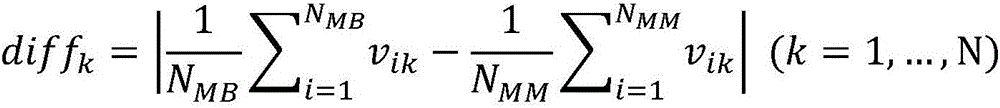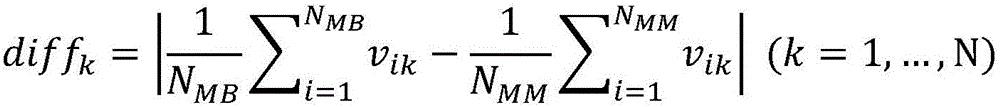Patents
Literature
879 results about "Thyroid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid, is an endocrine gland in the neck, consisting of two lobes connected by an isthmus. It is found at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones, namely the two thyroid hormones (thyroxine/T₄ and triiodothyronine/T₃), and calcitonin. The thyroid hormones primarily influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, but they also have many other effects, including effects on development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis.
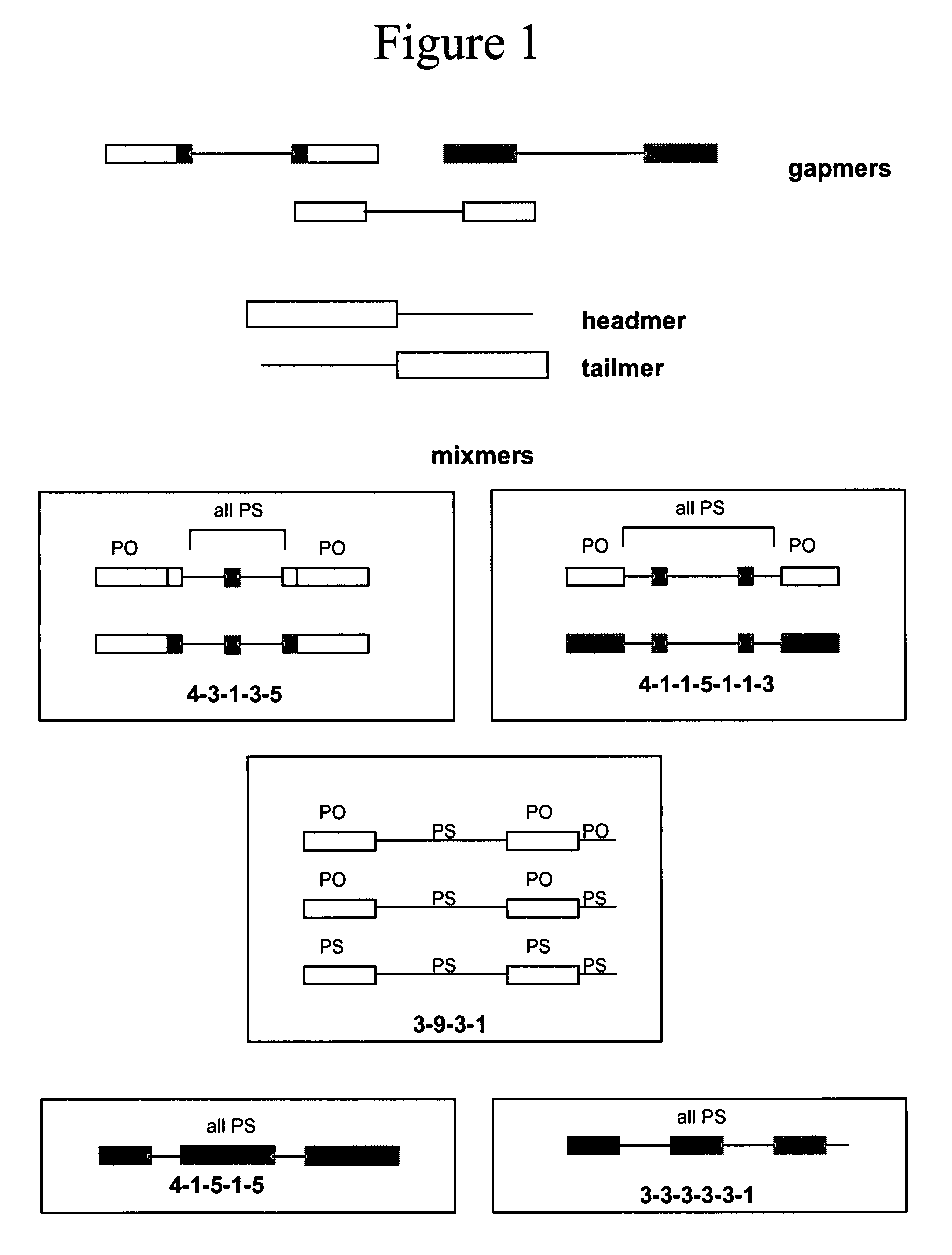
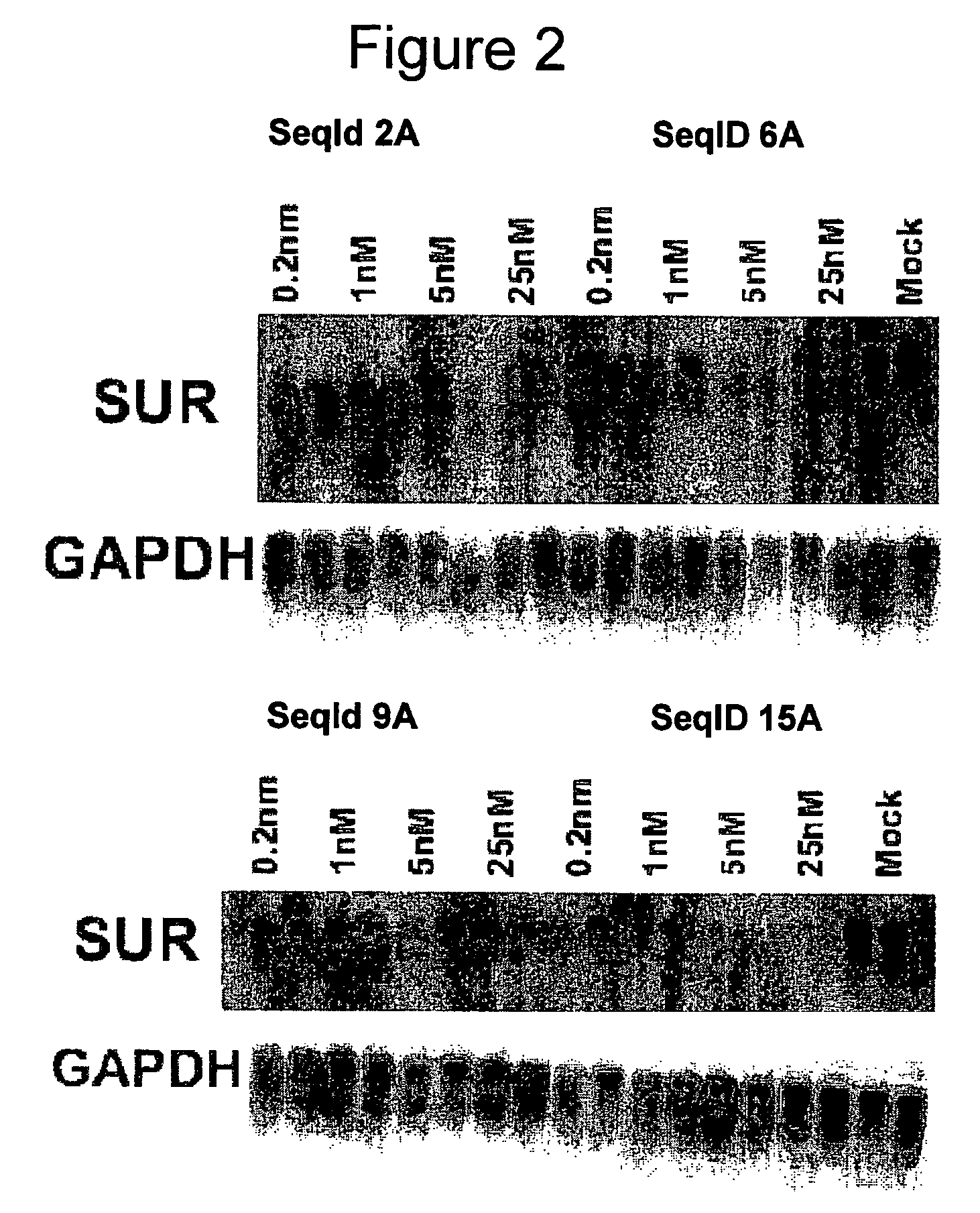
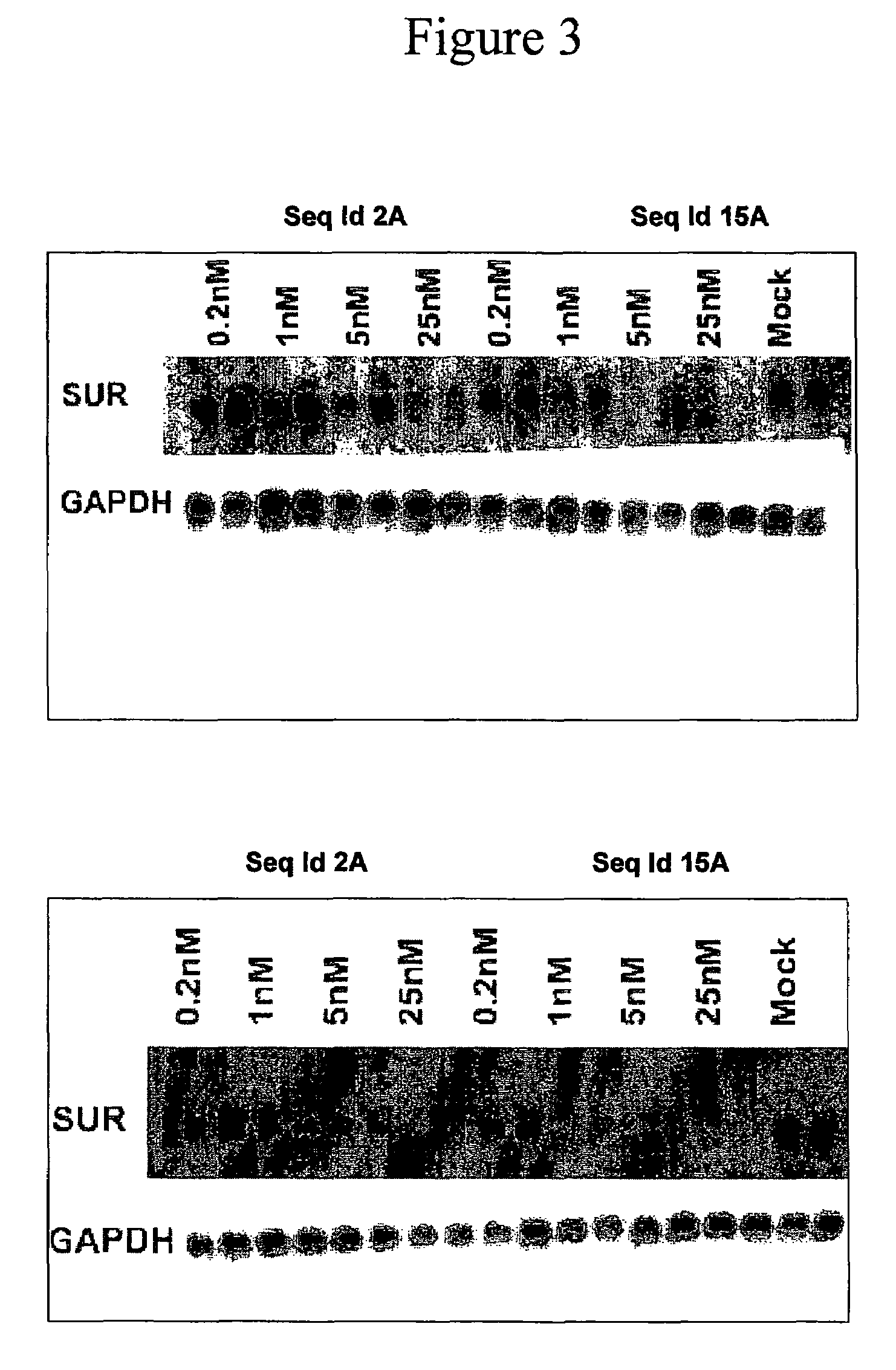
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
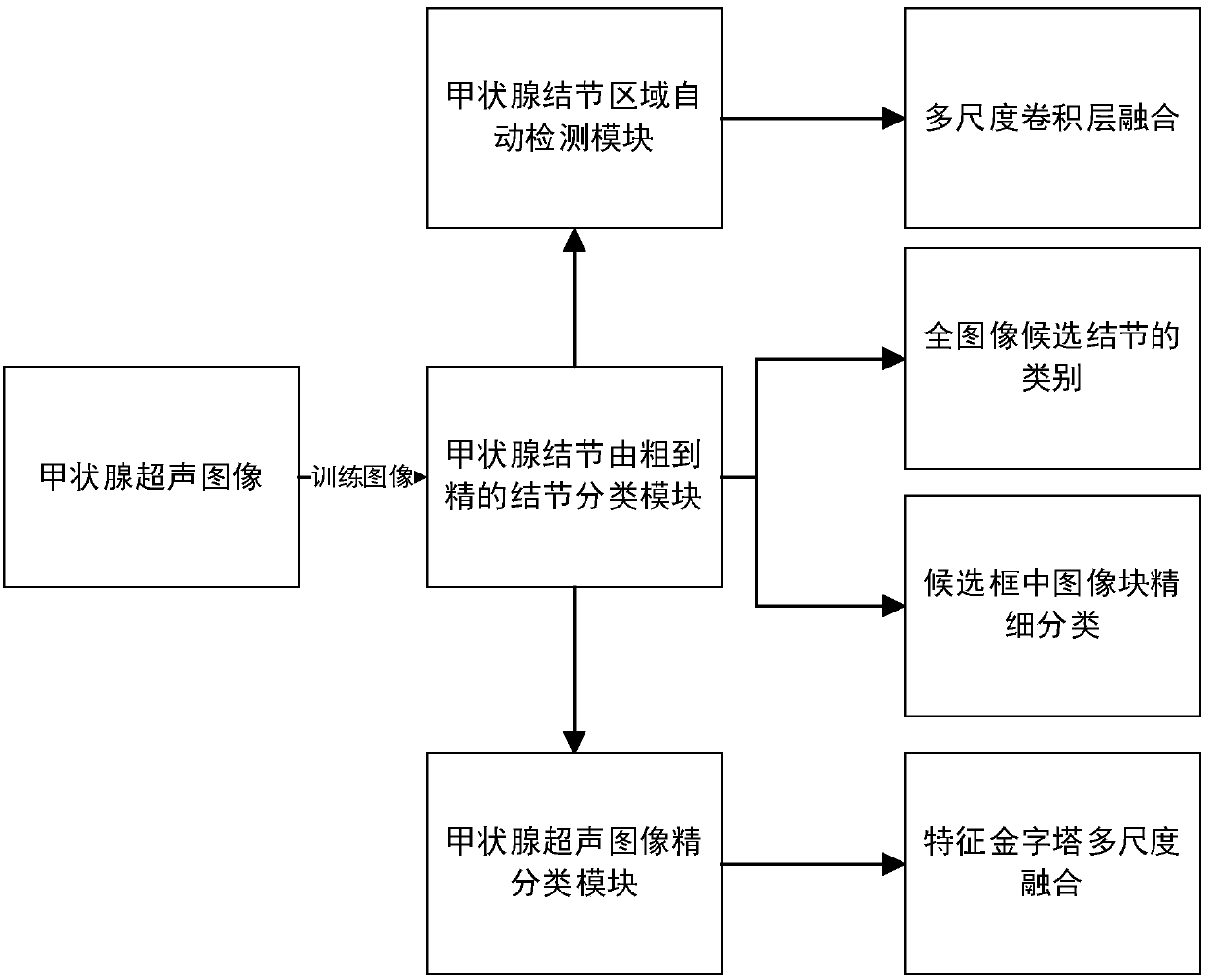
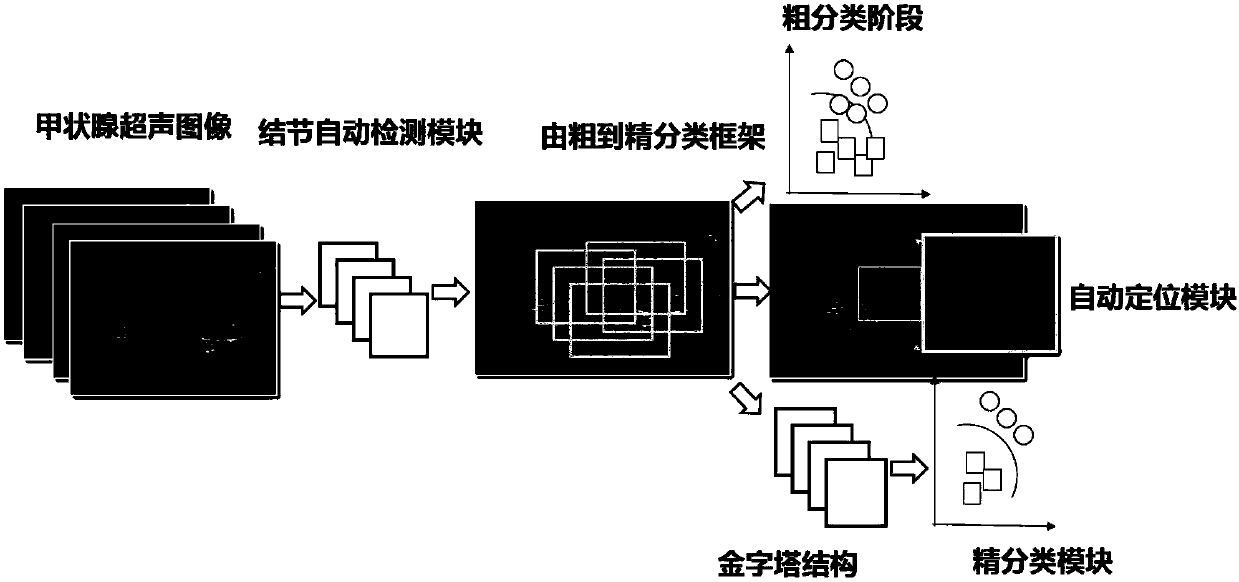
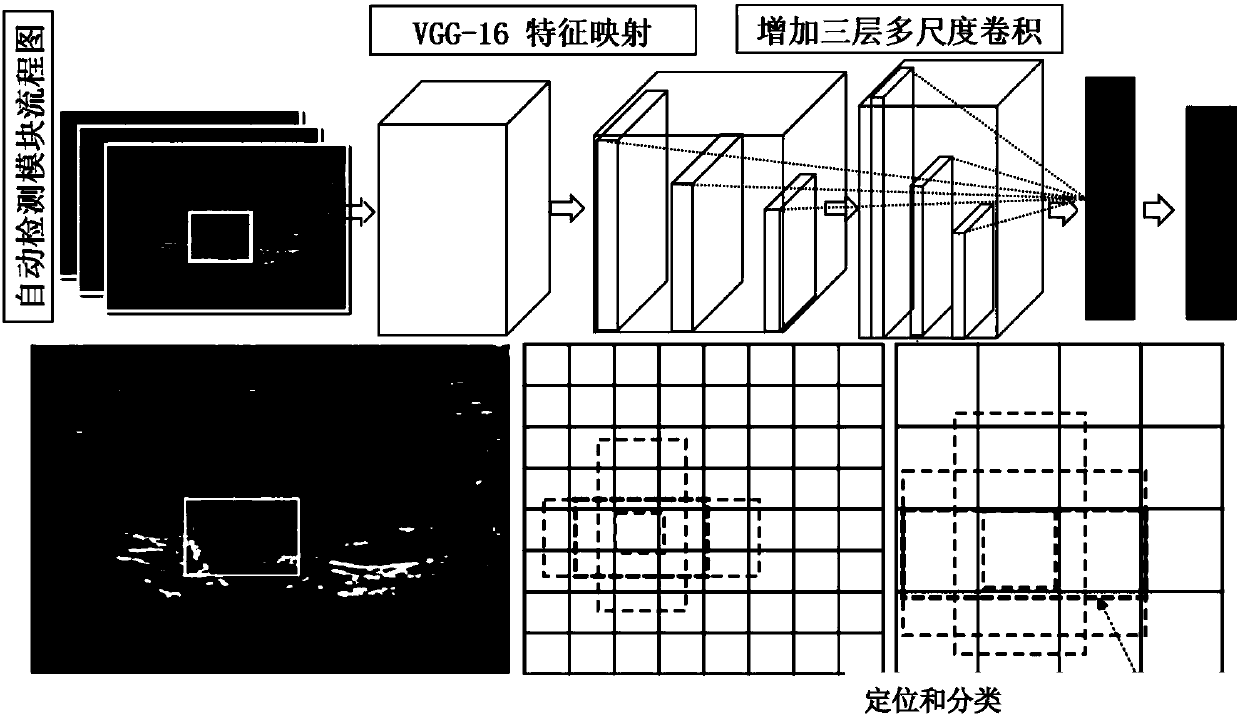
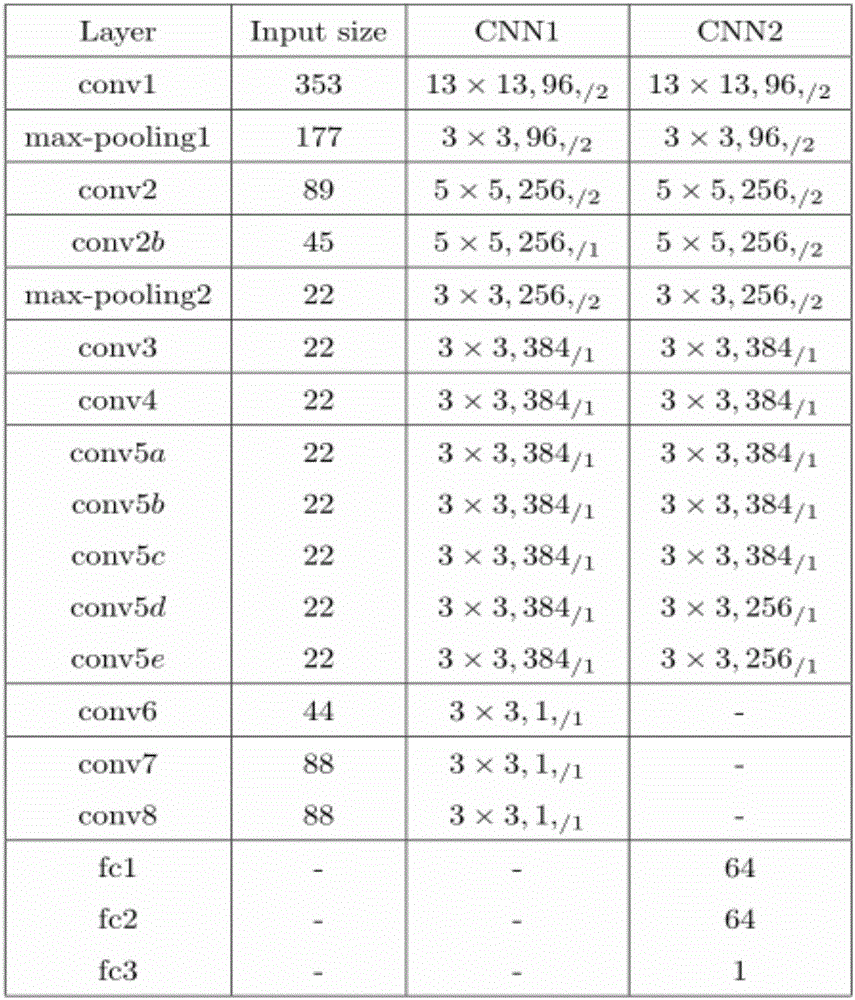
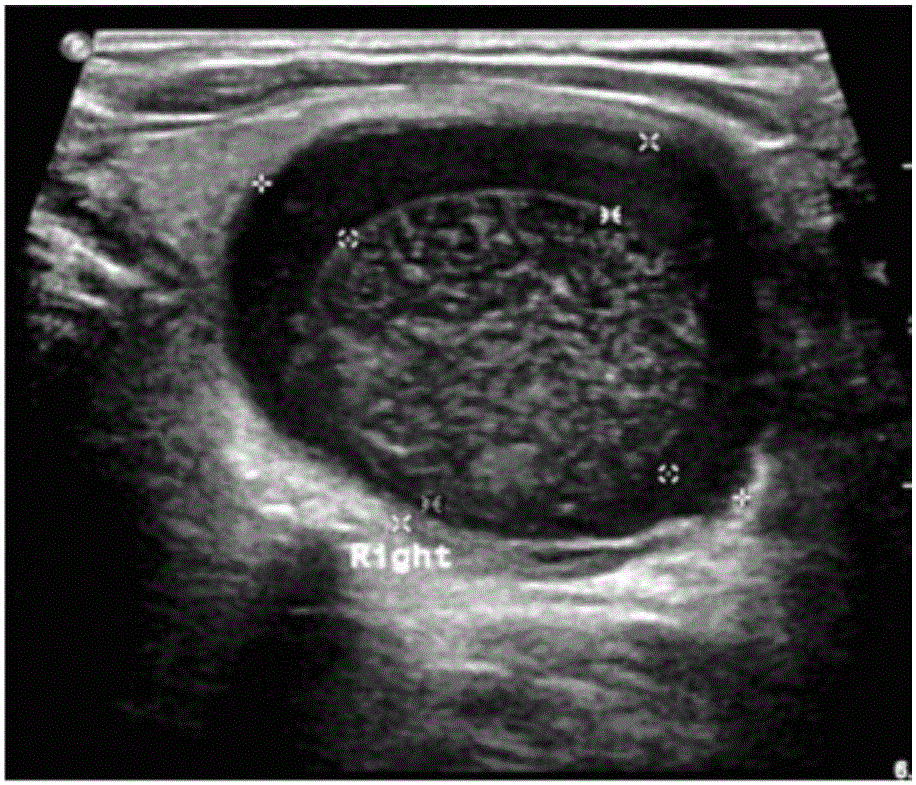
Thyroid ultrasound image nodule automatic diagnosis system based on multi-scale convolutional neural network
ActiveCN107680678AAccurate detectionAdapt to polymorphic automatic detectionImage enhancementImage analysisSemantic featureGlobal information
The invention provides a thyroid ultrasound image nodule automatic diagnosis system based on a multi-scale convolutional neural network. The system includes a thyroid nodule coarse-to-fine classification module, a thyroid nodule region automatic detection module, and a thyroid nodule fine classification module. The size features of different sensing regions are extracted through a multi-scale feature fusion convolutional neural network, and then, the context semantic features of a thyroid nodule can be extracted according to local and global information, and the thyroid nodule can be automatically located. Through multi-scale coarse-to-fine feature extraction based on a neural network and the design of a multi-scale fine classification AlexNet of a pyramid structure, the position of a focus and the probability that the focus is benign or malignant can be accurately predicted, doctors can be assisted in diagnosing a thyroid focus, and the objectivity of diagnosis is improved. The systemhas the characteristics of good real-time performance and high accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
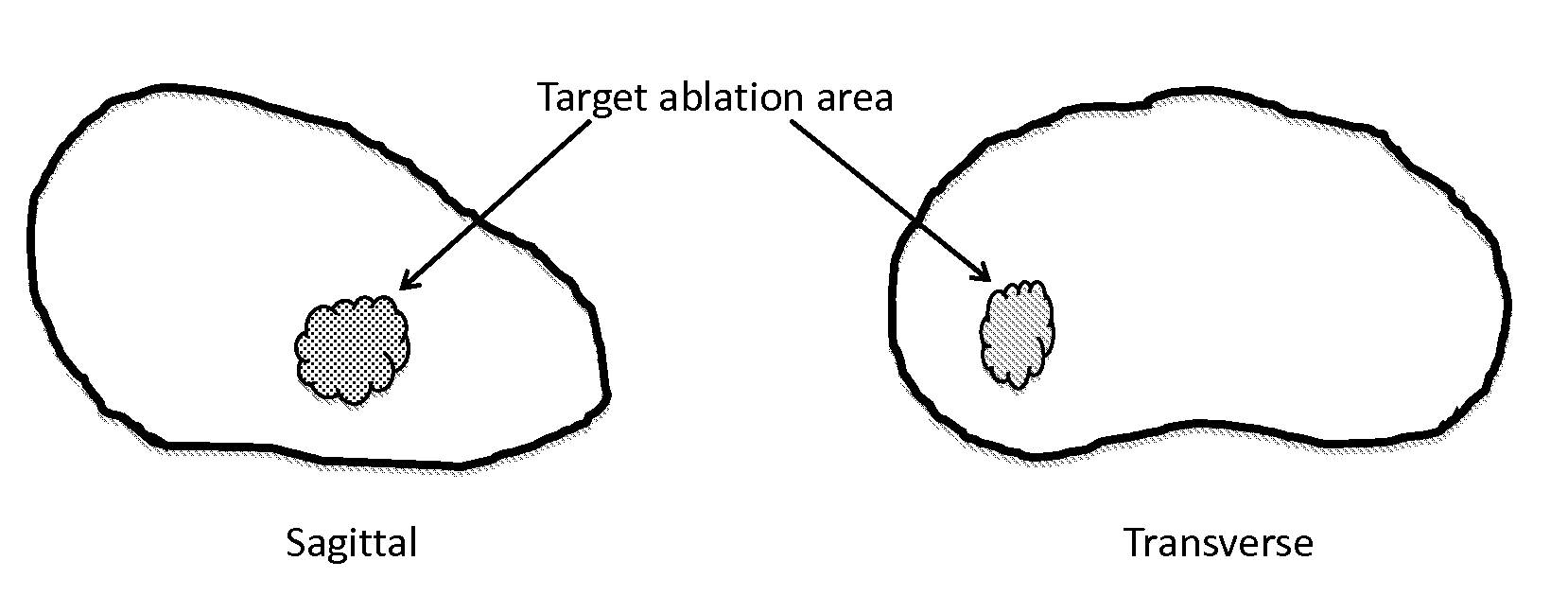
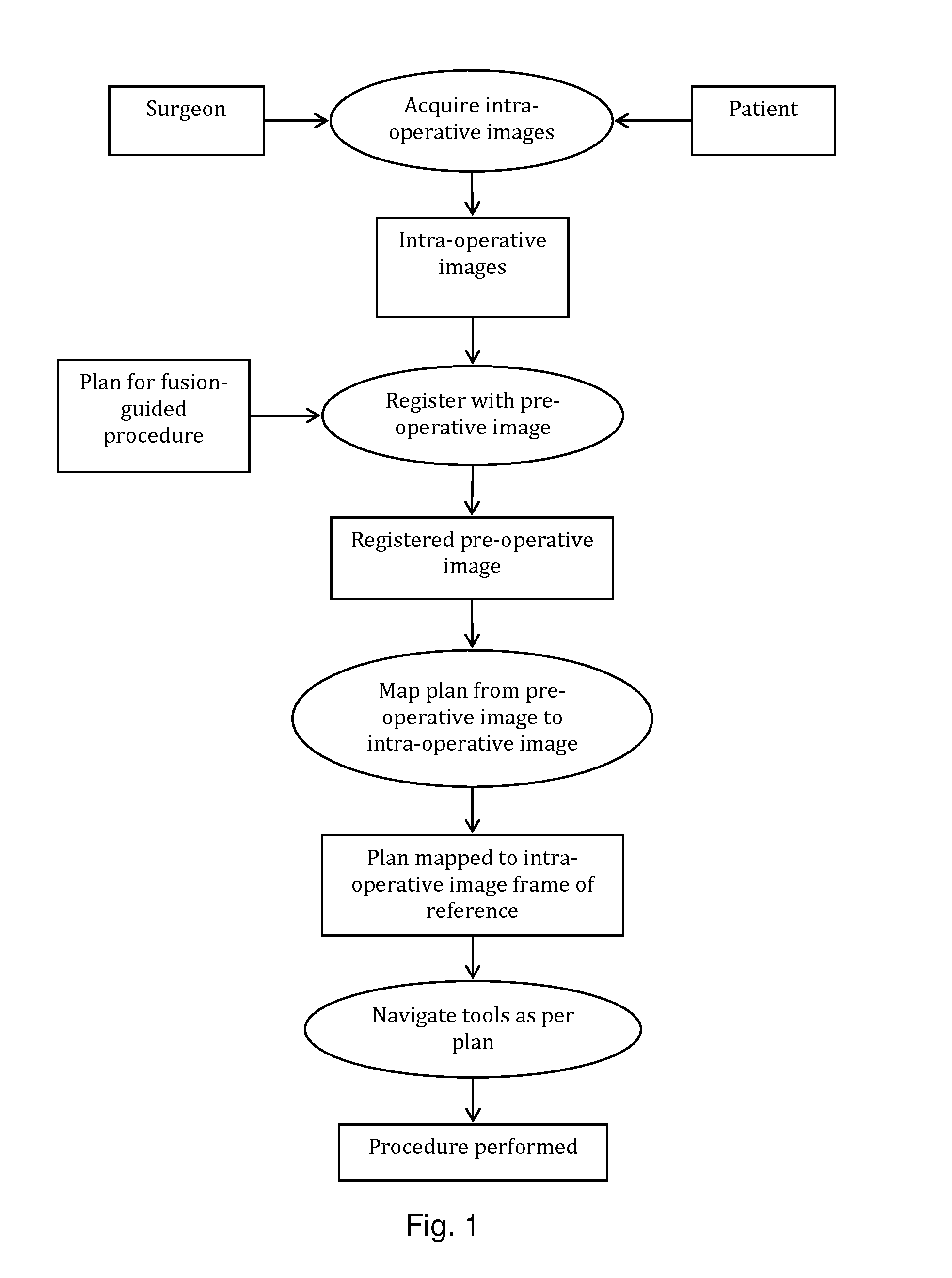
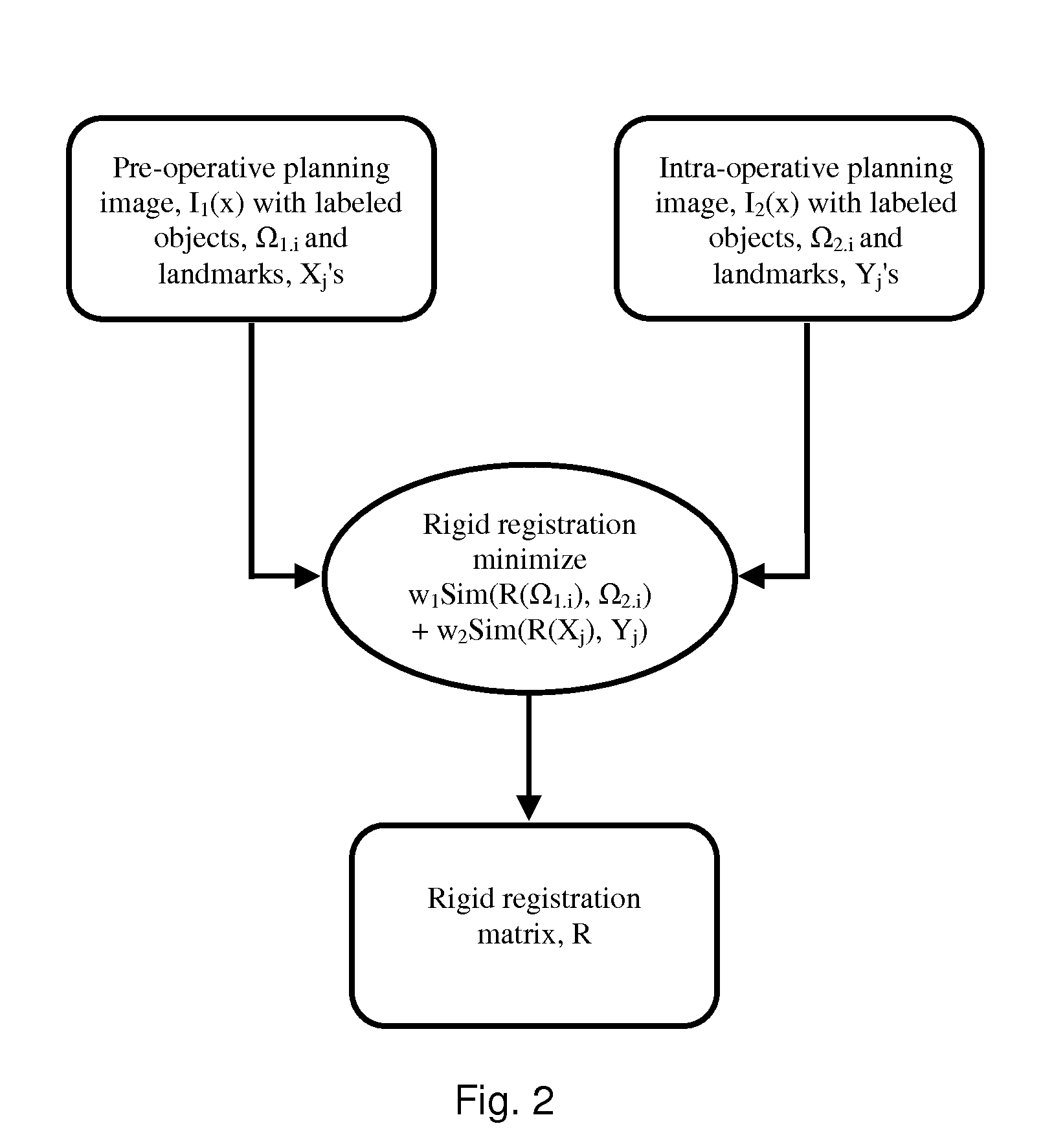
System and method for image guided medical procedures
InactiveUS20140073907A1Correction can be minimizedEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySoft tissue deformation
A system and method combines information from a plurality of medical imaging modalities, such as PET, CT, MRI, MRSI, Ultrasound, Echo Cardiograms, Photoacoustic Imaging and Elastography for a medical image guided procedure, such that a pre-procedure image using one of these imaging modalities, is fused with an intra-procedure imaging modality used for real time image guidance for a medical procedure for any soft tissue organ or gland such as prostate, skin, heart, lung, kidney, liver, bladder, ovaries, and thyroid, wherein the soft tissue deformation and changes between the two imaging instances are modeled and accounted for automatically.
Owner:CONVERGENT LIFE SCI
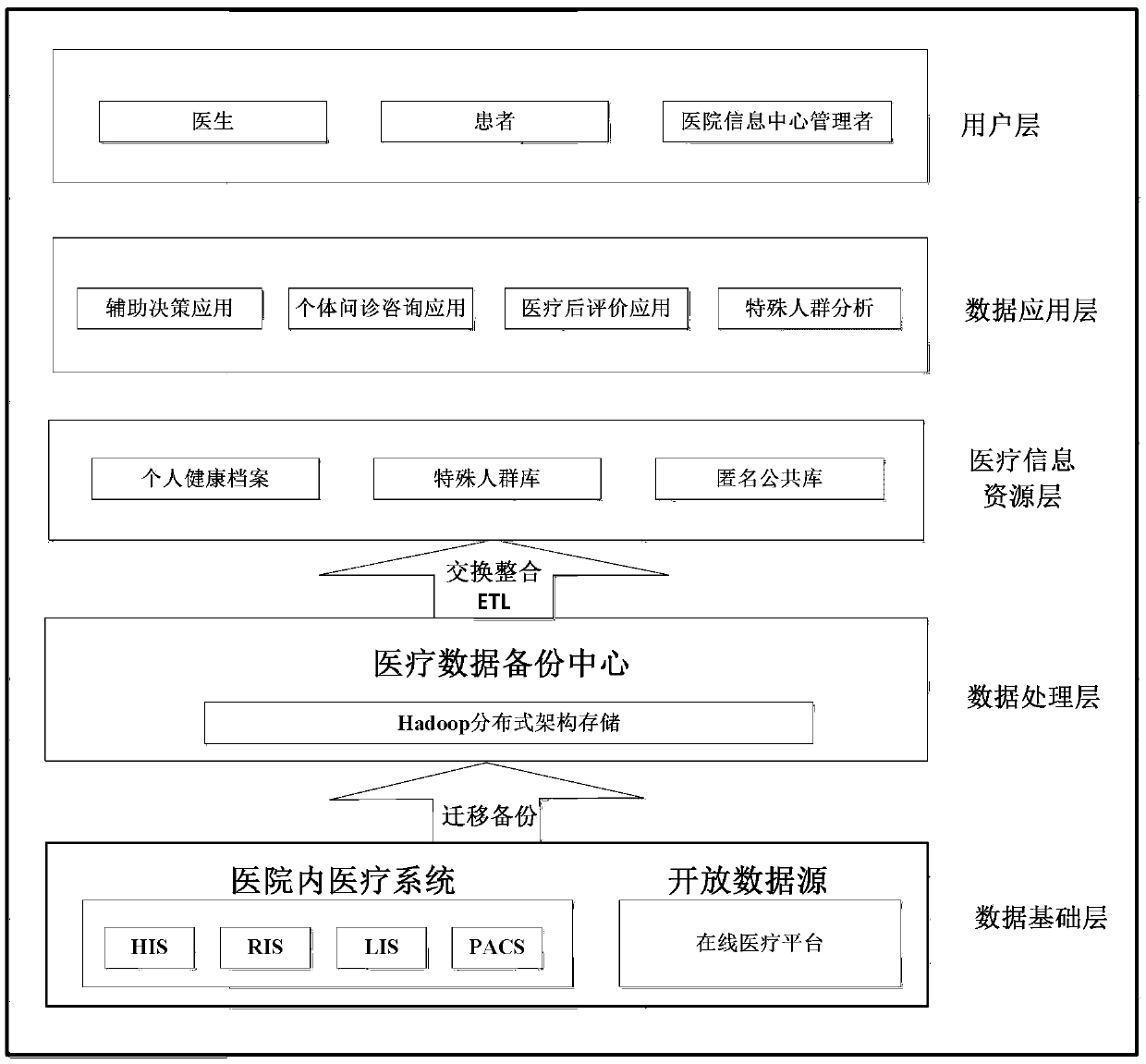
Clinical data mining analysis and aided decision-making method based on Internet integrated medical platform
The invention discloses a clinical data mining analysis and aided decision-making method based on an Internet integrated medical platform, and relates to the technical field of an Internet medical platform. The clinical data mining analysis and aided decision-making method includes data mining analysis and aided decision-making, wherein data mining analysis includes a multidimensional analysis algorithm module, a data mining algorithm module and a deep learning algorithm module; and aided remote decision-making includes four parts: a prediction module based on index parameters, a prediction module based on inspection report texts, a model training module and a structurized module. The clinical data mining analysis and aided decision-making method based on an Internet integrated medical platform selects several diseases as research objects for data collection and analysis, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes, thyroid nodules and breast tumors, and collects and integrates clinical medicaldata depended the integrated platform to realize data mining analysis and aided decision-making services for clinical data diseases, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes, thyroid nodules and breast tumors, so as to provide systematic support for clinical diagnosis of clinicians and disease research by researchers.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRIMAN INFORMATION & TECH
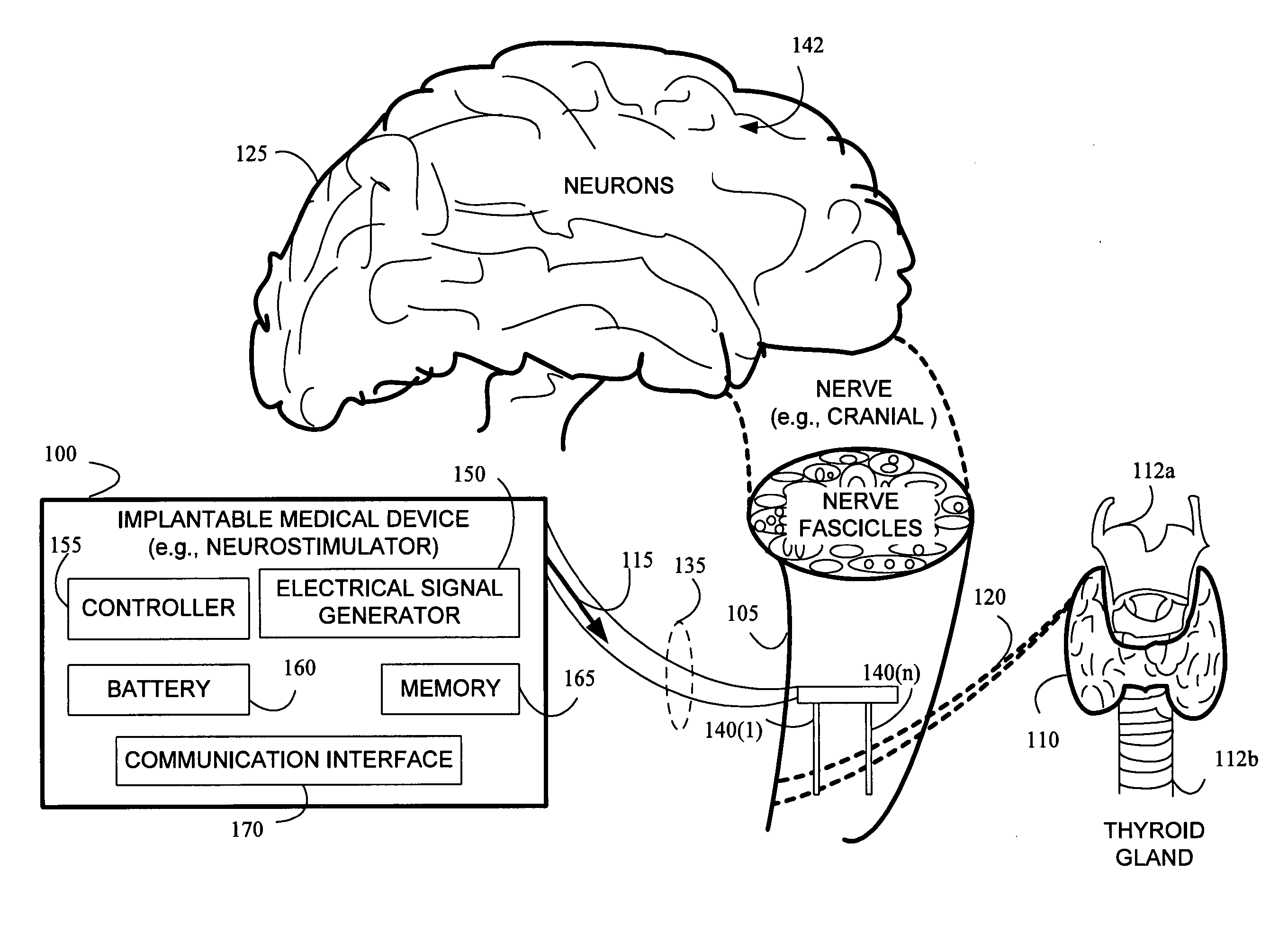
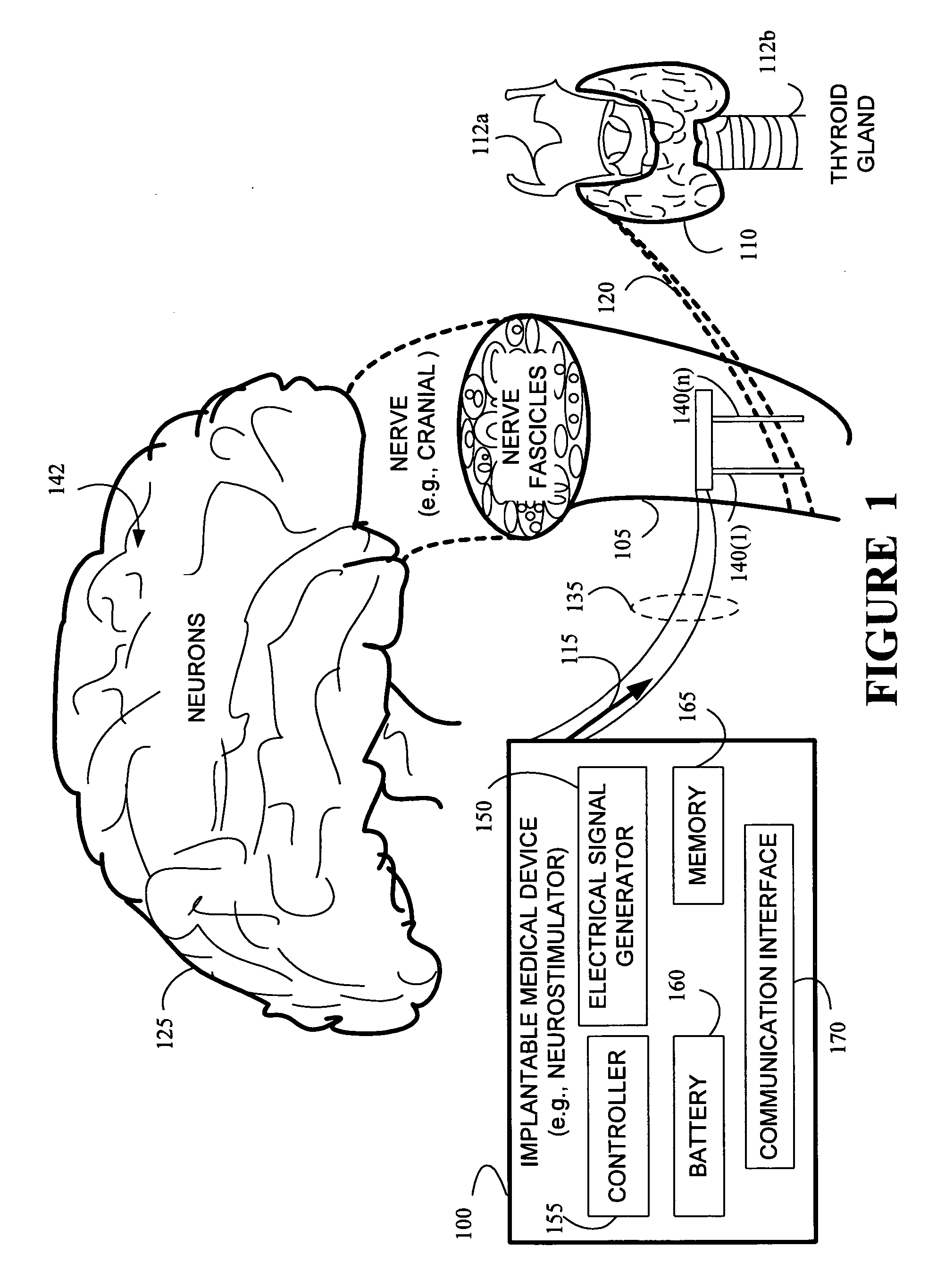
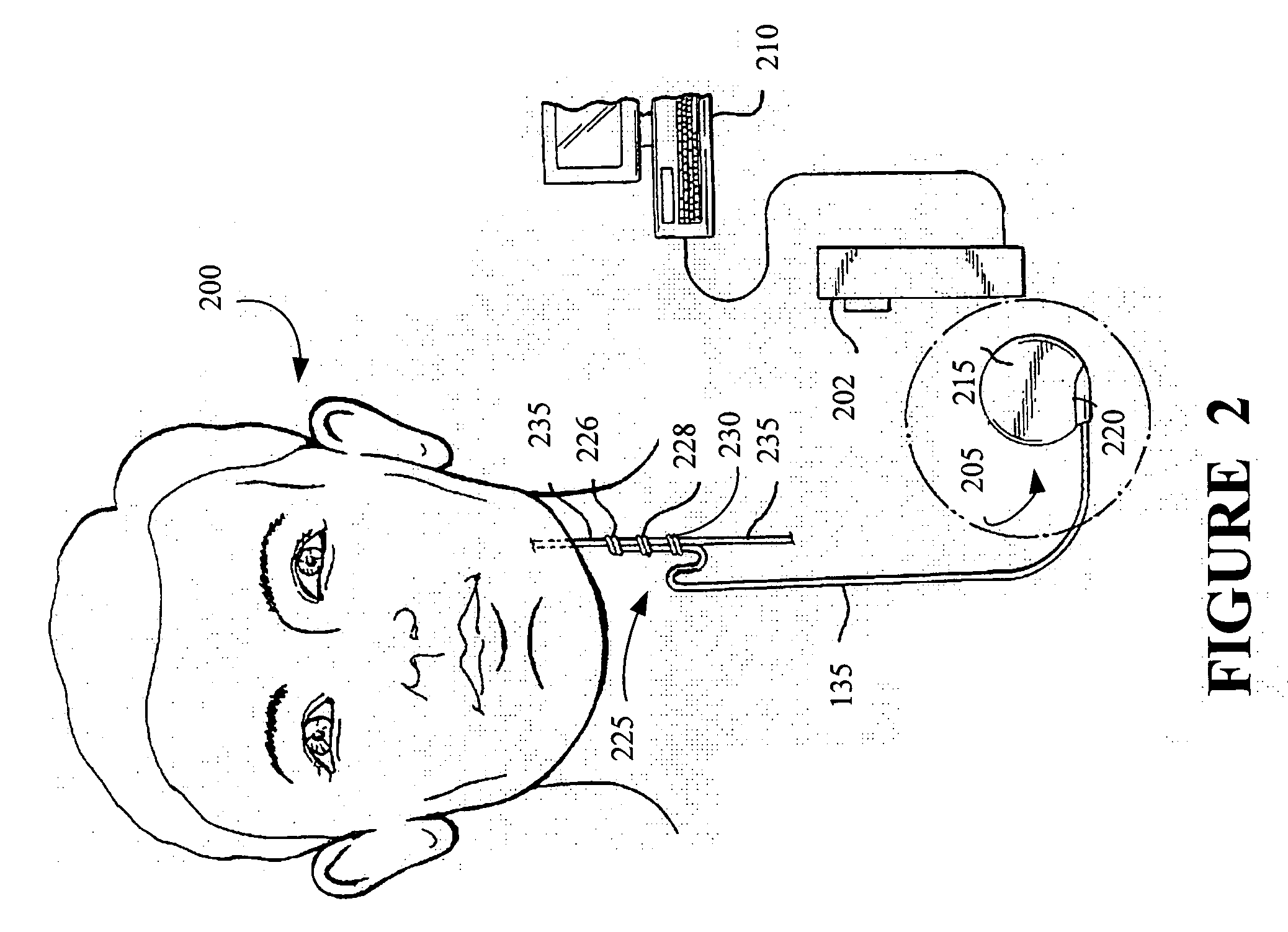
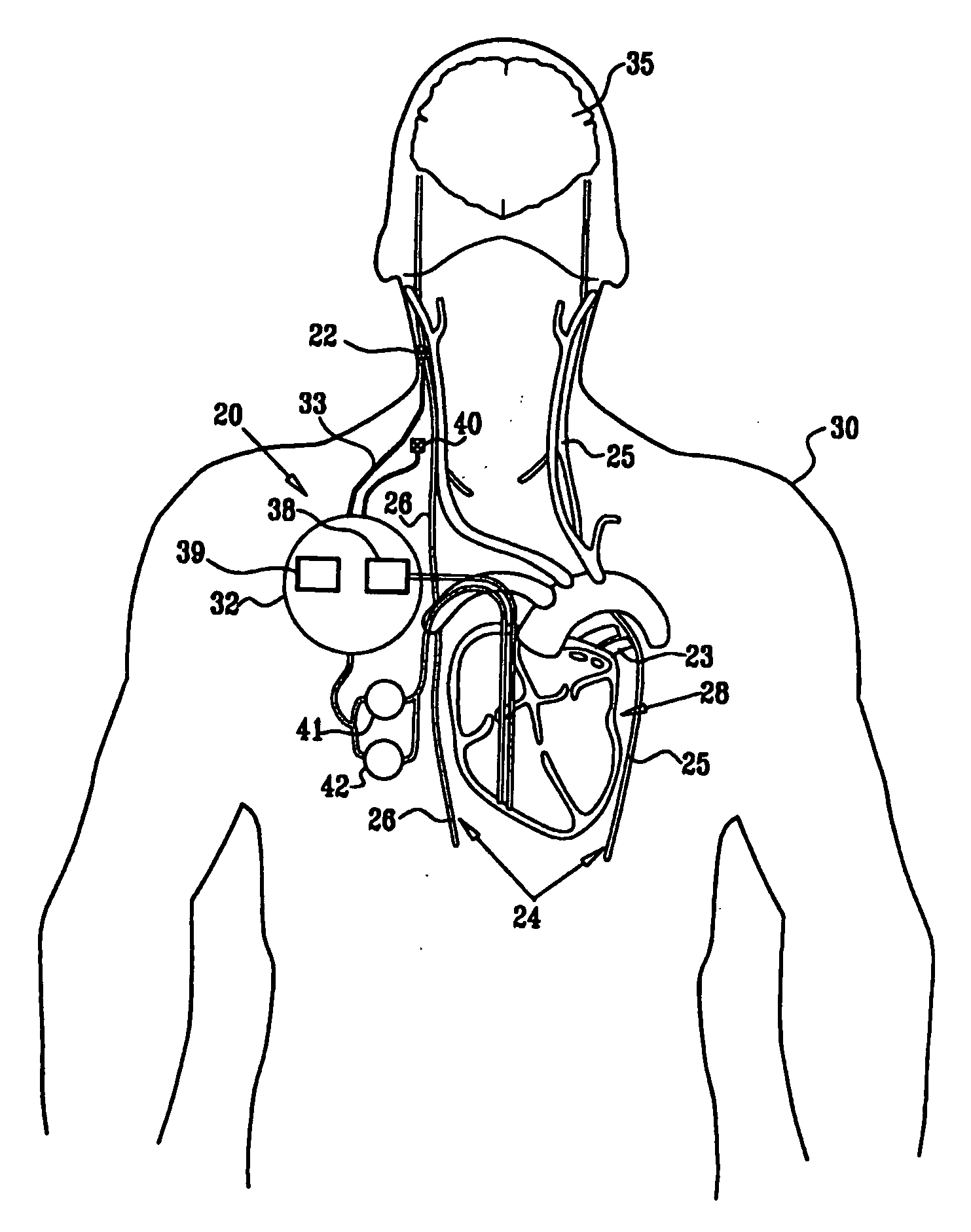
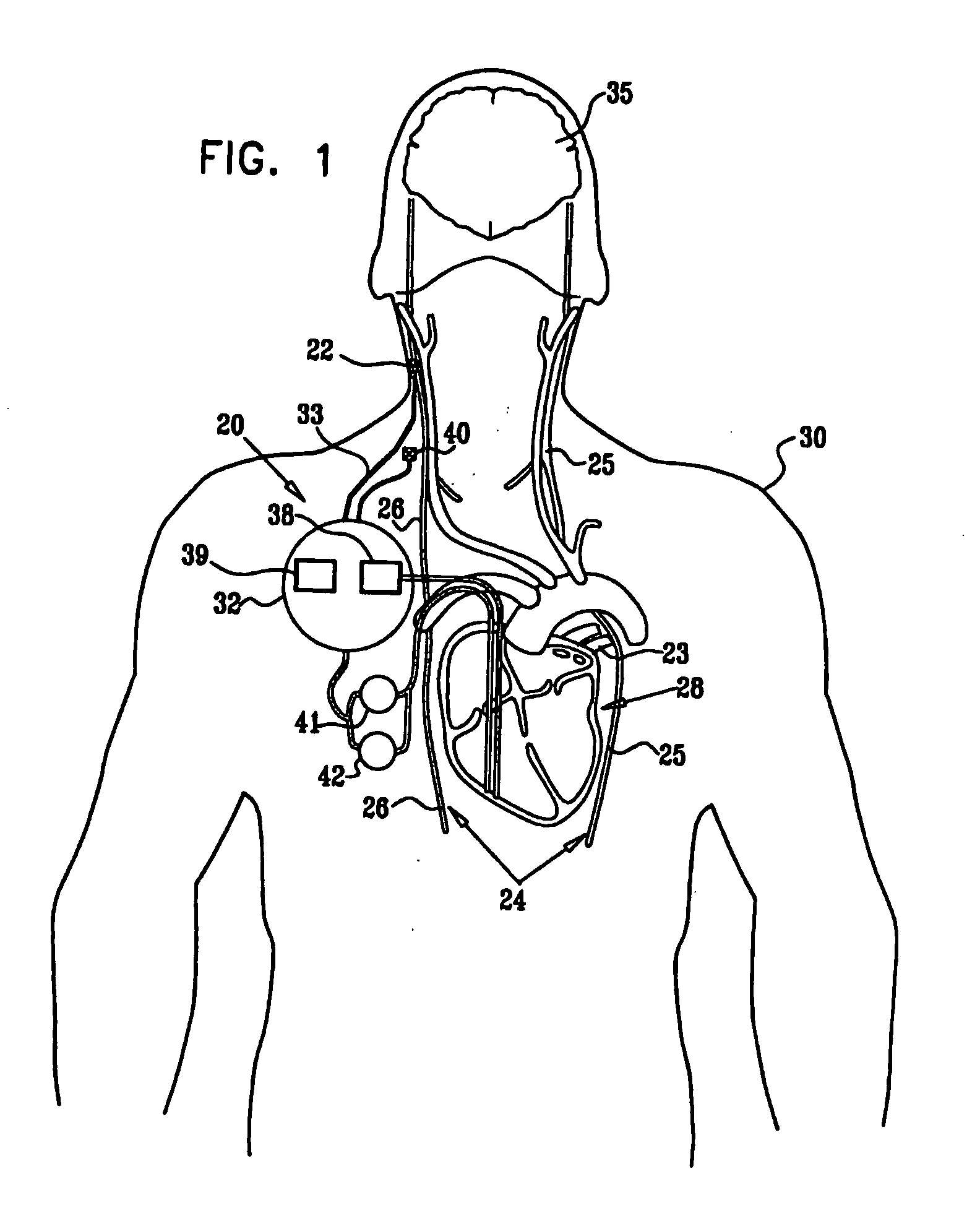
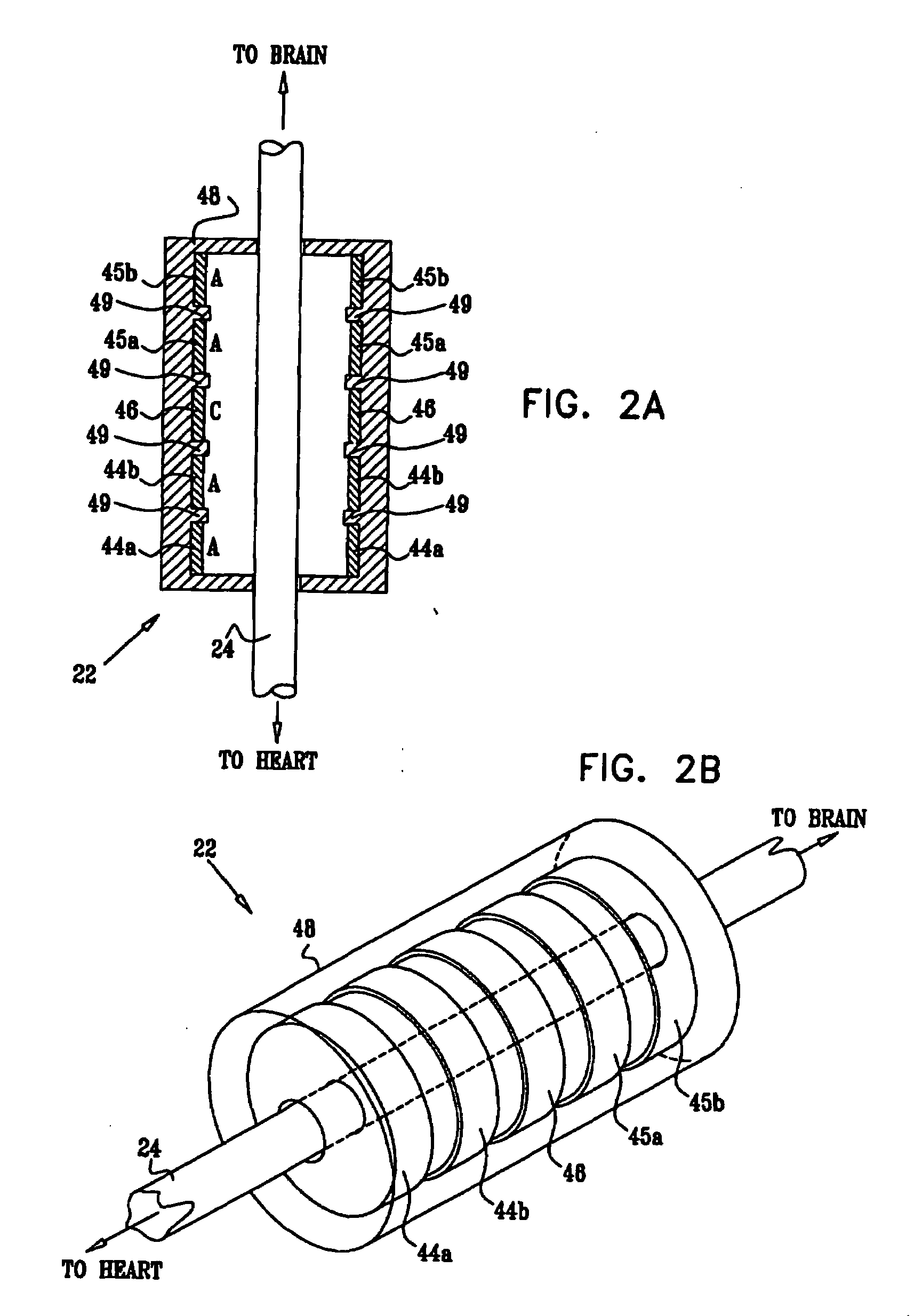
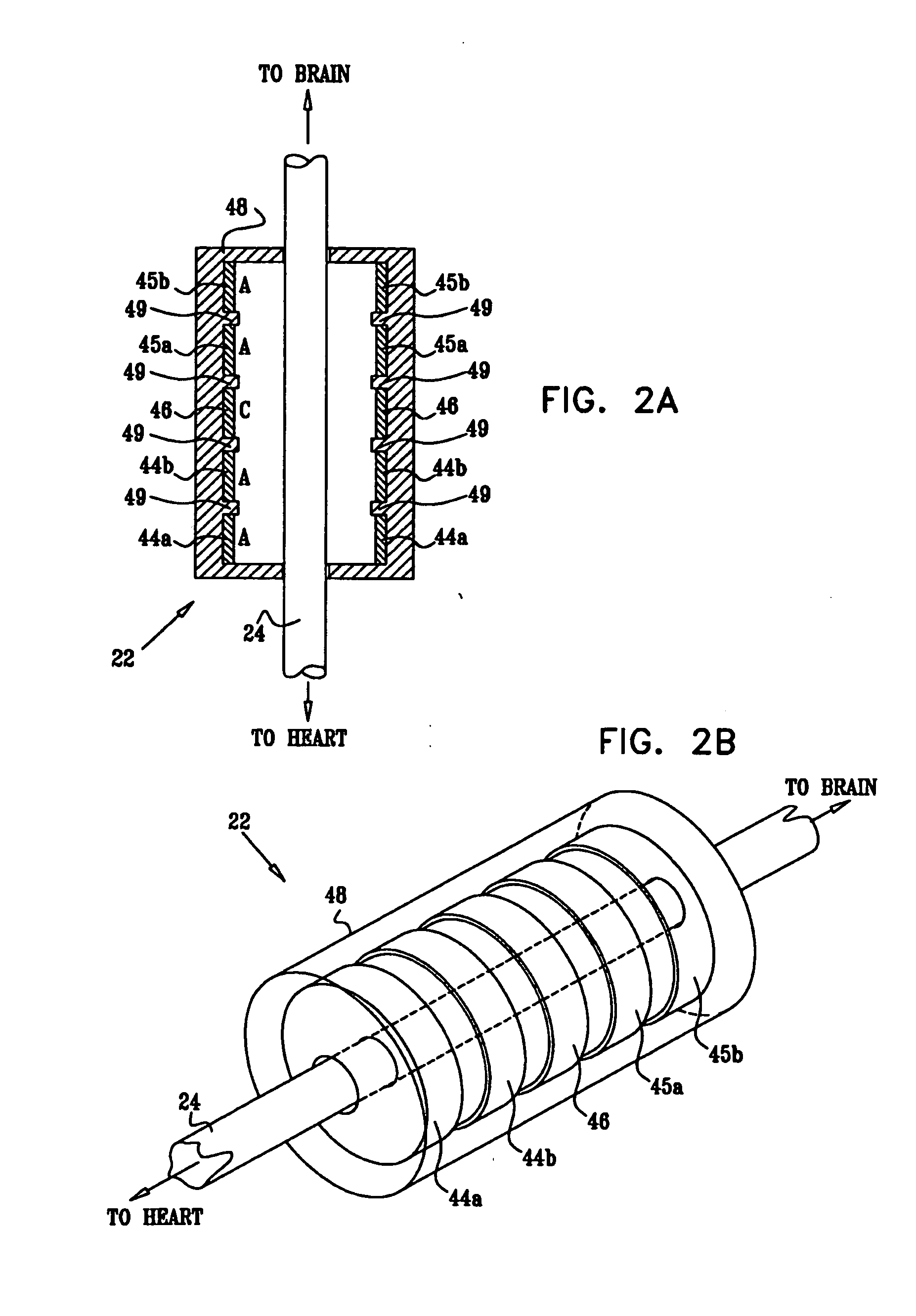
Stimulating cranial nerve to treat disorders associated with the thyroid gland
A method, system, and an apparatus for stimulating a cranial nerve of a patient to treat a disorder, such as a metabolic or an endocrine disorder associated with the thyroid gland with an implantable medical device are provided. The method comprises coupling an electrode to the cranial nerve selected from the group consisting of a vagus nerve, a trigeminal nerve, and a glossopharyngeal nerve. The method further includes generating an electrical signal to treat a disorder associated with the thyroid gland. The electrical signal may be applied to the cranial nerve using the electrode to provide electrical nerve stimulation therapy to the patient. For treating a patient with a metabolic or an endocrine disorder associated with the thyroid gland, a neurostimulator may be adapted to apply an electrical stimulus to the vagus nerve and / or a branch of the vagus nerve associated with the thyroid gland. By balancing hormonal imbalance, the neurostimulator may provide electrical nerve stimulation therapy to the patient, thereby treating a target metabolic or an endocrine disorder associated with the thyroid gland.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
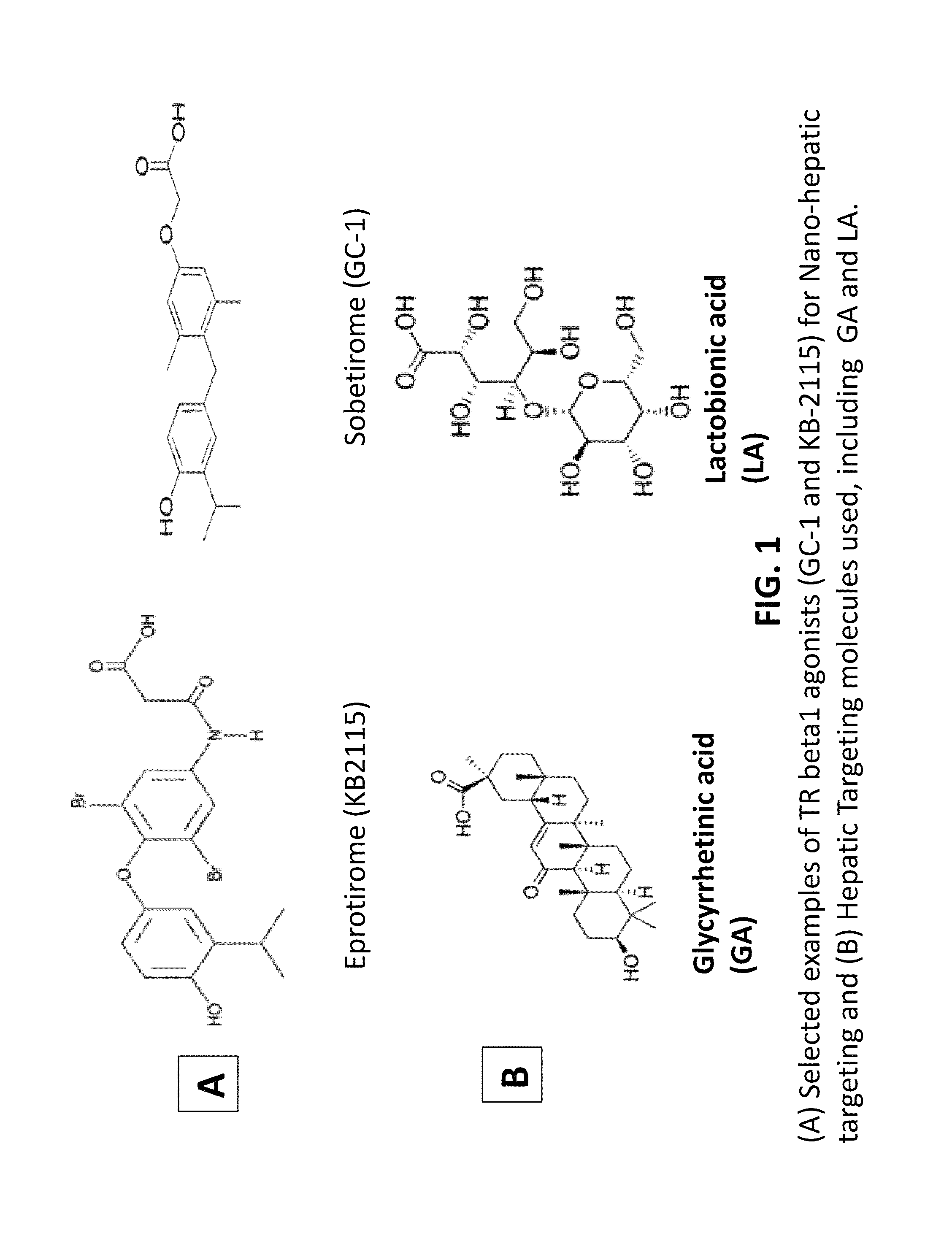
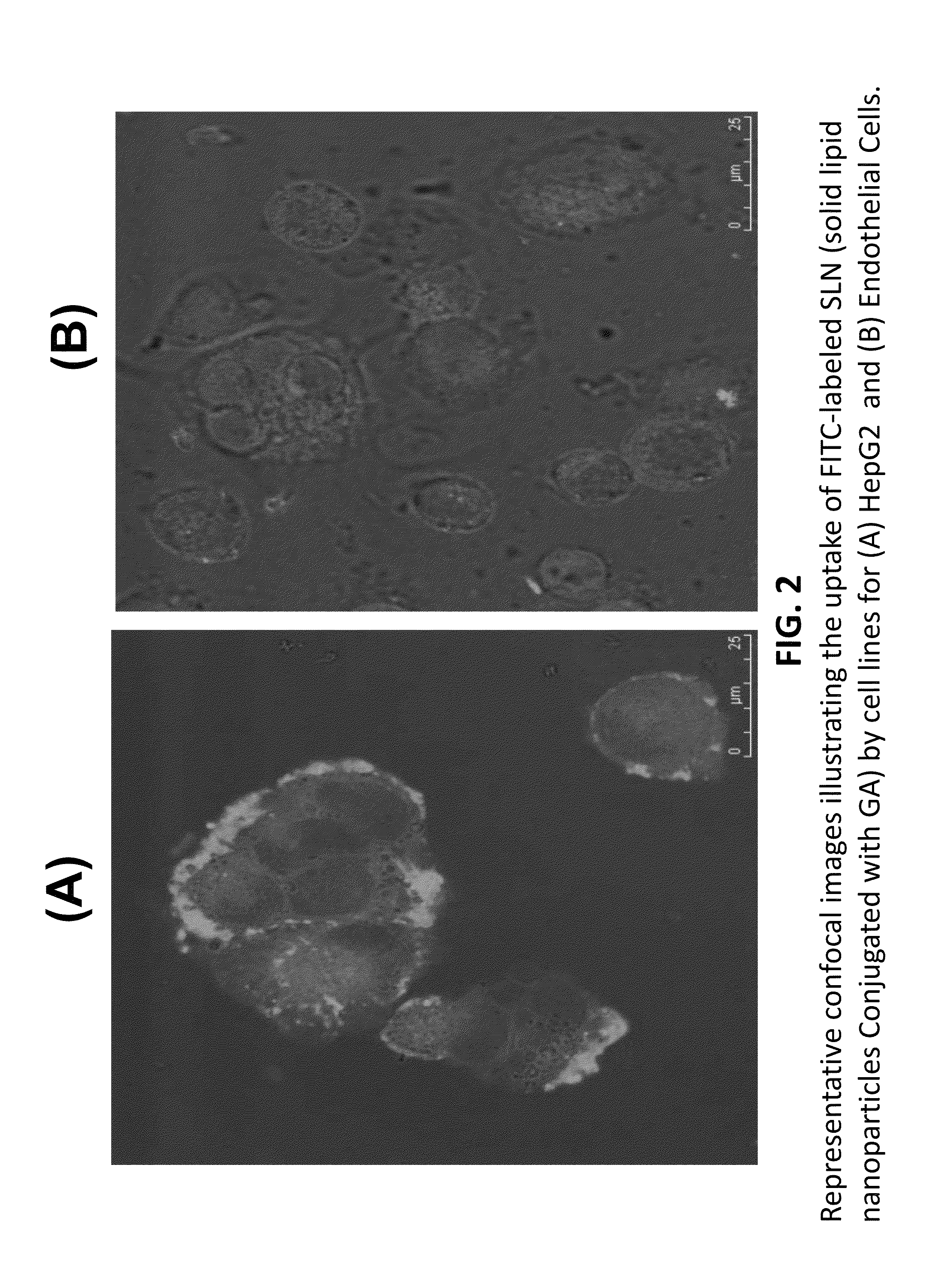
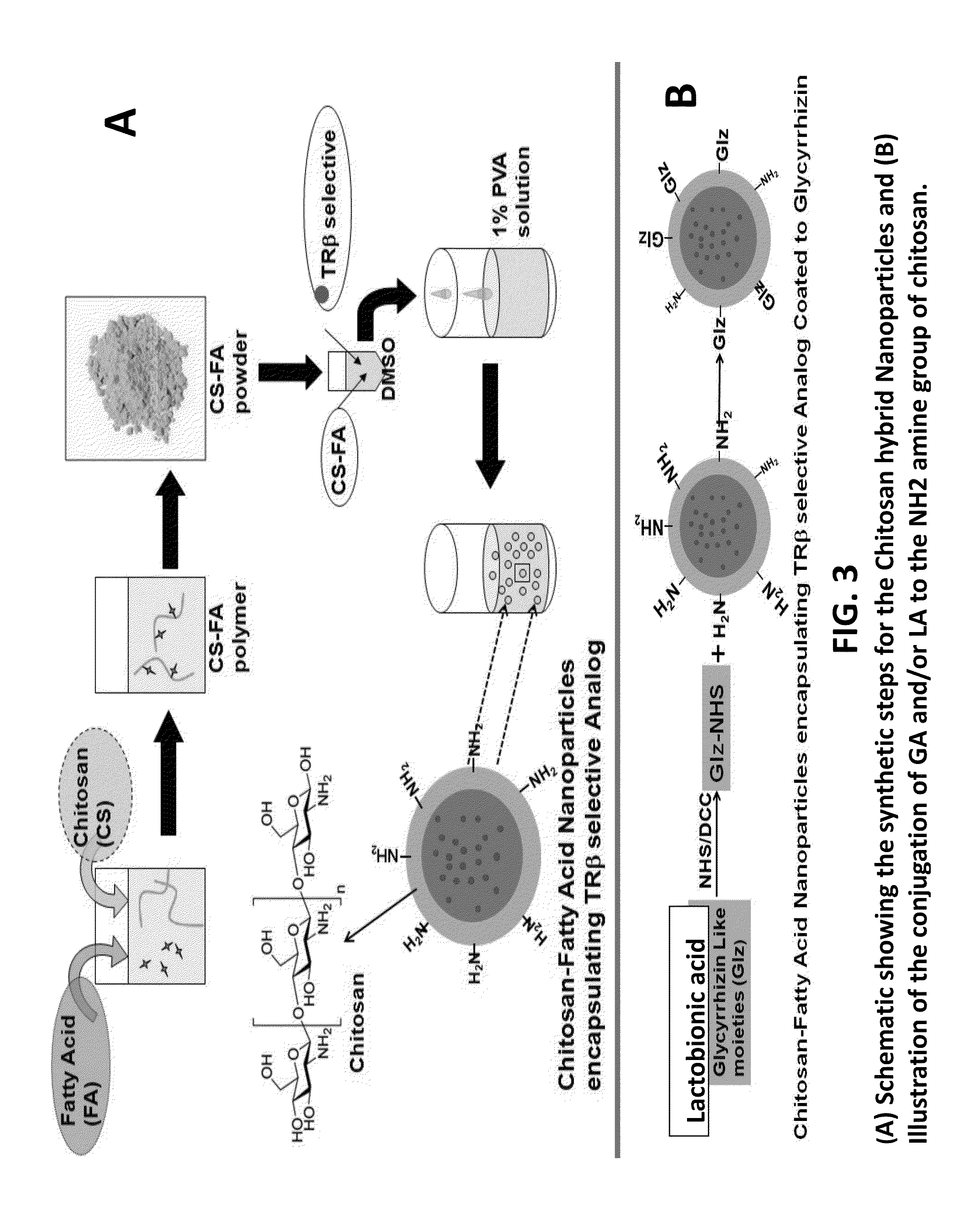
Nanoformulation and methods of use of thyroid receptor beta1 agonists for liver targeting
A composition and an associated method for hepatic targeted delivery of thyroid receptor beta1 (TRβ1) agonist to a liver of a subject. The composition includes hydrophobic nanoparticles, a liver targeting moiety exterior to each nanoparticle and covalently bonded to each nanoparticle, and at least one TRβ1 agonist encapsulated within each nanoparticle. The nanoparticles include chitosan hybrid nanoparticles, amine-modified PLGA nanoparticles, solid lipid nanoparticles, and combinations thereof. The liver targeting moiety includes Glycyrrhetinic acid (GA), Lactobionic acid (LA), or combinations thereof.
Owner:MOUSA SHAKER A
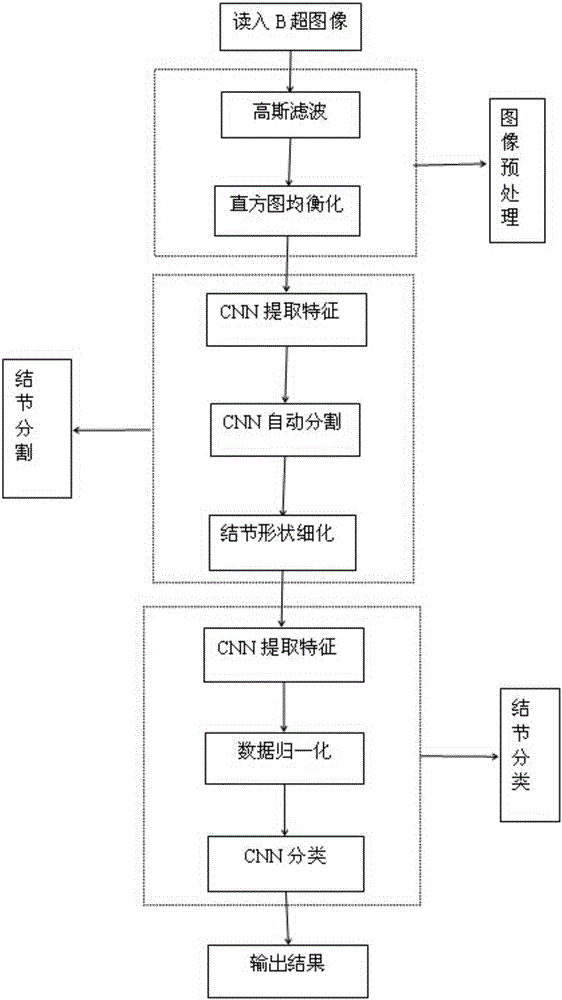
Method for automatically identifying whether thyroid nodule is benign or malignant based on deep convolutional neural network
ActiveCN106056595AImprove accuracyAvoid the complexity of manually selecting featuresImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsAutomatic segmentationNerve network
The invention relates to auxiliary medical diagnoses, and aims to provide a method for automatically identifying whether a thyroid nodule is benign or malignant based on a deep convolutional neural network. The method for automatically identifying whether the thyroid nodule is benign or malignant based on the deep convolutional neural network comprises the following steps: reading B ultrasonic data of thyroid nodules; performing preprocessing for thyroid nodule images; selecting images, and obtaining nodule portions and non-nodule portions through segmentations; averagely dividing the extracted ROIs (regions of interest) into p groups, extracting characteristics of the ROIs by utilizing a CNN (convolutional neural network), and performing uniformization; taking p-1 groups of data as a training set, taking the remaining one group to make a test, and obtaining an identification model through training to make the test; and repeating cross validation for p times, and then obtaining an optimum parameter of the identification model. The method can obtain the thyroid nodules through the automatic segmentations by means of the deep convolutional neural network, and makes up for the deficiency that a weak boundary problem cannot be solved based on a movable contour and the like; and the method can automatically lean and extract valuable feature combinations, and prevent the complexity of an artificial feature selection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DE IMAGE SOLUTIONS CO LTD
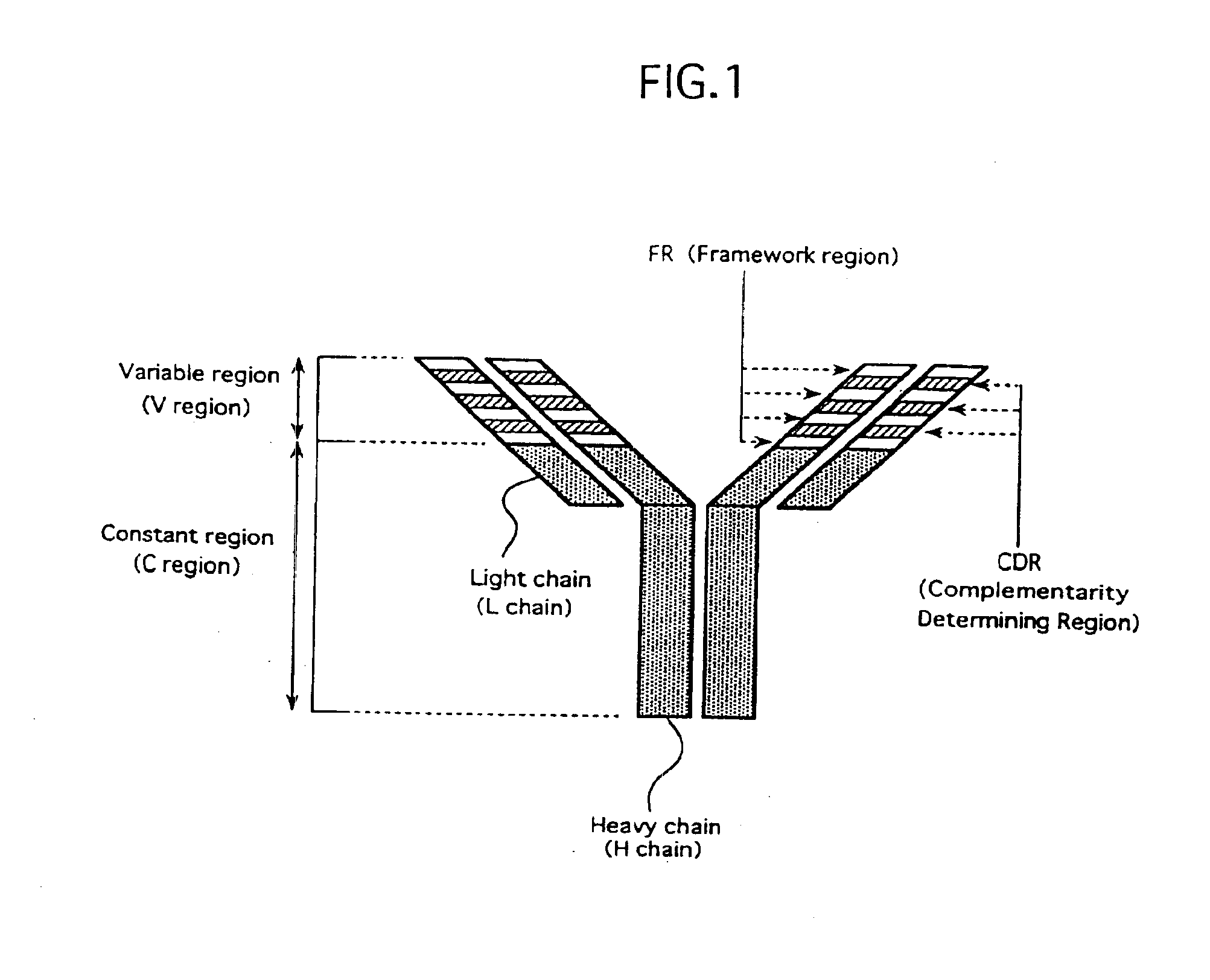
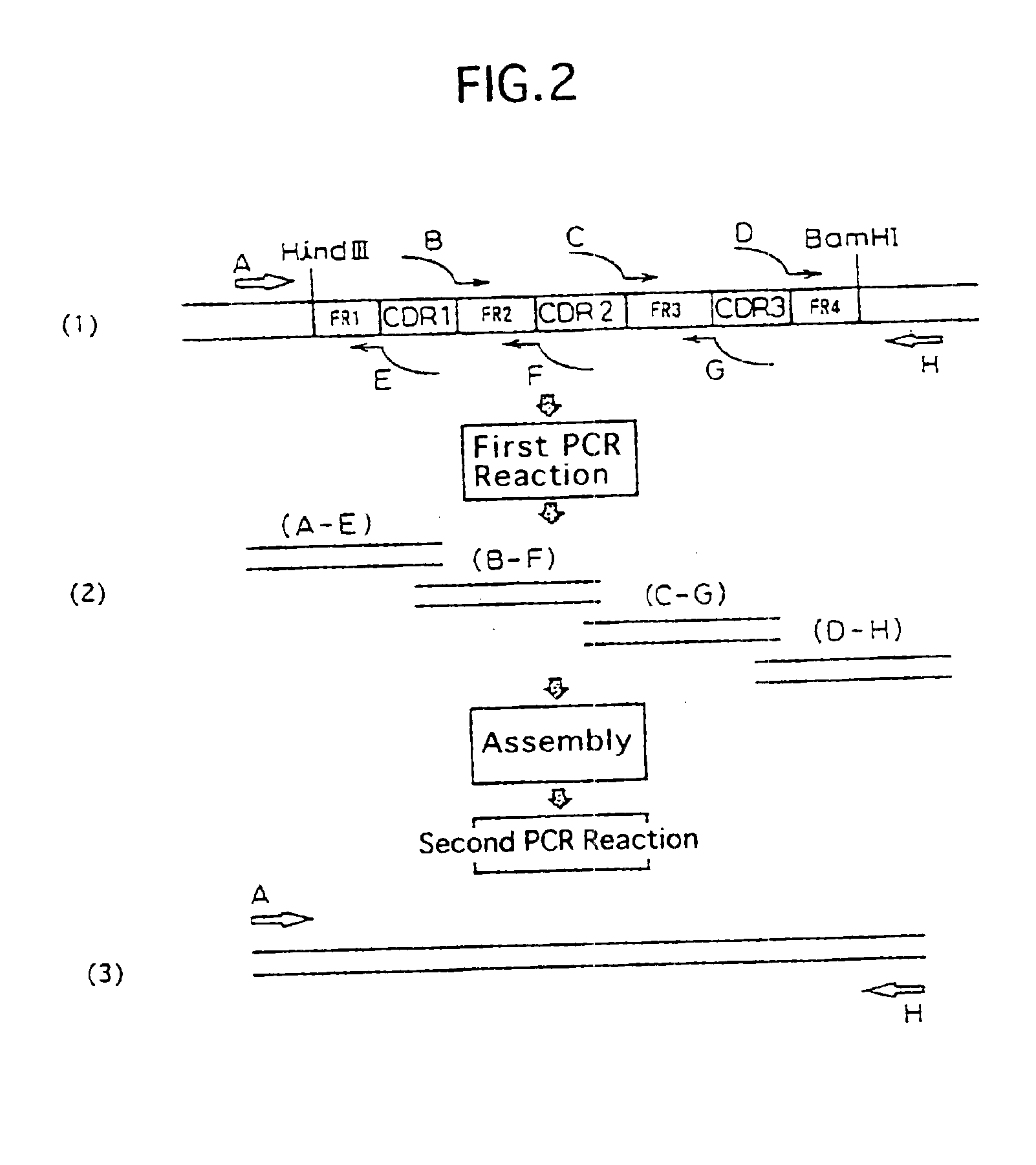
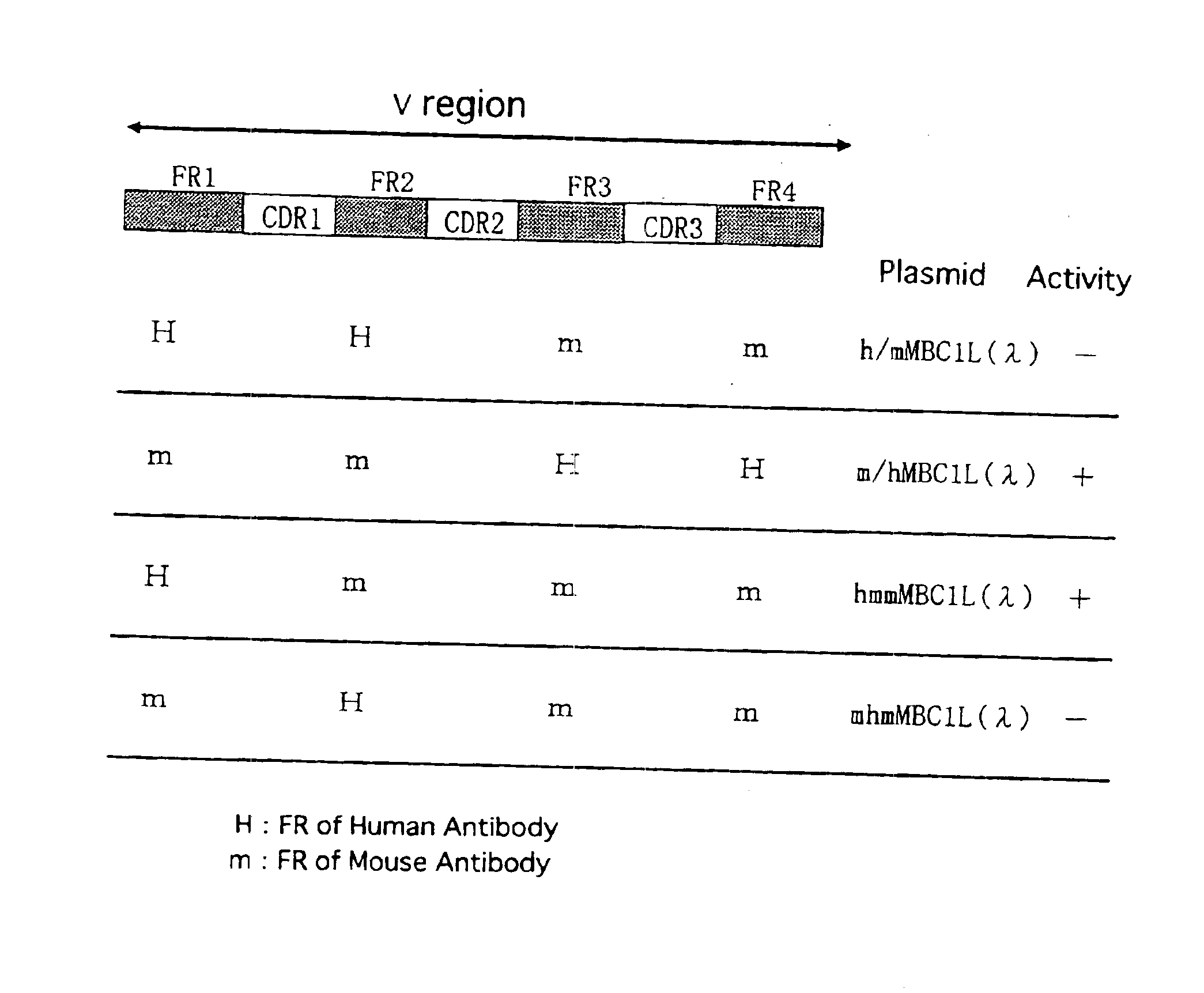
Antibody against human parathormone related peptides
InactiveUS6903194B1Improve hypophosphatemiaHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsThyroid hormonesA-DNA
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Foamable compositions, kits and methods for hyperhidrosis
The composition of the present invention is geared towards treating hyperhidrosis or any condition involving and / or promoting excessive sweating, typically involving the whole body, include hyperthyroidism or similar endocrine disorders; endocrine treatment for prostatic cancer or other types of malignant disorder; severe psychiatric disorders; obesity and menopause. The foamable composition of the present invention is suitable for treating palmar hyperhidrosis; axillary hyperhidrosis; plantar hyperhidrosis; hyperhidrosis of the trunk and / or the thighs; and facial hyperhidrosis; and any combination of them consisting of a therapeutic foamable composition including: an active agent, suitable for the treatment or prevention of hyperhidrosis.
Owner:VYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods to increase the effect of a neurotoxin treatment
InactiveUS20050214325A1Good curative effectReducing and inhibiting and interferingHormone peptidesBacterial antigen ingredientsGrowth retardantDisease
The present invention discloses compositions and methods for enhancing the effect (e.g., duration) of a neurotoxin treatment. The compositions herein include neurotoxins and neuron growth inhibitors. Such compositions are administered locally to treat or prevent conditions, such as dermatological conditions, urological conditions, thyroid conditions, optical conditions, and neurological conditions.
Owner:KYTHERA BIOPHARMLS INC
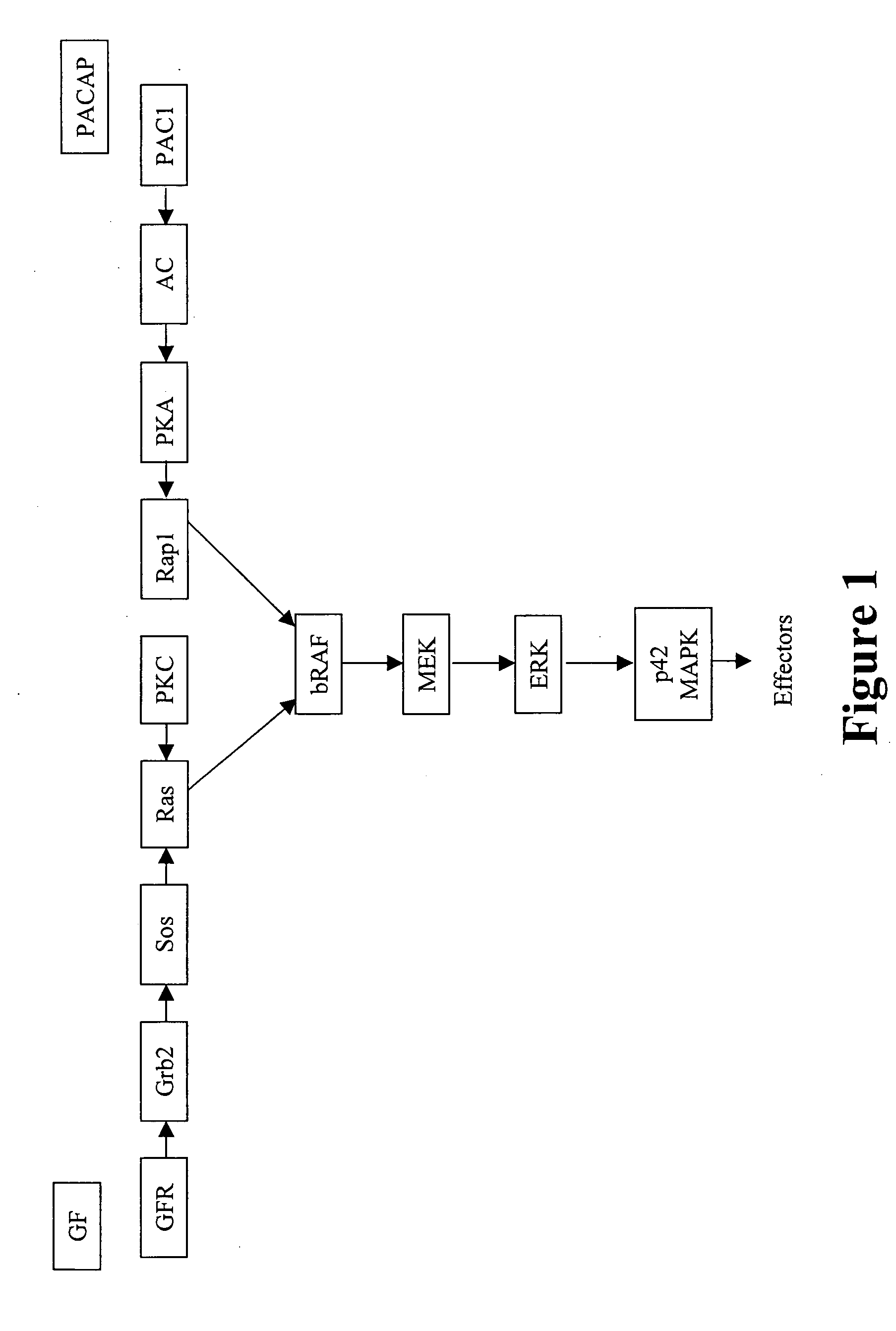
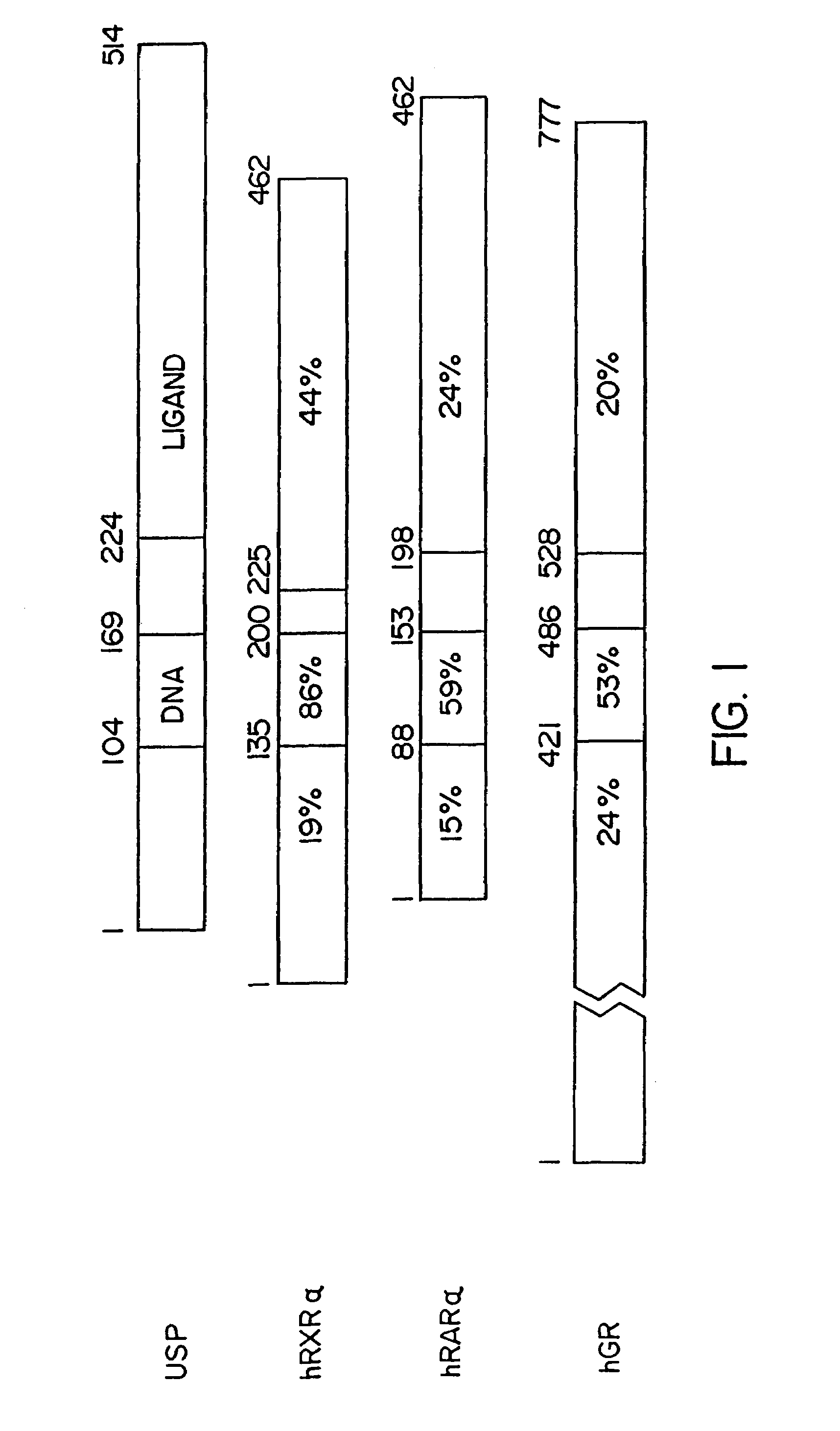
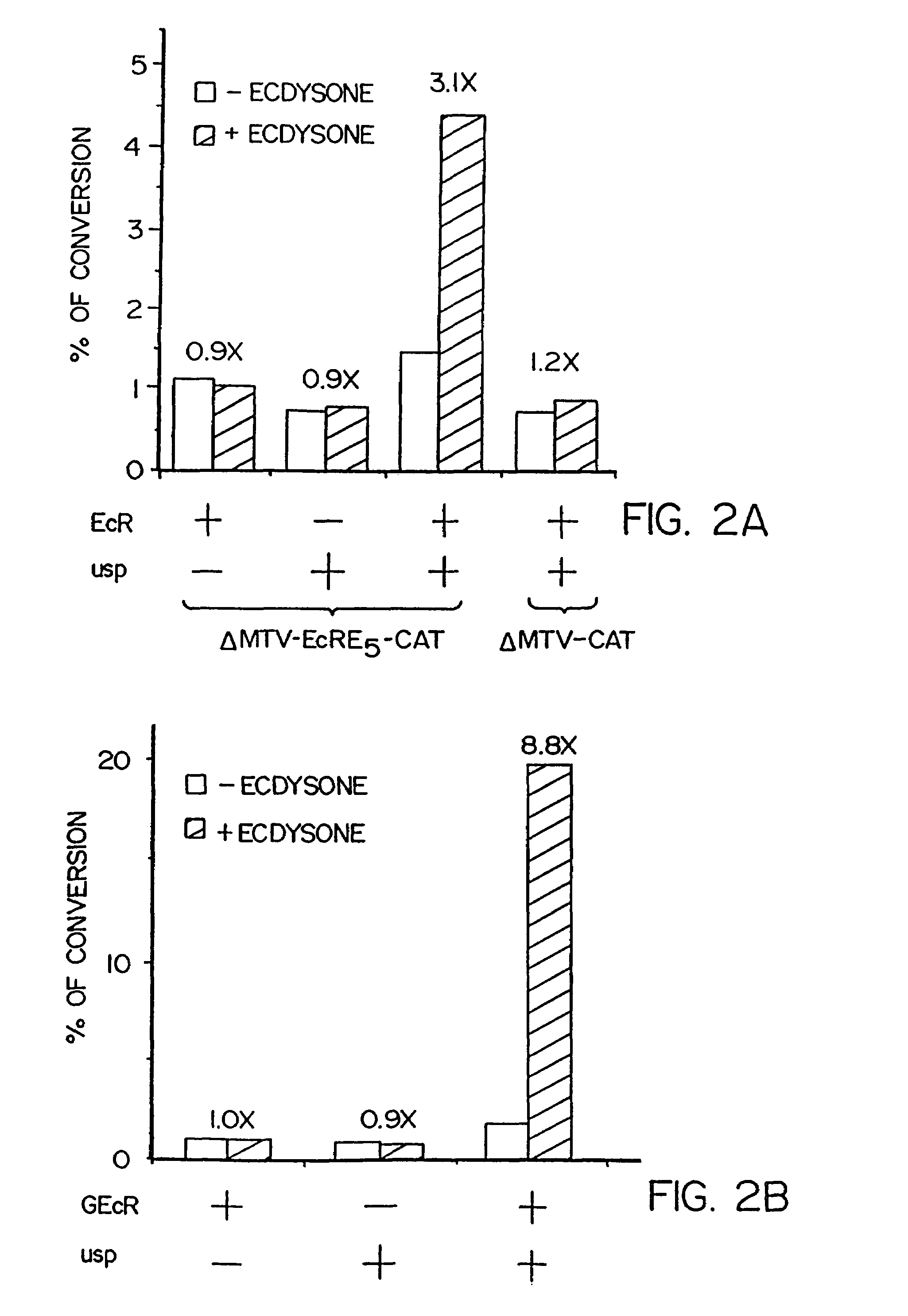
Multimeric forms of members of the steroid/thyroid superfamily of receptors with the ultraspiracle receptor
InactiveUS7119077B1Ability to modulateSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsHormones regulationEphA Receptors
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that various members of the steroid / thyroid superfamily of receptors can interact with the insect-derived ultraspiracle receptor, to form multimeric species. Accordingly, the interaction of at least one member of the steroid / thyroid superfamily of receptors with at least the dimerization domain of the ultraspiracle receptor modulates the ability of said member of the steroid / thyroid superfamily of receptors to transactivate transcription of genes maintained under hormone expression control in the presence of the cognate ligand for said member of the superfamily.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Multimeric forms of members of the steroid/thyroid superfamily of receptors
InactiveUS7038022B1Ability to modulatePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHormones regulationEphA Receptors
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that various members of the steroid / thyroid superfamily of receptors can interact to form multimeric species comprising a complex of more than one receptor. Accordingly, the interaction of a first receptor species with a second receptor species modulates the ability of the first receptor species to trans-activate transcription of genes maintained under hormone expression control in the presence of the cognate ligand for said first receptor.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Native soft tissue matrix for therapeutic applications
InactiveUS20050288796A1Promote ex vivo regenerationEfficient and effectiveAnti-incontinence devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue repairPerichondrium
A product for implantation within a soft tissue site of the human or animal body comprises a pulverized or morselized matrix of a substantially non-mineralized native soft tissue (NSTM) of the human or animal body, provided in a therapeutic amount to induce growth of native tissue or organs and healing at the tissue site. The NSTM is composed of at least one soft tissue selected from the group consisting of cartilage, meniscus, intervertebral disc, ligament, tendon, muscle, fascia, periosteum, pericardium, perichondrium, skin, nerve, blood vessels, and heart valves or from organs such as bladder, lung, kidney, liver, pancreas, thyroid, or thymus. Preferably, the NSTM is composed of a soft tissue of the same type of tissue native to the repair site. In another embodiment, the NSTM includes soft tissue of a different type than the tissue repair site.
Owner:AWAD HANI +2
Combined parasympathetic stimulation and drug therapy
InactiveUS20080125843A1Enhancing and sustaining efficacyImprove efficiencyHeart defibrillatorsMedical devicesNervous systemMyelitis
A method is provided for treating a subject, including applying a current to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, and an internal jugular vein of the subject. The method also includes configuring the current so as to treat a condition of the subject selected from the list consisting of: an autoimmune disease, an autoimmune inflammatory disease, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, myelitis, immune-mediated neuropathy, myositis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, inclusion body myositis, inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, Guillain Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, inflammation of the nervous system, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sjogren syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease, glomerulonephritis, thyroid autoimmune disease, sepsis, meningitis, a bacterial infection, a viral infection, a fungal infection, sarcoidosis, hepatitis, and portal vein hypertension.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
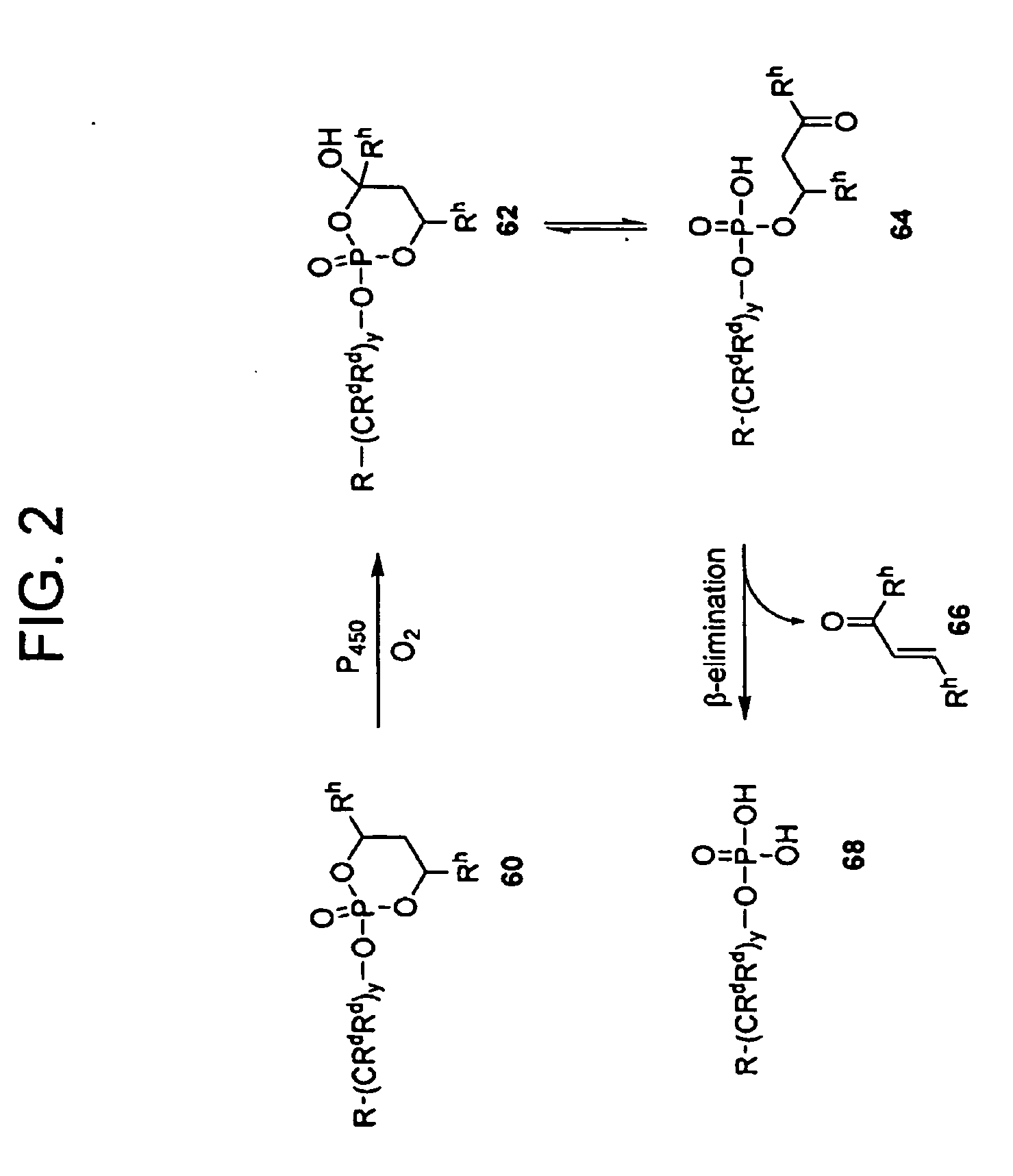
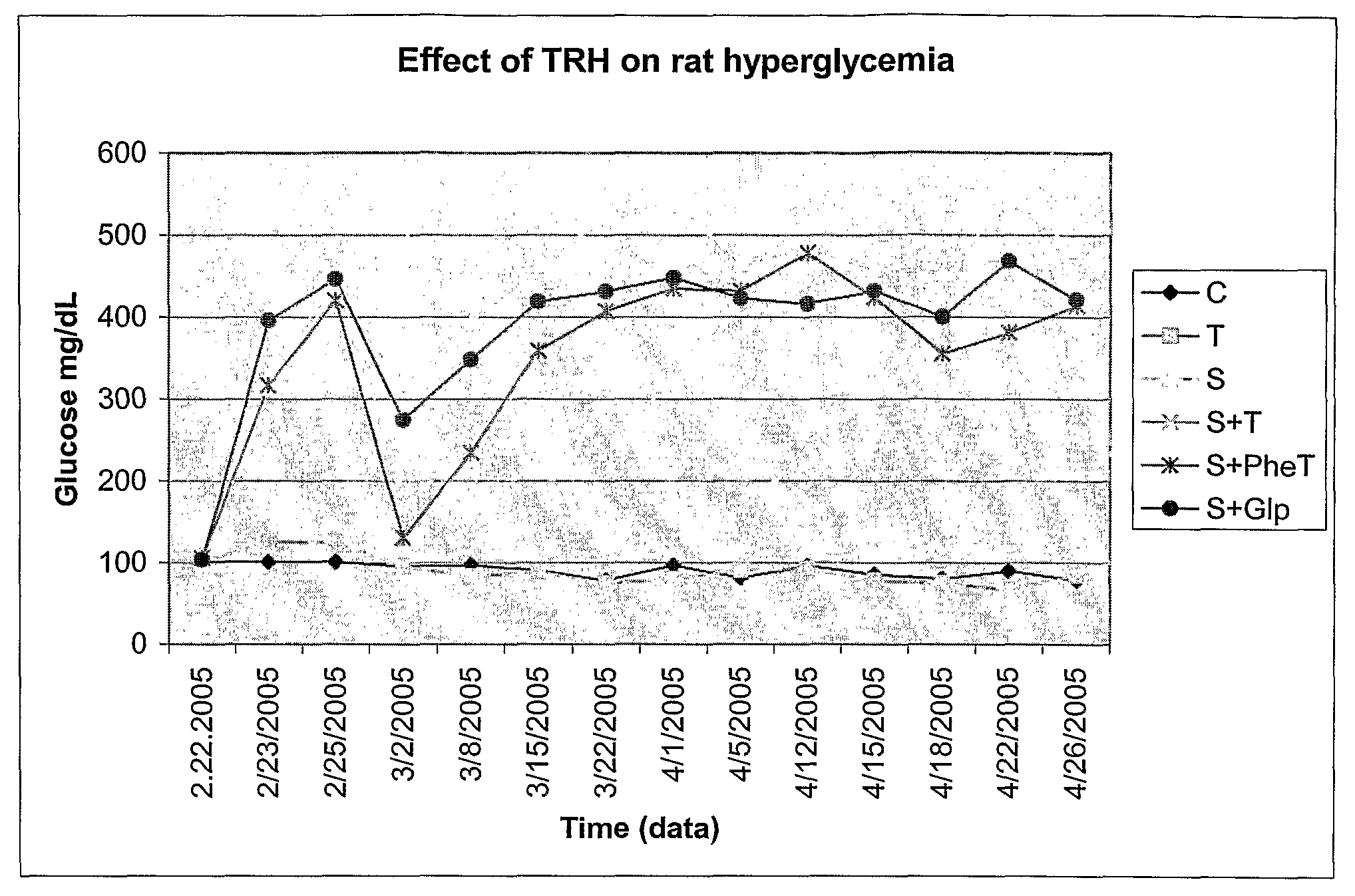
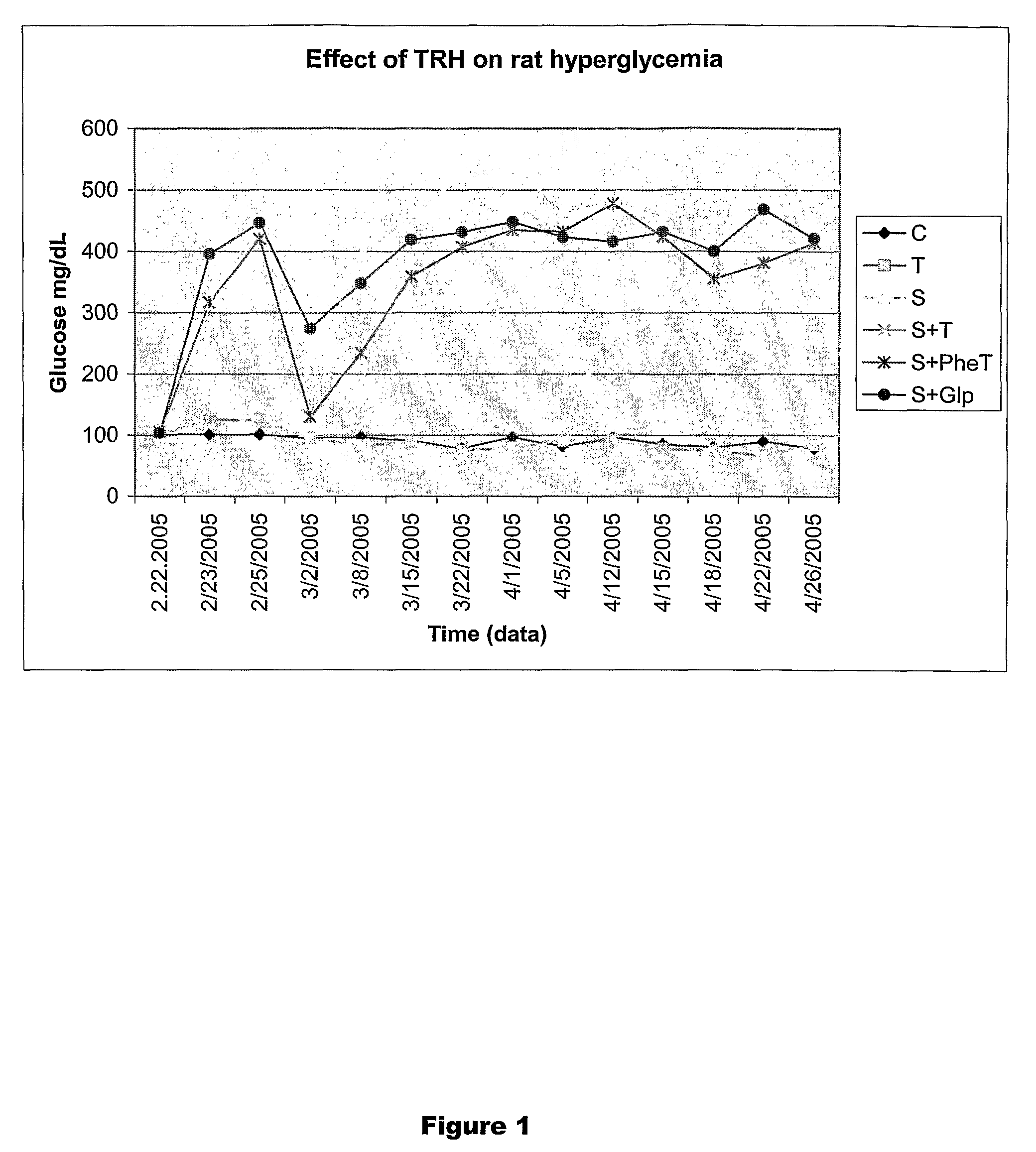
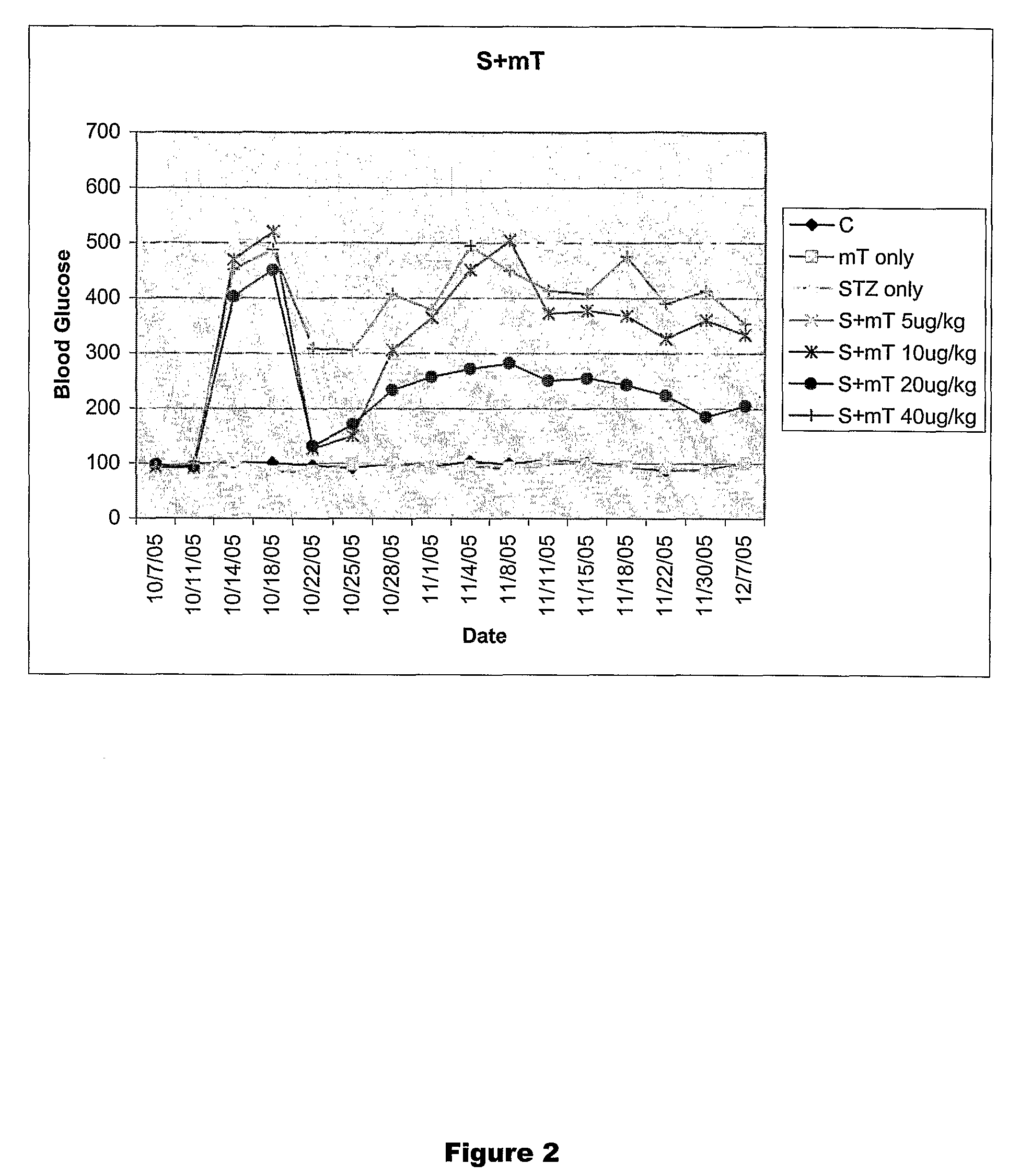
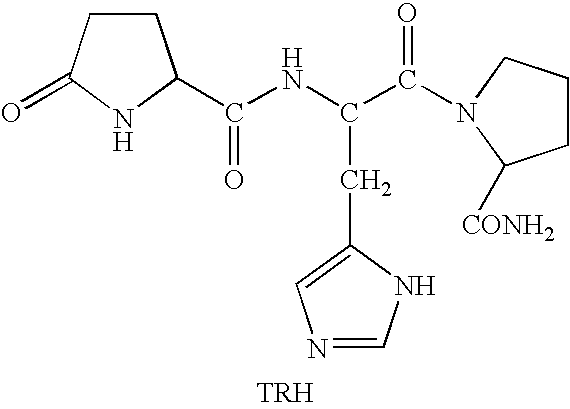
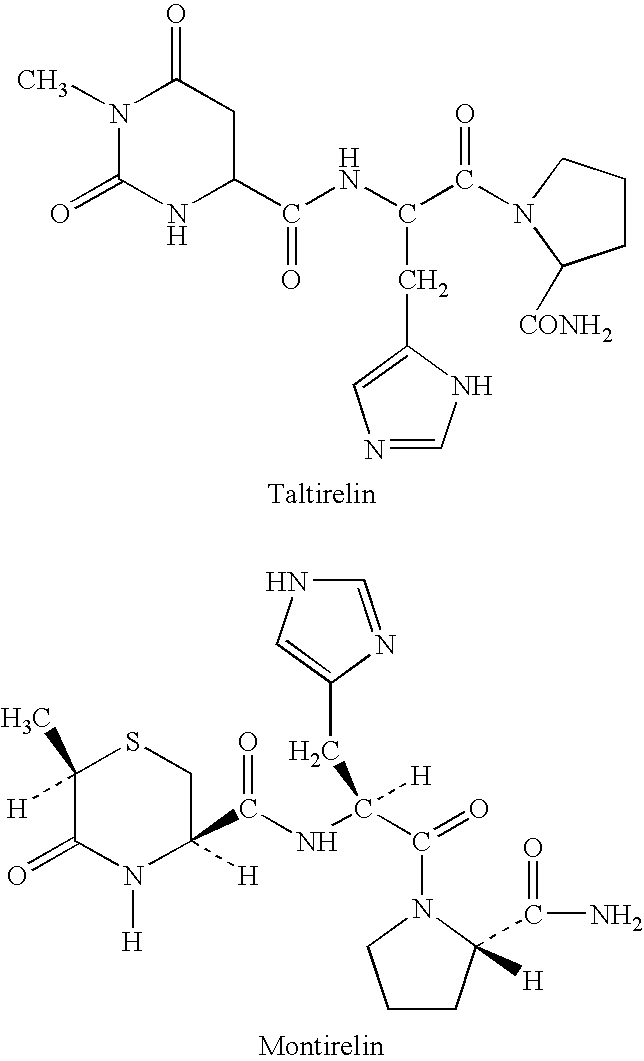
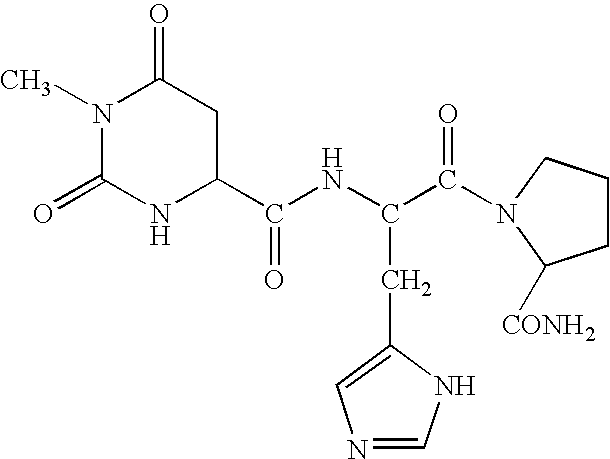
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogs and Method of Use
InactiveUS20080249028A1Modulating blood glucose levelMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute hyperglycaemiaThyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogue
The invention provides a method of modulating blood glucose levels by treating or preventing pancreas-related disorders with thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) or a TRH derivative. Diabetes mellitus, pancreatic islet destruction, pancreatic beta cell malfunction, and hyperglycemia-related malfunction are preferably treated or prevented.
Owner:PROSPECT CHARTERCARE +1
Methods for treating cancer-related fatigue
Methods for treating cancer patients suffering from severe and persistent fatigue, diagnosed as Cancer-Related Fatigue (CRF), with thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and peptidomimetic analogs of TRH.
Owner:TRH THERAPEUTICS
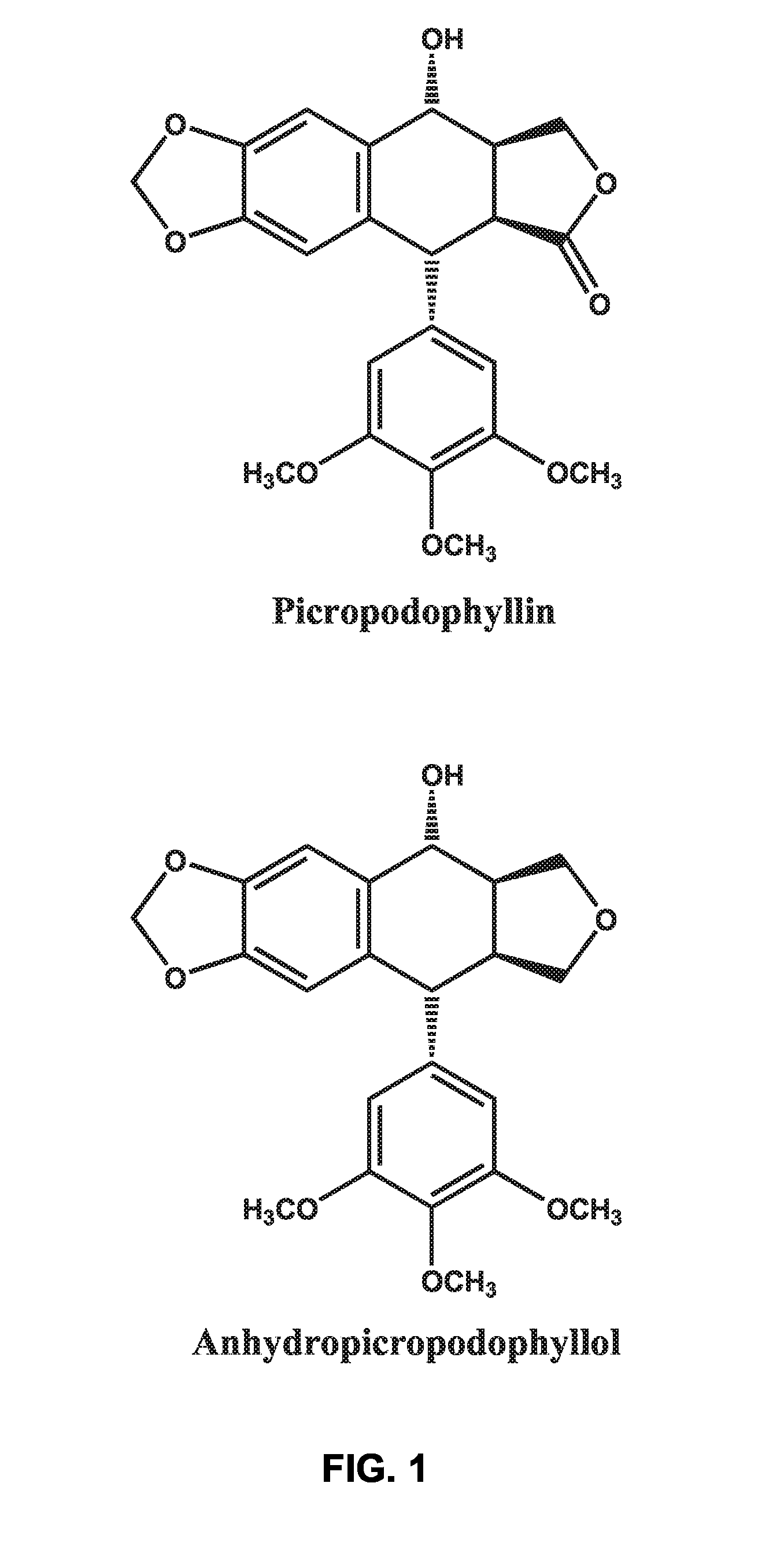
Use of cyclolignans for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and as contraceptives
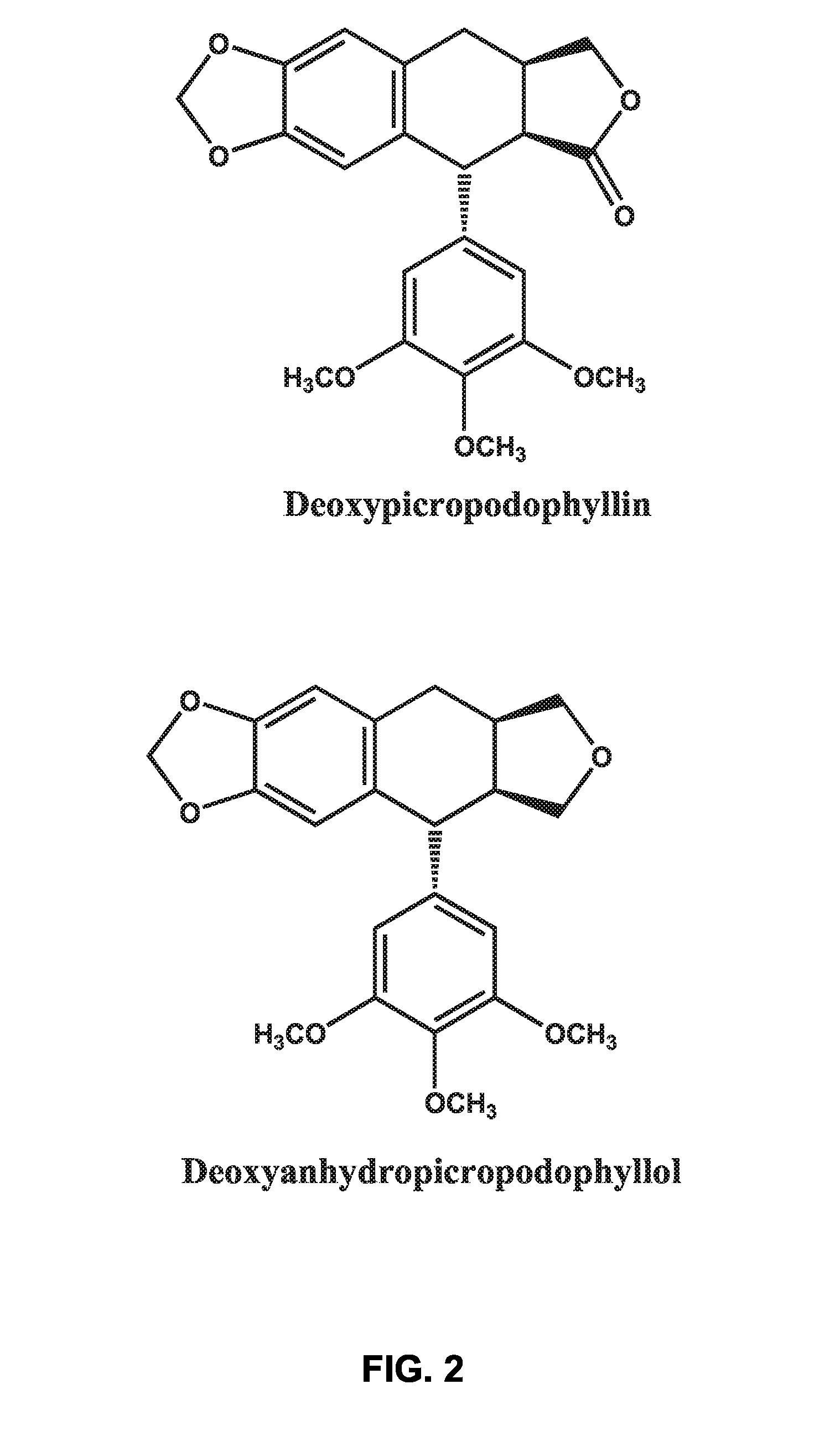
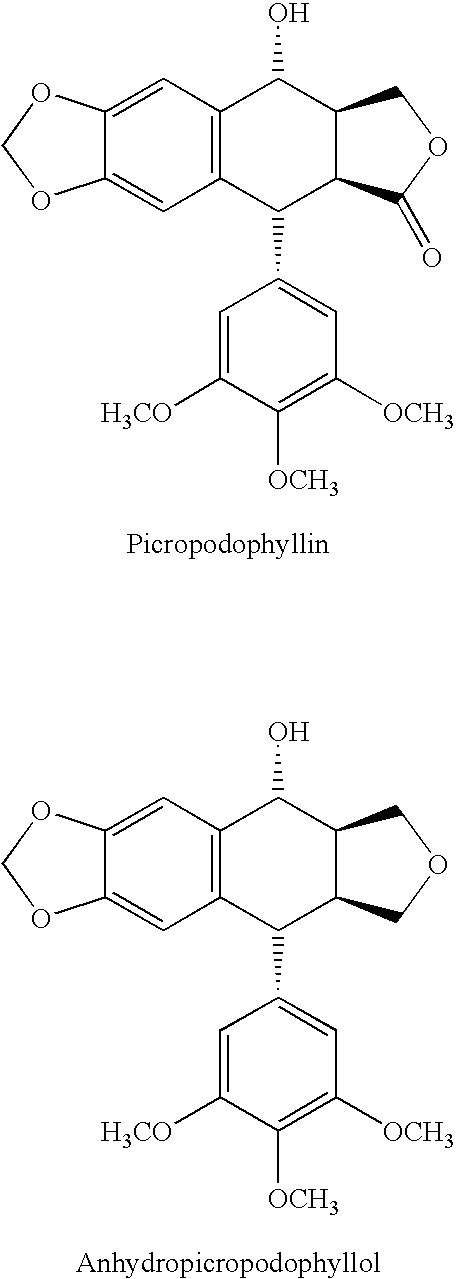
There is disclosed use of certain cyclolignans for prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2, nephropathy, retinopathy, macular degeneration, retinopathy of prematurity, central retinal vein occlusion, branch retinal vein occlusion, rubeotic glaucoma, thyroid eye disease, corneal graft rejection and corneal chemical burns; and for contraception. Preferred compounds are picropodophyllin, deoxypicropodophyllin and anhydropicropodophyllol. There is also described a method of treatment of an eye disease.
Owner:AXELAR
Inhibitors of proteasomal activity for stimulating hair growth
Compounds that inhibit the activity of NF-κB or inhibit the activity of the proteasome or both promote bone formation and hair growth and are thus useful in treating osteoporosis, bone fracture or deficiency, primary or secondary hyperparathyrdidism, periodontal disease or defect, metastatic bone disease, osteolytic bone disease, post-plastic surgery, post-prosthetic joint surgery, and post-dental implantation; they also stimulate the production of hair follicles and are thus useful in stimulating hair growth, including hair density, in subject where this is desirable.
Owner:OSTEOSCREEN IP +1
Foamable compositions and methods for disorders of the skin or mucosal surfaces
The composition of the present invention is geared towards treating hyperhidrosis or any condition involving and / or promoting excessive sweating, typically involving the whole body, include hyperthyroidism or similar endocrine disorders; endocrine treatment for prostatic cancer or other types of malignant disorder; severe psychiatric disorders; obesity and menopause. The foamable composition of the present invention is suitable for treating palmar hyperhidrosis; axillary hyperhidrosis; plantar hyperhidrosis; hyperhidrosis of the trunk and / or the thighs; and facial hyperhidrosis; and any combination of them consisting of a therapeutic foamable composition including: an active agent, suitable for the treatment or prevention of hyperhidrosis.
Owner:FOAMIX PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
Parasympathetic stimulation for heart conditions
InactiveUS20080125819A1Enhancing and sustaining efficacyImprove efficiencyHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsMyelitisNervous system
A method is provided for treating a subject, including applying a current to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, and an internal jugular vein of the subject. The method also includes configuring the current so as to treat a condition of the subject selected from the list consisting of: an autoimmune disease, an autoimmune inflammatory disease, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, myelitis, immune-mediated neuropathy, myositis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, inclusion body myositis, inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, Guillain Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, inflammation of the nervous system, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sjogren syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease, glomerulonephritis, thyroid autoimmune disease, sepsis, meningitis, a bacterial infection, a viral infection, a fungal infection, sarcoidosis, hepatitis, and portal vein hypertension.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
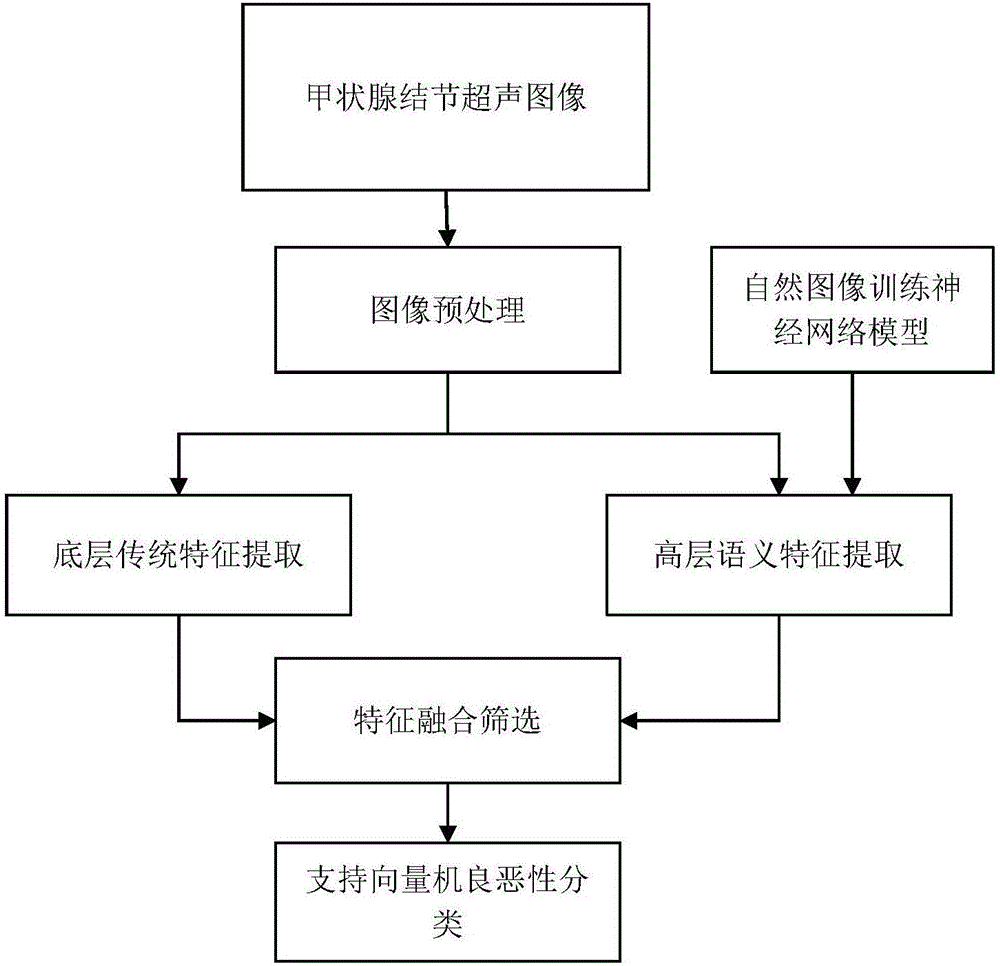
Transfer learning and feature fusion-based ultrasonic thyroid nodule benign and malignant classification method
ActiveCN106780448ADescribe the characteristics of the caseAvoiding Obstacles That Cannot Train Convolutional Neural NetworksImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationSupport vector machine classifier
The invention discloses a transfer learning and feature fusion-based ultrasonic thyroid nodule benign and malignant classification method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly preprocessing an ultrasonic image and zooming the ultrasonic image to a uniform size; extracting traditional low-level features of the ultrasonic image; extracting high-level semantic features of the ultrasonic image by using a model obtained in a natural image through deep neural network training through a transfer learning method; fusing the low-level features with the high-level features; carrying out feature screening by utilizing distinction degree of benign and malignant thyroid nodules so as to obtain a final feature vector which is used for training a support vector machine classifier; and carrying out final thyroid nodule benign and malignant classification. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the low-level features and the high-level features are fused, and salient feature screening is carried out, so that the problem that the ability of single features for describing thyroid nodule features on the level of semantic meaning is insufficient is solved, and the classification precision is effectively improved; and through importing the transfer learning, the problems that the medical sample images are few and the deep features can not be obtained by direct training are solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
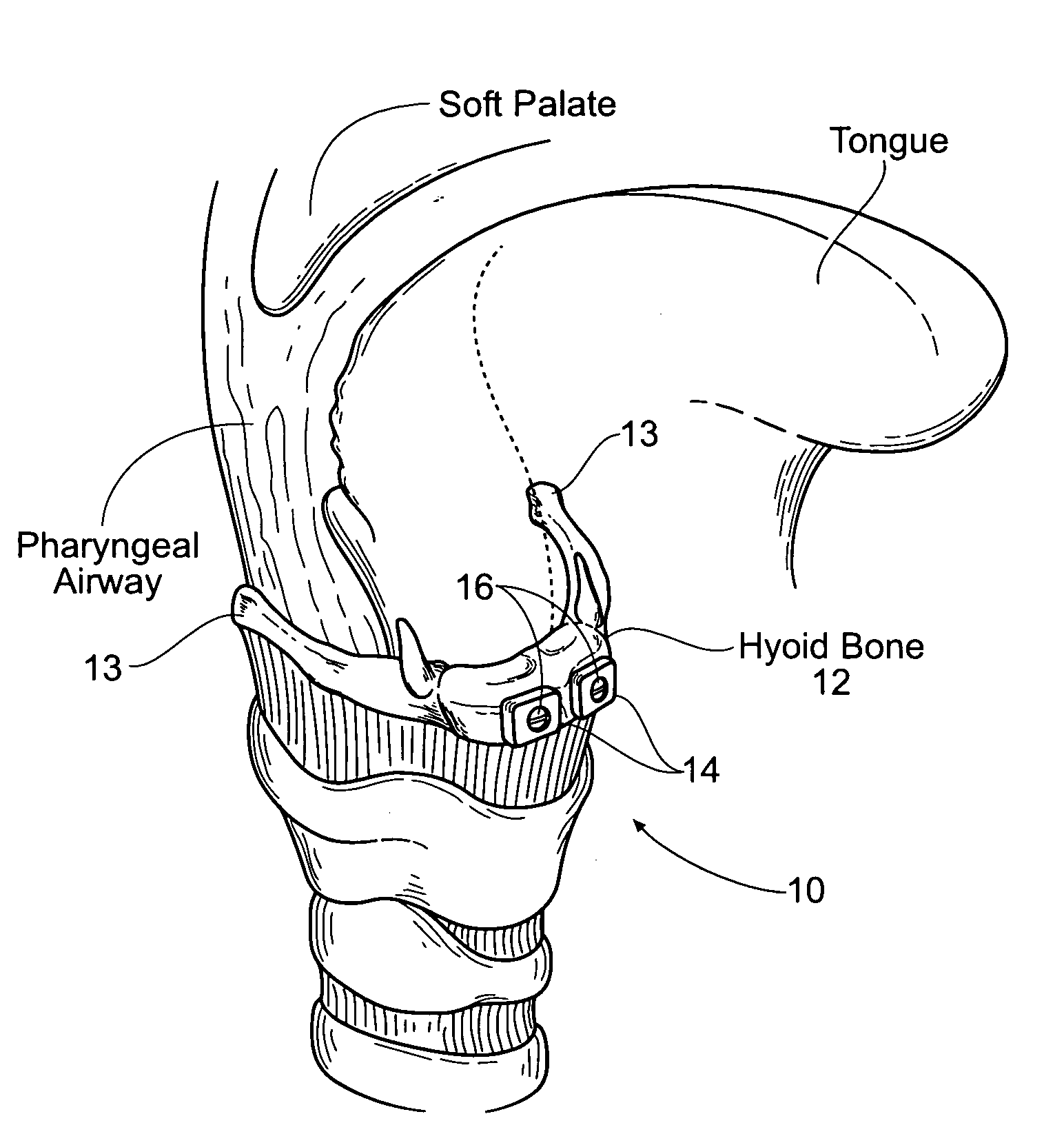
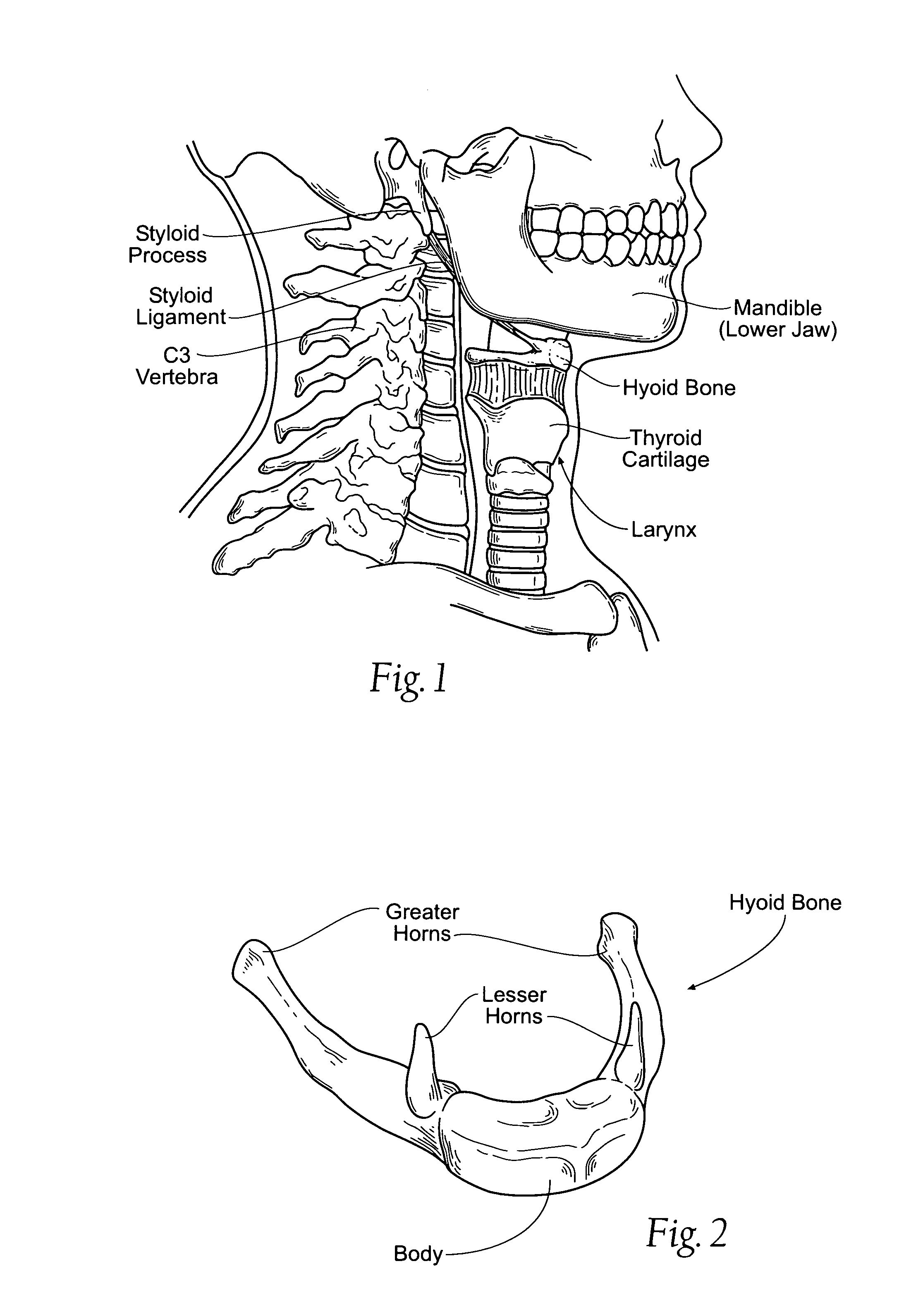
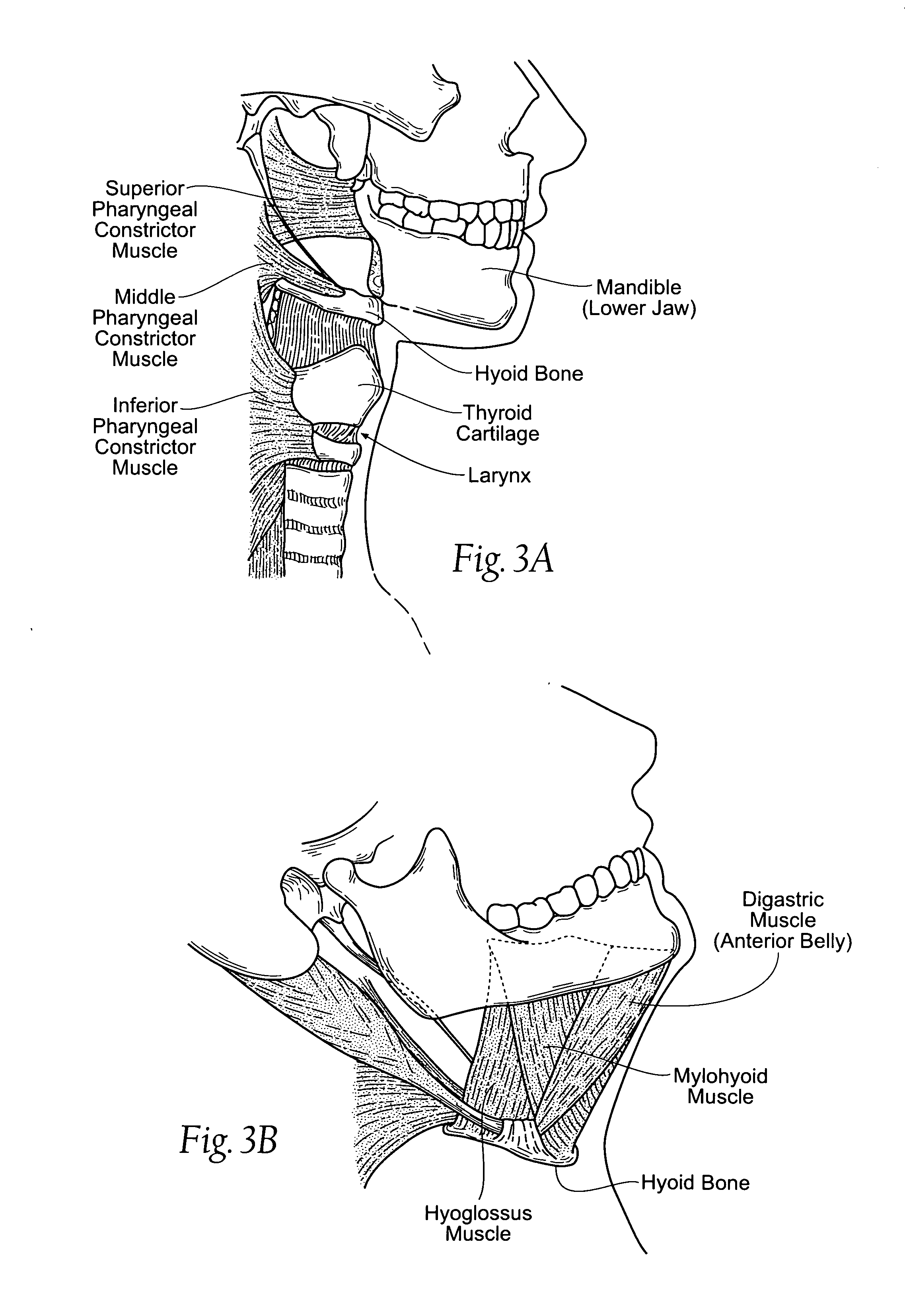
Devices, systems, and methods to move or restrain the hyoid bone
Systems and methods employ implants attached to the hyoid bone, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, or both the thyroid and cricoid cartilages and a source of magnetic force to move the hyoid bone, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, or both the thyroid and cricoid cartilages in the treatment of sleep disordered breathing, using attracting, repelling or a combination of attracting and repelling magnetic forces.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Thyromimetics for the Treatment of Fatty Liver Diseases
InactiveUS20090232879A1Low in fatPreventing and treating and ameliorating fatty liver diseaseBiocideMetabolism disorderSteatosisReceptor
The present invention is directed toward the use of thyromimetic compounds that are thyroid receptor ligands, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and to prodrugs of these compounds for preventing, treating, or ameliorating fatty liver diseases such as steatosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Antagonists of melanin concentrating hormone effects on the melanin concentrating hormone receptor
The present invention relates to the antagonism of the effects of melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) through the melanin concentrating hormone receptor which is useful for the prevention or treatment of eating disorders, weight gain, obesity, abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water / electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Use of gaseous nitric oxide as an anti-cancer agent
InactiveUS20070275100A1Effectively deliver gaseous NOEfficient procedureBiocideBronchoscopesCell phenotypeAnticarcinogen
The invention relates to a method for treating, controlling, or preventing cancerous cell phenotypes and growths in an animal involving the administration of gaseous nitric oxide to one or administration sites in a body. The invention generally is capable of treating cancers found in or on the adrenal gland, bladder, bones, brain, breast, cervix, colon, colorectum, esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney, liver, large intestine, lungs, mouth, ovaries, pancreas, parathyroid, pituitary gland, prostate, salivary gland, skin, small intestine, spleen, stomach, thymus, thyroid, testicles, urinary tract, uterus, vagina, and so forth.
Owner:PULMONOX TECH
Recombinant glycoproteins related to feline thyrotropin
Amino acid sequences of feline thyrotropin and polynucleotide sequences encoding feline thyrotropin are provided, as well as methods of making and using said sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
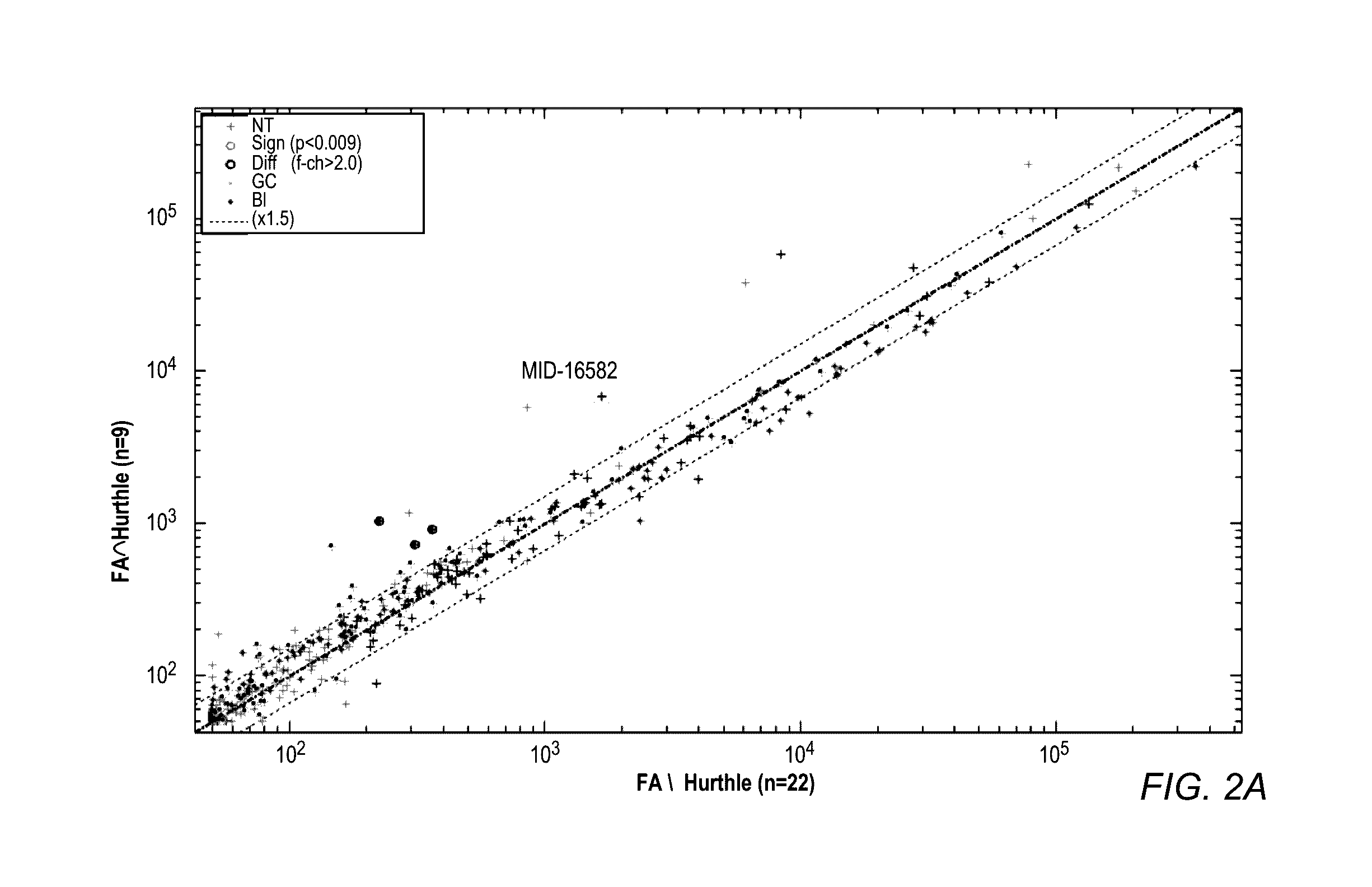
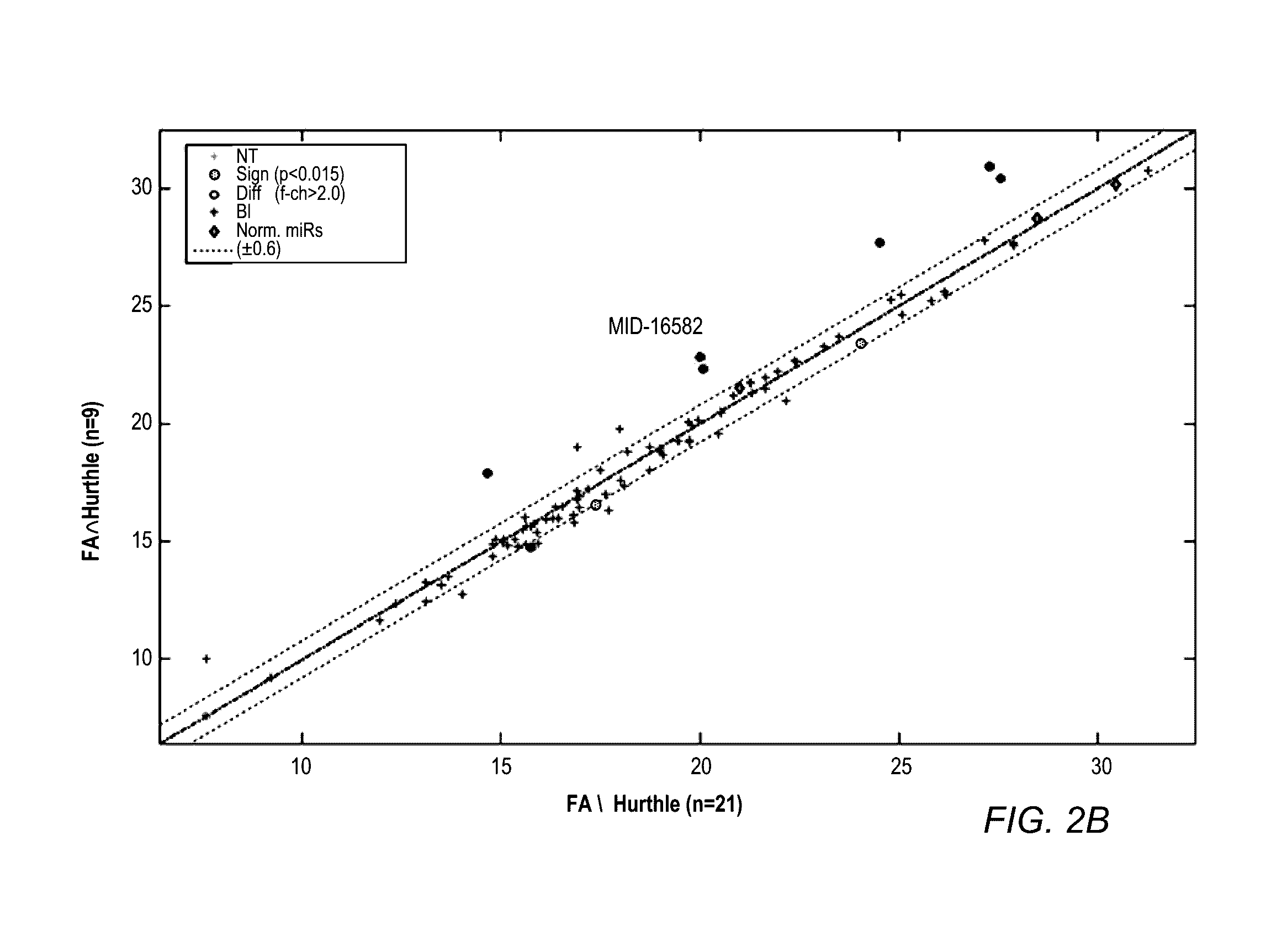
Mirna expression signature in the classification of thyroid tumors
The present invention provides a method for classification of thyroid tumors through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs in fine needle aspiration samples. Thyroid tumor classification according to a microRNA expression signature allows optimization of diagnosis and treatment, as well as determination of signature-specific therapy.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Thyroid tumor ultrasonic image recognition method and device
InactiveCN108520518AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationMalignant Thyroid Tumor
The invention discloses a thyroid tumor ultrasonic image recognition method and device, and the method comprises the steps: selecting a tumor region in a thyroid tumor ultrasonic image, extending a certain boundary scope and then performing cutting, carrying out the benign and malignant marking, and enabling the cut images to form a training set; training a selected CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) through the training set, and forming a thyroid tumor ultrasonic image recognition model; obtaining a to-be-recognized thyroid tumor ultrasonic image, selecting a tumor region and extending a certain boundary scope, and carrying out the benign and malignant recognition through the thyroid tumor ultrasonic image recognition model. The method and device are used for assisting a doctor to diagnose the benign and malignant thyroid tumors, obtain the accuracy of 90% or greater in the detection test of the benign and malignant thyroid tumors through the thyroid tumor ultrasonic image, and is ofgreat reference significance to the actual clinical diagnosis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT +1
Compositions and methods for regulating thyroid hormone metabolism and cholesterol and lipid metabolism via the nuclear receptor car
InactiveUS20050106635A1Regulating basal metabolic rateCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDyslipidemiaBlood lipids
Methods for identifying agents which alter thyroid hormone metabolism or cholesterol and lipid metabolism by modulating expression and / or activity of the nuclear receptor CAR are provided. Also provided are compositions containing such agents and methods of using such agents to alter thyroid hormone metabolism or cholesterol and lipid metabolism in a subject. Administration of such agents is useful in the treatment of conditions such as obesity, cholesterolemia and dyslipidemia.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com