Patents
Literature
2997results about "Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
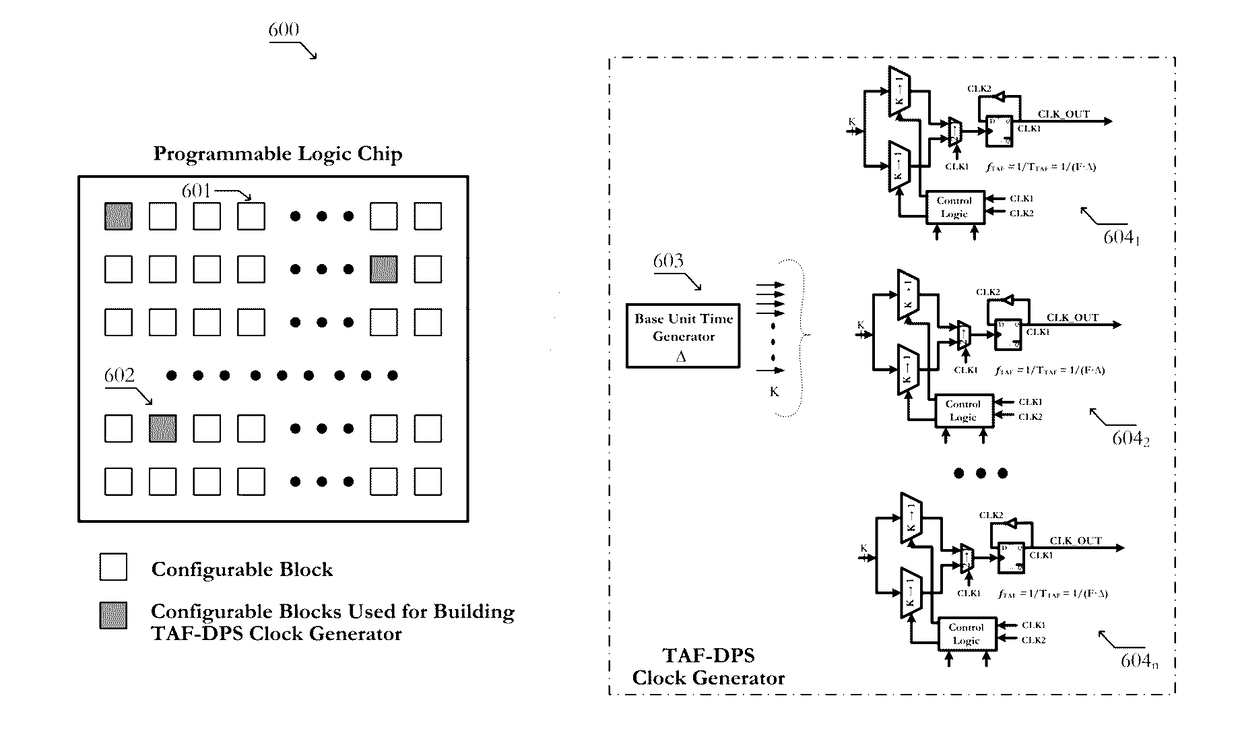
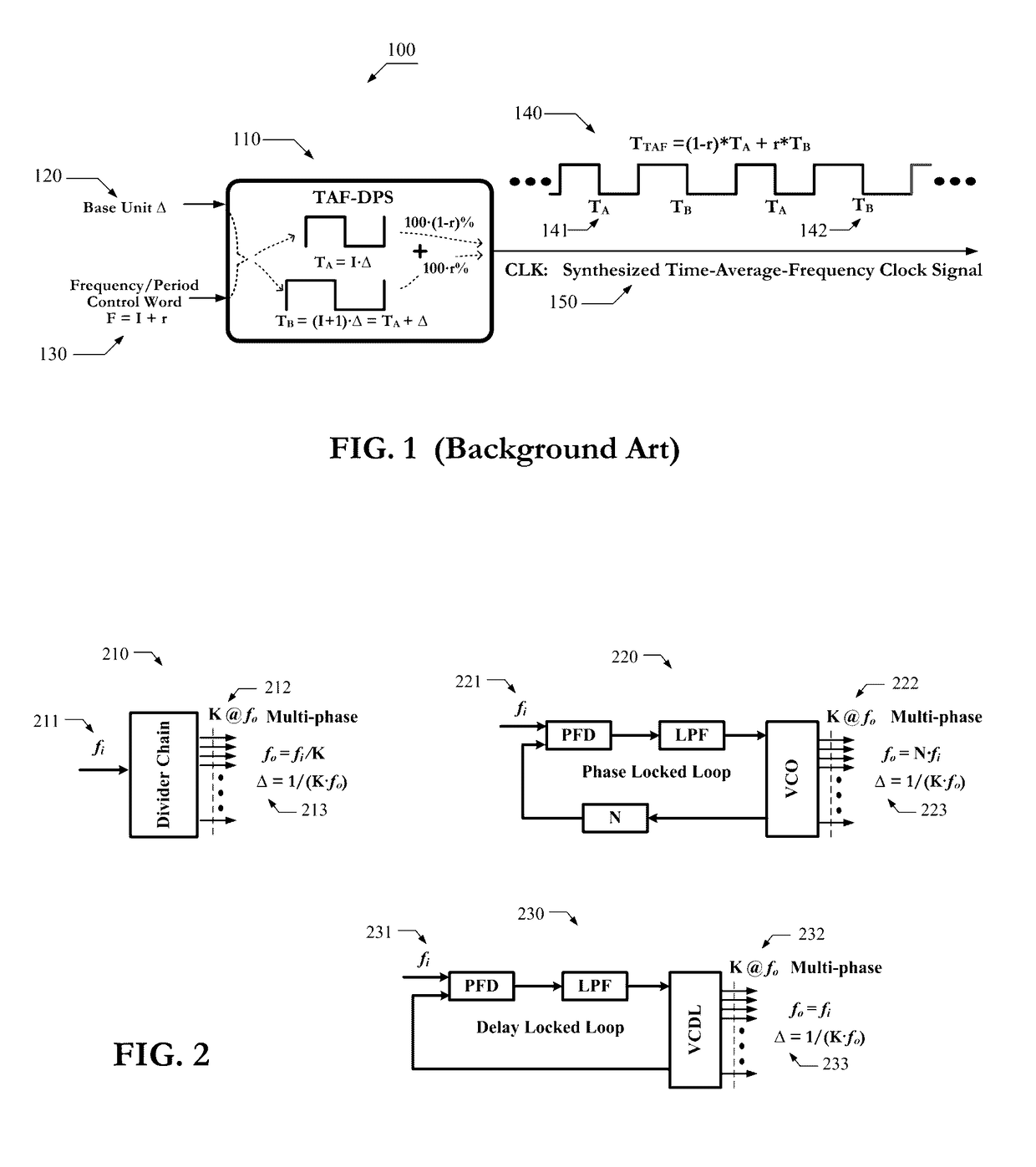
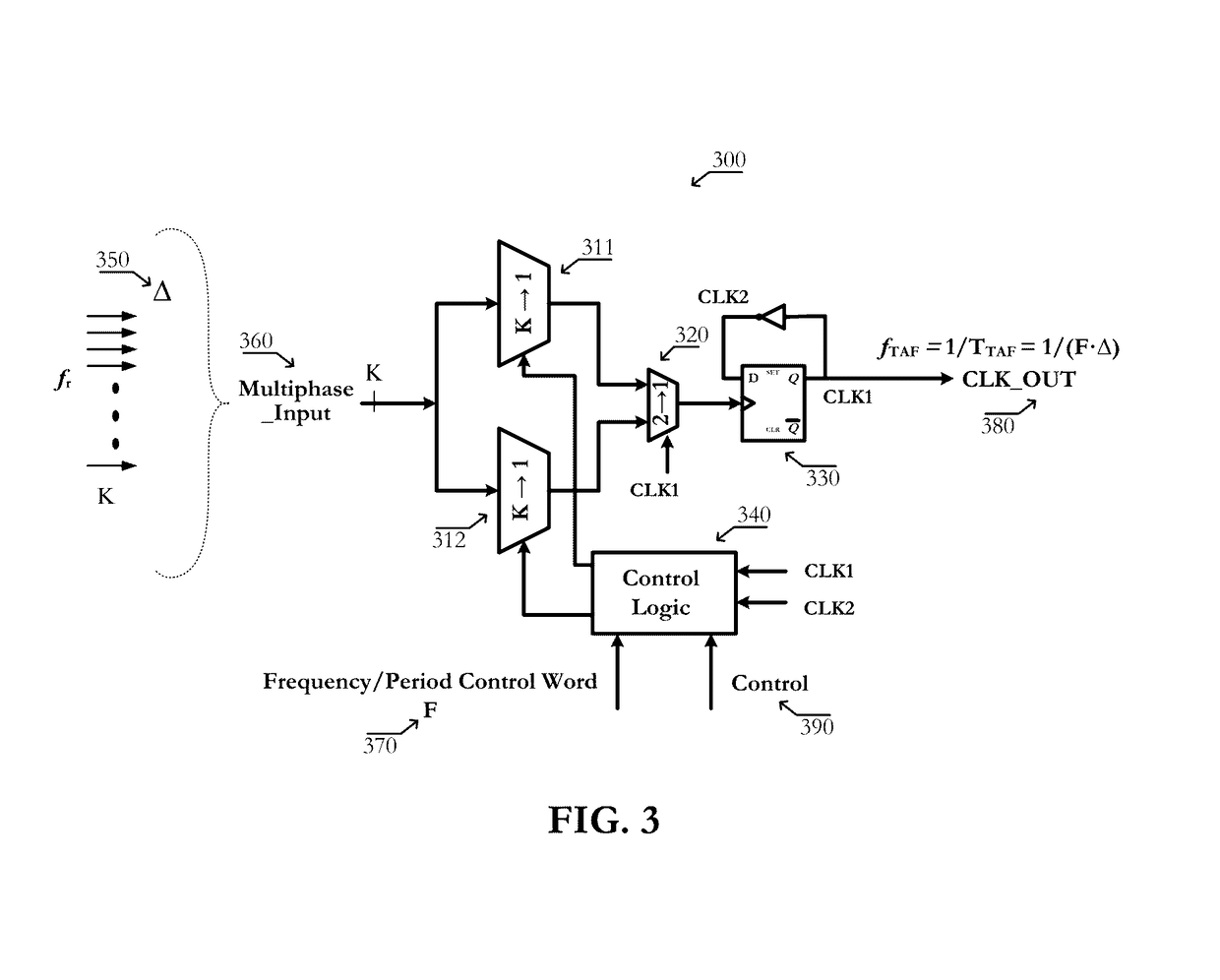
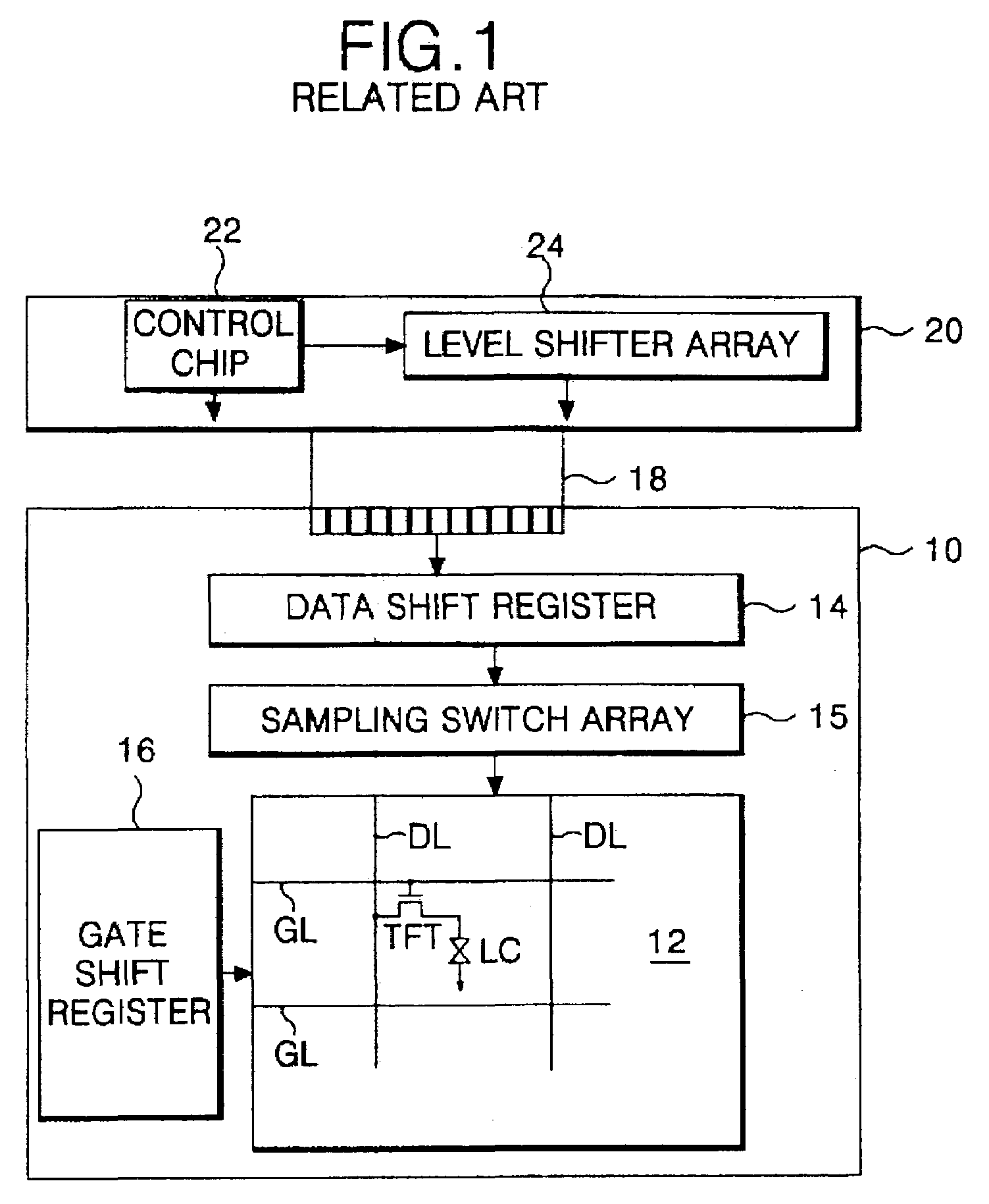
Circuits and methods of implementing time-average-frequency direct period synthesizer on programmable logic chip and driving applications using the same
ActiveUS9621173B1Innovative designPowerful frequency generation capabilityPulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsUnit generatorProgrammable logic device
Circuits of a TAF-DPS clock generator implemented on programmable logic chip comprise: 1) a base time unit generator created from configurable blocks, or on-chip PLL, or on-chip DLL, said base time unit generator produces a plurality of phase-evenly-spaced-signals; 2) a TAF-DPS frequency synthesizer created by configuring configurable blocks of said programmable logic chip, said TAF-DPS frequency synthesizer takes said plurality of phase-evenly-spaced-signals as its input. Methods of creating flexible clock signal to drive application comprise: 1) selecting one or more strategic areas in said programmable logic chip; 2) creating one or more TAF-DPS clock generator for each said area by using the configurable resource in said area; 3) creating control function to control the frequency and duty-cycle of the TAF-DPS clock generator output, said control function can be circuit created from configuring configurable blocks, said control function can also be achieved by software; 4) driving the circuits in application by the flexible clock generated from said TAF-DPS clock generator.
Owner:XIU LIMING
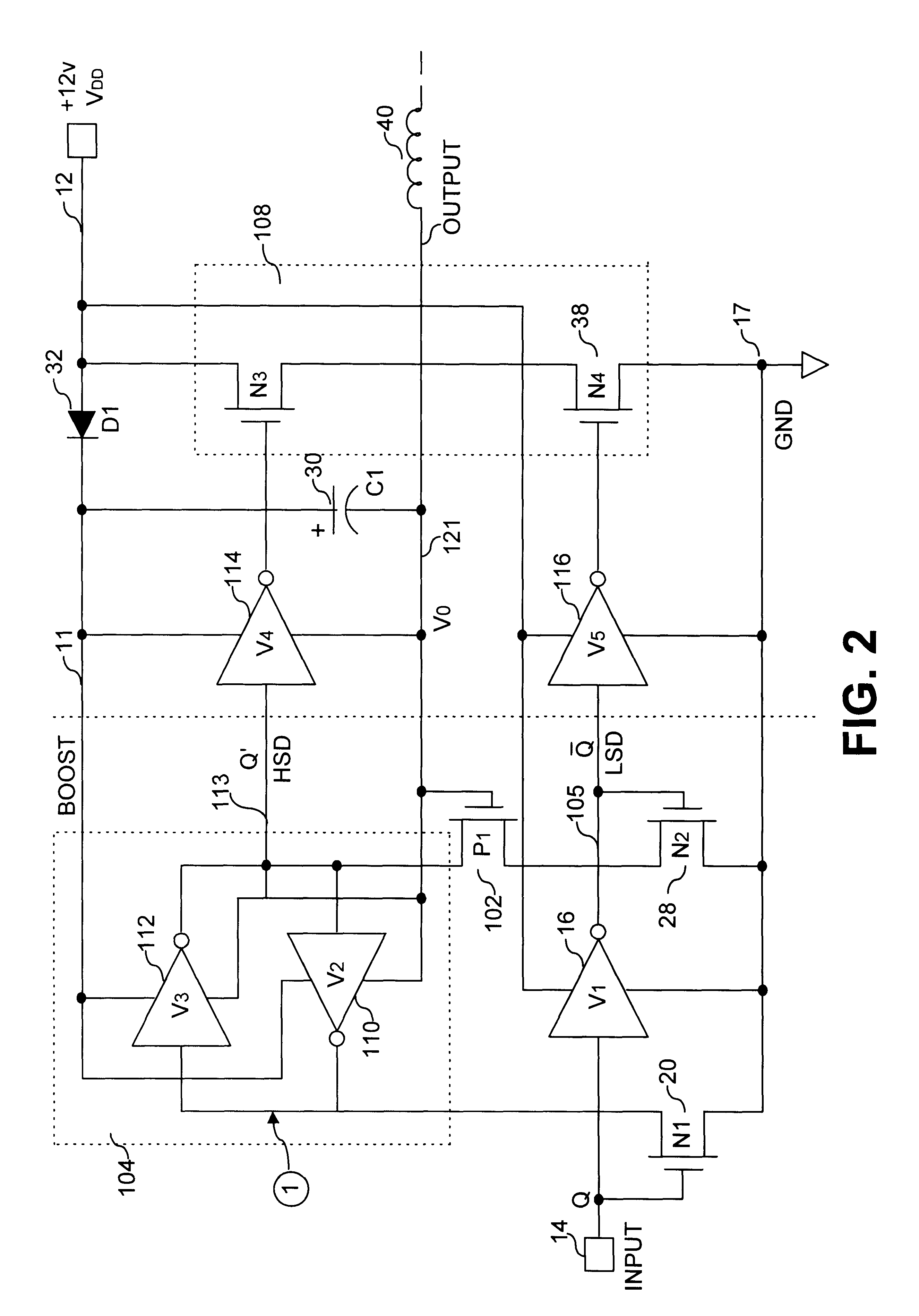
Fast Voltage Level Shifter Circuit
ActiveUS20110181340A1Pulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsField-effect transistorLevel converter
A voltage level shifting circuit with an input terminal and an output terminal. The level shifting circuit has a field-effect transistor (FET) switch with a gate attached to the input terminal, a drain attached to the output terminal and a source attached to a current changing mechanism. The current changing mechanism includes a current mirror circuit having an output connected between the source and an electrical earth. The output of the current mirror circuit is preferably adapted to change a current flowing between the drain and the source based on an input voltage applied to the gate.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
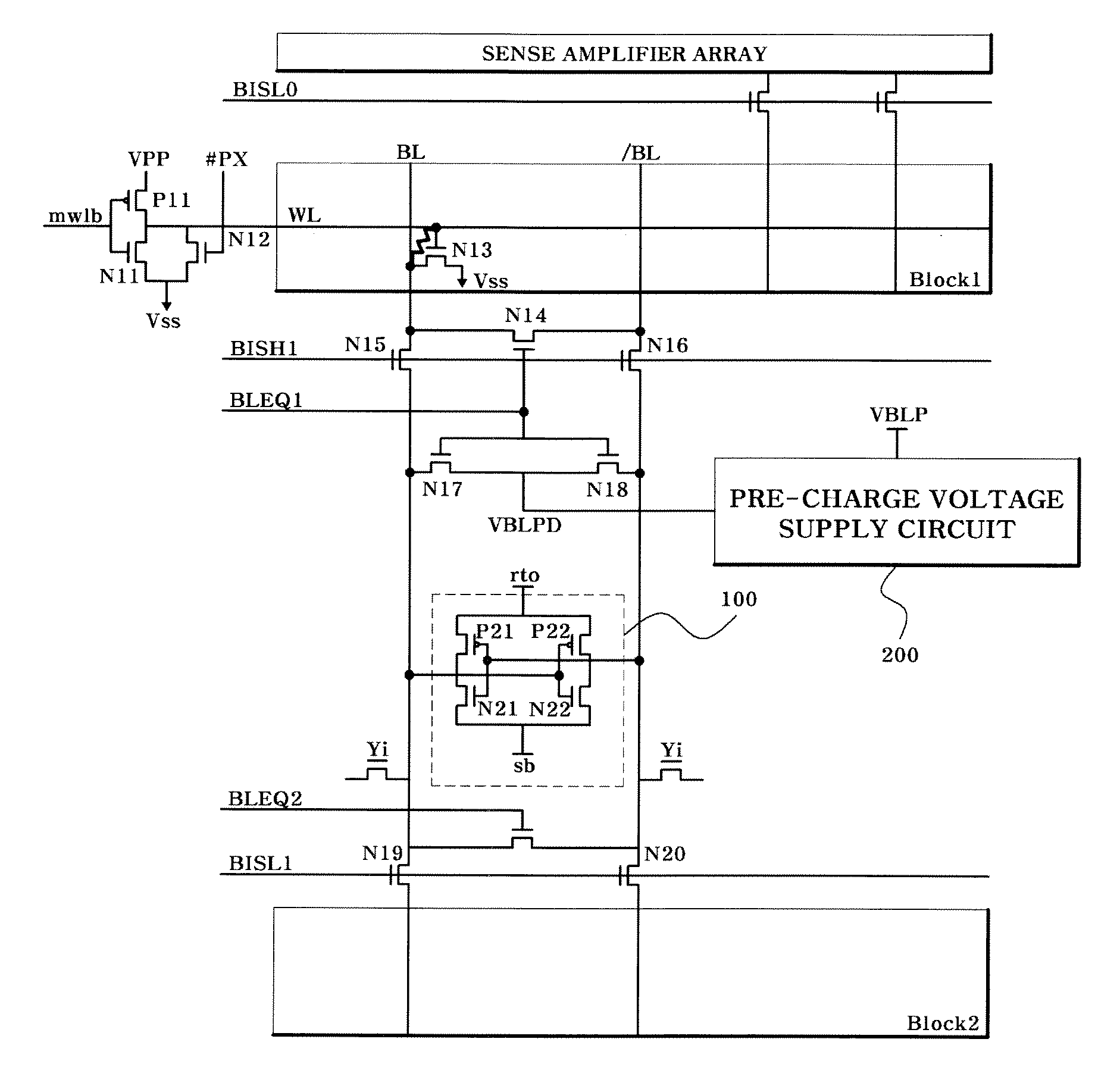
Pre-charge Voltage Supply Circuit of Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20060221738A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease in pre-charge speedLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDigital storageEngineeringPre-charge
A pre-charge voltage supply circuit of a semiconductor device is disclosed which includes a first switch which supplies a pre-charge voltage in response to a first signal having a predetermined voltage level, and has a turn-on resistance of a predetermined level, and a second switch which is connected in parallel to the first switch, supplies the pre-charge voltage in response to a second signal, and has a turn-on resistance lower than the turn-on resistance of the first switch.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
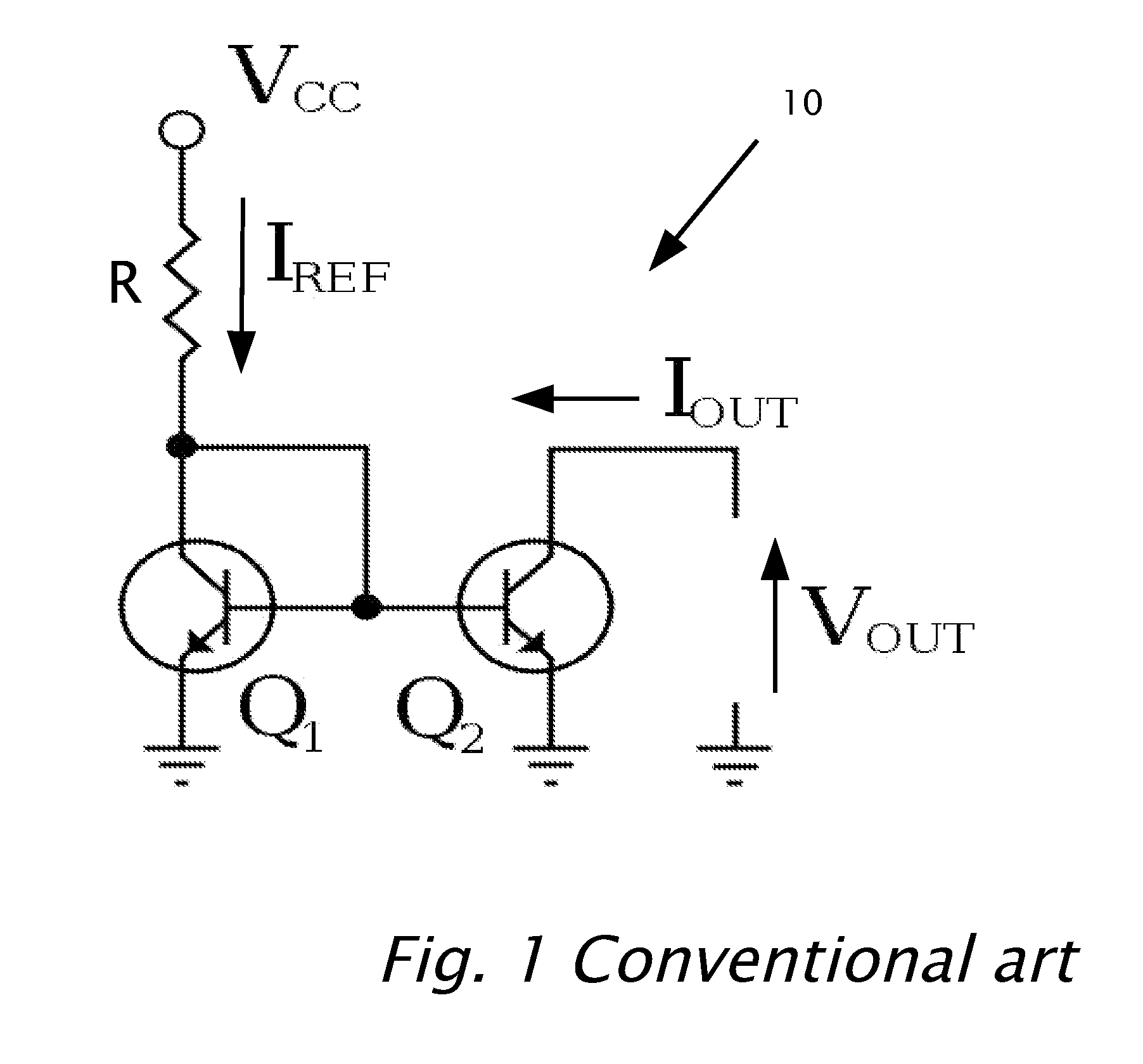
Self-biasing CMOS PECL receiver with wide common-mode range and multi-level-transmit to binary decoder
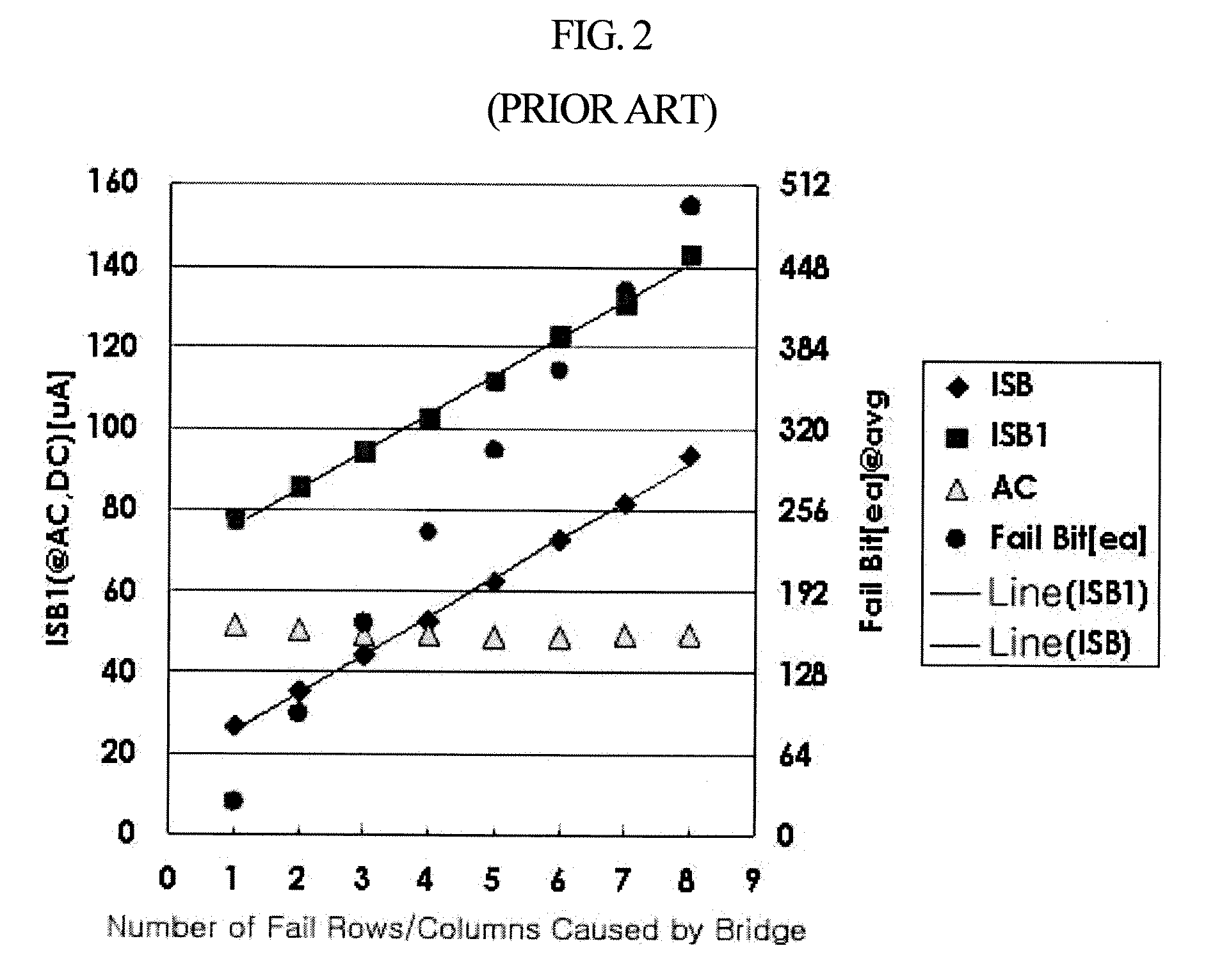
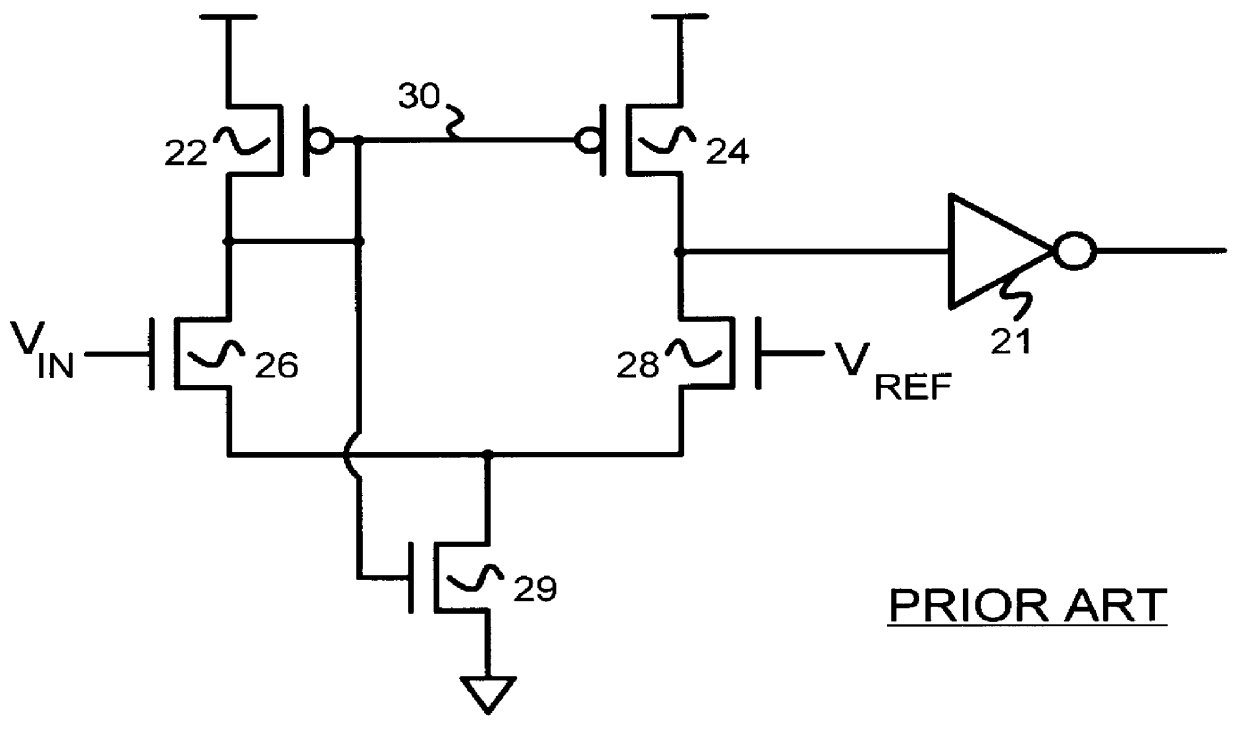
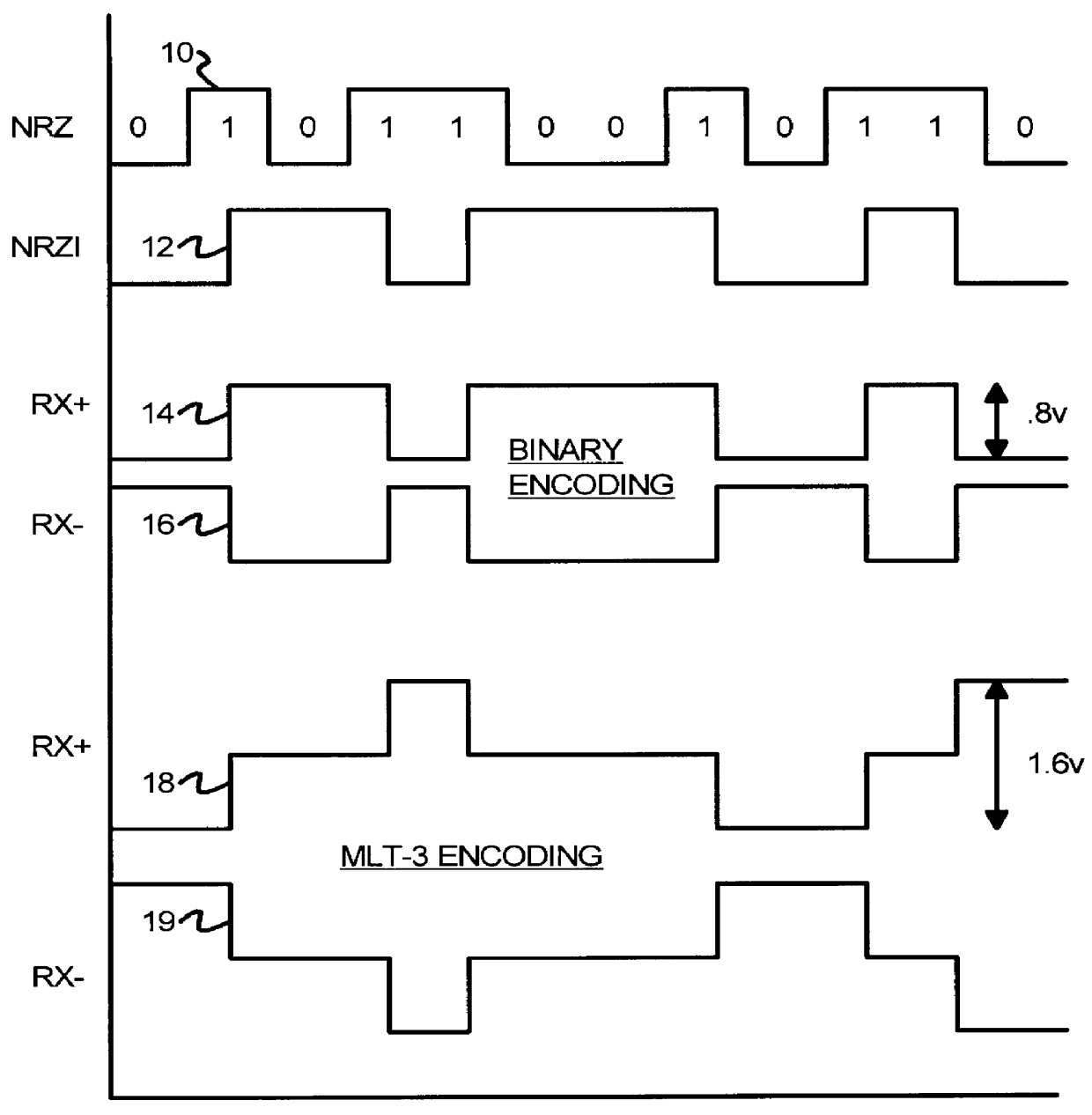
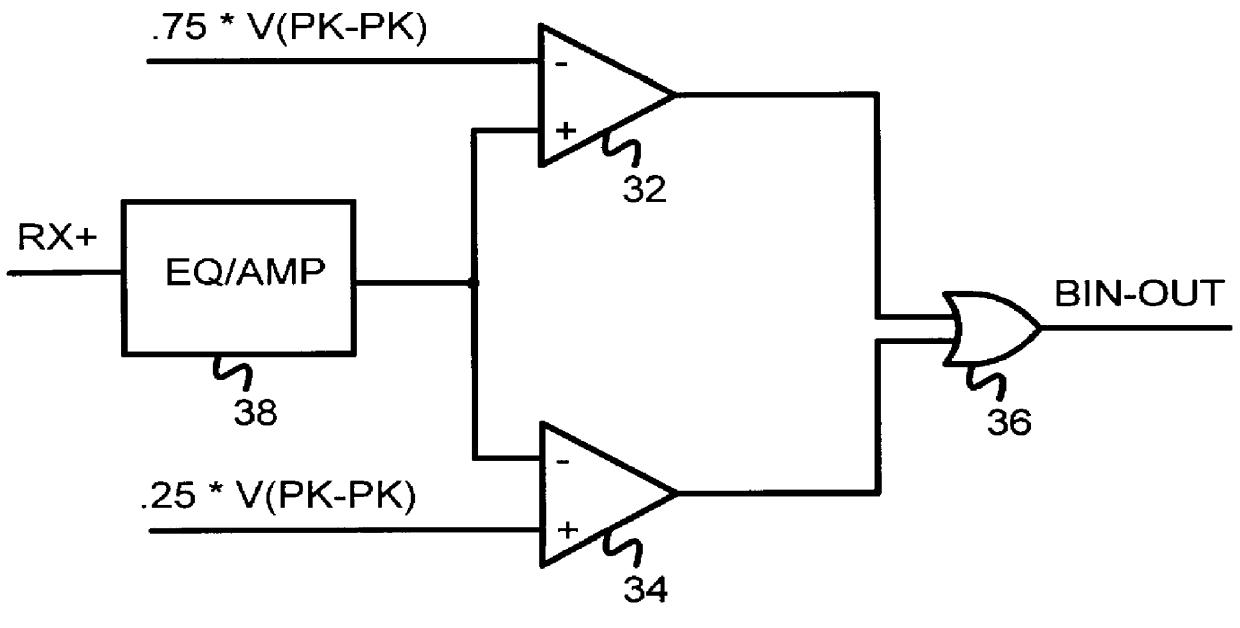
InactiveUS6049229AReduced Power RequirementsSimplify interconnect routingLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsThree levelEmitter-coupled logic
A pseudo-emitter-coupled-logic (PECL) receiver has a wide common-mode range. Two current-mirror CMOS differential amplifiers are used. One amplifier has n-channel differential transistors and a p-channel current mirror, while the second amplifier has p-channel differential transistors and an n-channel current mirror. When the input voltages approach power or ground, one type of differential transistor continues to operate even when the other type shuts off. The outputs of the two amplifiers are connected together and each amplifier receives the same differential input signals. The tail-current transistor is self-biased using the current-mirror's gate-bias. This self biasing of each amplifier eliminates the need for an additional voltage reference and allows each amplifier to adjust its biasing over a wide input-voltage range. Thus the common-mode input range is extended using self biasing and complementary amplifiers. The complementary self-biased comparators can be used for receiving binary or multi-level-transition (MLT) inputs by selecting different voltage references for threshold comparison. Using the same reference on both differential inputs eliminates a second reference for multi-level inputs having three levels. Thus binary and MLT inputs can be detected and decoded by the same decoder.
Owner:DIODES INC
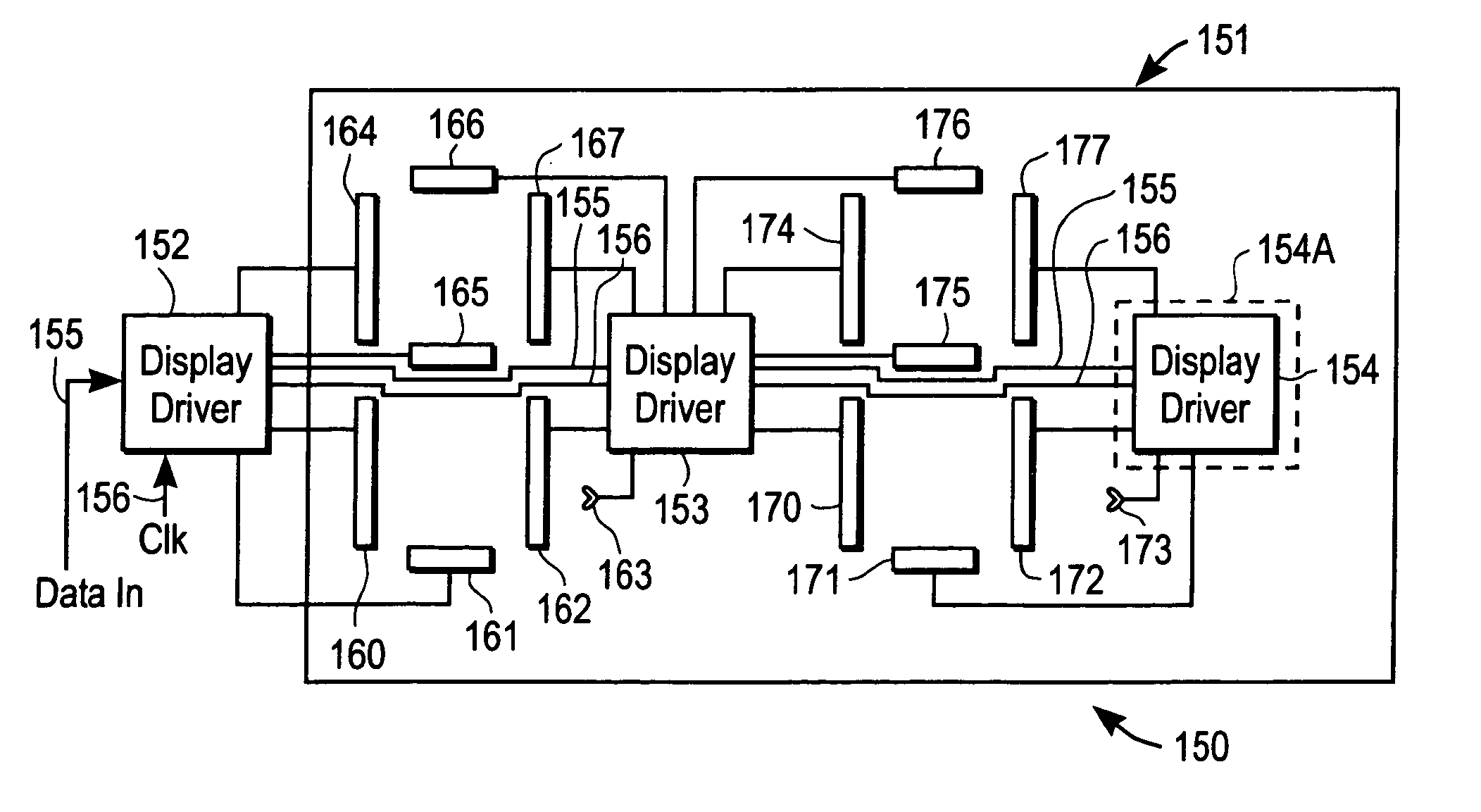
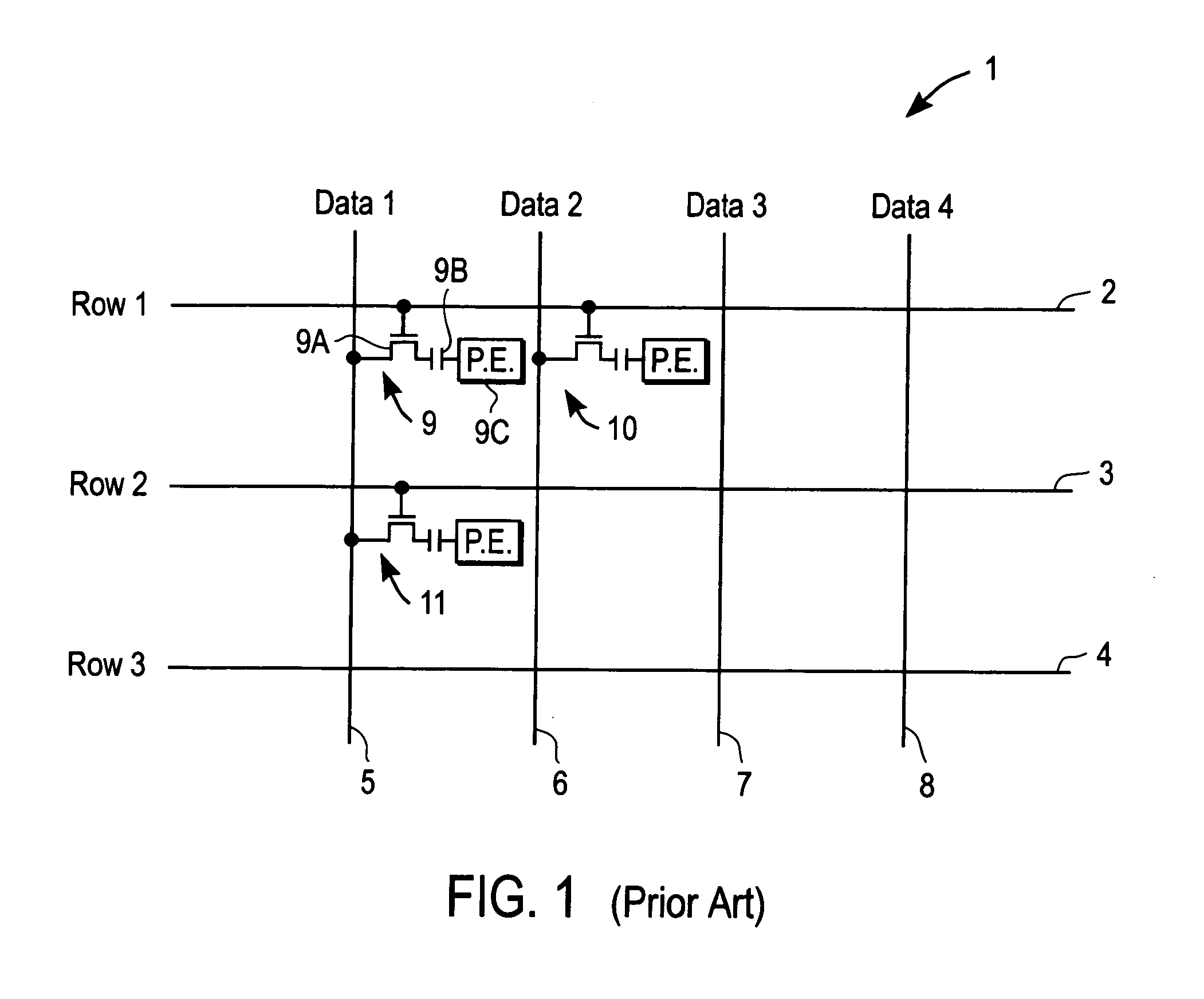
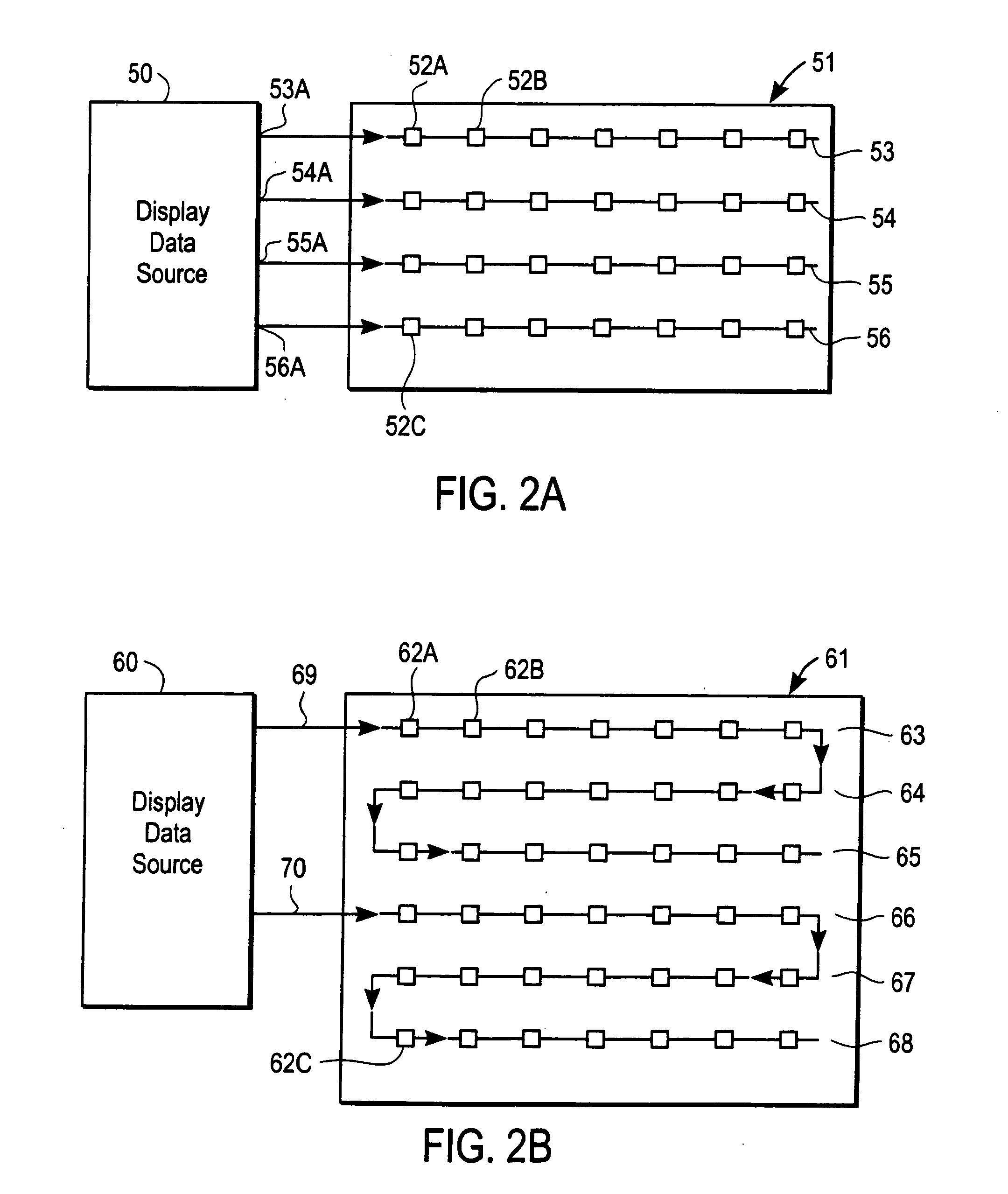
Display devices and integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050206585A1Static indicating devicesLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsShift registerEngineering
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Multi-function input/output driver
InactiveUS6856178B1Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorCMOSDifferential signaling
A high-speed I / O driver includes circuitry that is configurable to meet single-ended and differential I / O signal standards. For one embodiment, the driver includes four input circuits that can be configured to implement two CMOS inverters to process single-ended signals or configured to implement a differential circuit to process differential signals.
Owner:PROMISE TECHNOLOGY
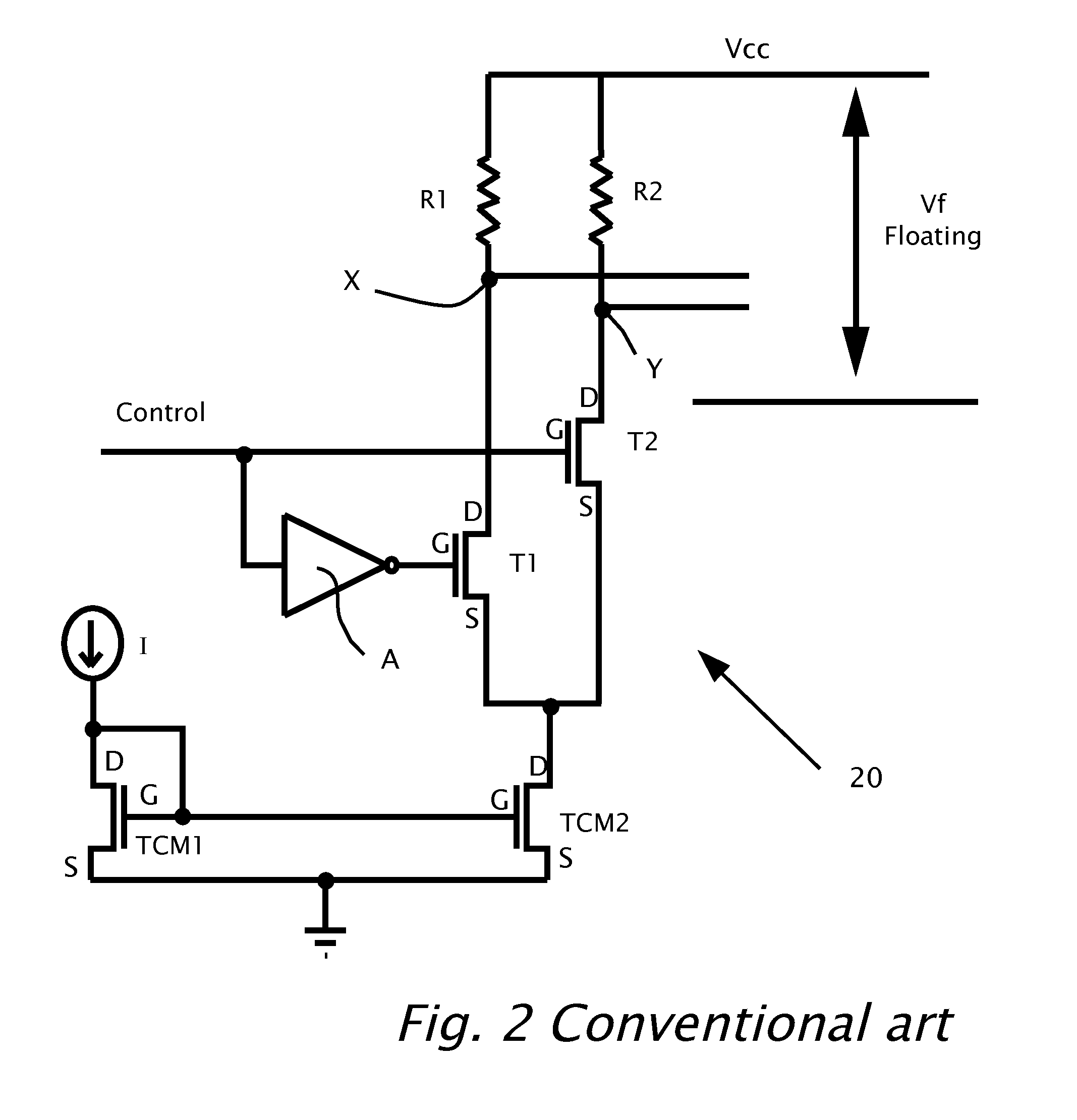
Clamped cascode level shifter circuit
InactiveUS6201429B1Preventing continuous current conductionHysteretic SwitchingPower reduction in field effect transistorsPulse automatic controlCascodeEngineering
An improved level shifter circuit that toggles a "flying Flip-Flop" comprising a cross-coupled inverter pair with control devices driven out of phase through a pair of cascode transistors. The cross-coupled inverter pair provides pull-up to the positive rail, clamping to a High Side-Common (HSC), and providing Hysteretic Switching. The cascode transistors restrict the pull-down of the control devices, thereby preventing continuous current conduction.
Owner:AME
Display devices and integrated circuits
InactiveUS6980184B1Static indicating devicesLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsShift registerProcessor register
Integrated circuits, assemblies with integrated circuits, display devices and electrical circuits. There are various different aspects and embodiments of these apparatuses described herein. According to one aspect, a display device includes a plurality of display drivers which includes a serial shift register, wherein the display drivers are located in the display area of the display device which is viewable. According to another aspect, an integrated circuit, which has a plurality of functionally symmetric interface pads, includes an instruction decoder which decodes instructions received through at least one of the pads. In another aspect, an integrated circuit (IC) includes a position detector which detects a position of the IC relative to a receptor substrate and provides a signal which is determined by the position; this IC may be used in an assembly which includes the receptor substrate. In another aspect, an IC includes a position detector which detects a position of the IC relative to a receptor substrate and also includes a configurable pad which is configurable, depending upon the position as one of at least two of the following: an input pad, an output pad, or a no-operation pad. According to another aspect, a layout of an IC has a plurality of functionally symmetric interface pads wherein two such pads are configurable pads. According to another aspect, an assembly includes a receptor substrate and an IC attached to the substrate, and the IC includes a first logic circuit which provides a first function, a second logic circuit which provides a second function, and a selector which selects between the two functions such that the IC performs only the selected function. Other aspects and methods are also described.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Versatile RSDS-LVDS-miniLVDS-BLVDS differential signal interface circuit
InactiveUS6992508B2Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDifferential signalingVoltage source
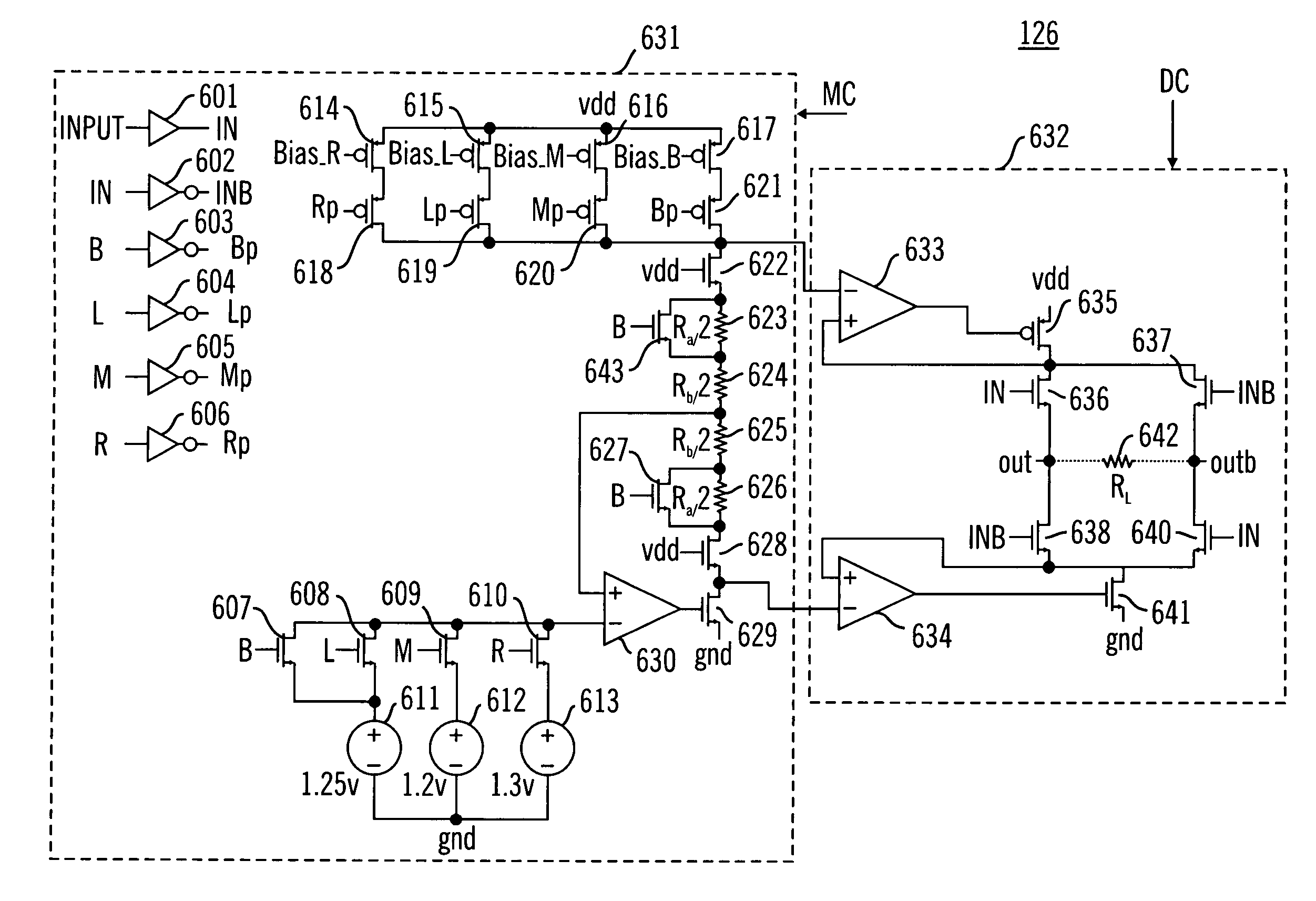
An electronic circuit includes a selectively configurable differential signal interface and a selection control input for selecting one of a plurality of standard differential signal interfaces for configuration of the differential signal interface. The selection control input selects one of the following plurality of standard differential signal interfaces: reduced swing differential signaling (RSDS), low voltage differential signaling (LVDS), mini low voltage differential signaling (mini-LVDS), and bussed low voltage differential signaling (BLVDS), for configuration of the differential signal interface. The electronic circuit may also include a plurality of selectable voltage sources (611, 612, 613) and a plurality of selectable current sources (614, 615, 616, 617), for selecting, in response to an input signal at the selection control input, at least one of an operating D.C. voltage, a standard differential signal voltage, and a standard differential signal current for the differential signal interface.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Broad output current scope low pressure difference linear manostat
InactiveCN101339443AIncreased unity-gain bandwidthImprove stabilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceCurrent range
A low dropout linear voltage regulator with wide output current range and low pressure difference, comprises an error amplifier in the folding common source and common gate structure, a buffer circuit, a driving element, a feedback circuit, a load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit and a multistage Miller compensation circuit, wherein the buffer circuit changes the low frequency pole into a medium frequency pole and a high frequency pole; the large load capacitance of the load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit pushes the main pole to the low frequency, causing the gain crossover point to push inwards, and generating a medium frequency zero point for counteracting the medium frequency pole connected serially with the equivalent series resistance; the stride multilevel Miller compensation circuit generates a medium high frequency pole and a medium high frequency zero point slightly smaller than the medium high frequency pole for advancing the phase margin, thereby not only adding the unity gain bandwidth, but also saving considerable chip area. When the output current has a large change range, the structure provided by the invention generates wider unity gain bandwidth, provides the phase margin of greater than 85 degrees, ensures the stability of the system and advances the low pressure difference linear voltage stabilization performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Integrated circuit output driver circuitry with programmable preemphasis
ActiveUS6940302B1Reliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
Programmable logic device integrated circuitry having differential I / O circuitry is provided. The differential I / O circuitry may include output drivers for providing differential digital output data signals across pairs of output lines. A user may program the I / O circuitry to accommodate different high-speed differential I / O signaling standards. The user may also program the I / O circuitry to provide a desired amount of preemphasis to the output data signals.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Level shifter circuit
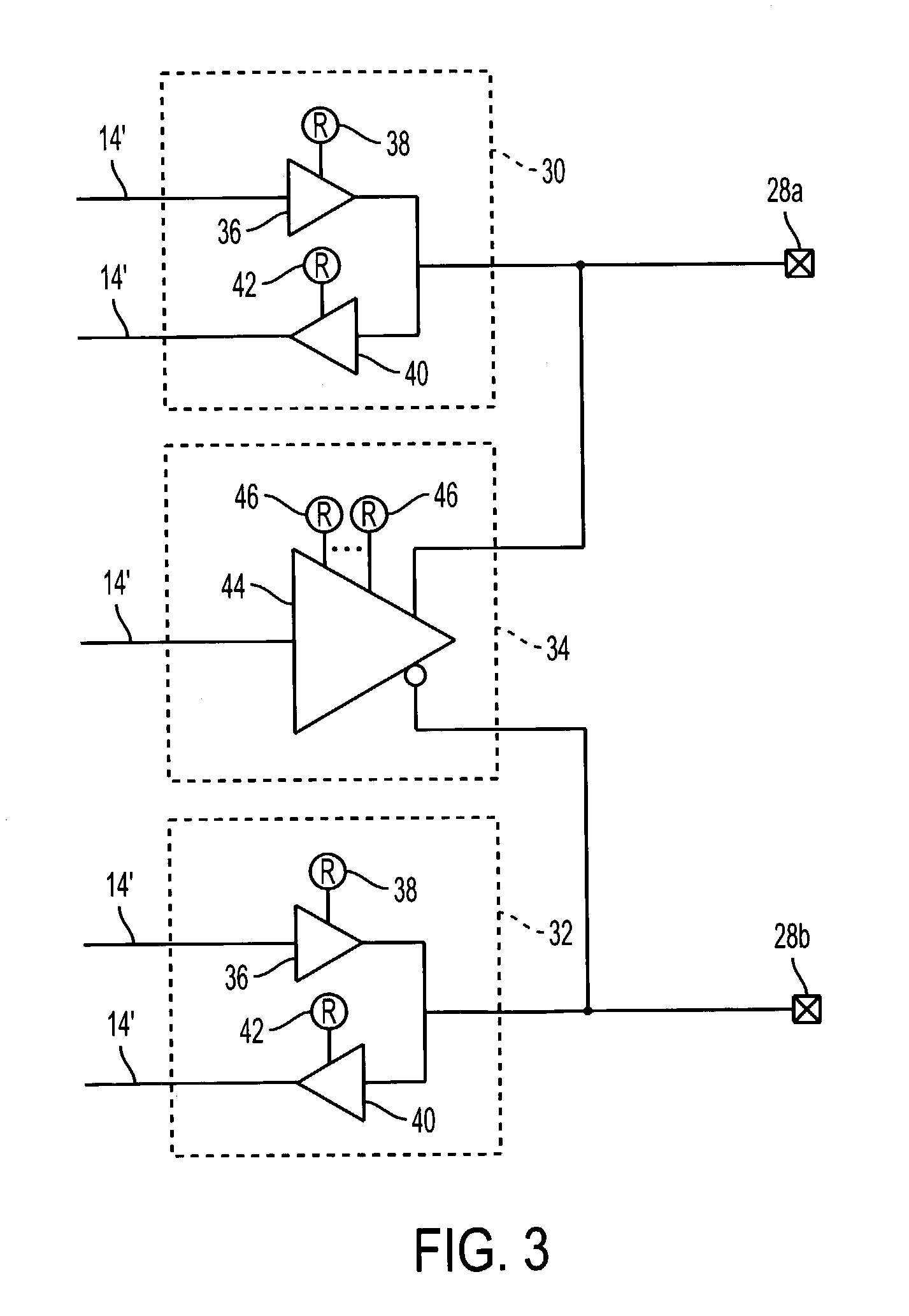
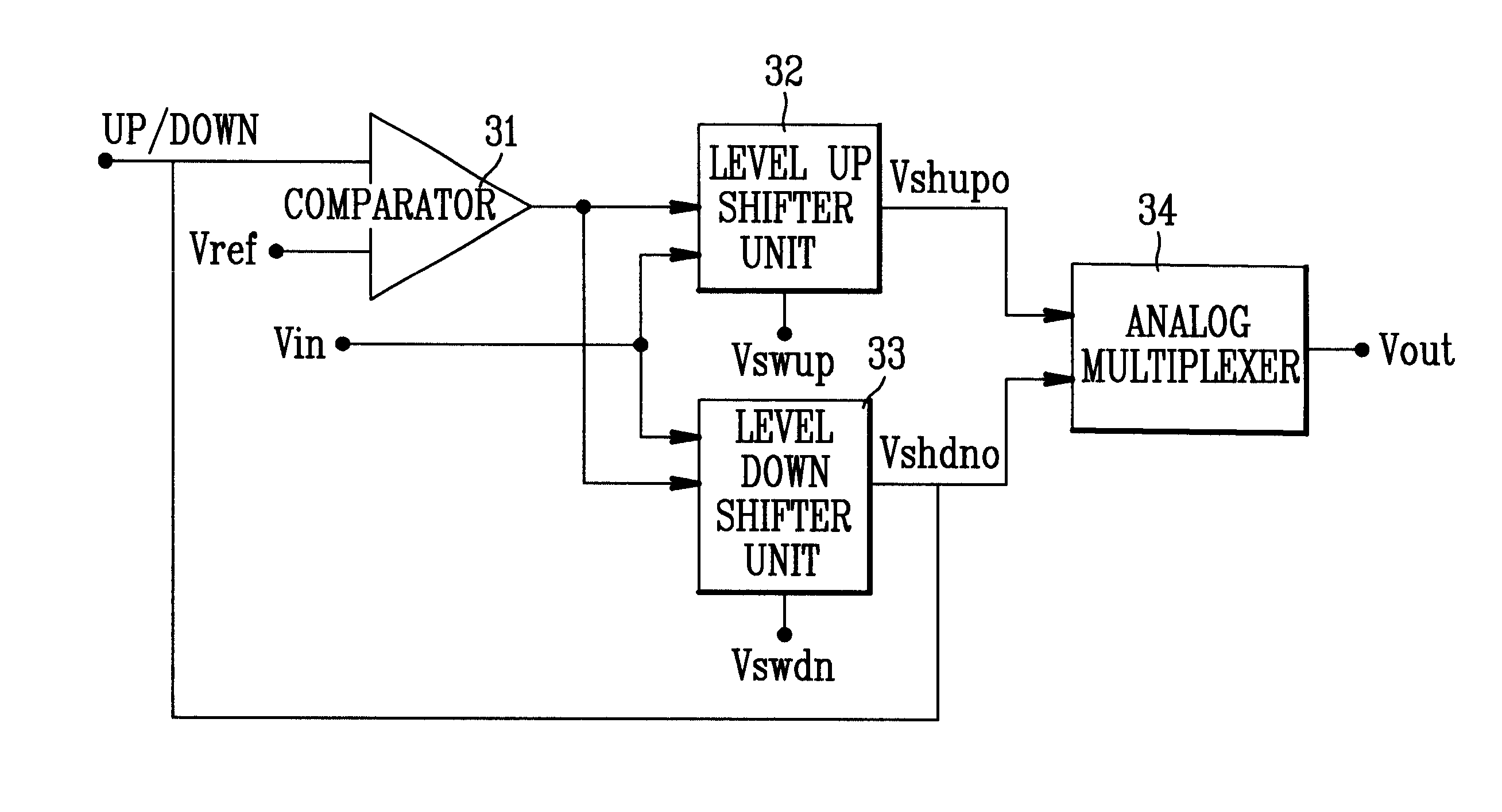
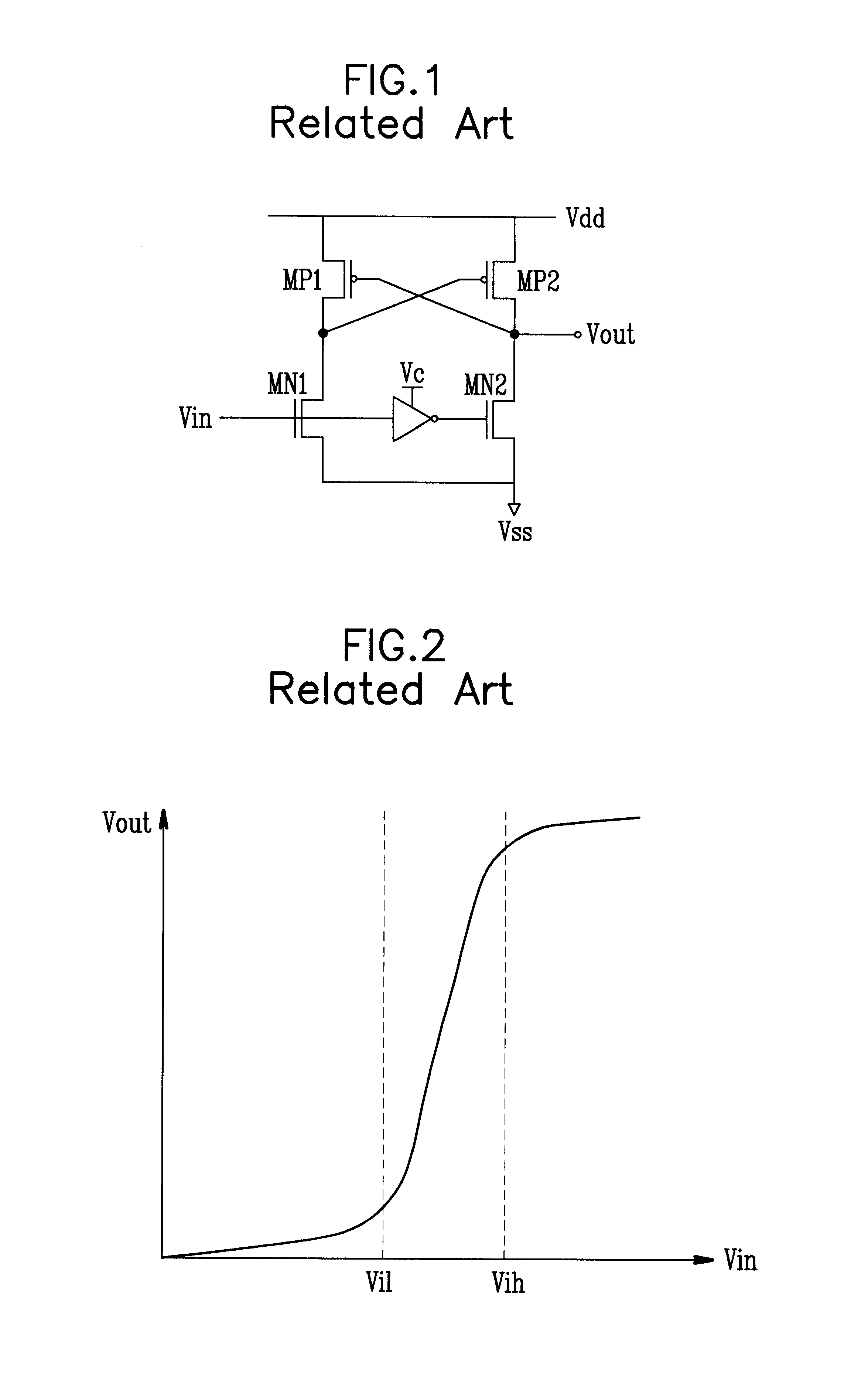
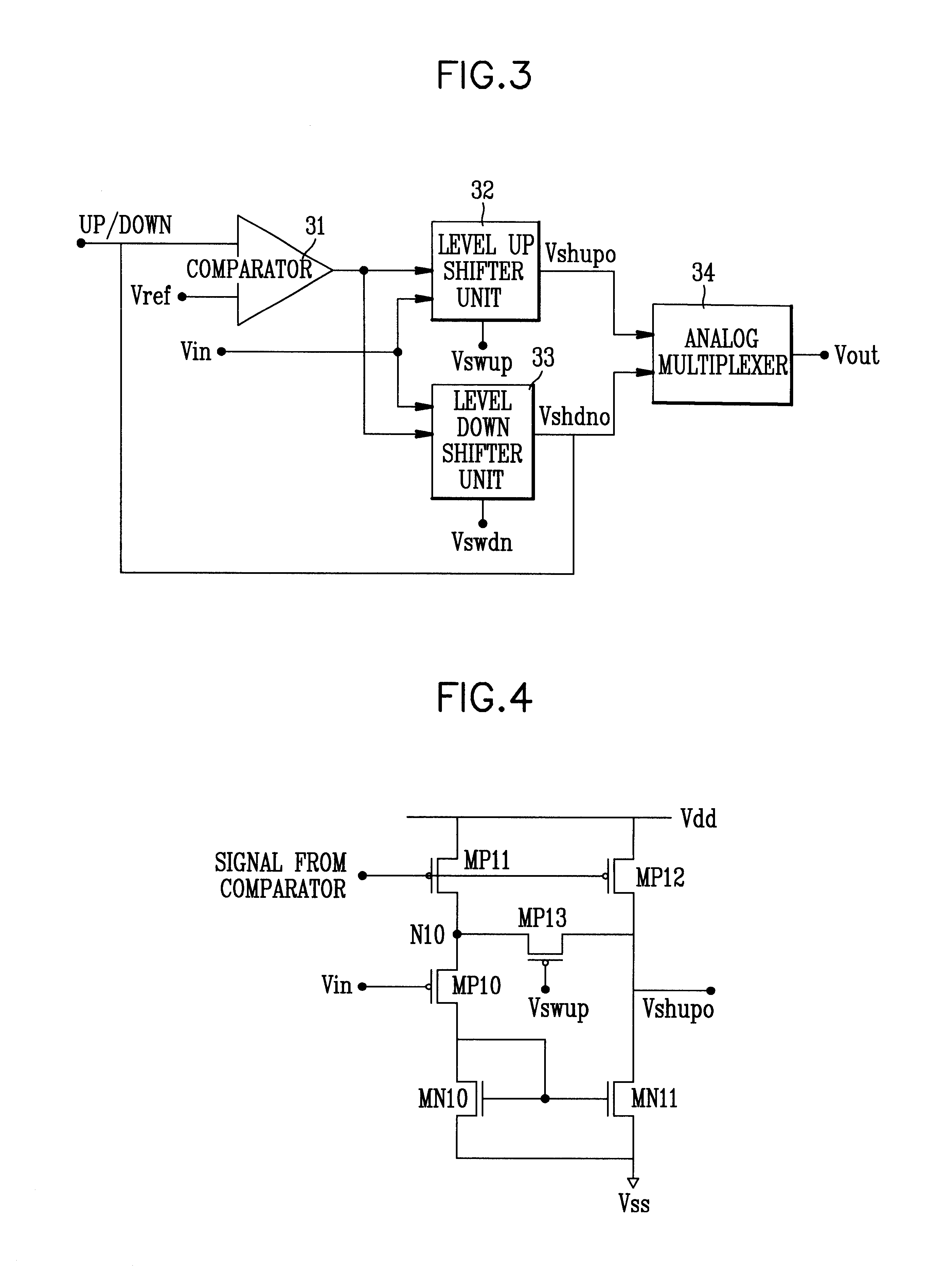
InactiveUS6222385B1Efficient level shift operationGuaranteed uptimeLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsLogic circuits using semiconductor devicesControl signalMultiplexer
Level shifter circuit which can make an efficient level shift to level up or level down according to a change of a digital logic characteristic, including a comparator for comparing an up / down control signal to a reference signal in disabling either one of the level up shifter or the level down shifter according to the up / down control signal, a level up shifter unit for leveling up of an input voltage in response to a level up shifter / level down shifter disable signal from the comparator, a level down shifter unit for leveling down of an input voltage in response to a level up shifter / level down shifter disable signal from the comparator; and an analog multiplexer for selectively providing a leveled up signal or a leveled down signal from the level up shifter unit or the level down shifter unit.
Owner:CHIAO TUNG HLDG LLC
Interchangeable CML/LVDS data transmission circuit
InactiveUS6847232B2Easy to operateReduce input voltageLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesDriver circuitTransceiver
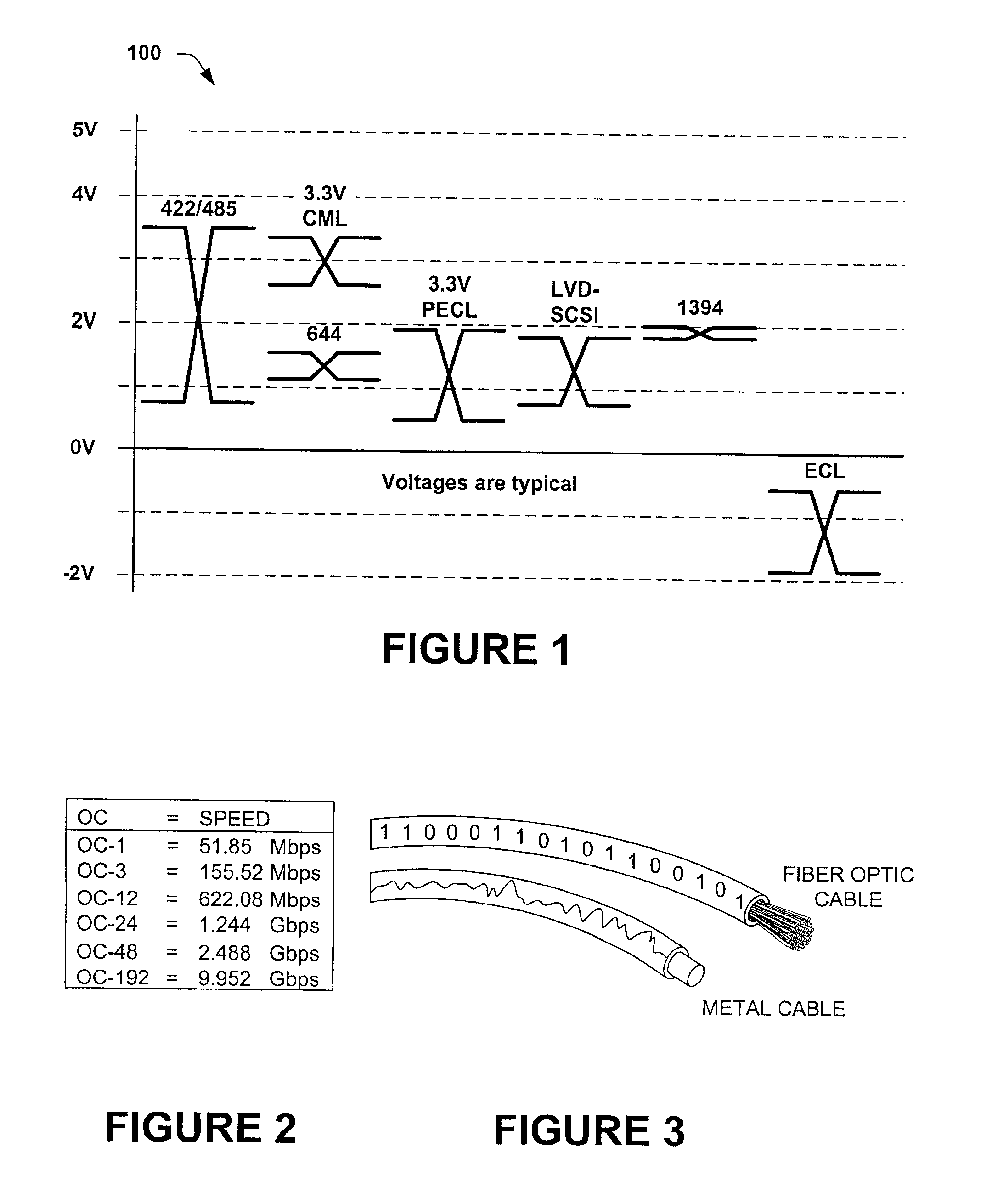
A system and method is described for a driver circuit used for high speed data transmission in LVDS and CML transceiver device applications. The transceivers are intended to receive a low voltage differential input signal and interchangeably drive a standard LVDS load with a TIA / EIA-644 compliant LVDS signal, and a standard CML load with a standard CML compatible signal. The driver circuit operates at speeds up to 1.36 Gbps, making it compatible with the OC-24 signaling rate for optical transmission. To accomplish this, the driver uses a mixed combination of voltage and current mode drive sections in the output circuit when coupled to LVDS loads, and when the driver is coupled to CML loads, operates purely in a current mode using only the current mode drive section. MOS transistors and a current source are used in the current mode switch portion to switch the drive with a constant current at the high speeds, and NPN transistors in the voltage mode output portion provide variable impedance for the output circuit. A common mode compensation circuit using a feedback voltage from the load generates a compensation signal for variable impedance control of the NPN transistors to yield a regulated voltage for the common mode dc voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Micropower RC oscillator
InactiveUS6462625B2Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsGenerator stabilizationElectrical resistance and conductanceClosed loop
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
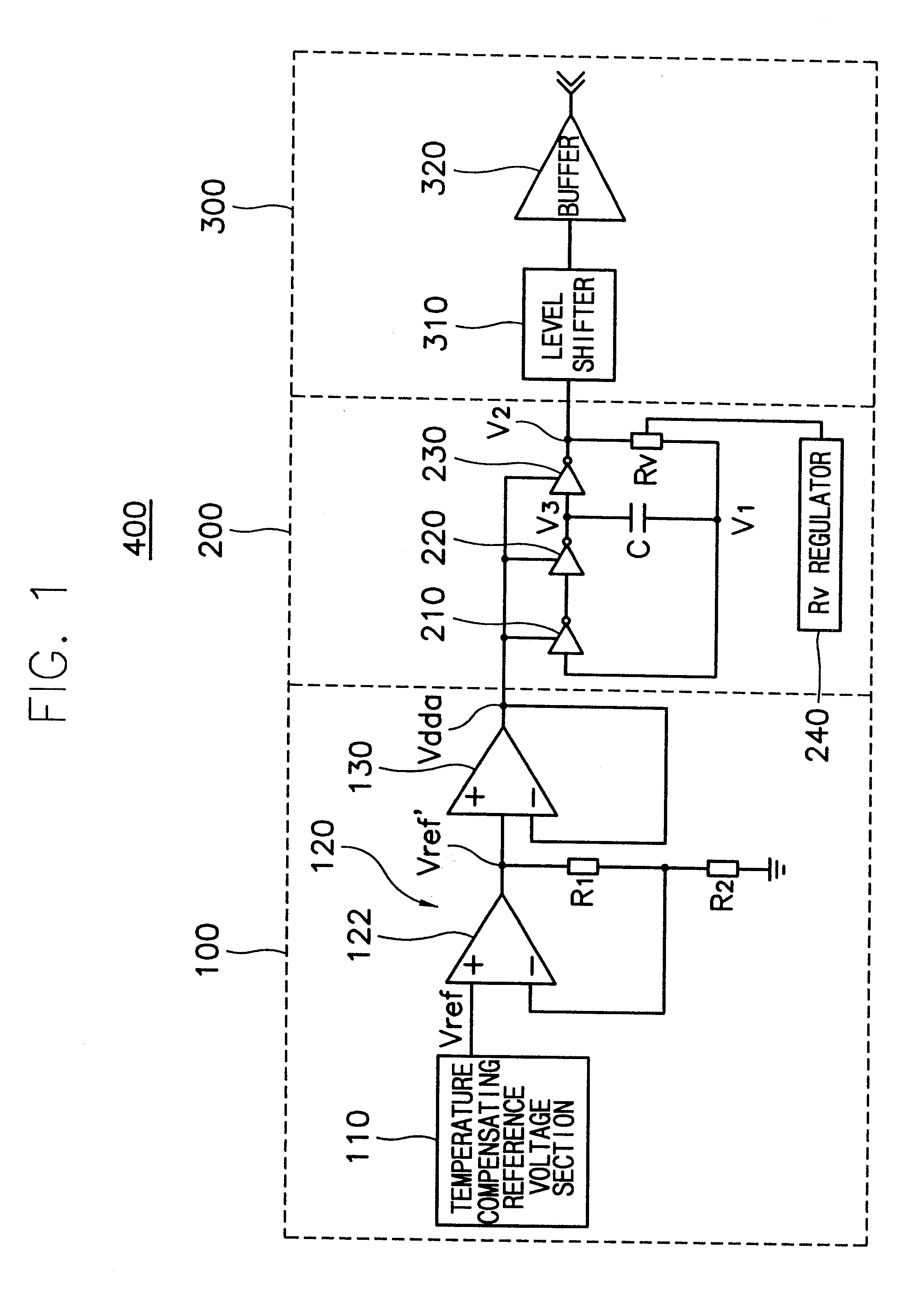
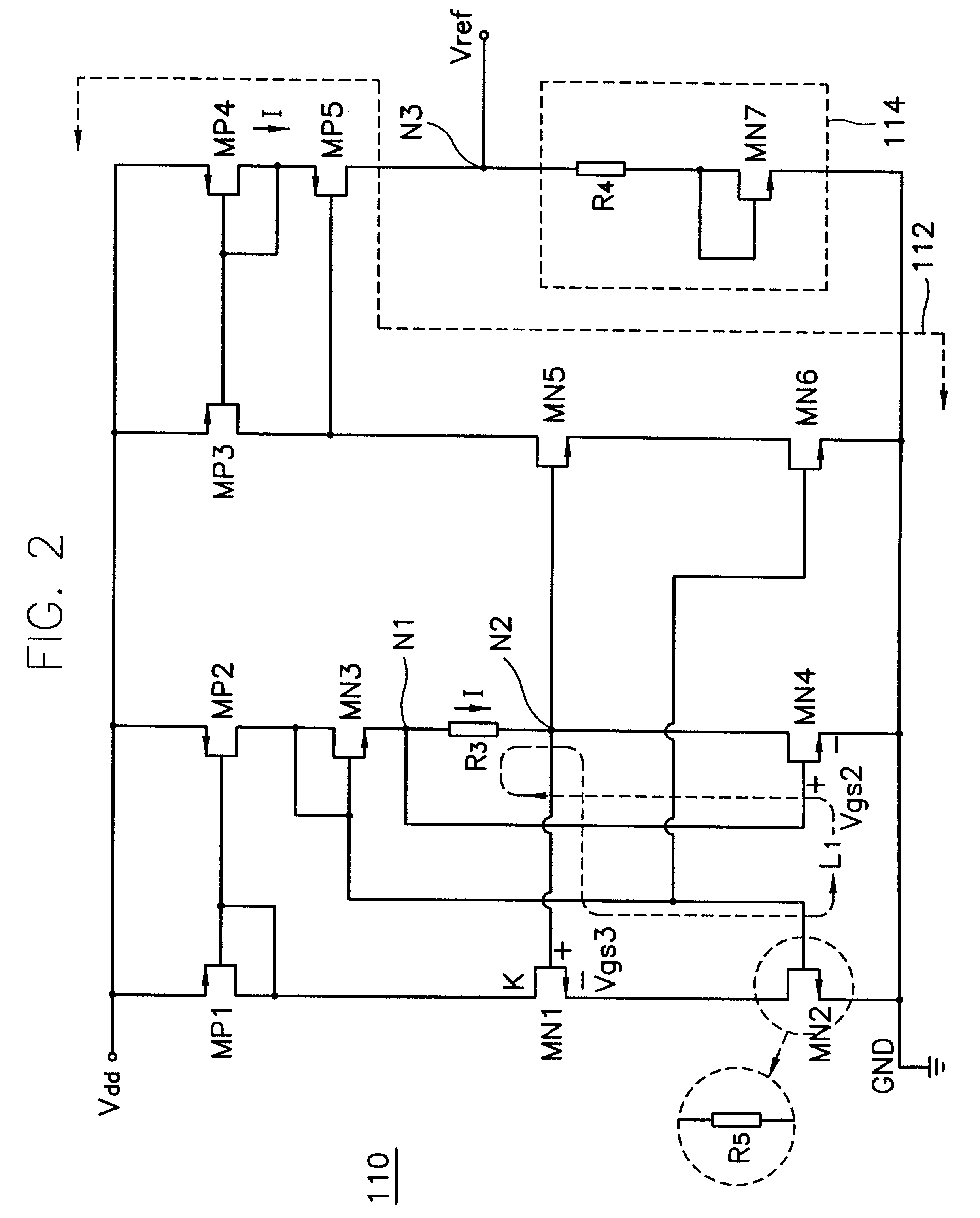
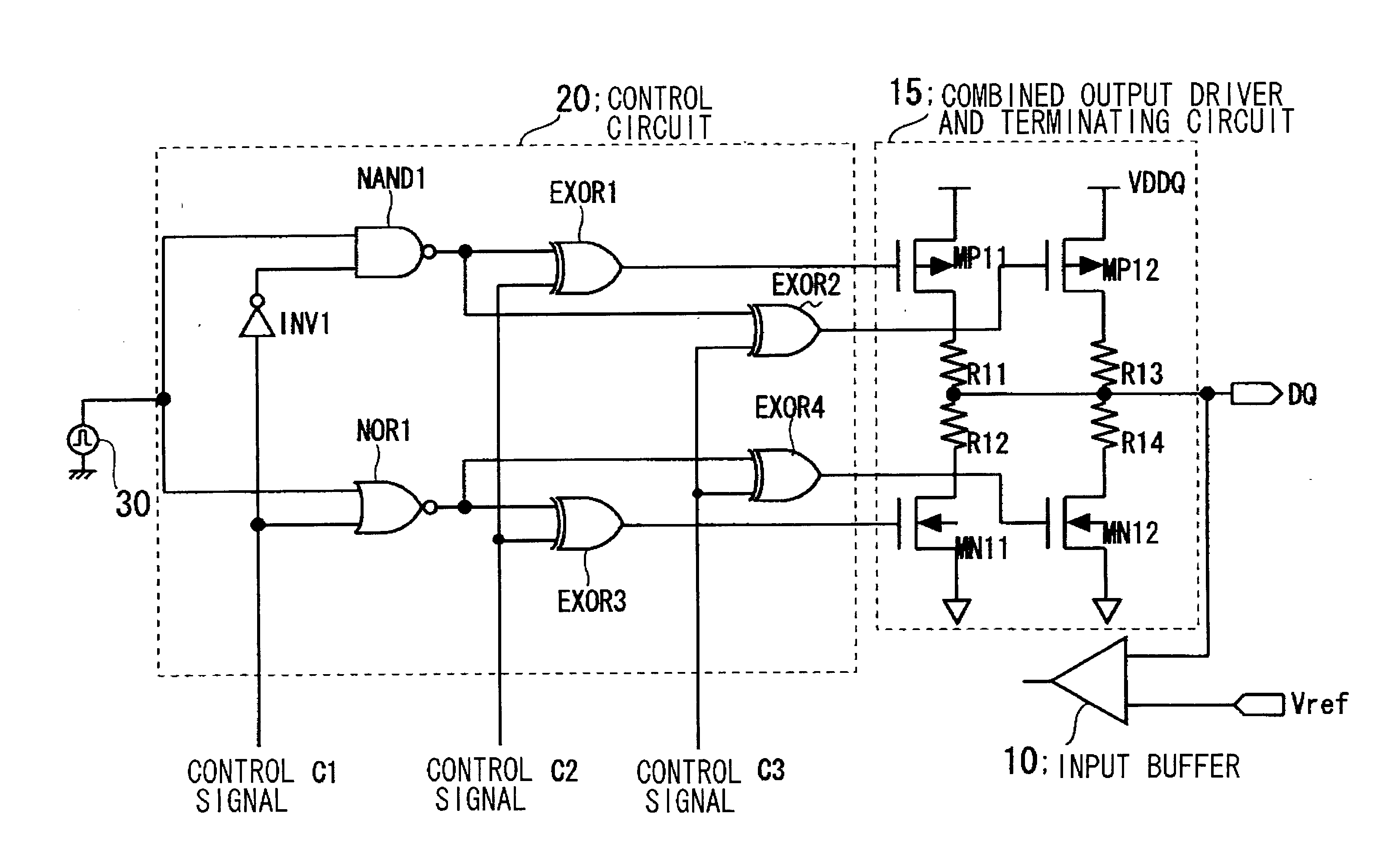
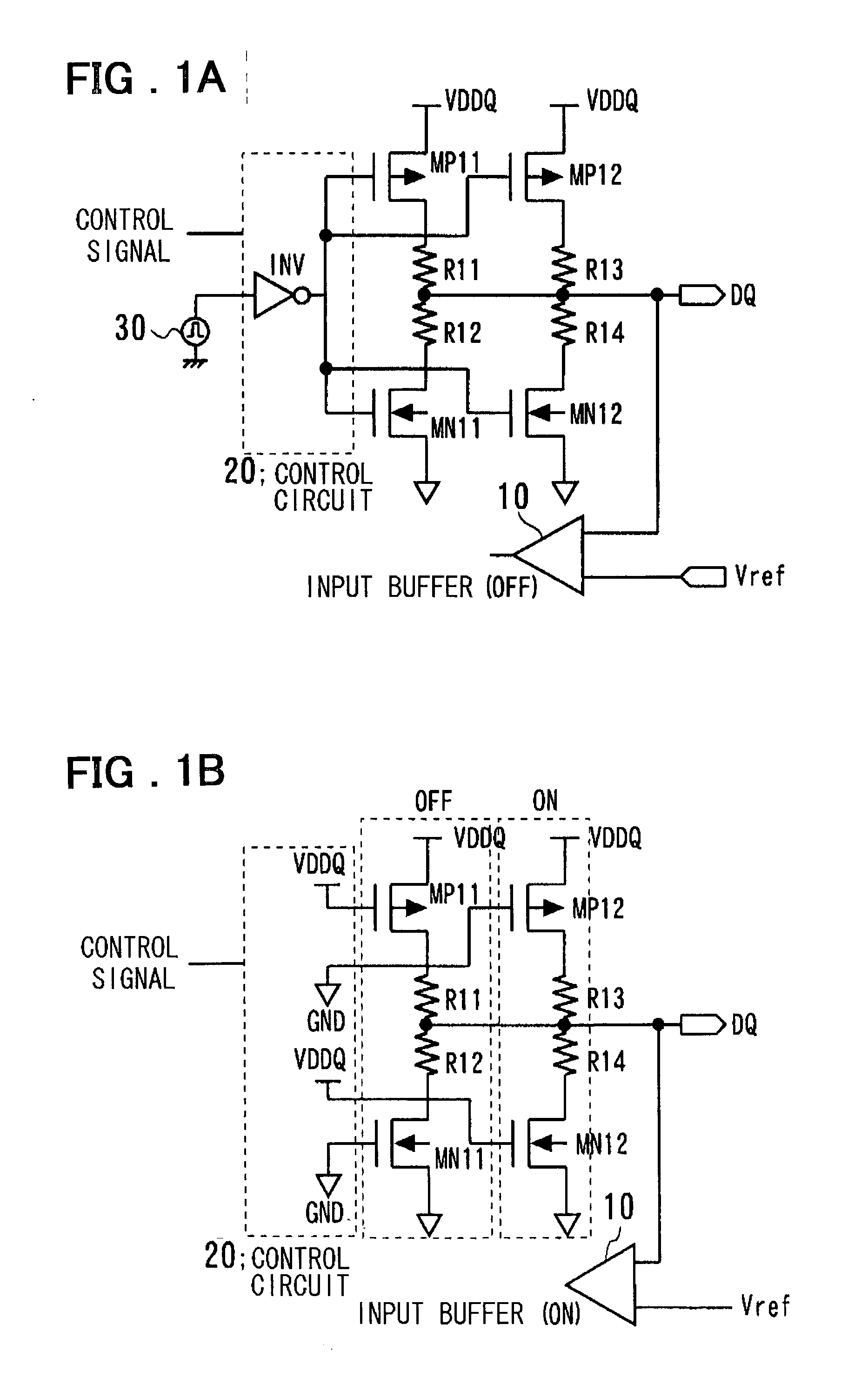
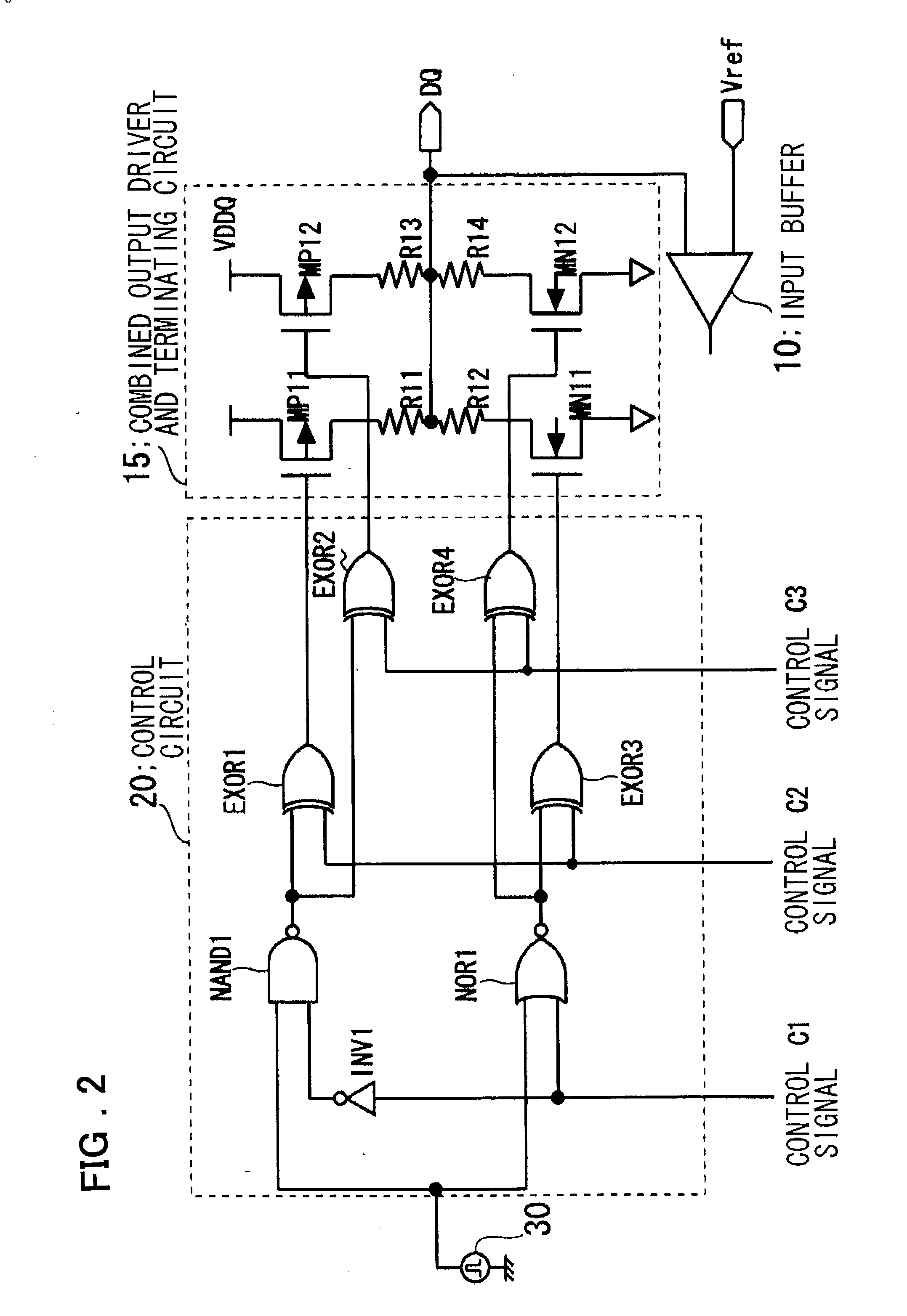
Input/output circuit, reference-voltage generating circuit, and semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20030080774A1Reliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsEngineeringVoltage reference
Disclosed is an input / output circuit having a terminating circuit that contributes to a smaller chip area. The input / output includes an output buffer having a first series circuit, which comprises a first transistor and a resistor and a second series circuit, which comprises a second transistor and a resistor, connected in parallel between a high-potential power supply and an input / output pin, as well as a third series circuit, which comprises a third transistor and a resistor and a fourth series circuit, which comprises a fourth transistor and a resistor, connected in parallel between the input / output pin and a low-potential power supply. The input / output circuit further includes an input buffer having an input terminal connected to the input / output pin, and a control circuit which, at the time of a signal output, performs control for supplying a signal, which is obtained by inverting the logic of output data, to gates of the first to fourth transistors, and which, at the time of a signal input, performs control for supplying the gates of the first and third transistors with the high-potential power supply voltage and low-potential power supply voltage, respectively, and the gates of the second and fourth transistors with the low-potential power supply voltage and high-potential power supply voltage, respectively.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Voltage level shifter
InactiveUS6043698APulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDc currentLow voltage
The present invention provides a voltage level shifter for use in a digital circuit having a low voltage portion and a high voltage portion. The voltage shifter comprises an interface circuit 20,32,60 that senses transitions in a low voltage digital signal from an old value to a new value and uses these to trigger latching of the new value. The latch can be a SR latch 34,62 with its set 40 and reset 42 inputs coupled to pulse generators 46,68,58,70 respectively responsive to rising and falling edges in the input low voltage signal being passed from the low voltage portion to the high voltage portion. Feedback from the output on the latch 62 can be controlled to limit the duration of the pulses from the pulse generators 68,70 and thereby reduce power consumption due to the dc current leakage associated with a low voltage to high voltage signal interface.
Owner:ARM LTD
Universally programmable output buffer
InactiveUS6975135B1Reduce variationReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsEngineeringVoltage
Output buffers are provided that are compatible with any differential output standard. The output buffers compensate for variations in process, the supply voltage, and temperature. The edge rate of an output buffer can be programmed to be compatible with different output standards. The edge rate of an output buffer can compensate for variations in process, voltage, and temperature. The output voltage of an output buffer can be adjusted to be compatible with different output standards.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
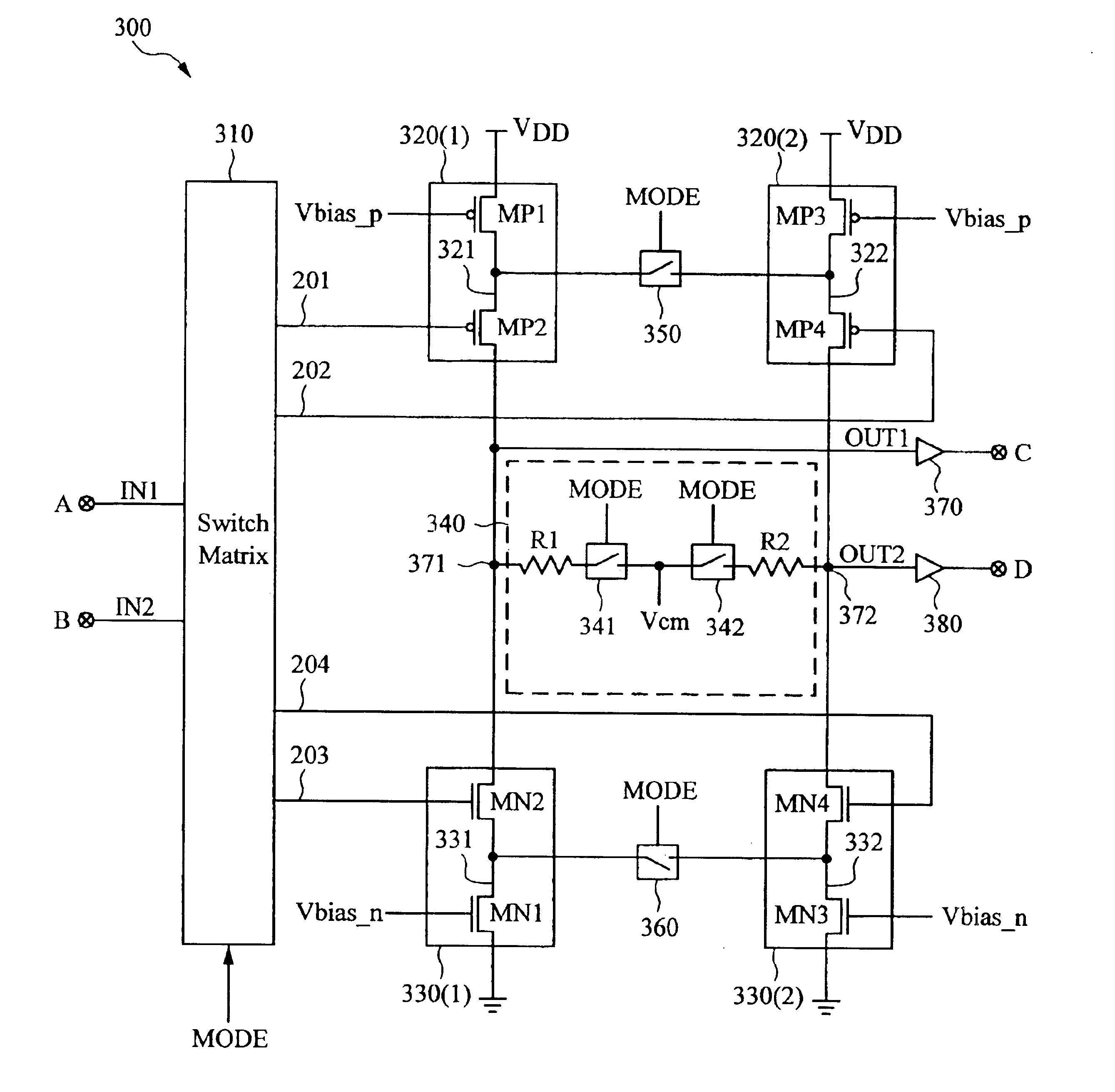
Differential to single-ended logic converter
InactiveUS6924668B2Easy to implementMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringSignal transition
The present invention is a converter stage for converting a differential logic input signal and a corresponding common mode differential logic signal each having a first single-ended logic signal and a complementary second single-ended logic signal into a single-ended logic output signal. The converter stage comprises a first and a second differential stage each having a first and a second MOS transistor and a first and second current source for the differential stages. According to the invention the current sources are controlled by the voltage level which is centered between the mid-potentials of the common mode level differential logic signal and the mid-potential of the differential logic input signal.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
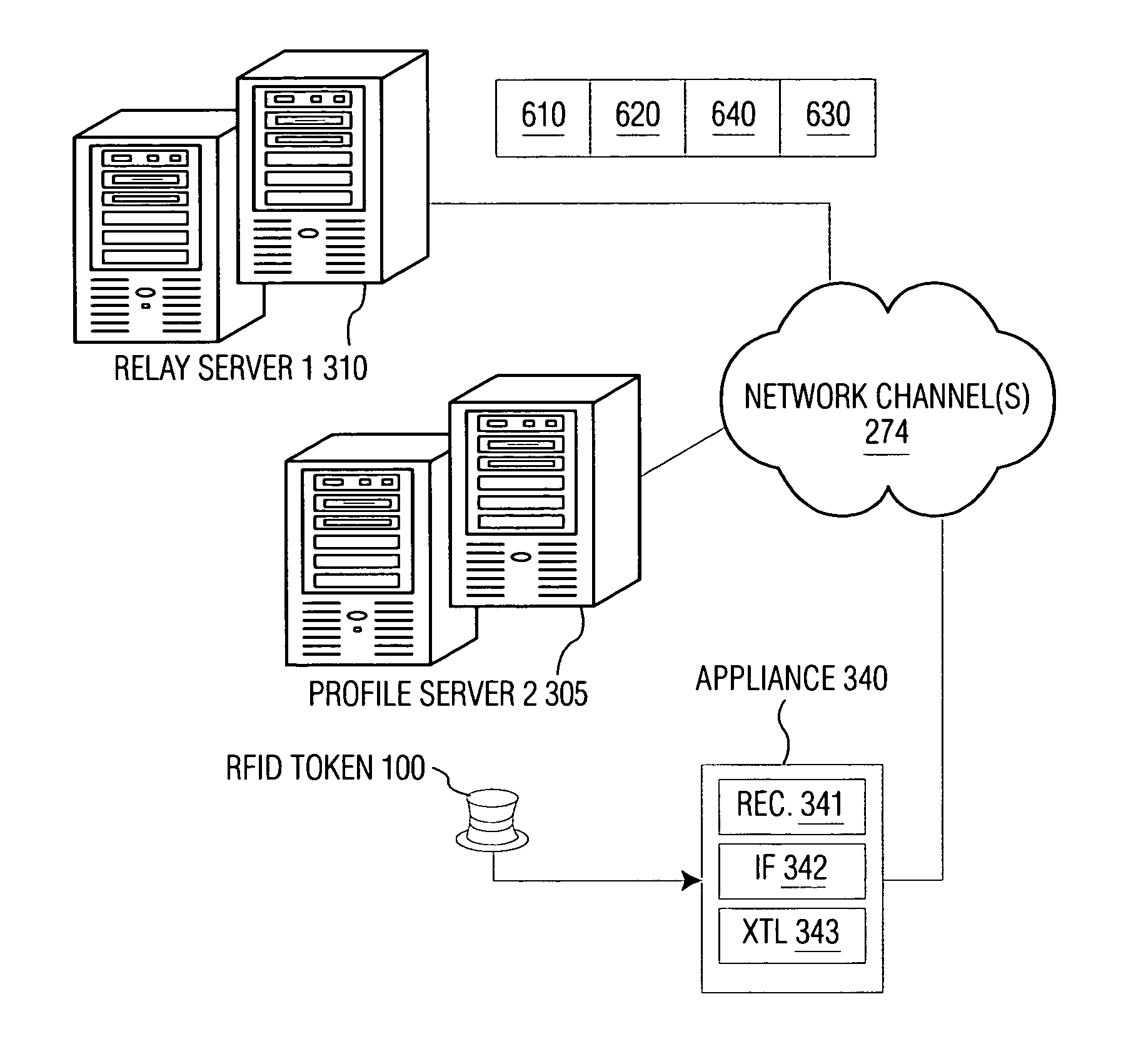
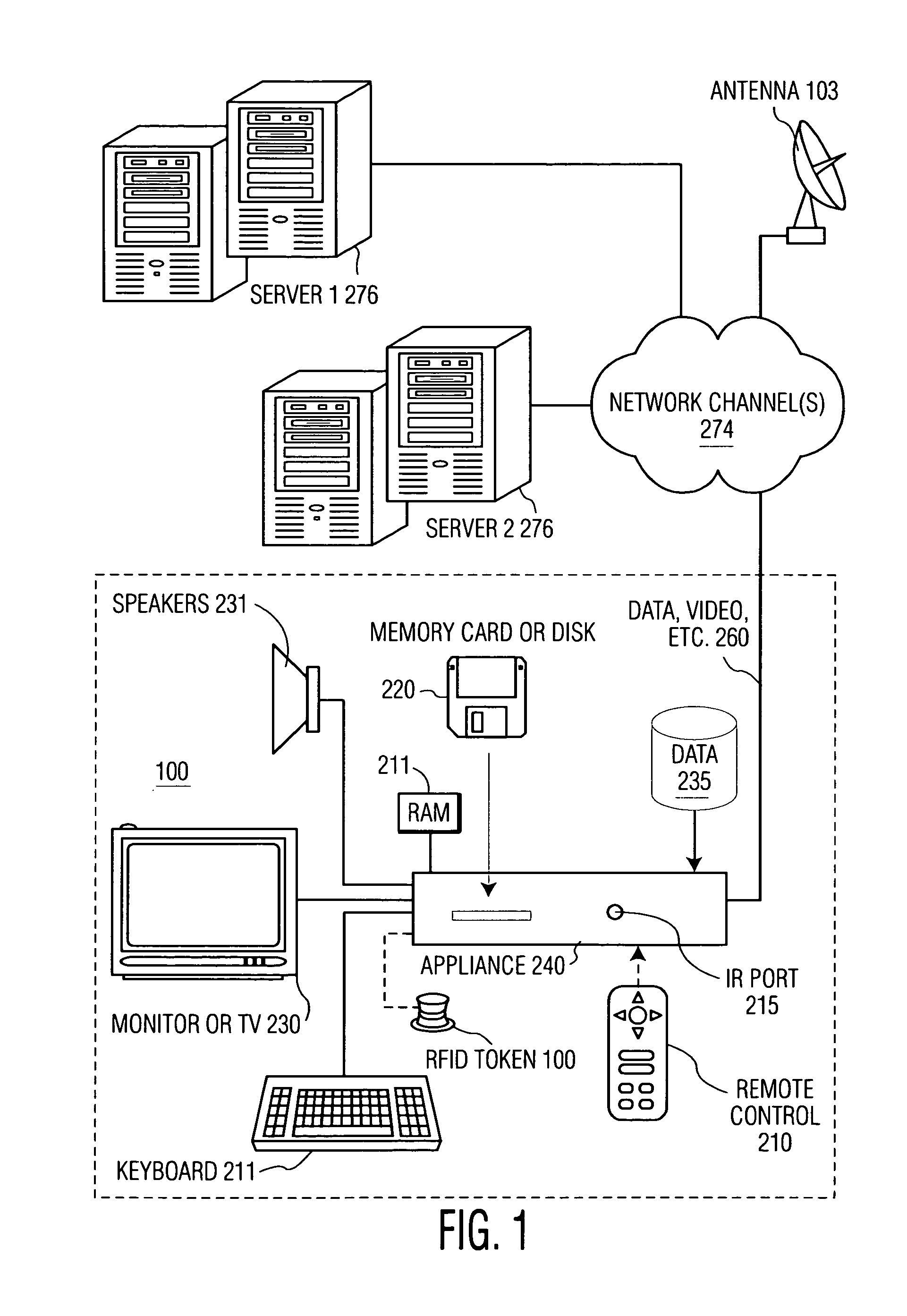
Token-based personalization of smart appliances
InactiveUS7933968B1Easy to solveValue maximizationLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsRead-only memoriesPersonalizationUser profile
A radio frequency identification (RFID) token is used with appliances to access profile data to personalize the appliance. Each token contains a pointer to a relay location on a network with a further pointer indicating a profile location where user-profile data is stored. When a user wants to use an appliance, he / she places the token near the appliance and the appliance accesses the data from the site indicated (pointed to) by the relay location. The profile location may contain many different types of data such as speed dial lists, media preferences, preferred product classifications, etc. The appliance could obtain just the information it required, for example if the database were XML-tagged, by filtering out irrelevant content and personalize itself accordingly. When multiple users wish to use a single appliance, for example a television, each may place his / her token near the appliance and the appliance may then combine relevant profile data accordingly to develop a single composite profile to use to personalize the appliance.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for providing two modes of I/O pad termination
InactiveUS6040714AReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDual modeEngineering
The present invention provides a method of providing two different modes of operation for an output driver on an integrated circuit. A first mode provides an open drain driver, such as an enhanced GTL+ driver, for high-speed data transmission. A second mode provides a totem pole output driver, such as a TTL or a LVTLL driver, which does not require additional circuitry for external terminations, as is required for open drain drivers. Thus, one embodiment of the present invention can be characterized as a method of providing a dual mode output from an integrated circuit. This method includes receiving an output mode signal indicating an enhanced GTL+ output mode or a totem pole output mode. This method also includes providing an enhanced GTL+ output signal if the mode signal indicates the enhanced GTL+ output mode, and providing a totem pole output signal if the mode signal indicates the totem pole output mode. Another embodiment of the present invention can be described as a method for providing a dual mode output from an integrated circuit. This method includes providing to the integrated circuit an output mode signal indicating a first output mode or a second output mode. It also includes coupling an output pin of the integrated circuit to an open drain bus with an active termination if the mode signal indicates the first mode, and coupling an output pin of the integrated circuit to an unterminated bus if the mode signal indicates the second output mode.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method of and apparatus for correctly transmitting signals at high speed without waveform distortion
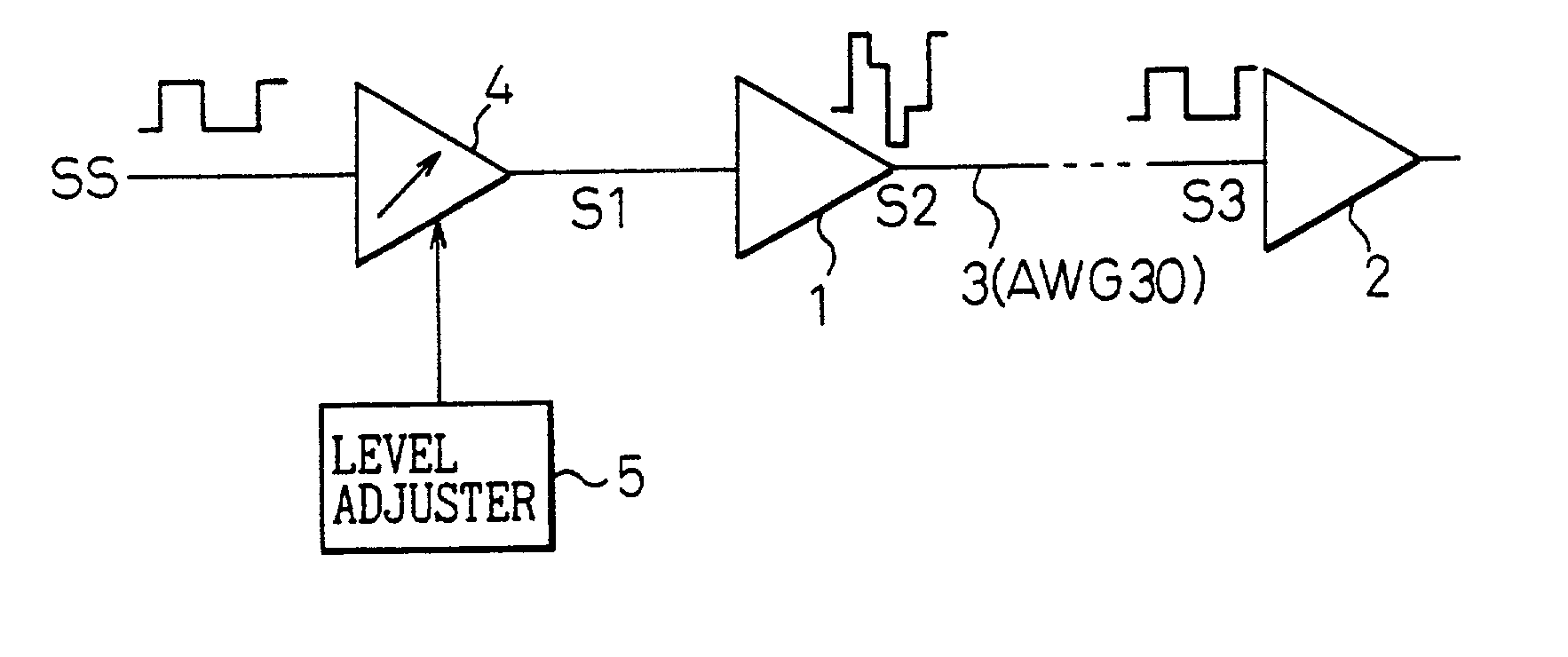
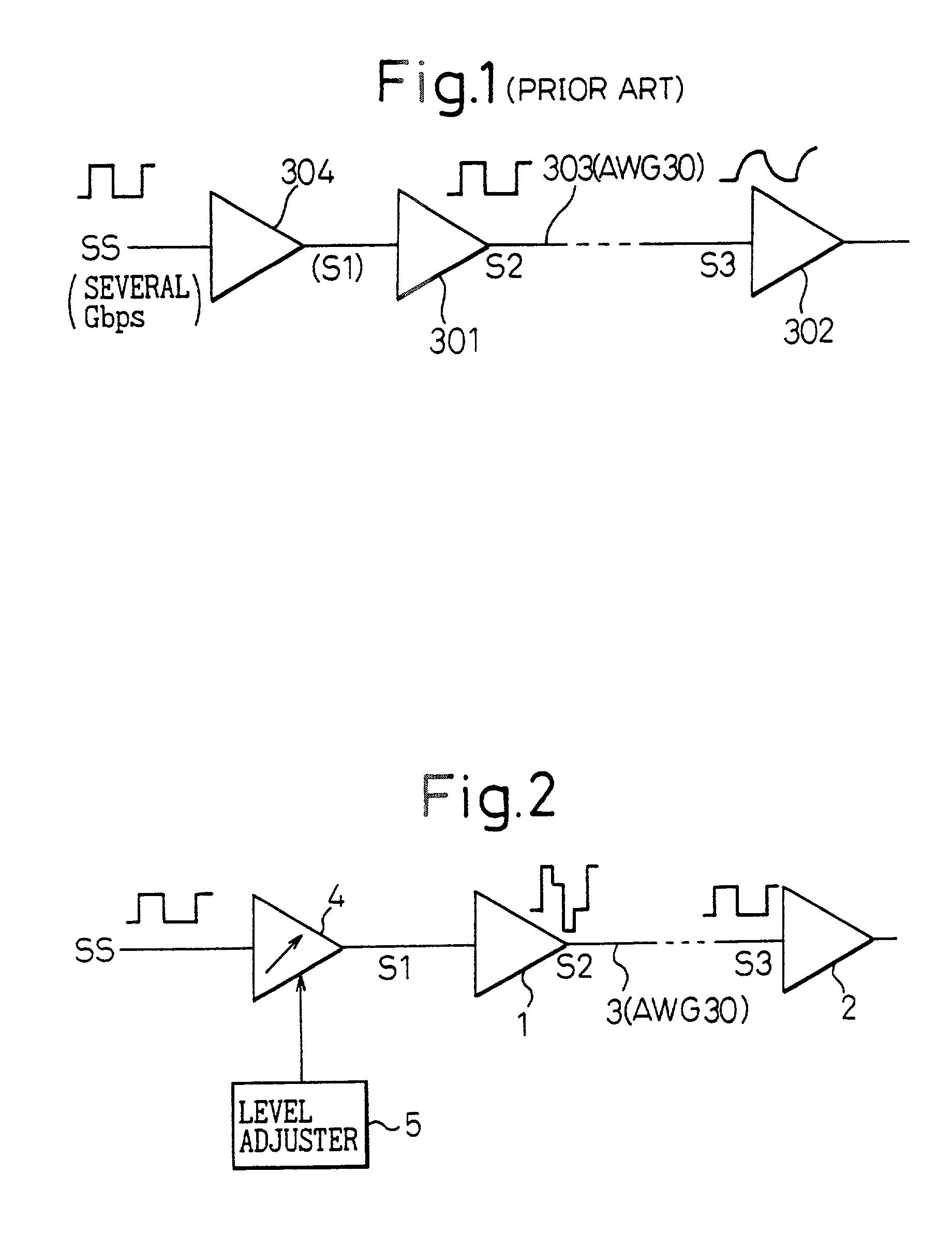
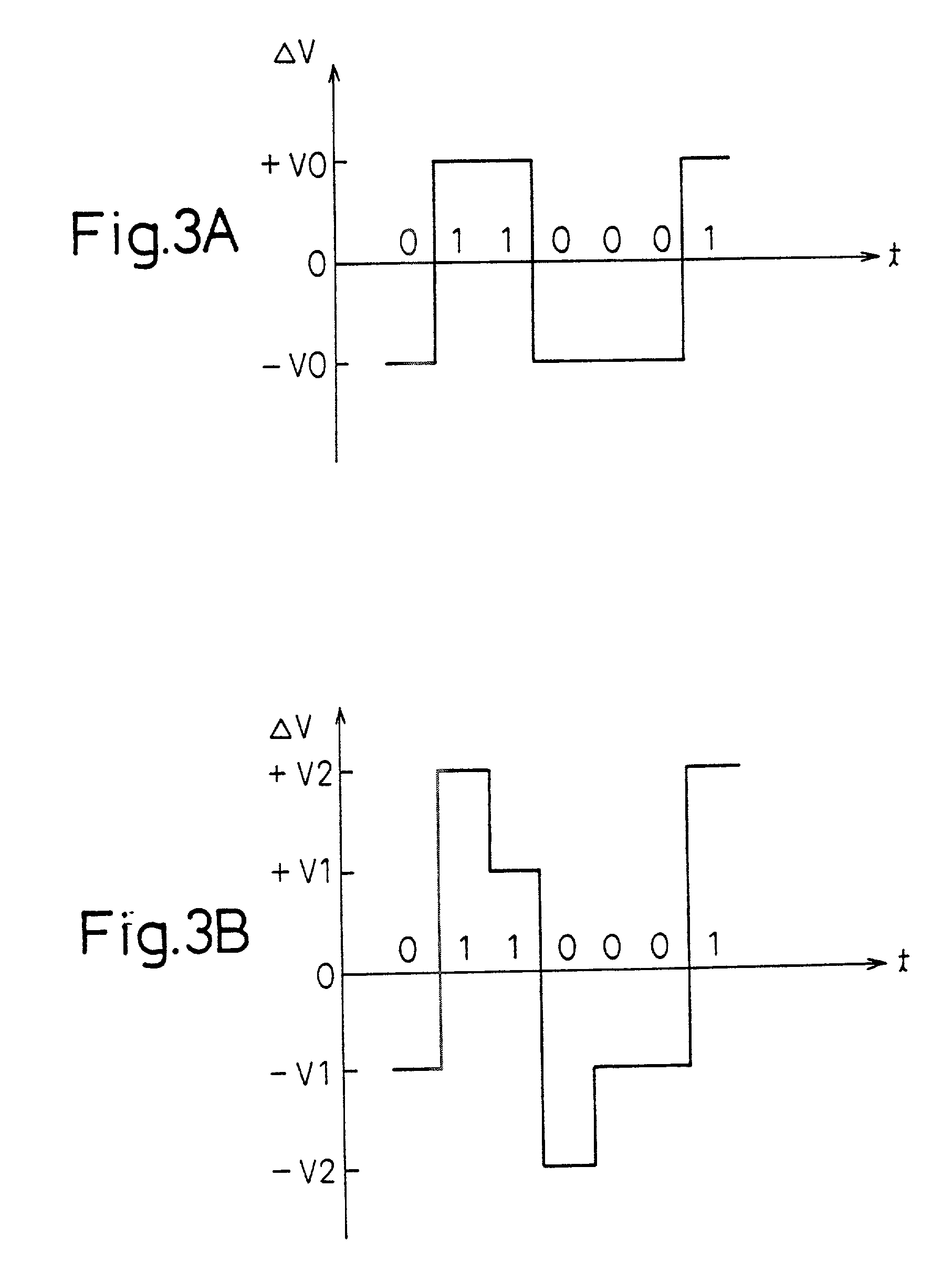
InactiveUS20020125933A1Eliminate distractionsAccurate transmissionCovering/liningsPulse automatic controlDriver circuitEngineering
A driver circuit transmits a signal to a receiver circuit through a signal transmission line. The driver circuit has an output driver, a front driver, and a level adjuster. The front driver drives the output driver, and the level adjuster adjusts the output level of the front driver. The output driver generates a signal whose level is variable in response to an output level of the front driver.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Repeater circuit with high performance repeater mode and normal repeater mode
ActiveUS7119580B2Reliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringRepeater
Repeater circuit with high performance repeater mode and normal repeater mode is provided and described. In one embodiment, switches are set to a first switch position to operate repeater circuit in the high performance repeater mode. In another embodiment, switches are set to a second switch position to operate the repeater circuit in the normal repeater mode.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
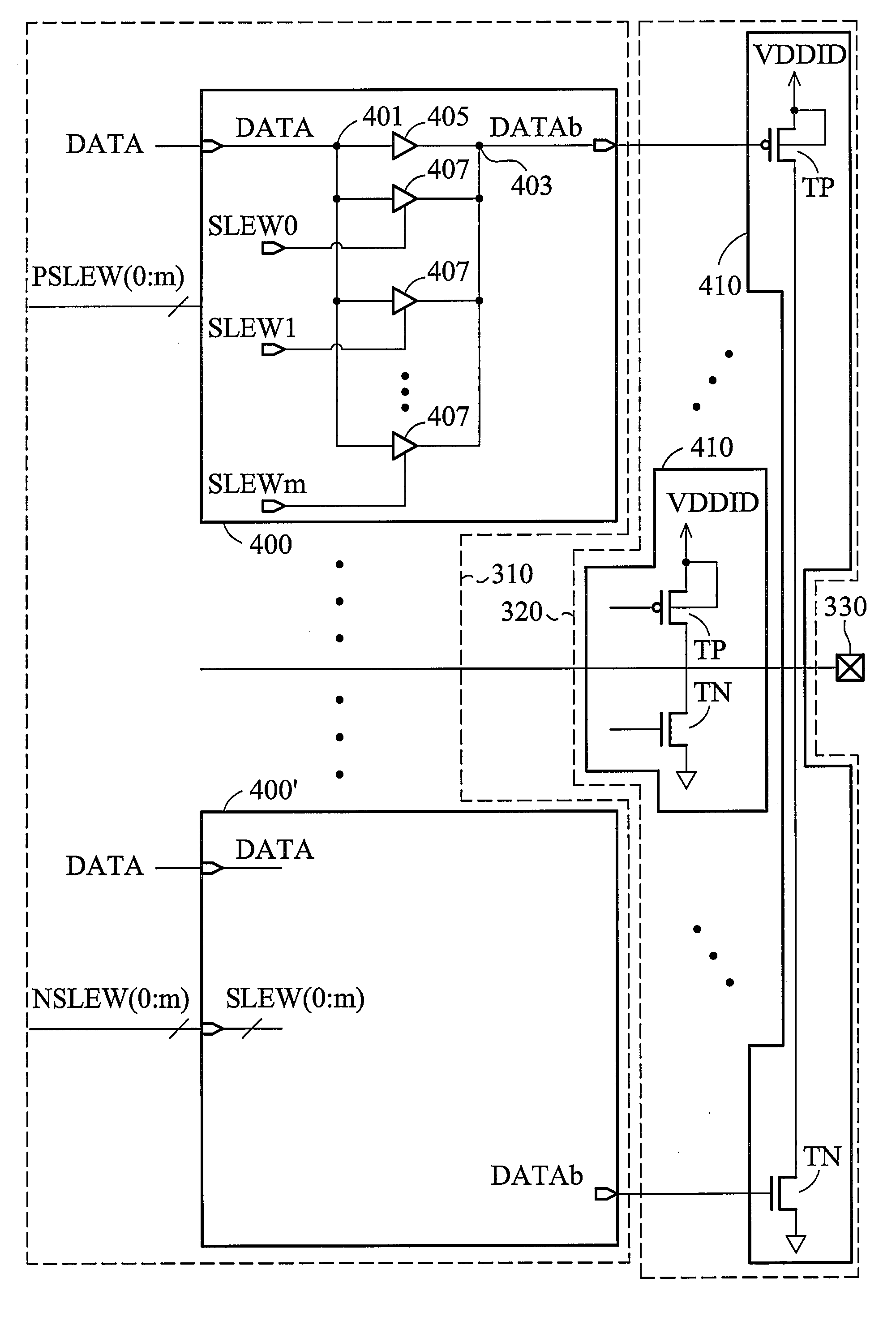
Slew rate controlled circuits
InactiveUS20080106297A1Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectronic switchingDriver circuitControl signal
A slew rate controlled output buffer. The slew rate controlled output buffer comprises a pre-driver circuit having a data input node and a data output node and a driver circuit coupled to the output node of the pre-driver circuit. The pre-driver circuit comprises a plurality of inverters connected in parallel, each having an input terminal coupled to the input node and an output terminal coupled to the output node, wherein at least one of the inverters is selectively disabled by a slew rate control signal via a slew rate controller. The driver circuit is driven by an output signal of the pre-driver circuit.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Multiple signal format output buffer
ActiveUS20050285629A1Reduce duplicationReduce needLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsSnubberIntegrated circuit
An output buffer circuit drives multiple signal formats. The output buffer circuit reduces duplication of output bond pads on an integrated circuit die. The output buffer circuit reduces a need for including conversion buffers on system boards. A single integrated circuit including the output buffer circuit may meet a variety of applications. The output buffer achieves these results with a programmable output voltage swing and a programmable output common mode voltage. In some embodiments of the present invention, an integrated circuit includes at least one single-ended buffer and at least one differential circuit coupled to a pair of outputs. One of the single-ended buffer and the differential circuit is selectively enabled to provide a signal to the outputs.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
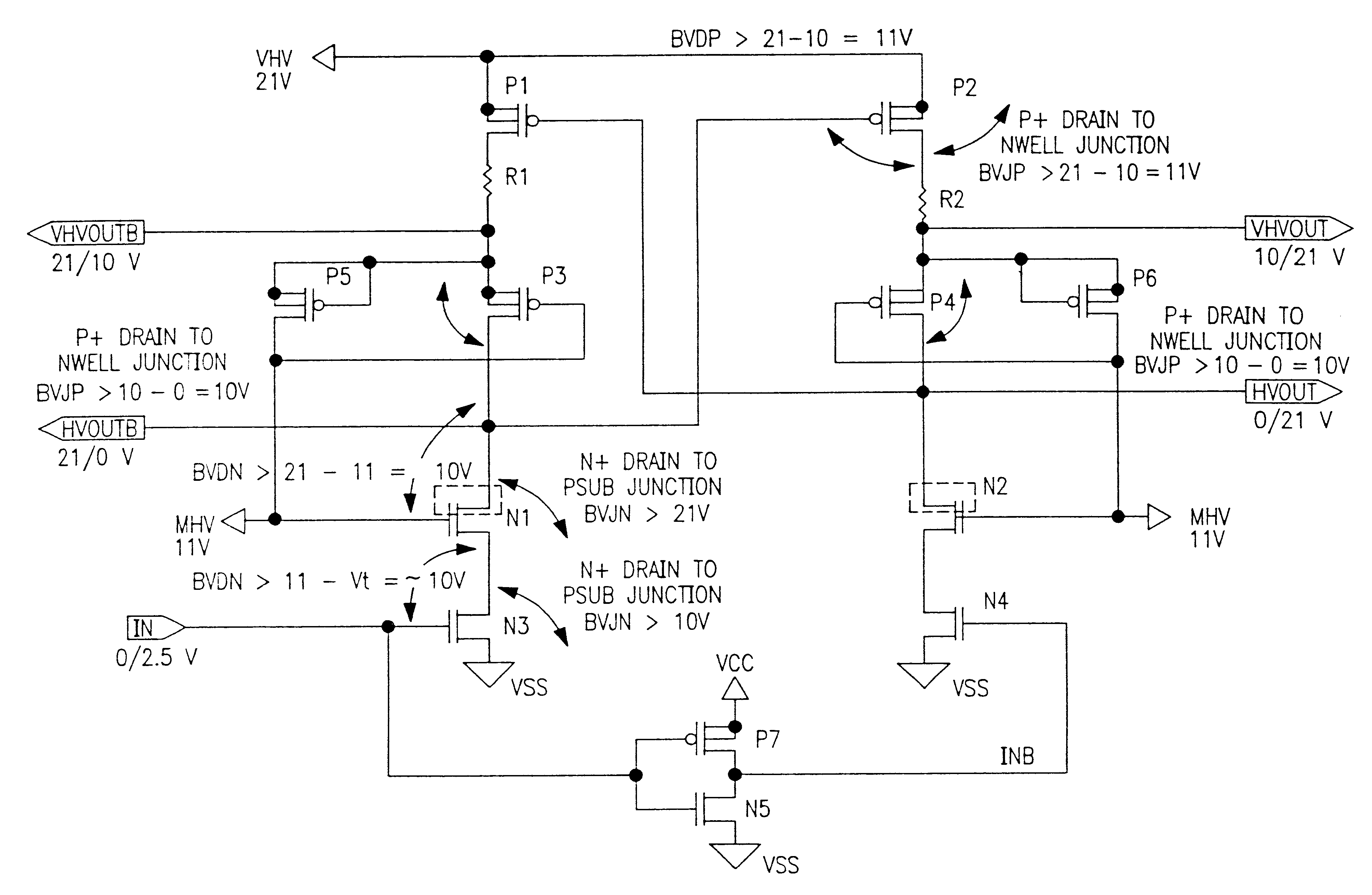
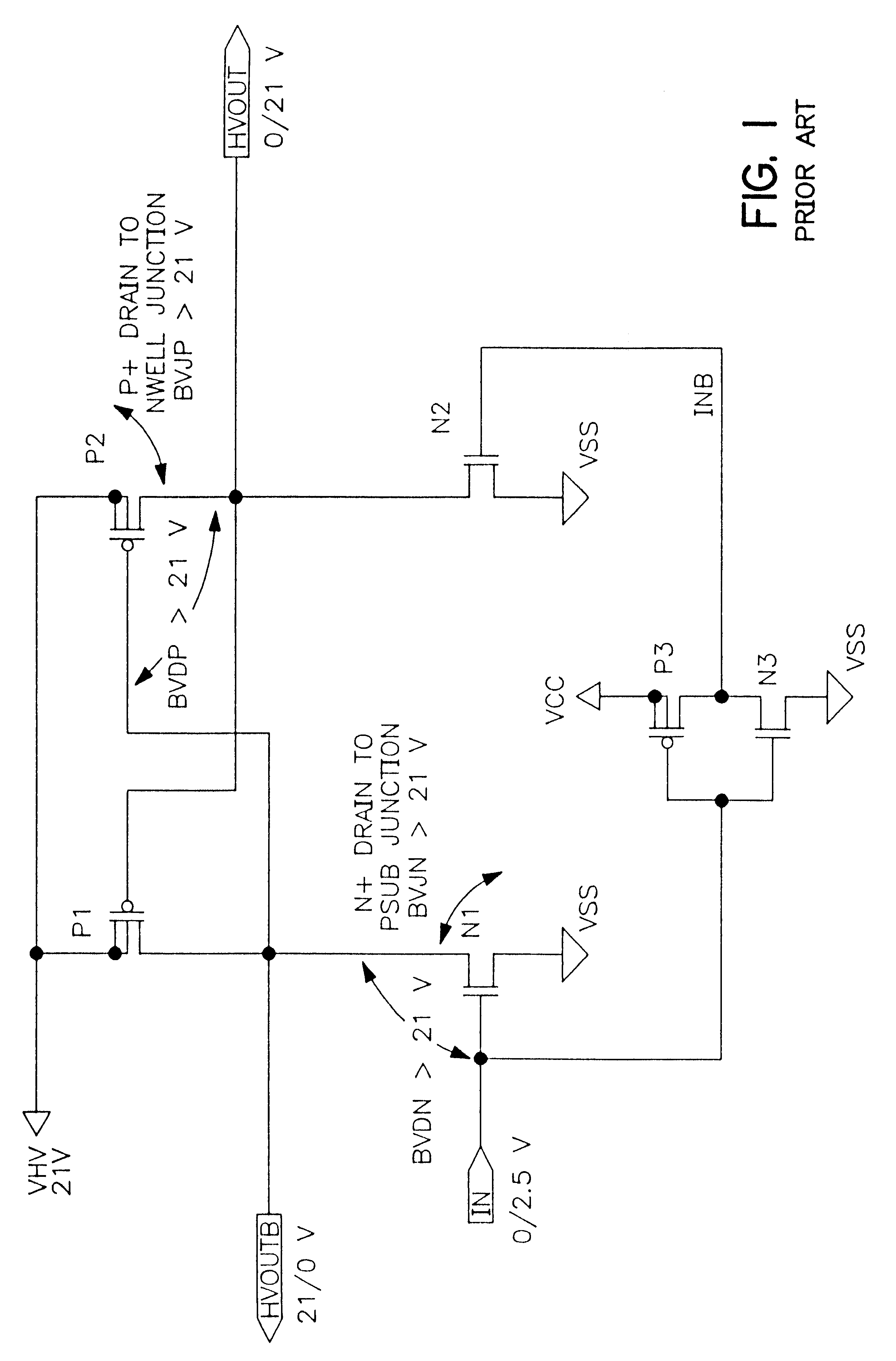
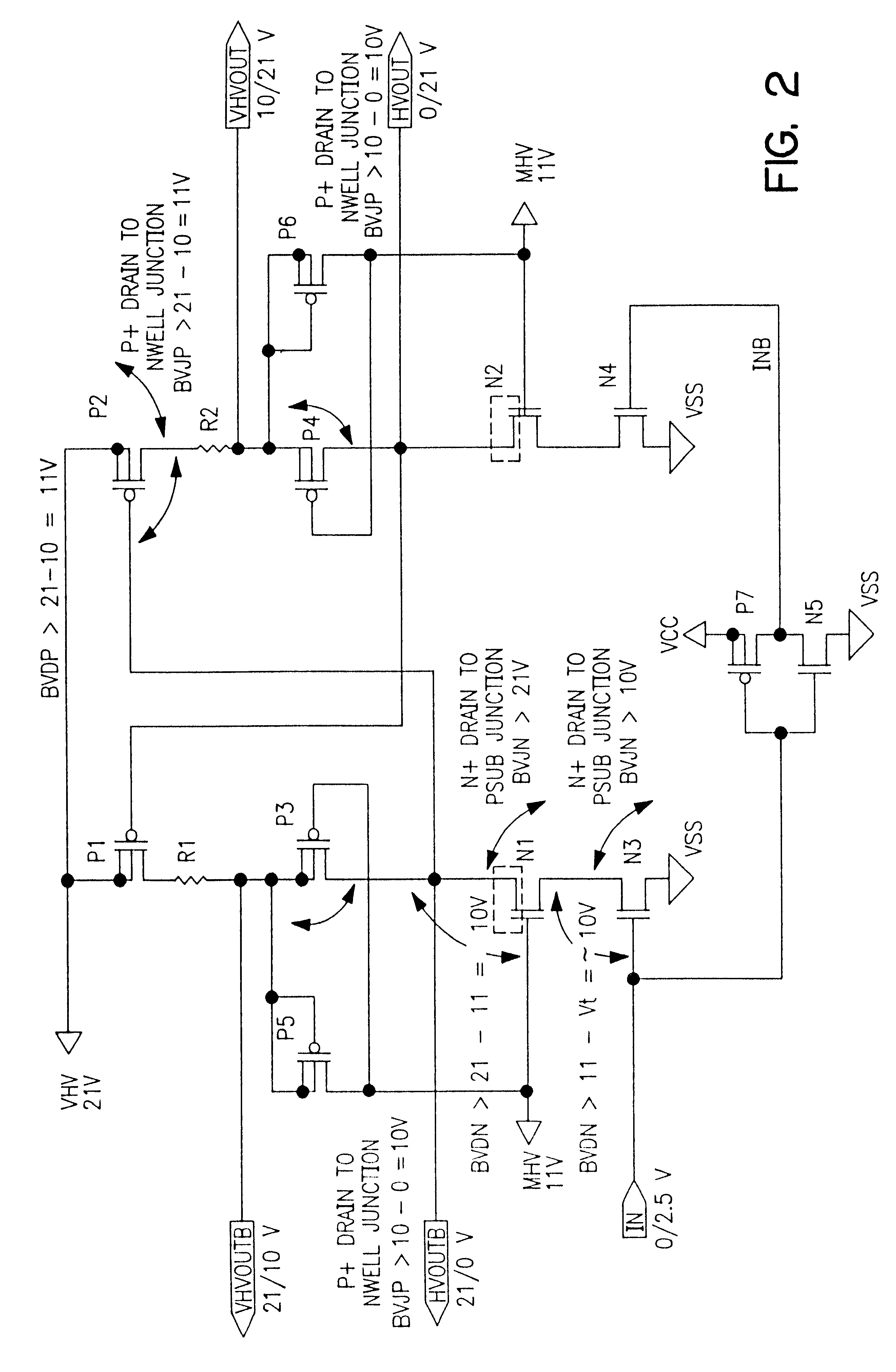
High voltage level shifter for switching high voltage in non-volatile memory integrated circuits
InactiveUS6437627B1High junction breakdownGated diode breakdownPulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsHigh voltage igbtLow voltage
A high voltage level shifter utilizing only low voltage PMOS and low voltage NMOS devices. The high voltage level shifter is used to distribute the high voltage almost equally among the PMOS devices and almost equally among the NMOS devices to meet the device electrical specification of low voltage MOS devices for various breakdown mechanisms. A layout technique is also used to achieve a much higher junction breakdown of N+ drain to P-substrate and a better gated diode breakdown of NMOS devices.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
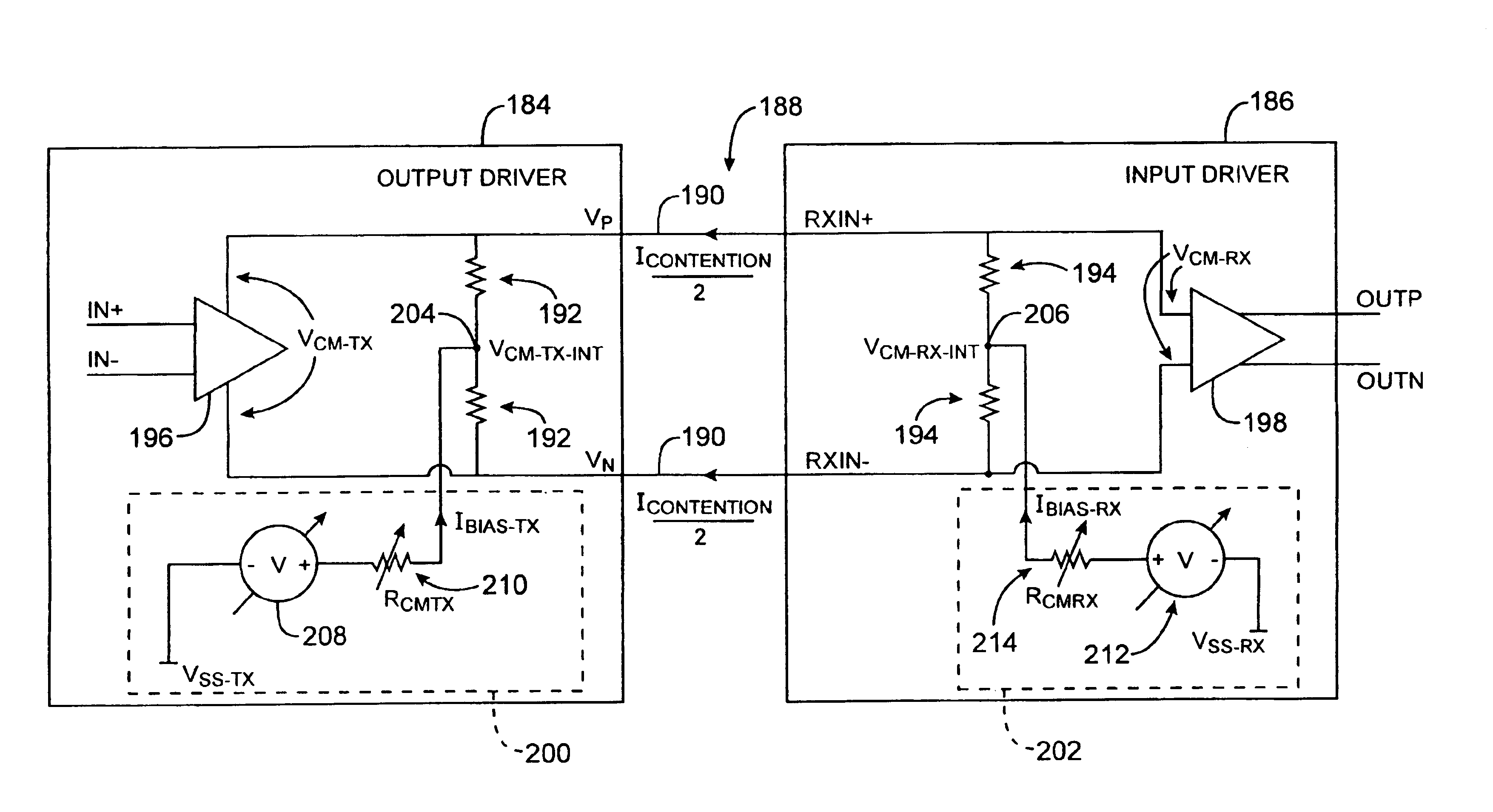
Adjustable differential input and output drivers
ActiveUS6864704B1Reduce resistanceIncrease currentReliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceTelecommunications link
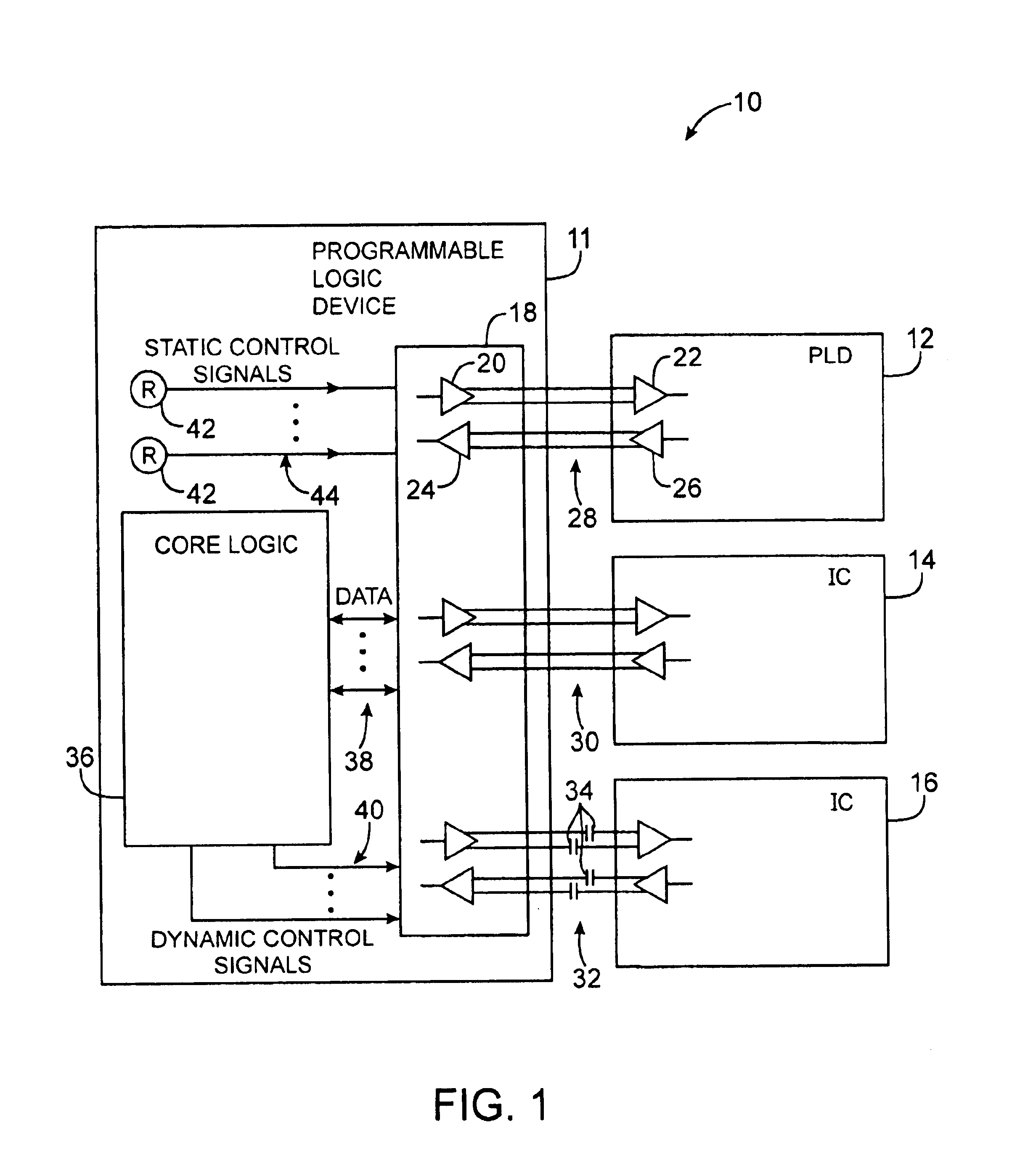
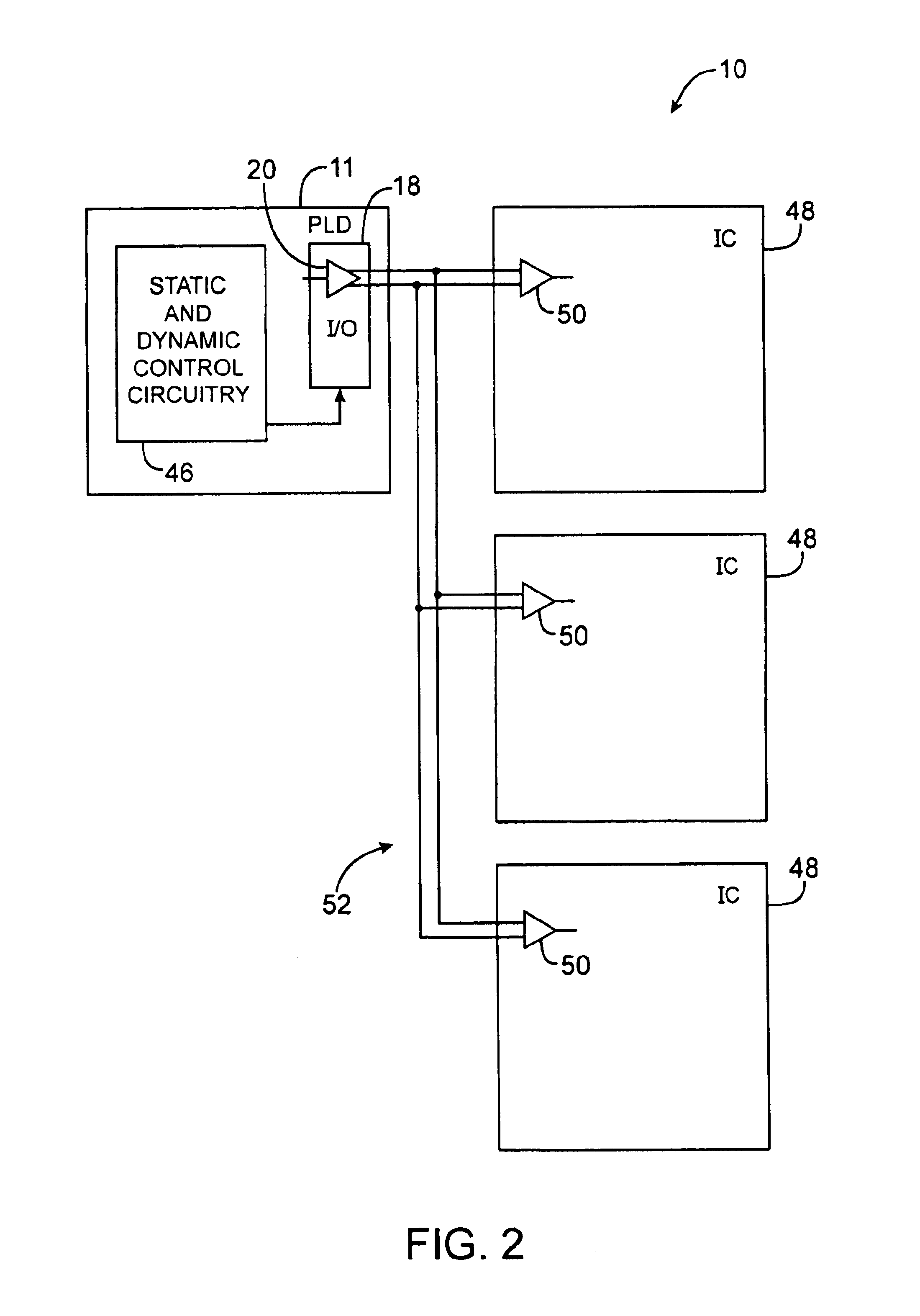
Systems and methods are provided using common-mode-voltage bias circuitry to make common-mode-voltage adjustments to differential driver circuitry in integrated circuit differential communications links. Adjustable bias circuitry may be controlled using static and dynamic control signals. Dynamic control signals can be produced by core logic on a programmable logic device or other integrated circuit. Static control signals can be produced by programmable elements. Bias circuit adjustments made at one end of a differential link can be used to improve performance at either end of the link or can be used to improve power consumption or to balance power and performance considerations. The same integrated circuit design can be used in both AC-coupled and DC-coupled environments. The bias circuitry can be formed from an adjustable current source and adjustable resistor. The current source and adjustable resistors can be controlled by the same control signals.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
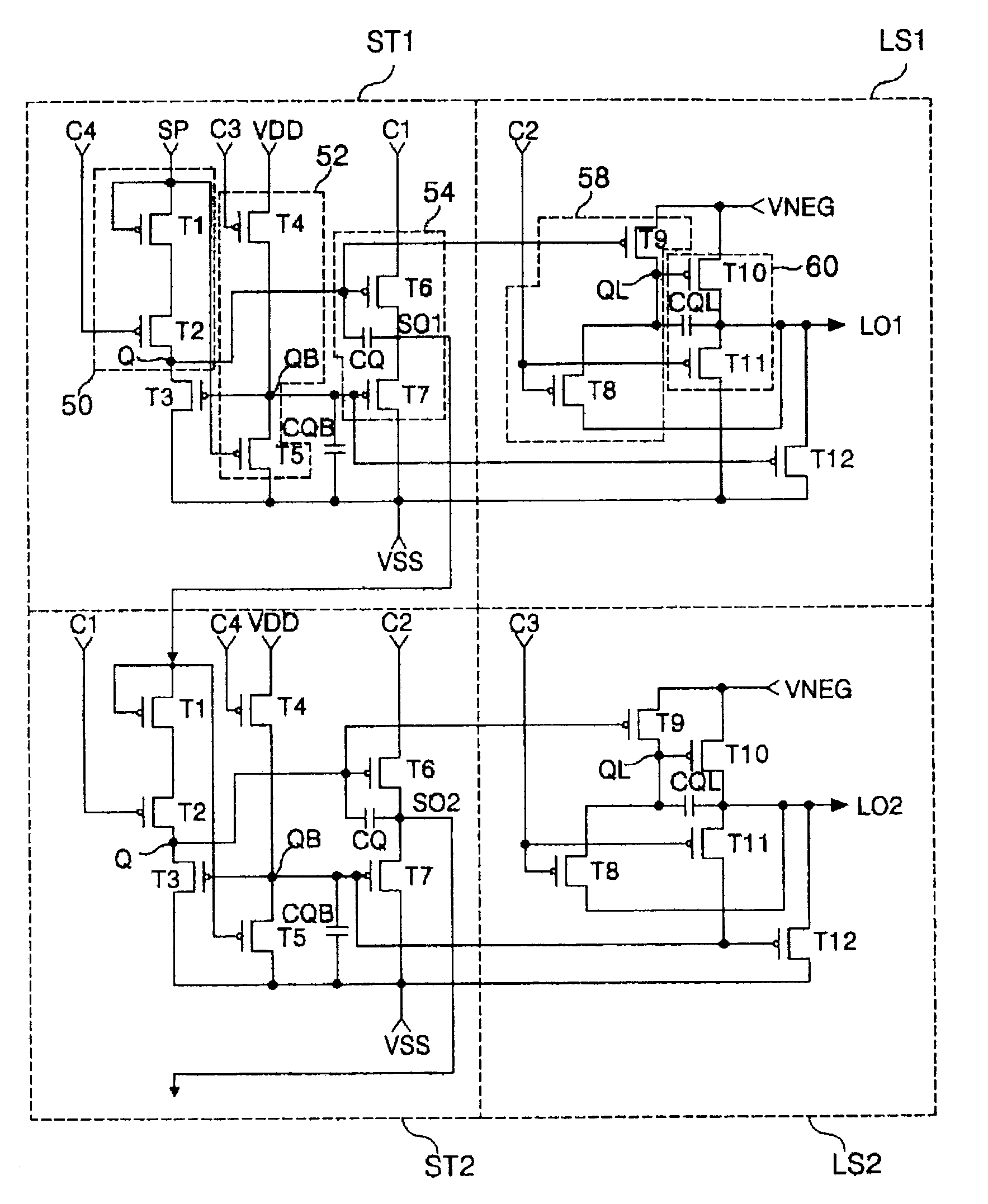
Shift register with a built in level shifter
ActiveUS7050036B2Lower levelStatic indicating devicesLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsShift registerEngineering
A shift register employs only a thin film transistor of the same type channel and has a level shifter built-in. A shift register with a built in level shifter includes a plurality of stages and a plurality of level shifters. The stages are connected in cascade to shift a start pulse inputted through an input terminal and sequentially output the shifted pulse. The level shifters level-shift a voltage level of the shifted pulse applied from each of the stages and outputting it.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Sampling level converter circuit, 2-phase and multiphase expanding circuit, and display device
InactiveUS20030076149A1Reduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Disclosed is a sampling level converter circuit having a fewer number of terminals and reduced power consumption, as well as an expanding circuit having such a sampling level converter circuit. The sampling level converter circuit includes first to third MOS transistors connected serially between a higher-potential power-supply and a lower-potential power-supply; a first capacitor connected to a connection node of the first and second MOS transistors; a fourth MOS transistor connected between an input terminal and the gate terminal of the third MOS transistor; and a second capacitor connected to the gate of the third MOS transistor. A sampling pulse signal is supplied to the gates of the first and second MOS transistors, and a signal obtained by inverting this sampling pulse signal is supplied to the gate of the fourth MOS transistor.
Owner:VISTA PEAK VENTURES LLC
Semiconductor device including voltage conversion circuit having temperature dependency
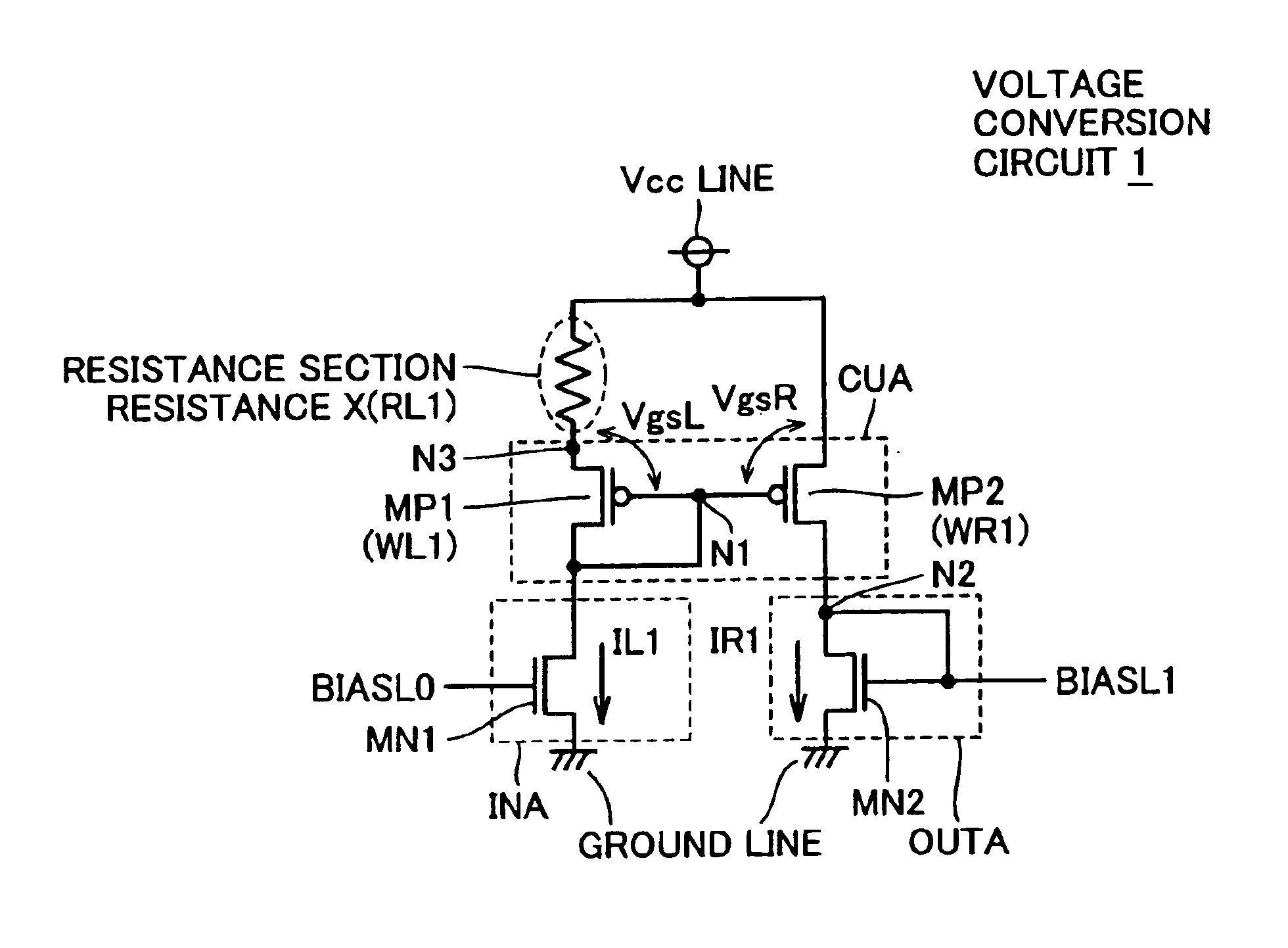
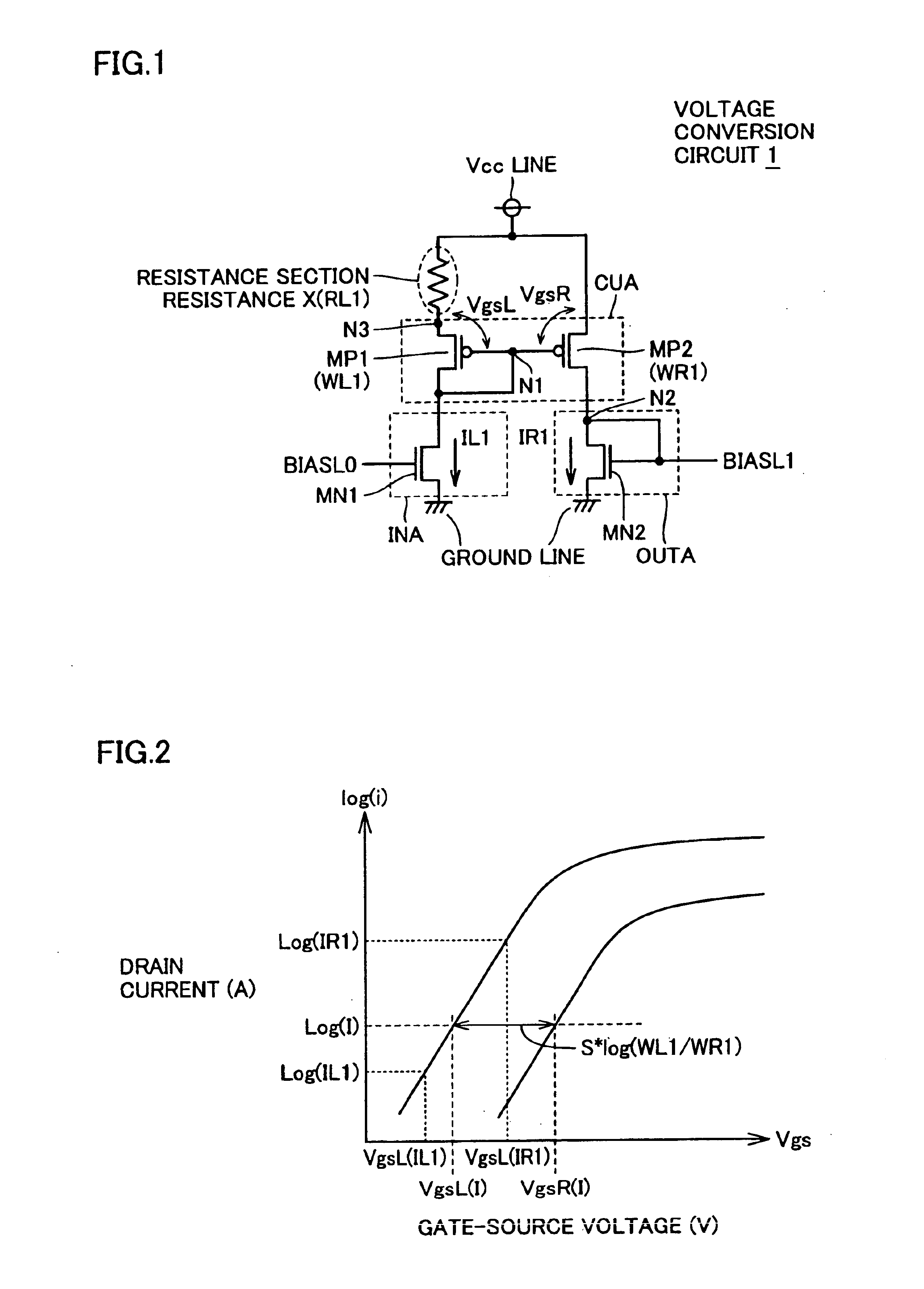
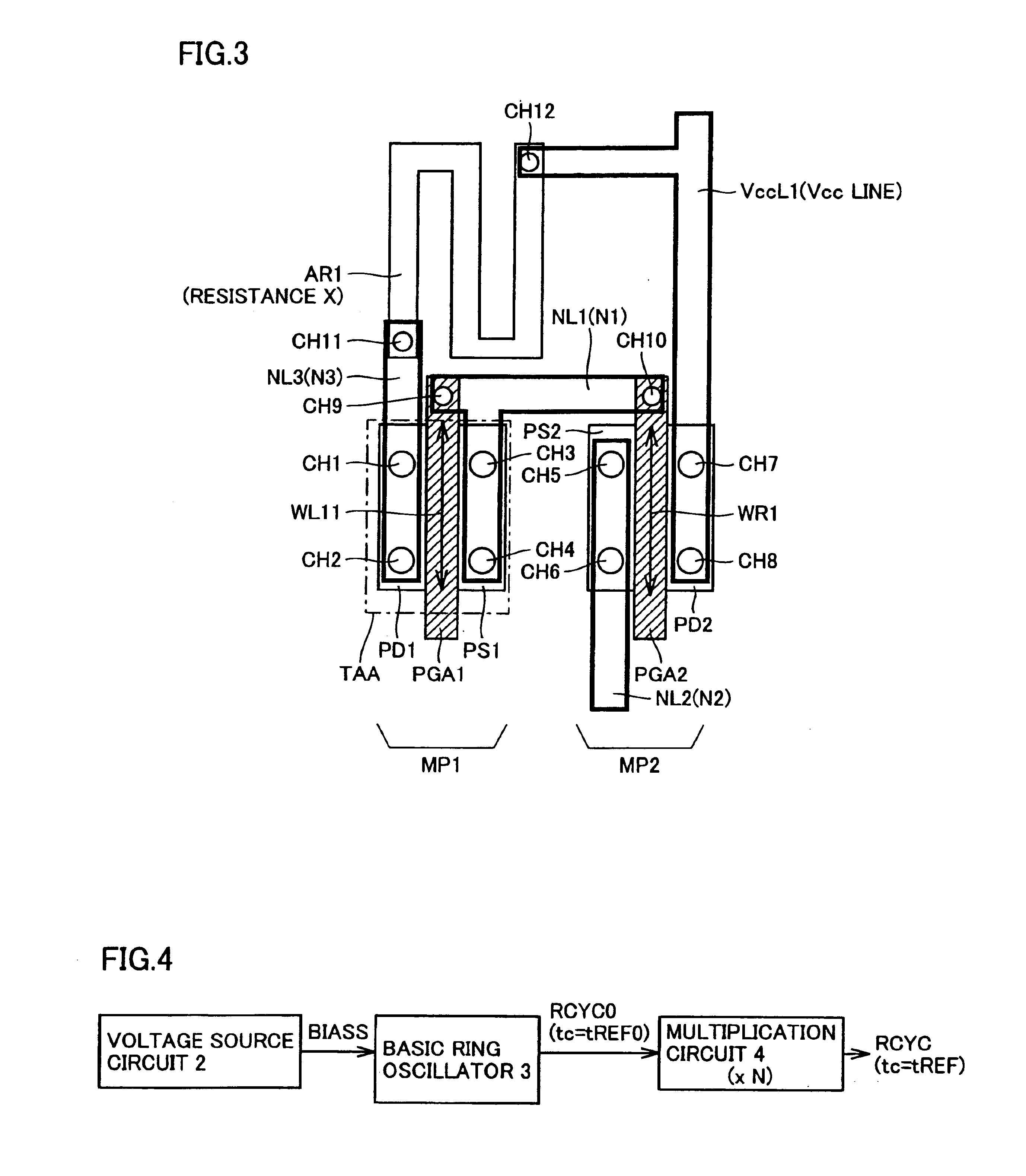
InactiveUS6850049B2Good temperature characteristicsReduce irregularitiesLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceSemiconductor
A semiconductor device according to the present invention has a configuration that a resistance section is connected to only one of a current-mirror section forming a voltage conversion circuit and an output section. With this configuration, it is possible to determine the temperature dependency of an output voltage according to S factors of transistors forming one of the current-mirror section and the output section and a resistance value of the resistance section, and to suppress manufacturing irregularities caused by irregularities of the transistors between the two sections and those among a plurality of resistance materials.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Level shifting circuit, driving device, LED print head, and image forming apparatus
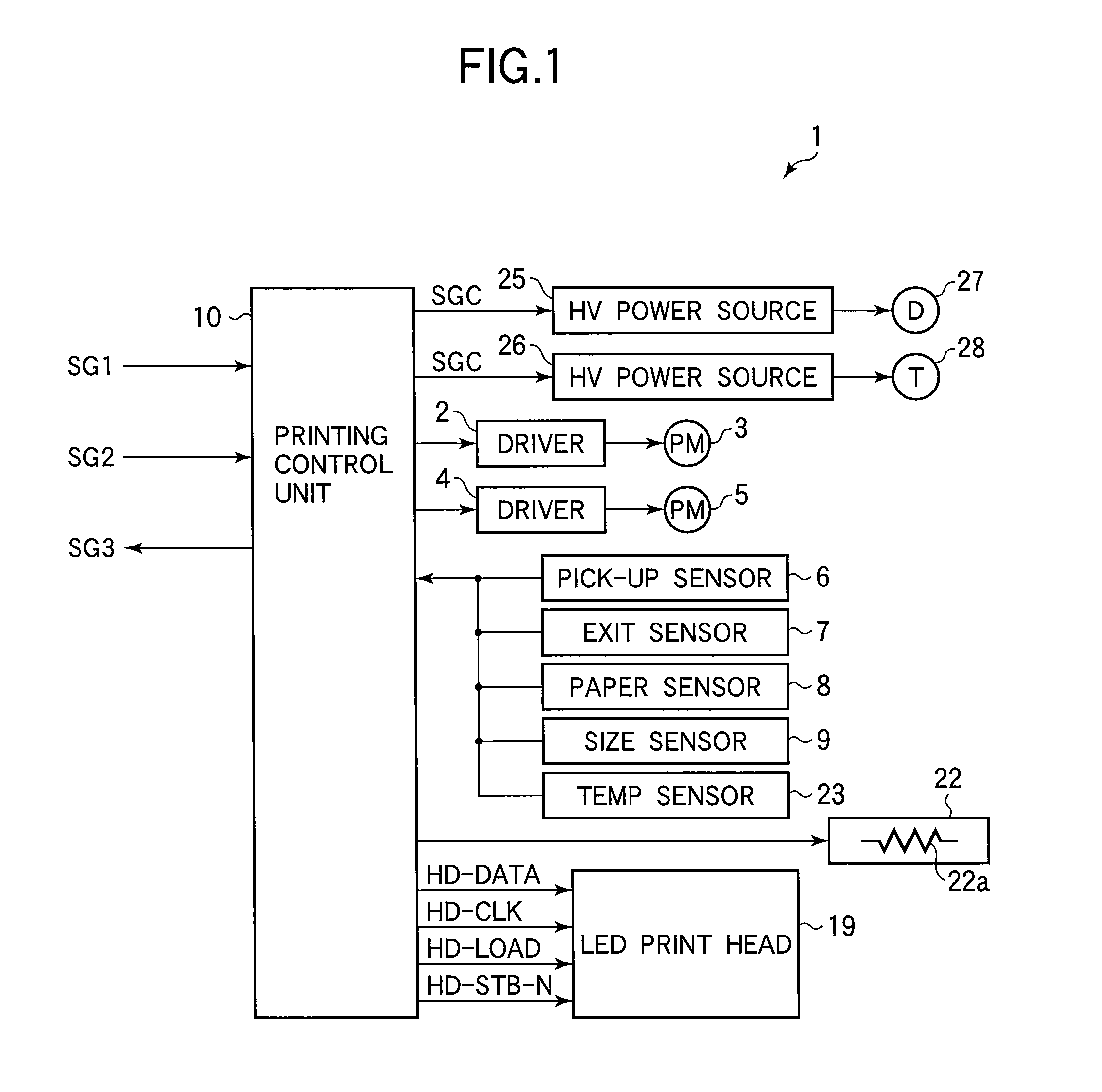
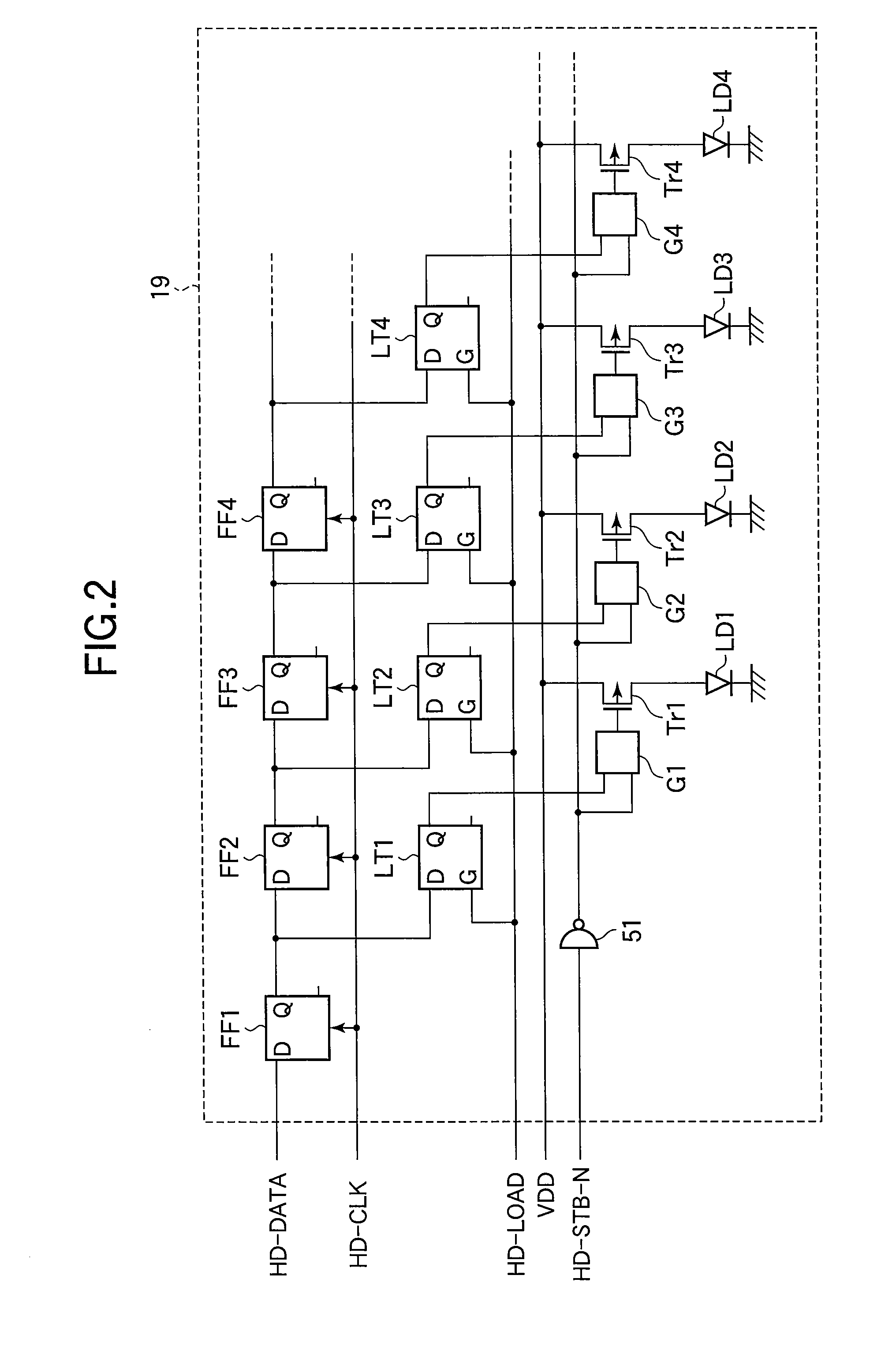
InactiveUS20080054979A1Small sizePulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsLevel shiftingEngineering
A level shifting circuit converts an input signal that varies between ground and a first voltage to a shifted signal that varies between ground and a second voltage higher than the first voltage. The level shifting circuit has two branches, in each of which a p-channel transistor and two n-channel transistors are connected in series between the second voltage and ground. When the two n-channel transistors in each branch are turned off, a clamping circuit clamps the node between them to the first voltage level, so that neither n-channel transistor has to withstand the full difference between the second voltage and ground. The level shifting circuit can accordingly be fabricated with transistors of small size, reducing the cost of driving circuits, light-emitting-diode print heads, and image forming apparatus in which the level shifting circuit is used.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
Popular searches
CAD circuit design Generating/distributing signals Special data processing applications Logic circuits using elementary logic circuit components Amplifier combinations Logic circuits using specific components Dc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stages Semiconductor devices Oscillations generators Reliability increase in field effect transistors
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com