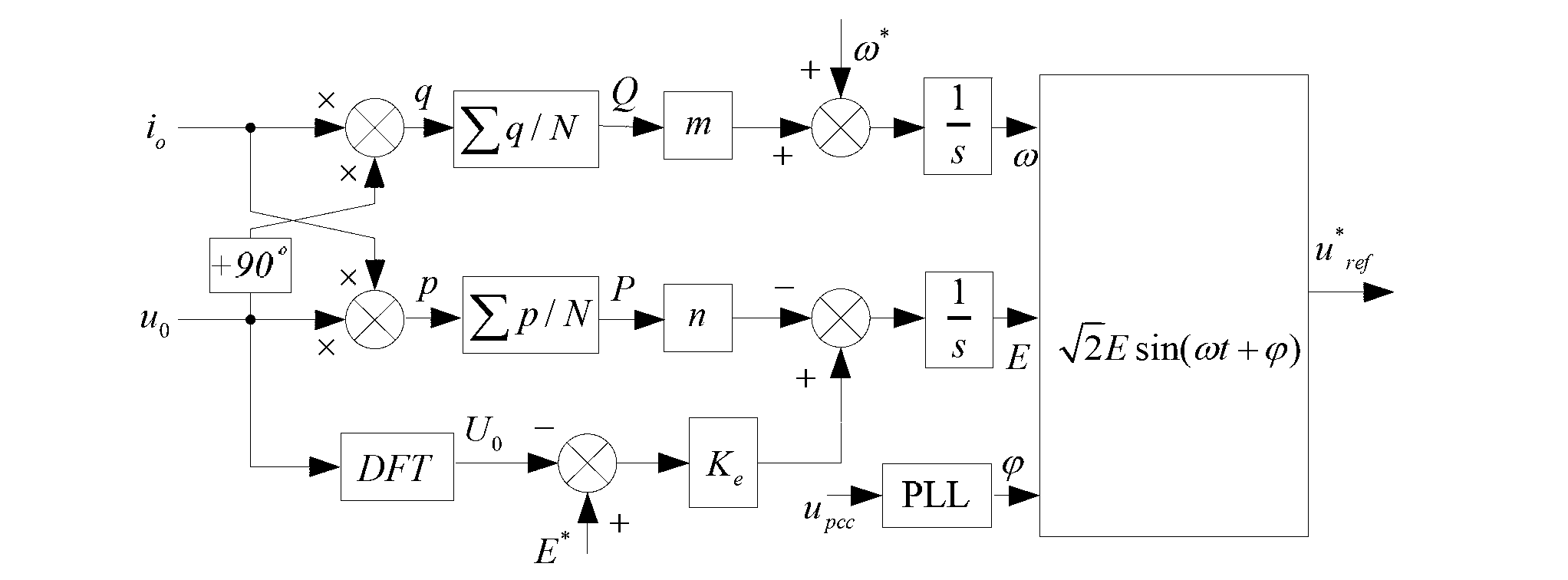
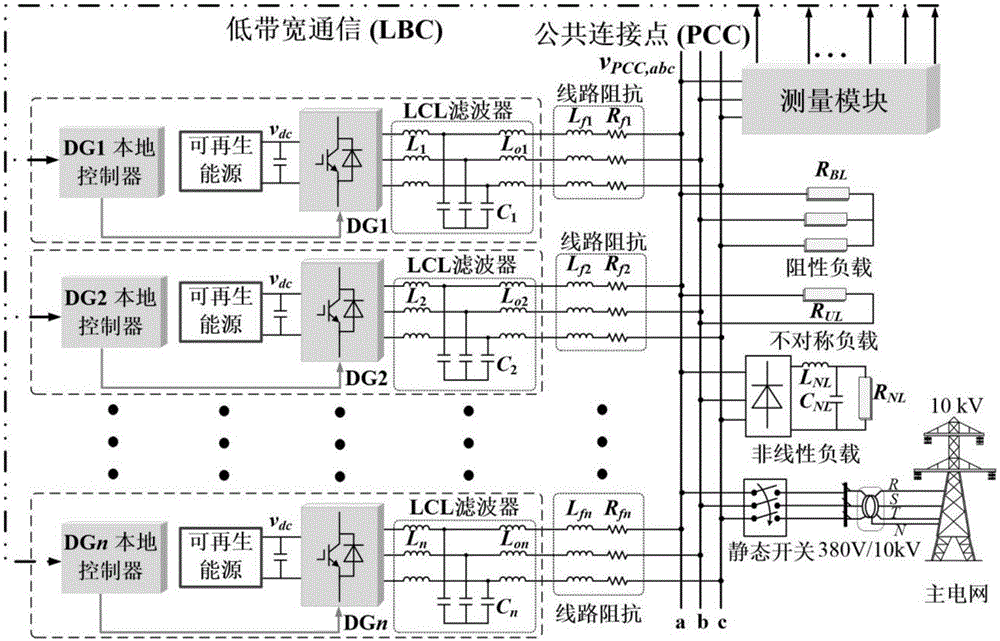
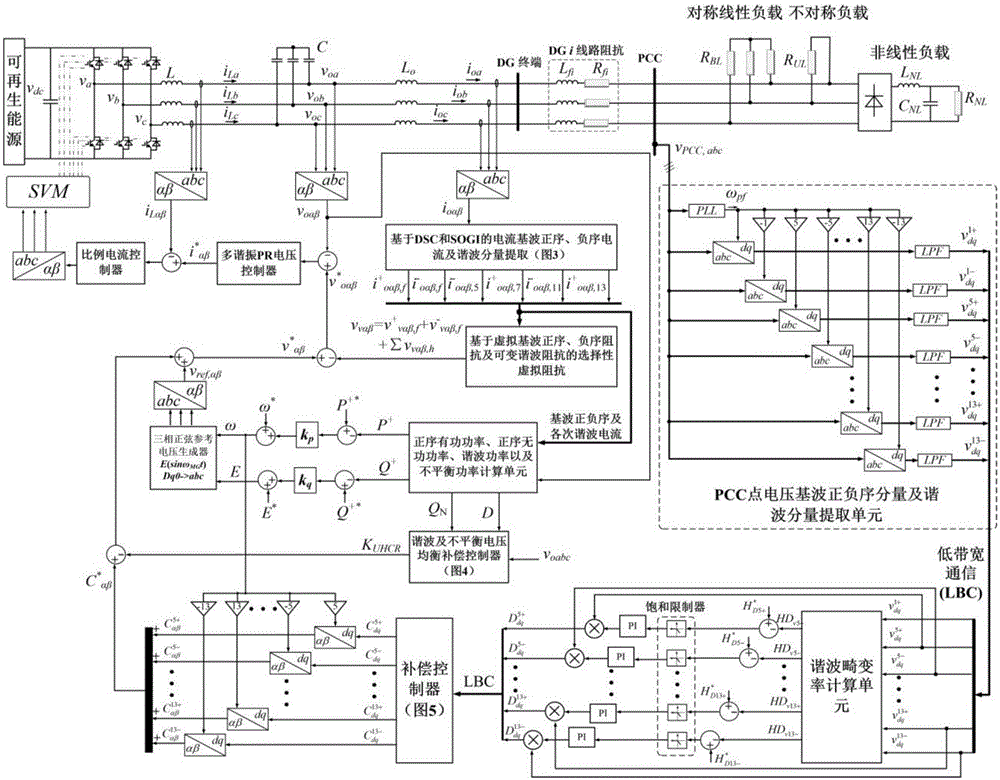
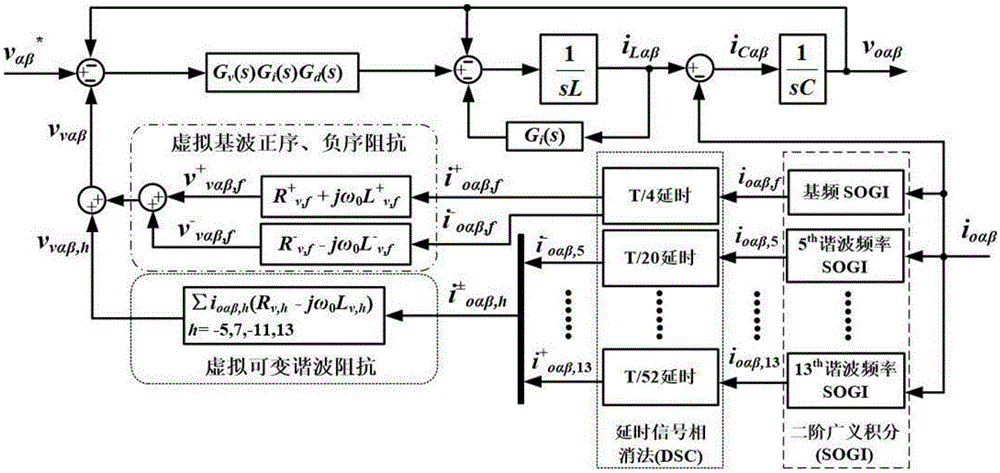
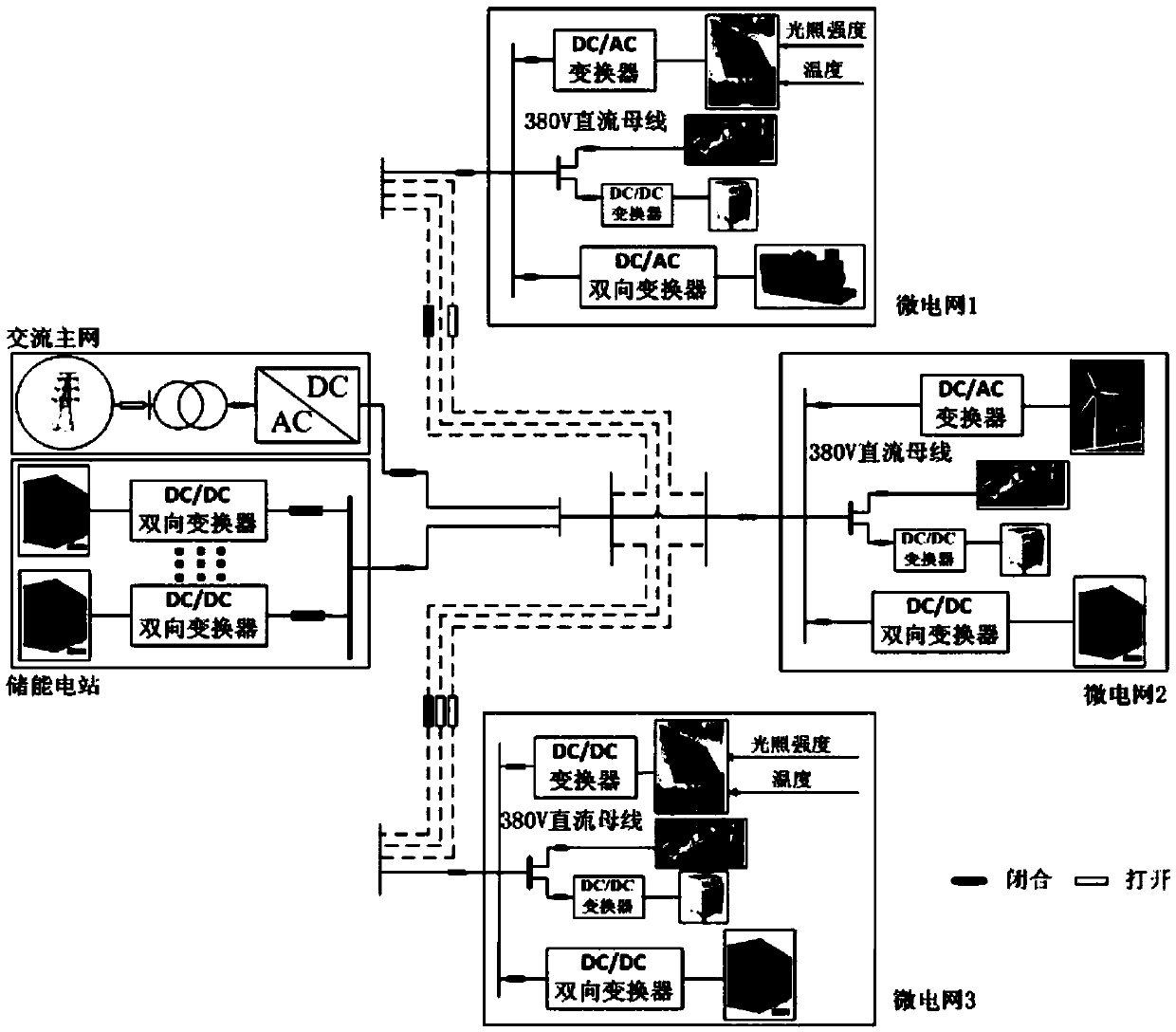
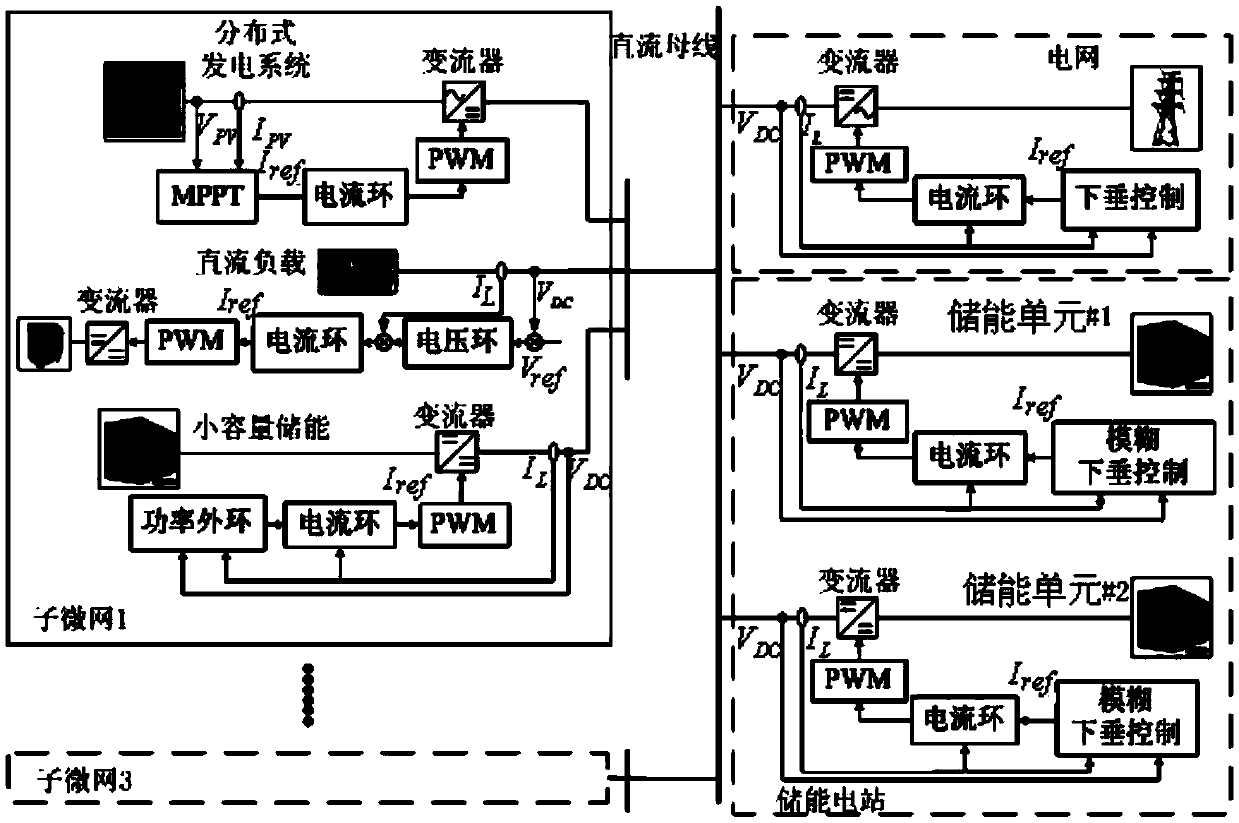
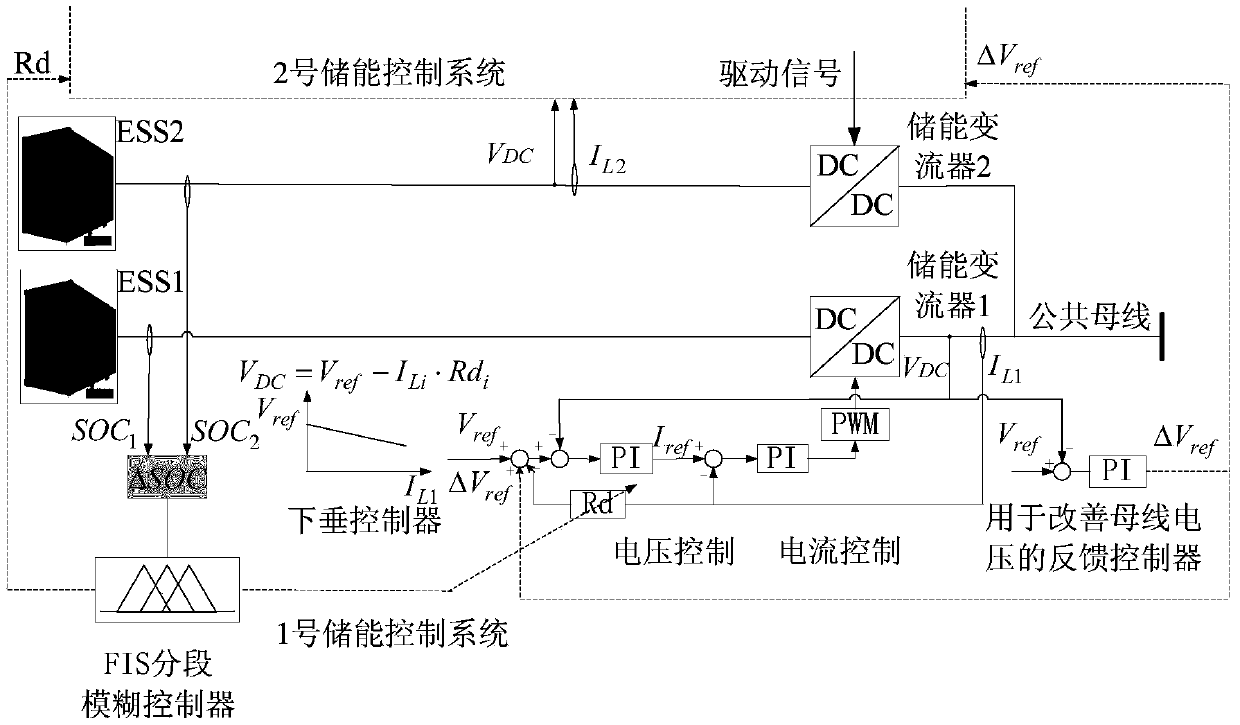
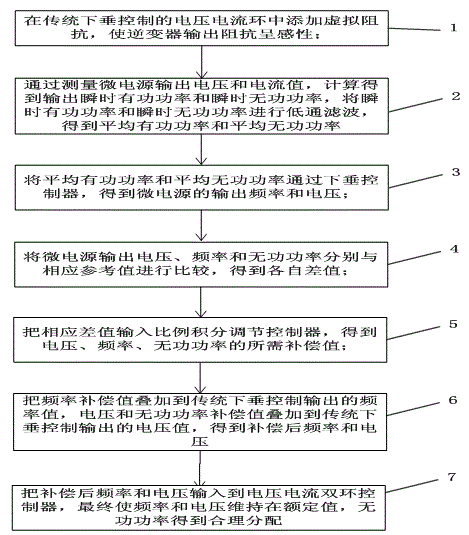
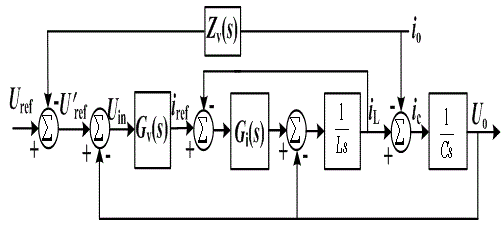
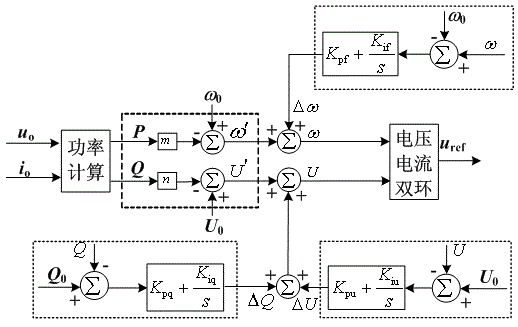
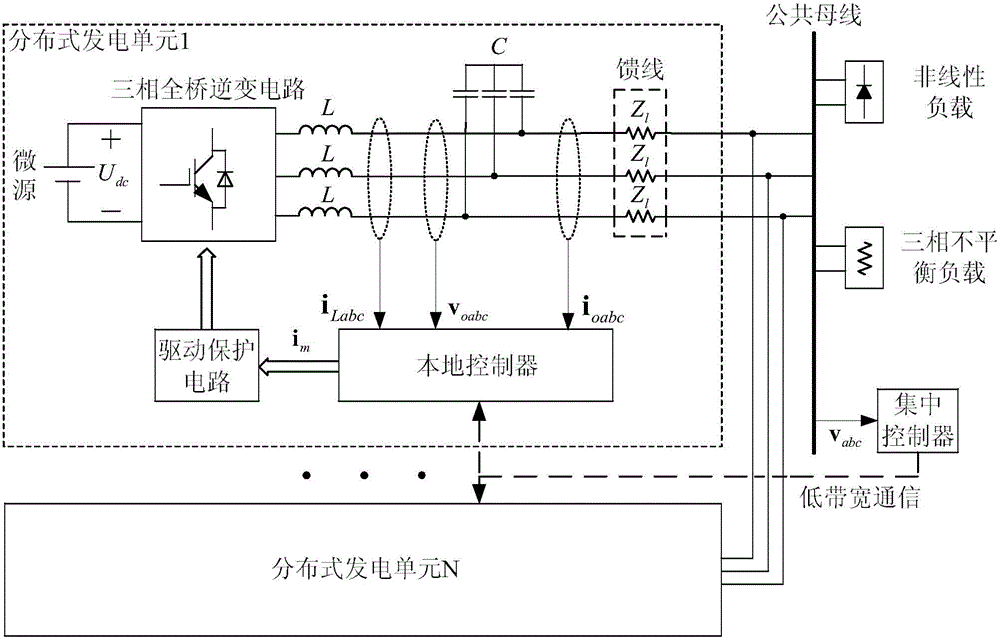
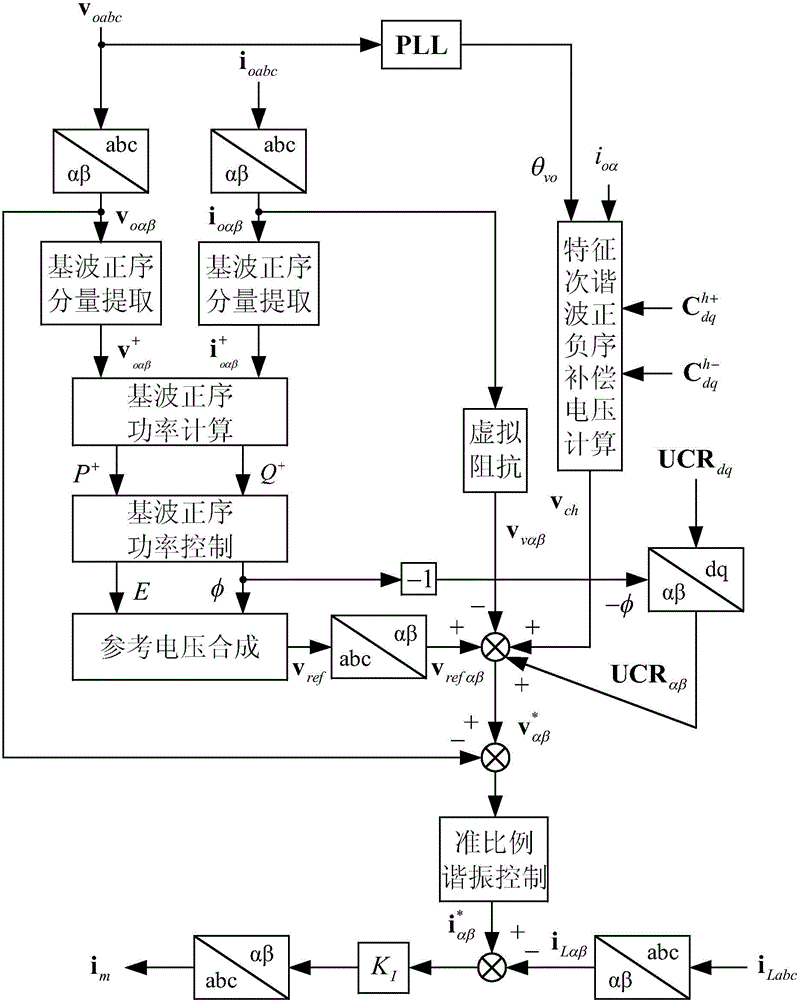
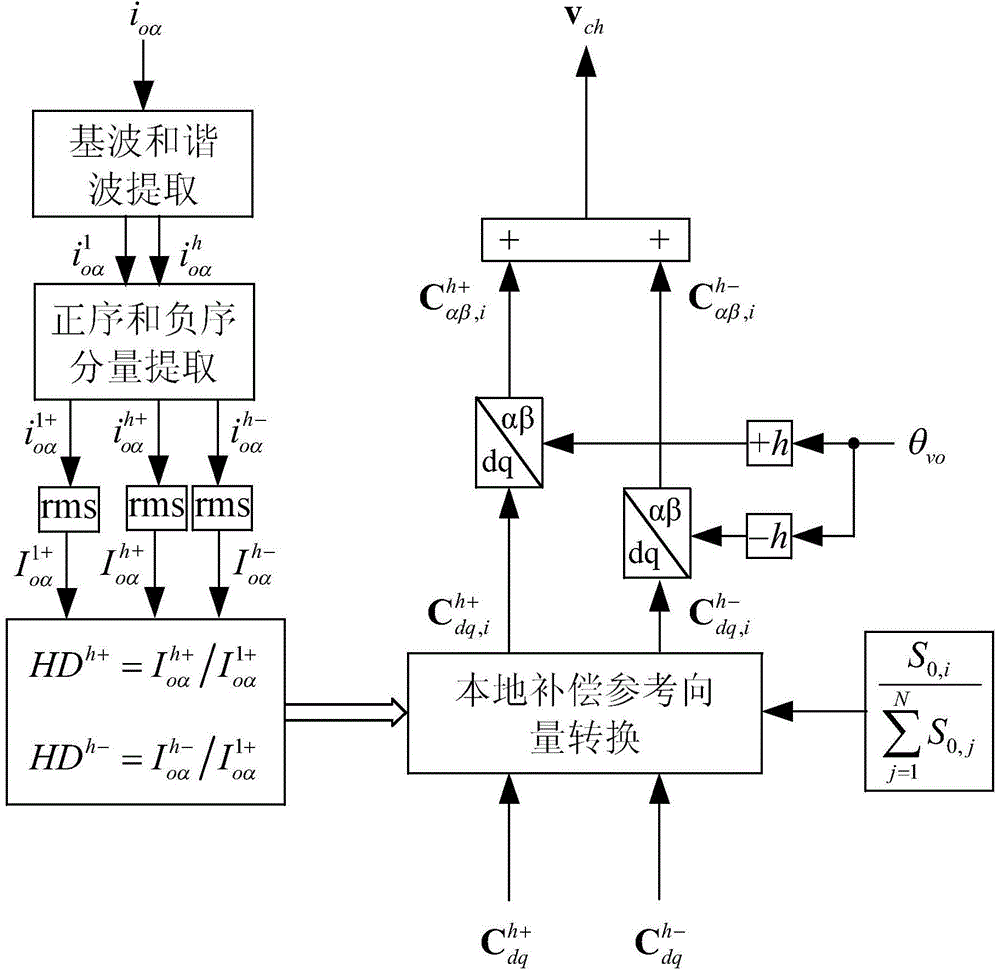
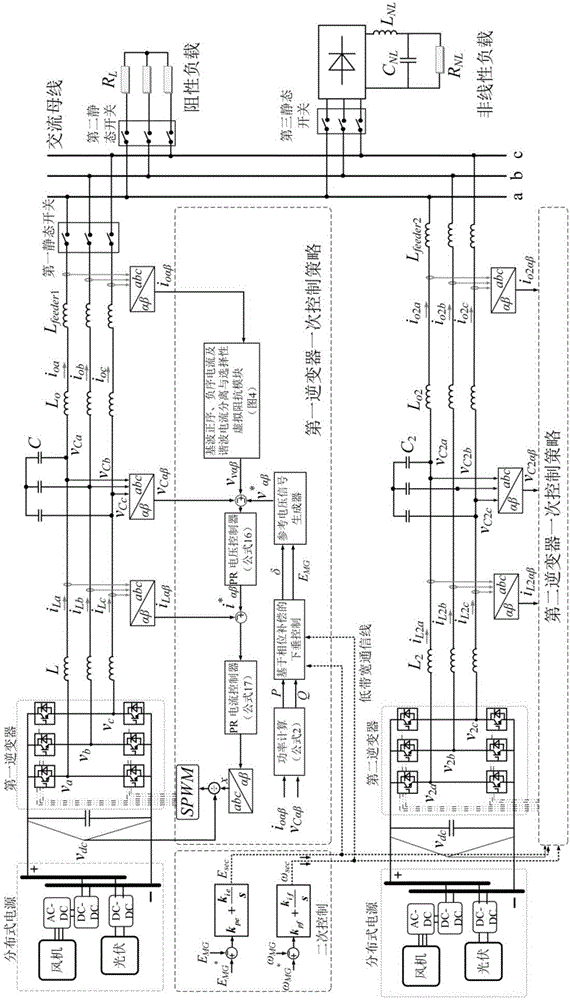
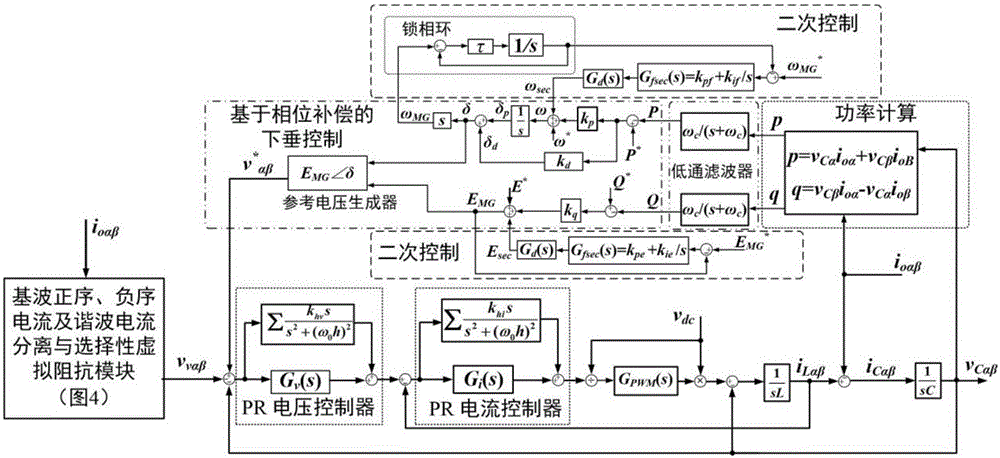
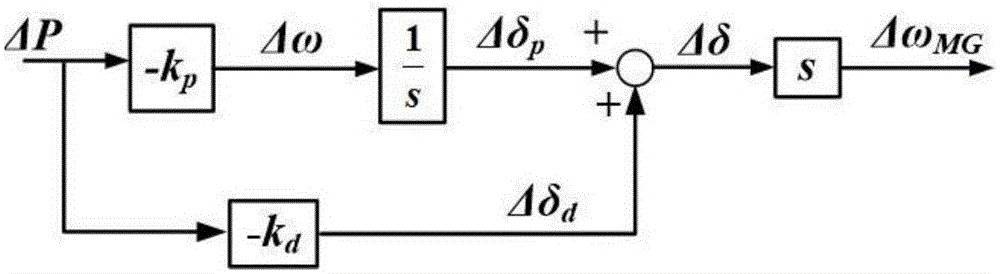
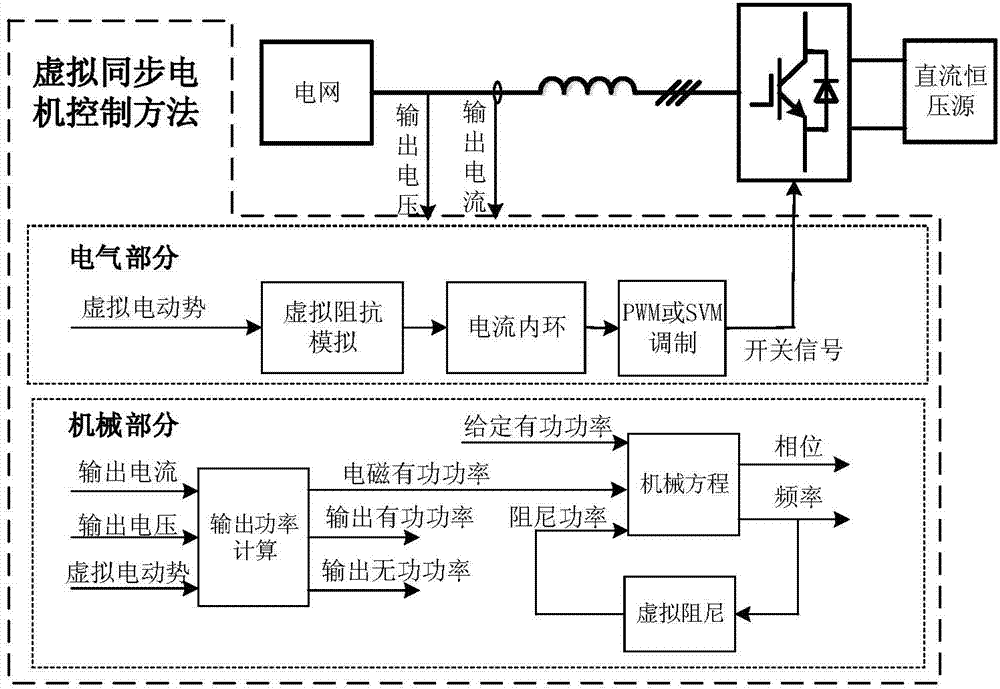
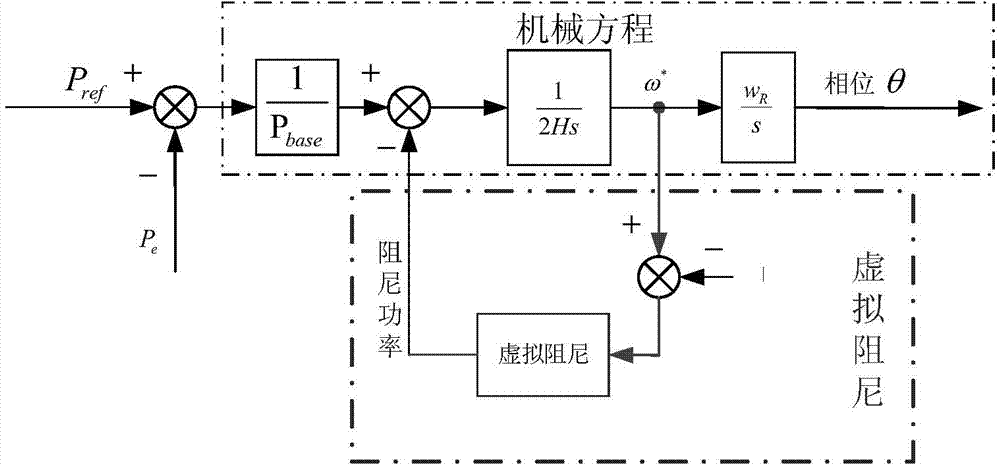
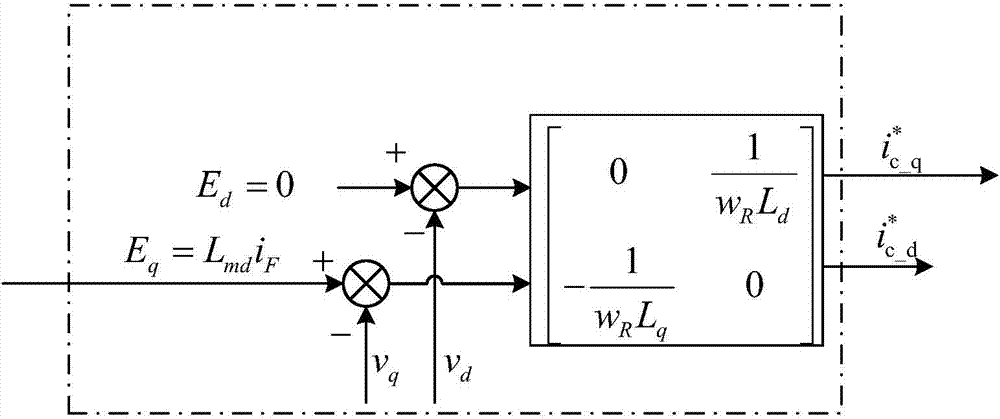
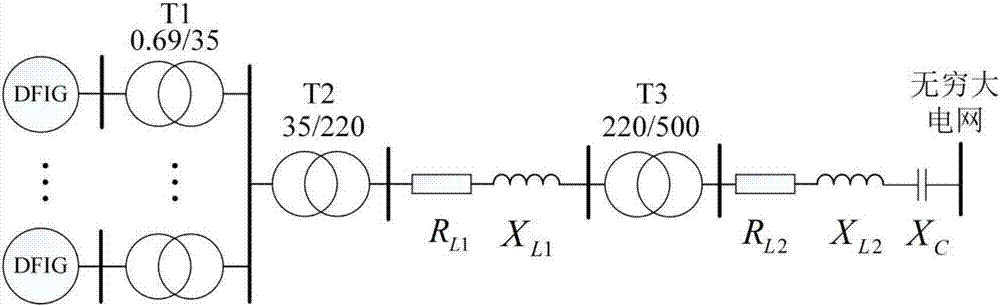
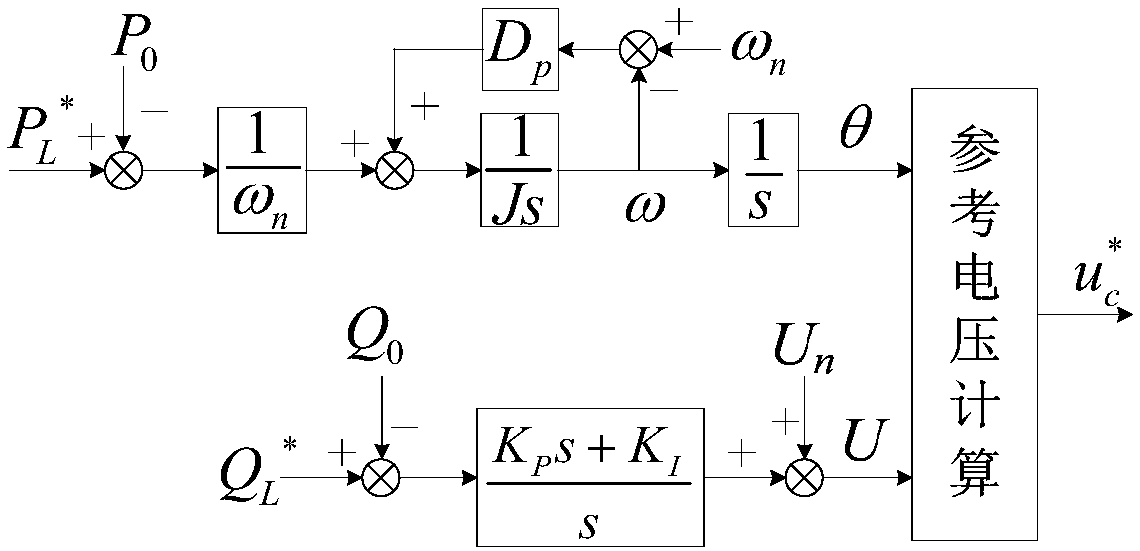
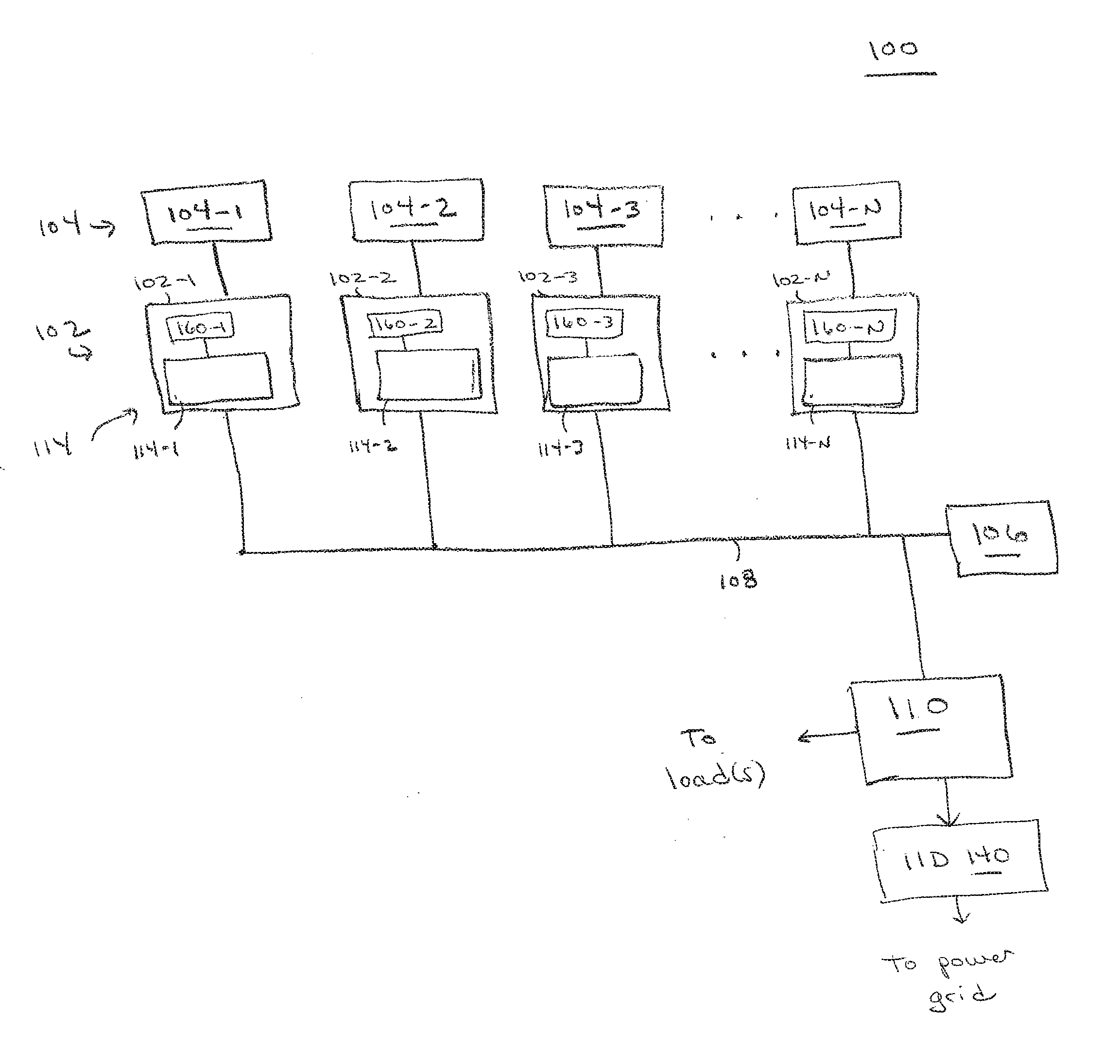
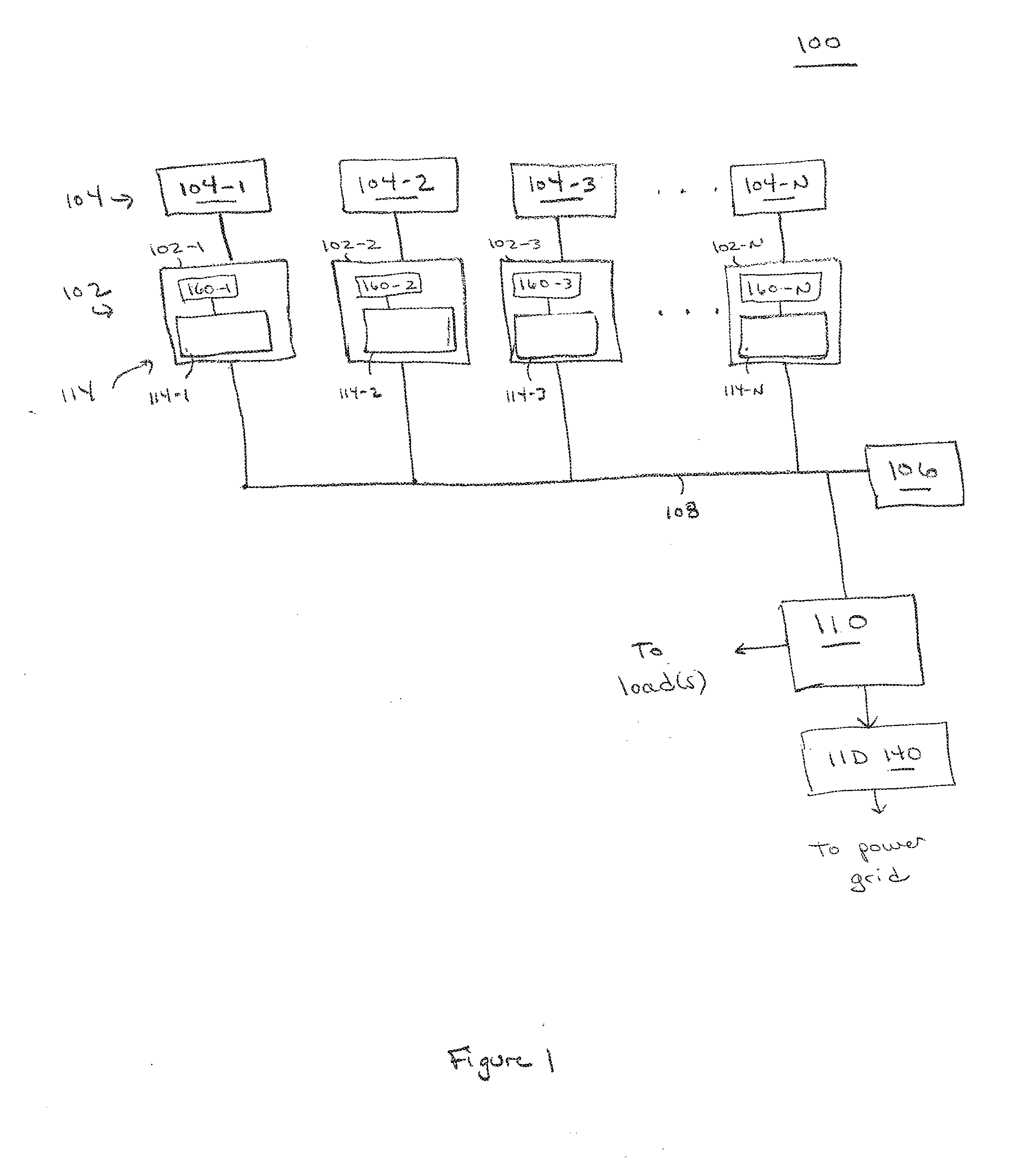
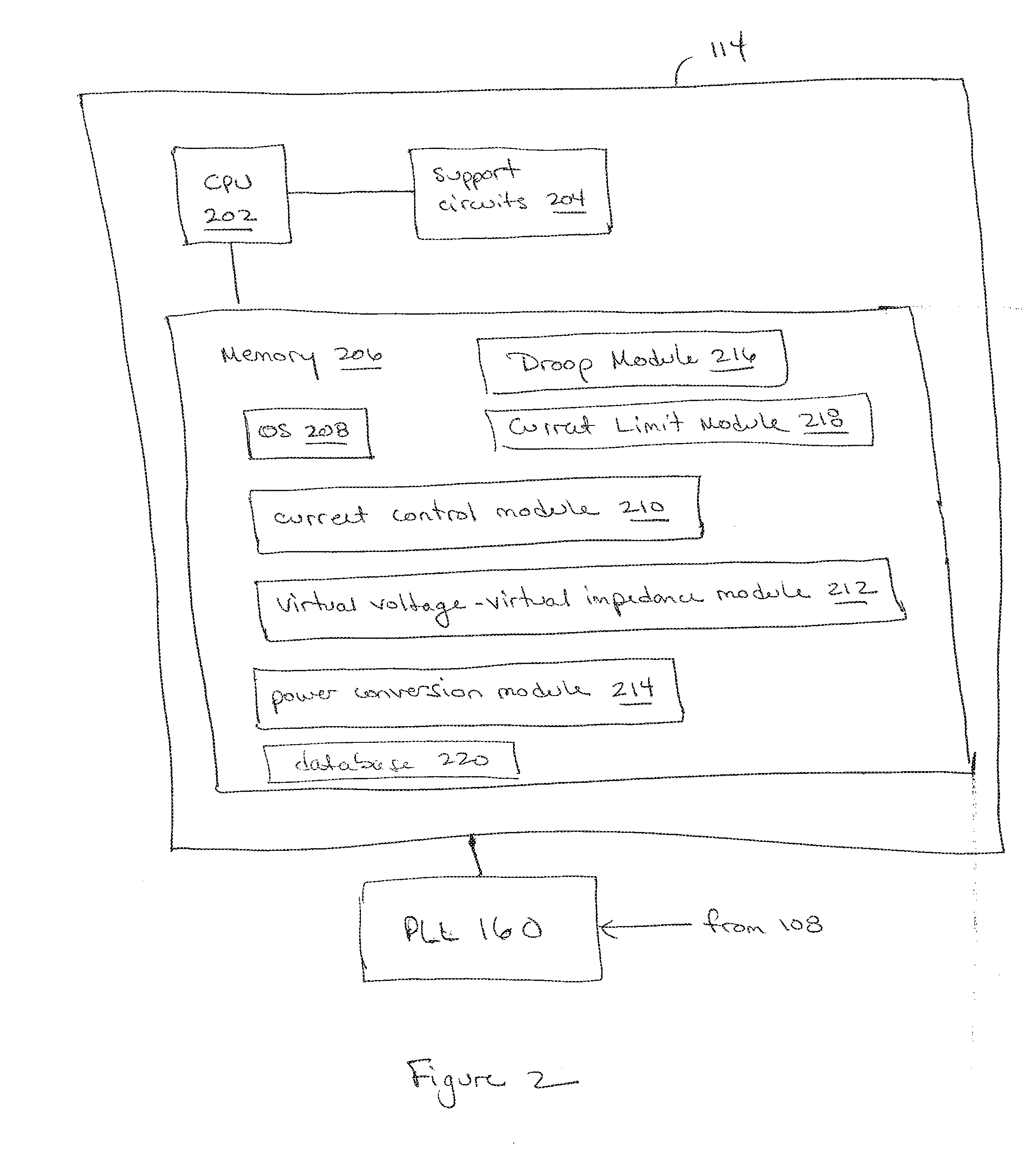
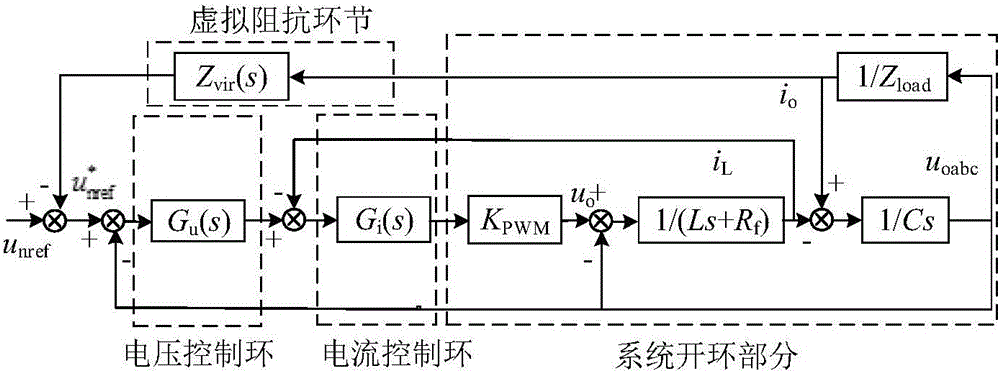
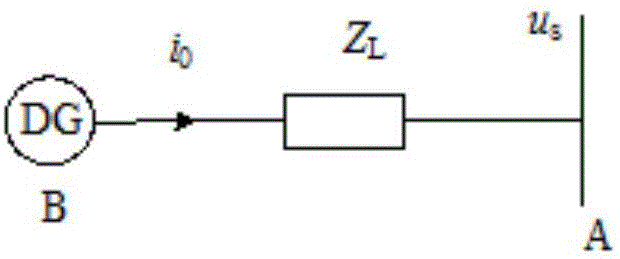
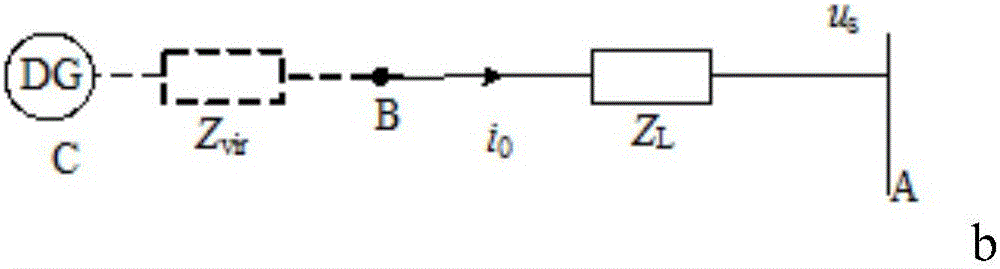
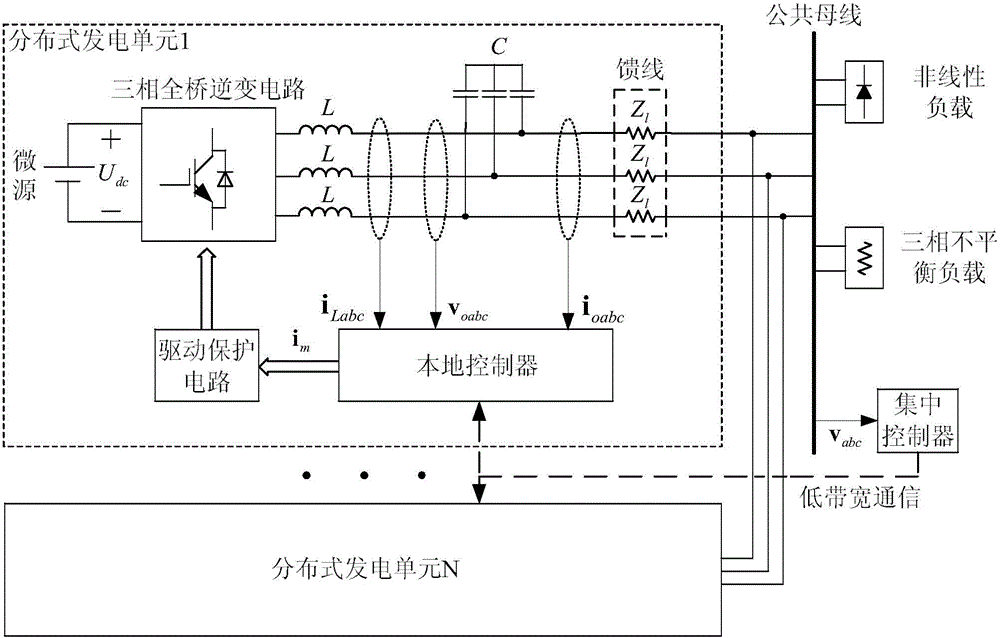
Patents
Literature
440 results about "Virtual impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for islanding microgrid control and optimization based on rotating coordinate virtual impedance
InactiveCN102623992AImprove impedance characteristicsCompensation errorEnergy industrySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMicrogridDynamic models
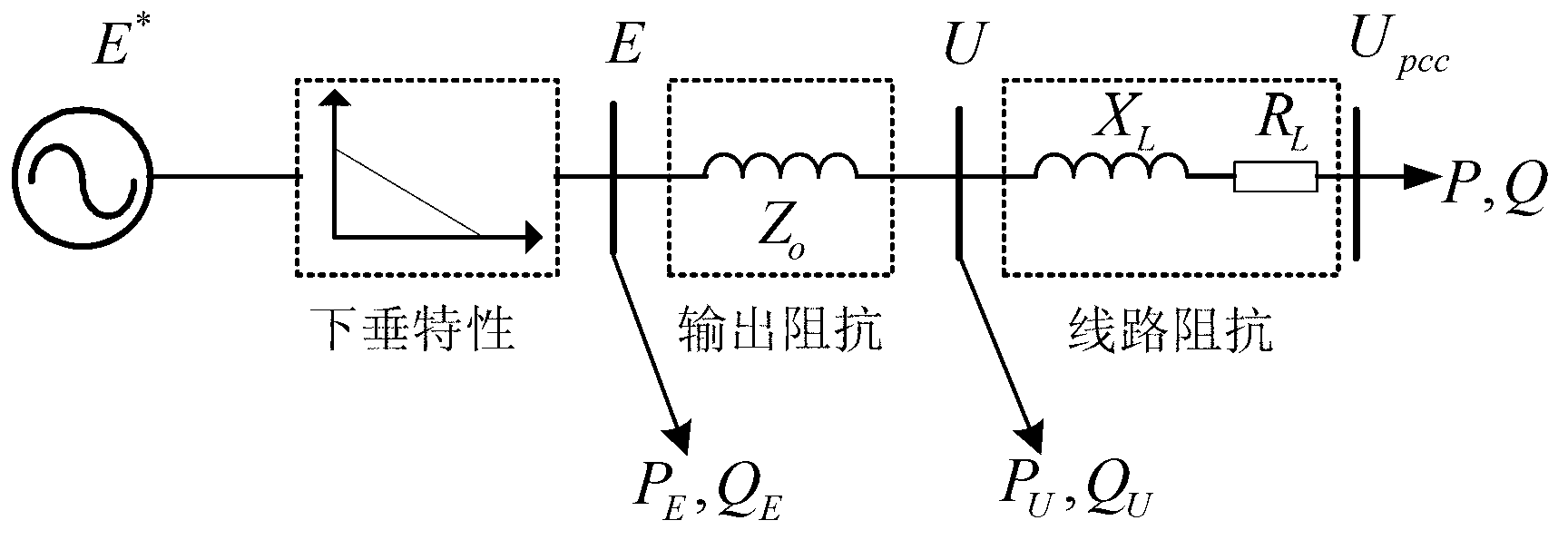
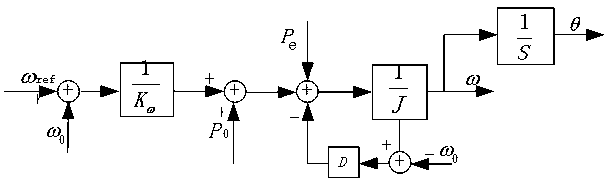
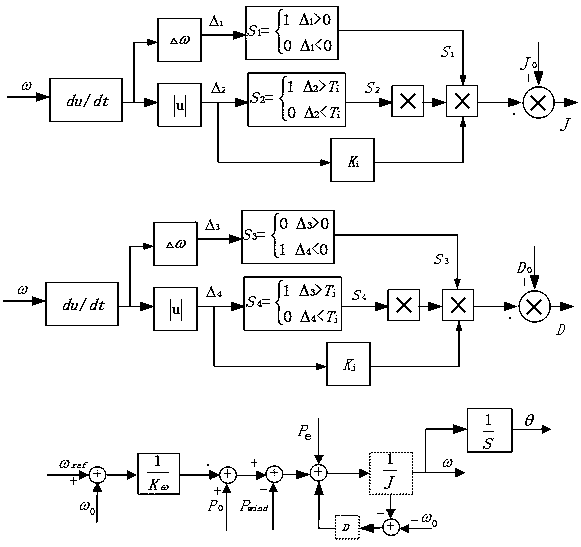
The invention discloses a method for islanding microgrid control and optimization based on rotating coordinate virtual impedance. Aiming to a fact that the actual microgrids have complicated impedance characteristics, the method for islanding microgrid control and optimization based on the rotating coordinate virtual impedance includes utilizing the coordinate rotation orthogonal transformation to design the coordinate rotation virtual impedance, improving the impedance characteristics of the microgrid, compensating errors of power distribution and improving power decoupling performance; establishing a complete small-signal dynamic model of the microgrid, wherein the small-signal dynamic model comprises distributed energy sources, power converters, loads and power grids, and guiding the selection of an optimal value on the basis of the small-signal dynamic analytical method; and simultaneously, providing a theoretical basis for the optimization selection of islanding microgrid control parameters by using the small-signal dynamic analytical method, wherein the islanding microgrid control parameters comprise droop control coefficients of the power distribution, process identifier (PI) parameters of a voltage current feedback controller, feedforward control coefficients and the like. The microgrid after being subjected to optimization design in an islanded operational mode is capable of effectively achieving power decoupling and improving the accuracy of the power distribution, the stability of the system and the dynamic performances.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Virtual-impedance-based inverter parallel running method
ActiveCN102157956AIncrease investmentEasy to useFlexible AC transmissionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower inverterVoltage amplitude
The invention provides a virtual-impedance-based inverter parallel running method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: for each inverter, introducing a virtual generator which is connected to a point with the inverter by virtual impedance; performing droop control on the virtual generators, regulating the frequency and voltage amplitude of each virtual generator by utilizing the active power and reactive power of the corresponding inverters respectively, and further calculating voltage directive values of the virtual generators; and based on the voltage directive values, further calculating output voltage directive values of the inverters, and controlling the inverters to output voltages to track the directive values, thereby realizing control over the voltages of the virtual generators and finally realizing the decoupling regulation of the active power and the reactive power. In the method, a control policy for the wireless parallel running of the inverters is realized by utilizing the virtual impedance; and compared with the conventional control methods, the invention is not required to remarkably increase hardware investment, and betters the using effects of droop characteristics to make applicable the droop characteristics to resistive environments.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Micro-grid multi-inverter parallel voltage control method for droop control of robust power
ActiveCN102842921AIncrease the output resistanceSmall output resistanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLow voltageVoltage reference
The invention discloses a micro-grid multi-inverter parallel voltage control method for droop control of robust power. The method comprises the following steps of: specific to each inverter in a micro-grid, computing and synthesizing an inverter output reference voltage by adopting a robust power droop controller; and introducing virtual complex impedance containing a resistance component and an inductive impedance component, and keeping inverter output impedance in a pure resistance state under a power frequency condition by adopting a multi-loop voltage control method based on virtual impedance and quasi-resonance PR (Proportional-Resonant) control, thereby realizing micro-grid multi-inverter parallel running and power equation, wherein the robustness of a micro-grid parallel system on numeric value computing errors, parameter drift, noise interference and the like is enhanced. Due to the adoption of the method, the defects of larger loop current of a parallel system, non-uniform power distribution and the like caused by the inductivity of the impedance output by inverters in the conventional droop method are overcome; and the method is suitable for multi-grid parallel uniform current control in a low-voltage micro-grid.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Microgrid system with asymmetric non-linear load and power balancing control method
InactiveCN105071405ASolving Harmonic ProblemsSolve balance problemsPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationMicrogridPower balancing
The invention dsiclsoes a microgrid system with an asymmetric non-linear load and a power balancing control method. The system comprises a plurality of DG units connected in parallel and line impedors connected with all DG units. The line impedors are connected to a microgrid bus by PCC points. A three-phase balancing resistive load, an asymmetric linear load, and a diode rectifier non-linear load of a load unit are connected to the microgrid bus by PCC points. A measurement module for measuring voltage fundamental wave positive sequence and negative sequence components and harmonic wave components of the PCC points is also connected to the microgrid bus. The microgrid bus is connected with a 10-kV main power grid by a static switch and a transformer successively. According to the invention, reactive and harmonic power balancing of the microgrid is realized by using a selective virtual impedance based on the virtual fundamental positive and negative sequence impedance and the virtual variable harmonic impedance; a harmonic and unbalancing voltage compensation controller enables equal division of an unbalanced power and a harmonic power to be realized; and a problem of unbalancing of the harmonic wave and the voltage of the microgrid can be solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Energy storage optimization and coordination control method for direct-current micro grid group
ActiveCN105514966AImprove securityImprove voltage qualityLoad balancing in dc networkDc source parallel operationPower stationState of charge
The invention relates to an energy storage optimization and coordination control method for a direct-current micro grid group. When multiple sub micro grids are operated in parallel, an energy storage system in each sub micro grid automatically adjusts power distribution according to the maximum charging and discharging power and the state of charge (SOC) of the corresponding energy storage system, and therefore the safety of the energy storage systems is improved while distributed generated power fluctuation can be smoothed and the bus voltage quality can be improved; when the energy storage systems of all the sub micro grids cannot effectively buffer the system power supply and demand, an energy storage power station needs to be connected to control stabilization of the bus voltage. According to the energy storage optimization and coordination control method for the direct-current micro grid group, the virtual impedance of droop controllers of all energy storage units in the energy storage power station is adjusted by adopting fuzzy control to achieve automatic distribution of the power among the different energy storage units and SOC balance, fuzzy input is segmented, the SOC balancing speed of the fuzzy input in different ranges is increased by adopting fuzzy control, bus voltage drop caused by droop control is compensated by adopting a bus voltage feedback control method, and the bus voltage quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Method for parallel operation control suitable to be used for microgrid inverter
ActiveCN104868500AImprove power qualityAllocation Accuracy ImprovementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentPower qualityMicrogrid
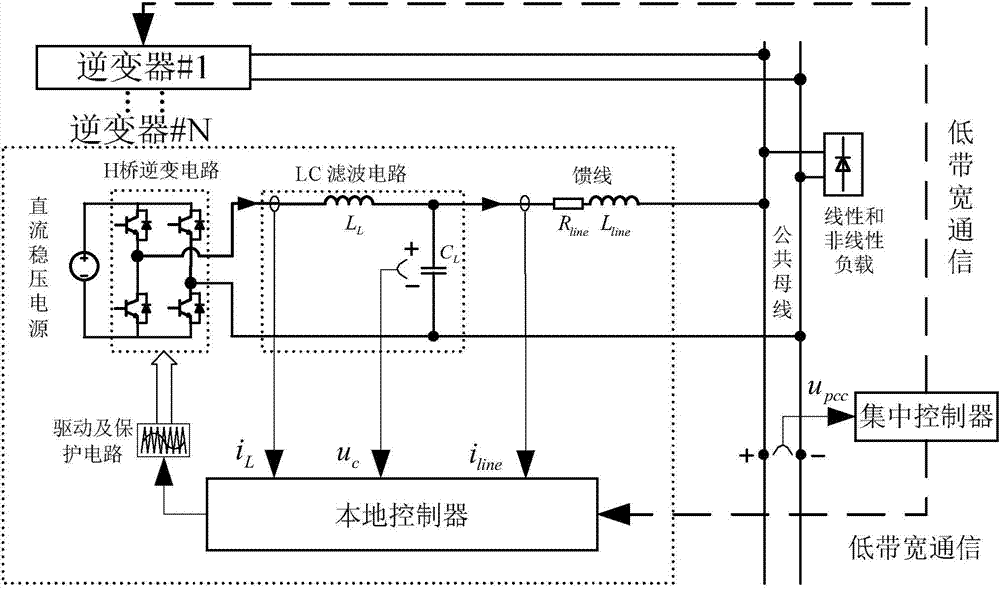
The invention discloses a method for parallel operation control suitable to be used for a microgrid inverter. The method comprises: step 1, adding virtual impedance in a voltage and current loop of conventional droop control; step 2, through measuring output voltage and current values of a micro power source, obtaining average active power and average reactive power; step 3, obtaining output frequency and voltage of the micro power source; step 4, comparing the output voltage, frequency, and reactive power of the micro power source with corresponding reference values, to obtain respective difference values; step 5, obtaining required compensation values of voltage, frequency, and reactive power; step 6, obtaining compensated frequency and voltage; step 7, inputting the compensated frequency and voltage to a voltage and current double-loop controller, and finally the frequency and voltage are maintained at rated values, the reactive power is distributed rationally. The method realizes technical effects of improving electric energy quality and rationally distributing reactive power, and distribution precision of the reactive power is relatively high.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Microgrid control method having functions of voltage unbalance compensation and harmonic suppression
InactiveCN104836258AEasy to receiveEfficient receptionEnergy industrySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReference vectorMicrogrid
The invention discloses a microgrid control method having functions of voltage unbalance compensation and harmonic suppression. An integrated controller acquires a common bus voltage and calculates an unbalance factor vector, a characteristic order harmonic component positive-sequence compensation reference vector and a characteristic order harmonic component negative-sequence compensation reference vector of the common bus voltage, and transmits the vectors to a local controller of every parallel inverter through low-bandwidth communication. In the local controller, a characteristic order harmonic positive- and negative-sequence compensation voltage vector is calculated and is superposed with a reference voltage vector, a virtual impedance voltage vector and the common bus voltage unbalance factor vector to synthesize and correct a voltage regulating reference vector, and unbalance compensation and harmonic suppression of the common bus voltage is carried out through inverter voltage and current control. By applying the method provided by the invention to a multi-inverter parallel system in which a common bus is connected with a three-phase unbalanced load and a nonlinear load, three-phase voltage balance of the microgrid can be maintained, output voltage distortion of three-phase inverters can be reduced, and output power of the parallel inverters can be accurately allocated.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Novel microgrid system, power balance control strategy and small-signal modeling method therefor
InactiveCN105162134AIncrease dampingGuaranteed stabilityEnergy industryReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationMicrogridPower Balance
The invention provides a novel microgrid system based on phase compensation and selective virtual impedance, a power balance control strategy and a small-signal modeling method therefor. The novel microgrid system comprises two paths of DG (distributed generation) units connected with an alternating current bus in parallel, a three-phase balance resistance load and a non-linear load; the DG unit comprises a distributed power supply, an inverter, an LCL type filter circuit, line impedance, two inverter primary strategy control modules and a secondary strategy control module that are connected in sequence; a first DG unit is connected with the alternating current bus through a first static switch; a second DG unit is connected with the alternating current bus through a second line impedance; and the three-phase balance resistance load and the non-linear load are connected with the alternating current bus through a second static switch and a third static switch separately. The invention provides a wattless and harmonic power balance control method for the novel microgrid system based on phase compensation droop control, selective virtual impedance and secondary control; and the wattless and harmonic power sharing of the microgrid under the nonlinear load can be effectively realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-module inverter wired parallel digital control method
ActiveCN103280999ASame output frequencySame amplitudeDc-ac conversion without reversalPower inverterComputer module
The invention discloses a multi-module inverter wired parallel digital control method. The method can be applicable to a single-phase inverter parallel system or a three-phase inverter parallel system. Connecting wires among the inverter modules are composed of a communication bus, a synchronizing signal bus and an output side alternating current bus, and the control part of the inverter modules mainly consists of a homogenization voltage-stabilizing loop, virtual impedance calculation and inverter voltage current double loop control. The reference voltage phases of the inverter modules are enabled to be the same through the synchronizing signal bus, a master machine guarantees the voltage effective value of the output alternating current bus to be constant, and a slave machine traces the master machine to enable the power of the inverters to be uniformly distributed. According to the multi-module inverter wired parallel digital control method, the output frequencies, the amplitudes and the phases of the modules can be enabled to be identical, the current sharing effect is good, the control method is simple and easy to implement and the reliability is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microgrid reactive power balanced allocation method based on impedance composite control
InactiveCN103236702AOptimal Impedance AdaptationEliminates adverse effects of impedance mismatchEnergy industryReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationTransient stateMicrogrid
The invention provides a microgrid reactive power balanced allocation method based on impedance composite control. The technical scheme includes that the microgrid reactive power balanced allocation method includes: dynamically changing a droop coefficient in real-time by a dynamic Q-U droop coefficient adjuster according to outputted active power and reactive power of VSI (vertical speed indicator), adjusting VSI output impedance according to output current by Q-U droop control based on virtual impedance compensation, compensating voltage drop generated by virtual impedance by a virtual impedance open-loop compensator according to active power and reactive power, and controlling Q-U droop properties in a closed-loop manner via a PI (power integrations) adjuster by an impedance closed-loop compensator. The microgrid reactive power balanced allocation method has the advantages that voltage drop generated by the virtual impedance is compensated by open loop and closed loop, so that voltage sag generated by virtual impedance is avoided when output impedance is corrected; and mismatching of line impedance is eliminated by adopting a dynamic variable coefficient method and a transient state variable coefficient method, and dynamic and steady averaging properties of reactive power are improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Current source type rectifier and grid-connected control method based on virtual resistor
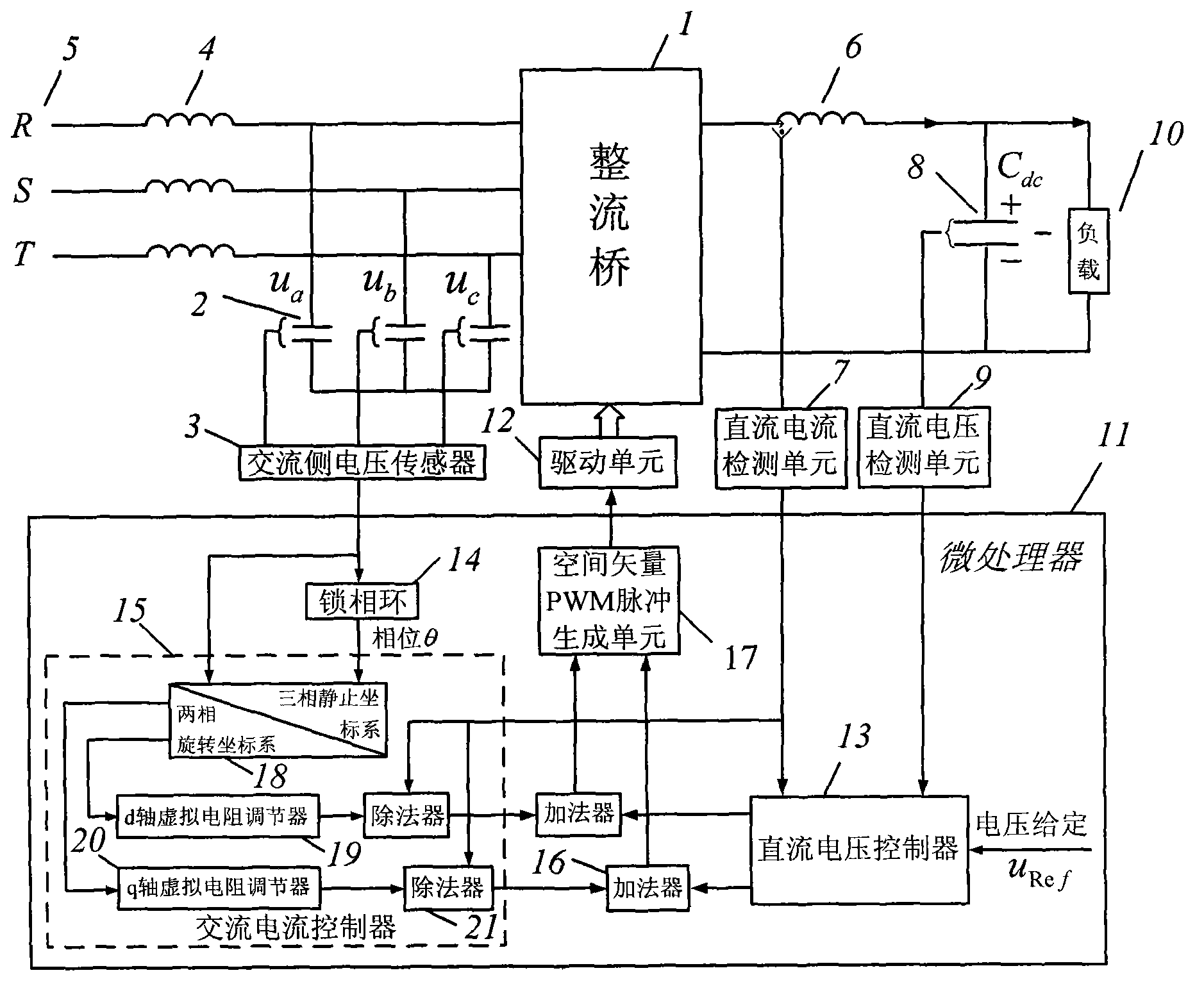
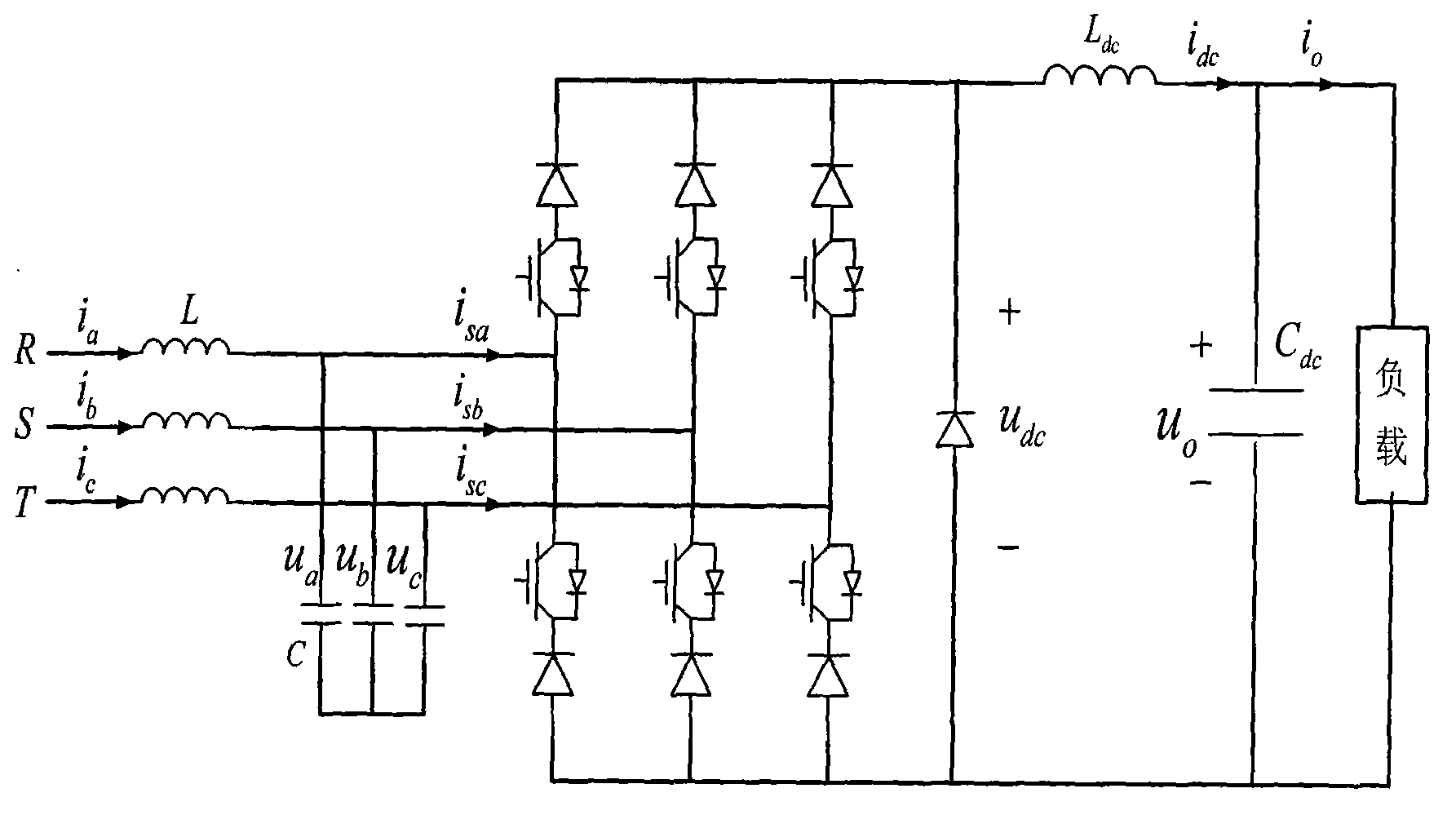
ActiveCN103078526ALow costReduce THDAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTotal harmonic distortionAlternating current
The invention discloses a current source type PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) rectifier and a grid-connected control method based on a virtual resistor. A grid-connected rectifier consists of commercial power, an alternating-current filtering inductor, an alternating-current filtering capacitor, a three-phase current source type rectifier, a direct-current inductor, a direct-current capacitor and a digital controller. Sampled alternating-current filtering capacitance voltage is transmitted to a microprocessor to perform digital phase locking, and after phase locking is finished, the alternating-current filtering capacitance voltage and phase are transmitted to an alternating-current controller. The alternating-current controller consists of a coordinate converter, a virtual impedance regulator and a divider. The coordinate converter converts the three-phase alternating-current filtering capacitance voltage into the voltage under a two-phase static coordinate system, after the voltage is regulated by the virtual resistance regulator, current passing through a virtual resistor is obtained, control amount of the alternating-current side is obtained through the divider, the control amount is superposed on the control amount on the direct-current side, a driving signal obtained through a PWM generator is transmitted to a driving plate, and after the signal is amplified by the driving plate, the connection and disconnection of a three-phase current source type rectifying bridge switch are controlled. The control effect of the virtual resistance regulator in the alternating-current controller is equivalent to the control effect that a resistor is directly connected in parallel on an alternating-current capacitor, so that oscillation can be effectively damped, loss is not caused, and ultraharmonics in grid-connected current can be effectively inhibited. The rectifier is high in dynamic response speed, stable in dynamic response and high in power factor, the total harmonic distortion rate of the grid-connected current is low, and the method can be applied to an uninterruptible power supply.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHICHENG CHAMPION GROUP +1
Voltage control type virtual synchronizing method of double-feed wind power generator set
ActiveCN108683198AAccurately offsets estimation errorsSpeed up the dynamic process of power regulationClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsControl mannerClosed loop
The invention discloses a voltage control type virtual synchronizing method of a double-feed wind power generator set. Through simulating inertia and a frequency-modulating and voltage-modulating characteristic of a synchronizer, the set can be different from a characteristic of no electric grid frequency change response in a traditional current control type, thereby possessing capability of supporting voltage and frequency of a weak power grid based on the voltage control type through virtual inertia. The method provides and realizes a VCT-DFIC virtual synchronous control structure of which an inner ring is controlled by an improved double-feed generator stator voltage rotor current double-closed-loop structure based on adaptive stator virtual impedance and transmission line sag voltage feedforward compensation in a control manner which includes crossed control between stator voltage and rotor current and furthermore an outer ring is controlled by a virtual synchronous realizing algorithm. The method realizes output power control in VCT-DFIG grid integration operation in a weak grid condition with any actual impedance and effective decoupling, and furthermore a designed control structure realizes higher inertia and frequency supporting capability of the double-feed generator.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
DC distribution system energy storage device adaptive virtual impedance droop control method
ActiveCN105305410ASuppress power oscillationsEliminate uneven distribution of powerLoad balancing in dc networkAc network load balancingCapacitanceClosed loop
The invention relates to a DC distribution system energy storage device adaptive virtual impedance droop control method, which is applied to multi-converter parallel control in a DC distribution system. The method comprises the steps of 1) acquiring electric power parameters of the DC distribution system, establishing a double closed-loop controller which consists a voltage outer loop and a capacitive current inner loop, and establishing a DC distribution system droop control model; 2) introducing virtual impedance ZD(s) into a part between converter output current and converter reference voltage signals of the double closed-loop controller in the DC distribution system droop control model so as to act as negative feedback, and acquiring equivalent output impedance Zov(s); and 3) enabling the equivalent output impedances Zov(s) corresponding to a plurality of lines to be equal through setting values of different virtual impedances ZD(s), and thus averaging output power and power distribution of the plurality of lines in the DC distribution system. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of shock suppression, simple algorithm, low cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Low-voltage micro-grid inverter control system based on virtual impedance and virtual power source
ActiveCN106712088ALow costAvoid adding filter inductanceAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLow voltageVirtual control
The invention discloses a low-voltage micro-grid inverter control system based on virtual impedance and a virtual power source. The control system comprises a droop controller, a virtual controller and a voltage / current dual-loop controller, and is characterized by establishing the droop controller capable of simulating the function of the virtual power supply through improvement of droop parameters, and carrying out tracking control on the voltage of the droop controller through fractional-order PID; by analyzing relation between virtual negative inductance and micro-source reactive power sharing, determining the value of virtual negative inductance required for accurate reactive power sharing, realizing virtual impedance in the virtual controller, and feeding back voltage drop of the virtual controller to the droop controller to participate in fractional-order PID tracking control of voltage of the virtual power source; and carrying out tracking control on inverter voltage through fractional-order PID in the voltage / current dual-loop controller, determining filtering parameters in the controller according to a transfer function of a filter, and carrying out optimization on fractional-order PID controller parameters through a difference genetic algorithm. The control system can ensure low-voltage micro-grid power decoupling and improve a reactive power sharing effect.
Owner:秦皇岛市睿能光电科技有限公司
Virtual synchronous generator fault current suppression method based on adaptive virtual impedance
InactiveCN111416393ACapable of fault ride-throughSuppress fault currentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVirtual synchronous generatorPower grid
The invention relates to a virtual synchronous generator fault current suppression method based on adaptive virtual impedance. When a power grid fails, the voltage of a power grid drops, a VSG can generate large fault current, particularly at the moment when a fault occurs and is removed, the VSG can generate large impact current; when the output current of the VSG exceeds the maximum value of thecurrent capable of being borne by an inverter, irreversible damage to the VSG system can be caused, and meanwhile, the stability of the power grid is further reduced. The VSG does not have a fault ride-through capability, so that the VSG can only have the fault ride-through capability through a reasonable control scheme. According to the method of the invention, VSG fault current is suppressed bythe self-adapting of virtual impedance and the modification of a VSG reference voltage during the fault, so that the VSG has the fault ride-through capability on the premise of not changing a controlstructure. The method has high control precision. With the method adopted, fault current and impact current can be effectively suppressed; and the control structure is not changed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Method for improving wireless internet stability of multiple inverters in microgrid by utilizing virtual impedance
InactiveCN101976851AImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower qualityElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a method for improving the wireless internet stability of a plurality of inverters in a microgrid by utilizing virtual impedance. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) calculating a droop control coefficient according to the requirement of the microgrid on power quality; (2) estimating a grid line parameter and calculating the stable range of the droop coefficient; (3) substituting the droop coefficient calculated in the step (1) into the range calculated in the step (2) for verifying; if the droop coefficient is not in the stable range, performing a step (4); if the droop coefficient can stabilize completely, performing a step (5); (4) according to a result calculated in the step (3), properly changing virtual inductance or resistance and repeating the step (2) and the step (3) in turn; and (5) realizing the droop control of the virtual impedance. In the method, feedback control is performed on an output voltage by utilizing output current of each micro power supply per se in the microgrid, so as to fulfill the aim of improving the stability of an overall microgrid system and save line conductors.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Virtual impedance voltage converter-based control method of virtual synchronous motor
ActiveCN104716886AOvercoming Impedance Simulation EffectsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage converterVirtual synchrony
The invention discloses a virtual impedance voltage converter-based control method of a virtual synchronous motor. Output voltage and current of a voltage converter is controlled to have the characteristic of a synchronous motor through electric and mechanical main parts of the virtual synchronous motor, wherein the electric part comprises a novel virtual impedance simulation algorithm, a conventional converter current inner ring and a modulation strategy and the mechanical part comprises a power calculating module, a rotor mechanical equation and a virtual damping module. The virtual impedance voltage converter-based control method of the virtual synchronous motor can be used for simulating winding impedance without introducing a differential term of current output by the converter, so that the influence on impedance simulation by an extra low pass filter is overcome, and the current inner ring control of a parallel converter is not sacrificed, and therefore, alternating current is controlled, and the converter has the capacity of preventing current fluctuation, overcurrent and even impact without quick current inner ring control. A silent pole motor and a non-salient pole motor can be simultaneously simulated.
Double-feed blower fan subsynchronous oscillation inhibition method based on virtual impedance control
ActiveCN107017646ASuppression of subsynchronous oscillation phenomenonChange the mode of operationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionAudio power amplifierTransfer function model
The invention discloses a double-feed blower fan subsynchronous oscillation inhibition method based on virtual impedance control, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a dq-axis component of a rotor current of a double-feed blower fan to serve as an input signal, and filtering a low-frequency component and a fundamental frequency component through a band-pass filter, and then obtaining a subsynchronous current component. The current component brings virtual impedance to a rotor loop through a proportional amplifier and a differentiation link, thereby achieving the effects of increasing the subsynchronous oscillation damping and inhibiting the subsynchronous oscillation. According to the invention, the method starts from the structure of a rotor controller, achieves the research of the relation between the rotor current and the output voltage of the rotor controller, and obtains the equivalent resistance of a rotor side controller, i.e., the virtual resistance value. Afterwards, a double-feed blower fan rotor current transfer function model is used for solving and obtaining a virtual inductance value needed by the virtual impedance control. The method is advantageous in that the method is simple in parameter configuration, is clear in physical concepts, improves a virtual resistance control strategy, is better in adaptability, is low in control cost, and can effectively inhibit the subsynchronous oscillation to a certain degree.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Distributed virtual synchronous-generator low voltage crossing control method
ActiveCN108092308AInhibit steady state overcurrentSuppresses instantaneous overcurrentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionVirtual synchronous generatorStable state
A distributed virtual synchronous-generator low voltage crossing control method is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps of using an improved virtual synchronous generator reactive powerring to accelerate a response speed of the reactive power ring and increase a reactive power support capability to a grid connection point; when a grid connection point voltage is detected to drop and an instantaneous overcurrent is detected, introducing virtual impedance control, correcting a voltage reference value and restraining the instantaneous overcurrent; using a balance current virtual synchronization control method to control positive and negative sequence currents, and when a grid connection voltage is imbalance, realizing balance control of an output current and restraining a stable state overcurrent; and according to a low voltage crossing requirement, resetting a power instruction value so that a system satisfies a reactive current injection requirement, and after a fault isremoved, setting the power instruction value to an original value. Through the above steps, low voltage crossing requirements of instantaneous and stable state overcurrent restraining, reactive current injection according to the requirement and the like are satisfied.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for time-domain droop control with integrated phasor current control
ActiveUS20160248253A1Conversion without intermediate conversion to dcSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTime domainTransverter
A method and apparatus for power converter current control. In one embodiment, the method comprises controlling an instantaneous current generated by a power converter such that that power converter appears, from the perspective of an AC line coupled to the power converter, as a virtual AC voltage source in series with a virtual impedance, wherein real and reactive phasor currents for the power converter are indirectly controlled by modifying amplitude and phase of a virtual AC voltage waveform that defines the virtual AC voltage source.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Improved droop control based microgrid auxiliary master-slave control method
ActiveCN105811421AAchieve output power decouplingQuality assurancePower network operation systems integrationEnergy industryPower qualityMicrogrid
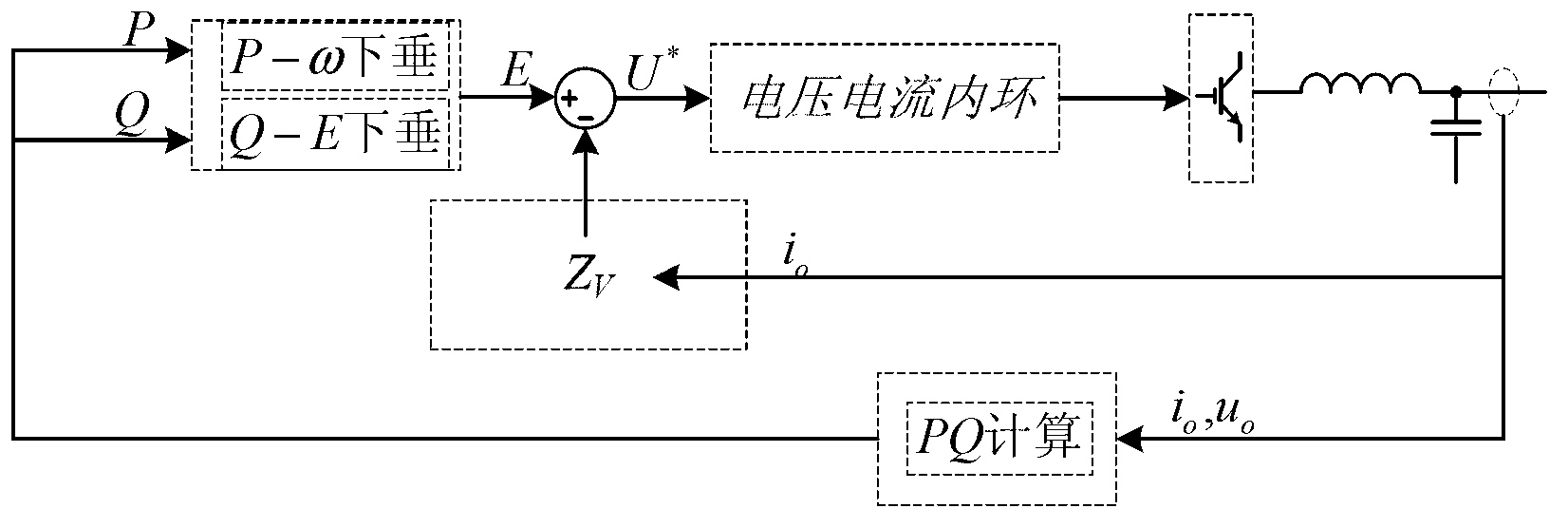
The invention relates to an improved droop control based microgrid auxiliary master-slave control method. The method is used for maintaining stability of the voltage and power of the microgrid. The microgrid comprises multiple DGs connected with alternating current buses respectively; each DG comprises a master-control DG, an auxiliary DG and a slave-control DG; the master-control DG and the slave-control DG are used as a master-control unit and a slave-control unit in the master-slave control method respectively; the inverter in the auxiliary DG adopts voltage and current dual-loop control; a load current io is multiplied by a dynamic virtual impedance Zvir, and the obtained product is used as an instruction voltage to be added in a feedback signal to a voltage loop, so that the output impedance of the inverter is sensitive. Compared with the prior art, the inverter of the auxiliary DG adopts the dynamic virtual impedance, so that matching between the output impedance of the inverter and the circuit impedance can be ensured, voltage drop can be effectively relieved, and the power quality is ensured; and in addition, the improved droop control is adopted, and an integral link is introduced in the reactive power control link, so that steady state voltage without static errors is realized, and the steady state performance of the system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Microgrid multi-inverter parallel operation control method adopting bus voltage compensation
InactiveCN104836235AEasy to receiveEfficient receptionPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionAc network voltage adjustmentMicrogridReference vector
The invention discloses a microgrid multi-inverter parallel operation control method adopting bus voltage compensation. An integrated controller acquires a common bus voltage and extracts a fundamental negative-sequence component, a characteristic order harmonic positive-sequence component and a characteristic order harmonic negative-sequence component of the common bus voltage, and transmits the common bus voltage components in a dq coordinate system to a local controller of every parallel inverter through low-bandwidth communication. In the local controller, a characteristic order harmonic positive- and negative-sequence compensation voltage vector is calculated and is superposed with a reference voltage vector and a virtual impedance voltage vector to synthesize and correct a voltage regulating reference vector, and imbalance compensation and harmonic suppression of the common bus voltage is carried out through inverter voltage and current control. By applying the method provided by the invention to an island microgrid multi-inverter parallel system in which a common bus is connected with a three-phase imbalance load and a nonlinear load, three-phase voltage balance of the microgrid can be maintained, output voltage distortion of three-phase inverters can be reduced, and output power of the parallel inverters can be accurately allocated.
Owner:国网山东省电力公司聊城供电公司 +1
Smooth switching control method for operating mode of micro-grid inverter of different capacity micro sources
InactiveCN104578168AReduce circulationRealize power distributionEnergy industrySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVoltage referenceControl theory
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Large-power high-frequency switch eliminator power comprehensive control method
ActiveCN103199718AAchieve matchingQuick responseAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringThree-phase
The invention discloses a large-power high-frequency switch eliminator power comprehensive control method which includes a front-stage three-phase voltage type rectifier control method and a back-stage high-frequency direct current / direct current (DC / DC) convertor control method. A parameter self-adaptation control dead beat control method based on power front feed is adopted in a front-stage three-phase voltage type rectifier, and quick response of a system and quick track of load change are achieved; and through parameter self-adaptation control, on-line dead beat controller parameter correction can be achieved, matching of control parameters and actual parameters can be achieved, bad influence on control performance because of parameter perturbation or drifting can be eliminated, and control robustness can be improved. A virtual impedance self-current-sharing control method based on output voltage feedback is adopted in a back-stage high-frequency DC / DC convertor, conflict between current-sharing control accuracy and load output voltage accuracy can be effectively solved, virtual impedance dereference can not influence output adjustment of load voltage, and adaptation capacity of the virtual impedance current-sharing method on occasions where accuracy demands on the output voltage are high is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Virtual impedance based DC-side fault current suppression method of modular multilevel converter (MMC)
ActiveCN105634257AInhibition of rising speedAchieve inhibitionPower conversion systemsDecoupling controllerDc current
The invention relates to a virtual impedance based DC-side fault current suppression method of a modular multilevel converter (MMC), belonging to the technical field of power transmission. A DC-side fault of the MMC can cause overcurrent of a switching device; and based on a traditional control strategy, a virtual impedance parallel circuit in a primary system is mapped to a controller by a feedback function, DC bus impedance is equivalently risen, thus, instantaneous rising speed of a fault current when a fault occurs in a DC side of the MMC is effectively prevented without increasing the fault current rising speed of other types of faults. In the core scheme, firstly, the DC bus voltage and current of a MMC system and the active power of a PCC point of an AC side are measured in real time; secondly, if the virtual impedance circuit is connected in series to a DC bus, the DC voltage deviation and the active power deviation are calculated when the DC current passes through the virtual circuit; and finally, the associated deviation correction quantity is additionally added to a measurement value of an active power type control quantity of a DQ decoupling controller for correction.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Fan grid-connected control method based on virtual synchronous generator parameter self-adaptive control
ActiveCN111277001AImprove stabilityReduce power fluctuationsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageVirtual synchronous generatorCurrent transducer
The invention relates to a fan grid-connected control method based on virtual synchronous generator parameter adaptive control. An AC bus output by a wind power plant is connected with a control system in parallel. The control system comprises an energy storage device, an inverter, a voltage sensor, a current sensor, a self-adaptive active-frequency control module, a reactive-voltage control module, a virtual impedance control module and an SVPWM control module, wherein the energy storage device is connected in parallel to an alternating current bus output by a wind power plant through an inverter; the voltage sensor and the current sensor respectively acquire the voltage of the grid-connected end of the control system and the wind power plant and the current output by the energy storage device, and inputs the voltage and current into the adaptive active-frequency control module, the reactive-voltage control module, the virtual impedance control module and the SVPWM control module forcalculation to obtain a driving signal of the inverter; and the output of the energy storage device is controlled to perform fan grid-connected control. The method is beneficial to improving the rapidity and stability of fan grid-connected control.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for averagely controlling parallel power of inverters of low-voltage micro-grid
InactiveCN104734202AHarmonic voltage distortion rate reductionSuppressed circulationEnergy industrySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsBusbarLow voltage
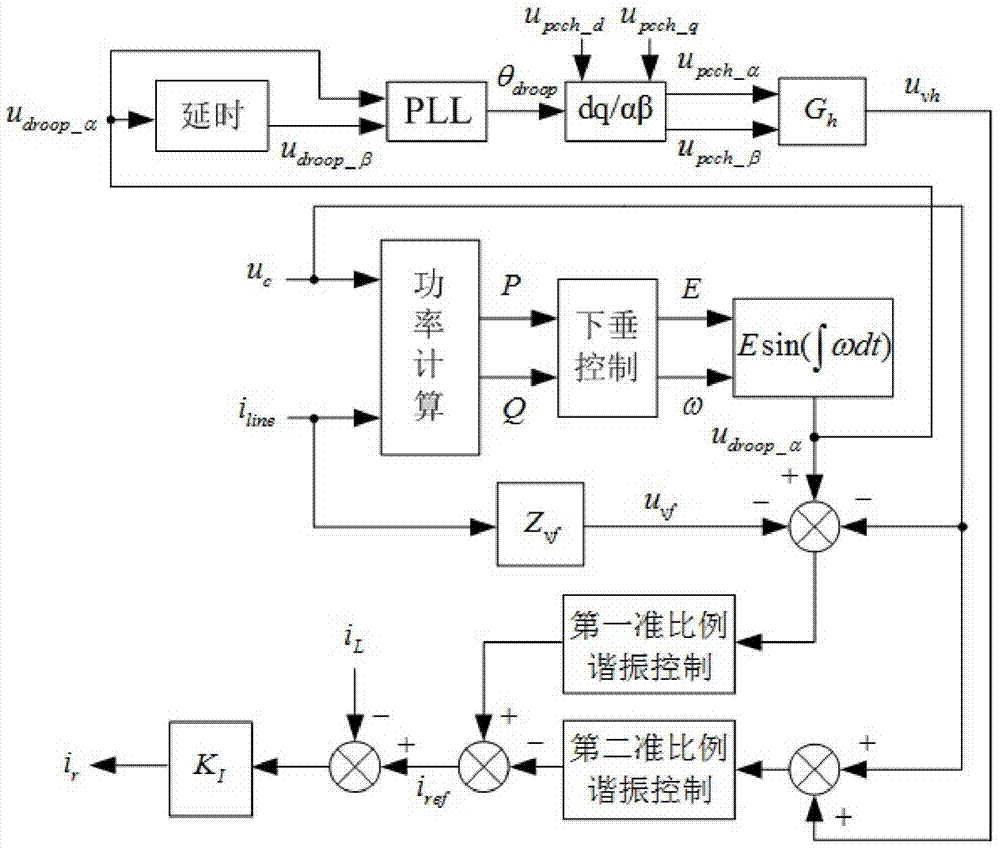
The invention provides a method for averagely controlling parallel power of inverters of a low-voltage micro-grid. A method of multiplying feeder line current and virtual complex impedances to obtain base wave virtual impedance voltage is used, output impedances of the inverters are designed to be ohmic and are matched with features of electrical parameters of a feeder line of the low-voltage micro-grid, and droop control output reference voltage is calculated and synthesized by a method of controlling power droop under the condition of ohmic equivalent output impedances; and a phase angle of the droop control output reference voltage is extracted and replaces a phase angle of common busbar voltage to perform dq / alpha beta coordinate transformation, and delay and distortion which are caused by the reason that the phase angle of the common busbar voltage is transmitted to a local controller from an integrated controller through low-bandwidth communication are avoided. When the method is used for a system for averagely controlling the parallel power of the inverters of the low-voltage micro-grid under the conditions that a nonlinear load exists, the feeder line impedances of the inverters are different, and the rated capacities of the inverters are different and the like, average control on the output power of the inverters can be realized, and circulation of the inverters can be restrained effectively.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Power conversion system and controlling method thereof and wind turbine power generation system
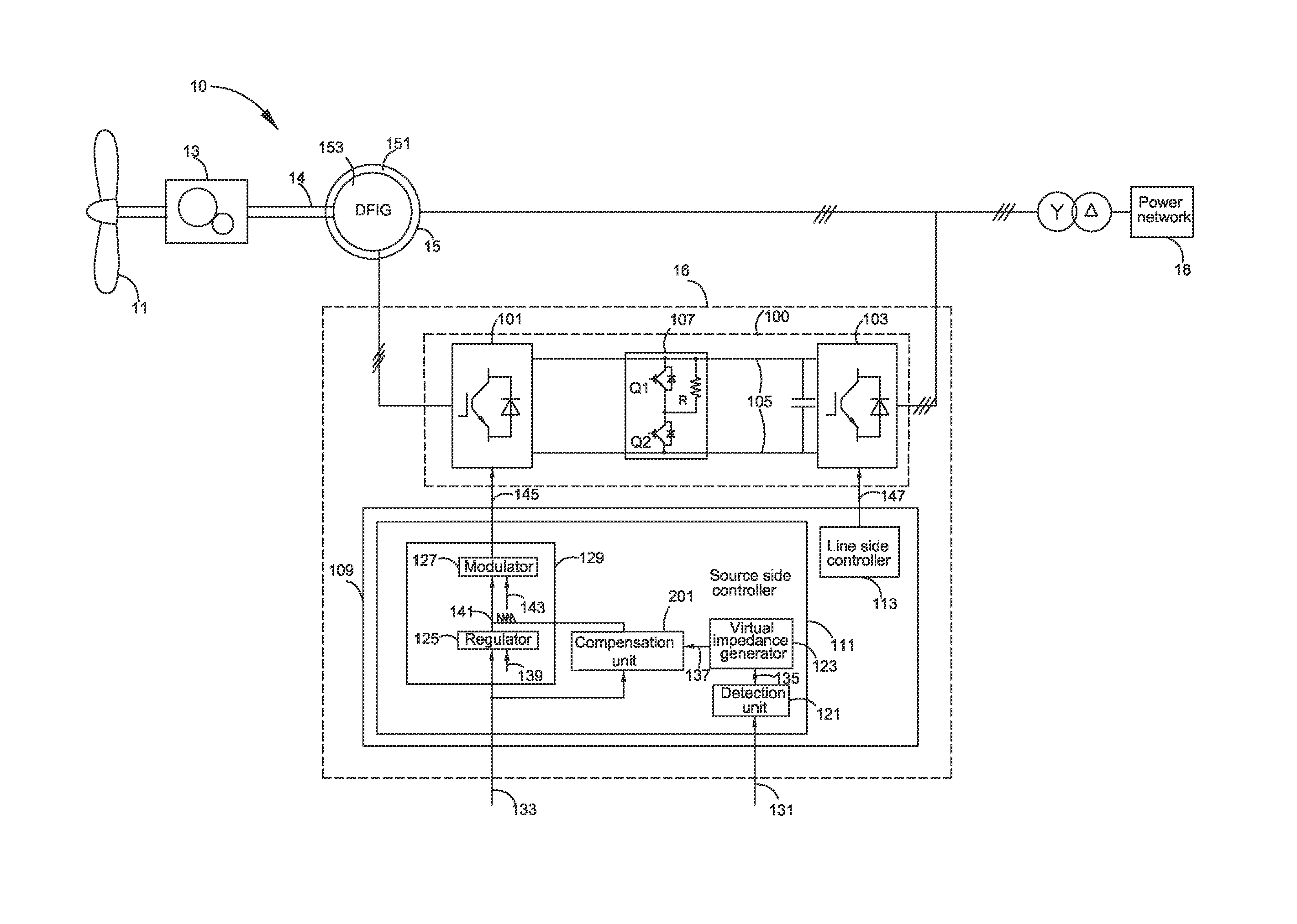
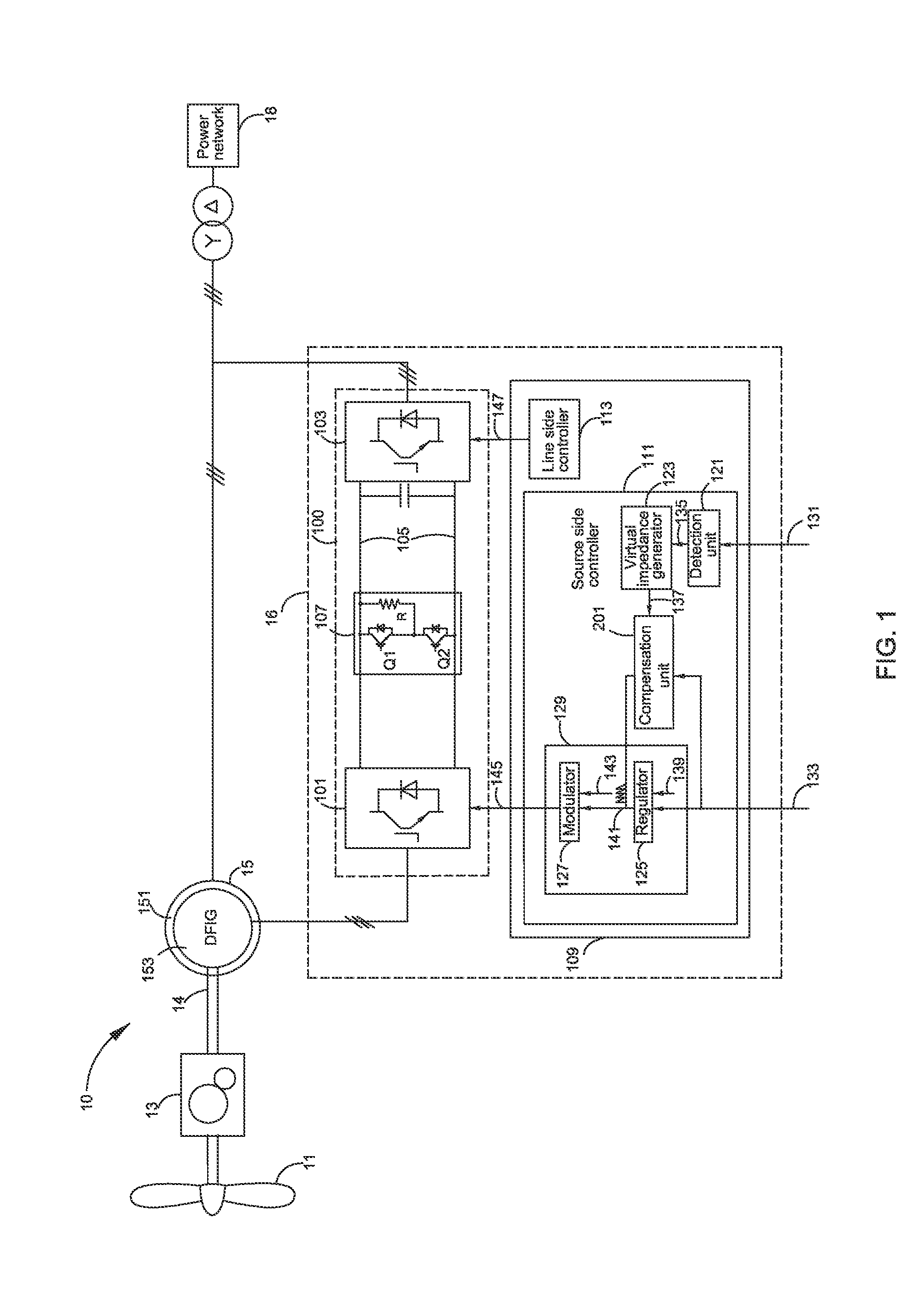
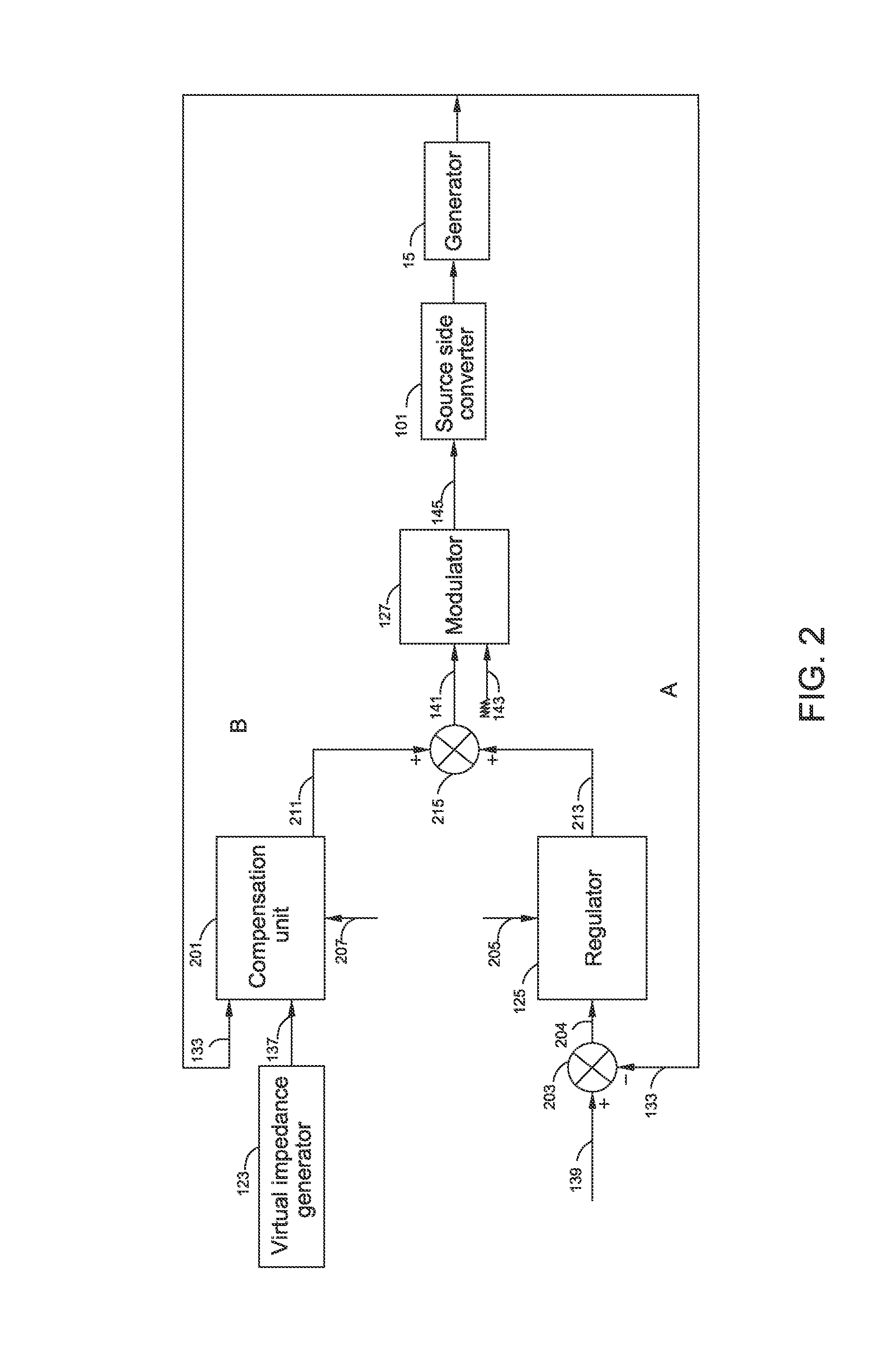
ActiveUS20160197559A1Extended service lifeLimit or eliminate torque transientsGenerator control circuitsElectric power transfer ac networkPower compensationSwitching signal
A system includes a source side converter for being electrically coupled to a generator of a power source, a line side converter for being electrically coupled to a power network, a DC link coupled between the source side converter and the line side converter, and a controller for generating source side switching signals based on a current or torque of the generator and a virtual impedance signal for system damping or reactive power compensation when at least one detected signal of the system is not normal. A method for controlling the system is also included.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-inverter micro-grid harmonic resonance suppression method based on adaptive virtual impedance remodeling
InactiveCN109698502AImprove output impedance characteristicsSuppression of series and parallel resonanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHarmonic reduction arrangementGrid impedanceEngineering
On the basis of the inverter-side current feedback control strategy, the invention presents a multi-inverter micro-grid harmonic resonance suppression method based on adaptive virtual impedance remodeling. The method includes a virtual impedance remodeling unit, a parameter adaptive adjustment unit and a grid impedance online detection unit. The virtual impedance remodeling unit can improve the output impedance characteristics of grid-connected inverters and inject certain damping components into a micro-grid. The parameter adaptive adjustment unit adaptively adjusts the control parameters ofthe virtual impedance remodeling unit and a current regulating controller according to the impedance parameters of the grid to maintain the stability of the system. The grid impedance online detectionunit provides the equivalent impedance of the grid as the input of the parameter adaptive adjustment unit. The method improves the characteristics of the current loop, and enables inverters to maintain stability under various grid impedance conditions. The method can solve the problems of complex control system, fixed control parameters and low efficiency of the regulation process in the existingmulti-inverter micro-grid system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low voltage micro-network droop control method based on 'virtual complex impedance'
InactiveCN109494709AReduce dropImprove power qualityAc network circuit arrangementsPower qualityPower coupling
The invention discloses a low voltage micro-network control policy based on 'virtual complex impedance'. The method comprises the steps that the introduction of traditional virtual impedance causes alarge voltage drop; a general droop control expression with a resistance ratio is proposed; virtual complex impedance is designed; the expression of virtual complex impedance is constructed to acquirethe virtual complex impedance expression related to the resistance ratio r; a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter mathematical model with virtual complex impedance is established; the output voltageand equivalent output impedance of an inverter are acquired; a virtual impedance value is set according to the total voltage drop of a system; and the new voltage value of the inverter is acquired. According to the invention, adaptive virtual impedance is used to adjust the equivalent output impedance of the micro-network parallel inverter, so that the impedance tends to be inductive; the virtualimpedance can be adaptively adjusted, which not only reduces voltage drop, but also achieves power equalization control; power coupling is reduced; and the power quality of a micro-source during operation is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com