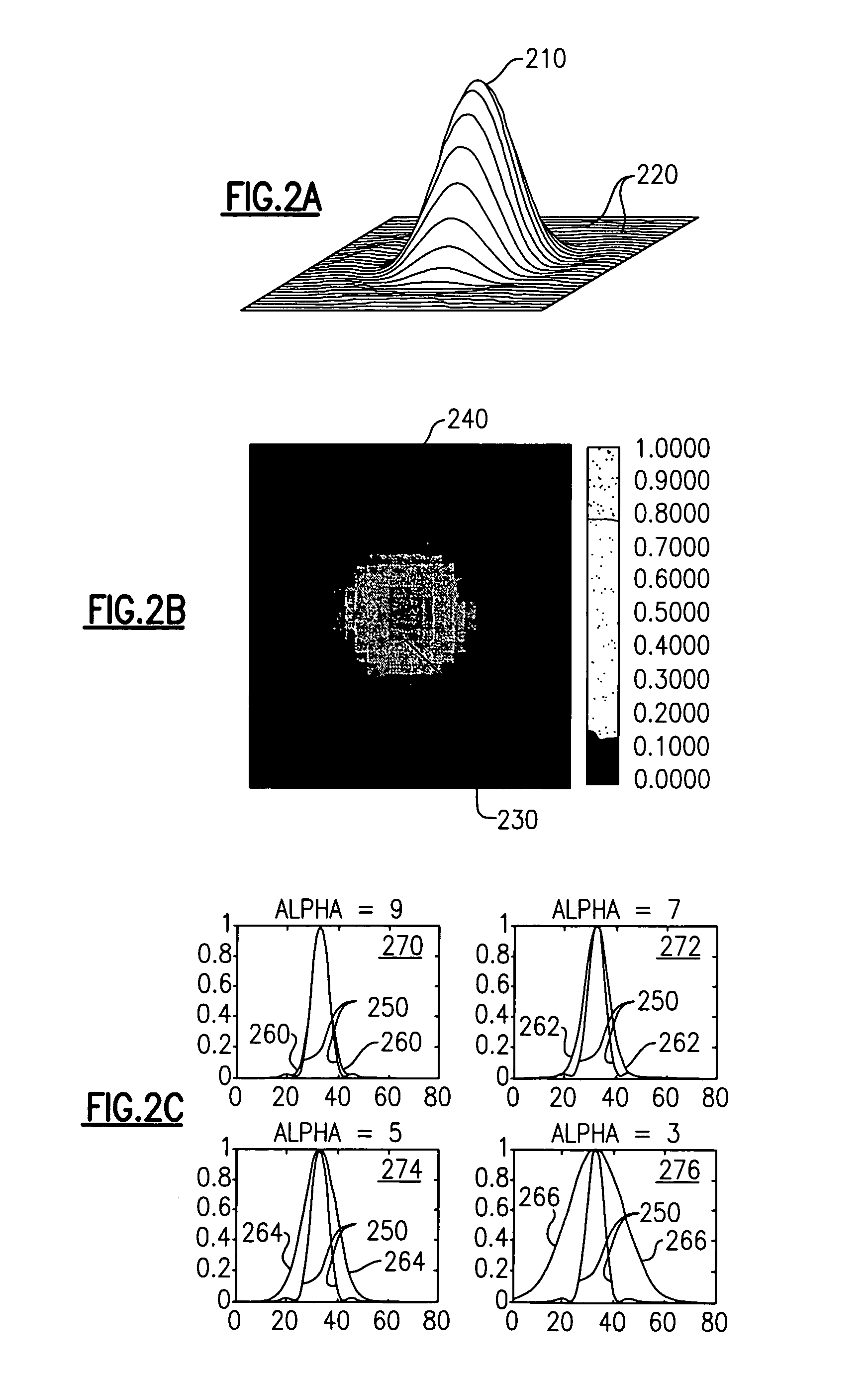
Patents
Literature
2651 results about "Working range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Each instrument used in analytical chemistry has a useful working range. This is the range of concentration (or mass) that can be adequately determined by the instrument, where the instrument provides a useful signal that can be related to the concentration of the analyte.
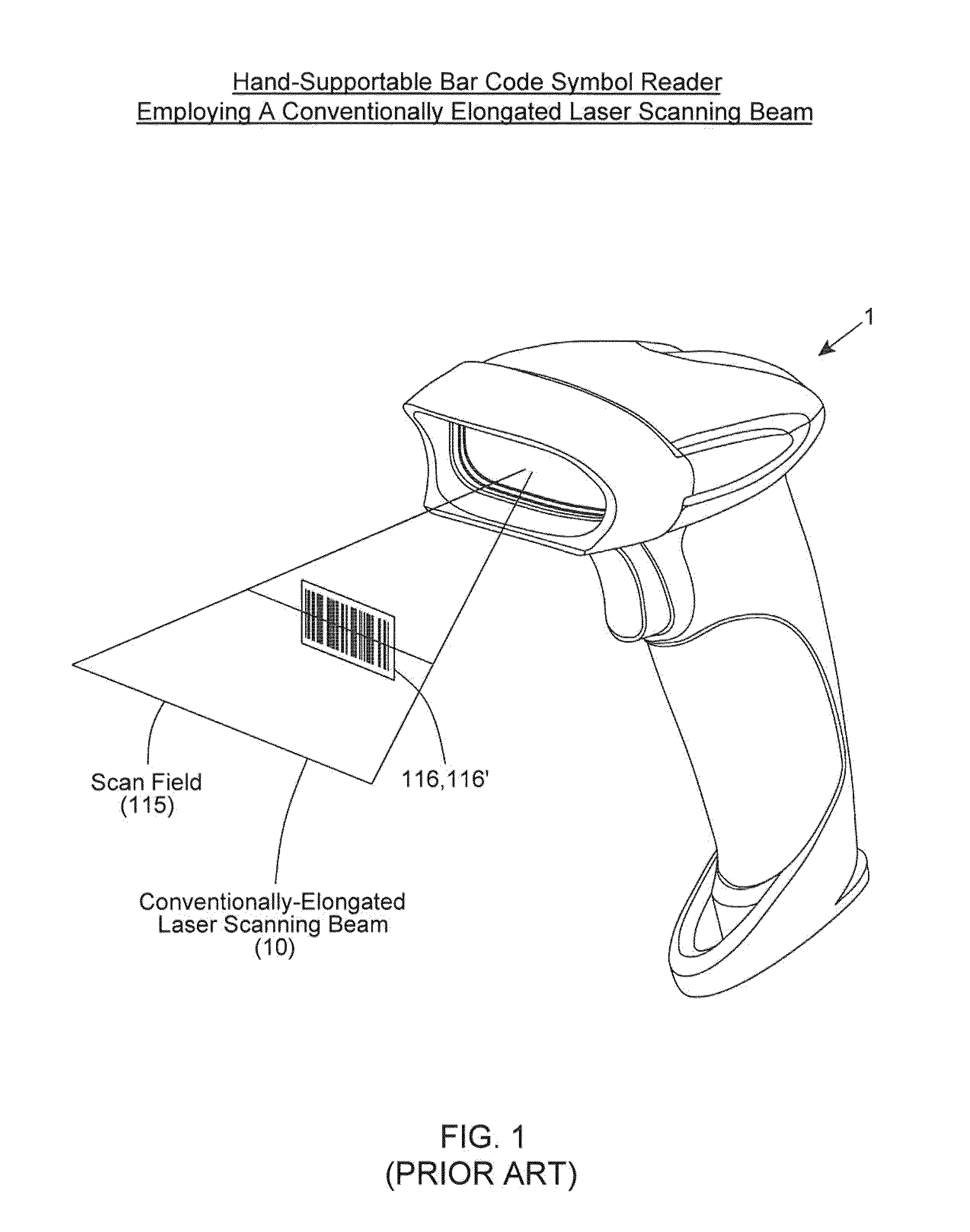
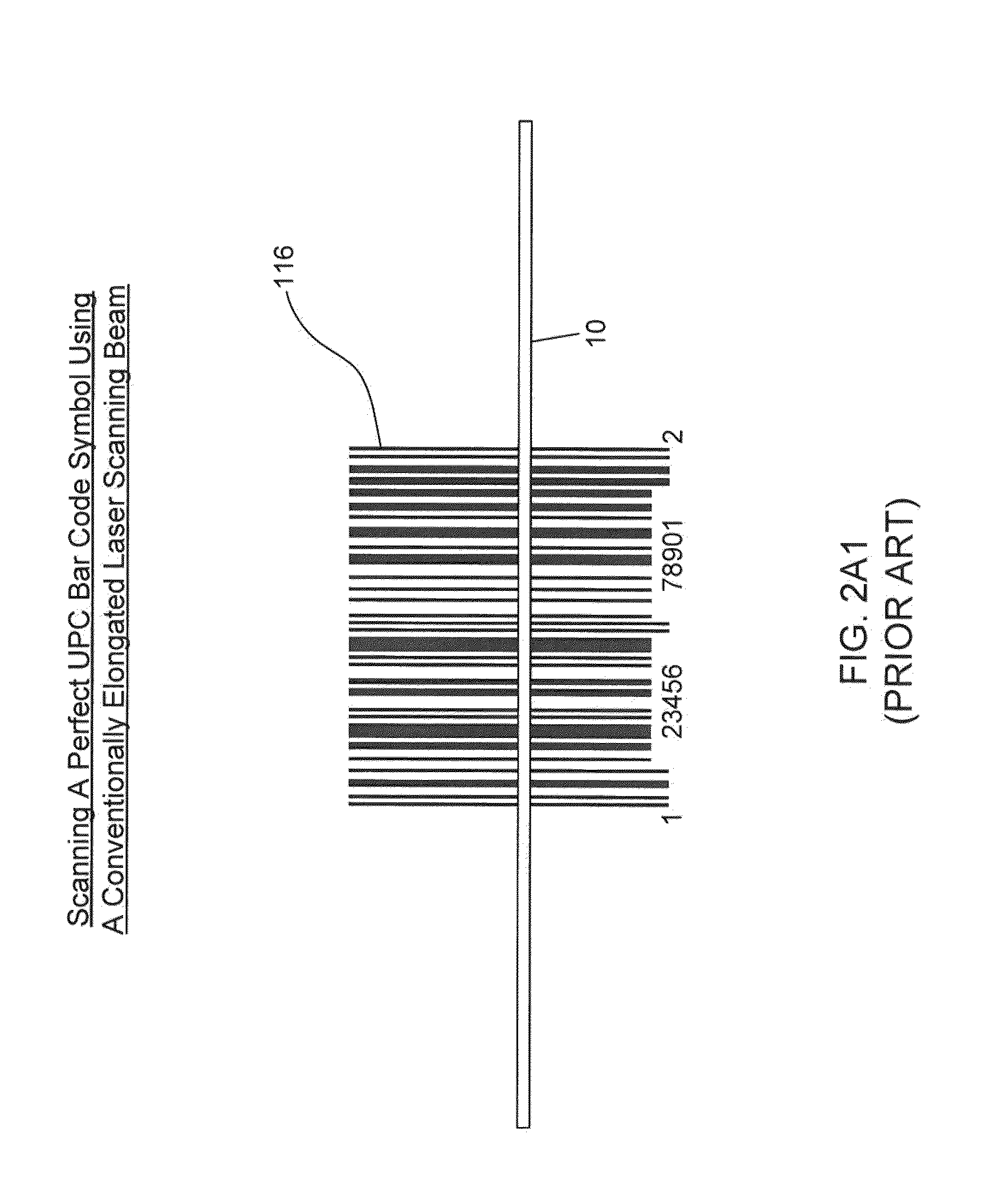
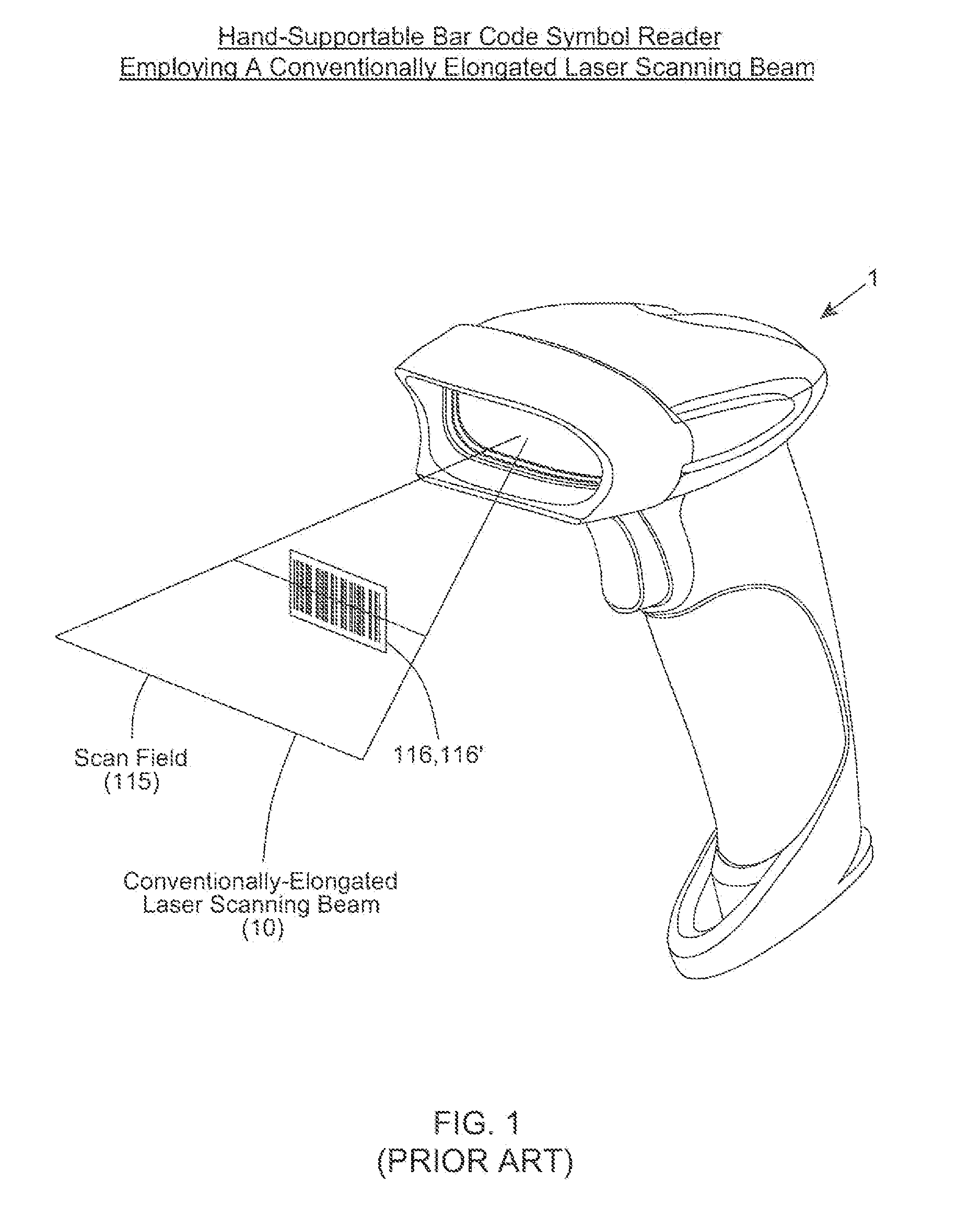
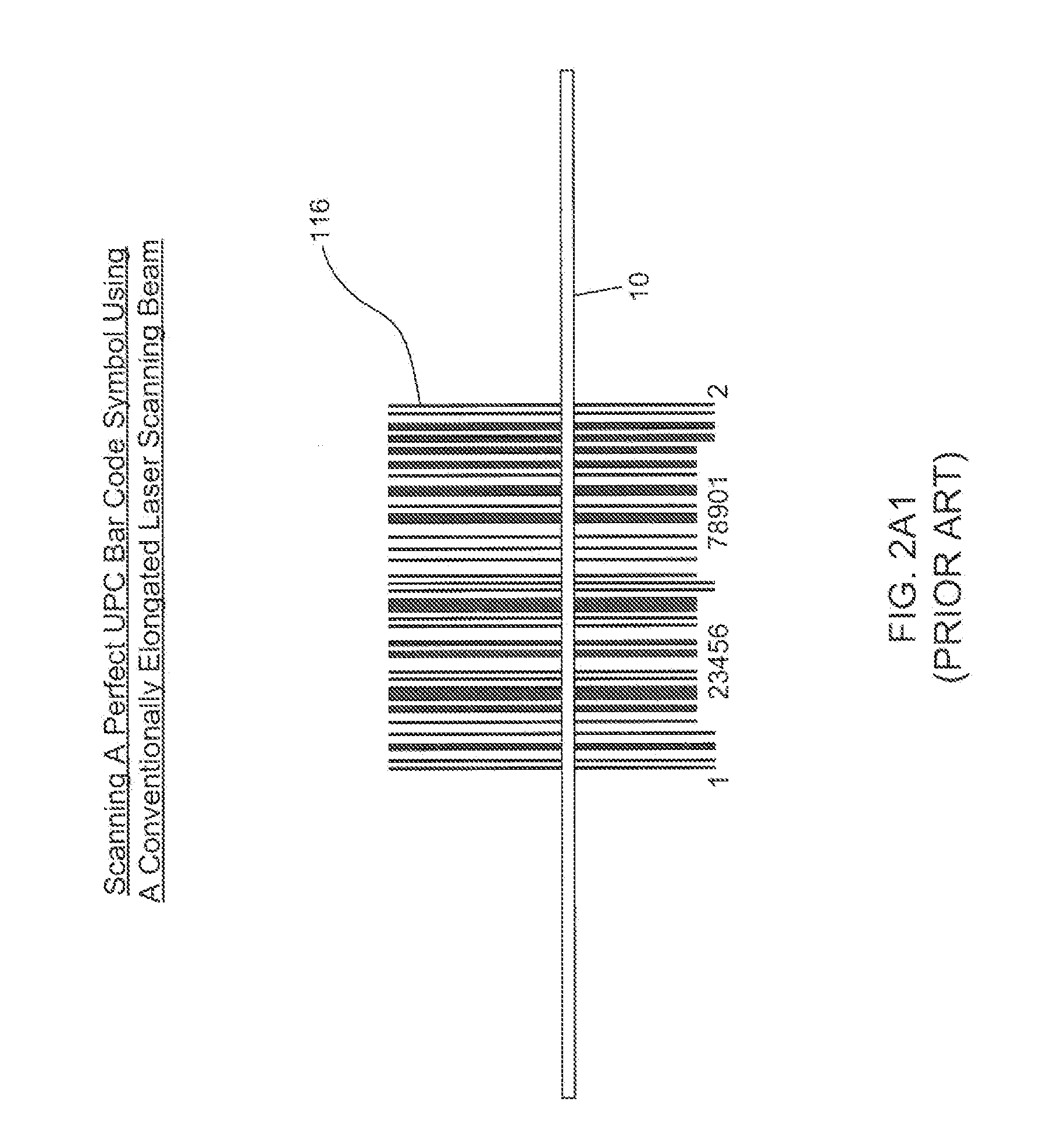
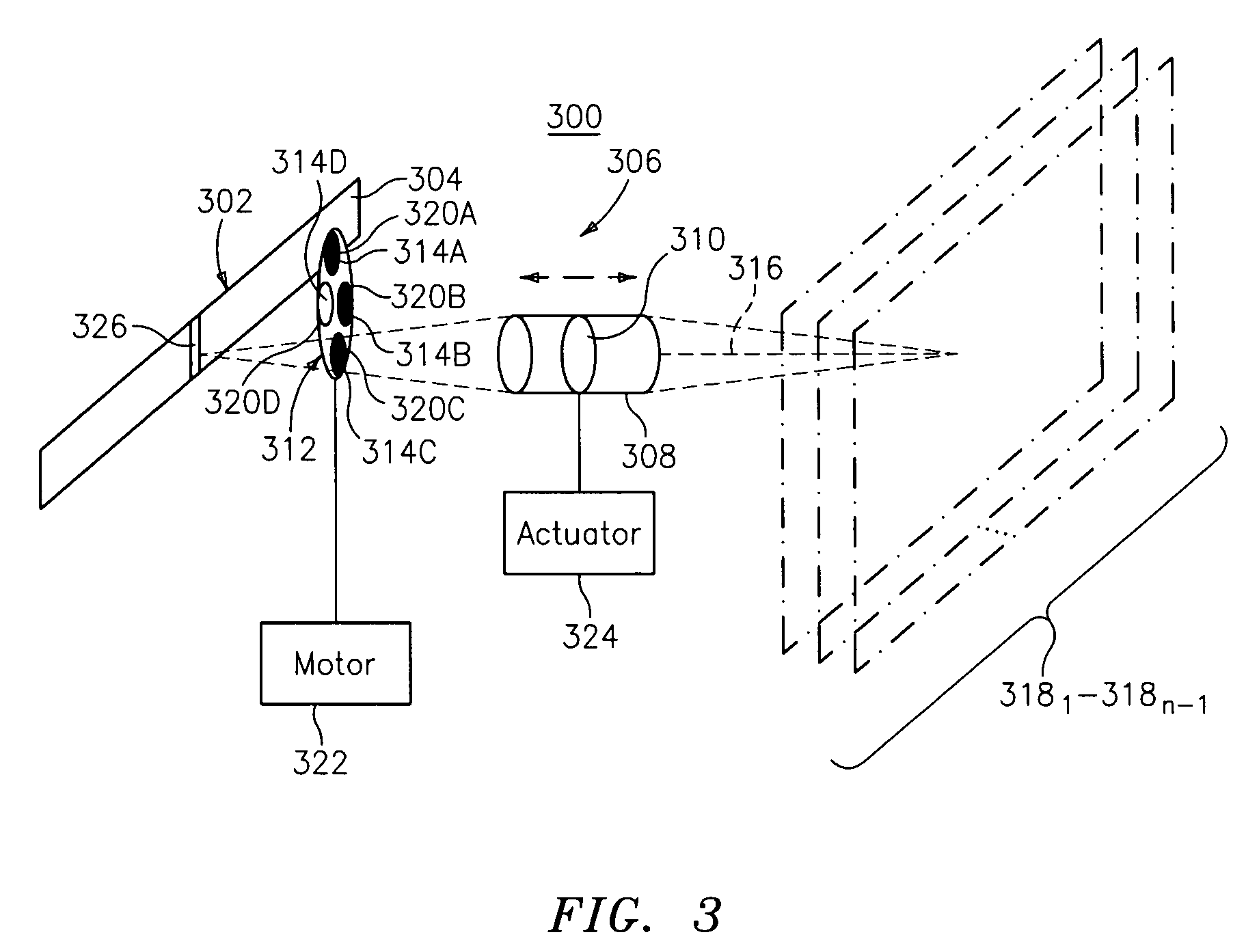
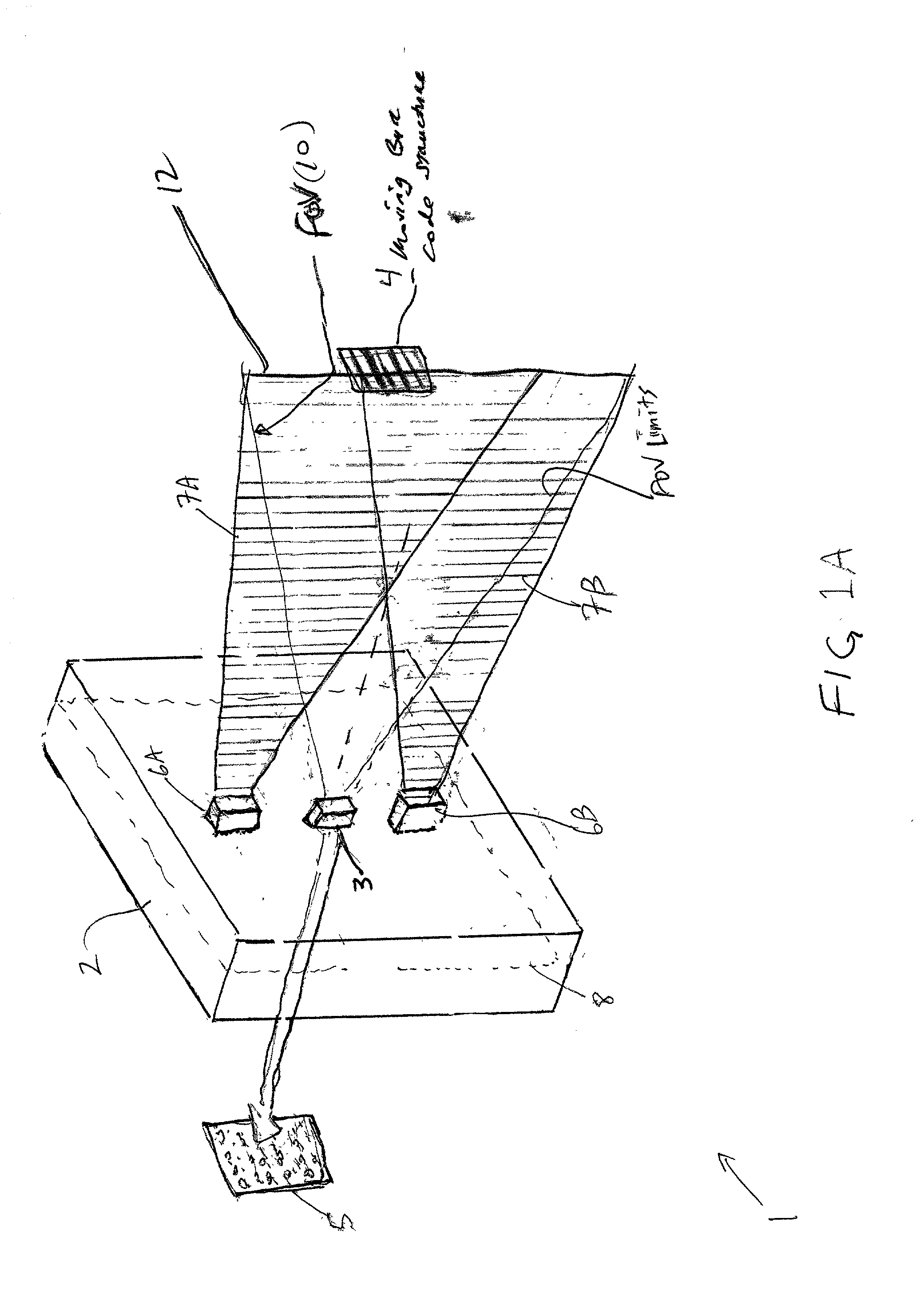
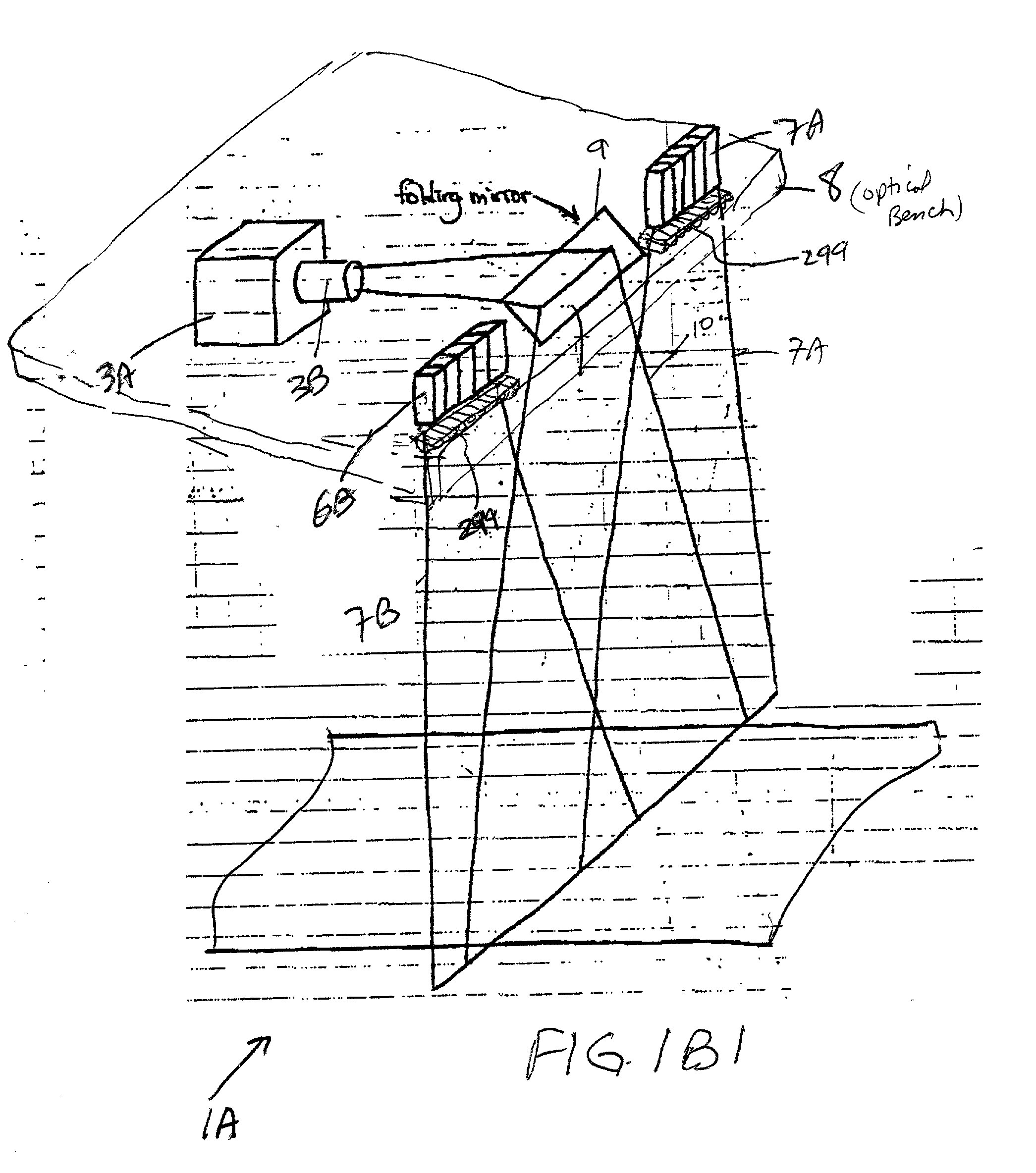
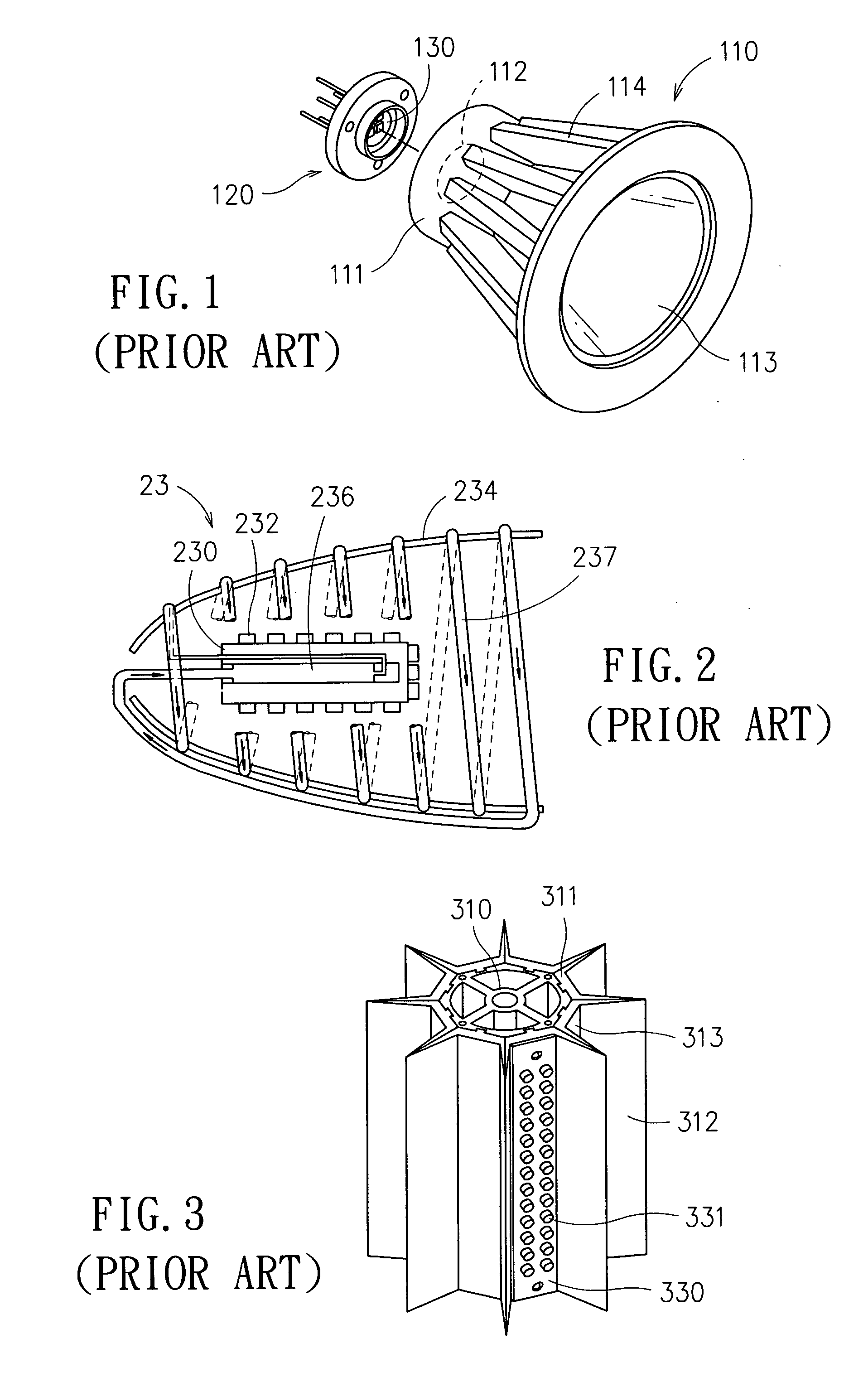
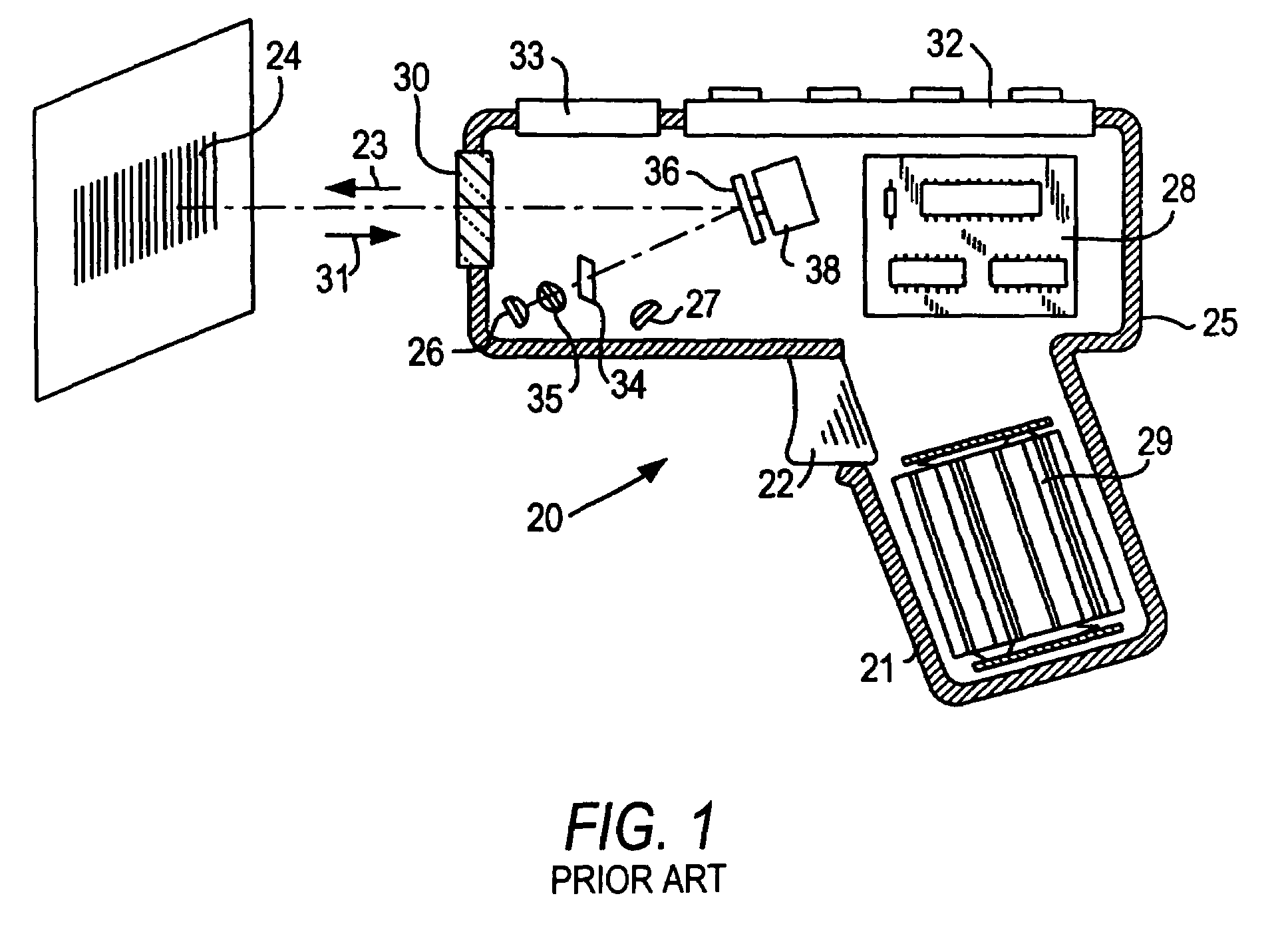
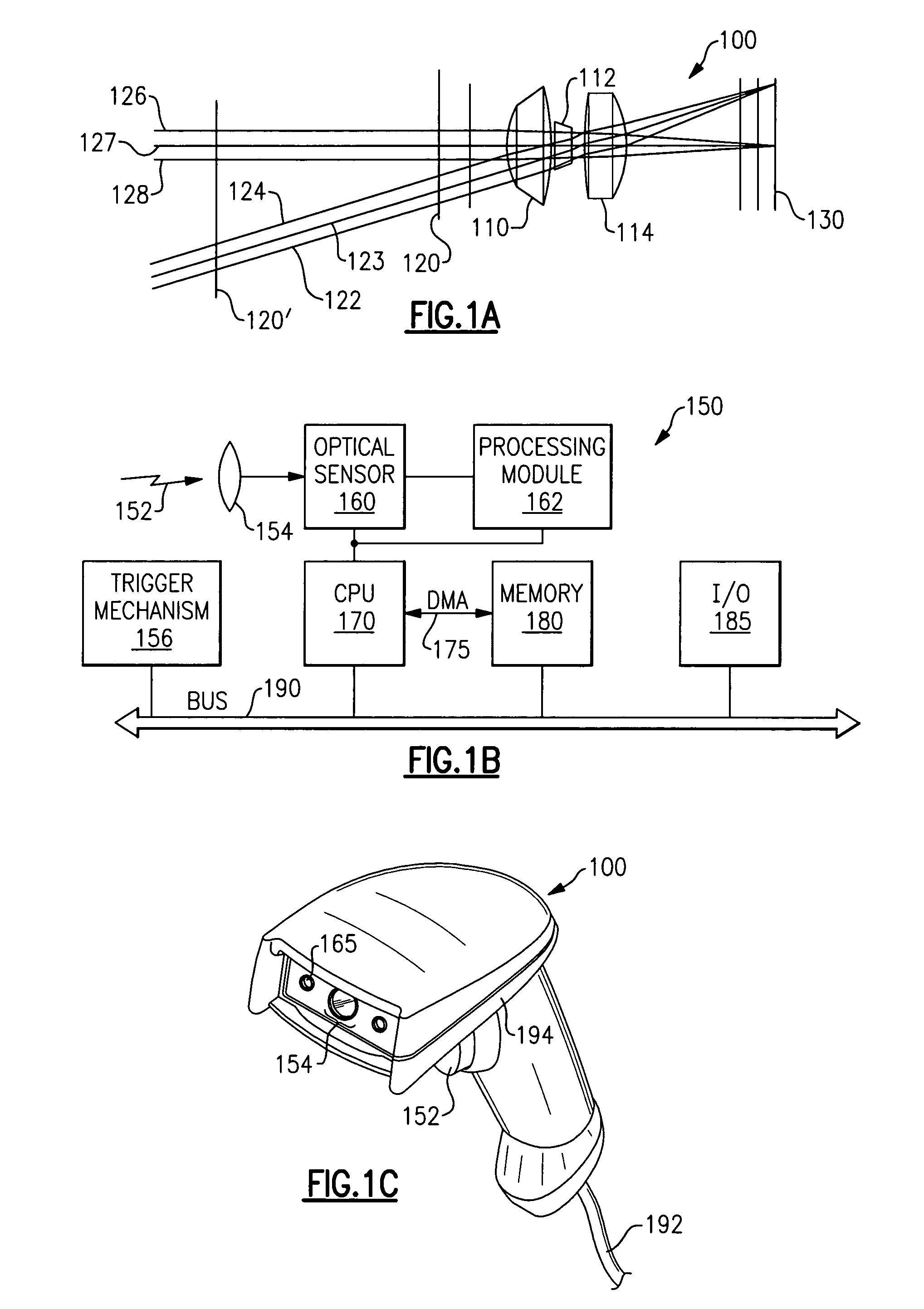
Bar code symbol reading system employing an extremely elongated laser scanning beam capable of reading poor and damaged quality bar code symbols with improved levels of performance
ActiveUS8376233B2Increase reflectionOptimized laser beam characteristicsTelevision system scanning detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionLaser scanningLight beam
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
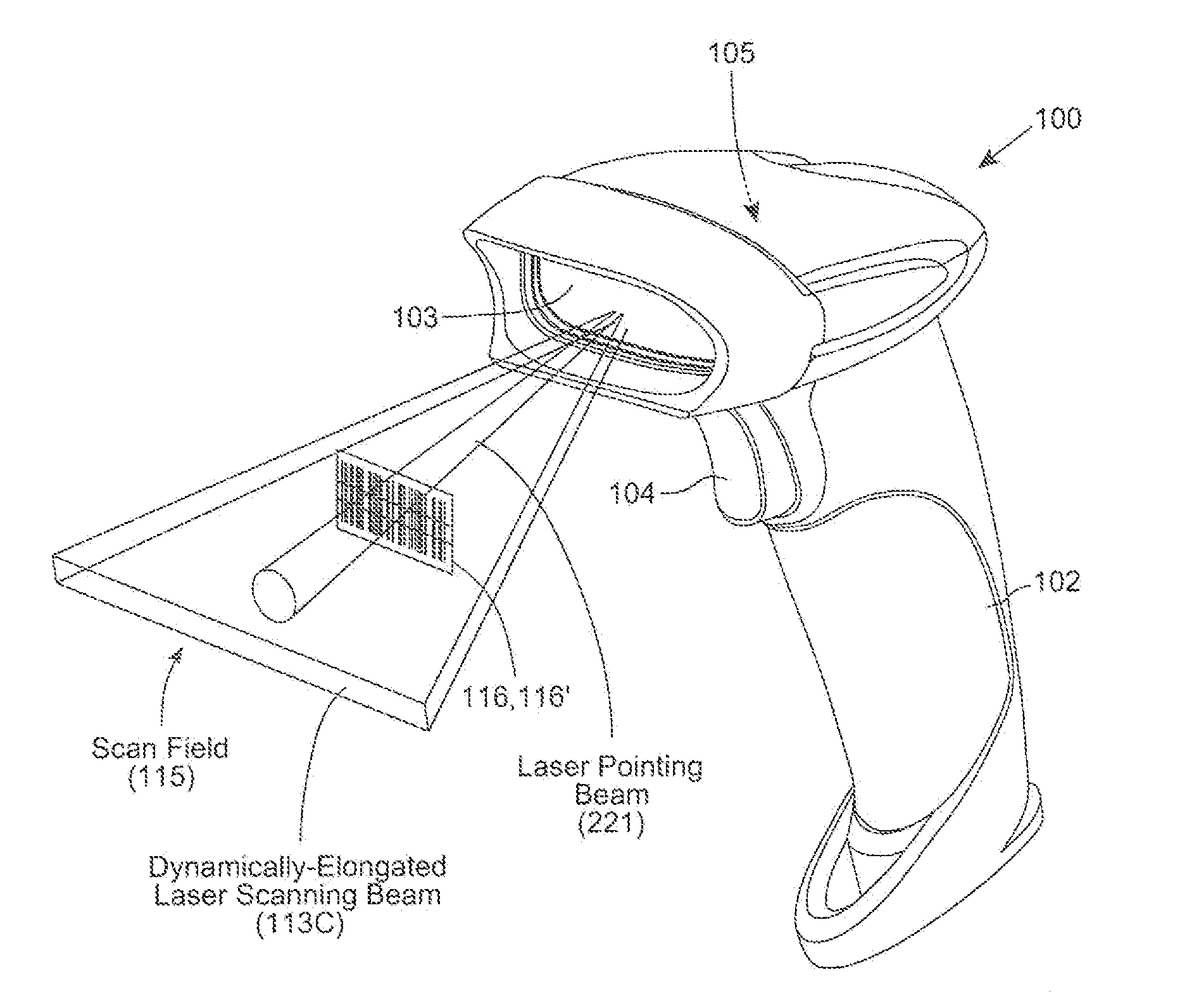
Code symbol reading system employing dynamically-elongated laser scanning beams for improved levels of performance
InactiveUS20130043312A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAverage out defectsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationLight beamLaser scanning
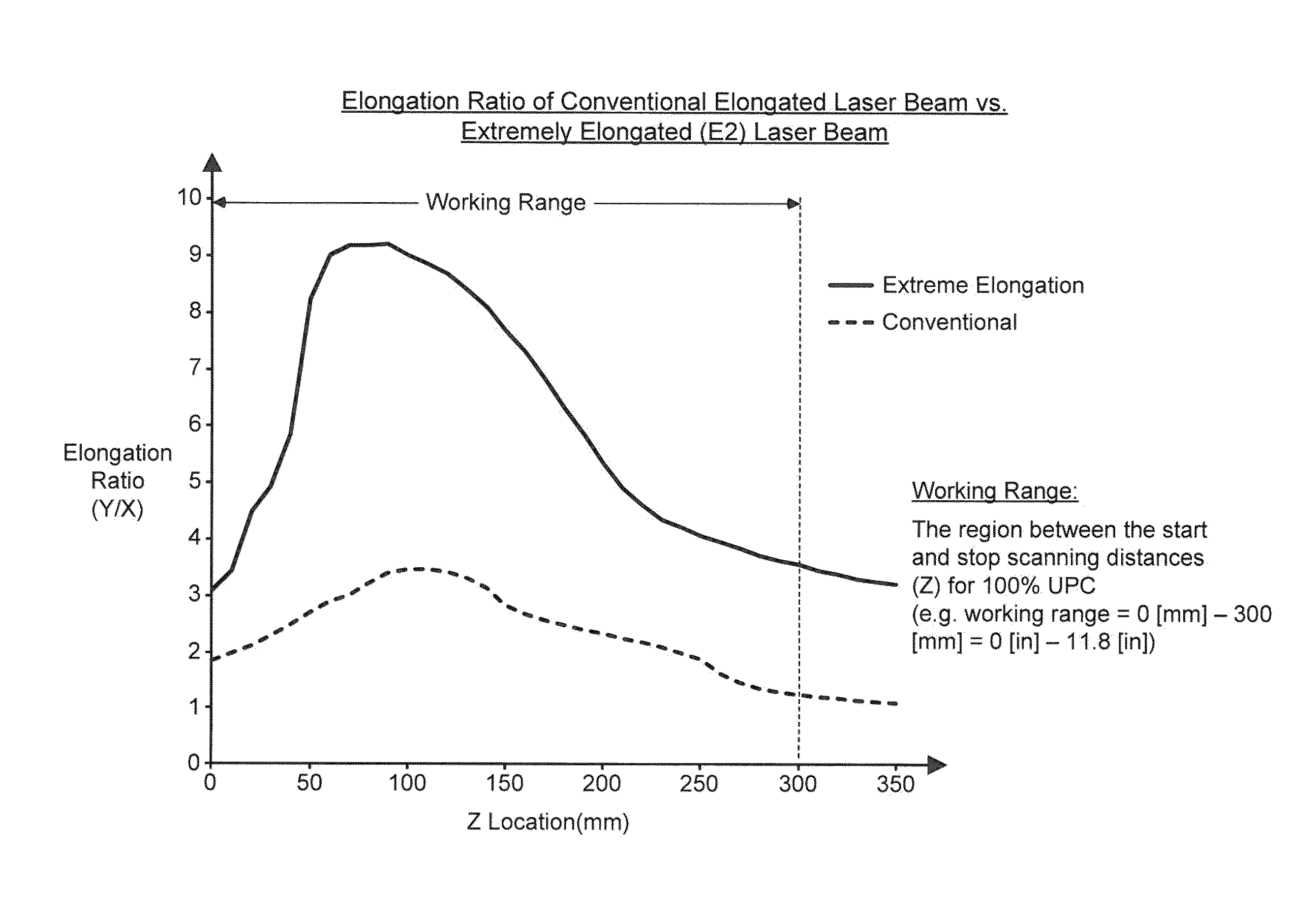
A laser scanning bar code symbol reading system for scanning and reading poor quality and damaged bar code symbols in flexible operating conditions. The system includes a housing having a light transmission window; a dynamically-elongated laser beam production module, including a multi-cavity visible laser diode (VLD), for producing a dynamically-elongated laser beam having (i) a direction of propagation extending along a z reference direction, (ii) a height dimension being indicated by the y reference direction, and (iii) a width dimension being indicated by the x reference direction, where x, y and z directions are orthogonal to each other. Each dynamically-elongated laser beam is characterized by an elongation ratio (ER) that is defined as Y / X where, for any point within the working range of the laser scanning bar code symbol reading system, extending along the z direction, (i) Y indicates the beam height of the dynamically-elongated laser beam measured in the Y reference direction, (ii) X indicates the beam width of the dynamically-elongated laser beam measured in the X reference direction, and (iii) the beam height (Y) and the laser beam width (X) are measured at 1 / e2 intensity clip level. A laser scanning mechanism is provided for scanning the dynamically-elongated laser beam out the light transmission window and across a scanning field defined external to the housing, in which a bar code symbol is present for scanning by the dynamically-elongated laser scanning beam.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Imaging arrangement and barcode imager for imaging an optical code or target at a plurality of focal planes
ActiveUS7090135B2Expand the scope of workCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationSensor arrayBarcode
Three non-complex imaging arrangements are provided where in two of the imaging arrangements a moveable carrier housing at least one objective lens is provided and, in the other imaging arrangement, at least one stationary objective lens and additional optical elements are provided. Each embodiment includes at least one fixed image sensor array for imaging thereon an optical code or target, such as a one-dimensional barcode symbol, or label, marking, picture, etc. Each imaging arrangement provides an extended working range of approximately 5–102 cm. The imaging arrangements are capable of being incorporated within a barcode imager to provide a non-complex barcode imager having an extended working range which is comparable to or greater than the working ranges of conventional image-based barcode imagers.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Arrangement and method of imaging one-dimensional and two-dimensional optical codes at a plurality of focal planes
ActiveUS7222793B2Expand the scope of workCharacter and pattern recognitionExposure controlOptical axisBarcode
A non-complex imaging arrangement is aligned along an imaging axis. A mirror assembly is configured to reflect an image from an optical axis, which intersects the imaging axis, toward the optics assembly. The imaging arrangement includes at least one fixed image sensor for imaging thereon an optical code or target, such as a one-dimensional or two-dimensional barcode symbol, or label, signature, marking, picture, etc. The imaging arrangement provides an extended working range of approximately 5–102 cm. The imaging arrangement is capable of being incorporated within a barcode imager to provide a non-complex barcode imager having an extended working range which is comparable to or greater than the working ranges of conventional image-based barcode imagers.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
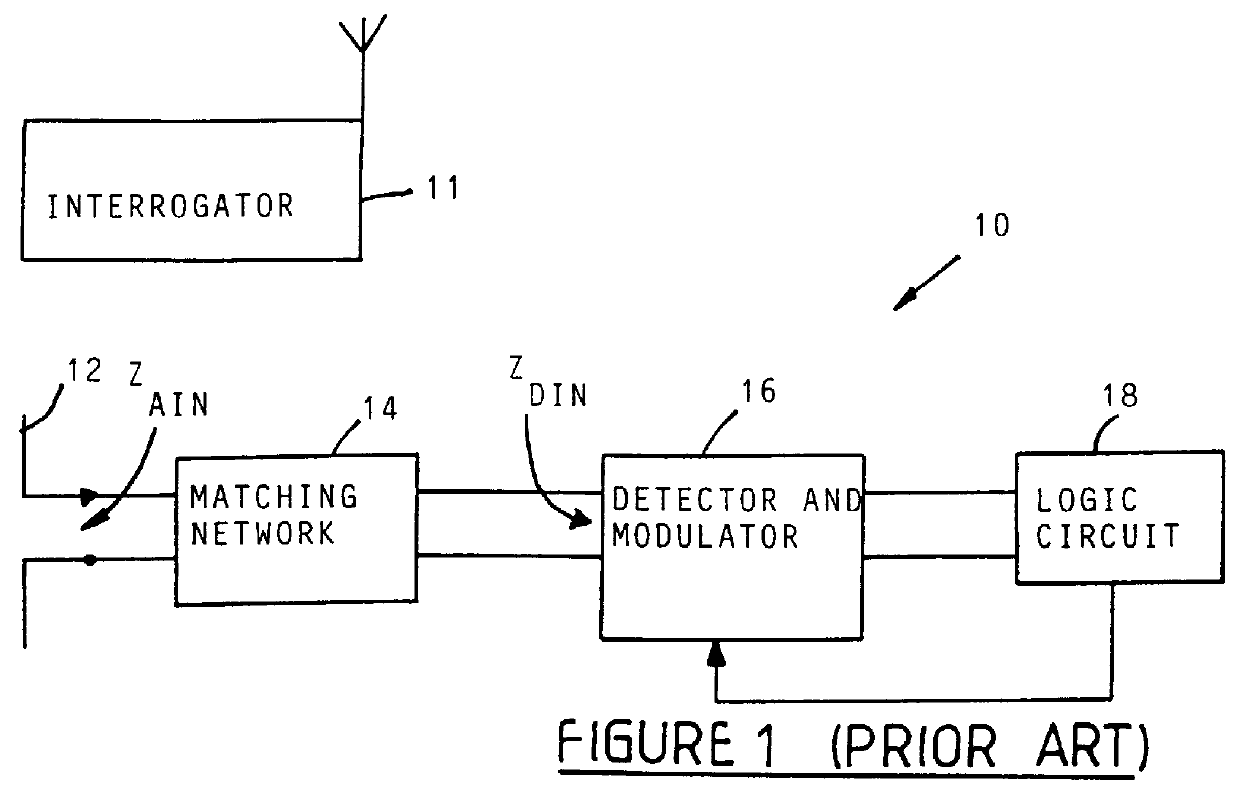
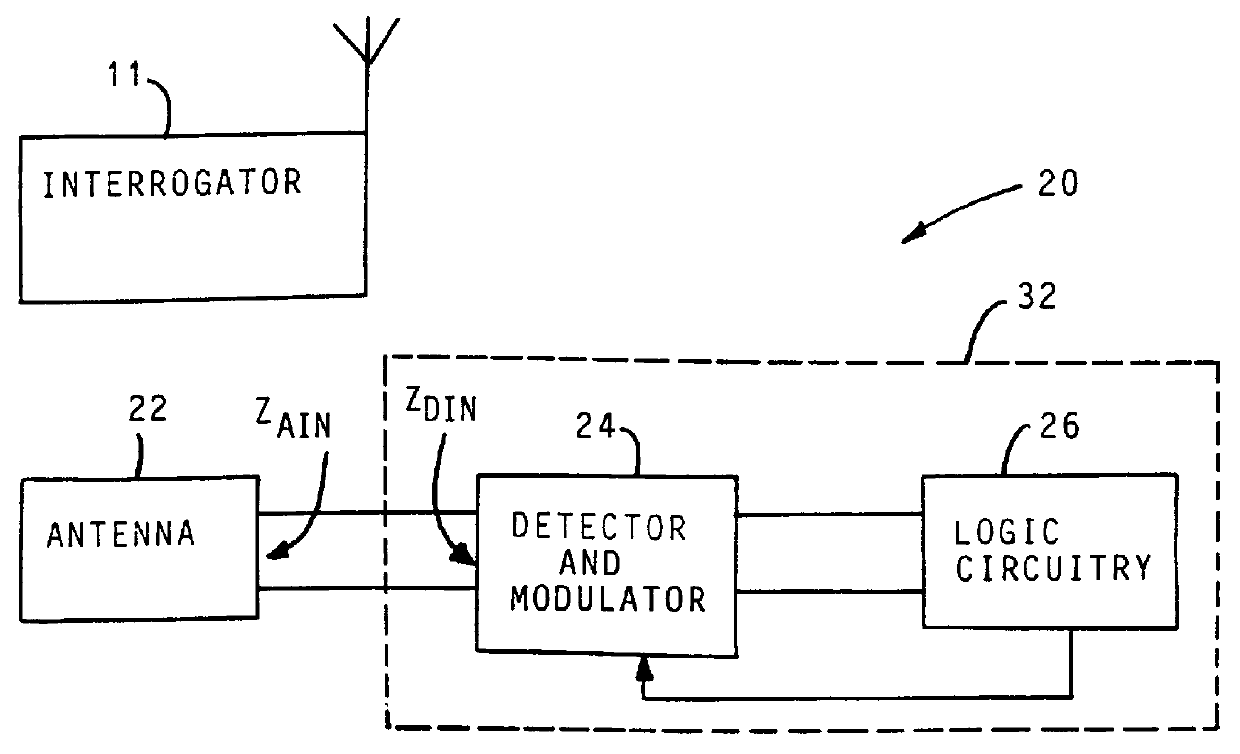
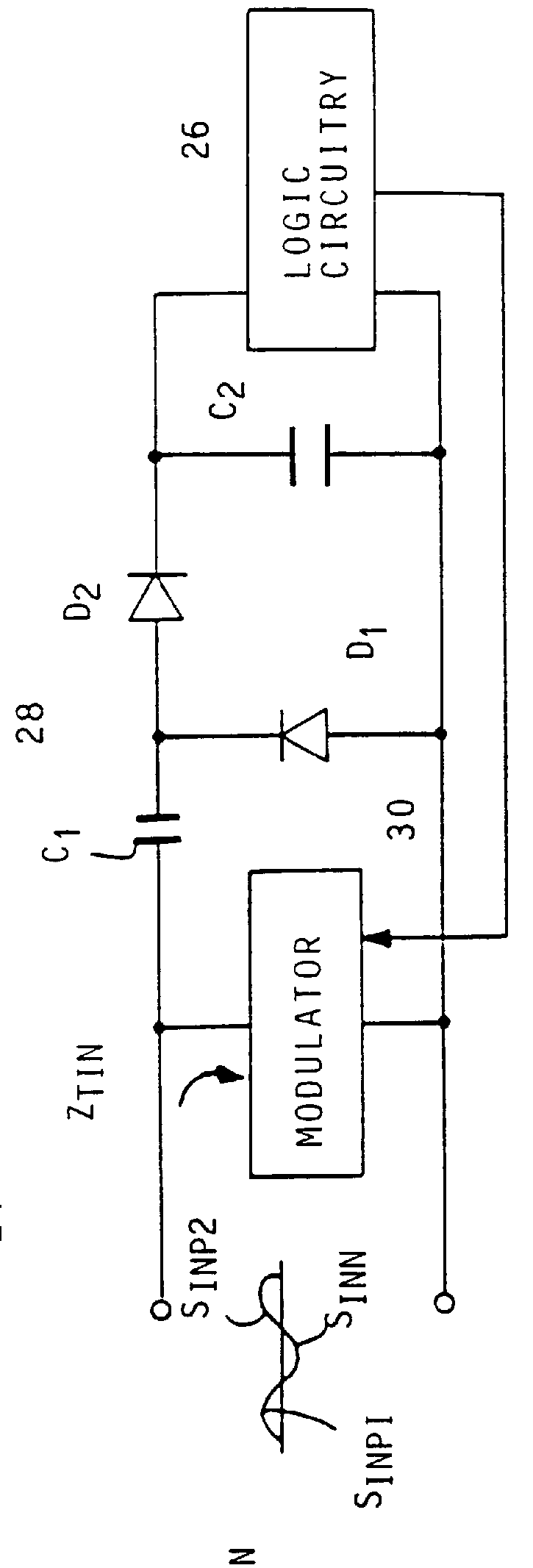
High impedance transponder with improved backscatter modulator for electronic identification system
InactiveUS6054925ATransmissionRecord carriers used with machinesElectronic identificationInput impedance
A transponder 20 for an electronic identification system transponder is characterized in that it presents a high input impedance (>400 OMEGA ) at an input thereof which is directly connected to an antenna 22 with a matched high input impedance. The transponder is aimed at improving the voltage recovered on capacitor C2 from an interrogation signal and thus the operational range of the system. The modulator 30 of the transponder is arranged to backscatter modulate the interrogation signal at a modulation depth of less than 80%, preferably in the order of 30%. This also results in an improvement of the operational range of the system.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
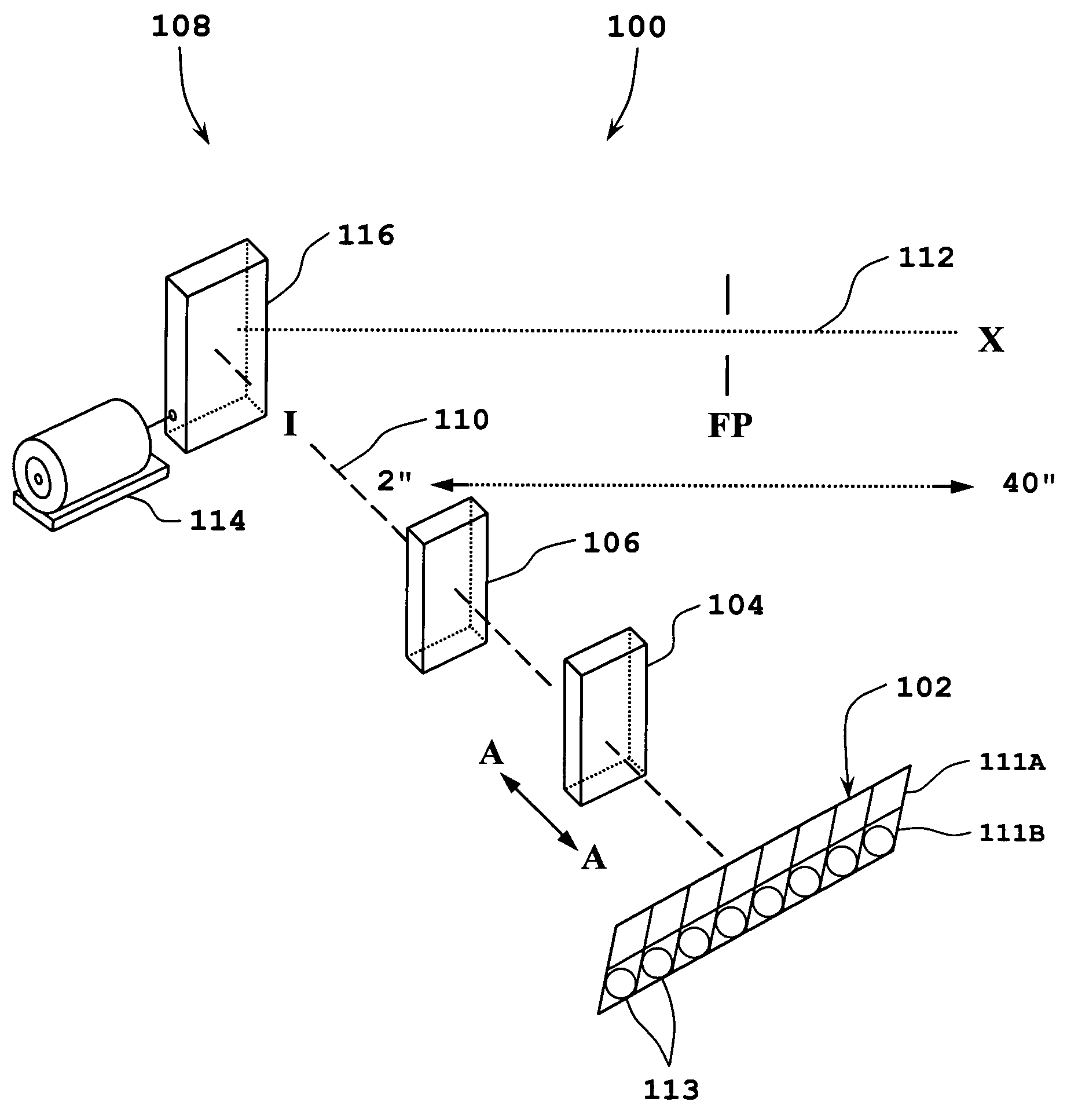
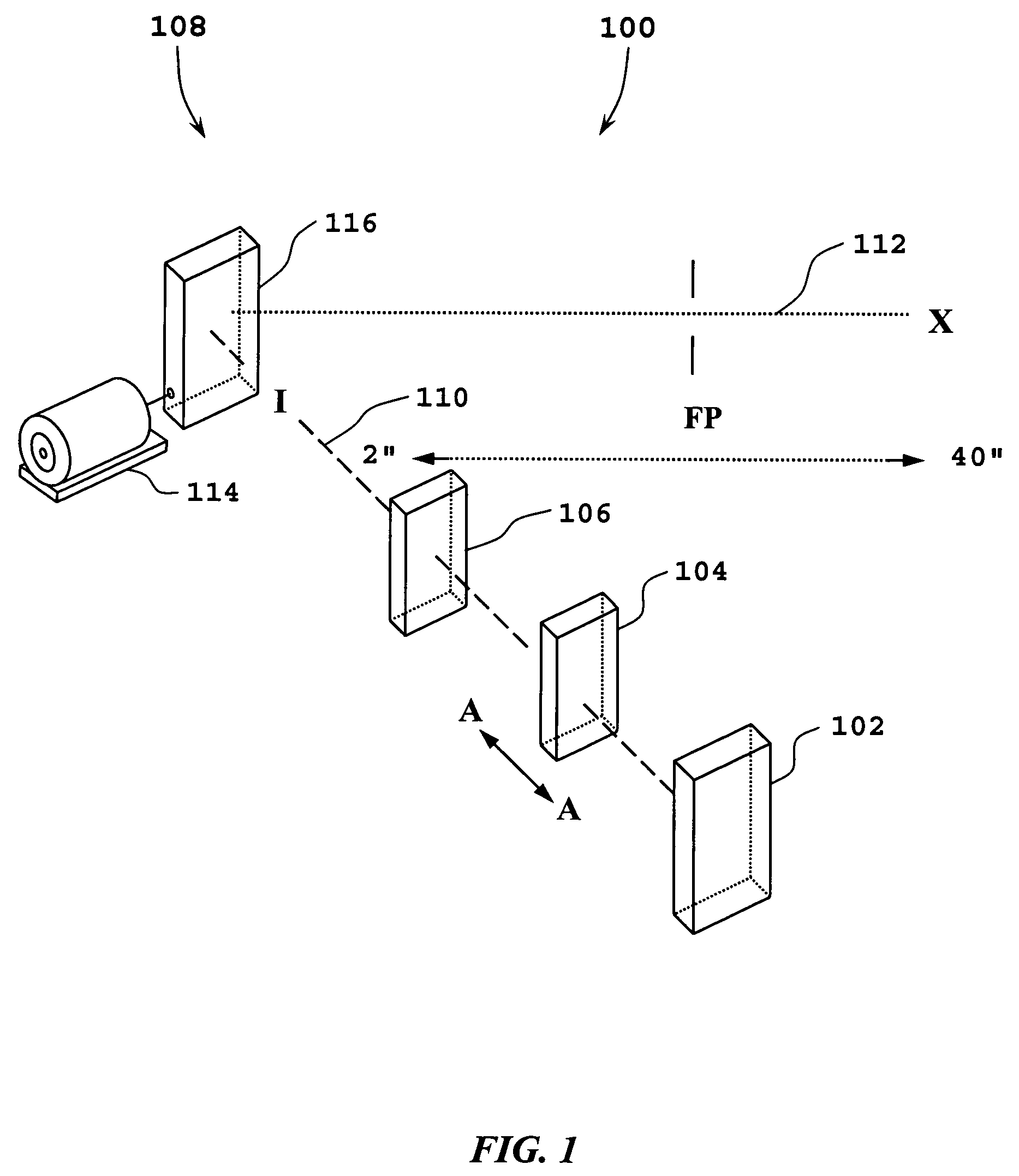
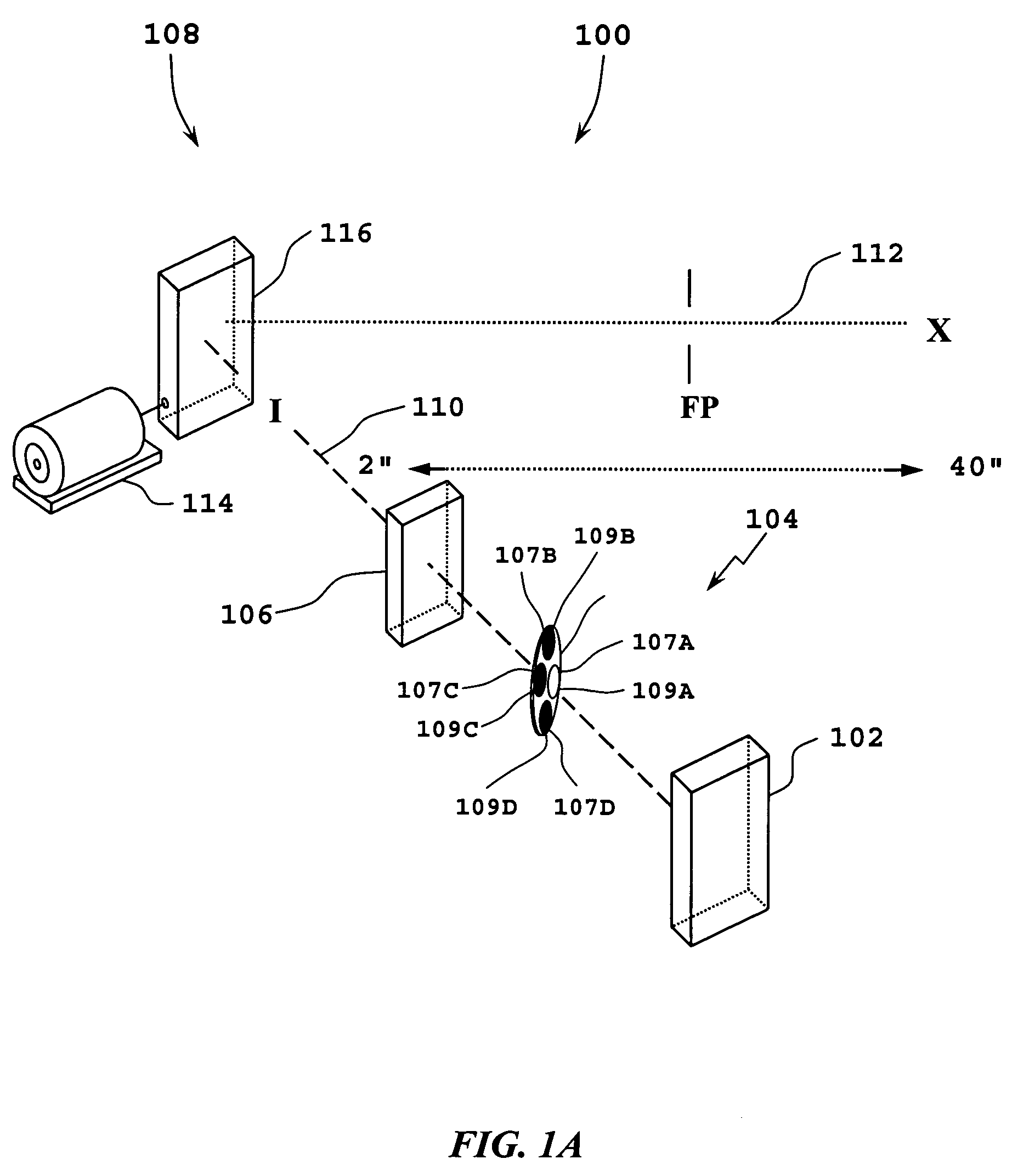
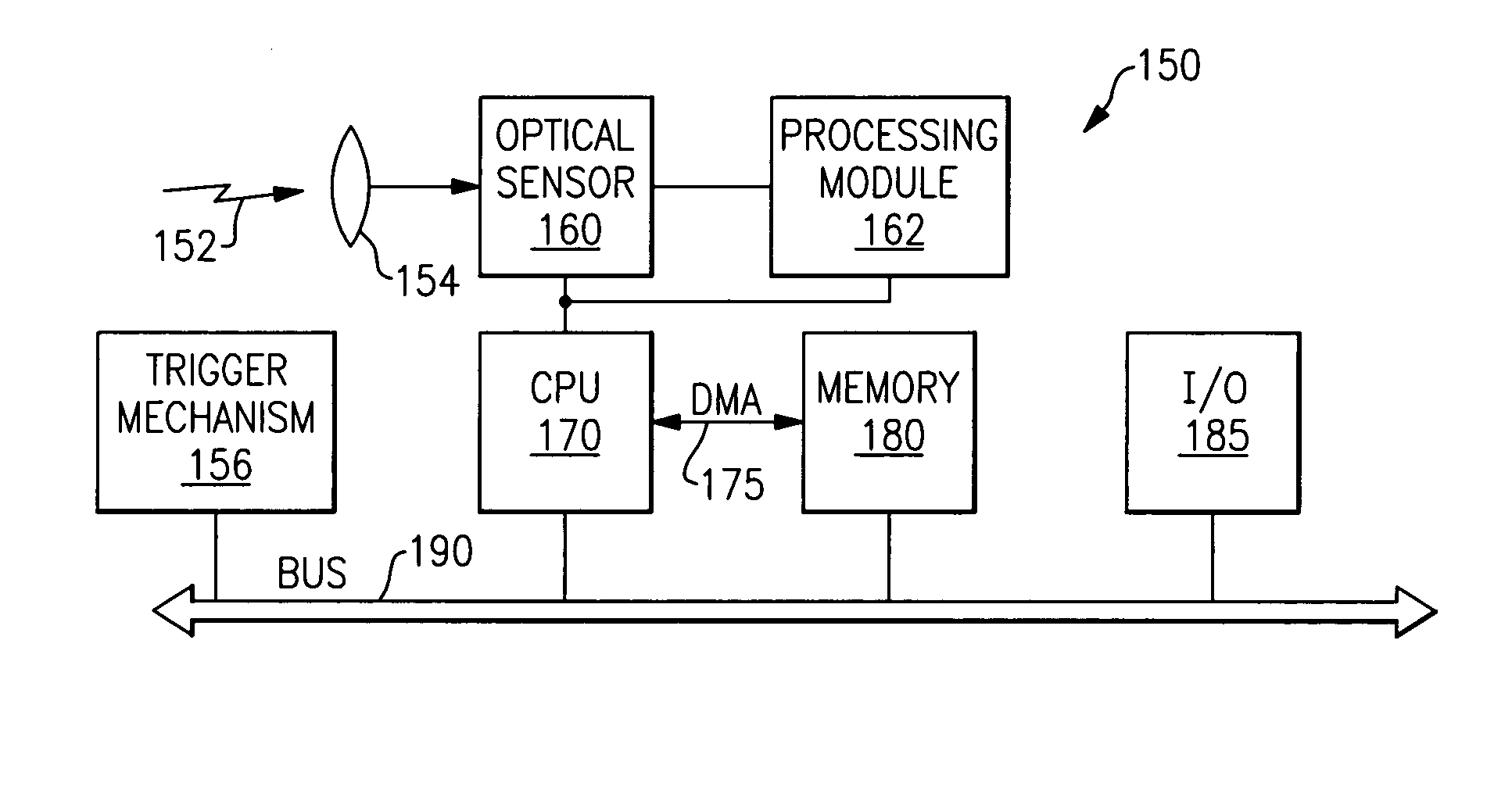
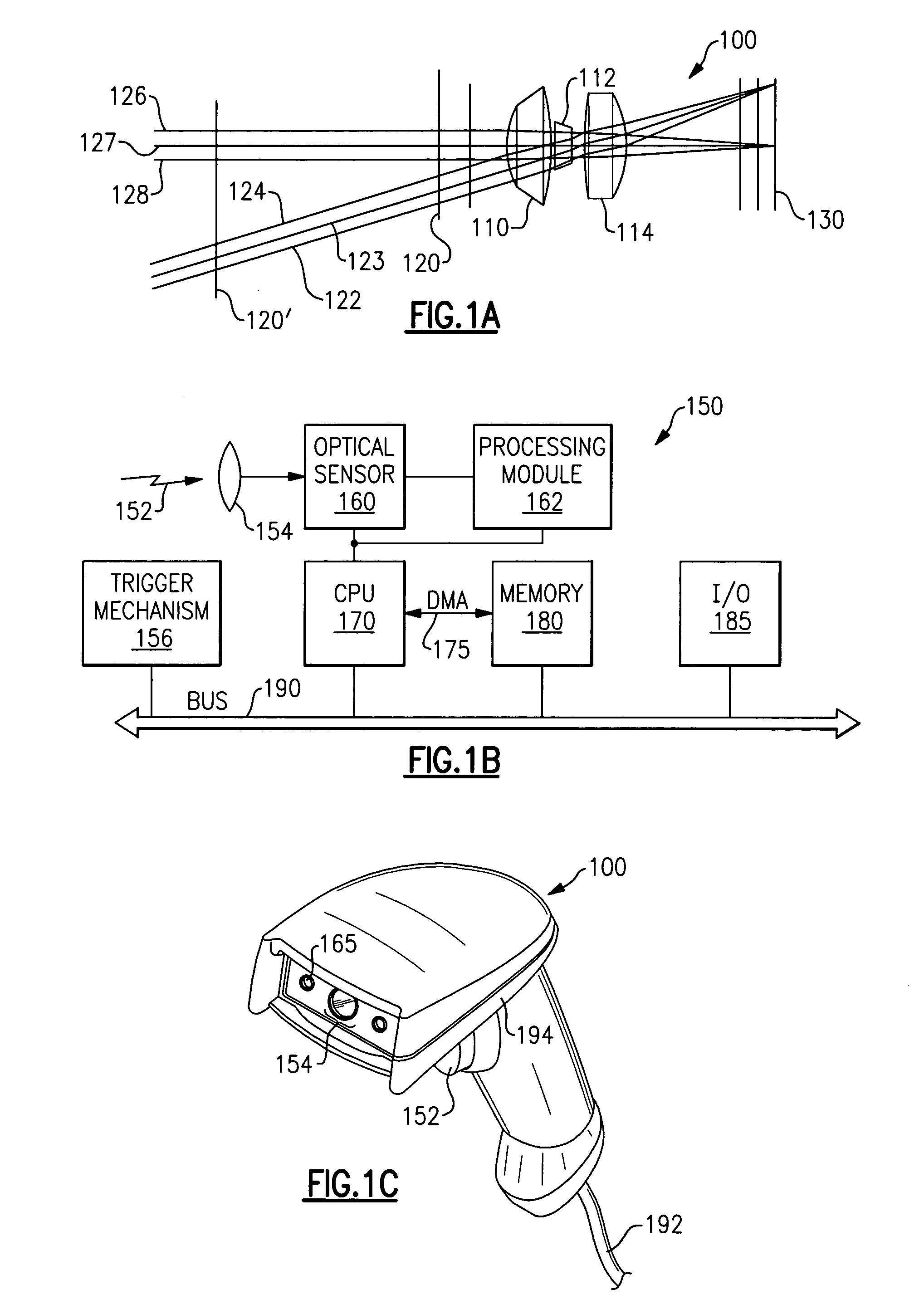
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
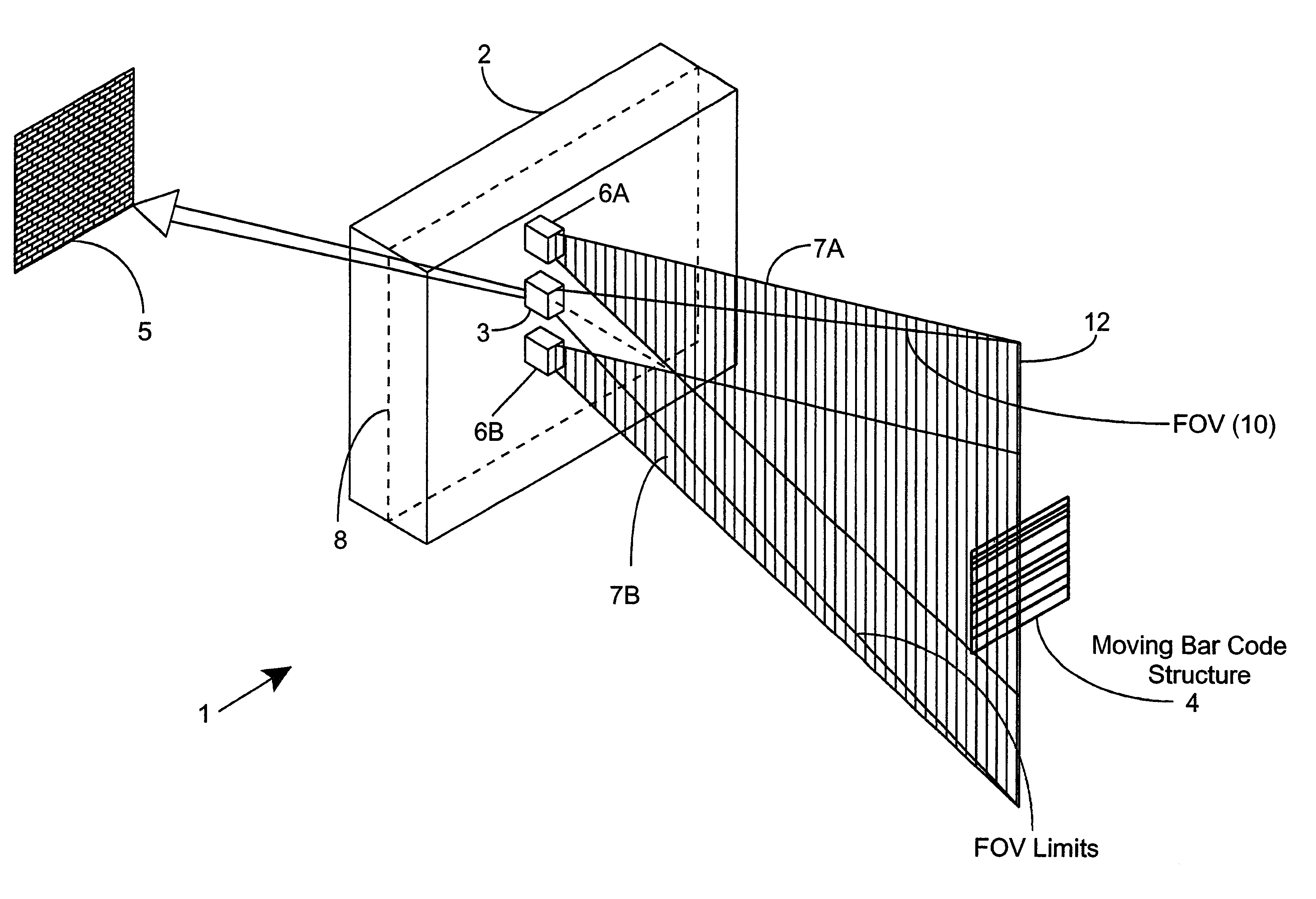
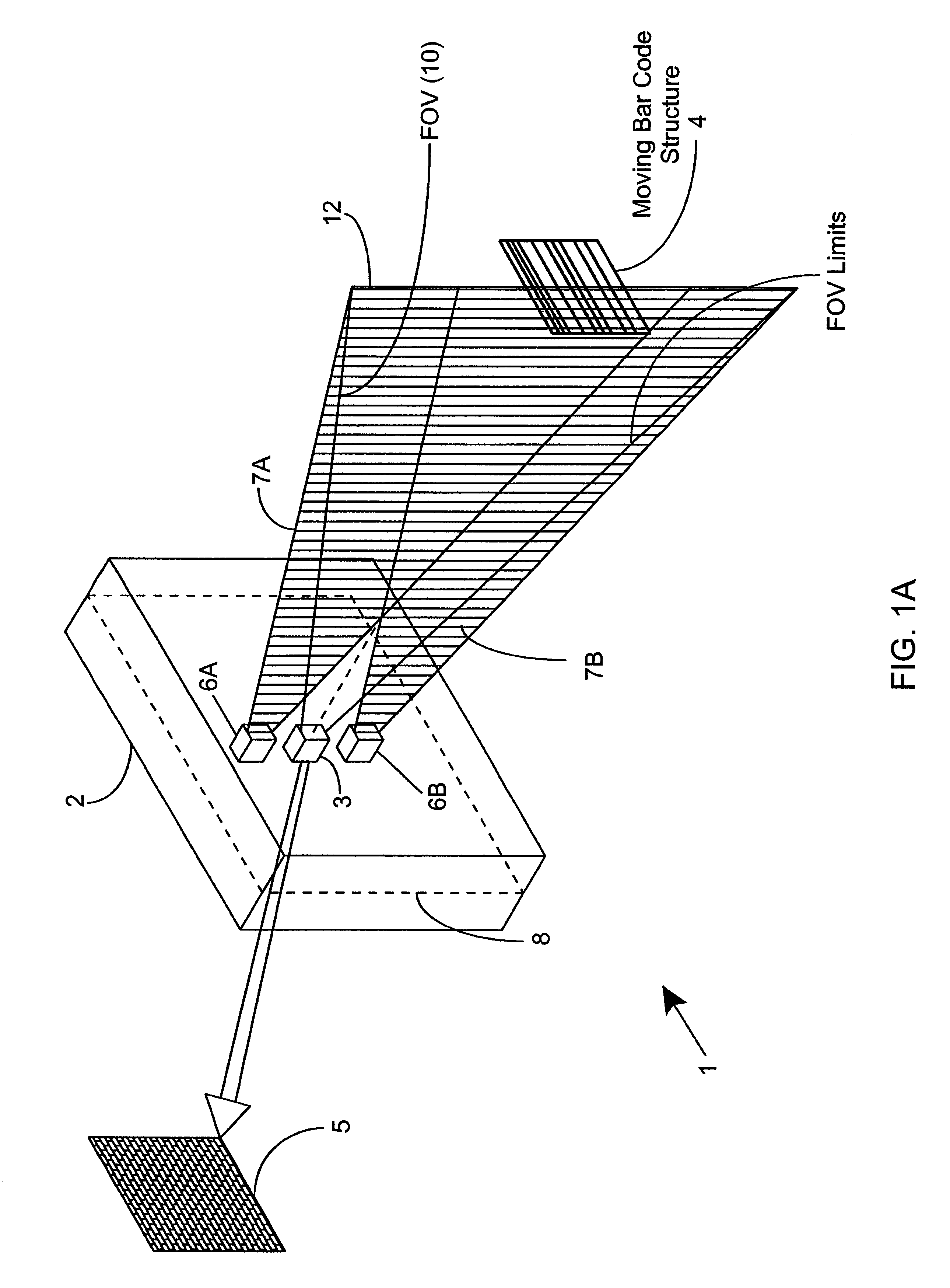
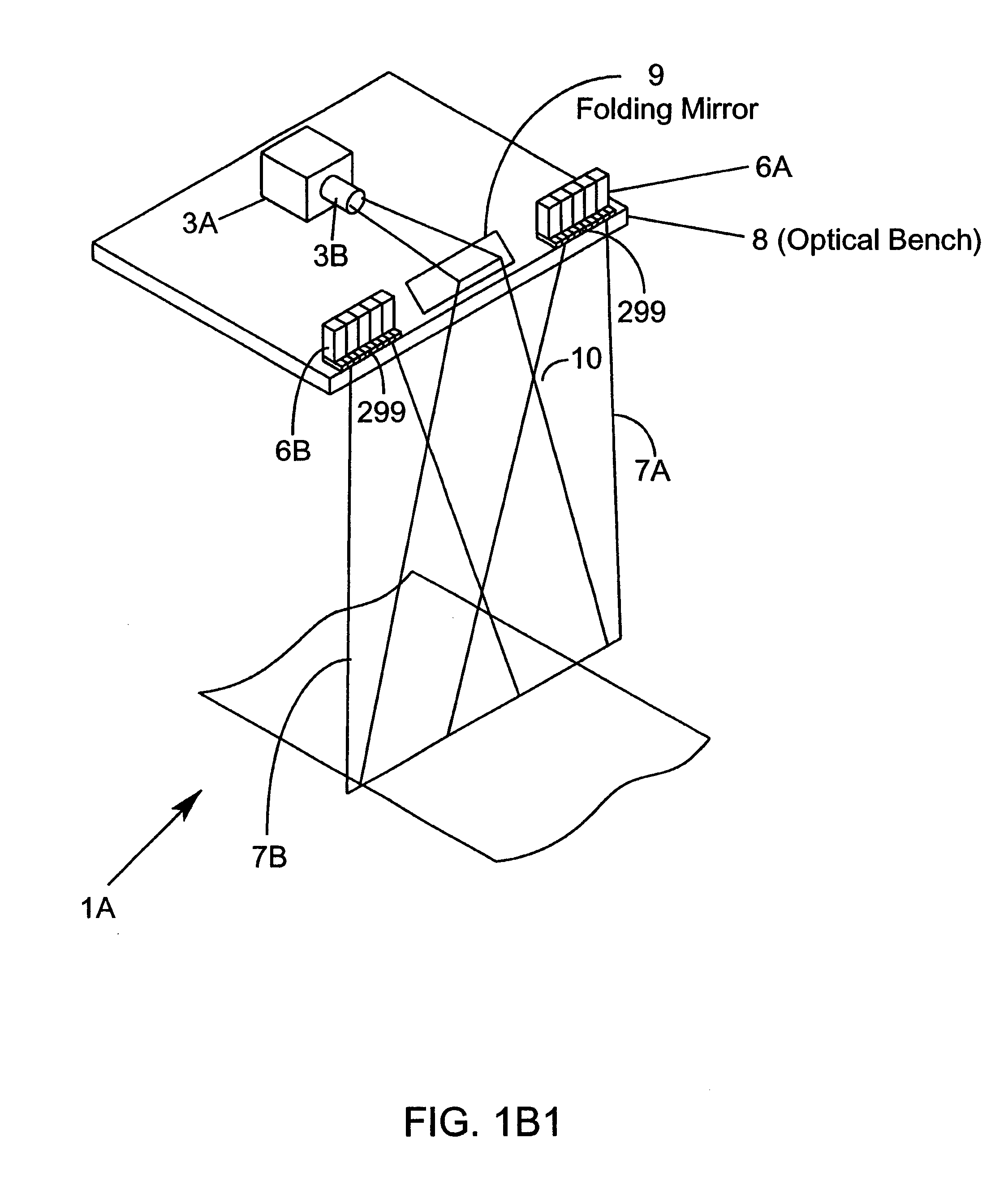
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Synthesis decoding and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20060213999A1Character and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesBarcodeLookup table
Systems and methods for successfully decoding optical images of objects of interest when such objects are situated outside a conventional working range of an imaging system, or when such objects are degraded. The systems and methods are based upon a comparison of computed signals corresponding to distorted images that would be obtained from known objects, such as barcodes, when viewed outside a working range, or when degraded, with actual signals obtained from the object of interest. The computed signals in one embodiment are recorded in a lookup table. An advantage of the systems and methods disclosed is that there results a smooth, monotonic probability of correctly decoding the image of interest, even beyond the working distance. A handheld or portable apparatus useful for practicing the invention is also disclosed.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
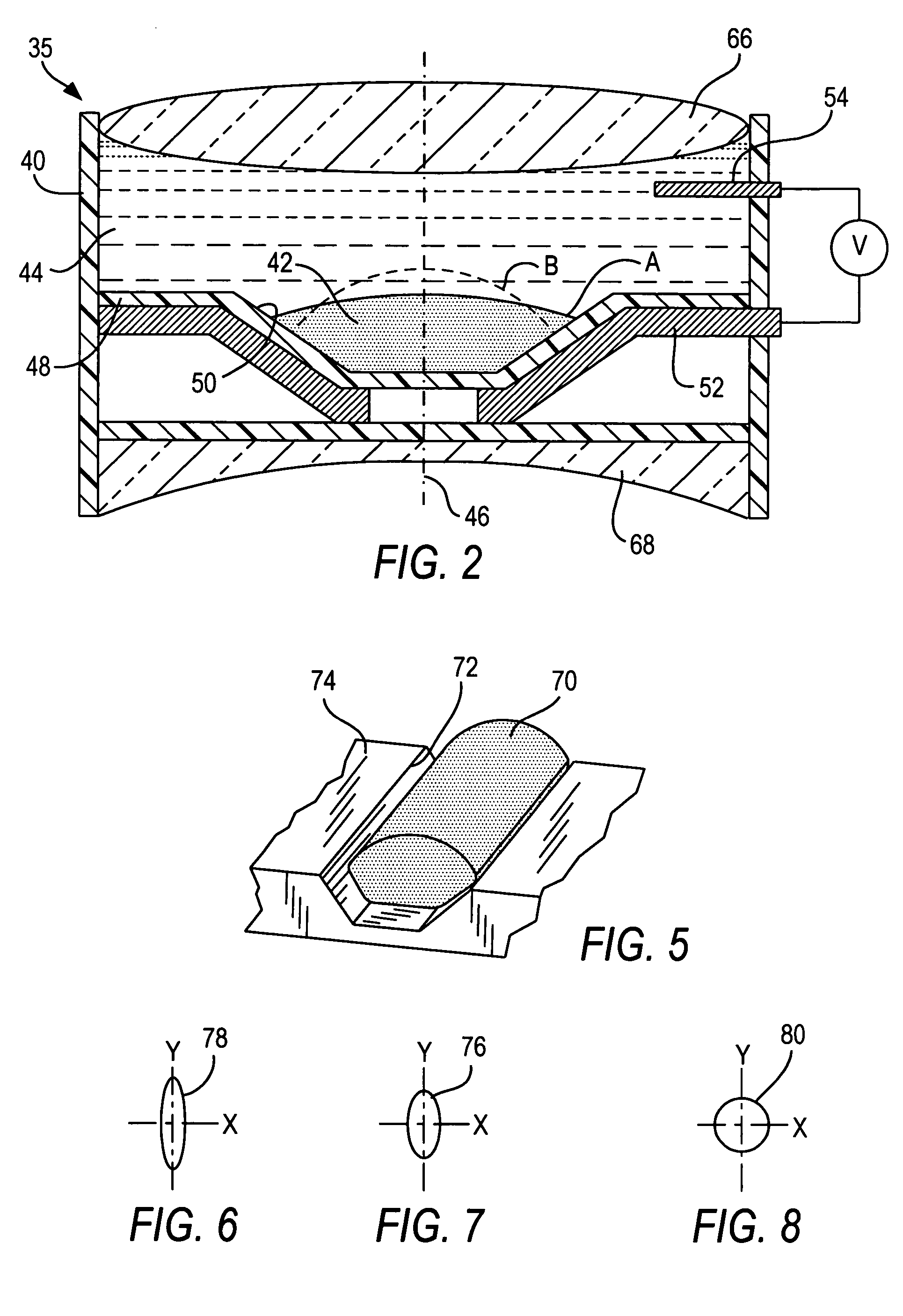
Optical adjustment for increased working range and performance in electro-optical readers
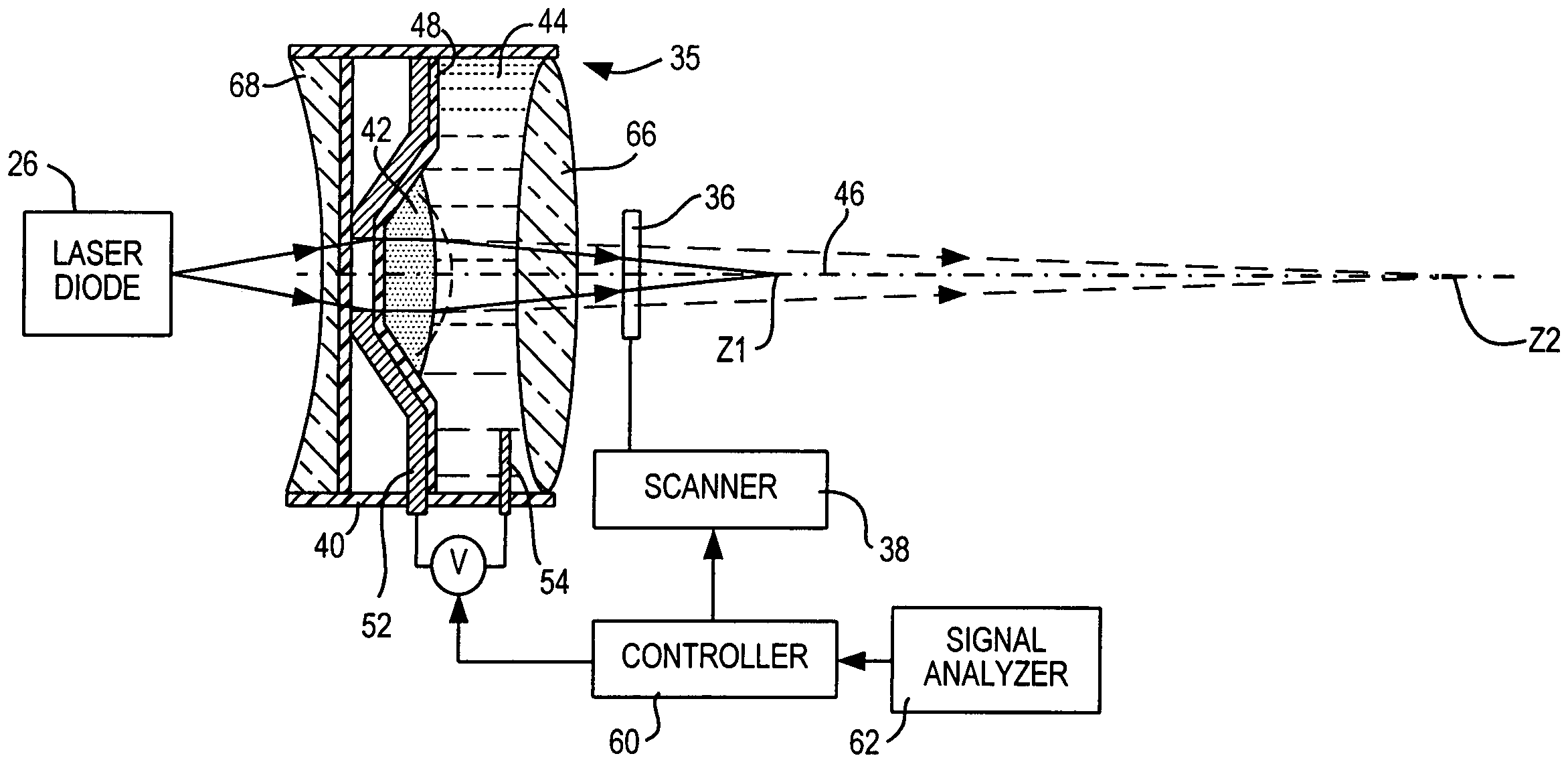
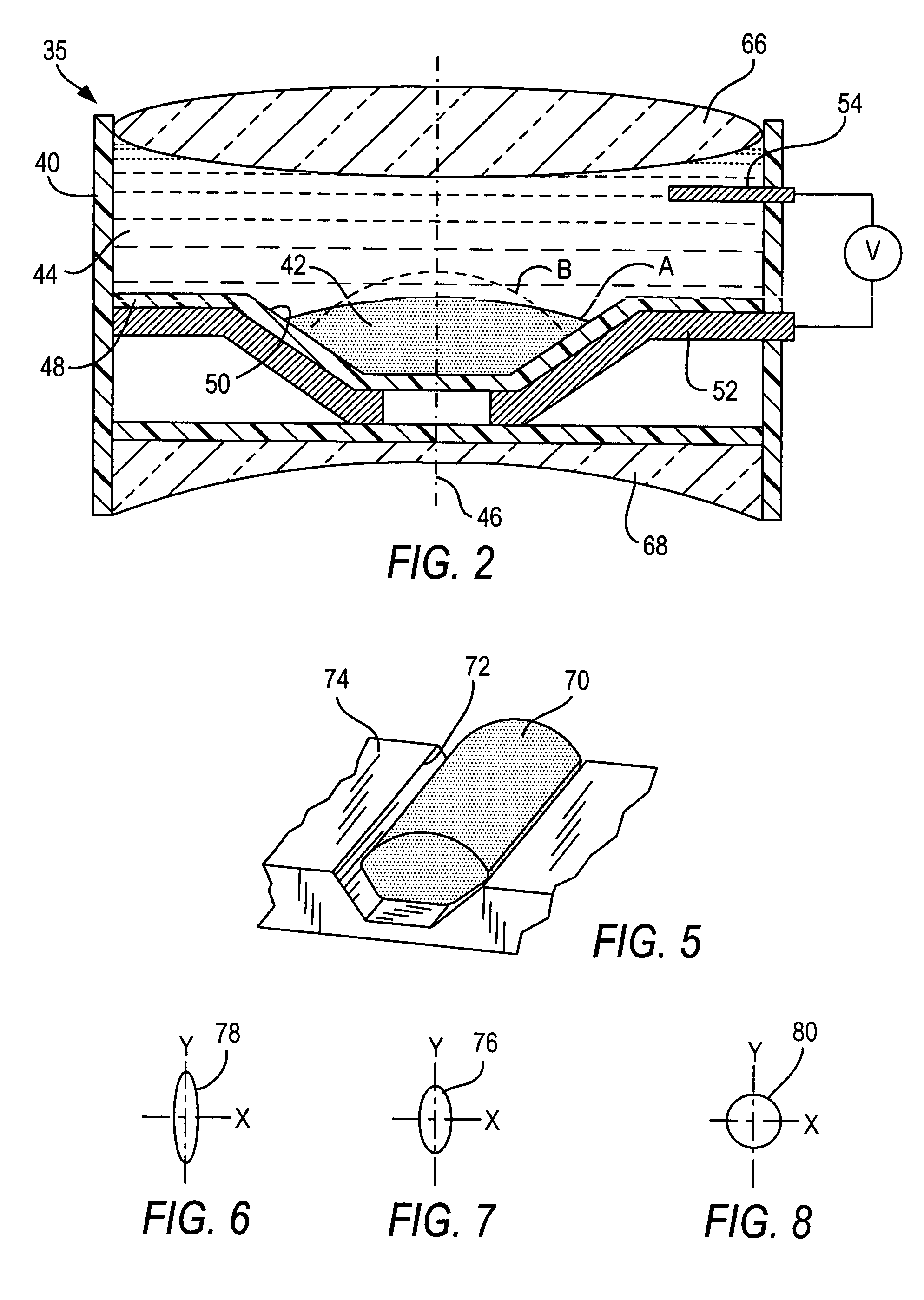
ActiveUS20050199725A1Improve performanceIncrease rangeProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementOpto electronicOptical reader
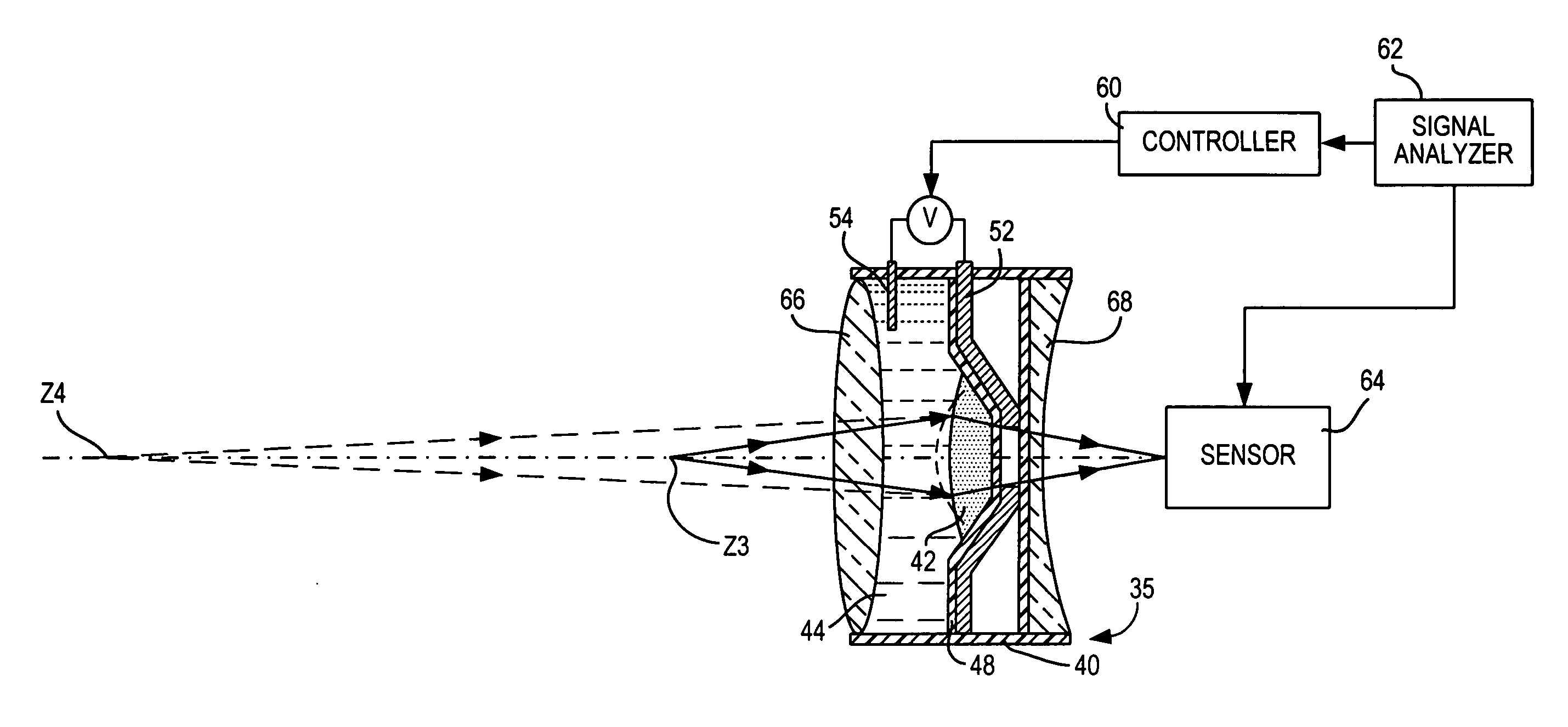
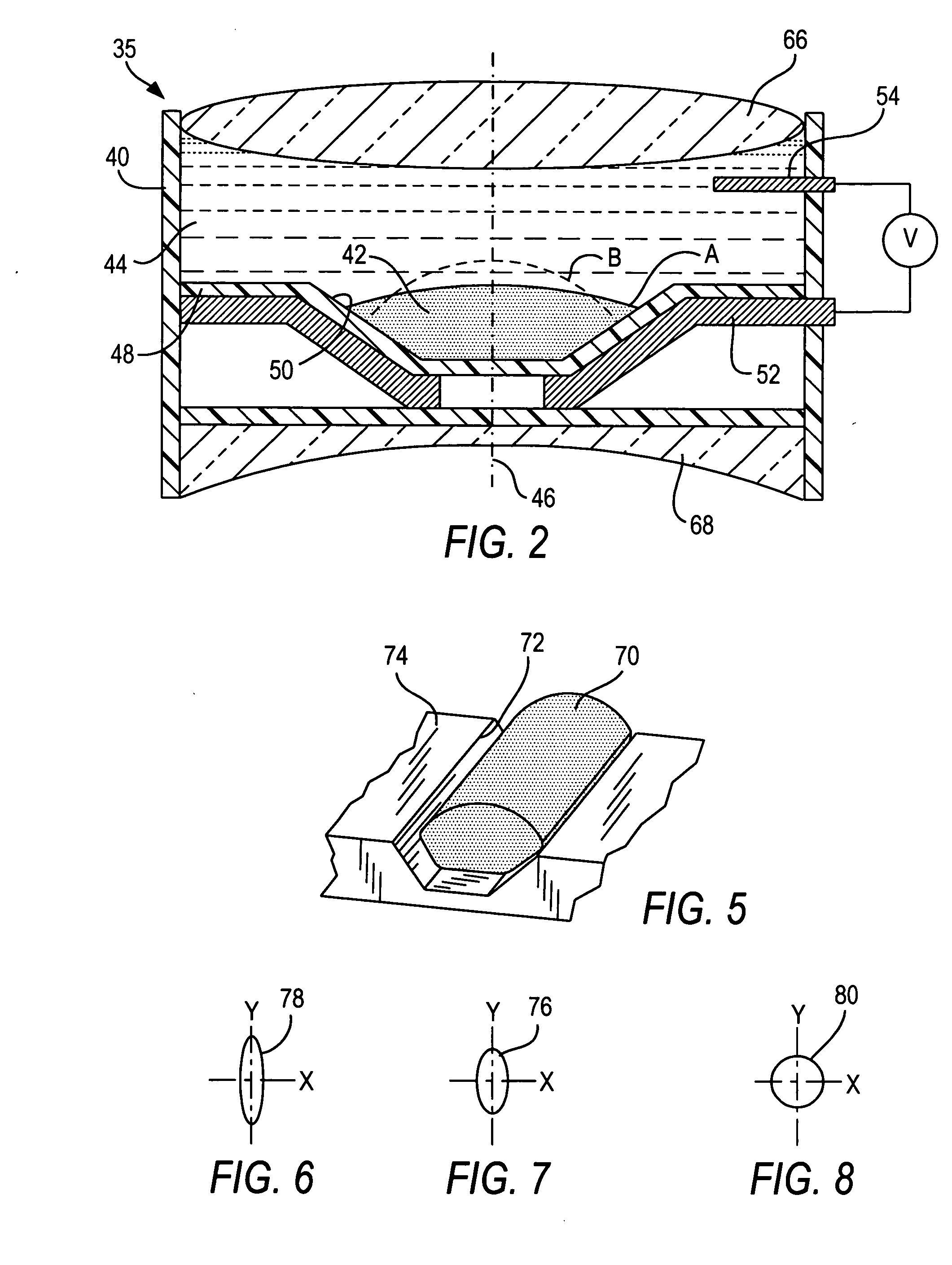
Working range is increased in an electro-optical reader or an imager for reading indicia by applying a voltage to a variable lens to change the shape of a liquid therein.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
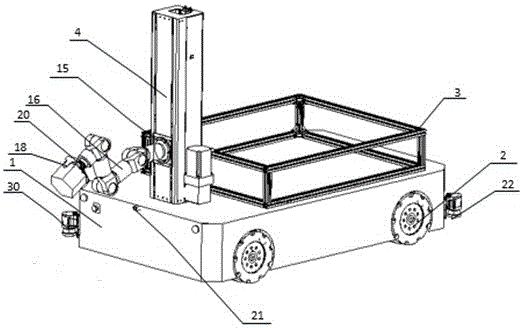
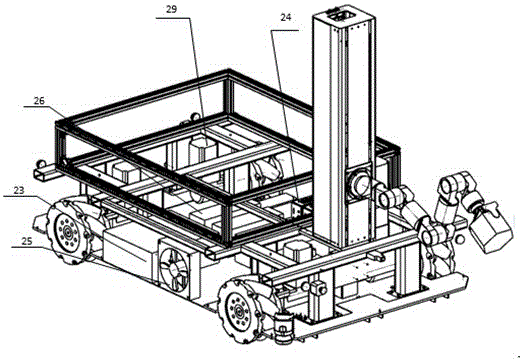
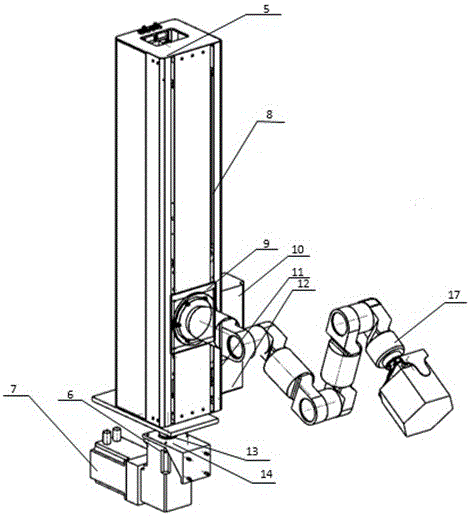
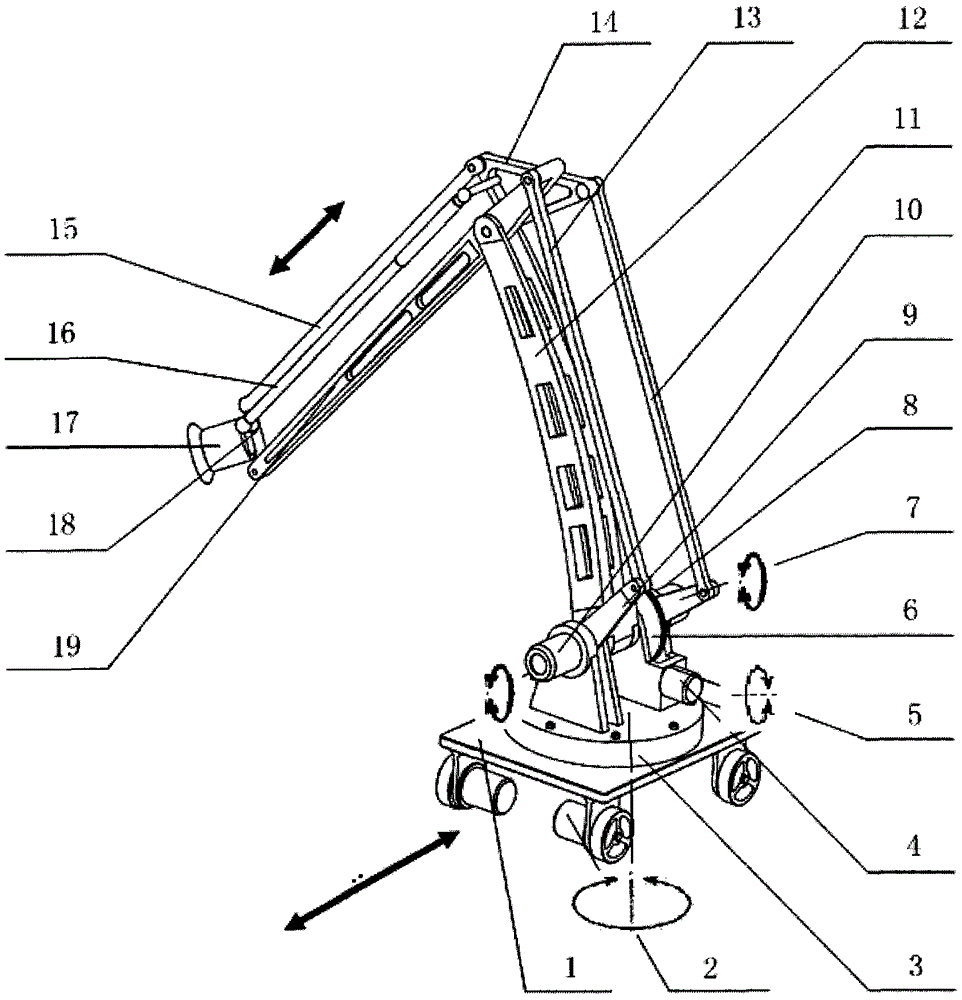
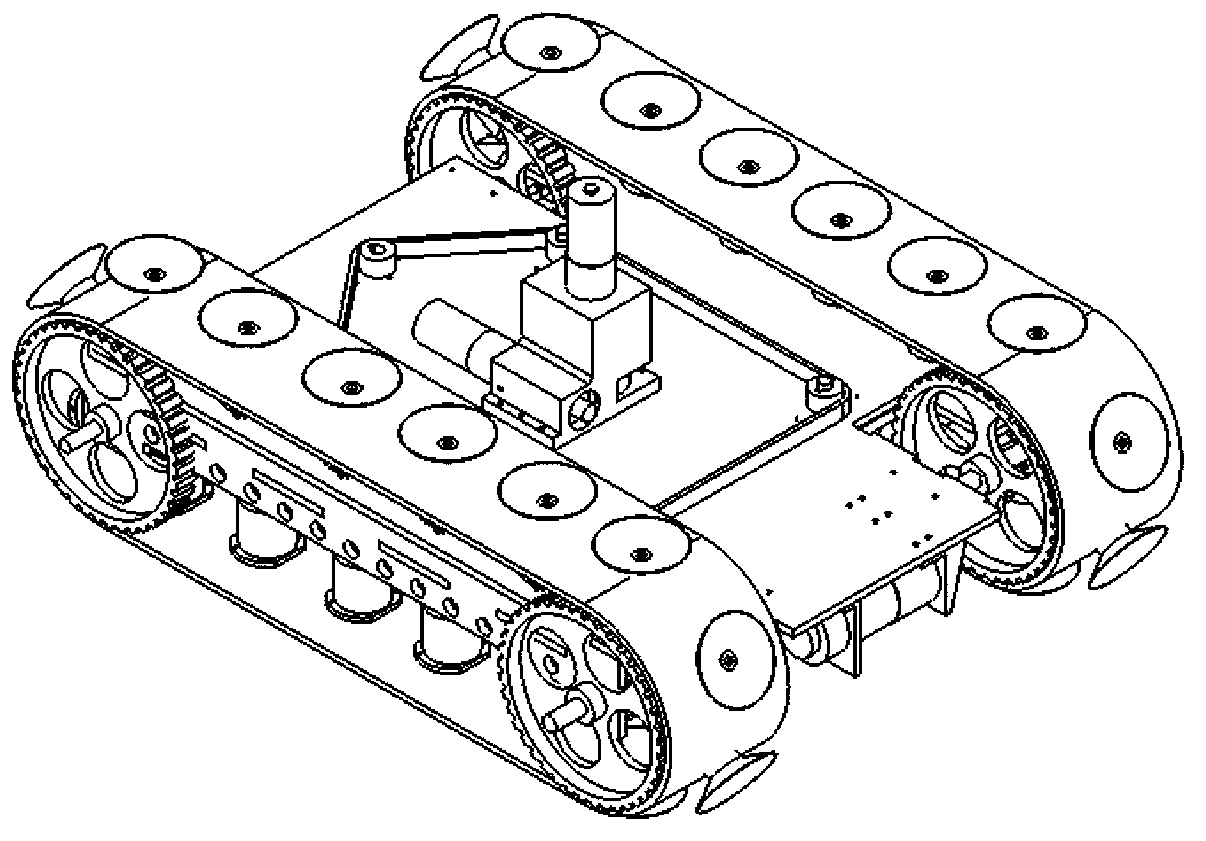
Omni-directional mobile transfer robot
InactiveCN106272415AImprove automationImprove completenessProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemSimulation
The invention discloses an omni-directional mobile transfer robot. The omni-directional mobile transfer robot comprises a mobile chassis, a carrying rack, a rotating mechanism, a lifting mechanism, a manipulator, a visual system, a laser sensor, a control system and a charging system. The mobile chassis is provided with Mecanum wheels for realizing omni-directional moving. The lifting mechanism can adjust the height of the manipulator. Rotational motion of a stand column at any angle can be realized through the rotating mechanism. Moreover, through cooperation of the manipulator having seven degrees of freedom, the working range is larger. Precision guidance can be realized through the laser sensor and the visual system. Operation is convenient. Motion is fast. The omni-directional mobile transfer robot is used for replacing manual operation, the working strength is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved. The omni-directional mobile transfer robot has high flexibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Spraying robot driven by multiple parallelogram links in parallel
InactiveCN104923431AReduce the safety of useImprove the safety of useProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpraying apparatusEngineeringMaximum pressure
The invention provides a spraying robot driven by multiple parallelogram links in parallel. The spraying robot comprises a pedestal (3), a big-arm driving motor (4), a small-arm driving motor (10), a pitch adjusting motor (8), a movable platform (18) and three paralleled parallelogram link mechanisms. The spraying robot is characterized in that the big-arm driving motor (4), the small-arm driving motor (10), and the pitch adjusting motor (8) are all arranged on one end of the pedestal (3), and the three paralleled parallelogram link mechanisms cooperate with one another to drive the movable platform (18). According to the invention, a three-parallelogram-link driving manner is employed, when the three parallelogram link mechanisms are designed, the maximum pressure angle is limited, in the working range, no matter the robot rotates to any position, the transmission performance of movements and forces can remain excellent.
Owner:SHANGHAI AIRCRAFT MFG +1
Process and device for using of low temperature heat for the production of electrical energy
The invention relates to the using of low temperature heat for the production of electrical energy by using of supercritical carbon dioxide as working fluid.It included a process and a device for process realizing with higher efficiency in relation to other known processes and with a wide temperature working range. This is related to a wider adjustability which allows an optimal operation both in summer and in winter operation without technical or constructional changes. The process is realizable without damages to the environment and is realizable with low effort. The relative emission of carbon dioxide is reduced in relation to other processes.Low temperature heat from a given heat source (1) is taken off by carbon dioxide at high supercritical pressure as heat transfer and working fluid in the process. Then the heated fluid is expanding in an expansion machine (2), which is connected with a generator (3) for the production of electric power. In this process the fluid will be cooled, then liquefied by using of a cold source (4) and in liquid state compressed to the working pressure.
Owner:TECHNIKUM CORP
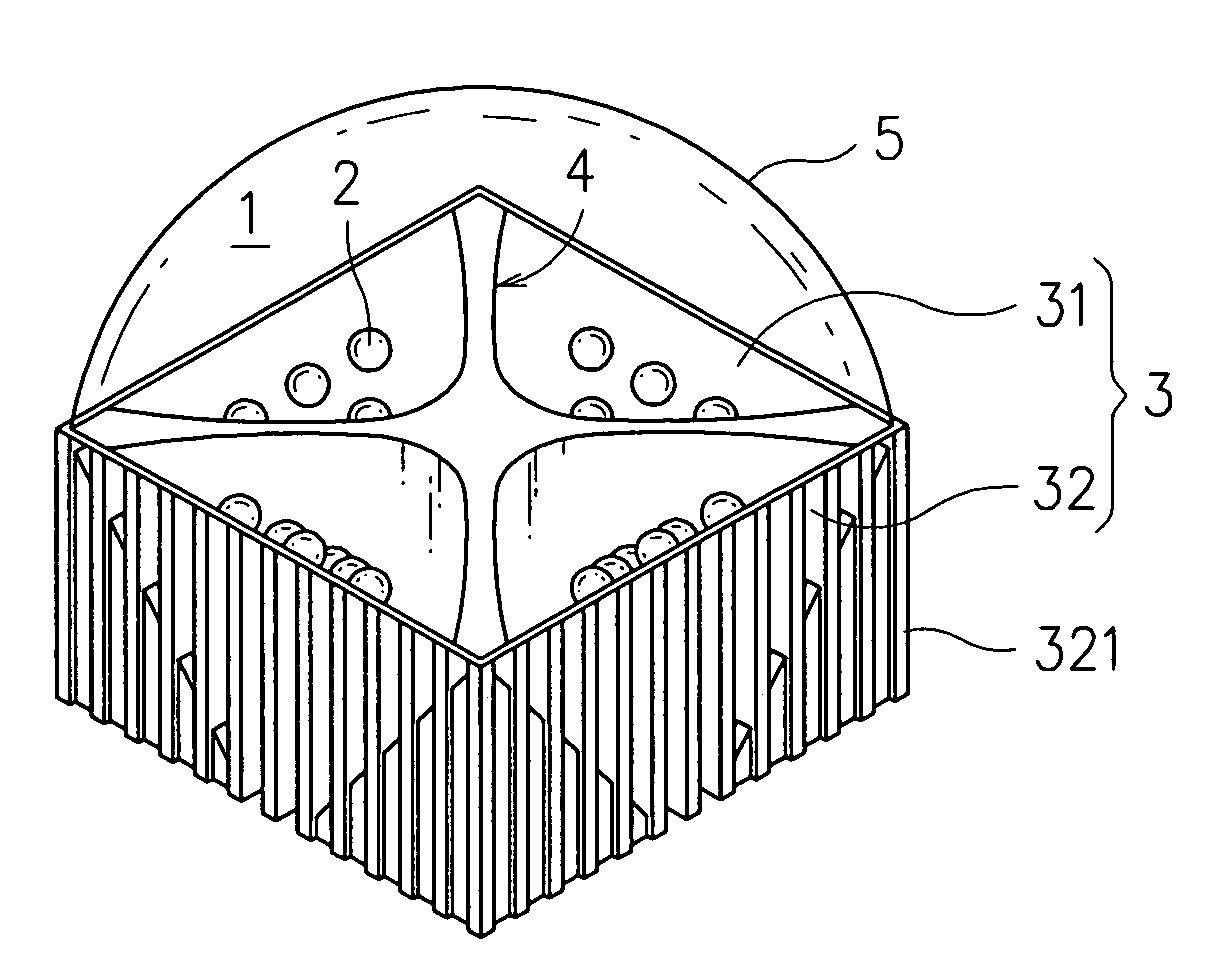
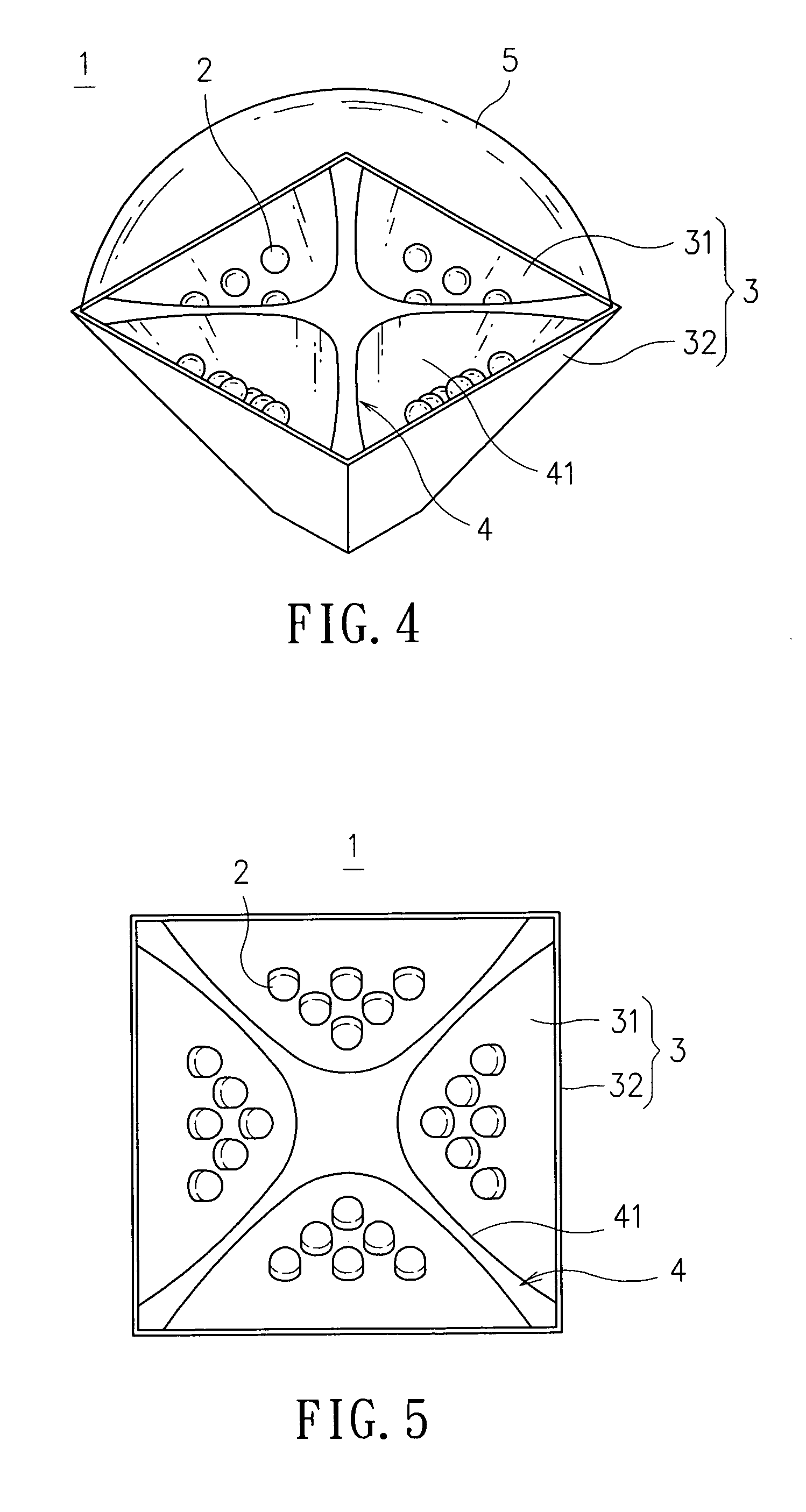
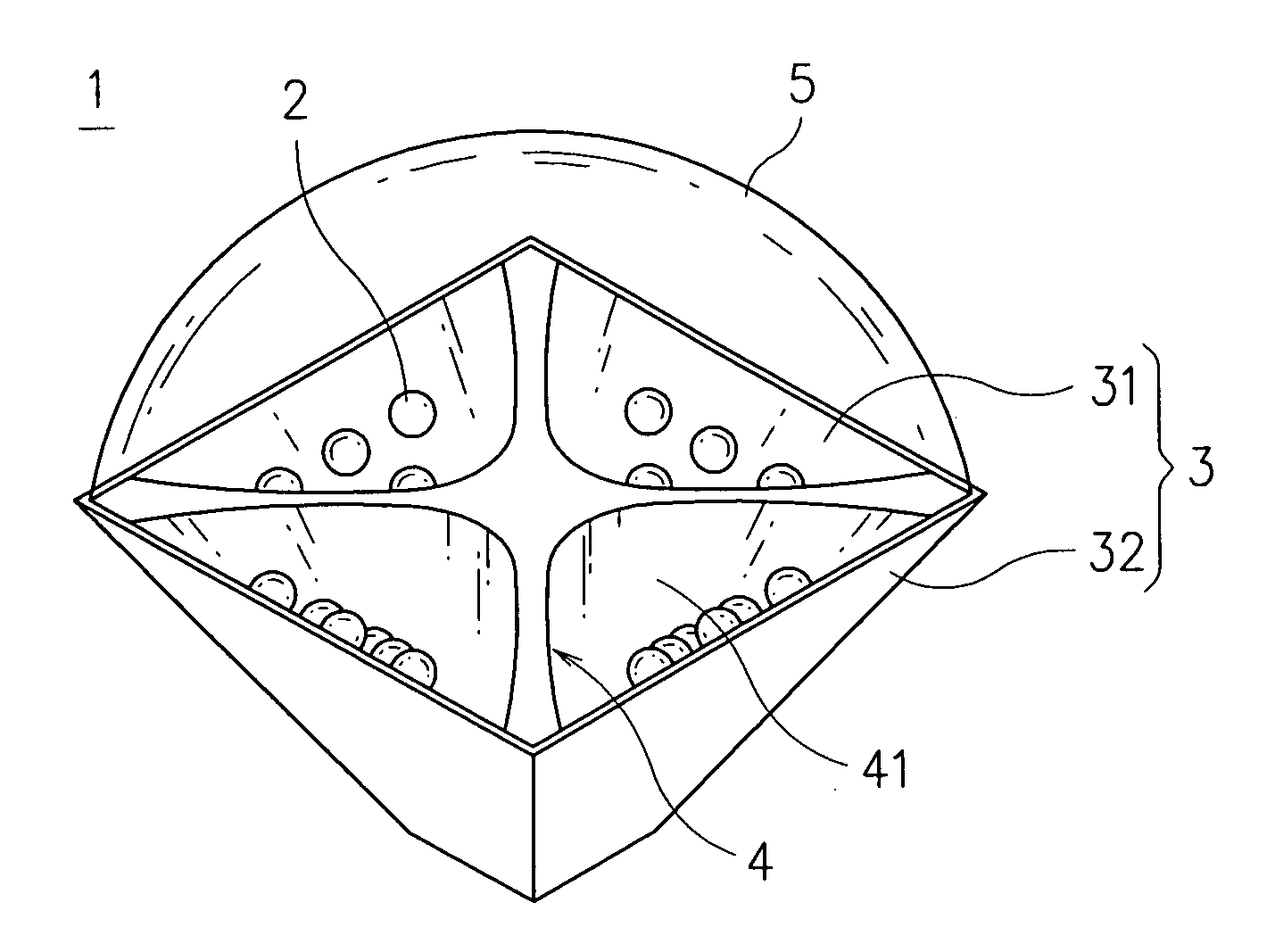
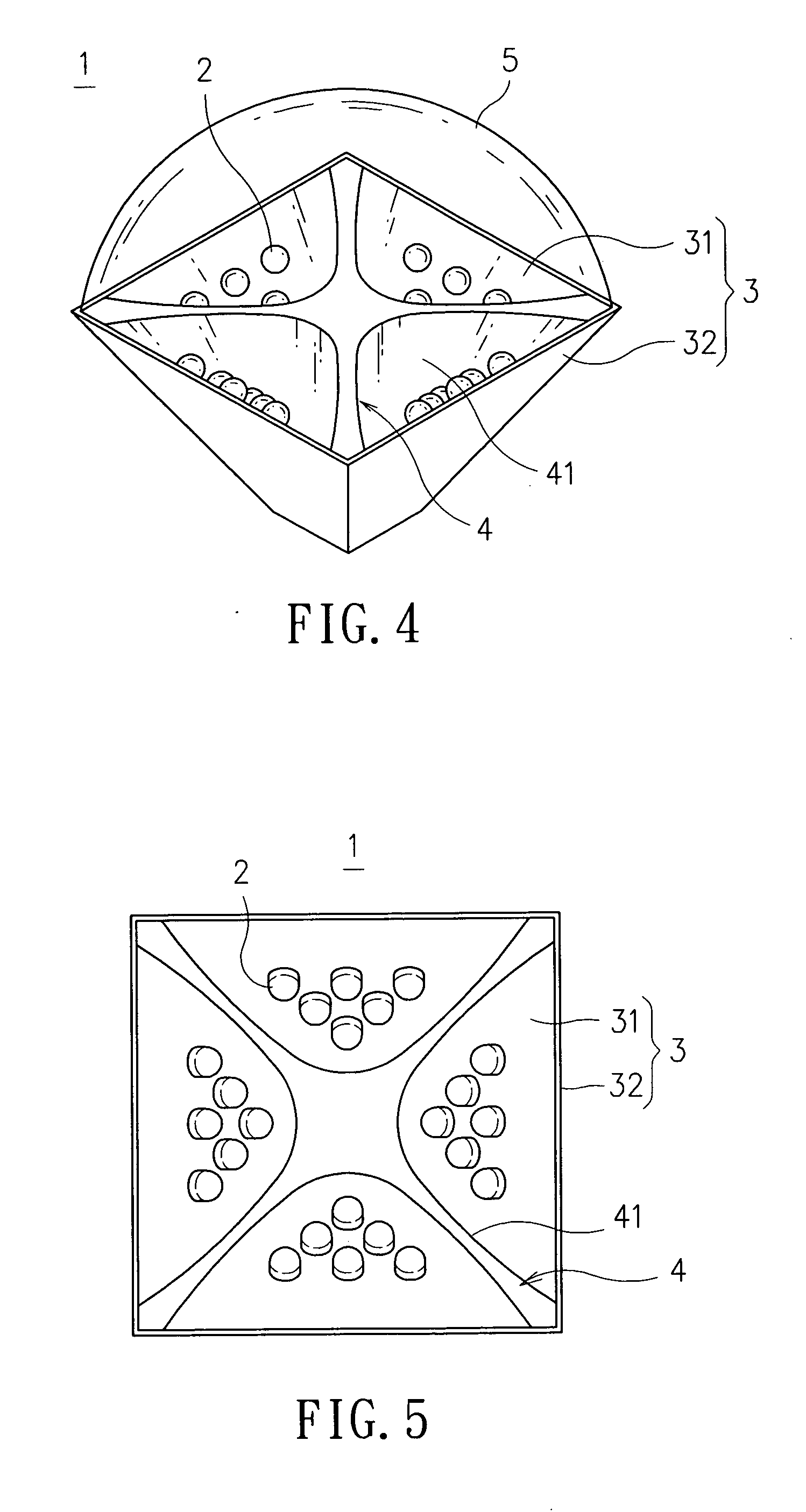
Illumination module
InactiveUS7461951B2Lower the volumeIncrease powerLighting applicationsVehicle headlampsComputer moduleLuminous flux
An illumination module is disclosed, which is comprised of a plurality of light sources, a plurality of light source substrates of high thermal conductivity, and a reflecting member for reflecting light. The plural light source substrates are arranged at positions corresponding to each other so as to form a polygon periphery of the illumination module, whereas the inner surface of the polygon periphery is enabled for at least one of the plural light sources to fit therein. The reflecting member is placed at the center of the module where it is corresponding to each of the plural light source substrates so as to reflect the light emitting from the light sources fitted thereon. In addition, a lens with light refraction ability is disposed at the light emitting end of the illumination module so as to enable the light illumination module to have light condensing / diffusing capability. Moreover, each light source substrate further comprises: a plurality of heat dissipating fins, being arranged at the outer surface thereof; and a assistant heat dissipating device; wherein the working range of the operation power and the luminous flux of the illumination module can be increased by the combined function provided by the heat dissipating fins and the assistant heat dissipating device. The assistant heat dissipating device can further comprise: a fan, being arranged at the bottom of the illumination module; and a heat pipe device, being fitted onto the light source substrate, for conducting waste heat to the heat dissipating fins to be dissipated.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Illumination module
InactiveUS20070115656A1Lower the volumeIncrease powerLighting applicationsVehicle headlampsOptoelectronicsLuminous flux
An illumination module is disclosed, which is comprised of a plurality of light sources, a plurality of light source substrates of high thermal conductivity, and a reflecting member for reflecting light. The plural light source substrates are arranged at positions corresponding to each other so as to form a polygon periphery of the illumination module, whereas the inner surface of the polygon periphery is enabled for at least one of the plural light sources to fit therein. The reflecting member is placed at the center of the module where it is corresponding to each of the plural light source substrates so as to reflect the light emitting from the light sources fitted thereon. In addition, a lens with light refraction ability is disposed at the light emitting end of the illumination module so as to enable the light illumination module to have light condensing / diffusing capability. Moreover, each light source substrate further comprises: a plurality of heat dissipating fins, being arranged at the outer surface thereof; and a assistant heat dissipating device; wherein the working range of the operation power and the luminous flux of the illumination module can be increased by the combined function provided by the heat dissipating fins and the assistant heat dissipating device. The assistant heat dissipating device can further comprise: a fan, being arranged at the bottom of the illumination module; and a heat pipe device, being fitted onto the light source substrate, for conducting waste heat to the heat dissipating fins to be dissipated.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
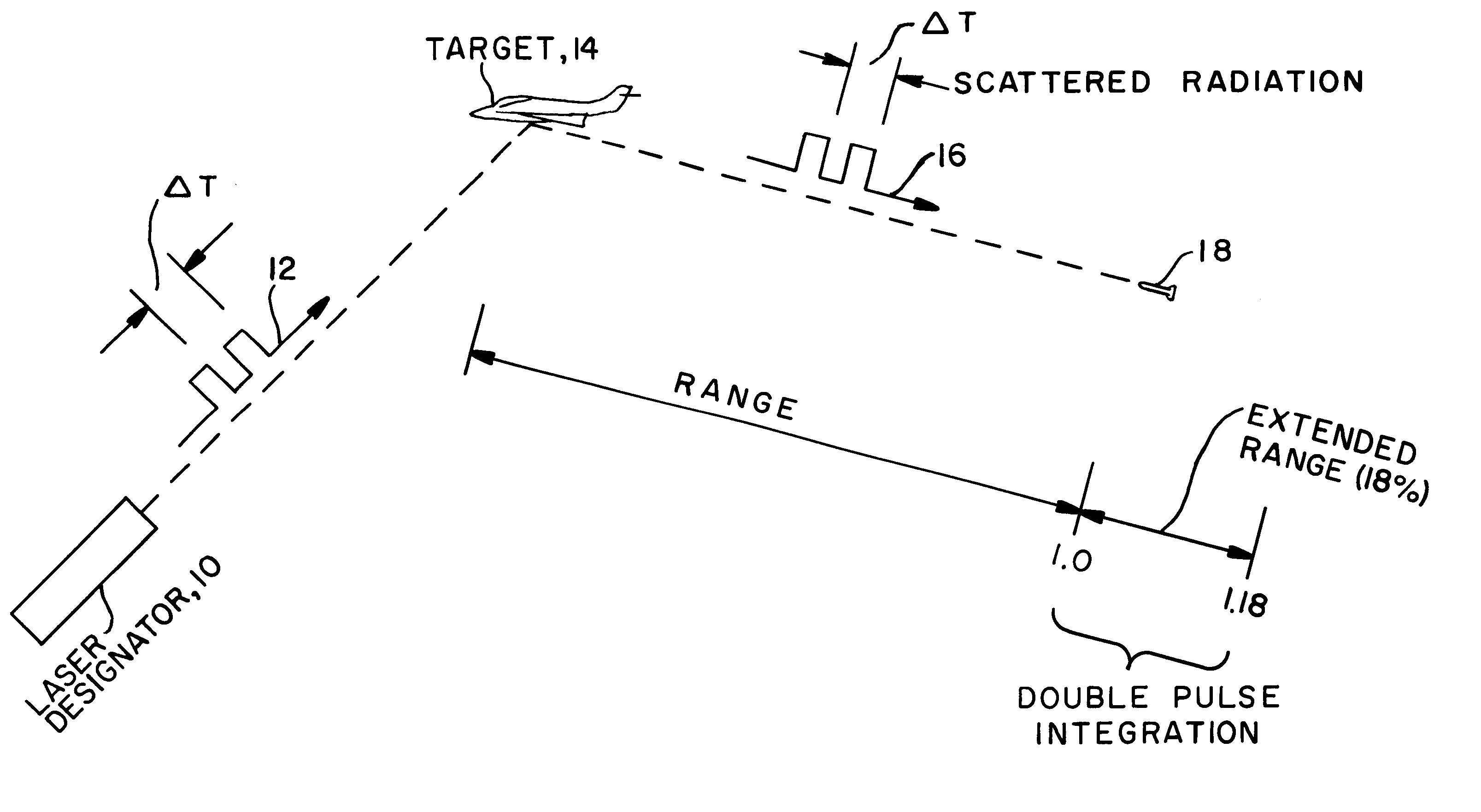
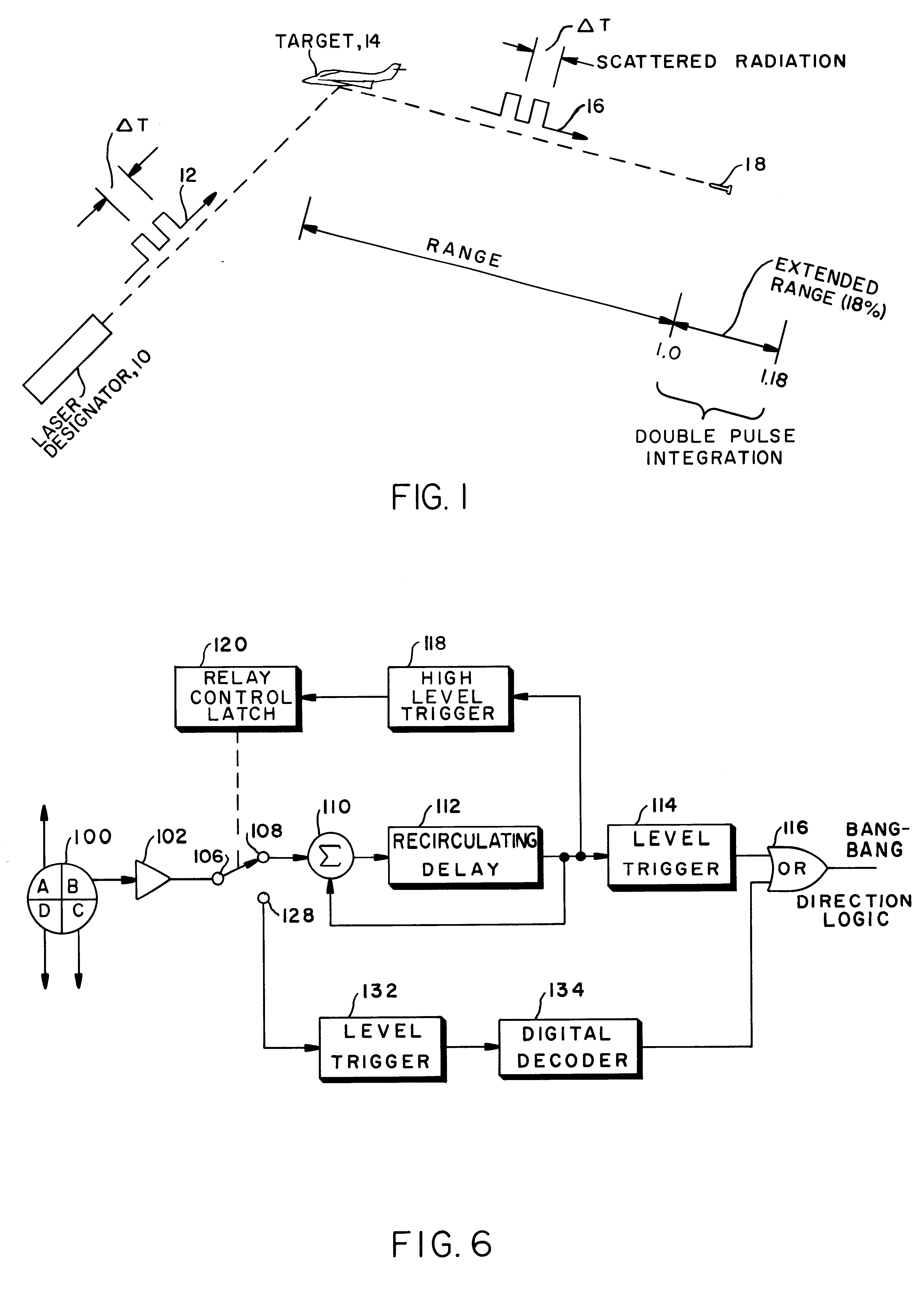
Extended range, light weight laser target designator
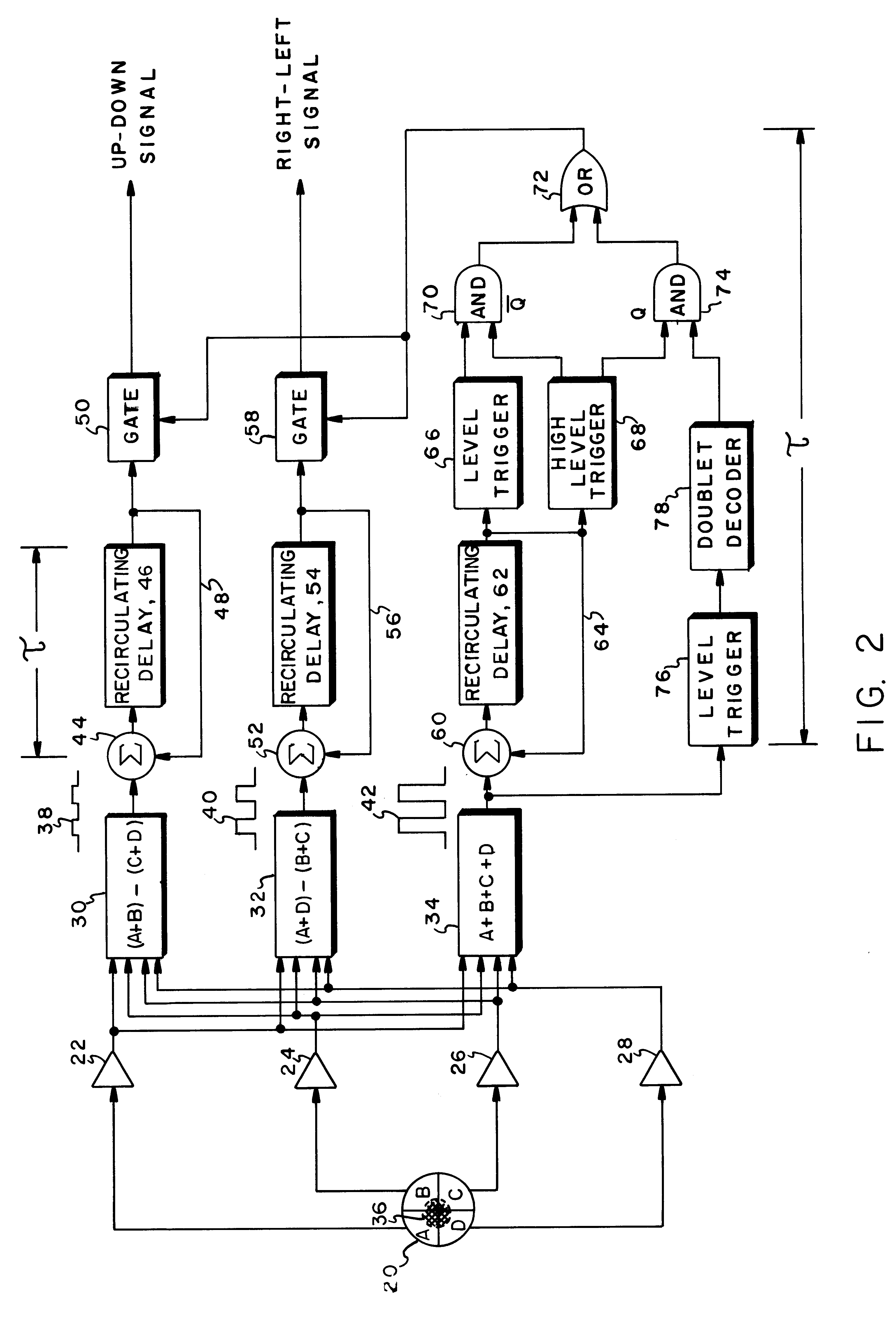
InactiveUS6926227B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce false alarm rateDirection controllersPosition fixationLaser targetCountermeasure
Pulse integration is utilized on board an optically guided missile or other ordinance device used as a part of a target designation system for extending the lock-on range of the missile by approximately 18%, when a double pulse laser is utilized to illuminate and designate the target. Pulse integration is accomplished with a recirculating delay unit which superimposes the first pulse on the second pulse, such that while the pulses add coherently, noise does not add in phase. The pulse integration technique therefore enhances the signal-to-noise ratio when the missile is at the outer limits of its operating range. When the missile is sufficiently close to the target, doublet decoding is actuated to offer countermeasure resistance. At this point, pulse integration may proceed in lieu of doublet decoding or may be dispensed with in view of the increased signal-to-noise ratio due to the close range of the missile to the target.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC +1
Low-pollution combustion chamber provided with premixing and pre-evaporating ring pipe
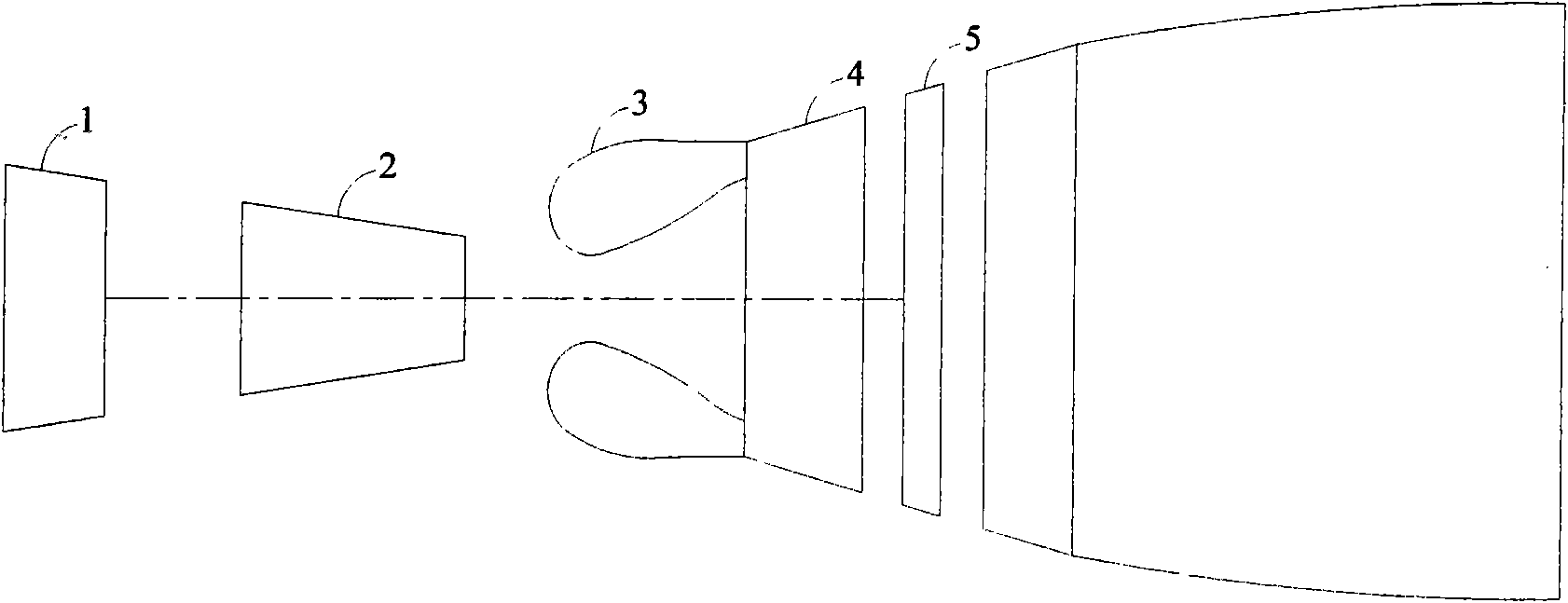
ActiveCN101788157AReduce pollutionFast evaporation blendingContinuous combustion chamberCombustion chamberCombustible gas
The invention relates to a low-pollution combustion chamber provided with a premixing and pre-evaporating ring pipe, which adopts a single-ring cavity structure and consists of a combustion chamber outer casing, a combustion chamber inner casing, an outer flame tube, an inner flame tube and a combustion chamber head part, wherein air used for combustion completely enters into the flame tubes from the combustion chamber head part; the scheme of fractional combustion can be adopted, and pre-combustion stage and a main-combustion stage are divided; the main-combustion stage comprises the premixing and pre-evaporating ring pipe, a main-combustion stage nozzle and a main-combustion stage swirler; fuel oil is evaporated and mixed inside the premixing and pre-evaporating ring pipe and then enters into the flame tubes after forming even mixed combustible gas, belonging to premixed combustion; a fuel nozzle is used for supplying the fuel oil for the pre-combustion stage and the main-combustion stage; the stable working range of the combustion chamber is mainly controlled by the pre-combustion stage, so that the stable combustion can be ensured to be carried out in the combustion chamber within wider working range, and a stable ignition source can be provided for the main-combustion stage; the pollution emission is mainly controlled by the main-combustion stage, and the equivalent weight ration of the premixed gas of the main-combustion stage can be controlled within the low-pollution combustion range, so that the pollution emission of the whole combustion chamber cam be ensured to be greatly reduced. The premixing and pre-evaporating structure has small size, simple structure and modularized characteristic, can reduce the pollution emission of the combustion chamber of an aircraft engine, and ensures good combustion stability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
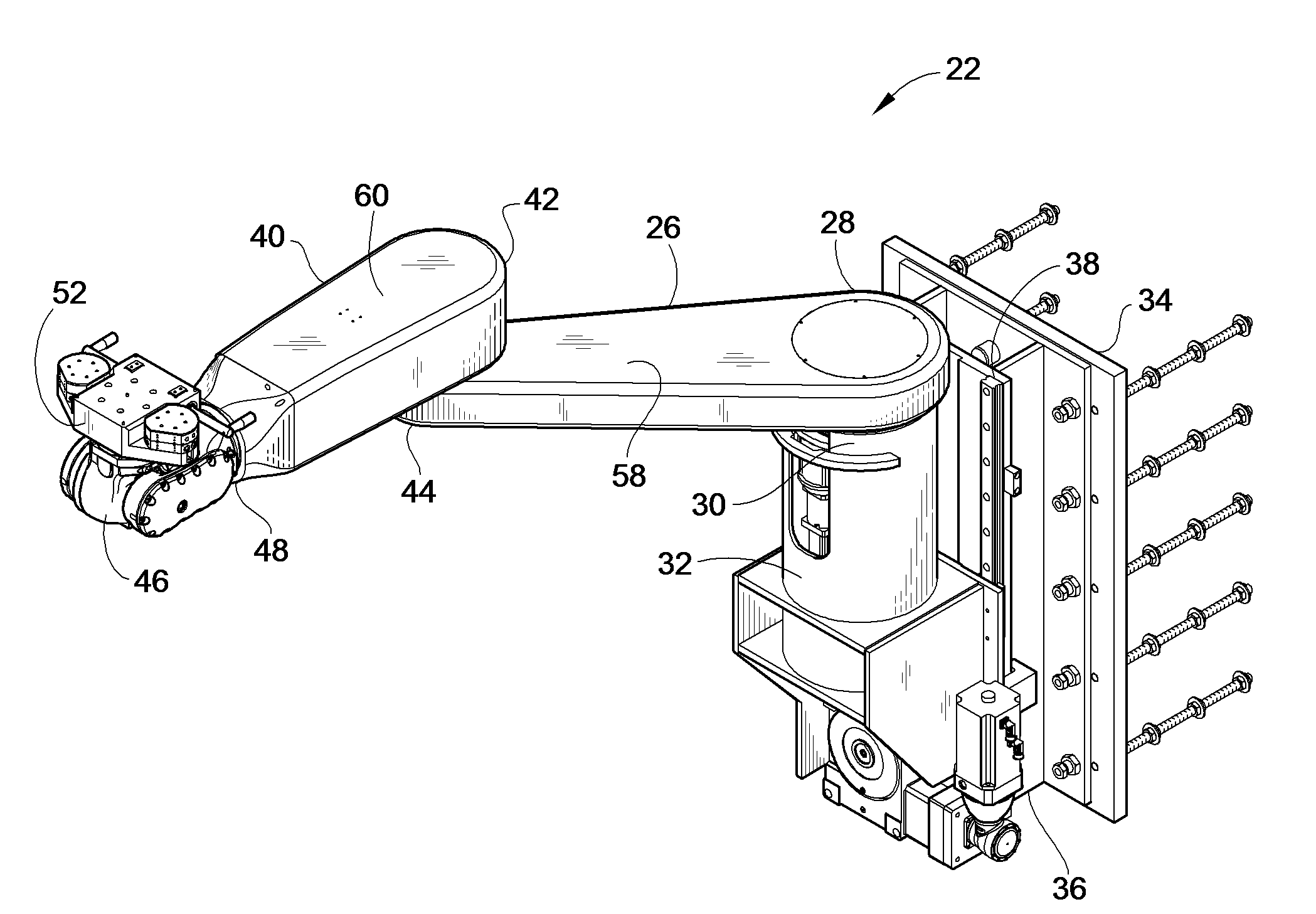
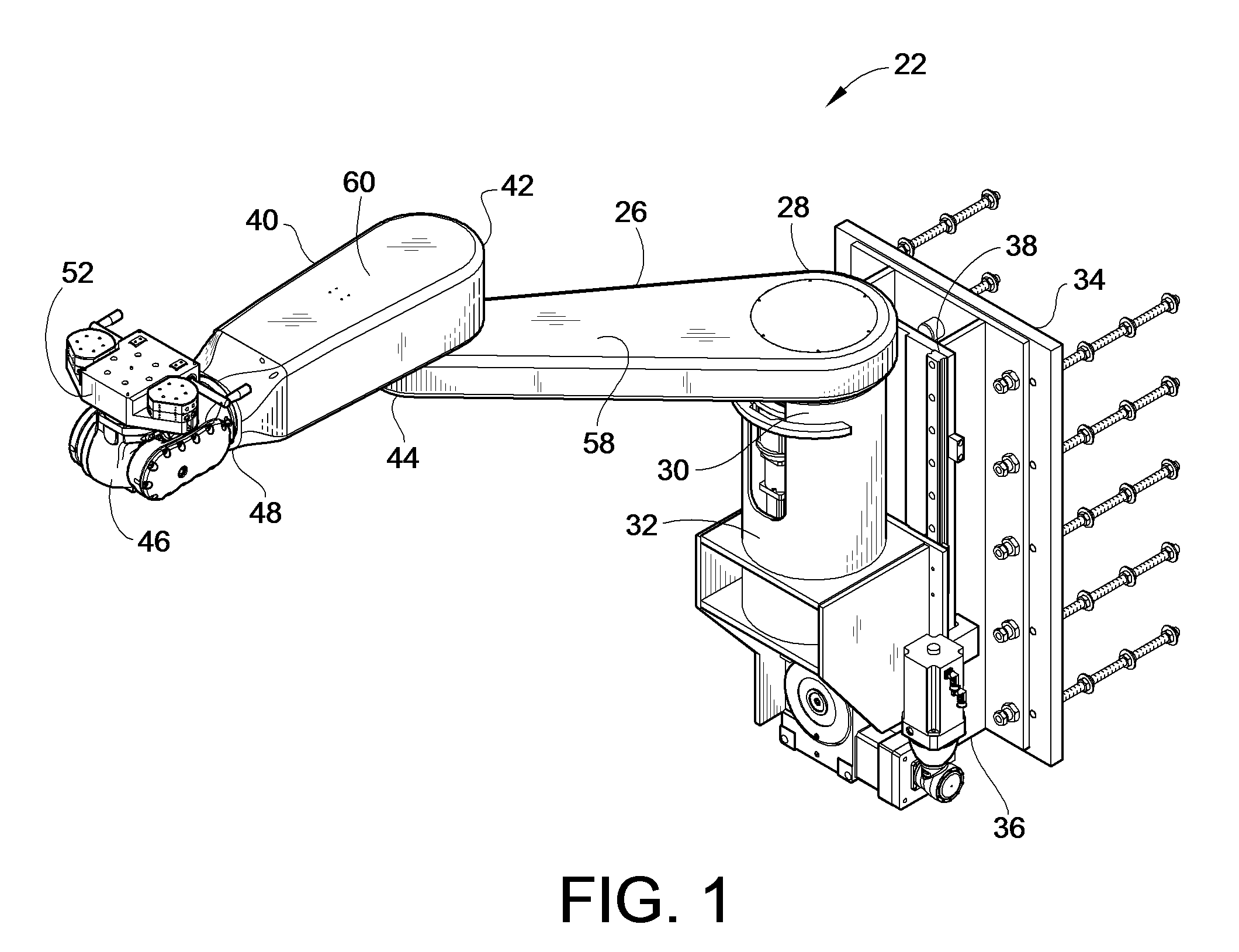
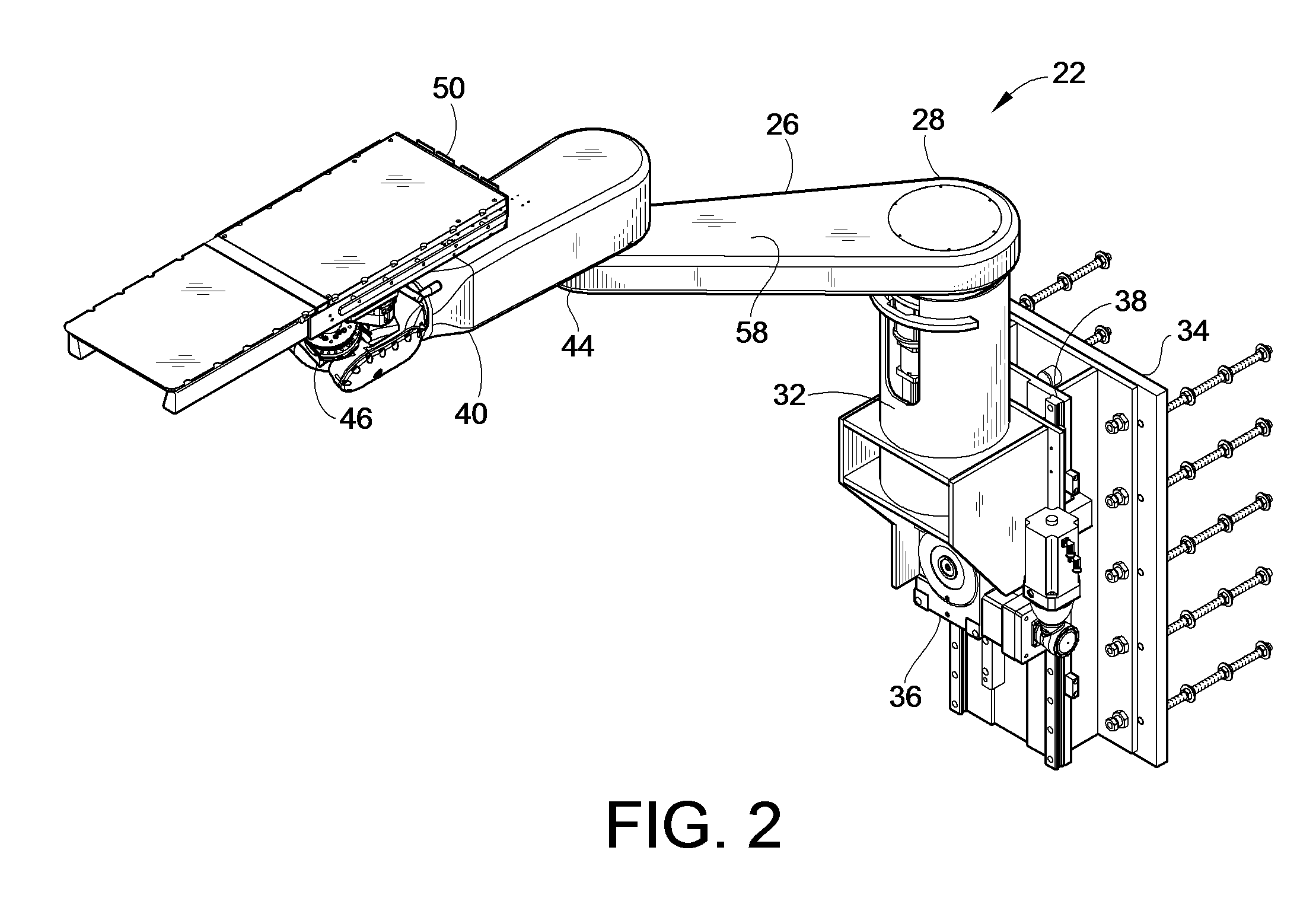
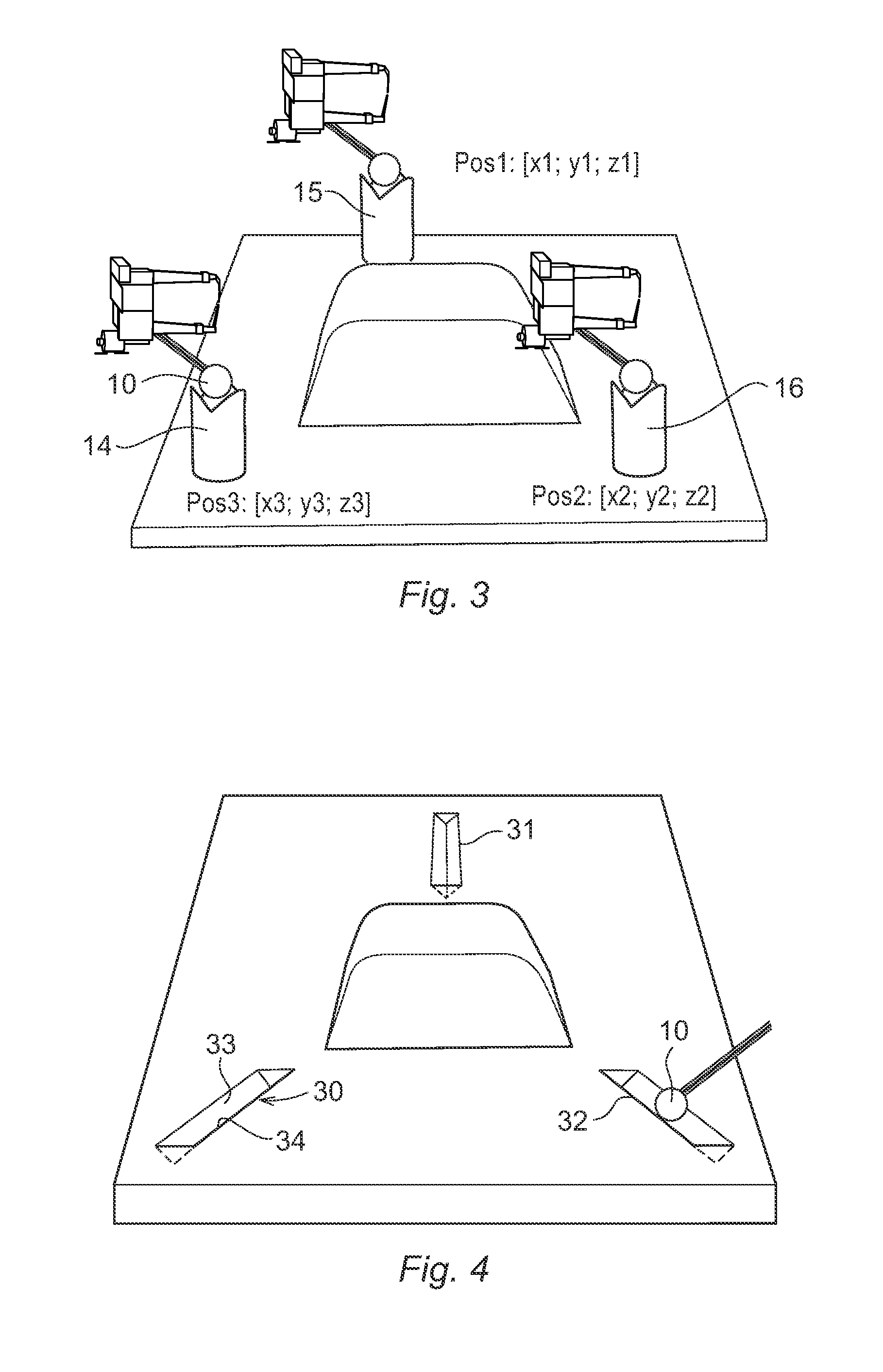
Patient Positioner System
ActiveUS20090070936A1Lower cost of capitalImprove throughputProgramme-controlled manipulatorOperating tablesRobotic systemsVision based
A computer controlled robot system for positioning a patient for radiation therapy or other medical procedures and the like. The robot is mounted at the top of a vertical shaft extending from the treatment room floor and includes horizontal arms arranged to maximize the available work envelope and eliminate “dead spots” in the envelope that the robot cannot reach. A double redundant coupling system for coupling devices to the robot is provided. A vision based docking system is employed for automatically coupling devices to the robot. Various enhanced safety features are provided, including device specific collision avoidance.
Owner:LUZADER DAVID J +2
Device and method for field calibration of vision measurement system
InactiveCN1605829AAddress flexibilitySolve for fast measuring cell calibrationImage analysisPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryTheodoliteVisual perception
The present invention is in-situ visual measurement system calibrating equipment and process. The calibrating equipment is 3D coordinate measuring system and stereo target, and the stereo target set inside the work range of the 3D coordinate measuring system consists of base plate as well as sensor calibrating target and system measured target, which are standard balls, set on two sides of the base plate. The 3D coordinate measuring system may be an industrial theodolite measurement system or a laser tracking instrument. The calibrating process includes calibrating the stereo target in the coordinate measuring system, acquiring the image of the sensor calibrating target, obtaining the conversion relation between the system measured target and the sensor calibrating target via coordination conversion, and other steps. The present invention can realize the in-situ measurement element calibration and overall system calibration.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method of and system for producing images of objects using planar laser illumination beams and image detection arrays
InactiveUS6629641B2Avoid disadvantagesLower Level RequirementsSemiconductor laser arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage detectionHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type scanning applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
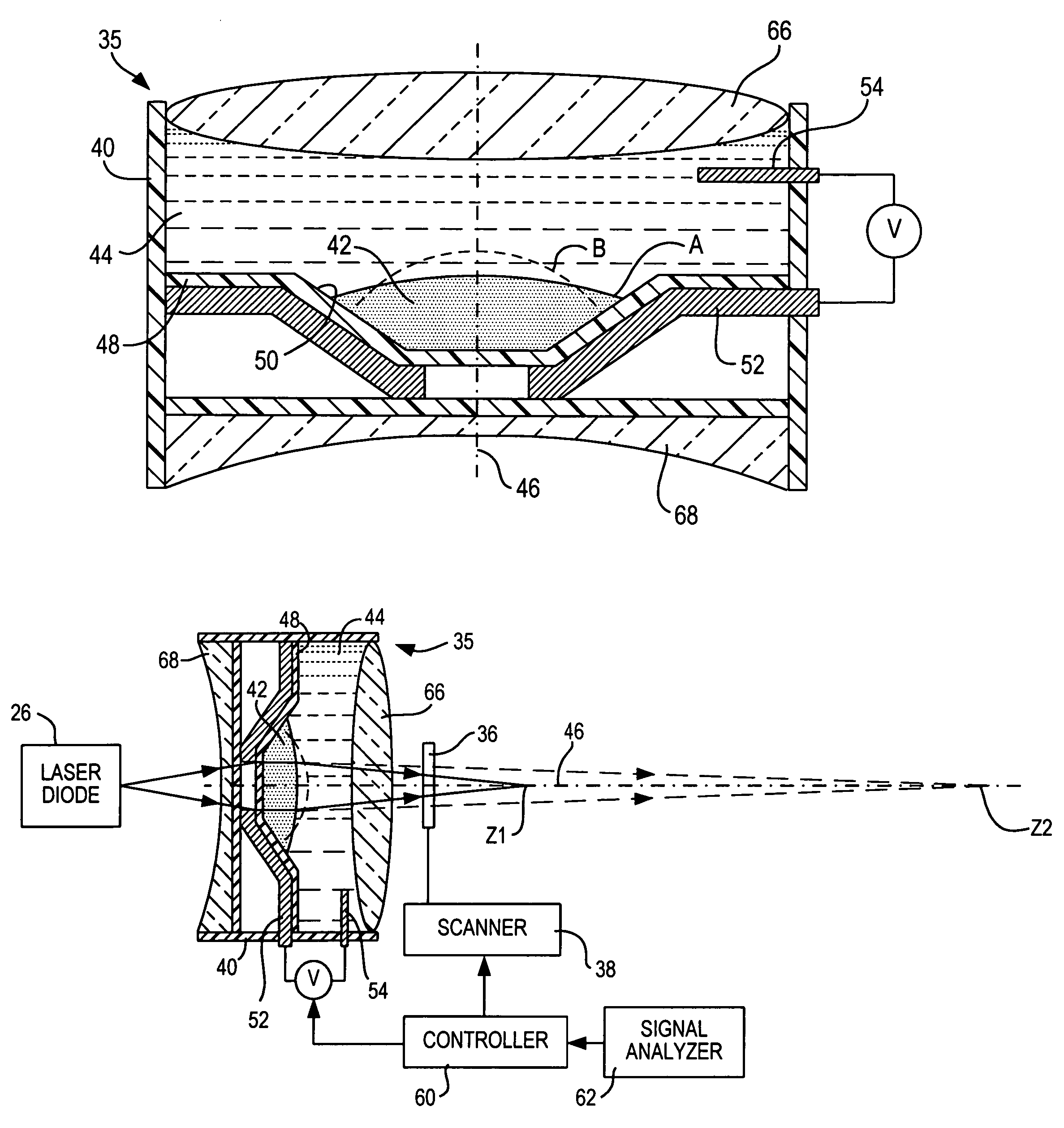
Optical adjustment of working range and beam spot size in electro-optical readers
ActiveUS7264162B2Guaranteed uptimeReliable and quiet in operationProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementLight beamBeam cross section
Working range and laser beam cross-section are adjusted in an electro-optical reader for reading indicia by applying control voltages to a pair of variable lenses to change the shape of a liquid therein. An aperture stop maintains a constant beam cross-section as an input to one of the lenses.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
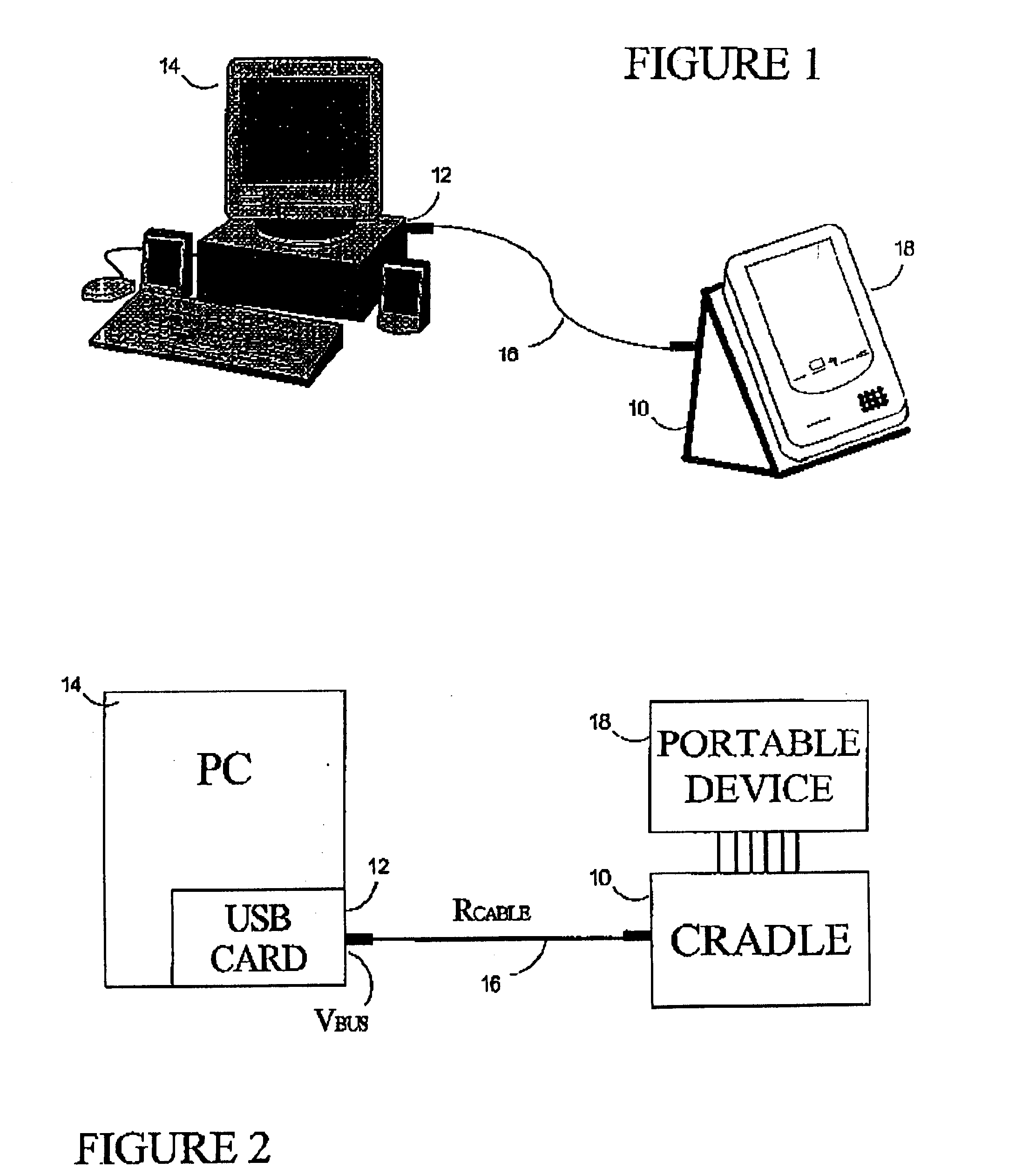
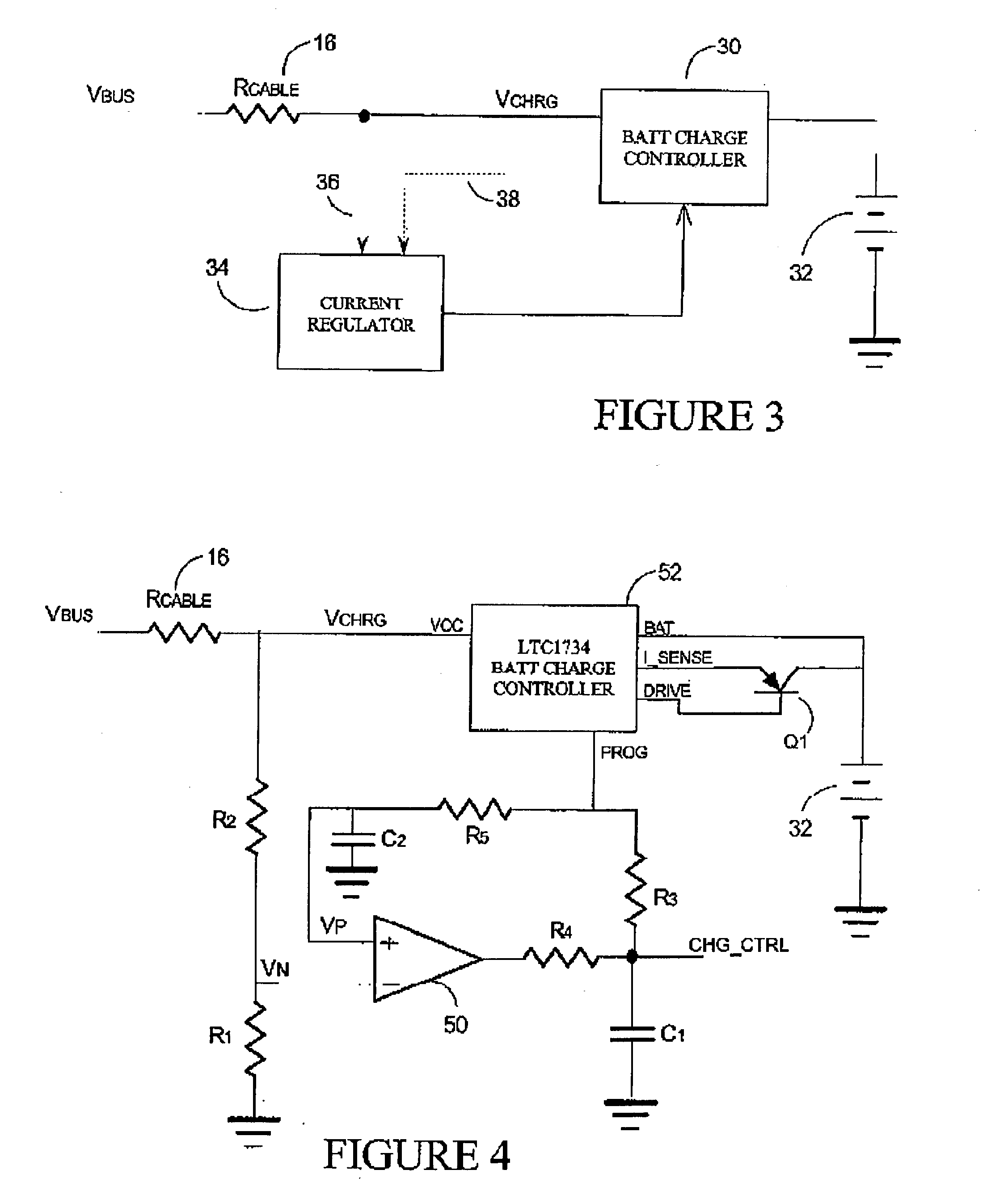
Circuit and method of operation for an adaptive charge rate power supply
InactiveUS20040164707A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingPower capabilityElectrical battery
A convenient source of charging power for portable communication devices is an integral power node of a computer data bus, such as a USB (universal serial bus) port. Unfortunately, USB ports have limited power capacity, making them generally incompatible with battery charge controllers (BCCs) which are designed to receive a steady, high capacity input. The invention provides a battery charging circuit which adjusts to the parameters of an external power supply such as a USB port by adding a regulating circuit to a standard BCC design. This regulating circuit maximizes the current drawn by the BCC, while keeping the voltage to the BCC above a preset minimum (the low voltage shut off level for the BCC). If the voltage to the BCC begins to drop, the regulating circuit reduces the current drawn, so the voltage rises and stays within the operating range of the BCC.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
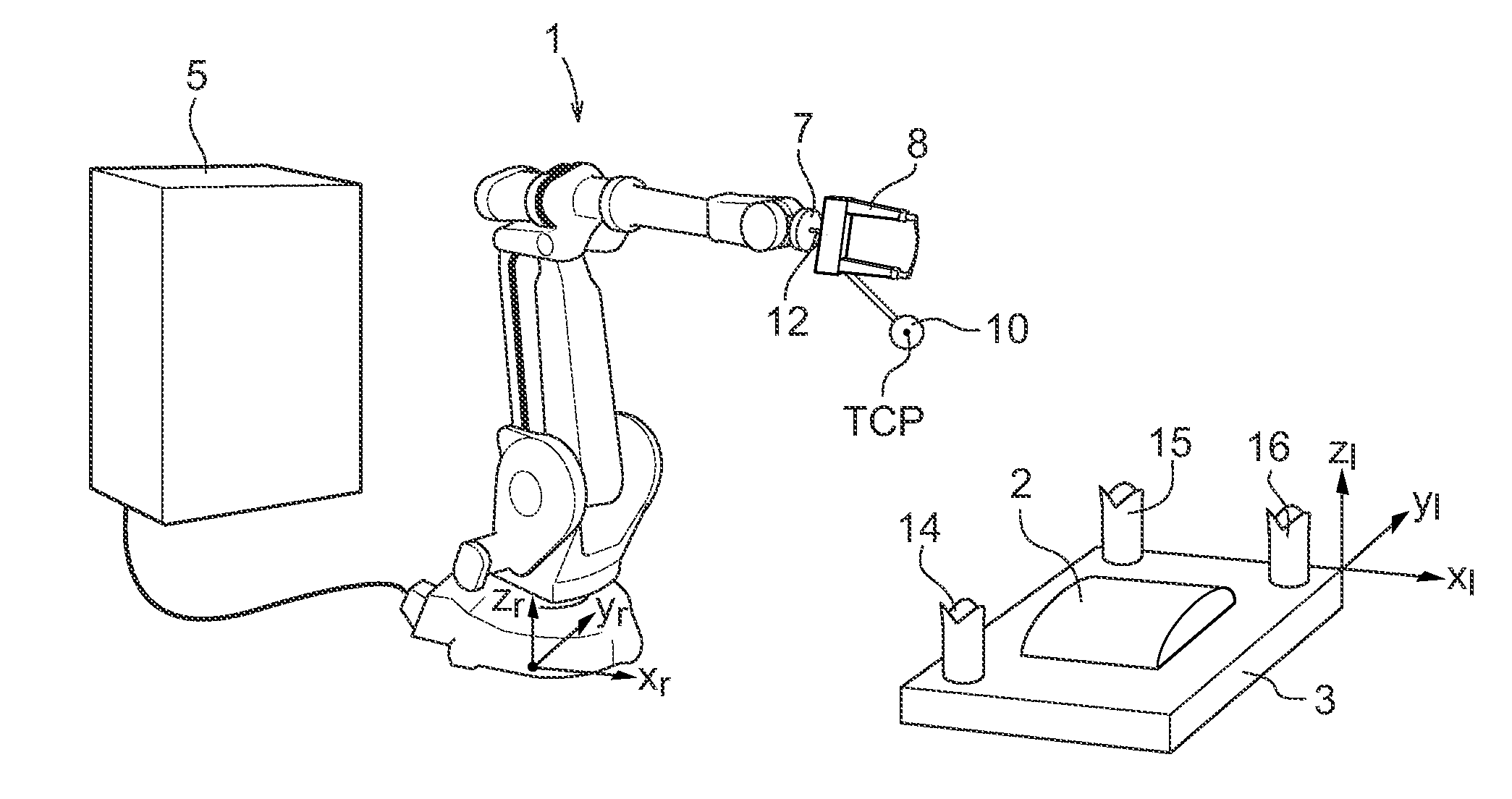
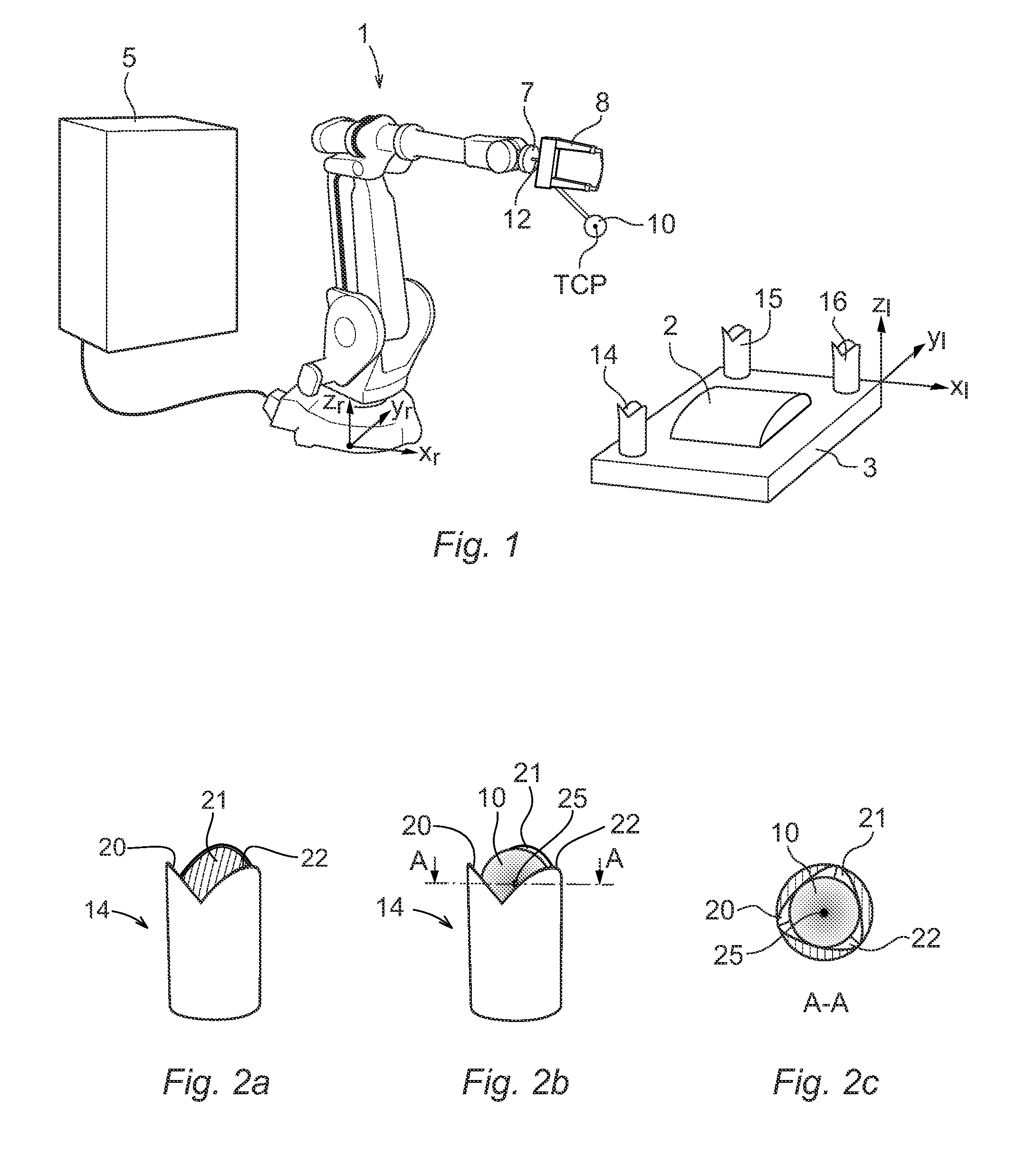
A method and system for determining the relation between a robot coordinate system and a local coordinate system located in the working range of the robot
InactiveUS20110046782A1Simple and quick and accurateProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlSituated computingEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a system for determining the relation between a local coordinate system located in the working range of an industrial robot (1) and a robot coordinate system. The method comprises: attaching a first calibration object (10) in a fixed relation to the robot, determining the position of the first calibration object in relation to the robot, locating at least three second calibration objects (14, 15, 16) in the working range of the robot, wherein at least one of the calibration objects is a male calibration object having a protruding part shaped as a sphere, and at least one of the calibration objects is a female calibration object comprising at least two nonparallel, inclining surfaces arranged to receive the sphere so that the sphere is in contact with the surfaces in at least one reference position, determining a reference position for each of the second calibration objects in the local coordinate system, for each second calibration object moving the robot until the sphere is in mechanical contact with the surfaces of the calibration object, reading the position of the robot when the sphere is in mechanical contact with all of the surfaces, and calculating the relation between the local coordinate system and the robot coordinate system based on the position of the first calibration object in relation to the robot, the reference positions of the second calibration objects in the local coordinate system, and the positions of the robot when the sphere is in mechanical contact with the surfaces of the second calibration objects.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
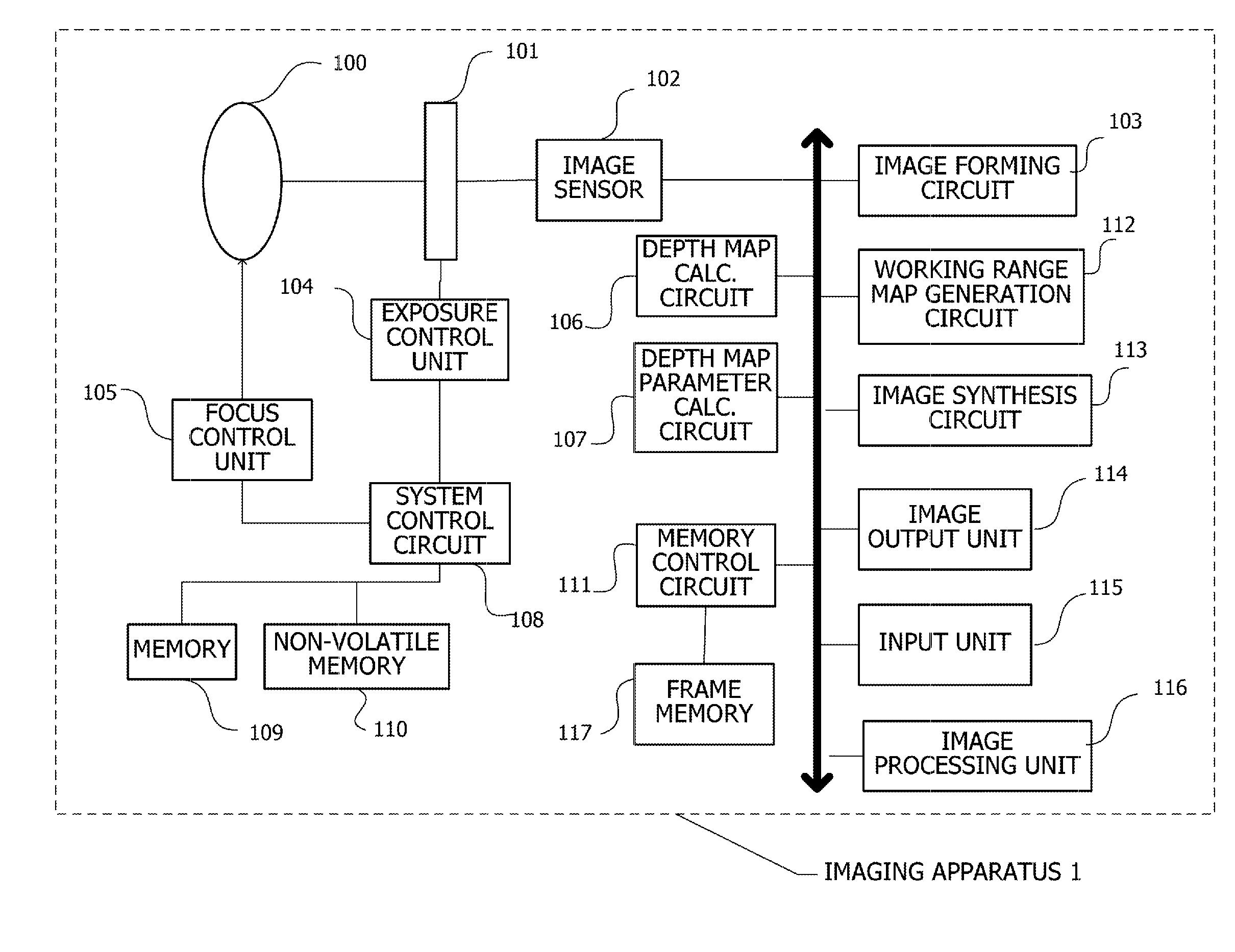
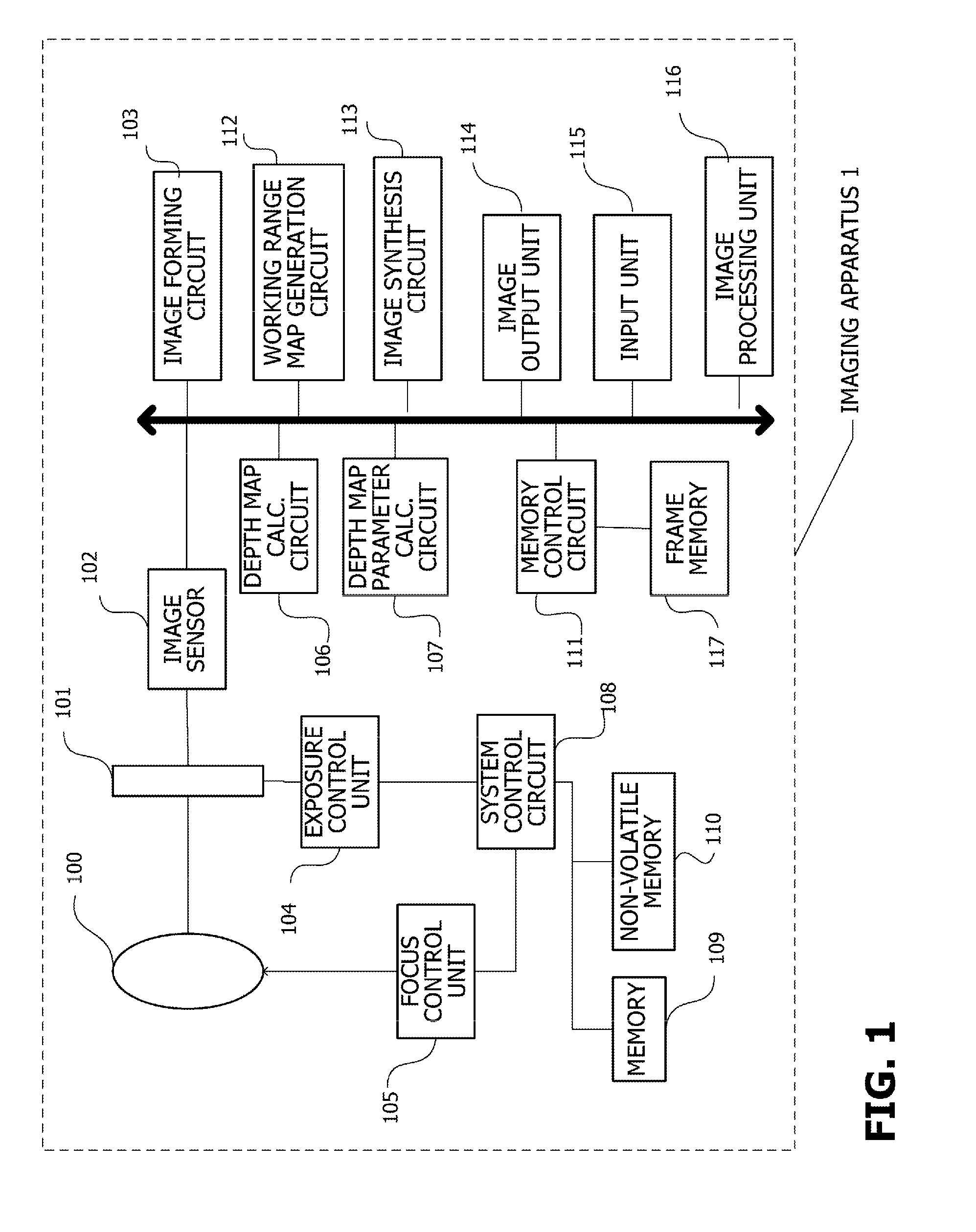
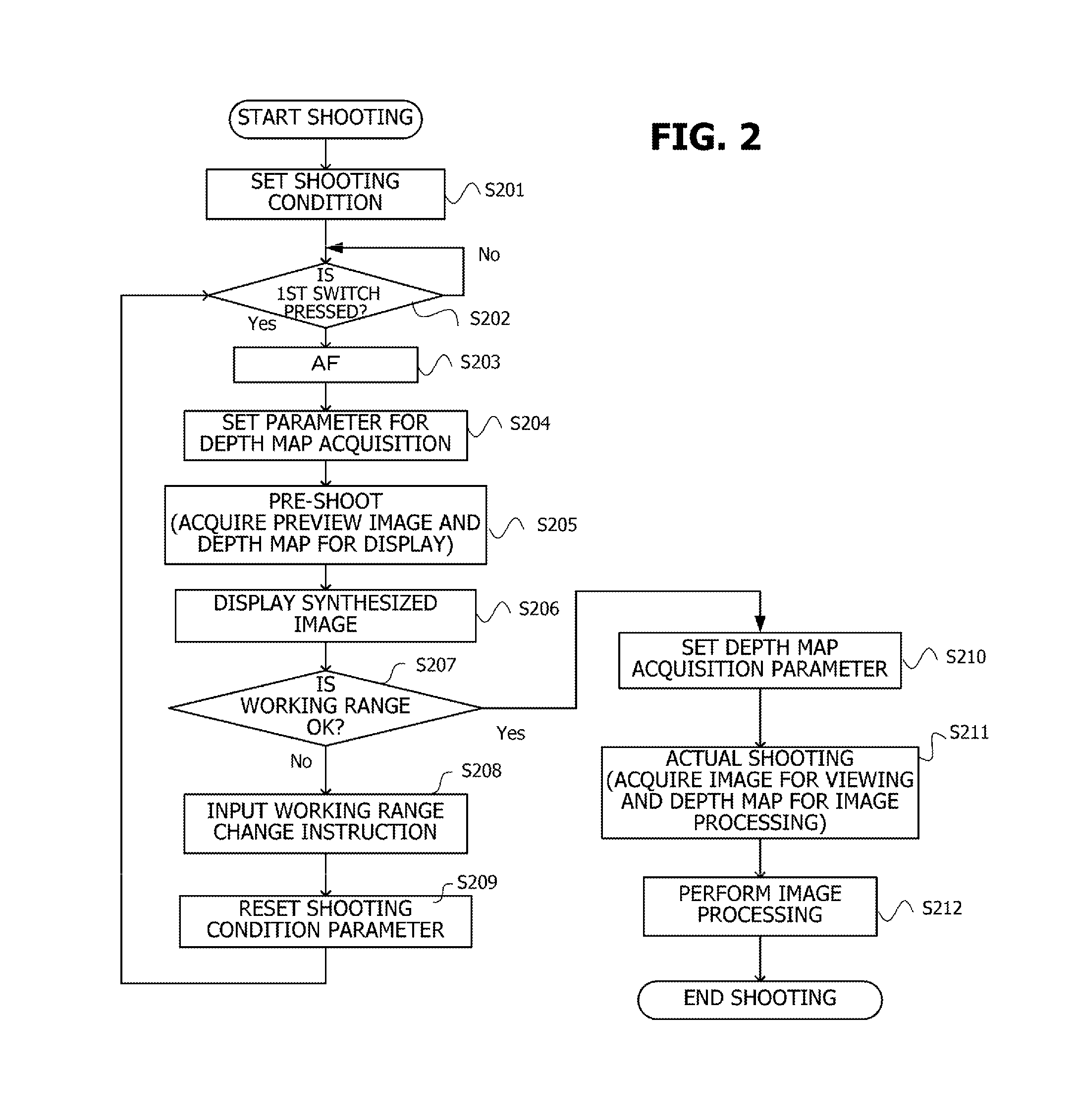
Imaging apparatus and method of controlling same
ActiveUS20150035824A1Easy to checkPossible to measureSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingImage acquisitionWorking range
An imaging apparatus comprising: an image acquisition unit configured to acquire an image; a depth map acquisition unit configured to acquire a first depth map; a working range map generation unit configured to generate a working range map showing a working range in the image on the basis of the first depth map; a synthesizing unit configured to synthesize the image and the working range map and to generate a synthesized image; and a display unit configured to display the synthesized image.
Owner:CANON KK
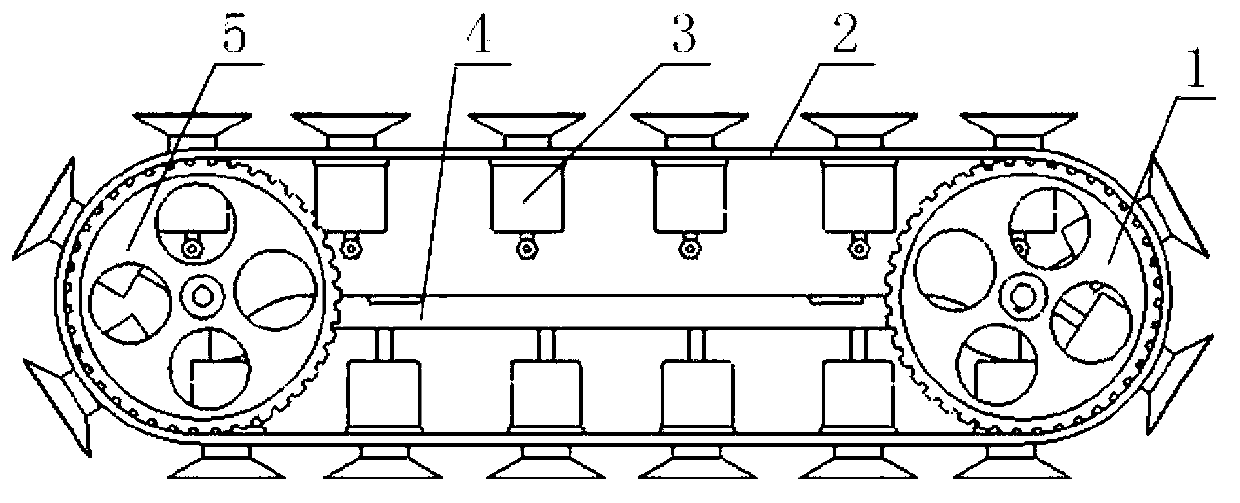
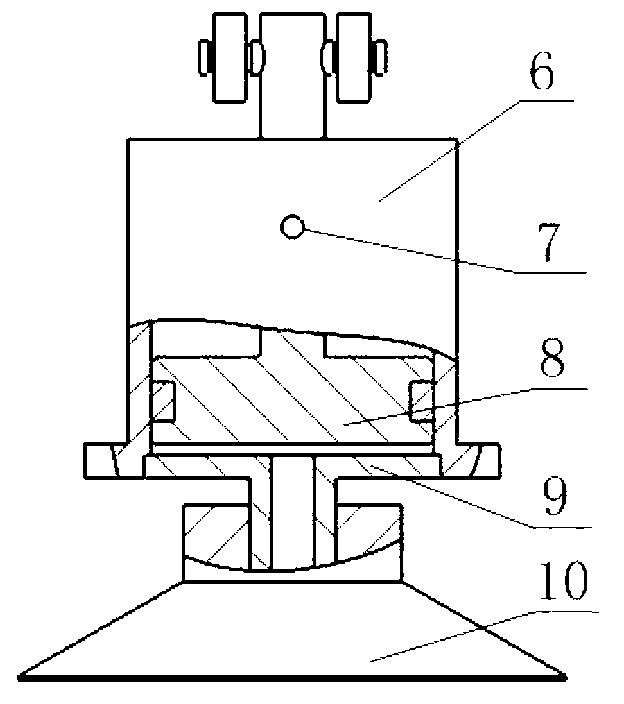
Cam-type negative pressure adsorption wall-climbing robot
The invention discloses a cam-type negative pressure adhering wall-climbing robot. By means of an inverse cam mechanism and a passive vacuum absorption mechanism, the negative pressure absorption function of a sucker is achieved and the limitation brought by a vacuum source device is eliminated. The adsorbing and detaching process of the vacuum sucker is easy through a mechanical structure. The structure is simple and the absorption force of the sucker is strong due to the negative pressure. By means of an adsorbing steering mechanism, the limitation of the minimum turning radius of a tracked robot is avoided and the pivot steering function is achieved. Adsorbing moving mechanisms are positioned on the two sides of a main baseboard of the robot; a steering power mechanism is fixed on the main baseboard; steering wheel components are connected with the steering power mechanism through flexible threaded rods; and by adjusting the position of a cam track groove, a steering auxiliary mechanism mounted on the main baseboard enables the adsorbing steering mechanism to work. The linear moving portion is connected with the linear steering portion through a screw transmission manner, the moving process of the robot is achieved through reasonable step arrangements, so that the cam-type negative pressure adsorption wall-climbing robot is easy to control and applicable to wide working range.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Optical adjustment for increased working range and performance in electro-optical readers
ActiveUS7201318B2Improve performanceIncrease rangeProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementOptical readerVoltage
Working range is increased in an electro-optical reader or an imager for reading indicia by applying a voltage to a variable lens to change the shape of a liquid therein.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for mounting a pneumatic tire
Method and apparatus for mounting a pneumatic tire Method for mounting a pneumatic tire (5) on a well base rim (26) of a motor vehicle wheel, in which the pneumatic tire (5) is grasped by means of a manipulator (1), brought up to a rim (26) held in a clamping device (27) and slipped with at least the one tire bead (20) facing the rim over a rim flange (28) by controlled movement of the manipulator (1). The apparatus suitable for this purpose comprises a manipulator (1) with an articulated arm (3) movable in three directions, which bears at its free end a gripper (2) for gripping and holding pneumatic tires (5), and a first mounting station (25) with clamping means (27) for releasably holding a rim (26), wherein the mounting station (25) is arranged within the working range of the manipulator (1).
Owner:SCHENCK ROTEC GMBH
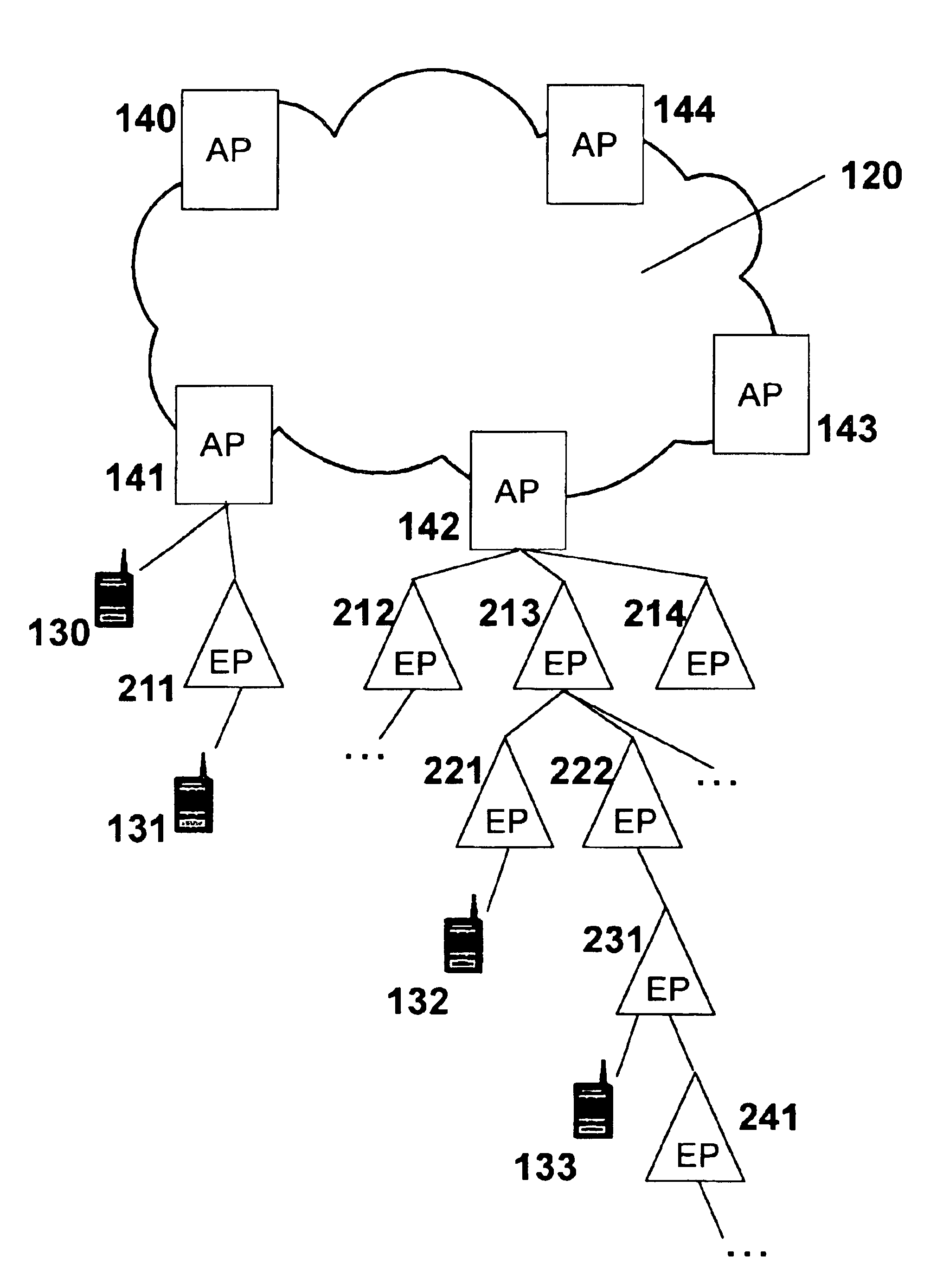
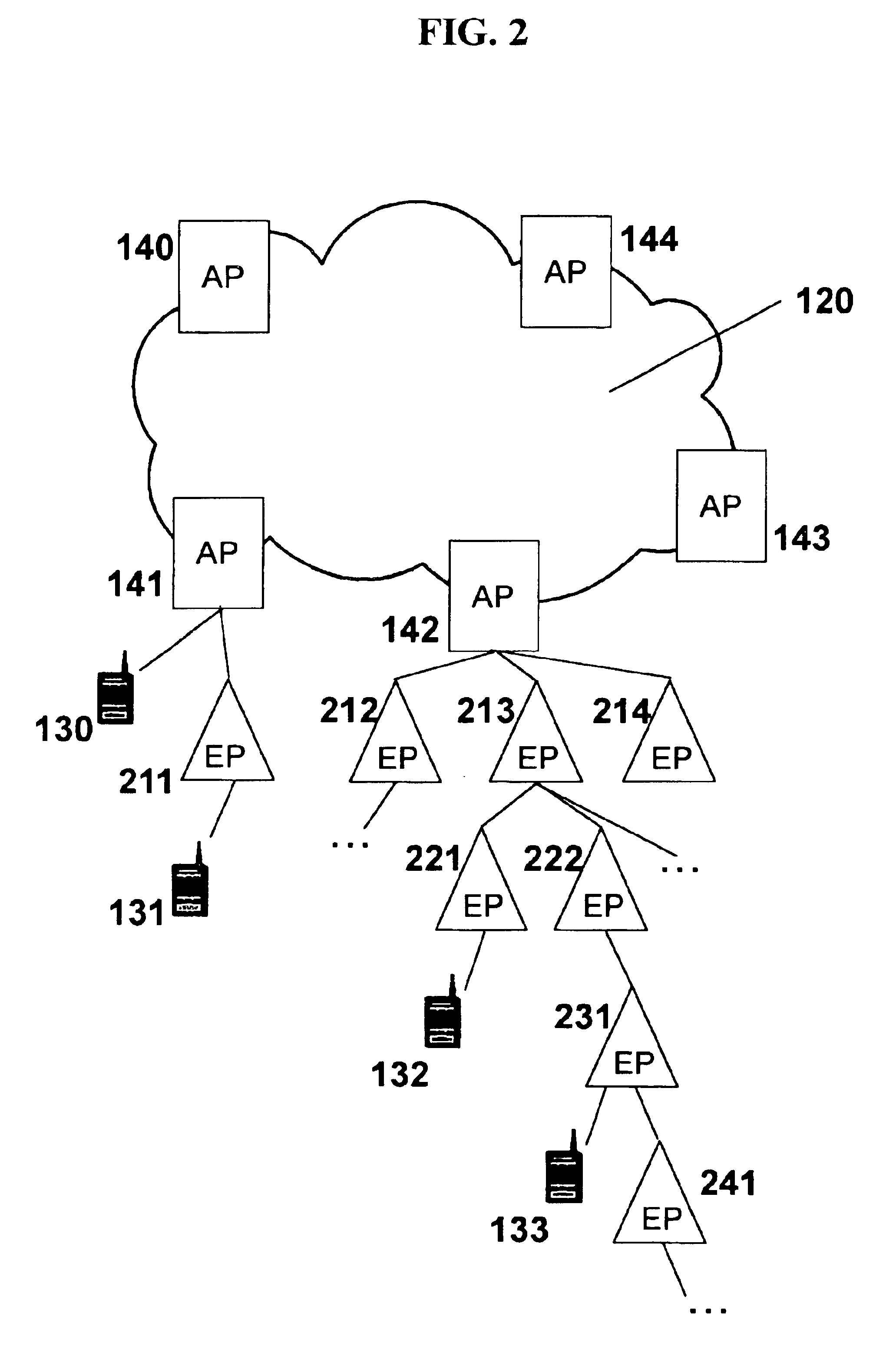
Extension mechanism and technique for enabling low-power end devices to access remote networks using short-range wireless communications means
InactiveUS6885847B1Increase the number ofMinimal added installationPower managementSpatial transmit diversityPointing deviceExtension mechanisms for DNS
The present invention provides methods, systems, devices, and computer program instructions for enabling low-power wireless devices (such as wireless telephones and personal digital assistants, or PDAs) to connect to a fast wired or wireless voice / data network. A novel relay point device, referred to as an “extension point”, is defined that flexibly extends the effective reach of network access points. Use of extension points enables the network infrastructure to be expanded (and subsequently re-configured, if necessary) simply and cost-effectively, requiring little or no additional physical wiring. The defined techniques provide an infrastructure that is scalable, supporting a large number of end users without substantial degradation to connection establishment time and data rates. Using the disclosed techniques, end devices are able to reach network services, and to communicate with other end devices, beyond the nominal working range of these devices and without limitation to the numbers of such devices.
Owner:REEFEDGE
System for linearly adjusting slope compensation voltage slope
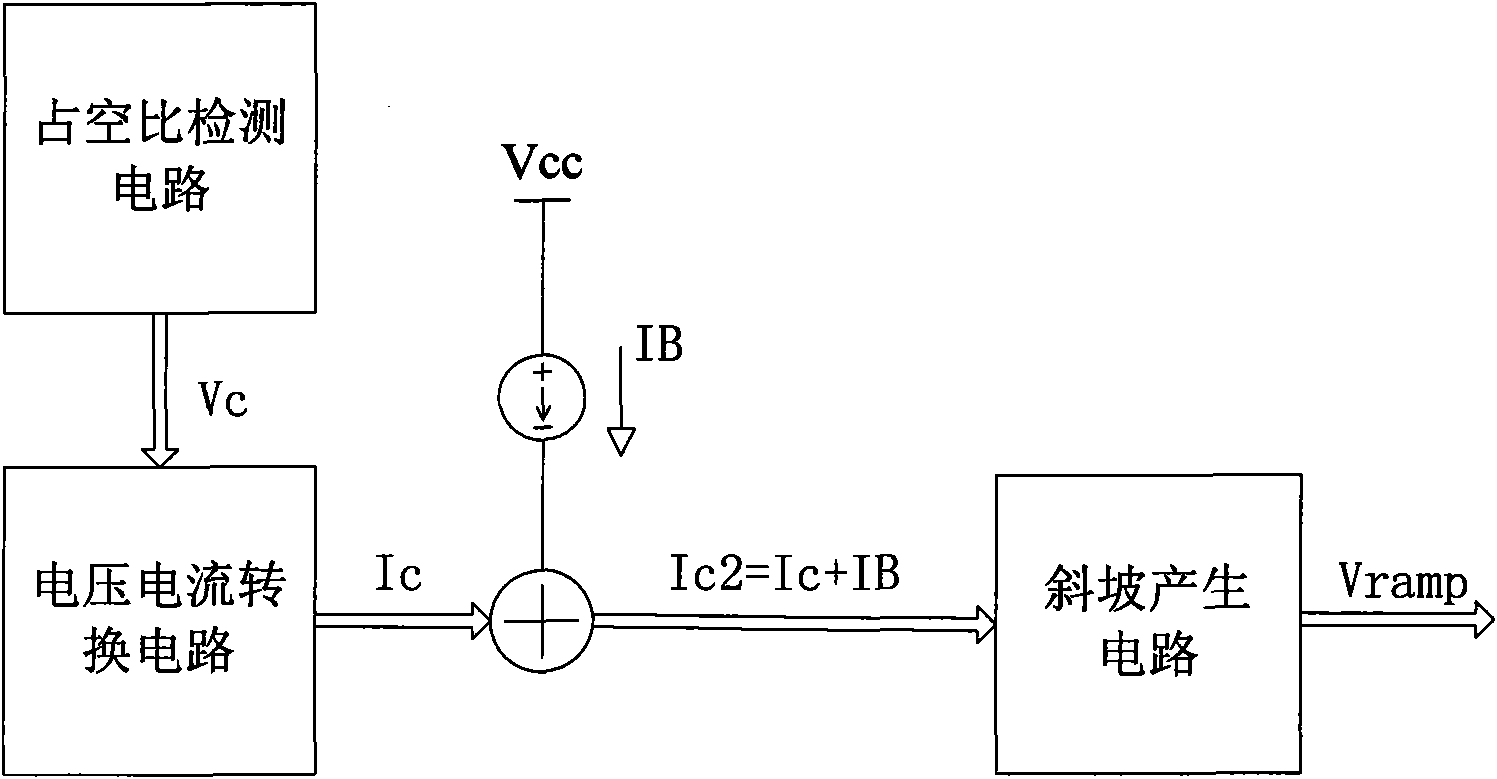
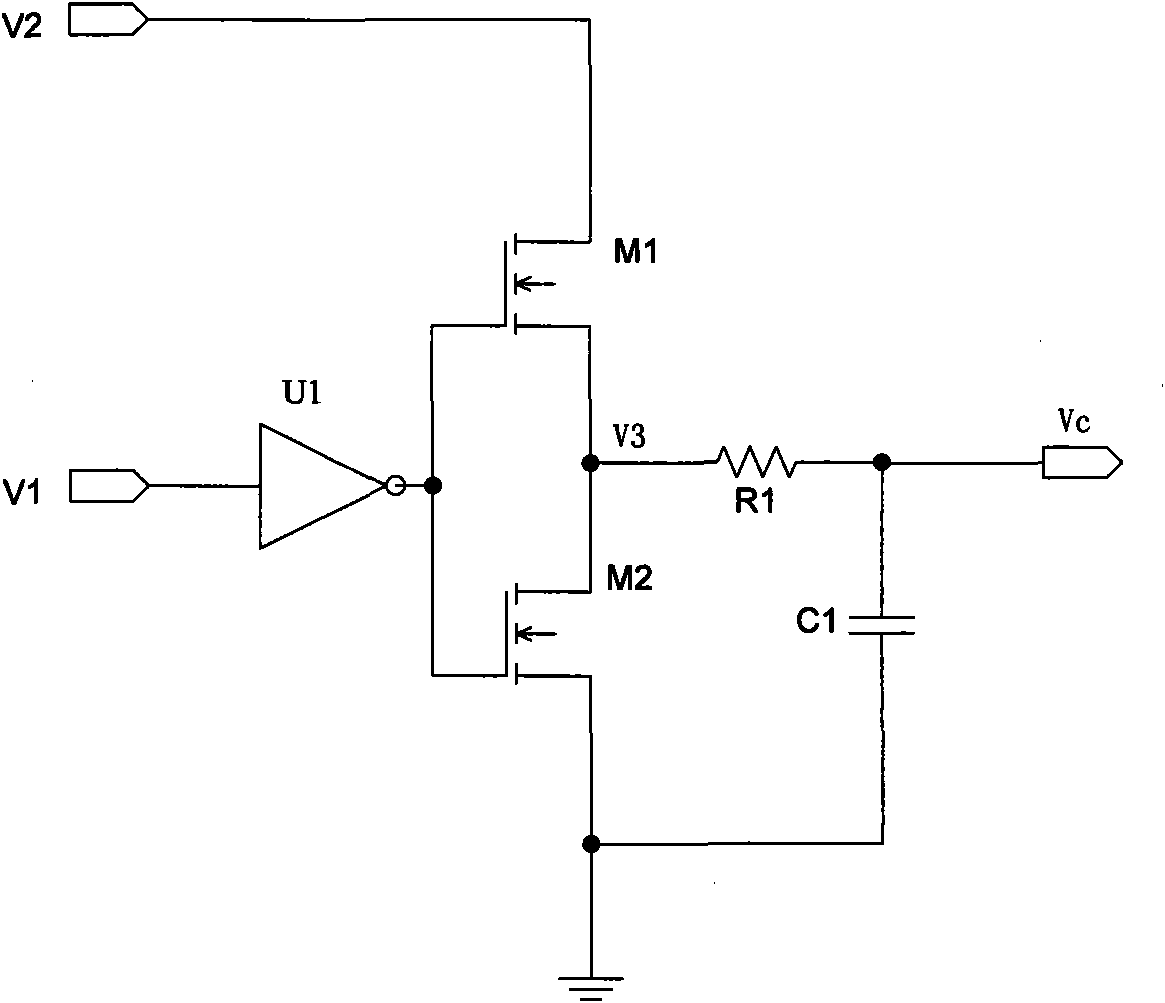
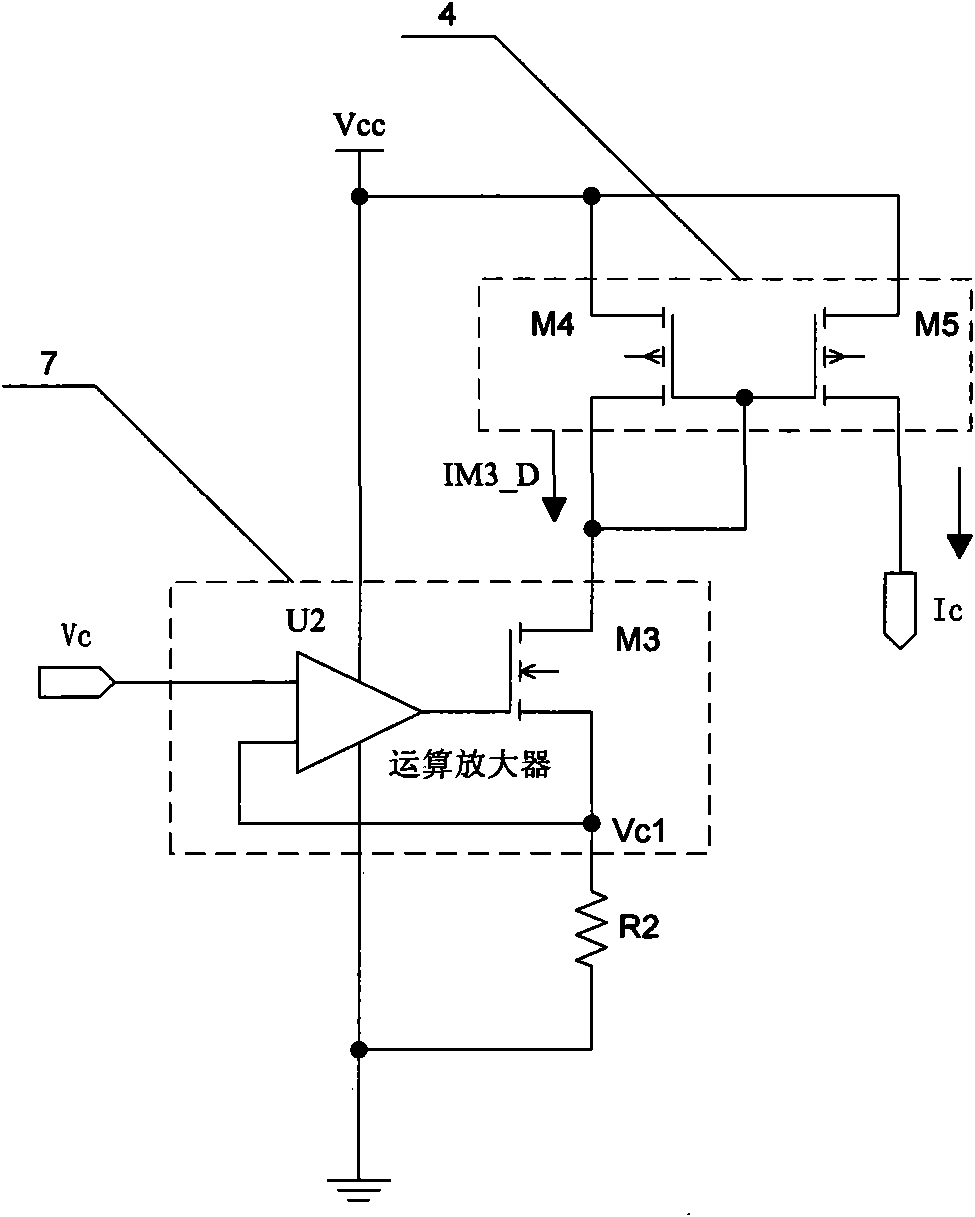
ActiveCN101795070AIncrease loading capacityEasy to adjustDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationReference currentLinear relationship
The invention discloses a system for linearly adjusting the slope compensation voltage slope. With a duty factor detection circuit, a voltage and current conversion circuit and a slope generation circuit, a duty factor of a switch signal in a peak current control mode chip is converted into a voltage signal forming a linear relationship with the duty factor by using the duty factor detection circuit, the voltage signal is linearly converted into a first current signal by using the voltage and current conversion circuit, and a second current signal formed by superposing the first current signal and a reference current source passes through the slope generation circuit to obtain slope compensation voltage, so that the invention achieves the function of linearly adjusting the slope of the slope compensation voltage according to the duty factor of the switch signal in the peak current control mode chip, well solves the problems that the peak current control mode chip is easy to generate over compensation during low duty factor and generate under compensation during high duty factor and ensures that the chip has favorable loading capacity and load regulating capacity in the work range of all duty factors.
Owner:NINGBO SEMICON INT CORP
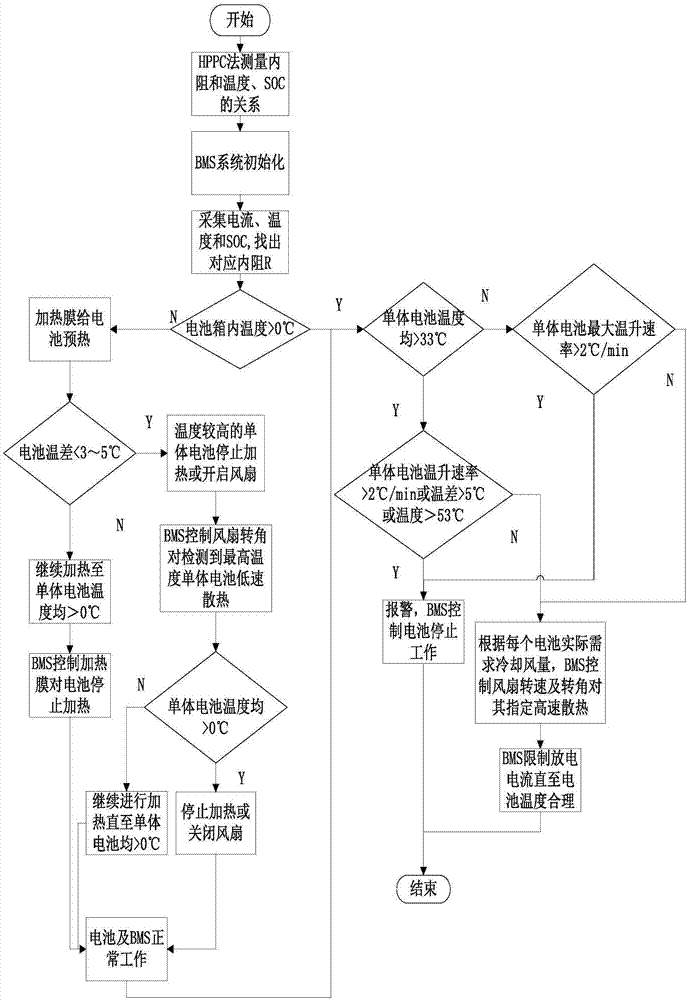
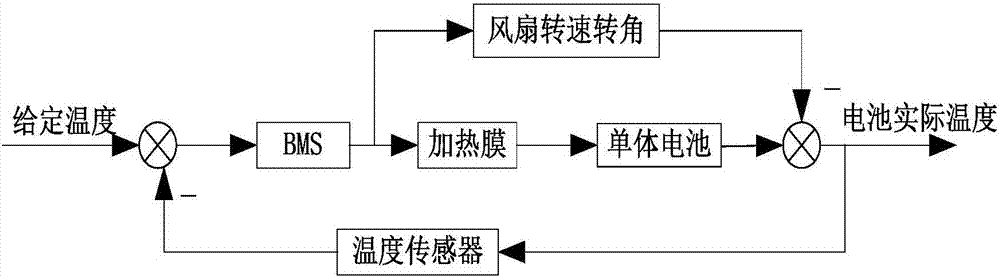
Electric automobile battery pack heat management and temperature balancing control method
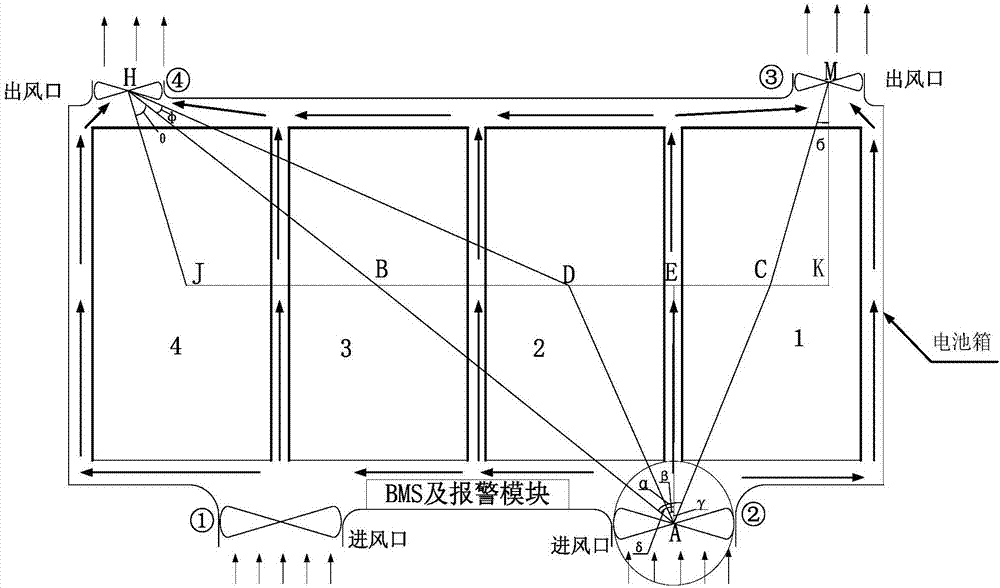
ActiveCN107579308AAvoid excessive temperature riseAvoid excessive local temperature differencesSecondary cellsVehicular energy storageTemperature controlHeat management
The invention discloses an electric automobile battery pack heat management and temperature balancing control method. According to the electric automobile battery pack heat management and temperaturebalancing control method, a battery module, a battery box, a BMS and a warning device are provided; a heating film is arranged at the periphery of the battery module; a plurality of temperature sensors are distributed in the battery box equidistantly and a plurality of fans capable of controlling rotation angles are arranged in the battery box; and the BMS evaluates the stage of the battery by monitoring the temperature of the battery pack through the temperature sensors, and performs heat management on the battery pack by taking 0 DEG C, 33 DEG C and 53 DEG C as temperature control thresholdvalues and combining temperature increasing rate and temperature difference as judgment conditions, wherein the temperature of the battery pack is maintained within the work range by the measures of selectively heating the heating film as well as accurately controlling the rotation angle of the fans, the starting time and the cooling air quantity. By the method, too high temperature increment andtoo large temperature difference of the battery are effectively avoided, battery temperature change stability and balanced characteristics are guaranteed and the service life of the lithium battery isprolonged.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Synthesis decoding and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7416125B2Character and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesComputer graphics (images)Barcode
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Method of adjusting the working range of a multi-analyte assay
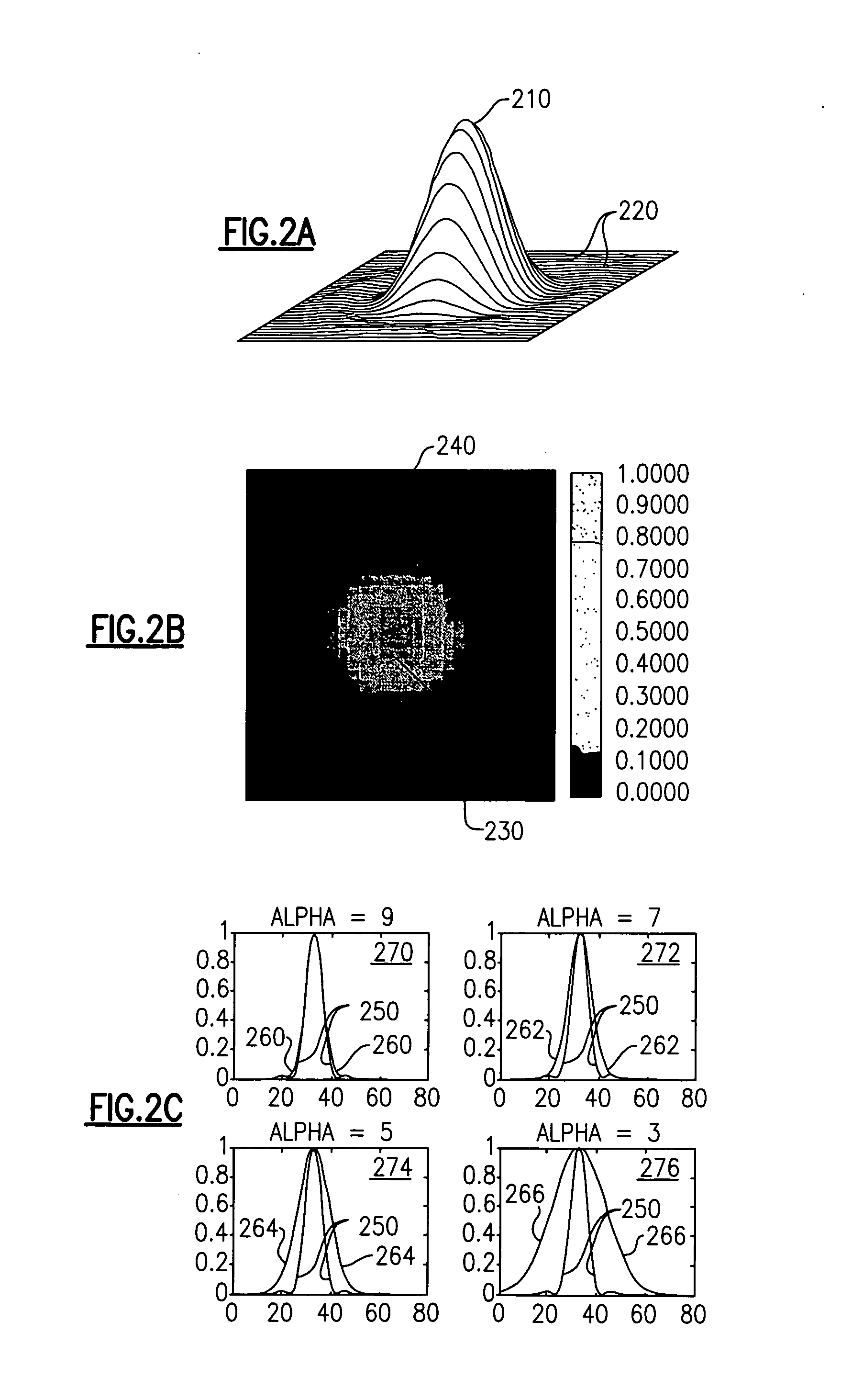
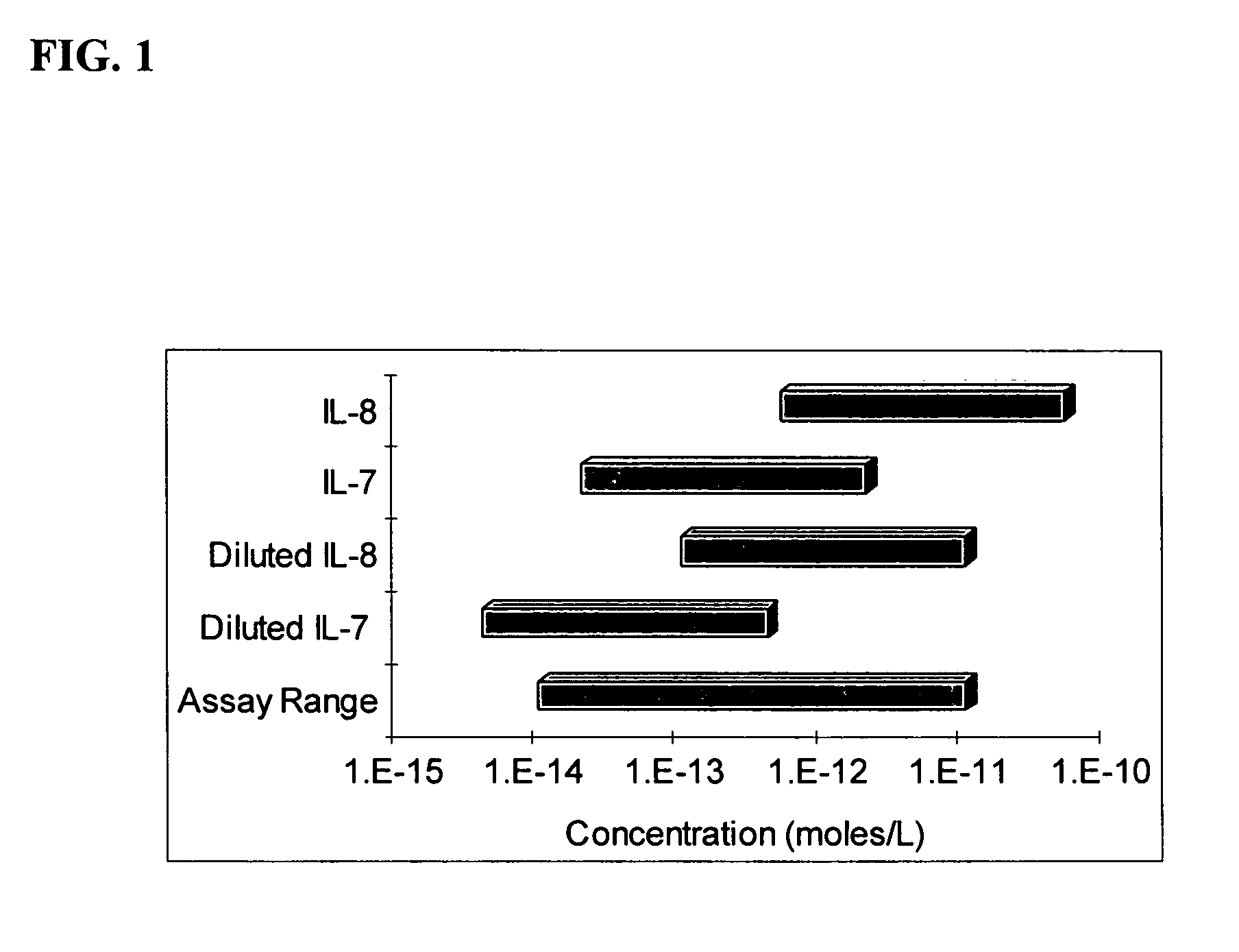
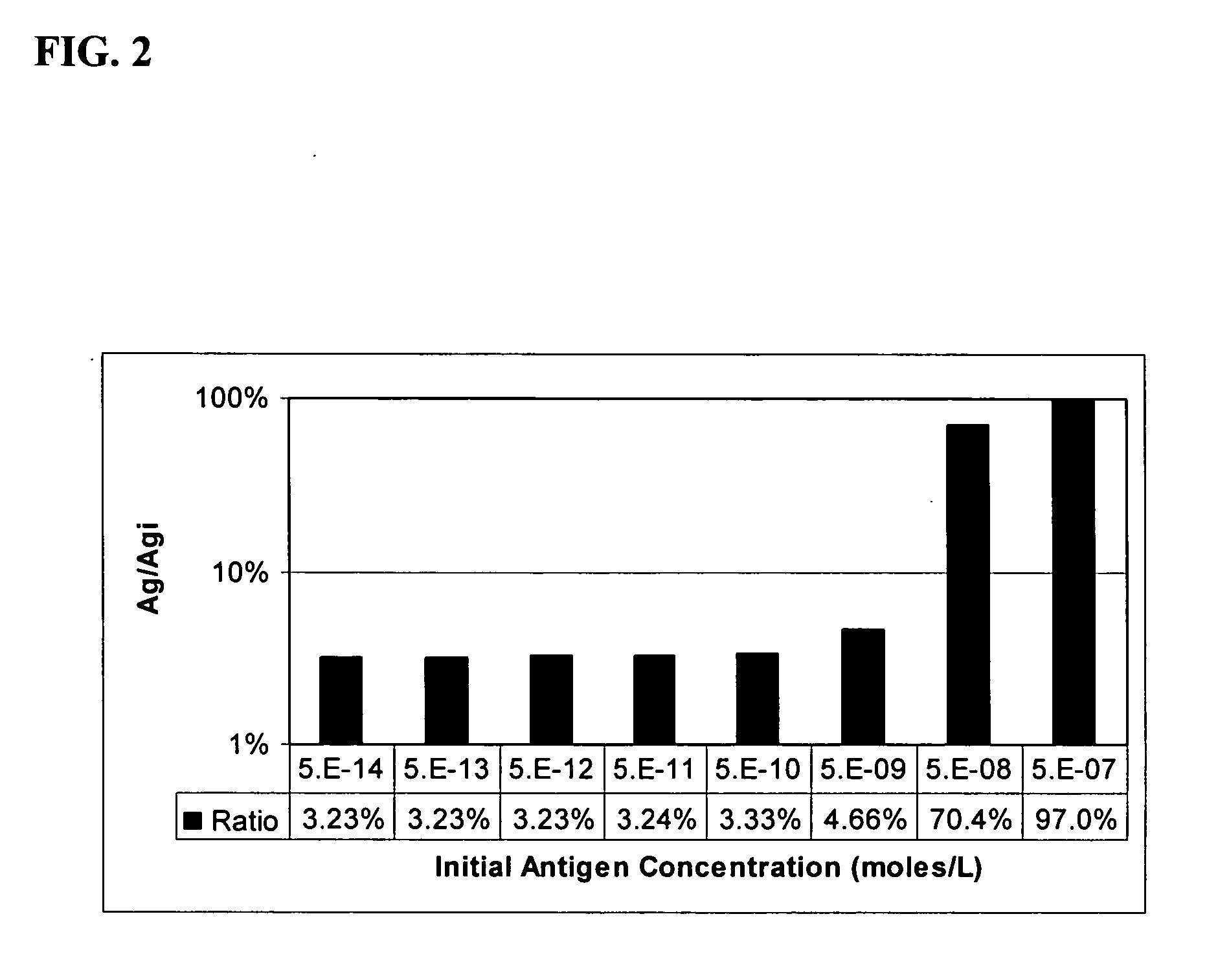
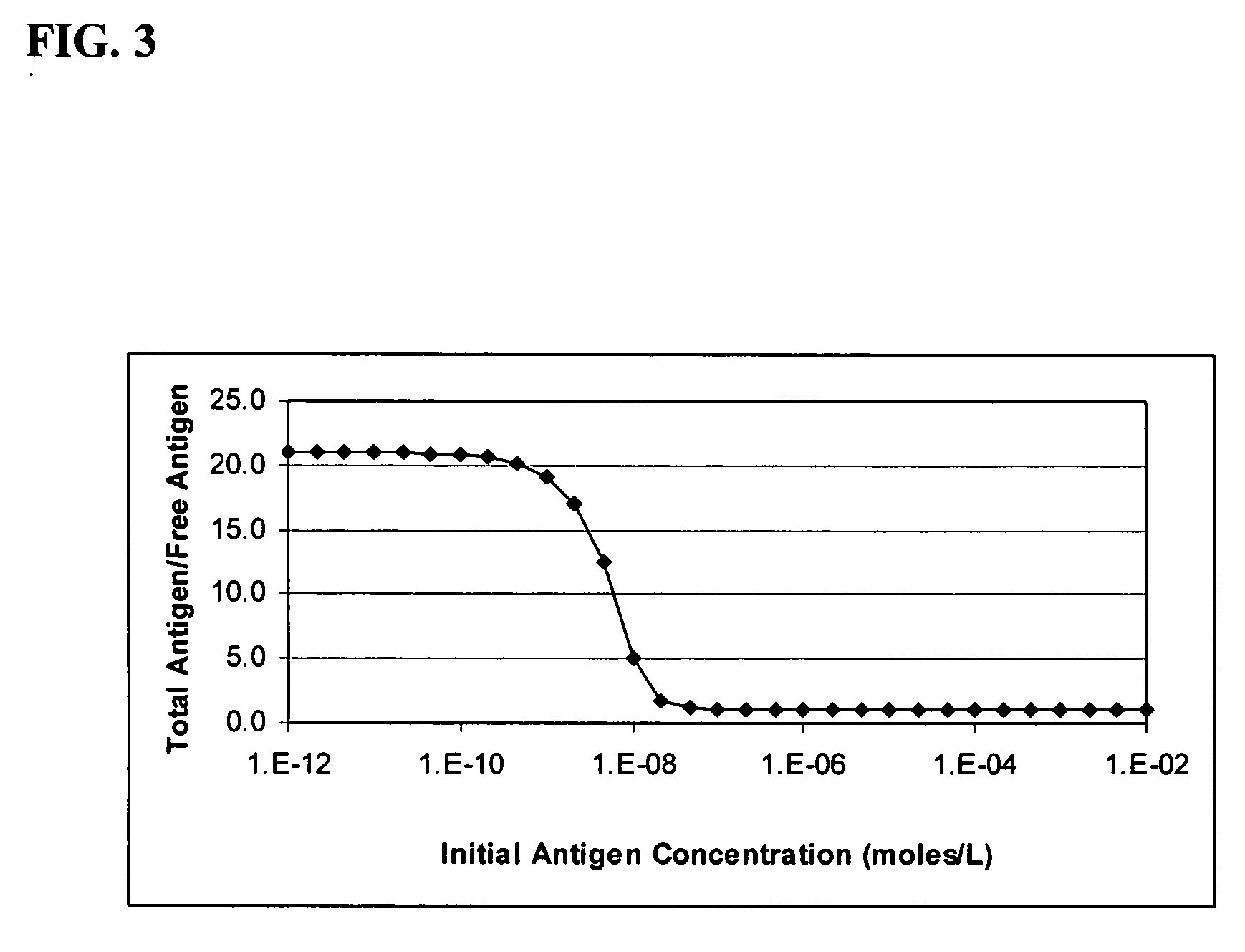
InactiveUS20060177873A1Reduce available analyte concentrationHinder availabilityBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsHigh concentrationMulti analyte
The invention features a method of adjusting the concentration of at least one but not all of a plurality of analytes in a fluid sample to match a known working range of detection of an analyte assay system, where each of the plurality of analytes may or may not be present within an expected initial concentration range having a high end and a low end, and at least one analyte has a high end expected concentration range that exceeds the high end of the working range of the assay system. The expected concentration of the high concentration analyte is adjusted by a proportional scaling constant, α, so that the high end of the adjusted expected concentration range is less than or equal to the high end of the working range, without adjusting the expected concentration range of at least one other of the plurality of analytes. Adjustment is preferably accomplished by adding to the solution phase of the assay one or more scaling agents, each scaling agent binding with specificity to an analyte and thereby preventing it from being detected by the assay system, e.g., by competing with binding to immobilized capture agent. This scaling method contrasts with prior methods, in which a concentration of available analyte is offset by a fixed amount to adjust the detectable threshold of the assay. Here, the amount of scaling agent is proportional to a scaling coefficient, and the scaling agent is present in the solution phase of the assay at high concentrations relative to analyte. Due to the equilibrium conditions established by the laws of mass transfer, the amount of free analyte remaining in solution in the presence of scaling agent is predictable and finite, and can be measured as a quantitative indicator of the initial concentration of the analyte in the sample.
Owner:COURTAGEN LIFE SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com