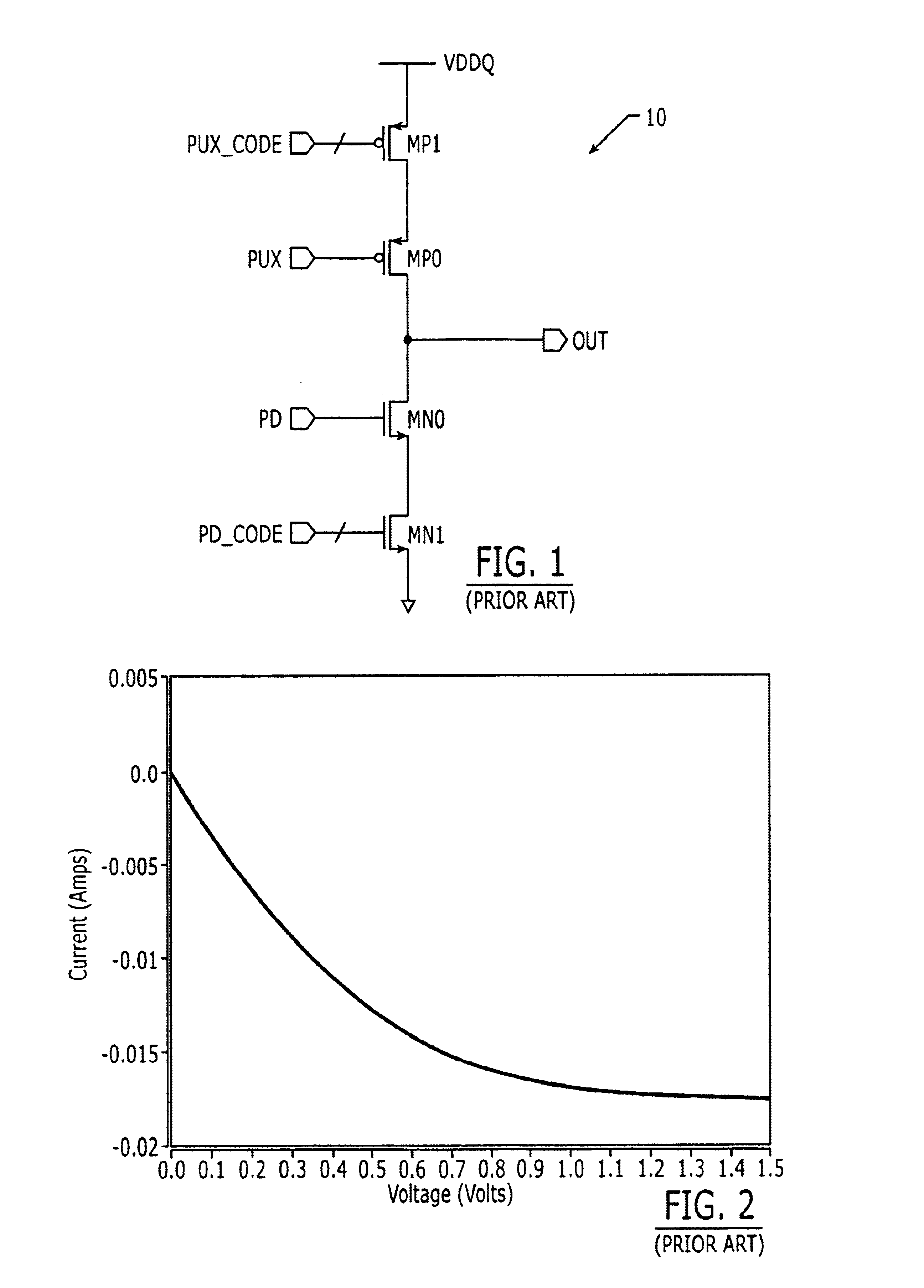
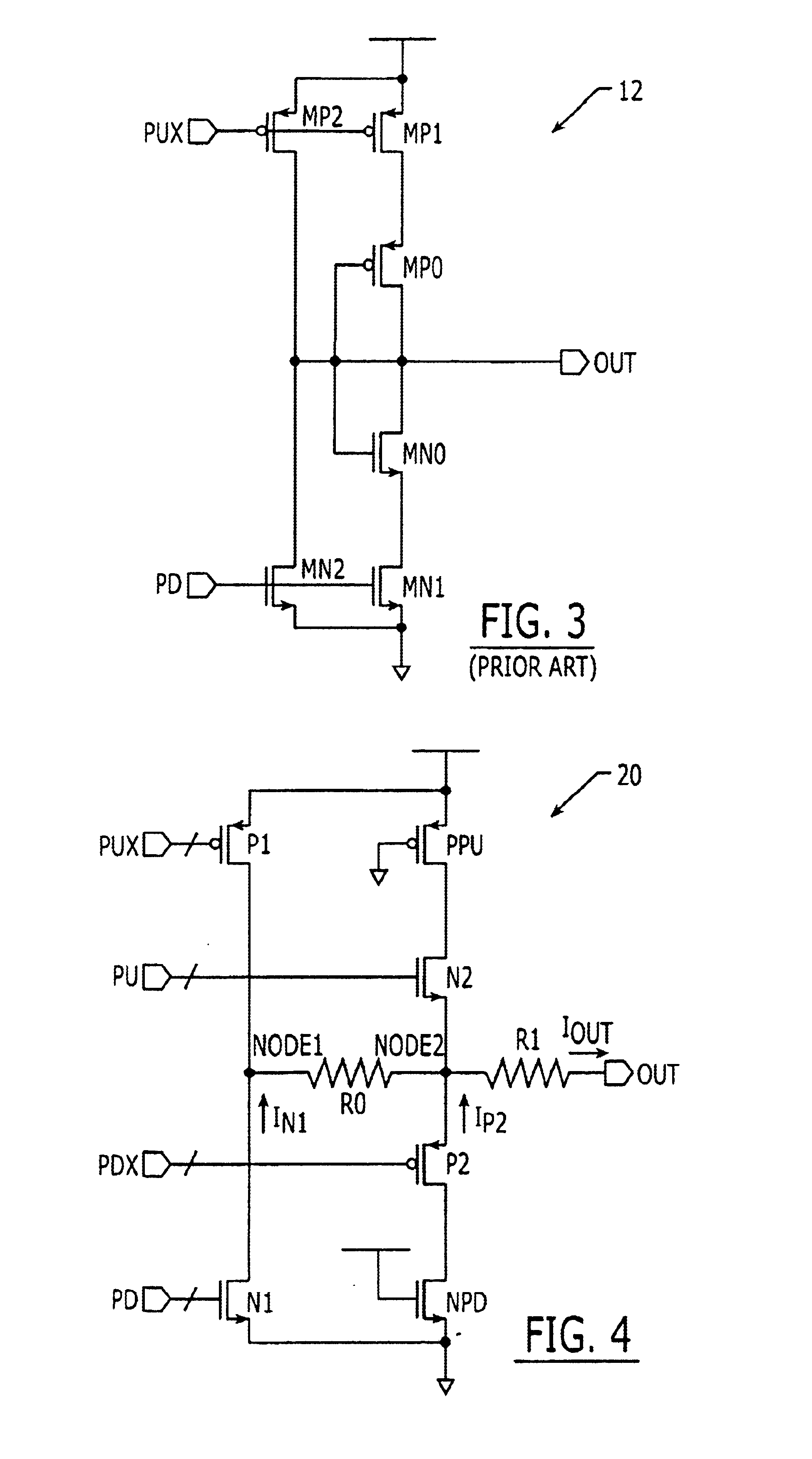
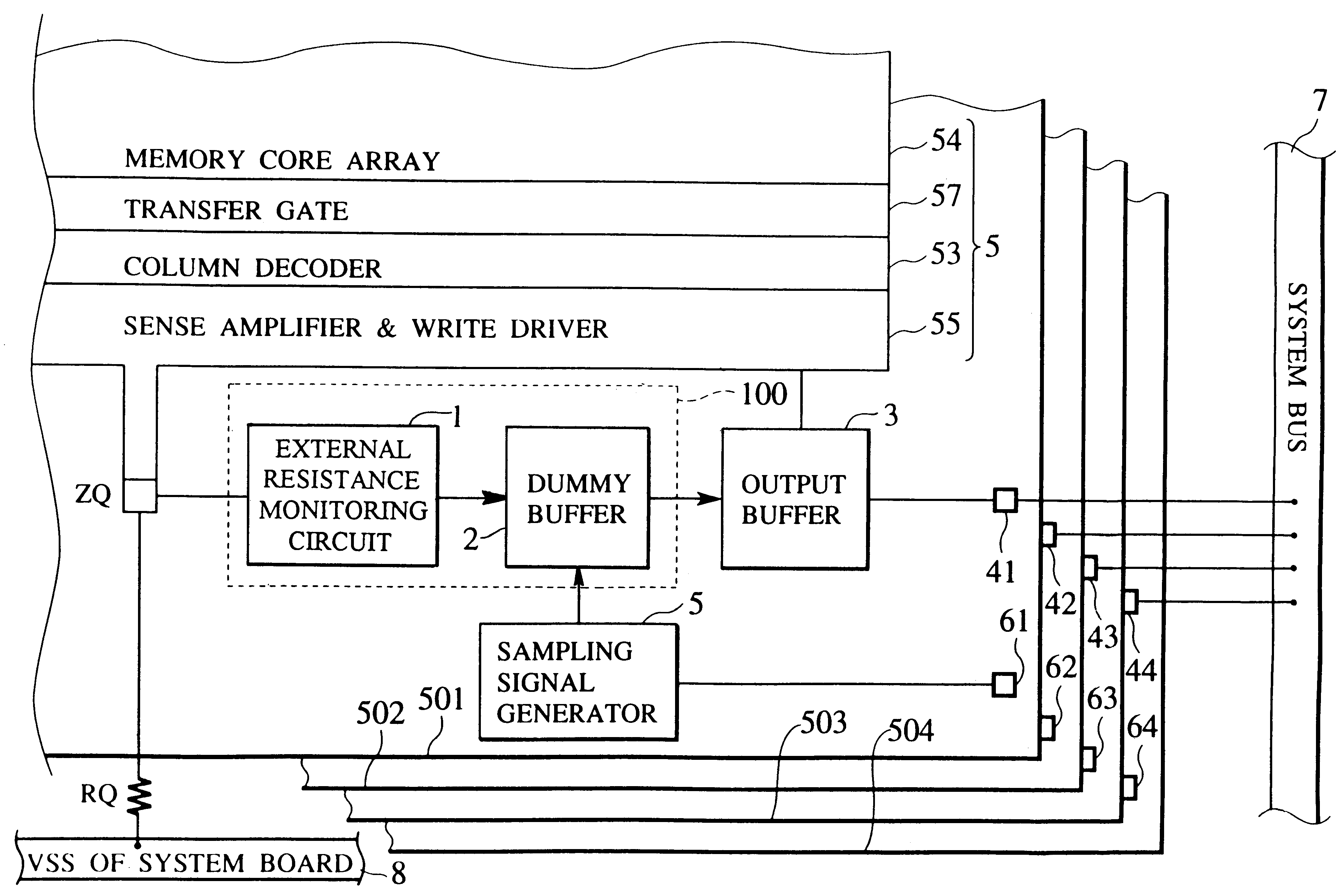
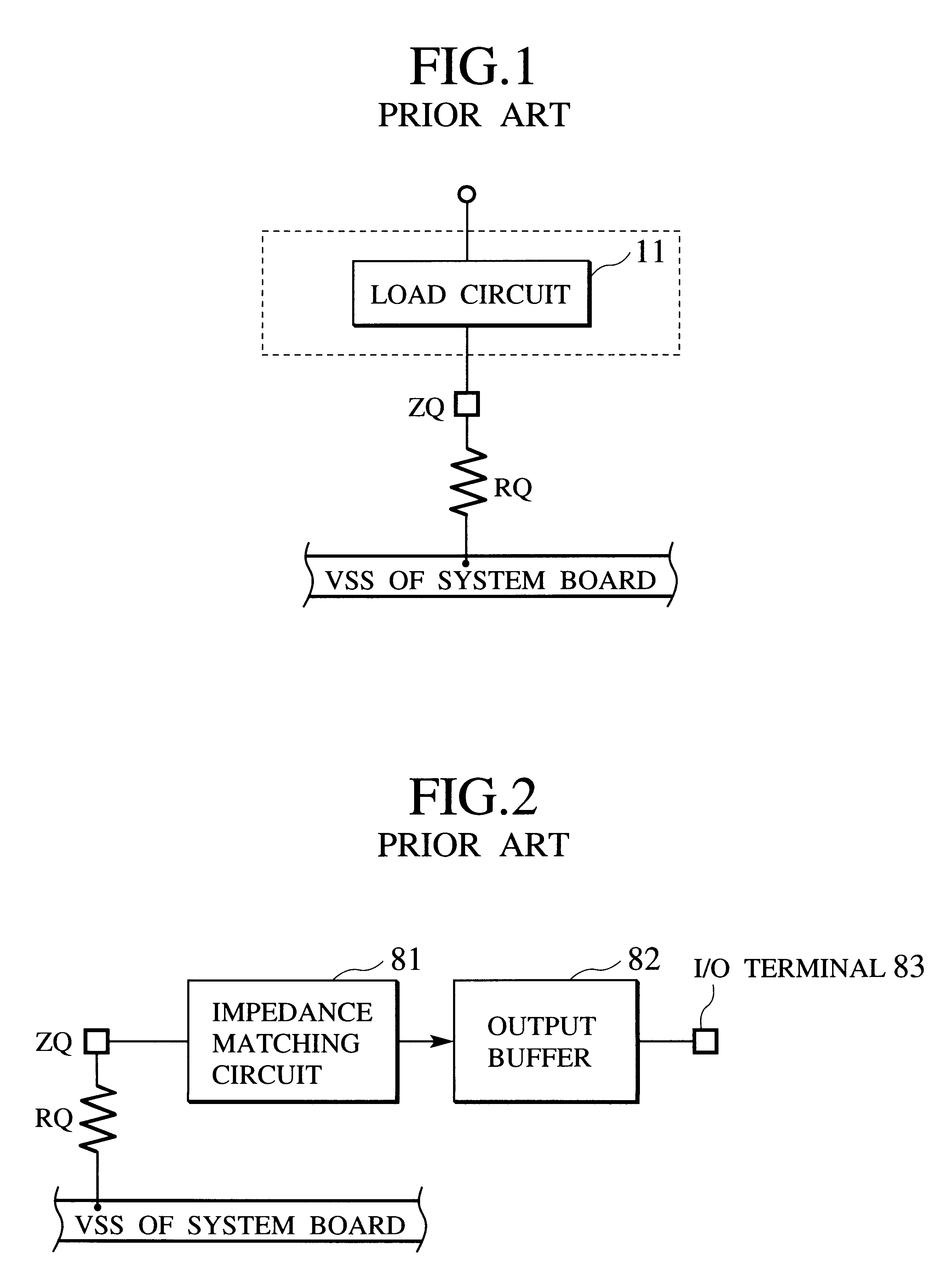
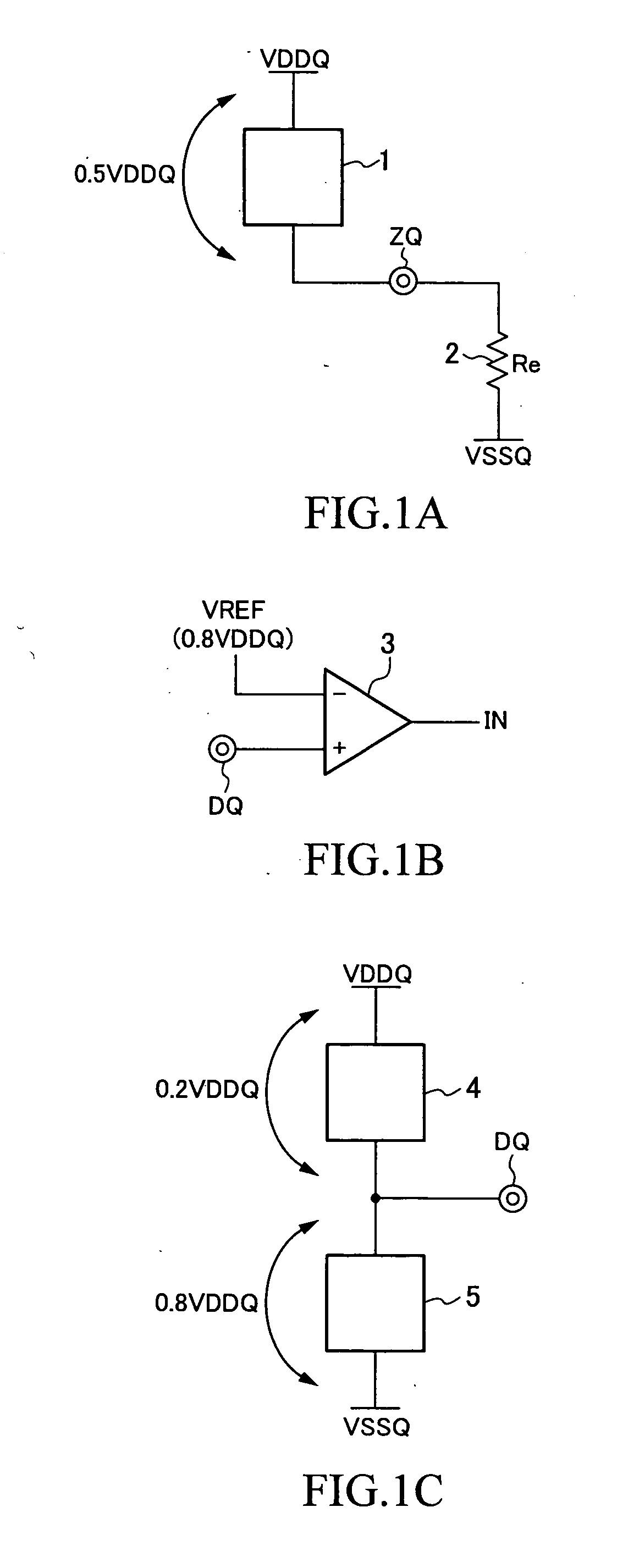
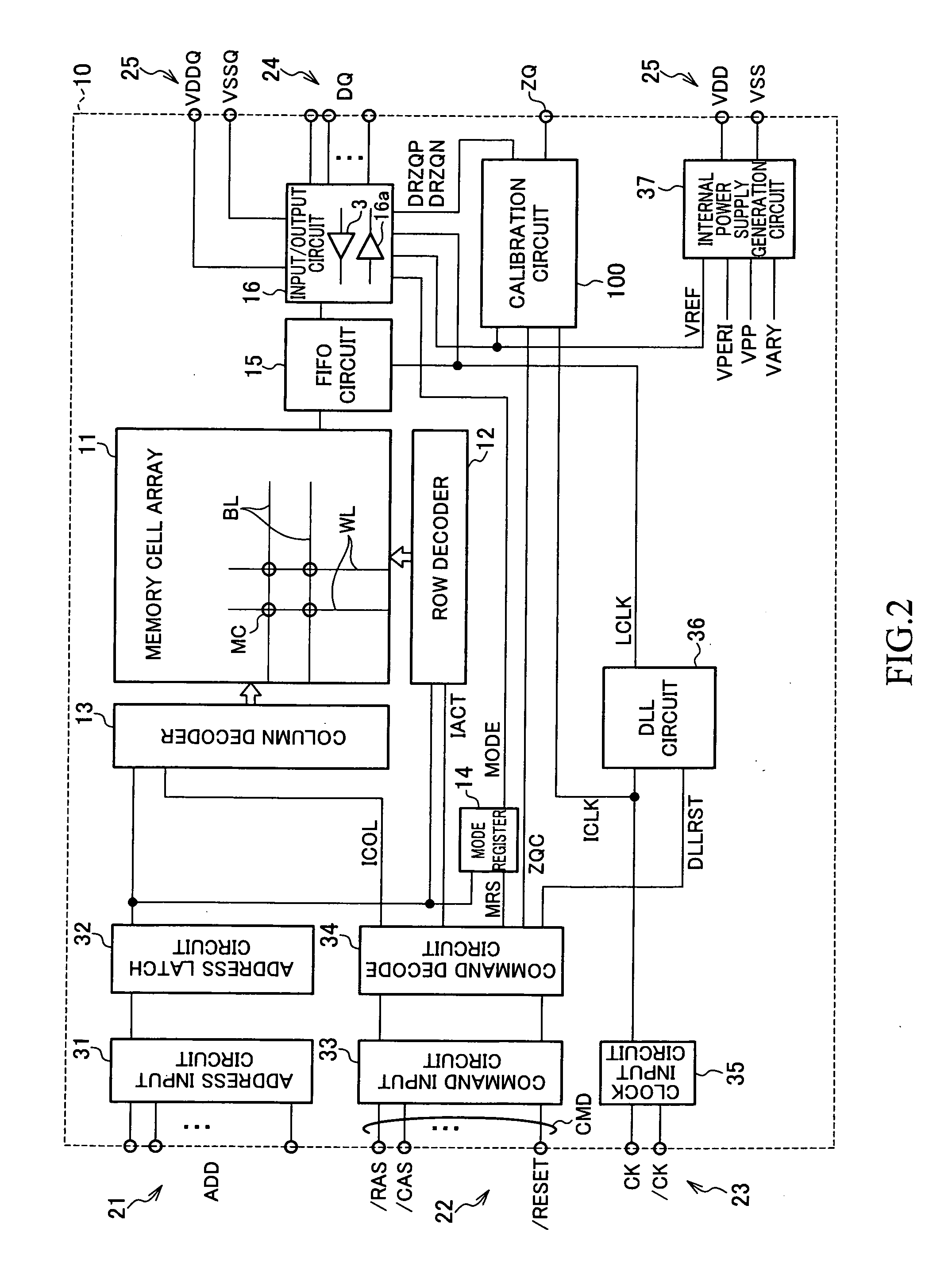
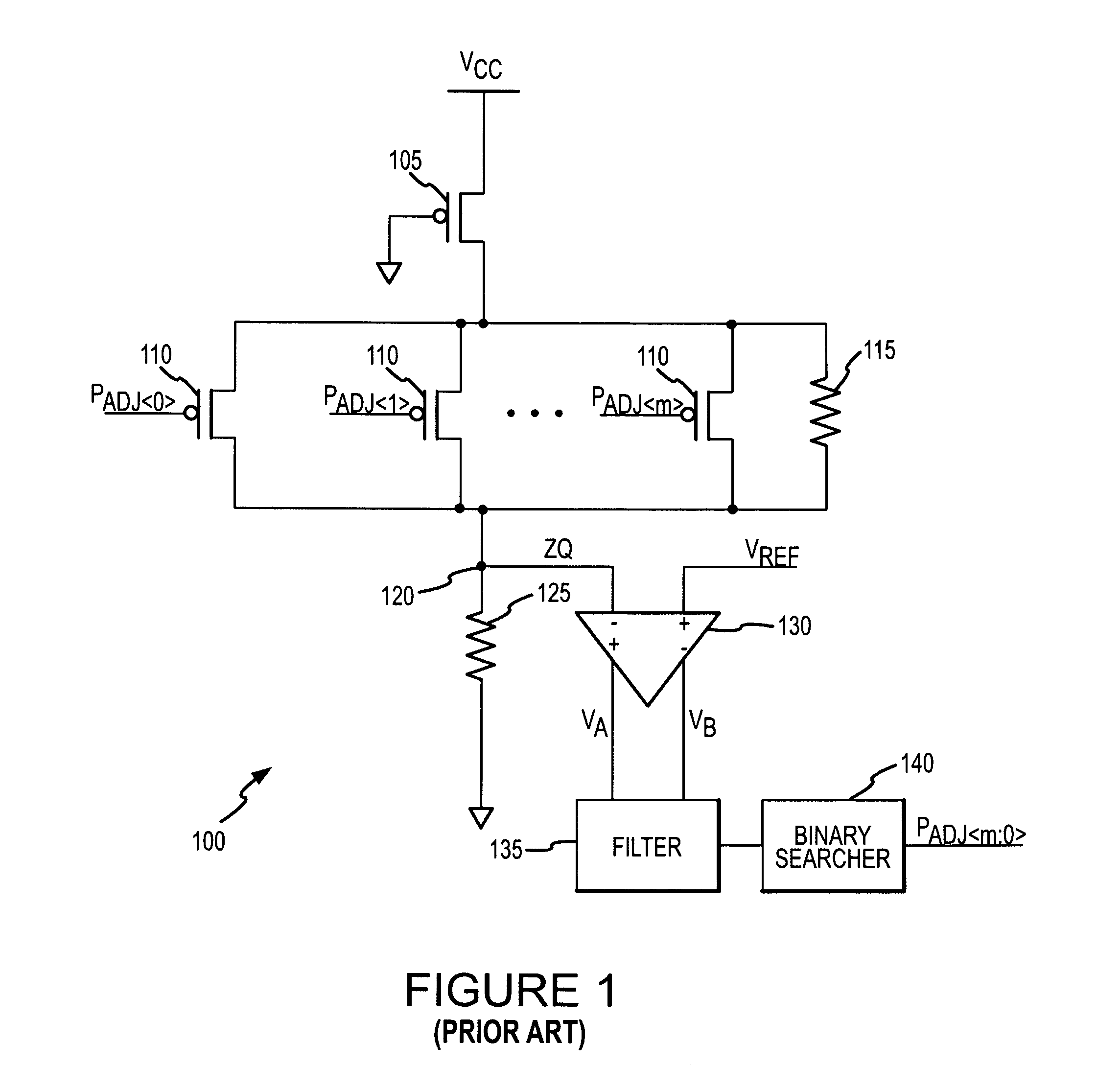
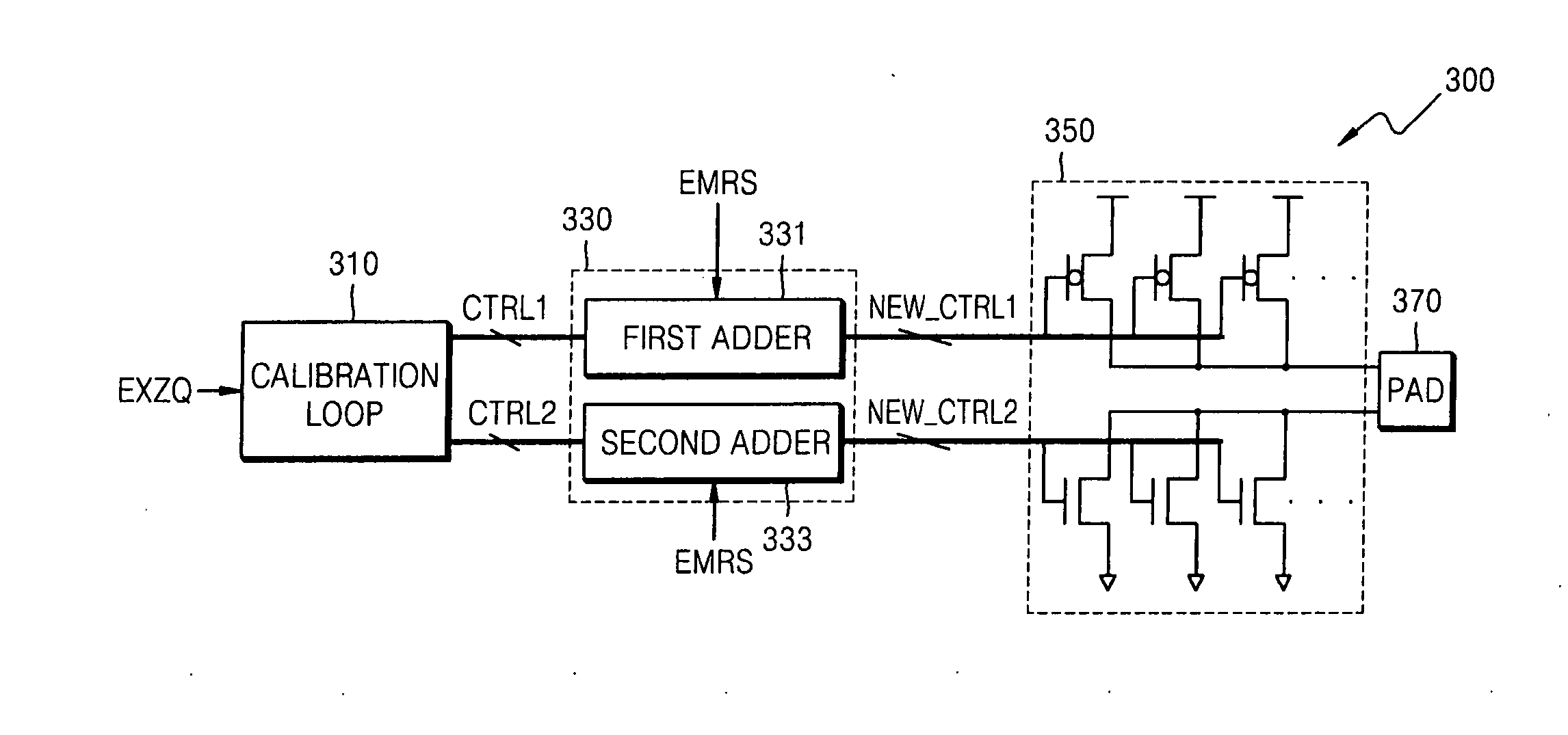
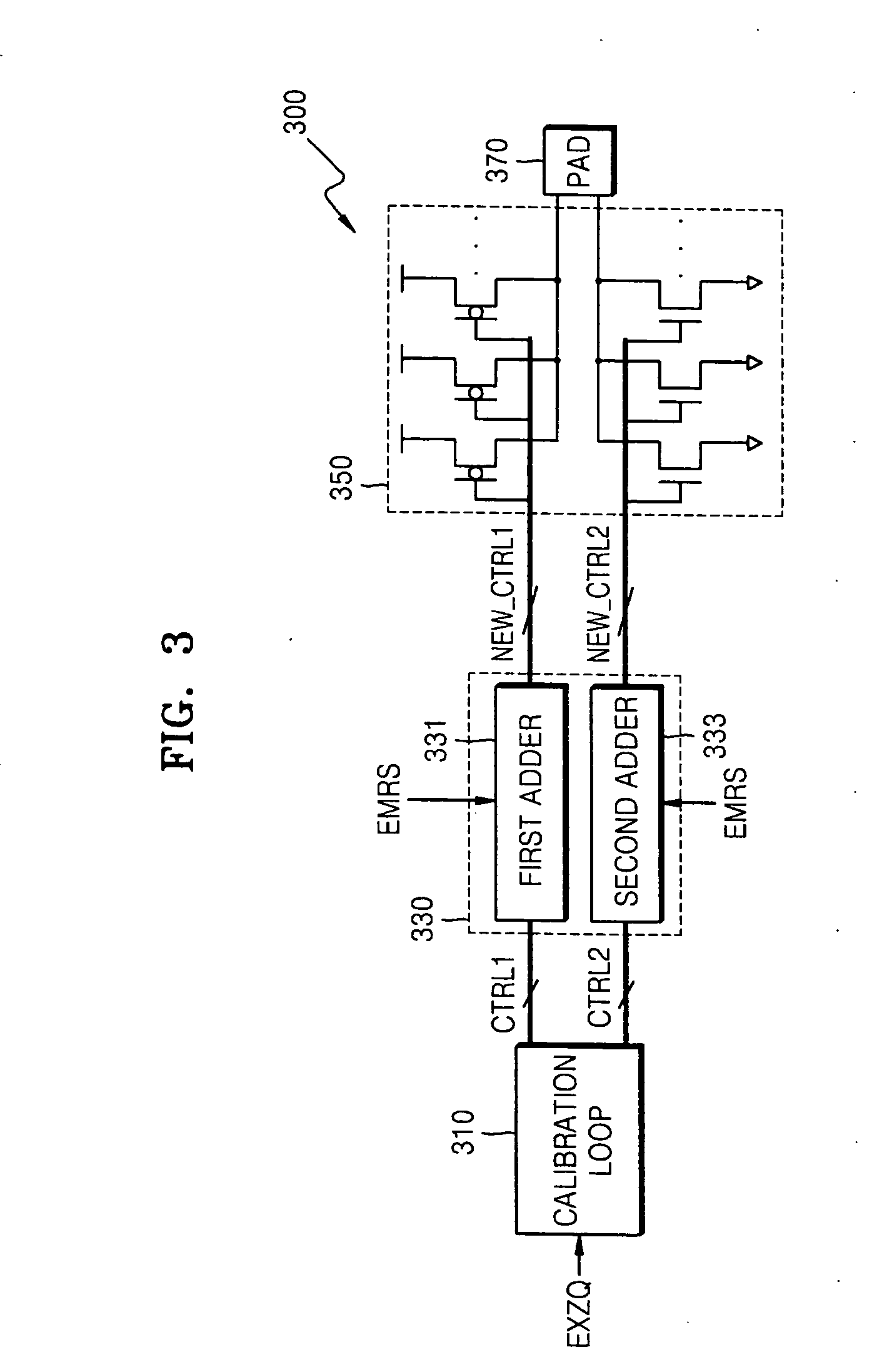
Patents
Literature
656results about "Input/output impedence modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
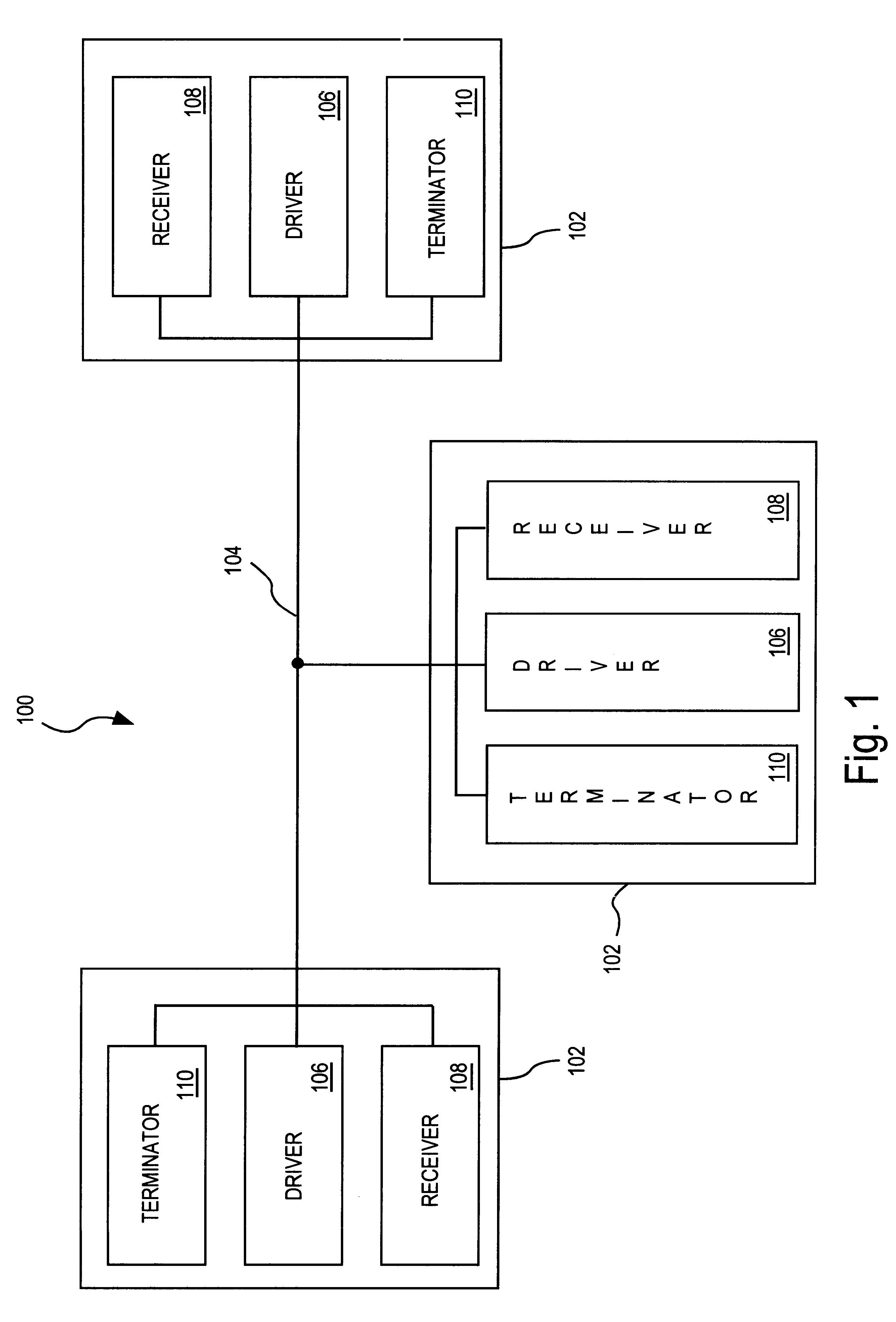
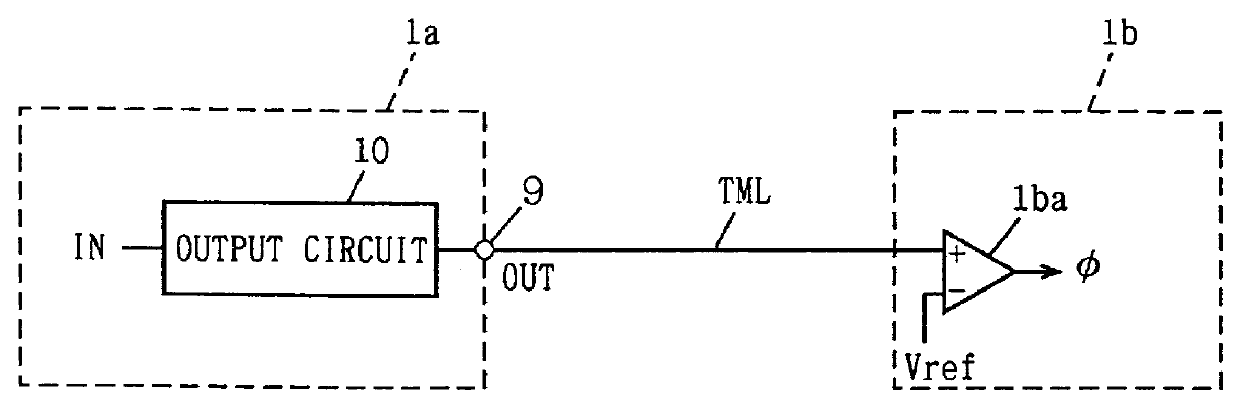
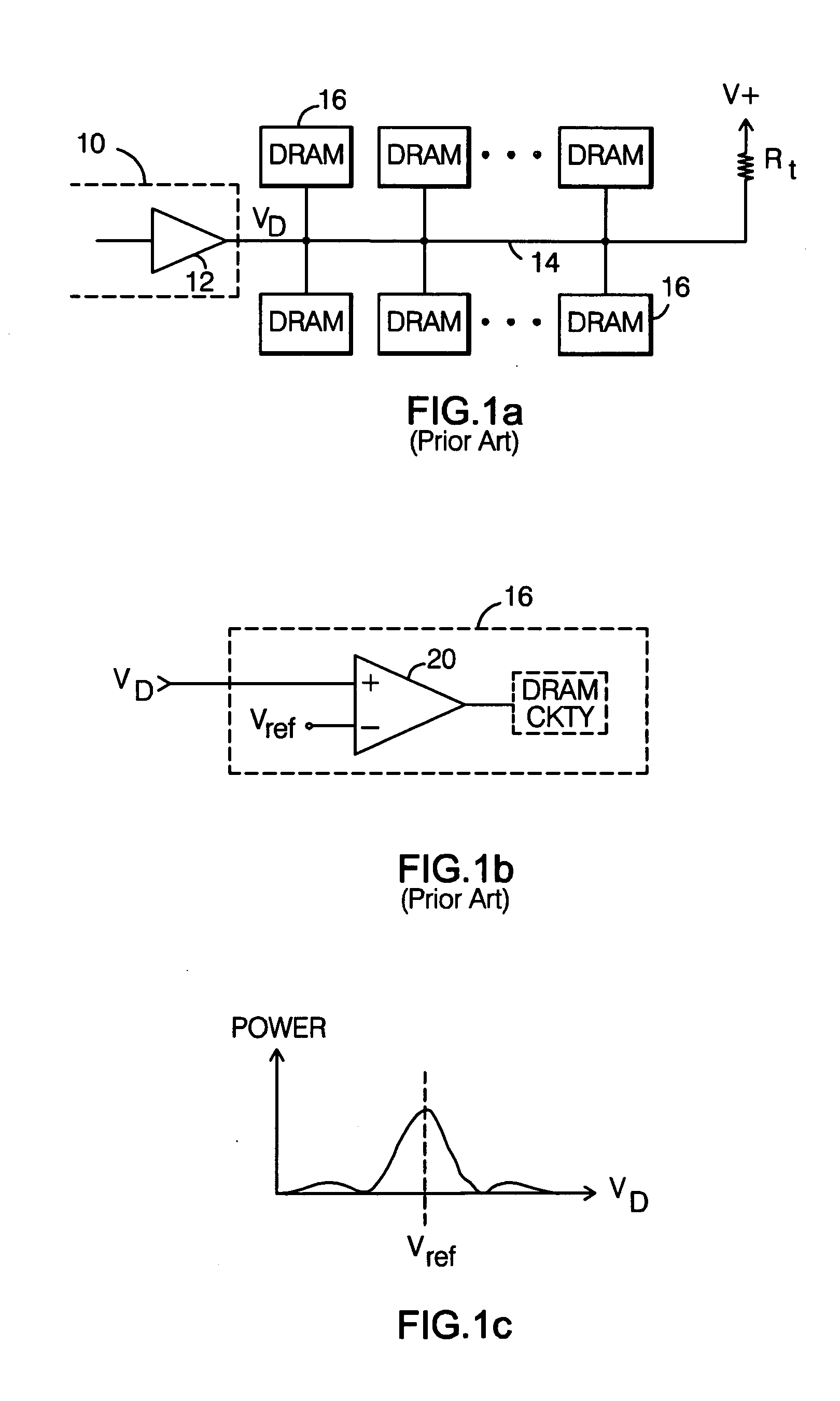
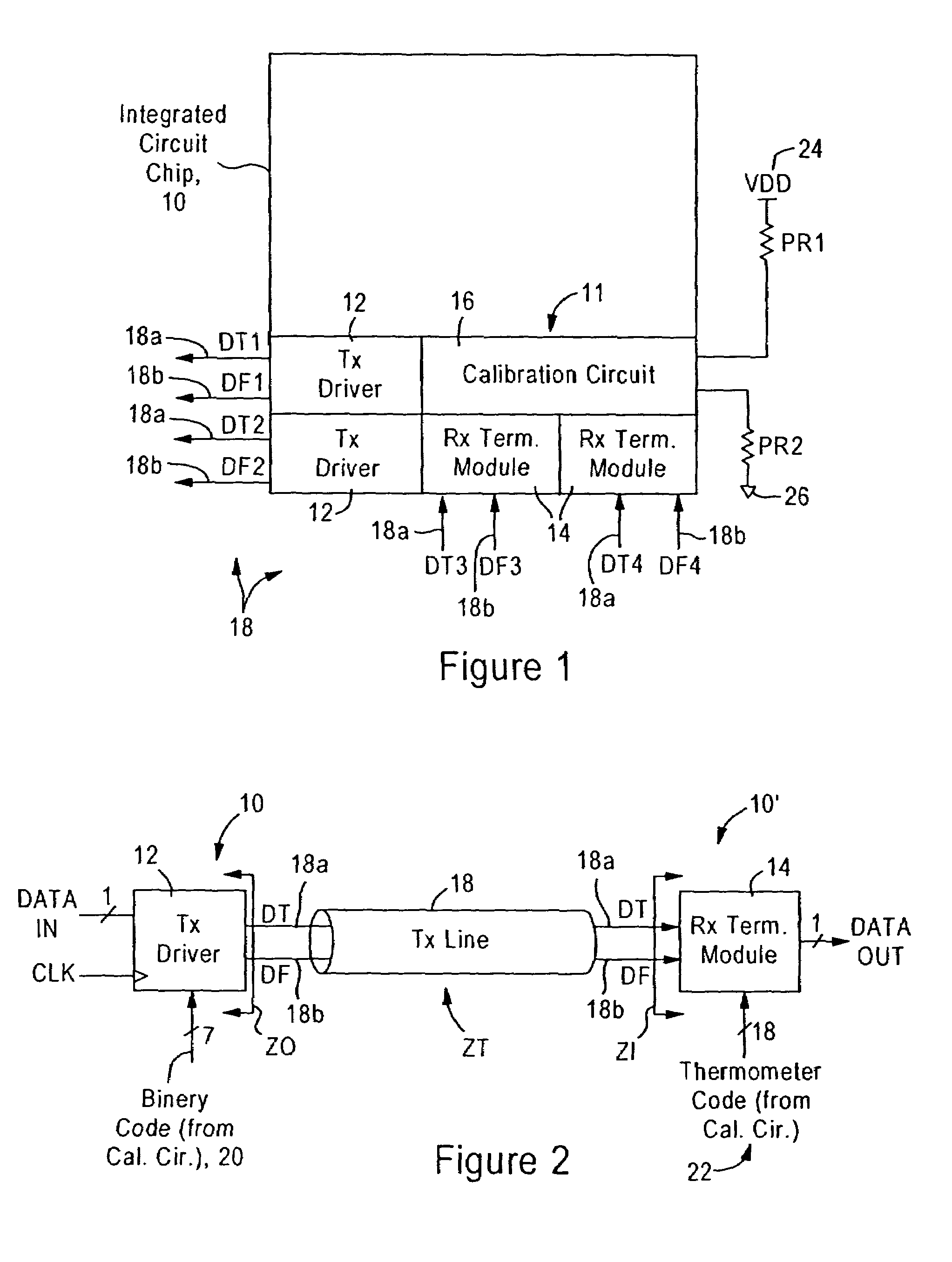
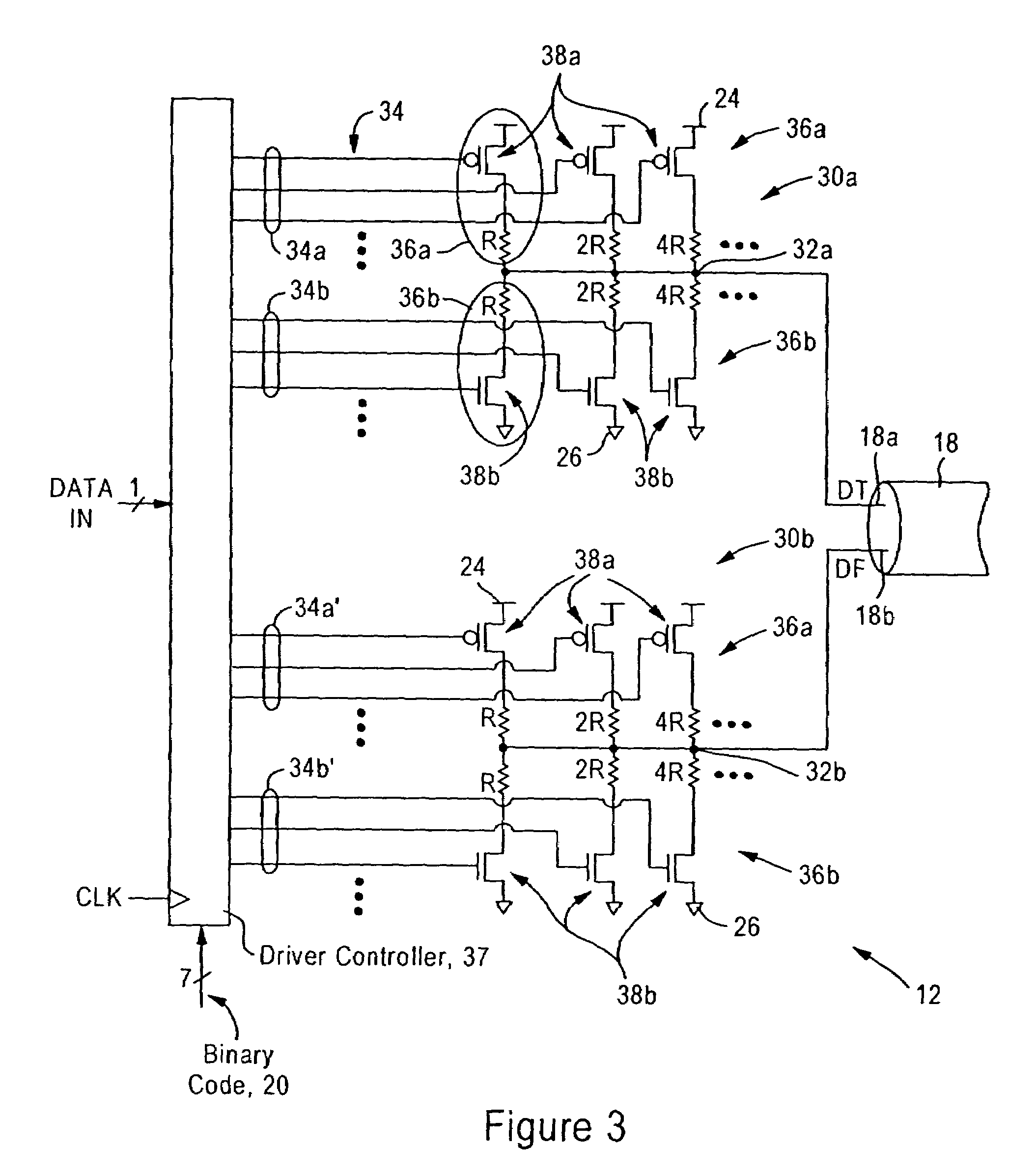
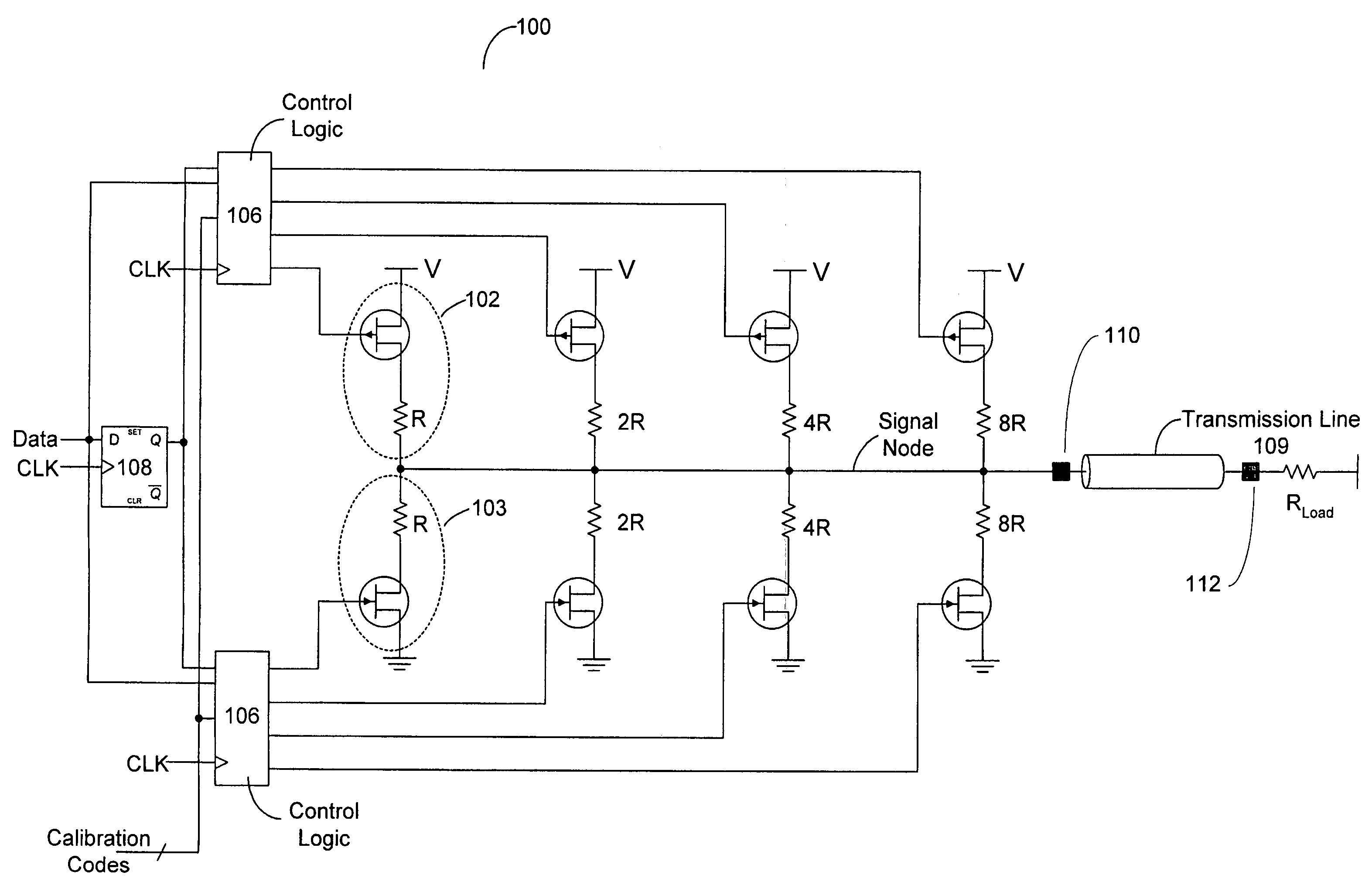
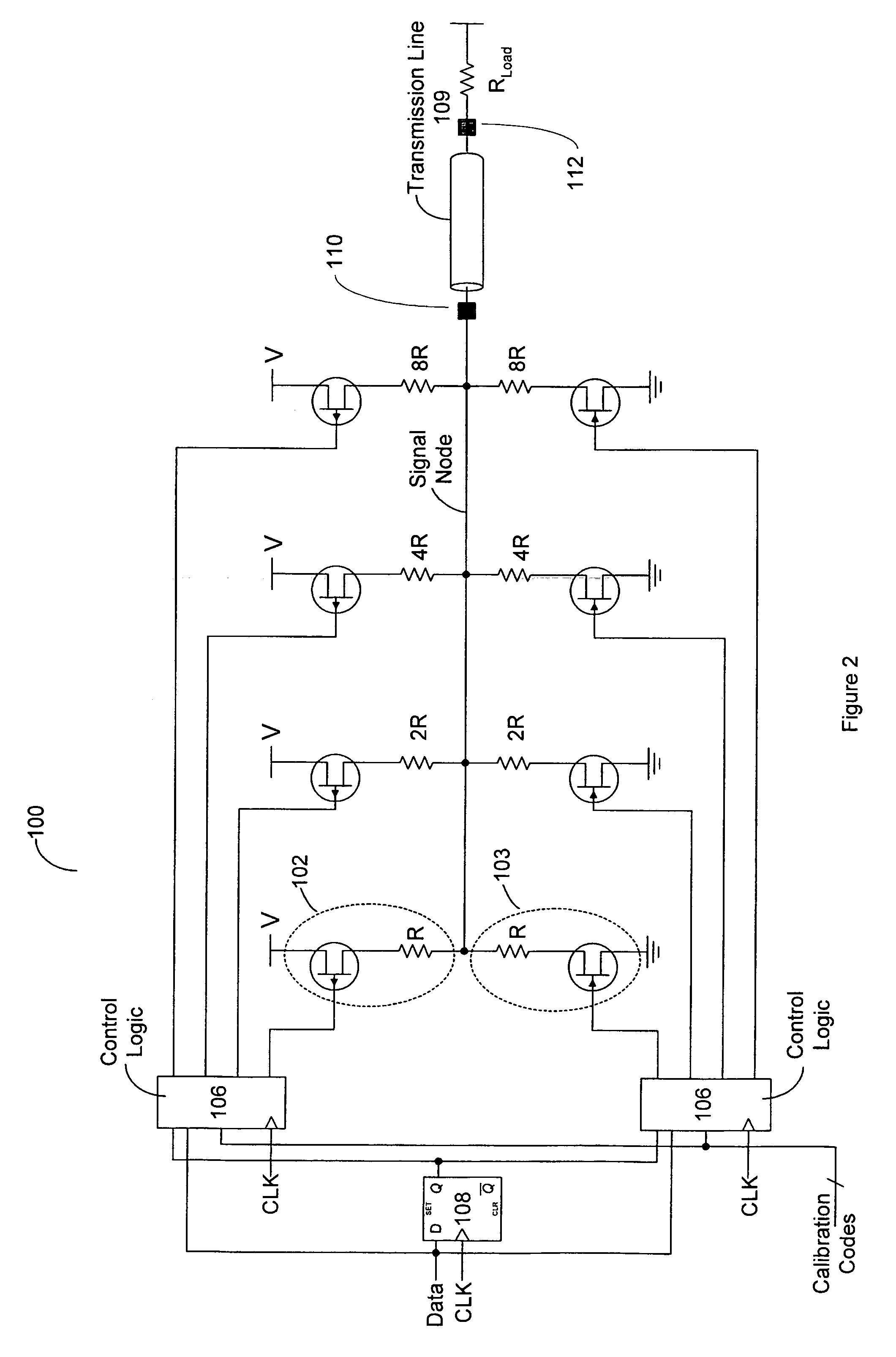
System and method for transmission-line termination by signal cancellation, and applications thereof
InactiveUS6937056B2Effective segmentationInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectric power transmissionNetwork termination
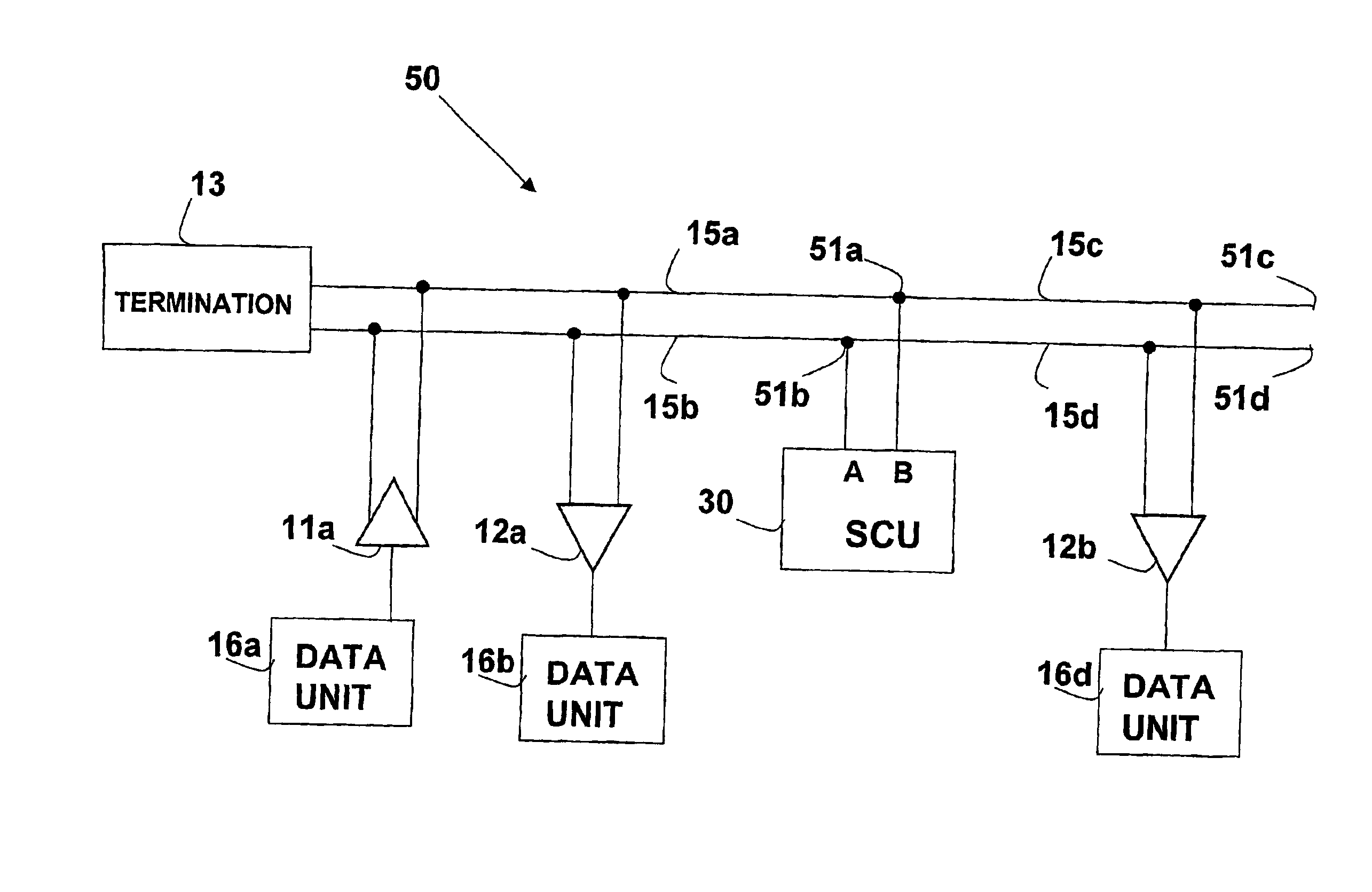
An active terminating device (30) for an electrical transmission line with optional line-receiving and line-driving capabilities. The basic device is a two-terminal unit, denoted as a Signal Canceling Unit (SCU), which sensesthe signal available at its terminals (34a, 34b), and applies negative feedback in order to cancel and absorb the signal. When applied to the end of a transmission line (15a, 15b) as part of wired communication network, the SCU functions as a terminator. When connected in the middle of such wired transmission line, the SCU splits the transmission line into two separate and isolated segments. In such a configuration, the SCU can be used to isolate a portion of a network from signal degradation due to noise or bridge-tap. Furthermore, the two isolated segments may each employ independent communications, such that no interference exists between the segments. In another embodiment, line receiver functionality is integrated into the SCU, designated as a Signal Canceling and Receiving Unit (SCRU) (90). The SCRU can perform all the SCU functions, and also serves as a line receiver in the communication network. In yet another embodiment, line driver functionality is integrated into the SCRU, designated as a Signal Canceling, Receiving and Transmitting Unit (SCRTU) (120). The SCRTU can perform all the SCRU functions, and also serves as a line driver in the communication network. Upon connecting multiple SCRTU's to a continuous transmission line, terminated independent point-to-point communication segments are formed.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
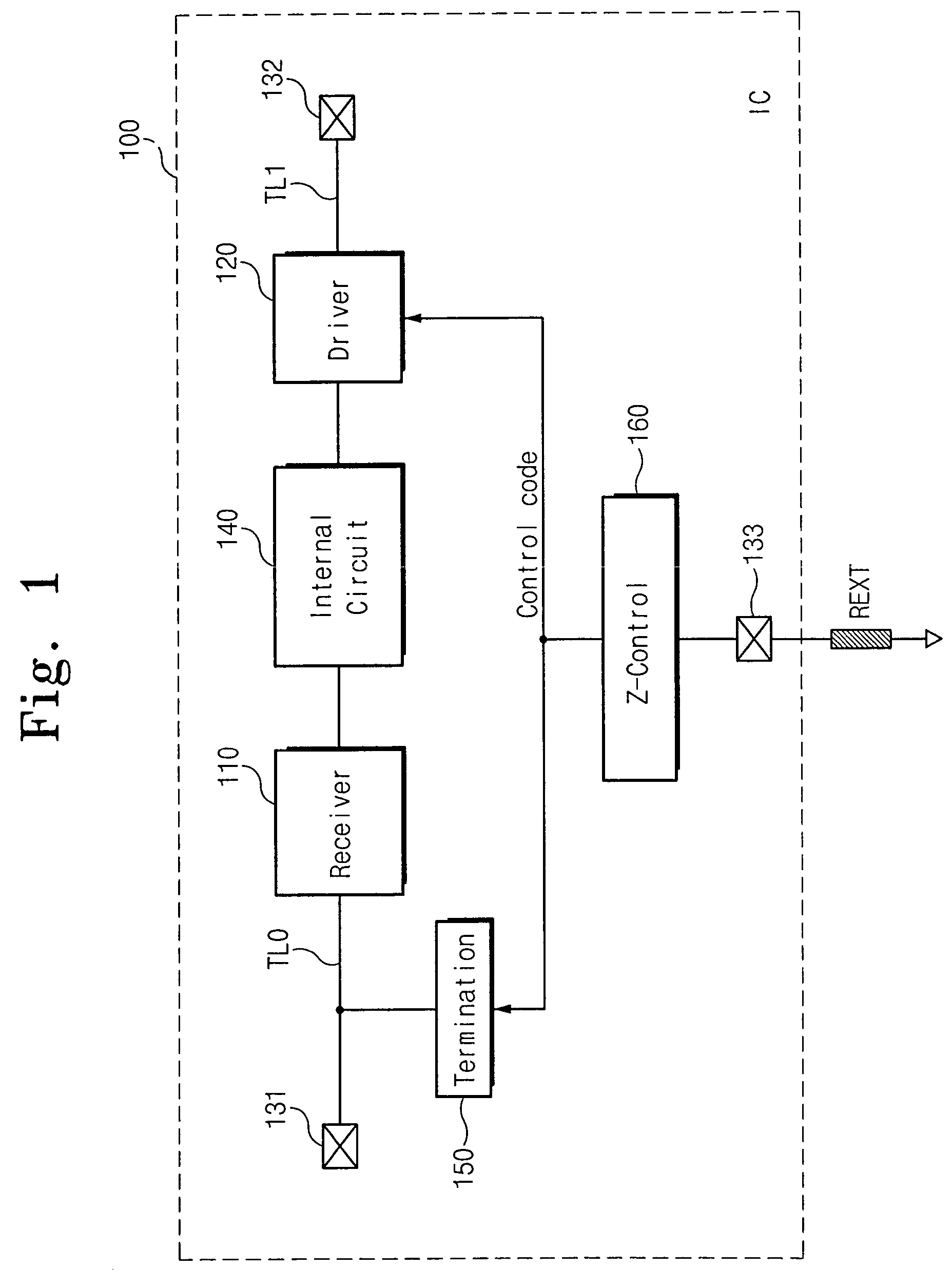
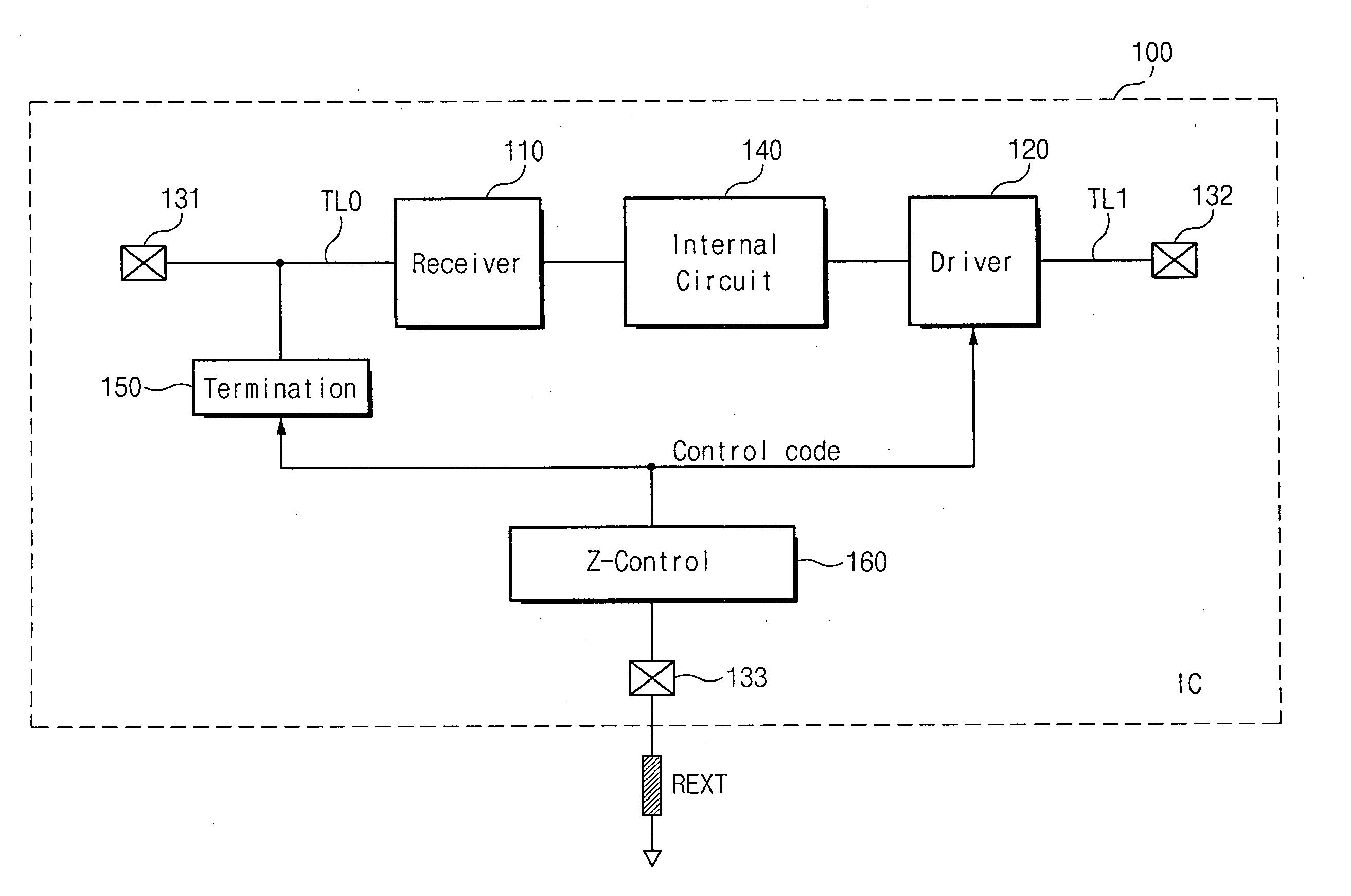
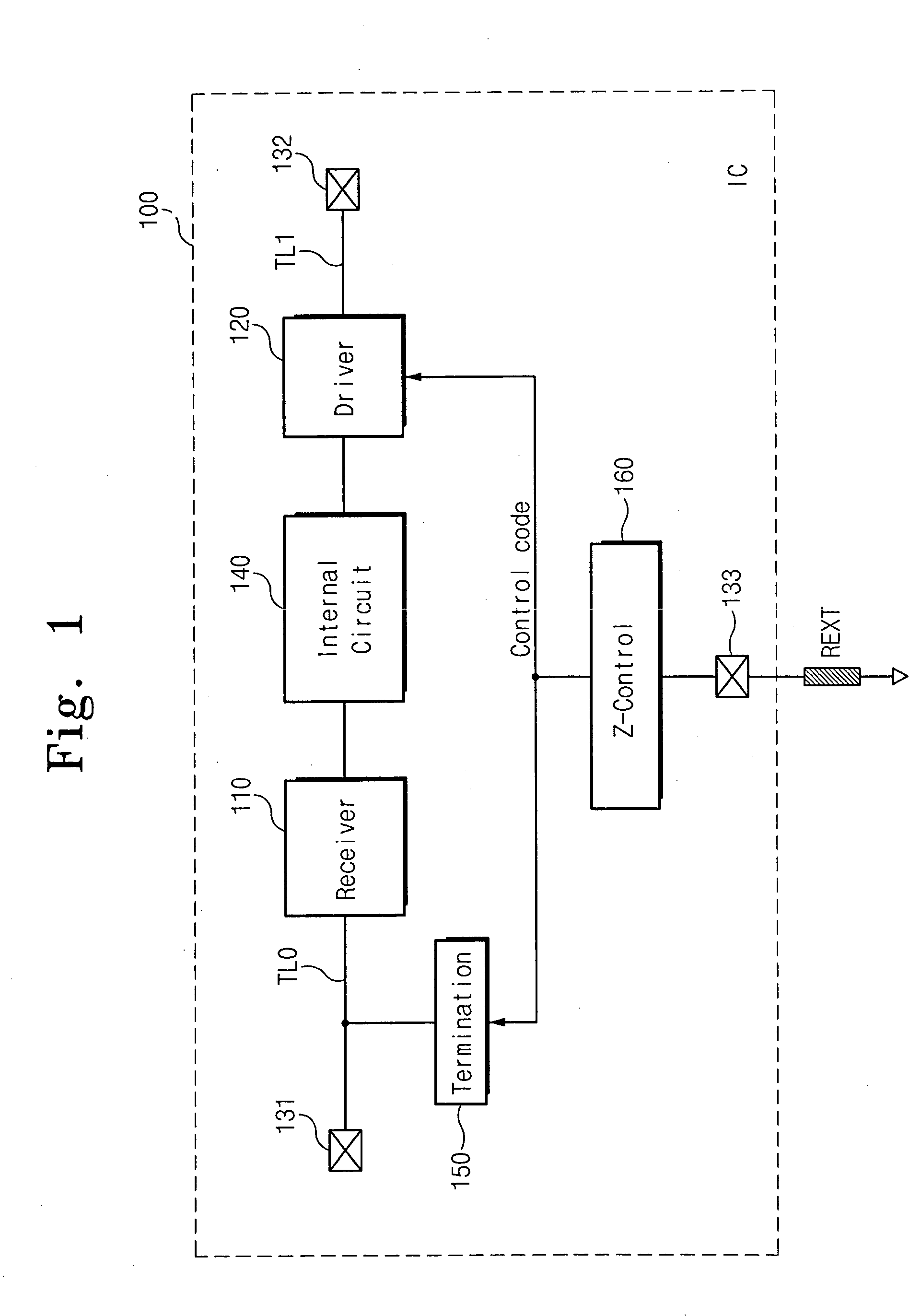
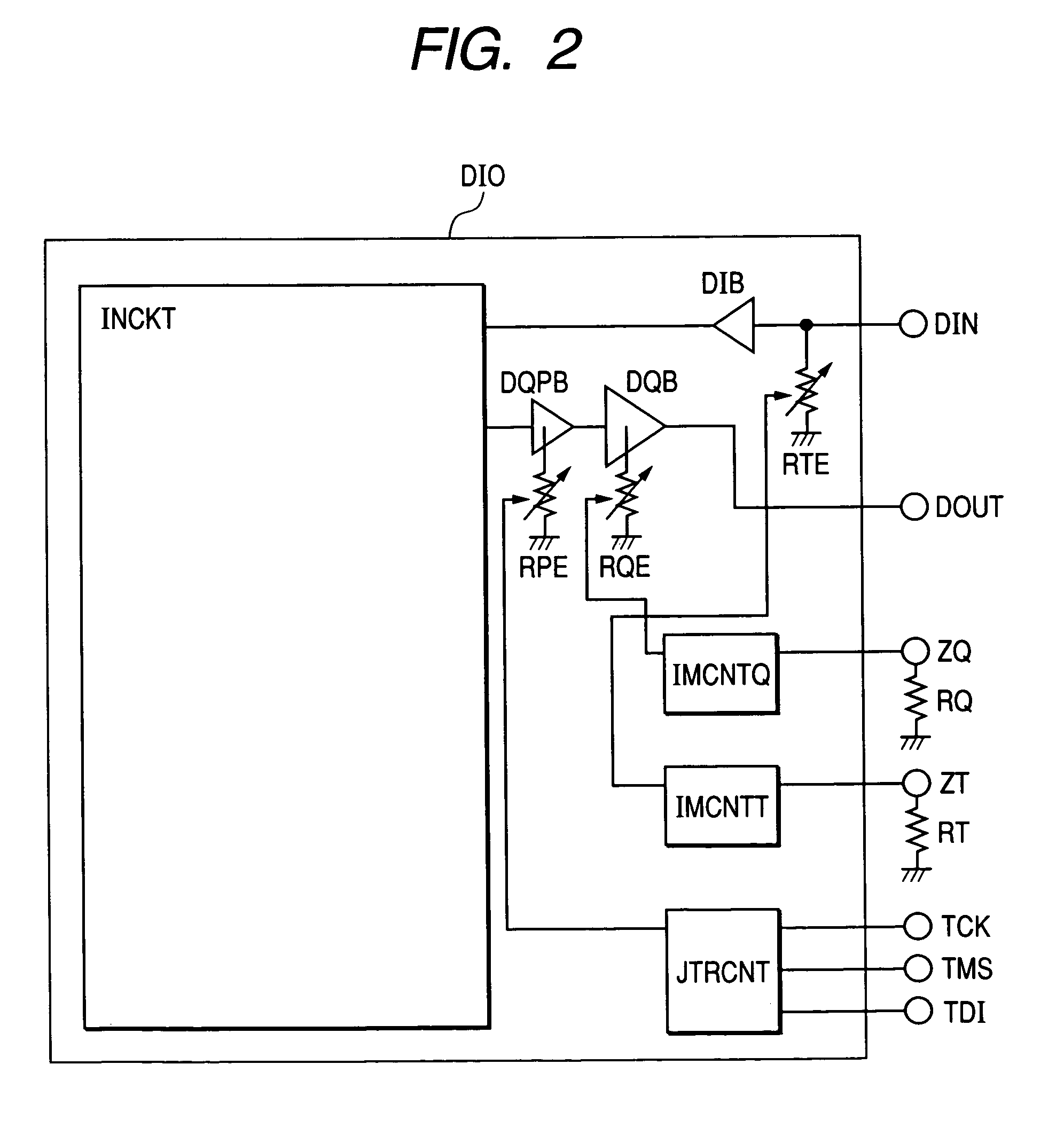
Semiconductor integrated circuit device capable of controlling impedance
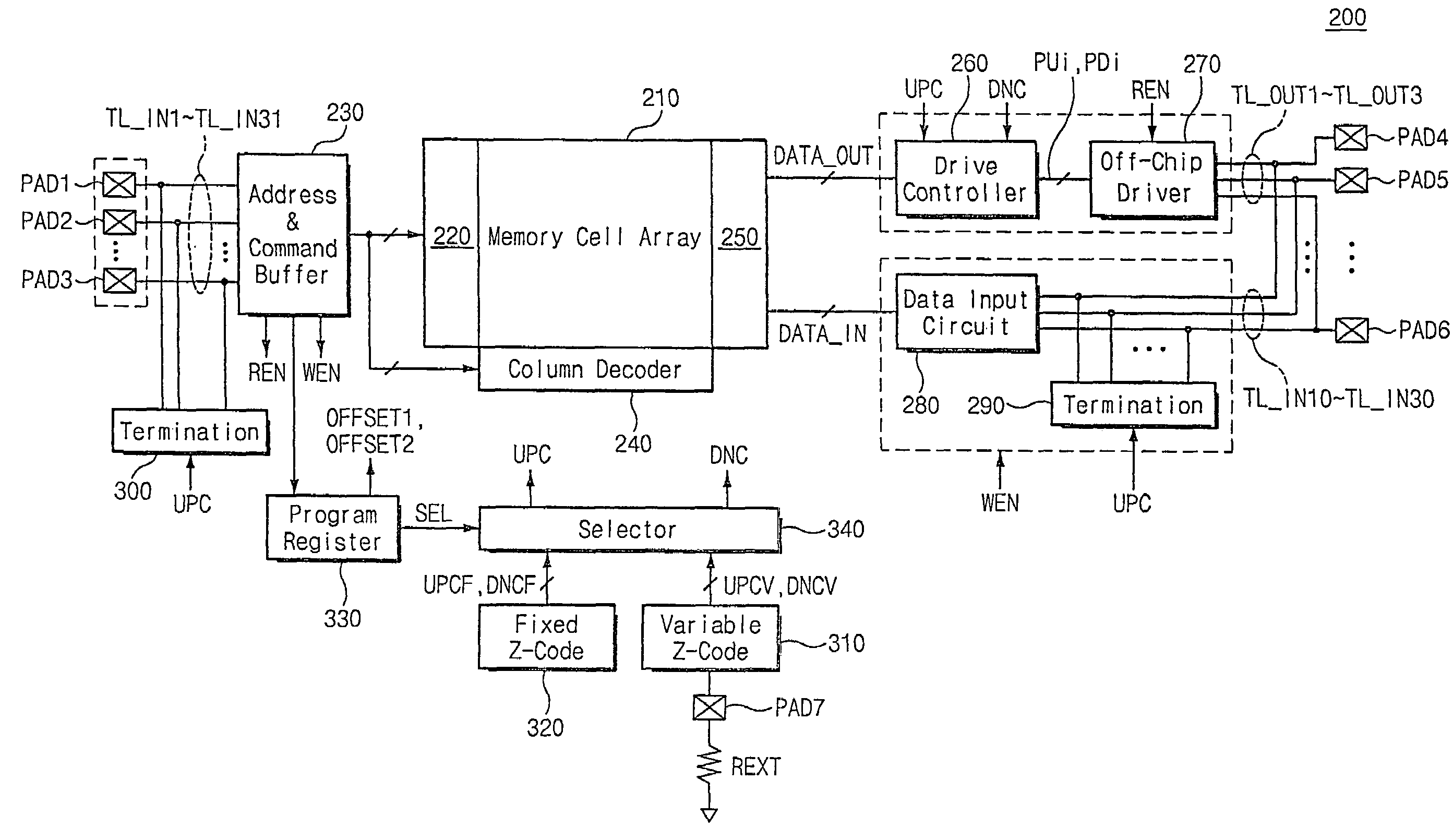
ActiveUS7148721B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsExternal referenceSemiconductor
A semiconductor integrated circuit device is connected to an external reference resistor, including an impedance control circuit for generating impedance control codes variable with impedances established by the external reference resistor. An input circuit receives an external signal through an input transfer line and forwards the external signal to an internal circuit. A termination circuit terminates the input transfer line in response to at least one of the impedance control code. An output circuit drives an output transfer line in accordance with an output signal. Impedance is variable with the control codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
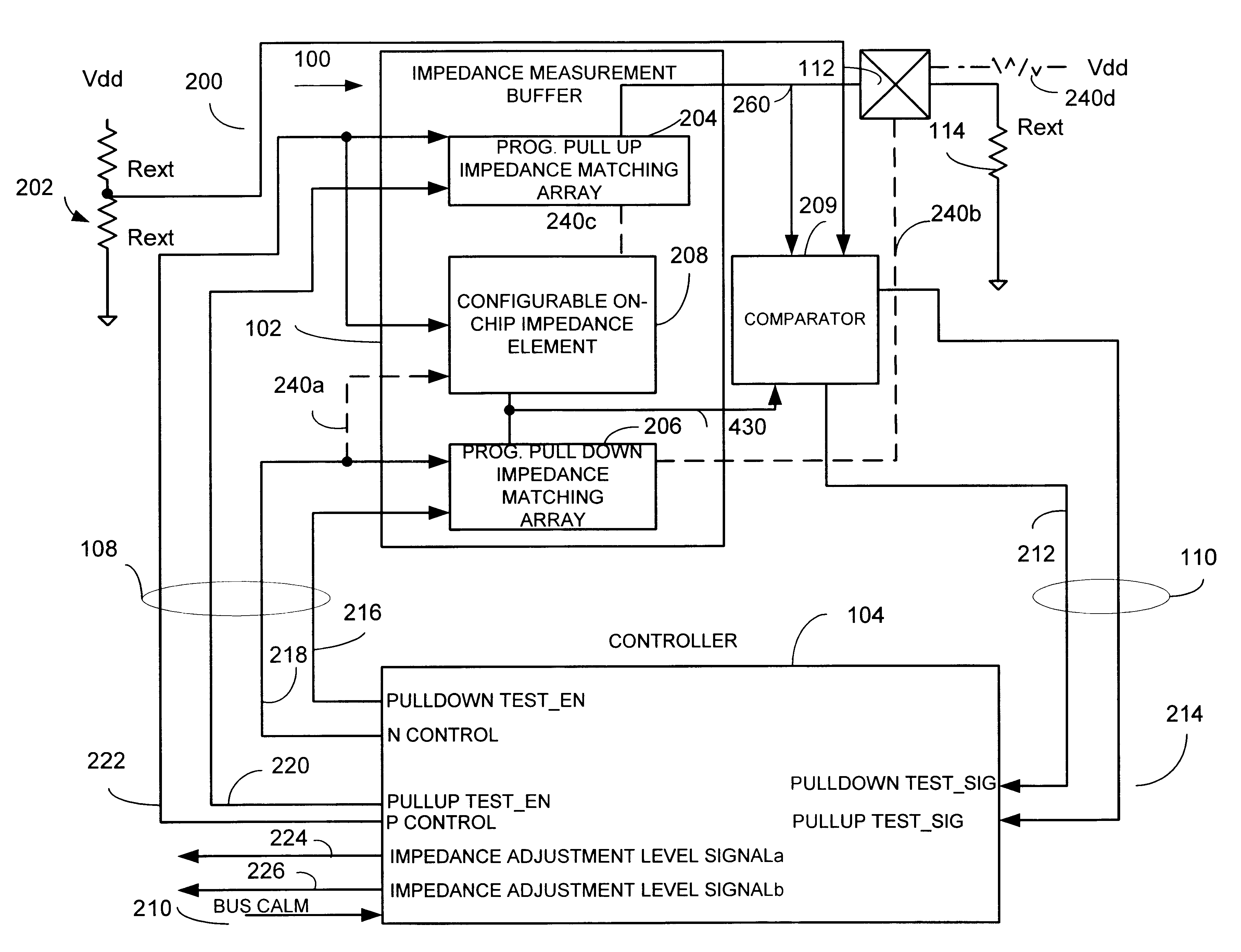
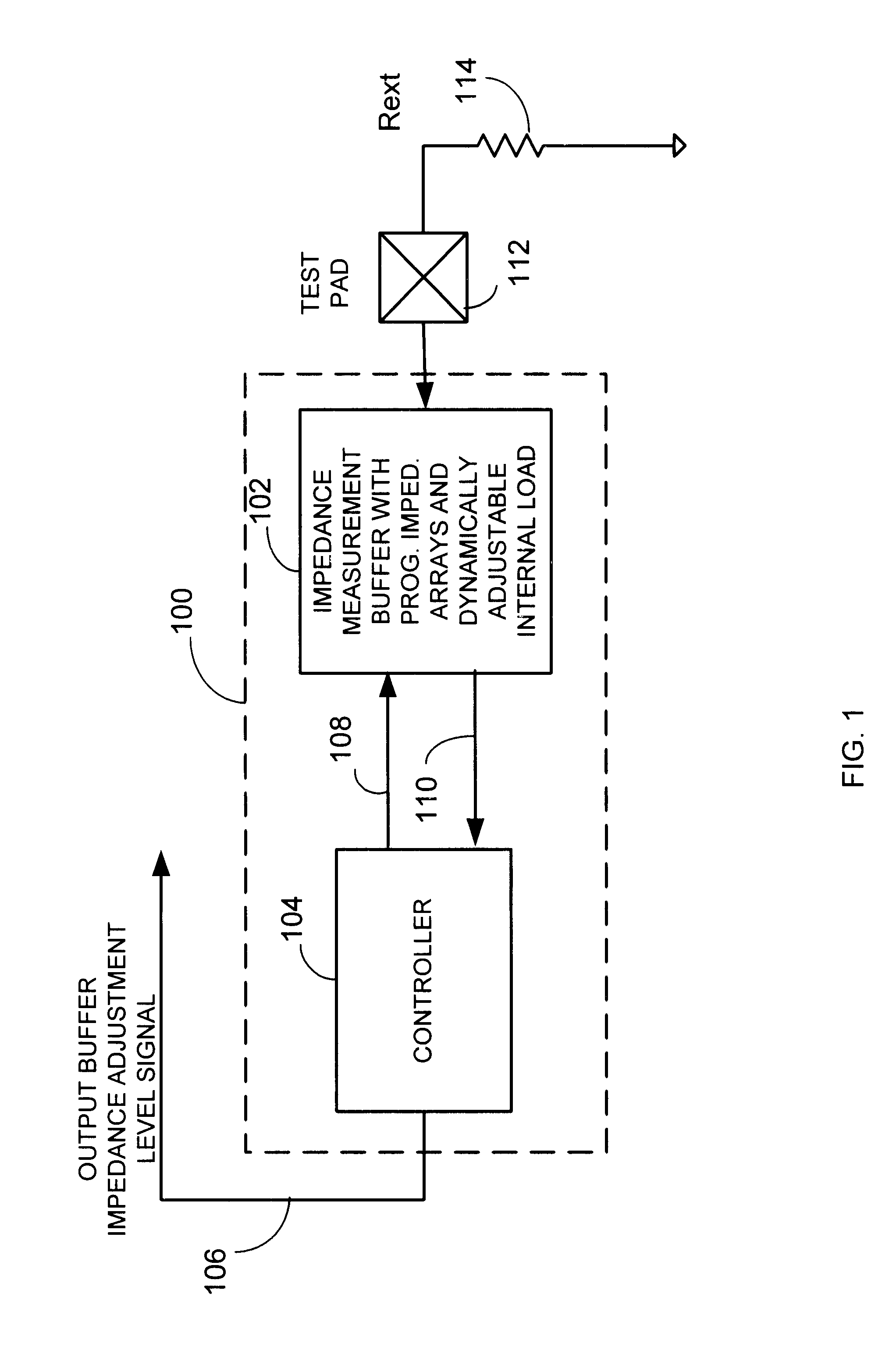
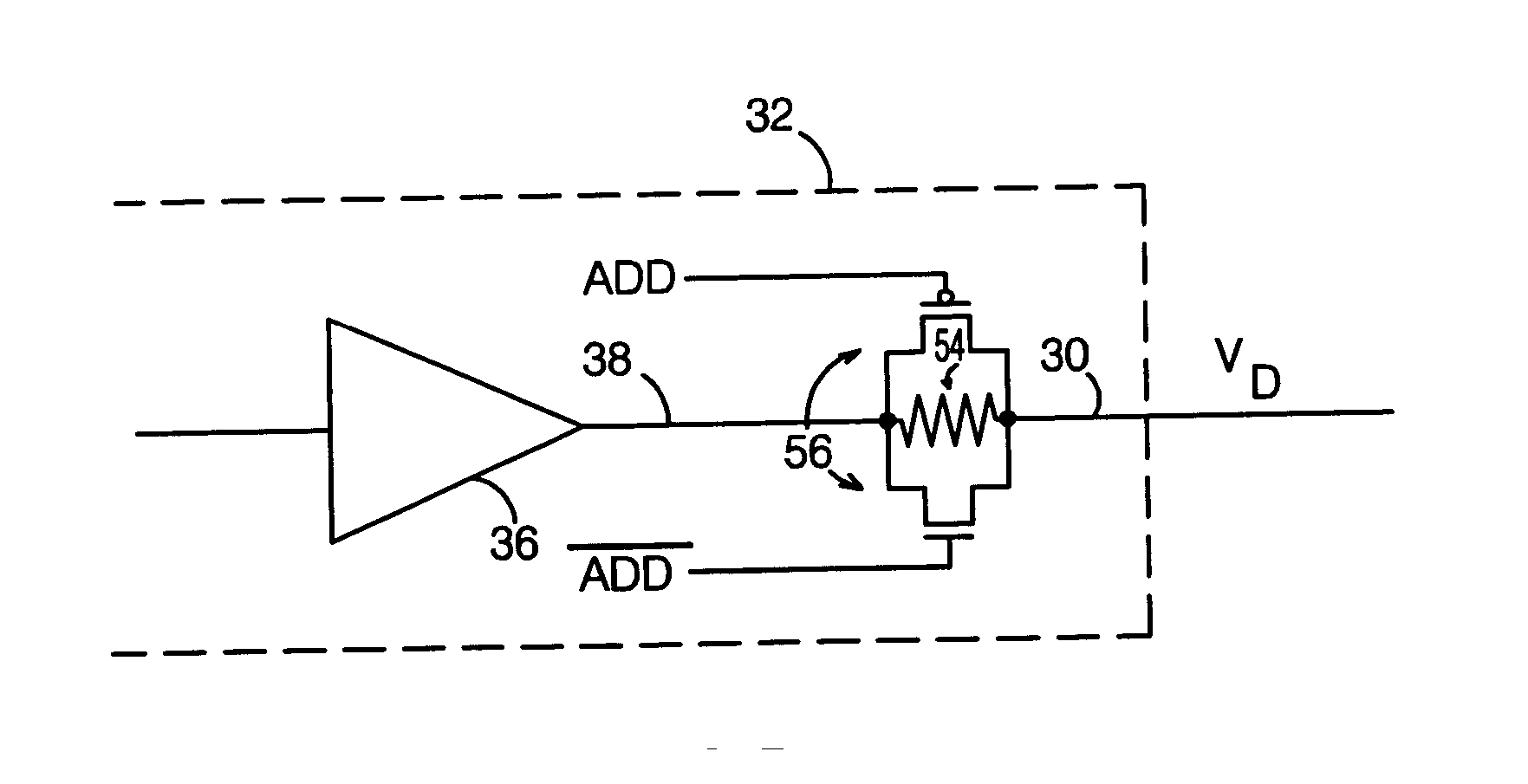
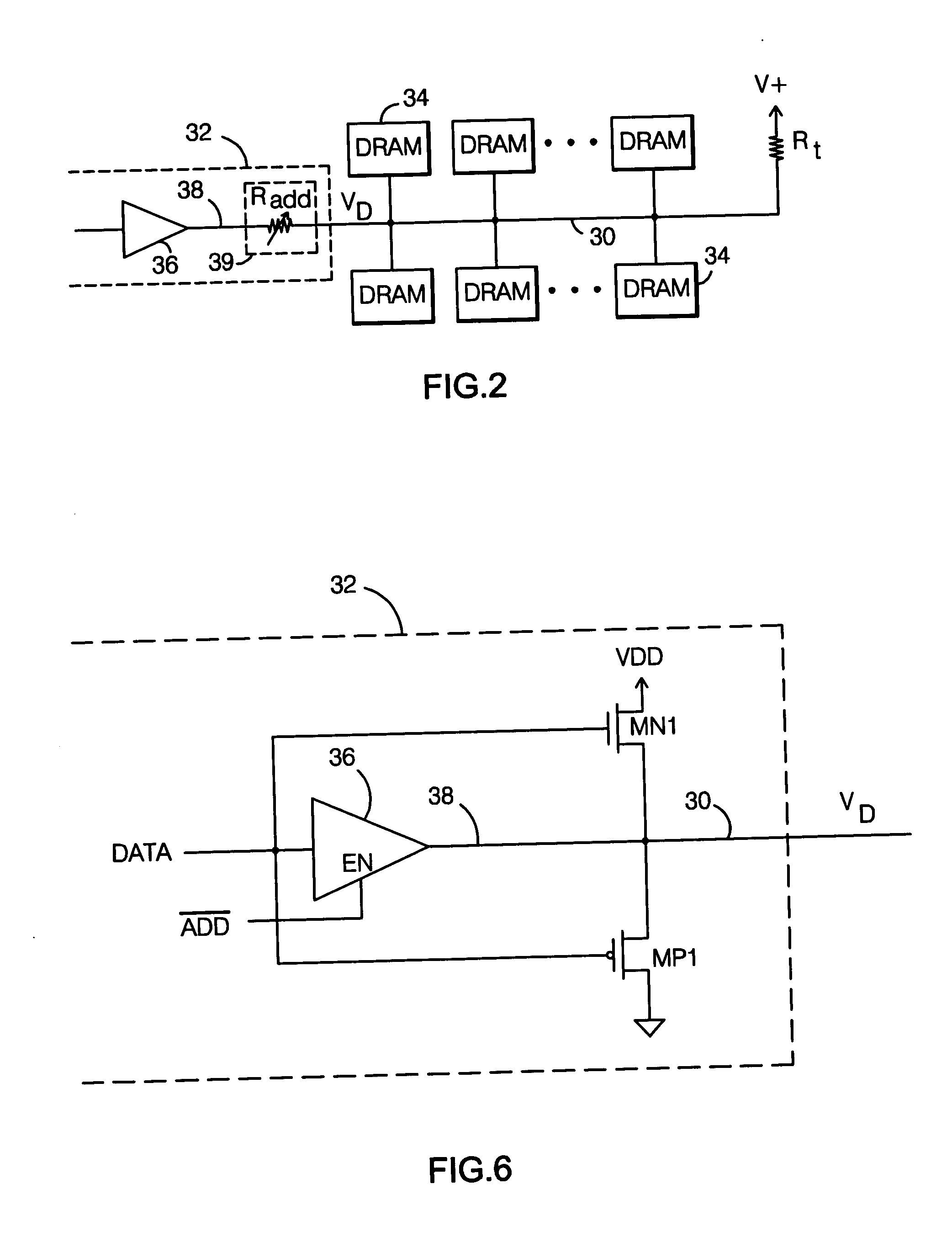
Dynamic impedance compensation circuit and method
InactiveUS6541996B1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDynamic impedanceEngineering
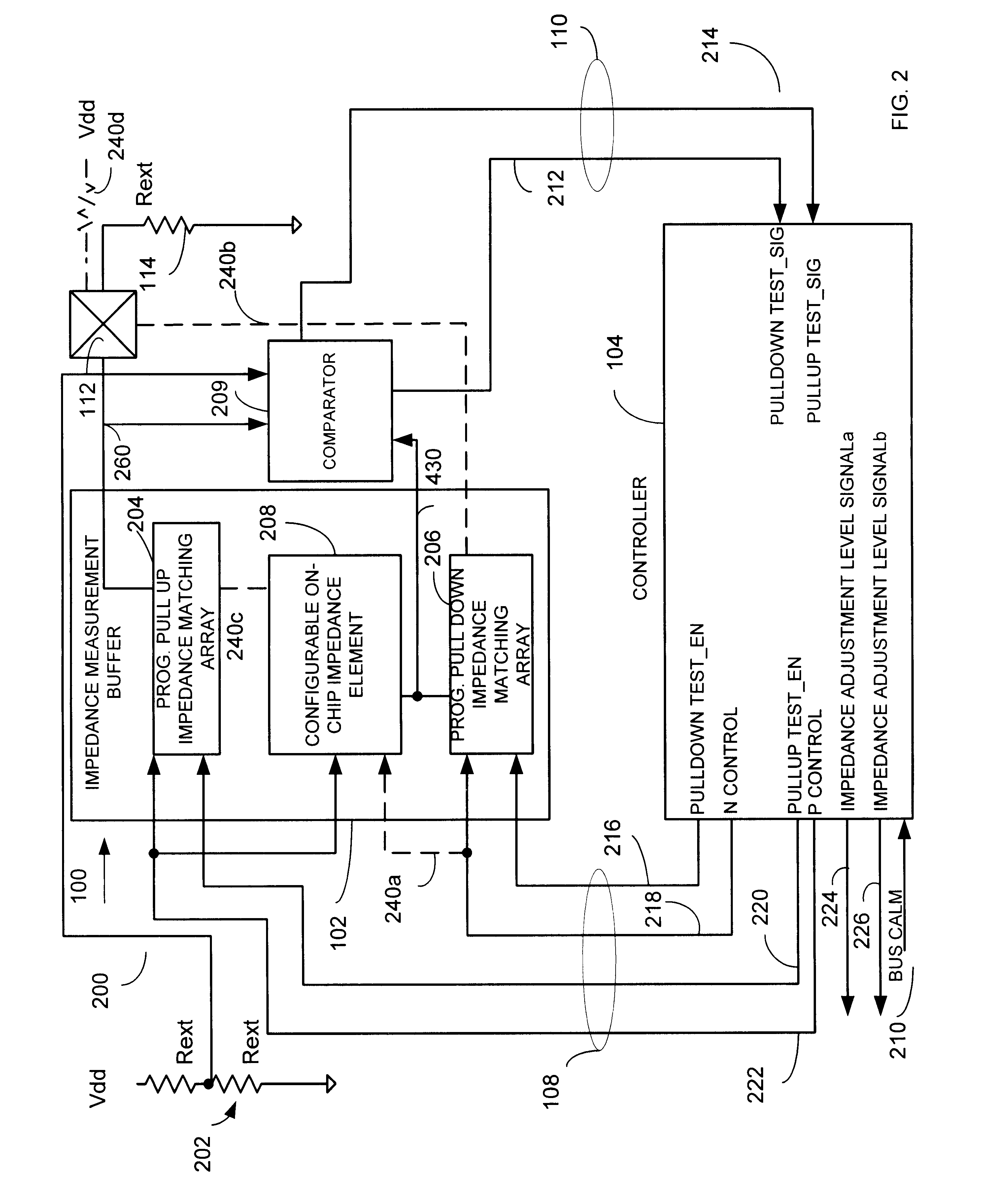
An impedance compensation circuit and method for an input / output buffer provides dynamic impedance compensation by using programmable impedance arrays and a dynamically adjustable on-chip load. Accordingly, among other advantages, only a single off-chip or external calibrated impedance resistor is used and only a single test pad is necessary.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Terminating transmission lines using on-chip terminator circuitry
InactiveUS6232792B1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceImpedance matching
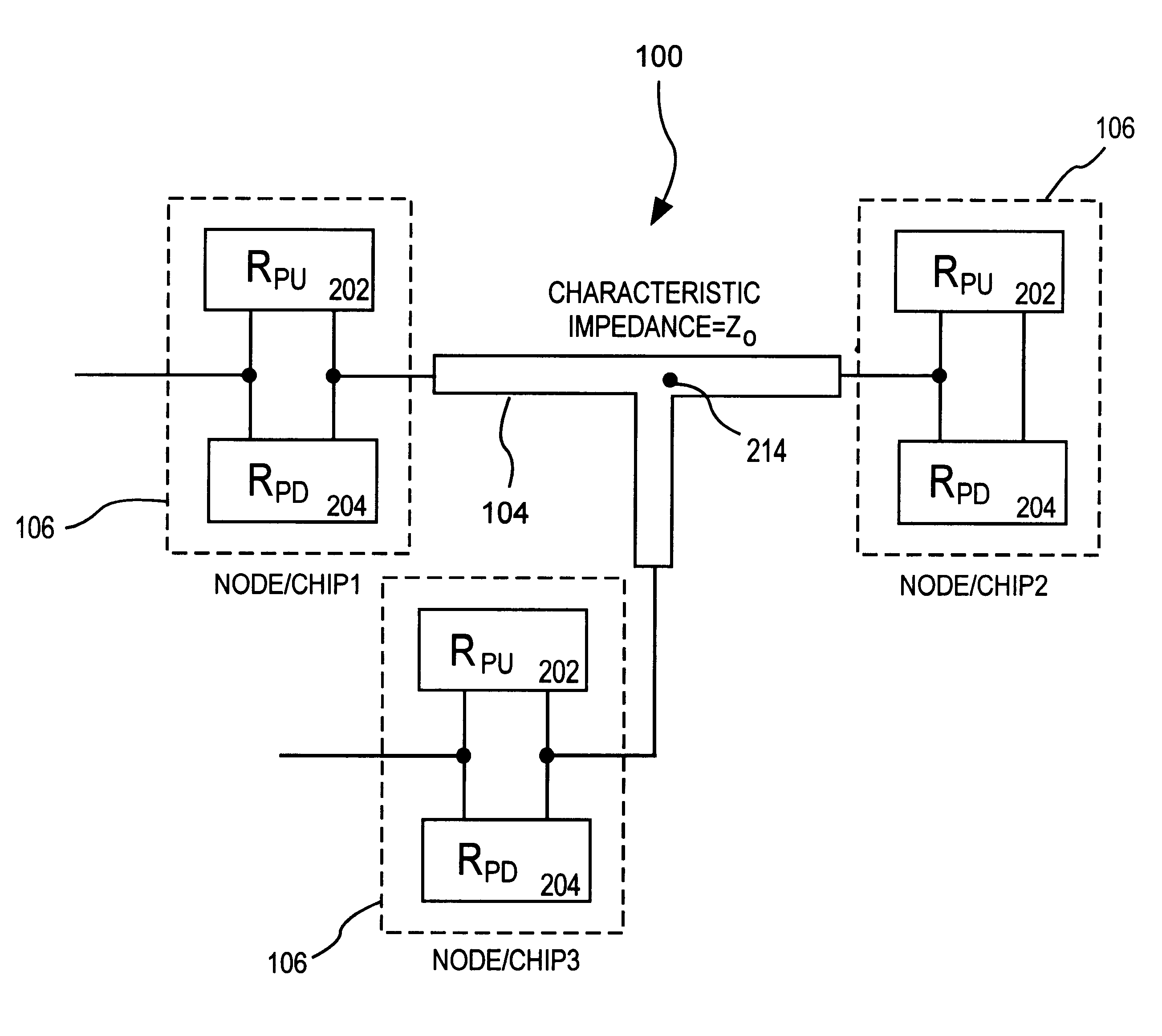
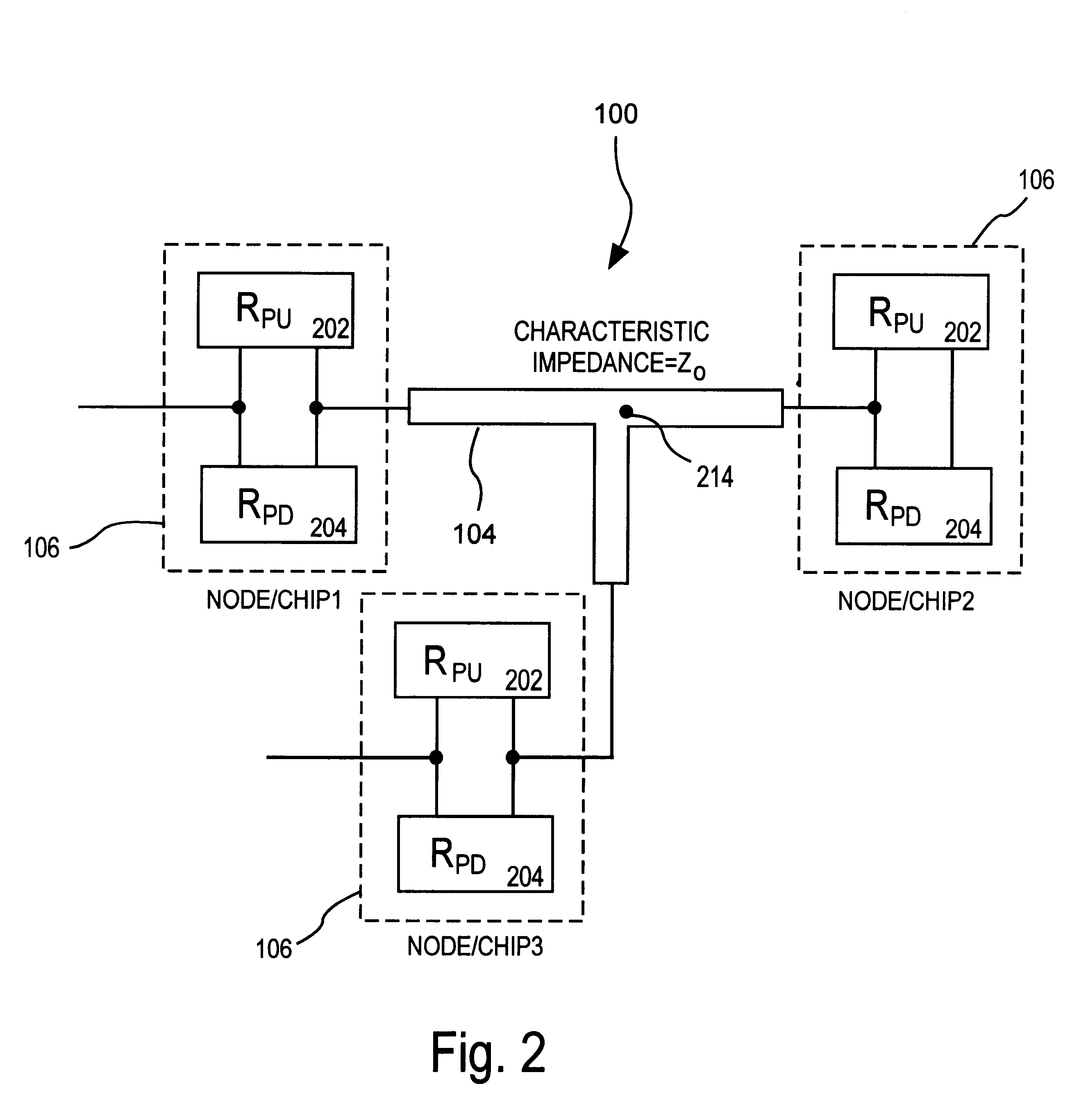
An information handling system is disclosed herein. The system includes at least one system transmission line having a characteristic impedance and a plurality of clusters, each cluster being coupled to each other cluster through at least one of the system transmission lines. Each cluster comprises at least one cluster transmission line each having a characteristic impedance equal to the characteristic impedance of the system transmission lines, and is coupled to a the system transmission line and a circuit chosen from the following: a driver, an on-chip terminator, an off-chip terminator; each driver having a pull-up circuit having an output resistance matching the characteristic impedance of the cluster transmission lines. A method for operating the system provided herein includes designating one of the drivers as an active driver, designating each driver other than the active driver as a terminating driver, causing each terminating driver to be configured in a nonactive pull-up terminating configuration; and causing the active driver to drive a signal onto the transmission line to which the active driver is connected.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
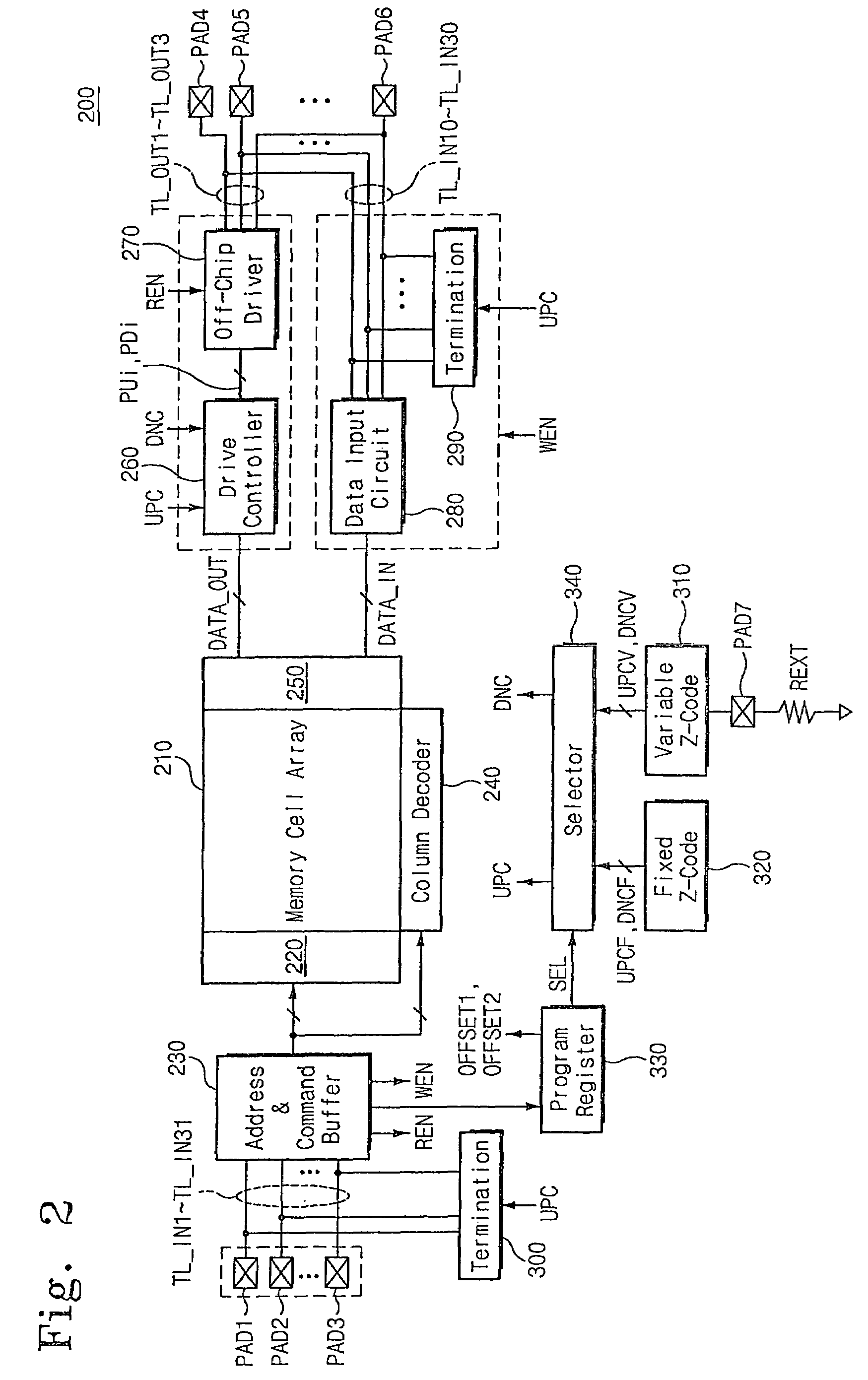
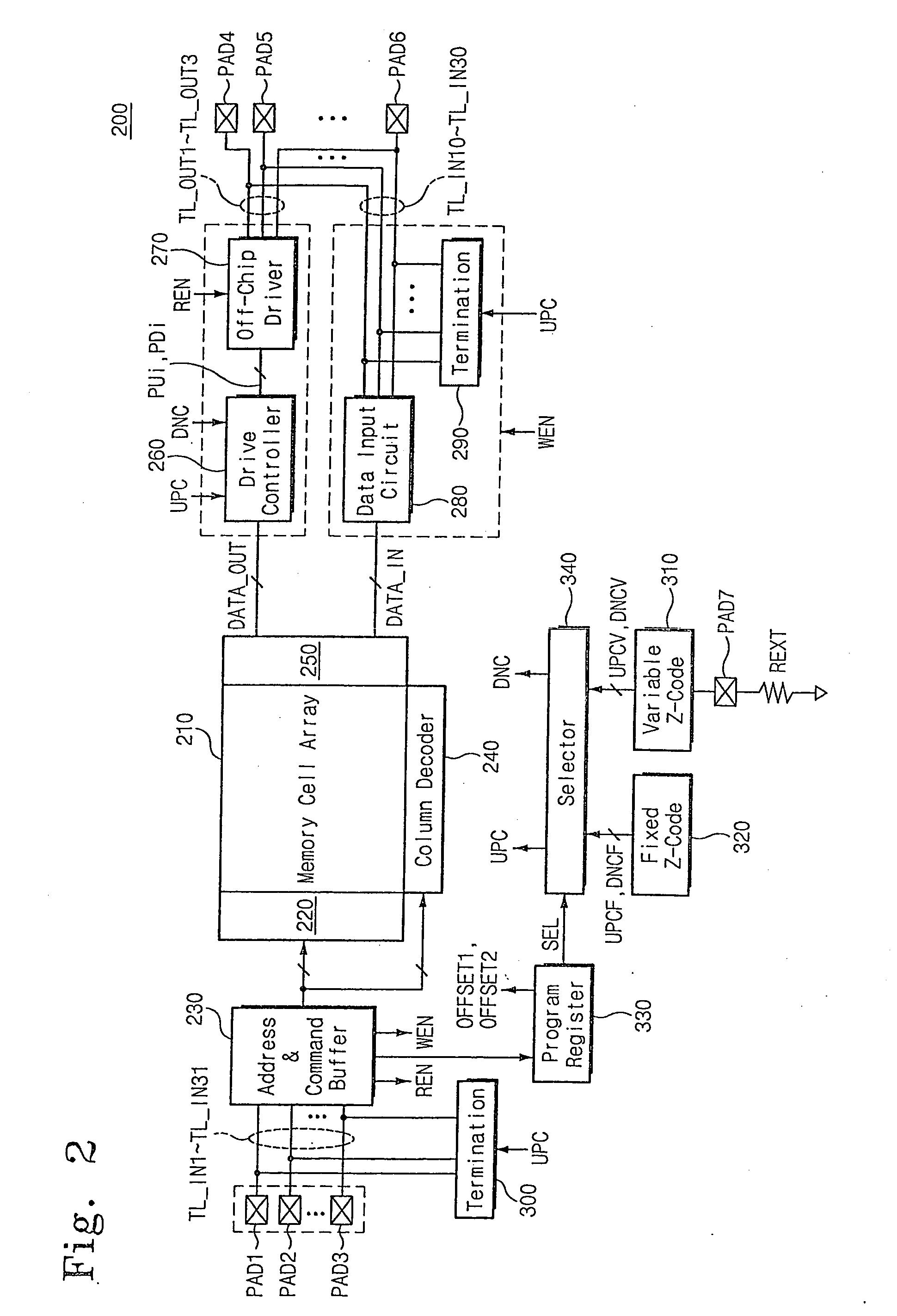
Semiconductor integrated circuit device capable of controlling impedance
ActiveUS20050040845A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsExternal referenceEngineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit device is connected to an external reference resistor, including an impedance control circuit for generating impedance control codes variable with impedances established by the external reference resistor. An input circuit receives an external signal through an input transfer line and forwards the external signal to an internal circuit. A termination circuit terminates the input transfer line in response to at least one of the impedance control code. An output circuit drives an output transfer line in accordance with an output signal. Impedance is variable with the control codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
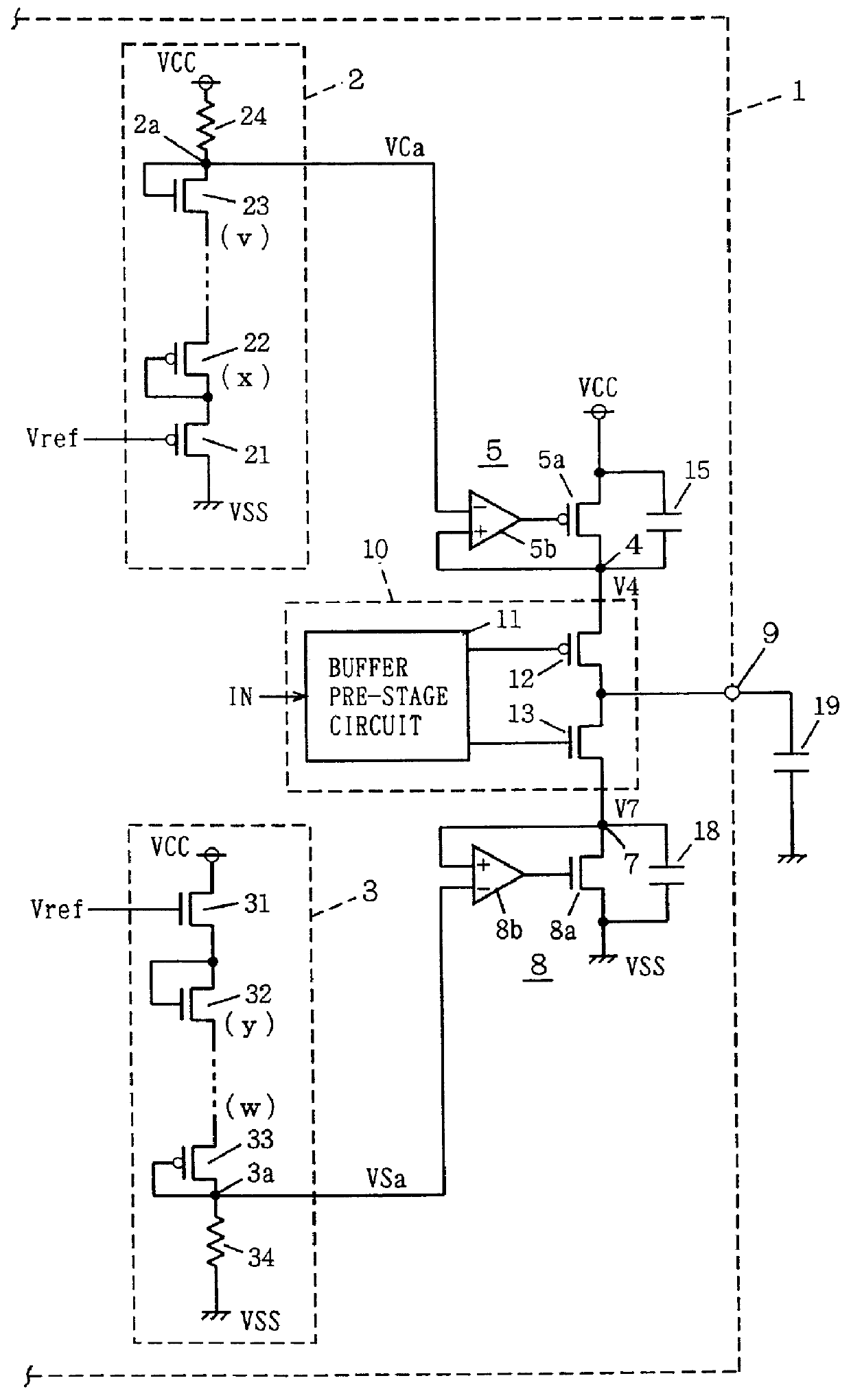
Semiconductor device allowing fast and stable transmission of signals
InactiveUS6087885AInput/output impedence modificationElectronic switchingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Internal power supply voltages at predetermined voltage levels are produced on output nodes of an output circuit in accordance with internal voltages generated by first and second voltage generating circuits which in receive a reference voltage on their inputs having high impedances. Stabilizing capacitors are connected to internal power supply nodes of this output circuit. The internal power supply voltage depends on MOS transistors operating in a source follower mode. During operation of the output circuit, charging and discharging currents are driven through the stabilizing capacitors, and an output signal having a limited amplitude can be reliably generated to an output node.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
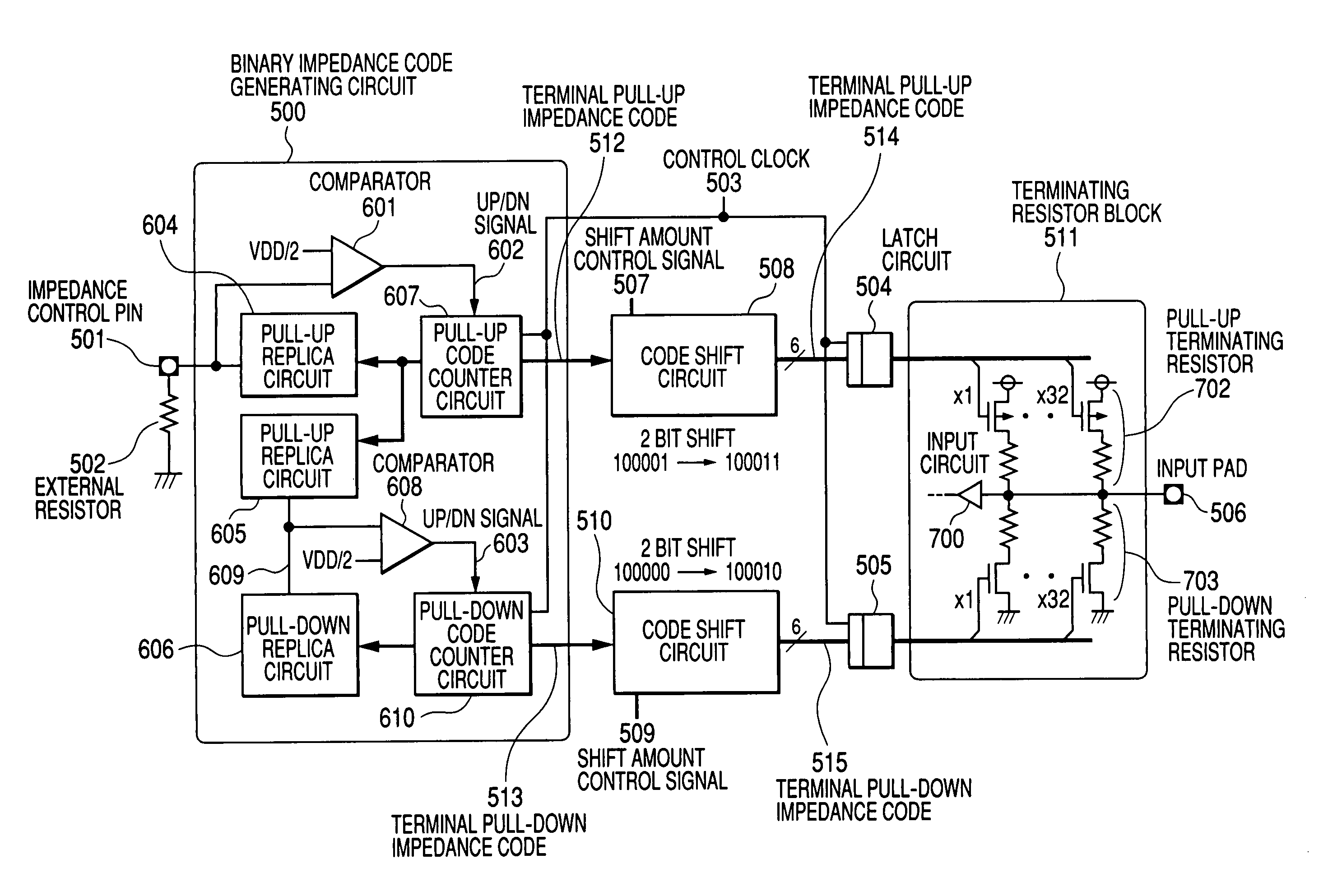
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
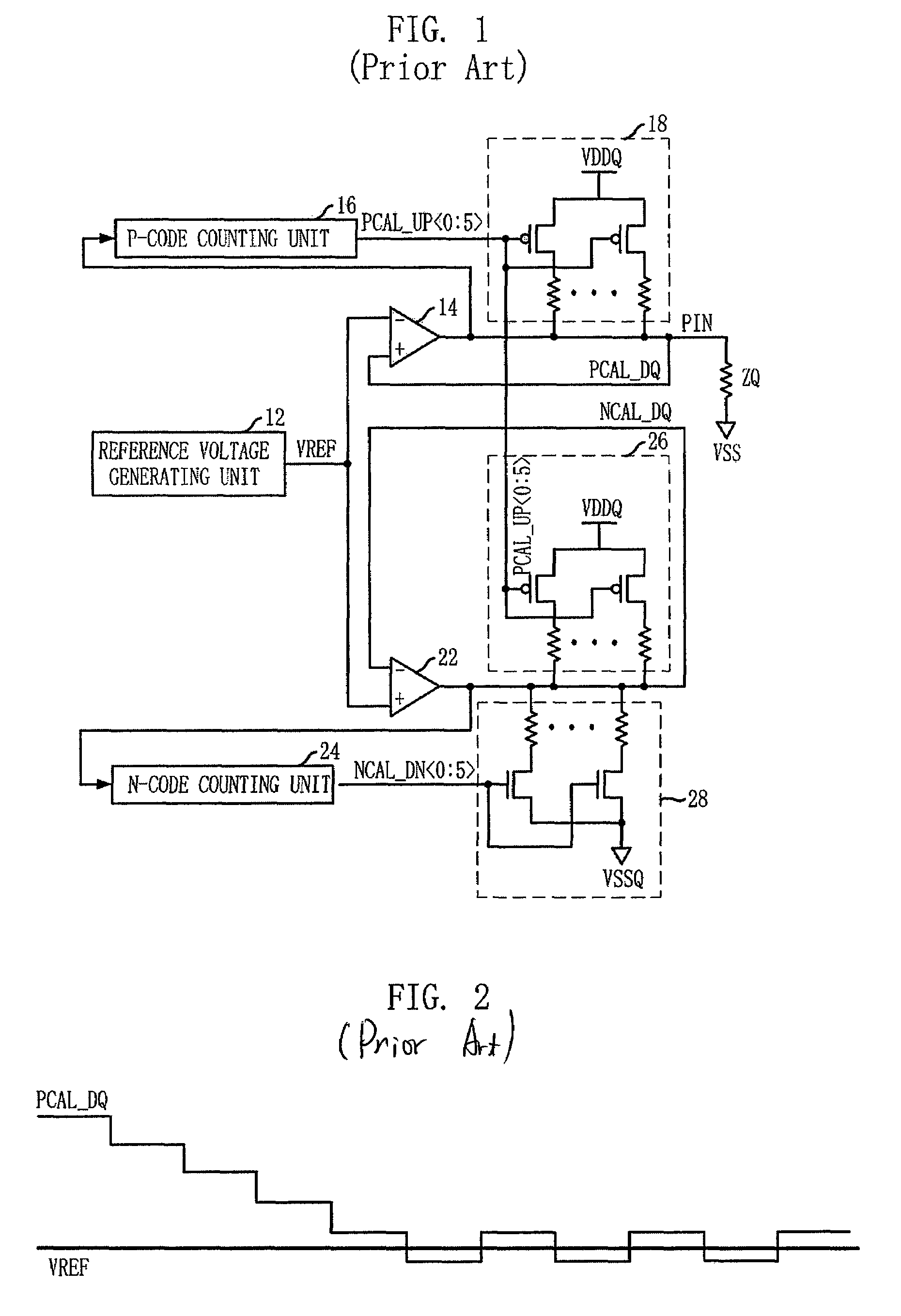
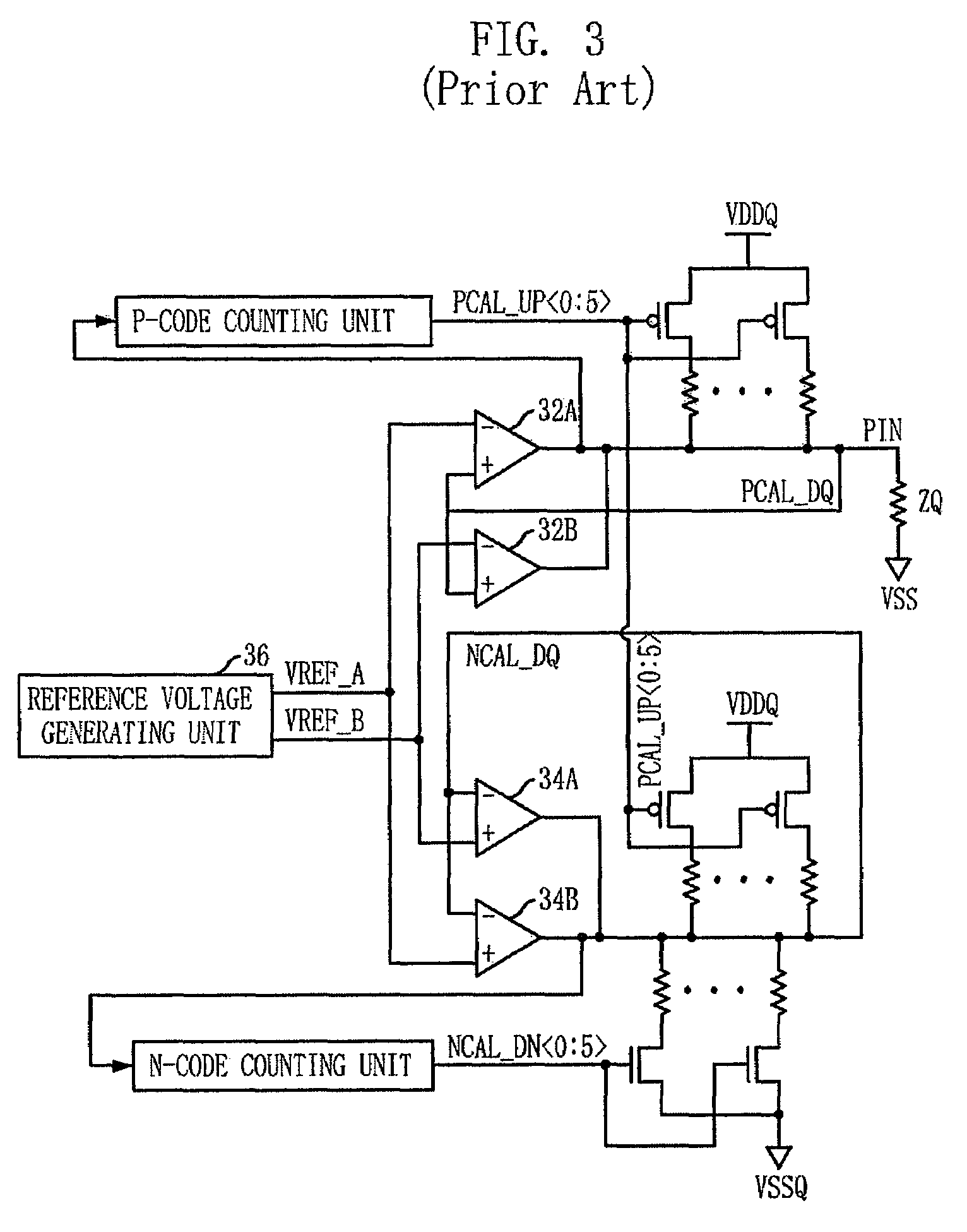
InactiveUS7038486B2Improve accuracyReduce yieldInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A plurality of sets of circuits are provided, each of which generates an impedance code through the use of an impedance control circuit in association with a resistive element connected to an external terminal, and each of which varies the impedance in accordance with such an impedance code. The impedance control circuit includes an impedance comparator which is formed equivalently to the resistive element and the plurality of sets of circuits, and which performs an impedance comparison with each of a plurality of replica circuits to form an up signal that increases the impedance and a down signal that decreases the impedance. Counters are provided adjacent to the individuals of the plurality of sets of circuits to thereby generate the impedance codes in response to the up signal and the down signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Output buffer with switchable output impedance
ActiveUS20070216445A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid unnecessary power consumptionInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitNormal mode
An output buffer with a switchable output impedance designed for driving a terminated signal line. The buffer includes a drive circuit, and a means for switching the output impedance of the drive circuit between a first, relatively low output impedance when the output buffer is operated in a ‘normal’ mode, and a second output impedance which is greater than the first output impedance when operated in a ‘standby’ mode. By increasing the drive circuit's output impedance while in ‘standby’ mode, power dissipation due to the termination resistor is reduced. When used in a memory system, additional power savings may be realized by arranging the buffer such that the increased impedance in ‘standby’ mode shifts the signal line voltage so as to avoid the voltage range over which a line receiver's power consumption is greatest.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
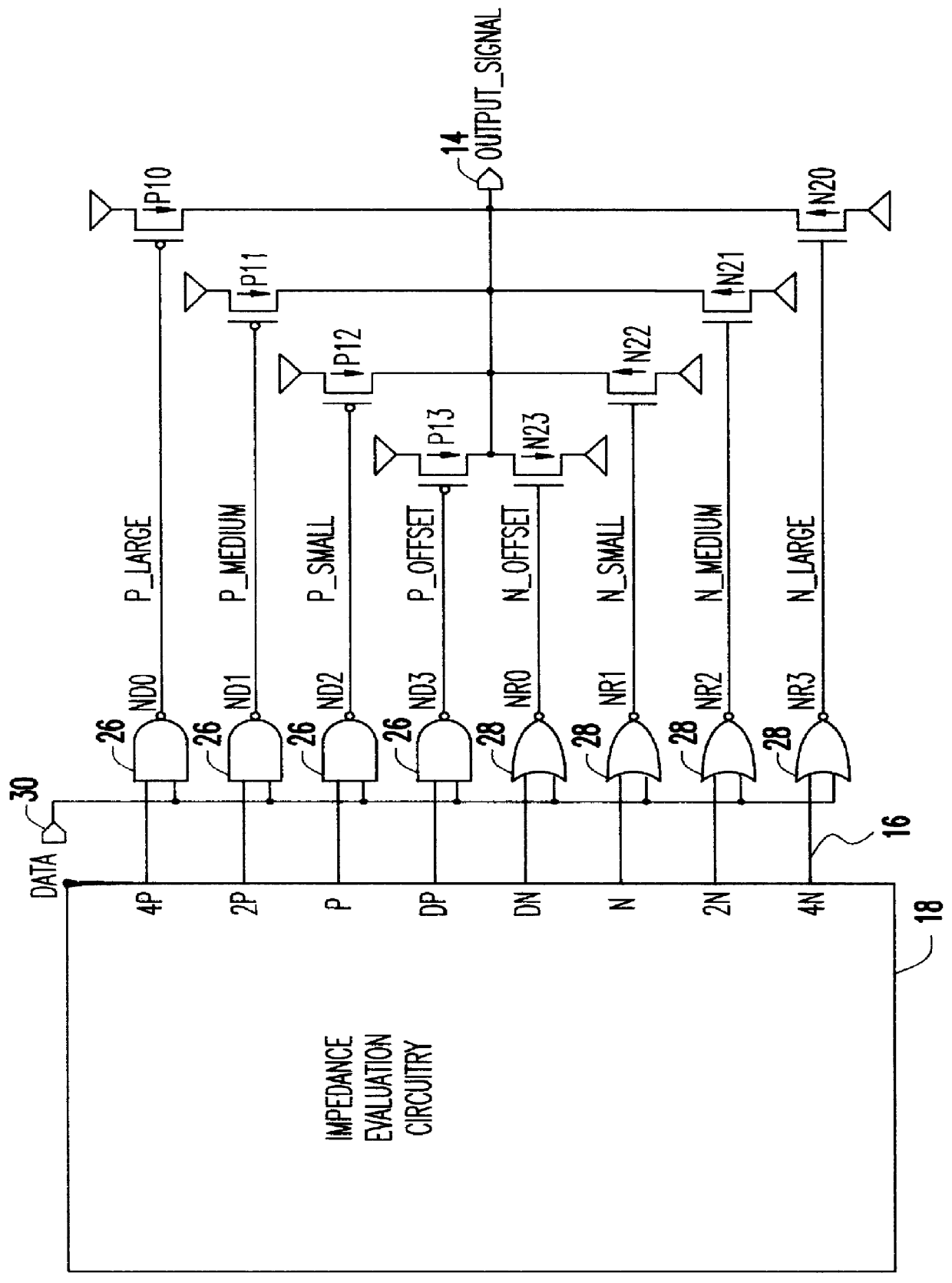
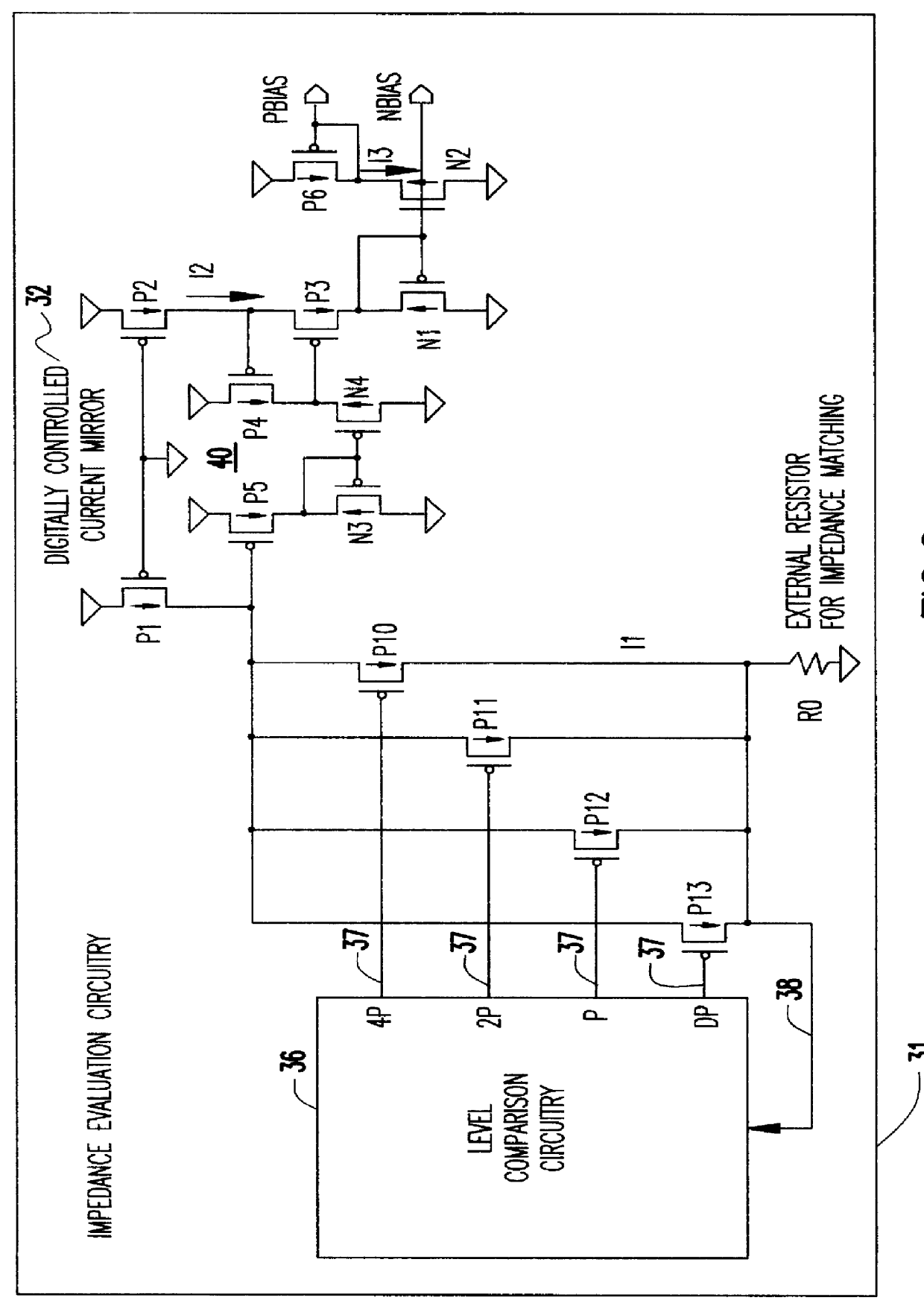
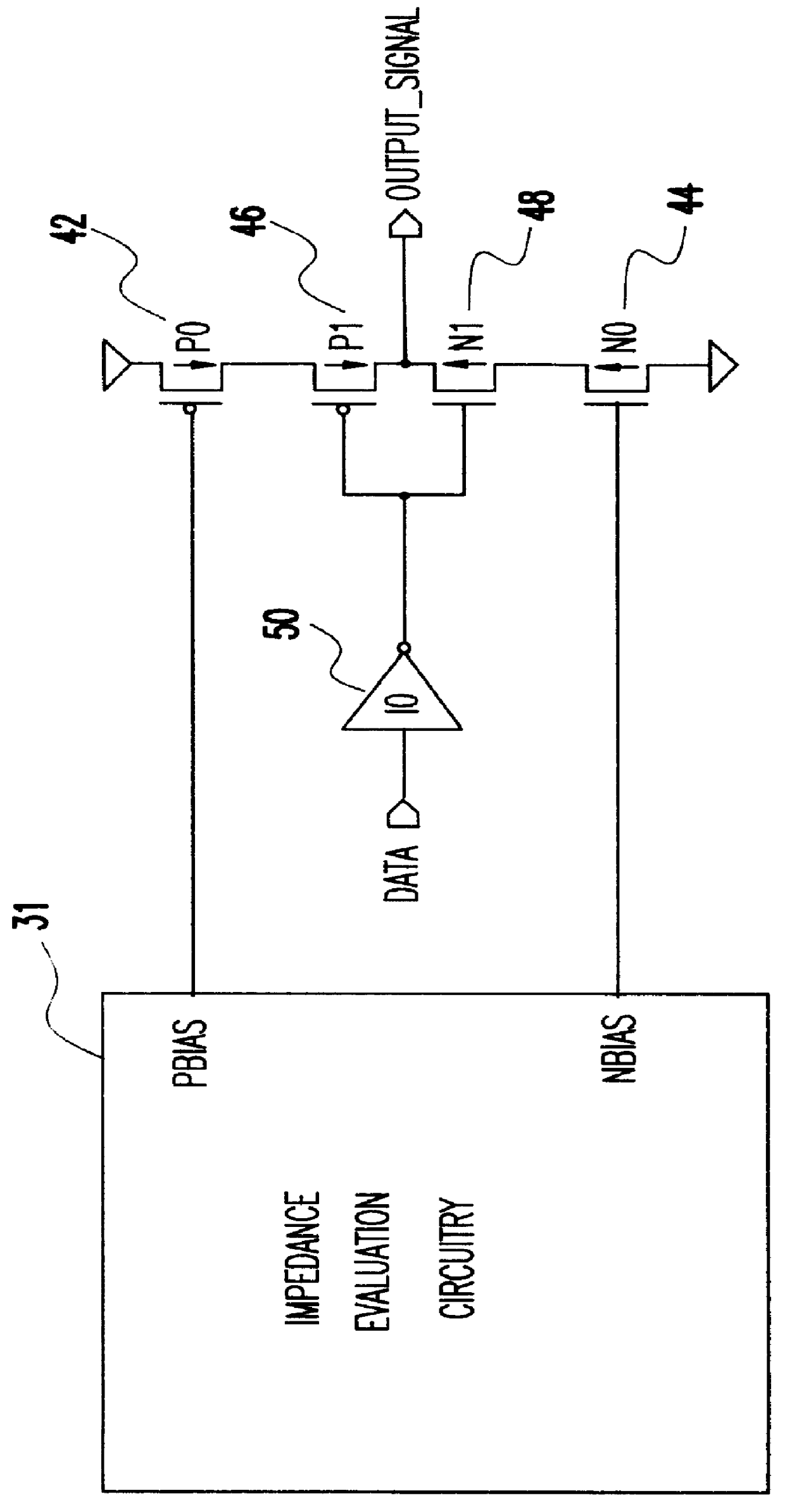
Variable impedance output driver circuit using analog biases to match driver output impedance to load input impedance
InactiveUS6133749AInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
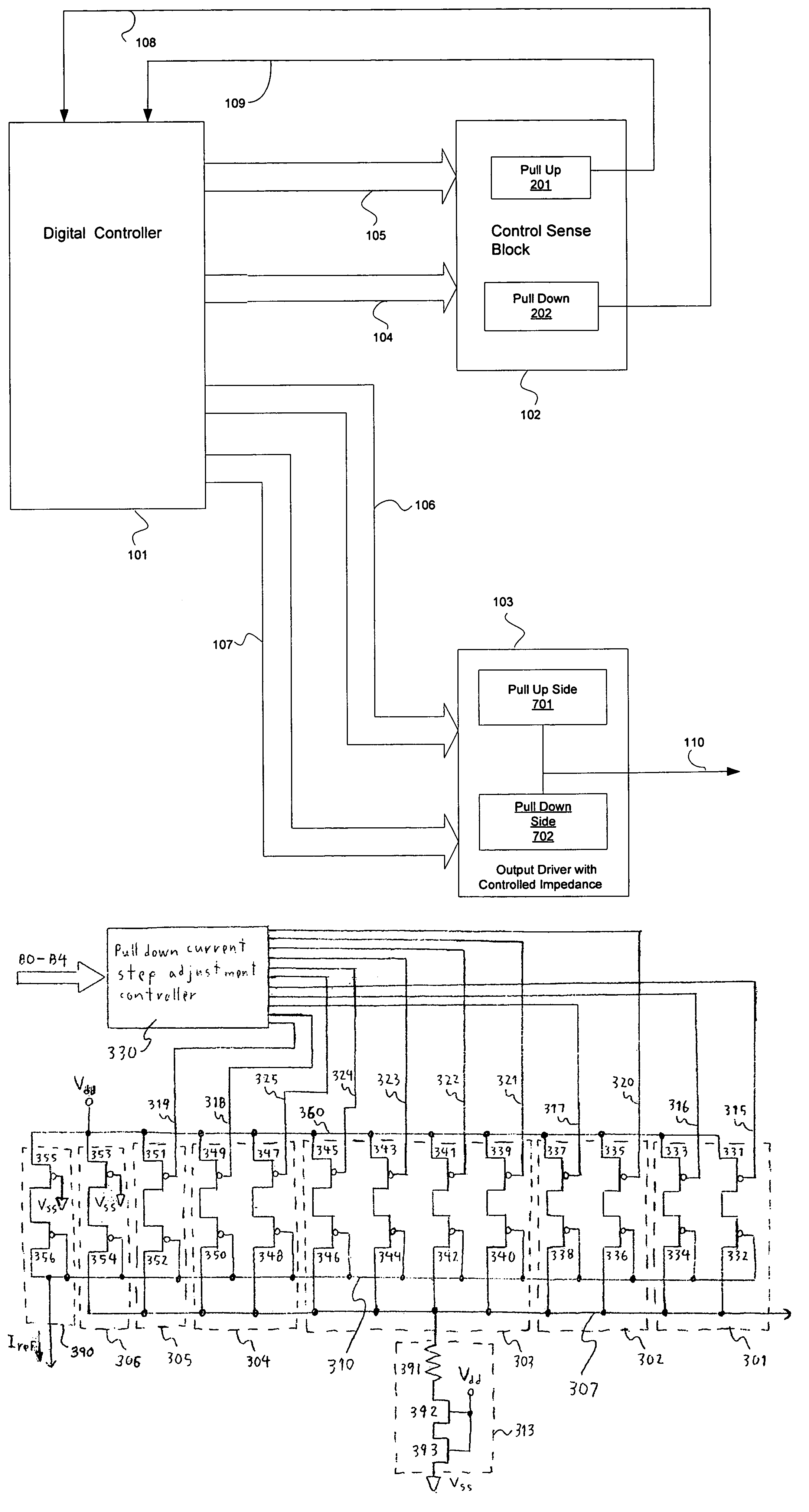
A programmable variable impedance output driver circuit uses analog biases to match driver output impedance to load input impedance. A current mirror is used to obtain a measurement of an external resistance value for matching the impedance of a driven load. The mirrored current generates the voltage "NBIAS" when passed through the resistively connected NFET. Similarly, the current is again mirrored and passed through a resistively connected PFET resulting in the voltage "PBIAS". The analog bias voltages, NBIAS and PBIAS are used to vary the impedance of complementary FETs in an impedance matched driver for a high degree of dI / dt control. The driver provides a high degree of flexibility because its turn-on and turn-off characteristics do not depend on a combination of digital control signals connected directly to the driving FETs as in the prior art. Instead, the PBIAS and NBIAS signals provide analog controls which may be applied to single transistors whose impedance changes as PBIAS and NBIAS increase or decrease.
Owner:IBM CORP
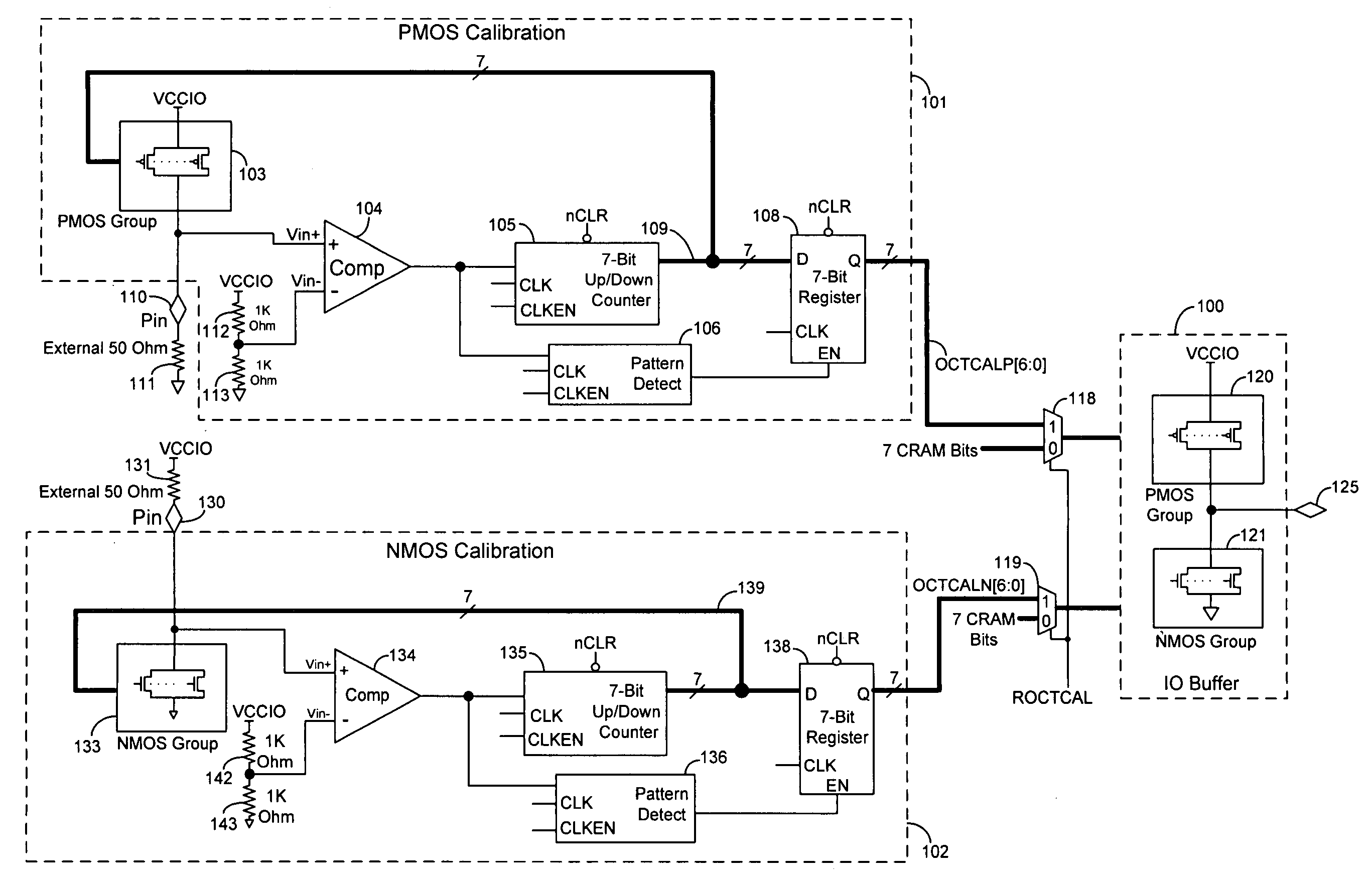
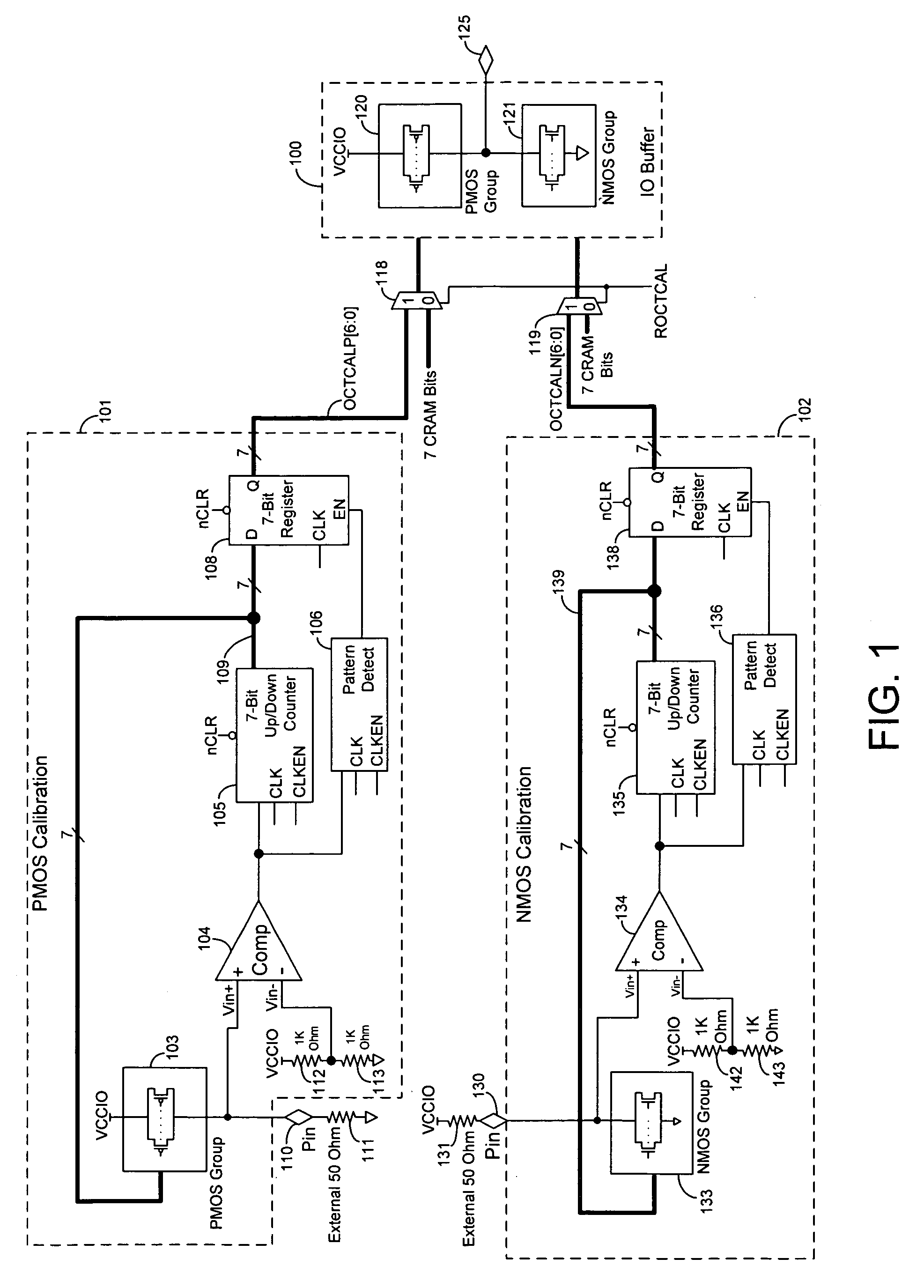
On-chip termination with calibrated driver strength
InactiveUS7221193B1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Techniques are provided for controlling an on-chip termination resistance in an input or output (IO) buffer using calibration circuits. Each calibration circuit monitors the voltage between an external resistor and a group of on-chip transistors. When the effective resistance of the group of transistors matches the external resistance, the calibration circuit causes the effective resistance of drive transistors in the IO buffer to match the effective resistance of the group of on-chip transistors.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
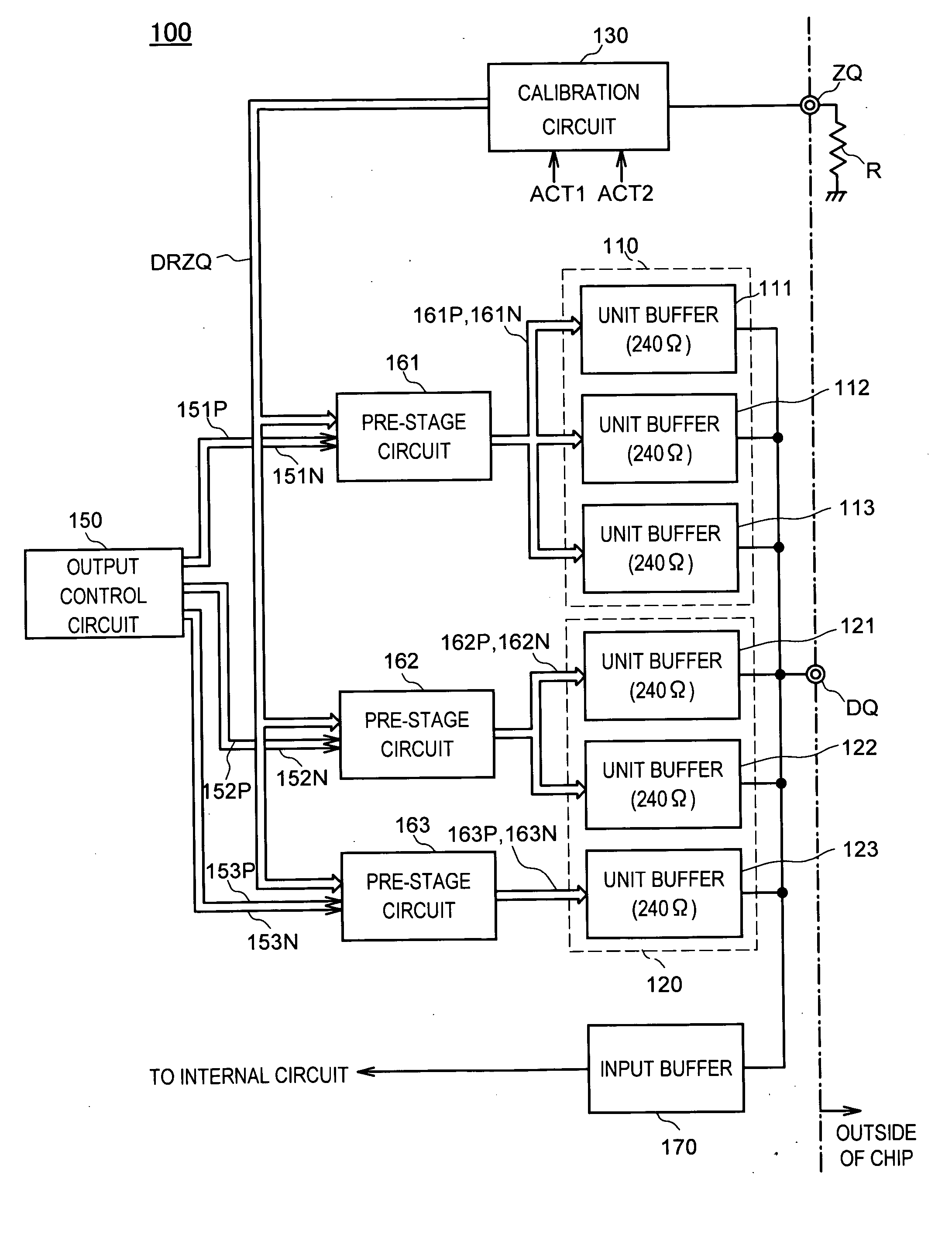
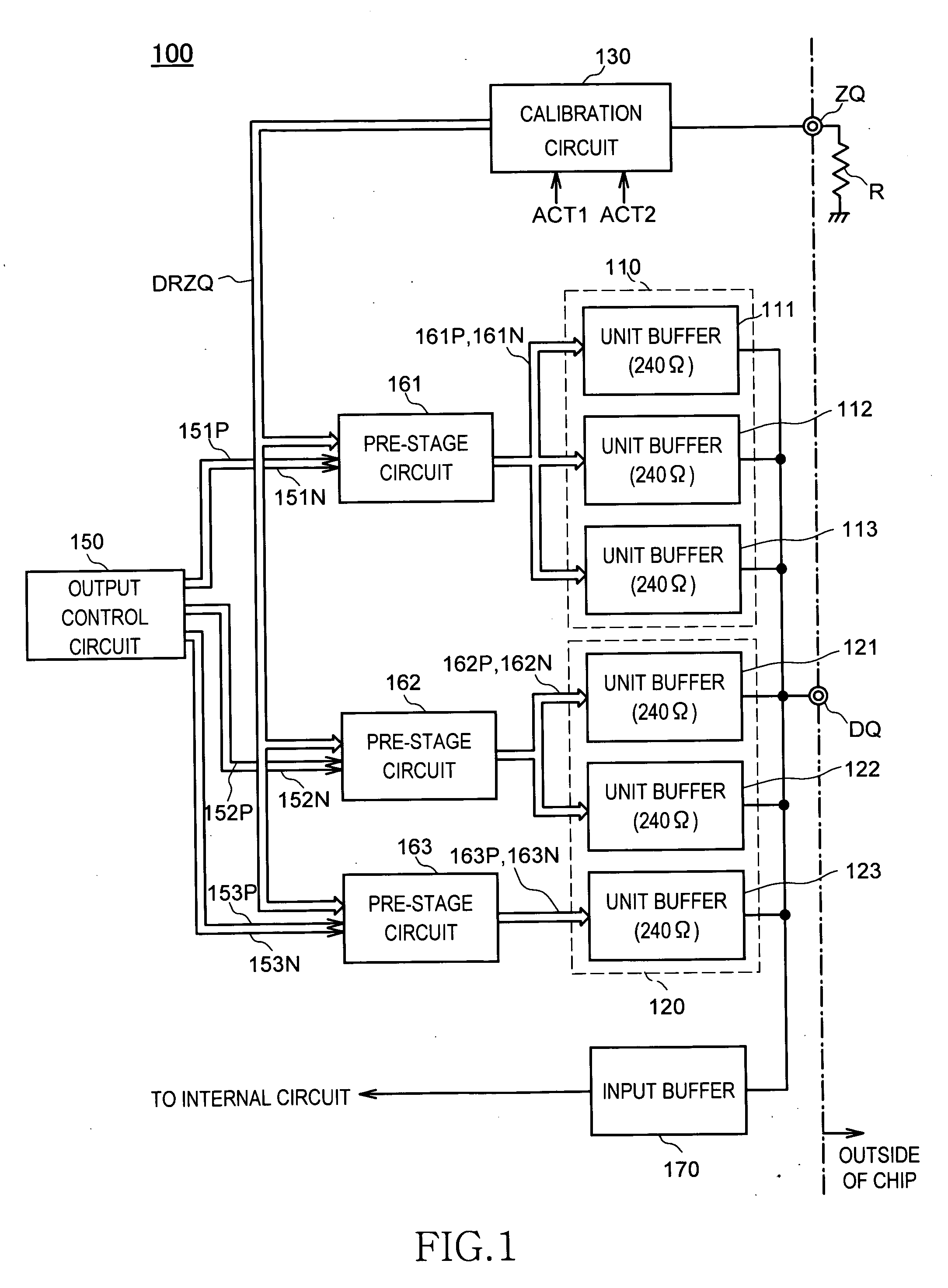
Output circuit for semiconductor device, semiconductor device having output circuit, and method of adjusting characteristics of output circuit
ActiveUS20060158198A1Reduce calibration timeReduce circuit sizeInput/output impedence modificationImpedence matching networksEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
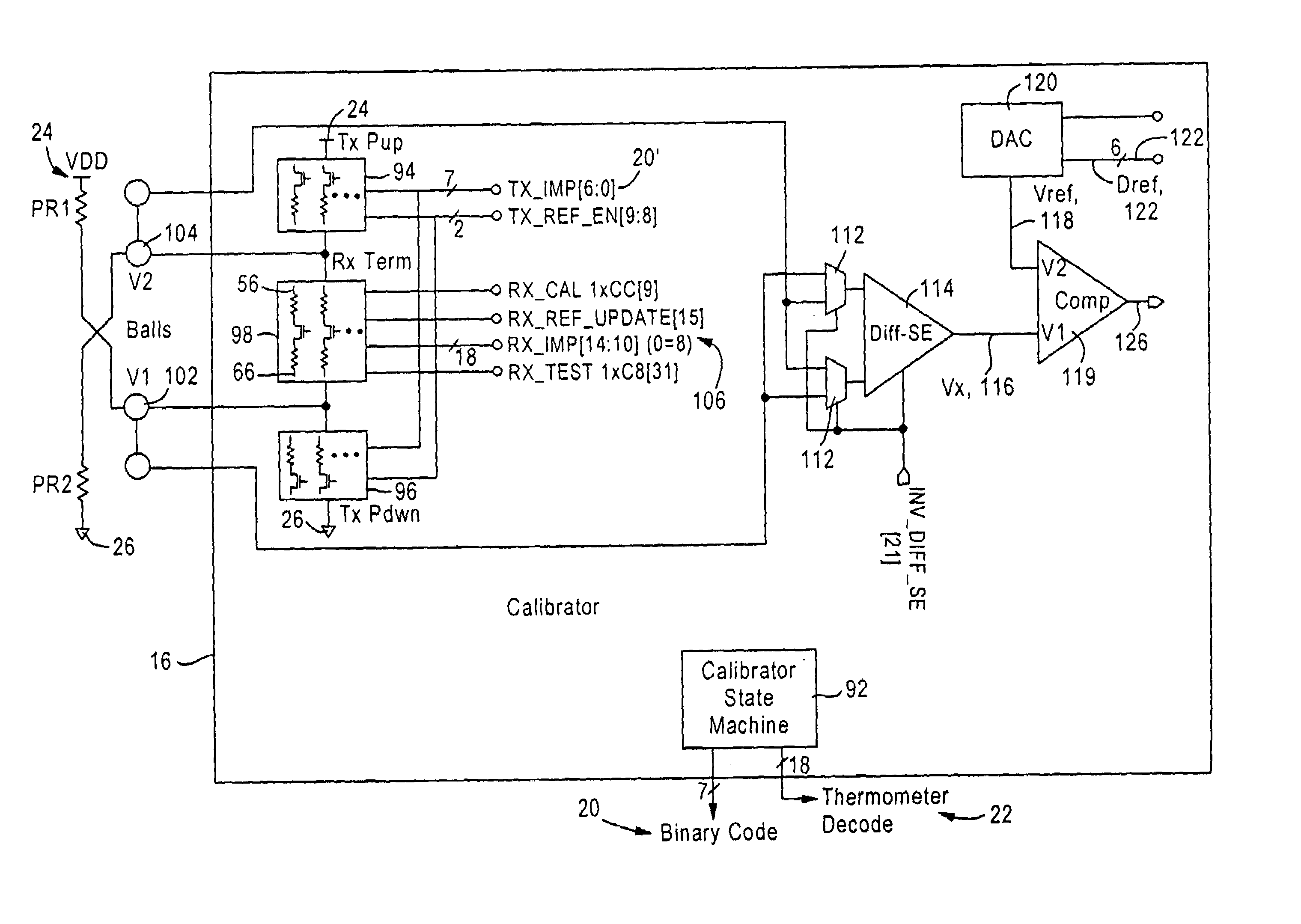
Voltage mode transceiver having programmable voltage swing and external reference-based calibration
ActiveUS7135884B1Reduce input capacitanceImprove the level ofInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsExternal referenceInput impedance
An integrated device includes a voltage mode transmit driver for matching an output impedance to an output transmission line based on a binary code, an input termination module configured for matching an input impedance to an input transmission line based on an input impedance calibration value using thermometer-based decoding. The voltage mode transmit driver includes, for each differential output signal, a resistor network circuit having pull-up circuits and pull-down circuits for changing the voltage on the differential output signal, and having binary weighted resistance values relative to each other. The input termination module includes pull-up circuits and pull-down circuits having inverse hyperbolic resistance values relative to each other, and using thermometer-based decoding to ensure a linear change in input impedance during transitions in the input impedance calibration value. A calibration circuit generates the binary code and the input impedance calibration value based on replicas of the pull-up and pull-down circuits.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
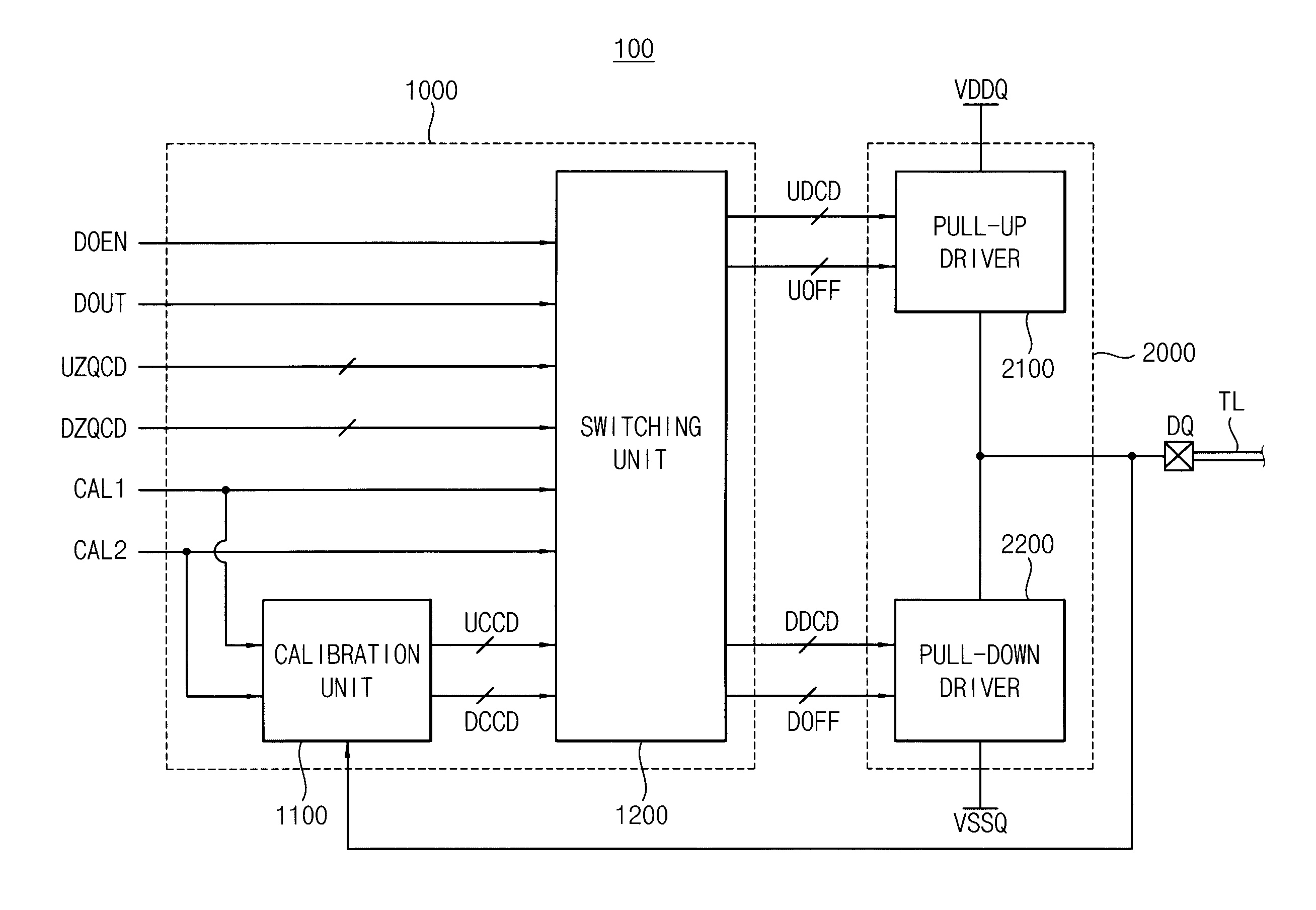
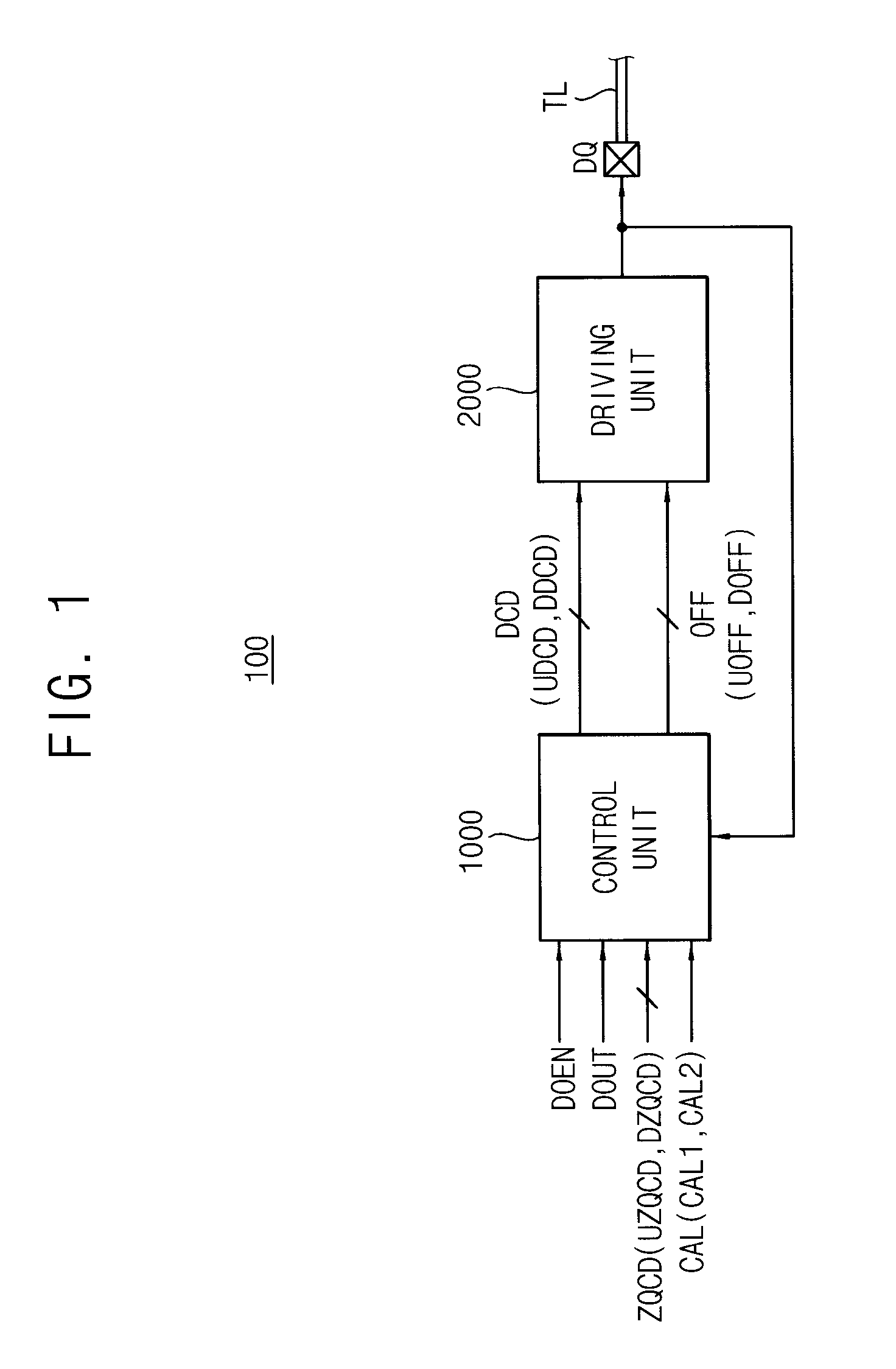
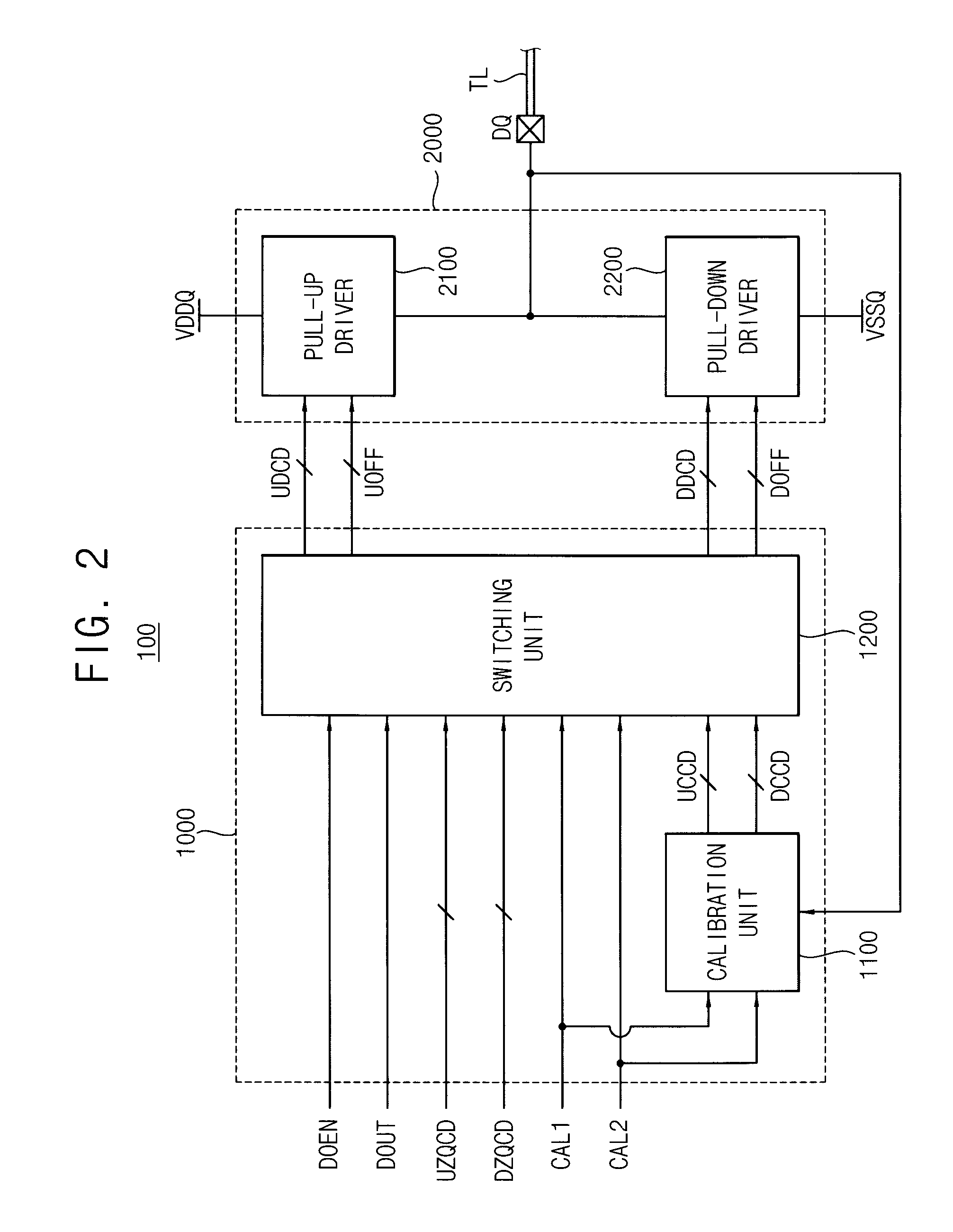
Data output buffer and memory device
A data output buffer includes a driving unit and a control unit. The driving unit selectively performs a termination operation that provides a termination impedance to a transmission line coupled to an external pin, and a driving operation that provides a drive impedance to the transmission line while outputting read data. The control unit adjusts a value of the termination impedance and a value of the drive impedance based on an output voltage at the external pin during a termination mode, and controls the driving unit to selectively perform one of the termination operation and the driving operation during a driving mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for dynamic impedance matching
InactiveUS7068065B1Improve performanceHigh levelInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsEngineeringImpedance matching
An integrated circuit provides dynamic, on chip resistor trimming, including a digital control loop for stabilizing impedance matching among multiple devices communicatively linked over a data transmission line. The digital control loop stabilizes input / output impedance matching of various devices to within a precise ohmic range that is far narrower than standard process variations, such as sheet resistance, within the components themselves. The impedance matching circuit also overcomes EMI problems normally associated with digital control and thus provides dynamic on-chip digital control without non-linearity and with tighter tolerance than is presently possible. Accordingly, the circuit boosts performance of peripheral devices that communicate over a standard USB port, without the need for a computer as a go between or intermediate interface. This makes device to device communication possible as between USB On-the-Go capable devices.
Owner:TAKLA NABIL
Output circuit for semiconductor device, semiconductor device having output circuit, and method of adjusting characteristics of output circuit
ActiveUS7215128B2Reduce calibration timeReduce circuit sizeInput/output impedence modificationImpedence matching networksEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Semiconductor device and driver control method
ActiveUS7768312B2Enhanced signalInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceP channel
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Transmit based equalization using a voltage mode driver
A driver circuit. In one embodiment, the driver circuit includes a plurality of pull-up circuits and a plurality of pull-down circuits. The driver circuit also includes control logic that is coupled to activate / deactivate the pull-up and pull-down circuits. The driver circuit may perform emphasized signal transmissions having a voltage swing of a first magnitude or de-emphasized signal transmissions having a voltage swing of a second magnitude, wherein the first magnitude is greater than the second magnitude. The control logic is further configured to activate and / or deactivate pull-up and / or pull-down circuits such that the driver circuit output impedance in the emphasized mode is substantially equal to the output impedance in the de-emphasized mode.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
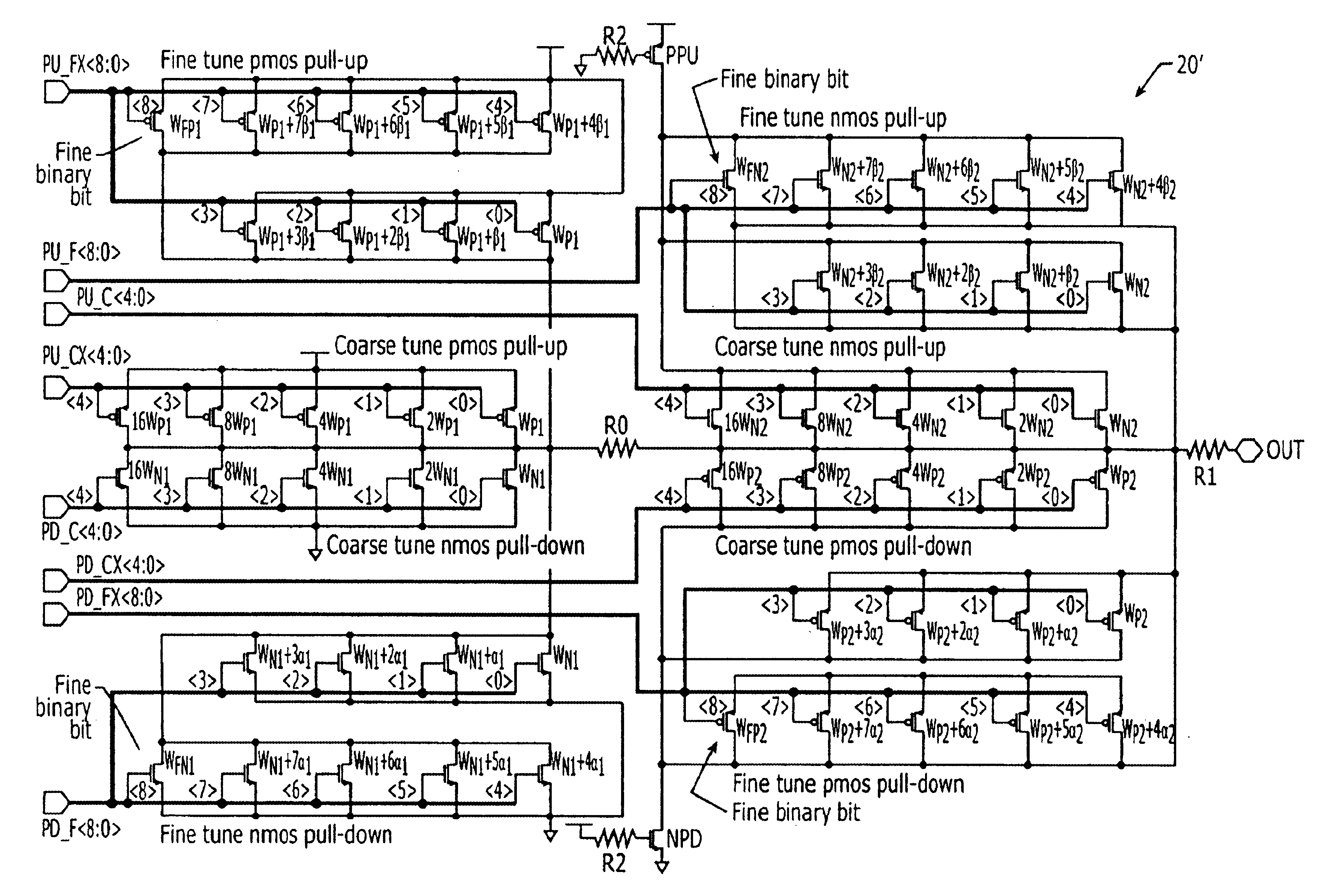
Impedance-matched output driver circuits having linear characteristics and enhanced coarse and fine tuning control
InactiveUS6894529B1Linear characteristicImprove output linearityInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitImpedance matching
Impedance-matched output driver circuits include a first totem pole driver stage and a second totem pole driver stage. The first totem pole driver stage includes at least one PMOS pull-up transistor and at least one NMOS pull-down transistor therein that are responsive to a first pull-up signal and a first pull-down signal, respectively. The second totem pole driver stage has at least one NMOS pull-up transistor and at least one PMOS pull-down transistor therein that are responsive to a second pull-up signal and second pull-down signal, respectively. The linearity of the output driver circuit is enhanced by including a first resistive element that extends between the first and second totem pole driver stages. The first resistive element has a first terminal, which is electrically coupled to drain terminals of the at least one PMOS pull-up transistor and the at least one NMOS pull-down transistor in the first totem pole driver stage, and a second terminal, which is electrically coupled to source terminals of the at least one NMOS pull-up transistor and the at least one PMOS pull-down transistor in the second totem pole driver stage.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Impedance matching circuit, high speed semiconductor integrated circuit employing the same and computer system employing the integrated circuit
InactiveUS6188237B1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsComputerized systemImpedance matching
A high speed impedance matching circuit suitable for use in high speed semiconductor integrated circuits matches the output impedance of a semiconductor device to the impedance of other devices such a computer system bus thereby reducing signal reflections caused by impedance mismatches and which can adversely affect the operation of a high speed computer system. The impedance of an output buffer is matched to the impedance of an external resistor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device, system with semiconductor device, and calibration method
InactiveUS20110102073A1Shorten the time periodReduce power consumptionInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsPower semiconductor devicePower flow
Variations of the impedance of each output driver of a semiconductor device can be reduced, and high-speed calibration is achieved. A calibration circuit including a replica circuit having the same configuration as each pull-up circuit or pull-down circuit included in an output driver of a semiconductor device is provided within a chip. During a first calibration operation, the replica circuit is provided with voltage conditions that allow the maximum current to flow through the output driver so that an impedance of the replica circuit is equal to a value of an external resistor. During a second calibration operation, table parameters obtained in the first calibration operation are used to adjust the impedance of the output driver without use of the replica circuit.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
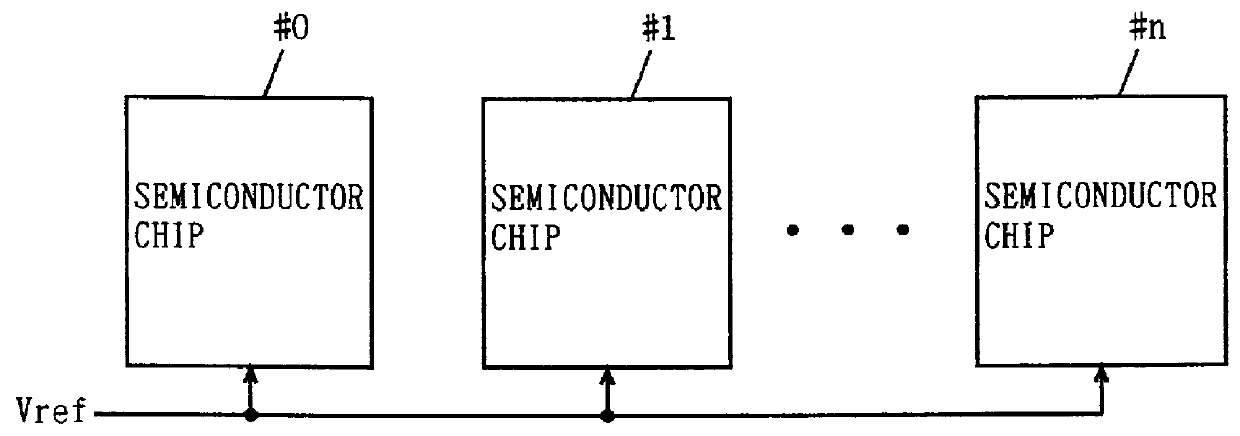
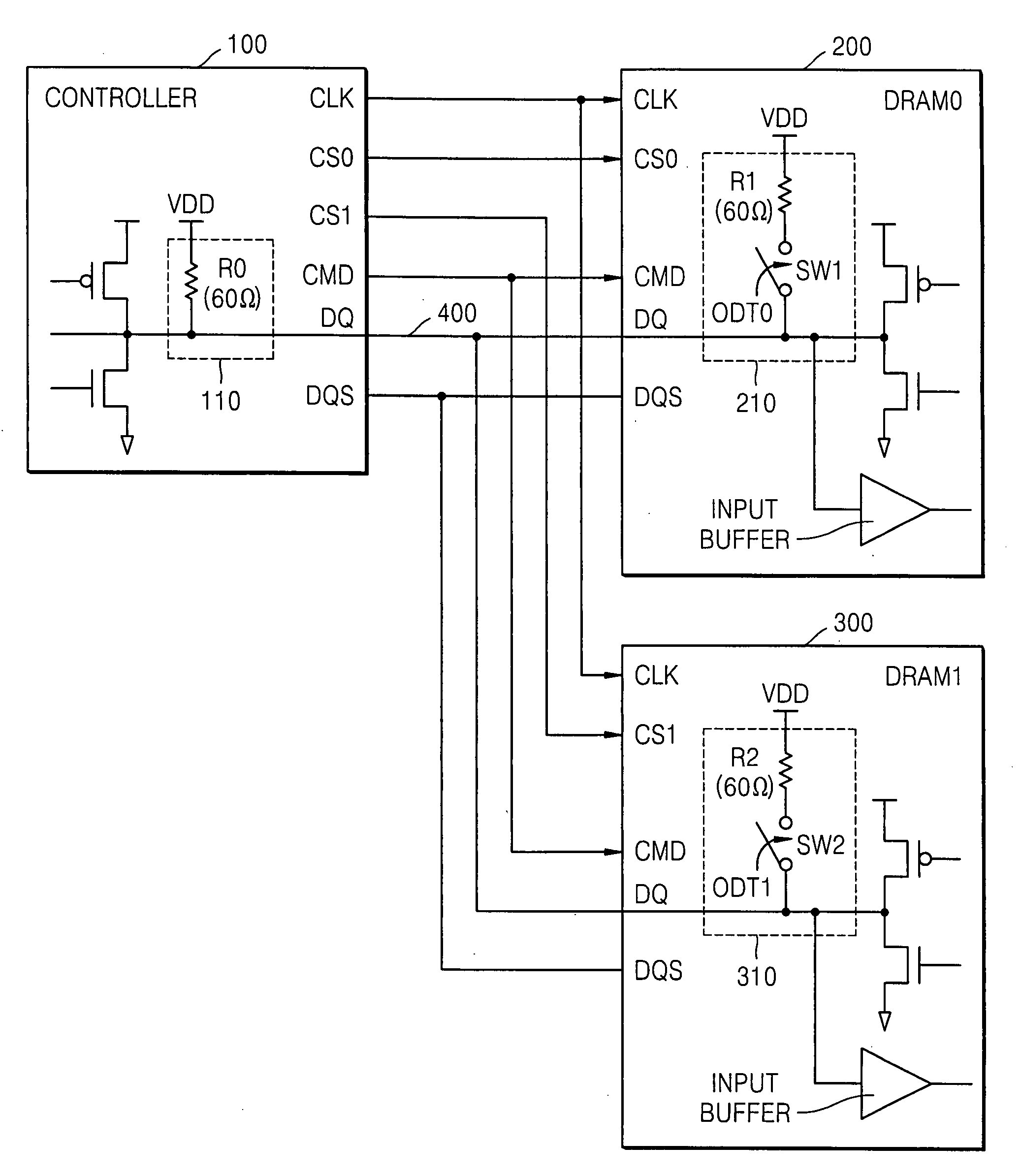
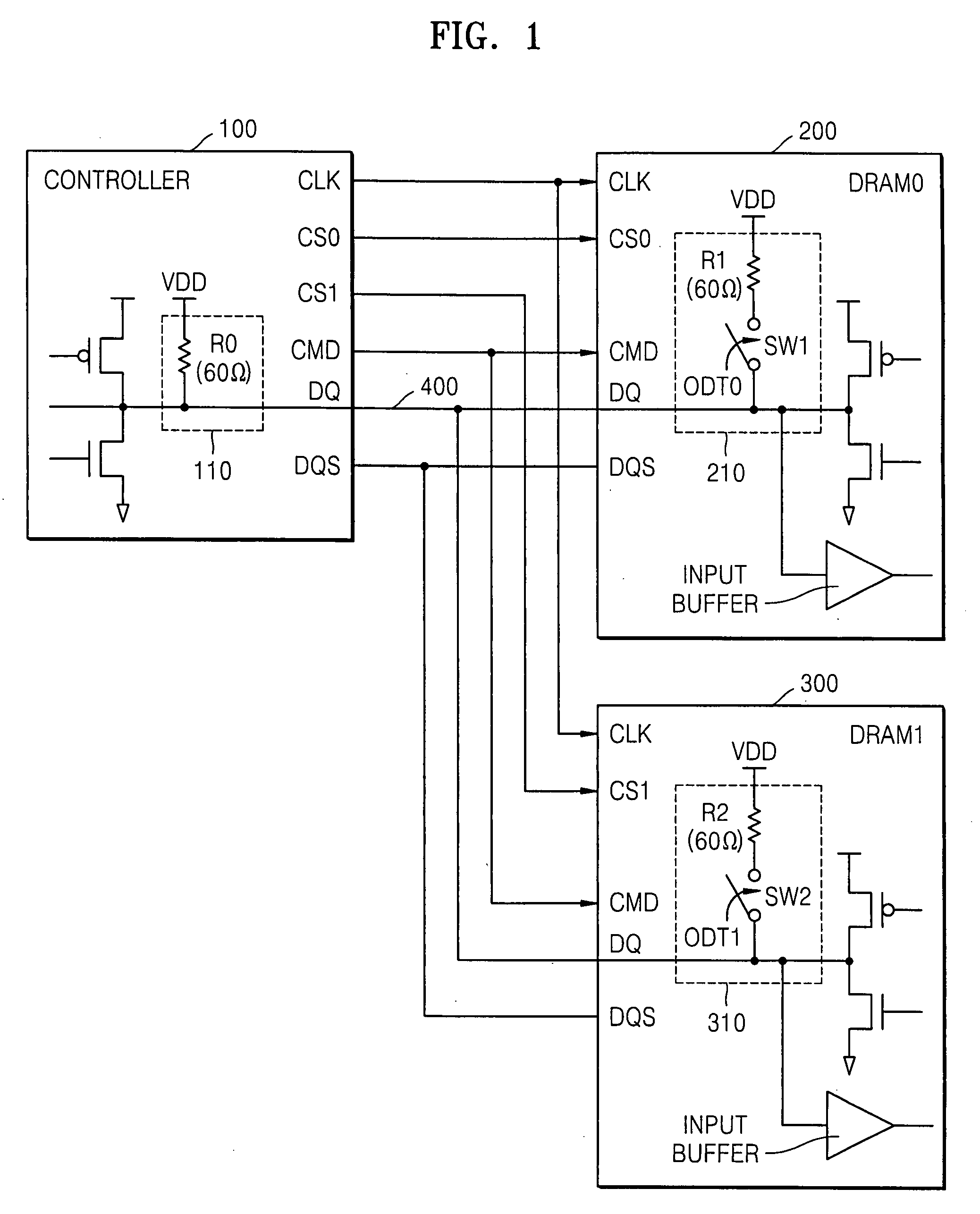
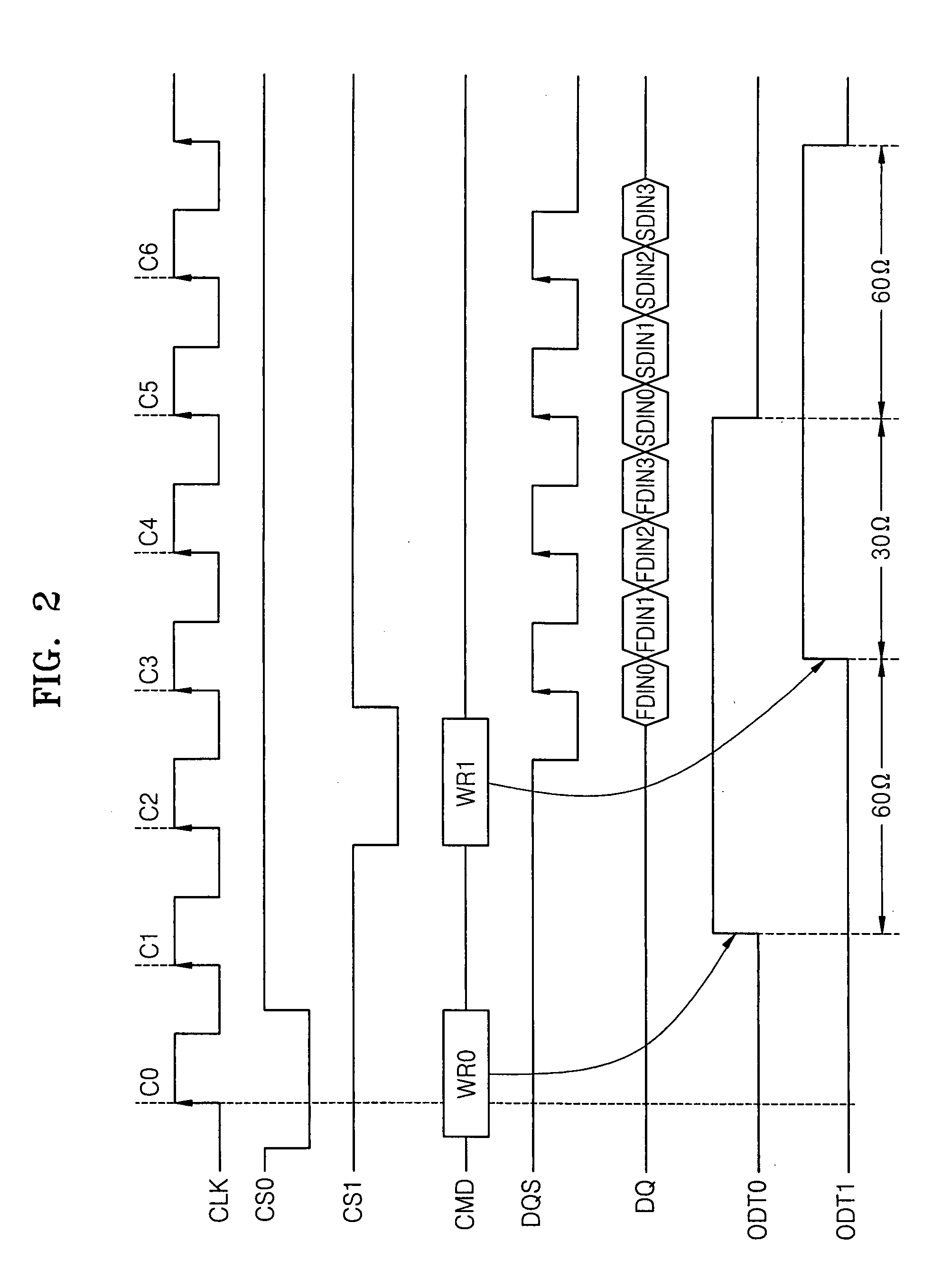
Method of controlling on-die termination of memory devices sharing signal lines
ActiveUS20080030221A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsControl memoryOn-die termination
A method of controlling On-Die Termination (ODT) resistors of memory devices sharing signal lines is provided. The ODT controlling method comprises setting an ODT control enable signal of each of the memory devices and address / command or data termination information to a mode register of the corresponding memory device, and controlling resistances of ODT resistors of the signal lines in the memory devices in response to the address / command or data termination information and termination addresses. When only one of the memory devices is activated, ODT resistors of the activated memory device are set to a first resistance. When all the memory devices are activated, ODT resistors of the memory devices are set to a second resistance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
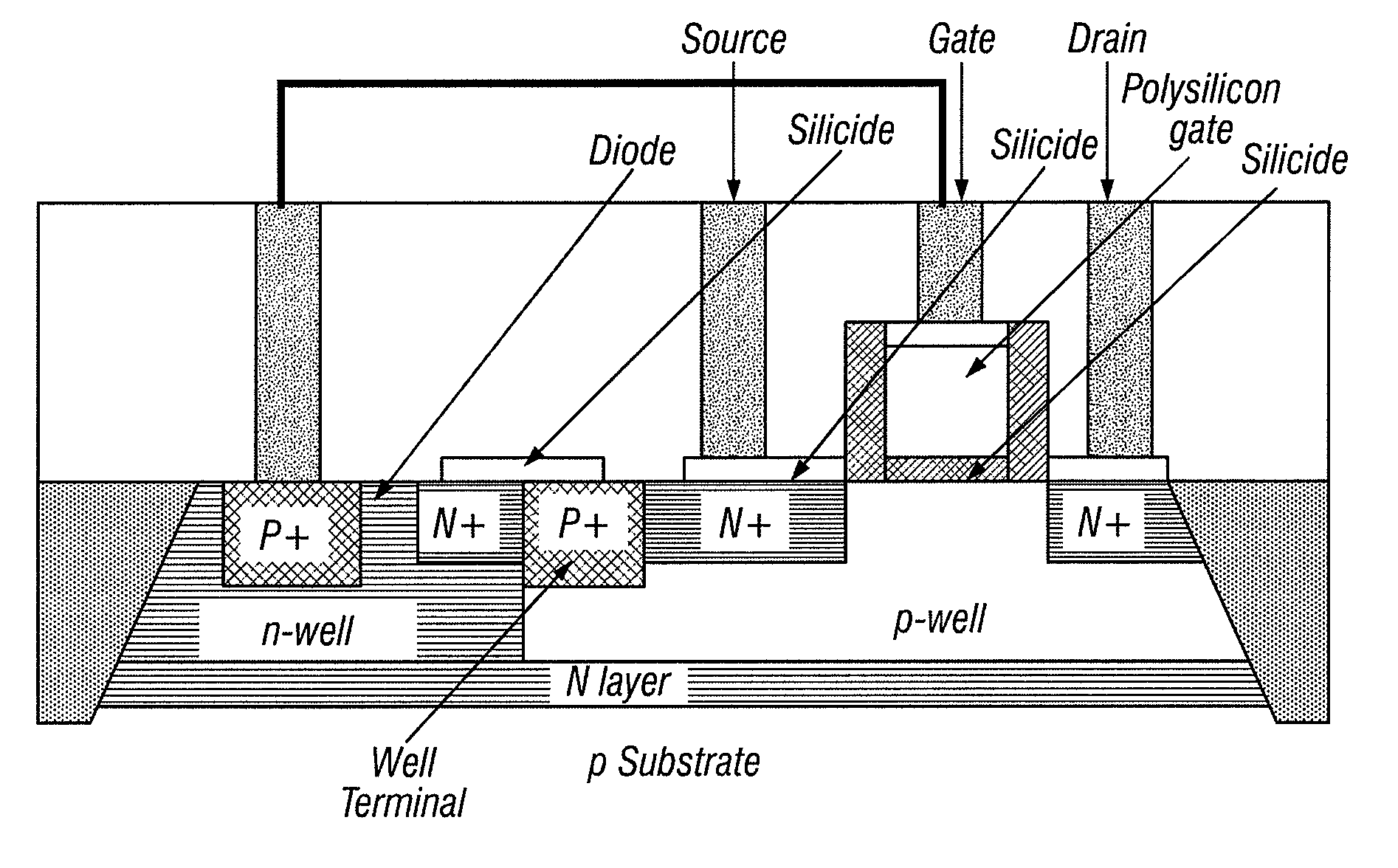
Apparatus and method for improving drive-strength and leakage of deep submicron MOS transistors
InactiveUS7683433B2Increase drive strengthReduce leakage currentTransistorInput/output impedence modificationCMOSEngineering
An apparatus and method of manufacture for metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors is disclosed. Devices in accordance with the invention are operable at voltages below 2V. The devices are area efficient, have improved drive strength, and have reduced leakage current. A dynamic threshold voltage control scheme comprised of a forward biased diode in parallel with a capacitor is used, implemented without changing the existing MOS technology process. This scheme controls the threshold voltage of each transistor. In the OFF state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage of the transistor increases, keeping the transistor leakage to a minimum. In the ON state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage decreases, resulting in increased drive strength. The invention is particularly useful in MOS technology for both bulk and silicon on insulator (SOI) CMOS. The use of reverse biasing of the well, in conjunction with the above construct to further decrease leakage in a MOS transistor, is also shown.
Owner:SEMI SOLUTIONS LLC
Input termination for delay locked loop feedback with impedance matching
ActiveUS7898288B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDelay-locked loopEngineering
A reference output circuit for generating an output clock signal for driving signals off of an integrated circuit chip uses a switched terminated load in combination with an output buffer to generate a feedback clock signal, which is used, in combination with a reference input clock signal, to generate the output clock signal. The switched terminated load uses transistors having the same size as transistors in the output buffer. The switched terminated load draws the same DC current as the output buffer. As a result, the switched terminated load and the output buffer have the same electro-migration performance. Pull-up and pull-down MOS impedances of the switched terminated load are easily adjusted during switching periods of the switched terminated load. The design of the switched terminated load minimizes variations in the terminated load impedance due to MOS impedance variations.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Semiconductor device and circuit board having the semiconductor device mounted thereon
InactiveUS20110193590A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsEngineeringElectrical impedance
To provide a semiconductor device including a first replica buffer connected to a calibration terminal, an impedance adjusting circuit that changes an impedance of the first replica buffer according to a comparison result between a potential of the terminal and a reference potential, and an impedance adjusting circuit that changes an impedance of a third replica buffer according to a comparison result between a potential of a connection node of a second replica buffer and the third replica buffer and a potential of the terminal. According to the present invention, both impedances of the first and third replica buffers are adjusted based on the potential of the terminal, and therefore an adjustment error of one of the replica buffers is not superimposed with an adjustment error of the other replica buffer.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
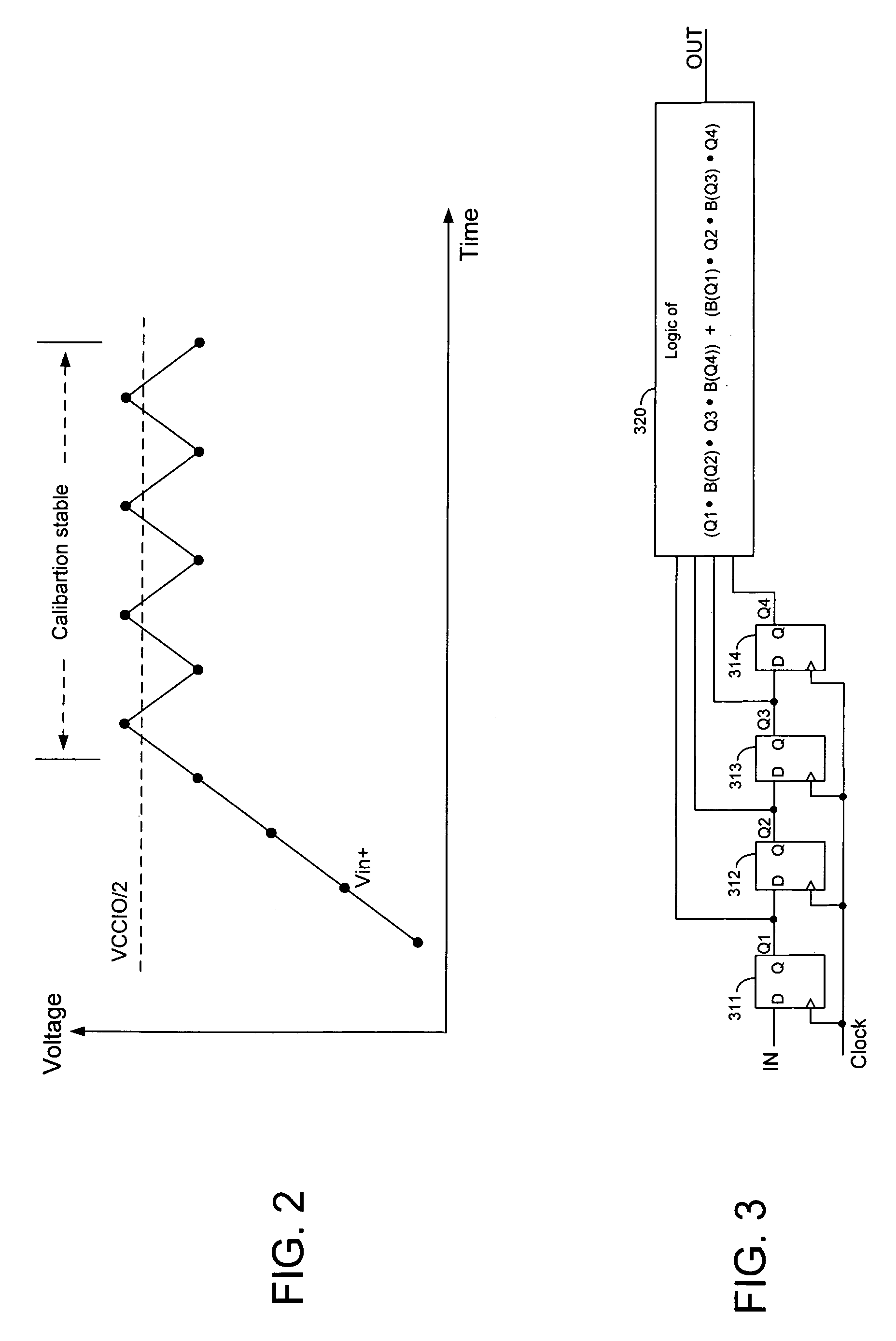
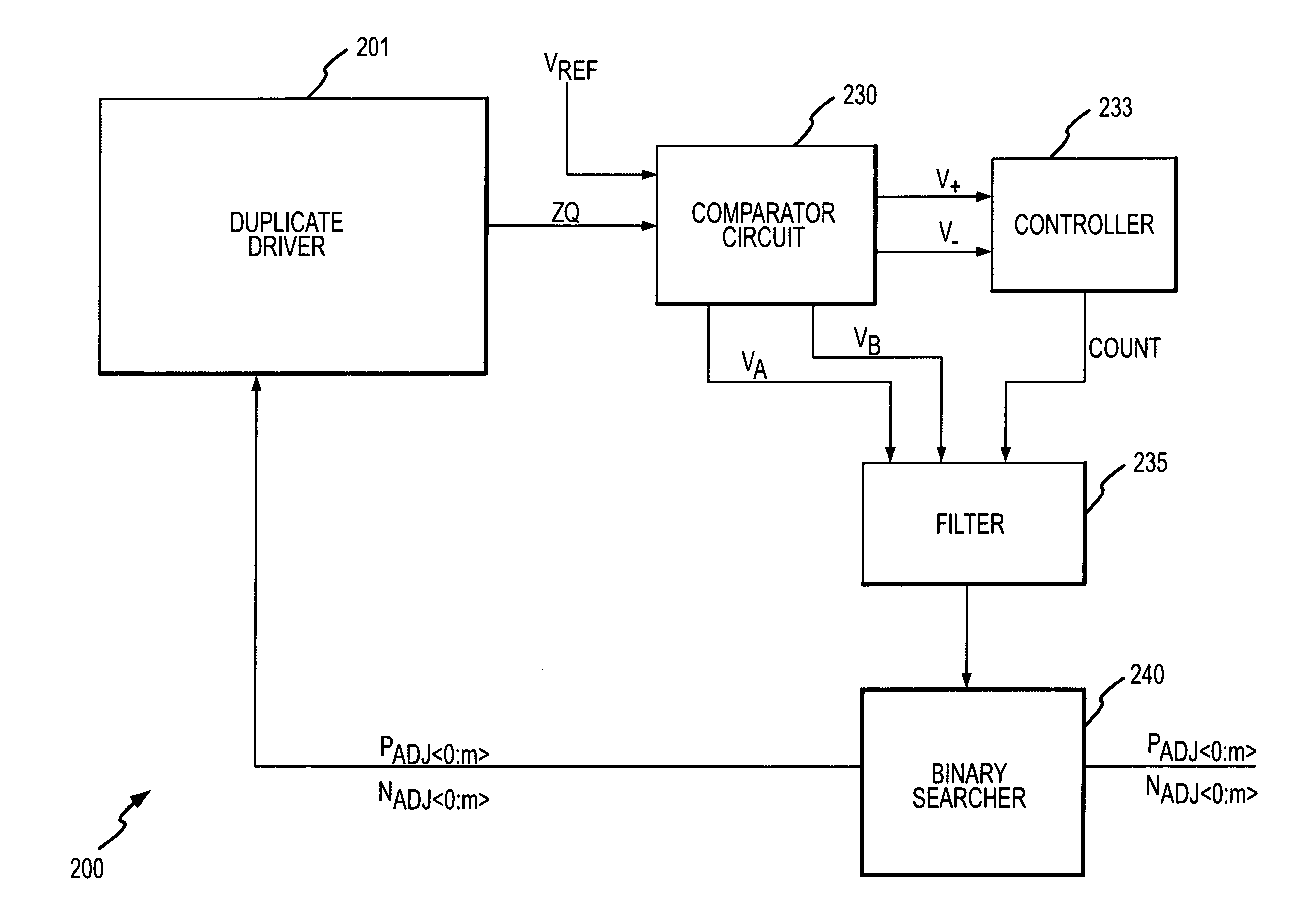
Digital calibration circuits, devices and systems including same, and methods of operation
ActiveUS7459930B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitComparators circuits
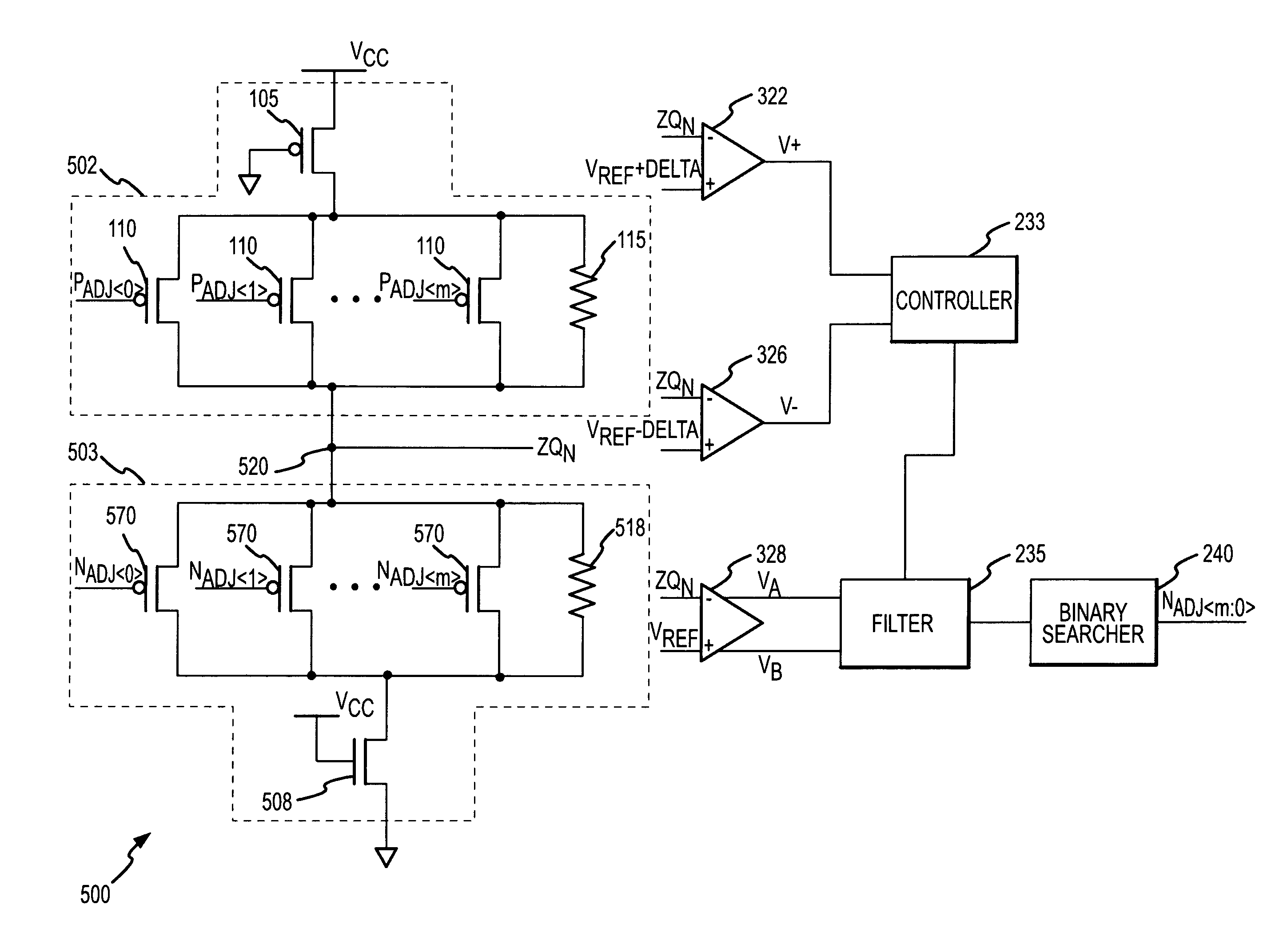
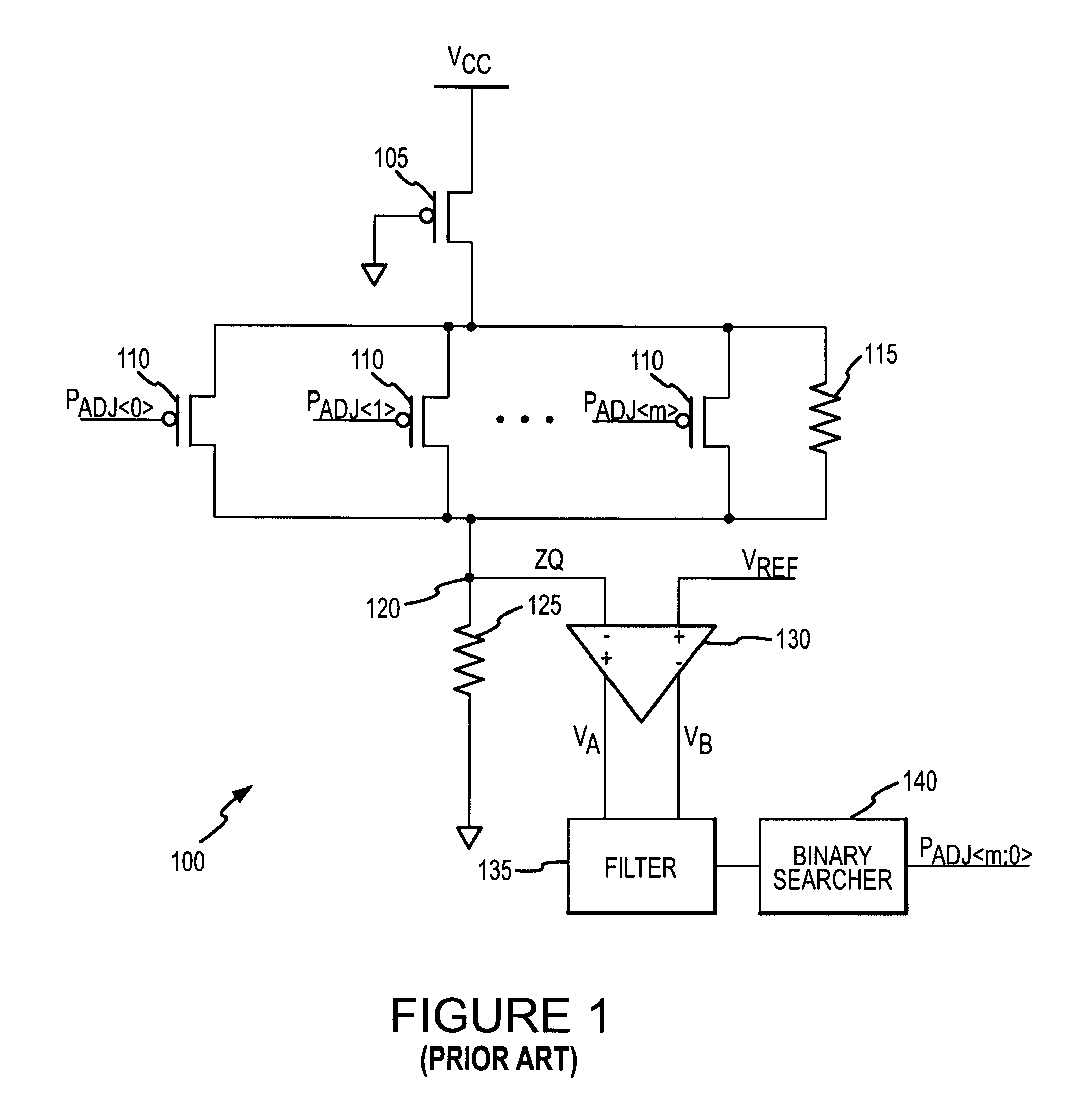
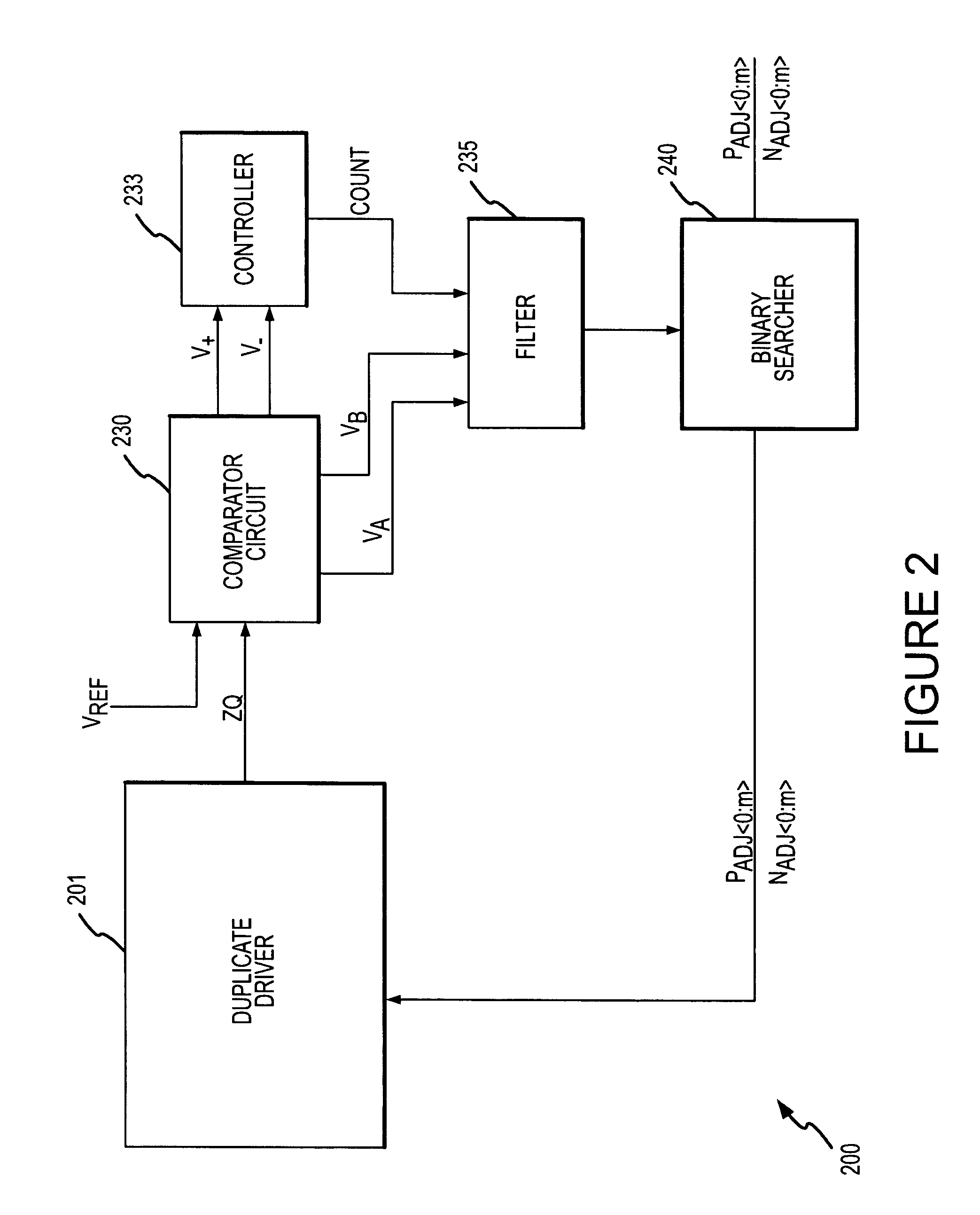
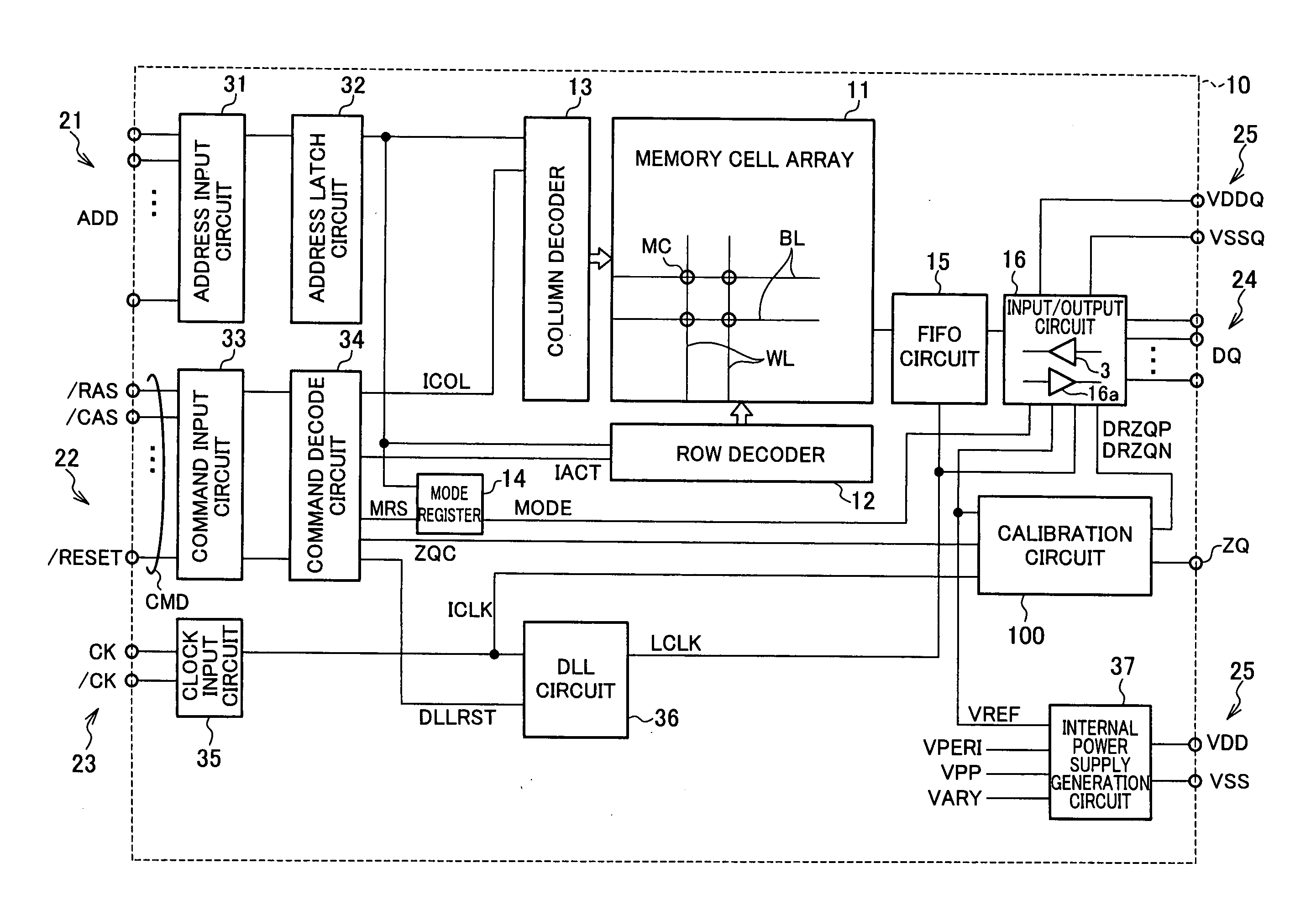
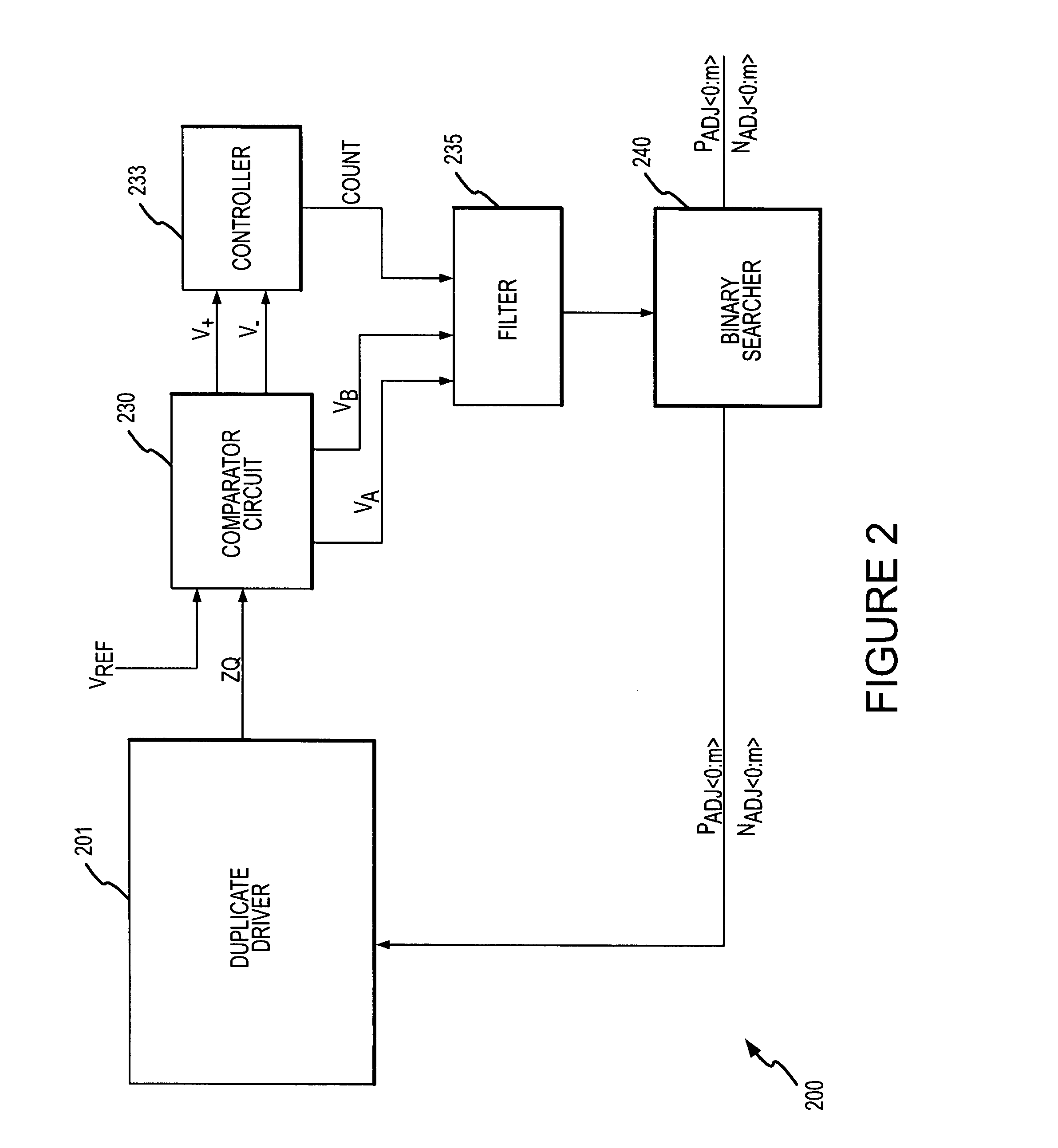
A calibration circuit for matching the output impedance of a driver by calibrating adjustments to the driver is described. The calibration circuit includes a driver circuit with a plurality of calibration transistors configured to receive a plurality of adjustment signals. The calibration circuit also includes a comparator circuit, and a binary searcher. The driver provides a signal corresponding to an output impedance to the comparator circuit. The output impedance signal is compared to a target impedance, and the comparator circuit then provides logic signals to the binary searcher representing whether the output impedance is greater than the target impedance. The binary searcher then selects a type of step size and count direction, in response to the logic signals, to count the number of steps for adjusting the calibration transistors of the driver.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device having impedance calibration function to data output buffer and semiconductor module having the same
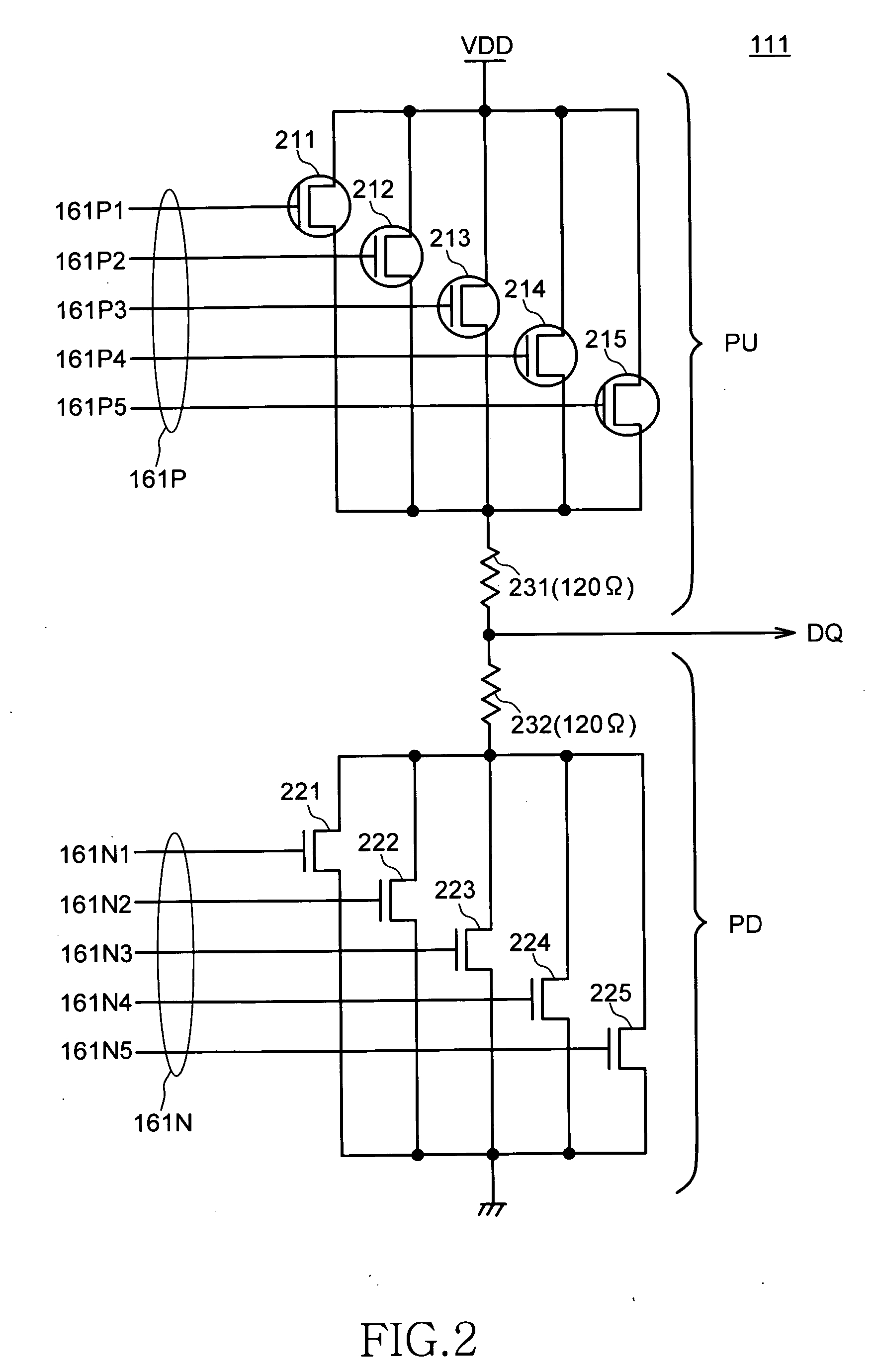
ActiveUS20130088257A1Impedance can be adjustedInput/output impedence modificationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsData terminalSemiconductor
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor device that includes a first transistor unit coupled to the data terminal, and a plurality of second transistor units coupled to the calibration terminal. The first transistor unit includes a plurality of first transistors having a first conductivity type connected in parallel to each other so that an impedance of the first transistor unit is adjustable. Each of the second transistor units includes a plurality of second transistors having the first conductivity type connected in parallel to each other so that an impedance of each of the second transistor units is adjustable. The semiconductor device further includes an impedance control circuit that reflects the impedance of each of the second transistor units to the first transistor unit.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Digital calibration circuits, devices and systems including same, and methods of operation
ActiveUS20080112246A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitComparators circuits
A calibration circuit for matching the output impedance of a driver by calibrating adjustments to the driver is described. The calibration circuit includes a driver circuit with a plurality of calibration transistors configured to receive a plurality of adjustment signals. The calibration circuit also includes a comparator circuit, and a binary searcher. The driver provides a signal corresponding to an output impedance to the comparator circuit. The output impedance signal is compared to a target impedance, and the comparator circuit then provides logic signals to the binary searcher representing whether the output impedance is greater than the target impedance. The binary searcher then selects a type of step size and count direction, in response to the logic signals, to count the number of steps for adjusting the calibration transistors of the driver.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20110057720A1Reduce power supply noiseAccurate reception of dataInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsControl signalEngineering
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device capable of controlling OCD and ODT circuits and control method used by the semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060226868A1Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsDevice materialControl signal
Provided is a semiconductor device capable of controlling an on-die-termination (ODT) circuit and an off-chip-driver (OCD) circuit and a control method used by the semiconductor device. The semiconductor device includes a control code generation unit generating a control code in response to a control signal, an addition unit adding an adjustment code to the control code to produce an adjusted control code, and an ODT circuit, wherein an impedance of the ODT circuit is adjusted in response to the adjusted control code. The semiconductor device can adjust the control code more precisely by adding or subtracting the adjustment code to or from the control code. Accordingly, the impedance of an OCD circuit or ODT circuit can be adjusted more precisely.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device with ZQ calibration circuit
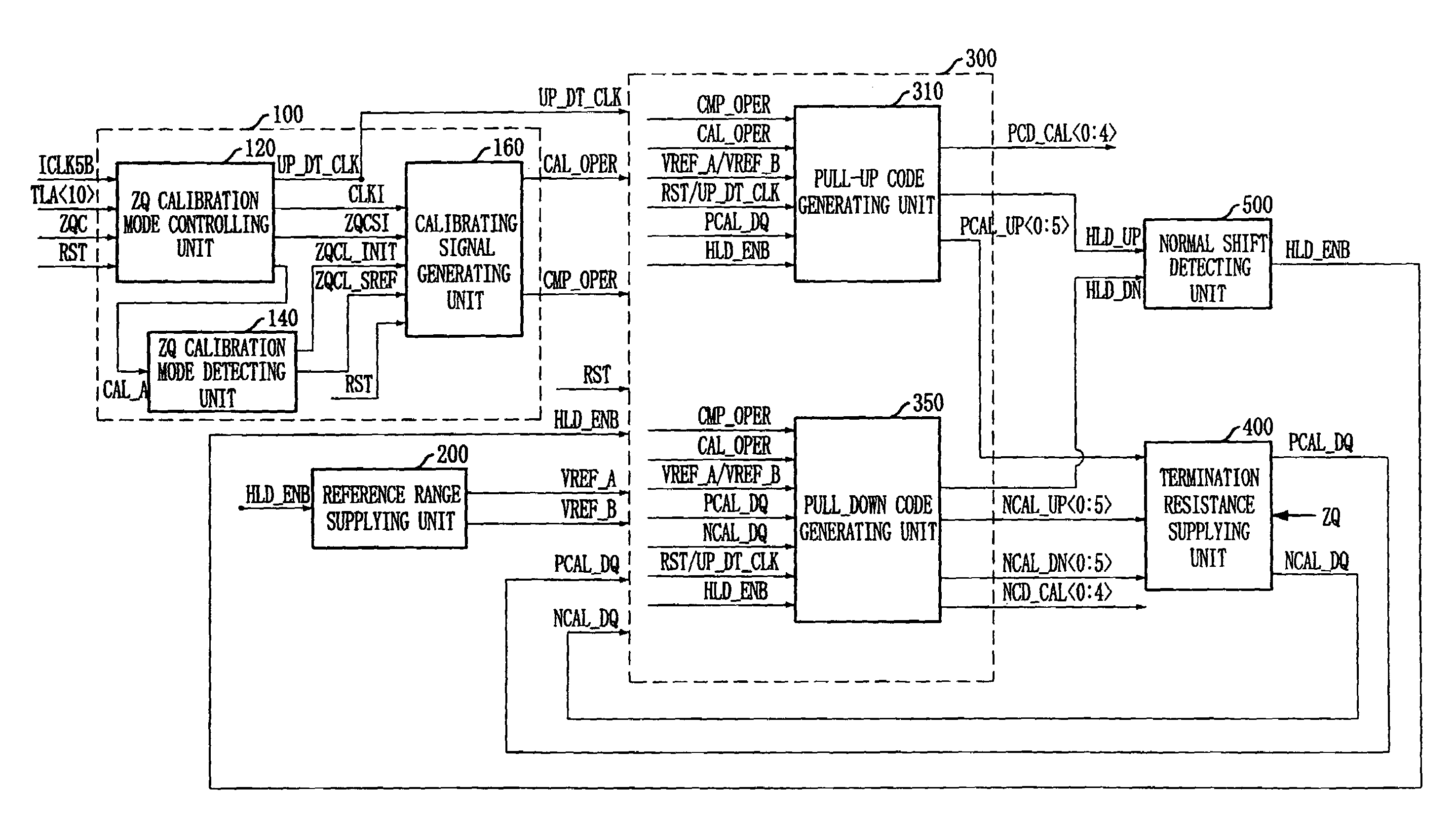
ActiveUS7528626B2Input/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsTarget signalEngineering
An impedance adjusting circuit of semiconductor memory devices is able to adjusting its termination resistance stably. The semiconductor memory device includes a reference range supplying unit for supplying a normal target range corresponding to a ZQ resistance and supplying a micro target range in response to a micro target signal, a termination resistance supplying unit for supplying an output resistance corresponding to a plurality of control codes, a code generating unit for generating the plurality of control codes in order to shift the output resistance within the normal target range and for adjusting the plurality of control codes to shift the output resistance within the micro target range in response to the micro target signal, and a normal shift detecting unit for detecting the output resistance arranged within the normal target range to generate the micro target signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com