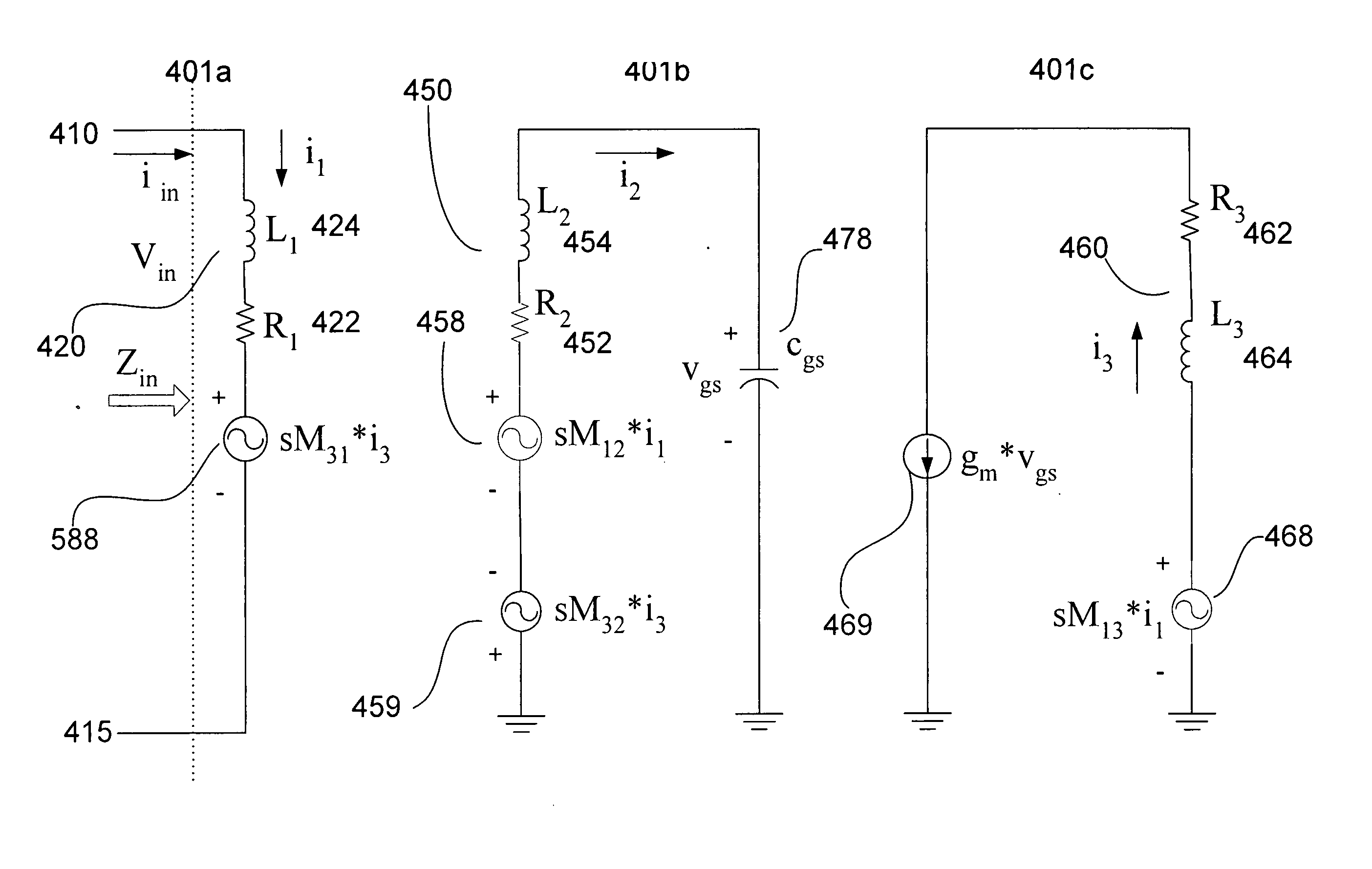
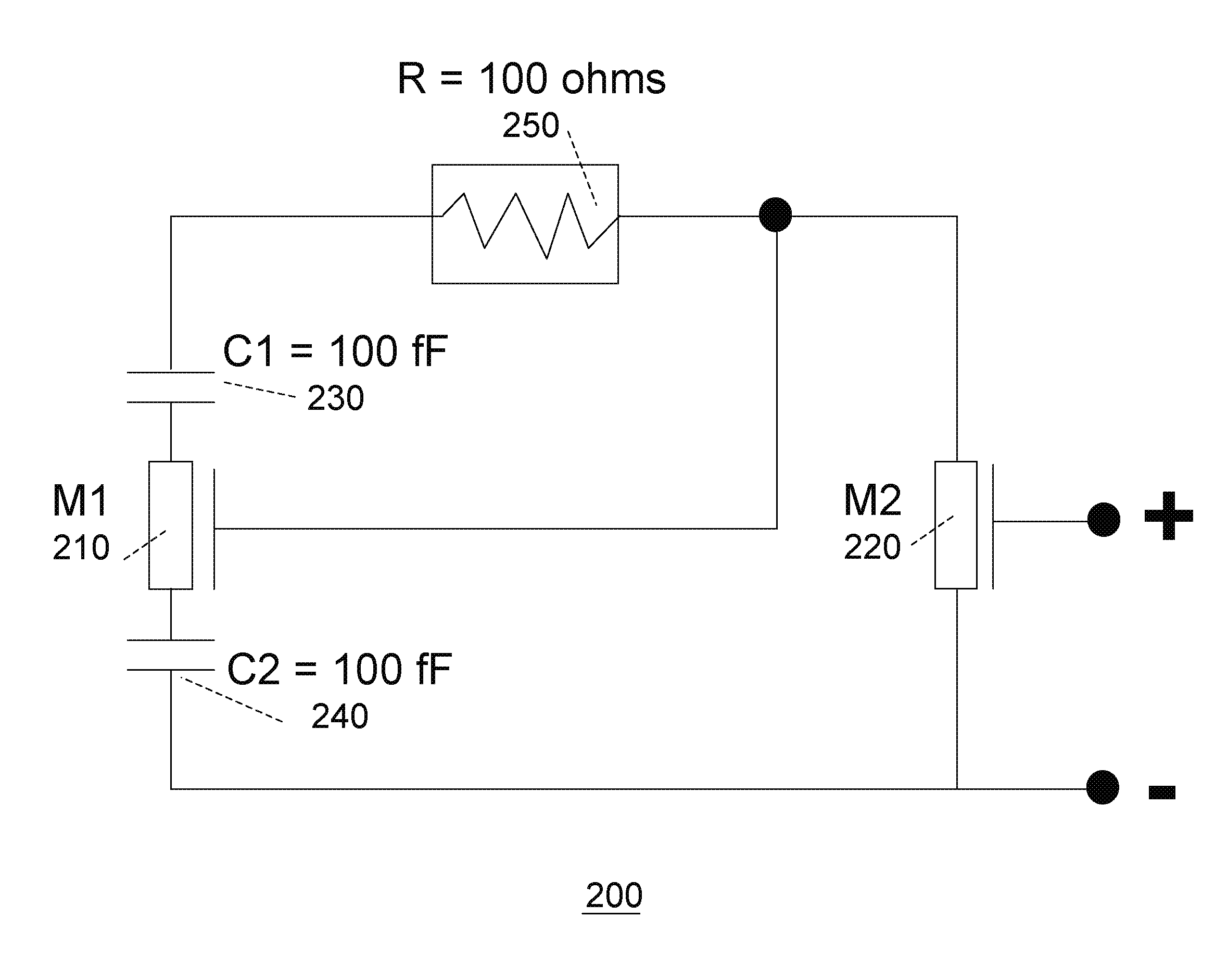
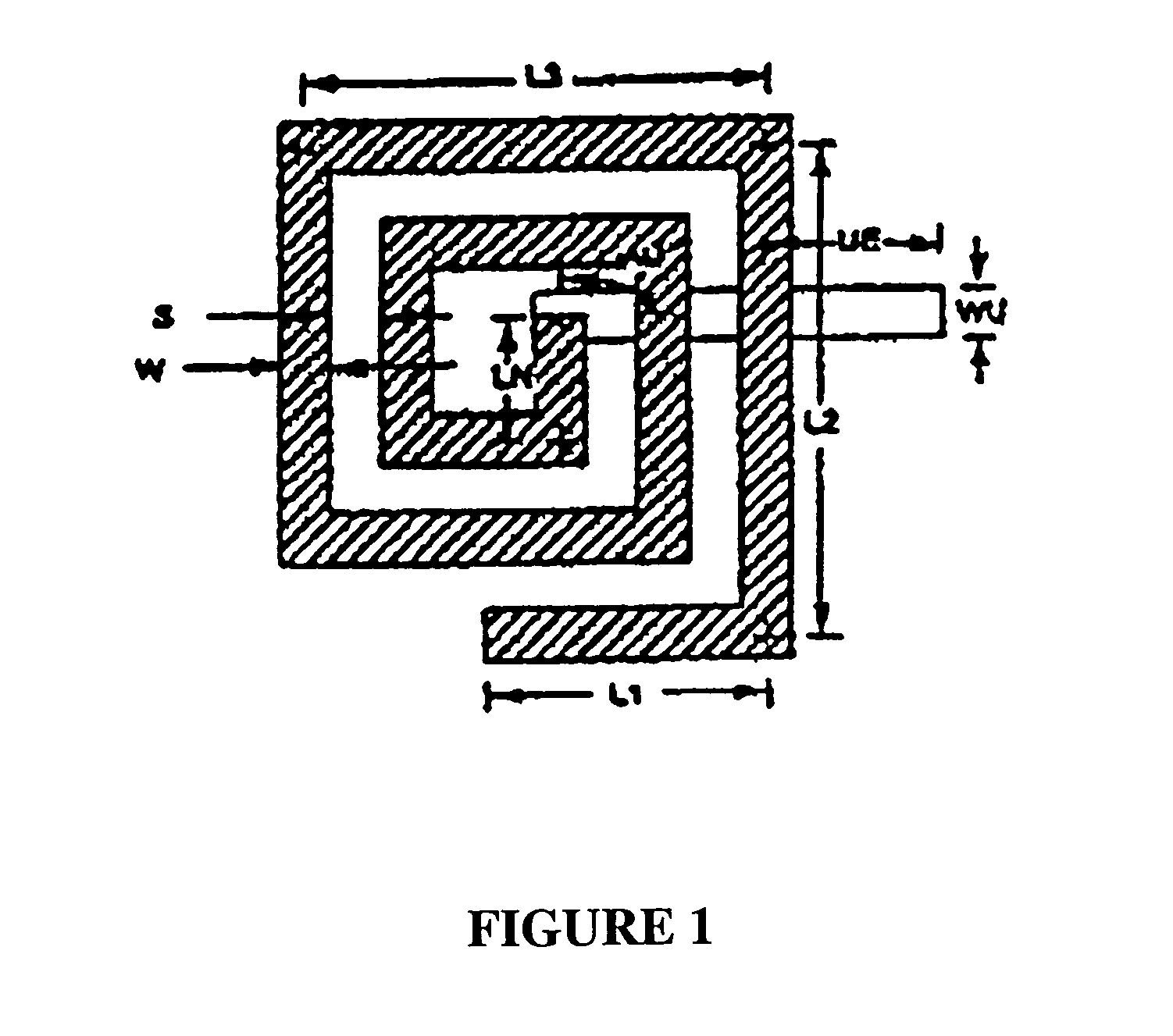
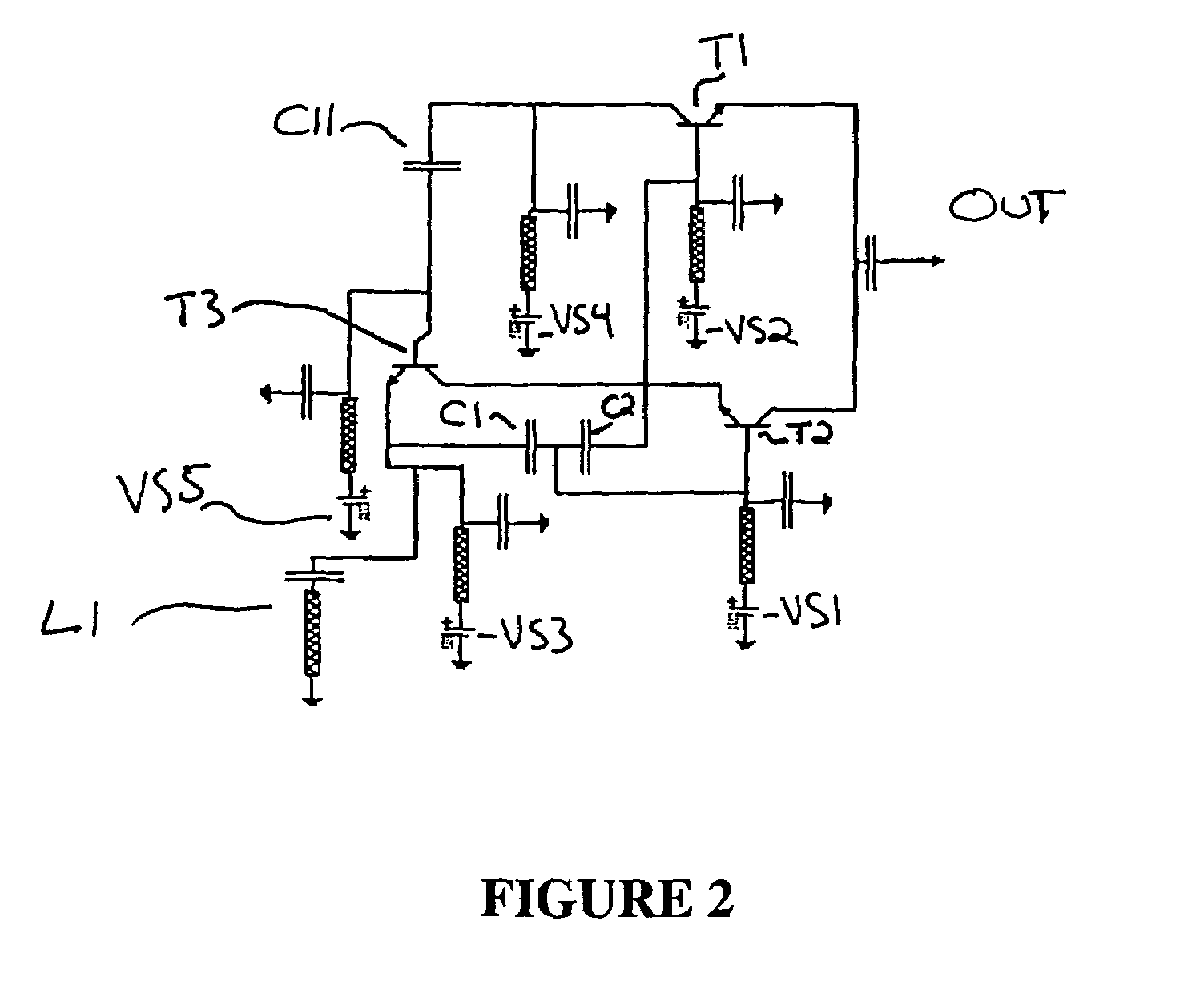
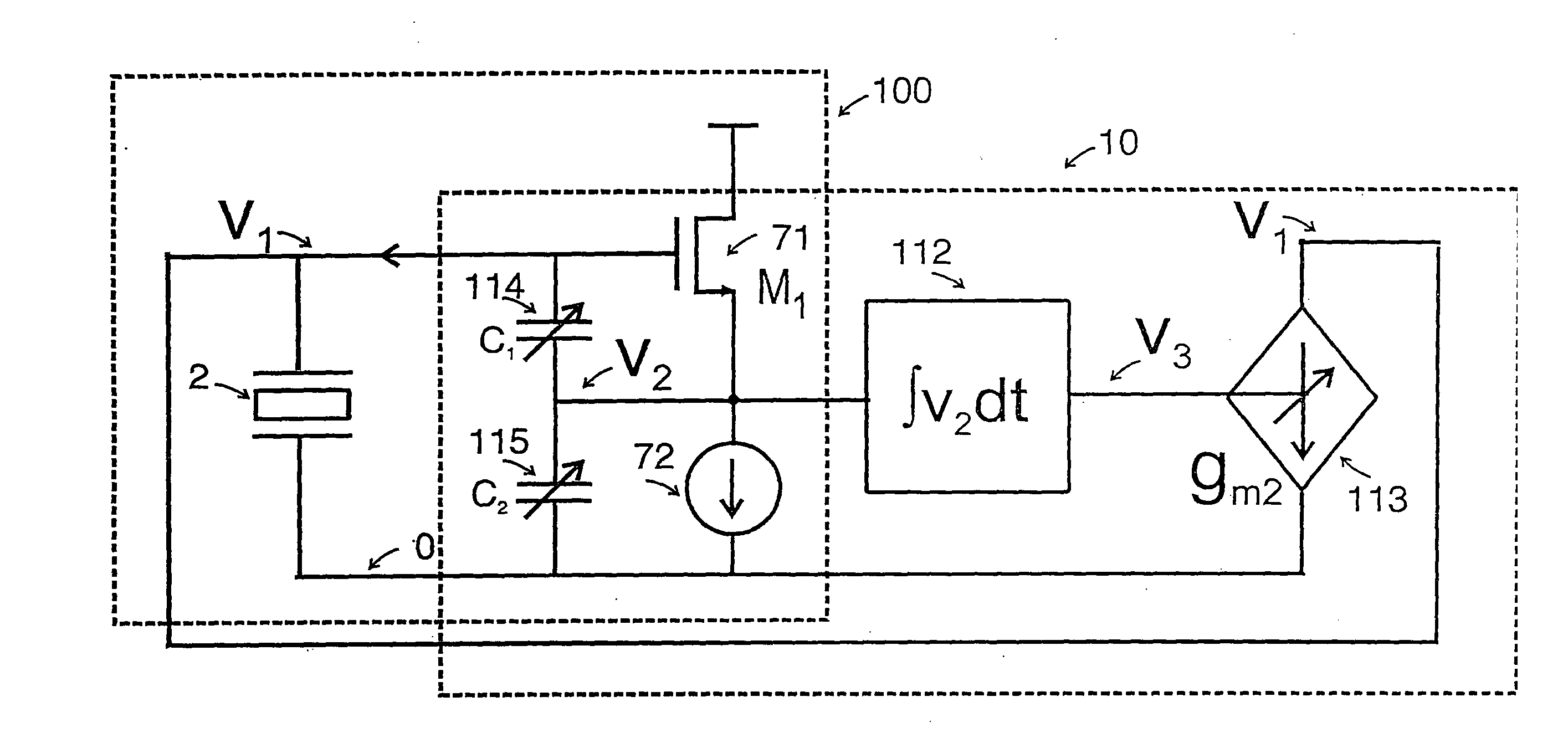
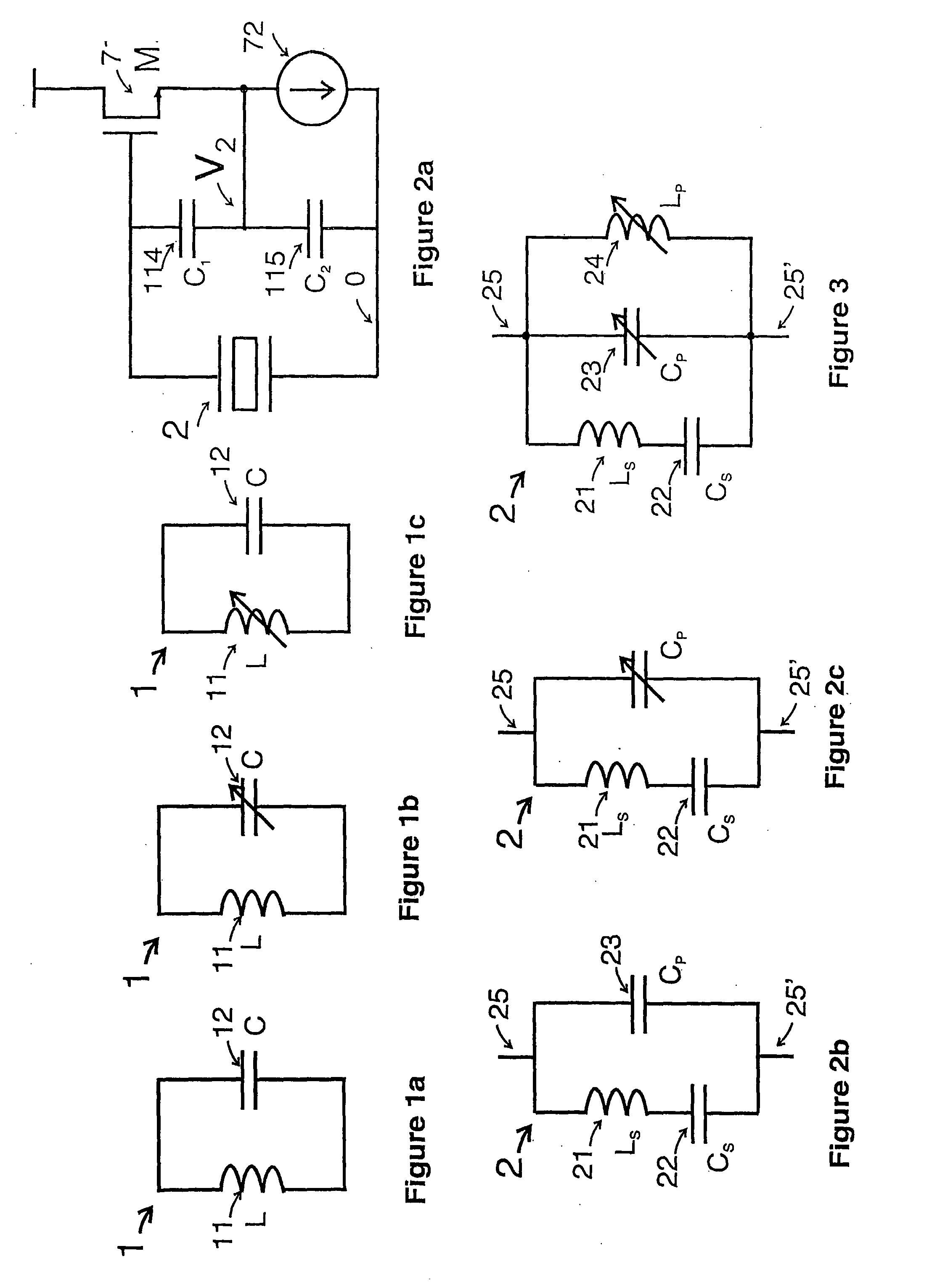
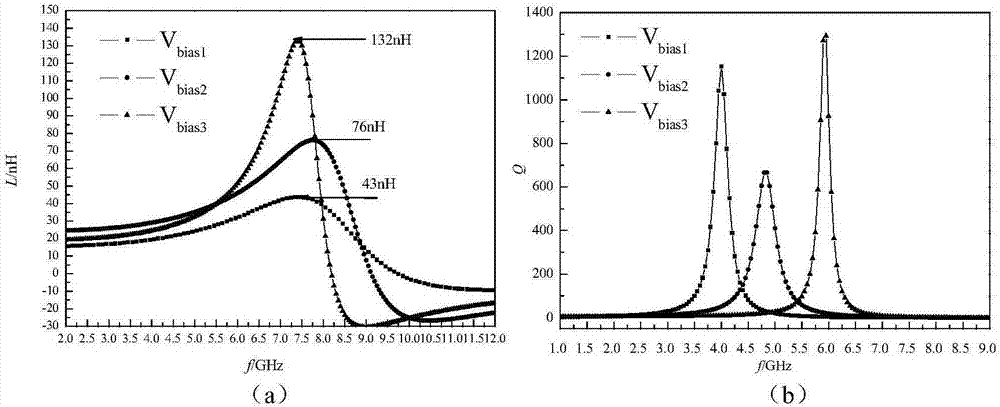
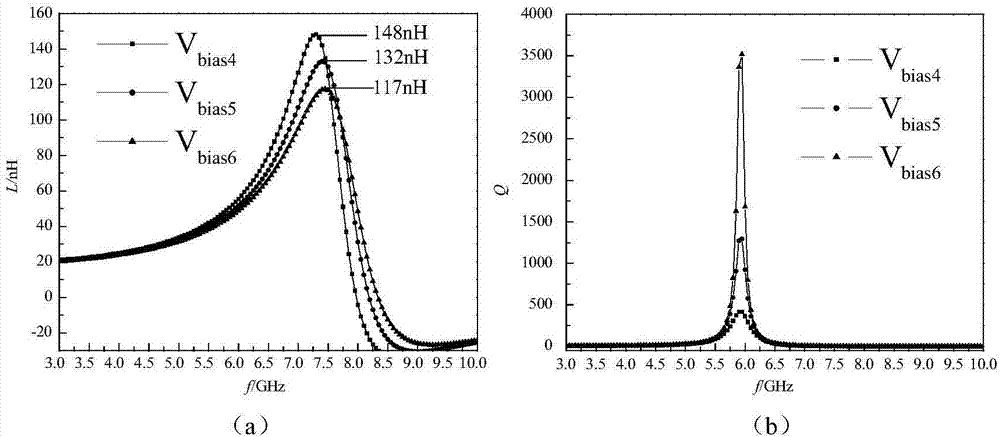
Patents
Literature
155results about "Network simulating reactances" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
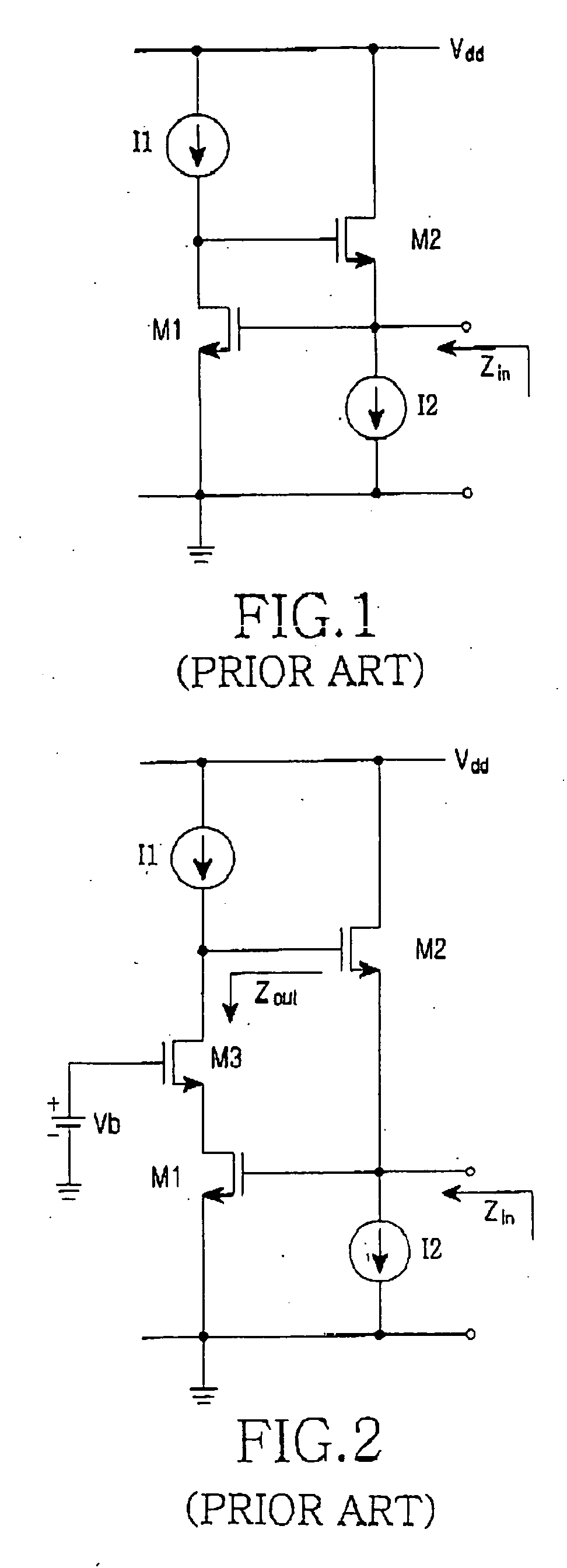
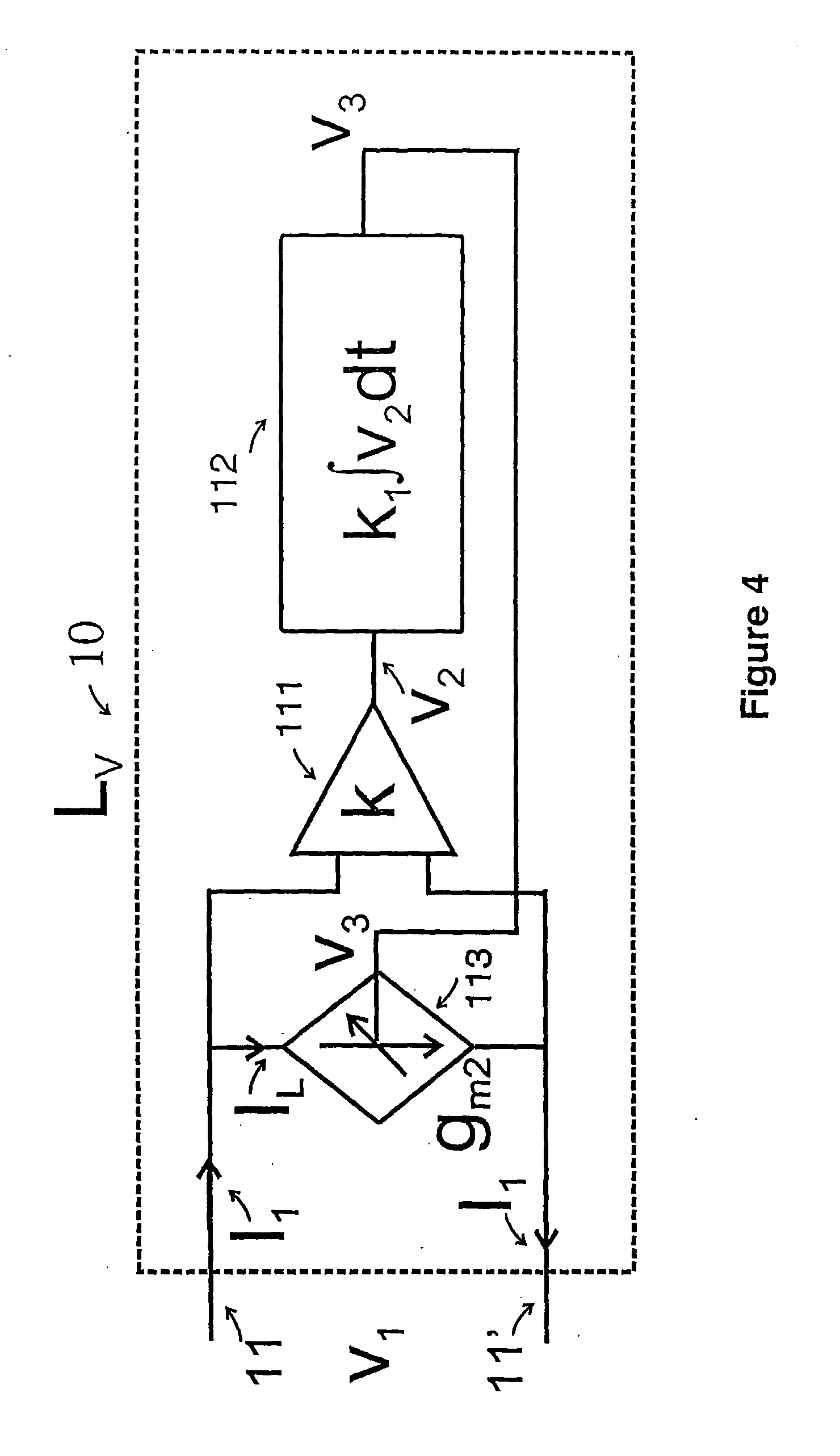
High-frequency active inductor
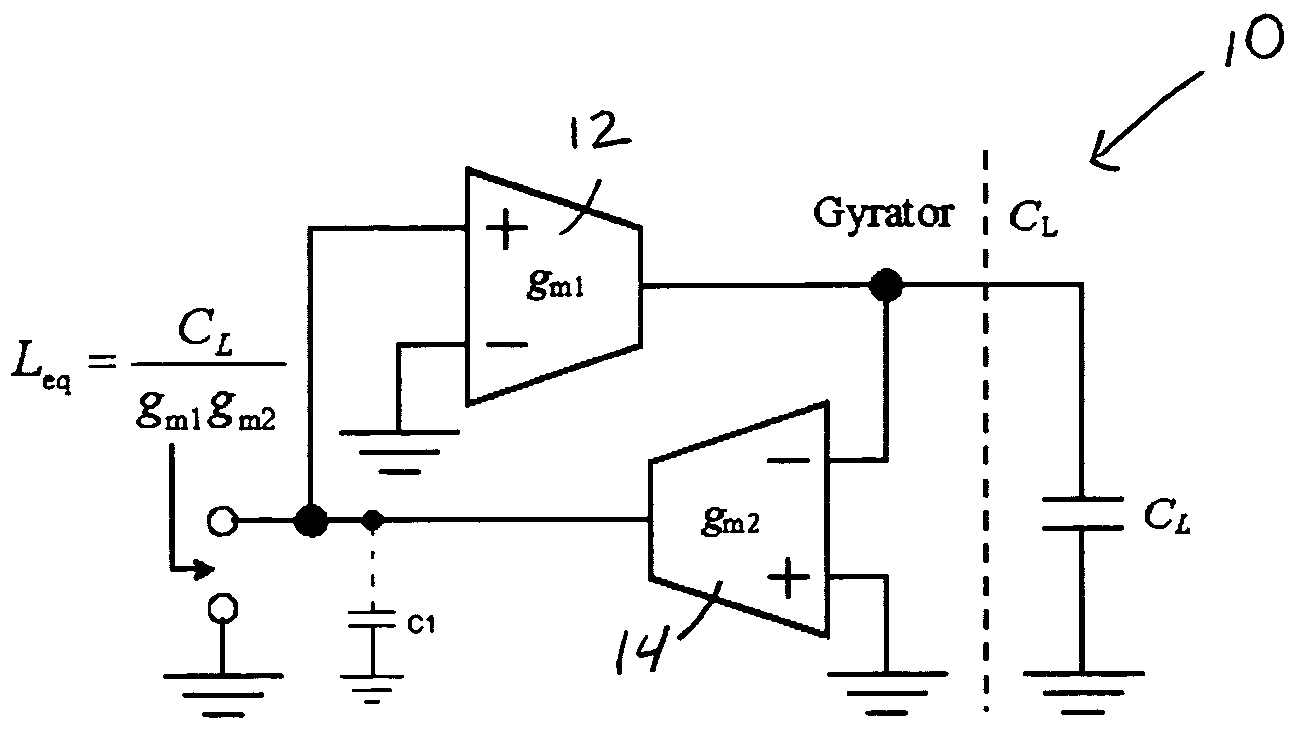
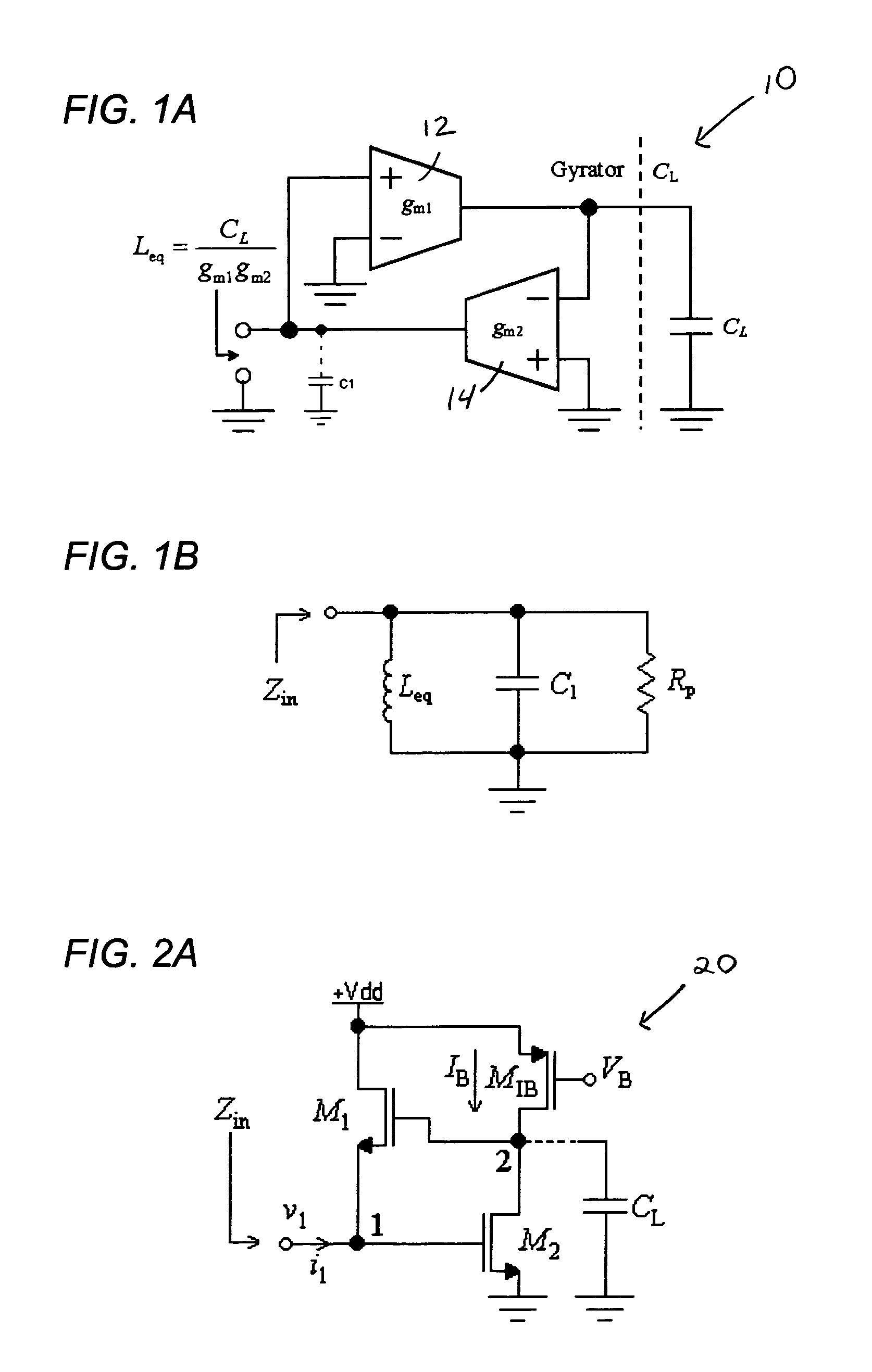
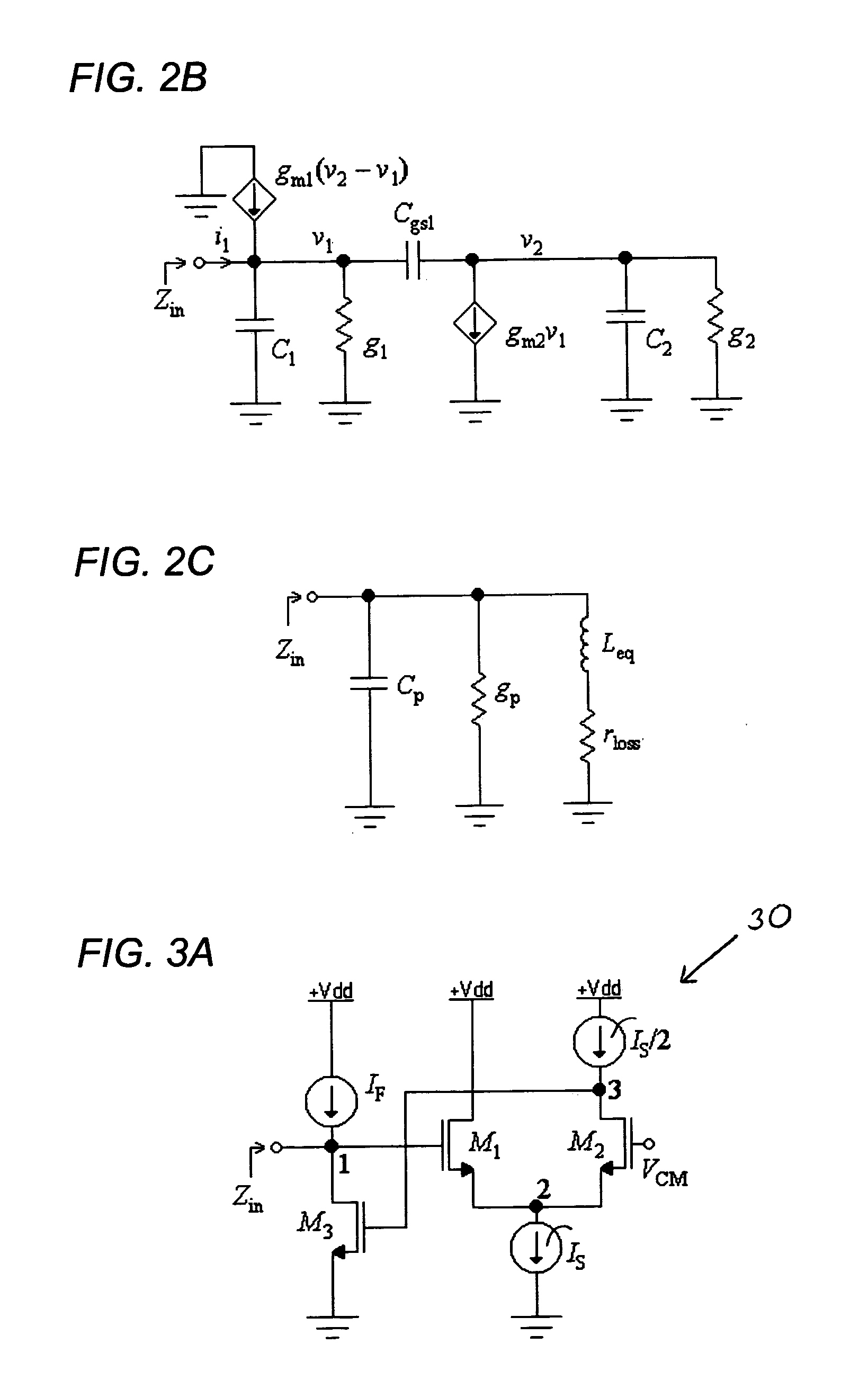
An active inductor circuit implemented in sub-micron CMOS semiconductor technology is usable at gigaHertz frequencies and includes an input node, a non-inverting transconductor circuit comprising a differential pair of NMOS transistors connected to the input node, an inverting transconductor circuit comprising an NMOS transistor connected to an output node of the non-inverting transconductor circuit and connected to the input node in a gyrator feedback configuration. Varactors coupled to the transconductor circuits tune the frequency and Q of the active inductor circuit.
Owner:PORTLAND STATE UNIV
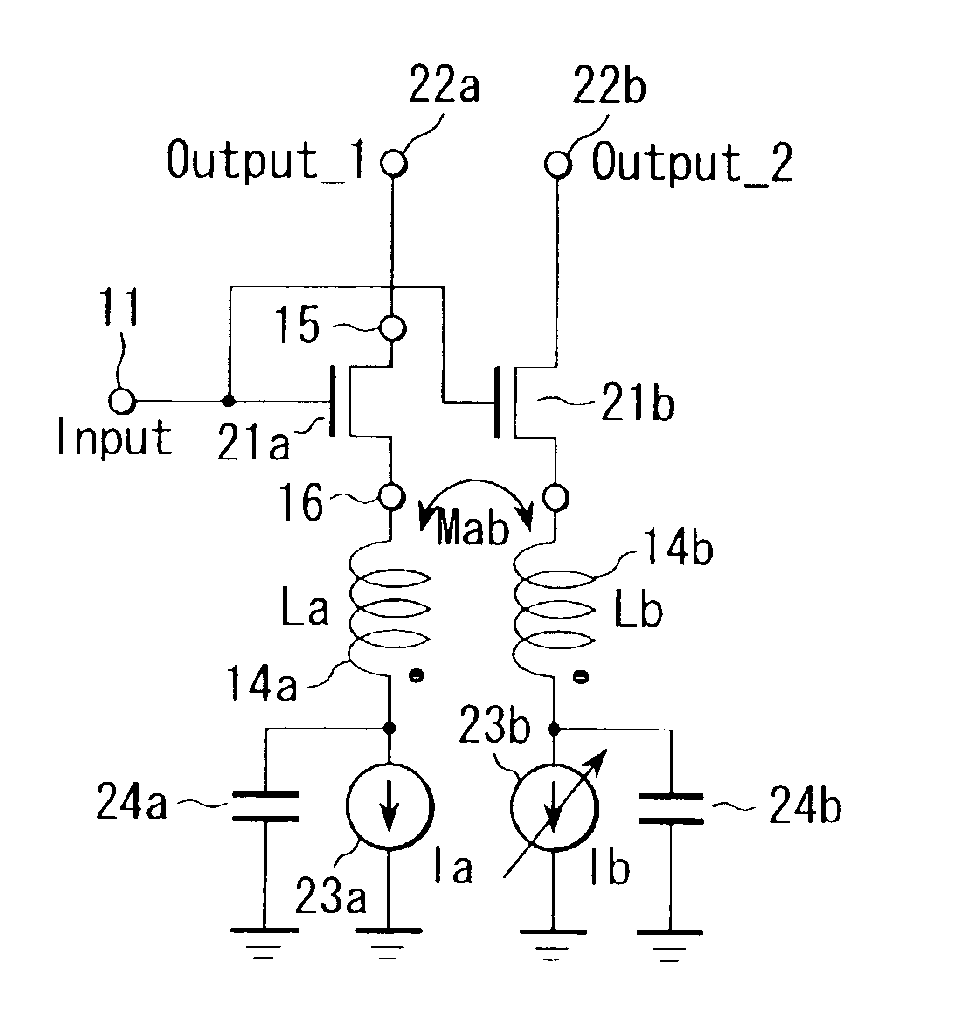
Variable inductor, oscillator including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this oscillator, and amplifier including the variable inductor and radio terminal comprising this amplifier
InactiveUS7098737B2Good electric characteristicMiniaturizationResonant circuit tuningGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierInductor
An amplifier comprises an amplifier circuit which comprises a first inductor as an impedance element for degeneration, and a control circuit which has a second inductor electro-magnetically connected to the first inductor, and changes a control current flowing through the second inductor to change an inductance value of the first inductor, thereby changing amplification characteristics of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Methods and apparatus for programmable active inductance
ActiveUS20080204171A1Improve linearityMultiple-port active networksNetwork simulating reactancesResistive circuitsInductor
Methods and apparatus are provided for programmable active inductance. The disclosed active inductor devices provide a tunable bandwidth with improved linearity. The disclosed active inductors have a variable frequency response corresponding to a variable inductance of the active inductor. The active inductor comprises a variable resistive circuit having an effective resistance, wherein the variable resistive circuit is comprised of at least one resistor that can be selectively bypassed in the variable resistive circuit to vary the effective resistive. The active inductor has an inductance that can be varied by varying the effective resistance.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High-frequency active inductor
InactiveUS20050083151A1Effective structureNetwork simulating reactancesDifferential amplifiersCMOSEngineering
An active inductor circuit implemented in sub-micron CMOS semiconductor technology is usable at gigaHertz frequencies and includes an input node, a non-inverting transconductor circuit comprising a differential pair of NMOS transistors connected to the input node, an inverting transconductor circuit comprising an NMOS transistor connected to an output node of the non-inverting transconductor circuit and connected to the input node in a gyrator feedback configuration. Varactors coupled to the transconductor circuits tune the frequency and Q of the active inductor circuit.
Owner:PORTLAND STATE UNIV
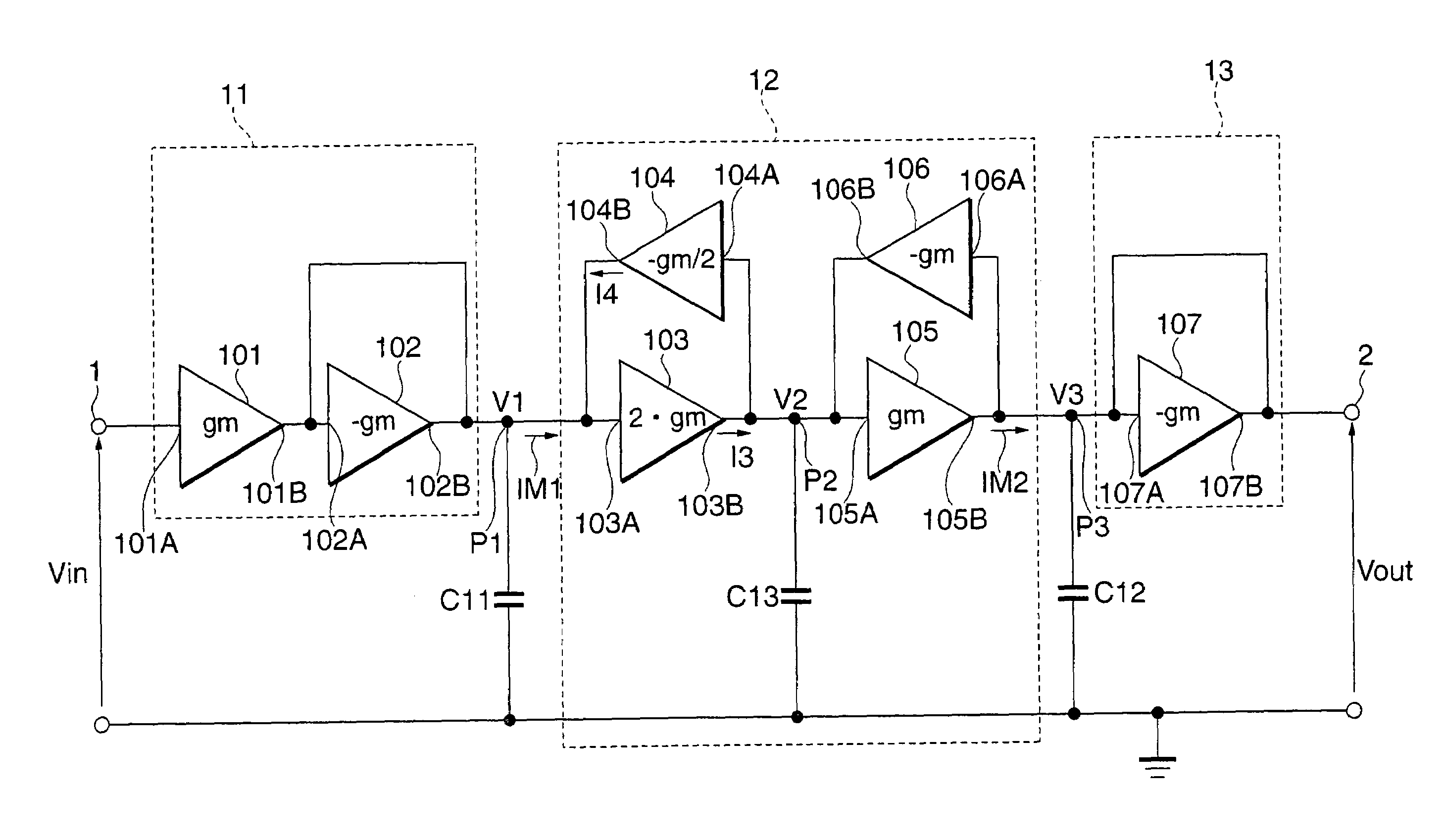
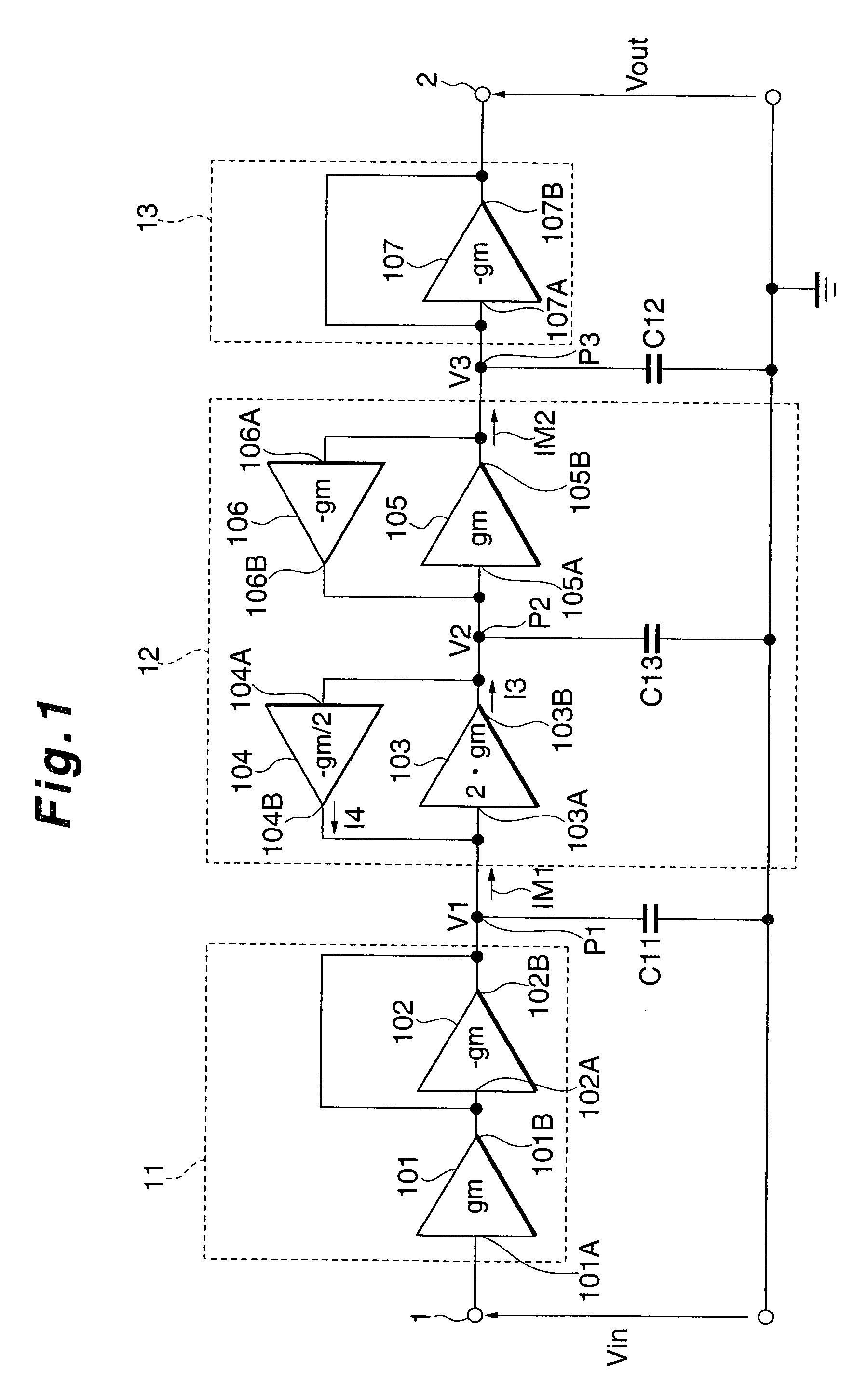
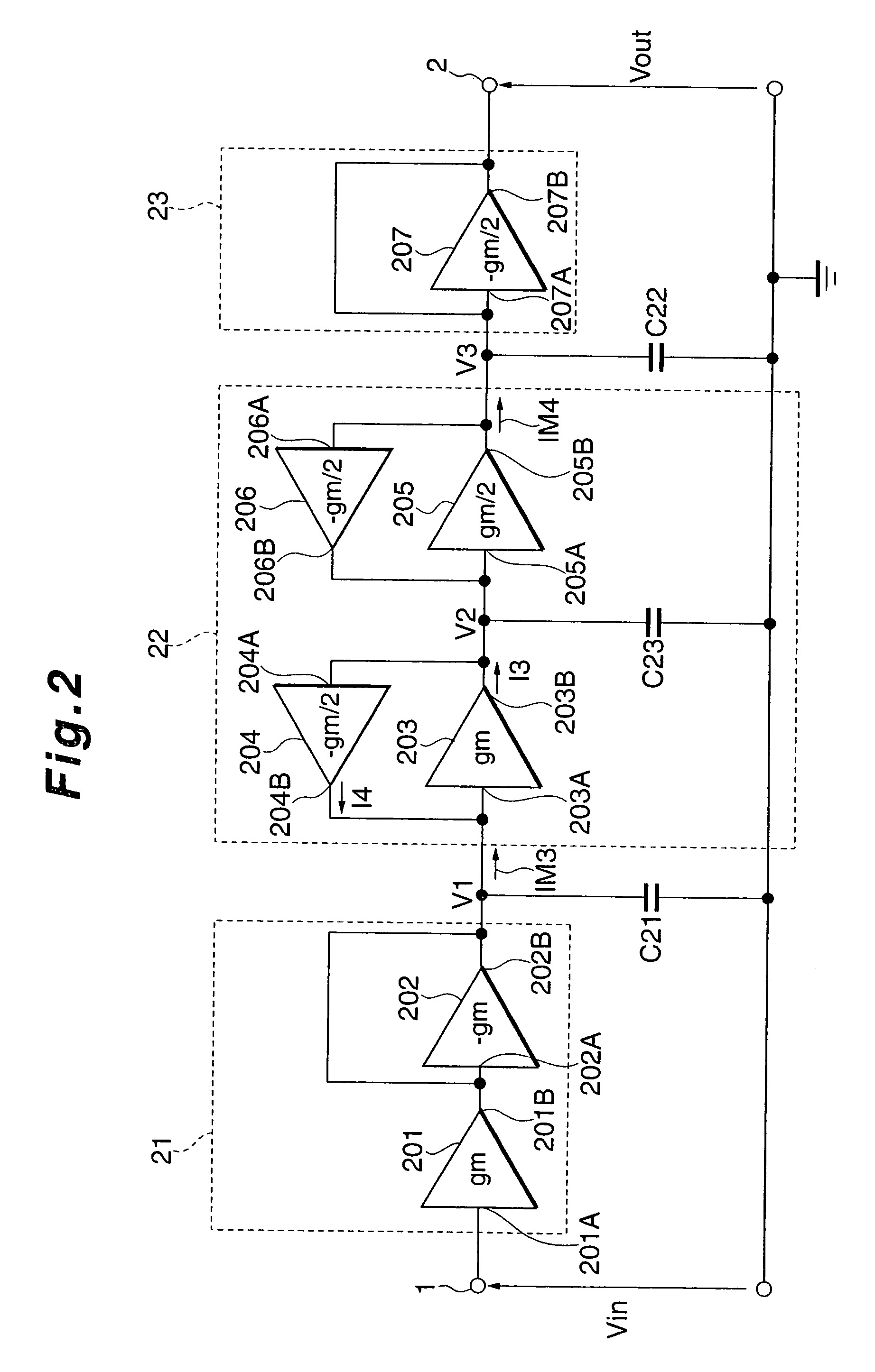
Filter circuit
InactiveUS20010048342A1Network simulating reactancesOscillations generatorsCapacitanceVoltage control
Input conversion noises of a filter circuit are reduced. The circuit has plural element circuits obtained by dividing the filter circuit so as to include at least one voltage controlled current source, at least one element circuit is an amplification element circuit having an amplifying function for amplifying an input signal to the filter circuit at a set amplification factor. The amplification element circuit has: a loop circuit constructed by plural intra-loop voltage controlled current sources in which mutual conductance values have a predetermined corresponding relation; and a corresponding capacitor connected to a contact in the loop circuit and having a capacitance depending on the corresponding relation so as to set a potential at the contact to a predetermined potential corresponding to the amplification factor, and amplification element circuit has an electric nature which is independent on the amplification factor when seeing from the input side of the filter circuit.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Tunable active inductor
An active inductor capable of tuning a self-resonant frequency, an inductance, a Q factor, and a peak Q frequency by applying a tunable feedback resistor to a cascode-grounded active inductor is disclosed. The tunable active inductor includes a first transistor having a source connected to a power supply voltage and a gate connected to first bias voltage; a second transistor having a drain connected to a drain of the first transistor and a gate connected to a second bias voltage; a third transistor having a drain connected to a source of the second transistor and a source connected to a ground voltage; a fourth transistor having a drain connected to a gate of the third transistor, a source connected to the ground voltage and a gate connected to a third bias voltage; a fifth transistor having a source connected to the drain of the fourth transistor and a drain connected to the power supply voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Broadband piezoelectric shunts for structural vibration control
InactiveUS6075309APiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A negative capacitance converter is used in combination with a buffer circuit to form an electrical shunt circuit. The negative capacitance converter and the buffer circuit, together, minimize or eliminate oscillations of a negative impedance generated by the electrical shunt circuit. Additionally, a specific configuration of the negative capacitance converter is used to provide optimum stability. The buffer circuit includes a Riordan-type circuit, with the negative capacitance converter being substituted for one of the impedance elements of the Riordan-type circuit. Resistors are used to replace the other impedance elements of the Riordan-type circuit. An additional capacitor is placed across one of the operational amplifiers of the Riordan-type circuit, in order to provide additional stability.
Owner:MCDONNELL DOUGLAS
Capacitance multiplier circuit
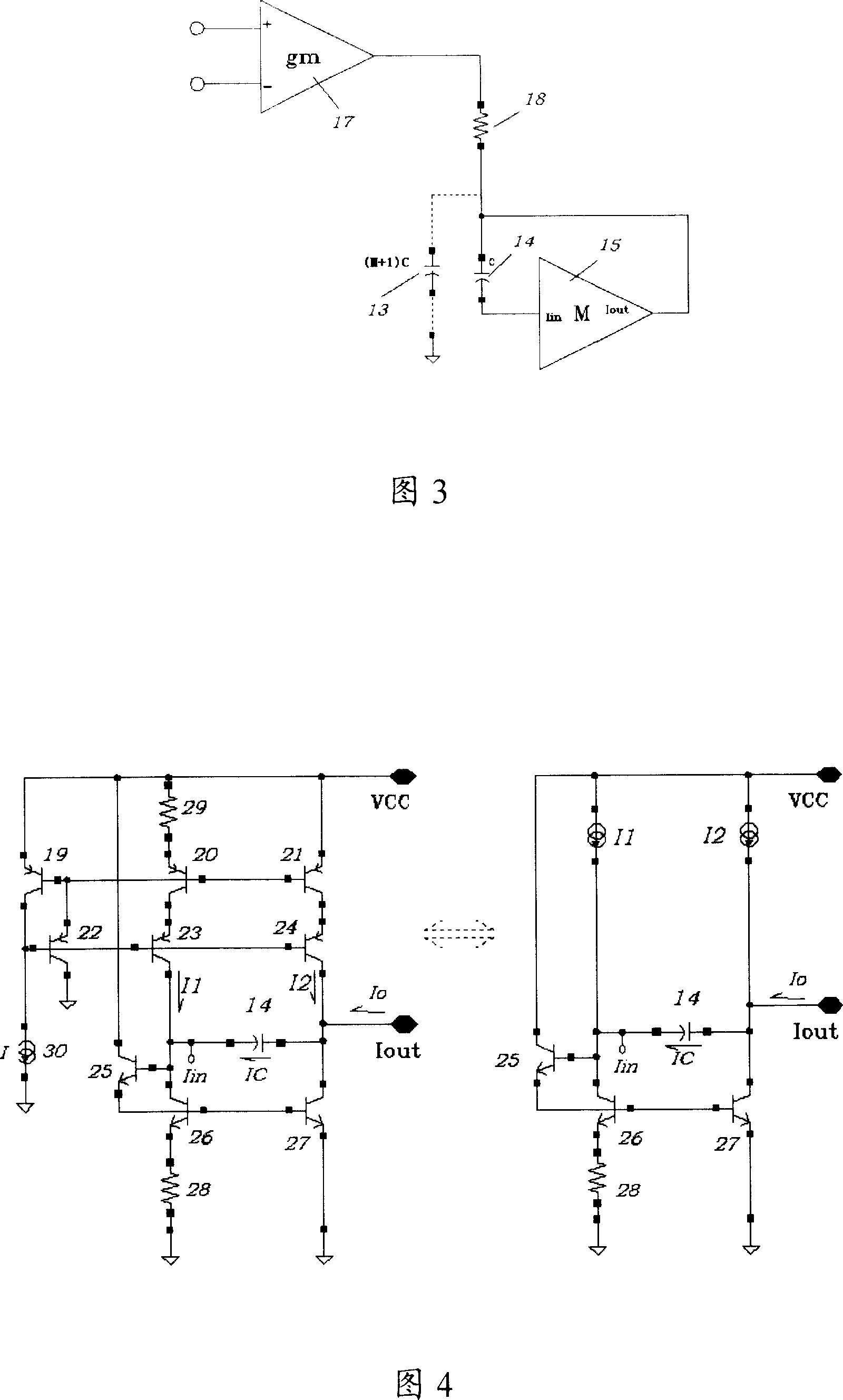
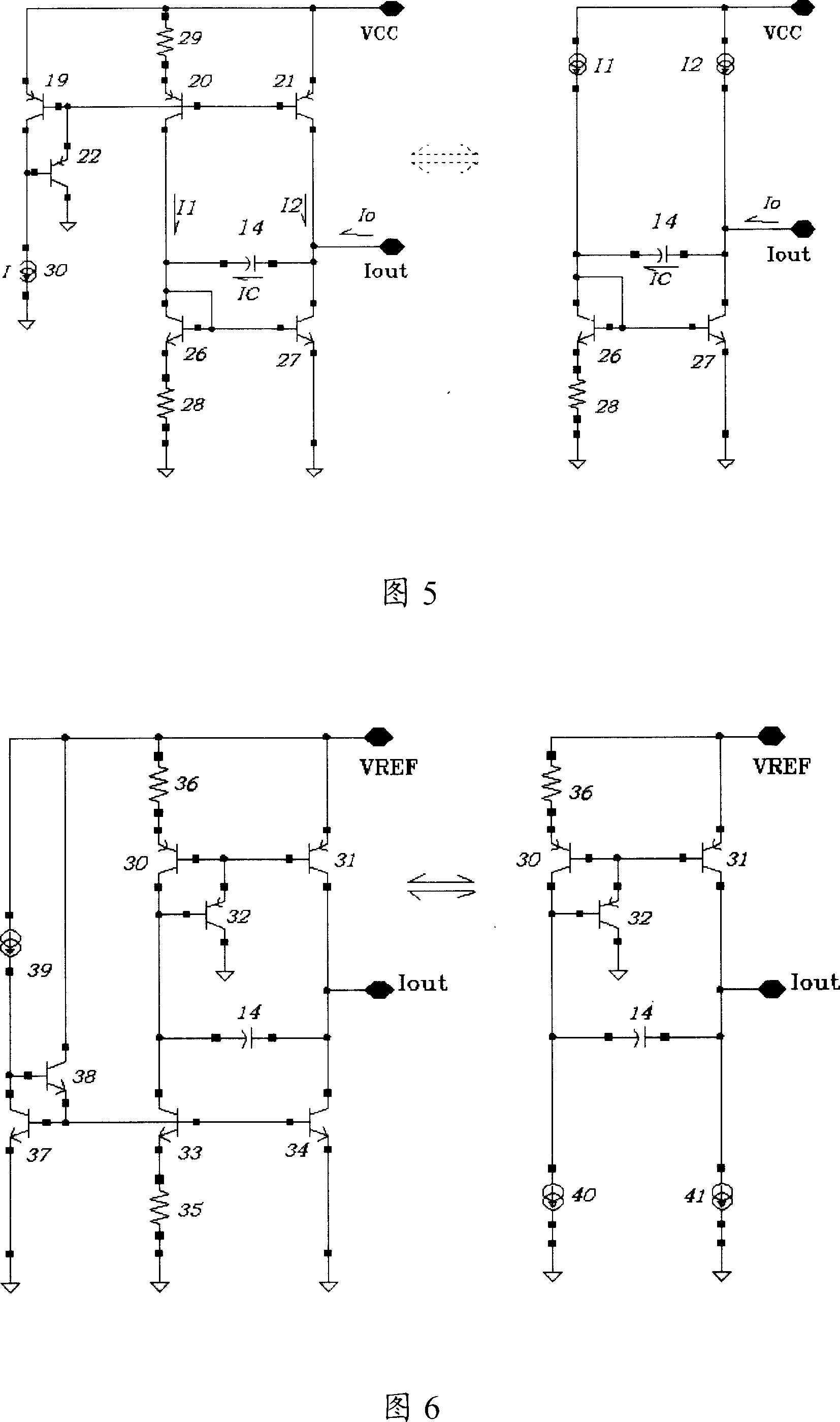
An integrated circuit including a capacitance multiplier having reduced parasitics and injected noise compared to conventional multiplier methods. The integrated circuit includes a reference capacitor and a current mirror arrangement coupled to the reference capacitor. The current mirror arrangement, which includes a current gain factor N, varies the capacitance of the reference capacitor by a factor of N+1, based on the reference capacitor current. The current mirror arrangement includes an operational amplifier operating in conjunction with two mirror transistors to form a current mirror arrangement having little or no series resistance. The current mirror also can include a plurality of resistors configured to reduce the noise from the capacitance multiplier, thus making the capacitance multiplier useful for applications that may require relatively low noise.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for an active negative-capacitor circuit to cancel the input capacitance of comparators
ActiveUS9124279B2Reduce voltageLower performance requirementsPower saving provisionsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCapacitanceEngineering
The differential output of a Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) is loaded by the input differential gate capacitance of a plurality of Analog to Digital converters (ADC) comparators and the differential metal layer traces to interconnect these comparators to the PGA. The differential capacitive load presented to the PGA is quite large and reduces the bandwidth of this interconnect between the PGA and ADC. To overcome the performance degradation due to the differential capacitive load, an active negative-capacitor circuit cancels the effect of the large input capacitance of the ADC comparators. This cancellation extends the gain characteristics of the interconnect between the PGA's output and the inputs of the first stage of the comparators. The active negative-capacitance is comprised of a cross pair NMOS with a capacitor connecting their sources where each NMOS is biased by a current source.
Owner:TENSORCOM
Method and system for bandwidth enhancement using hybrid inductors
ActiveUS8289067B2Computations using contact-making devicesNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Differential negative impedance converters and inverters with variable or tunable conversion ratios
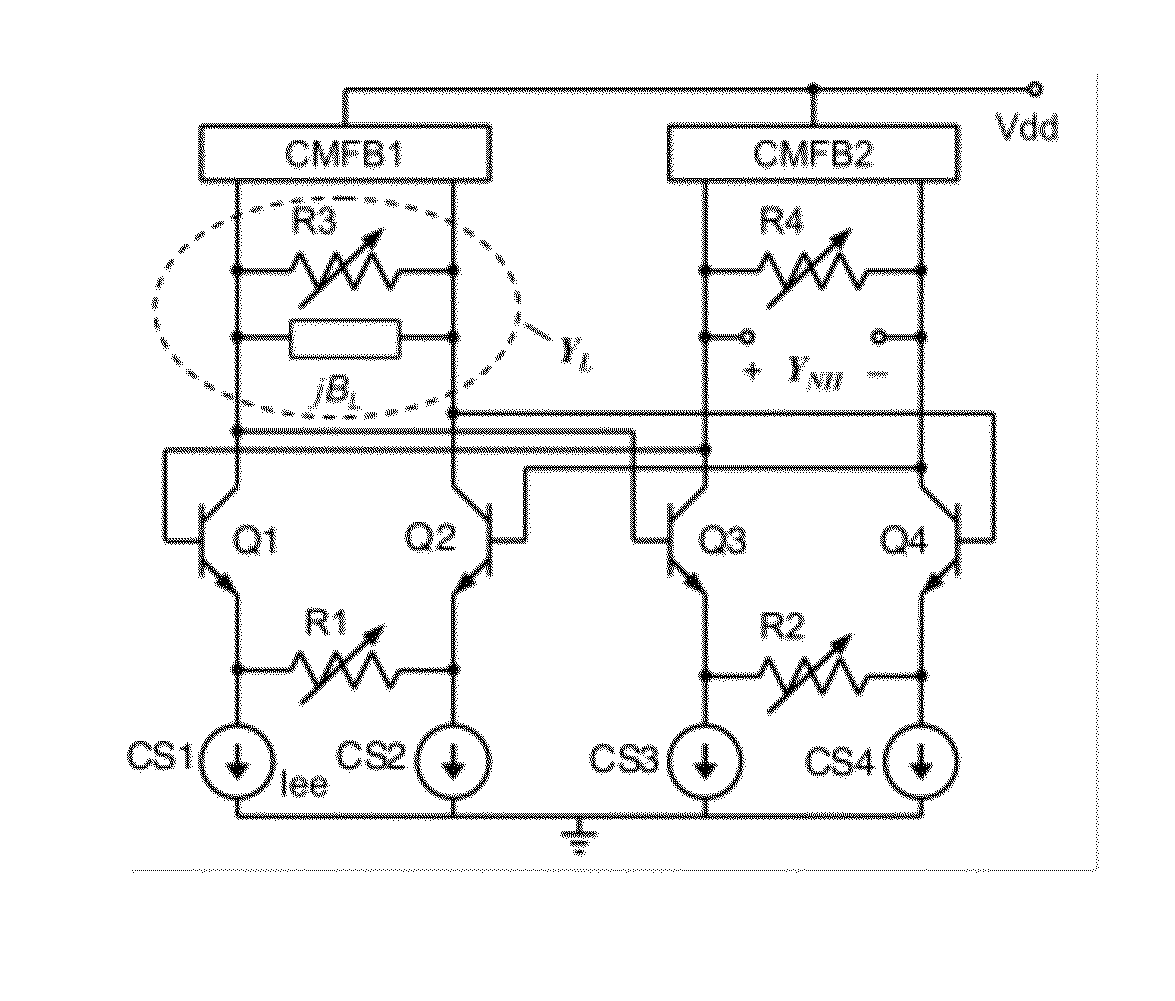
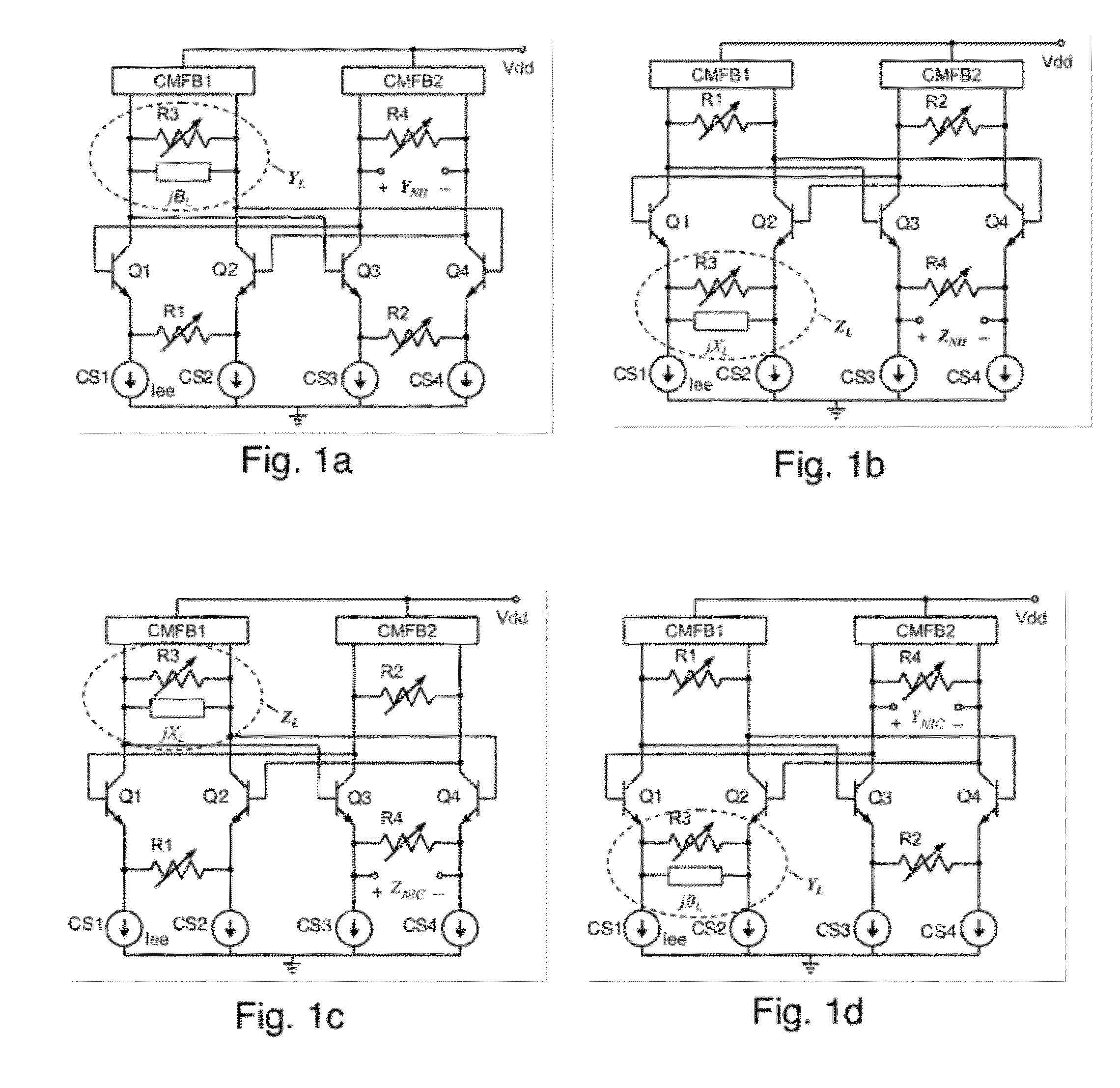
ActiveUS8988173B2Reduce parasitismImprove matchImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceEngineering
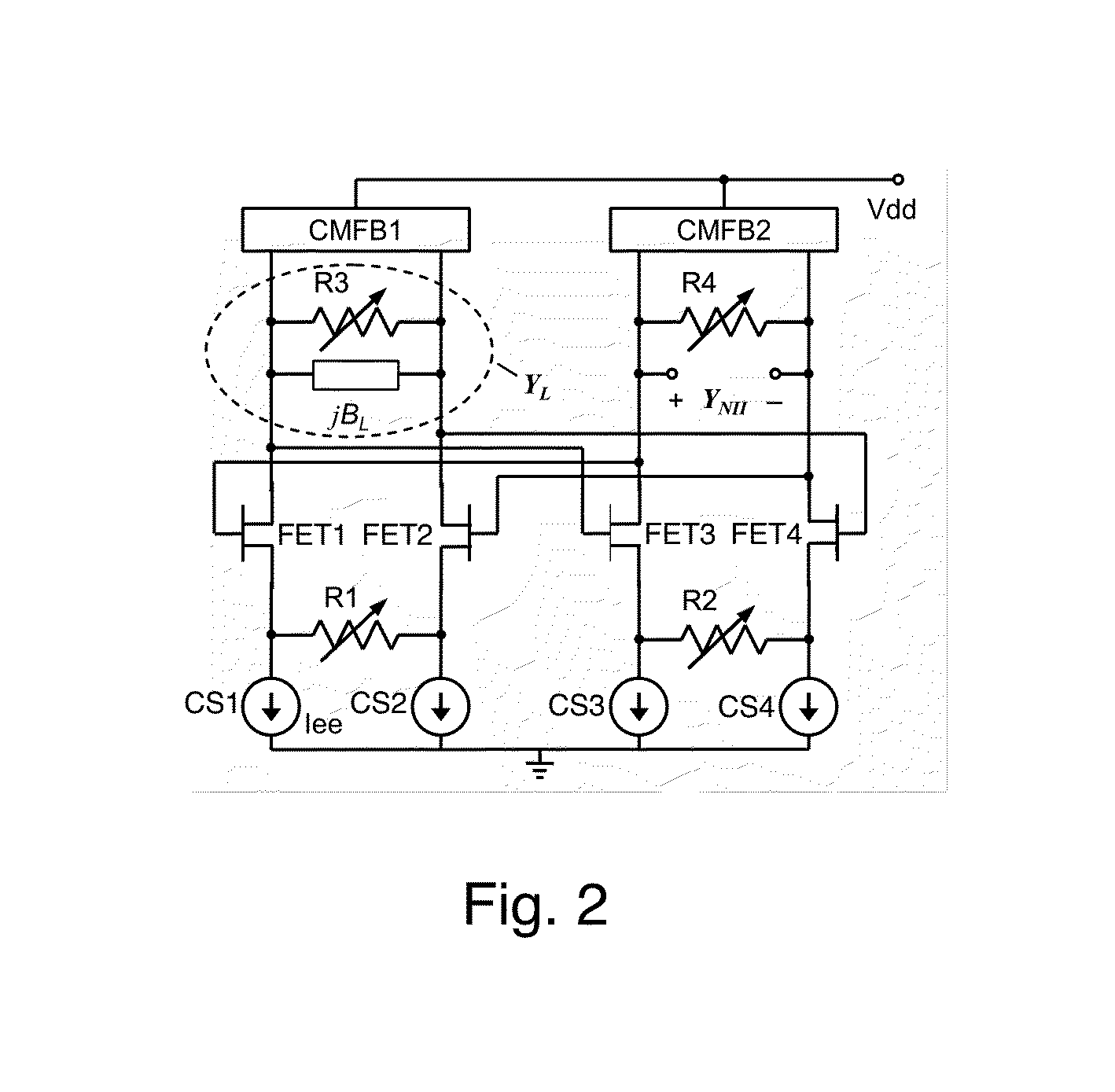
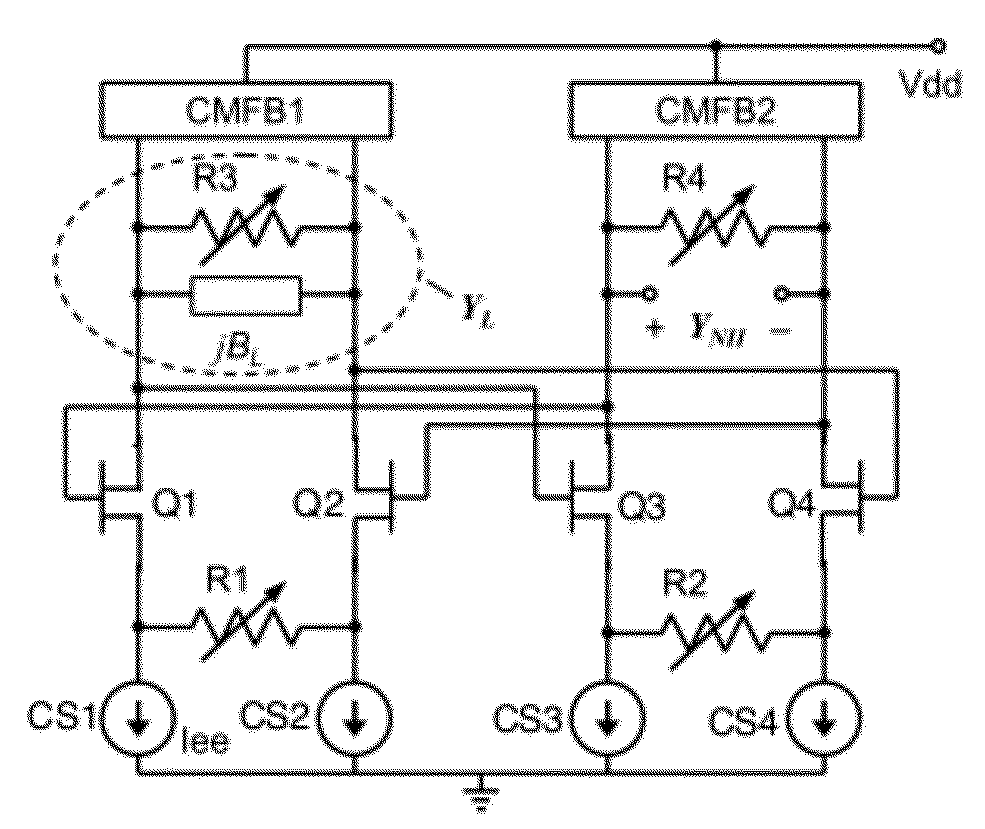
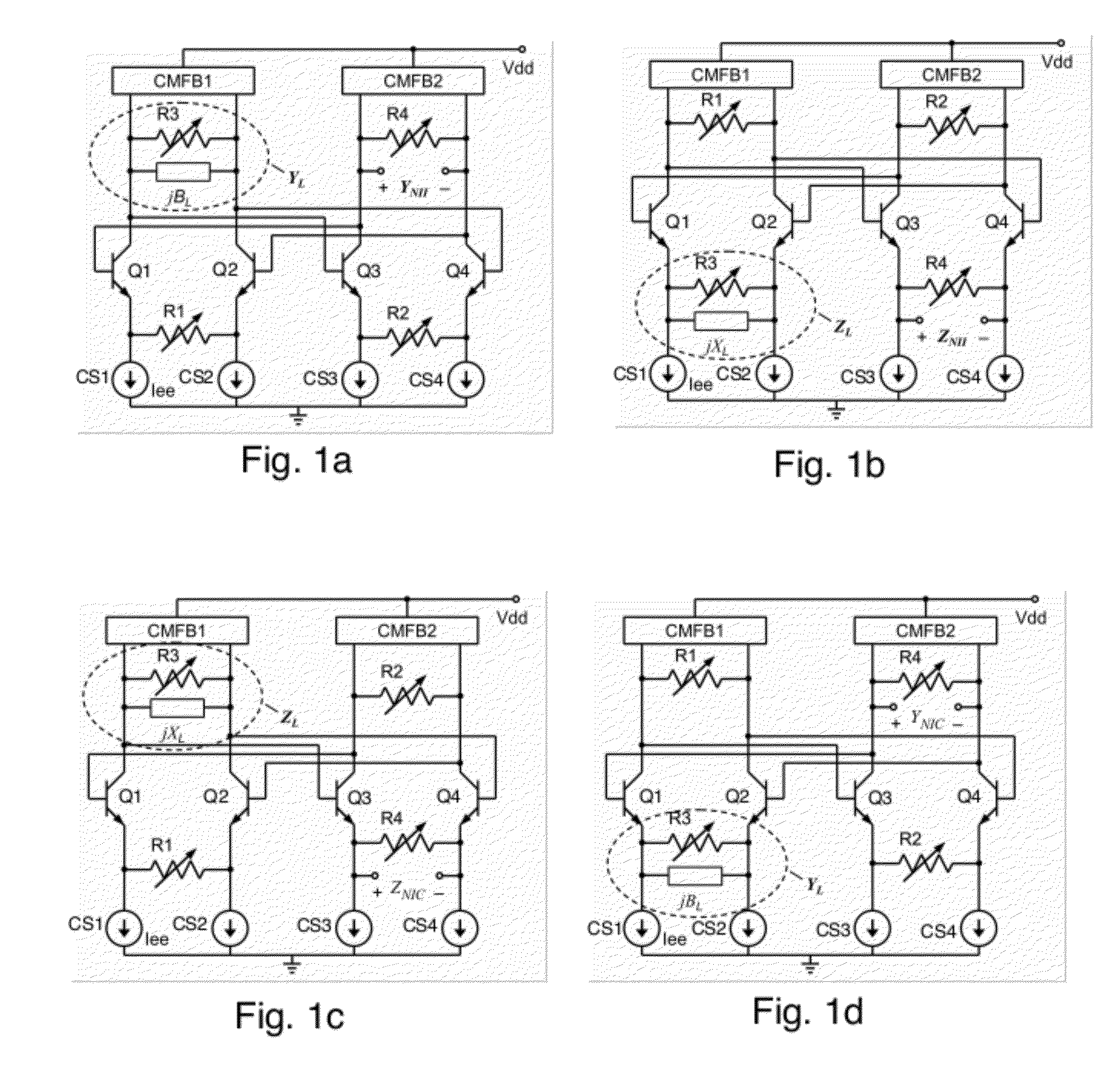
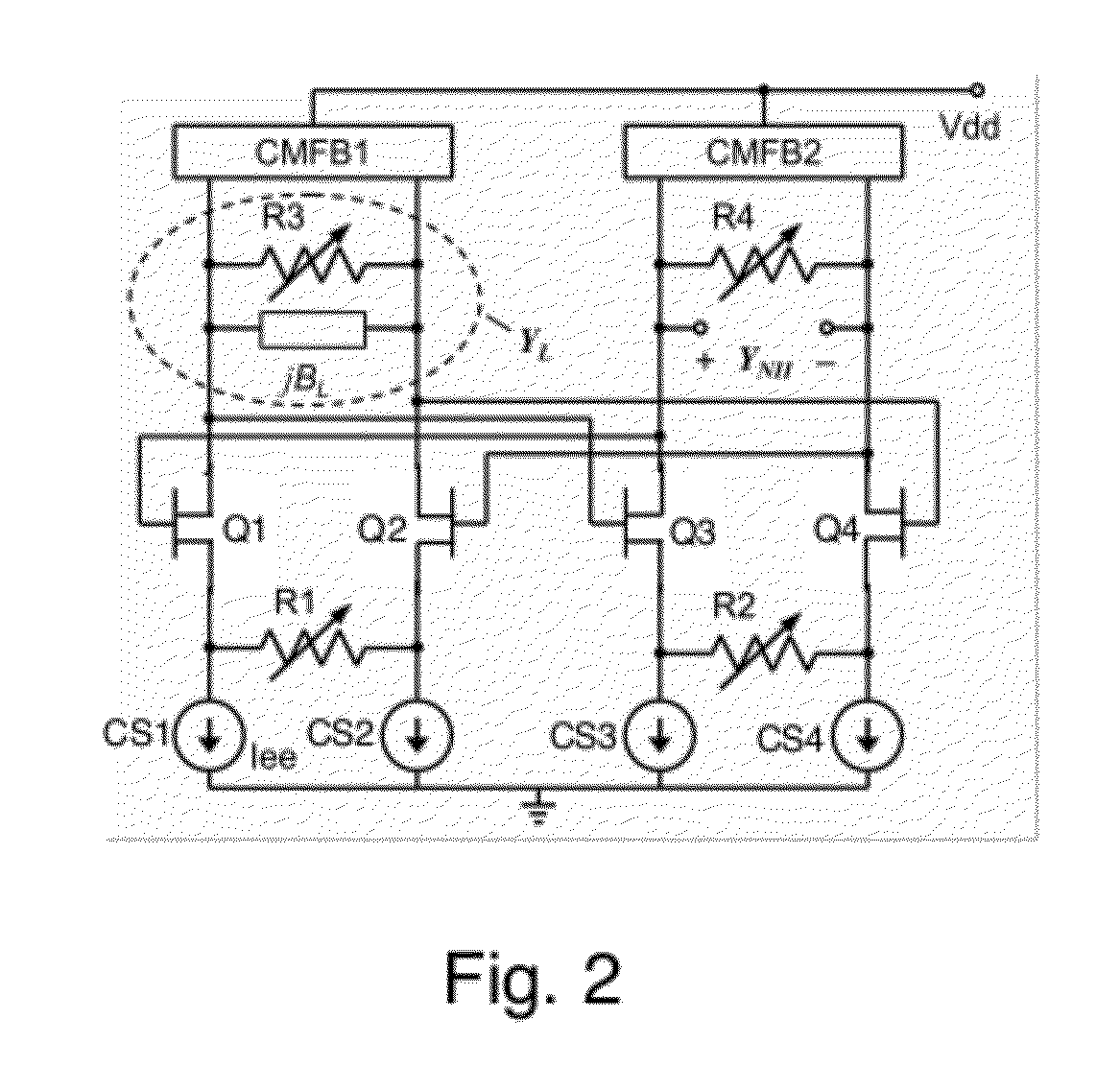
A differential circuit topology that produces a tunable floating negative inductance, negative capacitance, negative resistance / conductance, or a combination of the three. These circuits are commonly referred to as “non-Foster circuits.” The disclosed embodiments of the circuits comprises two differential pairs of transistors that are cross-coupled, a load immittance, multiple current sources, two Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) networks, at least one tunable (variable) resistance, and two terminals across which the desired immittance is present. The disclosed embodiments of the circuits may be configured as either a Negative Impedance Inverter (NII) or a Negative Impedance Converter (NIC) and as either Open-Circuit-Stable (OCS) and Short-Circuit-Stable (SCS).
Owner:HRL LAB
Active inductance parallel peaking structure
The invention discloses an active inductance parallel peaking structure which is characterized by comprising a load impedance circuit and a load impedance current control circuit, wherein the load impedance circuit is used for converting current from a transconductance circuit into circuit output voltage; the load impedance current control circuit is used for carrying out time domain delay and frequency domain low-pass filtering processing on the voltage of an output end of the load impedance circuit and electric potential translational and additional processing; the output end of the load impedance circuit is connected with an input end of the load impedance current control circuit; and an output end of the load impedance current control circuit is connected with an input end of the load impedance circuit.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP NO 771 RES INST
Tunable high quality factor inductor
InactiveUS20090167466A1Quality improvementQ factor of the inductor circuit is enhancedTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionDiscontinuous tuningInductorElectrical and Electronics engineering
An inductor circuit with high quality (Q) factor includes a primary inductor and a compensation sub-circuit. The compensation sub-circuit is electrically isolated from the primary inductor. The compensation sub-circuit is magnetically coupled with the primary inductor to compensate the loss in the primary inductor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES SINGAPORE PTE LTD +2
Active inductor for ASIC application
ActiveUS8115575B2Low costHigh quality factorNetwork simulating reactancesFrequency selective two-port networksEngineeringCircuit design
An apparatus and method for manufacturing low-cost high-density compact active inductor module using existing DRAM, SRAM and logic process integration. The elements of the active inductor modules are formed by three semiconductor devices including nMOS devices, deep-trench capacitors and a polysilicon or TaN resistor. The active inductor modules can be connected in a parallel and / or serial configuration to obtain a wide range of inductance values. The modular active inductors can be advantageously stored in an ASIC library to facilitate a flexible and convenient circuit design.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Impedance circuit, power supply device
InactiveUS20070103187A1Realizing negative impedance with easeEase in realizingReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringOutput impedance
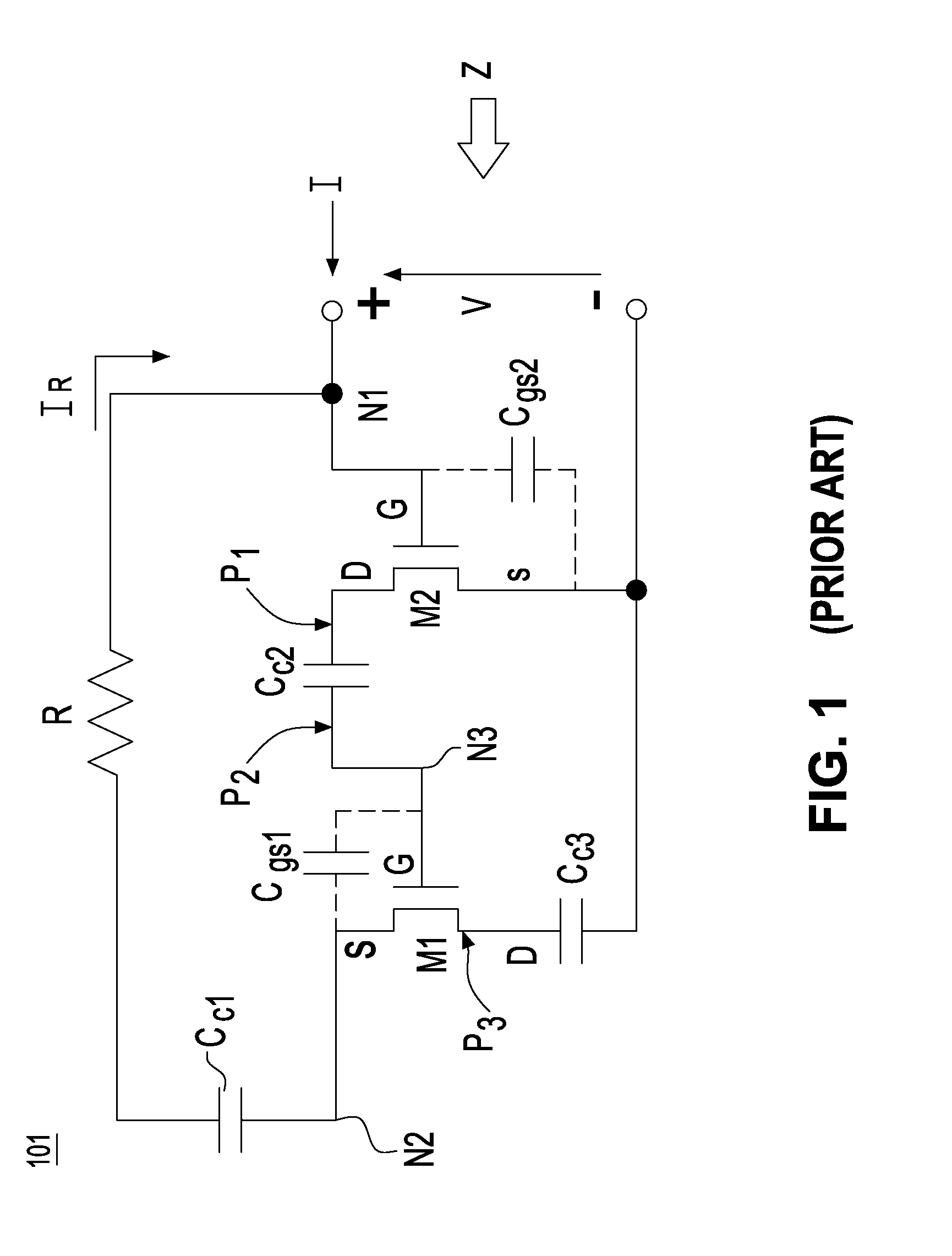
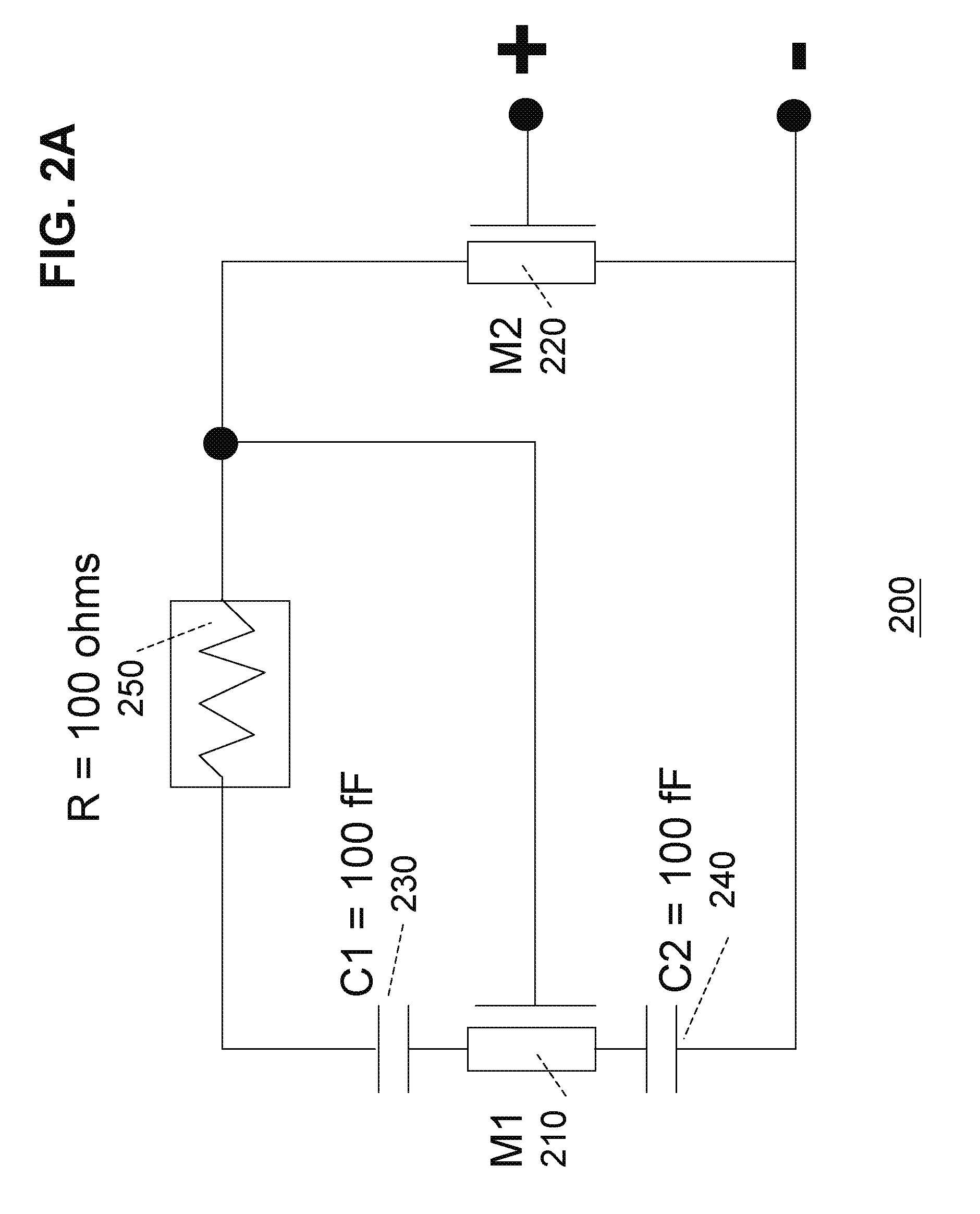
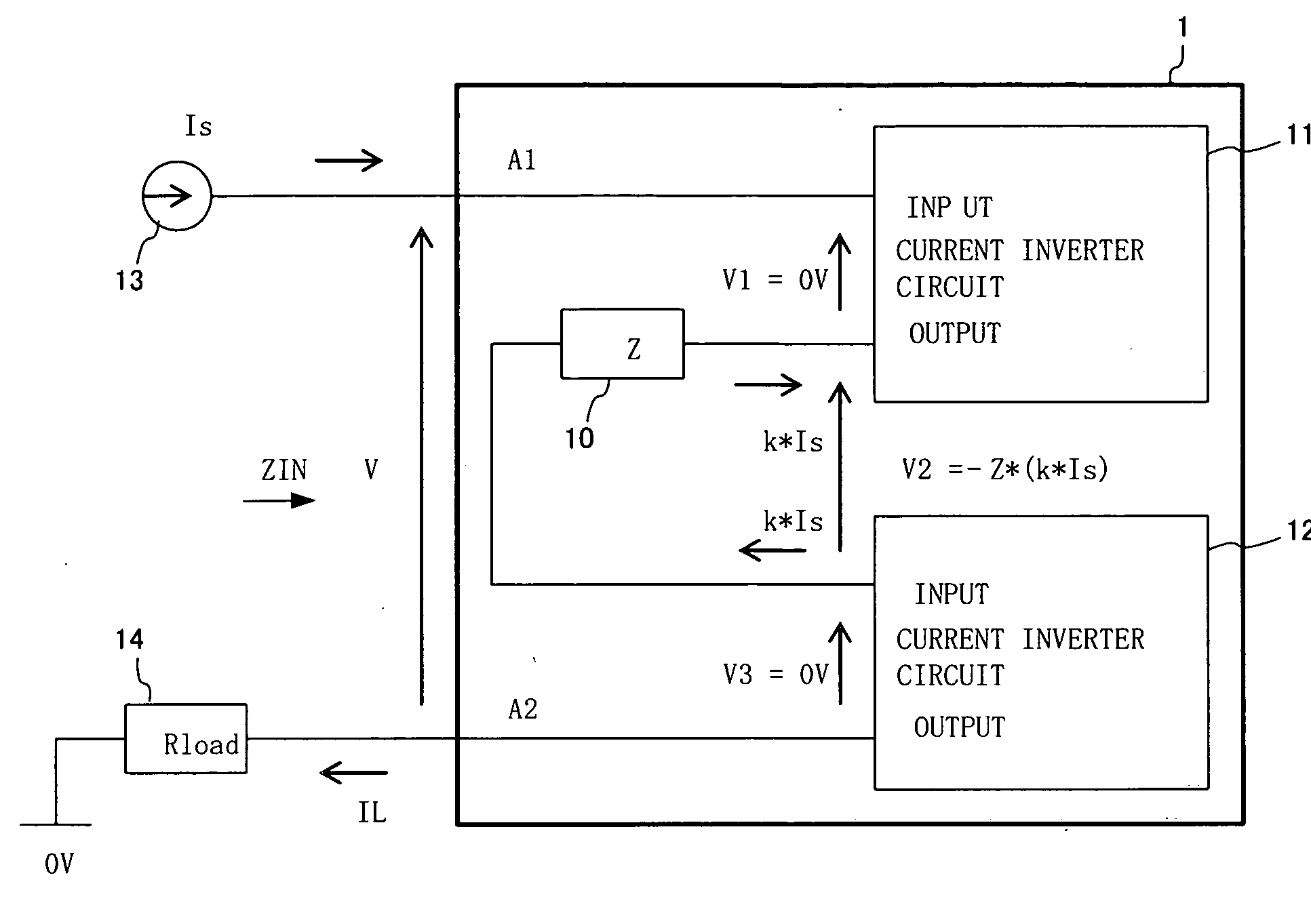
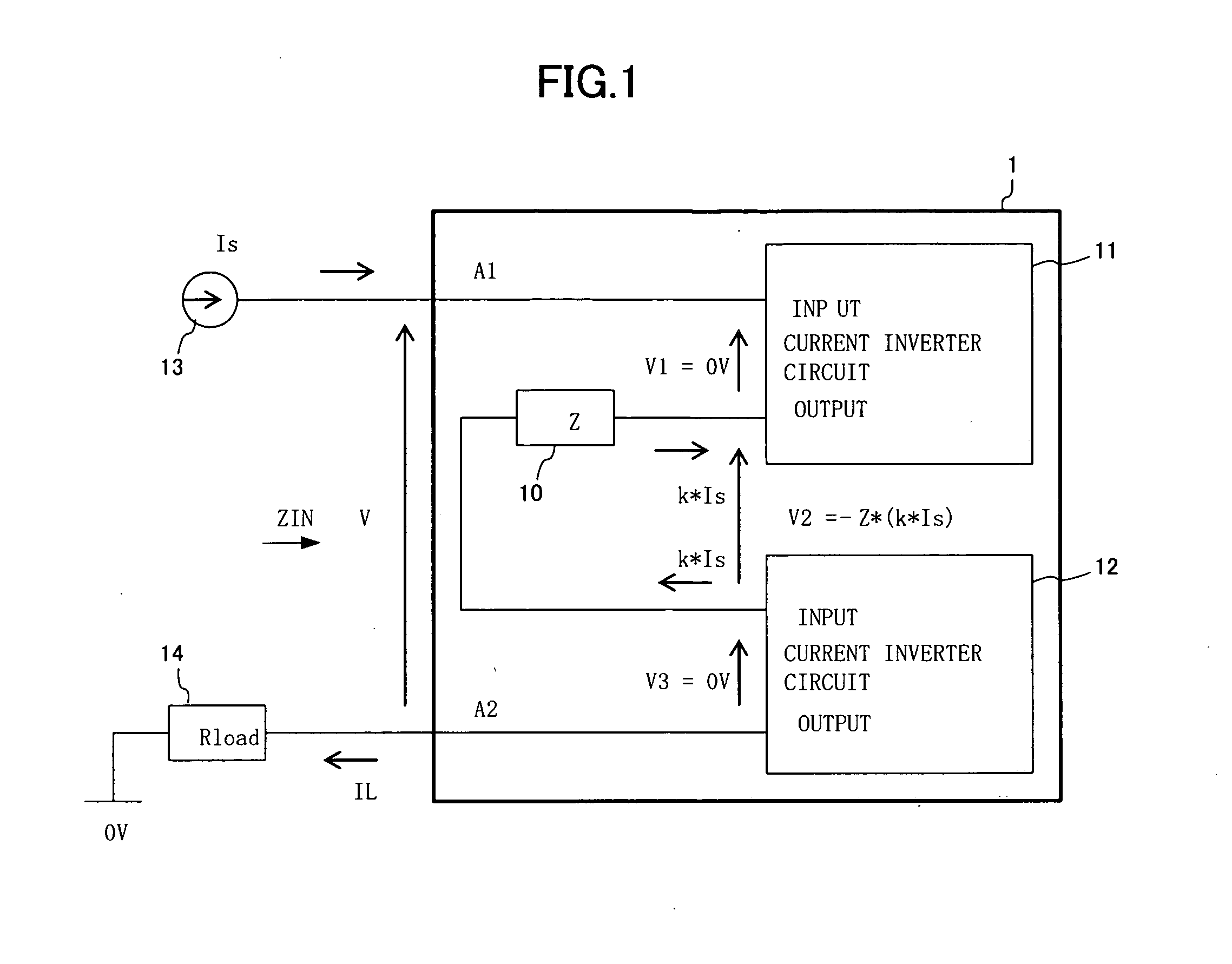
There is disclosed an impedance circuit which realizes negative impedance with ease, and a power supply device having negative output impedance. An impedance circuit 1 connected to an external circuit comprises: a current inverter circuit 11 having an input terminal connected to outside; a passive circuit 10 having an input terminal connected to an output terminal of the current inverter circuit 11; and a current inverter circuit 12 having an input terminal connected to an output terminal of the passive circuit 10 and an output terminal connected to outside. The current inverter circuits 11 and 12 work in cooperation with each other, to make magnitude of impedance of the impedance circuit 1 proportional to impedance of the passive circuit 10, and to invert the polarity of the impedance of the impedance circuit 1.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
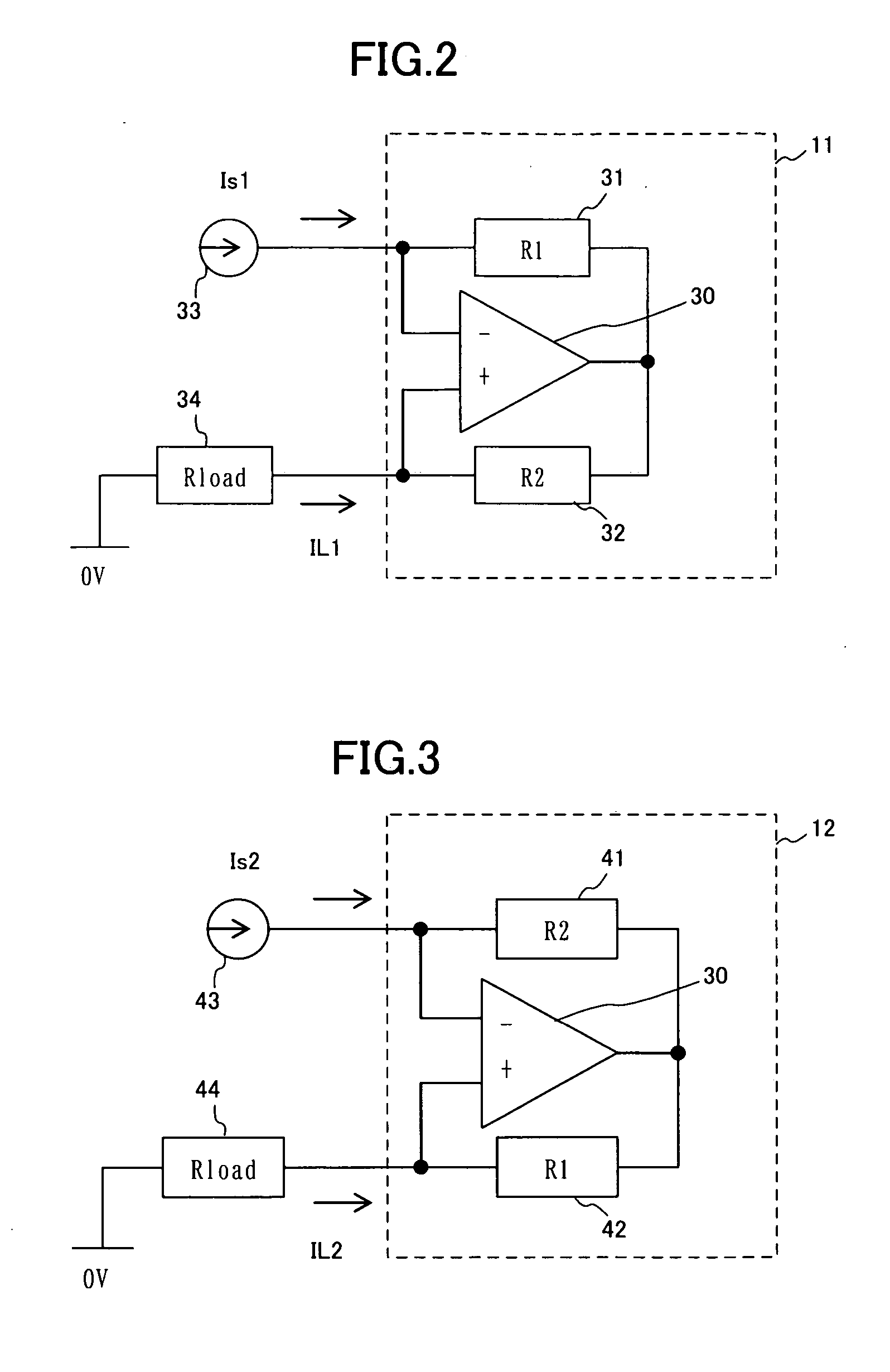
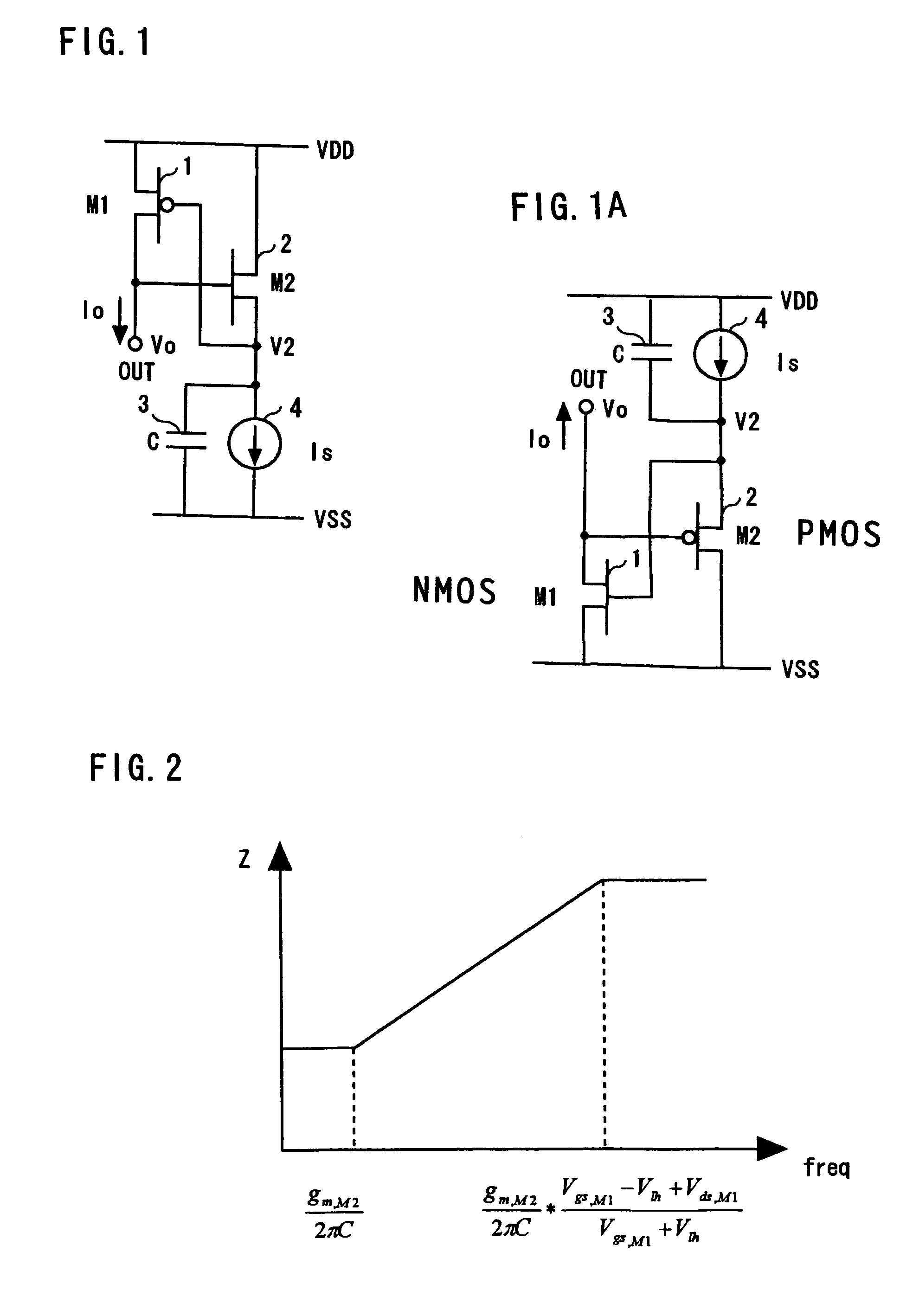
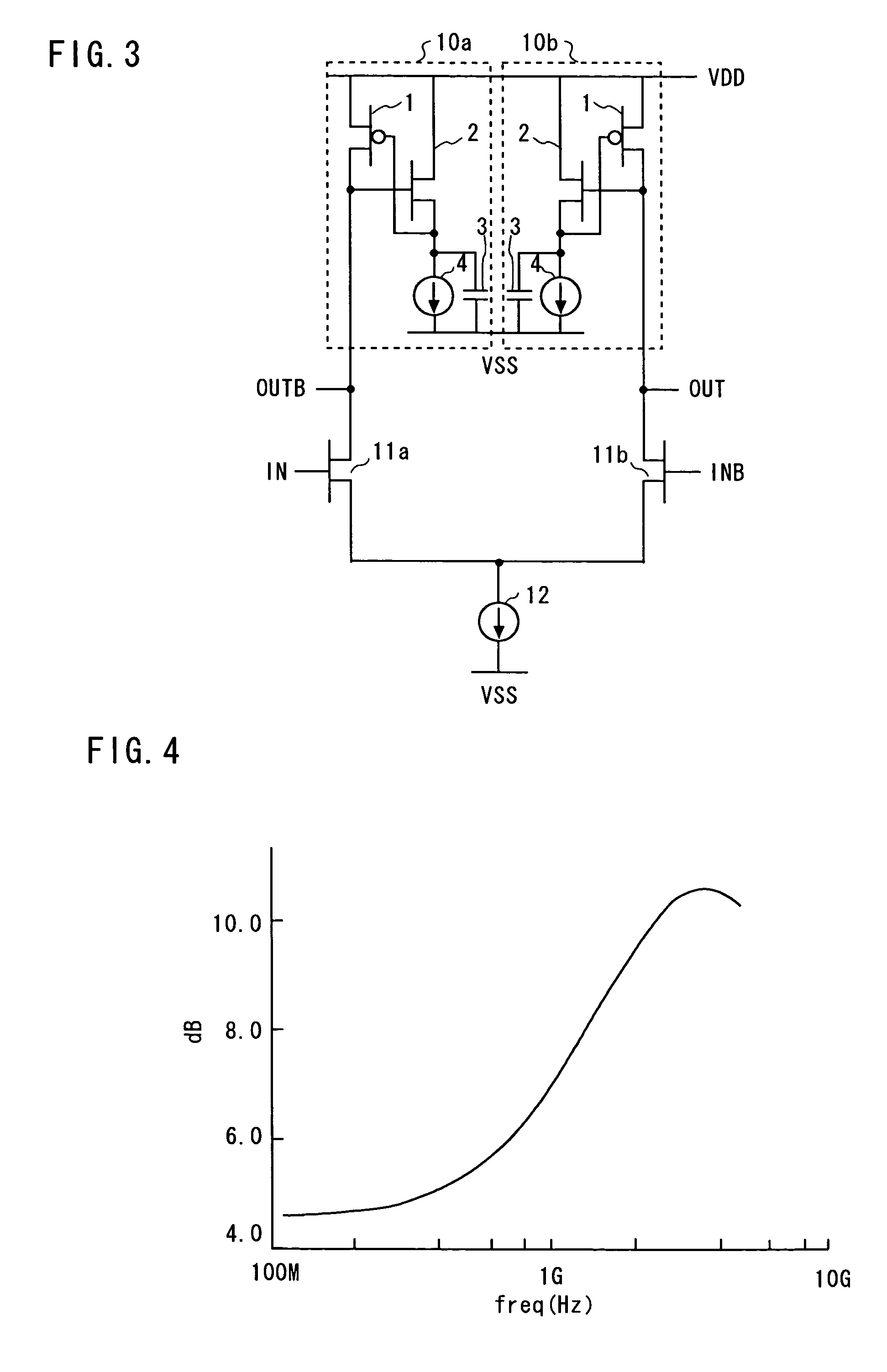
Active inductance circuit and differential amplifier circuit
InactiveUS7049888B2Reduce in quantitySmall voltage dropNetwork simulating reactancesDifferential amplifiersInductanceDifferential amplifier
An active inductance circuit comprising a signal terminal (OUT) and having voltage and current characteristics, as viewed from this terminal, which are identical to those of a circuit comprising an inductance, this active inductance circuit having a structure in which the drain terminal of a first MOS transistor M1 and the gate terminal of a second MOS transistor M2 different in conductivity type from the first MOS transistor are connected to the signal terminal, the gate terminal of the first MOS transistor is connected to the source terminal of the second MOS transistor, a capacitor and a current source are connected to the source terminal of the second transistor, the source terminal of the first MOS transistor and the drain terminal of the second MOS transistor are connected to a power source and other terminals of the capacitor and current source are connected to another power source.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
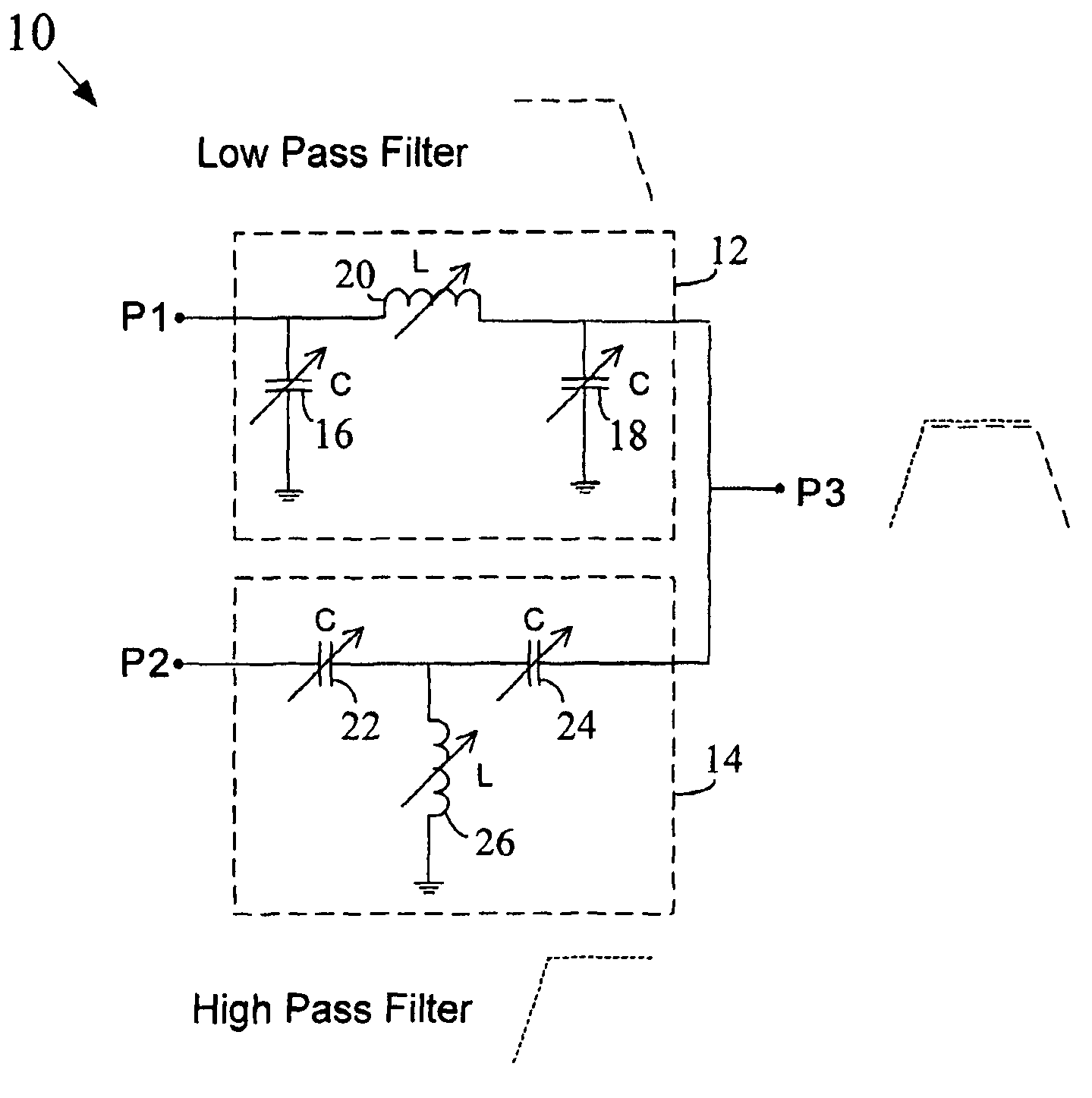
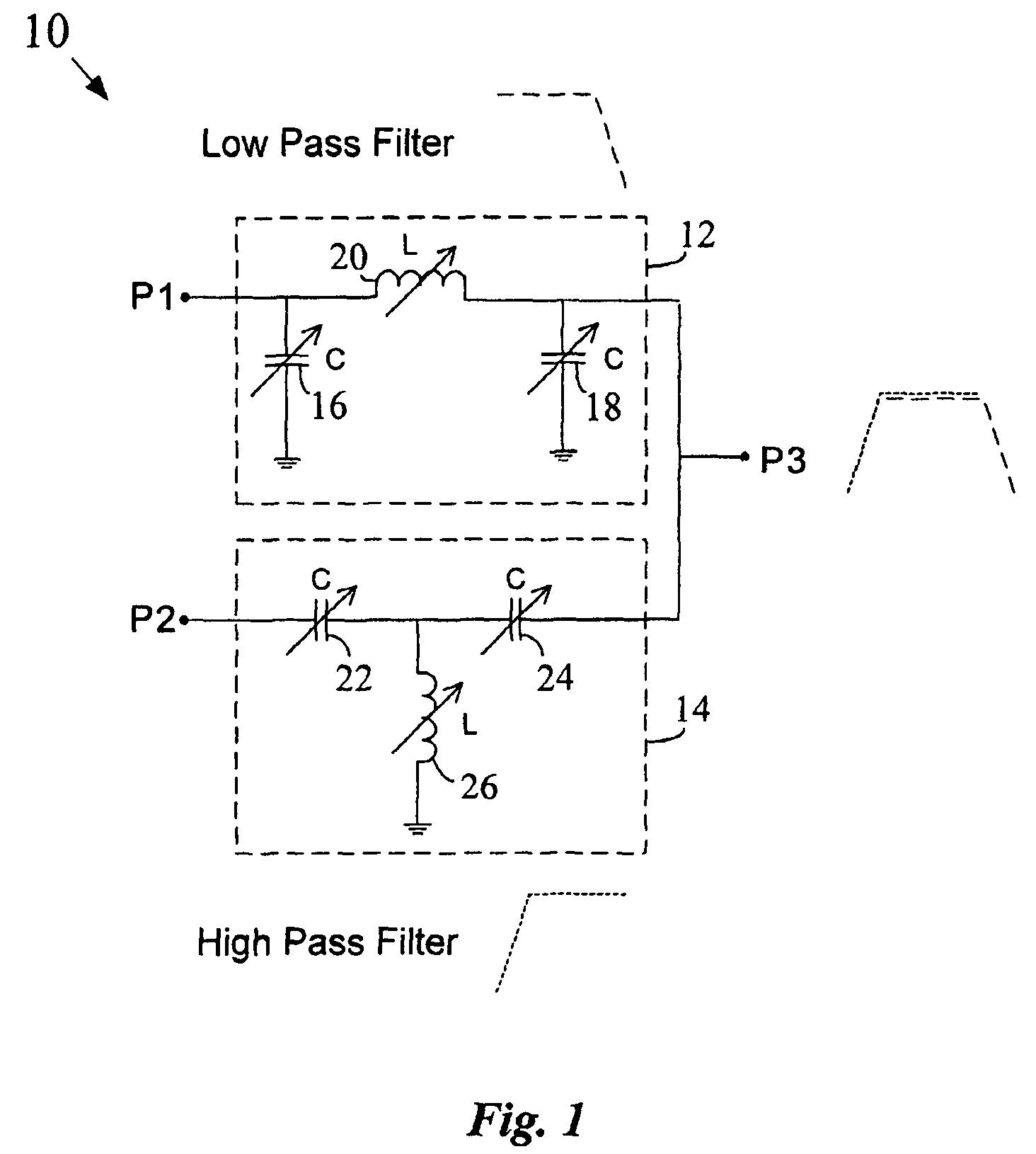
Digitally tuned, integrated baluns with enhanced linearity for multi-band radio applications
An integrated balun includes a low pass filter and a high pass filter that are formed on a semiconductor chip using tunable reactive elements. The outputs of the low pass filter and the high pass filter are tied together to form the single ended output of the balun. The inputs of the low pass filter and the high pass filter form the differential inputs of the balun. The low pass filter and the high pass filter each include a number of tunable networks for achieving the tunable reactive elements. Each tunable network includes at least one switching transistor and at least one fixed value reactive elements. In at least one embodiment, dynamic biasing circuitry may be provided to improve the linearity and reduce the insertion loss of the balun.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and its circuit for realizing multiplication capacitor
InactiveCN1988378AAchieve integrationReduce areaNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceIntegrated circuit
Owner:BCD SEMICON MFG
Gyrator with loop amplifiers connected to inductive elements
InactiveUS6025765AImprove phase noiseLarge oscillationImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceGyroscope
A gyrator includes shunt or feedback nodal capacitors and shunt lossy inductors without shunt load resistors. The effective nodal capacitance is reduced by the introduction of the shunt lossy inductors. The inductors act to discriminate against injected power supply noise, resulting in improved oscillator phase noise. The inductors produces less drop dc voltage than the resistive load, so that larger linear oscillation is obtained with improved oscillator phase noise.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Three-terminal, tunable active inductor
ActiveUS20060044099A1Controls are responsiveSmall parasitic capacitanceNetwork simulating reactancesContinuously variable inductances/transformersInductorTransconductance
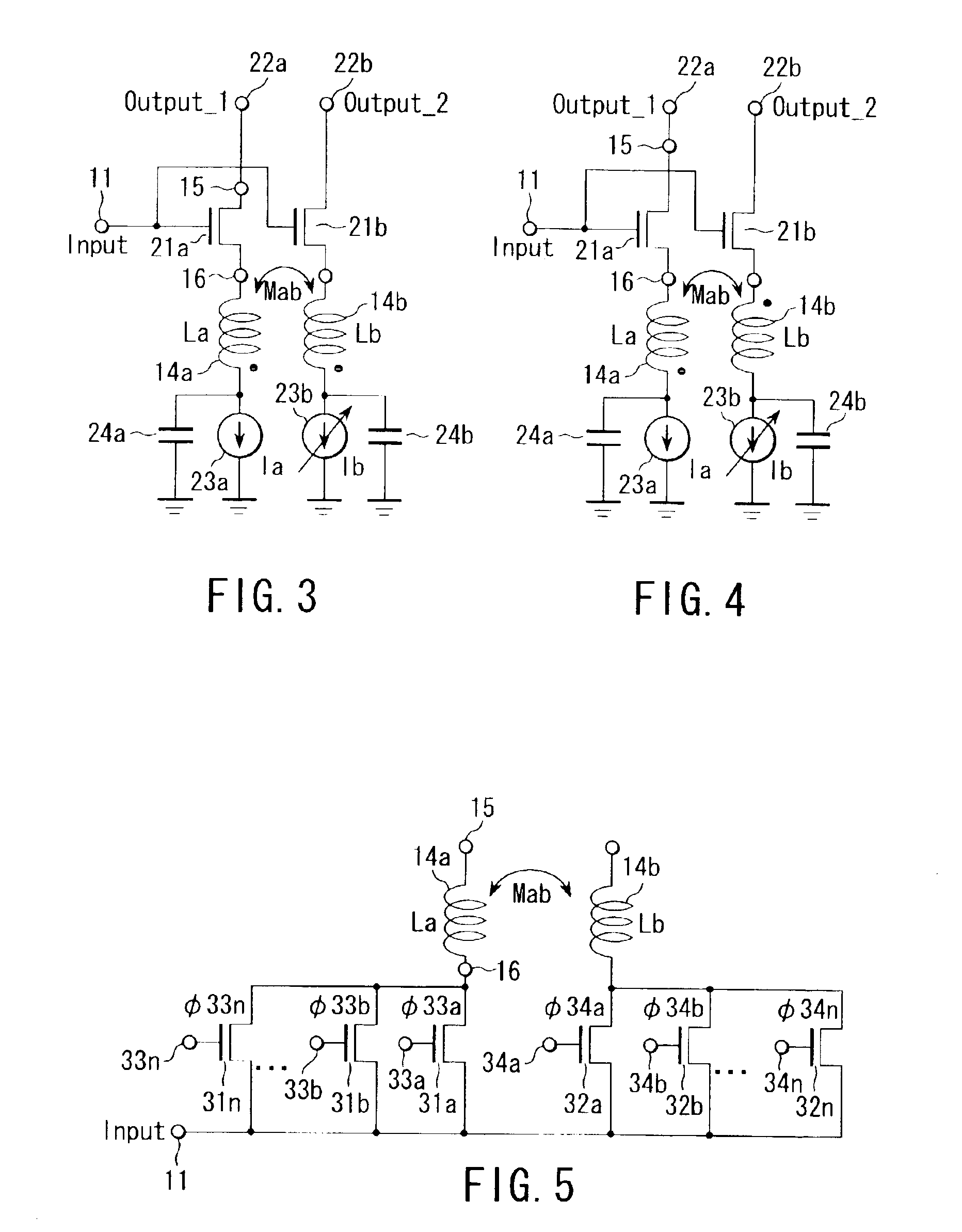
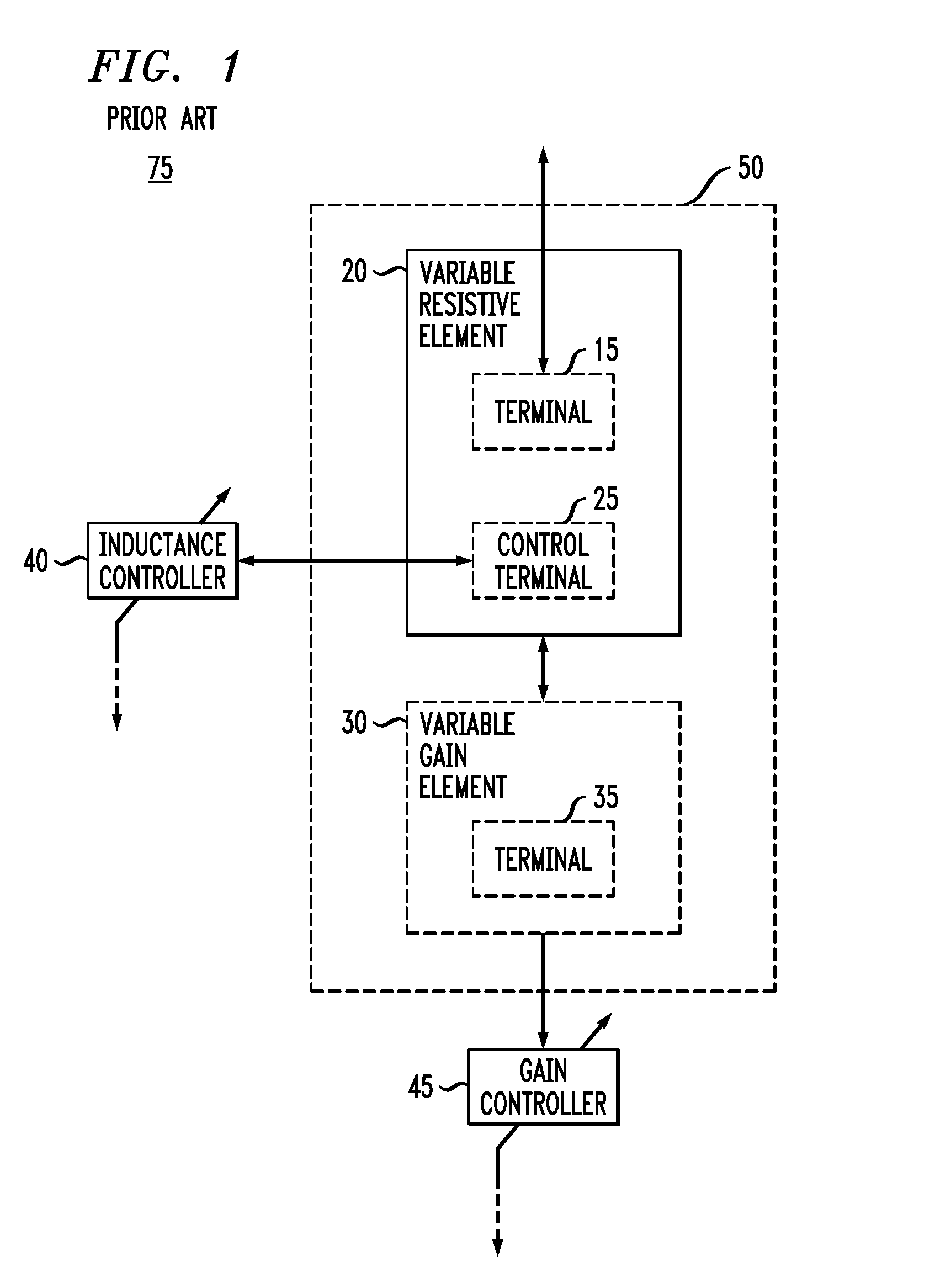
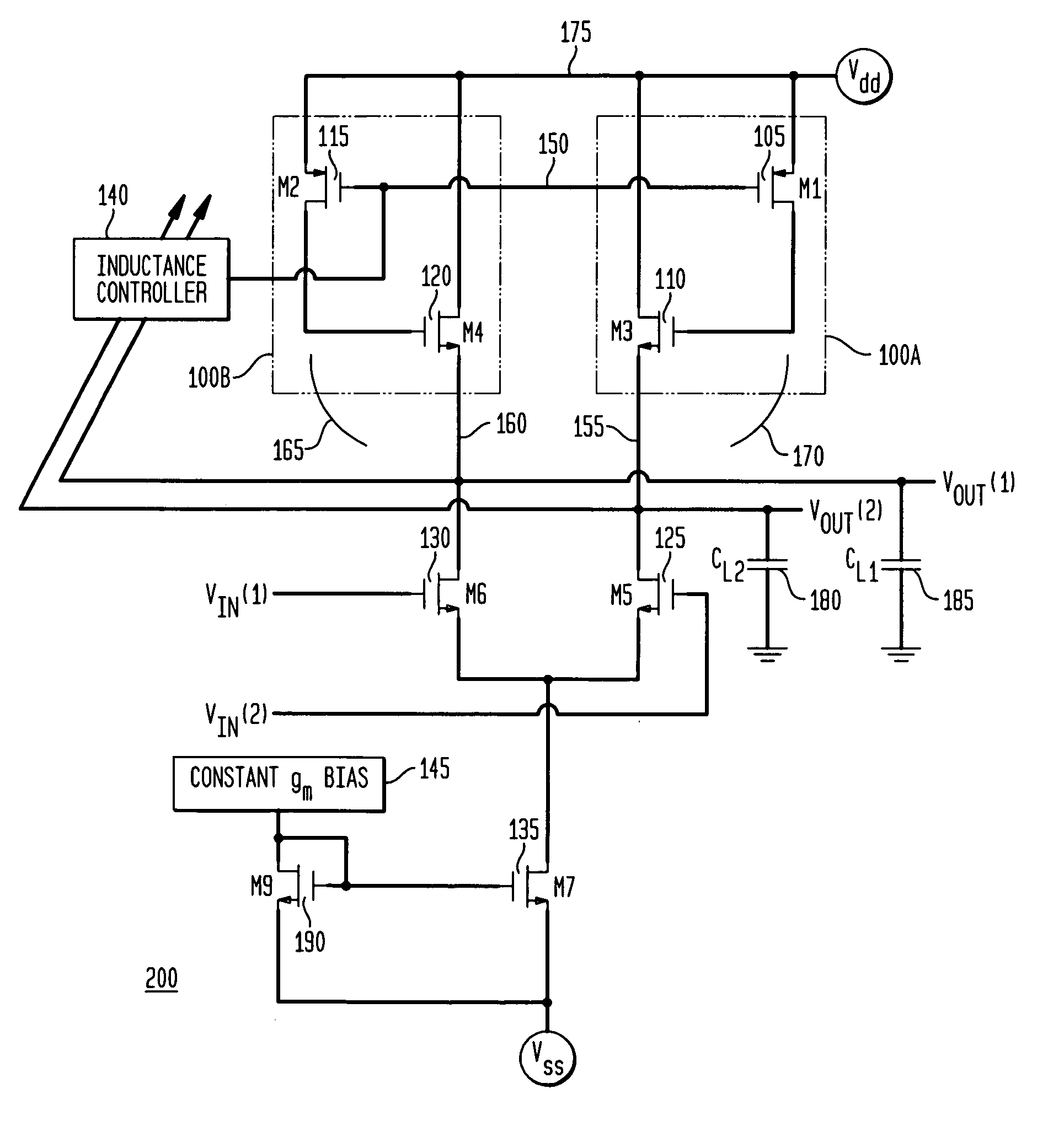
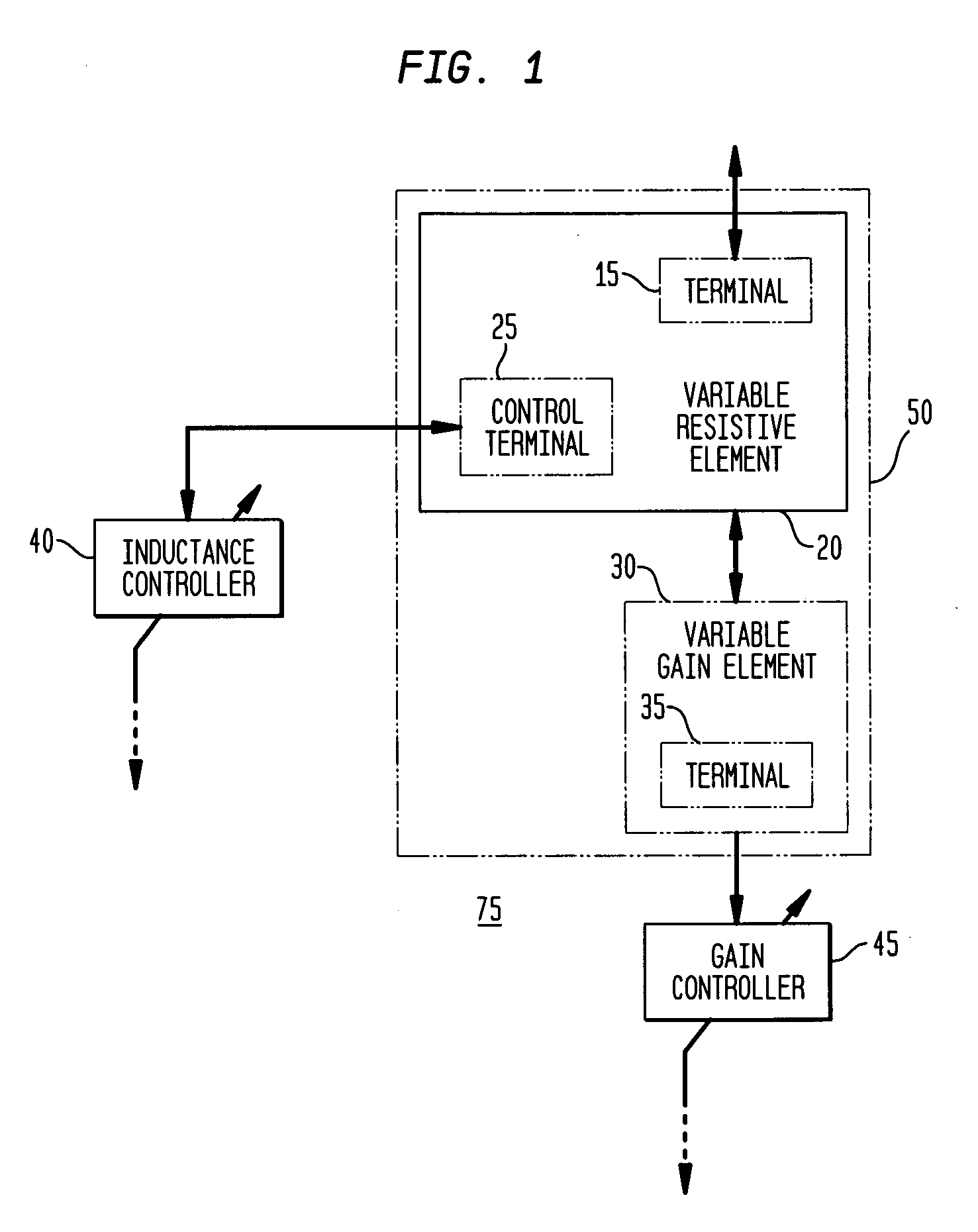
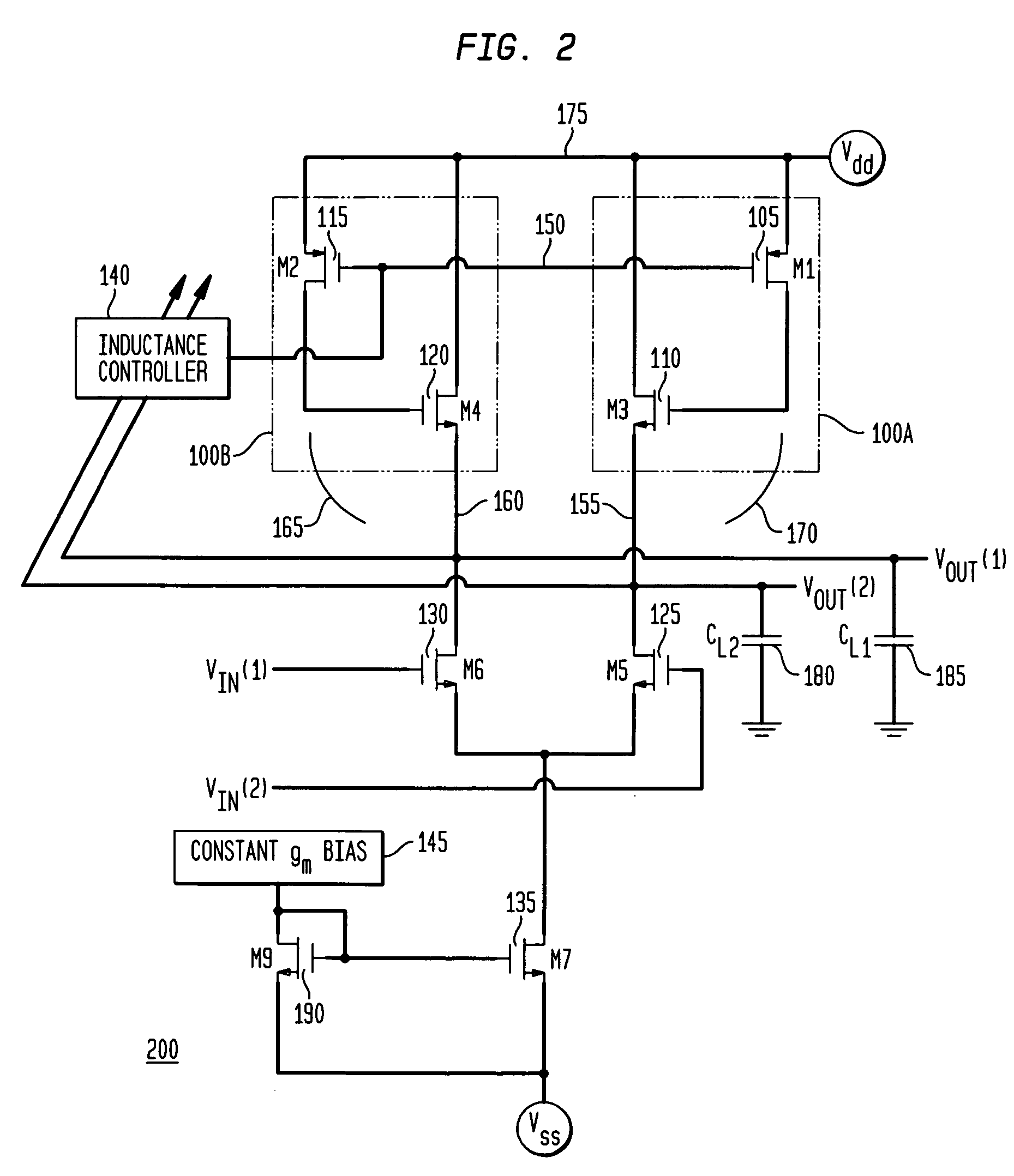
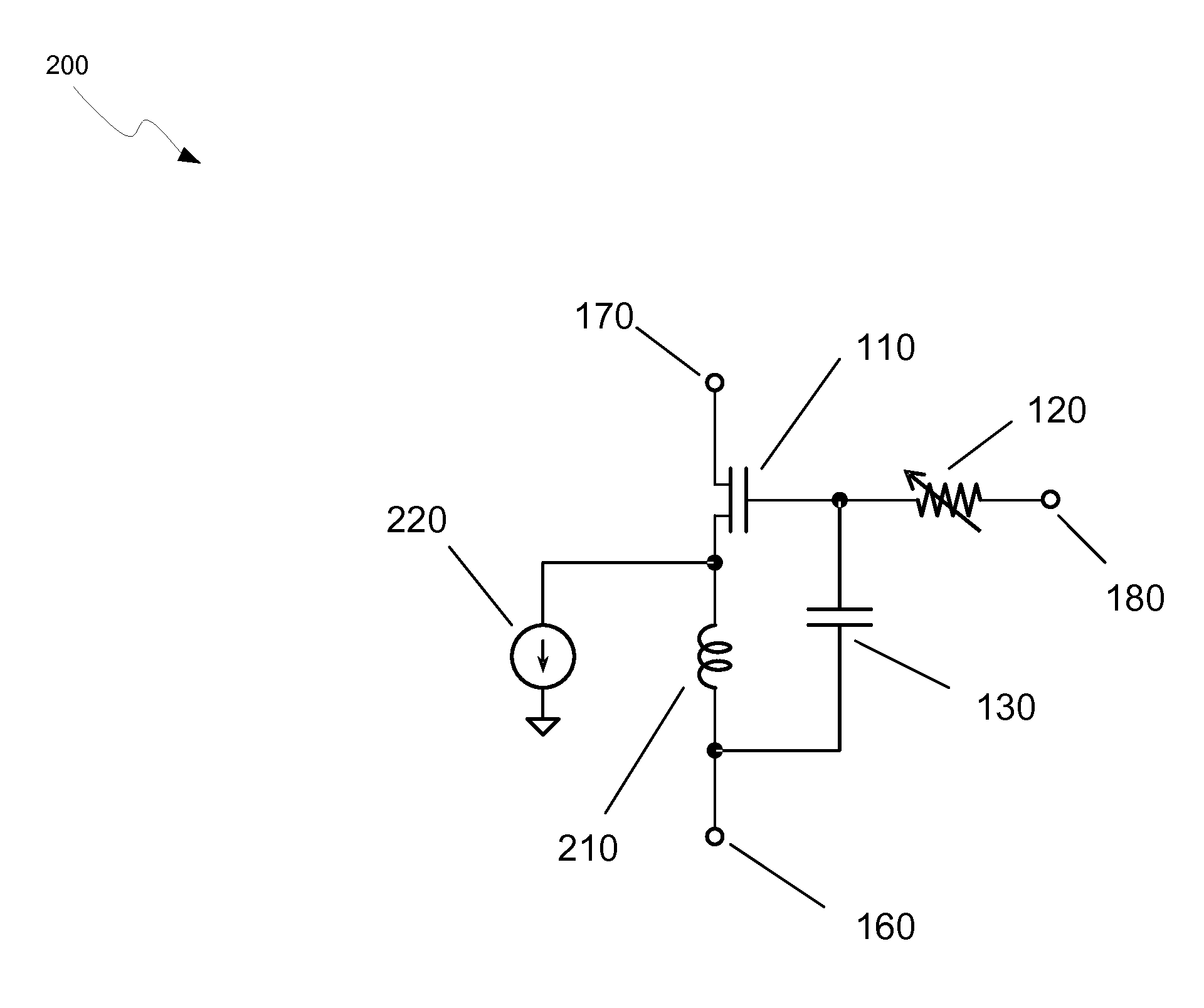
The present invention provides an active inductor apparatus and system, having a variable frequency response through inductance adjustment. The active inductor apparatus comprises a variable resistive element and a variable gain element, and the system further comprises an inductance controller and a gain controller. The variable resistive element has a first terminal and a second terminal, with the second terminal capable of receiving a first adjustment signal. The inductance controller is capable of providing the first adjustment signal to control and adjust a resistance level of the variable resistive element. The variable gain element has a third terminal capable of receiving a second adjustment signal. The gain controller is capable of providing the second adjustment signal to control and adjust a transconductance of the variable gain element. The frequency response of the active inductor apparatus and system is variable in response to adjustment of the resistance level of the variable resistive element and in response to adjustment of the transconductance of the variable gain element.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Method and system for bandwidth enhancement using hybrid inductors
ActiveUS20110063024A1High bandwidthComputations using contact-making devicesNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method and system for bandwidth enhancement using hybrid inductors are disclosed and may include providing an electrical impedance that increases with frequency via hybrid inductors comprising a transistor, a capacitor, an inductor, and a resistor. A first terminal of the hybrid inductors may comprise a first terminal of the transistor. A second terminal of the transistor may be coupled to a first terminal of the resistor and a first terminal of the capacitor. A second terminal of the resistor may comprise a second terminal of the hybrid inductors. A third terminal of the transistor may be coupled to a first terminal of an inductor, and a second terminal of the inductor may be coupled to a second terminal of the capacitor. The hybrid inductors may be configured by varying transconductance, resistance, and / or capacitance and may be utilized as an amplifier load.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Differential negative impedance converters and inverters with variable or tunable conversion ratios
ActiveUS20120256709A1Reduce parasitismGood device matchingImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceEngineering
A differential circuit topology that produces a tunable floating negative inductance, negative capacitance, negative resistance / conductance, or a combination of the three. These circuits are commonly referred to as “non-Foster circuits.” The disclosed embodiments of the circuits comprises two differential pairs of transistors that are cross-coupled, a load immittance, multiple current sources, two Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) networks, at least one tunable (variable) resistance, and two terminals across which the desired immittance is present. The disclosed embodiments of the circuits may be configured as either a Negative Impedance Inverter (NII) or a Negative Impedance Converter (NIC) and as either Open-Circuit-Stable (OCS) and Short-Circuit-Stable (SCS).
Owner:HRL LAB
Electronic circuit comprising a resonator to be integrated into a semiconductor product
InactiveUS7423502B2High quality coefficientImprove tuning effectNetwork simulating reactancesEngineeringInductance
An electronic circuit comprises a resonator meant to be integrated into a semiconductor product including a resonator having first and second resonant frequencies. The electronic circuit comprises: a first inductive partner element for canceling out said second resonant frequency, said partner element having a quality coefficient QI (f) having a first value in a predetermined frequency band and a second value outside said frequency band; a second capacitive partner element for adjusting tuning of said resonator to said first frequency.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Programmable passive inductor
ActiveUS20050275458A1Effective inductanceImprove performanceNetwork simulating reactancesTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsRelative magnitudeCoupling
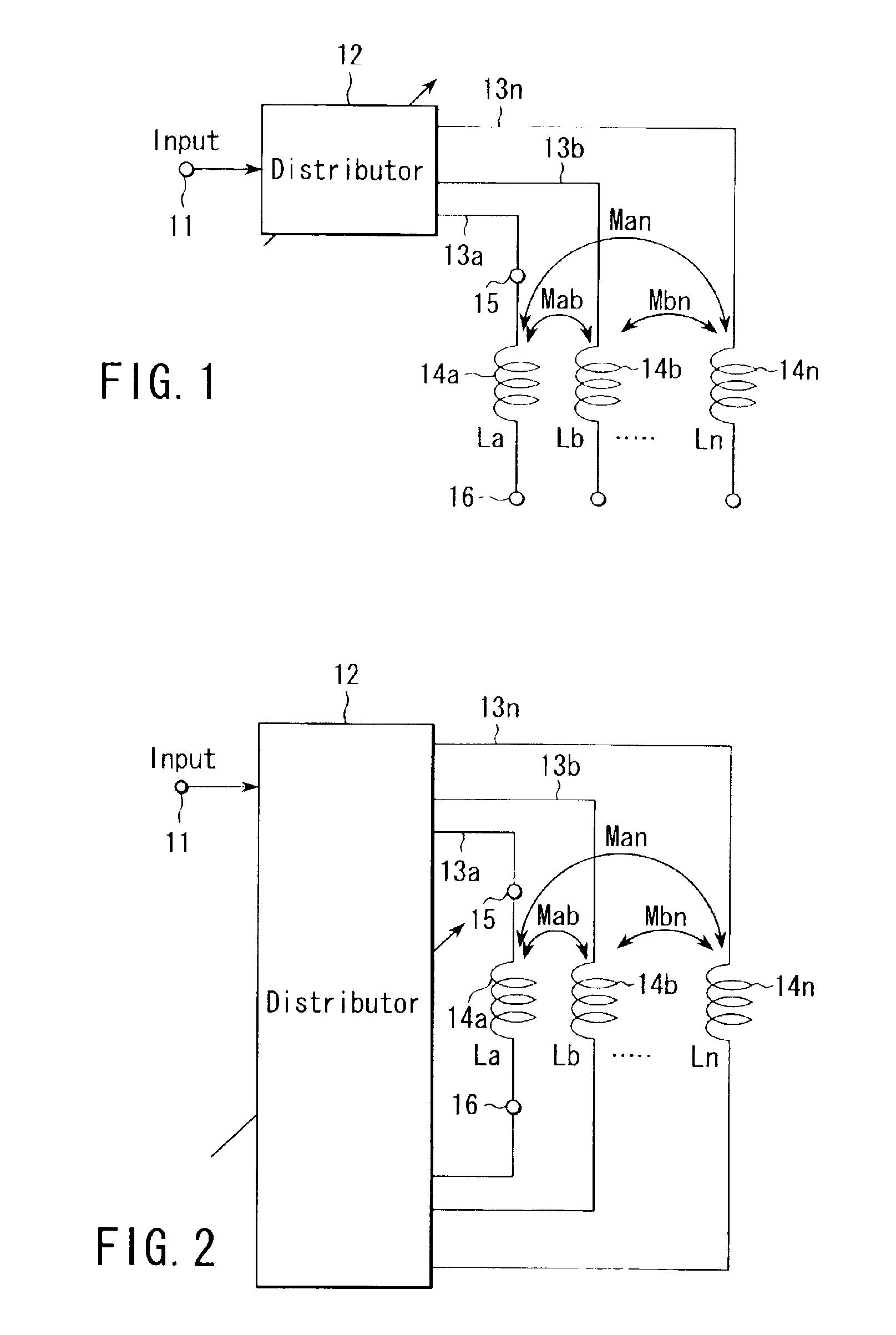
A programmable passive inductor includes two inductors or coils, each having a self-inductance, magnetically coupled together and having a mutual inductance proportional to a magnetic coupling factor. The relative magnitude of the currents through the two inductors can be dynamically varied, which changes the effective inductance.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
Variable inductor
A variable simulated inductor comprises an integrator connected to receive the voltage across the input to the circuit. The output of the inductor is connected to a control terminal of a transconductor connected across the input of the circuit. The gain of the transconductor is electronically controllable in order to control the inductance of the circuit. An oscillator using a variable simulated inductor and a piezoelectric resonator connected in parallel is also provided.
Owner:ACP ADVANCED CIRCUIT PURSUIT AG
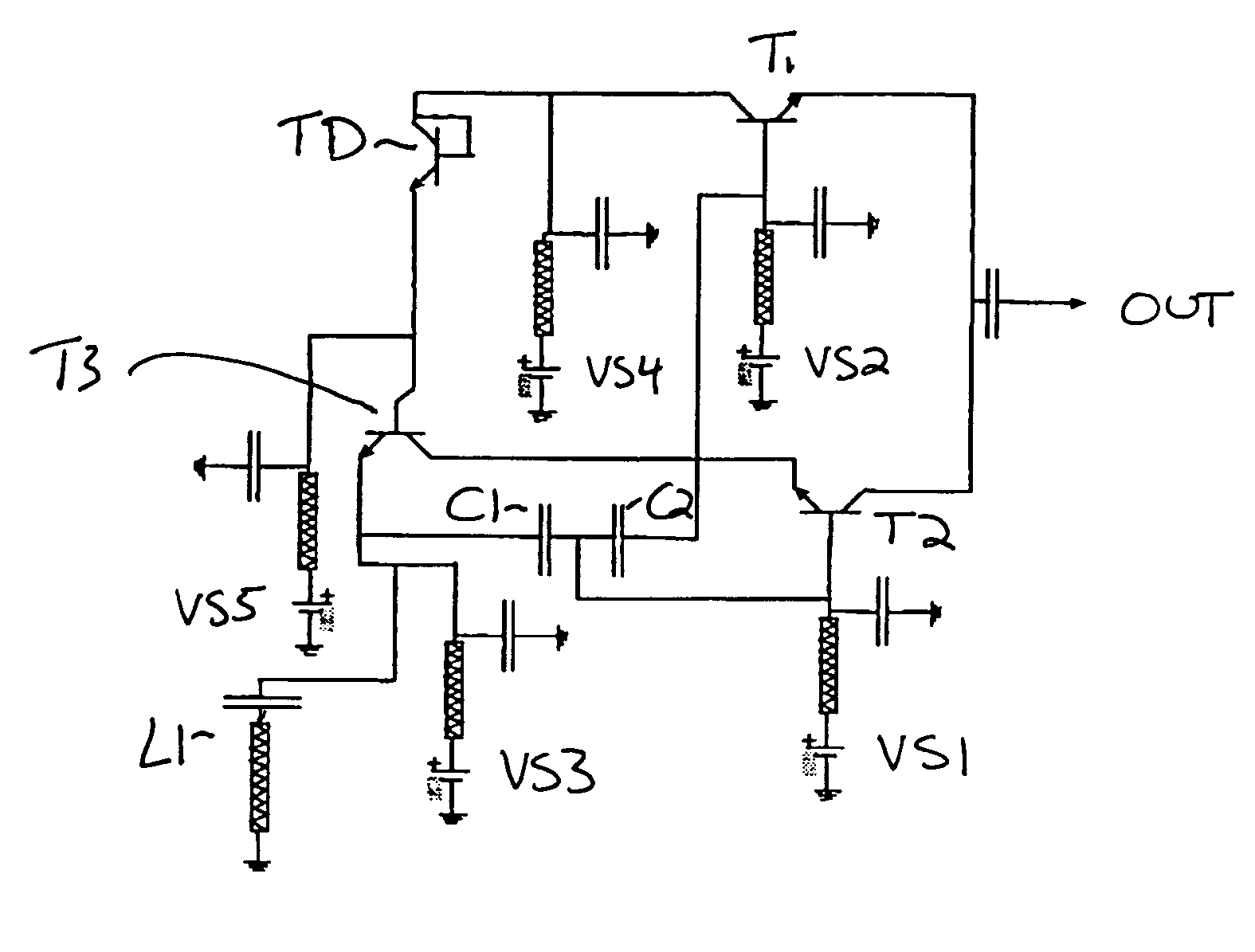
Active inductors using bipolar silicon transistors
InactiveUS7020450B2Pulse automatic controlNetwork simulating reactancesTransceiverAudio power amplifier
An active inductor includes bipolar transistors T1, T2, T3 and TD (TD being arranged in diode), where T1's emitter is connected to an output port and to T2's collector. T2's base is connected to a first voltage line and between two connected capacitors. T2's emitter is connected to T3's collecter. An end of one capacitor is connected to T1's base and to a second voltage line. An end of the other capacitor is connected to T3's emitter and to a third voltage line. T1's collector is connected to a fourth voltage line and to TM's collecter, which is connected to TM's base. TM's emitter is electrically connected to T3's base. Preferably, the transistors T1–T3 and TD are Silicon based, and the active inductor is fabricated on a single substrate comprising Silicon. The active inductor is incorporated into adaptive oscillators and amplifiers and an improved transceiver.
Owner:NEC CORP
Variable inductor
A variable simulated inductor comprises an integrator connected to receive the voltage across the input to the circuit. The output of the inductor is connected to a control terminal of a transconductor connected across the input of the circuit. The gain of the transconductor is electronically controllable in order to control the inductance of the circuit. An oscillator using a variable simulated inductor and a piezoelectric resonator connected in parallel is also provided.
Owner:ACP ADVANCED CIRCUIT PURSUIT
Phase-shifting circuit and multibit phase shifter
ActiveUS20070273456A1Small sizeReduce lossMultiple-port networksNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitancePhase shifted
A phase-shifting circuit includes: a first parallel circuit which is connected across input and output terminals of a high frequency signal, composed of a first inductor and a first switching element that exhibits a through state in an ON state and a capacitive property in an OFF state, and produces parallel resonance at a prescribed frequency when the first switching element is in the OFF state; a series circuit composed of a second inductor and a third inductor and connected in parallel with the first parallel circuit; a capacitor having its first terminal connected to a point of connection of the second and third inductors; and a second parallel circuit which is connected across a second terminal of the capacitor and a ground, composed of a fourth inductor and a second switching element that exhibits a through state in an ON state and a capacitive property in an OFF state, and produces parallel resonance at a prescribed frequency when the second switching element is in the OFF state. The phase-shifting circuit establishes by switching an operation mode of setting the first switching element at the ON state and the second switching element at the OFF state, or an operation mode of setting the first switching element at the OFF state and the second switching element at the ON state.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Active filter circuit with reduced noise
InactiveUS7009446B2Reduce noiseNetwork simulating reactancesOscillations generatorsCapacitanceEngineering
Input conversion noises of a filter circuit are reduced. The circuit has plural circuit arrangements obtained by dividing the filter circuit so as to include at least one voltage controlled current source, and at least one circuit arrangement is an amplification circuit having an amplifying function for amplifying an input signal to the filter circuit at a set amplification factor. The amplification element circuit has: a loop circuit constructed by plural intra-loop voltage controlled current sources in which mutual conductance values have a predetermined corresponding relation; and a corresponding capacitor connected to a node in the loop circuit and having a capacitance depending on the corresponding relation so as to set a potential at the node to a predetermined potential corresponding to the amplification factor, and amplification element circuit has an electric nature which is independent of the amplification factor when seeing from the input side of the filter circuit.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
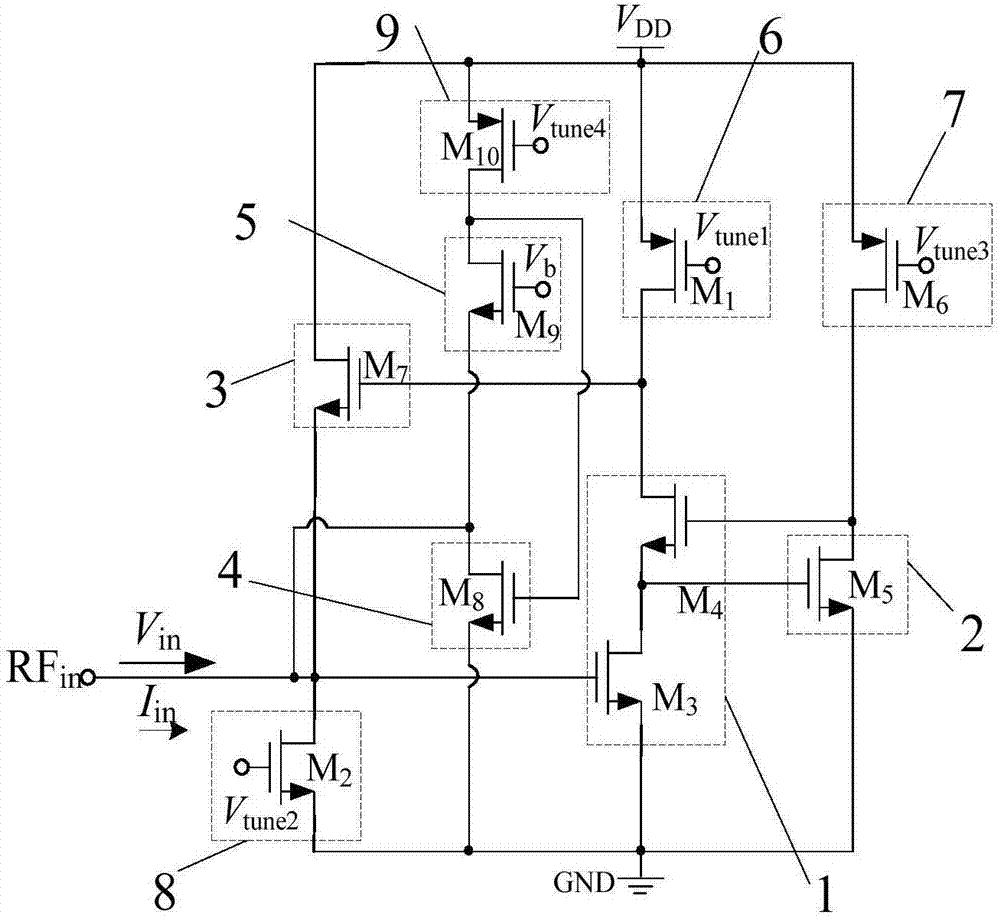
Broadband active inductor with high Q values and coarsely tunable and finely tunable inductance value
ActiveCN107124157AIncrease the inductance valueIncrease output impedanceNetwork simulating reactancesBroadbandInductor
The invention discloses a broadband active inductor with high Q values and a coarsely tunable and finely tunable inductance value. The broadband active inductor comprises a first transconductance unit (1), a modulation unit (2), a second transconductance unit (3), a third transconductance unit (4), a fourth transconductance unit (5), a first tunable bias circuit (6), a second tunable bias circuit (7), a third tunable bias circuit (8) and a fourth tunable bias circuit (9). The modulation unit is connected with the first transconductance unit and is used for increasing the Q values and bandwidth of the active inductor. The first transconductance unit, the modulation unit and the second transconductance unit form a master circuit. The third transconductance unit and the fourth transconductance unit form a slave circuit. The master circuit and the slave circuit are connected in parallel. The equivalent capacitance for synthesizing the inductance in the whole circuit is increased, so the inductance value of the active inductor is improved. According to the active inductor, the high Q peaks of the active inductor under different frequencies are realized, the Q peaks can be tuned, and the inductance value of the active inductor is coarsely tuned and finely tuned.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com