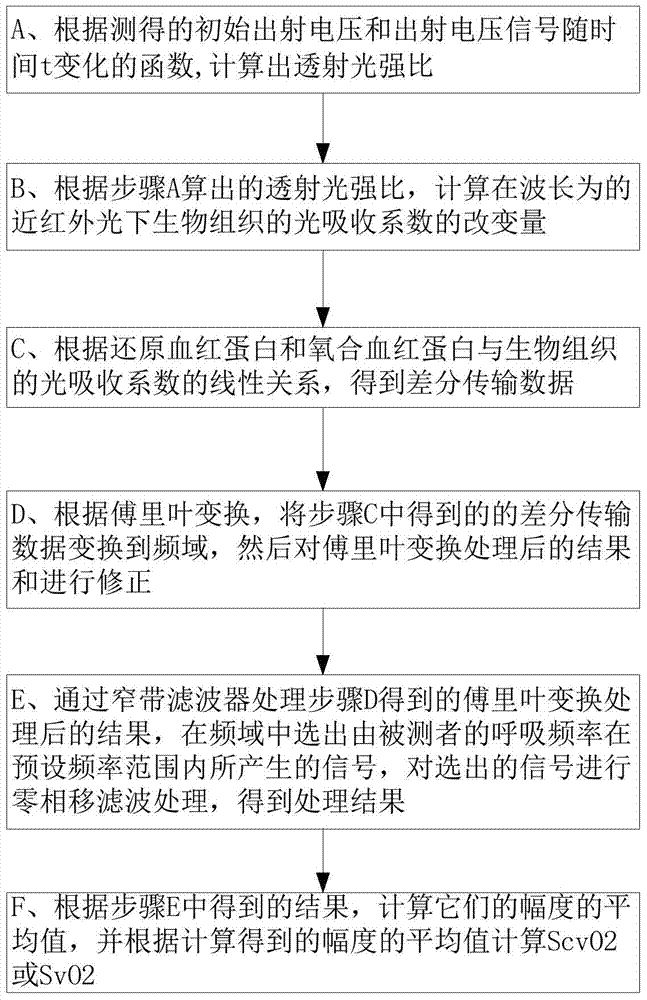
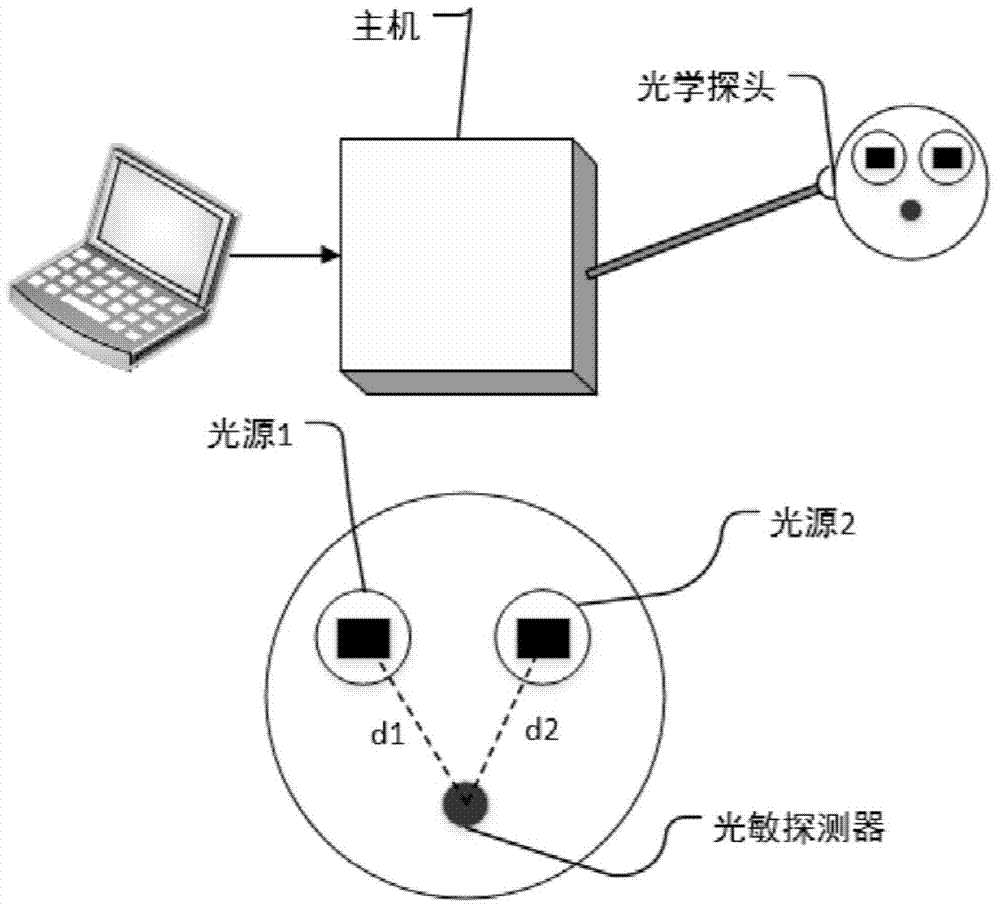
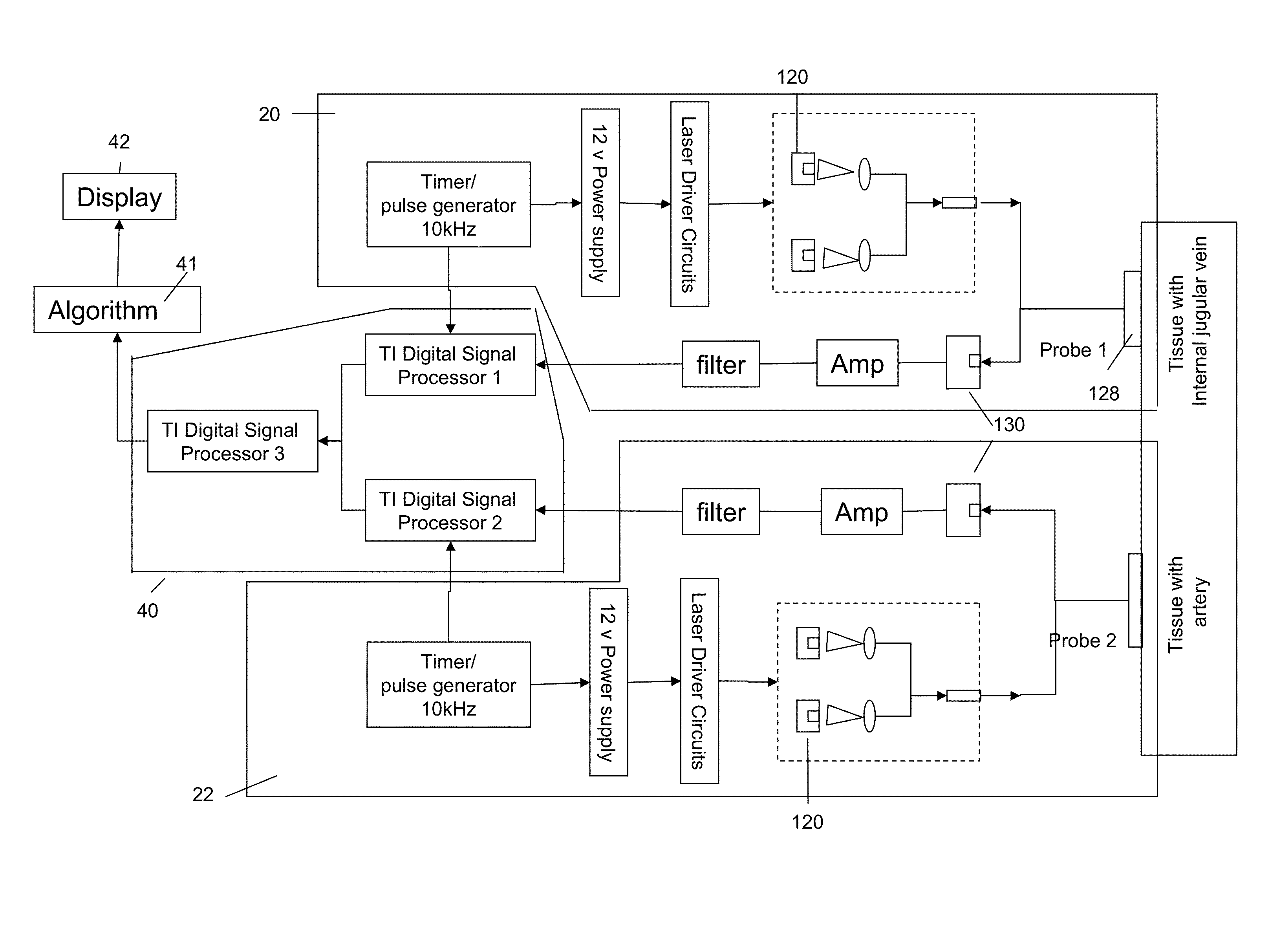
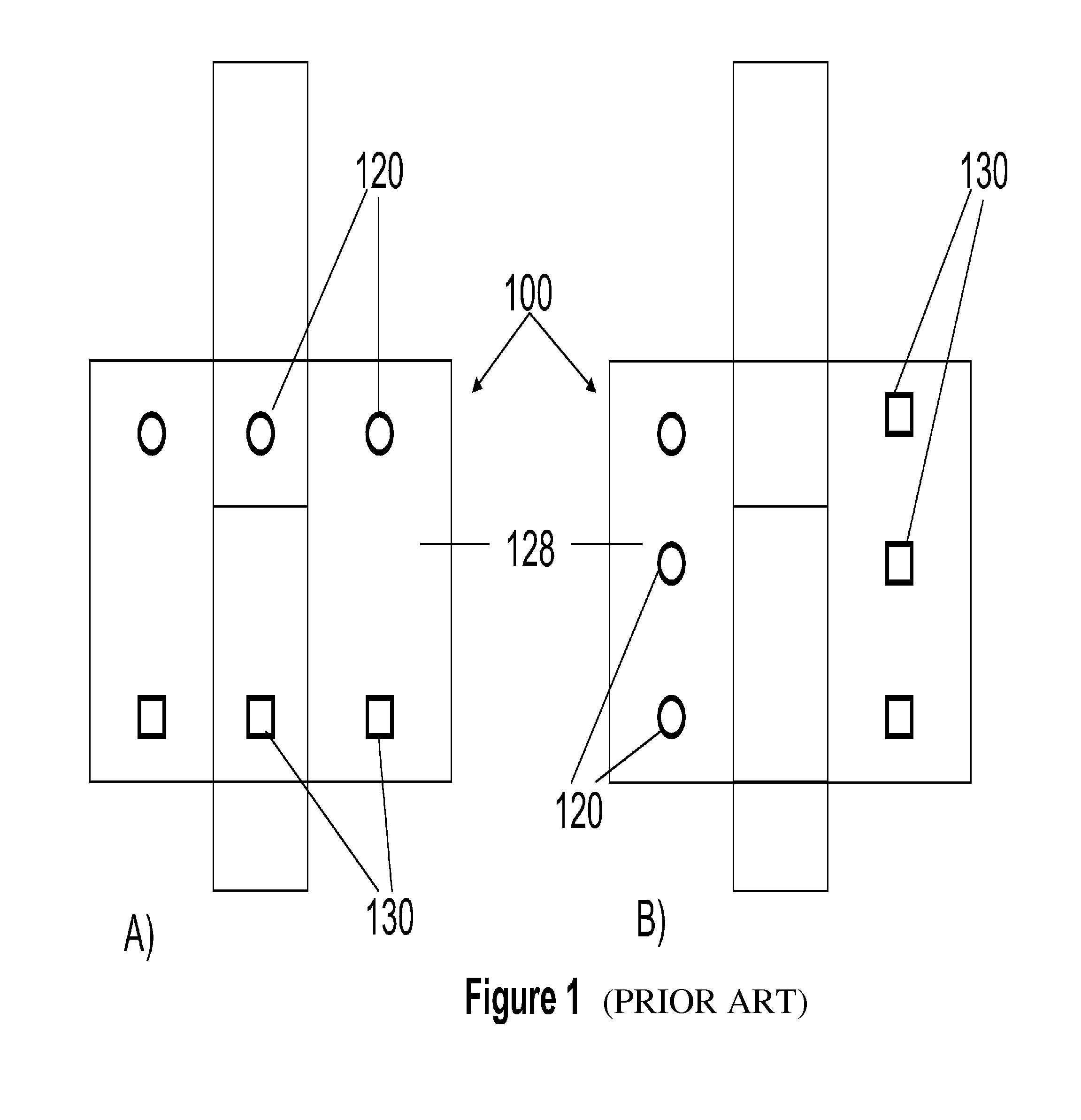
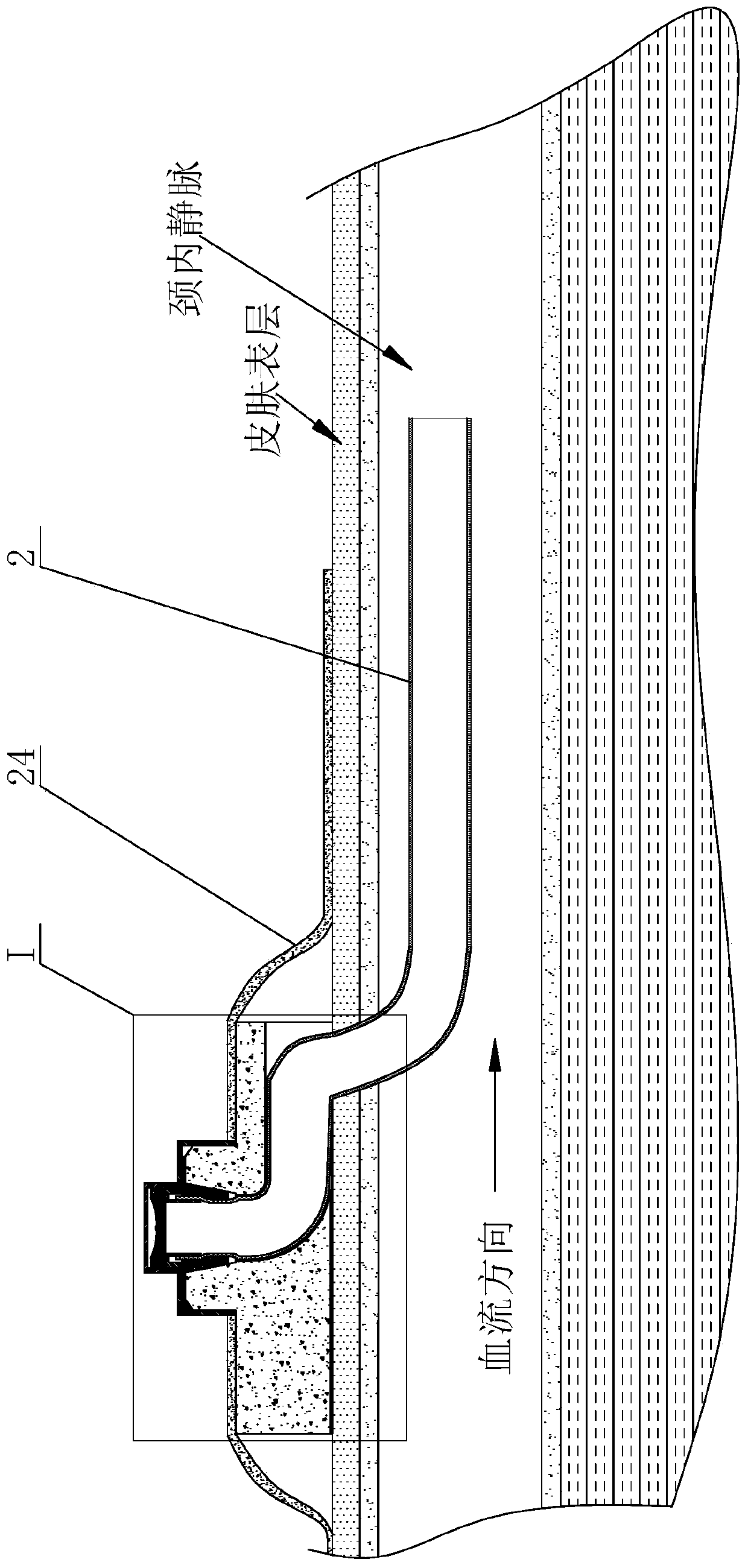
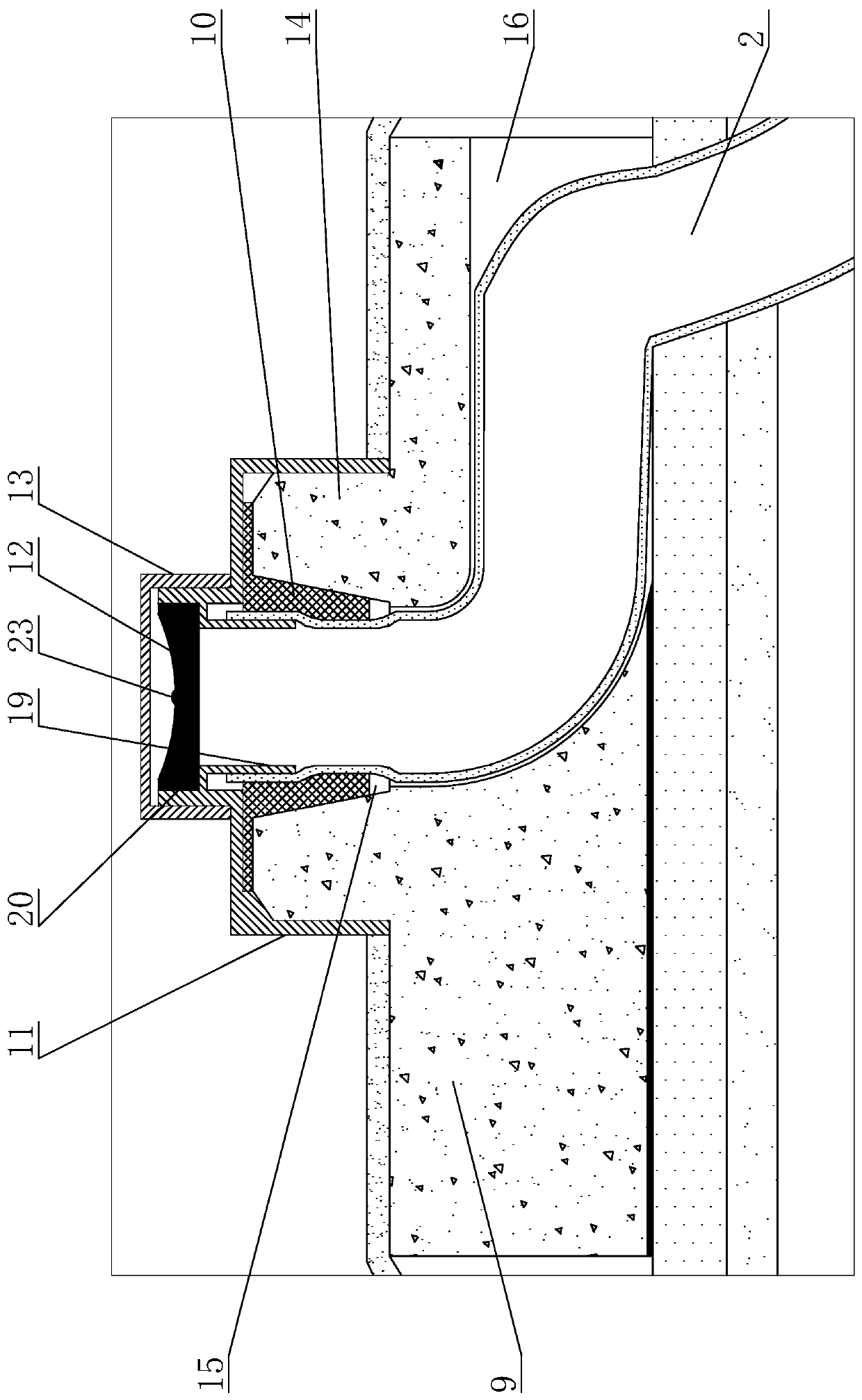
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Internal jugular vein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
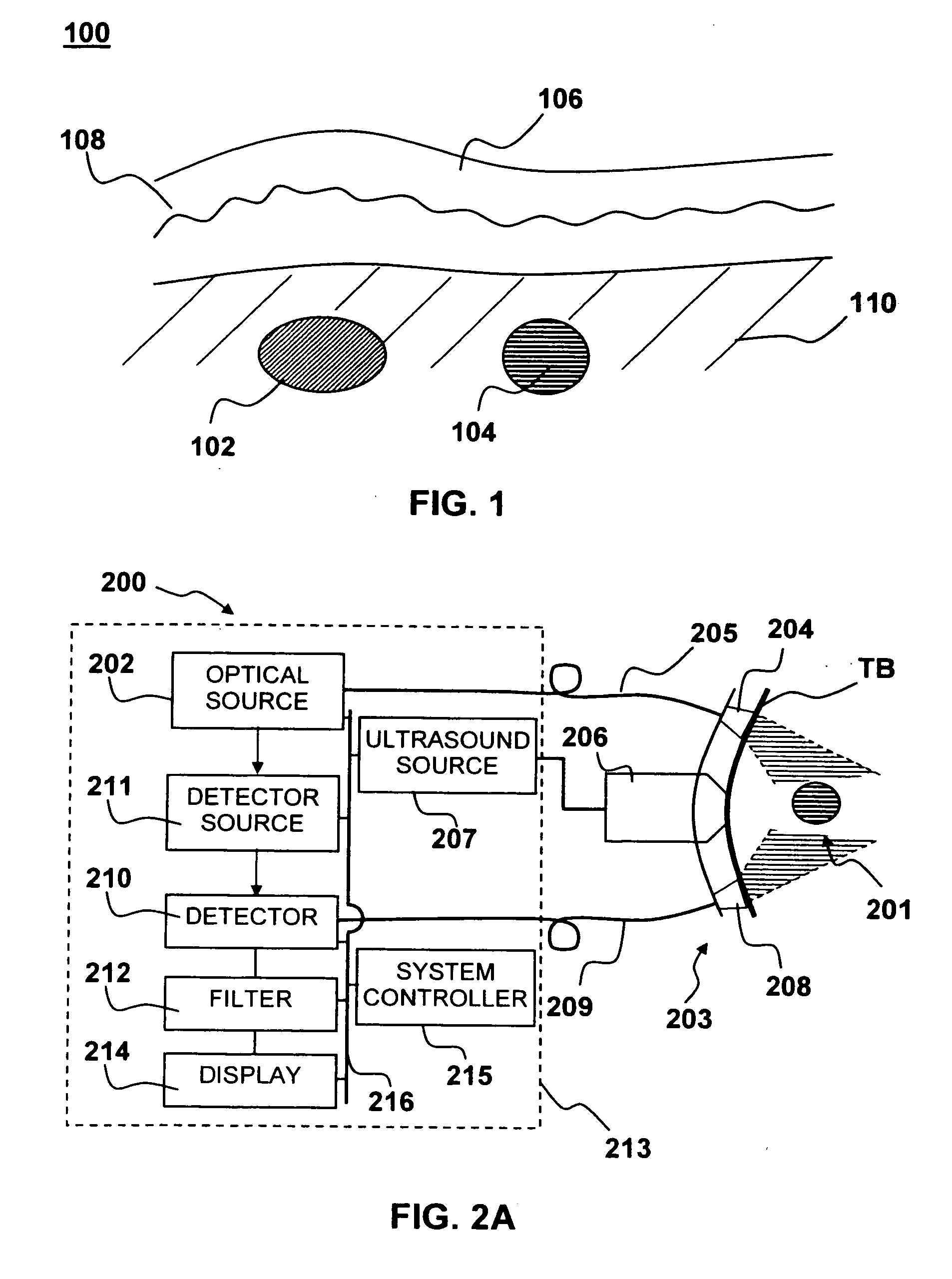
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. The vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.
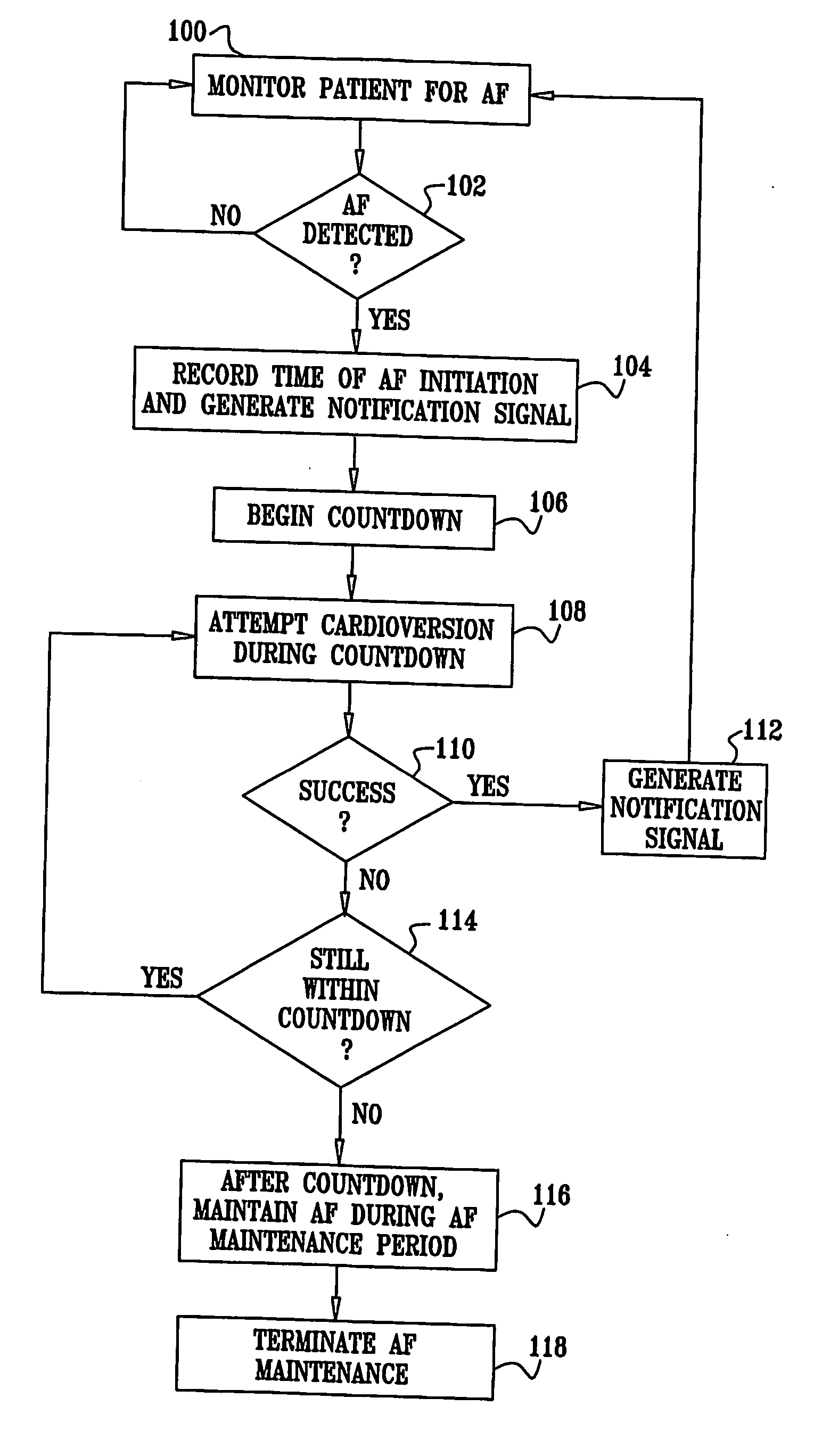
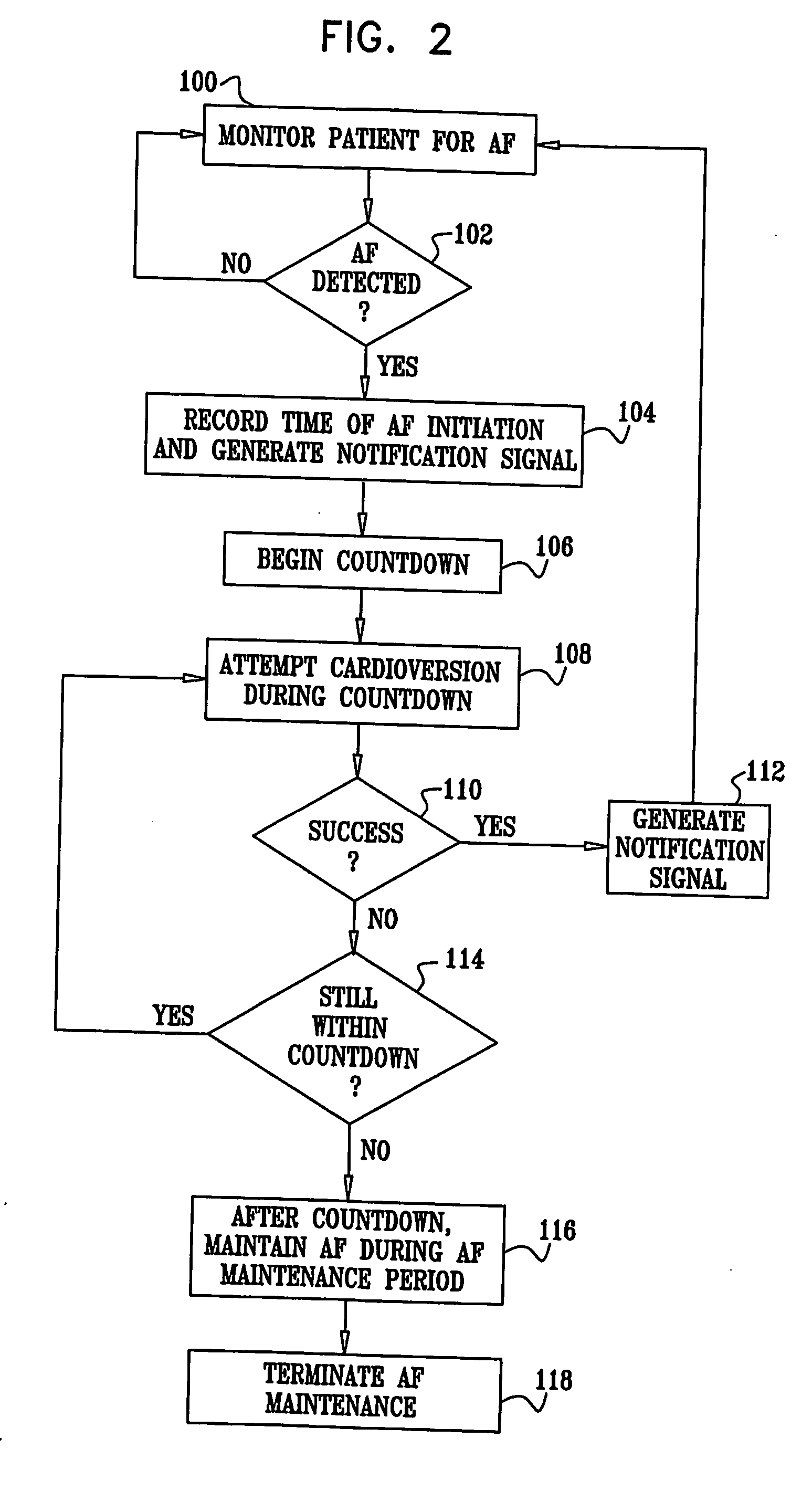
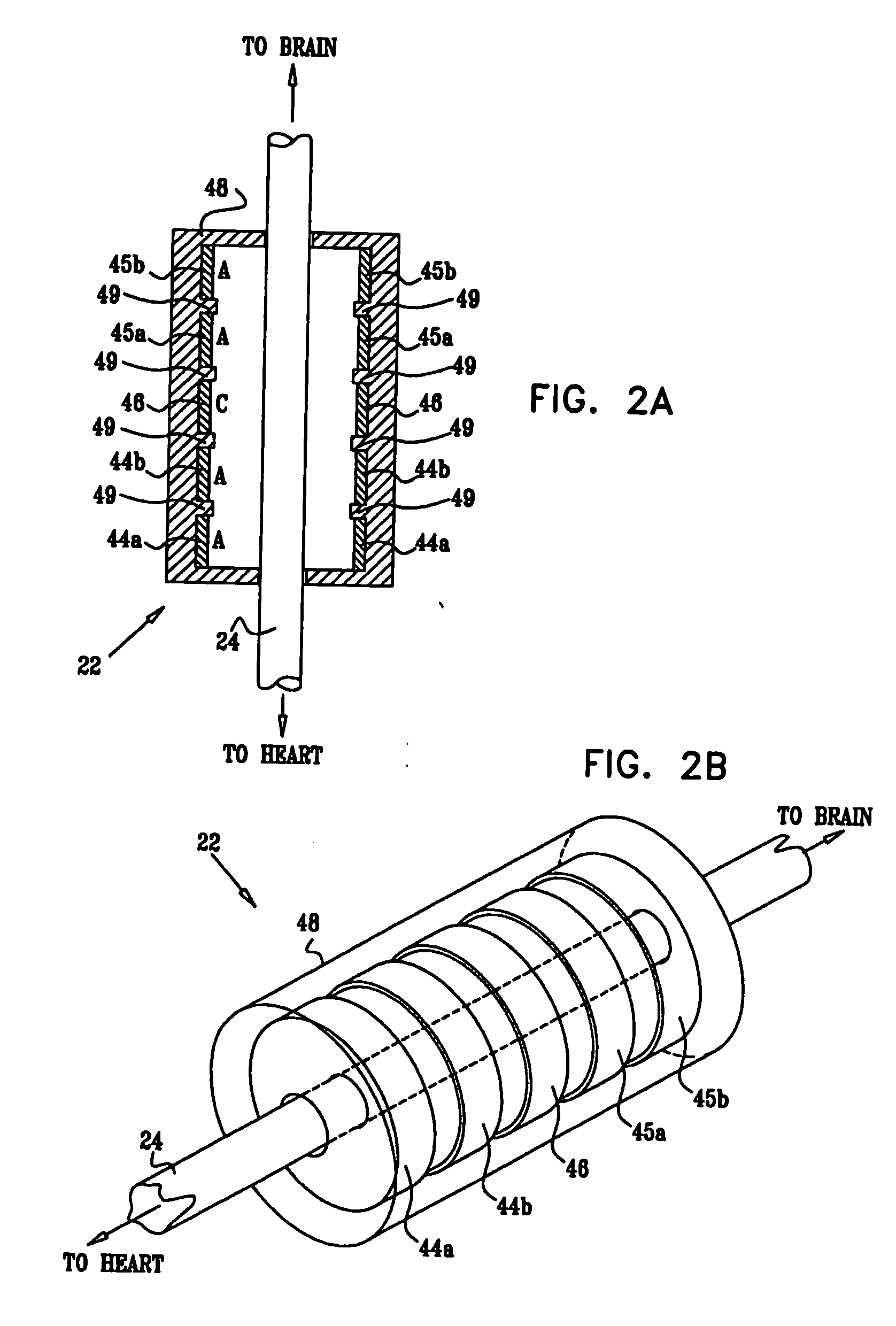
Retrograde perfusion monitoring and control system
InactiveUS6110139AOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsOrgan systemCardiopulmonary bypass time
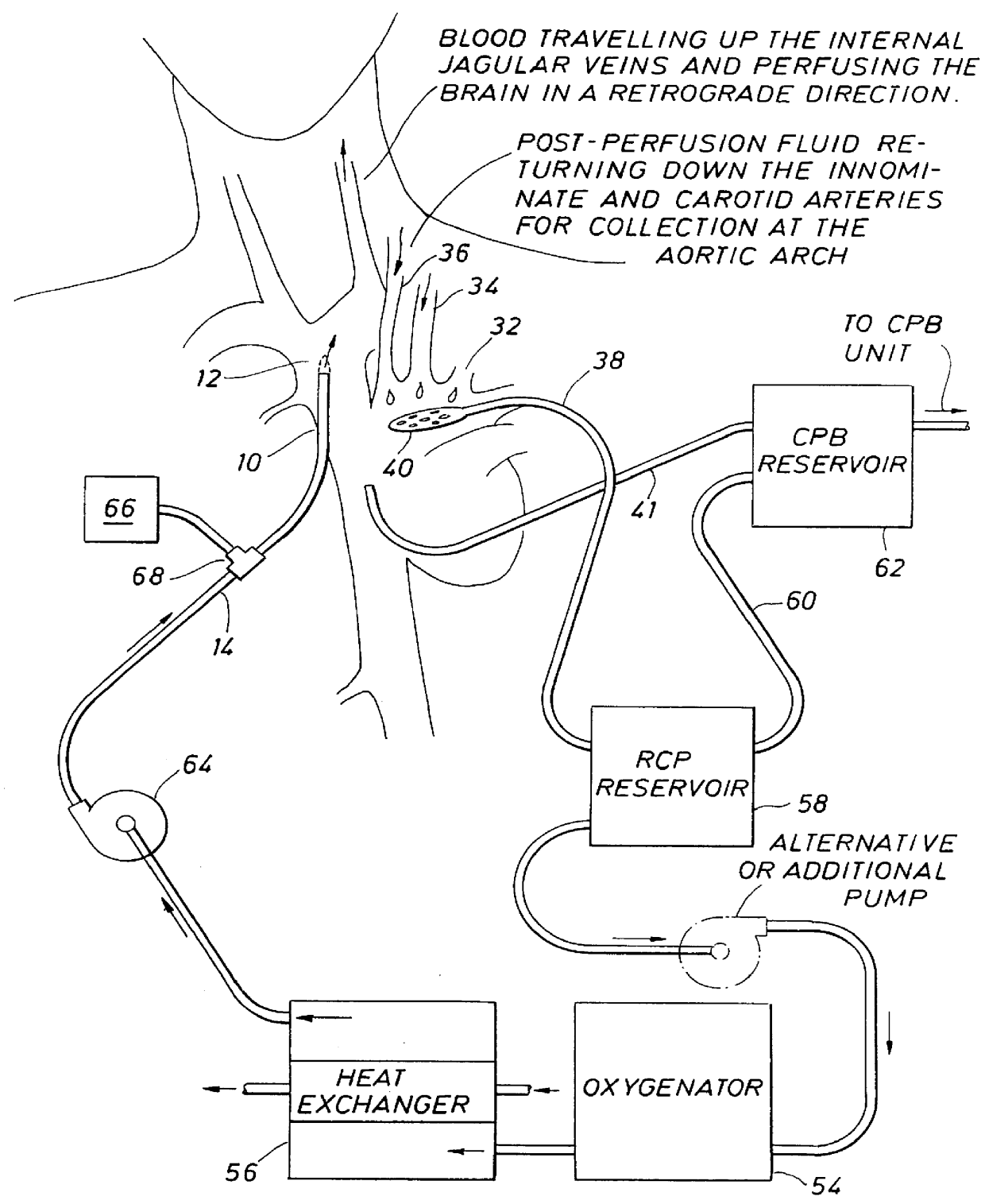
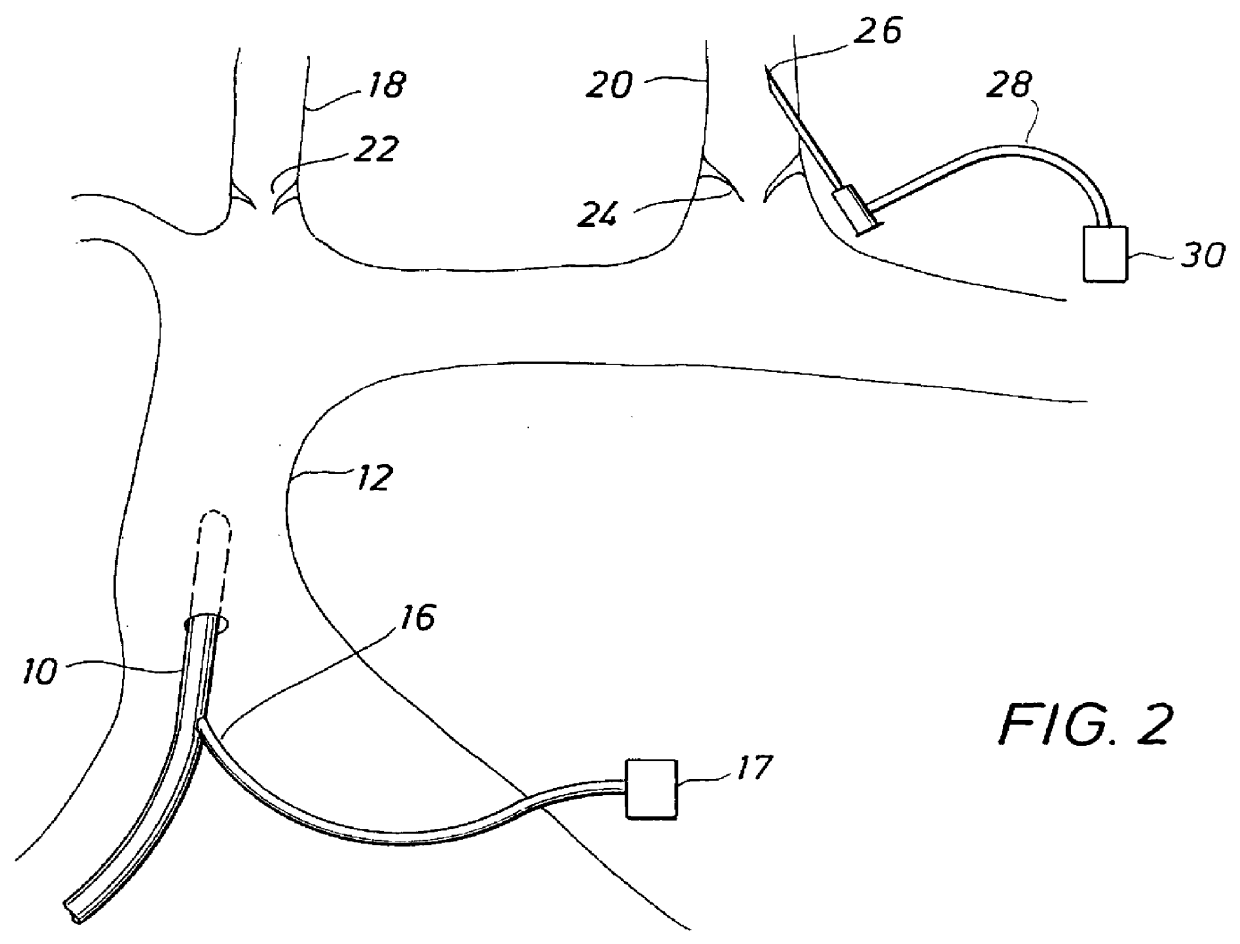
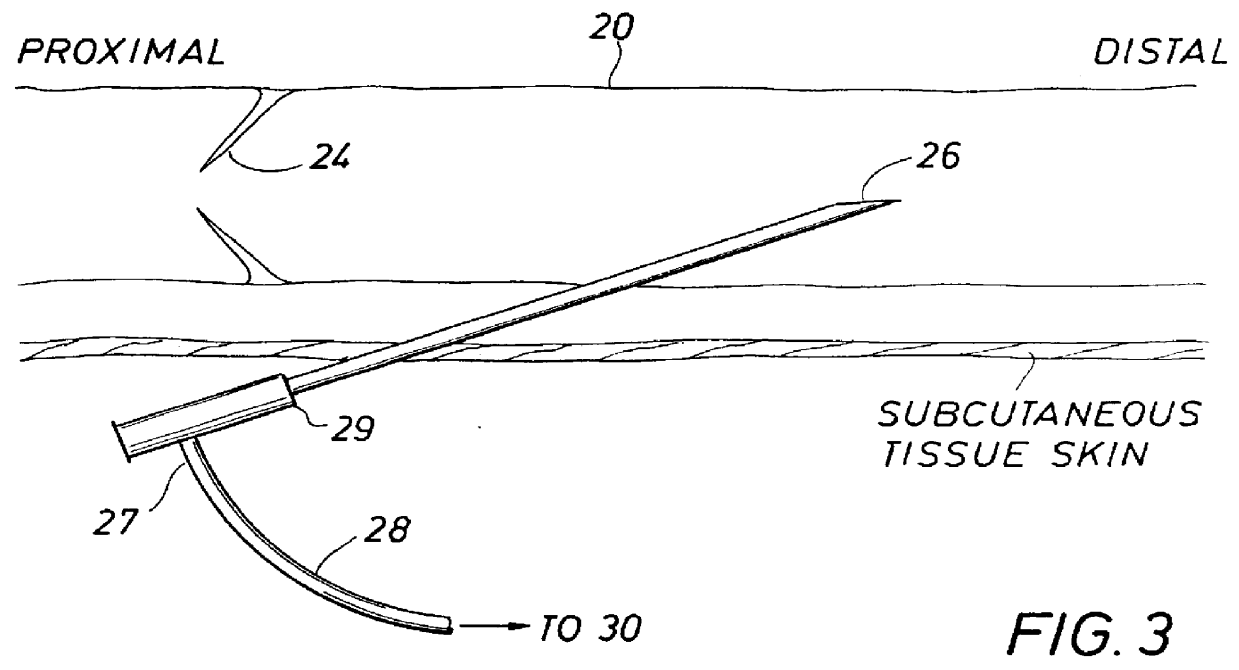
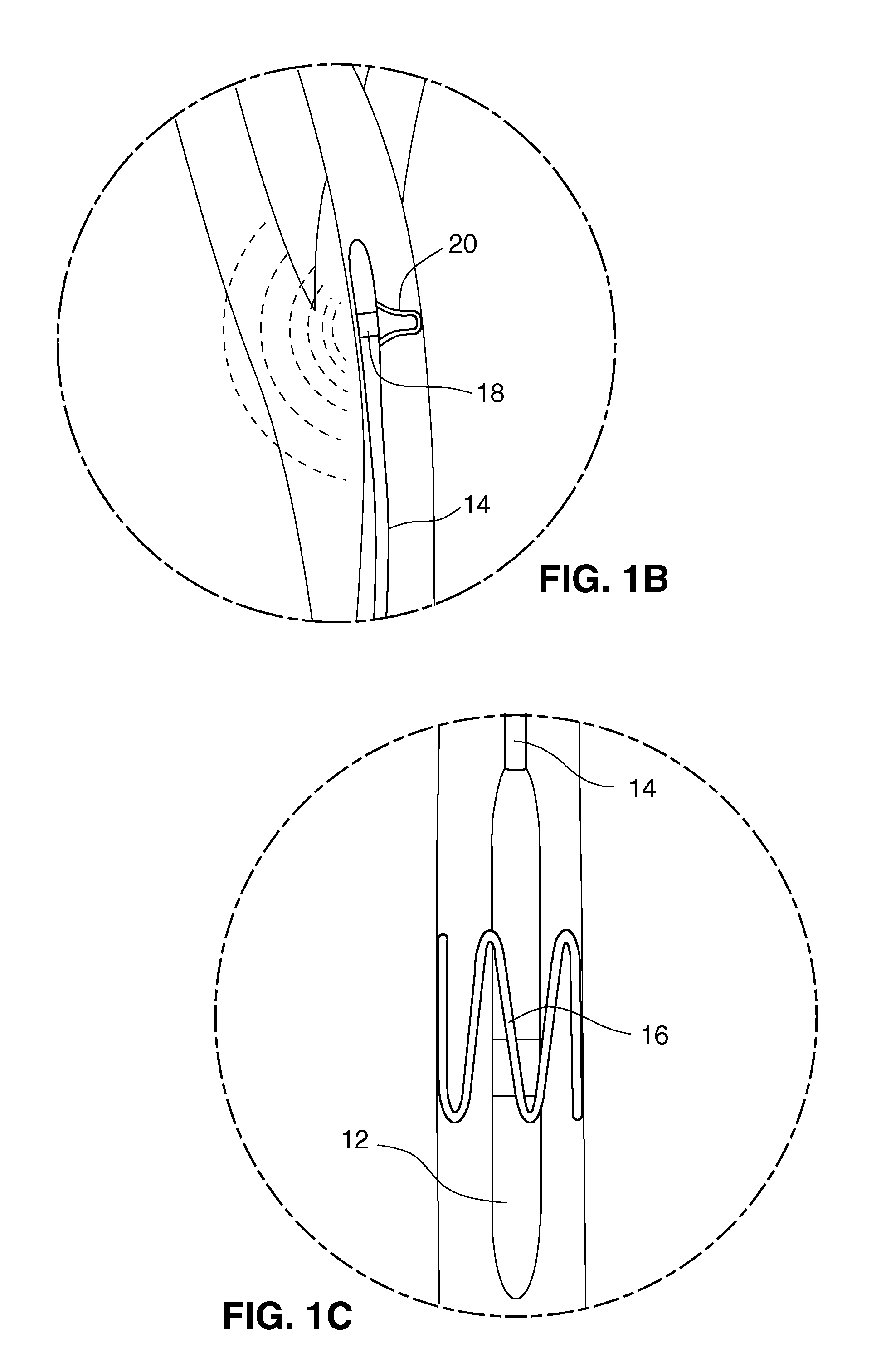
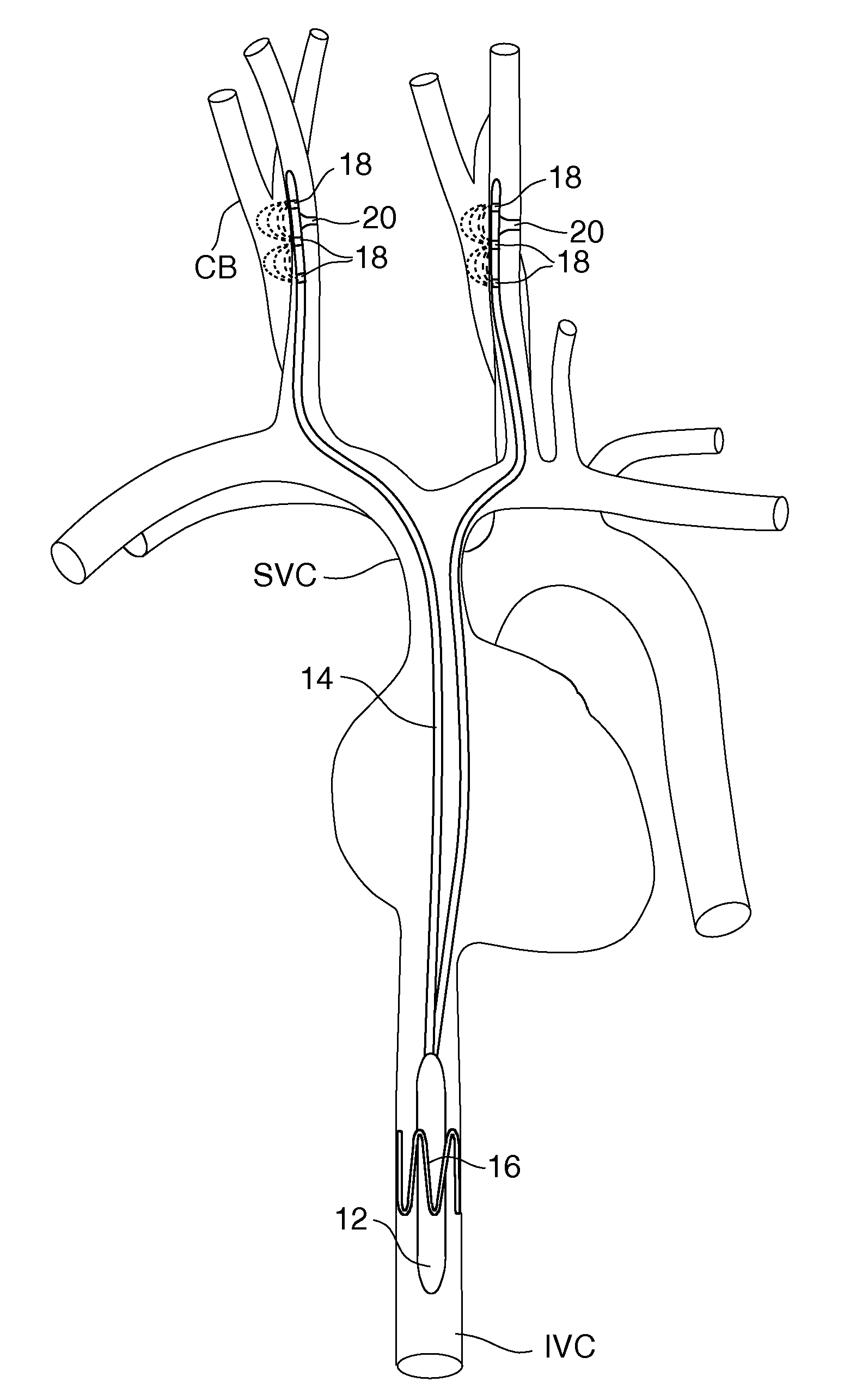
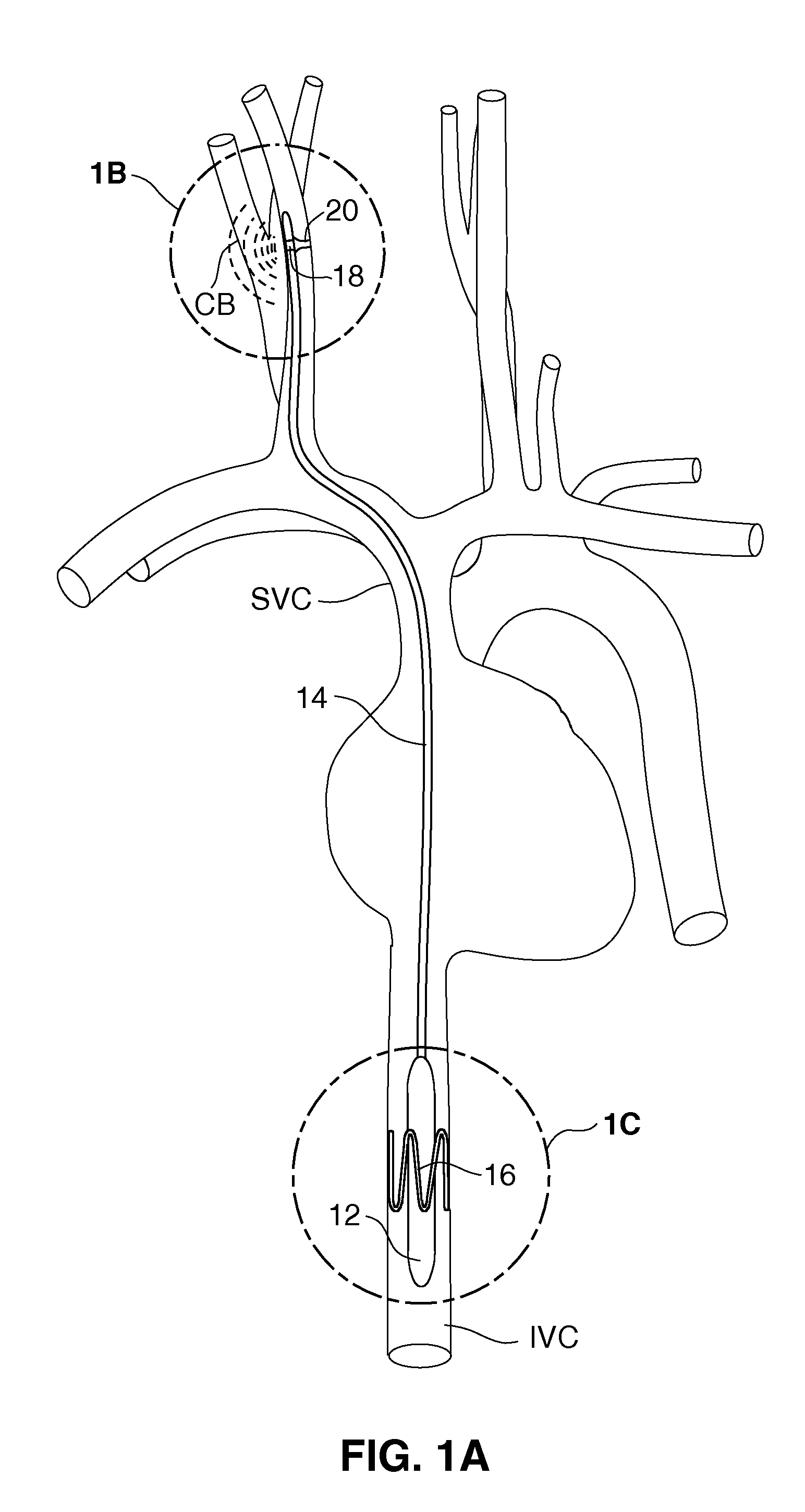
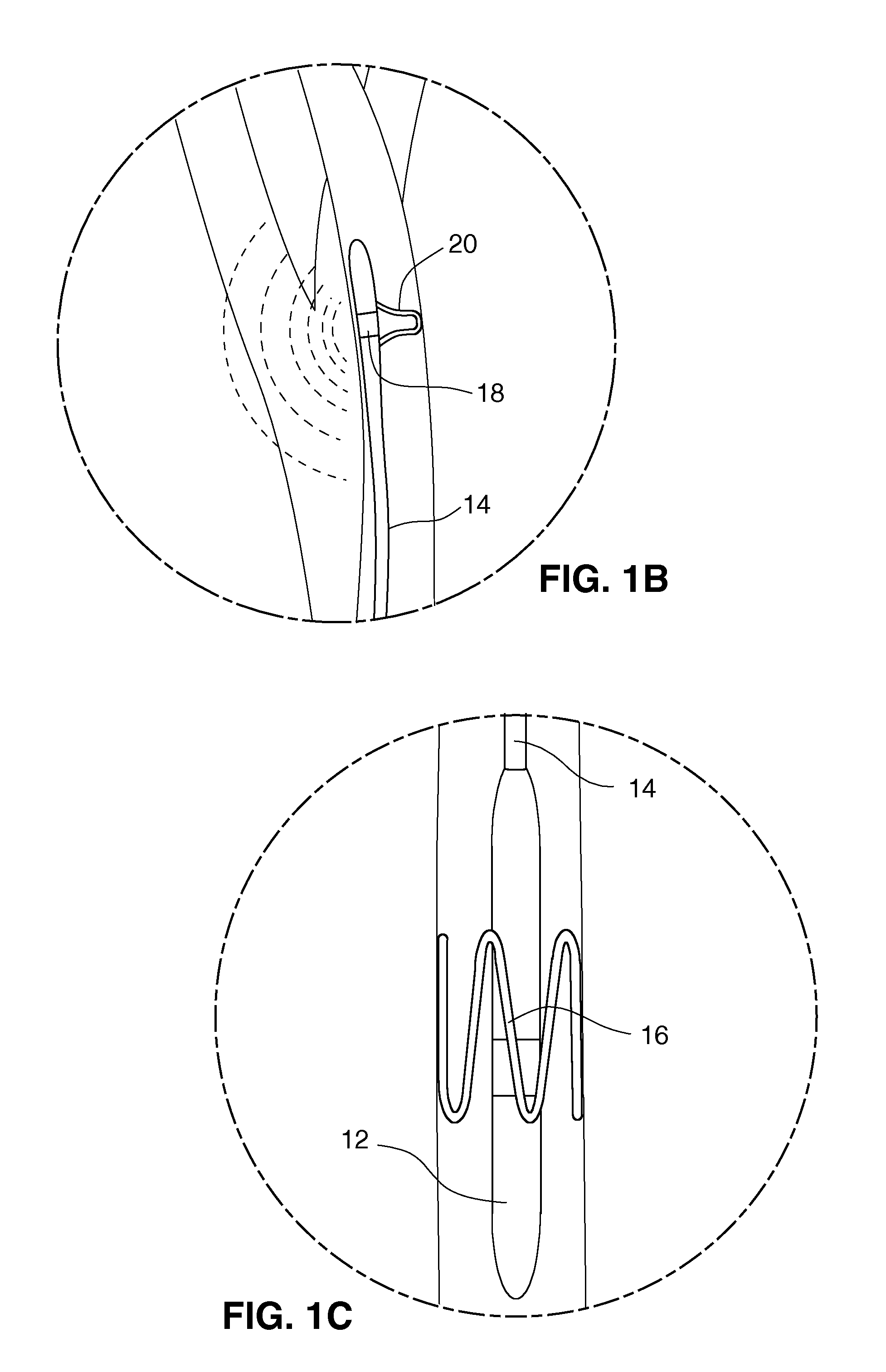
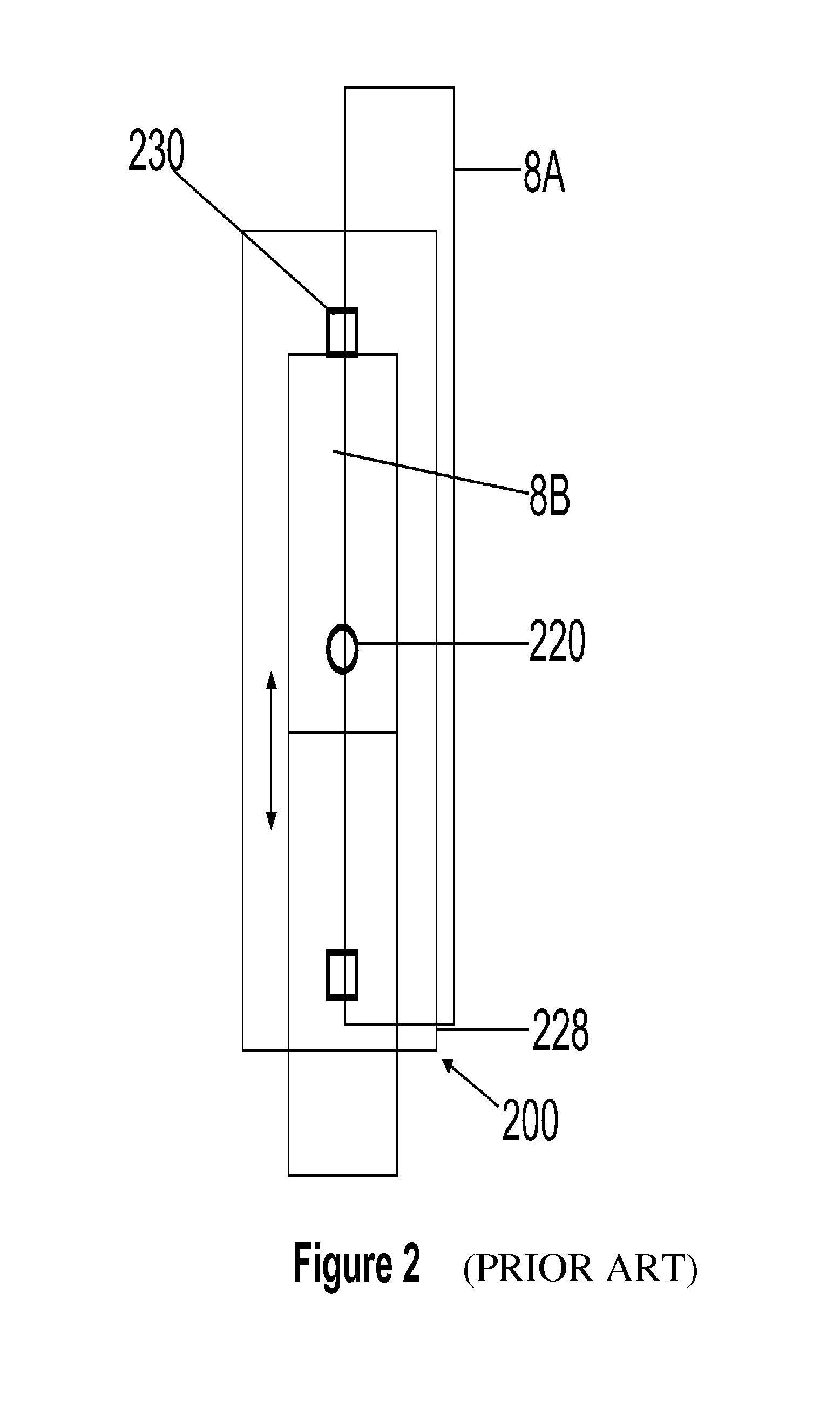
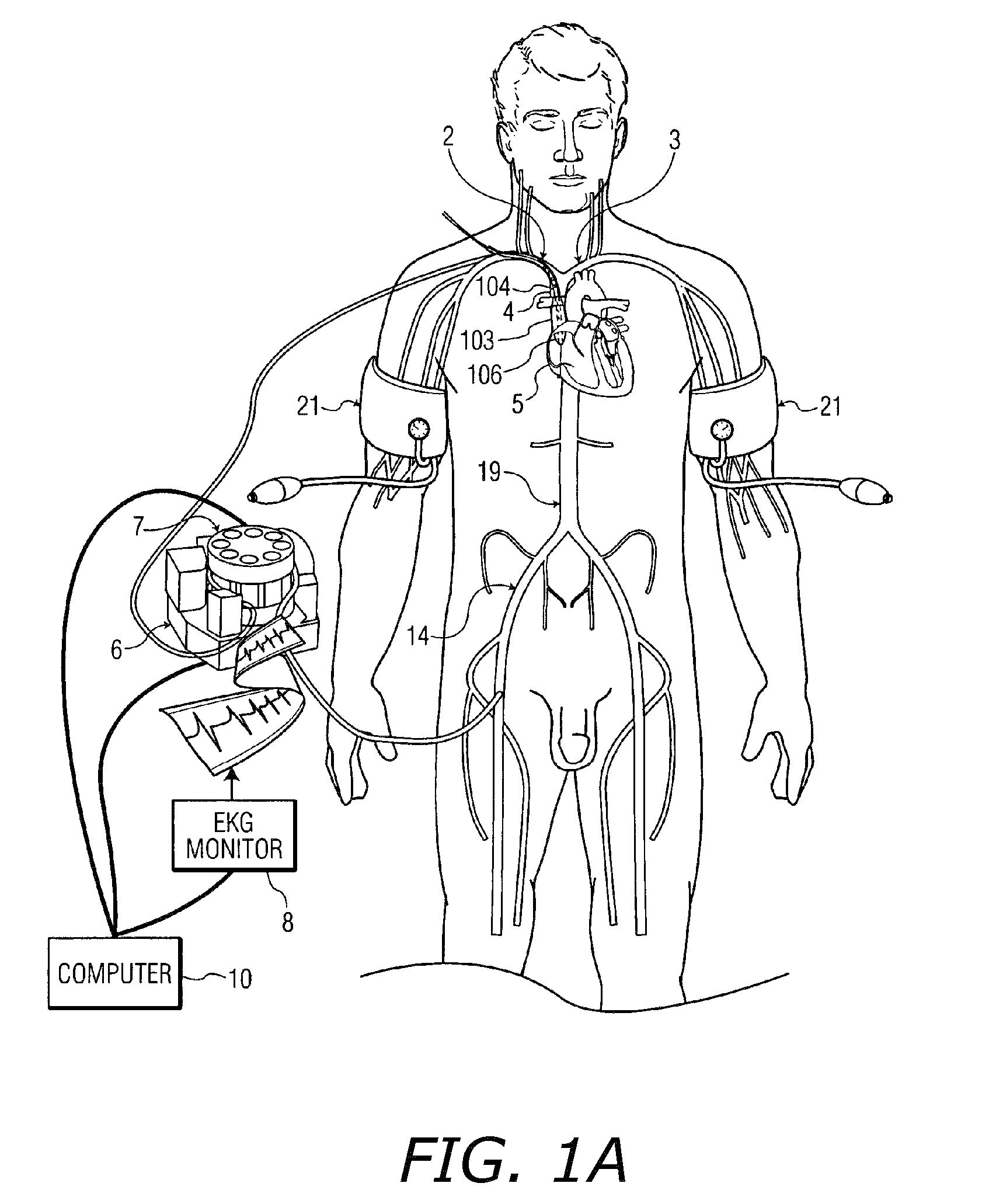
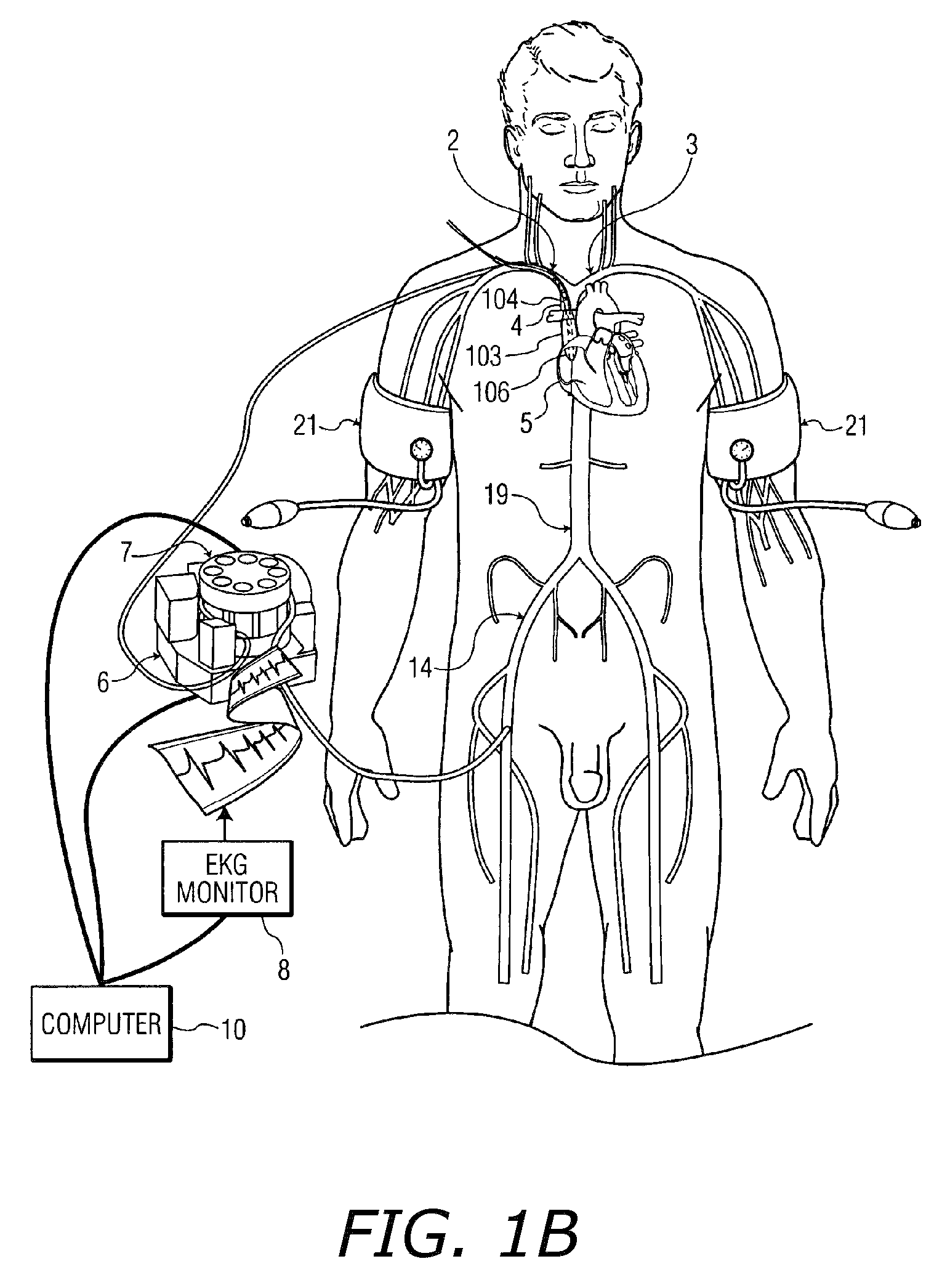
Apparatus and methods for performing retrograde perfusion, especially during cardiopulmonary bypass operations, including dedicated pediatric scaled apparatus for retrograde perfusion of an adult human organ, organ system, or limb, especially the brain, employing small scale oxygenators and heat exchangers such as are designed for pediatric surgery; also including methods and apparatus for retrograde cerebral perfusion, using nonselective infravalvular cannulation of the superior vena cava, estimating the efficacy of cerebral perfusion by monitoring fluid flow across a valve of an internal jugular vein, modification of inflow pressure and administration of pharmacologic agents, and increasing fluid flow into a brain by occlusion of an inferior vena cava distal to its junction with an azygos vein.
Owner:LOUBSER PAUL GERHARD
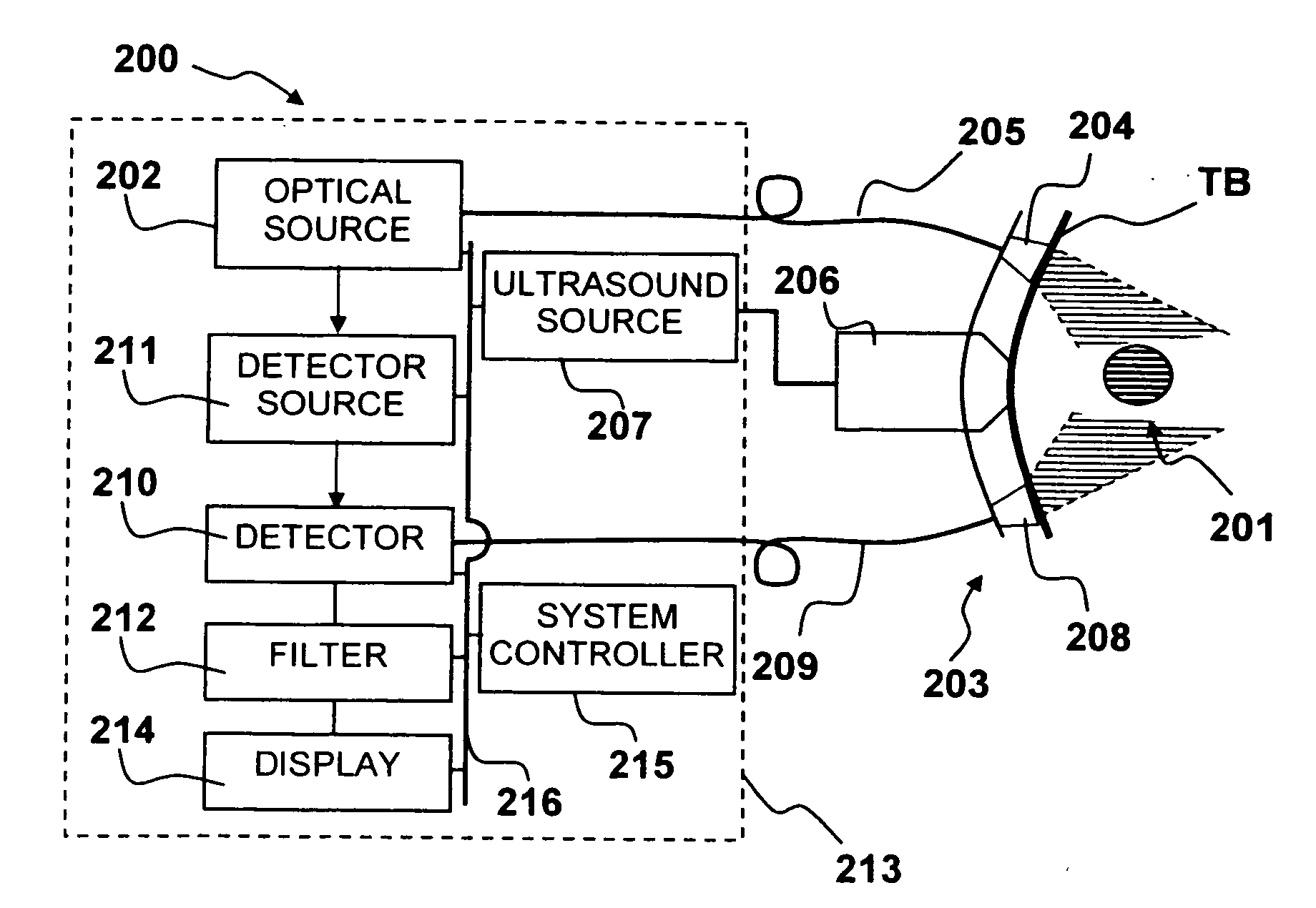
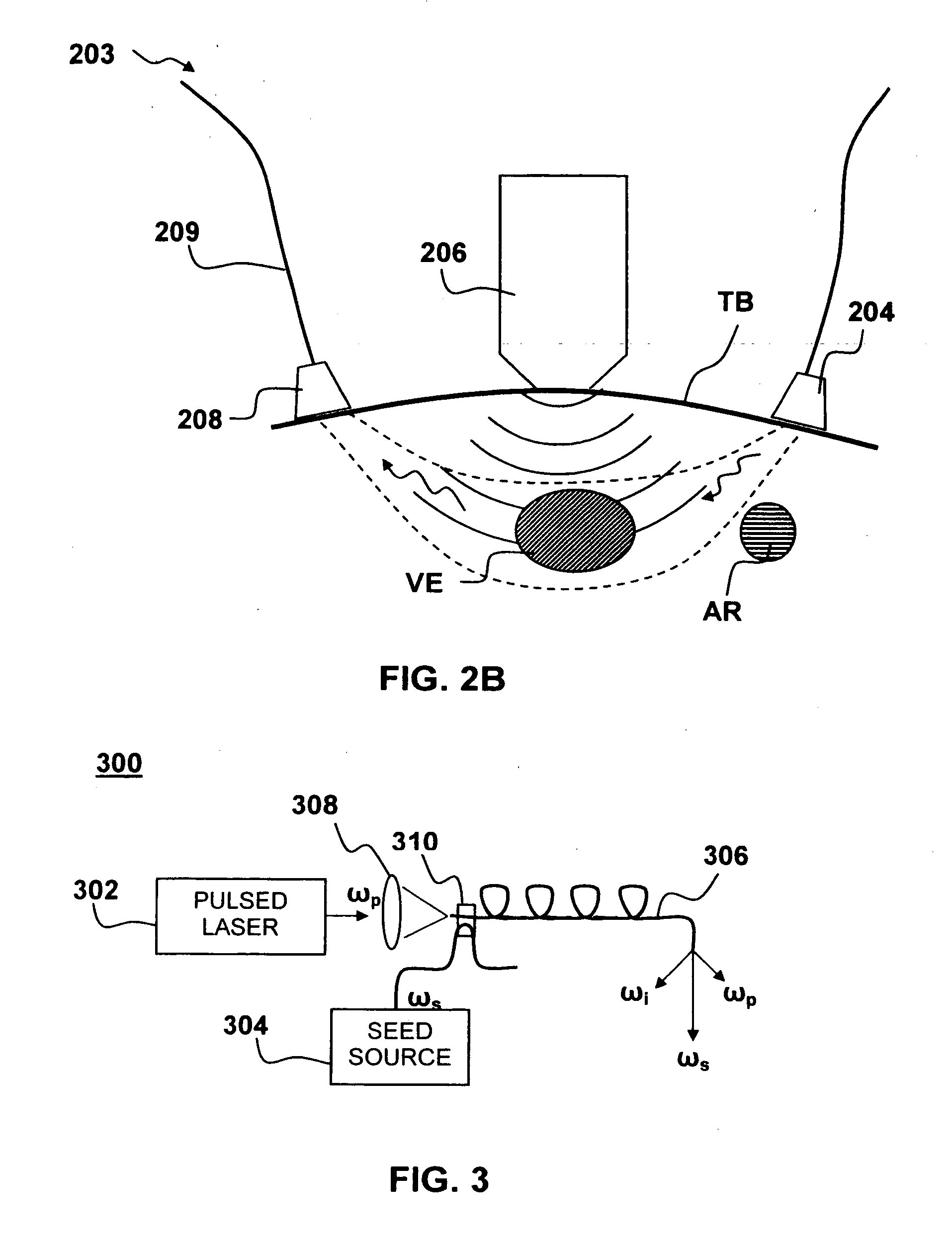
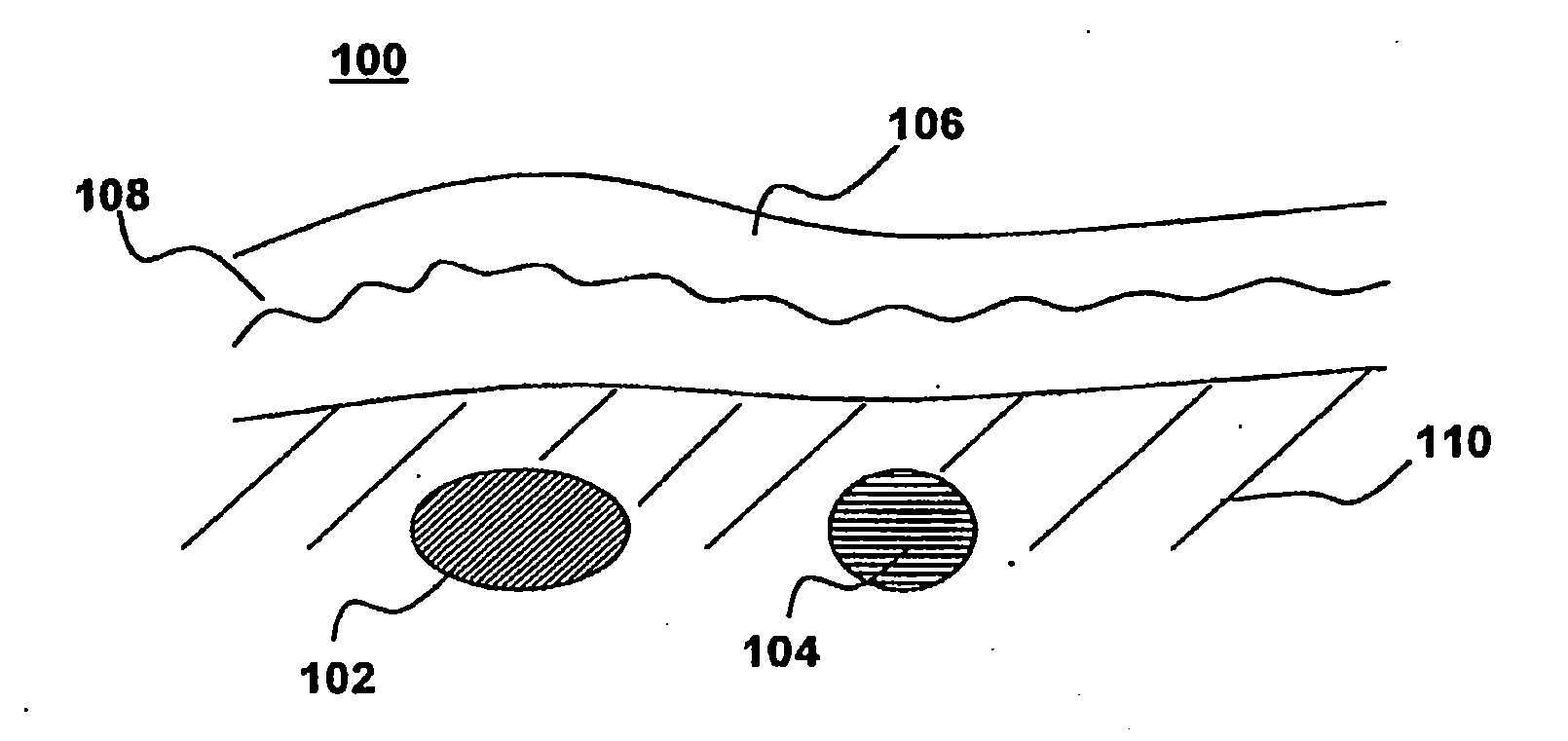
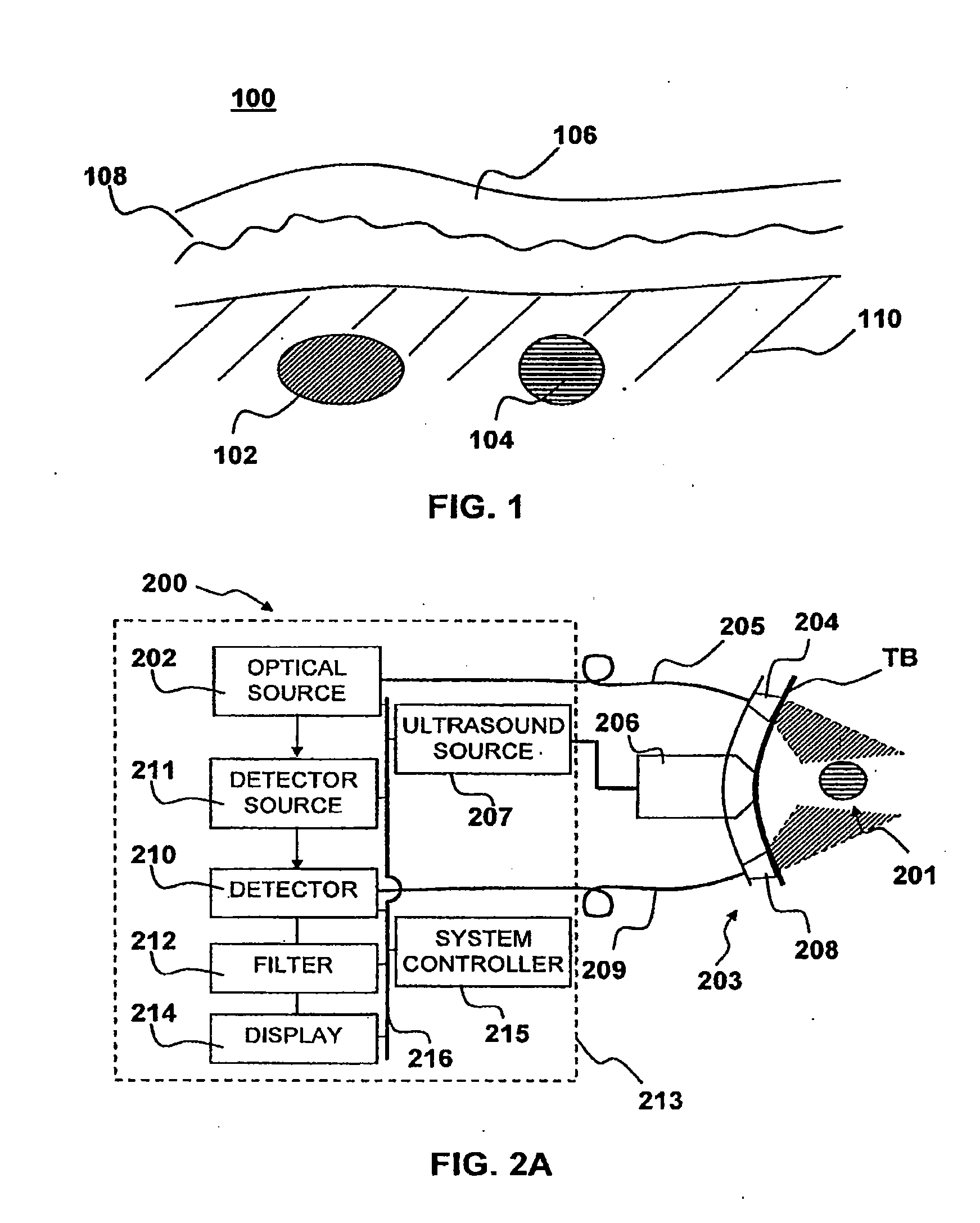
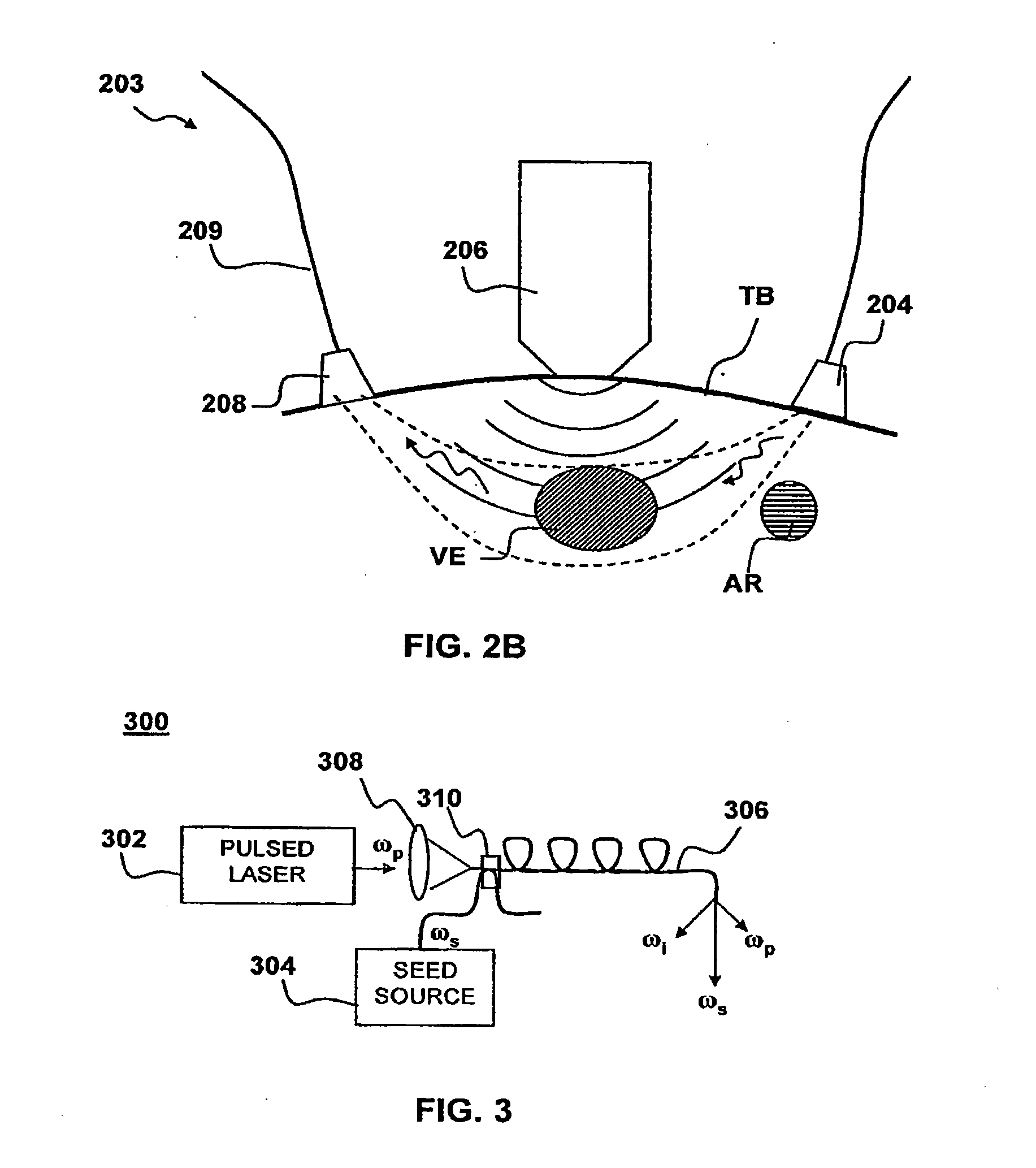
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of parameters relating to blood
InactiveUS20060253007A1Reduce disadvantagesImprove accuracyDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionNon invasiveThree vessels
Medical diagnostic system, apparatus and methods are disclosed. Optical transmitters generate radiation-containing photons having a specific interaction with at least one target chromophore in a target structure, preferably a blood vessel such as the interior jugular vein. The optical transmitters transmit the radiation into at least a first area including a substantial portion of the target structure and into a second area not including a substantial portion of the target structure. Optical receivers detect a portion radiation scattered from at least the first area and the second area. A processor estimates oxygenation, pH or cardiac output based on the scattered radiation detected from the first area, and the scattered radiation from the second area.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
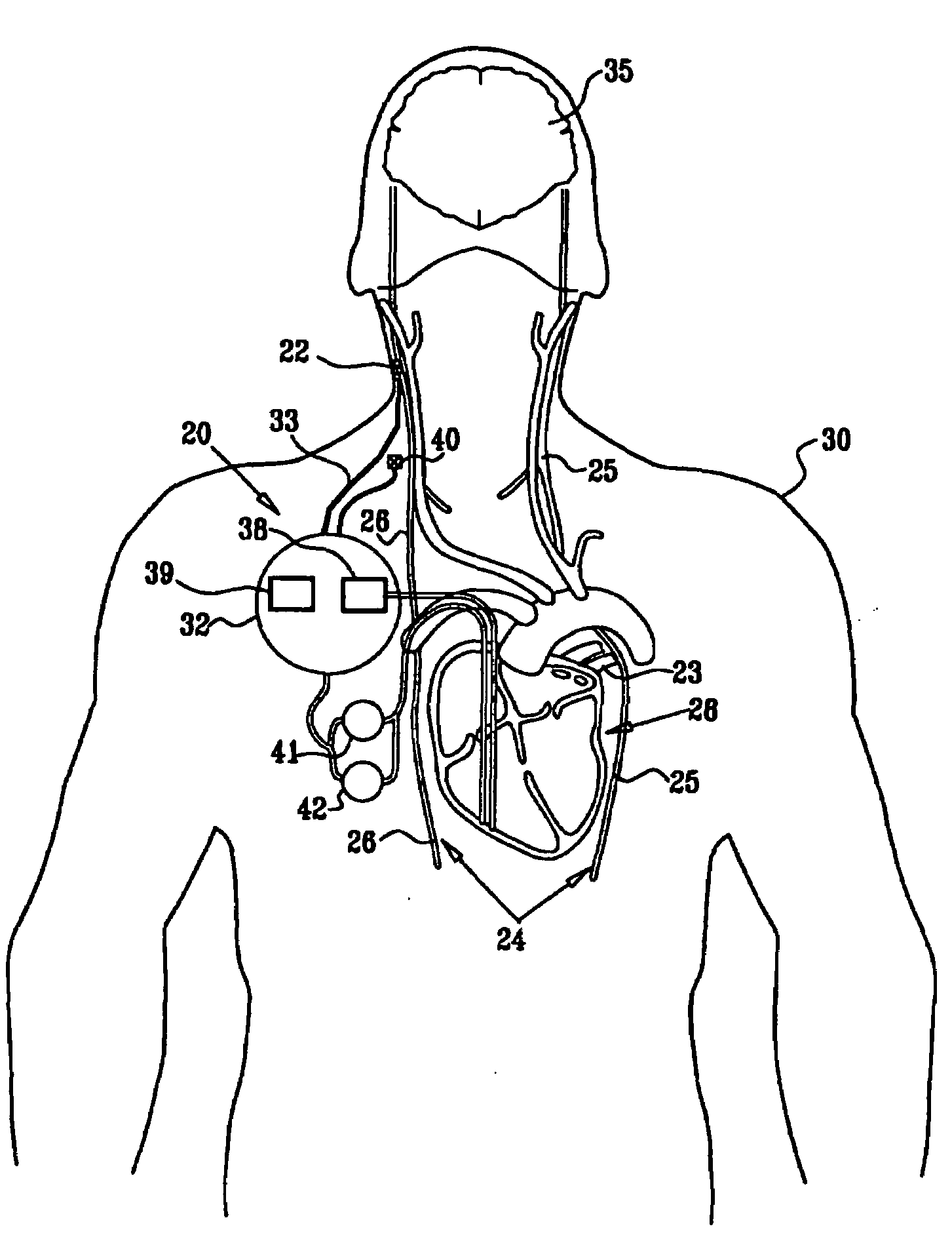
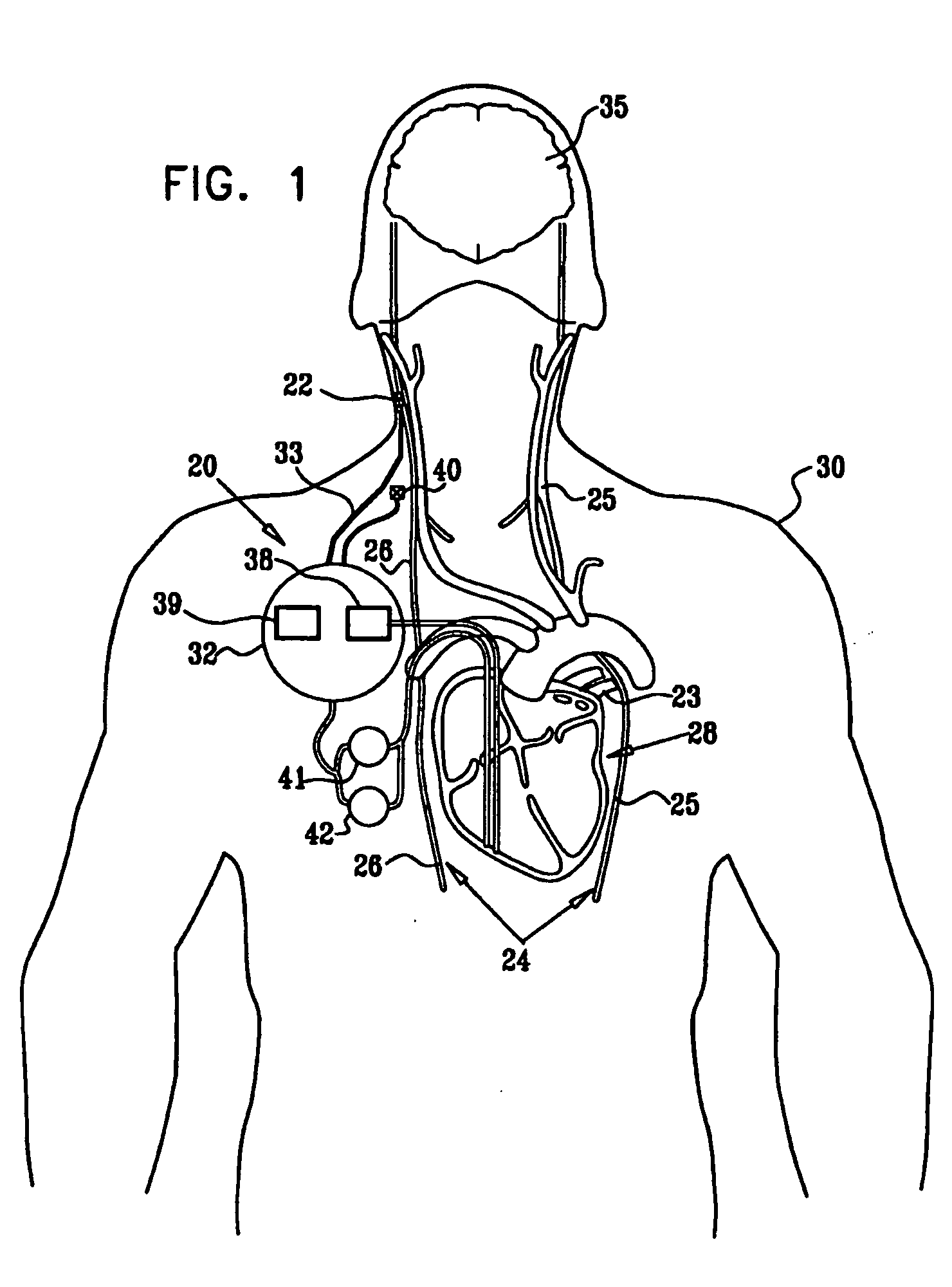
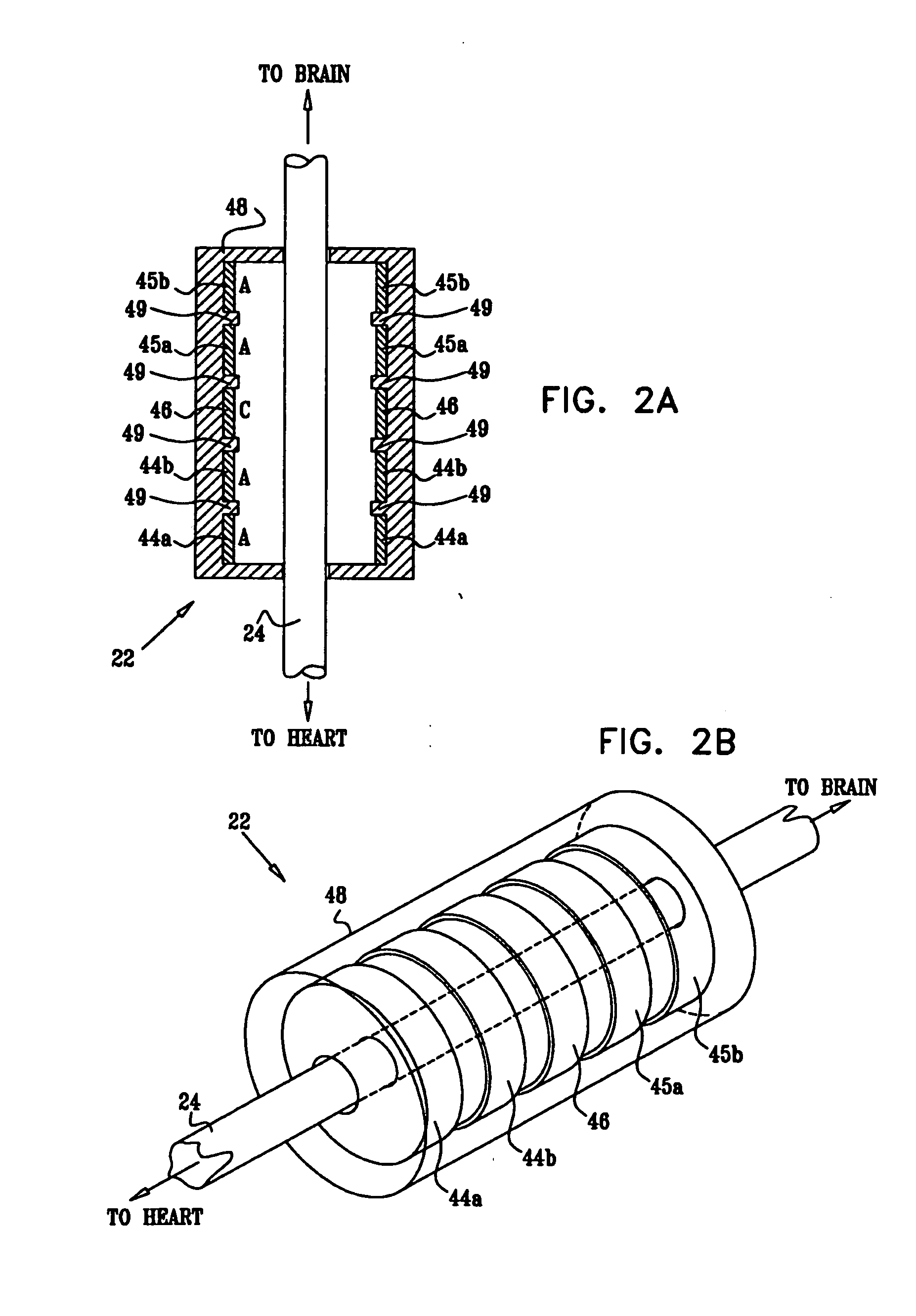
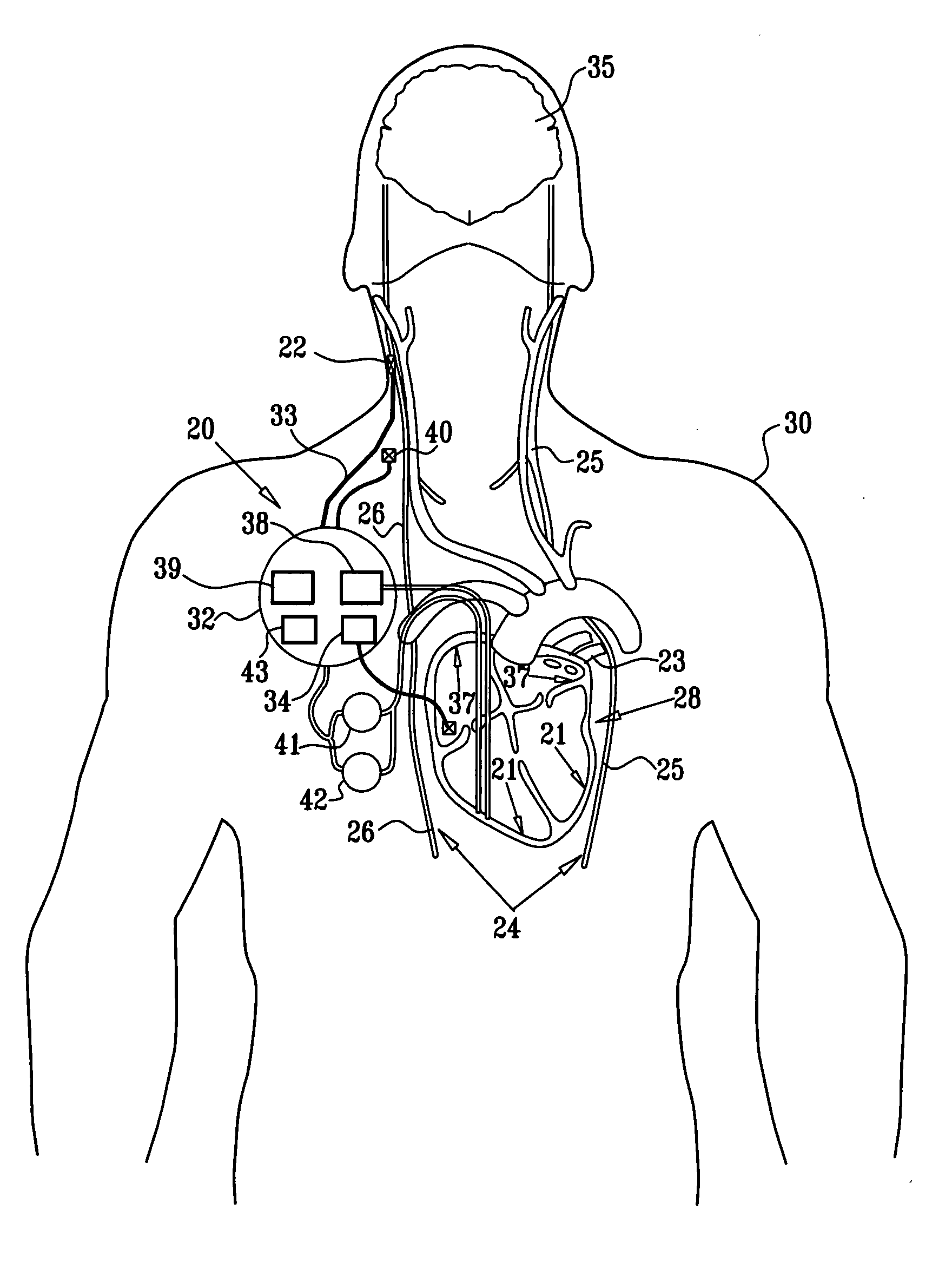
System and method for transvascularly stimulating contents of the carotid sheath
Methods and systems are disclosed for stimulating contents of the carotid sheath using an intravascular pulse generator and lead. The lead carries an energy delivery device such as an electrode, which is anchor within the portion of the internal jugular vein that is disposed within the carotid sheath. The energy delivery device is energized to transvenously direct energy to target contents of the carotid sheath external to the internal jugular vein. Such target contents may include nervous system elements associated with the carotid sinus baroreceptors, the carotid sinus nerve and associated nerve branches, and or the vagus nerve and associated nerve branches. The system may be used to control blood pressure and / or to lower heart rate and may be suitable for treatment of hypertension, heart failure, or other conditions.
Owner:NUXCEL2 LLC
System and method for transvascularly stimulating contents of the carotid sheath
Methods and systems are disclosed for stimulating contents of the carotid sheath using an intravascular pulse generator and lead. The lead carries an energy delivery device such as an electrode, which is anchor within the portion of the internal jugular vein that is disposed within the carotid sheath. The energy delivery device is energized to transvenously direct energy to target contents of the carotid sheath external to the internal jugular vein. Such target contents may include nervous system elements associated with the carotid sinus baroreceptors, the carotid sinus nerve and associated nerve branches, and or the vagus nerve and associated nerve branches. The system may be used to control blood pressure and / or to lower heart rate and may be suitable for treatment of hypertension, heart failure, or other conditions.
Owner:NUXCEL2 LLC
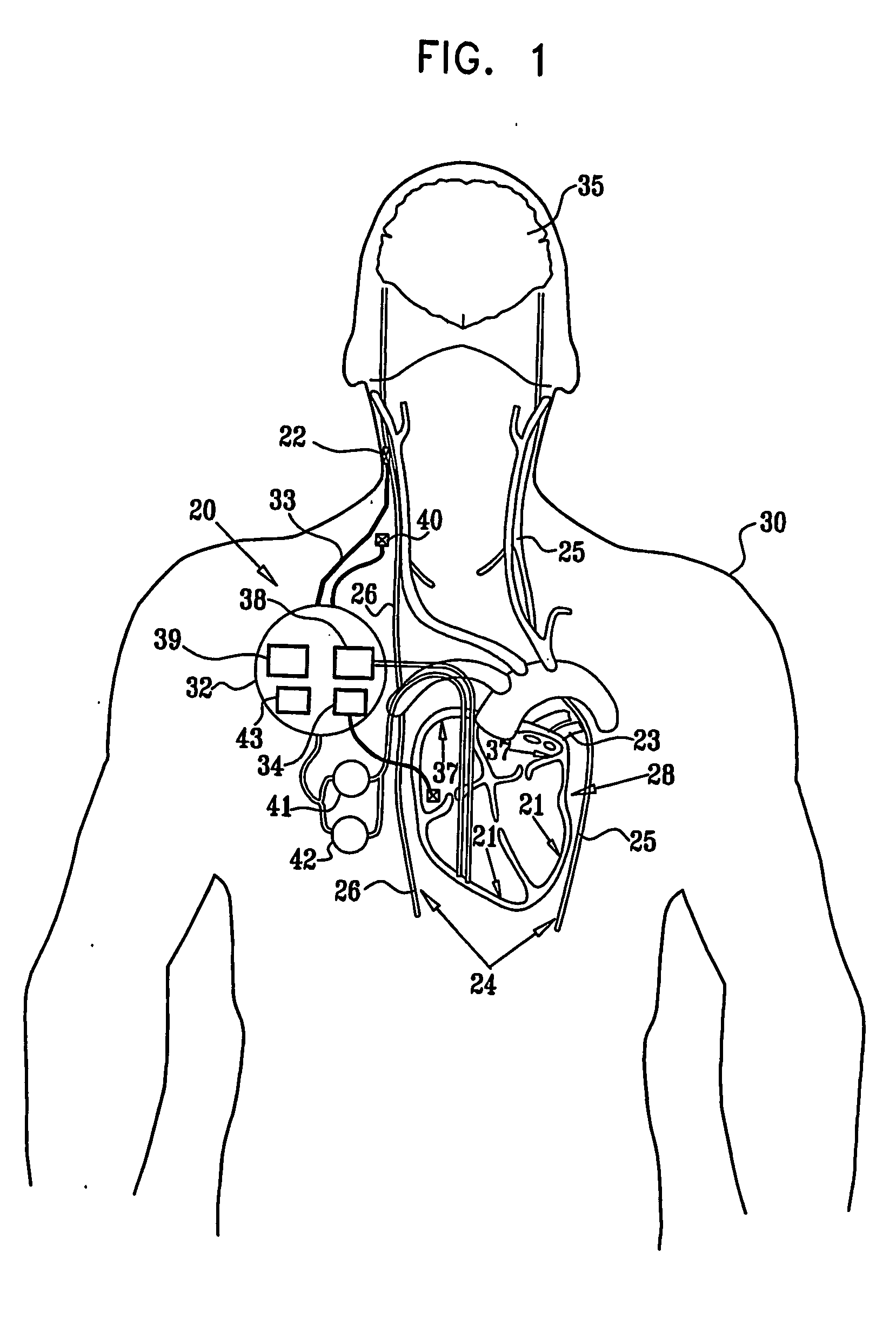
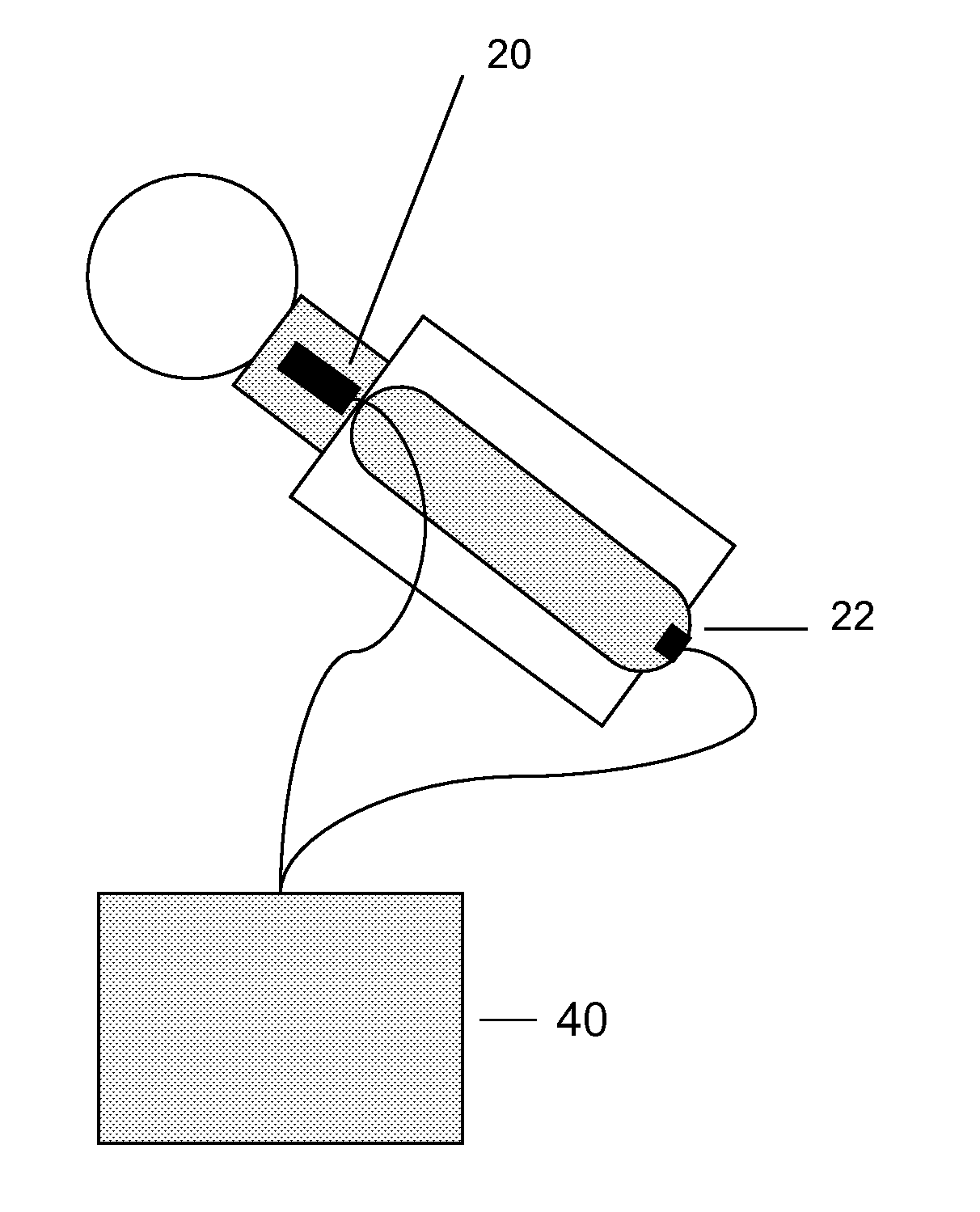
Vagal stimulation for anti-embolic therapy
InactiveUS20060271115A1Increase volumeIncrease stimulationSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsEmbolization TherapyBlood flow
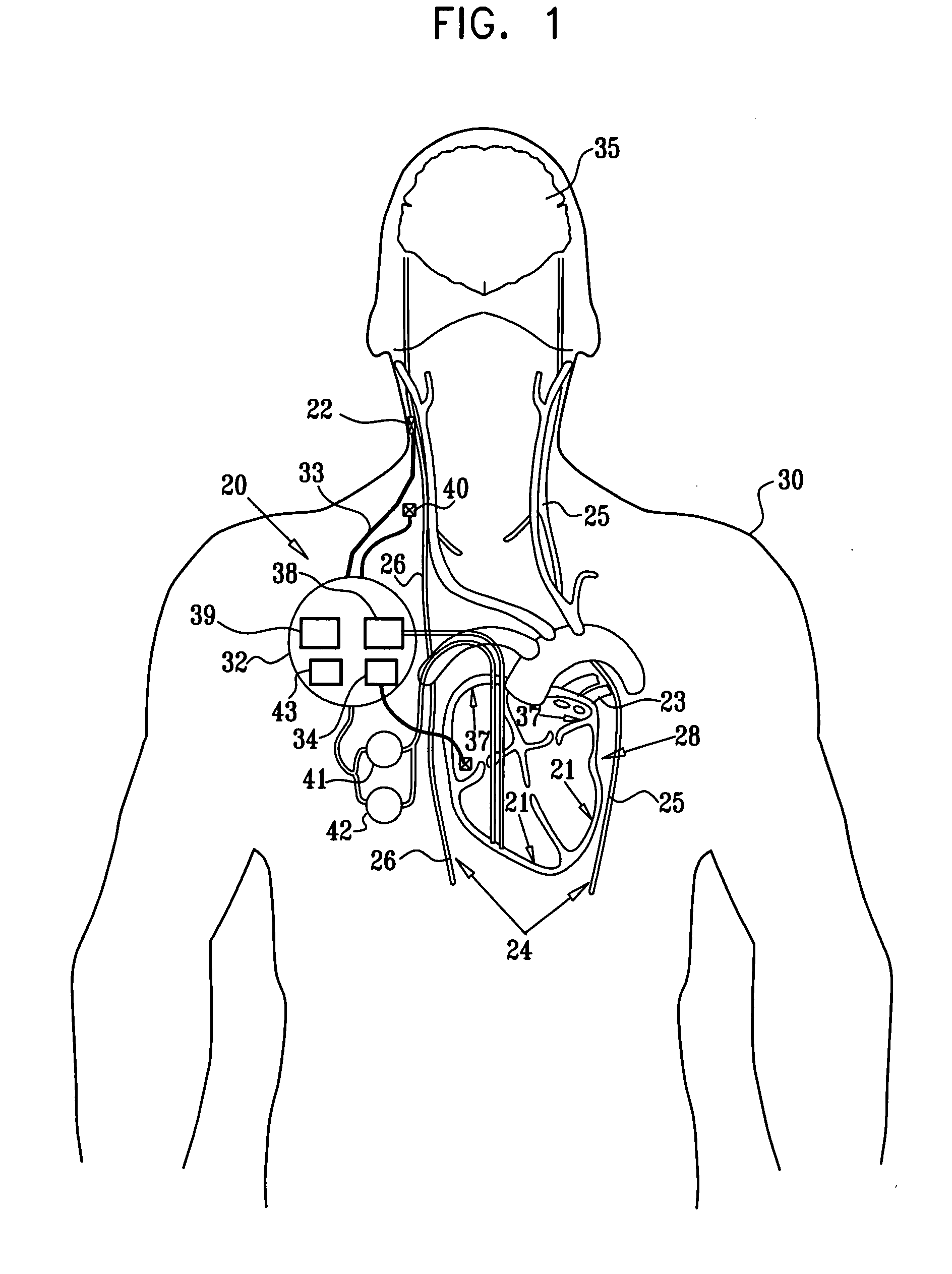
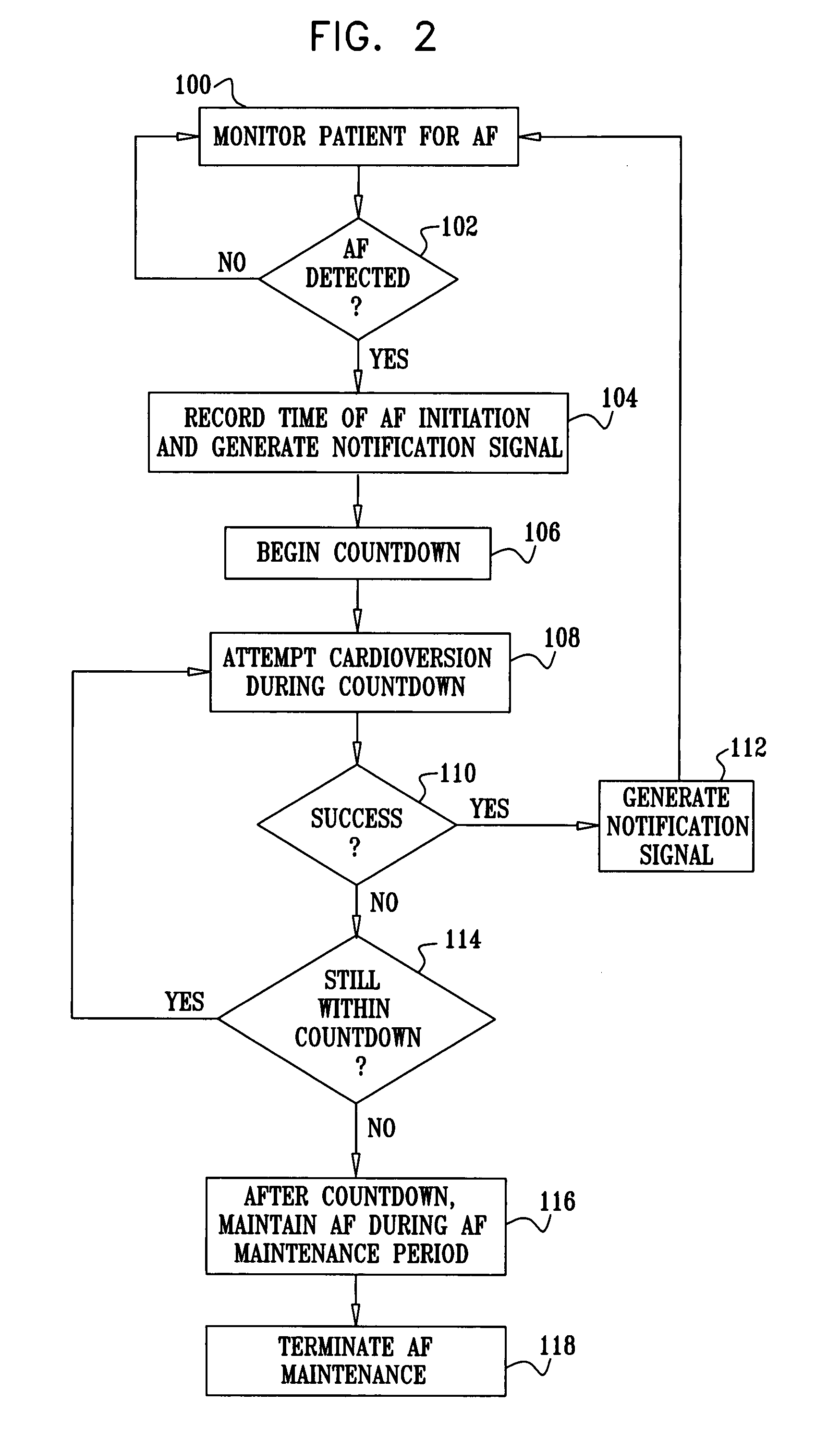
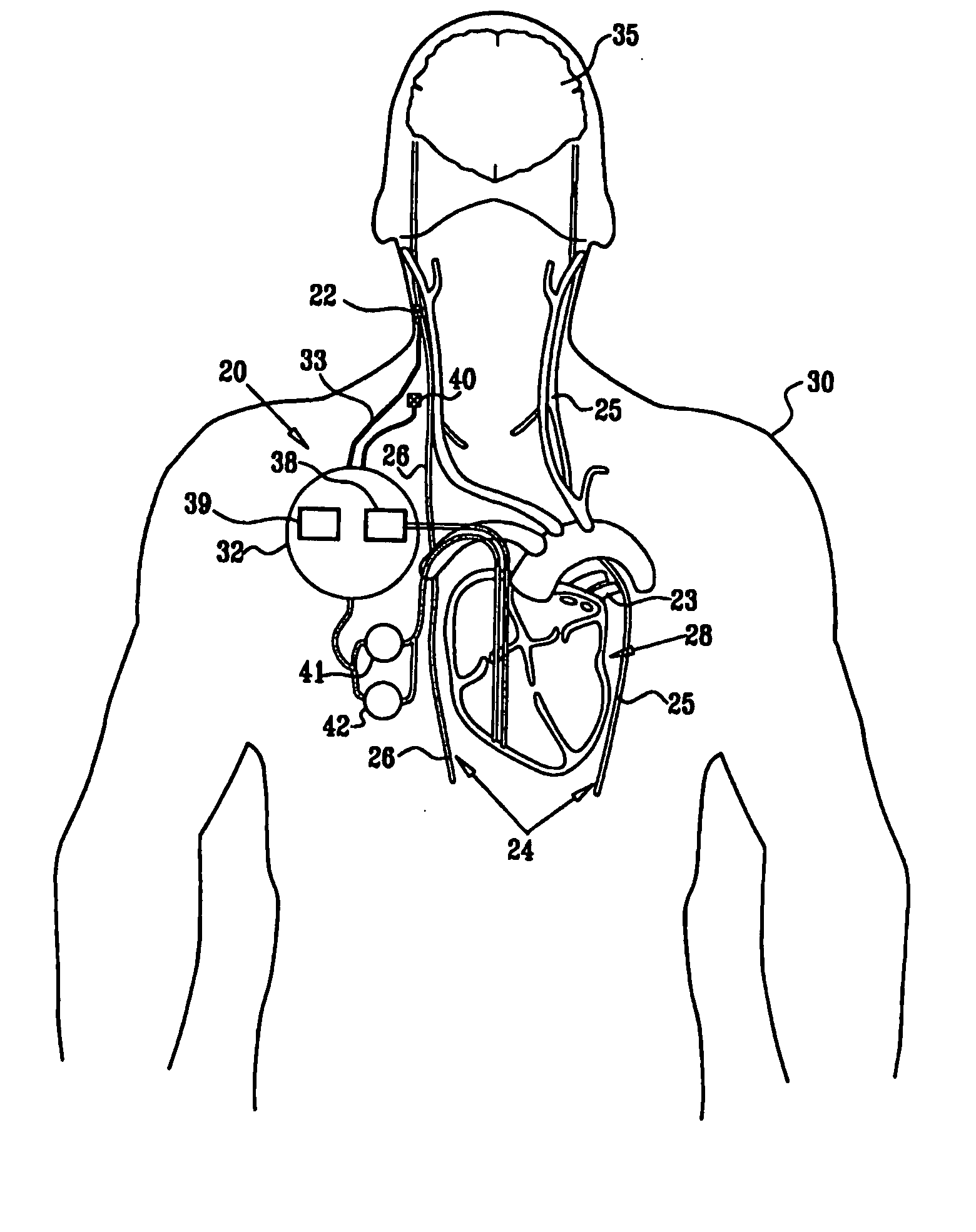
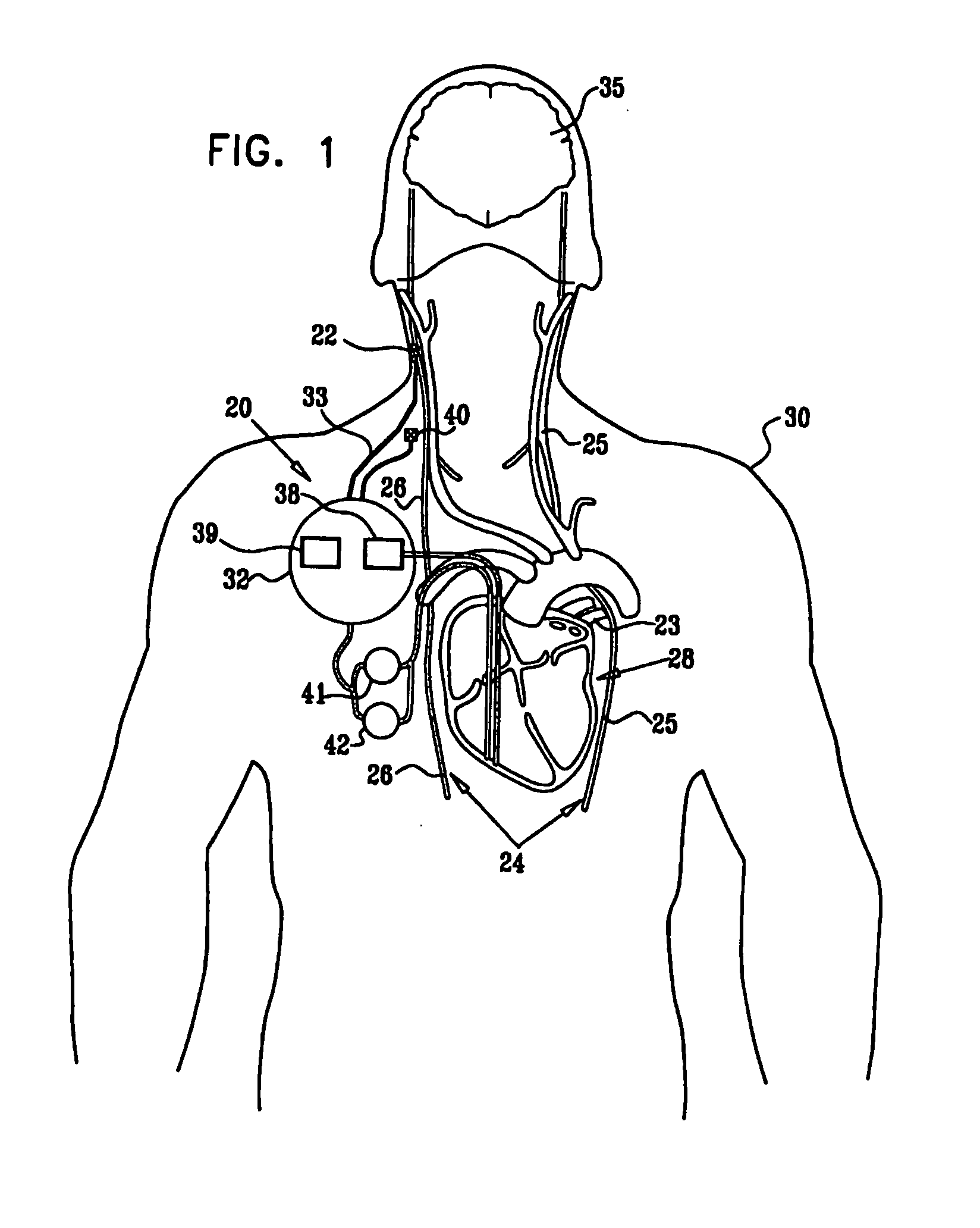
Apparatus (20) for treating a subject (30) suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device (22), adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject (30) selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve (24) of the subject (30), an epicardial fat pad of the subject (30), a pulmonary vein of the subject (30), a carotid artery of the subject (30), a carotid sinus of the subject (30), a vena cava vein of the subject (30), and an internal jugular vein of the subject (30), and a control unit (32), adapted to drive the electrode device (22) to apply an electrical current to the site, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intravascular system and method for blood pressure control
InactiveUS20100211131A1Spinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesNervous systemBlood vessel
An intravascular lead is used to deliver energy for stimulating nervous system targets using energy delivery elements (e.g. electrodes) that are in direct contact with the nervous system targets. The lead may be positioned within the internal jugular vein and the nervous system targets may include the carotid artery / carotid sinus bulb and / or associated baroreceptor afferents, and / or surrounding nervous system targets in the region of the internal jugular vein, such as the carotid sinus nerve and / or associated nerve branches and / or the vagus nerve and / or associated nerve branches. Stimulation energy travels along a conductive bridge that extends from the intravascular lead to the nervous system target, or is relayed from the intravascular lead to another device disposed within or surrounding the target structure.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL AUTONOMICS
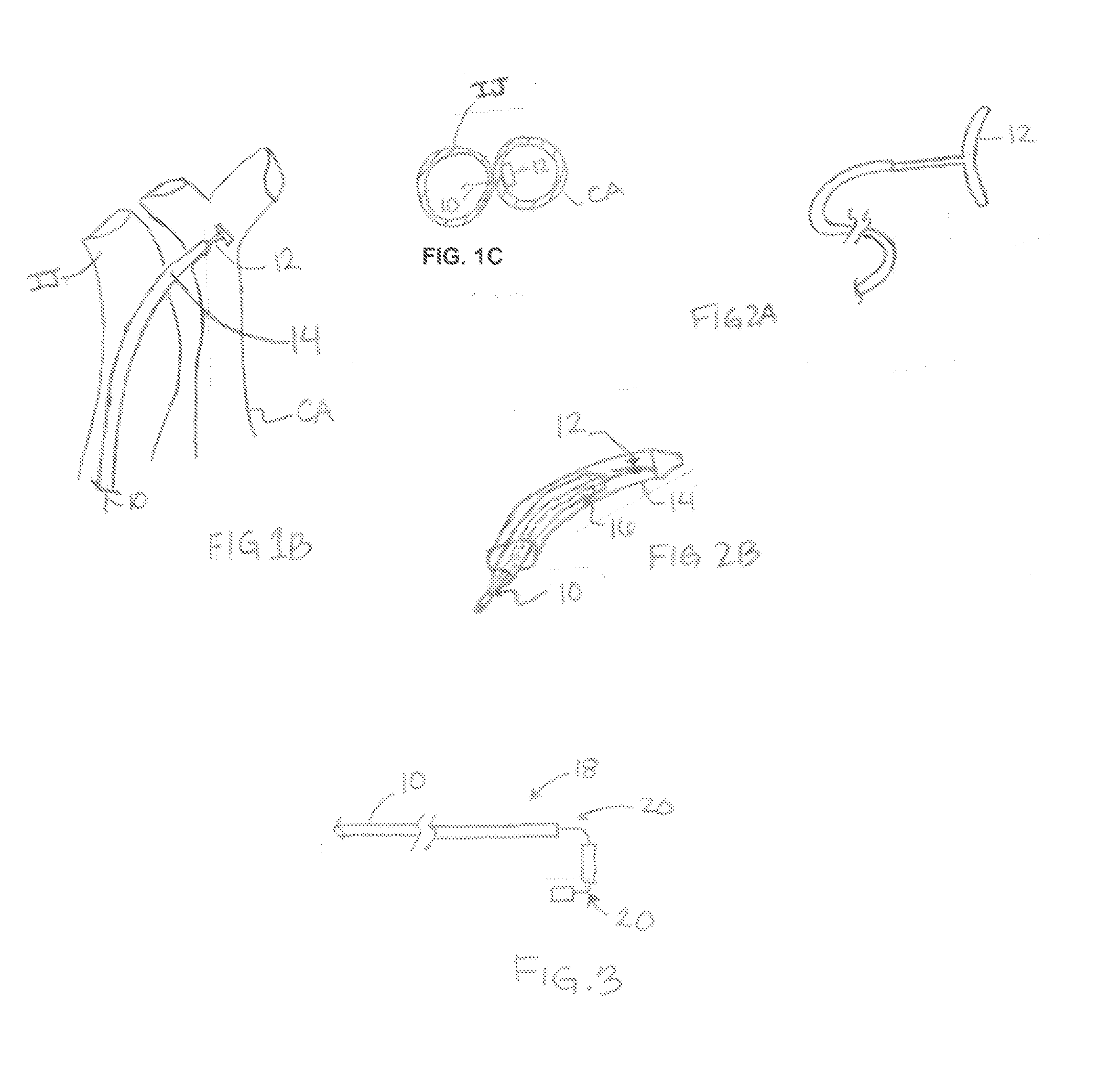
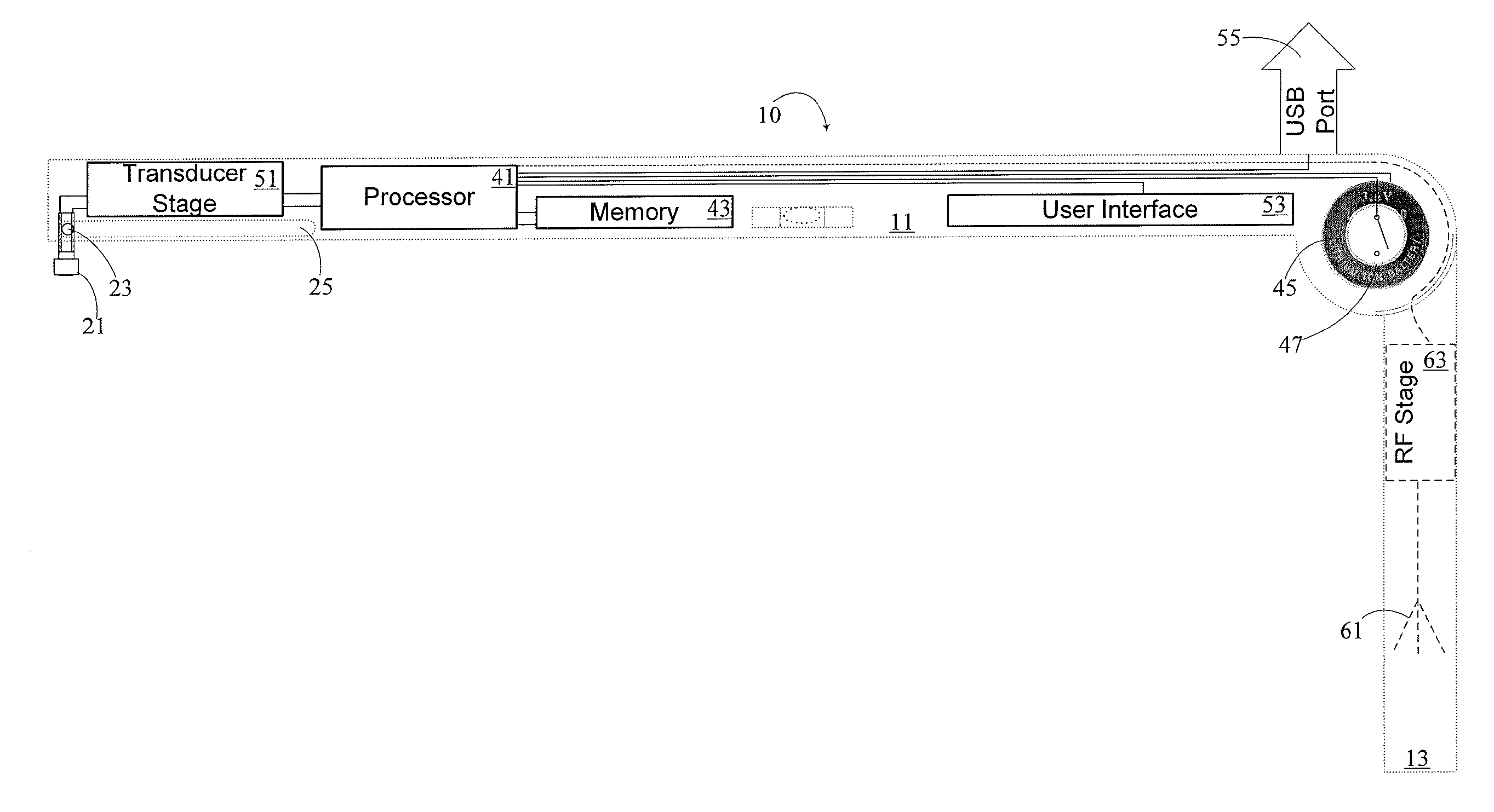
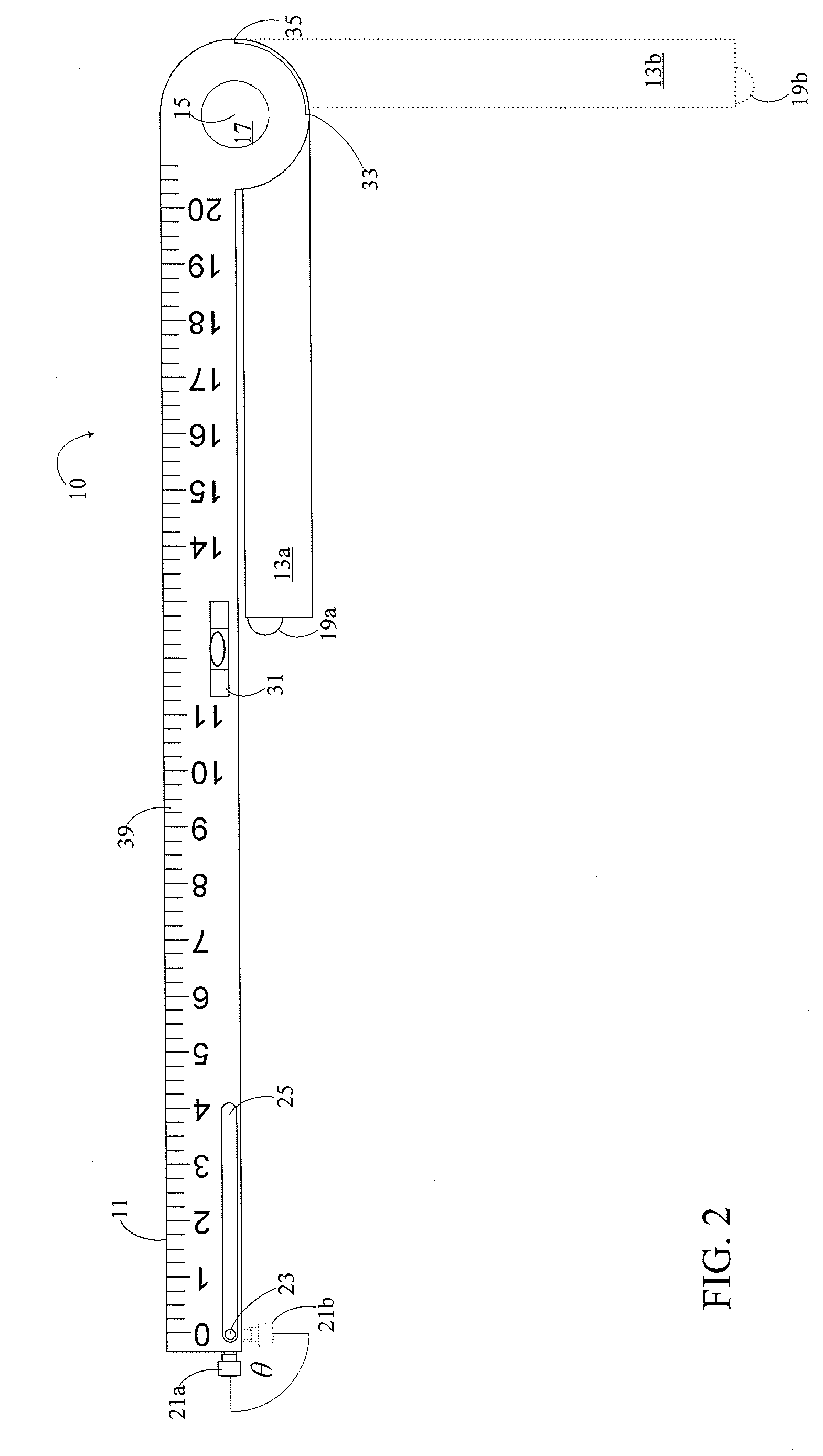
Jugular venous pressure ruler
A JVP ruler and a method for its use in measuring a jugular venous pressure in a patient, includes orienting the JVP ruler such that the second arm is collinear with a vertical line originating at a right atrium of the patient and such a the first arm is horizontal and having a transducer end situated opposite the pivot end of the first arm. The JVP Ruler has first and second arms elongate and situated to be in perpendicular relation one to the other. The arms meet and terminate at a pivot located at the pivot ends of the arms respectively, the transducer end being generally above a pulse point, the pulse point being a point on the skin of the patient where variations of the jugular venous pressure within the internal jugular vein are exhibited as at least vertical displacement of the skin.
Owner:PUSWELLA AMAL LESLY
Parasympathetic stimulation for heart conditions
InactiveUS20080125819A1Enhancing and sustaining efficacyImprove efficiencyHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsMyelitisNervous system
A method is provided for treating a subject, including applying a current to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, and an internal jugular vein of the subject. The method also includes configuring the current so as to treat a condition of the subject selected from the list consisting of: an autoimmune disease, an autoimmune inflammatory disease, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, myelitis, immune-mediated neuropathy, myositis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, inclusion body myositis, inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, Guillain Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, inflammation of the nervous system, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sjogren syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease, glomerulonephritis, thyroid autoimmune disease, sepsis, meningitis, a bacterial infection, a viral infection, a fungal infection, sarcoidosis, hepatitis, and portal vein hypertension.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vagal stimulation for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20080091241A1Reduce frequencyIncreased riskSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsBlood flowThrombus
Apparatus (20) for treating a subject (30) suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device (22), adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject (30) selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve (24) of the subject (30), an epicardial fat pad of the subject (30), a pulmonary vein of the subject (30), a carotid artery of the subject (30), a carotid sinus of the subject (30), a vena cava vein of the subject (30), and an internal jugular vein of the subject (30), and a control unit (32), adapted to drive the electrode device (22) to apply an electrical current to the site, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Minimal-heart-rate reduction parasympathetic stimulation
ActiveUS20080275514A1Enhancing and sustaining efficacyImprove efficiencyHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesMyelitisNervous system
A method is provided for treating a subject, including applying a current to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, and an internal jugular vein of the subject. The method also includes configuring the current so as to treat a condition of the subject selected from the list consisting of: an autoimmune disease, an autoimmune inflammatory disease, multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, myelitis, immune-mediated neuropathy, myositis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, inclusion body myositis, inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, Guillain Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, inflammation of the nervous system, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sjogren syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease, glomerulonephritis, thyroid autoimmune disease, sepsis, meningitis, a bacterial infection, a viral infection, a fungal infection, sarcoidosis, hepatitis, and portal vein hypertension.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
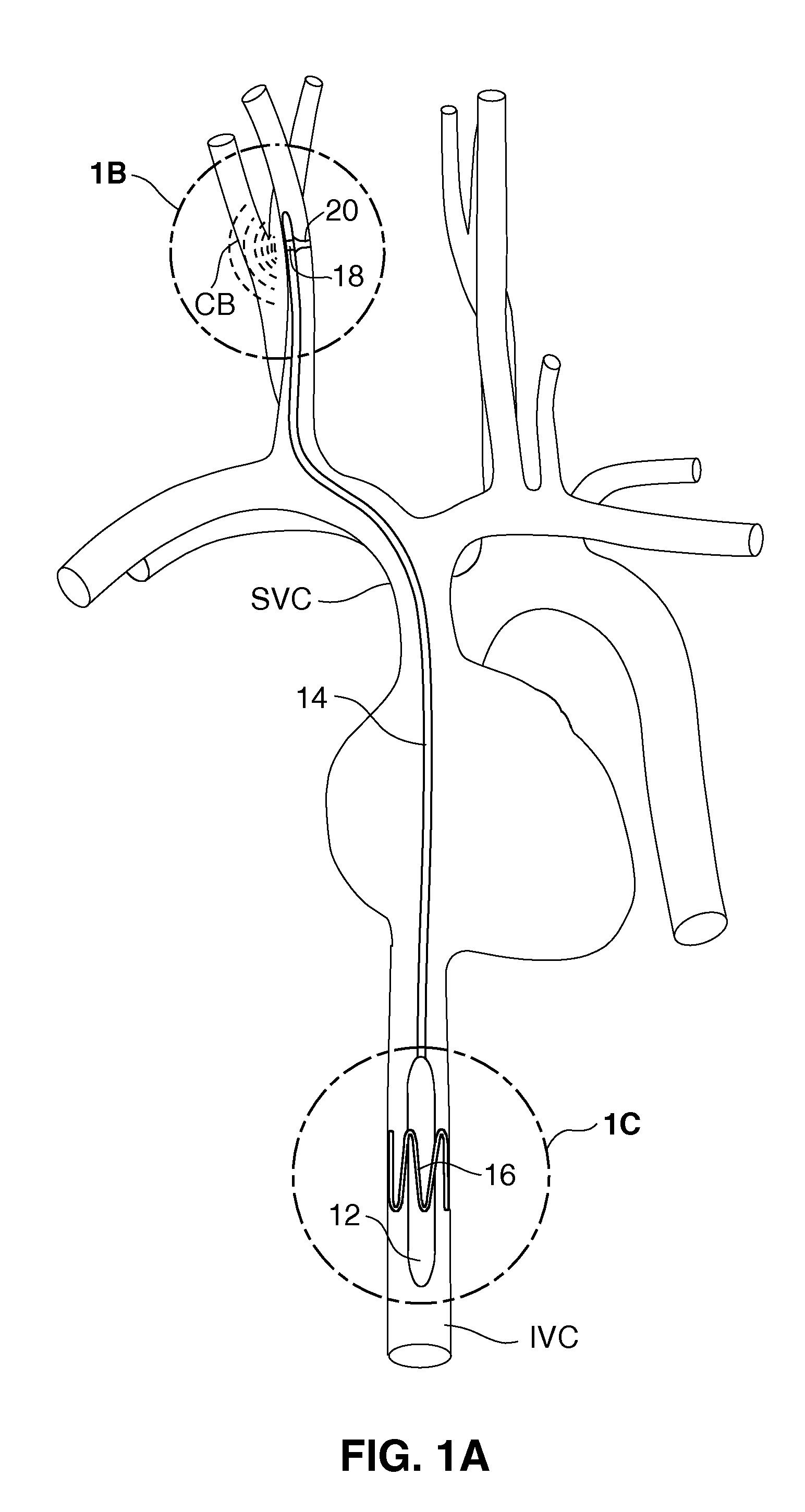
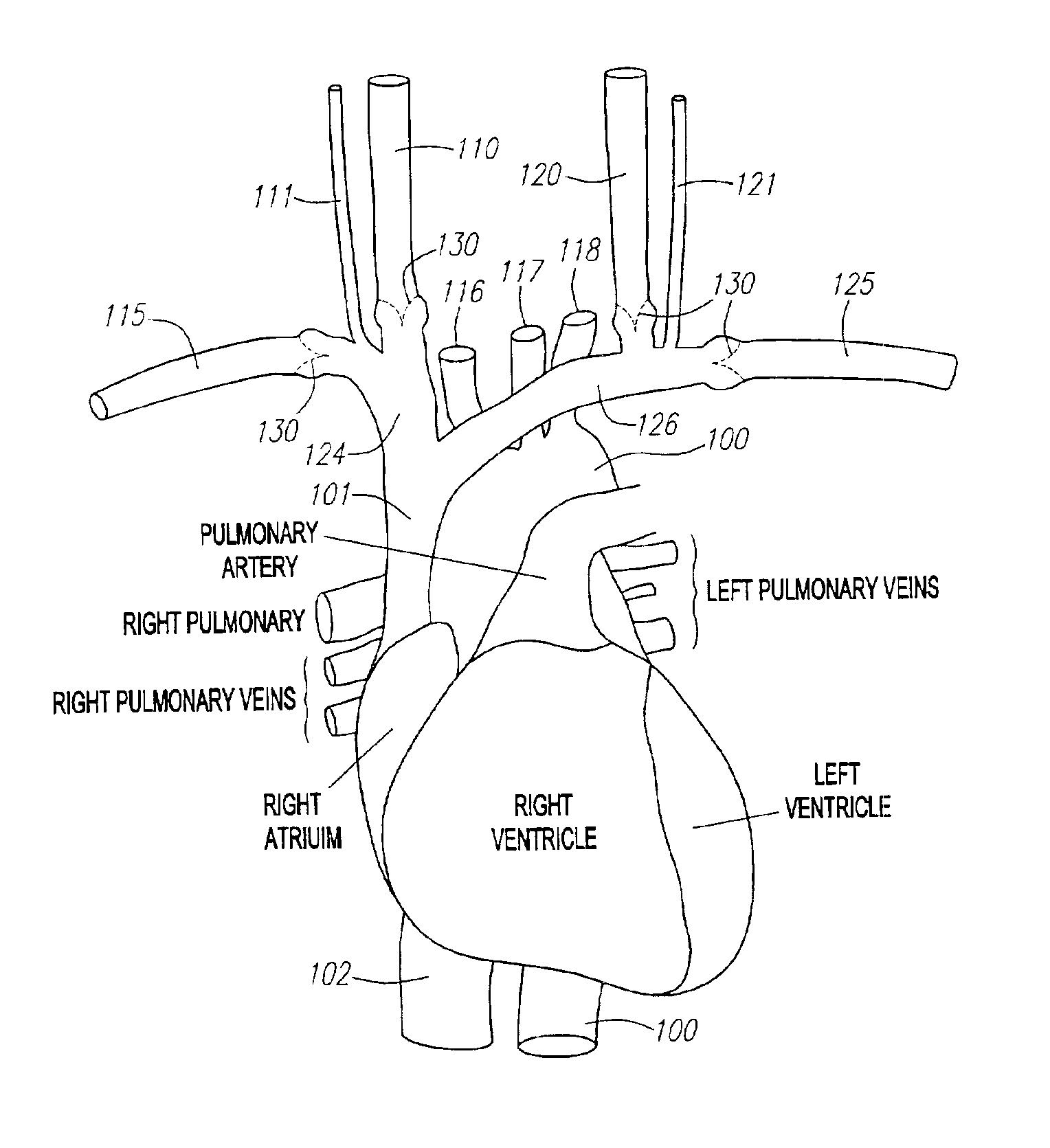
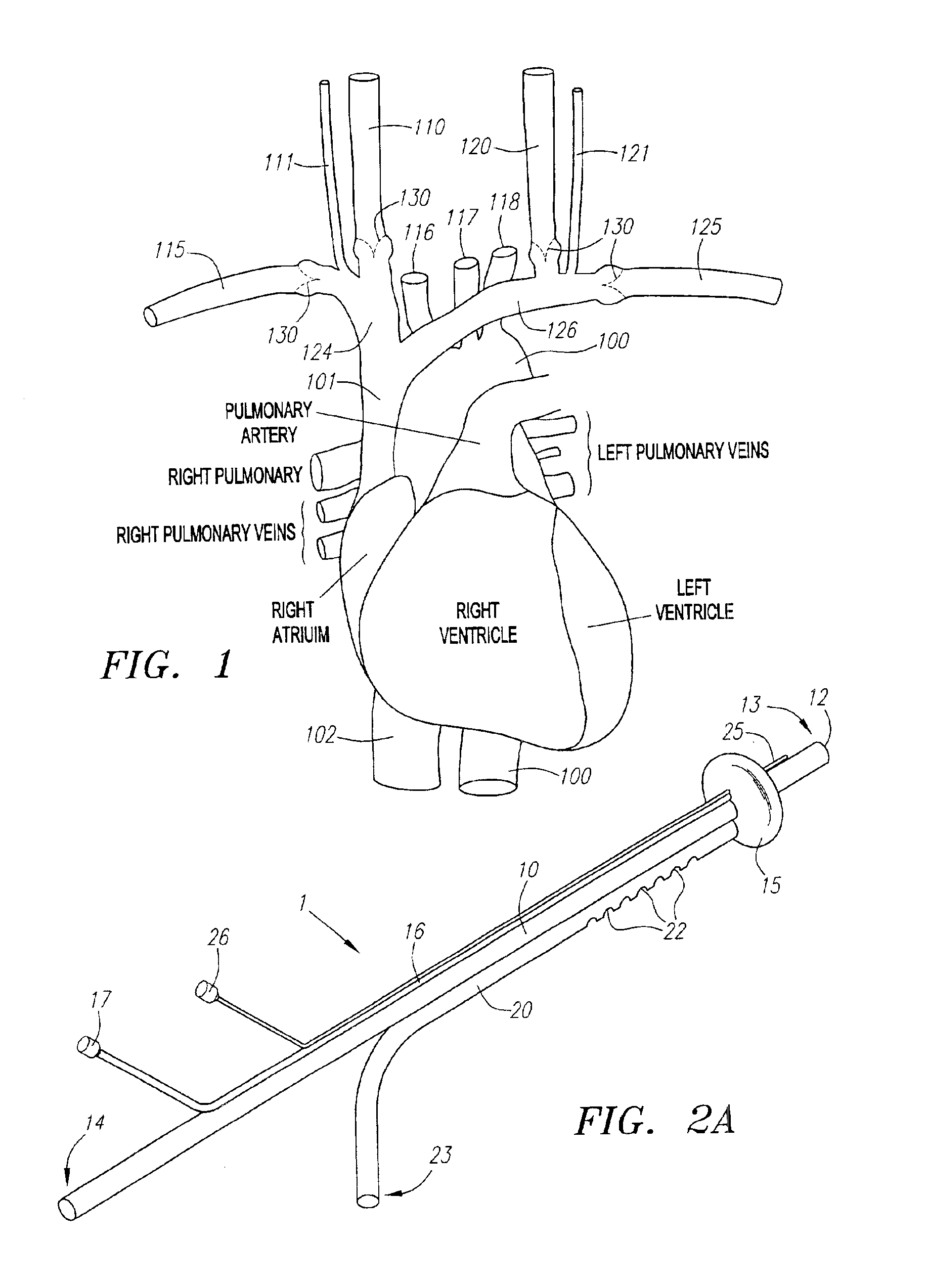
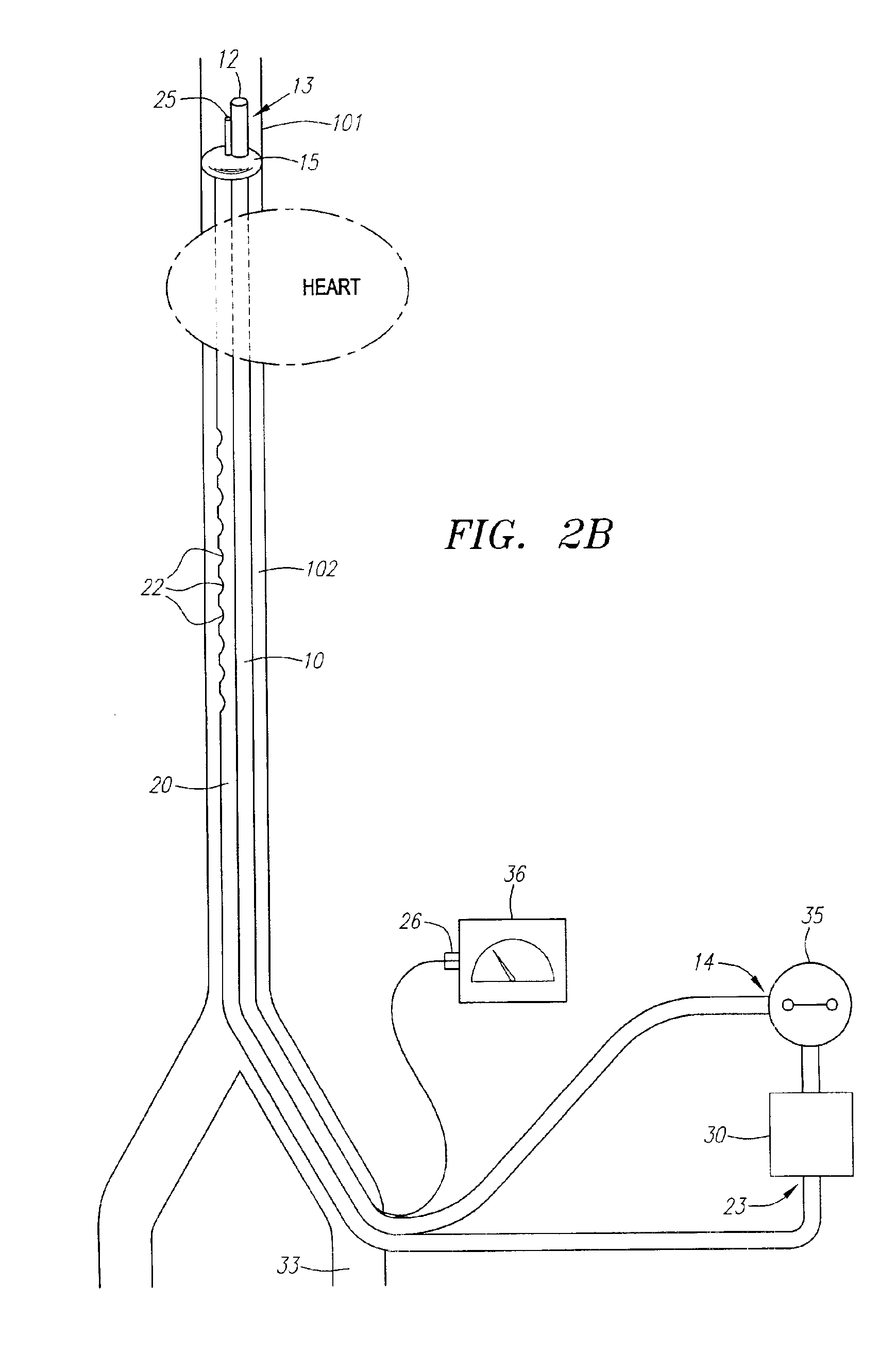
Retrograde venous perfusion with isolation of cerebral circulation
InactiveUS6896663B2Minimizes backflowMinimize damageOther blood circulation devicesSurgeryPerfusionMedical treatment
A medical device for providing retrograde venous perfusion to the cerebral vasculature for treatment of global or focal cerebral ischemia is disclosed. The device includes a catheter having an infusion port at its distal end, venous drainage port(s), and an expandable occluder disposed between the infusion port and drainage port(s). The catheter can be inserted into the superior vena cava or the internal jugular vein. The catheter is attached proximally to a pump and an oxygenator with or without a cooling system. Alternatively, the device includes two catheters, each having a lumen communicating with a distal infusion port and an occluder mounted proximal to the port. The catheters can be inserted into the internal jugular veins distal to jugular venous valves. Methods of using the devices to provide retrograde venous perfusion and isolated cerebral hypothermia are disclosed.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of parameters relating to blood
InactiveUS20100152559A1Improve accuracyDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionCalorescenceNon invasive
Medical diagnostic system, apparatus and methods are disclosed. Optical transmitters generate radiation-containing photons having a specific interaction with at least one target chromophore in a target structure, preferably a blood vessel such as the interior jugular vein. The optical transmitters transmit the radiation into at least a first area including a substantial portion of the target structure and into a second area not including a substantial portion of the target structure. Optical receivers detect a portion radiation scattered from at least the first area and the second area. A processor estimates oxygenation, pH or cardiac output based on the scattered radiation detected from the first area, and the scattered radiation from the second area.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
System and method for non-invasive monitoring of cerebral tissue hemodynamics
A method and system are provided which are useful for the non-invasive determination and monitoring of cerebral tissue oxygenation. The method comprises the steps of generating at least first and second jugular venous output signals against time based on the reflection of at least first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from an external tissue site on the patient in the proximity of the internal jugular vein; obtaining corresponding first and second cardiac arterial output signals for the first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from the patient, and separating the first and second cardiac arterial output signals from the first and second jugular venous output signals, respectively, to generate first and second cerebral venous output signals; and determining cerebral tissue oxygenation based on the first and second cerebral venous output signals. A system useful to monitor cerebral tissue oxygenation may comprise a first module for optically generating at least first and second jugular venous output signals against time at at least first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from the patient; a second module for generating first and second cardiac arterial output signals at the first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from the patient; and a signal processing means adapted to separate the first and second cardiac arterial output signals from the first and second jugular venous output signals, respectively, to yield first and second cerebral venous output signals, for the determination of cerebral tissue oxygenation.
Owner:MESPERE LIFESCI
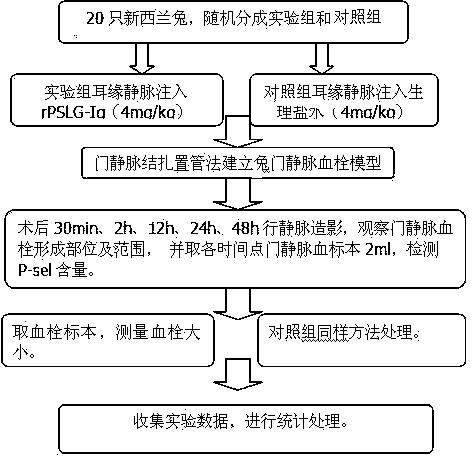
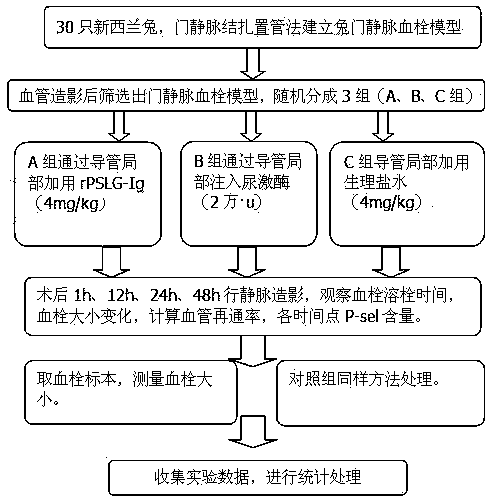
Rabbit portal vein thrombosis model
The invention relates to model preparation, particularly to a rabbit portal vein thrombosis model which establishes a rabbit portal vein thrombosis model by a portal vein ligation catheterization method. The experimental animal adopts a New Zealand white rabbit; the experimental process comprises the steps of preoperative preparation: a preoperative experimental rabbit fasts all night and freely drinks water; anaesthetization; operation method: make the preoperative preparations including shaving feathers at the operating area after anaesthetization, disinfection and the like, enter the belly layer by layer, separate a portal vein, insert a 2Fr internal jugular vein tube by a catheterization method, ligate the portal vein using the tube as the inner support, suture and fix, lead to outside of body, and then conducting firm fixing. The model of the invention causes partial blood stasis, annular oppressed damage of blood vessel endothelium by ligating the portal vein, simultaneously carries out tube stimulation, starts intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation processes, increases the incidence of thromboembolism, and provides passages for the later partially collecting blood specimen, dynamic venogram, partial injection and the like; the first PVT occurrence time is about 30 min after the model is found via the portal vein radiography, and the model formation rate is higher than 75%.
Owner:HUZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
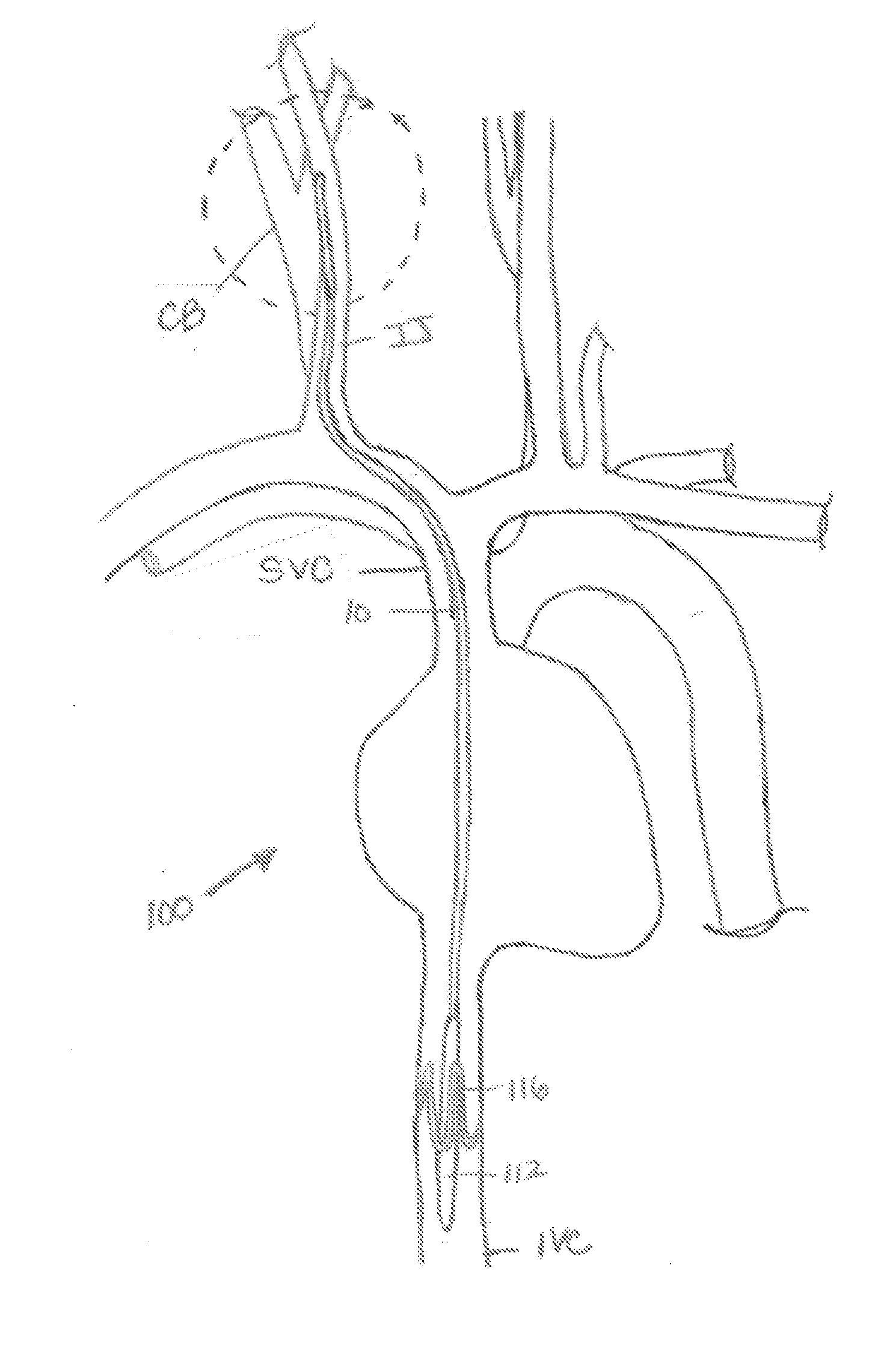
System, Methods and Apparatus for Cerebral Protection
ActiveUS20100241047A1Maintain their viabilityIncrease blood flowStentsBalloon catheterPerfusionGuide wires
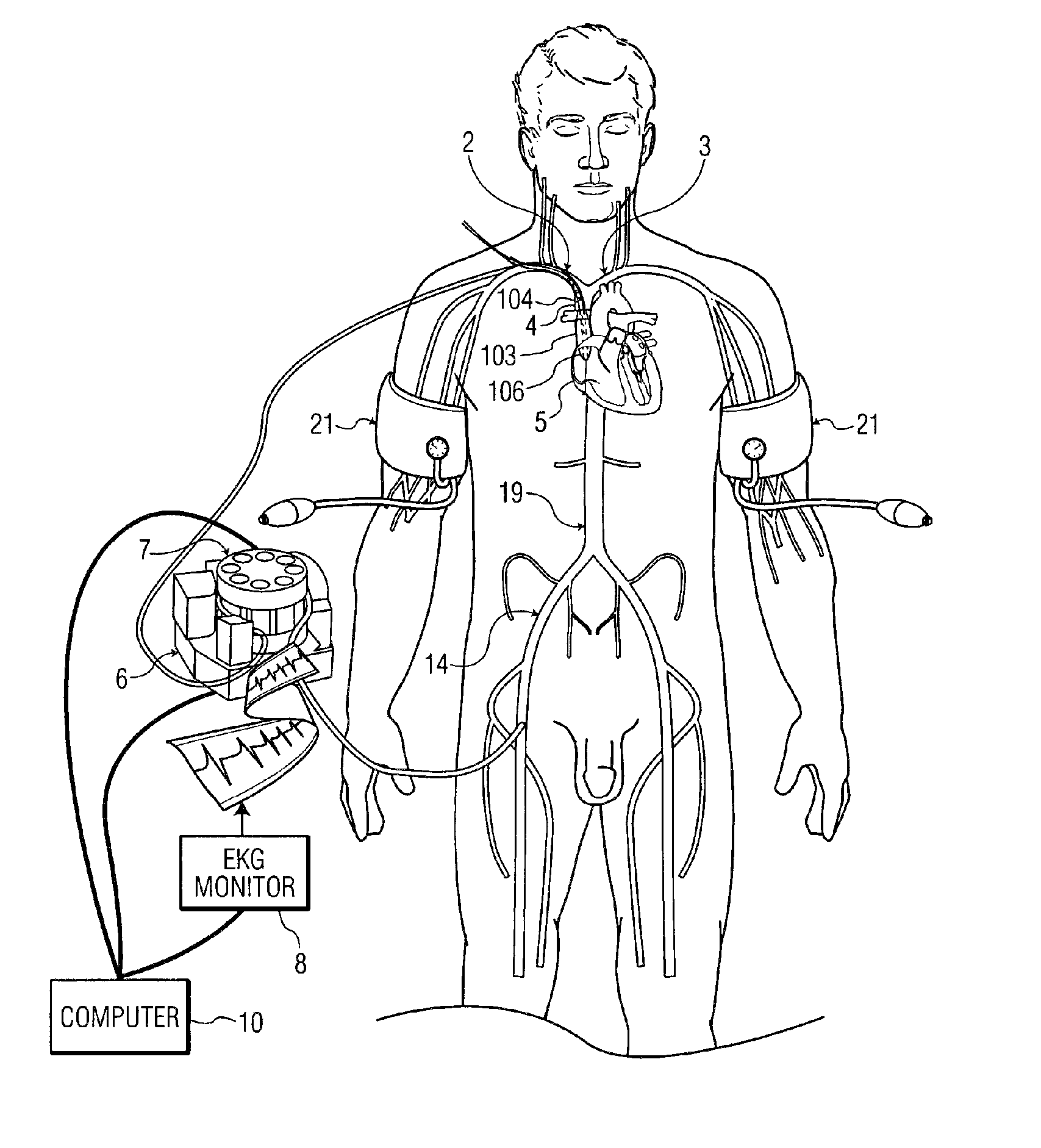
A device, system and method for perfusing an oxygenated medium in the cerebral vasculature. In the case of bihemispheric brain perfusion, it includes positioning pressure cuffs on upper extremities; providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon; inserting the catheter into a subclavian or femoral vein; advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned substantially in the superior vena cava junction substantially proximal to the take-off of the left innominate vein. During a perfusion mode, the cuffs and balloon are inflated causing an increase in cerebral blood flow, retrogradely; and oxygenated blood which may be cooled is pumped from a femoral artery into the catheter for a suitable period. During a non-perfusion mode the cuffs and balloon are deflated. The catheter has at least two regions, namely, guide wire and fluid delivery regions. Optionally, a separate balloon inflation region may be provided. In the case of unilateral (single hemisphere) brain perfusion, it includes providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon, inserting the catheter into a subclavian, jugular or femoral vein, advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned in the internal jugular vein on the side ipsilateral to the side of the brain requiring perfusion. In this unilateral scenario where the balloon is inflated in the ipsilateral internal jugular vein, no pressure cuffs are needed and only the balloon is inflated and deflated during the perfusion and non-perfusion modes respectively.
Owner:YACOUBIAN VAHE STEPHAN +1
Non-invasive dynamic measurement of intracranial reserve space
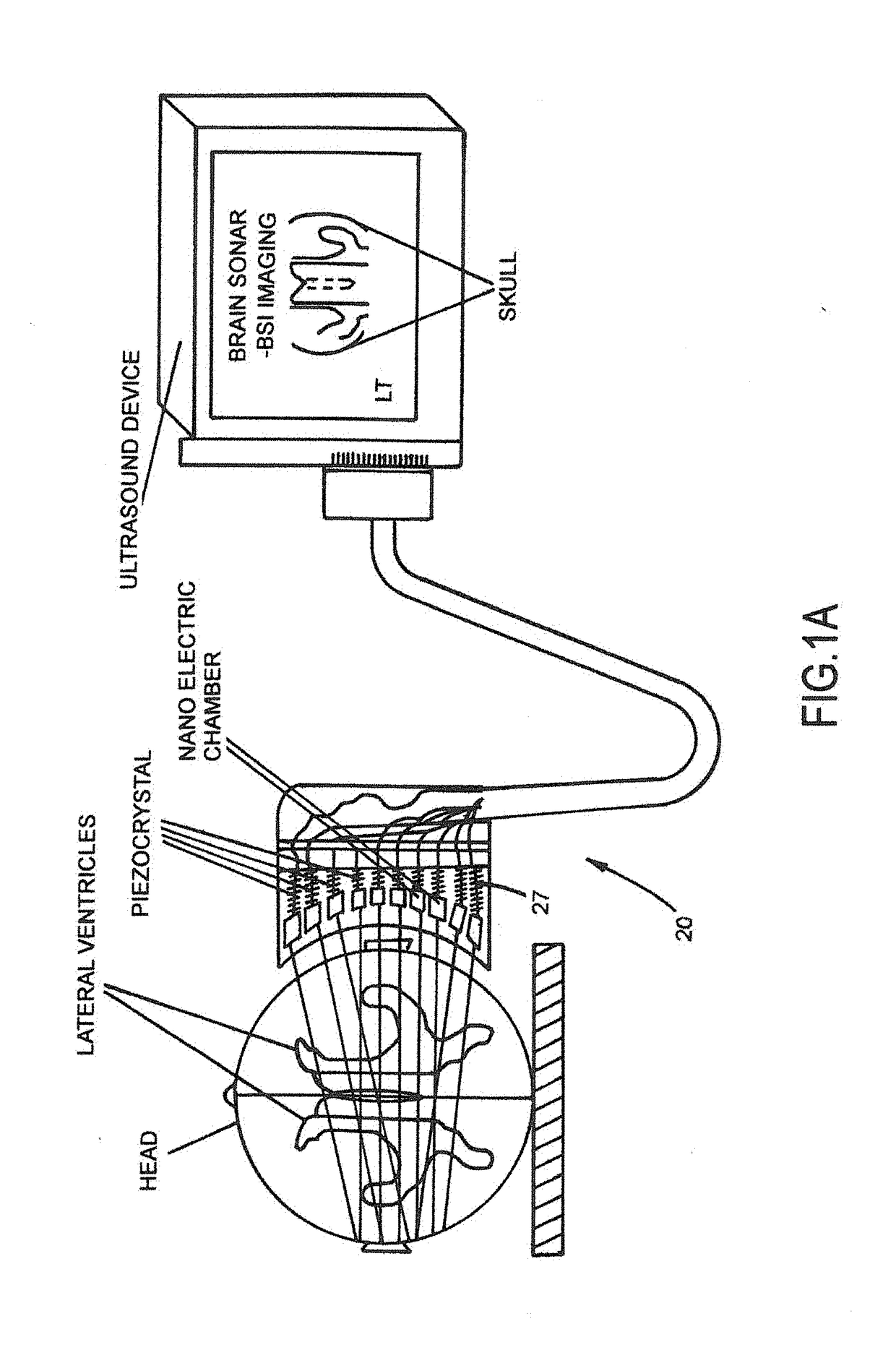
System for non-invasive measuring of an intracranial reserve space (ICRS) parameter of a mammalian subject, comprising a multi-frequency ultrasound probe configured, beginning at a start time, to emit and receive ultrasound waves into and from the subject's head and to produce a signal of brain tissue pulsation; an instrument configured to non-invasively partially occlude an internal jugular vein (IJV) starting at the start time and including a second ultrasound probe producing a second signal; and a computer system configured to receive the signal, the second signal and the start time, the computer system also configured, using one or more processors, to derive from the signal an intracranial brain tissue pulsation waveform and from the second signal images of the IJV, and to determine a length of time from the start time to a subsequent time at which the waveform is sufficiently compressed so as to exhibit a predefined decline in variability.
Owner:MICHAELI DAVID +1
Optical non-invasive detection method for oxygen saturation of mixed venous blood and oxygen saturation of central venous blood
InactiveCN104739425AEasy to implementComfortable and easy measurementDiagnostics using lightSensorsVenous bloodNon invasive
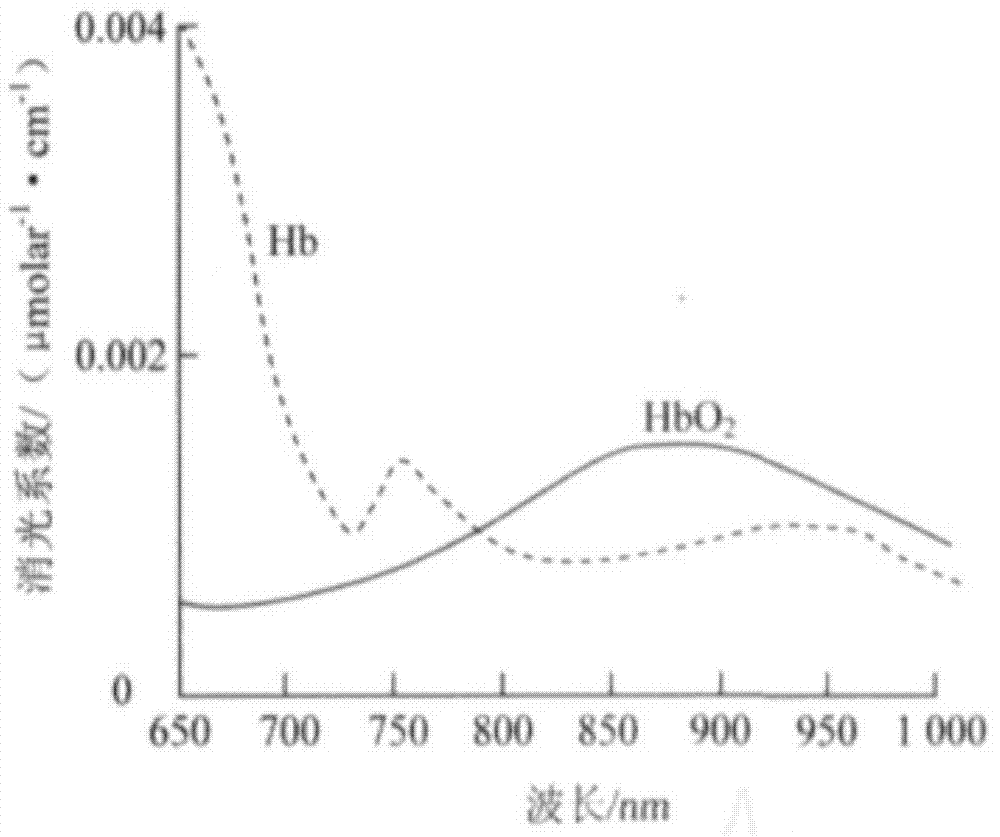
The invention discloses an optical non-invasive detection method for oxygen saturation of mixed venous blood and oxygen saturation of central venous blood. Infrared light is adopted, an absorption spectrum of reflected light is measured, and specific mixed and central vein calculation methods are provided. Compared with existing testing methods for blood oxygen saturation, the optical non-invasive detection method not only achieves non-invasive detection but also can achieve real-time continuous monitoring. The specific algorithms are simple, effective and easy to achieve. During measurement, any part of a human body does not need to be clamped, only the body surface needs to be attached to, then the purpose can be achieved by measuring the absorption spectrum of the reflected light, a patient feels more comfortable during measurement, and measurement is simpler and more convenient. Besides, when the oxygen saturation of central venous blood is measured, jugular veins and subclavian veins are preferably selected for a target deep-layer vascular structure, and measurement is more accurate.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for non-invasive monitoring of cerebral tissue hemodynamics
A method and system are provided which are useful for the non-invasive determination and monitoring of cerebral tissue oxygenation. The method comprises the steps of generating at least first and second jugular venous output signals against time based on the reflection of at least first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from an external tissue site on the patient in the proximity of the internal jugular vein; obtaining corresponding first and second cardiac arterial output signals for the first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from the patient, and separating the first and second cardiac arterial output signals from the first and second jugular venous output signals, respectively, to generate first and second cerebral venous output signals; and determining cerebral tissue oxygenation based on the first and second cerebral venous output signals. A system useful to monitor cerebral tissue oxygenation may comprise a first module for optically generating at least first and second jugular venous output signals against time at at least first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from the patient; a second module for generating first and second cardiac arterial output signals at the first and second wavelengths of light, respectively, from the patient; and a signal processing means adapted to separate the first and second cardiac arterial output signals from the first and second jugular venous output signals, respectively, to yield first and second cerebral venous output signals, for the determination of cerebral tissue oxygenation.
Owner:MESPERE LIFESCI
Guiding steel wire guiding method and device in subclavian vein catheterization
InactiveCN103100138AIncrease success ratePrevent stray entryGuide wiresSyringe needleSubclavian vein catheterization
Provided is a guiding steel wire guiding method in a subclavian vein catheterization. At first, magnetic materials are arranged on a guiding steel wire, and in the process that the guiding steel wire is propelled from the tail end of a needle cylinder to the top end of the needle cylinder, a magnet guide device is utilized to absorb the top end of the guiding steel wire and is arranged outside a guiding steel wire top end path arranged in advance. A guiding steel wire guiding device comprises a puncture needle cylinder, wherein a syringe needle is arranged at the top end of the needle cylinder, a piston is arranged in the needle cylinder and provided with a guiding steel wire channel, the guiding steel wire is arranged in the guiding steel wire channel, the top end of the guiding steel wire penetrates through an inner cavity of the needle cylinder and a needle hole in the syringe needle, the magnet guide device is arranged on the outer side of the top end of the guiding steel wire, and an interval is arranged between the magnet guide device and the top end of the guiding steel wire. According to the guiding steel wire guiding method and the guiding steel wire guiding device, the guiding steel wire can avoid entering abnormal parts of jugular veins and the like, the success rate of subclavian vein puncture is obviously improved, and pain and financial burdens of patients are lightened. Therefore, the method is safe, noninvasive, economical, and environment-friendly.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System, methods and apparatus for cerebral protection
ActiveUS8628490B2Maintain their viabilityIncrease blood flowStentsBalloon catheterPerfusionCBF - Cerebral blood flow
A device, system and method for perfusing an oxygenated medium in the cerebral vasculature. In the case of bihemispheric brain perfusion, it includes positioning pressure cuffs on upper extremities; providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon; inserting the catheter into a subclavian or femoral vein; advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned substantially in the superior vena cava junction substantially proximal to the take-off of the left innominate vein. During a perfusion mode, the cuffs and balloon are inflated causing an increase in cerebral blood flow, retrogradely; and oxygenated blood which may be cooled is pumped from a femoral artery into the catheter for a suitable period. During a non-perfusion mode the cuffs and balloon are deflated. The catheter has at least two regions, namely, guide wire and fluid delivery regions. Optionally, a separate balloon inflation region may be provided. In the case of unilateral (single hemisphere) brain perfusion, it includes providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon, inserting the catheter into a subclavian, jugular or femoral vein, advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned in the internal jugular vein on the side ipsilateral to the side of the brain requiring perfusion. In this unilateral scenario where the balloon is inflated in the ipsilateral internal jugular vein, no pressure cuffs are needed and only the balloon is inflated and deflated during the perfusion and non-perfusion modes respectively.
Owner:YACOUBIAN VAHE STEPHAN +1
Puncturing device for deep vein catheterization
InactiveCN107811685AThe puncture went wellReduce labor intensitySurgical needlesCatheterNeedle penetrationVein
The invention discloses a puncture device for deep vein catheterization, which comprises a puncture fixing device and a puncture needle. Needle, the bottom end of the syringe connector is located on the outer wall of the puncture needle and is sleeved with a push block, through the puncture fixing device, it is convenient for the doctor to use the puncture to puncture the patient, and the angle of the puncture needle can be adjusted by adjusting the angle of the puncture fixing device , so as to ensure the puncture angle of the puncture needle when using the subclavian vein puncture method and the internal jugular vein puncture method, and avoid accidentally injuring other blood vessels of the patient when the puncture needle is used for puncture. It can control the penetration speed of the puncture needle, and can also control the puncture needle to complete the needle return, which reduces the labor intensity of the doctor and makes the puncture go smoothly.
Owner:曾庆春
Cervical gear for automatically blocking internal jugular vein blood flow for peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) puncture
PendingCN110575344AImprove fitImprove comfortOperating tablesInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryVeinPediatrics
The invention discloses a cervical gear for automatically blocking internal jugular vein blood flow for peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)puncture. The cervical gear includes a first support plate, a driving box, a micro air pump, and a detection component,a second support plate is arrangedon the inner side of the first support plate, hinges are mounted below the left and right sides ofthe first support plate correspondingly, fixing rodsare connected below the hinges, support plates aremounted below the fixing rods,the driving box is arranged on the front surface of the support plate, and a pressure plate is embedded to theinner side of the support plate. The cervical gearfits to the neck of a patient, the comfort effect is high, the overall structure is simple, wearing of thecervical gearis convenient,the operation is convenient, the second support plate can be rotated with respect to the first support plate, the automatic head turning operation of the patient is then realized, the problemthata medical staff is needed to assist the patient to turn the head in the prior art is solved, the burden of the medical staff is advantageously reduced, and the pressure plate canrealize automatic compression of the internal jugular vein of the patient, the problem thatthe medical staff is needed to perform the pressing operation in the prior art is solved,and practicality ishigh.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
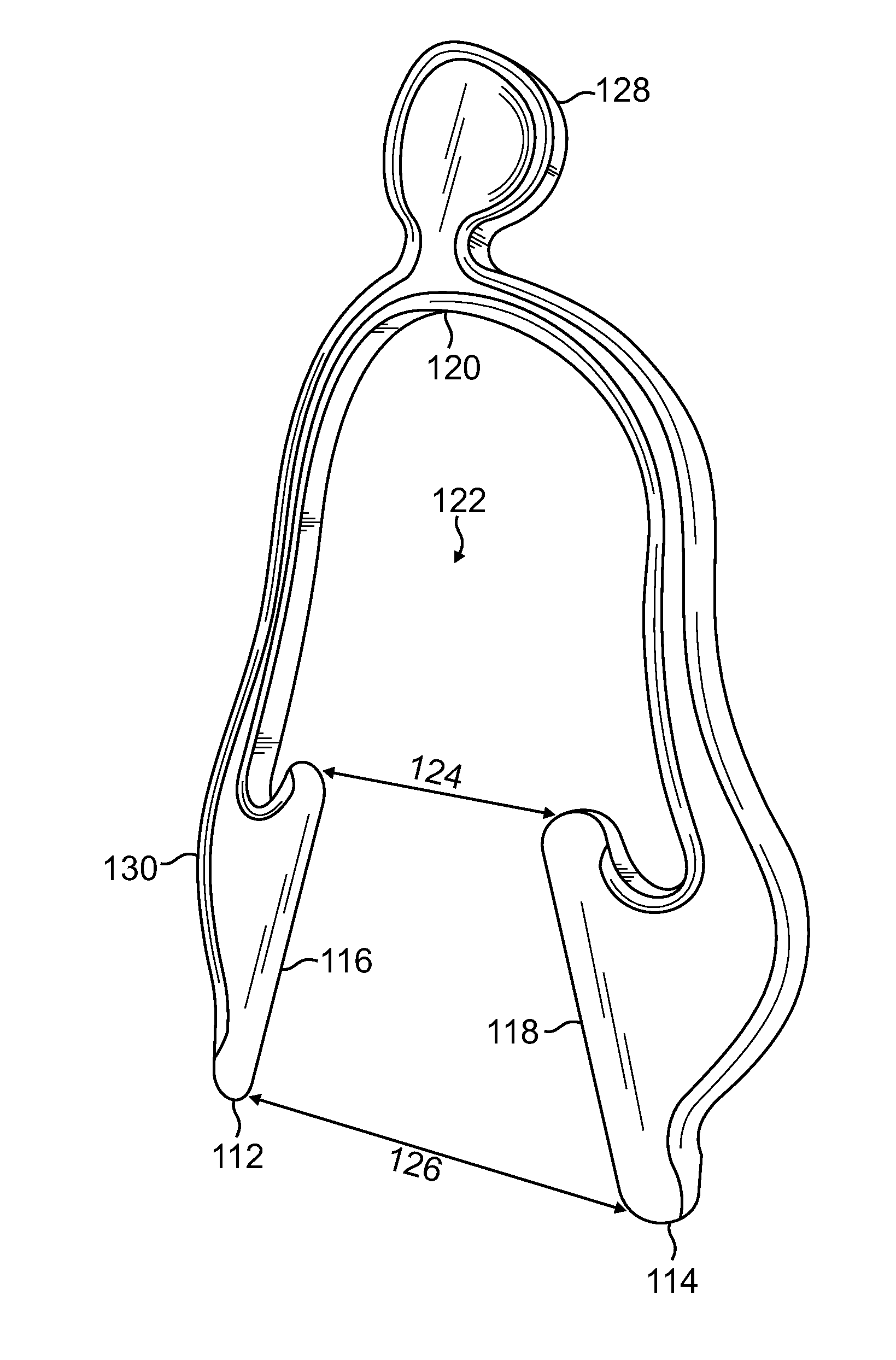
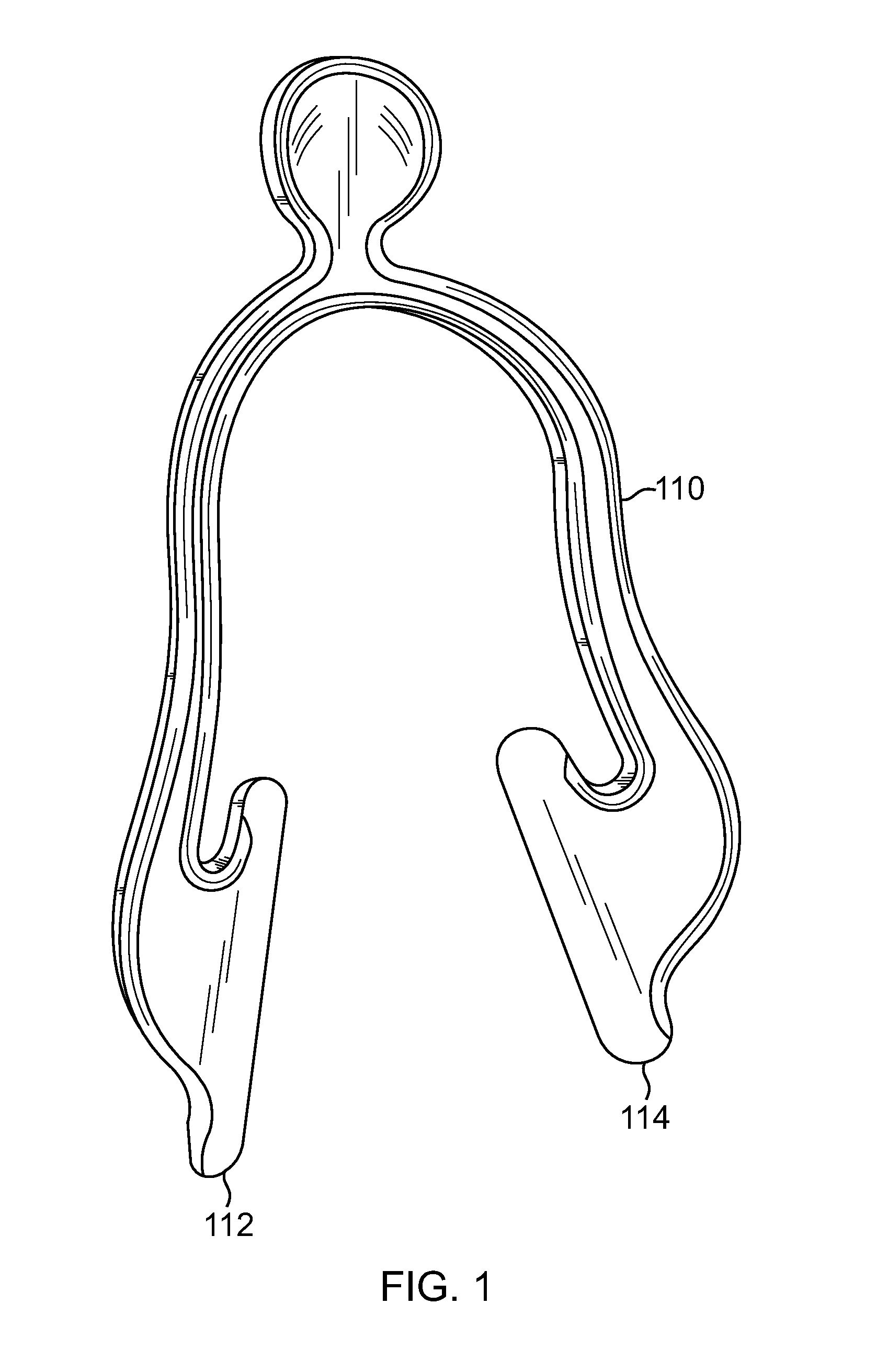
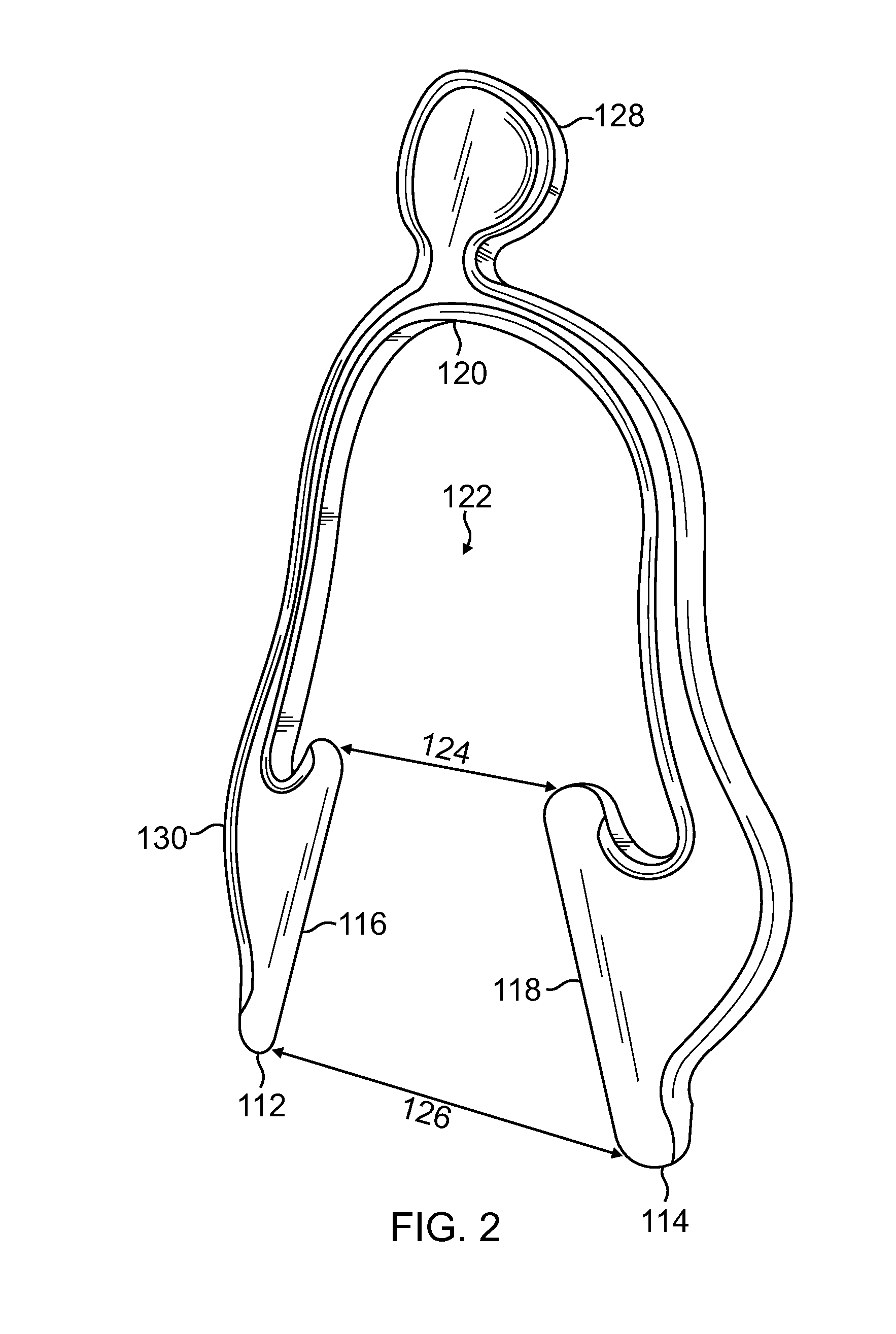
Apparatus and Method for Providing IV Access to the External Jugular Vein
A device for locating and distending the external jugular vein is provided by a wish-bone shaped apparatus designed to engage the neck of a patent and apply sufficient pressure on the neck that the external jugular vein becomes distended due to pressure placed on the patient's neck. The device includes two distally placed flat portions that resiliently engage the patient's neck without causing choking or hindrance in breathing.
Owner:FOSTER MICHAEL +1
Teaching model of internal jugular vein puncture
The invention relates to a teaching model of internal jugular vein puncture. The model includes a puncture module, a substrate, and simulated epidermis. The puncture module includes simulated muscle and simulated blood vessels arranged in the simulated muscle according to the anatomic positions; an accommodating cavity for accommodating the puncture module is formed in the substrate, and the simulated epidermis is arranged on the surface of a body, covers the surface of the puncture module and simulates the neck skin of the human body. The cost is very low, the raw materials are simple and easy to obtain, and thus the model can be well popularized; the manufacturing method is simple and can be completed manually without consuming a large amount of labor. Since the puncture module and the simulated epidermis are arranged, many functions are achieved, and people can practice a series of related operation such as body surface positioning, negative pressure needling, fluid pumpback, judgment of arteries and veins, pressure measurement, hand fixation, guiding-wire placement, pulling of a puncture needle, guiding-wire pressing, catheter placement, pull-out of a guiding wire, and catheterfixation.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Collection device and collection method for internal jugular vein indwelling blood sample of tree shrew
PendingCN110974257ASimple designEasy to useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsJugular veinInternal jugular vein
The invention discloses a collection device and a collection method for an internal jugular vein indwelling blood sample of a tree shrew, and mainly relates to the technical field of tree shrew experimental blood collection. The collection device comprises a puncture needle, an indwelling blood sampling hose and an indwelling box, wherein the puncture needle comprises a detachable part and a needle handle; the detachable part comprises two detachable needle body parts and two detachable needle body fixing shells; and the indwelling box comprises a seat body, a tube body pressing and holding fixed rubber plug, a clamping seat, a sealing plug and a protective cap. The collection method is a use method of the blood sample collection device. The collection device and the collection method provided by the invention have the following beneficial effects: the collection device can be used for a plurality of times of blood collection through one-time blood vessel puncture, is applicable to continuous blood collection or time-phased indwelling blood collection, and is good in fixing effect and not prone to falling off; the movement of the neck of the tree shrew cannot influence the indwelling blood collection tube indwelled in the jugular vein; and the indwelling blood collection tube indwelled in the jugular vein cannot damage the vein wall. Meanwhile, the indwelling blood sampling device can also be used for medicine administration.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for remaining PICC catheter through jugular vein by virtue of double-channel technique
InactiveCN111790041APlay a fixed roleReduce tube complicationsGuide wiresSurgical needlesVeinDirect puncture
The invention provides a method for remaining PICC catheter through a jugular vein by virtue of a double-channel technique. The method comprises the following steps: after jugular vein puncture is successfully carried out through ultrasonic guidance and the catheter is fed to a length of a preset pipe, establishing a subcutaneous tunnel with a length of 1cm at the same level of a puncture point byvirtue of a tunnel puncture needle, establishing a relatively long subcutaneous tunnel from an outside end of the subcutaneous tunnel to a site which is far from the lower part of a midclavicular line by two cross fingers, enabling the puncture to penetrate into the two tunnels and penetrate out of a body surface outlet in the site, trimming the catheter, and fixing the catheter at a wall of thechest. According to the method, various difficult problems of a current manner of directly remaining the PICC catheter through direct puncture through the jugular vein are solved, the operation quality is high, complications of a patient with the catheter can be reduced, the life quality is improved, and the method is capable of remarkably reliving the physiological, mental and economic burdens ofthe patient and the working intensity of medical workers and increasing the satisfaction degree of the patient.
Owner:XIANGYANG CENT HOSPITAL
Method for manufacturing bovine jugular vein valved conduit
The invention relates to an improved method for manufacturing a medical bovine jugular vein valved conduit. The bovine jugular vein valved conduit needs to be fixed before being implanted into human body. A fixing treatment method is improved. The method is characterized in that during fixing, a tube cavity is fully filled with fixing liquid, and the conduit is soaked into a container containing the fixing liquid after the two tail ends of blood vessel are ligated. The method has the advantages that the valved conduit can be fixed fully to better enhance the tissue strength and durability; moreover, the original shape of blood vessel can be well kept, wrinkling, twisting and knotting are avoided, convenience is brought to anastomosis in surgeries, pain of a patient and trouble of an operator are reduced, the surgical risk is lowered, and the use safety is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN PLASTICS RES INST CO LTD
Trimebutine maleate suppository and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102462657AAvoid the first pass effectImprove bioavailabilityDigestive systemSuppositories deliveryDrug administrationHepatic first pass effect
The invention relates to a trimebutine maleate suppository and a preparation method thereof. The trimebutine maleate suppository comprises a suppository shell and a content, wherein the content comprises 2 percent to 10 percent of trimebutine maleate, 40 percent to 90 percent of water-soluble base materials and 5 percent to 15 percent of humectants according to the percentage by weight. The trimebutine maleate suppository disclosed by the invention has the advantages that through an anus drug administration manner, active pharmaceutical ingredients enter into an inferior vena cava through an inferior rectal vein and an anal vein via an internal iliac vein after bypassing a liver and enter into systemic circulation, so a liver first pass effect is effectively avoided, the pharmaceutical bioavailability is improved, oral administration is not used, adverse reactions of a patient, which is produced during the oral administration, is avoided, and the compliance of the patient is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHARPLY PHARM R&D INSTIT +2
ECMO skill training simulation teaching system
An ECMO skill training simulation teaching system comprises simulated ECMO equipment, a simulated ECMO pipeline, a simulated monitoring system, a simulated human body model, an ultrasound-guided artery-vein puncture module, an artery and vein blood circulation device, a respiratory movement simulation device, a plurality of electrocardiogram simulation devices, a plurality of cardiopulmonary palpation auscultation simulation devices and an arterial blood pressure measurement simulation device. A simulated console, a simulated air-oxygen mixer, a simulated oxygenator, a simulated centrifugal pump and a variable-temperature water tank are arranged. A power control box is arranged. The simulation human body model is provided with a right carotid artery, an internal jugular vein, bilateral femoral arteries, veins and an ultrasound-guided puncture module. A pump box is provided with an artery and vein circulation device. Vivid critical scenes of various cardiopulmonary diseases can be set by simulating respiratory movement, electrocardiogram monitoring, cardiopulmonary touch auscultation and blood pressure measurement. The system can be connected with simulated ECMO or real ECMO equipment for training and examination such as pipeline pre-flushing, artery and vein puncture catheterization and monitoring, the whole ECMO skill training process is achieved, the simulation effect is highly simulated, and the training effect is remarkably improved.
Owner:营口东峰工贸有限公司
Methods and compositions for treating vascular-related degenerative neurological disorders
Methods and compositions for treating a patient having a vascular-related degenerative neurological disorder are disclosed. The methods comprising the steps of administering autologous bone marrow stem cells into an internal jugular vein of the patient and subsequently occluding the vein so as to create a local retrograde flow of the stem cells in the cranial veins of the patient. The further step of administering the autologous bone marrow stem cells to the patient's spinal canal subsequent to the administration of the cells to the jugular vein may also be performed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions for use in such methods. The neurodegenerative disorder commonly treated by the present invention is multiple sclerosis.
Owner:BROESKA HENRY DOUGLAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com