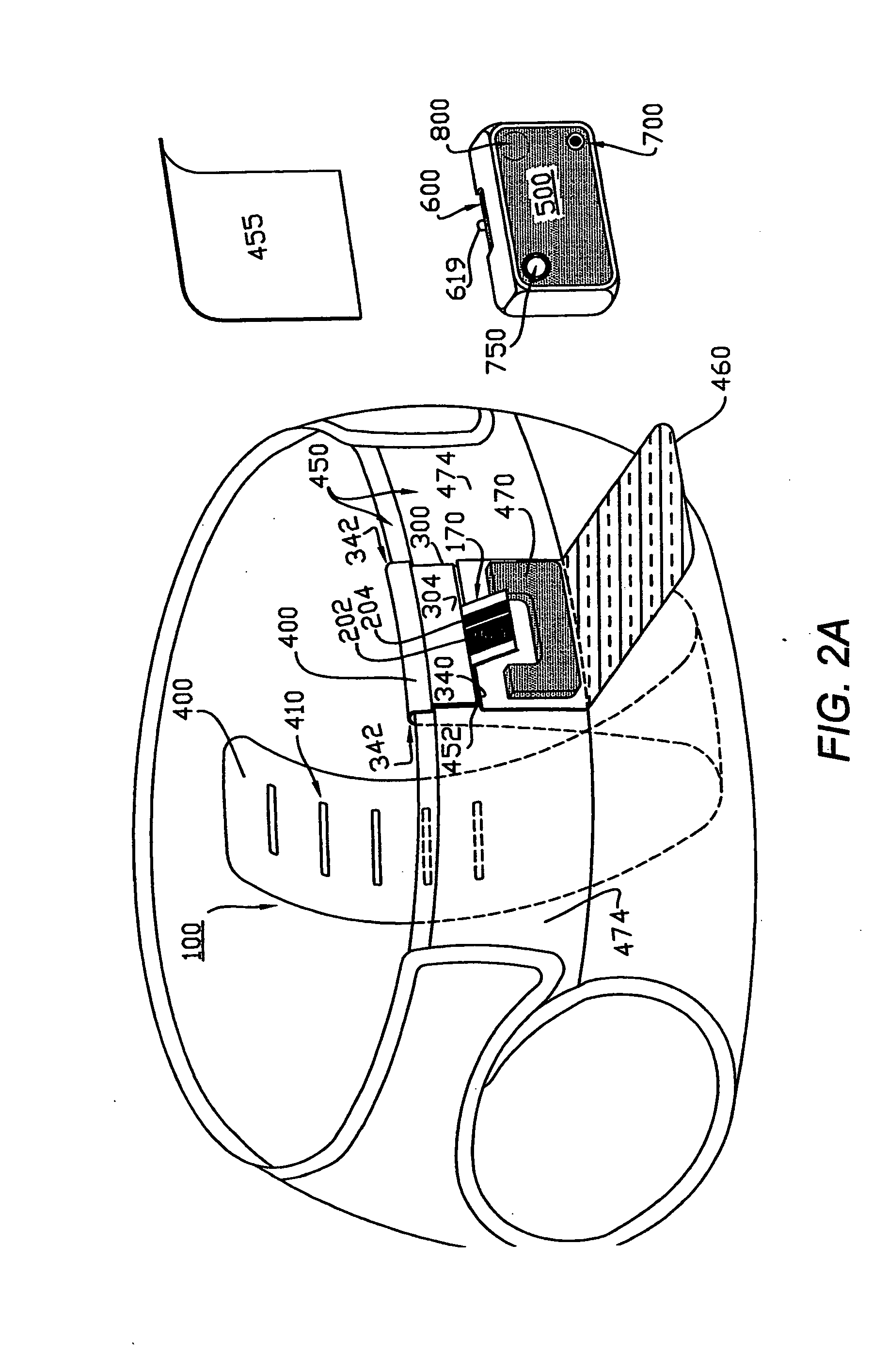
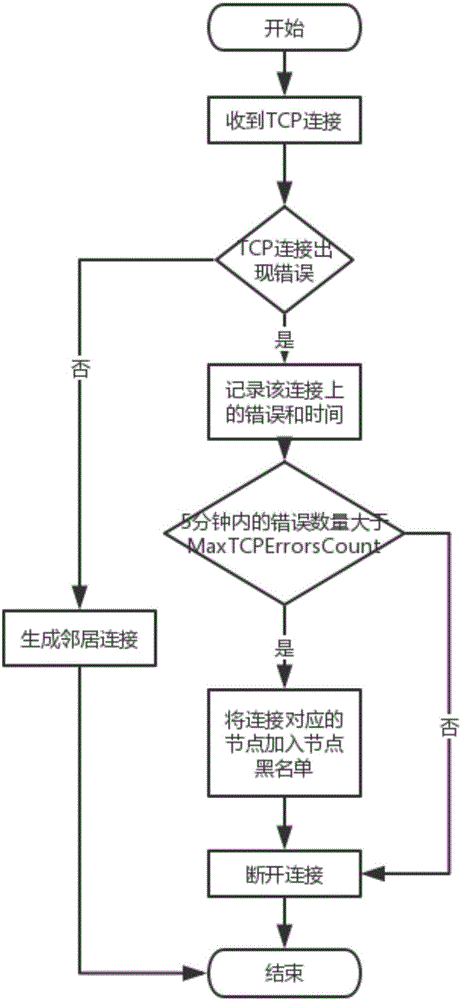
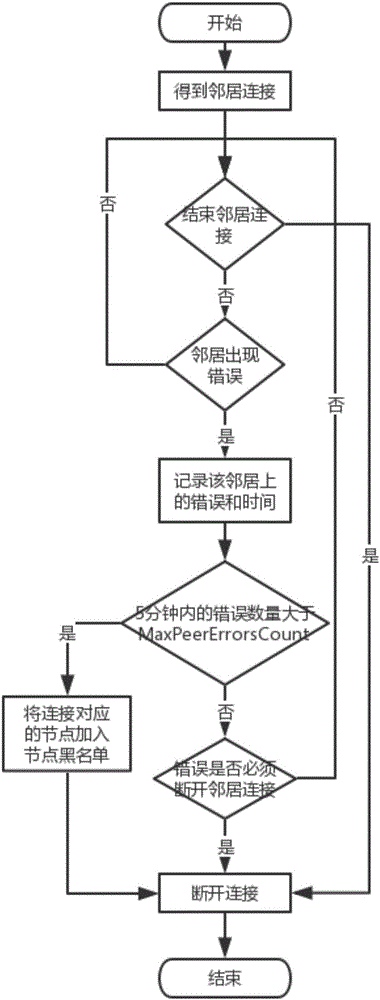
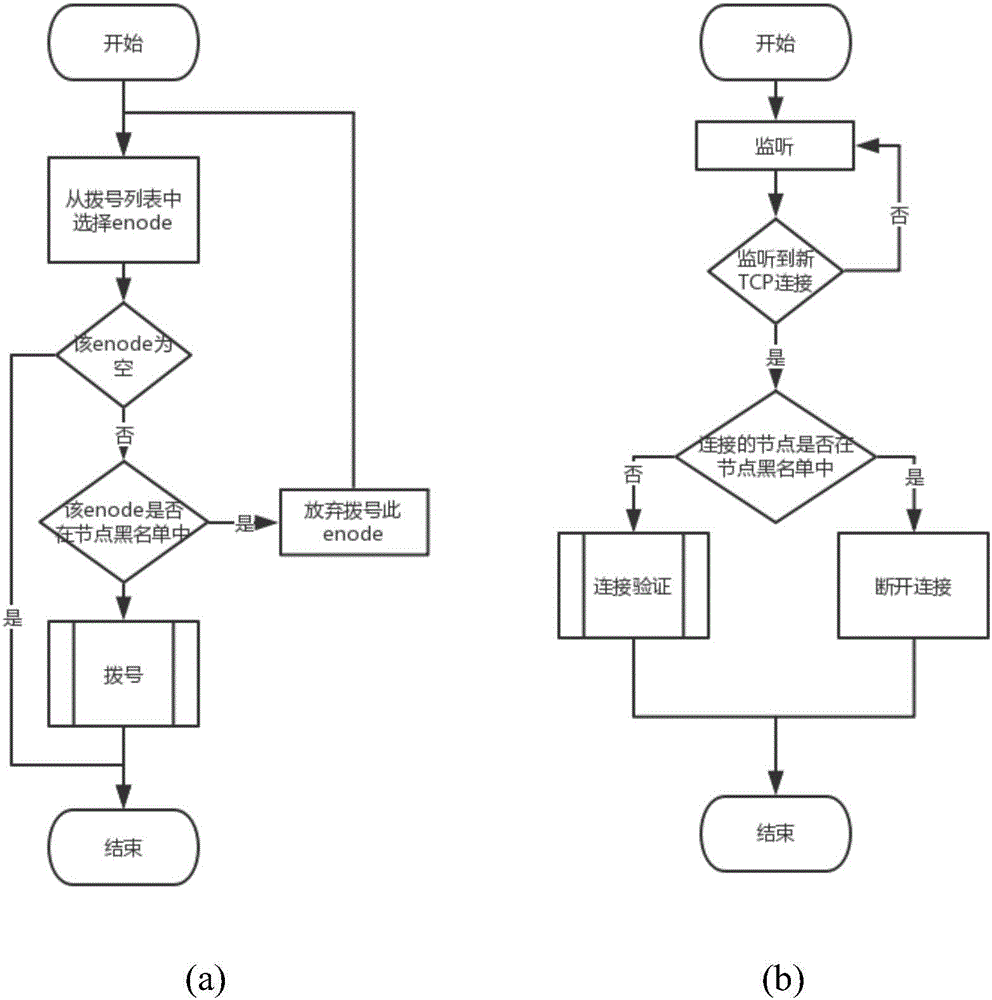
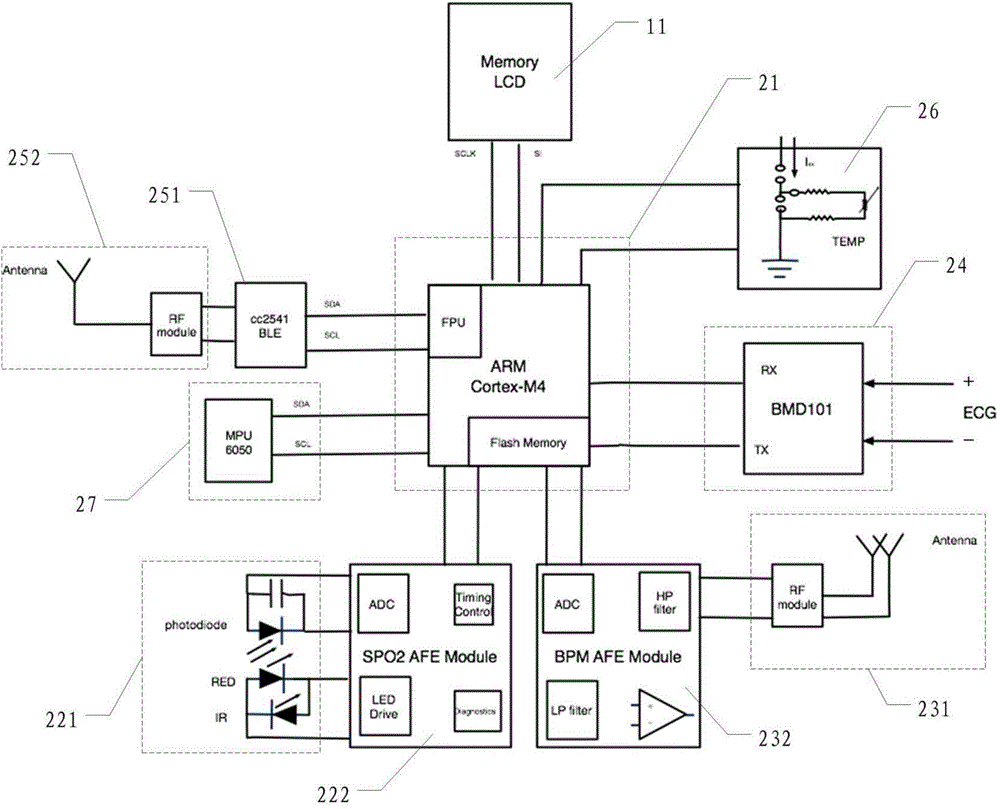
Patents
Literature
1731 results about "Monitor unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
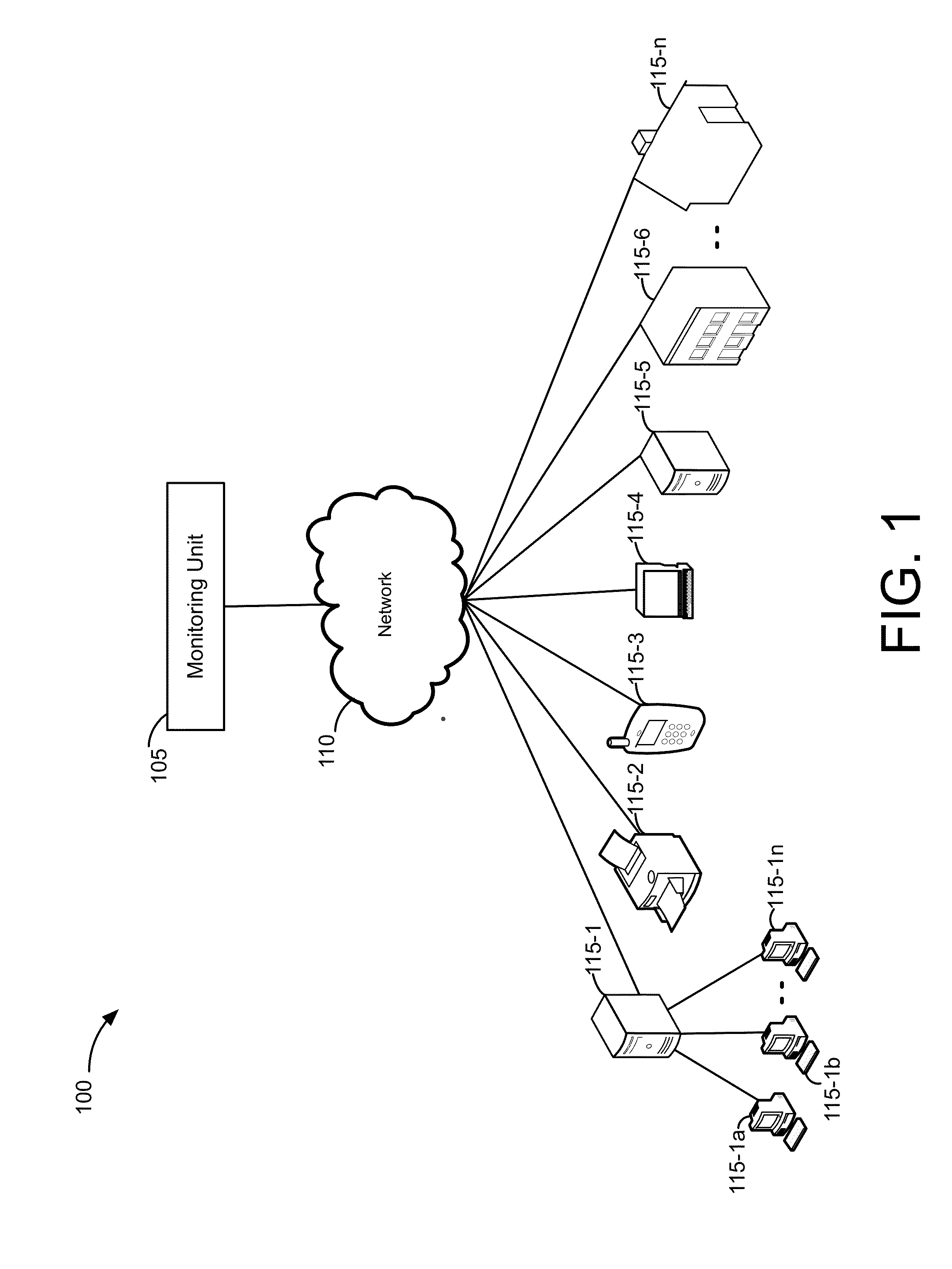
A monitor unit (MU) is a measure of machine output from a clinical accelerator for radiation therapy such as a linear accelerator or an orthovoltage unit. Monitor units are measured by monitor chambers, which are ionization chambers that measure the dose delivered by a beam and are built into the treatment head of radiotherapy linear accelerators.
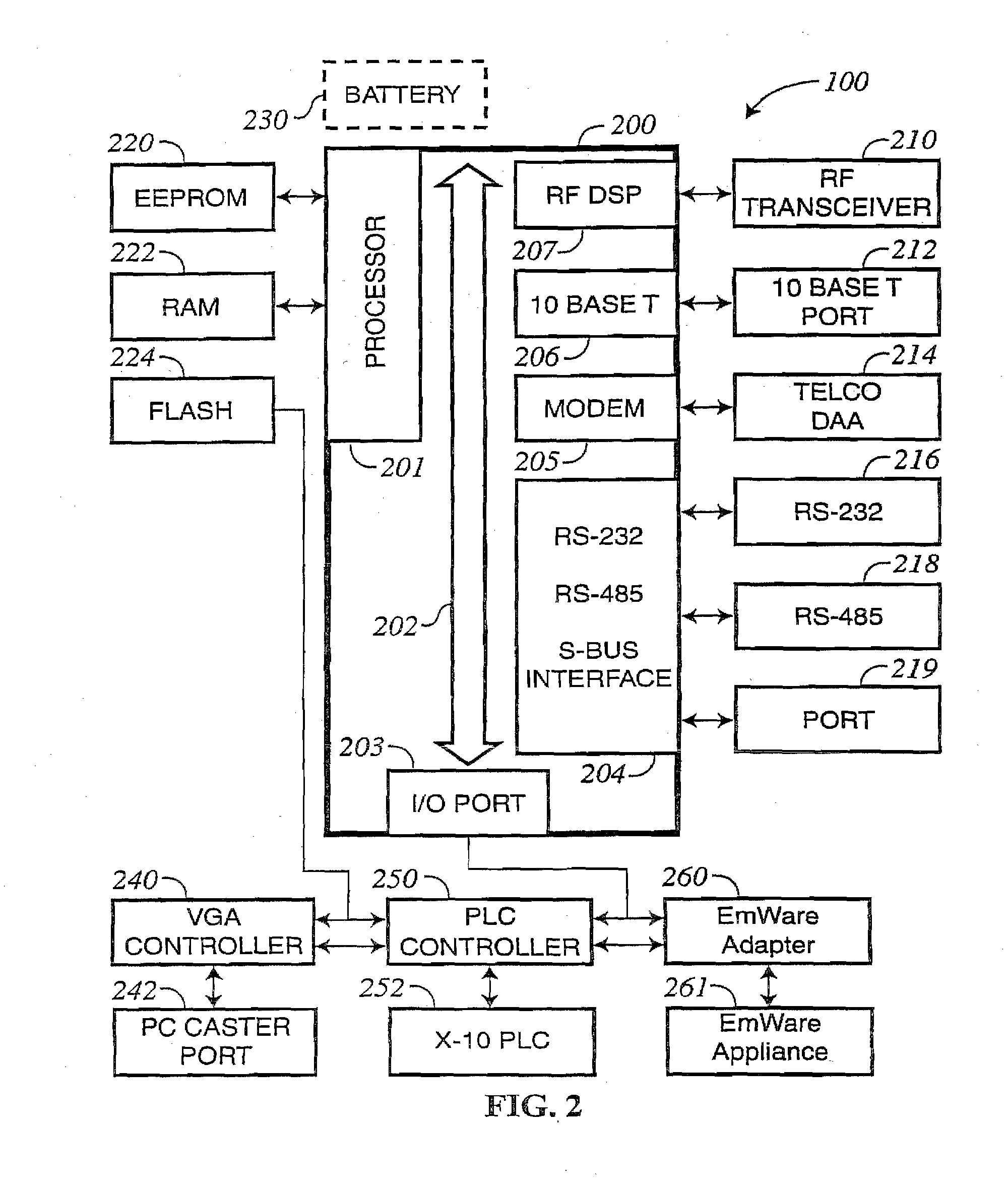
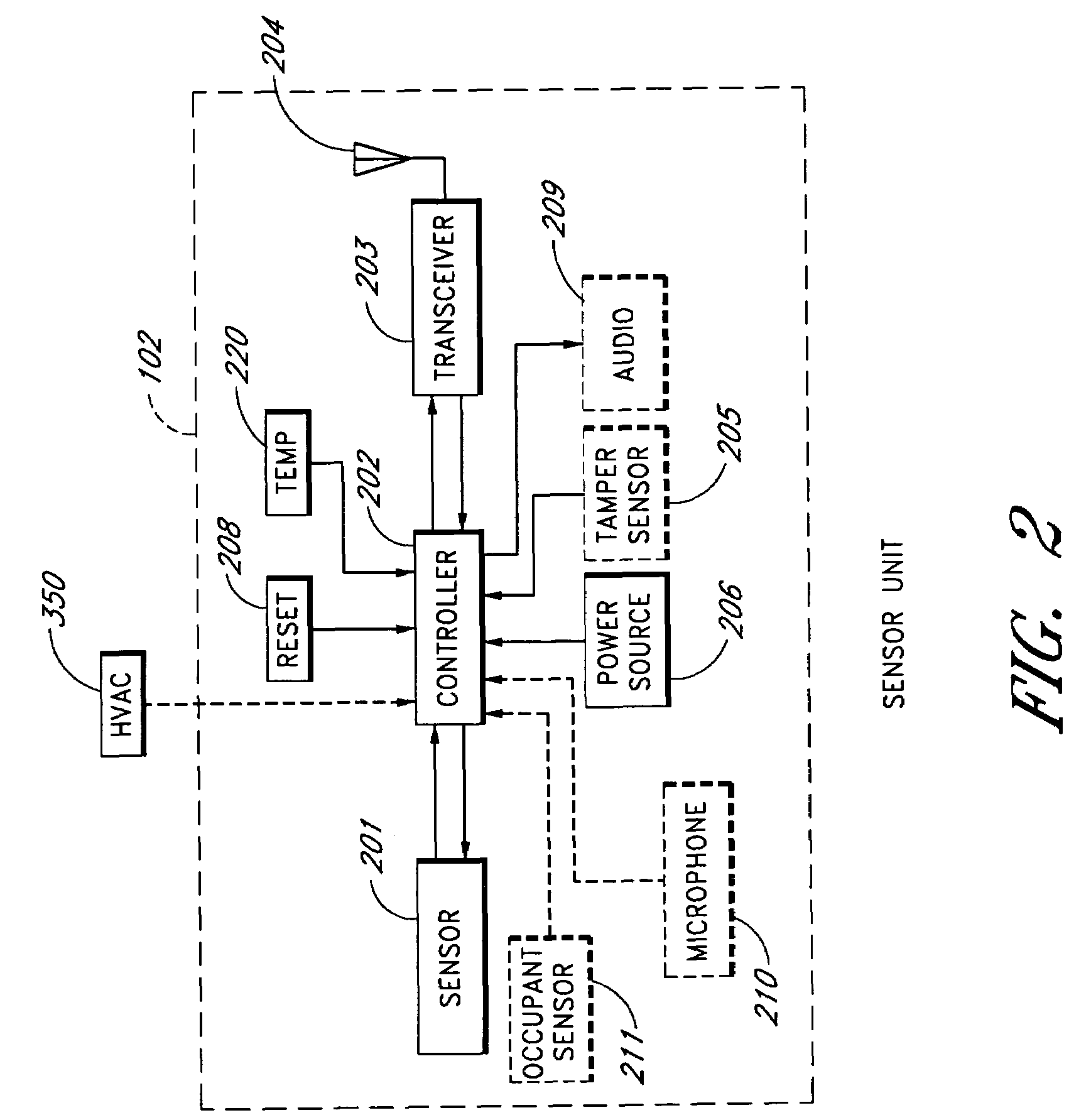
Elimination-absorber monitoring system
InactiveUS6246330B1Complicating power requirementEffectively overcome problemBaby linensAlarmsMonitoring systemEngineering
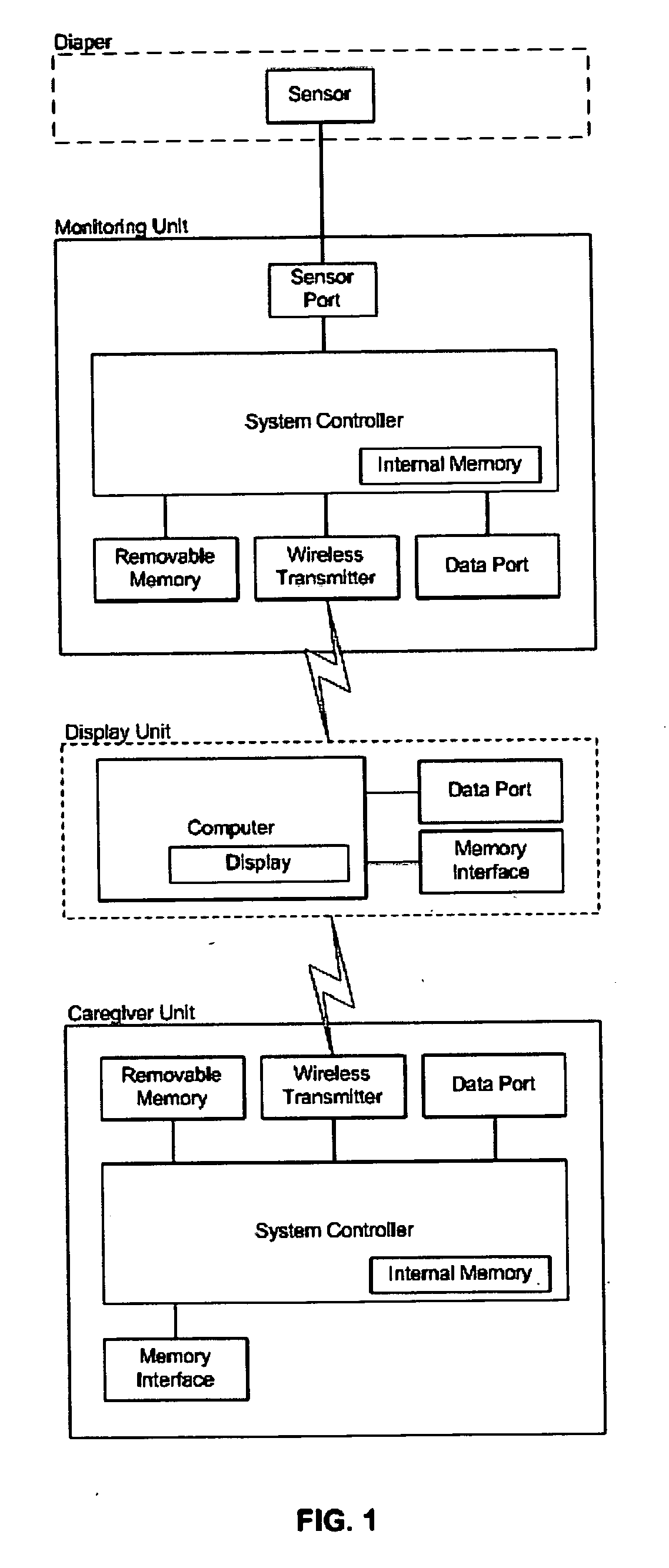
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Refrigeration monitor unit
InactiveUS20070220907A1Food quality is not compromisedAvoid damageProgramme controlPower network operation systems integrationRefrigeration compressorControl system
A control unit is attached to or embedded within a refrigeration appliance to monitor electric power voltage and / or frequency supplied by the mains. If the unit detects a sag or peak in either the voltage or frequency, the control unit either separates any high demand elements of the appliance from the mains to reduce demand in a sag or energizes the elements in a peak. When the control system separates the refrigeration compressor from the mains, a food spoilage monitoring system monitors the food storage compartments. This system utilizes food industry temperature and time algorithms to ensure the food does not spoil. If food spoilage could occur, the unit re-energizes the compressor to allow it to lower the temperature provided the power is sufficient to operate the compressor unit without damaging it. Once the sensed temperature is restored to a safe level, the unit separates the compressor from the mains.
Owner:RANCO OF DELAWARE
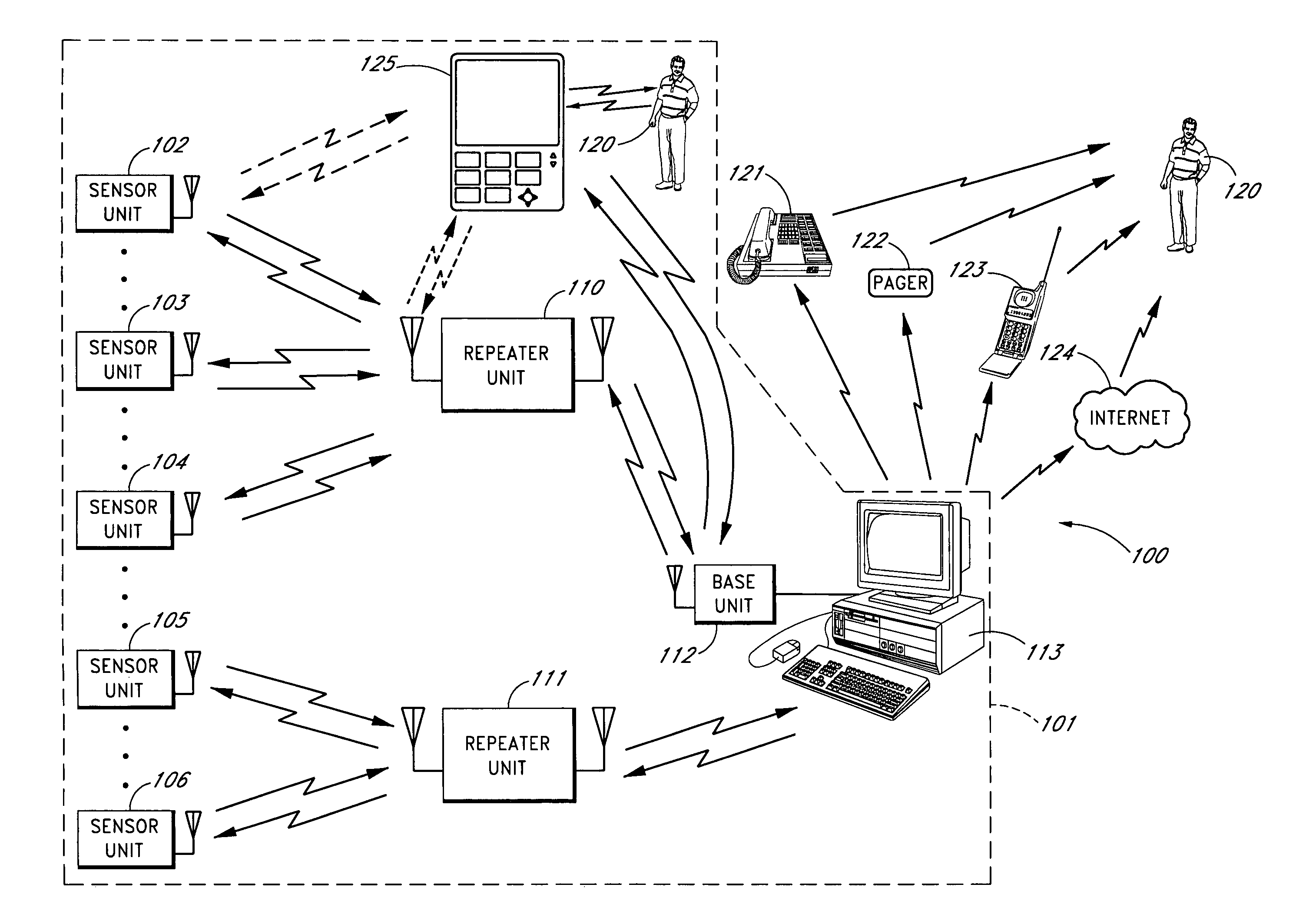
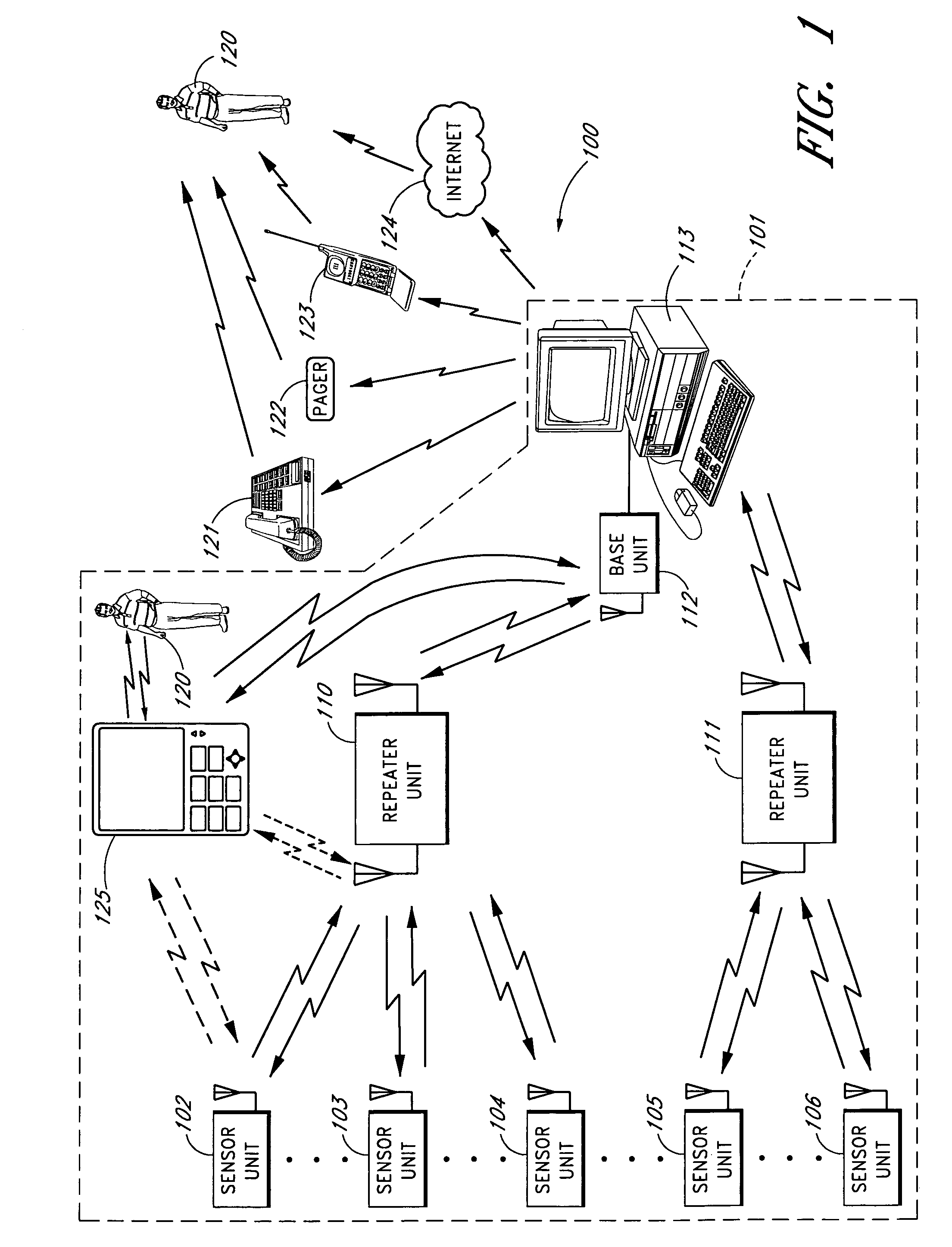
Wireless medical monitoring apparatus and system
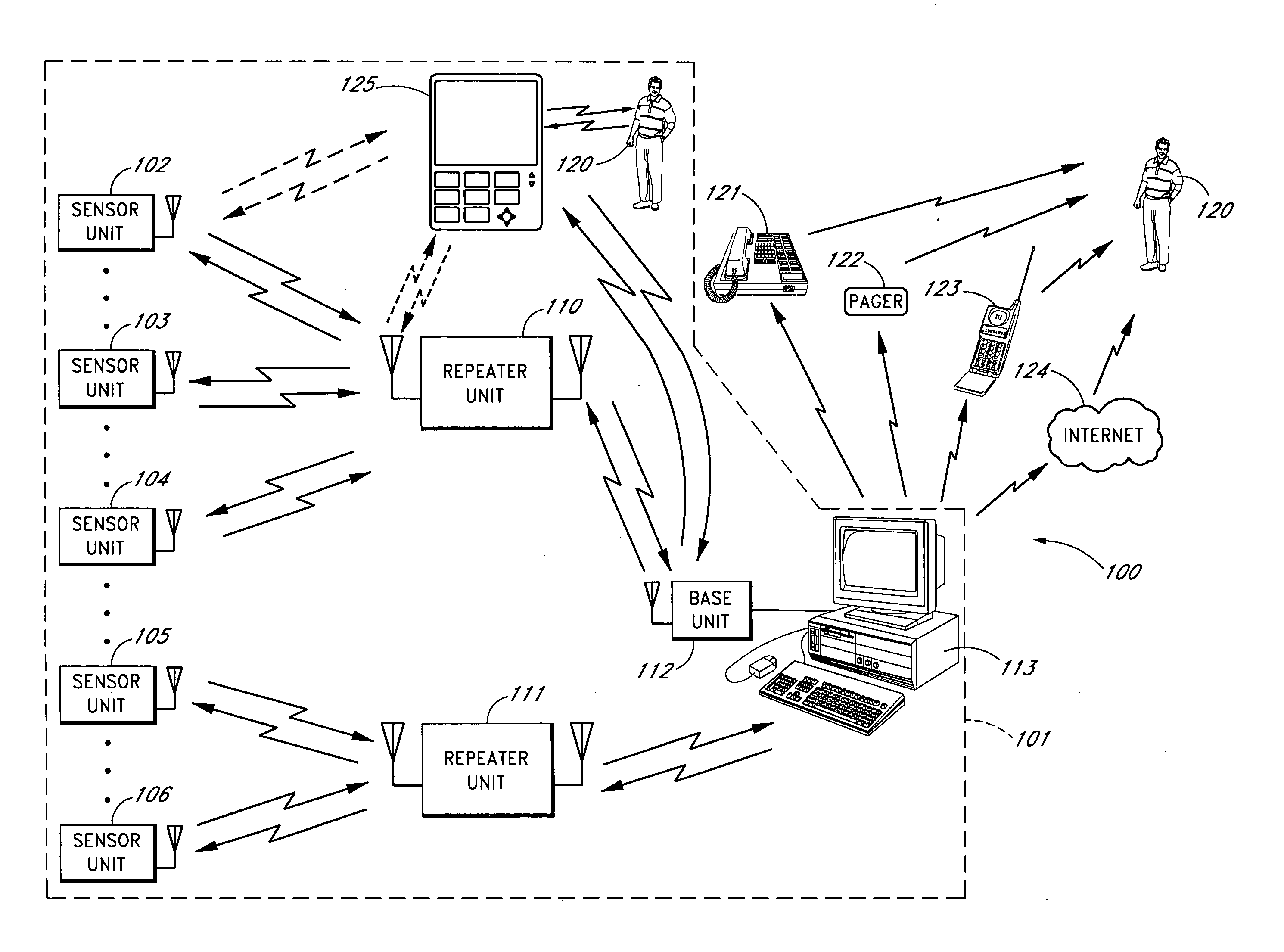
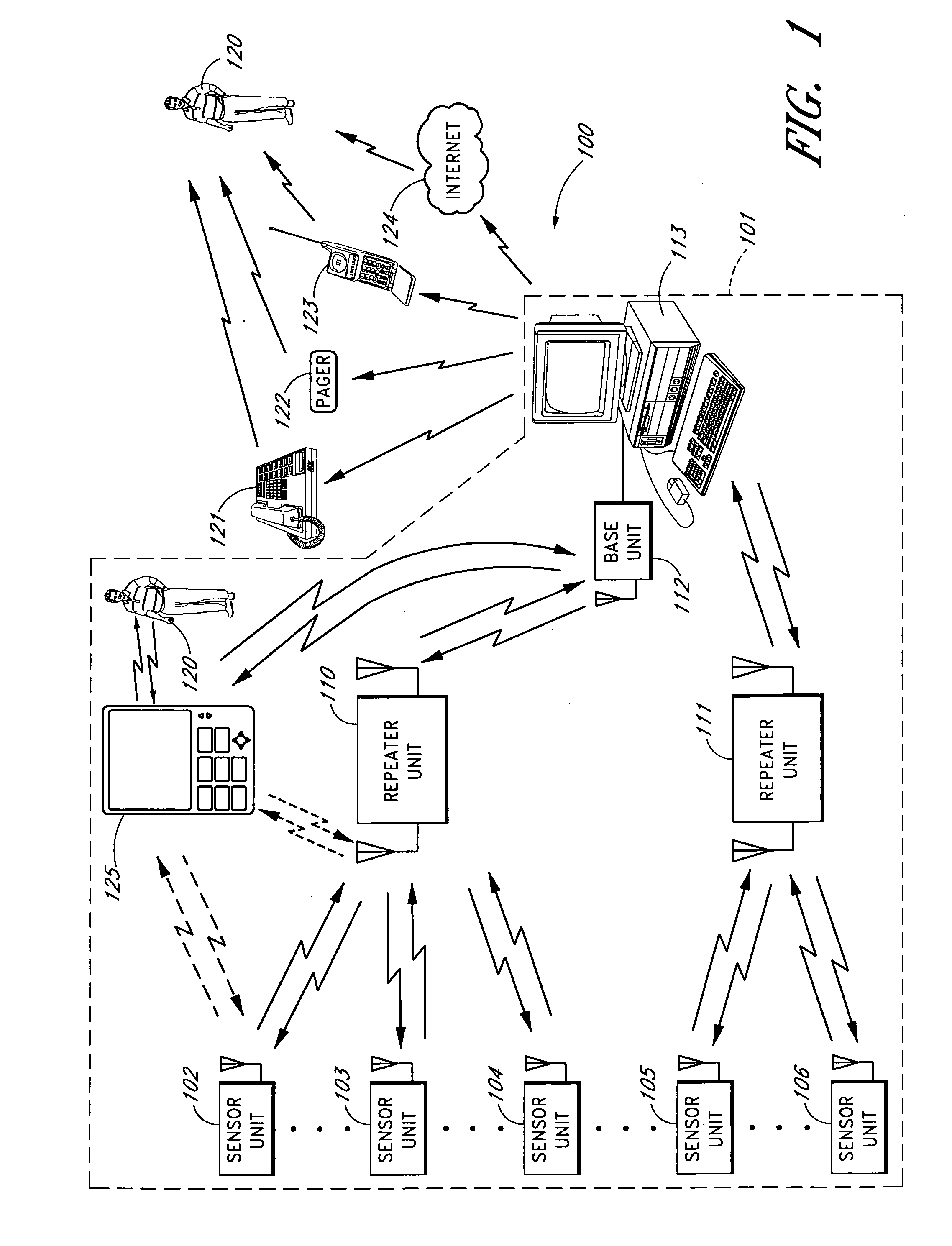
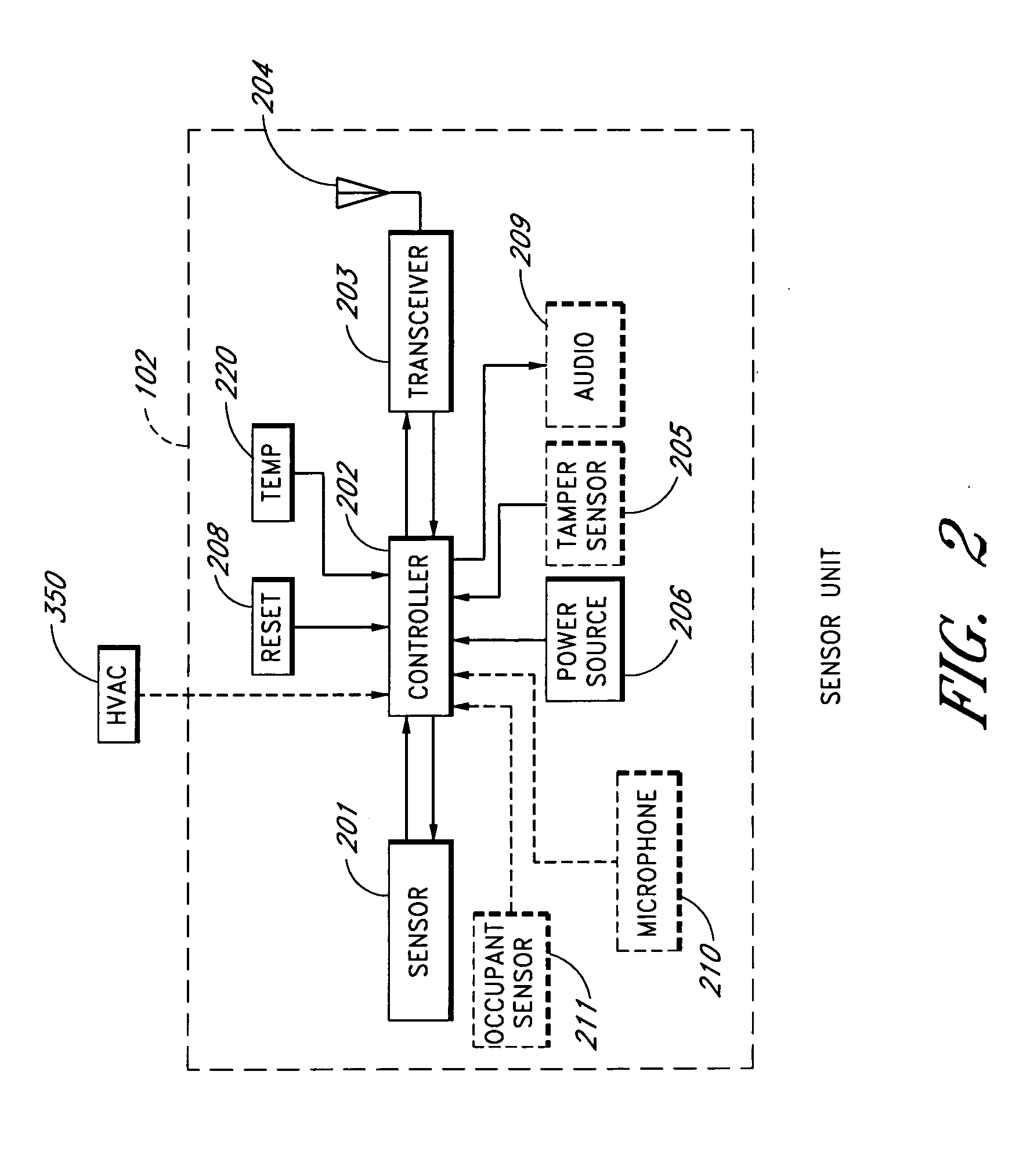
An apparatus for monitoring an electrical signal from a patient's body includes a disposable electrode patch having a thin flexible housing with an adhesive exterior, a power source, a printed circuit board, a plurality of electrodes, a converter for converting a detected electrical signal from the patient's body to a digital signal, a processor for processing the digital signal, and a transmitter connected for transmitting the processed digital signal as a wireless signal. A monitoring unit communicating with the electrode patch includes a power source, a transceiver, a global positioning receiver, a processor, at least one communication port for external communications, and a display. A system of the invention includes a plurality of patients having medical monitors wirelessly communicating biometric information to a central processor for archiving and accessing.
Owner:HALTHION MEDICAL TECH INC
Portable monitoring unit
ActiveUS20070139183A1Quickly apprisedReduce harmSub-station arrangementsTransmission systemsMonitoring siteTransceiver
A sensor system that provides an adjustable threshold level for the sensed quantity is described. The adjustable threshold allows the sensor to adjust to ambient conditions, aging of components, and other operational variations while still providing a relatively sensitive detection capability for hazardous conditions. The adjustable threshold sensor can operate for extended periods without maintenance or recalibration. A portable monitoring unit working in communication with the sensor system provides immediate communication of conditions detected by the sensors. The portable monitoring unit allows building or complex management to be in communication with a sensor system at all times without requiring someone to be physically present at a monitoring site. The portable monitoring unit can be equipped with an auditory device for alerting management or a screen for displaying pertinent information regarding an occurring situation so that management can quickly identify and resolve the problem. In addition, the portable monitoring unit can also be equipped with function keys that allow the portable monitoring unit to send instructions back to the sensor system. In one embodiment, the portable monitoring unit also includes a second transceiver for communications over a short wave radio frequency, or with a cellular phone system.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
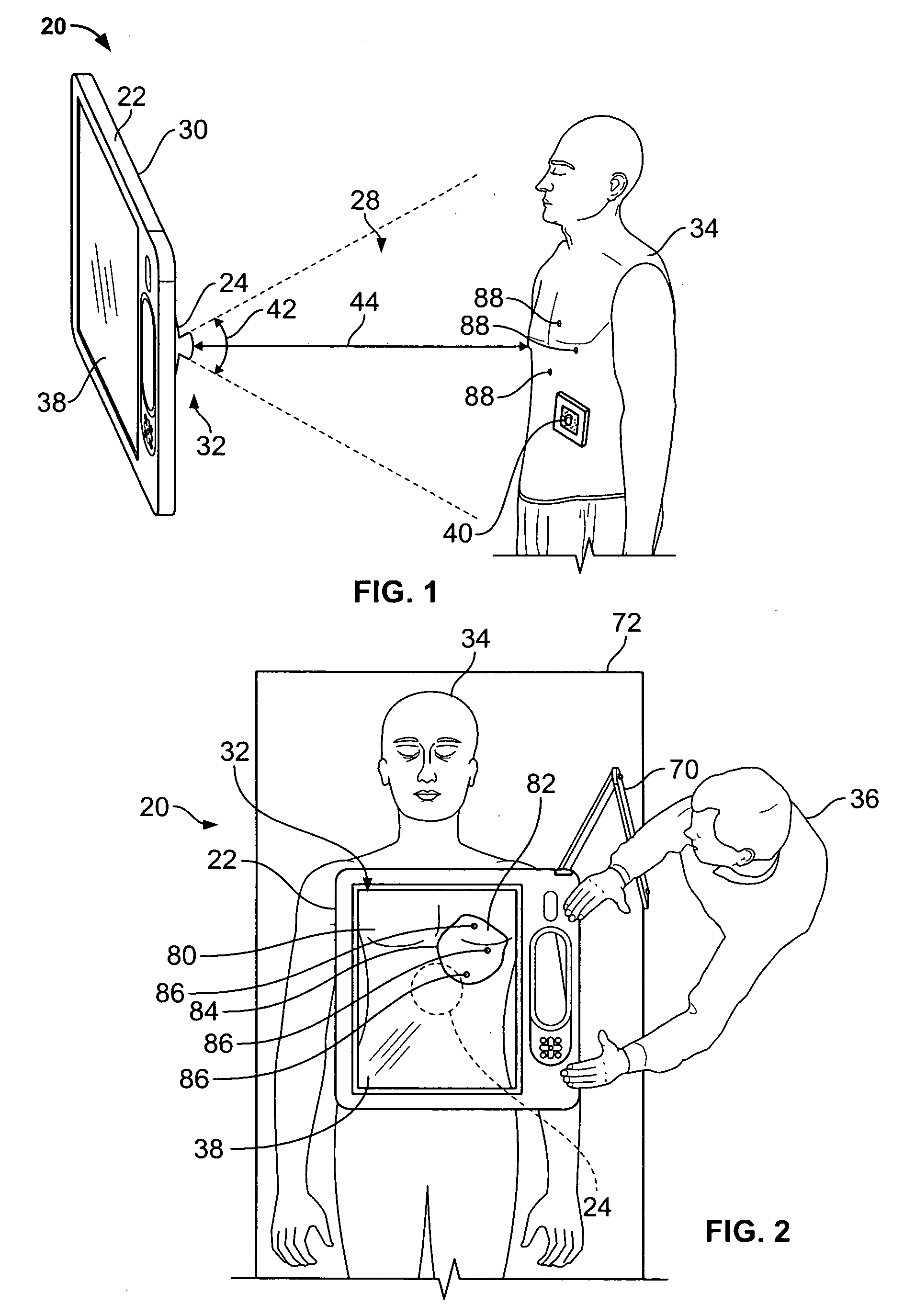
System for and method of visualizing an interior of body
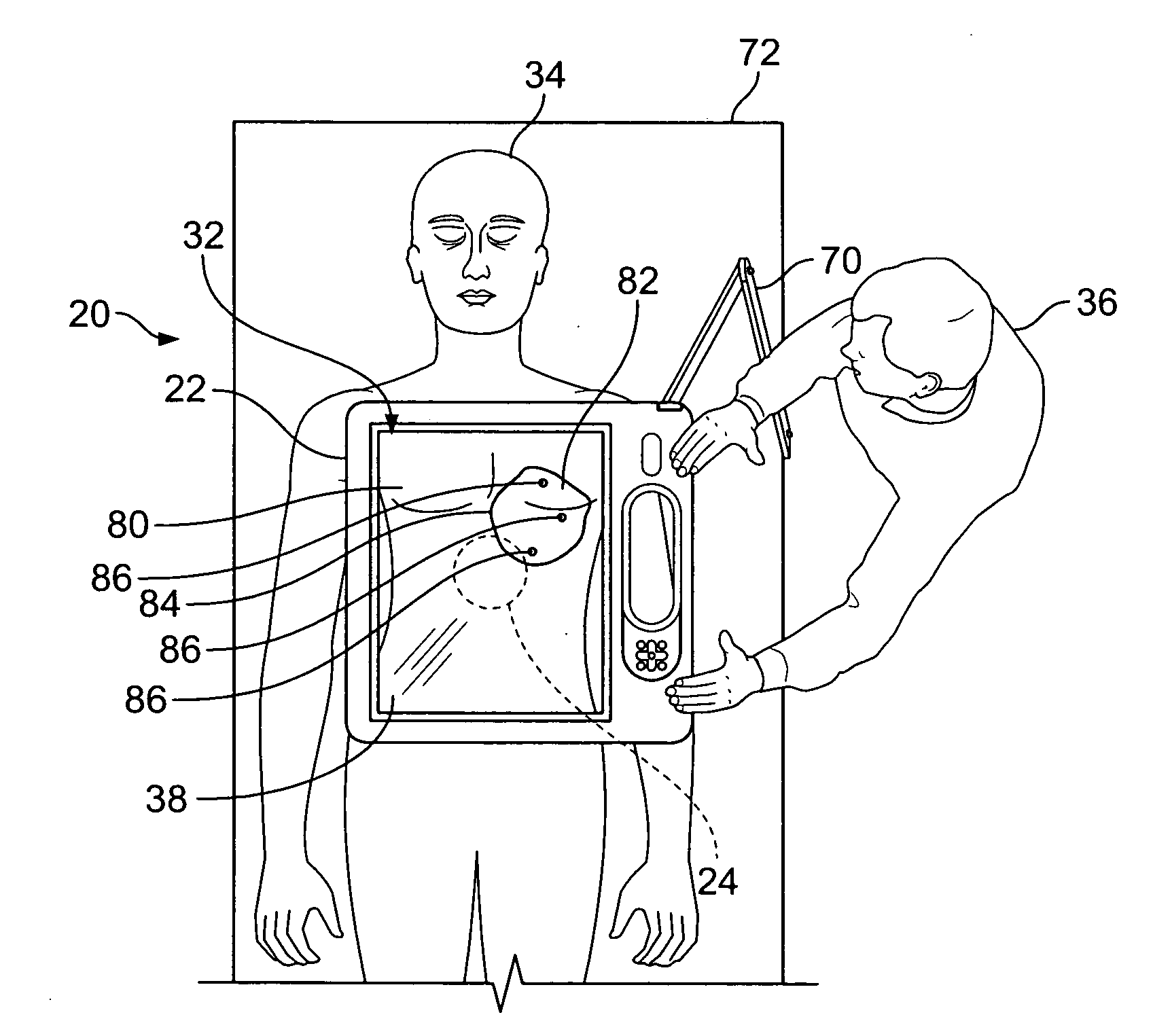
A navigation system includes a display monitor, a CPU, and a camera, wherein the camera is mounted to a back side of the display monitor to form a monitor unit. One or more reference units are placed on a body while acquiring an image data set, and are tracked during a surgical operation by the monitor unit to register and correlate a position of a visual image of an exterior surface of the body with the image data set including information concerning internal structures of the body. The image data set is displayed on the display monitor superimposed in registration over the visible image of the exterior of the body with an angle of view and aperture in accordance with the actual position of the camera, whereby the display monitor displays the internal structures corresponding to the line-of-sight of the camera and the observer.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Elimination - absorber monitoring system
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Method and system for finding
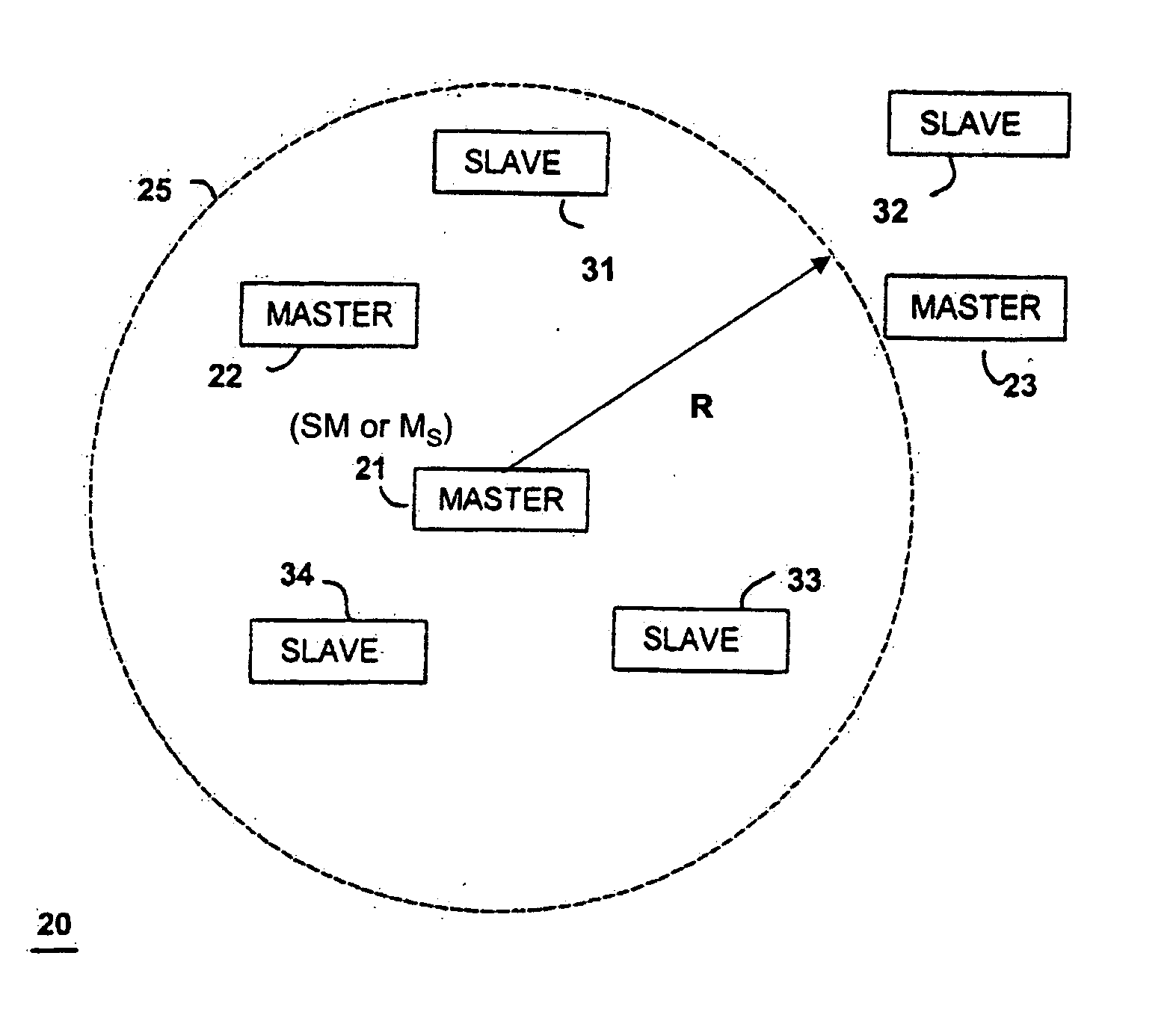
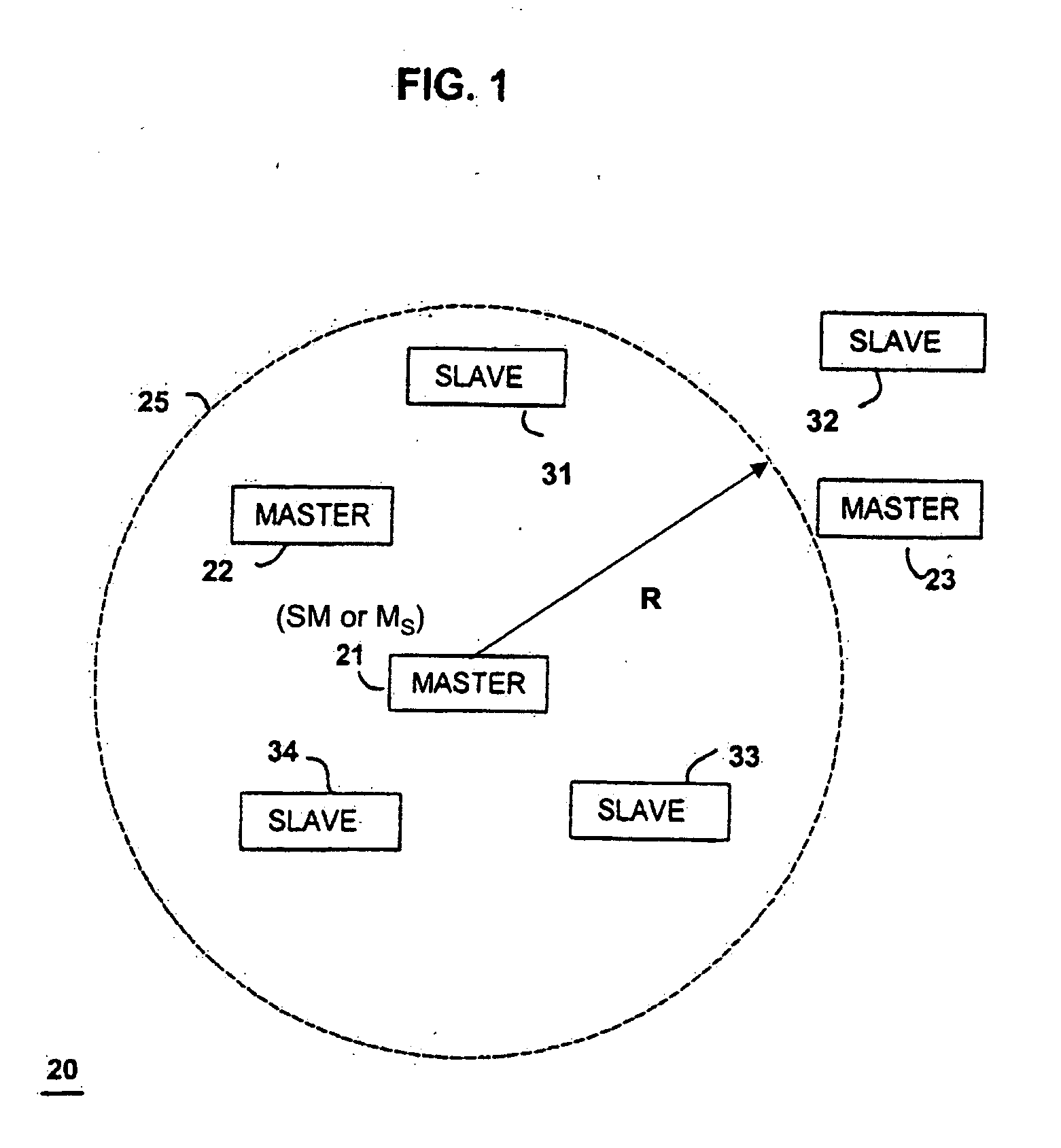
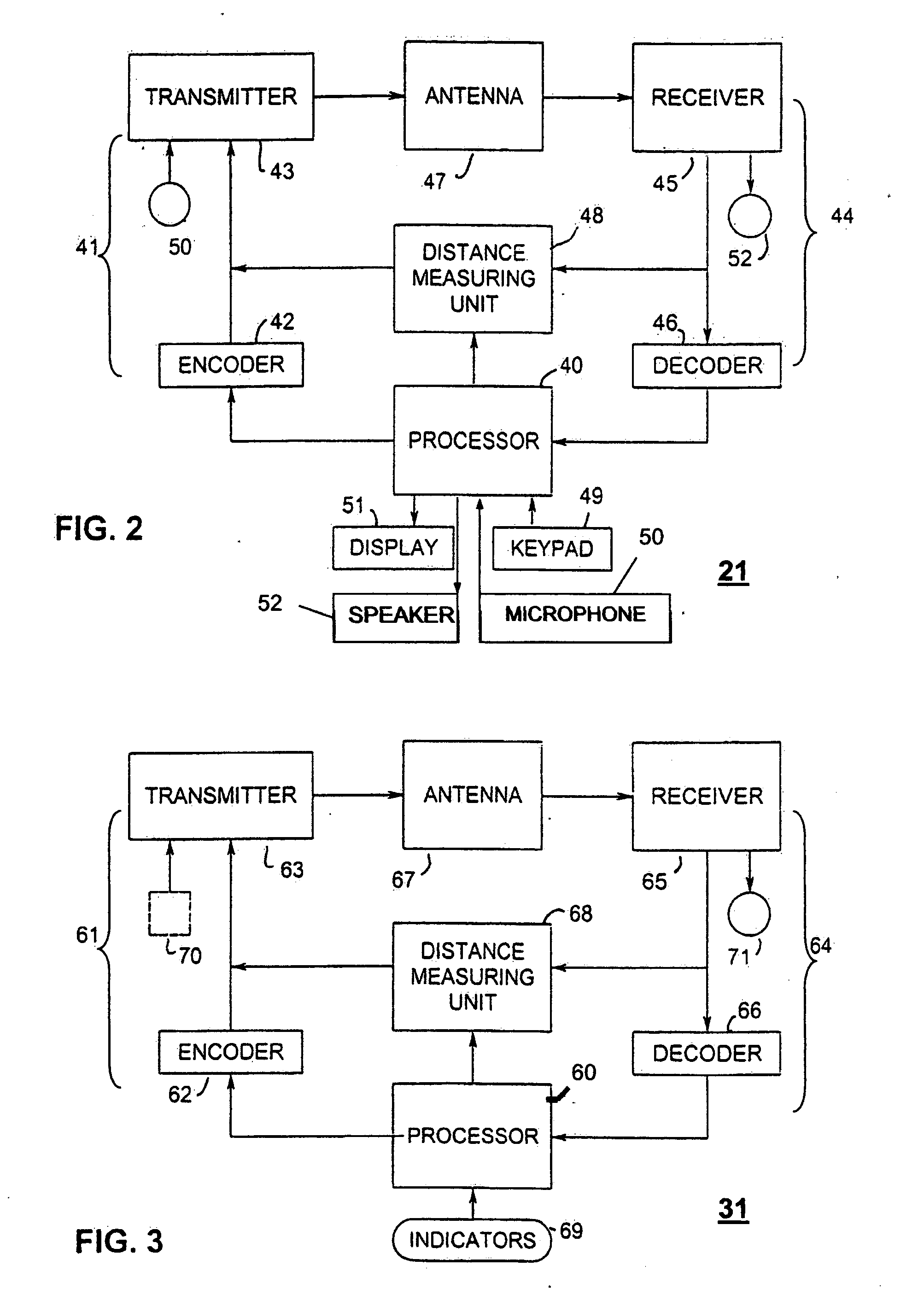
ActiveUS20060012476A1Simplified triangulationUser-device interaction is minimized—eliminatingElectric signalling detailsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalUser deviceTransceiver
A wireless system and method for determining the location of a fixed or mobile subject or object includes a transponder disposed on the target, a transceiver for monitoring the location of the target, a wireless communication system operating on at least one Radio Frequency (RF) band configured to allow communication between the transponder and the transceiver, and a processor configured to find the target by virtual triangulation based on values of position information received from the transponder and the transceiver. The processor is configured to determine virtual triangulation based on successive values of the position information using at least three points P1, P2 and P3 of the transponder respective of the transceiver. The processor can include a means for position ambiguity reduction (PAR) configured to find the target by correcting the direction to the location of the target T based on the values of the position information. The processor can also determine the position of the target based on the average speed of the motion of the user of the transponder respective of the transceiver. Furthermore, the processor can determine virtual triangulation based on successive values of the position information from user input on the transceiver. The method finding the target T (“finder” techniques) based on one or more position determination principles including determining the position of the target using virtual triangulation between the master or monitoring unit and at least one target T, whereby the monitoring device Ms measures the distance between it and the slave unit and, alternatively, in addition to measuring the distance between itself and the slave unit, between itself and another monitoring unit, or the monitoring device Ms measures the distance between its own successive locations. The present invention also discloses methods for finding with virtual triangulation by: (1) finding with virtual triangulation by generating position information in real-time, in the case of (i) stationary and moving target, and or (ii) in the case of the presence of obstacles; (2) finding with virtual triangulation relating to the average speed of the motion of operator; and or (3) finding with simplified virtual triangulation, whereby the user-device interaction is minimized—eliminating the need for monitoring device Ms to measure the distance between its own successive locations as well as the user's signaling to the monitoring or master unit when in motion or during stops.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
Portable monitoring unit
ActiveUS7528711B2Quickly apprisedReduce harmSub-station arrangementsTransmission systemsMonitoring siteRelevant information
A sensor system that provides an adjustable threshold level for the sensed quantity is described. The adjustable threshold allows the sensor to adjust to ambient conditions, aging of components, and other operational variations while still providing a relatively sensitive detection capability for hazardous conditions. The adjustable threshold sensor can operate for extended periods without maintenance or recalibration. A portable monitoring unit working in communication with the sensor system provides immediate communication of conditions detected by the sensors. The portable monitoring unit allows building or complex management to be in communication with a sensor system at all times without requiring someone to be physically present at a monitoring site. The portable monitoring unit can be equipped with an auditory device for alerting management or a screen for displaying pertinent information regarding an occurring situation so that management can quickly identify and resolve the problem. In addition, the portable monitoring unit can also be equipped with function keys that allow the portable monitoring unit to send instructions back to the sensor system. In one embodiment, the portable monitoring unit also includes a second transceiver for communications over a short wave radio frequency, or with a cellular phone system.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
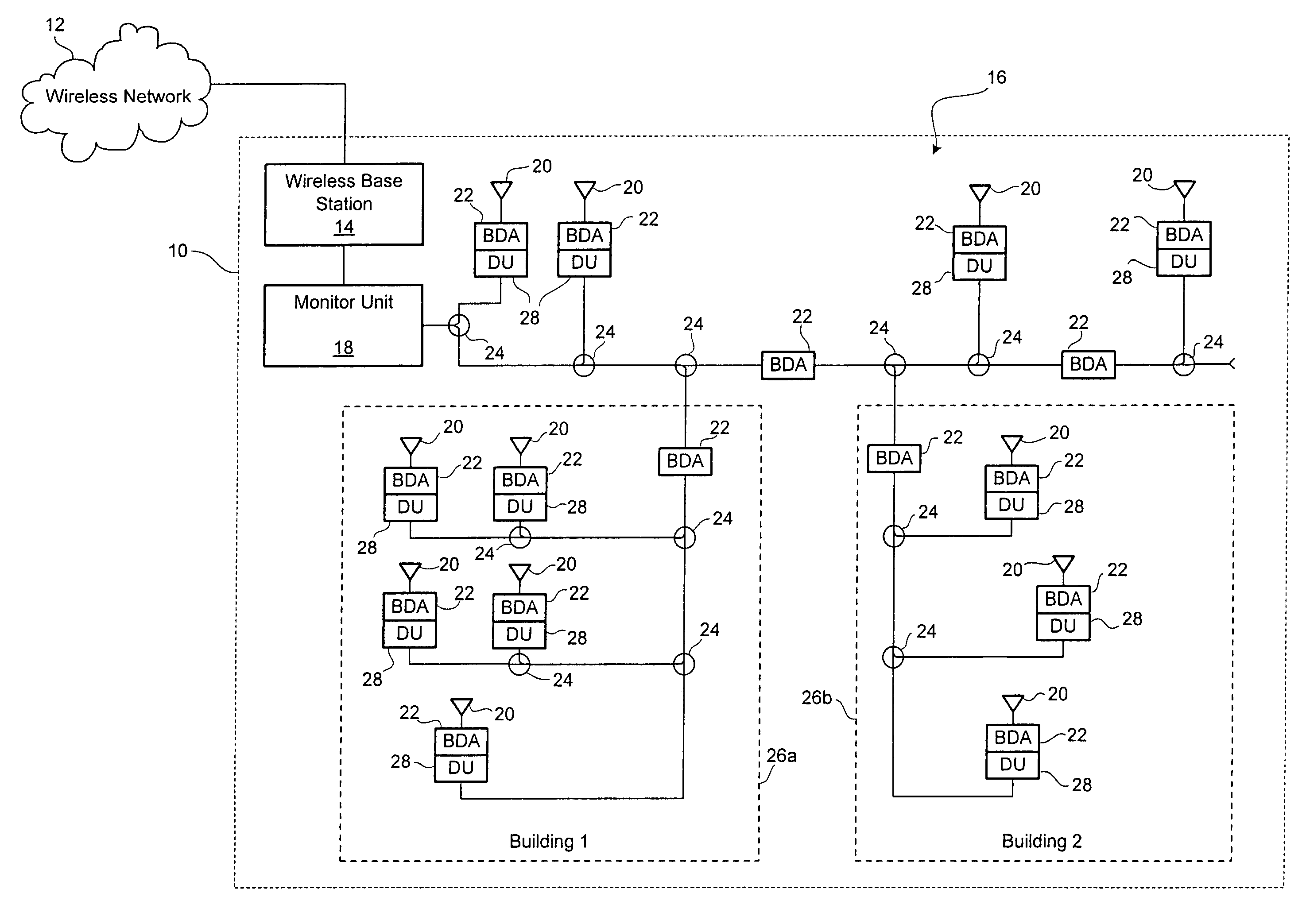
System and method for emergency 911 location detection
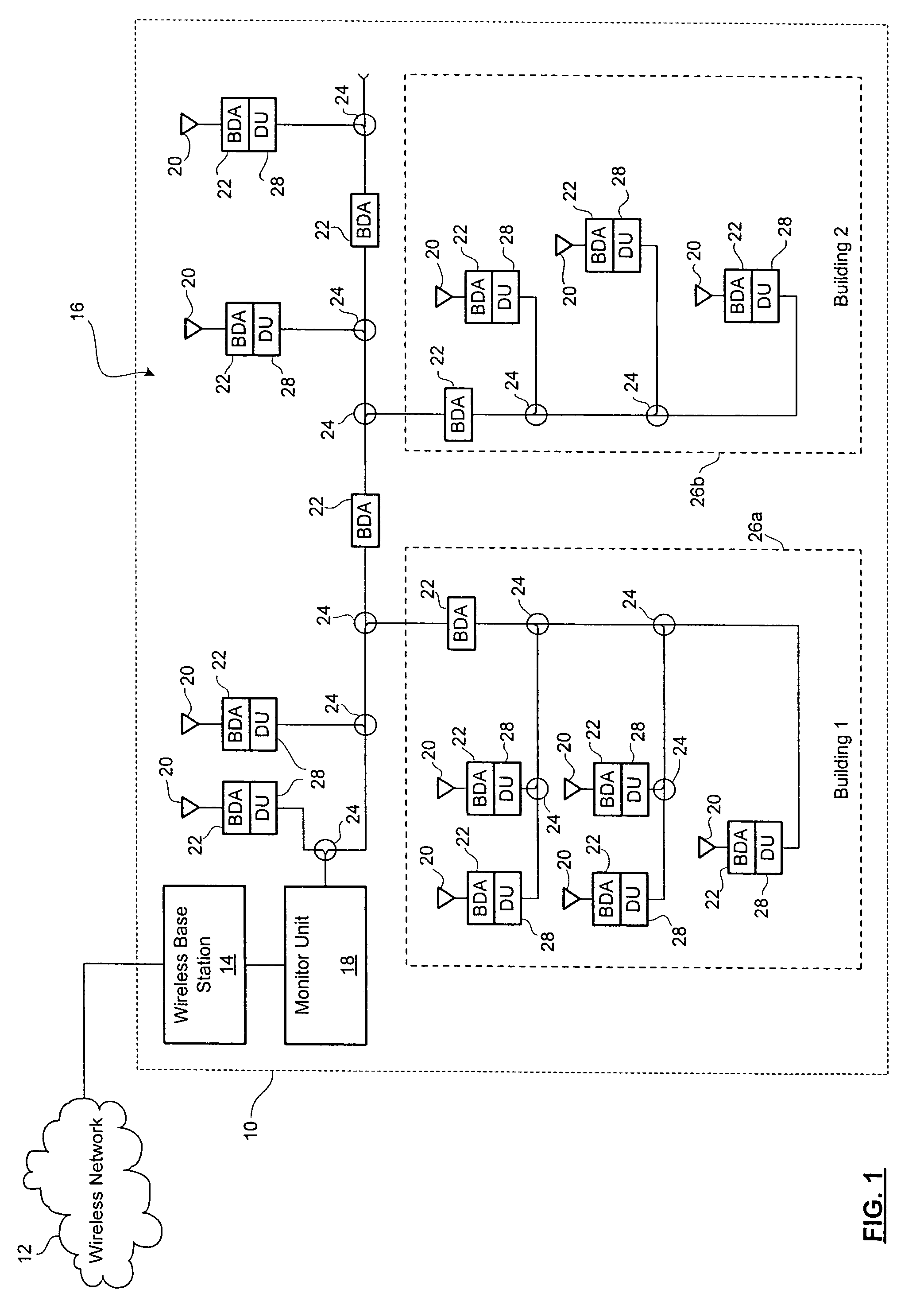
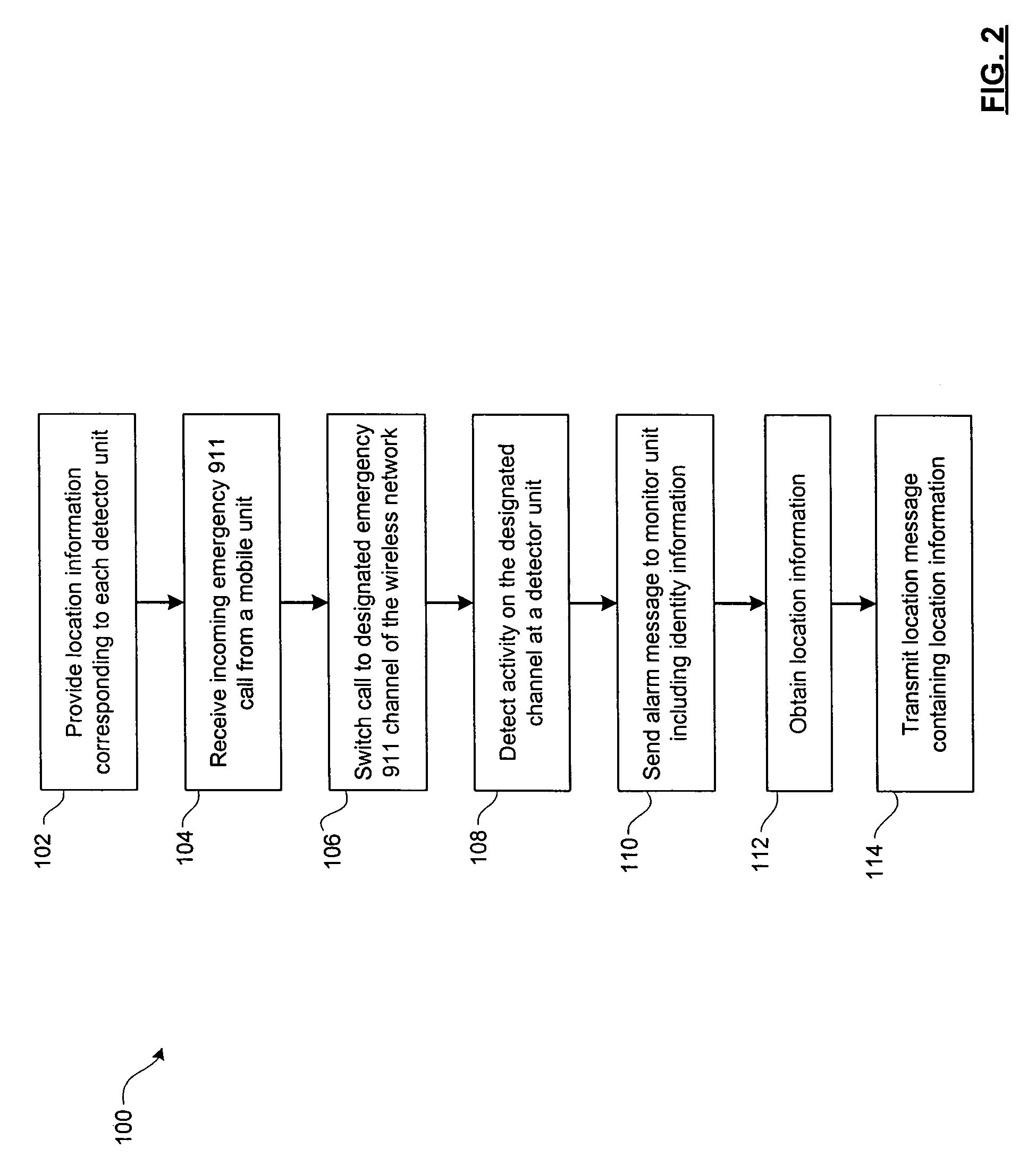
InactiveUS7315735B2Position fixationTelephonic communicationLocation detectionDistributed antenna system
A location detection system for locating a mobile device placing an emergency 911 call within a facility having a distributed antenna system. The location detection system includes one or more detection units located within the distributed antenna system and being associated with one or more antennas. Each detection unit monitors a dedicated emergency 911 channel for activity and alerts a monitor unit if activity is detected. The monitor unit determines the location of the antenna receiving the emergency 911 call based upon the identity of the detection unit.
Owner:P G ELECTRONICS
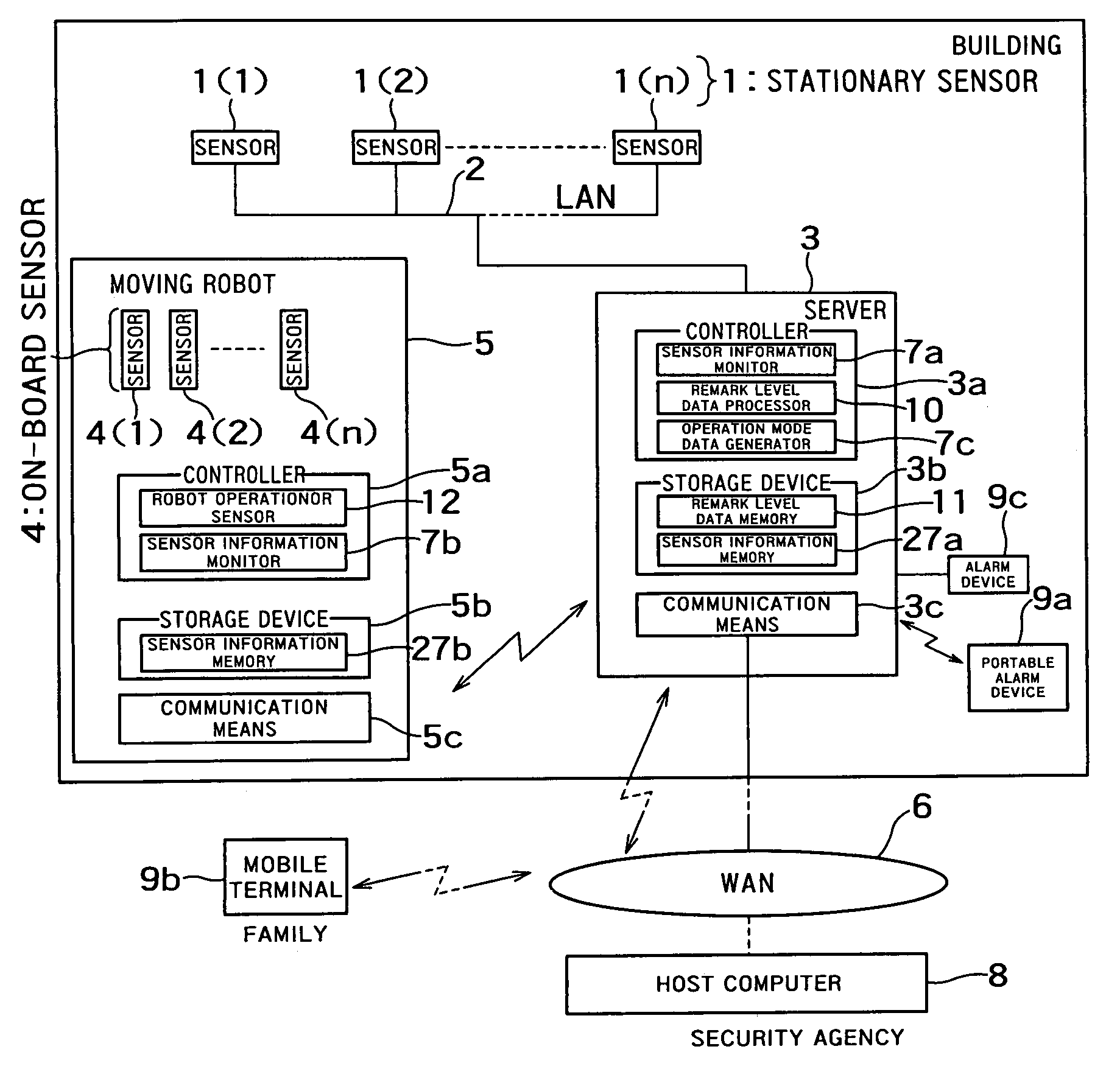
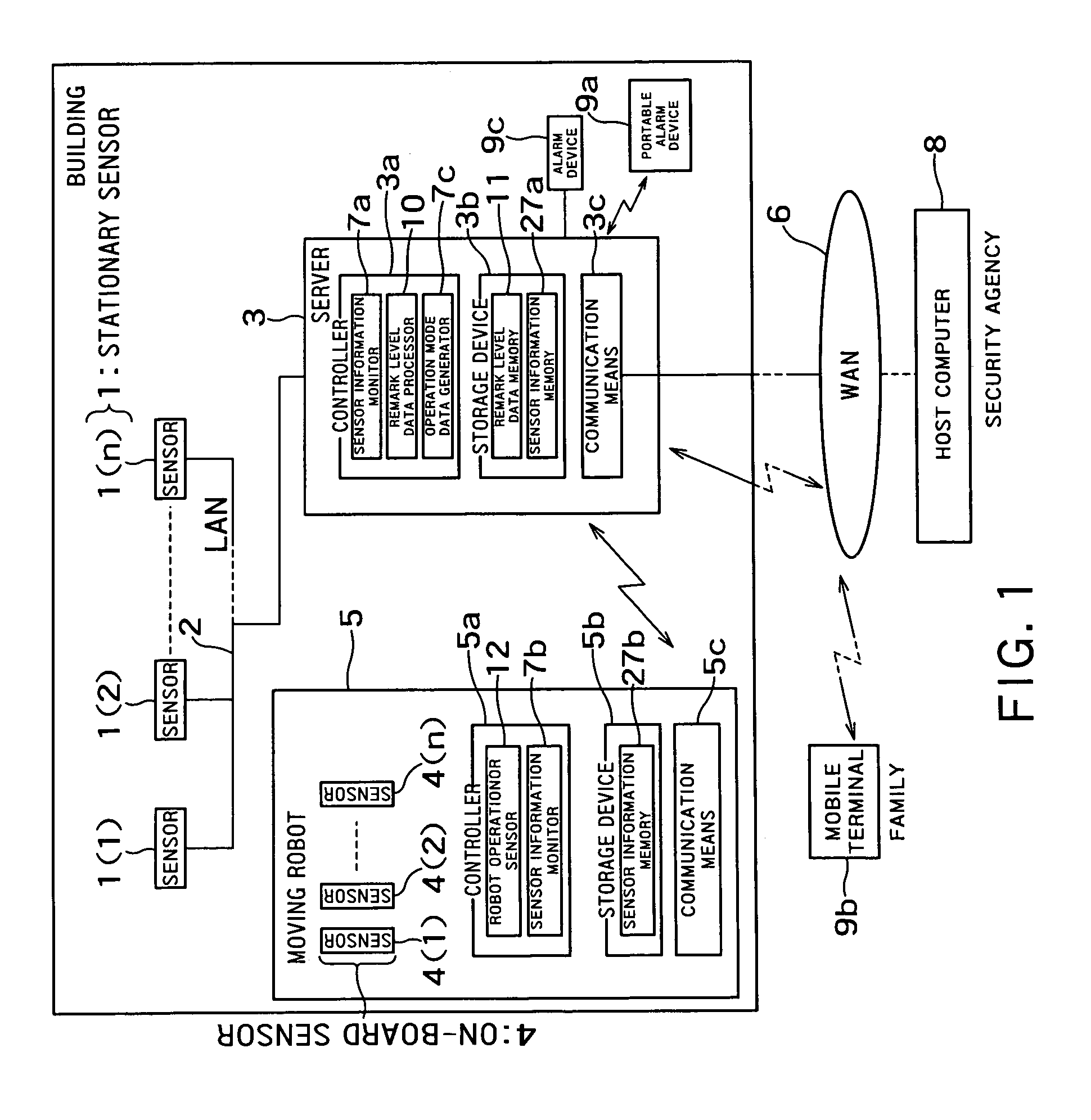
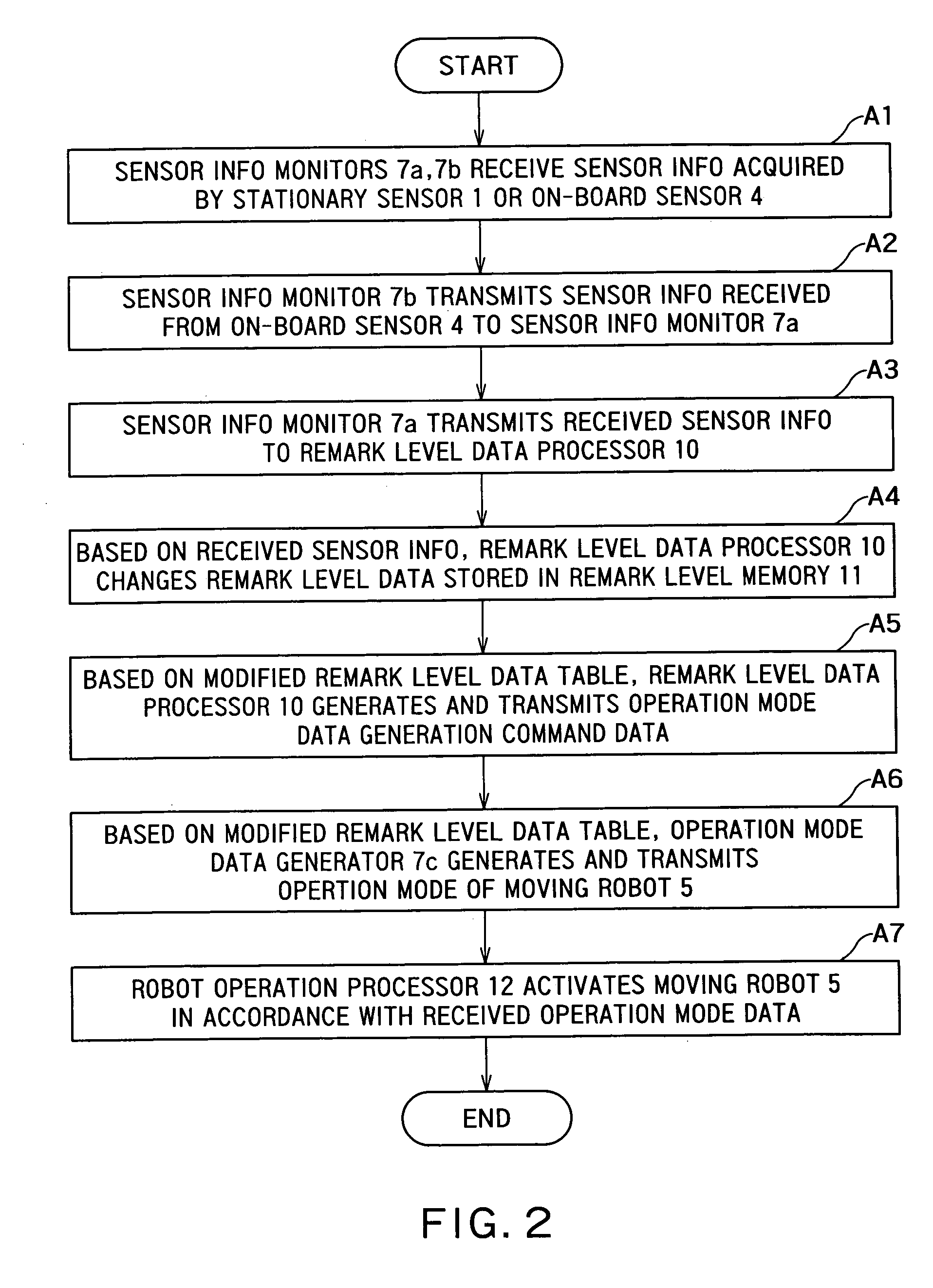
Security system and moving robot
A security system comprises a first sensor disposed in an area to be monitored in a building to monitor the area; a moving robot having a robot main body, a second sensor for monitoring the area to be monitored and a robot operation processor for moving the robot main body according to an operation mode data indicating an operation of the robot main body; a controller including first and second sensor information monitor units for collecting first sensor information and second sensor information which are acquired by the first and second sensors, and an operation mode data generator for generating the operation mode data from the first sensor information or the second sensor information and transmitting the operation mode data to the robot operation processor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Wireless communication protocol for a medical sensor system
ActiveUS20070109117A1Improve stabilityElectric signal transmission systemsSensorsLine sensorCommunications system
In one embodiment the present invention provides a wireless communication system for medical sensor data. This communications system includes a portable unit that connects to a wireless sensor and a monitor unit that connects to a sensor monitor. Once activated, the units will self organize into a wireless communication structure controlled by the portable unit. As other pairs of units activate, they can self-organize their transmissions by joining an existing network or by creating new networks.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
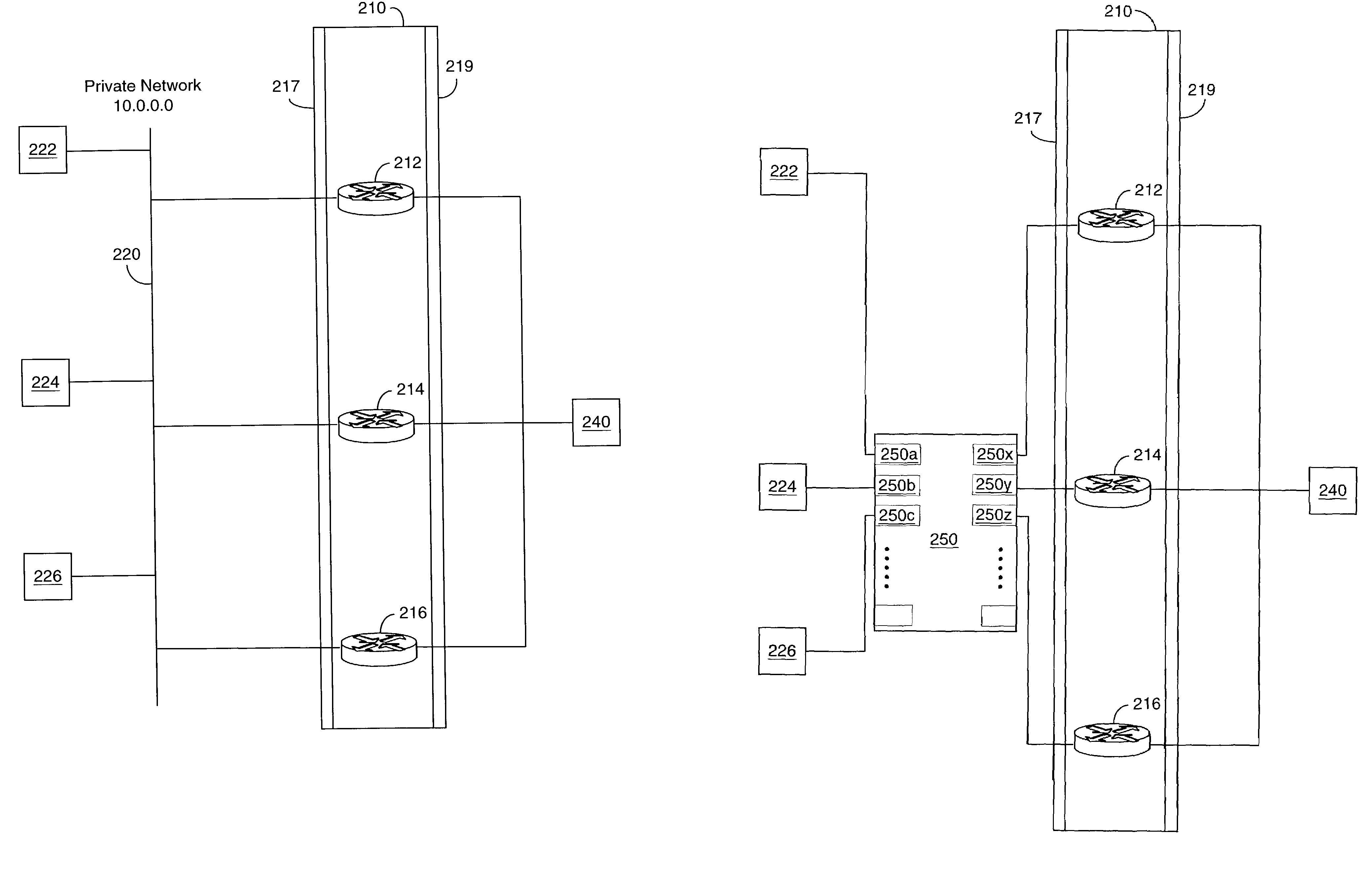
IP redundancy with improved failover notification
Redundant gateway methods, apparatus and systems use more than one gateway device in a gateway device group for communications directed outside of a LAN. Failover services are thus provided in the event that an active router or other gateway device fails. A failover monitoring unit includes a memory and a processor coupled to the memory. The monitoring unit also includes gateway ports connected to the processor. Each gateway port is configured to connect a gateway device to the monitoring unit. The monitoring unit is configured to collect and store redundancy group data pertaining to a redundancy group comprising a plurality of gateway devices connected to the monitoring unit. The redundancy group includes an active gateway device and one or more standby gateway devices. The monitoring unit monitors the gateway ports to detect failure of an active gateway device. When a failure is detected, the monitoring unit notifies each redundancy group standby gateway device of the active gateway device failure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for controlling wellbore equipment
InactiveUS20050096846A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyTelecommunications linkRemote control
The present invention generally provides a method for remotely controlling and / or monitoring at least one parameter of well bore equipment. In one aspect, a method for remotely controlling and / or monitoring at least one parameter of well bore equipment is provided, including: collecting data corresponding to the at least one parameter by a sensor module monitoring the at least one parameter of the well bore equipment; transmitting the collected data to a remote control / monitoring unit via a communication link; analyzing the collected data to determine if the parameter is within predefined limits; if the parameter is not within predefined limits, then transmitting control data from the control / monitoring unit to the well bore equipment for modifying the operation of the well operation equipment so that the parameter will conform to the predefined limits or stopping operation of the wellbore equipment.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Microwave array applicator for hyperthermia
InactiveUS20100036369A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease surface areaMicrowave therapySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringElectromagnetic field
Apparatus (10) for treating skin tissue with microwave radiation (e.g. having a frequency of 1 GHz to 300 GHz) is disclosed in which an array of radiating elements (18), e.g. patch antennas are arranged on a flexible treating surface (16) for locating over and conforming with a region of skin tissue (24) to be treated. The radiating elements (18) receive microwave energy from a feed structure and are configured to emit outwardly a electromagnetic field which permits the region of skin to a substantially uniform penetration depth. Each radiating element (18) may have an independently controllable power supply to permit relative adjustment of the field across the treatment surface. Each radiating element may have a monitoring unit to allow adjust based on detected reflected power. Each independently controllable power supply may include a dynamic impedance matching unit.
Owner:UNIV OF WALES BANGOR
Auditory alarms for physiological data monitoring
ActiveUS6947780B2Strengthen associationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationVisual perception
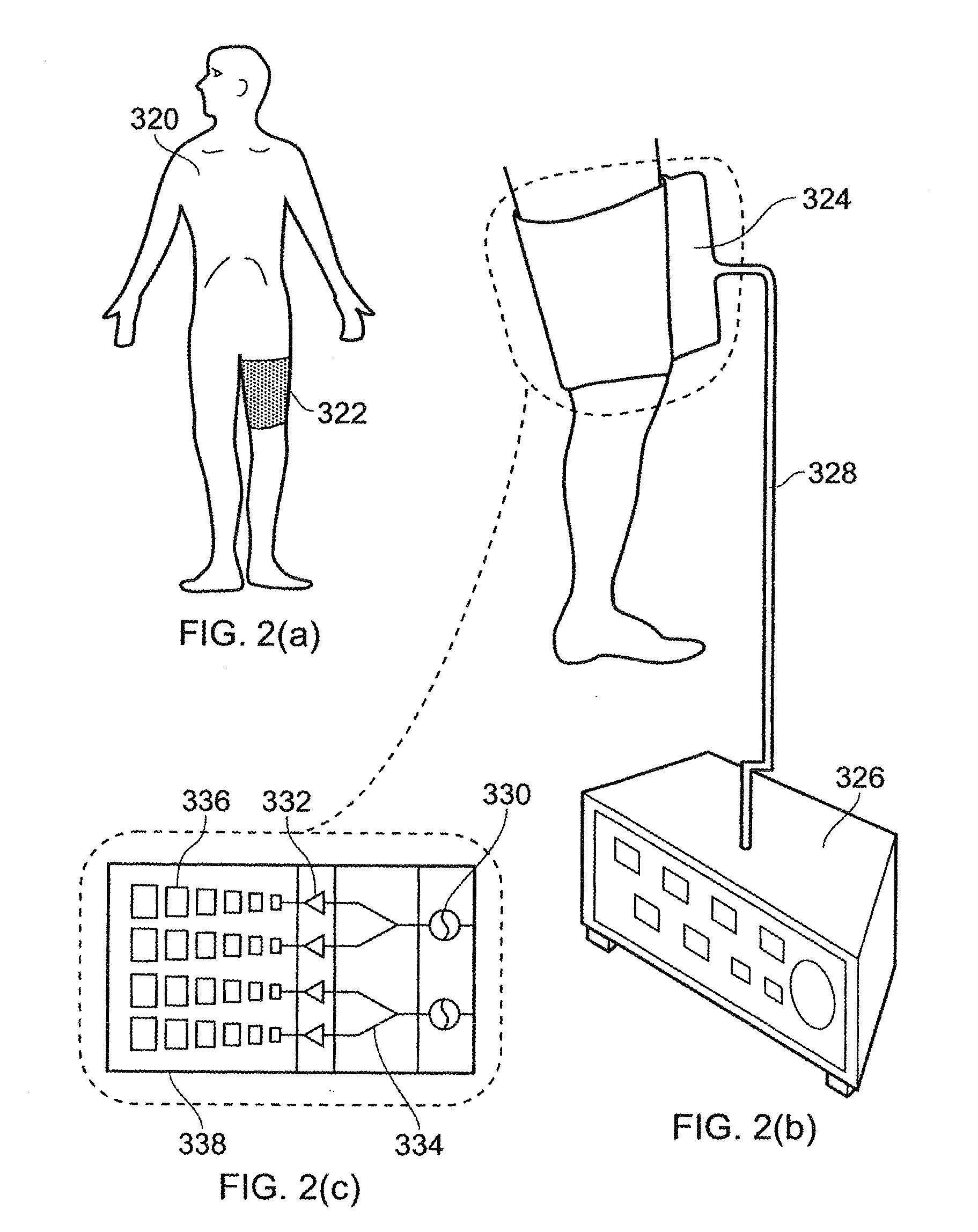
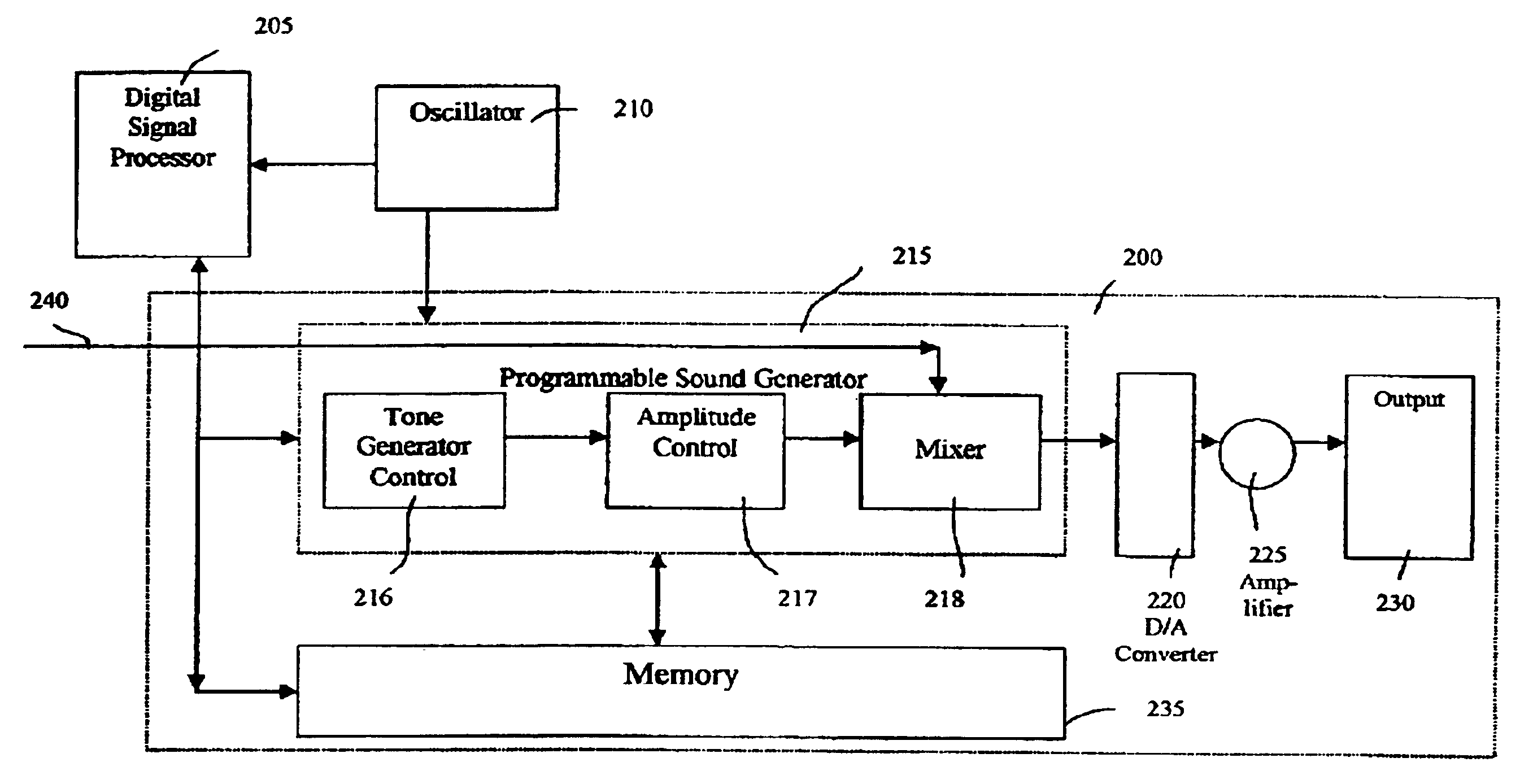
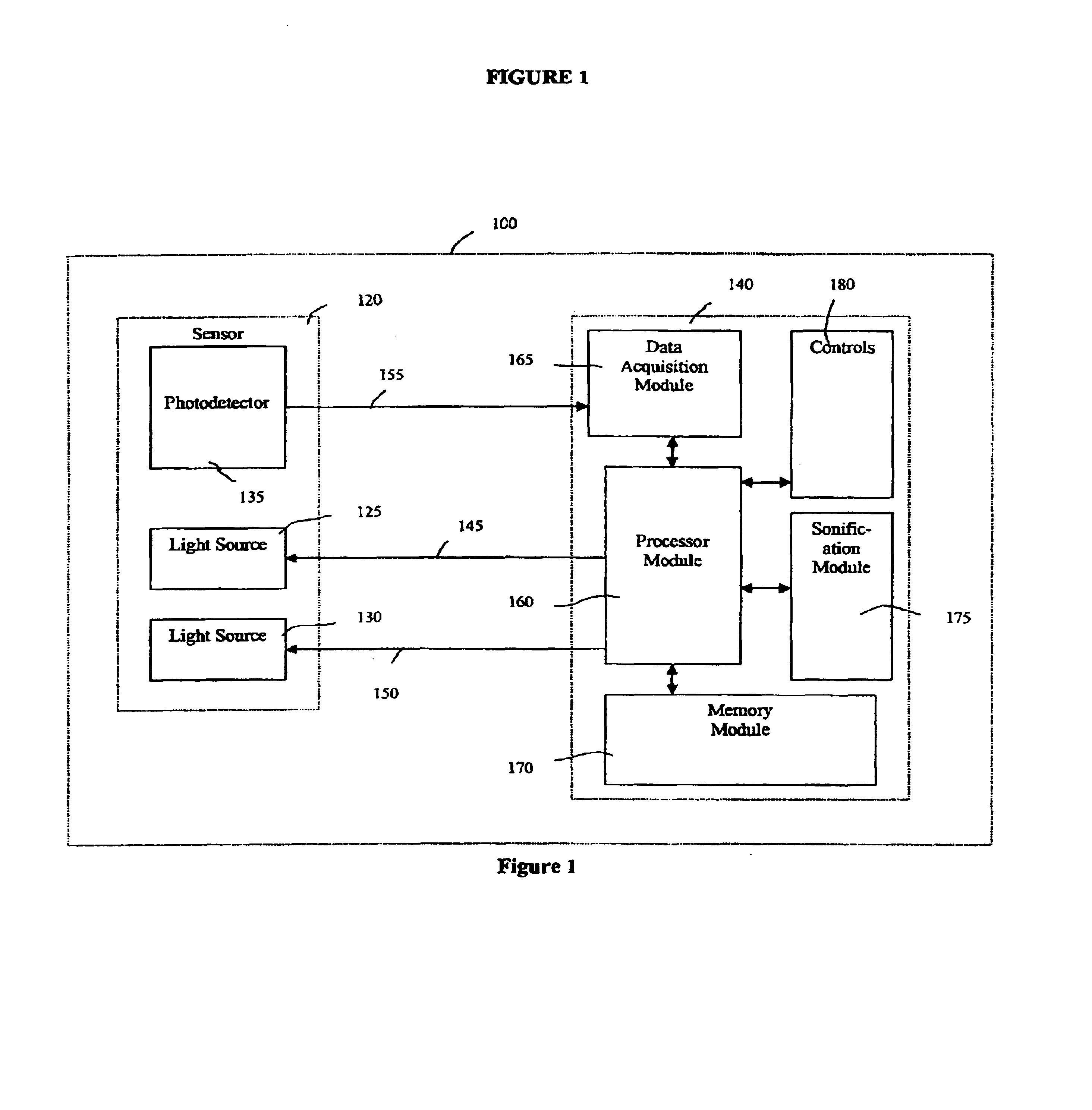
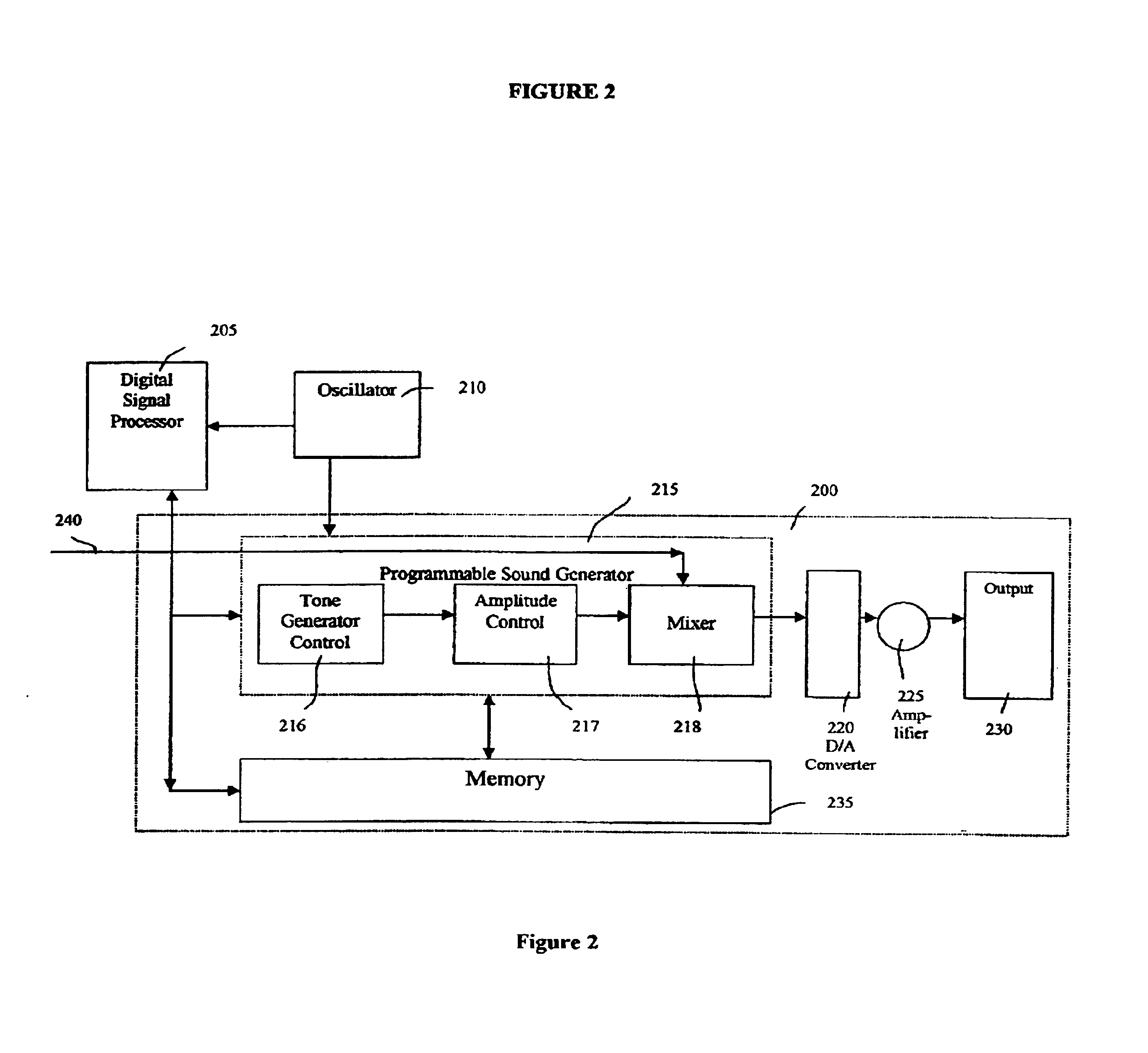
The present invention provides methods and devices for monitoring physiological data such that a health care provider is able to effectively monitor a patient's health status, including, for example, blood flow characteristics, without having to maintain constant visual contact. In one embodiment of the present invention, a physiological data monitoring system measures at least one physiological characteristic wherein the physiological data monitoring system comprises a sensor unit and a monitoring unit in data communication with the sensor unit. The monitoring unit has a sonification module that comprises one programmable sound generator module to produce a plurality of signals indicative of a physiological parameter and a memory module for storing a plurality of control parameters for managing the programmable sound generator module, wherein the plurality of signals produced have a plurality of frequencies modified in accordance with at least one physiological data value. More specifically, the present invention provides a pulse oximetry sonification system that generates fixed frequency singular and / or combined amplitude-adjusted dual audio tones corresponding to predetermined transition and / or intermediate points over a range of SpO2 measurements.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
Node monitor system applied to block chain
The present invention discloses a node monitor system applied to a block chain. The node monitor system comprises a monitor unit of a block chain node and a monitor program independent from the block chain node. The monitor unit comprises a network monitor module, a block chain monitor module, a behavior monitor module, a state monitor module, and a log monitor module. In the monitor system, the monitor unit deployed on each node is used to monitor the node and collect monitoring data, so as to discover the abnormality of the block chain node, and lower the impact of the abnormality; then the monitor processing module makes the abnormal node prominent, the reason of the abnormal node is analyzed rapidly by using the collected data and the abnormal node is positioned rapidly by using the collected data, and then the abnormality is processed and controlled. The node monitor system can be widely used for monitoring nodes of a public chain, an alliance chain and a private chain, and is particularly suitable for the alliance chain and the private chain.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNXIANG NETWORK TECH
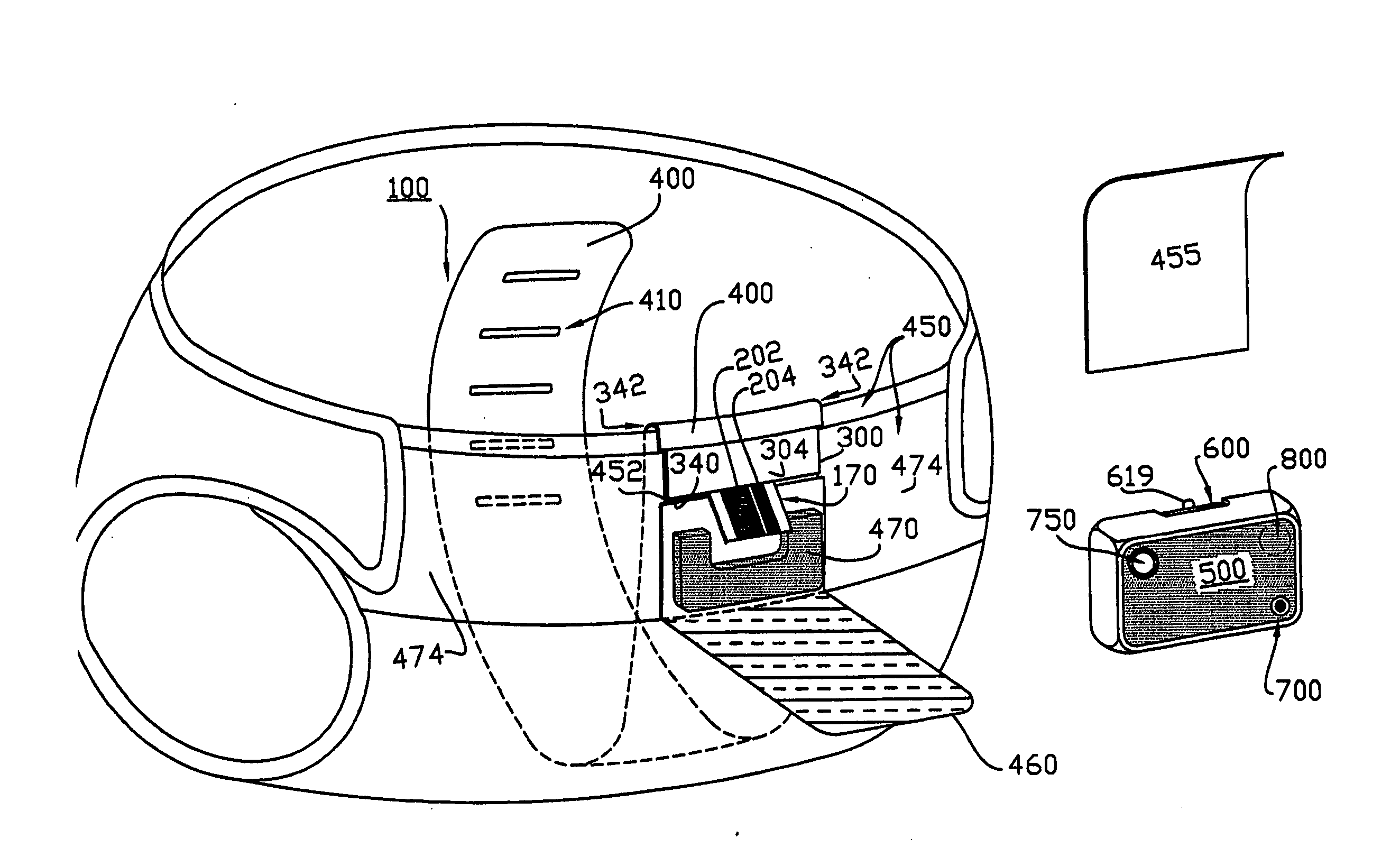
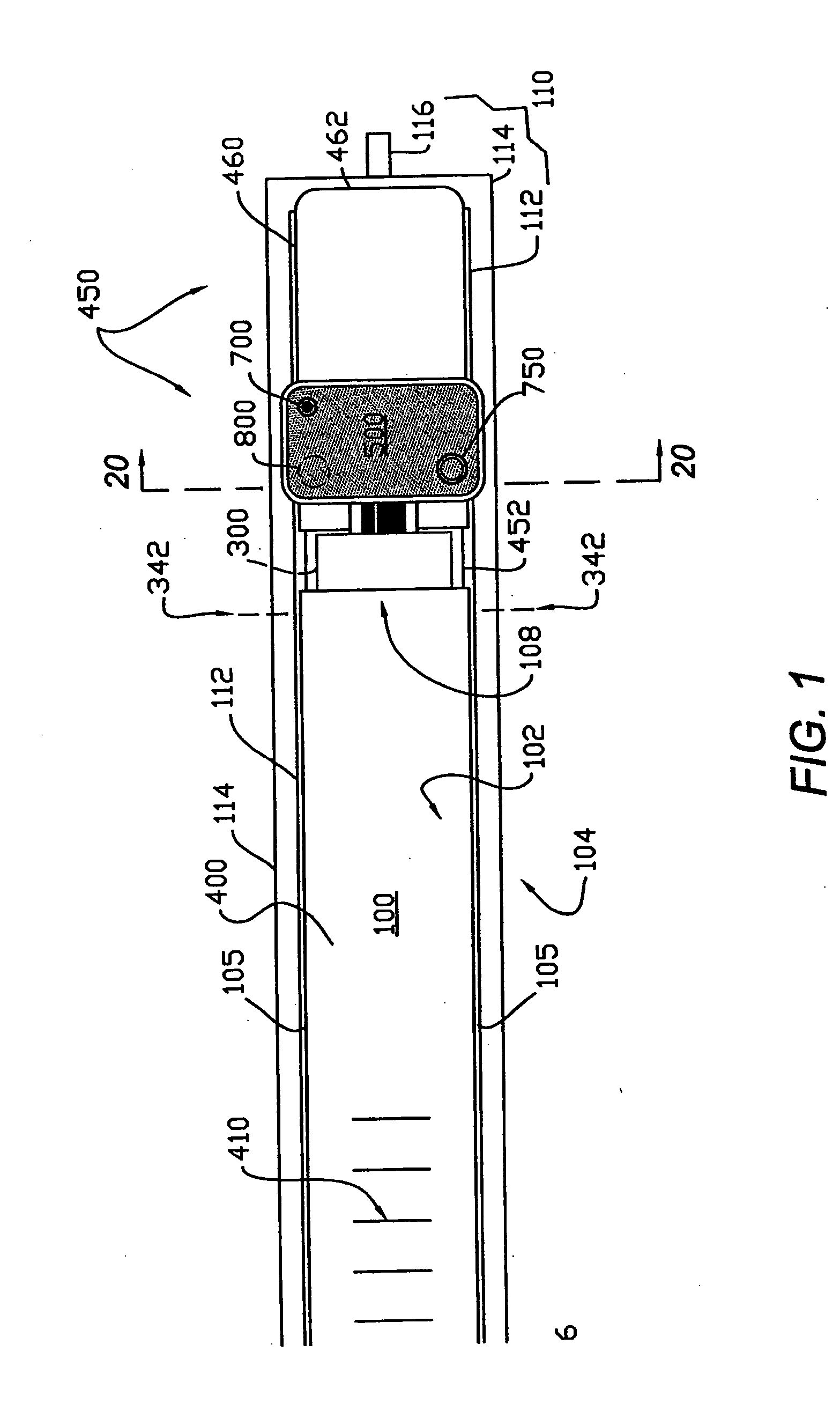
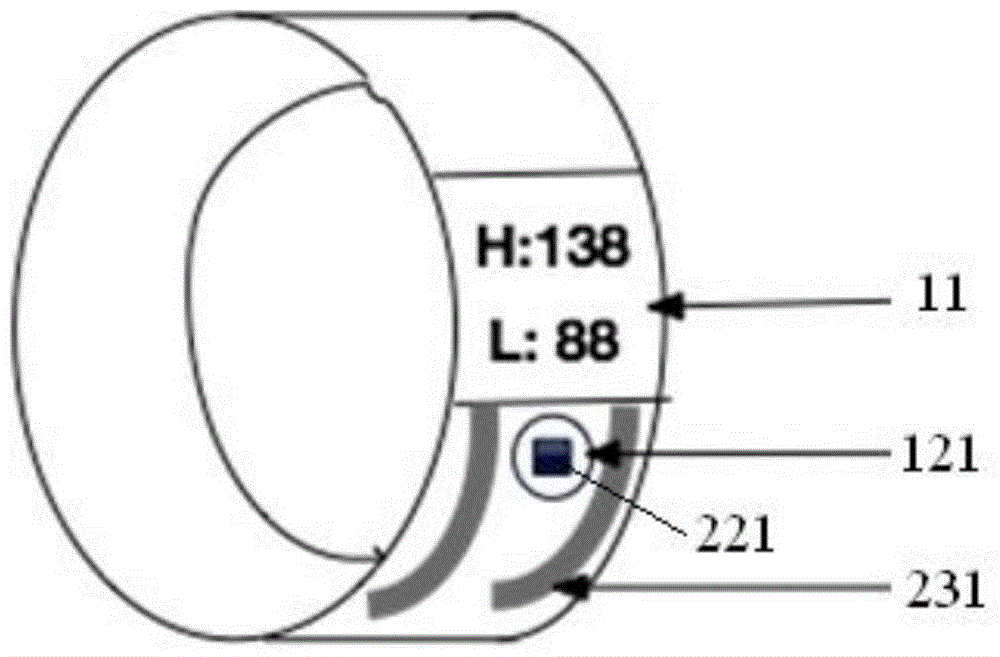
Wearable intelligent hand ring and method for continuously monitoring human body physiological signs
InactiveCN104055499AImplement parallel processingOverall healthDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyData synchronization
The invention discloses a wearable intelligent hand ring and method for continuously monitoring human body physiological signs. The intelligent hand ring comprises a hand ring body; a monitoring circuit is embedded in the hand ring body; the monitoring circuit comprises a main control unit and multiple monitoring units; each monitoring unit monitors the various human body physiological signs which are processed by a main control unit. The wearable intelligent hand ring and method for the continuously monitoring the human body physiological signs have the following beneficial effects of integrating multiple sensing circuits, being capable of collecting multiple human body physiological signs and realizing the parallel processing on various collected data; the collected human body physiological signs are analyzed by adopting a unique data analysis method, so the human body healthy condition can be comprehensively accurately obtained; a user can regularly start the monitoring function by triggering of one hand or controlling of the main control unit, and the need that the human body physiological signs of the user are monitored anytime anyplace for 24 hours is met; the intelligent hand ring is provided with a wireless communication unit, and data synchronization can be performed between the intelligent hand ring and a mobile terminal, so the user can learn the physiological signs and the healthy condition in real time.
Owner:YUEXIANG QUSHI TECH BEIJING
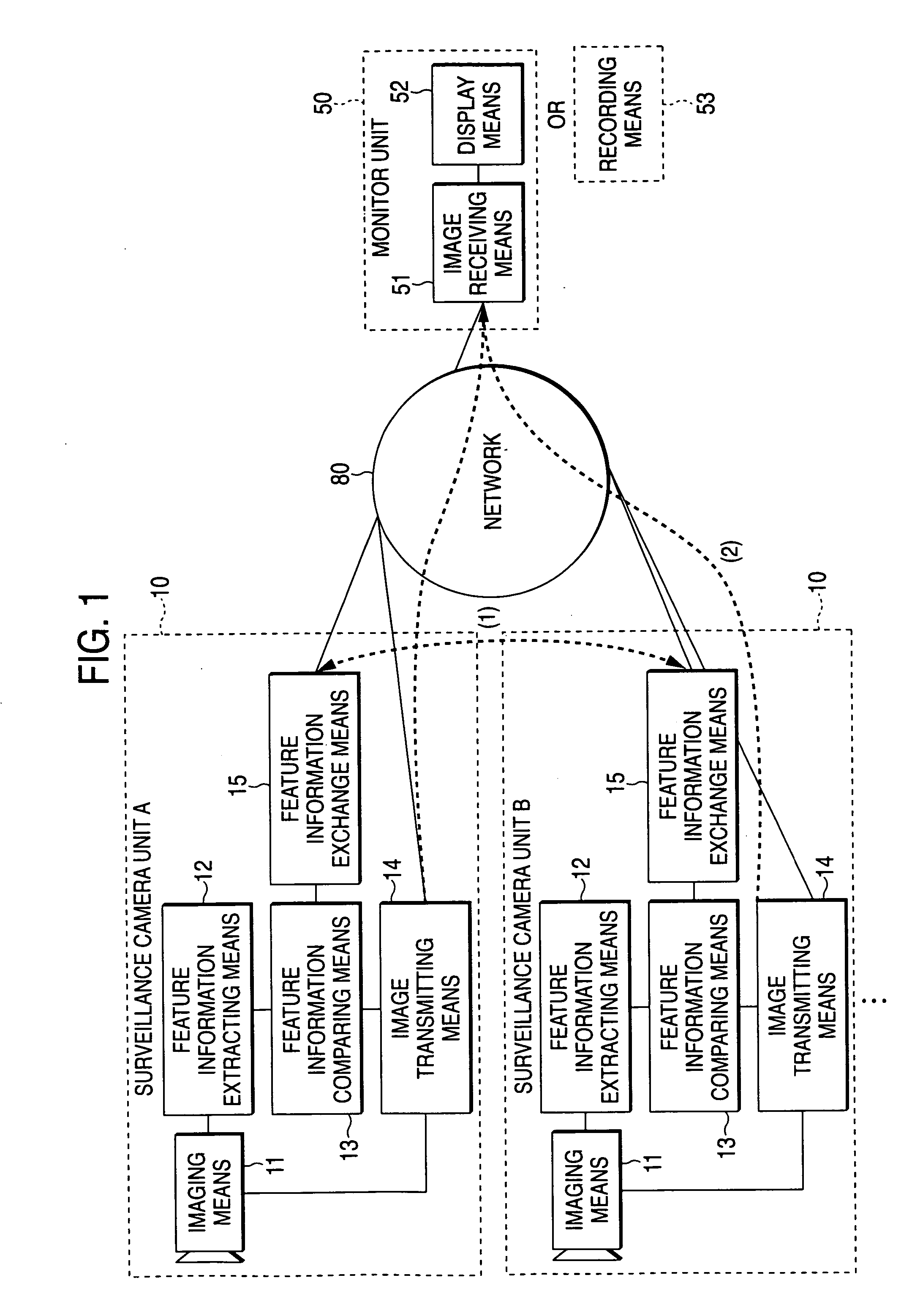
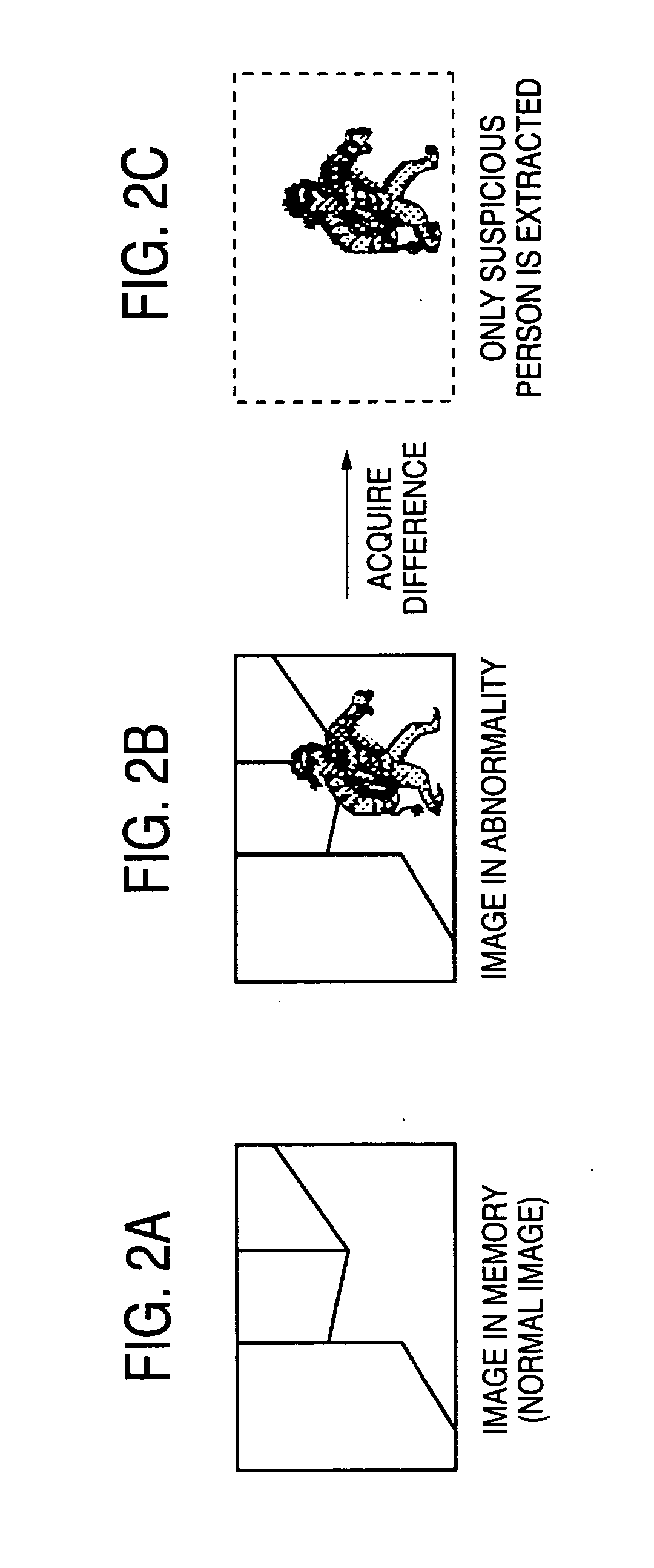
Surveillance system and a surveillance camera
ActiveUS20050057653A1Stable trackingCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsMonitoring systemSurveillance camera
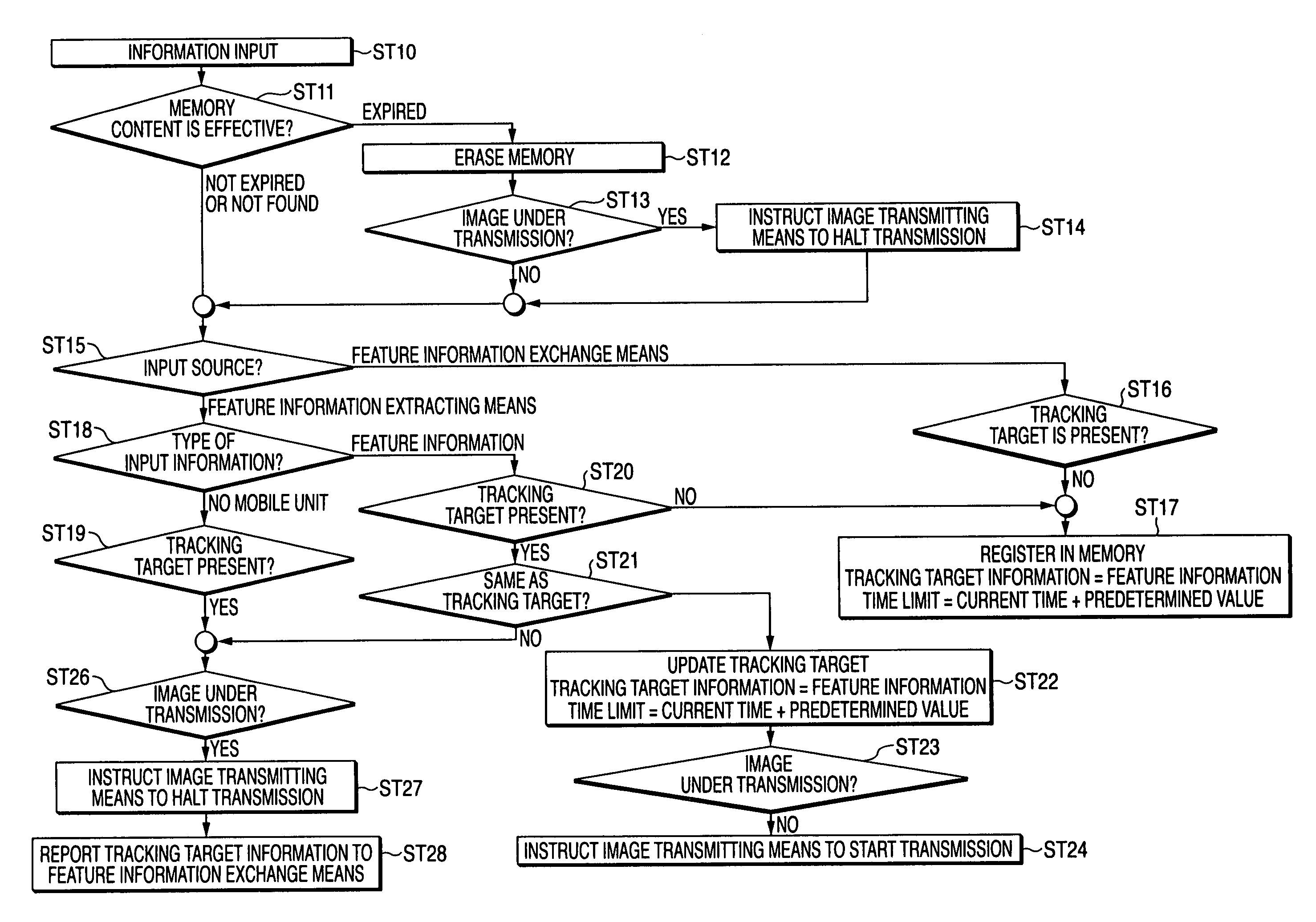
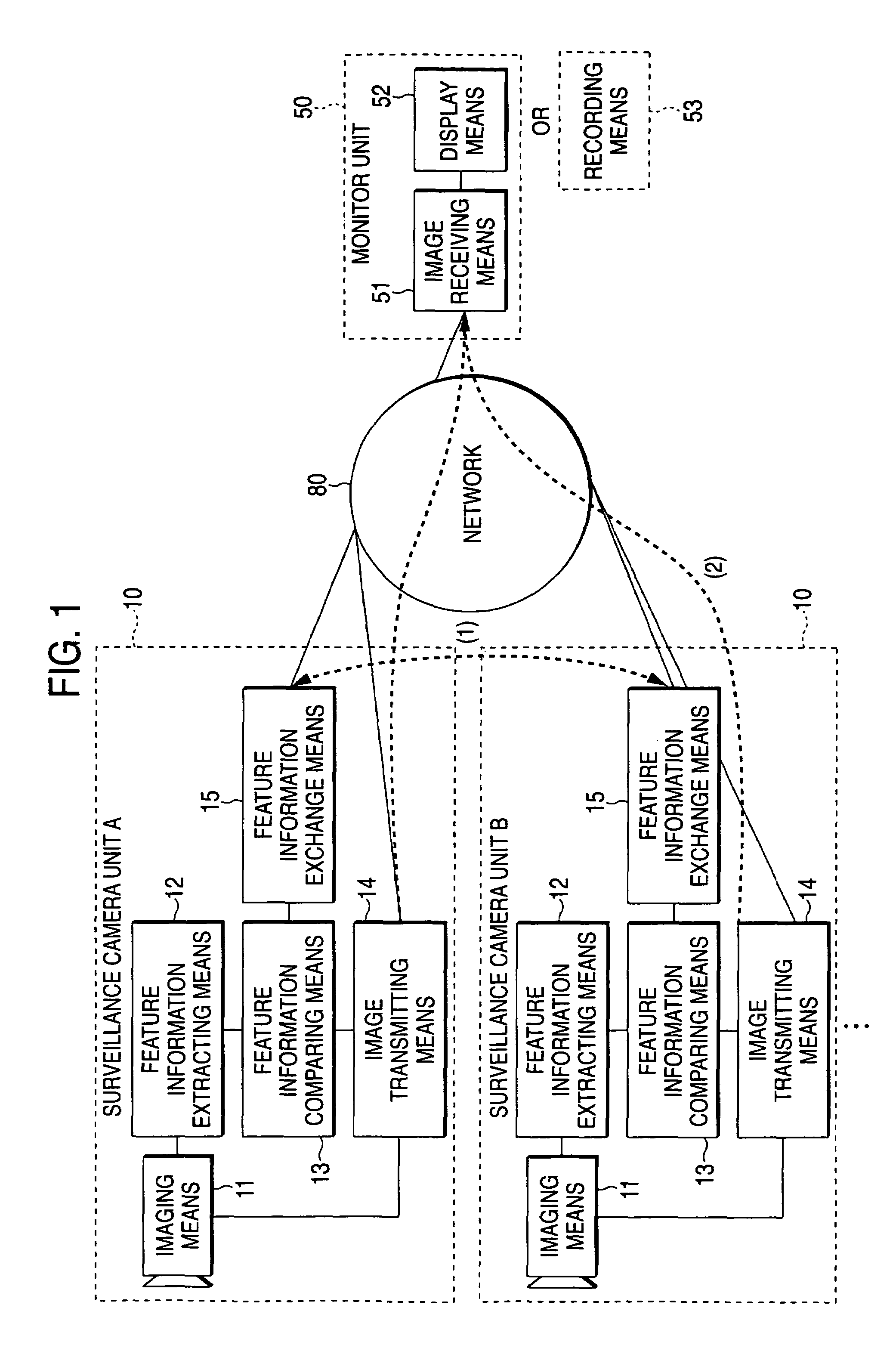
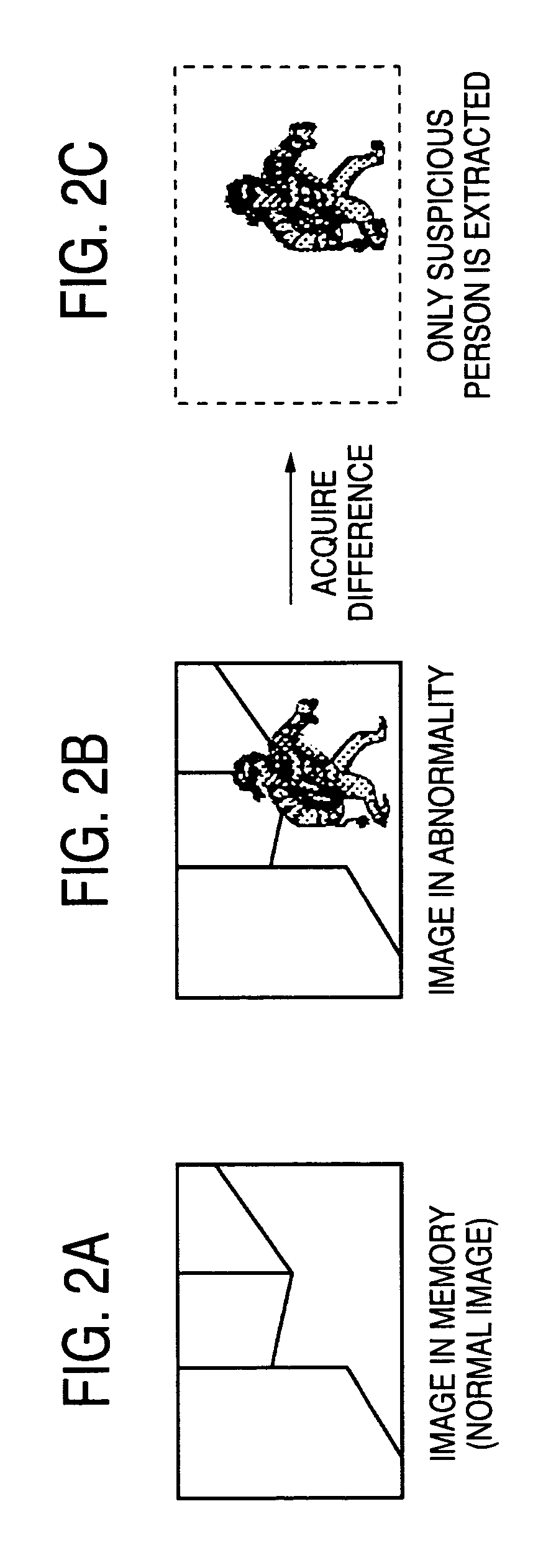
The surveillance system is a system that a plurality of surveillance camera units cooperatively acquire image of a movable object. Each of the surveillance camera units is equipped with a image recognition function. A surveillance camera unit that has recognized the feature information on the movable object in the image picked up transmits the image to a monitor unit via a network and the feature information on the movable object to the other surveillance camera unit via the network. A surveillance camera unit that has recognized the feature information received from the other camera unit in the image picked up transmits the image to the monitor unit via the network as well as transmits the feature information on the movable object to the other surveillance camera unit via the network. This makes it possible to keep tracking of a target even in a space including more blind spots.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
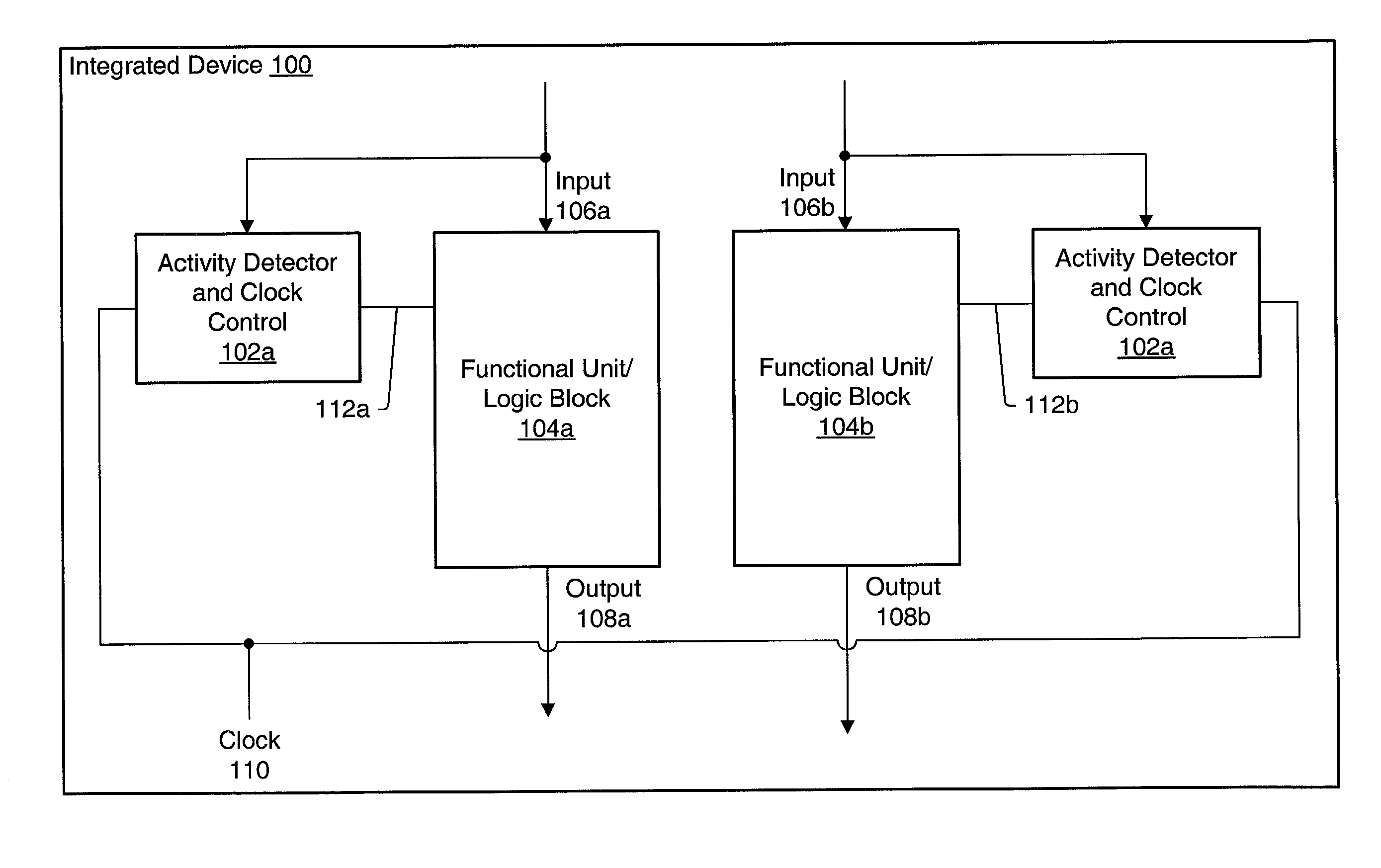
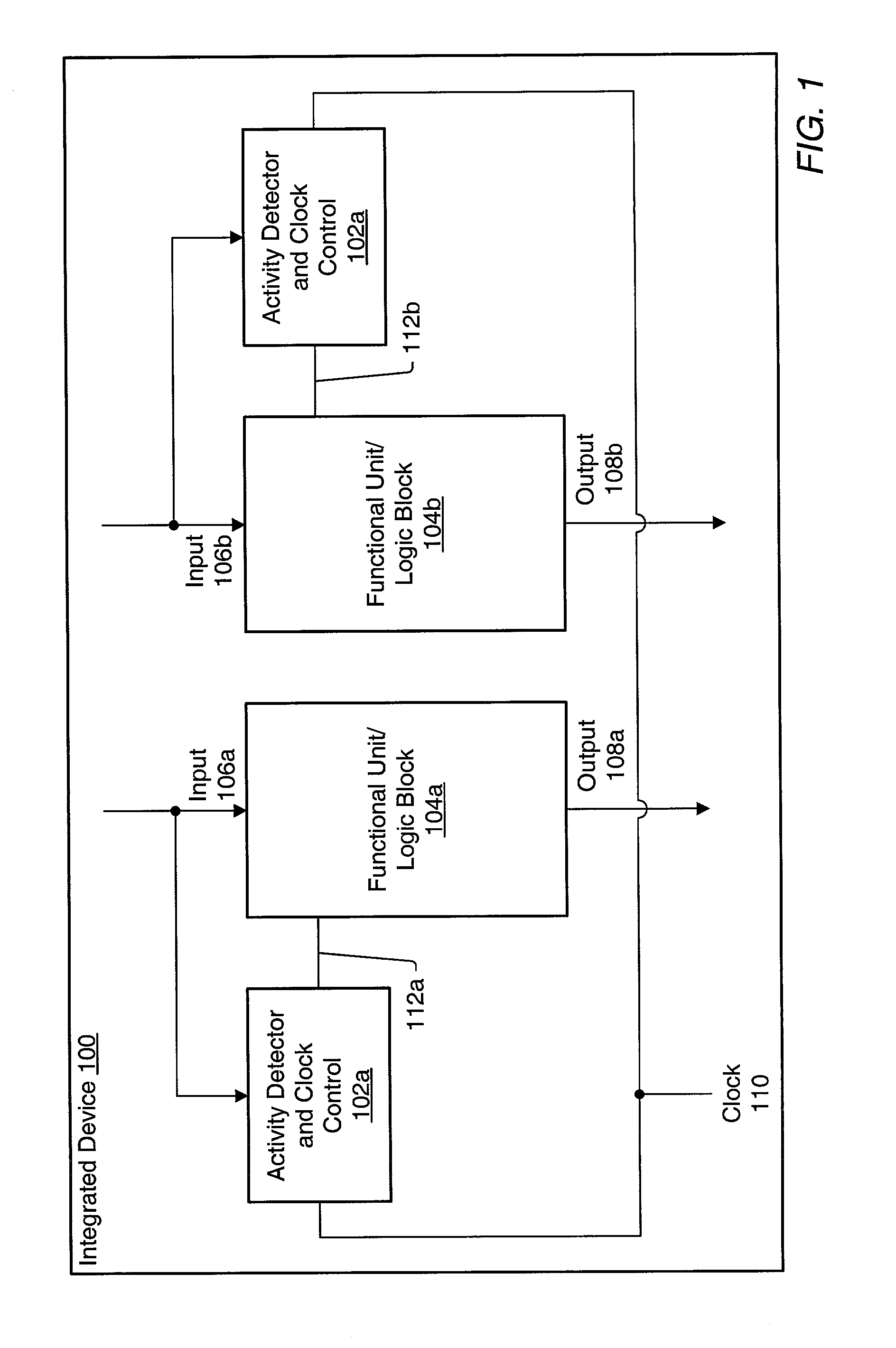
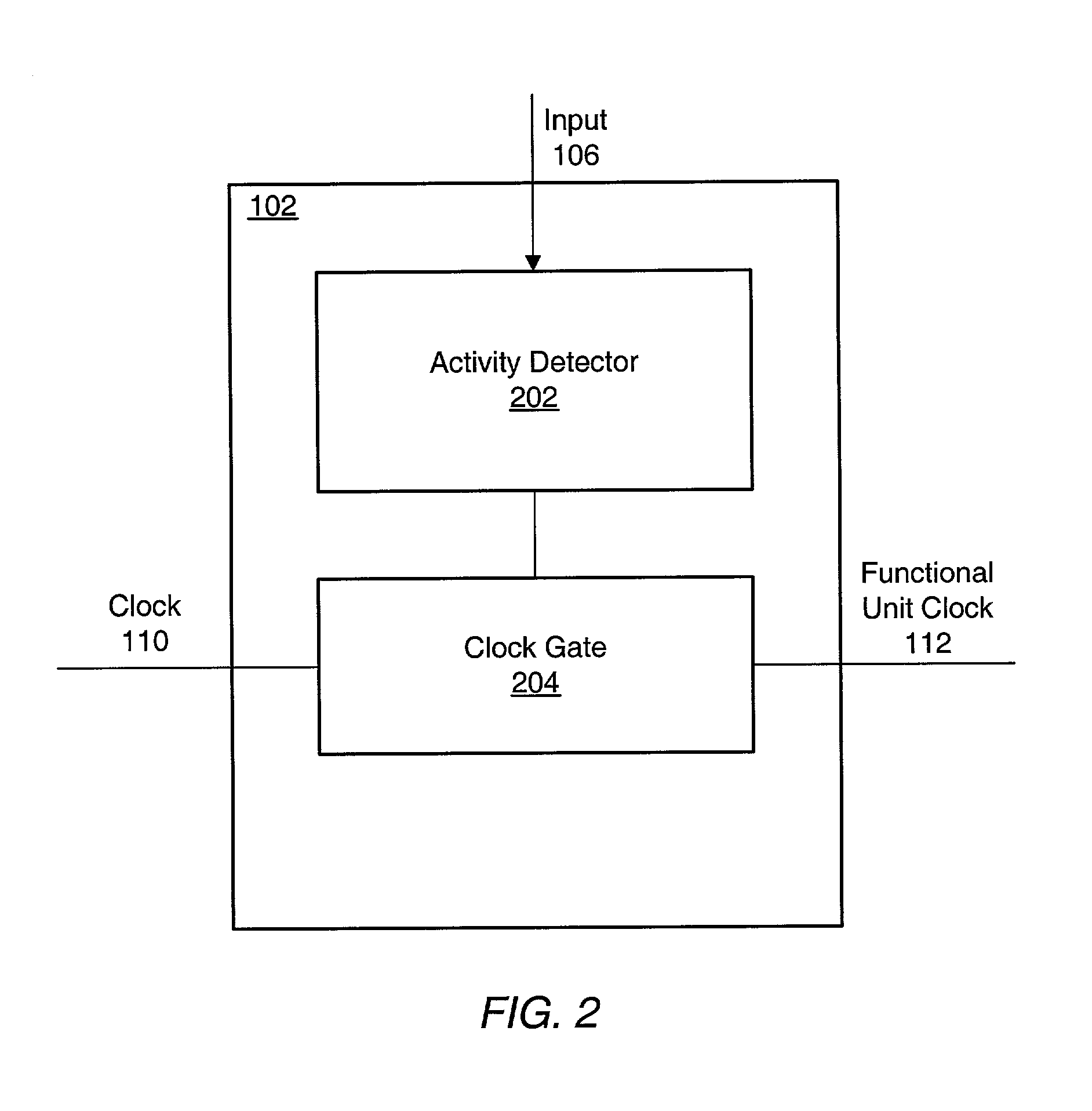
Clock control of functional units in an integrated circuit based on monitoring unit signals to predict inactivity
ActiveUS6983389B1Reduce overall static and dynamic power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingEngineeringEmbedded system
An integrated circuit may have separate clock control for a number of different functional units. Ancillary to some of the functional units may be an activity detector and clock control unit which monitors input to its functional unit to determine when the functional unit will be inactive. When an activity detector and clock control unit determines that a particular functional unit is or will be inactive, it may disable clocking to its functional unit while the functional unit is inactive. When activity detector and clock control unit determines that activity will resume for its functional unit, it enables clocking to its functional unit. Thus, the activity detector and clock control unit for each such functional unit functions to control clocking to its respective functional unit so that during periods of inactivity, inactive functional units are not clocked to reduce the overall static and / or dynamic power consumption for the integrated device.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Surveillance system and a surveillance camera
ActiveUS7227569B2Stable trackingCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The surveillance system is a system that a plurality of surveillance camera units cooperatively acquire image of a movable object. Each of the surveillance camera units is equipped with a image recognition function. A surveillance camera unit that has recognized the feature information on the movable object in the image picked up transmits the image to a monitor unit via a network and the feature information on the movable object to the other surveillance camera unit via the network. A surveillance camera unit that has recognized the feature information received from the other camera unit in the image picked up transmits the image to the monitor unit via the network as well as transmits the feature information on the movable object to the other surveillance camera unit via the network. This makes it possible to keep tracking of a target even in a space including more blind spots.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
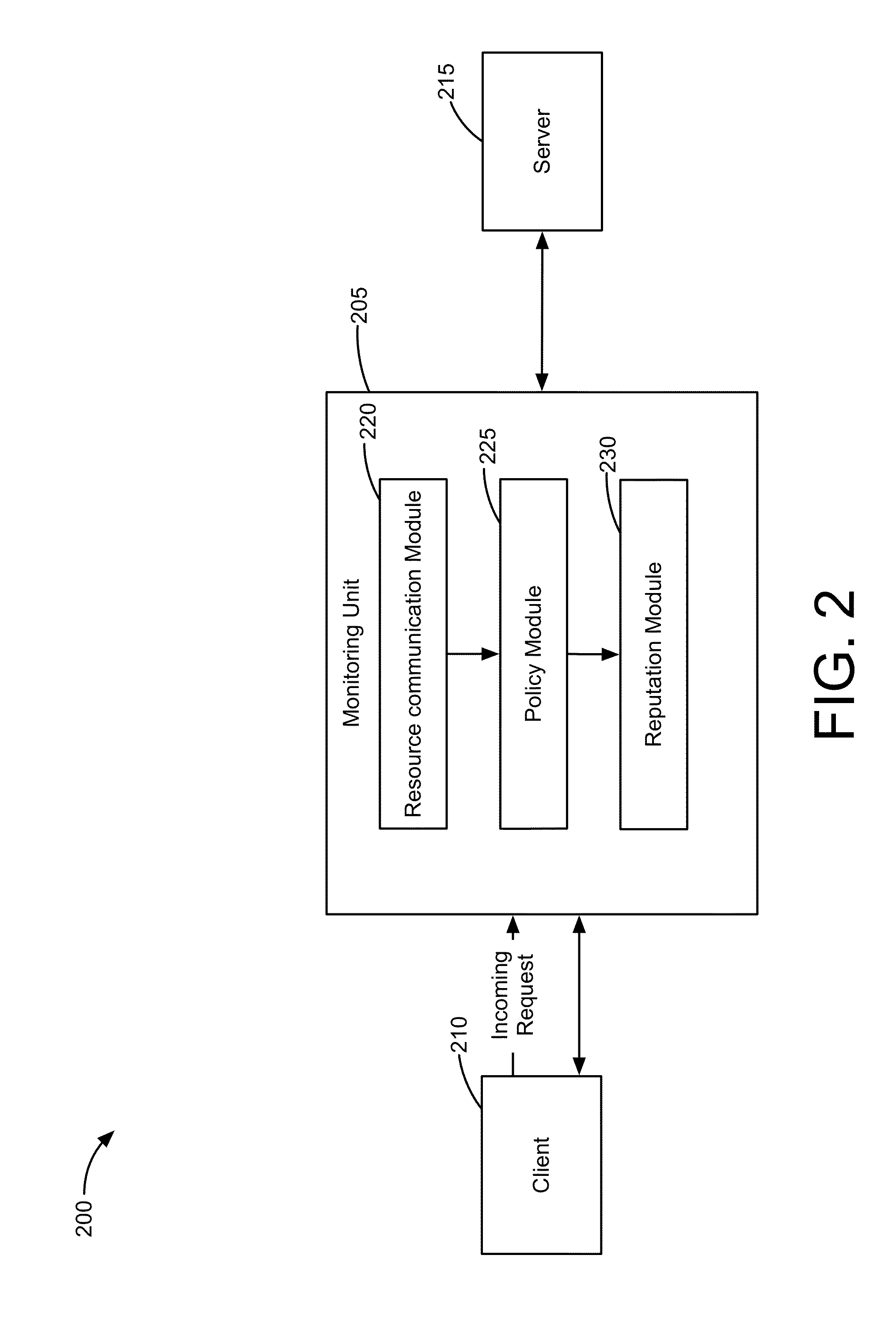
Detecting malicious resources in a network based upon active client reputation monitoring
ActiveUS20130312097A1Facilitates display of reputationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionMonitoring systemMonitor equipment
Systems and methods for detecting malicious resources by analyzing communication between multiple resources coupled to a network are provided. According to one embodiment, a method is performed for client reputation monitoring. A monitoring unit within a network observes activities relating to multiple monitored devices within the network. For each observed activity, the monitoring unit assigns a score to the observed activity based upon a policy of multiple polices established within the monitoring unit. For each of the monitored devices, the monitoring unit maintains a current reputation score for the monitored device based upon the score and a historical score associated with the monitored device. The monitoring unit classifies one of the monitored devices as potentially being a malicious resource based upon its current reputation score.
Owner:FORTINET
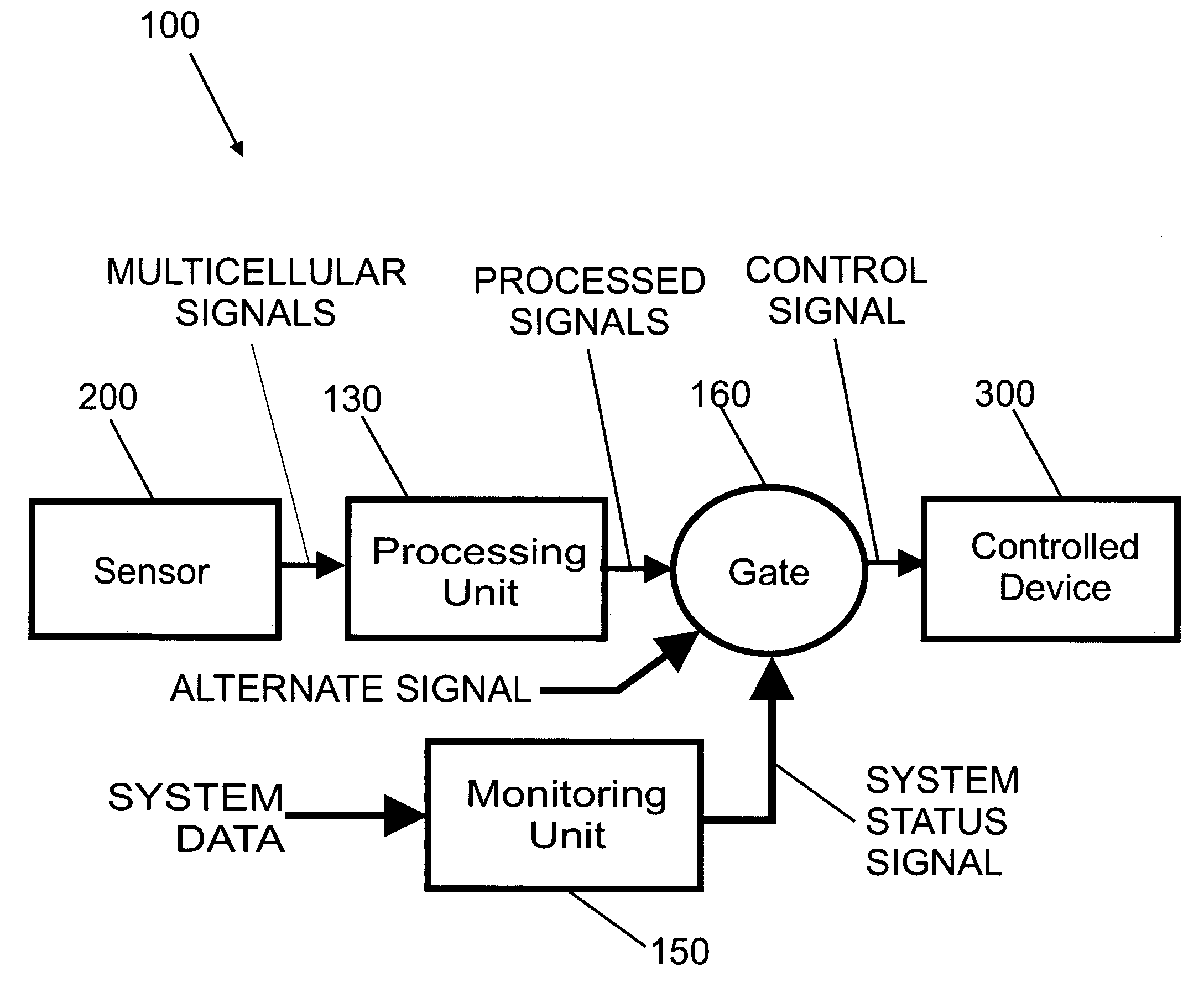
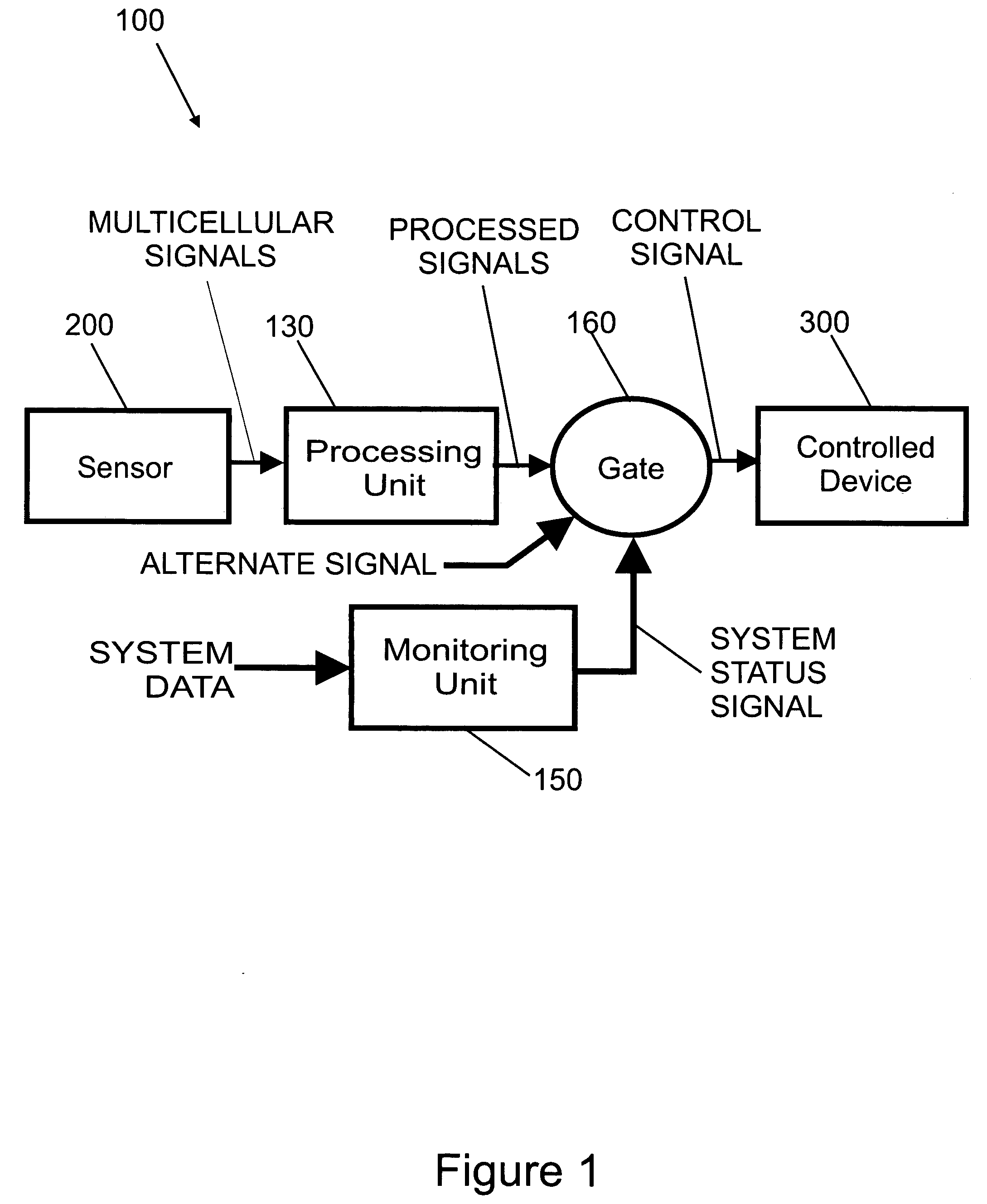
Biological interface system with gated control signal
Various embodiments of a biological interface system and related methods are disclosed. The biological interface system may comprise a sensor comprising a plurality of electrodes for detecting multicellular signals emanating from one or more living cells of a patient, a processing unit configured to receive the multicellular signals from the sensor and process the multicellular signals to produce a processed signal, and a signal gate configured to receive the processed signal from the processing unit and an alternative signal generated by the system, the signal gate being configured to transmit a control signal to a controlled device based on either the processed signal or the alternative signal. A monitoring unit may receive system data and process the system data to produce a system status signal. The system status signal may be used to determine which of the processed signal and the alternative signal is to be used as the control signal.
Owner:CYBERKINETICS NEUROTECH SYST +1
Support of non-trivial scheduling policies along with topological properties
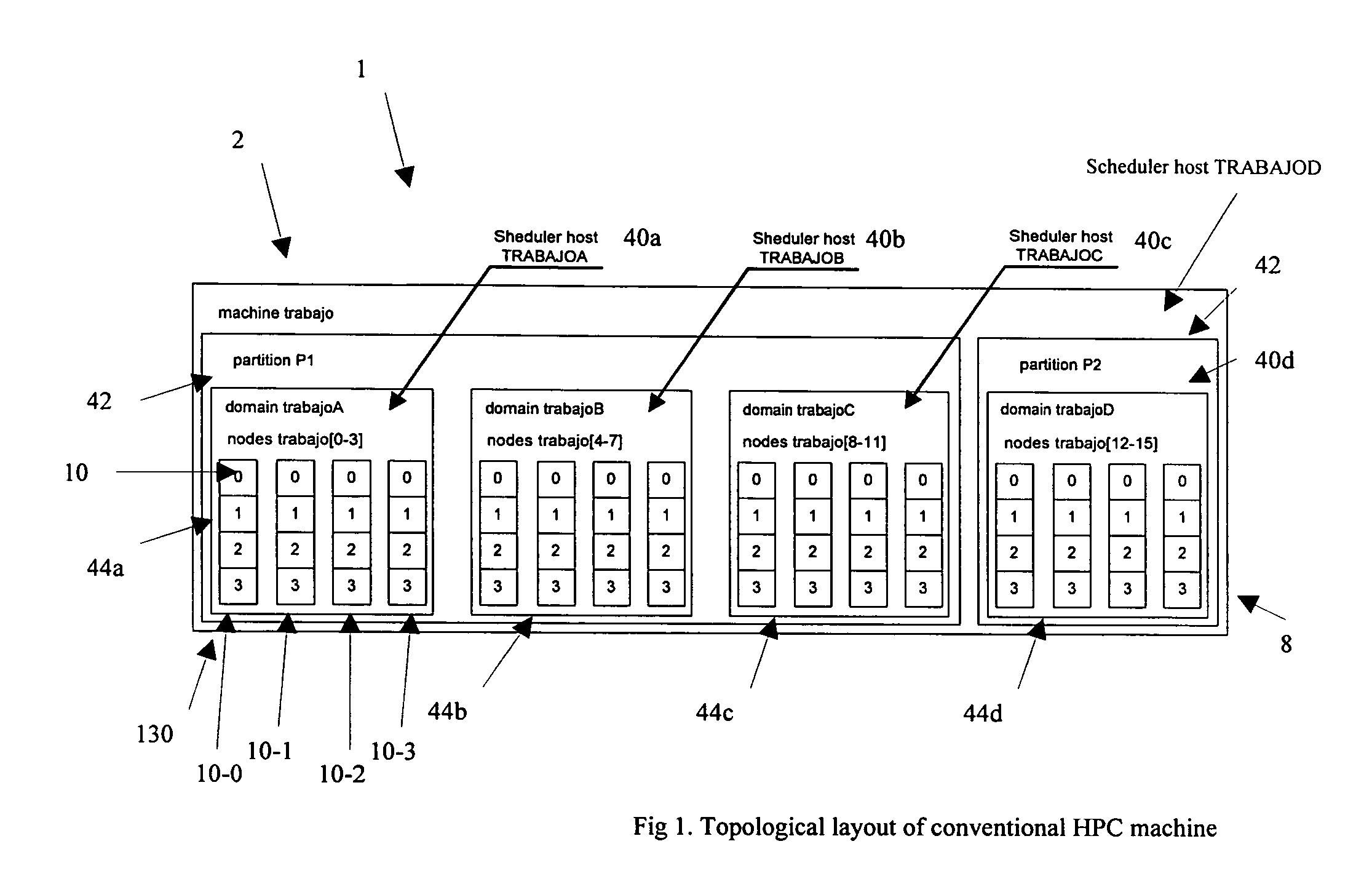
InactiveUS7596788B1Fulfil requirementsMaximize efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationResource allocationMulti processorTopological order
Systems and methods for scheduling jobs in a multiprocessor machine are disclosed. The status of resources in the multiprocessor machine is periodically determined. The status indicates the resources available to execute jobs. This information is accumulated by the topology-monitoring unit and provided to the topology library. The topology library also receives a candidate host list which lists all resources available to execute the job being scheduled based on non-trivial scheduling. The topology library unit generates a free map F indicating the interconnection of the resources available to execute the job. The topology monitoring unit matches jobs to the resources available to execute the jobs, based on resource requirements including shape requirements indicative of interconnections of resources required to execute the job. The topology monitoring unit dispatches the job to the portion of the free map F which matches the shape requirements of the job.
Owner:IBM CORP
Arrangement for anaesthetising a living creature
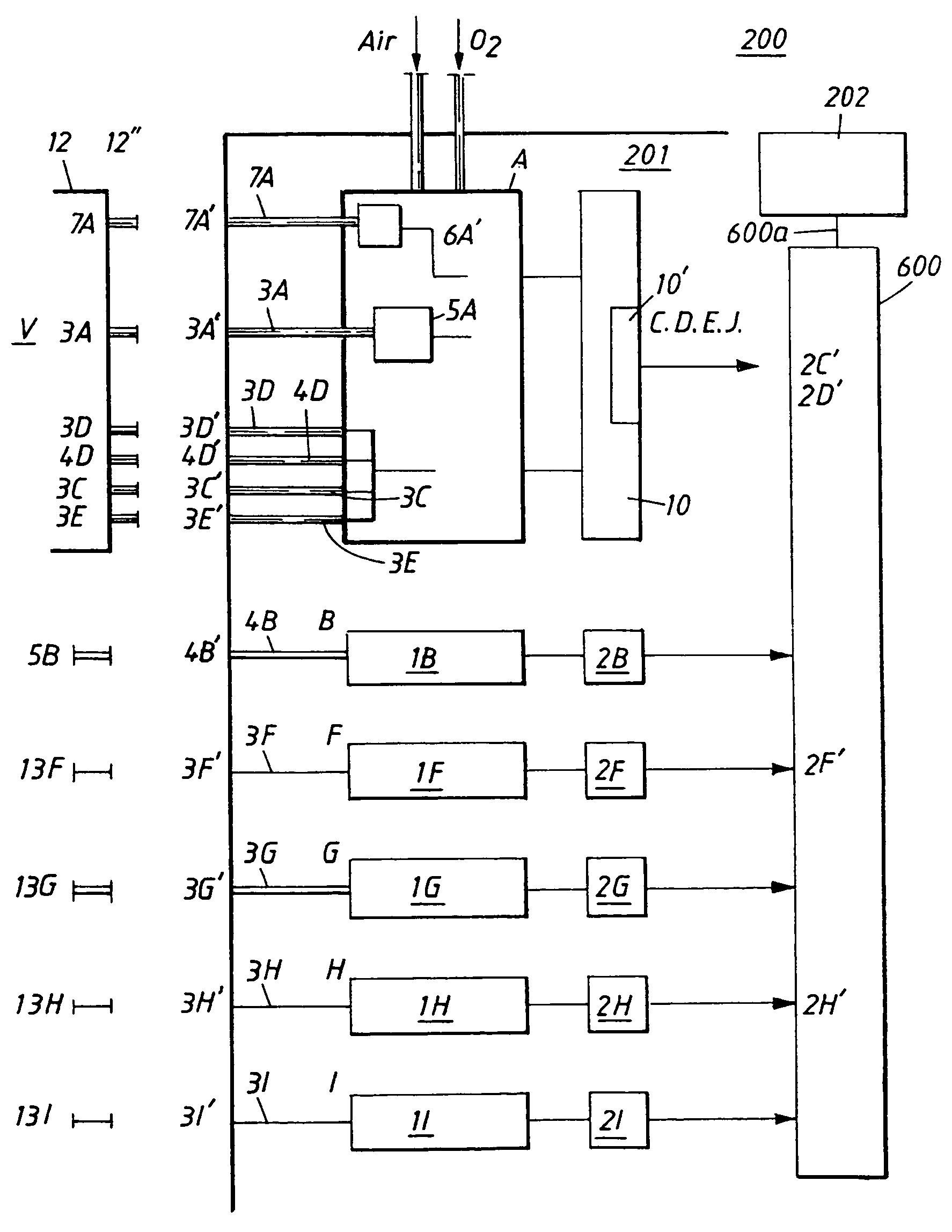
InactiveUS7040315B1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesUnit of timeBiomedical engineering
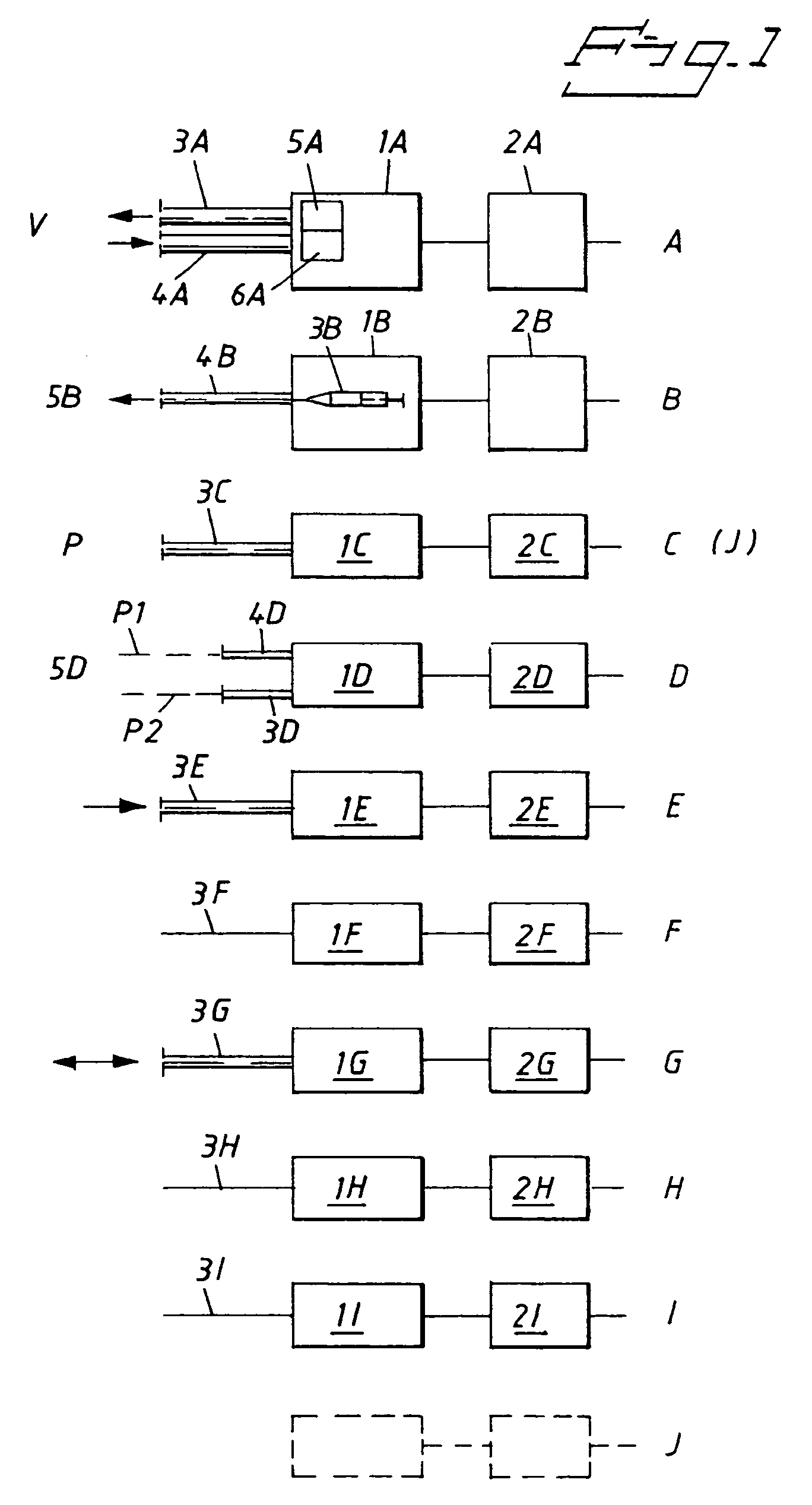
The invention relates to an arrangement (200) for anaesthetising a living creature (V) and for maintaining said creature in an anaesthetised state, by administering thereto an infused volume of anaesthesia inducing pharmaceutical (22) in liquid phase per unit of time, with the aid of one or more lung ventilator units (A) and one or more infusion units (B). Chosen parts of the lung ventilator unit, with the exception of external insufflation hose, expiration valve, measuring probe and a number of hoses (12), and selected parts of the infusion unit (B), with the exception of cannula (5B) and hose (4B) are mutually combined to form a single equipment unit (201). Some of the parts of the equipment unit are mutually coordinated with respect to communication via a computer unit (600) included in the equipment unit, and the computer unit is adapted to monitor unit related criteria and creature related criteria.
Owner:ANEO AB
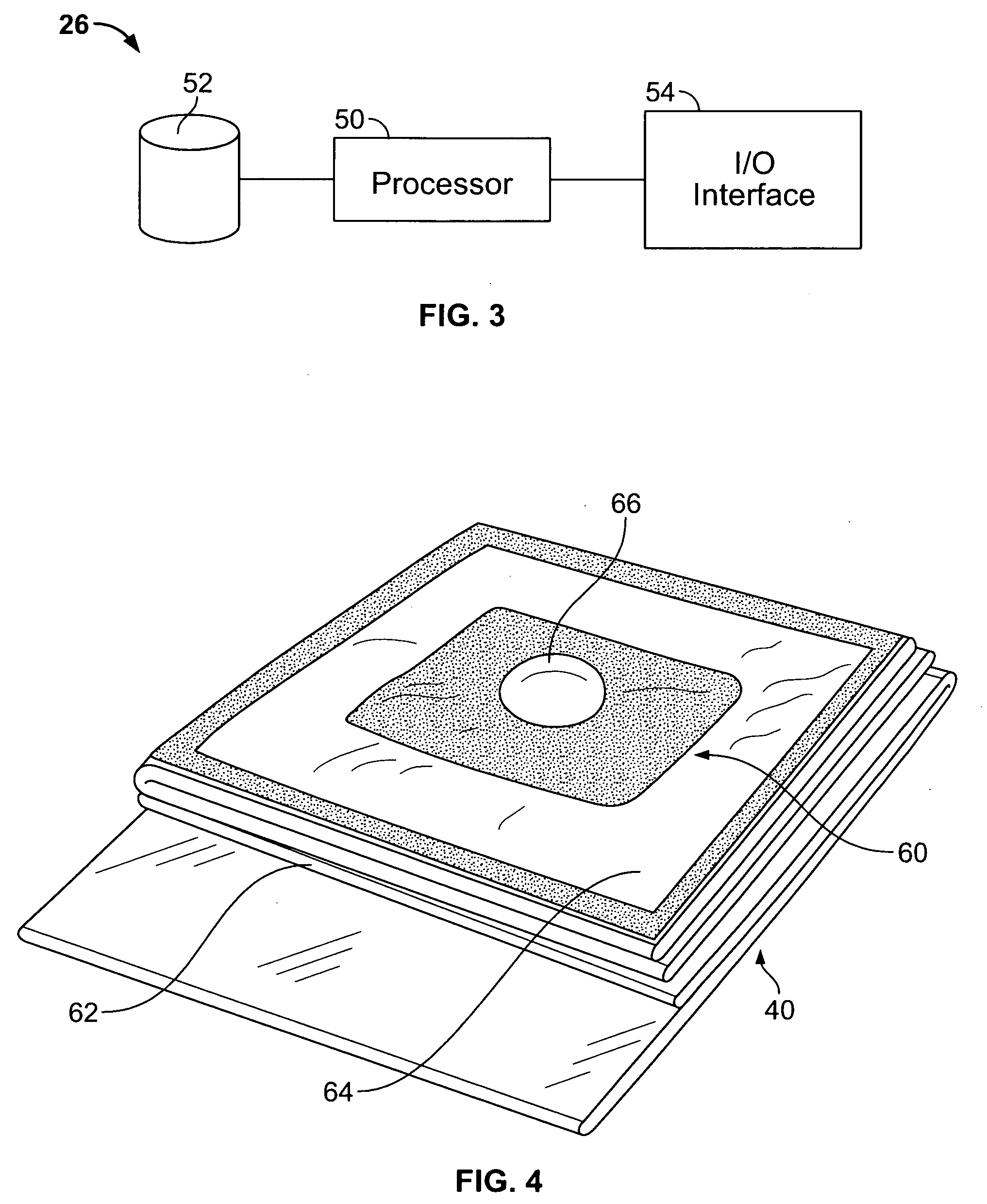
Patient monitoring system
ActiveUS20050033250A1Degree of accountability improvedImprove quality of careBaby linensAlarmsMonitoring systemEngineering
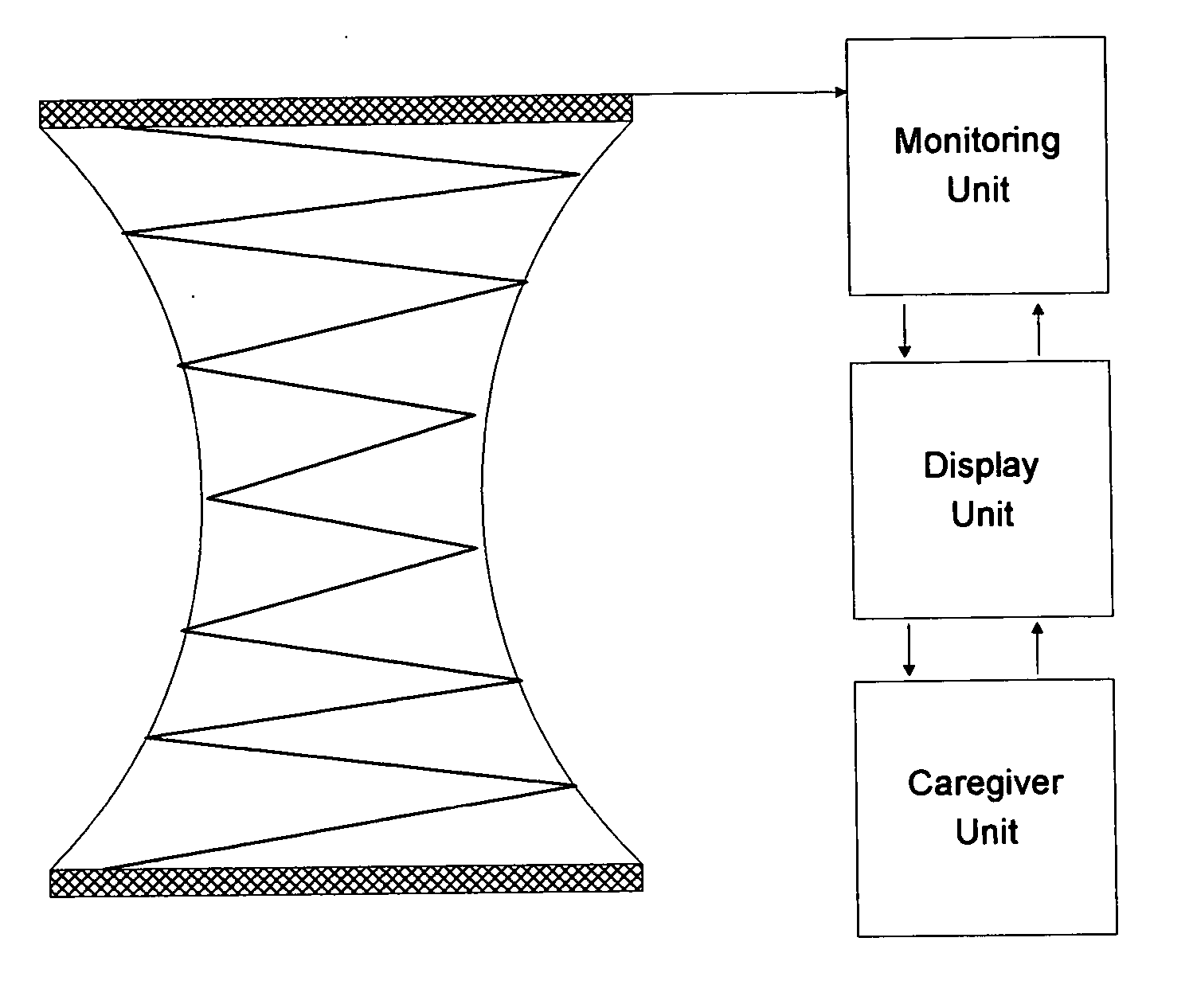
A patient monitoring system according to one embodiment includes a real-time wetness sensor configured to detect the rate of change in wetness occurring within an associated diaper, and automatically adjusting the sensitivity of the sensor to account for a wetness event unrelated to urination. A monitoring unit may be utilized in such a manner that the monitoring system controller-monitors the wetness sensor and generates data associated with detected-wetness events relative to the diaper. A wireless transmitter configured with the monitoring unit and in communication with the monitoring system controller may be further utilized to send the generated data, through a host computer, to a caregiver unit having a caregiver system controller in communication with the host computer. The caregiver can then check the status of the patient, provide a service, and annotate the patients history by transmitting the recorded observation and service provided back to the base station.
Owner:ZEALACARE LLC
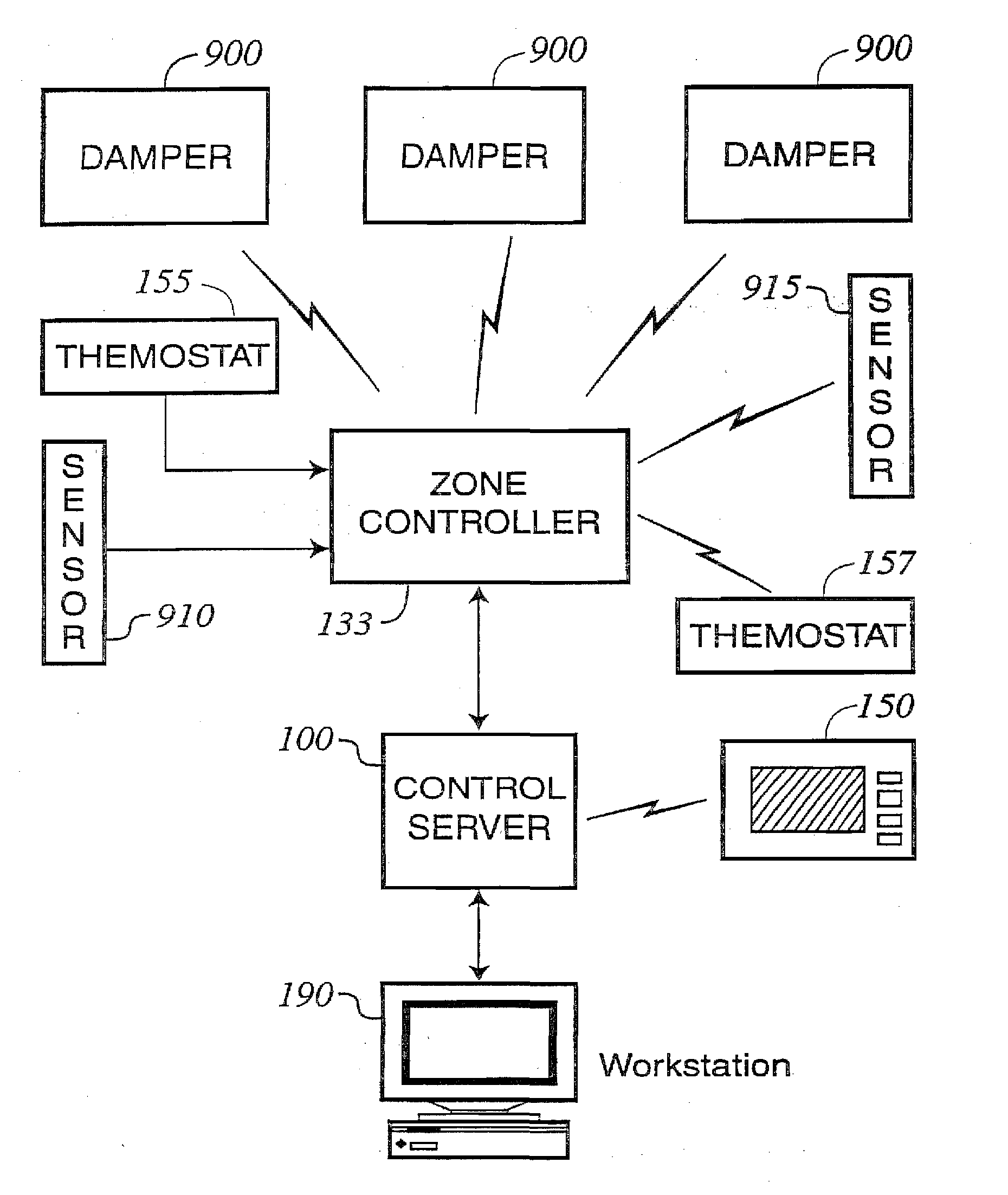
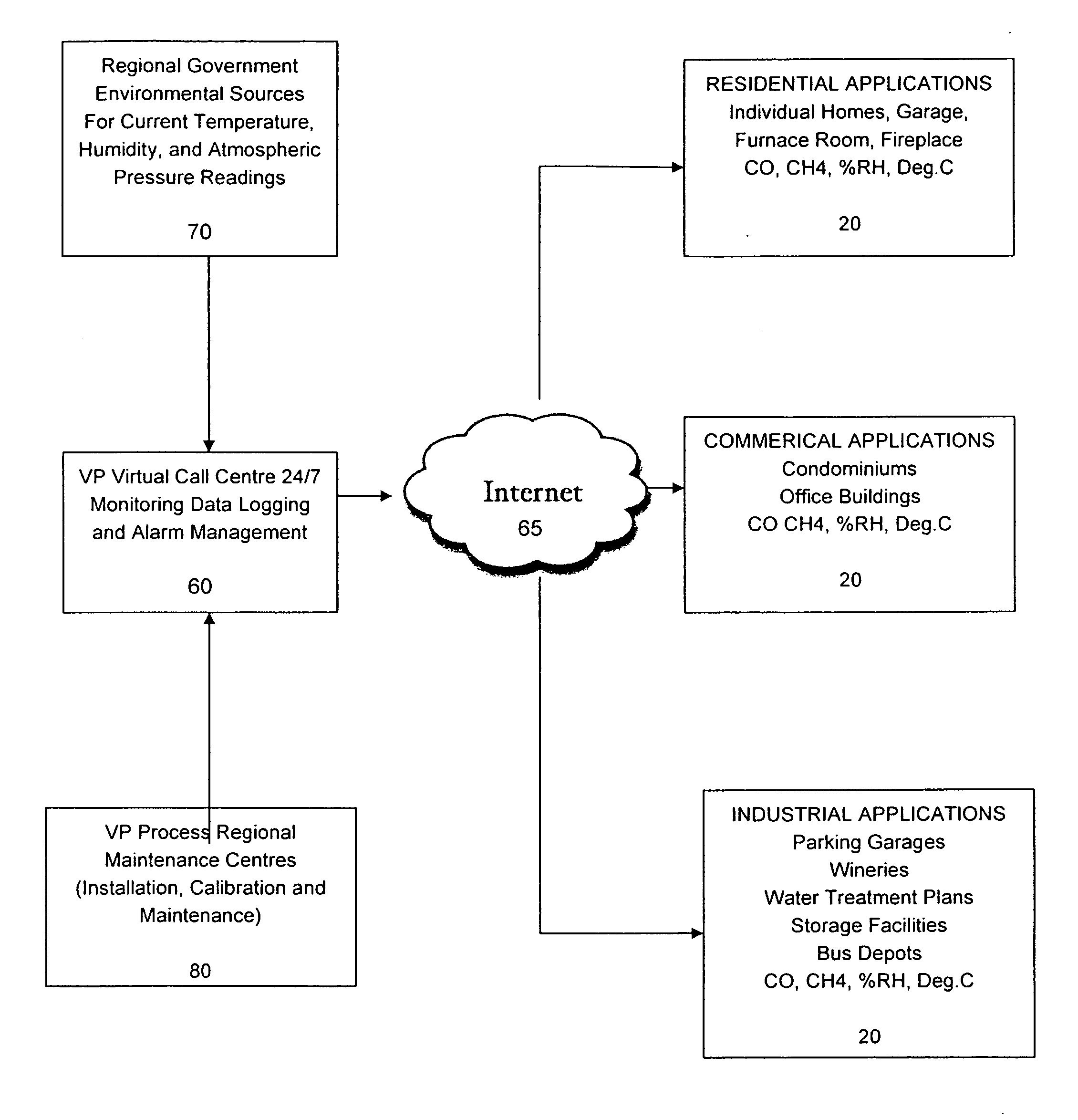
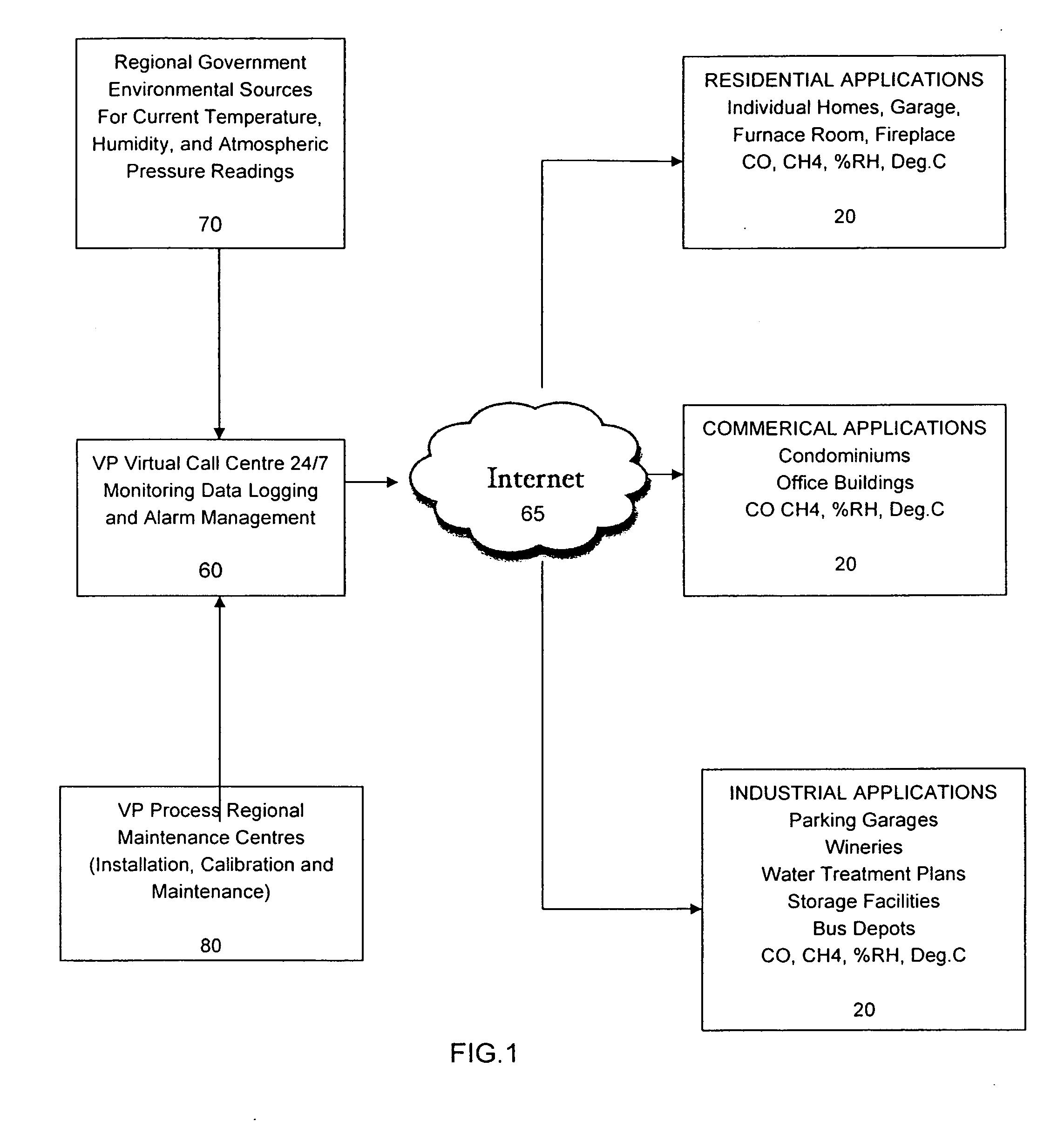
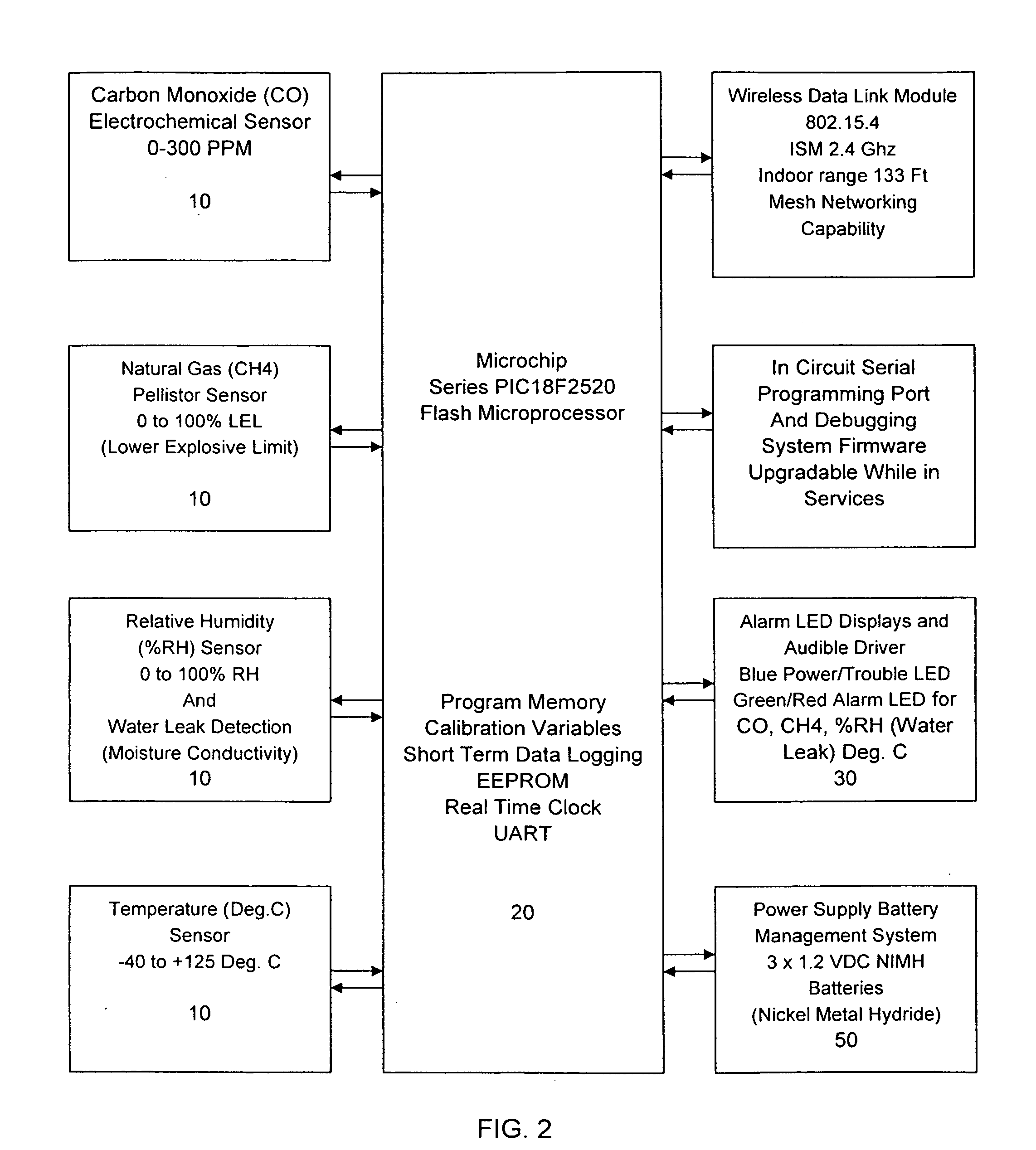
Environmental monitoring and control system
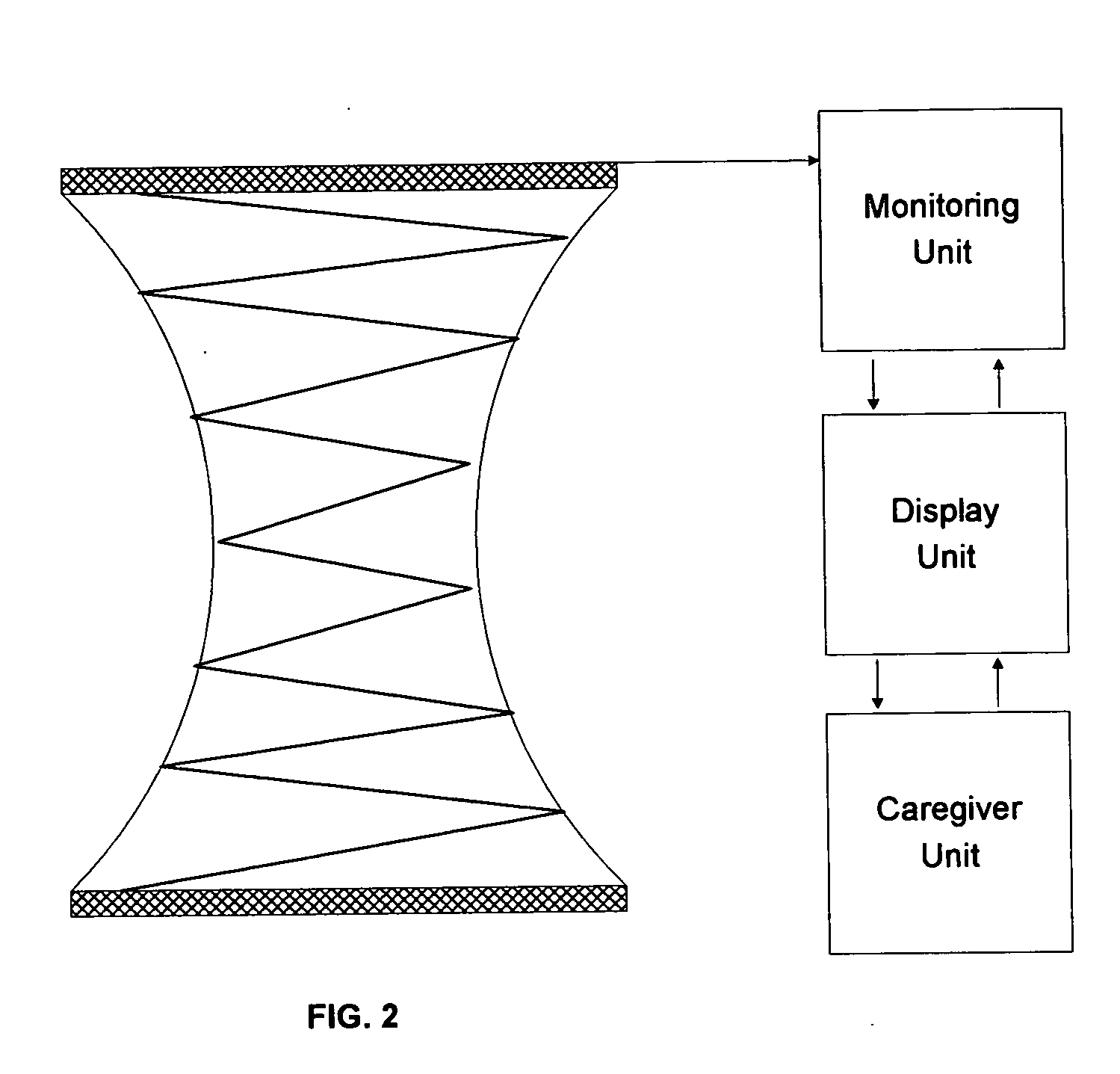
A wireless environmental monitoring system is disclosed comprising at least one monitor unit in wireless communication with a remote monitoring centre by way of the Internet and a server unit wherein the server unit is in wireless communication with both the monitor unit and the remote monitoring centre. The monitor unit comprises at least one sensor configured to detect an anomalous environmental condition such as the presence of or undesirable change in environmental variables. The monitor unit further comprises an alarm system and a relay output wherein the relay output is configured to trigger an event in response to the anomalous environmental condition to mitigate damage that may be caused by the anomalous environmental condition. The remote monitoring centre is configured to receive and monitor the operational parameters of the monitor unit to interpret an anomalous environmental condition detected by the monitor unit in light of operational variations which may affect the accuracy of the monitor unit. The remote monitoring centre is also configured to receive and communicate environmental data to the monitor unit to establish the base threshold level used to determine an anomalous environmental condition.
Owner:SINKEVICIUS VYTAS +1
Method and apparatus for controlling wellbore equipment
InactiveUS7264050B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDrilling rodsTelecommunications linkRemote control
The present invention generally provides a method for remotely controlling and / or monitoring at least one parameter of well bore equipment. In one aspect, a method for remotely controlling and / or monitoring at least one parameter of well bore equipment is provided, including: collecting data corresponding to the at least one parameter by a sensor module monitoring the at least one parameter of the well bore equipment; transmitting the collected data to a remote control / monitoring unit via a communication link; analyzing the collected data to determine if the parameter is within predefined limits; if the parameter is not within predefined limits, then transmitting control data from the control / monitoring unit to the well bore equipment for modifying the operation of the well operation equipment so that the parameter will conform to the predefined limits or stopping operation of the wellbore equipment.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
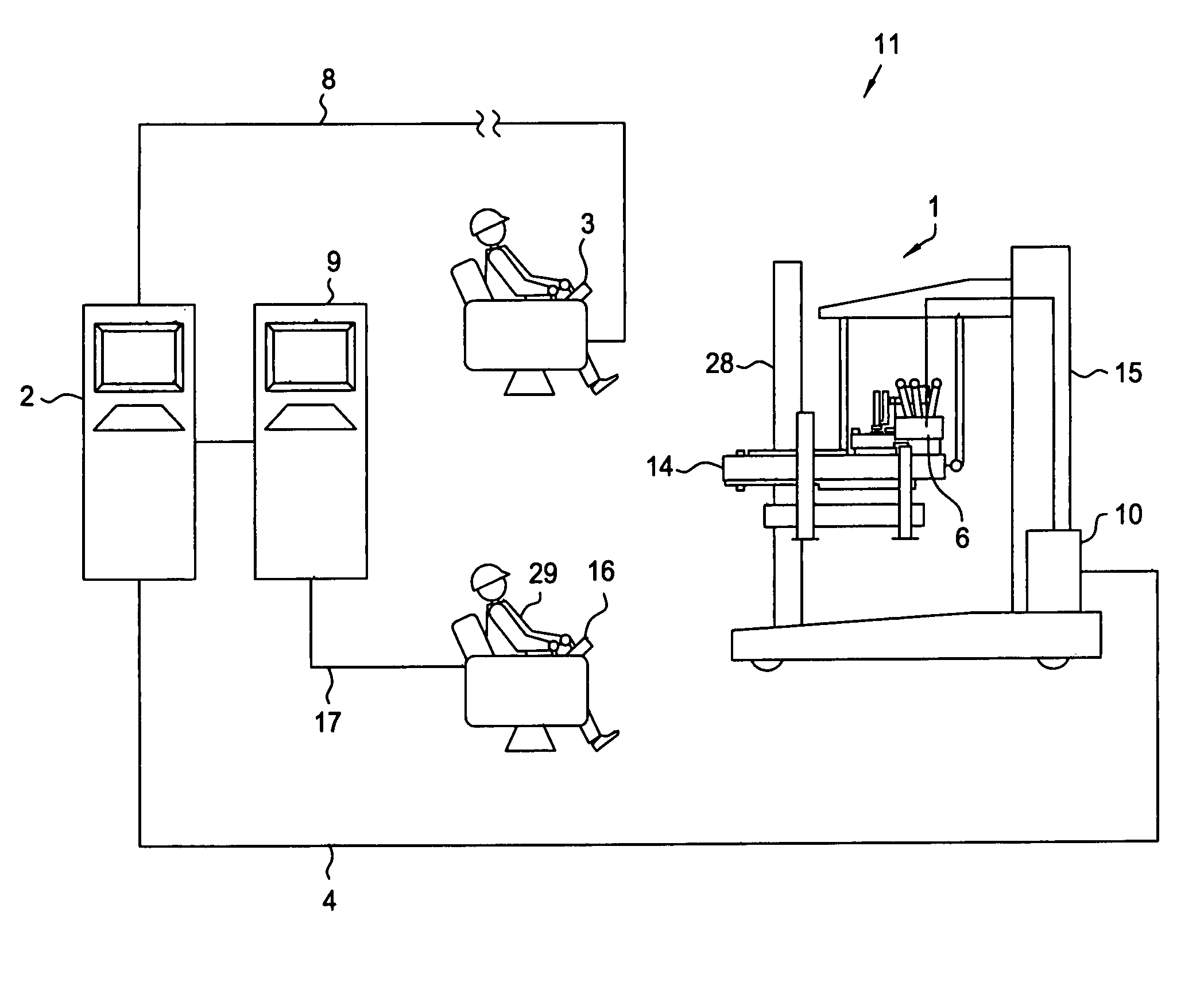
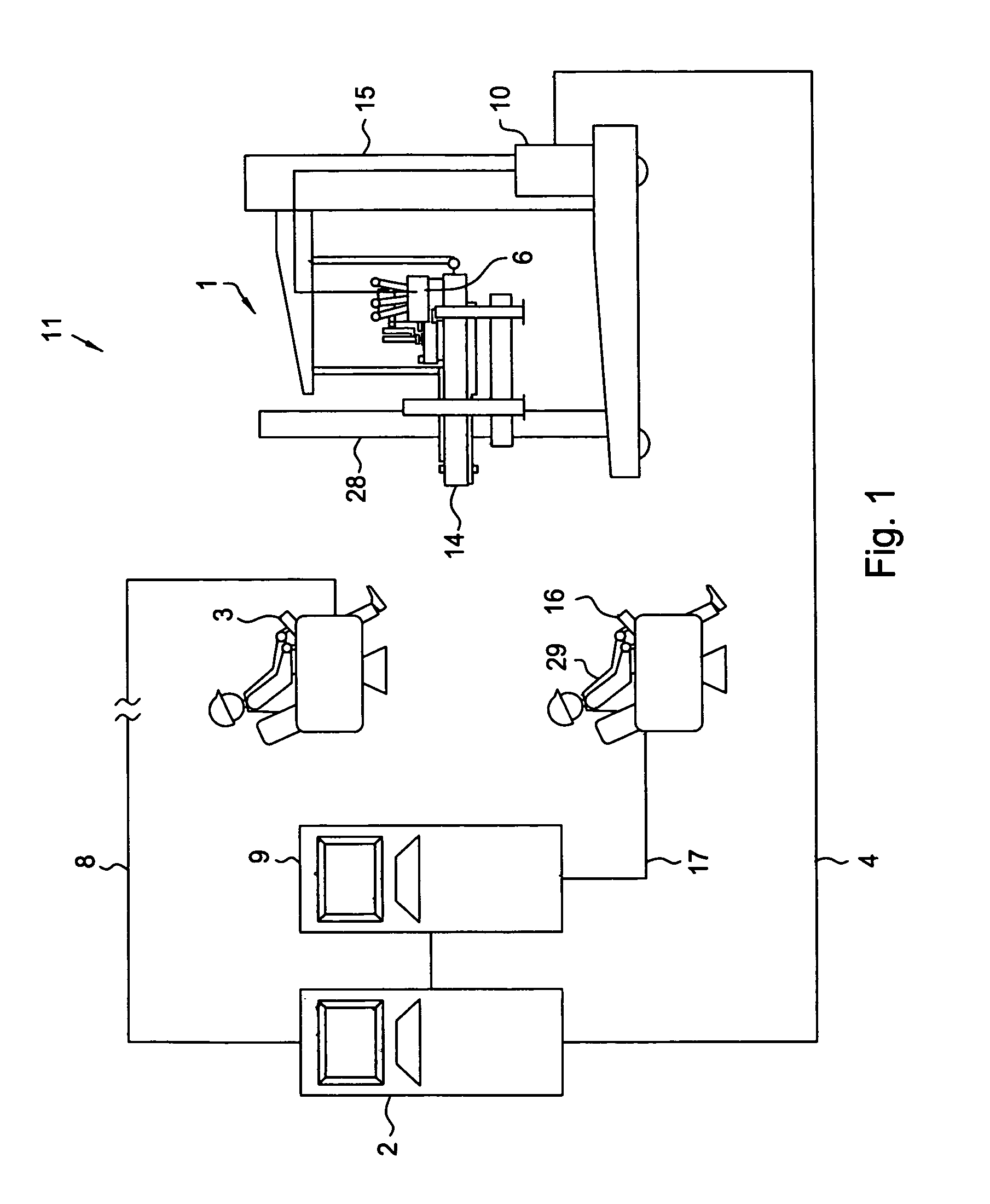
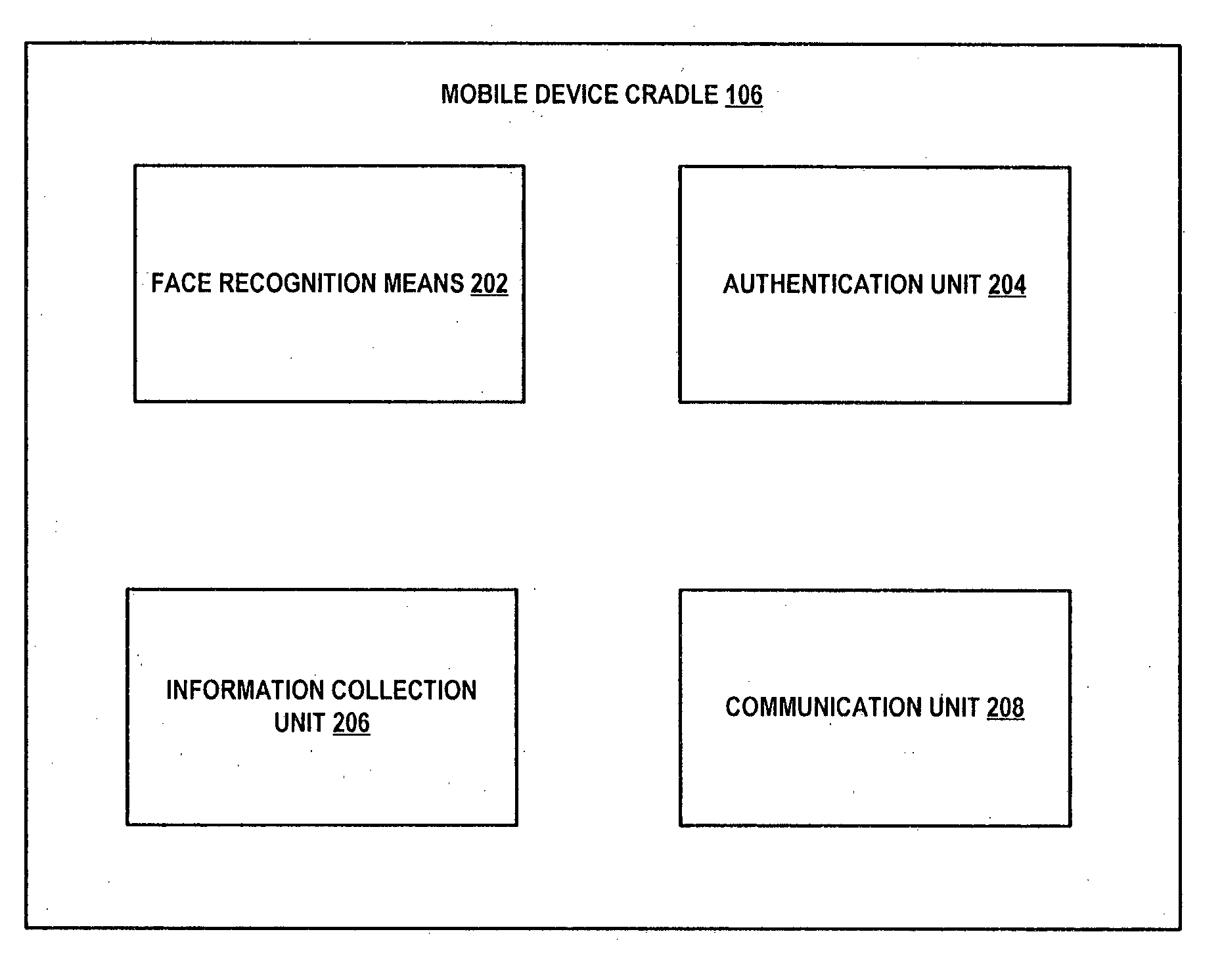
Multi-purpose intelligent cradle for a vehicle
InactiveUS20130005414A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesAnti-theft devicesCommunication unitMobile device
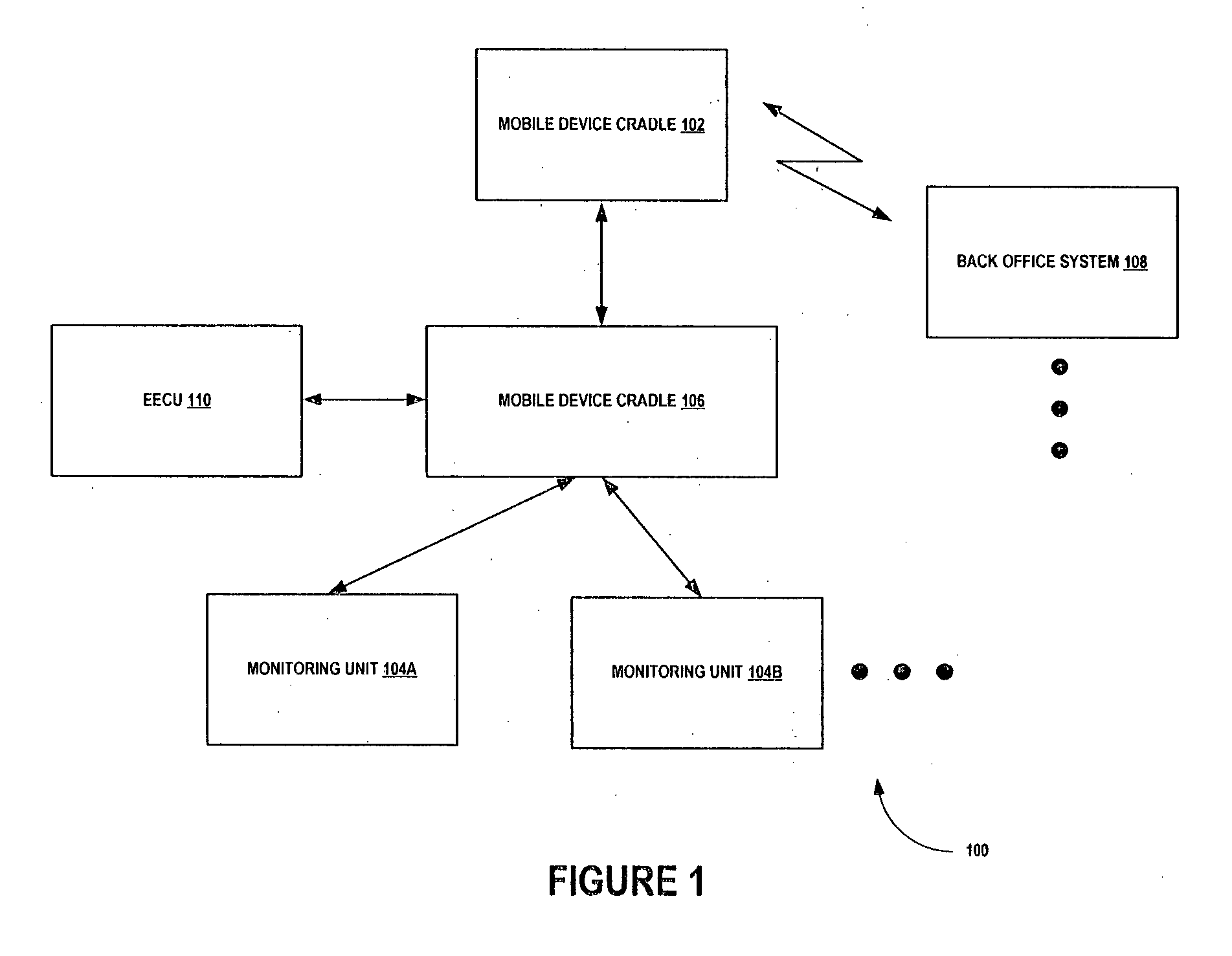
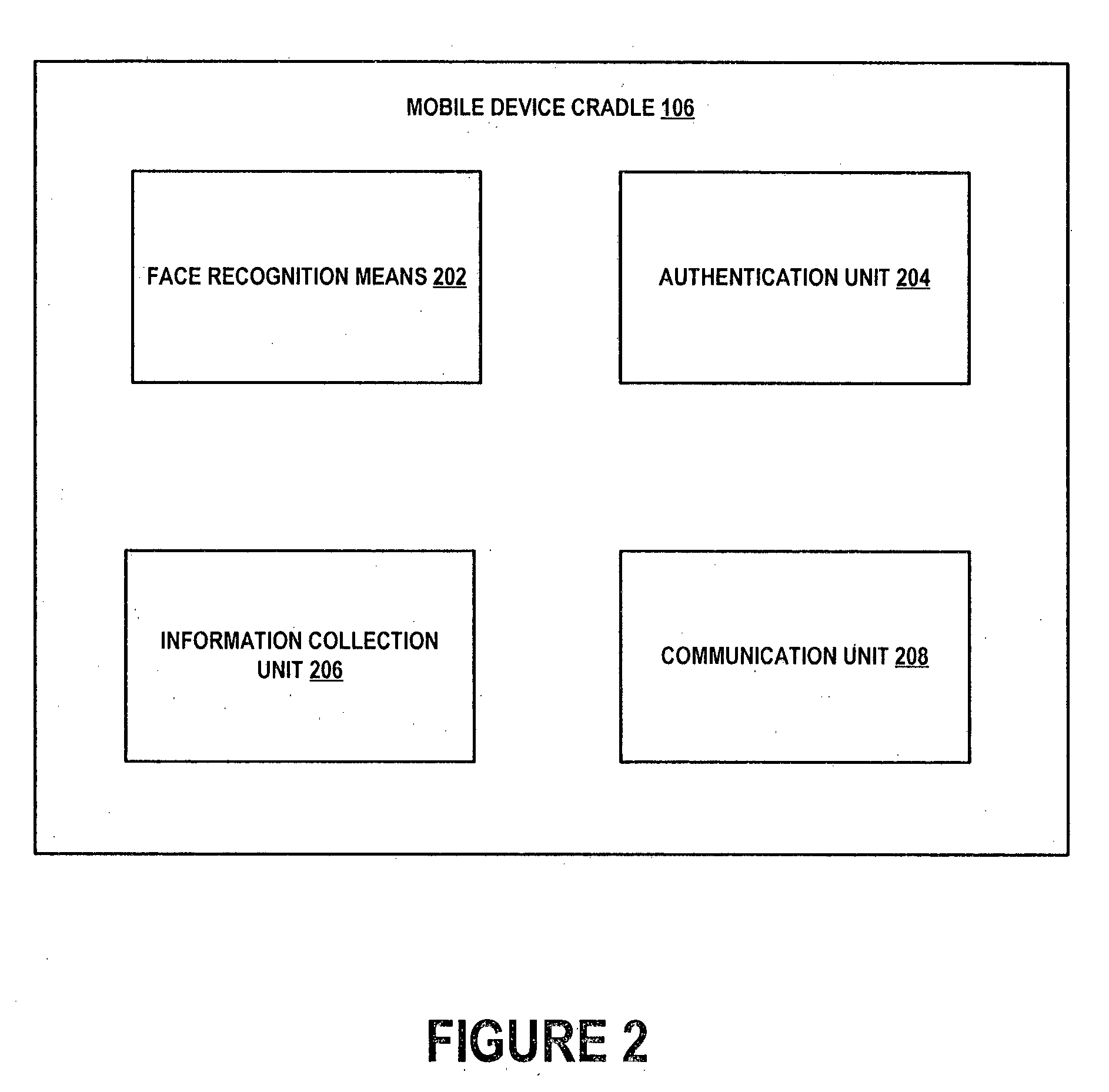
The present invention provides a mobile device cradle for a vehicle. The cradle may include docking members for receiving a mobile device of a driver of the vehicle. The cradle may also include a face recognition means for periodically capturing a face of the driver, environmental conditions, and traffic conditions. Further, the cradle may include an authentication unit for authenticating the mobile device and the face of the driver captured by the face recognition means and for providing an authentication signal for starting the vehicle to an electronic engine control unit (EECU). Furthermore, the cradle may include an information collection unit for collecting dynamic information associated with the driver and the vehicle from monitoring units. Moreover, the cradle may also include a communication unit for communicating the dynamic information to back office system(s) communicatively coupled to the mobile device via a wireless communication network.
Owner:BINDRA GURBRINDER SINGH +3
Building information total management system and method
InactiveCN102063116ARealize integrated all-round managementRealize all-round managementProgramme total factory controlGas supply equipmentPublic infrastructure
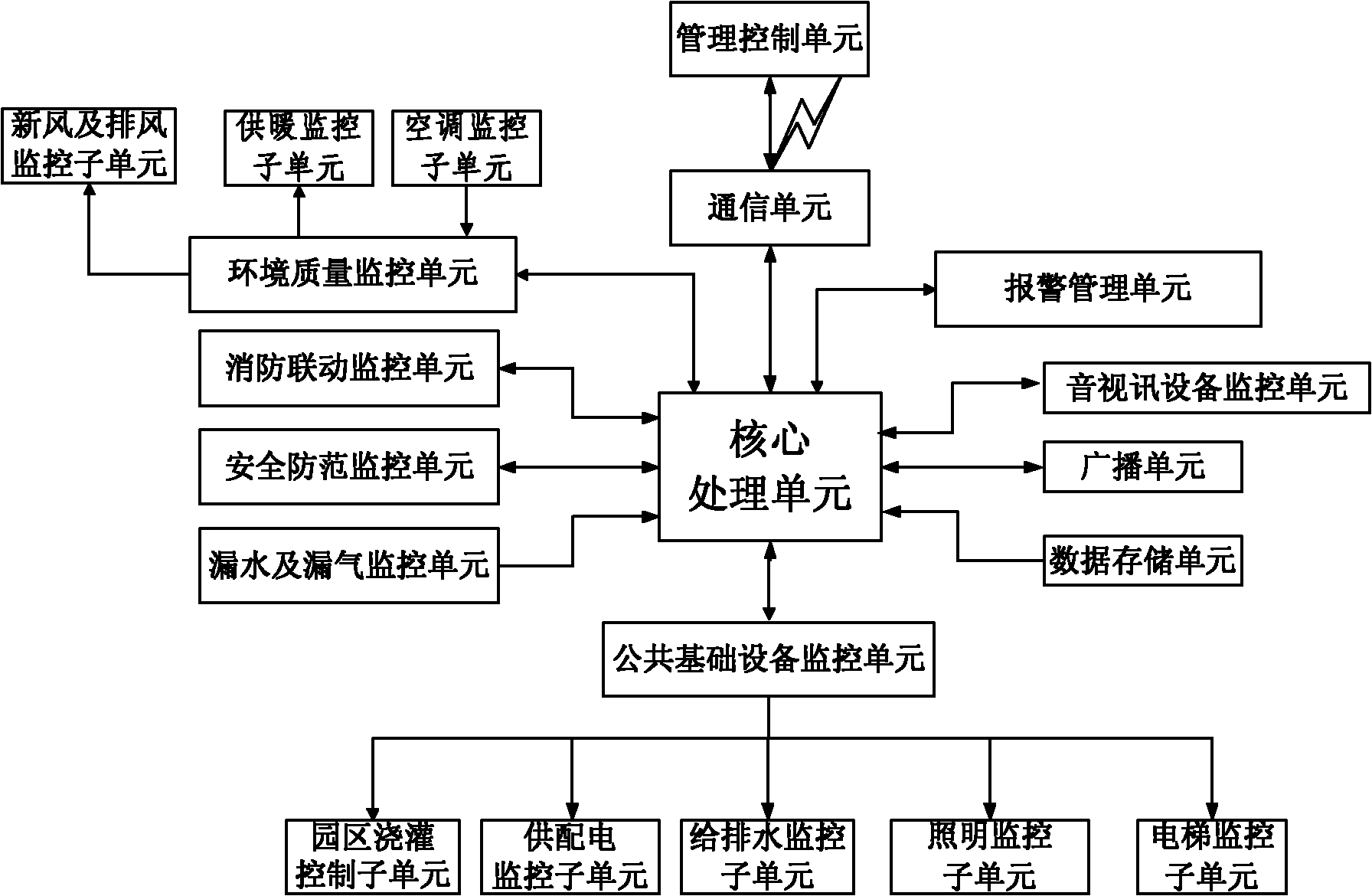
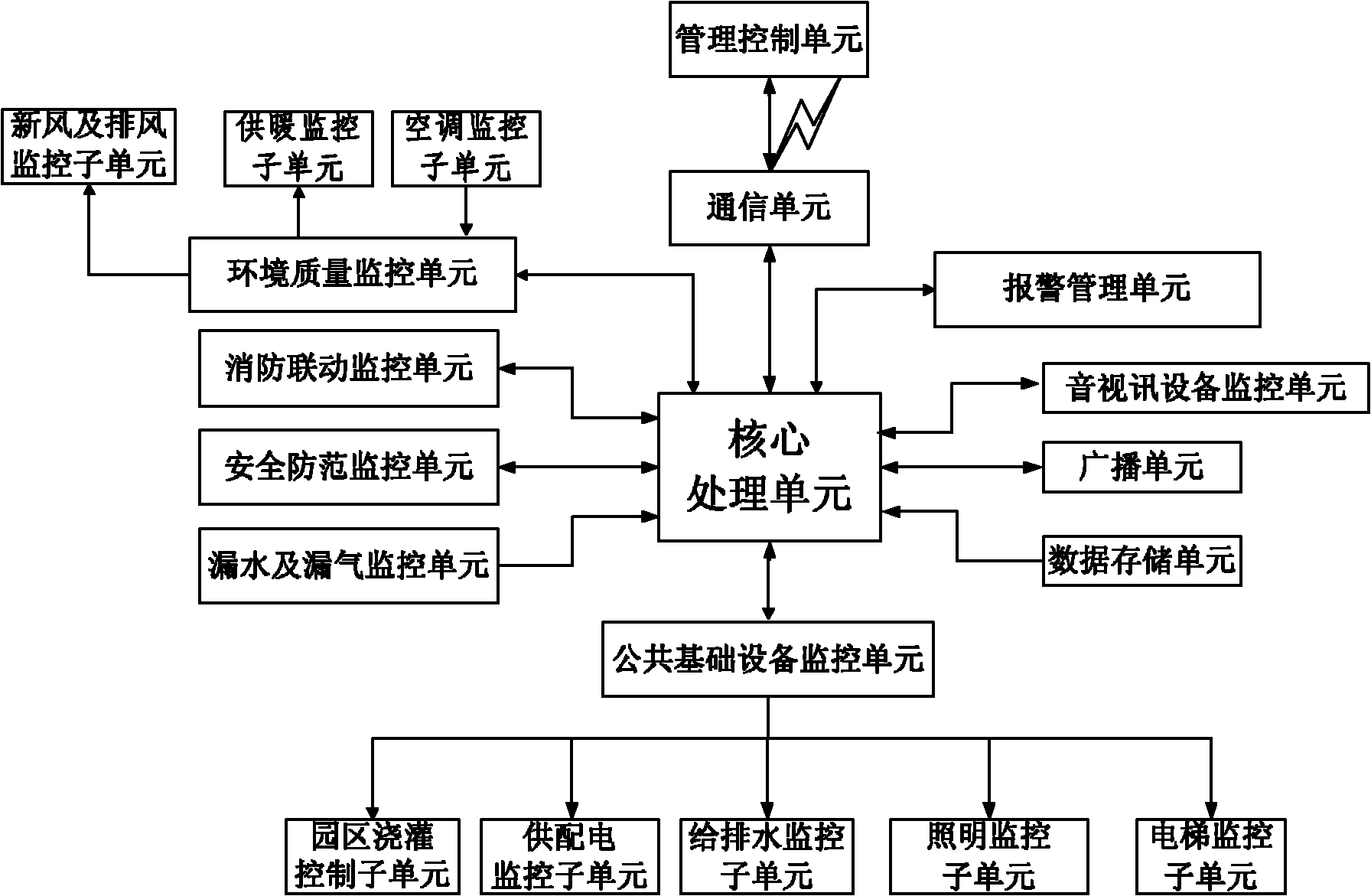
The invention discloses a building information total management system and method. The system comprises a fire control linkage monitoring unit, a public infrastructure monitoring unit, a security monitoring unit, a water and gas leakage monitoring unit, an environment quality monitoring unit, a management controlling unit, a core processing unit and an alarm managing unit, wherein the fire control linkage monitoring unit is used for obtaining smoke and fire detection information; the public infrastructure monitoring unit is used for obtaining working state information of public infrastructures; the security monitoring unit is used for obtaining monitoring data of security monitoring equipment; the water and gas leakage monitoring unit is used for obtaining detection information for representing water / gas leakage of water / gas supply equipment; the environment quality monitoring unit is used for obtaining environment quality detection information; the management monitoring unit is used for receiving a control command of a user and sending the control command to the core processing unit; the core processing unit is used for forwarding the detection information of the monitoring / detection unit and alarm information to the management monitoring unit and forwarding the control command of the management controlling unit to an appointed monitoring / detecting unit to control corresponding building equipment to operate; and the alarm managing unit is used for selecting an alarm mode according to the event grade of the alarm information.
Owner:海南义利达高新技术实业有限公司
Remote health monitoring system
InactiveUS6171237B2Easy to collectGood adhesionSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEngineeringEmergency medicine
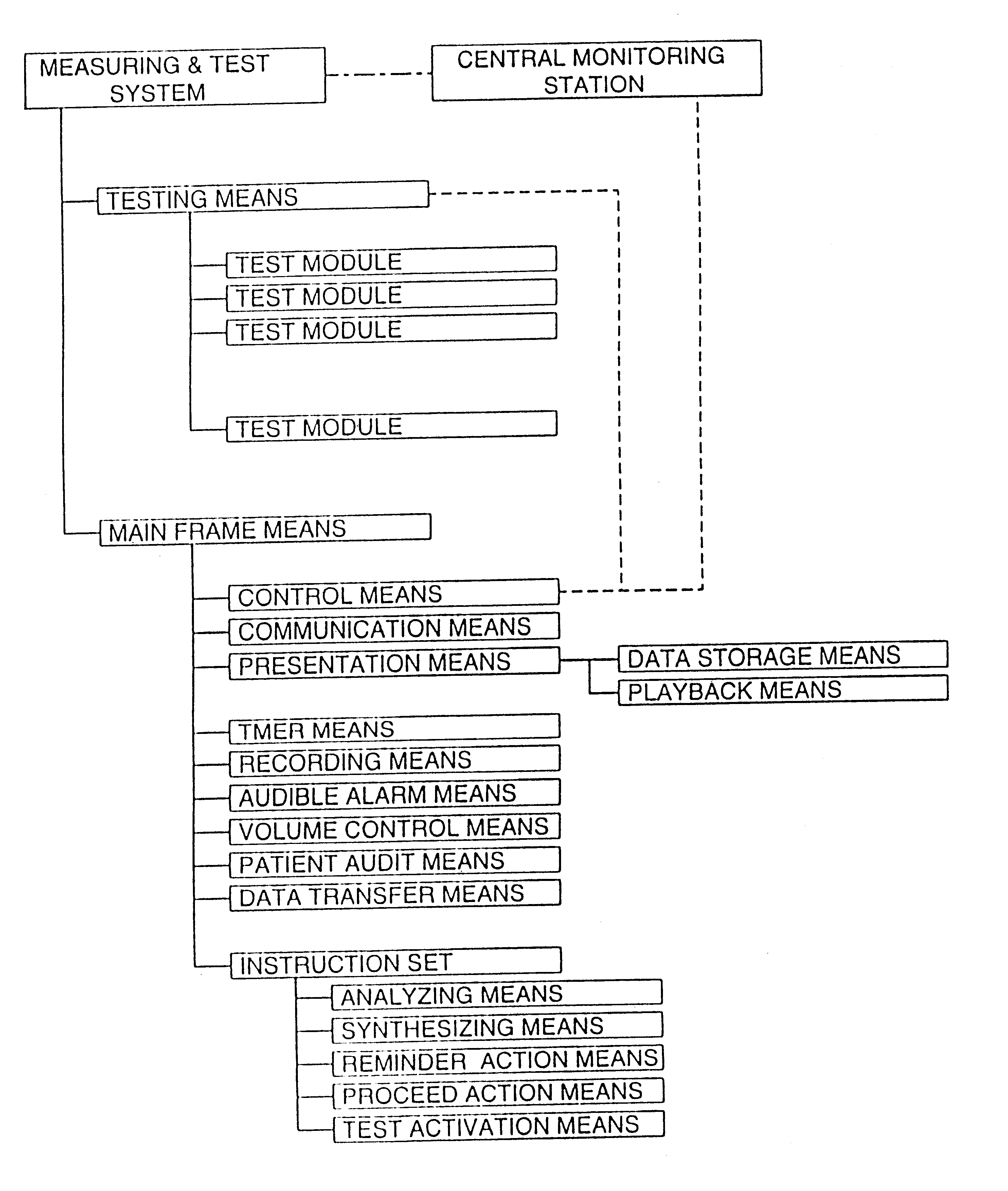
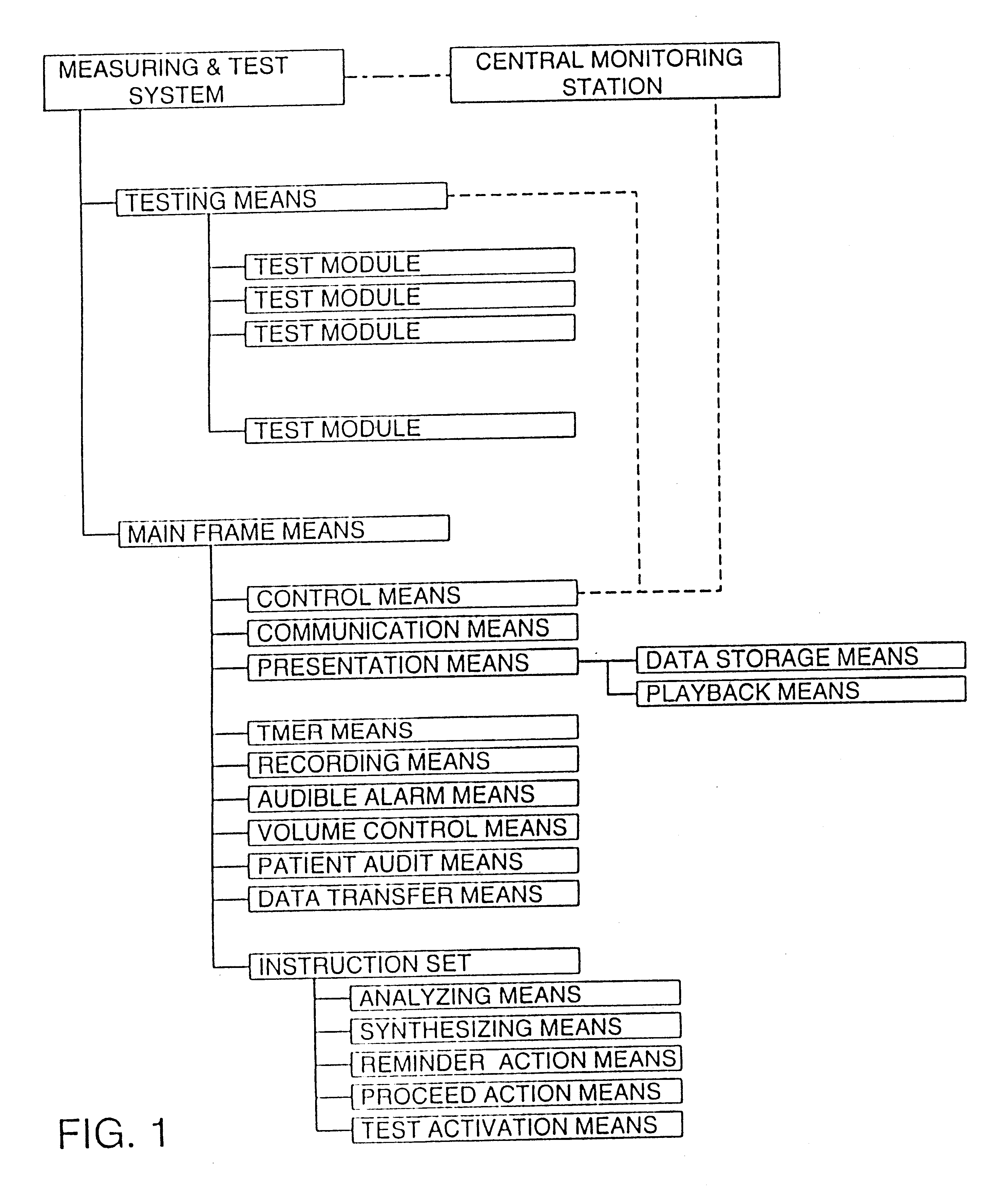
A computer control system operates with an instruction set to provide automated administration of health care to a patient. In a preferred embodiment of the invention a central monitoring station receives data from a plurality of remote testing units. Each of the testing units is custom configured for a particular patient and is made to provide optimal care for that individual alone. Similarly one monitoring unit may serve multiple patients and transmit the data to a central monitoring computer via the telephone lines. Medical procedures are then administered to the patient and results taken as data. The data is made available to the central monitor so that proper medical interpretation is enabled. A number of novel steps in the programming of the system are taken to assure that the right patient is being monitored, that the patient is being tested properly and that the system is being monitored appropriately.
Owner:AVITALL BOAZ +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com