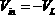Patents
Literature
31 results about "Negative inductance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
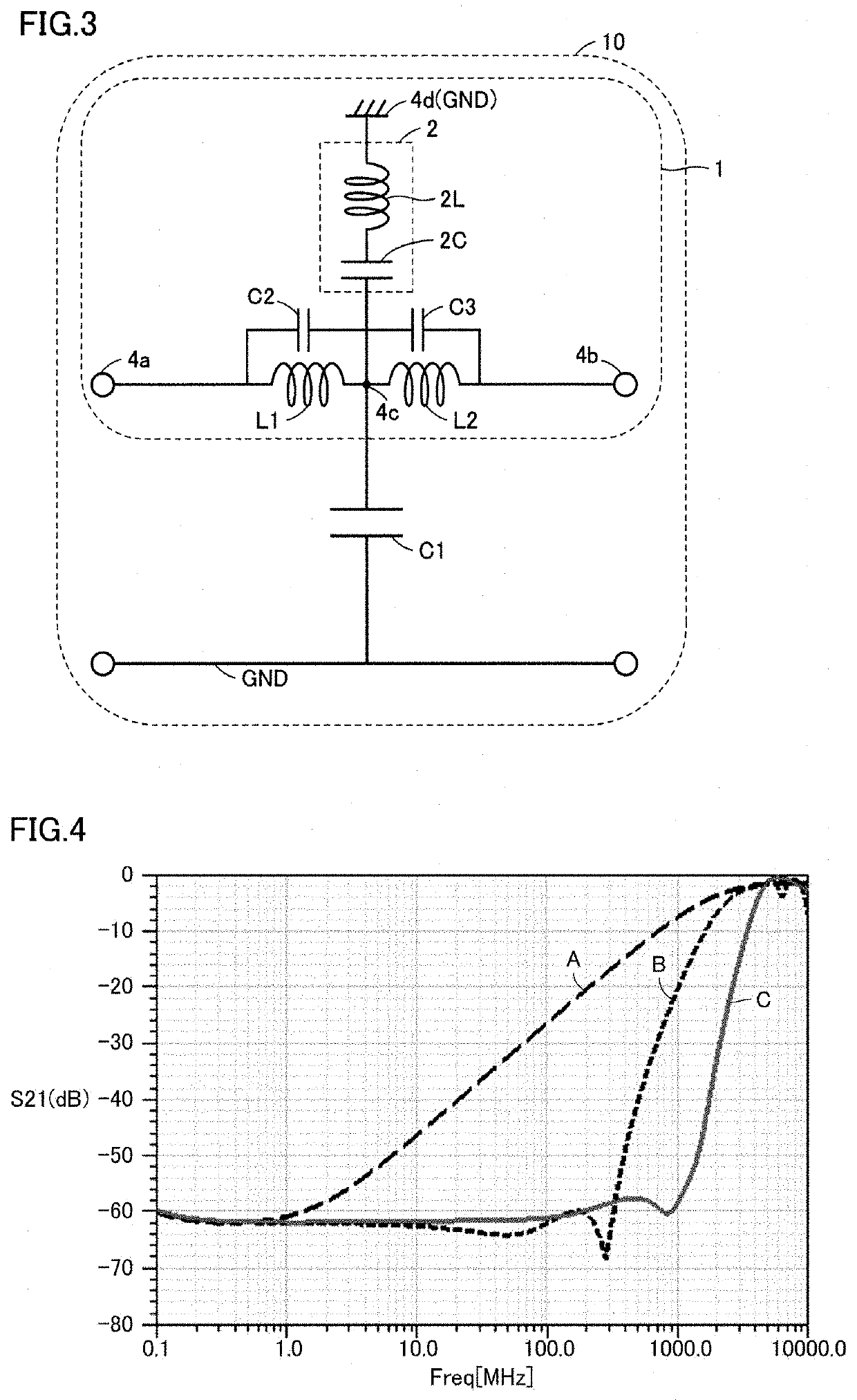
At a fixed frequency, a negative inductance can be seen as a capacitor which presents the same impedance as an inductor but with opposite phase. Over a range of frequencies, a negative inductance is not generally directly physically realisable.
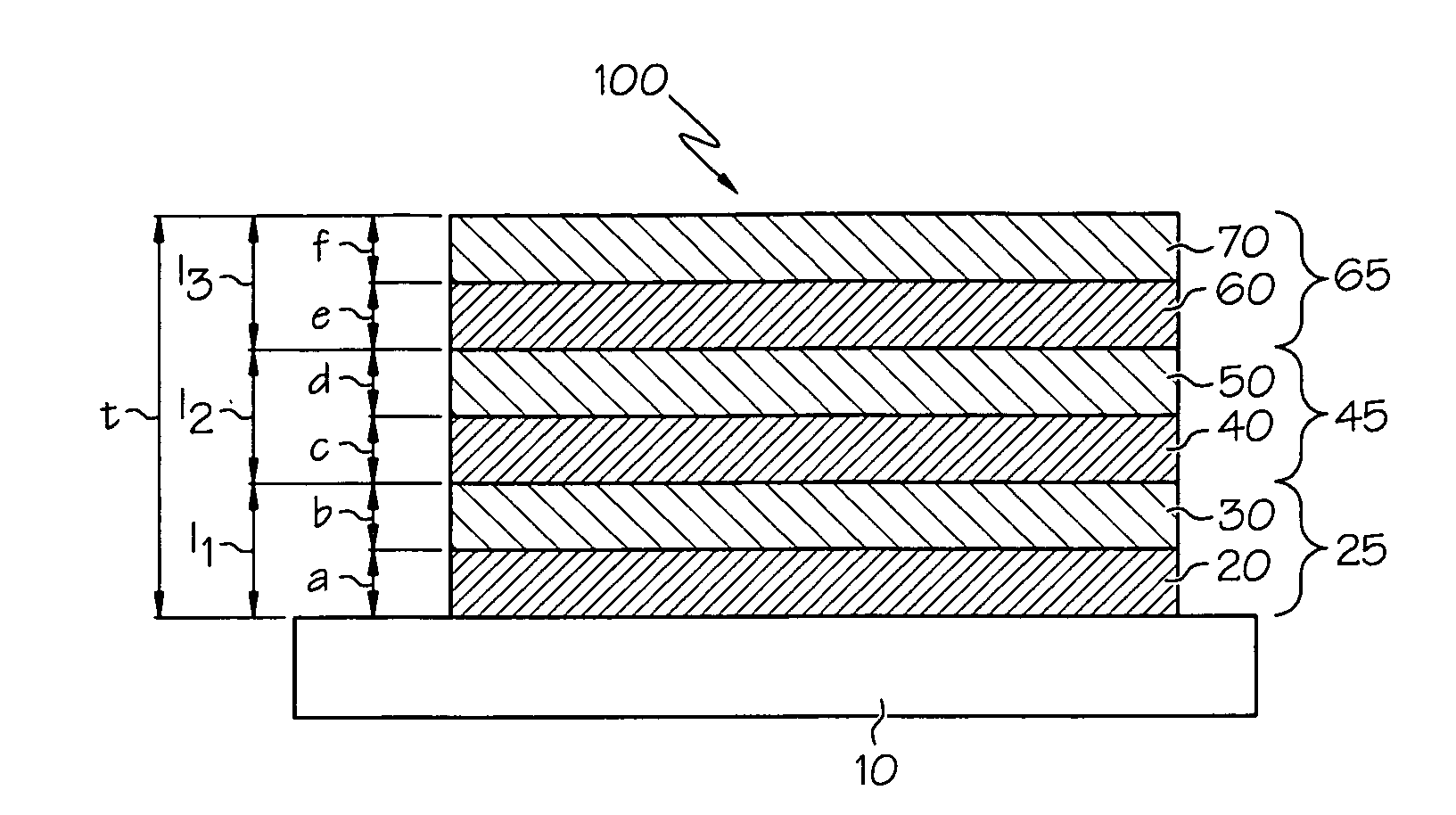
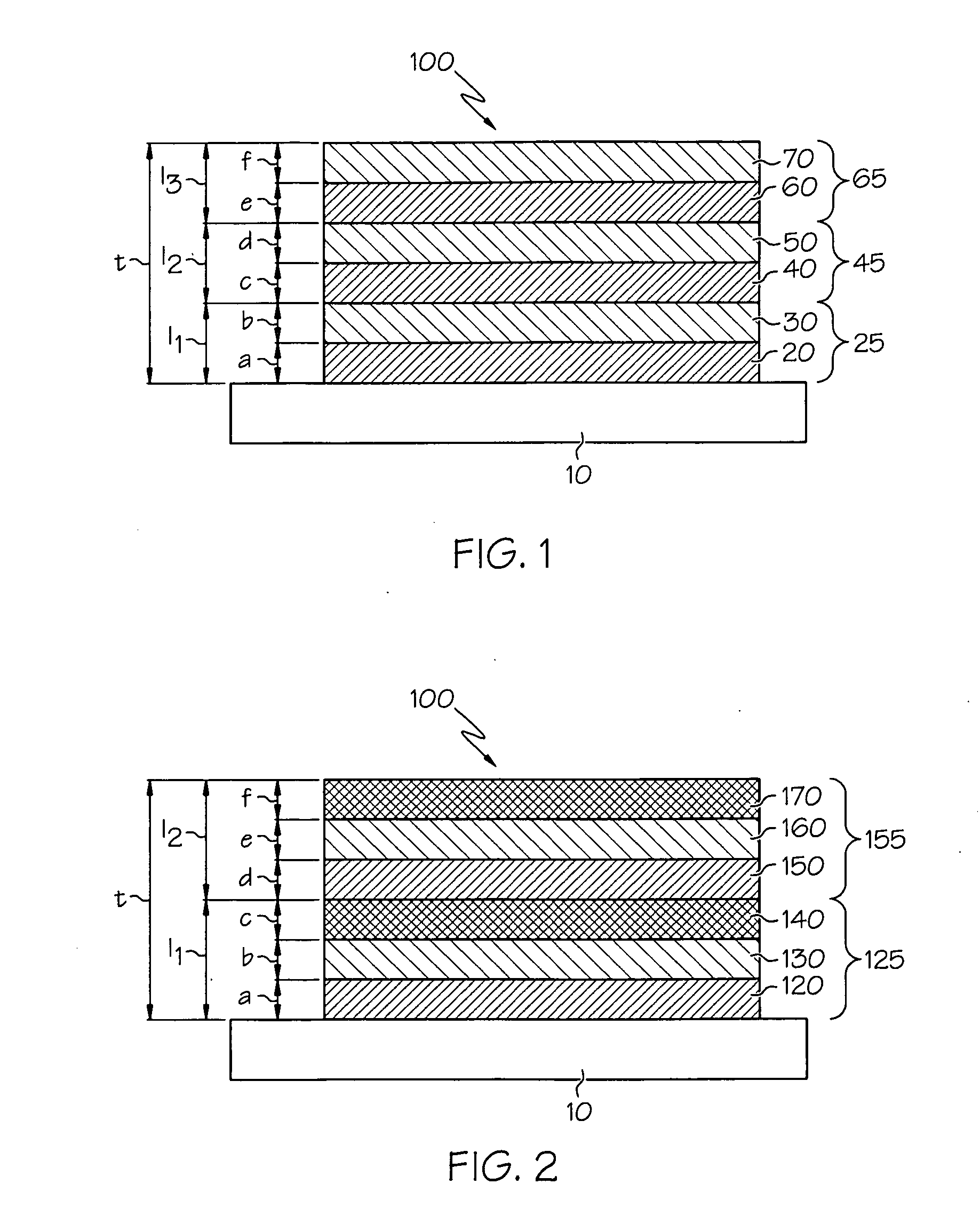
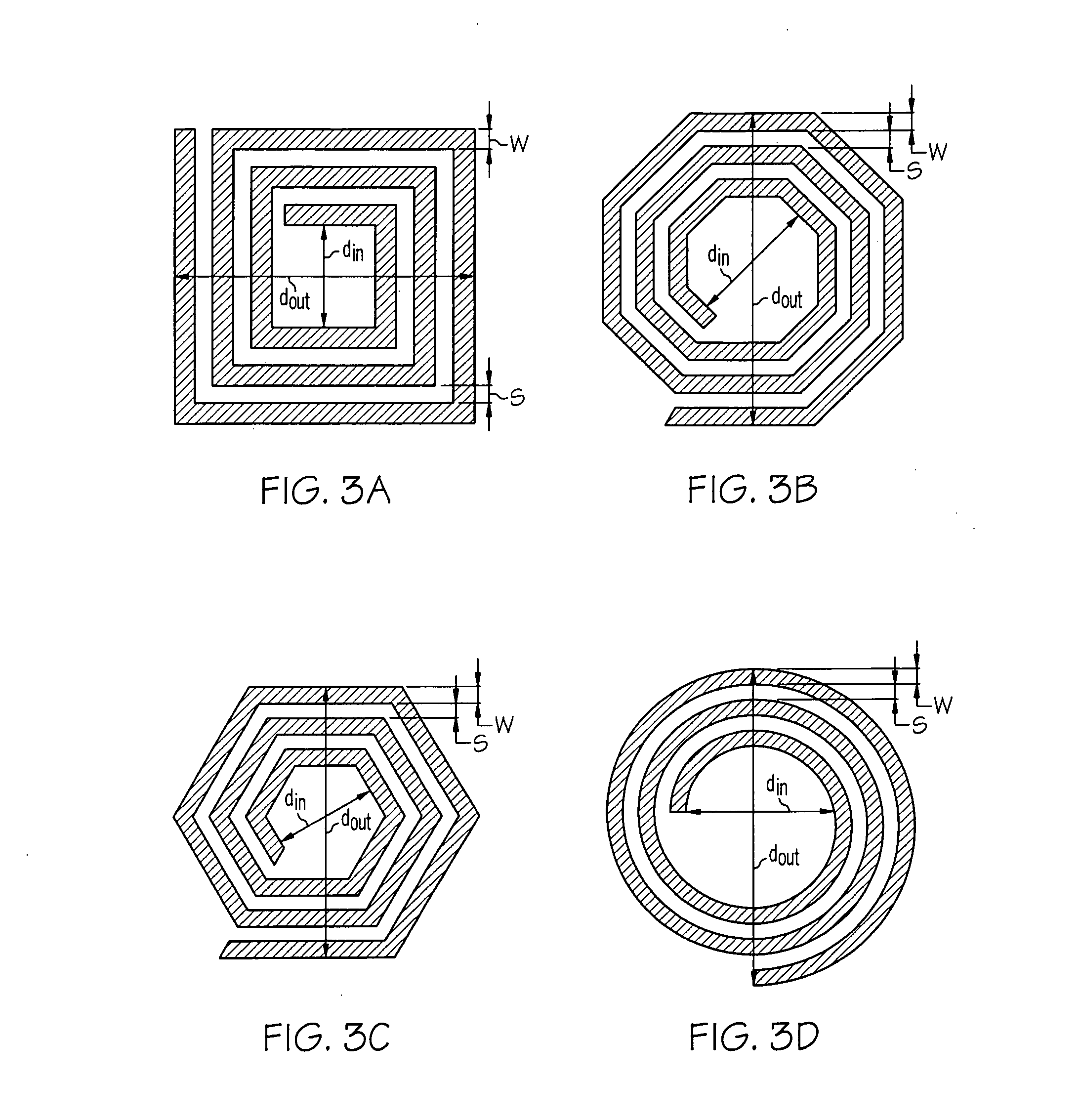
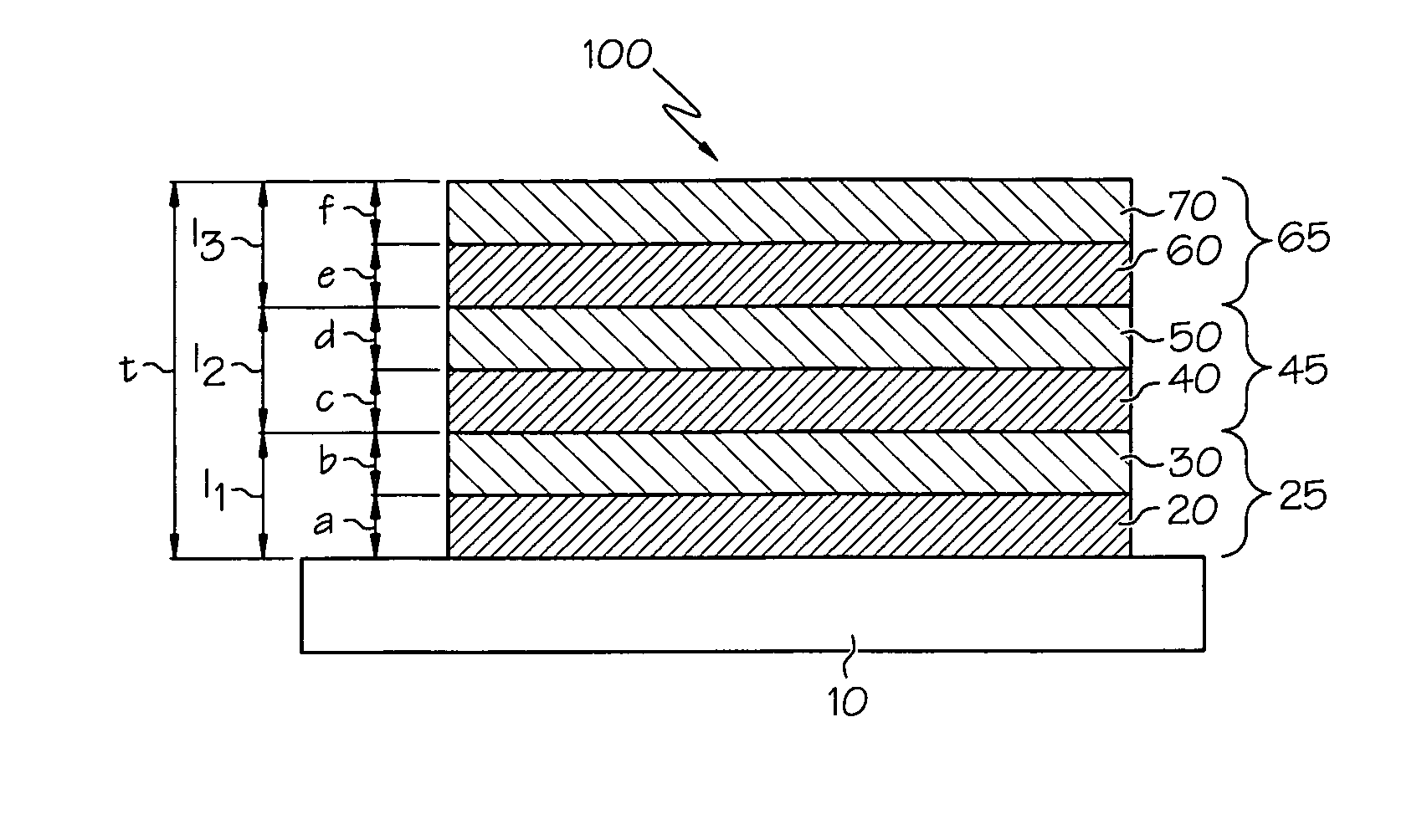
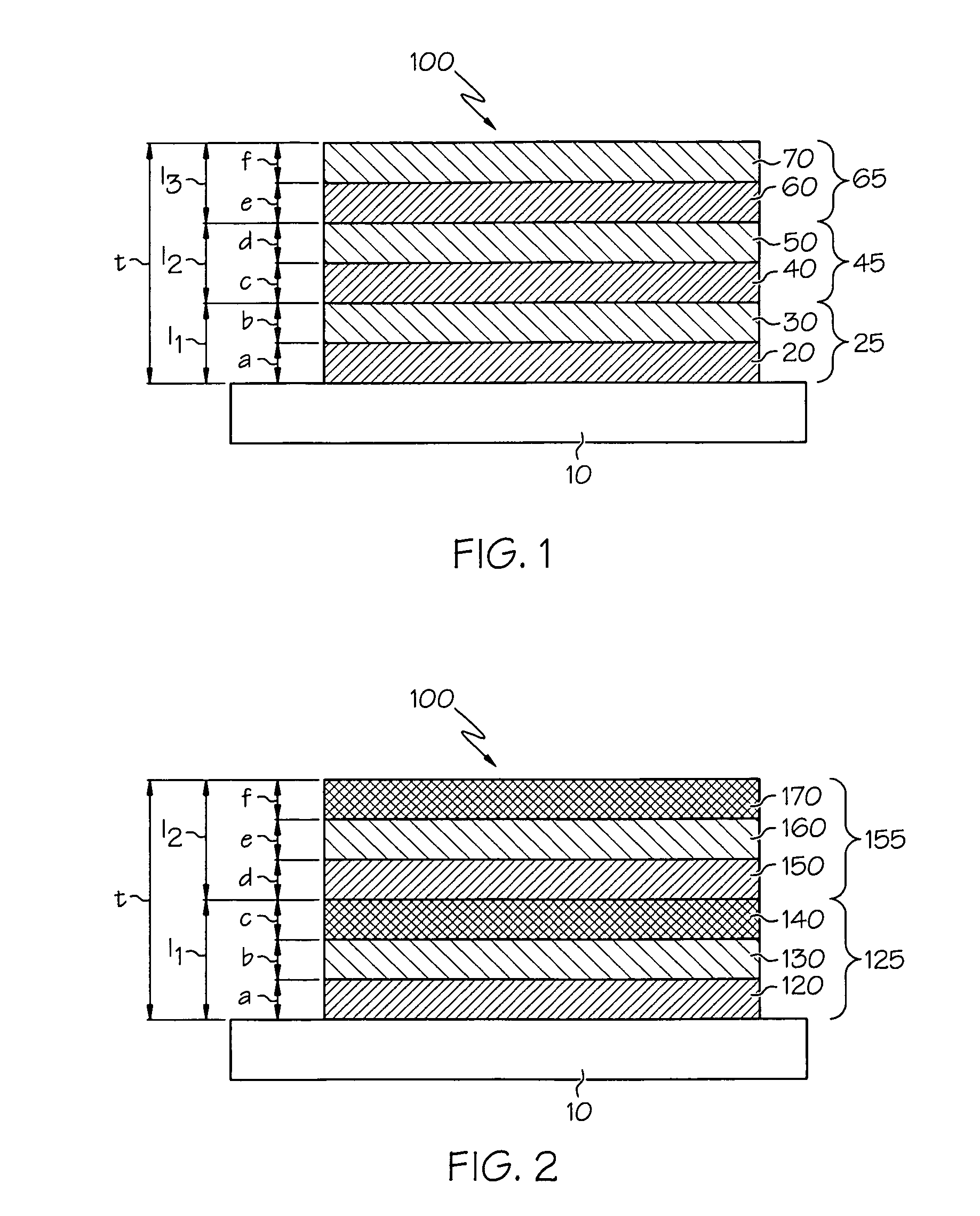
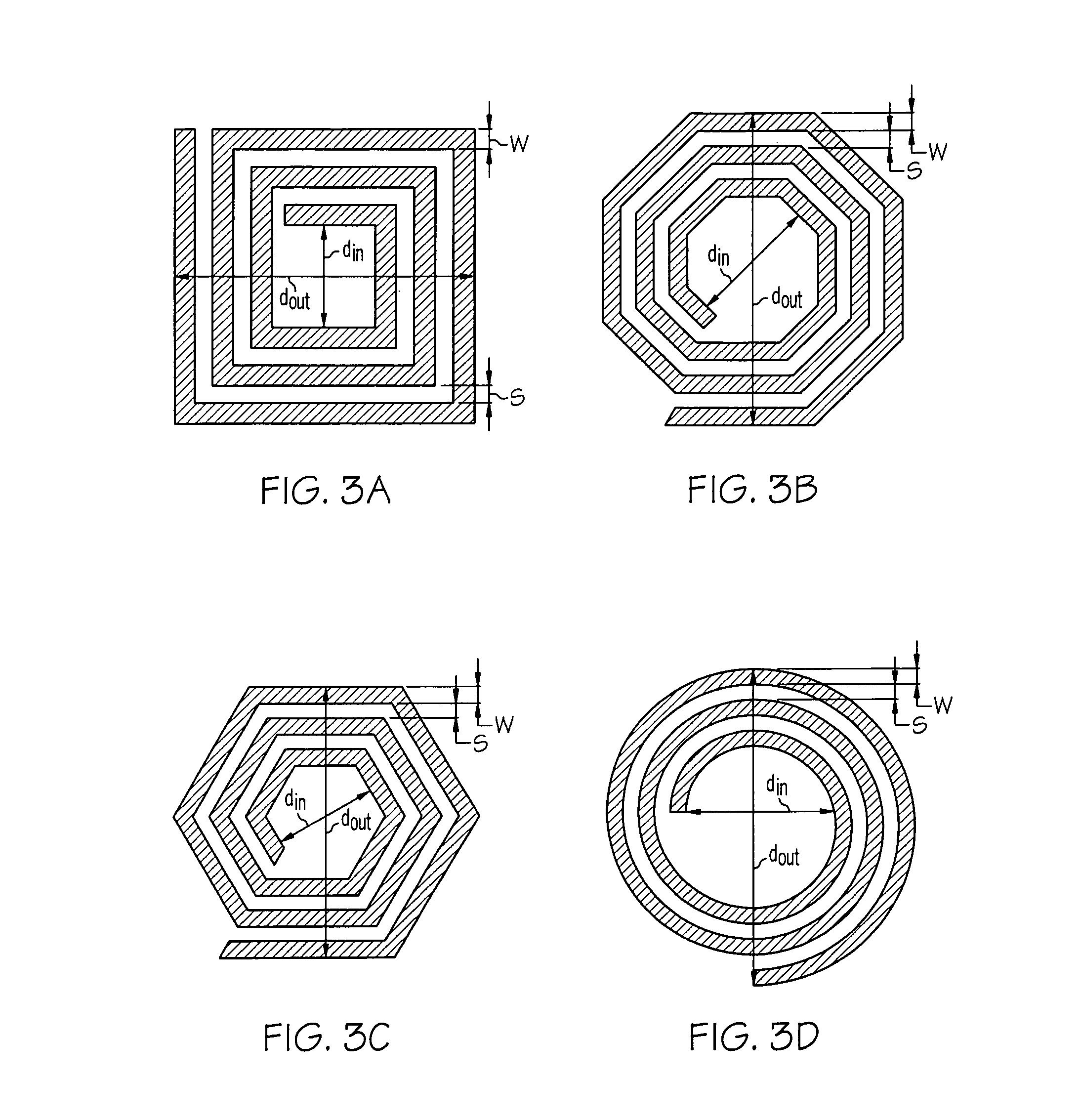
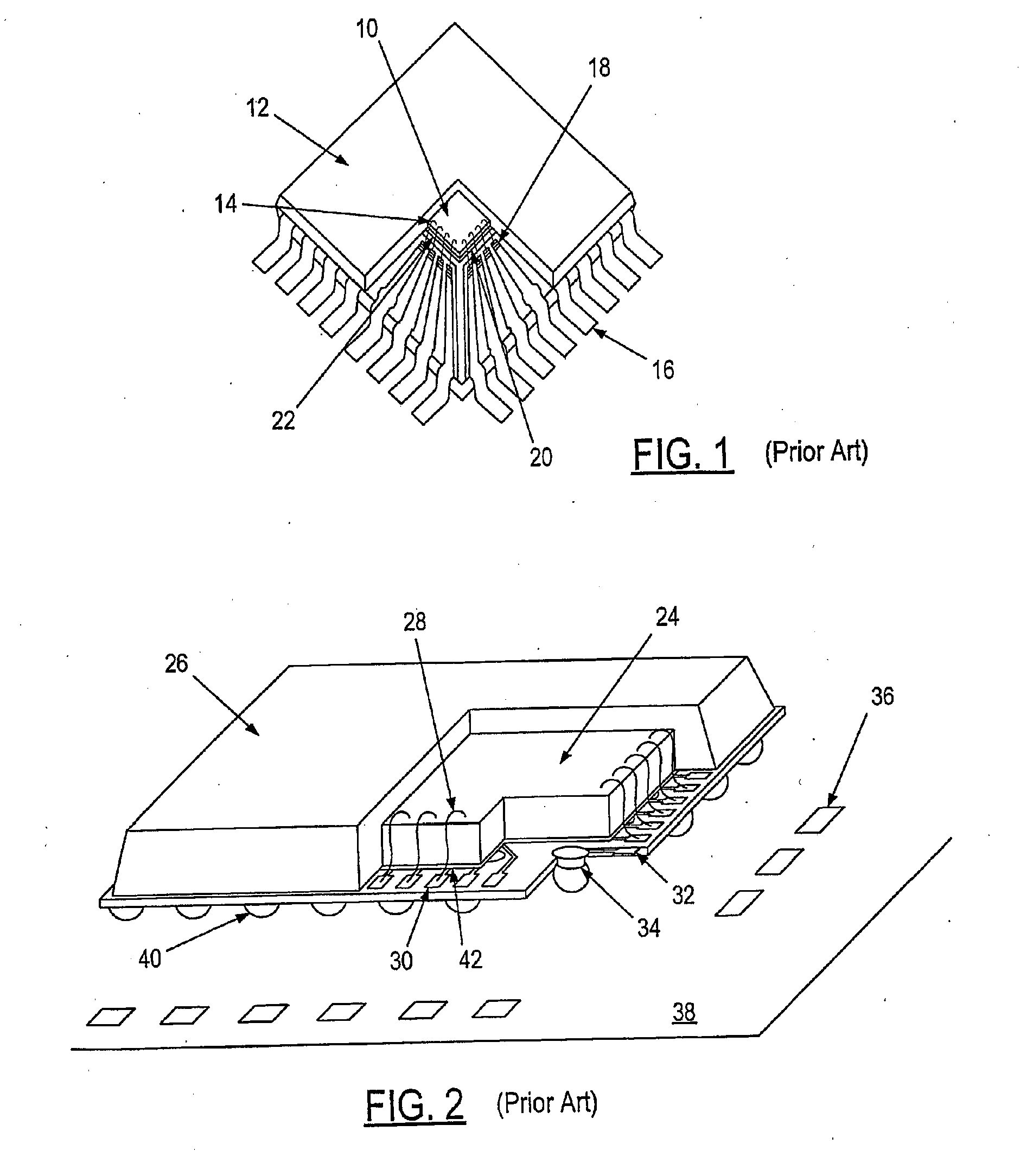
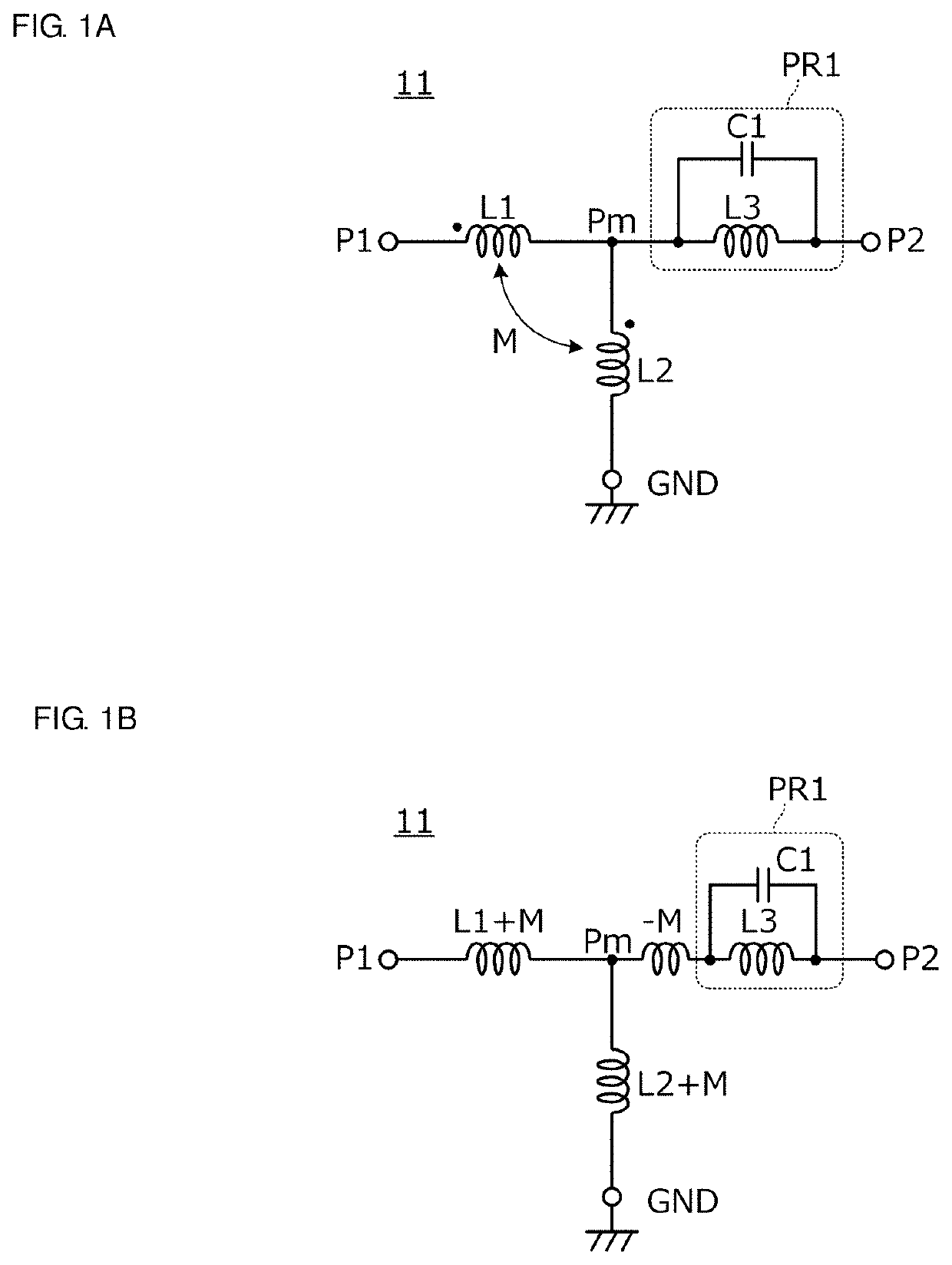
Thin film structures with negative inductance and methods for fabricating inductors comprising the same
ActiveUS20090261936A1Transformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical conductorEngineering
An inductor structure comprising a substrate and a planar conductor structure on a surface of the substrate, and methods for fabricating an inductor structure. The planar conductor structure may comprise a vertical stack of three or more multilayer films. Each multilayer film may comprise a first layer of a first metal, defining a first vertical thickness, and a second layer of a second metal, defining a second vertical thickness. The metals and thicknesses are chosen such that the inductor exhibits a negative electrical self-inductance when an electrical signal is transmitted from a first contact point to a second contact point.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
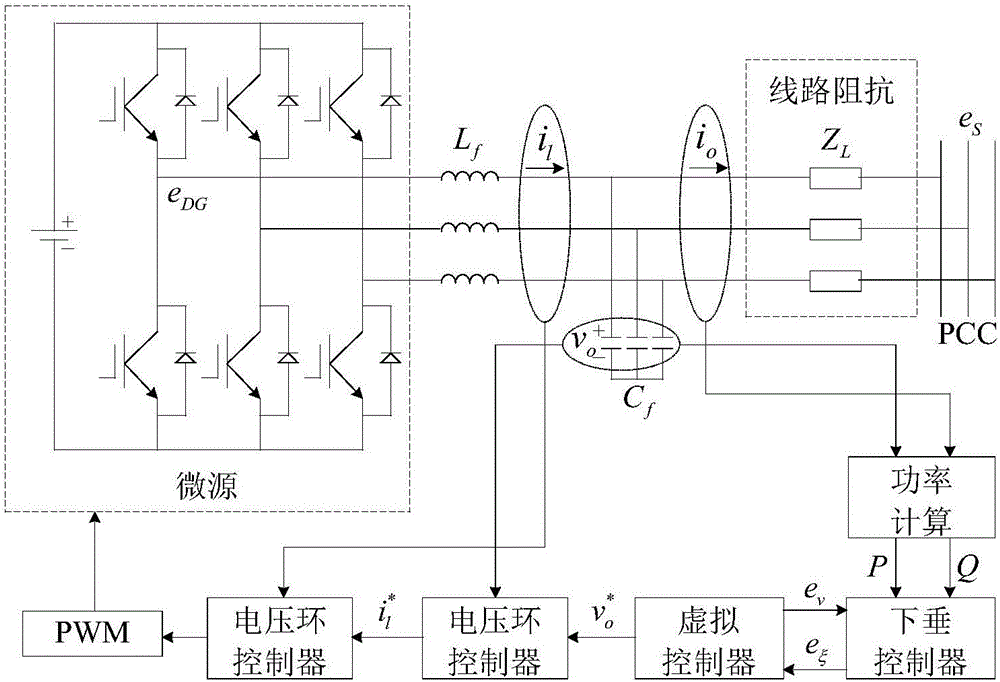
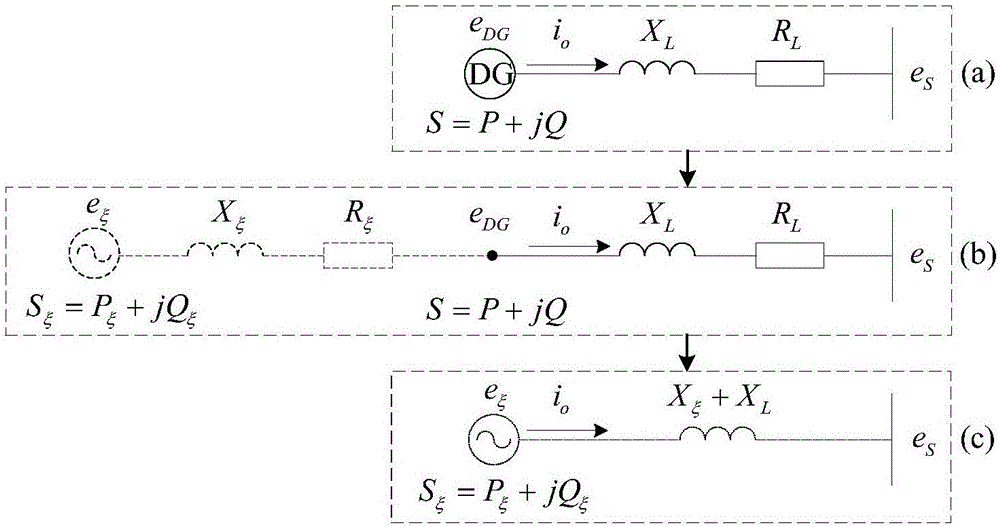
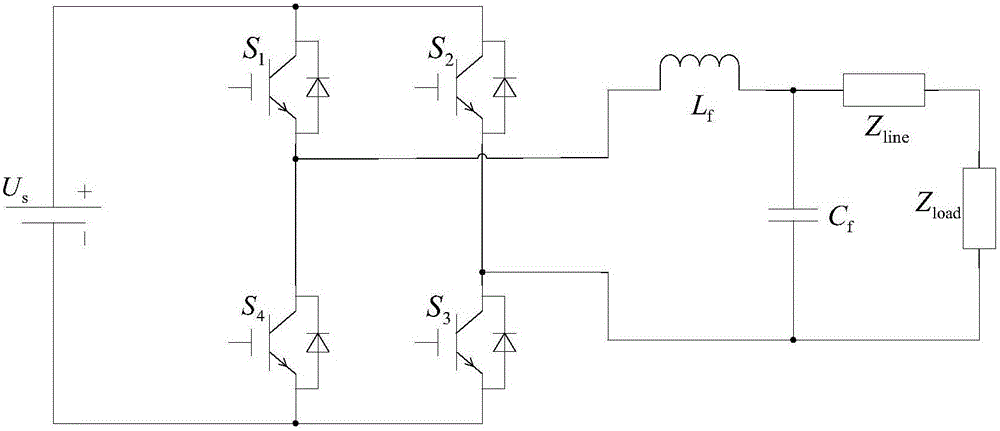
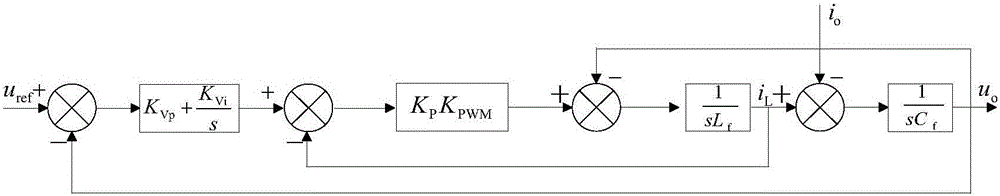
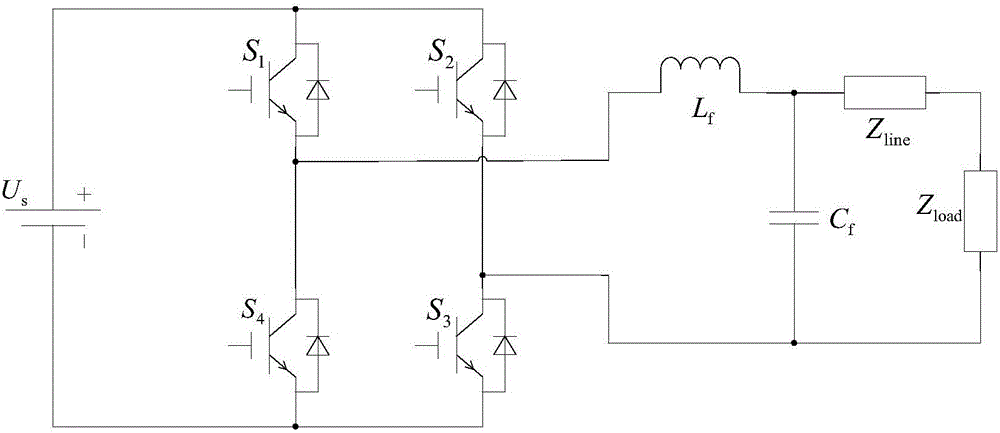
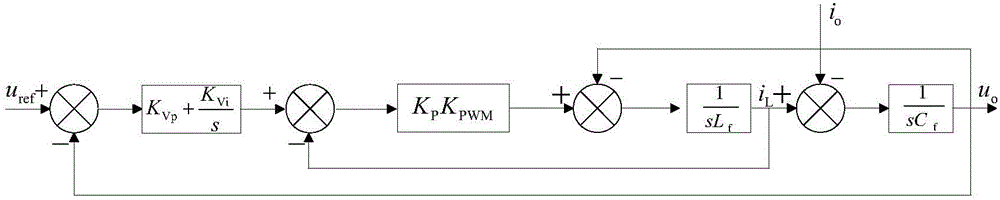
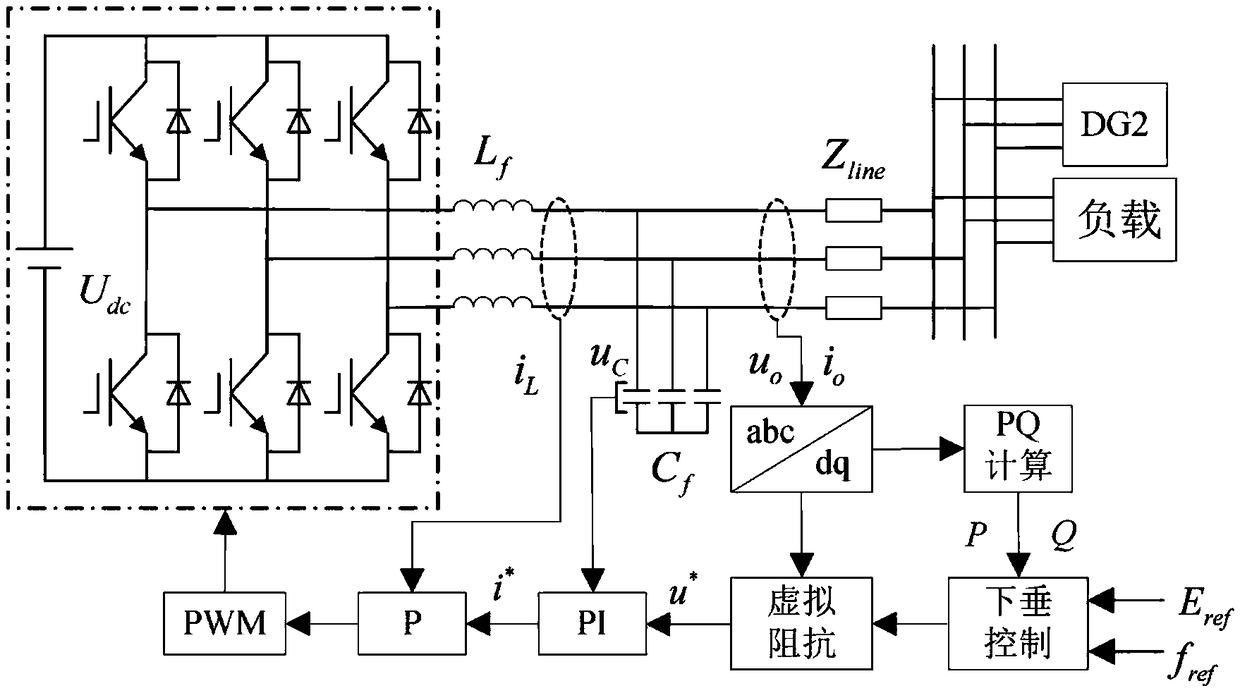
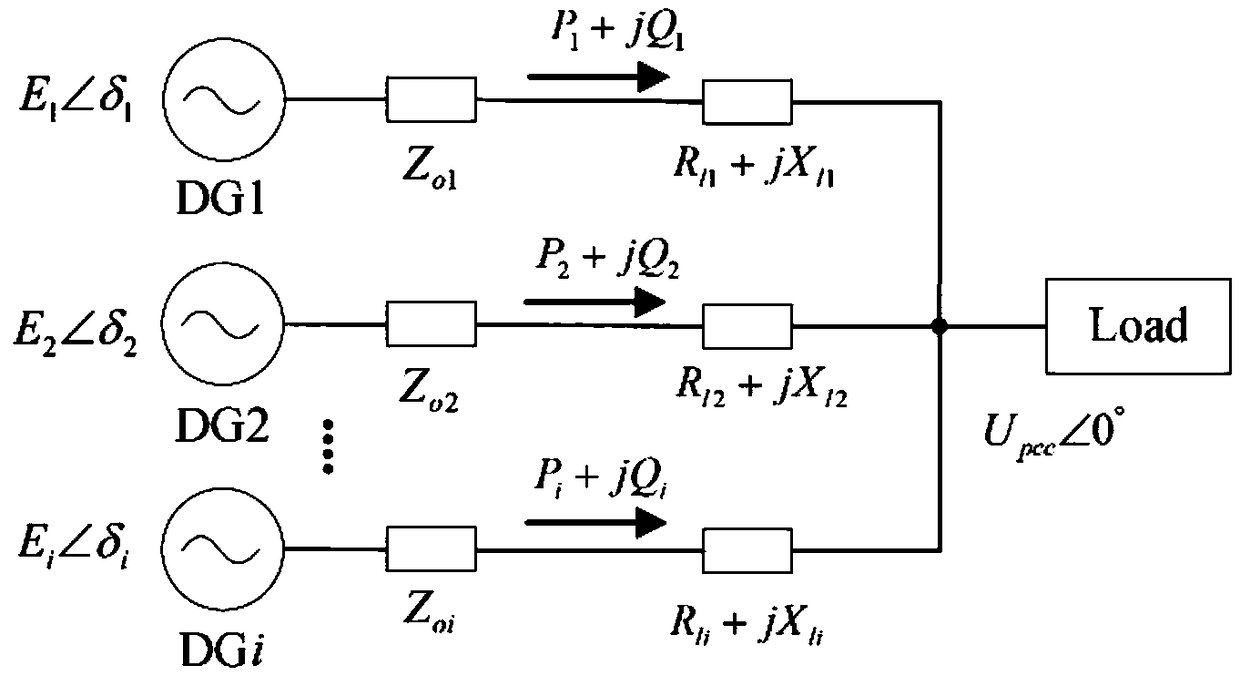
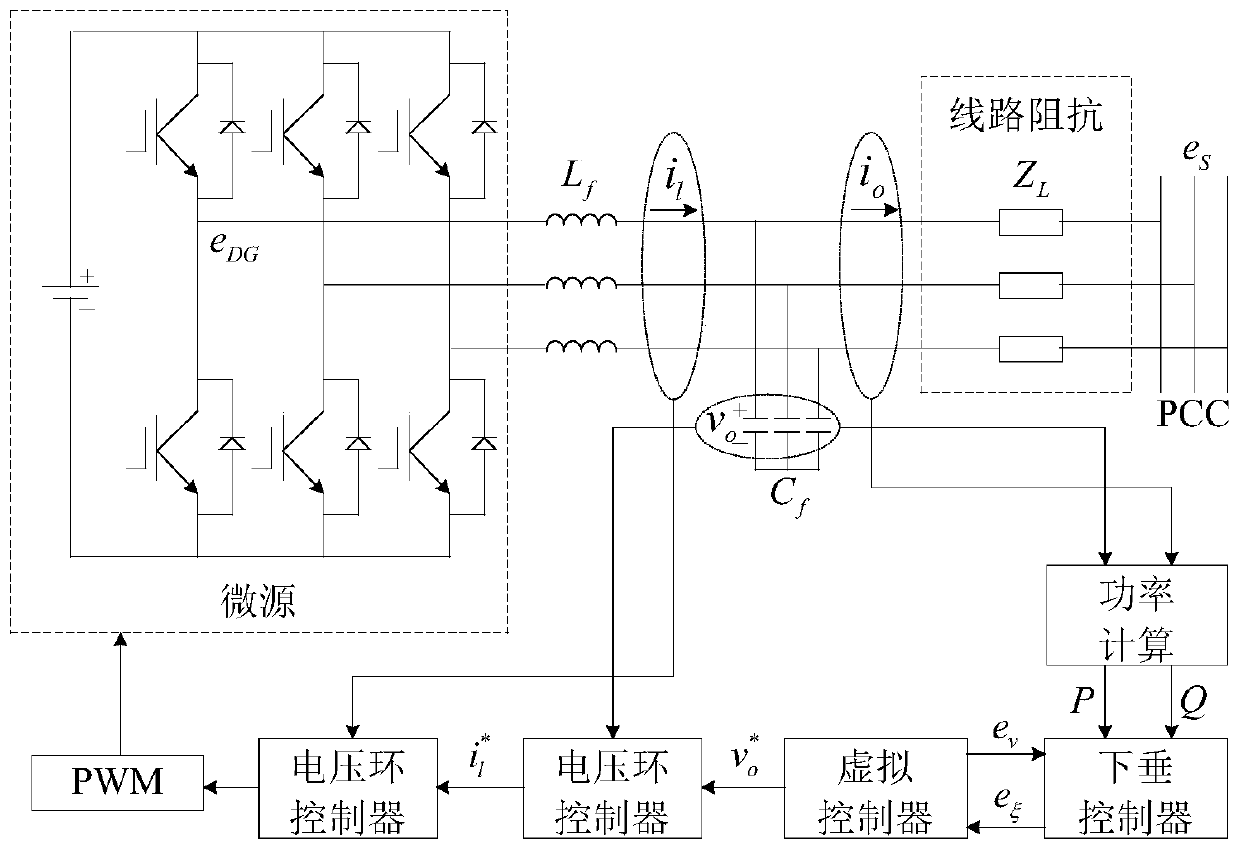
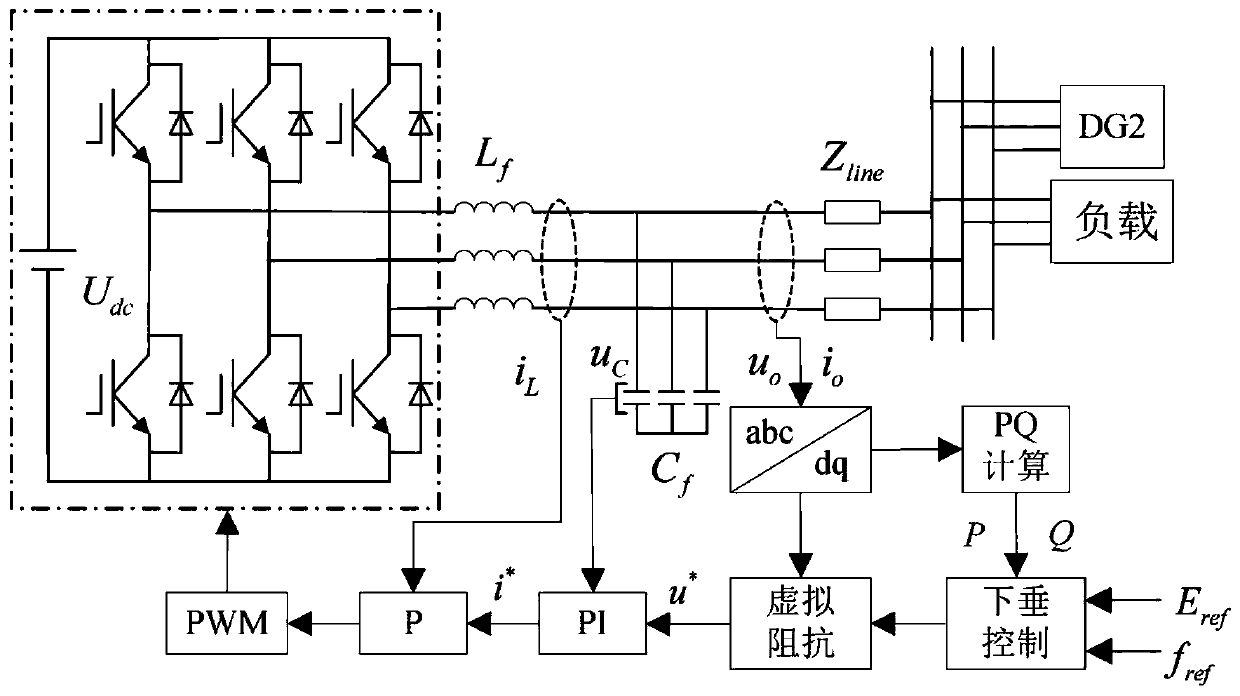
Low-voltage micro-grid inverter control system based on virtual impedance and virtual power source
ActiveCN106712088ALow costAvoid adding filter inductanceAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLow voltageVirtual control
The invention discloses a low-voltage micro-grid inverter control system based on virtual impedance and a virtual power source. The control system comprises a droop controller, a virtual controller and a voltage / current dual-loop controller, and is characterized by establishing the droop controller capable of simulating the function of the virtual power supply through improvement of droop parameters, and carrying out tracking control on the voltage of the droop controller through fractional-order PID; by analyzing relation between virtual negative inductance and micro-source reactive power sharing, determining the value of virtual negative inductance required for accurate reactive power sharing, realizing virtual impedance in the virtual controller, and feeding back voltage drop of the virtual controller to the droop controller to participate in fractional-order PID tracking control of voltage of the virtual power source; and carrying out tracking control on inverter voltage through fractional-order PID in the voltage / current dual-loop controller, determining filtering parameters in the controller according to a transfer function of a filter, and carrying out optimization on fractional-order PID controller parameters through a difference genetic algorithm. The control system can ensure low-voltage micro-grid power decoupling and improve a reactive power sharing effect.
Owner:秦皇岛市睿能光电科技有限公司
Single-phase inverter parallel control method based on virtual complex impedance
InactiveCN106026744AReduce power couplingReduce the equivalent output impedanceAc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceMicrogrid
The invention proposes a single-phase inverter parallel control method based on virtual complex impedance, and the virtual complex impedance consists of virtual negative inductance and virtual positive resistance. The high frequency burr in the output of an inverter is filtered through an LC filter, and the output of the inverter is connected to an output AC bus through a line. Because of the existing of the filter inductance, the output impedance of the inverter is inductive, but not purely inductive. After the virtual complex impedance is added, the method can counteract the inductiveness generated by the filter inductance, thereby enabling the equivalent output impedance of the inverter to be resistive. The control method is suitable for a multi-inverter parallel control system in a low-voltage microgrid.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
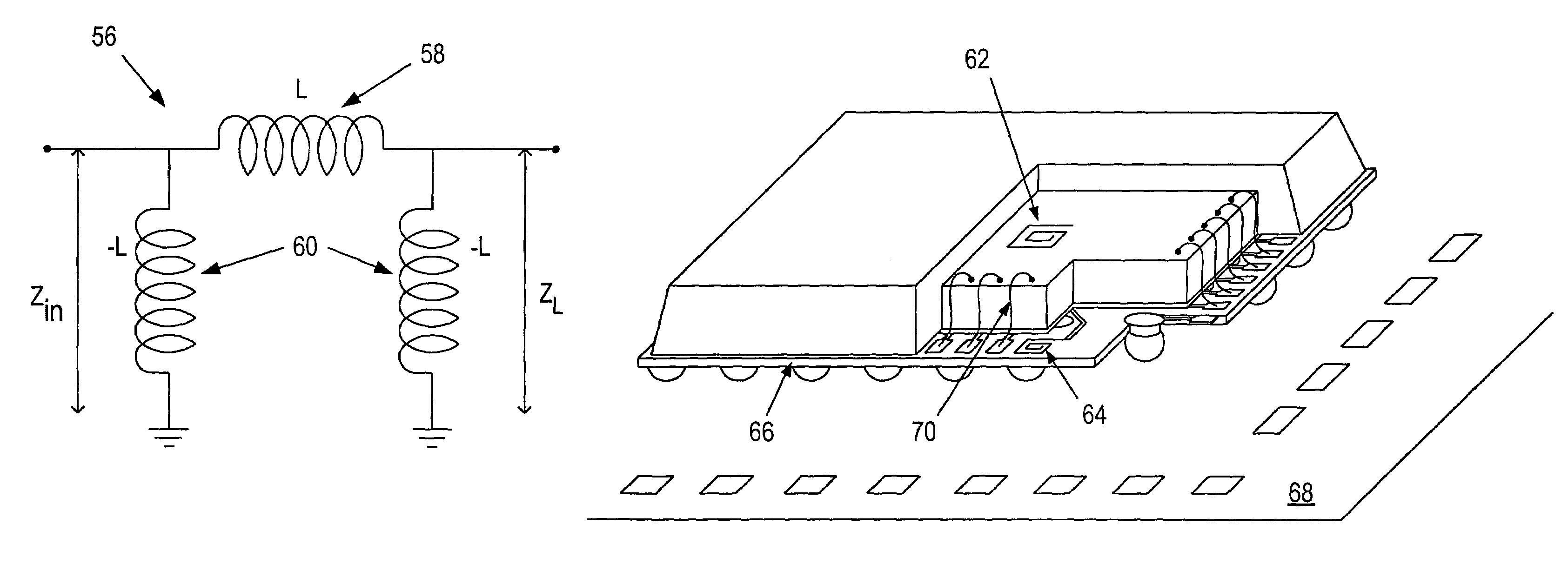
Integrated circuit incorporating wire bond inductance
InactiveUS7342300B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingComputer module
The invention relates to the field of electronics, more particularly to the wire bonds incorporated into an integrated circuit package such as a quad flat pack, a ball grid array or hybrid style module. The present invention takes the normally undesirable wire bond inductance and uses it in an operational circuit where positive inductance is required. The circuit in which the wire bond inductance is used is located primarily in the integrated circuit die housed in the integrated circuit package, but may also include off-die components. In one example, a wire bond is used as the required series inductance in a discrete circuit impedance inverter which consists of two shunt-to-ground negative inductances and one series positive inductance. One of the negative inductances is located on-die, while the other is located off-die.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Active broadband matching method of short-wave frequency-band electrically small antenna and matching circuit thereof
InactiveCN104202007AGood offsetting effectMultiple-port networksTransmissionCapacitanceTransmission line transformer
The invention discloses an active broadband matching method of a short-wave frequency-band electrically small antenna and a matching circuit thereof, the electrically small antenna is matched by a non-Forster reactive element and a passive broadband matching network, the non-Forster reactive element is realized by a negative impedance converter, the negative impedance converter and the passive broadband matching network are cascaded into an active broadband matching network with two ports, one port of the matching network is connected with the electrically small antenna, and said two ports are connected with an emitter / receiver. In the invention, the non-Forster reactive element and the passive broadband matching network are comprehensively considered, led loss is regulated in realization process of the non-Forster reactive element, single traditional negative capacitor can be replaced by in series connecting a negative capacitor and a negative inductor to better neutralize the impedance imaginary part, a transmission line transformer is led into the matching network, and the deviation between a testing value and a design value can be compensated by slightly adjusting the transformation ratio of the transmission line transformer.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Differential negative impedance converters and inverters with variable or tunable conversion ratios
ActiveUS8988173B2Reduce parasitismImprove matchImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceEngineering
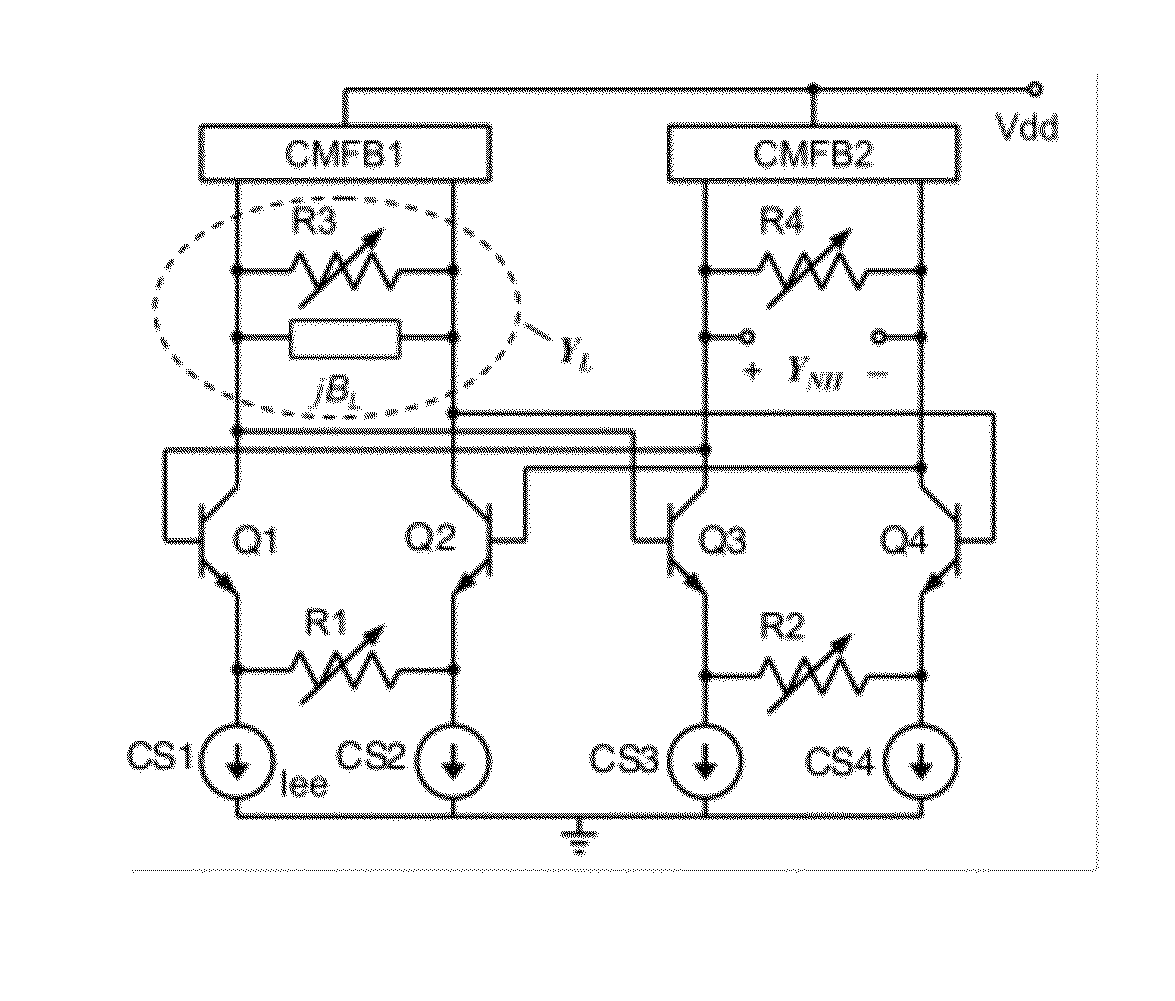
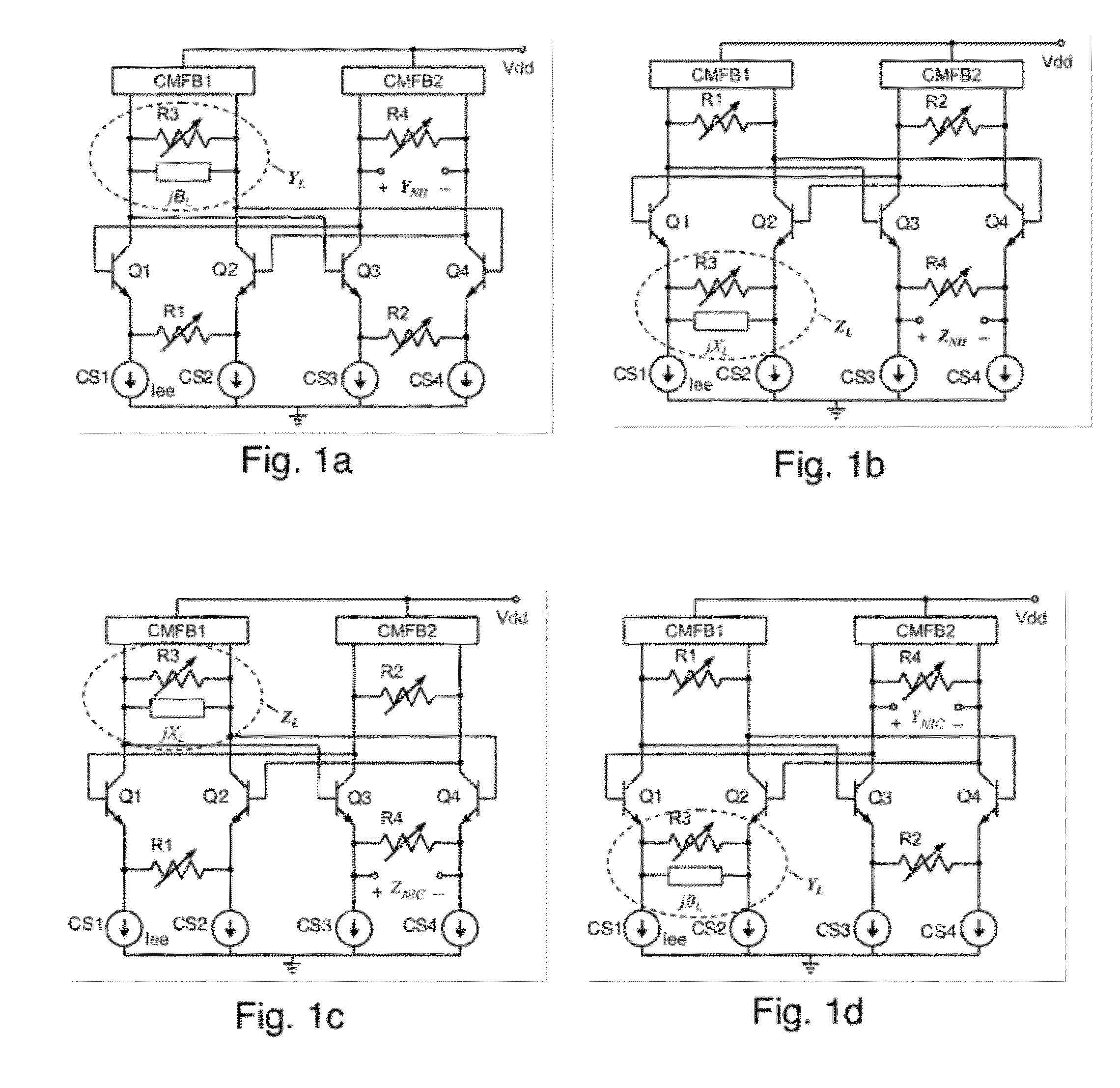
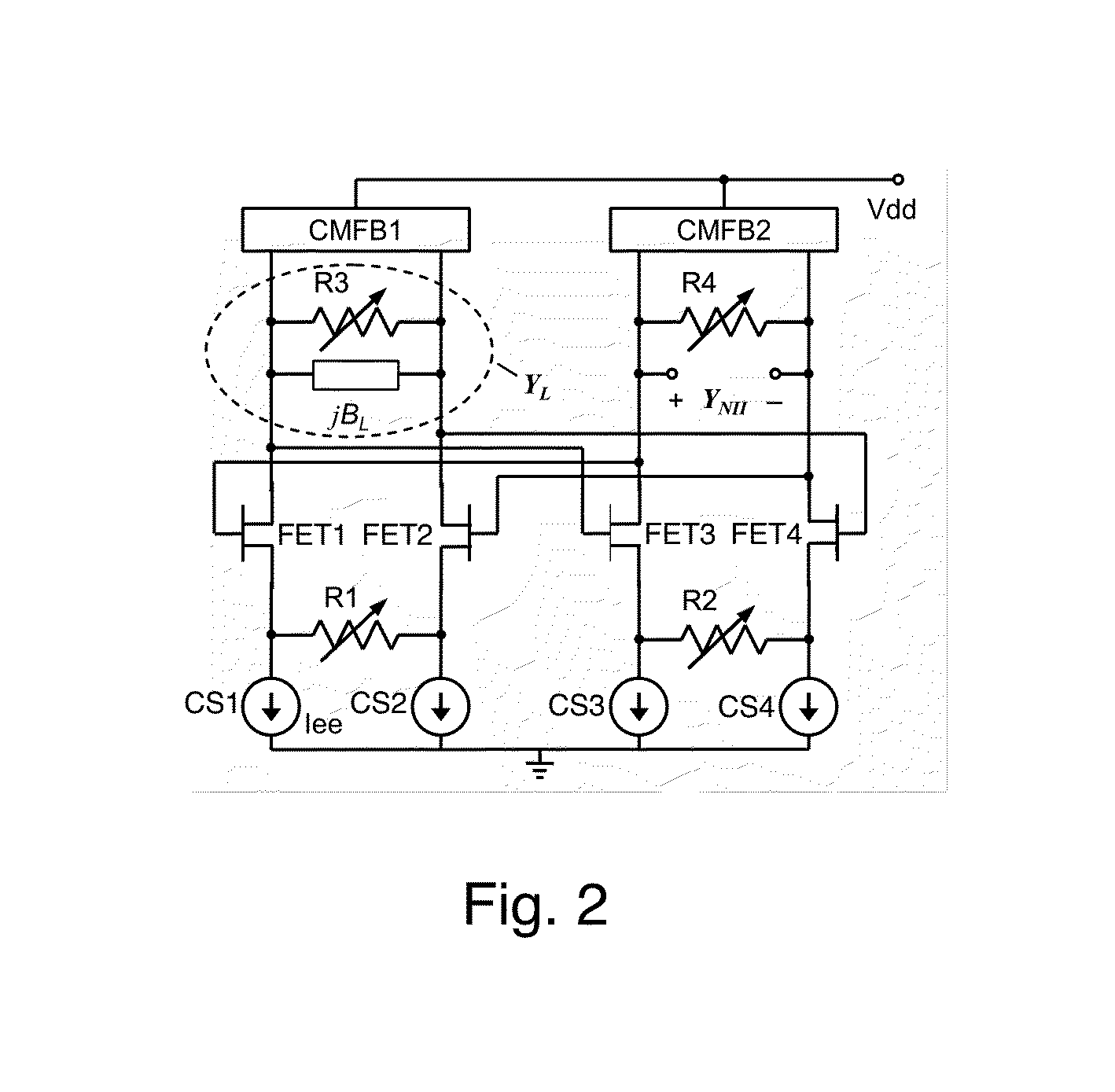
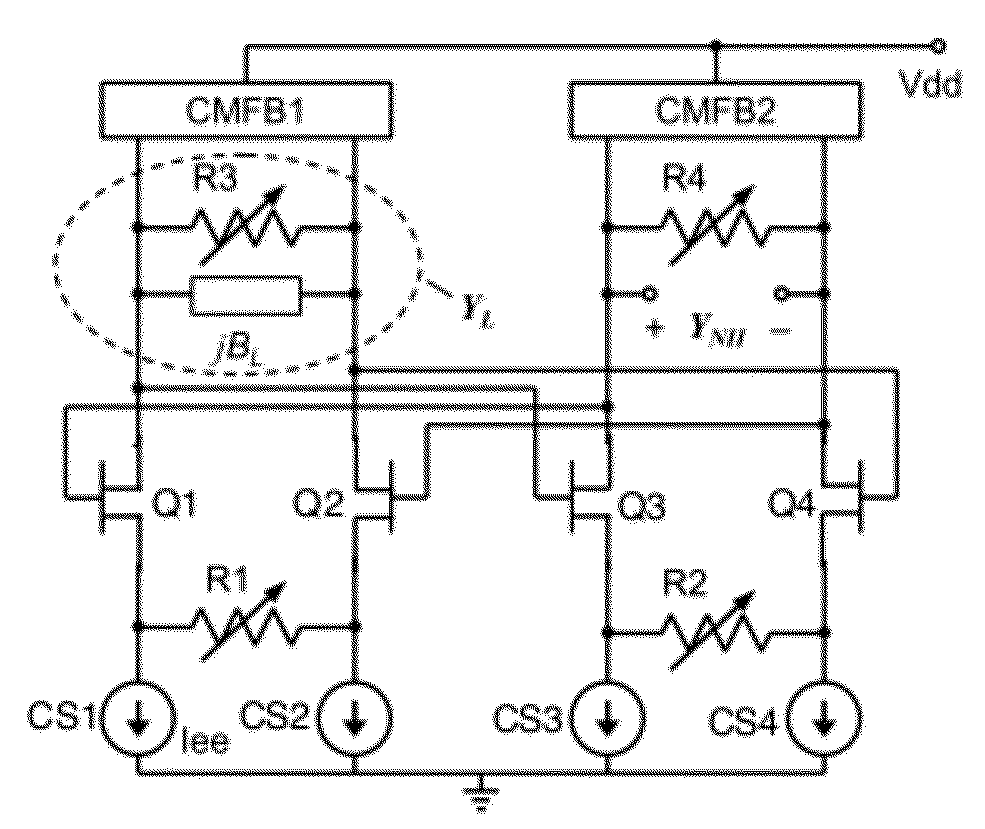
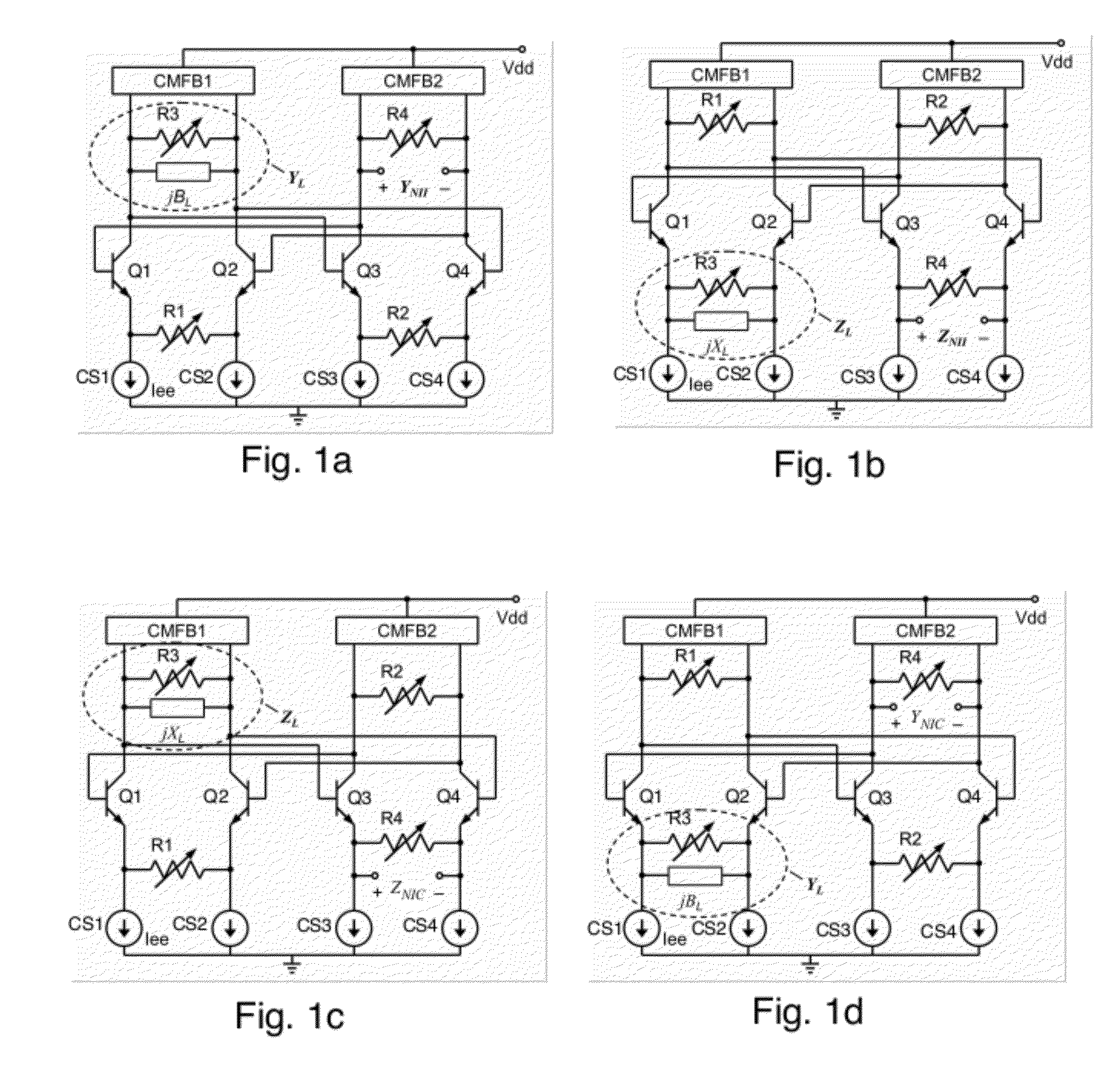
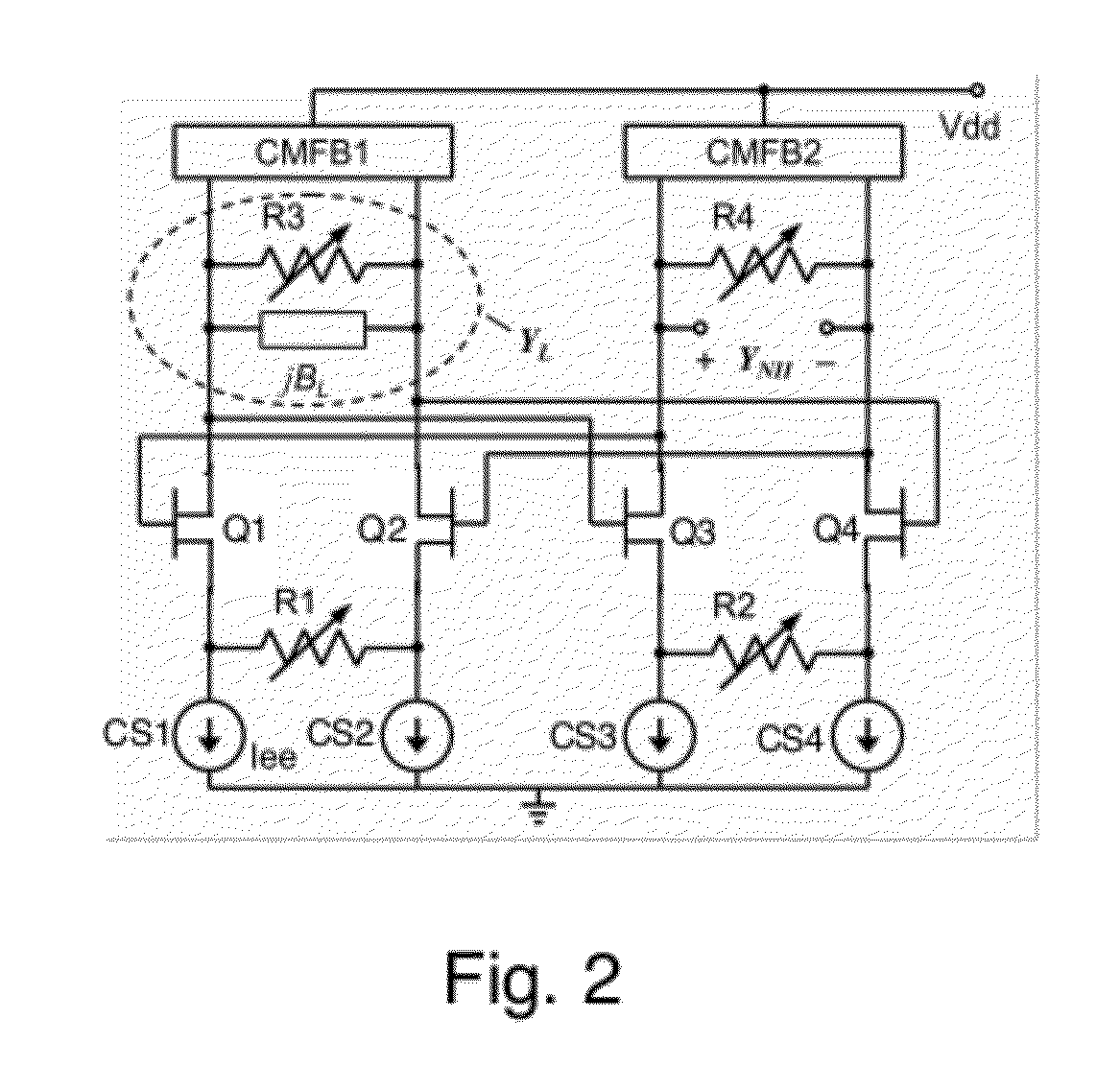
A differential circuit topology that produces a tunable floating negative inductance, negative capacitance, negative resistance / conductance, or a combination of the three. These circuits are commonly referred to as “non-Foster circuits.” The disclosed embodiments of the circuits comprises two differential pairs of transistors that are cross-coupled, a load immittance, multiple current sources, two Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) networks, at least one tunable (variable) resistance, and two terminals across which the desired immittance is present. The disclosed embodiments of the circuits may be configured as either a Negative Impedance Inverter (NII) or a Negative Impedance Converter (NIC) and as either Open-Circuit-Stable (OCS) and Short-Circuit-Stable (SCS).
Owner:HRL LAB
Differential negative impedance converters and inverters with variable or tunable conversion ratios
ActiveUS20120256709A1Reduce parasitismGood device matchingImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceEngineering
A differential circuit topology that produces a tunable floating negative inductance, negative capacitance, negative resistance / conductance, or a combination of the three. These circuits are commonly referred to as “non-Foster circuits.” The disclosed embodiments of the circuits comprises two differential pairs of transistors that are cross-coupled, a load immittance, multiple current sources, two Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) networks, at least one tunable (variable) resistance, and two terminals across which the desired immittance is present. The disclosed embodiments of the circuits may be configured as either a Negative Impedance Inverter (NII) or a Negative Impedance Converter (NIC) and as either Open-Circuit-Stable (OCS) and Short-Circuit-Stable (SCS).
Owner:HRL LAB
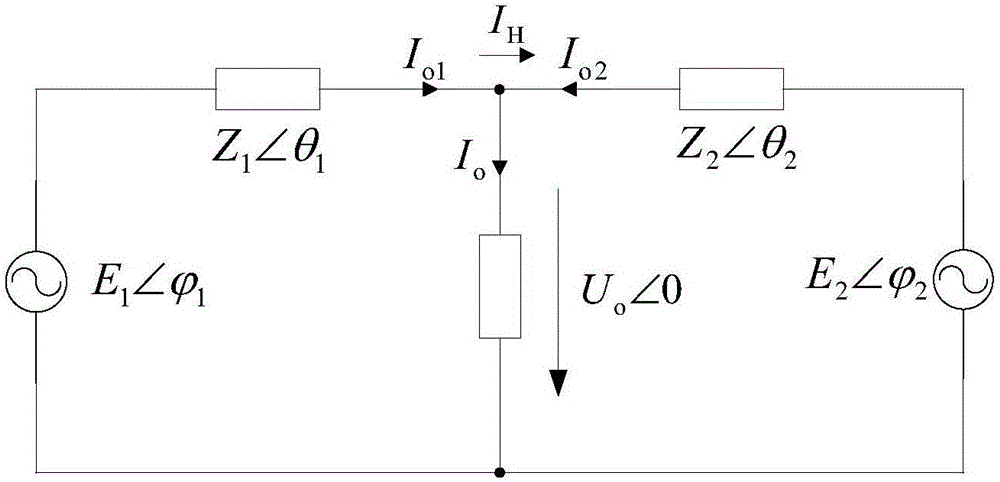
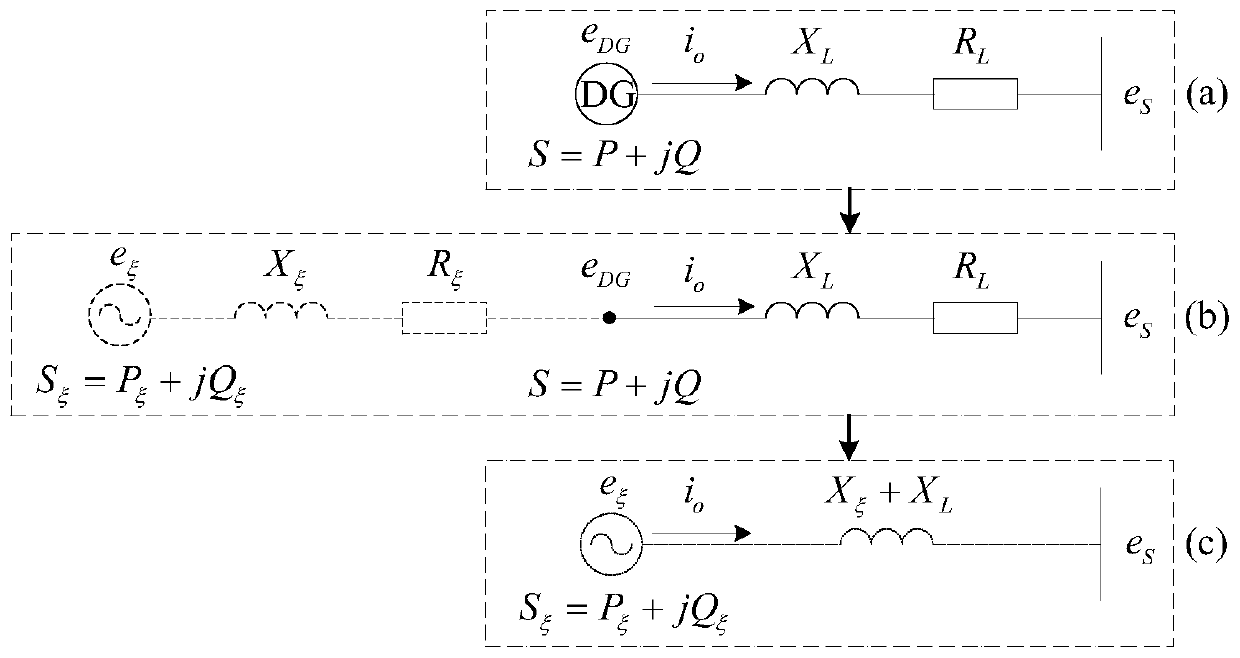
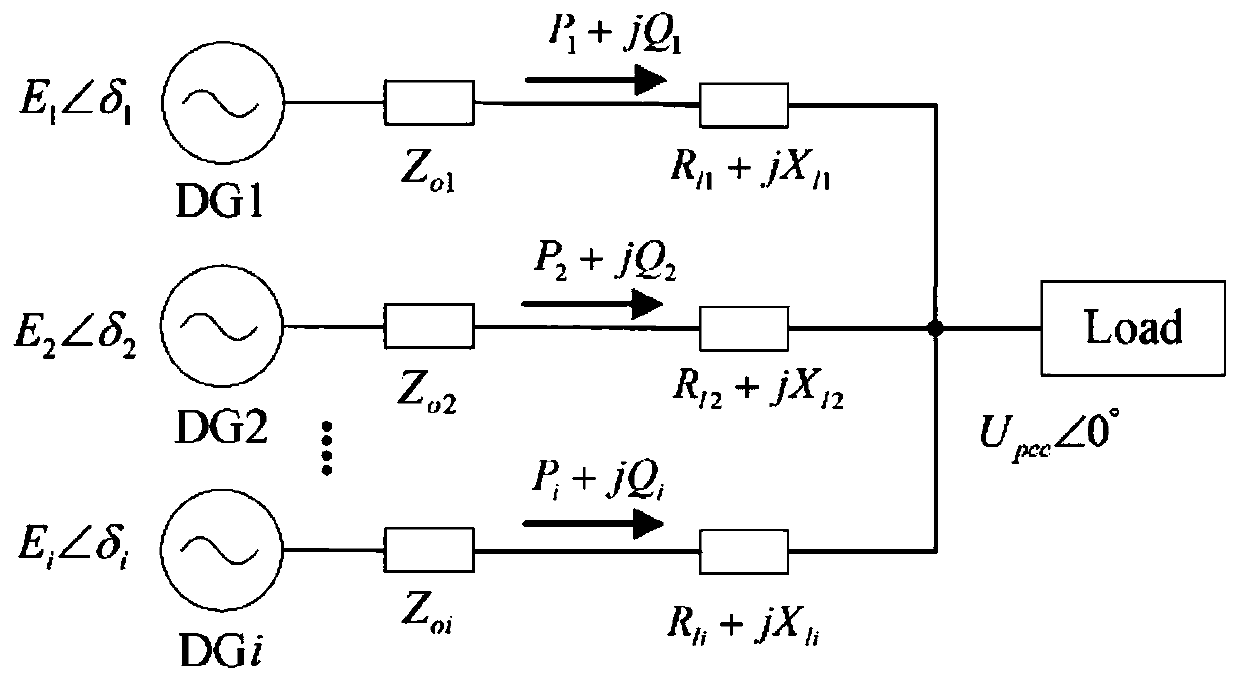
Inverter virtual impedance vector diagram analysis method
ActiveCN105826950AAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsClosed loop feedbackSimulation
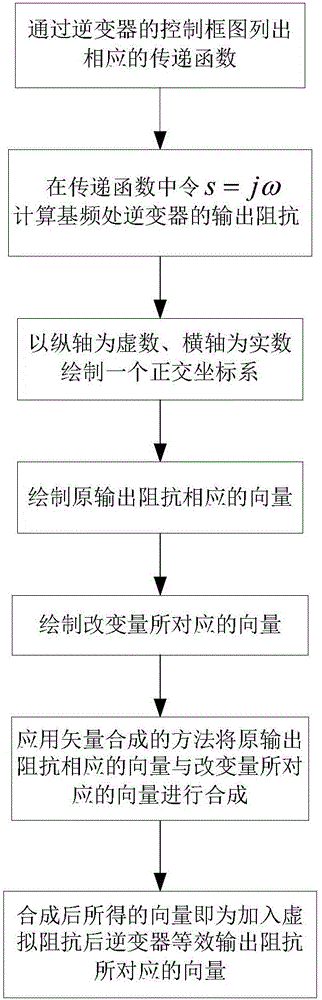
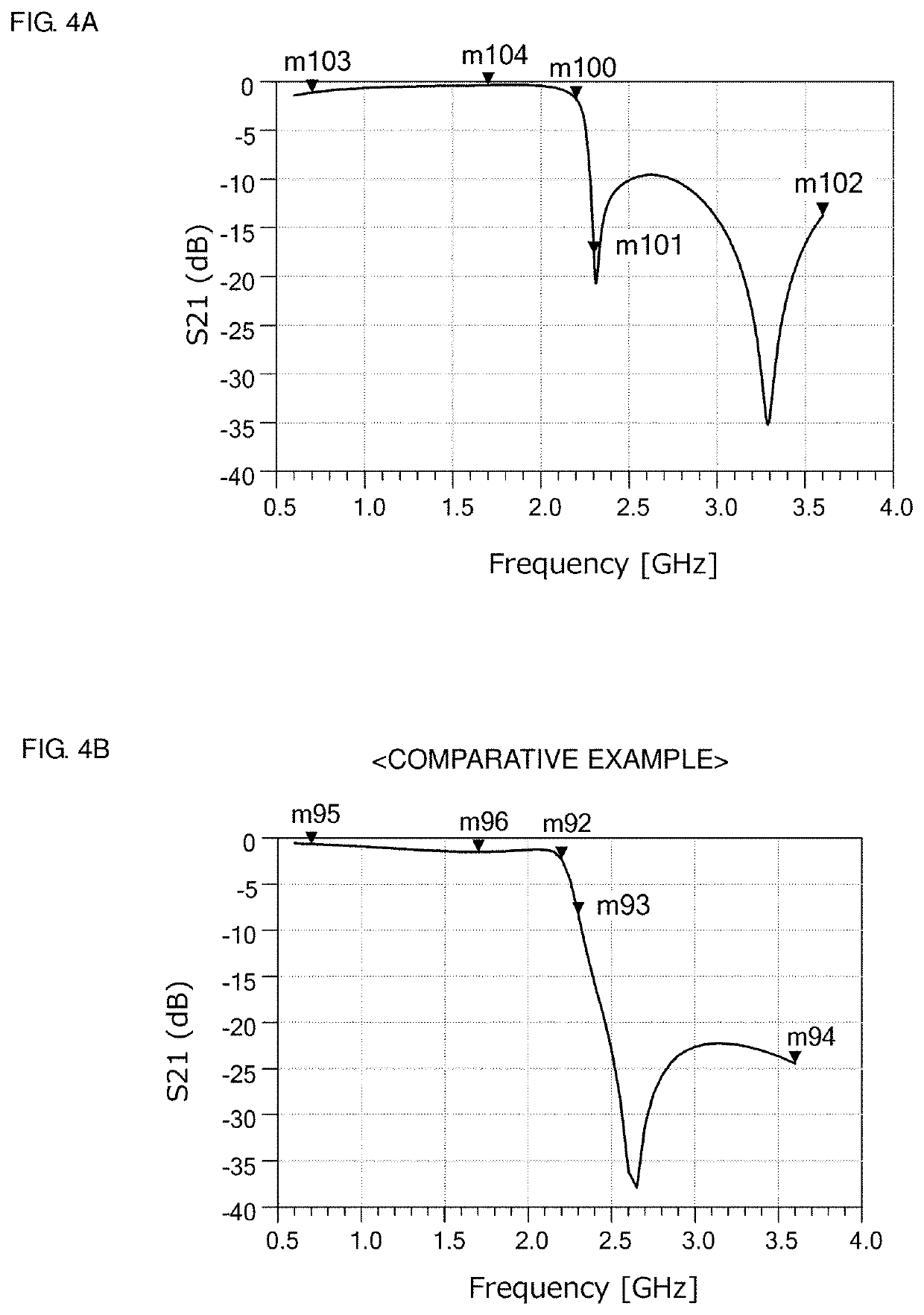
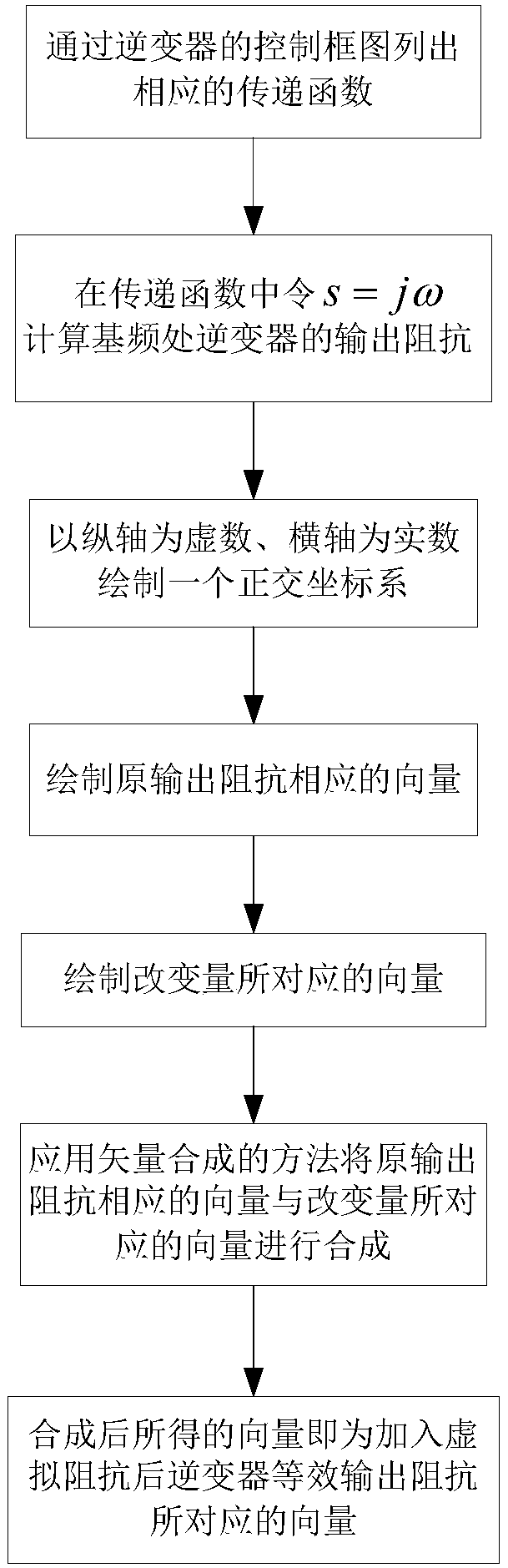
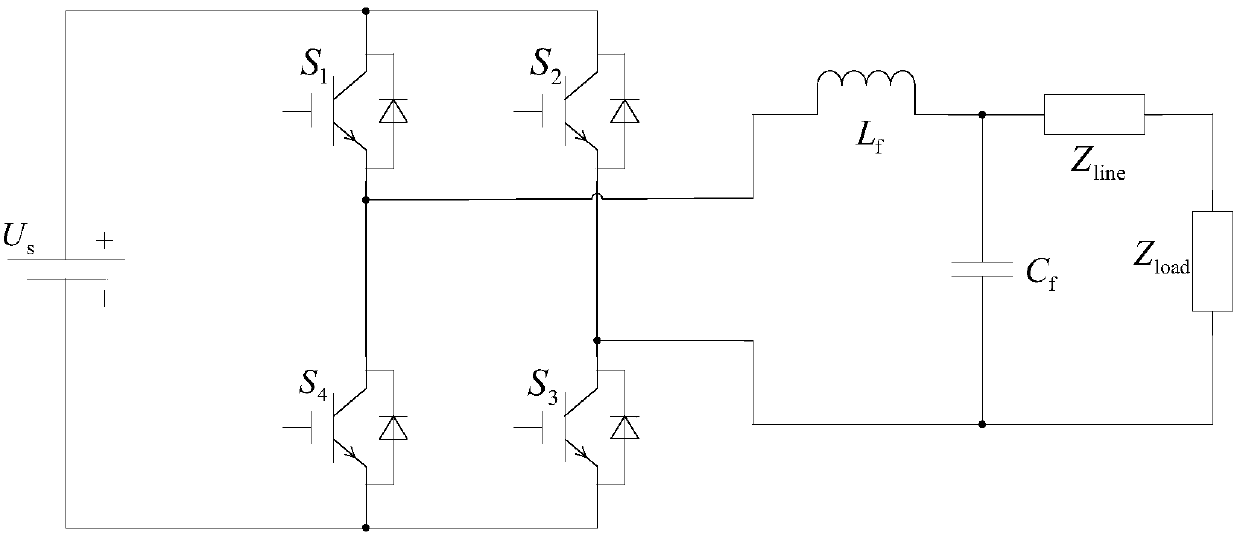
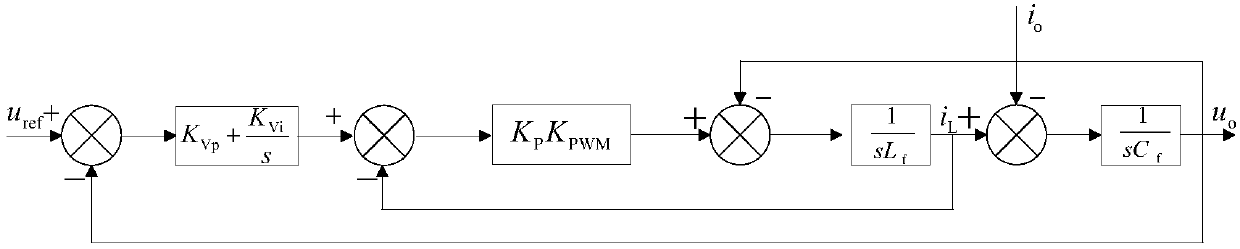
The invention provides an inverter virtual impedance vector diagram analysis method. The size and nature of output impedance at the fundamental frequency of an inverter are analyzed under different types of virtual impedances added. By introducing virtual impedance, the size and nature of the original output impedance of an inverter can be changed, and an inverter output impedance can be acquired as needed. A virtual impedance module is added on the basis of the original voltage and current double-closed-loop feedback control system. The adopted current feedback is inductive current feedback. Thus, the change in output impedance at the fundamental frequency of an inverter under five conditions, namely, adding virtual positive inductance, adding virtual negative inductance, adding virtual positive resistance, adding virtual negative resistance, and adding virtual complex impedance composed of virtual positive resistance and virtual negative inductance, can be analyzed and verified based on a vector diagram and a corresponding Bode diagram.
Owner:东台城东科技创业园管理有限公司
Optically powered and controlled non-foster circuit
ActiveUS9425769B1Impedence matching networksImpedence convertorsElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
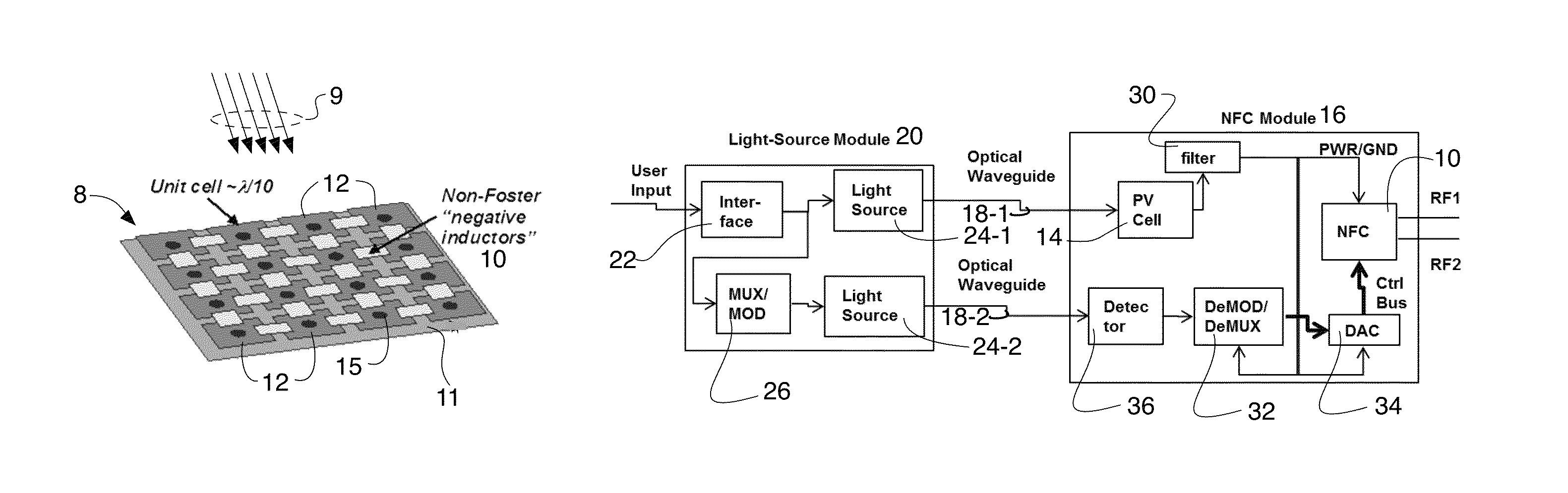
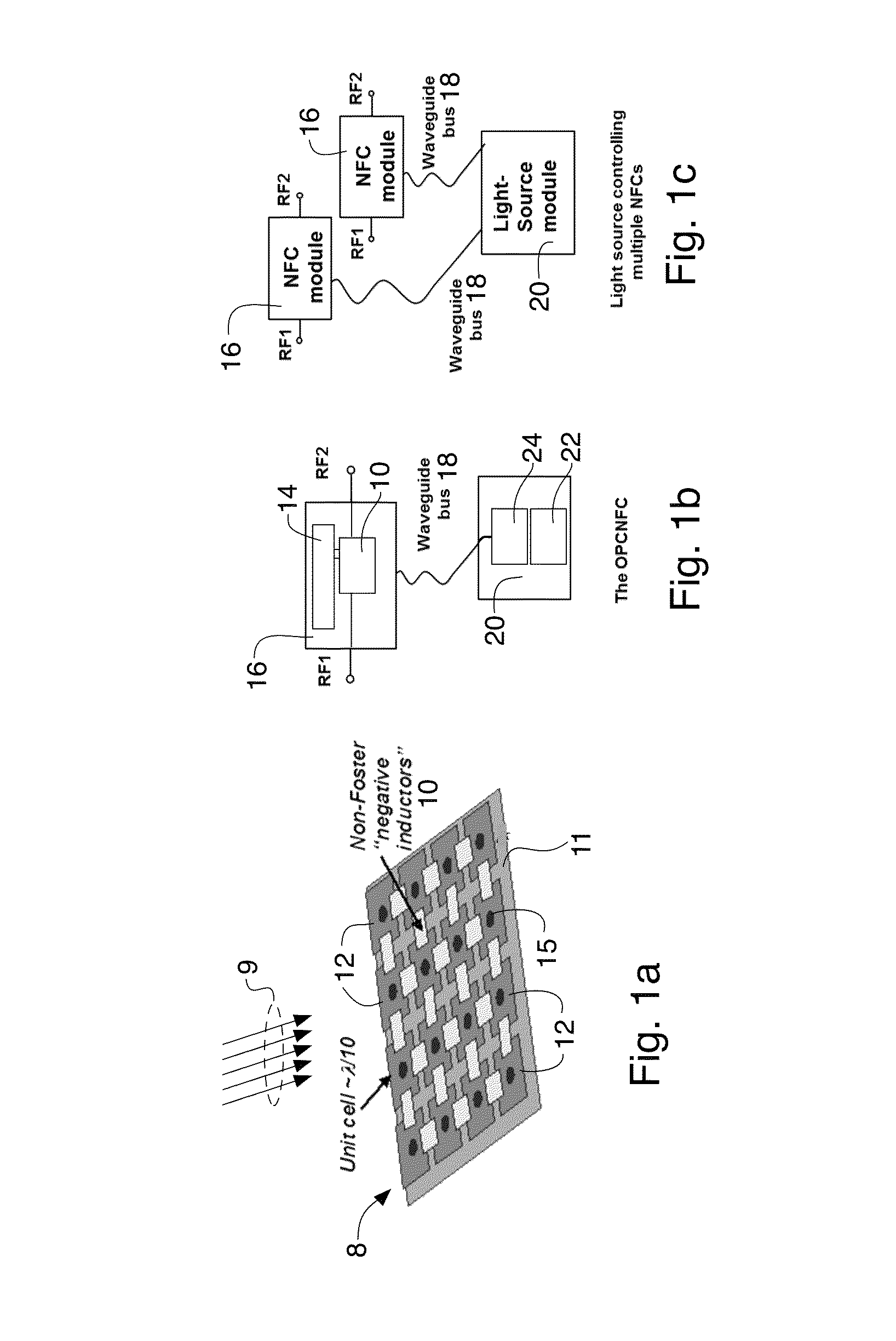
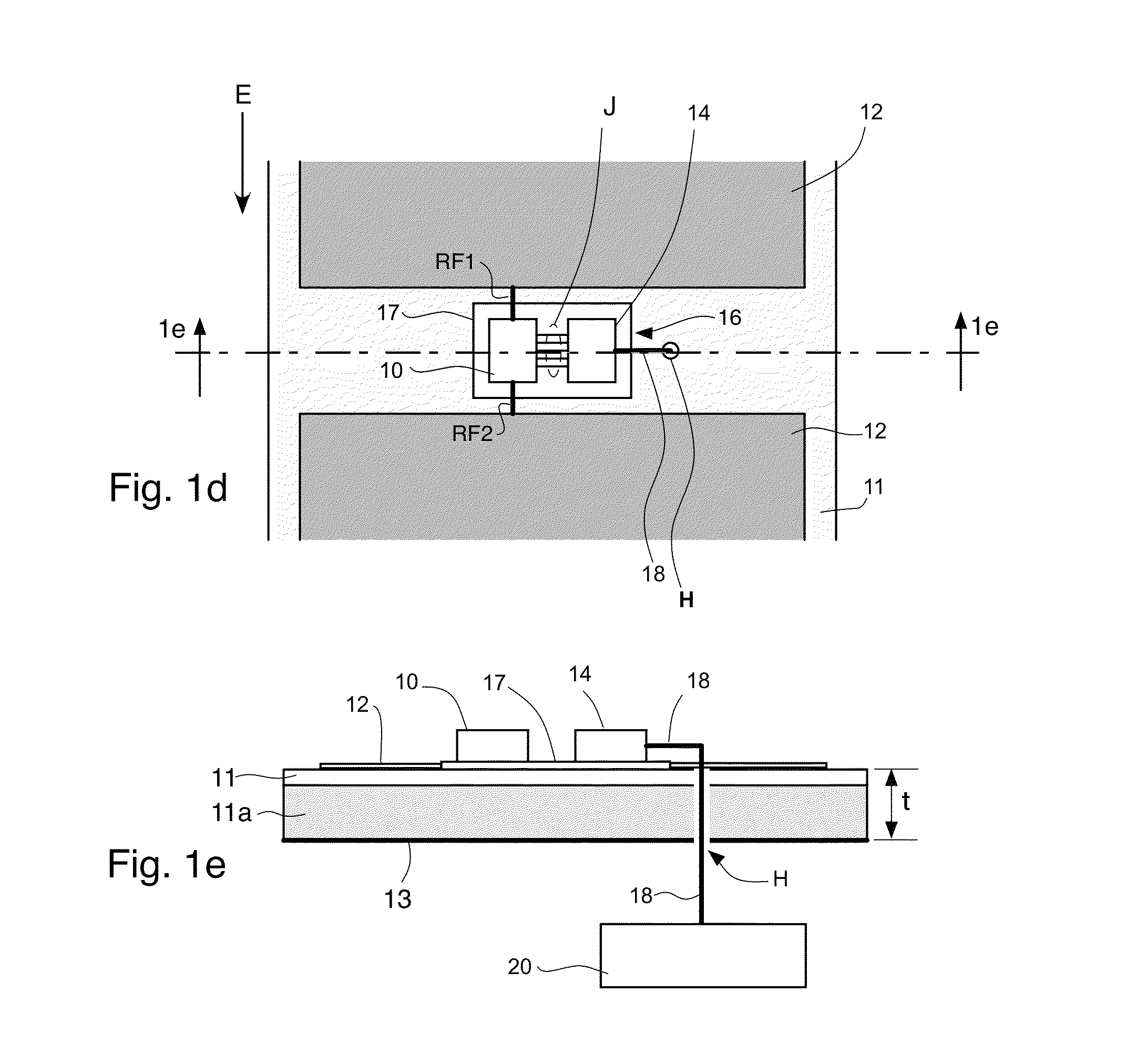
This invention is the Optically Powered and Controlled Non-Foster Circuit (OPCNFC) that is electrically floating; i.e., it does not have any metallic electrical / conductive connection to a power supply, ground, or control signal. Rather power and control signals are applied to the OPCNFC using optical energy. The Non-Foster Circuit (NFC) synthesizes negative inductance, negative capacitance, and / or negative resistance between metallic patches disposed in an array of an Artificial Impedance Surface (AIS).
Owner:HRL LAB
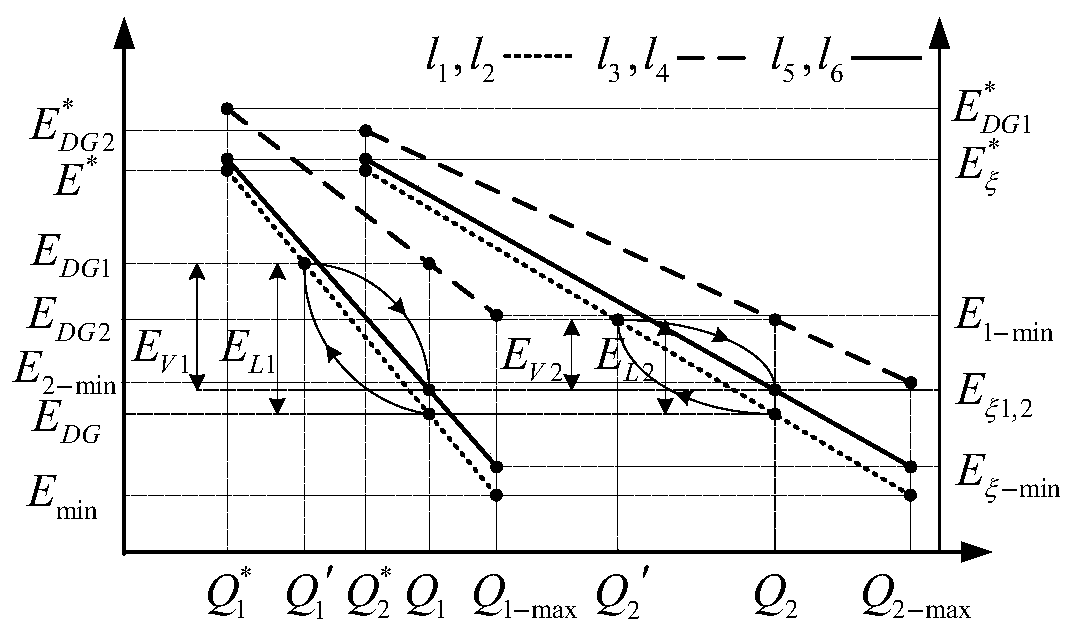
Low-voltage micro-grid distributed control method and system based on adaptive virtual impedance
ActiveCN109449999AReduce the uneven distribution of active powerReduce the deviation of output powerSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceLow voltage
The invention provides a low-voltage micro-grid distributed control method and system based on adaptive virtual impedance. The method comprises the following steps: generating adaptive virtual resistance by using a product of a ratio of active power output by a local inverter and voltage magnitude and a virtual impedance coefficient; determining virtual negative inductance according to an inductive reactance part of equivalent output impedance of the local inverter, so that the equivalent output impedance of the local inverter has a resistance property; obtaining the adaptive virtual impedanceaccording to the complex accumulation of the adaptive virtual resistance and the virtual negative inductance; according to a dq-axis current component of the adaptive virtual impedance and local inverter outlet three-phase current, generating dq-axis virtual voltage; and using the dq-axis virtual voltage to compensate a voltage reference value obtained by resistance droop control to obtain finalreference voltage.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
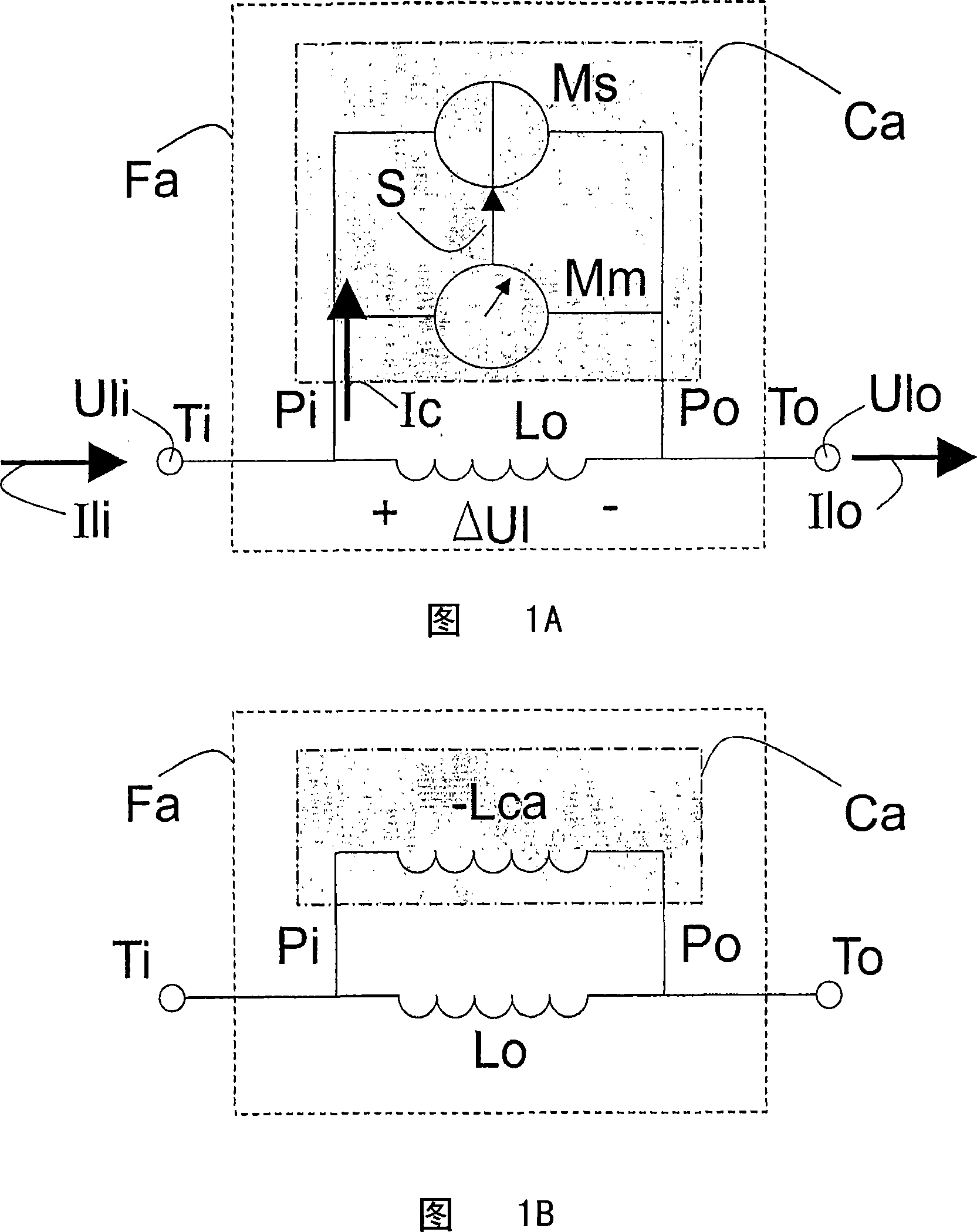
Active electromagnetic interference filter circuit for suppressing a line conducted interference signal
InactiveCN101010874AMultiple-port networksImpedence convertorsElectromagnetic interferenceConducted Interference
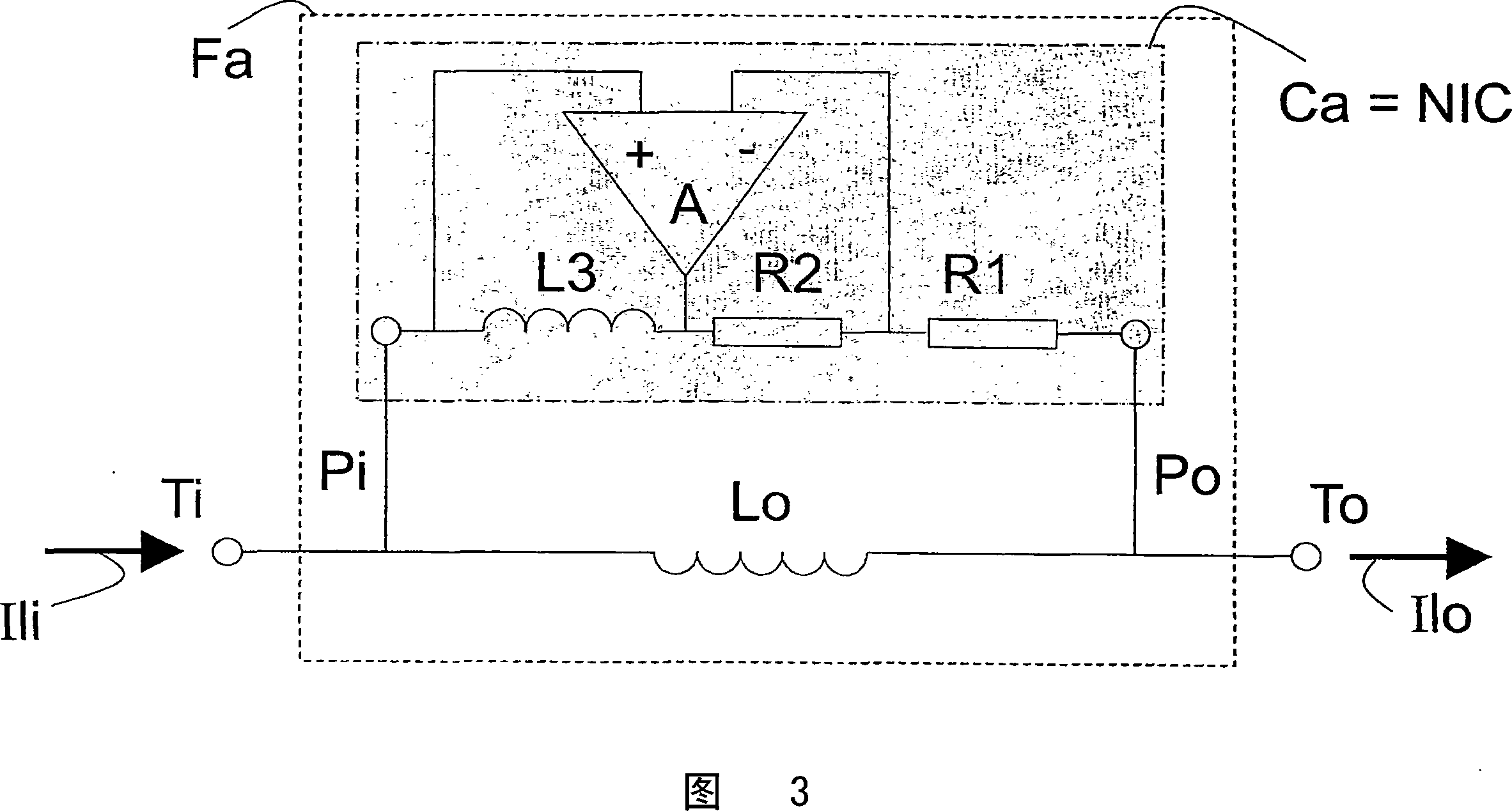
The invention relates to an Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) filter circuit (Fa) for suppressing a Line Conducted Interference (LCI) signal. The EMI filter circuit (Fa) comprises a filter inductance (Lo) to carry a supply current (Isup) between a supply voltage (Vsup) and a load (L). The EMI filter circuit (Fa) further comprises an active circuit (Ca), arranged in parallel with the filter inductance (Lo). The active circuit (Ca) comprises a sensing circuit (Mm) to sense the LCI signal and further comprises a suppressing circuit (Ms) to suppress the LCI signal. In an embodiment of the active EMI filter circuit (Fa), the active circuit (Ca) comprises a negative inductance generating circuit to create a negative inductance value. Selecting the negative inductance generating circuit to create an inductance value (Lca) larger than the inductance value of the filter inductance (Lo) creates a resulting inductance (Lr) which is higher compared to the inductance value of the filter inductance (Lo). In one embodiment, the negative inductance generating circuit comprises a negative impedance converter.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Linearly polarized active artificial magnetic conductor
An active artificial magnetic conductor comprising an array of unit cells, each unit cell comprising an electrically conductive patch that is connected with an electrically conductive patch of neighboring unit cell in a column of unit cells using a non-Foster negative inductor and having RF isolating plates or walls between rows of unit cells. These isolating plates or walls eliminate undesirable cross coupling between the non-Foster negative inductors. The electrically conductive patches may be formed by metallic patches preferably arranged in the 2D array of such patches. Each patch preferably has a rectilinear shape.
Owner:HRL LAB
Thin film structures with negative inductance and methods for fabricating inductors comprising the same
ActiveUS7956715B2Transformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical conductorEngineering
An inductor structure comprising a substrate and a planar conductor structure on a surface of the substrate, and methods for fabricating an inductor structure. The planar conductor structure may comprise a vertical stack of three or more multilayer films. Each multilayer film may comprise a first layer of a first metal, defining a first vertical thickness, and a second layer of a second metal, defining a second vertical thickness. The metals and thicknesses are chosen such that the inductor exhibits a negative electrical self-inductance when an electrical signal is transmitted from a first contact point to a second contact point.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
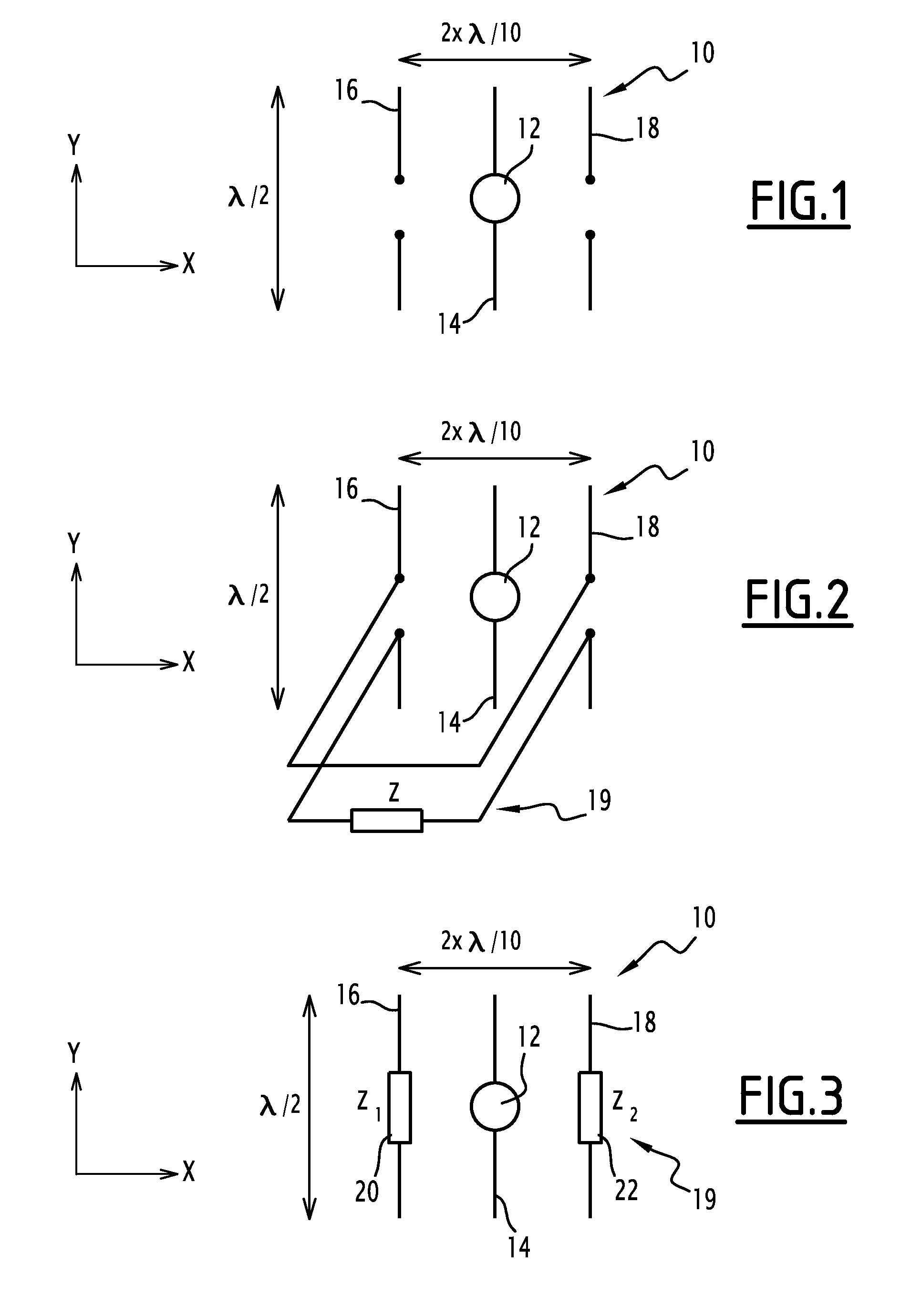
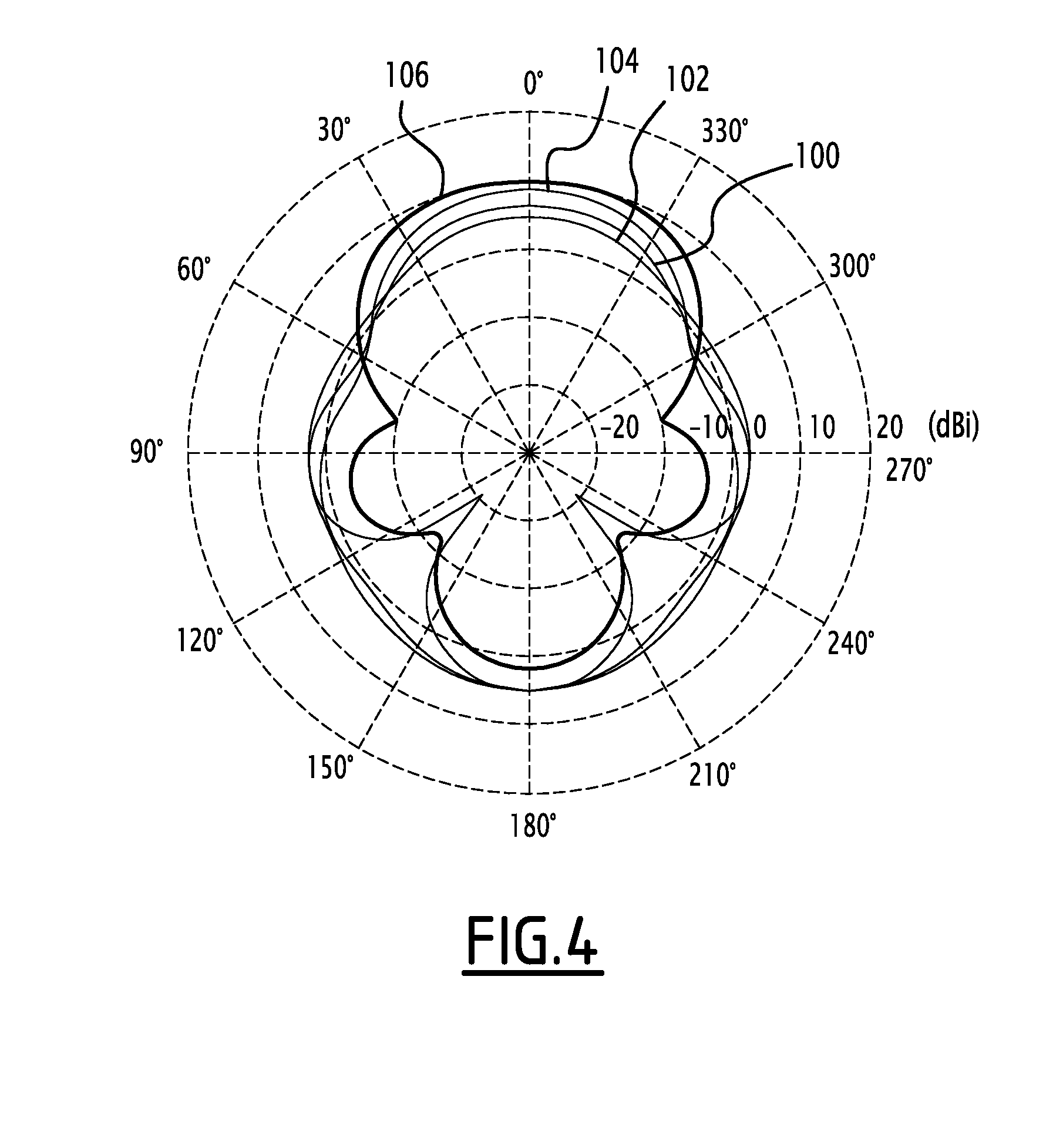
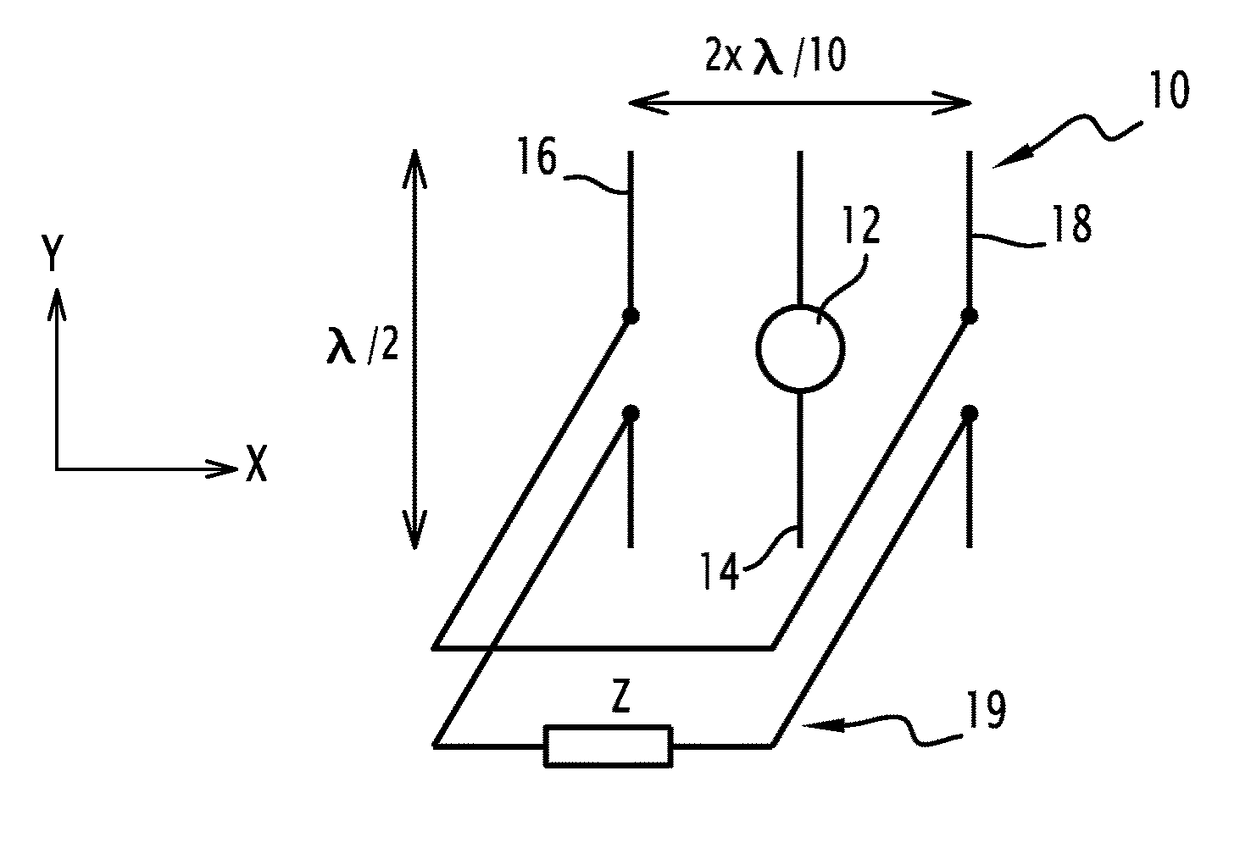
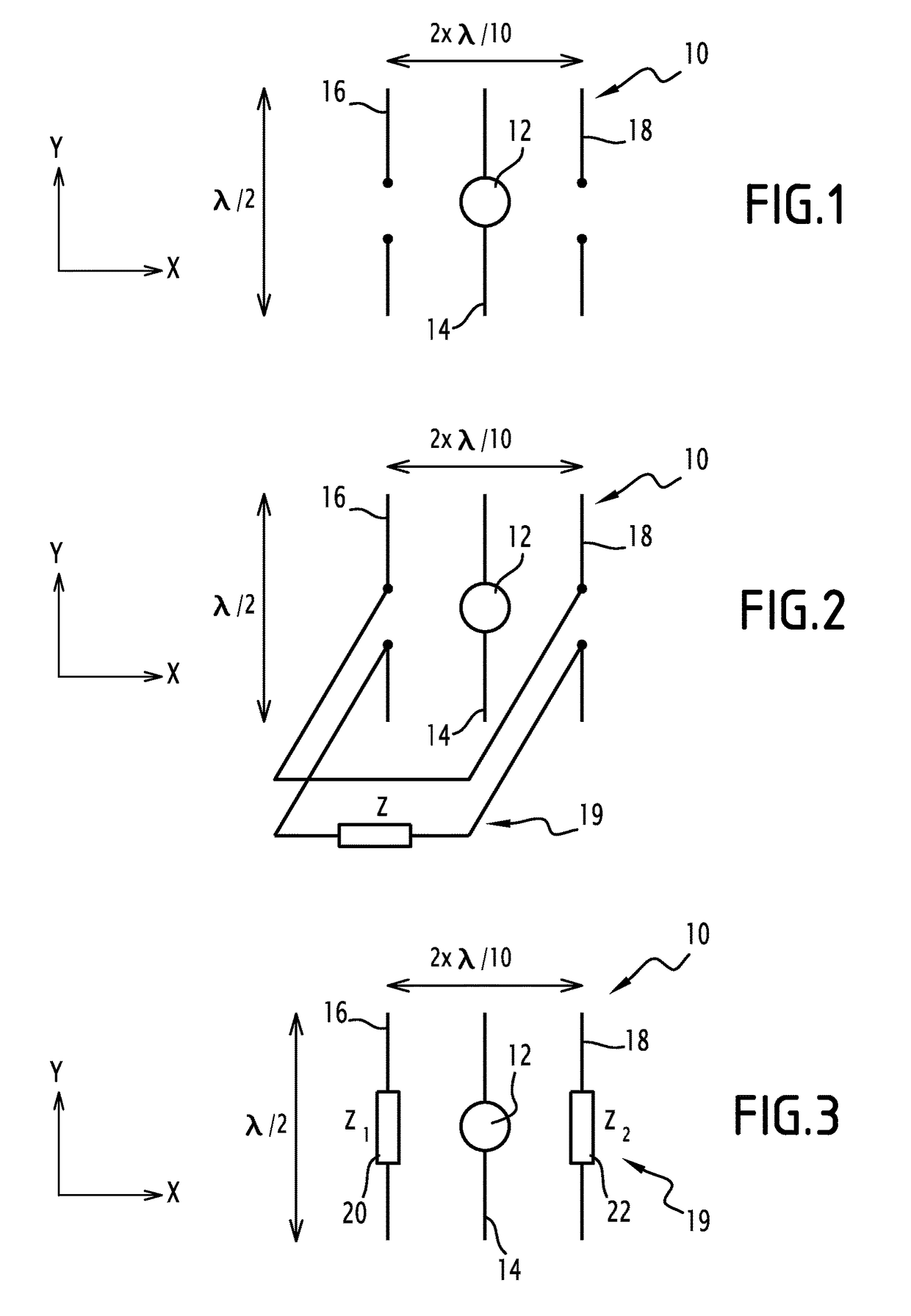
Antenna array
ActiveUS20150054700A1Improve directivityReduce compactnessAntenna arraysAntenna earthingsCapacitanceNegative inductance
This antenna array includes at least one primary antenna, at least one secondary antenna and at least one load coupled to a secondary antenna. The load includes two separate components, a first component being a resistor and a second component being selected from an inductor or a capacitor. The antenna array can include one or more of the following characteristic features, taken into consideration individually or in accordance with any technically possible combinations: the first component has negative resistance; the second component has negative inductance or a negative capacitance; at least one load has an adjustable impedance. The antenna array may be used in a system, such as a vehicle, a terminal, a mobile telephone, a wireless network access point, a base station, or a radio frequency excitation probe.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
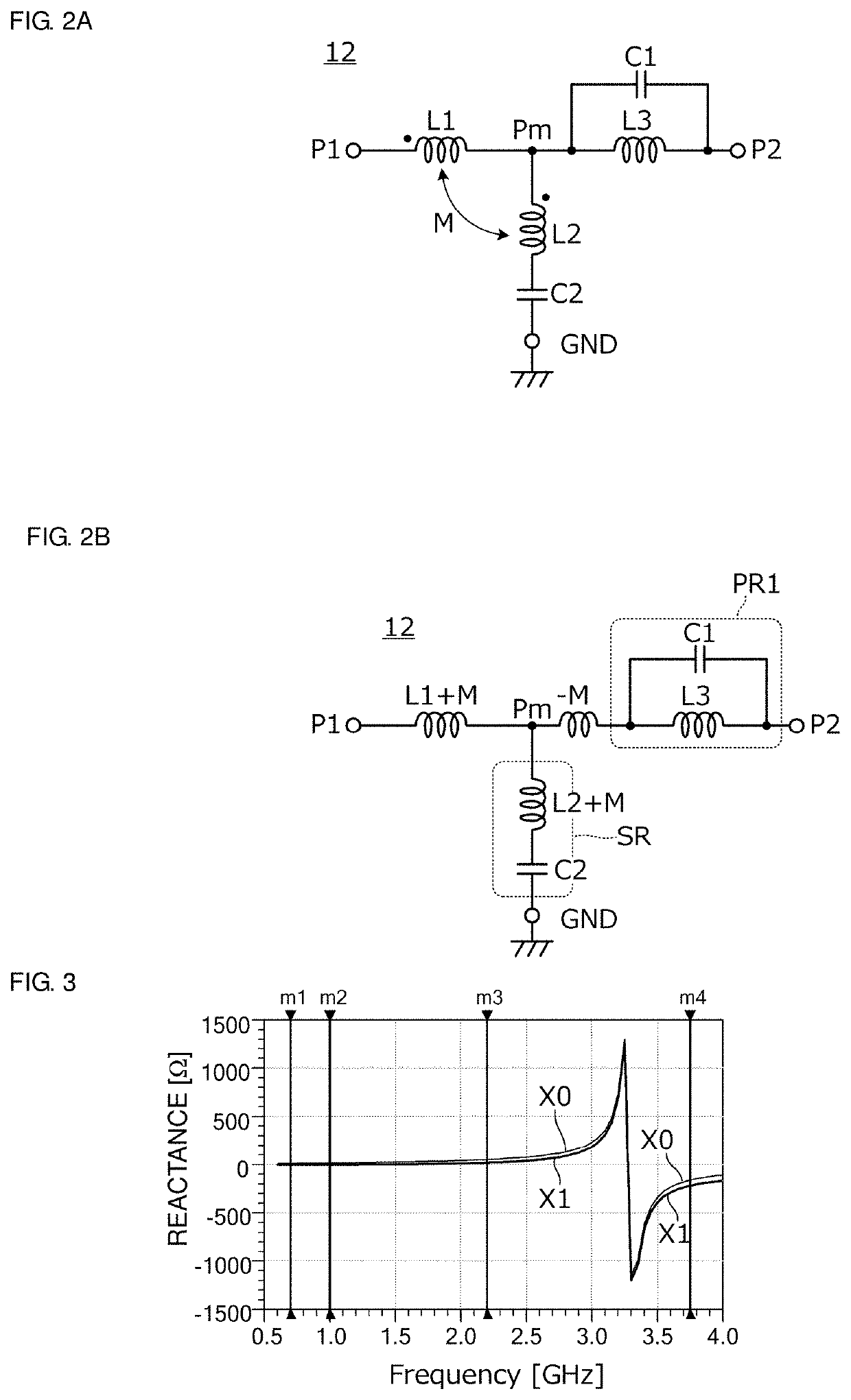
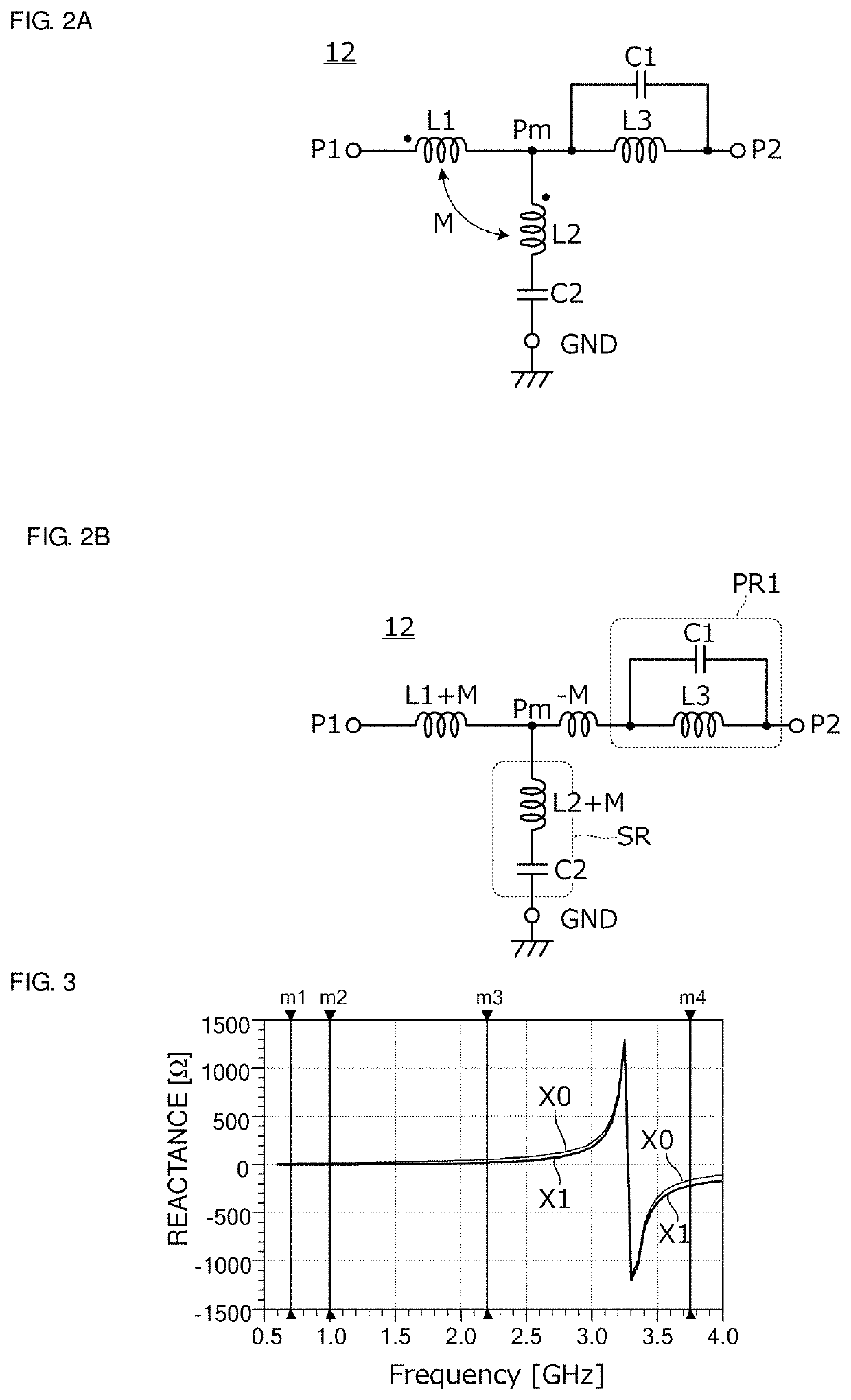
Coil component and filter circuit including same
ActiveUS20200279684A1Reduce frequencyIncrease the frequency bandMultiple-port networksTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsHemt circuitsNegative inductance
A coil component includes a first coil and a second coil that magnetically couples with the coil and causes a negative inductance to be generated. The coil component further includes an electrode that is provided at a position adjacent to or in the vicinity of a port of each of the first and second coils.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
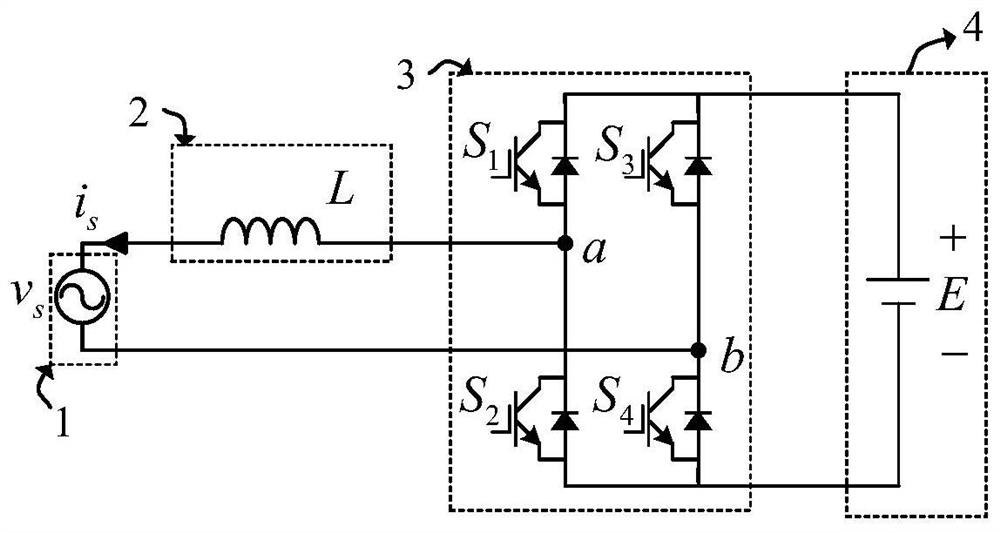
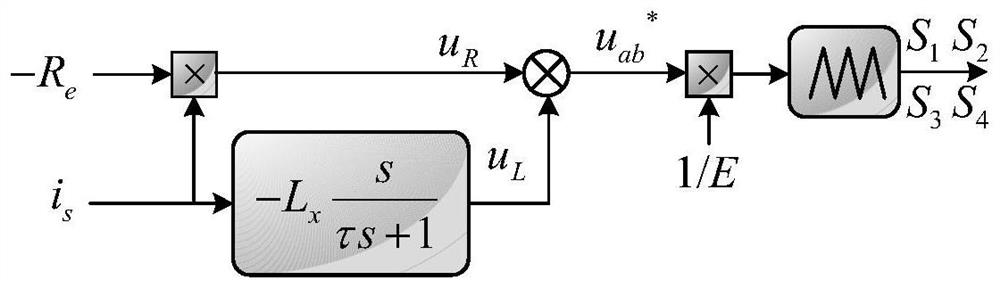
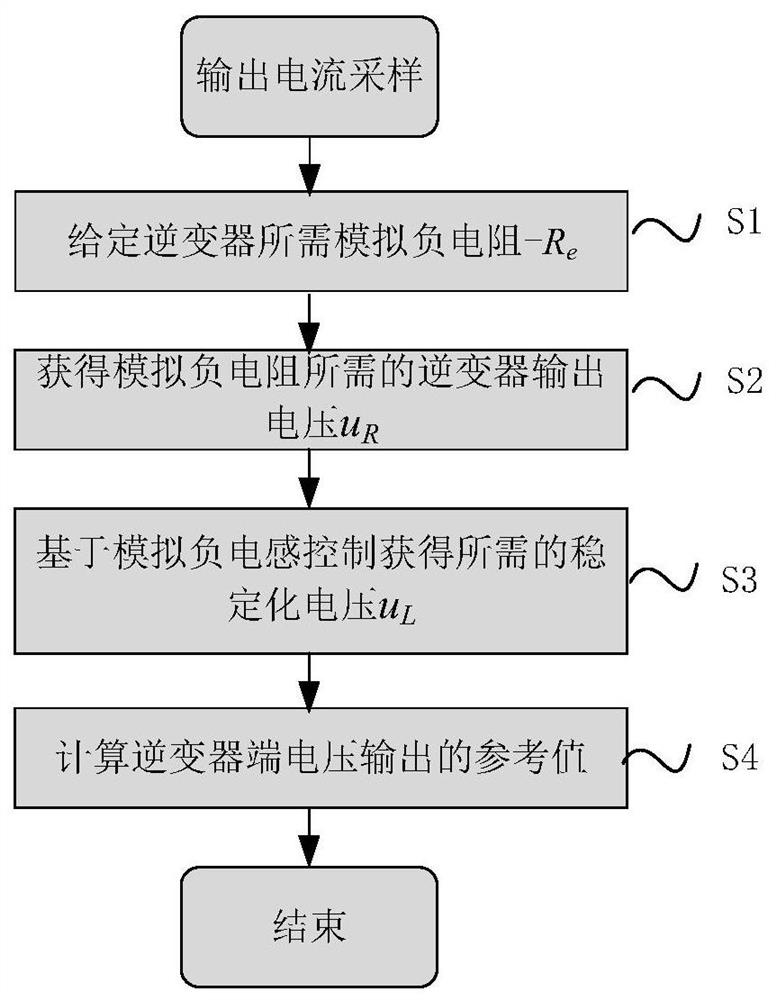
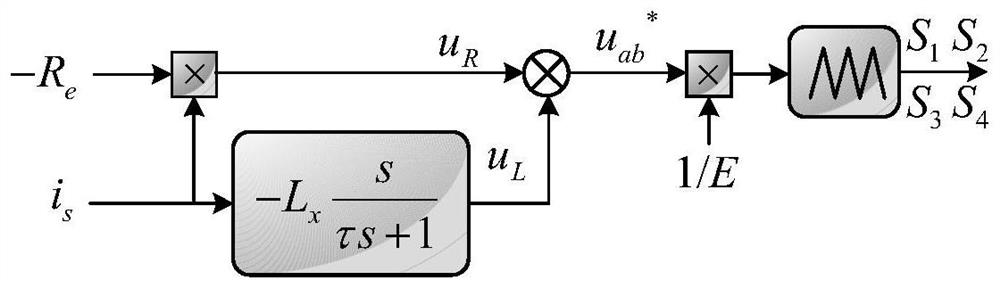
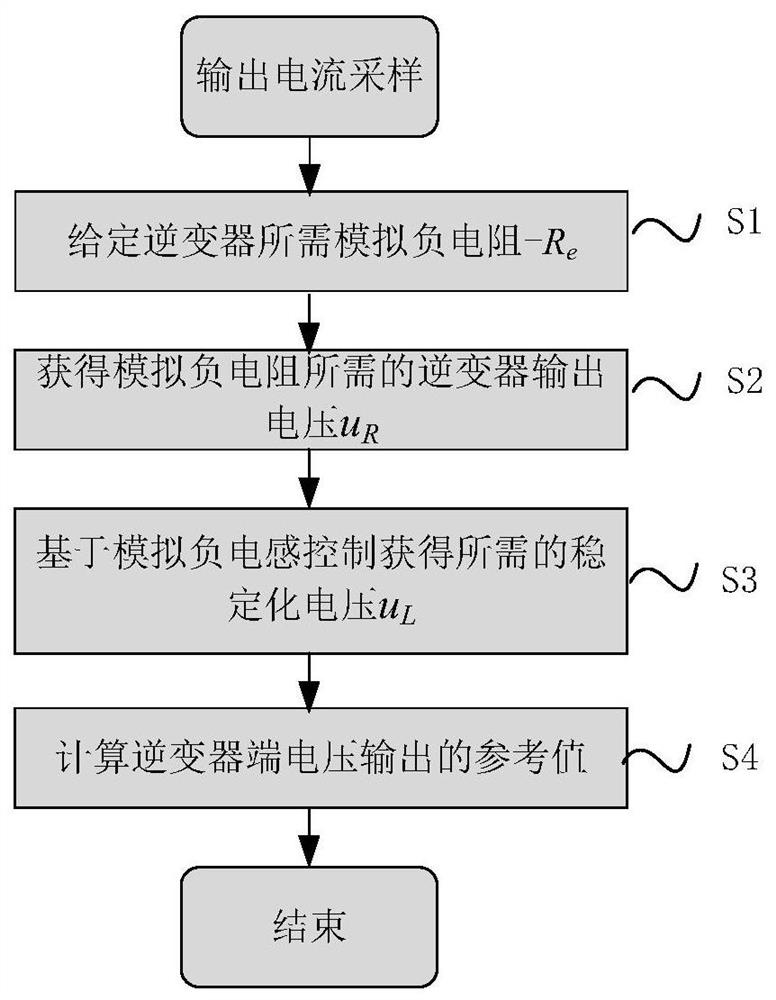
Inverter control method without power grid voltage sensor
ActiveCN113037119AGuaranteed uptimeImprove power qualityAc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceStabilization control
The invention provides an inverter control method without a power grid voltage sensor. The inverter control method comprises two parts, namely analog negative resistance control and stabilization control based on analog negative inductance. The analog negative resistance control is used for transmitting the power of an inverter to a power grid and ensuring that the output current of the inverter is kept sine. The stabilization control based on analog negative inductance is used for making up for unstable poles caused by the analog negative resistance control so as to realize safe and stable operation of the inverter. In addition, according to the method, only the output current of the inverter is sampled, so the reliability of a system is improved, and sensor cost is reduced. Meanwhile, the method is easy to control, has small calculation amount and is suitable for practical application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Antenna array
ActiveUS9634401B2Improve directivityReduce compactnessAntenna arraysAntenna earthingsCapacitanceEngineering
This antenna array includes at least one primary antenna, at least one secondary antenna and at least one load coupled to a secondary antenna. The load includes two separate components, a first component being a resistor and a second component being selected from an inductor or a capacitor. The antenna array can include one or more of the following characteristic features, taken into consideration individually or in accordance with any technically possible combinations: the first component has negative resistance; the second component has negative inductance or a negative capacitance; at least one load has an adjustable impedance. The antenna array may be used in a system, such as a vehicle, a terminal, a mobile telephone, a wireless network access point, a base station, or a radio frequency excitation probe.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Integrated circuit incorporating wire bond inductance
ActiveUS20080001683A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead bondingEngineering
The invention relates to the field of electronics, more particularly to the wire bonds incorporated into an integrated circuit package such as a quad flat pack. a ball grid array or hybrid style module. The present invention takes the normally undesirable wire bond inductance and uses it in an operational circuit where positive inductance is required. The circuit in which the wire bond inductance is used is located primarily in the integrated circuit die housed in the integrated circuit package, but may also include off-die components. In one example, a wire bond is used as the required series inductance in a discrete circuit impedance inverter which consists of two shunt-to-ground negative inductances and one series positive inductance. One of the negative inductances is located on-die, while the other is located off-die.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Filter circuit, filter circuit element, and multi/demultiplexer
ActiveUS20200252041A1Reduce and prevent insertion lossReduced insertion lossMultiple-port networksTransmissionMagnetic field couplingLow-pass filter
A low pass filter includes a first inductor, a second inductor magnetic-field-coupled to the first inductor, a third inductor, and a first capacitor. The first inductor is electrically connected between a first port and an intermediate node, being a node to which the second inductor is electrically connected, between the first inductor and the second port. The second inductor is electrically connected between the intermediate node and a ground terminal. The third inductor is electrically connected between the intermediate node and the second port, and a first parallel resonant circuit is defined by the third inductor and the first capacitor. The first inductor and the second inductor are coupled to each other in such a relationship that a negative inductance is generated between the intermediate node and the third inductor due to magnetic field coupling between the first inductor and the second inductor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
A vector diagram analysis method of virtual impedance of inverter
ActiveCN105826950BAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsControl systemClosed loop feedback
The invention provides an inverter virtual impedance vector diagram analysis method. The size and nature of output impedance at the fundamental frequency of an inverter are analyzed under different types of virtual impedances added. By introducing virtual impedance, the size and nature of the original output impedance of an inverter can be changed, and an inverter output impedance can be acquired as needed. A virtual impedance module is added on the basis of the original voltage and current double-closed-loop feedback control system. The adopted current feedback is inductive current feedback. Thus, the change in output impedance at the fundamental frequency of an inverter under five conditions, namely, adding virtual positive inductance, adding virtual negative inductance, adding virtual positive resistance, adding virtual negative resistance, and adding virtual complex impedance composed of virtual positive resistance and virtual negative inductance, can be analyzed and verified based on a vector diagram and a corresponding Bode diagram.
Owner:东台城东科技创业园管理有限公司
Low-voltage microgrid inverter control system based on virtual impedance and virtual power
ActiveCN106712088BLow costAvoid adding filter inductanceAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMicrogridVirtual control
The invention discloses a low-voltage micro-grid inverter control system based on virtual impedance and virtual power supply. The control system is divided into a droop controller, a virtual controller, and a voltage / current double-loop controller; by improving the droop parameters, a virtual inverter capable of simulating The droop controller with power supply function uses fractional order PID to track and control the droop controller voltage; by analyzing the relationship between virtual negative inductance and micro-source reactive power sharing, determine the value of virtual negative inductance required for accurate reactive power sharing , realize the virtual impedance in the virtual controller, feed back the voltage drop of the virtual controller to the droop controller, and participate in the fractional-order PID tracking control of the virtual power supply voltage; use the fractional-order PID to track the inverter voltage in the voltage / current dual-loop controller Control, according to the transfer function of the filter to determine the filter parameters in the controller, using the differential genetic algorithm to optimize the parameters of the fractional order PID controller. The invention can ensure the power decoupling of the low-voltage micro-grid and improve the effect of equal sharing of reactive power.
Owner:秦皇岛市睿能光电科技有限公司
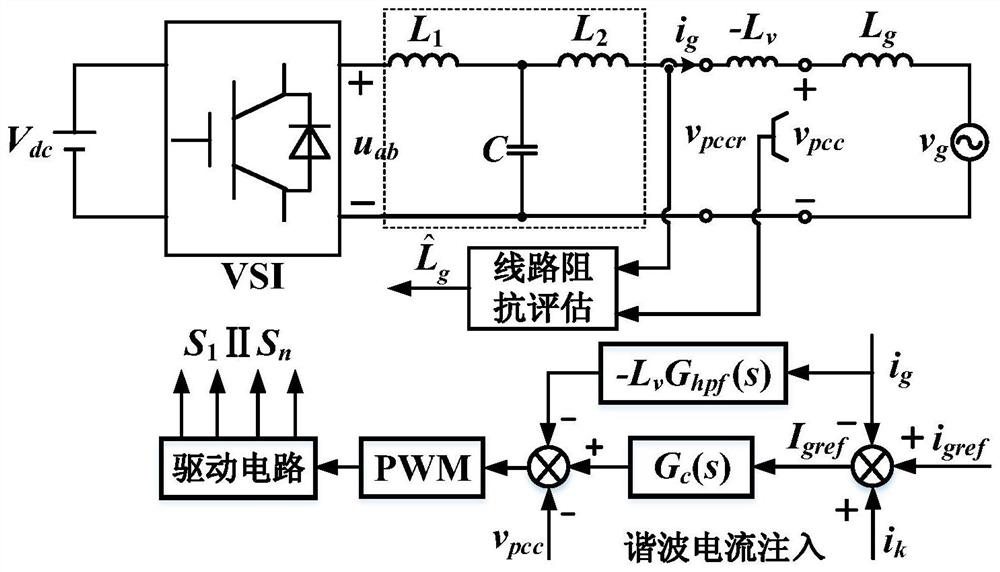
Control method for improving stability of grid-connected inverter under low short circuit ratio
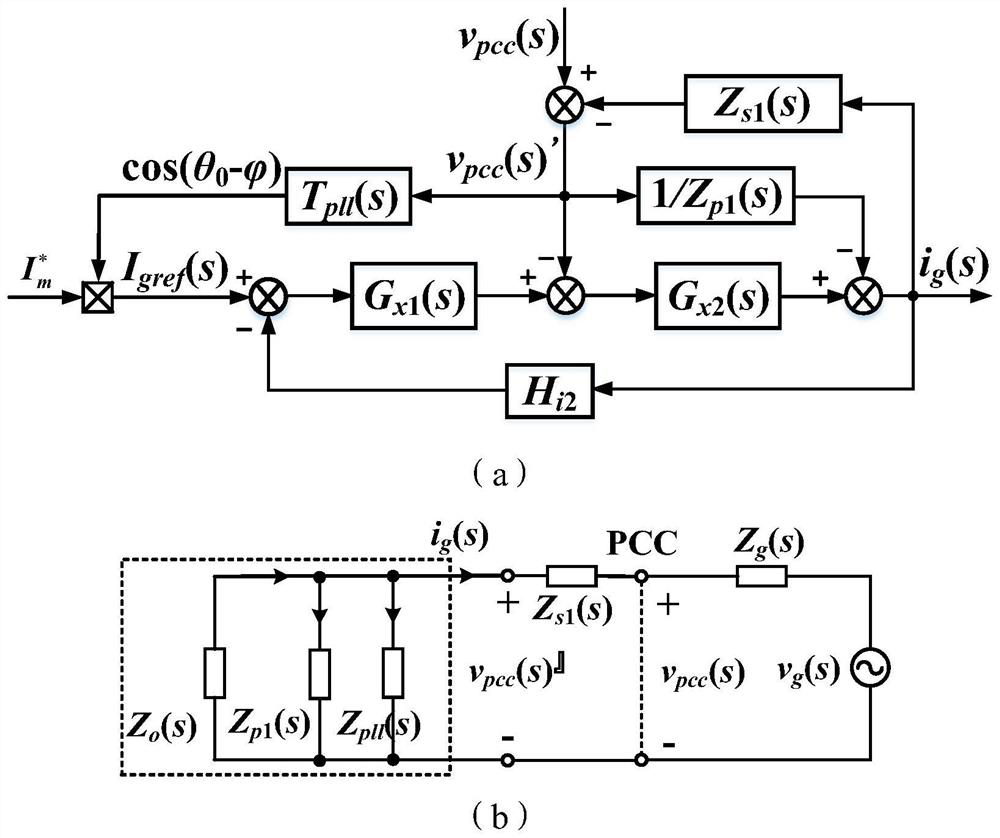
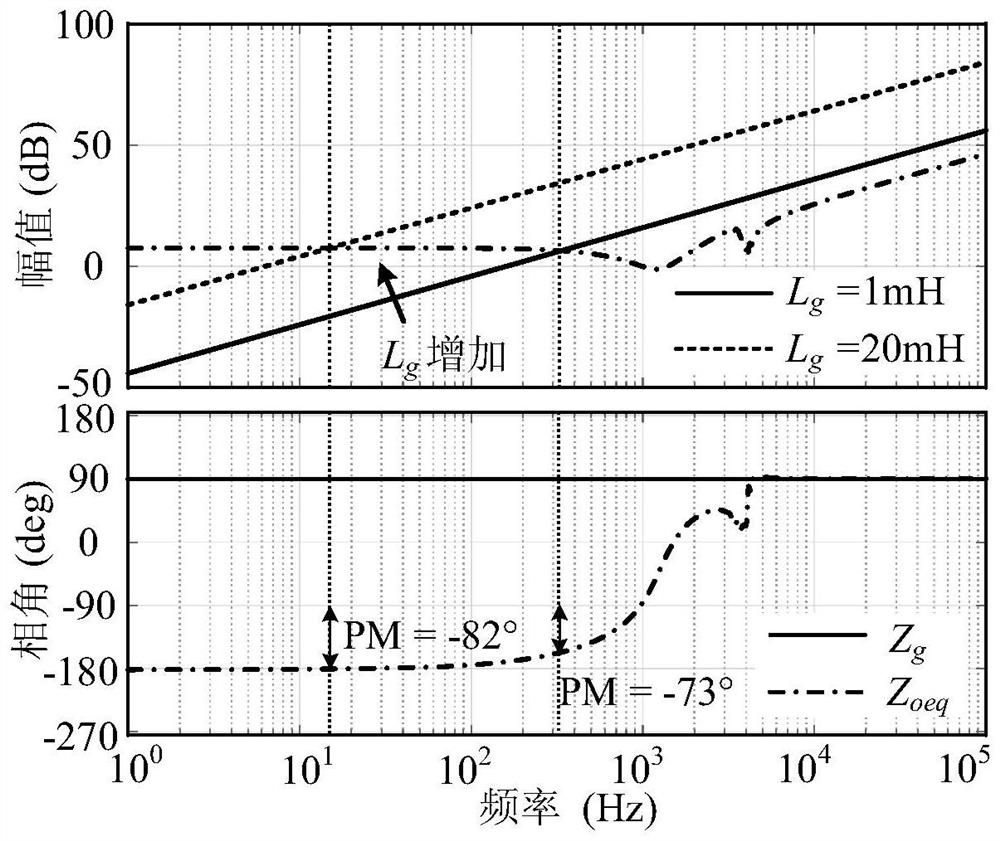
PendingCN114499257AGuaranteed stabilityImprove robustnessAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCarrier signalNegative inductance
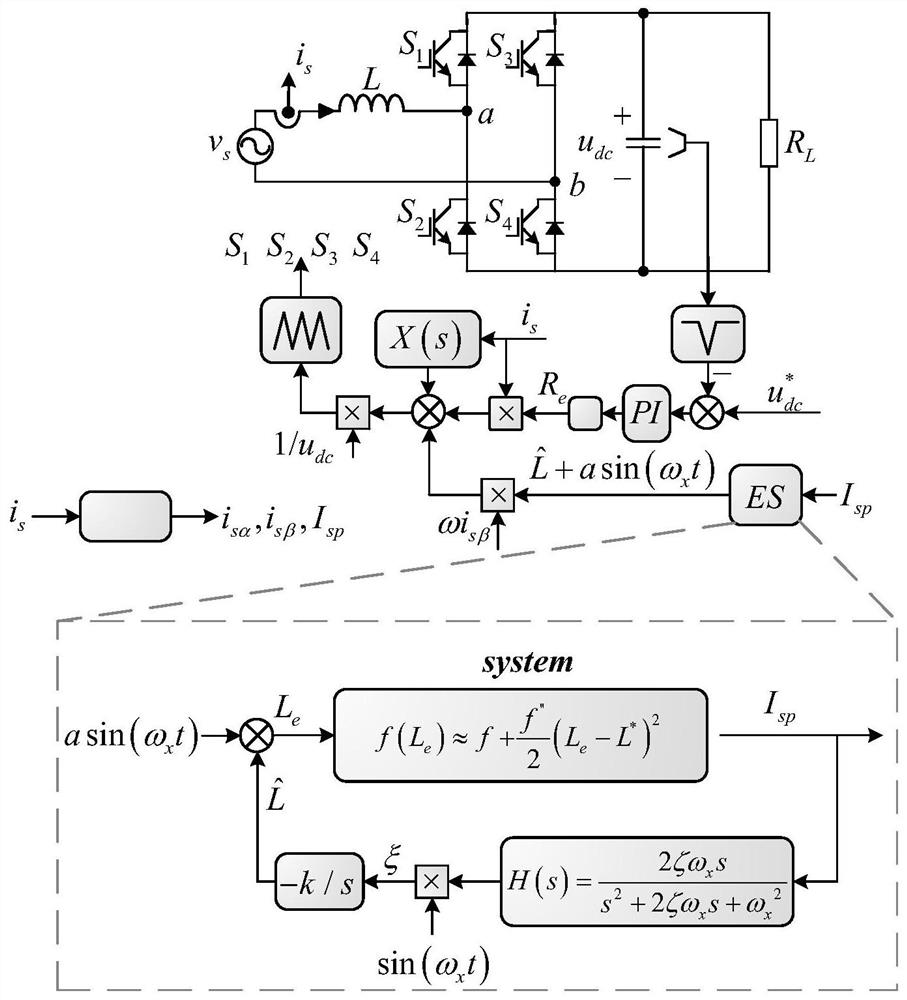
The invention discloses a control method for improving the stability of a grid-connected inverter under a low short circuit ratio, and the method comprises the steps: sampling a PCC point voltage, a grid-connected current, and a DC bus voltage; the grid-connected inverter obtains the voltage phase of the PCC point through the PLL; obtaining a grid-connected current reference value according to the PCC point voltage phase and current amplitude information obtained by PLL locking, and adding the grid-connected current reference value to the actively injected inter-harmonic current reference to obtain the total reference of the grid-connected current; harmonic response components in PCC point voltage and grid-connected current are extracted through a discrete Fourier transform algorithm, so that power grid line impedance is evaluated, and then a line inductance value is obtained. Feeding back the product of the virtual negative inductance and the grid-connected current to a current loop controller according to the evaluated line inductance value and the line negative inductance with the virtual inductance value larger than the current loop controller, obtaining a final modulation signal, comparing the modulation signal with a carrier signal, and generating a PWM signal to drive an inverter switching tube.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
Filter circuit, filter circuit element, and multi/demultiplexer
ActiveUS11228295B2Attenuation in a stop frequency band is increasedReduce and prevent insertion lossMultiple-port networksTransmissionCapacitanceMagnetic field coupling
A low pass filter includes a first inductor, a second inductor magnetic-field-coupled to the first inductor, a third inductor, and a first capacitor. The first inductor is electrically connected between a first port and an intermediate node, being a node to which the second inductor is electrically connected, between the first inductor and the second port. The second inductor is electrically connected between the intermediate node and a ground terminal. The third inductor is electrically connected between the intermediate node and the second port, and a first parallel resonant circuit is defined by the third inductor and the first capacitor. The first inductor and the second inductor are coupled to each other in such a relationship that a negative inductance is generated between the intermediate node and the third inductor due to magnetic field coupling between the first inductor and the second inductor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
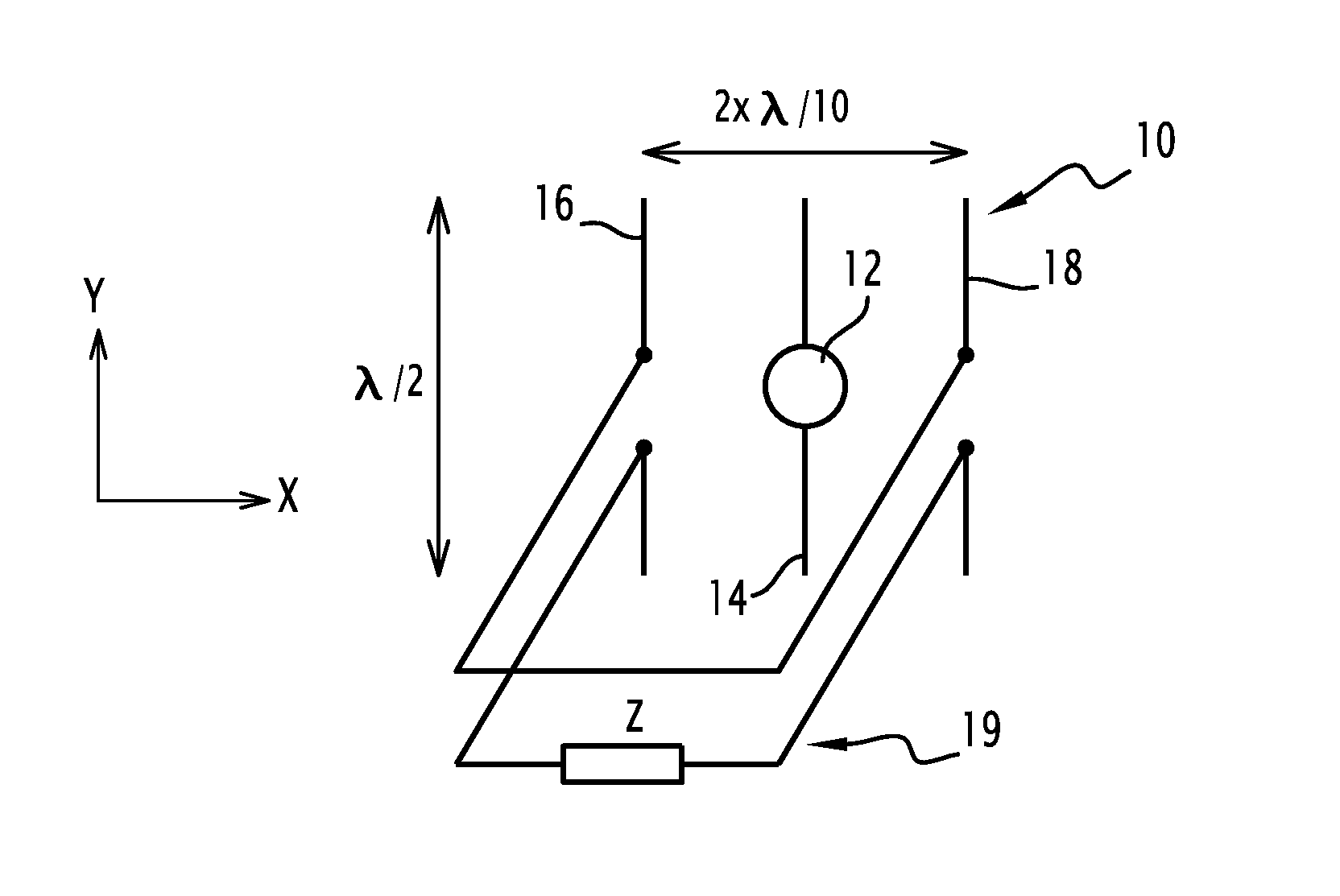
Switched mode negative inductor
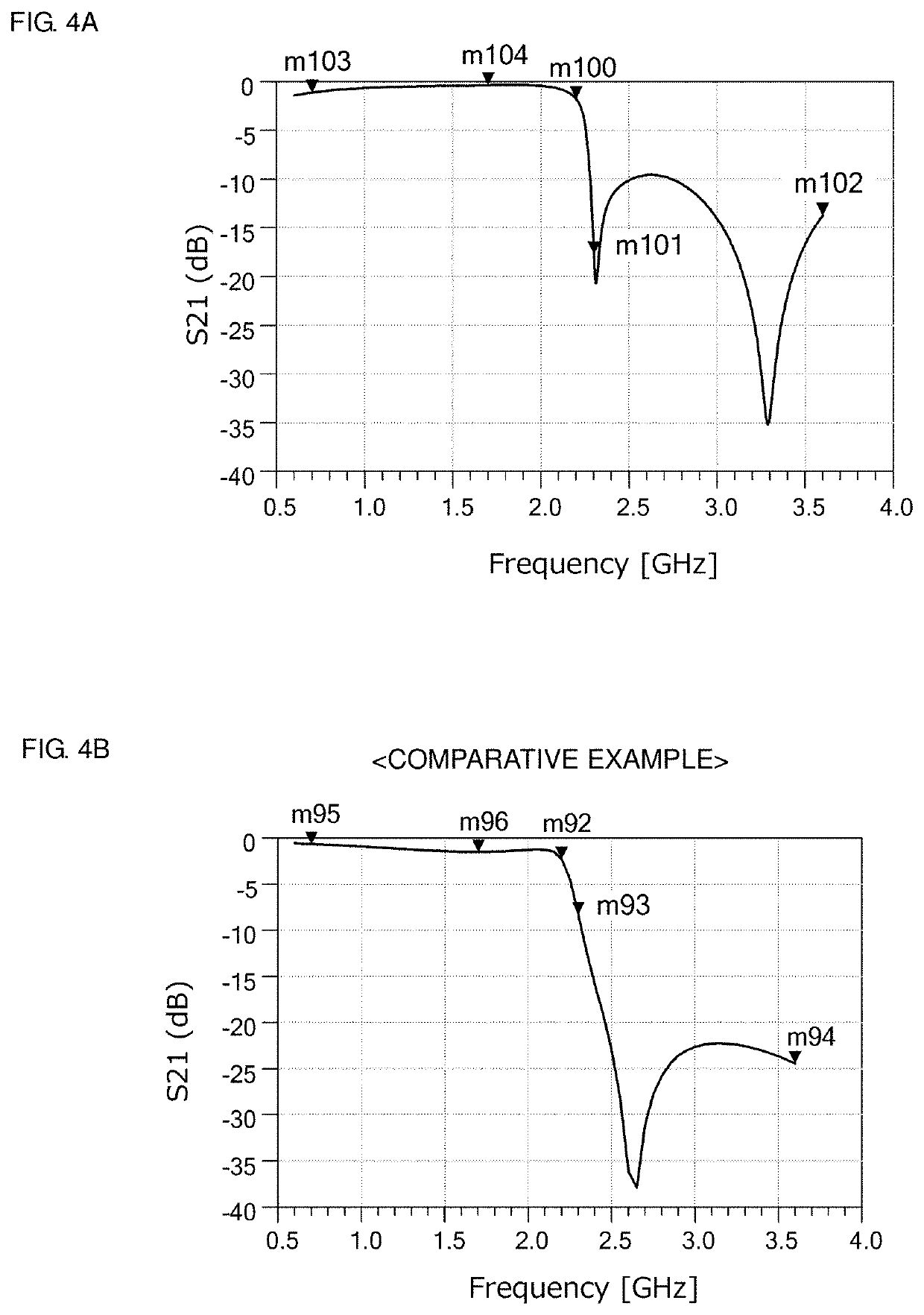
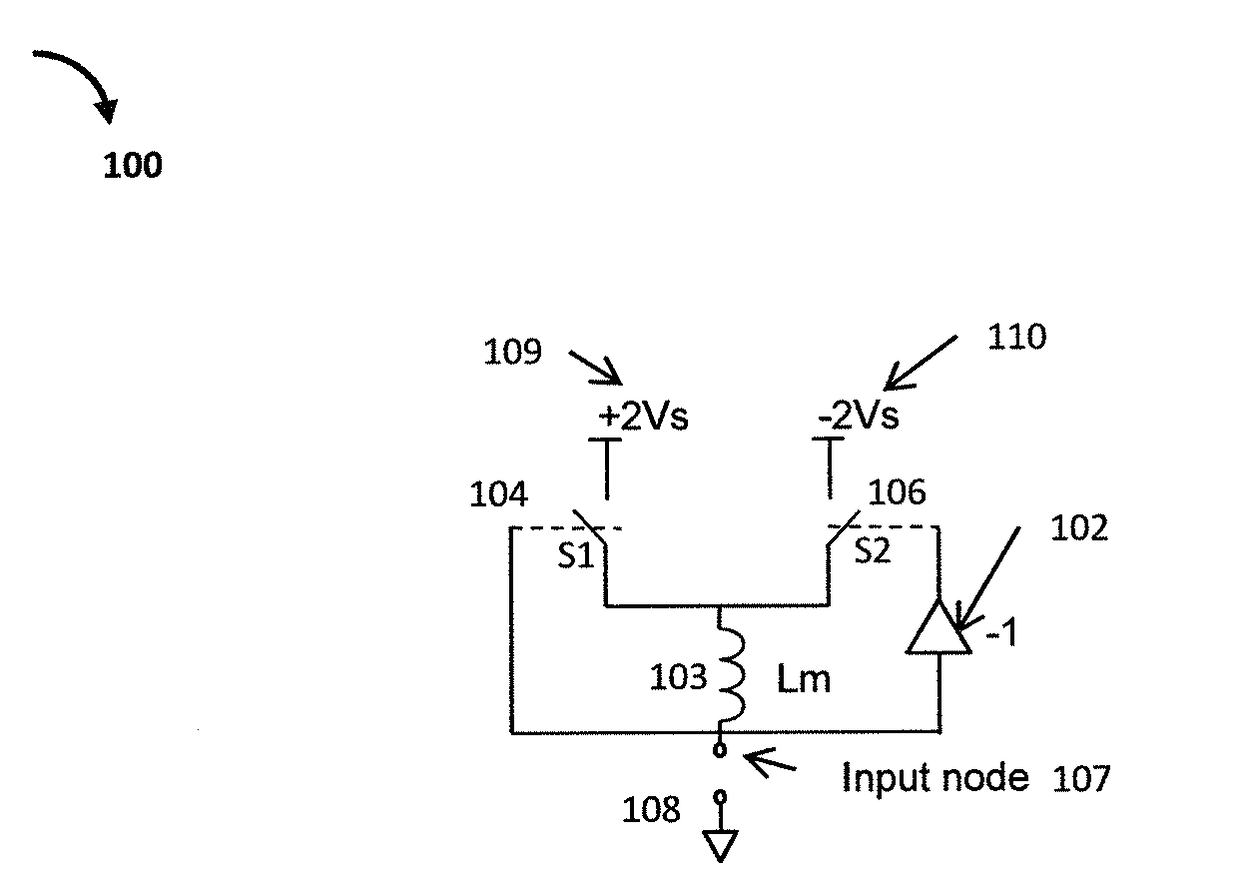
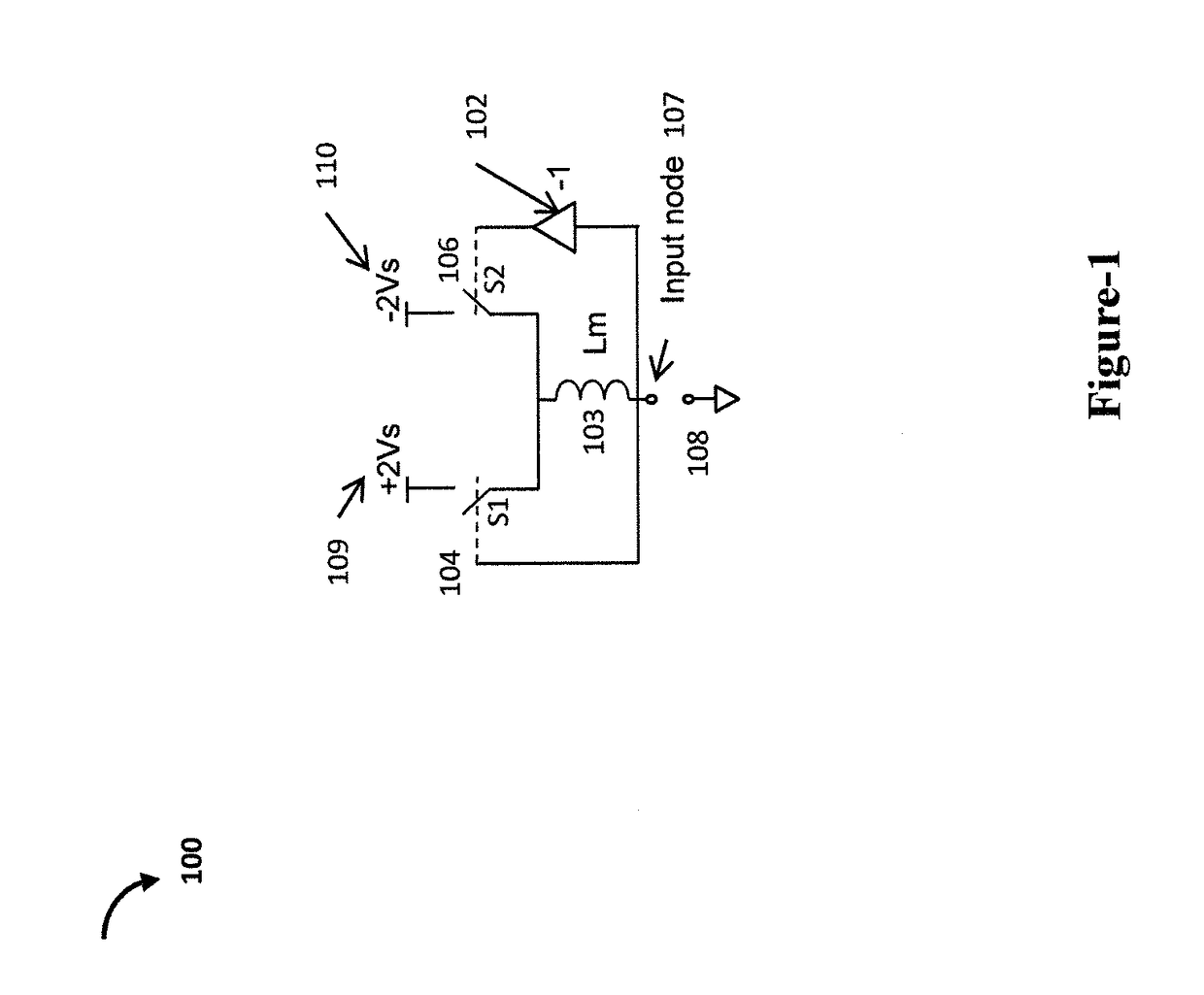
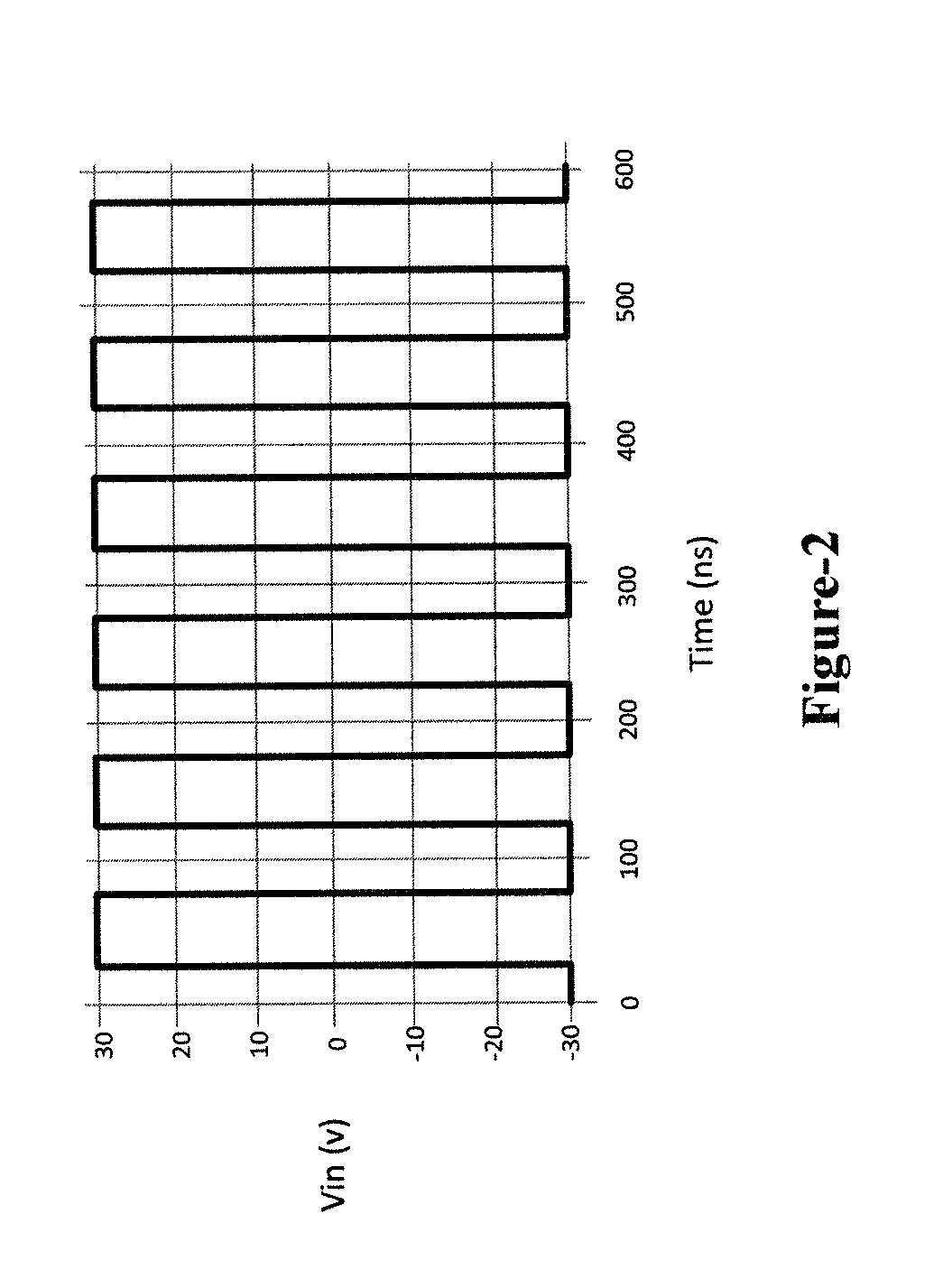
ActiveUS9923548B1Network simulating reactancesFrequency selective two-port networksControl switchVoltage source
A switched mode negative inductance circuit includes an input node responsive to a voltage signal. The circuit also includes first and second voltage sources, first and second controlled switches having first poles coupled to the first and second voltage sources, respectively and an inductor having a first electrode coupled to second poles of the first and second controlled switches and a second electrode coupled to the input node. The input node is coupled to a control electrode of the first controlled switch, and to a control electrode of the second controlled switch through a voltage inverting circuit. The disclosure also illustrates balanced negative inductance circuits and implementation approaches using NMOS transistors.
Owner:HRL LAB
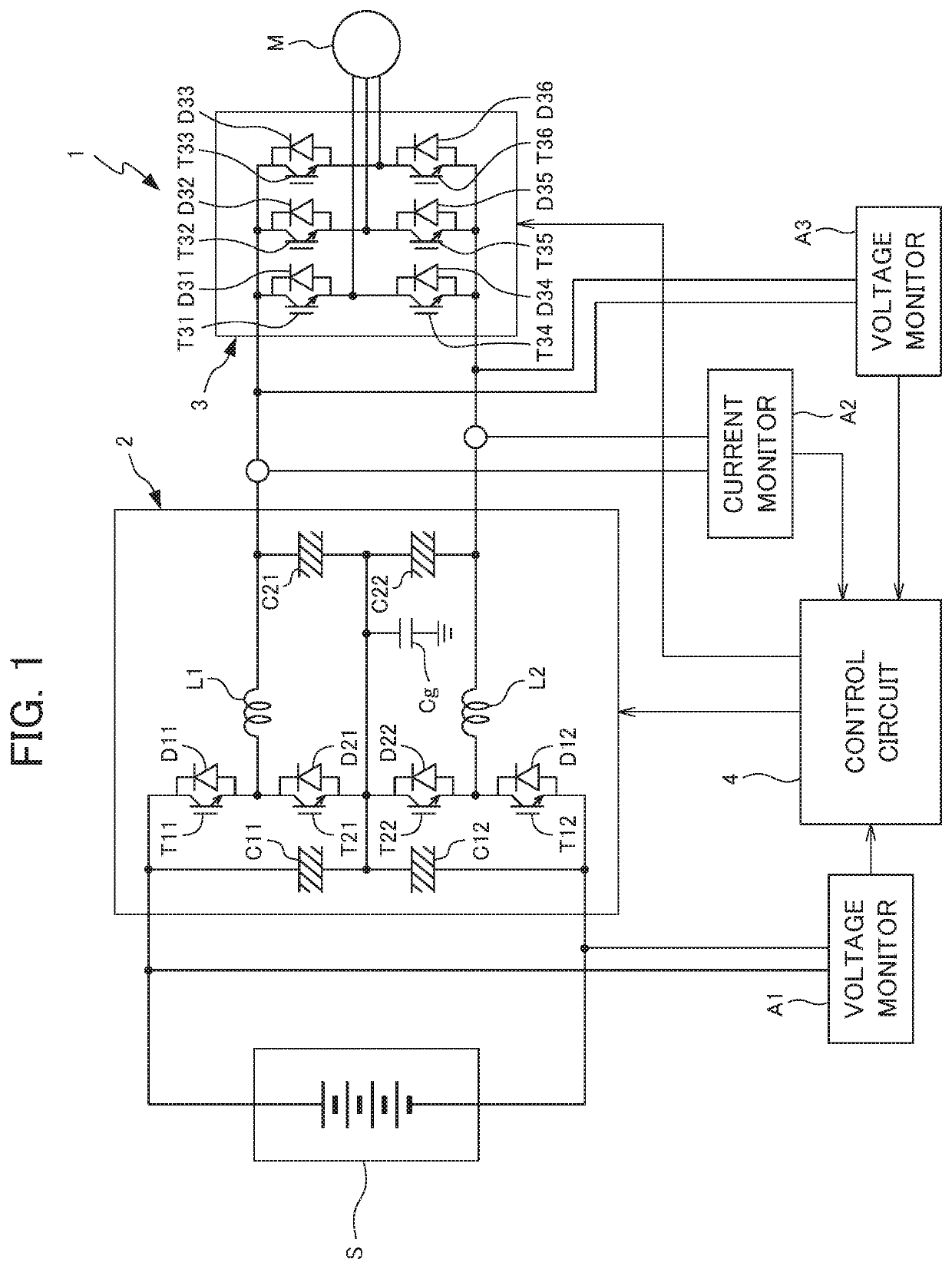
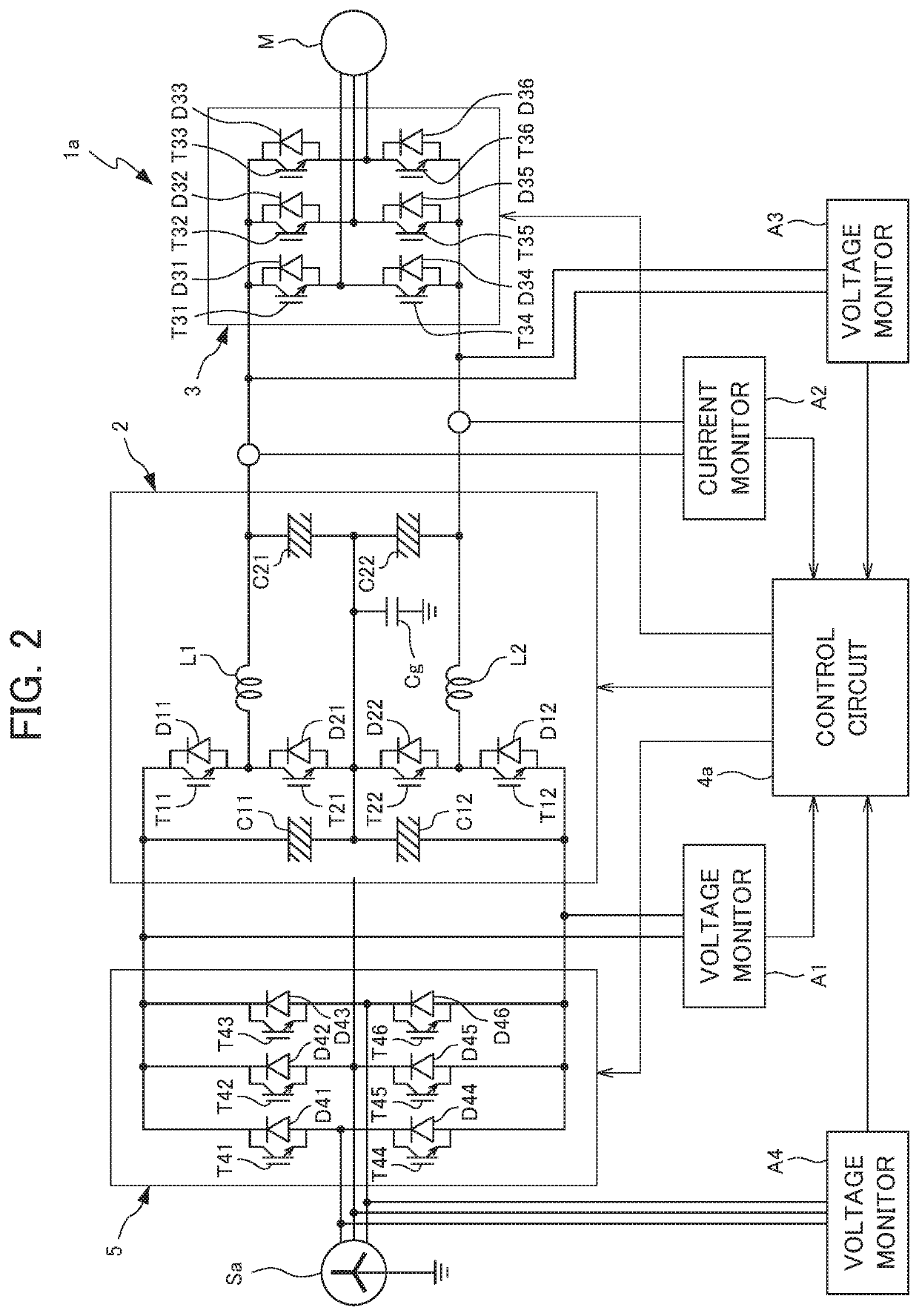
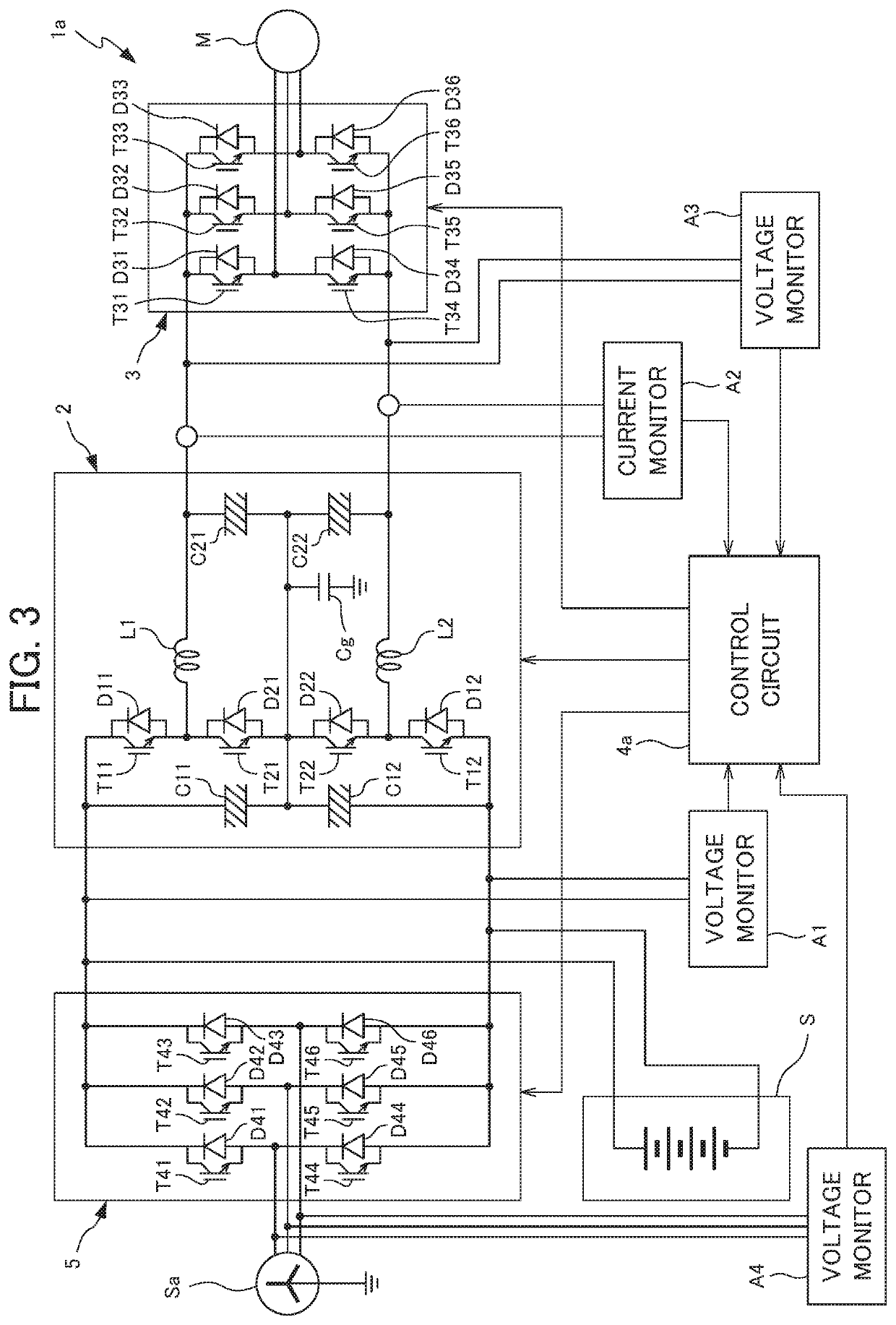
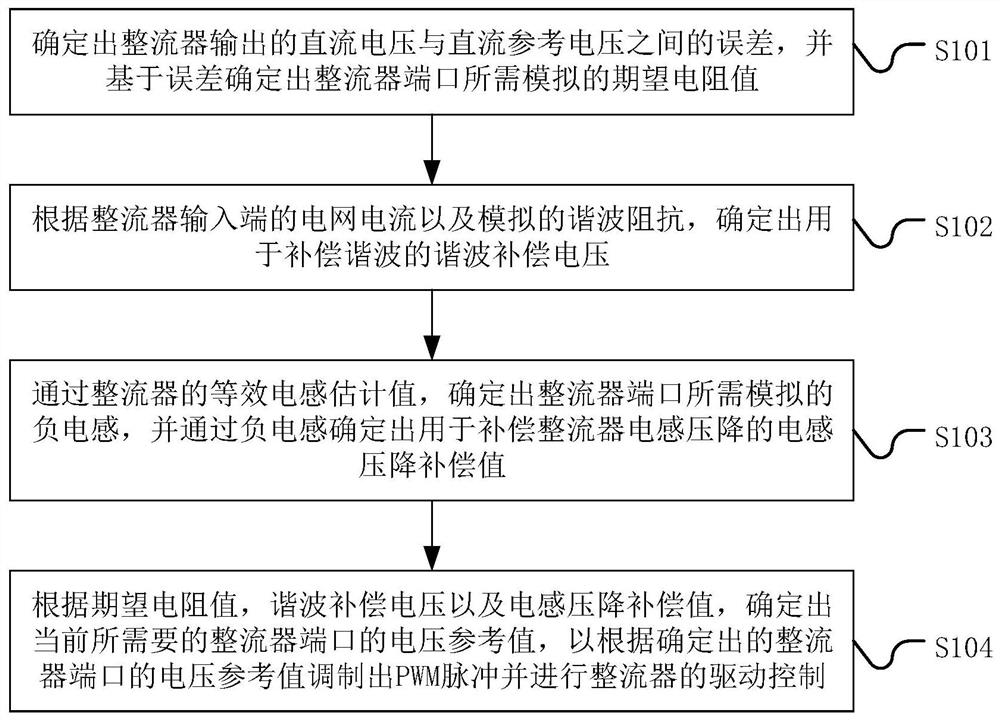
A rectifier and its control method and control system
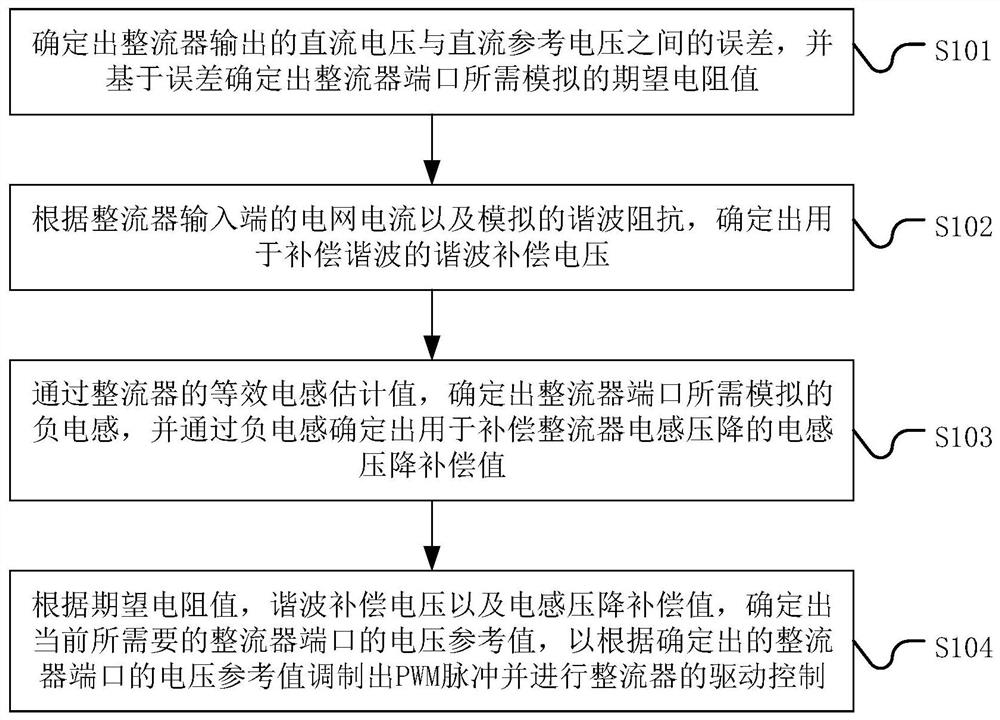
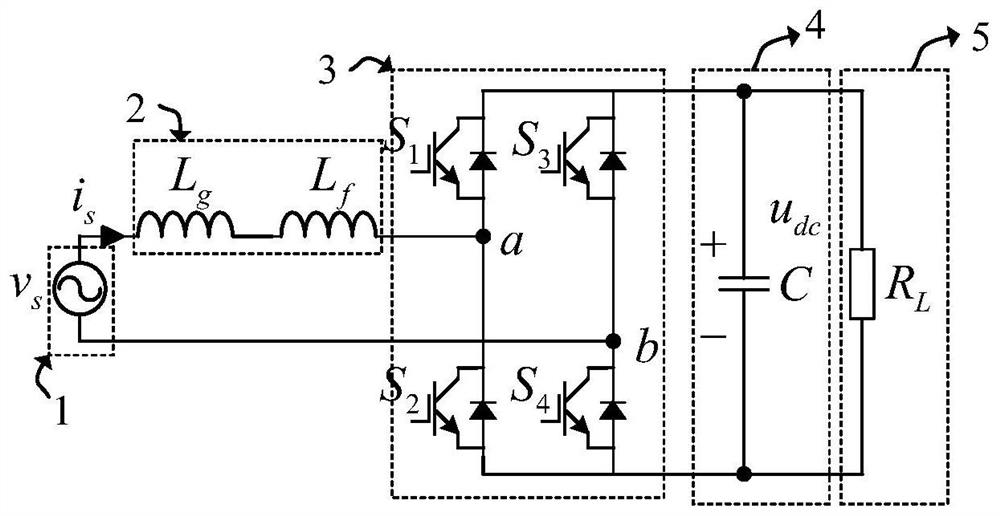
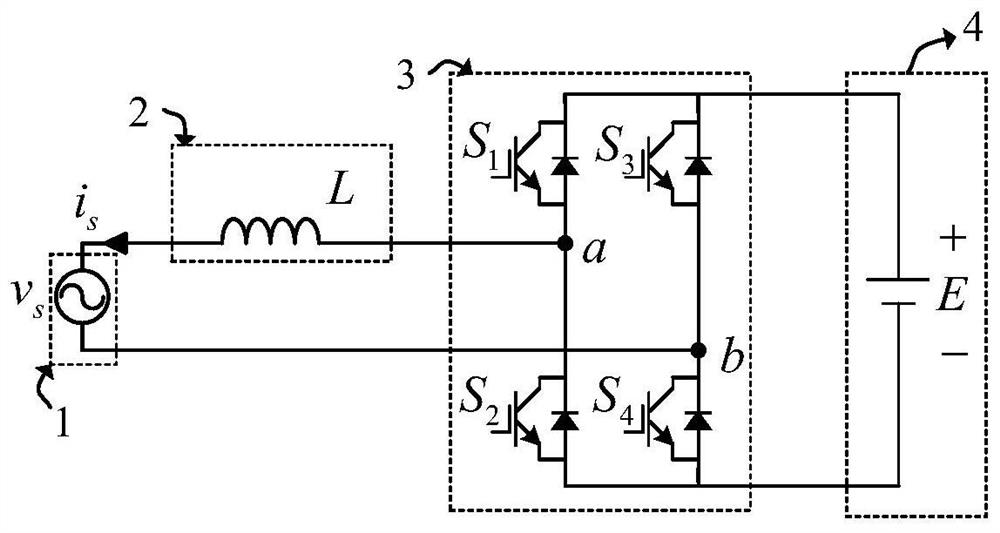
ActiveCN113507227BImprove power factorEliminate errorsAc-dc conversionHarmonic reduction arrangementPower factorVoltage reference
The present application discloses a rectifier and a control method and control system thereof, including: determining an error between a DC voltage output by the rectifier and a DC reference voltage, and determining an expected resistance value to be simulated at a port of the rectifier based on the error; The grid current at the input end and the simulated harmonic impedance determine the harmonic compensation voltage for compensating harmonics; through the estimated value of the equivalent inductance of the rectifier, determine the simulated negative inductance of the rectifier port, and determine the negative inductance through the negative inductance. The inductance voltage drop compensation value used to compensate the inductance voltage drop of the rectifier; according to the expected resistance value, harmonic compensation voltage and inductance voltage drop compensation value, determine the current required voltage reference value of the rectifier port to modulate the PWM pulse and carry out Drive control of the rectifier. By applying the solution of the present application, when there is no grid voltage sensor, the current harmonics of the rectifier are effectively reduced, and a high power factor is achieved.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
An inverter control method without grid voltage sensor
ActiveCN113037119BGuaranteed uptimeImprove power qualityAc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceStabilization control
The invention provides an inverter control method without a grid voltage sensor. The inverter control method includes two parts: analog negative resistance control and stabilization control based on analog negative inductance. The analog negative resistance control is used to realize the power transmission of the inverter to the grid while ensuring that the output current of the inverter remains sinusoidal. The stabilization control based on the analog negative inductance is used to make up for the unstable pole caused by the analog negative resistance control, so as to realize the safe and stable operation of the inverter. In addition, this method only samples the output current of the inverter, which improves the reliability of the system and reduces the sensor cost. At the same time, the method is simple to control and has a small amount of calculation, so it is suitable for practical applications.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Low-voltage microgrid distributed control method and system based on adaptive virtual impedance
ActiveCN109449999BReduce the deviation of output powerReduce the impact of impedanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMicrogridLow voltage
The invention provides a low-voltage micro-grid distributed control method and system based on adaptive virtual impedance. The method comprises the following steps: generating adaptive virtual resistance by using a product of a ratio of active power output by a local inverter and voltage magnitude and a virtual impedance coefficient; determining virtual negative inductance according to an inductive reactance part of equivalent output impedance of the local inverter, so that the equivalent output impedance of the local inverter has a resistance property; obtaining the adaptive virtual impedanceaccording to the complex accumulation of the adaptive virtual resistance and the virtual negative inductance; according to a dq-axis current component of the adaptive virtual impedance and local inverter outlet three-phase current, generating dq-axis virtual voltage; and using the dq-axis virtual voltage to compensate a voltage reference value obtained by resistance droop control to obtain finalreference voltage.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
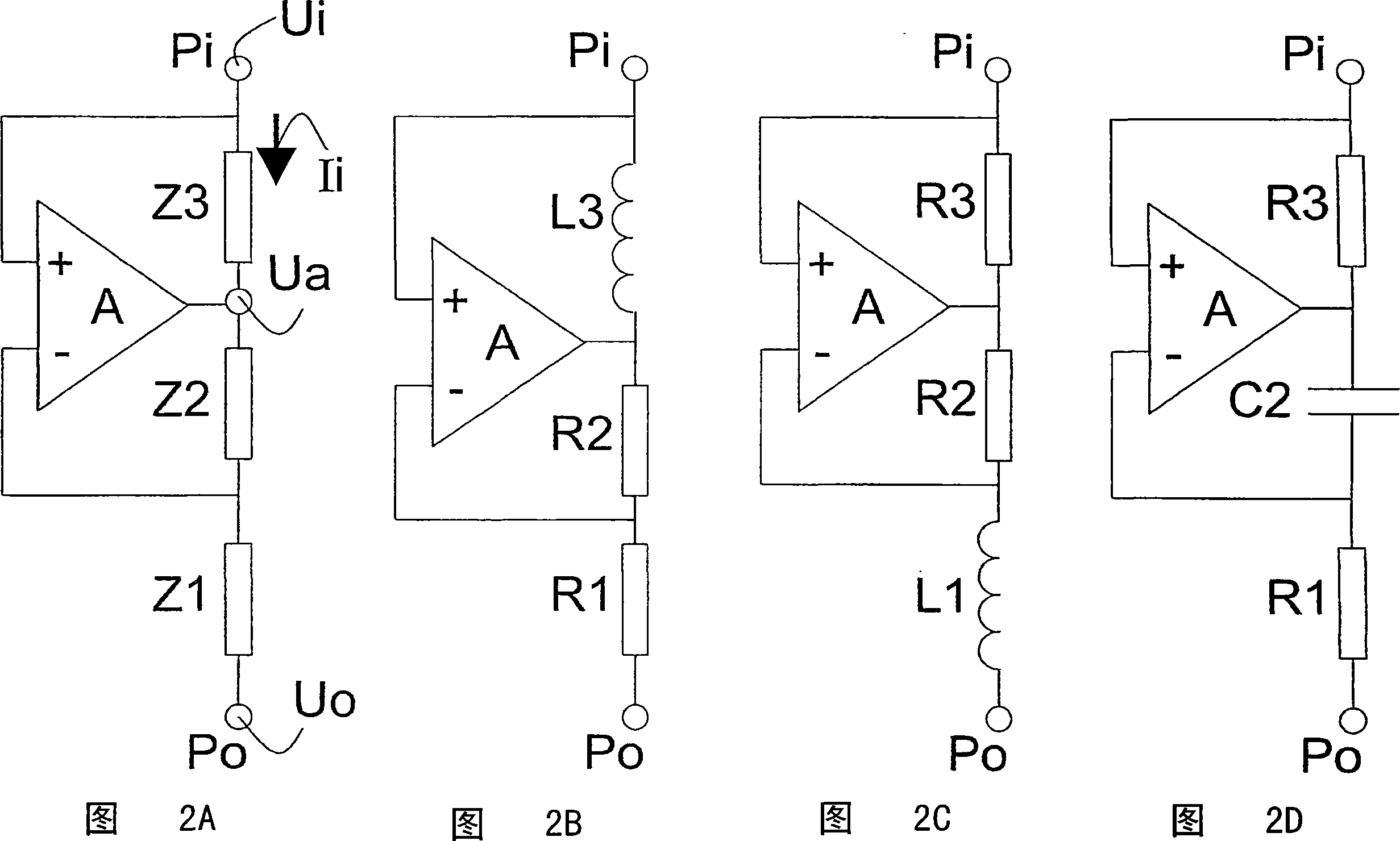
Negative capacitance device, negative inductance device, and circuit including same
PendingCN112448680ANegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention relates to a negative capacitance device, a negative inductance device, and a circuit including the same. According to one embodiment, a negative capacitance device is provided having afirst terminal and a second terminal. The negative capacitance device includes: a first operational amplifier having a first non-inverting input terminal connected to the first terminal of the negative capacitance device, a first inverting input terminal connected to the second terminal of the negative capacitance device, and a first output terminal; a first capacitor connected between the first non-inverting input terminal and the first output terminal of the first operational amplifier; a first resistor connected between the first inverting input terminal and the first output terminal of thefirst operational amplifier; and a second resistor connected between the first inverting input terminal of the first operational amplifier and the second terminal of the negative capacitance device.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Power supply and power system having a step-down circuit and an inverse-conversion circuit
Owner:FANUC LTD
Rectifier and control method and control system thereof
ActiveCN113507227AImprove power factorEliminate errorsAc-dc conversionHarmonic reduction arrangementPower factorVoltage reference
The invention discloses a rectifier and a control method and system thereof, and the method comprises the steps: determining an error between a DC voltage outputted by the rectifier and a DC reference voltage, and determining an expected resistance value needed to be simulated by a rectifier port based on the error; determining harmonic compensation voltage for compensating harmonic according to the power grid current of the input end of the rectifier and the simulated harmonic impedance; according to the equivalent inductance estimation value of the rectifier, determining negative inductance needing to be simulated at the port of the rectifier, and determining an inductance voltage drop compensation value used for compensating the inductance voltage drop of the rectifier through the negative inductance; according to the expected resistance value, the harmonic compensation voltage and the inductance voltage drop compensation value, determining a currently required voltage reference value of a rectifier port so as to modulate PWM pulses and perform driving control of the rectifier. By applying the scheme of the invention, the current harmonic of the rectifier is effectively reduced without a power grid voltage sensor, and a high power factor is realized.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com