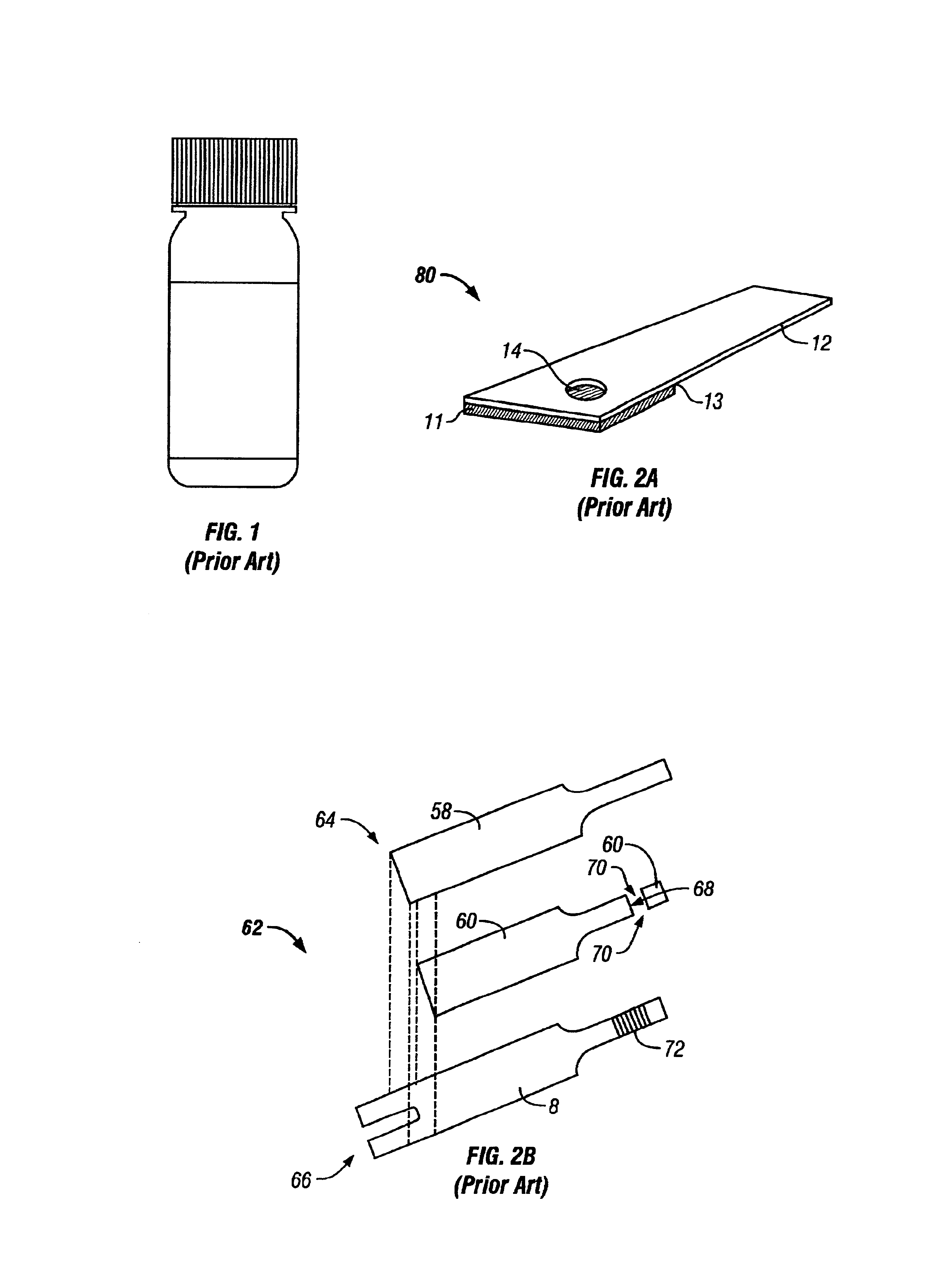
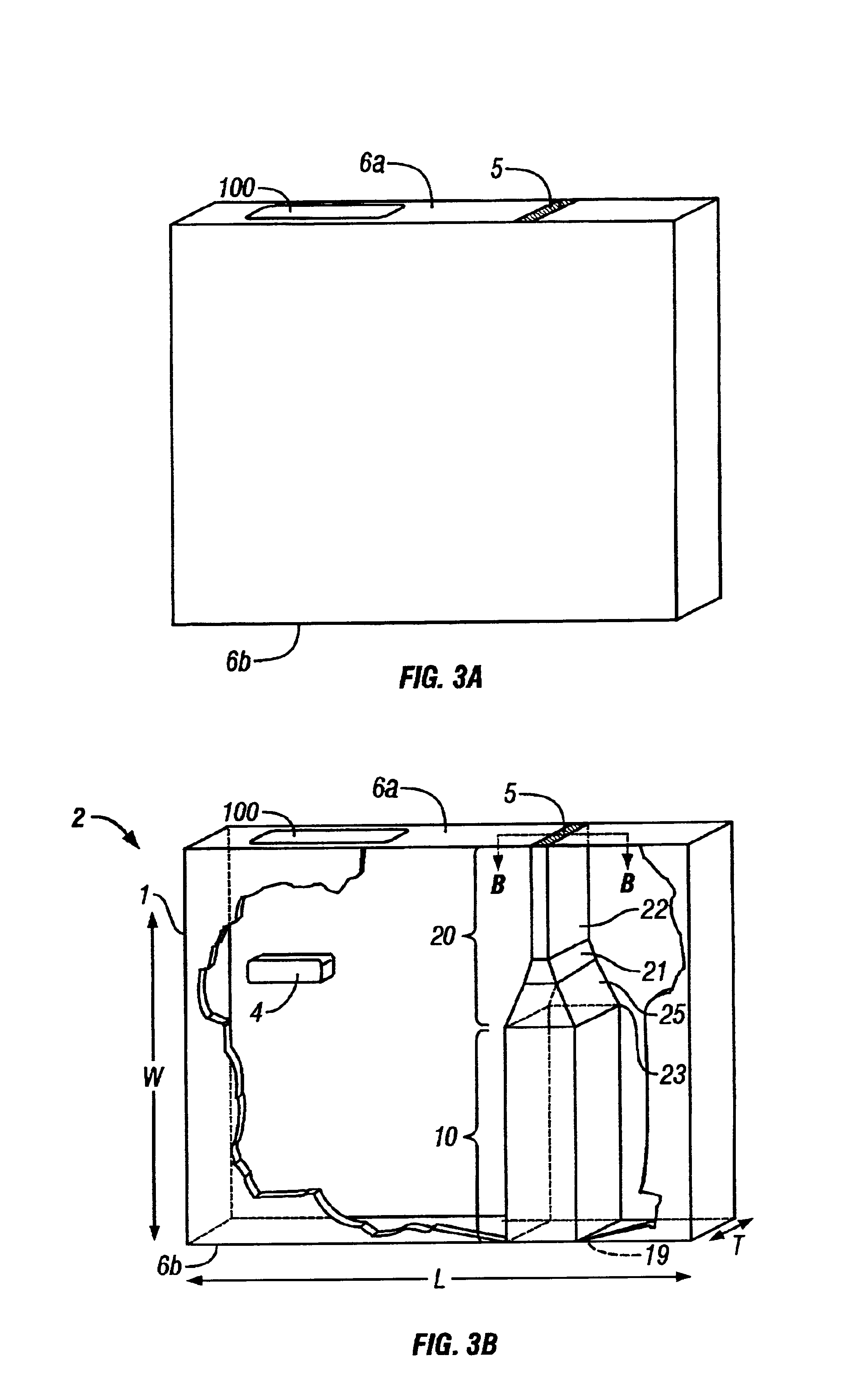
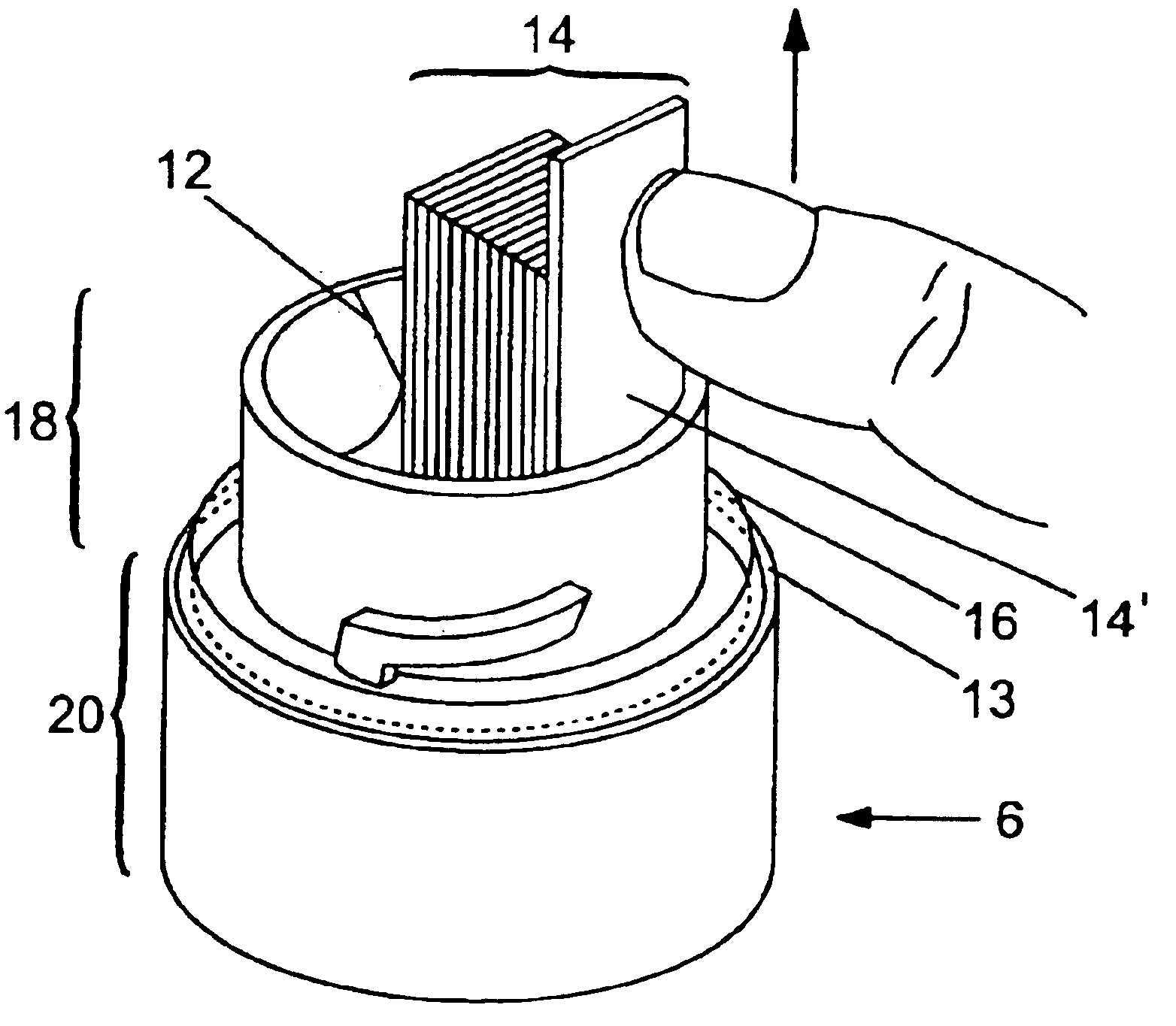
Patents
Literature
374 results about "Test Strip (device)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
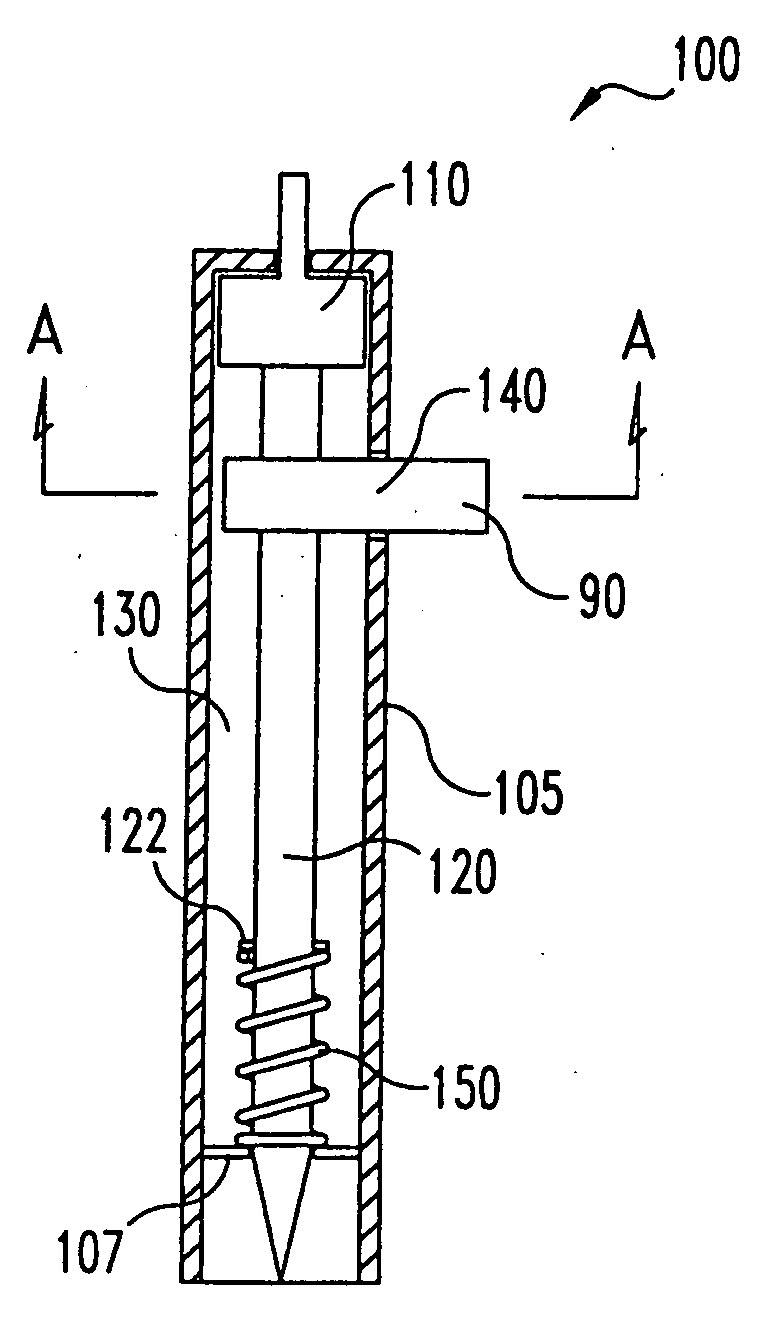
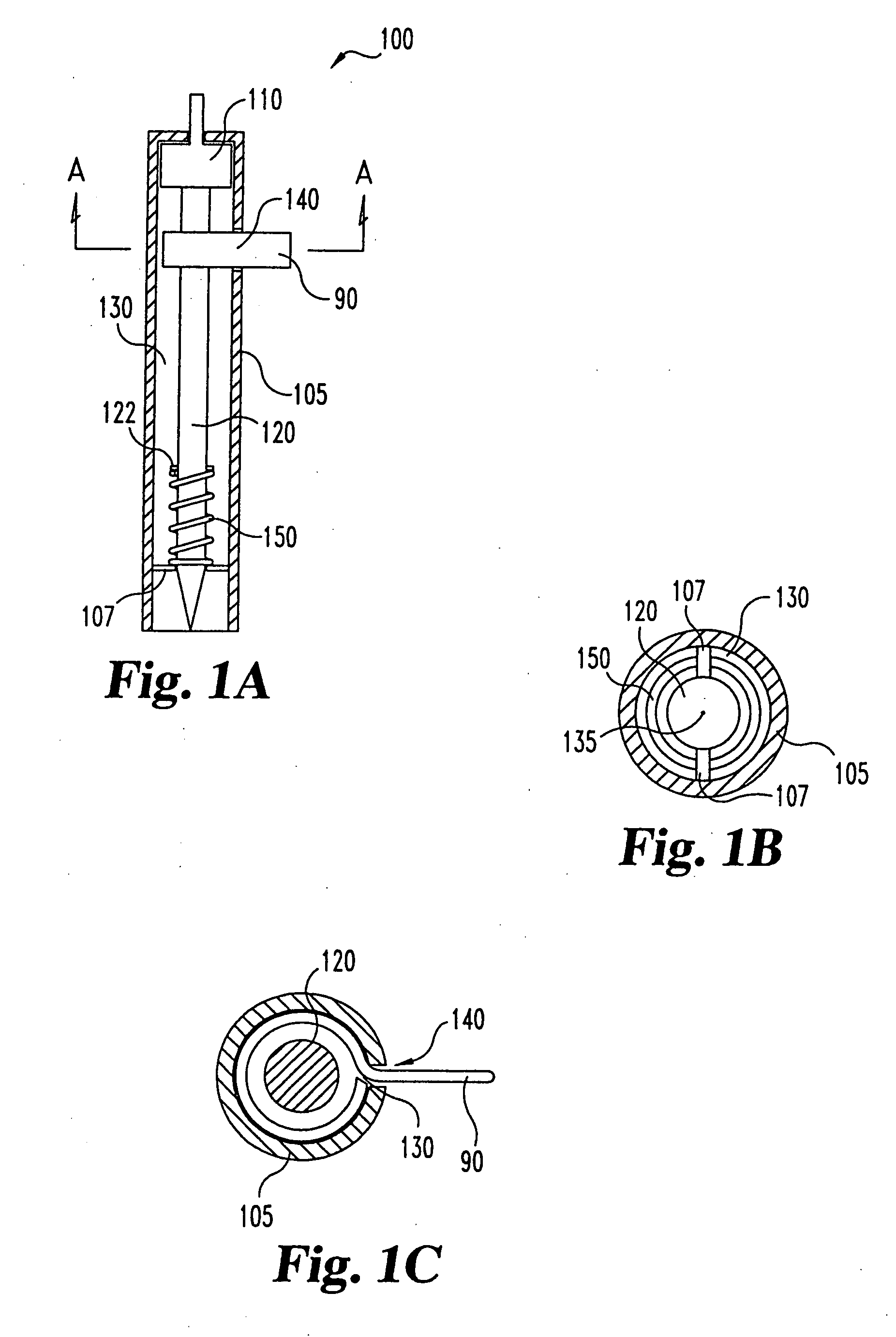
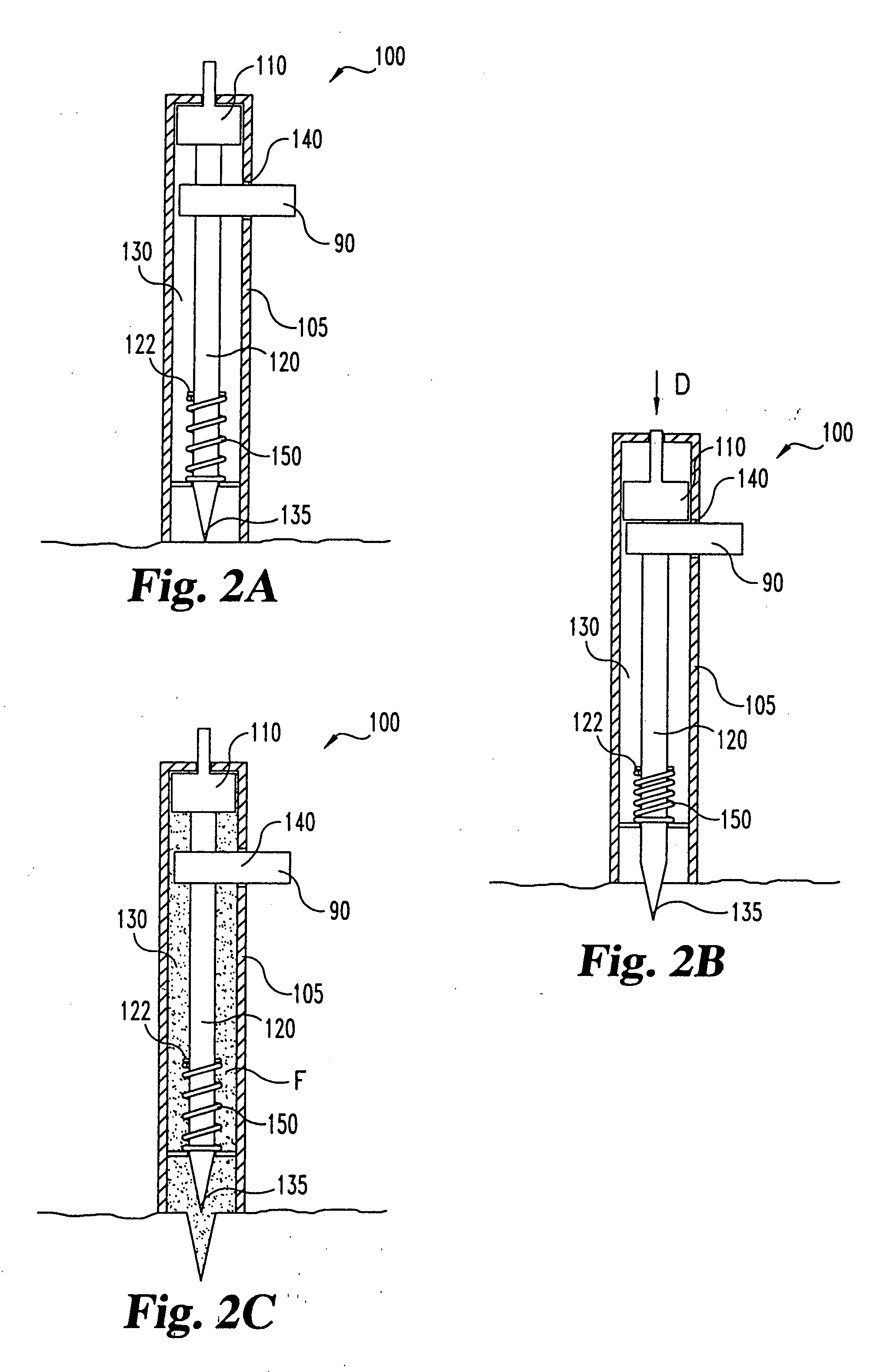
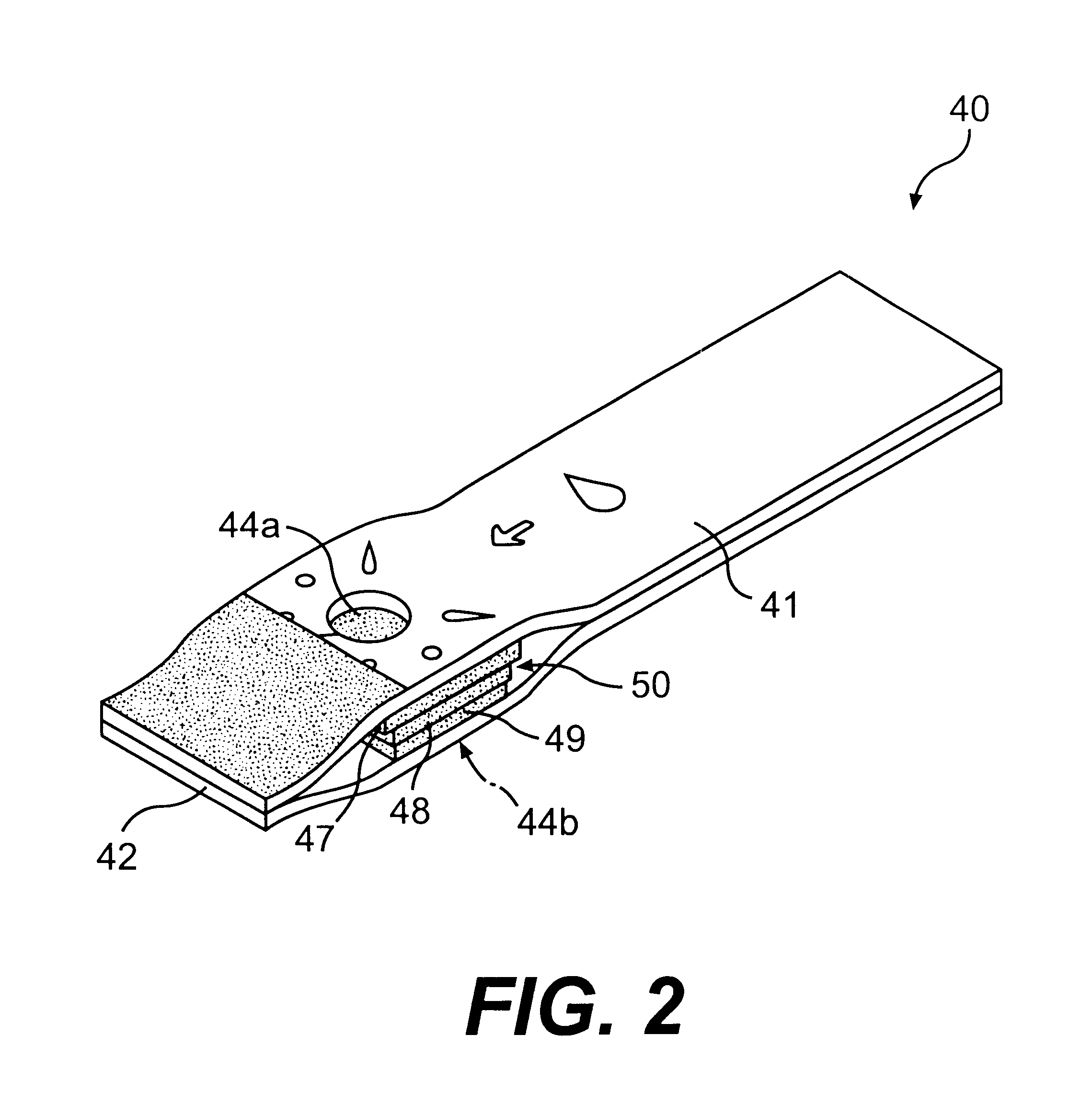
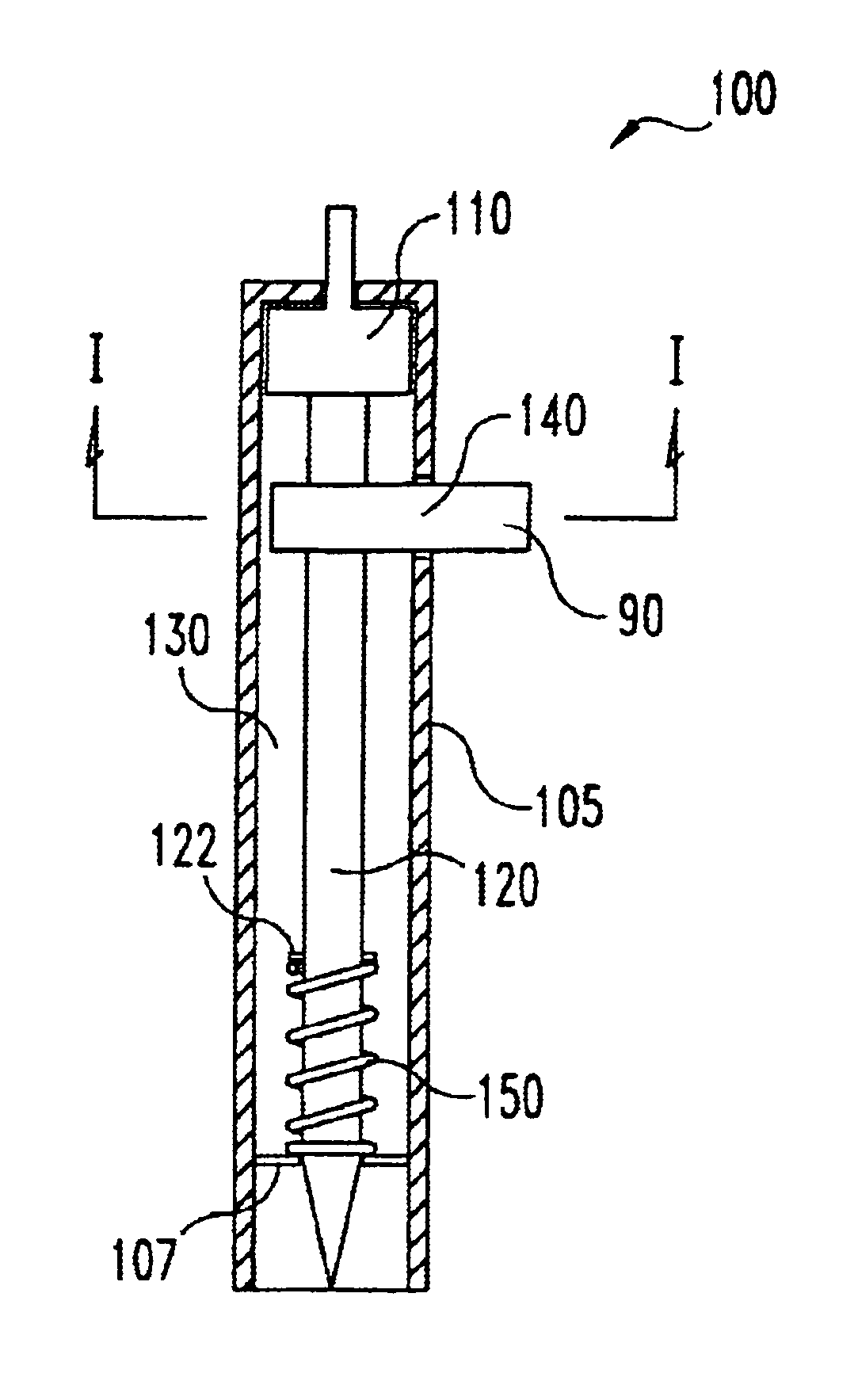
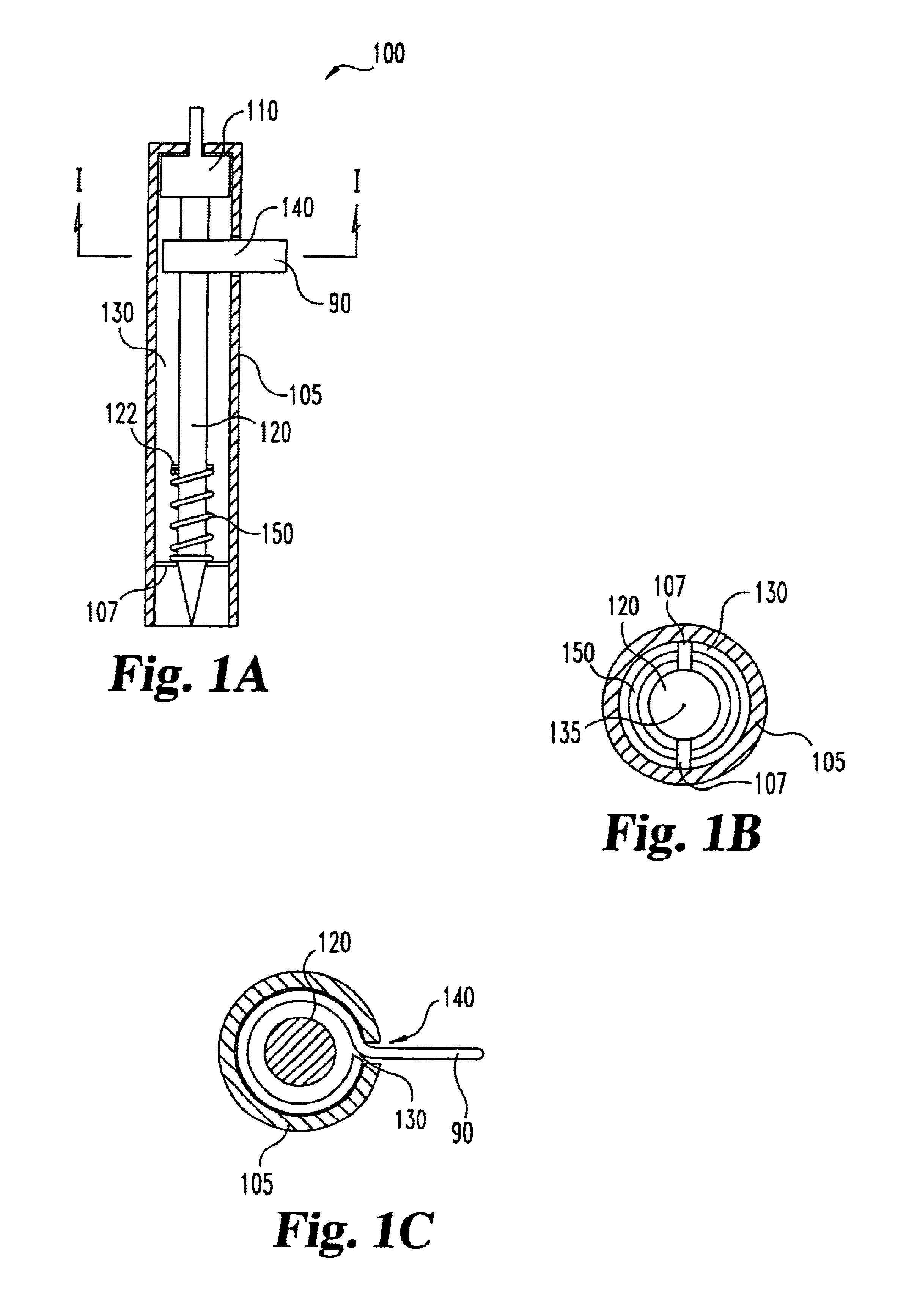
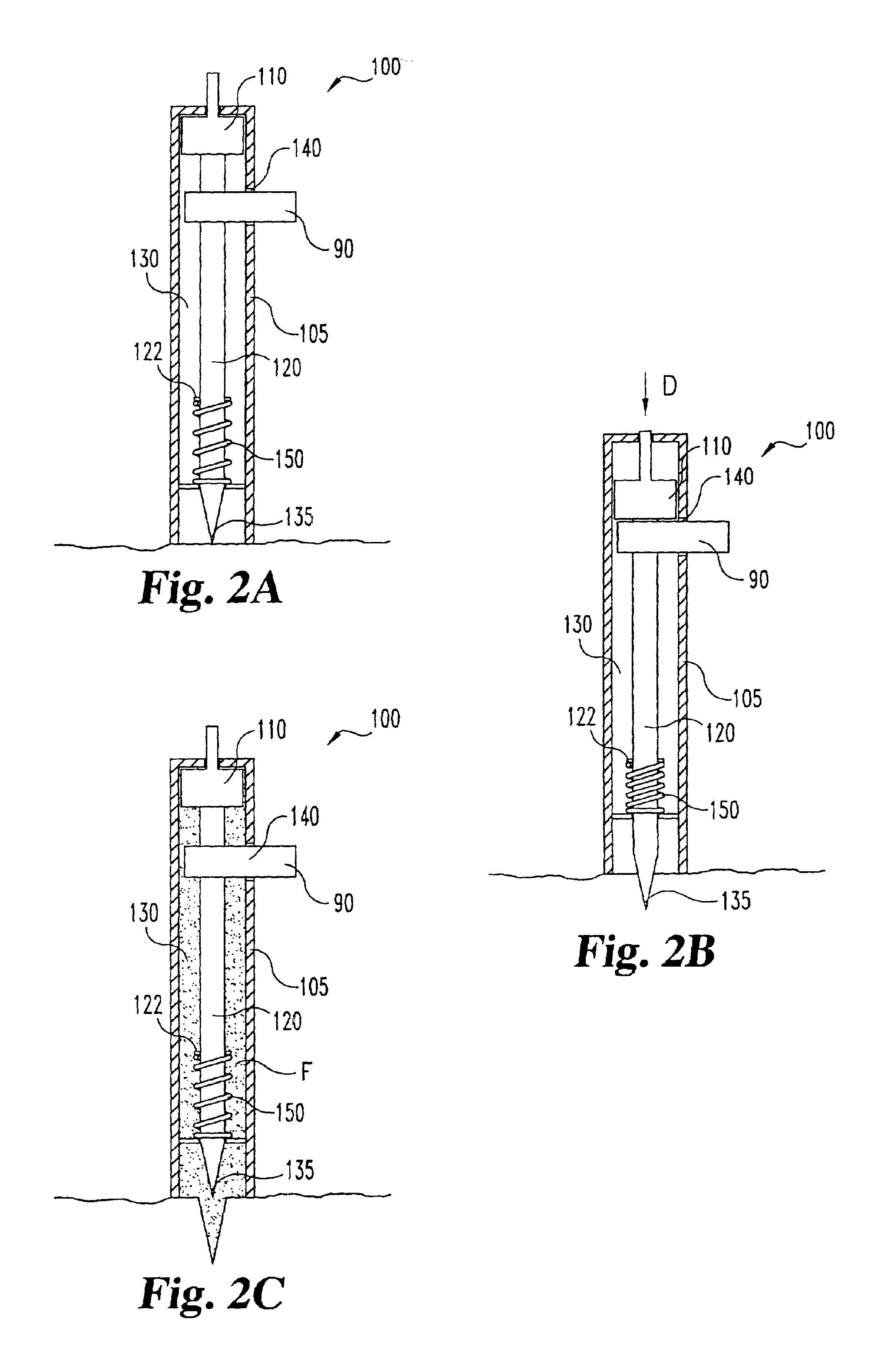
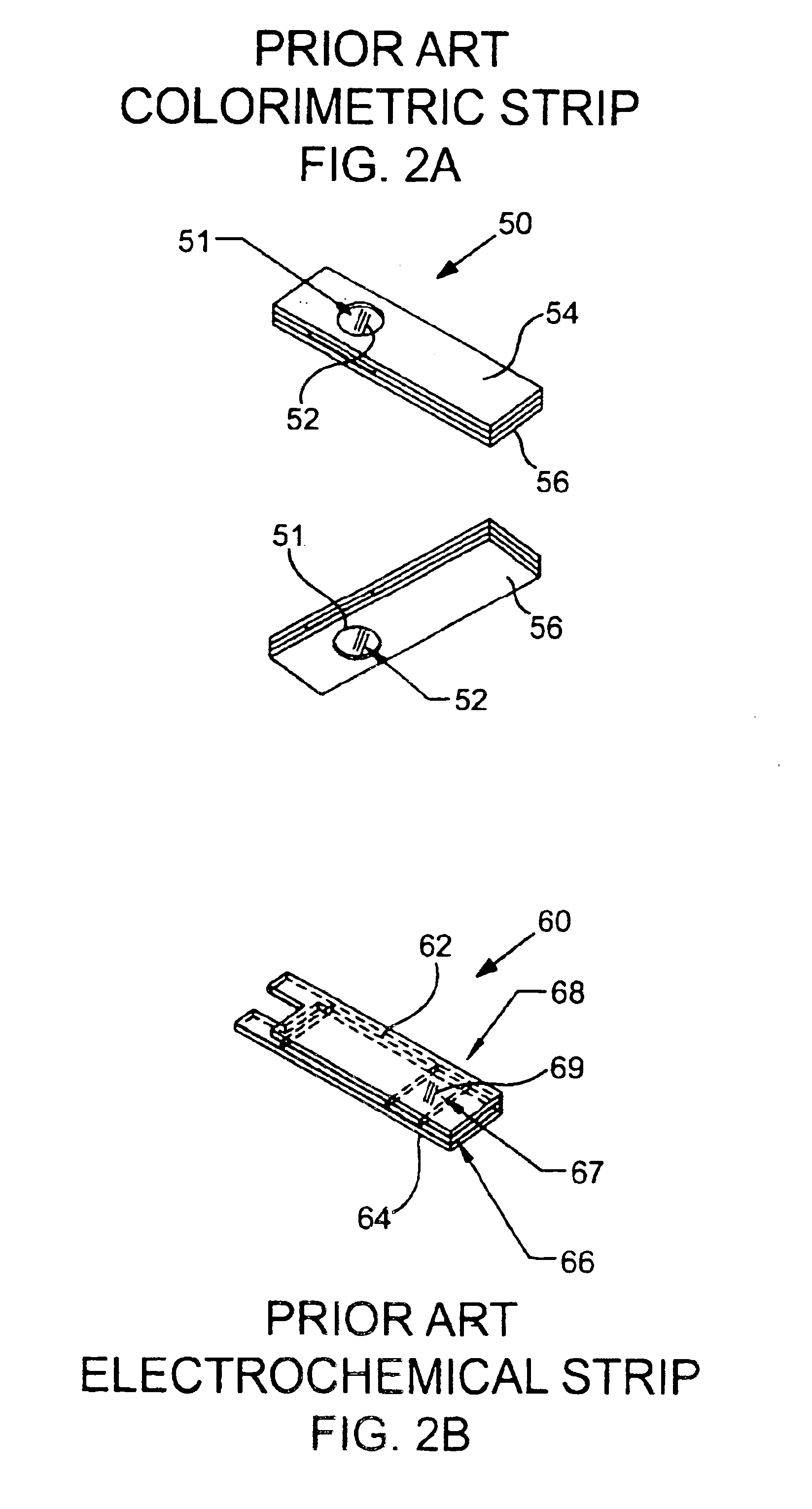
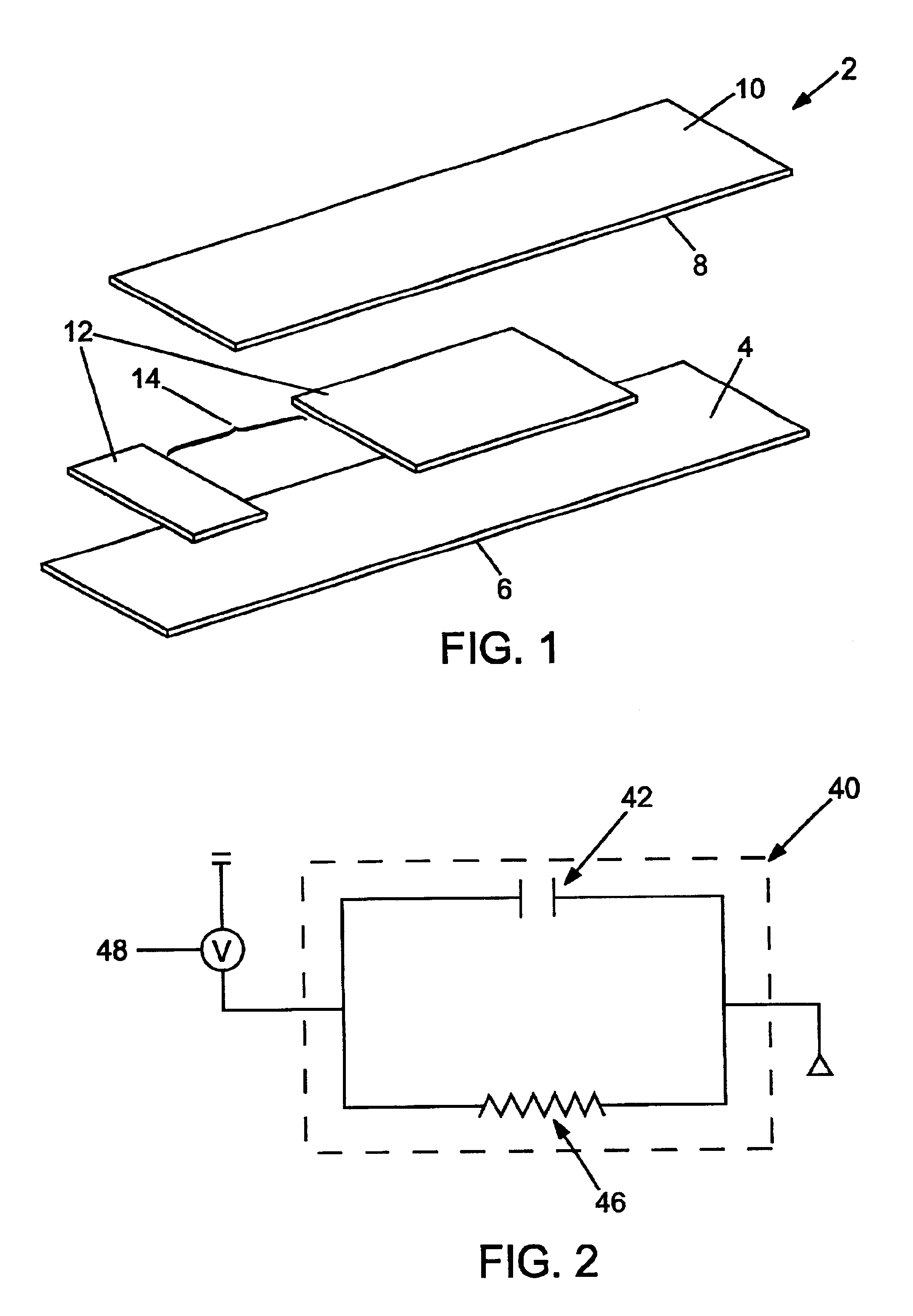
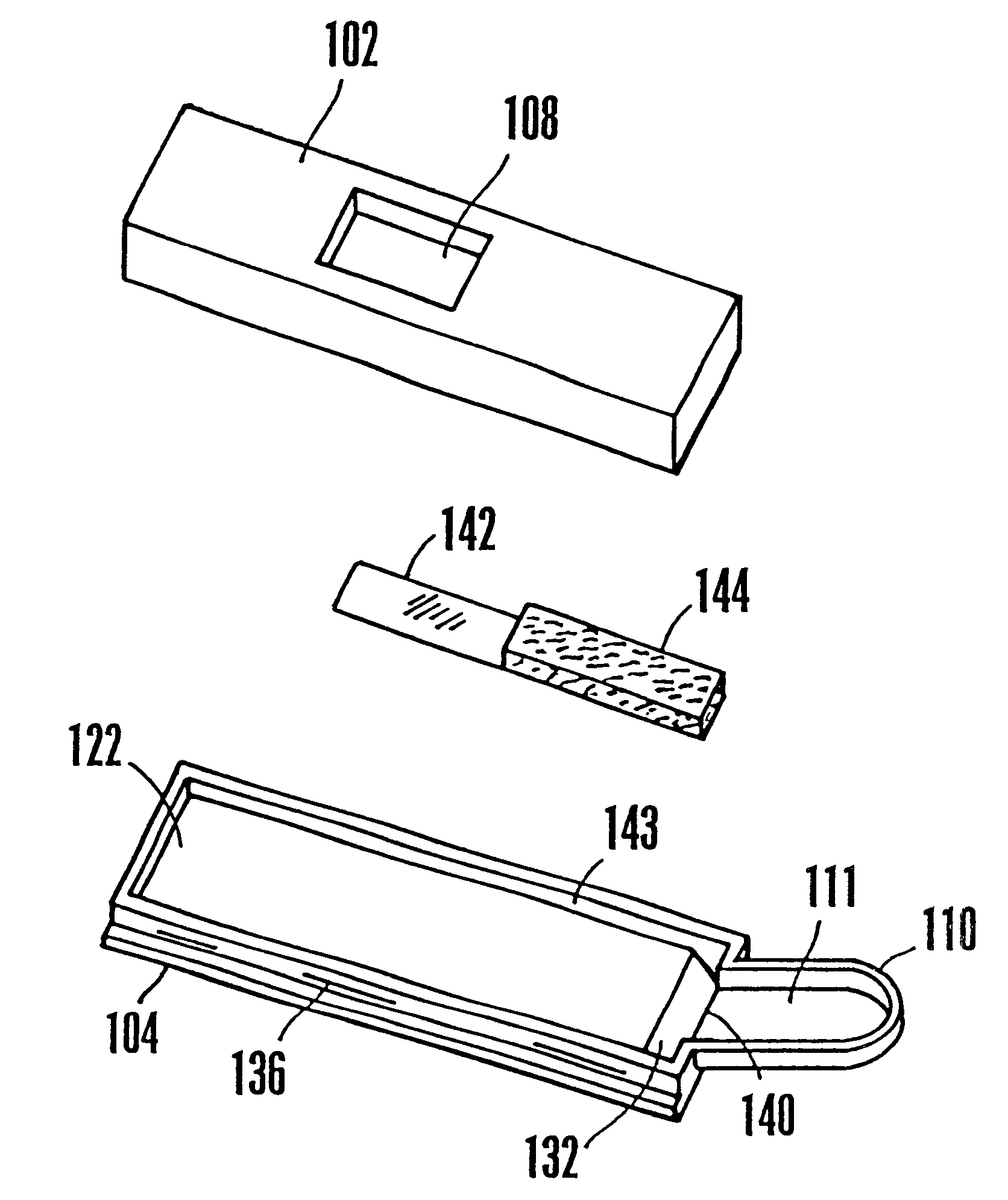
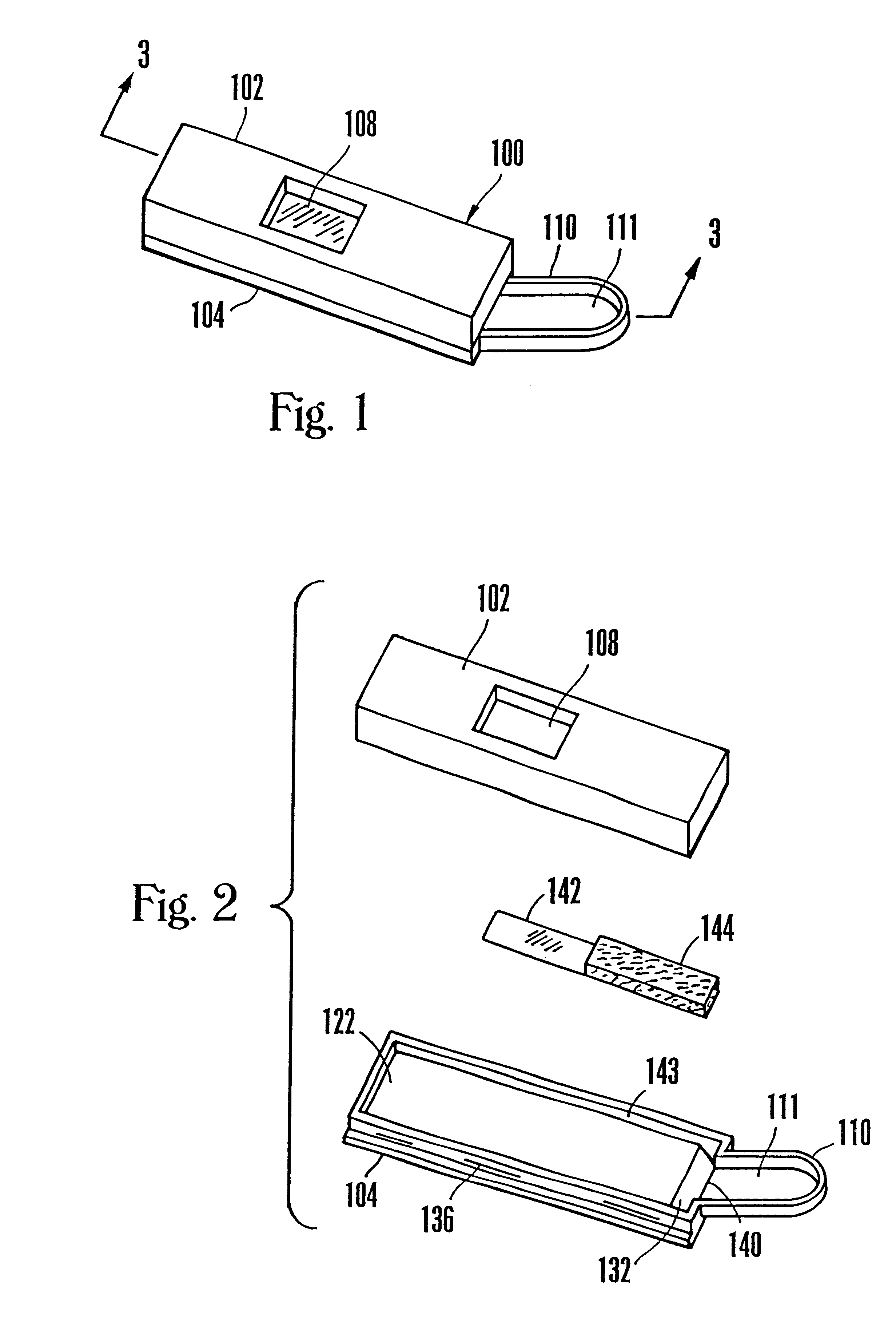
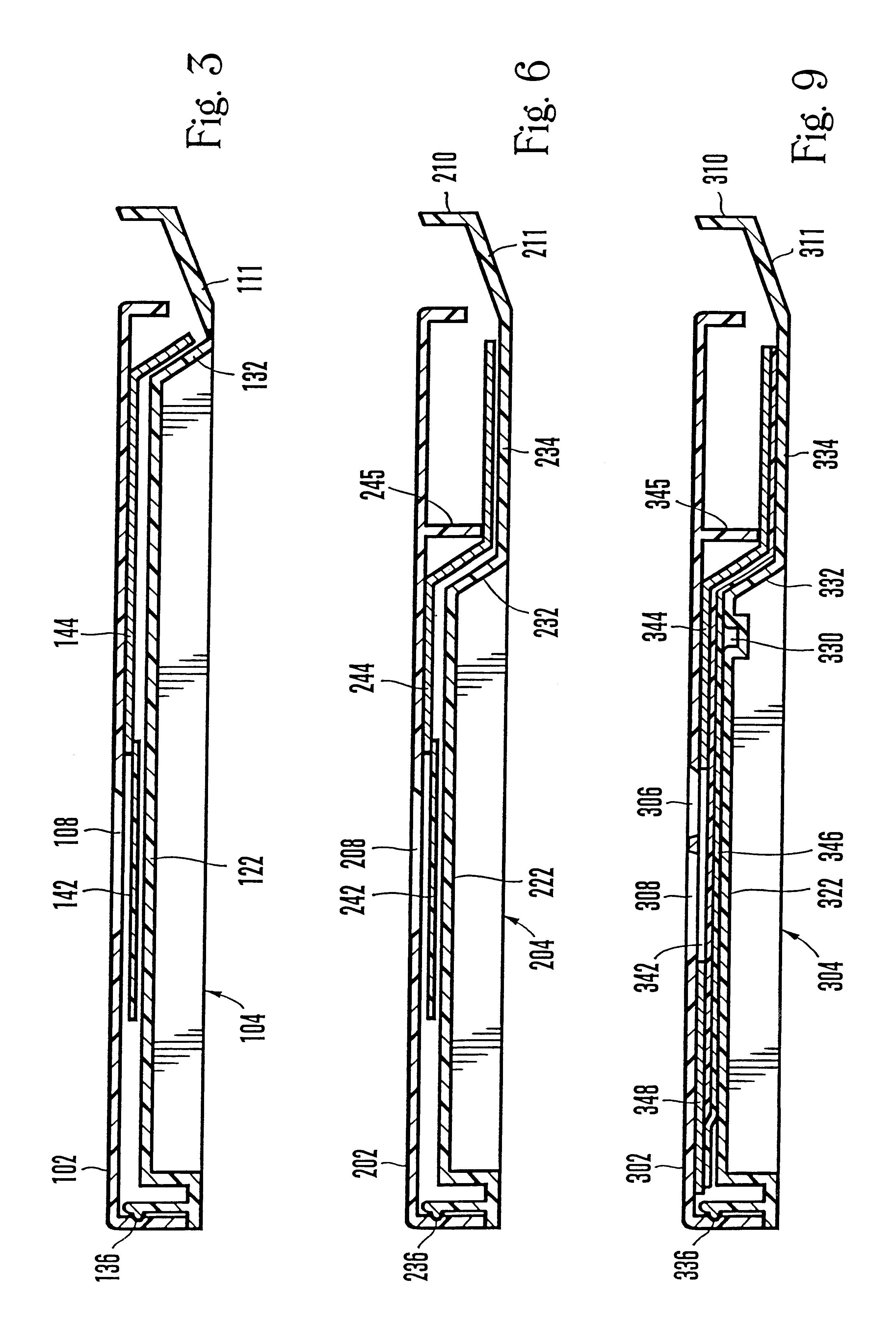
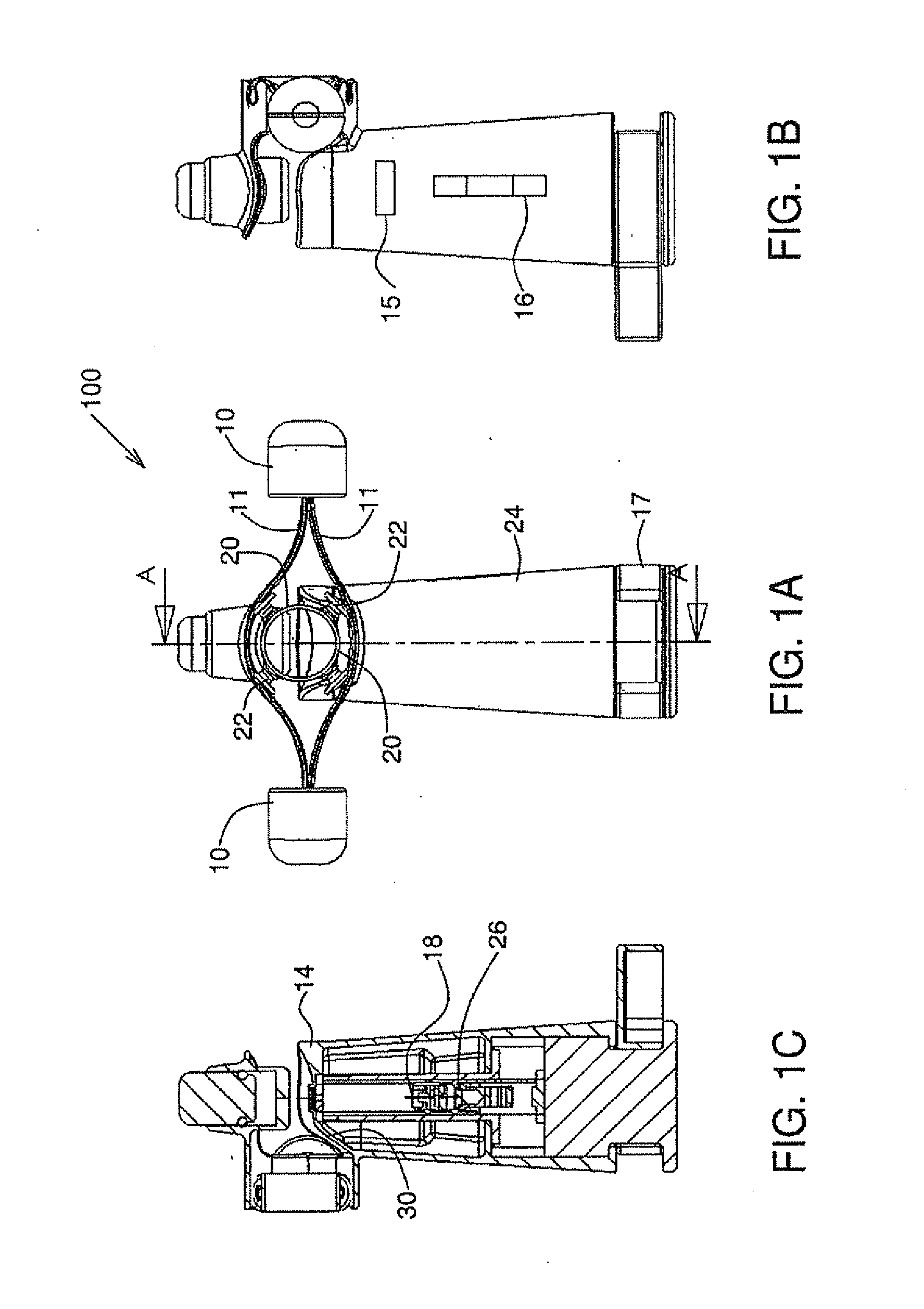
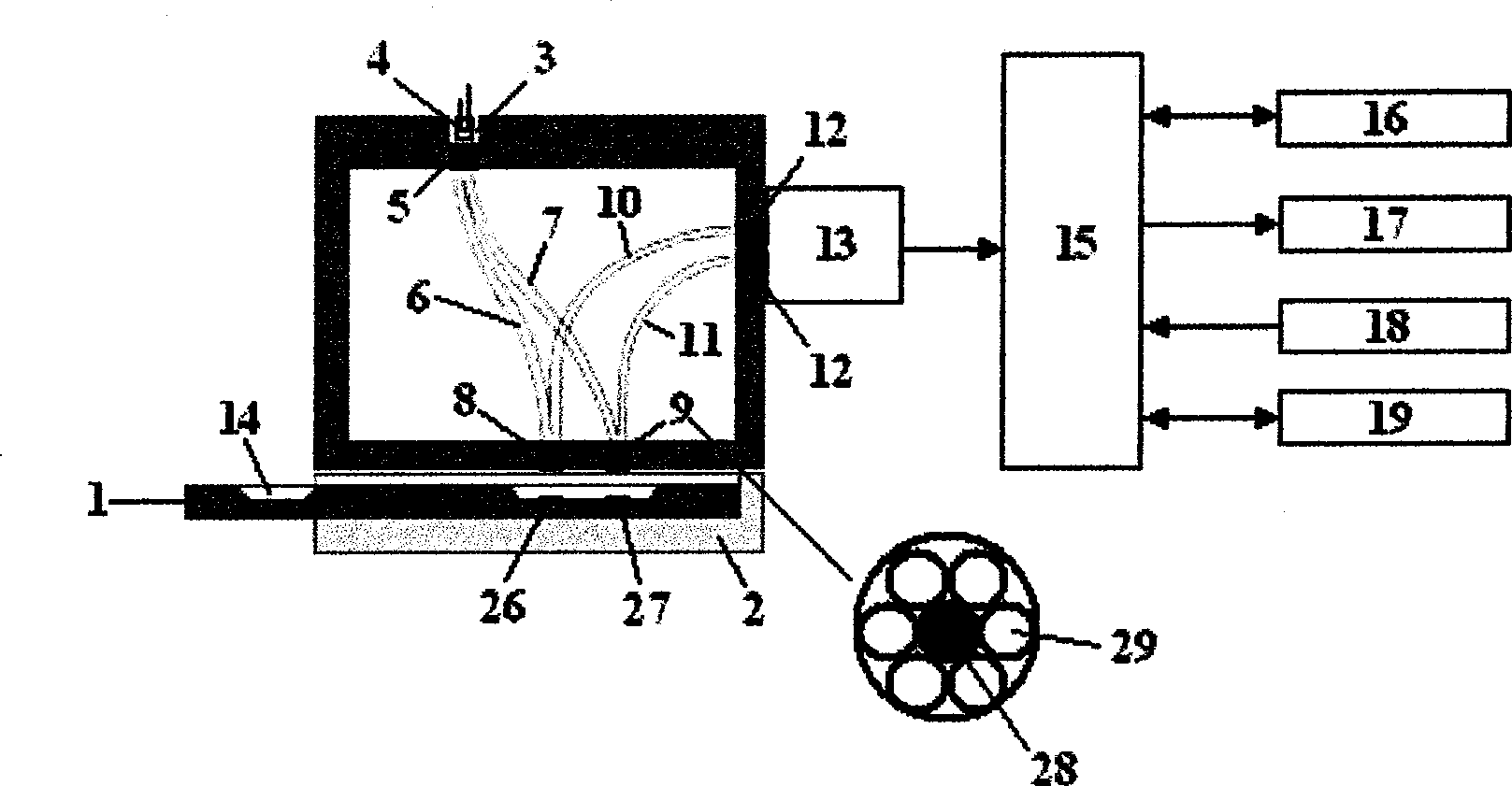
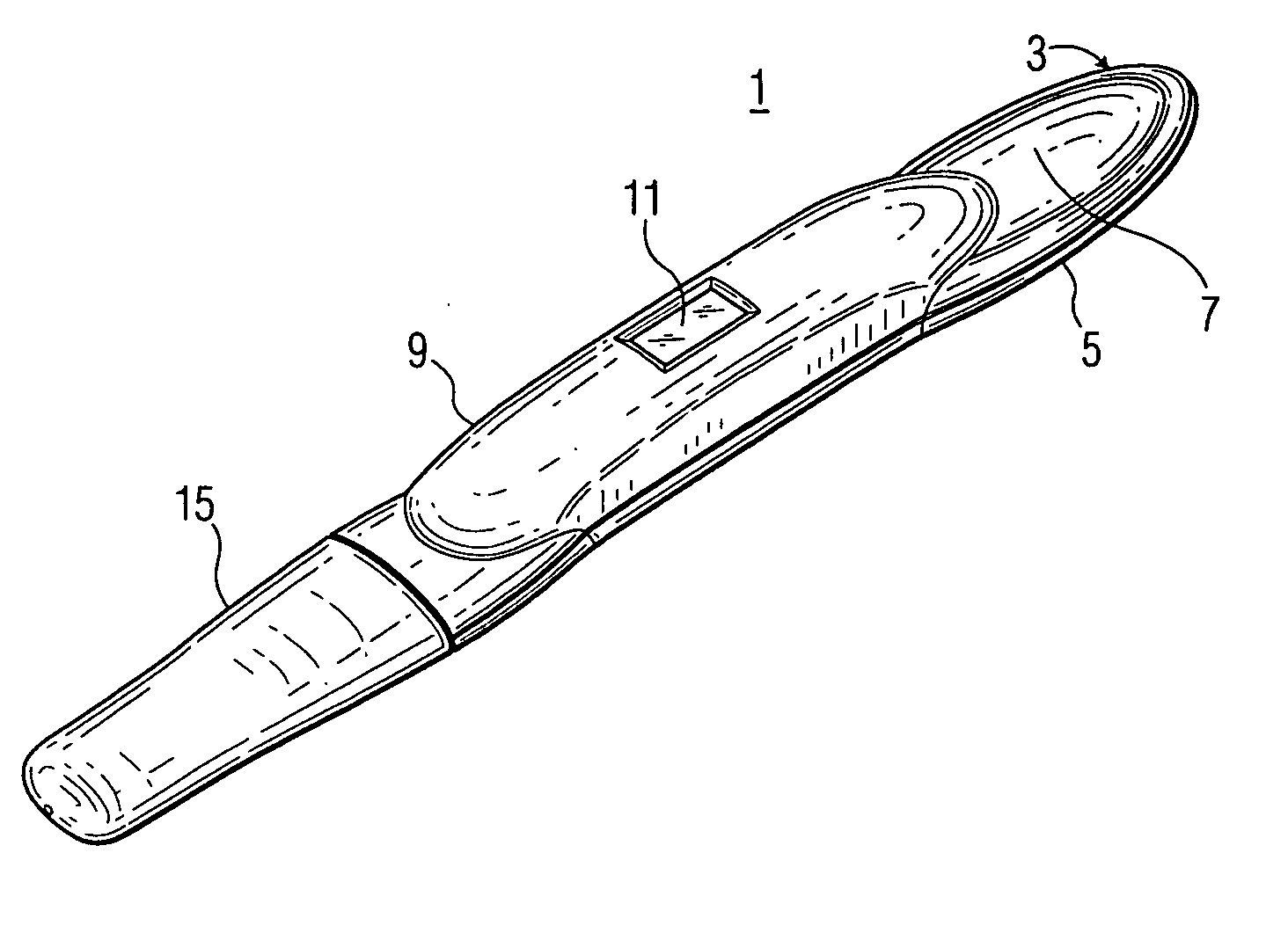
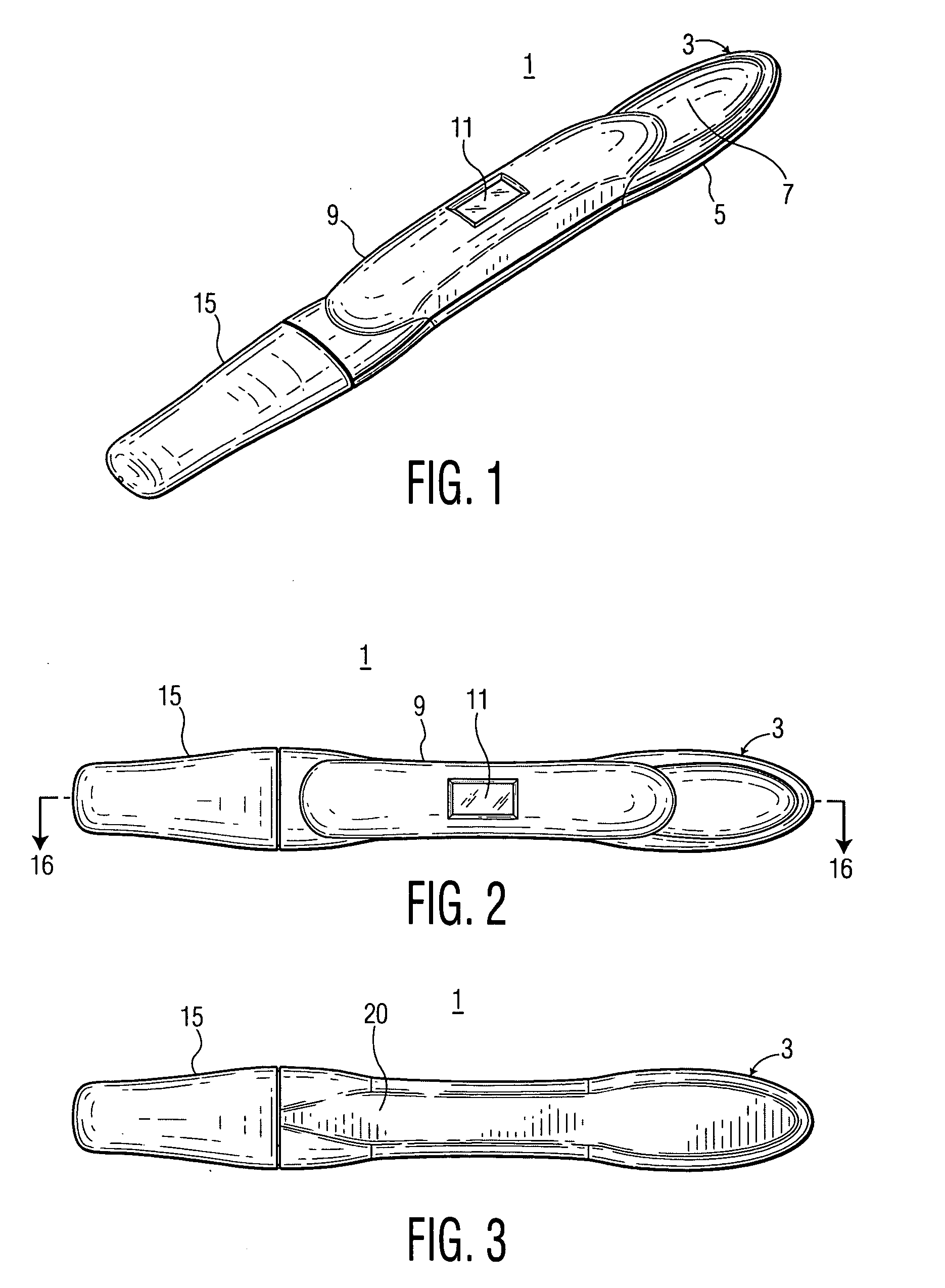
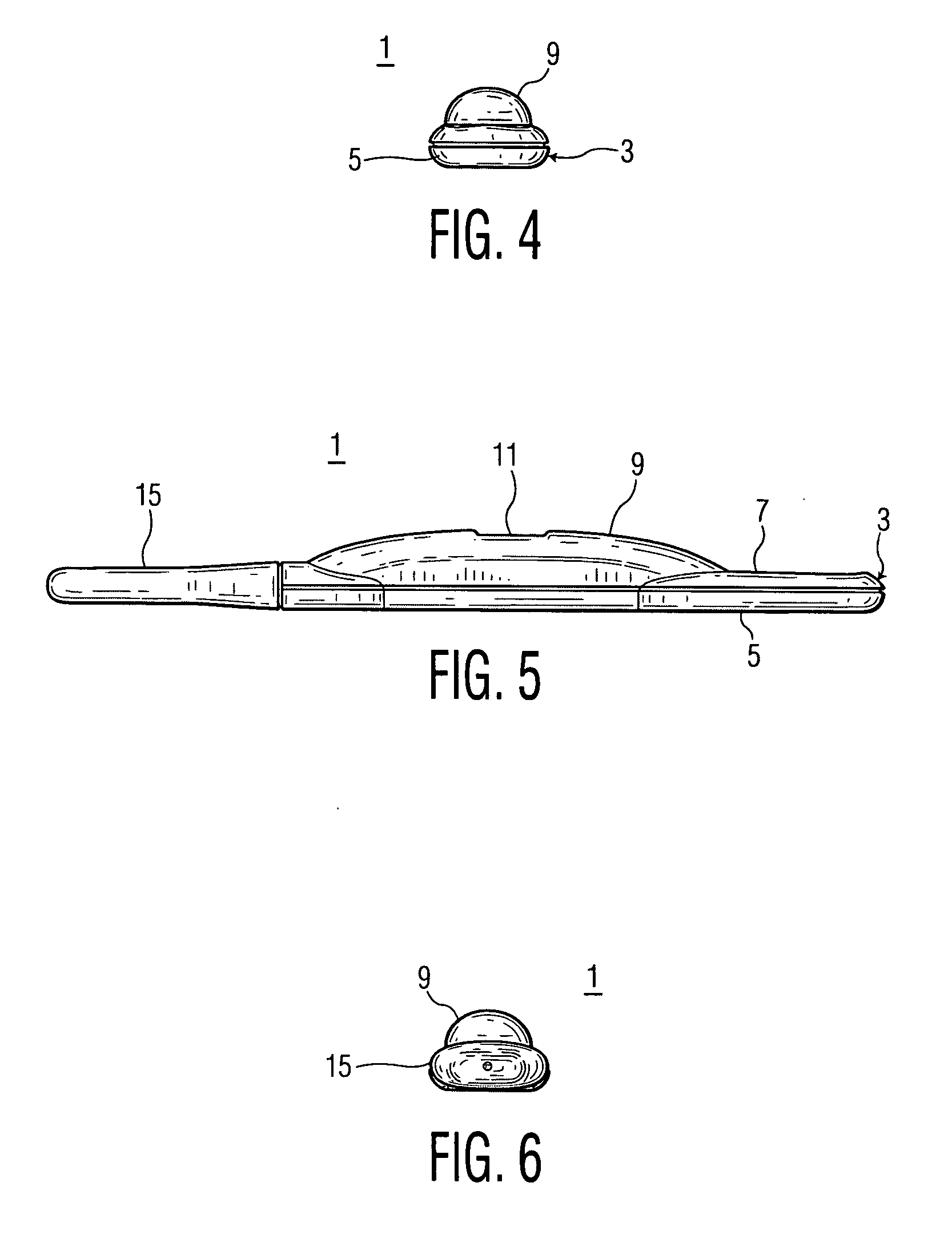
Lancet device having capillary action
InactiveUS20050004494A1Material minimizationReduced structureSamplingSurgeryVisual inspectionBody fluid
A device for sampling body fluid, the device comprising, a main body, a lancet disposed within the main body, a carrier disposed within the main body fixedly attached to the lancet, a biasing means in communication with the lancet and the carrier, an annular space disposed within the main body adjacent the lancet, and a means for measuring a body fluid. Wherein the means for measuring the body fluid may include micro-porous test strips, an electronic testing device, an optical / reflectance testing measuring device, or a visual inspection.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Elimination-absorber monitoring system
InactiveUS6246330B1Complicating power requirementEffectively overcome problemBaby linensAlarmsMonitoring systemEngineering
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS6541266B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
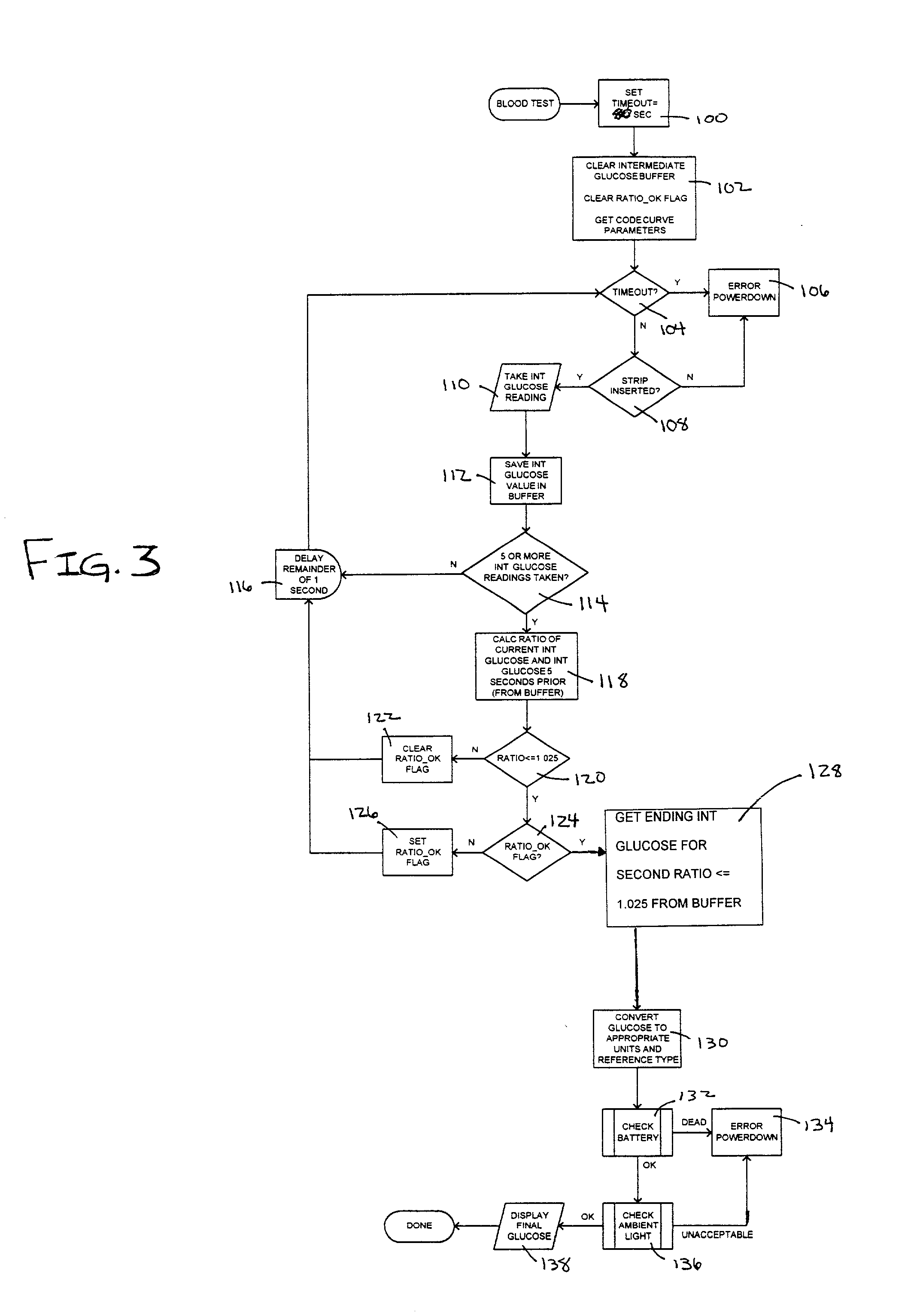
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such as glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Physiological sample collection devices and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20030143113A2Good repeatabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTest stripsBiomedical engineering
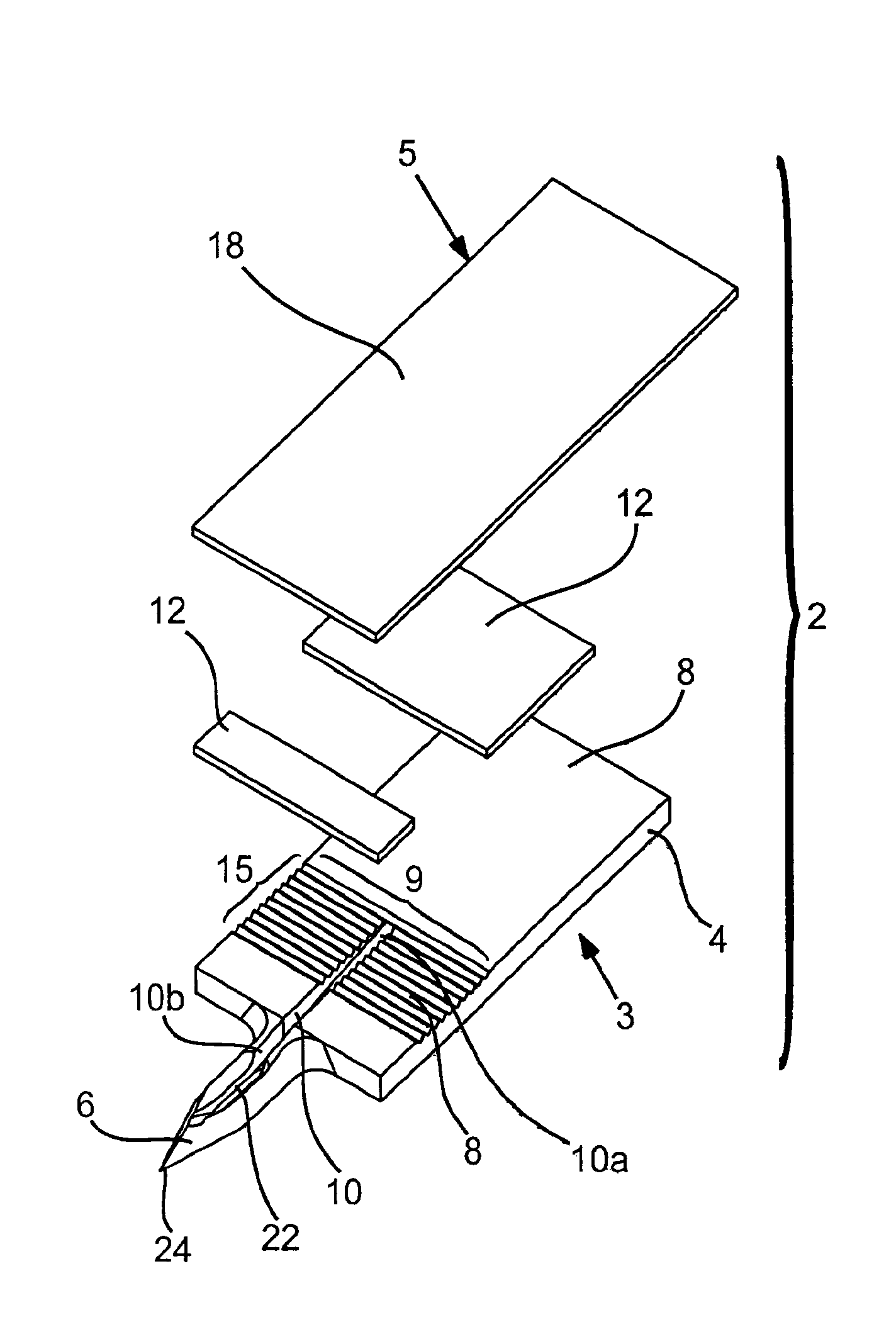
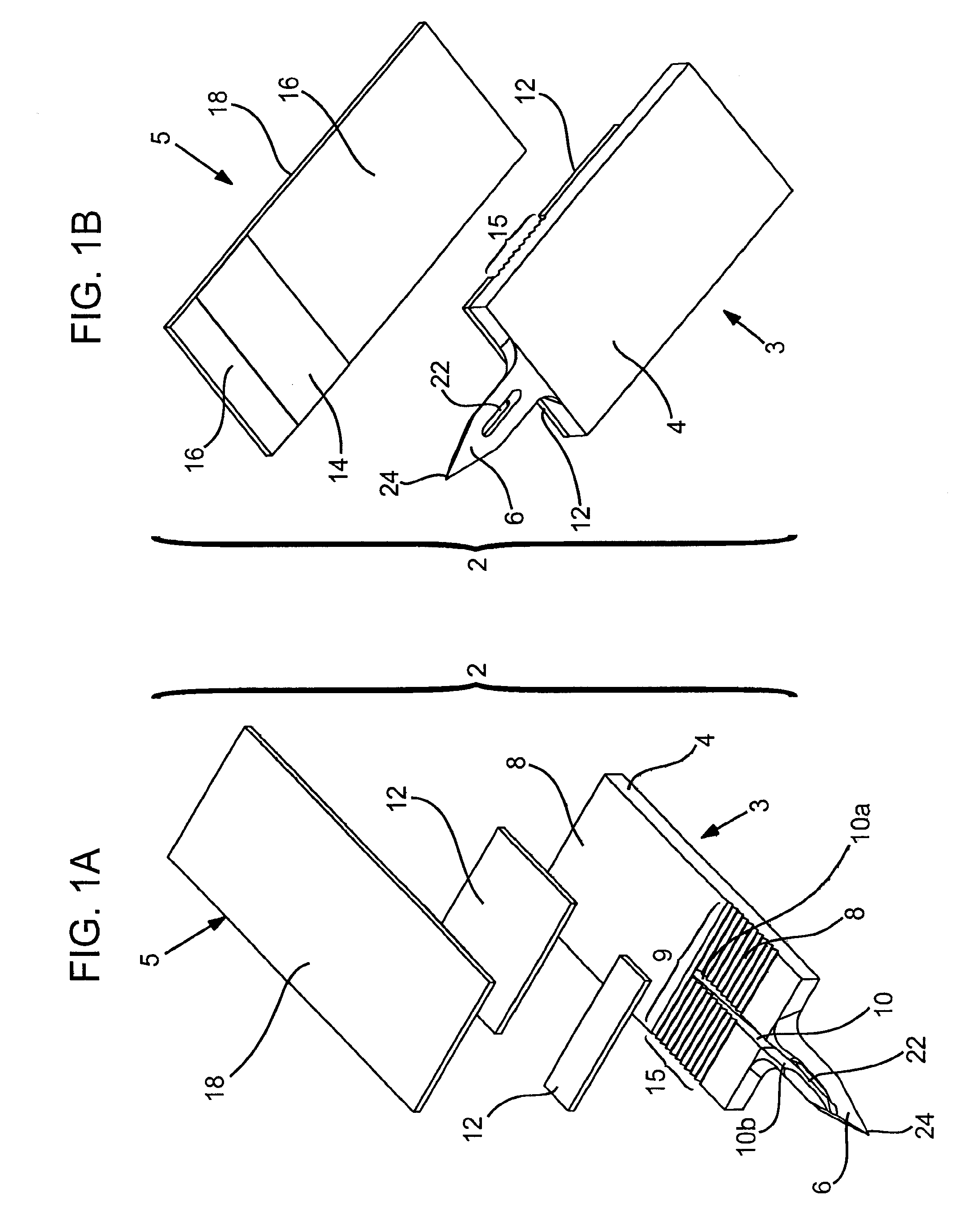
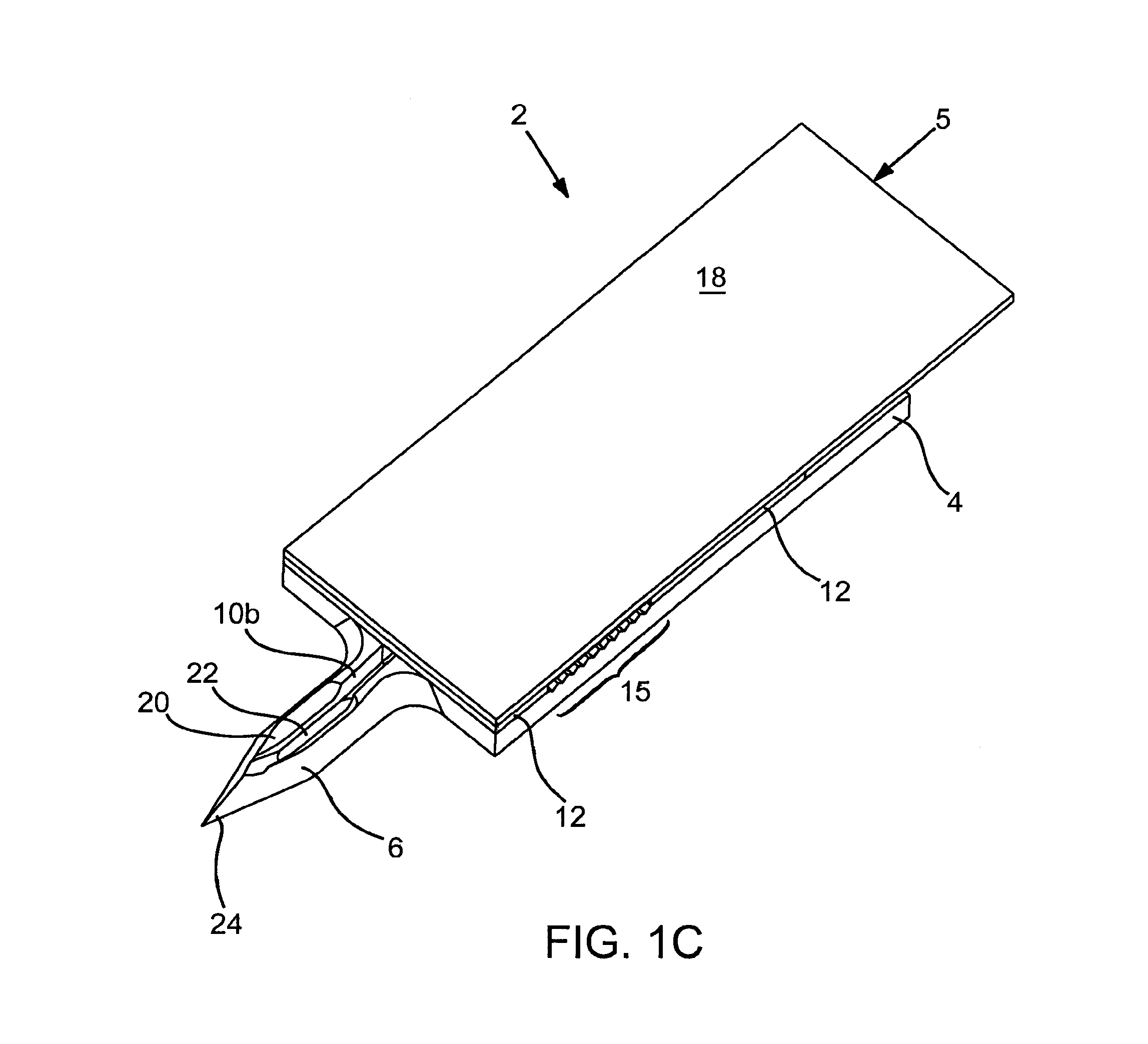
Abstract of Disclosure Devices, systems and methods are provided for piercing the skin, accessing and collecting physiological sample therein, and measuring a characteristic, e.g., an analyte concentration, of the sampled physiological sample. The subject devices are in the form of a test strip which include a biosensor and at least one skin-piercing element which is a planar extension of a portion of the biosensor. At least one fluid pathway resides within a portion of the biosensor and within the skin-piercing element. The skin-piercing element has a space-defining configuration therein which acts as a sample fluid pooling area upon penetration into the skin. Systems are provided which include one or more test strip devices and a meter for making analyte concentration measurements. Methods for using the devices and systems are also provided.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS6946299B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorGlucose polymers
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the sample chamber. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS7160251B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorElectrode pair
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the sample chamber. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Elimination - absorber monitoring system
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS6964871B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorEngineering
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber or other testing zone, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the testing zone. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Lancet device having capillary action
InactiveUS6866675B2Minimizes material and structureSamplingSurgical needlesVisual inspectionCapillary action
A device for sampling body fluid, the device comprising, a main body, a lancet disposed within the main body, a carrier disposed within the main body fixedly attached to the lancet, a spring in communication with the lancet and the carrier, an annular space disposed within the main body adjacent the lancet, and a testing device for measuring a body fluid. The testing device may include micro-porous test strips, an electronic testing device, an optical / reflectance testing measuring device, or a visual inspection.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
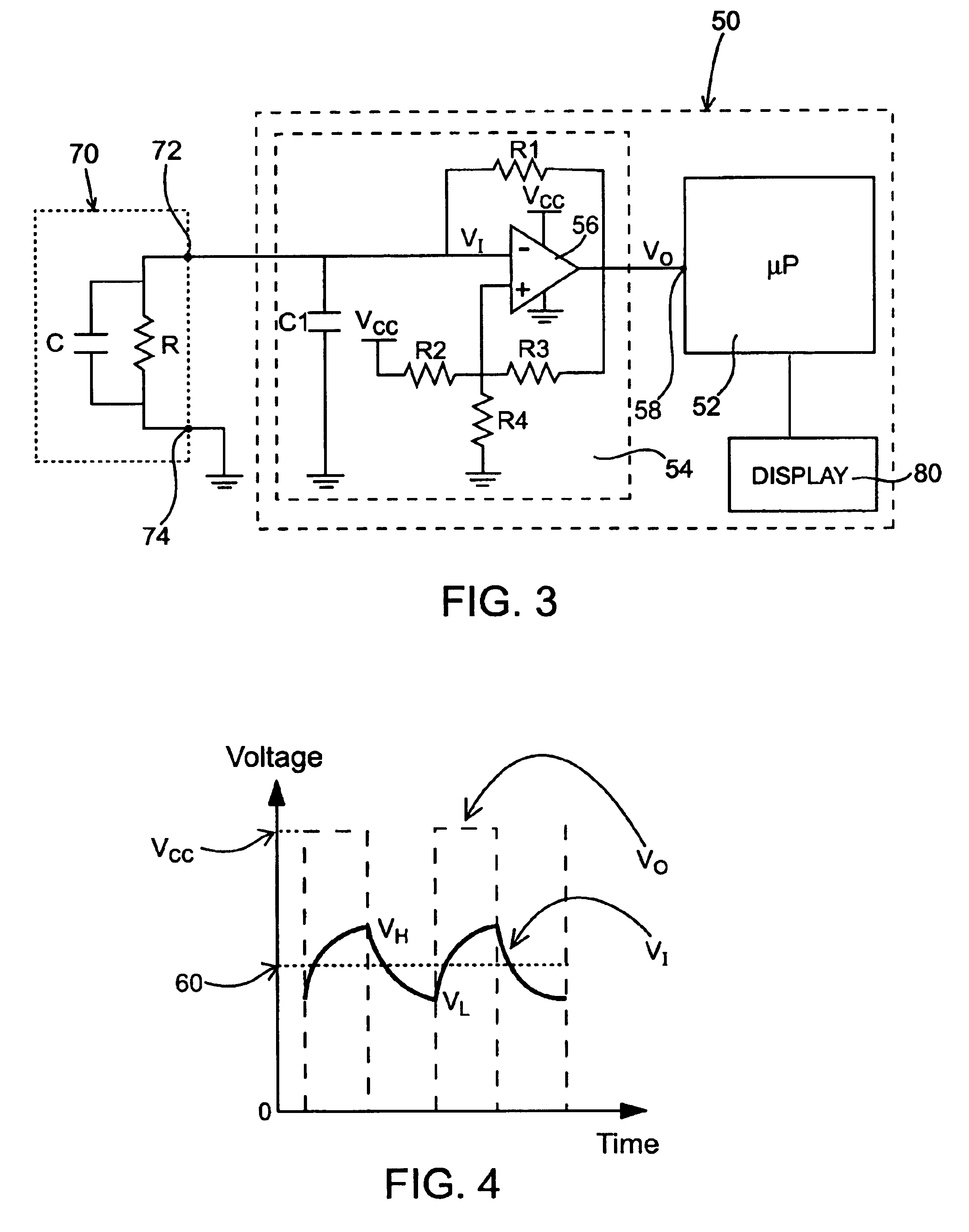
Analyte concentration determination meters and methods of using the same
InactiveUS6881578B2The process is simple and convenientEase and low cost manufactureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteEngineering
Devices and methods for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. The subject devices are meters characterized by having an internal structure that includes a test strip selecting element having a continuously reduced cross-sectional area configured to select a single test strip at a time and means for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample applied to the selected test strip. In the subject methods for containing at least one test strip and dispensing a single test strip at a time, a meter having at least one test strip contained therein is provided. The meter is positioned with respect to the ground to cause the single test strip to move from a contained position to a dispensed position. The subject invention also includes kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
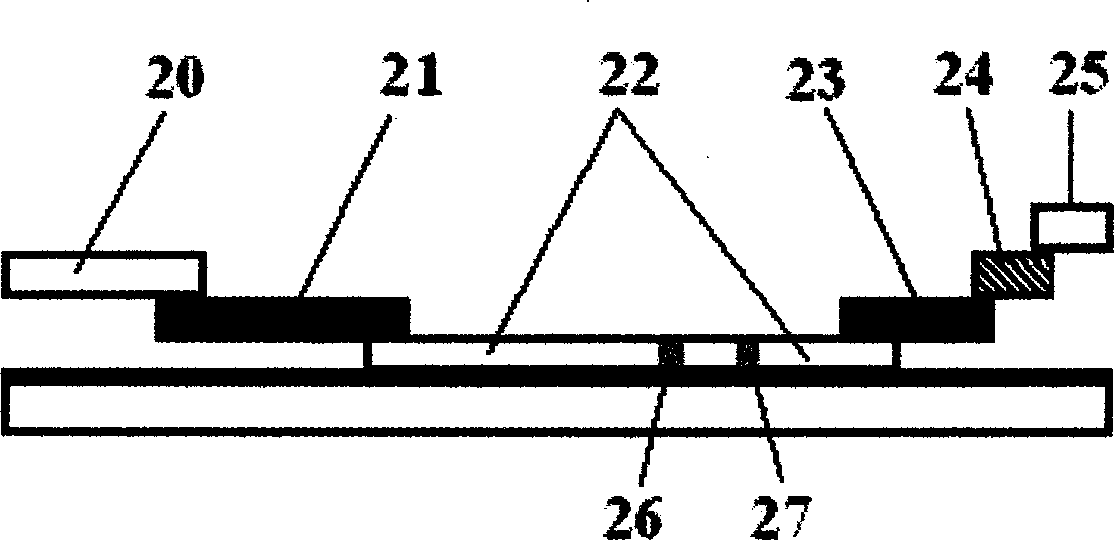
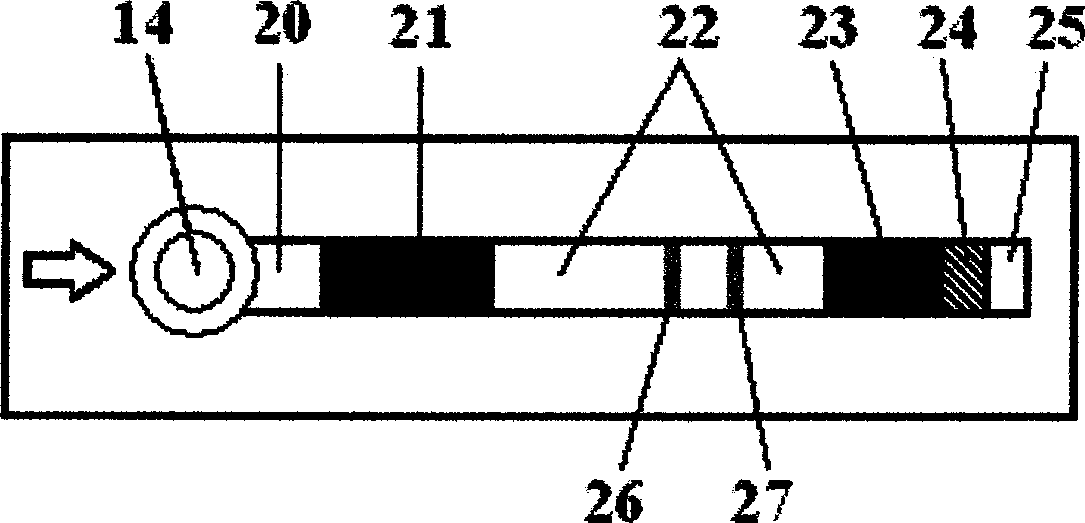
Test strip dispenser
InactiveUS6872358B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesEngineeringTest strips
Devices for dispensing test strips and methods of using the same are provided. The subject devices are characterized by having a housing made of a cover and a base configured to retain a plurality of test strips. In certain embodiments, the height of the base is less than the height of each of the test strips, such that a portion of each of the test strips extends beyond the distal or top edge of the base. The subject devices may further be characterized as having a substantially air and moisture tight seal. In using the subject devices, a plurality of test strips stored in a subject device are provided. A single test strip is removed from the subject device by moving the test strip distal to the remaining test strips. Also provided by the subject invention are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Consolidated body fluid testing device and method
InactiveUS20030109777A1Increase flowSufficient supplyCatheterSensorsTest fixtureBiomedical engineering
A body fluid testing device includes a body member and a tissue penetrator carried by the body member. A test strip holder is carried by the body member, and a test strip is carried by the test strip holder. The test strip is capable of receiving a body fluid thereon and processing the body fluid into a form suitable for yielding test results relating to the content of the body fluid.
Owner:KLOEPFER DR HANS
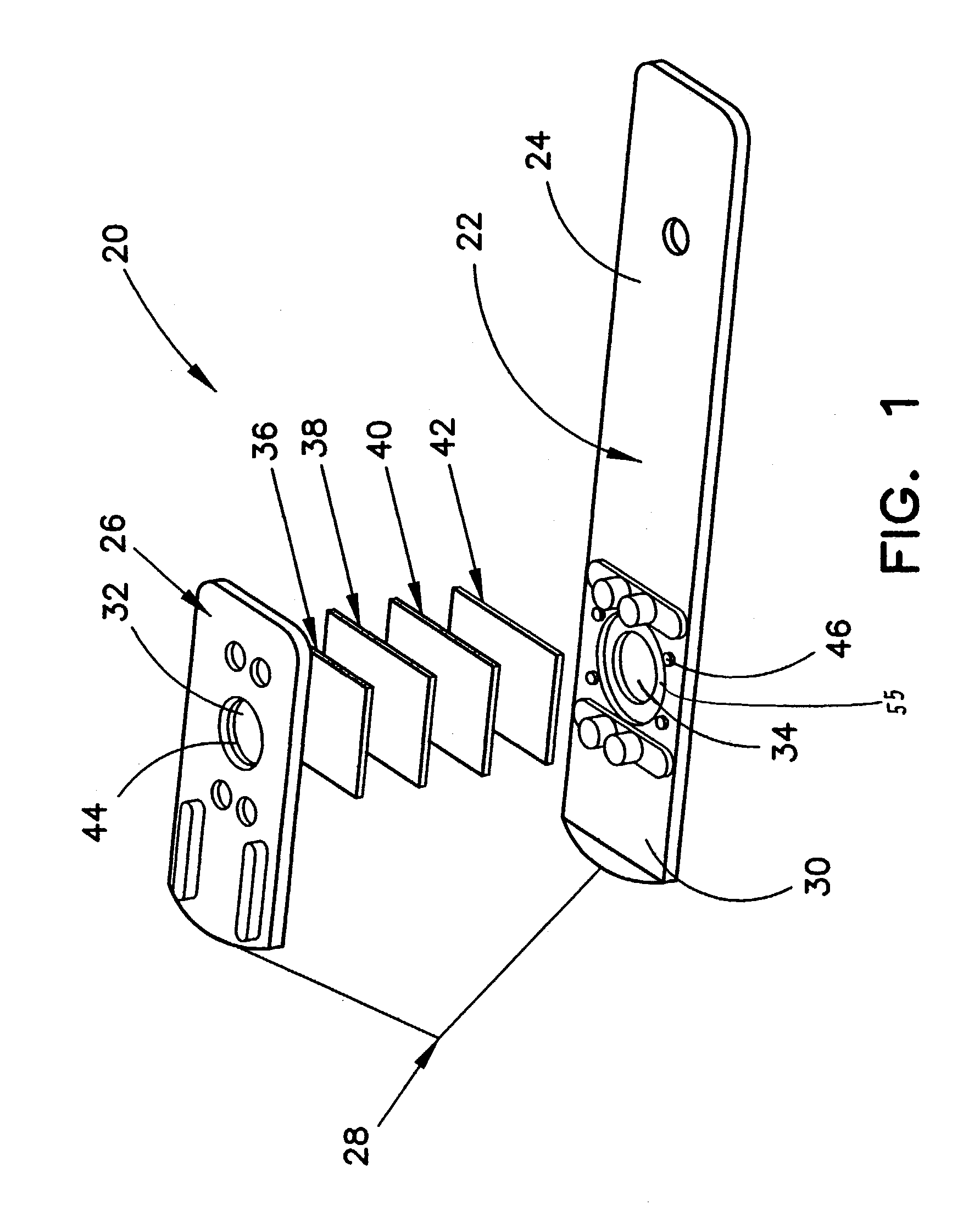
Multiple analyte assay device with sample integrity monitoring system
InactiveUS6514769B2Avoid pollutionImprove securityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSamplingMulti analyteSample integrity
An assay device, a fluid analyte sample separator device and methods for use of thereof for determining whether the integrity of a fluid analyte sample has been compromised and for contemporaneously assaying the sample for the presence or absence of multiple analytes, such as drugs of abuse. The device is composed of a housing having separate slots therein for insertion of one or more analyte test strips, one end of which protrudes from the housing, and one or more units of a sample integrity monitoring system. The device may be used in dipstick or cassette form. An analyte sample separator for division of sample and retention of uncontaminated sample for further testing is also provided. The analyte test strips and sample integrity monitoring system are replaceable, so that the panel of analytes and of sample condition parameters tested can be customized.
Owner:ASSURANCE BIOTECH
Determination of sample volume adequacy in biosensor devices
InactiveUS6872298B2Accurate measurementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteTest strips
Systems and methods are provided for determining whether a volume of biological sample is adequate to produce an accurate analyte concentration measurement. Certain such systems and methods provide the additional function of compensating for a sample volume determined to be less than adequate in order to proceed with an accurate analyte concentration measurement. The present invention is employed with a biosensor, such as an electrochemical test strip to which the sample volume of biological solution is deposited, and a meter configured to receive such test strip and to measure the concentration of selected analytes within the biological sample.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
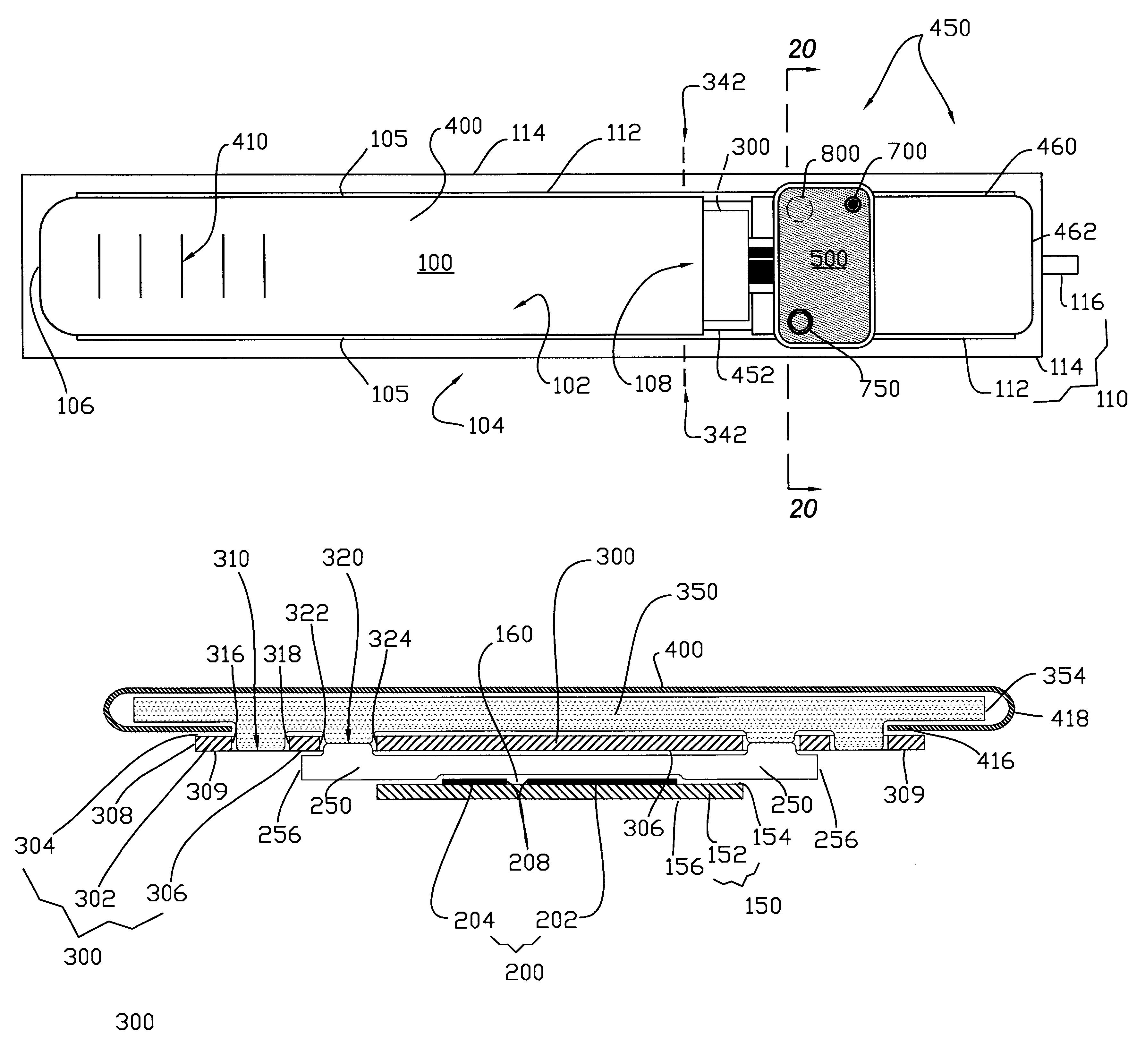
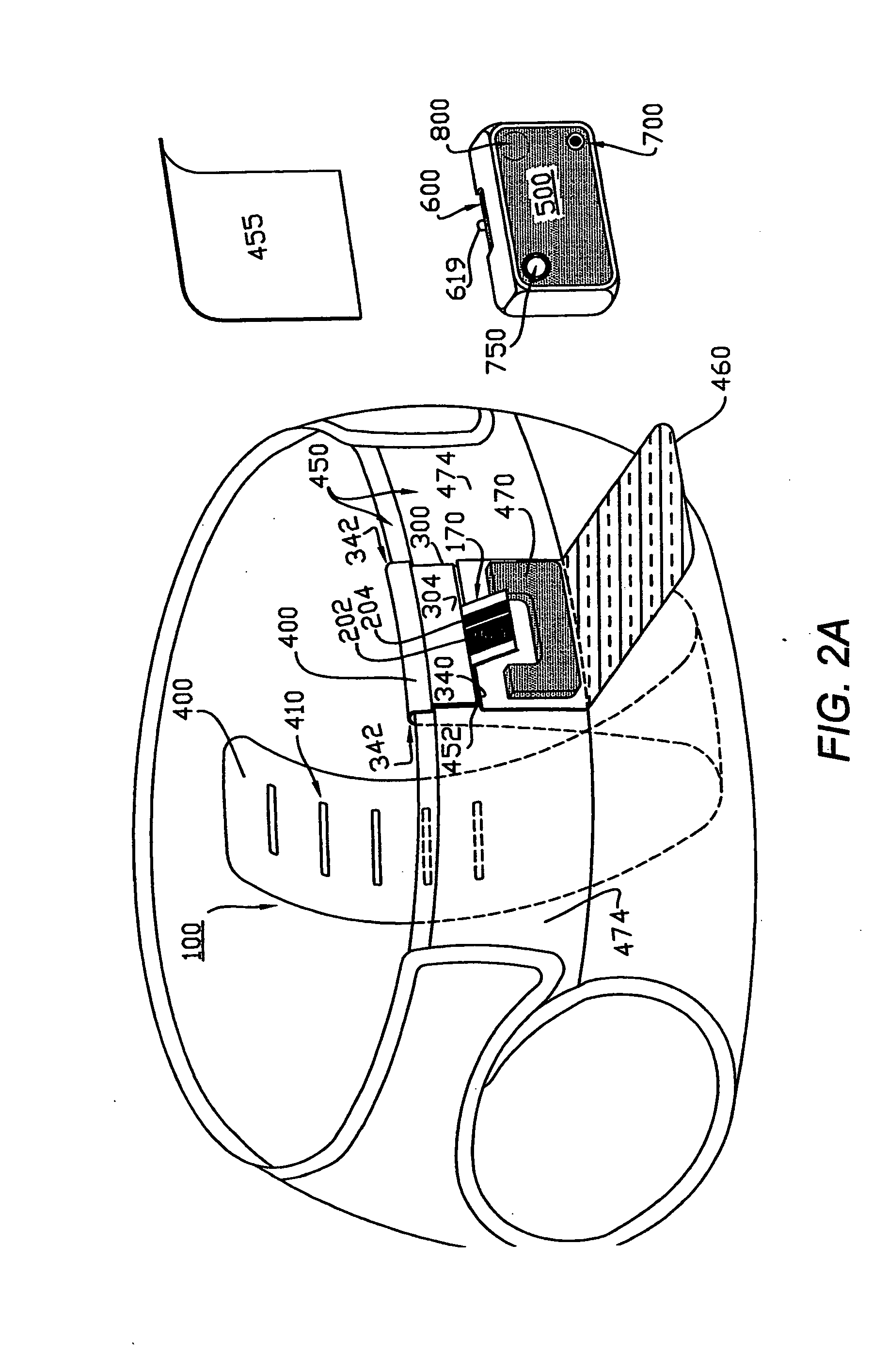
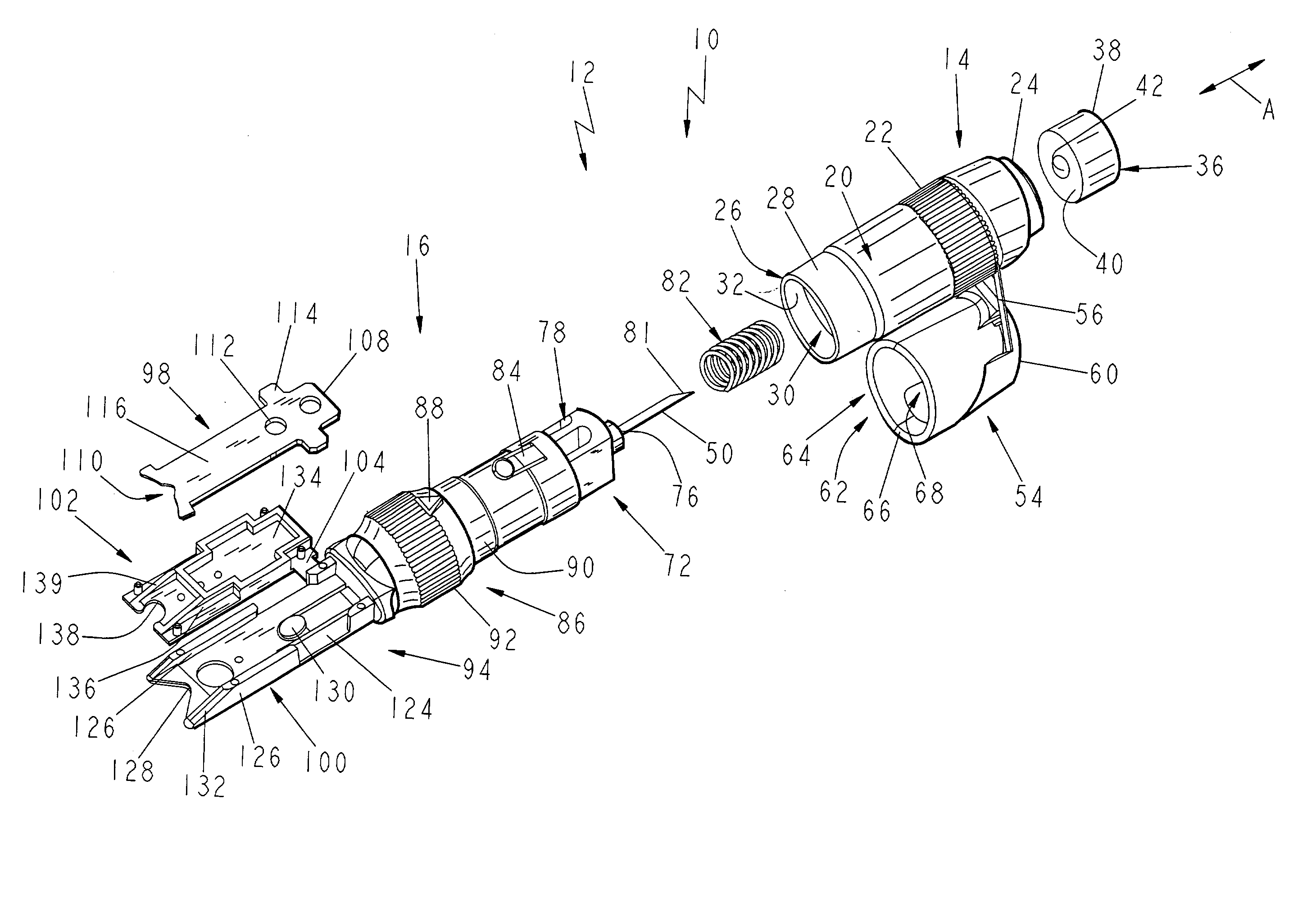
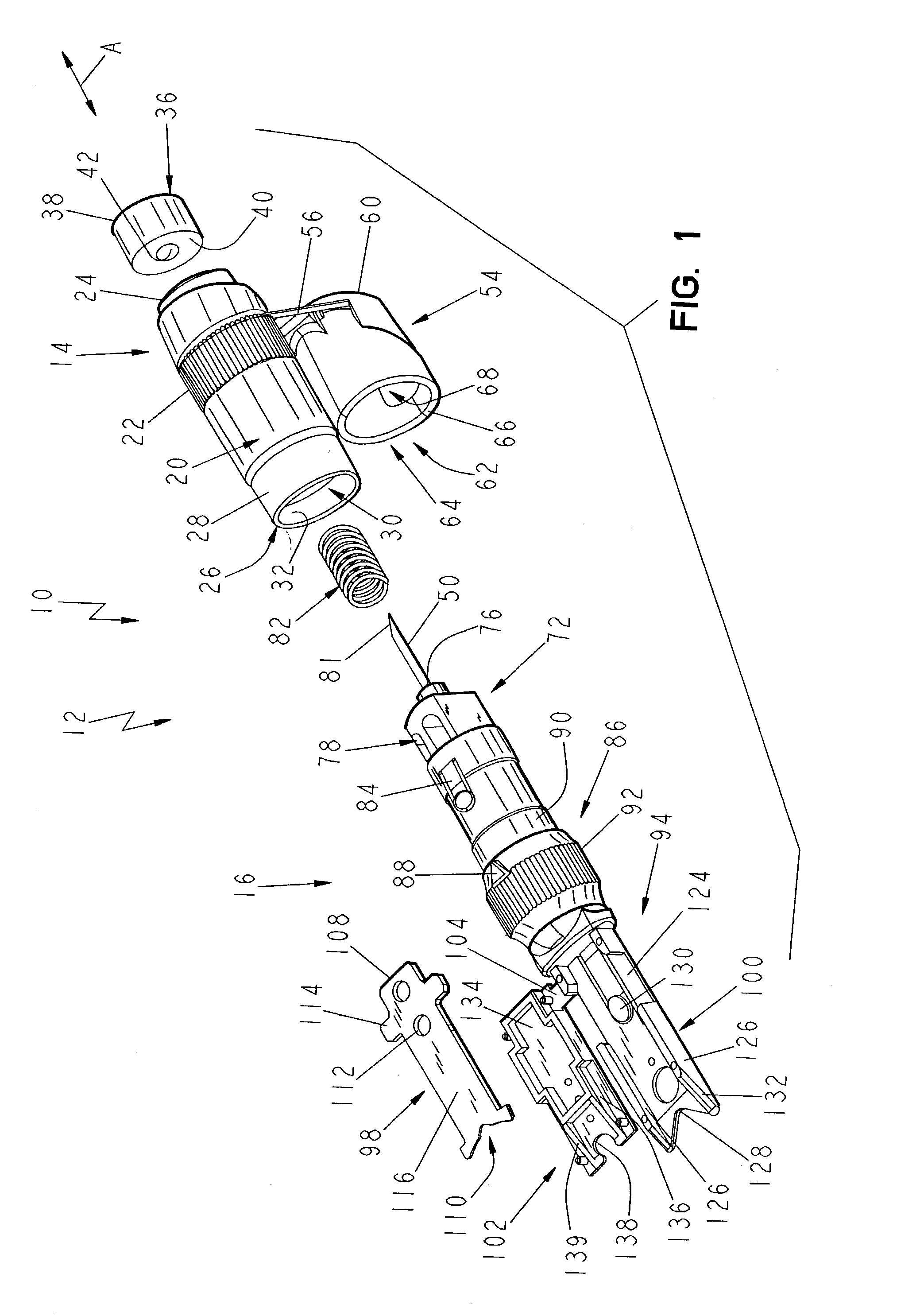
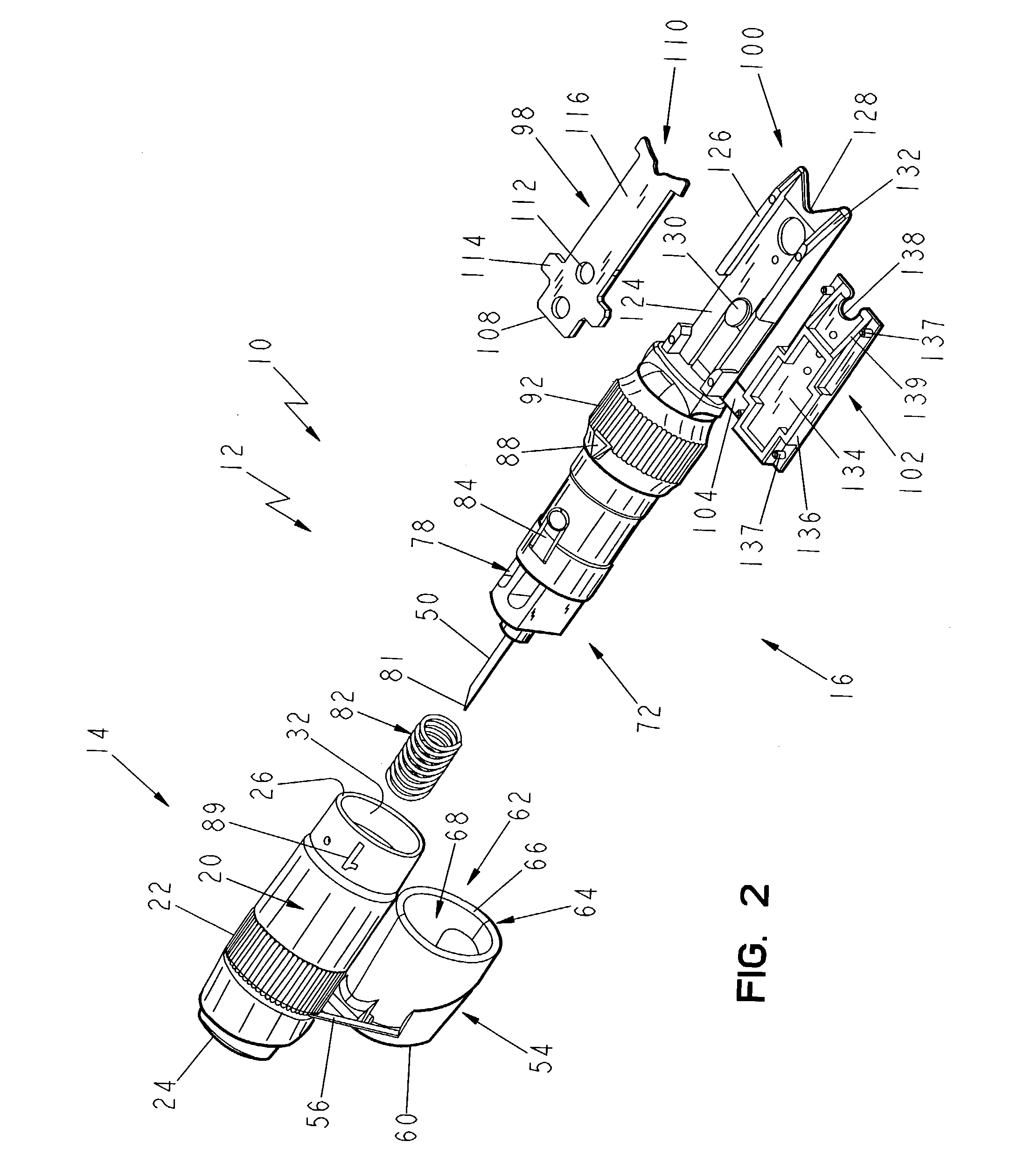
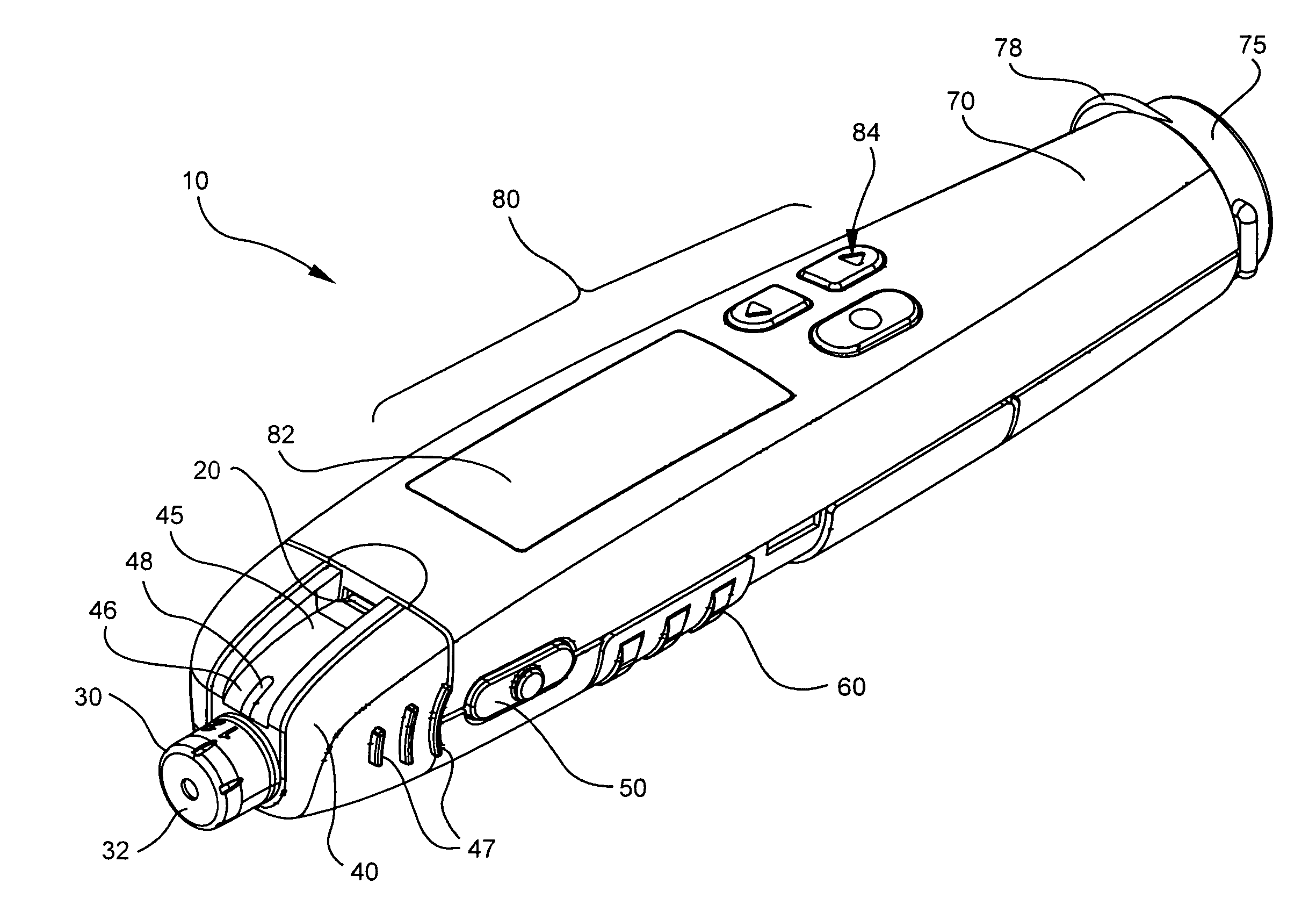
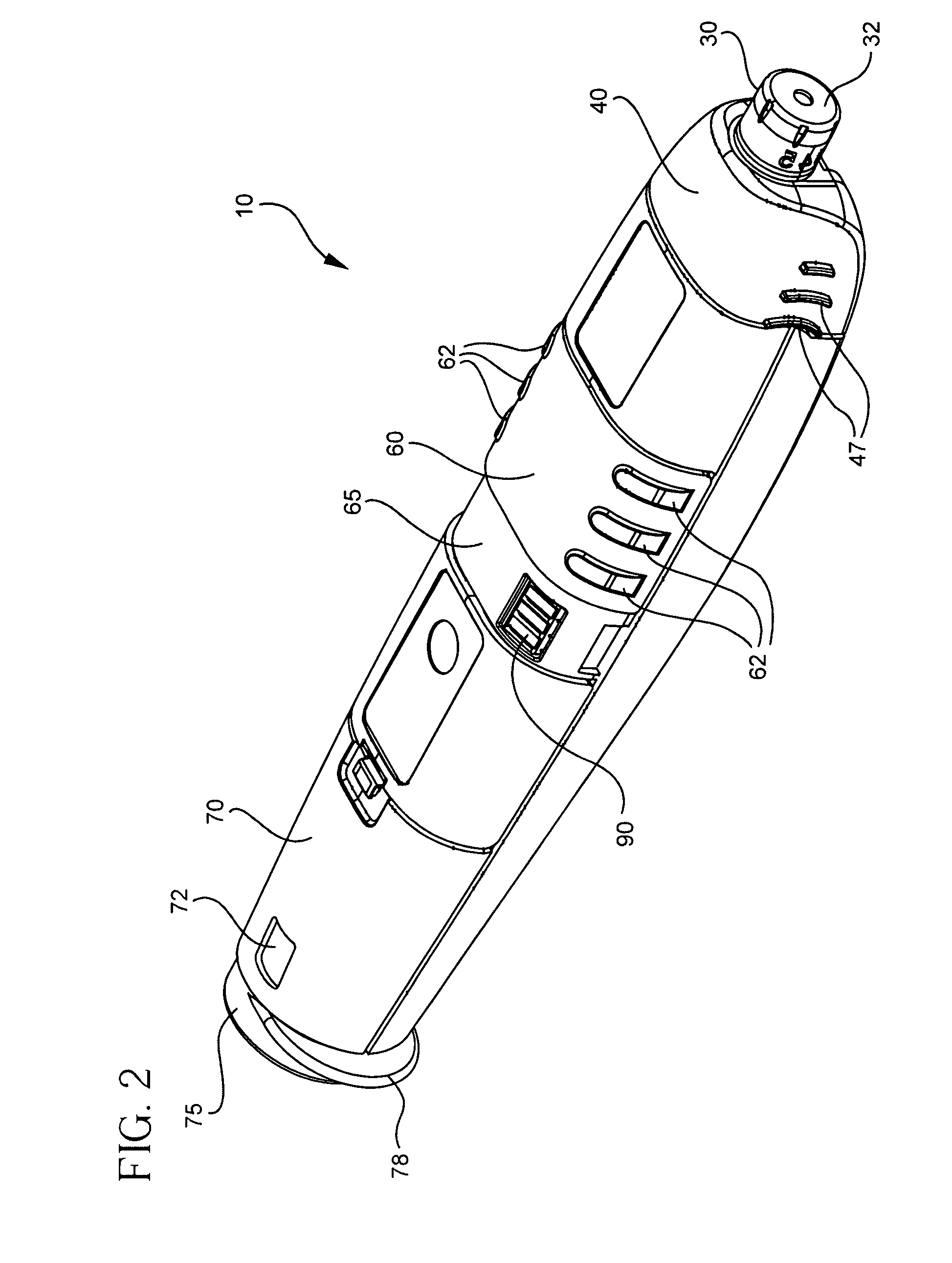
Blood glucose meter having integral lancet device and test strip storage vial for single handed use and methods for using same
ActiveUS20080058631A1Facilitates one-handed opening and closing of the vialEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementSensorsData connectionBlood glucose meters
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Multiple analyte assay device with sample integrity monitoring system
InactiveUS20020001854A1Avoid pollutionImprove securitySamplingBurette/pipette supportsAnalyteSample integrity
An assay device, a fluid analyte sample separator device and methods for use of thereof for determining whether the integrity of a fluid analyte sample has been compromised and for contemporaneously assaying the sample for the presence or absence of multiple analytes, such as drugs of abuse. The device is composed of a housing having separate slots therein for insertion of one or more analyte test strips, one end of which protrudes from the housing, and one or more units of a sample integrity monitoring system. The device may be used in dipstick or cassette form. An analyte sample separator for division of sample and retention of uncontaminated sample for further testing is also provided. The analyte test strips and sample integrity monitoring system are replaceable, so that the panel of analytes and of sample condition parameters tested can be customized.
Owner:ASSURANCE BIOTECH
Optical arrangement for assay reading device
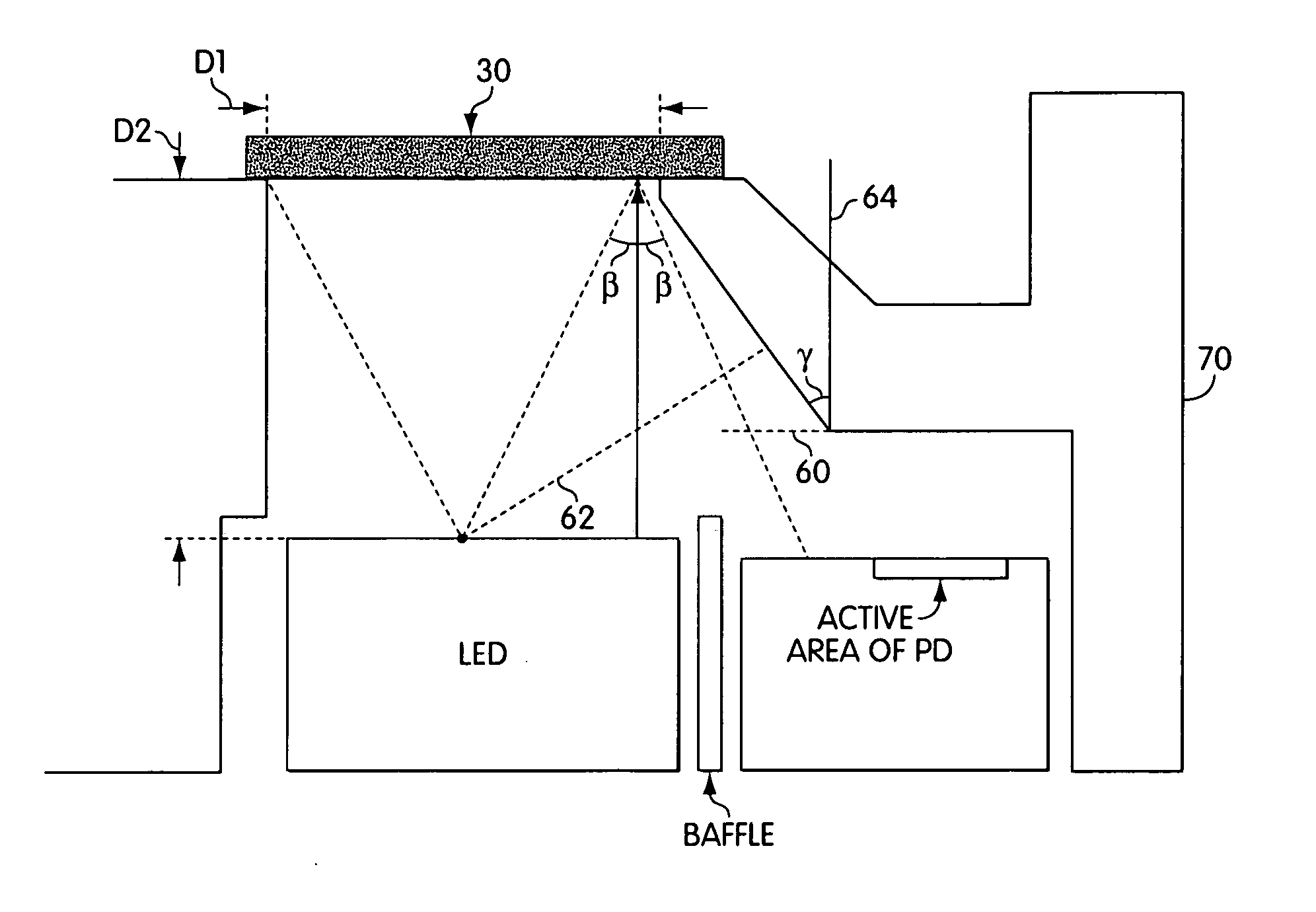
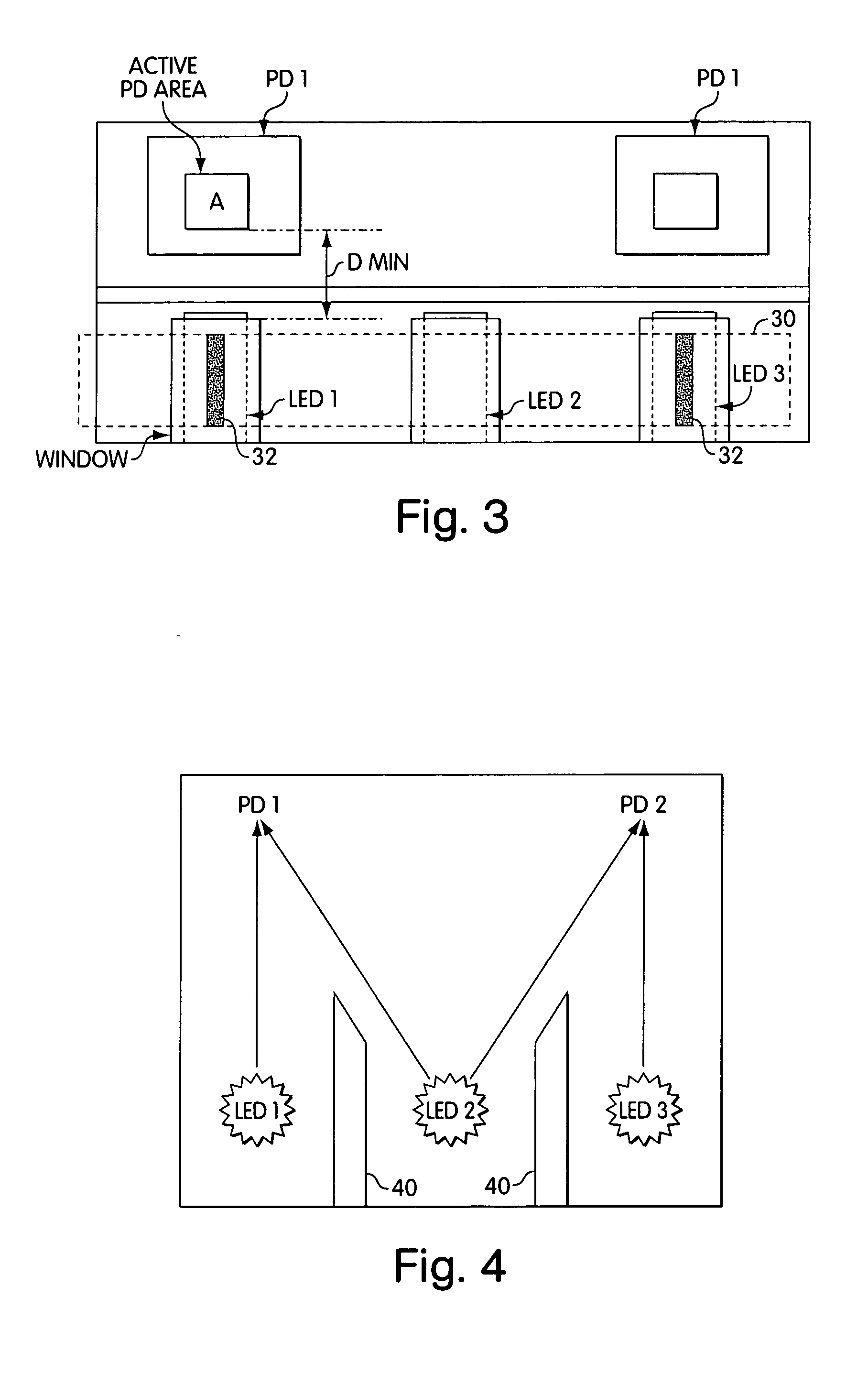
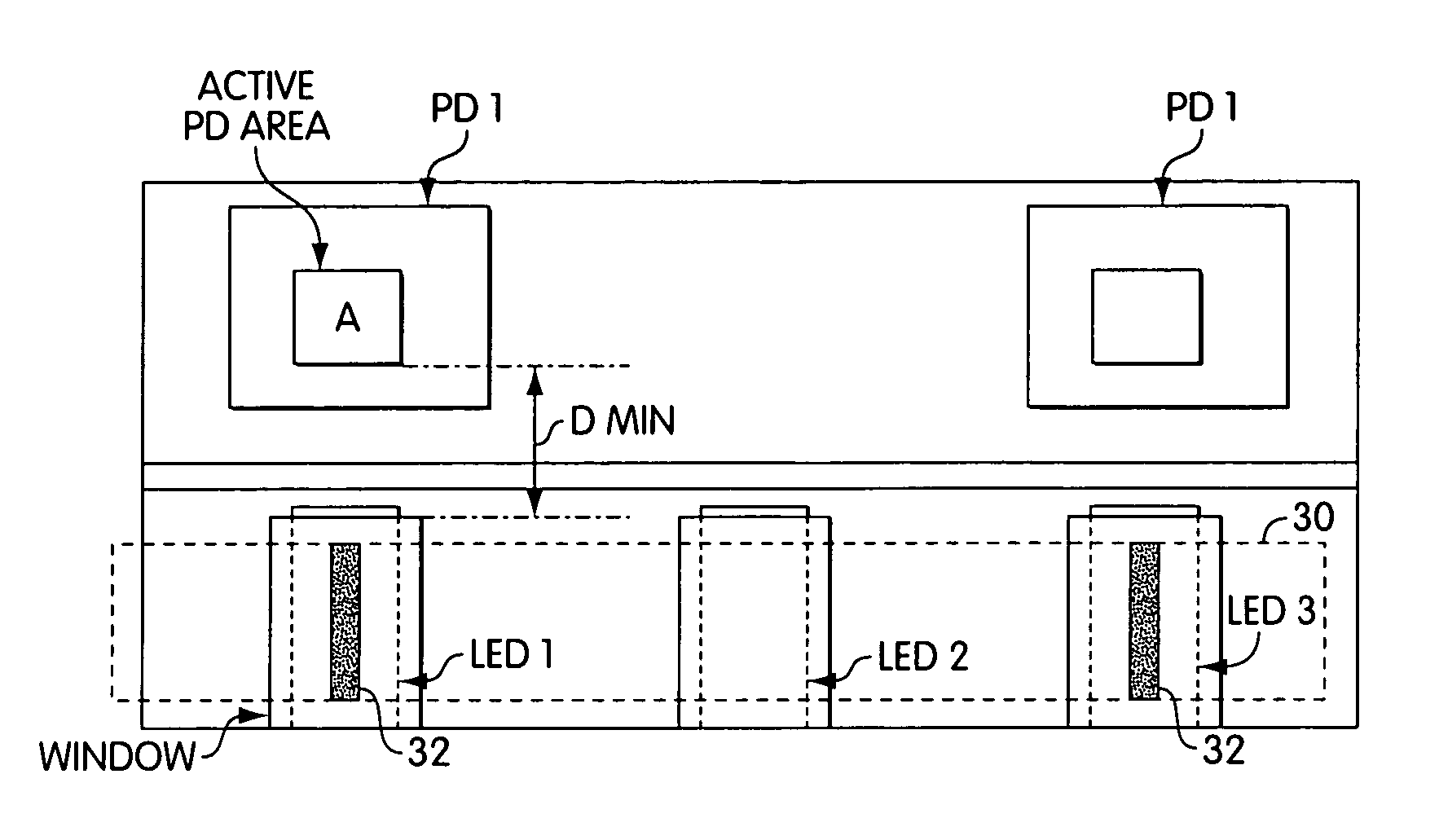
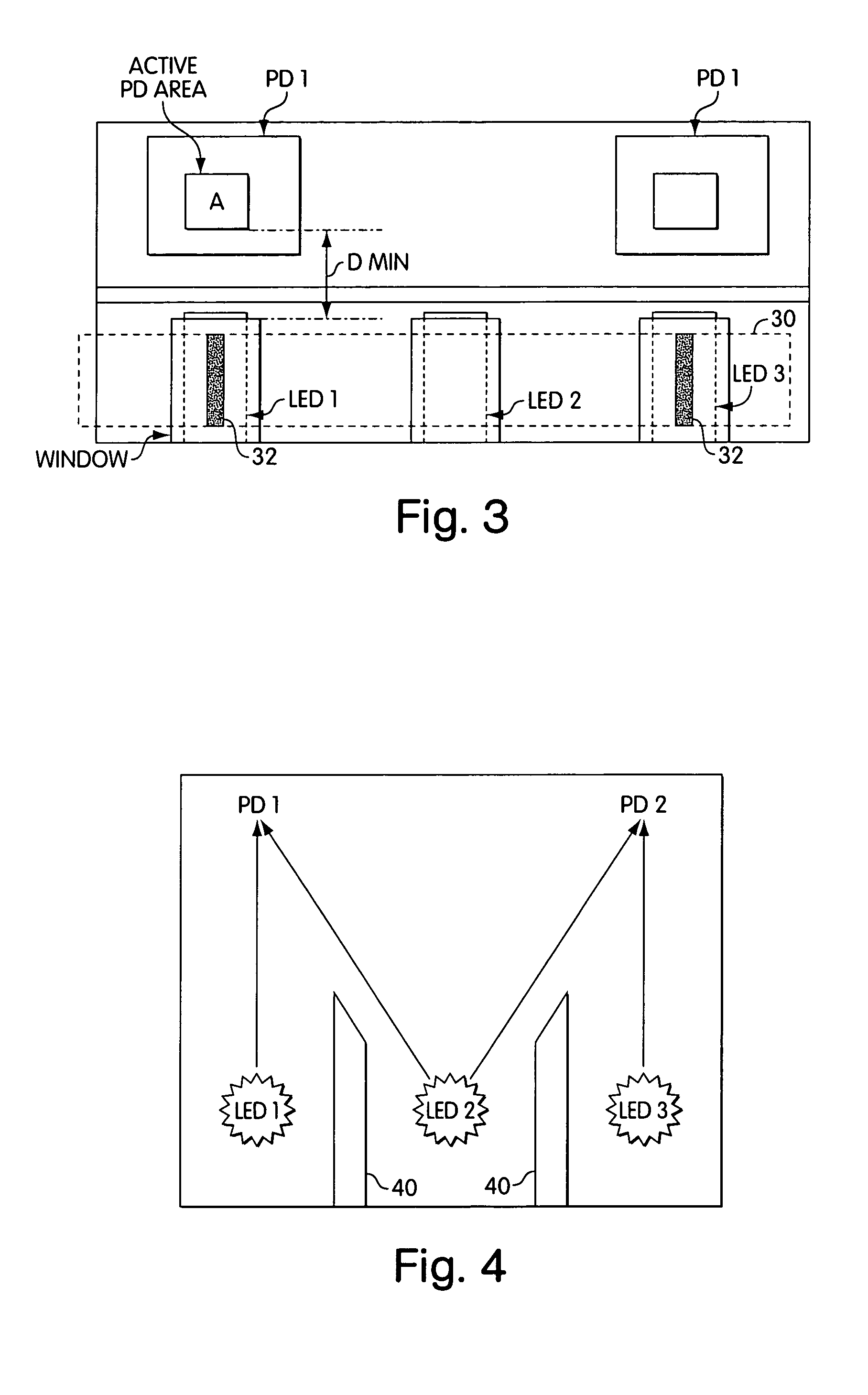
ActiveUS20050036148A1Closely arrangedScattering properties measurementsInvestigating moving sheetsPhotodetectorOpto electronic
Disclosed, in one aspect, is an assay result reading device for reading the result of an assay performed using a test strip, the device comprising: a light source or sources, said light source / s emitting light incident upon at least two, spatially separated zones of the test strip; and a photodetector which detects light emanating from each of the two said zones; in a further aspect is disclosed an assay result reading device for reading the result of an assay performed using a test strip, the device comprising: at least one light source incident upon a zone of the test strip; and at least two photodetectors both of which are able to detect some of the light emanating from the zone of the test strip illuminated by the light source.
Owner:ABBOTT RAPID DIAGNOSTICS INT UNLTD
Fluid sample distriution system for test device
InactiveUS6203757B1Evenly distributedAnalysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresDistribution systemTest fixture
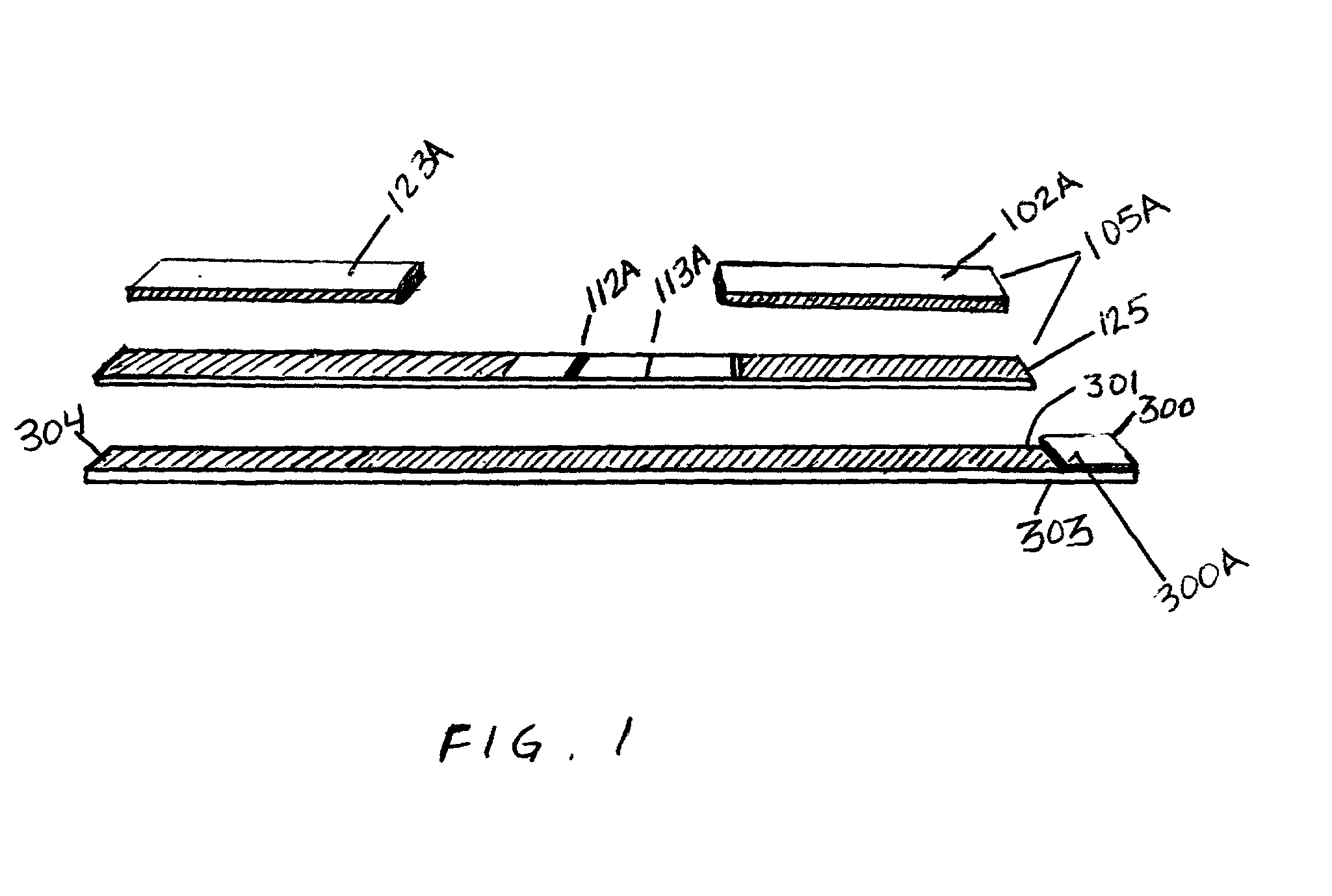
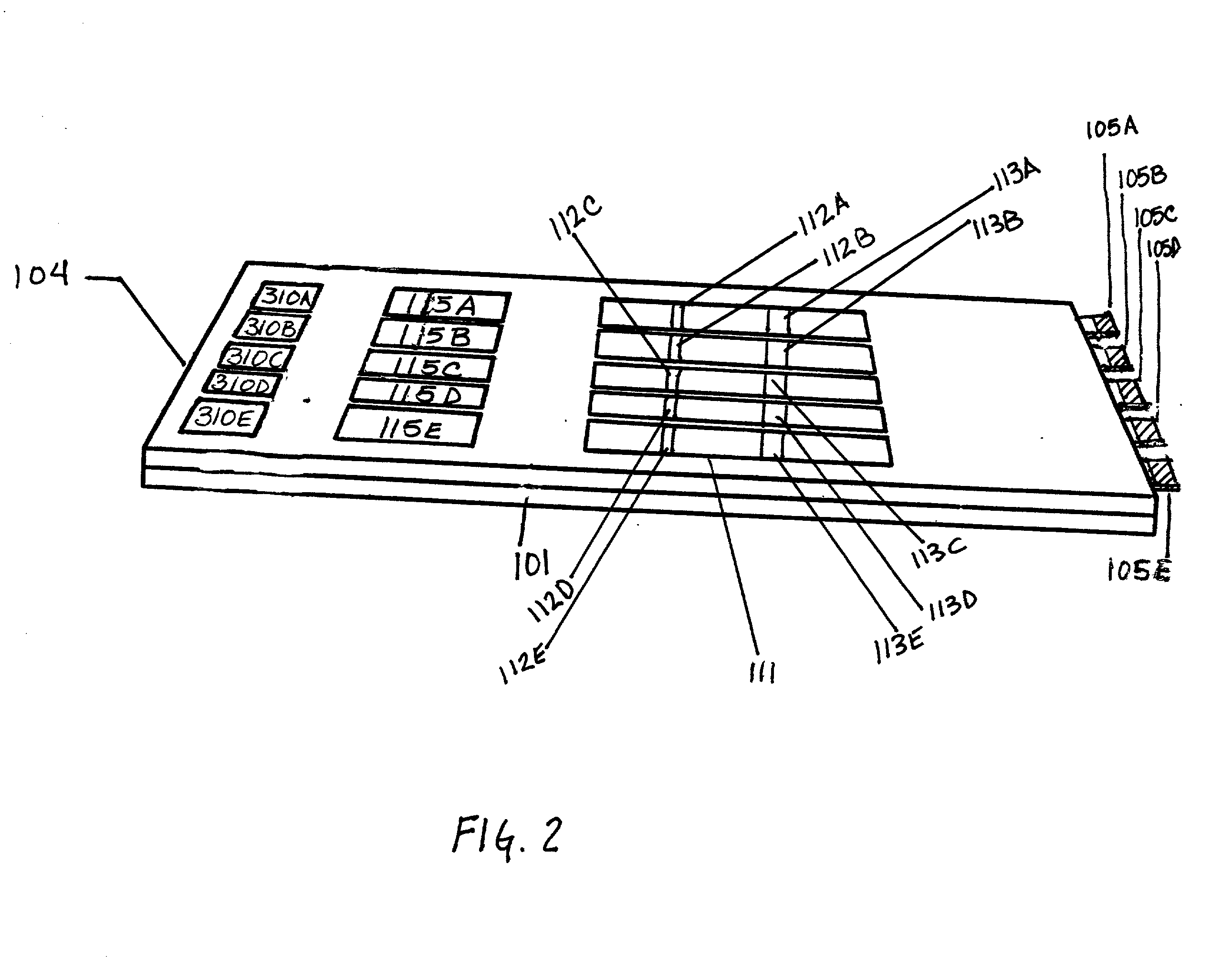
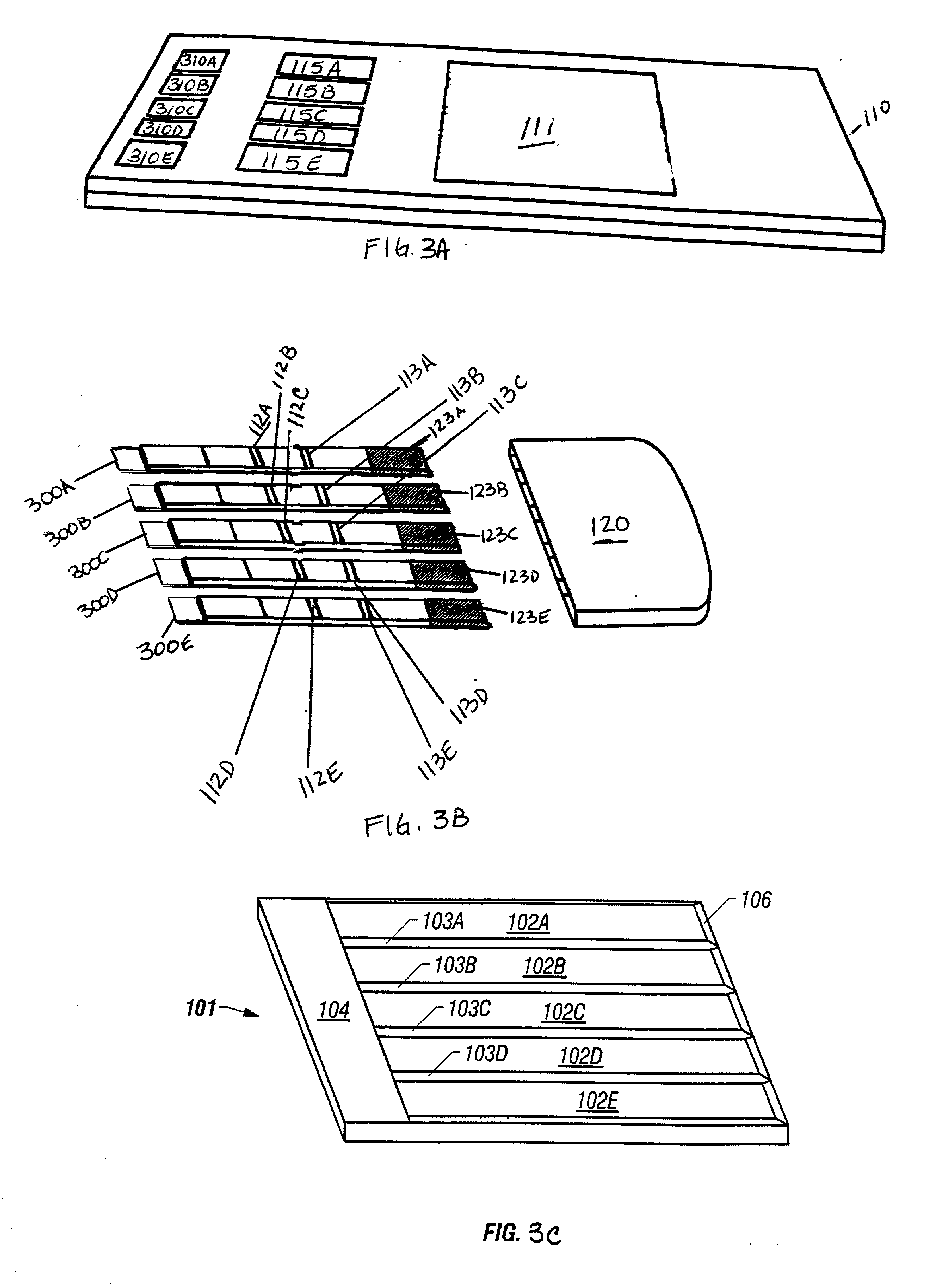
Diagnostic products having multiple test strips within a unitary diagnostic test device, or test icon, are described herein. In the preferred embodiments of the diagnostic test device of this invention, a fluid sample distribution system is provided wherein a sample collection and distribution port is provided in the housing for receipt of a biologic fluid sample and the channeling of such sample onto a sample receiving web. The sample receiving web, which is located within the test device, is in fluid communication with an array of test strips, and is configured to deliver an aliquot of biologic fluid sample to the test site of each such test strip at essentially the same rate. In the preferred embodiments of this invention, the sample receiving web comprises at least one base segment and at least one branched segment. Each of the base and branched segments can be formed or cut from a common sheet of material or from separate sheet material and thereafter placed in contiguous relationship one another. The relative placement of the sample receiving web within the test device is coincident with a portion of each test strip and designed to effect the balanced distribution and delivery of an aliquot of the biologic fluid sample to the test site of each of the test strips within the test device.
Owner:BIONIKE
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS20020146835A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical physicsWhole blood units
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such a glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Even fluid front for liquid sample on test strip device
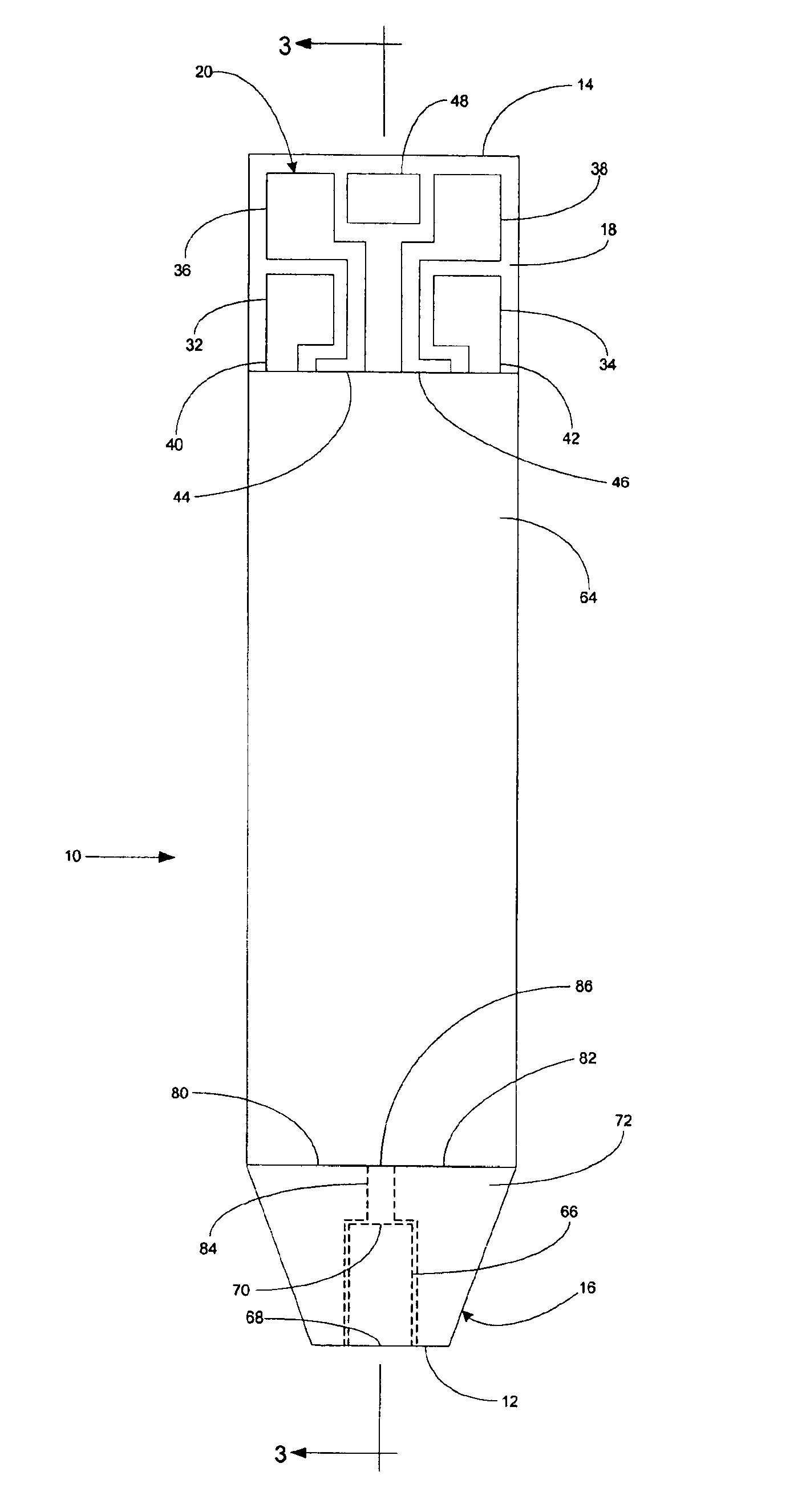
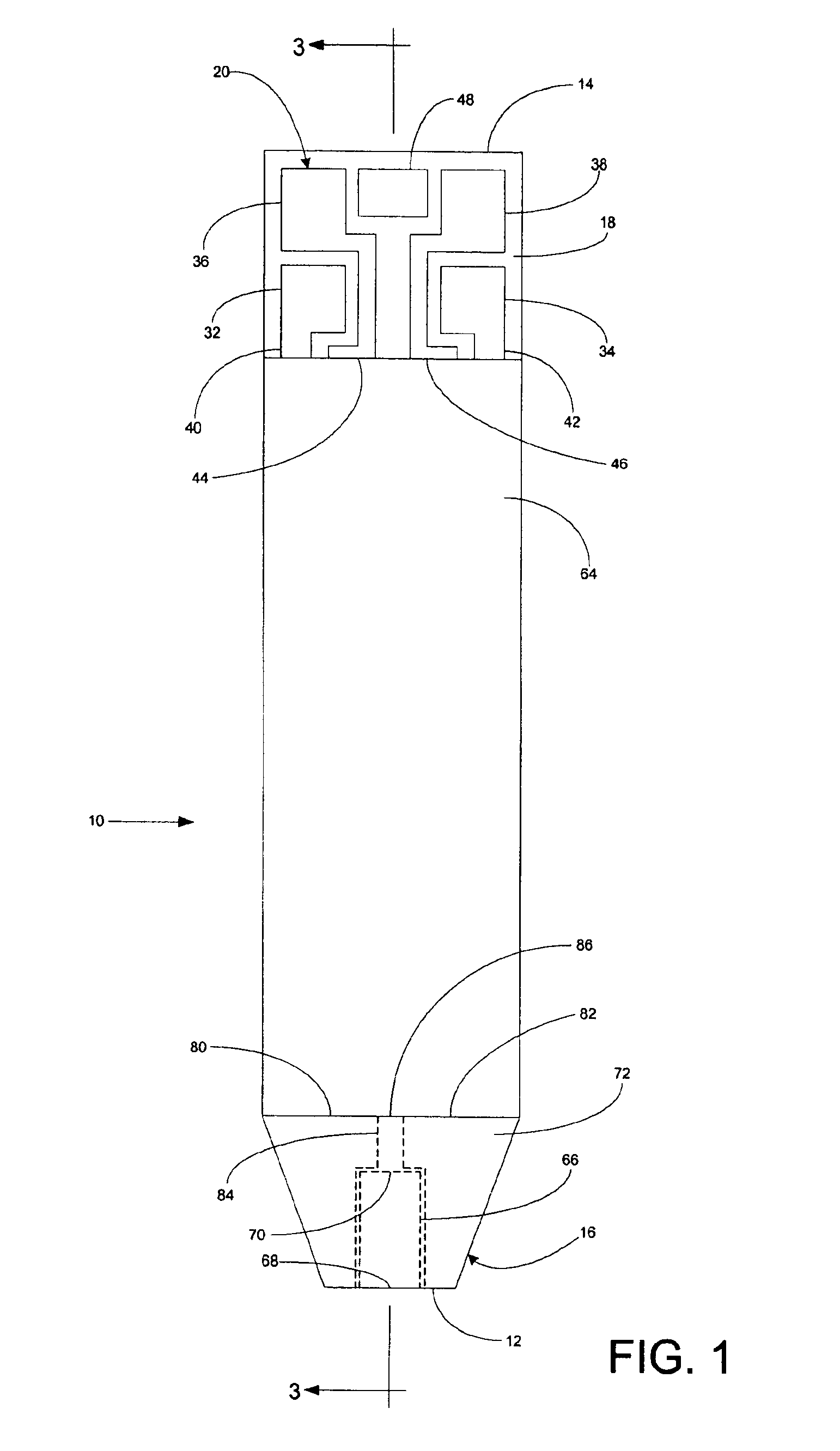
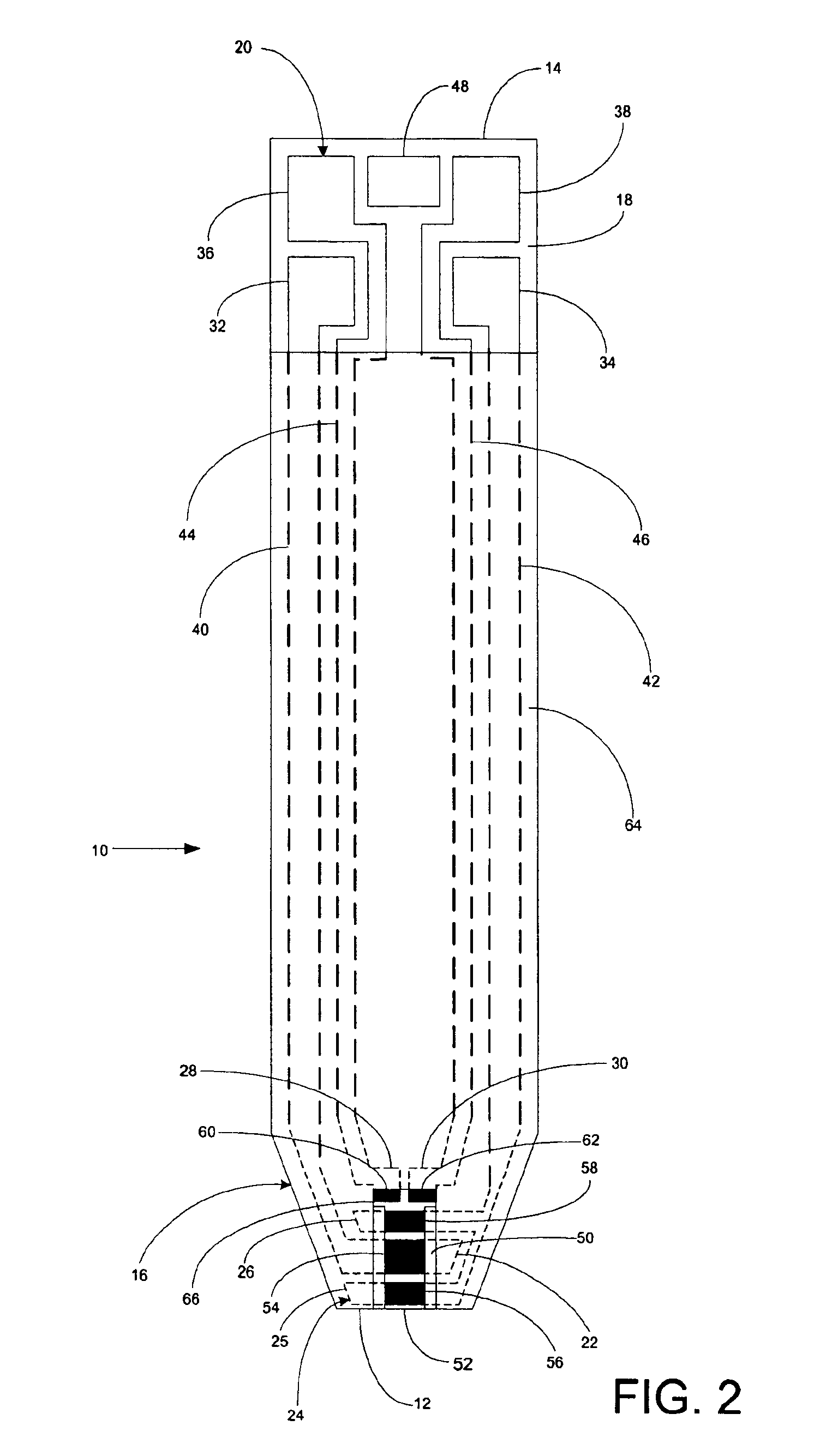
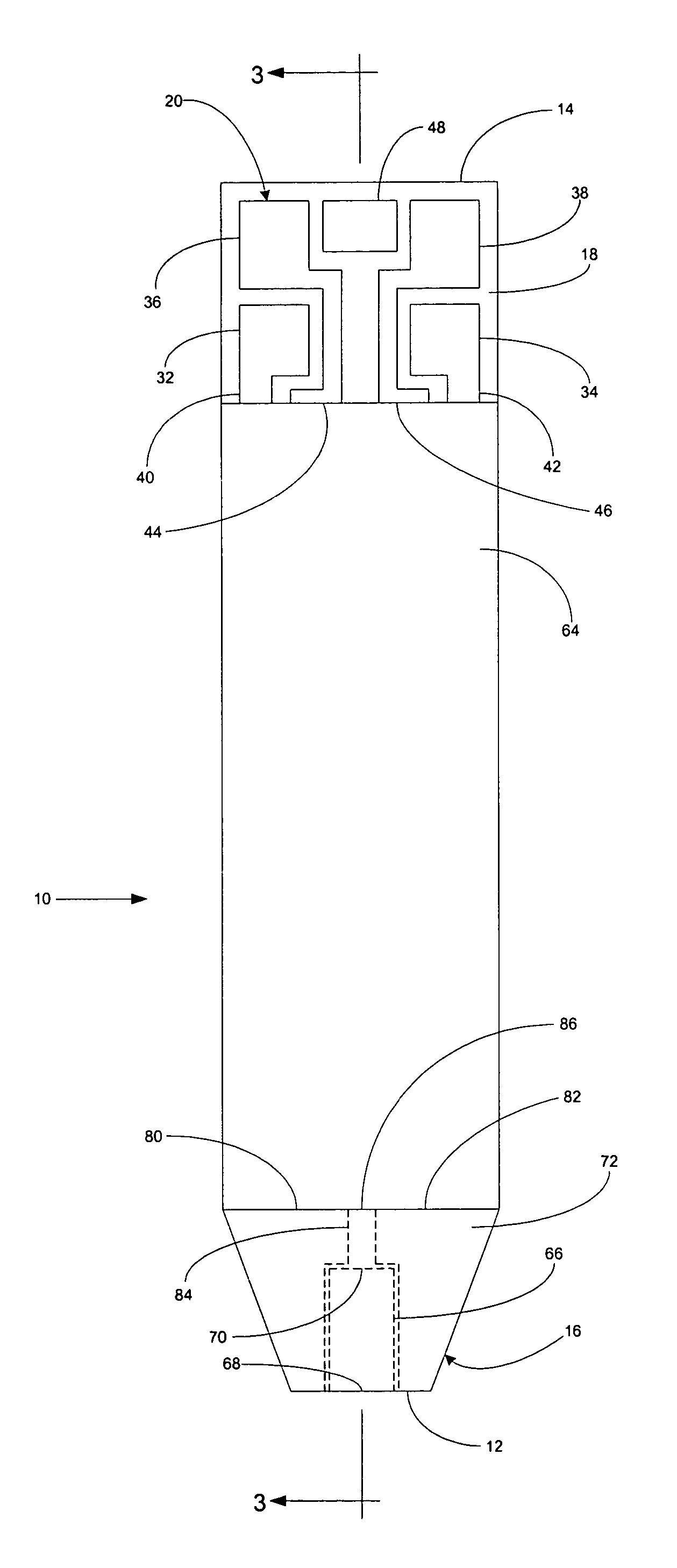
InactiveUS6372514B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMembrane configurationTest Strip (device)
Test strip device for accepting a liquid sample and forming an even fluid front across the test strip. When the sample is applied to a contacting surface, it runs down the surface where it collects between the contacting surface and a slope surface. As the sample collects, it evenly reaches fluid flow contact with an absorbent membrane. As a result, the sample forms an even fluid front across the membrane, improving the performance of the test strip device. Methods for using the device to accept a sample and to detect an analyte in the liquid sample are also provided.
Owner:SYNTRON BIORES
Optical arrangement for assay reading device
ActiveUS7315378B2Closely arrangedInvestigating moving sheetsScattering properties measurementsAssayPhotodetector
Owner:ABBOTT RAPID DIAGNOSTICS INT UNLTD
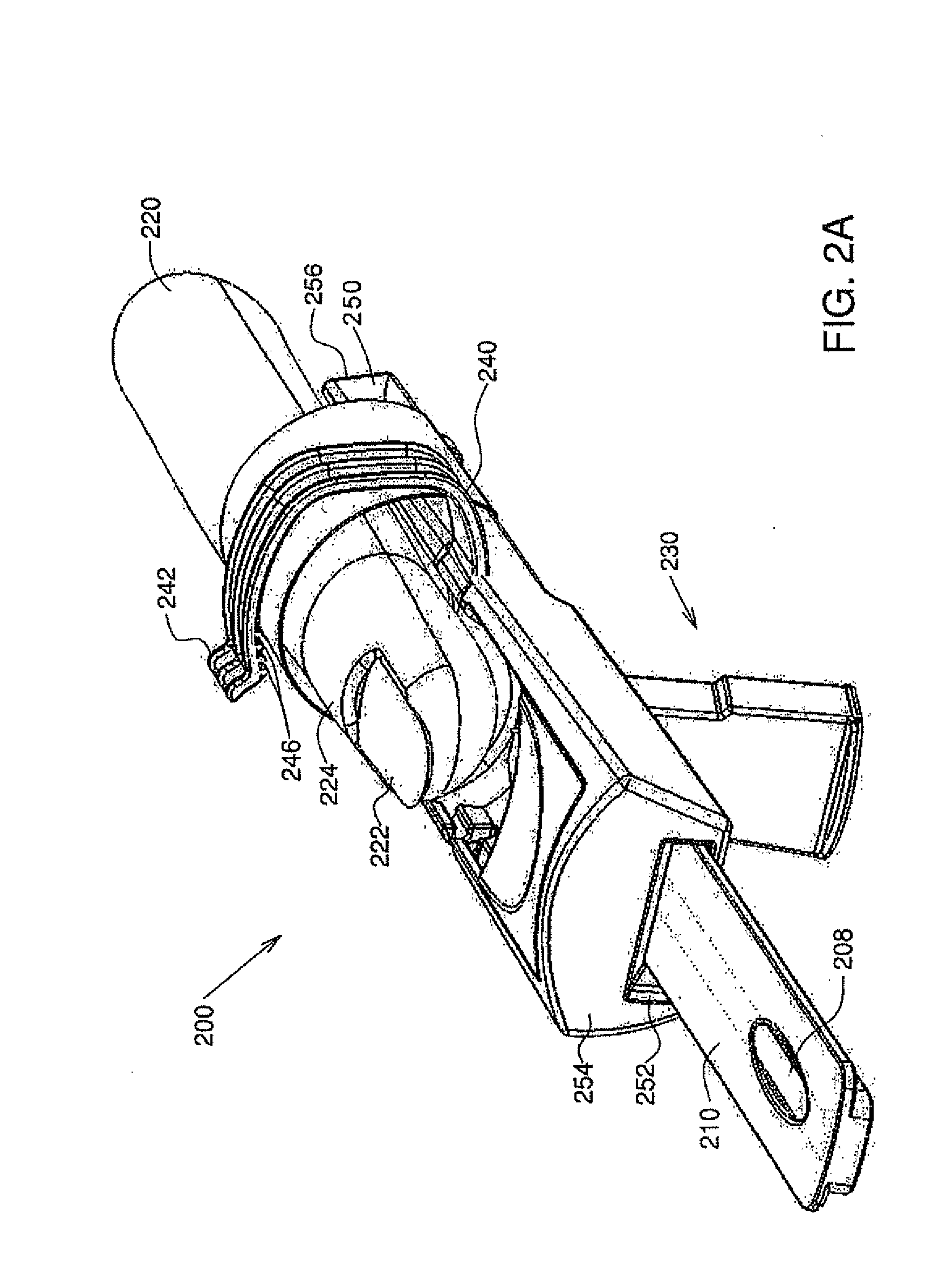
Devices and methods for reduced-pain blood sampling
Systems, methods and devices are provided for invasive reduced-pain blood sampling and testing, the devices including, a horizontally-disposed finger support element configured to support the finger thereupon, a finger holding element adapted, in a closed position, to radially grip the finger on said support element near to a tip thereof and configured to force blood into said tip, a lancet housing element disposed vertically underneath the finger support element for piercing the finger tip with a lancet while said finger tip is gripped by said finger holding element and supported by said finger support element; and a test strip conveying element adapted to be received by the finger support element after retraction of the lancet housing element thereby bringing a test strip into direct contact with a predetermined volume of blood from said finger support element thereby effecting a blood test.
Owner:RAPIDX LTD
Method and system for intelligently identifying and reading immunity-chromatography test strip and application thereof
InactiveCN101769925AGuaranteed accuracyHigh degree of intelligenceMaterial analysis by optical meansColor measuring using electric radiation detectorsConvertersMedicine
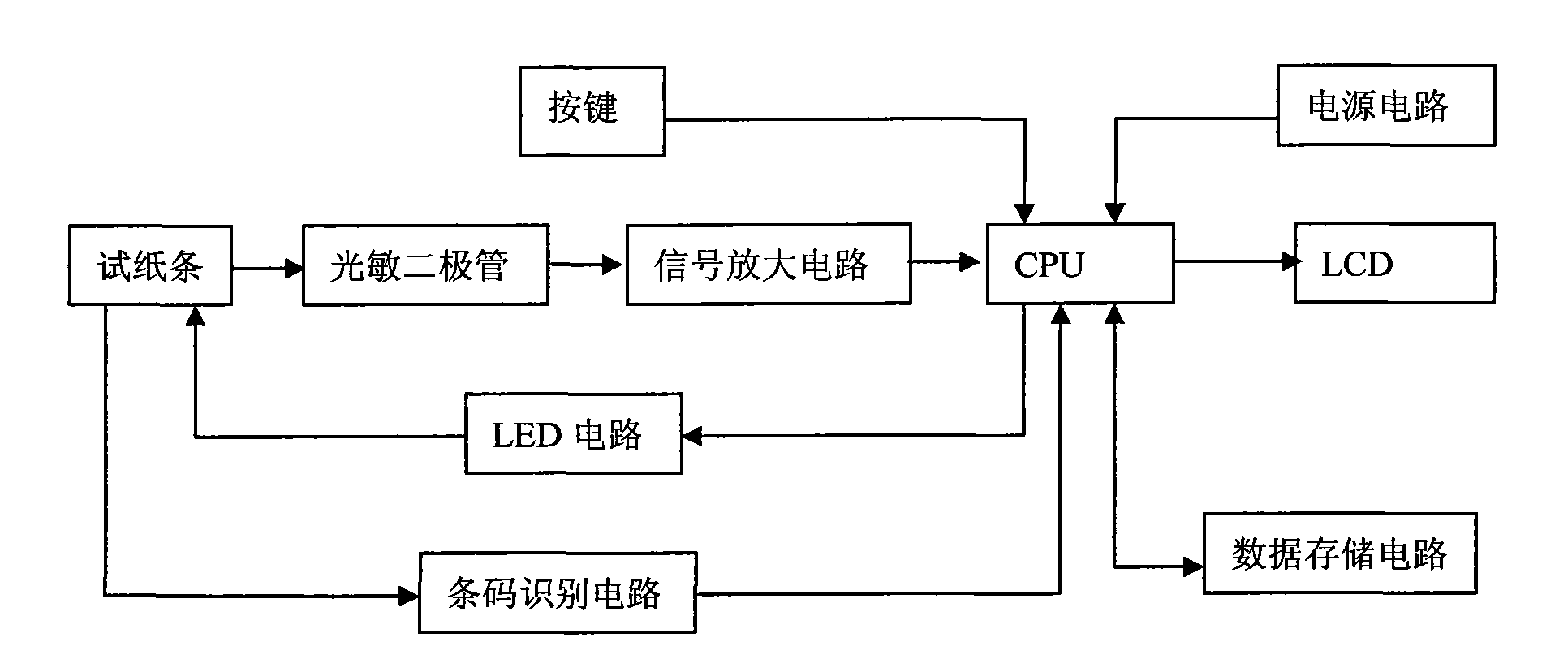
The invention discloses a method an a system for intelligently identifying and reading an immunity-chromatography test strip and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: the immunity-chromatography test strip with a bar code is arranged in a test strip test jack; light emitted by a light source in a bar code identification circuit is irradiated on the bar code of the immunity-chromatography test strip with the bar code by a lens; the emitted light is converted into an electric signal by a photoelectric converter; the signal is transmitted to a CPU by an amplification and rectification circuit; and the CUP fetches an analysis programme corresponding the type of the immunity-chromatography test strip with the bar code according to the received electric signal from the bar code identification circuit. The system obtained according to the method has high intelligent degree and simple operation. The operator only needs to insert the immunity-chromatography test strip with the bar code in a designated position of the device and then makes a loading end of the immunity-chromatography test strip in contact with a sample so as to know the result of the test item by a display screen.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WONDFO BIOTECH
System and method for quantitative detection of test strips on basis of continuous fluorescent-substance markers
ActiveCN101592659AEmitting characteristic wavelengths with high fluorescence brightnessHigh fluorescence brightnessBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAcquired characteristicFluorescence
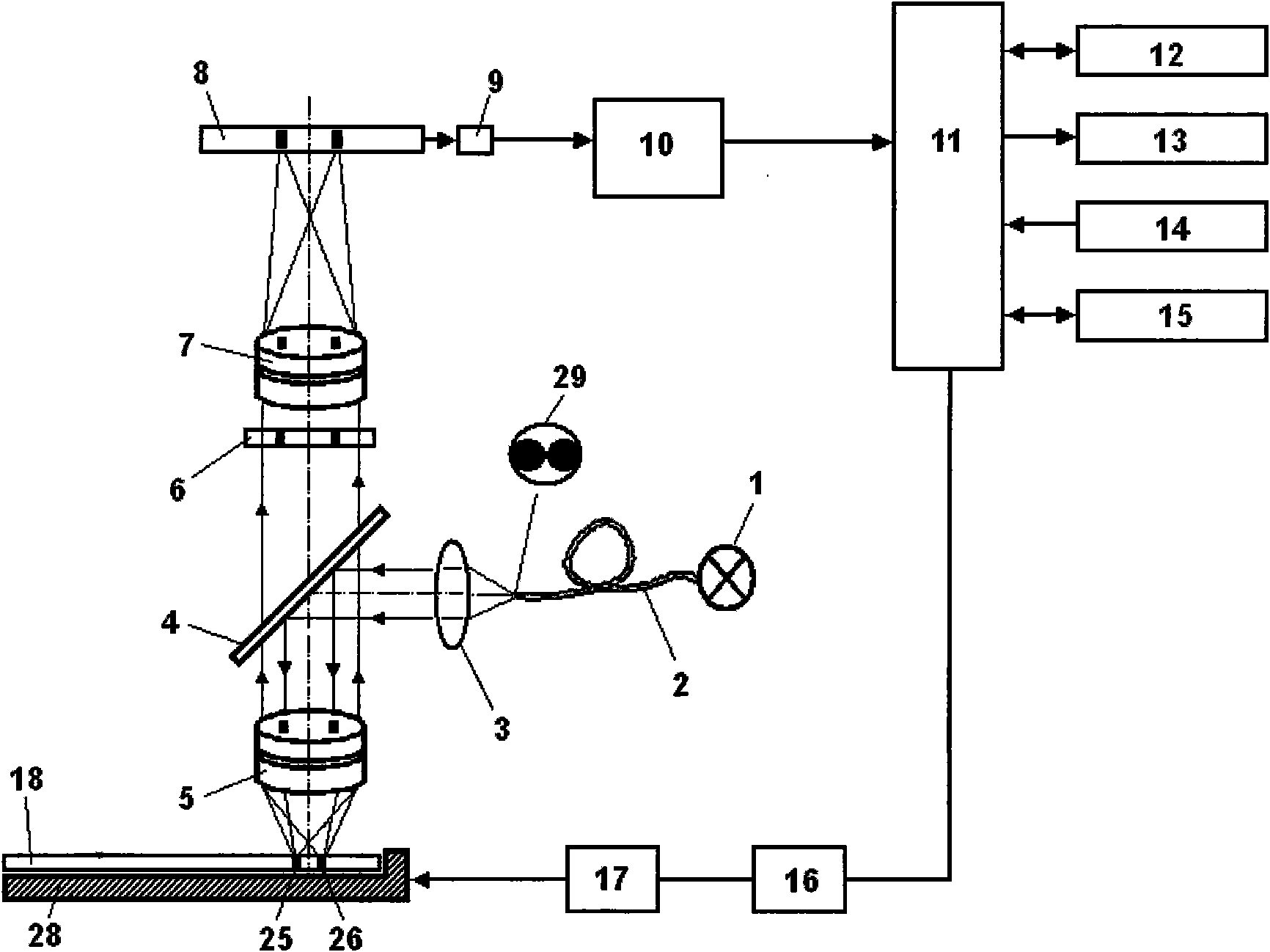
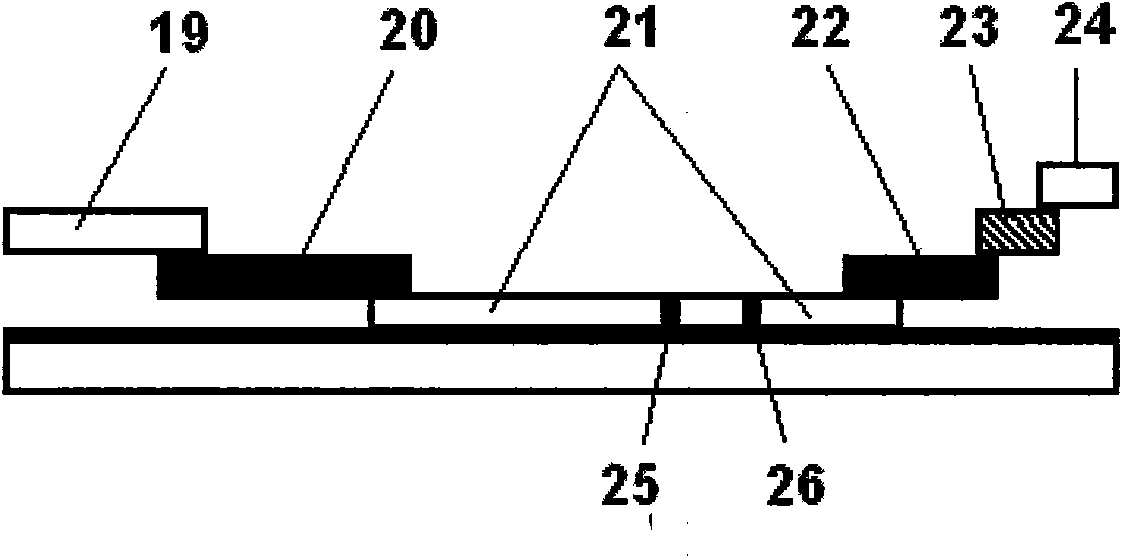
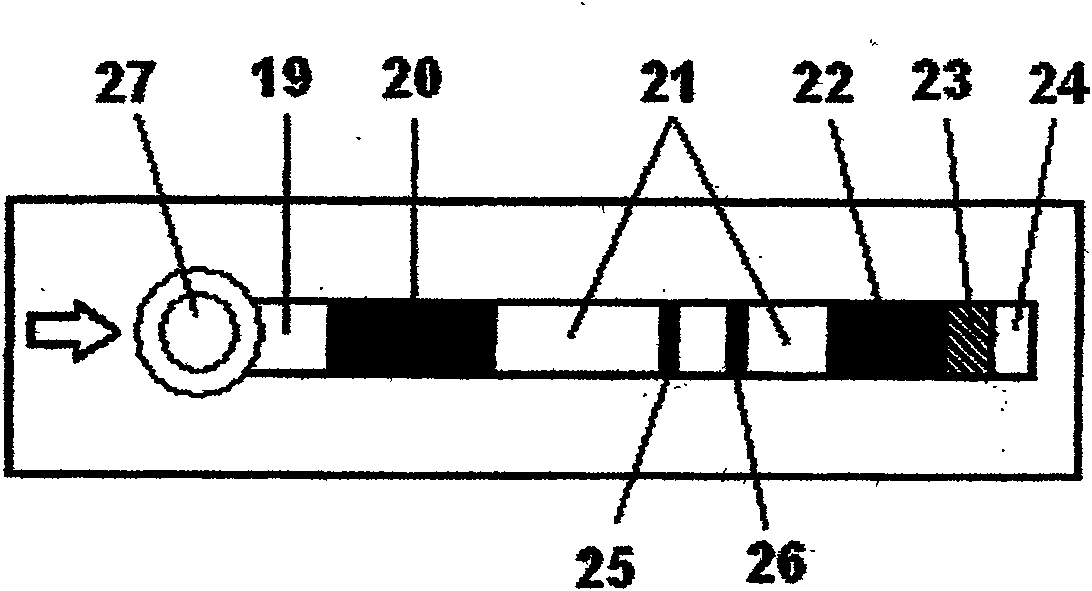
The invention belongs to the field of bio-medical instruments, and in particular relates to a system and a method for quantitative detection of test strips on the basis of continuous fluorescent-substance markers. The system comprises a continuous fluorescent-substance marker test strip, a test strip frame, a lighting system, an imaging system, a fluorescent image receiver, a signal amplifier, an analog / digital converter, a data processing-controlling system, an output display device, a printer, a keyboard and an IC card matched with the test strip. The data processing-controlling system reads parameters of the IC card and then controls the test strip frame to move so as to ensure that the light emitted by the lighting system is reflected via a dichroic mirror and then automatically scans the test strip; acquired characteristic wavelength reflection fluorescence is transmitted to the data processing-controlling system for optical density identification and concentration calculation via the fluorescent image receiver, the signal amplifier and the analog / digital converter; and the output display device displays results. The invention can quickly and accurately realize the quantitative or qualitative detection of single-component and multi-component samples. The system has the characteristics of high detection sensitivity, objective results, flexible use and the like.
Owner:马义才
Quantum dot marking test strip quantitative detection system based on CMOS image sensor
InactiveCN101368907AAccurately Realize Qualitative DetectionThe test results are objectiveBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCMOSDisplay device
Disclosed is a CMOS image sensor-based on quantum dot marking test strip quantitative detection system, which comprises a quantum dot marking test strip, a test strip frame, a scanning system, a CMOS image sensor, a data-processing device, an output display device, a printer, a keyboard and an IC card matched with the test strip. After reading the IC card parameters, the data-processing device controls the test strip to move, so that the scanning system can automatically scan a detection band and a quality control band of the test strip; the collected signals are transmitted to the data-processing device through the CMOS image sensor, so that the optical density of the detection band and the quality control band can be identified and processed with concentration computing and technical analysis; and the test results are transmitted to the output display device and displayed. The invention can accurately achieve one-component and multi-component quantitative, semi-quantitative or qualitative detection of samples and can dynamically monitor the immunochromatographic reaction process. The system has high sensitivity, objective result and flexible operation.
Owner:马义才
Method for determining HDL concentration from whole blood or plasma
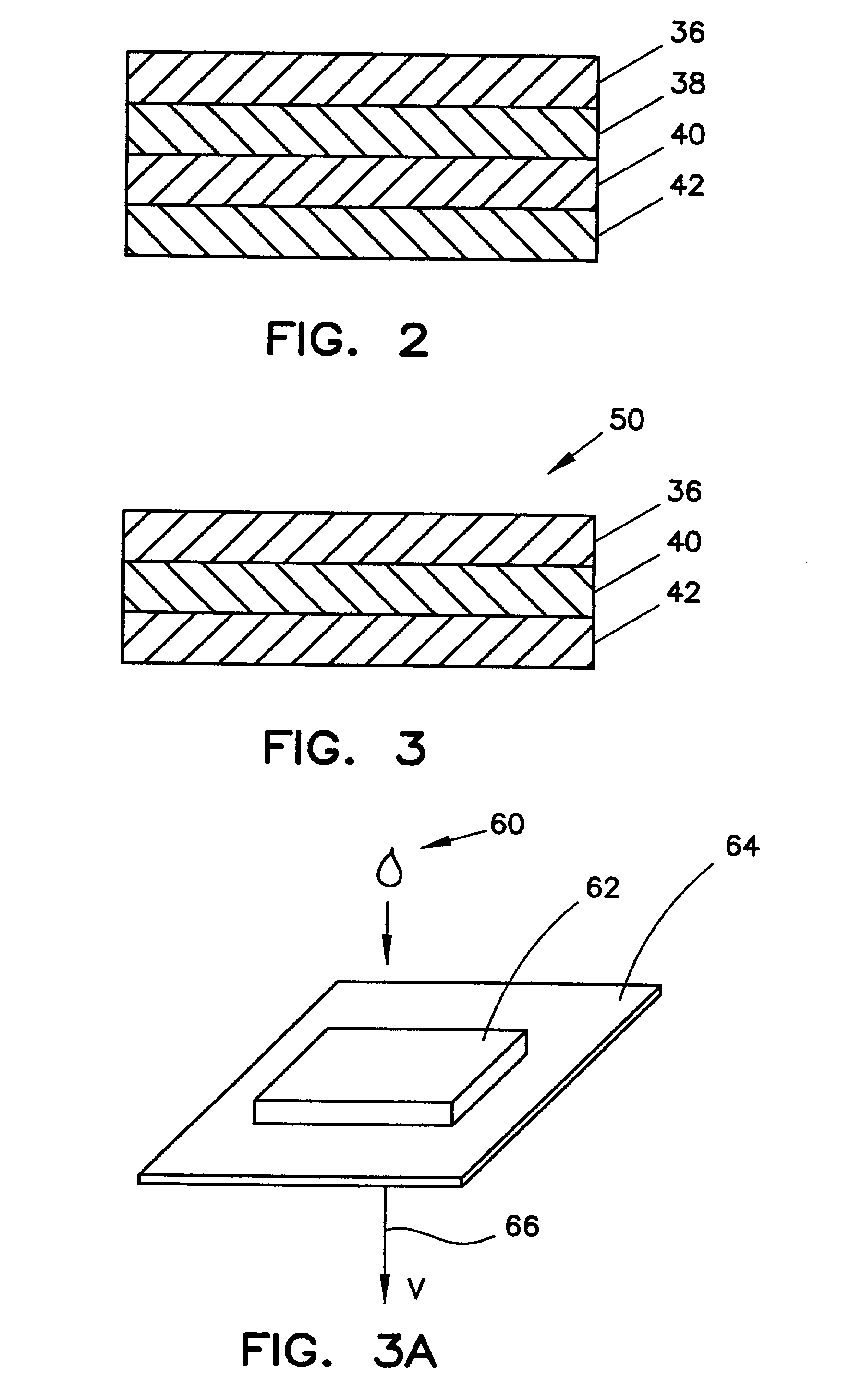
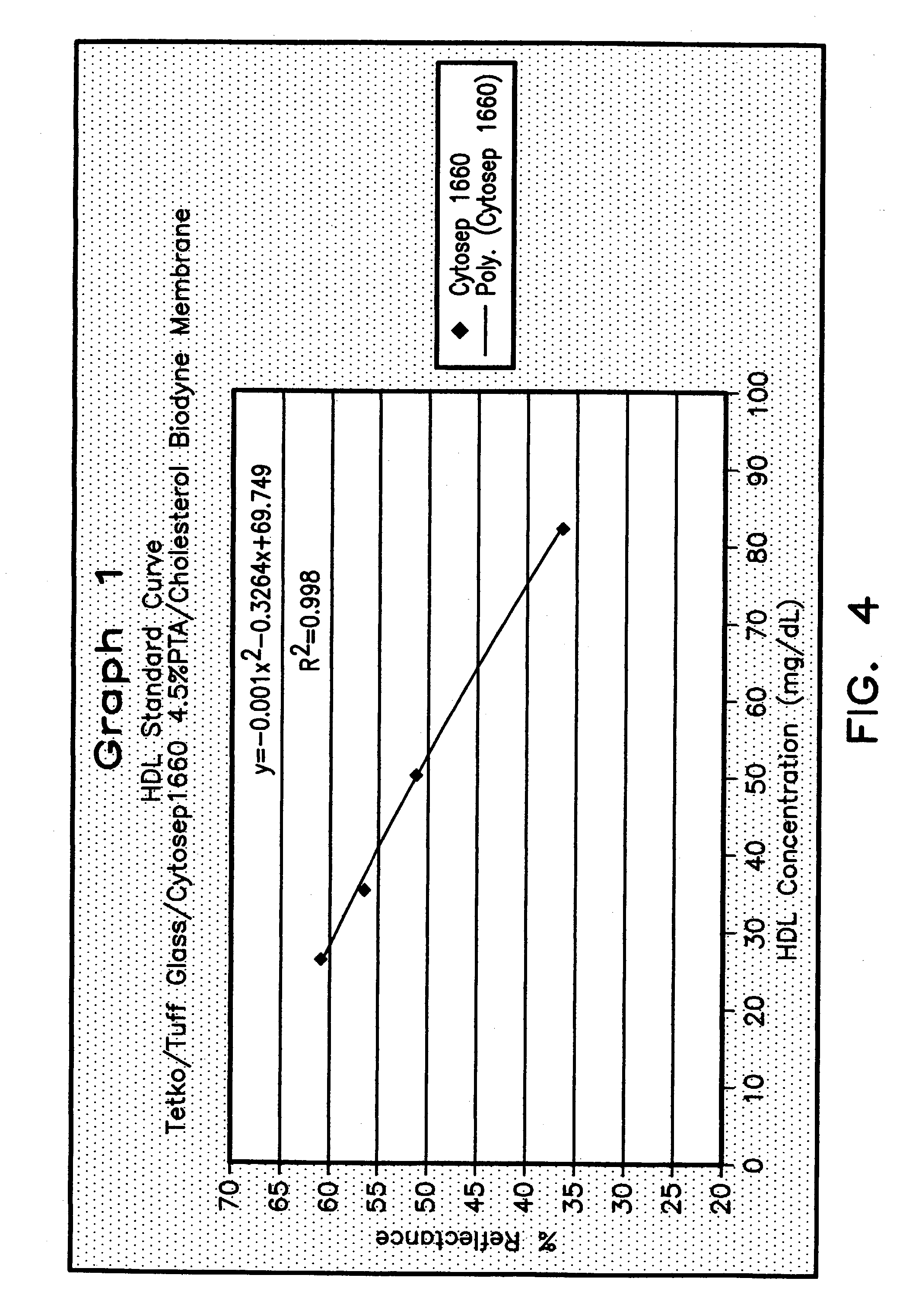
ActiveUS7087397B2Avoid flowEasy and fast assemblyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerCholesterol
A multilayer test strip and method of using the test strip for determining concentration of HDL cholesterol in a whole blood sample. The inventive test strip includes a two-stage blood separation mechanism, including a first glass fiber matrix which separates most of the blood cells and an adjacent, second matrix preferably also containing glass fibers that separates the remainder of the blood cells. The second layer also precipates and retains non-HDL cholesterol, thereby providing plasma that is substantially free of red blood cells and substantially free of non-HDL cholesterol to a reaction layer. Precipitation and retention on non-HDLs takes place by a vertical or dead-end filtration in a single layer. The reaction layer produces a color, the intensity of which is proportional to the concentration of HDL cholesterol in the blood sample which is applied to the test strip. Advantageously, the inventive test strip is a vertical flow device, which can be made more compact and operates more efficiently than a lateral flow device.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
Extraction method and apparatus for high-sensitivity body fluid testing device
ActiveUS20080166820A1Rapid and efficient mannerQuick and accurate testBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBottleSaliva
An extraction method and apparatus is provided for obtaining quick, safe and highly sensitive testing of any of a variety of body fluids including saliva, blood, urine or other fluids for drugs of abuse or other analytes. The apparatus includes a latchable extraction wand for obtaining body fluid samples from a subject which is adapted to maximize the portion of the body fluid sample that will go into a graduated bottle containing a buffer solution, and a testing device wherein the sample will be received and into which test strips can be inserted to determine levels of drugs of abuse or other analyte in the sample. In one of the methods of the invention, energy is imparted to the sample and buffer solution, such as by shaking, and this facilitates the reduction of sample viscosity, such as by promoting the breakdown of mucins when the sample is saliva.
Owner:HEALGEN SCI LLC
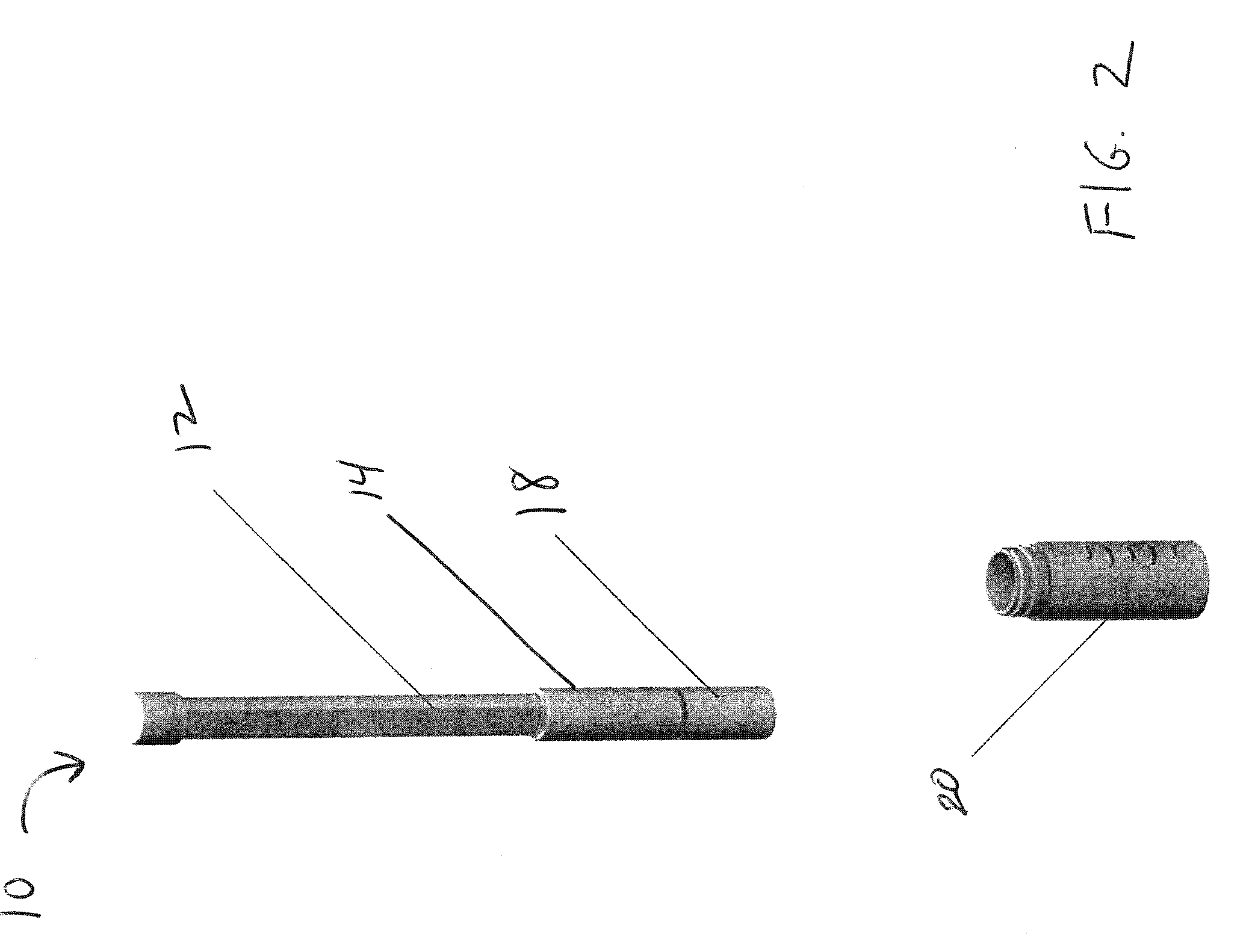
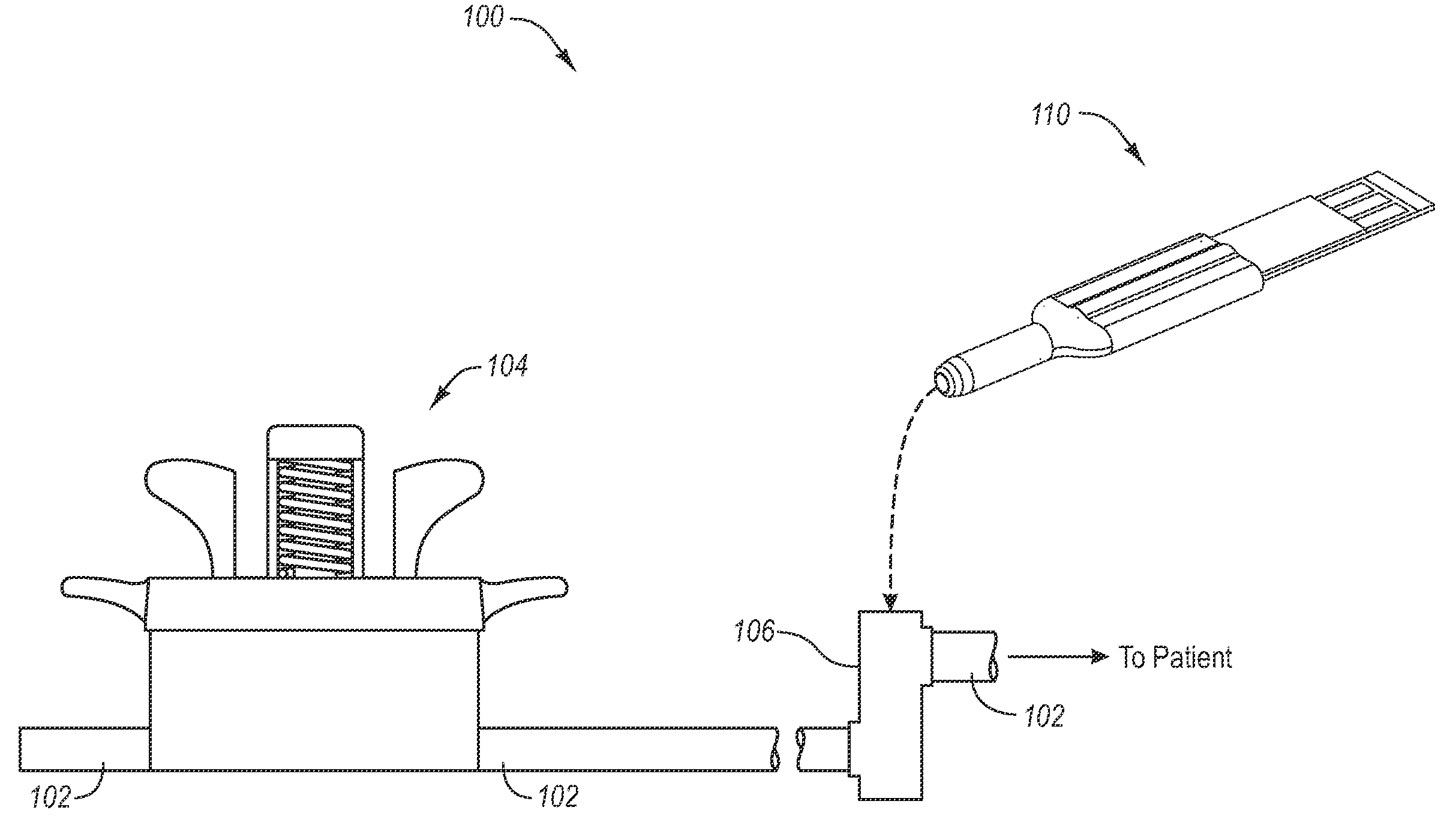
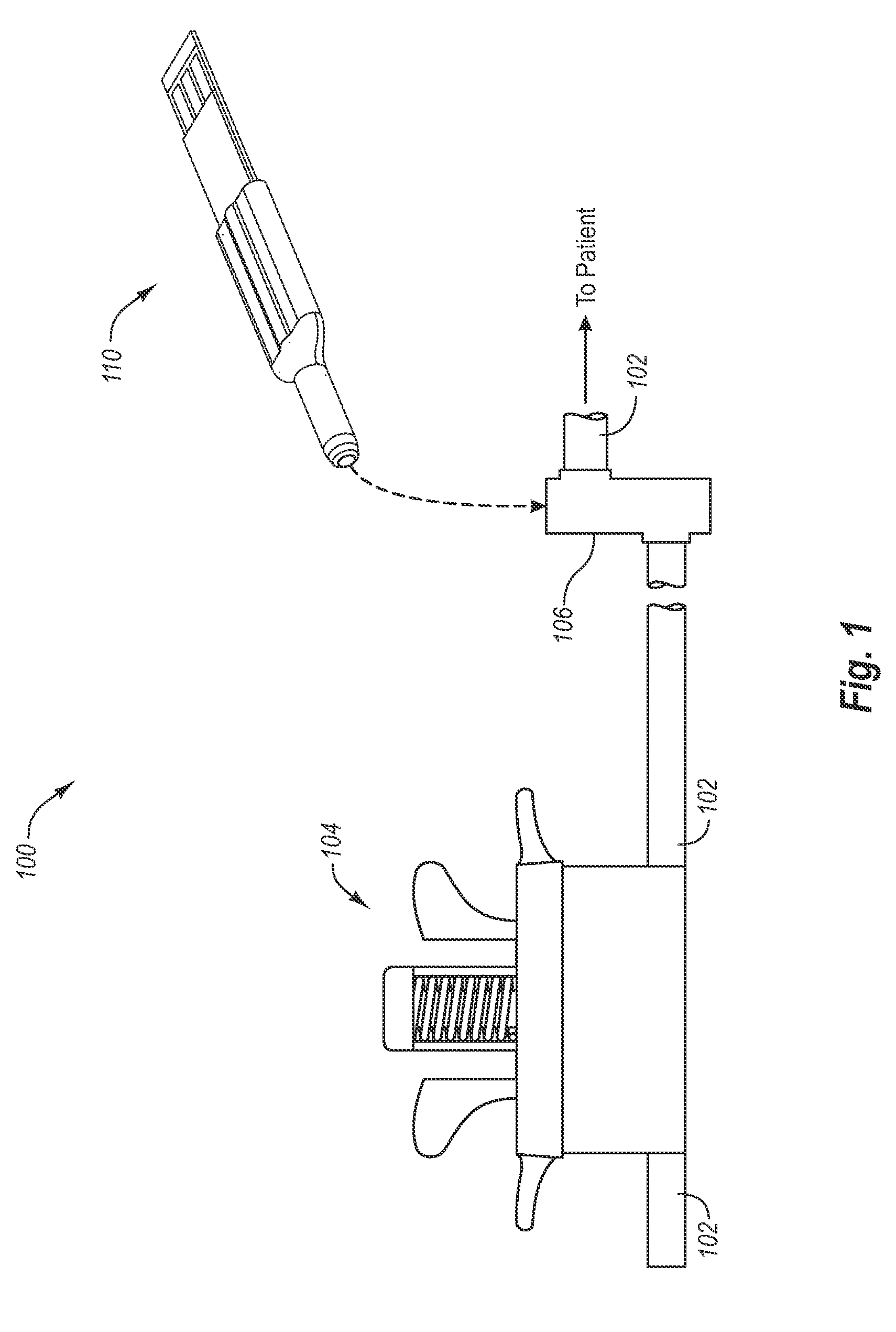
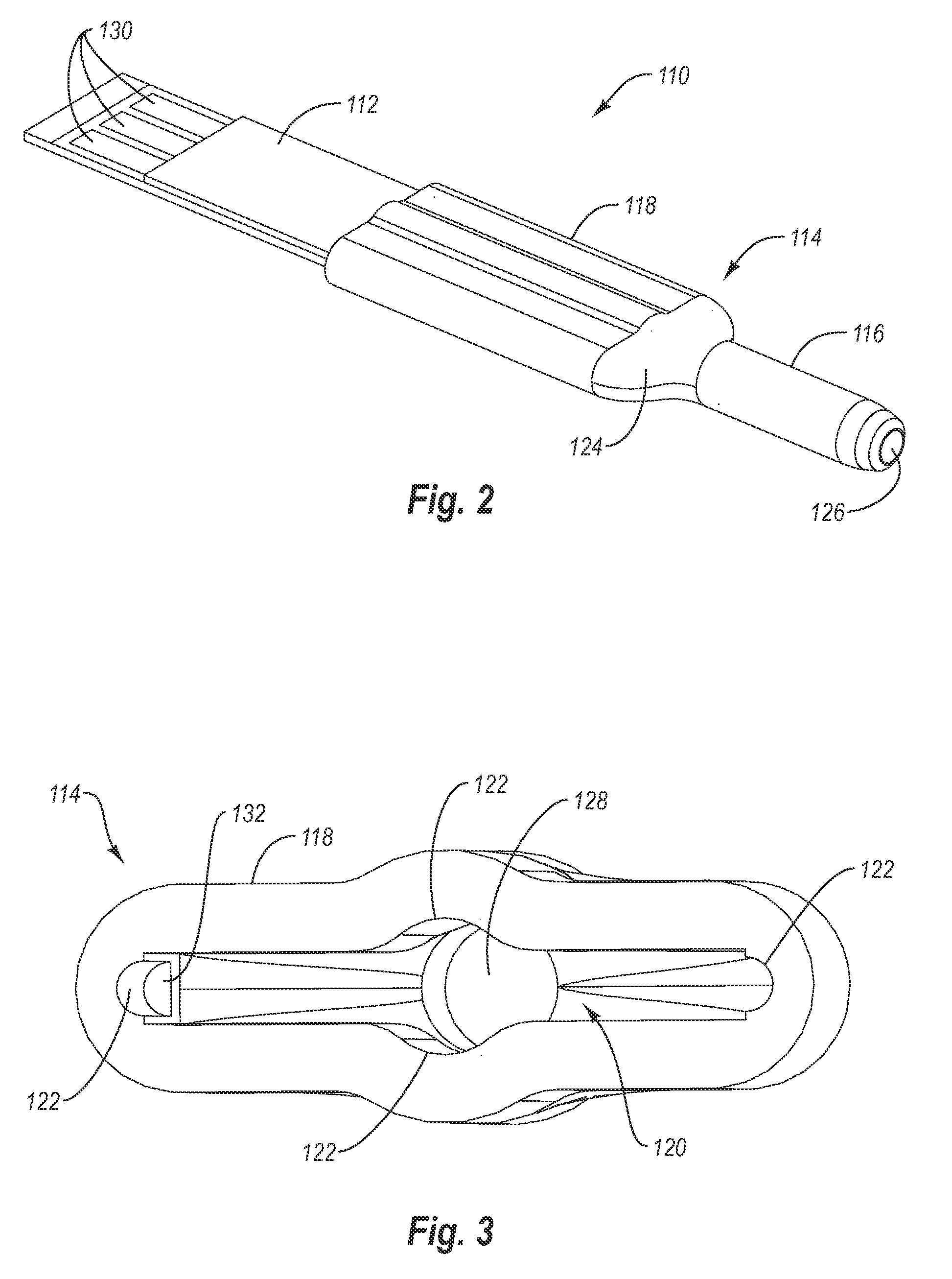
Bodily fluid sampling systems, methods, and devices
InactiveUS20090099431A1Shorten the timeReduce painCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringBody fluid
A fluid sampling system is disclosed comprising a fluid drawing device, a fluid sampling device, and an analysis device. The fluid drawing device can be used to draw bodily fluid into a sample port of an IV tube. The fluid sampling device can be used to access the sample port to obtain a fluid sample. The fluid sampling device can include a test strip housing for receiving a test strip therein. Extending from an end of the test strip housing is a blunt canula that can be inserted into the sample port to obtain the fluid sample and communicate the fluid sample to the test strip. The test strip housing is configured to allow the second end of the test strip to be received within an analysis device to facilitate analysis of the fluid sample.
Owner:GLUCOR SYST
Electronic analyte assaying device
ActiveUS20060008896A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteAssay
The invention is an electronically processed single-step test device for detecting the presence of a preselected analyte in a fluid. The device includes a hollow rectangular outer casing, disposed within co-joined upper and lower sections of the casing are assay material, an electronic processing system, and a LCD display. The LCD display is observable through a viewing window. The assay material is a sorptive material including a fluid sample application region in the form of a sample wick in fluid communication with a test strip. The test strip includes an analyte capture region adjacent to a light shield. The electronic processing system includes red and green LEDs which are alternately pulsed or energized over predetermined periods of time to determine if fluid test results show a marker or markers in the capture region indicative of the presence of a preselected analyte in the fluid. If so, Yes+ is displayed on the LCD. If not, No− is displayed on the LCD.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
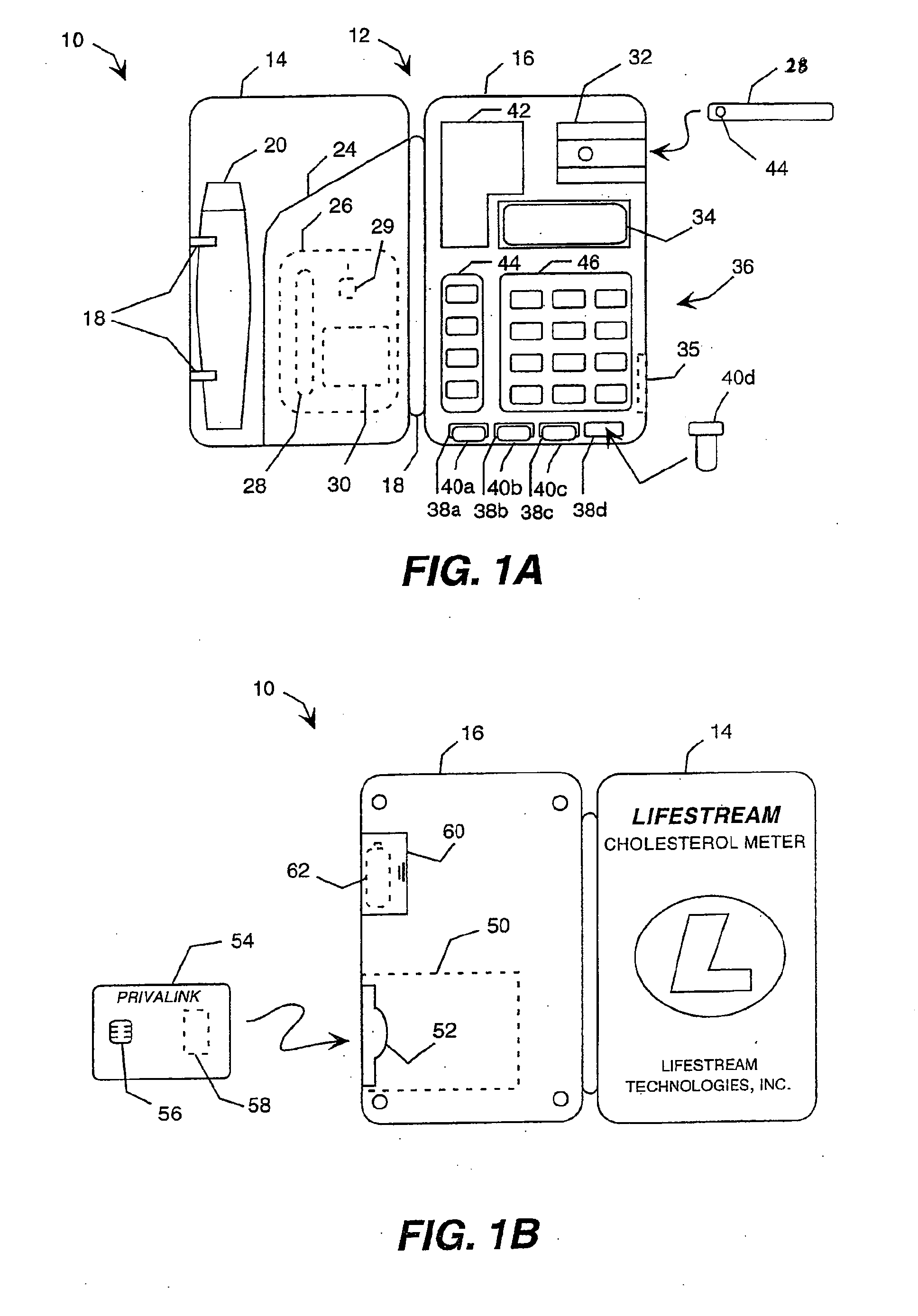
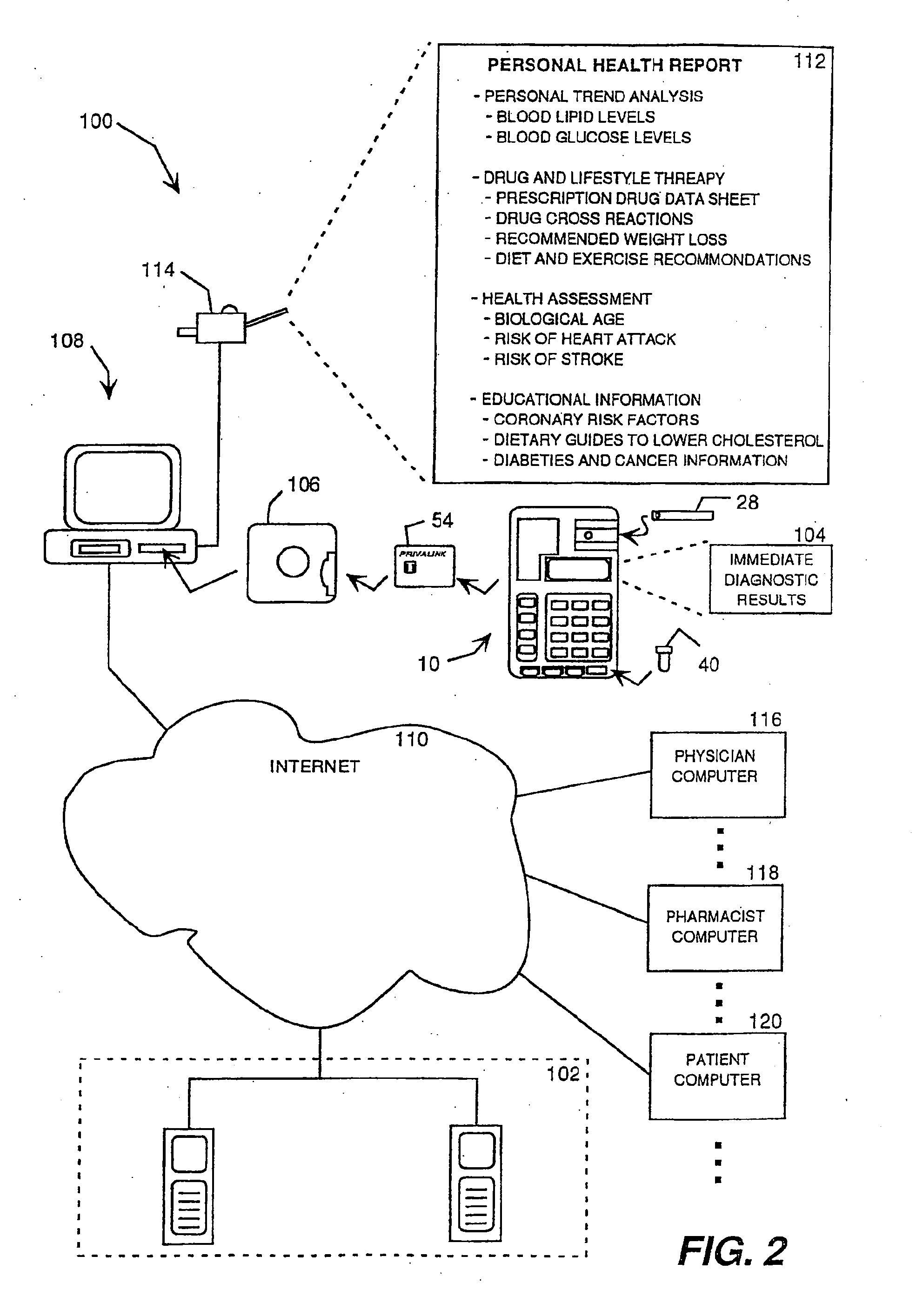
Health monitoring and diagnostic device and network-based health assessment and medical records maintenance system
InactiveUS20100169123A1Low costReduce inconvenienceDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMedical recordEmergency medicine
A health monitoring and diagnostic device (LIFESTREAM cholesterol meter) configured as a self-contained testing and diagnostic unit in a clam-shell type case. One side of the case includes a spring-loaded finger stick and a compartment for carrying one or more packages of disposable items including a test strip, a needle for the finger stick, and an alcohol swipe. The other half of the case includes a test strip reader, a key pad, and a liquid crystal display. The meter reads a test strip carrying a droplet of blood and receives additional diagnostic information from the patient, such as age, gender, weight, and family history of heart disease. Within minutes, the meter displays test results, including total cholesterol levels. The meter also displays additional diagnostic results, such as the patient's “cardiac age,” recommended weight loss, and a cardiac risk assessment. The meter also works in connection with a network-based comprehensive health analysis and reporting system. The meter writes patient data to a smartcard. This patient data typically includes patient identification information, the test results, the diagnostic information, and the diagnostic results. A computer station reads the smartcard and establishes a network connection with a health report server over the Internet. The computer then downloads the patient data to the health report server, which prepares a comprehensive health report. Within minutes, this report is transmitted back to the computer station, where it is printed out and delivered to the patient.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com