Patents
Literature
804results about "Power reduction in field effect transistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110175646A1Suppress power consumptionPrevent degradationTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsProgrammable logic deviceLow leakage
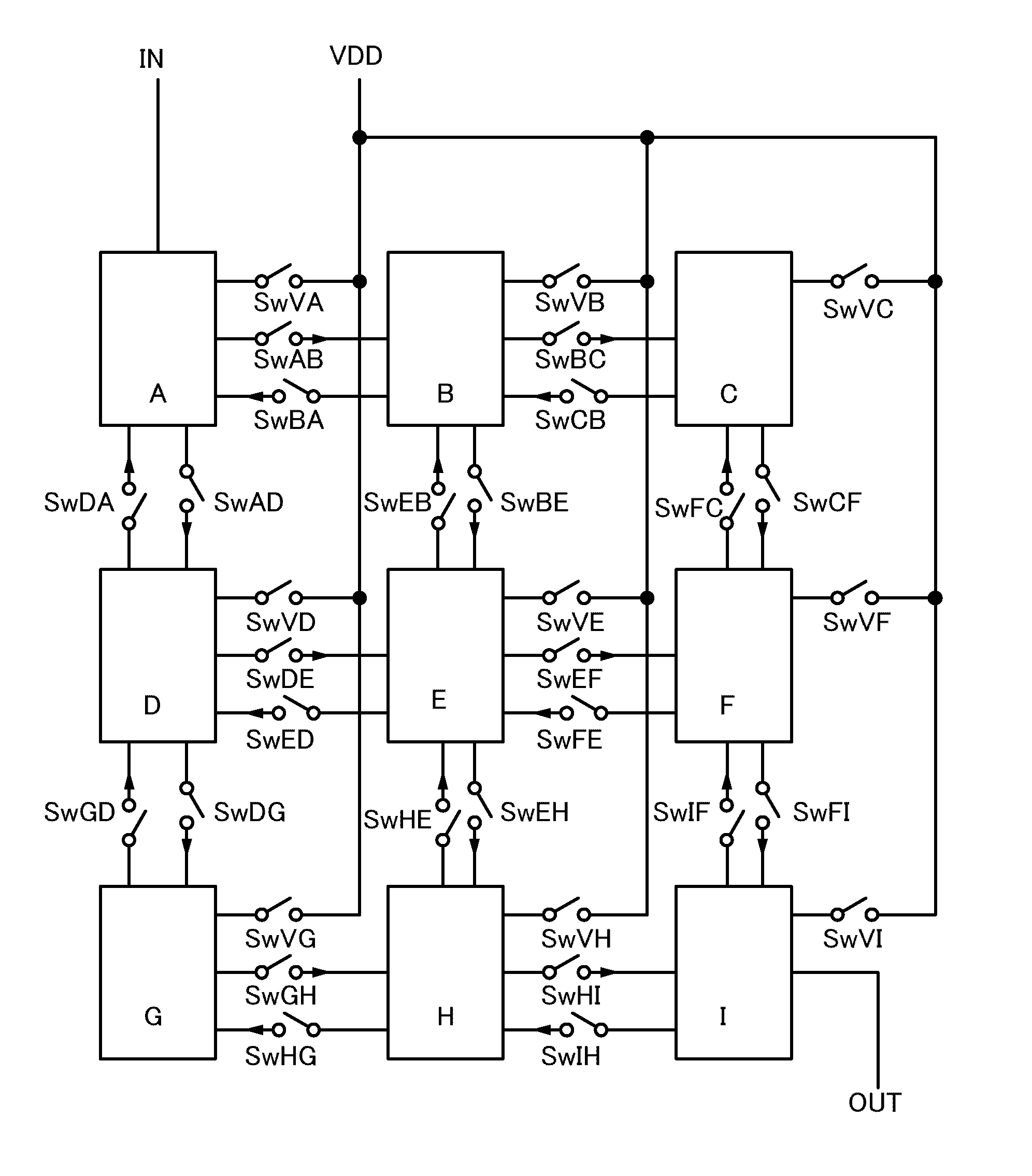
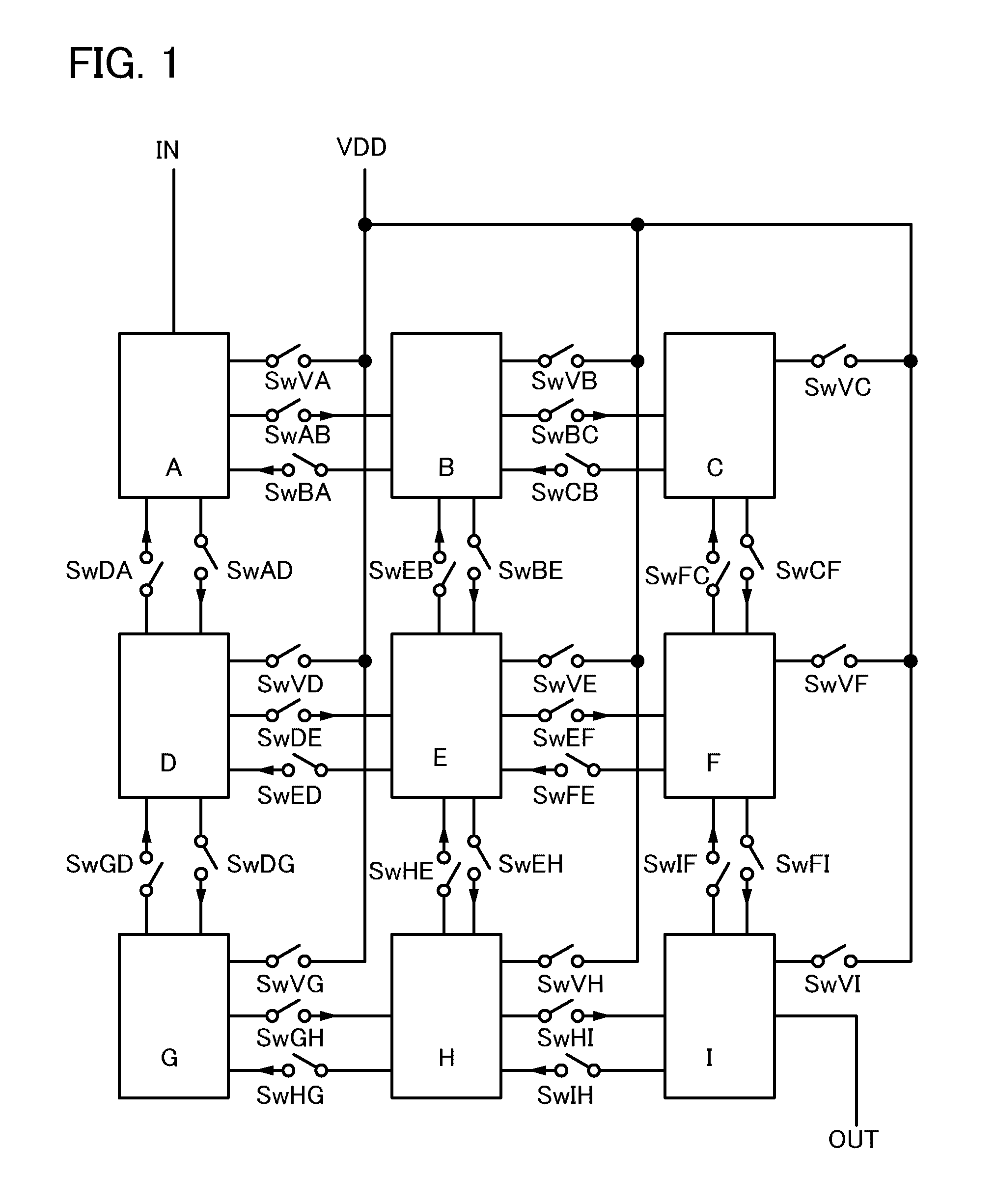
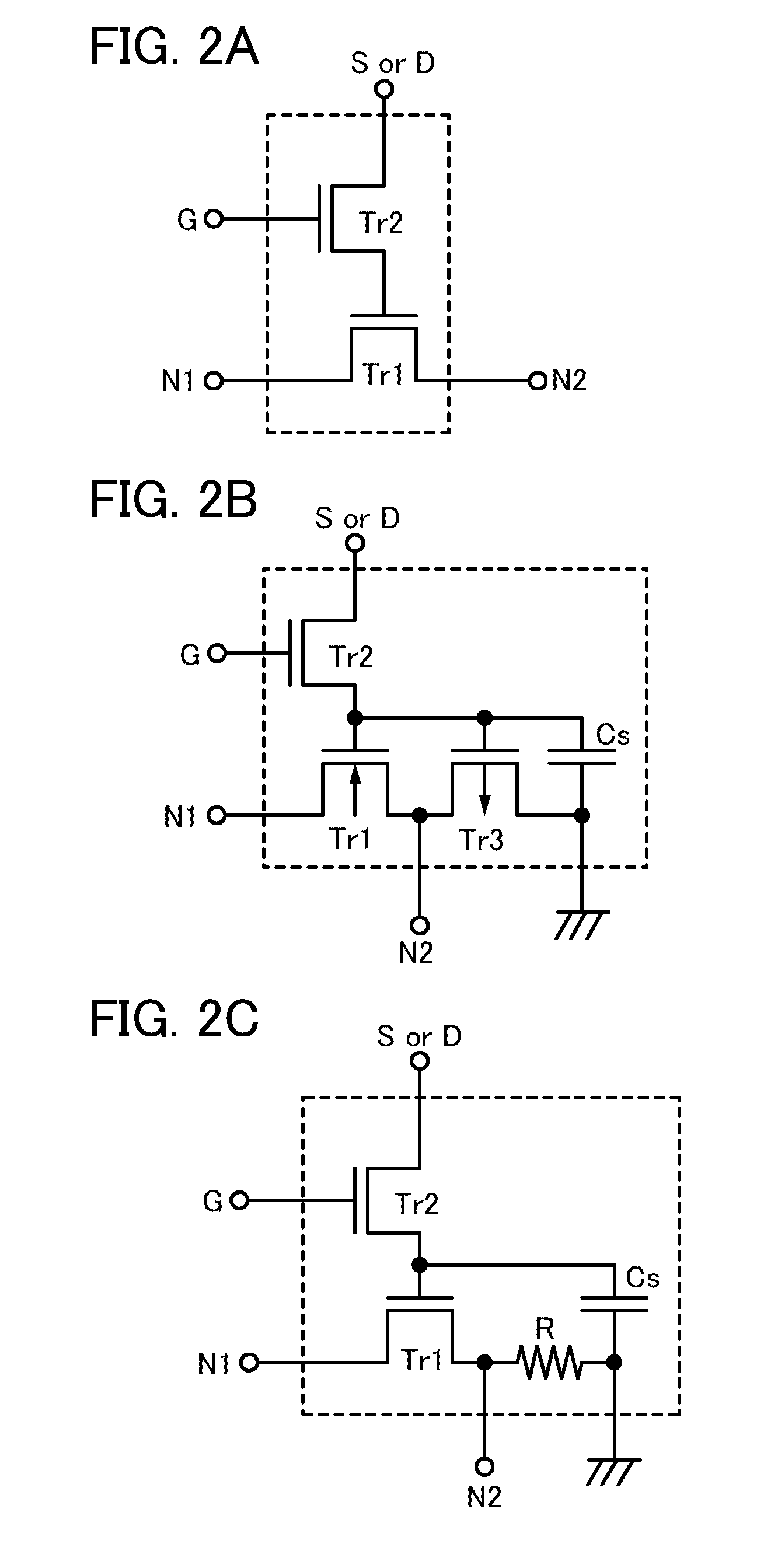
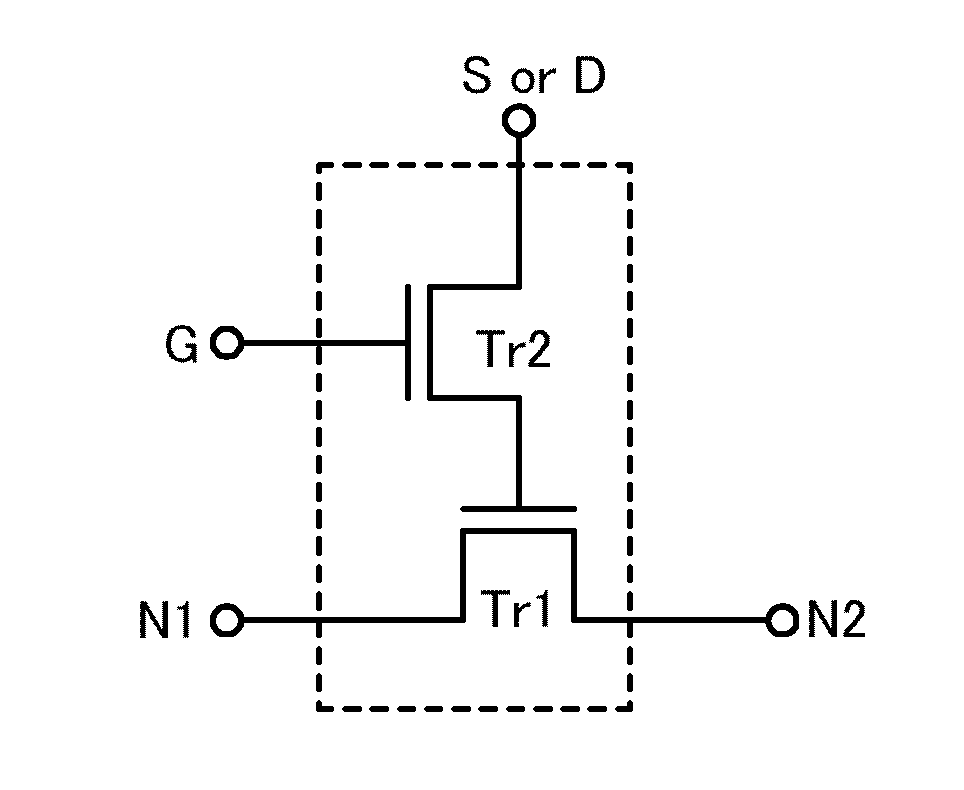
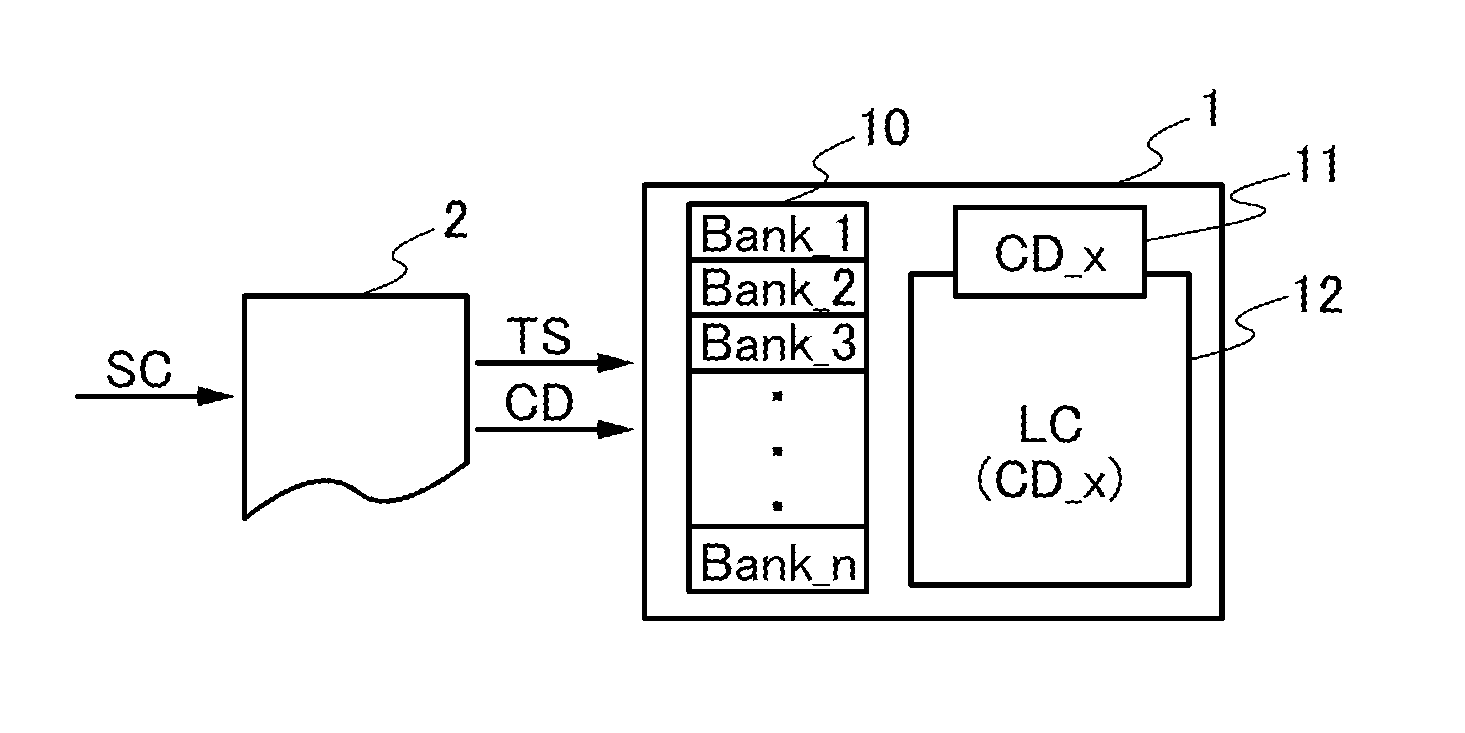
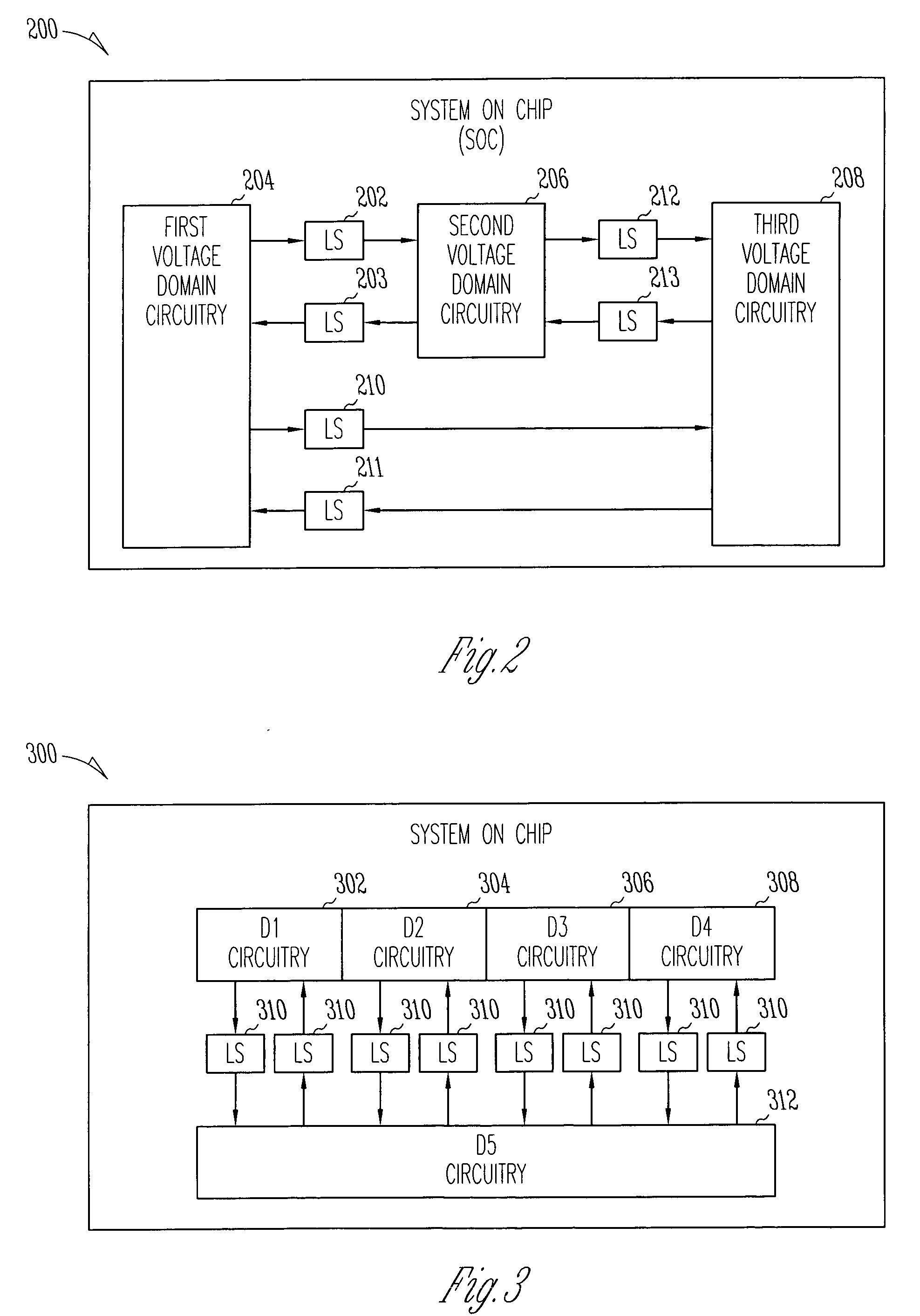
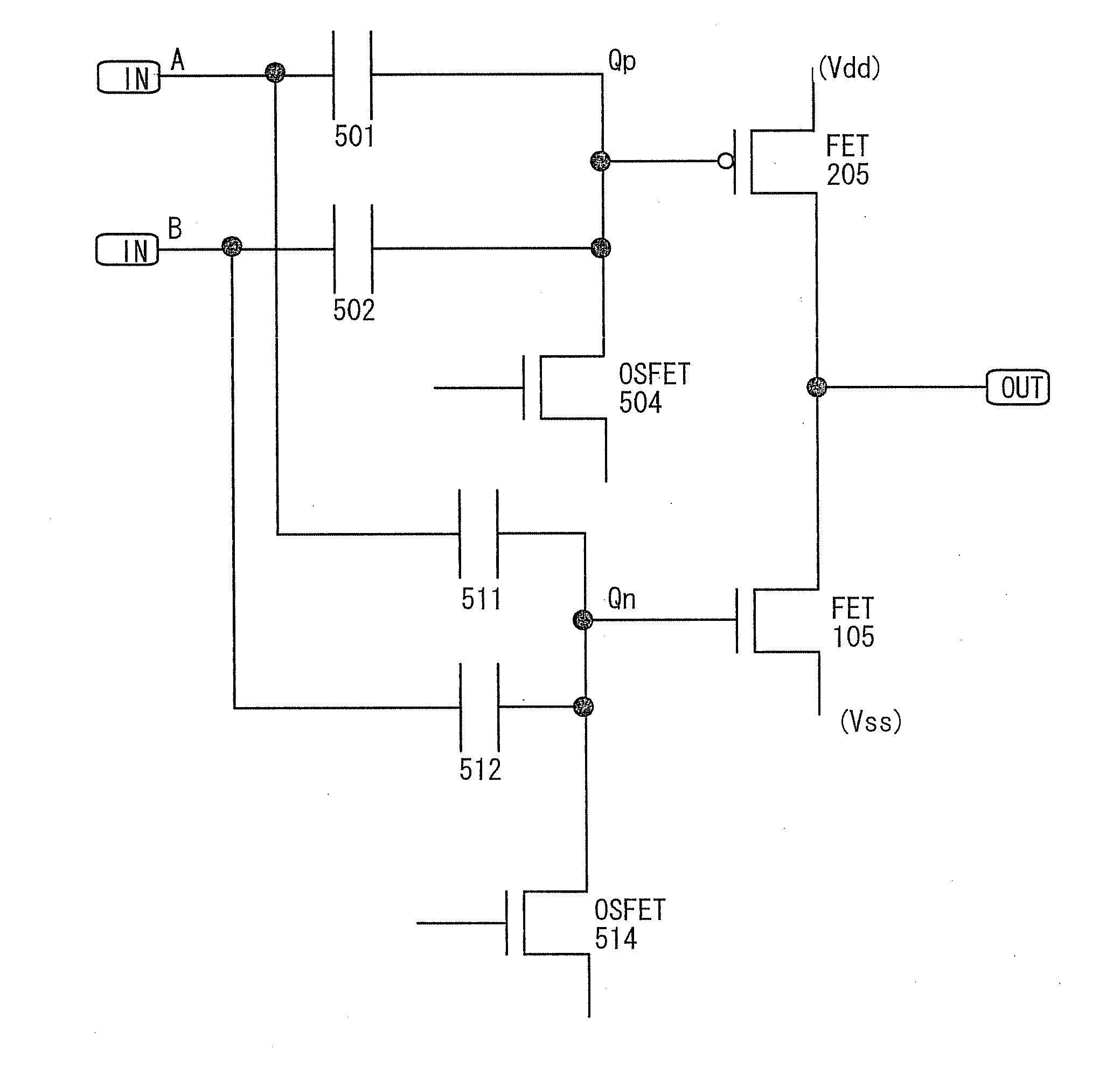
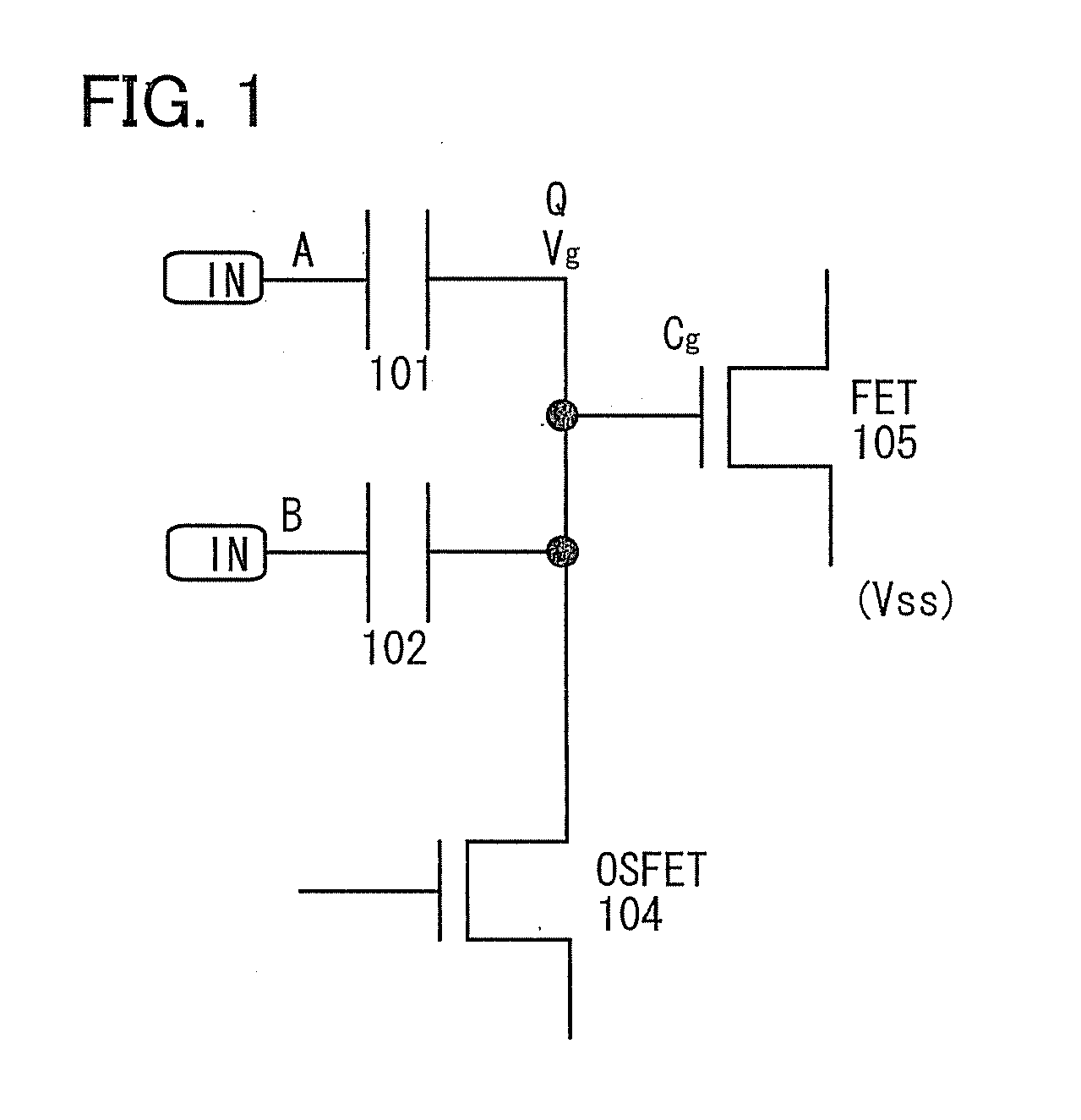
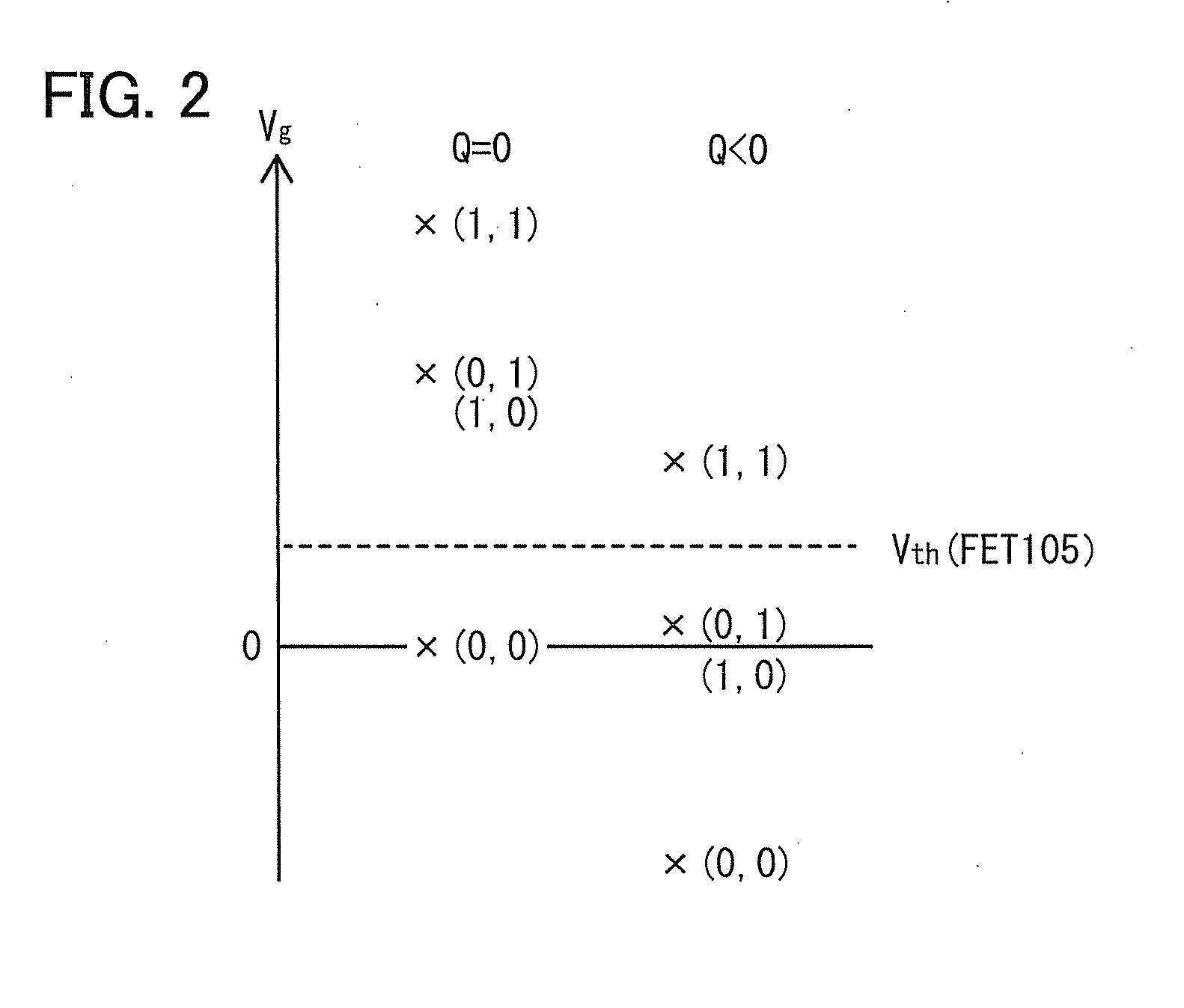
It is an object to provide a semiconductor device in which power consumption can be reduced. It is another object to provide a highly reliable semiconductor device using a programming cell, such as a programmable logic device (PLD). In accordance with a change in a configuration of connections between basic blocks, power supply voltage furnishing to the basic blocks is changed. That is, when the structure of connections between the basic blocks is such that a basic block does not contribute to a circuit, the supply of the power supply voltage to this basic block is stopped. Further, the supply of the power supply voltage to the basic blocks is controlled using a programming cell formed using a field effect transistor whose channel formation region is formed using an oxide semiconductor, the field effect transistor having extremely low off-state current or extremely low leakage current.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device, storage medium on which cell library is stored and designing method for semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20020079927A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesMOSFETDrain current
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
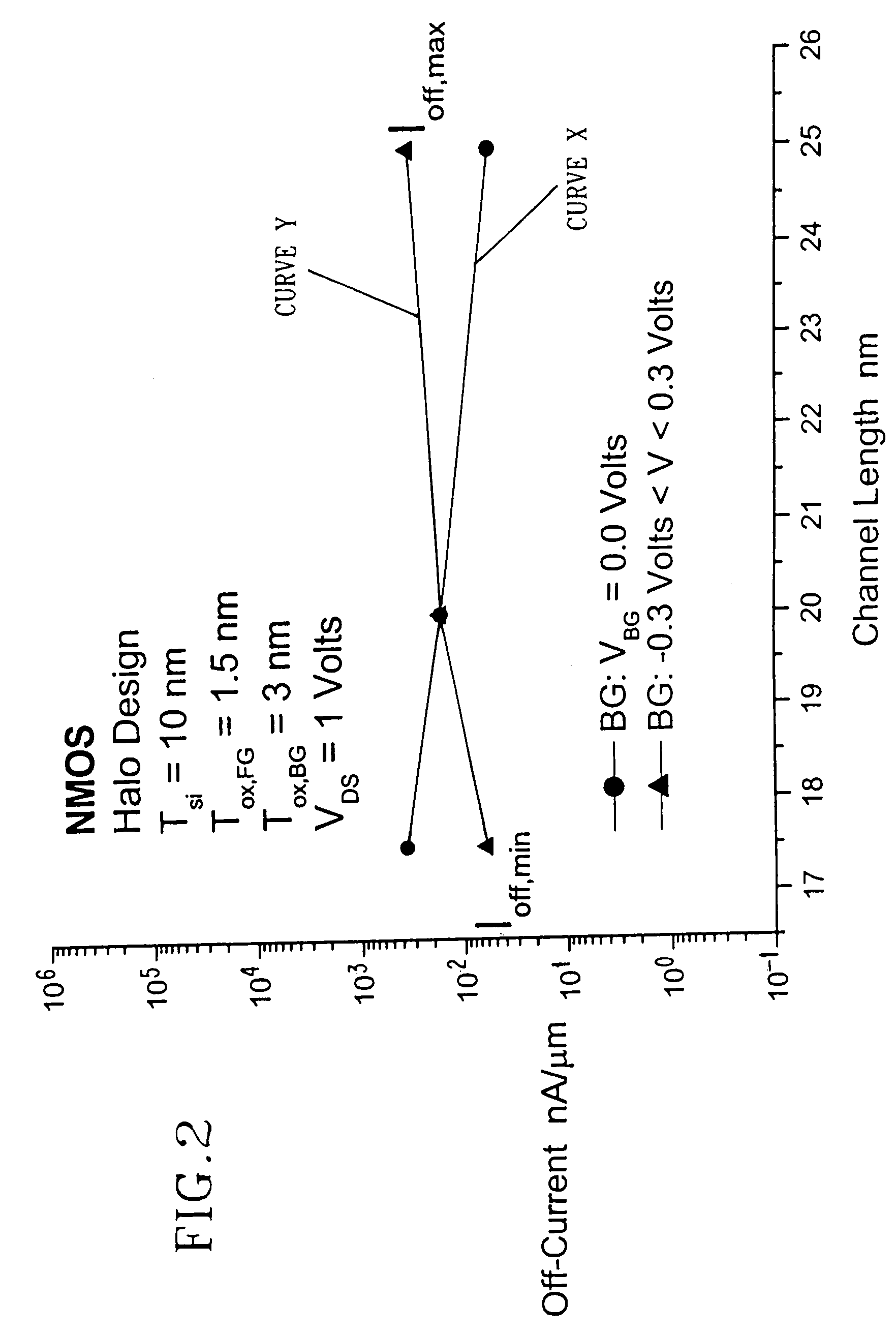
Threshold voltage roll-off compensation using back-gated MOSFET devices for system high-performance and low standby power
InactiveUS7089515B2Power reduction in field effect transistorsDetecting faulty computer hardwareMOSFETStandby power
A method for compensating the threshold voltage roll-off using transistors containing back-gates or body nodes is provided. The method includes designing a semiconductor system or chip having a plurality of transistors with a channel length of Lnom. For the present invention, it is assumed that the channel length of these transistors at the completion of chip manufacturing is Lmax. This enables one to set the off-current to the maximum value of I-offmax which is done by setting the threshold voltage value to Vtmin. The Vtmin for these transistors is obtained during processing by using the proper implant dose. After manufacturing, the transistors are then tested to determine the off-current thereof. Some transistors within the system or chip will have an off-current value that meets a current specification. For those transistor devices, no further compensation is required. For other transistors within the system or chip, the off-current is not within the predetermined specification. For those transistors, threshold voltage roll-off has occurred since they are transistors that have a channel length that is less than nominal. For such short channel transistors, the threshold voltage is low, even lower than Vtmin, and the off-current is high, even higher than I-offmax. Compensation of the short channel transistors is achieved in the present invention by biasing the back-gate or body node to give increased threshold voltage about equal to Vtmin and hence an off-current that meets the predetermined specification, which is about equal to I-offmax.
Owner:ETHICON INC +1
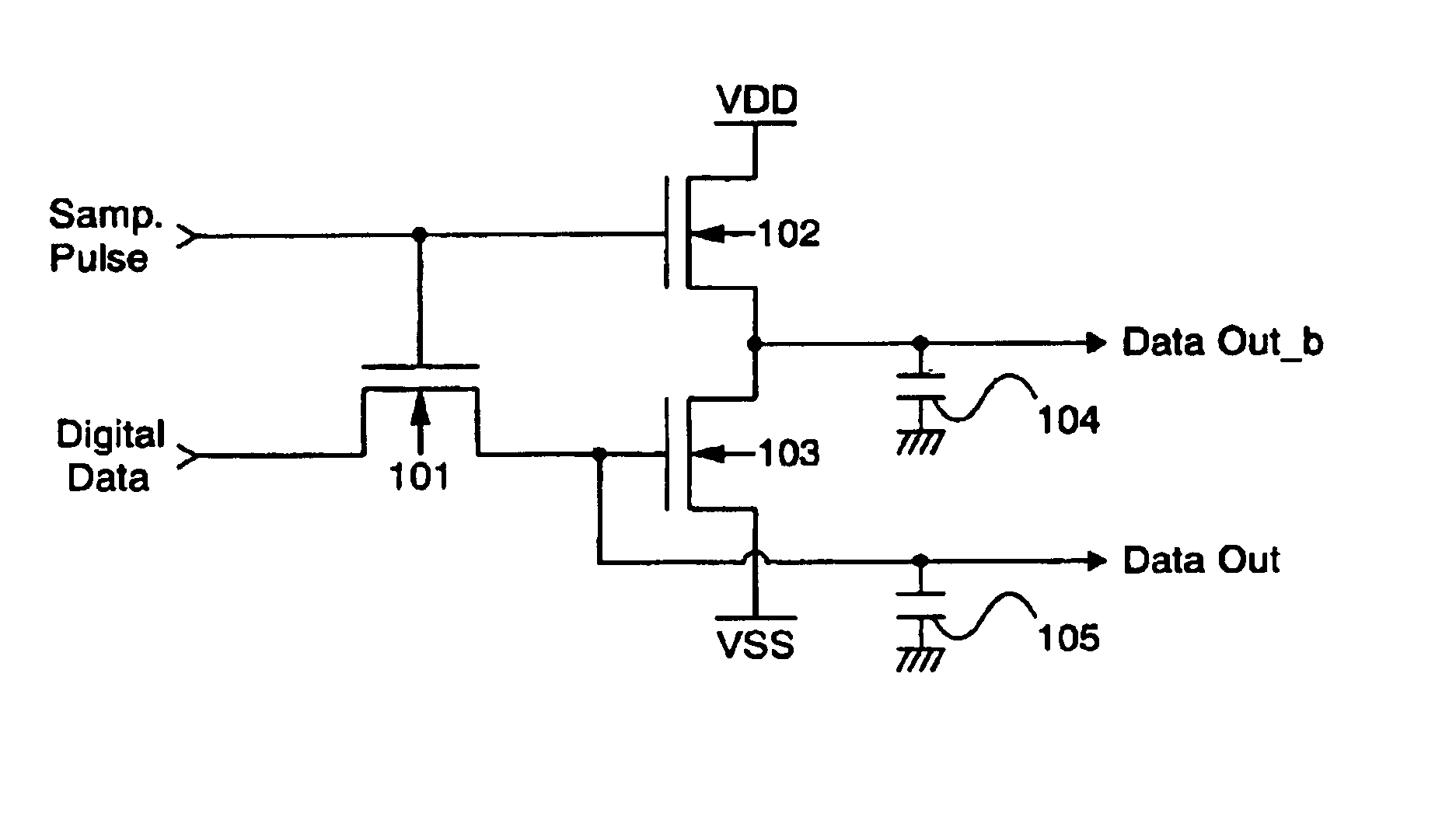
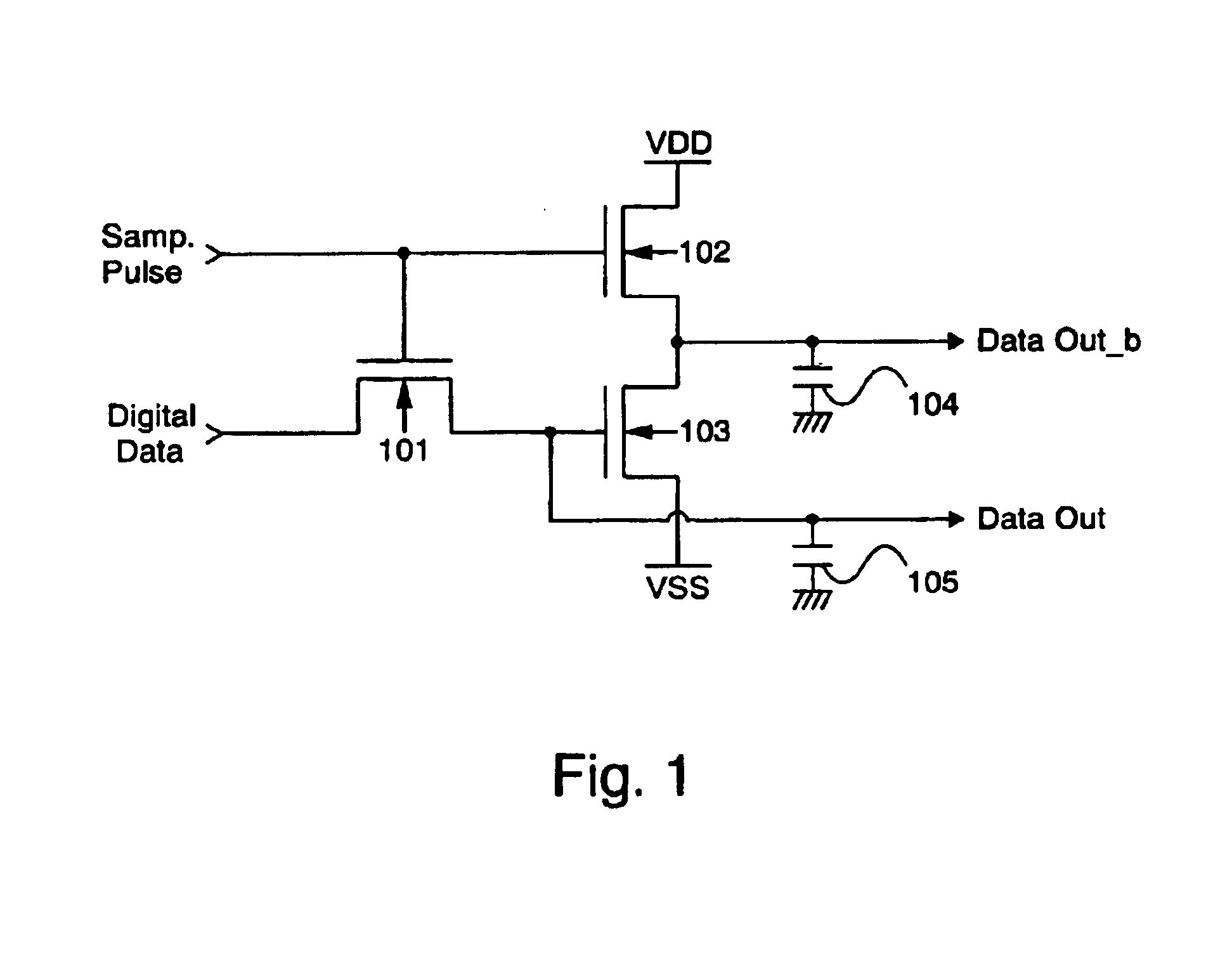
Semiconductor device and display device
InactiveUS7068076B2Obstruction is producedPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital videoDevice material
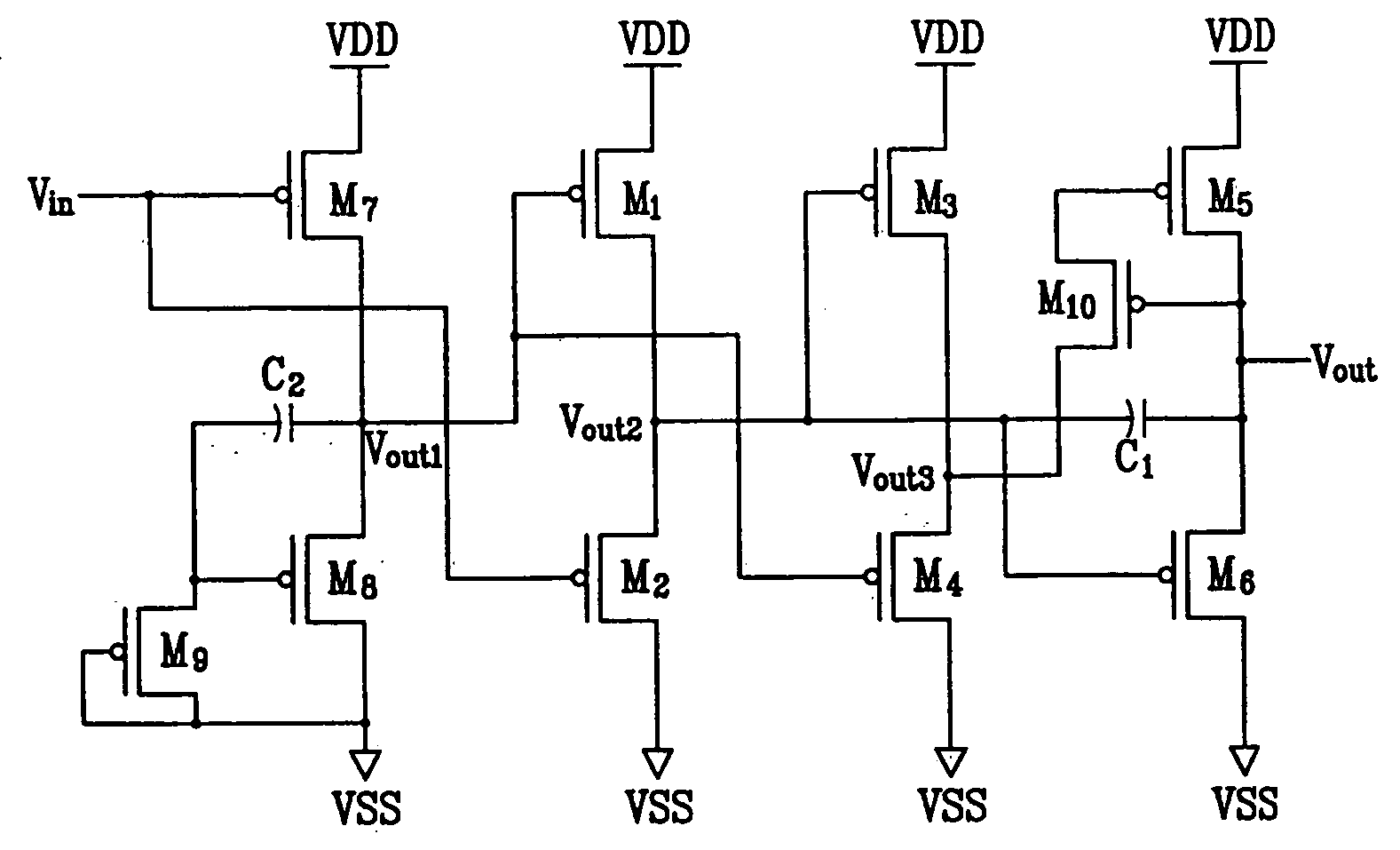
A circuit capable of reducing a consumption current is provided for a digital display device composed of unipolar TFTs. There is provided a latch circuit for holding a digital video signal. According to the latch circuit, when the digital video signal is inputted to an input electrode of a TFT (101), a non-inverting output signal is outputted from an output electrode of the TFT (101) and an inverting output signal is outputted from output electrodes of TFTs (102 and 103). Two line outputs of non-inversion and inversion are obtained. Thus, when a buffer located in a subsequent stage is operated, a period for which a direct current path is produced between a high potential and a low potential of a power source can be shortened, thereby contributing to reduction in a consumption current.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8547753B2Improve versatilityReduce designPower reduction in field effect transistorsTransistorProgrammable logic deviceHemt circuits
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Clamped cascode level shifter circuit
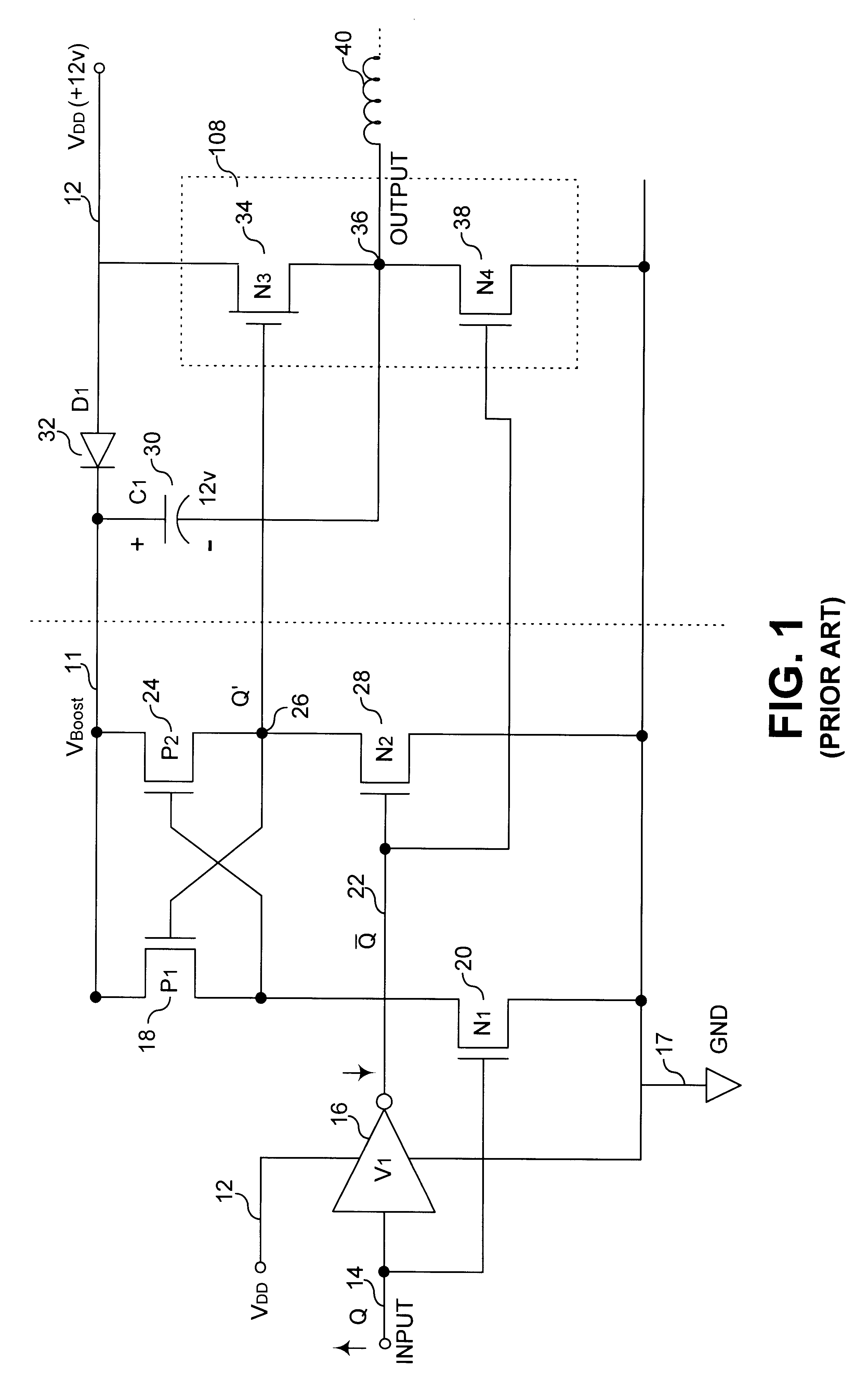
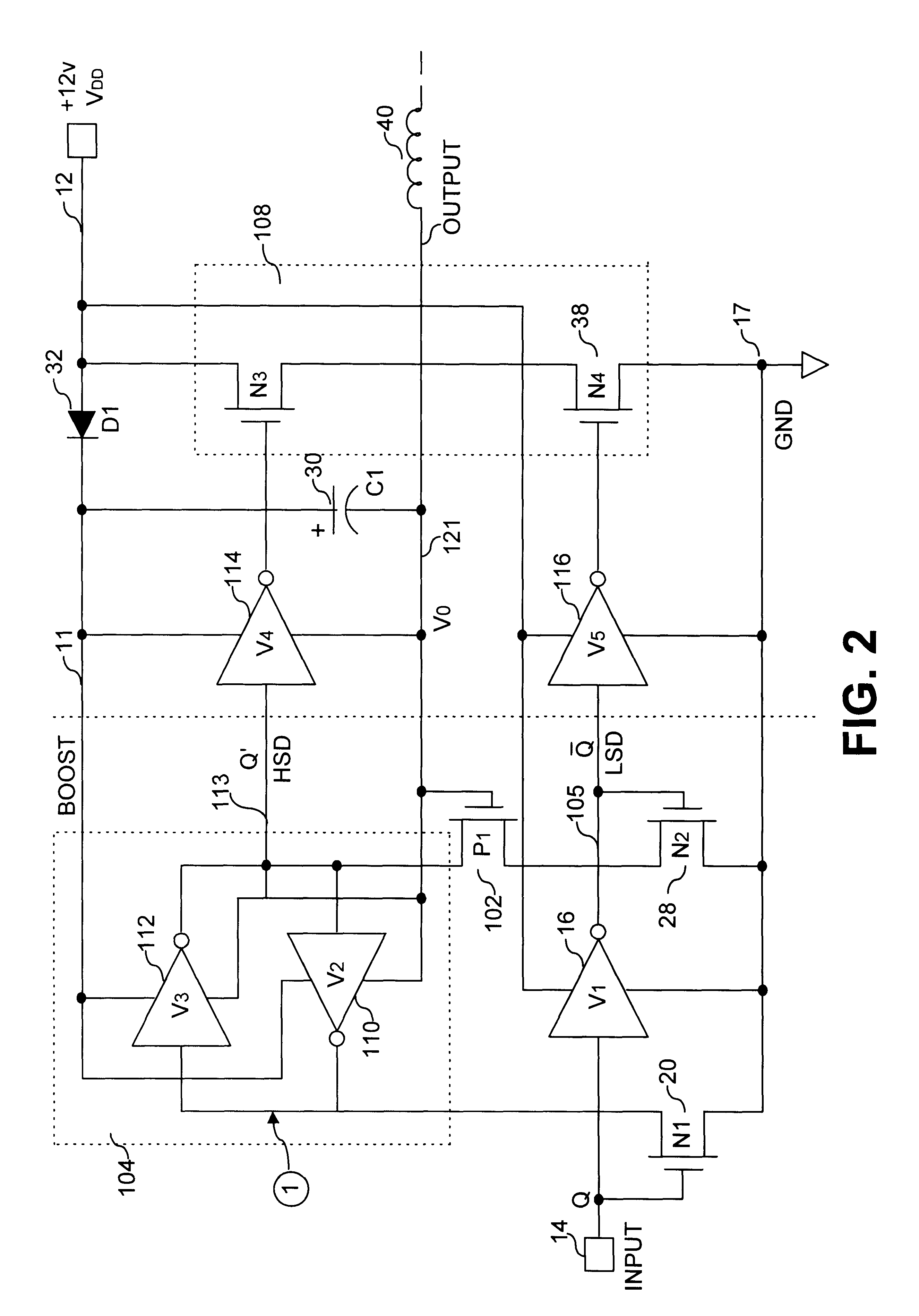
InactiveUS6201429B1Preventing continuous current conductionHysteretic SwitchingPower reduction in field effect transistorsPulse automatic controlCascodeEngineering
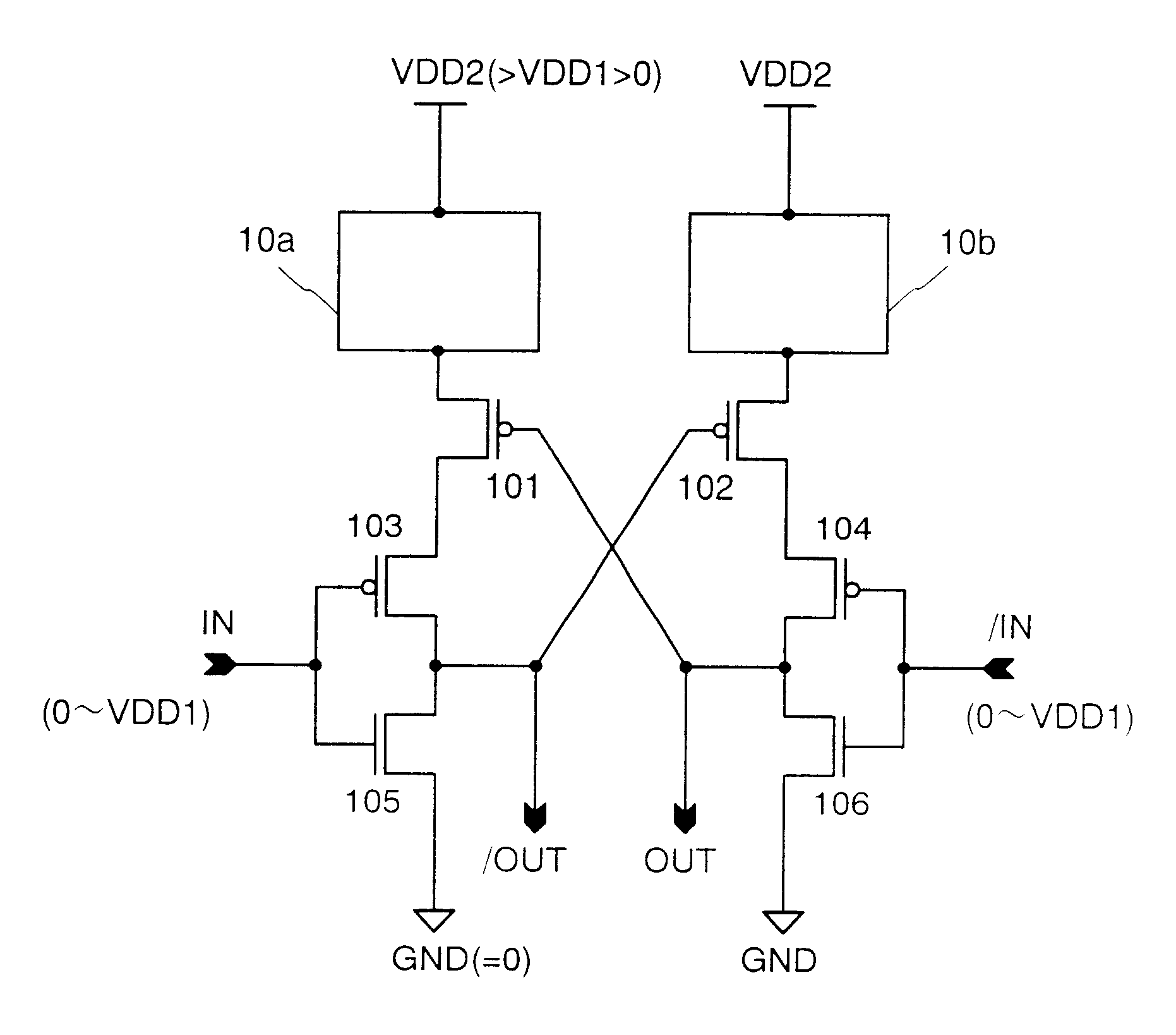
An improved level shifter circuit that toggles a "flying Flip-Flop" comprising a cross-coupled inverter pair with control devices driven out of phase through a pair of cascode transistors. The cross-coupled inverter pair provides pull-up to the positive rail, clamping to a High Side-Common (HSC), and providing Hysteretic Switching. The cascode transistors restrict the pull-down of the control devices, thereby preventing continuous current conduction.
Owner:AME
Semiconductor integrated circuit
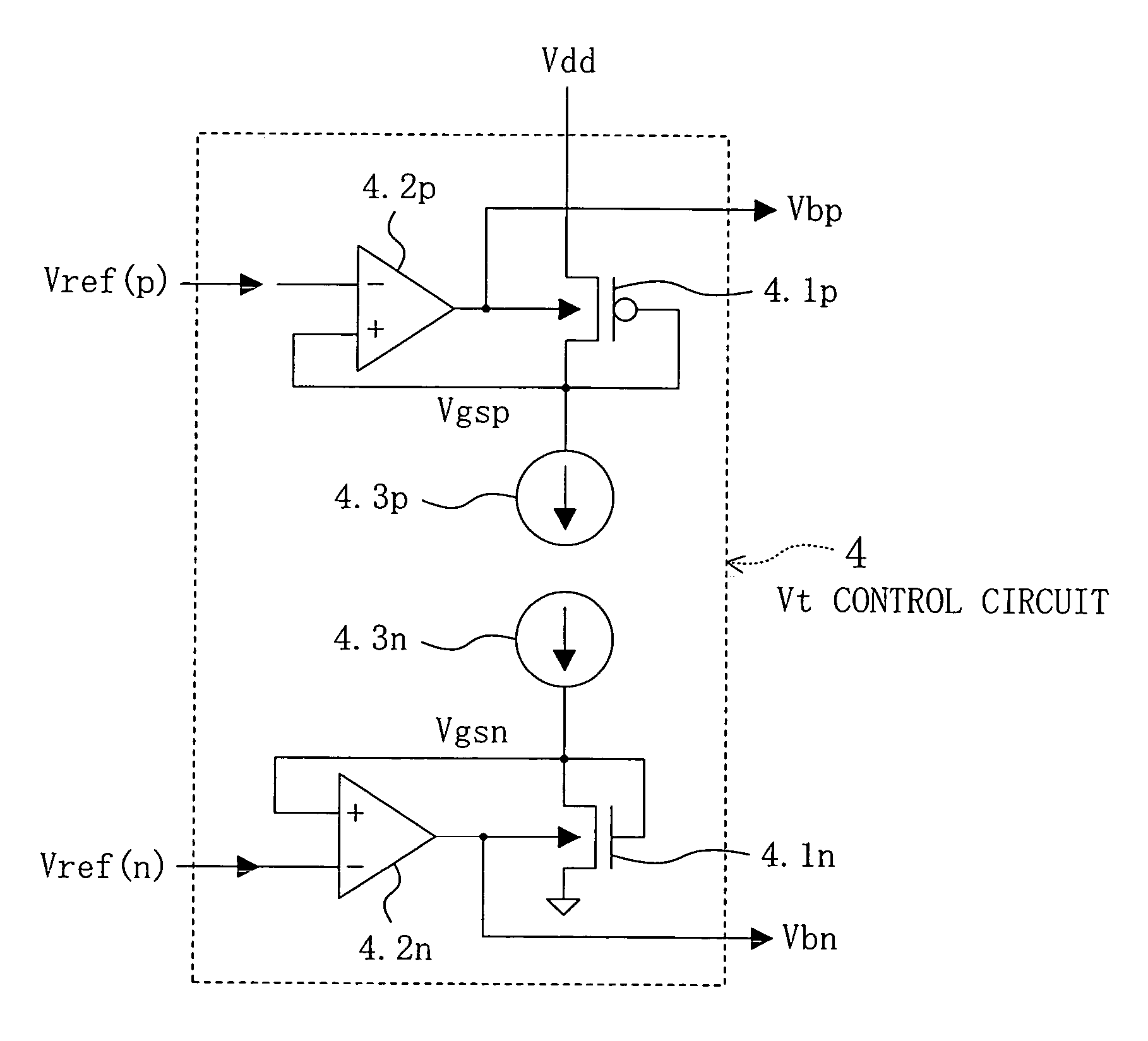
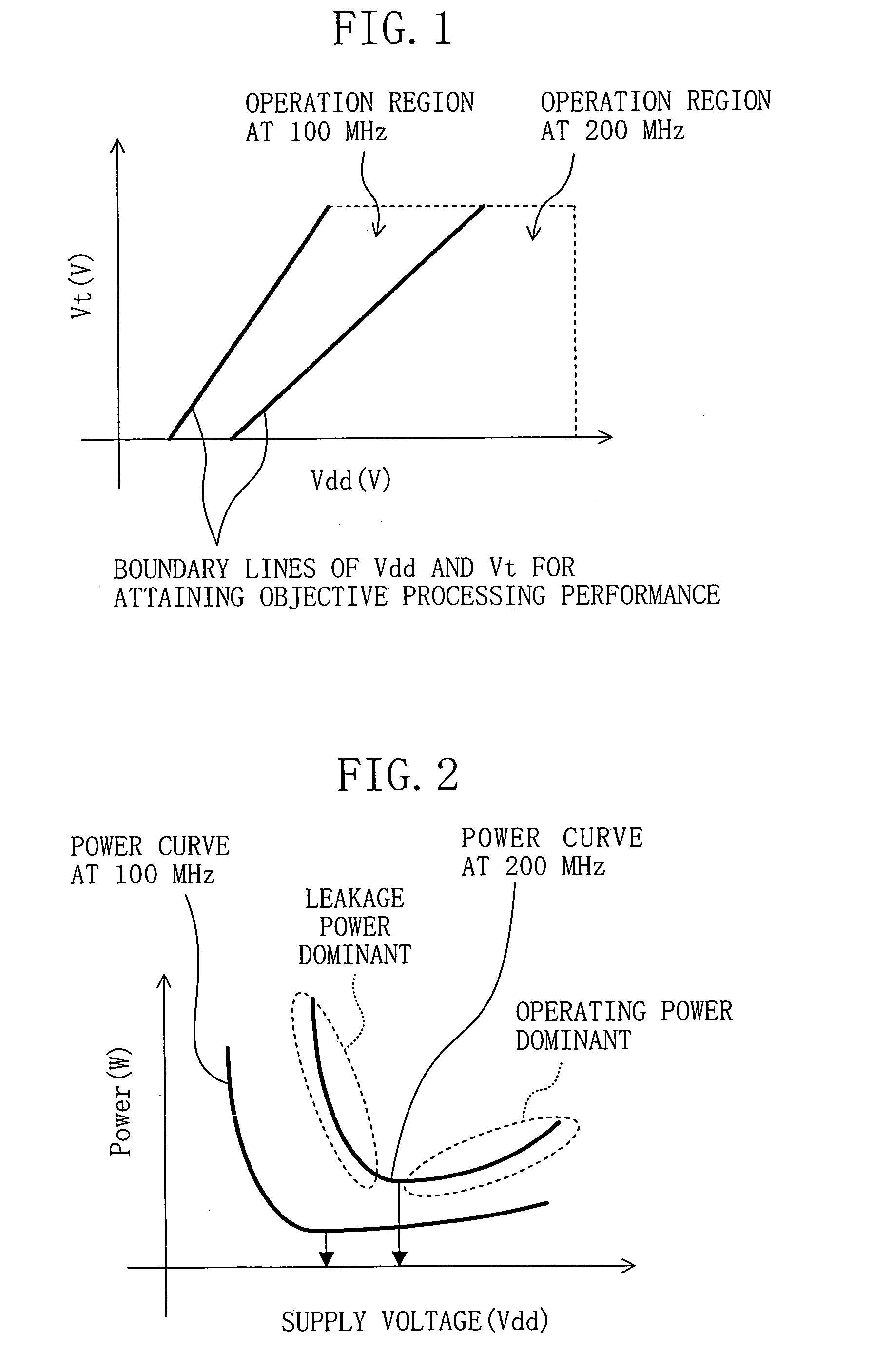
InactiveUS20050116765A1Increase probabilityReduce power consumptionTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsEngineeringControl circuit
In a semiconductor integrated circuit, respective semiconductor circuits are disposed in different regions partitioned in accordance with their operation probabilities per unit time, and a supply voltage and a threshold voltage are correlatively controlled in each region. A target value for controlling the threshold voltage is determined in accordance with the operation probability of the semiconductor circuit. A threshold voltage control circuit controls substrate voltages of p-type and n-type MOS transistors included in the semiconductor circuit so that the threshold voltage can be constant at the target value regardless of the temperature change occurring in use. Simultaneously, a supply voltage control circuit controls the supply voltage for the semiconductor circuit so that an objective operating frequency can be attained. As a result, a semiconductor integrated circuit with low power consumption can be obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
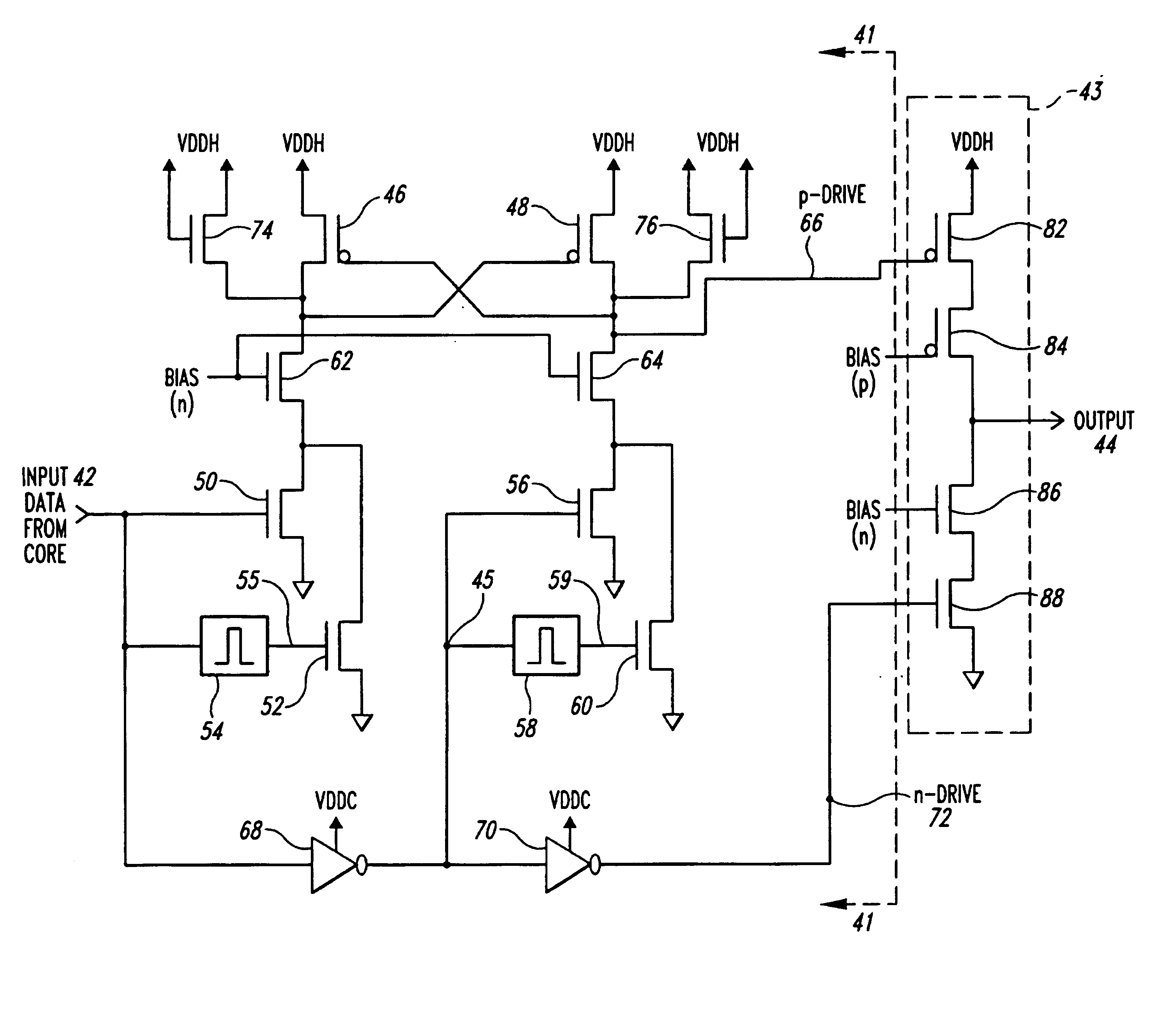
Level shifter
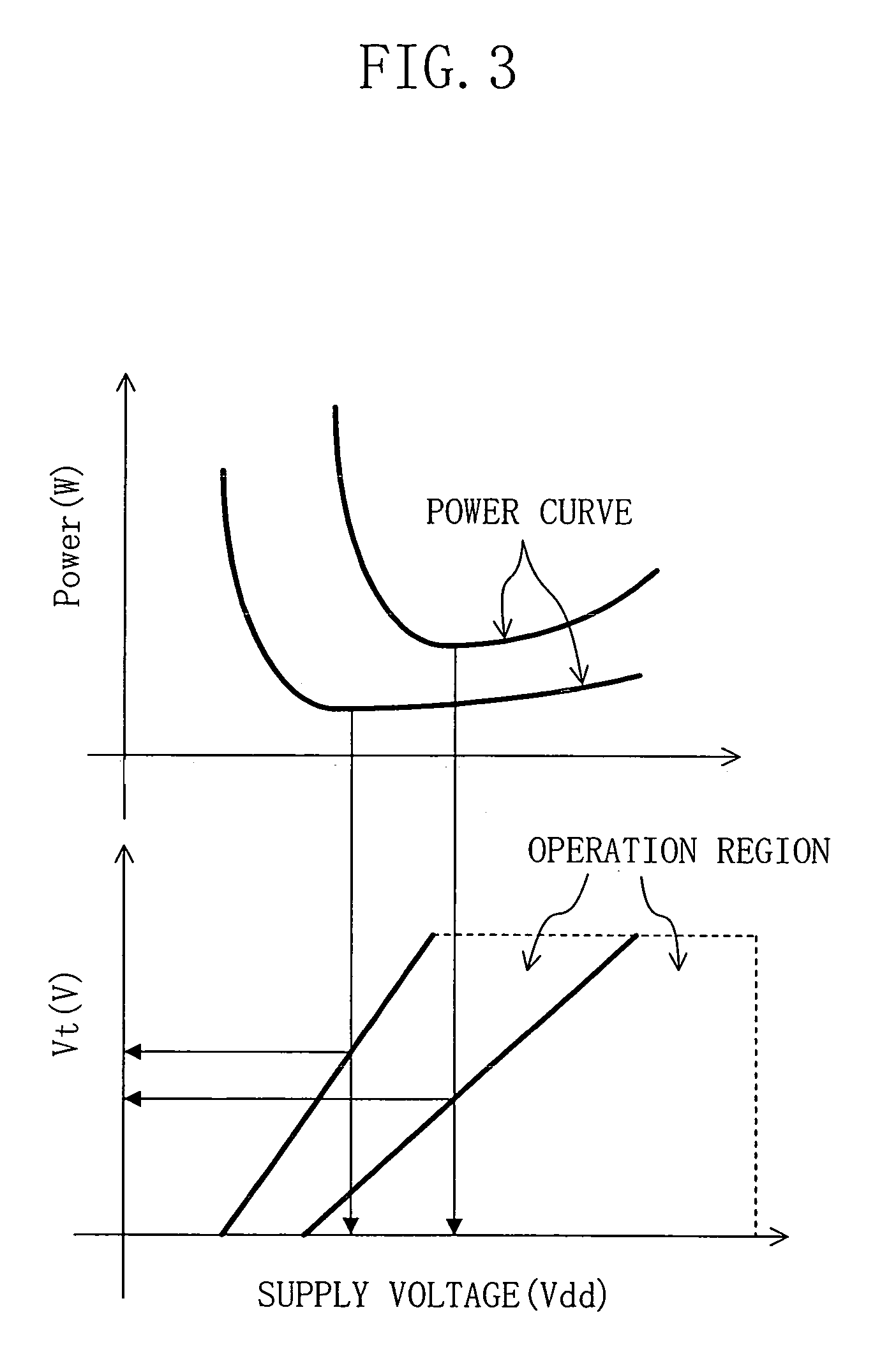
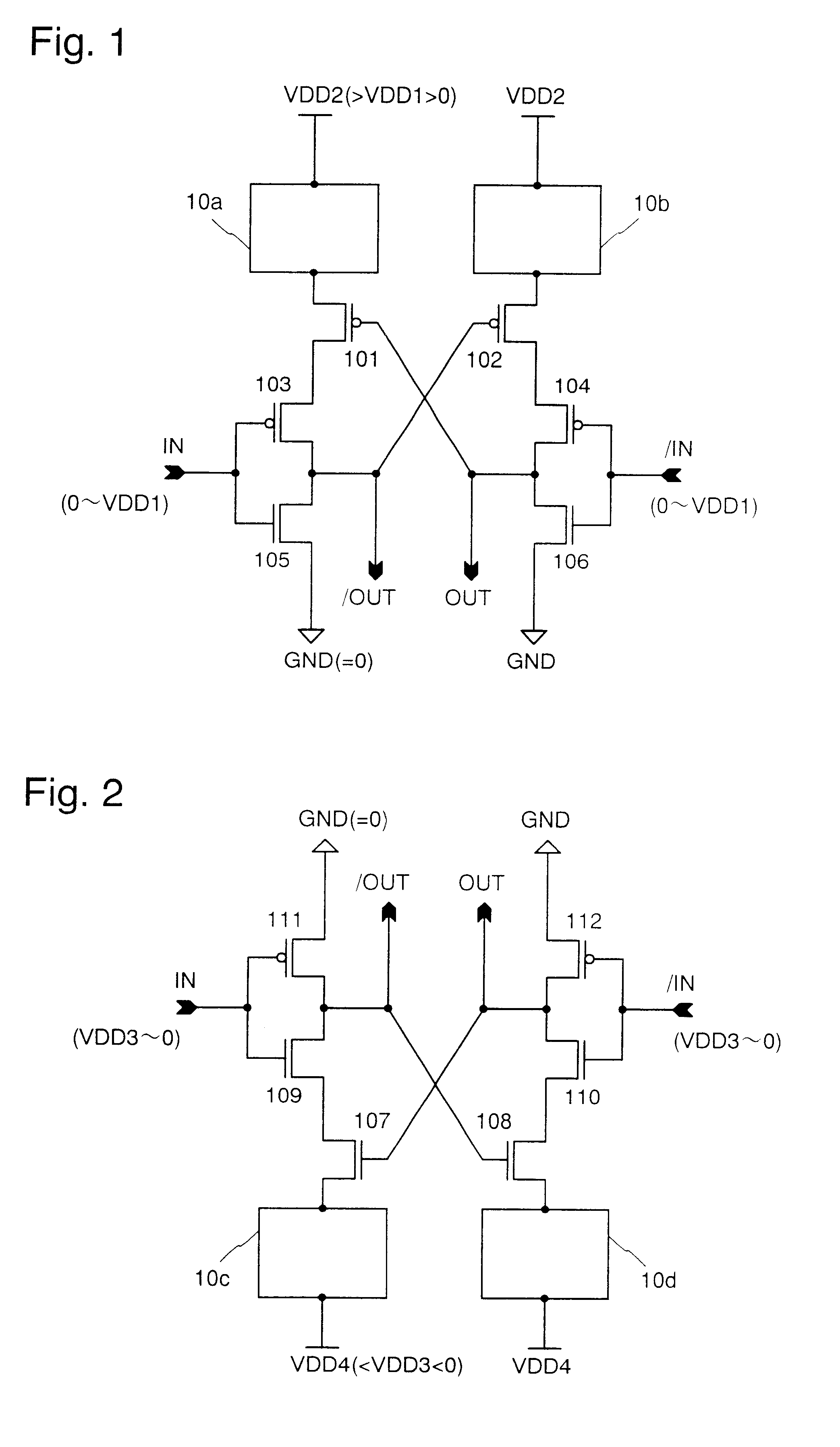
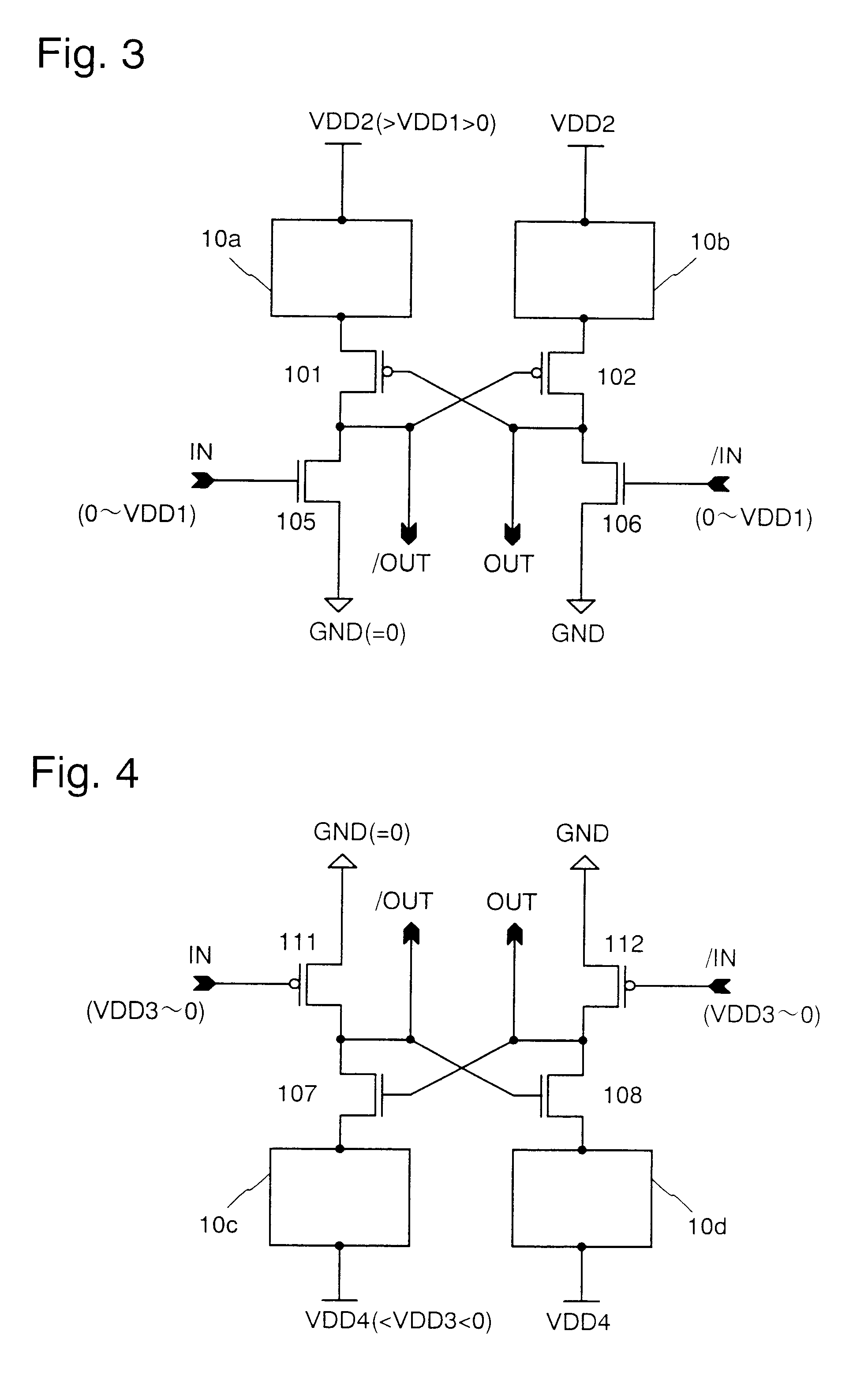
InactiveUS6384808B2Level conversion of voltage amplitudes having a large difference easyHigh speedPower reduction in field effect transistorsTelevision system detailsVoltage regulationElectric field
A compact level shifter is provided, which has a low consumption power and speedy operation, capable of easily performing a level conversion of voltage levels having a large difference. A voltage regulating circuit (10a), a P channel MOS electric field effect transistor (hereinafter referred to as PMOST), a PMOST (103), and an N channel MOS electric field effect transistor (hereinafter referred to as NMOST) (105) are connected in series between 2 power sources. Similarly, a voltage regulating circuit (10b), a PMOST (102), a PMOST (104), and an NMOST (106) are connected in series between 2 power sources. During the flow of a penetrating current in a transient period of a level conversion operation, a power source voltage is effectively reduced by the above-mentioned voltage regulating circuit, whereby the level conversion of the voltage level having a large difference is made easy.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
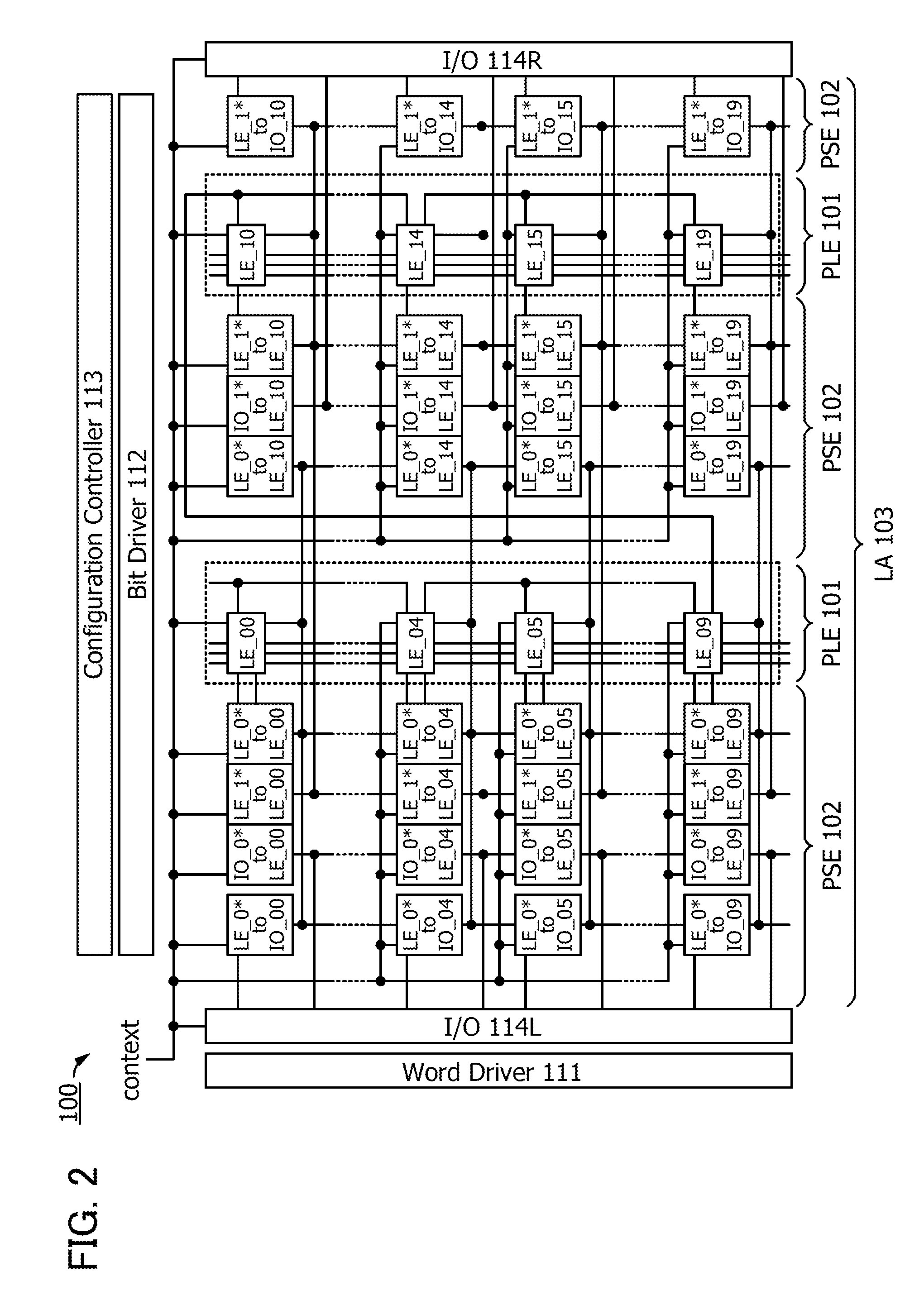
Programmable logic device
InactiveUS20130293263A1Reduce power consumptionShort startup timePower reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceSoftware engineering
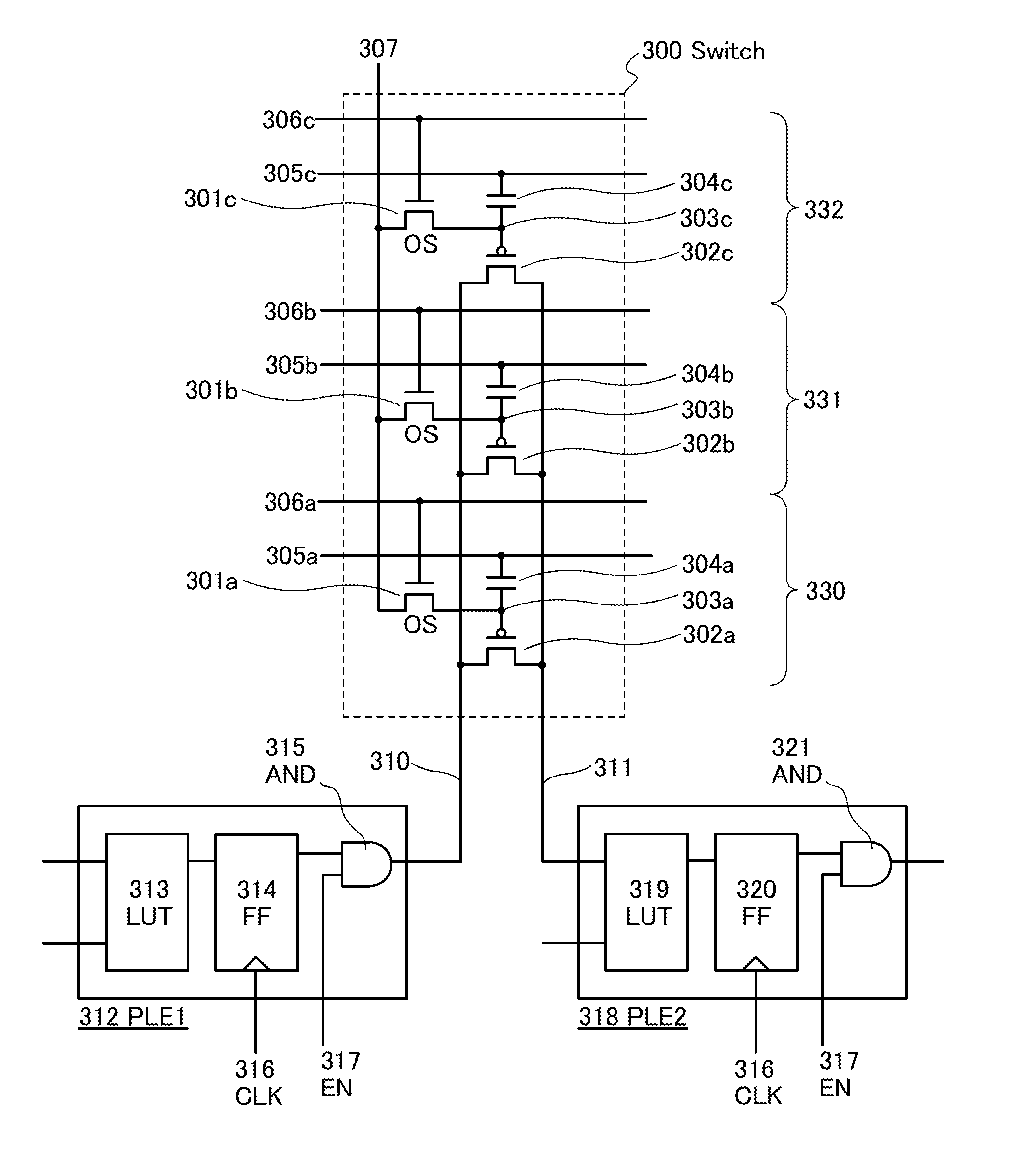
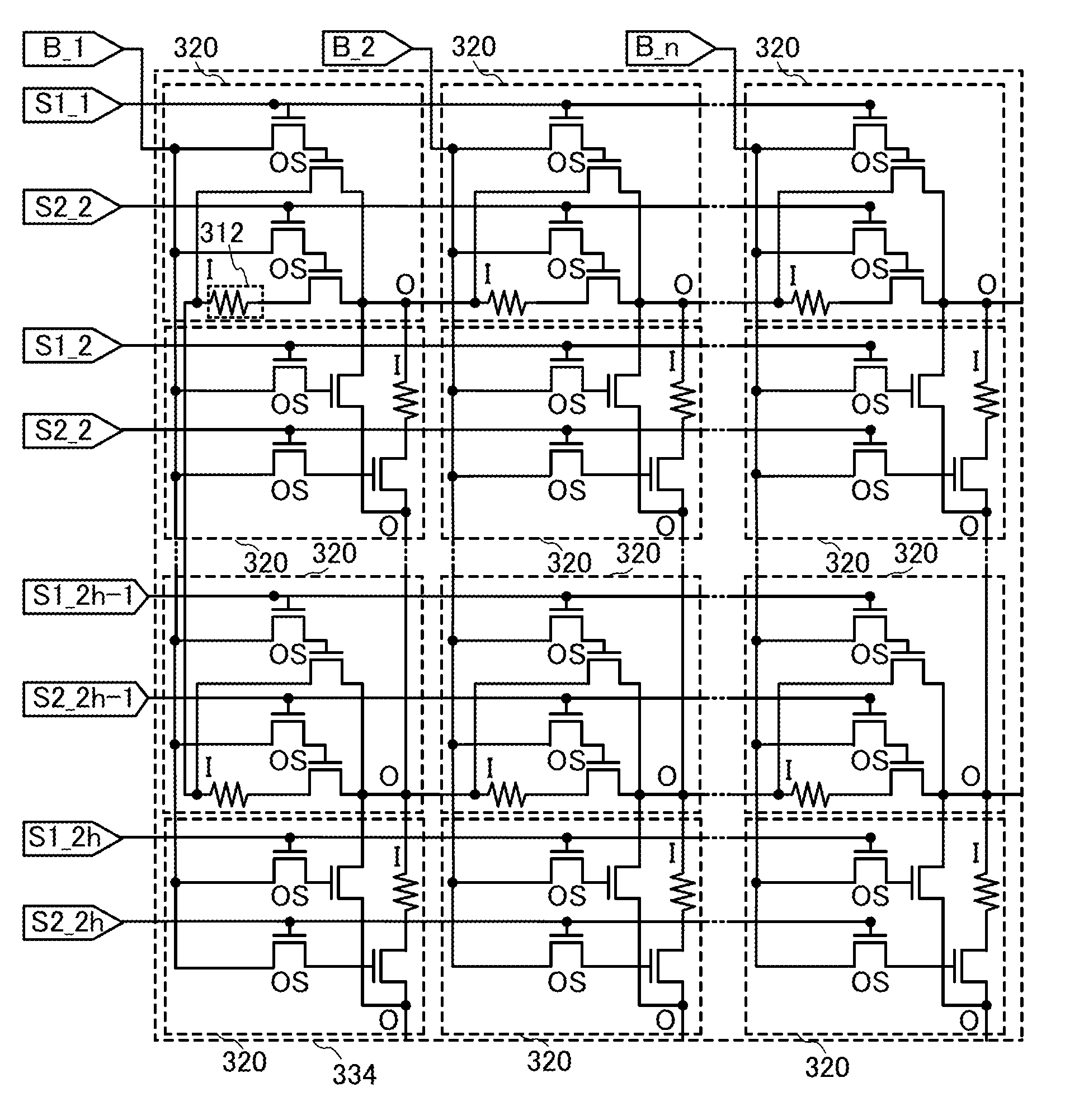
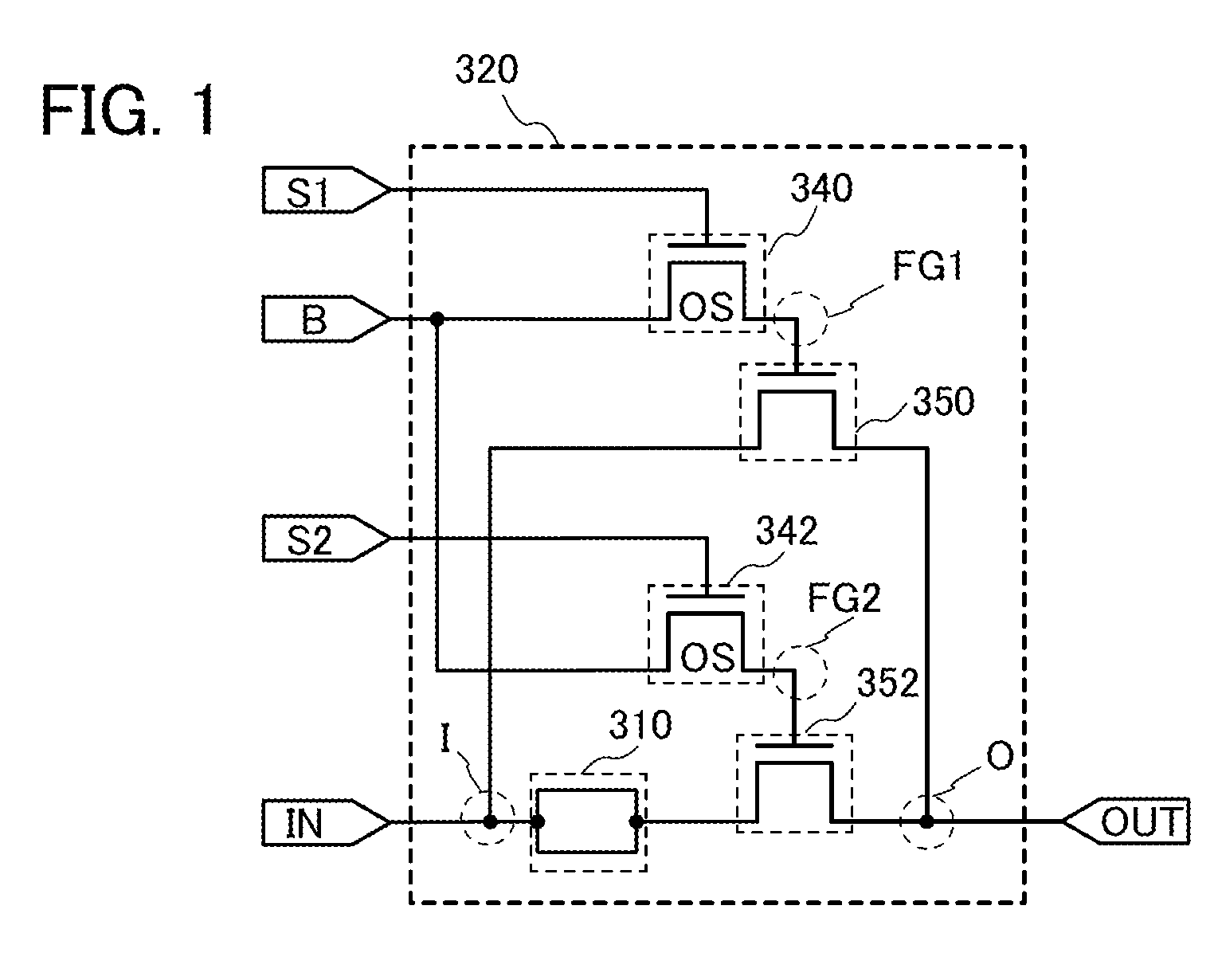
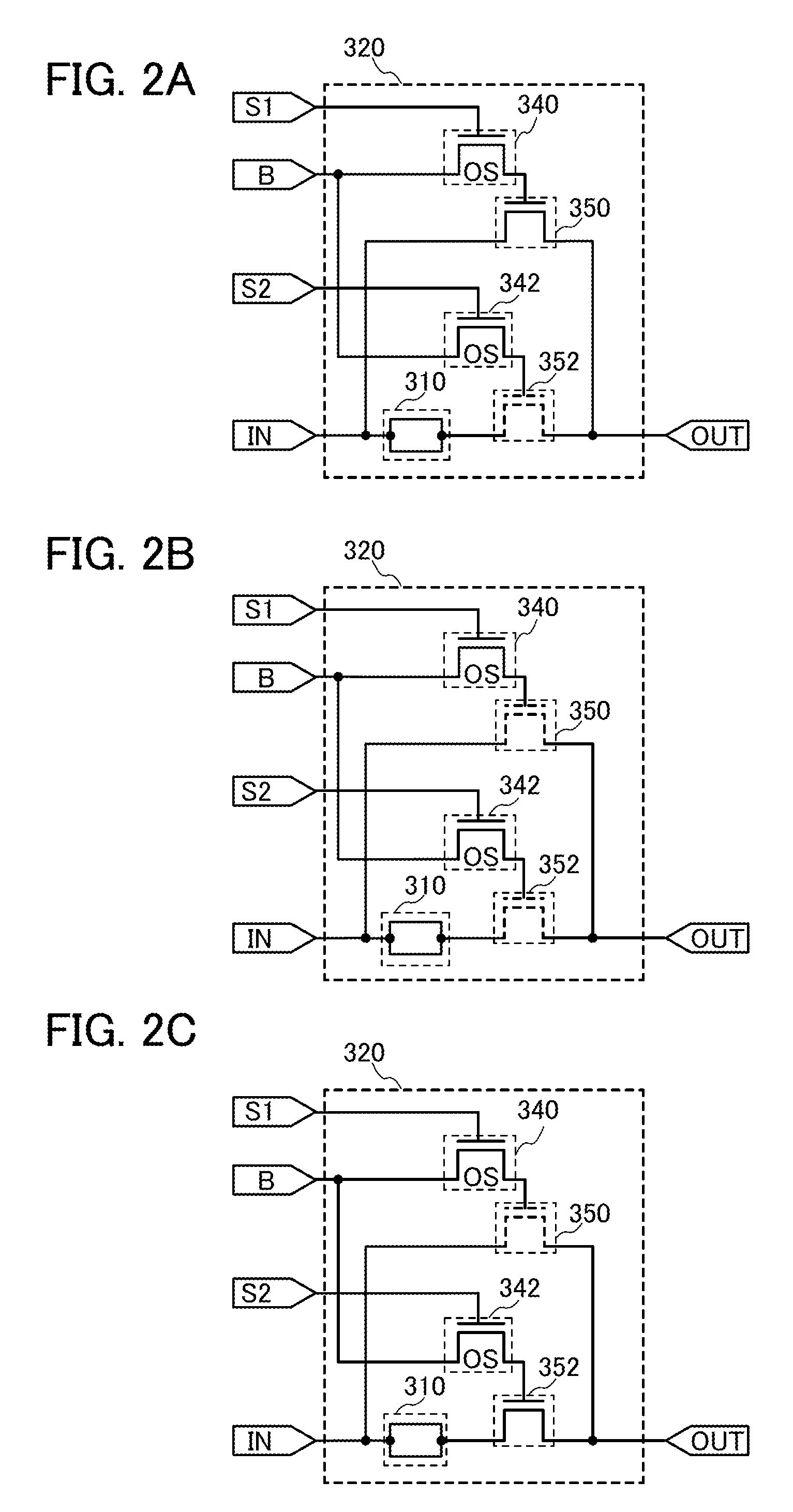
Disclosed is a programmable logic device (PLD) which can undergo dynamic configuration at a high speed. The PLD includes a plurality of programmable logic elements (PLEs) and a switch for selecting electrical connection between the PLEs. The switch includes a plurality of circuit groups each of which includes first and second transistors. The second transistors of the circuit groups are electrically connected in parallel with one another. In each of the circuit groups, the electrical conduction between a source and a drain of the second transistor is determined based on configuration data held at a node between the gate of the second transistor and a drain of the first transistor, which allows the selection of the electrical connection and disconnection between the programmable logic elements by the selection of one of the circuit groups.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device, recording medium stored with cell library, and method for designing semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS6380764B1Power reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionMOSFETDrain current
Disclosed is a semiconductor integrated circuit device constructed of MOSFETs in which there is attained a harmony between increase in consumption power due to a leakage current and operating speed of the MOSFETs in a suitable manner, and among a plurality of signal paths in the semiconductor integrated circuit device, a path which has a margin in delay is constructed with MOSFETs each with a high threshold voltage, while a path which has no margin in delay is constructed with MOSFETs each with a low threshold voltage which has a large leakage current but a high operating speed, in light of a delay with which a signal is transmitted along a signal path.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Programmable logic device
InactiveUS20120293206A1Raise the potentialLayer deterioratesPower reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceEngineering
An object is to provide a programmable logic device having logic blocks connected to each other by a programmable switch, where the programmable switch is characterized by an oxide semiconductor transistor incorporated therein. The extremely low off-state current of the oxide semiconductor transistor provides a function as a non-volatile memory due to its high ability to hold a potential of a gate electrode of a transistor which is connected to the oxide semiconductor transistor. The ability of the oxide semiconductor transistor to function as a non-volatile memory allows the configuration data for controlling the connection of the logic blocks to be maintained even in the absence of a power supply potential. Hence, the rewriting process of the configuration data at starting of the device can be omitted, which contributes to the reduction in power consumption of the device.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Programmable LSI
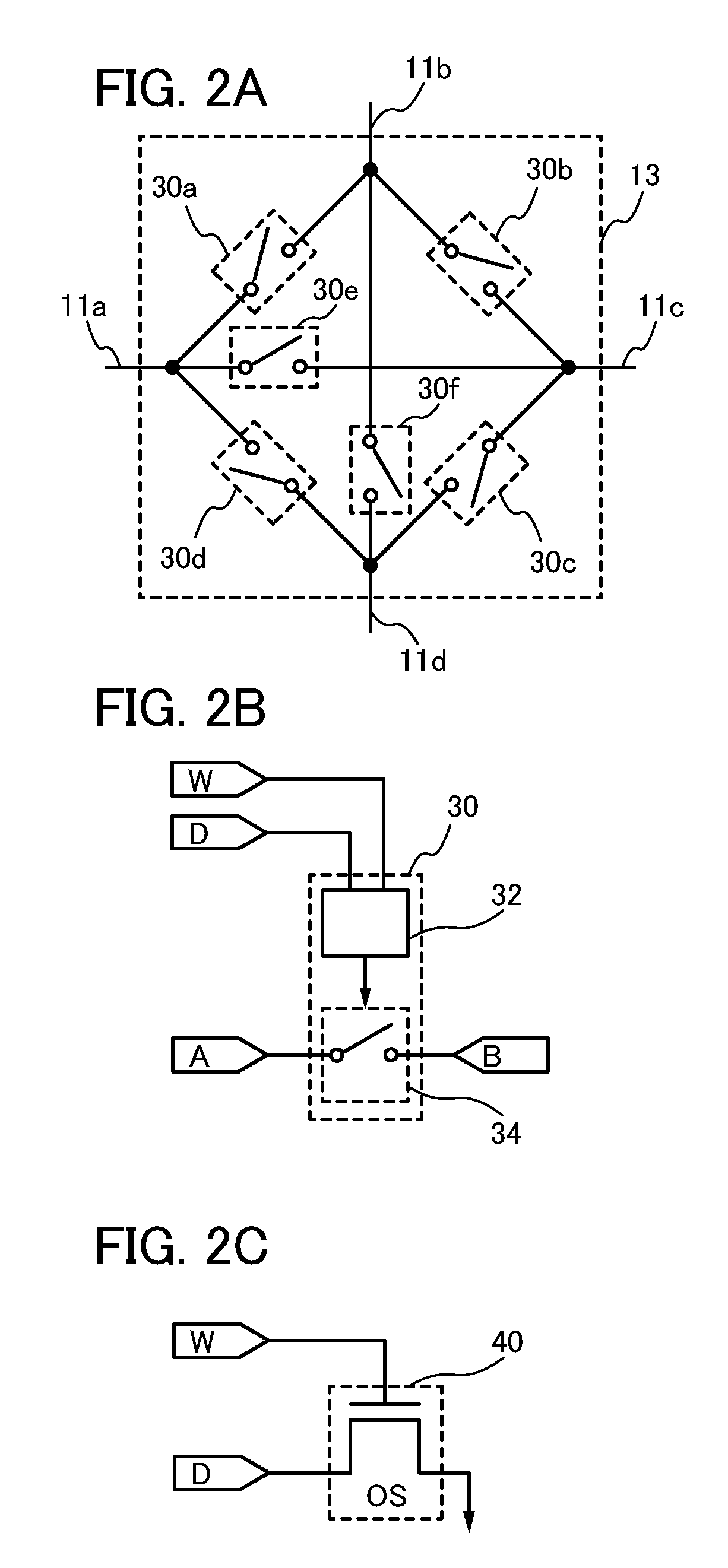
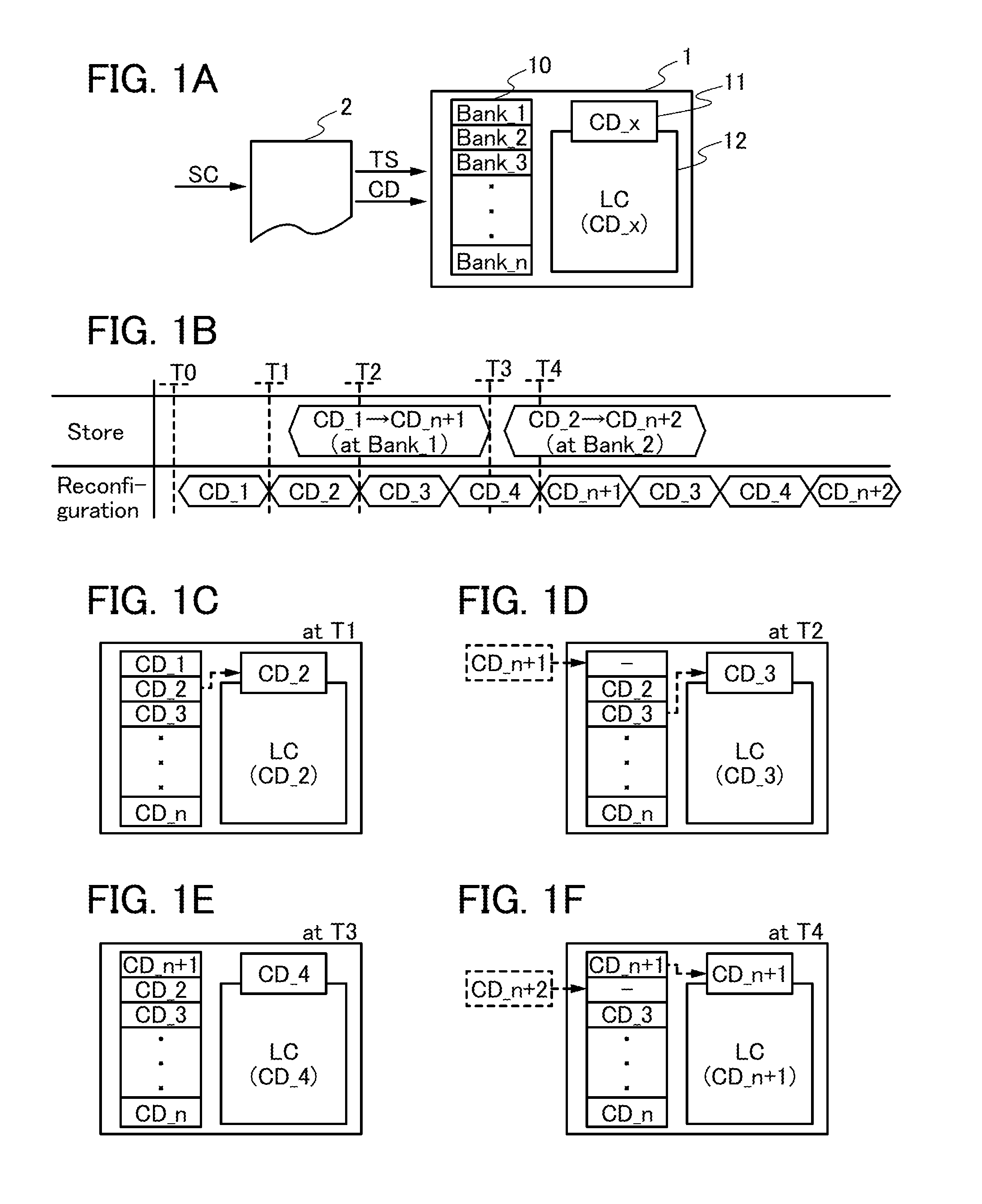
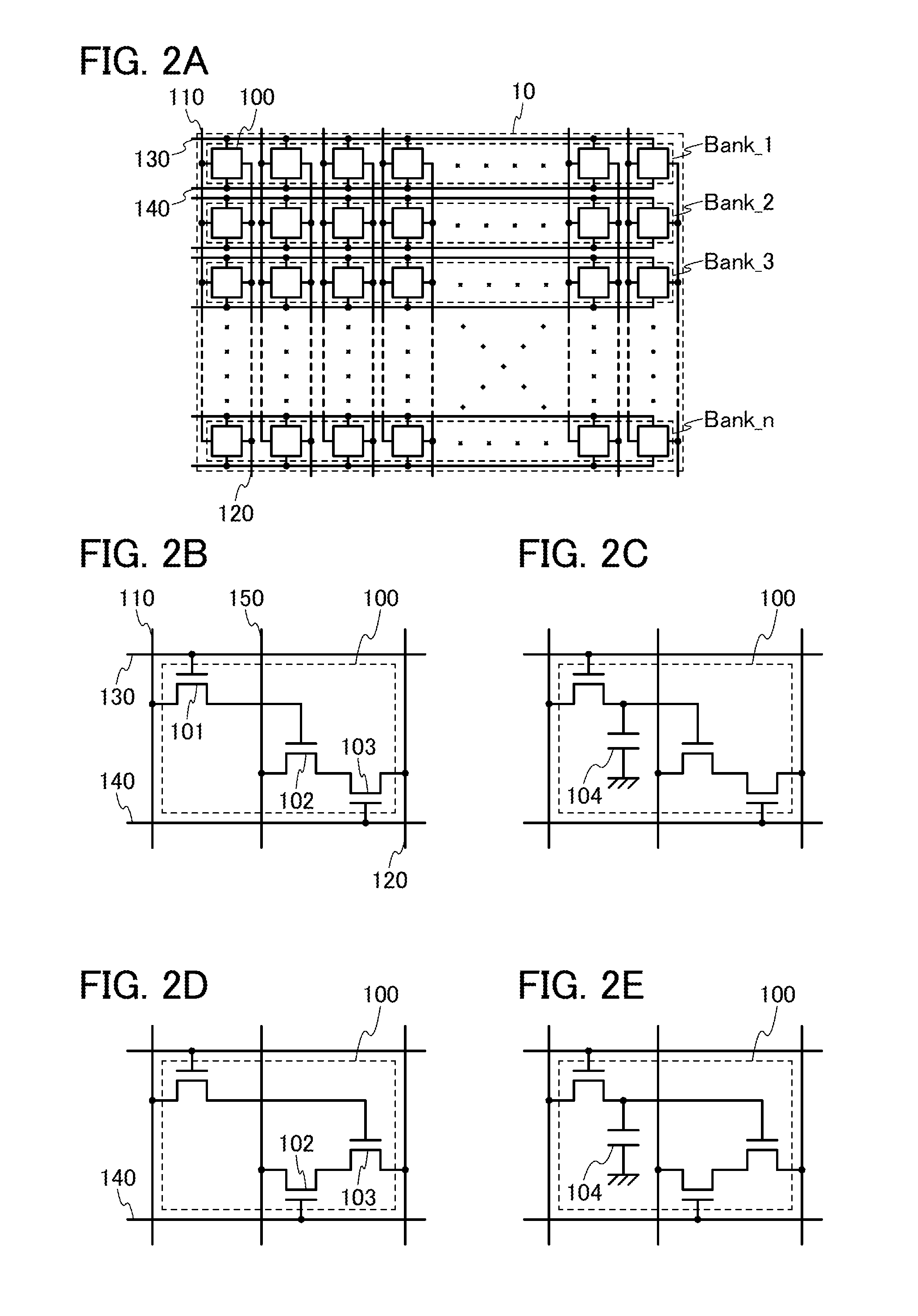
ActiveUS20130285697A1Operation delay can be suppressedReduce circuit areaPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsTime scheduleData needs
An object is to achieve both suppression of operation delay and reduction in power consumption of a programmable LSI. A compiler generates, from source code, configuration data needed in a programmable LSI and a time schedule that shows a timing of using the data in the programmable LSI (a timing at which the data is held in a configuration memory) and a timing of storing the data in the programmable LSI before the data is used. Supply of new configuration data to the programmable LSI from the outside (storage of new configuration data) and data rewrite in the configuration memory in the programmable LSI (circuit reconfiguration) are performed independently and concurrently on the basis of the time schedule.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Adaptive supply voltage body bias apparatus and method thereof
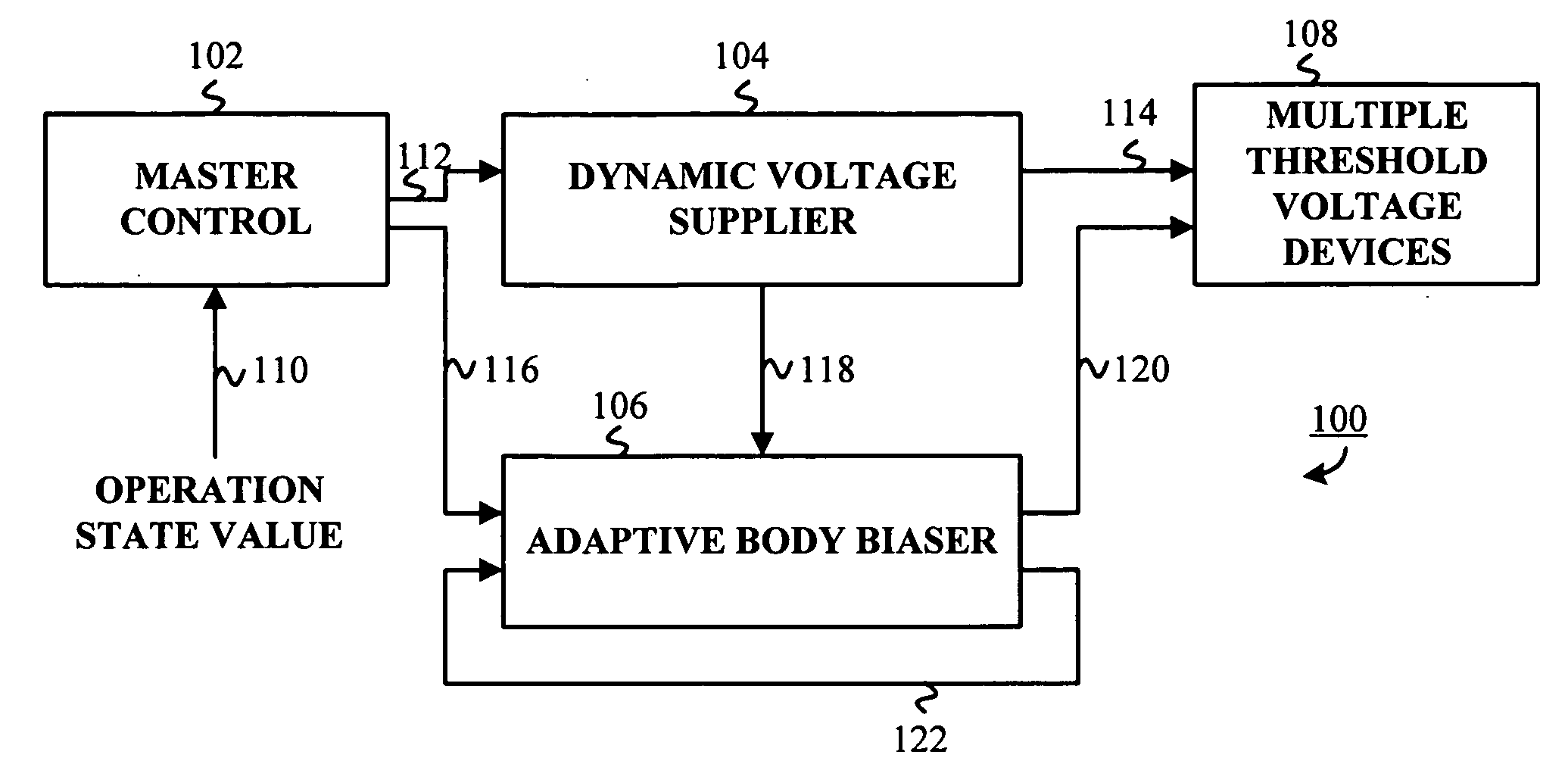
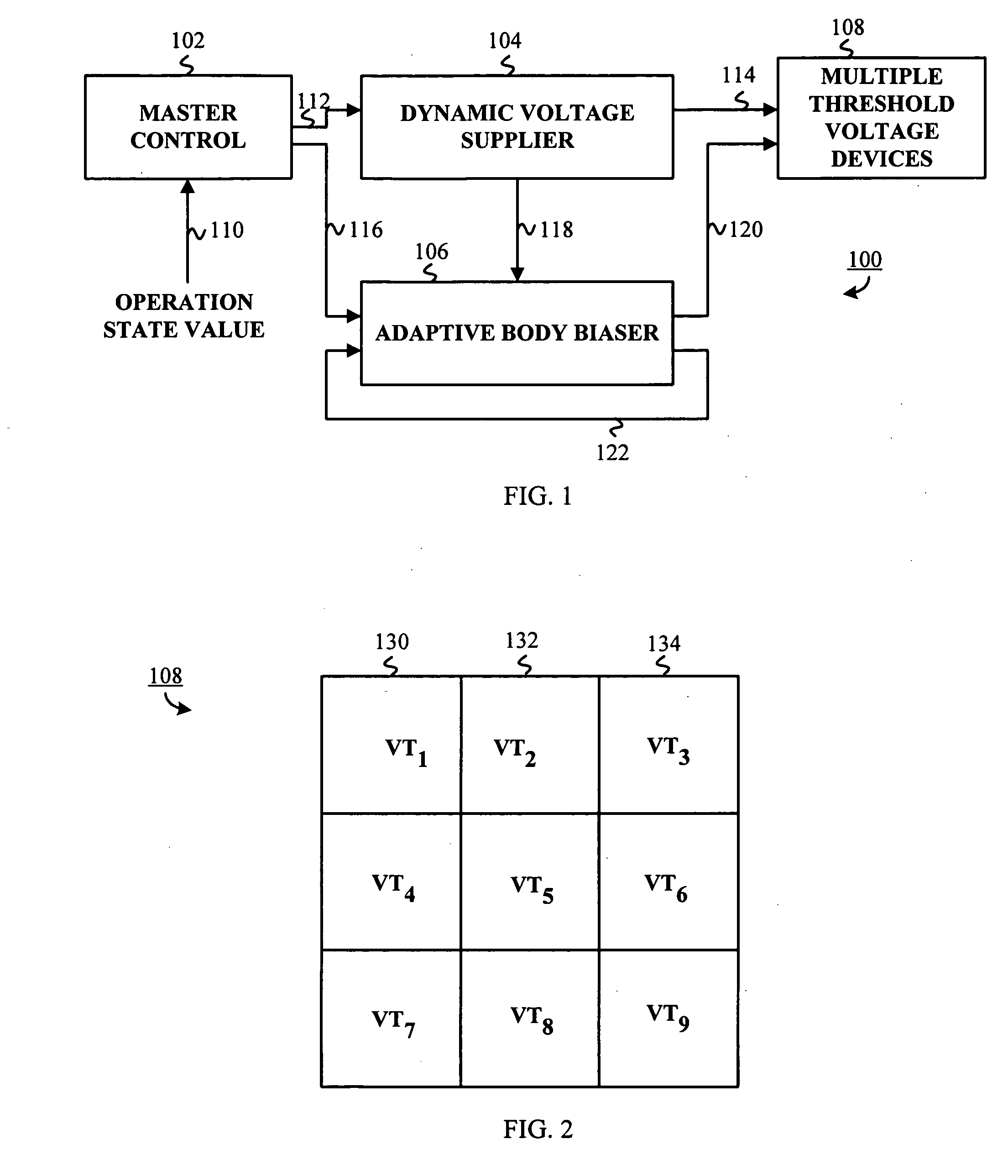
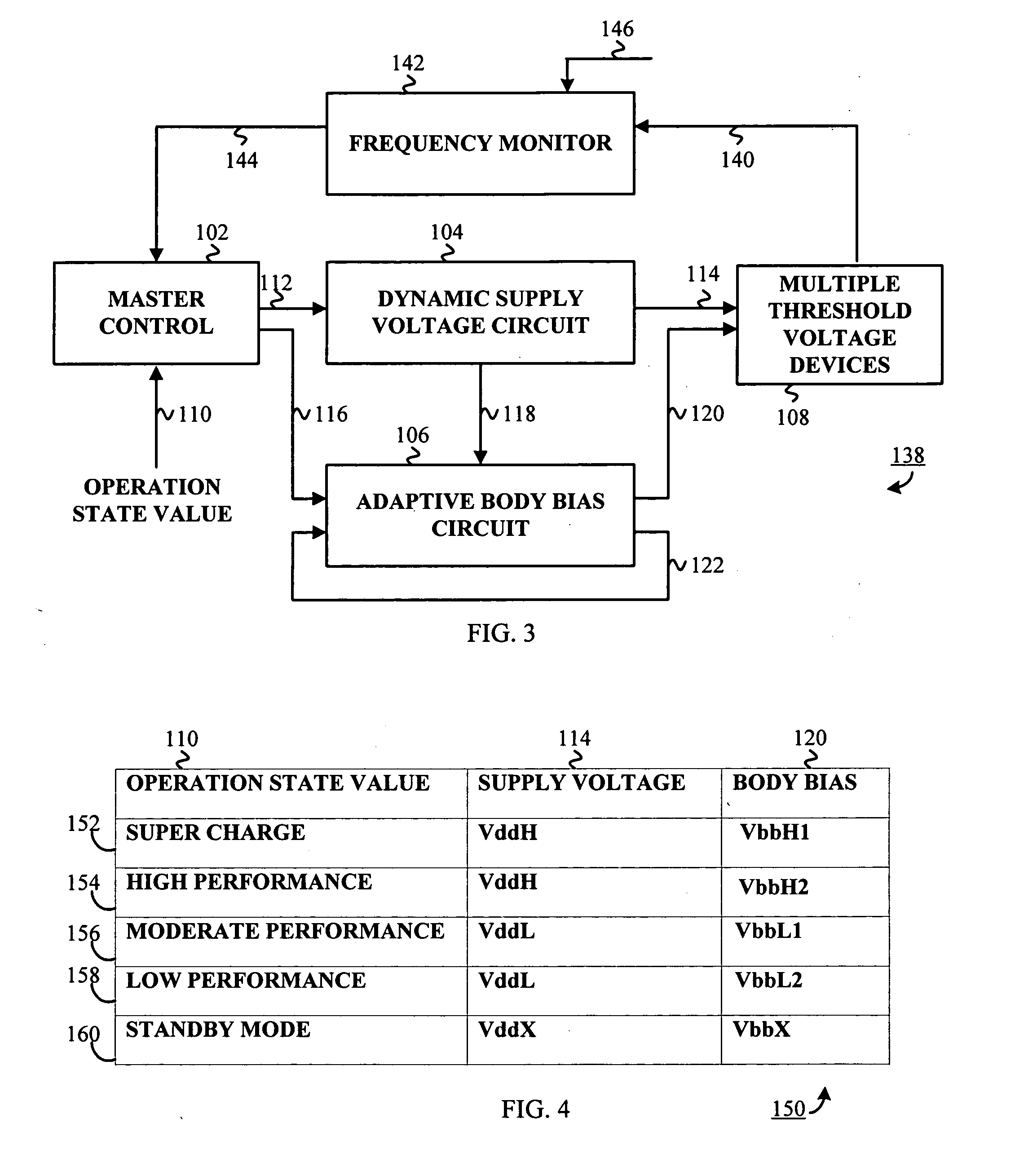
InactiveUS20050225376A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalMaster controllerSelf adaptive
An adaptive supply voltage and body bias apparatus includes a master controller including an operation state value. The apparatus and method includes a dynamic voltage supplier coupled to the master controller operative to receive a supply voltage indicator. The apparatus and method includes an adaptive body biaser coupled to the master controller operative to receive a body bias indicator. Furthermore, the apparatus and method includes a plurality of computing devices each having one of a plurality of threshold voltages. The plurality of computing devices are operative to receive the supply voltage from the dynamic voltage supplier and a bias voltage from the adaptive body biaser for optimized power supply in conjunction with reduction of power leakage in view of the varying threshold voltage of the computing devices.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Clock network fishbone architecture for a structured ASIC manufactured on a 28 NM CMOS process lithographic node
InactiveUS8629548B1Low levelEasy constructionPower reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic cellAnd logic unit
A clock architecture for a Structured ASIC chip, manufactured using a CMOS process is shown. A via-configurable logic block (VCLB) architecture in the Structured ASIC has a core region containing memory and logic cells arranged in columns that are supplied by a clock network having a global clock network tree and a low-level clock mesh to distribute the global clock signal in a repeating pattern. The clock mesh has a fishbone configuration in outline and allows for scalable expansion of the clock network. In one embodiment 36 global clocks may be provided to the Structured ASIC, with four clocks per logic cell. The VCLB Structured ASIC chip is manufactured on a 28 nm CMOS process lithographic node, having several metal layers but preferably is programmable on a single via layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Low-power output controlled circuit
InactiveUS6653878B2High power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierSwitched current
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Pulse translation method from low to high voltage level in half and full bridge application
InactiveUS7236020B1Minimize power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorFull bridgeControl signal
A switched bridge circuit comprises a first switch, a second switch, and a non-overlapping pulse generator. The first switch is coupled to a load. The second switch is coupled to said load. The non-overlapping pulse generator is coupled to the first switch and the second switch and coupled to receive an input signal. The non-overlapping pulse generator in response to the input signal generates a first control signal and a second control signal that respectively control the first and second switches. The pulses in the first and second control signals are not overlapped so that the first and second switches are not simultaneously enabled.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
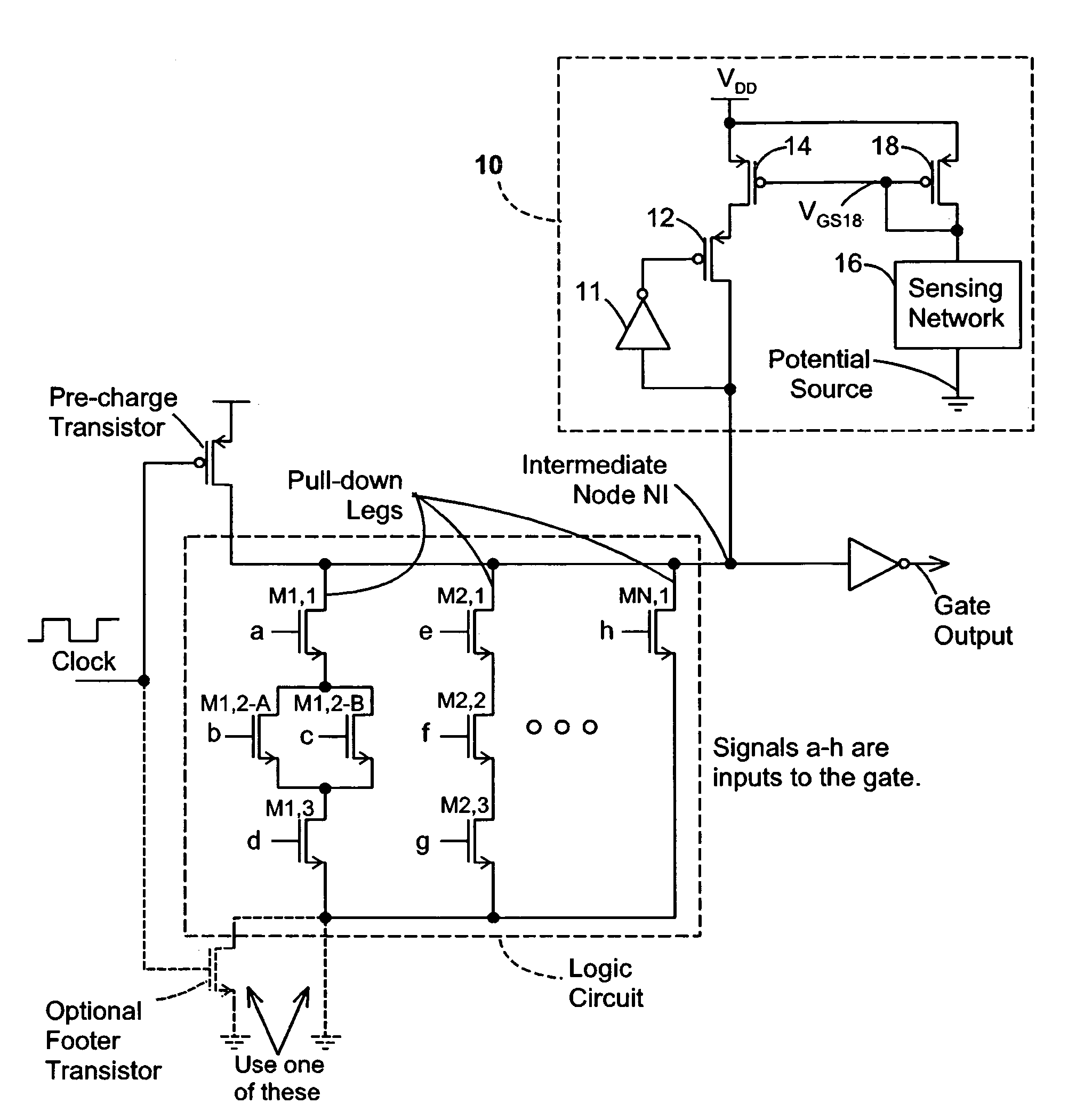
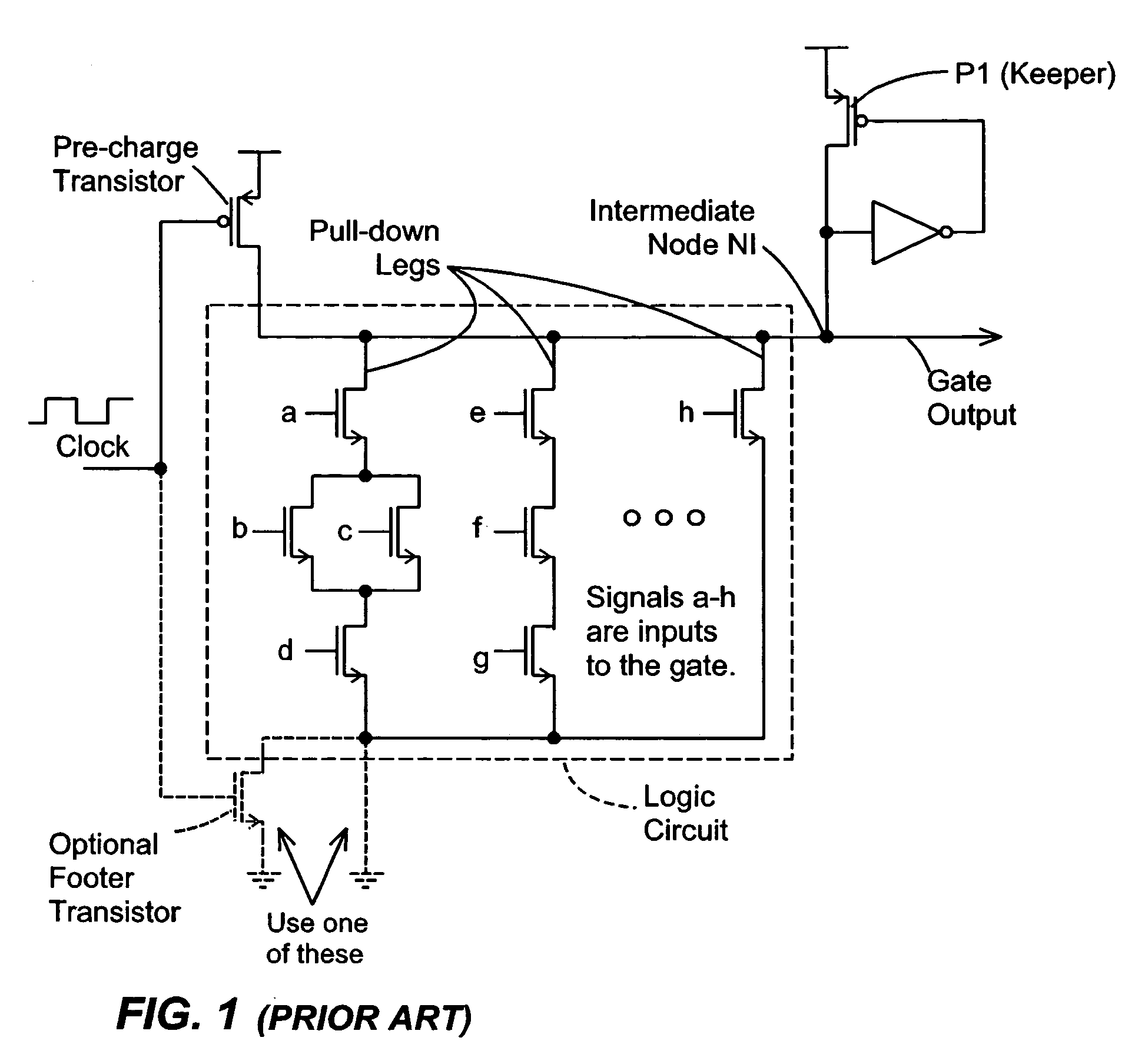
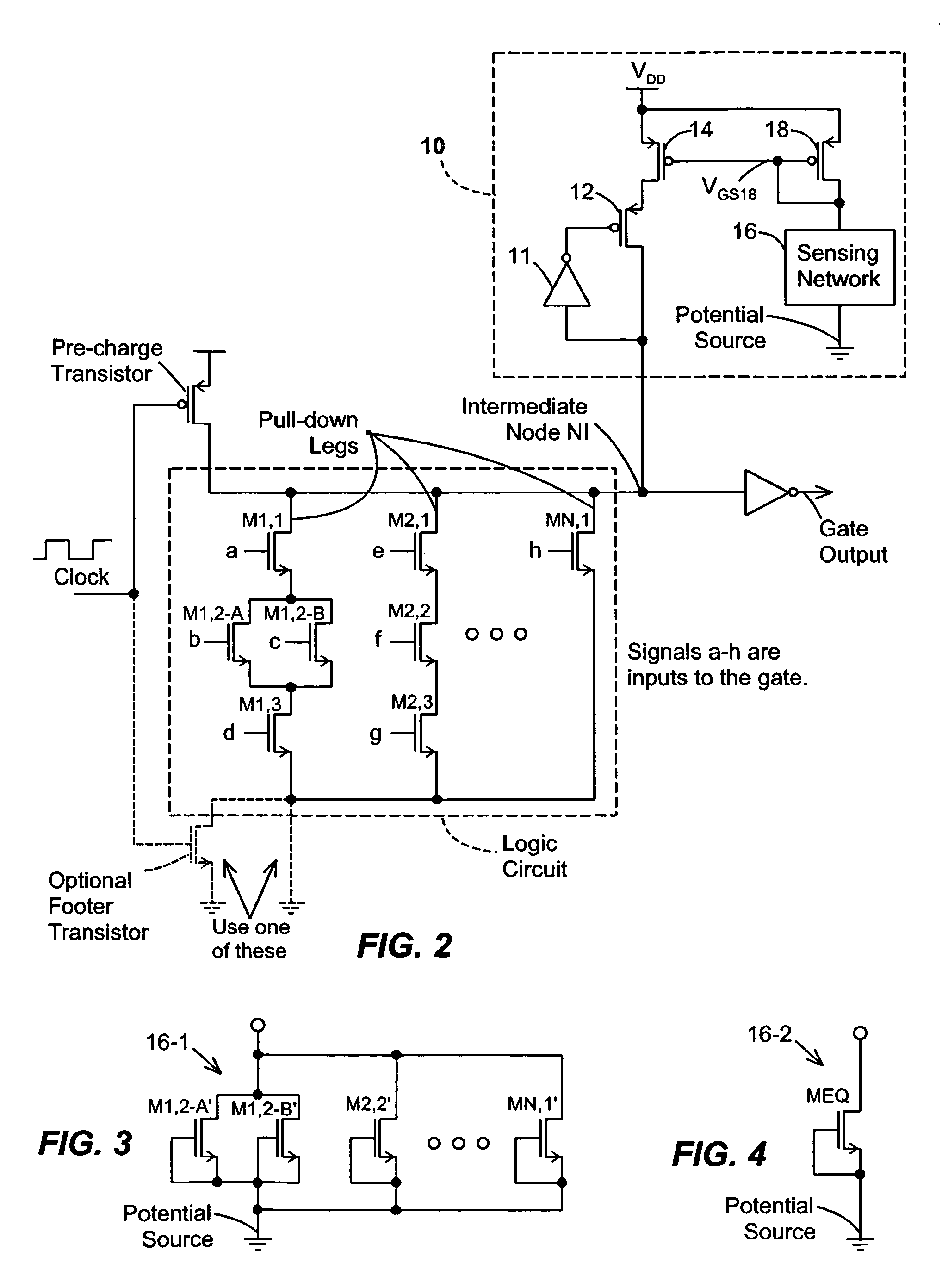
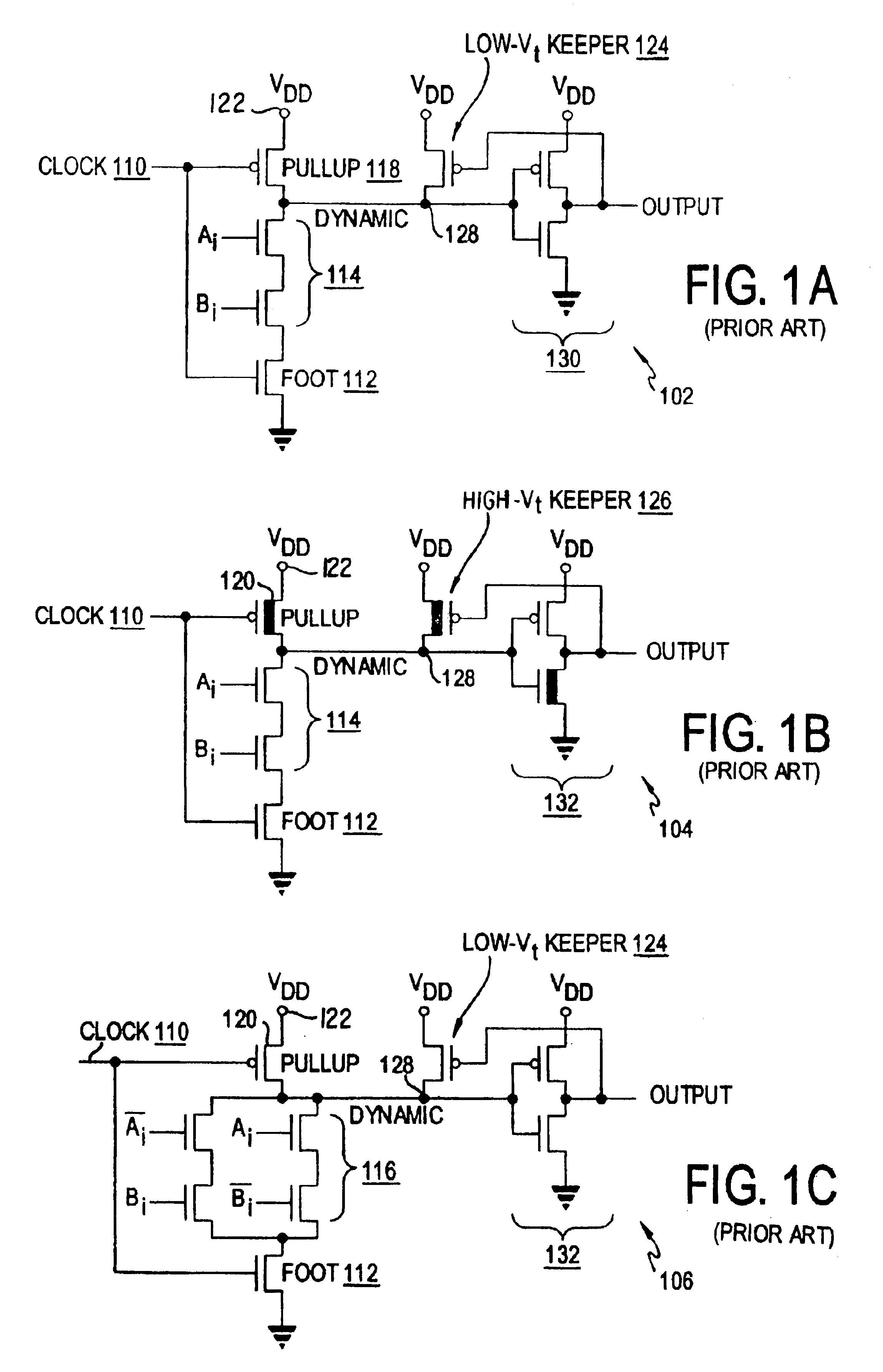
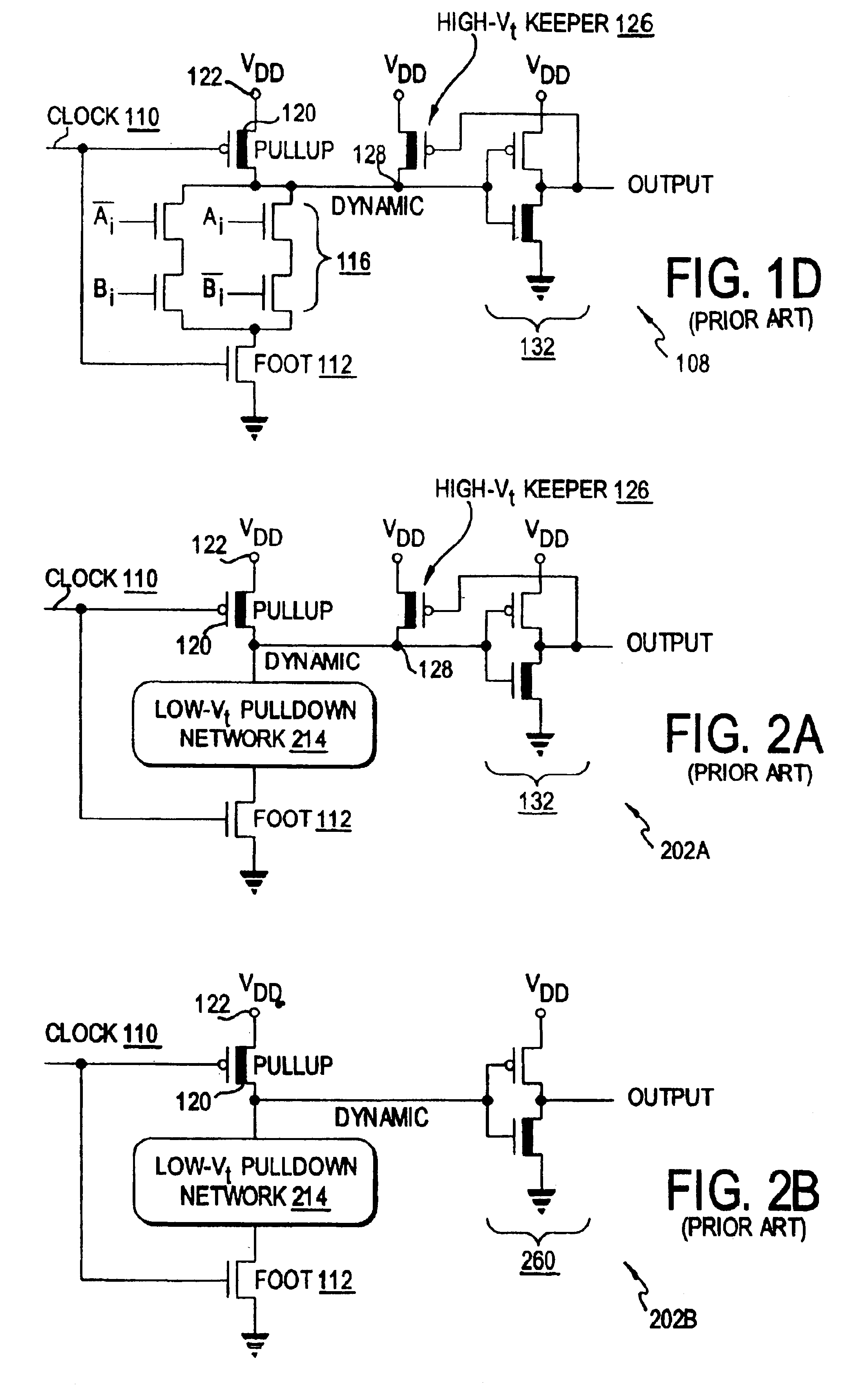
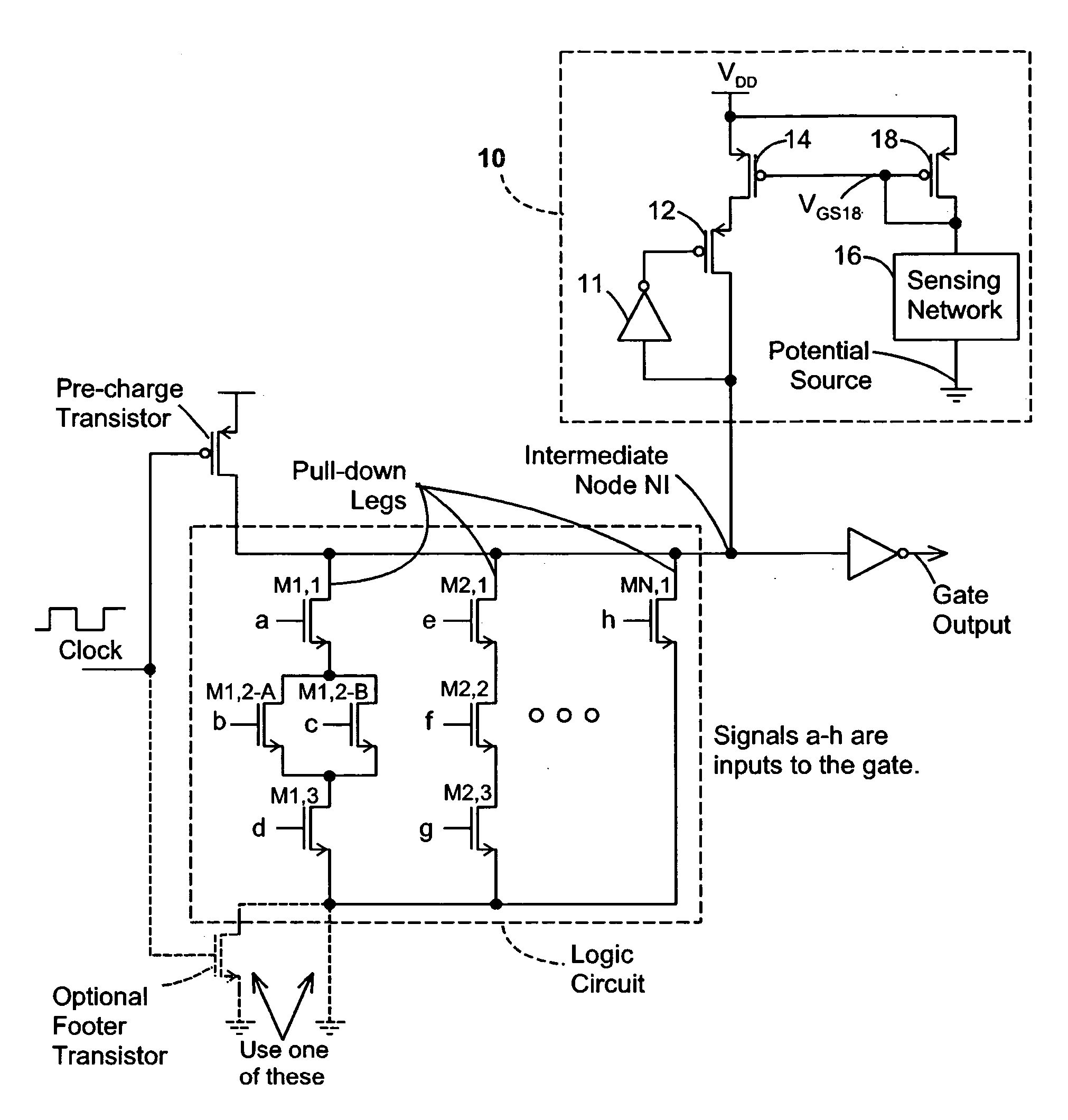
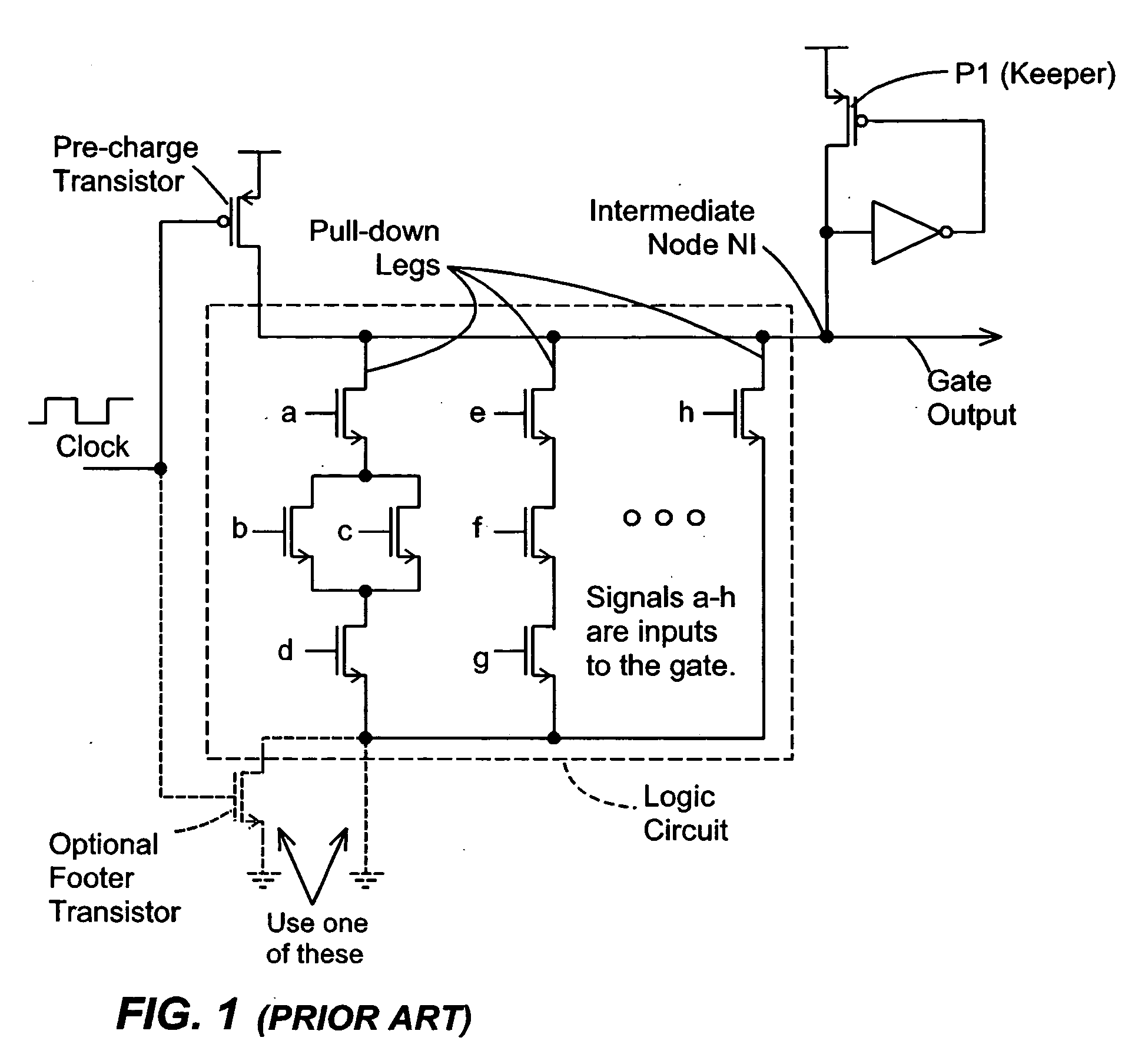
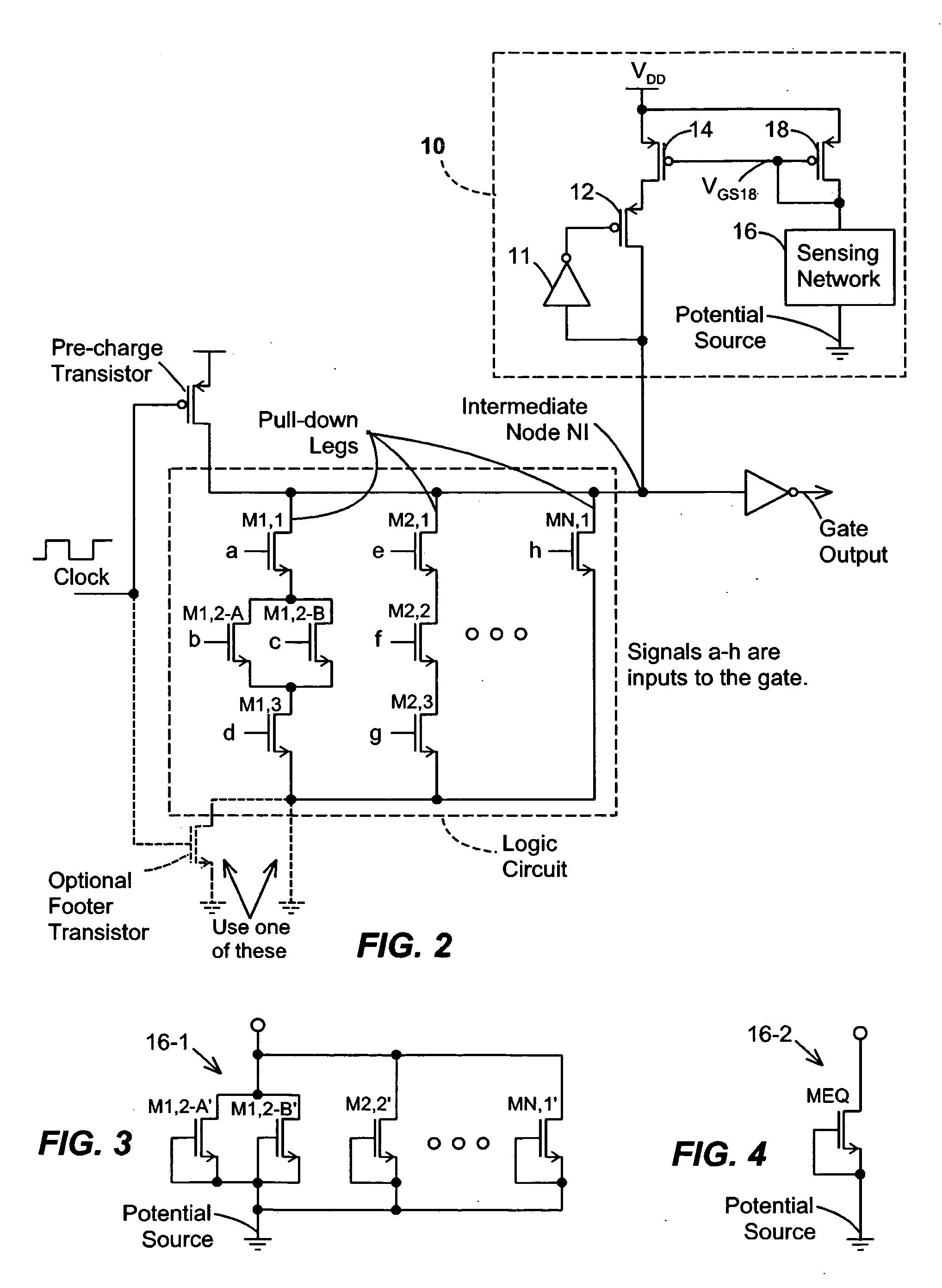
Keeper circuits having dynamic leakage compensation
ActiveUS7256621B2High conductanceMinimize impactPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate leakage currentDrain current
Disclosed are keeper circuits for electronic circuits that selectively maintain the voltage level of an intermediate circuit node at a desired level. In one exemplary embodiment, a keeper transistor either provides current or drains current from the intermediate node to maintain the desired voltage level in response to a signal to do so. The keeper circuit works against a leakage current that either drains current from the node or supplies current to the node. A current-setting transistor is coupled in series with the keeper transistor to set the maximum current through the keeper circuit to a value that is related to this leakage current, preferably tracking the leakage current. With this construction, the current-setting transistor is able to track variations in the leakage current caused by variations in the manufacturing process, and thereby provide dynamic leakage compensation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
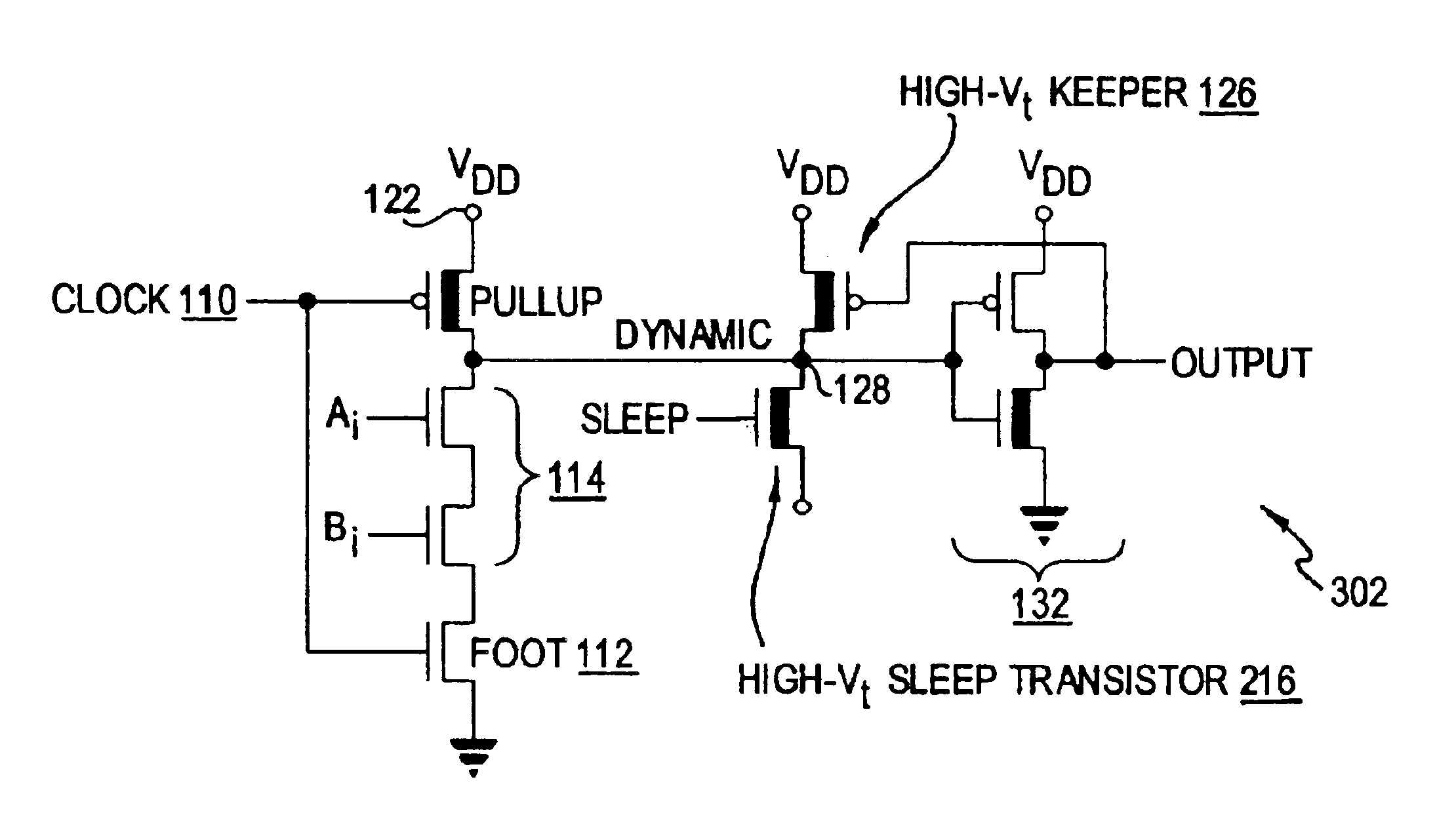
Dual threshold voltage and low swing domino logic circuits
InactiveUS6900666B2Lowering standby leakage energyReducing leakage energyPower reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalDomino logicGate voltage
A domino logic circuit is configured to reduce power consumption. In a first embodiment, a sleep switch grounds the dynamic node during sleep mode. In a second embodiment, a low-swing circuit at the output reduces the output and keeper transistor gate voltage swings. A third embodiment combines those two techniques.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
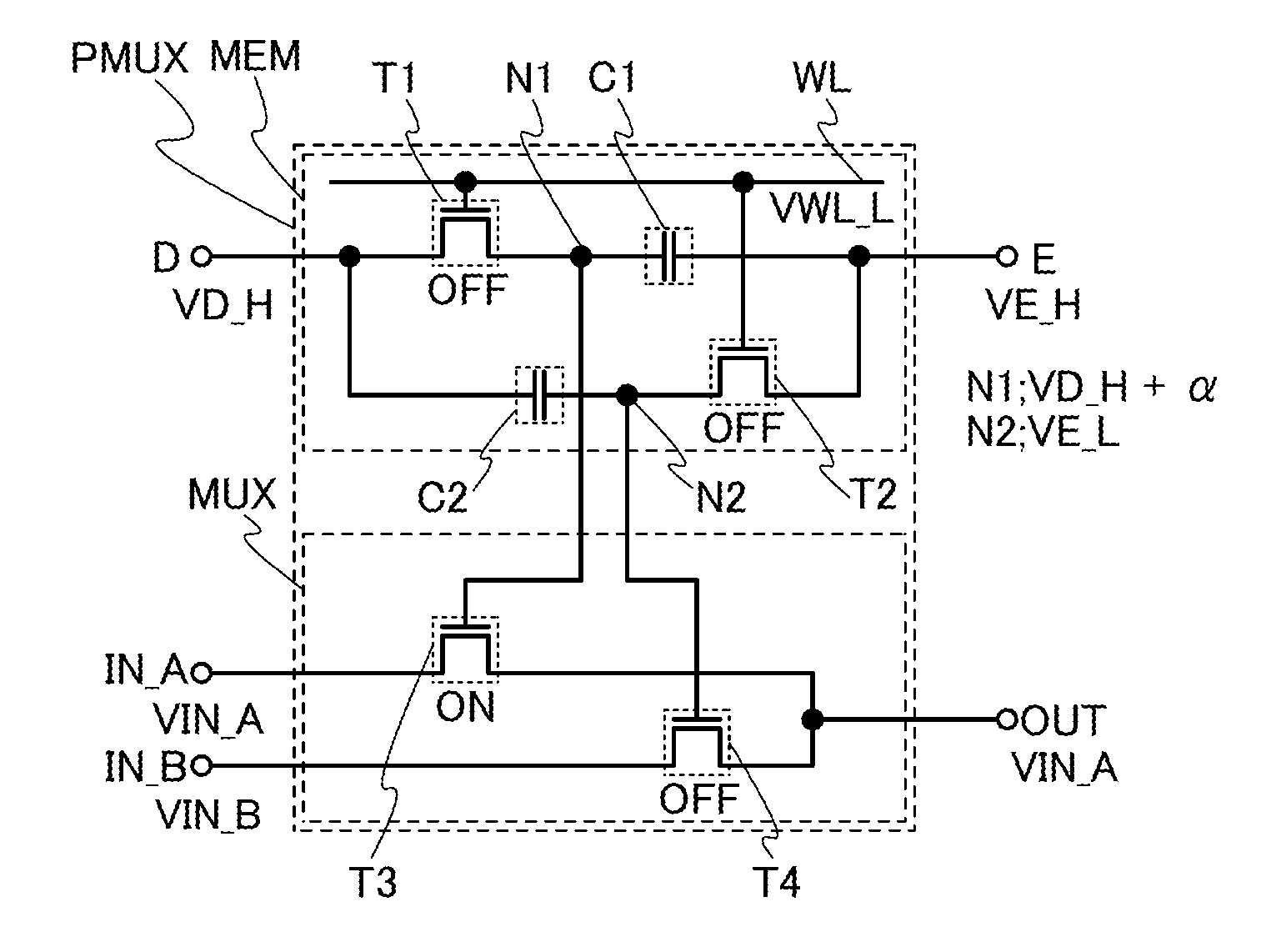
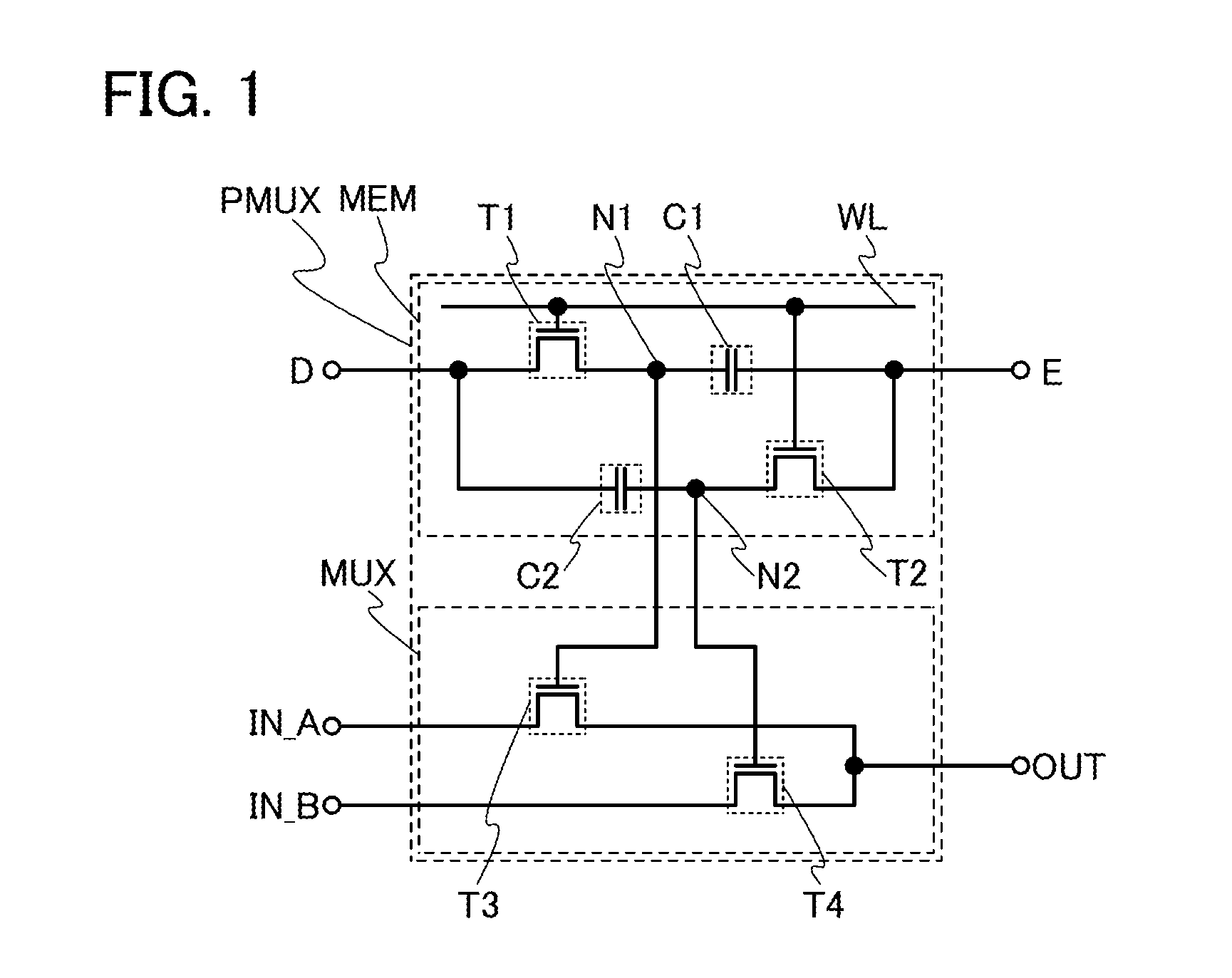
Method for driving semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130314125A1Supply is stoppedReduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsDigital storagePower semiconductor deviceMultiplexer
A method for driving a semiconductor device capable of reducing an area of a multiplexer and reducing its power consumption is provided. In a method for operating a semiconductor device including a memory and a multiplexer, a first transistor is connected to a first capacitor, and a second transistor is connected to a second capacitor. In the multiplexer, in a third transistor, a source is connected to a first input terminal and a drain is connected to an output terminal and, in a fourth transistor, a source is connected to a second input terminal and a drain is connected to the output terminal. Further, a step of holding a first potential in a node to which the first transistor, the first capacitor, and a gate of the third transistor are connected and holding a second potential higher than the first potential in the node is included.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Integrated header switch with low-leakage PMOS and high-leakage NMOS transistors
ActiveUS7164291B2High currentLower unit costPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectronic switchingControl signalLow voltage
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Programmable logic device
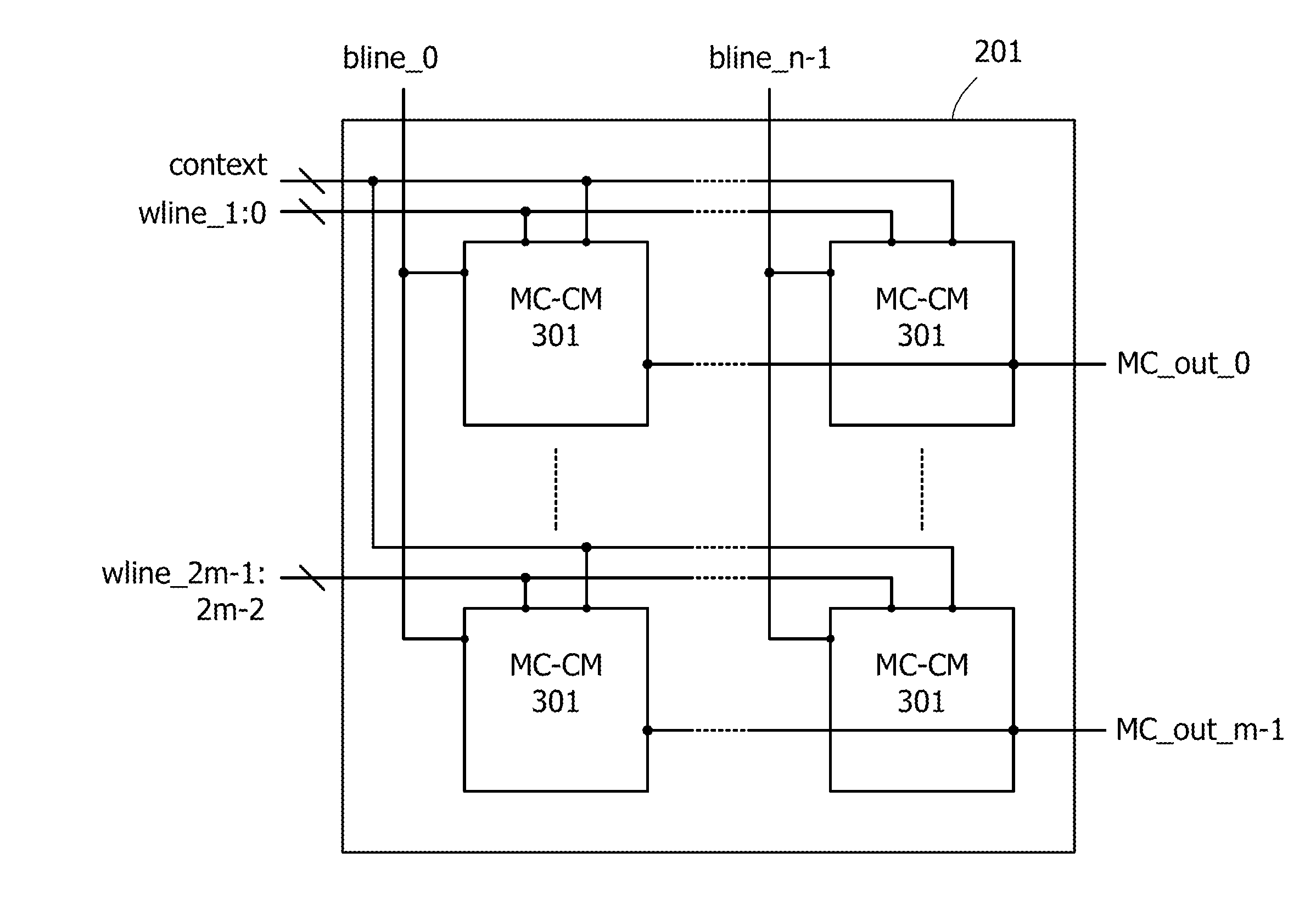
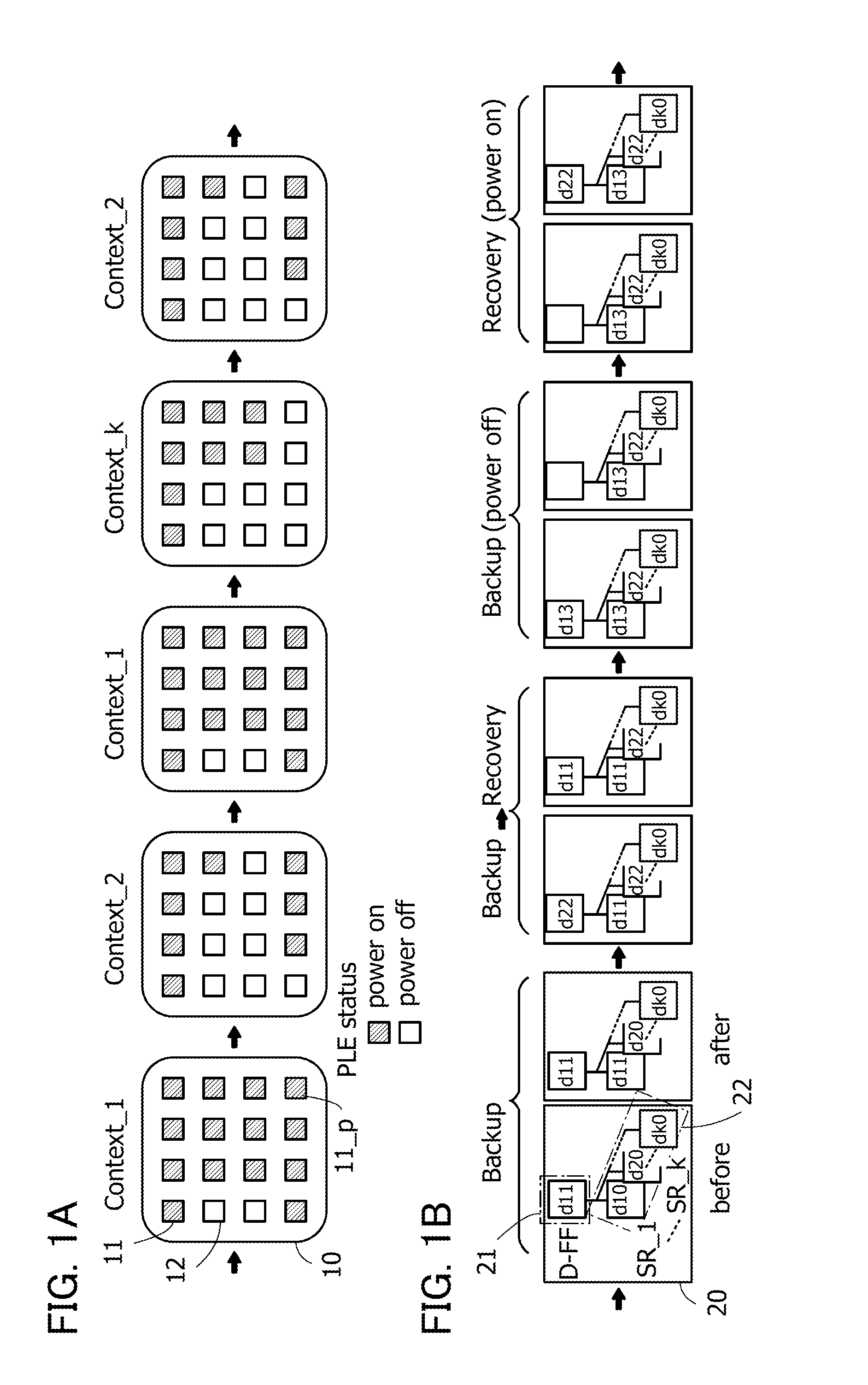
ActiveUS20140368235A1Novel structureData retentionPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsMultiple contextProcessor register
Data of a register in a programmable logic element is retained. A volatile storage circuit and a nonvolatile storage circuit are provided in a register of a programmable logic element whose function can be changed in response to a plurality of context signals. The nonvolatile storage circuit includes nonvolatile storage portions for storing data in the register. The number of nonvolatile storage portions corresponds to the number of context signals. With such a structure, the function can be changed each time context signals are switched and data in the register that is changed when the function is changed can be backed up to the nonvolatile storage portion in each function. In addition, the function can be changed each time context signals are switched and the data in the register that is backed up when the function is changed can be recovered to the volatile storage circuit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Voltage translator circuit formed using low voltage transistors
InactiveUS7068091B1Reduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsPulse automatic controlVoltage converterProcessing type
A circuit for use in conjunction with a portion of a core of an integrated circuit, for shifting a signal from a first voltage level to a second voltage level, wherein the circuit is formed using the same process type transistors (i.e., low voltage transistors) as are used in the core of the integrated circuit.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Low-leakage level shifter with integrated firewall and method
ActiveUS20050285623A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalVoltage referenceLow leakage
A level shifter may reduce leakage current and provide firewall protection between circuits of different voltage domains when one voltage domain is in a standby mode. The level shifter may either couple or decouple input circuitry from a reference voltage in response to a firewall enable signal, may translate signals between a first voltage domain and a second voltage domain when the firewall enable signal is deasserted, and may generate an output signal having a predetermined one of either a high or low state when the firewall enable signal is asserted.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120306533A1Switch accuratelyReduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceNODAL
A programmable analog device and an analog device that can retain data even when supply of a power supply potential is interrupted and consumes less power. In a semiconductor device, first to fourth transistors are used as switches in a unit cell including an analog element, and the output of the unit cell switches between a conducting state, a non-conducting state, and a conducting state through the analog element by controlling the potential of a first node where the first transistor and the second transistor are connected and the potential of a second node where the third transistor and the fourth transistor are connected.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device
InactiveUS20120293242A1Lower average currentTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsCapacitorLogic circuitry
As semiconductor devices including semiconductors, logic circuits are given. Logic circuits include dynamic logic circuits and static logic circuits and are formed using transistors and the like. Dynamic logic circuits can store data for a certain period of time. Thus, leakage current from transistors causes more severe problems in dynamic logic circuits than in static logic circuits. A logic circuit includes a first transistor whose off-state current is small and a second transistor whose gate is electrically connected to the first transistor. Electric charge is supplied to a node of the gate of the second transistor through the first transistor. Electric charge is supplied to the node through a first capacitor and a second capacitor. On / off of the second transistor is controlled depending on a state of the electric charge. The first transistor includes an oxide semiconductor in a channel formation region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Keeper circuits having dynamic leakage compensation
ActiveUS20060214695A1High conductanceMinimize impactPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate leakage currentDrain current
Disclosed are keeper circuits for electronic circuits that selectively maintain the voltage level of an intermediate circuit node at a desired level. In one exemplary embodiment, a keeper transistor either provides current or drains current from the intermediate node to maintain the desired voltage level in response to a signal to do so. The keeper circuit works against a leakage current that either drains current from the node or supplies current to the node. A current-setting transistor is coupled in series with the keeper transistor to set the maximum current through the keeper circuit to a value that is related to this leakage current, preferably tracking the leakage current. With this construction, the current-setting transistor is able to track variations in the leakage current caused by variations in the manufacturing process, and thereby provide dynamic leakage compensation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
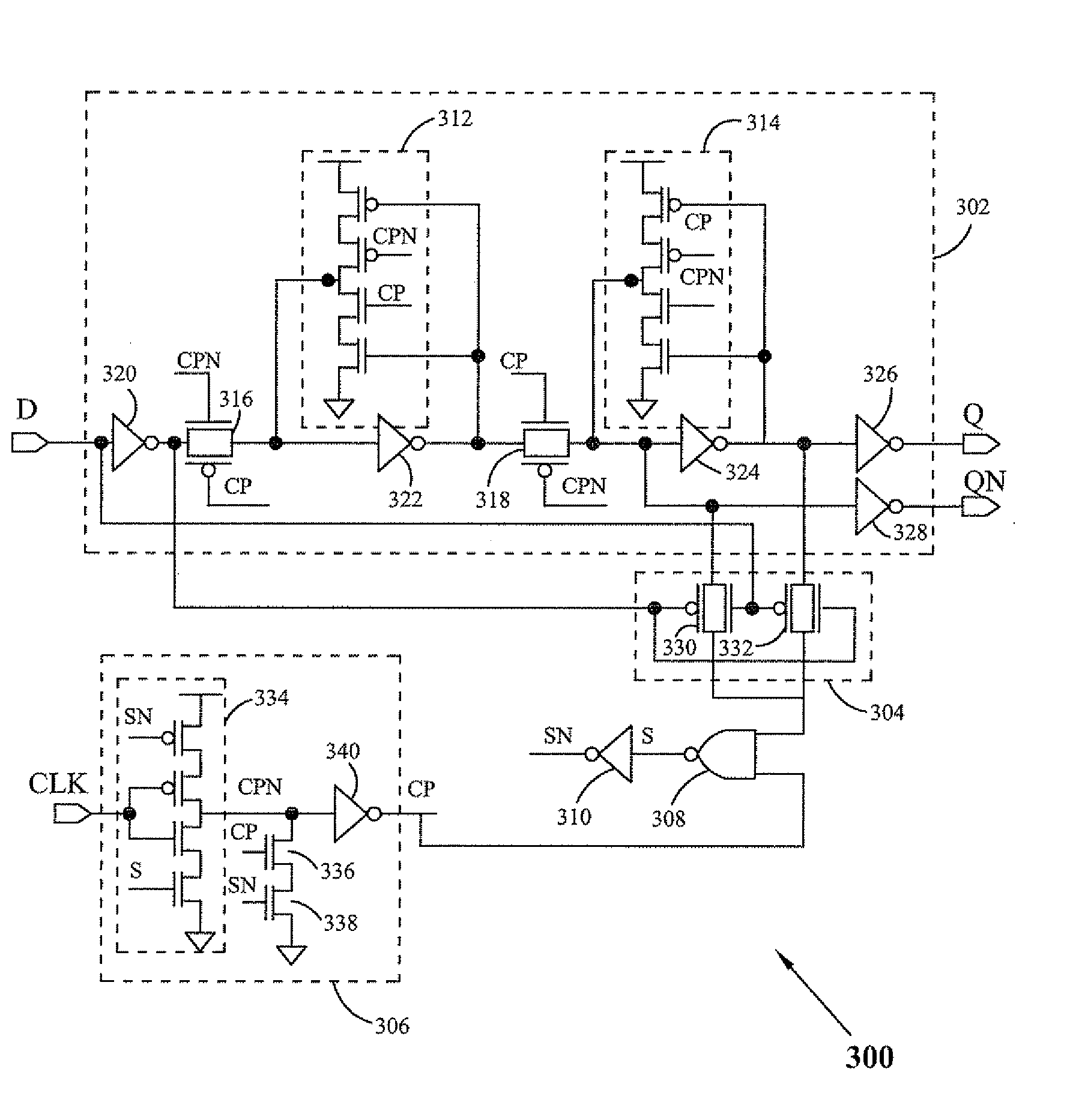
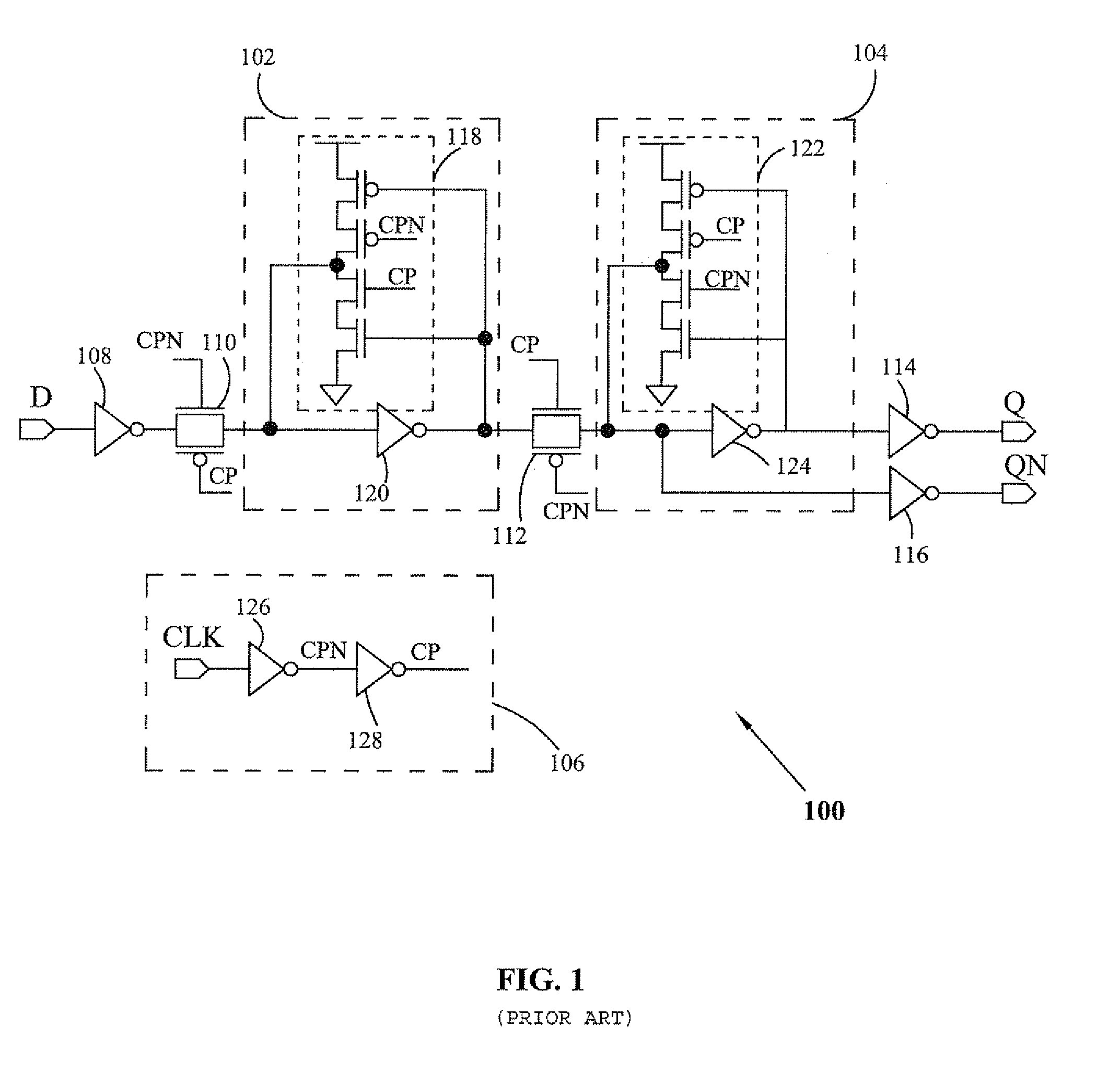
Low power flip-flop circuit
InactiveUS20080218234A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid it happening againPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorLeading edgeEngineering
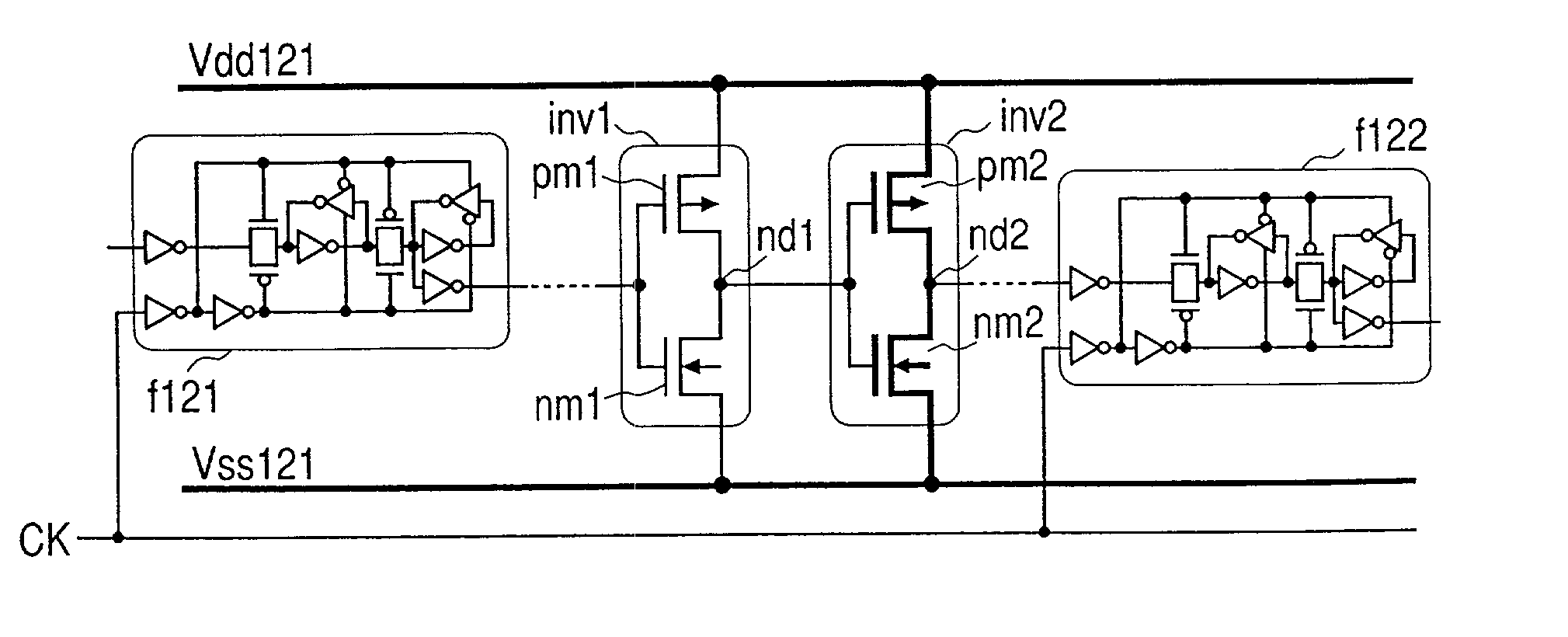
A flip-flop circuit having low power consumption includes a sensing circuit, and a clock generating circuit. The flip-flop is leading edge triggered and operates on an internally generated pseudo clock signal. The sensing circuit senses a change in an input signal and an output signal of the flip-flop. The clock generating circuit generates a pseudo clock signal with a sharp rise and fall based upon an external clock signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
Power saving termination circuits for dram modules
InactiveUS20100327902A1Reduce power consumptionReduce reflective effectInput/output impedence modificationPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceLow frequency
The present invention provides power saving methods by replacing termination resistors used to support SSTL DRAM interfaces with RC termination circuits; the RC termination circuits consumes significant less power relative to prior art termination resistors at low frequency and behave as a matching impedance at high frequency. Similar methods and structures are also applicable for PCIe, SATA, or MIPI differential interfaces.
Owner:UNIRAM TECH
Buffer circuit and active matrix display using the same
ActiveUS20040164978A1Reduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCapacitanceActive matrix
A buffer circuit includes first to sixth transistors. The first transistor is coupled between a first power source and a first node, and has a gate for receiving a first signal having a first signal level. The second transistor is coupled between the first node and a second power source, and has a gate for receiving a second signal having a second signal level, which is an inverse of the first signal level. The third transistor has a gate coupled to the first node, and is coupled between the first power source and a second node. The fourth transistor is coupled between the second node and the second power source, and has a gate for receiving the first signal. The fifth transistor has a gate coupled to the second node, and is coupled between the first power source and an output end. The sixth transistor has a gate coupled to the first node, and is coupled between the output end and the second power source. In addition, a capacitance is formed between the gate of the sixth transistor and the output end.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Apparatus for and method of range sensor based on direct time-of-flight and triangulation
ActiveUS20170097417A1Improve eyesightIncrease autonomyPower reduction in field effect transistorsTelevision system detailsObject basedTriangulation
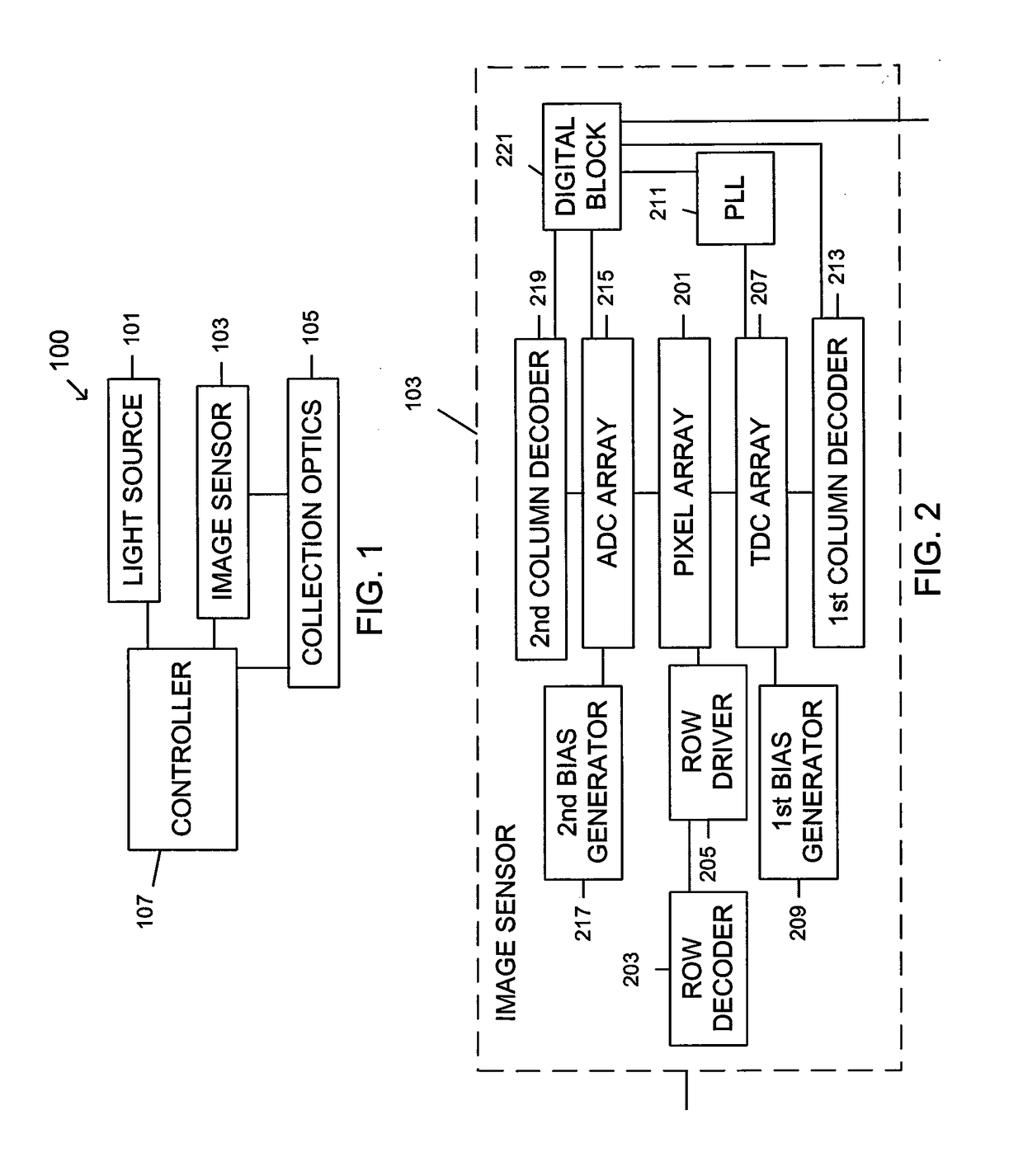
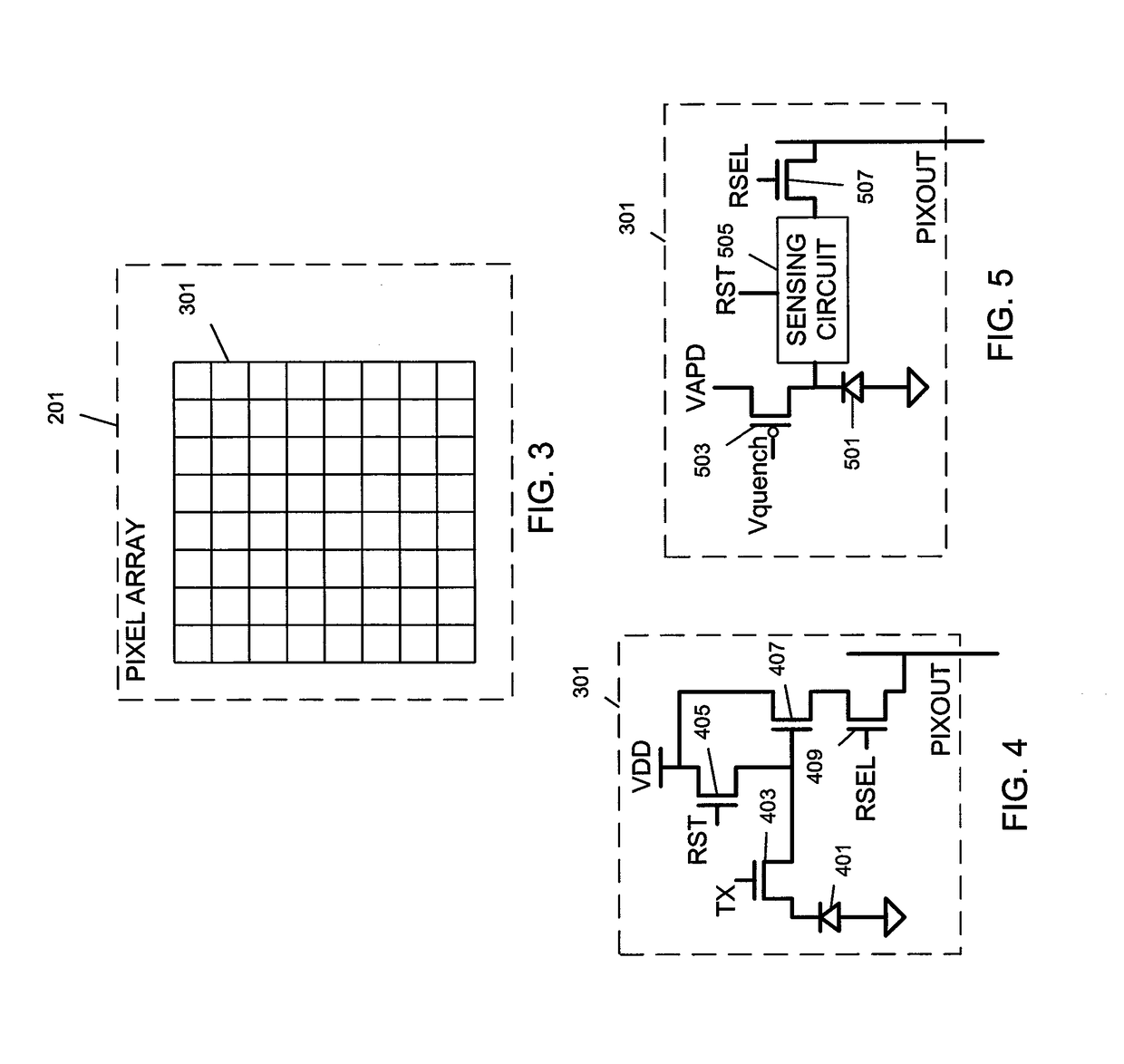
A range sensor and a method thereof. The range sensor includes a light source configured to project a sheet of light at an angle within a field of view (FOV); an image sensor offset from the light source; collection optics; and a controller connected to the light source, the image sensor, and the collection optics, and configured to determine a range of a distant object based on direct time-of-flight and determine a range of a near object based on triangulation. The method includes projecting, by a light source, a sheet of light at an angle within an FOV; offsetting an image sensor from the light source; collecting, by collection optics, the sheet of light reflected off objects; and determining, by a controller connected to the light source, the image sensor, and the collection optics, a range of a distant object based on direct time-of-flight and a range of a near object based on triangulation simultaneously.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Popular searches
Diode Computation using denominational number representation Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Computer aided design Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Special data processing applications Memory systems Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements Semiconductor devices Static indicating devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com