Patents
Literature
3428 results about "Resistive element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The resistive element is a thin bulk metal foil that is cemented on a ceramic substrate. The foil thickness is several micrometers. Inherent to the mechanical design, they feature a very low temperature coefficient of resistance. They are used for applications with high precision requirements.
Energy harvesting circuits and associated methods
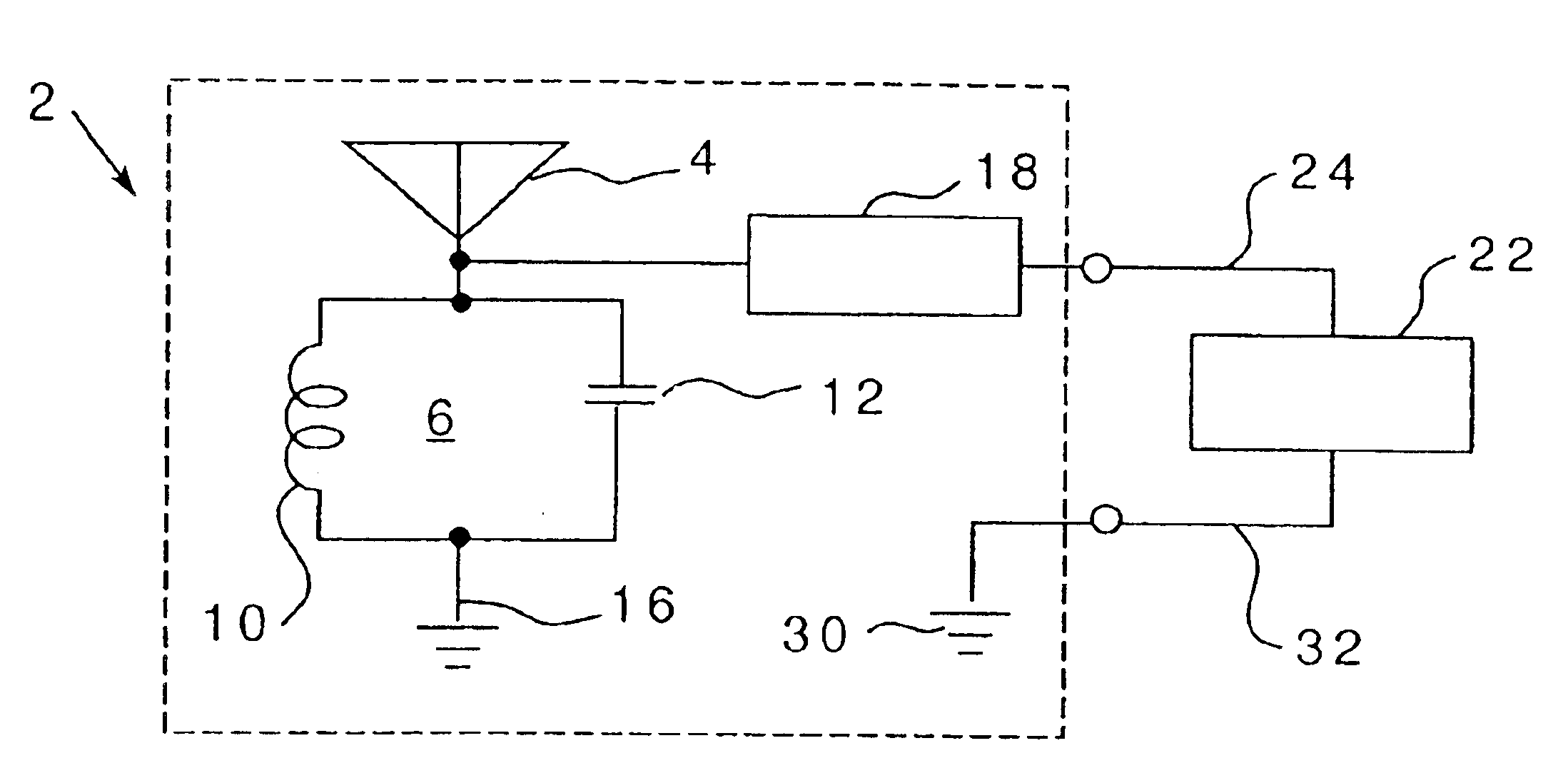
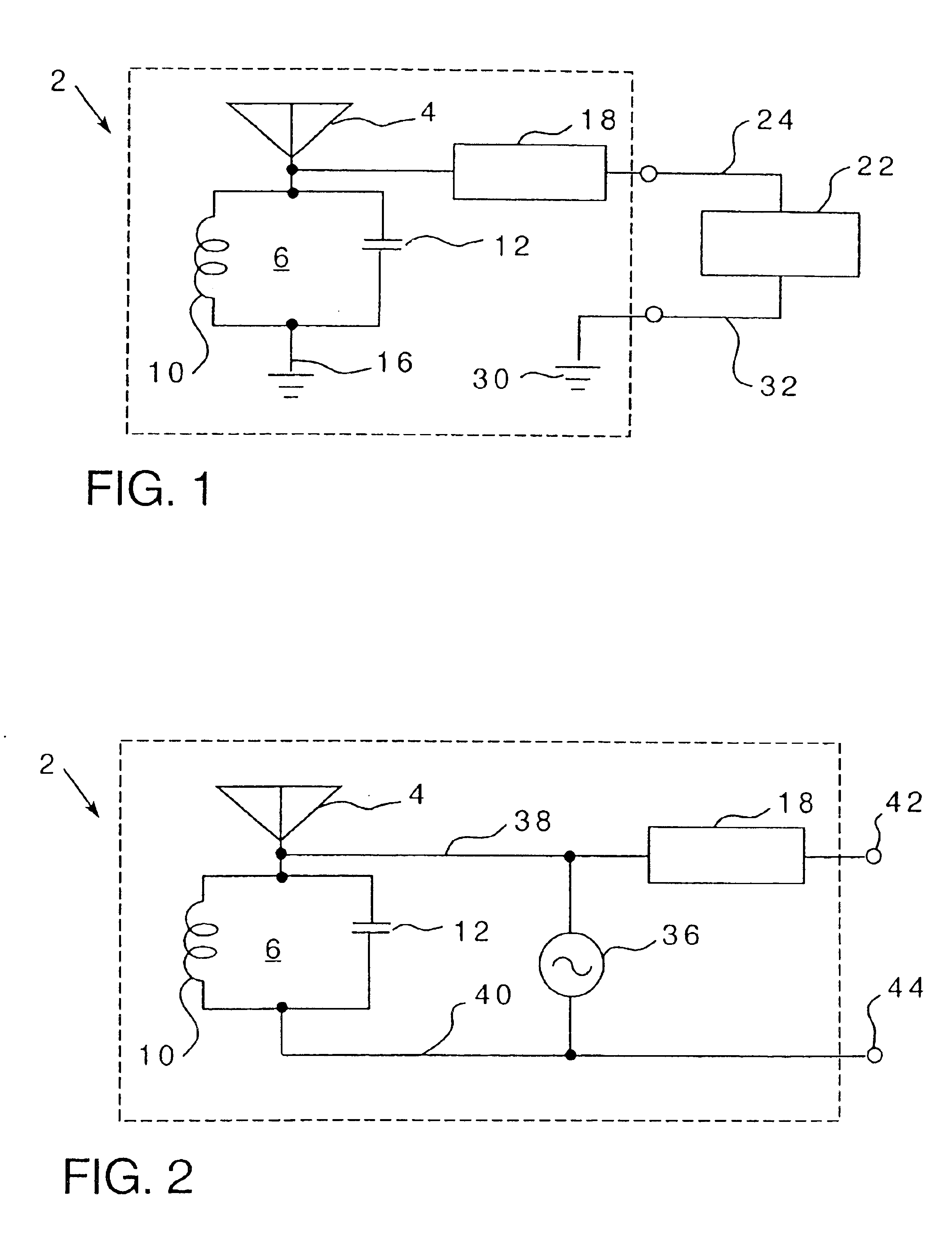
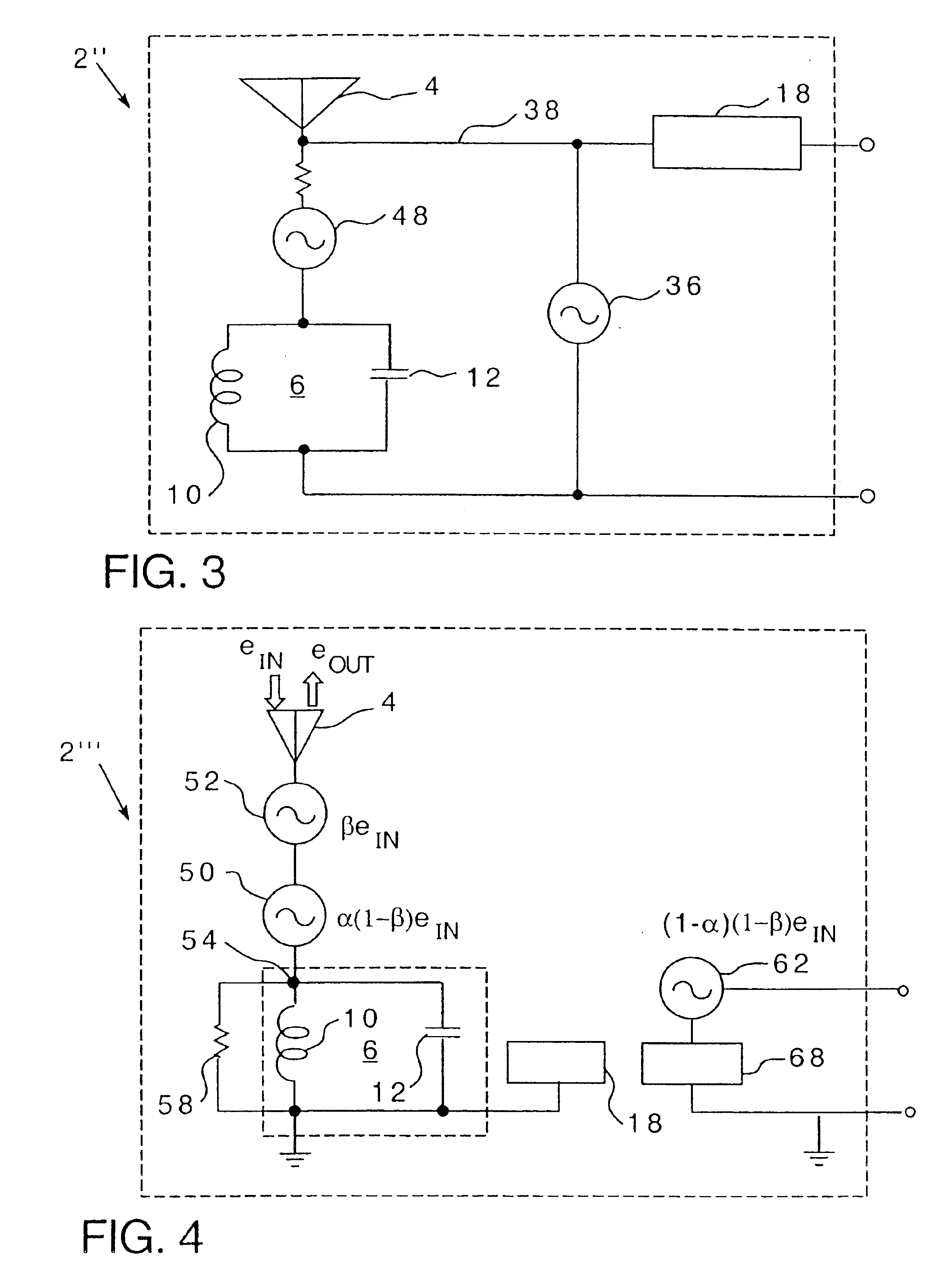
InactiveUS6856291B2Advantageously employedAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna feed intermediatesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An inherently tuned antenna has a circuit for harvesting energy transmitted in space and includes portions that are structured to provide regenerative feedback into the antenna to produce an inherently tuned antenna which has an effective area substantially greater than its physical area. The inherently tuned antenna includes inherent distributive inductive, inherent distributive capacitive and inherent distributive resistive elements which cause the antenna to resonate responsive to receipt of energy at a particular frequency and to provide feedback to regenerate the antenna. The circuit may be provided on an integrated circuit chip. An associated method is provided.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Conductivity reconstruction based on inverse finite element measurements in a tissue monitoring system
InactiveUS7169107B2Low and high conductivityReduce conductivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical devicesElectrical impedance tomographyEngineering
An impedance model of tissue is useful for describing conductivity reconstruction in tissue. Techniques for determining and mapping conductivity distribution in tissue supply useful information of anatomical and physiological status in various medical applications. Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) techniques are highly suitable for analyzing conductivity distribution. Electrical characteristics of tissue include resistive elements and capacitive elements. EIT techniques involve passing a low frequency current through the body to monitor various anatomical and physiological characteristics. The system can interrogate at multiple frequencies to map impedance. Analytical techniques involve forward and inverse solutions to boundary value analysis to tissue characteristics.
Owner:INOTECH MEDICAL SYST
Programmable Resistive RAM and Manufacturing Method
Integrated circuit nonvolatile memory uses programmable resistive elements. In some examples, conductive structures such as electrodes are prepared, and the programmable resistive elements are laid upon the prepared electrodes. This prevents contamination of the programmable resistive elements from previous fabrication steps.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method for same
InactiveUS20100219392A1Large capacityLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStorage cellTransistor
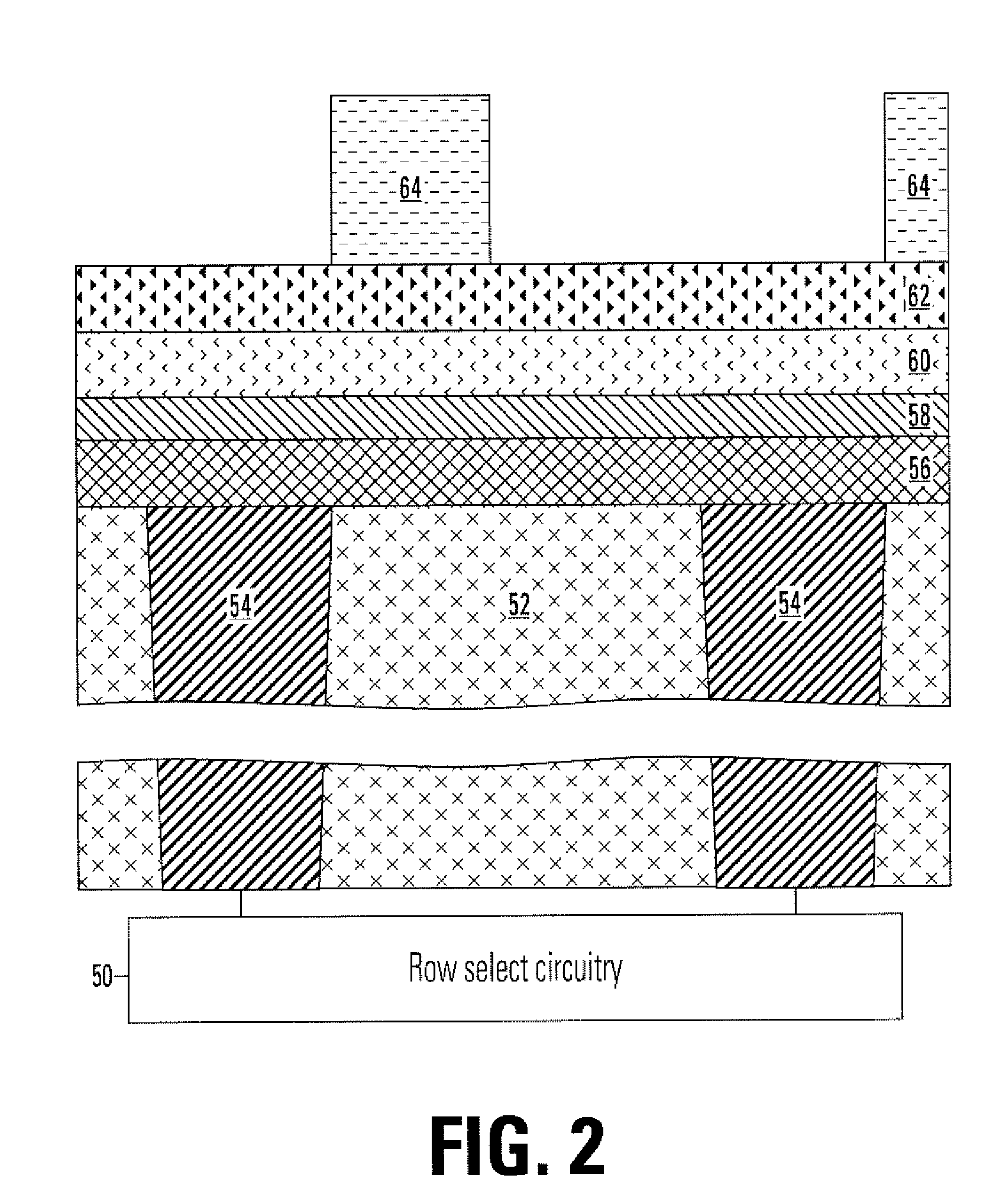
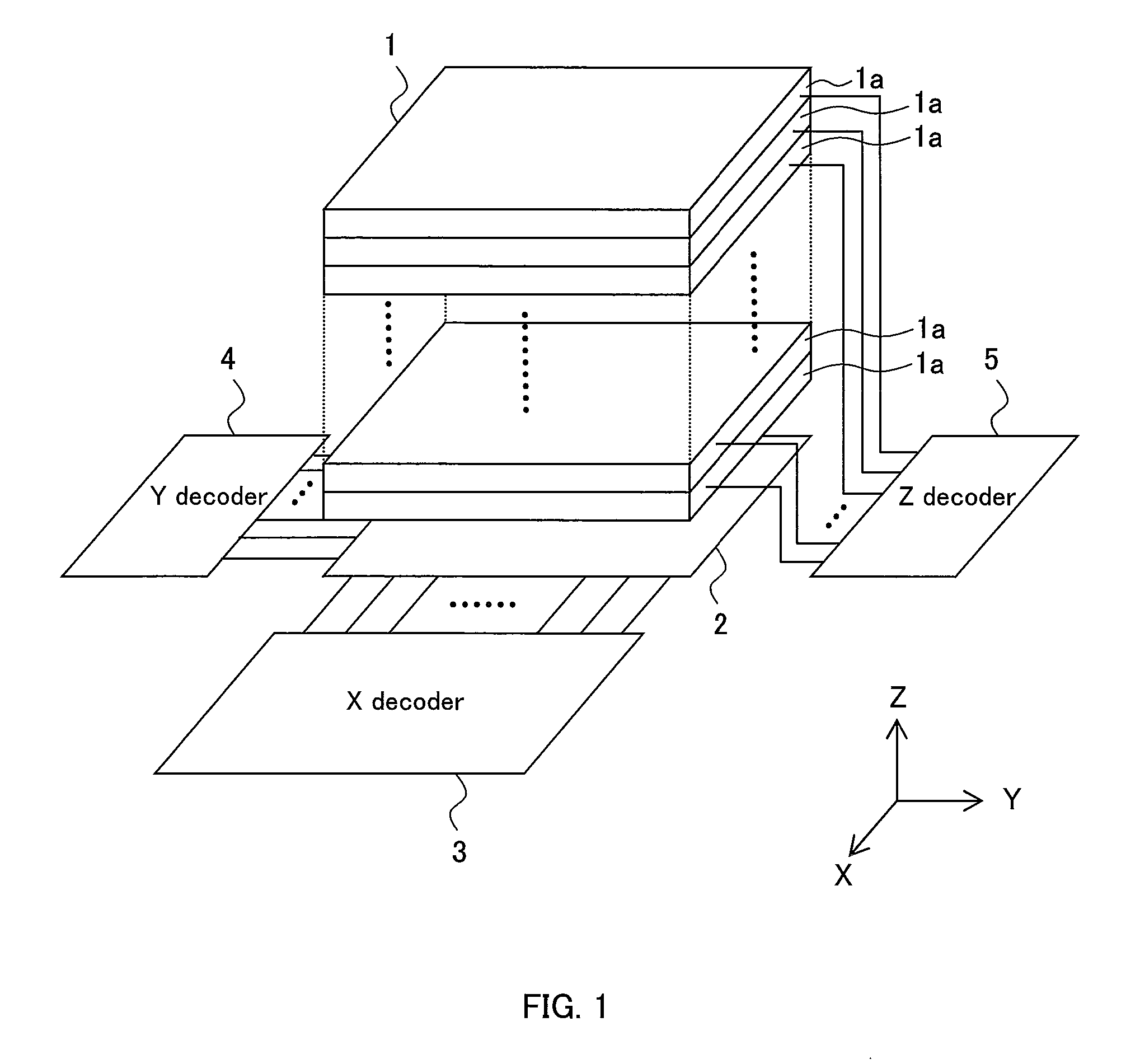
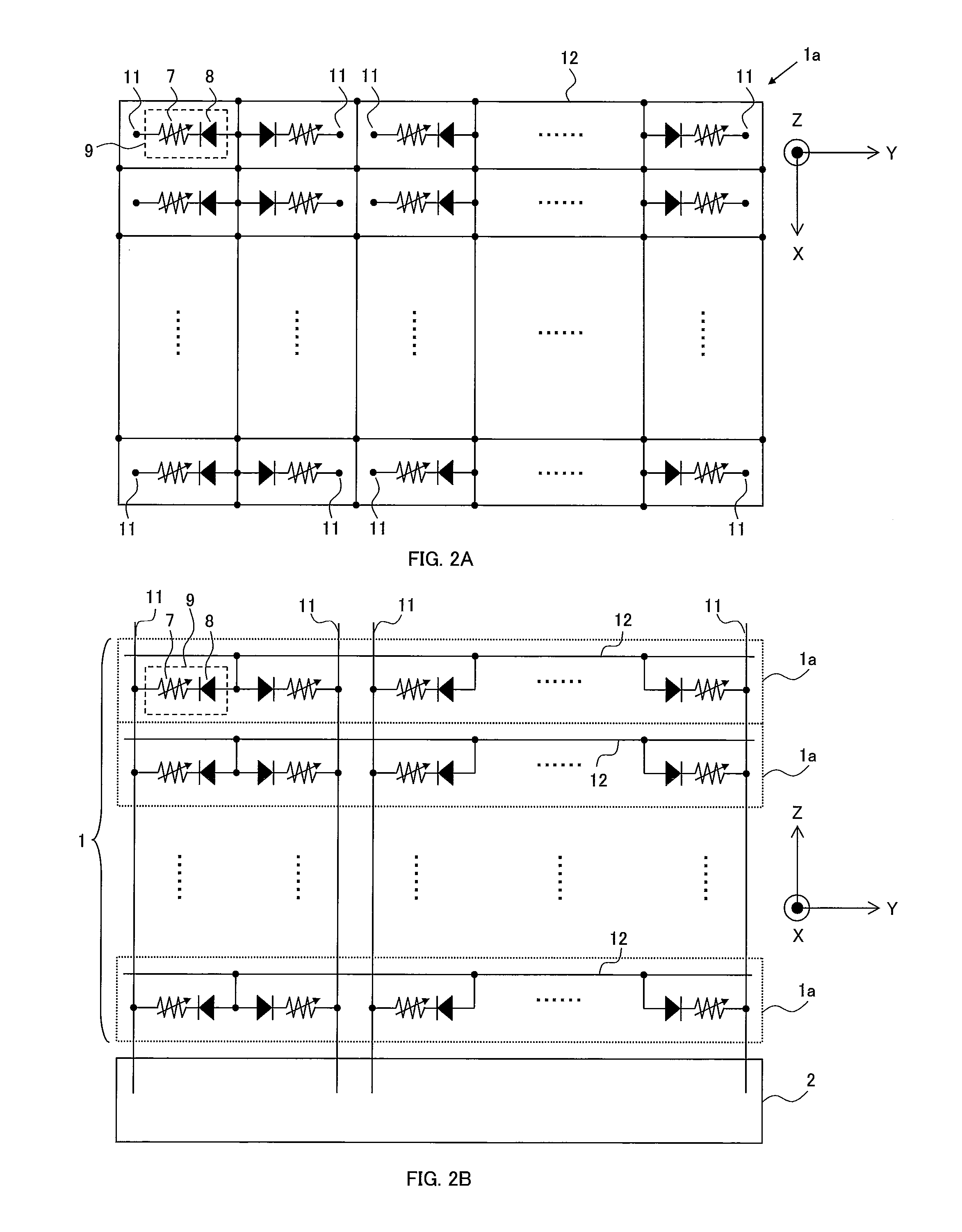
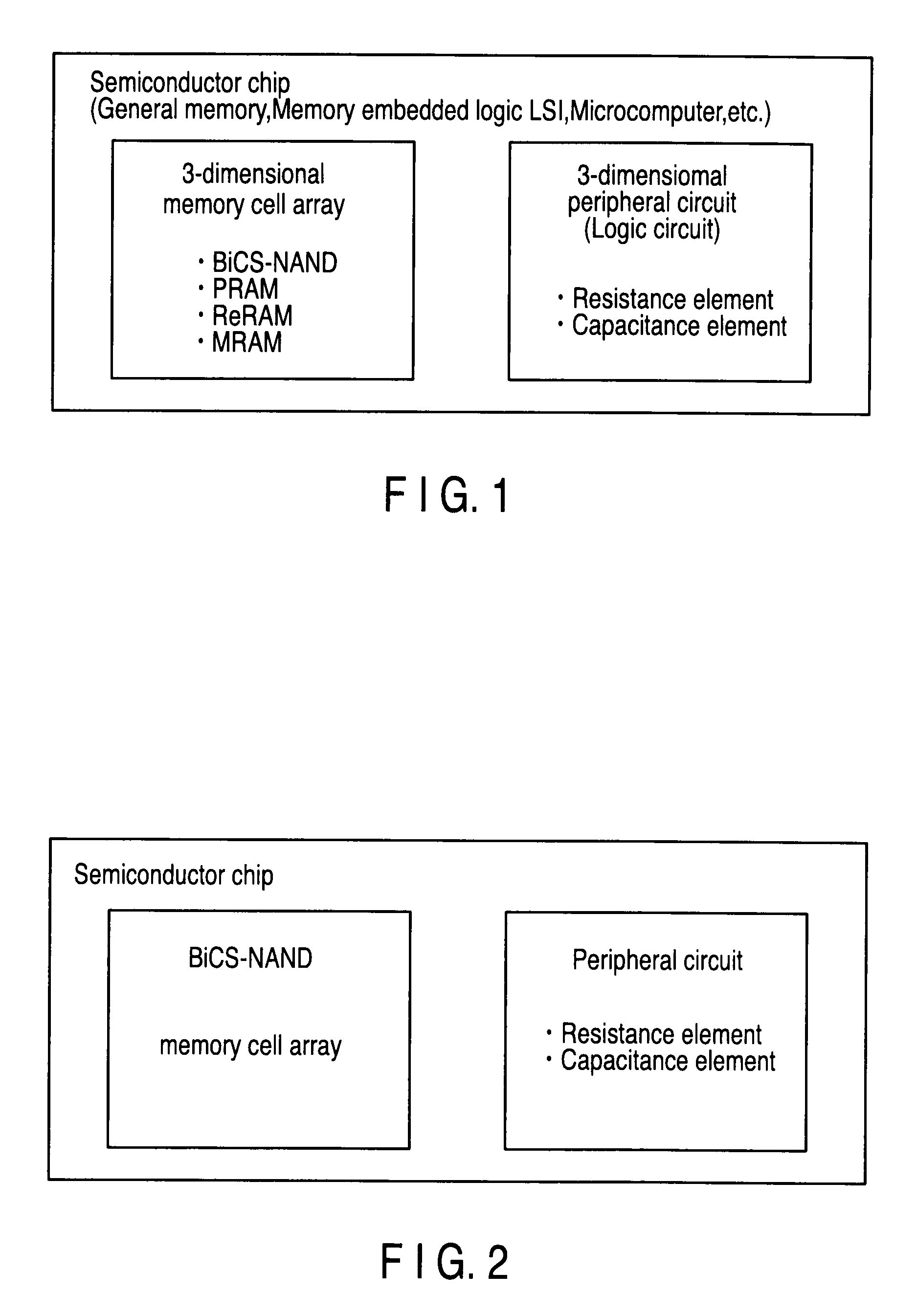
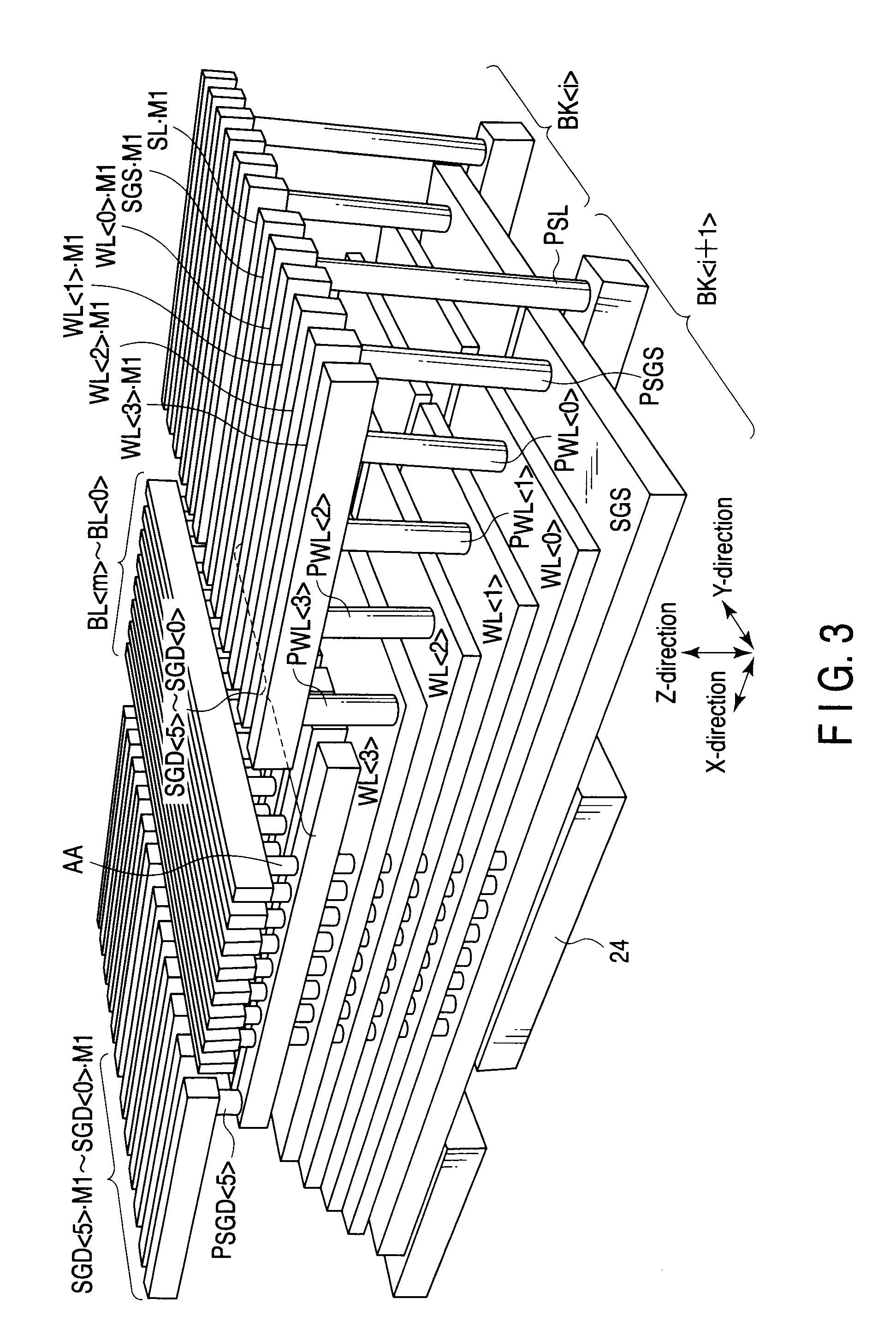
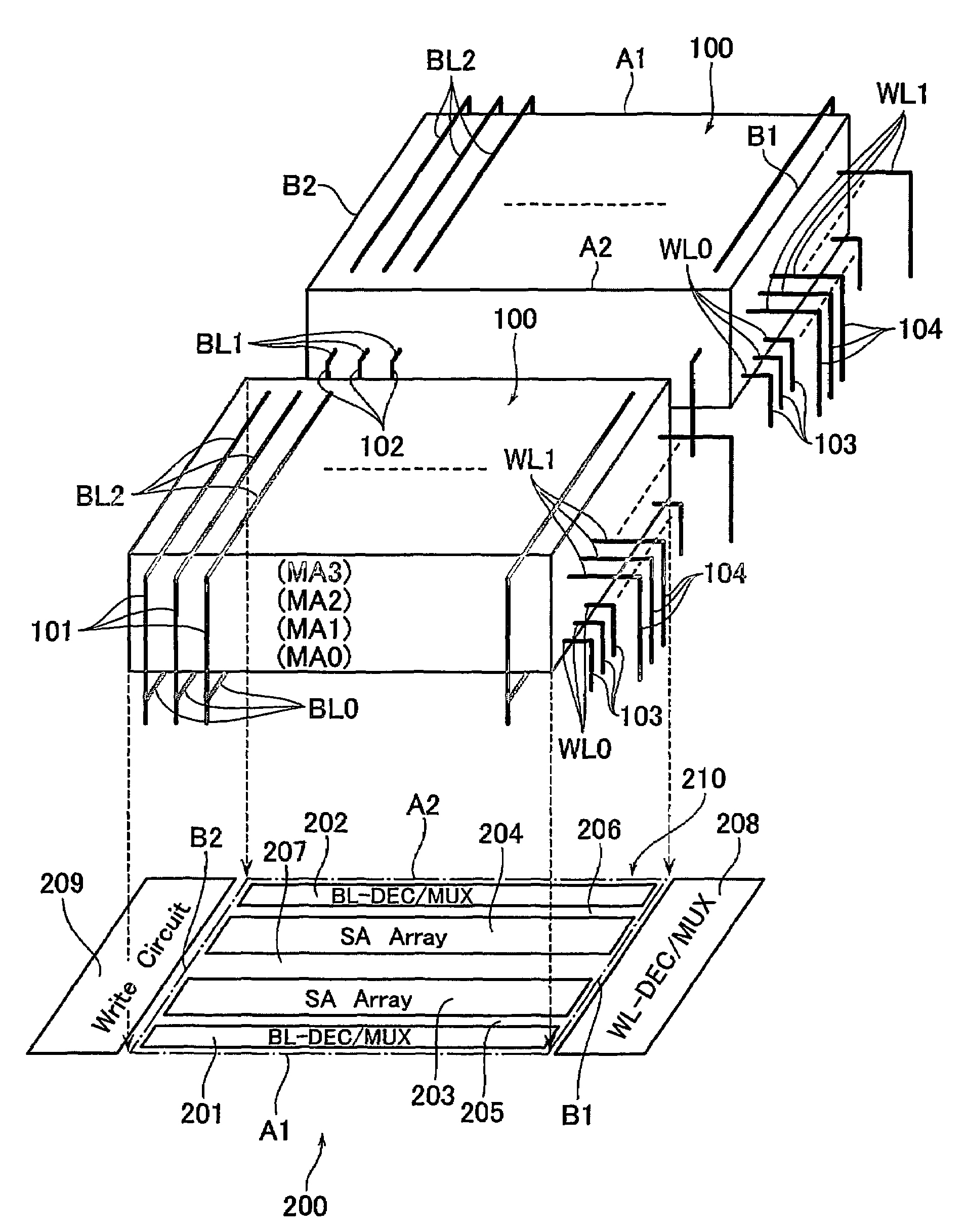
A three-dimensional memory cell array of memory cells with two terminals having a variable resistive element is formed such that: one ends of memory cells adjacent in Z direction are connected to one of middle selection lines extending in Z direction aligned in X and Y directions; the other ends of the memory cells located at the same point in Z direction are connected to one of third selection lines aligned in Z direction; a two-dimensional array where selection transistors are aligned in X and Y directions is adjacent to the memory cell array in Z direction; gates of selection transistors adjacent in X direction, drains of selection transistors adjacent in Y direction and sources of selection transistors are connected to same first selection line, second selection line, and different middle selection lines, respectively; and first, second and third selection lines are connected to X, Y and Z decoders, respectively.
Owner:SHARP KK
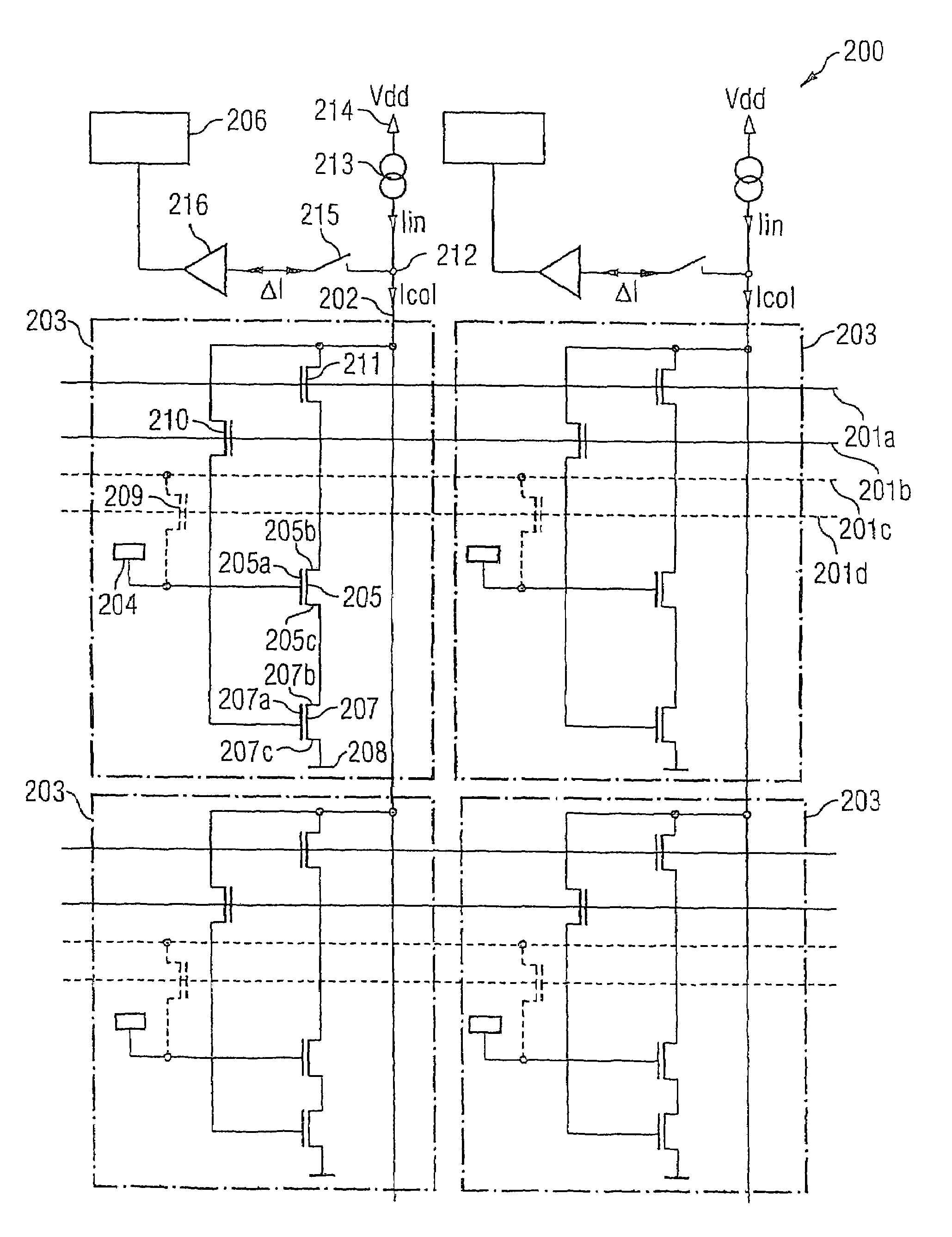
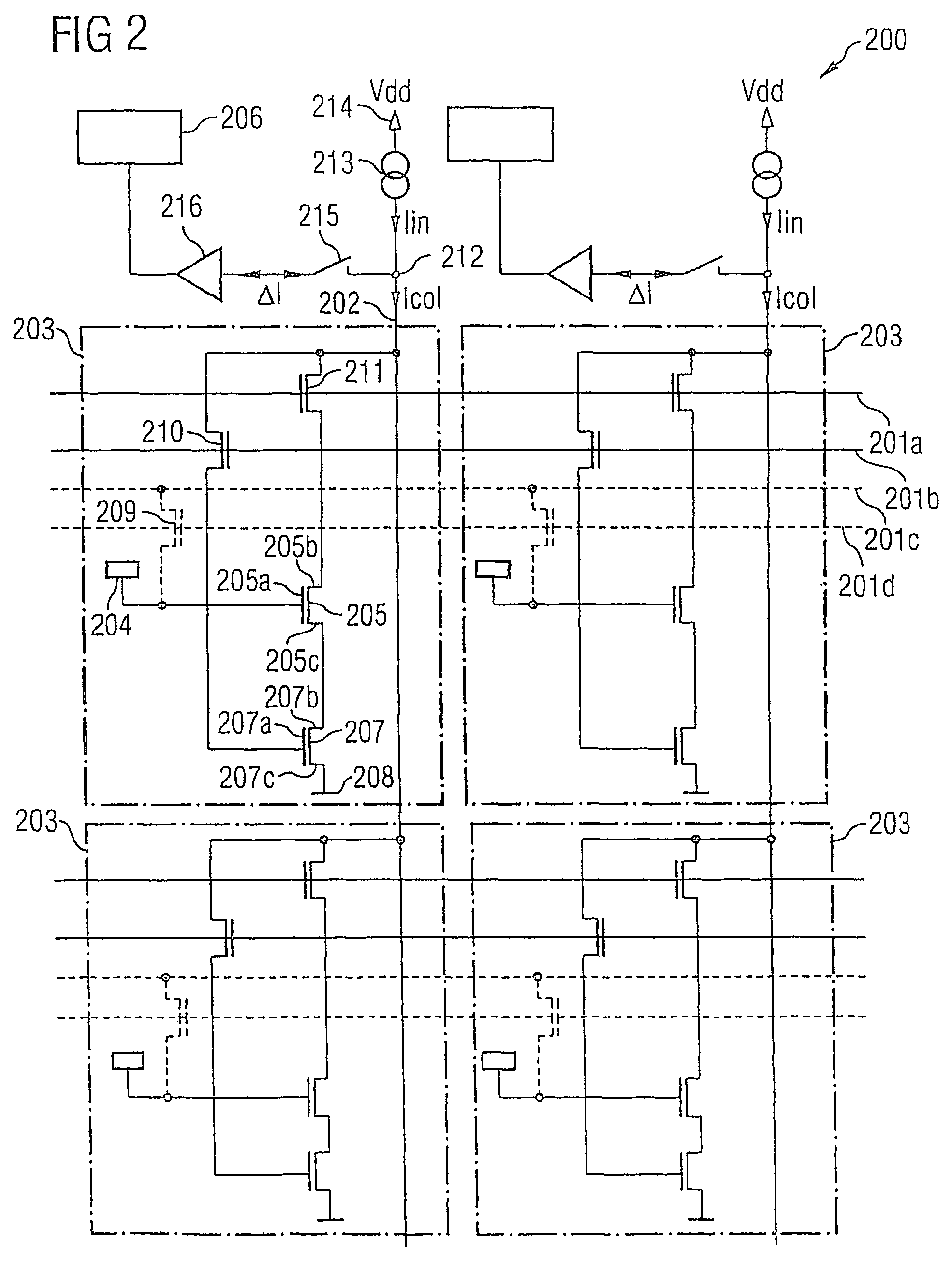
Active-matrix display, the emitters of which are supplied by voltage-controlled current generators
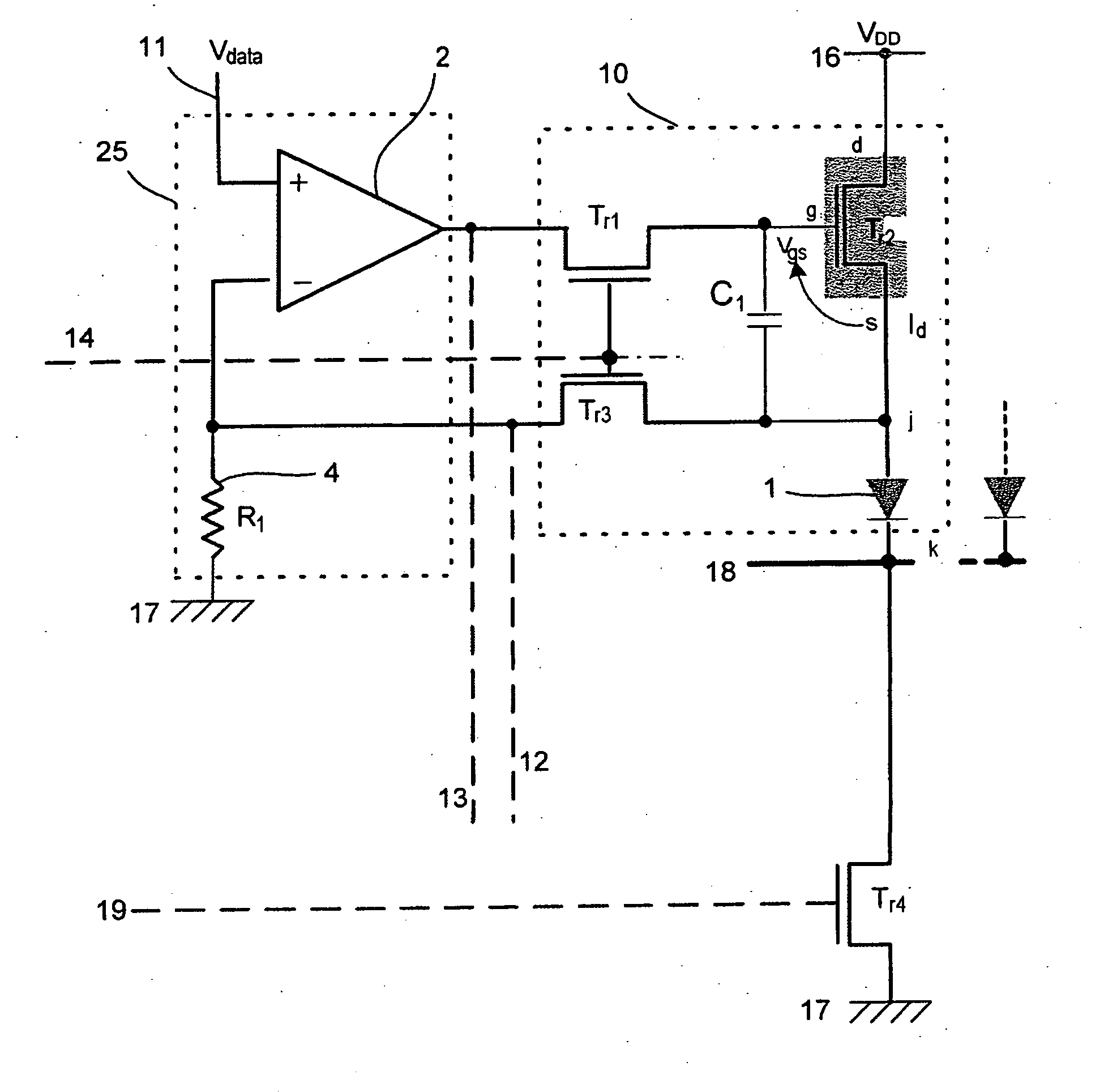
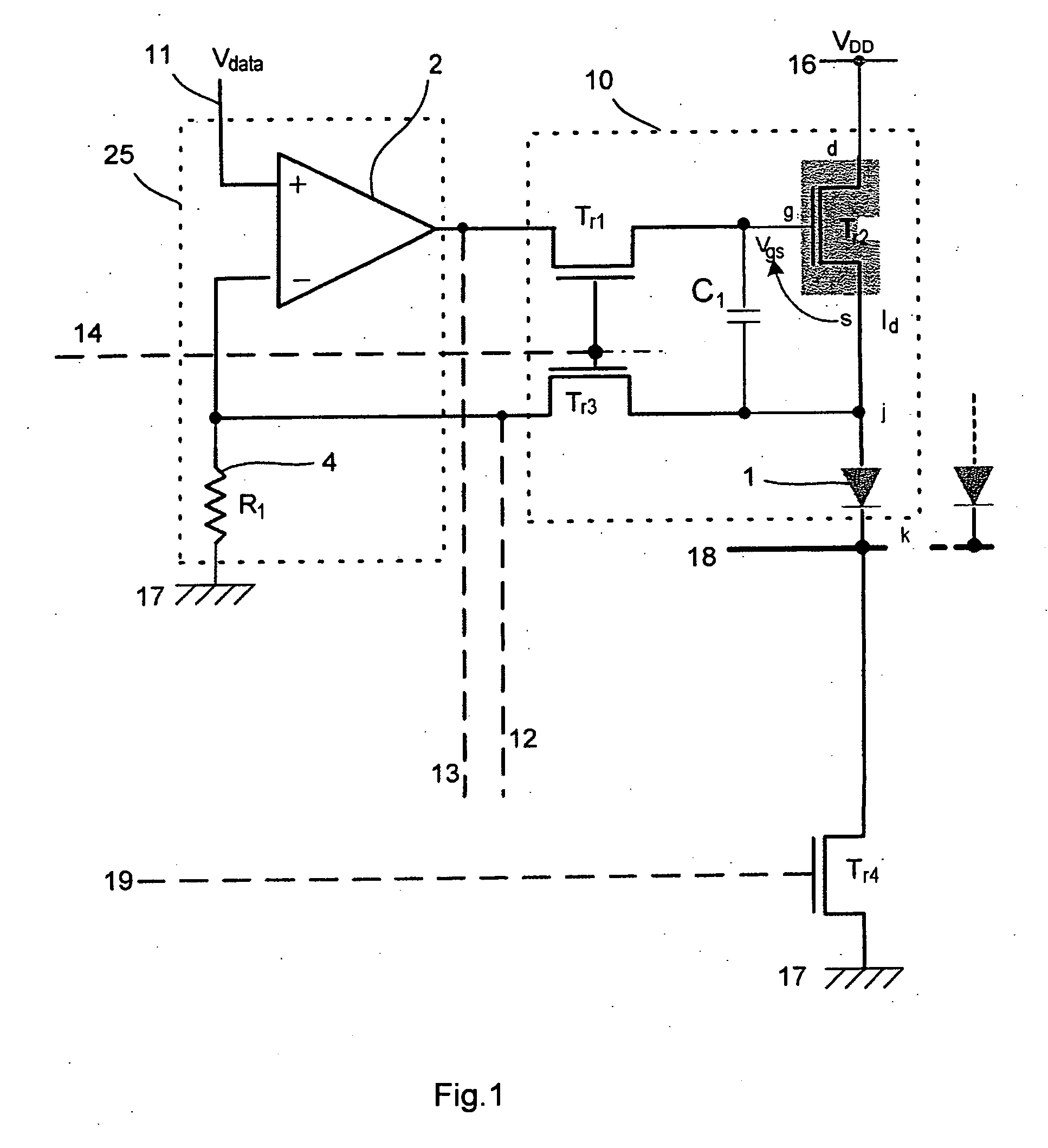
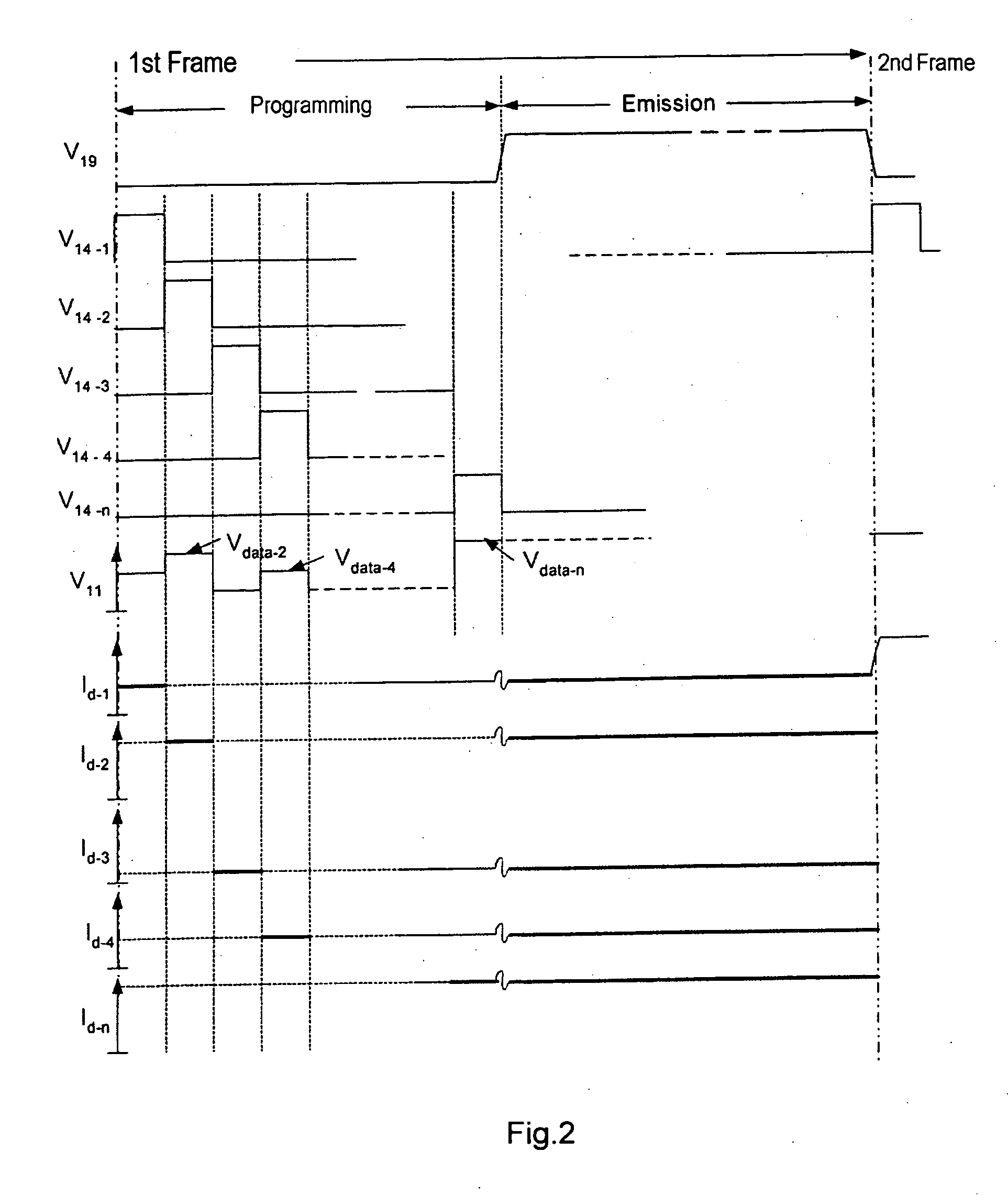
The display comprises an array of pixel circuits each comprising an emitter 1 in series with a current modulation transistor, and at least one address circuit, which integrates, for each column, a differential amplifier and a passive element preferably a resistive element, which cooperate with the current modulation transistors so as to form, during address phases in which the emitters are switched “out of the circuit”, a voltage-programmable current generator. After the address phases, thanks to a suitable switch, the emitters are switched “into the circuit” and supplied with the preprogrammed current. Such a display allows the image display quality to be inexpensively improved.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Programmable Resistive RAM and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20070158690A1Low costReduce the numberSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceReduced size
Programmable resistive RAM cells have a resistance that depends on the size of the programmable resistive elements. Manufacturing methods and integrated circuits for programmable resistive elements with uniform resistance are disclosed that have a cross-section of reduced size compared to the cross-section of the interlayer contacts.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device allowing shrinking of memory cell
InactiveUS7208751B2Reducing memory cell sizeSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesComputer scienceStorage cell
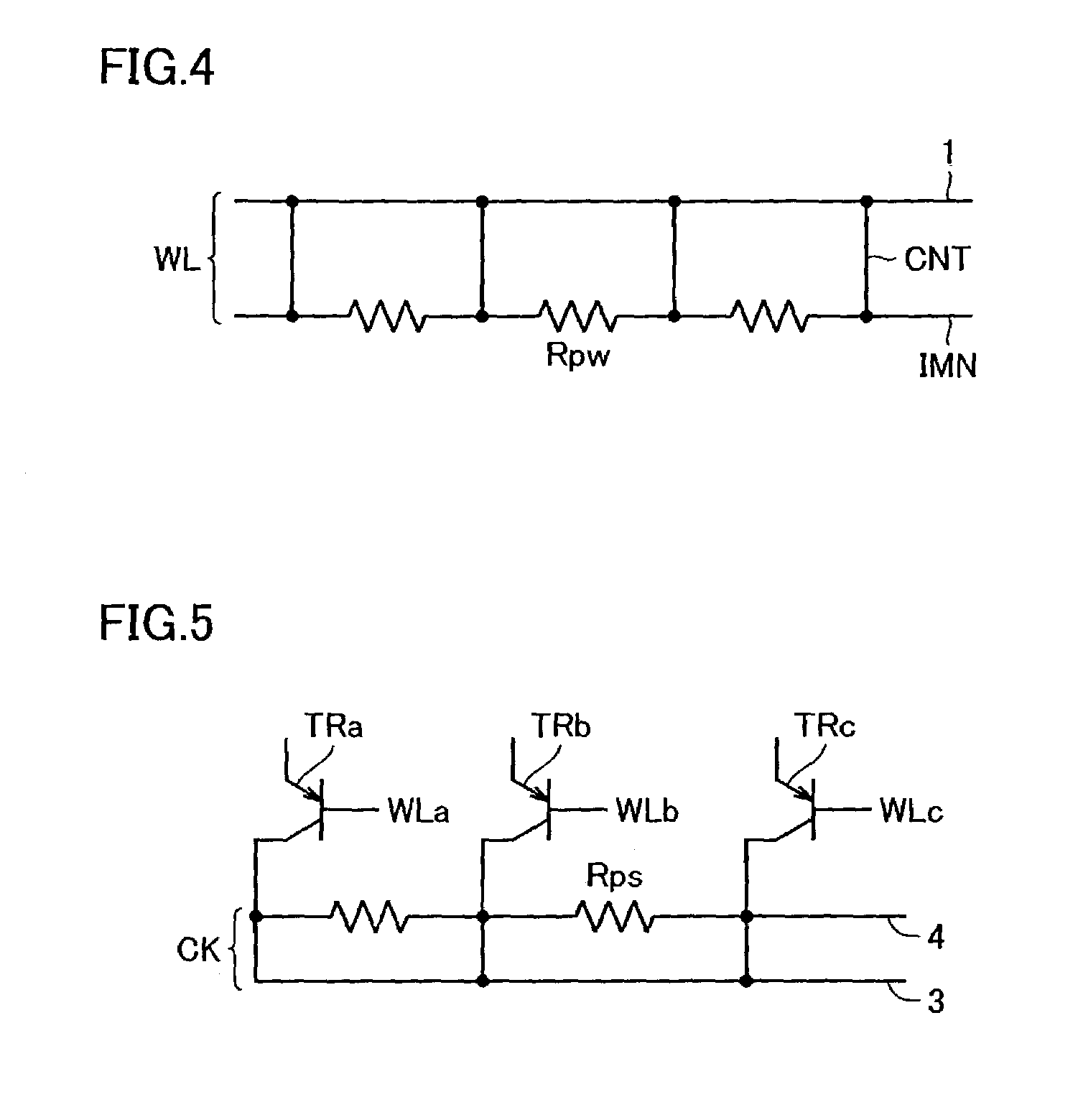
Dummy cells are disposed in alignment with memory cells arranged in rows and columns in a memory array. The memory cell includes a variable resistance element and a select transistor having a collector connected to a substrate region and selecting the variable resistance element in response to a row select signal. Corresponding to a row of memory cells, there is provided a word line connecting to memory cells on corresponding row and transmitting the row select signal, and a word line shunting line electrically connected at predetermined intervals to each word line. Moreover, corresponding to a row of dummy cells and a column of dummy cells, there is provided substrate shunt lines electrically connected to the substrate region. The voltage distribution in the substrate region is eliminated to achieve stable operating characteristics of the memory cell transistor. In addition, a word line is driven at high speed by a word line shunt structure.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Programmable resistive device and memory using diode as selector
Building programmable resistive devices in contact holes at the crossover of a plurality of conductor lines in more than two vertical layers is disclosed. There are plurality of first conductor lines and another plurality of second conductor lines that can be substantially perpendicular to each other, though in two different vertical layers. A diode and / or a programmable resistive element can be fabricated in the contact hole between the first and second conductor lines. The programmable resistive element can be coupled to another programmable resistive device or shared between two programmable devices whose diodes conducting currents in opposite directions and / or coupled to a common conductor line. The programmable resistive memory can be configured to be programmable by applying voltages to conduct current flowing through the programmable resistive element to change its resistance for a different logic state.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Resistance element, method of manufacturing the same, and thermistor
InactiveUS20050040371A1Easy and stable coatingLow resistivityMaterial nanotechnologyCurrent responsive resistorsResistive elementCarbon nanotube
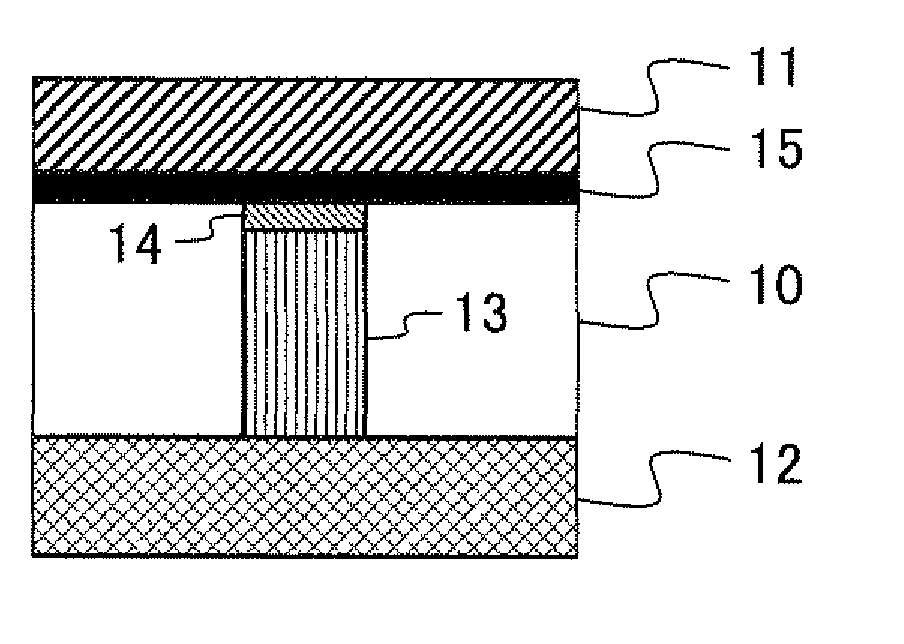
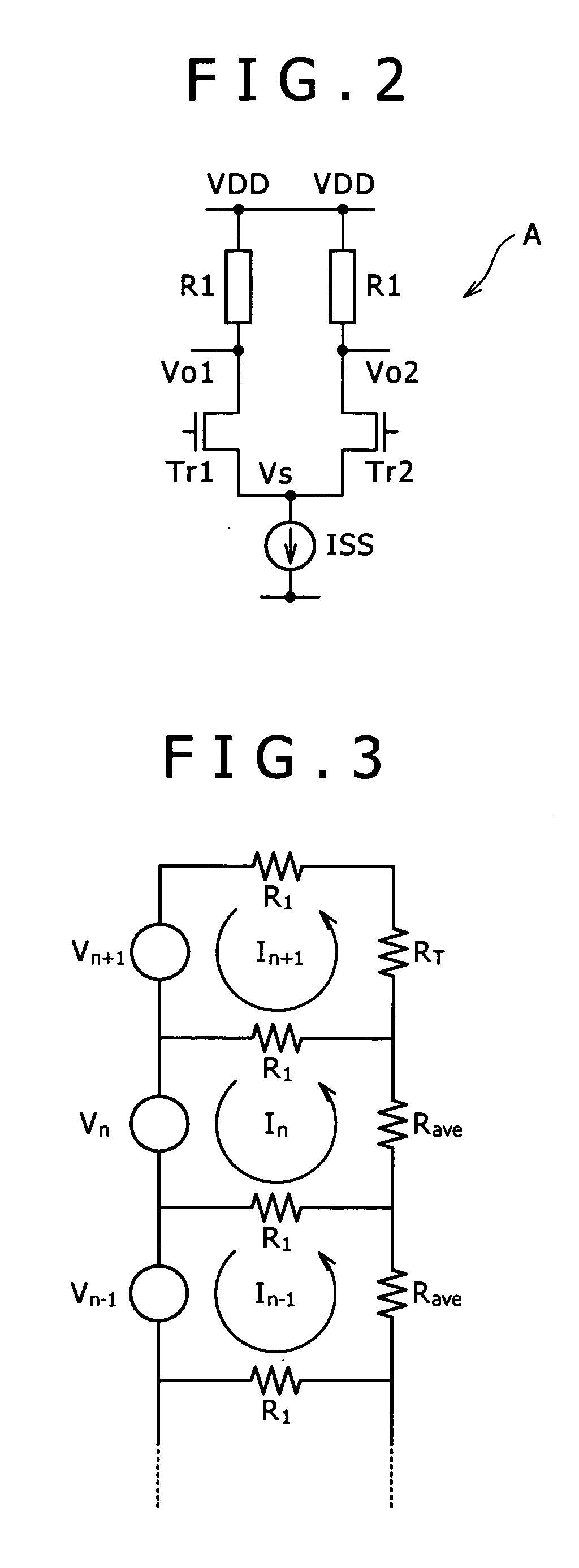
To provide a resistance element having an electric resistance body with excellent stability and a method of manufacturing the same. The resistance element includes an electric resistance body, on a base body surface, consisting of a carbon nanotube structure layer 14, which configures a mesh structure in which at least plural carbon nanotubes are cross-linked to one another. The method of manufacturing the resistance element includes: an applying step of applying the base body surface 12 with a liquid solution containing carbon nanotubes having functional groups; and a cross-linking step of forming the carbon nanotube structure layer 14, used as an electric resistance body, that configures a mesh structure in which the plural carbon nanotubes are cross-linked to one another through curing of the liquid solution after application.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Semiconductor device
A semiconductor device is comprised of a semiconductor substrate, conductive layers stacked above the semiconductor substrate, which is comprised of a conductive polysilicon, and a metal layer provided above the conductive layers. Both ends of the conductive layers have stairsteps respectively. The conductive layers are connected in series by a metal layer which is provided on the stairsteps. The conductive layers connected in series comprise a resistance element.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
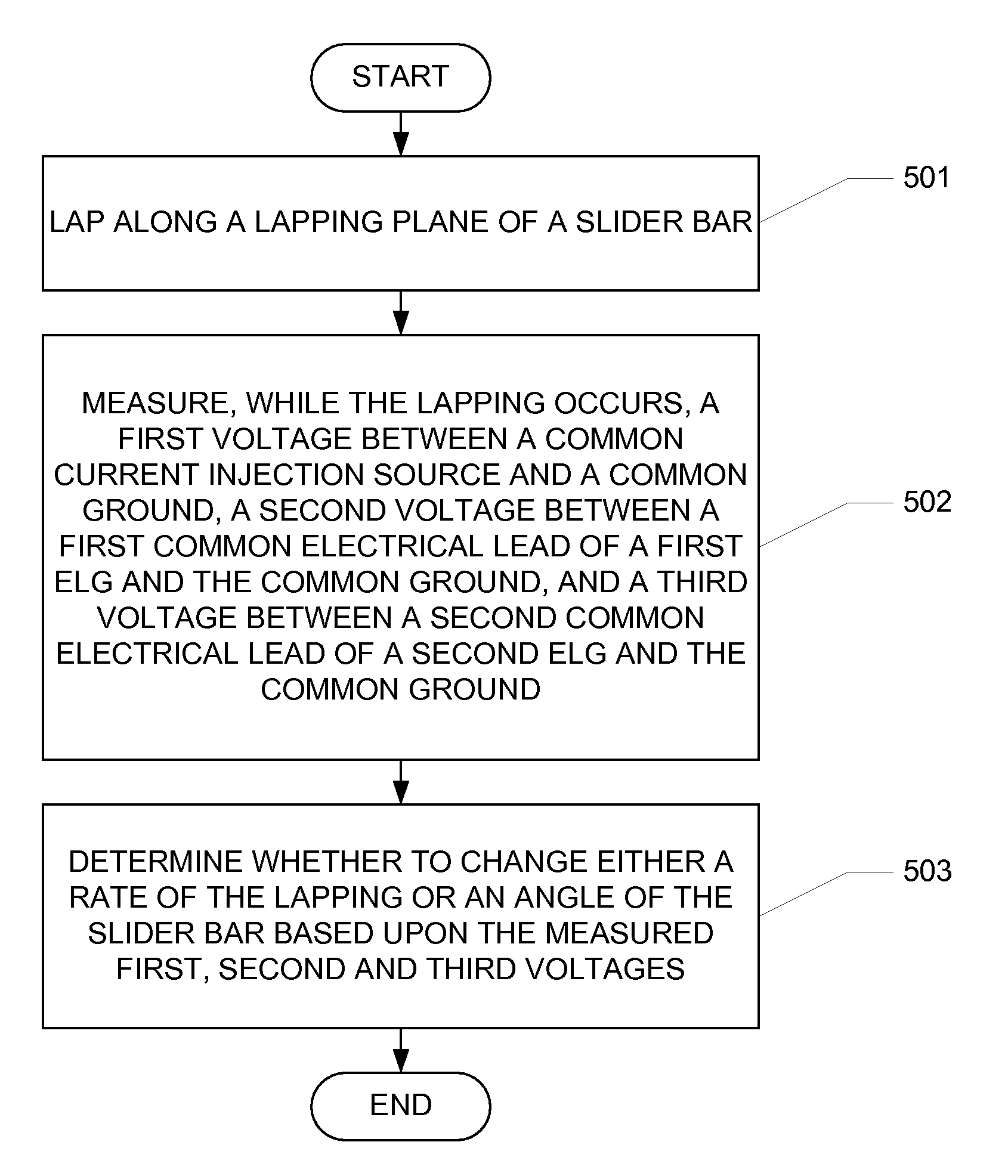
Four pad self-calibrating electronic lapping guide
Lapping guides for use in fabrication of a magnetic recording head are provided. The lapping guides comprise a first differential electronic lapping guide (ELG) disposed in a first layer of the magnetic recording head. The first differential ELG has a first resistive element and a second resistive element between which is disposed a first common electrical lead. The lapping guides further comprise a second differential ELG disposed in a second layer of the magnetic recording head. The second differential ELG has a third resistive element and a fourth resistive element between which is disposed a second common electrical lead. The first and second differential ELGs share a common ground and a common current injection source. Remaining lapping distances at the first and second layers of the magnetic recording head are determined by measuring changing voltages across the first, second, third and fourth resistive elements, respectively.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Dynamic spinal stabilization device
InactiveUS20070288009A1Reduce movementIncrease strainInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElectrical resistance and conductanceSpinal column
The present invention provides a dynamic stabilization device positionable about a portion of a spinal column. The stabilization device may generally include a first component and a second component, where the first and second components are movably coupled to one another to define an arcuate path of motion. The stabilization device may also include one or more adjustment elements positionable within first and second adjustment openings to affect the path of motion between the first and second components and / or the behavior and characteristics of the movement. In addition, one or more resistive elements may be adjustably positionable within either and / or both of the first and second adjustment openings to provide resistance and / or dampening of the forces experienced as the first and second components move relative to one another. The stabilization device may further define a joint having three degrees of freedom to adapt to movement of a spinal column.
Owner:DISC MOTION TECH
Three-dimensional programmable resistance memory device with a read/write circuit stacked under a memory cell array
A programmable resistance memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, at least one cell array, in which memory cells are arranged and formed above the semiconductor substrate. Each of the memory cells has a stack structure of a programmable resistance element and an access element, the programmable resistance element storing a high resistance state or a low resistance state based on the polarity of voltage application in a non-volatile manner. The access element has a resistance value in an off-state in a certain voltage range that is ten time or more as high as that in a select state. A read / write circuit is formed on the semiconductor substrate and underlying the cell array for data reading and data writing in communication with the cell array.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
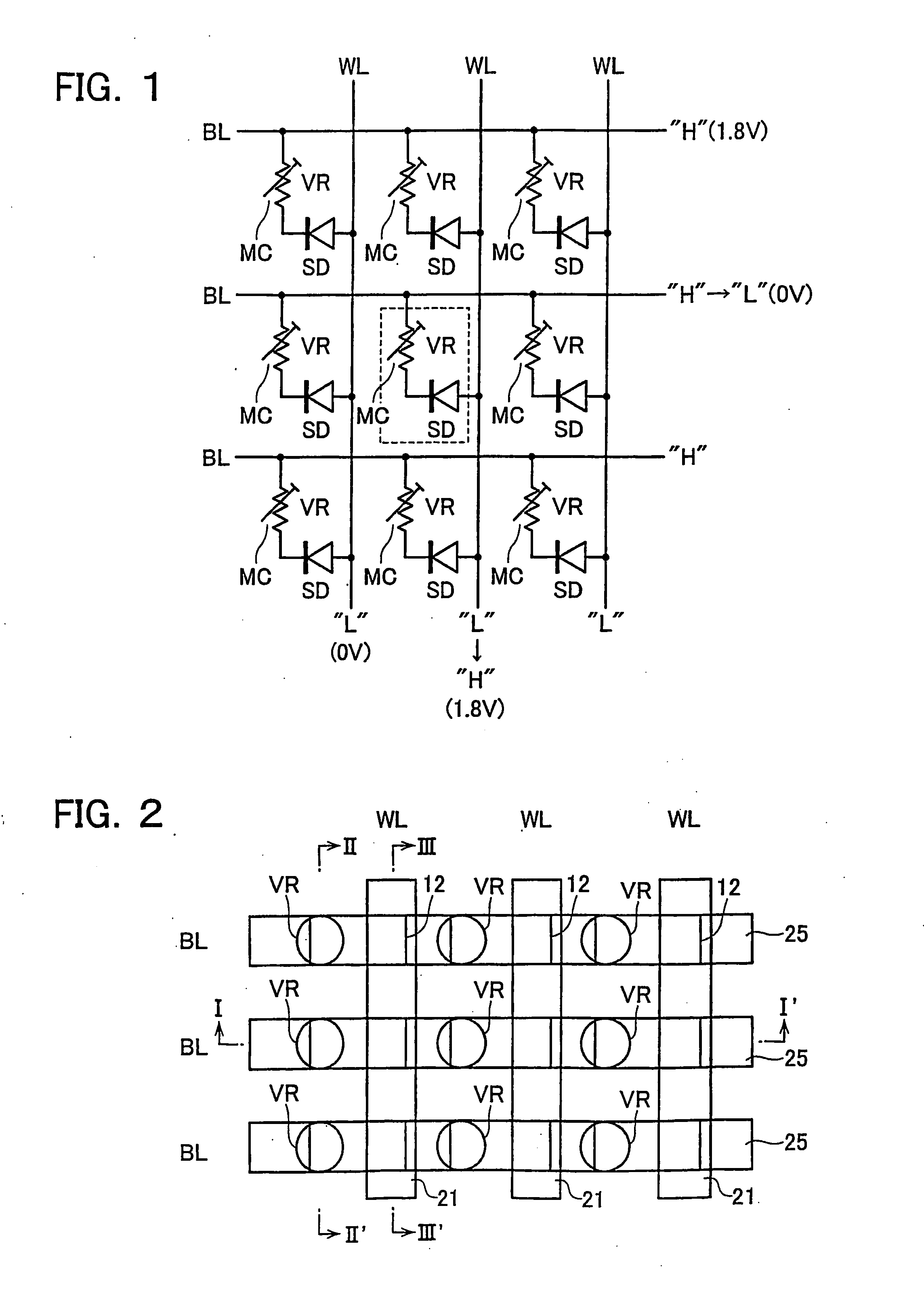
Phase-Change Memory Device
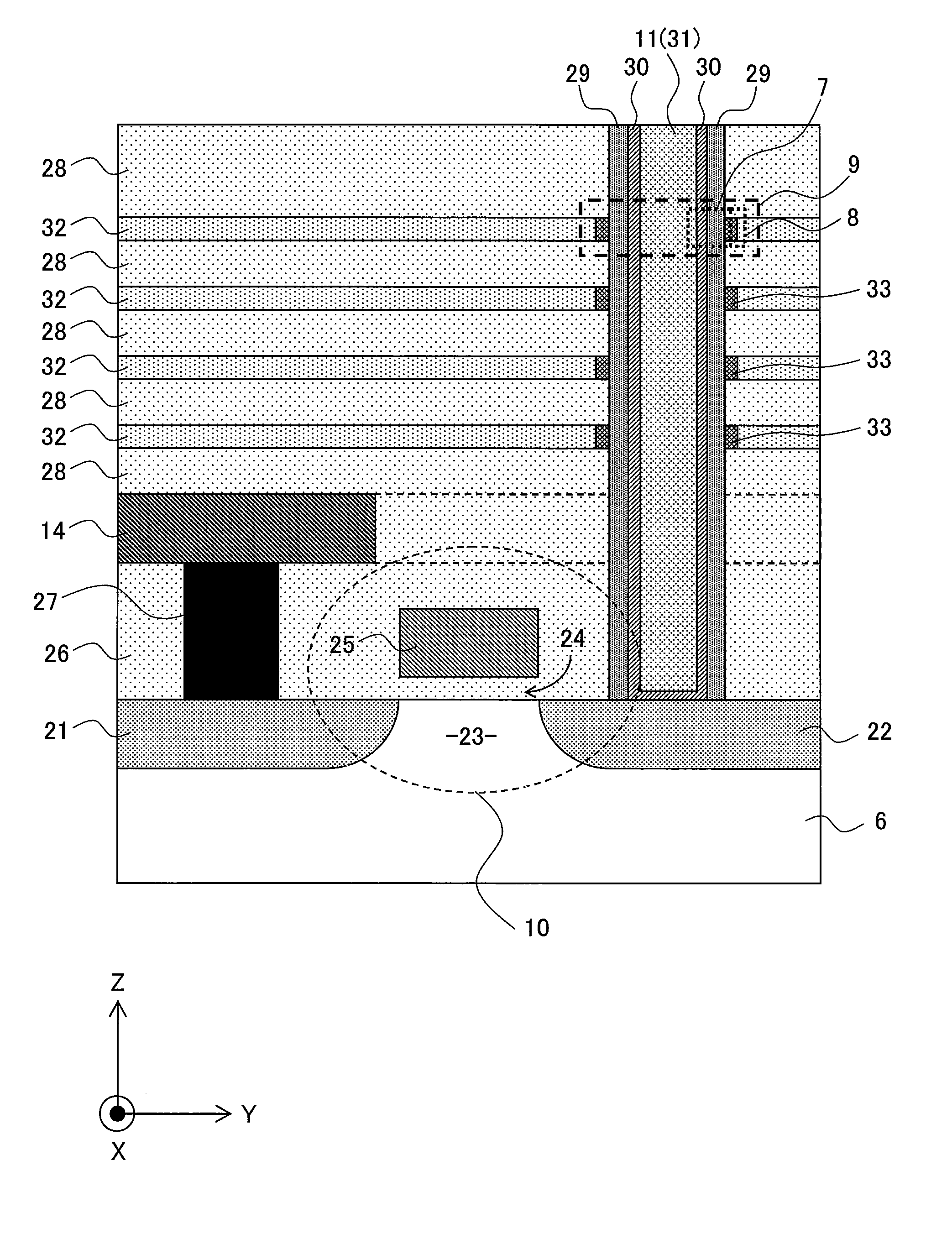
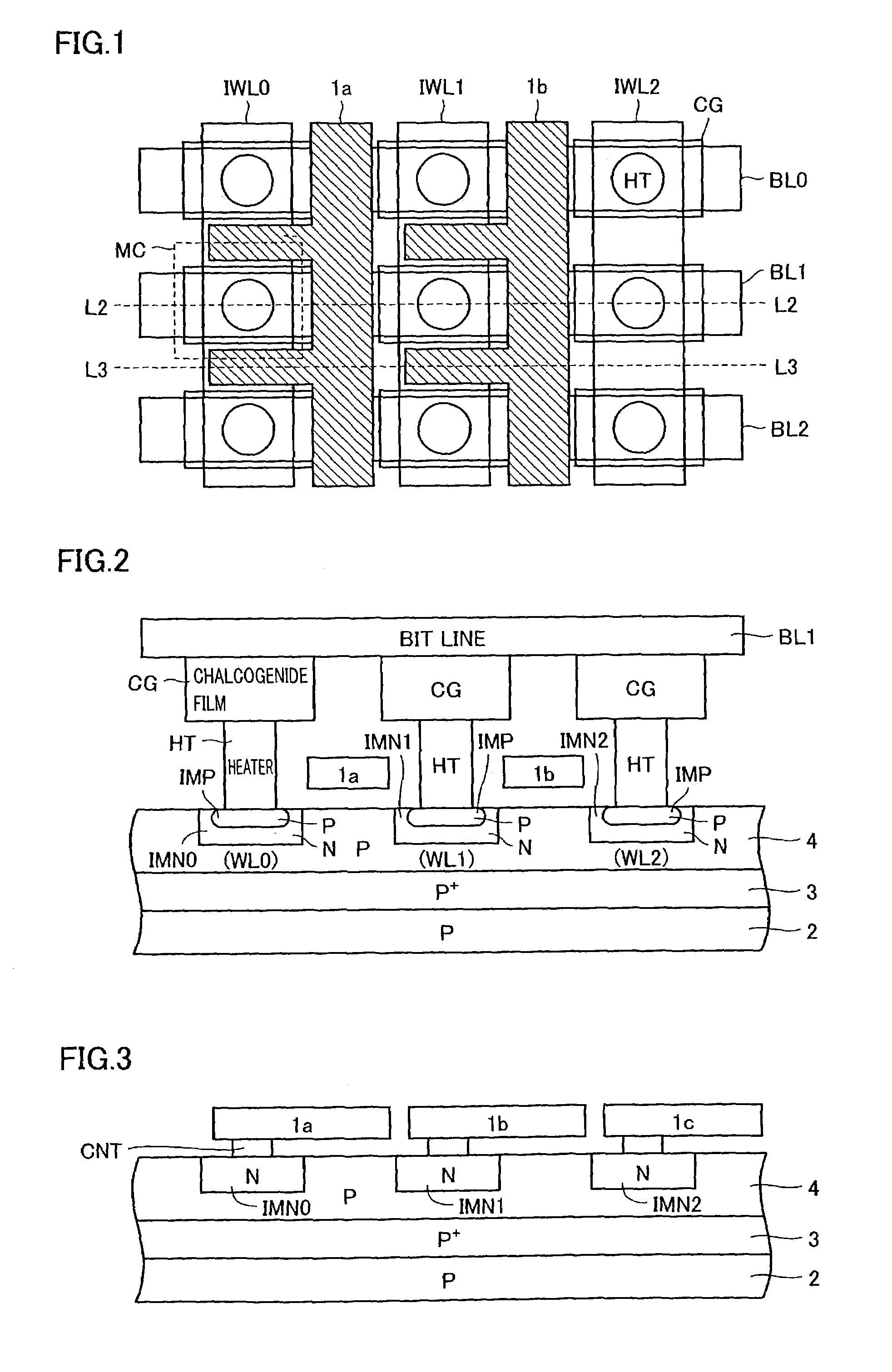
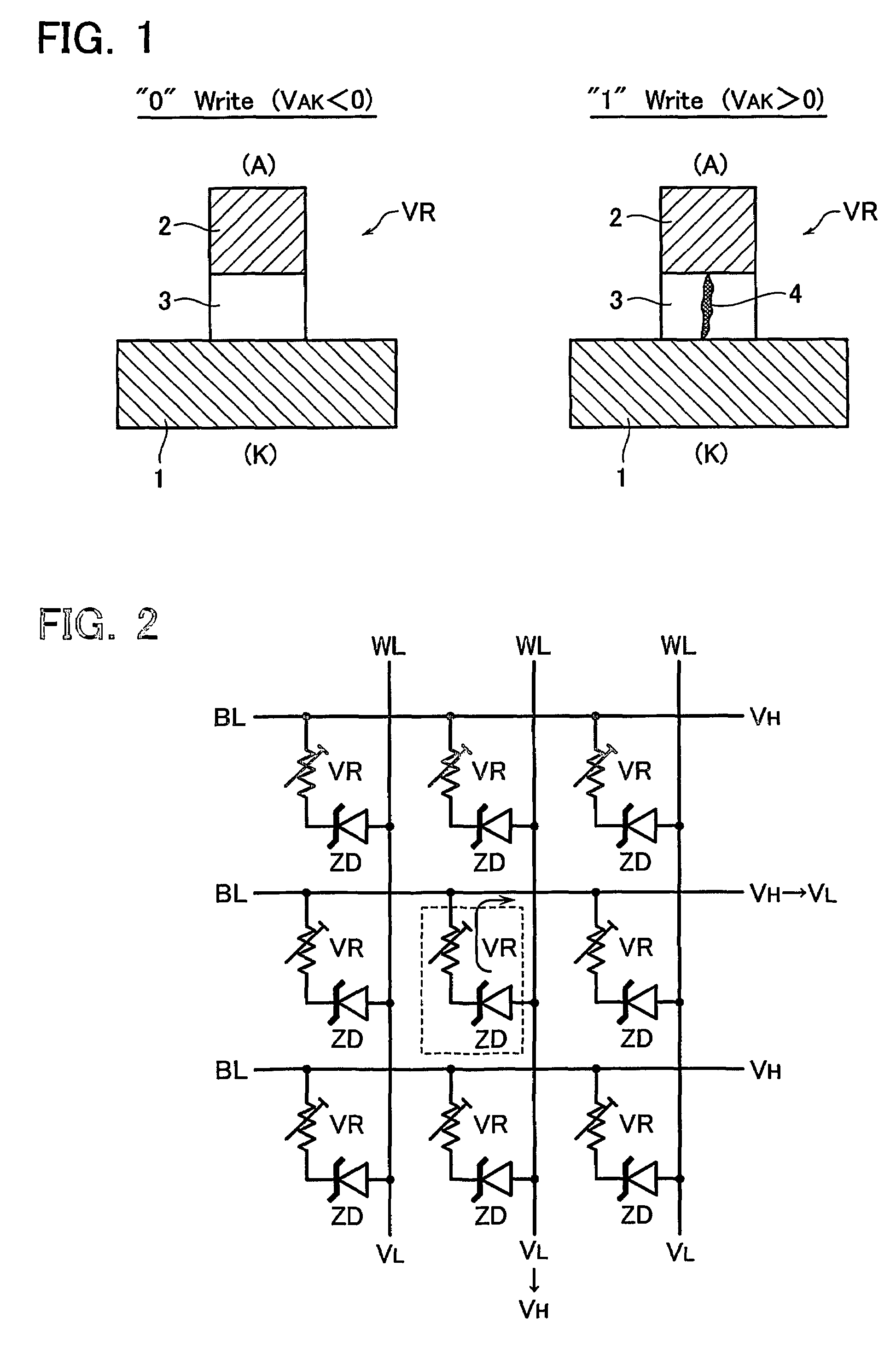
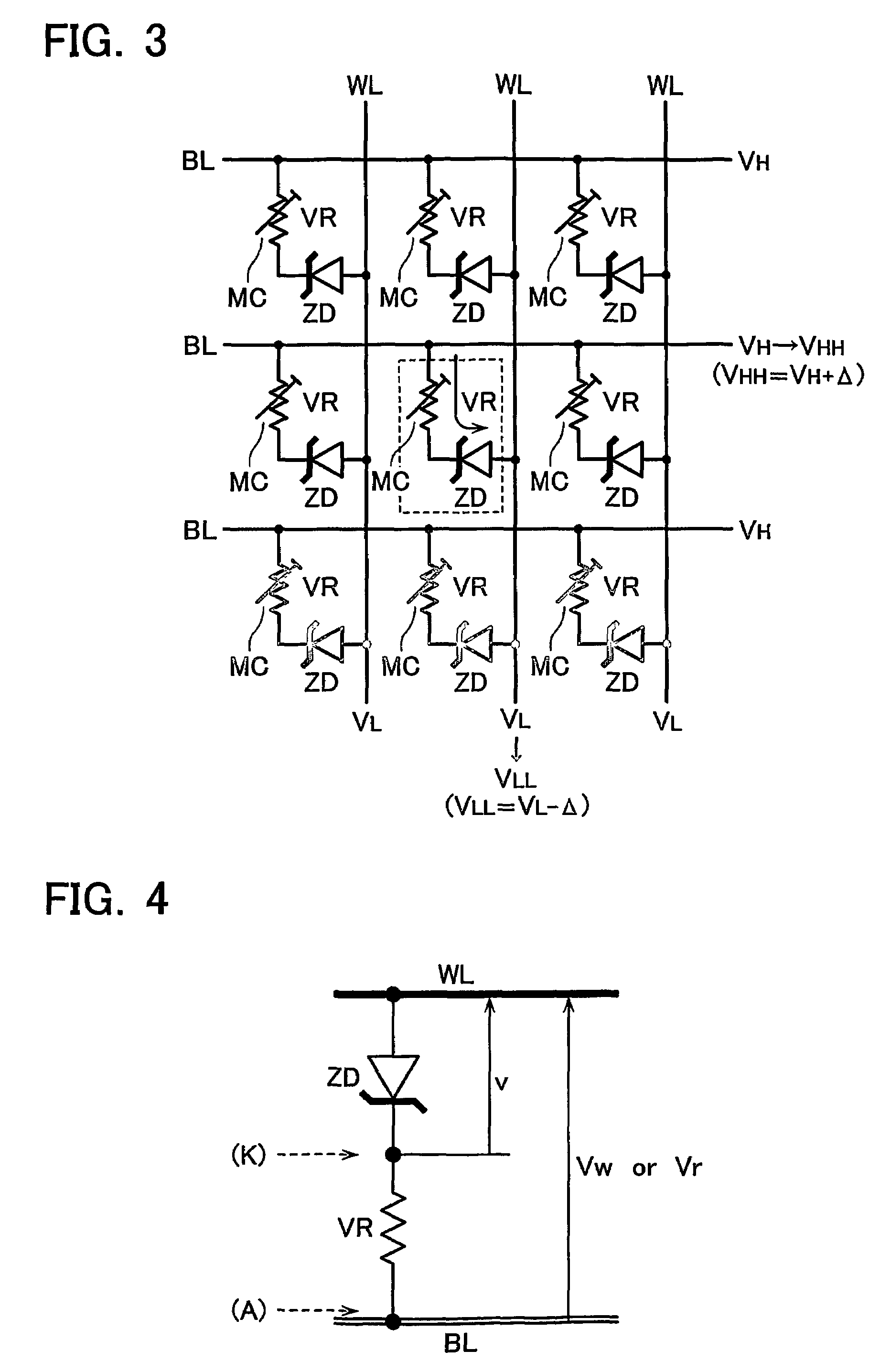
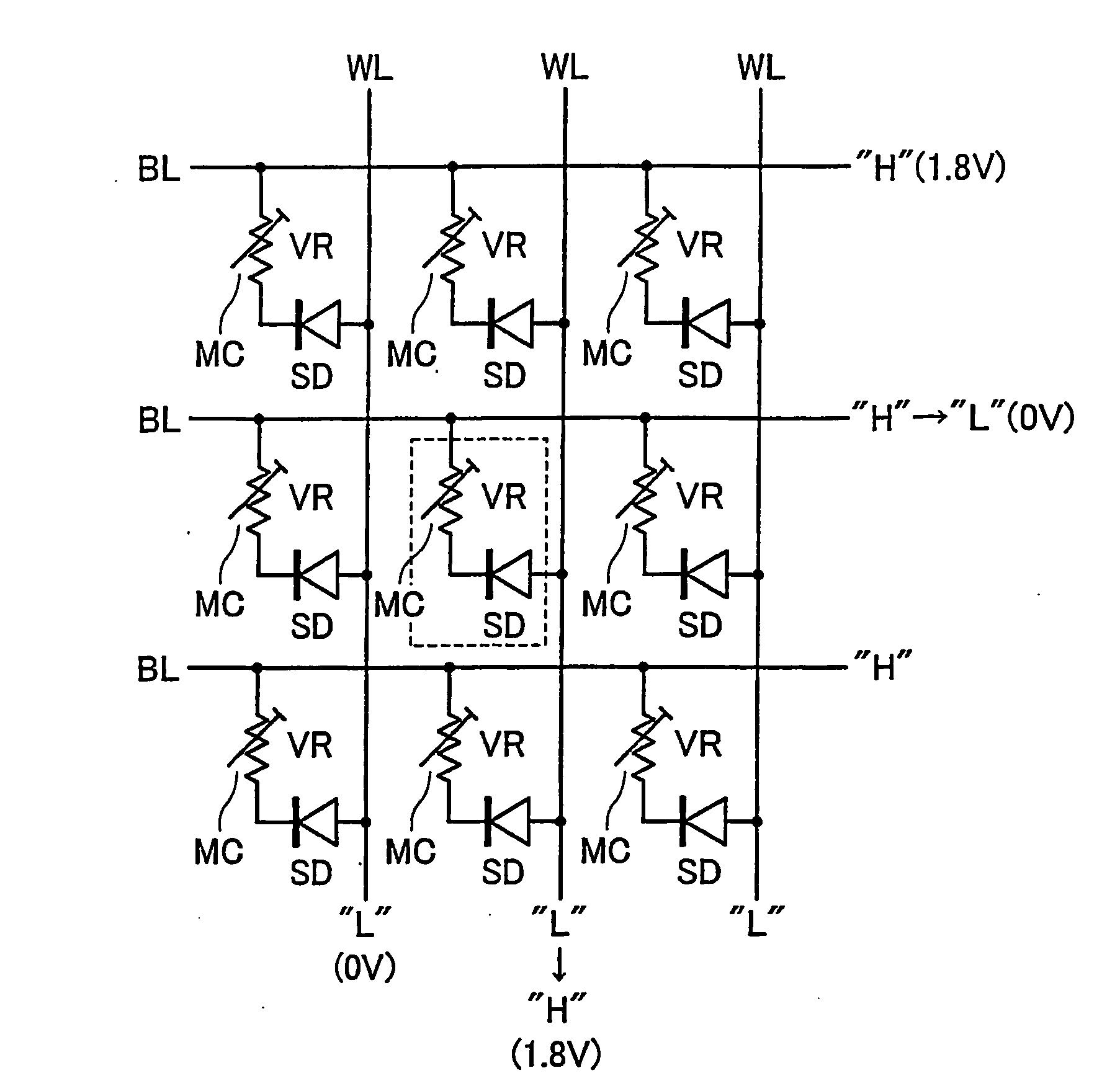
A phase-change memory device has a plurality of first wiring lines WL extending in parallel to each other, a plurality of second wiring lines BL which are disposed to cross the first wiring lines WL while being separated or isolated therefrom, and memory cells MC which are disposed at respective cross points of the first wiring lines WL and the second wiring lines BL and each of which has one end connected to a first wiring line WL and the other end connected to a second wiring line BL. The memory cell MC has a variable resistive element VR which stores as information a resistance value determined due to phase change between crystalline and amorphous states thereof, and a Schottky diode SD which is connected in series to the variable resistive element VR.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electro-resistance element, method of manufacturing the same and electro-resistance memory using the same
InactiveUS20080048164A1Reduce leakageFew associated short-circuitsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceOptoelectronics
An electro-resistance element that develops less leakage and fewer associated short-circuits even when an electro-resistance layer is made thinner, a method of manufacturing the same and an electro-resistance memory using the same are provided. The electro-resistance element includes a first electrode, a second electrode, an electro-resistance layer stacked between the first and the second electrodes and an insulating layer (a tunnel barrier layer). The tunnel barrier layer has a thickness in a range from 0.5 nm to 5 nm both inclusive. The electro-resistance layer is a layer having a plurality of states in which electric resistance values are different and being switchable between the states by applying a voltage or a current between the first and the second electrodes. The electro-resistance layer contains transition metal oxide as its main component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for starting power converters
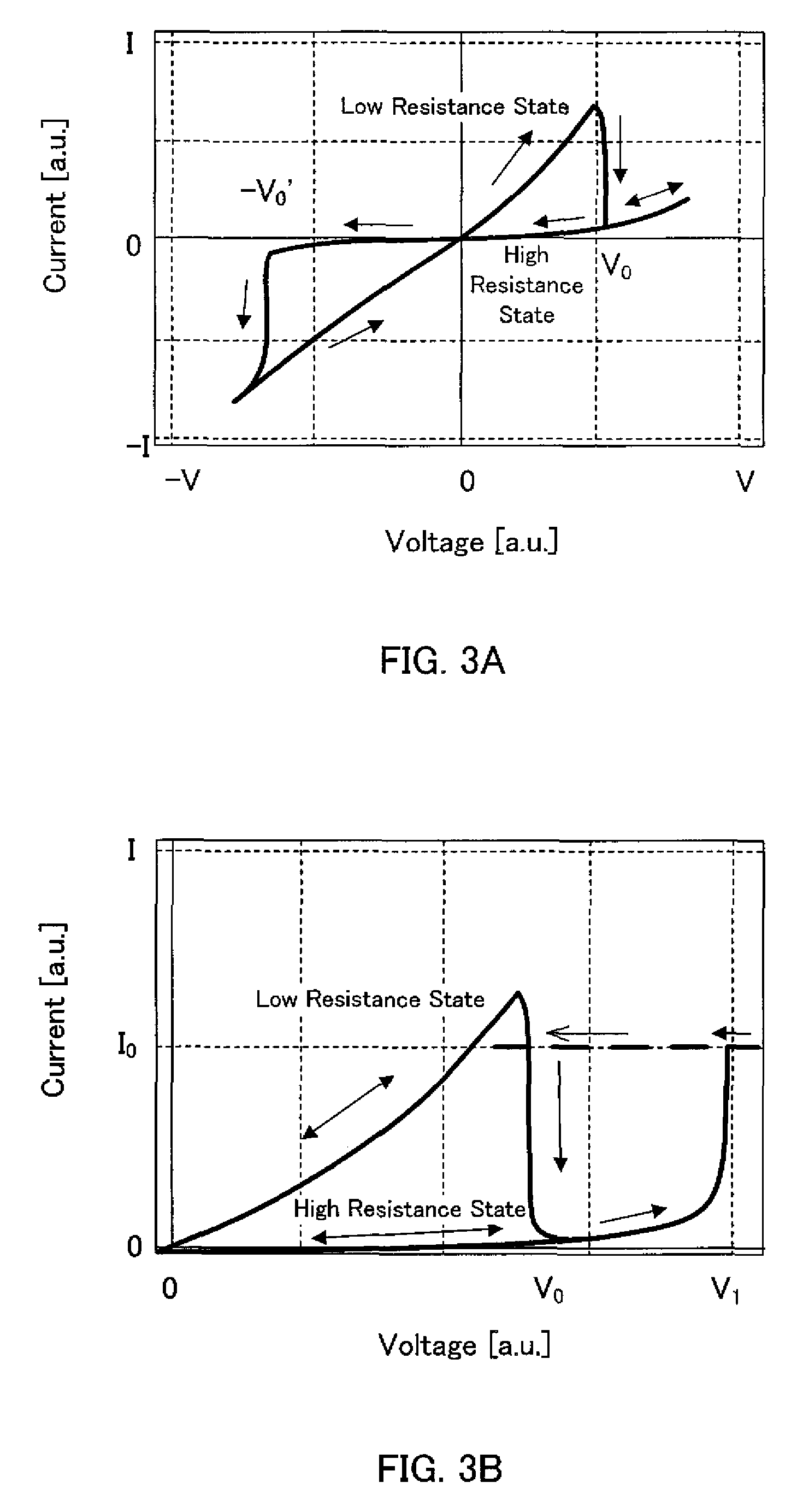
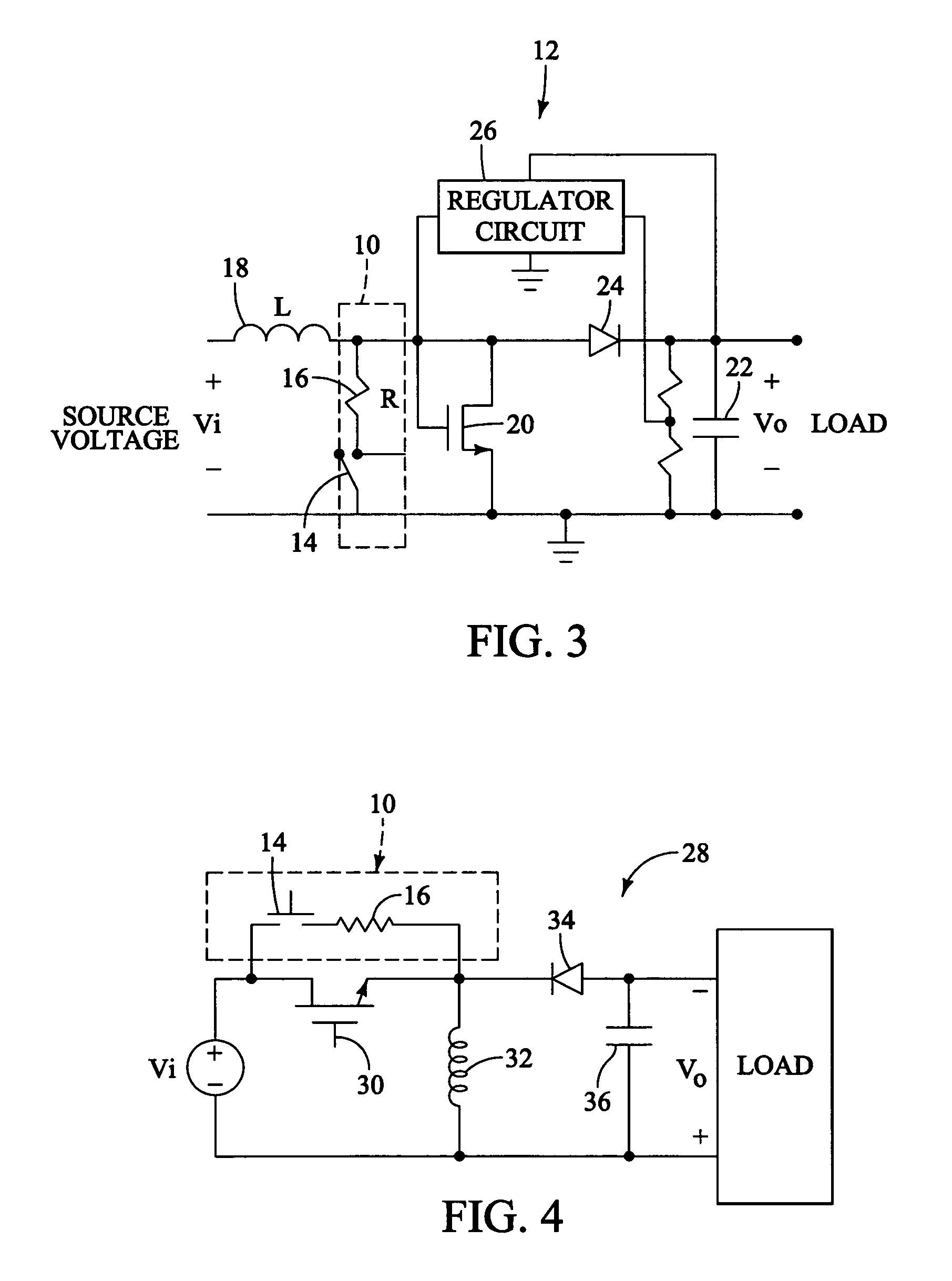
InactiveUS7078883B2Power supply linesDc-dc conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceResistive element
A startup circuit for starting a power converter for converting an input voltage to an output voltage includes a switch connected in series with a resistive element. The startup circuit is connected in parallel with a trigger switch in the power converter for enabling the power converter to generate the output voltage. When closed or activated, the switch in the startup circuit charges an energy storing device in the power converter. The energy storing device activates the trigger switch as the charge is released.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Direct resistance measurement corrosion probe
InactiveUS7034553B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A direct resistance measurement probe for measuring corrosion levels and material loss. The probe includes a hollow body having a resistive element at one end that is exposed to the environment. The probe can have an internal or external power source that is electrically connected to the resistive element. A meter measures the electrical resistance of the resistive element providing data from which corrosion rates may be ascertained. A temperature sensing device measures the temperature of the resistive element. A pressure sensing device measures the pressure of the environment that the resistive element is subjected to. The probe does not use a comparative or ratiometric reference element.
Owner:GILBOE DEREK
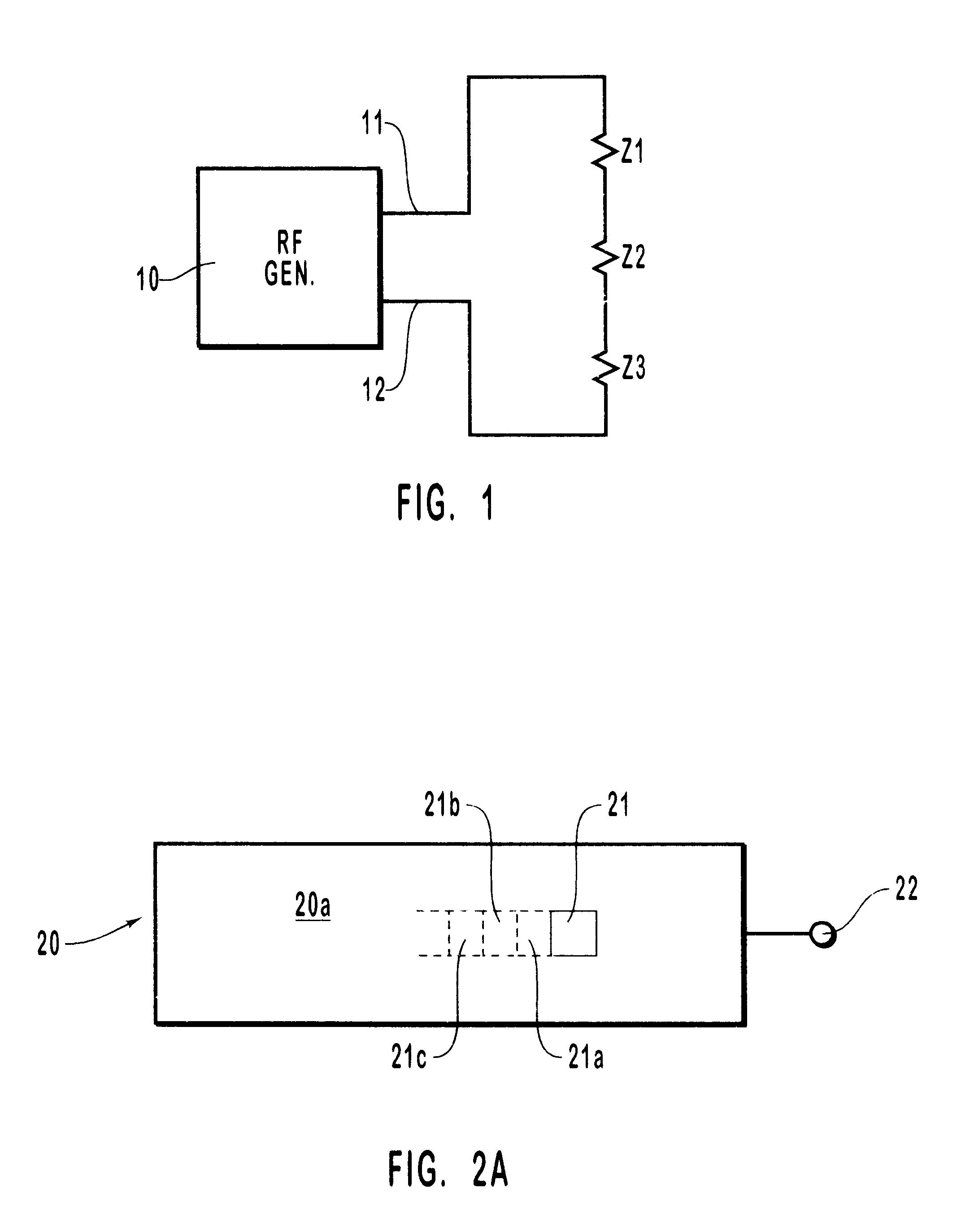
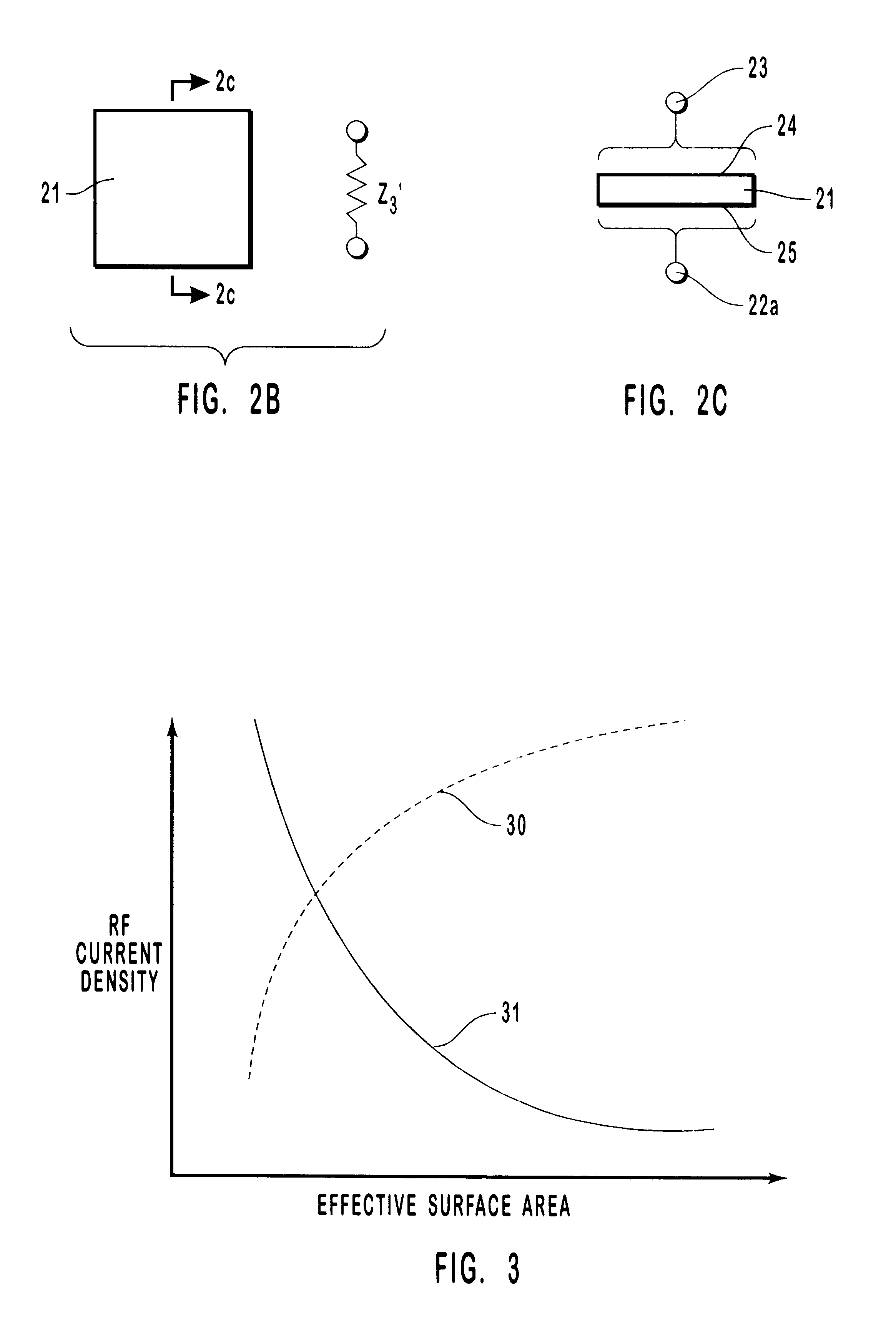
Self-limiting electrosurgical return electrode
InactiveUS6454764B1Eliminate burnsReduce the possibilityElectrotherapyDiagnosticsCapacitanceElectrical connection
A self-limiting electrosurgical return electrode for use with electrosurgery. Through the selection of impedance characteristics for the electrode materials of the principal body of the electrode, and through tailoring of electrode geometries, the return electrode of the present invention is self-regulating and self-limiting as to current density and temperature rise so as to prevent patient trauma. The electrosurgical return electrode includes a sheet of material having an effective bulk impedance equal to or greater than about 4,000 OMEGA.cm and one or more connectors for making electrical connection to the sheet. The effective bulk impedance of the sheet may arise from resistive components, capacitive components, inductive components, or combinations thereof. The configuration of the presently described return electrode allows the electrode to self-limit the electrode's current densities, thereby preventing burning of a patient during surgery. Furthermore, through employment of washable surface areas, the electrode is made readily cleanable, disinfectable, sterilizable, and reusable. An optional sleeve is provided for cooperative use with the electrode.
Owner:MEGADYNE MED PROD INC US
Multiple-Bit Programmable Resistive Memory Using Diode as Program Selector
ActiveUS20120314472A1Small cell sizeLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageResistive elementPolycrystalline silicon
A method and system for multiple-bit programmable resistive cells having a multiple-bit programmable resistive element and using diode as program selector are disclosed. The first and second terminals of the diode having a first and second types of dopants can be fabricated from source / drain of MOS in a well for MOS devices or fabricated on the same polysilicon structure. If a multiple-bit programmable resistive cell has 2n (n>1) distinct resistance levels to store n-bit data, at least 2n−1 reference resistance levels can be designated to differential resistances between two adjacent states. Programming multiple-bit programmable resistive elements can start by applying a program pulse with initial program voltage (or current) and duration. A read verification cycle can follow to determine if the desirable resistance level is reached. If the desired resistance level has not been reached, additional program pulses can be applied.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Biosensor circuit and sensor array consisting of a plurality of said biosensor circuits and biosensor array
InactiveUS7019305B2Highly integratedHigh degree of miniaturizationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayDevice form
Biosensor circuit arrangement including a substrate, a sensor element formed in or on a surface region of the substrate with a physical parameter, which is coupled to a substance to be examined, the type of coupling having a resistive component, the sensor element having an electrically conductive sensor electrode that is coupled to the substance to be examined, the sensor element having a measuring transistor the gate terminal of which is coupled to the electrically conductive sensor electrode, and the physical parameter being the threshold voltage of the measuring transistor, and a calibration device formed in or on the substrate, the calibration device being set up such that it is used to at least partly compensate for an alteration of the value of the physical parameter of the sensor element.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050227440A1Simple processEfficient preparation methodTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialMetal silicide
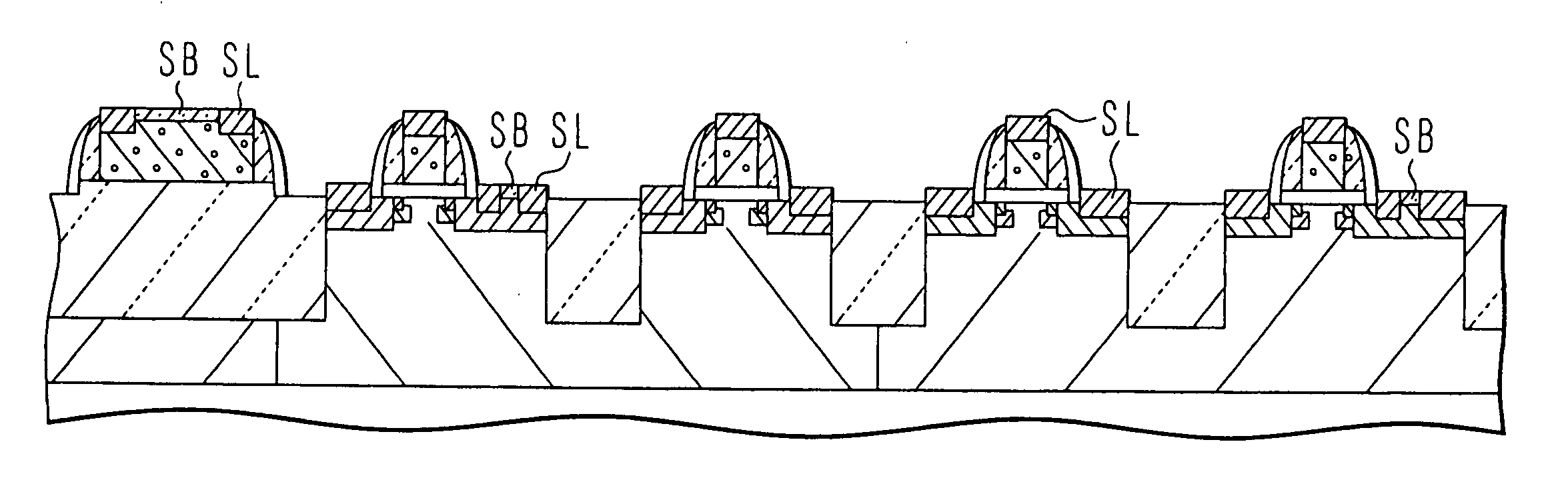
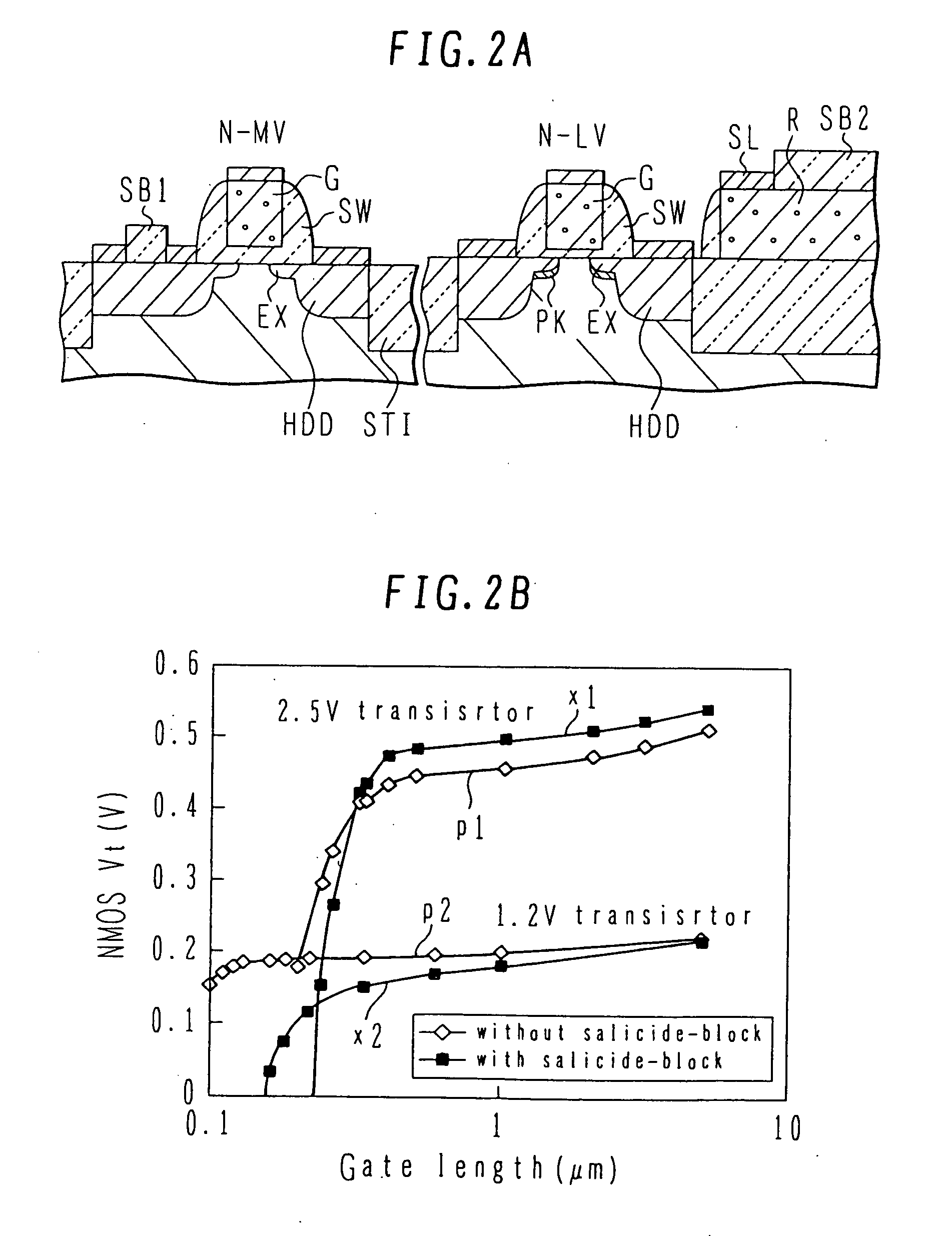
A semiconductor device manufacturing method includes, forming isolation region having an aspect ratio of 1 or more in a semiconductor substrate, forming a gate insulating film, forming a silicon gate electrode and a silicon resistive element, forming side wall spacers on the gate electrode, heavily doping a first active region with phosphorus and a second active region and the resistive element with p-type impurities by ion implantation, forming salicide block at 500° C. or lower, depositing a metal layer covering the salicide block, and selectively forming metal silicide layers. The method may further includes, forming a thick and a thin gate insulating films, and performing implantation of ions of a first conductivity type not penetrating the thick gate insulating film and oblique implantation of ions of the opposite conductivity type penetrating also the thick gate insulating film before the formation of side wall spacers.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Variable resistive element, manufacturing method for same, and non-volatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS8054674B2Improve processingSimple compositionSolid-state devicesDigital storageInterfacial oxidePower flow
Provided is a variable resistive element which performs high speed and low power consumption operation. The variable resistive element comprises a metal oxide layer between first and second electrodes wherein electrical resistance between the first and second electrodes reversibly changes in accordance with application of electrical stress across the first and second electrodes. The metal oxide layer has a filament, which is a current path where the density of a current flowing between the first and second electrodes locally increases. A portion including at least the vicinity of an interface between the certain electrode, which is one or both of the first and second electrodes, and the filament, on an interface between the certain electrode and the metal oxide layer is provided with an interface oxide which is an oxide of at least one element included in the certain electrode and different from the oxide of the metal oxide layer.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
AD converter
InactiveUS8106806B2Reduce power consumptionReduce areaElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
Owner:SONY CORP
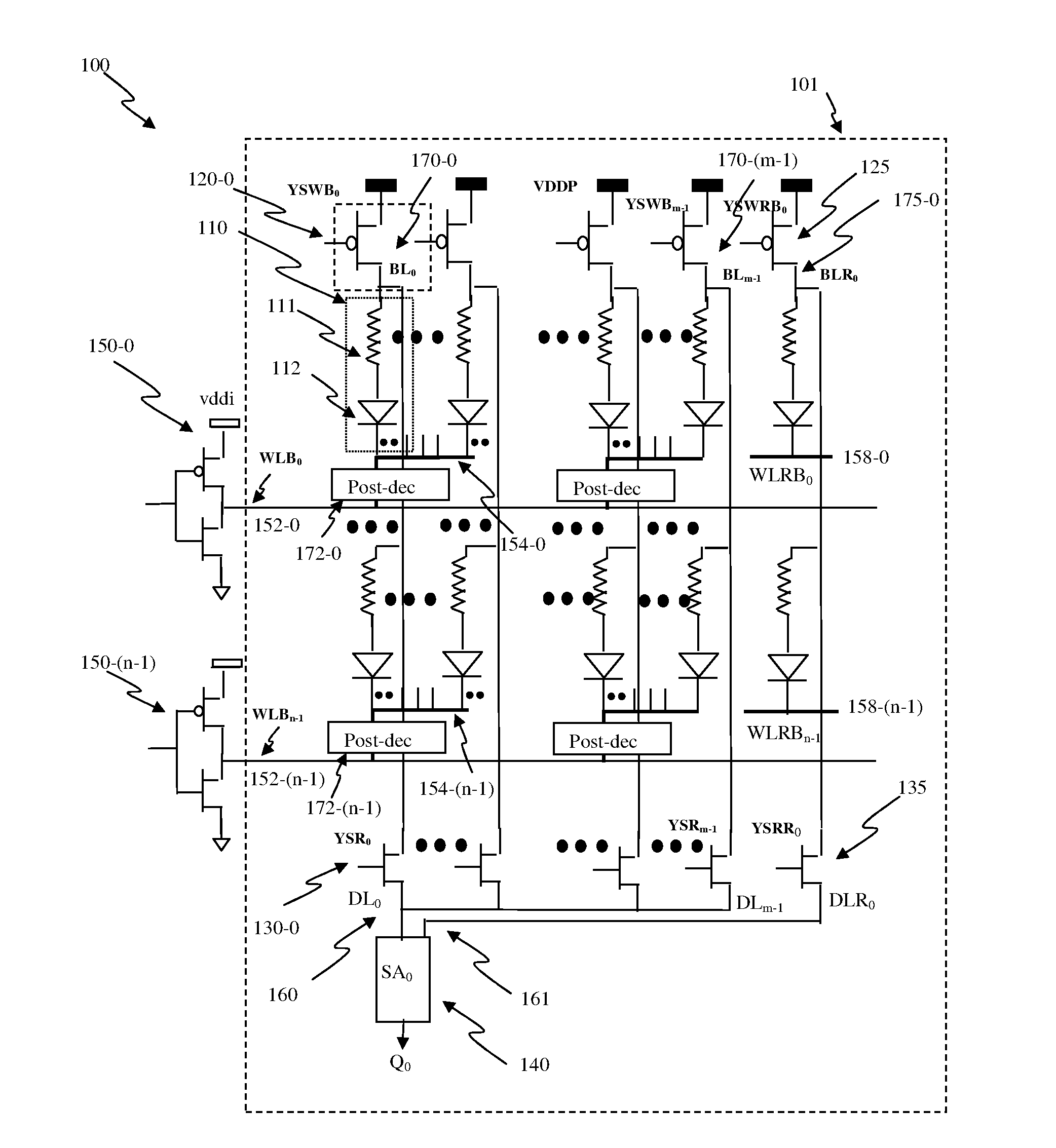
Nonvolatile memory device having two or more resistance elements and methods of forming and using the same
ActiveUS20060131554A1Solid-state devicesDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceDevice form
A nonvolatile memory device having two or more resistors and methods of forming and using the same. A nonvolatile memory device having two resistance layers, and more particularly, to a nonvolatile memory device formed and operated using a resistance layer having memory switching characteristics and a resistance layer having threshold switching characteristics. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device may include a lower electrode; a first resistance layer having at least two resistance characteristics formed on the lower electrode, a second resistance layer having threshold switching characteristics formed on the first resistance layer, and an upper electrode formed on the second resistance layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device with magnetoresistance elements and method of writing data into the same
InactiveUS20050036361A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriver circuitMagnetic reluctance
A semiconductor memory device includes memory cells, first wirings, a first current driver circuit, and a second current driver circuit. The memory cell includes a magneto-resistive element having a first ferromagnetic film, an insulating film formed on the first ferromagnetic film, and a second ferromagnetic film formed on the insulating film. The first wiring is provided in close proximity to and insulated from the magneto-resistive element. The first current driver circuit supplies a first current to the first wiring in a write operation to produce a magnetic field around the magneto-resistive elements. The second current driver circuit supplies a second current between the first and second ferromagnetic films via the insulating film in a write and a read operation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Programmable Resistive Memory Unit with Multiple Cells to Improve Yield and Reliability
ActiveUS20120320657A1Small cell sizeLow costRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPolycrystalline silicon
A method and system for a programmable resistive memory to improve yield and reliability has a plurality of programmable resistive units. Each programmable resistive unit can have at least one programmable resistive cell. Each programmable resistive cell can have a programmable resistive element with a first end coupled to a first supply voltage line and a second end coupled to at least one diode serving as program selector. Each diode can have at least first and second terminals with first and second types of dopants, with the second terminal being coupled to a second supply voltage line. The first and second terminals of the diode can be fabricated from source / drain of MOS in a well for MOS devices or fabricated on the same polysilicon structure.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure, and magneto-resistive element and spintronics device each using same
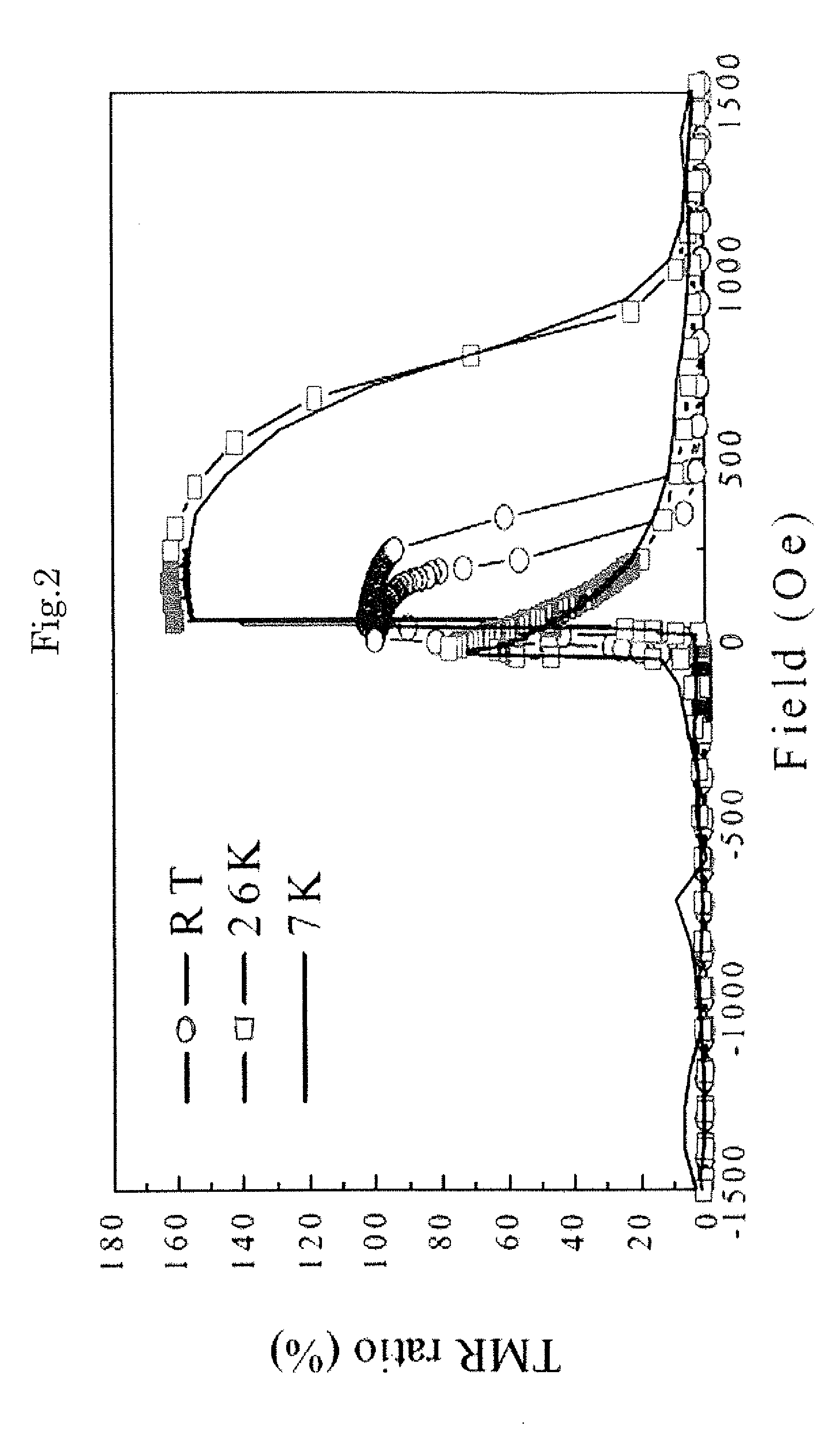
ActiveUS20120091548A1Quality improvementLarge TMRNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceAlloy
Disclosed is a ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure which is characterized by having a tunnel barrier layer that comprises a non-magnetic material having a spinel structure. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure is also characterized in that the non-magnetic material is substantially MgAl2O4. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction is also characterized in that at least one of the ferromagnetic layers comprises a Co-based full Heusler alloy having an L21 or B2 structure. The ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure is also characterized in that the Co-based full Heusler alloy comprises a substance represented by the following formula: Co2FeAlxSi1-x (0≦x≦1). Also disclosed are a magnetoresistive element and a spintronics device, each of which utilizes the ferromagnetic tunnel junction structure and can achieve a high TMR value, that cannot be achieved by employing conventional tunnel barrier layers other than a MgO barrier.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070029676A1Improve reliabilityImprove manufacturing yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialElectrical connection
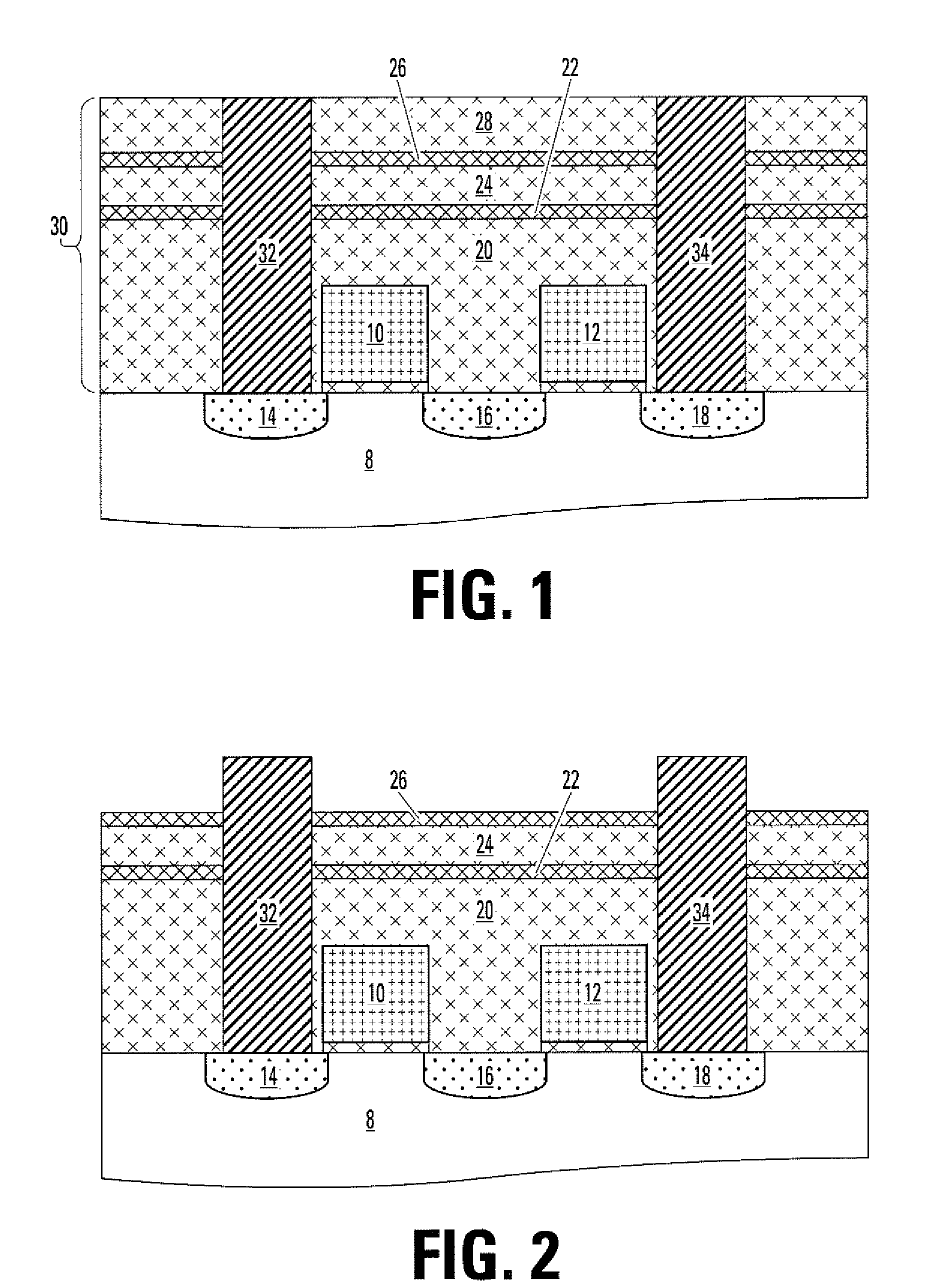
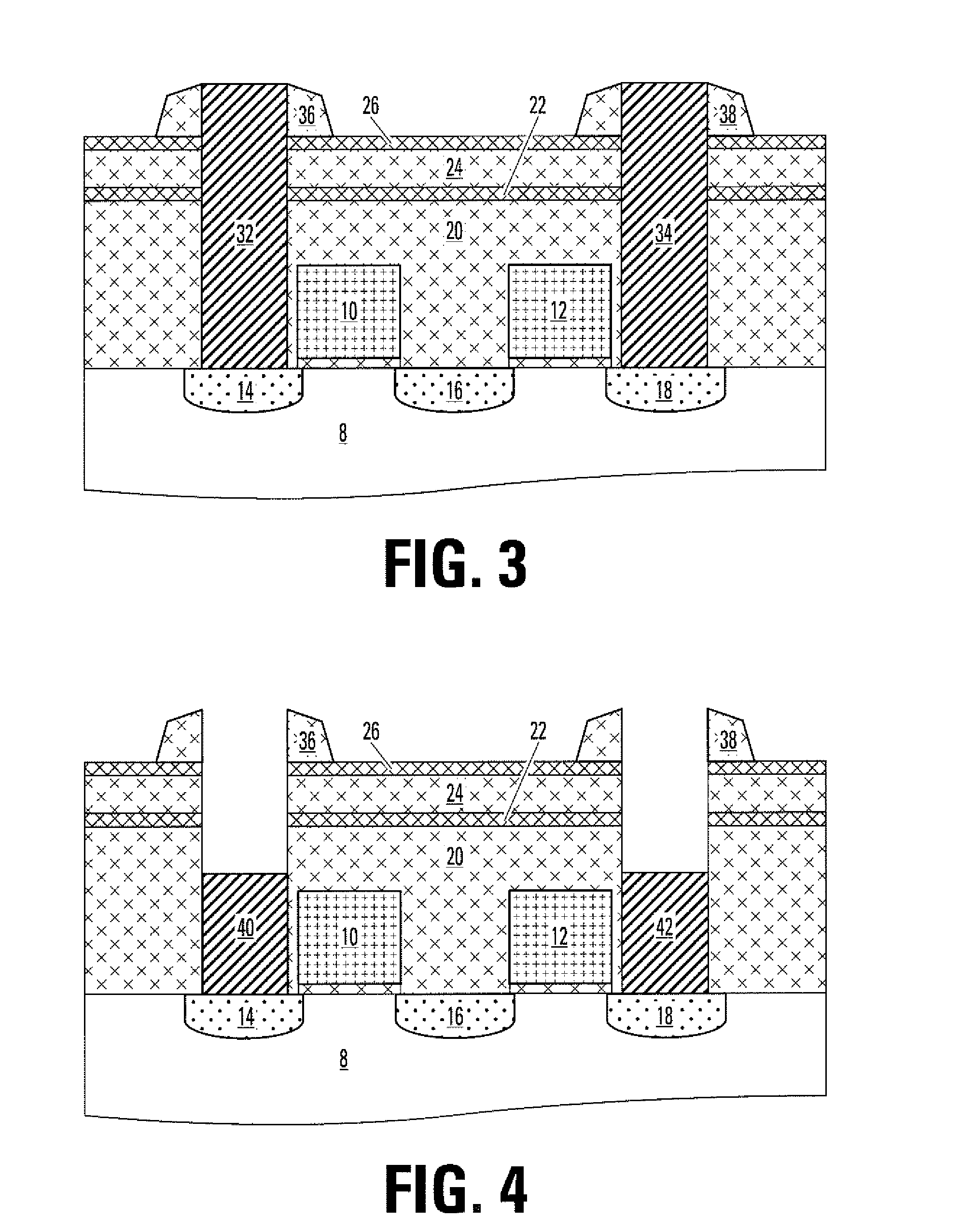
A resistor element formed of a peel-preventive film, a recording layer made of chalcogenide, and an upper electrode film is formed on a semiconductor substrate, first and second insulation films are formed so as to cover the resistor element, a via hole for exposing the upper electrode film is formed through the first and second insulation films, and a plug for electrical connection to the upper electrode film is formed in the via hole. To form the via hole, the first insulation film made of silicon nitride is used as an etching stopper to perform dry etching on the second insulation film. Then, dry etching is performed on the first insulation film to expose the upper electrode film from the via hole.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
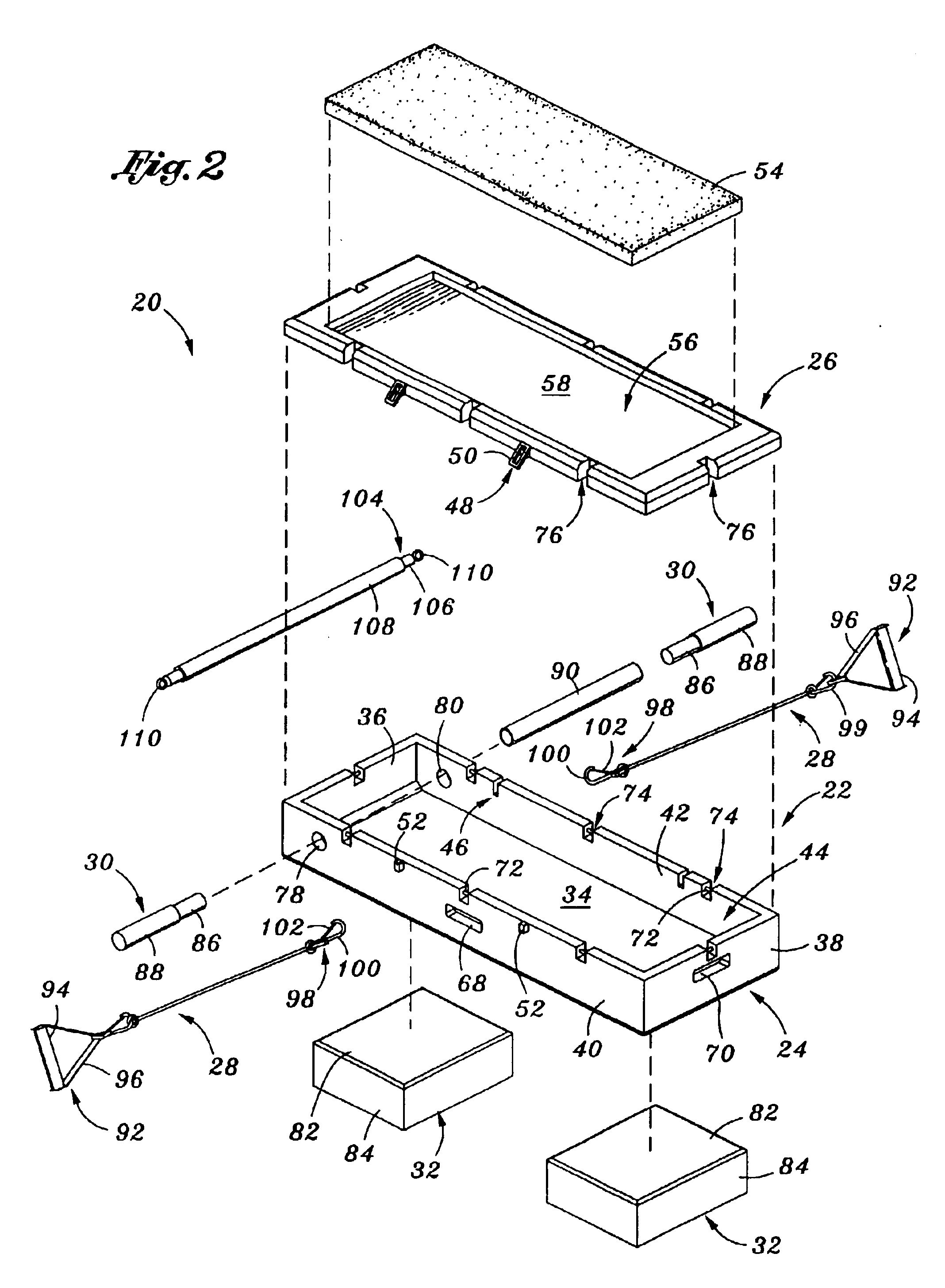
Exercise apparatus
InactiveUS6908417B2Resilient force resistorsSpace saving gamesElectrical resistance and conductanceInterior space
An exercise apparatus, a method of using the apparatus, and a method of exercising are disclosed. In one or more embodiments, the exercise apparatus comprises an exercise platform comprising a base and a lid, the platform defining an interior space accessible by moving the lid from a closed to an open position with respect to the base, at least one handle associated with the platform for use by a user in moving the exercise apparatus, at least one wheel movably mounted to the base and permitting the platform to be rolled along a surface, at least one riser for use in supporting the platform upon a surface to increase a height thereof and sized to fit within the interior space when not in use, at least one resistive element for selective attachment to the platform for use in an exercise by a user, at least one mount associated with the platform to which the at least one resistive element may be attached, and at least one hand / foot peg for use with the platform.
Owner:POWERBOX FITNESS
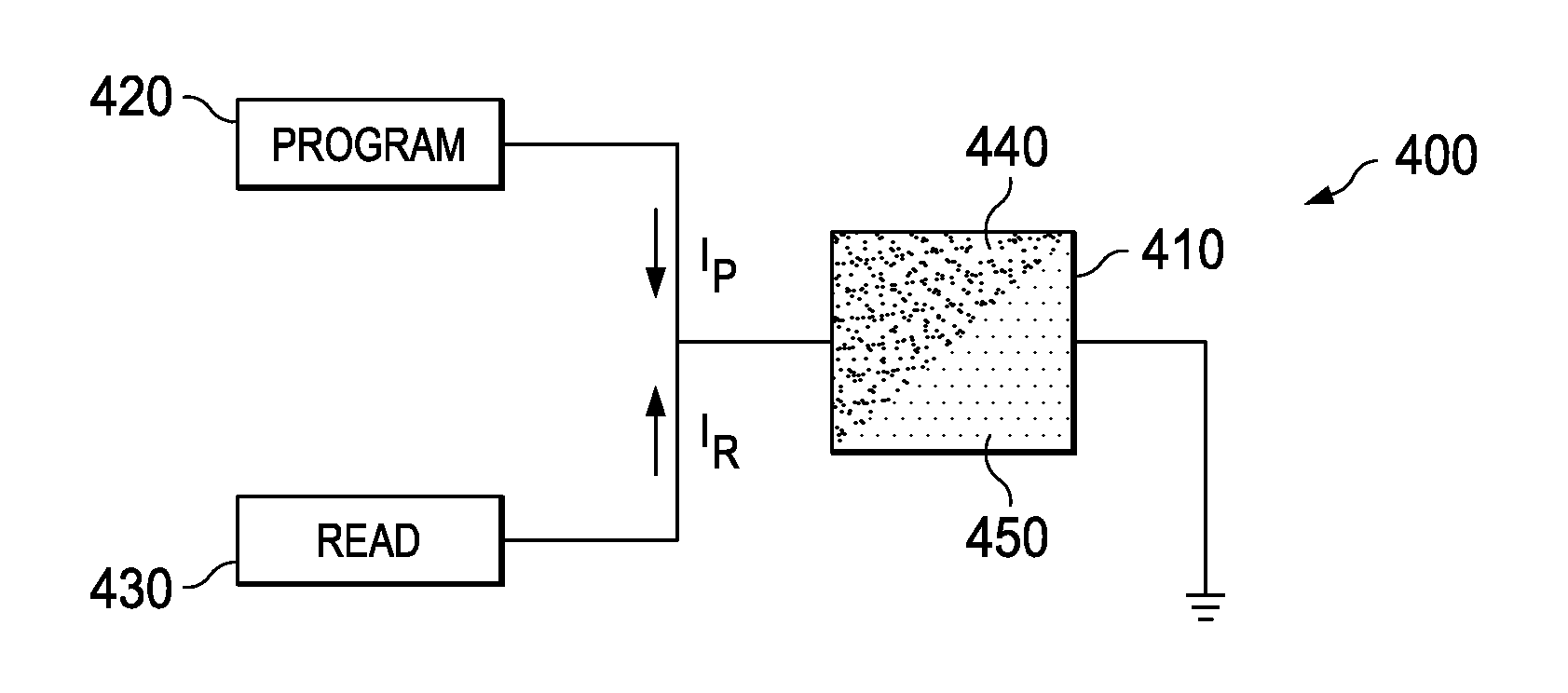
Modification of logic by morphological manipulation of a semiconductor resistive element
An electronic device includes a substrate with a resistive element located thereover. The resistive element includes a semiconductor region. A read module is configured to determine a resistance of the resistive element. A programming module is configured to cause a current to flow through the semiconductor region. The current is sufficient to induce a change of morphology of at least a portion of the semiconductor region.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com