Patents
Literature
8018 results about "Electrical resistivity and conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) and its inverse, electrical conductivity, is a fundamental property of a material that quantifies how strongly it resists or conducts electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter ρ (rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-meter (Ω⋅m). For example, if a 1 m × 1 m × 1 m solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the resistance between these contacts is 1 Ω, then the resistivity of the material is 1 Ω⋅m.
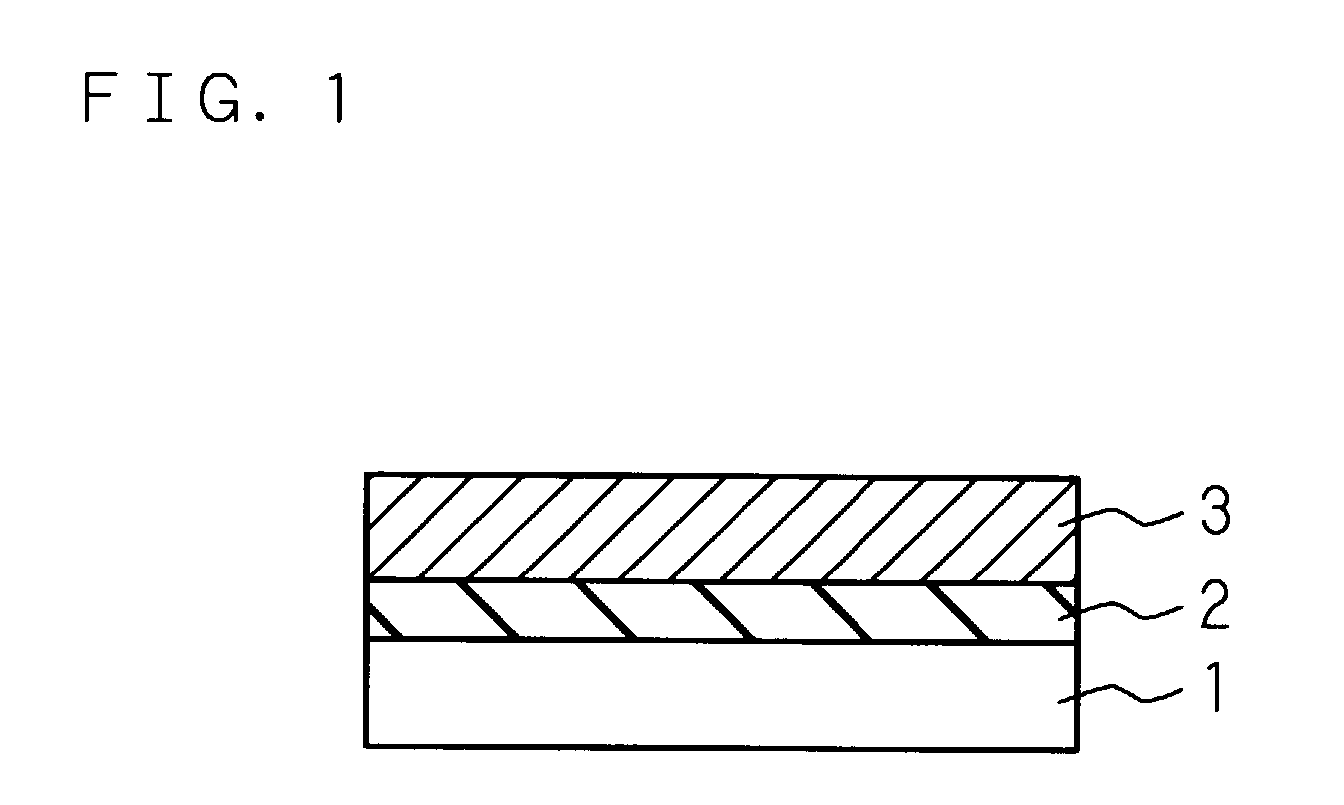
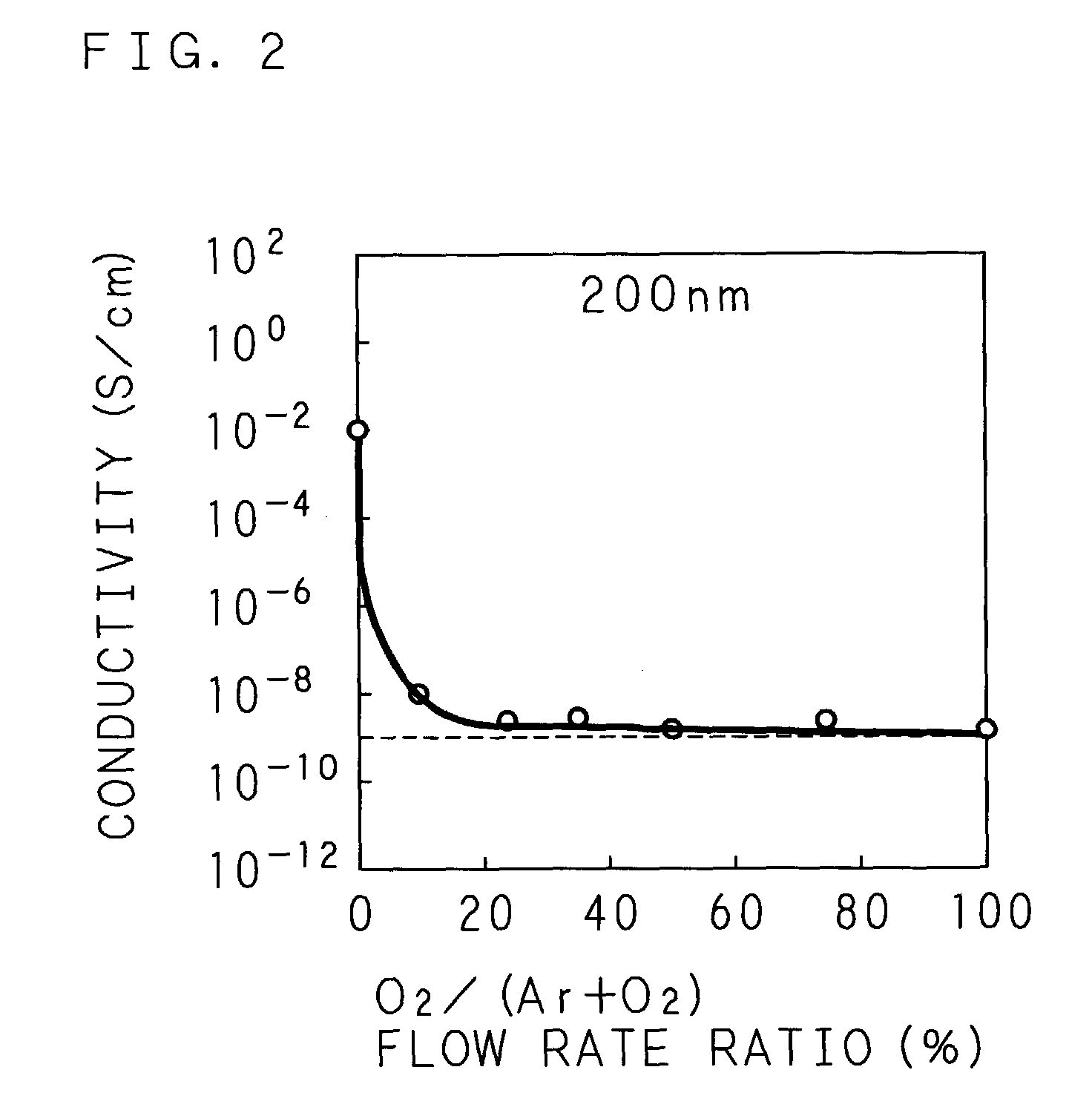
Method for forming ZnO film, method for forming ZnO semiconductor layer, method for fabricating semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS7049190B2High crystallinityLow costTransistorPolycrystalline material growthX-rayElectrical resistivity and conductivity
A ZnO buffer layer having an electric conductivity of 1×10−9 S / cm or lower or alternatively a ZnO buffer layer having a diffraction peak of a crystal face other than (002) and (004) in X-ray diffraction is formed on a substrate by sputtering. A ZnO semiconductor layer is formed on the ZnO buffer layer. The ZnO semiconductor layer is formed under the condition that the flow rate ratio of an oxygen gas in a sputtering gas is lower than that in the formation of the ZnO buffer layer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Absorbent article comprising a synthetic polymer derived from a renewable resource and methods of producing said article
An absorbent article is disclosed having a topsheet, a backsheet joined with the topsheet, an absorbent core disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet, and a synthetic superabsorbent polymer derived from a first renewable resource via at least one intermediate compound, wherein said superabsorbent polymer exhibits a defined Saline Flow Conductivity value and Absorption Against Pressure value. Alternately, an absorbent article is disclosed having a synthetic polyolefin derived from a first renewable resource via at least one intermediate compound. The synthetic polyolefin exhibits defined performance characteristics making the polyolefin particularly useful in certain components of the absorbent article. Methods for making the aforementioned absorbent articles are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Elimination-absorber monitoring system
InactiveUS6246330B1Complicating power requirementEffectively overcome problemBaby linensAlarmsMonitoring systemEngineering
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Method of monitoring glucose level
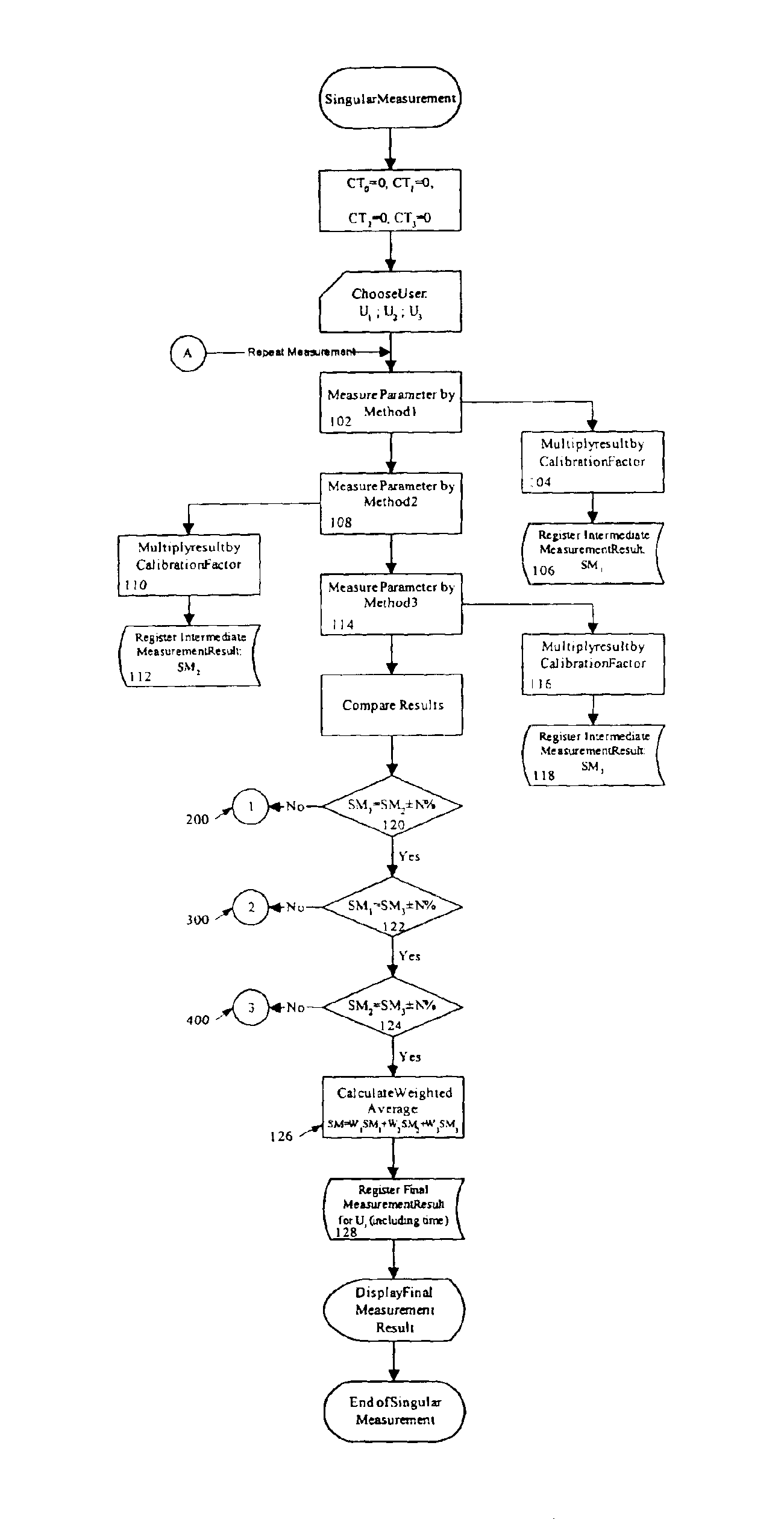
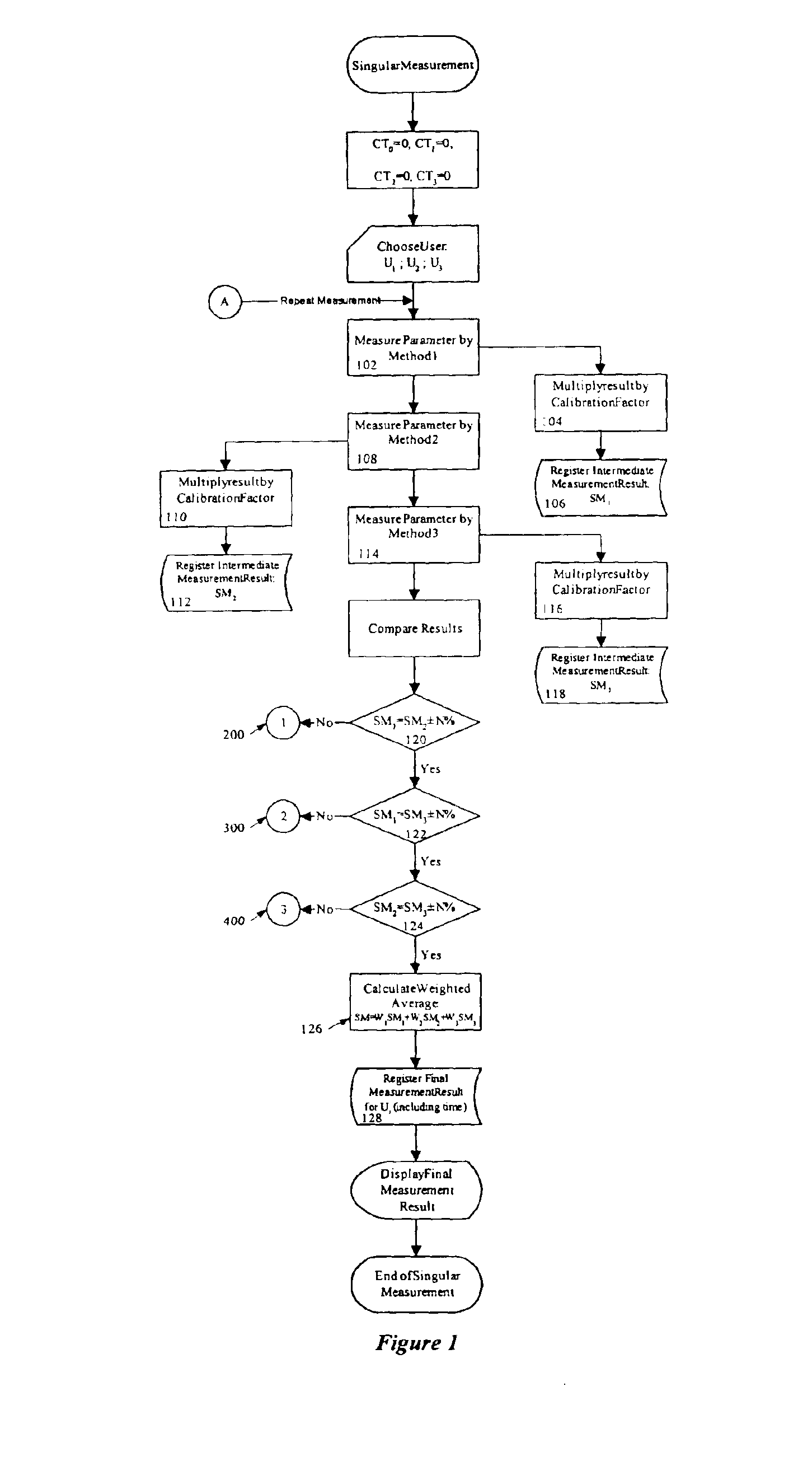
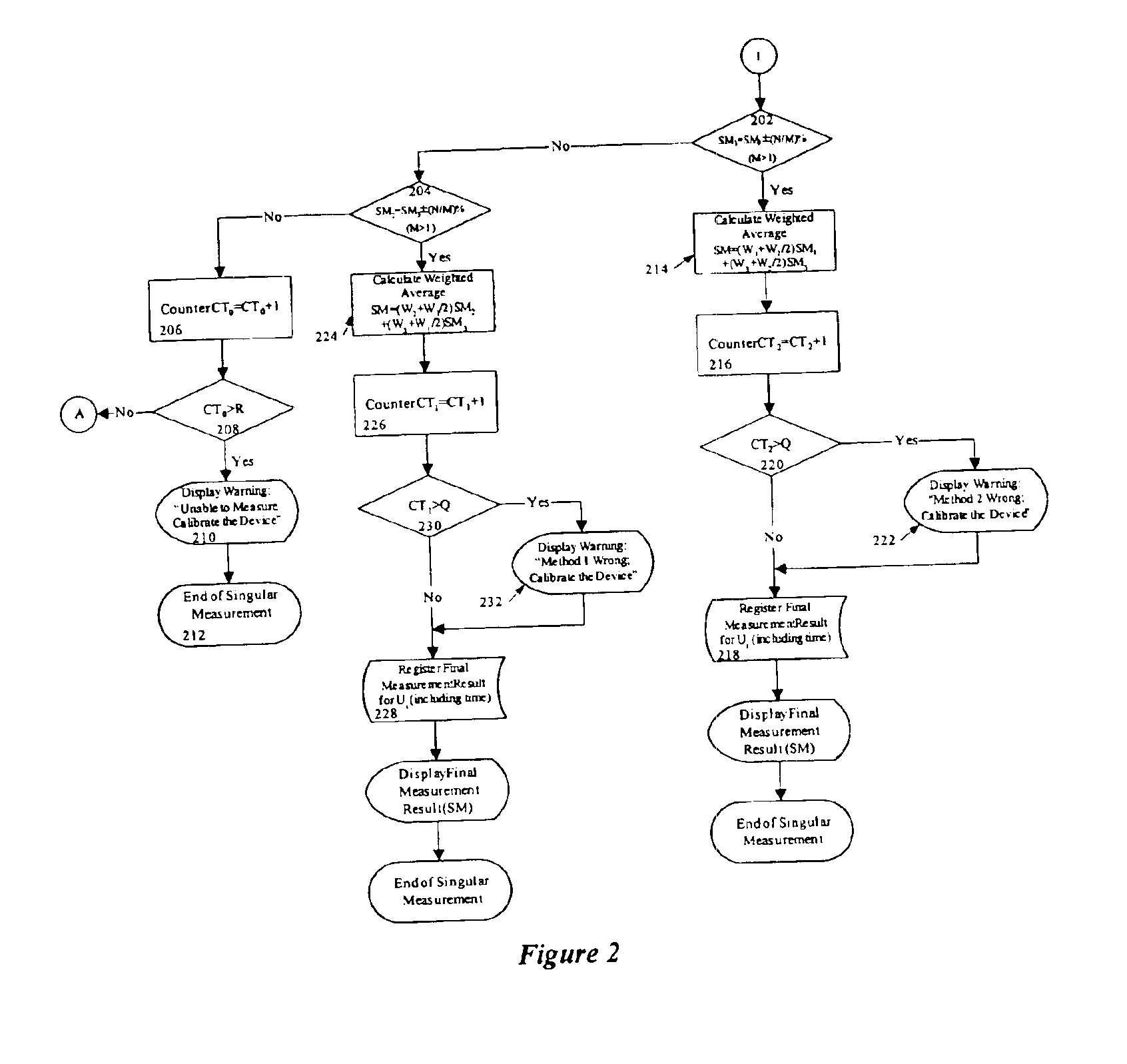
The method of monitoring or measuring the concentration of glucose level in human and animal blood uses a non-invasive technique and includes measurements of the speed of sound through the blood, the conductivity of the blood, and the heat capacity of the blood, or by non-invasive measurement of any other parameters that can be used to calculate the glucose level. Thereafter, the glucose level for each of the three measurements is calculated and the final glucose value is determined by a weighted average of the three calculated glucose values.
Owner:JMS DIVERSIFIELD HLDG
Absorbent Article Comprising A Synthetic Polymer Derived From A Renewable Resource And Methods Of Producing Said Article
Owner:HIRD BRYN +1
Conductivity reconstruction based on inverse finite element measurements in a tissue monitoring system
InactiveUS7169107B2Low and high conductivityReduce conductivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical devicesElectrical impedance tomographyEngineering
An impedance model of tissue is useful for describing conductivity reconstruction in tissue. Techniques for determining and mapping conductivity distribution in tissue supply useful information of anatomical and physiological status in various medical applications. Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) techniques are highly suitable for analyzing conductivity distribution. Electrical characteristics of tissue include resistive elements and capacitive elements. EIT techniques involve passing a low frequency current through the body to monitor various anatomical and physiological characteristics. The system can interrogate at multiple frequencies to map impedance. Analytical techniques involve forward and inverse solutions to boundary value analysis to tissue characteristics.
Owner:INOTECH MEDICAL SYST
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050045919A1Increase the areaFine granularitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A programmable semiconductor device has a switch element in an interconnection layer, wherein in at least one of the inside of a via, interconnecting a wire of a first interconnection layer and a wire of a second interconnection layer, a contact part of the via with the wire of the first interconnection layer and a contact part of the via with the wire of the second interconnection layer, there is provided a variable electrical conductivity member, such as a member of an electrolyte material. The via is used as a variable electrical conductivity type switch element or as a variable resistance device having a contact part with the wire of the first interconnection layer as a first terminal and having a contact part with the wire of the second interconnection layer as a second terminal. By varying the electrical conductivity of the switch element, the state of connection of the via with the wire of the first interconnection layer and the state of connection of the via with the wire of the second interconnection layer may be variably set to a shorted state, an open-circuited state or to an intermediate state A two-state switch element includes an ion conductor for conducting metal ions interposed between the first and second electrodes. The second electrode is formed of a material lower in reactivity than the first electrode. The electrical conductivity across the first and second electrodes is changed by the oxidation-reduction reaction of the metal ions. There are provided first and second transistors of opposite polarities, connected to the first electrode, and third and fourth transistors of opposite polarities, connected to the second electrode.
Owner:NEC CORP
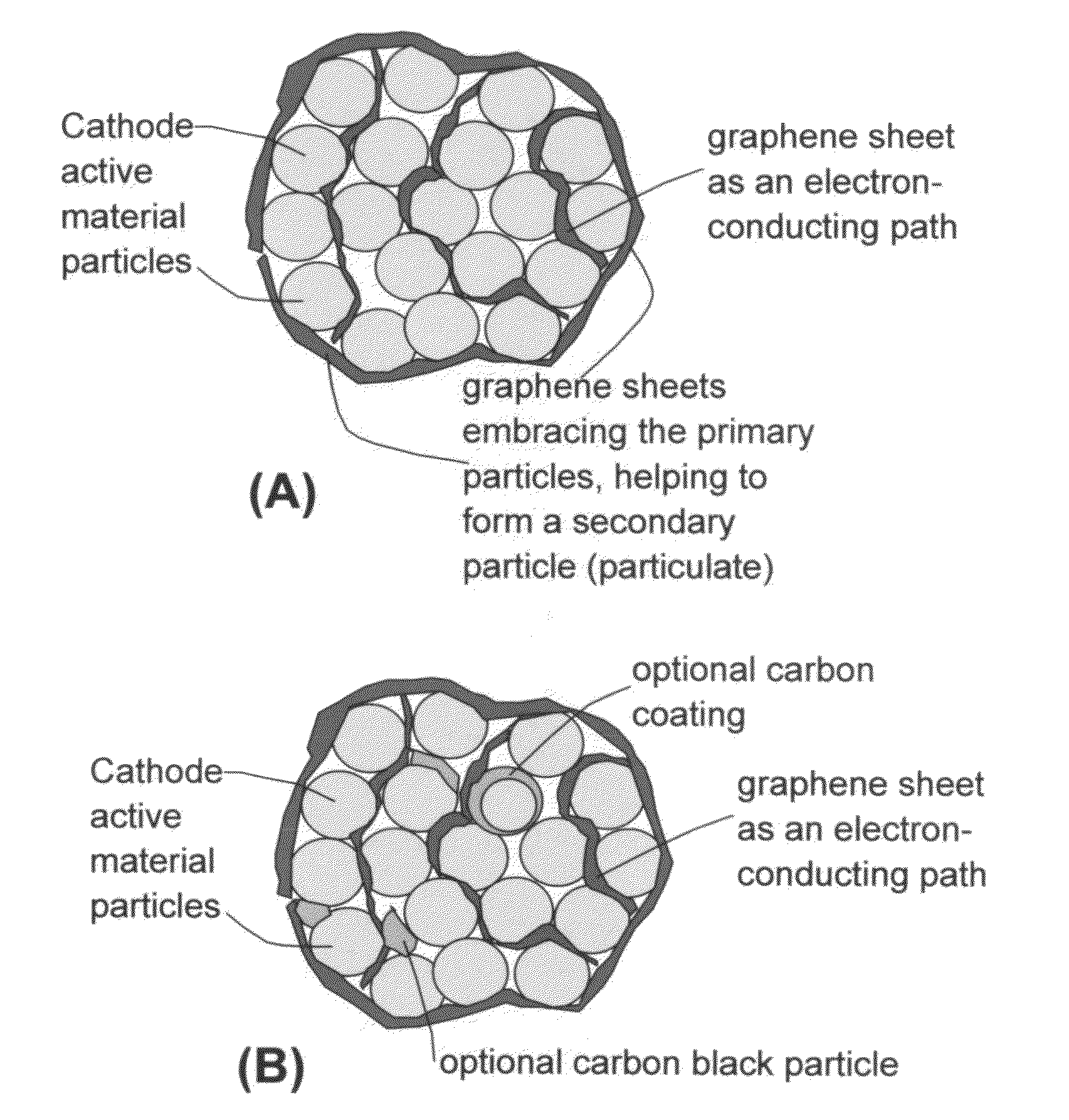
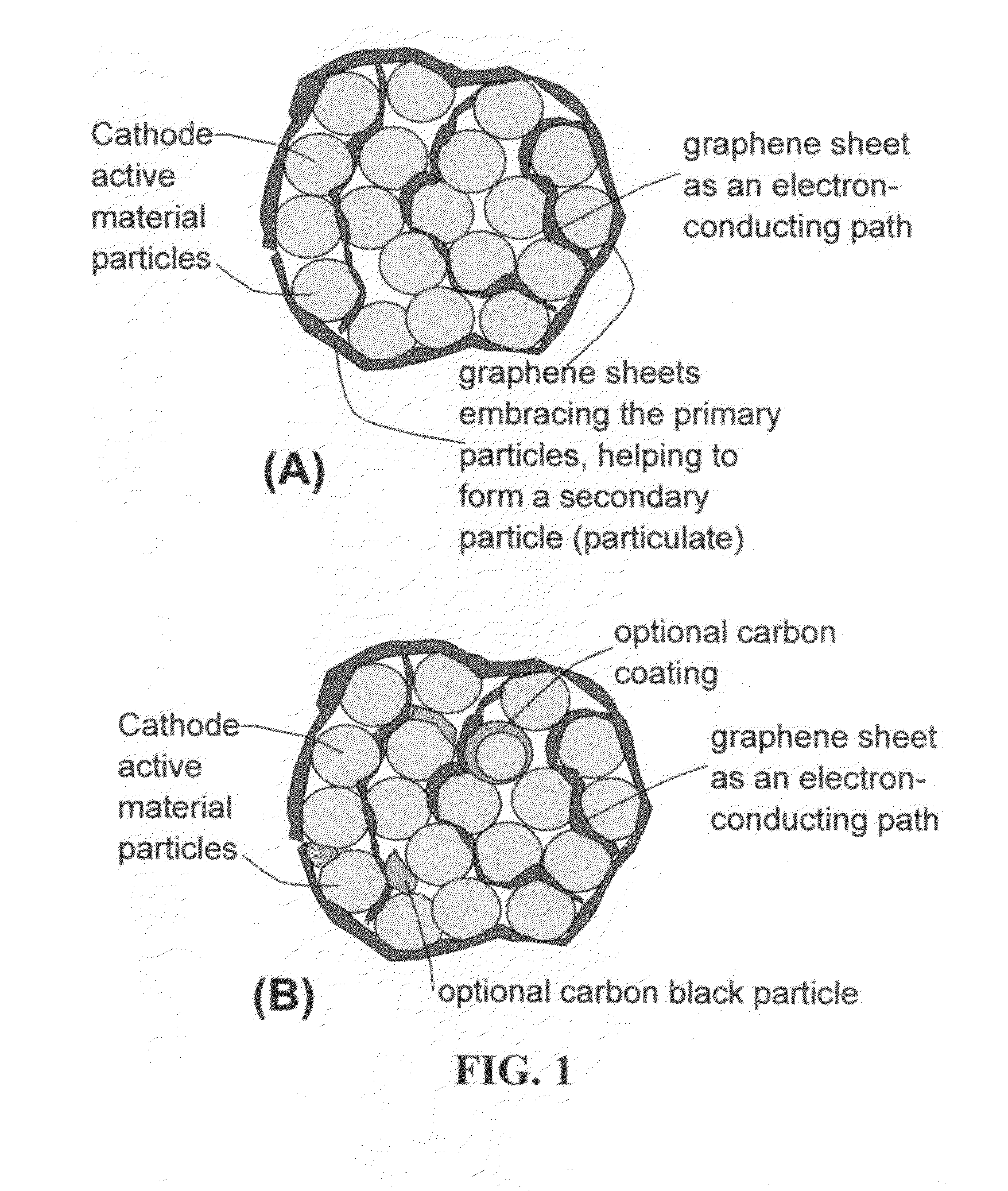
Graphene-Enhanced cathode materials for lithium batteries
ActiveUS20120058397A1Short timeEasy dischargeNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesCvd graphene
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium battery cathode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine cathode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm (preferably sub-micron or nano-scaled), and the graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into an individual discrete particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the cathode active material particles, and wherein the particulate has an electrical conductivity no less than 10−4 S / cm and the graphene is in an amount of from 0.01% to 30% by weight based on the total weight of graphene and the cathode active material combined.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Electro-optic display and materials for use therein
InactiveUS20070035808A1Improve conductivityHigh viscosityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesives without carriersAdhesiveDisplay device
An electro-optic display comprises a layer (130) of a solid electro-optic material, at least one electrode disposed adjacent the layer (130) of electro-optic material, and a layer (180) of a lamination adhesive interposed between the layer (130) of electro-optic material and the electrode, the lamination adhesive (180) having a higher electrical conductivity in a direction perpendicular to the layer of lamination adhesive than in the plane of the layer.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Ionically conductive membranes for protection of active metal anodes and battery cells
InactiveUS20040191617A1Improve propertiesImprove ionic conductivitySolid electrolytesSolid electrolyte cellsChemical stabilityBattery cell
Disclosed are ionically conductive membranes for protection of active metal anodes and methods for their fabrication. The membranes may be incorporated in active metal negative electrode (anode) structures and battery cells. In accordance with the invention, the membrane has the desired properties of high overall ionic conductivity and chemical stability towards the anode, the cathode and ambient conditions encountered in battery manufacturing. The membrane is capable of protecting an active metal anode from deleterious reaction with other battery components or ambient conditions while providing a high level of ionic conductivity to facilitate manufacture and / or enhance performance of a battery cell in which the membrane is incorporated.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Elimination - absorber monitoring system
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Microelectronic device and method for label-free detection and quantification of biological and chemical molecules
InactiveUS6482639B2Sensitive and accurate detectionWide scope of practical and worthwhile utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceField-effect transistor
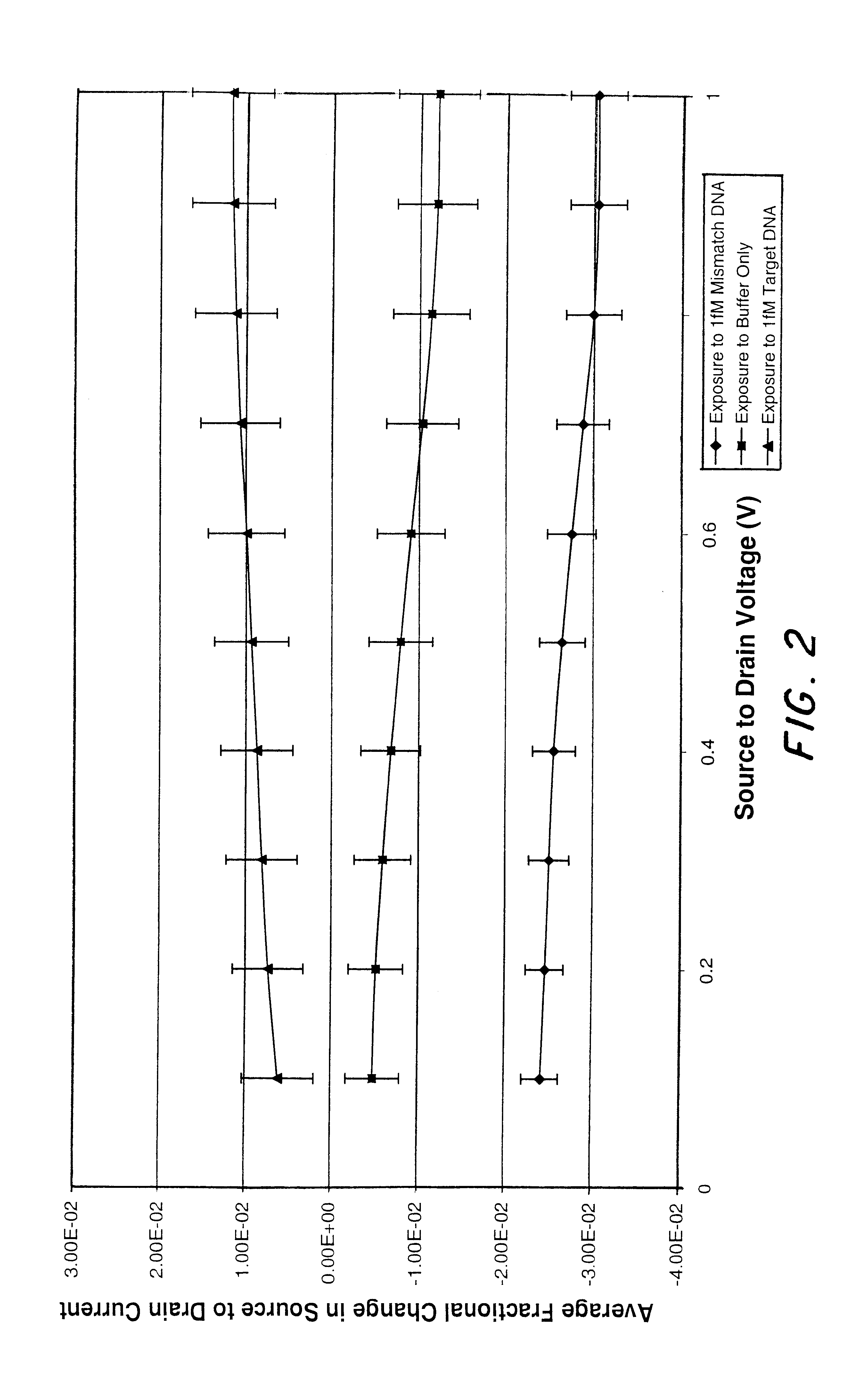
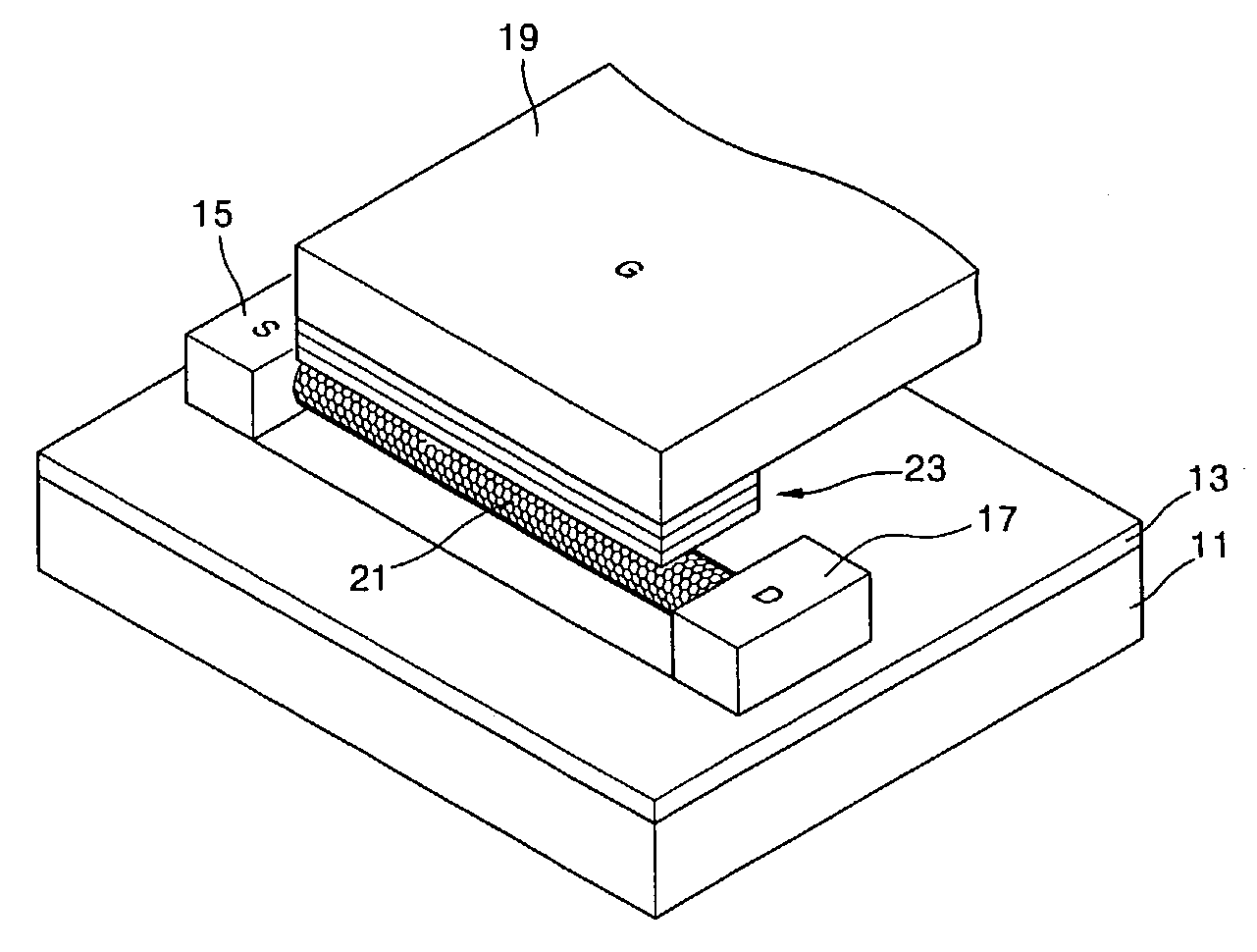
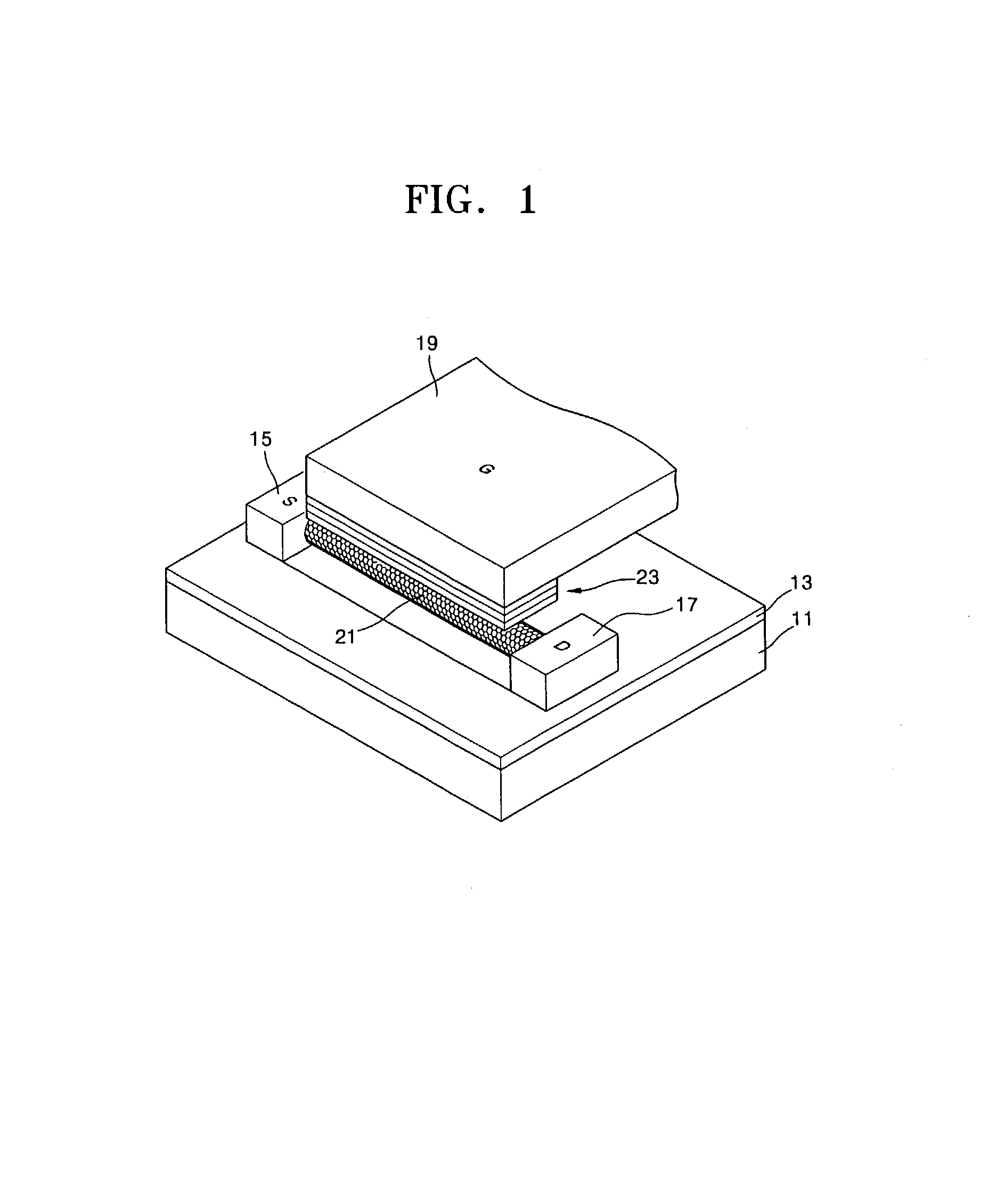
Molecular recognition-based electronic sensor, which is gateless, depletion mode field effect transistor consisting of source and drain diffusions, a depletion-mode implant, and insulating layer chemically modified by immobilized molecular receptors that enables miniaturized label-free molecular detection amenable to high-density array formats. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The conductivity of the active channel is determined by the potential of the sample solution in which the device is immersed and the device-solution interfacial capacitance. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The interfacial capacitance is determined by the extent of occupancy of the immobilized receptor molecules by target molecules. Target molecules can be either charged or uncharged. Change in interfacial capacitance upon target molecule binding results in modulation of an externally supplied current through the channel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Memory device utilizing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7015500B2Increase in malfunctionIncrease resistanceTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationDevice formCarbon nanotube
A fast, reliable, highly integrated memory device formed of a carbon nanotube memory device and a method for forming the same, in which the carbon nanotube memory device includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a carbon nanotube having high electrical and thermal conductivity, a memory cell having excellent charge storage capability, and a gate electrode. The source electrode and drain electrode are arranged with a predetermined interval between them on the substrate and are subjected to a voltage. The carbon nanotube connects the source electrode to the drain electrode and serves as a channel for charge movement. The memory cell is located over the carbon nanotube and stores charges from the carbon nanotube. The gate electrode is formed in contact with the upper surface of the memory cell and controls the amount of charge flowing from the carbon nanotube into the memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for synthesis of carbon-coated redox materials with controlled size
ActiveUS20040033360A1Low costReduce the numberMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitorsCross-linkRedox
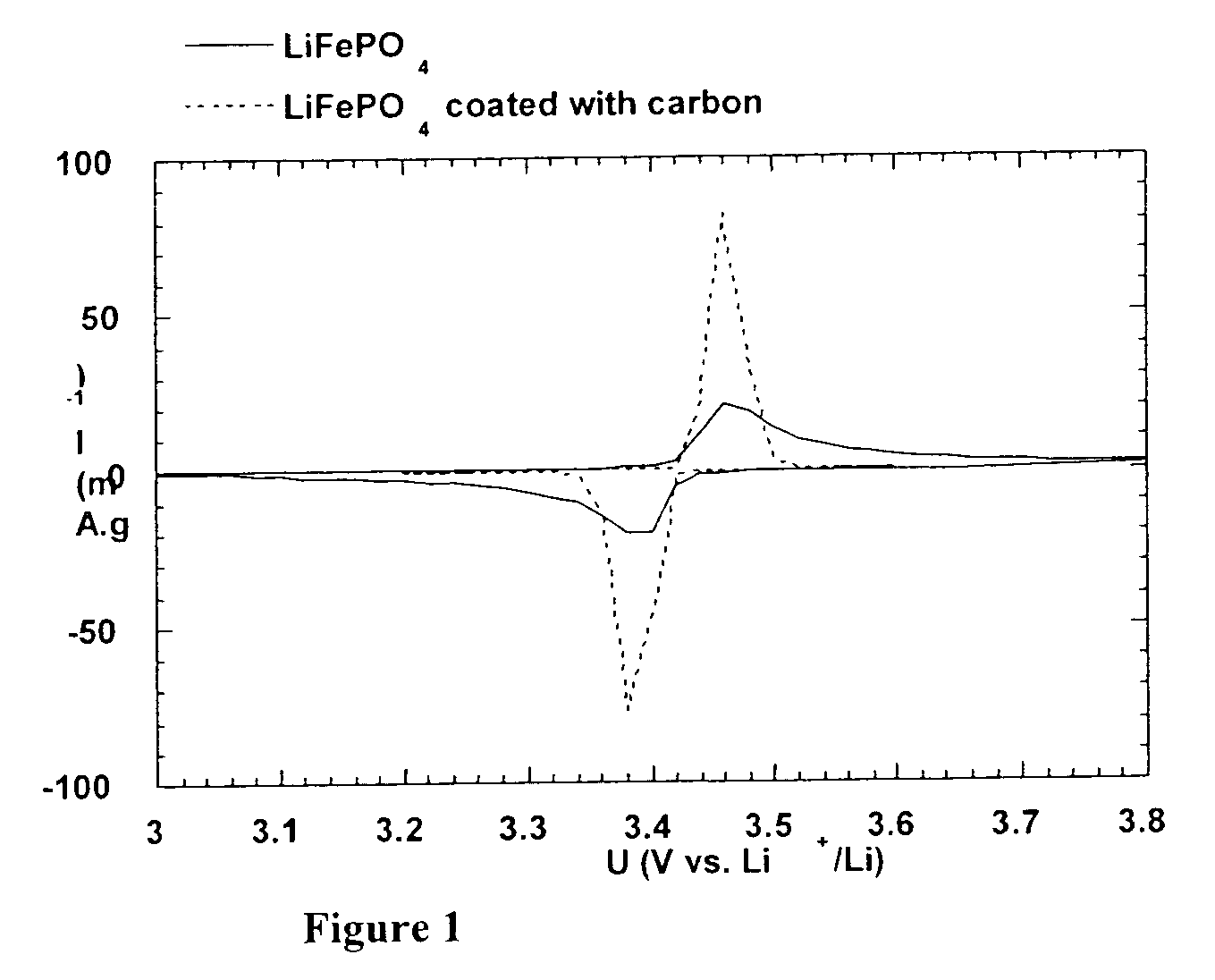
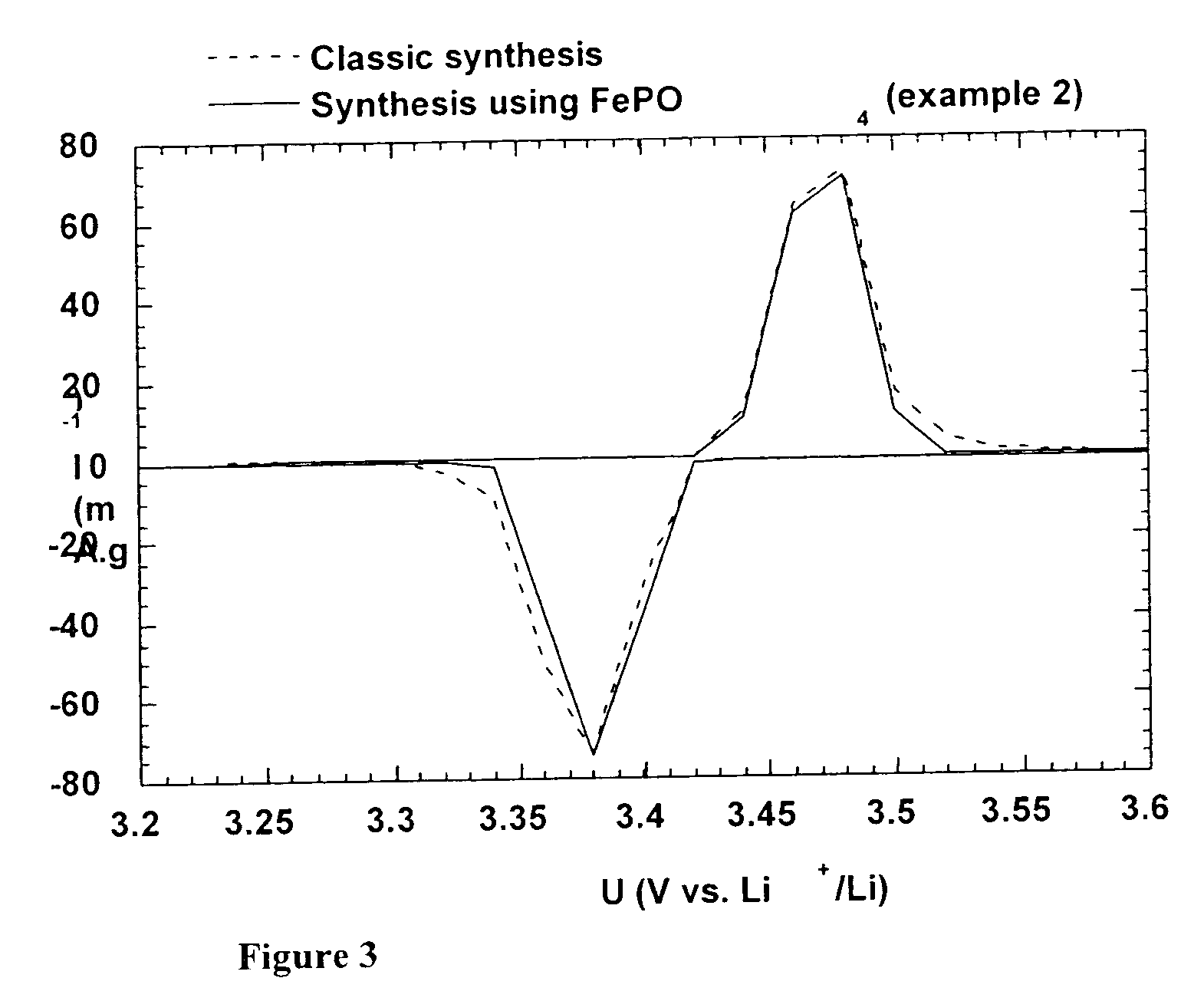
A method for the synthesis of compounds of the formula C-LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, where C represents carbon cross-linked with the compound LixM1-yM'y(XO4)n, in which x, y and n are numbers such as 0<=x<=2, 0<=y<=0.6, and 1<=n<=1.5, M is a transition metal or a mixture of transition metals from the first period of the periodic table, M' is an element with fixed valency selected among Mg<2+>, Ca<2+>, Al<3+>, Zn<2+> or a combination of these same elements and X is chosen among S, P and Si, by bringing into equilibrium, in the required proportions, the mixture of precursors, with a gaseous atmosphere, the synthesis taking place by reaction and bringing into equilibrium, in the required proportions, the mixture of the precursors, the procedure comprising at least one pyrolysis step of the carbon source compound in such a way as to obtain a compound in which the electronic conductivity measured on a sample of powder compressed at a pressure of 3750 Kg.cm<-2 >is greater than 10<-8 >S.cm<-1>. The materials obtained have excellent electrical conductivity, as well a very improved chemical activity.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
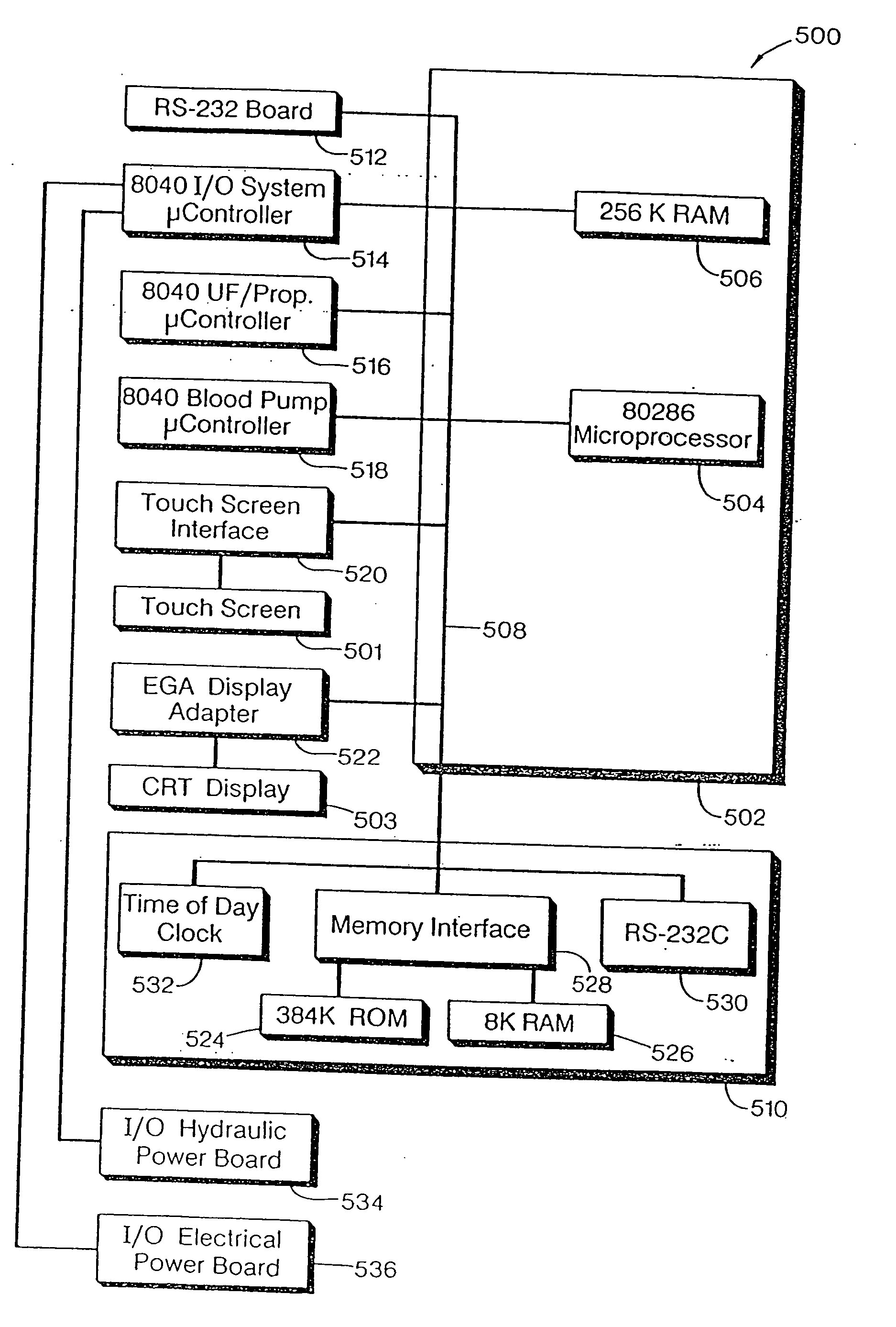
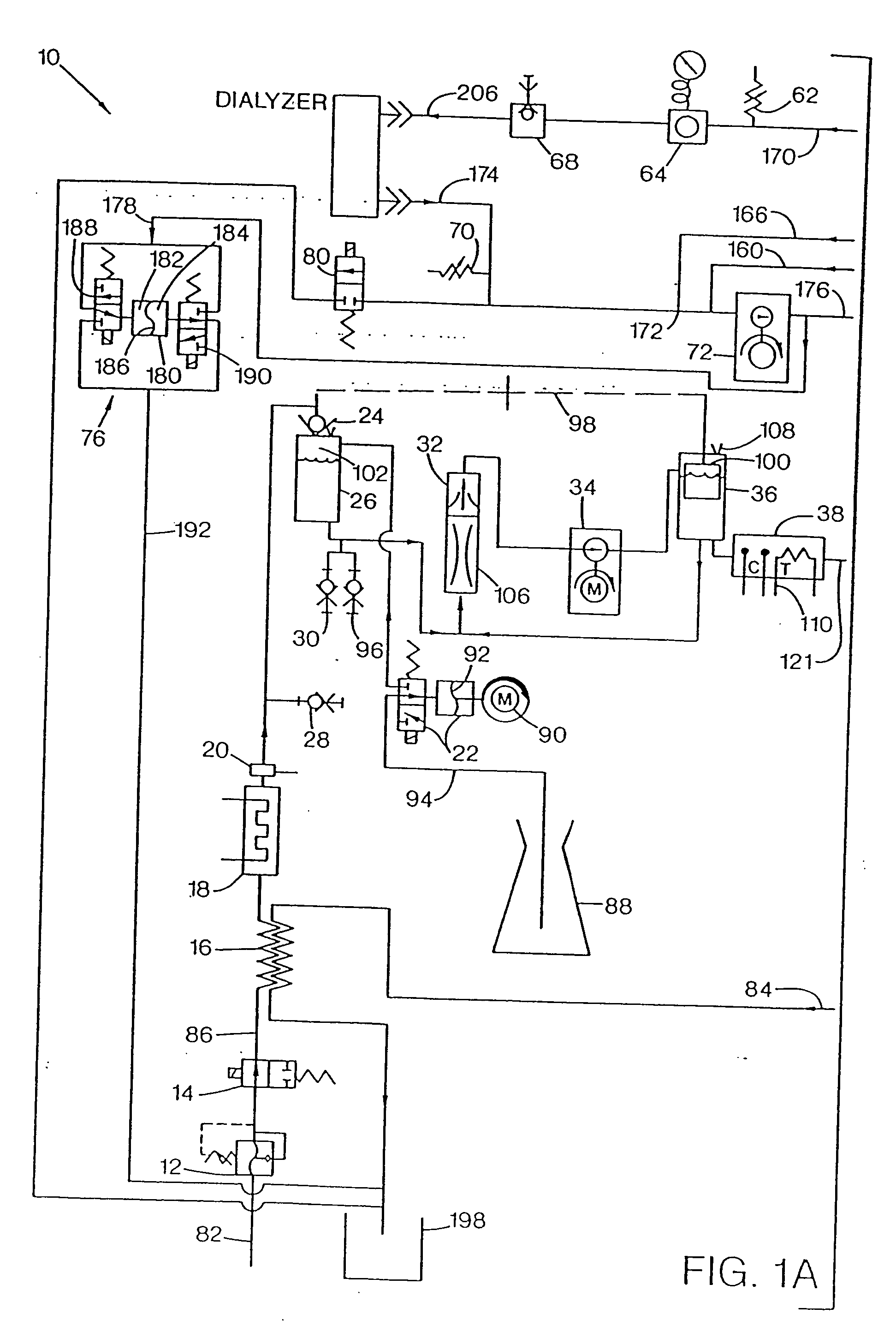
Method and apparatus for kidney dialysis
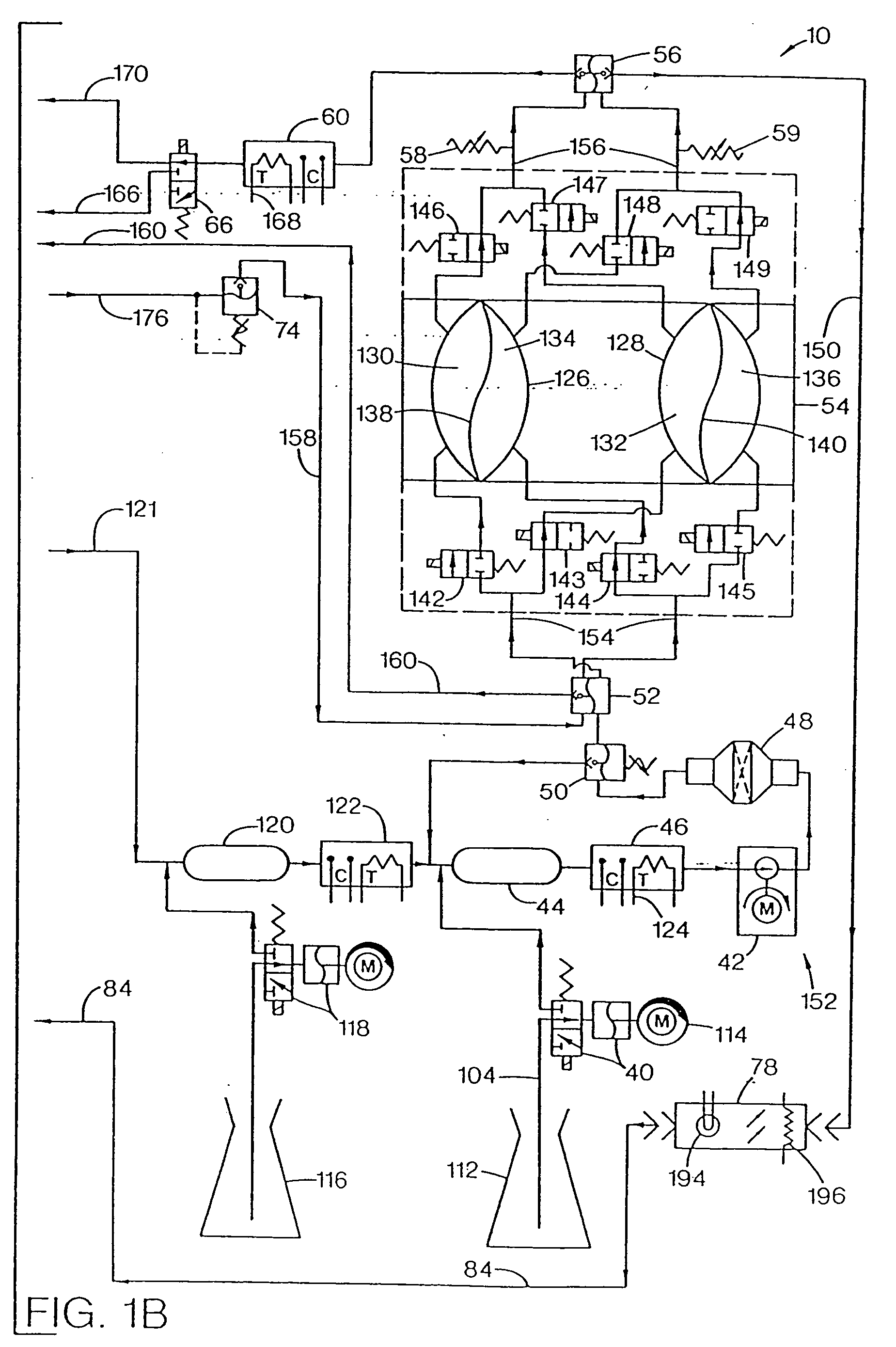
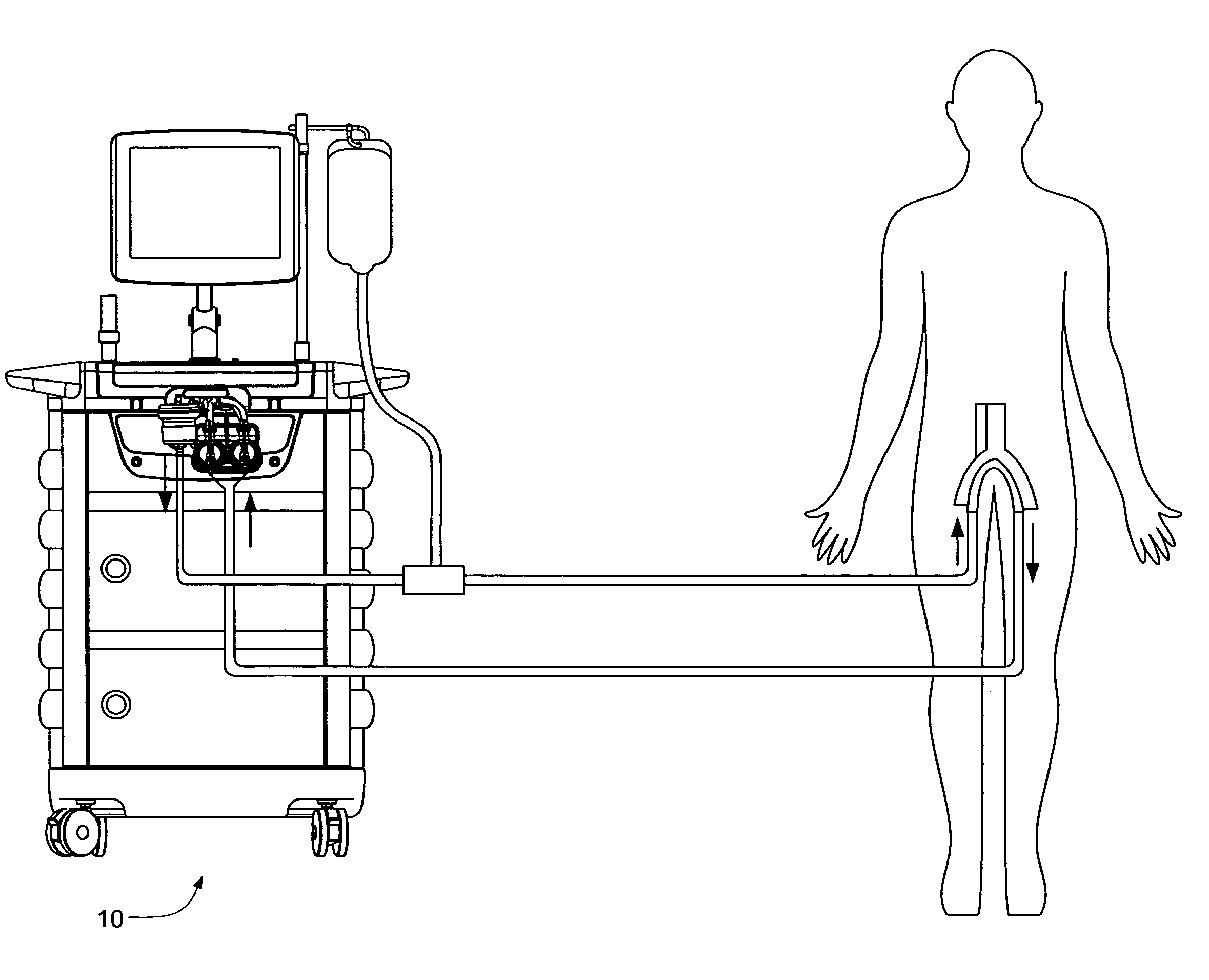
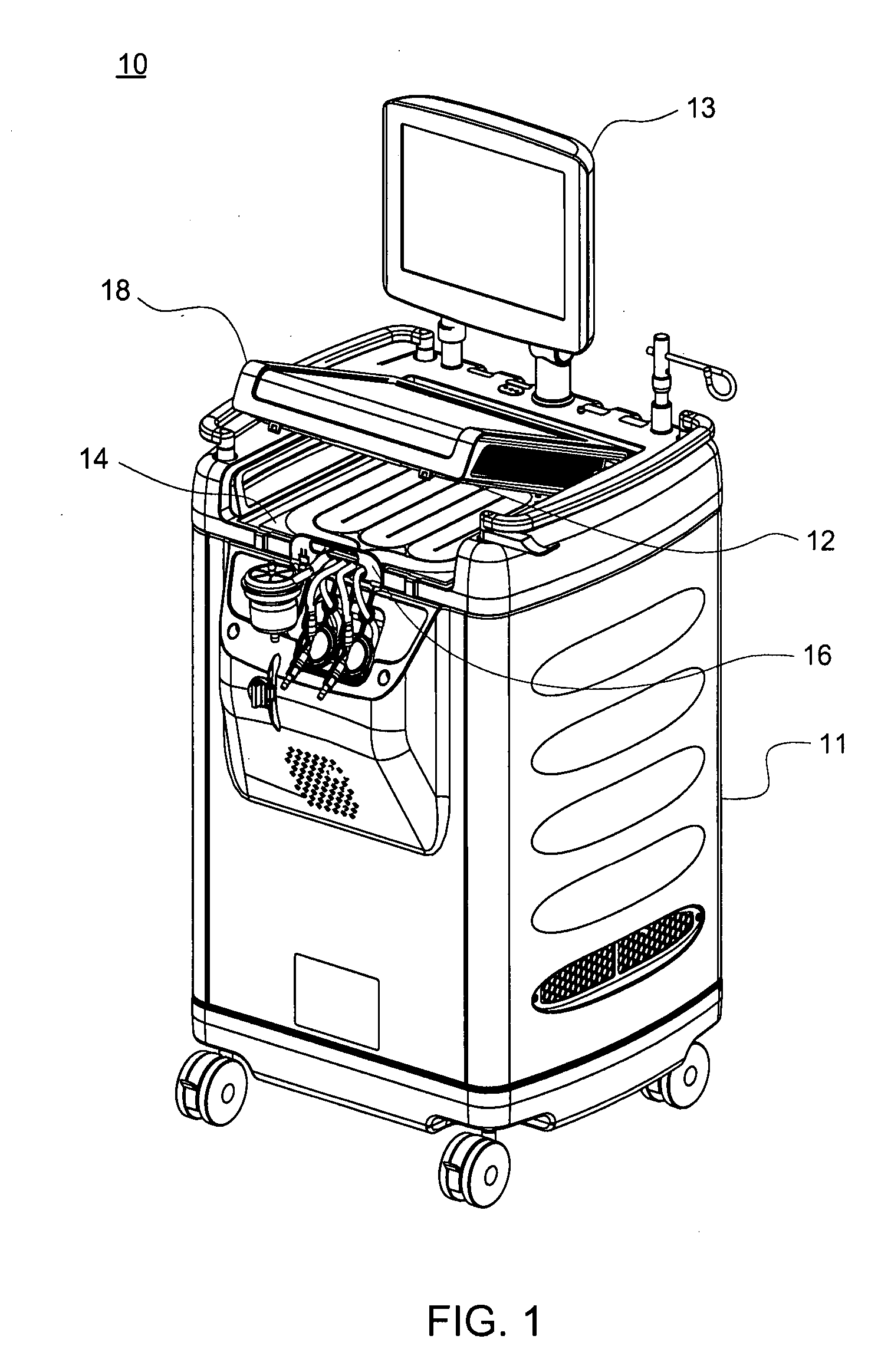
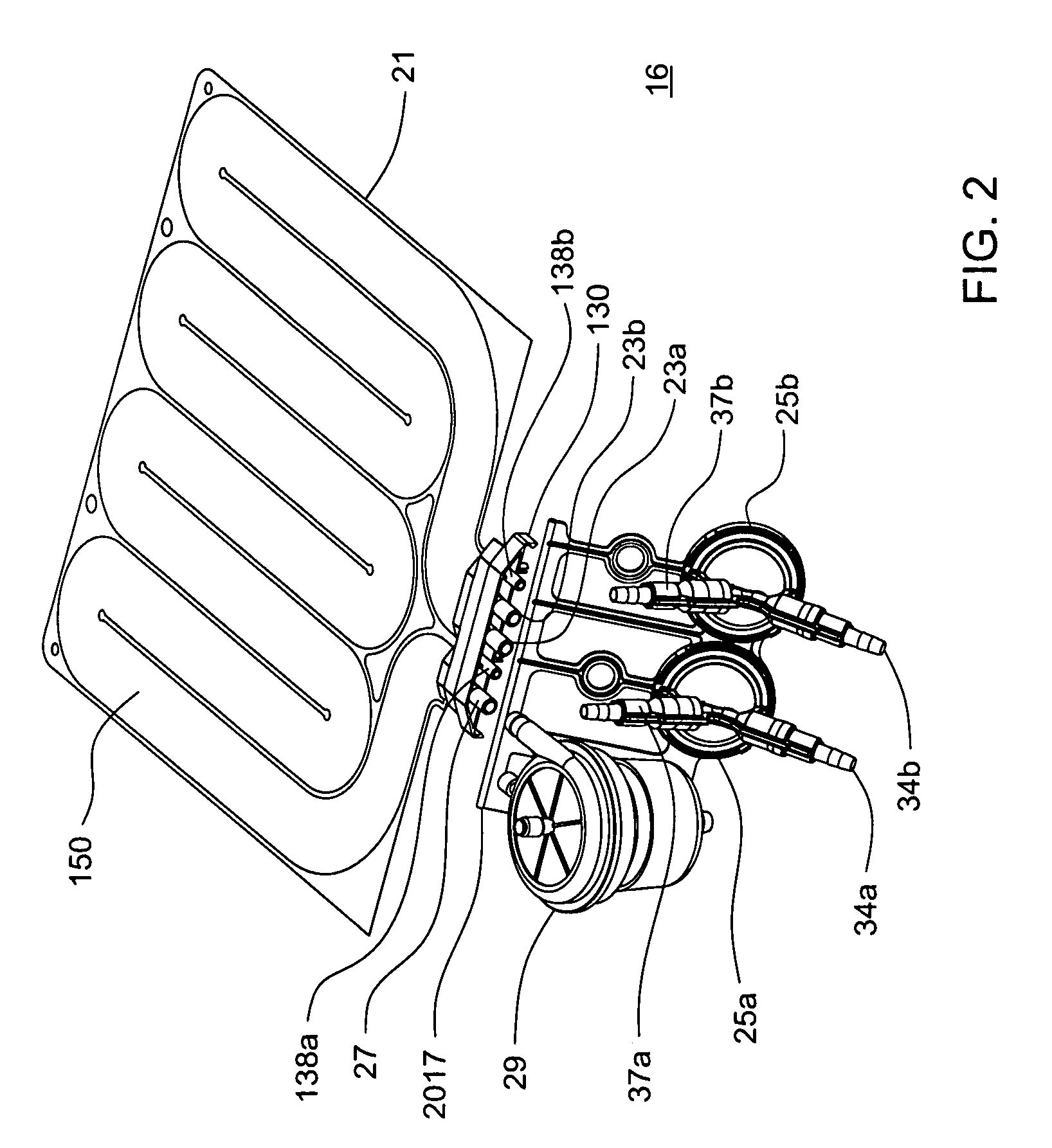
InactiveUS20050045540A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSolvent extractionUltrafiltrationElectrical resistivity and conductivity
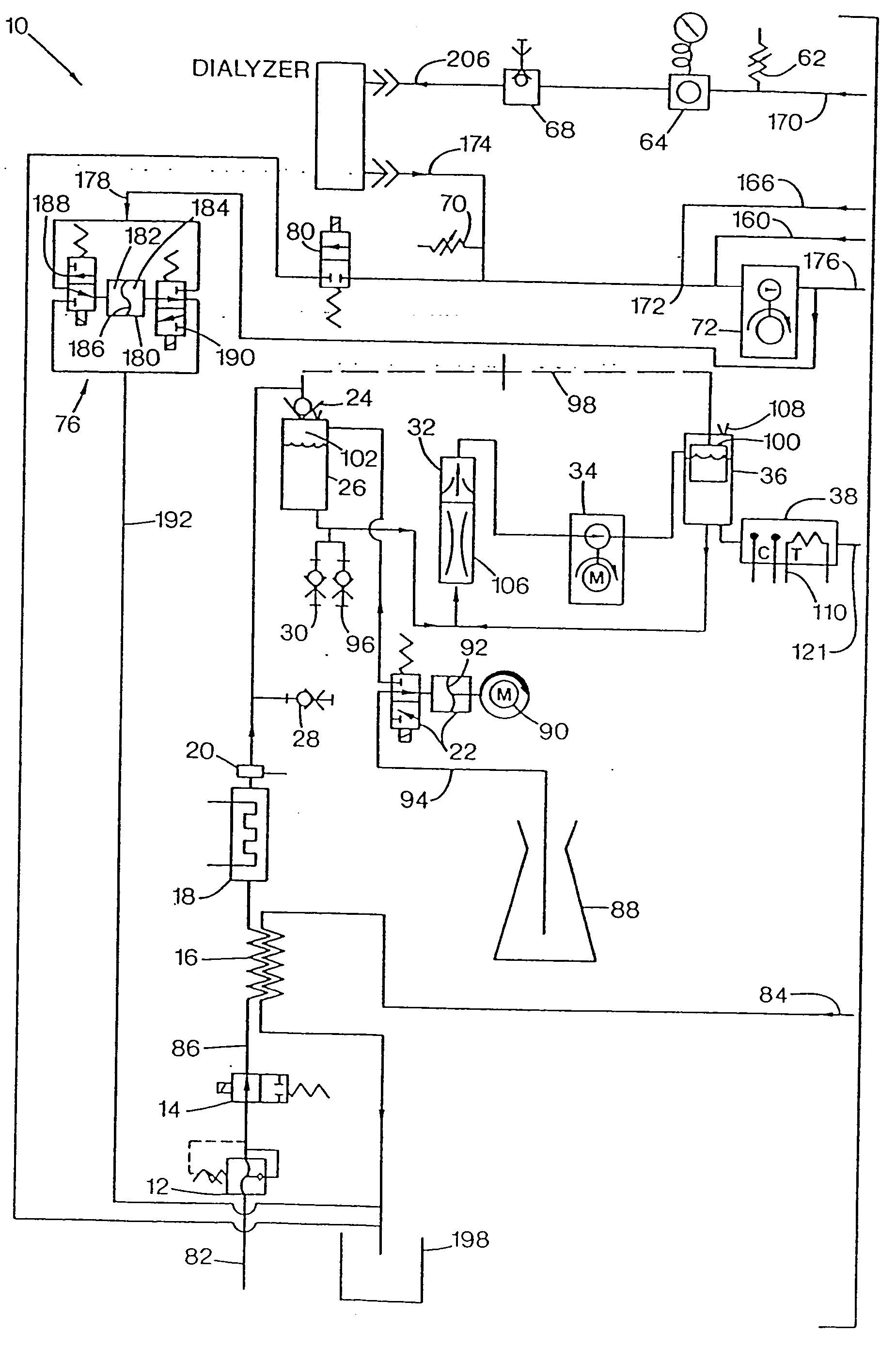
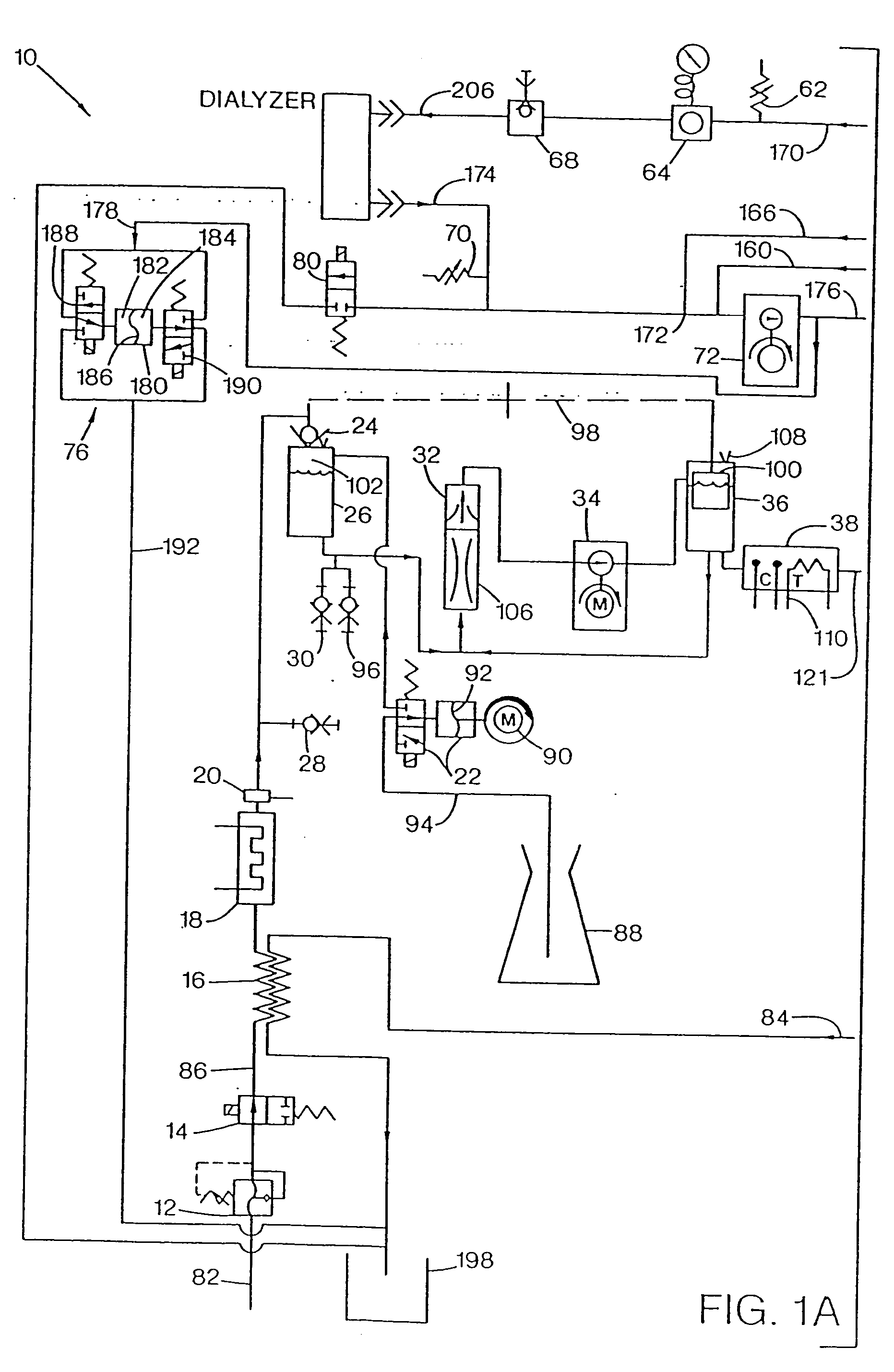
A number of improvements relating to methods and apparatuses for kidney dialysis are disclosed. These include checking of dialysate bypass status using flow measurement; using a flow sensor to confirm the absence of ultrafiltration during bypass; automatic testing of ultrafiltration function by removal of a discrete volume from a portion of the dialysate flow path coupled with a pressure test of that part of the flow path; using a touch screen user interface; bar graph profile programming of ultrafiltration, sodium, and bicarbonate parameters; using a RAM card to upload treatment instructions to, and to download treatment data from, the machine; automatic setting of proportioning mode (acetate or bicarbonate) based on connections of concentrate lines; predicting dialysate conductivity values based on brand and formulation of concentrates; minimizing no-flow dead time between dialysate pulses; initiating operation in a timed mode from a machine power-off condition; preserving machine mode during machine power-fail condition; calibration scheduling and reminding; automatic level adjusting; and blood leak flow rate detecting.
Owner:CONNELL MARK E +9
Thermal and conductivity sensing systems, devices and methods
A sensing probe is described. The sensing probe includes a probe housing having a probe tip. A thermal sensor in the housing is also included. The thermal sensor has a sensing end and a connector end, where the sensing end is thermally coupled to the probe tip. Also included are at least two leads. The leads transfer electrical signals that are used to determine temperature and conductivity. Also included is a thermal well. The thermal well includes a hollow housing of a thermally conductive material. The housing has an outer surface and an inner surface. The inner surface is a predetermined shape so as to form a mating relationship with a sensing probe. The mating thermally couples the inner surface with a sensing probe. In some embodiments, the thermal well is located on a disposable portion and the sensing probe on a reusable portion.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
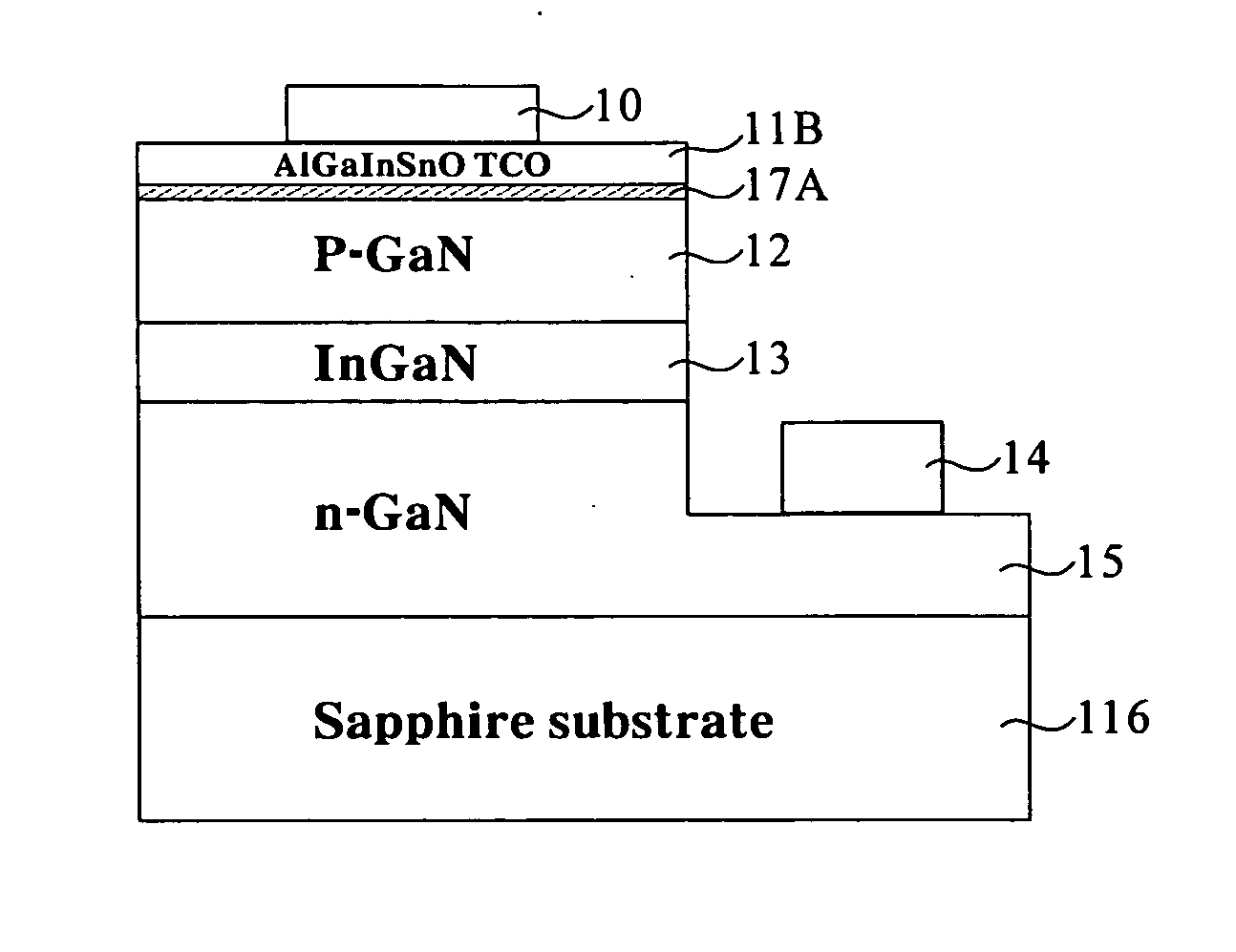
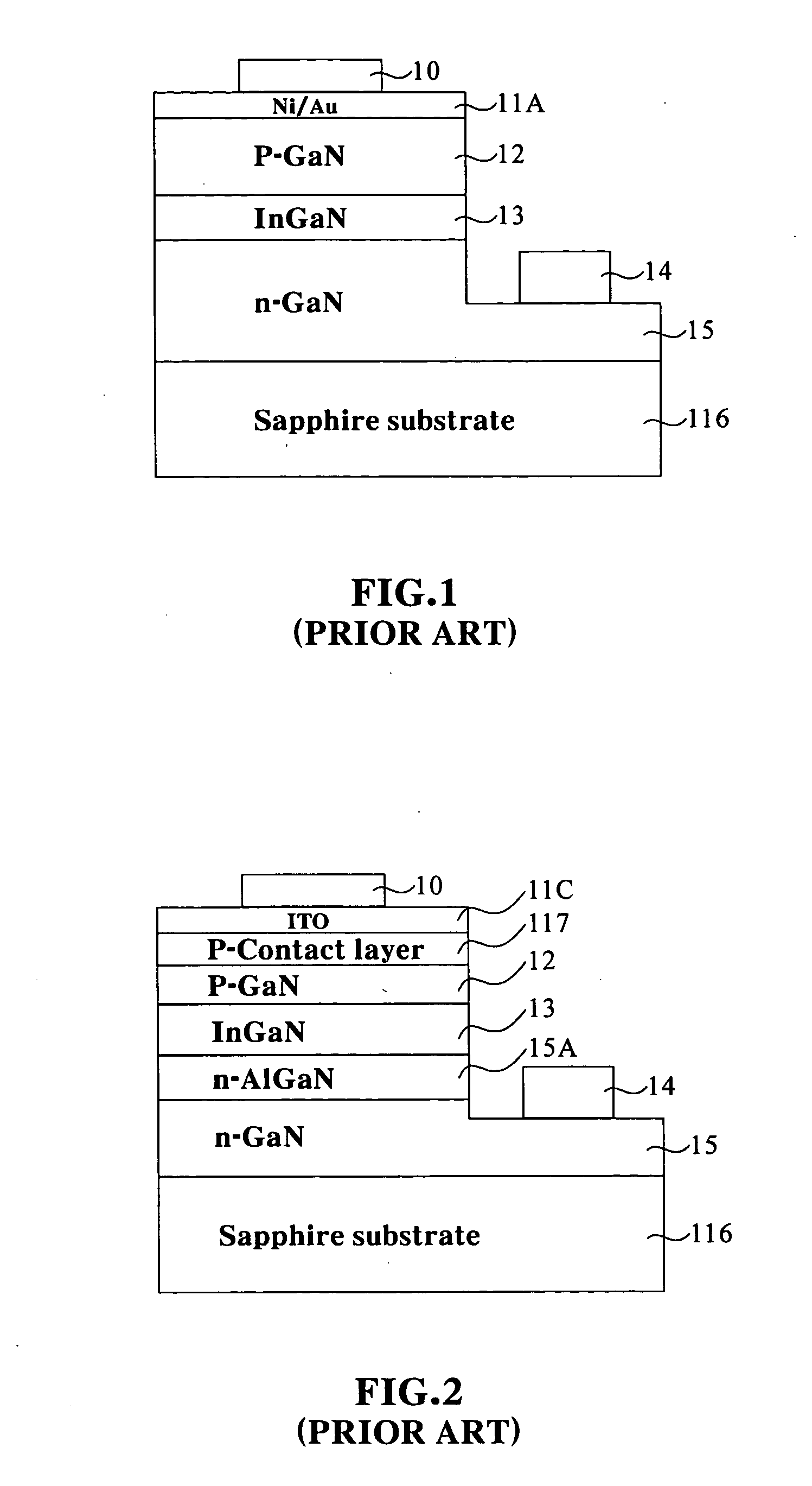
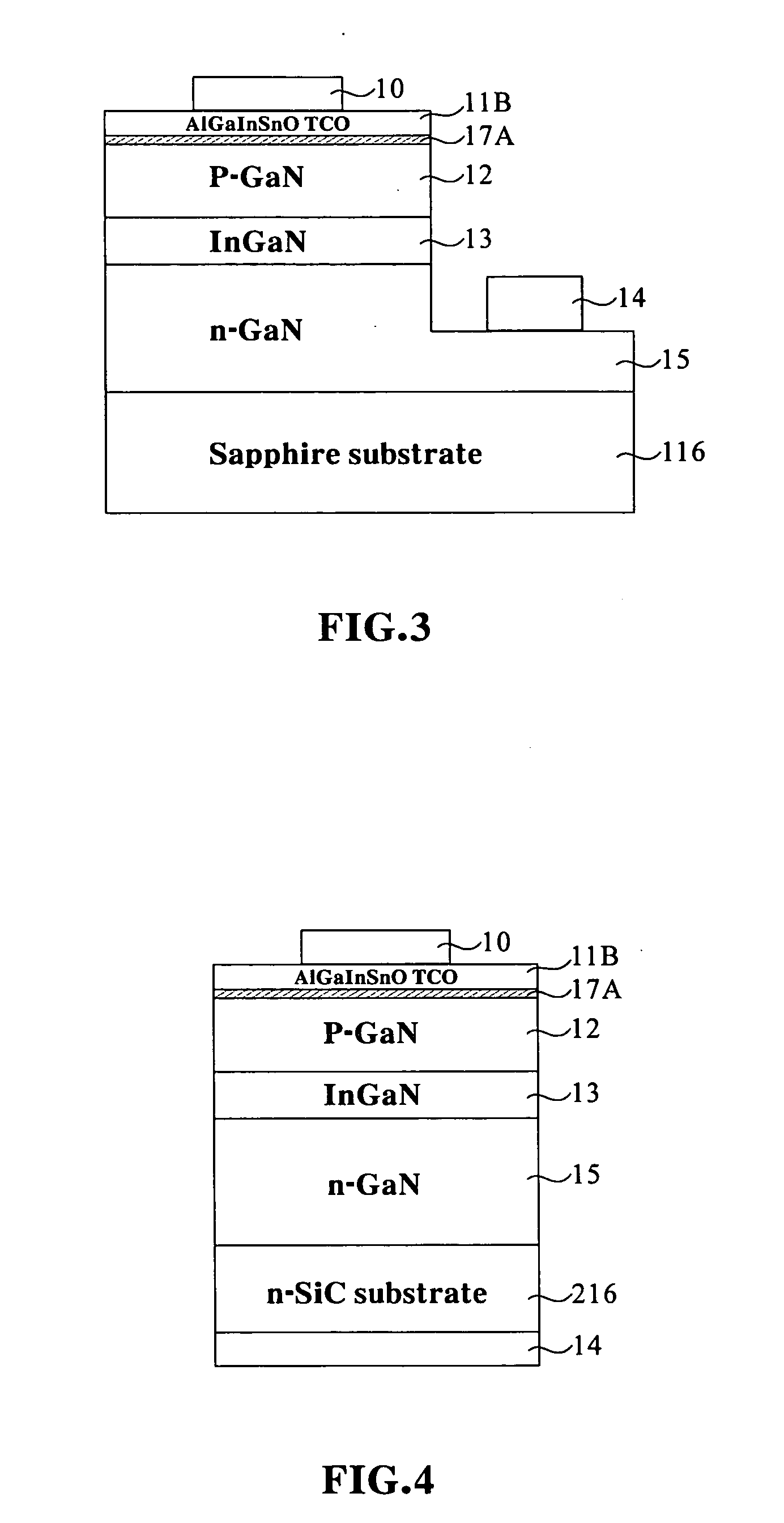
High brightness gallium nitride-based light emitting diode with transparent conducting oxide spreading layer
InactiveUS20050230701A1Reduce contact resistanceReduce the impactFibre treatmentSolid-state devicesOptical propertyGallium
A new transparent conducting oxide (TCO), which can be expressed as AlxGa3−x−yIn5+ySn2−zO16−2z; 0≦x<1, 0<y<3, 0≦z<2, has been used to improve the brightness and current spreading in GaN base LED process. The optical properties of this system are superior to regular Ni / Au transparent conducting layer in blue-green region, and the new Al2O3—Ga2O3—In2O3—SnO2 system is able to increase the brightness at 1.5˜2.5 time to compare to regular process. Furthermore, the new transparent conducting oxide thin film has the highest conductivity, which is better than the Ni / Au transparent conducting thin film.
Owner:ARIMA OPTOELECTRONICS
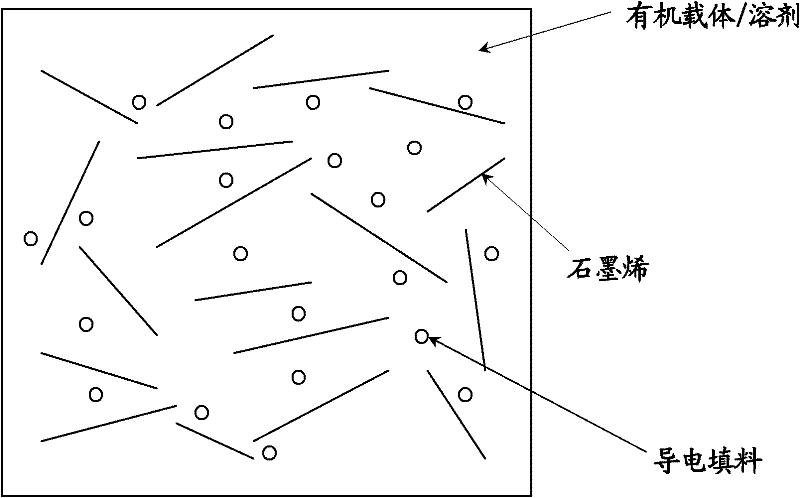
General electronic paste based on graphene filler
ActiveCN102254584AImprove conductivityConductivity regulationNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialNano structuringConductive coating
The invention discloses general electronic paste based on graphene filler. The electronic paste contains graphene-containing conductive filler, an organic carrier, a solvent and an auxiliary agent. Because the graphene has good electronic conductivity and a unique two-dimensional laminar nano structure, the graphene forms a conductive network in the organic carrier more easily, and the electric conductivity of the electronic paste is improved by adding the graphene. Further, the conductive filler also contains a conductive material with relatively high electric conductivity, so that the electric conductivity of the electronic paste is further improved. Because the graphene and the conductive material are compounded to form the conductive filler, the electronic paste has good electric conductivity. The electronic paste can obtain a relatively wide electric conductivity range by changing the category of the conductive material mixed with the graphene and adjusting the relative proportion of the graphene to the conductive material of different category. The electric conductivity of the electronic paste is 1*10<-3>S / cm to 1*10<3>S / cm. The paste can be widely applied, and can be particularly used as a conductive coating or adhesive.
Owner:NINGBO GRAPHENE INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Single-sided lateral-field and phototransistor-based optoelectronic tweezers
ActiveUS7956339B2Good flexibilityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentDielectrophoretic forceCell culture media
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electromagnetic imaging method and device
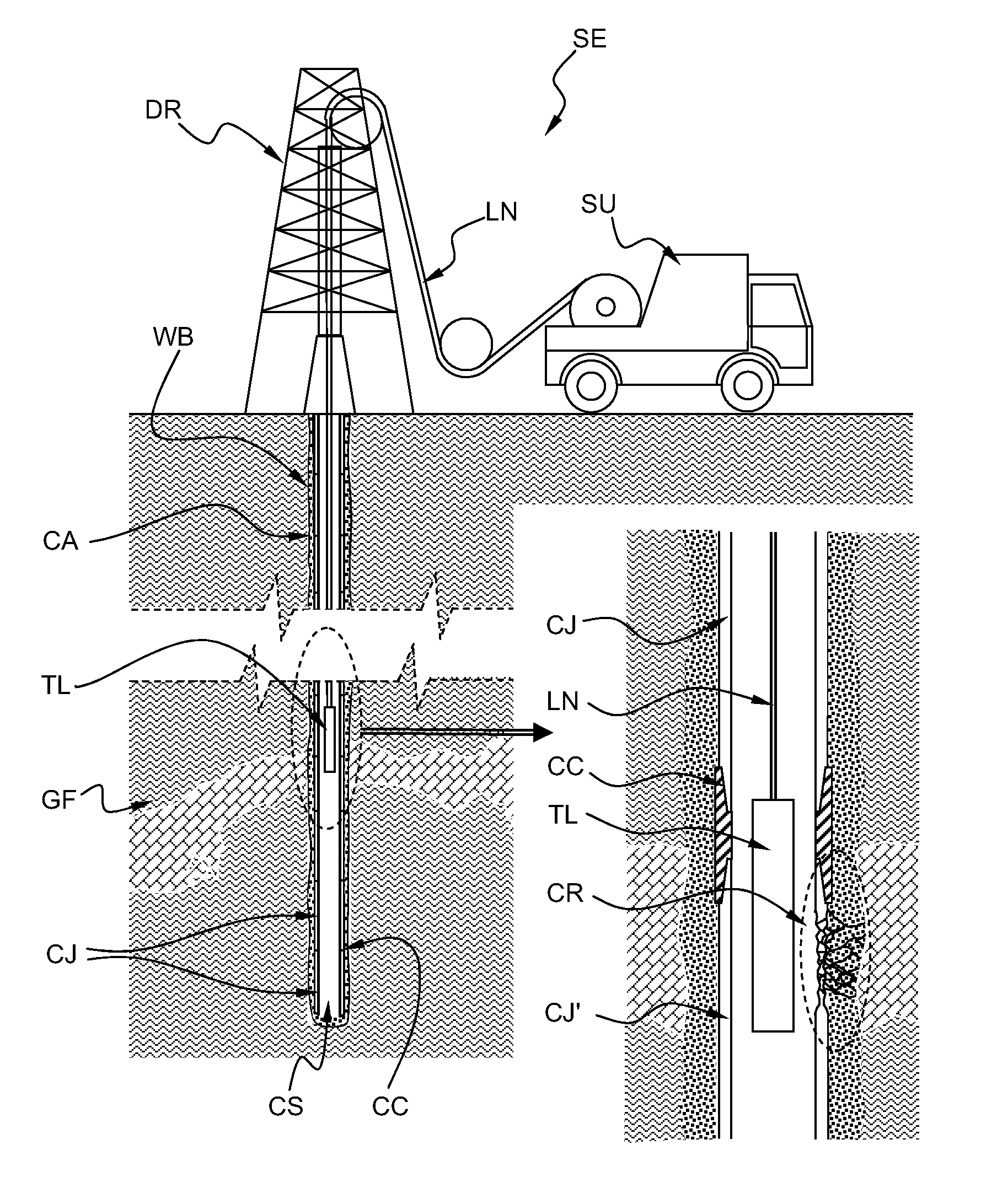
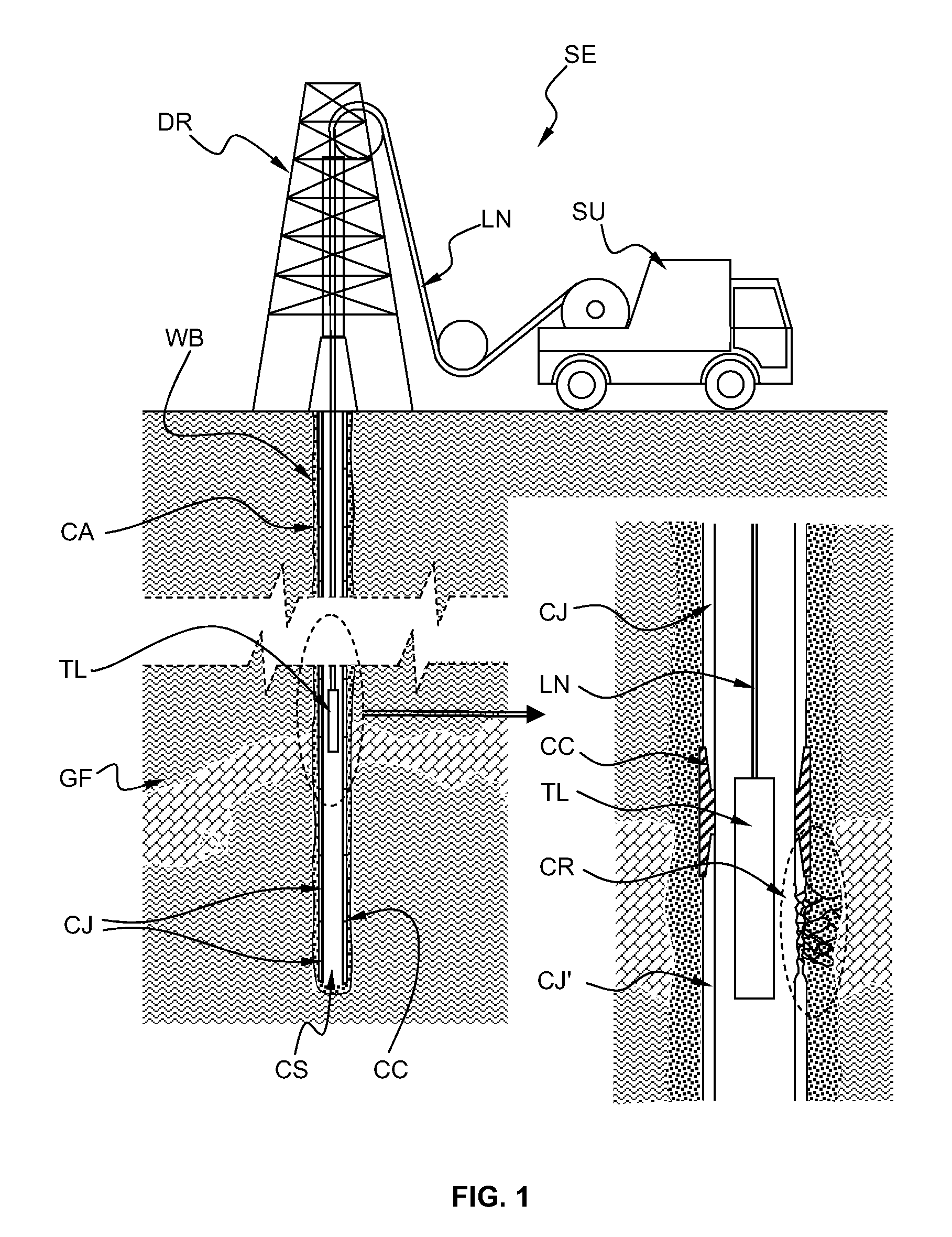
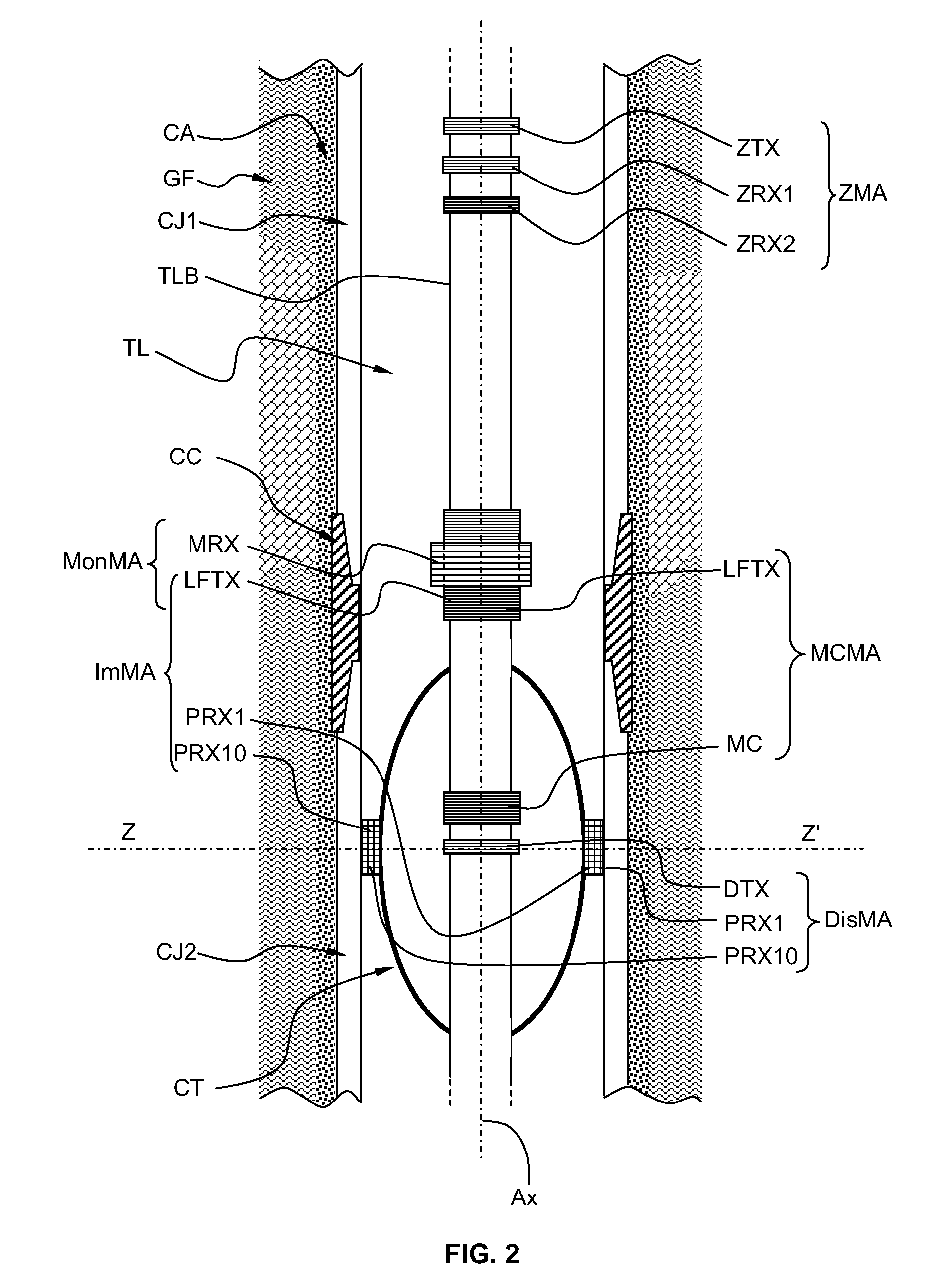
InactiveUS20090195244A1Accurate electromagnetic imageImprove accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsTransmitter coilElectrical resistivity and conductivity
An electromagnetic imaging method for electromagnetically measuring physical parameters of a pipe CJ, CC by means of a plurality of measuring arrangement ZMA, MCMA, MonMa, ImMA comprising a plurality of transmitter coil ZTX, LFTX, DTX and a plurality of receiver coil ZRX1, ZR2, MRX, MC, PRX1, PRX2, PRX3, PRX4, PRX5, PRX6, PRX7, PRX8, PRX9, PRX10, PRX11, PRX12, PRX13, PRX14, PRX15, PRX16, PRX17, PRX18, the transmitter coils and receiver coils being associated so as to form the plurality of measuring arrangement, the plurality of measuring arrangement being adapted to be positioned into the pipe and displaced through the pipe, the physical parameters being measured for a plurality of position along the pipe, the method comprising the steps of:a) determining a first value of an average ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity and a first value of an average inner diameter of the pipe Z-MES,b) determining an average electromagnetic thickness of the pipe MC-MES,c) determining a second value of the average ratio of magnetic permeability to electrical conductivity and a second value of the average inner diameter of the pipe Mon-MES according to excitation frequencies which are substantially lower than the excitation frequencies used to determine the first values Z-MES,d) determining a first image EMTIM of the pipe electromagnetic thickness and the pipe defects Im-MES,e) discriminating the defects at an inside perimeter of the pipe from the defects at an outside perimeter of the pipe Dis-MES, andf) forming a corrected first image IOFIM of the pipe taking into account a position of the defects.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Semiconductor device comprising a contact structure based on copper and tungsten
ActiveUS20070099414A1Reduce resistanceLower resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInter layerDevice material
By providing contact plugs having a lower plug portion, formed on the basis of well-established tungsten-based technologies, and an upper plug portion, which may comprise a highly conductive material such as copper or a copper alloy, a significant increase in conductivity of the contact structure may be achieved. For this purpose, after the deposition of a first dielectric layer of the inter-layer stack, a planarization process may be performed so as to allow the formation of the lower plug portions on the basis of tungsten, while, after the deposition of the second dielectric layer, a corresponding copper-based technology may be used for forming the upper plug portions of significantly enhanced conductivity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
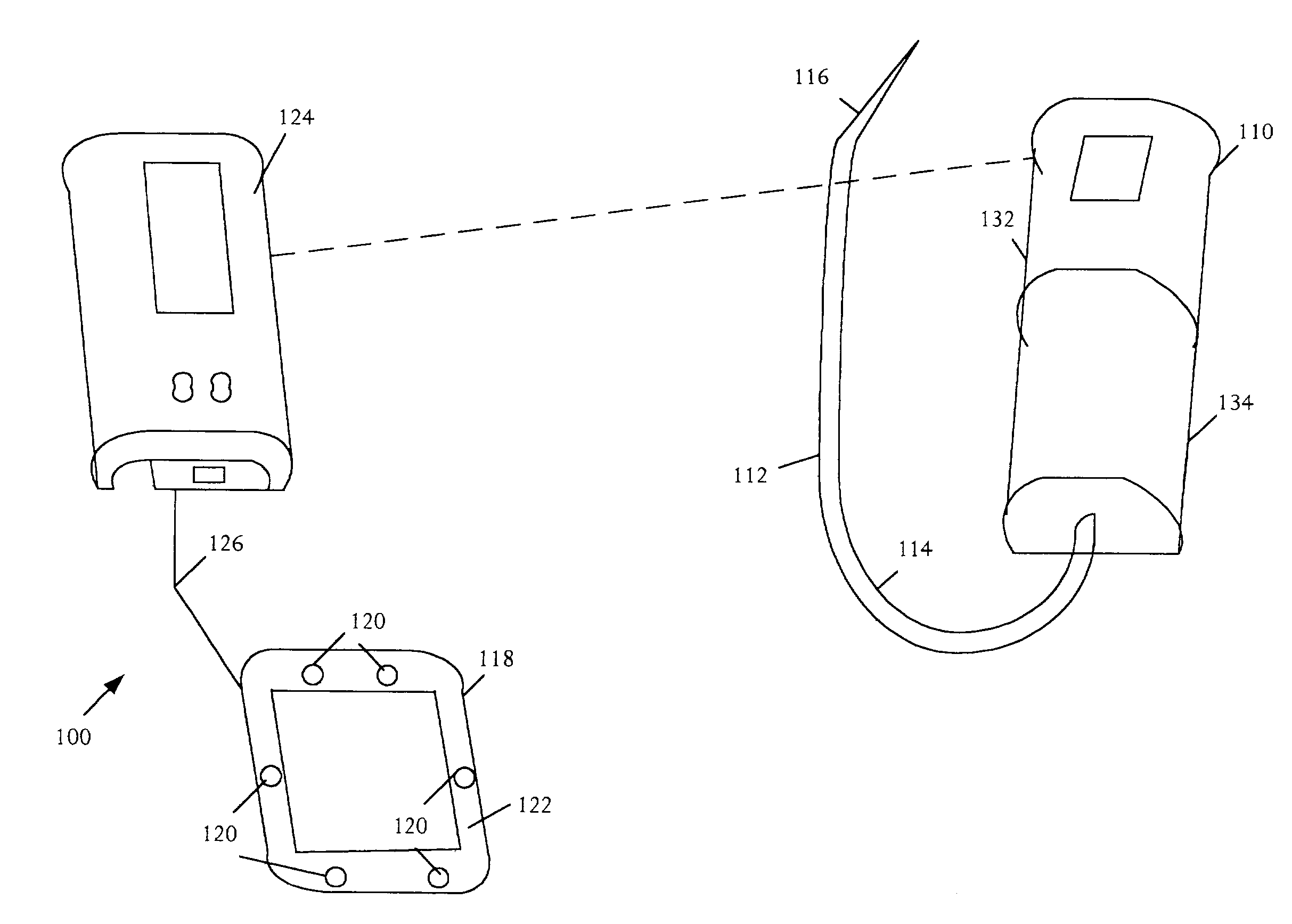
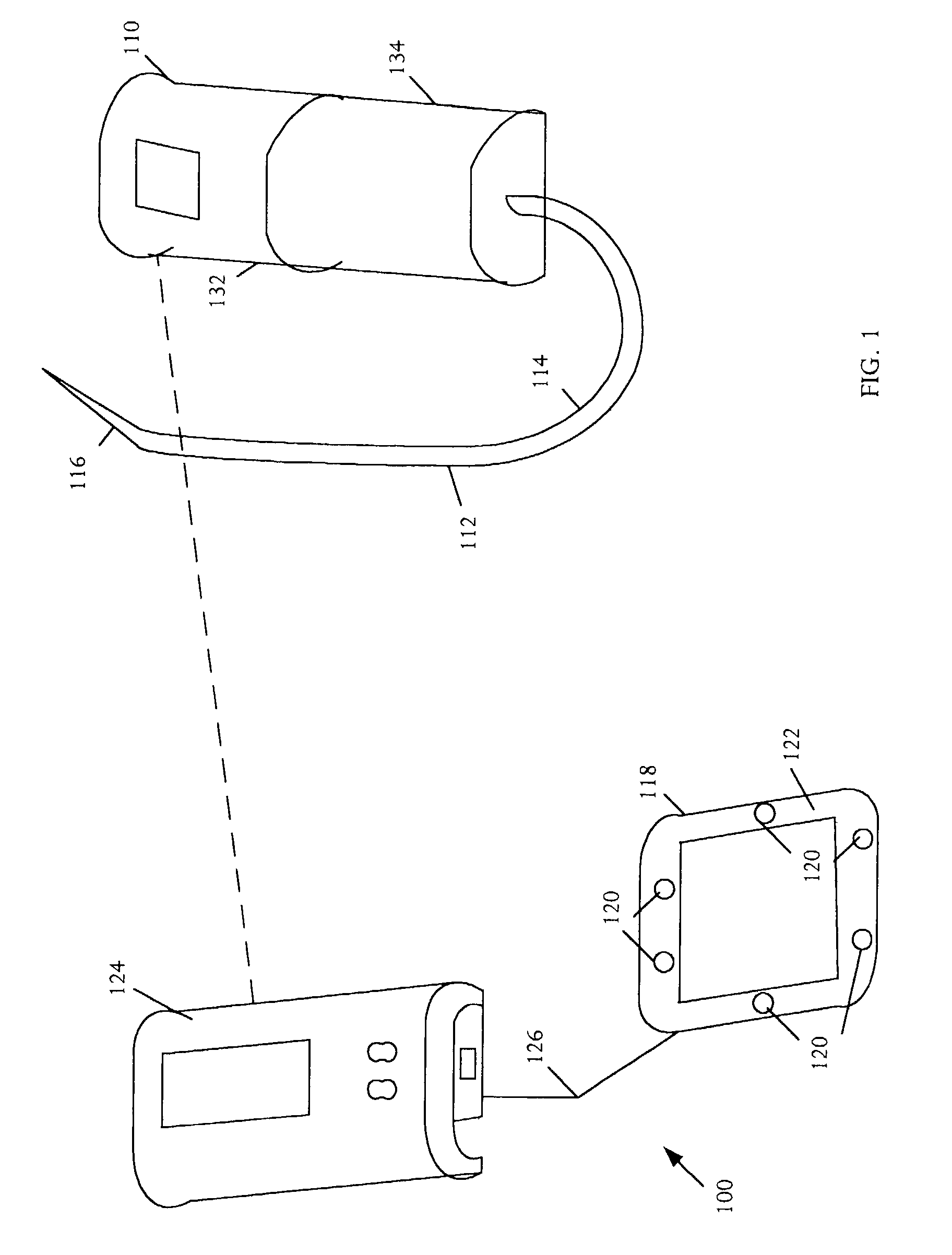
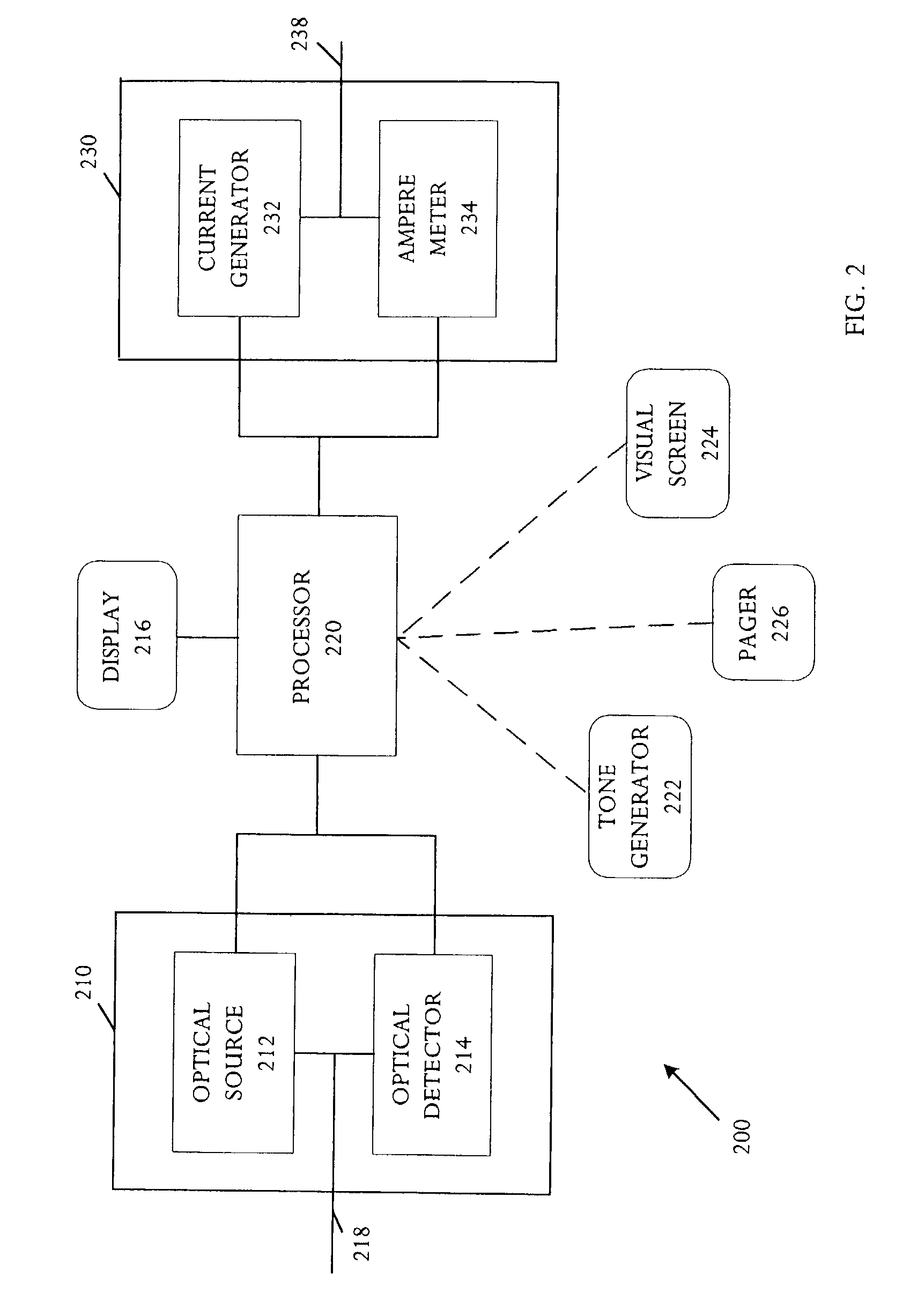
Integrated Biometric Sensing and Display Device
InactiveUS20120271121A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyBiometric dataWavelength filter
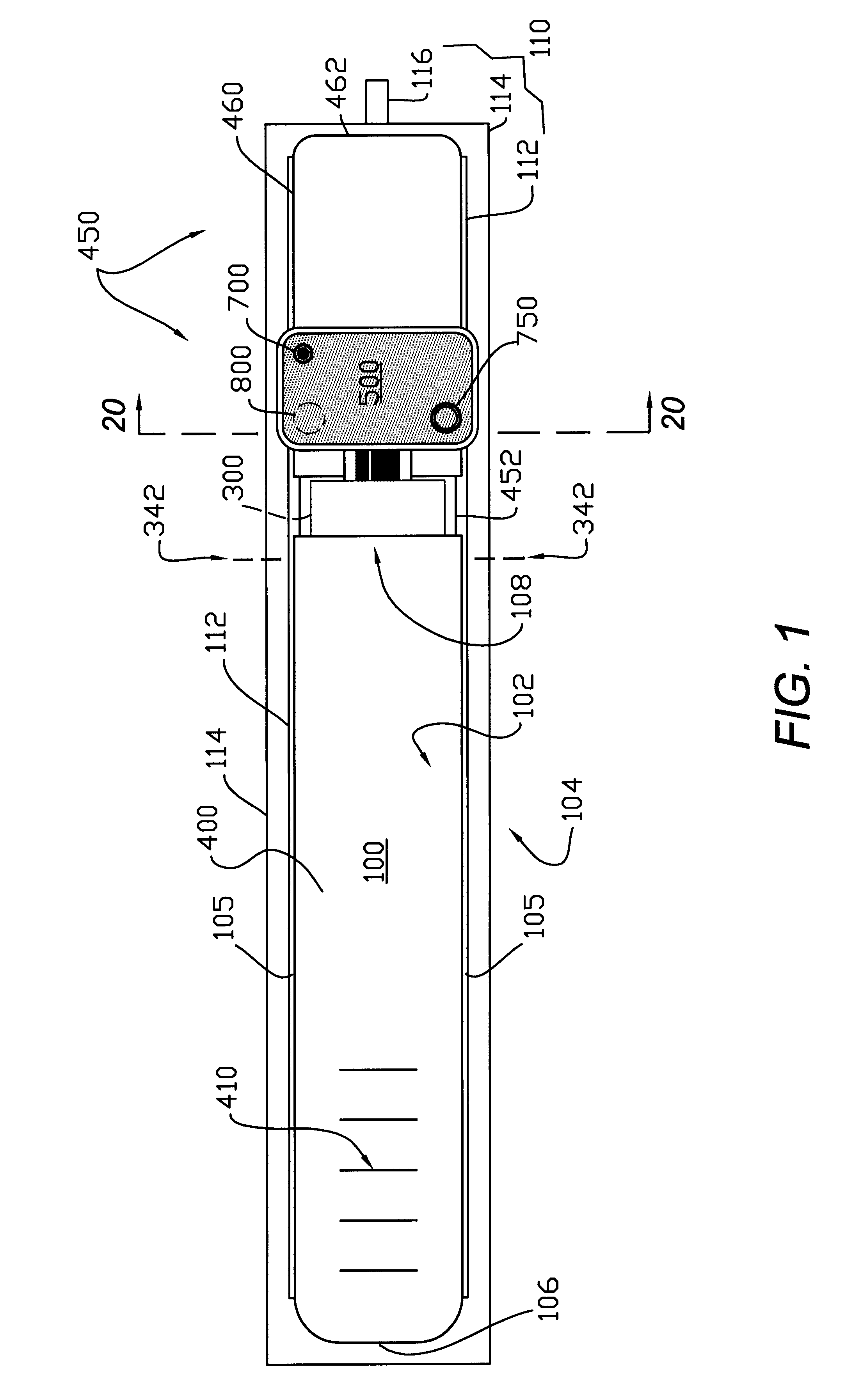
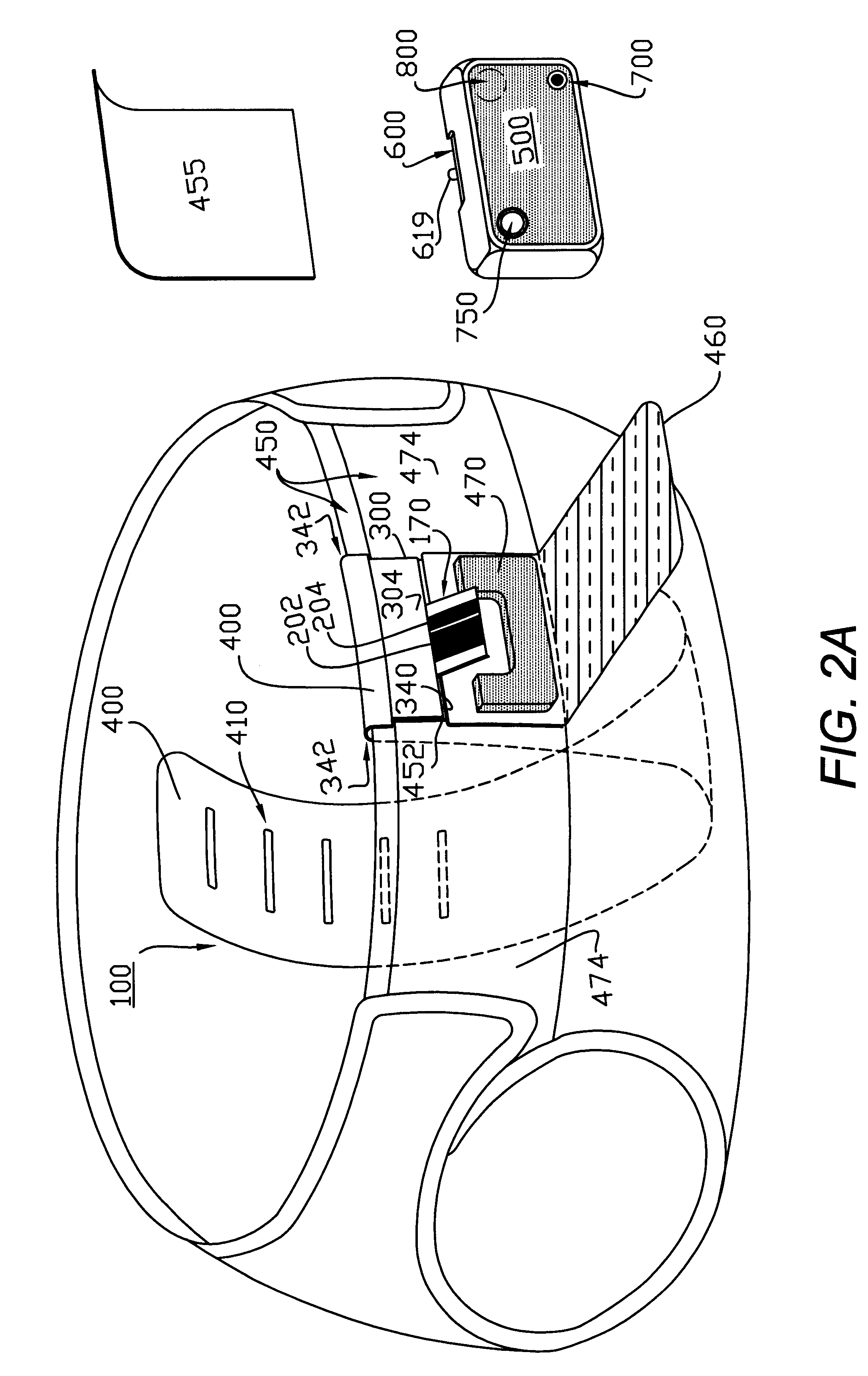
A biometric device configured to be attached to a portion of a body of a user measures biometric data of the user. The device includes an optical emitter, a wavelength filter, an optical sensor and a processor, for sending a light to the body of a user, receiving light received from the user, filtering and processing it to measure biometric data of the user, including for example, heart rate and blood flow rate. In addition, the biometric device may include other sensors, such as a galvanic skin response sensor, an ambient temperature sensor, skin temperature, motion sensor, etc., to enable the biometric device to measure arousal or conductivity changing events, ambient temperature, user temperature and motion associated with the user. Additionally, information from each sensor may be used to further filter noise in one or more signals received by the sensors to provide biometric data to the user.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Antenna coil and rfid-use tag using it, transponder-use antenna
InactiveUS20050007296A1Improve rigidityHigh frequencyLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreOther printing matterAir coreNon magnetic
An antenna coil includes an air-core coil wound helically in a plane and a plate magnetic core member inserted in the air-core coil to be approximately parallel with a plane of the air-core coil. The magnetic core member is formed by a soft magnetic metal, an amorphous or ferrite, or a composite member of a powder, flake and plastic, or rubber. The magnetic core member is formed by performing an injection molding operation or a compressing molding operation of the composite member. Alternatively, the magnetic core member is a magnetic coating formed by applying and drying the composite member. A non-magnetic conductive plate that has a conductivity is layered on a surface of the air-core coil through which the magnetic core member is inserted. The conductive plate is made of a copper, a copper alloy, an aluminum or an aluminum alloy having 0.01 to 2 mm thickness. The antenna coil is operated by relatively high frequency while it is rigid relatively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
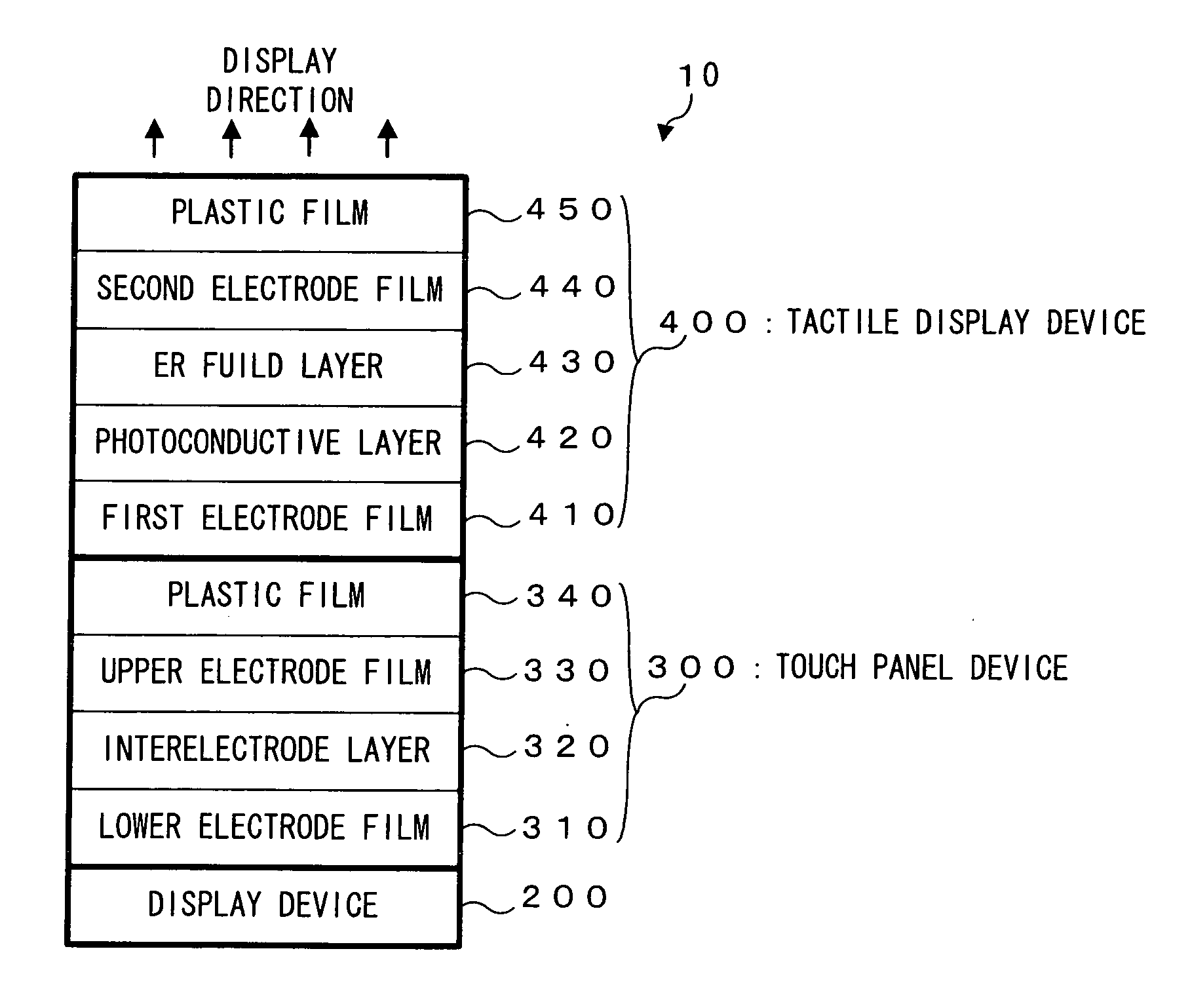
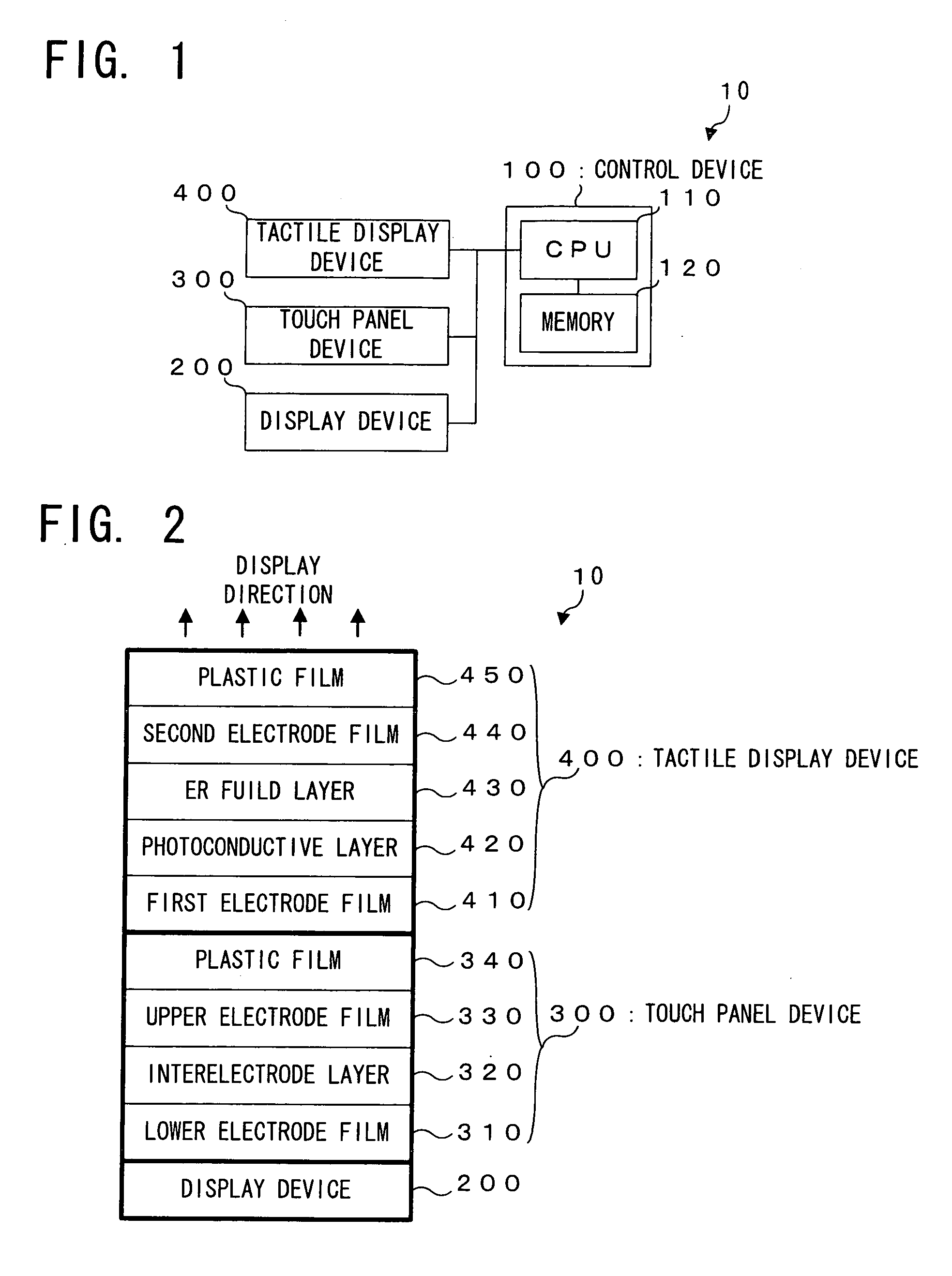
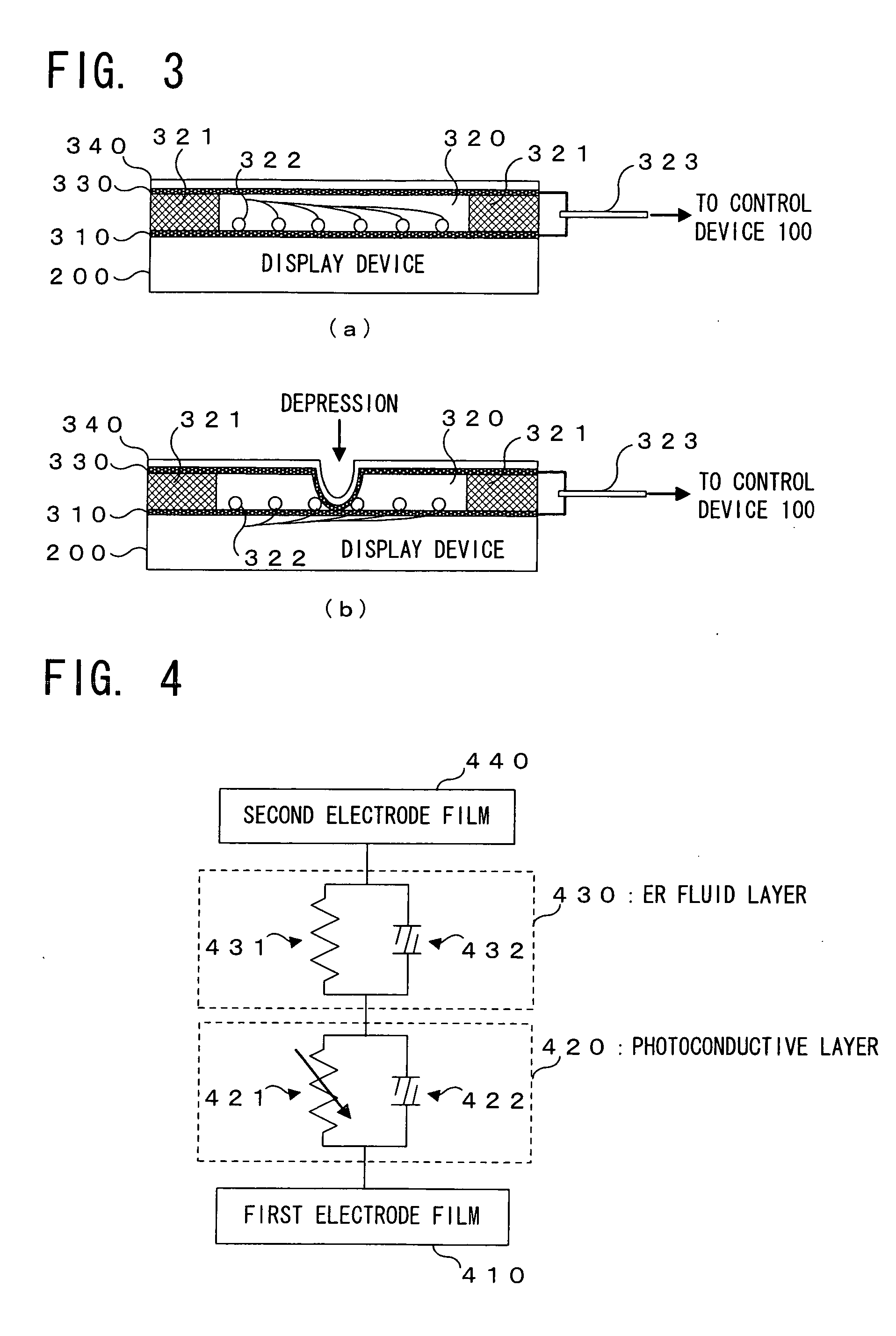
Tactile display device and touch panel apparatus with tactile display function
InactiveUS20050285846A1Easy constructionSimple structureCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHaptic displayDisplay device
Conductivity of a photoconductive layer 420 changes in accordance with a display pattern made of black and white, which is displayed on a display device 200 of a touch panel apparatus with tactile display function 10. With this change of the conductivity, viscosity of an electrorheological fluid layer 430 changes in accordance with this display pattern. This change of the viscosity is presented to an operator, as tactile information corresponding to the display pattern displayed as the visual information.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
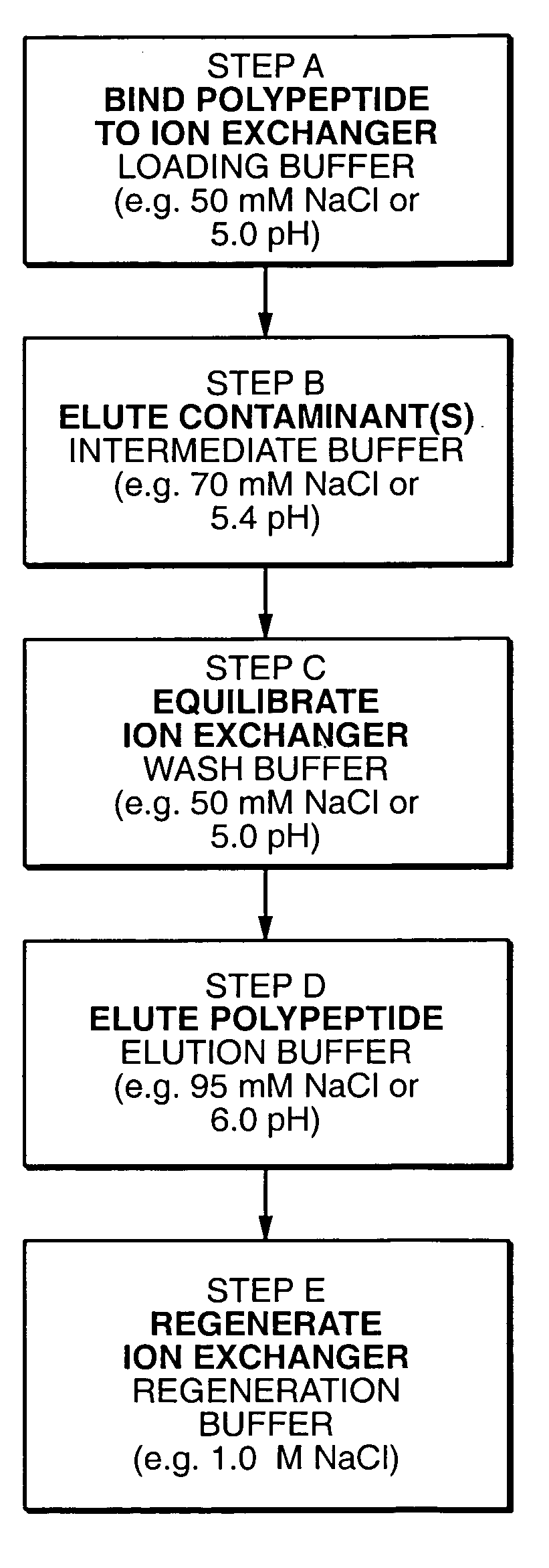
Protein purification
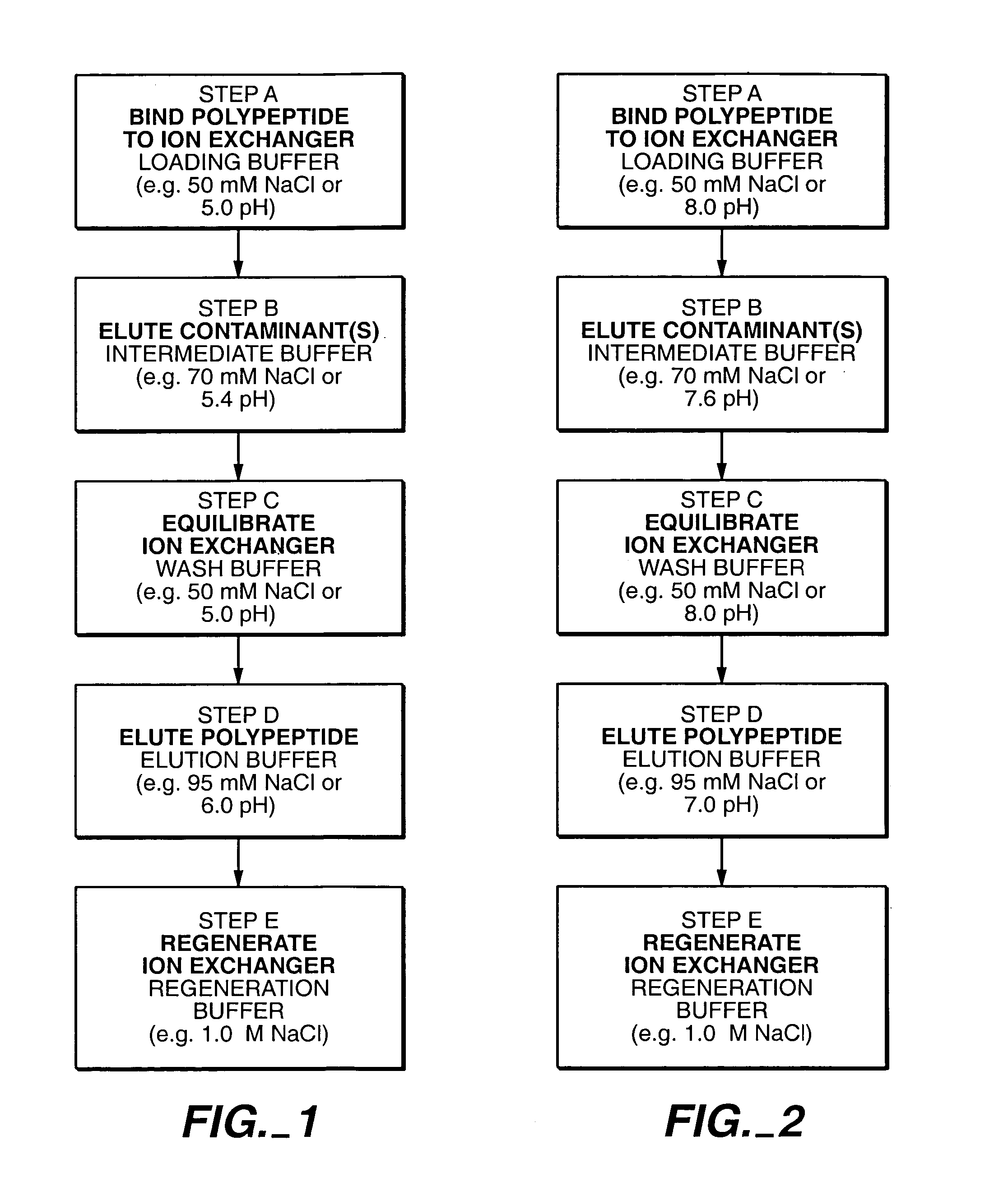
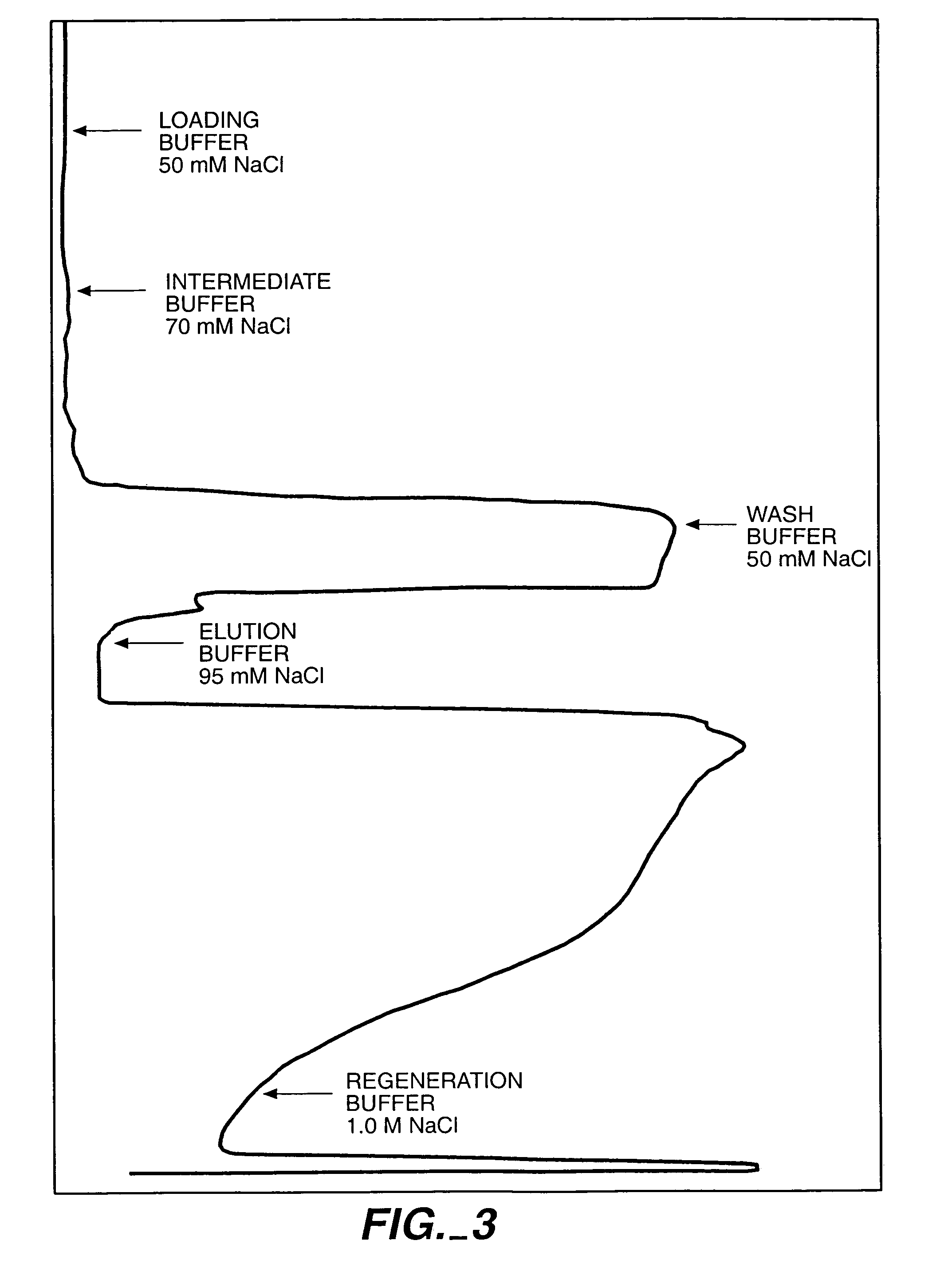
InactiveUS7074404B2High recovery ratePeptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsIon chromatographyMulti pollutant
A method for purifying a polypeptide by ion exchange chromatography is described which involves changing the conductivity and / or pH of buffers in order to resolve a polypeptide of interest from one or more contaminants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method and apparatus for kidney dialysis
InactiveUS20050242034A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOther blood circulation devicesUltrafiltrationDischarge measurements
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
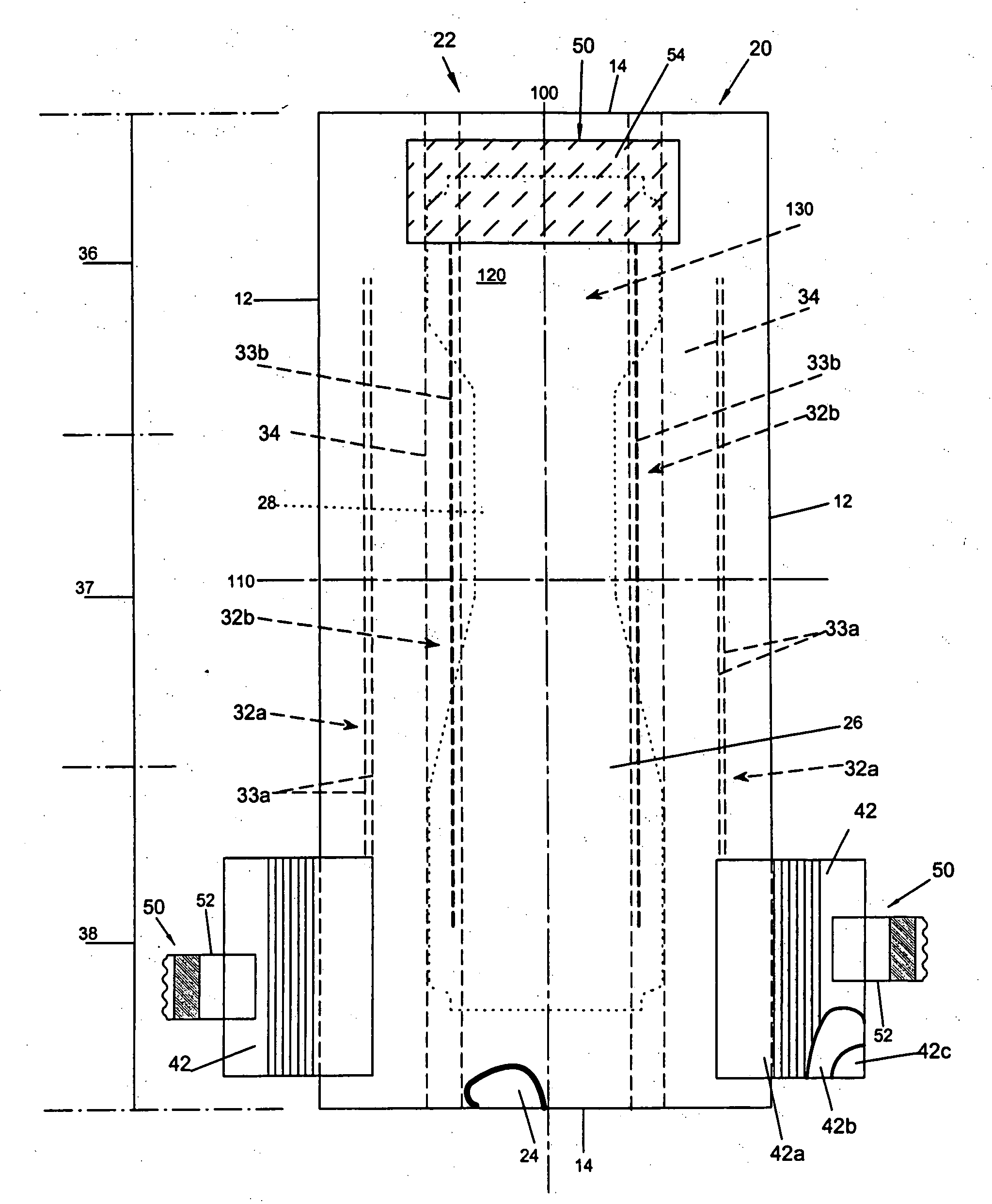
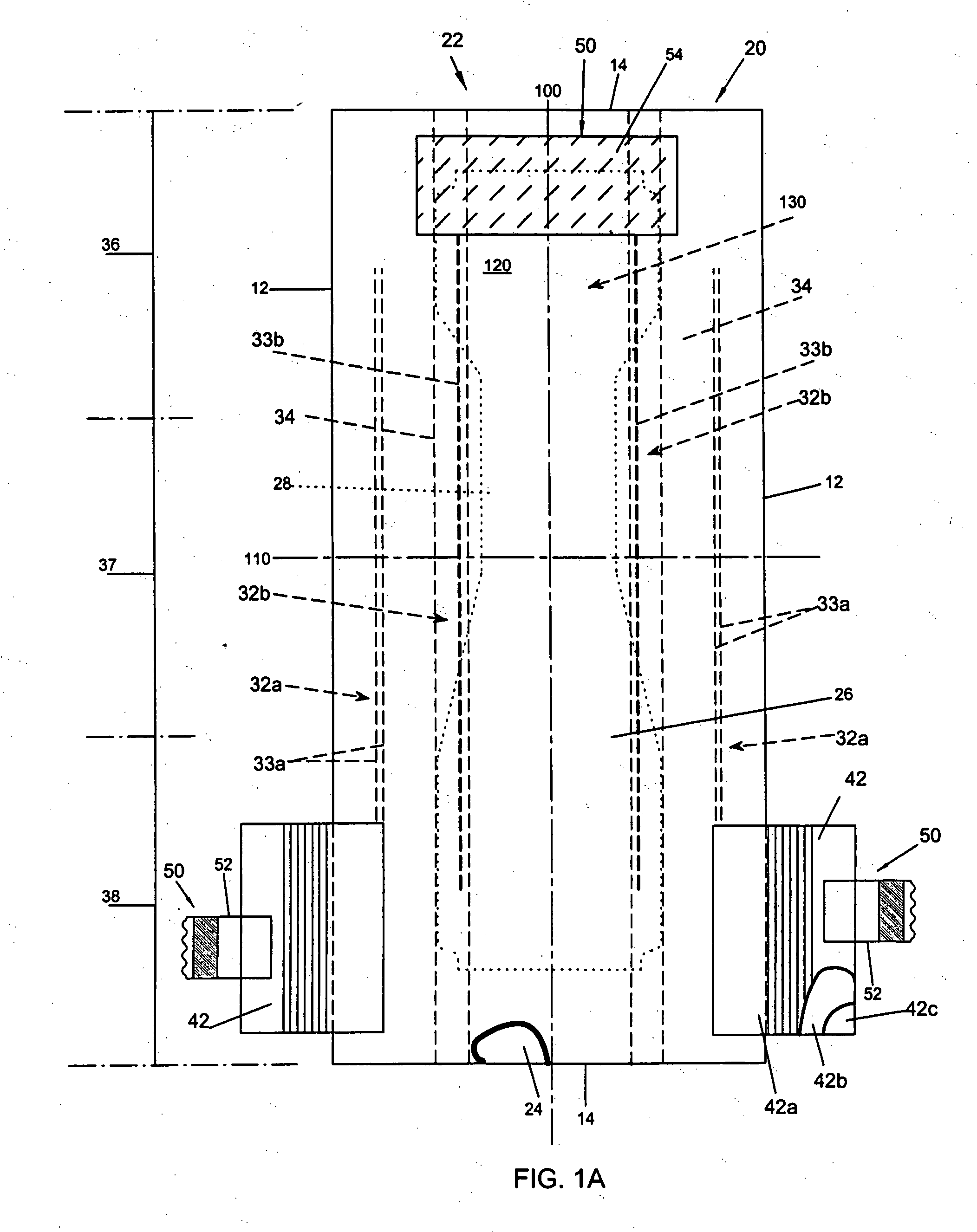
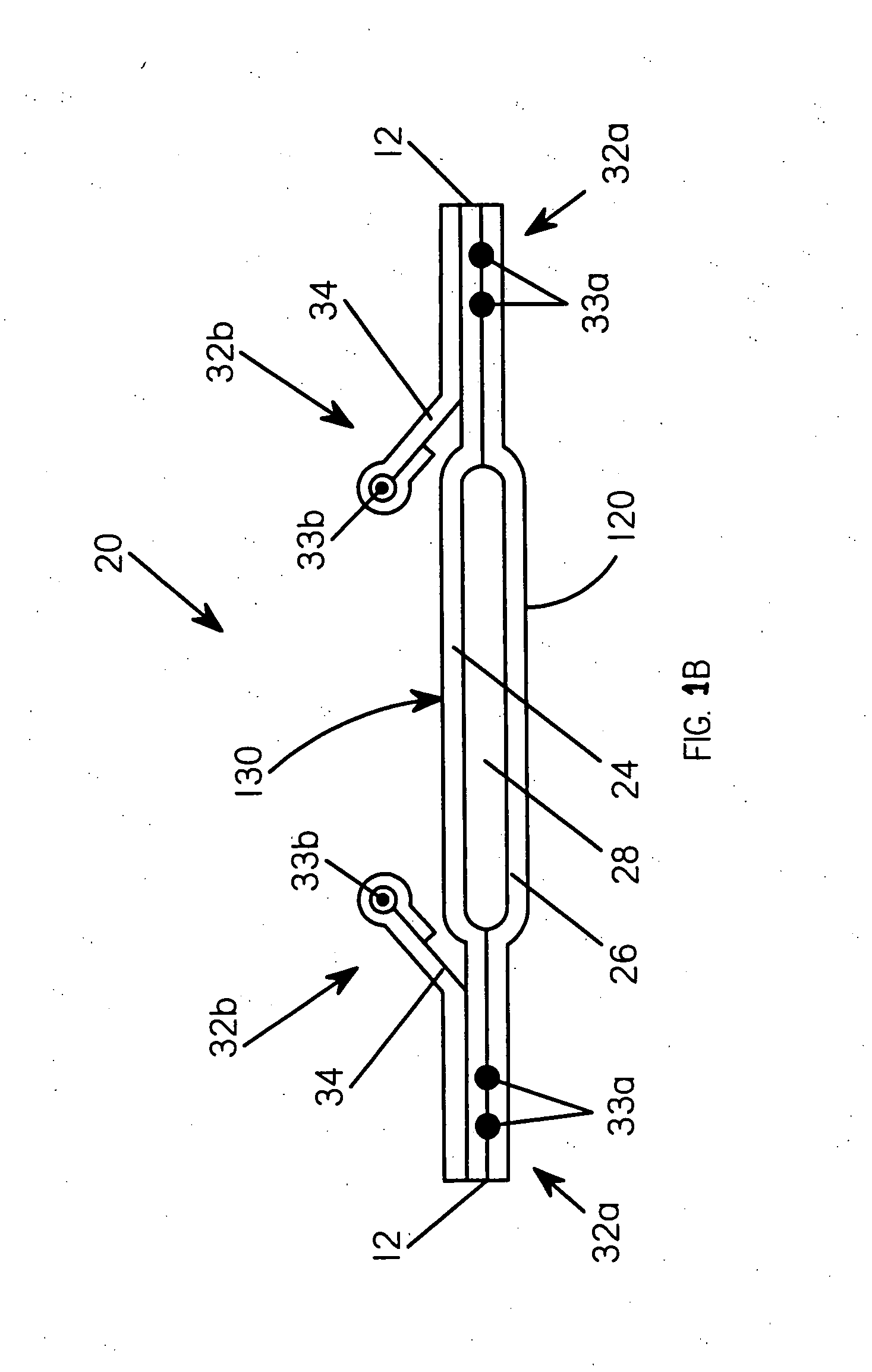
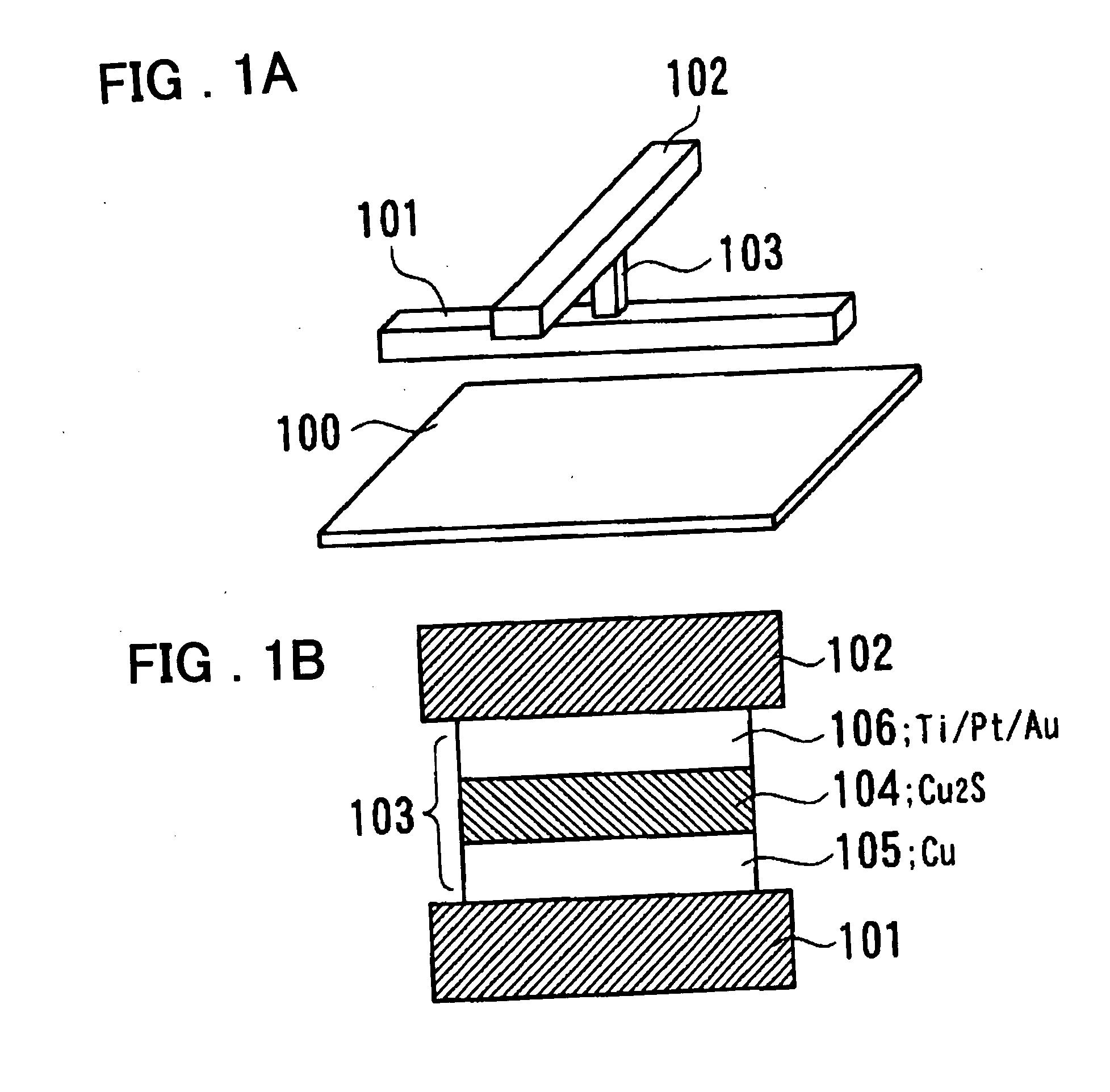
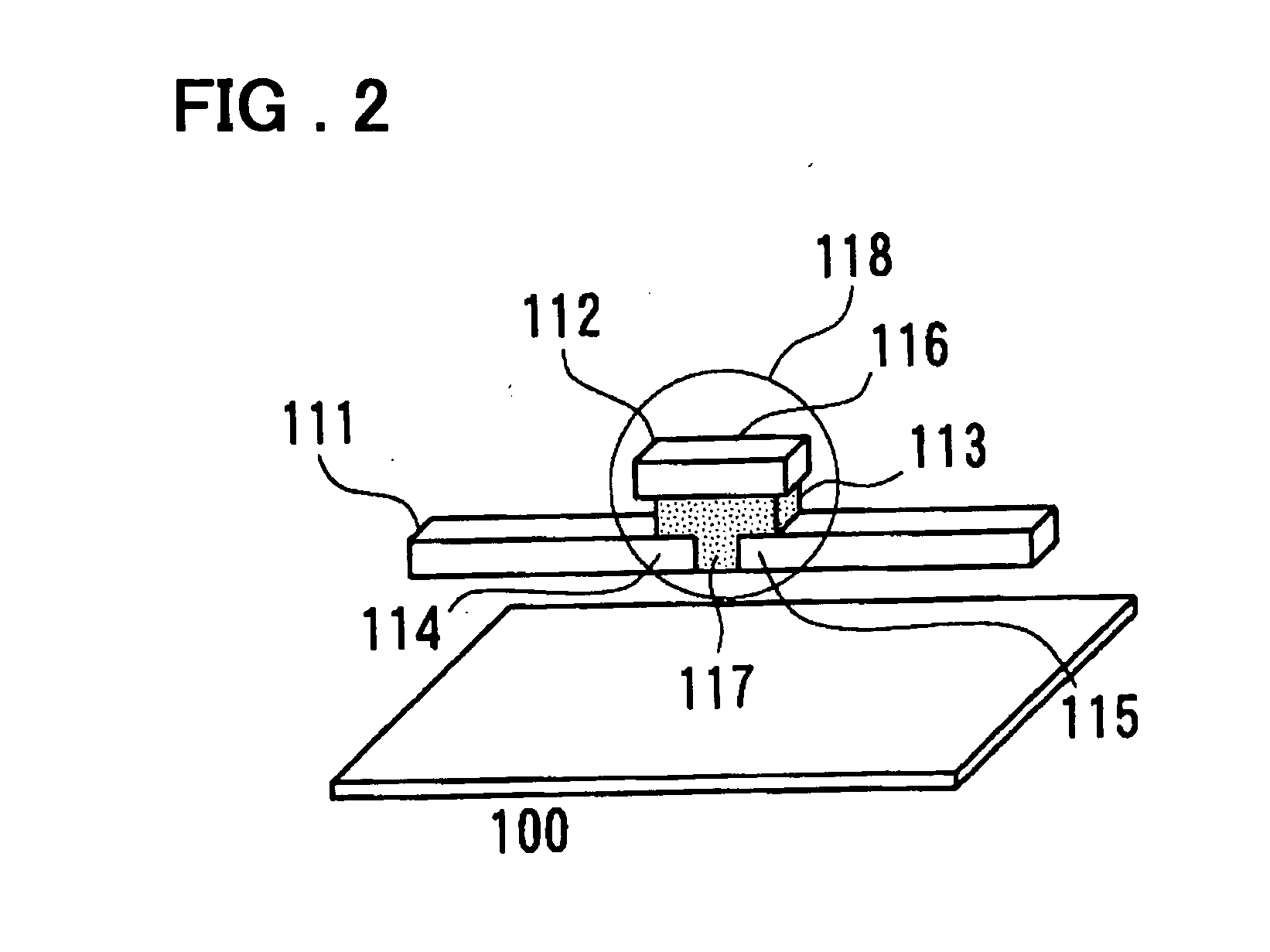
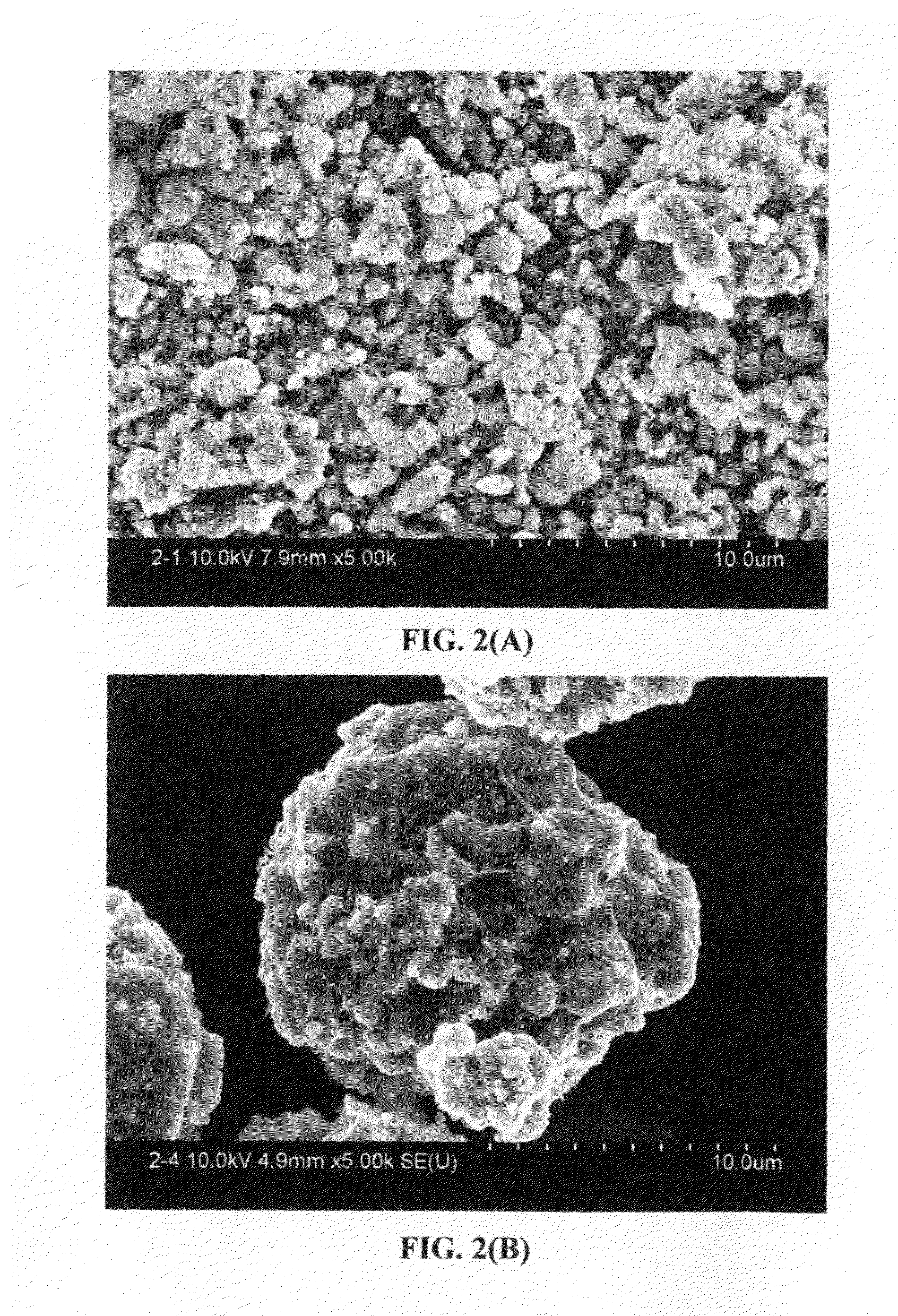
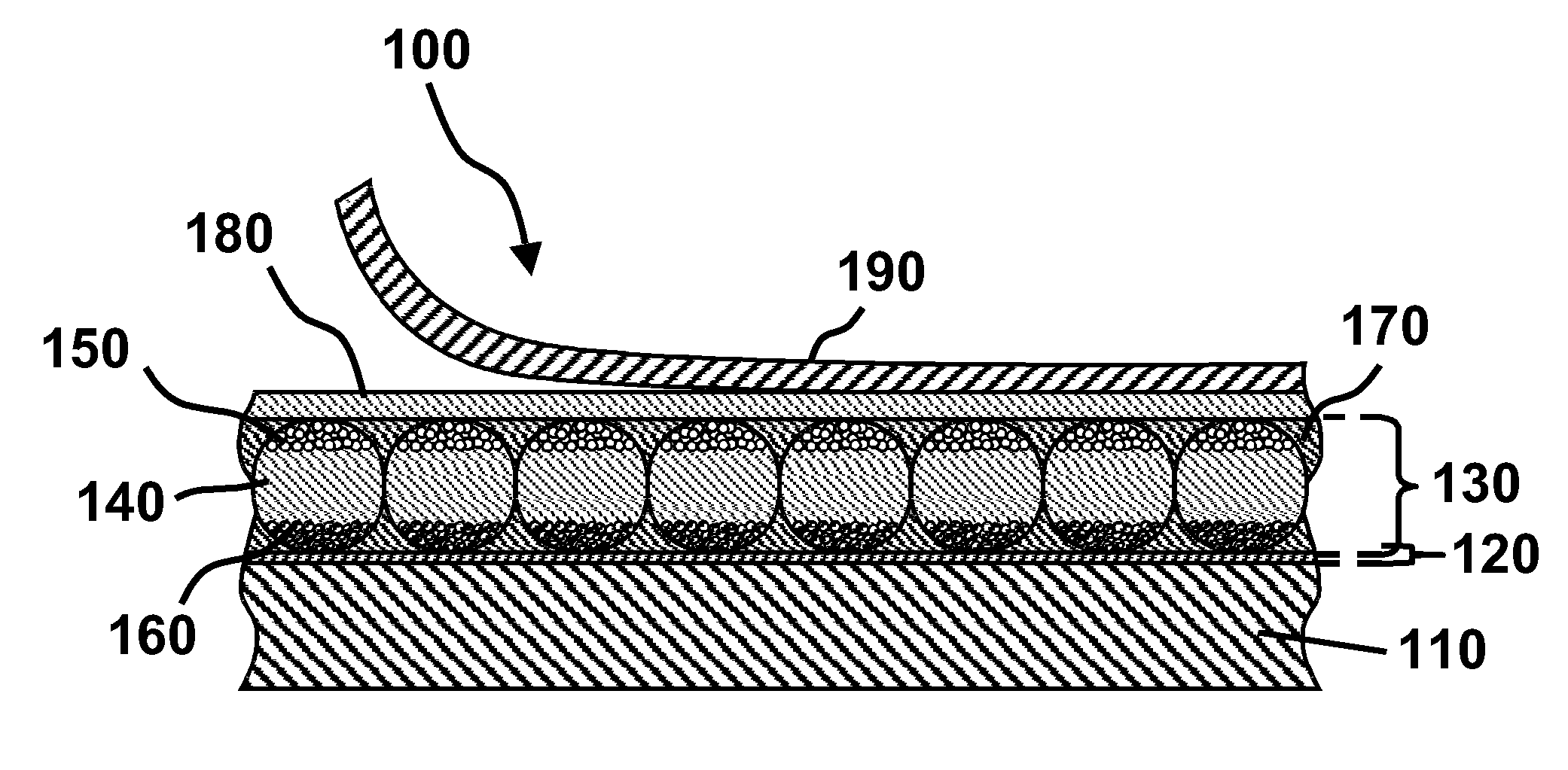
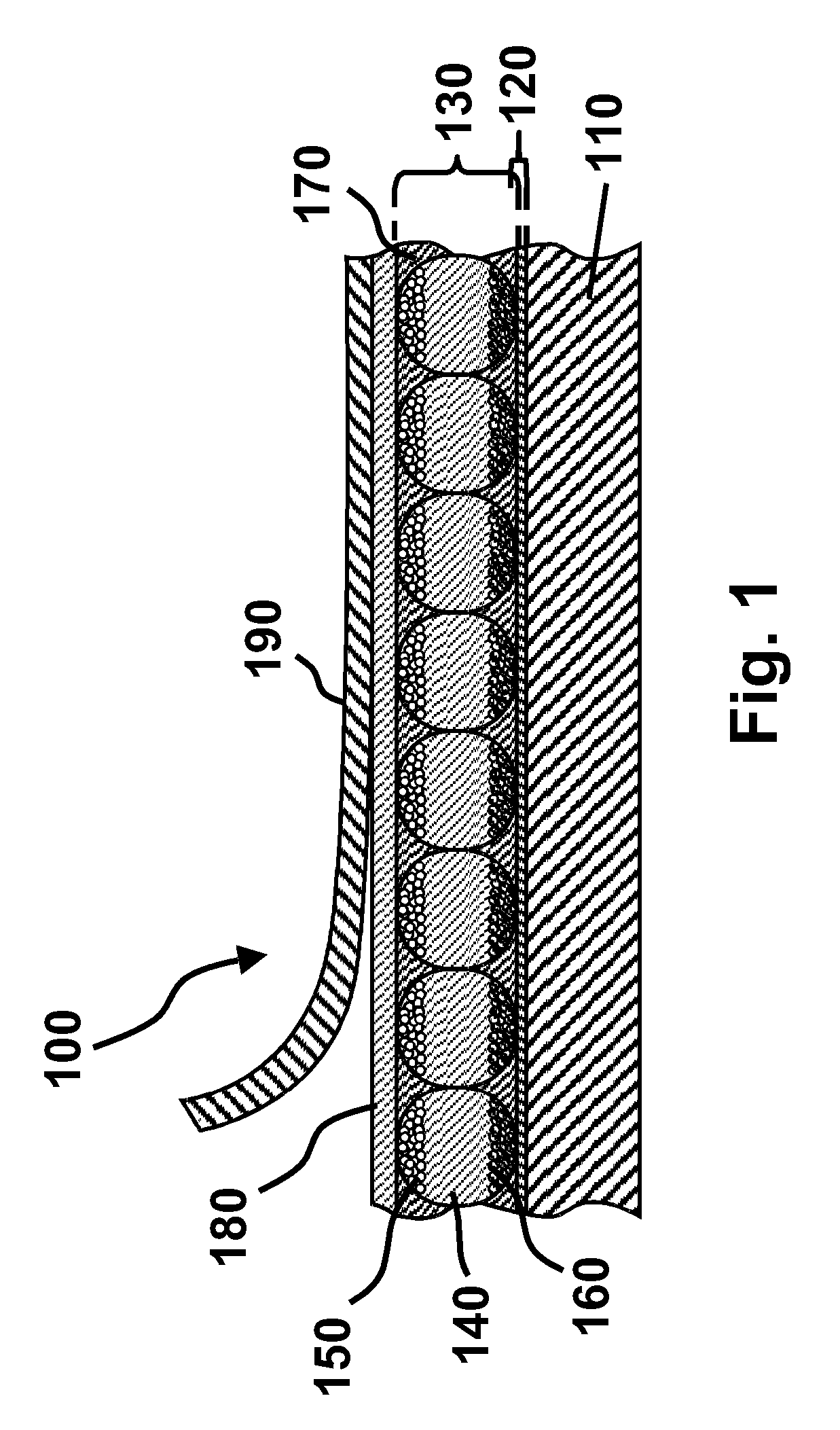
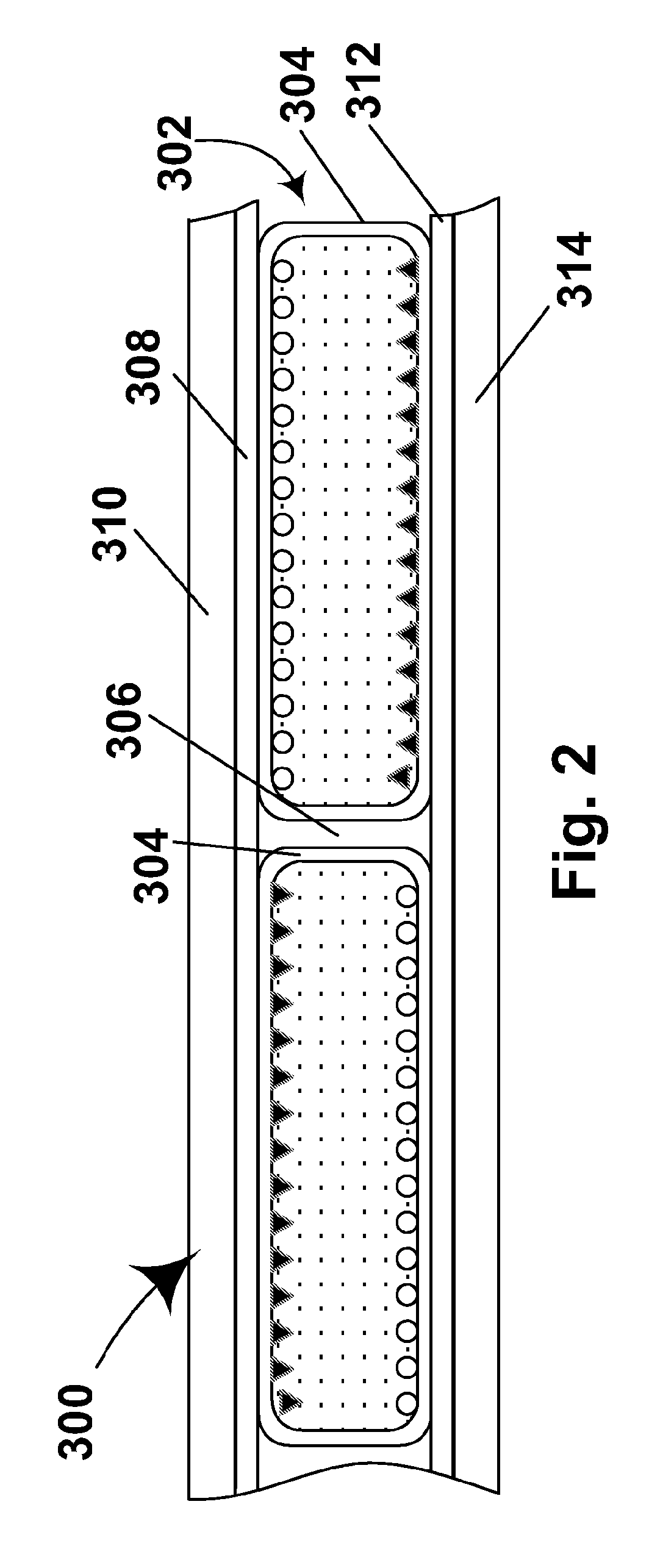
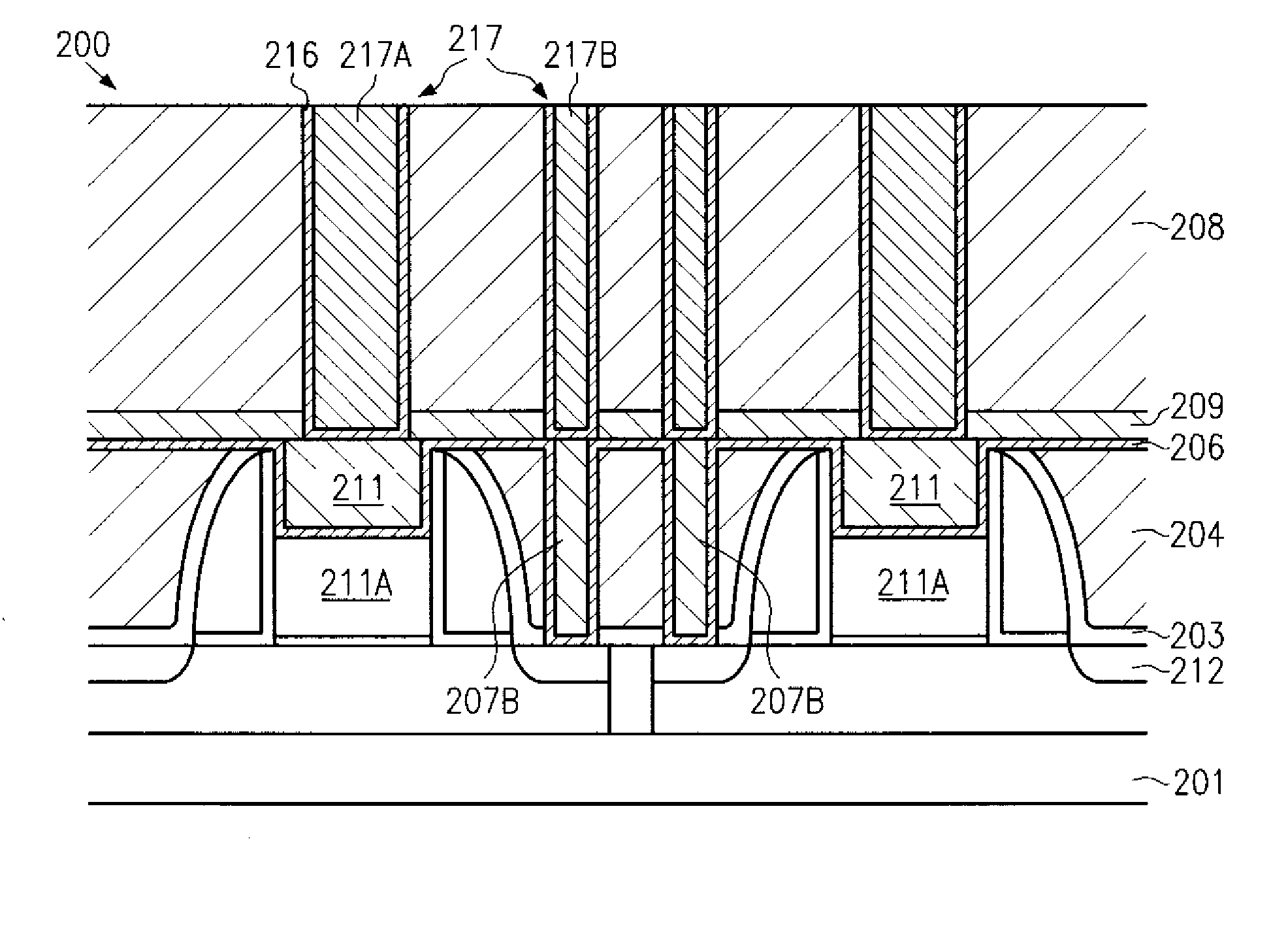
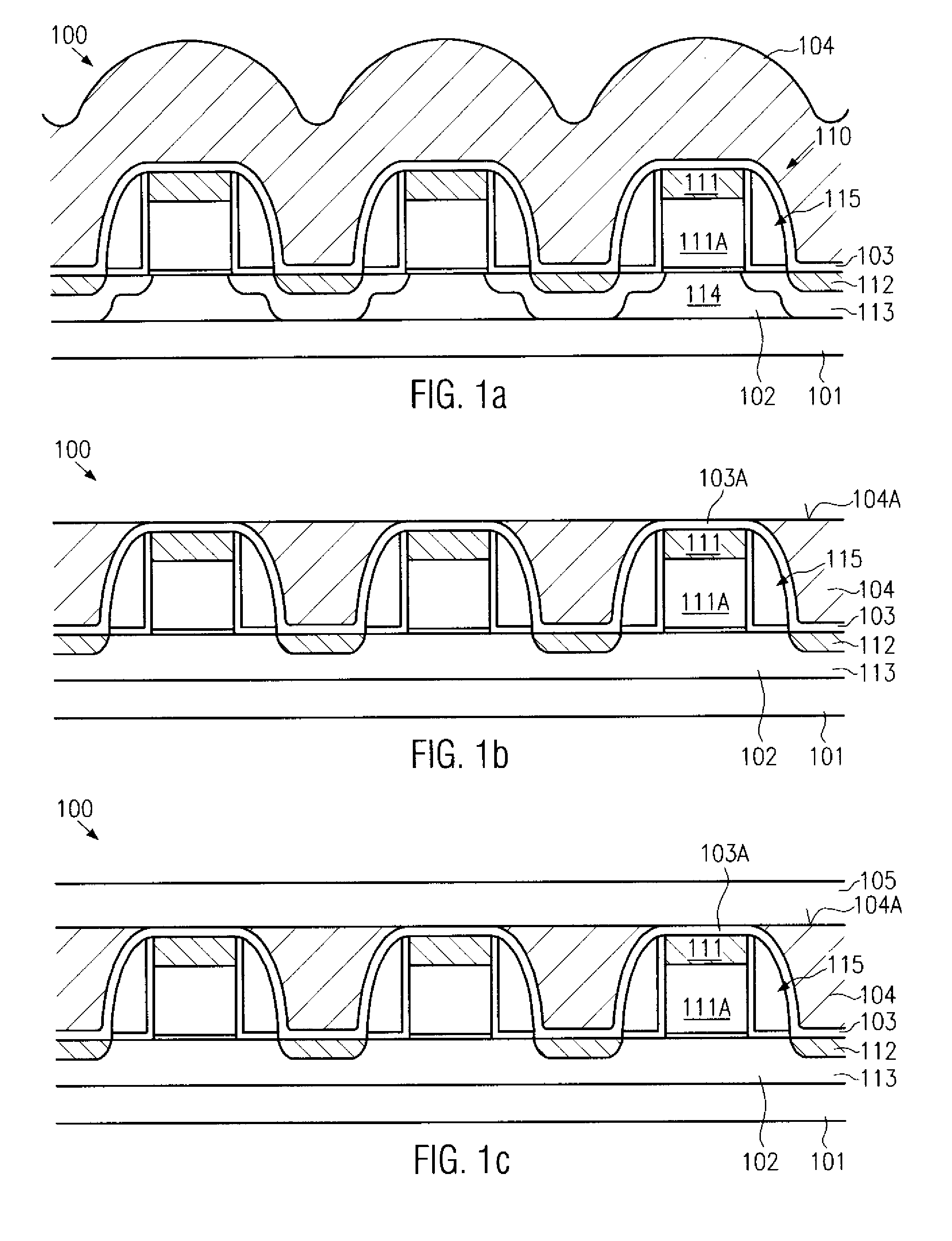
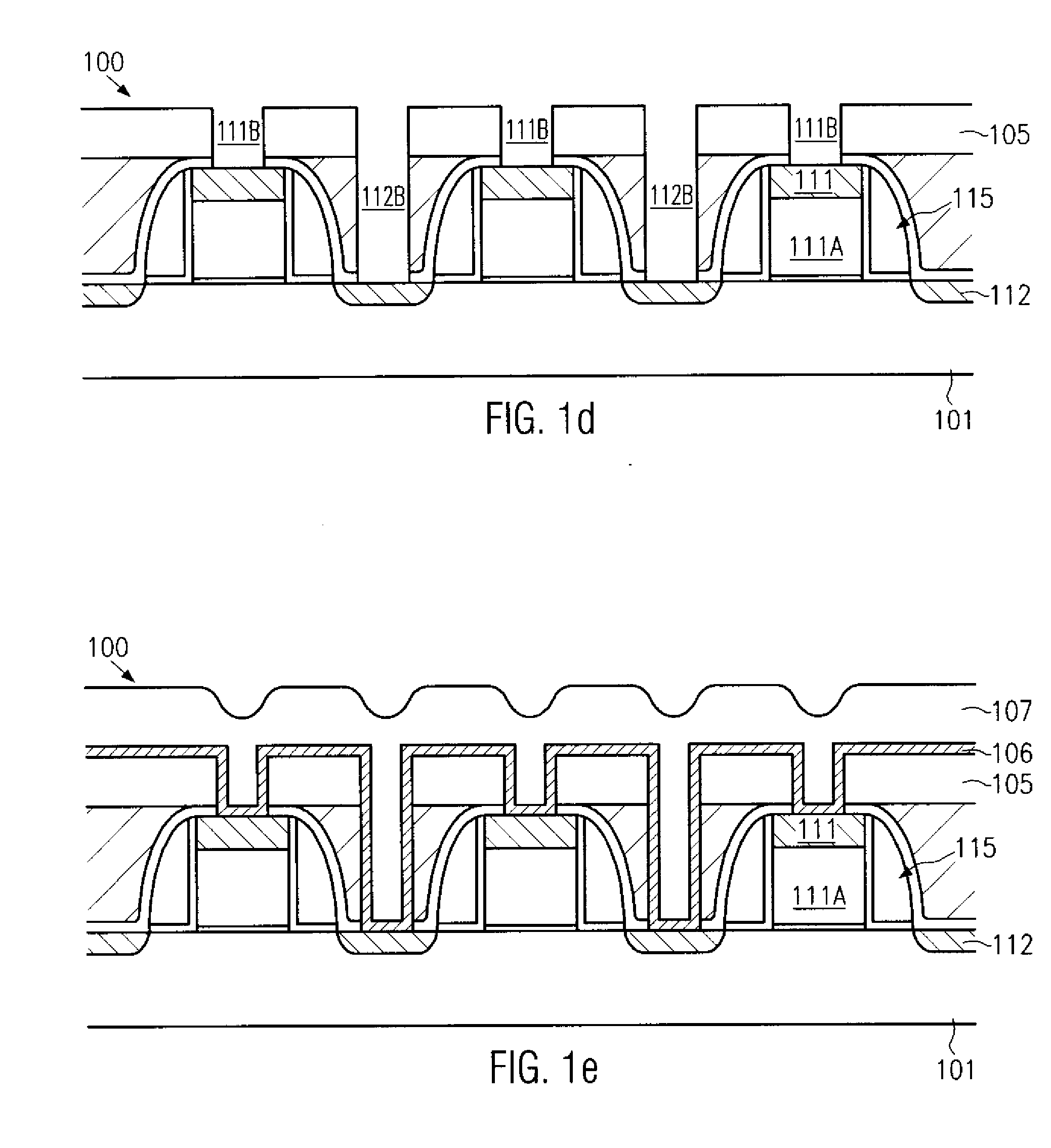
[superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof]
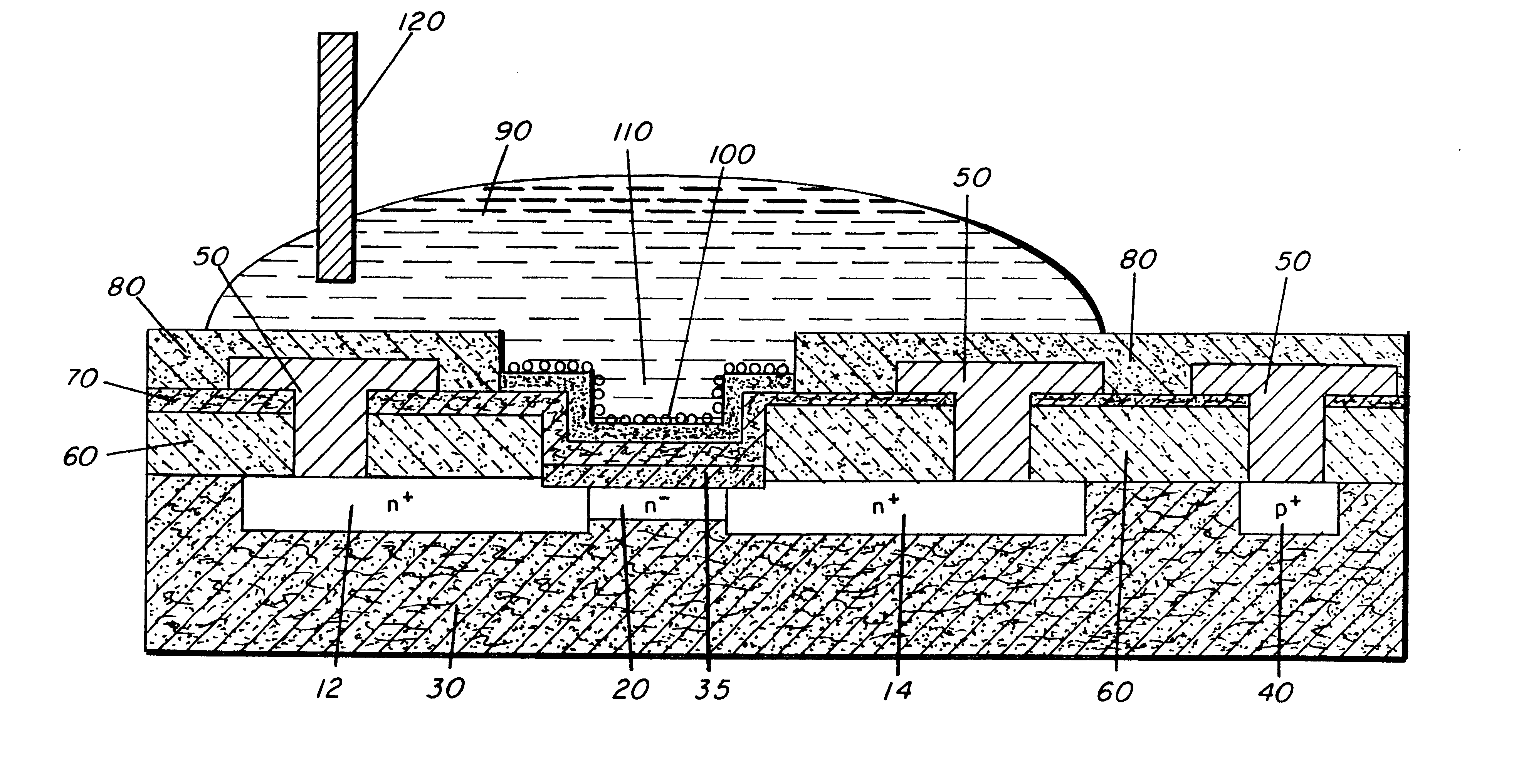
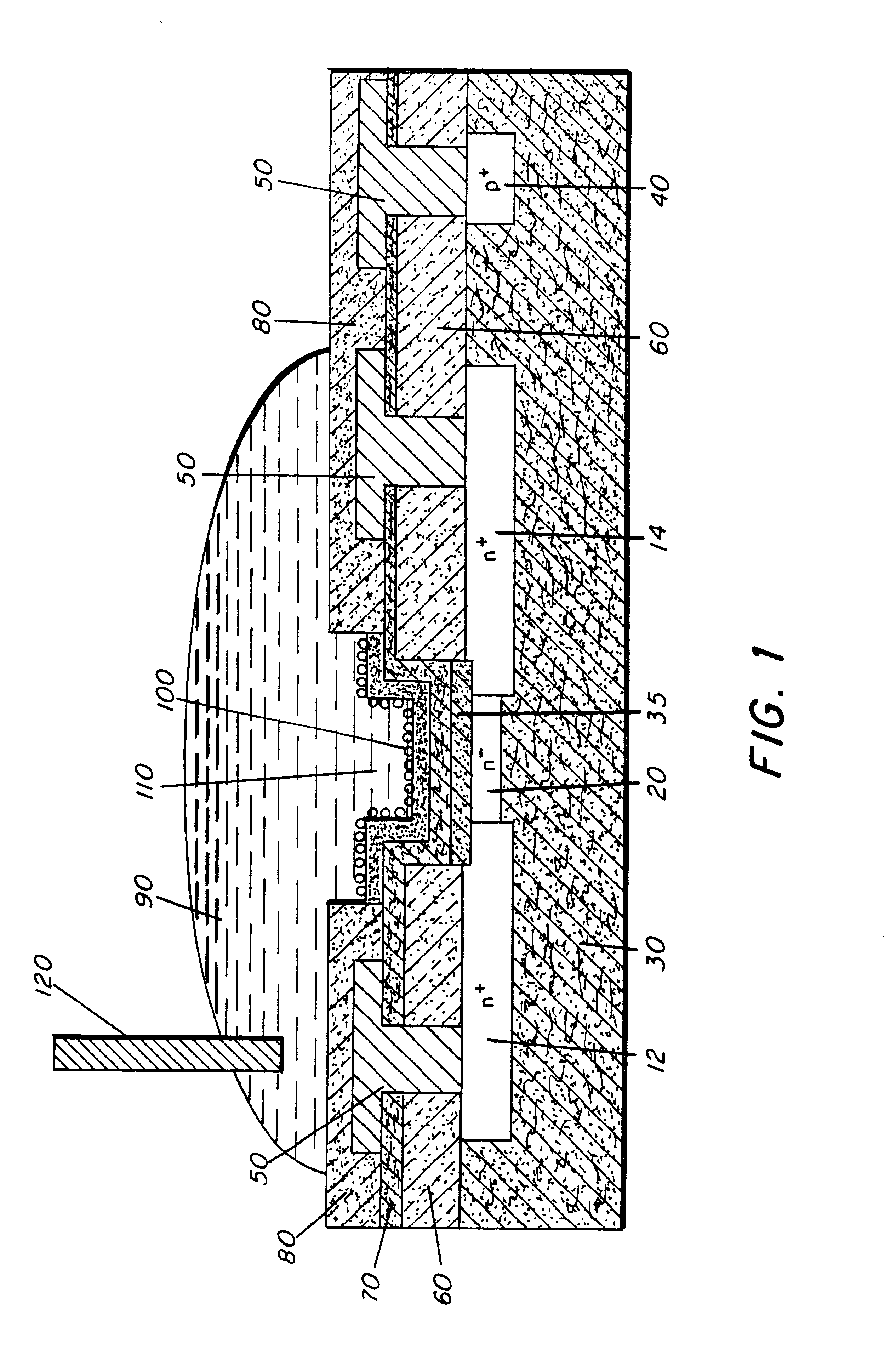
InactiveUS20050242411A1Reduce resistanceIncrease heightSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A superjunction Schottky device is described. The Schottky device includes a back metal layer, a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type, superjunction cells on the substrate, a lightly-doped JBS (Junction Barrier Schottky) region of the first conductivity type on each superjunction cell, and a front conductor layer. The superjunction cells include numerous charge-balanced junctions that extend substantially vertically, and the front conductor layer is disposed contacting with the JBS region to form a Schottky contact.
Owner:TAURUS MICROPOWER
Automatic atherectomy system
InactiveUS20070270688A1Improve conductivityReduce conductivityExcision instrumentsDiagnostic recording/measuringAtherectomyEngineering
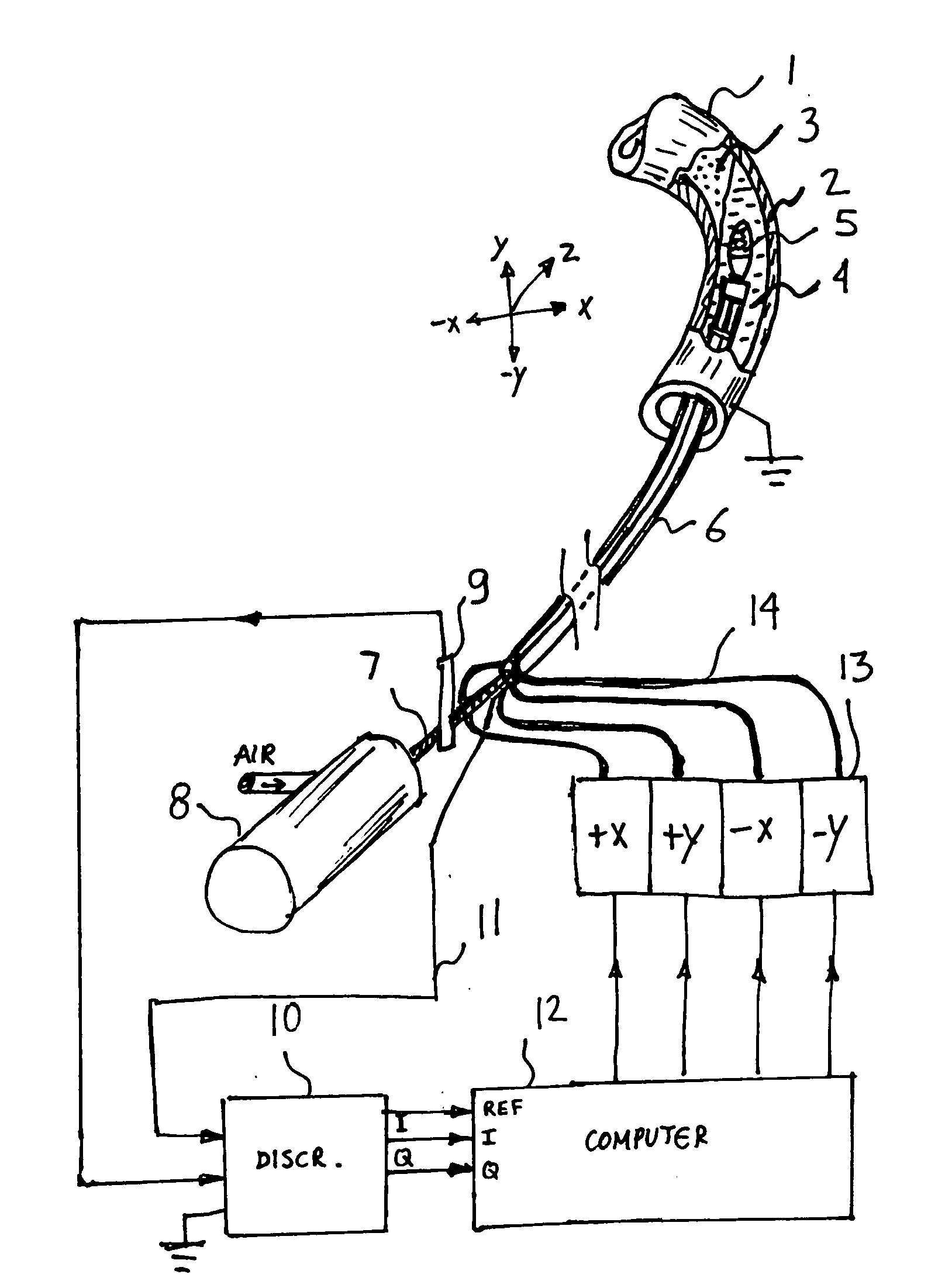
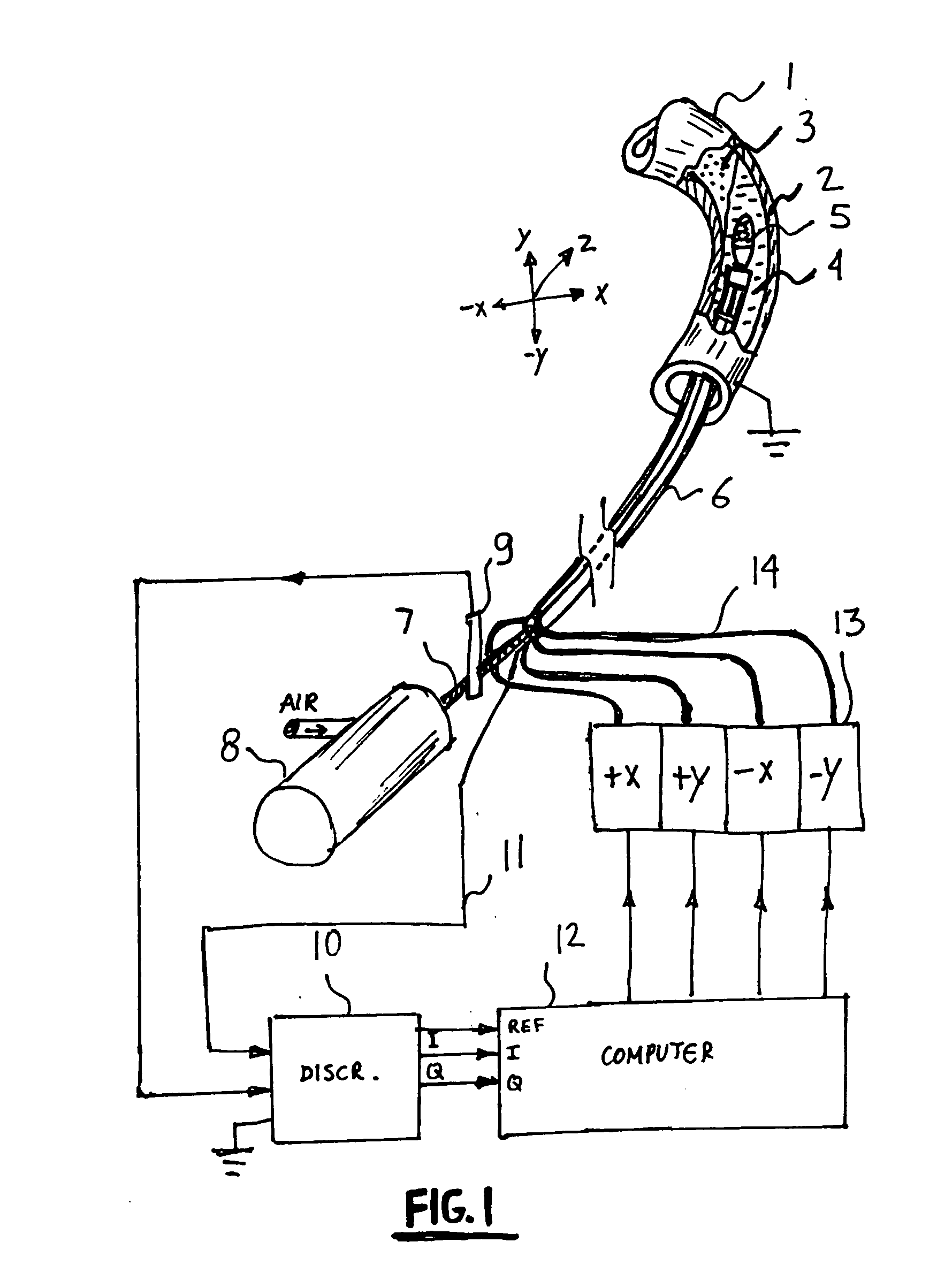
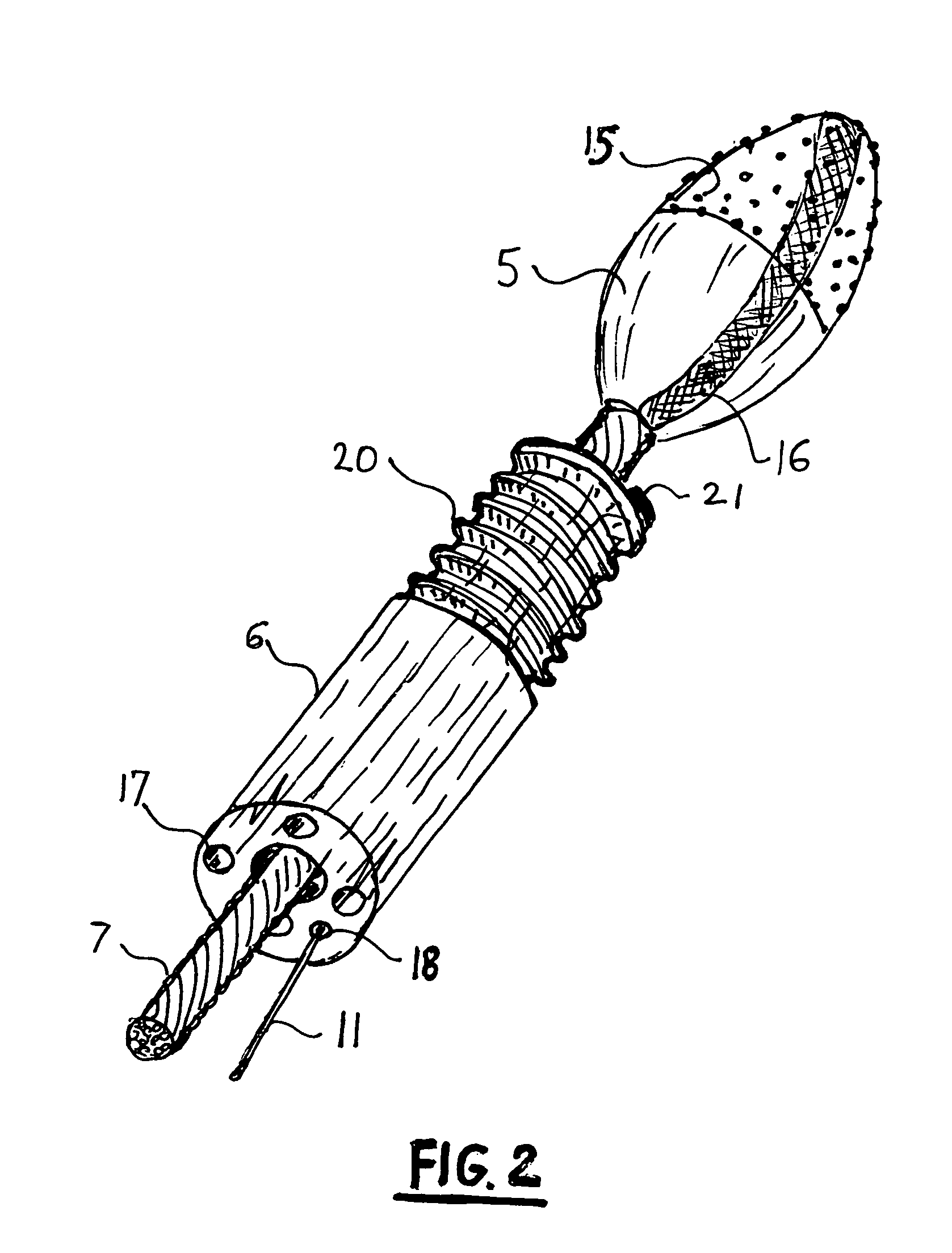
An automatic atherectomy system uses the rotary burr at the tip of a catheter as a sensing device, in order to measure both the electrical conductivity and permittivity of the surrounding tissue at multiple frequencies. From these parameters it is determined which tissue lies in the different directions around the tip. A servo system steers the catheter tip in the direction of the tissue to be removed. In non-atherectomy applications the rotary tip can be replaced with any desired tool and the system can be used to automatically steer the catheter to the desired position. The steering is done hydraulically, by pressurizing miniature bellows located near the catheter tip.
Owner:KARDIUM
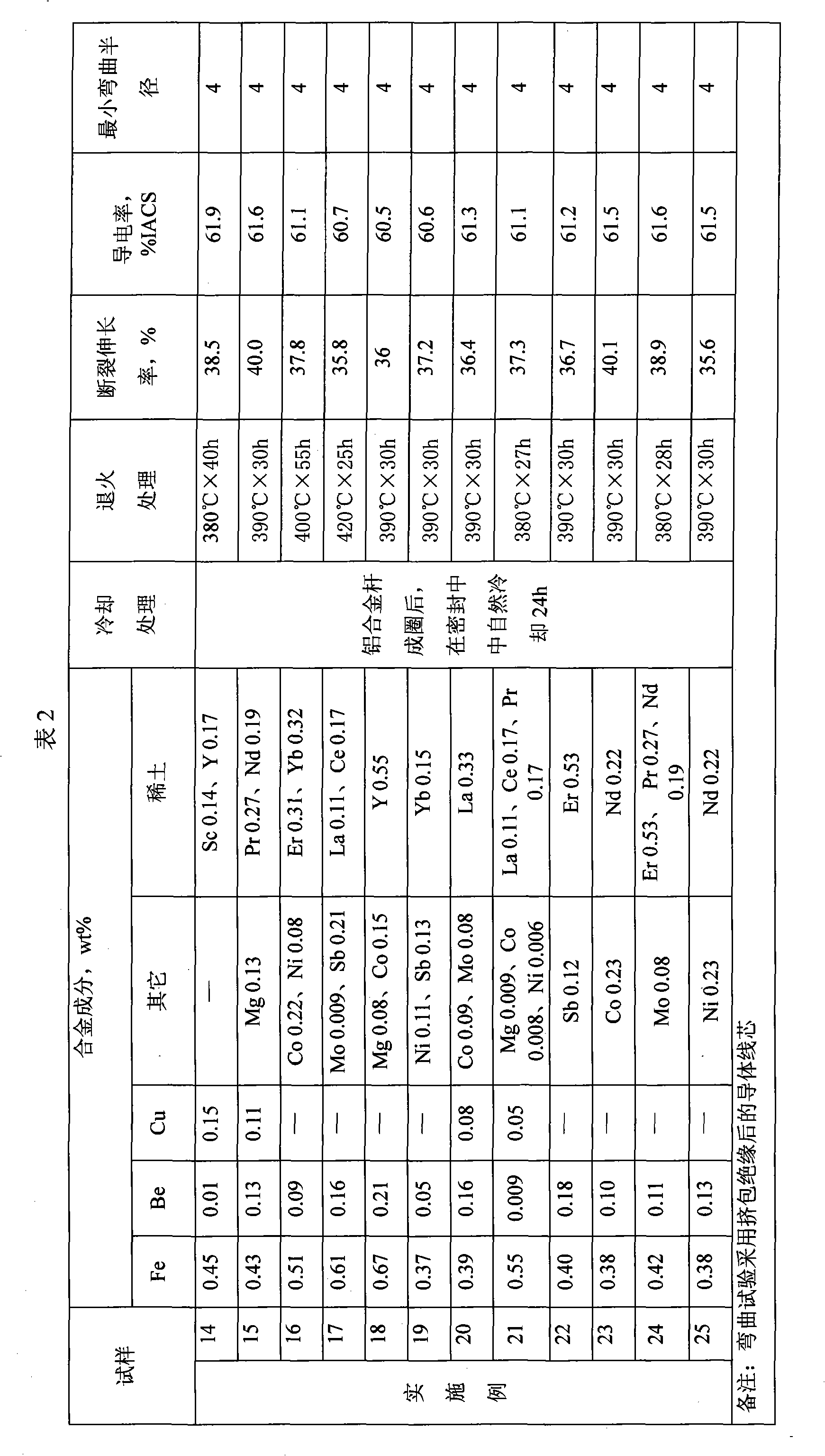
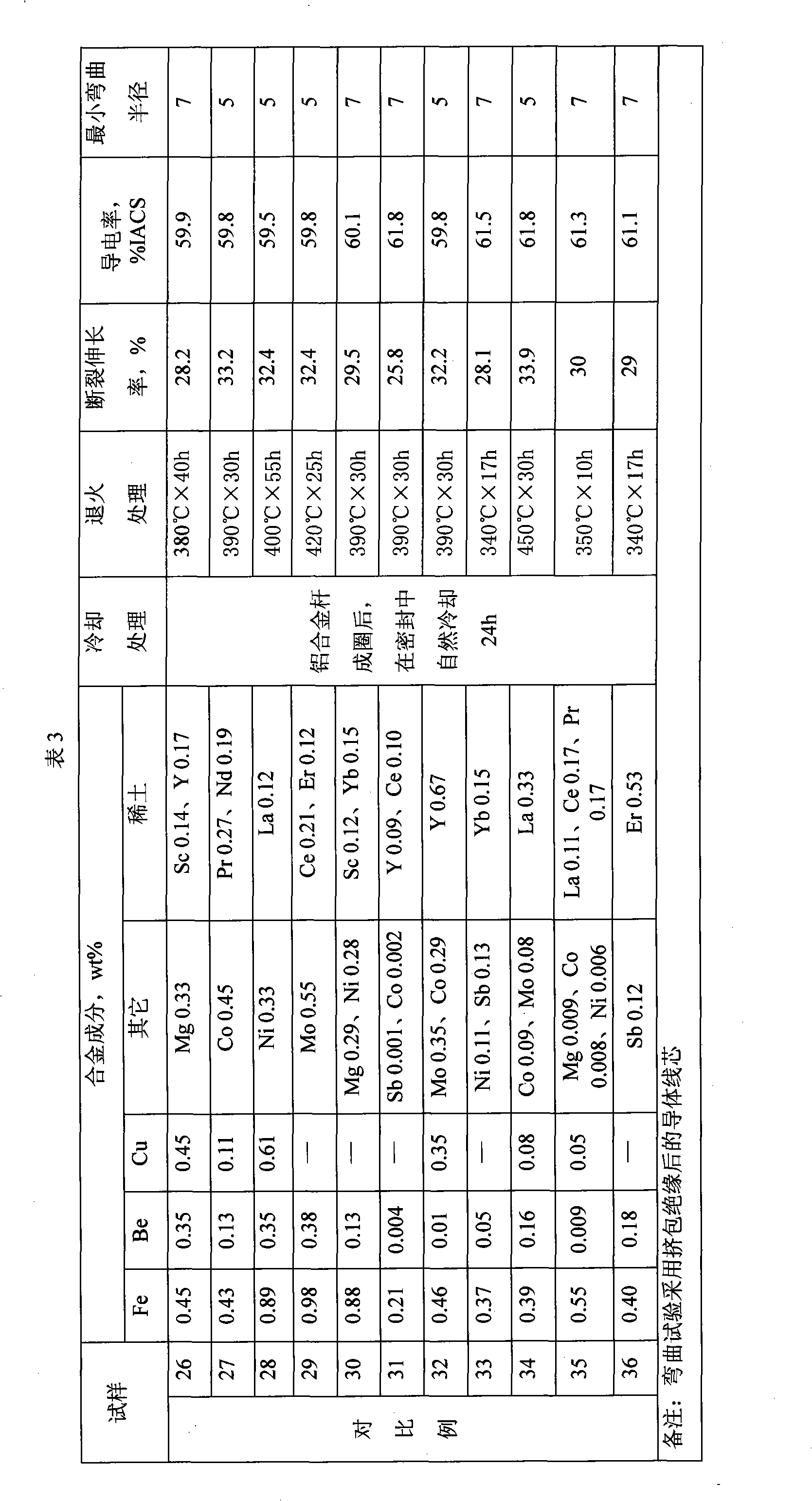
Super-soft aluminum alloy conductor and preparation method thereof
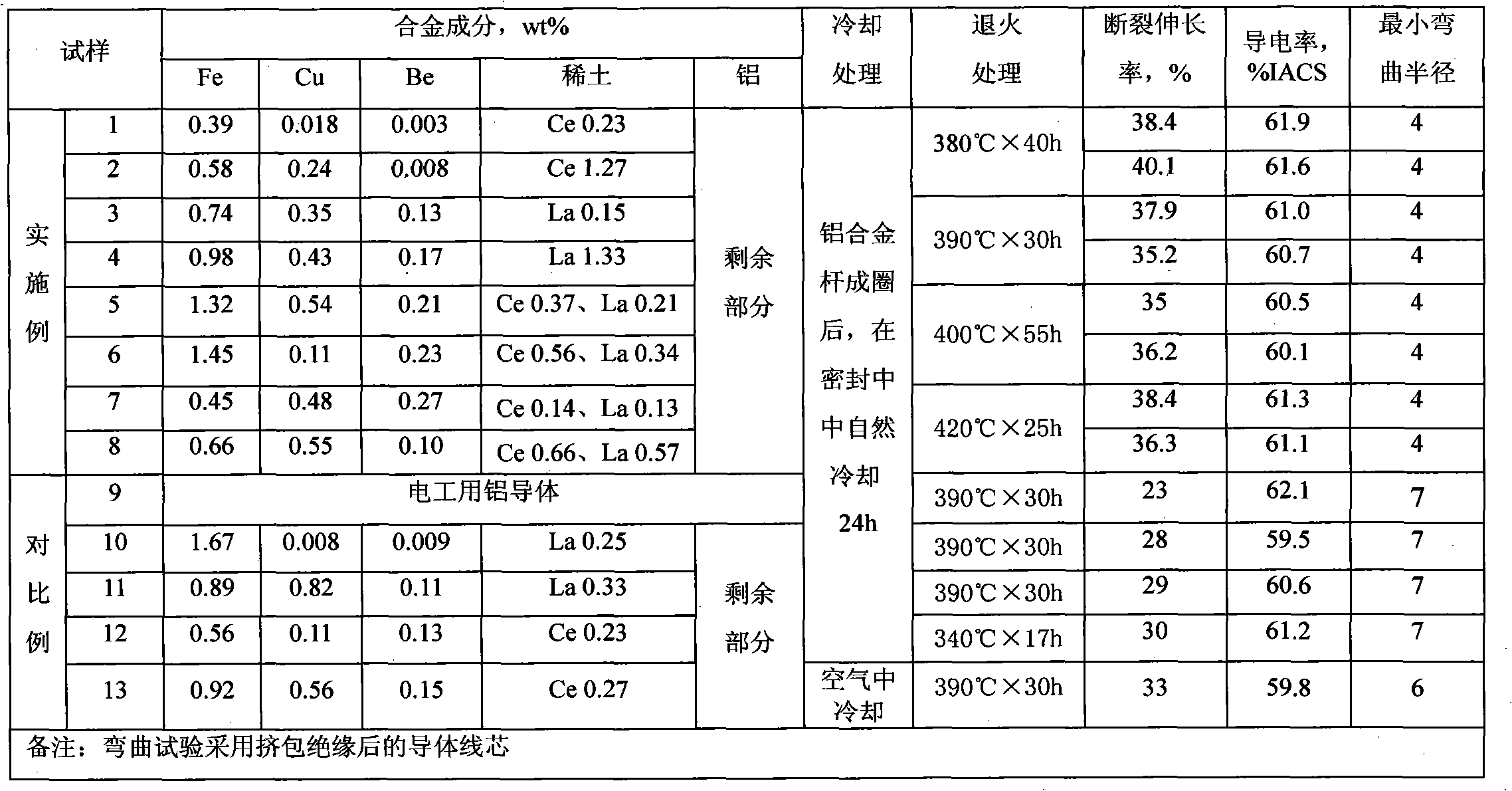
The invention provides a super-soft aluminum alloy conductor and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum alloy conductor comprises the following materials in percentage by weight: 0.3 to 1.5 percent of Fe, 0.001 to 0.3 percent of Be, 0.005 to 0.6 percent of Cu, 0.1 to 1.5 percent of rare earth, less than or equal to 0.08 percent of Si, less than or equal to 0.15 percent of total inevitable impurities, and the balance of aluminum. The aluminum alloy is drawn into an aluminum alloy wire by melting, continuous casting and continuous rolling, and the aluminum alloy wire is put into an annealing furnace and annealed for 20 to 40 hours at the temperature of between 380 and 420 DEG C to form the aluminum alloy conductor, wherein the annealing is performed in a sealed heat insulation device under the protection of nitrogen. The aluminum alloy has extremely good toughness and elongation performance, the coefficient of elongation reaches or exceeds 35 percent and even can reach 40 percent, and the electric conductivity can reach 60 percent IACS.
Owner:ANHUI JOY SENSE CABLE
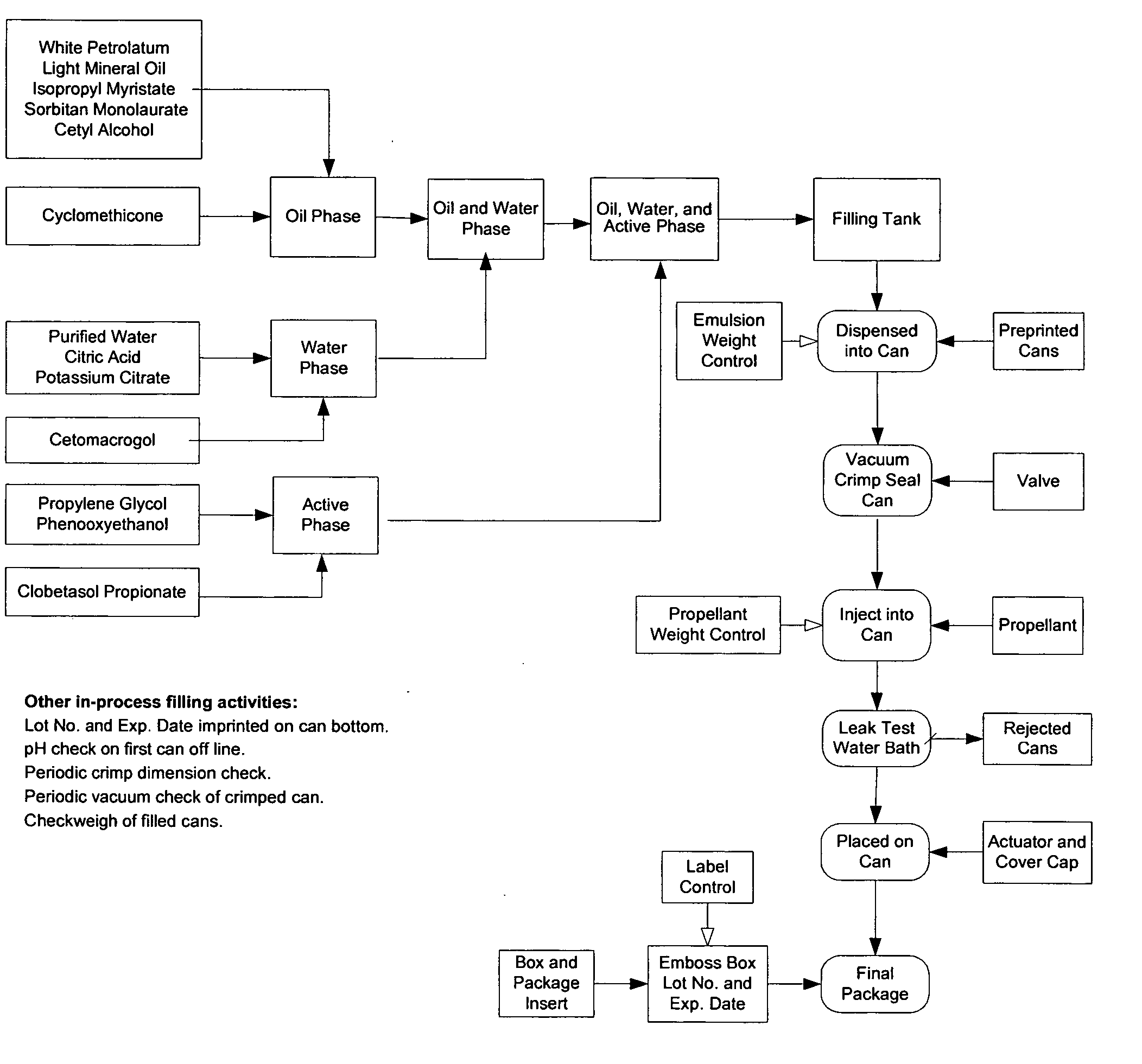
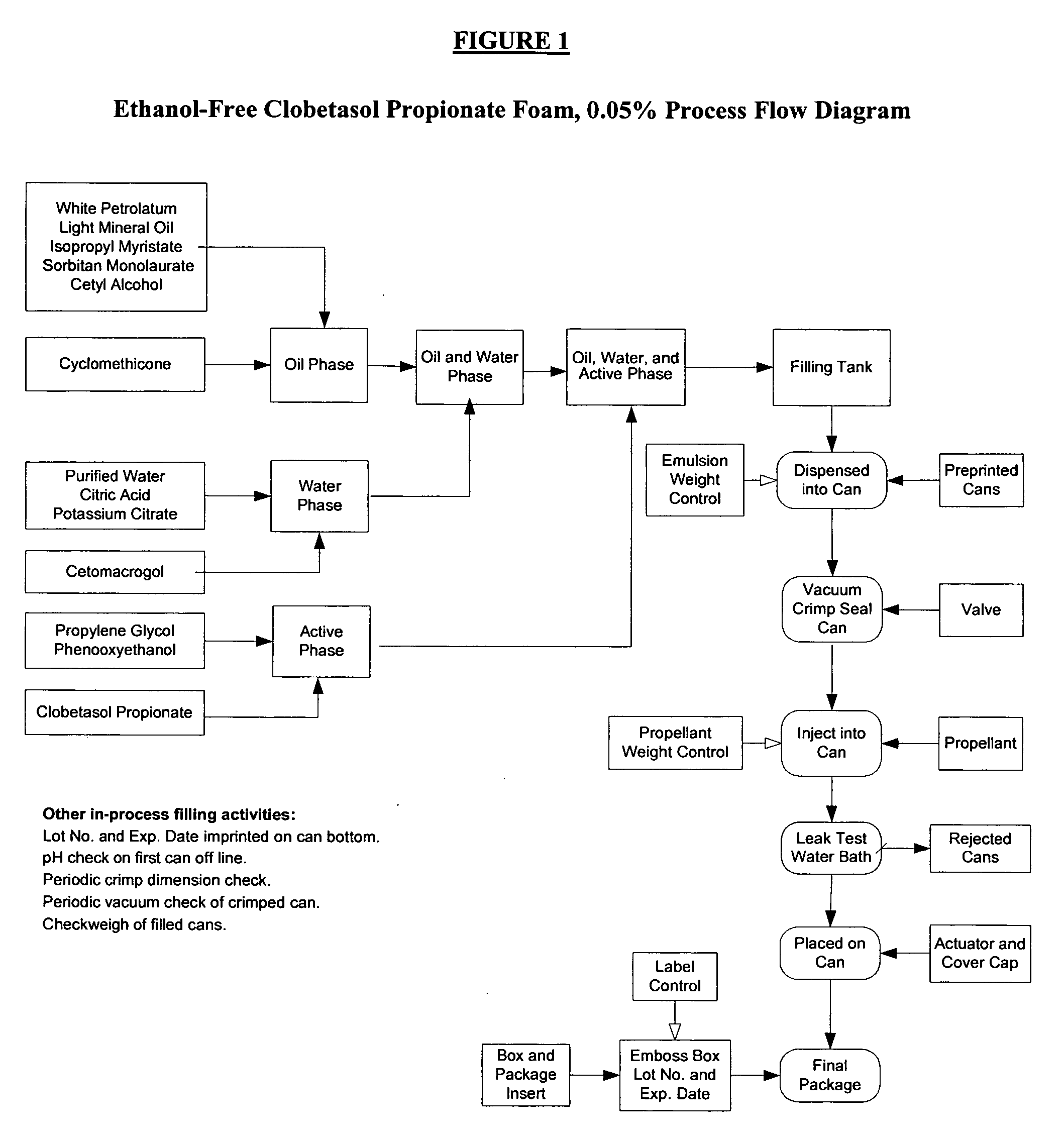
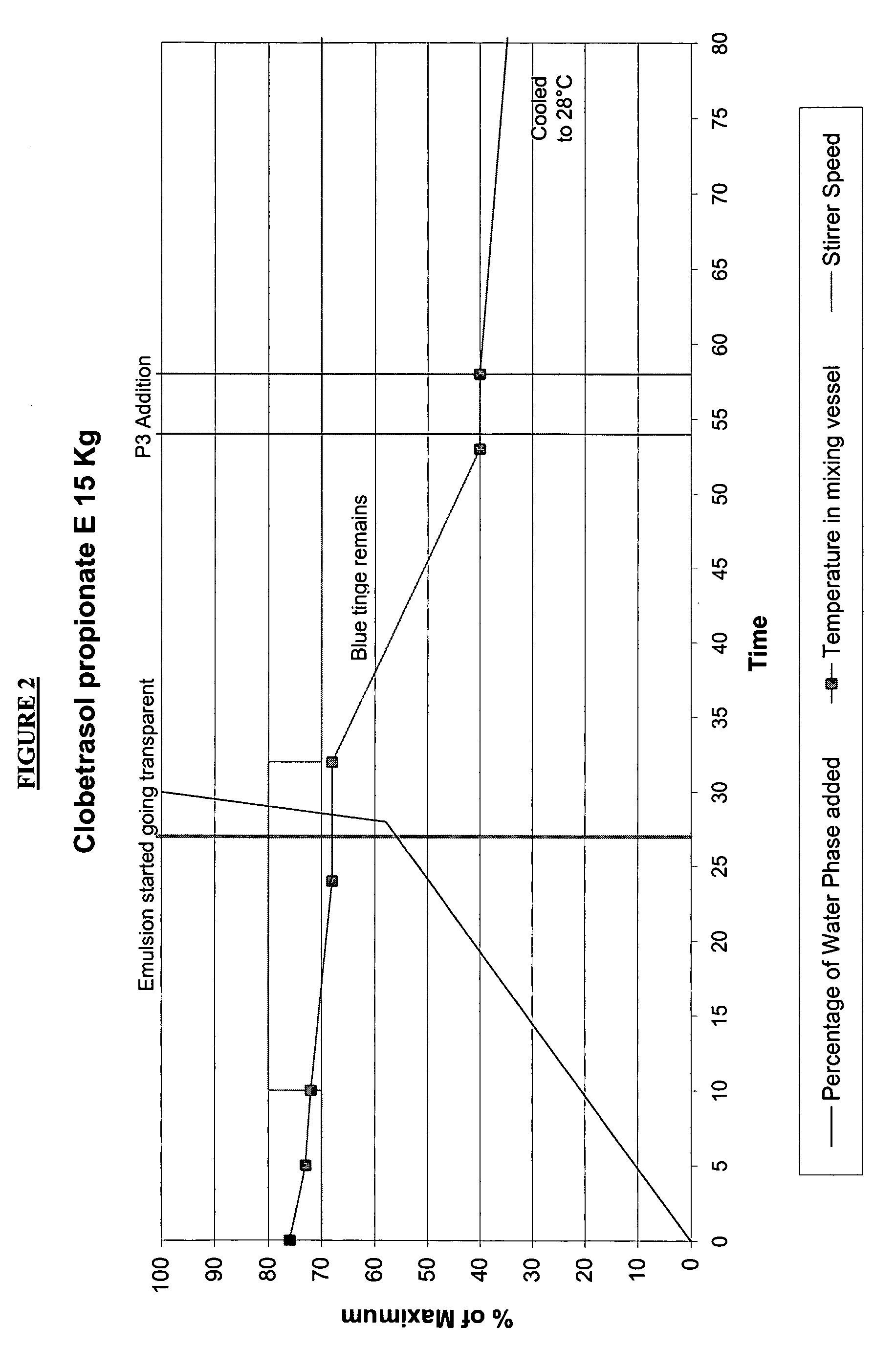
Microemulsion process and composition
ActiveUS20060057168A1Quality improvementCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsVegetable oilSilanes
There is provided a process for the preparation of an oil in water (O / W) microemulsion or sub-micron emulsion composition for dermal delivery of at least one pharmaceutically active ingredient, the method including the steps of a) Admixing a first part including at least one of the group consisting of animal, mineral or vegetable oils, silanes, siloxanes, esters, fatty acids, fats, halogen compounds or alkoxylated alcohols; and one or more lipophilic surfactants, and a second part including water and at least one hydrophilic surfactant to achieve homogeneity, b) heating the mix of step a) to a phase assembly temperature in the range of 40-99° C., preferably 45-95° C., more preferably 65-85° C. with continuous mixing to obtain a microemulsion or sub-micron emulsion, c) allowing said microemulsion or sub-micron emulsion to cool, and d) adding a third part to said microemulsion or sub-micron emulsion at a temperature between 2° C. and said phase assembly temperature, said third part if necessary being premixed and heated until the components are dissolved and including at least one component selected from the group consisting of non-surfactant amphiphilic type compound, surfactant and water with the proviso that when the third part includes water it also includes a non-surfactant amphiphilic type compound and / or surfactant. The phase assembly temperature can be determined visually by the achievement of translucence in the composition or by measures such as conductivity which peaks and then is maintained at a plateau whilst phase assembly occurs. It has been found that whilst if a non-surfactant amphiphilic type compound such as the polyol is added together with the second part as would conventionally be the case, a microemulsion or sub-micron emulsion is not formed, by adding the so called third part, phase assembly occurs at a lower temperature than would be expected and moreover, this phase appears to assist in maintaining the microemulsion or sub-micron emulsion characteristics of the formulation during storage at normal temperatures.
Owner:STIEFEL WEST COAST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![[superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof] [superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8a8473c2-2c5a-4498-8a31-fcdb4f4c6324/US20050242411A1-20051103-D00000.png)
![[superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof] [superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8a8473c2-2c5a-4498-8a31-fcdb4f4c6324/US20050242411A1-20051103-D00001.png)
![[superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof] [superjunction schottky device and fabrication thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8a8473c2-2c5a-4498-8a31-fcdb4f4c6324/US20050242411A1-20051103-D00002.png)