[0004] 1) Xu Jinming, Xie Shaojun and Tang Ting published "Adaptive Current Control of
LCL Filter Grid-connected
Inverter under Weak
Power Grid" on August 25, 2014 in "Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical
Engineering" Volume 34 Issue 24, which pointed out that Under the weak grid, the grid voltage proportional feedforward will form a
positive feedback channel, which will greatly reduce the
stability margin of the grid-connected inverter, and even lead to
system instability. This paper proposes an adaptive current control method based on grid impedance measurement
However, this method relies on accurate grid impedance values, which makes the
algorithm more complicated. In addition, the proposed stability compensation scheme contains a differential link, which will face the problem of
noise interference in
engineering applications.
[0005] 2) Xu Fei, Tang Yu and Gu Wei published "
Resonance Feedforward Control Strategy of LCL Grid-connected
Inverter under Weak Grid Conditions" published in "Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical
Engineering" on September 20, 2016, Volume 36, Issue 18 , this paper proposes an improved feed-forward control method using the second-order generalized
integrator to realize the band-pass filter characteristics, so as to improve the stability of the system under weak grid. However, this method will greatly increase the current command step of the grid-connected inverter, etc. The overshoot in the dynamic process deteriorates the dynamic performance of the grid-connected system
[0006] 3) Qian Qiang, Xie Shaojun and Ji Lin published "A Current Control Strategy to Improve the Adaptability of the
Inverter to the
Power Grid" on November 20, 2016 in the "Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical
Engineering", Volume 36, Issue 22. This paper improves the
stability margin of the grid-connected inverter by reducing the feed-forward
gain of the grid voltage to improve the stability of the grid-connected inverter to a certain extent, but this method will make the fundamental wave
gain of the grid-connected inverter It is greatly reduced, which is not conducive to the tracking of the current fundamental wave command, and increases the steady-state error between the grid-connected current feedback value and the command value; moreover, this scheme will also reduce the dynamic performance of the grid-connected inverter, which is not suitable for dynamic performance demanding occasions
[0007] To sum up, in view of the problem that the stability of the grid-connected inverter is greatly reduced by the direct feed-forward control of the traditional grid voltage in the case of a weak grid, the existing technology has the following problems:
[0008] (1) The existing adaptive current control method based on grid impedance measurement relies on accurate grid impedance values, resulting in a more
complex algorithm, and because the stability compensation scheme contains a differential link, it will face the problem of
noise interference in
engineering applications;
[0009] (2) The existing improved feed-forward control method using the second-order generalized
integrator to realize the band-pass filter characteristics will greatly increase the overshoot in the dynamic process such as the current command step of the grid-connected inverter, and deteriorate the dynamics of the grid-connected system performance;
[0010] (3) The existing method of reducing the feed-forward
gain of the grid voltage will greatly reduce the fundamental wave gain of the grid-connected inverter, which is not conducive to the tracking of the current fundamental wave command, and increases the stability between the grid-connected current feedback value and the command value. State error, and reduce the dynamic performance of the grid-connected inverter, not suitable for occasions with high dynamic performance requirements;
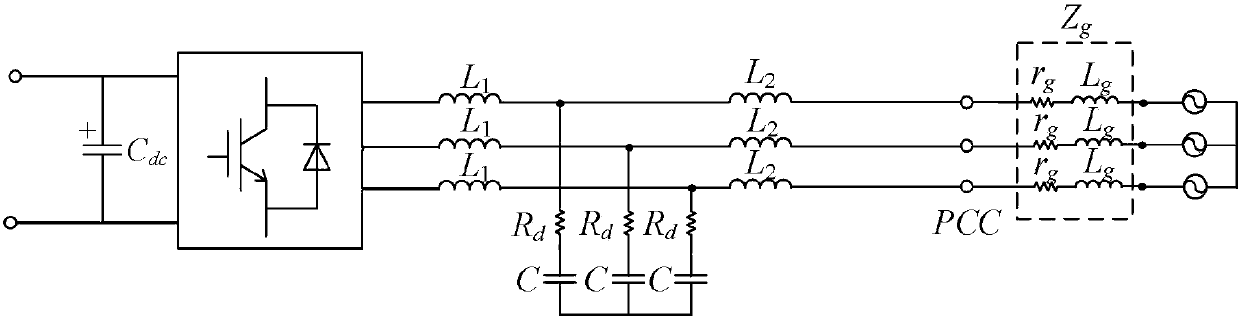
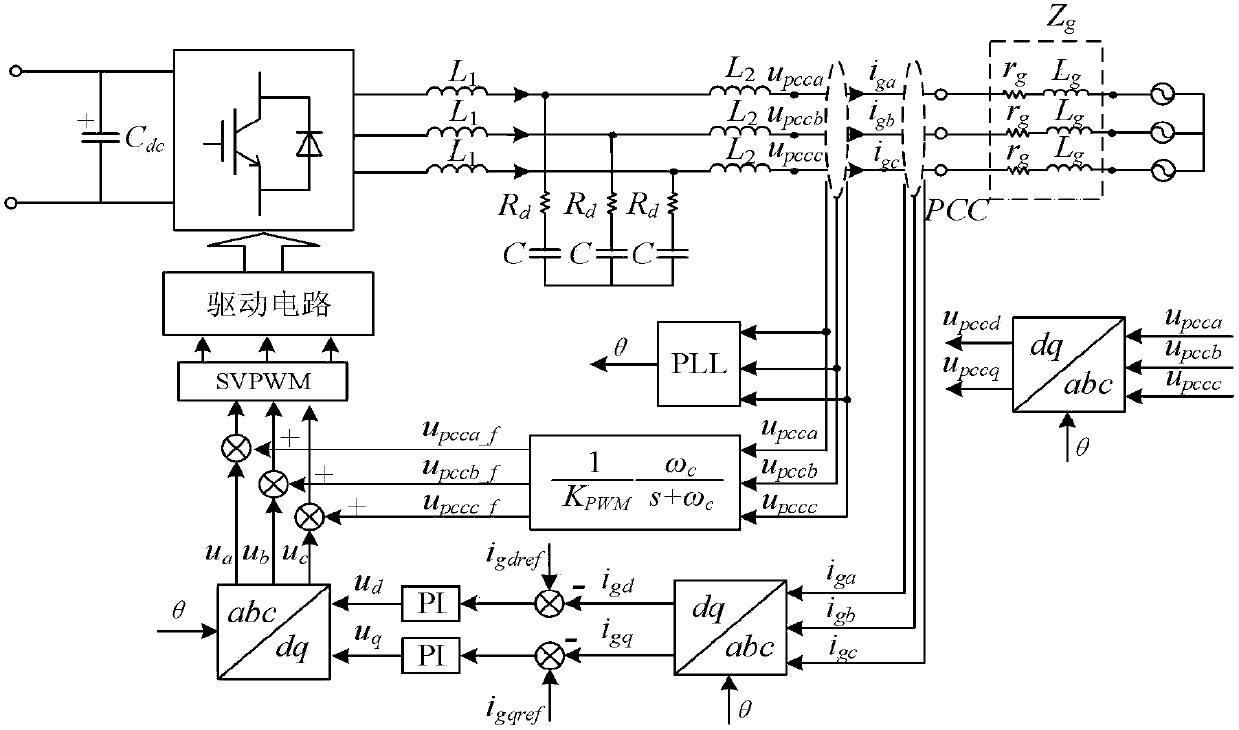
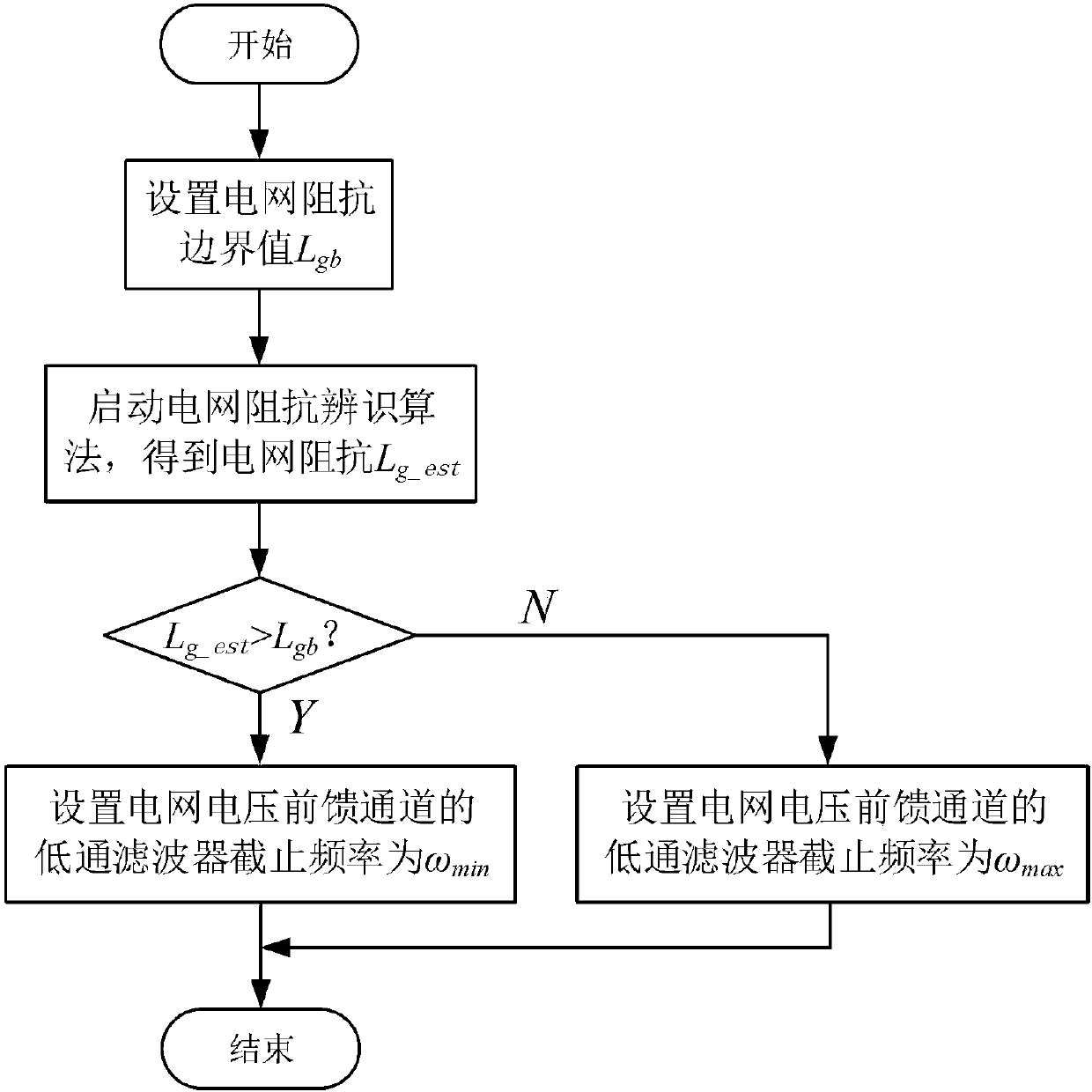
[0011] (4) None of the schemes proposed in the existing literature involve the realization of grid voltage feed-forward lag compensation control based on grid impedance
adaptation by identifying the grid impedance, that is, when the grid impedance is large, the grid voltage feed-forward A low-pass filter with a lower
cut-off frequency is added to the channel, and a low-pass filter with a higher
cut-off frequency is added to the grid voltage feedforward channel when the grid impedance is small, so as to realize that the inverter can adapt to a wide range of grid impedance changes. Grid stability issues
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More