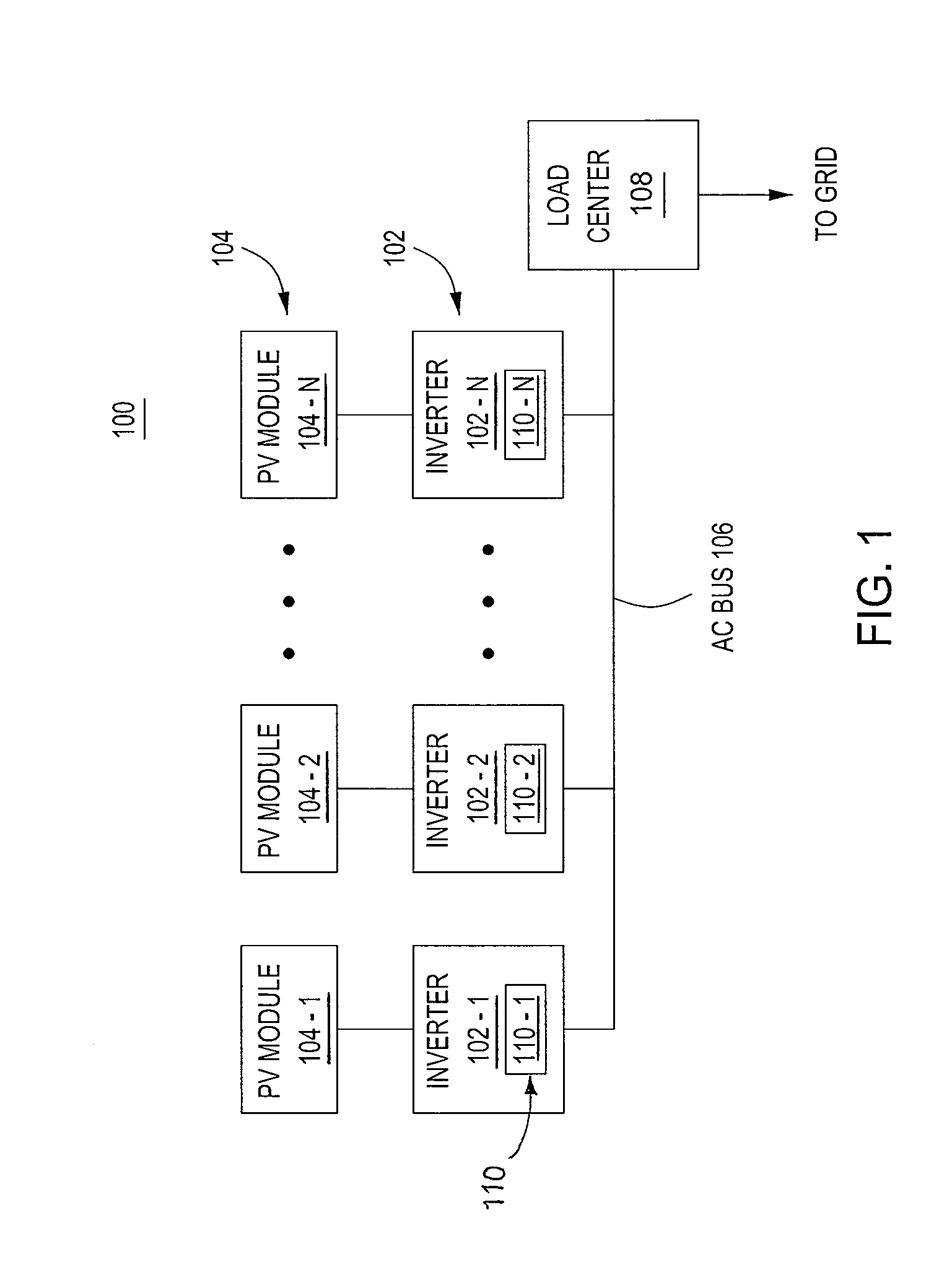
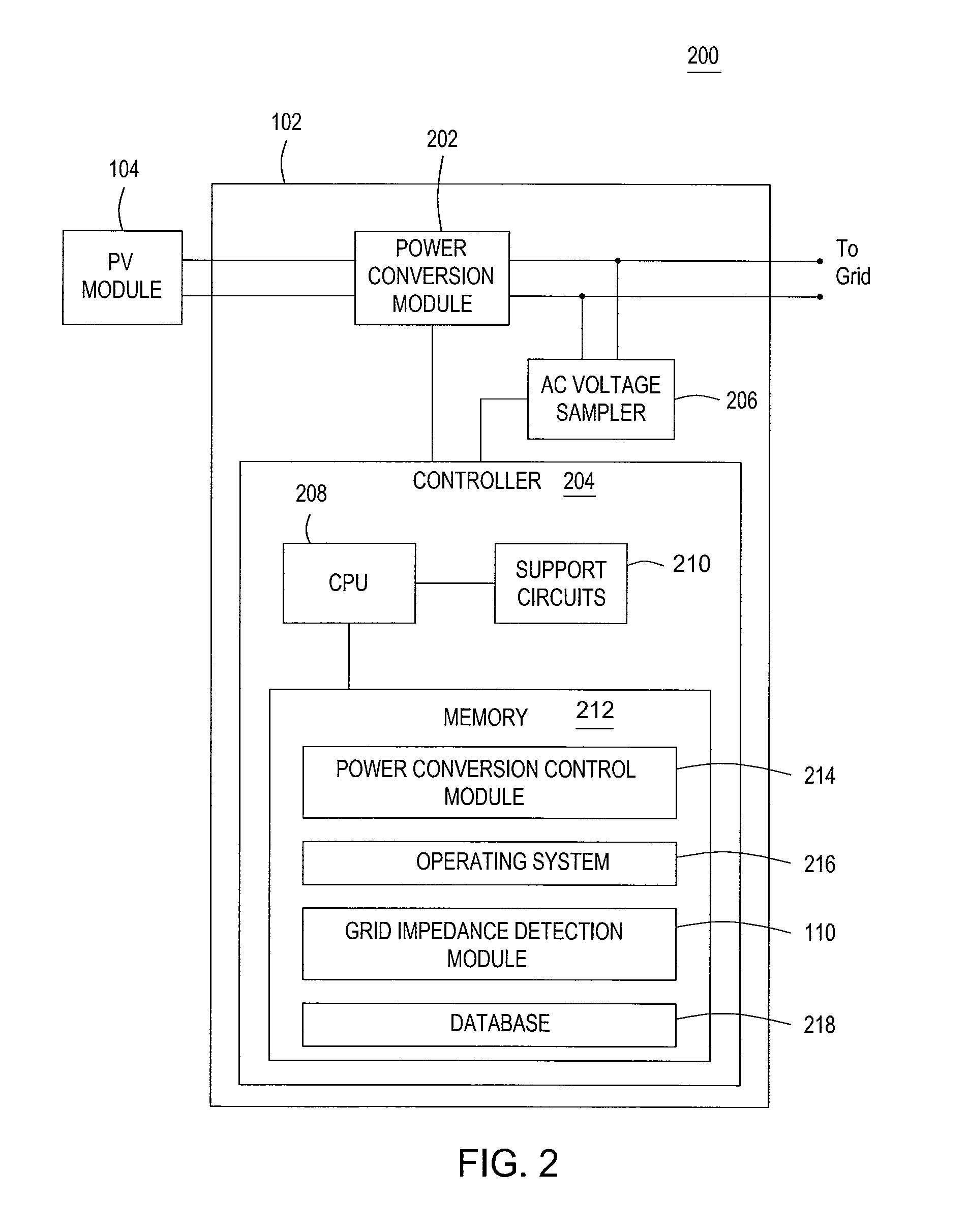
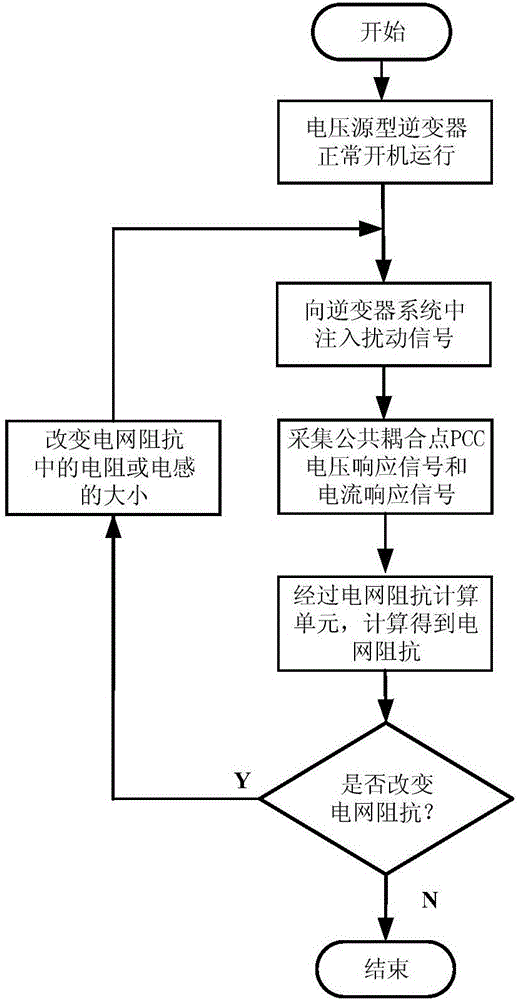
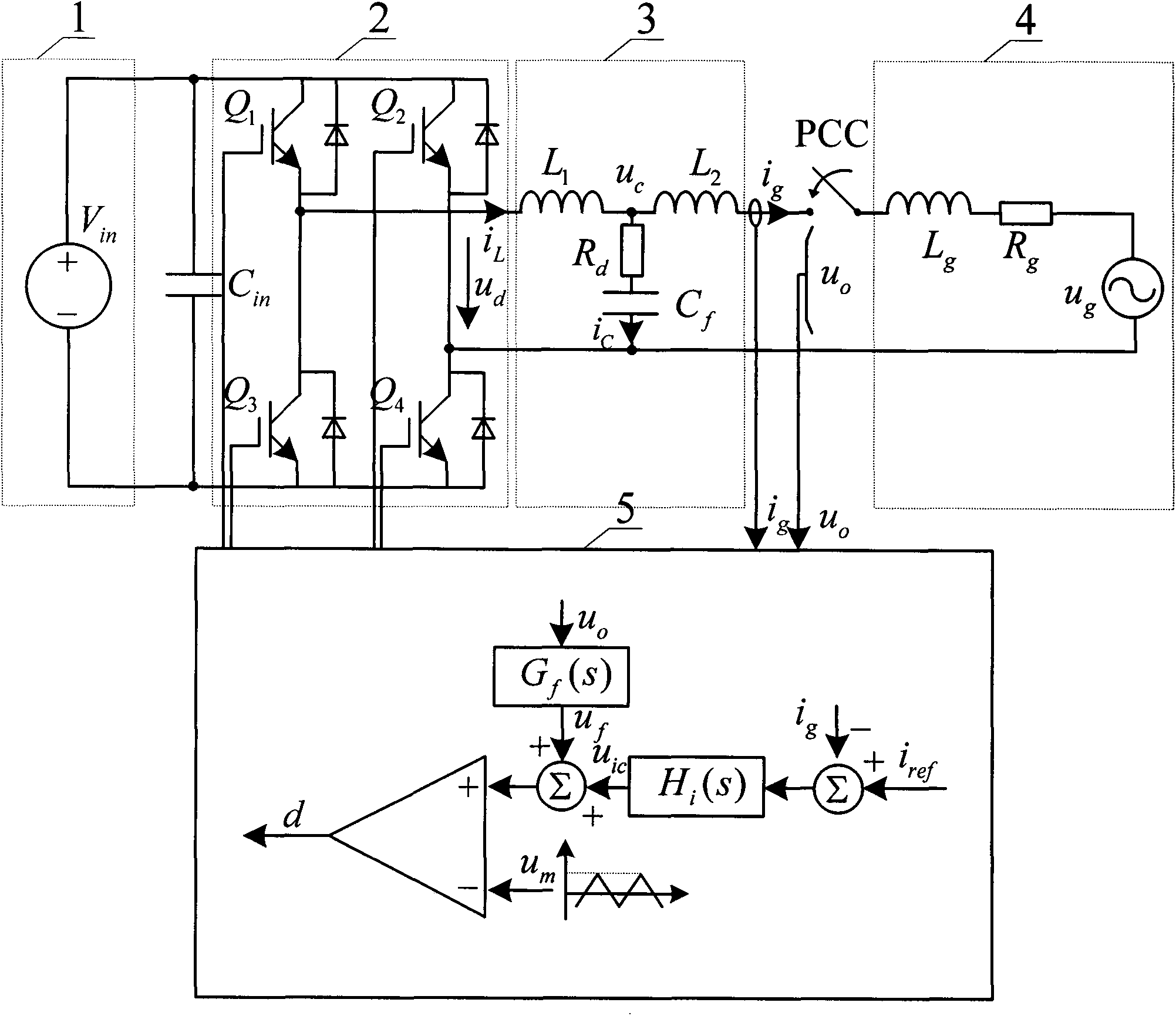
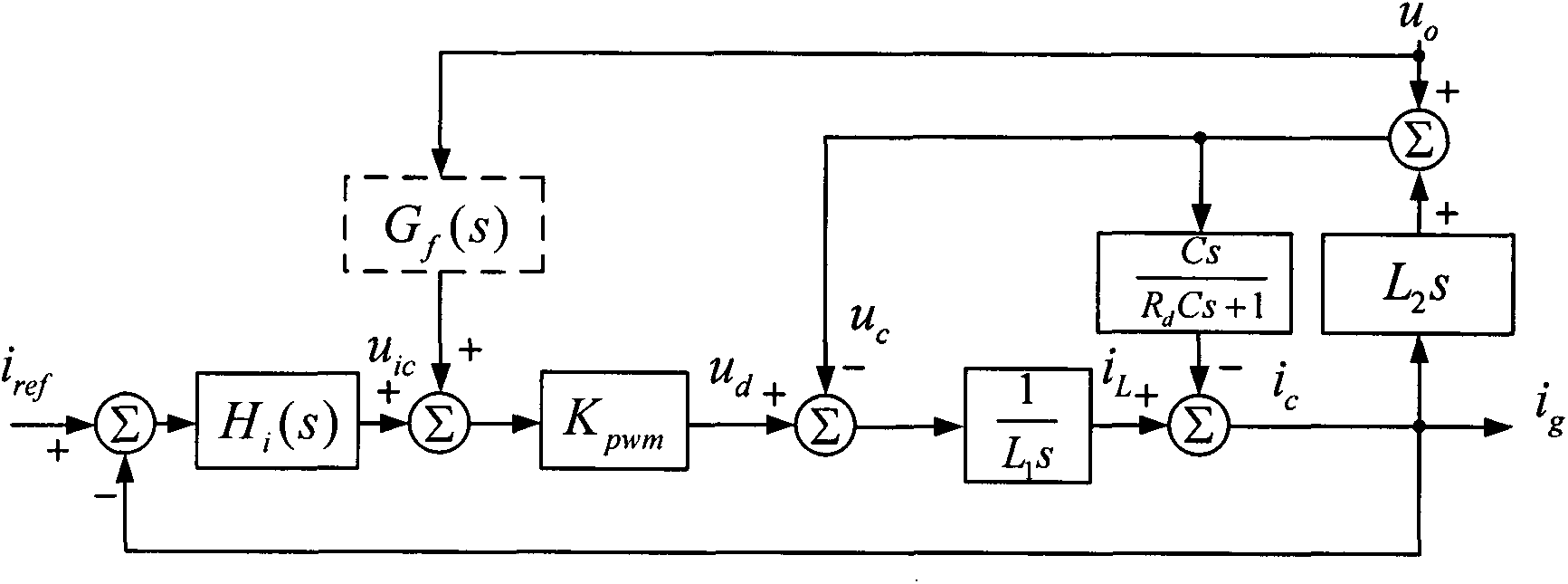
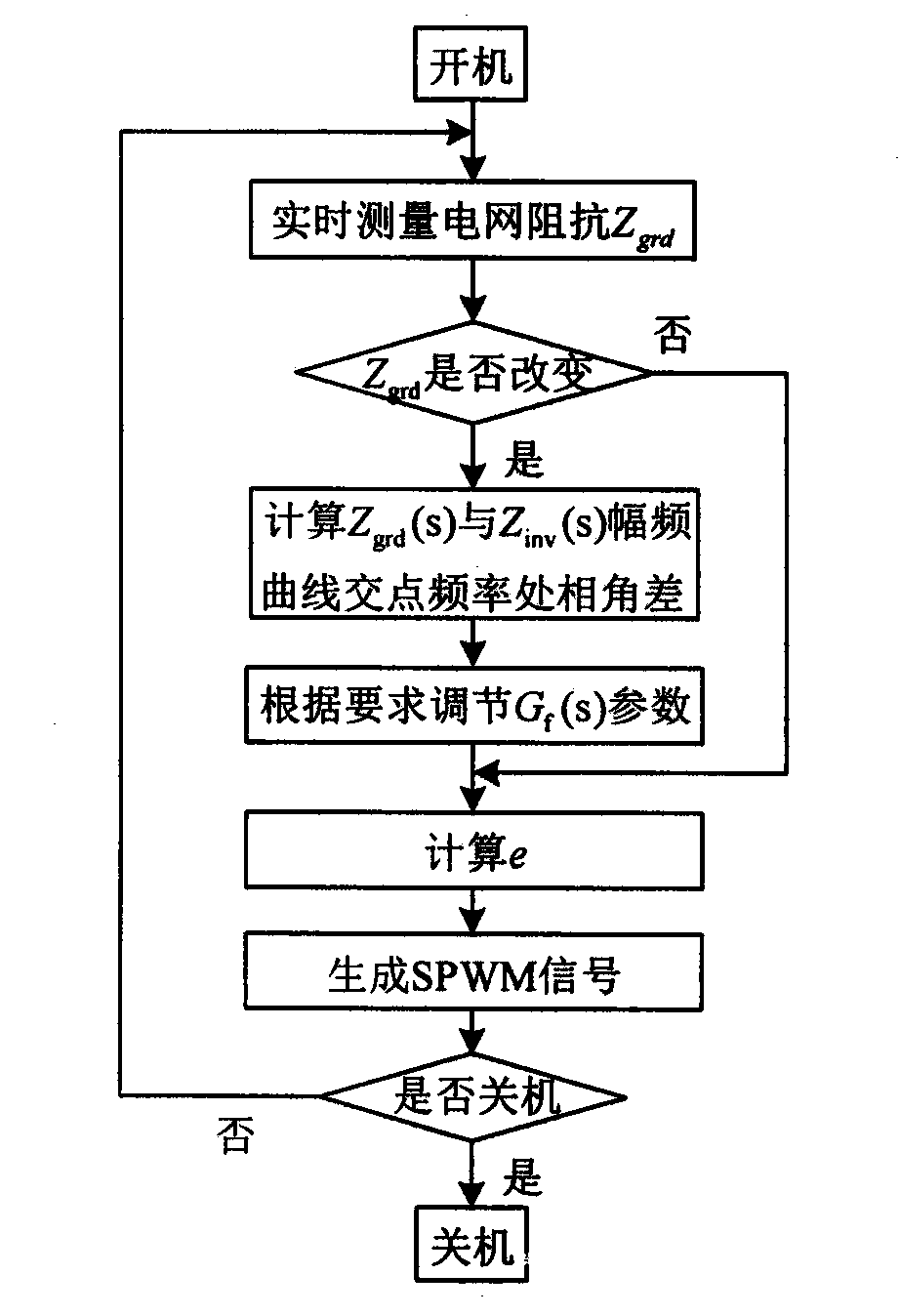
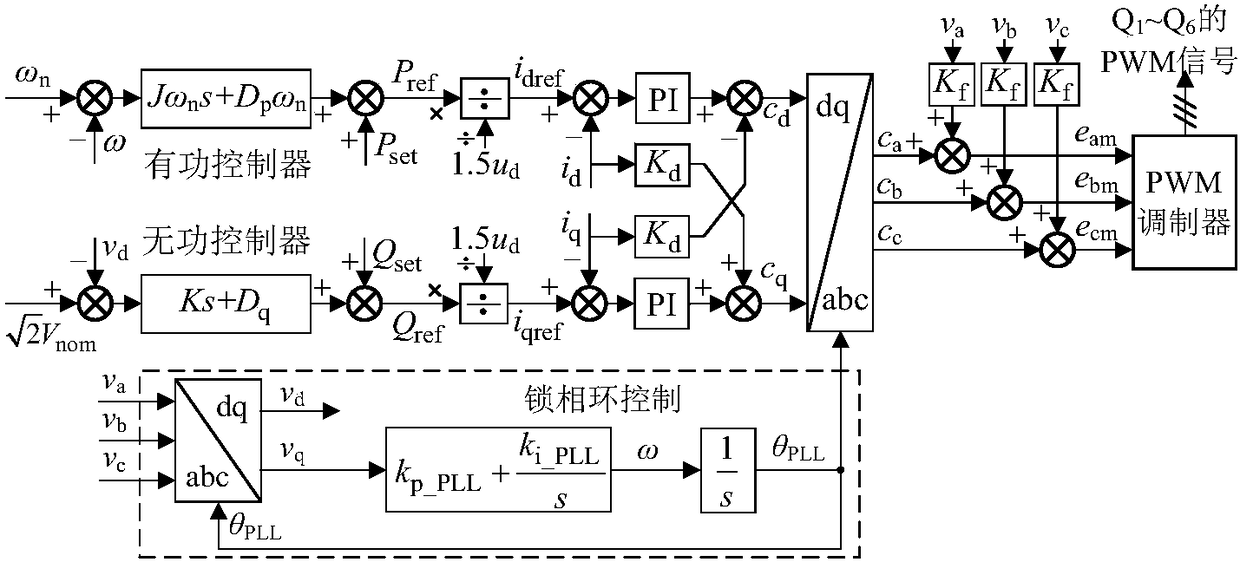
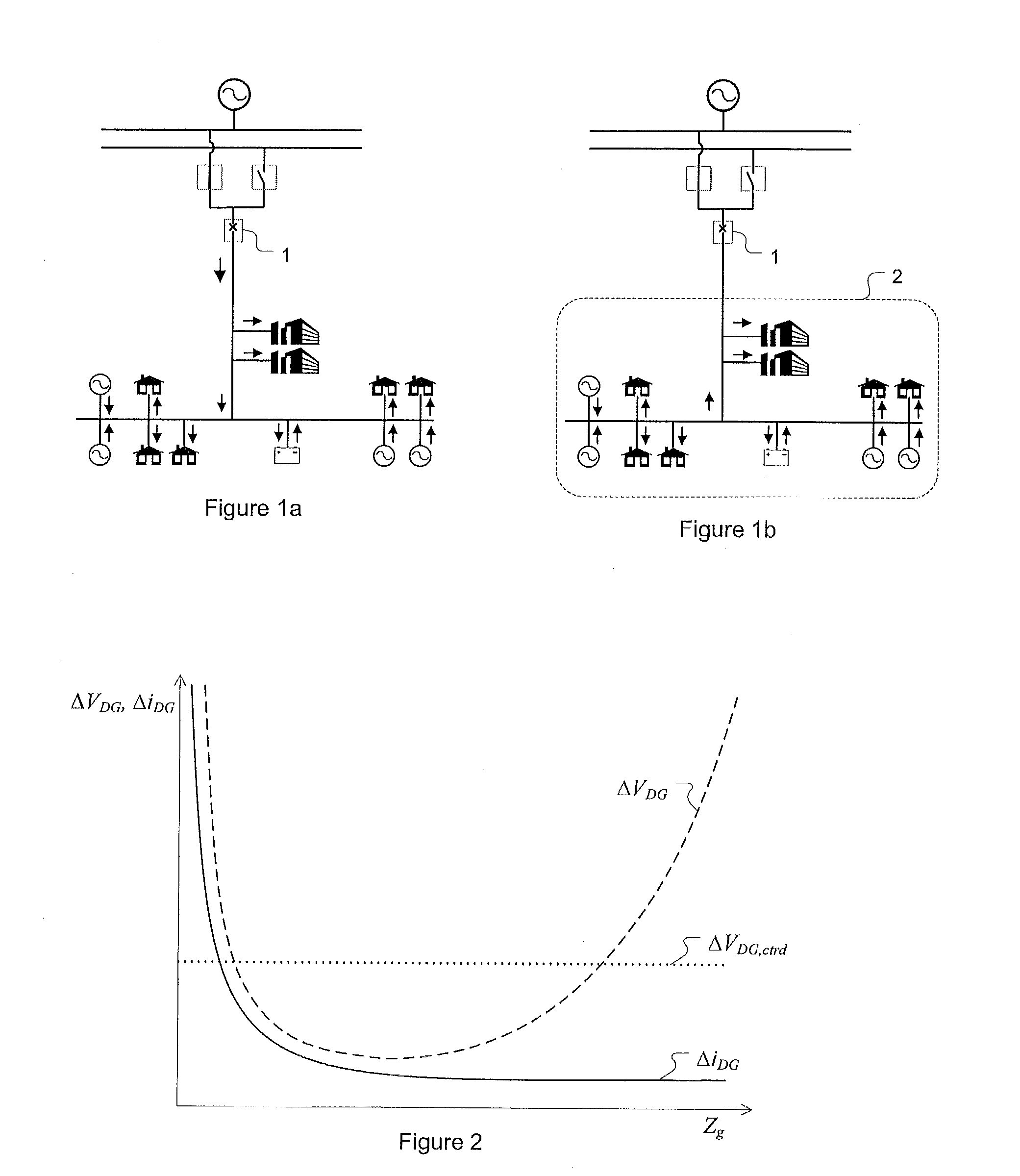
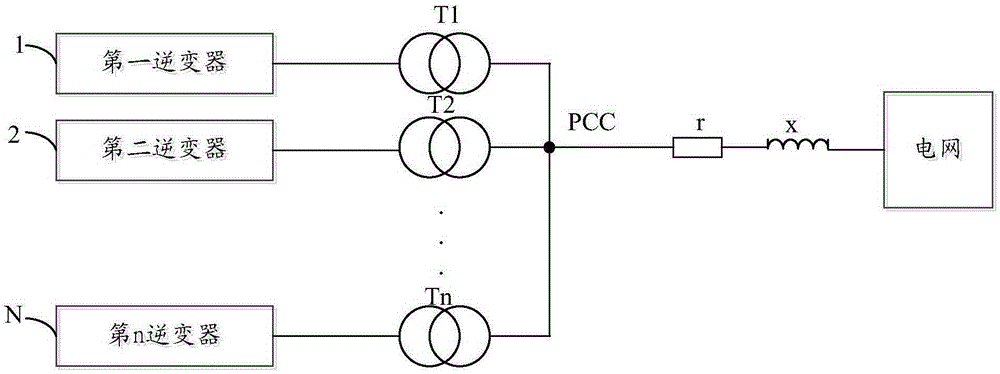
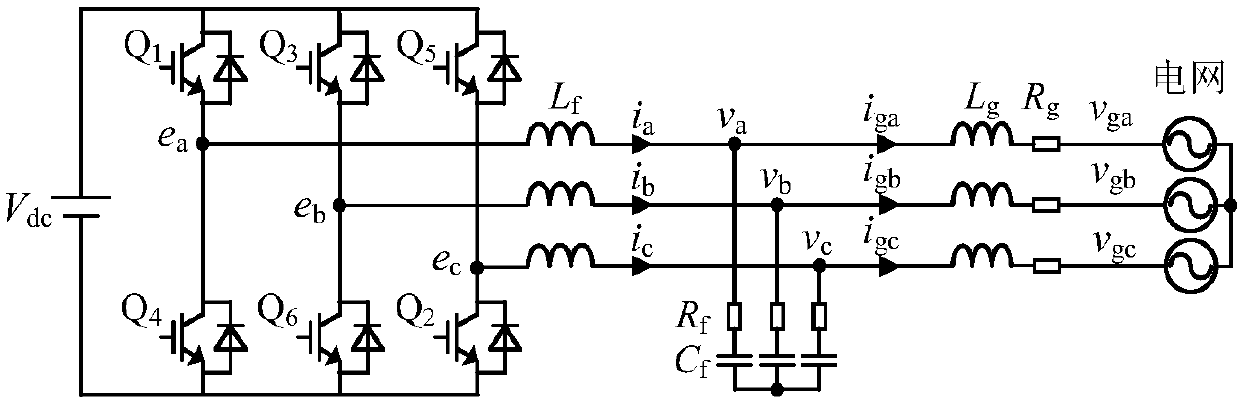
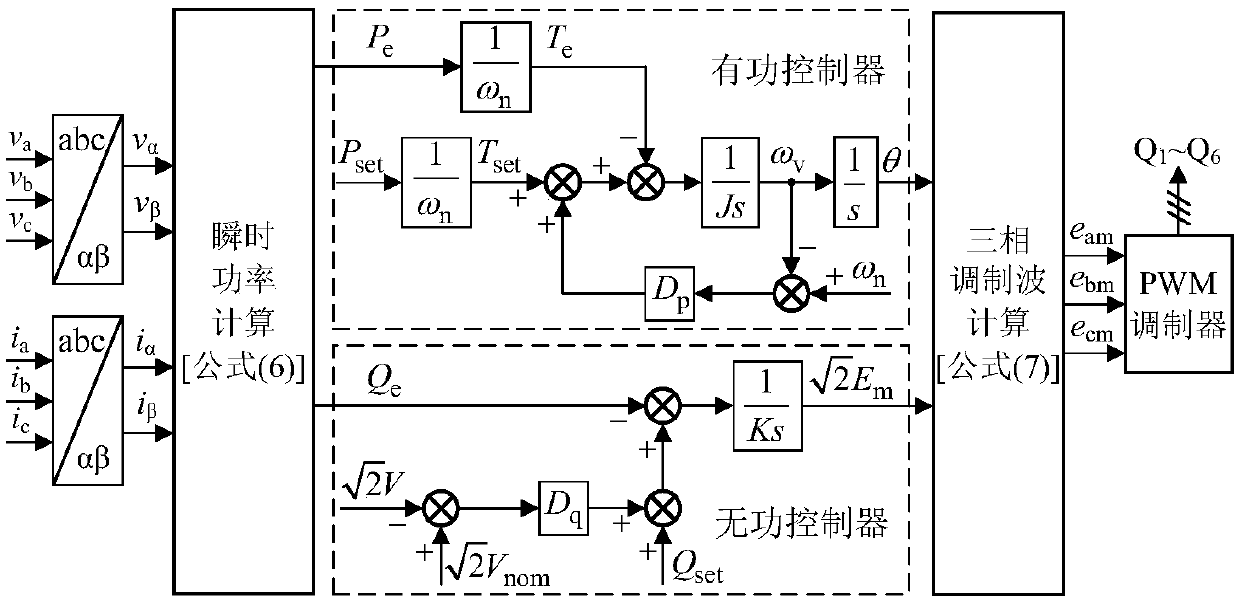
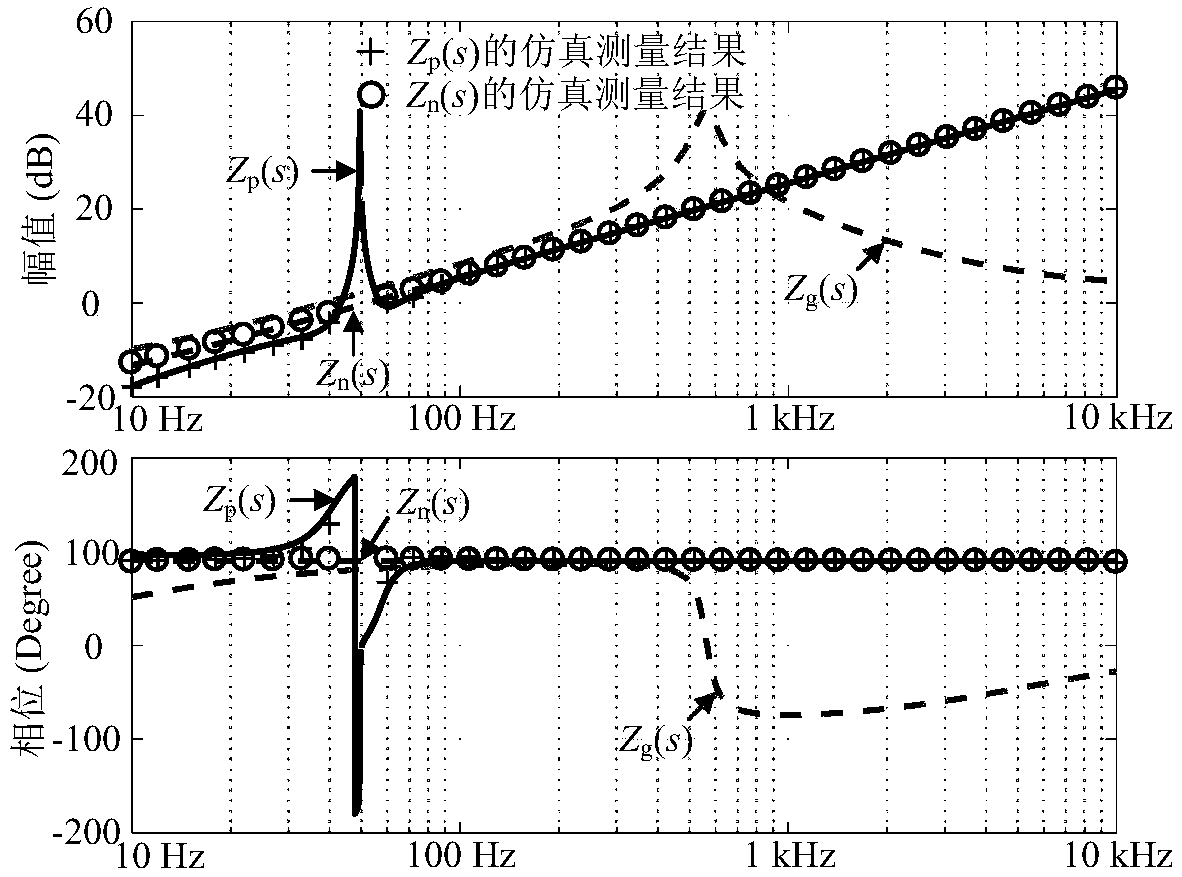
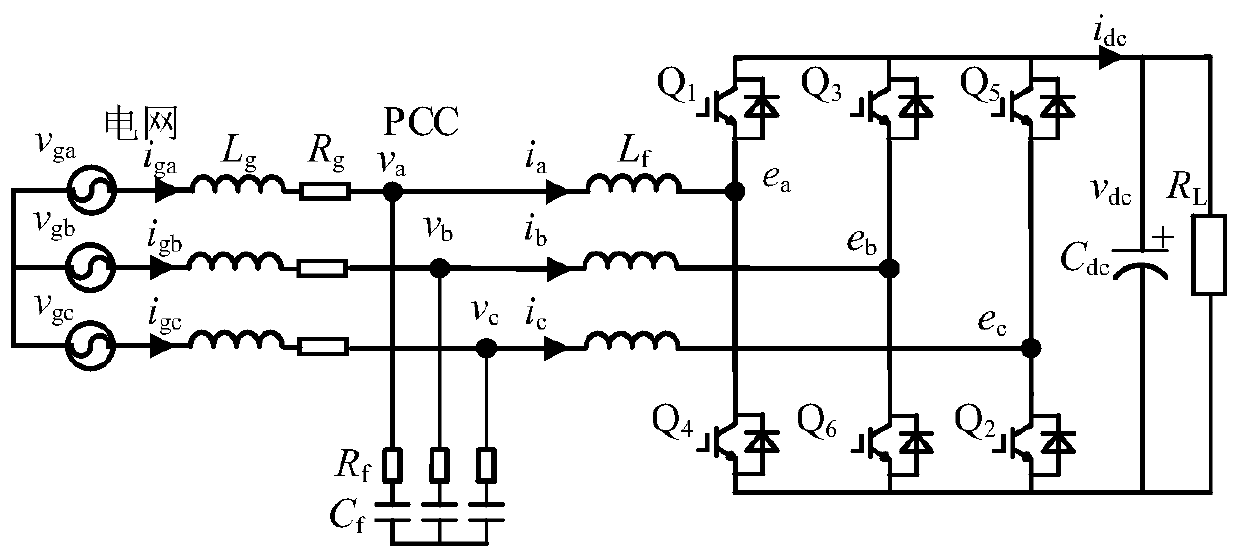
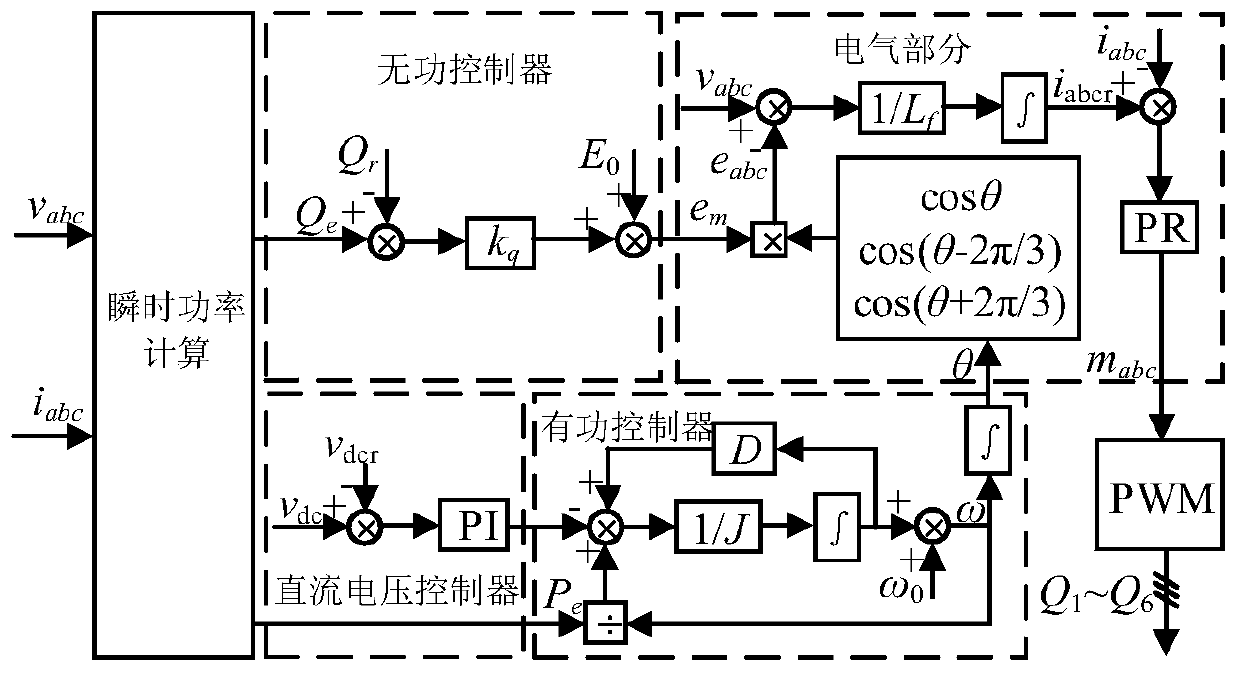
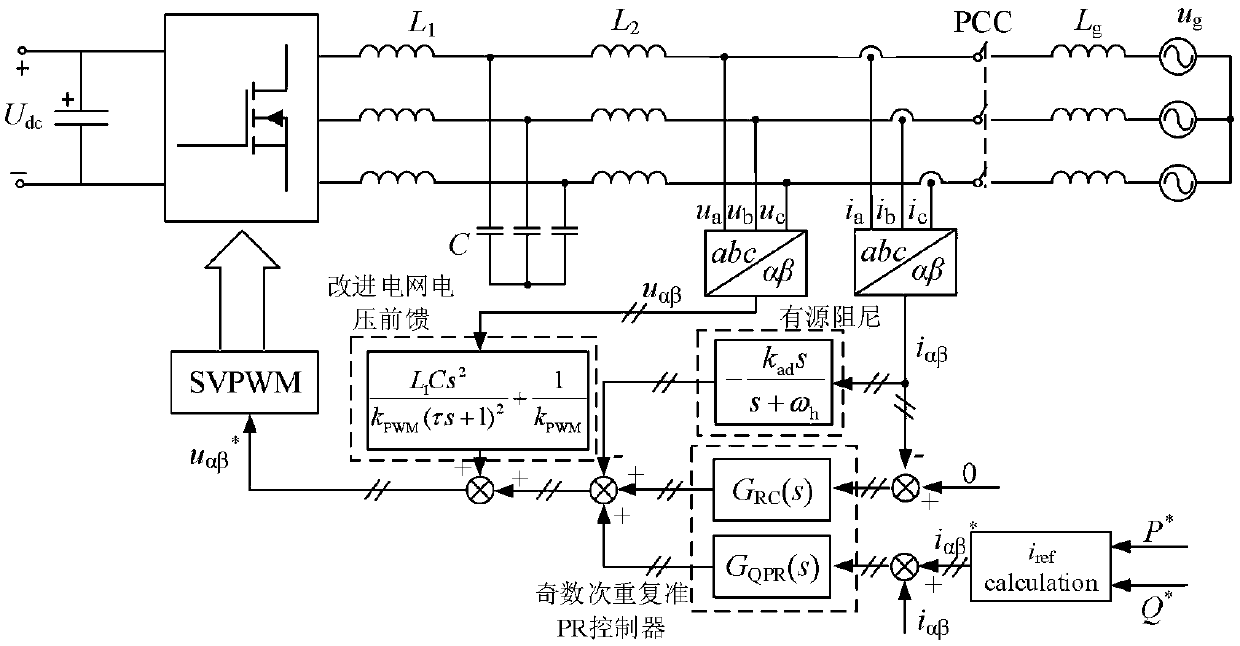
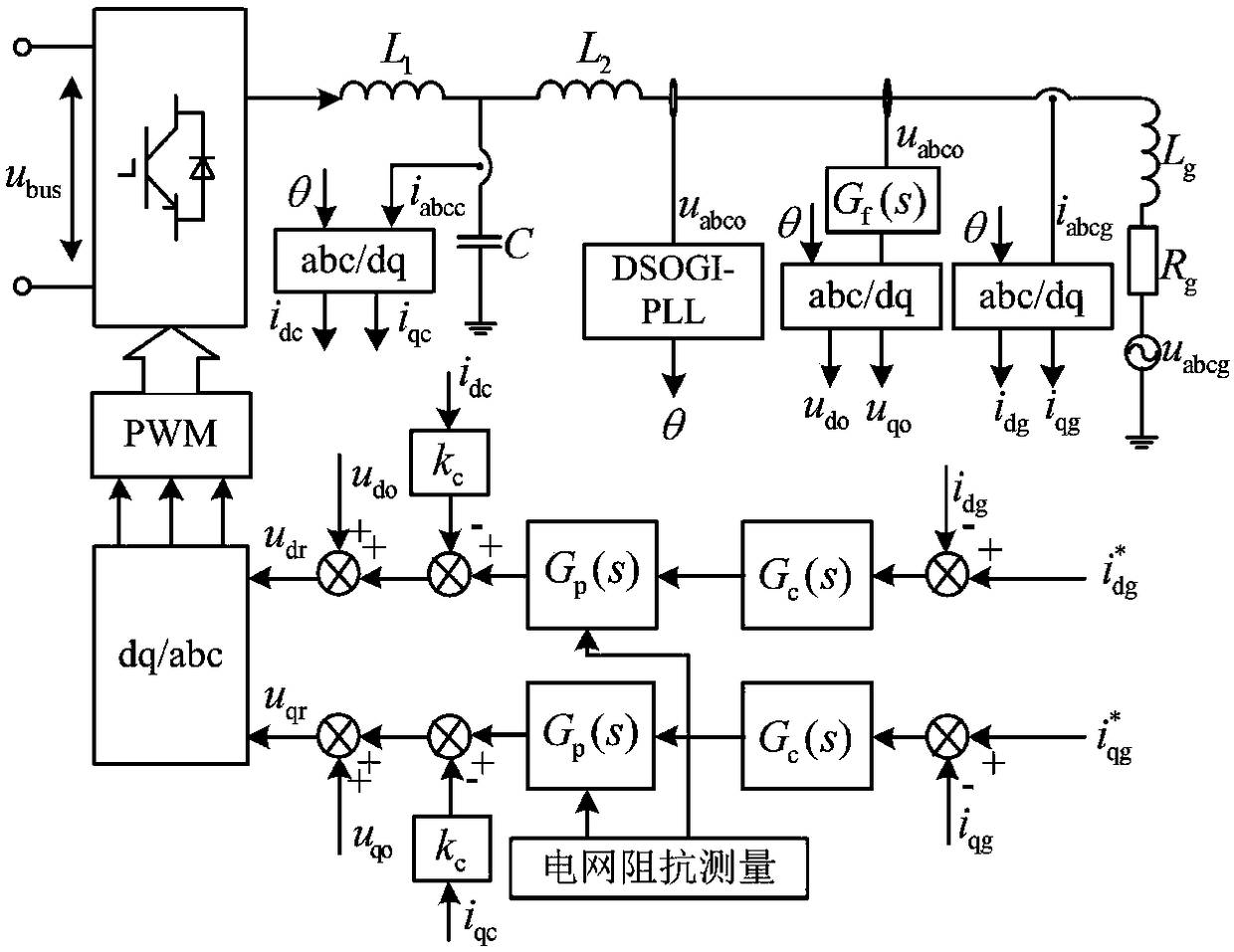
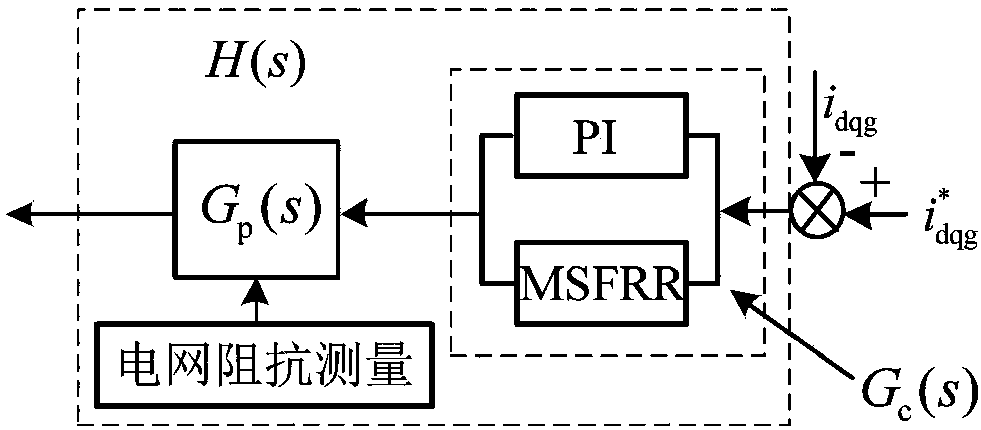
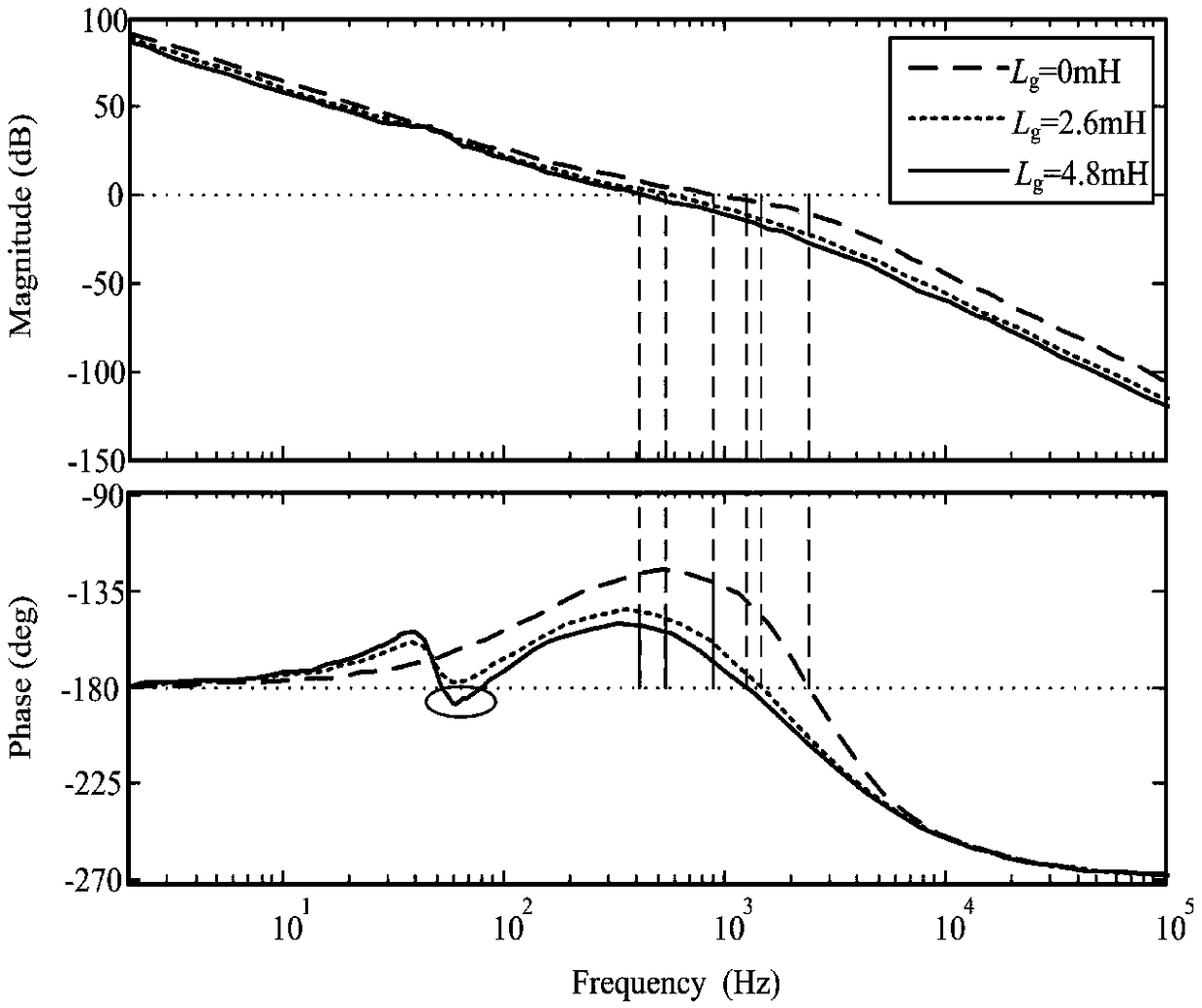
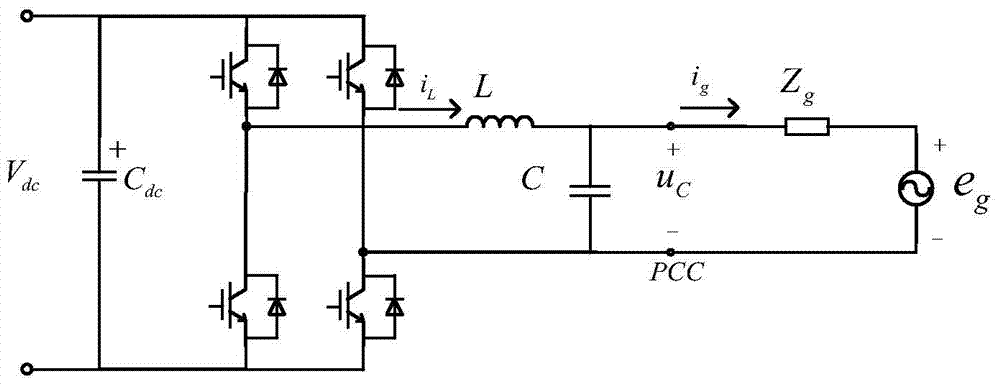
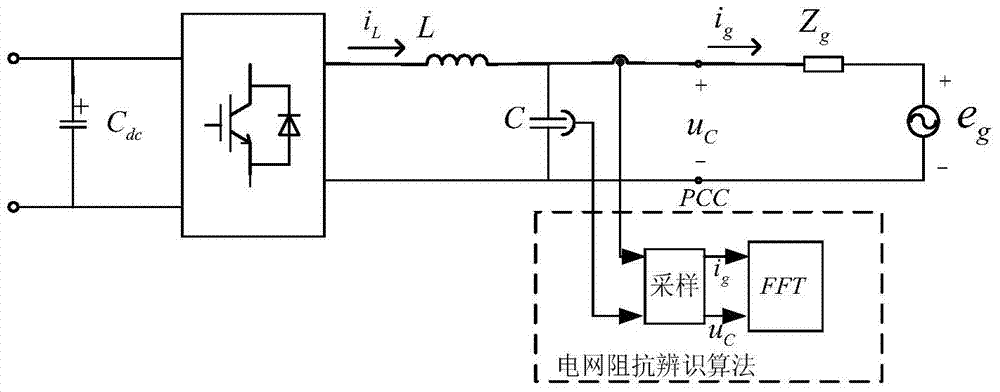
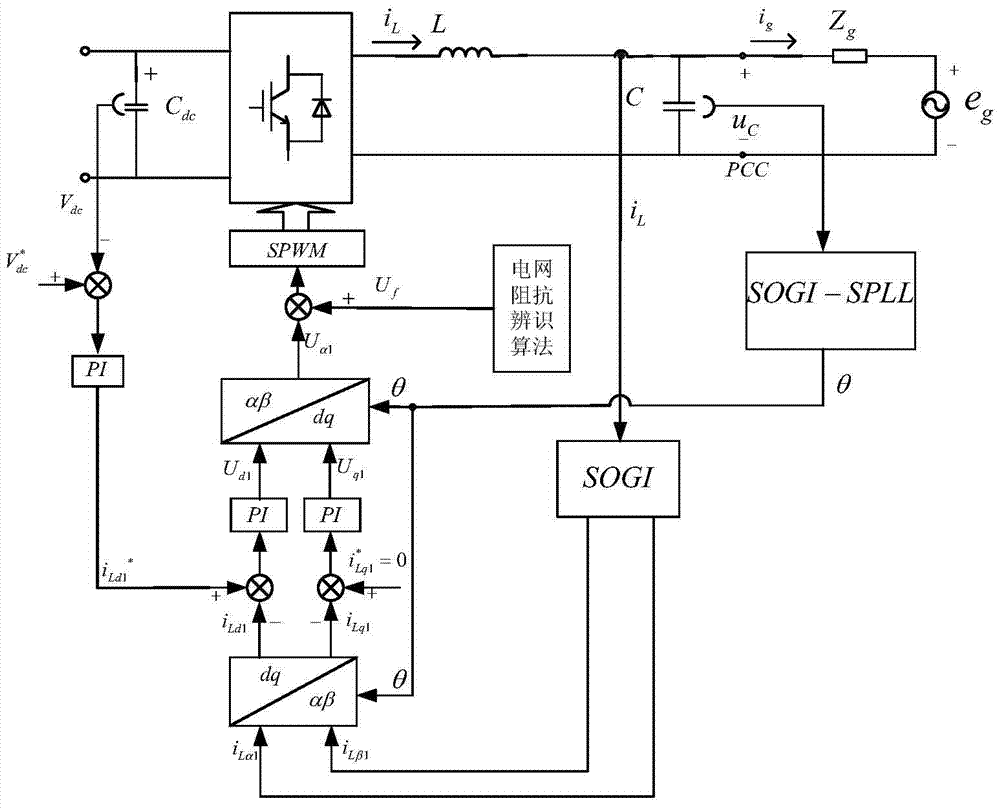
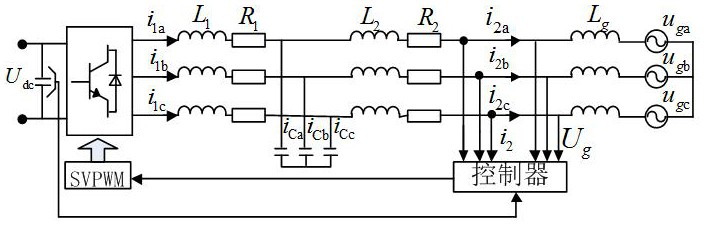
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Grid impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
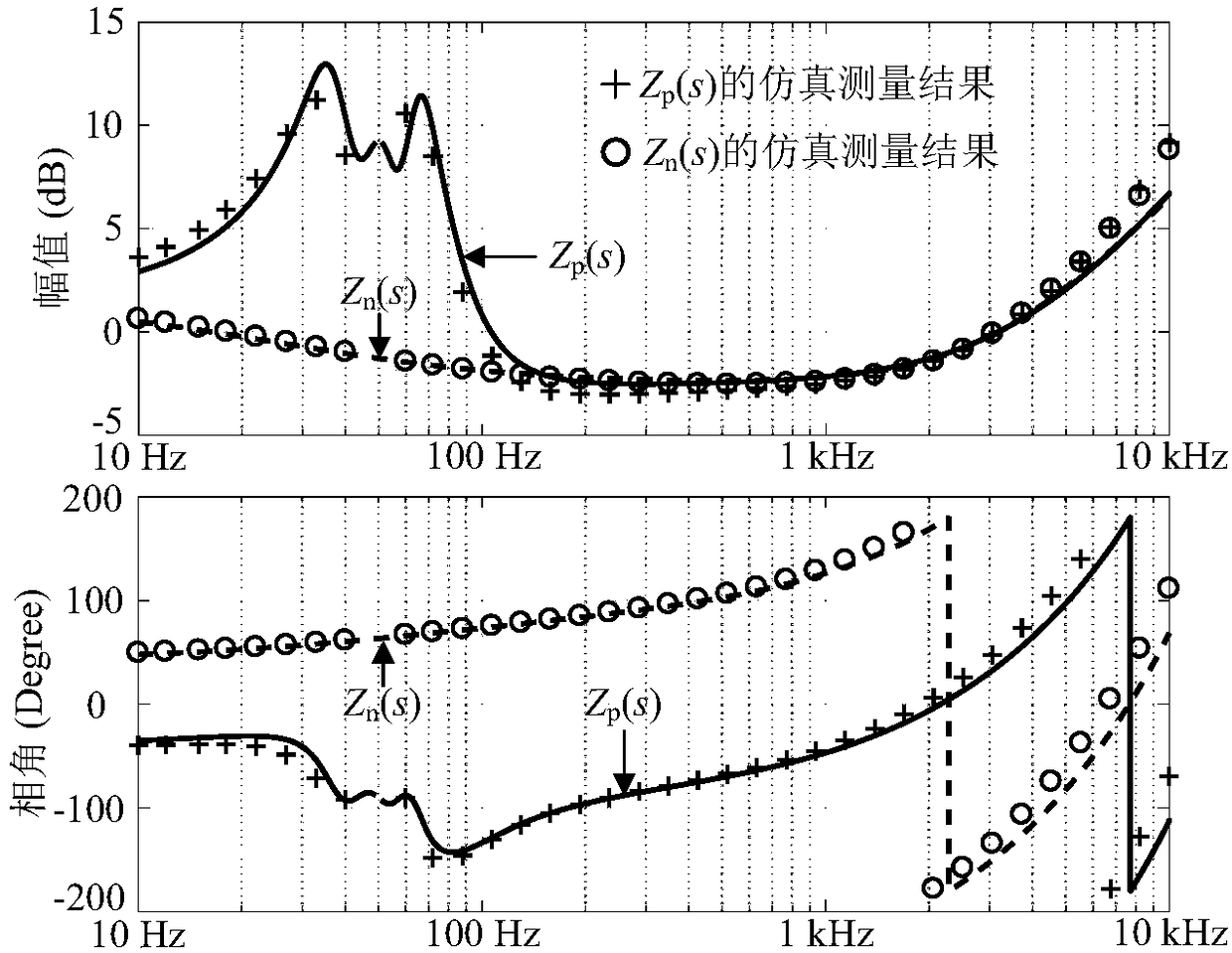
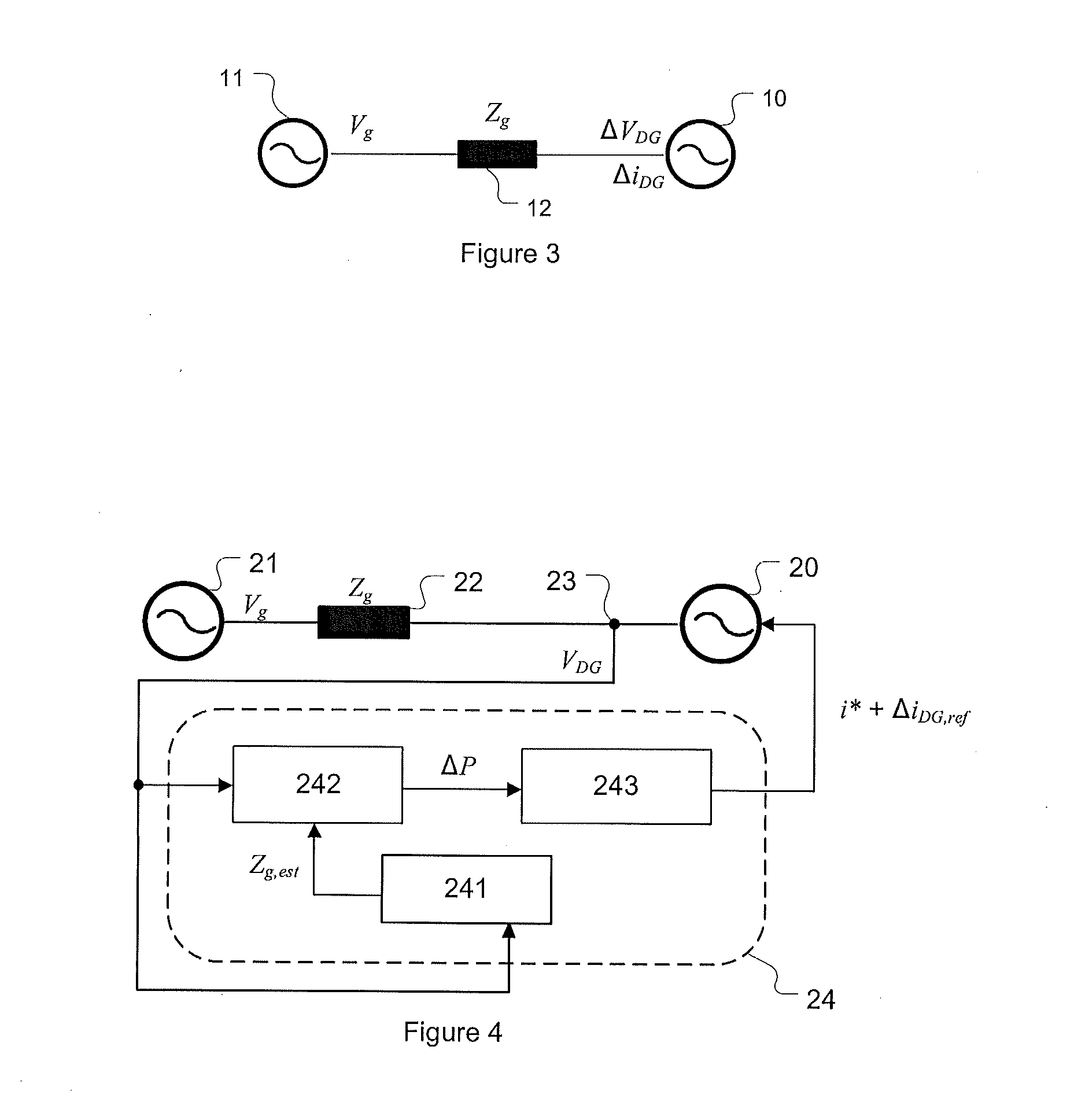
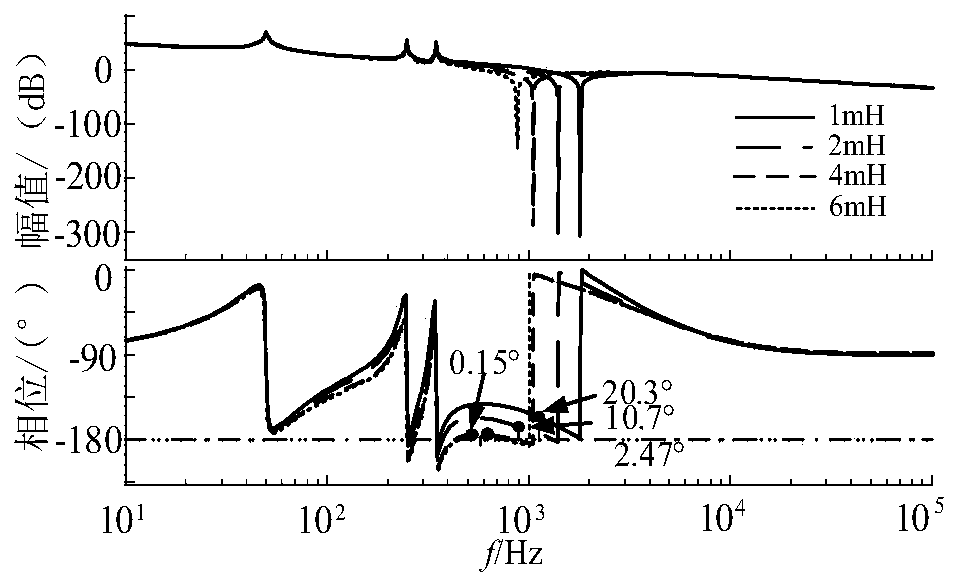
The measured grid impedances , and determined straightforward from only the line to neutral line The absolute values of the impedances are linearly increasing due to the inductive part. The phase angle is rising from 0° and approaches 90°. At higher frequencies the account of the skin effect is growing.
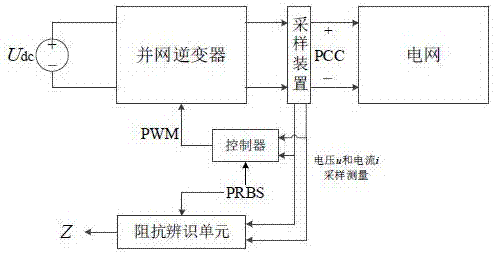
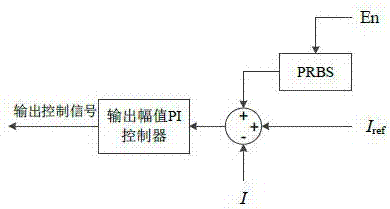
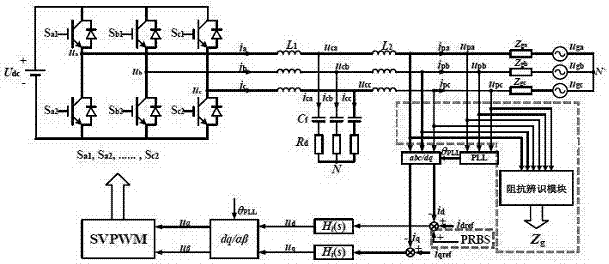
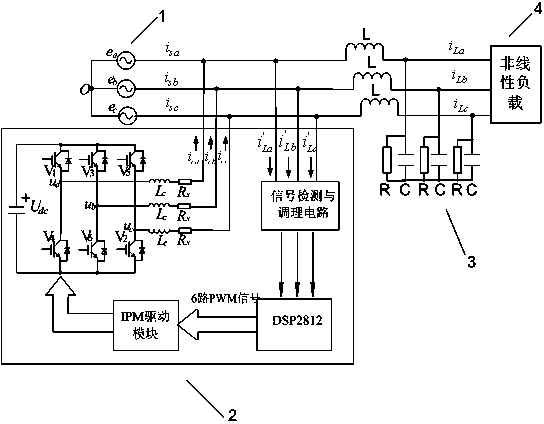
PRBS disturbance injection-based power grid impedance online identification method and device
ActiveCN107121609AAvoid Harmonic OscillationCapable of harmonic disturbance injectionElectrical testingImpedence measurementsElectrical engineering technologyGrid connected inverter
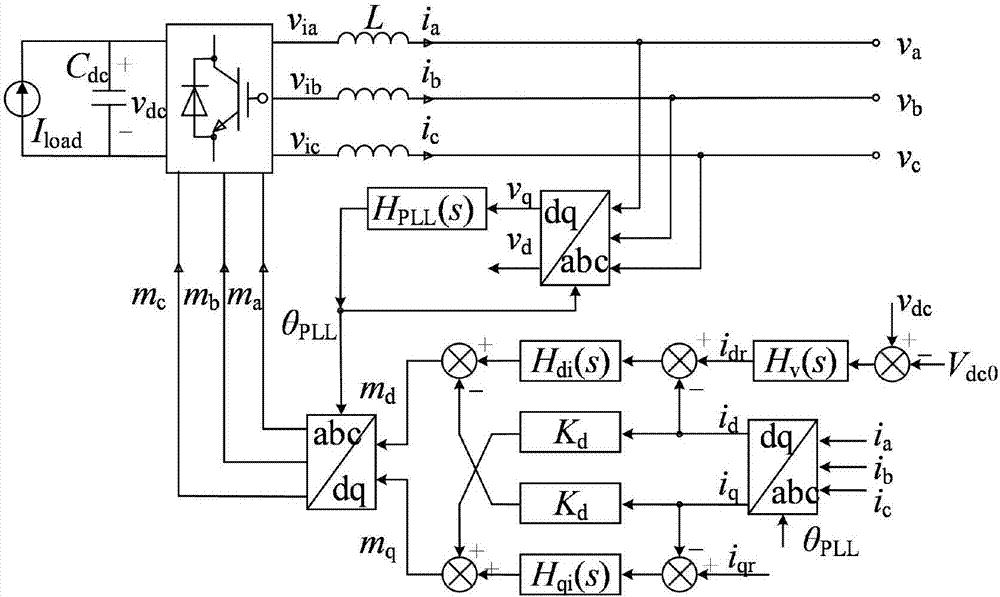
The present invention relates to the technical field of electrical engineering and discloses a PRBS disturbance injection-based power grid impedance online identification device. The device is mainly composed of a grid-connected inverter, a current loop controller, a sampling device and an impedance identification unit. The device is characterized in that the grid-connected inverter is connected with the current loop controller. When the grid-connected state is stable, the grid-connected inverter injects the PRBS disturbance into the power grid. During the injection process of a PRBS signal, a built-in output voltage THD is fed back to the controller, so that the THD value of the output voltage of the inverter is ensured to be smaller than 5%. The sampling device is connected with the PCC part of the power grid and is used for sampling and recording the voltage and the current at the PCC part of the power grid. The impedance identification unit is used for subjecting the sampled data of the sampling device to DFT analysis, and taking the average value of the amplitude and the average value of the phase of each harmonic component of the voltage and the current during the current sampling period. The method of the invention is high in precision, high in speed, strong in real-time property, wide in frequency range, lower in measuring cost and difficulty, and better in stability.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method and apparatus for grid impedance detection
A method and apparatus for monitoring an AC line for impedance change. In one embodiment, the method, comprises superimposing a tone on an AC current coupled to the AC line, wherein the tone is a higher frequency than an AC voltage waveform on the AC line; applying a correlation over a sampled AC voltage waveform, obtained by sampling the AC voltage waveform, to generate a correlated signal; and determining whether at least one change in characteristic of the correlated signal occurs.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
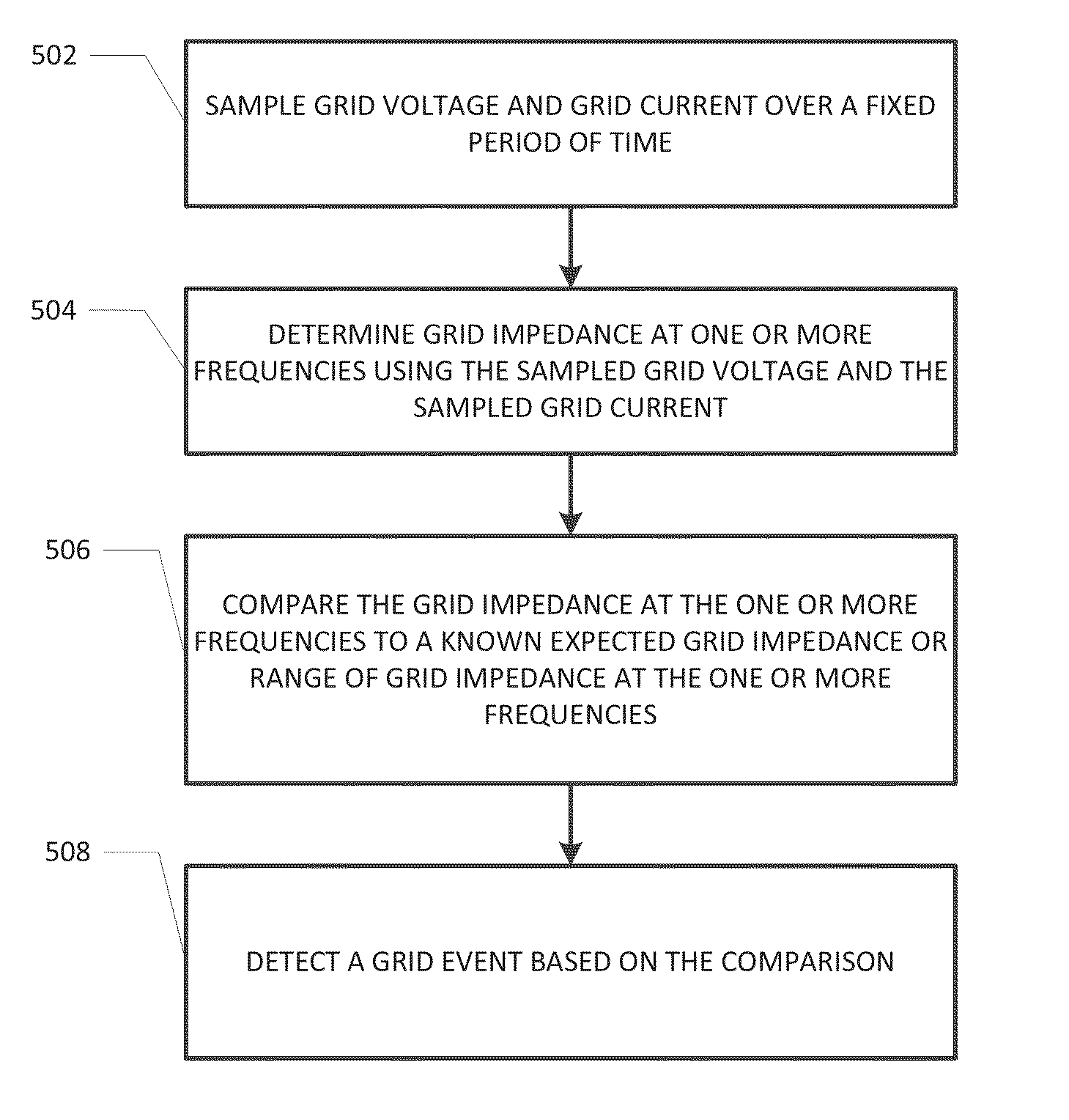
System and method for detecting a grid event
A method for detecting a grid event is provided. The method includes sampling grid voltage and grid current over a fixed period of time; determining grid impedance at one or more frequencies using the sampled grid voltage and the sampled grid current; comparing the grid impedance at the one or more frequencies to a known expected grid impedance at the one or more frequencies; and detecting a grid event based on the comparison.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
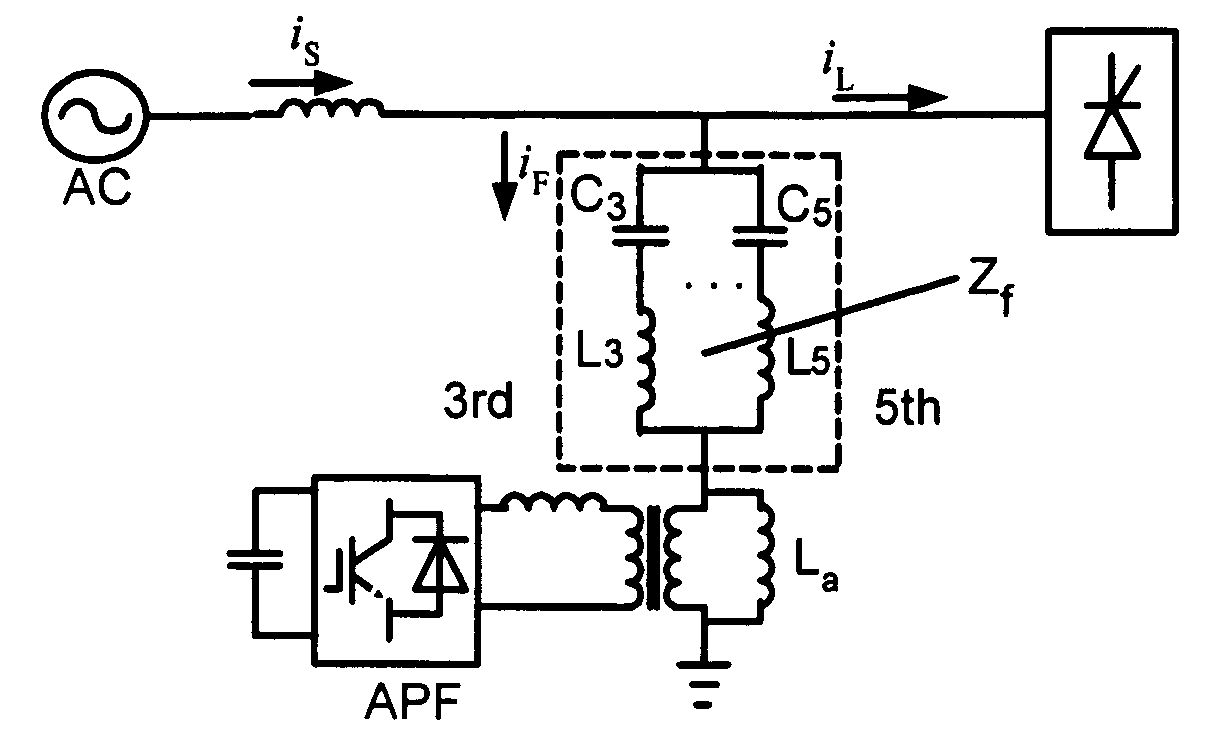
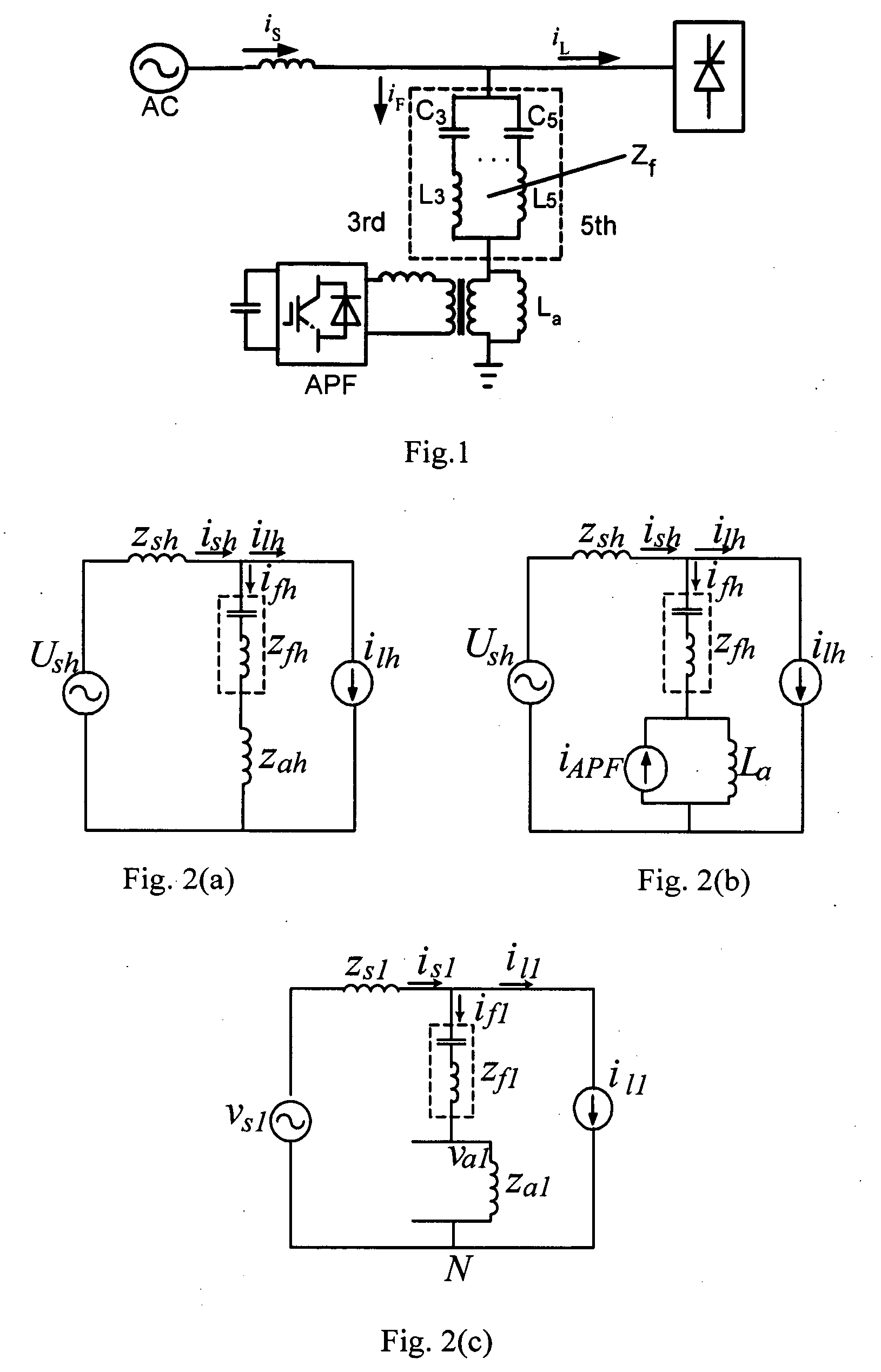
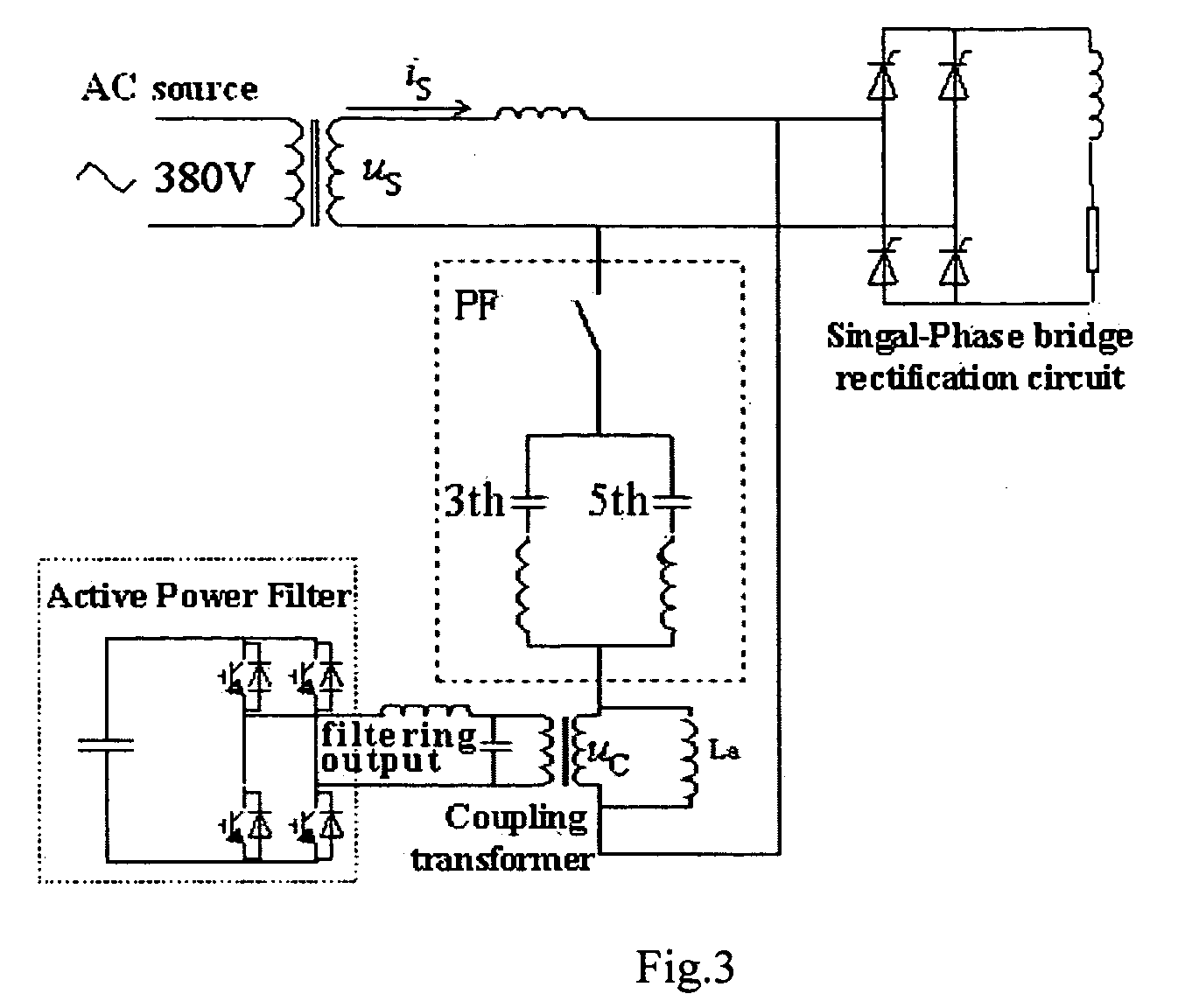
Hybrid parallel active power filter for electrified railway system
InactiveUS20050083627A1Add significant costImprove filtering resultInterference suppressionActive power filteringGrid impedanceControl manner
An exemplary parallel hybrid power filter apparatus for the electrified railway is described. The apparatus may include a group of LC reactive filter being purely tuned, an additional inductance, an active power filter and a coupling transformer. The active power filter may be controlled, e.g., as a current source in a composite control manner and can be connected in parallel to the additional inductance via the coupling transformer. The power filter can be connected to the reactive filter in series to form the parallel hybrid filtering system, and may be connected to the power grid via the circuit breaker or a thyristor. This exemplary system can be installed either in the traction substations or in the locomotives directly, or performed by ameliorating the original reactive filter. The active power filter does not add significant amount of cost, and may be simple and reliable in a control manner for the capacity of the APF is so small as to be less than one percent of that of the harmonics source. The power filter can also inhibit the impact of the “background harmonics” of the electrified railway on the reactive filter, and prevent the reactive filter and the grid impedance from resonance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
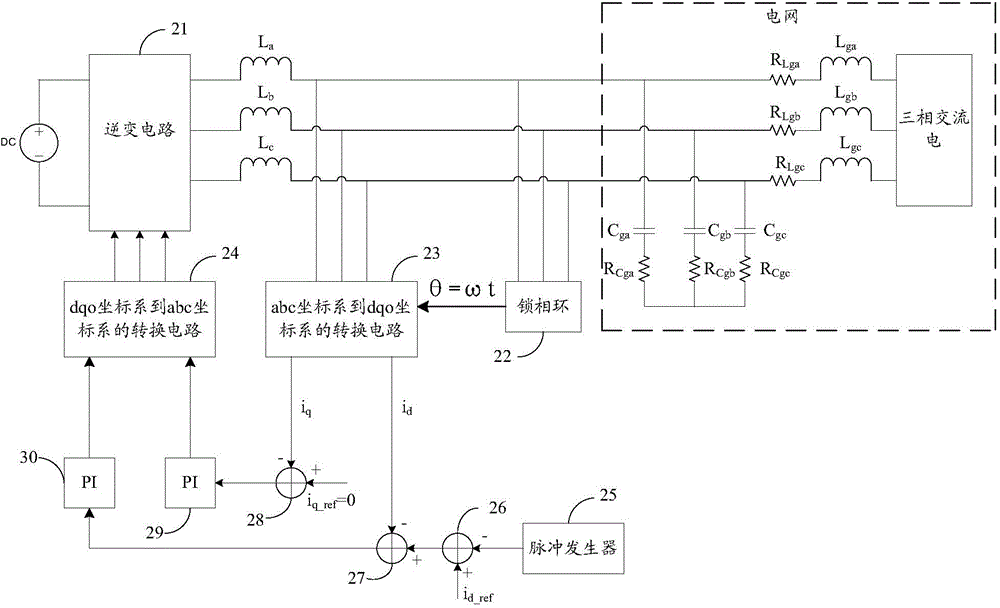
Method for adaptively controlling hybrid damping of grid-connection inverter applicable to weak grid access conditions
ActiveCN103545838AReasonable frequency characteristicsPR parameter increaseAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDamping factorGrid impedance
The invention relates to a method for adaptively controlling hybrid damping of a grid-connected inverter applicable to weak grid access conditions. Most existing methods are used for optimally controlling fixed impedance of grids at present, but grid access conditions of grid-connected inverters are dynamic and varied, so that adaptive control under different grid impedance conditions has high application value. The method includes measuring impedance information of a weak grid by a harmonic injection process; enabling a controller to adaptively modify loop parameters and active damping coefficients; ensuring a wide stability margin and a proper control bandwidth of a control system. The method has the advantages that the novel method for adaptively controlling the hybrid damping is based on real-time measurement on impedance of the grid, and optimal control parameters in a DSP (digital signal processor) are automatically selected, so that the control bandwidth and a phase margin of the inverter under different grid impedance access conditions can be guaranteed, and the grid-connected inverter can safely and reliably run under the various grid impedance conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Stability analysis method for grid-connected inverter system under coexistence condition of multiple frequency coupling factors
ActiveCN107994606AAccurate Analysis of StabilityAvoid errorsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsGrid connected inverterNyquist stability criterion
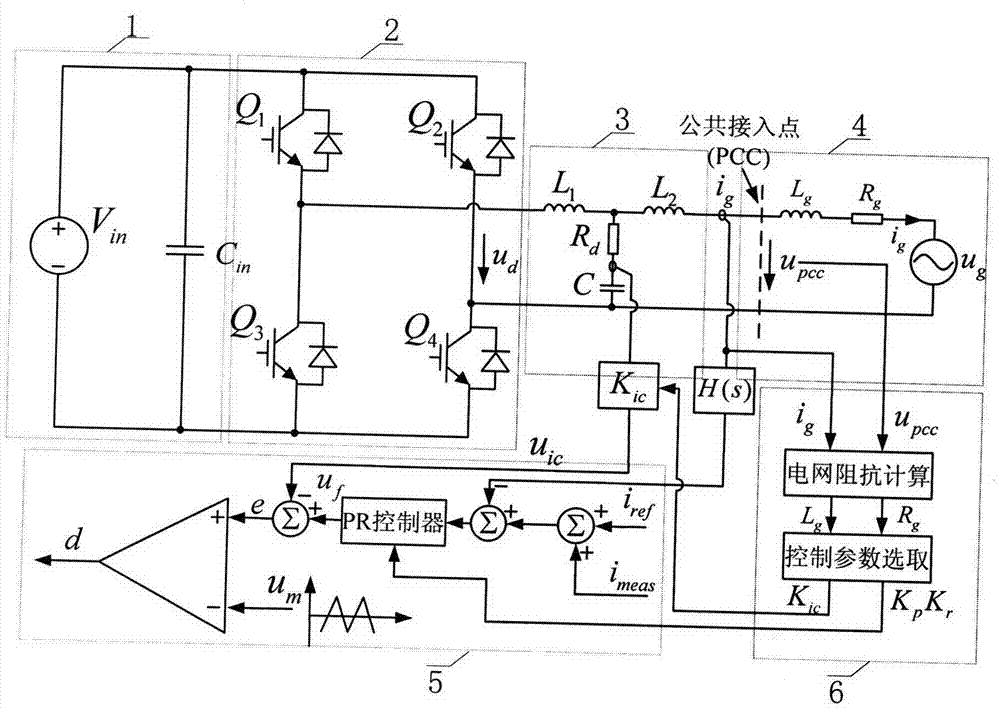
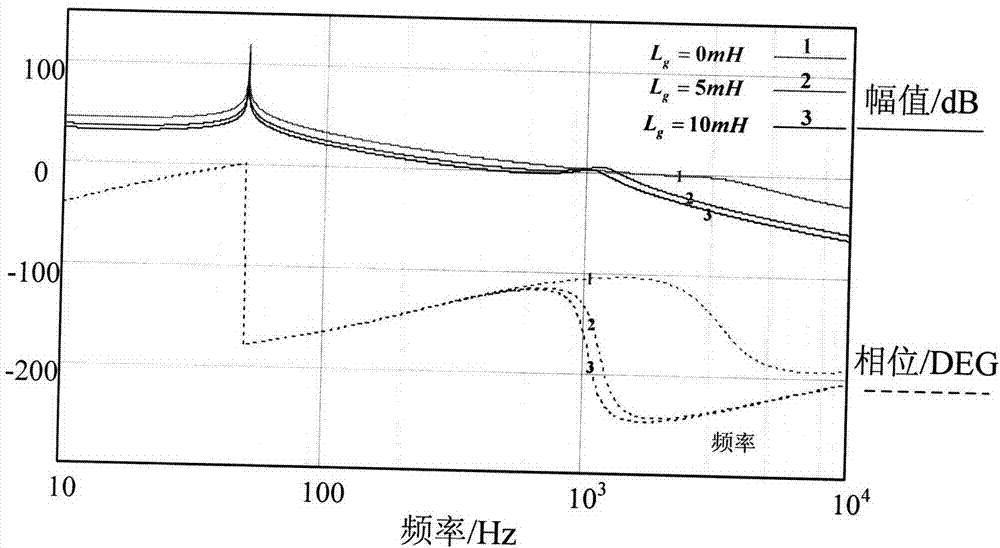
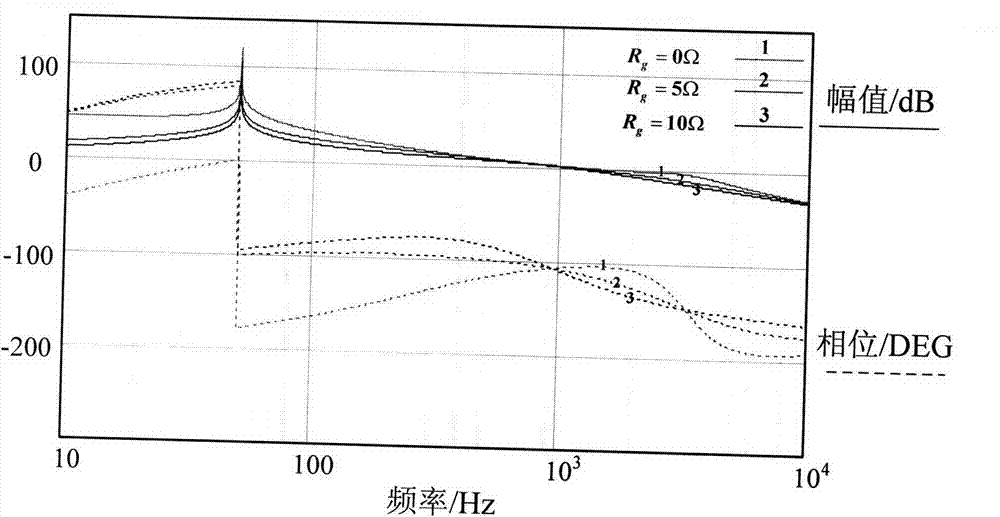
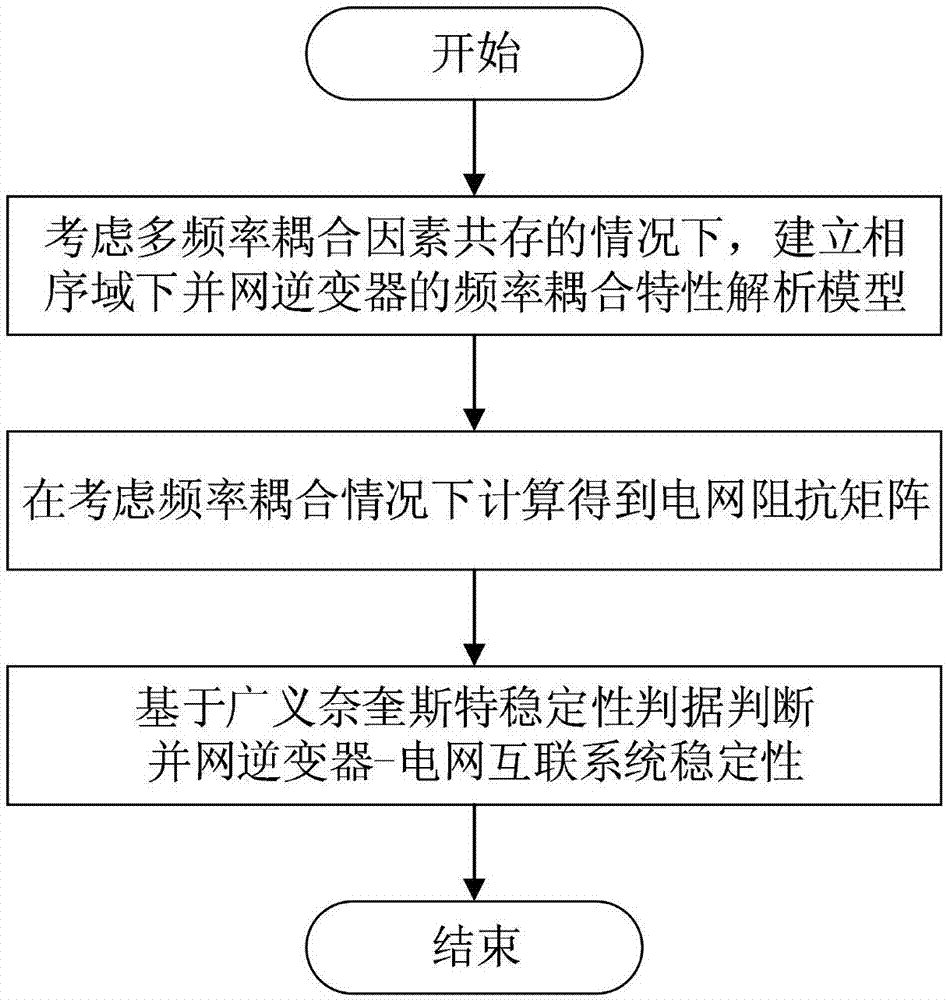
The invention discloses a stability analysis method for a grid-connected inverter system under the coexistence condition of multiple frequency coupling factors. The method is applied to a grid-connected inverter system, wherein the situation that multiple frequency coupling factors coexist is considered. A frequency coupling characteristic analysis model of a grid-connected inverter is establishedin a phase sequence coordinate system, and a power grid impedance matrix is obtained through calculation under the condition that the frequency coupling is considered. The method is realized based onthe generalized Nyquist stability criterion, and the stability of the grid-connected inverter system is judged by utilizing the generalized impedance ratio matrix of the grid impedance matrix and thefrequency coupling characteristic matrix of the grid-connected inverter. Therefore, the method can be used for analyzing the system stability under the complex condition of the coexistence of multi-frequency coupling factors. Compared with an existing stability analysis method based on the impedance of the grid-connected inverter, the method is more complete. Therefore, analysis errors caused byignoring frequency coupling are avoided. The stability of the grid-connected inverter system under the complex condition can be analyzed more accurately.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Verification method and experimental device for grid impedance recognition
ActiveCN106771786AAvoid the effects of background harmonicsSimplify the extraction processInductance measurementsElectrical testingGrid impedanceValidation methods
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Phase angle margin compensation-based system impedance active control method of grid -connected inverter
ActiveCN103354359ATo achieve the purpose of harmonic injectionImprove accuracyHarmonic reduction arrangementAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesGrid-tie inverterControl signal
The invention relates to a phase angle margin compensation-based system impedance active control method of a grid-connected inverter. Because the changing impedance exists in a power grid, a dynamic interaction influence exists between the grid-connected inverter and the power grid and thus the grid-connected current waveform quality is influenced, so that the weakening of the impedance interaction influence is crucial to improvement of the grid-connected current quality. According to the invention, the impedance active control method is characterized in that real-time grid impedance information is obtained in real time and thus a phase angle margin at an inverter output impedance amplitude-frequency curve intersection point frequency is solved; a voltage feedforward control method is employed and a phase angle margin of the inverter impedance at the impedance intersection point frequency is compensated in real time; operation is carried out on a voltage feedforward link output and a current ring PI result so as to obtain an SPWM control signal. According to the invention, because the active impedance control method with the phase angle margin compensation function is used, the harmonic resonance generated by the dynamic interaction influence between the inverter and the power grid near the impedance intersection point frequency can be effectively suppressed, so that the rid-connected current waveform quality of the inverter is improved and the grid-connected stability is enhanced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multi-inverter micro-grid harmonic resonance suppression method based on adaptive virtual impedance remodeling
InactiveCN109698502AImprove output impedance characteristicsSuppression of series and parallel resonanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementGrid impedanceEngineering
On the basis of the inverter-side current feedback control strategy, the invention presents a multi-inverter micro-grid harmonic resonance suppression method based on adaptive virtual impedance remodeling. The method includes a virtual impedance remodeling unit, a parameter adaptive adjustment unit and a grid impedance online detection unit. The virtual impedance remodeling unit can improve the output impedance characteristics of grid-connected inverters and inject certain damping components into a micro-grid. The parameter adaptive adjustment unit adaptively adjusts the control parameters ofthe virtual impedance remodeling unit and a current regulating controller according to the impedance parameters of the grid to maintain the stability of the system. The grid impedance online detectionunit provides the equivalent impedance of the grid as the input of the parameter adaptive adjustment unit. The method improves the characteristics of the current loop, and enables inverters to maintain stability under various grid impedance conditions. The method can solve the problems of complex control system, fixed control parameters and low efficiency of the regulation process in the existingmulti-inverter micro-grid system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Impedance modeling and stability analysis method of current controlled virtual synchronous generator
ActiveCN108418253AHigh expressionHigh precisionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVirtual synchronous generatorNew energy
The invention discloses an impedance modeling and stability analysis method of a current controlled virtual synchronous generator. In consideration of the influence of the active controller, the reactive controller, the current inner loop control and the phase locked loop of the current controlled virtual synchronous generator, a wideband small signal modeling method for current controlled virtualsynchronous generator based on sequence impedance model is provide to solve the problem of small signal impedance modeling of current controlled virtual synchronous generator. Based on a built wideband small signal impedance model, a grid impedance model and a Nyquist stability criterion, the influence of grid impedance, current controlled virtual synchronous generator grid-connected number and phase-locked loop control bandwidth on system stability is analyzed. The invention provides a model and method for analyzing the small disturbance stability in scenes of the current controlled virtualsynchronous generator connected to a micro grid and a new energy field station.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for detecting islanding conditions of distributed generator
InactiveUS20120239215A1Minimize impactMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlDistributed generatorIslanding
A method and apparatus are provided for detecting islanding conditions for distributed generators connected to a grid. The method includes estimating a grid impedance, and inducing, on the basis of the estimated grid impedance, a variation on a value of a first electrical quantity of the grid. The method also includes monitoring a grid response to the variations, and determining islanding conditions on the basis of the monitored response.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
High-bandwidth high-isolation low on-resistance CMOS analog switch circuit and realizing mode thereof
InactiveCN101931387AImprove transmission bandwidthDoes not affect isolationElectronic switchingGrid impedanceEngineering
The invention provides a CMOS switch circuit with wider bandwidth, high isolation and low on-resistance, which is used for multi-path high-frequency analog signal switching. By adopting the technology of floating trap and grid impedance control, the problem that the on-resistance and the transmission bandwidth of the traditional CMOS analog switch circuit are restricted with each other can be solved, so that the signal transmission bandwidth of the CMOS switch under the same on-resistance and isolation can be greatly improved.
Owner:上海英联电子科技有限公司
Power grid impedance on-line detection method on the basis of inverter
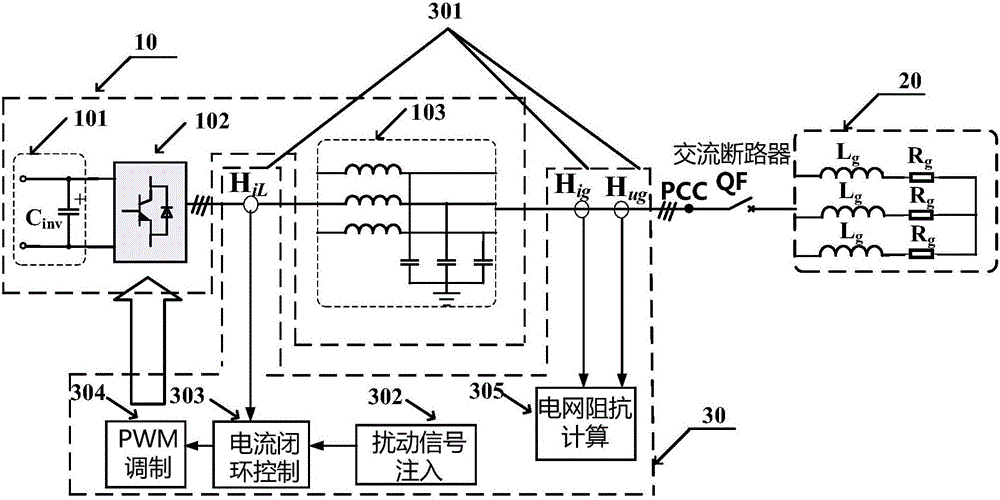
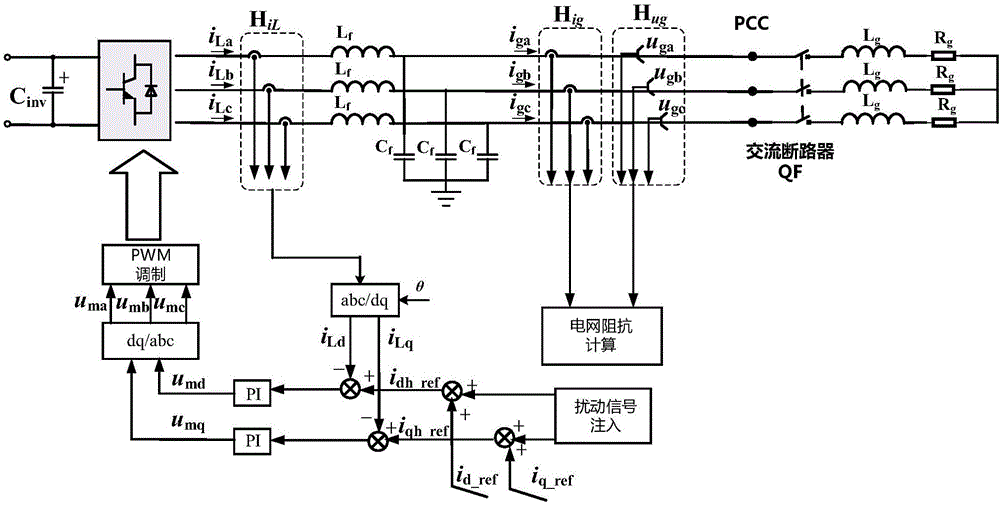
ActiveCN105259414AReduce disturbanceReduce harmonic componentsResistance/reactance/impedencePower qualityPower inverter
The present invention relates to a power grid impedance on-line detection method on the basis of an inverter. The power grid impedance on-line detection method on the basis of the inverter comprises the following steps: (1) the amplitude of an output voltage of a voltage inverter is regulated through adoption of an axle voltage regulation method after the synchronous grid connection of the inverter, an output frequency of the voltage inverter is regulated to accord with the frequency of the power grid, and voltage values, VPCC1 and VPCC2, of a PPC point in two states are acquired; and (2) a power grid impedance value is calculated. Compared with the prior art, the power grid impedance on-line detection method on the basis of an inverter is easy to operate, is high in measurement accuracy, and has small influence on quality of electric energy, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Stability analysis method based on doubly-fed wind power plant grid-connected system output impedance model
PendingCN110994668AImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationNew energyGrid impedance
The invention relates to the technical field of new energy power generation grid-connected stability control, in particular to a stability analysis method based on a doubly-fed wind power plant grid-connected system output impedance model. According to the method, a doubly-fed fan small signal output impedance model by considering three parts of a phase-locked loop, a current loop and a power loopis established under a synchronous rotating coordinate system to obtain a synchronous rotating coordinate system doubly-fed wind power plant grid-connected small signal impedance model through the doubly-fed fan output impedance model; a power grid small signal impedance model is established under the synchronous rotating coordinate system; the ratio of the output impedance of the doubly-fed windpower plant to the impedance of the power grid is calculated, and the stability of the doubly-fed wind power plant grid-connected system is determined according to a generalized Nyquist criterion. The stability analysis method can be used for analysis of the stability of the doubly-fed wind power plant grid-connected system and a powerful theoretical basis is provided for analyzing subsynchronous / super-synchronous oscillation caused by the fact that a large-scale wind power plant is connected into a power grid.
Owner:STATE GRID GASU ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +4
System and method for controlling a power generating unit
ActiveUS20190131795A1Wind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityData set
A method for controlling a power output of a power generating unit includes receiving at least two measurement data sets from a location of integration of a power generating unit to an electrical grid. Each measurement data set includes a plurality of electrical parameters. The method further includes generating a grid model of the electrical grid based on the at least two measurement data sets. The grid model is characterized by an equivalent grid voltage and an equivalent grid impedance. The method further includes computing a strength value of the electrical grid based on the grid model, using the at least two measurement data sets. The method also includes controlling the power output of a power generating unit based on the strength value of the electrical grid.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Capacitor voltage feedforward control method of grid-connected inverter under weak power grid
ActiveCN111245017AReduce usageLow costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementCapacitor voltageGrid impedance
The invention relates to a capacitor voltage feedforward control method of a grid-connected inverter under a weak power grid. The method belongs to the field of grid-connected inverter control, and comprises the following steps: S1, performing feedback control by using inverter side current i1, and performing phase locking, active damping and feedforward compensation by using capacitor voltage uCto obtain a capacitor voltage feedforward control system of a grid-connected inverter under a weak power grid; S2, performing active damping negative feedback design under a weak power grid on the capacitor voltage feedforward control system obtained in the step S1; and S3, on the basis of the step S2, designing a capacitor voltage feedforward compensation control strategy for the capacitor voltage feedforward control system. On the premise of ensuring the performance of the control system, the use of voltage and current sensors is reduced, and the hardware cost of the system is reduced; and the dynamic performance and stability of the control system are improved, so that the grid-connected inverter always has enough stability margin under the characteristic that the impedance of the powergrid changes in a relatively wide range.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method and system for inhibiting voltage fluctuation of photovoltaic power station
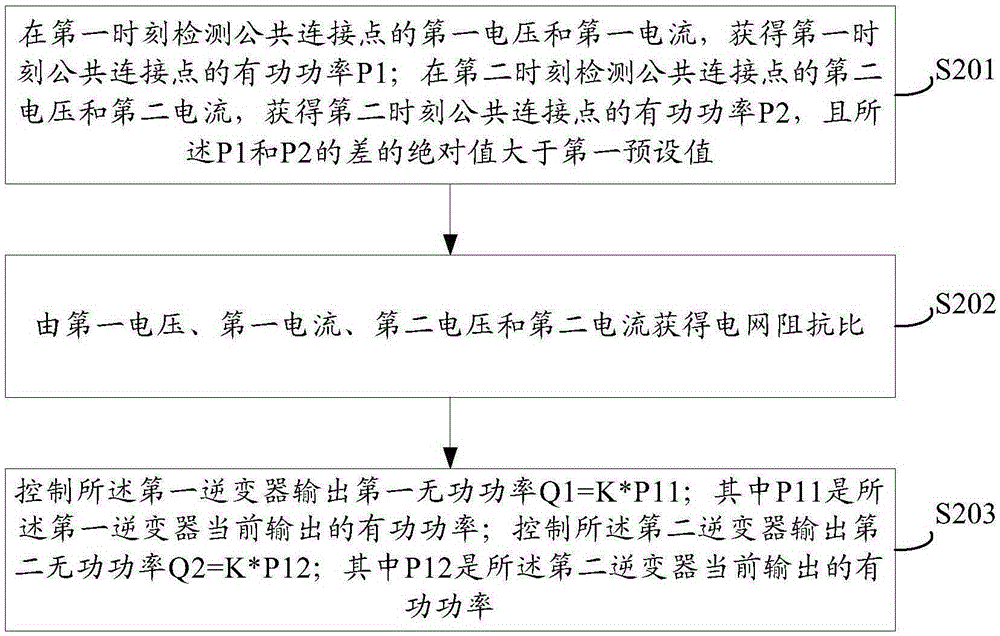
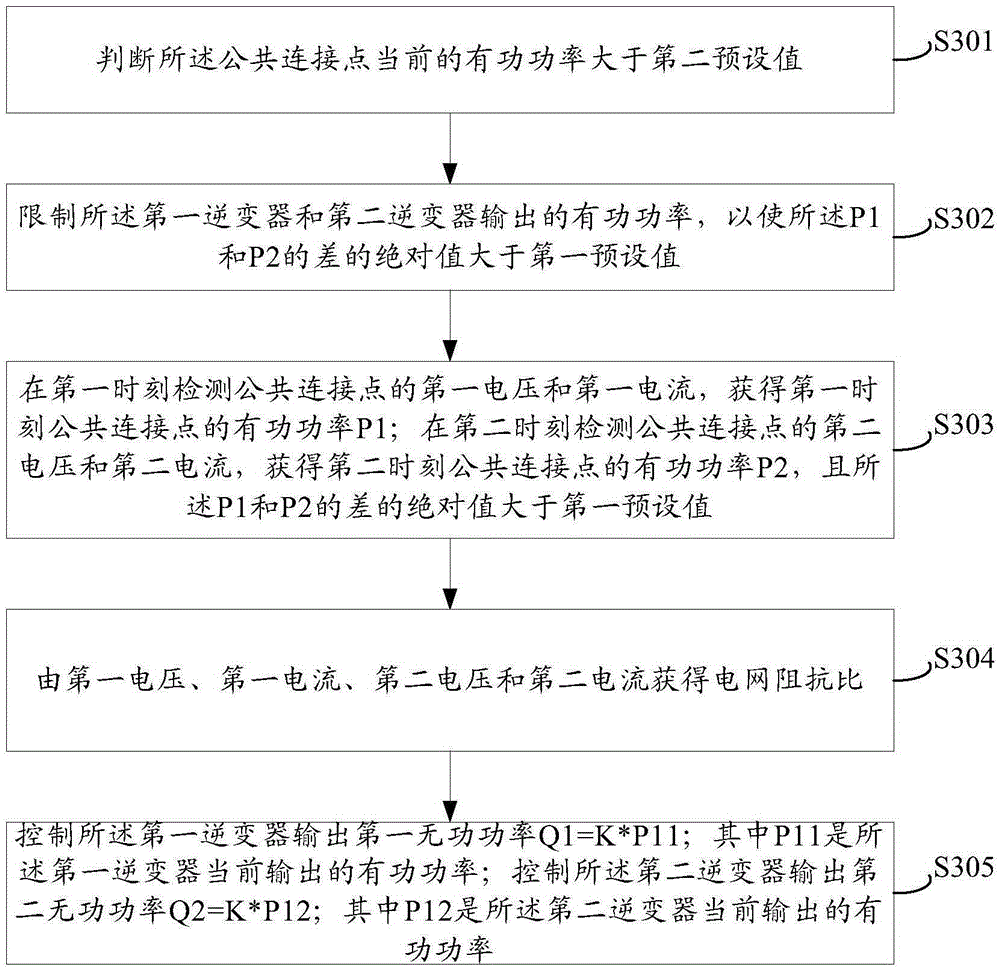
ActiveCN105262149ASuppresses voltage fluctuationsReal-time requirements are not too highSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentPower inverterGrid impedance
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and system for inhibiting voltage fluctuation of a photovoltaic power station. The method includes the steps that a first voltage Vp1 and a first current Ip1 of a public coupling point are detected at a first moment, and active power P1 of the public coupling point at the first moment is obtained through the Vp1 and the Ip1; a second voltage Vp2 and a second current Ip2 of the public coupling point are detected at a second moment, active power P2 of the public coupling point at the second moment is obtained through the Vp2 and the Ip2, and the absolute value of the difference of the P1 and the P2 is larger than the first preset value; the grid impedance ratio is obtained through the Vp1, the Ip1, the Vp2 and the Ip2; a first inverter is controlled to output first reactive power Q1, and Q1=K*P11; the P11 is active power currently output by the first inverter; a second inverter is controlled to output second reactive power Q2, and Q2=K*P12; the P12 is active power currently output by the second inverter. The method is simple, the real-time request of communication is not high, and the inverters do not need to be controlled in real time to conduct reactive power adjustment; the reactive power output by the inverters needs to be adjusted only when the grid impedance ratio changes.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Impedance modeling and stability analysis method for voltage-control virtual synchronous generator
ActiveCN108281986AHigh precisionHigh expressionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVirtual synchronous generatorNyquist stability criterion
The invention discloses an impedance modeling and stability analysis method for a voltage-control virtual synchronous generator. The influence of a virtual synchronous generator active controller is considered in order to provide a voltage-control virtual synchronous generator broadband small-signal modeling method based on a sequence impedance model, overcoming the difficulties in voltage-controlvirtual synchronous generator small-signal impedance modeling. On the basis of an established broadband small-signal sequence impedance model, a grid impedance model and Nyquist stability criterion,the influences of grid impedance and the number of voltage-control virtual synchronous generator grid-connected units upon system stability are analyzed. The results show that in any case of high gridimpedance and the large number of the virtual synchronous generator grid-connected units, a virtual synchronous generator grid-connected system can stably run. The models and method are provided forthe small disturbance stability analysis in the scenes, such as voltage-control virtual synchronous generators connected to a grid, and new energy stations; the popularization and application of the voltage-control virtual synchronous generators are benefited.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Sequence impedance modeling and stability analysis method of load virtual synchronous machine
ActiveCN110768299AHigh precisionThe stability analysis method is simple and effectiveSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower controllerLoop control
The invention discloses a sequence impedance modeling and stability analysis method of a load virtual synchronous machine. Influences of a direct-current voltage controller, a reactive power controller, an active power controller, an alternating-current controller and positive and negative sequence disturbance frequency coupling of a load virtual synchronous machine are comprehensively considered,a harmonic linearization method is adopted to establish an accurate sequence impedance model of a load virtual synchronous machine, so a problem of small signal impedance modeling of the load virtualsynchronous machine under the influence of multi-loop control and frequency coupling is solved. The influence of different power grid impedances on the stability of a grid-connected system of the load virtual synchronous machine is analyzed by utilizing the established sequence impedance model of the load virtual synchronous machine, the established power grid impedance model and the establishedNyquist stability criterion. Analysis results show that the load virtual synchronous machine can still operate stably under the condition of large power grid impedance, namely a weak power grid, and does not interact with the power grid easily to generate oscillation. The invention provides a model and a method for analyzing the stability of the small signal of the load virtual synchronous machineaccessed to the power grid, and popularization and application of the load virtual synchronous machine are facilitated.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
LLCL grid-connected inverter resonance suppression method adapting to power grid impedance change
PendingCN110718934AImprove anti-interference abilityQuality improvementSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementCapacitanceGrid connected inverter
The invention relates to the technical field of grid-connected inverter harmonic resonance control methods, and aims to provide an LLCL grid-connected inverter resonance suppression method adapting topower grid impedance change. The method mainly comprises a third-order LLCL filter, a power grid voltage feedforward control strategy and a capacitance current feedback control strategy. According tothe power grid voltage feedforward control strategy, a voltage feedforward channel is added on the basis of a weighted current control strategy; the interference of power grid voltage is effectivelysuppressed by adopting a power grid voltage feedforward strategy, thereby effectively suppressing resonance peaks, reducing a grid-connected harmonic content, and introducing the capacitive current feedback on the basis of a power grid voltage feedforward control strategy. The invention has the beneficial effects that a traditional power grid voltage feedforward control method is reserved, so theinfluence of power grid voltage distortion on the grid-connected current is eliminated, the harmonic peak of the system at the resonant frequency is effectively restrained by introducing capacitive current feedback, the harmonic content of the grid-connected current is reduced, and the grid-connected quality of the grid-connected current is improved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
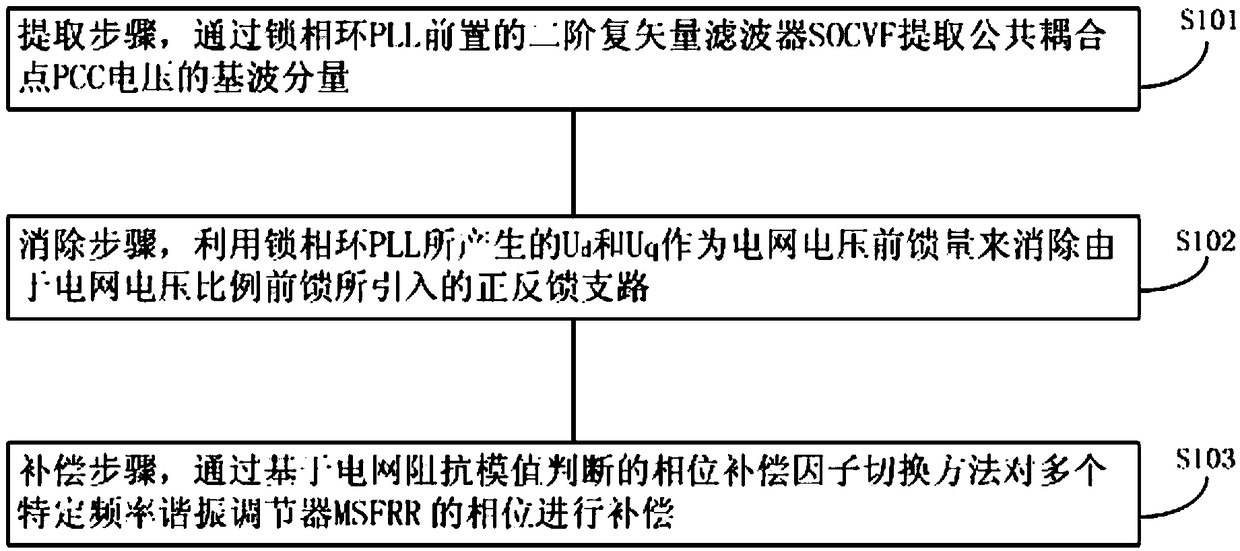
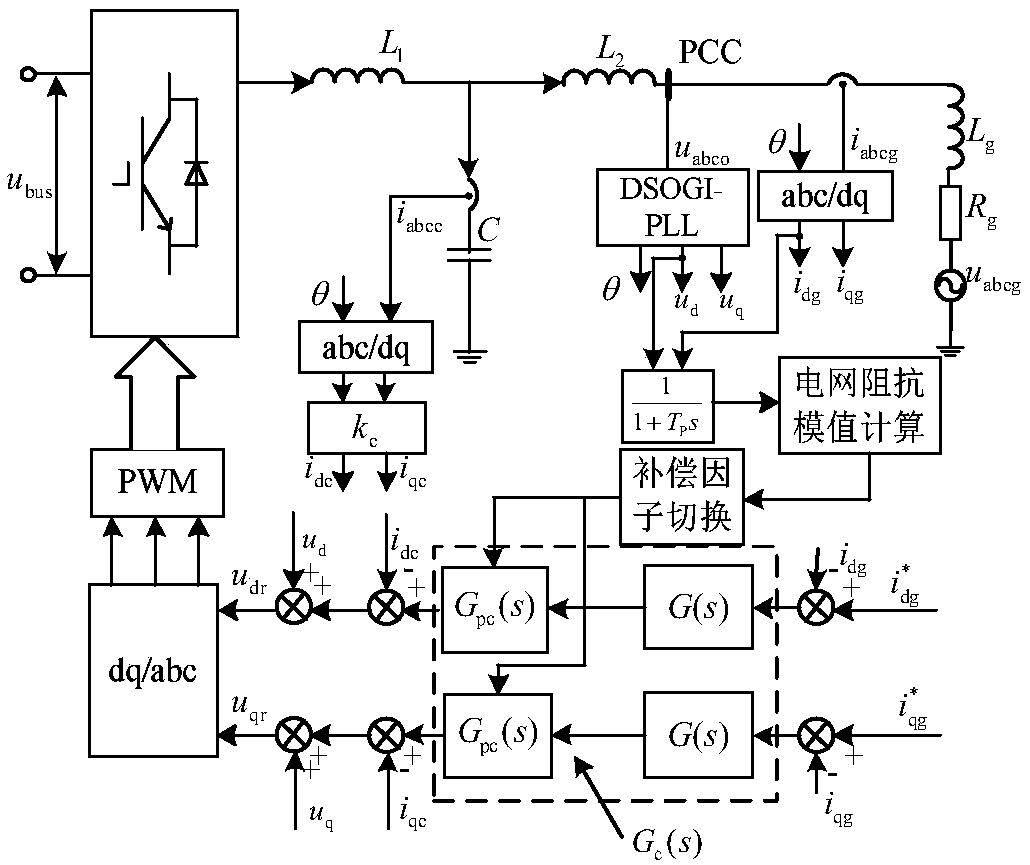
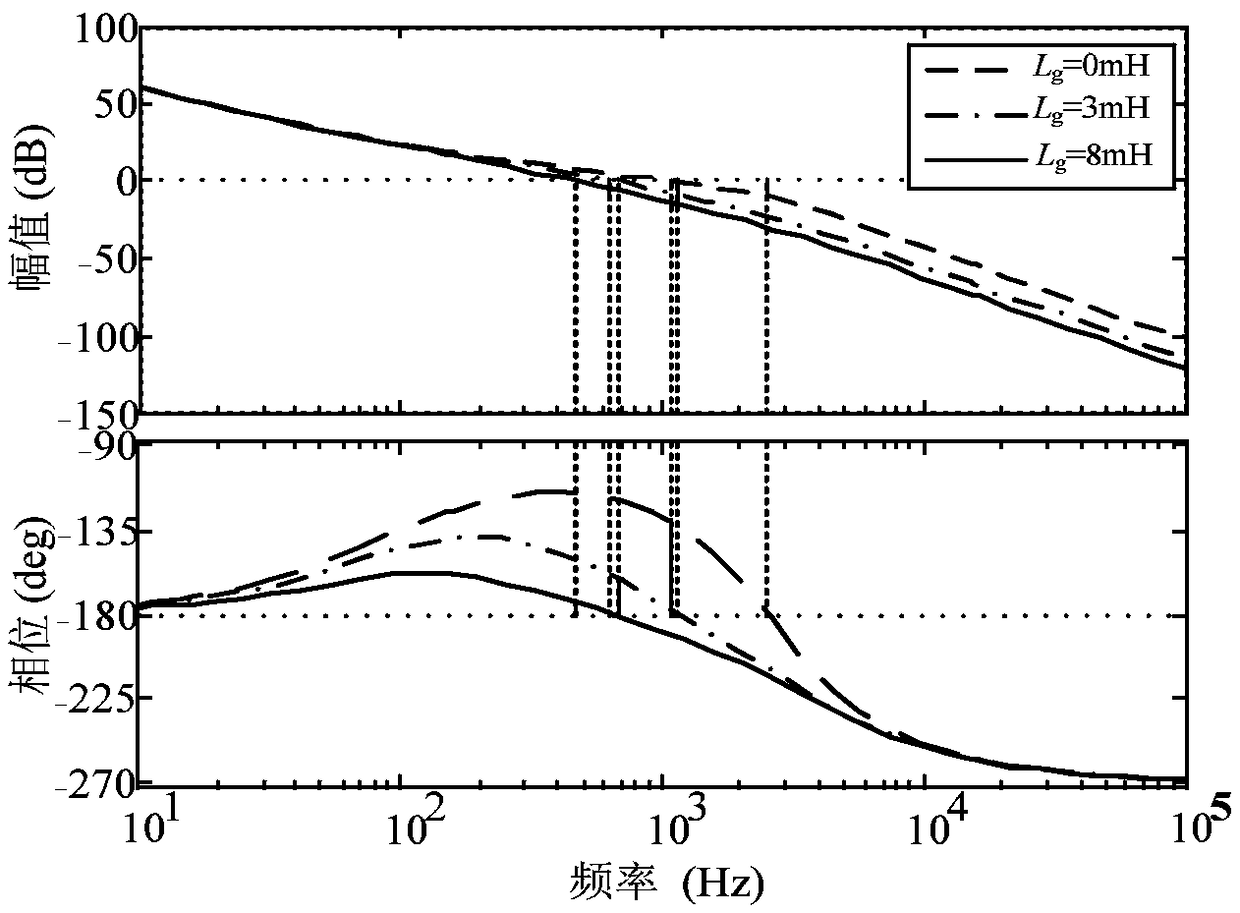
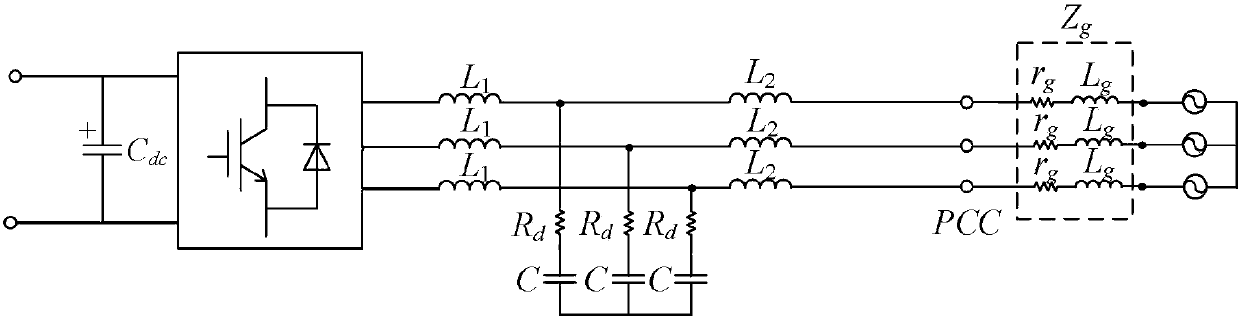
SOCVF feedforward and phase compensation factor switching control method for grid-connected inverter in weak power network
ActiveCN109193792AEliminate the effects ofEnhanced inhibitory effectSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionGrid impedancePower factor
The invention provides a SOCVF feedforward and phase compensation factor switching control method of grid-connected inverter under weak power network. The method comprises: The fundamental component of the PCC voltage at the common coupling point is extracted by SOCVF in front of the PLL, Ud and uq generated by PLL are used as voltage feedforward quantities to eliminate the positive feedback branch introduced by voltage proportional feedforward. The phase compensation factor switching method based on impedance modulus judgment is used to compensate the phase of MSFRR. The invention provides acontrol method for grid-connected inverter under weak power network, so as to eliminate the influence of grid impedance on the grid-connected control system of the inverter. The stability of the system is greatly improved, and the adaptability of the system is strong, and the power factor is high, and the ability to suppress the background harmonics of the power network is improved, so that the inverter control system can maintain a high shear frequency, phase margin and gain margin, and the system 's rapidity and stability is enhanced.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Voltage feedforward lag compensation control method based on impedance self-adaption under weak power grid
ActiveCN107895966AFeedforward Control Inhibition PreservedImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsGrid-tie inverterLow-pass filter
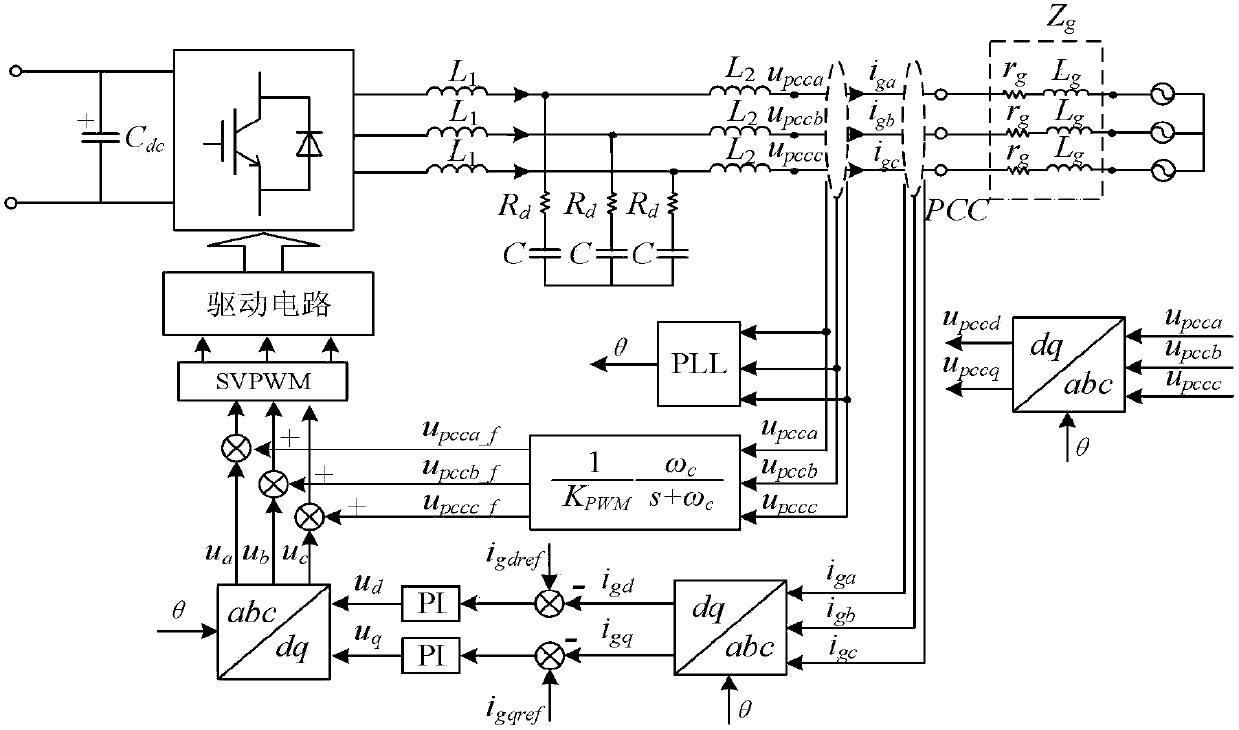
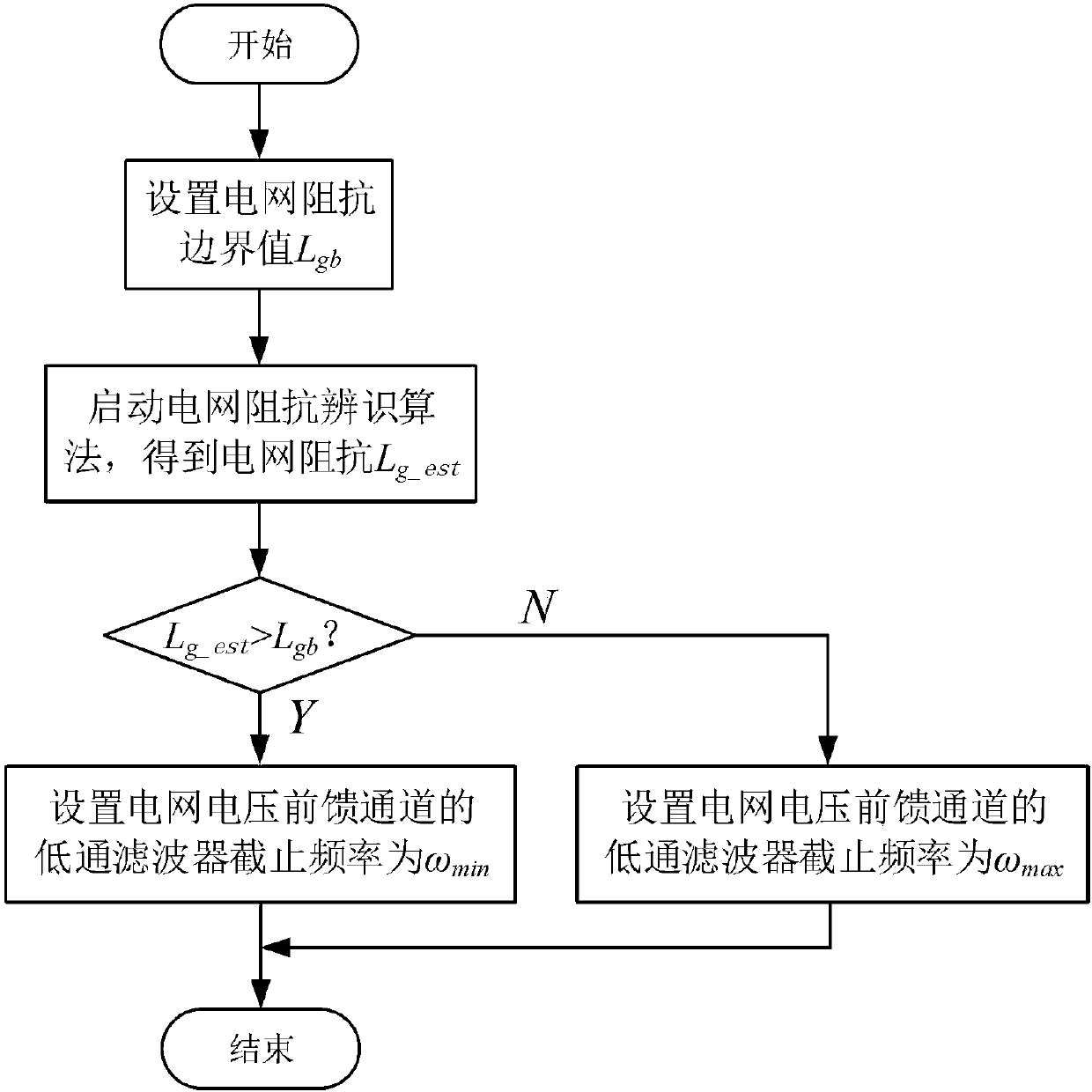
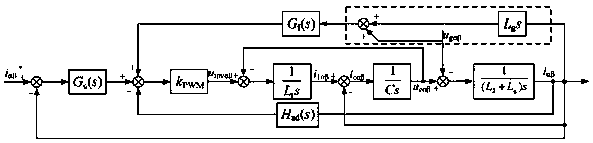
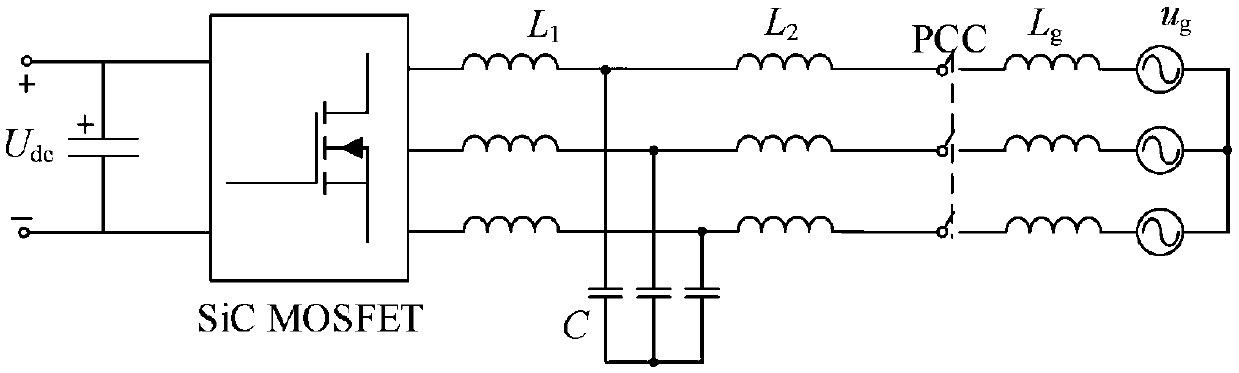
The invention discloses a grid voltage feedforward lag compensation control method based on grid impedance self-adaption under a weak power grid. The method realizes grid voltage feedforward lag compensation control based on grid impedance self-adaption by identifying grid impedance for the problem of stability of a grid-connected inverter due to conventional grid voltage direct feedforward control under the weak power grid, that is, when grid impedance is large, adding a low-pass filter, the cutoff frequency of which is low, to a grid voltage feedforward channel, and when the grid impedance is small, adding a low-pass filter, the cutoff frequency of which is high, to the grid voltage feedforward channel. The method not only keeps the capability of the conventional grid voltage feedforwardcontrol in suppressing power grid background harmonics, but also greatly increases stability of the grid-connected inverter under the condition of great change of the power grid impedance, and improves grid-connected current quality of the grid-connected inverter.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Composite robust control method of high-frequency SiC photovoltaic grid-connected inverter under weak power grid
ActiveCN111245004AMake the most of power densityImprove power densityEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionThermodynamicsGrid connected inverter
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Improved regulator applied to grid-connected inverter under weak grid
InactiveCN108448583AIncreased phase angle stability marginImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementGrid impedancePhase compensation
The invention discloses an improved regulator applied to a grid-connected inverter under a weak grid. The structure of the improved regulator is PI+MSFRR+OPC, wherein the MSFRR is a plurality of specific frequency resonance regulators, the OPC is an online phase compensator, Gc(s) a regulator with the parallel connection of the PI and the MSFRR, Gp(s) is a transfer function of the OPC, the Gc(s) is connected in series with the Gp(s), grid impedance is obtained by the grid impedance on-line measurement technology to update a phase compensation factor in real time, and thus the online phase compensation control is achieved. Through the improved regulator, the phase margin of a system is improved, at the same time, the system has a high open-loop shear frequency, while the stability of the system is ensured, the dynamic response speed of the system is accelerated, and the adaptability of the system to the grid impedance is improved. While the shear frequency is improved, an open-loop gainis increased, which means that the open-loop gain of specific sub-harmonic is increased synchronously, thus a steady-state error is reduced, the suppression of grid background harmonics is enhanced,the THD of grid-connected current is effectively reduced, and the quality of the grid-connected current is improved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Hybrid electric power filter
InactiveCN103368179ANot easy to resist interferenceReduce capacity requirementsActive power filteringHarmonic reduction arrangementGrid impedancePower grid
The invention discloses a hybrid electric power filter, which is characterized by consisting of a power supply, an active electric power filter, a single-level LC passive filter and a non-linear load, wherein the power supply is connected with the active electric power filter and the single-level LC passive filter in parallel and then is connected with the non-linear load in series; the LC passive filter takes the effect of harmonic wave and reactive compensation; the object compensated by the active electric power filter is system current filtered by the passive filter. Harmonic content in the system current is greatly reduced, so that the capability requirement on the active electric power filter is not high, the active filer can improve the filtering characteristic of the LC passive filter, and the defects that the passive filter is easily affected by power grid impedance and is easily syntonic with the power grid impedance are overcome. The hybrid electric power filter is not easily affected by the power grid impedance, the structure is simple, and the capacity requirement on the active filter is very small.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Power grid impedance measurement method and device
The invention provides a power grid impedance measurement method and a device and solves a problem that one phase of a three-phase AC current supposed to have the largest current or voltage deformation degree has the smallest current or voltage deformation degree because of injected pulses when the single-polarity pulses are injected to a current given of a d axis at the peak time of a certain phase current in the prior art employing an active injection mode to measure power grid impedance. The method comprises steps that a pulse signal is applied to a power grid on the current given of the d axis at the first time, and the first time is the time when a current of any phase of the three-phase AC current is not a peak value; the voltage and the current of the power grid during pulse signal applying are determined; the power grid impedance is determined according to the determined voltage and the determined current of the power grid.
Owner:EMERSON NETWORK POWER CO LTD
Dual-mode control method for LC-type grid-connected inverter based on grid impedance self-adaptation
InactiveCN105356507BGuaranteed uptimeImprove stabilityAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHysteresisPower inverter
The invention discloses a power grid impedance self-adaption based LC type grid-connected inverter dual-mode control method. According to the invention, a power grid impedance boundary value of mutual switching between a current source grid-connected mode and a voltage source grid-connected mode of an inverter is determined at first, the inverter adopts a current source grid-connected mode control method when the power grid impedance boundary value is less than a switching boundary value, and the inverter adopts a voltage source grid-connected mode control method when the power grid impedance boundary value is greater than the switching boundary value; and an impedance hysteresis loop based switching mode is adopted in order to improve the stability in switching. The method disclosed by the invention solves a defect that the inverter can only operate stably within a small power grid impedance variation range when adopting a single current source or voltage source grid-connected mode under different power grid impedance conditions, and stable operations of the inverter within a large power grid impedance variation range are realized through mutual switching between the current source power-grid mode and the voltage source grid-connected mode.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
High-stability control method of LCL type grid-connected inverter system under weak power grid
PendingCN114884125AReduce usageLow costGeometric CADSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAdaptive filterIntegrator
The invention discloses a high-stability control method of an LCL type grid-connected inverter system under a weak power grid, and belongs to the technical field of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter control. The problem that a conventional grid-connected inverter is likely to be unstable in a weak power grid environment is solved. Aiming at the influence of power grid impedance increase and small signal disturbance on a phase-locked loop and an LCL filter in a grid-connected inverter system under a weak power grid, a double-grid-connected current loop feedback active damping strategy of a second-order generalized integral is adopted, a self-adaptive second-order resonance integrator active damping feedback function is constructed, a proportional resonance function is used as a current loop controller, and the grid-connected inverter system is controlled by the proportional resonance function. Virtual impedance correction is carried out on the control system, and a voltage feedforward controller is designed; a double-second-order adaptive filter-based sequence-dividing phase-locked loop is designed; through demonstration, reasonable virtual impedance correction is added, the use of measuring devices in hardware can be reduced while a good damping effect is achieved, the hardware cost is saved, and the control strategy can ensure the stability and robustness of the system.
Owner:ZHONGYUN INTERNATIONAL ENGINEERING CO LTD
Method for adaptively improving stability of LCL grid-connected inserter system under condition of weak grid
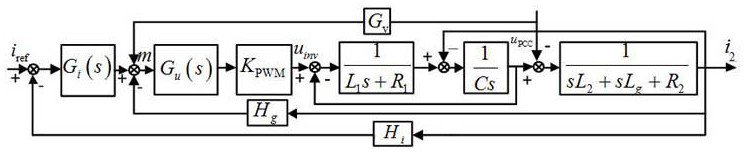
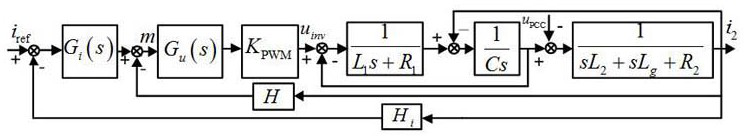
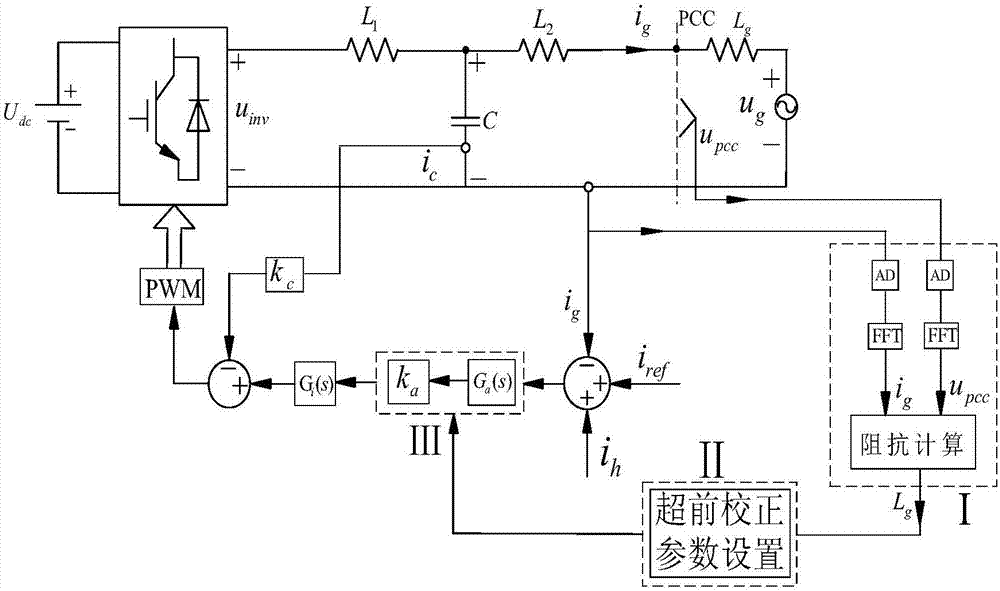
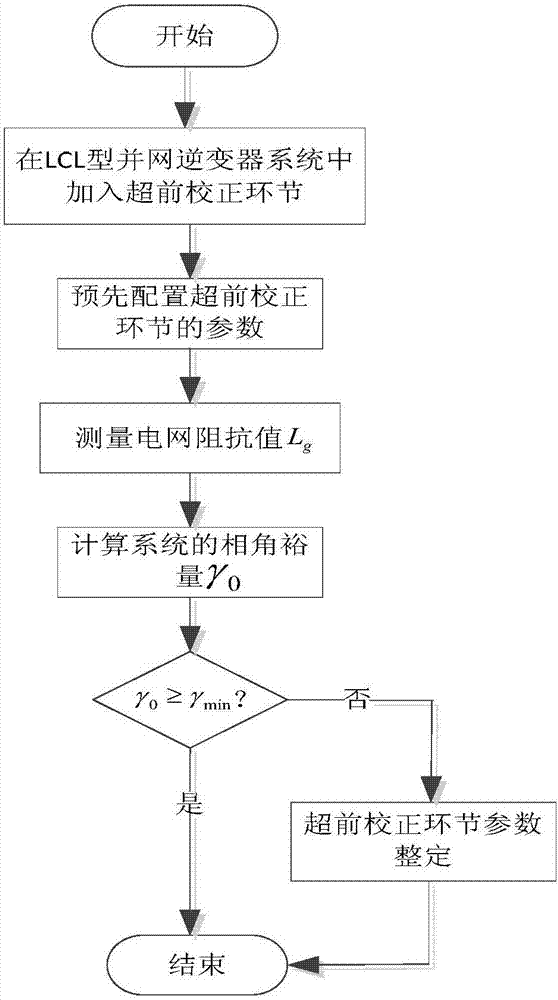
ActiveCN106877401AImprove stabilitySufficient phase marginSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc-ac conversion without reversalGrid impedanceEngineering
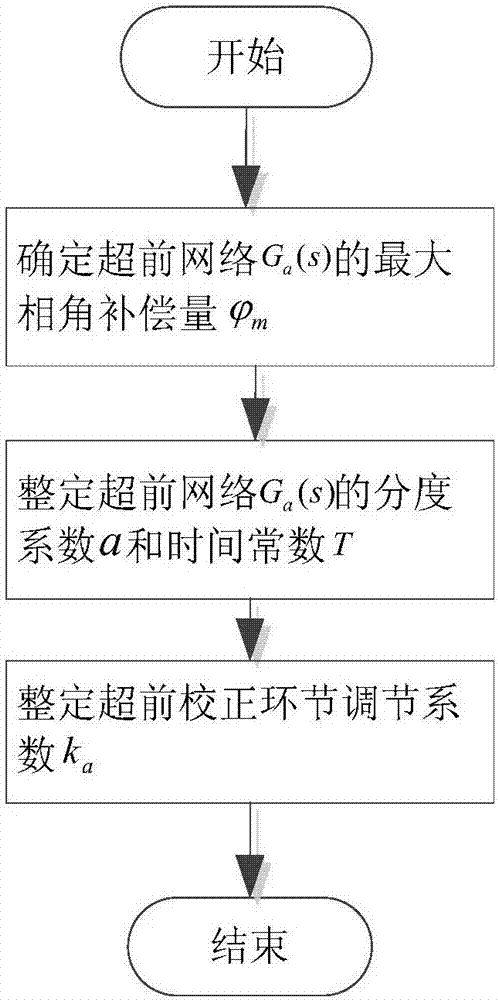
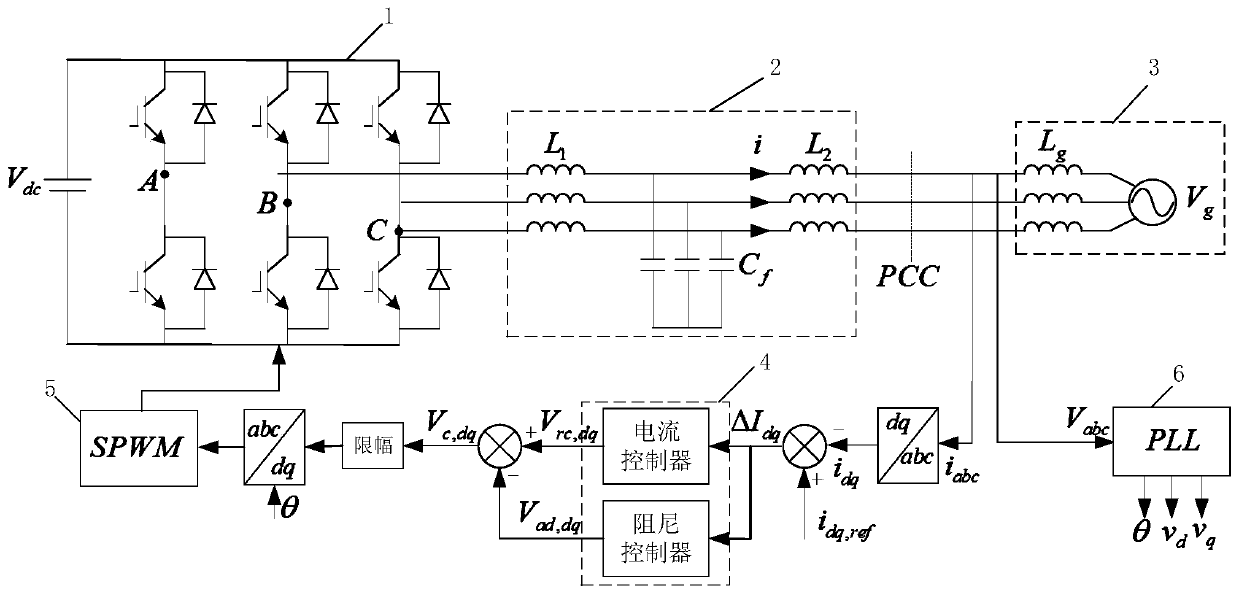
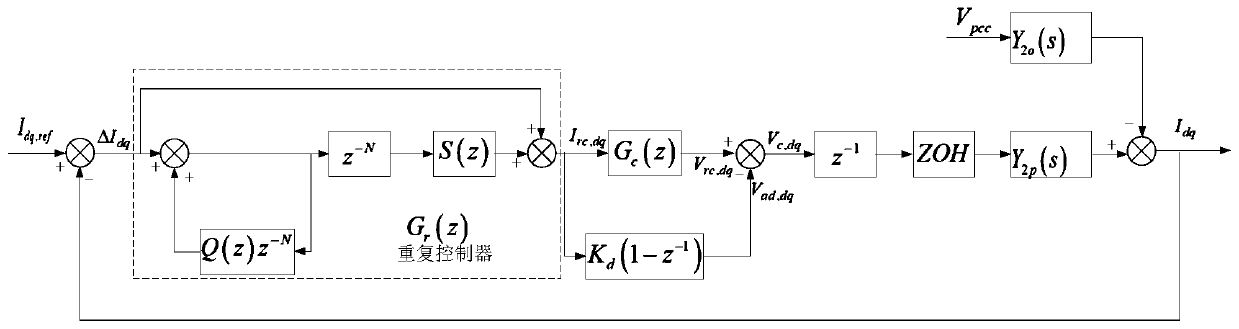
A method for adaptively improving the stability of an LCL grid-connected inserter system under the condition of a weak grid comprises the following steps: adding a lead correction link to the LCL grid-connected inserter system, and pre-configuring the parameters of the lead correction link; measuring the inductive impedance (Lg) of the grid through a small signal injection method; judging whether there is a need to set the parameters of the lead correction link; if there is no need to set the parameters of the lead correction link, ending the process; and if there is a need to set the parameters of the lead correction link, setting the indexing coefficient (a) and the time constant (T) of a lead network in the lead correction link, and setting the adjustment coefficient (ka) of the lead correction link. According to the invention, the lead correction link is added to the LCL grid-connected inserter system, the impedance of the grid is measured through the small signal injection method, and the parameters of the lead correction link are set to make compensation for the system phase when the phase angle margin of the system is insufficient. By adaptively adjusting the parameters of the lead correction link to make compensation for the phase margin of the system according to the result of grid impedance measurement, enough stable margin can be kept for the system, and safe and stable operation of the system can be ensured.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
Output impedance remodeling method for grid-connected inverter parallel system
ActiveCN110729752AGood harmonic suppression effectGuaranteed uptimeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementGrid connected inverterGrid impedance
The invention discloses an output impedance remodeling method for a grid-connected inverter parallel system. According to the output impedance remodeling method, the amplitude intersection point of the output admittance Yc (s) and load admittance Yload (s) of a grid-connected inverter is determined through an impedance analysis method, so that possible resonant frequency points between a grid-connected inverter and a power grid are found out; the parameters of a PI controller and a repetitive controller are adjusted, so that the passivity of the output impedance of the grid-connected inverterat the resonant frequency points is remodeled, and therefore, interactive resonance between the grid-connected inverter and the power grid is avoided; the PI controller is designed to ensure the closed-loop stability of the system; the repetitive controller is designed to ensure the stability of the repetitive controller; the output impedance of the grid-connected inverter and the passivity of theimpedance of the power grid are analyzed, so that the possible resonant frequency points can be found out; and the parameters of the controller are corrected, so that the output impedance of the grid-connected inverter is passive at the points.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com