Patents
Literature
4298 results about "Differential amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs Vᵢₙ⁻ and Vᵢₙ⁺ and one output Vₒᵤₜ in which the output is ideally proportional to the difference between the two voltages Vₒᵤₜ=A(Vᵢₙ⁺-Vᵢₙ⁻) where A is the gain of the amplifier.
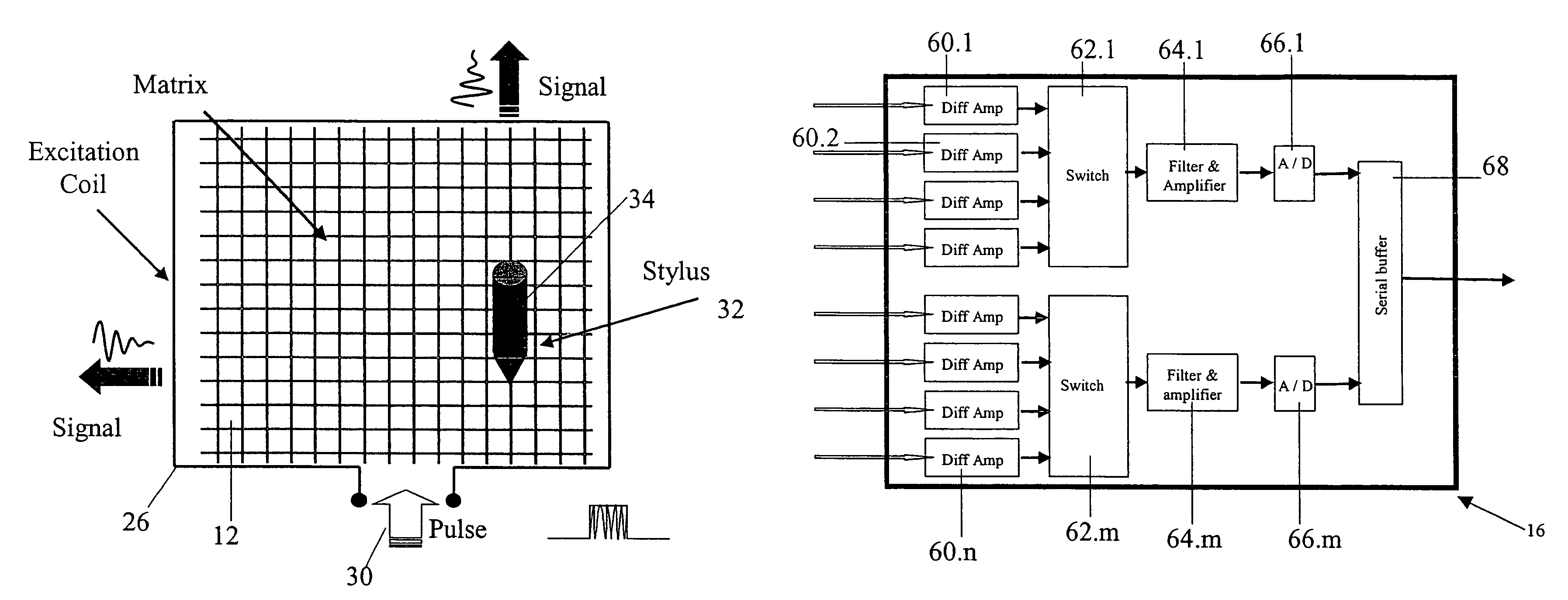
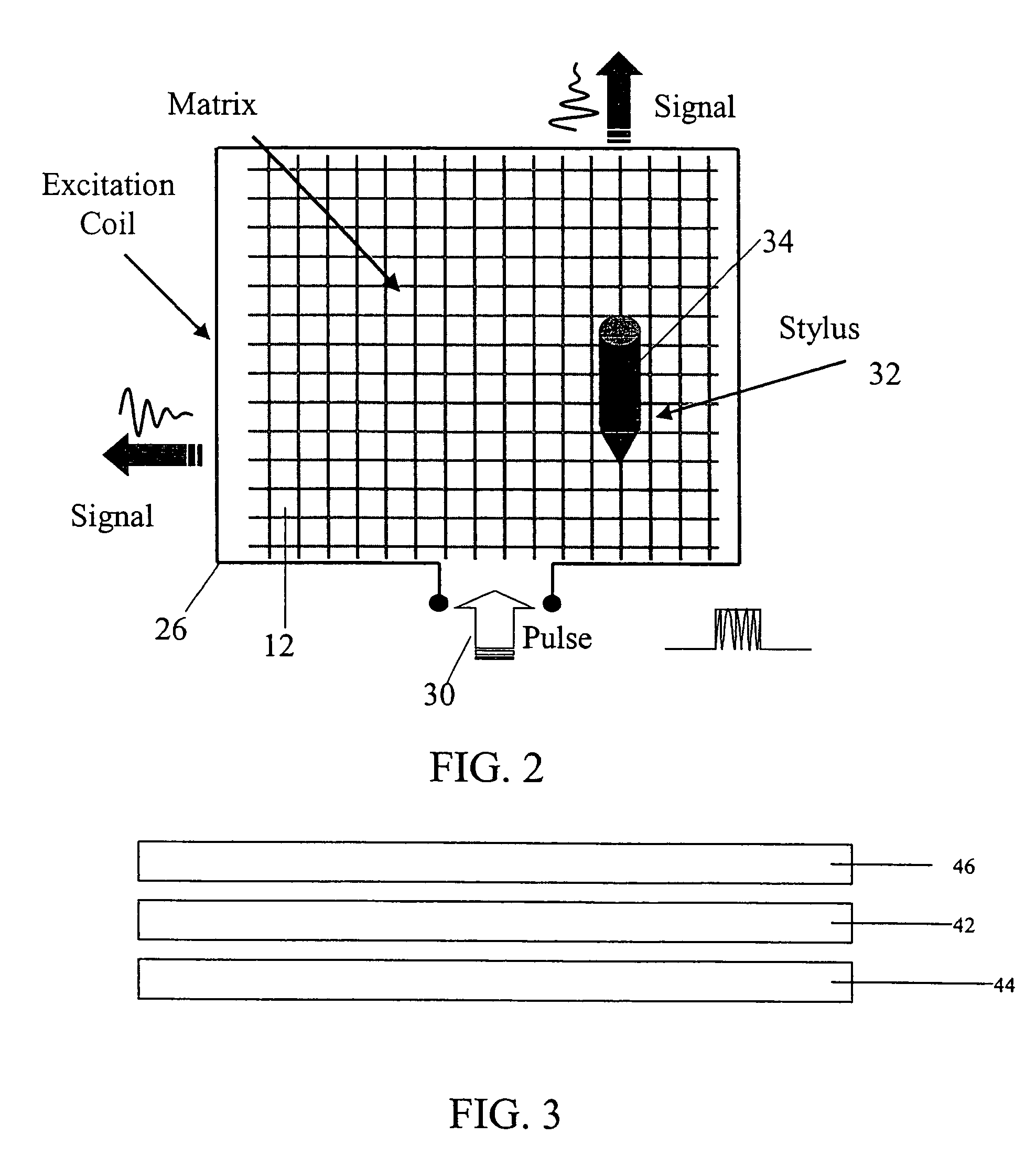
Transparent digitiser
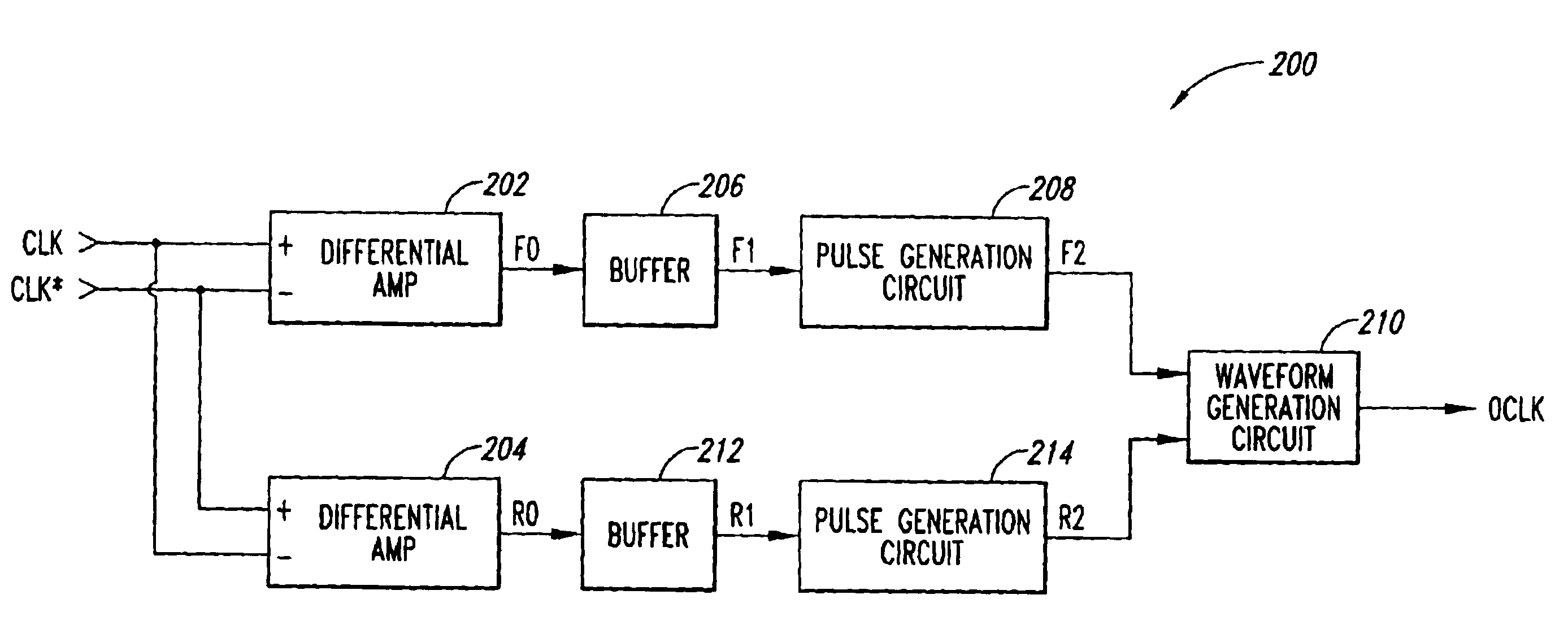
ActiveUS7292229B2Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital converterDifferential amplifier
A digitizer for user interaction via an object with an electronically refreshable display screen, the digitizer comprising: a transparent sensing arrangement of detectors located at said electronically refreshable display screen for detecting an electric field of said object, said detectors having outputs, and an arrangement of differential amplifiers associated with said outputs, thereby to apply differential detection between said outputs.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
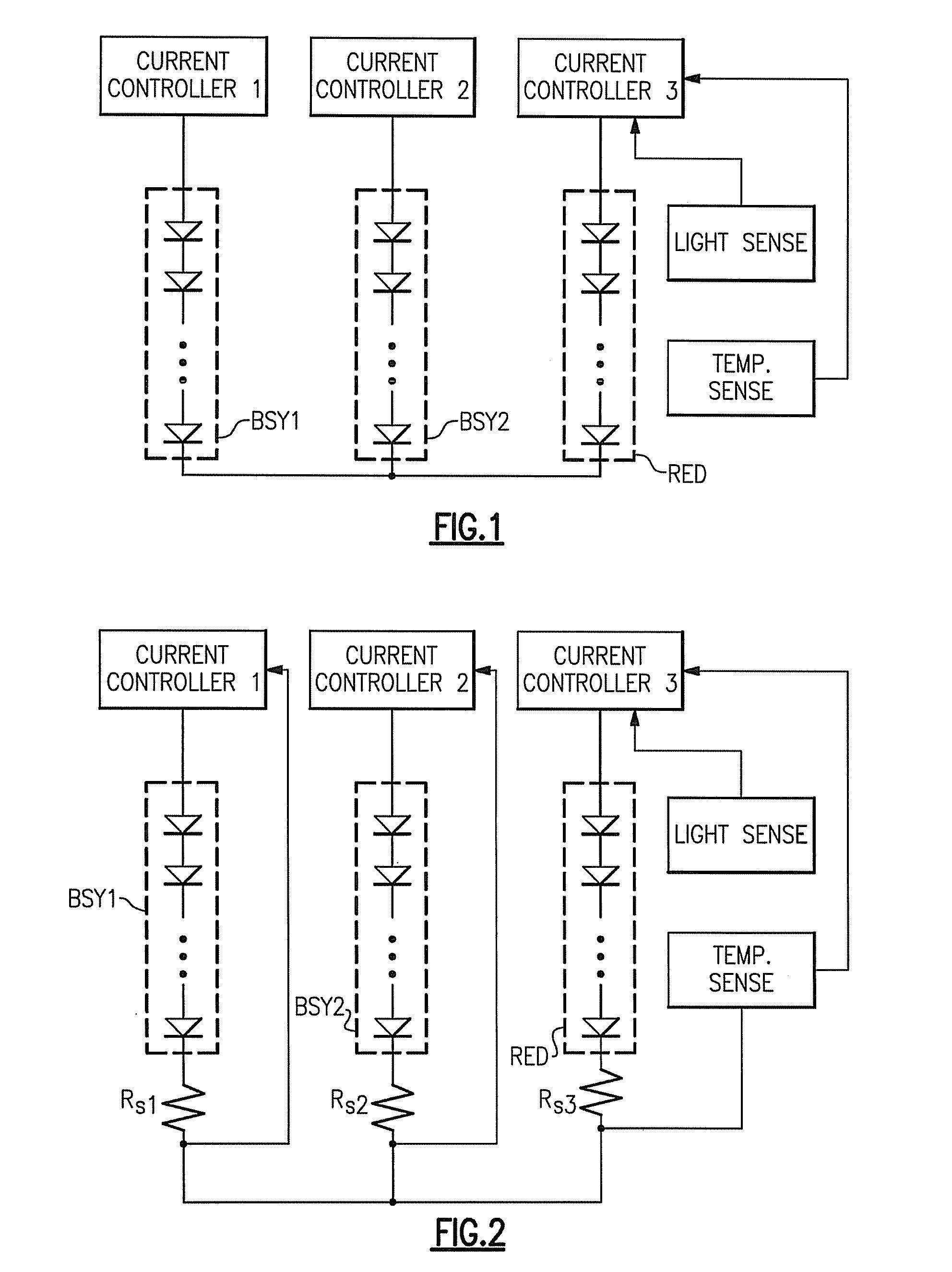
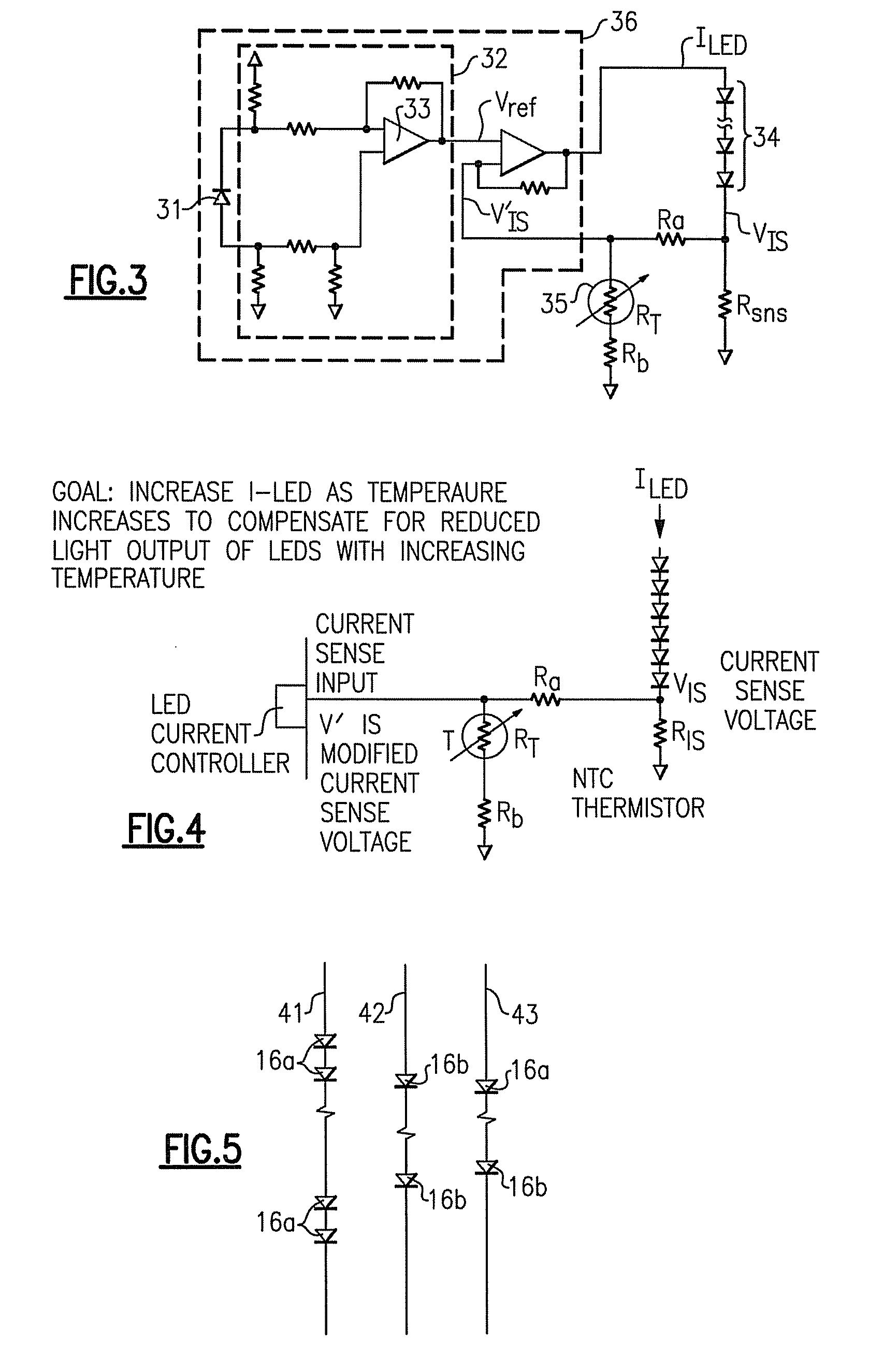
Lighting devices and methods for lighting
ActiveUS20080309255A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight sensingLight equipment
A lighting device comprises groups of solid state light emitters, a sensor and circuitry. If the emitters are illuminated, the sensor is exposed to combined light from the groups, and senses only a portion of the combined light. The circuitry adjusts current applied to at least one of the emitters based on an intensity of the light sensed. Also, a device comprising emitters, a circuit board and a sensor, at least one of the emitters being positioned on the first circuit board and the sensor being spaced from the circuit board. Also, a lighting device comprising emitters, a sensor, and circuitry which adjusts current applied an emitters based on detection by the first sensor, the circuitry comprising a differential amplifier circuit. Also, a lighting device, comprising light emitters and circuitry which adjusts current applied to only some of the emitters based on ambient temperature. Also, methods of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
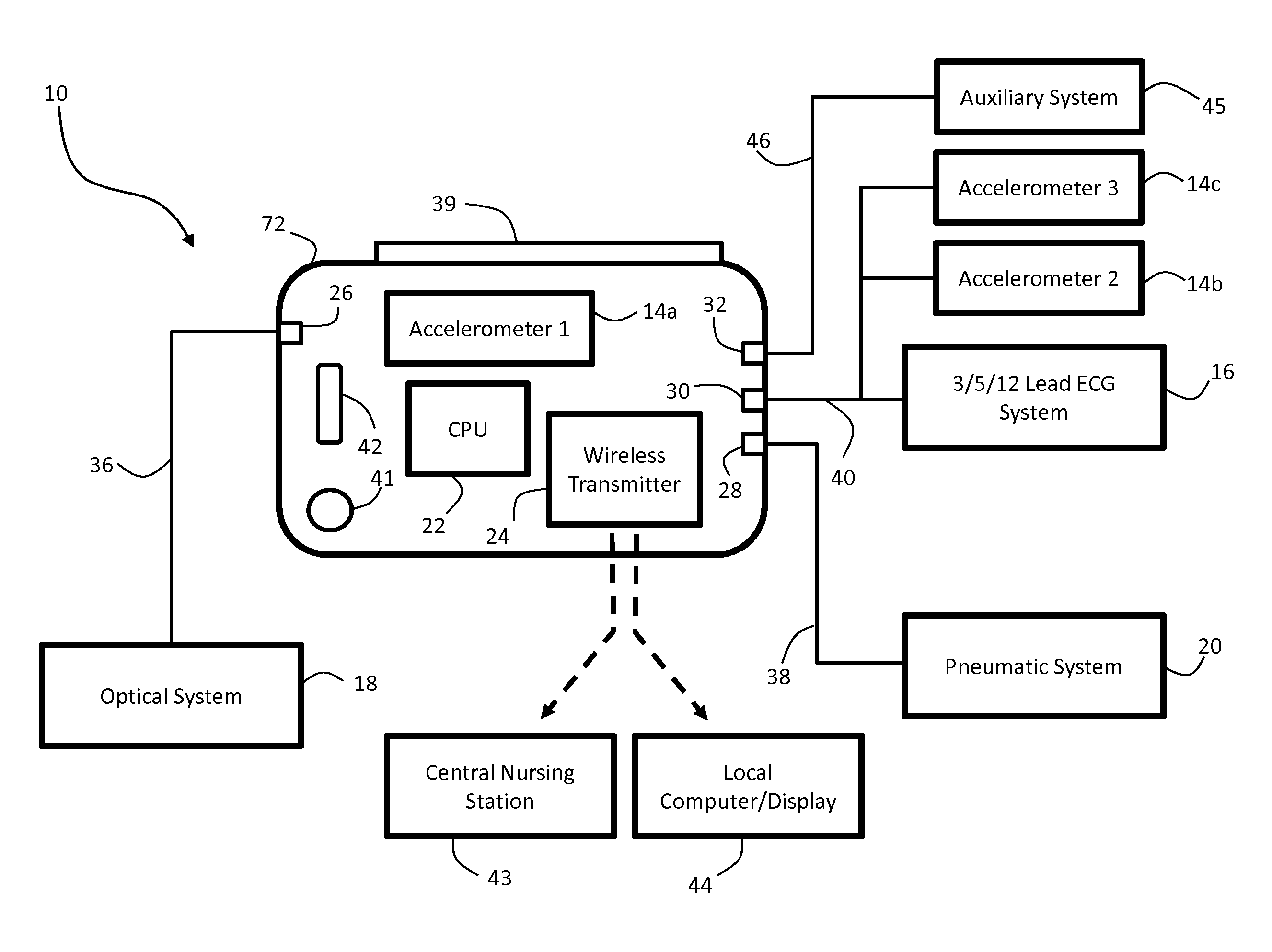
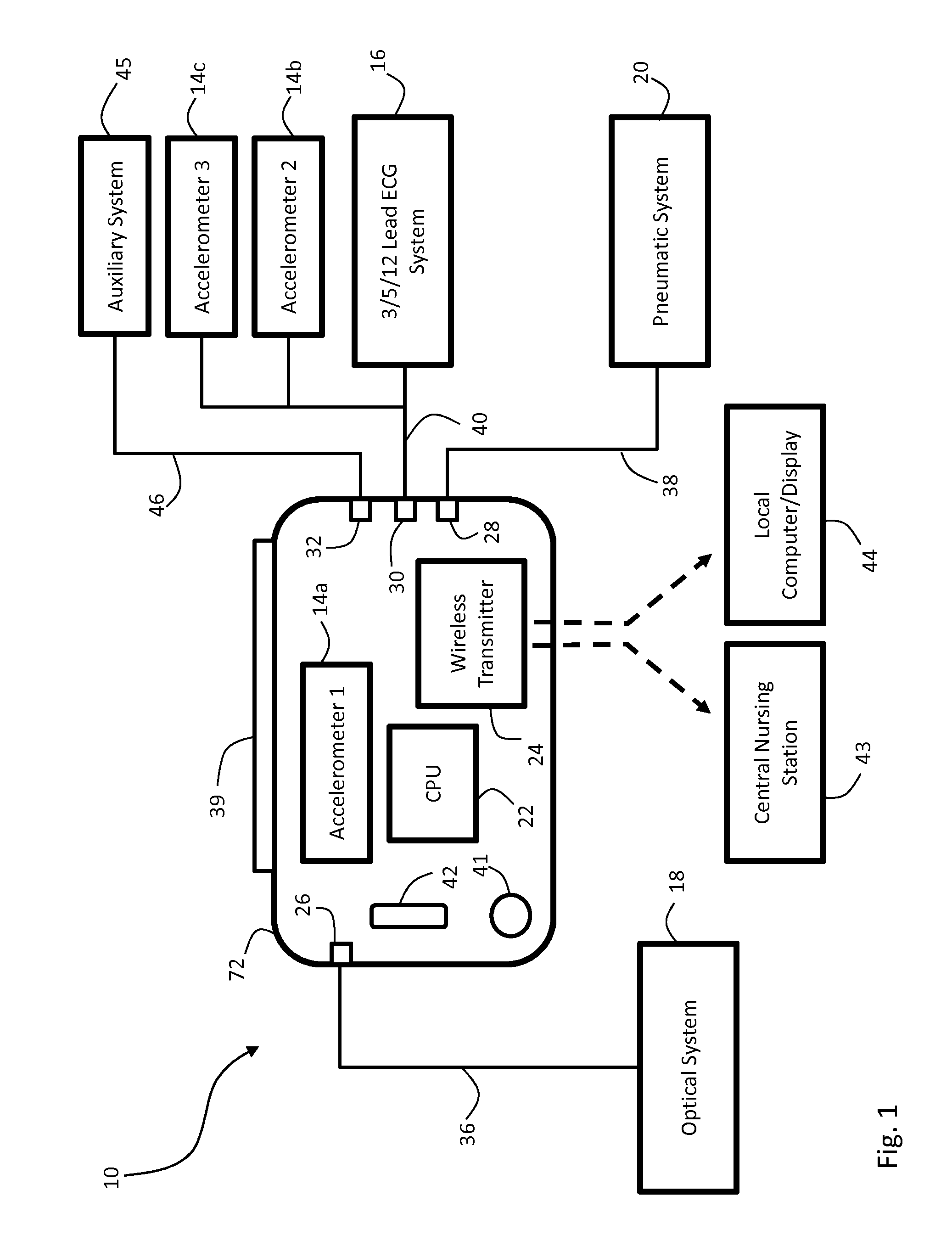
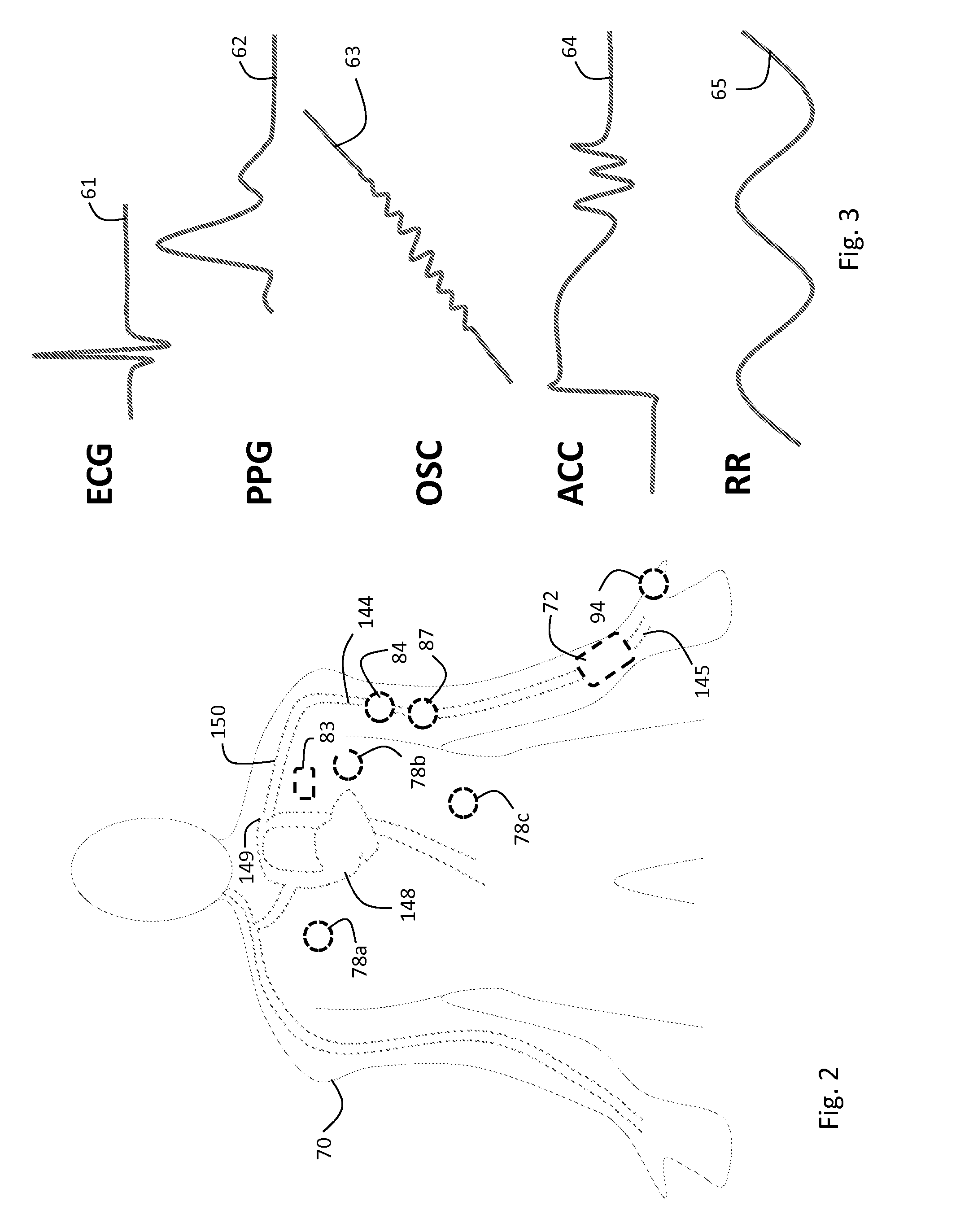
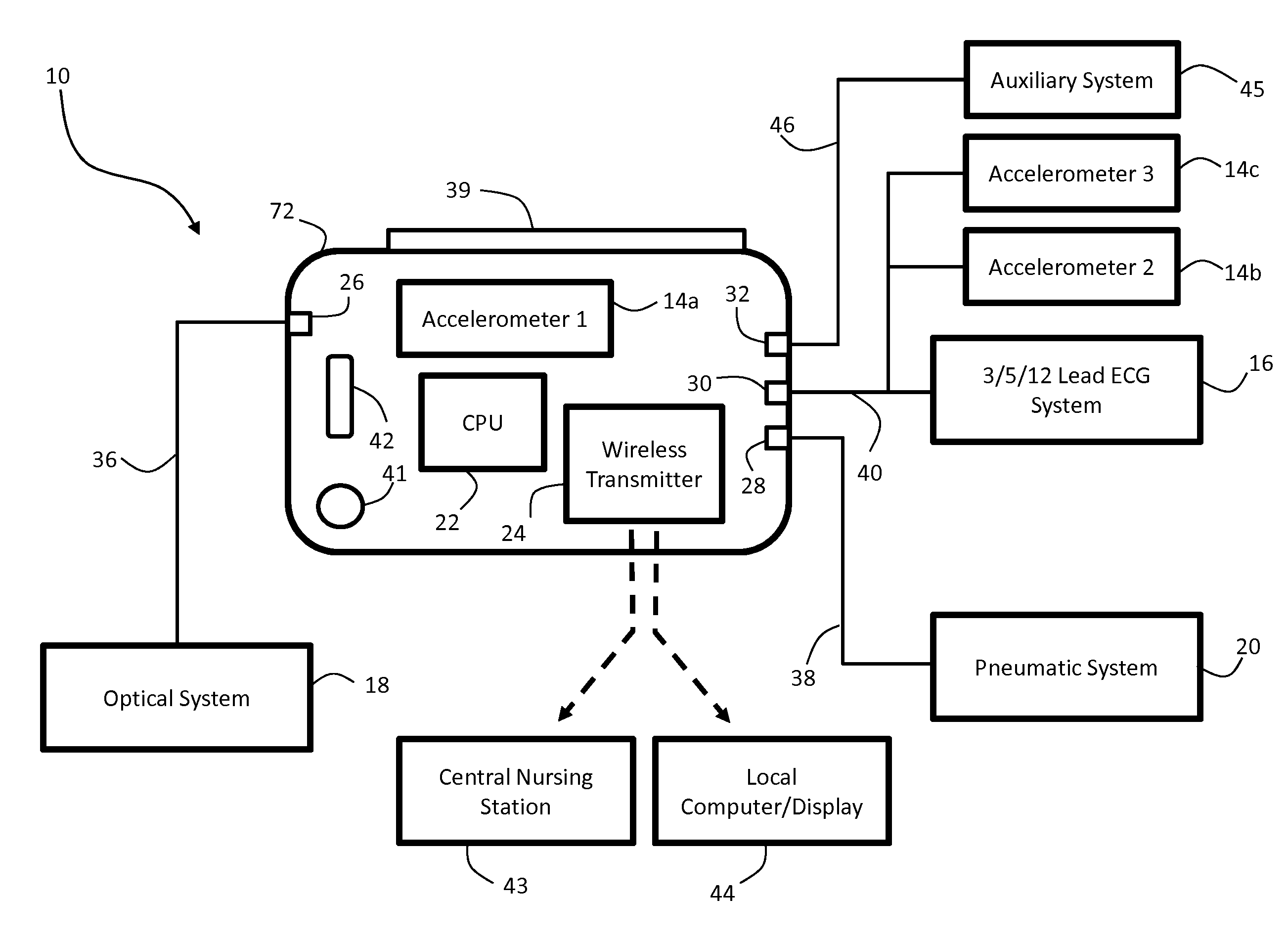
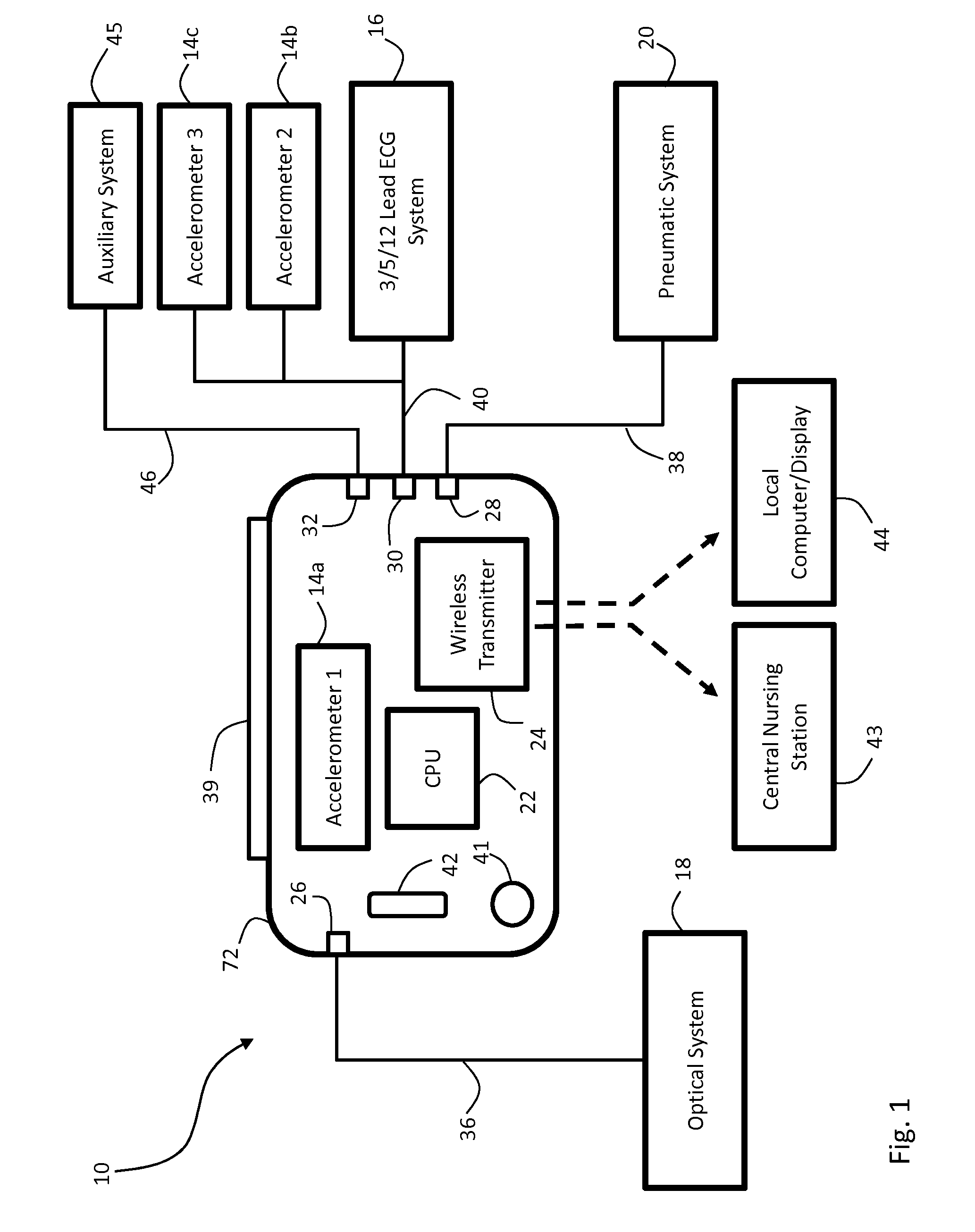
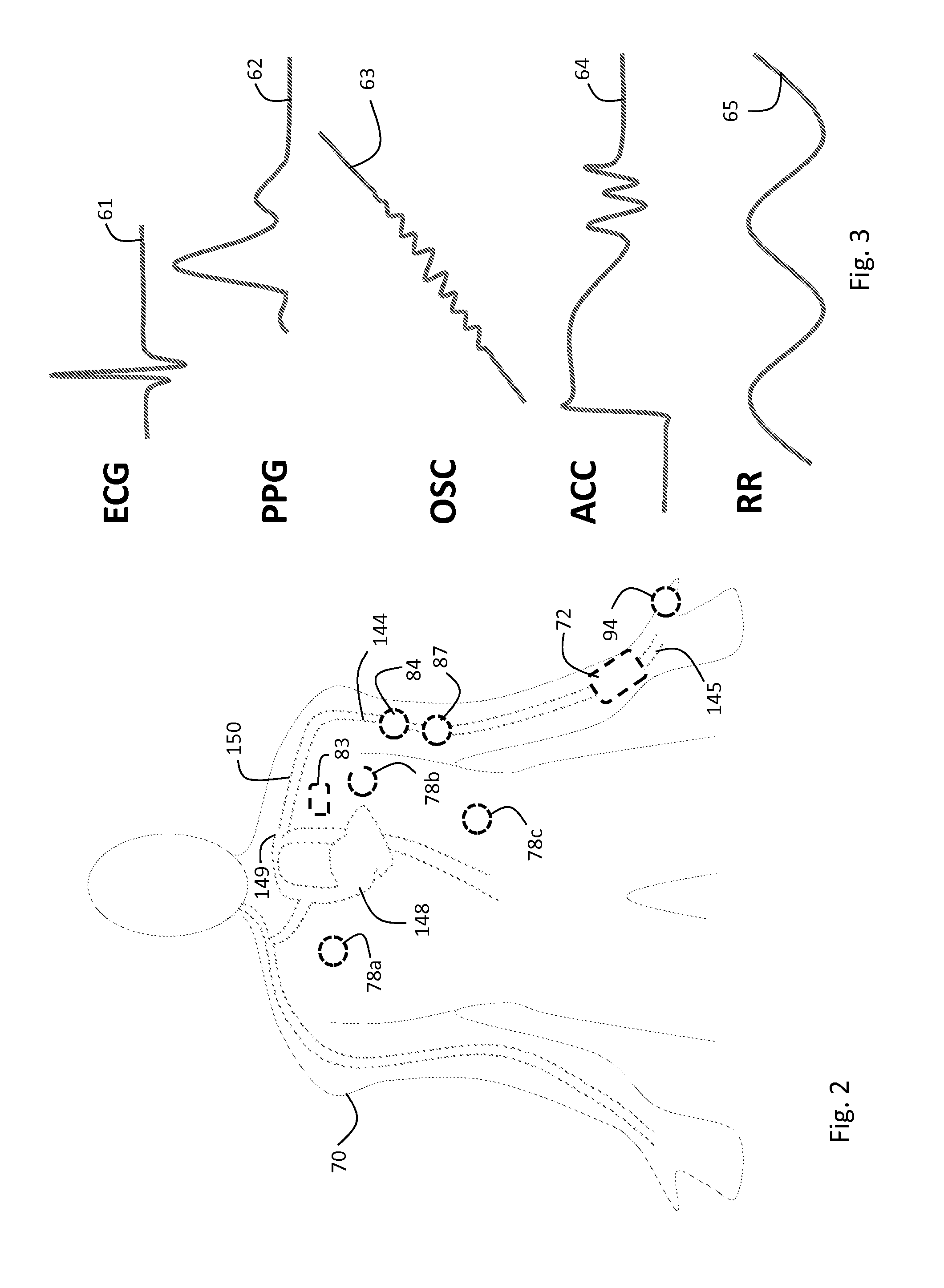
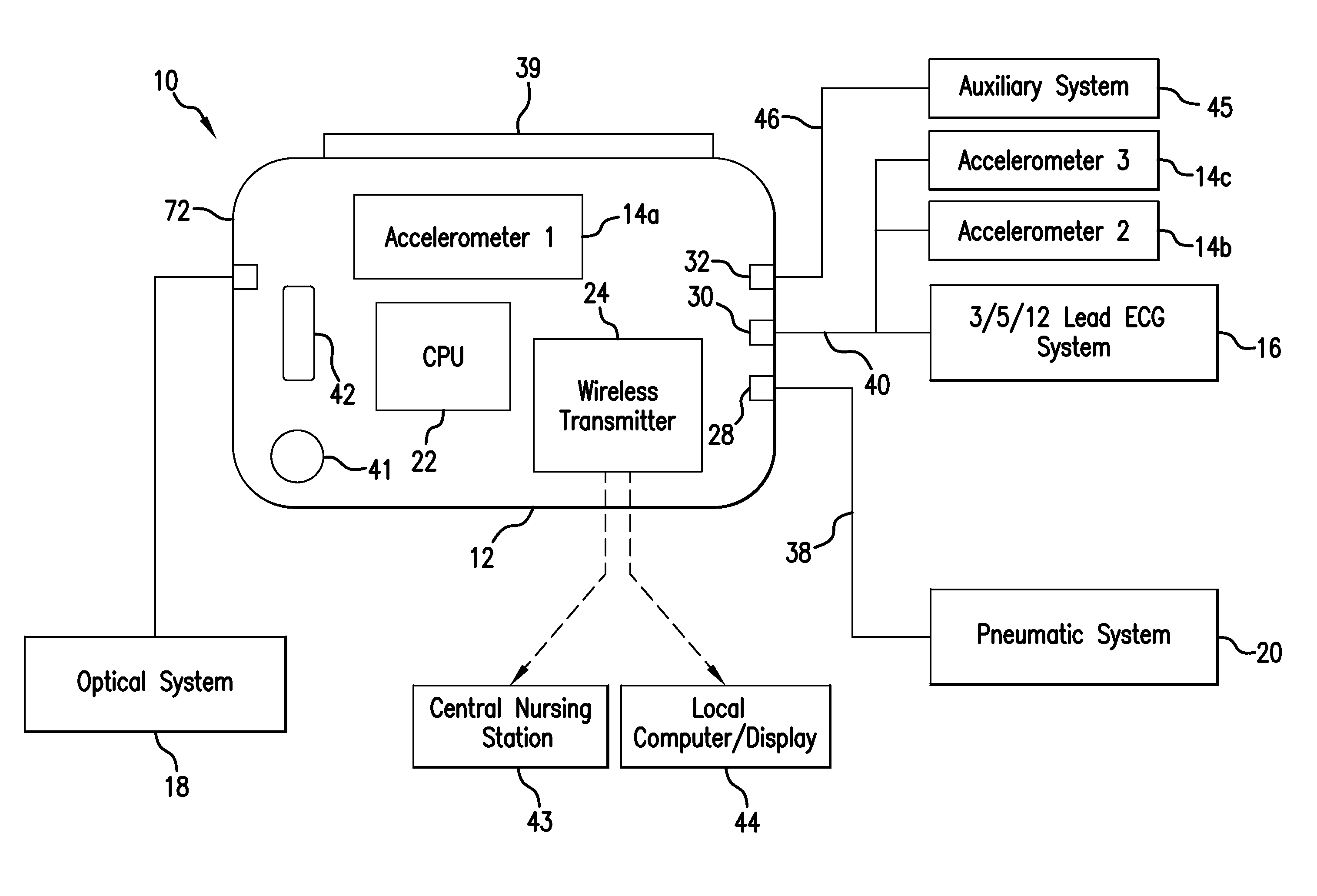
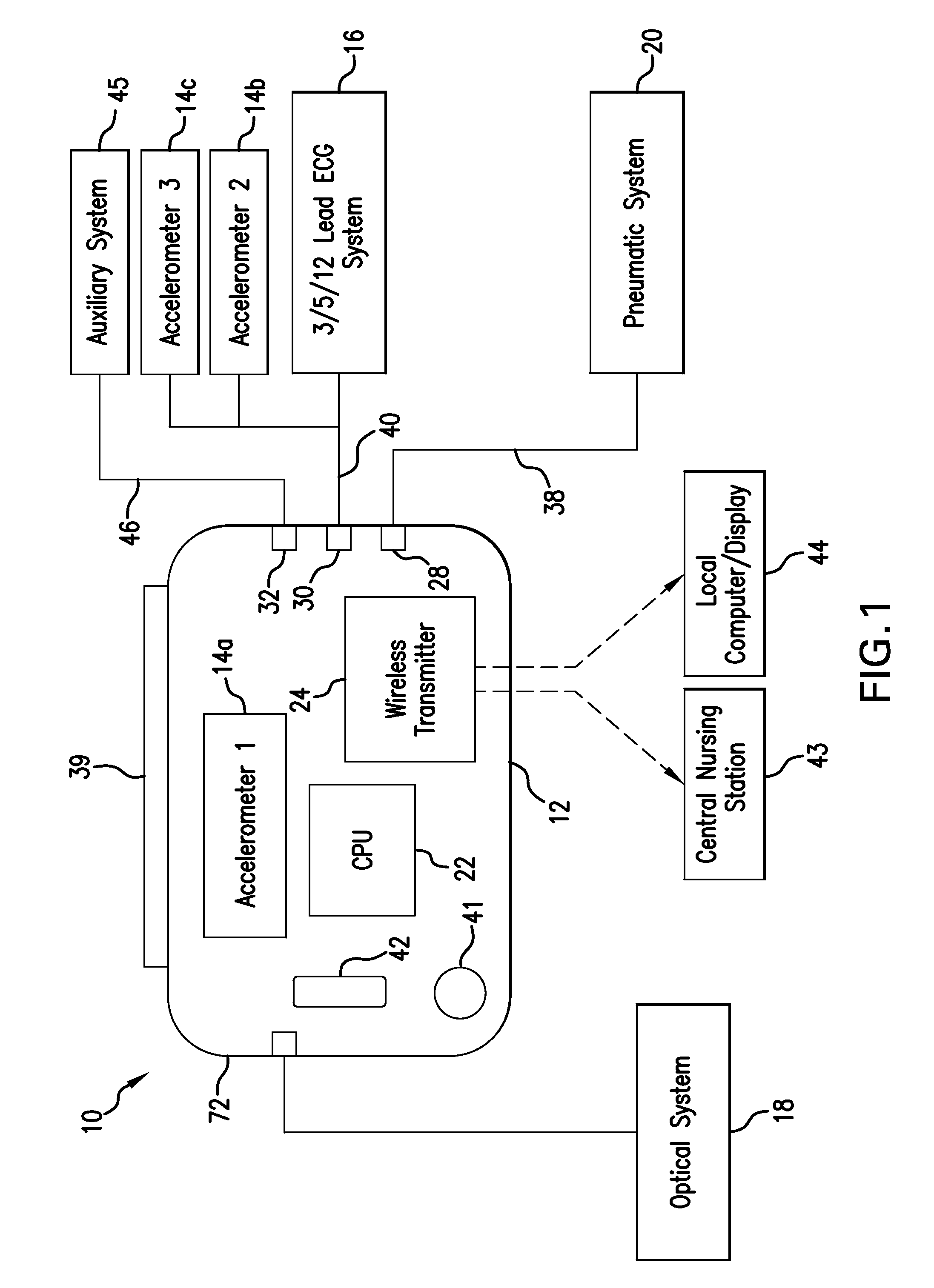
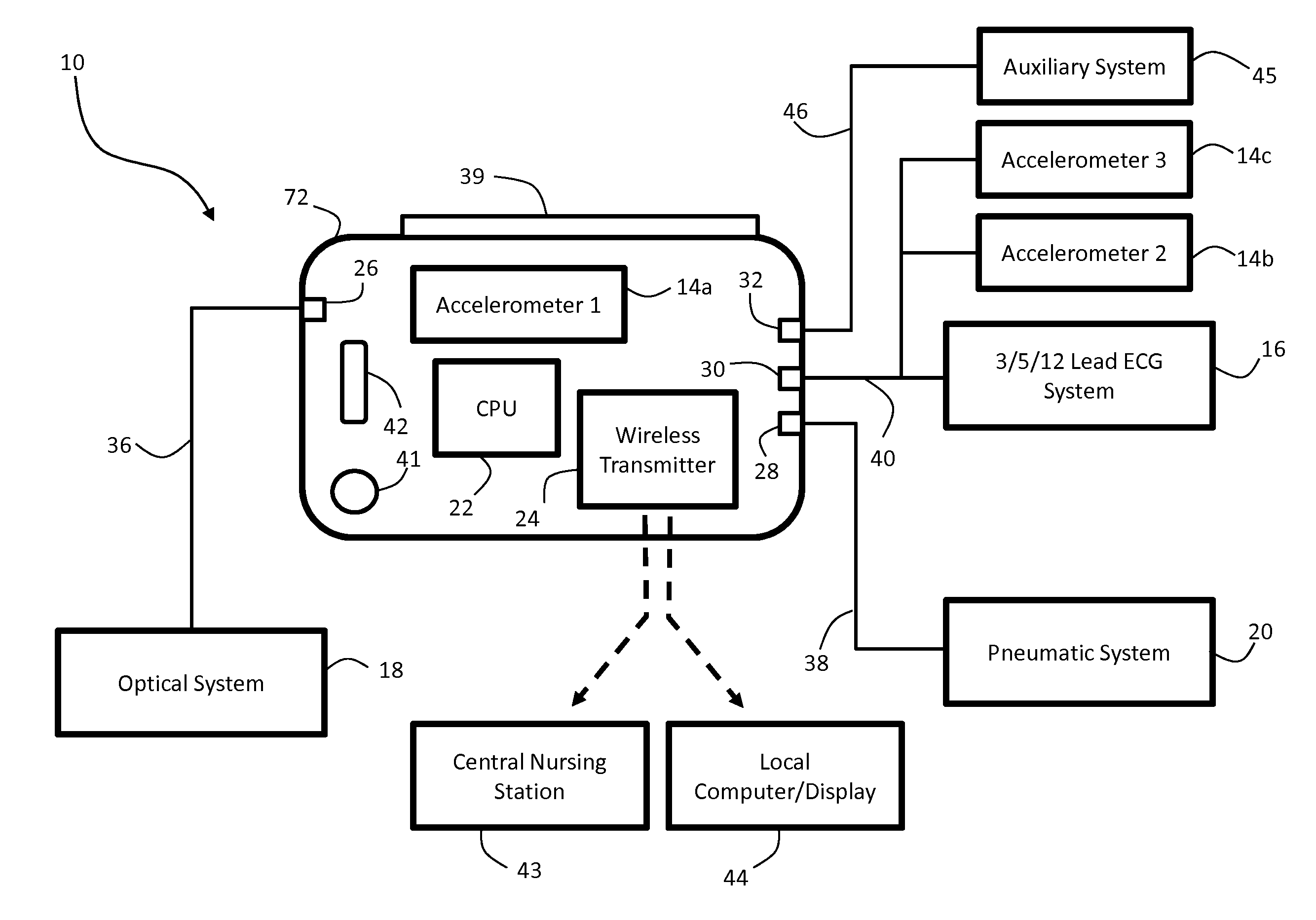
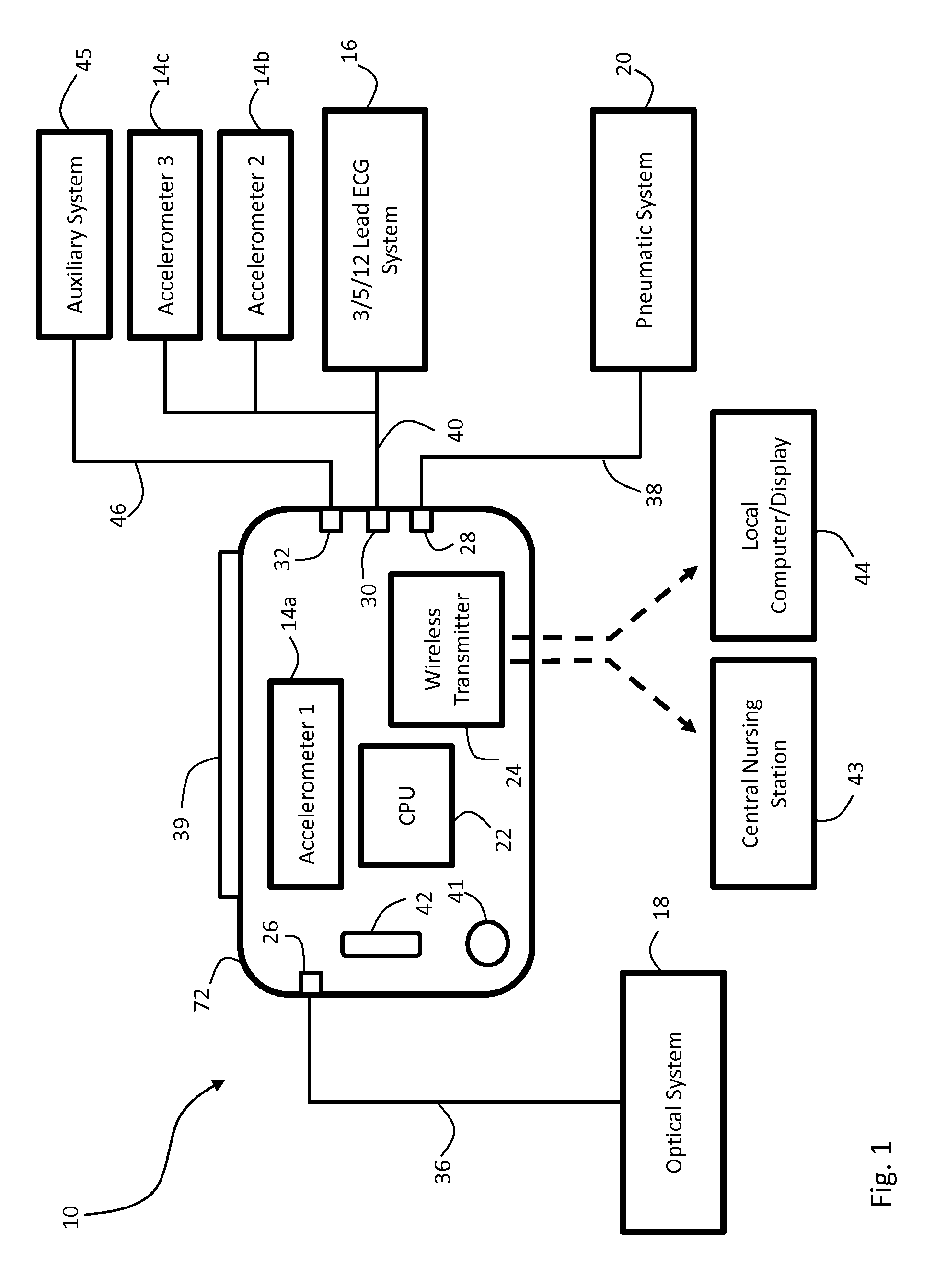
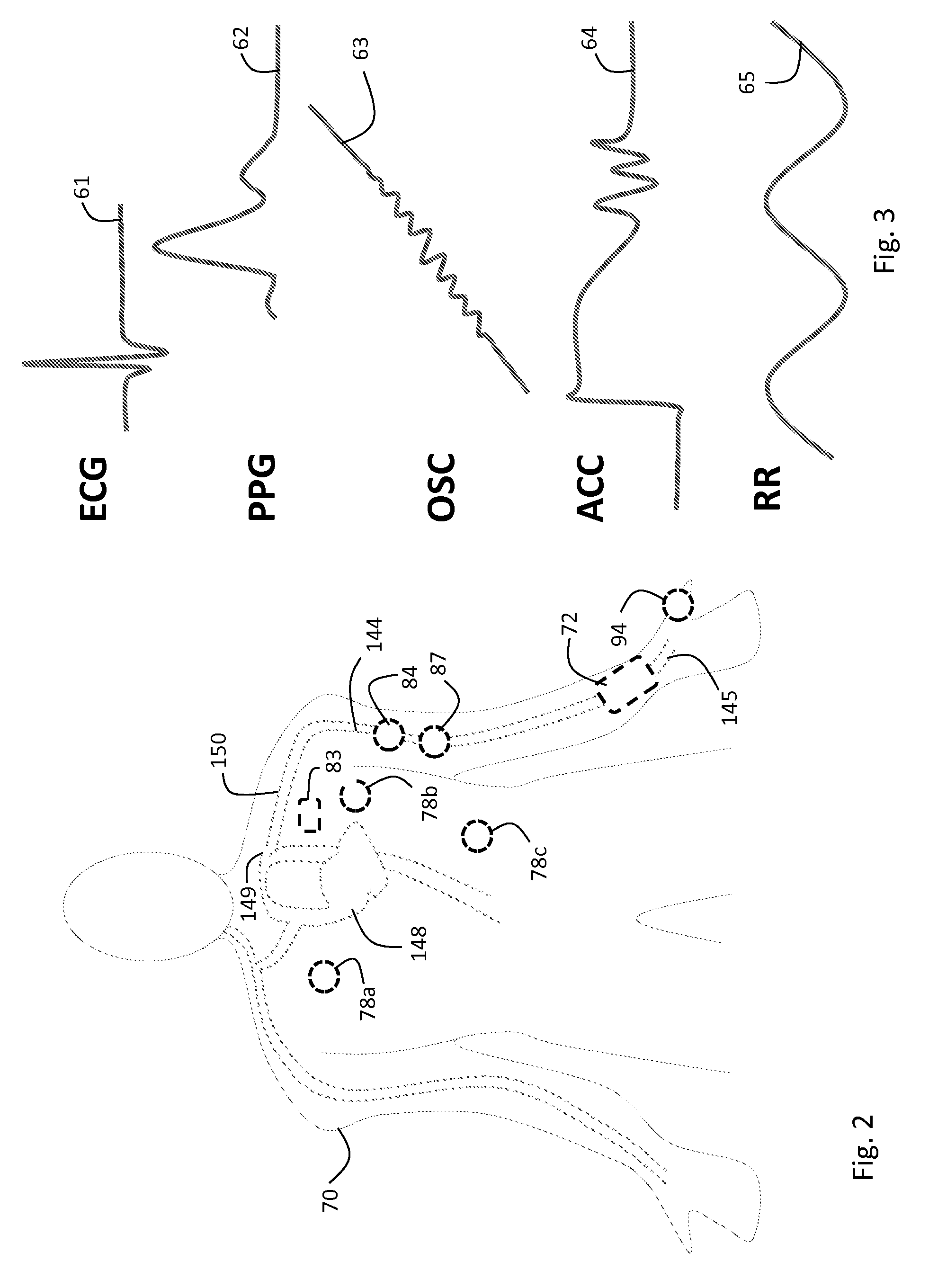
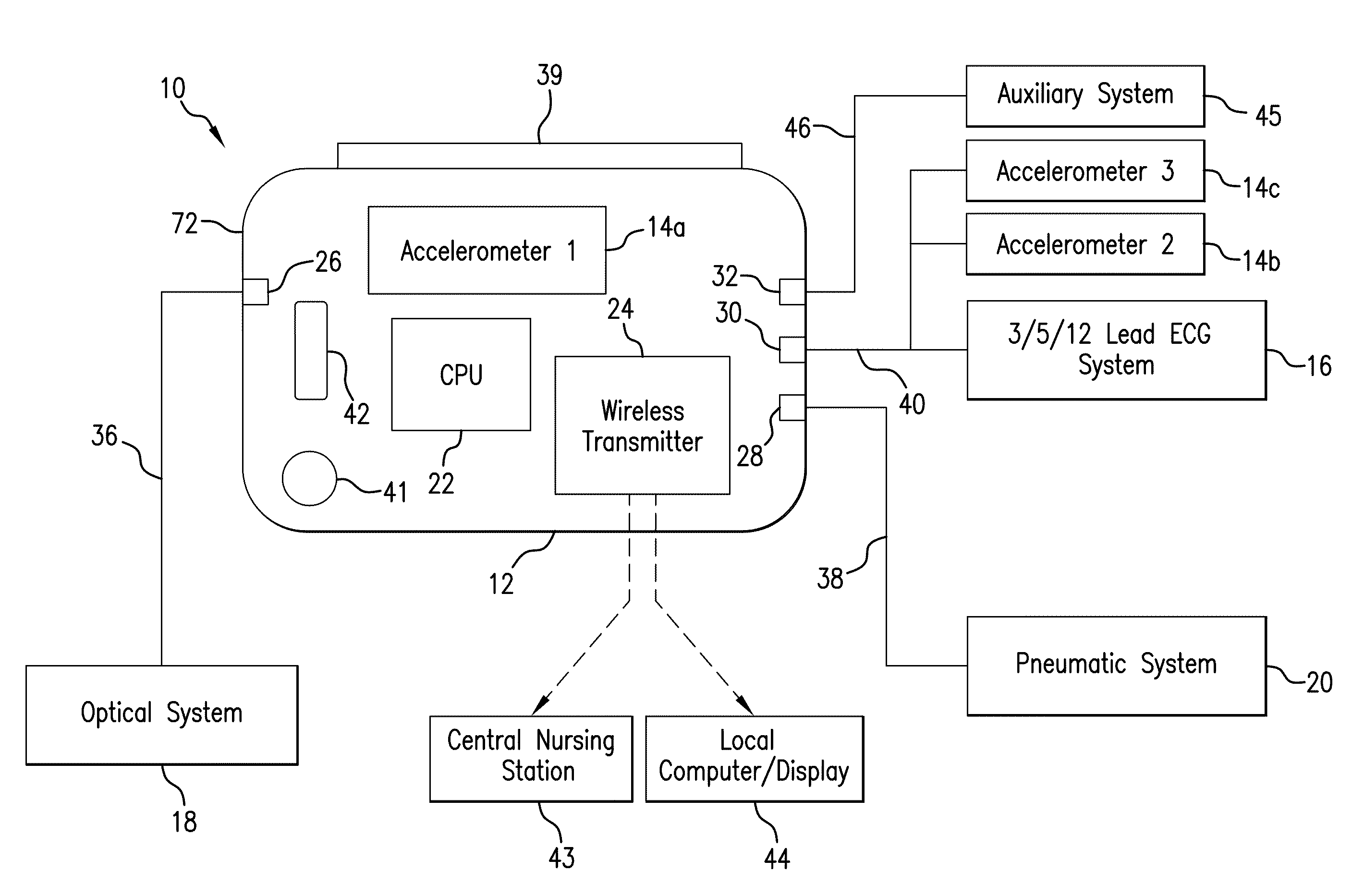
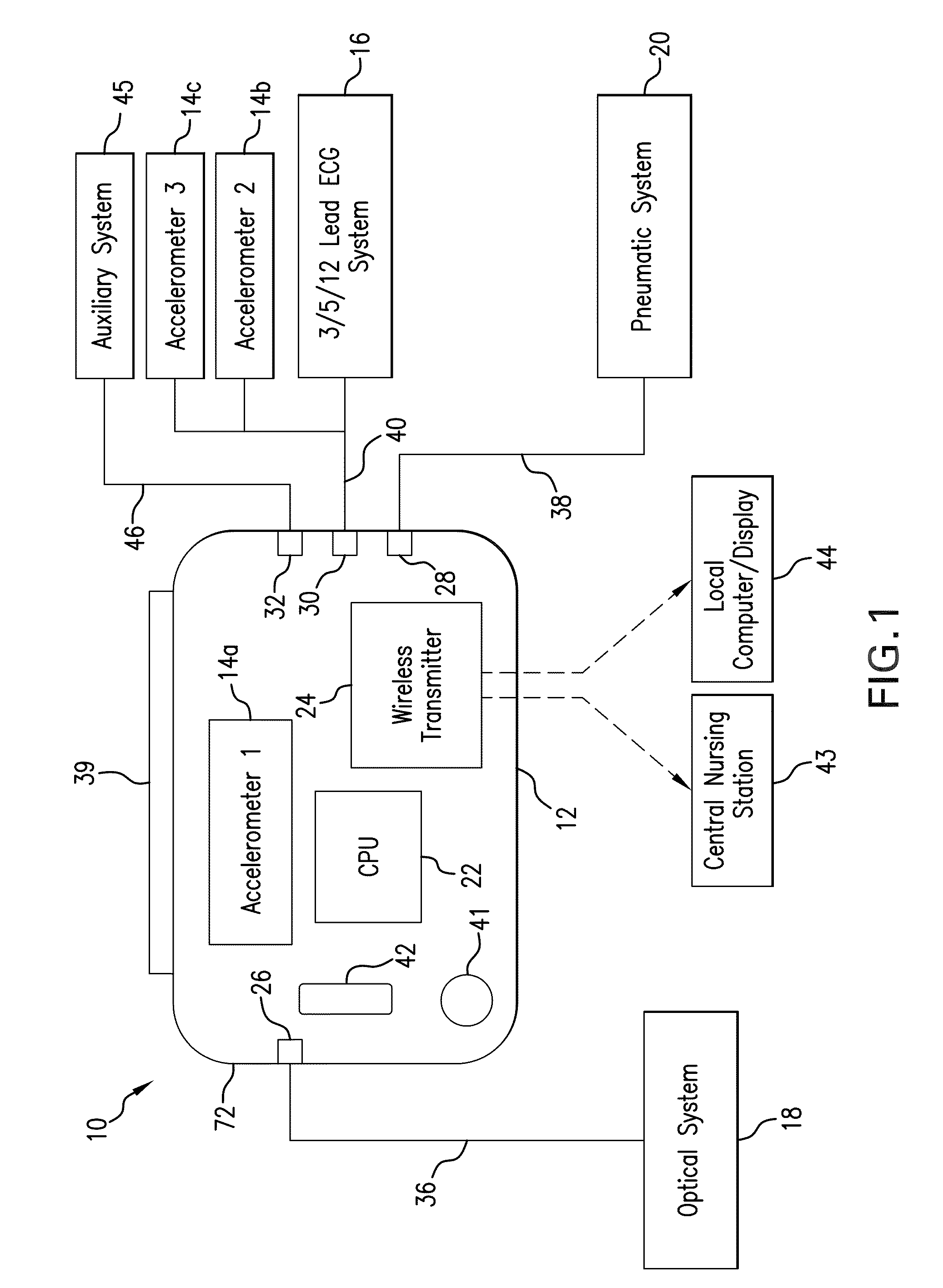
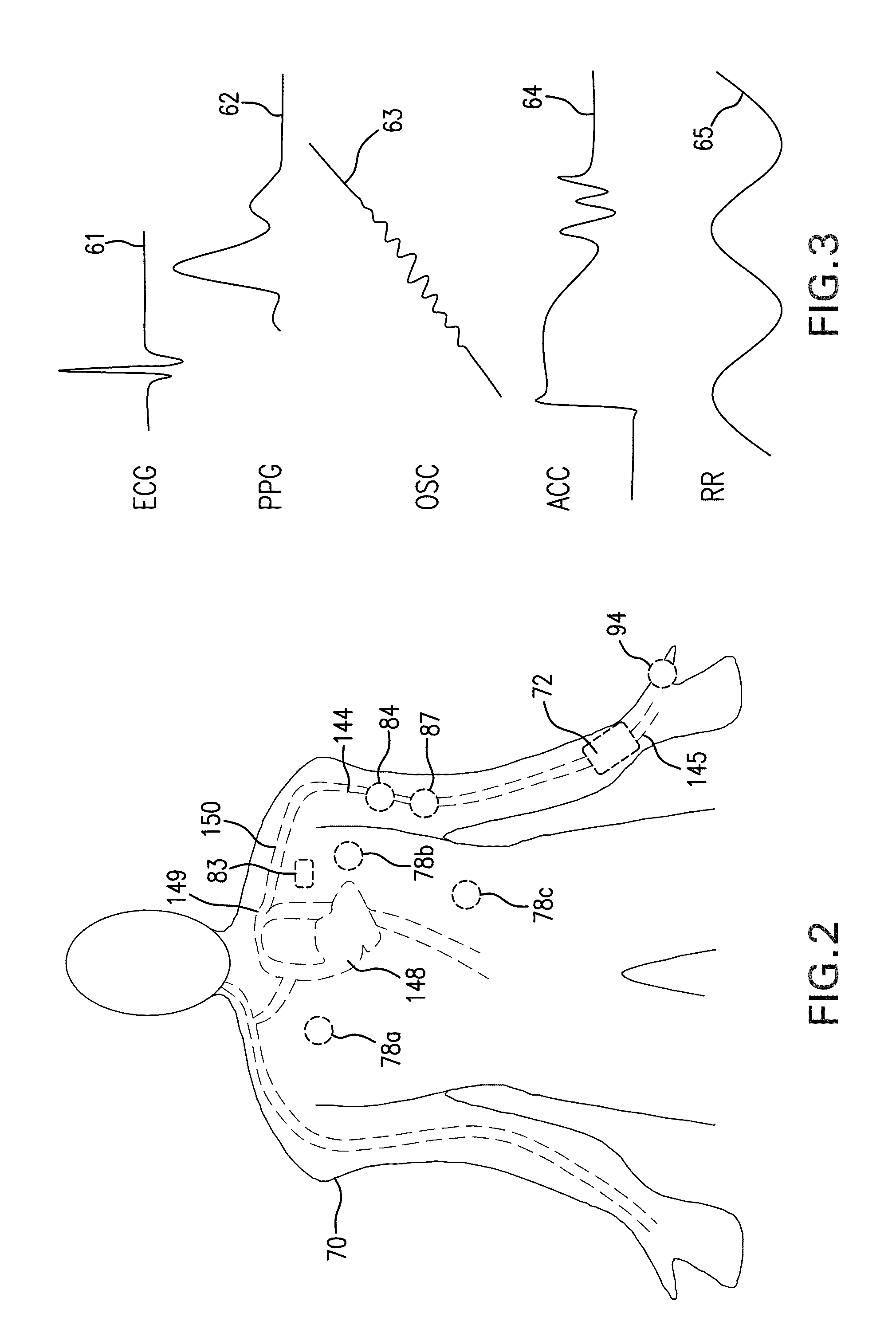
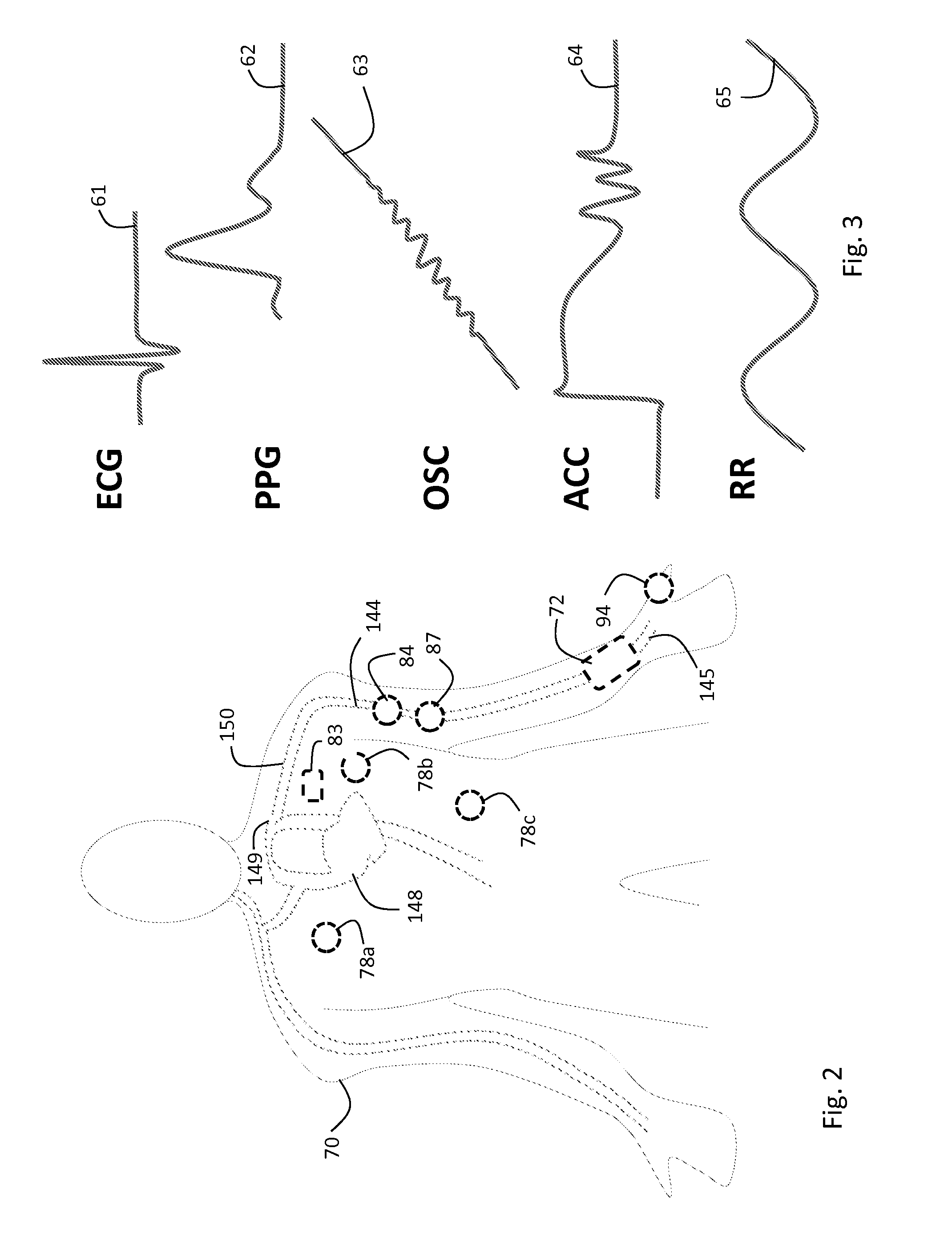
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110066051A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsDigital dataTransceiver
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
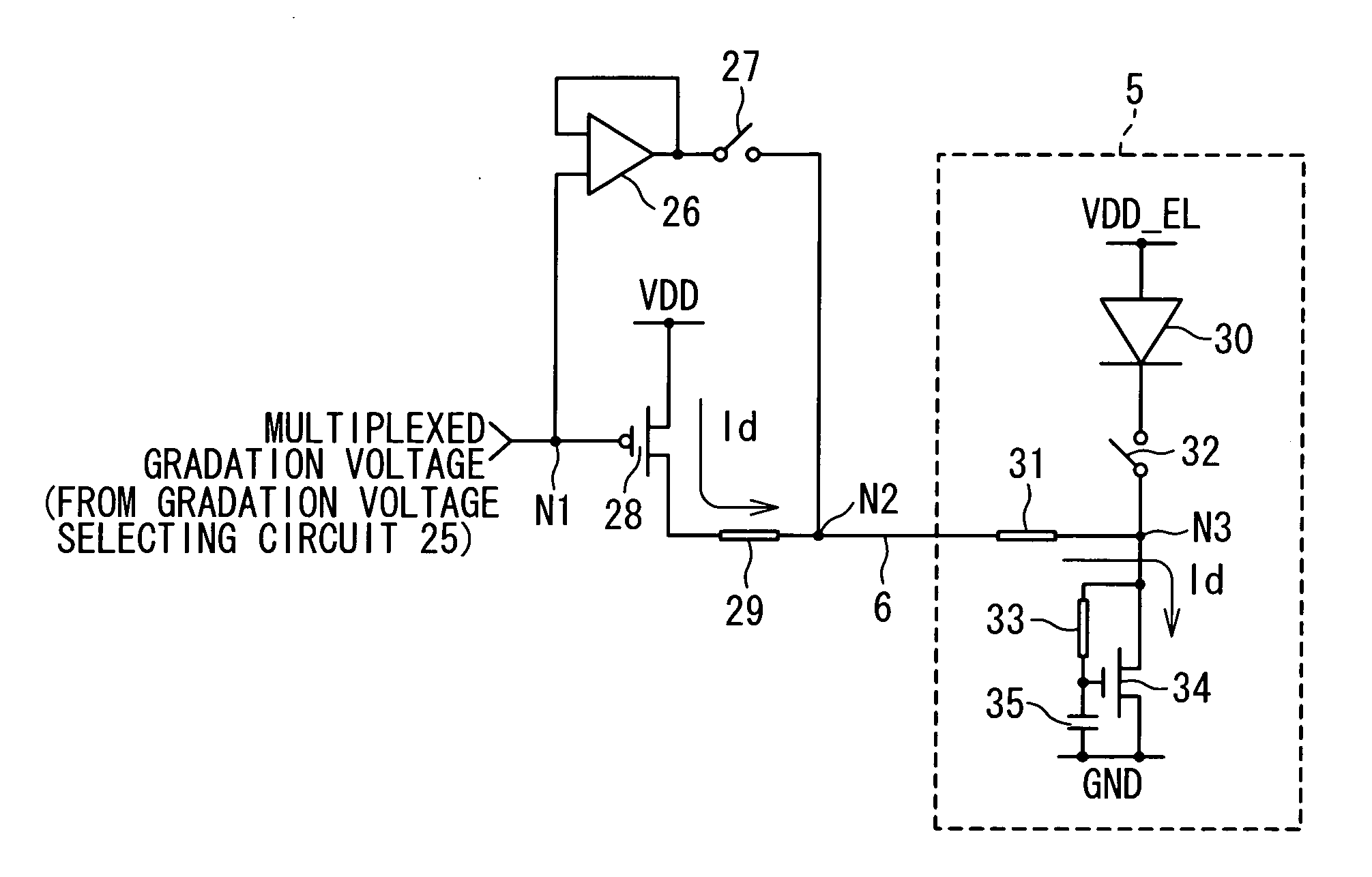
Display apparatus, and driving circuit for the same
ActiveUS20070001939A1Reduce the valueReduce circuit sizeStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringDifferential amplifier
A drive circuit which outputs an output signal to an output terminal, includes a drive transistor configured to output a gradation current to the output terminal; a single differential amplifier; a resistance element connected with the drive transistor; and a plurality of switches. The plurality of switches are controlled such that a precharge voltage is outputted from the differential amplifier to the output terminal in a first period while blocking off an output from the drive transistor and such that a gradation current is outputted from the drive transistor to the output terminal in a second period after the first period.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Active-matrix display, the emitters of which are supplied by voltage-controlled current generators
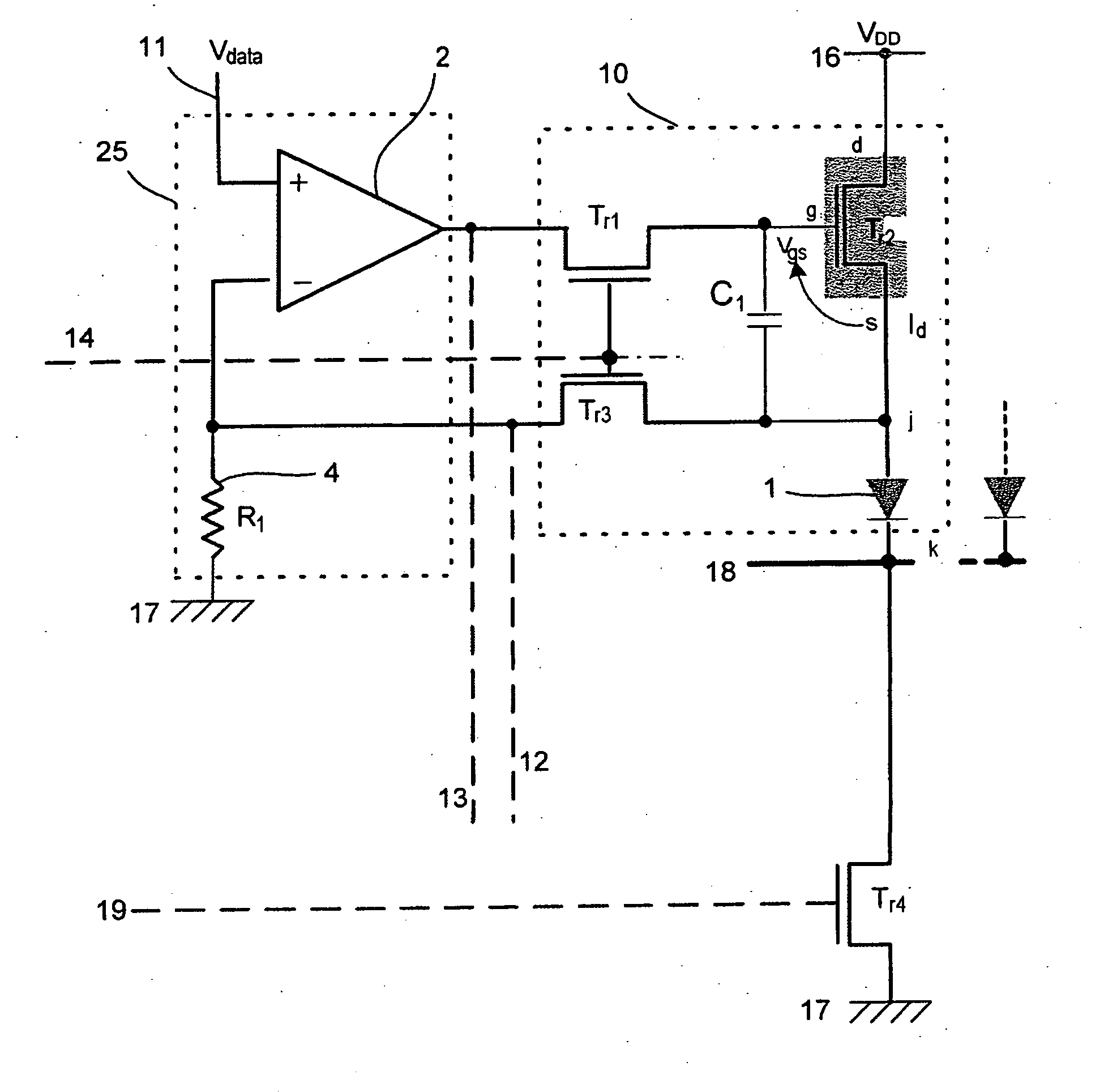
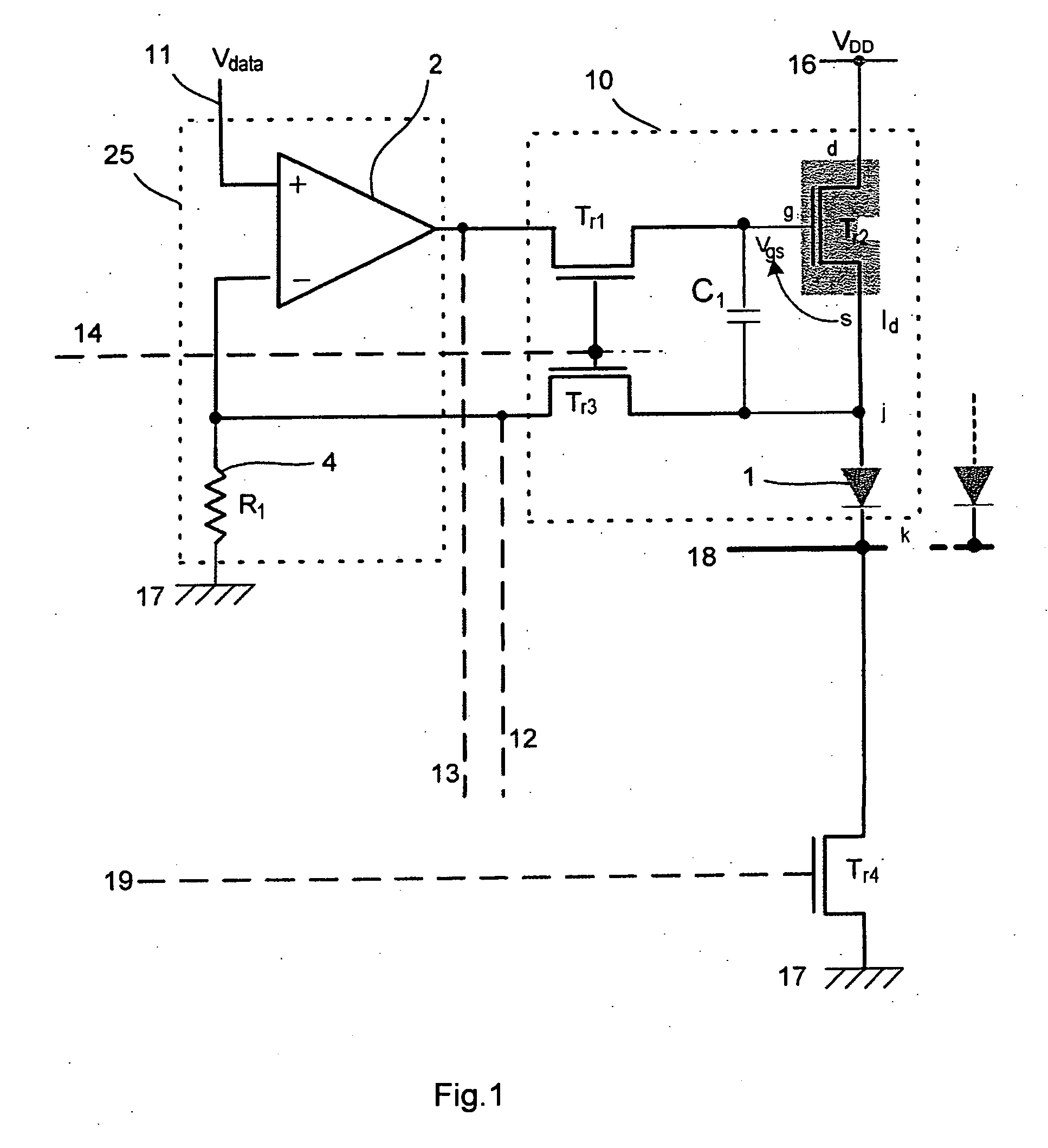
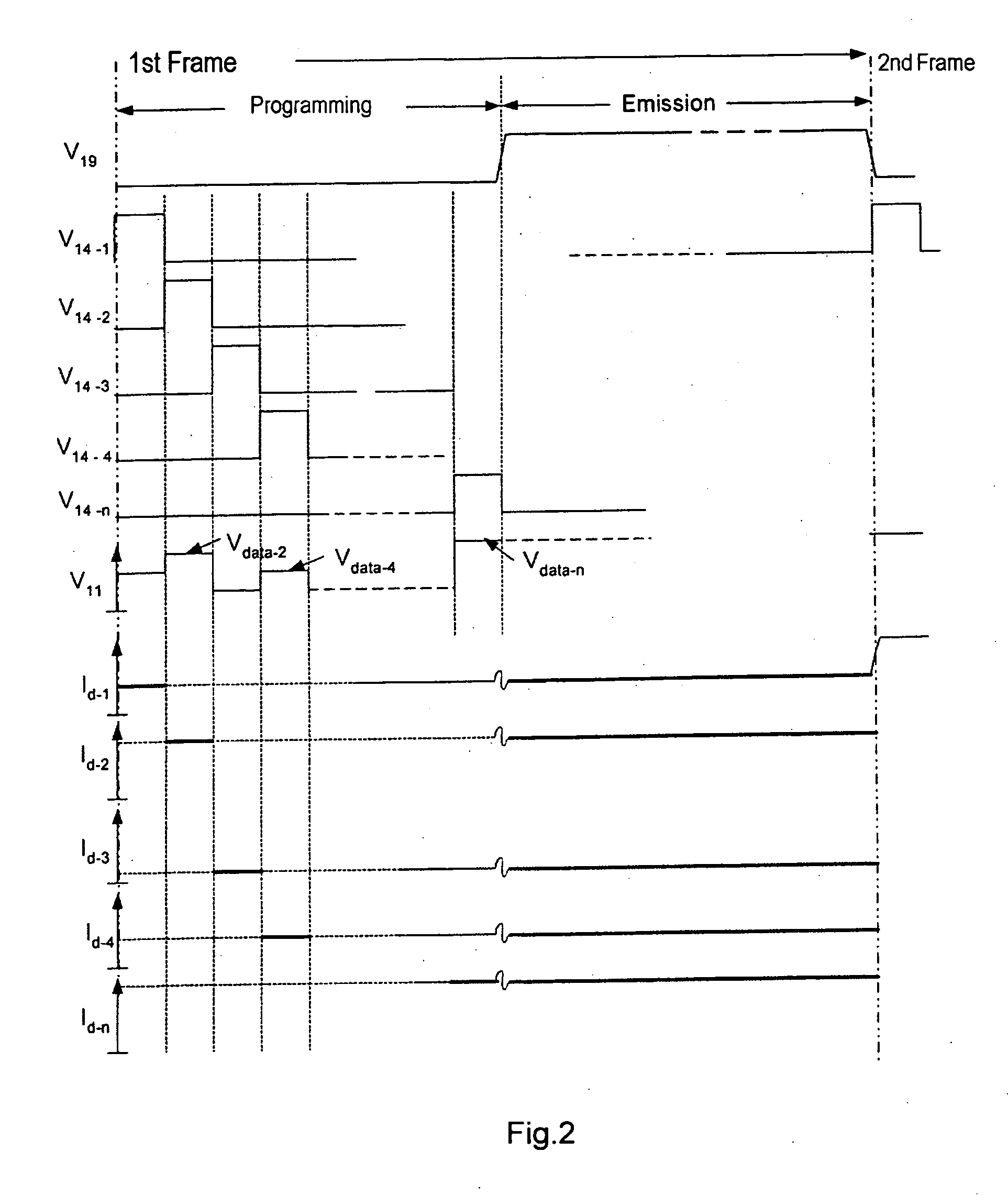
The display comprises an array of pixel circuits each comprising an emitter 1 in series with a current modulation transistor, and at least one address circuit, which integrates, for each column, a differential amplifier and a passive element preferably a resistive element, which cooperate with the current modulation transistors so as to form, during address phases in which the emitters are switched “out of the circuit”, a voltage-programmable current generator. After the address phases, thanks to a suitable switch, the emitters are switched “into the circuit” and supplied with the preprogrammed current. Such a display allows the image display quality to be inexpensively improved.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Signal transmission apparatus and interconnection structure
ActiveUS7446567B2Sufficient capabilitySimple and scalableReliability increasing modificationsBatteries circuit arrangementsLine pairHarmonic
Apparatus for transmitting a digital signal within, for example, an integrated circuit includes a signal transmission line with a directional coupler at one or both ends. The directional coupler blocks the direct-current component of the digital signal while transmitting the alternating-current component, including enough higher harmonics to transmit a well-defined pulse waveform. A suitable directional coupler consists of two adjacent line pairs in materials with different dielectric constants. The apparatus may also include a driver of the inverter type, a receiver of the differential amplifier type, a terminating resistor, and a power-ground transmission line pair for supplying power to the driver. An all-metallic transmission-line structure is preferably maintained from the output interconnections in the driver to the input interconnections in the receiver.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +11
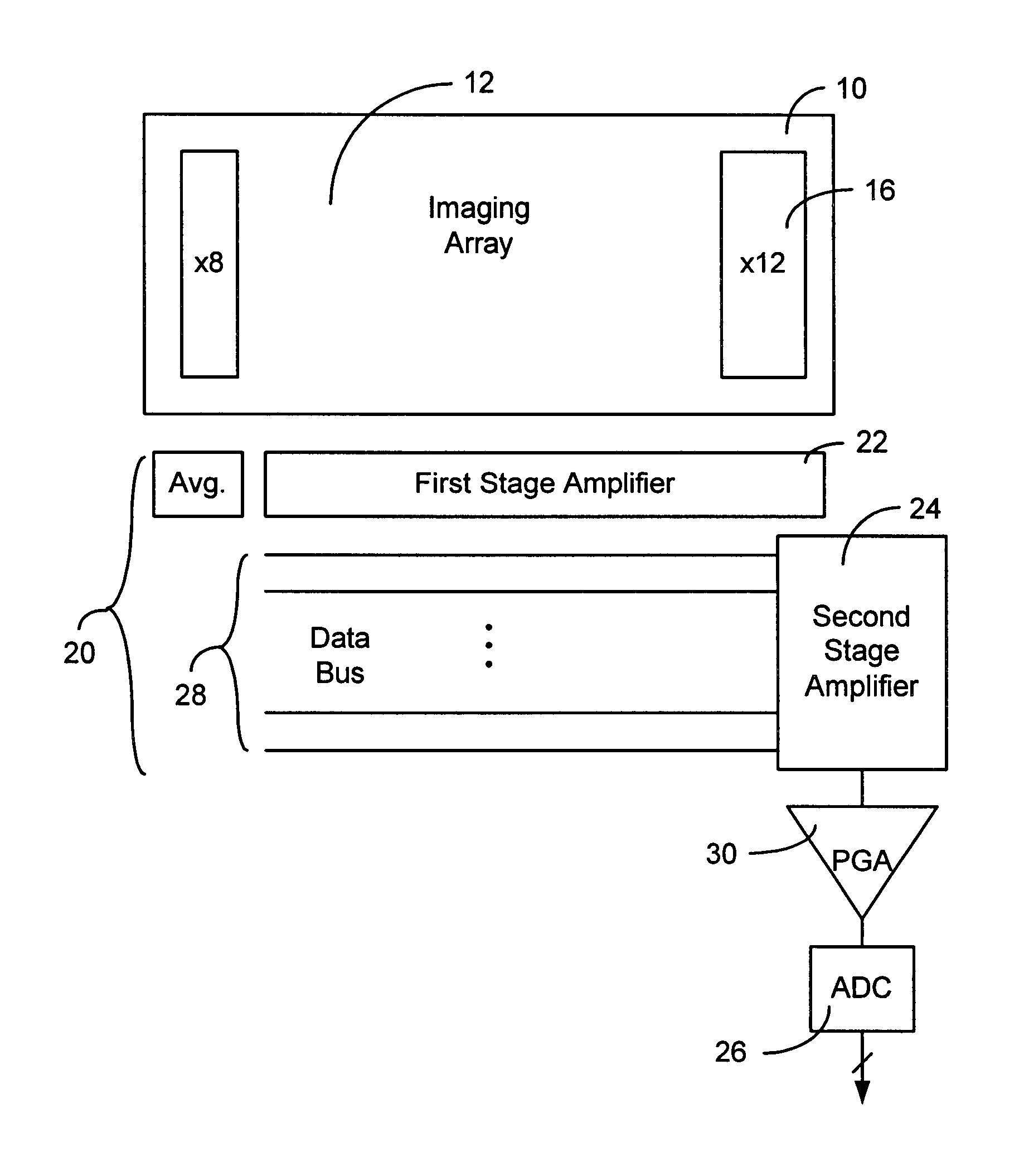
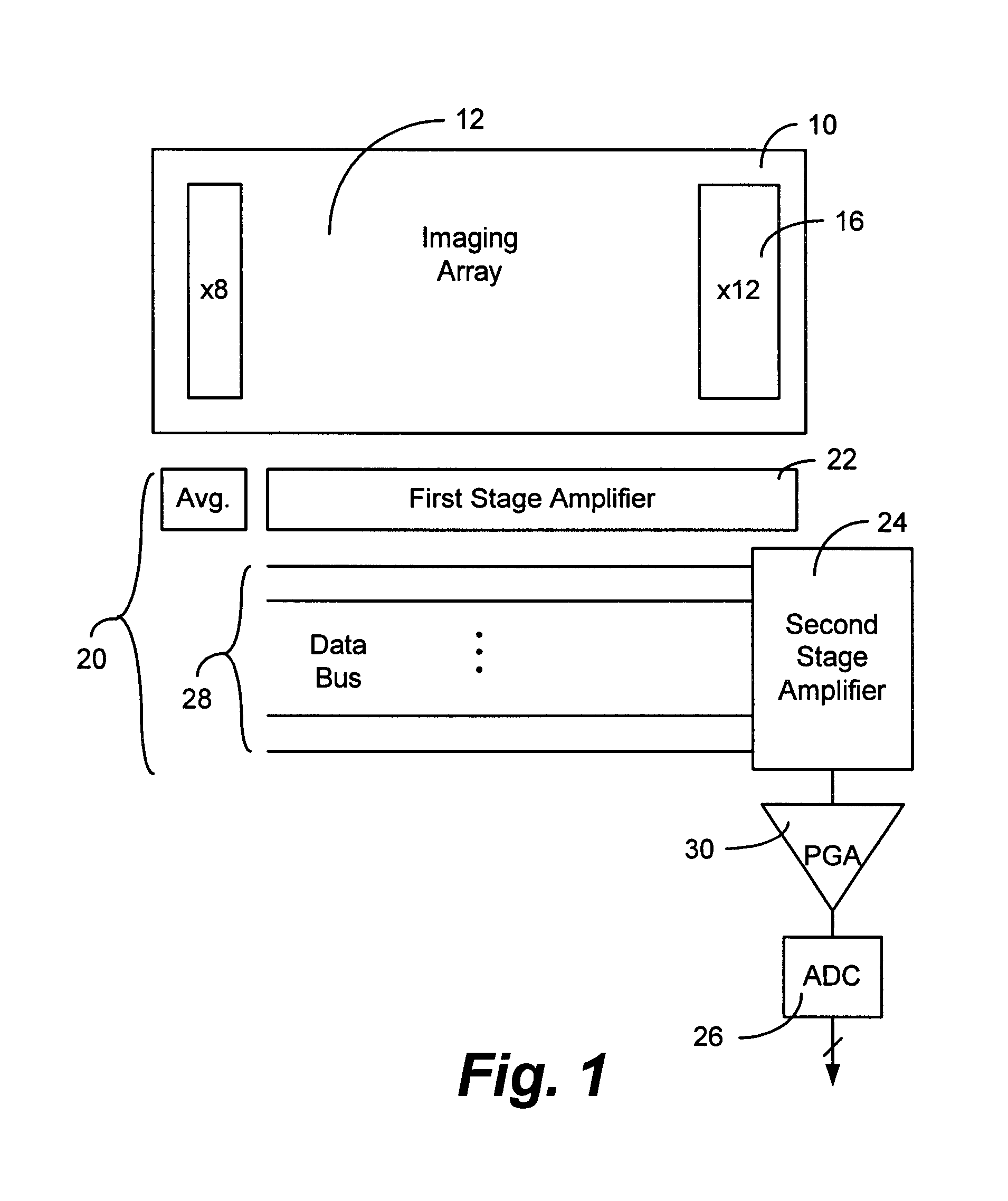
Electrical sensing apparatus and method utilizing an array of transducer elements
Many electrical sensing devices include an array of transducer elements for converting external stimuli to electrical indications. Novel technologies to realize improvements in low power consumption, low noise, and analog output path which occupies minimal die area while maintaining certain data rates are disclosed. A two stage pipeline architecture of the invention in the analog output path maintains fast pixel rates with minimal ADC (analog digital converter) arrangement. A novel power supply and the use of differential amplifiers in connection with a black signal level as a reference voltage are also described.
Owner:M RED INC
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110066010A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionElectrocardiographyPerson identificationDigital dataTransceiver
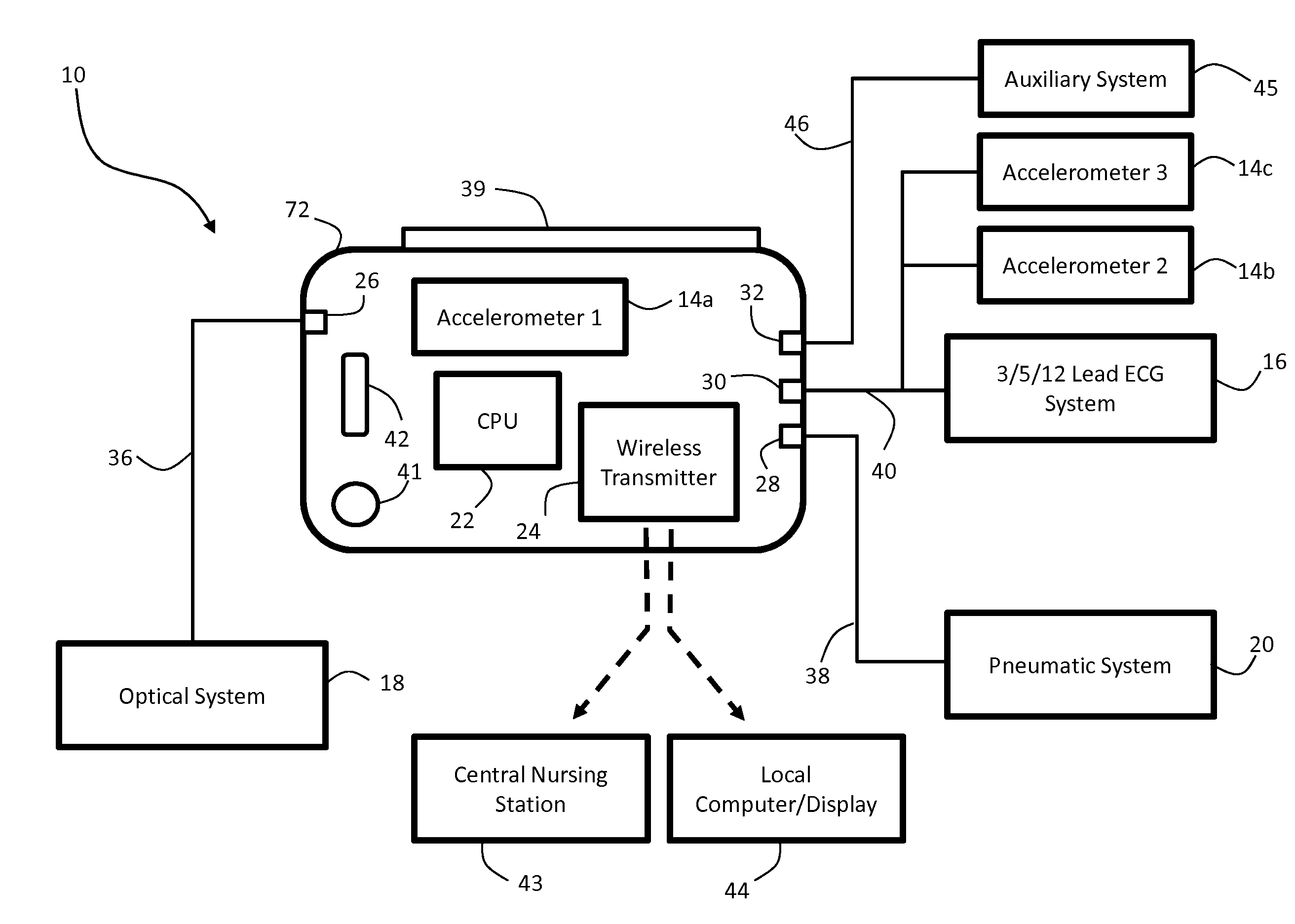
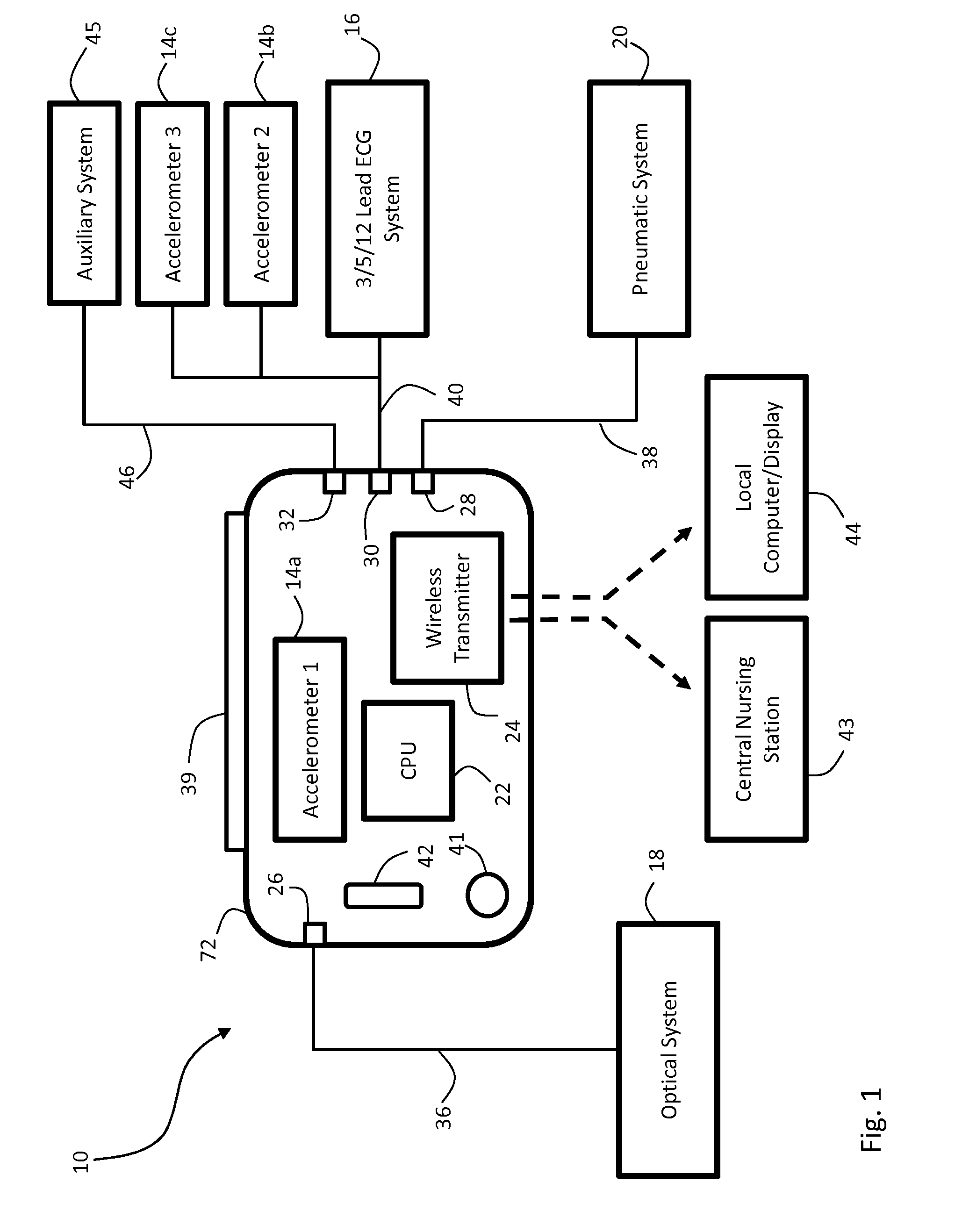
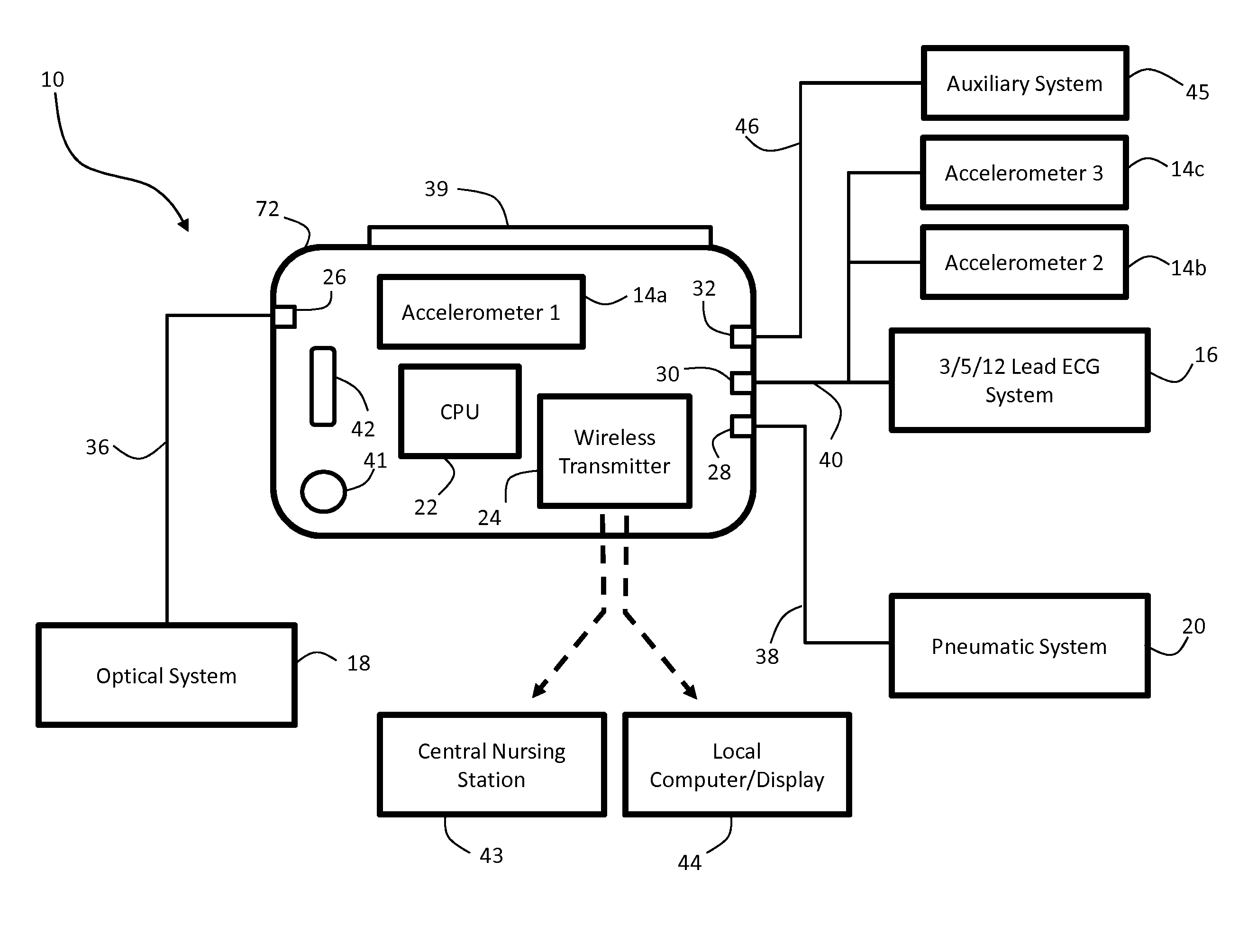
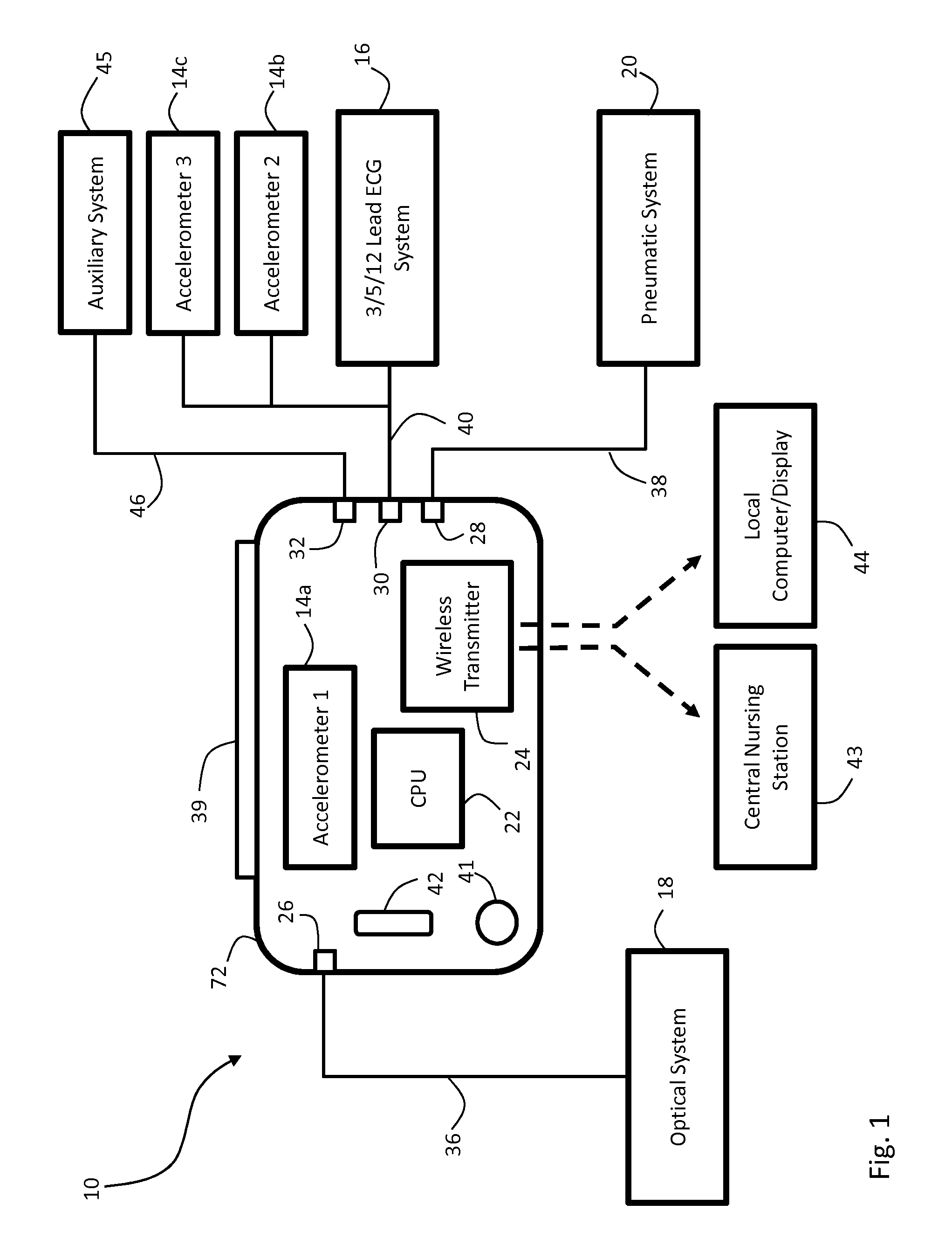
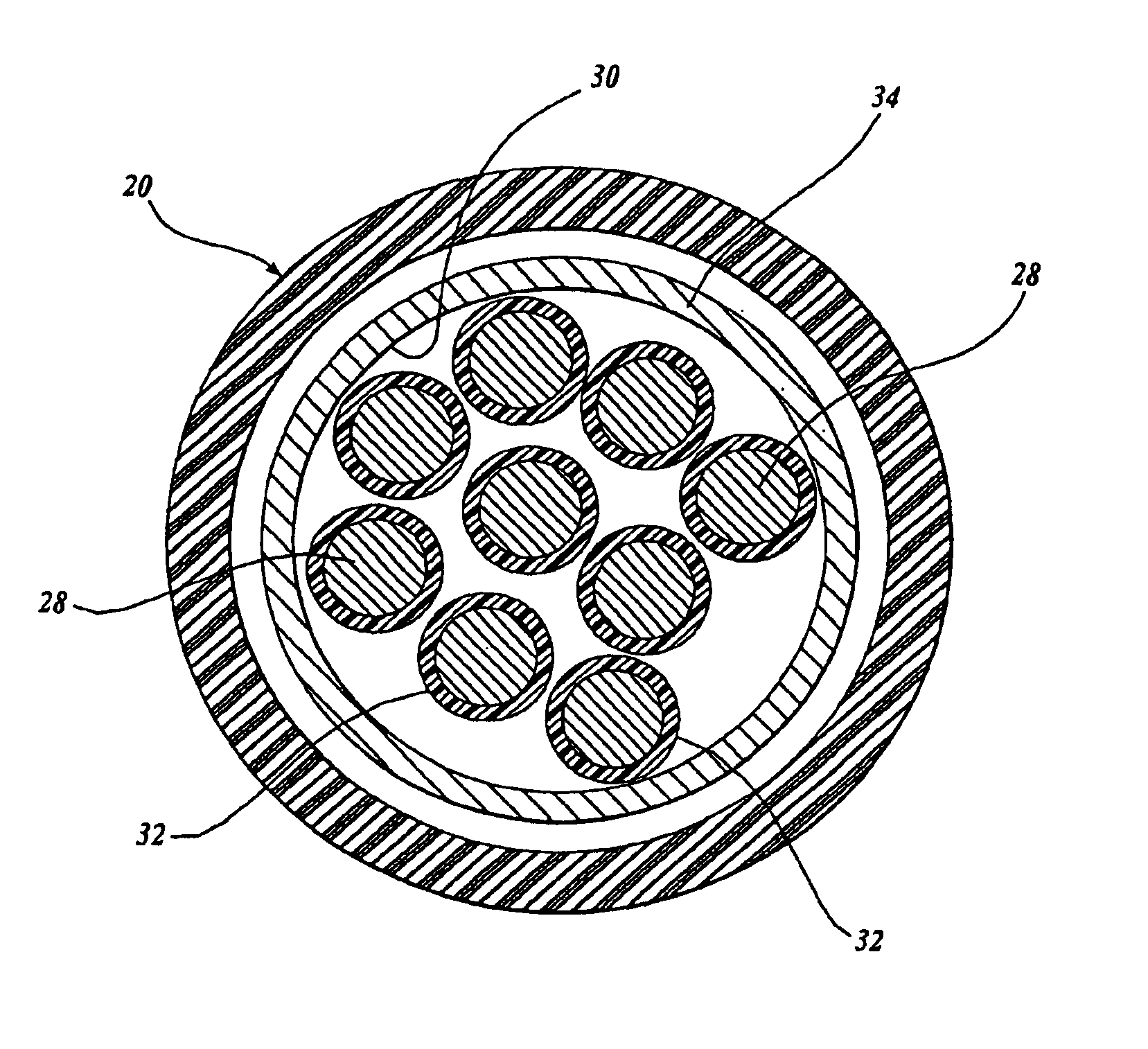
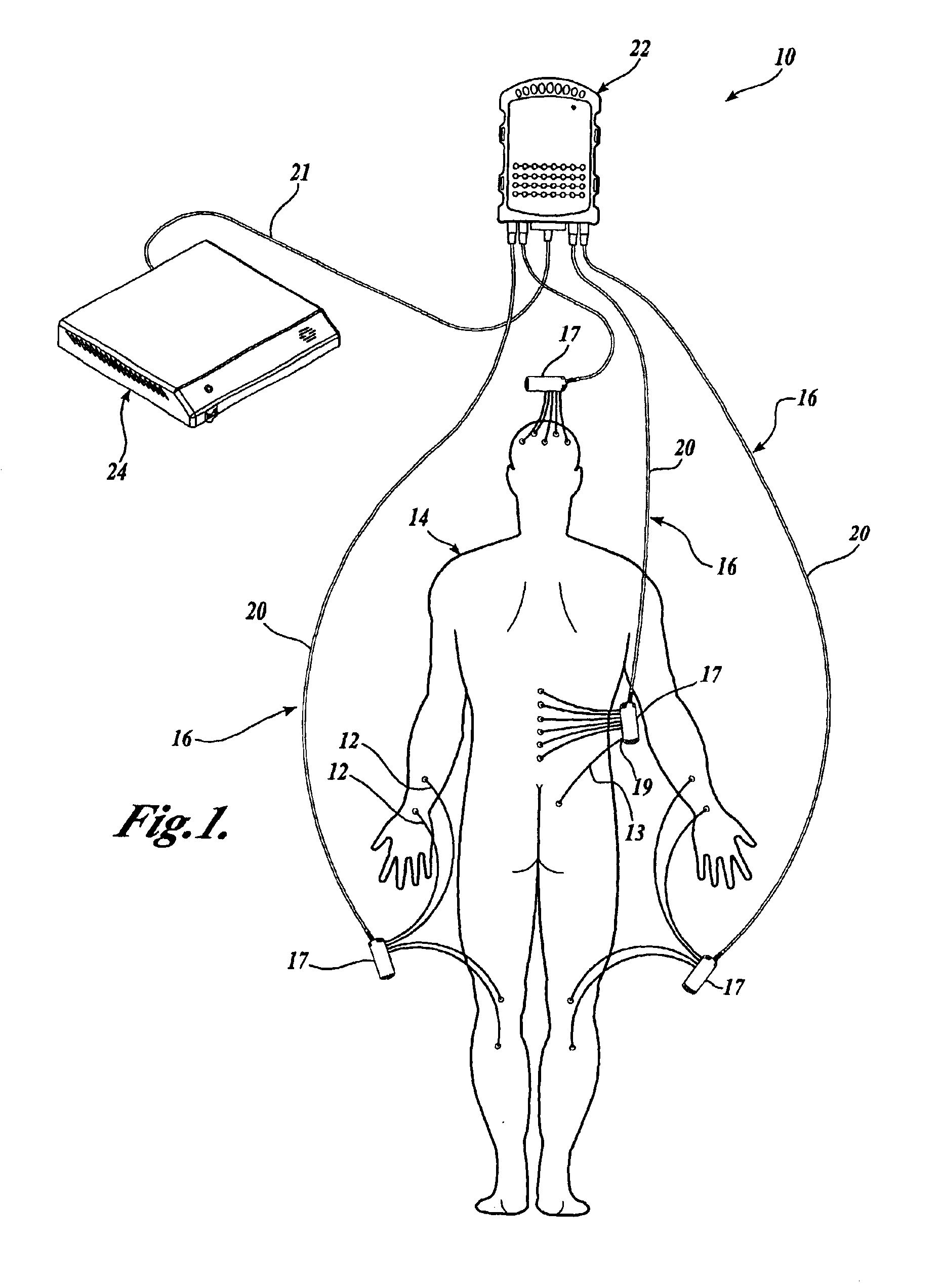
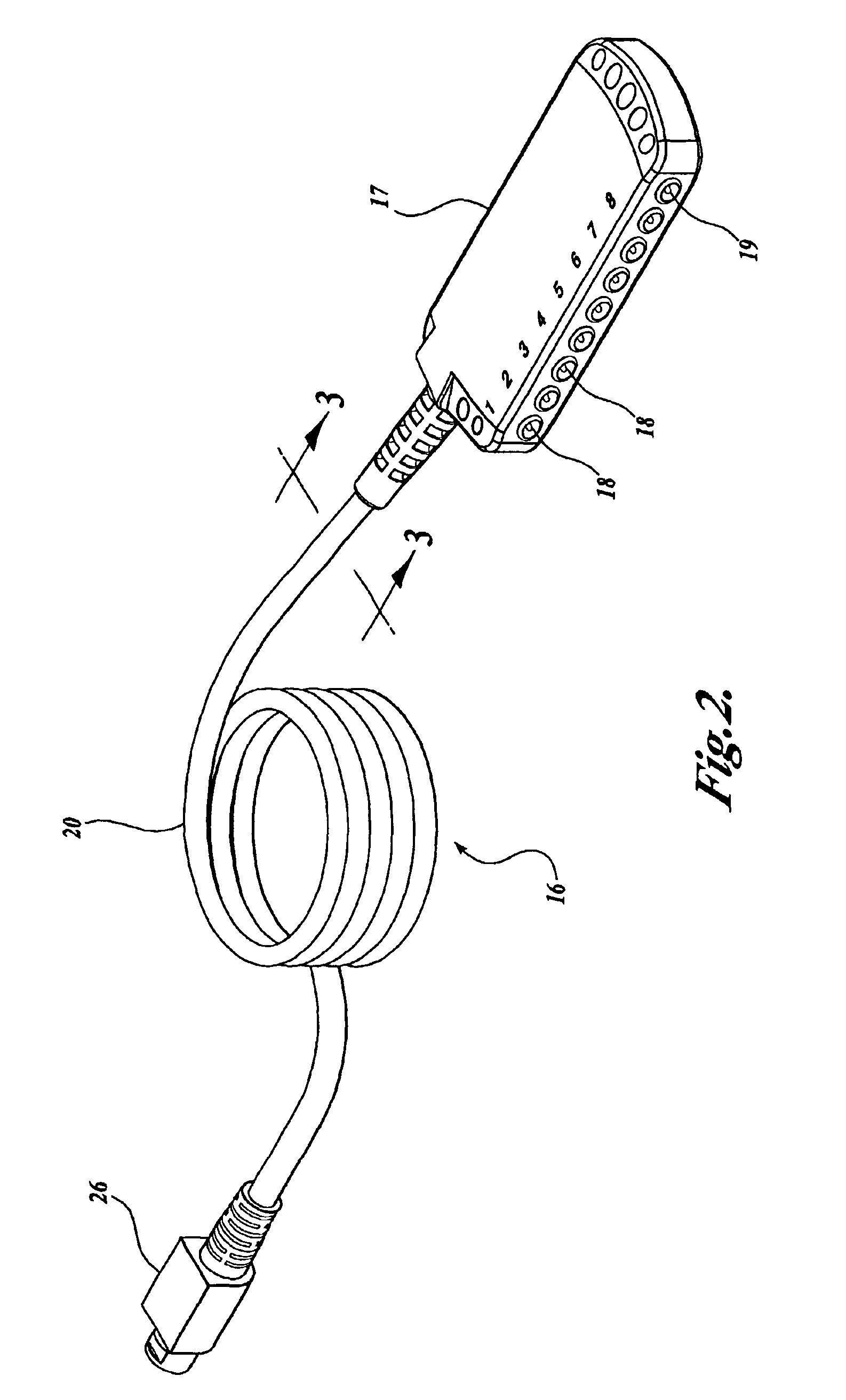
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Low skew clock input buffer and method
InactiveUS6847582B2Reliability increasing modificationsDigital storageAudio power amplifierLogic state
An input buffer includes first and second cross-coupled differential amplifiers. Each amplifier drives a buffer signal from a first logic state to a second logic state at a first slew rate when input signal transitions from a first logic state to a second logic state and a complementary input signal transitions from the second logic state to the first logic state, and drives the buffer signal from the second logic state to the first logic state at a second slew rate when the signal transitions are the complement of these previous transitions. An output circuit generates a first edge of an output signal when the buffer signal from the first amplifier transitions from the first logic state to the second logic state and generates a second edged of the output signal when the buffer signal from the second amplifier transitions from the first to the second logic state.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
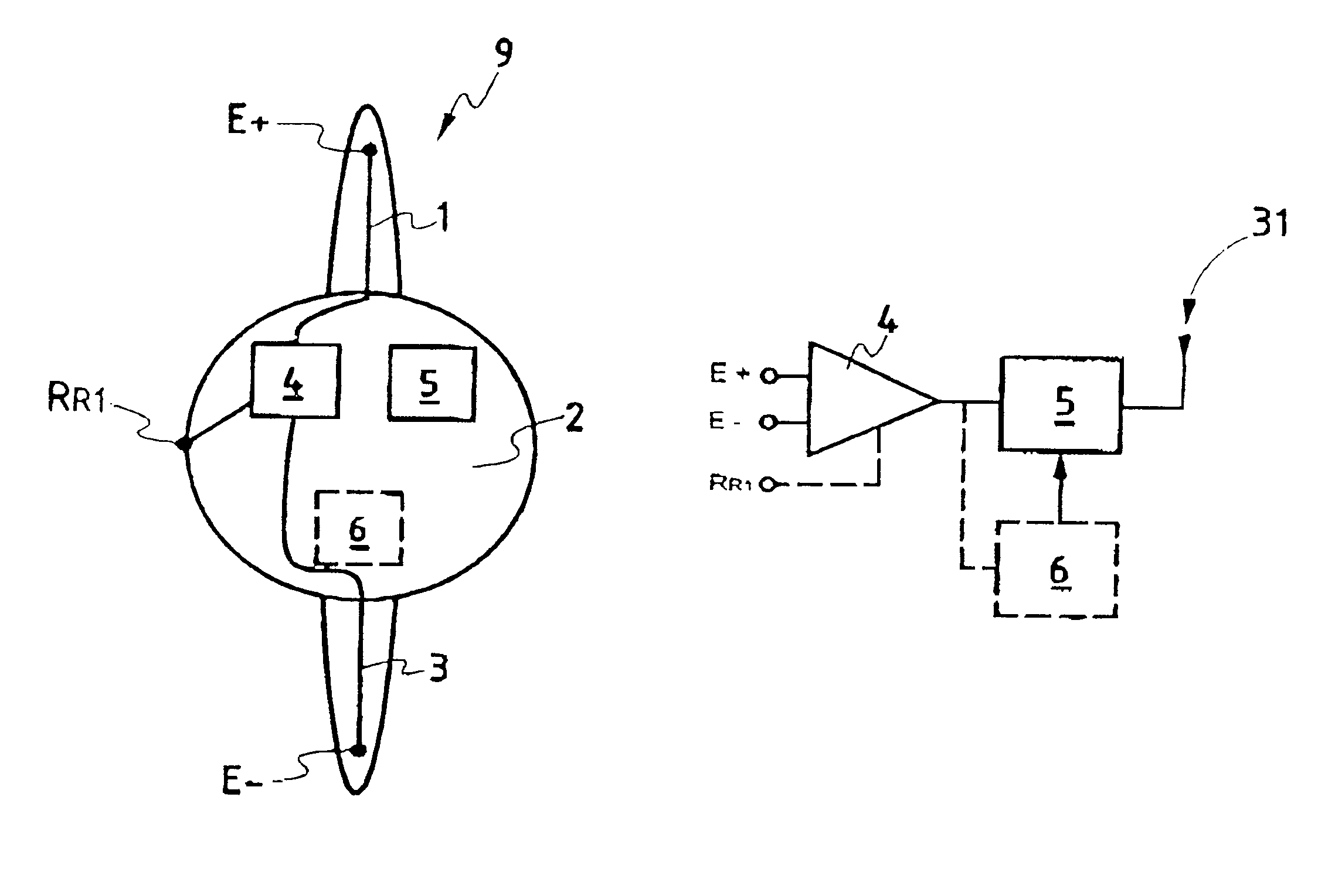
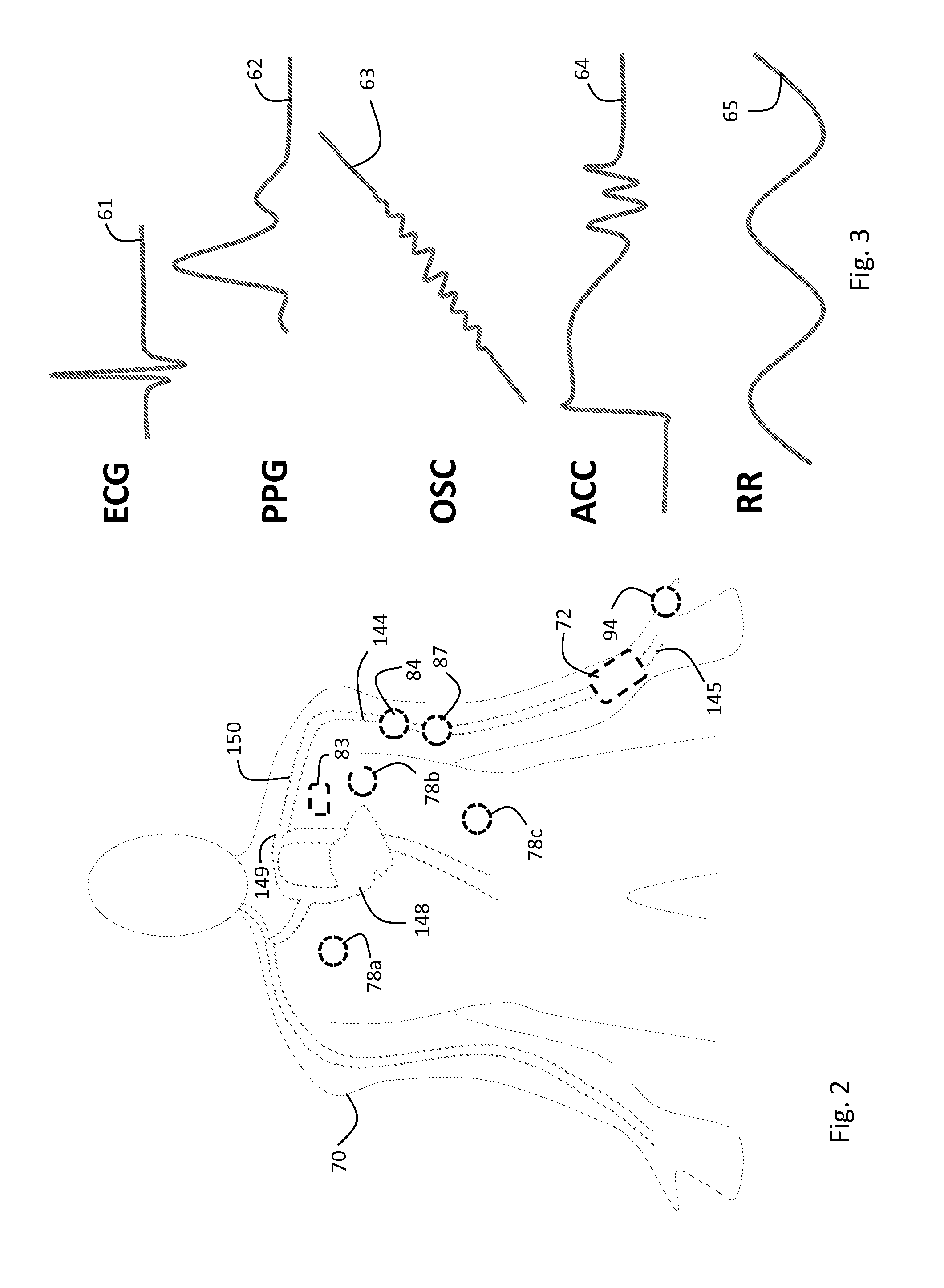
Method and apparatus for picking up auditory evoked potentials
InactiveUS6428484B1Avoid the needElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyImplanted deviceAuditory system
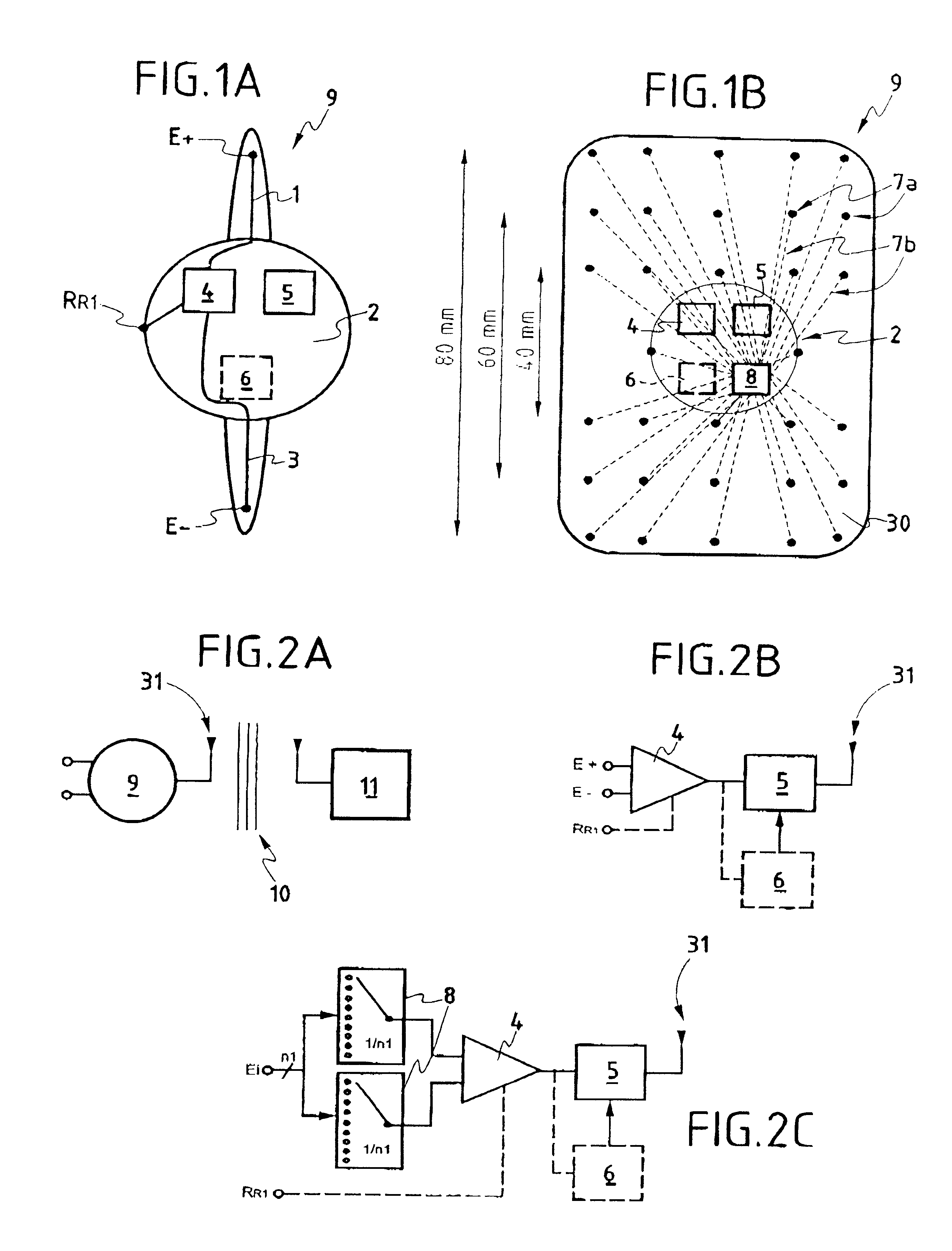
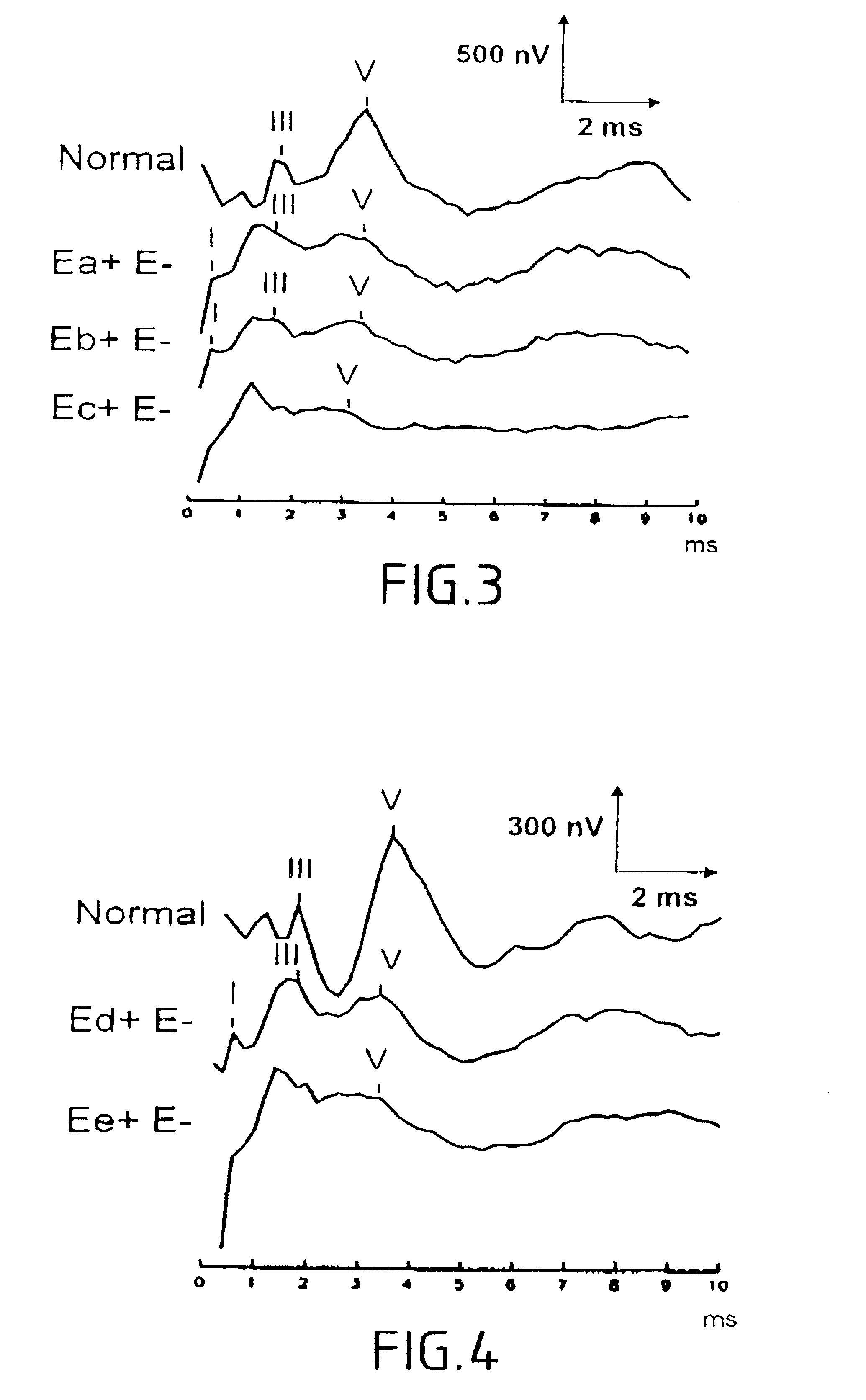
The present invention relates to a device for picking up biological electrical signals, and more precisely auditory evoked potentials generated by acoustic and / or electrical and / or mechanical stimulation of the cochlear, or of a portion of the auditory system in man or animal. The implantable device for measuring or picking up auditory evoked potentials comprises at least two extracochlear pickup electrodes connected to the inputs of a differential amplifier.
Owner:NEURELEC FIFTY PERCENT INTEREST
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110066009A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDigital dataTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
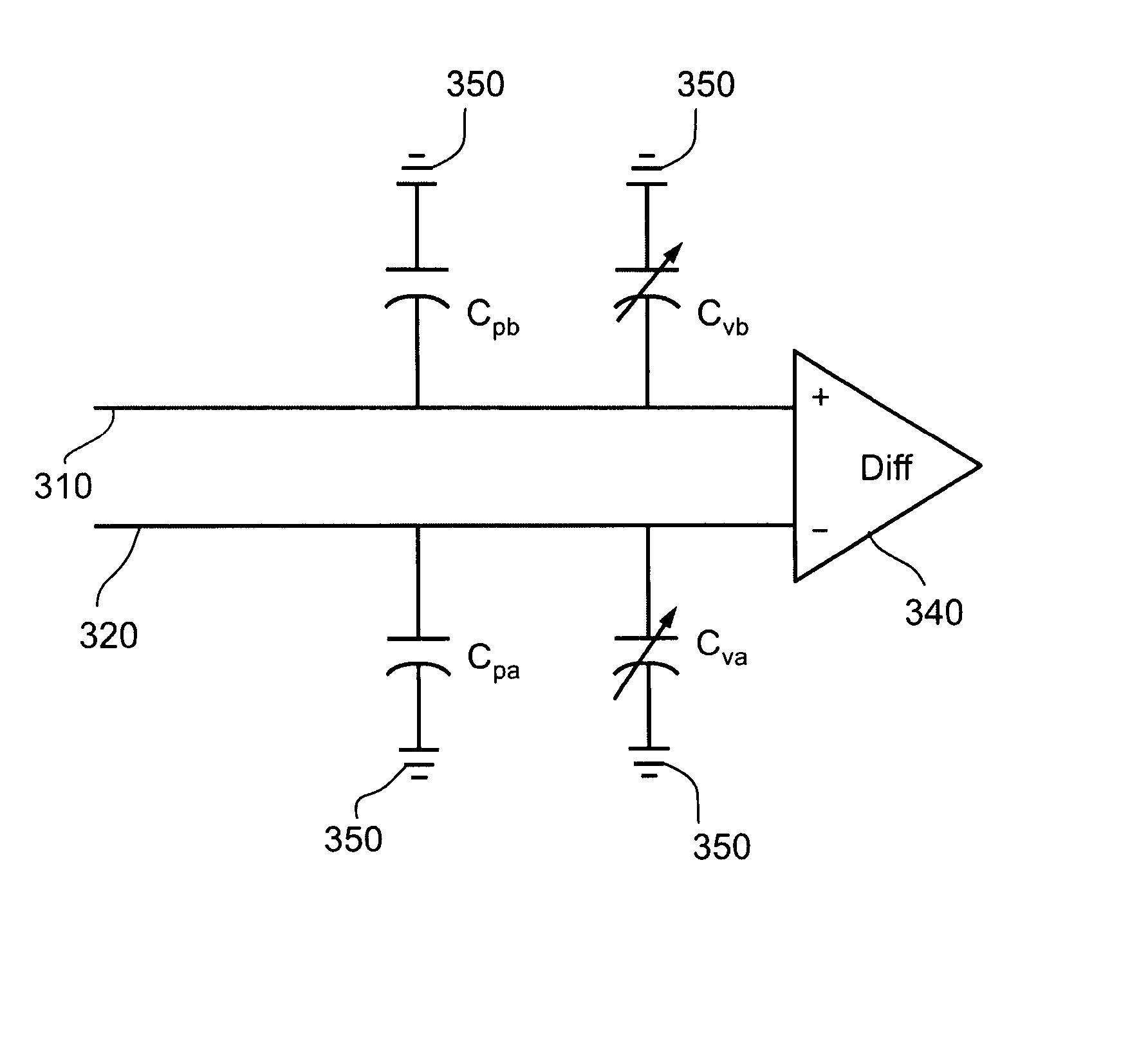
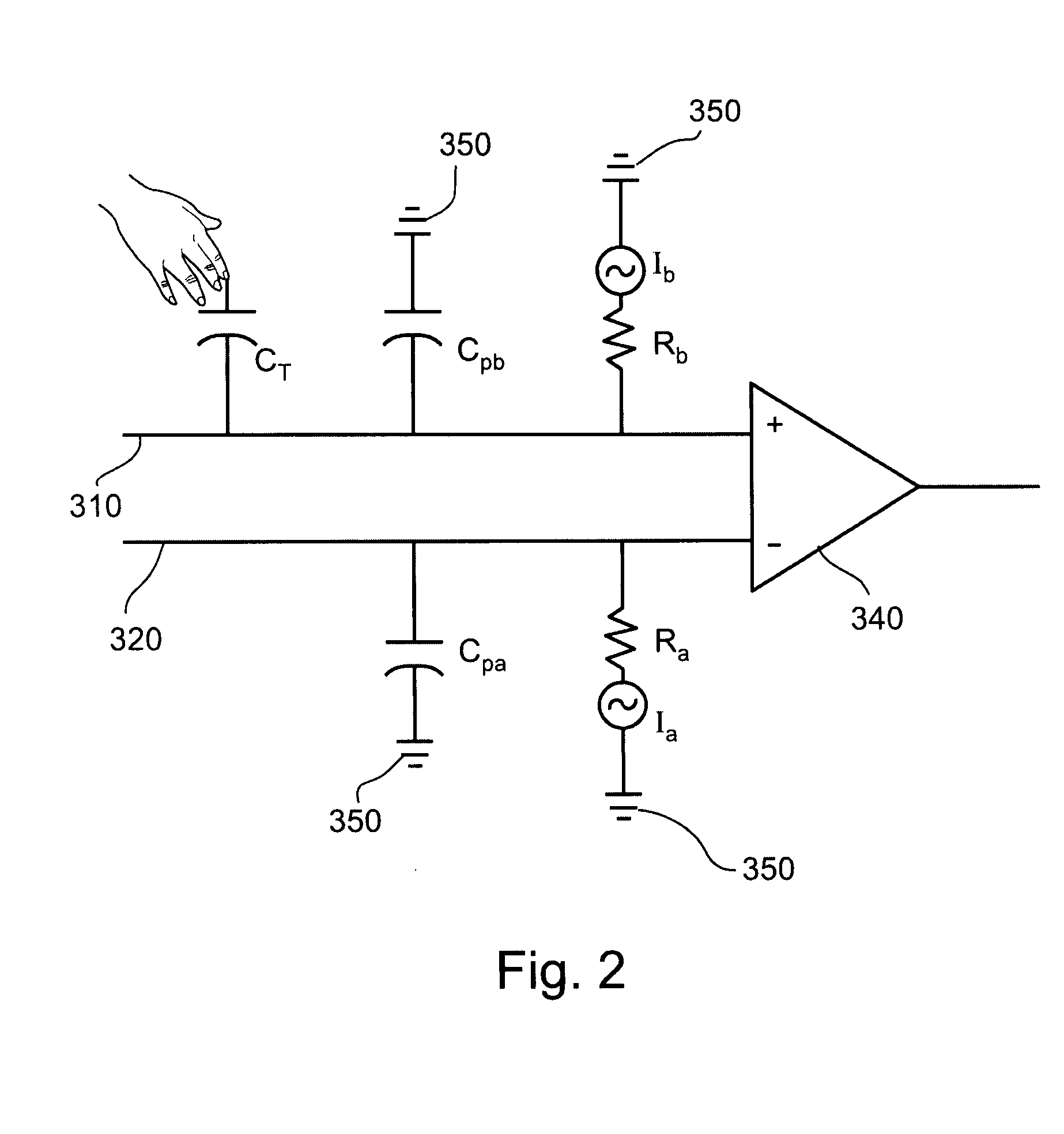
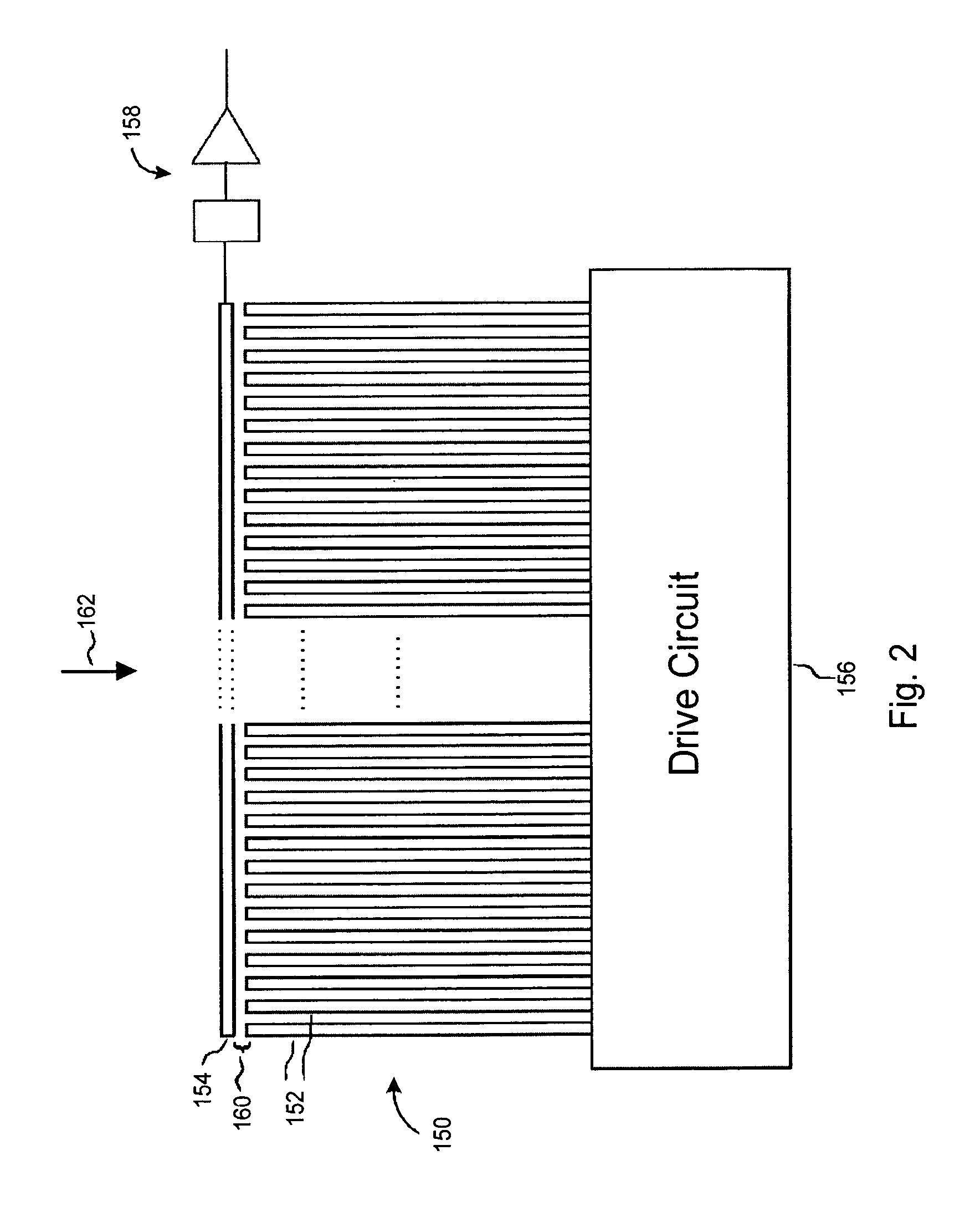
Variable capacitor array
InactiveUS20070268272A1Minimize output signalInput/output processes for data processingParasitic capacitanceDifferential amplifier
A digitizer includes a digitizer sensor comprising at least one pair of conductive lines coupled to at least one differential amplifier through which a difference signal is detected, and at least one capacitor operative to balance differences in parasitic capacitance between the conductive lines of the at least one pair of conductive lines.
Owner:N TRIG
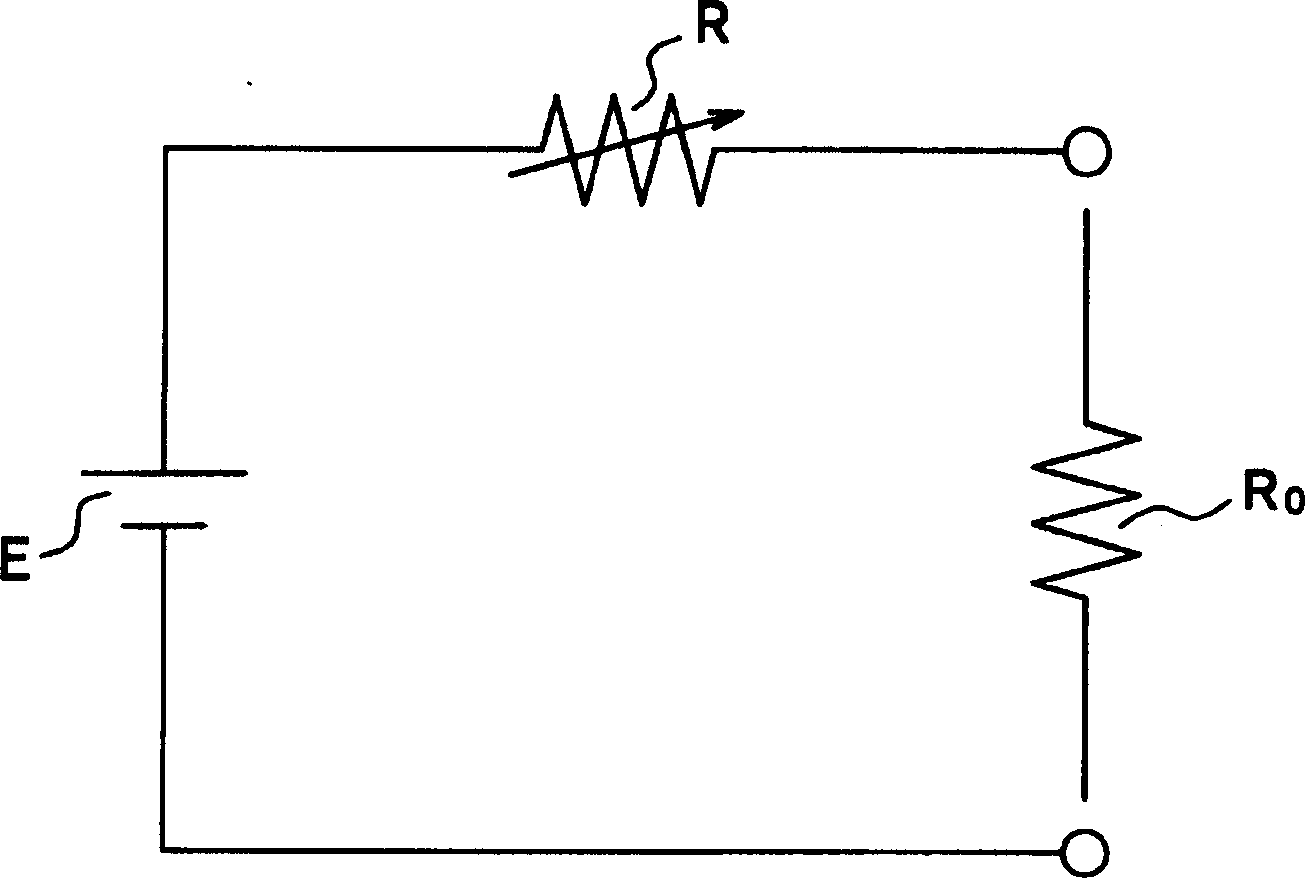
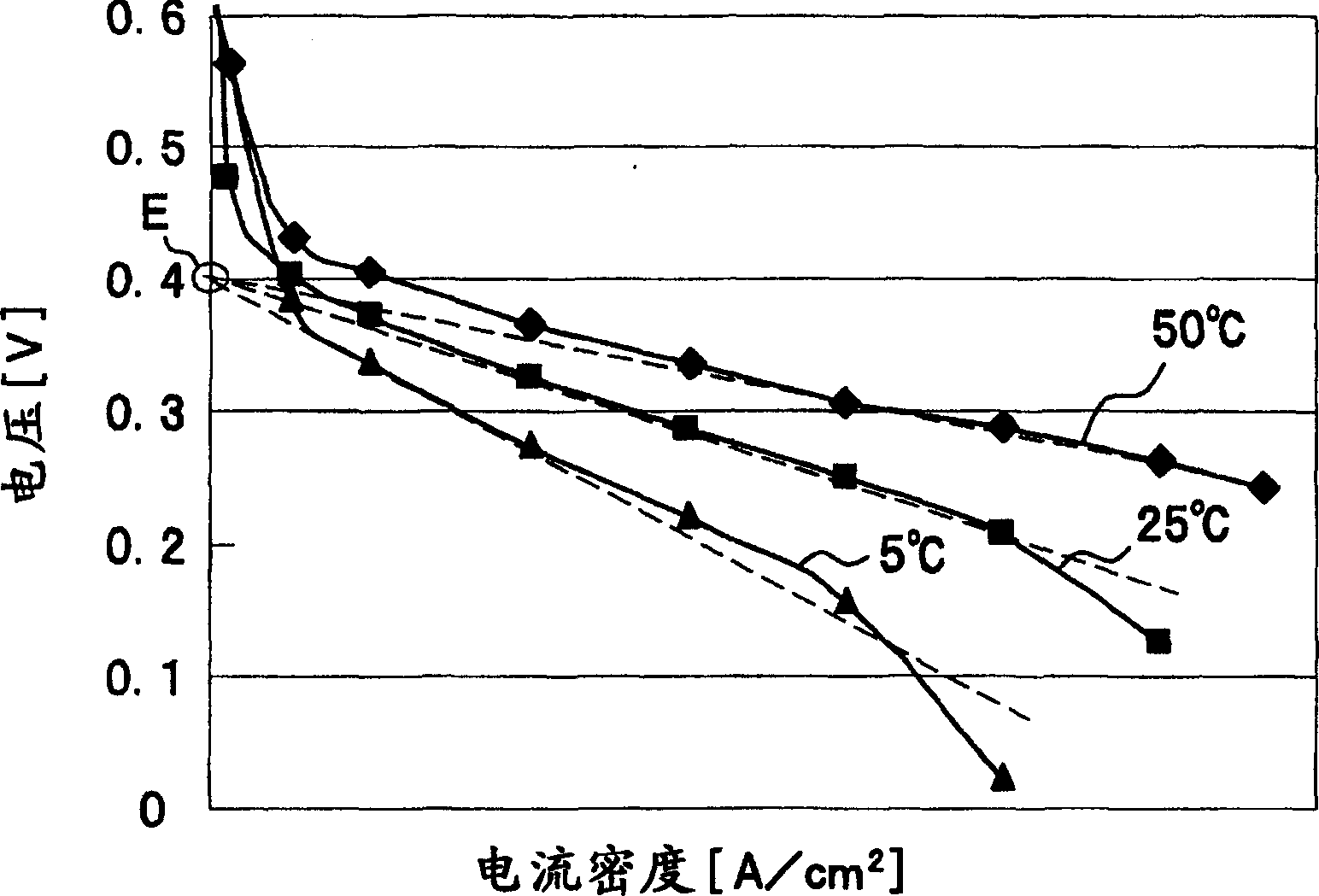
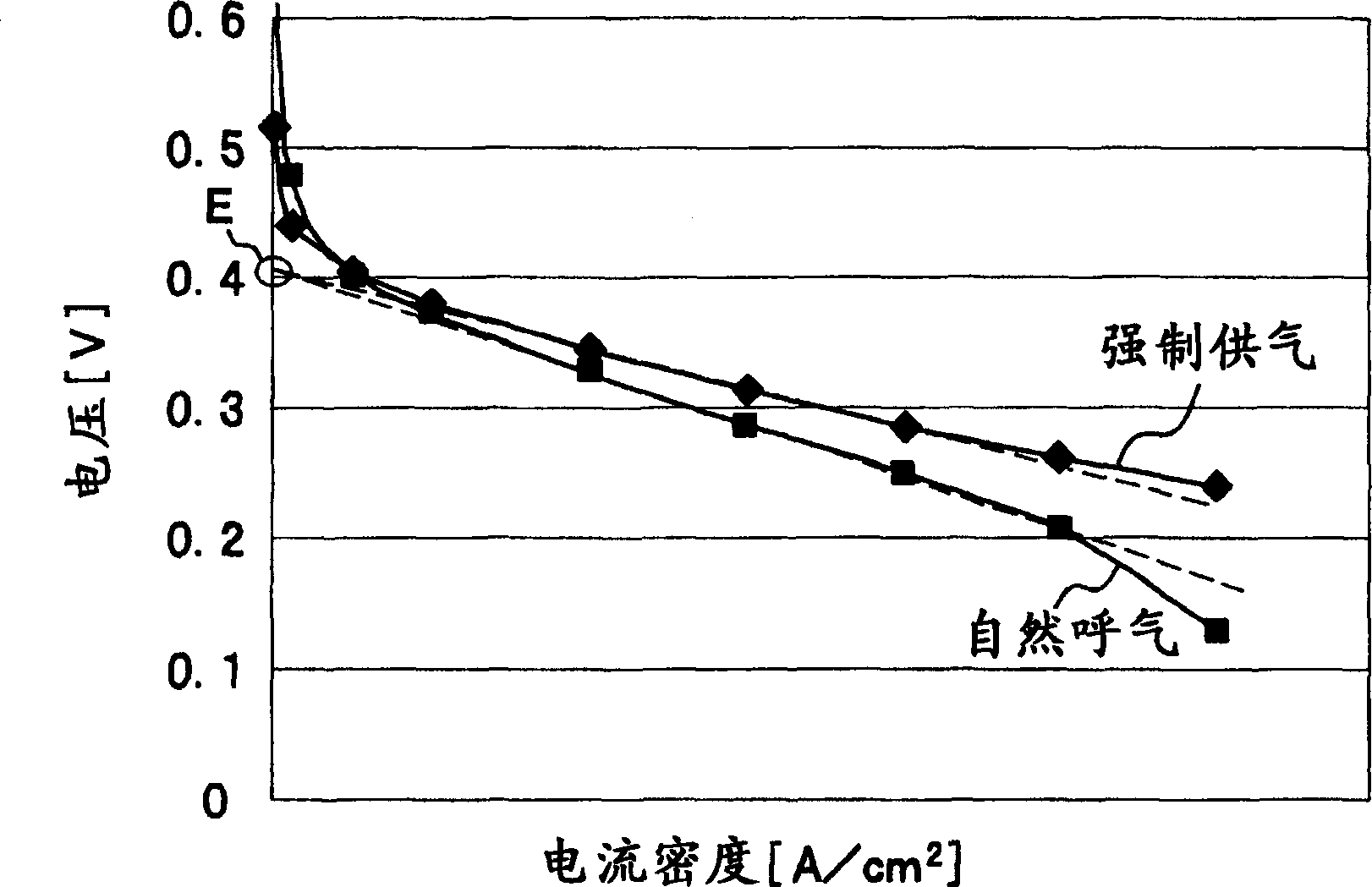
Mehotd for determining a maximum power point voltage of a fuel cell, as well as fuel cell control system and power controller used in the fuel cell control system
InactiveUS20060222916A1Reduce output powerAccurately determineMechanical power/torque controlFuel cell heat exchangePower controllerFuel cells
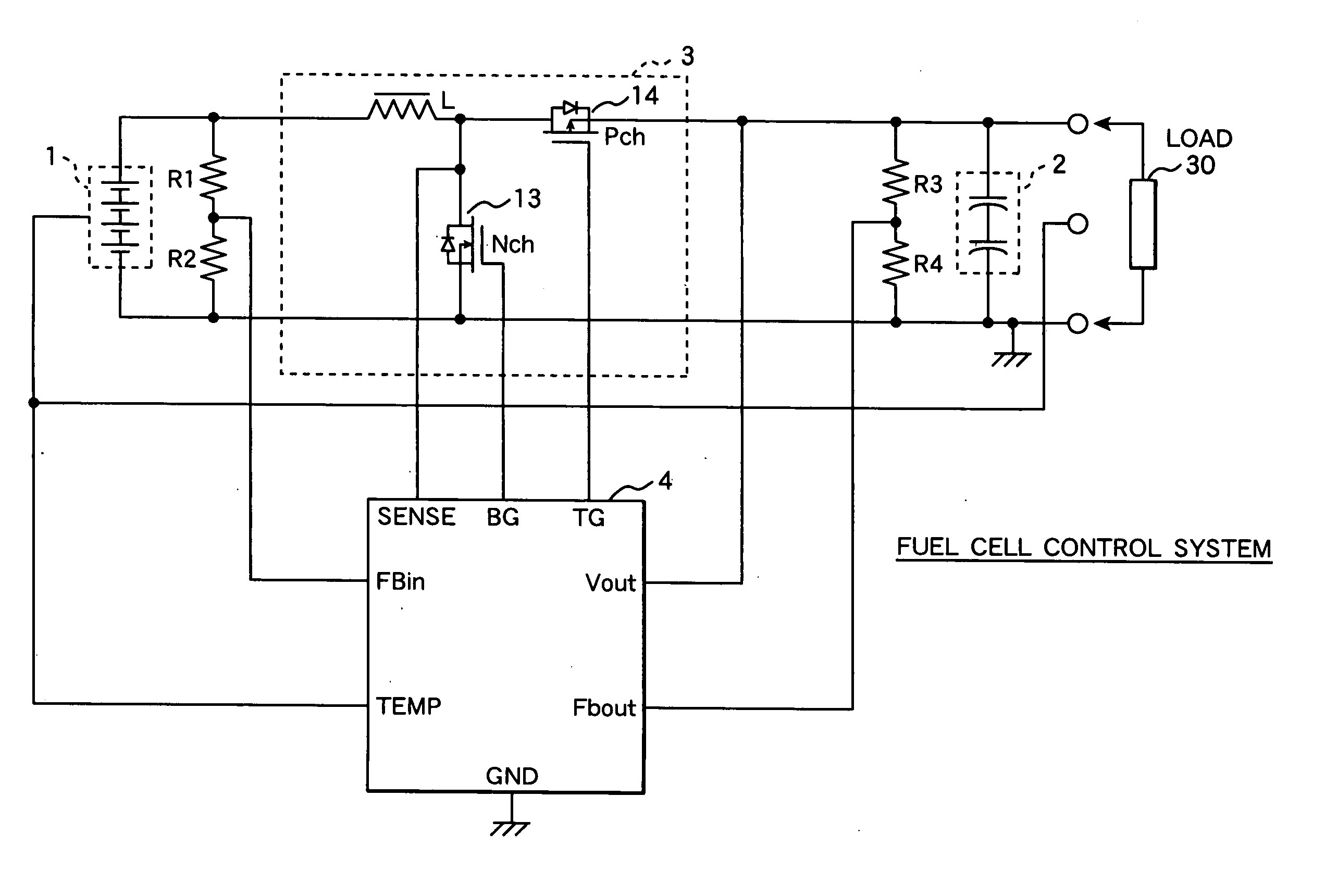
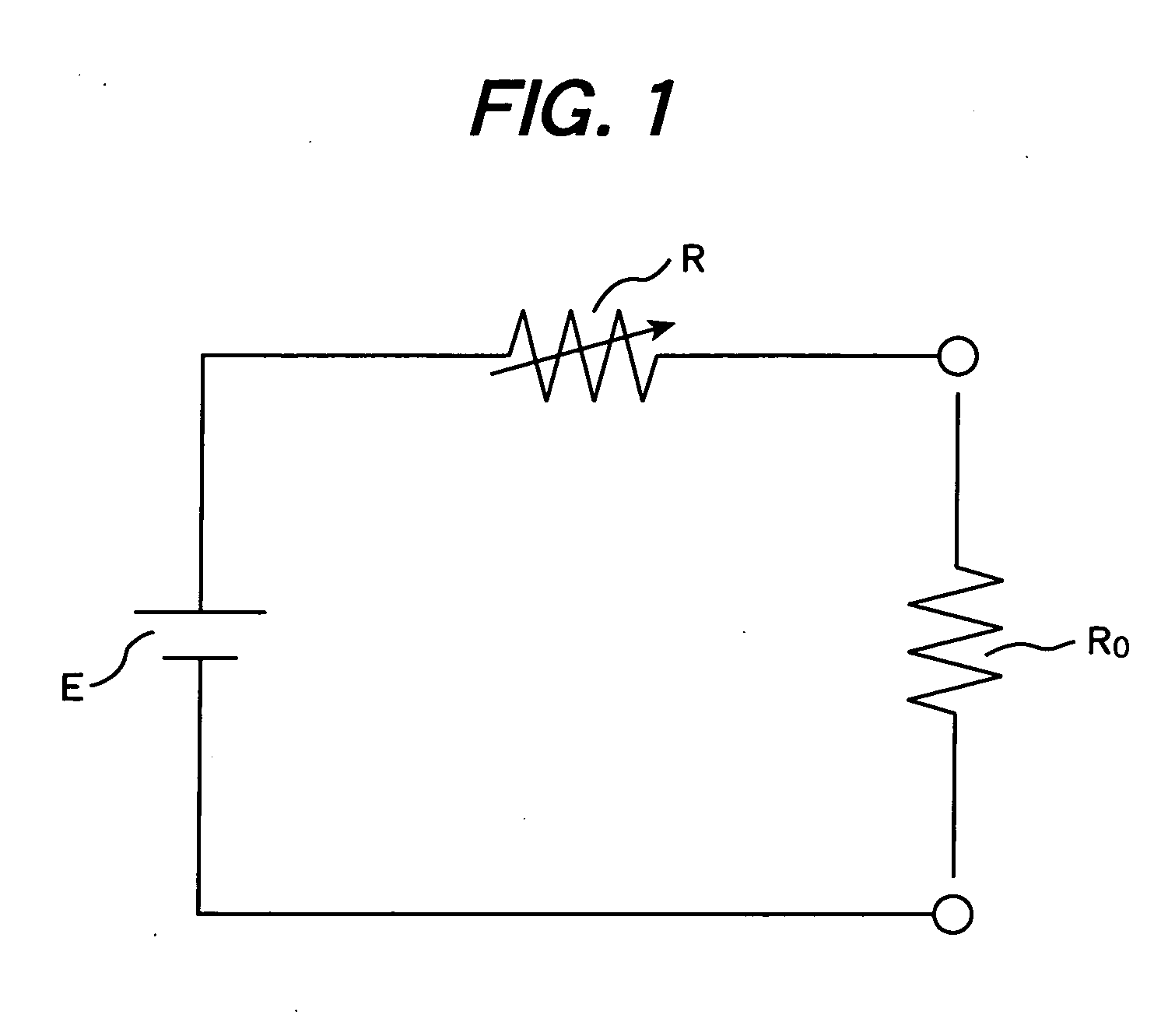
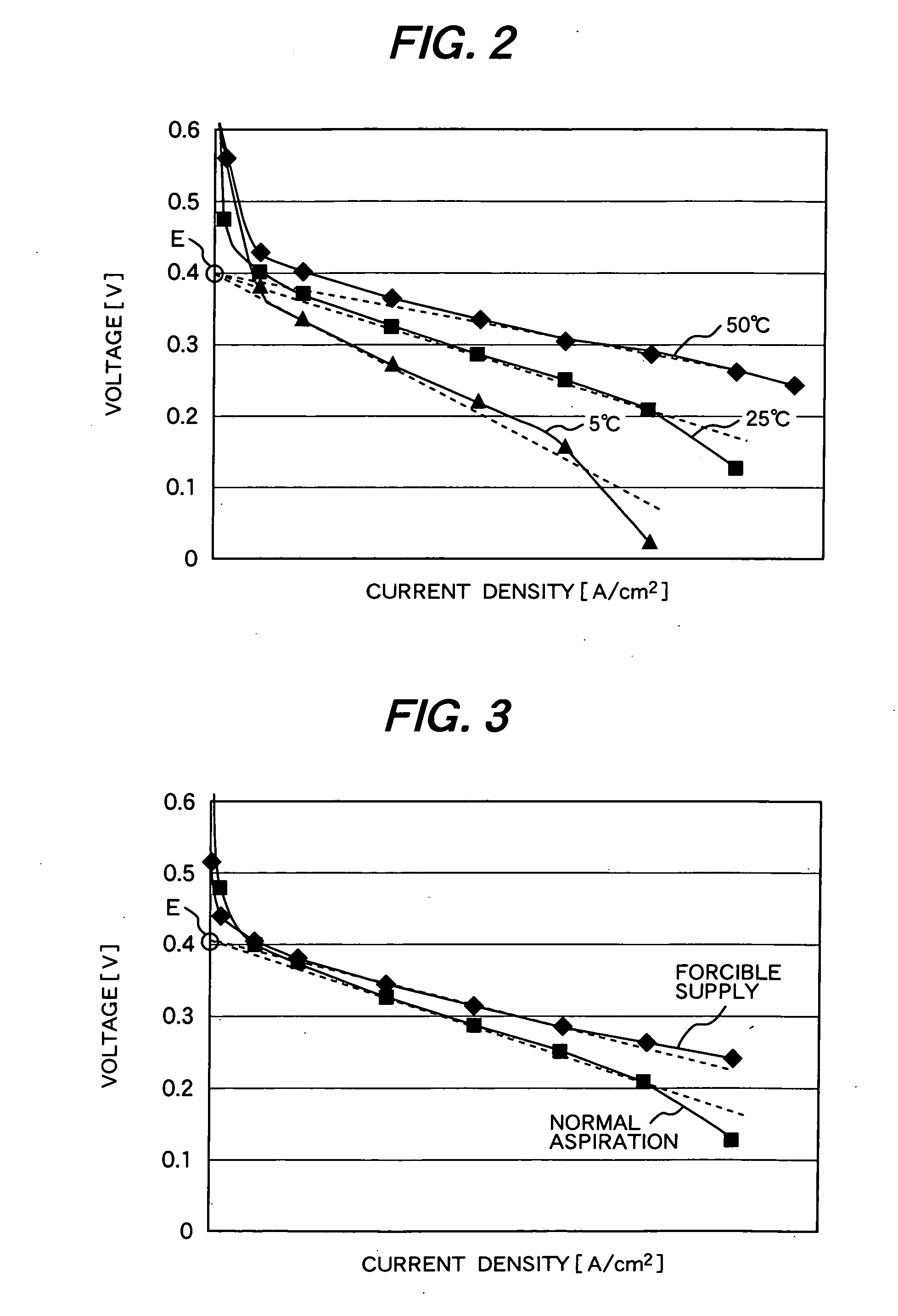
A detection voltage, which is obtained by dividing the voltage of a fuel cell 1 by resistors, is compared with a first reference voltage Vref1 by a differential amplifier. The differential voltage is input to a control section. The control section performs PWM control for the circuit section according to the difference. The first reference voltage Vref1 is set according to the dividing ratio of the resistors, based on the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. To determine the output voltage for maximum power generation, a characteristic curve representing a current-voltage characteristic is approximated by an approximating line within a range excluding an area in which the output voltage changes abruptly when the output current is nearly zero, and an extrapolated voltage is obtained on the extension line of the approximating line at an output current of zero. Fifty percent of the extrapolated voltage is then determined as the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. Thus, a fuel cell control system that identifies a highly precise output voltage for power generation at a maximum power point and controls power so that the maximum power point is not exceeded could be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
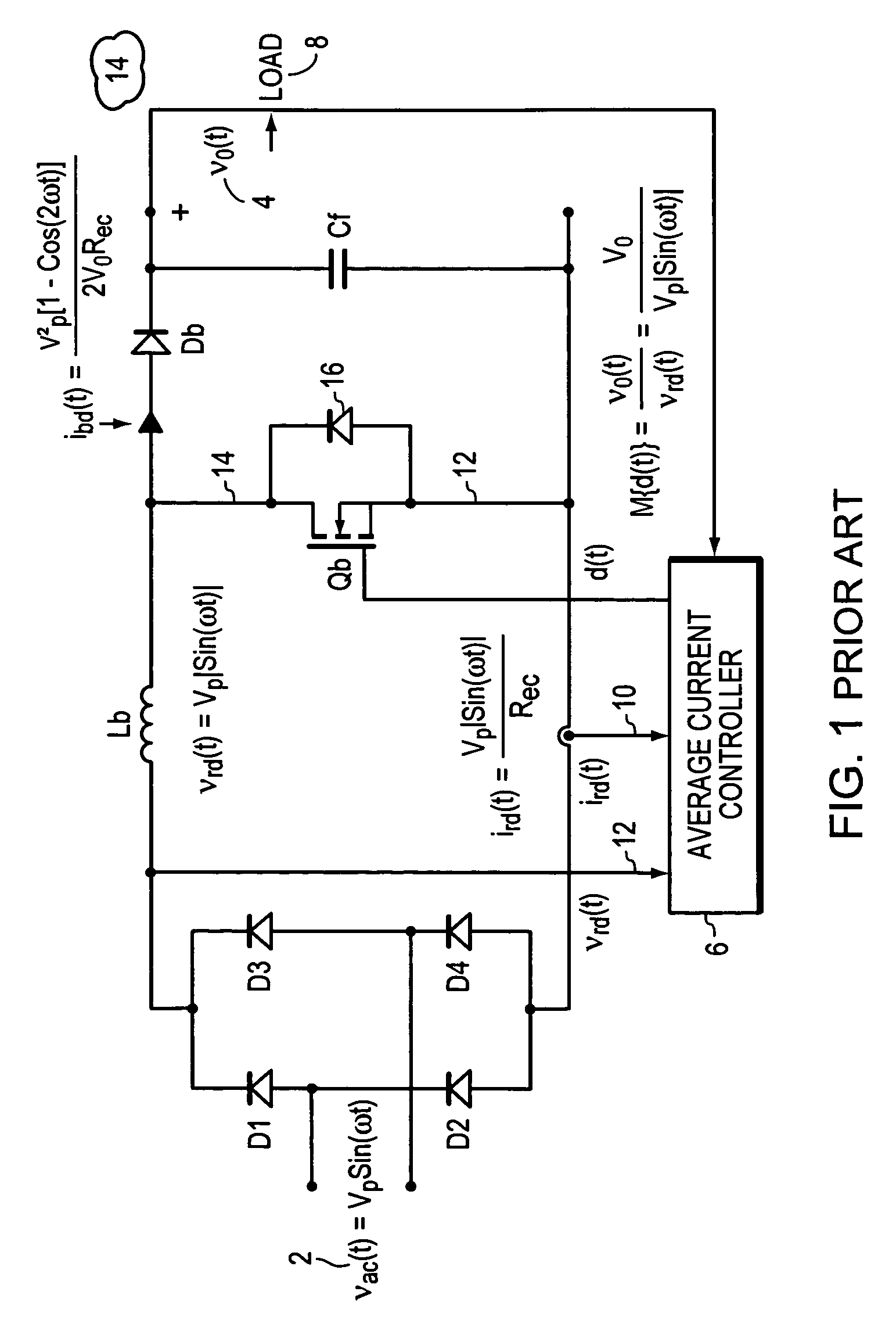
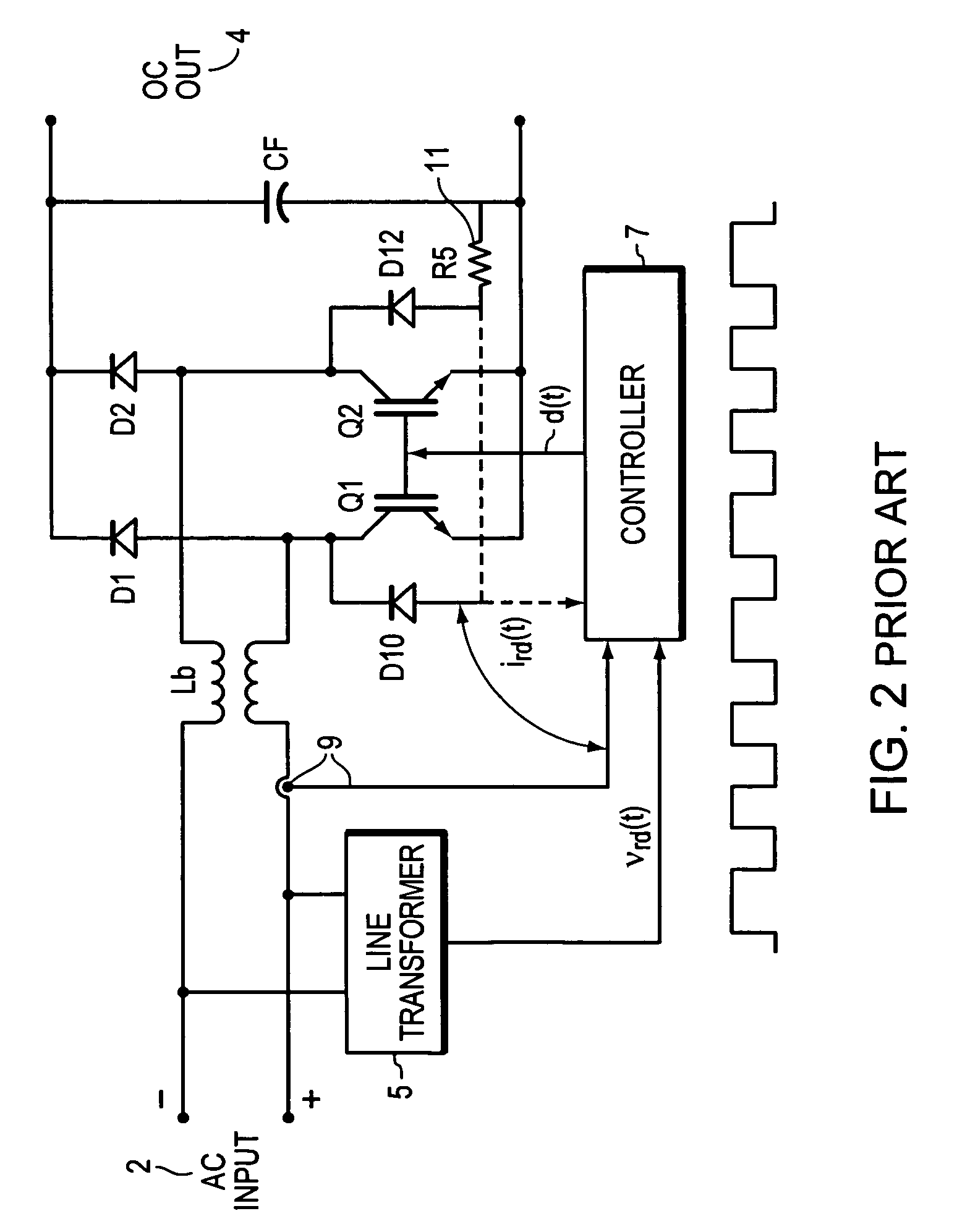
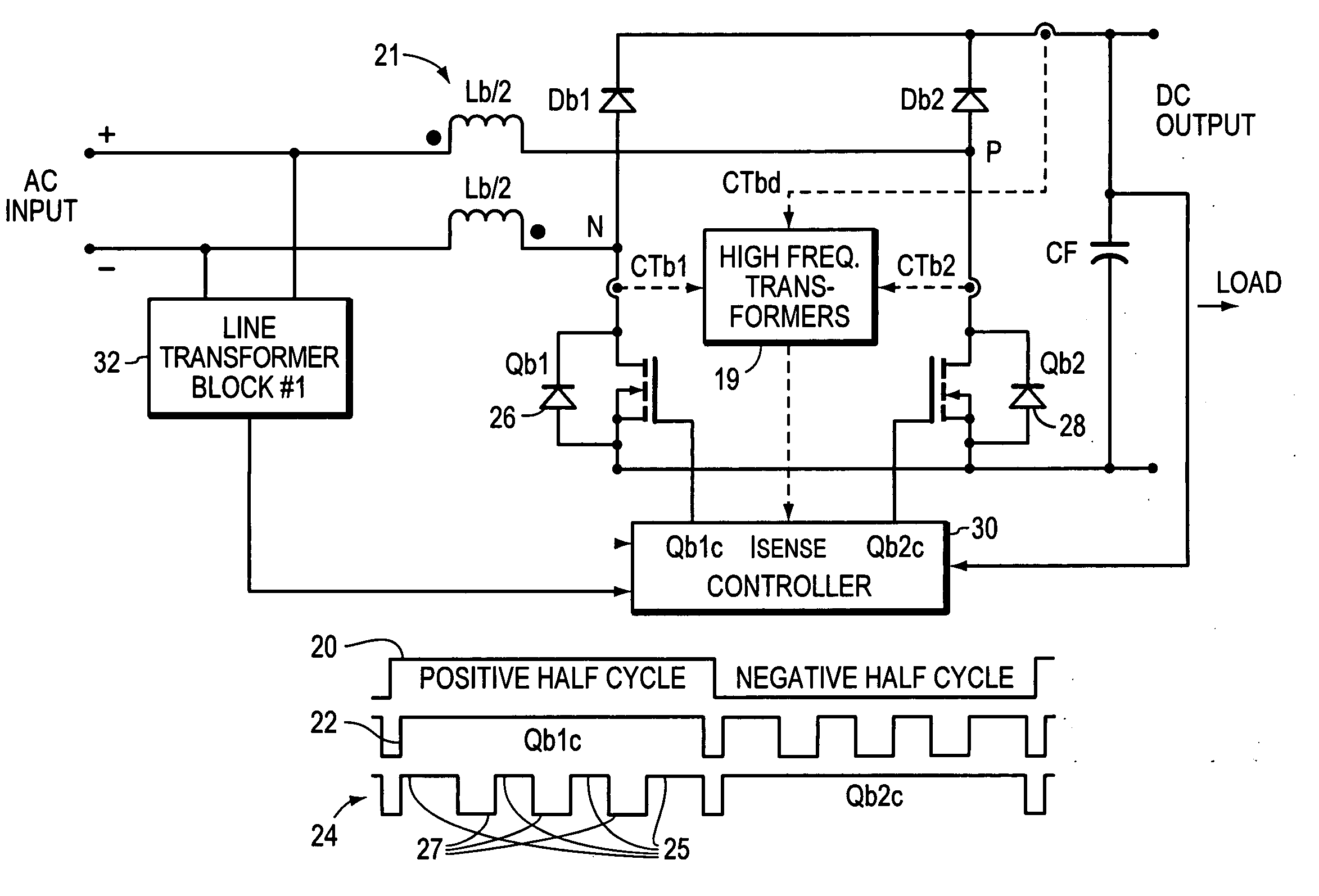
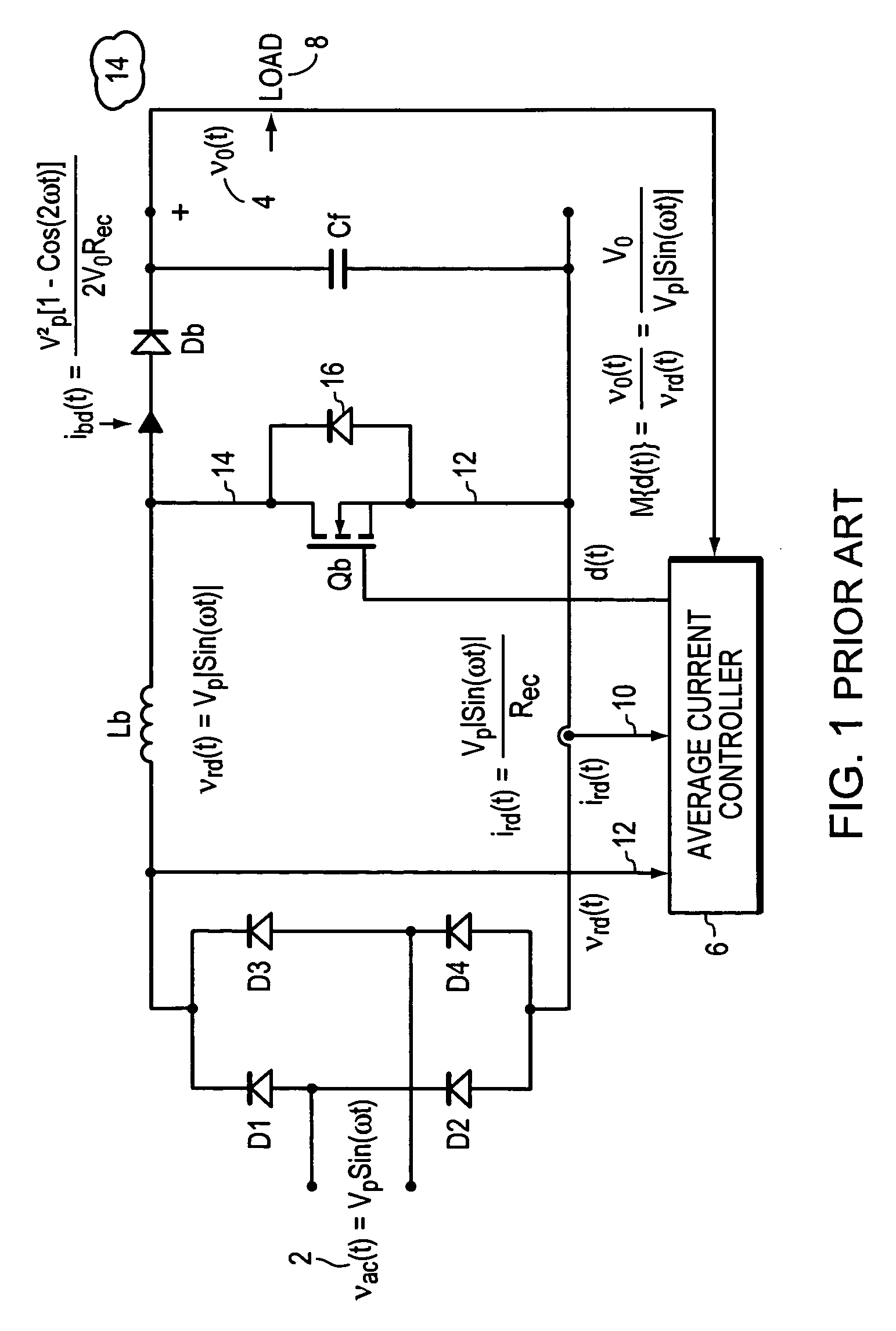
Vrms and rectified current sense full-bridge synchronous-rectification integrated with PFC
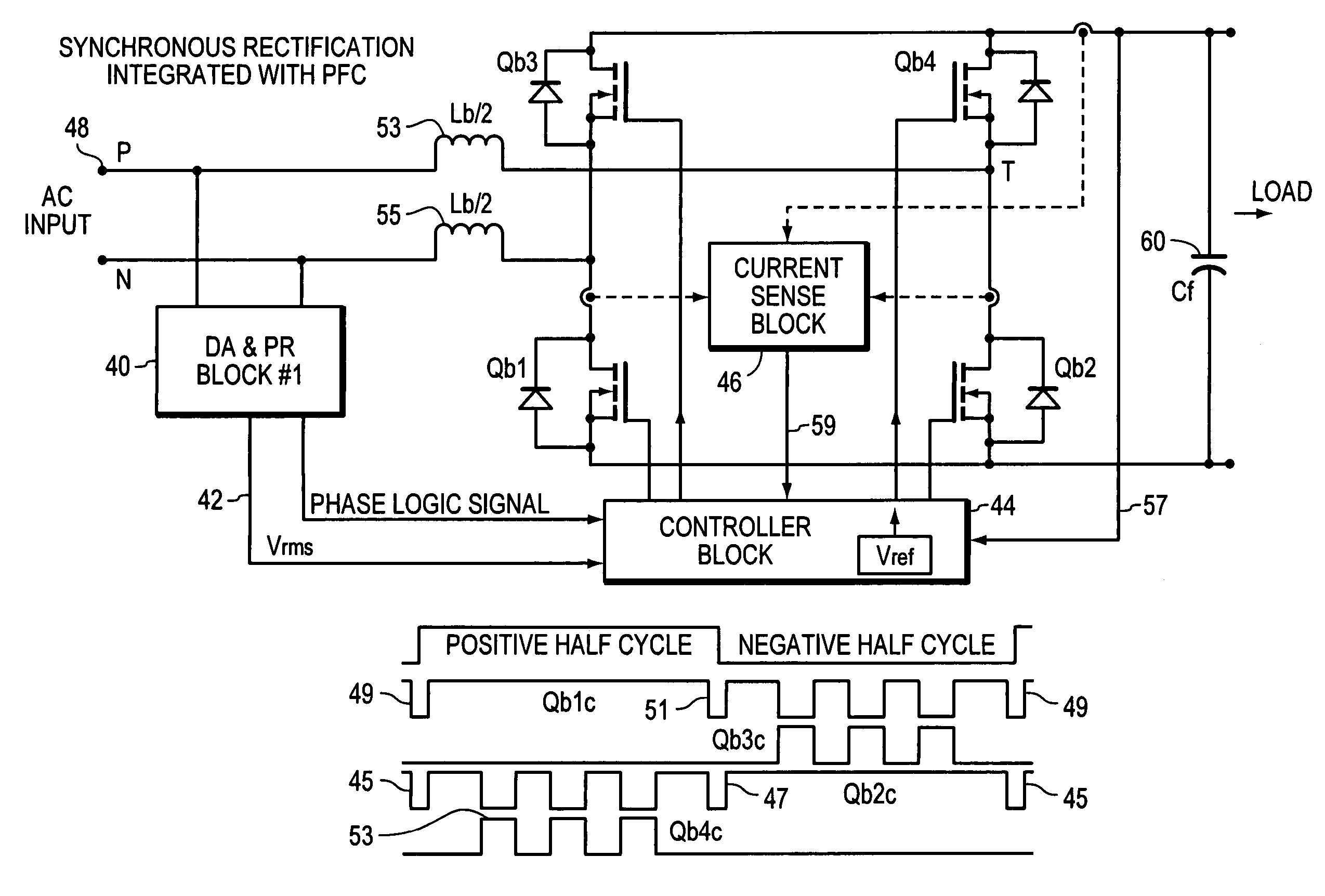
ActiveUS7269038B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETFull bridge
A synchronous full bridge rectifier is controlled to provide a power factor near unity. The full bridge rectifiers are transistors each with a controlling input. The AC input signal and currents within the circuit are sensed and sent to a controller. In response, the controller output control signals to turn on / off the rectifying MOSFETS on a timely basis to form a power factor of near one with respect to the AC input signal. The full wave rectifier is made of N-channel MOSFET's, some with fast body diodes. The MOSFET's are rectifiers and PFC control elements. The result is a one stage synchronous rectifier with PFC. A solid state precision analog differential amplifier senses the AC line waveform and high frequency current transformers sense the currents. The controller accepts the inputs of the amplifier and the sensed currents and outputs control signals that turn on and off the four MOSFET's. The timing of turning on / off is arranged so that the current drawn from the AC source is sinusoidal and matches the phase of the sinusoidal AC source.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Vrms and rectified current sense full-bridge synchronous-rectification integrated with PFC
ActiveUS20070058402A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETPower factor
A synchronous full bridge rectifier is controlled to provide a power factor near unity. The full bridge rectifiers are transistors each with a controlling input. The AC input signal and currents within the circuit are sensed and sent to a controller. In response, the controller output control signals to turn on / off the rectifying MOSFETS on a timely basis to form a power factor of near one with respect to the AC input signal. The full wave rectifier is made of N-channel MOSFET's, some with fast body diodes. The MOSFET's are rectifiers and PFC control elements. The result is a one stage synchronous rectifier with PFC. A solid state precision analog differential amplifier senses the AC line waveform and high frequency current transformers sense the currents. The controller accepts the inputs of the amplifier and the sensed currents and outputs control signals that turn on and off the four MOSFET's. The timing of turning on / off is arranged so that the current drawn from the AC source is sinusoidal and matches the phase of the sinusoidal AC source.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Transmission line input structure test probe
InactiveUS7019544B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsDifferential signalingCharacteristic impedance
A differential electrical test probe tip for sensing a plurality of electric signals and generating a differential signal including an elongate common substrate having a two signal test points at one end and a differential amplifier at the second end. Two transmission lines are on the common substrate, each connecting a respective signal test point a signal input of the differential amplifier. The characteristic impedances of the two transmission lines are substantially equal. In one preferred embodiment, the common substrate is a flexible substrate. In one preferred embodiment an over-mold, which may have gaps therein, at least partially encloses the common substrate, the first transmission line, and the second transmission line.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
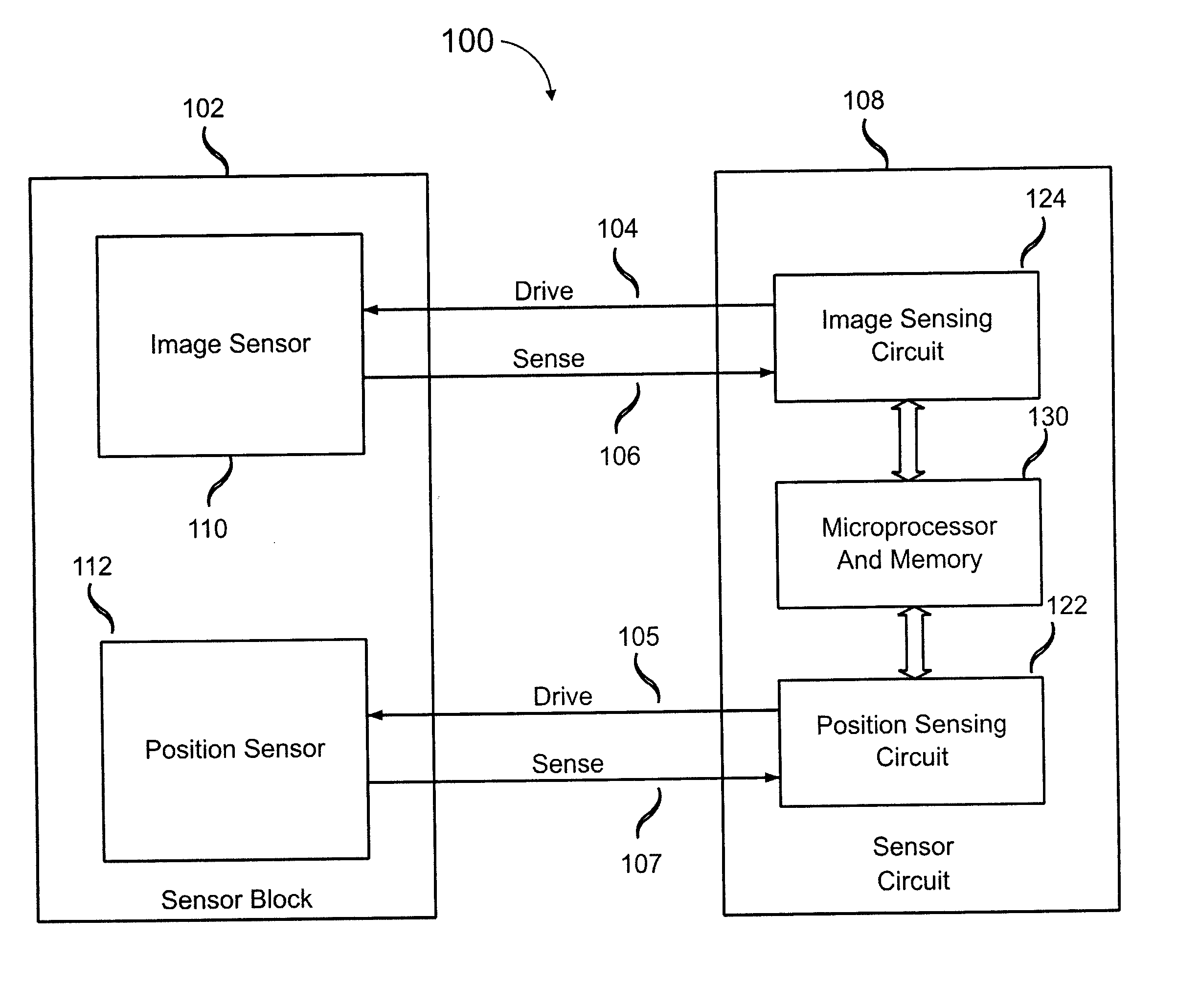
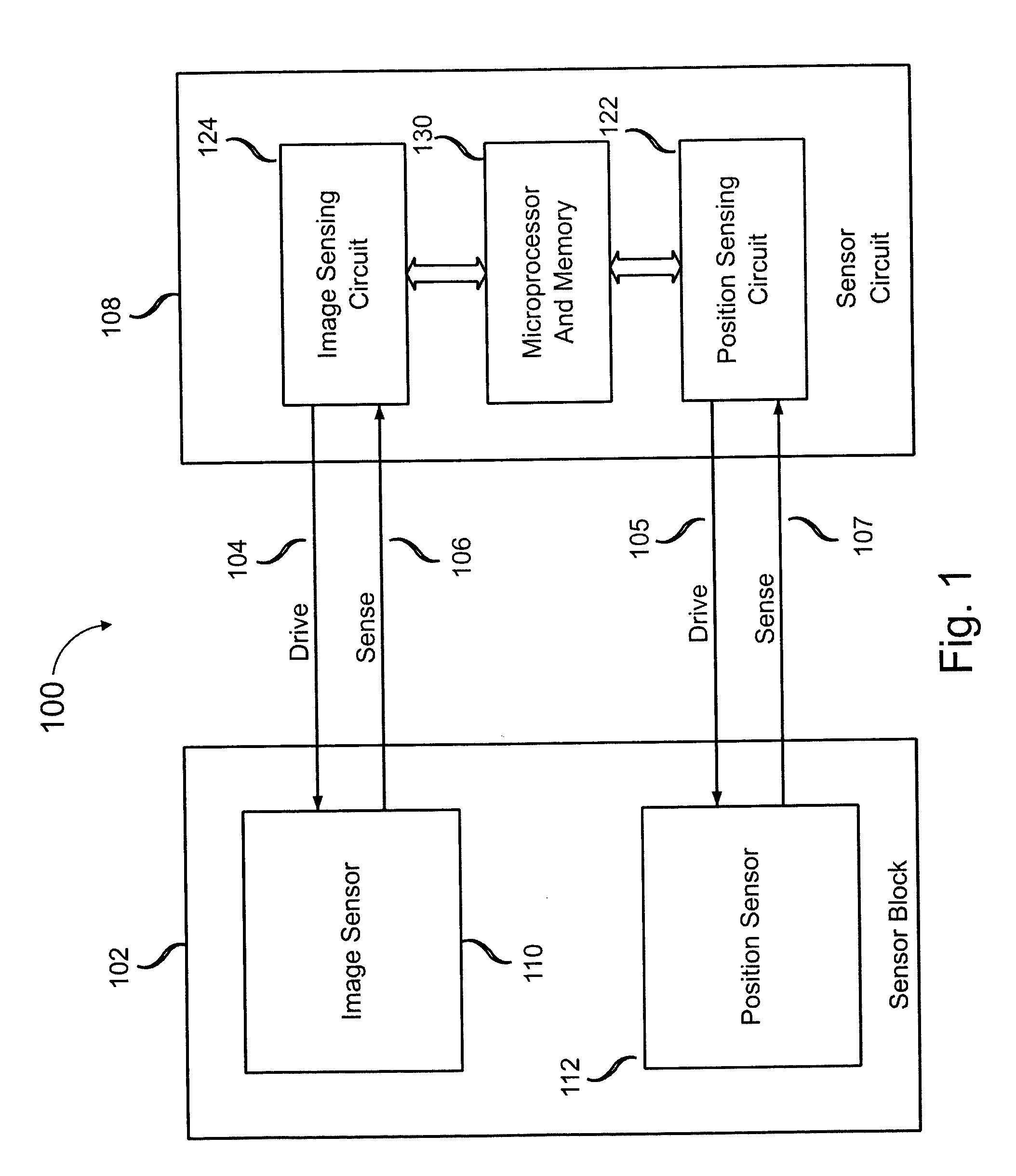
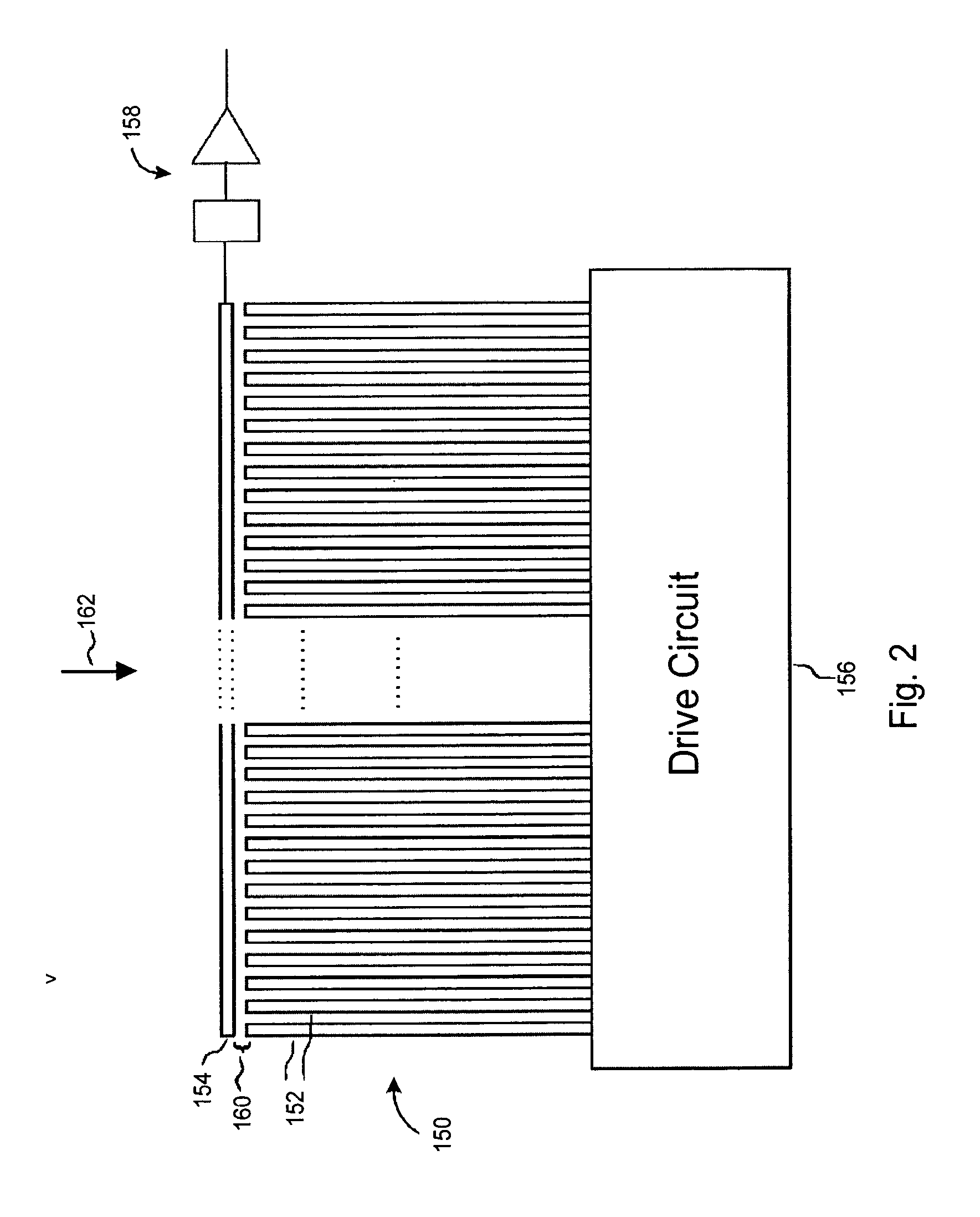
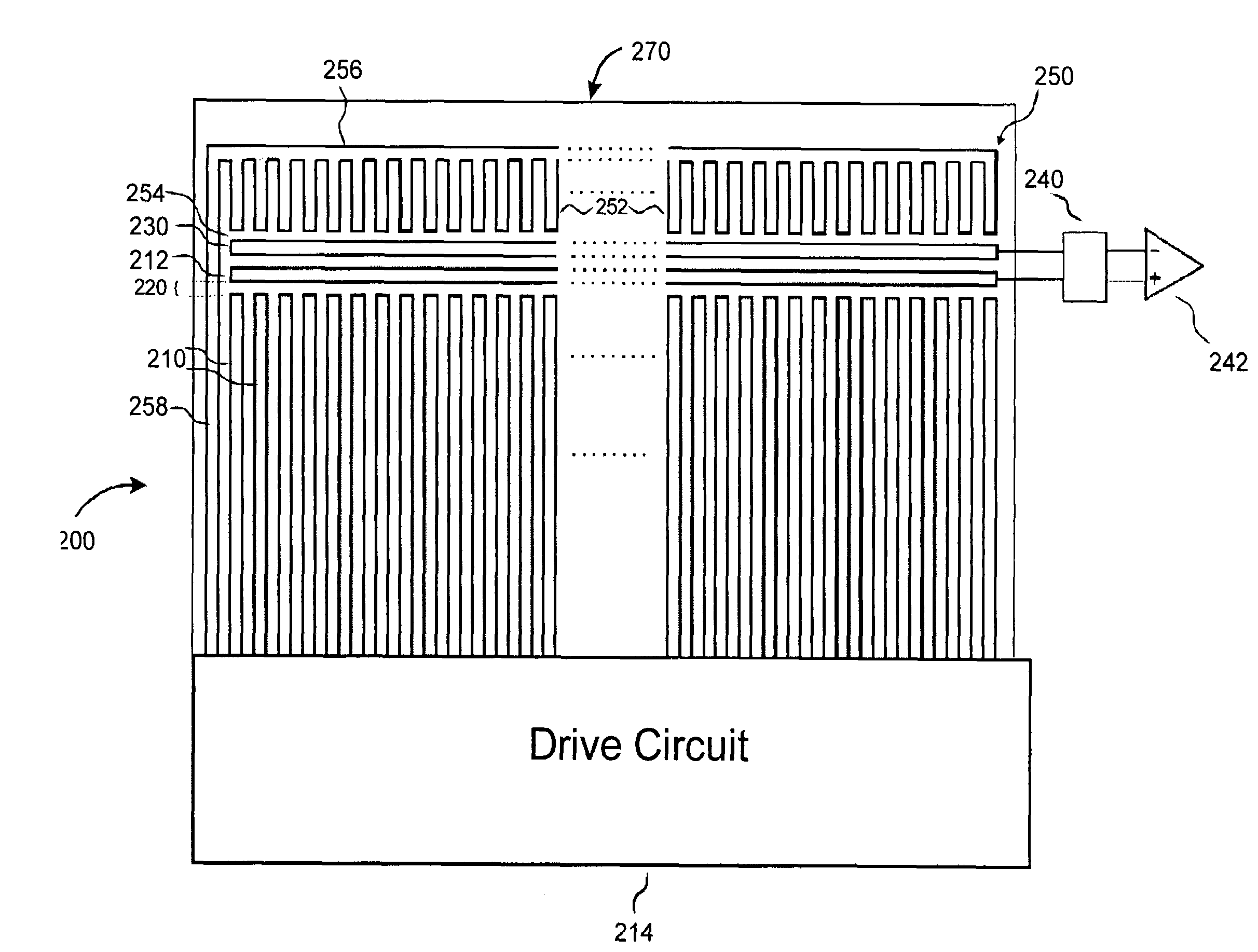
Electronic fingerprint sensor with differential noise cancellation
ActiveUS20070031011A1Resistance/reactance/impedencePerson identificationImage signalDifferential amplifier
Image sensing apparatus includes an image pickup plate disposed generally orthogonally with respect to an expected direction of movement of an object, such as a finger, multiple image drive plates in spaced relation to the image pickup plate to define sensor gaps between respective image drive plates and the image pickup plate, and a reference plate disposed substantially parallel to the image pickup plate. The reference plate is spaced from the image pickup plate to permit common mode noise and coupling to be cancelled and is spaced from the image drive plates to permit a differential image signal to develop between the image pickup plate and the reference plate. A differential amplifier coupled to the image pickup plate and the reference plate provides noise cancellation. The apparatus may further include a comb plate spaced from the reference plate and coupled to a reference potential, such as ground.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +1
Method for determining a maximum power point voltage of a fuel cell and use thereof
A detection voltage, which is obtained by dividing the voltage of a fuel cell 1 by resistors, is compared with a first reference voltage Vref 1 by a differential amplifier. The differential voltage is input to a control section. The control section performs PWM control for the circuit section according to the difference. The first reference voltage Vref 1 is set according to the dividing ratio of the resistors, based on the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. To determine the output voltage for maximum power generation, a characteristic curve representing a current-voltage characteristic is approximated by an approximating line within a range excluding an area in which the output voltage changes abruptly when the output current is nearly zero, and an extrapolated voltage is obtained on the extension line of the approximating line at an output current of zero. Fifty percent of the extrapolated voltage is then determined as the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. Thus, a fuel cell control system that identifies a highly precise output voltage for power generation at a maximum power point and controls power so that the maximum power point is not exceeded could be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
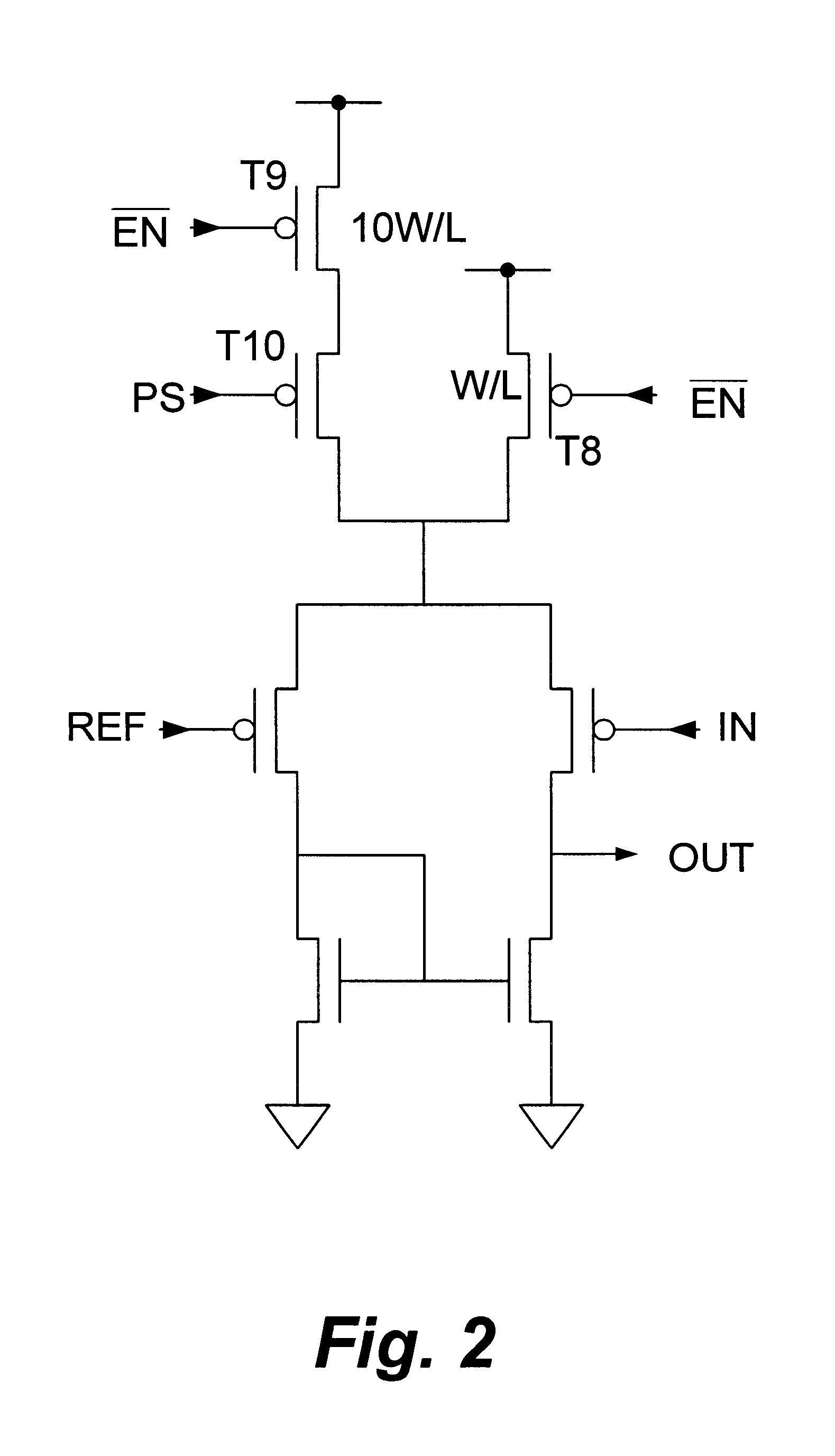
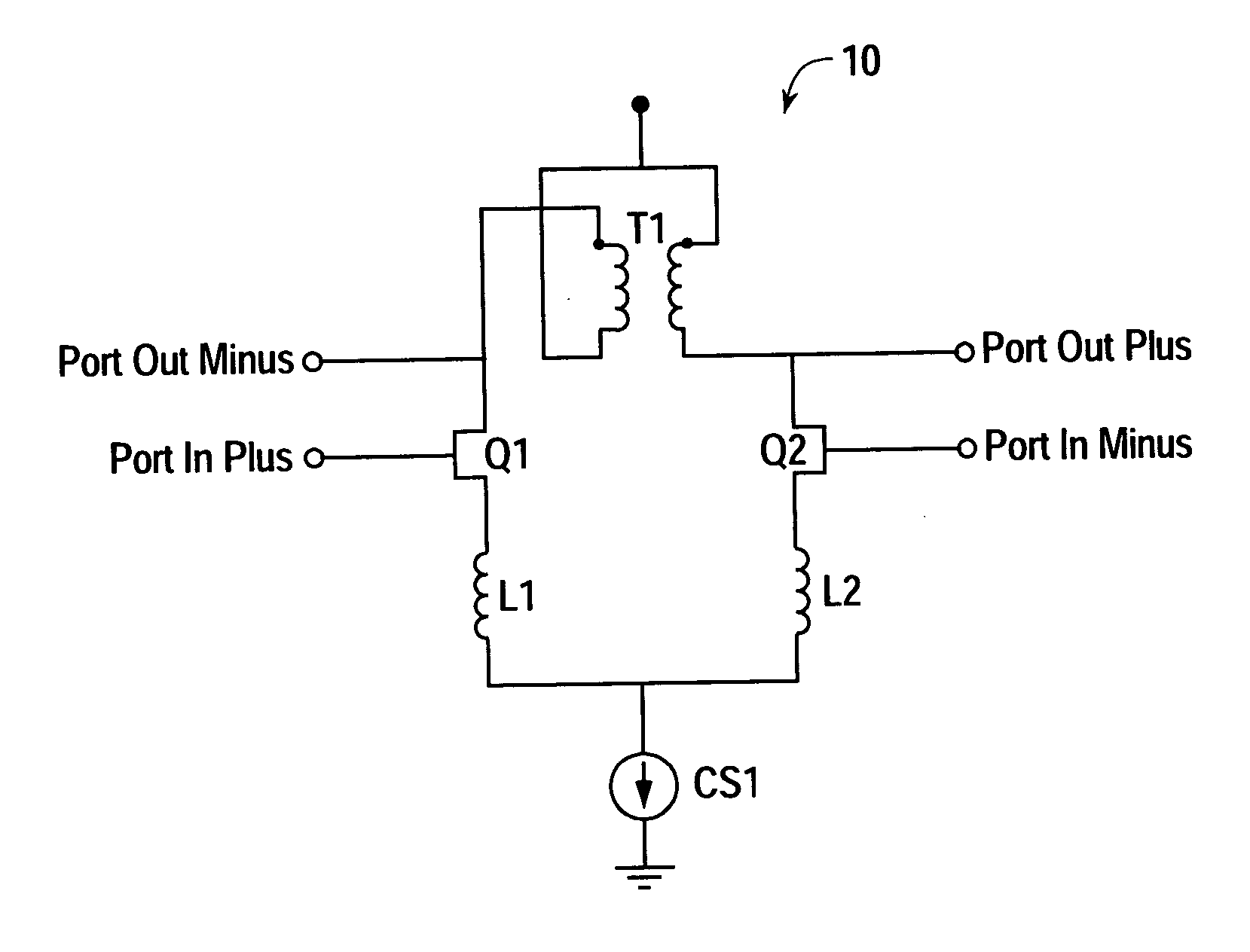
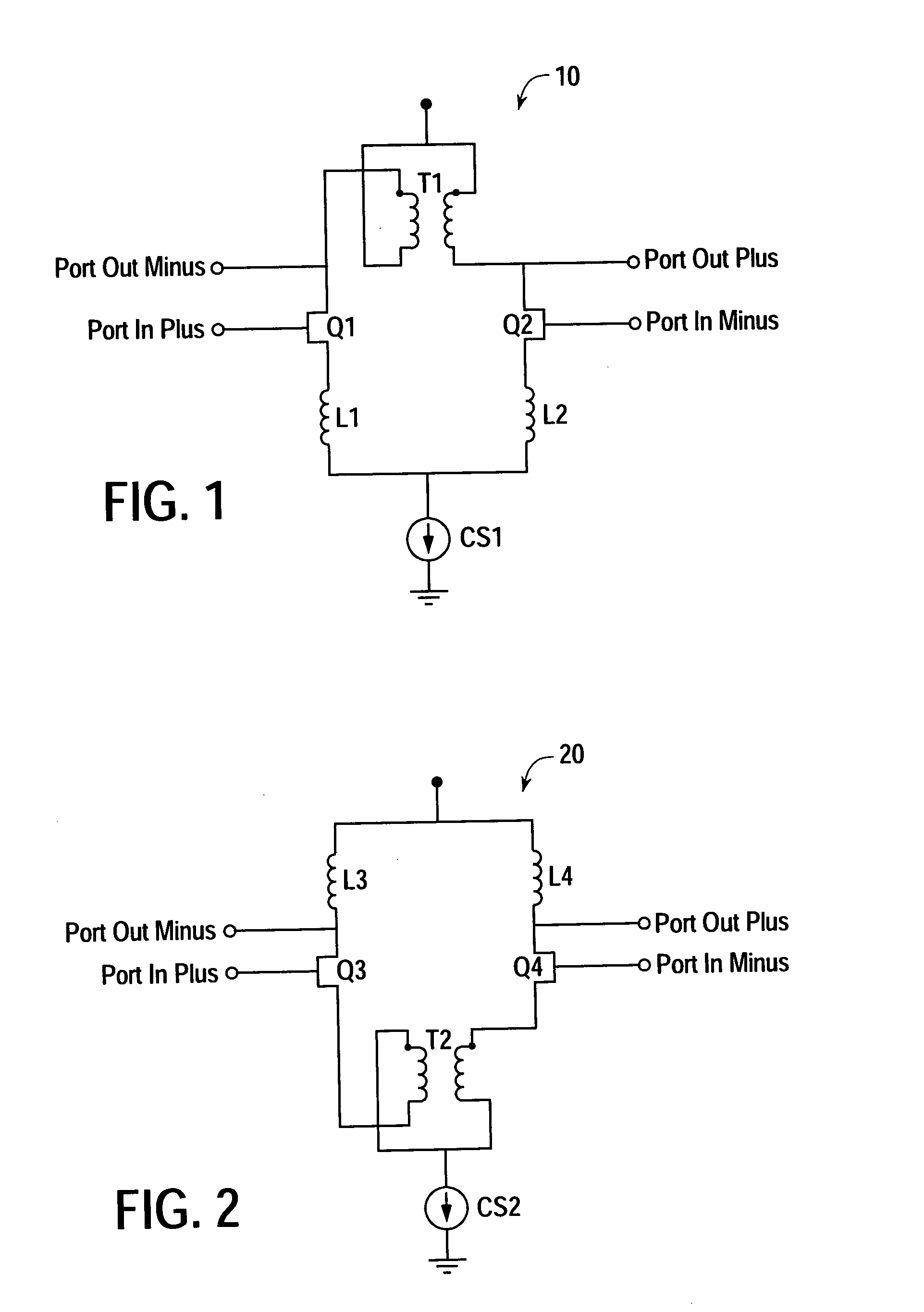
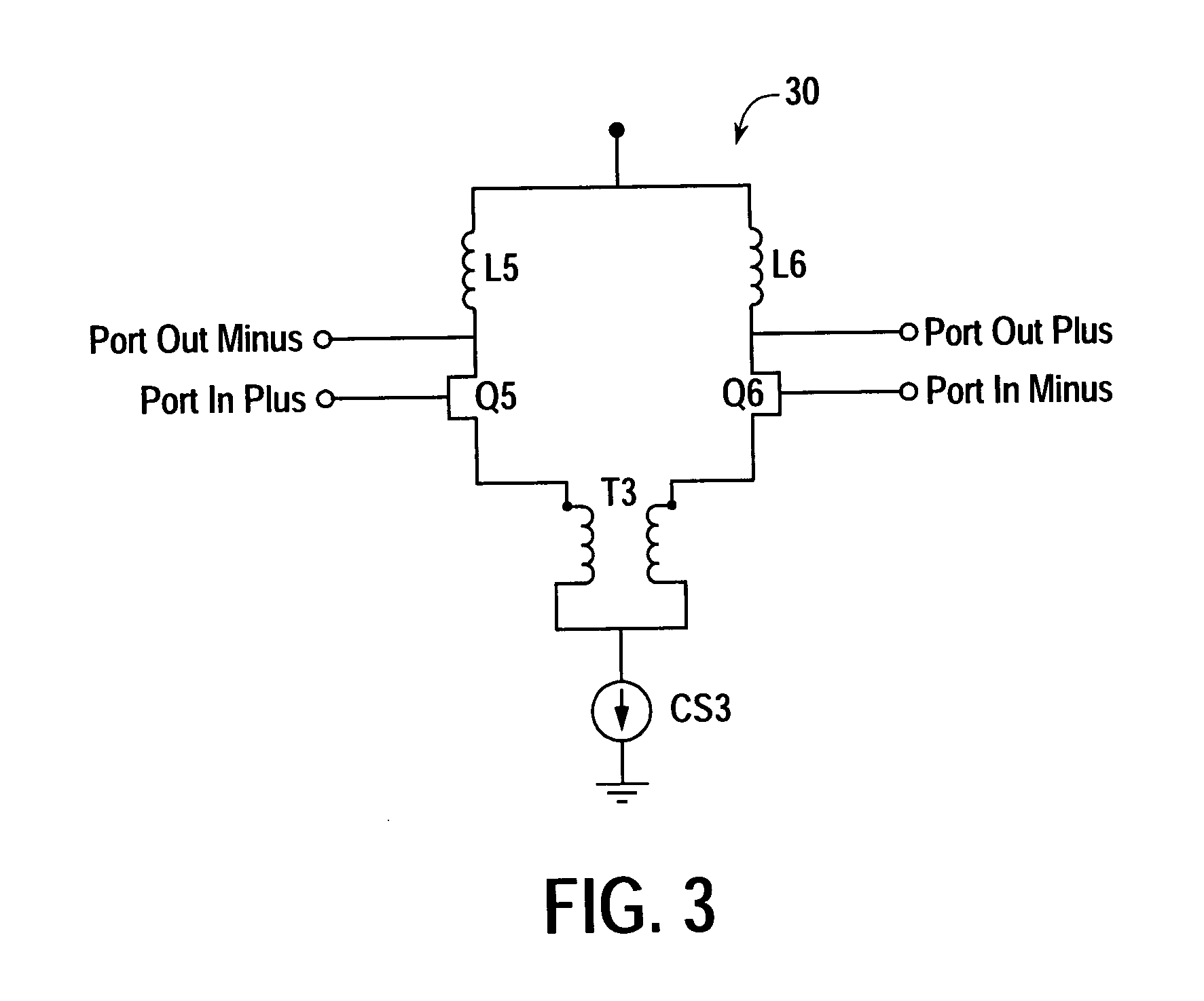
Coupled-inductance differential amplifier
ActiveUS20050062533A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersSmall form factorEngineering
A differential amplifier that employs mutually coupled inductors to provide desired levels of inductance in a substantially smaller form factor in comparison to individual inductor components. Mutually coupled inductors according to the present teachings may also be used to increase common mode rejection in a differential amplifier.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transparent digitiser
ActiveUS20080023232A1Easy to useHigh frequency resolutionTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital converterDifferential amplifier
A digitizer for user interaction via an object with an electronically refreshable display screen, the digitizer comprising: a transparent sensing arrangement of detectors located at said electronically refreshable display screen for detecting an electric field of said object, said detectors having outputs, and an arrangement of differential amplifiers associated with said outputs, thereby to apply differential detection between said outputs.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS8527038B2Improve securityMinimize corruptionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDigital dataTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110066045A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionElectroencephalographyInertial sensorsDigital dataTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn vital sign monitor
InactiveUS20110066044A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionElectroencephalographyInertial sensorsDigital dataTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
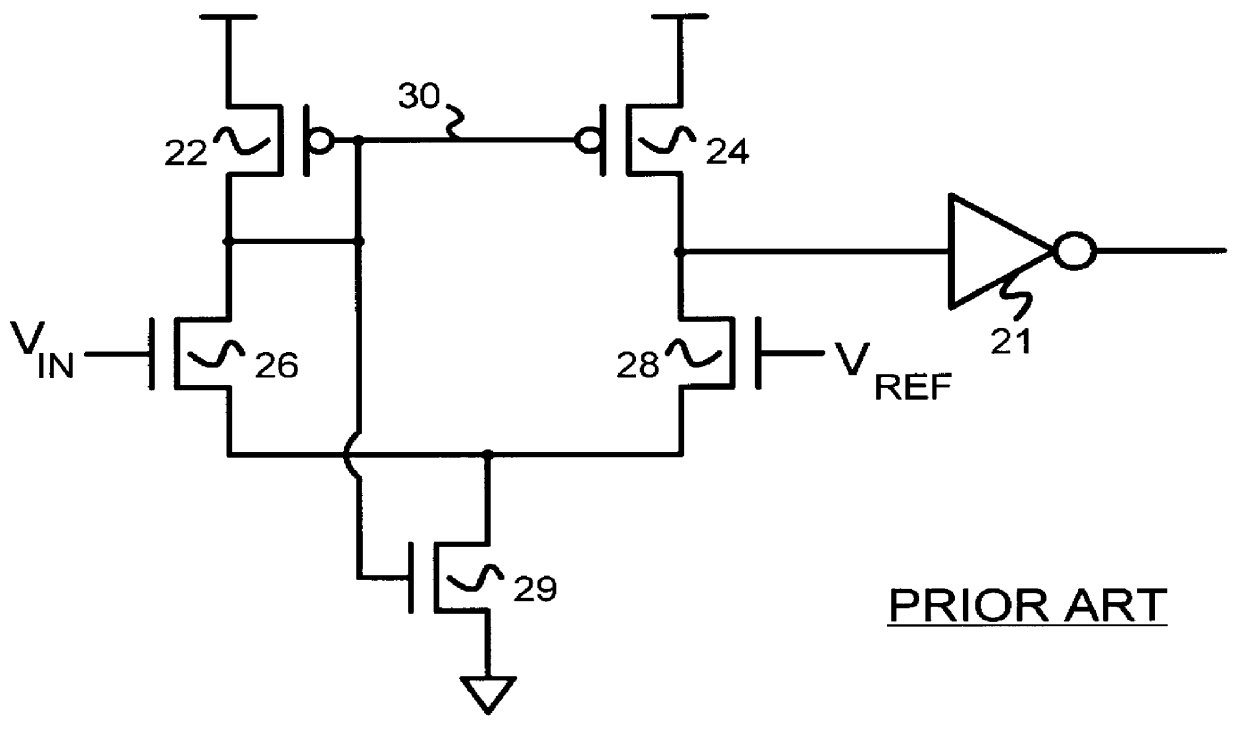
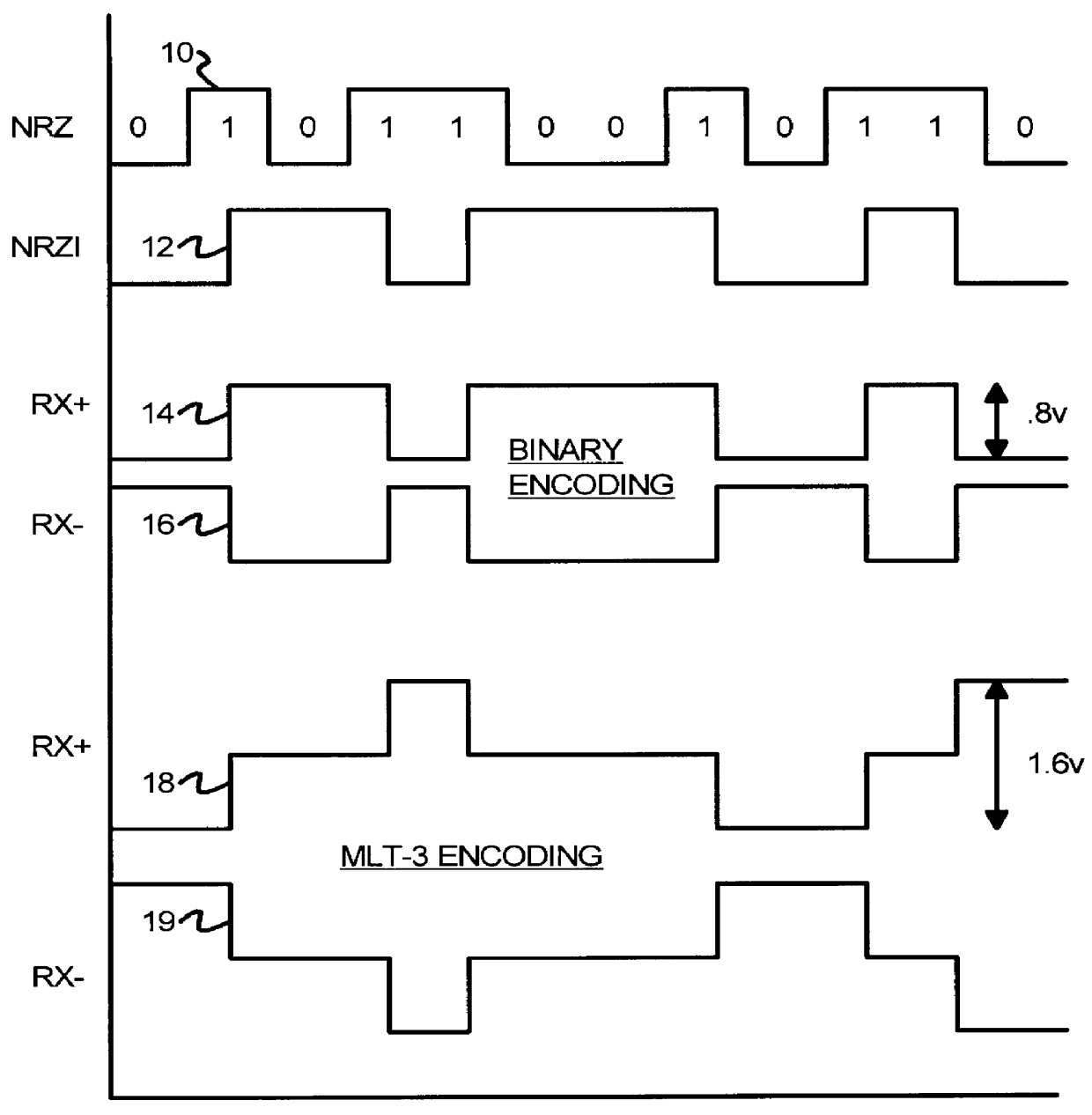
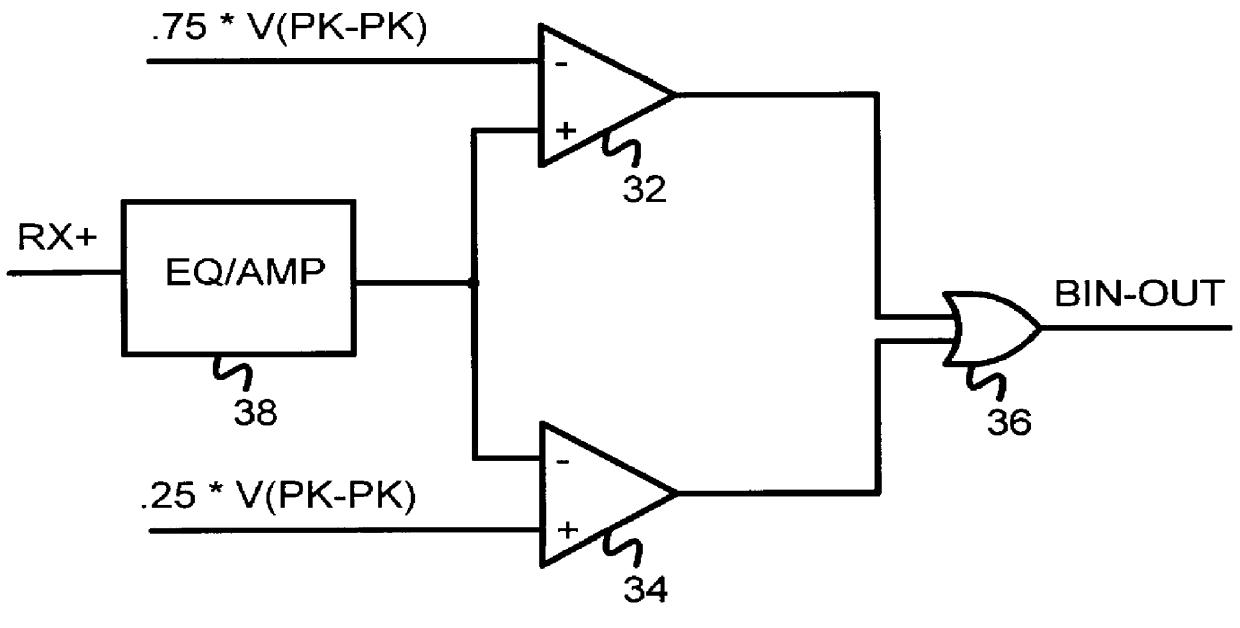
Self-biasing CMOS PECL receiver with wide common-mode range and multi-level-transmit to binary decoder
InactiveUS6049229AReduced Power RequirementsSimplify interconnect routingLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsThree levelEmitter-coupled logic
A pseudo-emitter-coupled-logic (PECL) receiver has a wide common-mode range. Two current-mirror CMOS differential amplifiers are used. One amplifier has n-channel differential transistors and a p-channel current mirror, while the second amplifier has p-channel differential transistors and an n-channel current mirror. When the input voltages approach power or ground, one type of differential transistor continues to operate even when the other type shuts off. The outputs of the two amplifiers are connected together and each amplifier receives the same differential input signals. The tail-current transistor is self-biased using the current-mirror's gate-bias. This self biasing of each amplifier eliminates the need for an additional voltage reference and allows each amplifier to adjust its biasing over a wide input-voltage range. Thus the common-mode input range is extended using self biasing and complementary amplifiers. The complementary self-biased comparators can be used for receiving binary or multi-level-transition (MLT) inputs by selecting different voltage references for threshold comparison. Using the same reference on both differential inputs eliminates a second reference for multi-level inputs having three levels. Thus binary and MLT inputs can be detected and decoded by the same decoder.
Owner:DIODES INC
Current sensor
InactiveUS20060071655A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyMagnetic measurementsDynamo-electric motor metersElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
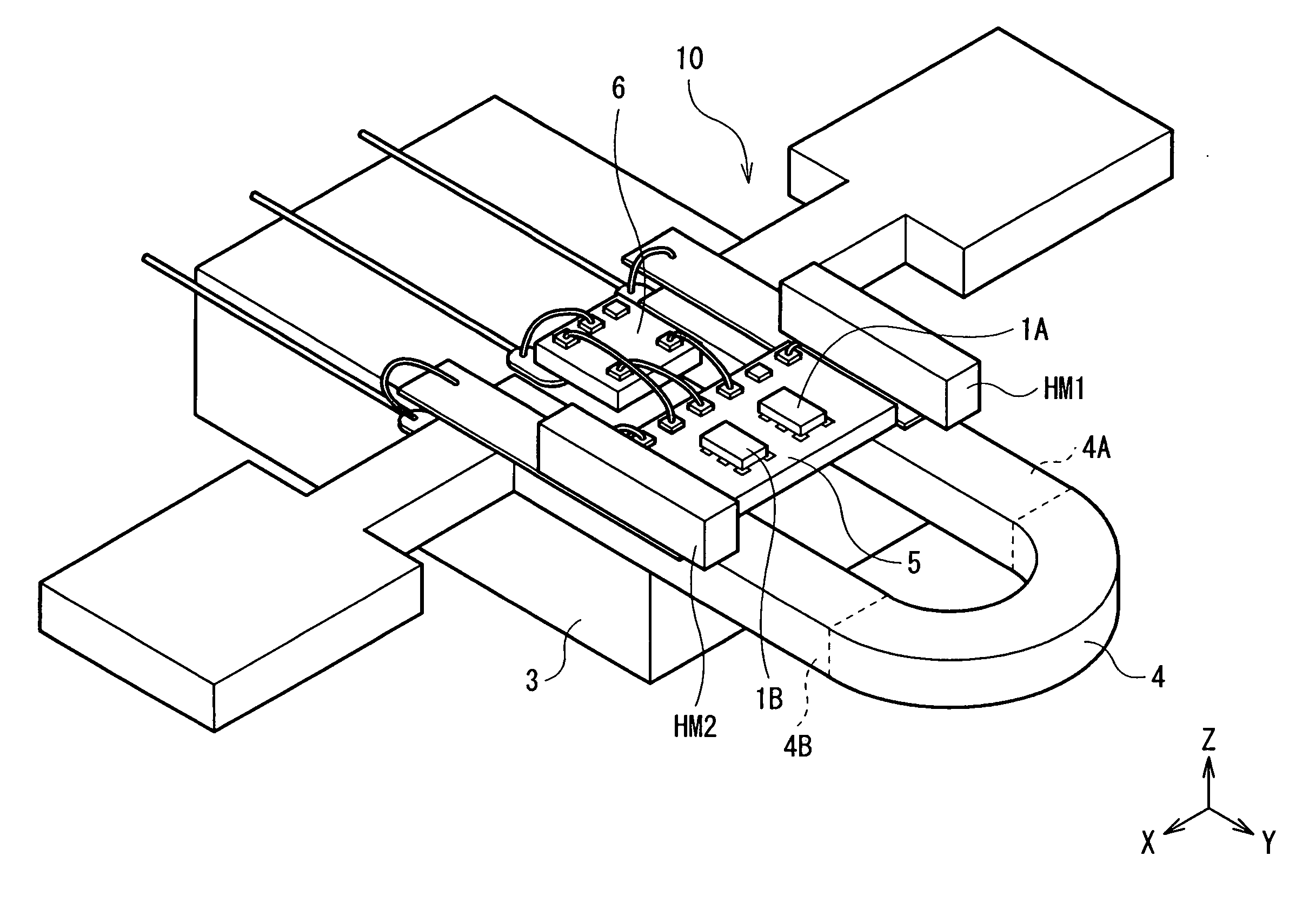
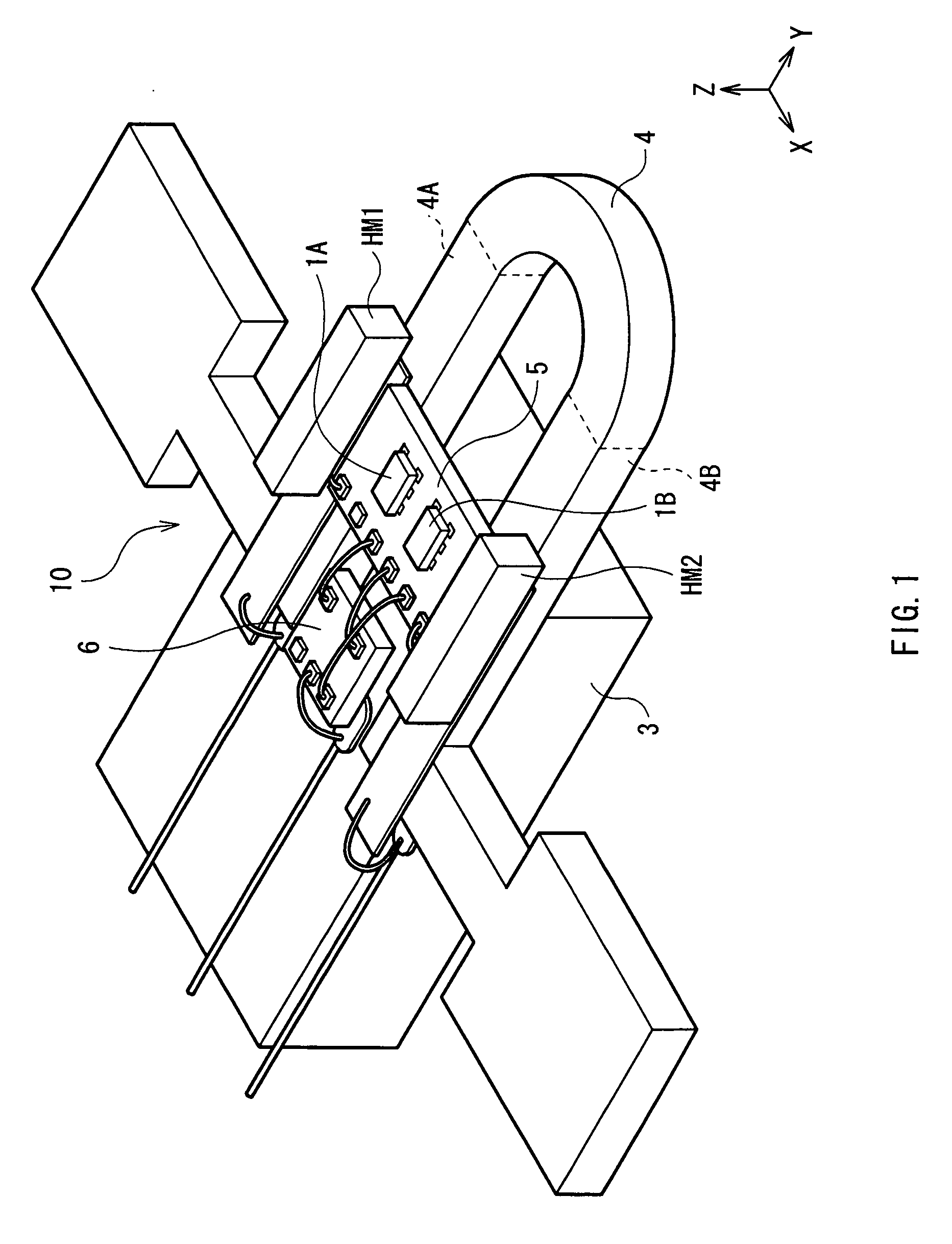
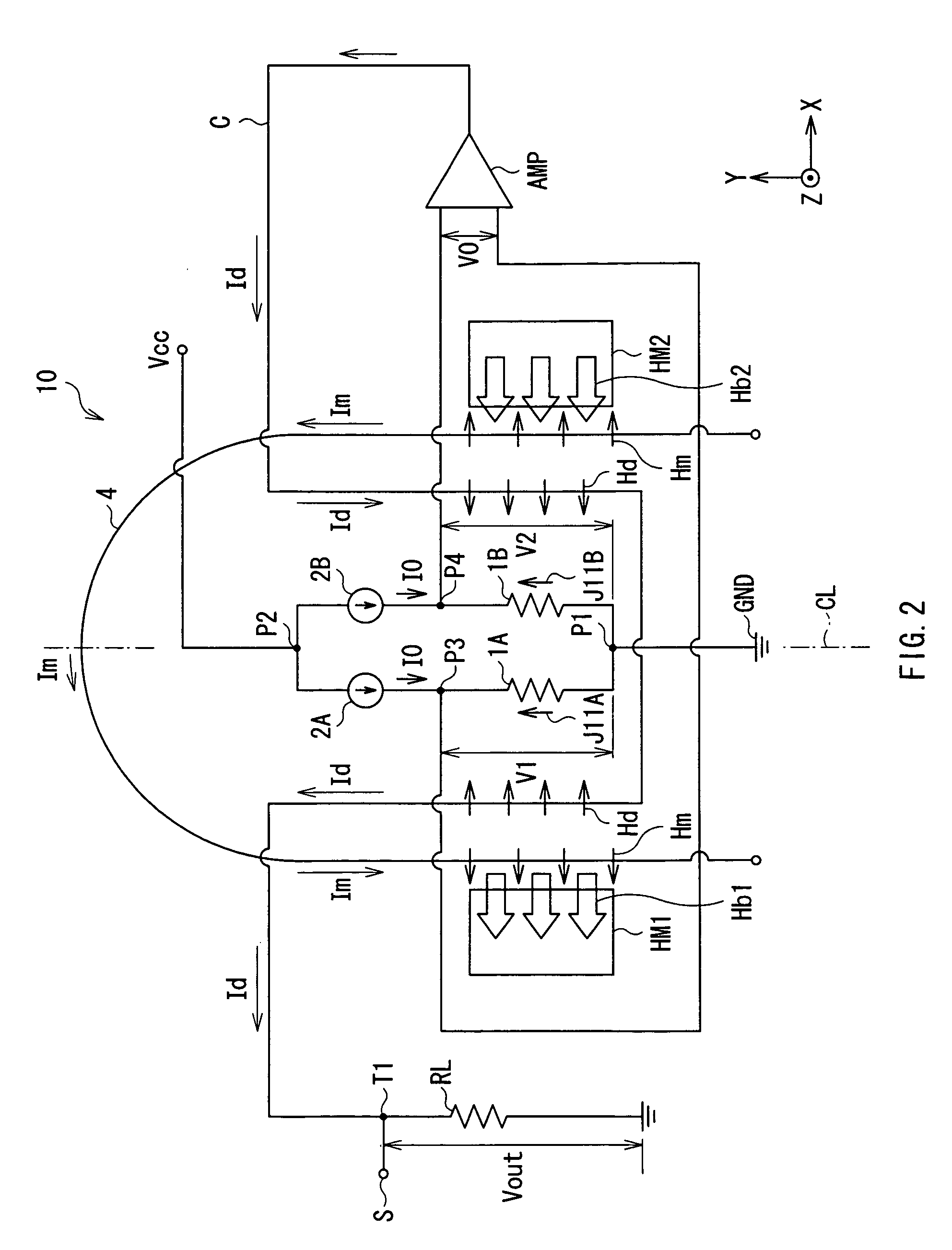
The present invention provides a current sensor capable of adjusting an offset value at a zero magnetic field more easily and detecting a current magnetic field generated by a current to be detected with high sensitivity and high precision. The current sensor has: first and second magnetoresistive elements disposed along a conductor so that resistance values change in directions opposite to each other in accordance with a current magnetic field generated by a current to be detected flowing in the conductor; and first and second constant current sources that supply constant currents equal to each other to the first and second magnetoresistive elements, respectively. The current sensor further includes a differential amplifier that detects the difference between voltage drops occurring in the first and second magnetoresistive elements by the constant current. The current to be detected is detected on the basis of the difference between the voltage drops.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method for measuring currents in a motor controller and motor controller using such method
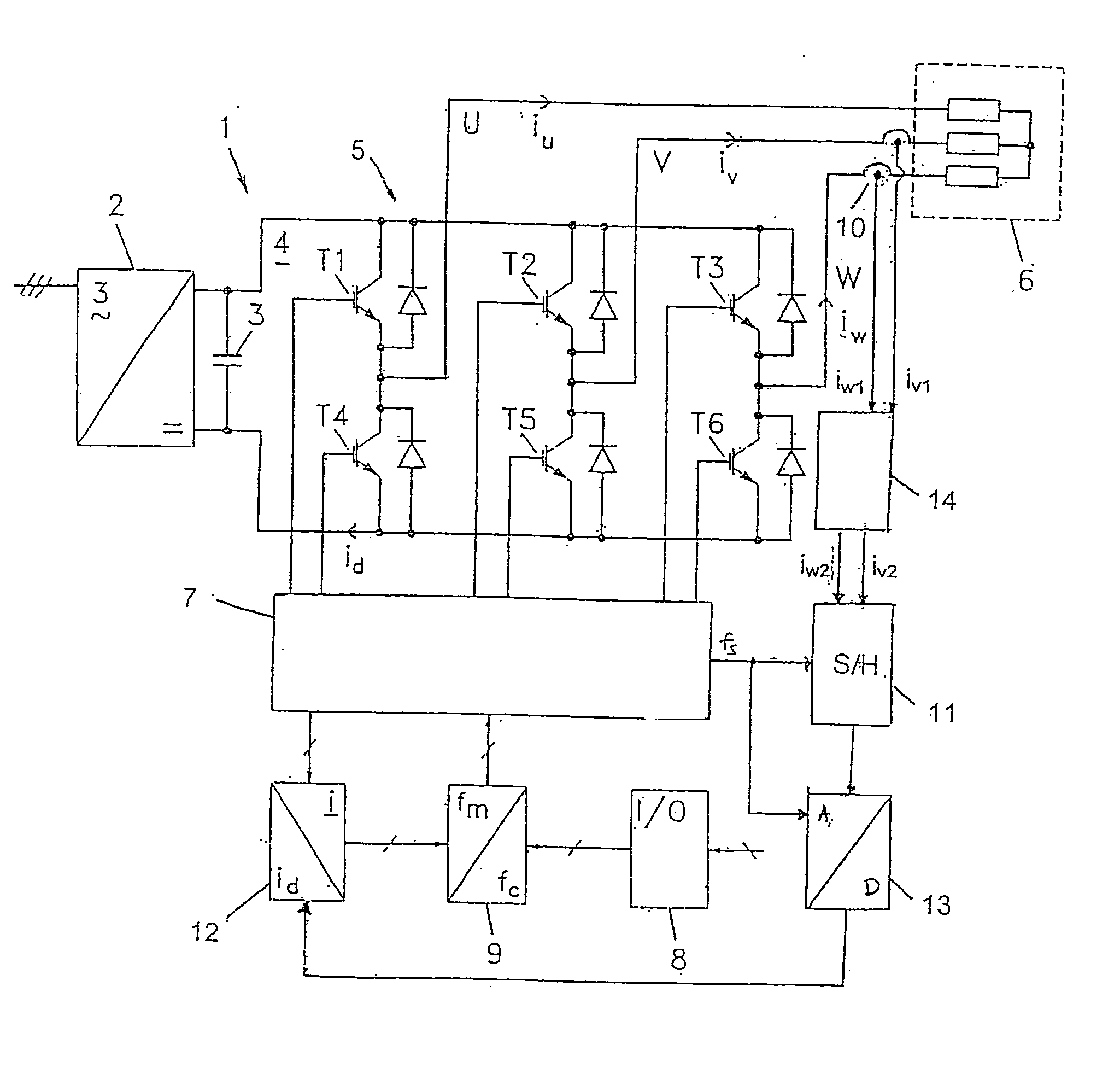
InactiveUS20050190094A1Increase heightReduce random noiseElectric signal transmission systemsField or armature current controlSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Differential transmission
The invention relates to a method for measuring currents in a motor controller. Some current sensing devices placed on the motor wires or inside the motor controller provide low amplitude output signals thus complicating sampling and data processing. In order to improve the signal / noise ratio, an oversampling technique is disclosed which makes used of a differential transmission of the output signal. Further, by applying intelligent sorting techniques on the sampled data, a substantial improvement in the signal / noise ratio can be obtained. The invention also concerns a motor controller using this method, and discloses the use of a power card and a control card, where the current sensing device is placed on the power card and a differential amplifier is placed on the control card. The gain of the differential amplifier is controlled by components placed on the power card as well as on the control card.
Owner:DANFOSS DRIVES
Body-worn vital sign monitor
ActiveUS20110066050A1Improve securityMinimize corruptionElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsDigital dataTransceiver
The invention provides a body-worn monitor featuring a processing system that receives a digital data stream from an ECG system. A cable houses the ECG system at one terminal end, and plugs into the processing system, which is worn on the patient's wrist like a conventional wristwatch. The ECG system features: i) a connecting portion connected to multiple electrodes worn by the patient; ii) a differential amplifier that receives electrical signals from each electrode and process them to generate an analog ECG waveform; iii) an analog-to-digital converter that converts the analog ECG waveform into a digital ECG waveform; and iv) a transceiver that transmits a digital data stream representing the digital ECG waveform (or information calculated from the waveform) through the cable and to the processing system. Different ECG systems, typically featuring three, five, or twelve electrodes, can be interchanged with one another.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Electronic fingerprint sensor with differential noise cancellation
Image sensing apparatus includes an image pickup plate disposed generally orthogonally with respect to an expected direction of movement of an object, such as a finger, multiple image drive plates in spaced relation to the image pickup plate to define sensor gaps between respective image drive plates and the image pickup plate, and a reference plate disposed substantially parallel to the image pickup plate. The reference plate is spaced from the image pickup plate to permit common mode noise and coupling to be cancelled and is spaced from the image drive plates to permit a differential image signal to develop between the image pickup plate and the reference plate. A differential amplifier coupled to the image pickup plate and the reference plate provides noise cancellation. The apparatus may further include a comb plate spaced from the reference plate and coupled to a reference potential, such as ground.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +1
System and device for reducing signal interference in patient monitoring systems
InactiveUS6870109B1Reduce signal interferenceBioelectric signal measurementPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsShielded cableMonitoring system
A system and device for mitigating interference in patient physiological monitoring is provided, particularly in surgical environments. One or more sets of electrodes are placed on a patient's body and connected to corresponding terminals of an input extender. The terminals of the input extender are connected to a set of signal wires encased by a ferrous shielded cable. The ferrous shielded cable connects to a signal processing unit, which includes a differential amplifier and an active drive topology to drive the shield with a common mode signal. The signal processing unit connects to physiological monitoring equipment.
Owner:CADWELL INDS
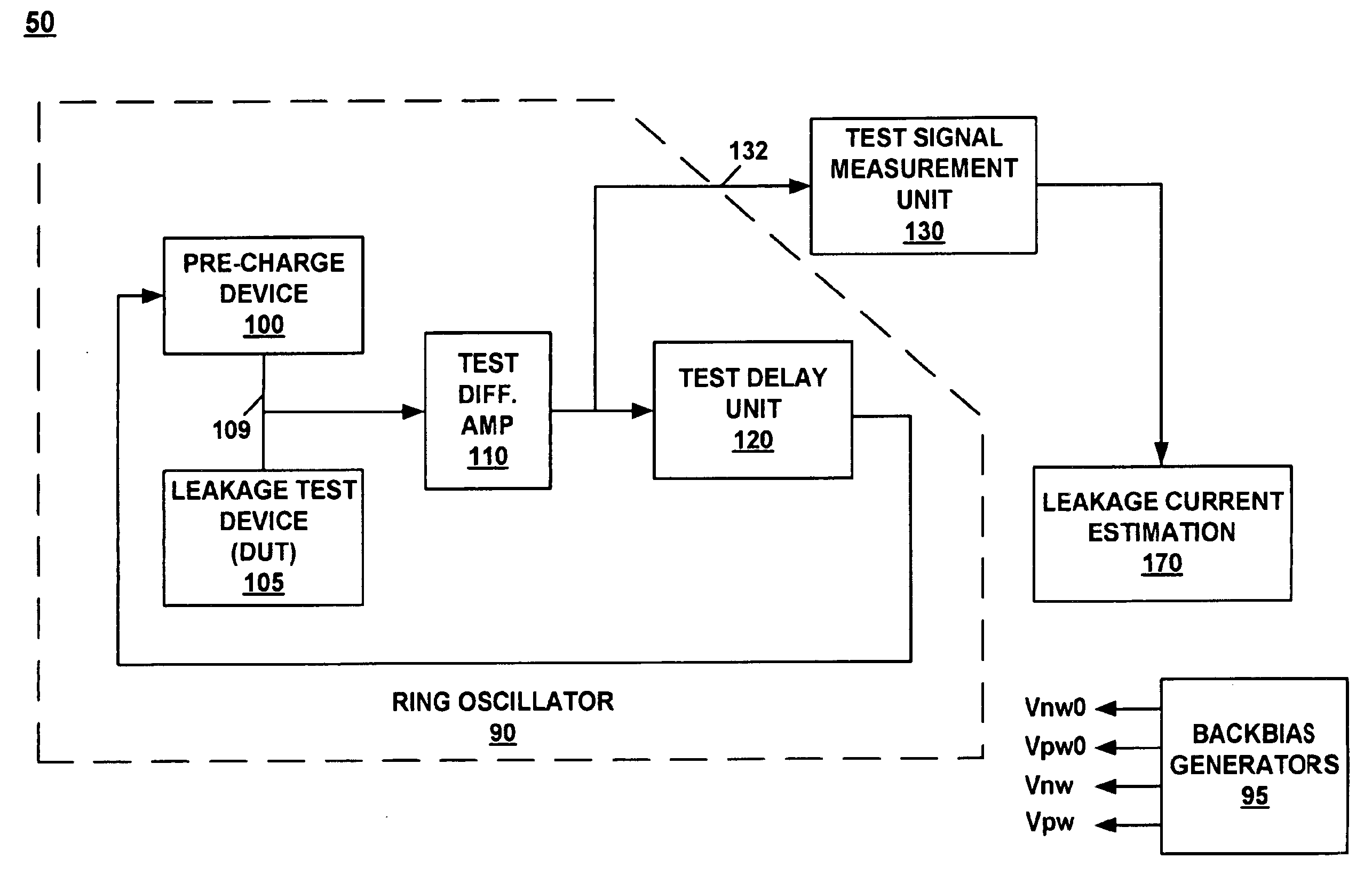
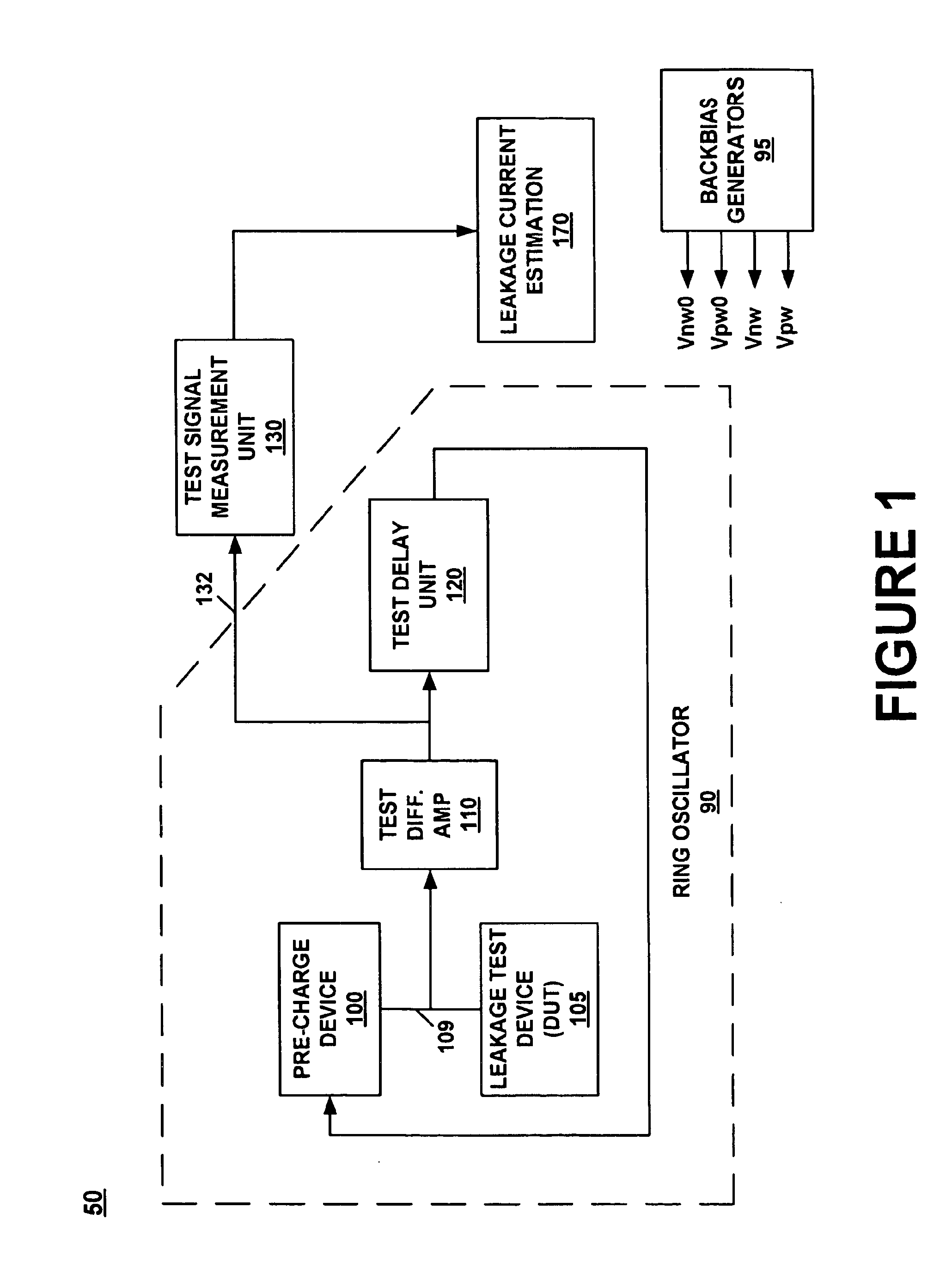
System and method for measuring transistor leakage current with a ring oscillator with backbias controls
A circuit and method thereof for measuring leakage current are described. The circuit includes a pre-charge device subject to a first backbias voltage and a leakage test device subject to a second backbias voltage. The leakage test device is coupled to the pre-charge device. The leakage test device is biased to an off state. A differential amplifier is coupled to the pre-charge device and the leakage test device. A delay unit is coupled to the differential amplifier and to an input of the pre-charge device. The pre-charge device is turned on and off at a frequency that corresponds to said leakage current.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com