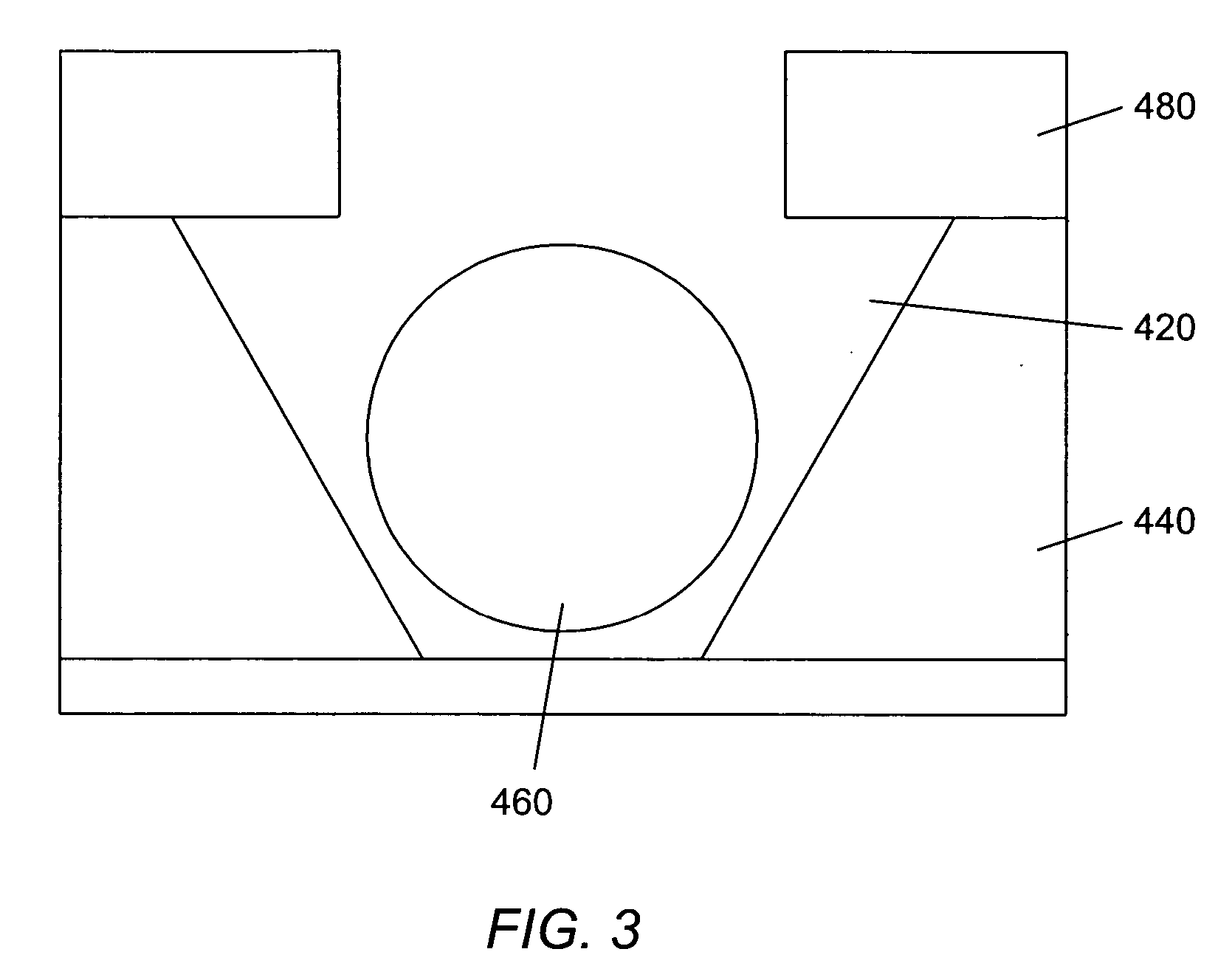
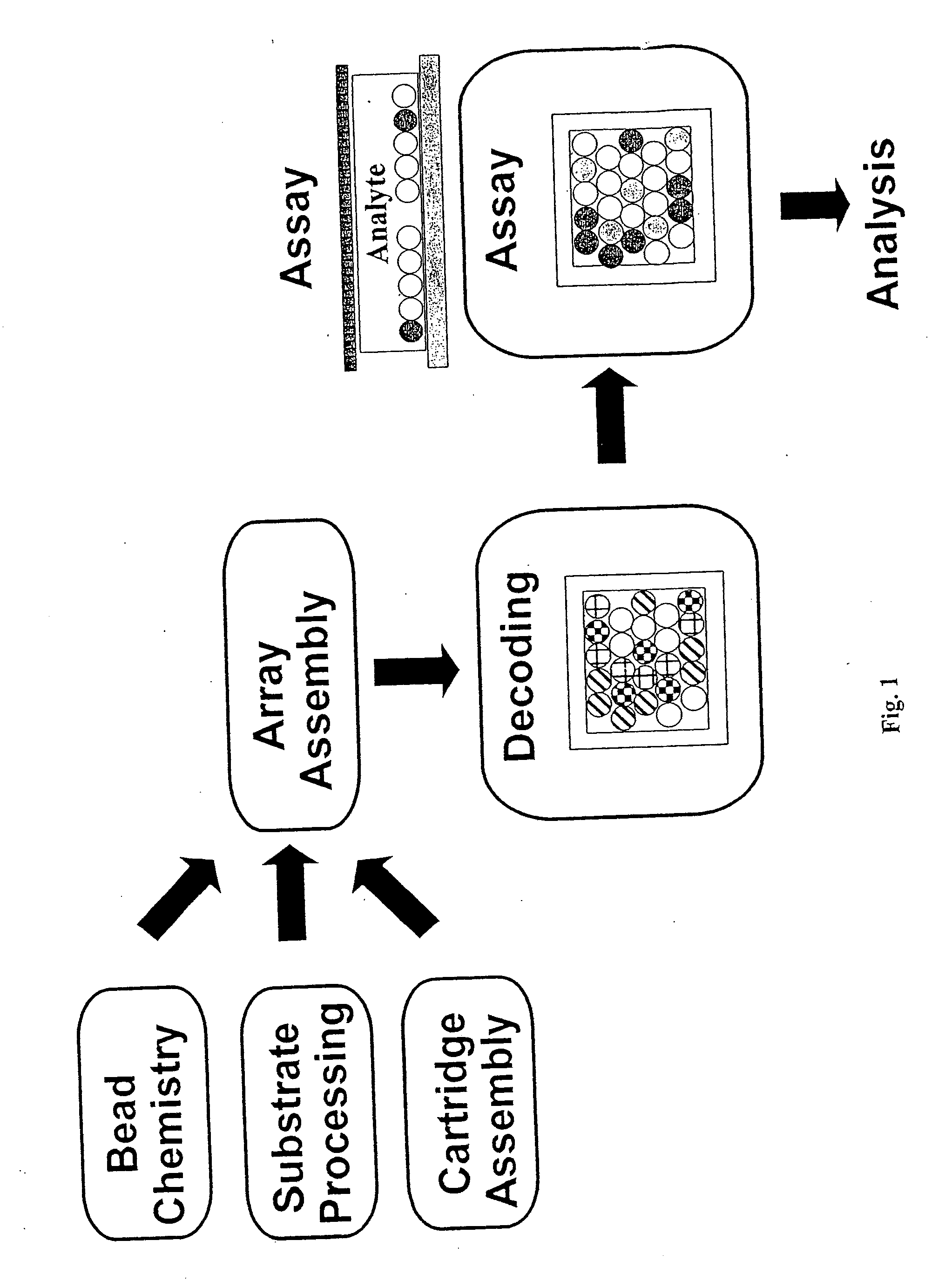
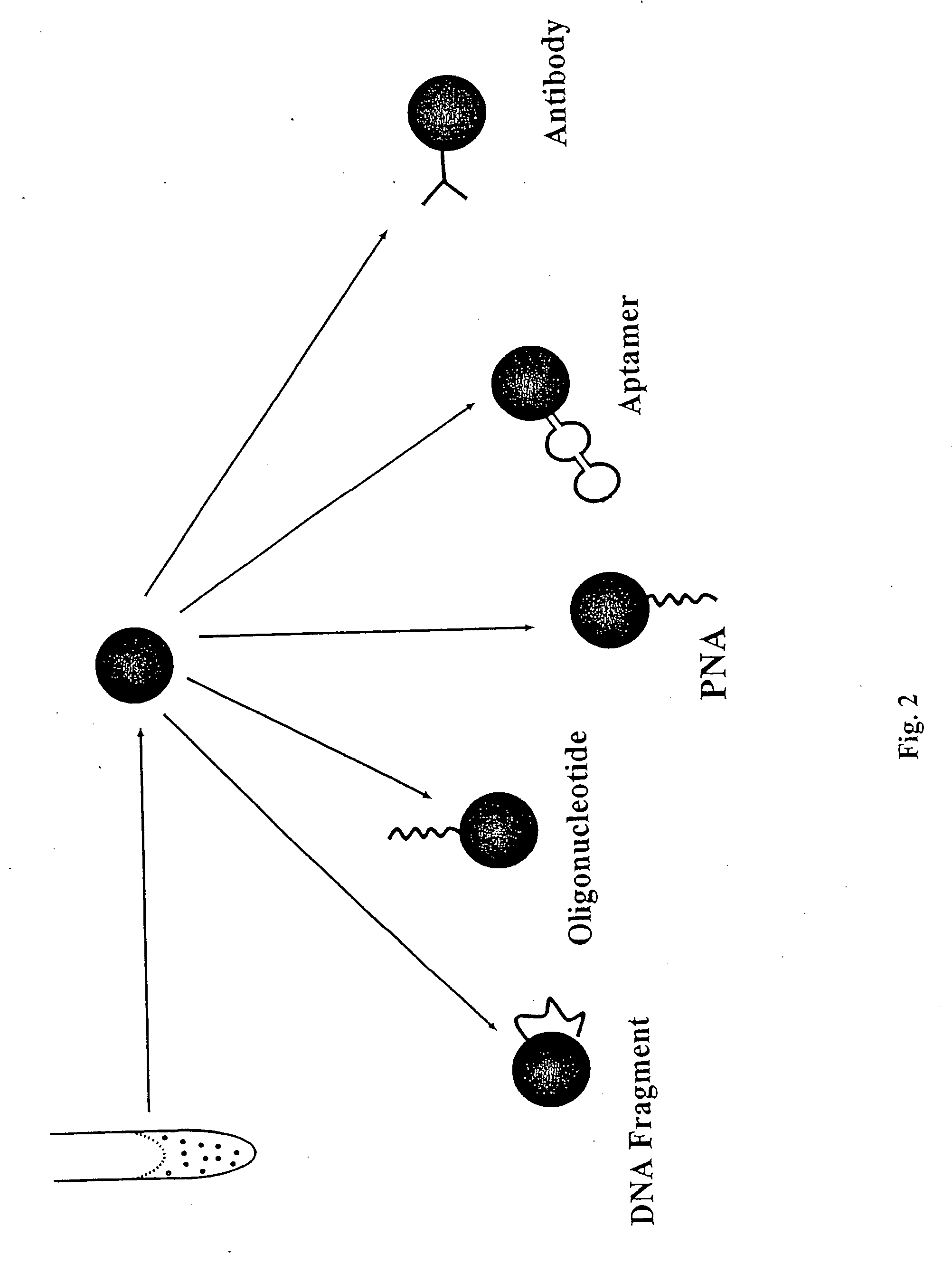
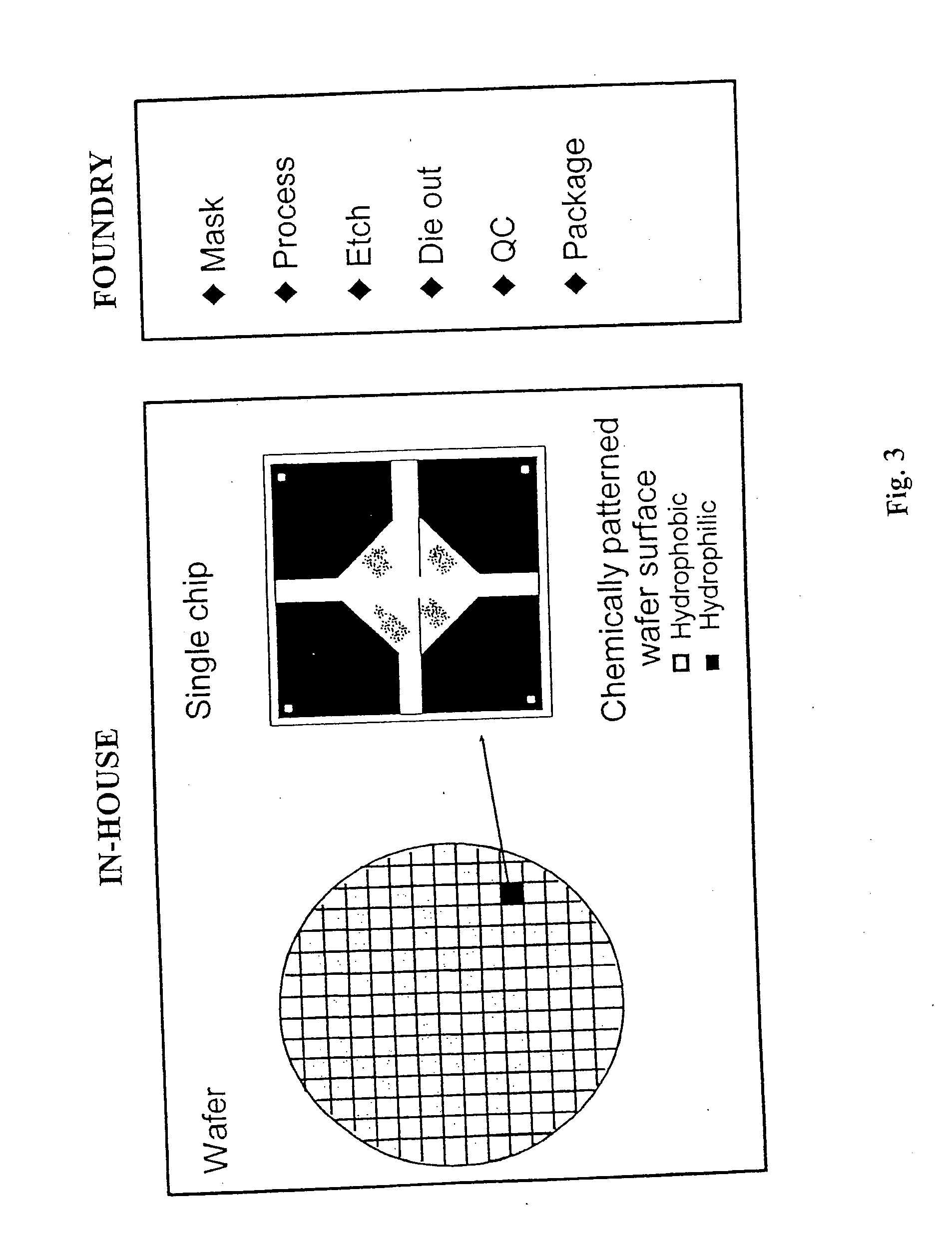
Patents
Literature
136 results about "Multi analyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
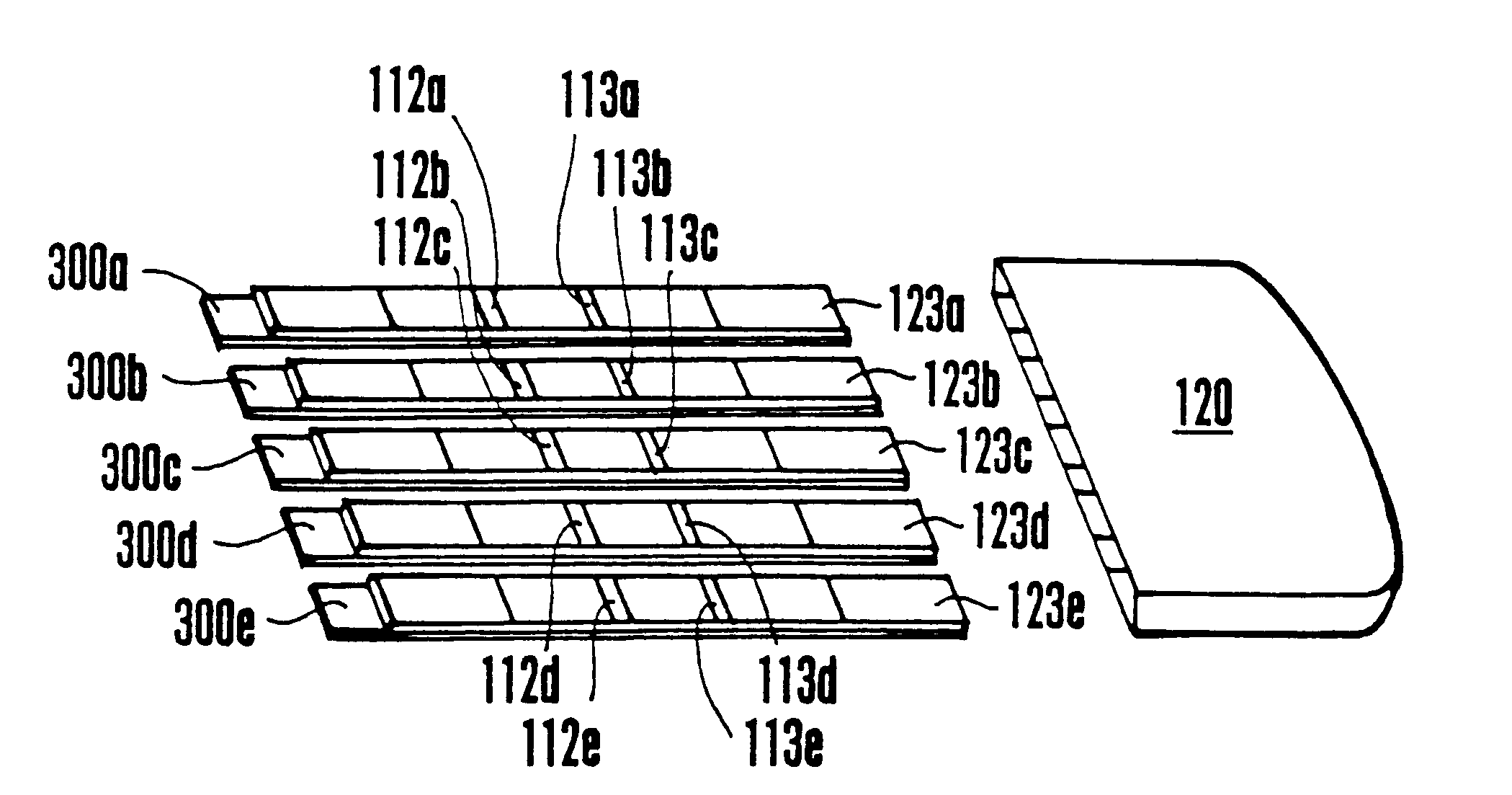
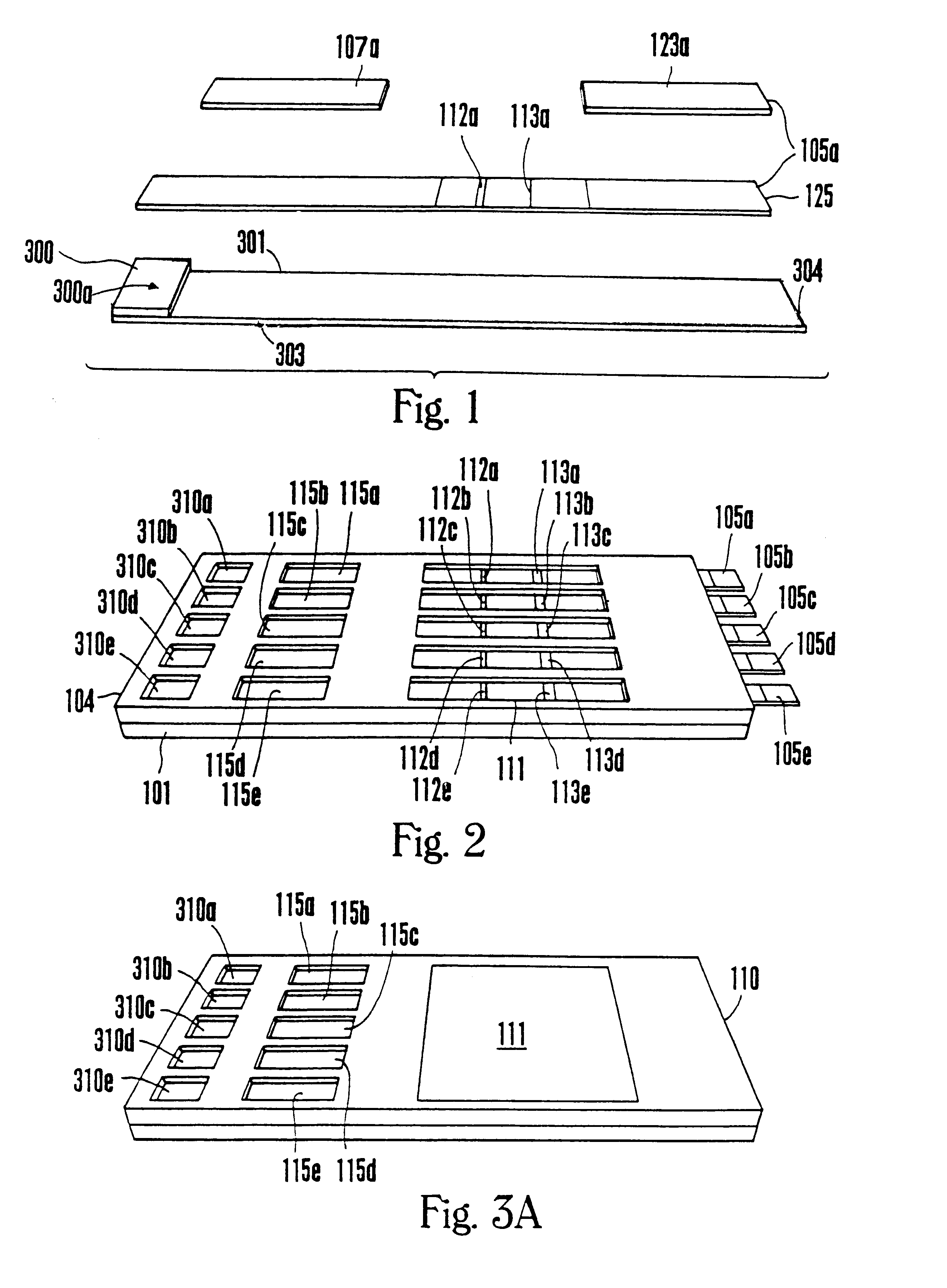
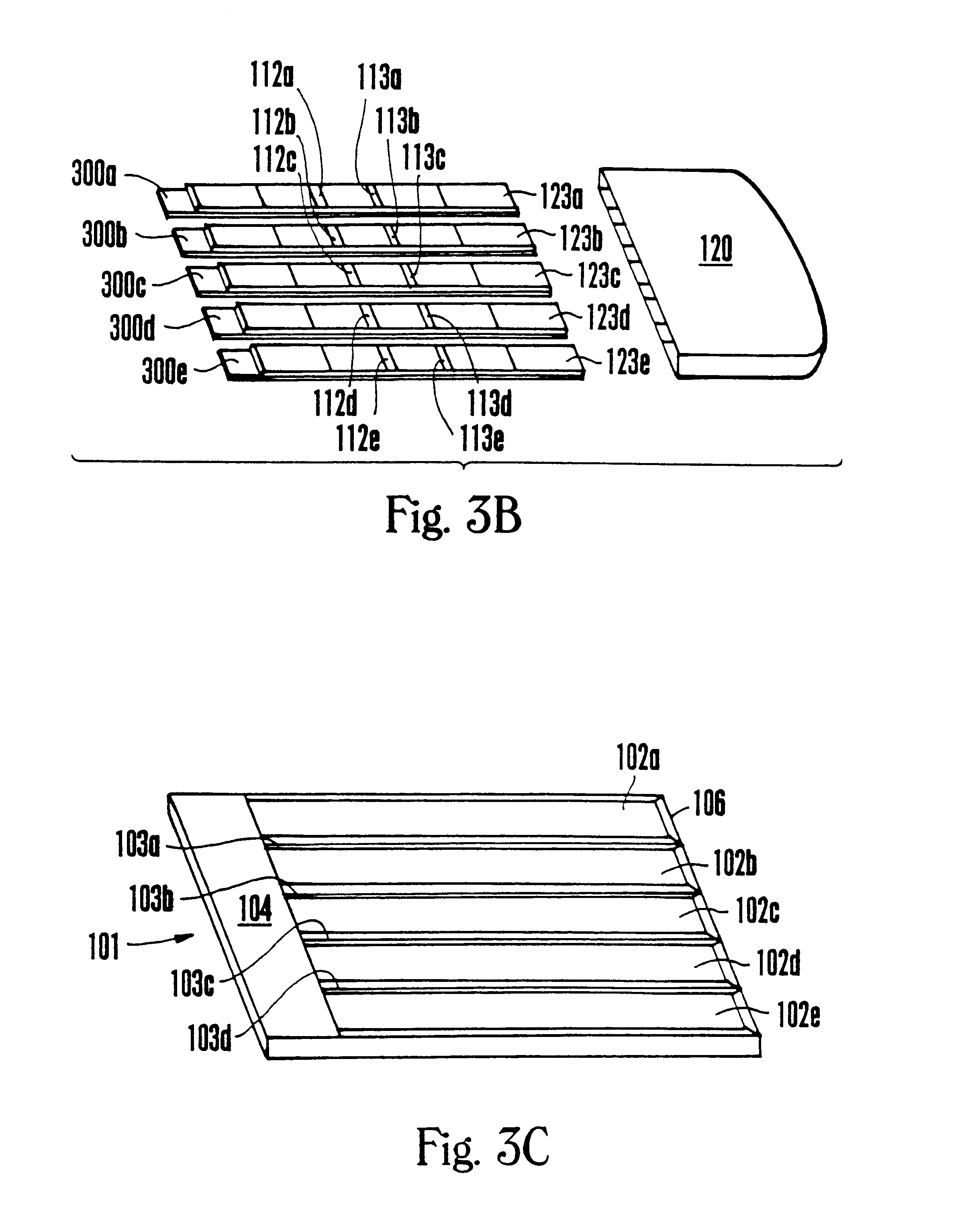
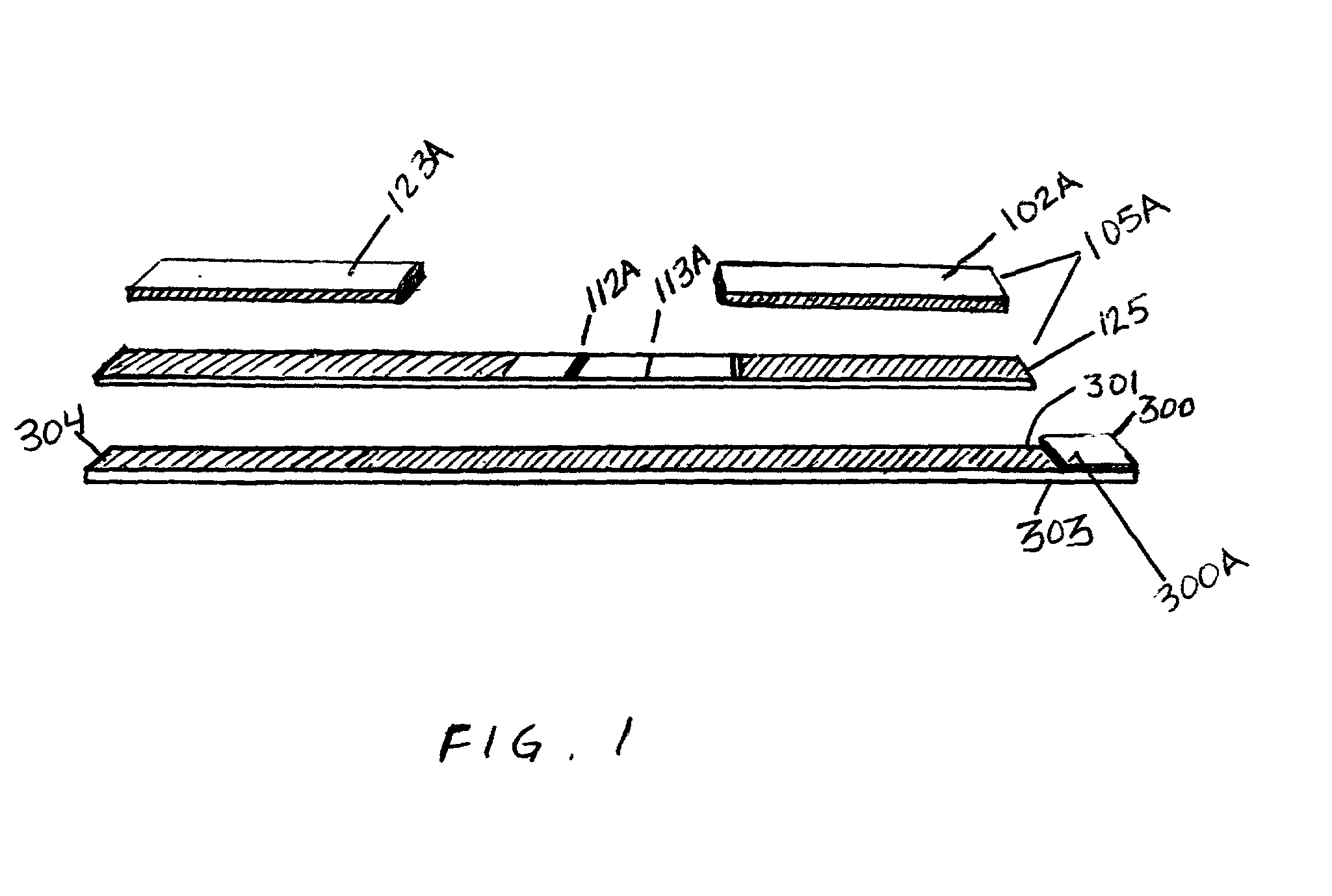
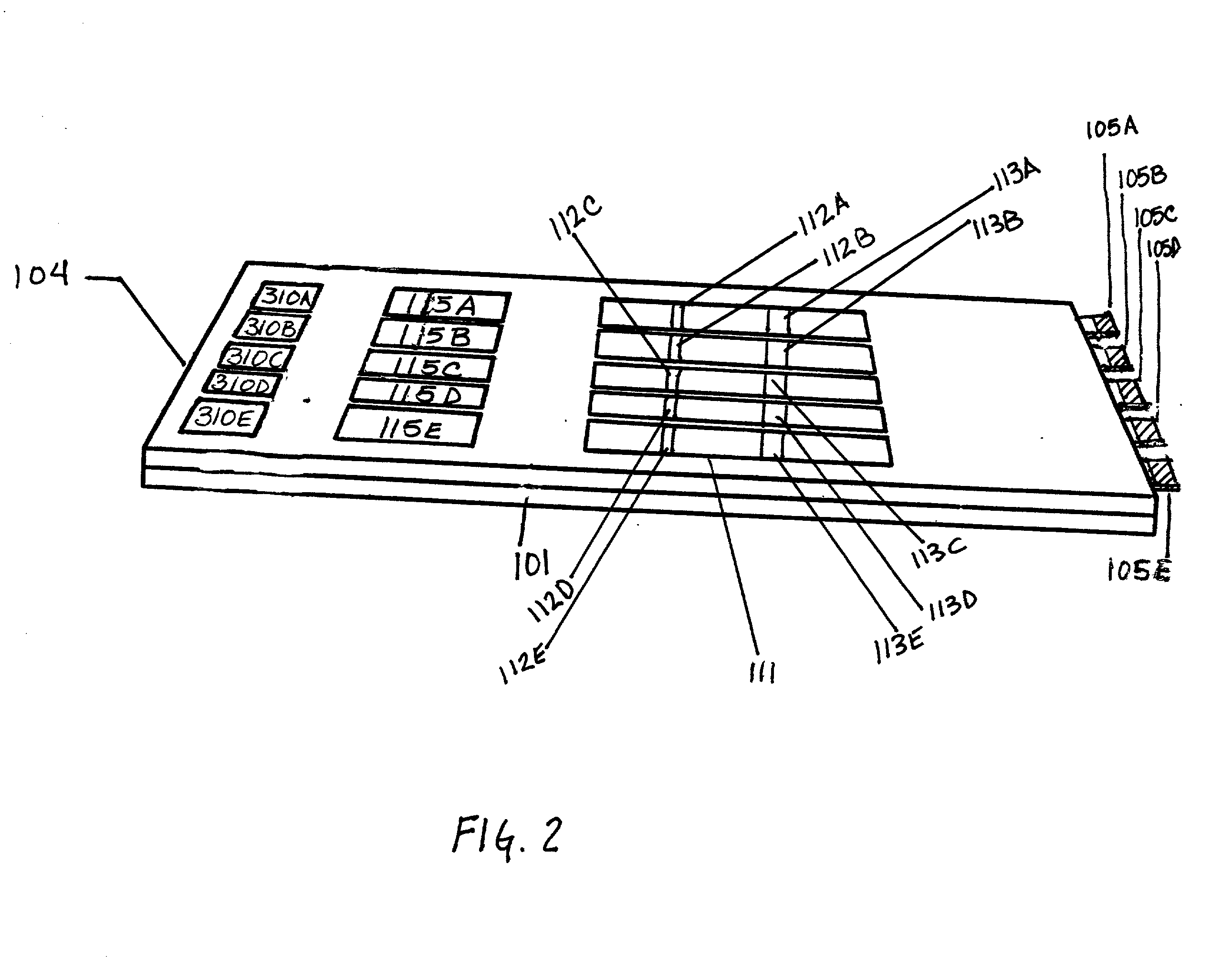
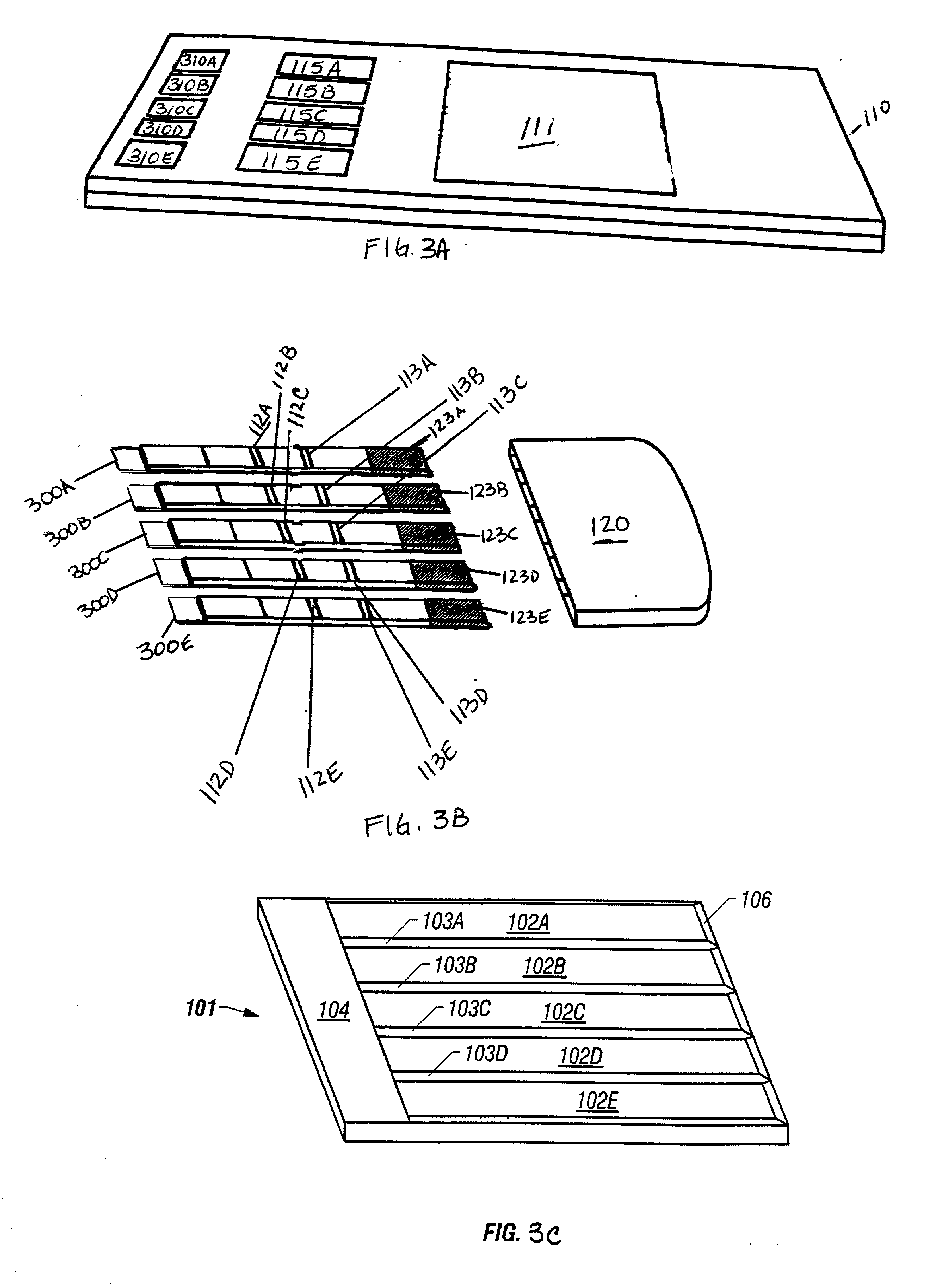
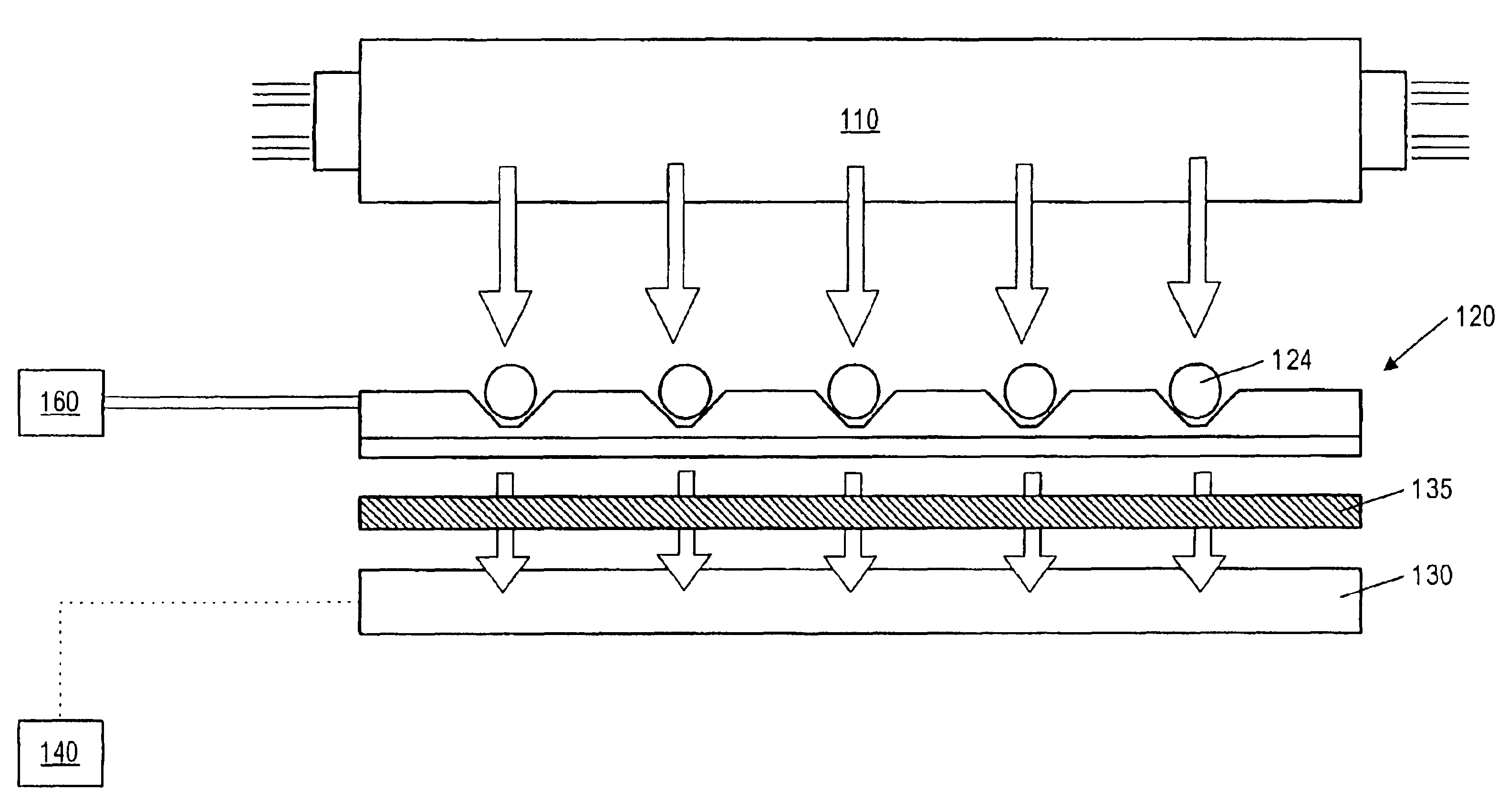
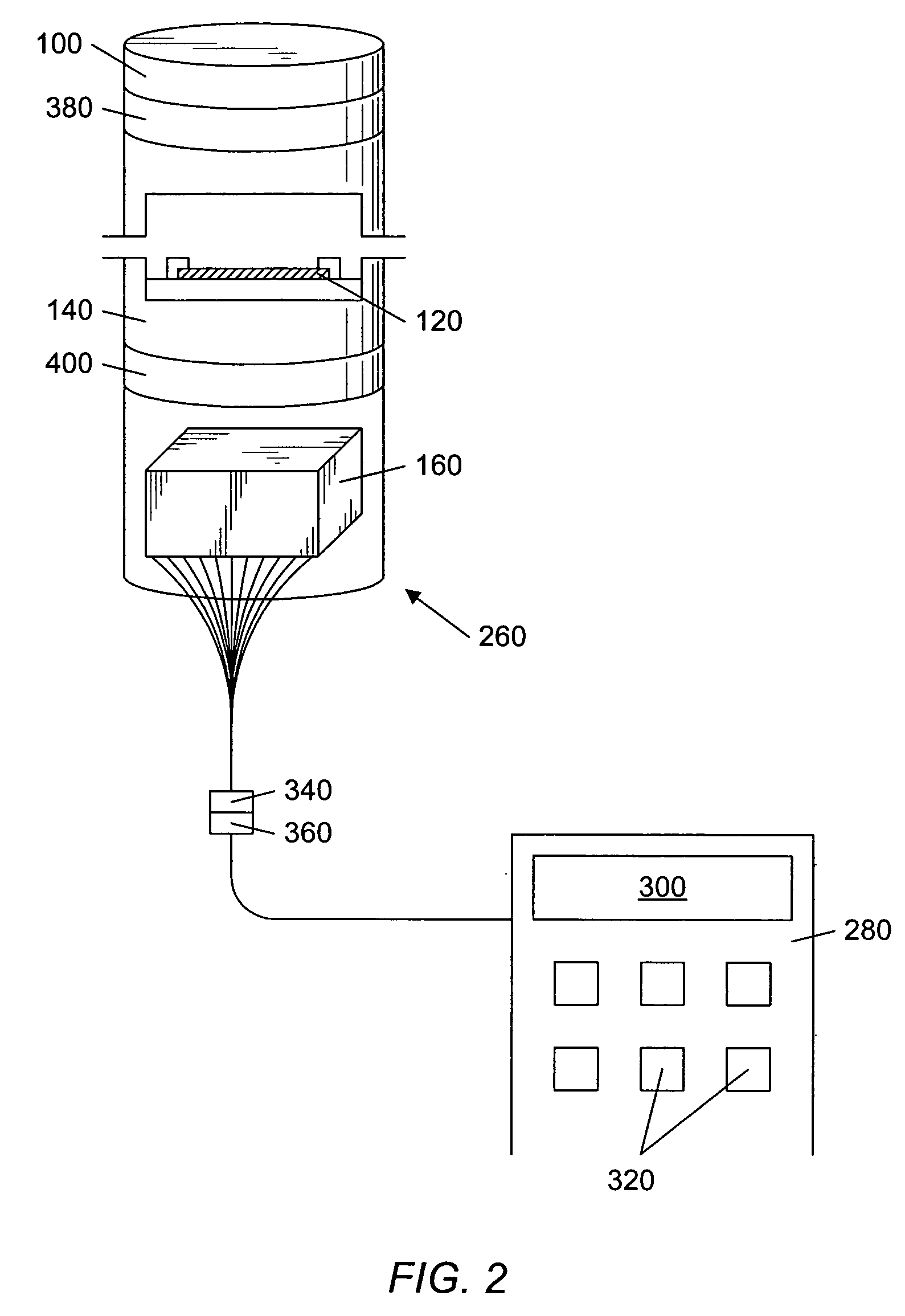
Multiple analyte assay device with sample integrity monitoring system
InactiveUS6514769B2Avoid pollutionImprove securityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSamplingMulti analyteSample integrity
An assay device, a fluid analyte sample separator device and methods for use of thereof for determining whether the integrity of a fluid analyte sample has been compromised and for contemporaneously assaying the sample for the presence or absence of multiple analytes, such as drugs of abuse. The device is composed of a housing having separate slots therein for insertion of one or more analyte test strips, one end of which protrudes from the housing, and one or more units of a sample integrity monitoring system. The device may be used in dipstick or cassette form. An analyte sample separator for division of sample and retention of uncontaminated sample for further testing is also provided. The analyte test strips and sample integrity monitoring system are replaceable, so that the panel of analytes and of sample condition parameters tested can be customized.
Owner:ASSURANCE BIOTECH
System and method for the analysis of bodily fluids
InactiveUS20050136548A1Quick checkFixed microstructural devicesOrganic chemistry methodsSensor arrayMulti analyte
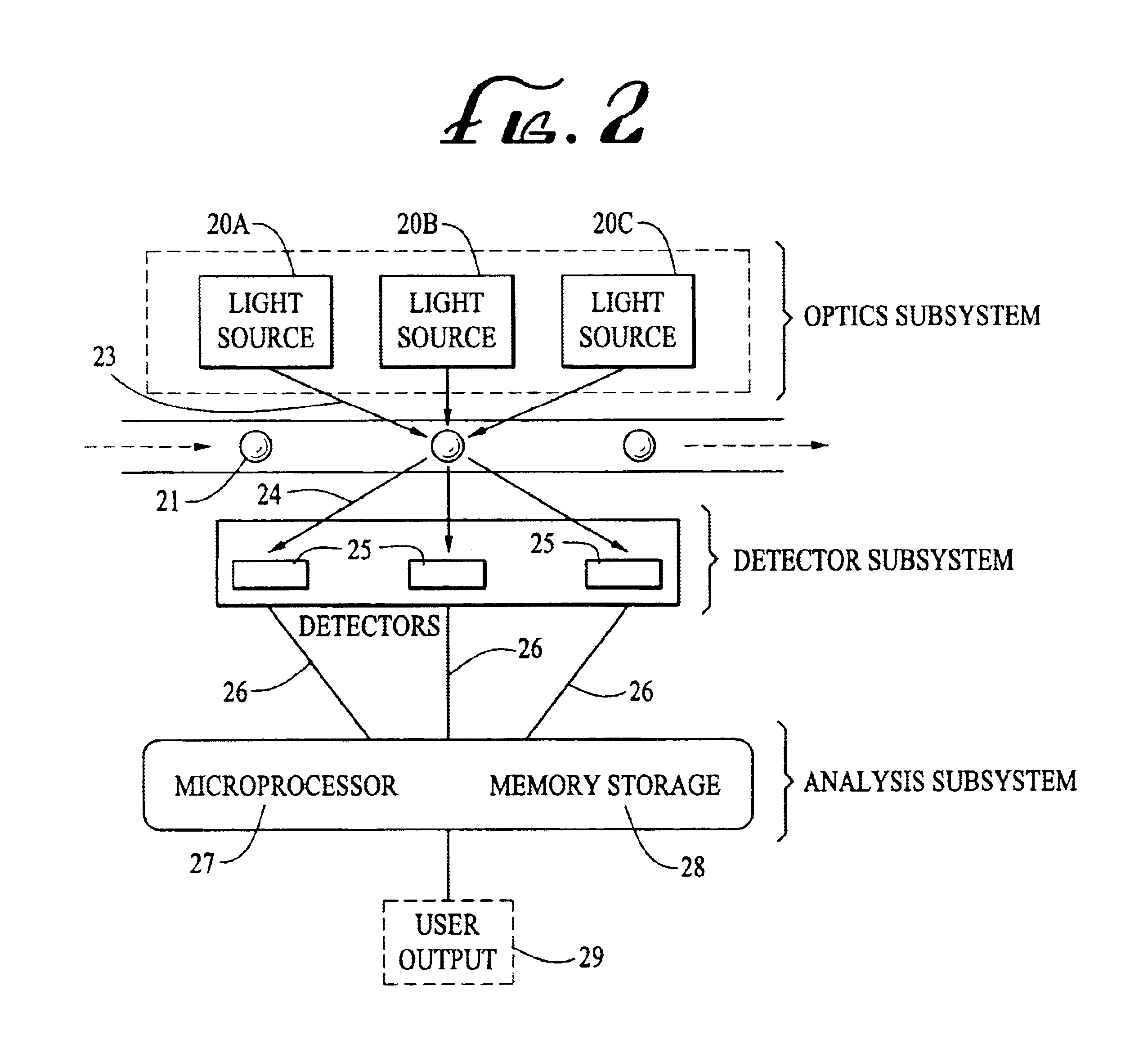
A system for the rapid characterization of multi-analyte fluids, in one embodiment, includes a light source, a sensor array, and a detector. The sensor array is formed from a supporting member into which a plurality of cavities may be formed. A series of chemically sensitive particles are, in one embodiment positioned within the cavities. The particles may be configured to produce a signal when a receptor coupled to the particle interacts with the analyte. Using pattern recognition techniques, the analytes within a multi-analyte fluid may be characterized.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Multianalyte sensor
InactiveUS20060078908A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTarget analysisAnalyte
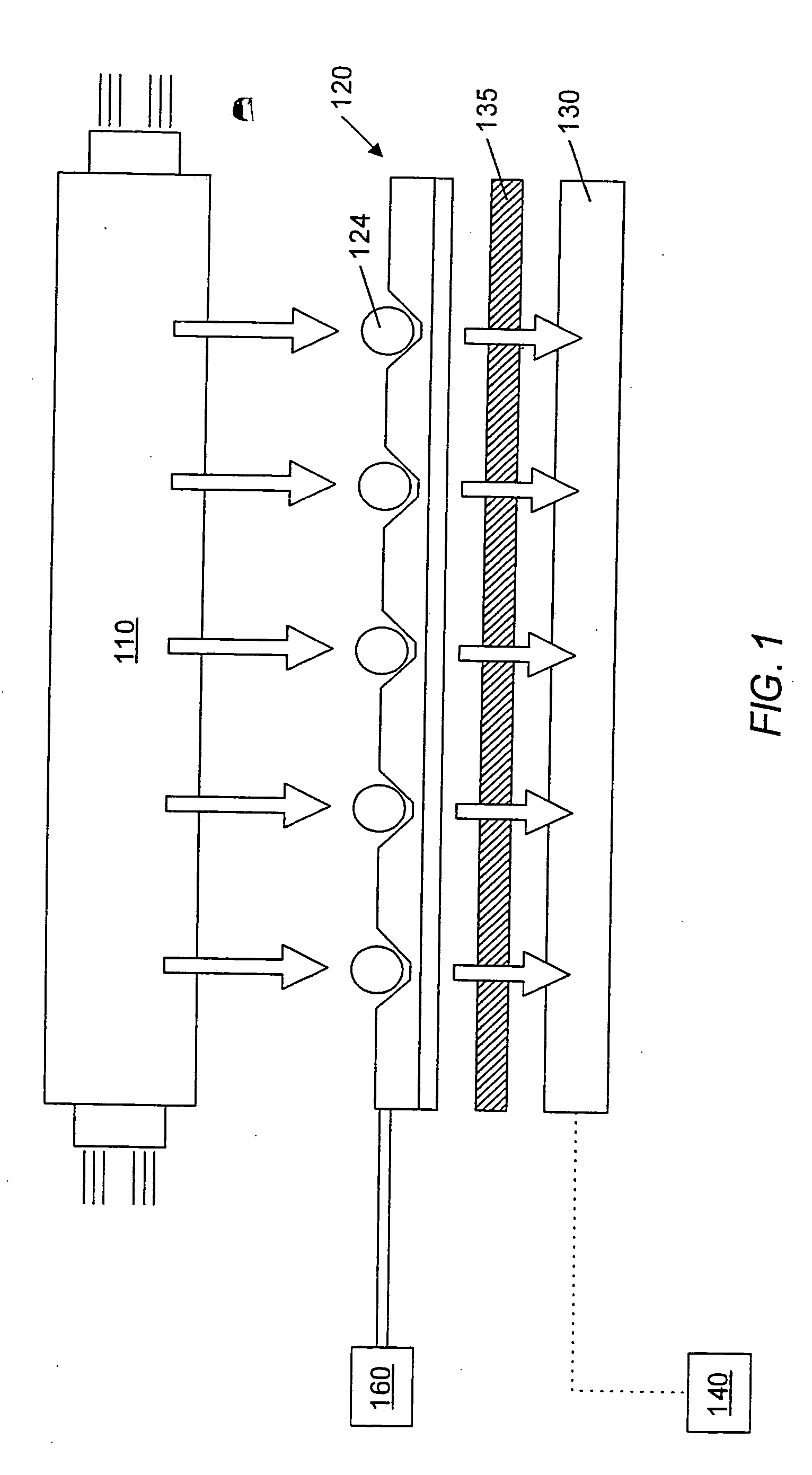
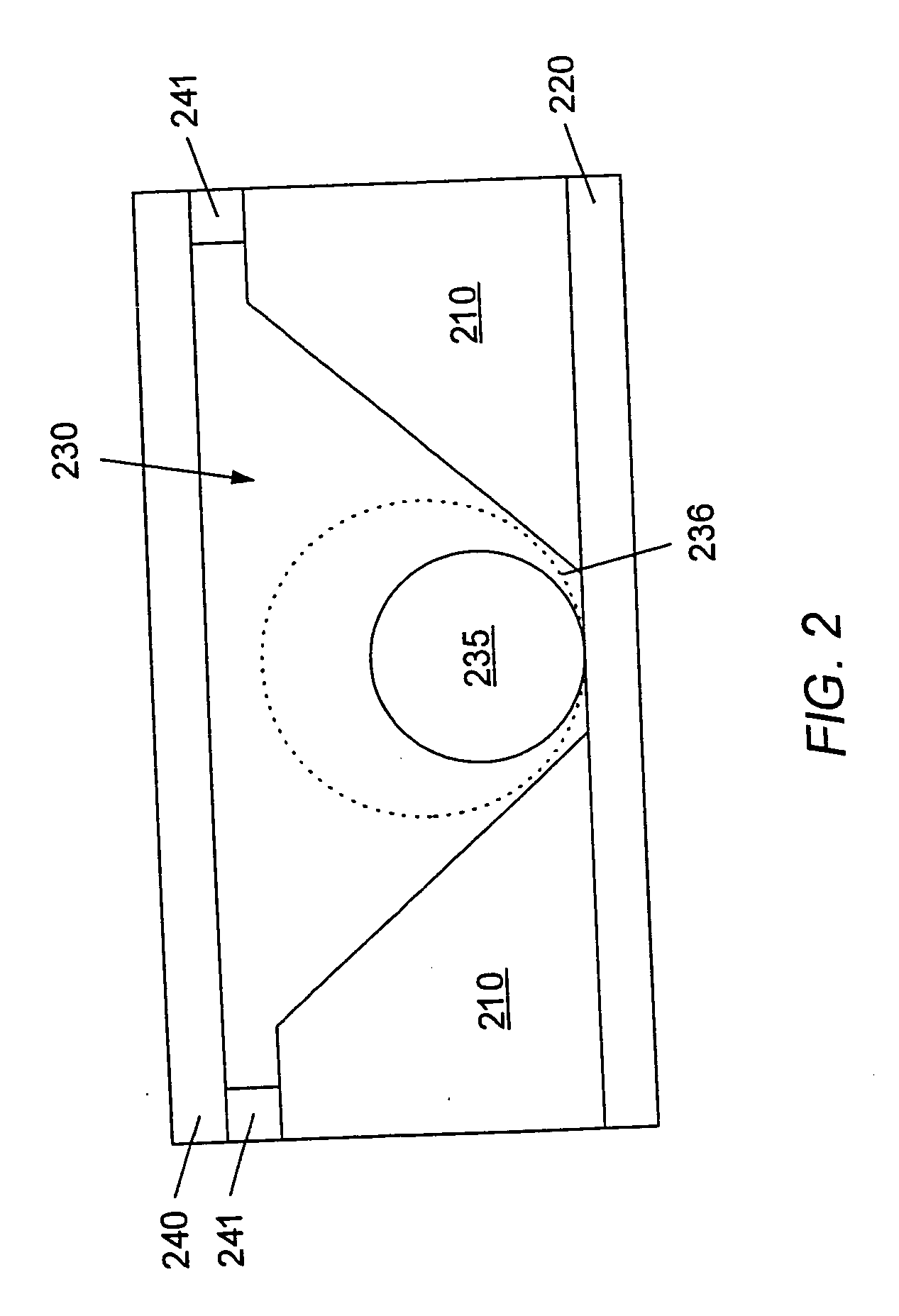
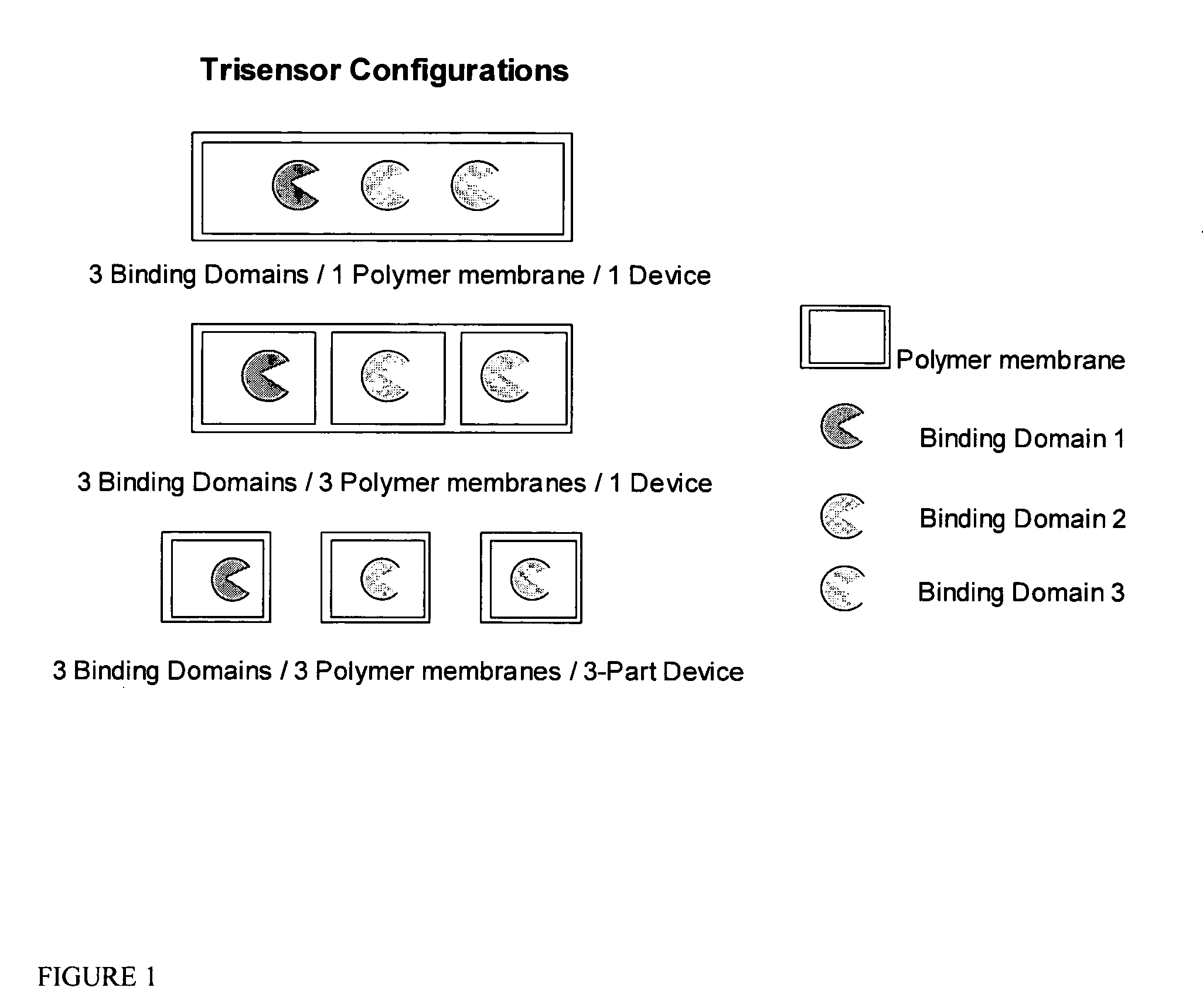
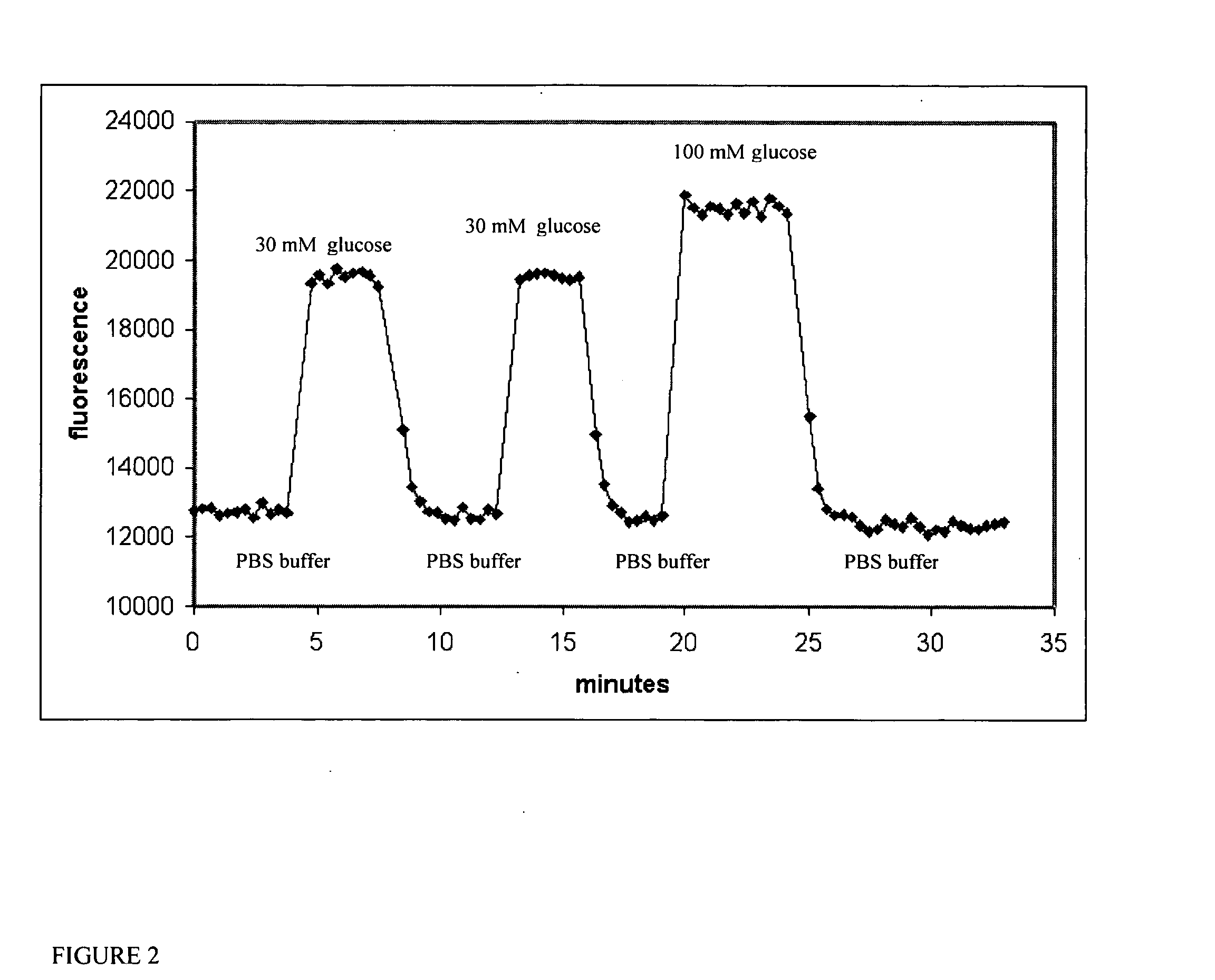
The invention relates to devices for continuously measuring the concentrations of more than one target analyte. Specifically, the devices comprise a plurality of analyte binding domains, with each domain being capable of specifically and reversibly binding to at least one of the target analytes. The devices further comprise a membrane surrounding these binding domains that is permeable to the target analytes. The devices convey binding information to a detector. The invention also relates to methods of using the devices, including monitoring chronic disease states in an individual.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Detection of multiple analytes from a single sample using a multi-well, multi-analyte flow-through diagnostic test device
InactiveUS7052831B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle sampleDiagnostic test
The present invention provides a method and device for conducting a rapid in vitro enzyme immunoassay test for the direct and qualitative detection of two or more viral antigens from specimens of symptomatic patients. The method for immunoassay of viral antigens is performed on a membrane. Non-immunological capture of viral antigens takes place by absorption onto the membrane. Captured antigen binds to a detection reagent that includes a label conjugated to a specific antibody. The test is a differentiated test such that two or more viral antigens may be distinguished from each other in a single test. The invention also includes a kit for performing an assay in accordance with the method of the present invention, wherein the kit comprises the device of the present invention.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Multiple analyte assay device with sample integrity monitoring system
InactiveUS20020001854A1Avoid pollutionImprove securitySamplingBurette/pipette supportsAnalyteSample integrity
An assay device, a fluid analyte sample separator device and methods for use of thereof for determining whether the integrity of a fluid analyte sample has been compromised and for contemporaneously assaying the sample for the presence or absence of multiple analytes, such as drugs of abuse. The device is composed of a housing having separate slots therein for insertion of one or more analyte test strips, one end of which protrudes from the housing, and one or more units of a sample integrity monitoring system. The device may be used in dipstick or cassette form. An analyte sample separator for division of sample and retention of uncontaminated sample for further testing is also provided. The analyte test strips and sample integrity monitoring system are replaceable, so that the panel of analytes and of sample condition parameters tested can be customized.
Owner:ASSURANCE BIOTECH
Fluid based analysis of multiple analytes by a sensor array
InactiveUS6908770B1Quick checkOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSensor arrayMulti analyte
A system for the rapid characterization of multi-analyte fluids, in one embodiment, includes a light source, a sensor array, and a detector. The sensor array is formed from a supporting member into which a plurality of cavities may be formed. A series of chemically sensitive particles are, in one embodiment positioned within the cavities. The particles may be configured to produce a signal when a receptor coupled to the particle interacts with the analyte. Using pattern recognition techniques, the analytes within a multi-analyte fluid may be characterized.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Integrated nanomechanical sensor array chips
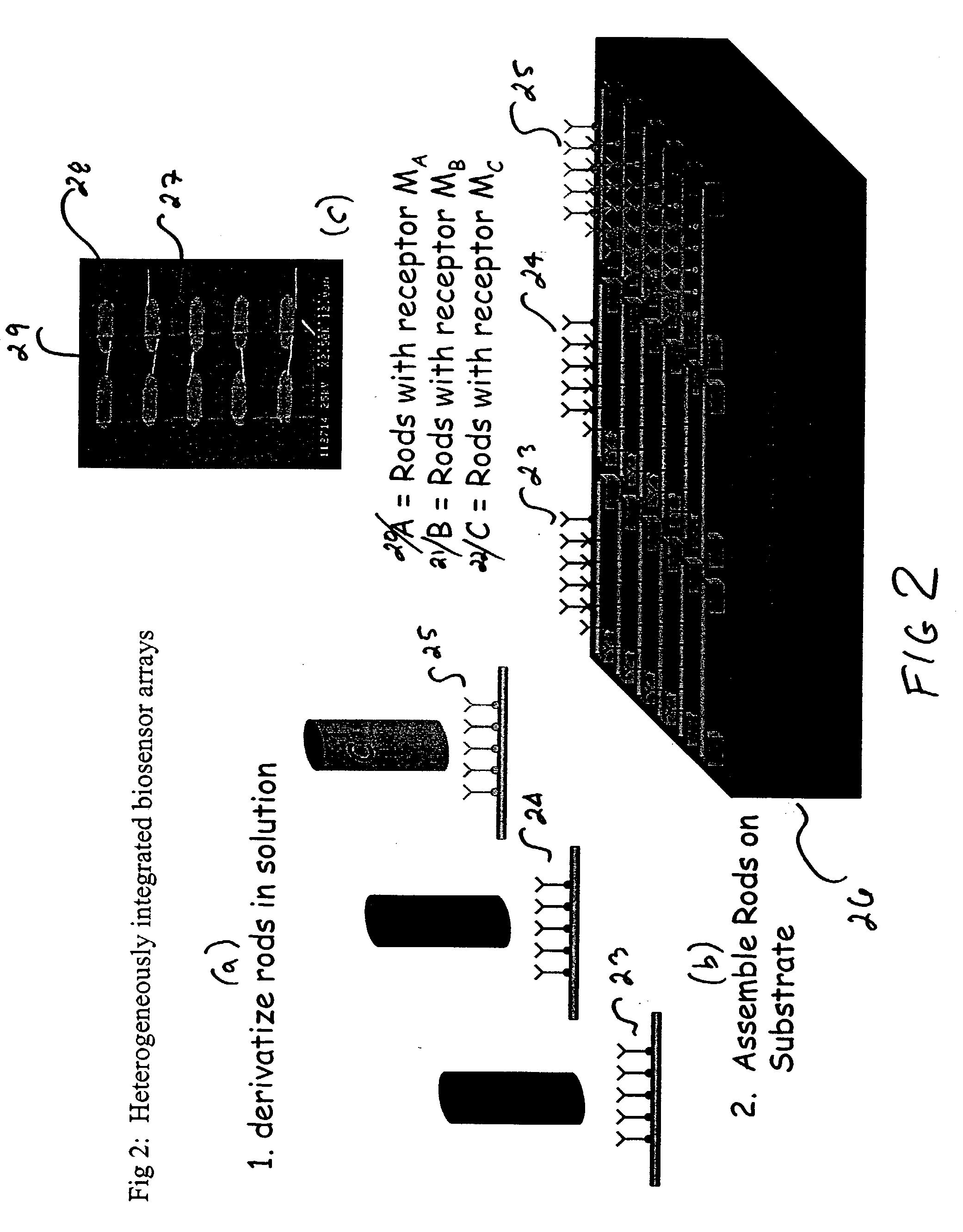
The invention provides sensor, preferably biosensor devices and method of fabrication. The devices have significant advantages over the prior art methods having compatibility with future trends in clinical diagnostics and chemical detection. The underlying principle involves the integration of nanometer diameter, micron long metal or semiconductor rods onto a substrate to form a suspended nanomechanical cantilevers. The cantilever rods are rigidly attached to the substrate on one or both ends, and resonate at a characteristic frequency depending on the diameter, length, and stiffness of the rod. The metal or semiconductor rods are integrated onto the substrate using electrofluidic or fluidic assembly techniques. A receptor coating is placed on the metal or semiconductor rods prior to or following rod alignment using self-assembly chemistries. Sensing is accomplished when the target agent binds to the receptor substance, causing a change in the mass of the cantilever rod, and a corresponding change in the resonant frequency. This change in resonant frequency can be detected using an electrical readout. The sensing circuitry is integrated with CMOS or TFT technologies to form compact multi-analyte senor arrays on single crystal silicon, glass, or polymeric substrates. Circuits can also be included on the substrate to transmit the array data via wireless methods to a remote workstation for analysis. Devices may be integrated on chips with other analysis devices.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
System and method for multi-analyte detection
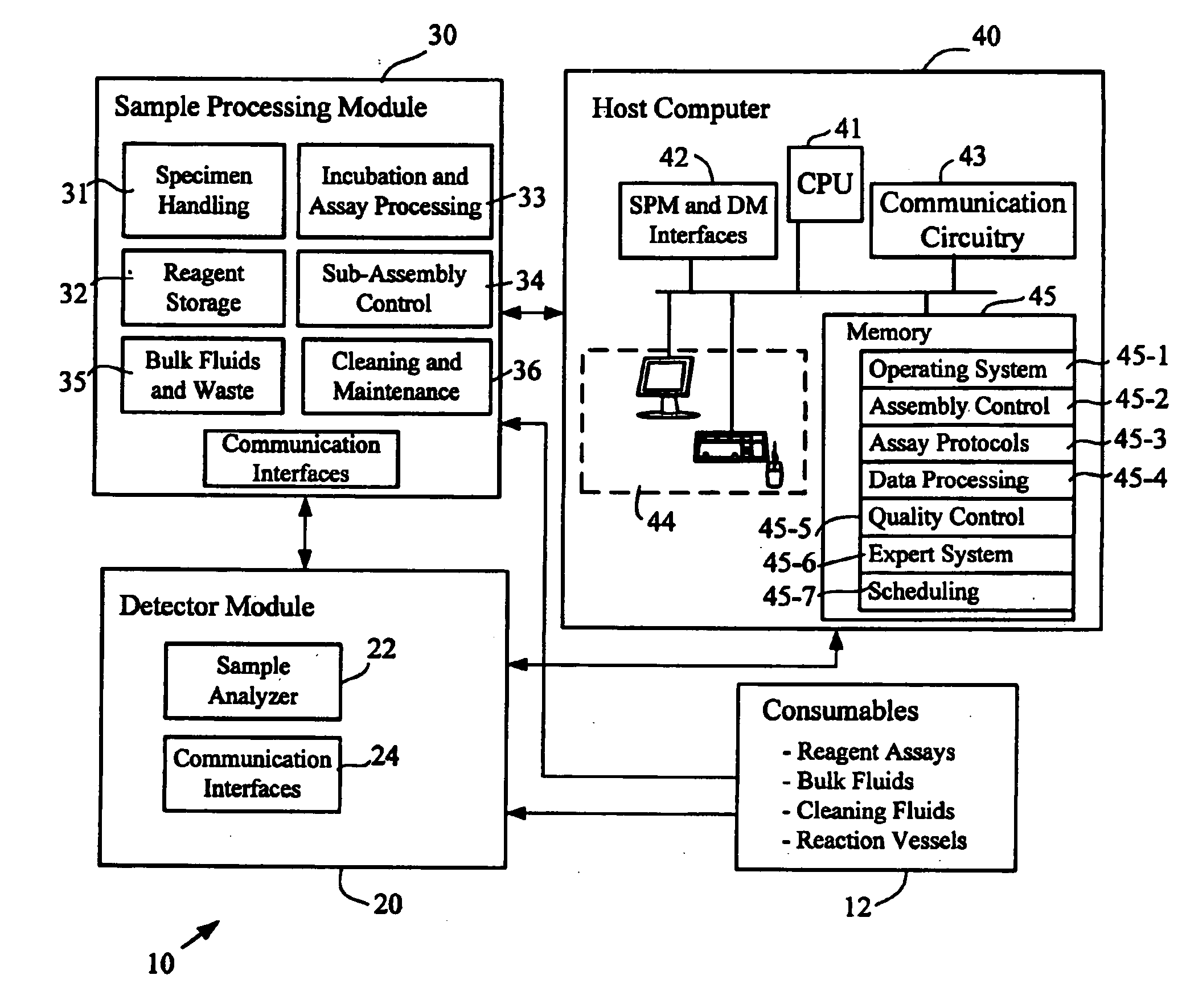
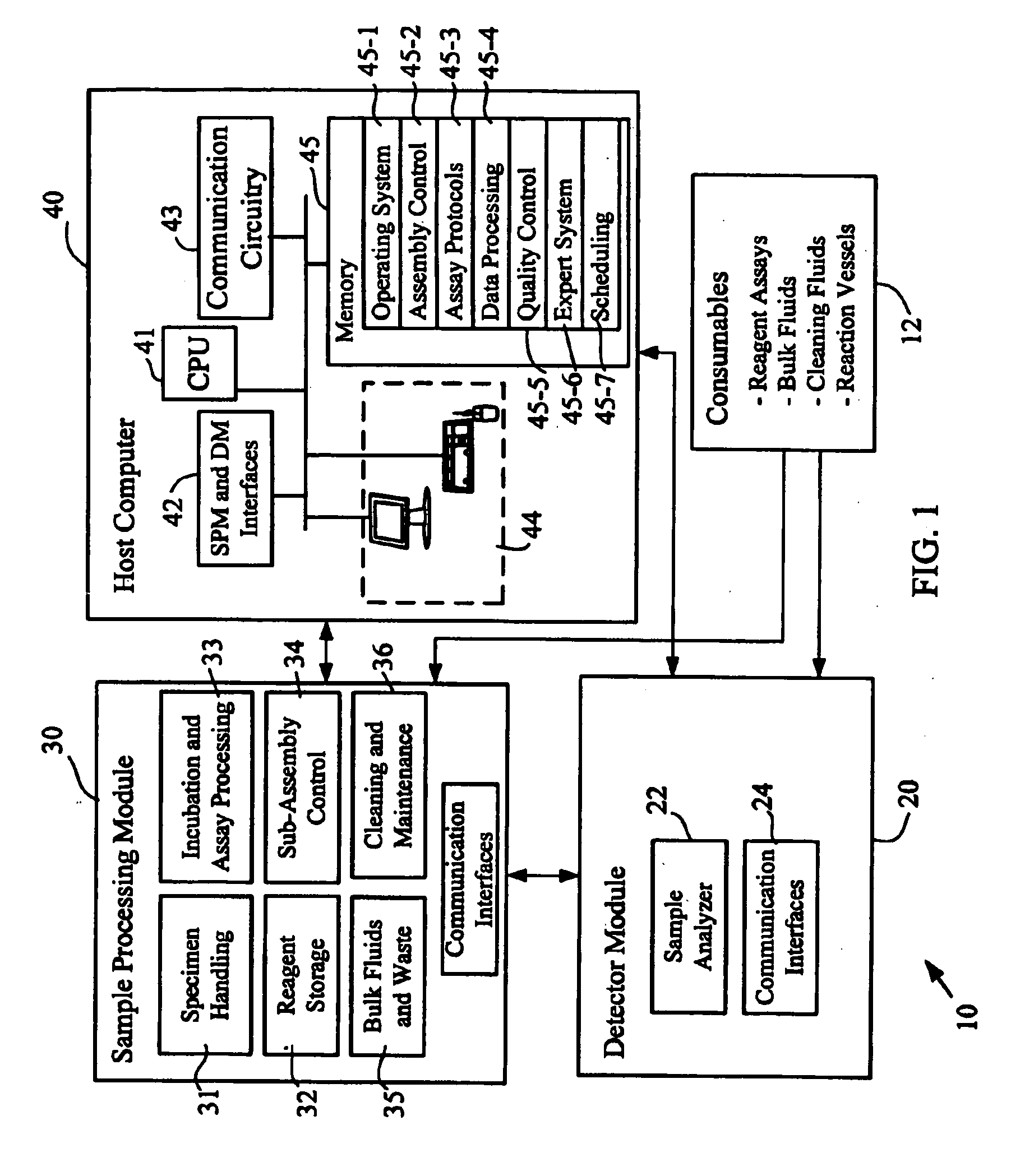
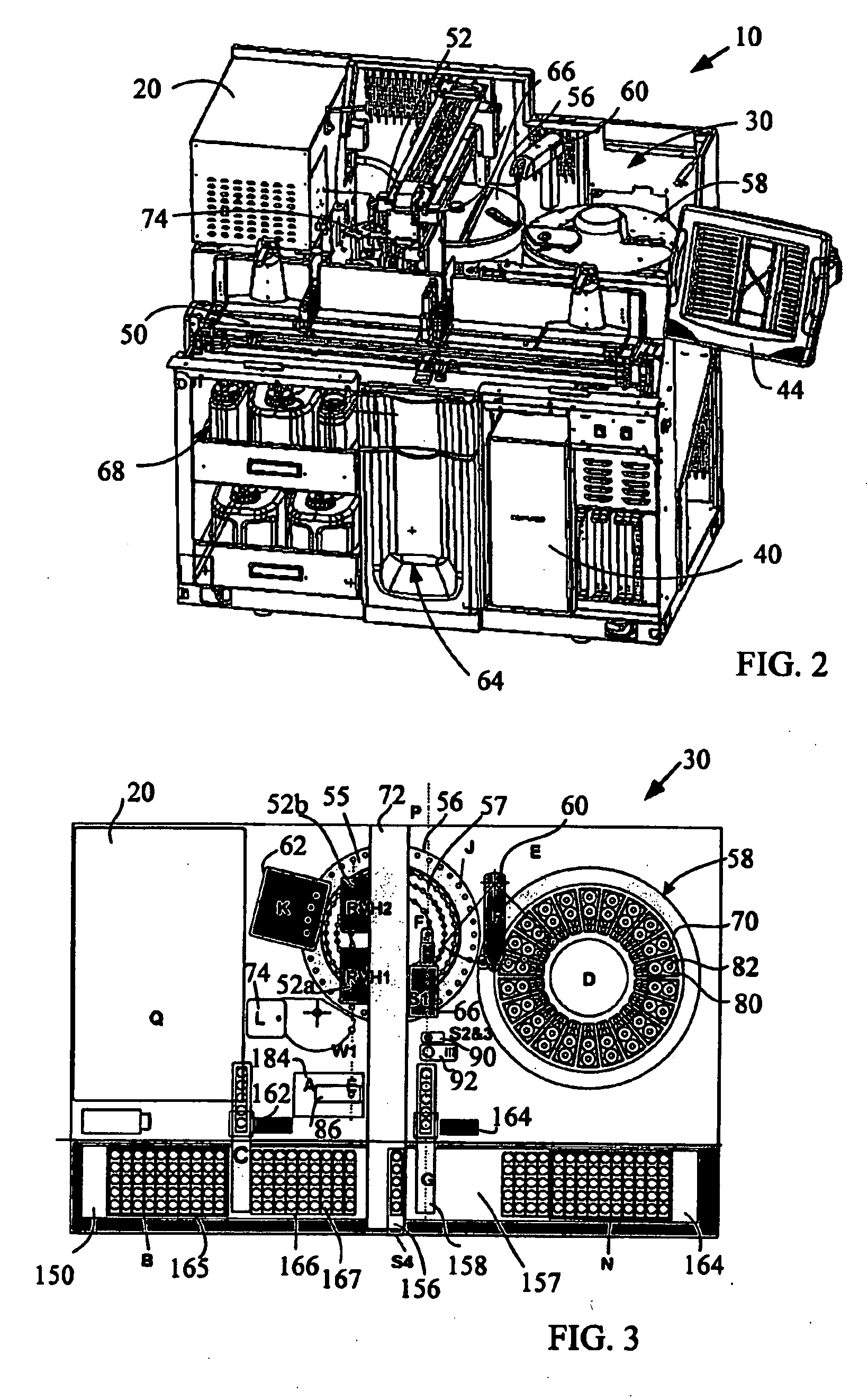
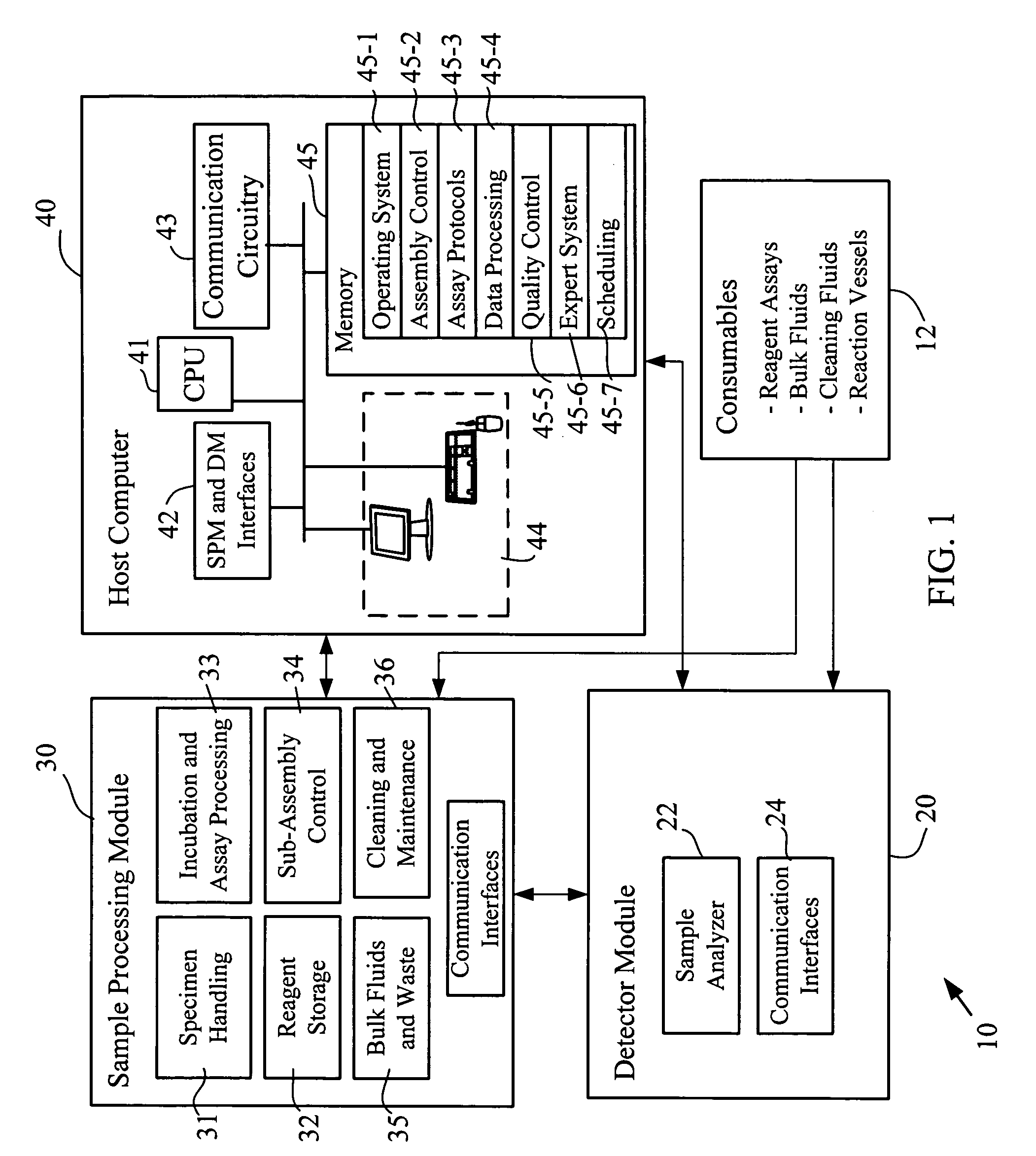
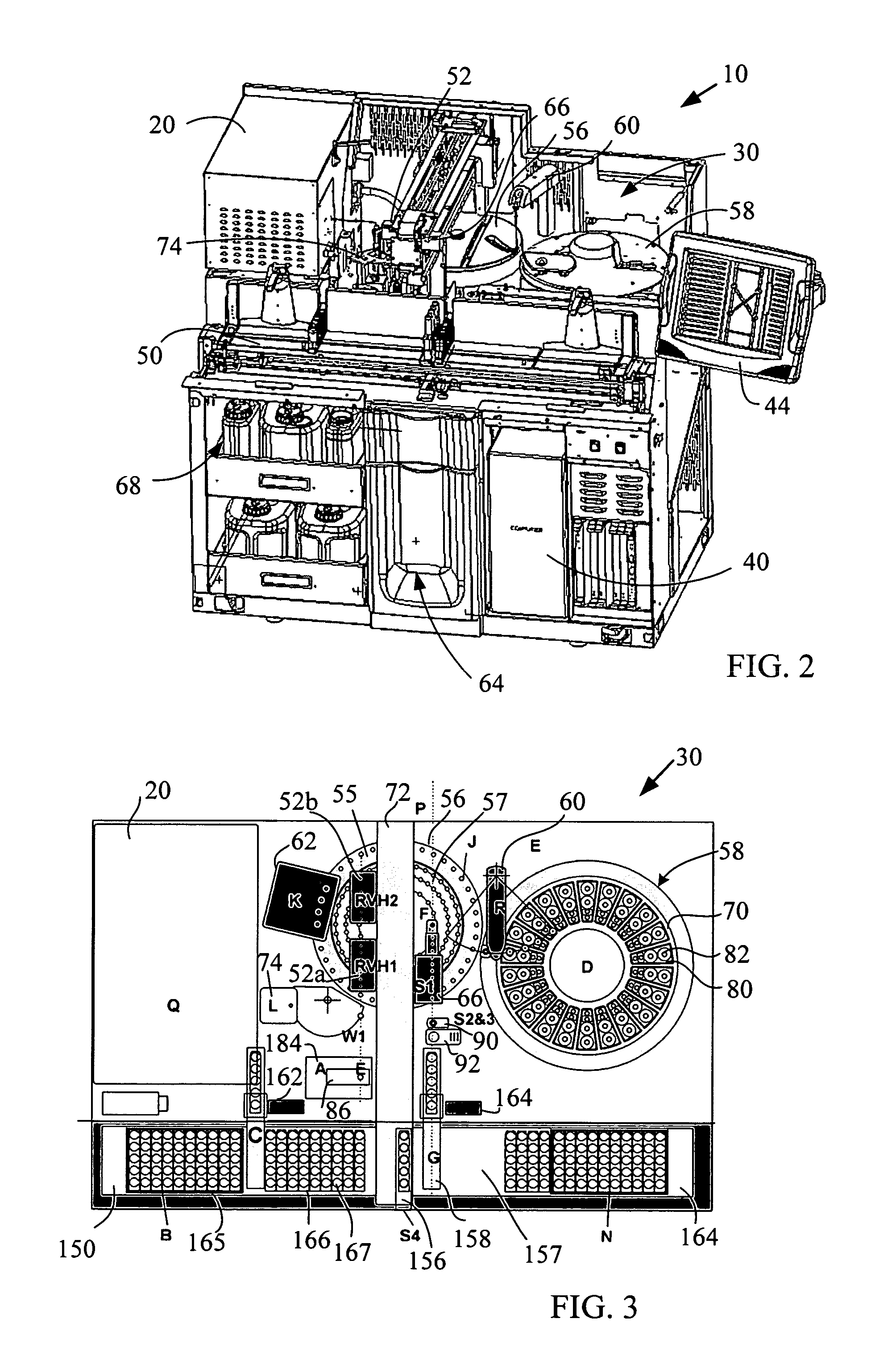
ActiveUS20090068062A1Improve throughputAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementMulti analyteEngineering
The present invention provides a system and method for the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in a sample. The detection system includes a housing that holds a reagent carousel rotatably coupled thereto. Further included in the housing is an incubator carousel rotatably coupled thereto. The housing also includes magnetic material that is associated with the incubation carousel for assisting in separation beads from reagent and wash solution. A robot, associated with the housing is configured to manipulate at least either the reagent carousel or the incubator carousel and transfer materials between these carousels. Reaction vessels hold samples and reaction vessels handlers move the reaction vessels. Sample analysis is determined by at least one laser based detector.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Portable sensor array system
InactiveUS7316899B2Quick checkFixed microstructural devicesOrganic chemistry methodsSensor arrayMulti analyte
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
System and method for multi-analyte detection
ActiveUS7220385B2Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMulti analyteEngineering
The present invention provides a system and method for the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in a sample. The detection system includes a housing that holds a reagent carousel rotatably coupled thereto. Further included in the housing is an incubator carousel rotatably coupled thereto. The housing also includes magnetic material that is associated with the incubation carousel for assisting in separation beads from reagent and wash solution. A robot, associated with the housing is configured to manipulate at least either the reagent carousel or the incubator carousel and transfer materials therebetween. Reaction vessels hold samples and reaction vessels handlers move the reaction vessels. Sample analysis is determined by at least one laser based detector.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
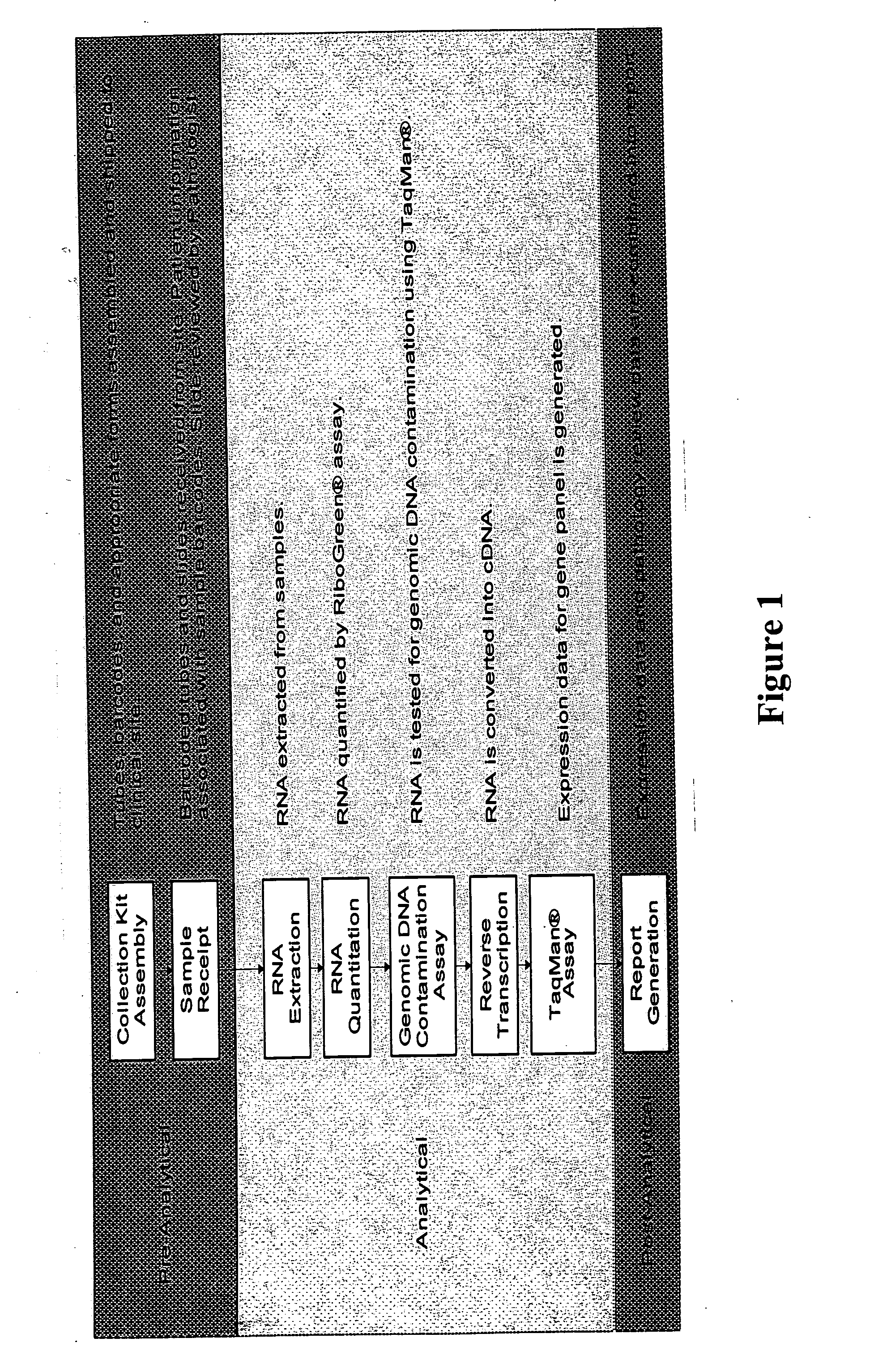
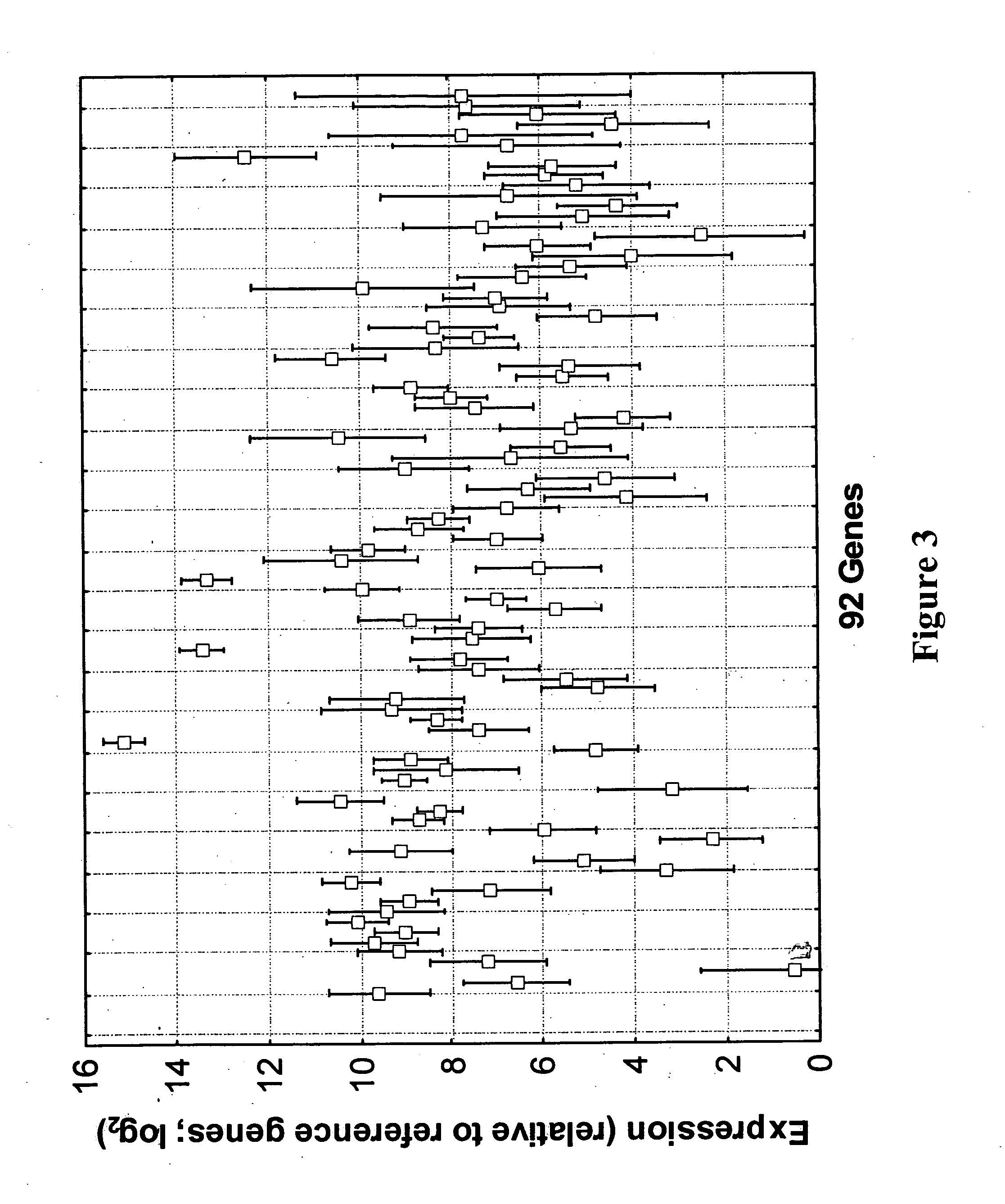
qRT-PCR assay system for gene expression profiling
InactiveUS20050095634A1High precisionSensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMulti analytePcr assay
The invention concerns an integrated, qRT-PCR-based system for analyzing and reporting RNA expression profiles of biological samples. In particular, the invention concerns a fully optimized and integrated multiplex, multi-analyte method for expression profiling of RNA in biological samples, including fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples. The gene expression profiles obtained can be used for the clinical diagnosis, classification and prognosis of various pathological conditions, including cancer.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Multiplexed nanoscale electrochemical sensors for multi-analyte detection
Provided are nanoscale devices suitable for multiplexed, parallel detection of multiple analytes and methods for fabricating such devices.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
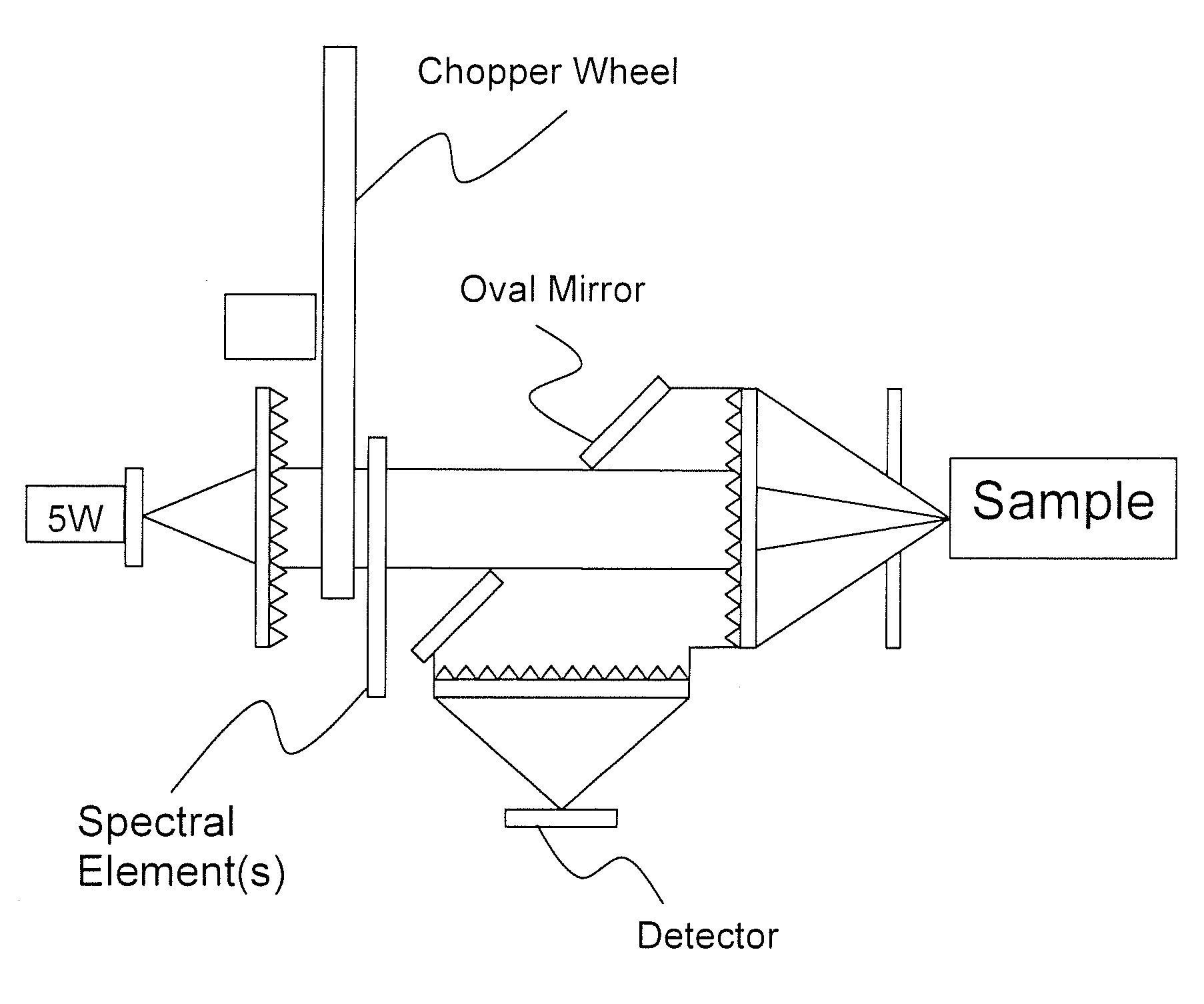
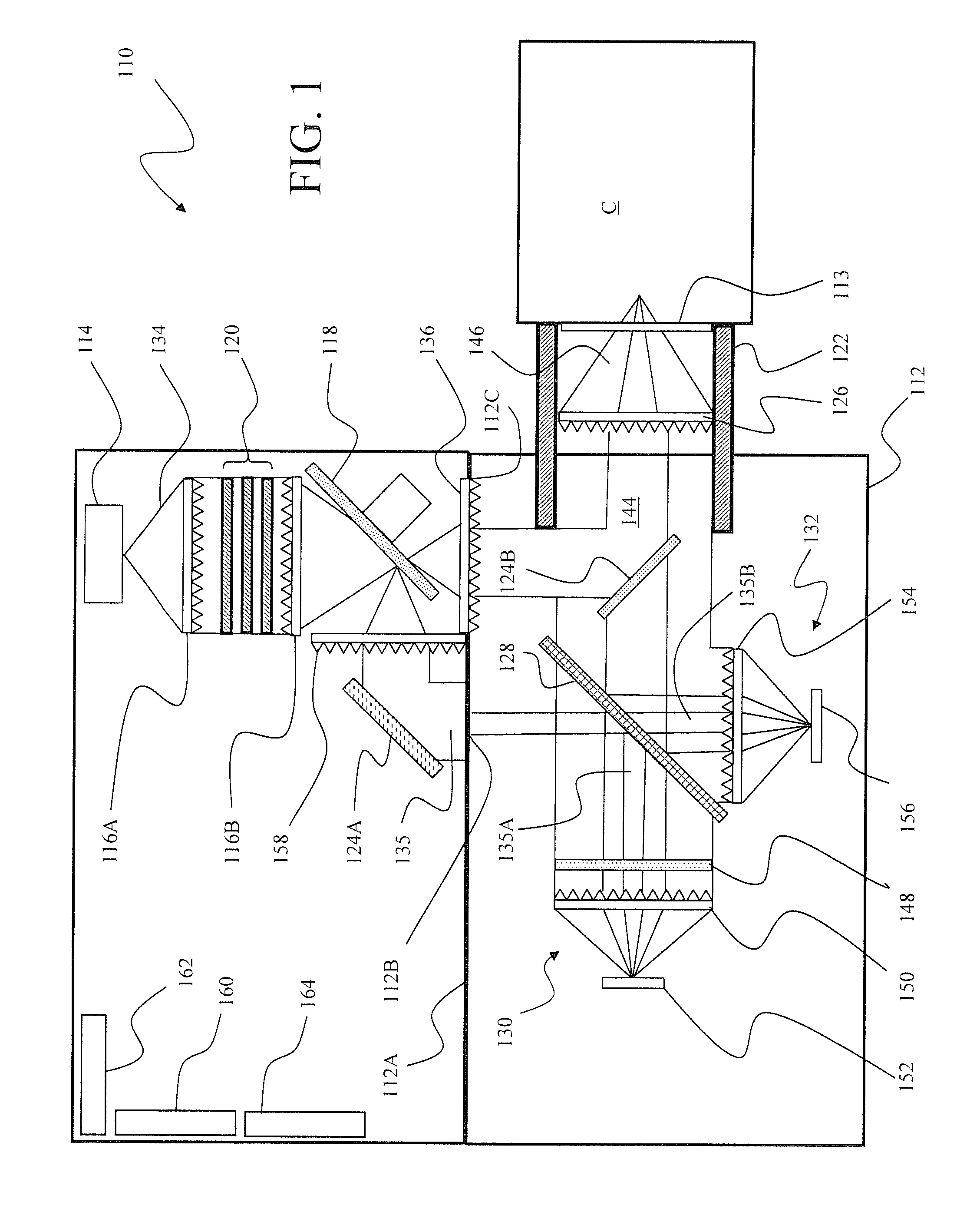
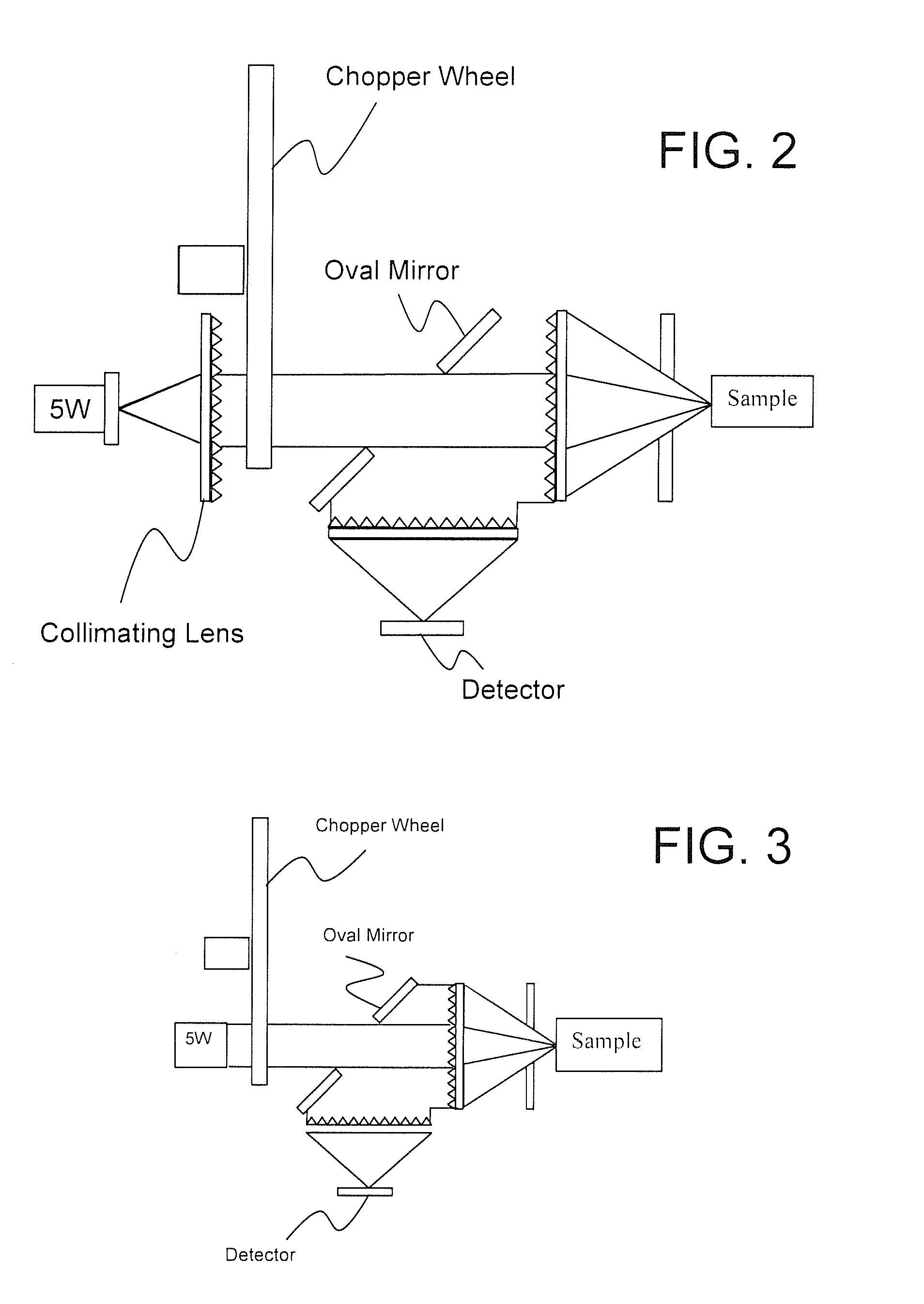
Novel multi-analyte optical computing system
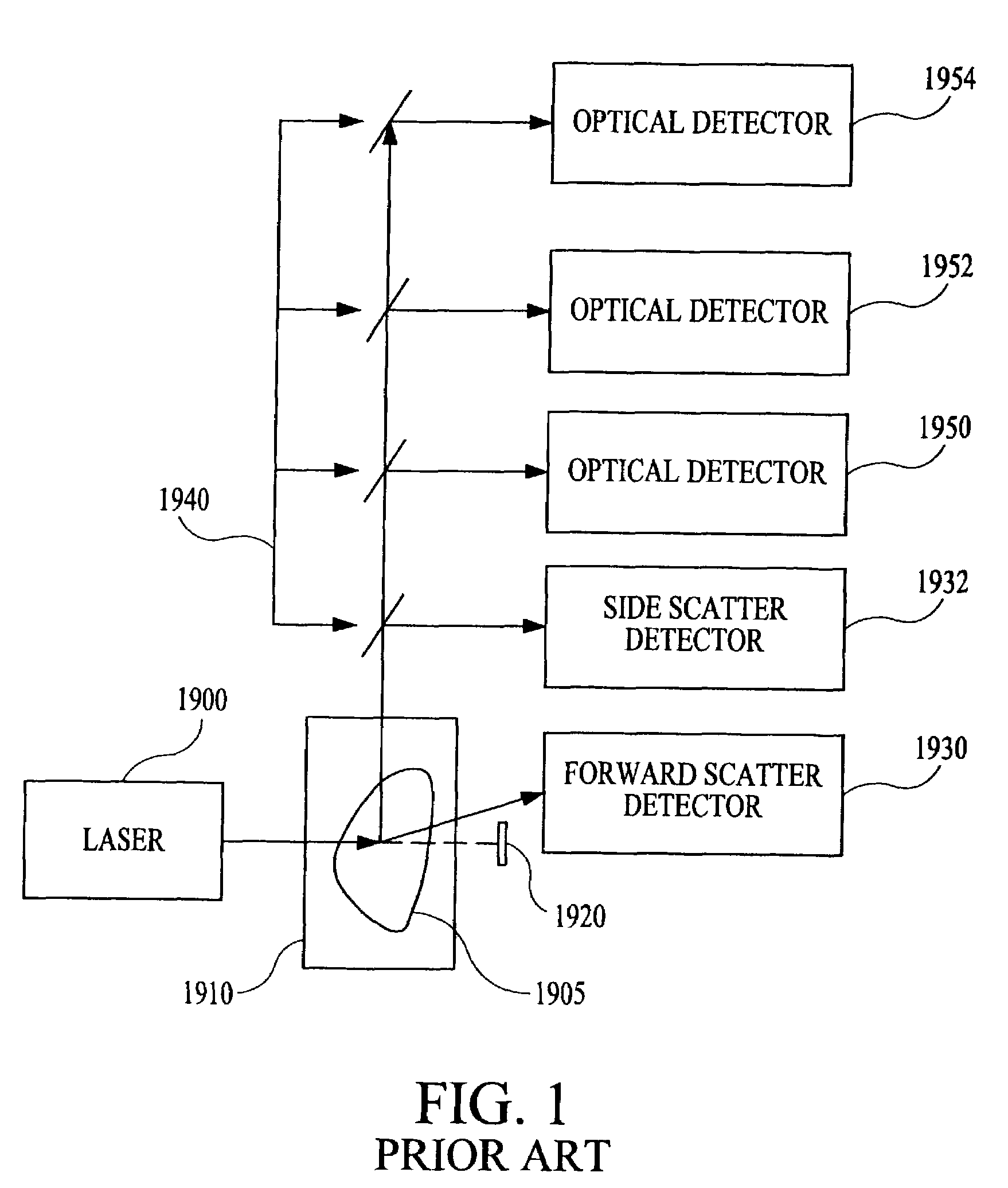
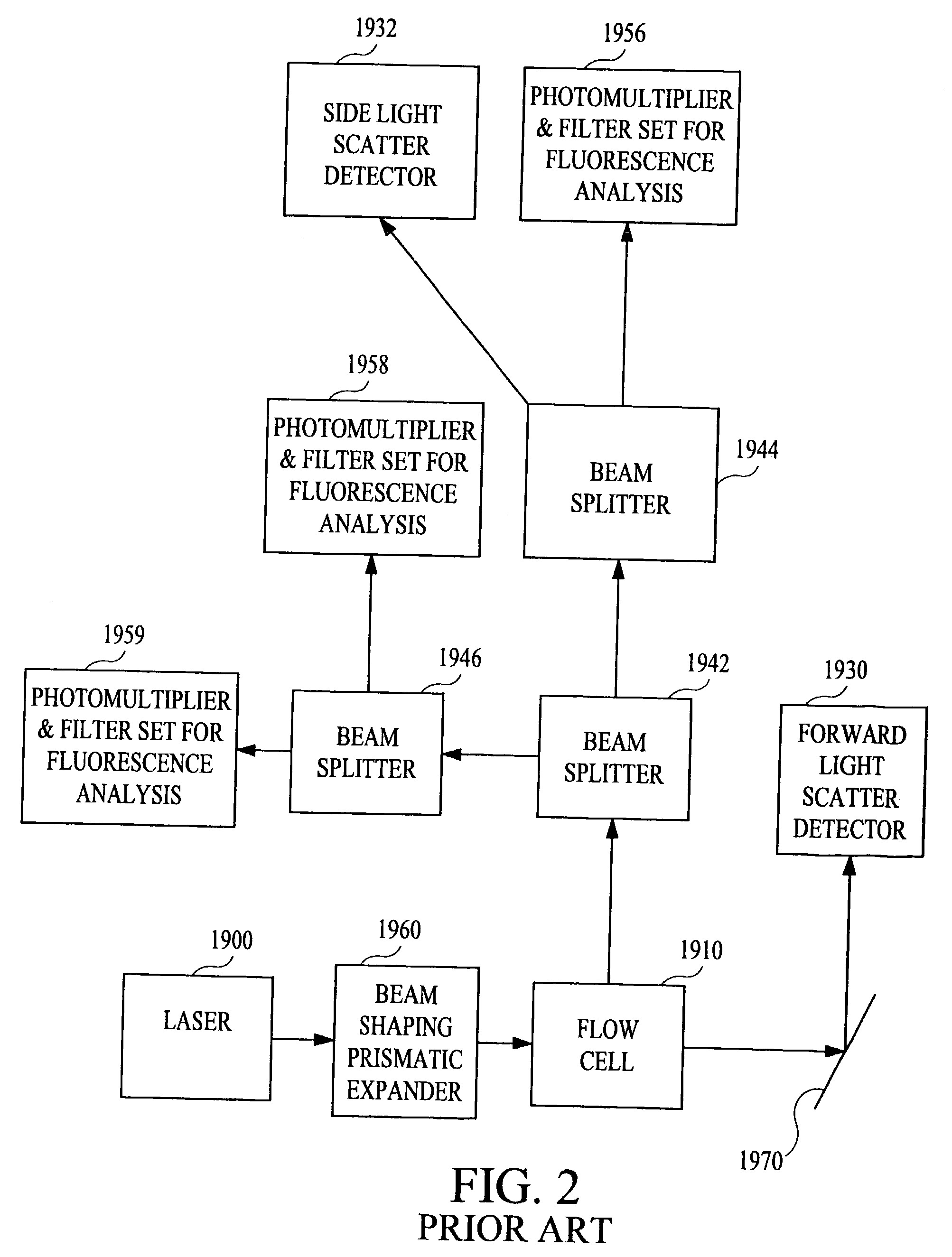
The present subject matter relates to methods of high-speed analysis of product samples. Light is directed to a portion of a product under analysis and reflected from or transmitted through the product toward a plurality of optical detectors. Signals from the detectors are compared with a reference signal based on a portion of the illuminating light passing through a reference element to determine characteristics of the product under analysis. The products under analysis may be stationary, moved by an inspection point by conveyor or other means, or may be contained within a container, the container including a window portion through which the product illuminating light may pass.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Multi-analyte diagnostic system and computer implemented process for same
InactiveUS7267798B2Remove any variabilitySignificant comprehensive benefitsSpecific gravity using centrifugal effectsVolume/mass flow measurementMulti analyteBiology
A multi-analyte diagnostic system for use with a computer. The diagnostic system includes a flow analyzer including a co-planar light source-optical detector array, the flow analyzer being communicatable with the computer. The diagnostic system also includes a memory medium readable by the computer and storing computer instructions. The instructions include the following steps. A biological sample is run through the flow analyzer. The identity and quantity of at least one analyte of interest in the biological fluid is determined substantially simultaneously to the sample-running step.
Owner:LUMINEX
Multi-modality contrast and brightfield context rendering for enhanced pathology determination and multi-analyte detection in tissue
ActiveUS20120200694A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresDiagnostic Radiology Modality
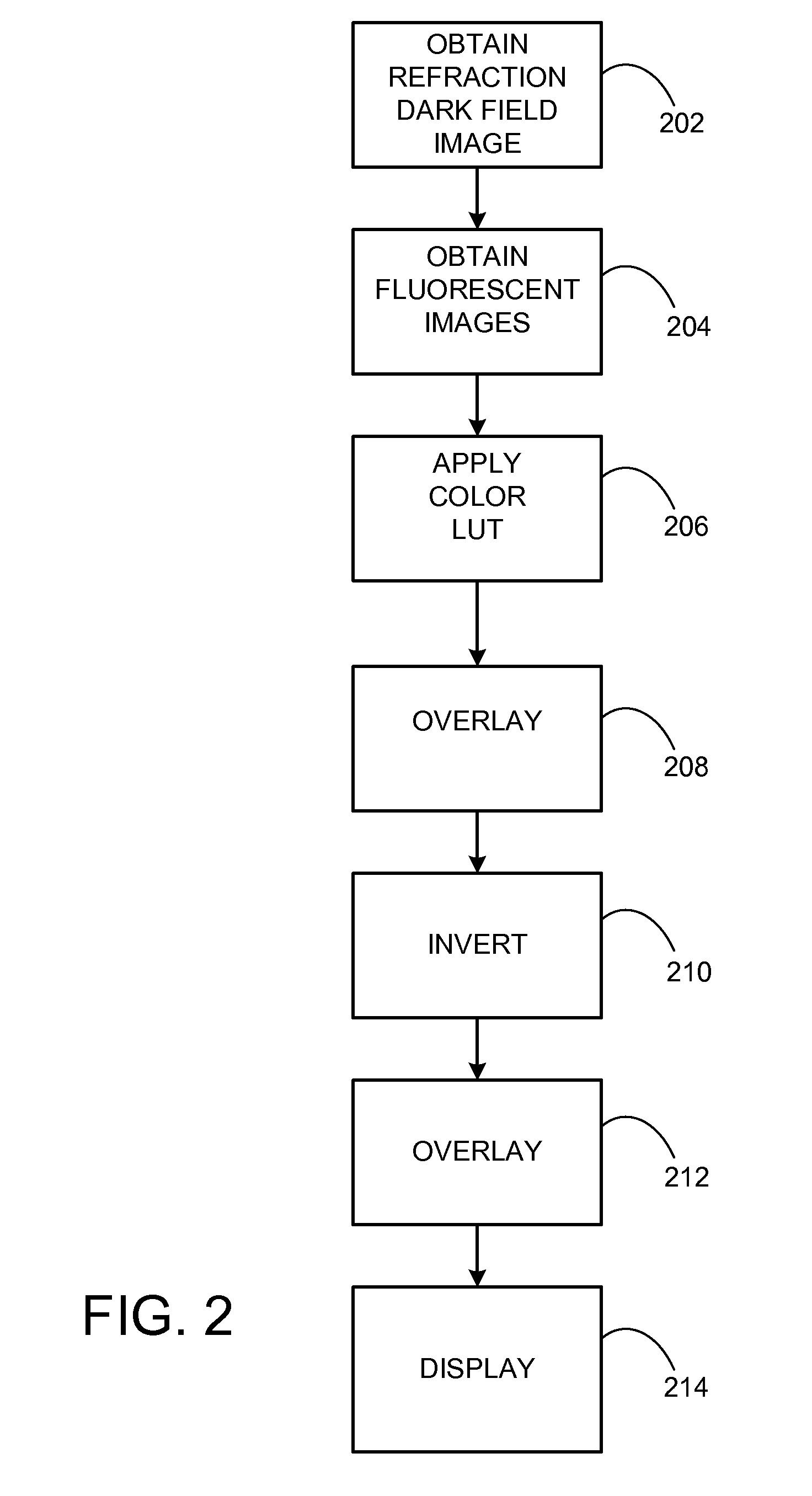
Multiple modality contrast can be used to produce images that can be combined and rendered to produce images similar to those produced with wavelength absorbing stains viewed under transmitted white light illumination. Images obtained with other complementary contrast modalities can be presented using engineered color schemes based on classical contrast methods used to reveal the same anatomical structures and histochemistry, thereby providing relevance to medical training and experience. Dark-field contrast images derived from refractive index and fluorescent DAPI counterstain images are combined to produce images similar to those obtained with conventional H&E staining for pathology interpretation. Such multi-modal image data can be streamed for live navigation of histological samples, and can be combined with molecular localizations of genetic DNA probes (FISH), sites of mRNA expression (mRNA-ISH), and immunohistochemical (IHC) probes localized on the same tissue sections, used to evaluate and map tissue sections prepared for imaging mass spectrometry.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
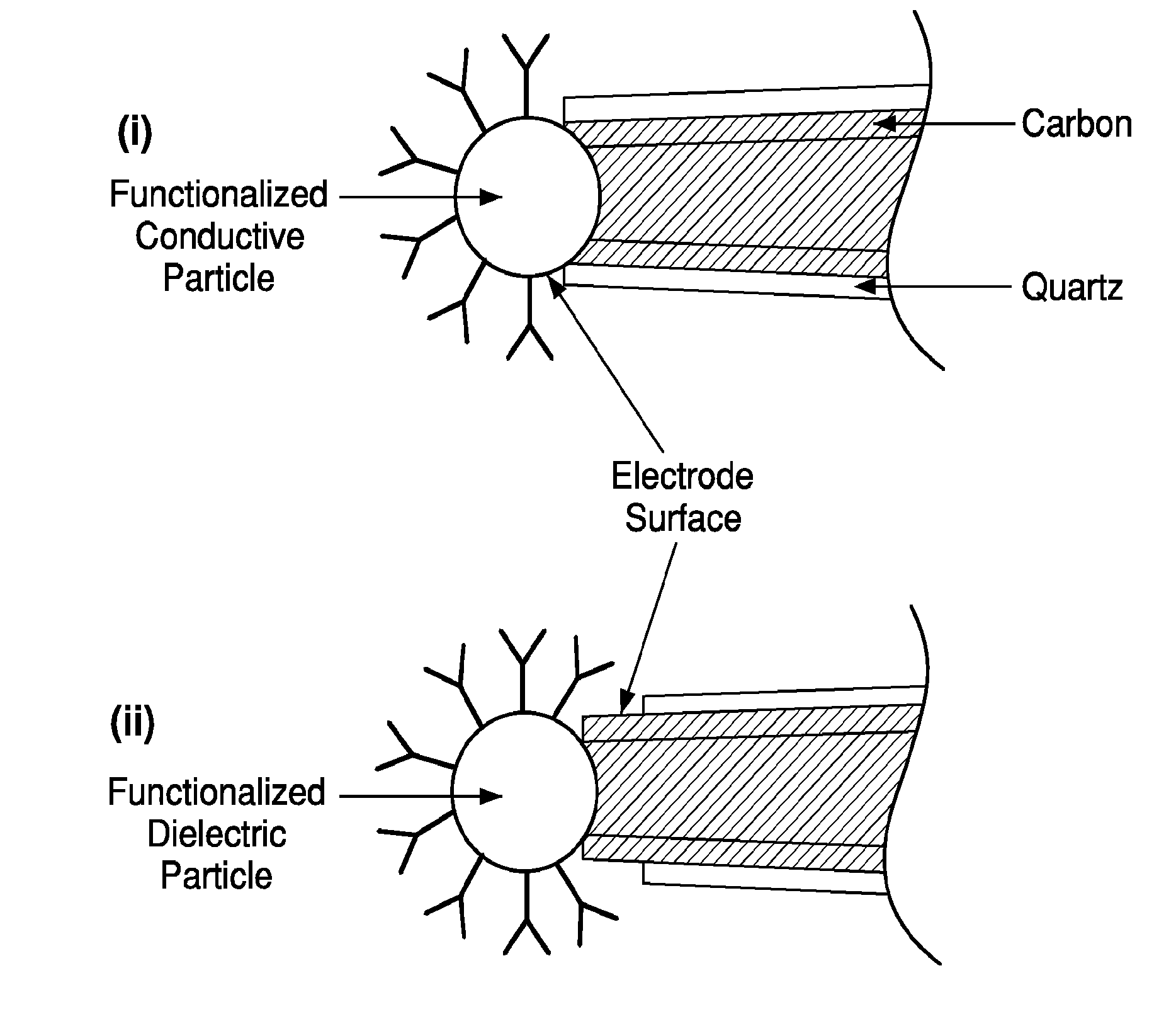
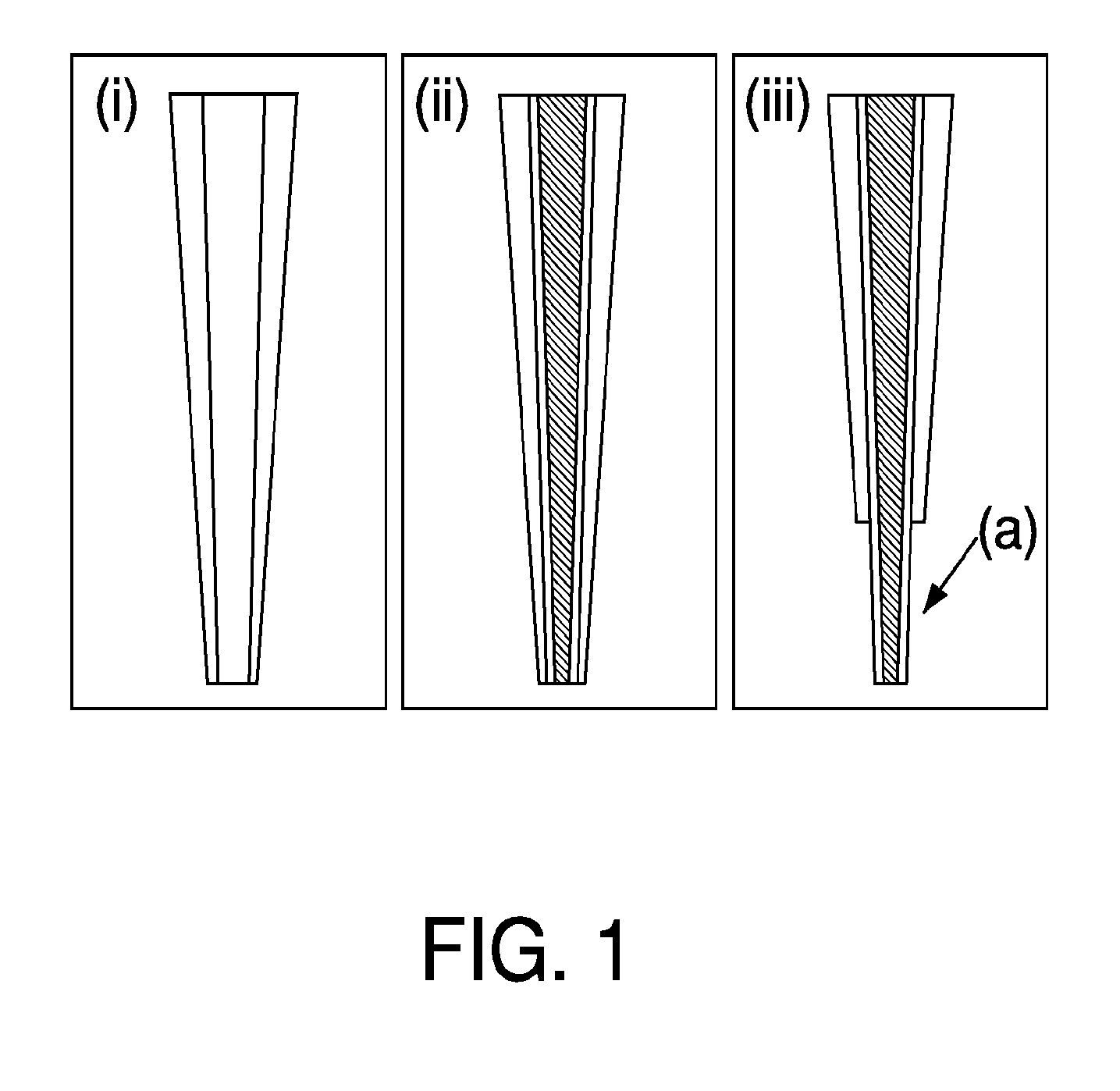
Fluidic units and cartridges for multi-analyte analysis
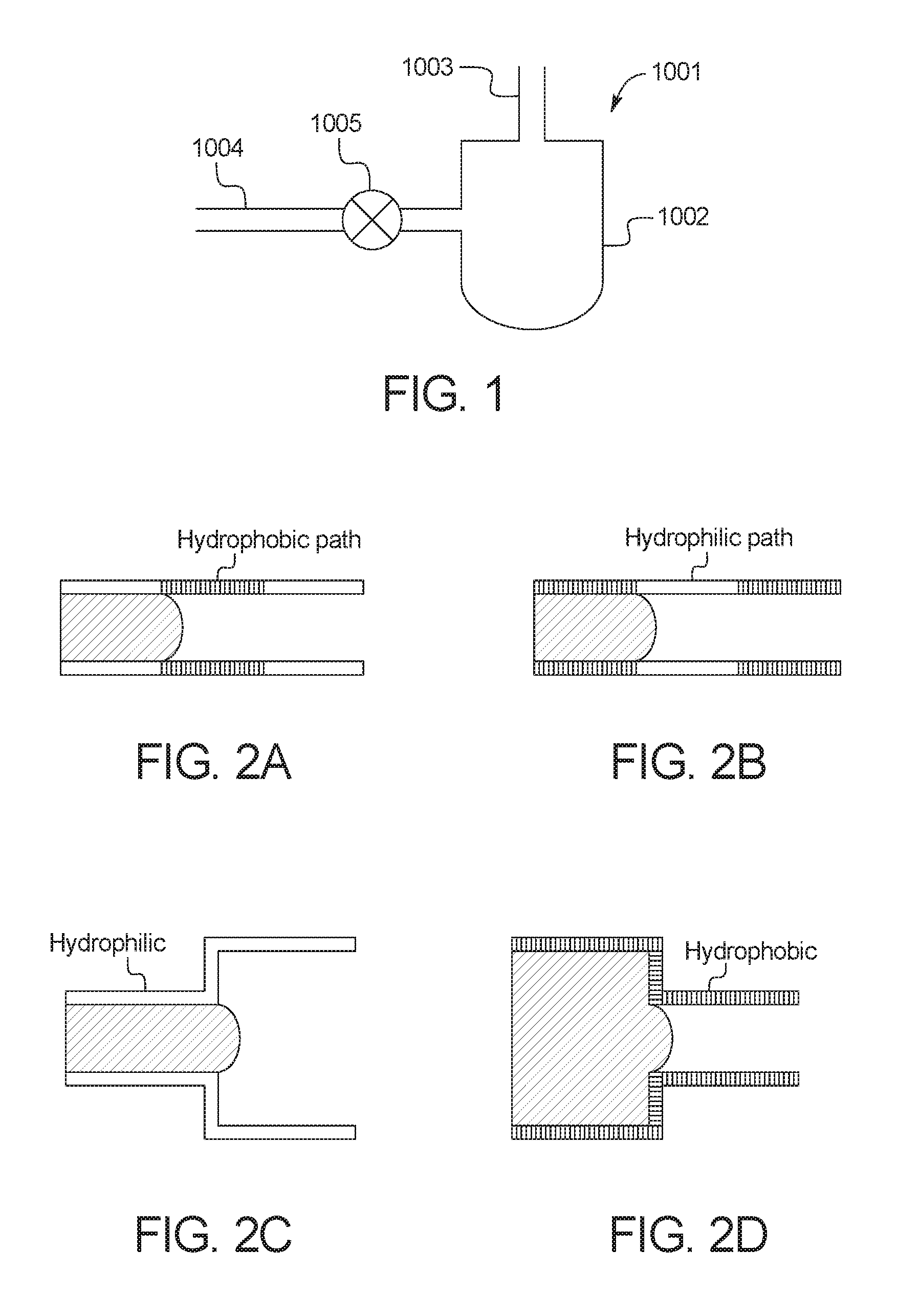
ActiveUS20160361715A1Reduce and eliminate effectPreparing sample for investigationSurgeryMulti analytePressure difference
A fluidic device for a cartridge for testing biological samples is disclosed herein. In an embodiment, the fluidic device includes a fluidic chamber, at least one microfluidic channel in fluid communication with the fluidic chamber, a venting port configured to apply a pneumatic force to the fluidic chamber, at least one passive valve located within the at least one microfluidic channel and configured to allow or stop fluid flow through the at least one microfluidic channel based on a pressure difference, and a controller configured to control the pneumatic force applied to the fluidic chamber via the venting port.
Owner:CYTOCHIP INC
Method of adjusting the working range of a multi-analyte assay
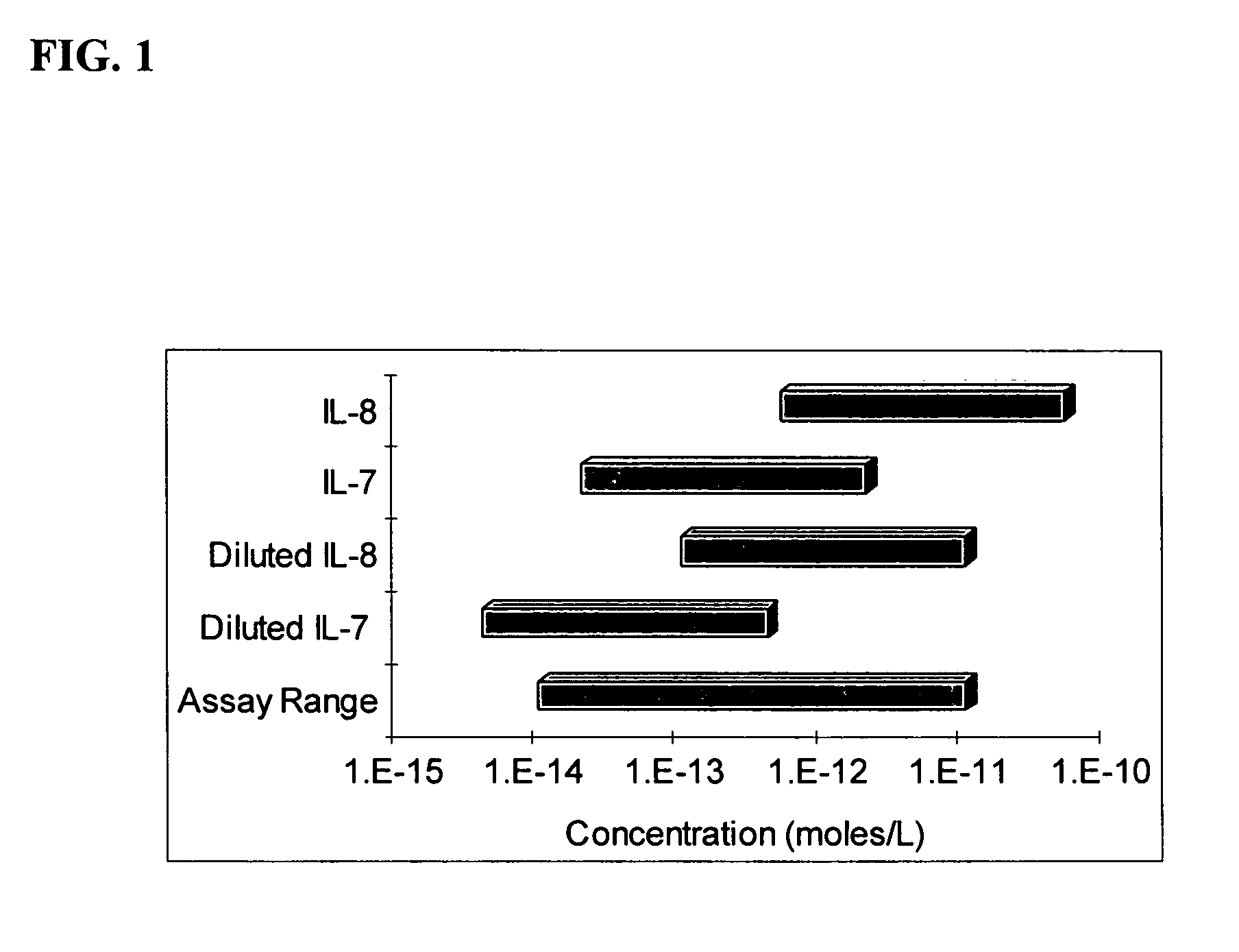
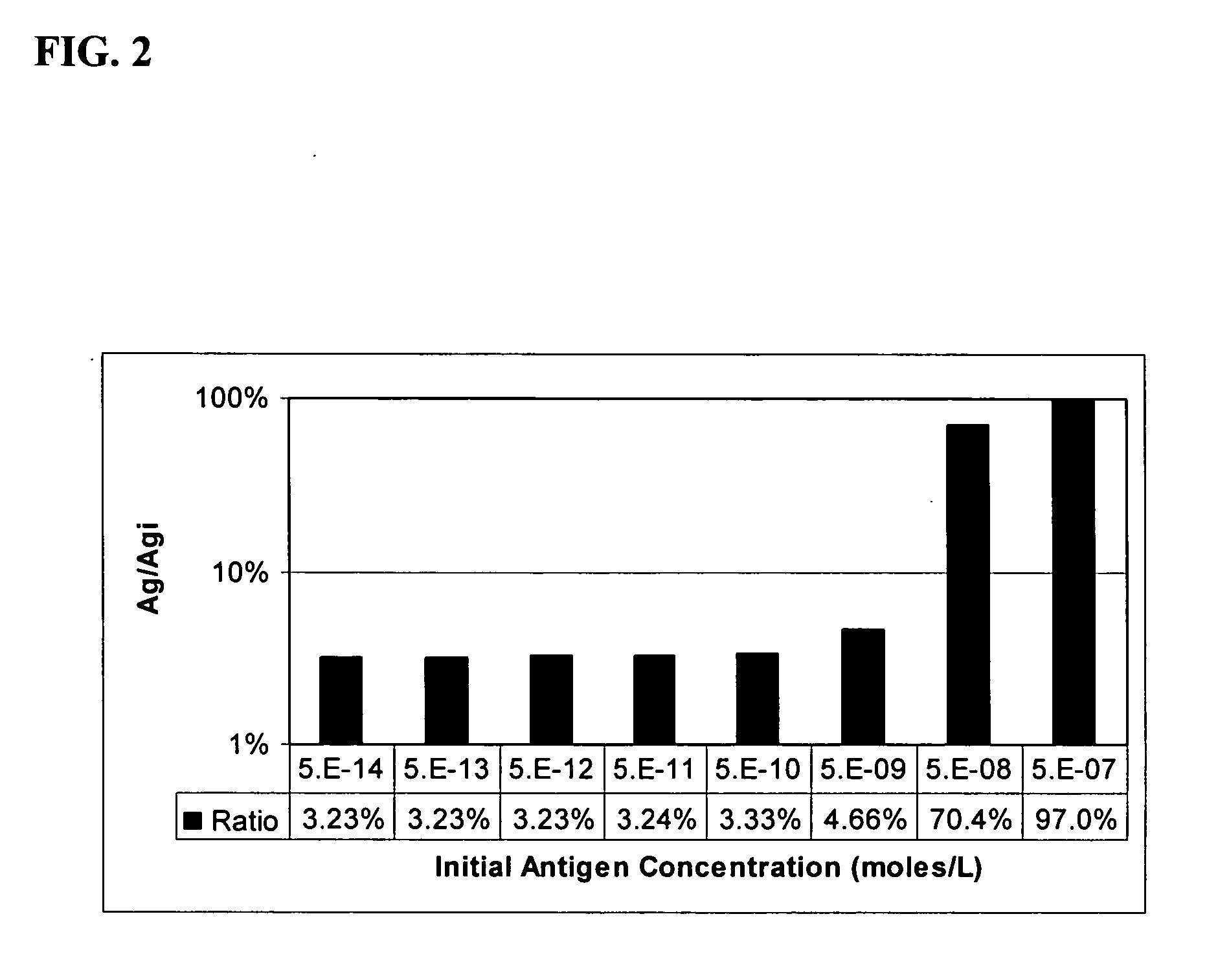
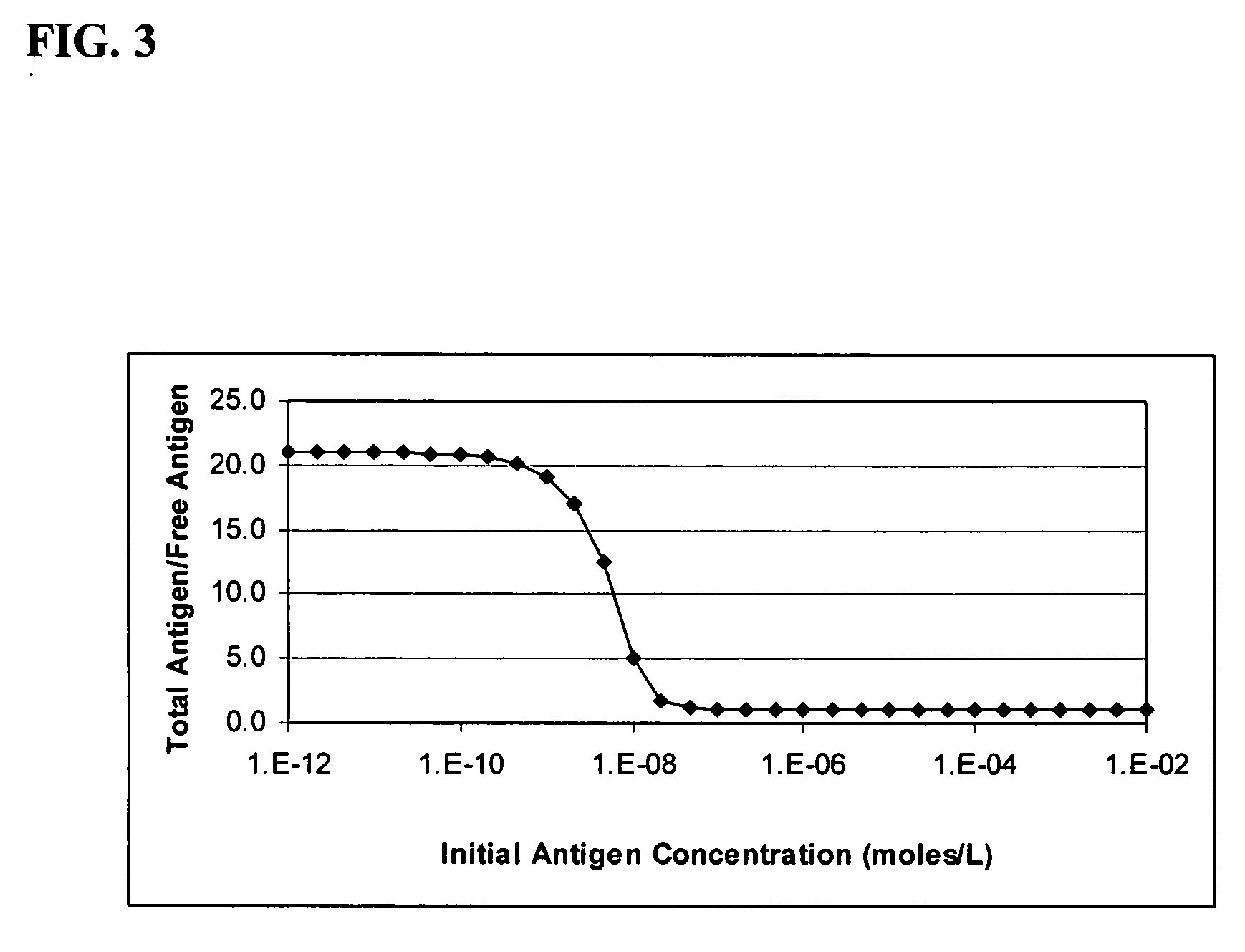
InactiveUS20060177873A1Reduce available analyte concentrationHinder availabilityBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsHigh concentrationMulti analyte
The invention features a method of adjusting the concentration of at least one but not all of a plurality of analytes in a fluid sample to match a known working range of detection of an analyte assay system, where each of the plurality of analytes may or may not be present within an expected initial concentration range having a high end and a low end, and at least one analyte has a high end expected concentration range that exceeds the high end of the working range of the assay system. The expected concentration of the high concentration analyte is adjusted by a proportional scaling constant, α, so that the high end of the adjusted expected concentration range is less than or equal to the high end of the working range, without adjusting the expected concentration range of at least one other of the plurality of analytes. Adjustment is preferably accomplished by adding to the solution phase of the assay one or more scaling agents, each scaling agent binding with specificity to an analyte and thereby preventing it from being detected by the assay system, e.g., by competing with binding to immobilized capture agent. This scaling method contrasts with prior methods, in which a concentration of available analyte is offset by a fixed amount to adjust the detectable threshold of the assay. Here, the amount of scaling agent is proportional to a scaling coefficient, and the scaling agent is present in the solution phase of the assay at high concentrations relative to analyte. Due to the equilibrium conditions established by the laws of mass transfer, the amount of free analyte remaining in solution in the presence of scaling agent is predictable and finite, and can be measured as a quantitative indicator of the initial concentration of the analyte in the sample.
Owner:COURTAGEN LIFE SCI
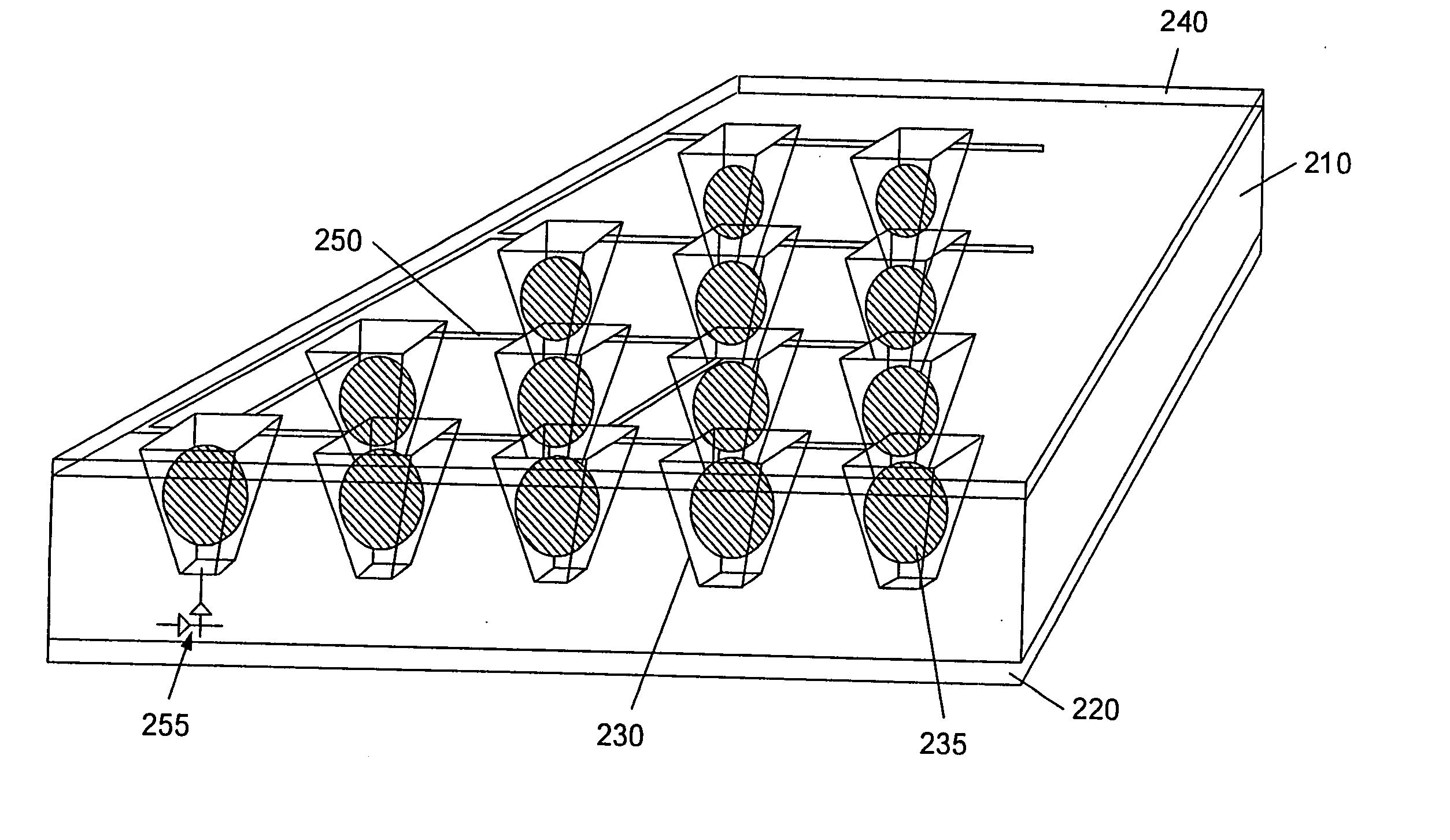
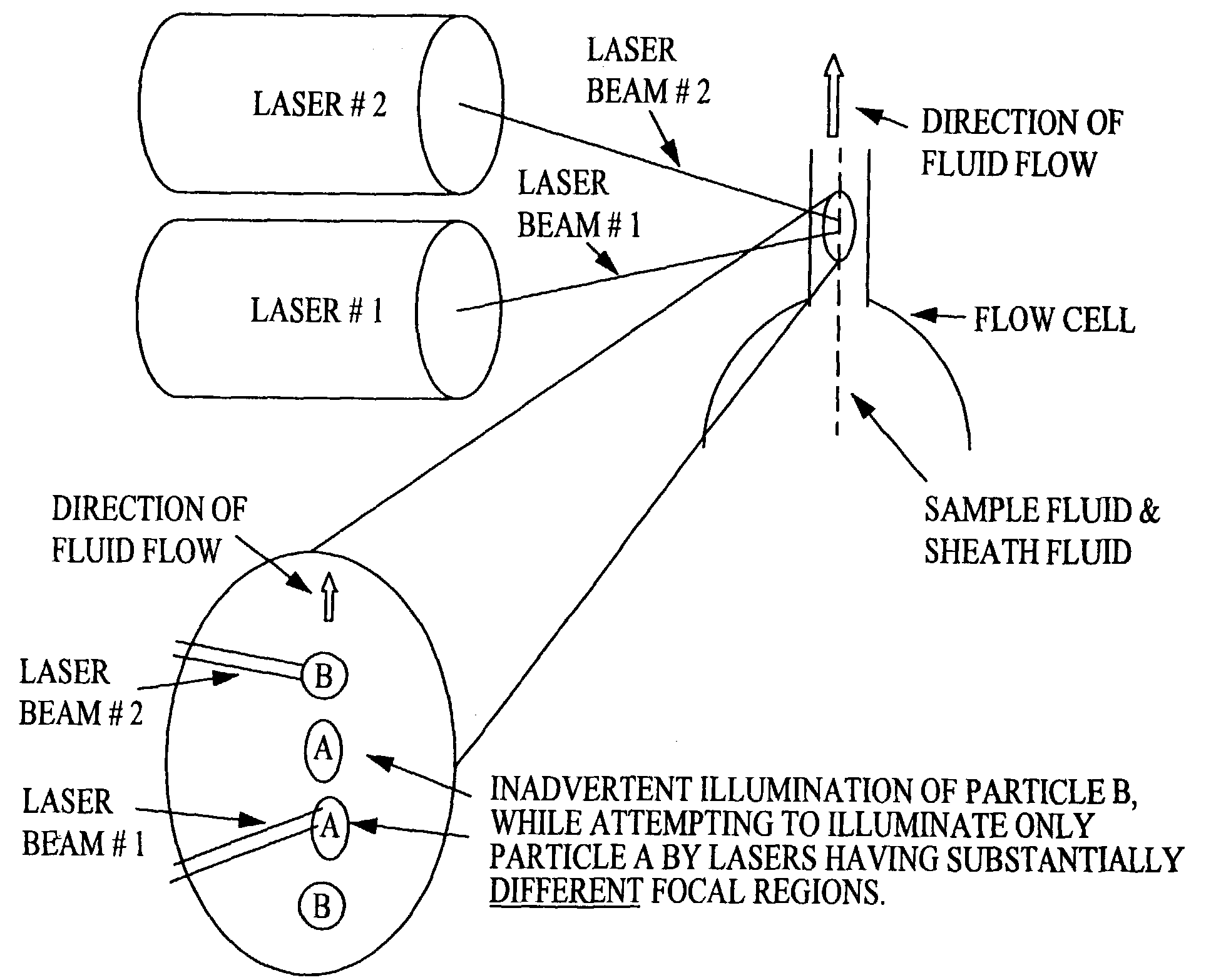
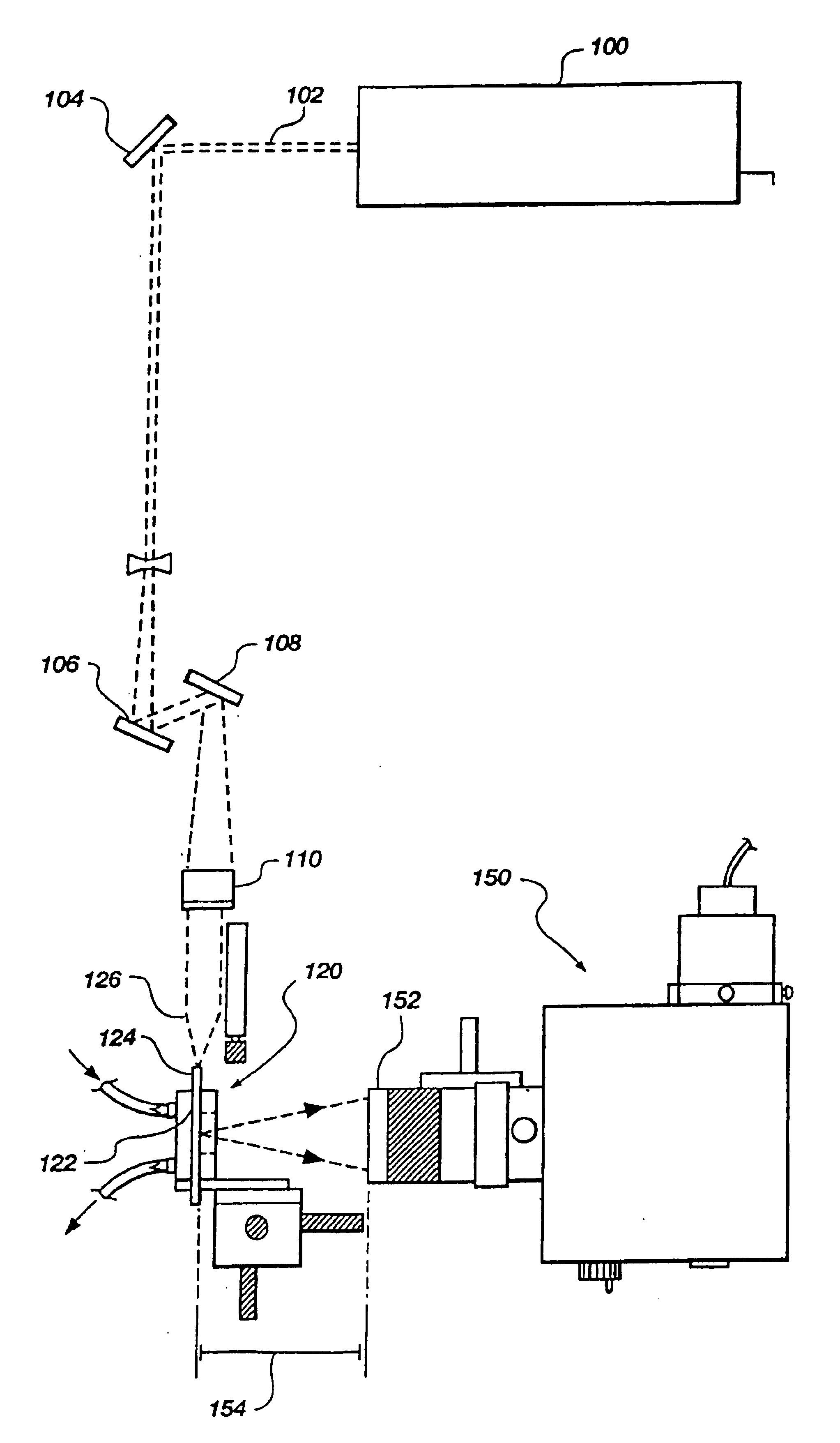
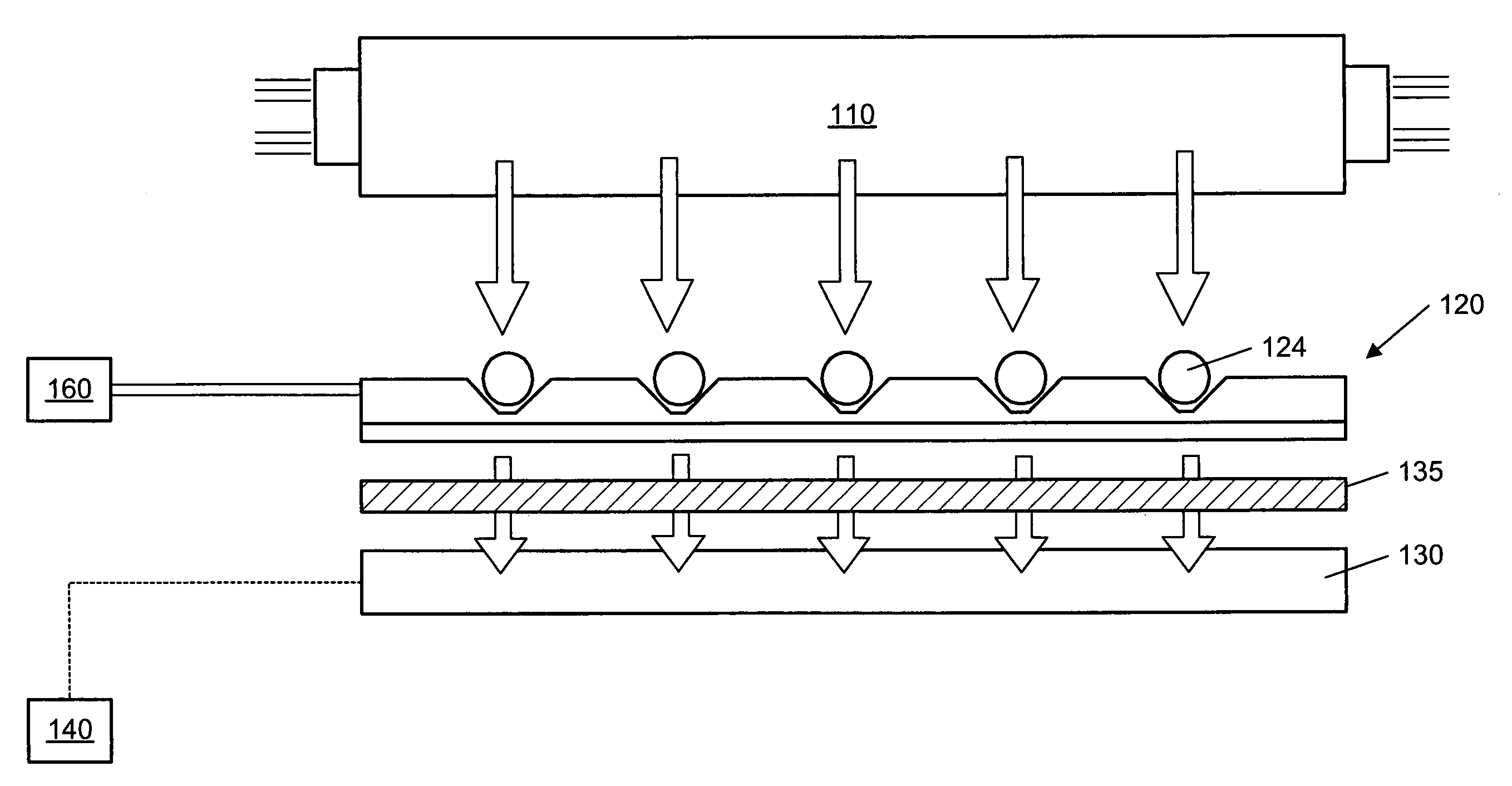
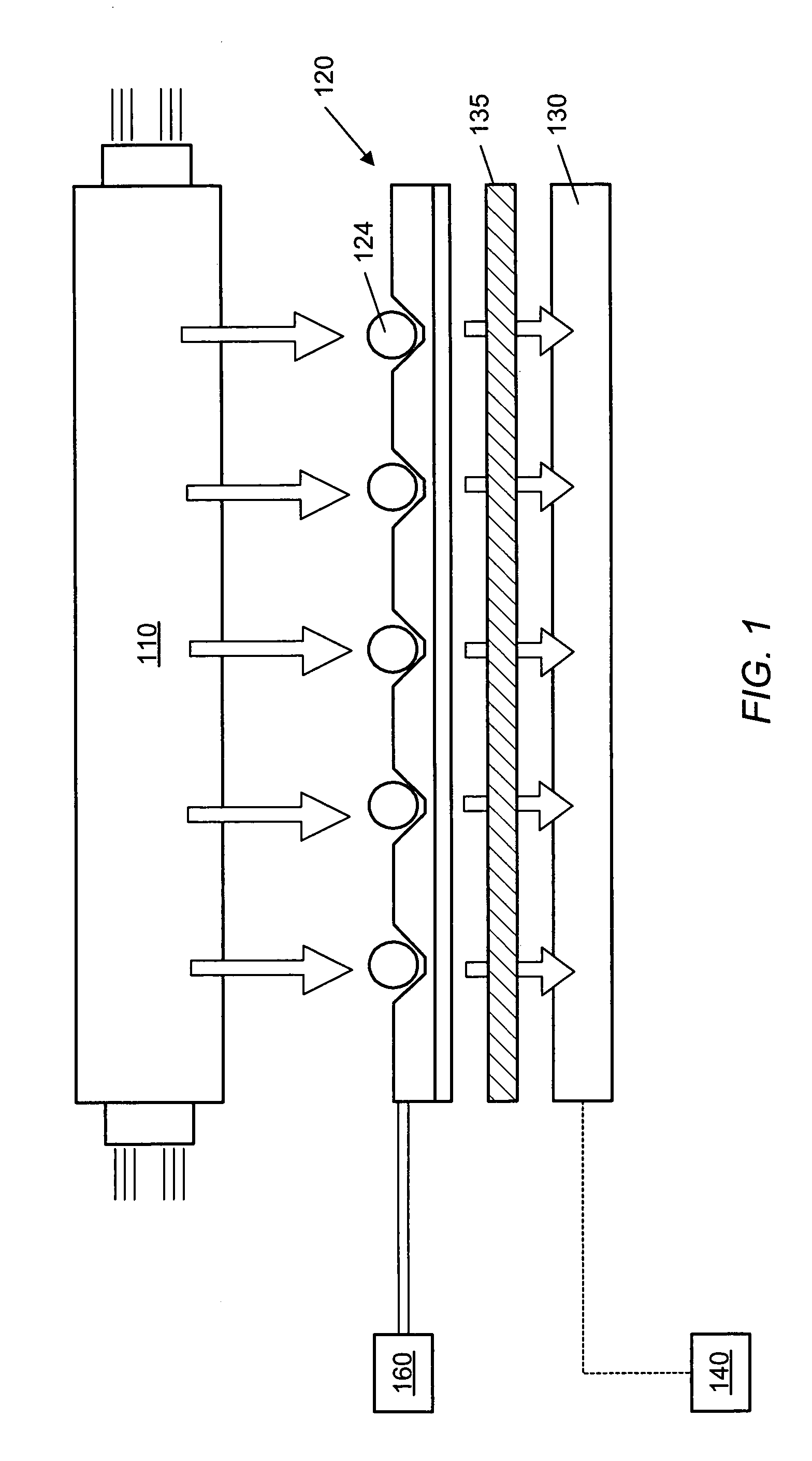
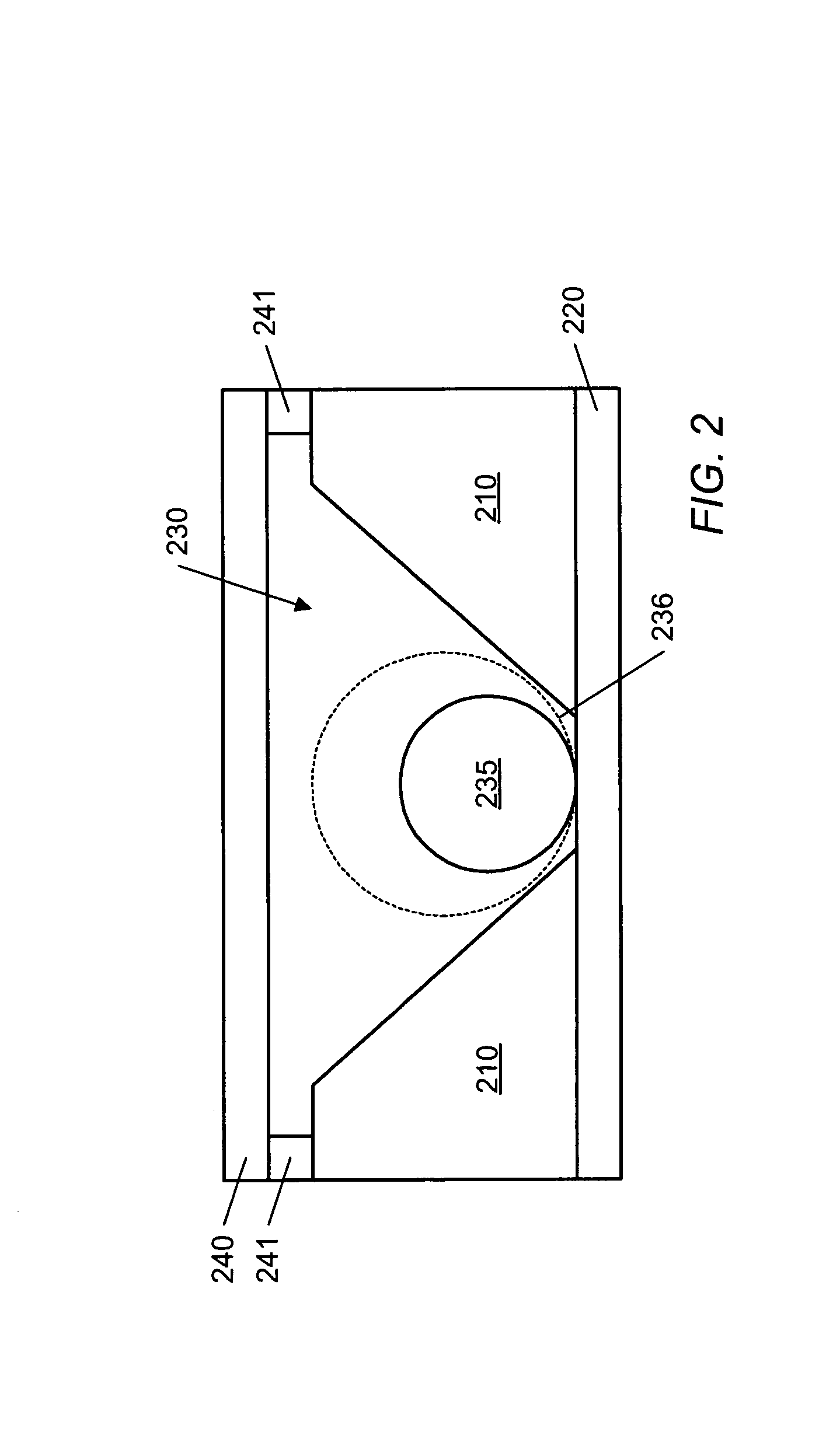
Apparatus and methods for multi-analyte homogeneous fluoro-immunoassays
InactiveUS6979567B2Reduce nonspecific bindingEasy to prepareBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMulti analyteLaser light
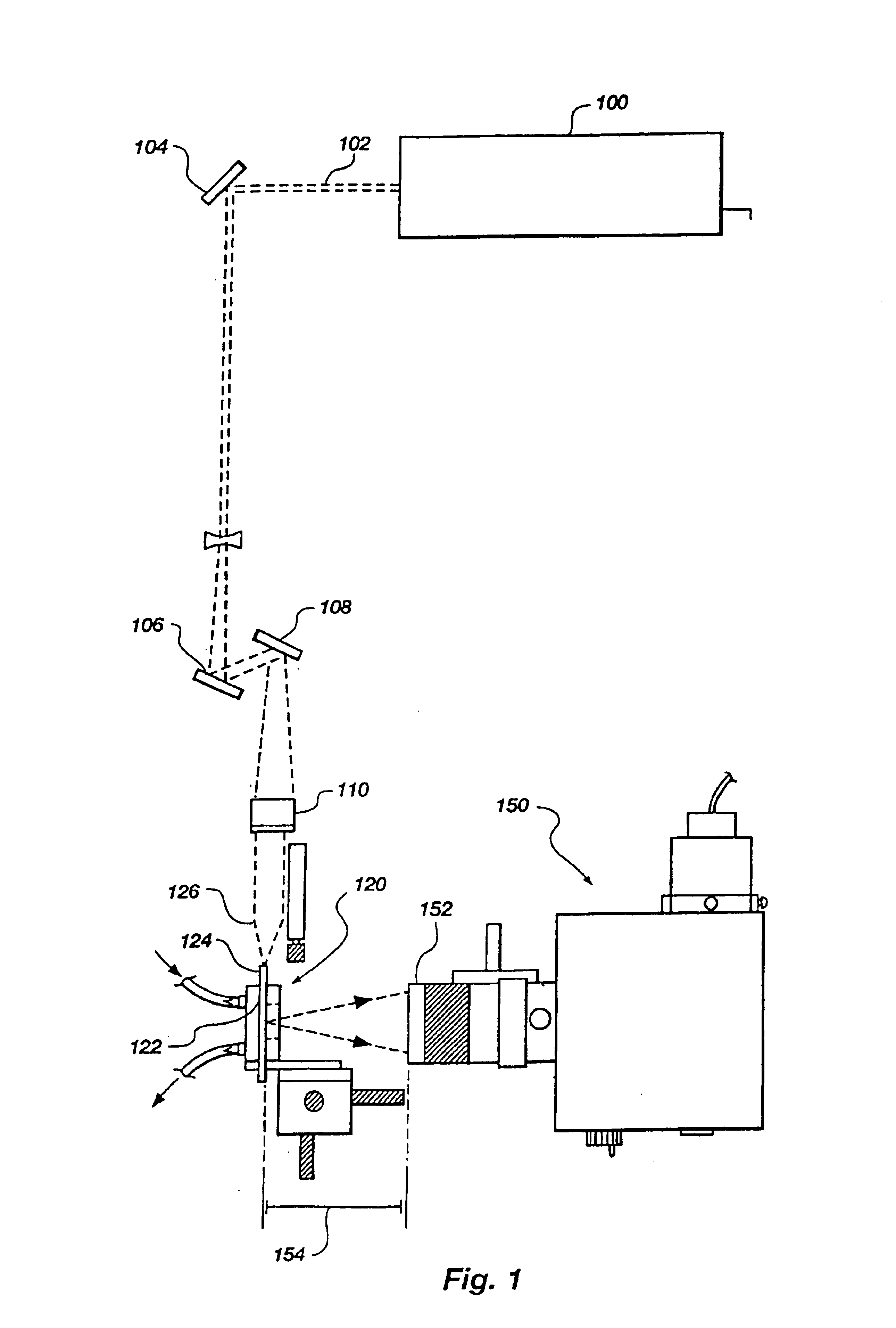
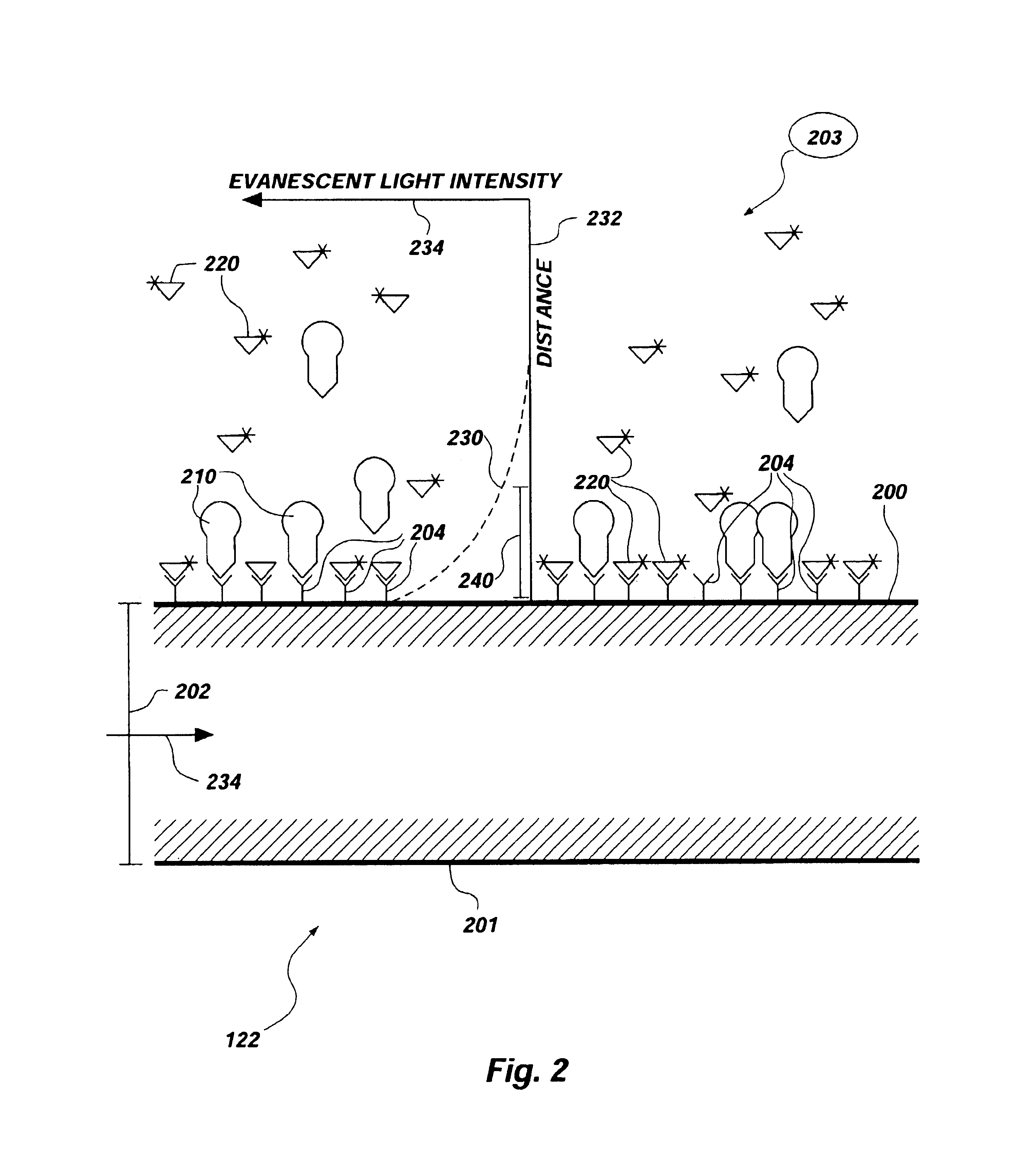
Methods and apparatus for evanescent light fluoroimmunoassays are disclosed. The apparatus employs a planar waveguide with an integral semicylindrical lens, and has multi-analyte features and calibration features, along with improved evanescent field intensity. A preferred embodiment of the biosensor and assay method has patches of capture molecules, each specific for a different analyte disposed adjacently within a single reservoir. The capture molecules are immobilized to the patches on the waveguide surface by site-specific coupling of thiol groups on the capture molecules to photo-affinity crosslinkers, which in turn are coupled to the waveguide surface or to a nonspecific binding-resistant coating on the surface. The patches of different antibodies are produced by selectively irradiating a portion of the waveguide surface during the process of coupling the photo-affinity crosslinkers, the selective irradiation involving a mask, a laser light source, or the like.
Owner:BIOCENTX
Method and system for the analysis of saliva using a sensor array
ActiveUS7651868B2Quick checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsSensor arrayMulti analyte
A system for the rapid characterization of analytes in saliva. In one embodiment, a system for detecting analytes includes a light source, a sensor array, and a detector. The sensor array is formed from a supporting member, in which a plurality of cavities may be formed. A series of chemically sensitive particles, in one embodiment, are positioned within the cavities. The particles may produce a signal when a receptor, coupled to the particle, interacts with the cardiovascular risk factor analyte and the particle-analyte complex is visualized using a visualization reagent. Using pattern recognition techniques, the analytes within a multi-analyte fluid may be characterized. In an embodiment, each cavity of the plurality of cavities is designed to capture and contain a specific size particle. Flexible projections may be positioned over each of the cavities to provide retention of the particles in the cavities.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Method and apparatus for the delivery of samples to a chemical sensor array
InactiveUS7022517B1Quick checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayMulti analyte
A system for the rapid characterization of multi-analyte fluids, in one embodiment, includes a light source, a sensor array, and a detector. The sensor array is formed from a supporting member into which a plurality of cavities may be formed. A series of chemically sensitive particles are, in one embodiment positioned within the cavities. The particles may be configured to produce a signal when a receptor coupled to the particle interacts with the analyte. Using pattern recognition techniques, the analytes within a multi-analyte fluid may be characterized.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Analyte detection system
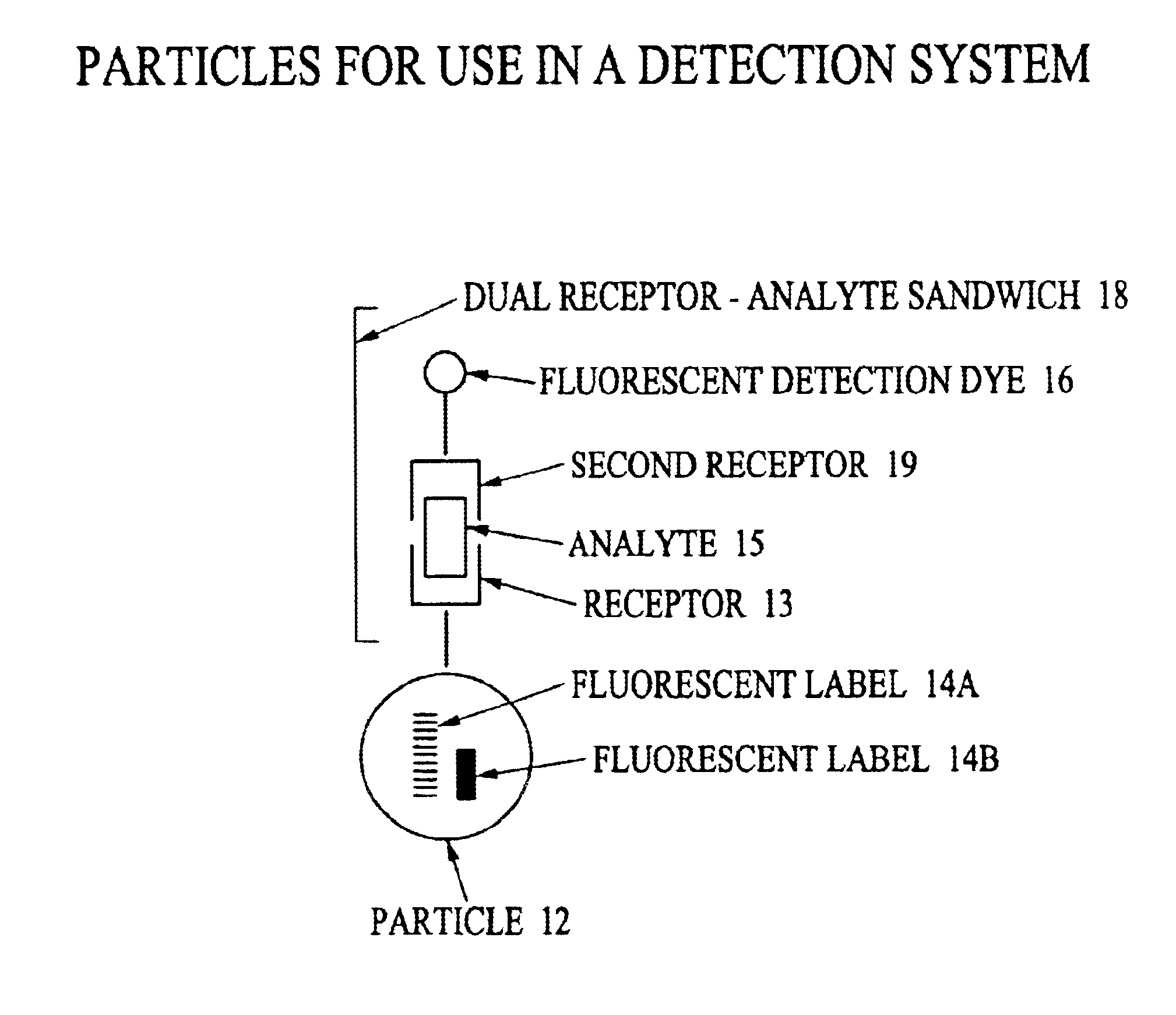
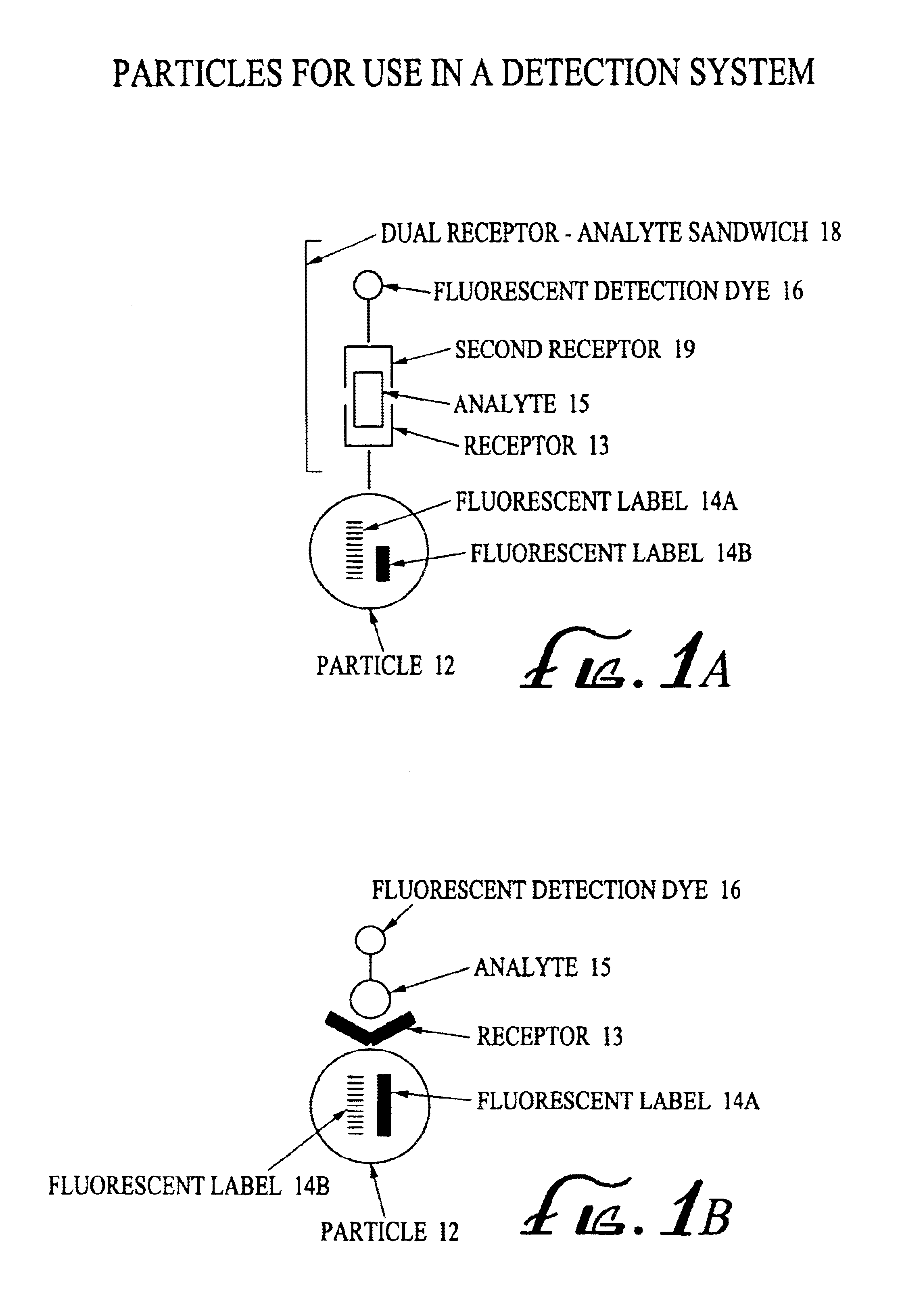
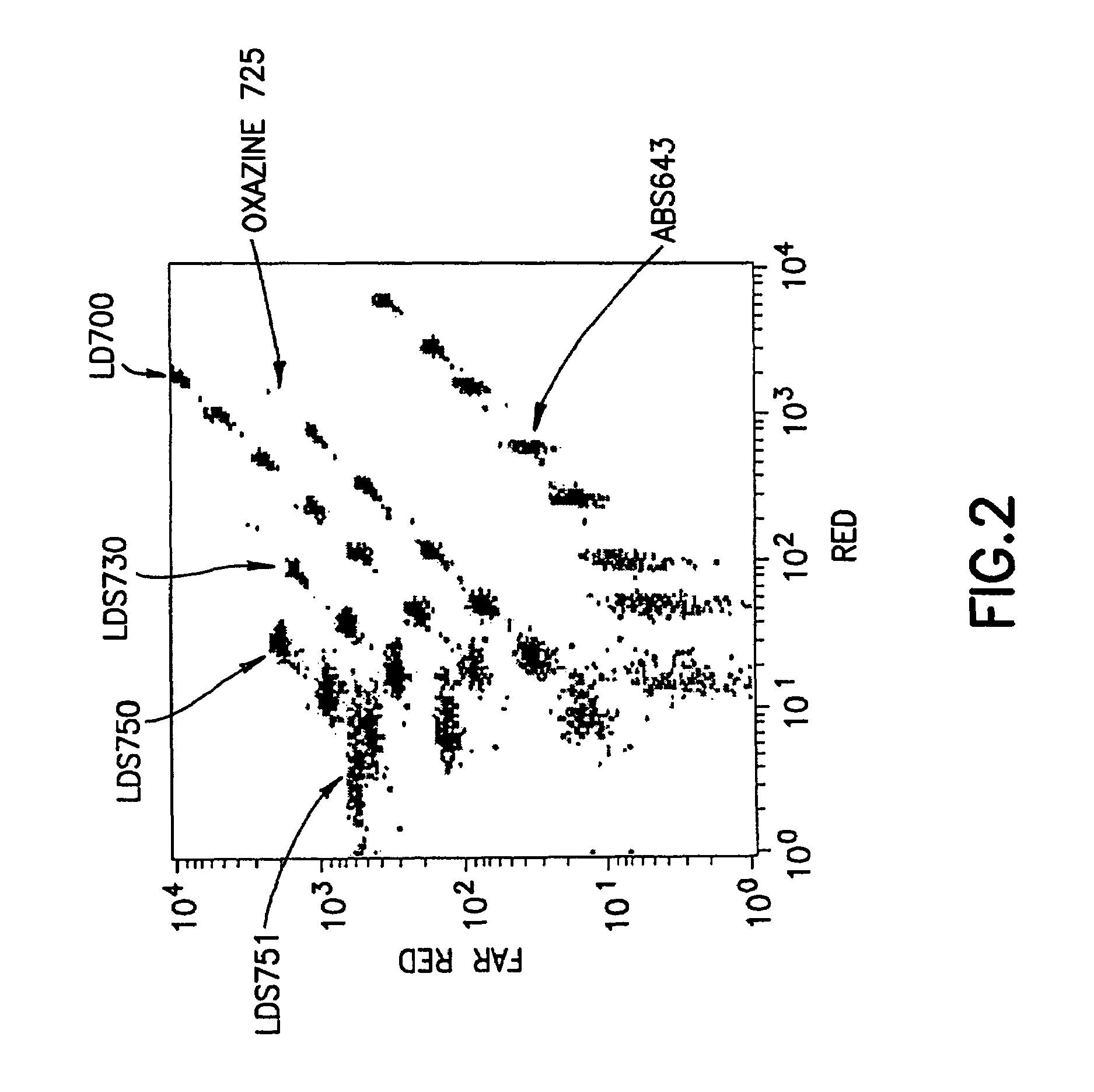
InactiveUS6838289B2Effective timeEasy to operateMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorInfraredMulti analyte
An analyte detection system utilizing a combination of fluorescent labels for labeling particles and an analyte specific fluorescent analyte detection dye. The particles contain a combination of fluorescent labels for coding the particles and an analyte specific fluorescent dye. The particles can be used to identify and quantify analytes in an analytical sample by reaction of the analytical sample with the particles. An analytical device can identify the particles according to the combination of fluorescent labels. The device can then correlate the identified particle with the analyte specific fluorescent analyte detection dye. Multiple subpopulations of particles can be used to identify and quantify multi-analytes in a single analytical sample. Near infrared (NIR) fluorescent labels useful in the detection system are also provided.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Application of nano-gold directly bonded with luminol in immunoassay
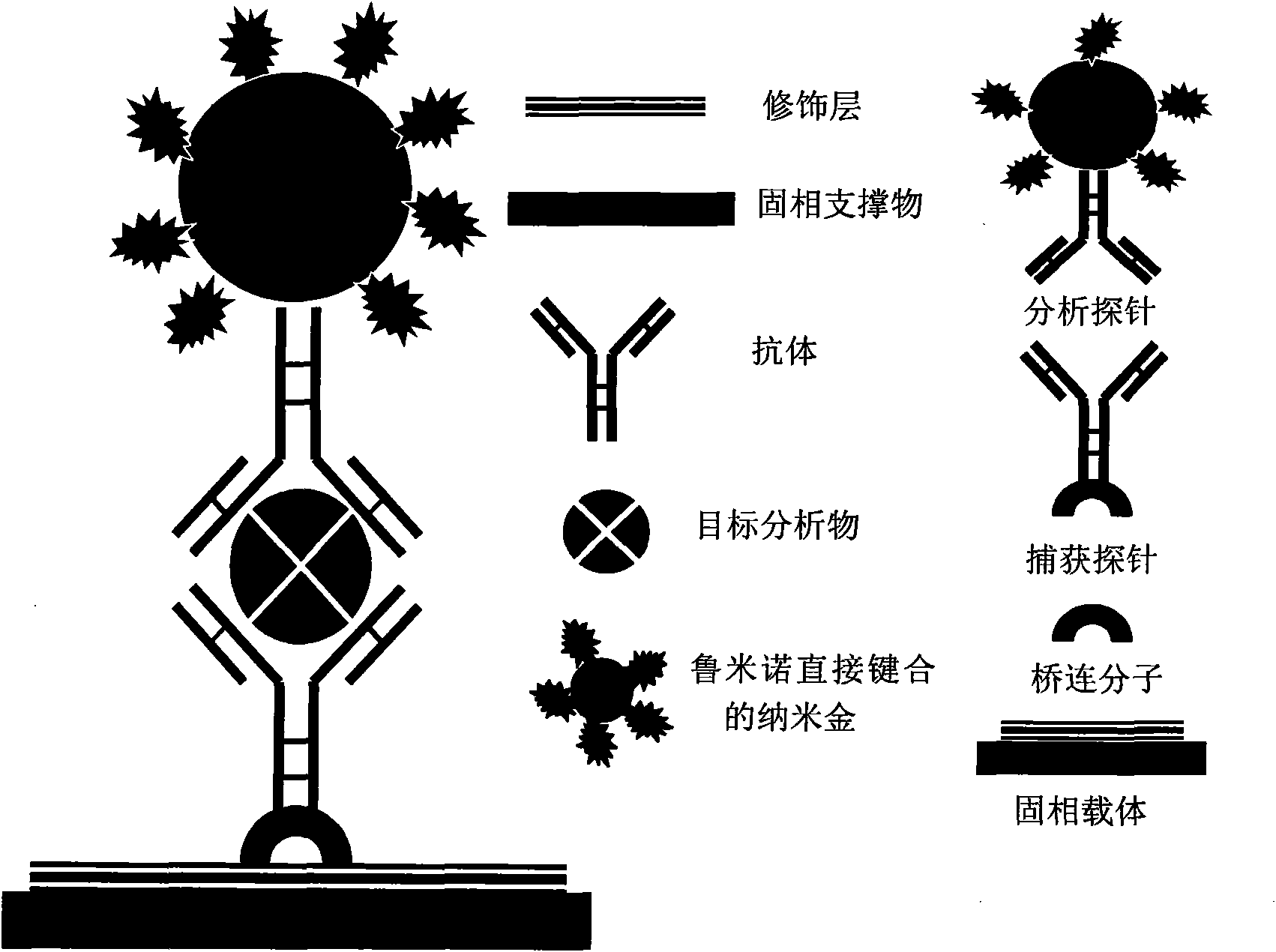
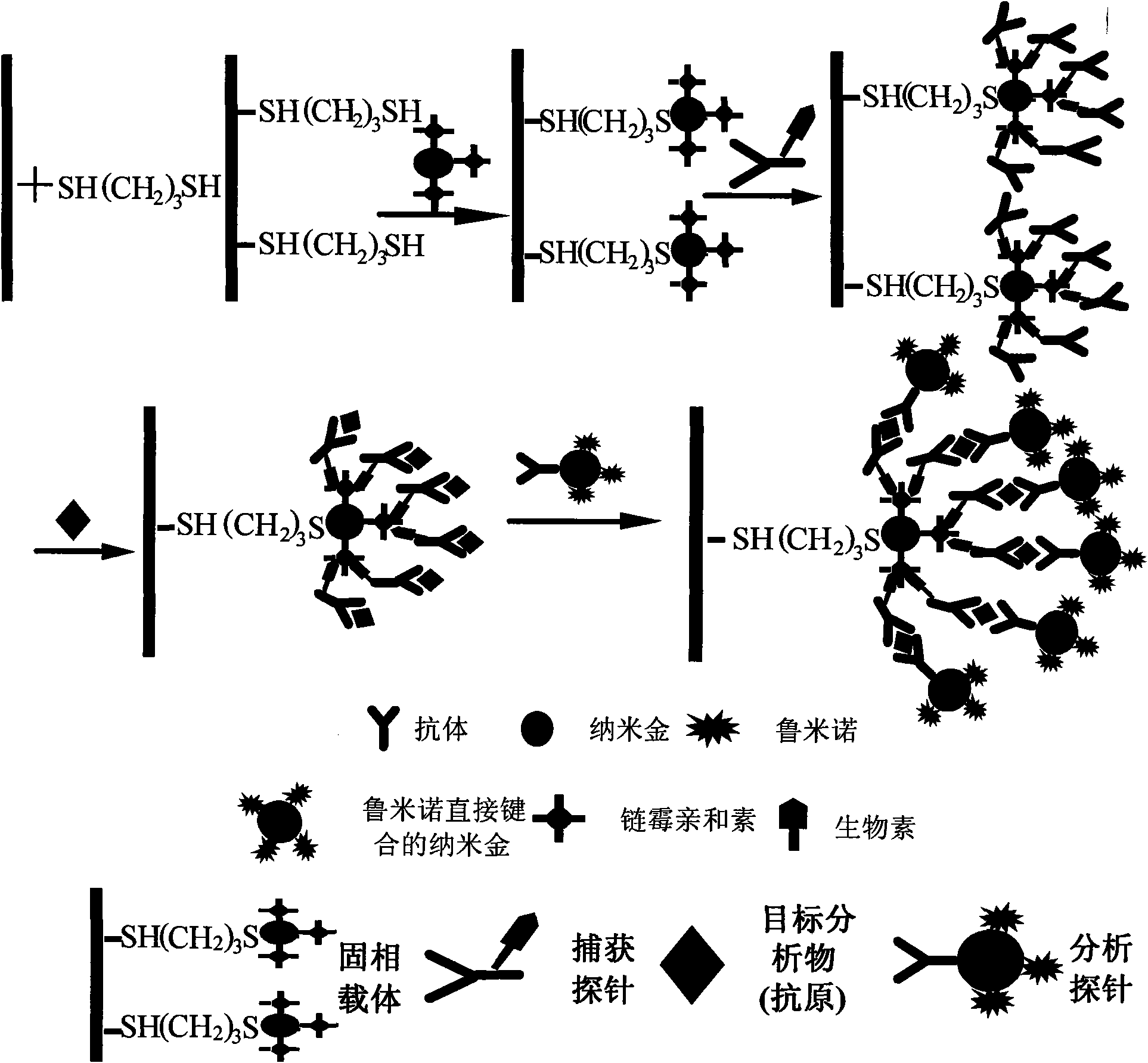
ActiveCN101900723ASimple methodFast wayAnalysis by electrical excitationBiological testingMulti analyteLinearity
The invention discloses an application of nano-gold directly bonded with luminol in an immunoassay. The invention is characterized in that the immunoassay probe of a nano-gold directly bonded with luminol comprises antibodies which are labeled by the nano-golds directly bonded with luminol, wherein the nano-gold directly bonded with luminol are prepared through reducing chloroauric acid by the luminol at a single step; a chemiluminescence immunoassay method is based on the immunoassay probe of the nano-gold directly bonded with luminol; and a kit is used for carrying out the immunoassay method. The chemiluminescence immunoassay method of the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity (for instance, the detection limit can reach 1.0pg / mL for detecting human IgG), wide range of linearity, good repeatability, simple operation, low cost and the like, can be applied to detect multi-analyte in various samples and has key application prospect in fields, such as clinical diagnosis and cure, drug analysis, food security detection, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for the analysis of saliva using a sensor array
ActiveUS20050214863A1Quick checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsSensor arrayMulti analyte
A system for the rapid characterization of analytes in saliva. In one embodiment, a system for detecting analytes includes a light source, a sensor array, and a detector. The sensor array is formed from a supporting member, in which a plurality of cavities may be formed. A series of chemically sensitive particles, in one embodiment, are positioned within the cavities. The particles may produce a signal when a receptor, coupled to the particle, interacts with the cardiovascular risk factor analyte and the particle-analyte complex is visualized using a visualization reagent. Using pattern recognition techniques, the analytes within a multi-analyte fluid may be characterized. In an embodiment, each cavity of the plurality of cavities is designed to capture and contain a specific size particle. Flexible projections may be positioned over each of the cavities to provide retention of the particles in the cavities.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Multianalyte molecular analysis using application-specific random particle arrays
ActiveUS20060240416A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular analysisMagnetite Nanoparticles
The present invention provides a method for the generation of novel libraries of encoded magnetic particles from sub-libraries of by the generation of novel sub-libraries of magnetic nanoparticles and encoded particles. The sub-libraries are functionalized on demand are useful in the formation of arrays. The present invention is especially useful for performing multiplexed (parallel) assays for qualitative and / or quantitative analysis of binding interactions of a number of analyte molecules in a sample.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
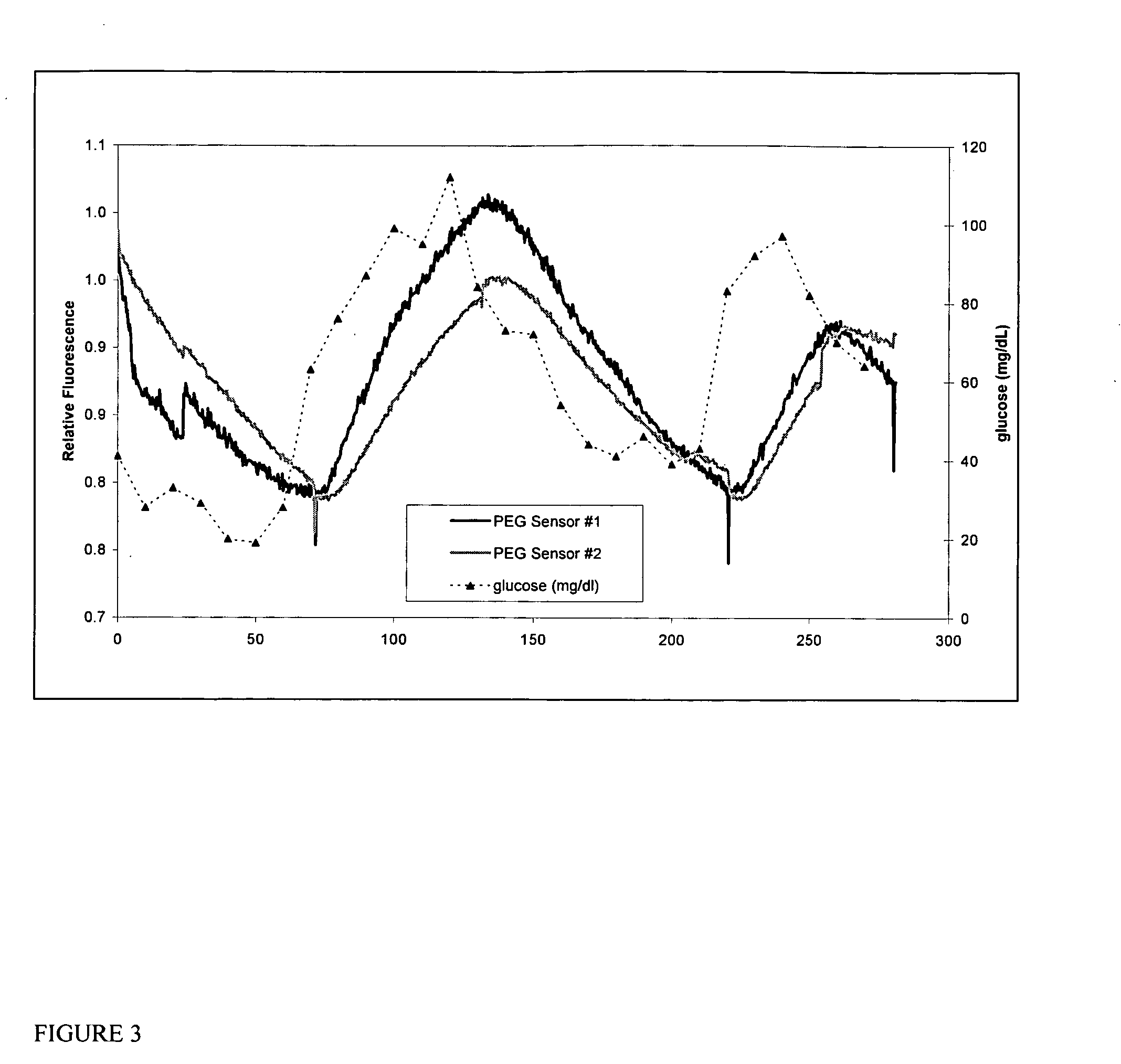
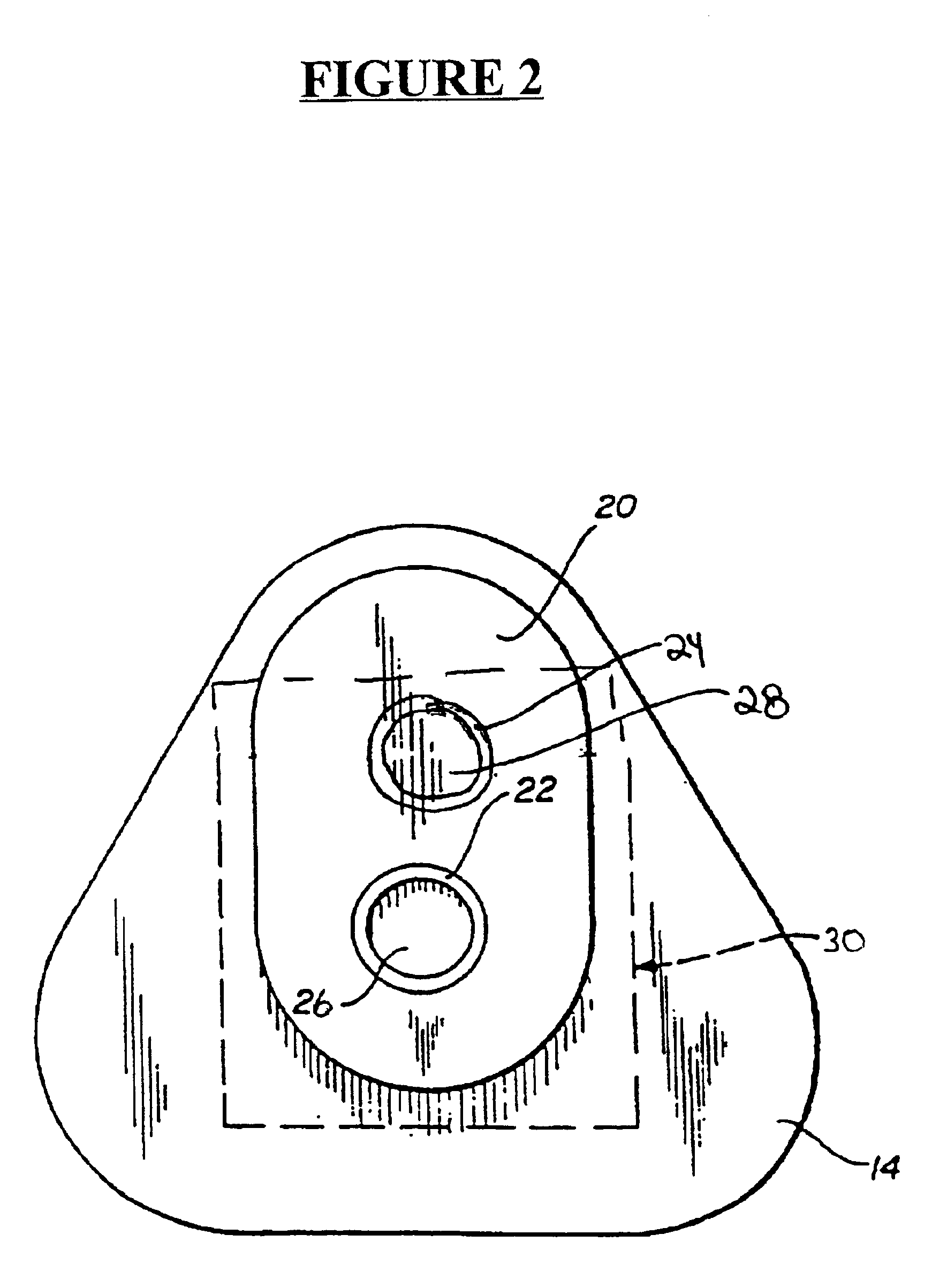
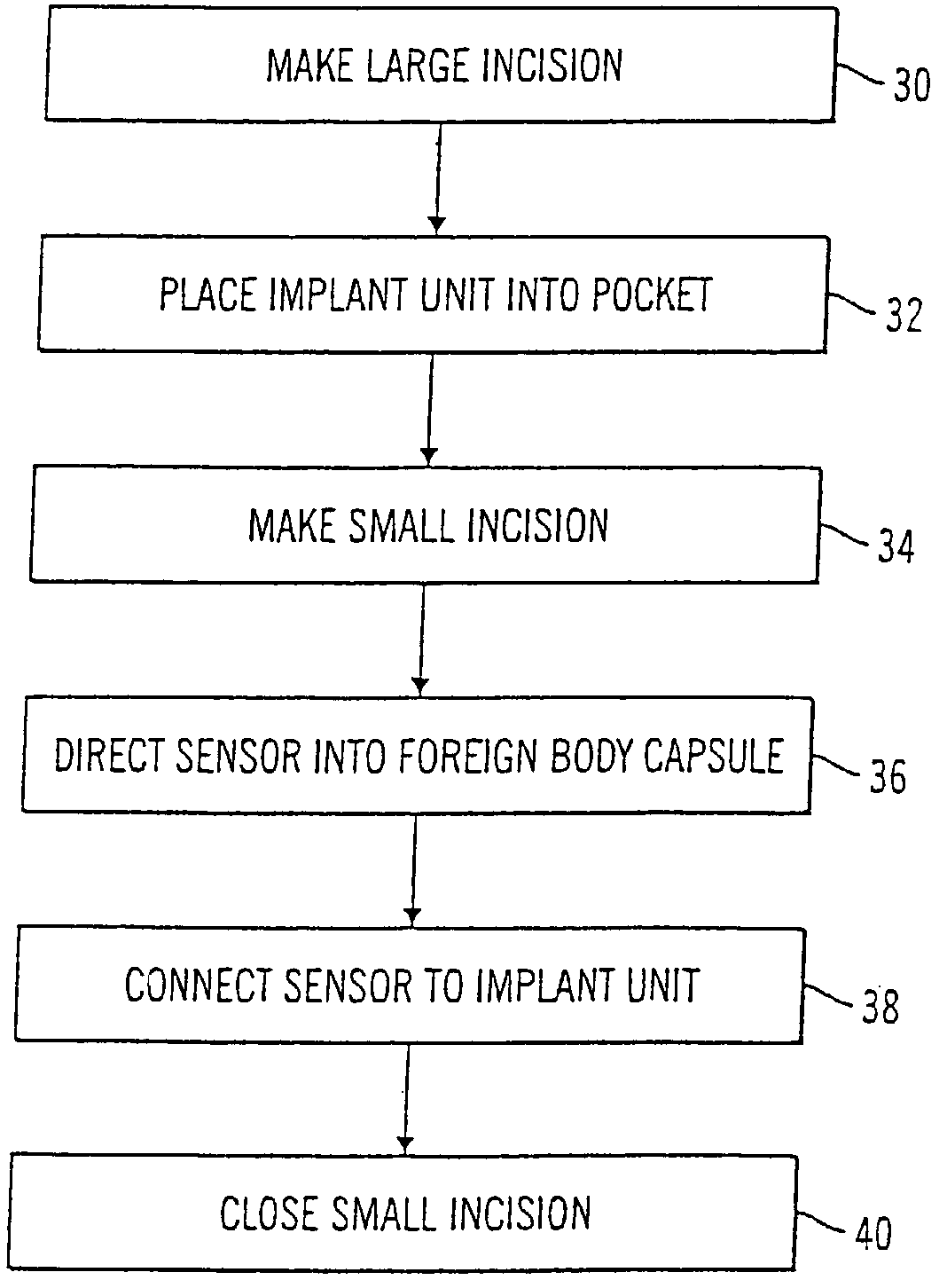
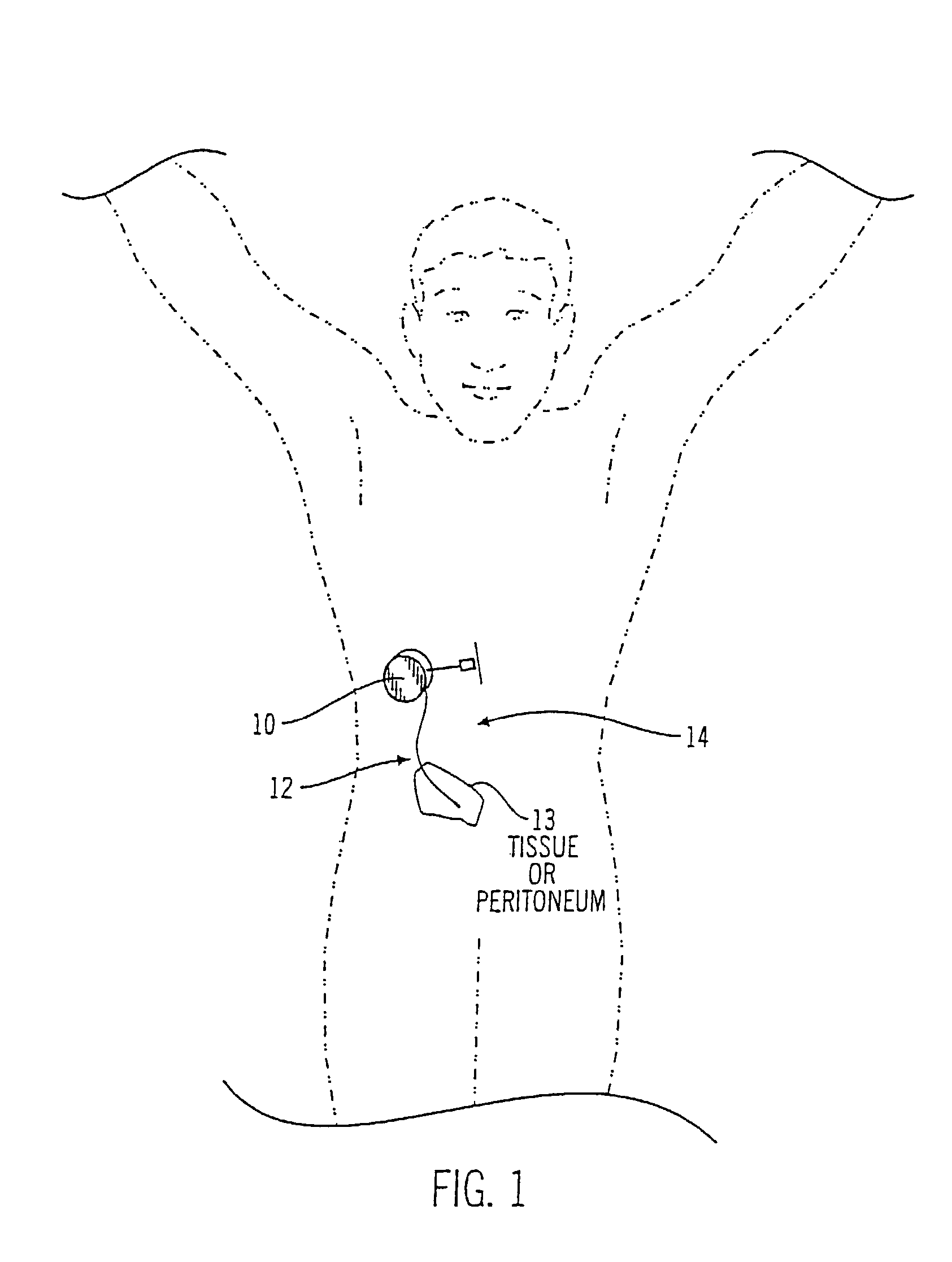
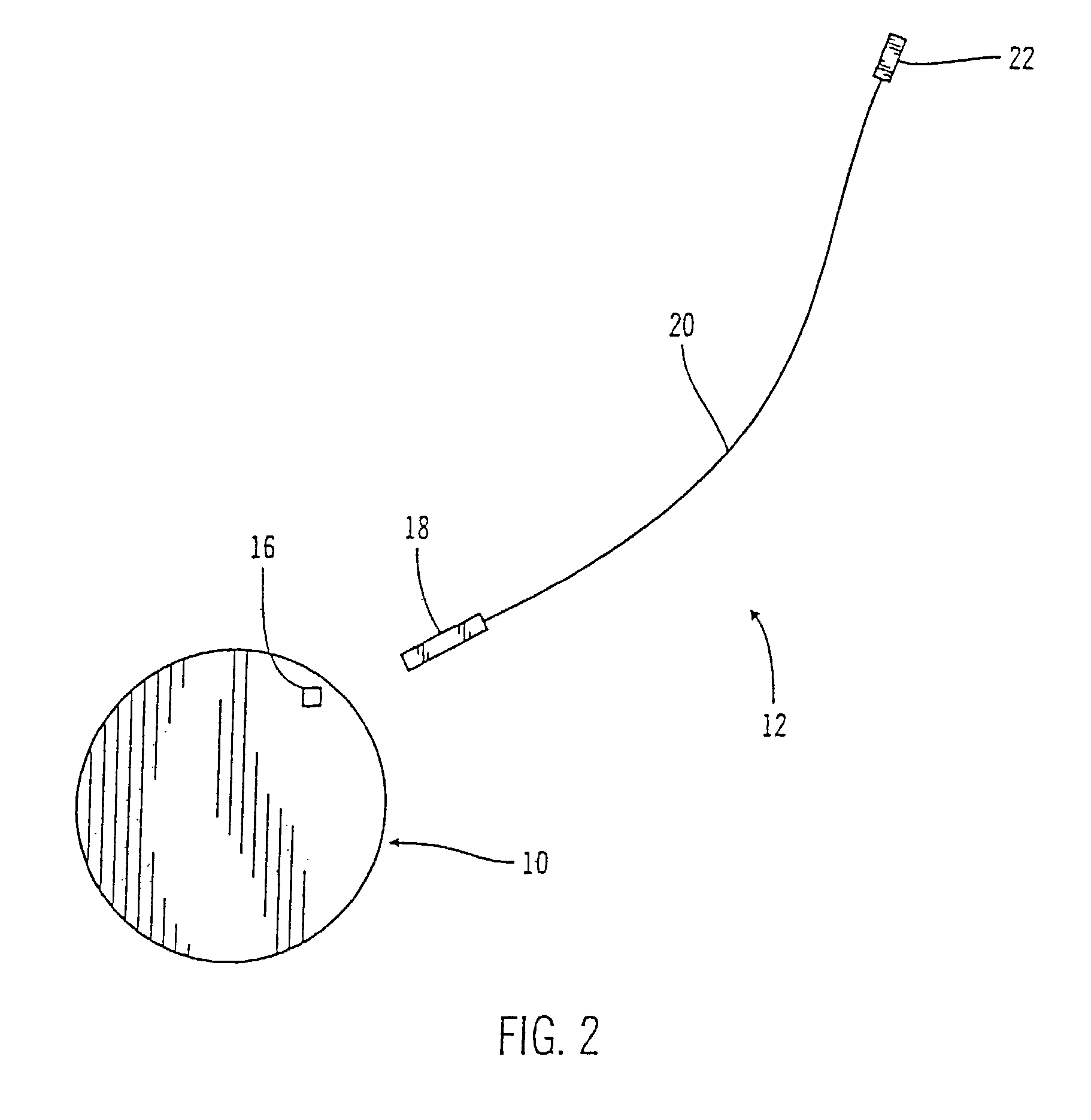
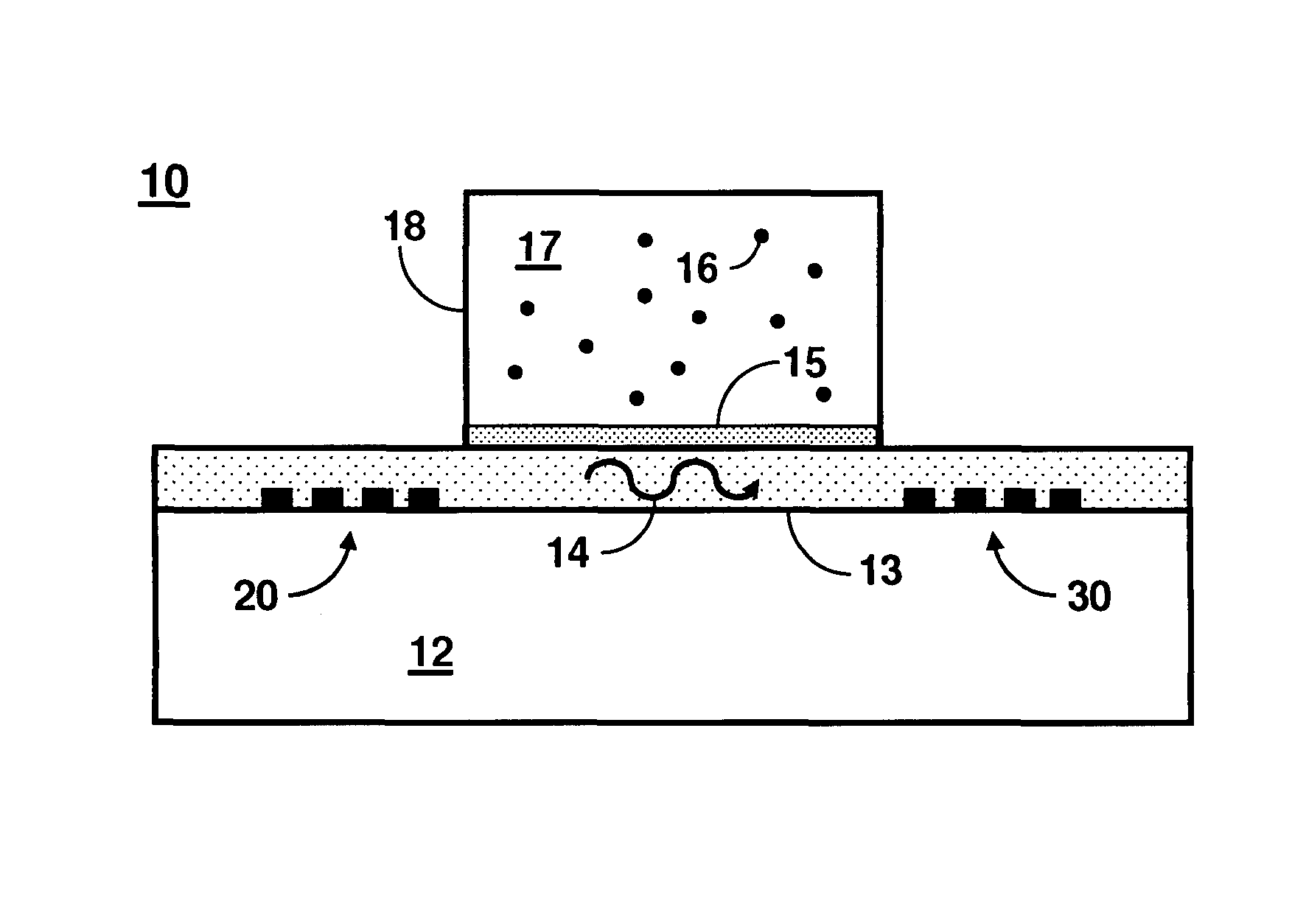
Implantable sensor method and system
ActiveUS7736309B2Accurate measurementReduce noiseBioelectric signal measurementSurgical needlesMulti analytePeritoneal space
Systems and methods for non-vascular sensor implantation and for measuring physiological parameters in areas of a body where the physiological parameters are heterogeneous. An implant unit is implanted in an area of a body and a foreign body capsule is allowed to form around the implant unit area. A sensor may be directed into a body cavity such as, for example, the peritoneal space, subcutaneous tissues, the foreign body capsule, or other area. A subcutaneous area of the body may be tunneled for sensor placement. Spatially separated sensing elements may be used for detecting individual amounts of the physiological parameter. An overall amount of the physiological parameter may be determined by calculating a statistical measurement of the individual sensed amounts in the area. Another embodiment of the invention, a multi-analyte measuring device, may include a substrate having an electrode array on one side and an integrated circuit on another side.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Fluid based analysis of multiple analytes by a sensor array
InactiveUS20050164320A1Quick checkBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayMulti analyte
A system for the rapid characterization of multi-analyte fluids, in one embodiment, includes a light source, a sensor array, and a detector. The sensor array is formed from a supporting member into which a plurality of cavities may be formed. A series of chemically sensitive particles are, in one embodiment positioned within the cavities. The particles may be configured to produce a signal when a receptor coupled to the particle interacts with the analyte. Using pattern recognition techniques, the analytes within a multi-analyte fluid may be characterized.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Multiplex microparticle system
ActiveUS7507588B2Simplify creationNone provides advantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMulti analyteMicroparticle
Arrays of microparticle populations, each population labeled with a single fluorescent dye, are provided for use in multiplex assays. The populations form a virtual multidimensional array wherein each microparticle is identified by fluorescence intensity in two different fluorescence detection channels. The arrays are useful in a variety of assays, including multiplex, multi-analyte assays for the simultaneous detection of two or more analytes by, for example, flow cytometry, and a labeling reagents in, for example, microscopy. The use of singly-dyed microparticles to form multidimensional arrays greatly simplifies the creation of multiplex assays.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Biomarkers
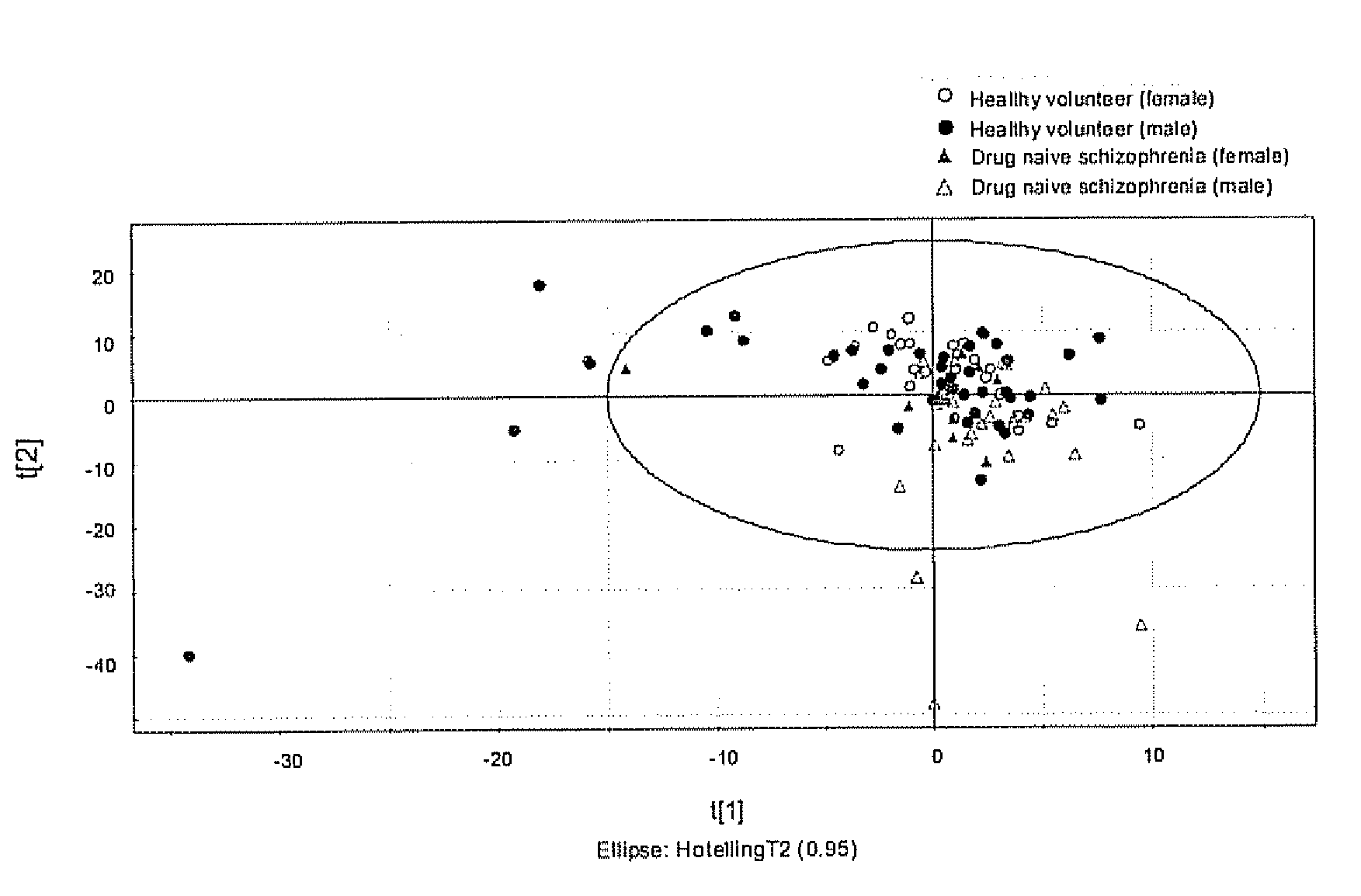
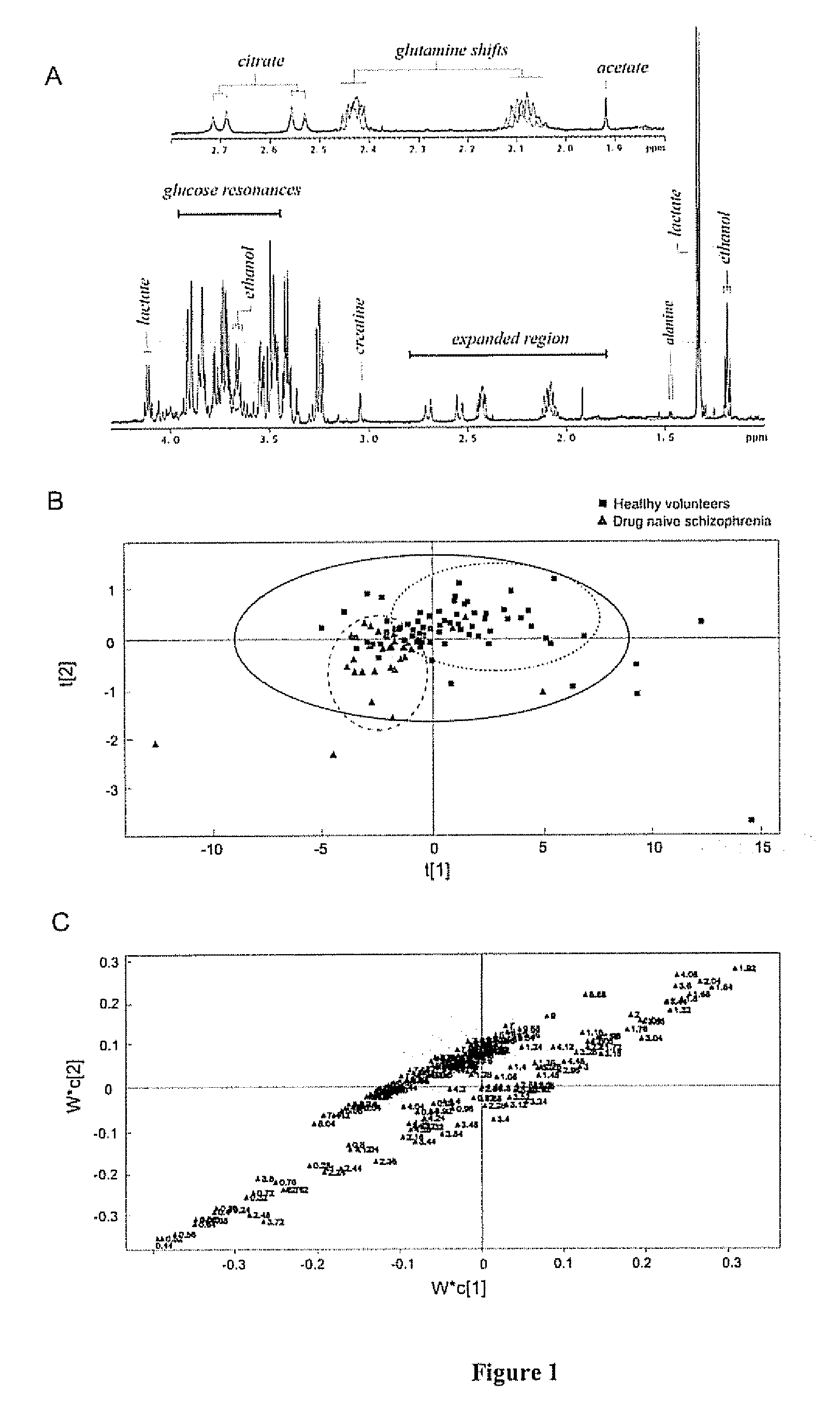
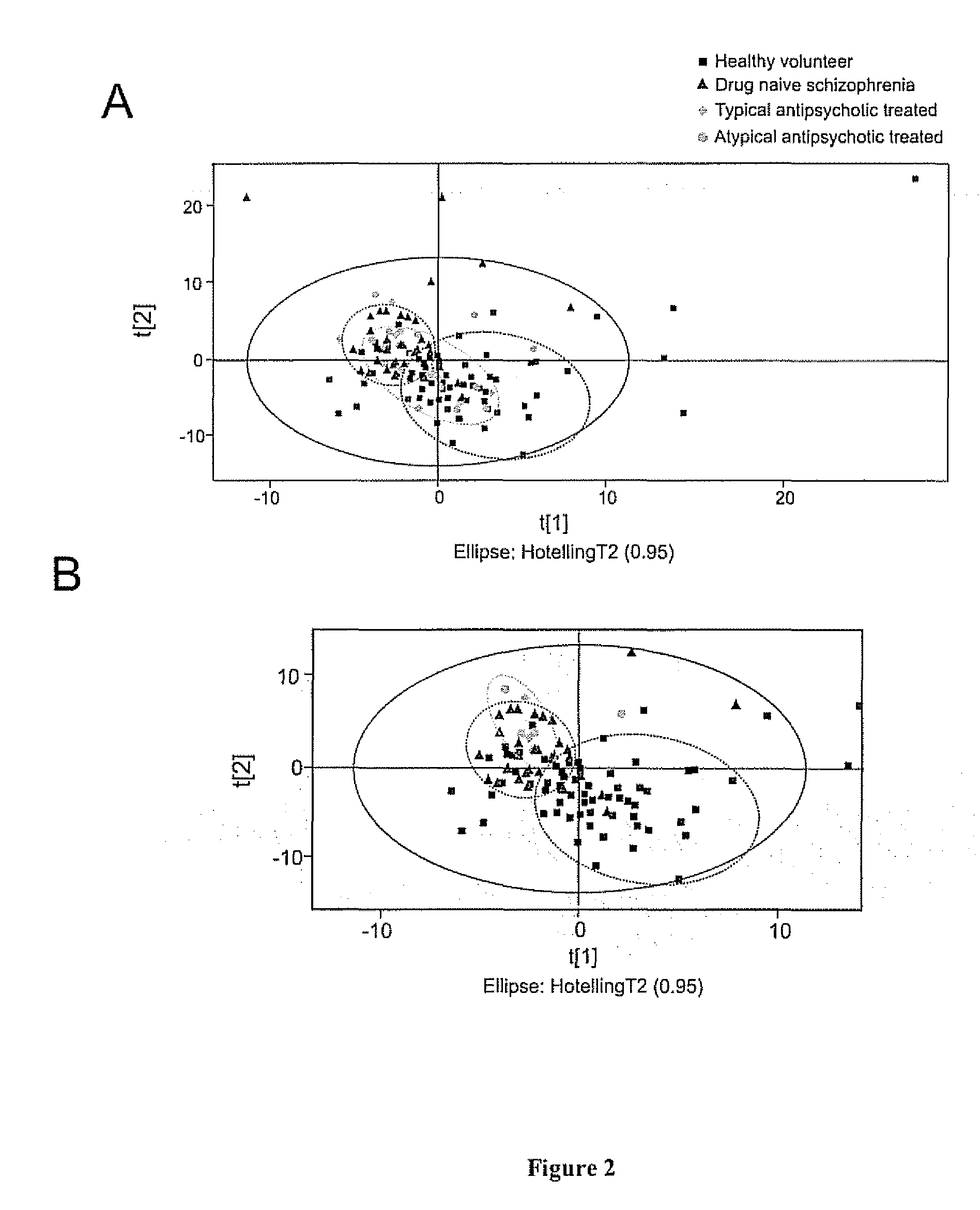
InactiveUS20080220530A1Minimal sample preparationSuppress water NMR resonanceMagnetic measurementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBipolar mood disorder
The invention relates to methods for diagnosing or monitoring psychotic disorders such as schizophrenic or bipolar disorders, comprising measuring the level of one or more biomarker(s) present in a cerebrospinal fluid sample taken from a test subject, said biomarker(s) being selected from the group consisting of: glucose, lactate, acetate species and pH. The invention also relates to methods of diagnosing or monitoring a psychotic disorder in a subject comprising providing a test sample of CSF from the subject, performing spectral analysis on said CSF test sample to provide one or more spectra, and, comparing the one or more spectra with one or more control spectra. The invention also relates to sensors, biosensors, multi-analyte panels, arrays, assays and kits for performing methods of the invention.
Owner:PSYNOVA NEUROTECH LTD
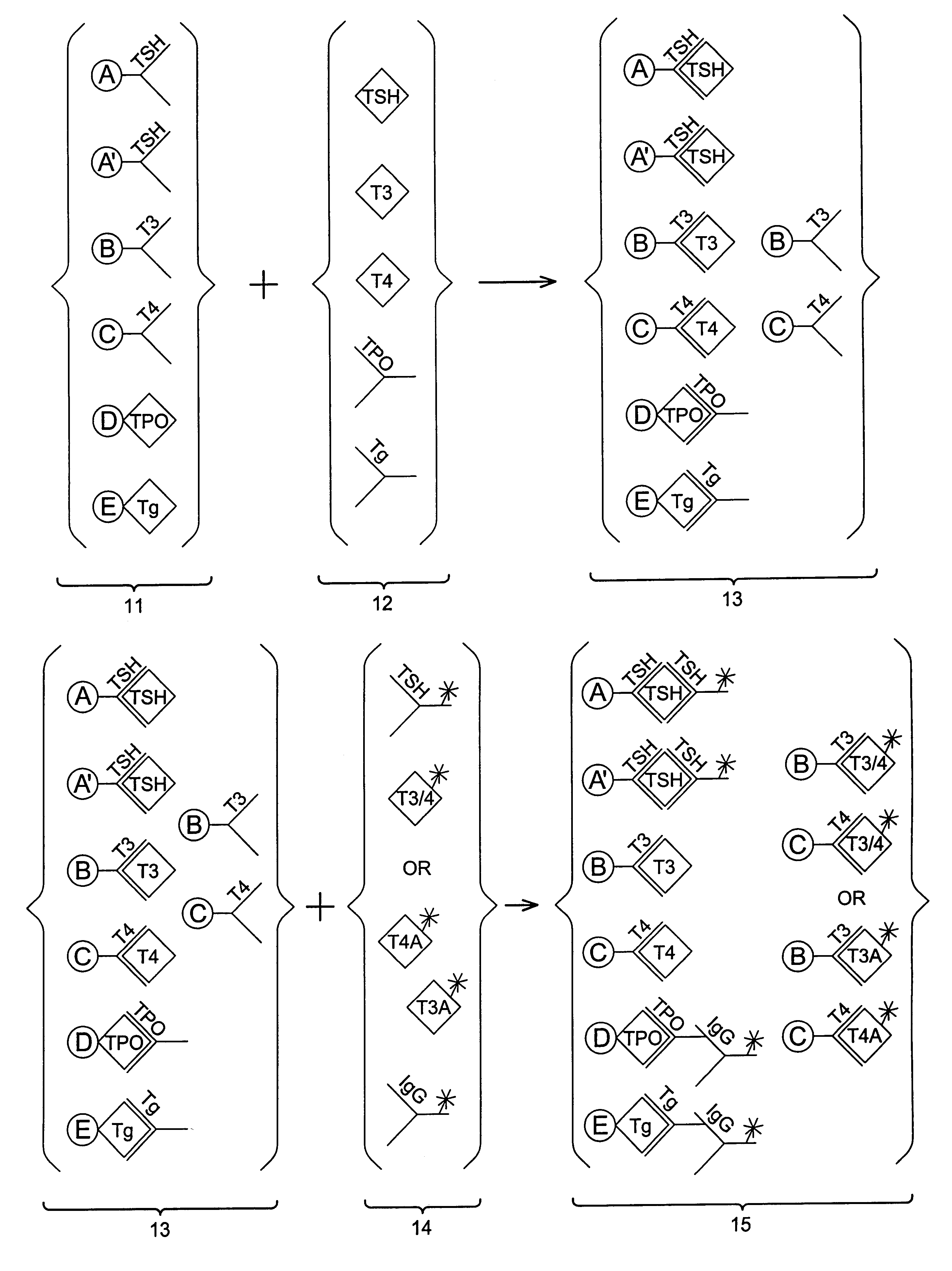
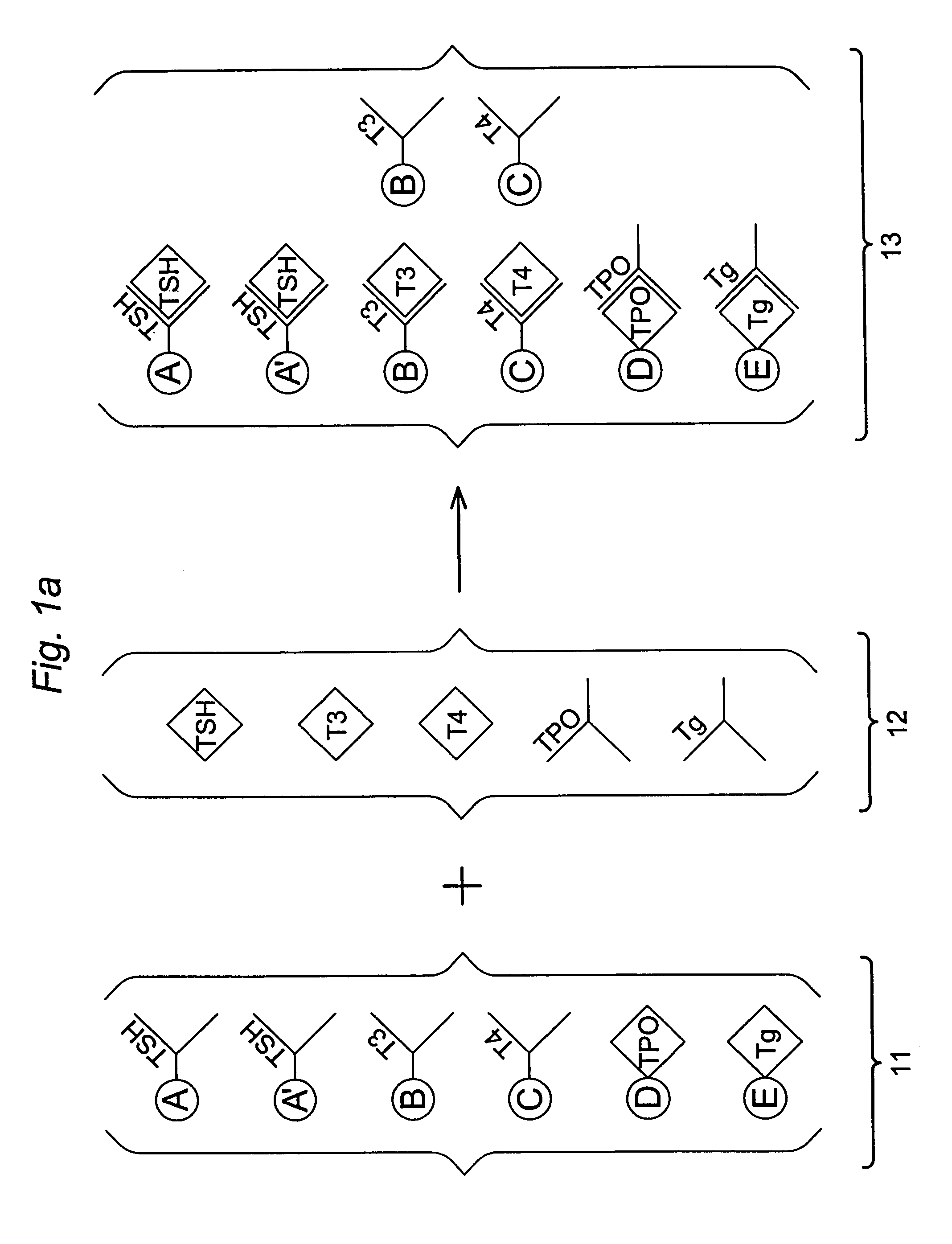
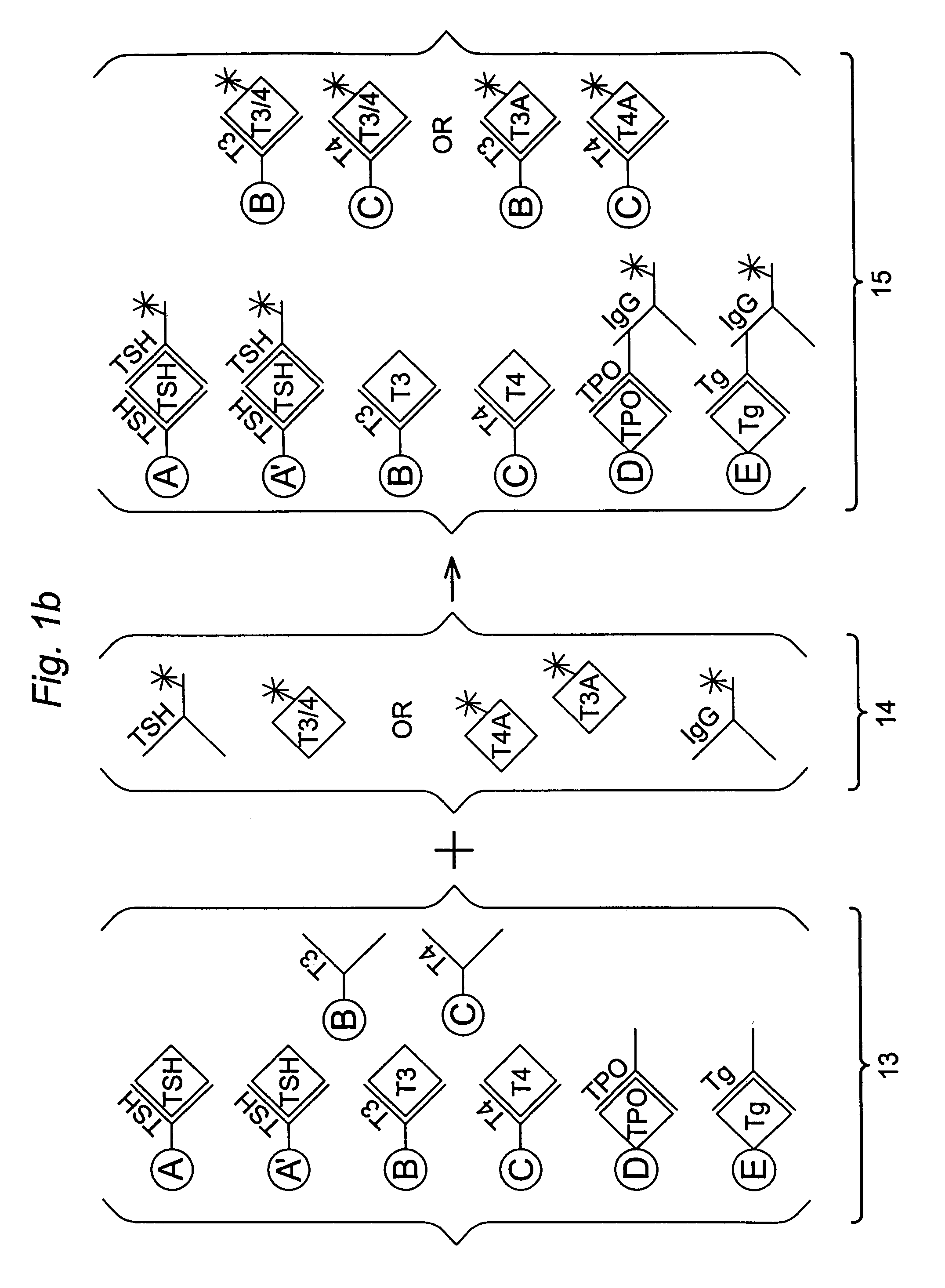
Multi-analyte diagnostic test for thyroid disorders
InactiveUS7271009B1Reduce signalingIncrease ratingsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseMulti analyte
Immunological assays for several biological markers for thyroid disorders in a biological sample are performed in a single test with a combination of sandwich-type, sequential competitive, and serological assays by the use of particles classified into groups that are distinguishable by flow cytometry, one group for the assay of each marker. Each group of particles is coated with a different immunological binding member, and coating densities, co-coating materials, and special buffer solutions are used to adjust for differences in the sensitivities and dynamic ranges of each of the markers in the typical sample.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
High-frequency shear-horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor
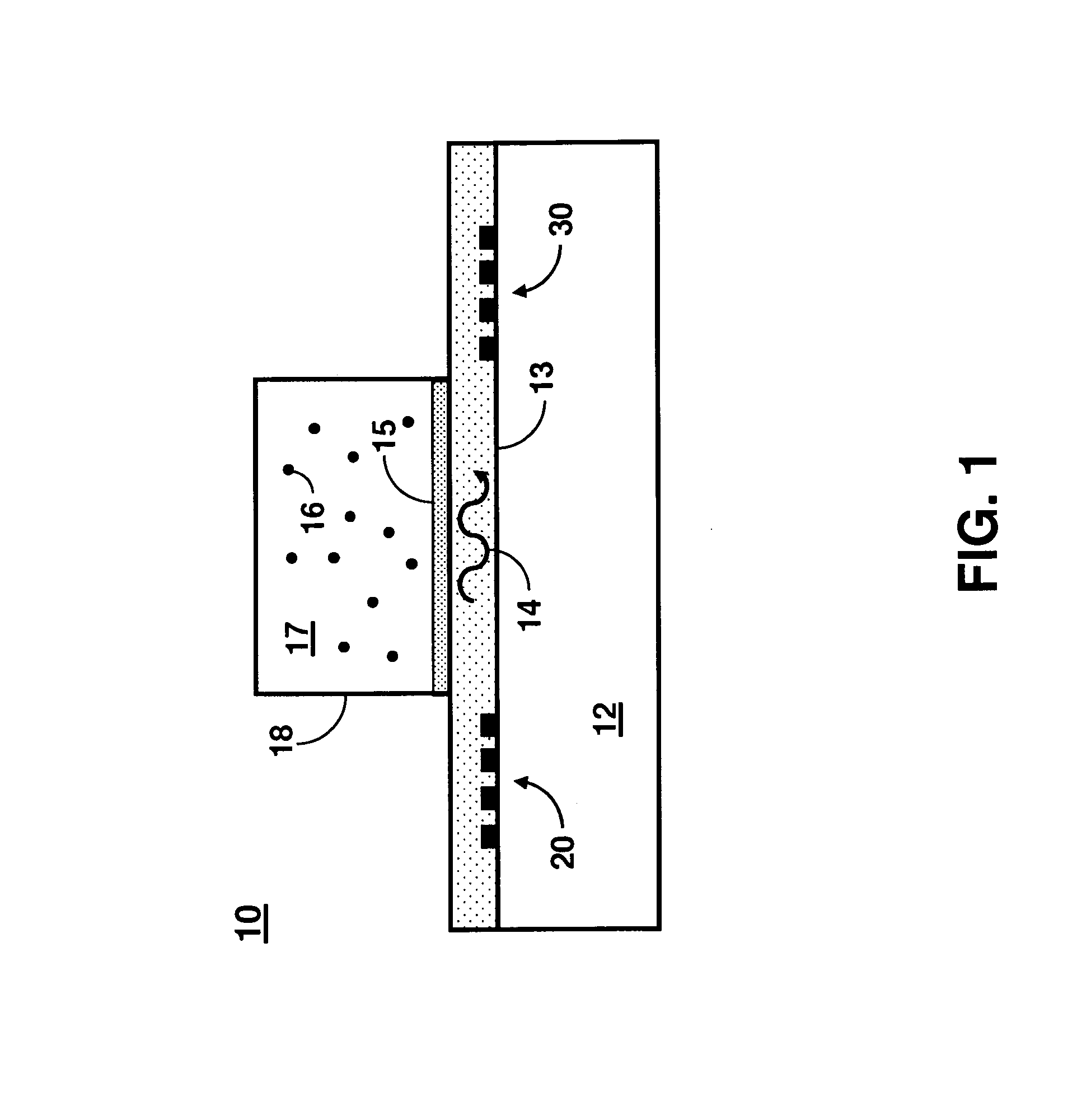
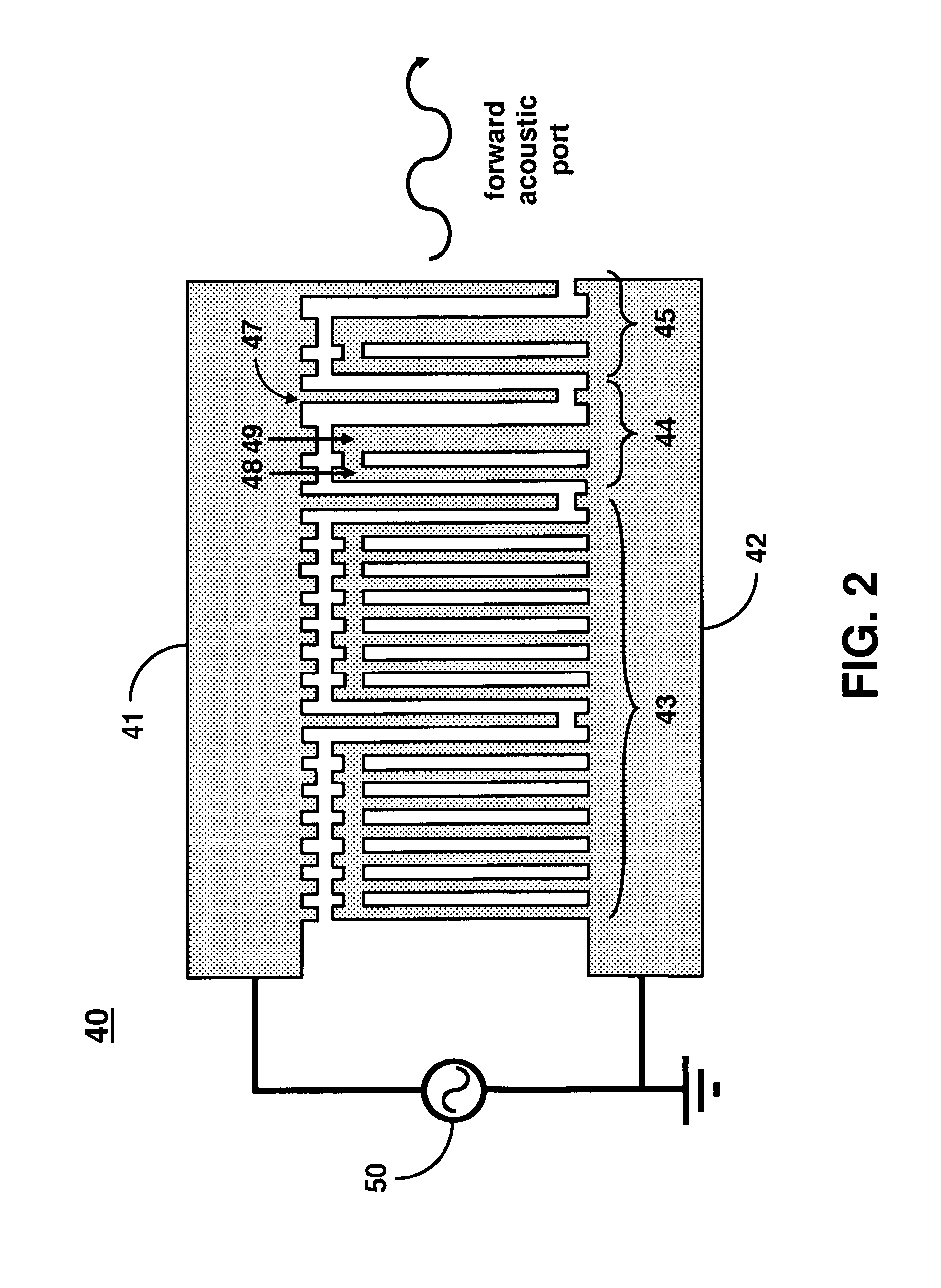
ActiveUS8436509B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMulti analyteImpedance matching
A Love wave sensor uses a single-phase unidirectional interdigital transducer (IDT) on a piezoelectric substrate for leaky surface acoustic wave generation. The IDT design minimizes propagation losses, bulk wave interferences, provides a highly linear phase response, and eliminates the need for impedance matching. As an example, a high frequency (˜300-400 MHz) surface acoustic wave (SAW) transducer enables efficient excitation of shear-horizontal waves on 36° Y-cut lithium tantalate (LTO) giving a highly linear phase response (2.8° P-P). The sensor has the ability to detect at the pg / mm2 level and can perform multi-analyte detection in real-time. The sensor can be used for rapid autonomous detection of pathogenic microorganisms and bioagents by field deployable platforms.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com