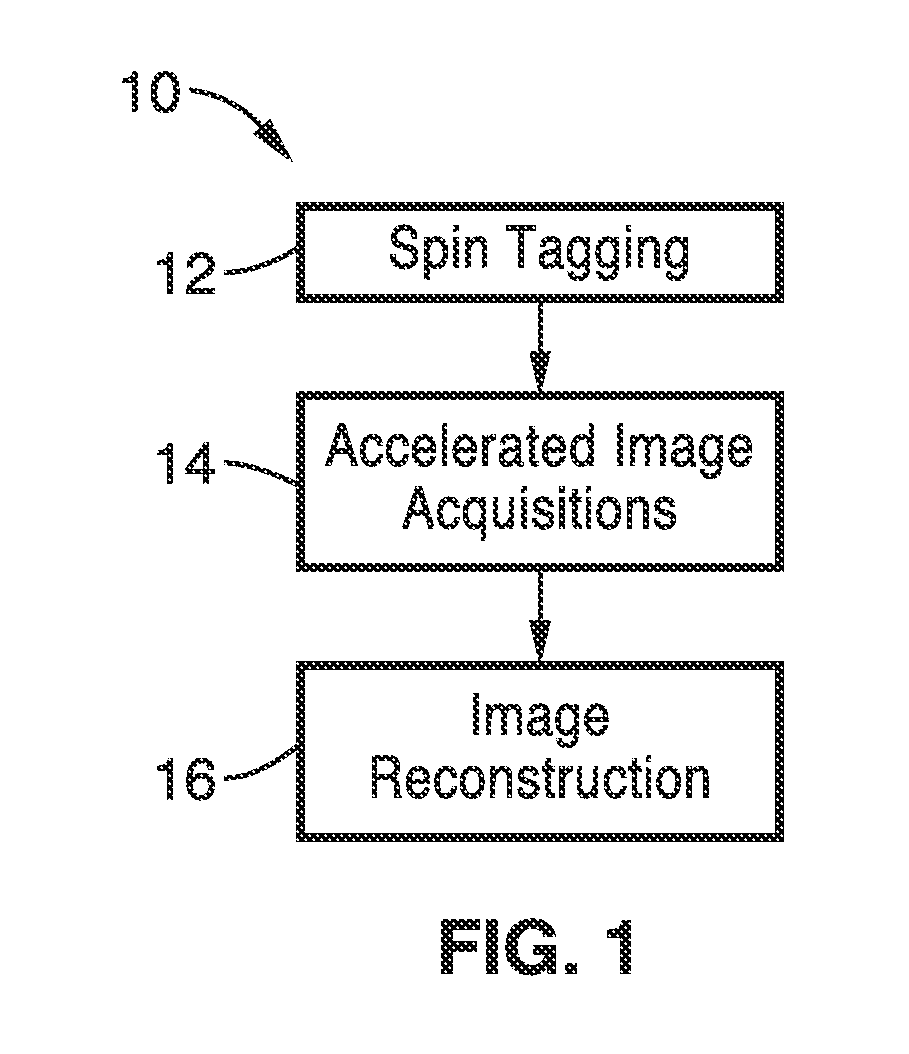
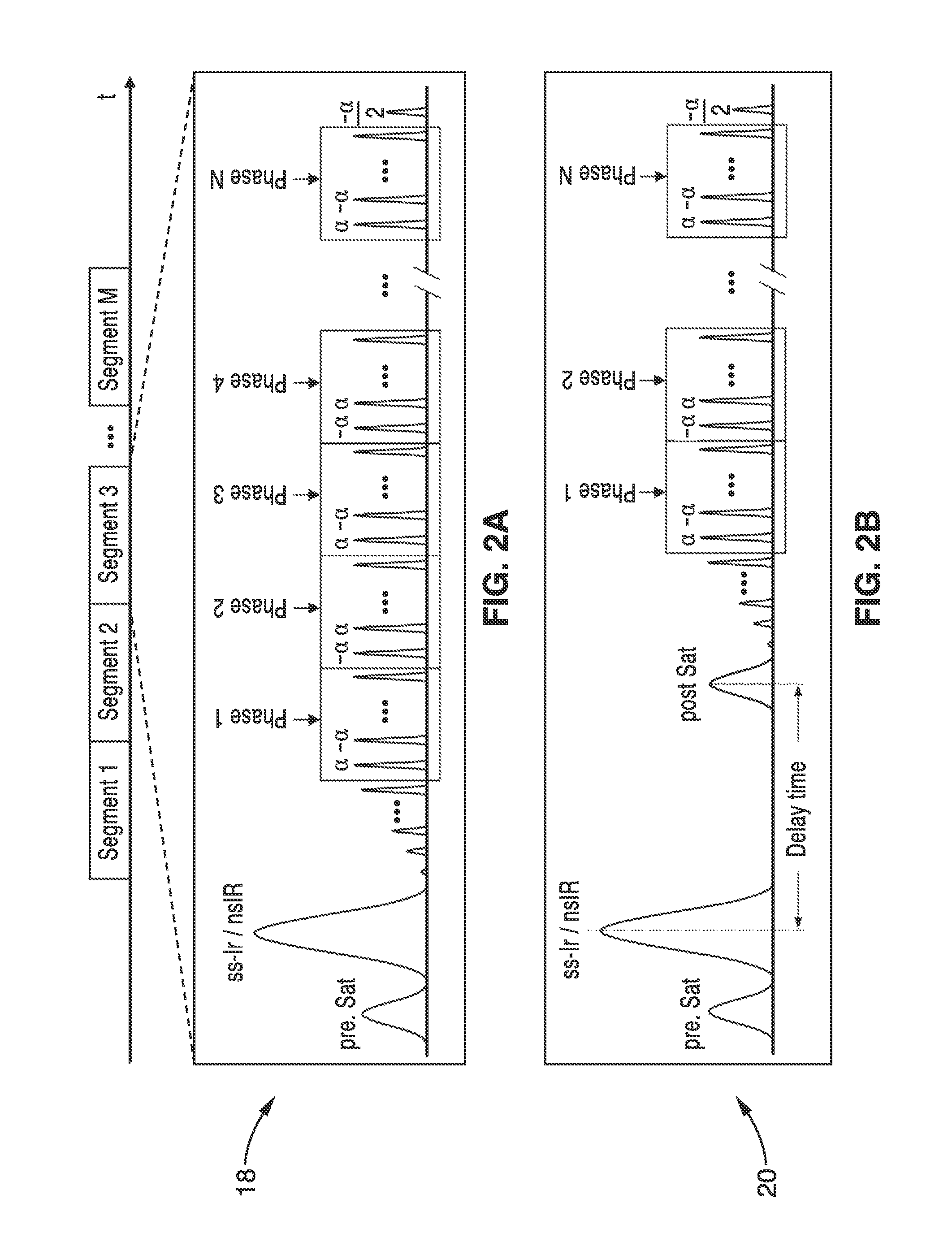
Patents
Literature
345 results about "CBF - Cerebral blood flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is the blood supply to the brain in a given period of time. In an adult, CBF is typically 750 millilitres per minute or 15% of the cardiac output.
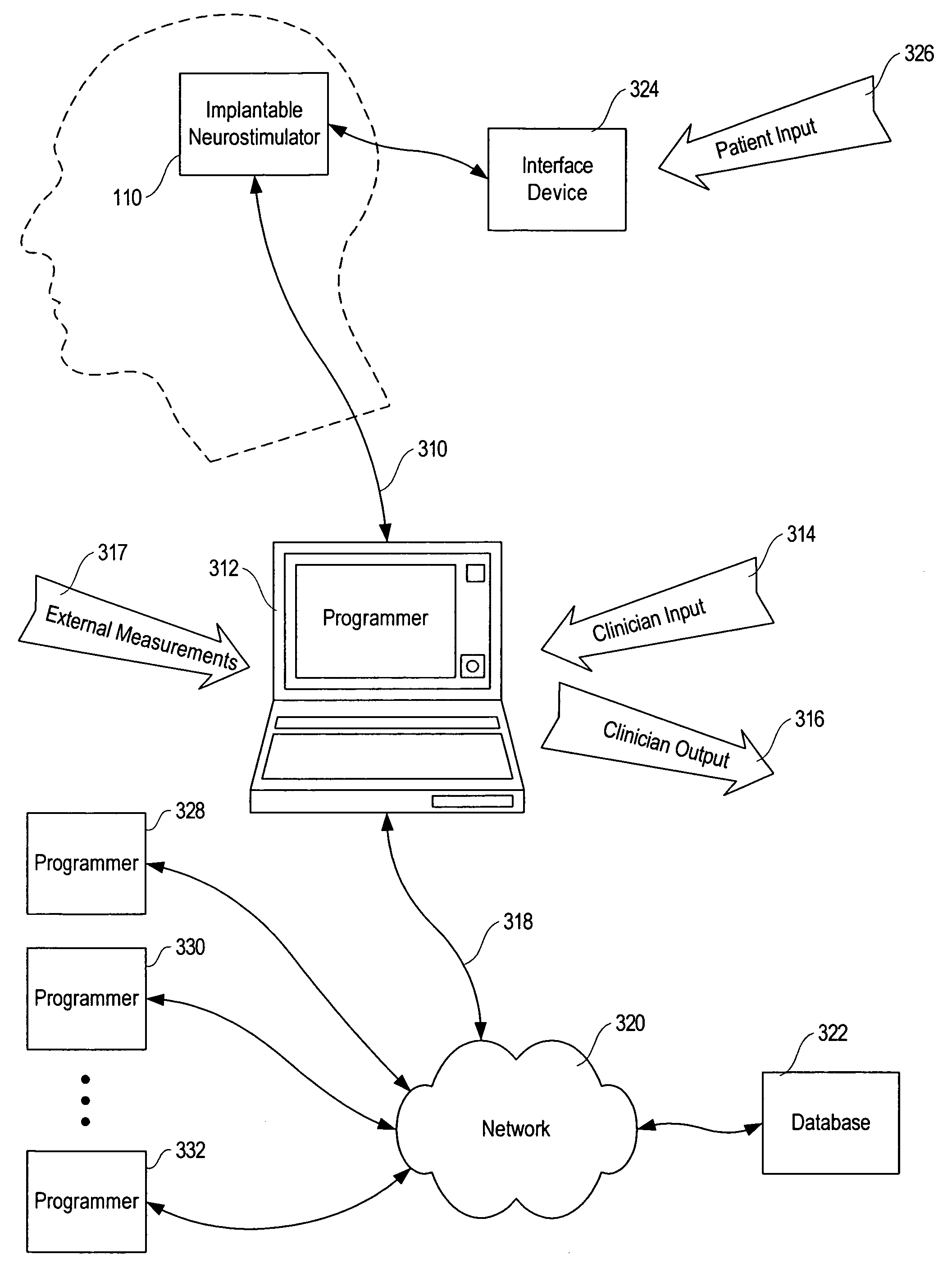
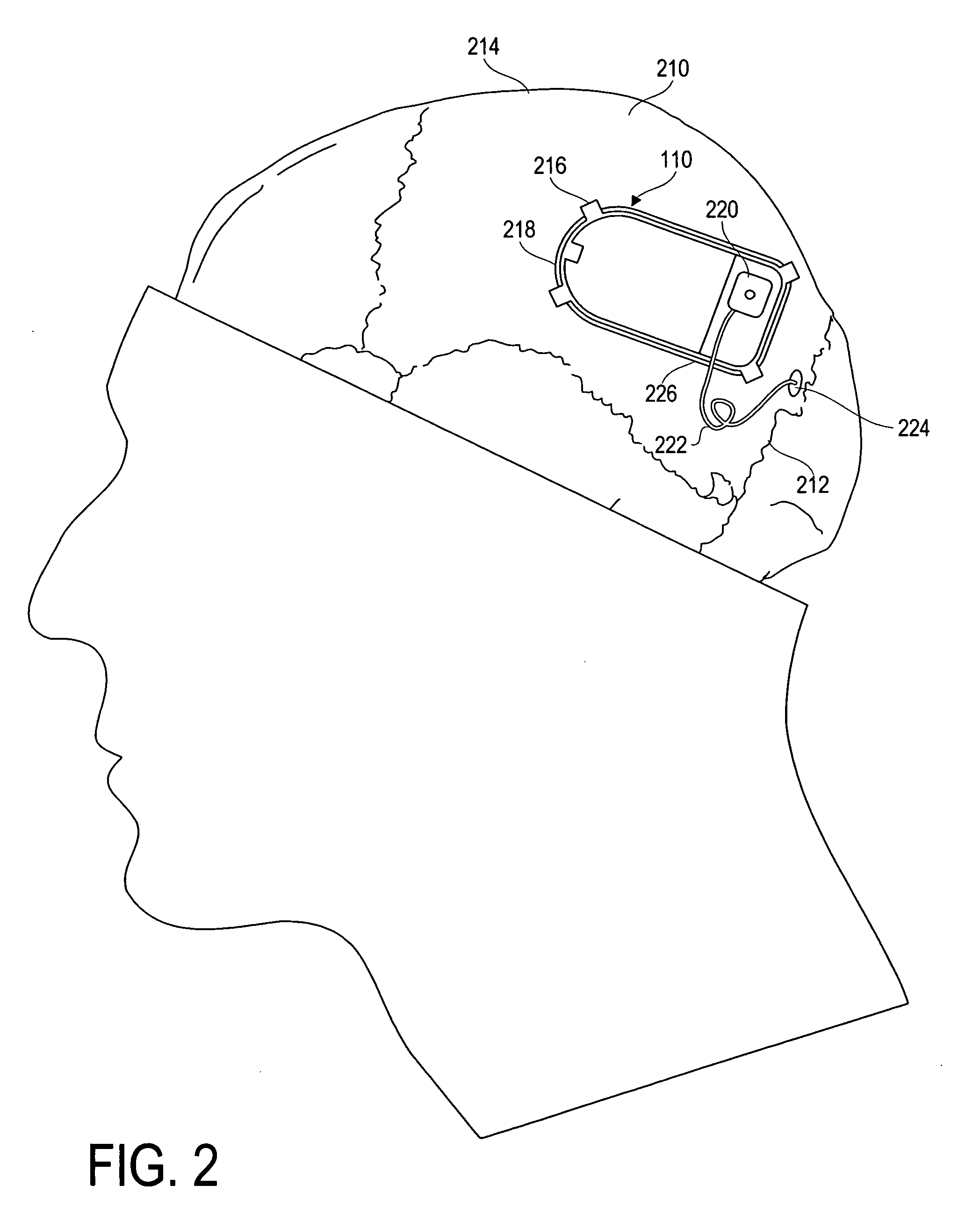
Modulation and analysis of cerebral perfusion in epilepsy and other neurological disorders
InactiveUS20060265022A1Increase perfusionReduce perfusionElectroencephalographyUltrasound therapyDiseaseNervous system
A system including an implantable neurostimulator device capable of modulating cerebral blood flow to treat epilepsy and other neurological disorders. In one embodiment, the system is capable of modulating cerebral blood flow (also referred to as cerebral perfusion) in response to measurements and other observed conditions. Perfusion may be increased or decreased by systems and methods according to the invention as clinically required.
Owner:NEUROPACE
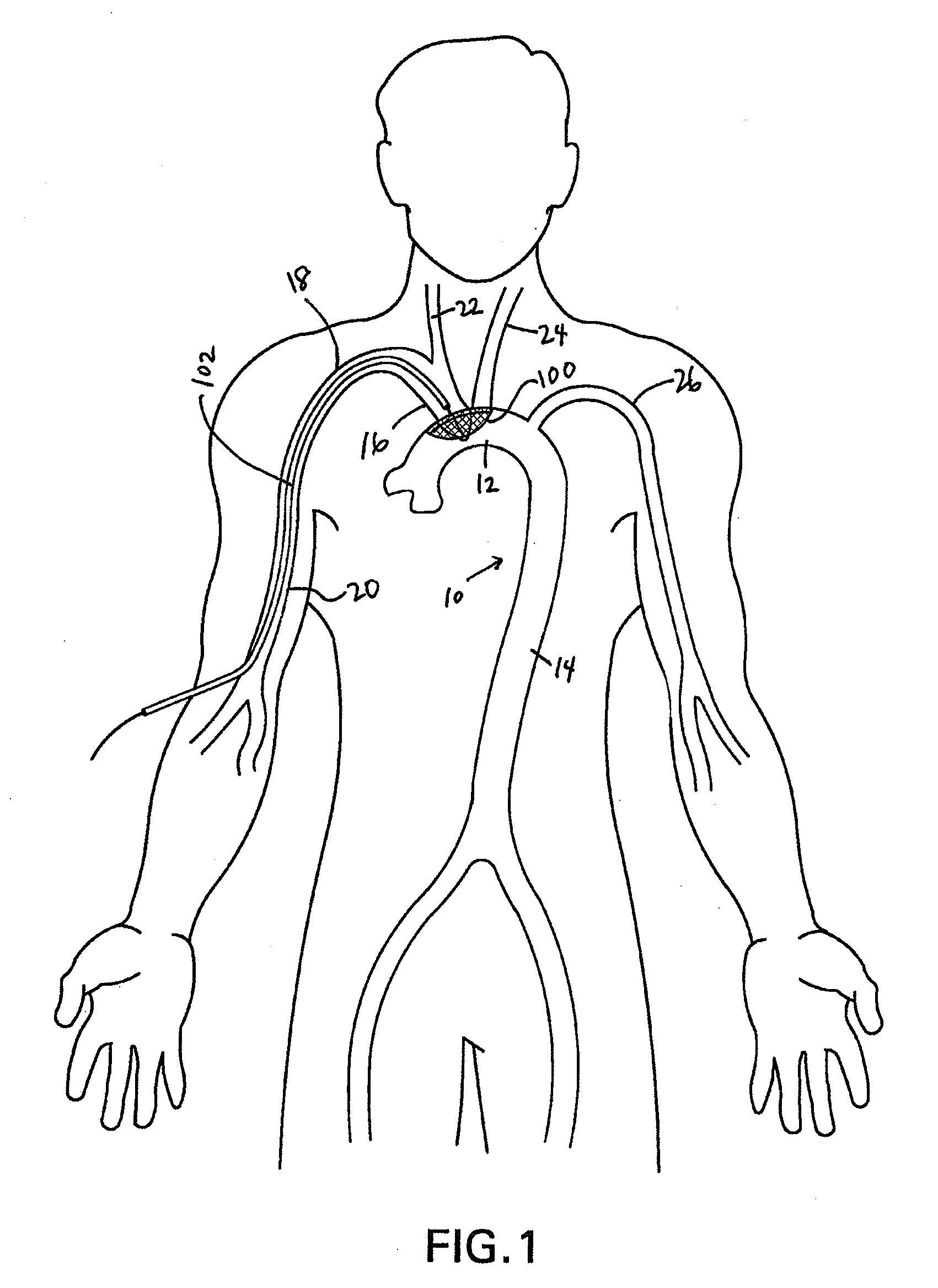
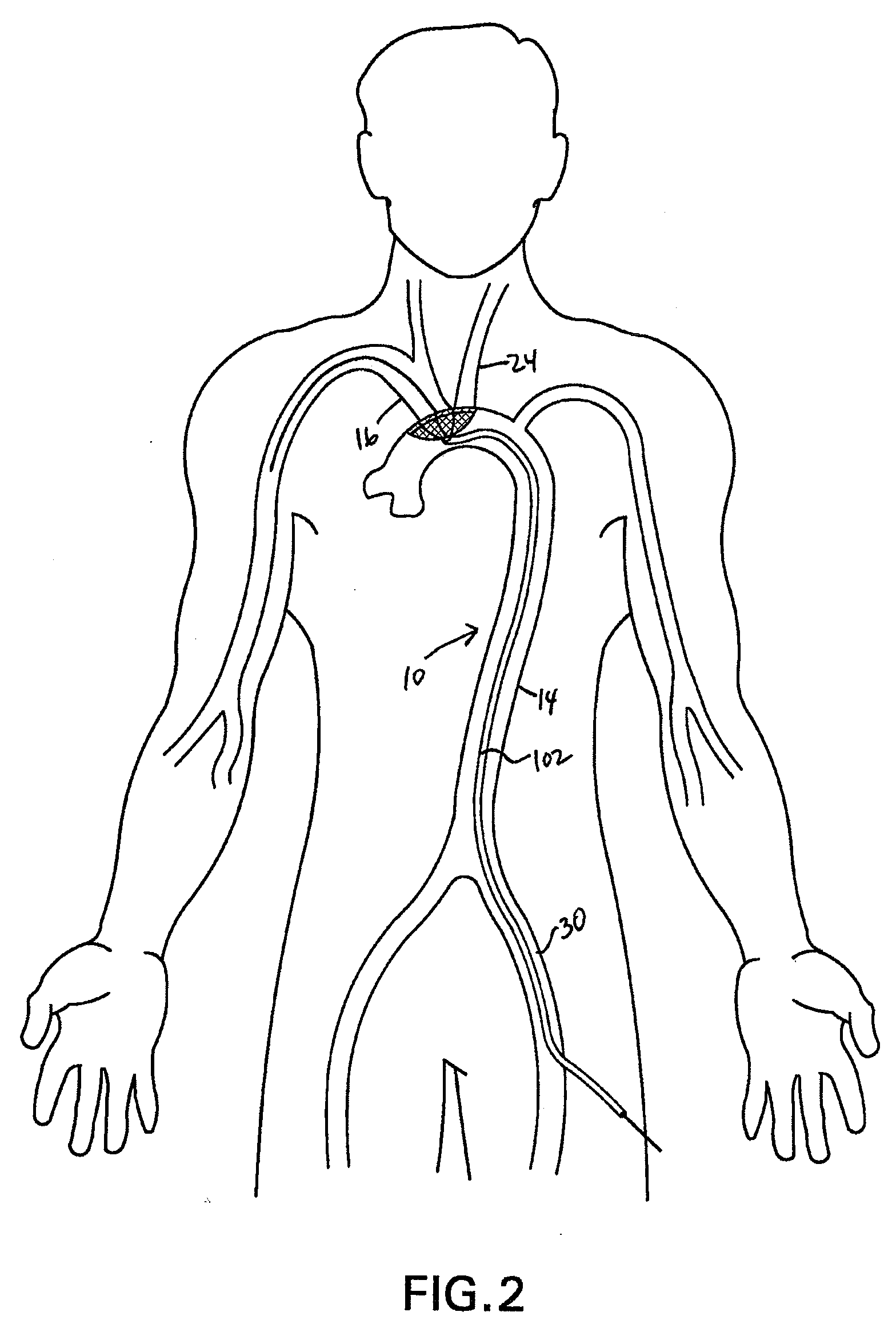
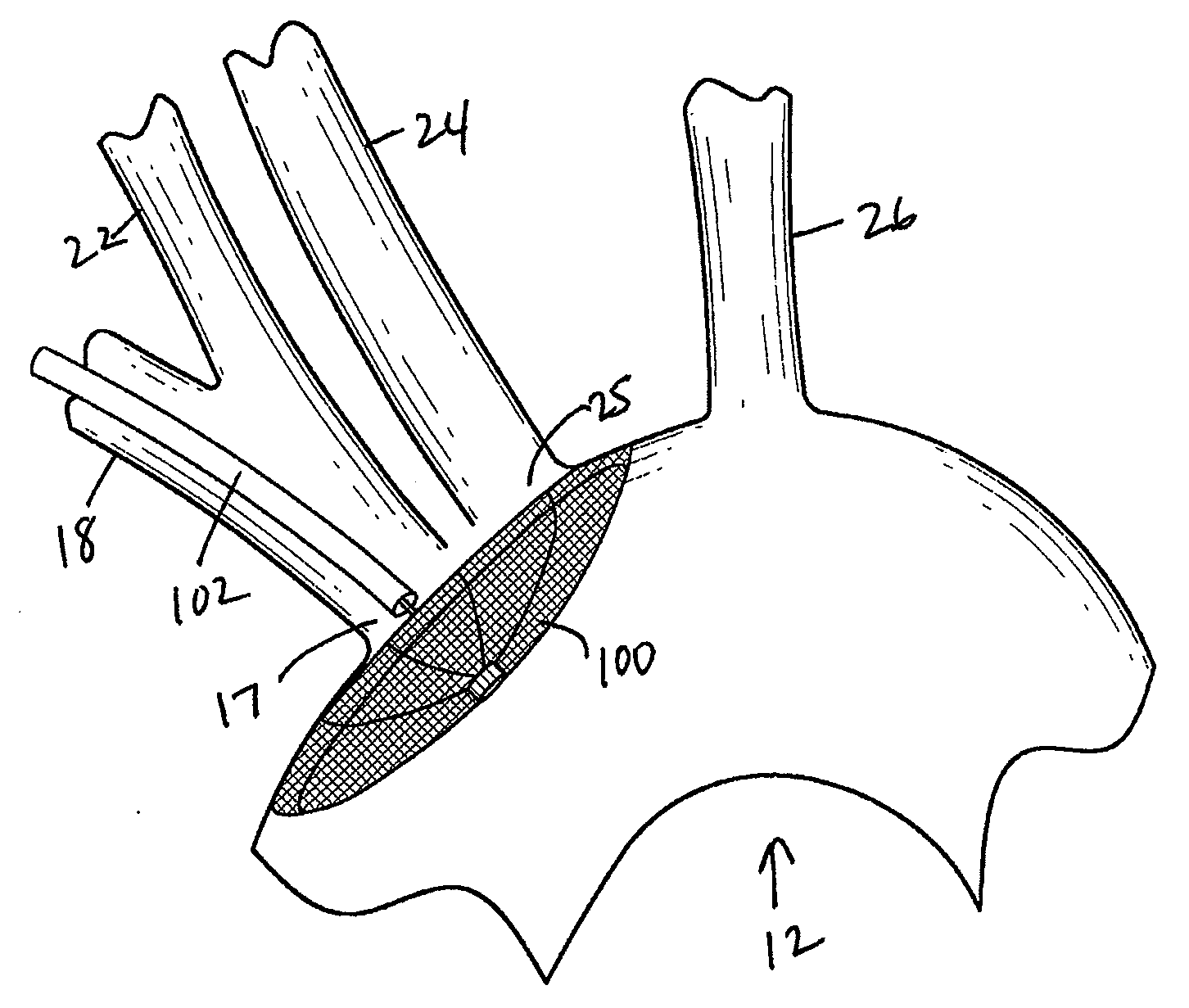
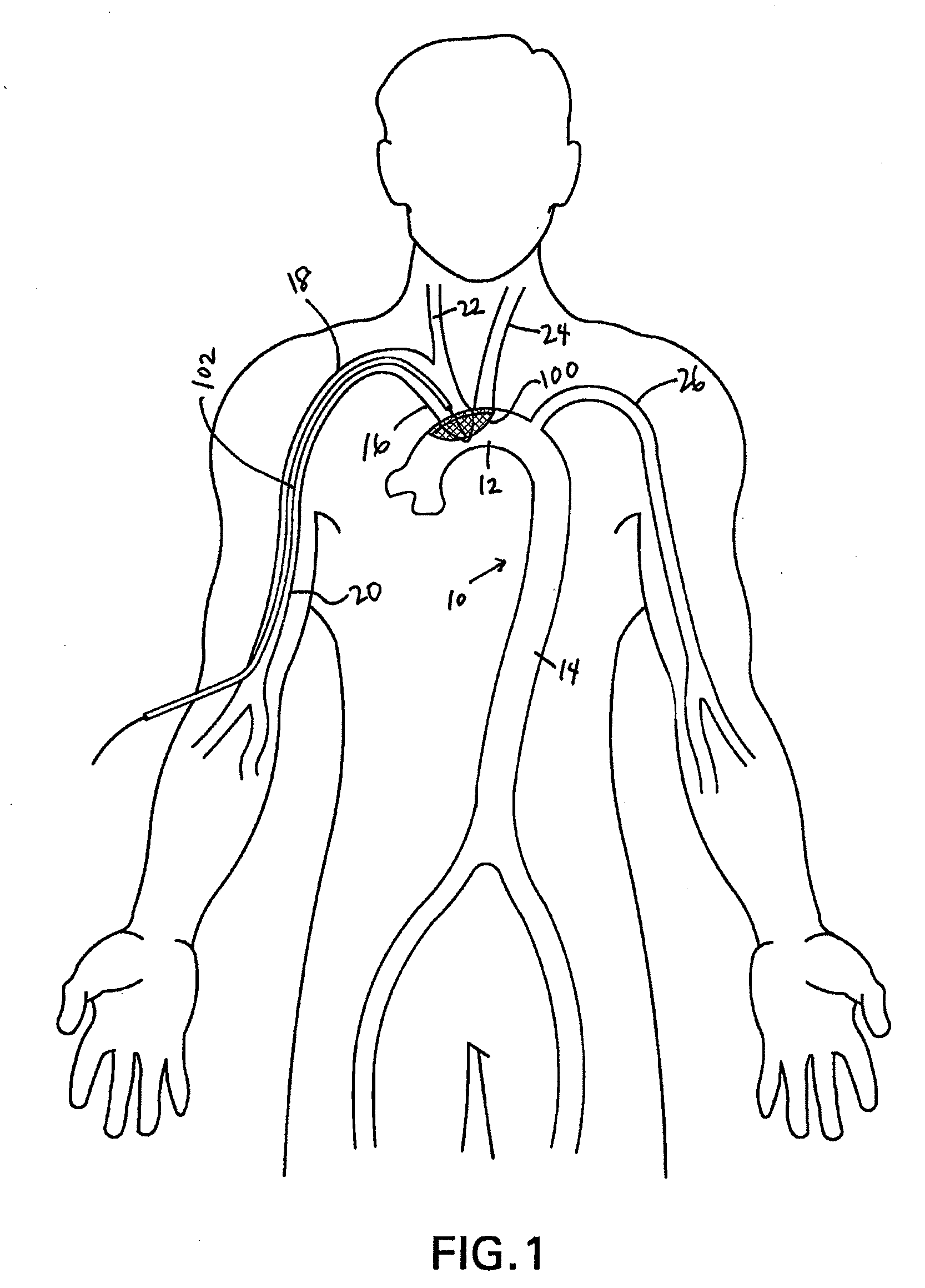
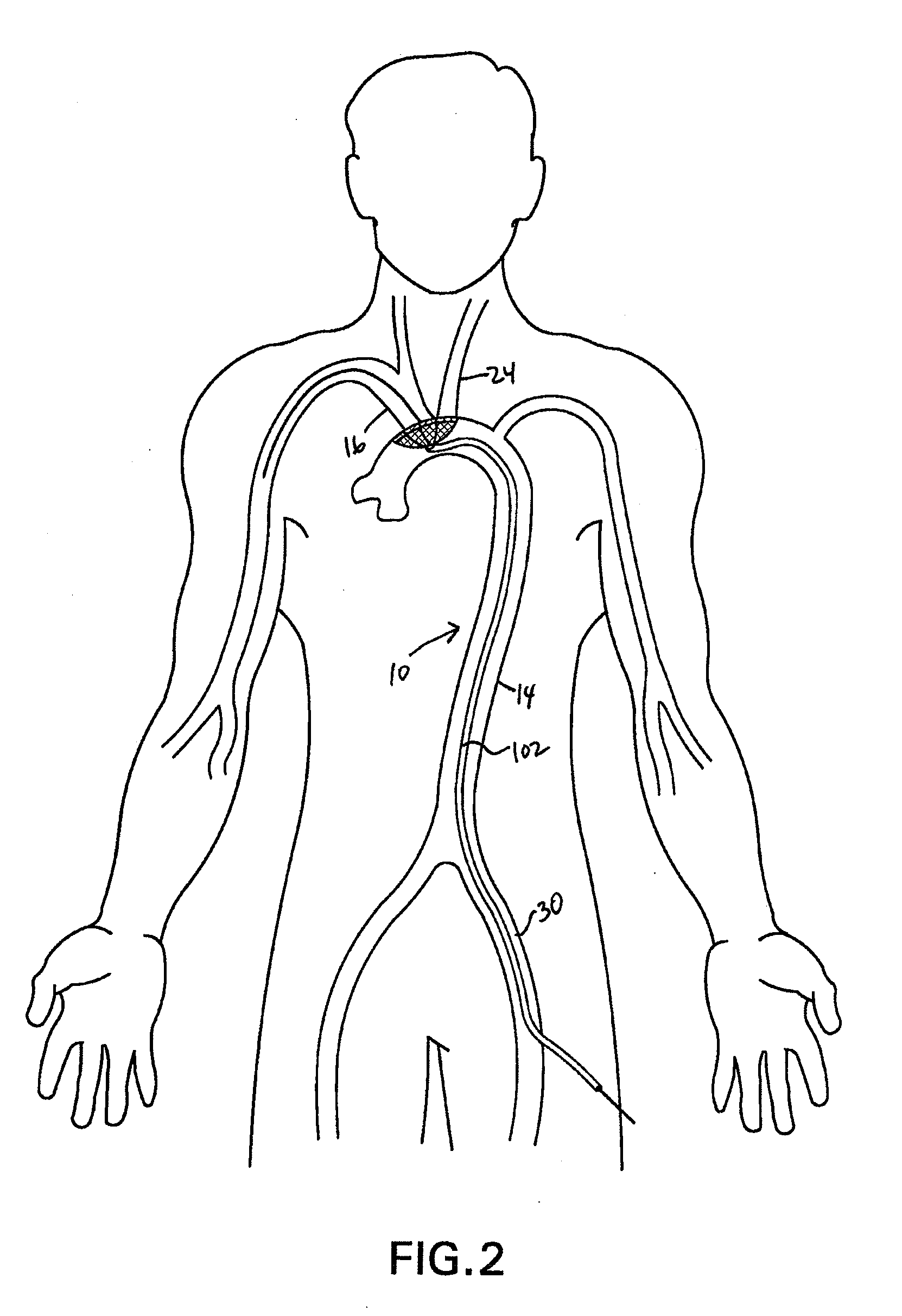
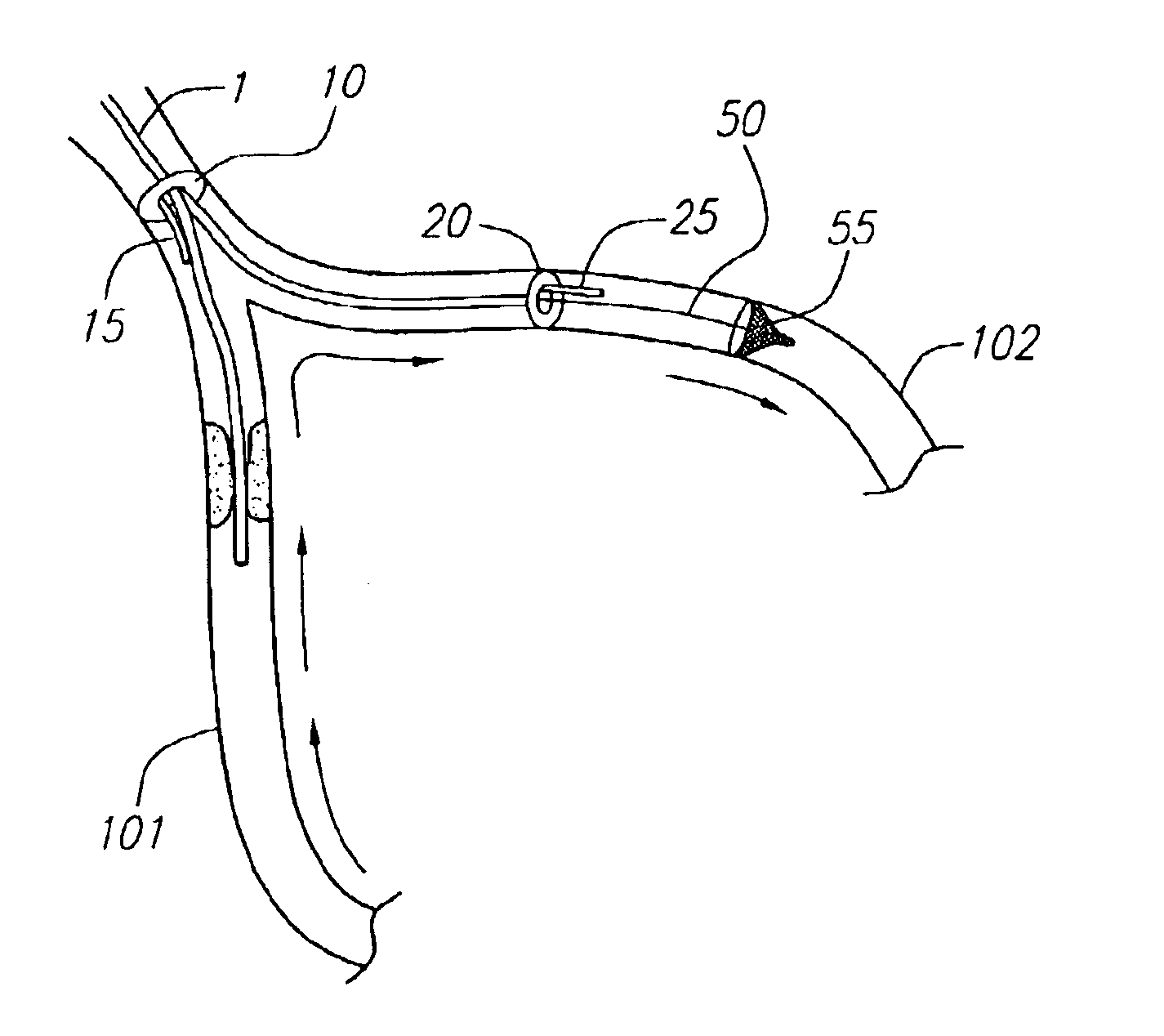
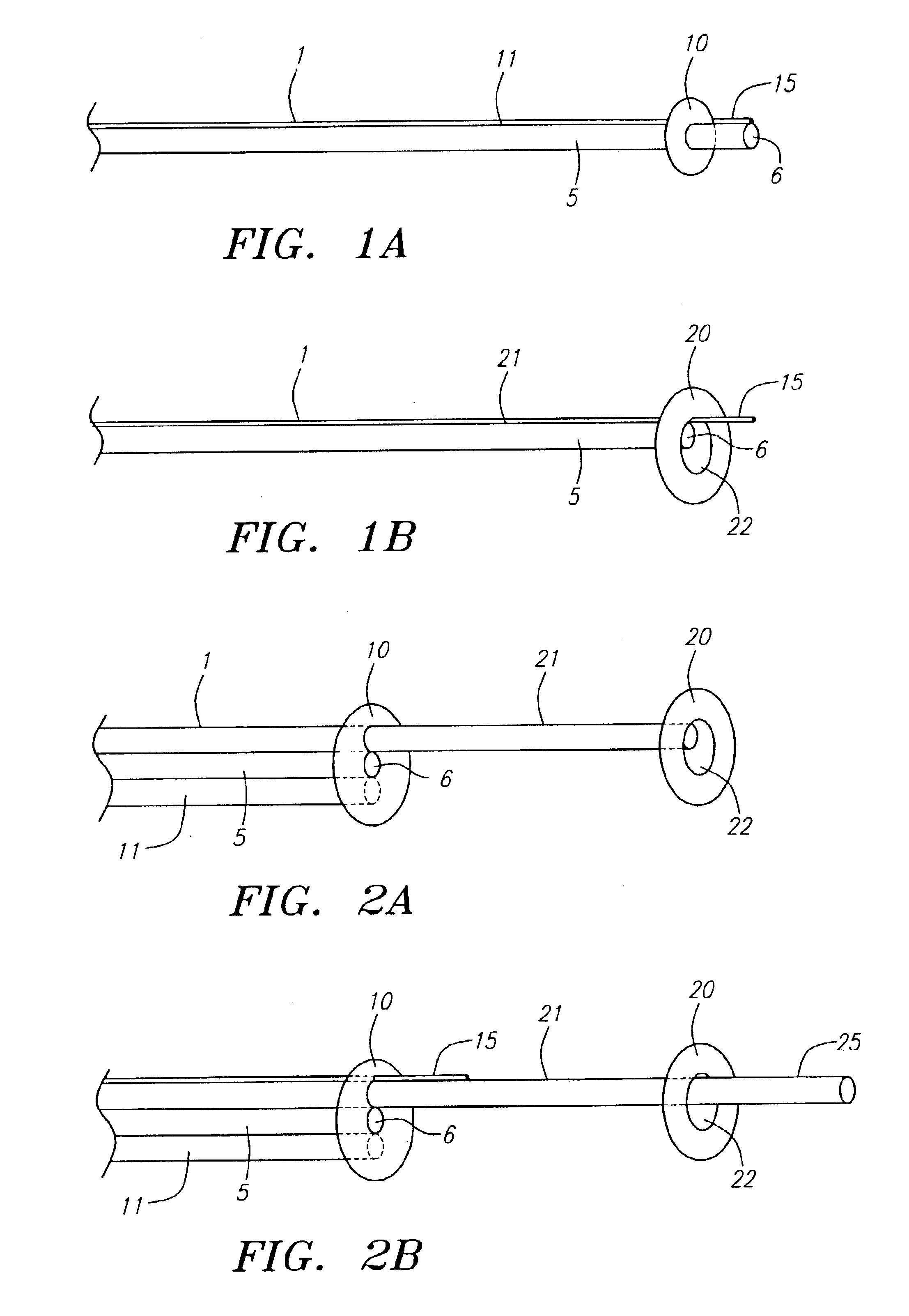
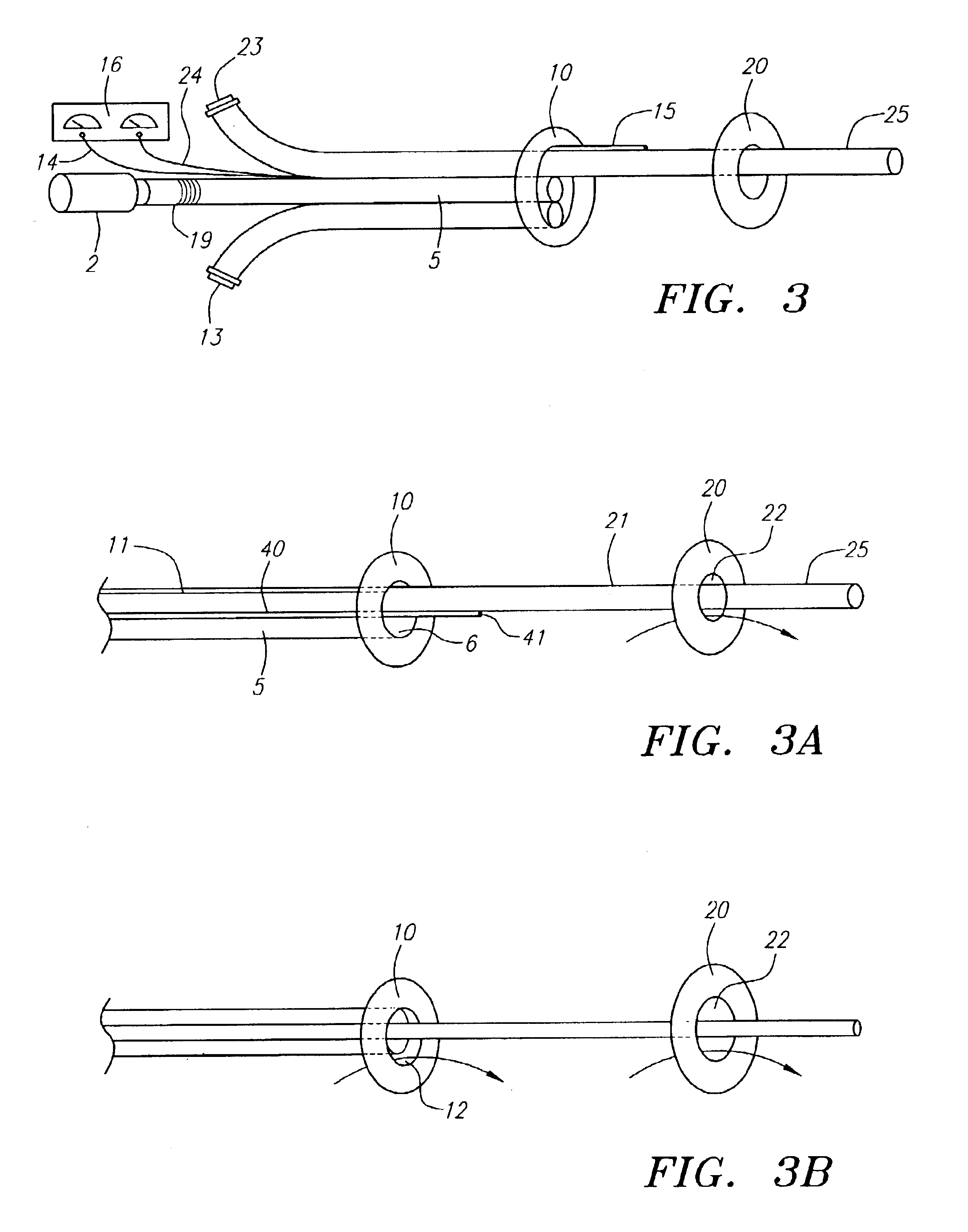
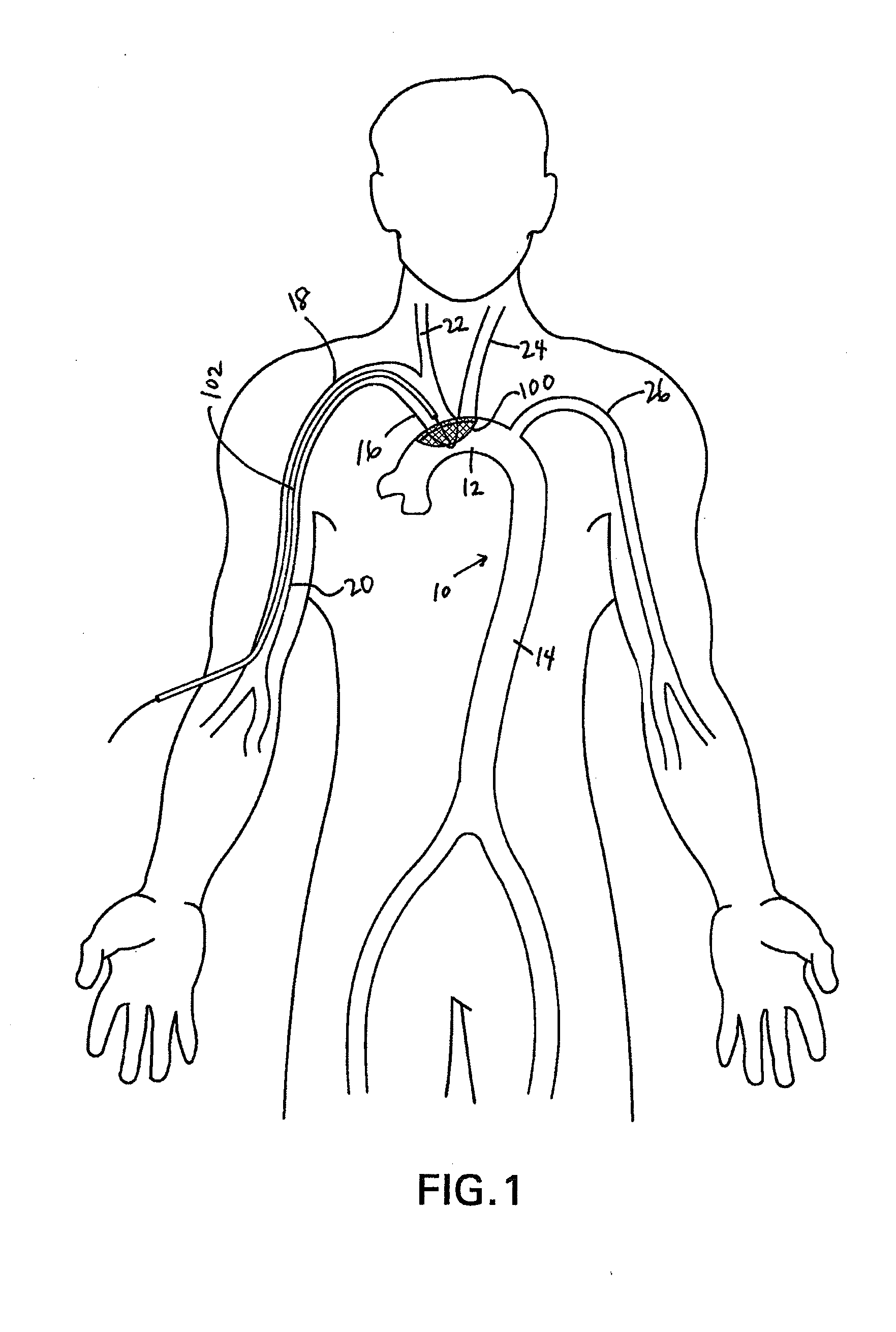
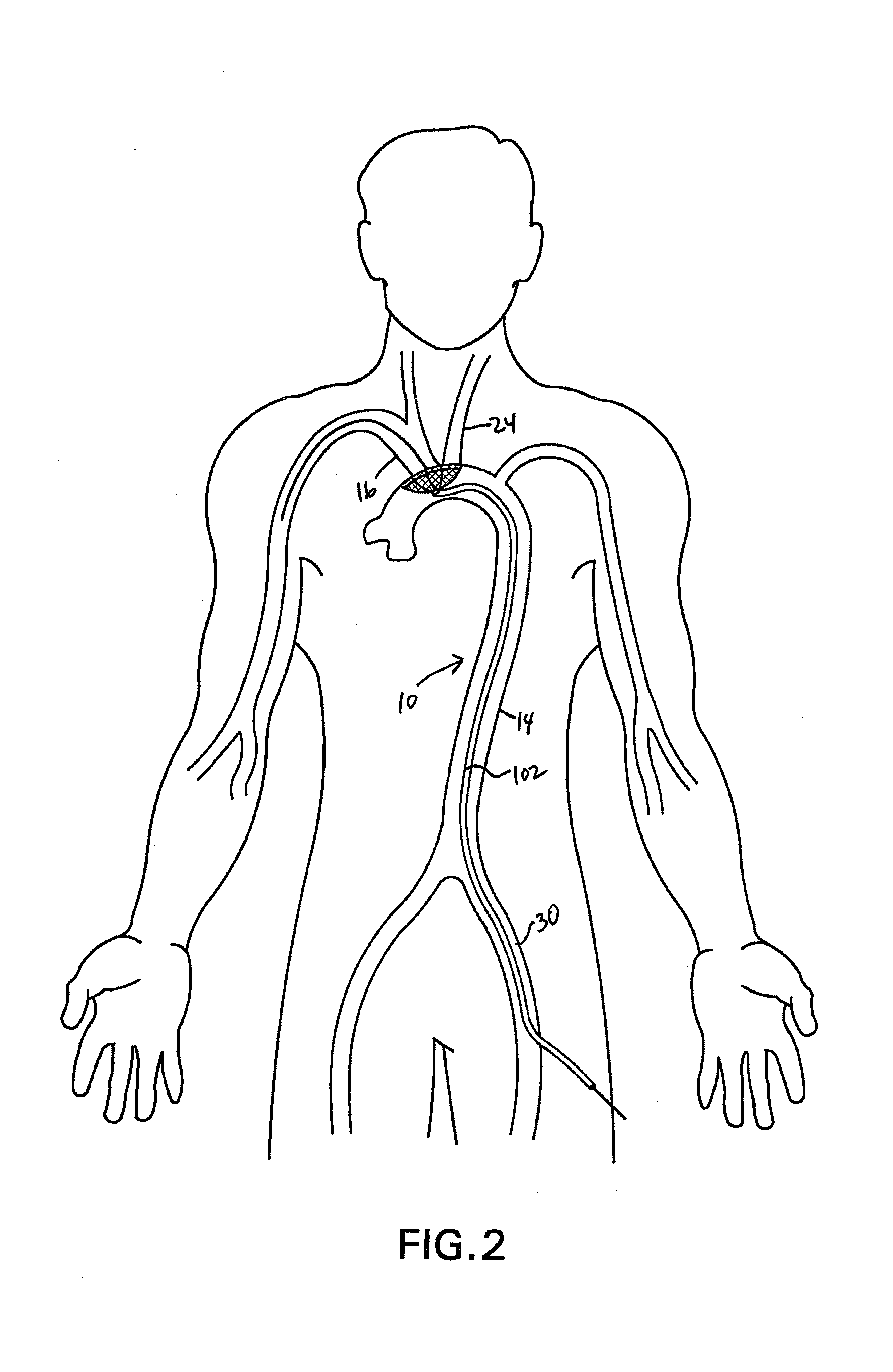
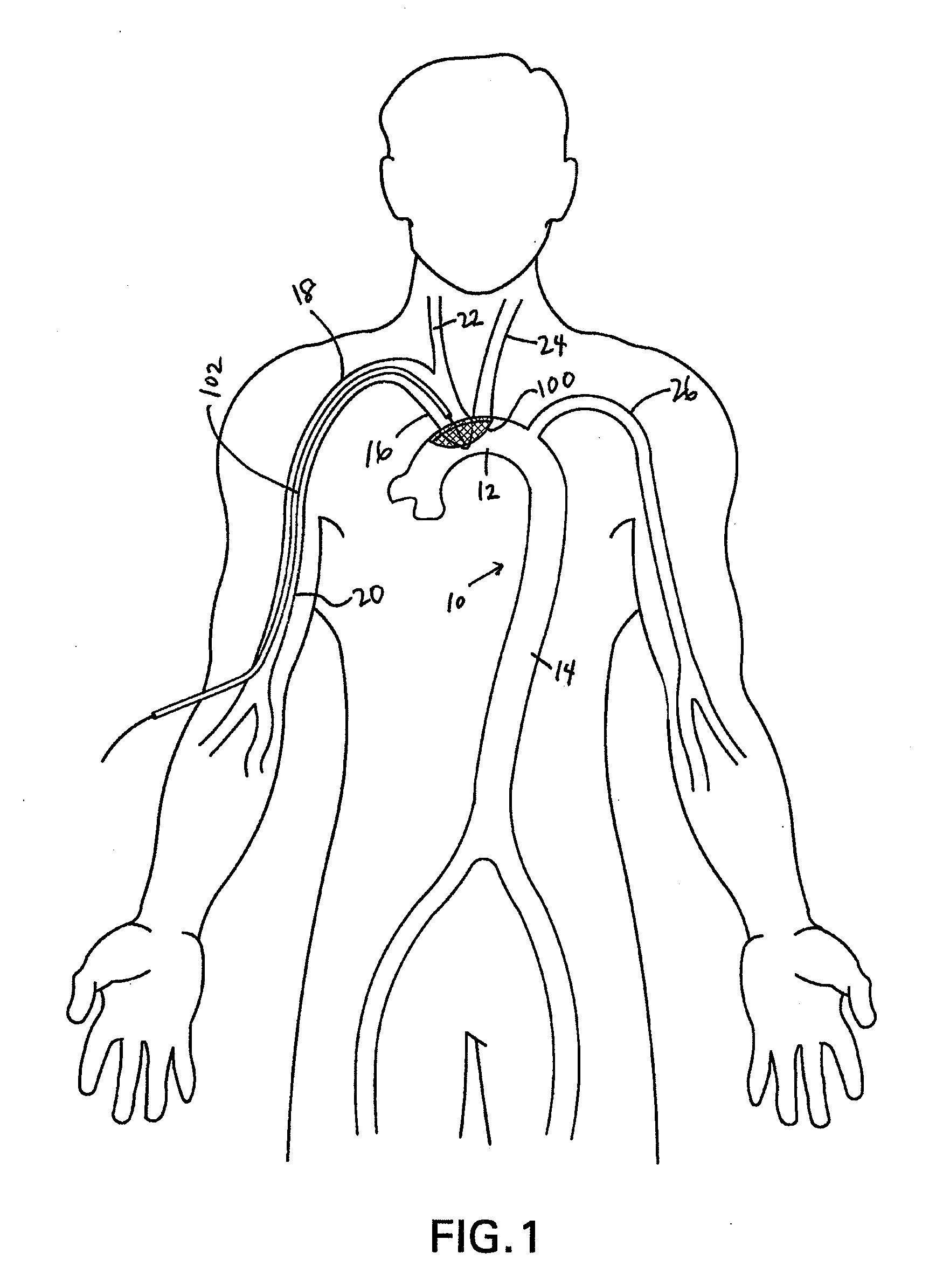
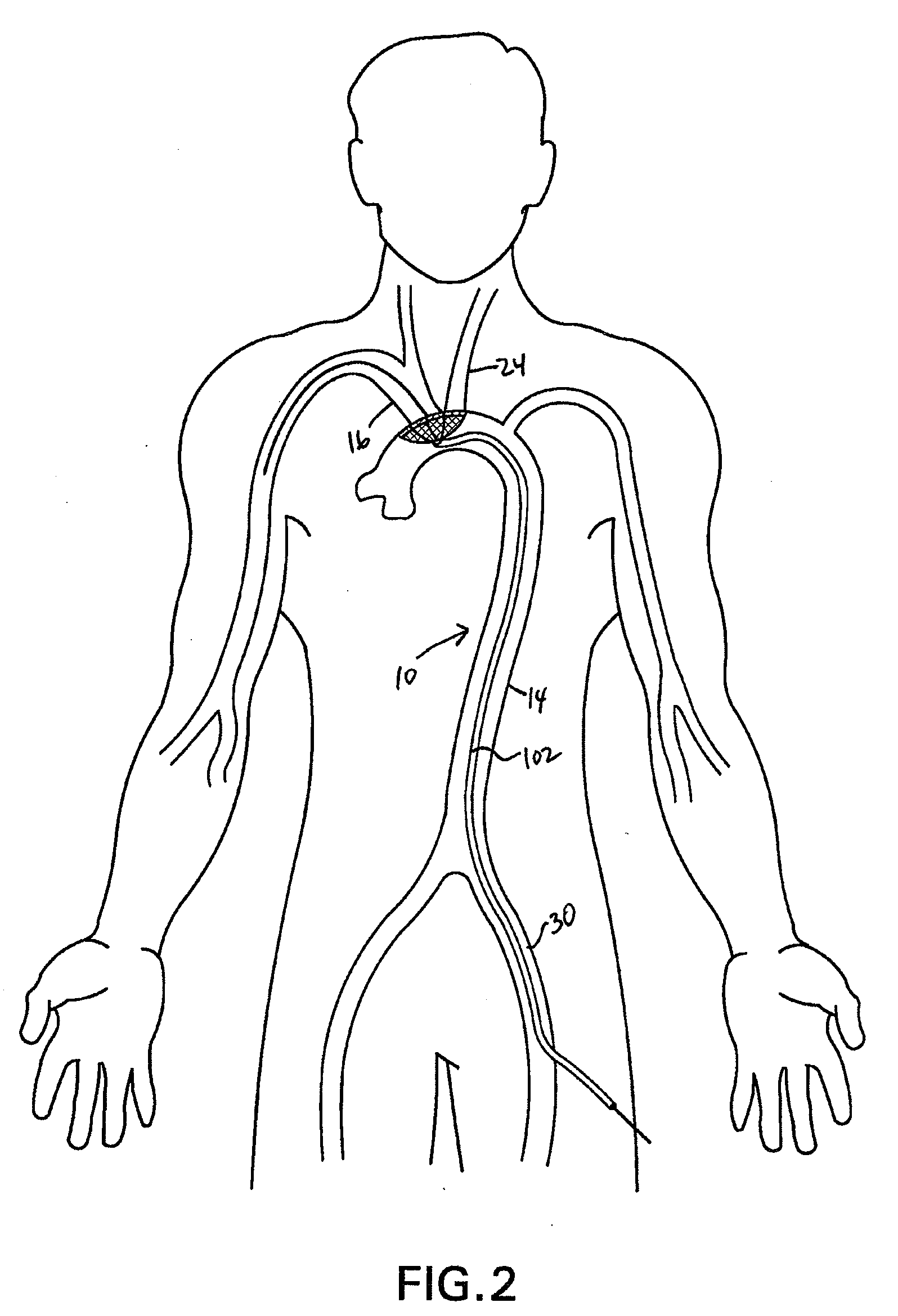
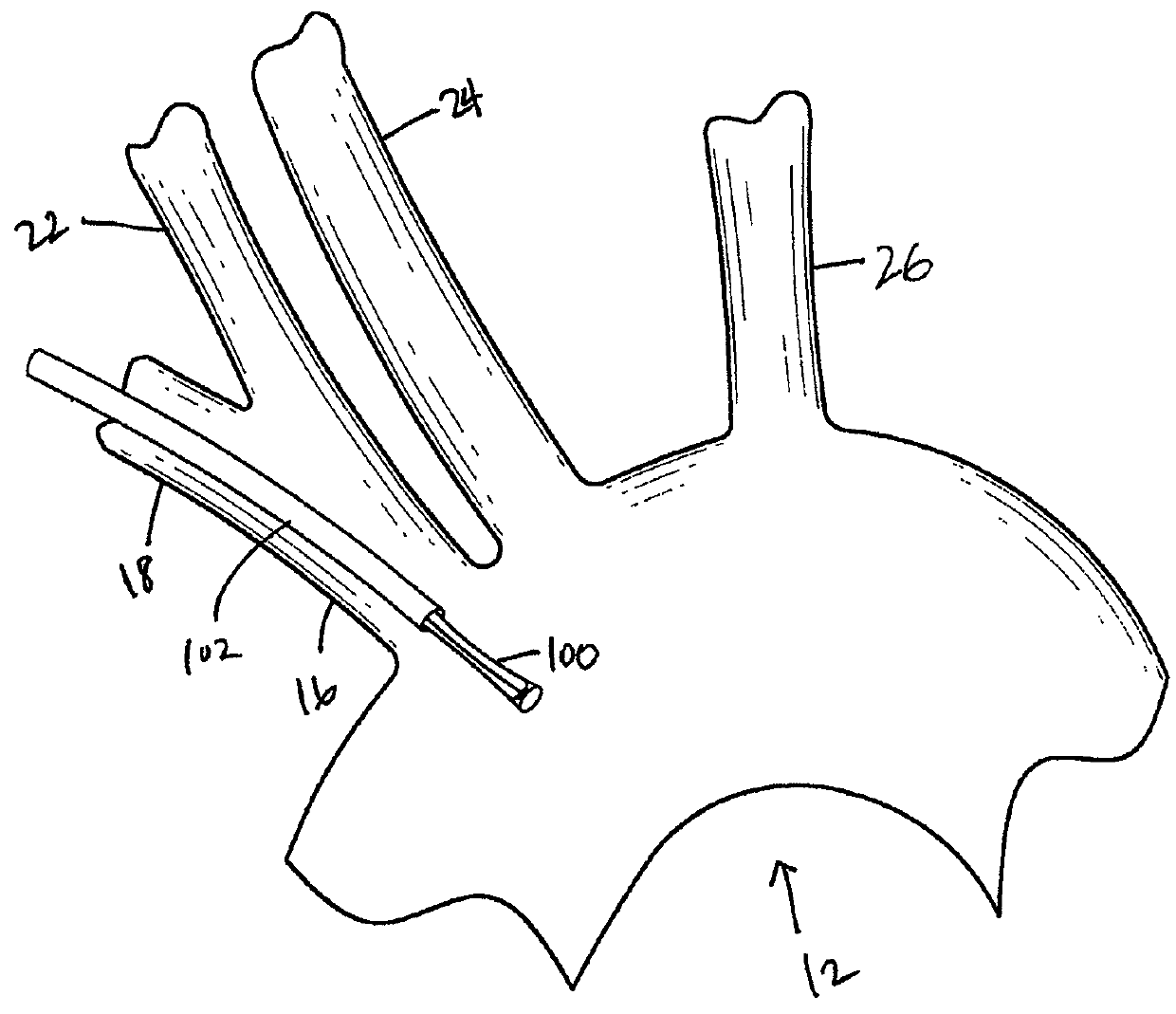
Methods of reducing embolism to cerebral circulation as a consequence of an index cardiac procedure
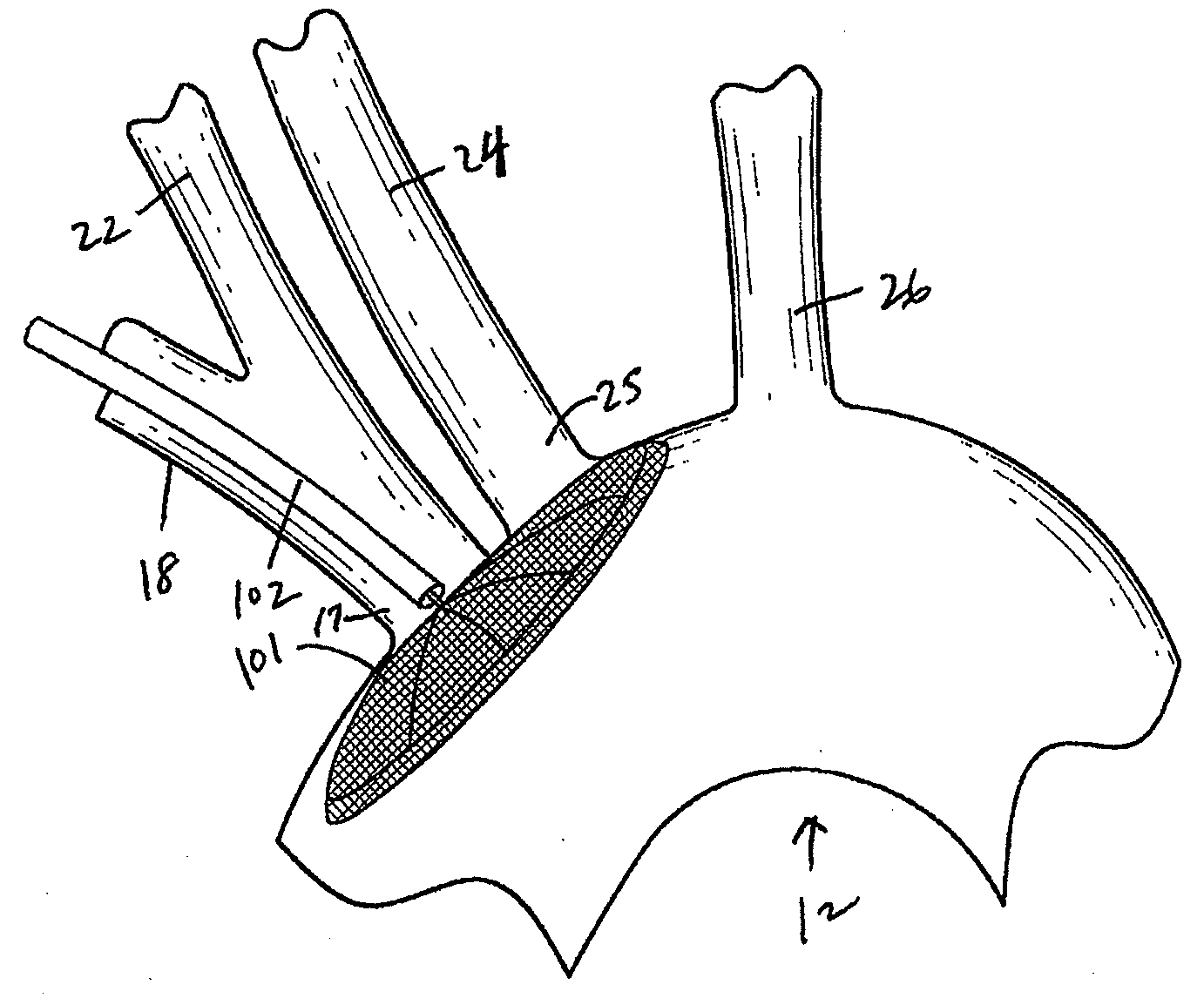
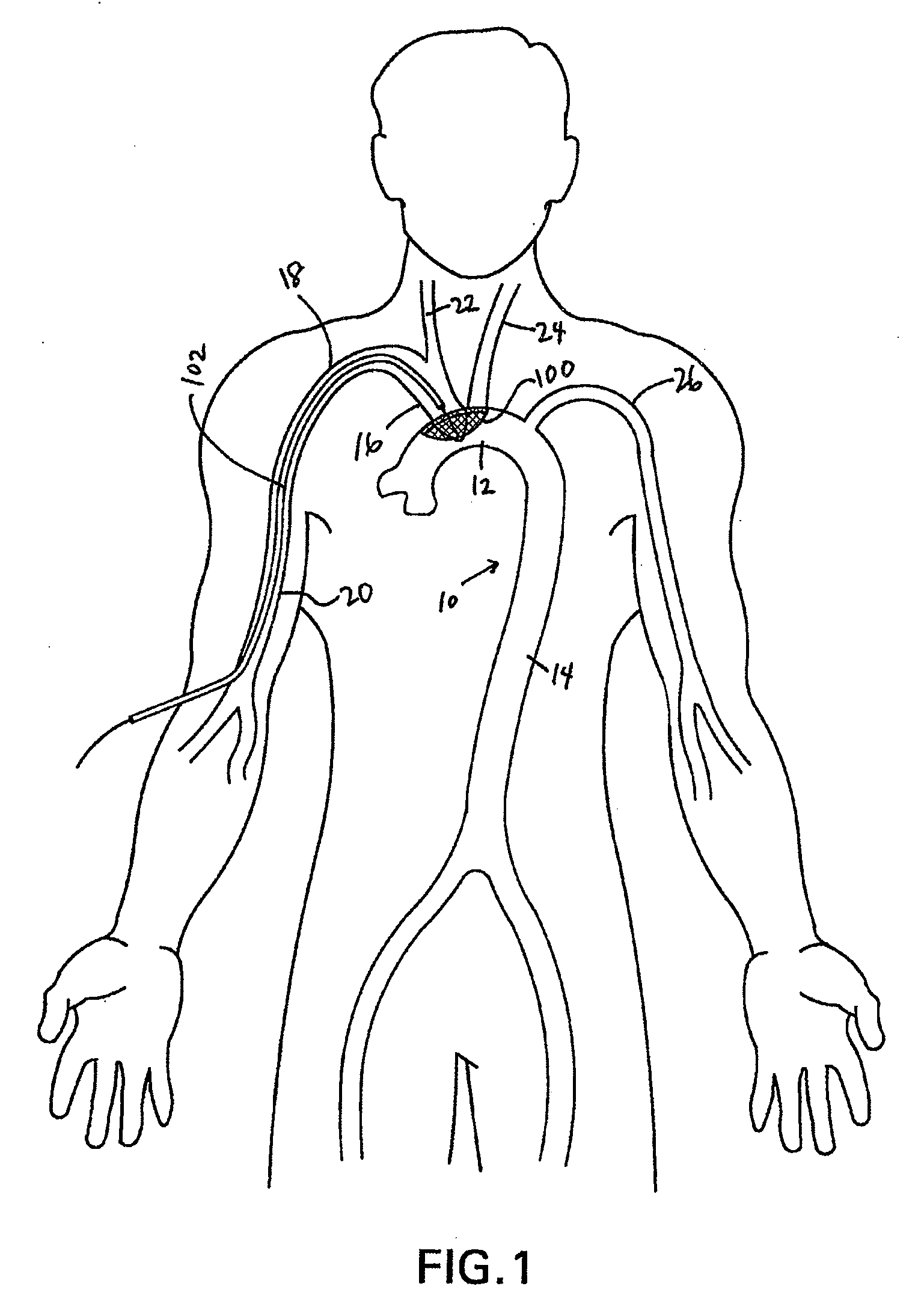
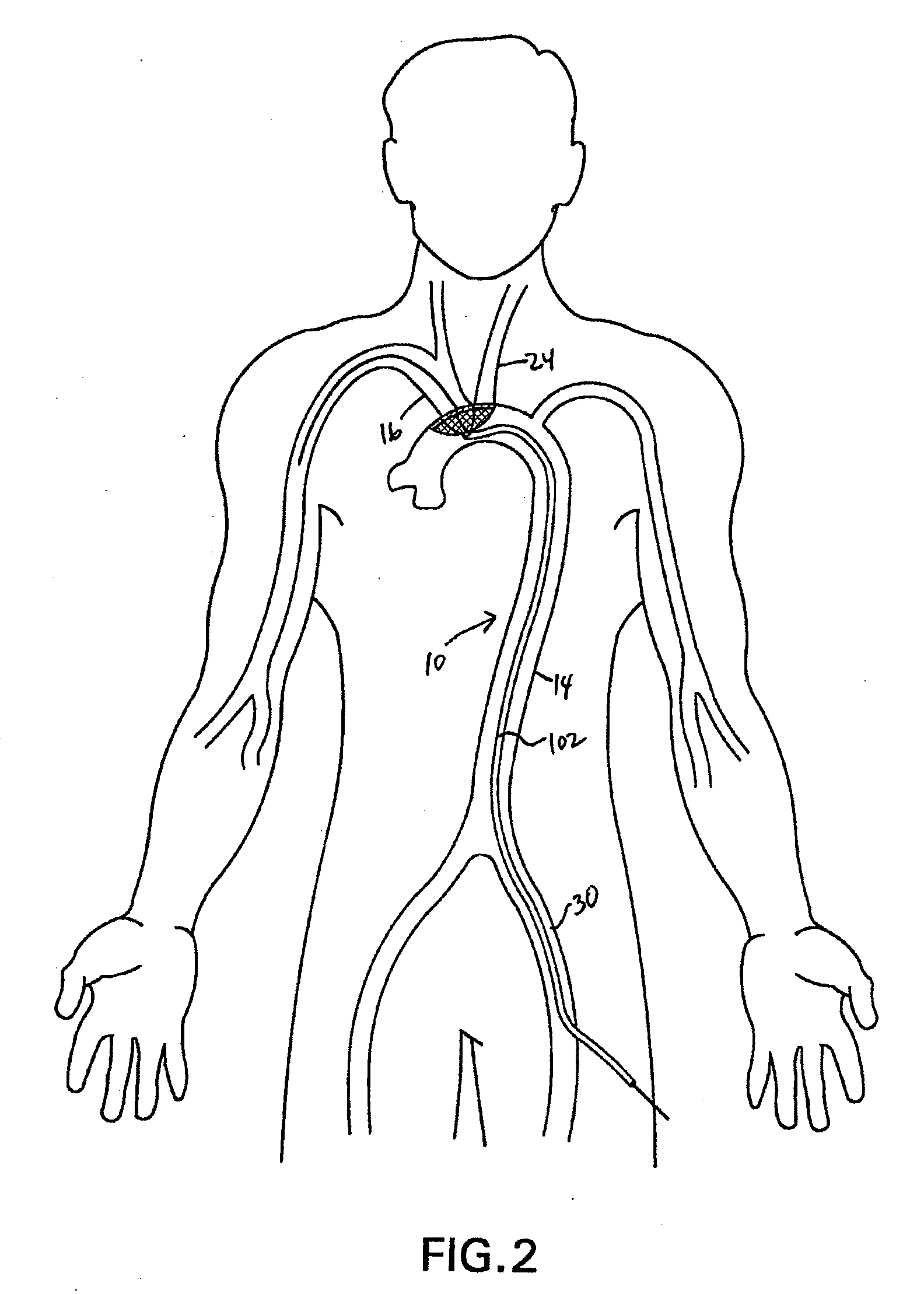
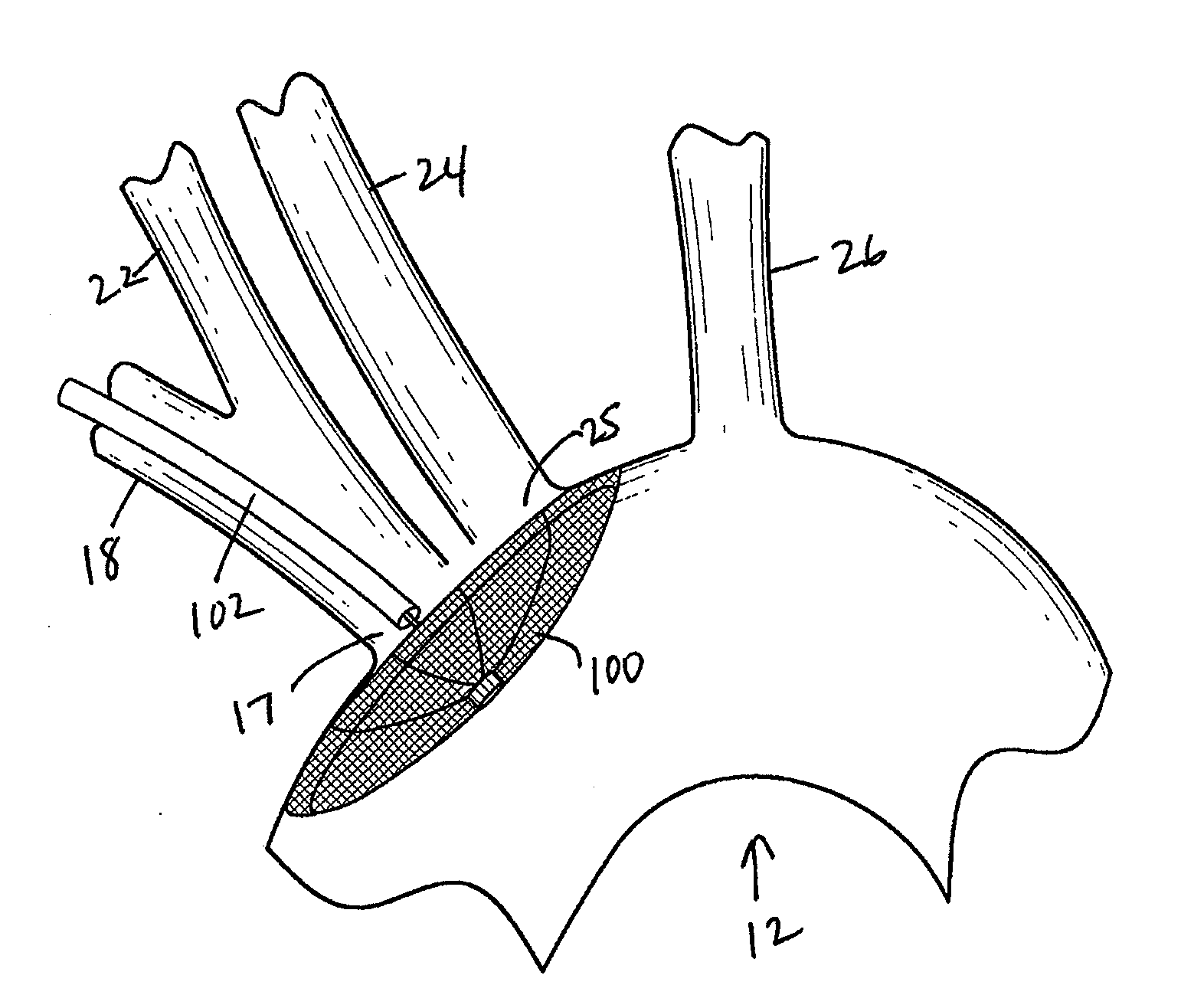
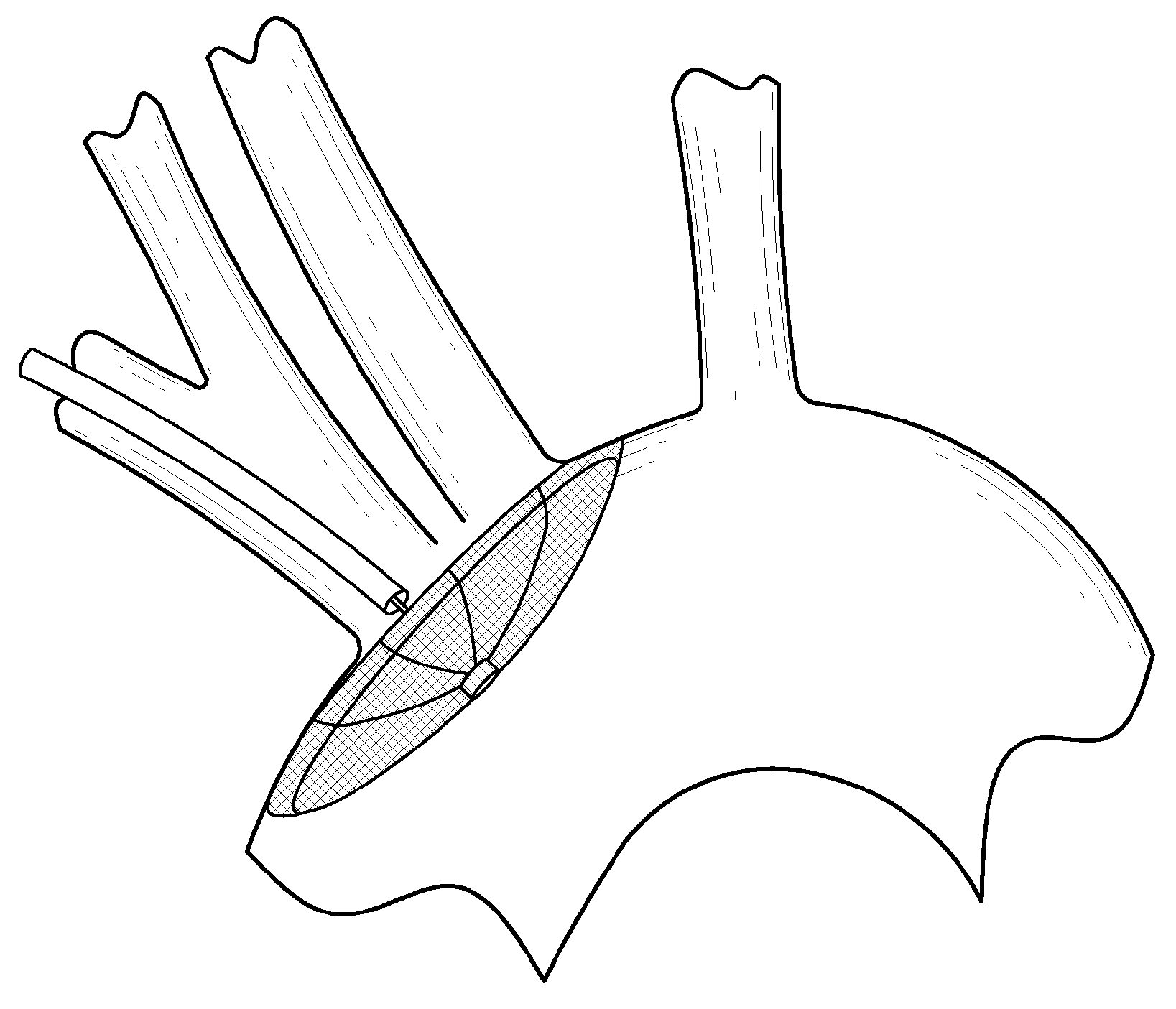
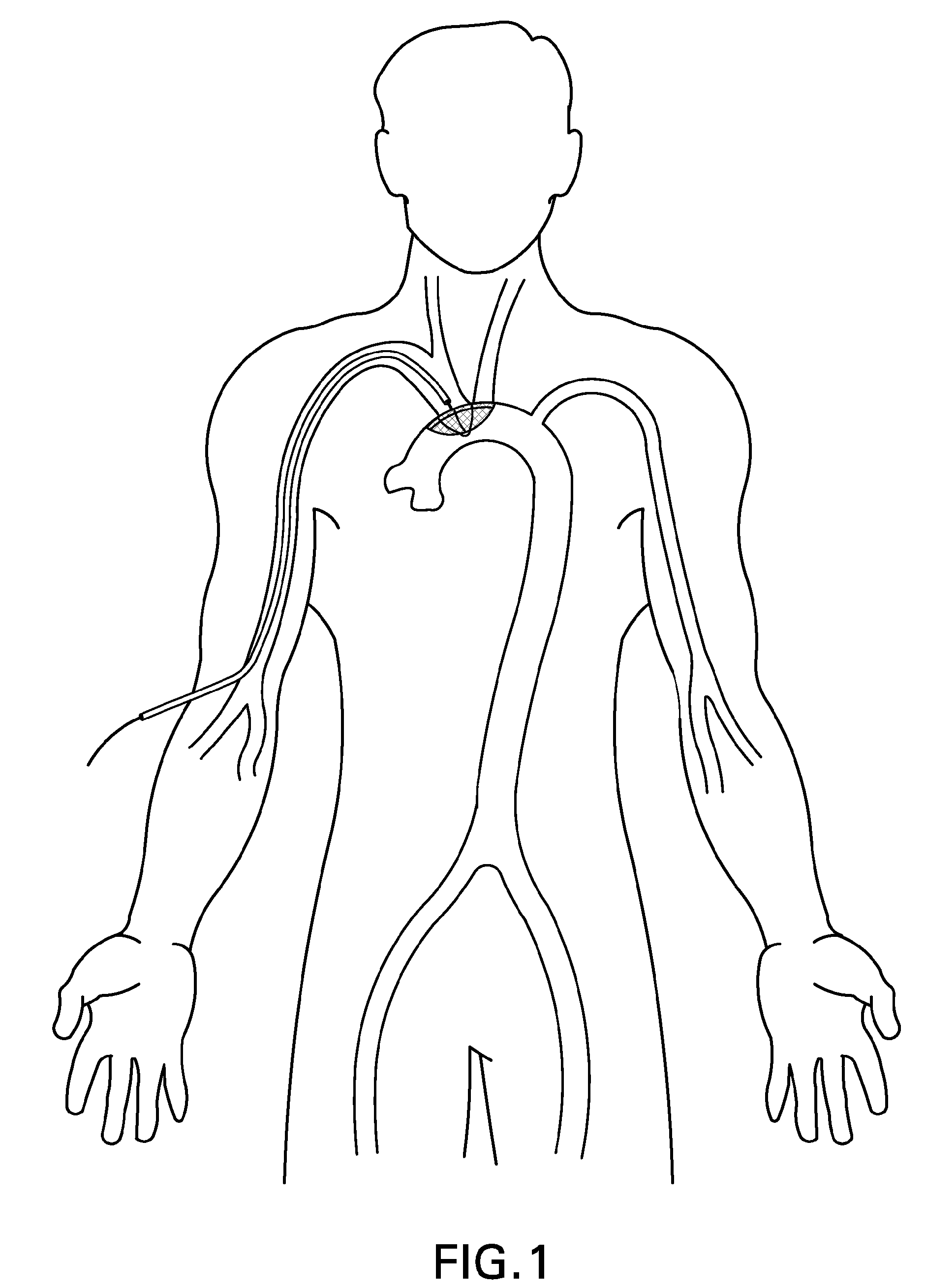
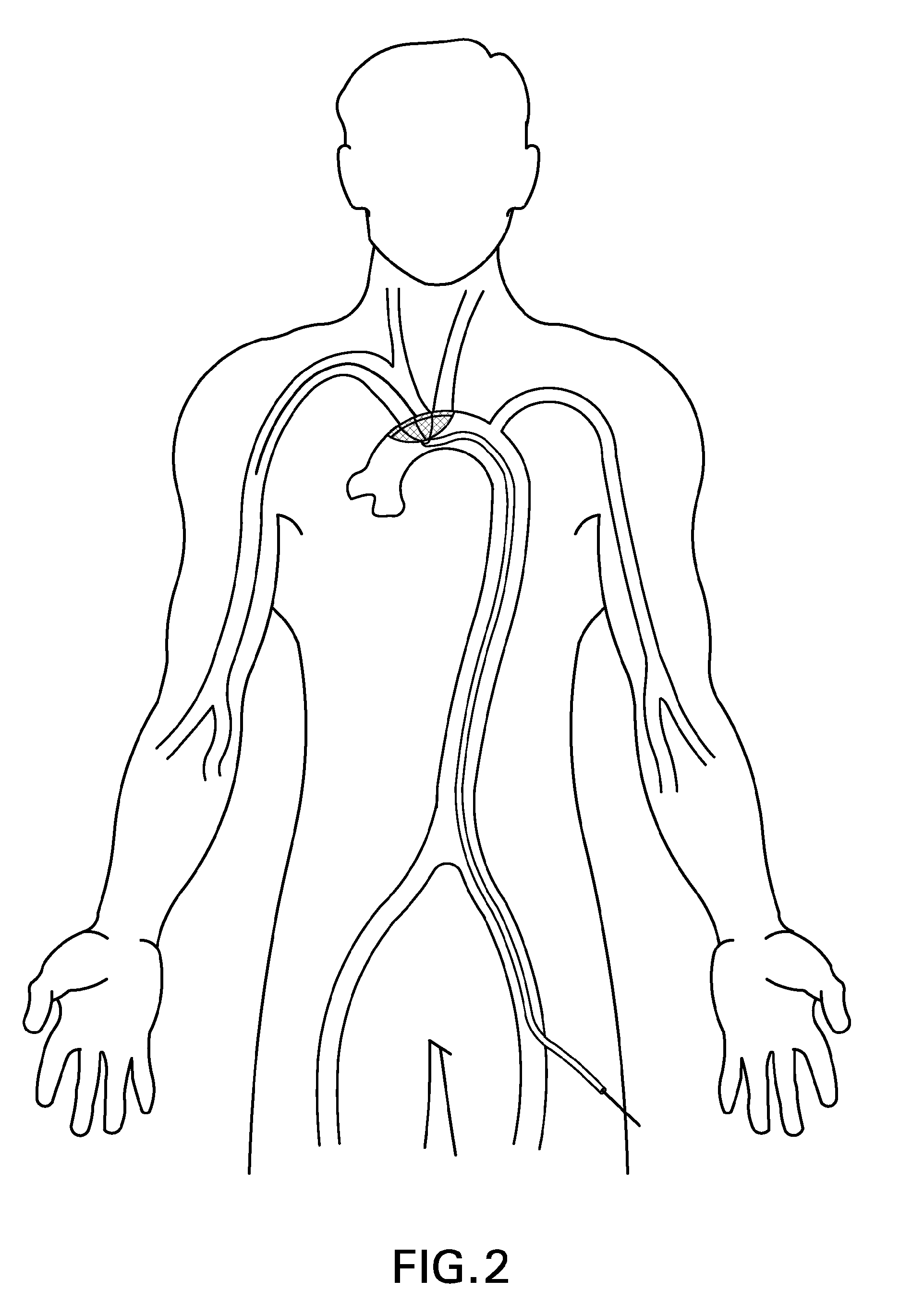
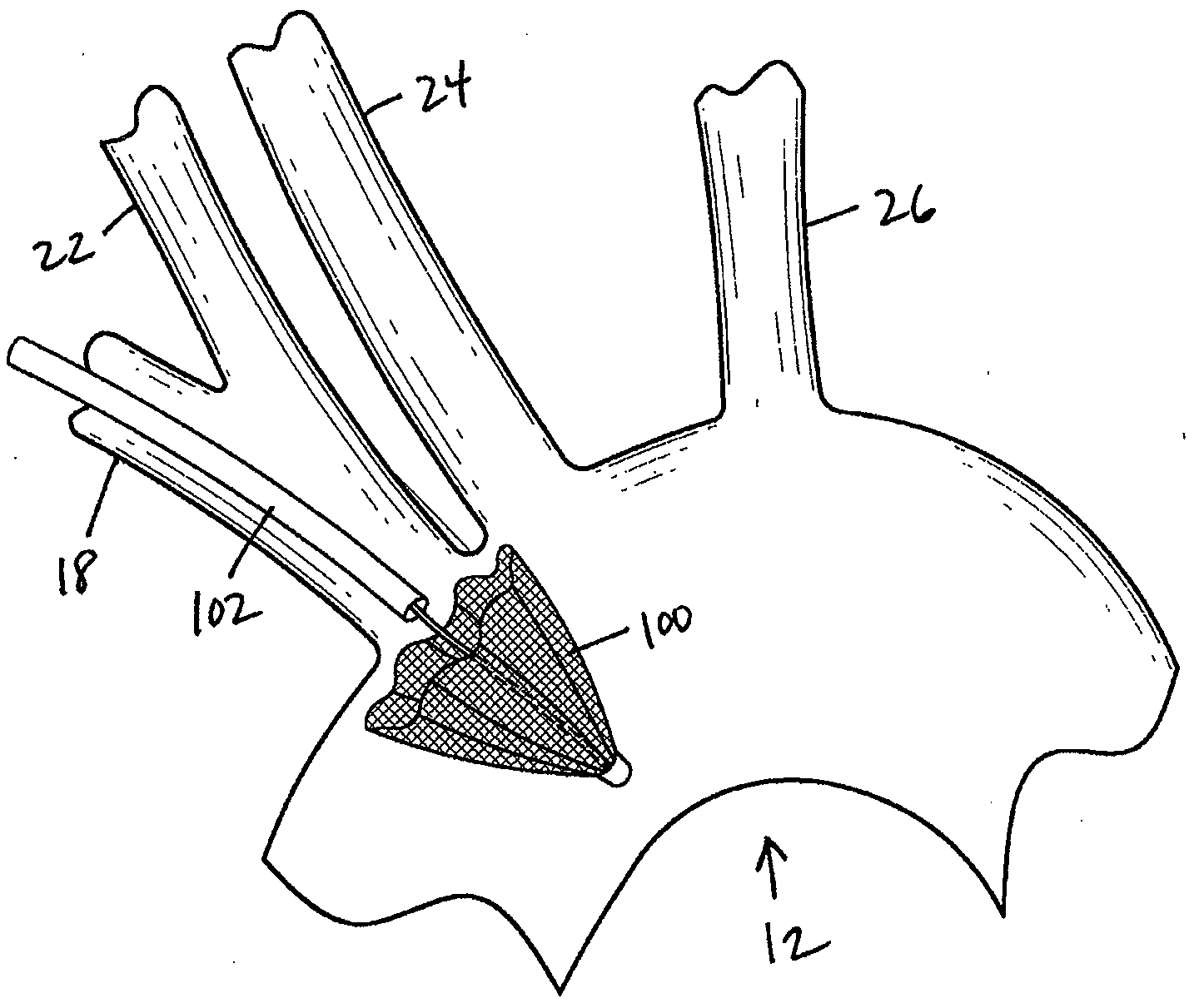
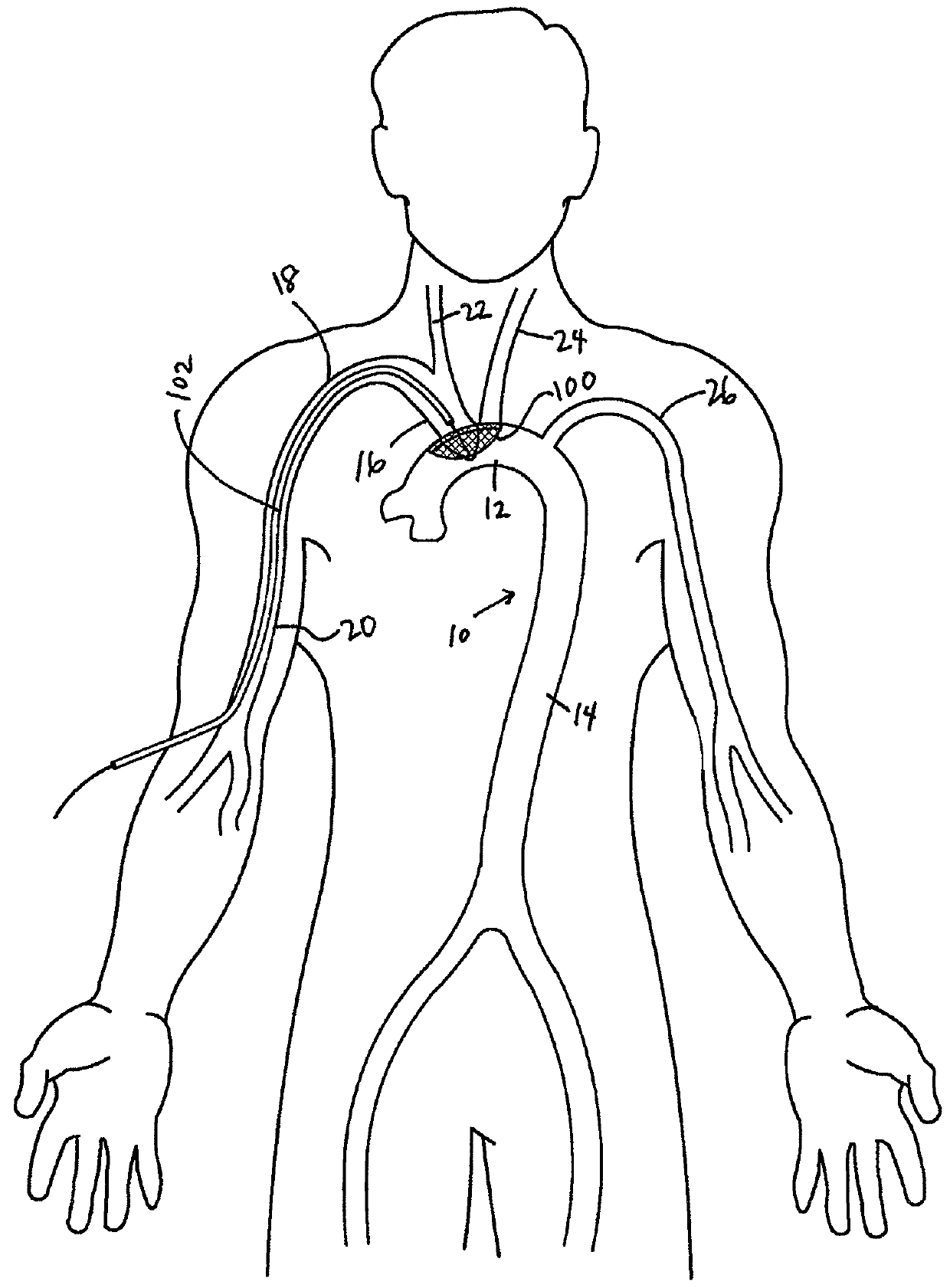
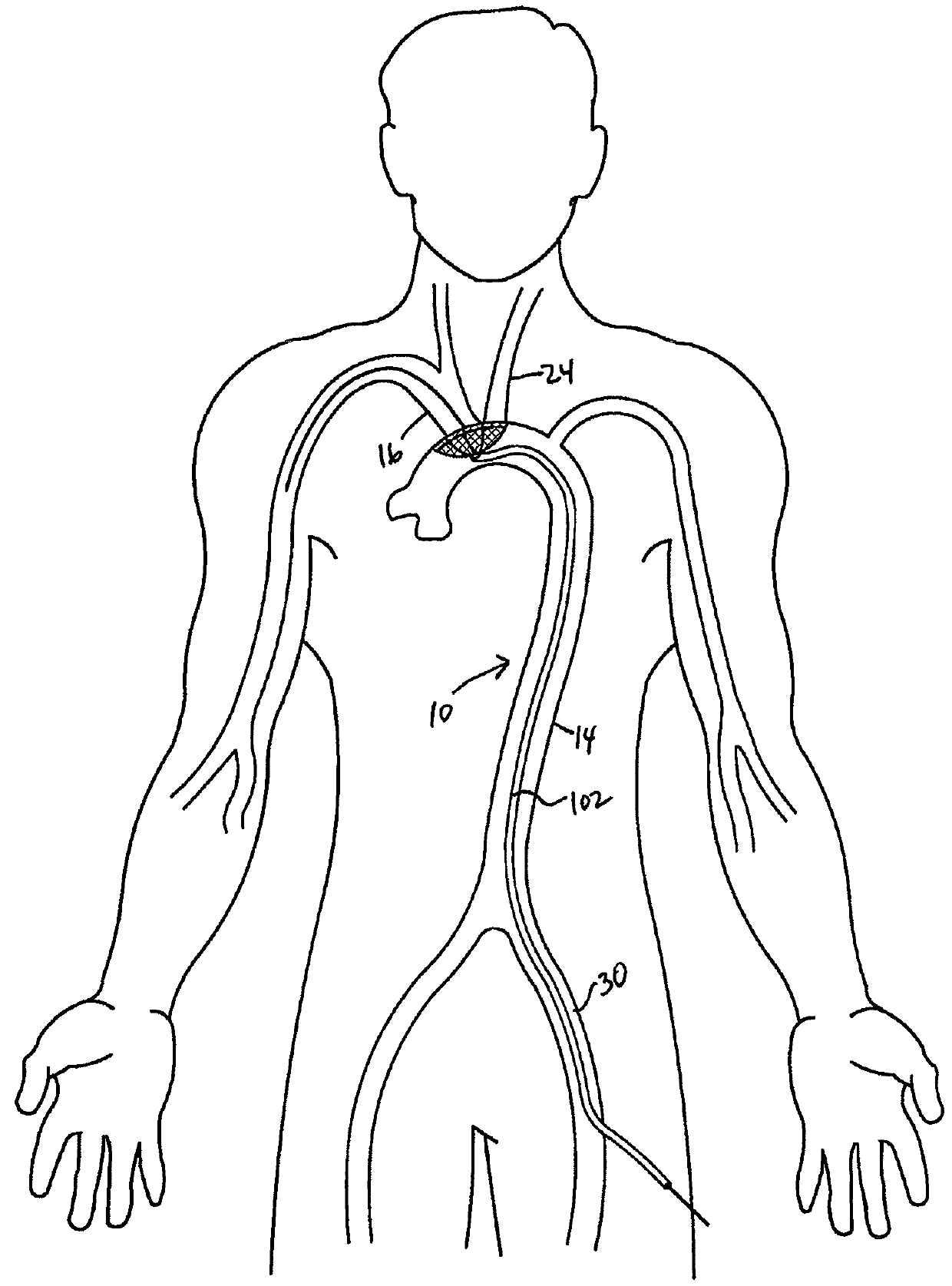
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Methods of deploying and retrieving an embolic diversion device
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
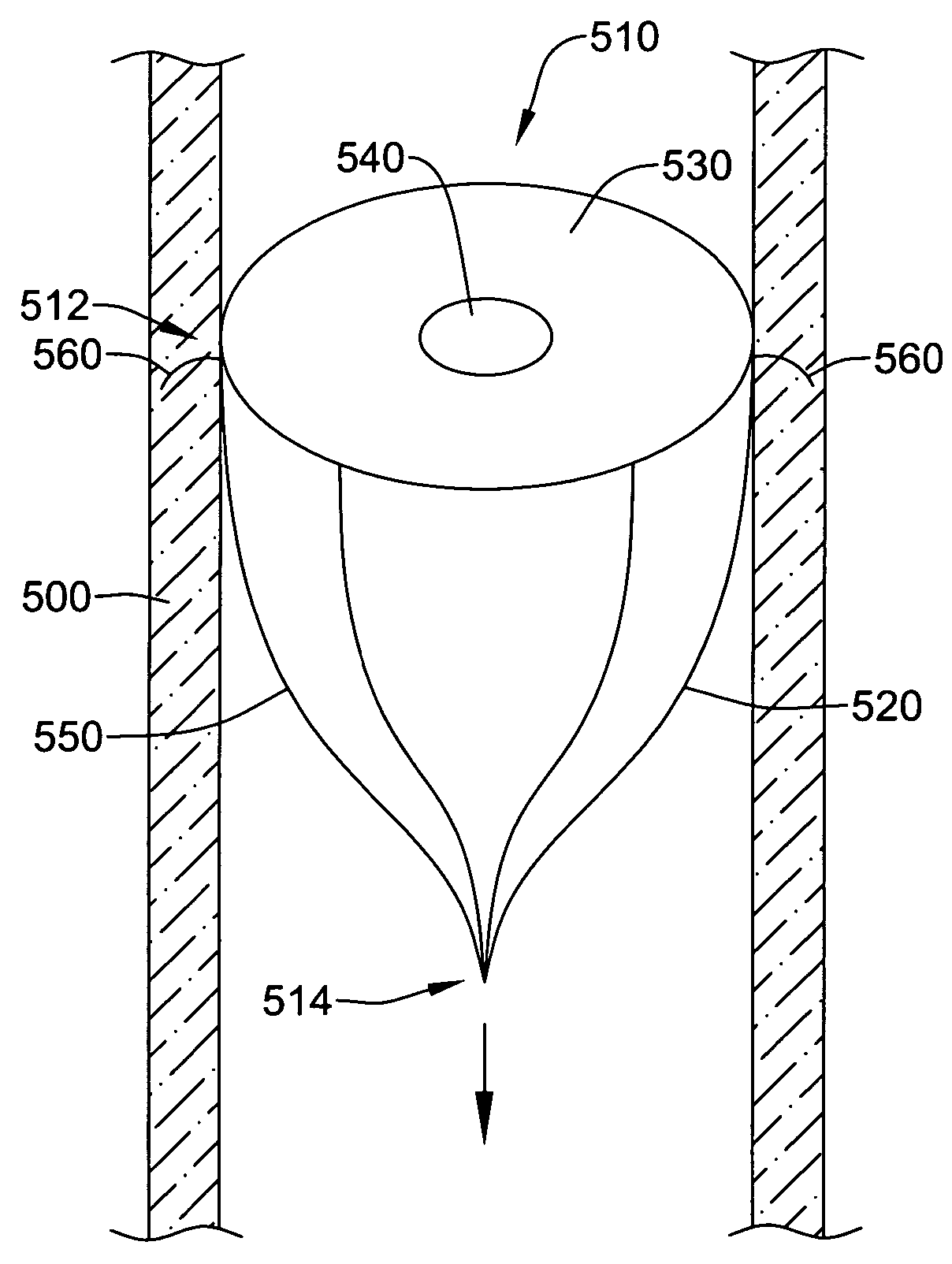
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal in arteries having collateral blood flow
InactiveUS6840949B2Prevention of distal embolizationReversed blood flowStentsBalloon catheterAtherectomyPercutaneous angioplasty
The invention provides a medical device having a catheter and one or more expandable constricting / occluding members. The catheter is adapted for use with therapeutic or diagnostic devices, including an angioplasty / stent catheter and an atherectomy catheter. The constrictor / occluder is mounted at the distal end of the catheter. Manometers may be mounted distal to one or more constrictors for measuring pressure distal to the constrictor(s). Methods of using the devices are disclosed for preventing distal embolization during extracranial or intracranial carotid artery, vertebral artery, or coronary artery procedures, or procedures involving any vessel having collateral flow by reversing flow in the diseased vessel.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Embolic deflection device
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. The deflector shaft could have a first portion and a second portion, the second portion being more flexible than the first portion. The deflector frame can include one, two, or more movable structures, such as hinges. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Embolic deflection device
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
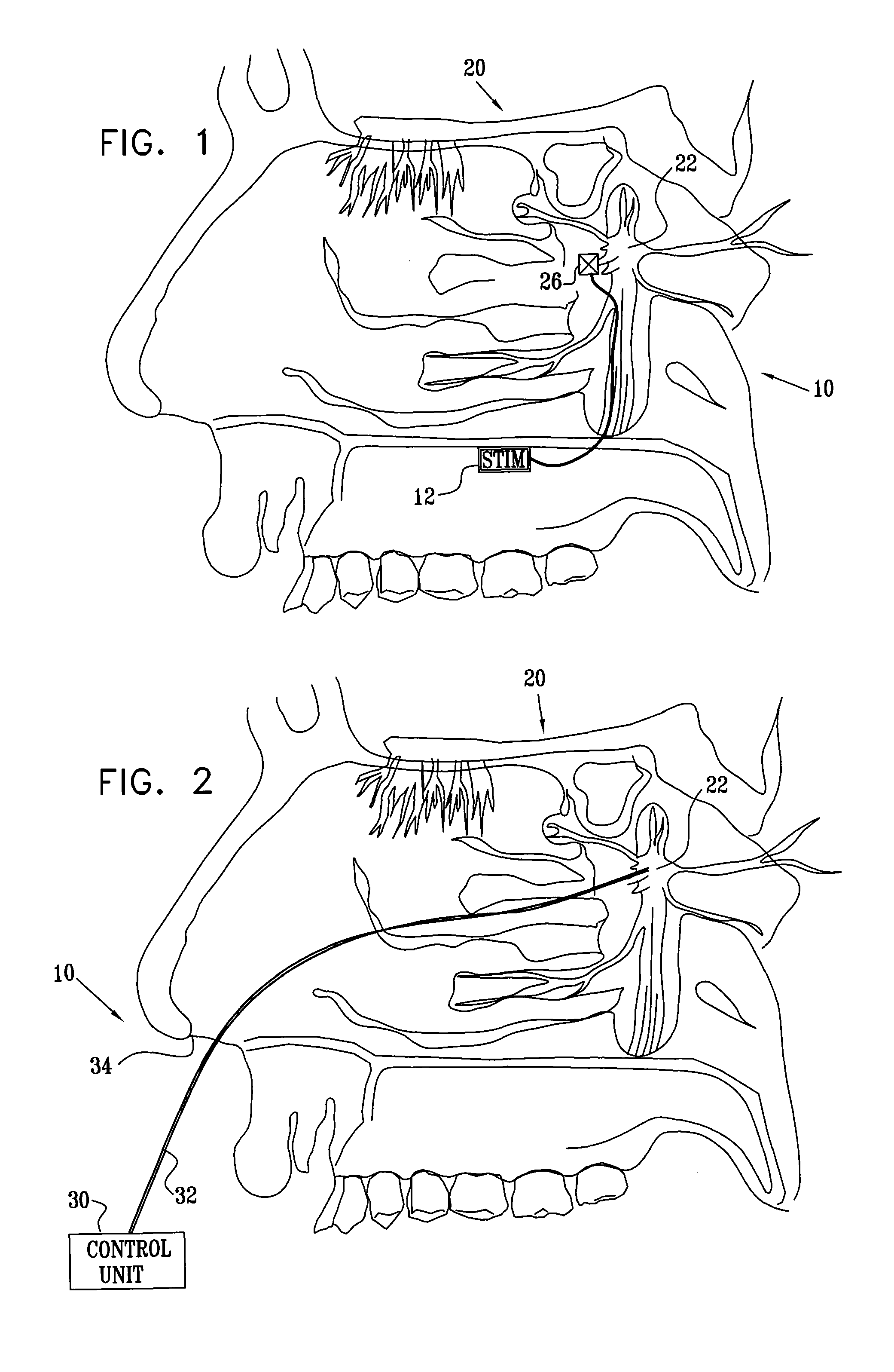
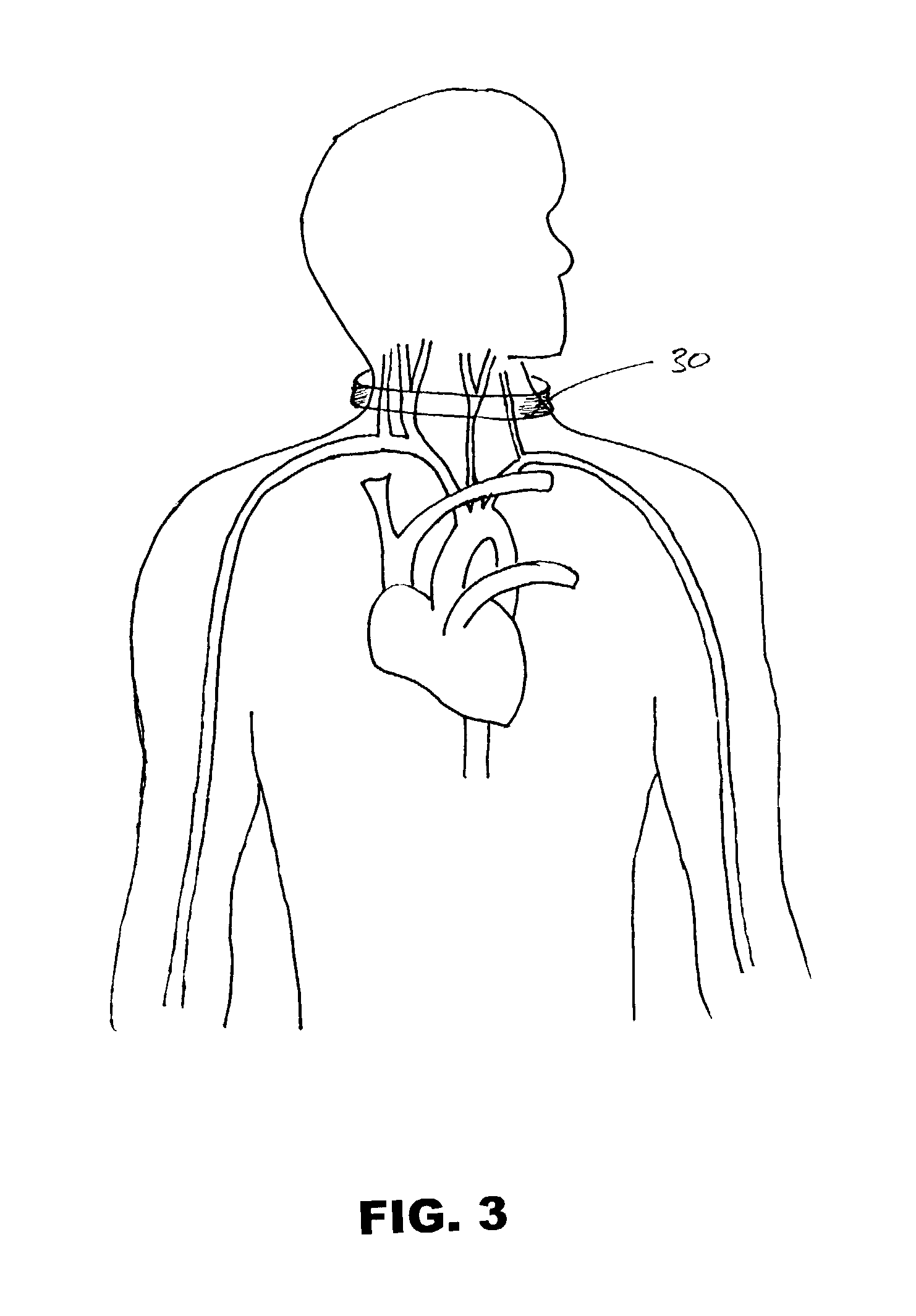
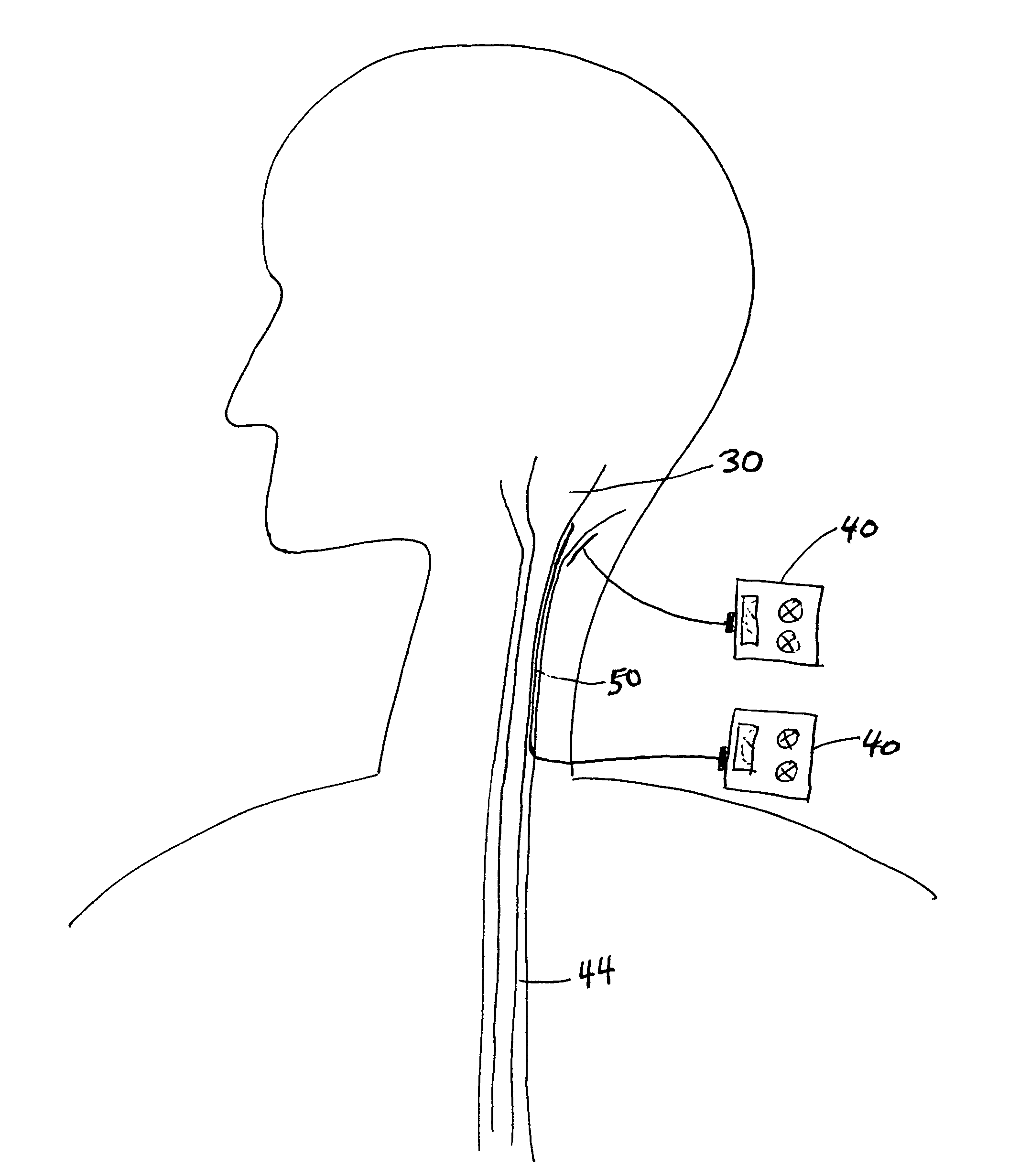
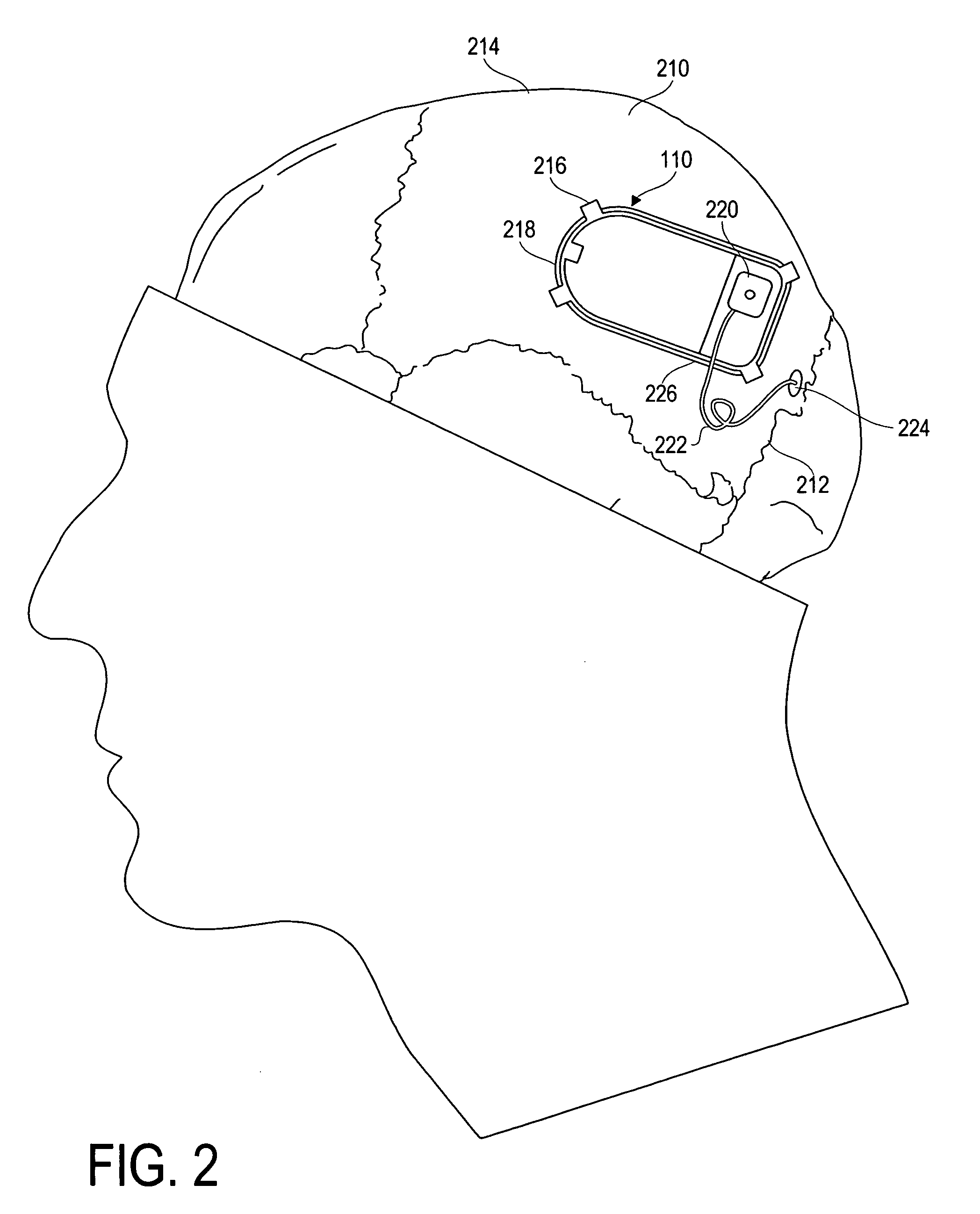
Stimulation for treating brain events and other conditions
ActiveUS20070083245A1Increase cerebral blood flowReduce harmSpinal electrodesDeep petrosal nerveMedicine
Apparatus for treatment is provided, including one or more electrodes, configured to be applied to a site of a subject, and adverse cerebrovascular condition treatment functionality. The functionality comprises a control unit configured to drive the one or more electrodes to apply electrical stimulation to the site during a plurality of stimulation periods which includes at least first and last stimulation periods, set an inter-period interval between initiation of the first stimulation period and initiation of the last stimulation period to be at least 24 hours, and configure the stimulation during the first and last stimulation periods to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF) of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. The site is selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve. Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
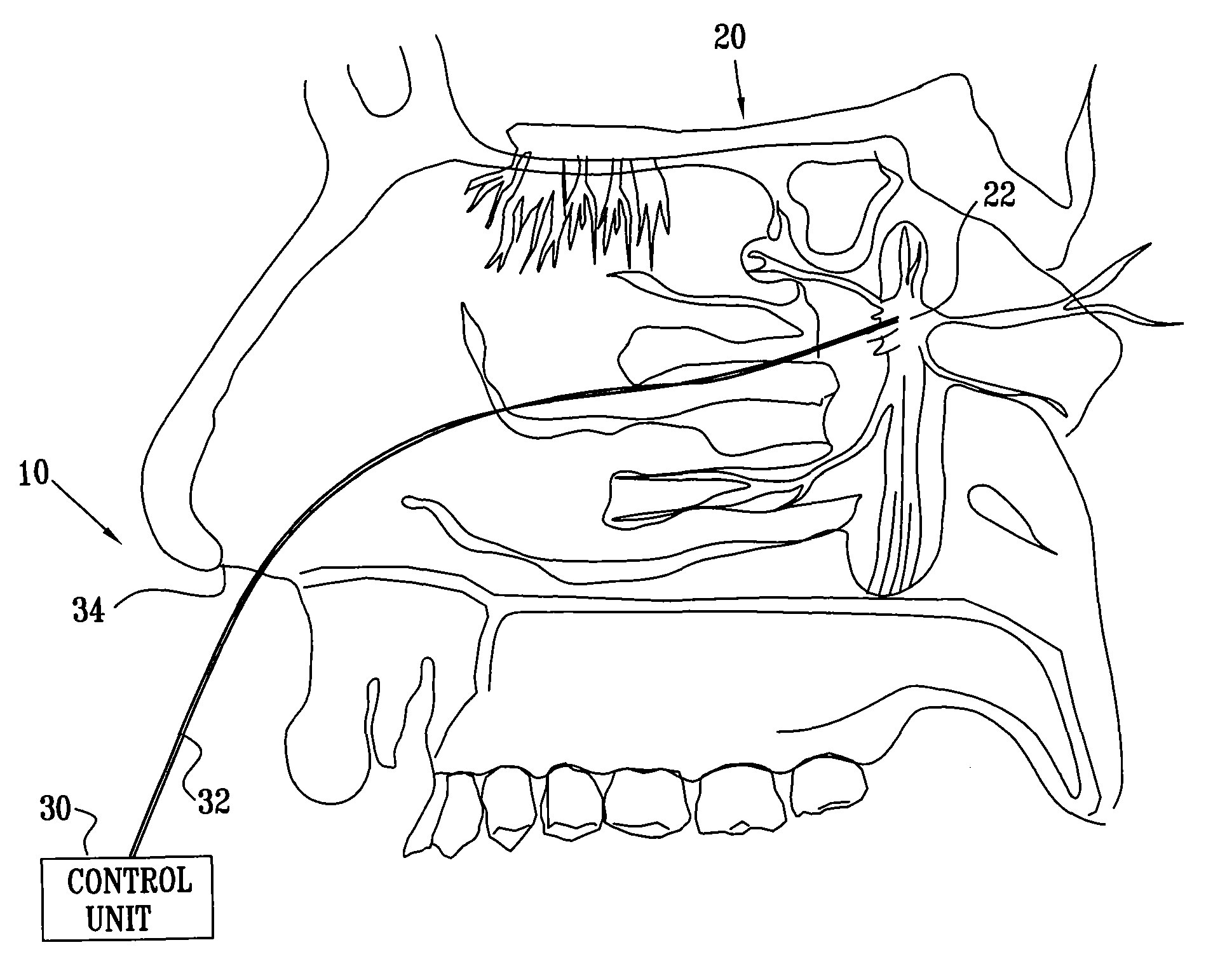
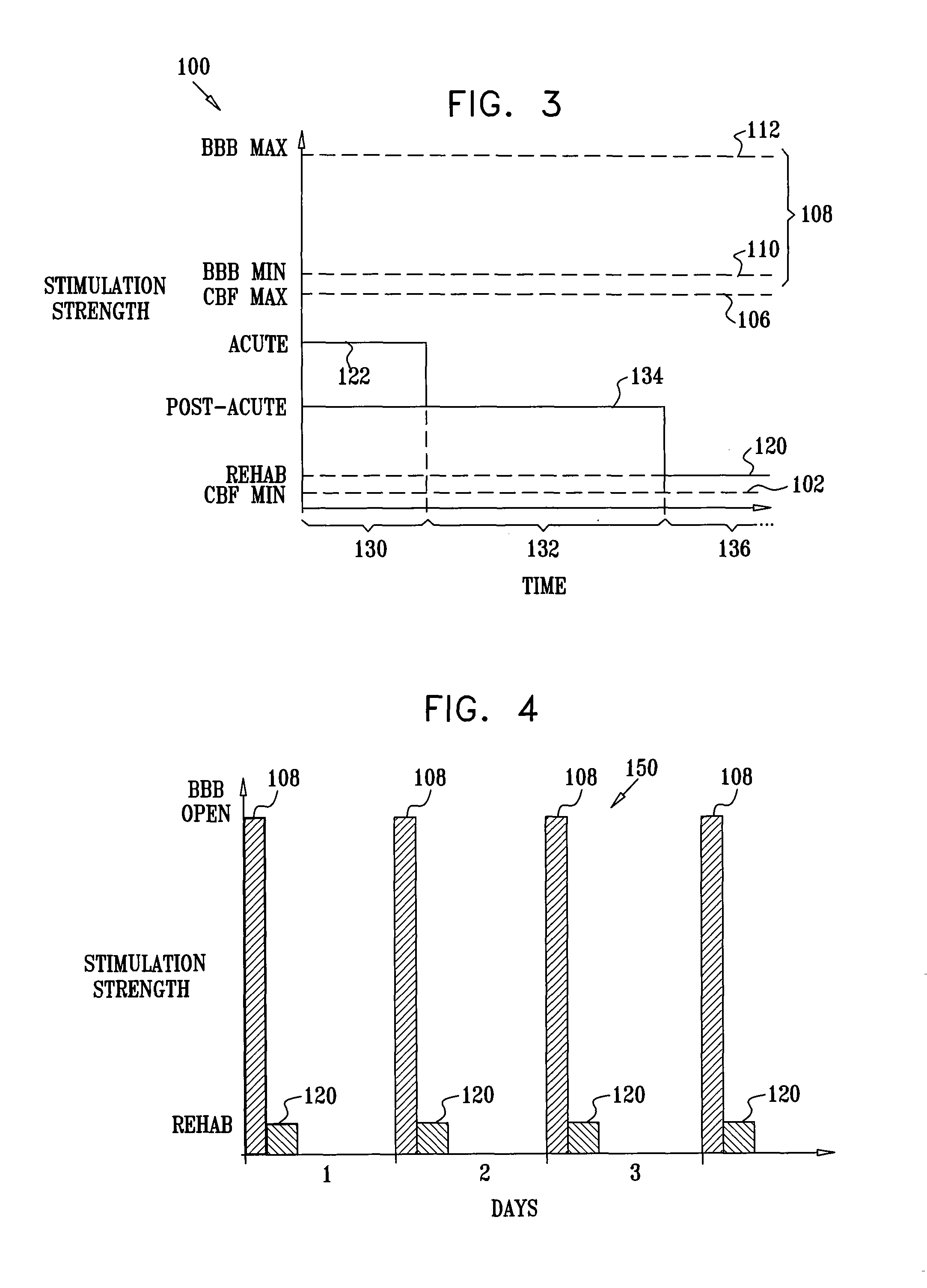
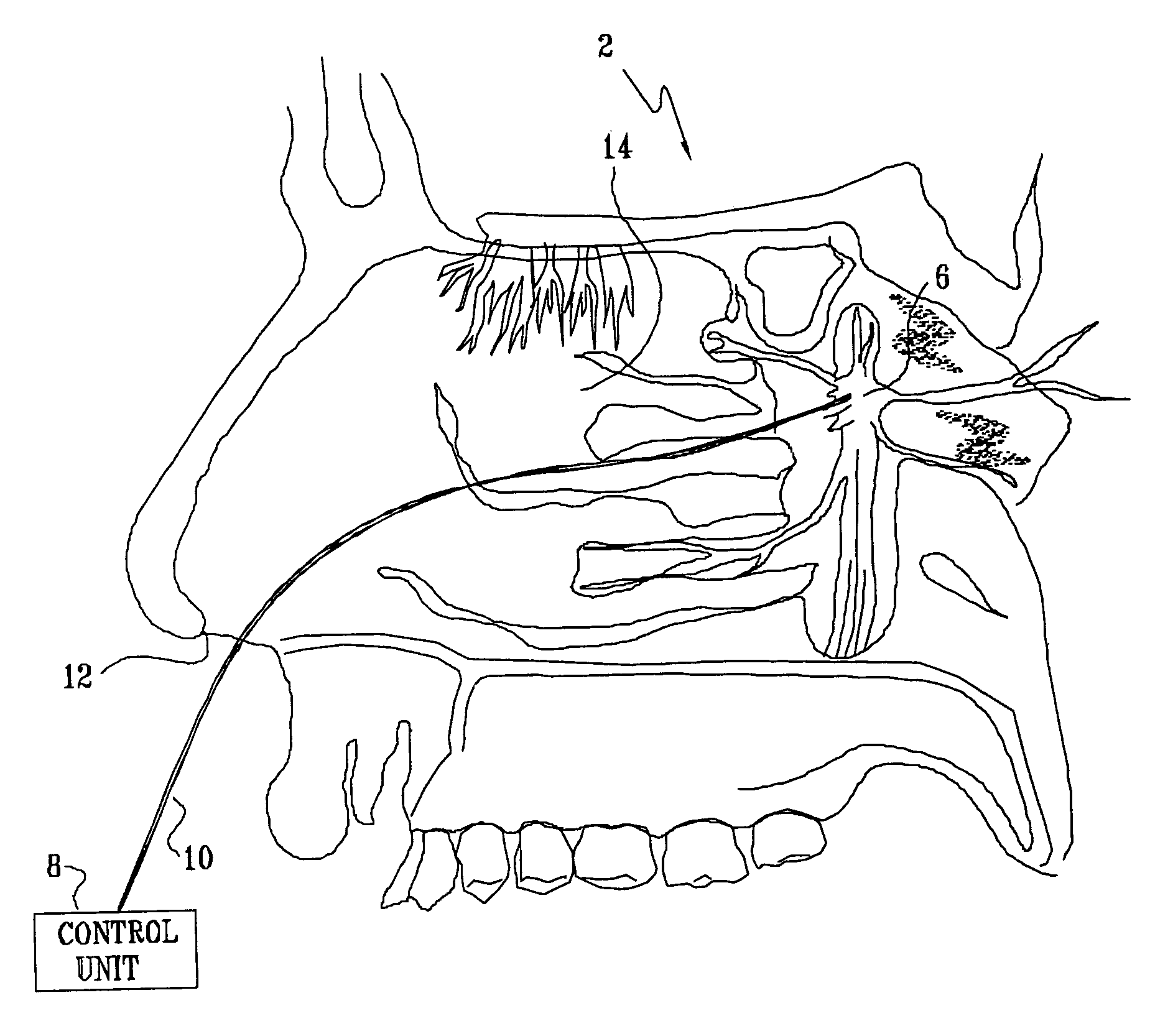
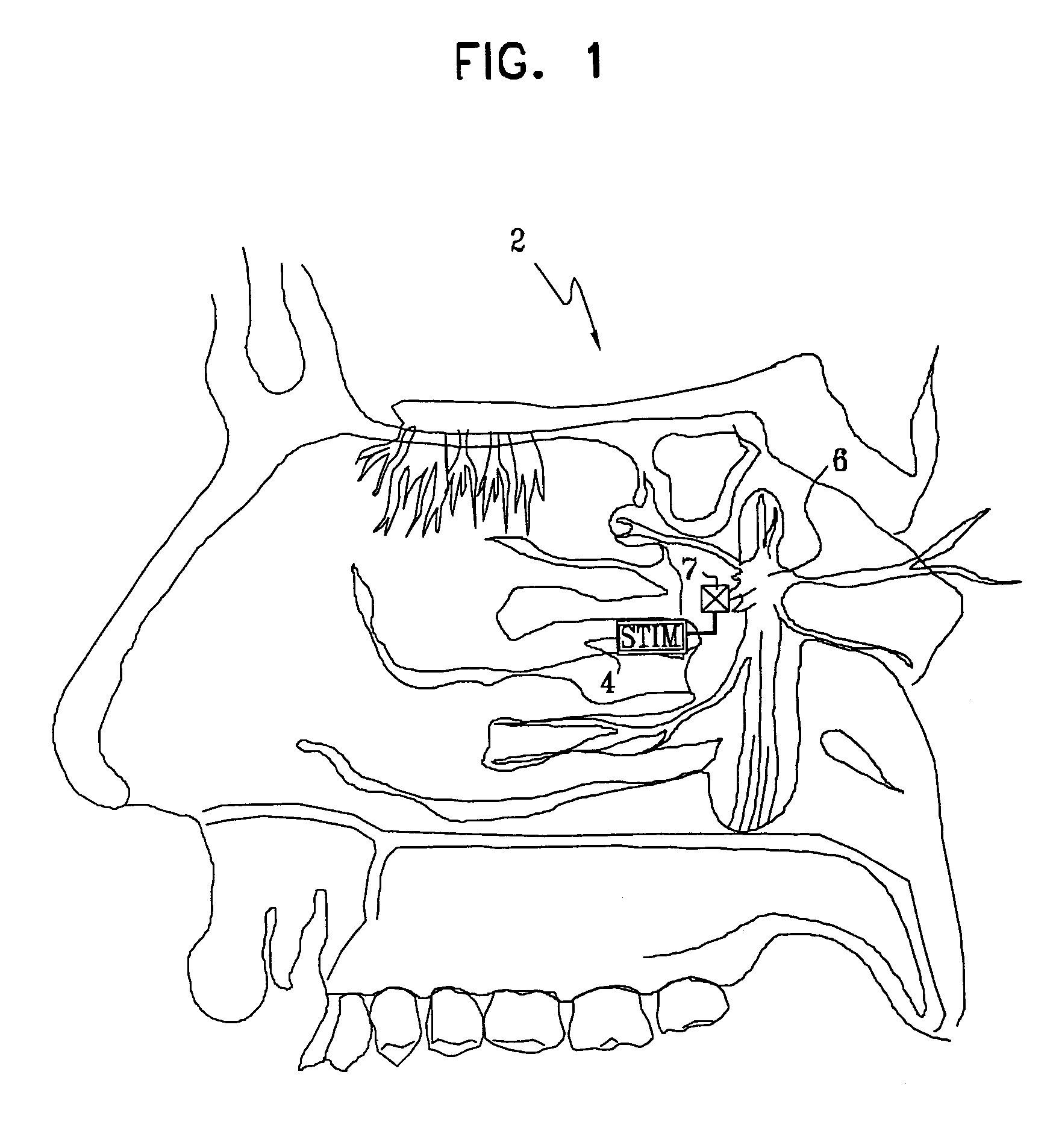
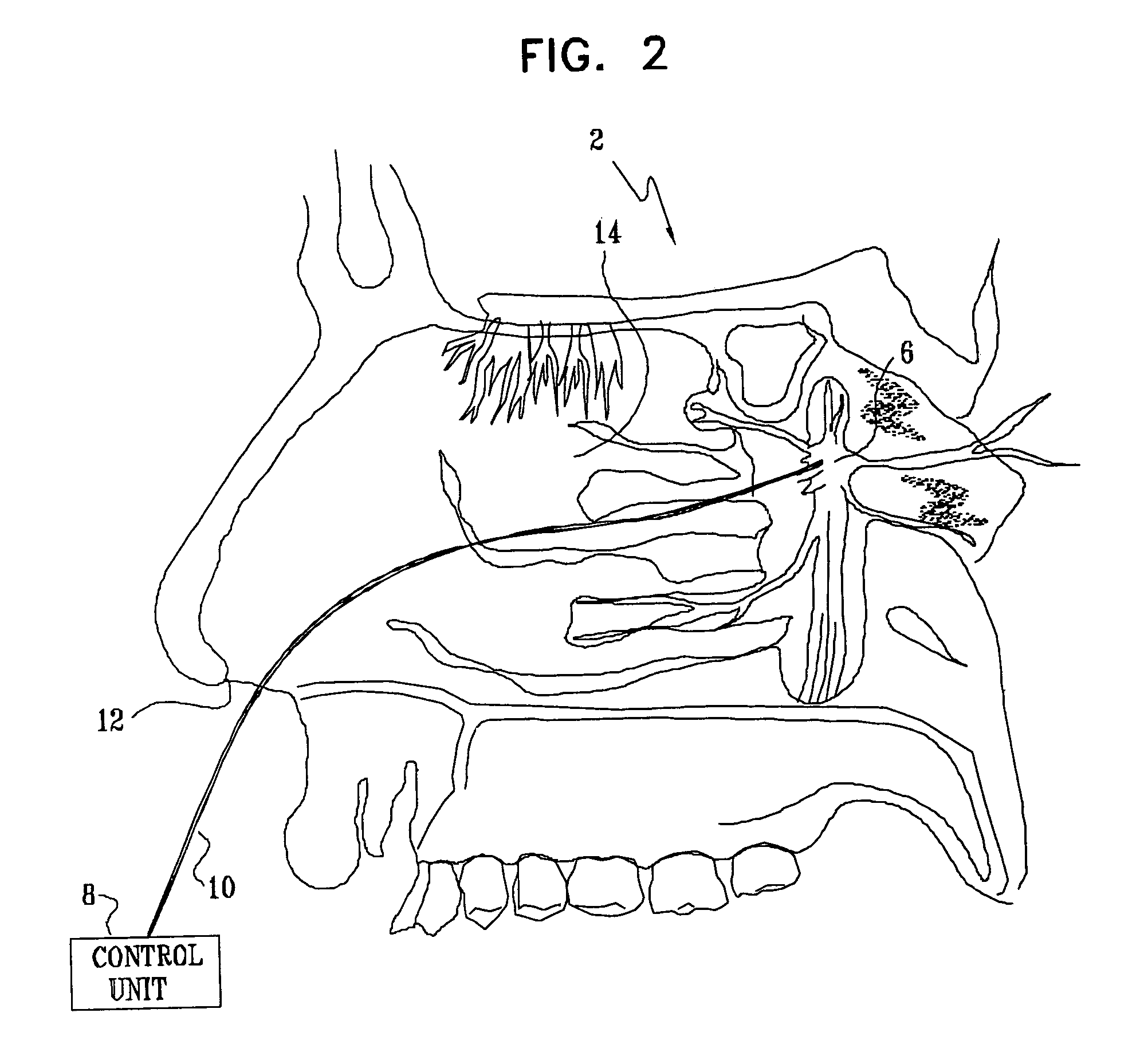
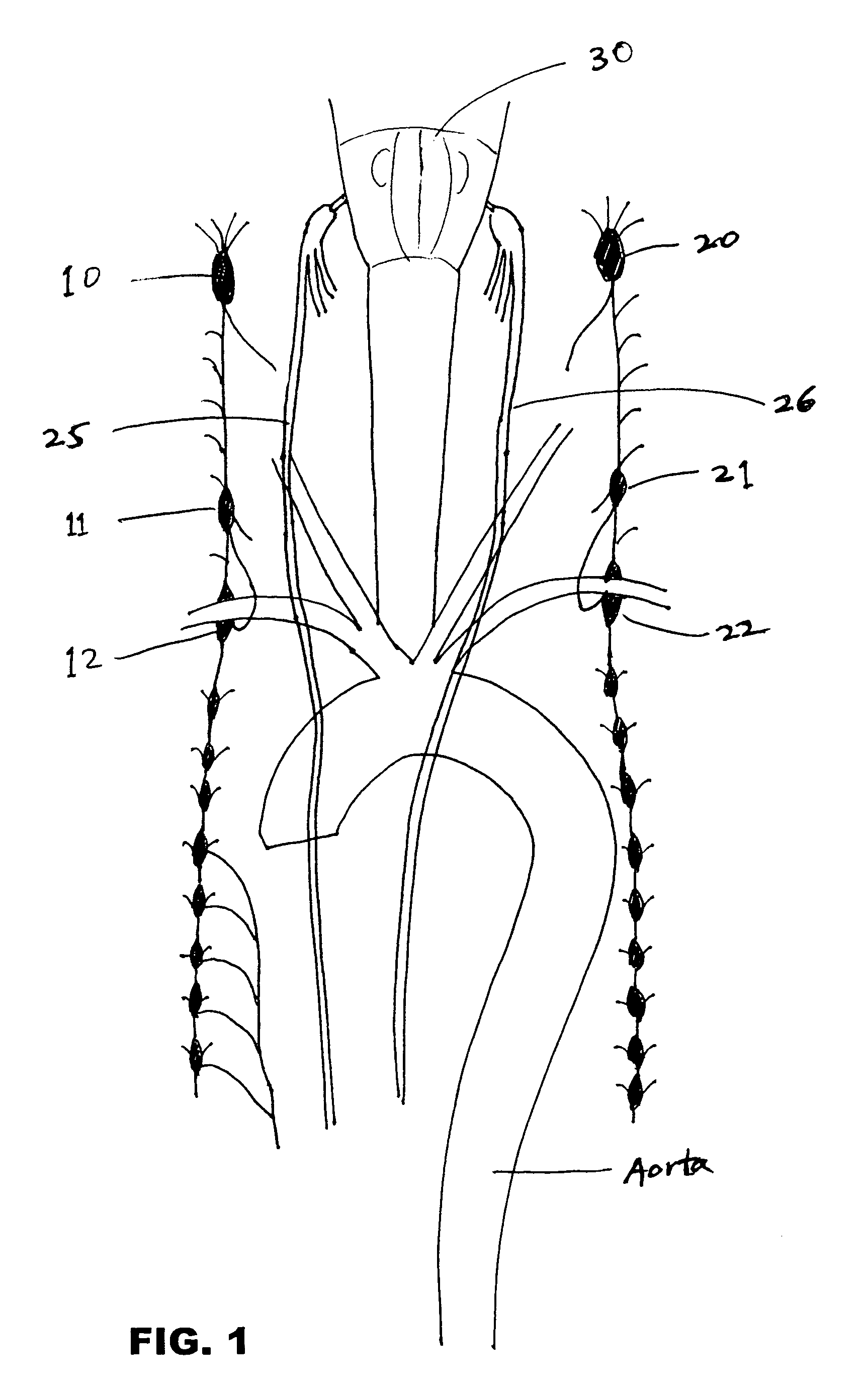
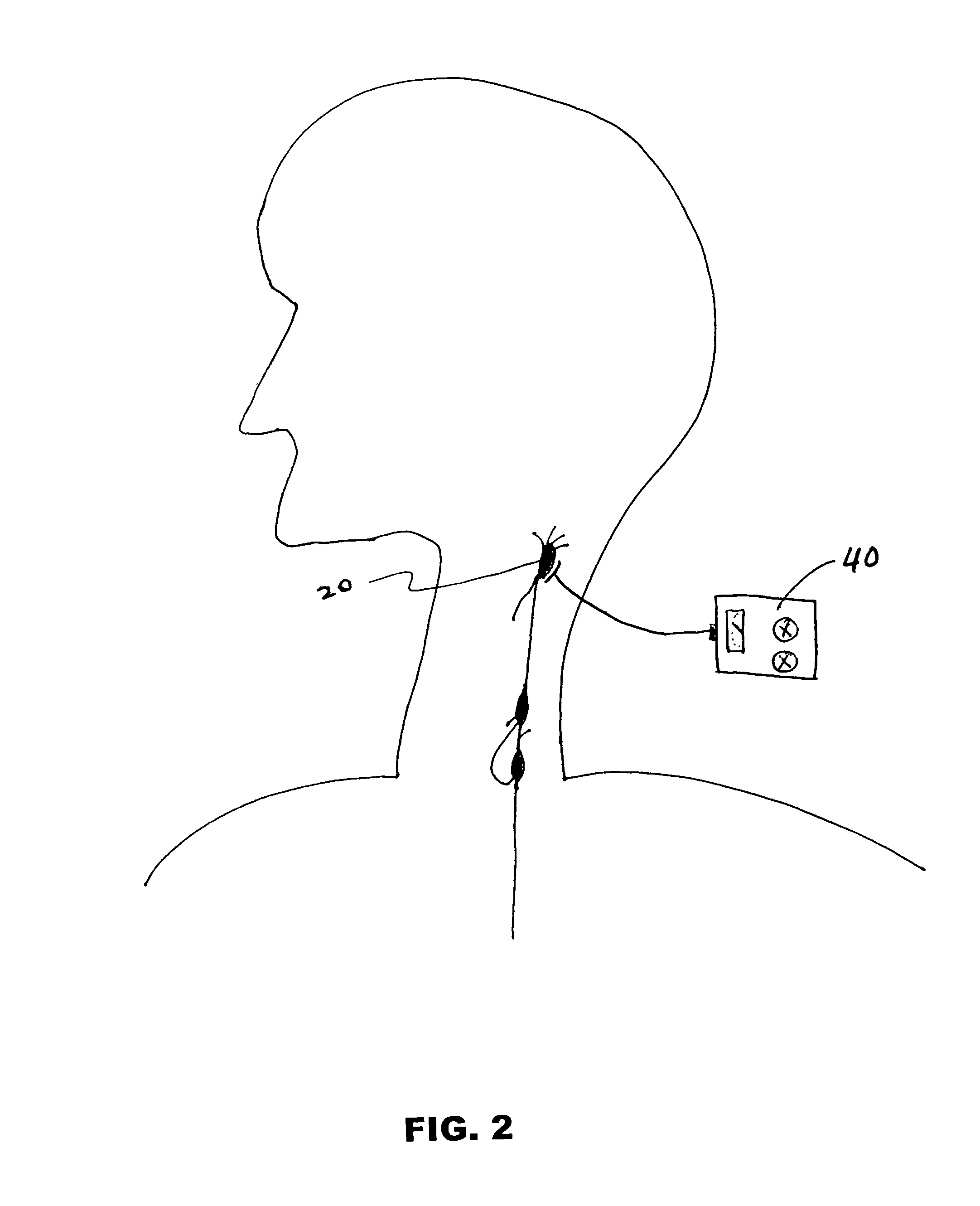
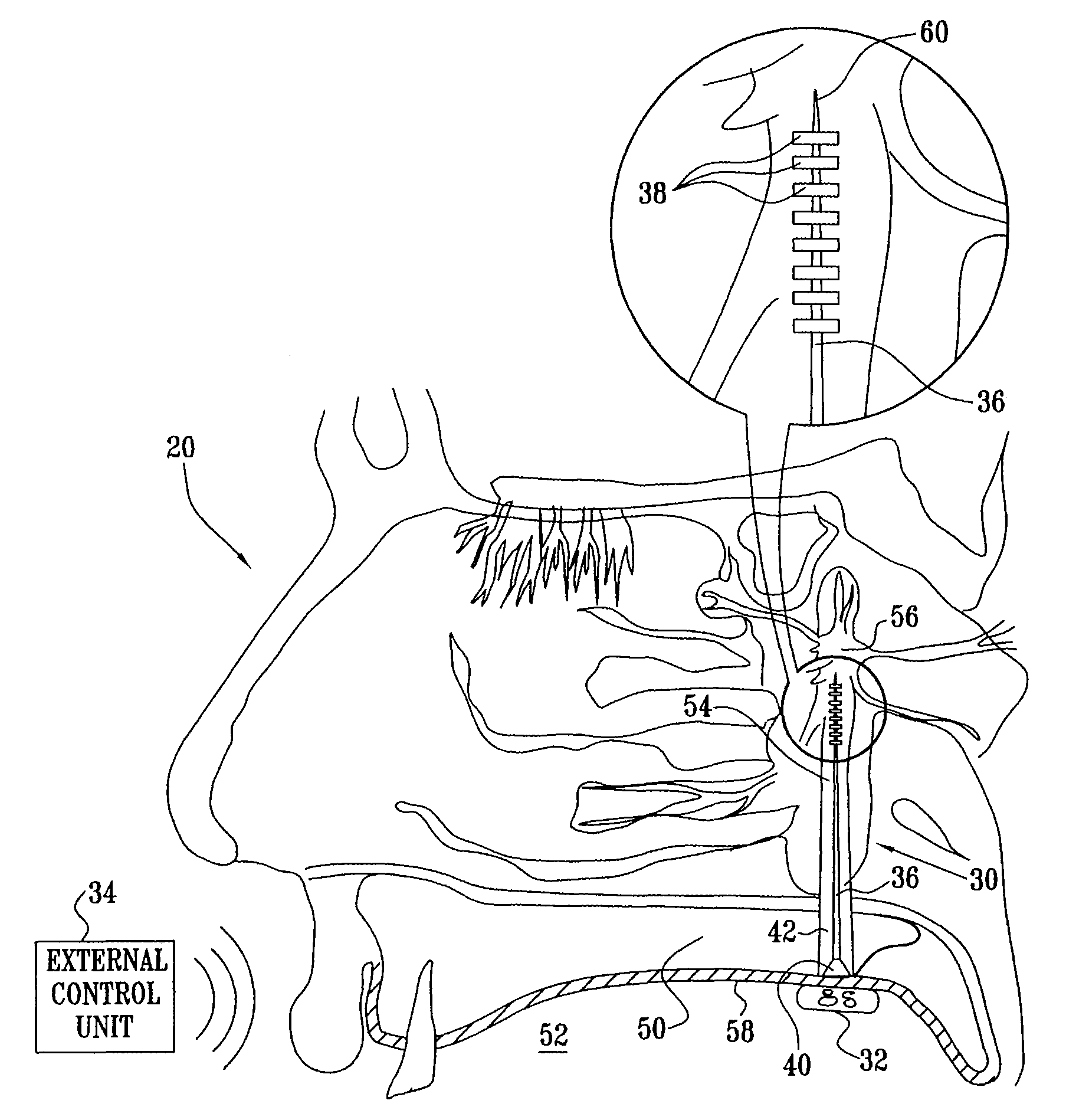
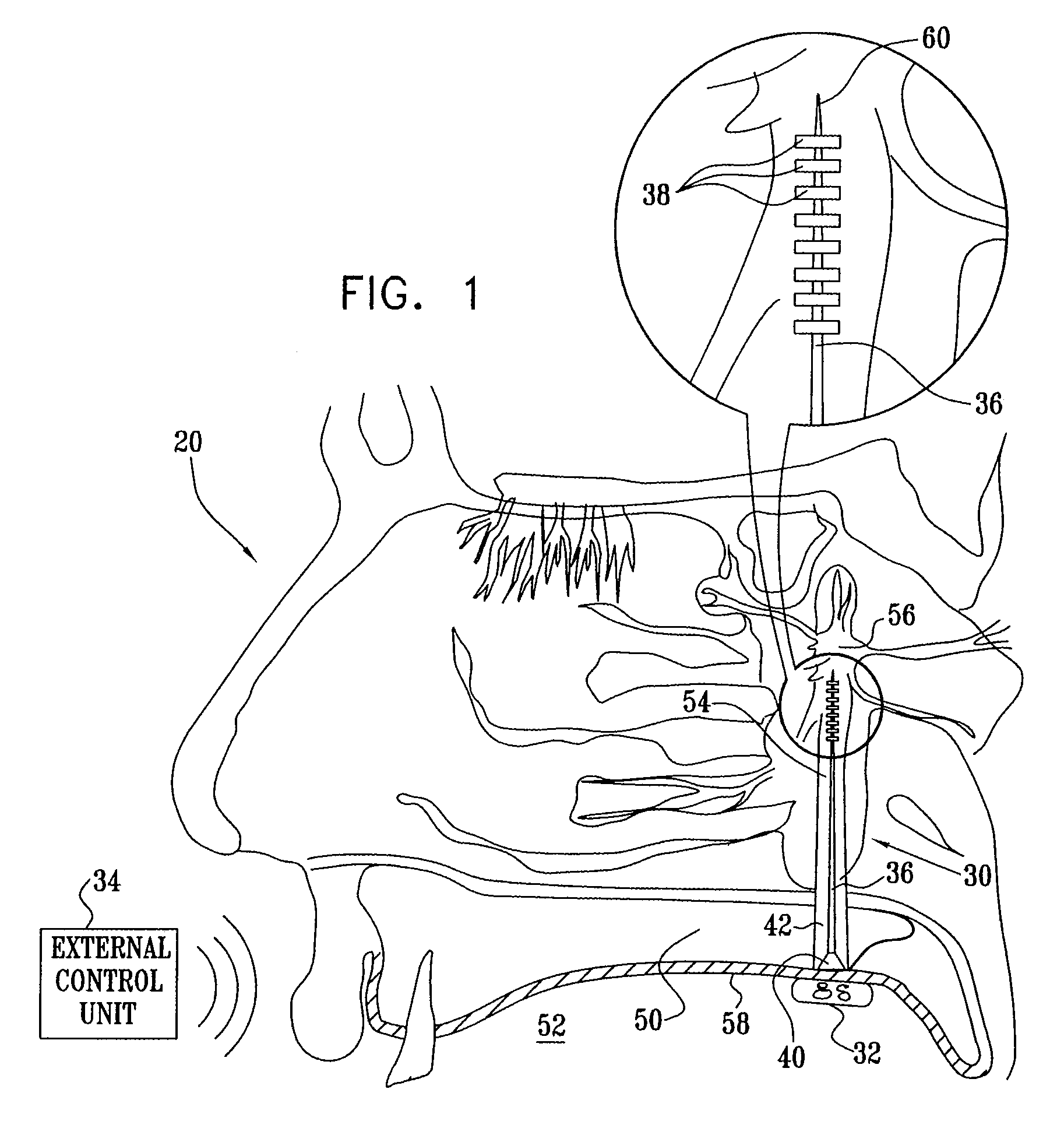
Method and apparatus for stimulating the sphenopalatine ganglion to modify properties of the BBB and cerebral blood flow
InactiveUS7120489B2Promote absorptionPermeability of BBB is increasedHead electrodesBlood flow measurement devicesCerebral blood volumeRetinal blood flow
Apparatus for modifying a property of a brain of a patient is provided, including one or more electrodes (7), adapted to be applied to a site selected from a group of sites consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) (6) of the patient and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG. A control unit (8) is adapted to drive the one or more electrodes to apply a current to the site capable of inducing (a) an increase in permeability of a blood-brain barrier (BBB) of the patient, (b) a change in cerebral blood flow of the patient, and / or (c) an inhibition of parasympathetic activity of the SPG.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
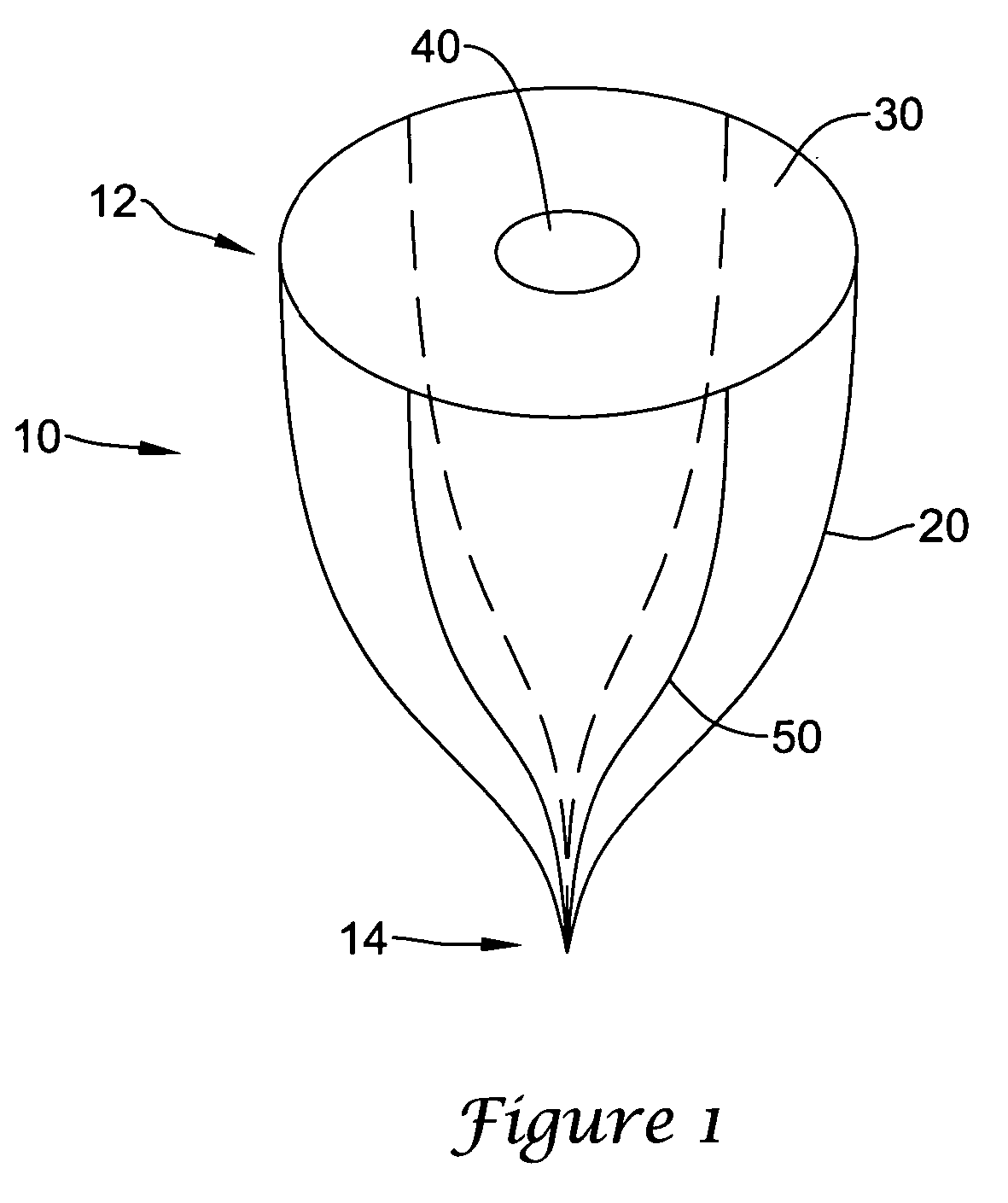
Embolic Protection Device and Method of Use
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (greater than 100 microns in the preferred embodiment) from entering either the right or left carotid arteries by deflecting emboli downstream in the blood flow. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The device has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the device.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG +1
Methods of diverting embolic debris away from the cerebral circulation
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Diversion device to increase cerebral blood flow
ActiveUS20060058833A1Increasing cerebral perfusionIncrease perfusionDilatorsOcculdersPartial obstructionBlood flow
Methods and devices provide for temporary partial aortic occlusion to achieve diversion of blood flow to the brain in patients suffering from cerebral ischemia. The device includes an expandable frame and membrane that is inserted into the aorta to partially occlude blood flow.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Methods and devices for non-invasive cerebral and systemic cooling
ActiveUS20100211140A1Minimize neurologic deficitMaximize coolingTracheal tubesHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsNasal cavityWhole body
A method for providing and adjusting cerebral cooling in response to changes in a physiological parameter. A spray having a boiling point between 38-300° C. is delivered to the surface of a patient's nasal cavities. The spray causes cooling by direct heat transfer through the nasopharynx and hematogenous cooling through the carotids and the Circle of Willis. A physiological parameter, such as cerebral temperature, changes in cerebral blood flow or brain oxygenation is monitored. The delivery rate of the spray is adjusted in response to the physiological parameter.
Owner:BRAINCOOL +1
Modulation and analysis of cerebral perfusion in epilepsy and other neurological disorders
A system including an implantable neurostimulator device capable of modulating cerebral blood flow to treat epilepsy and other neurological disorders. In one embodiment, the system is capable of modulating cerebral blood flow (also referred to as cerebral perfusion) in response to measurements and other observed conditions. Perfusion may be increased or decreased by systems and methods according to the invention as clinically required.
Owner:NEUROPACE
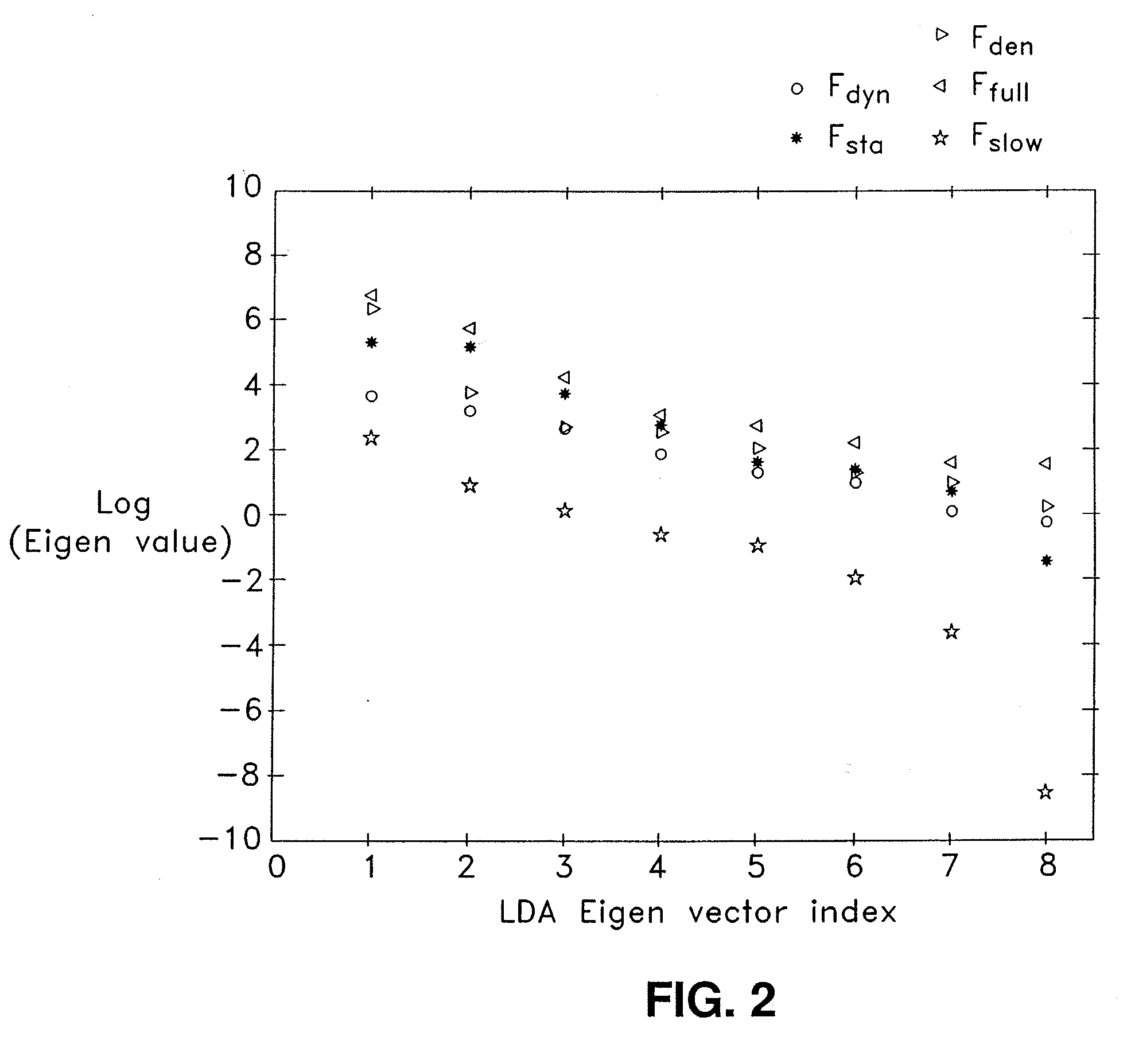
Method and Apparatus For Non-Invasive Assessment of Hemodynamic and Functional State of the Brain
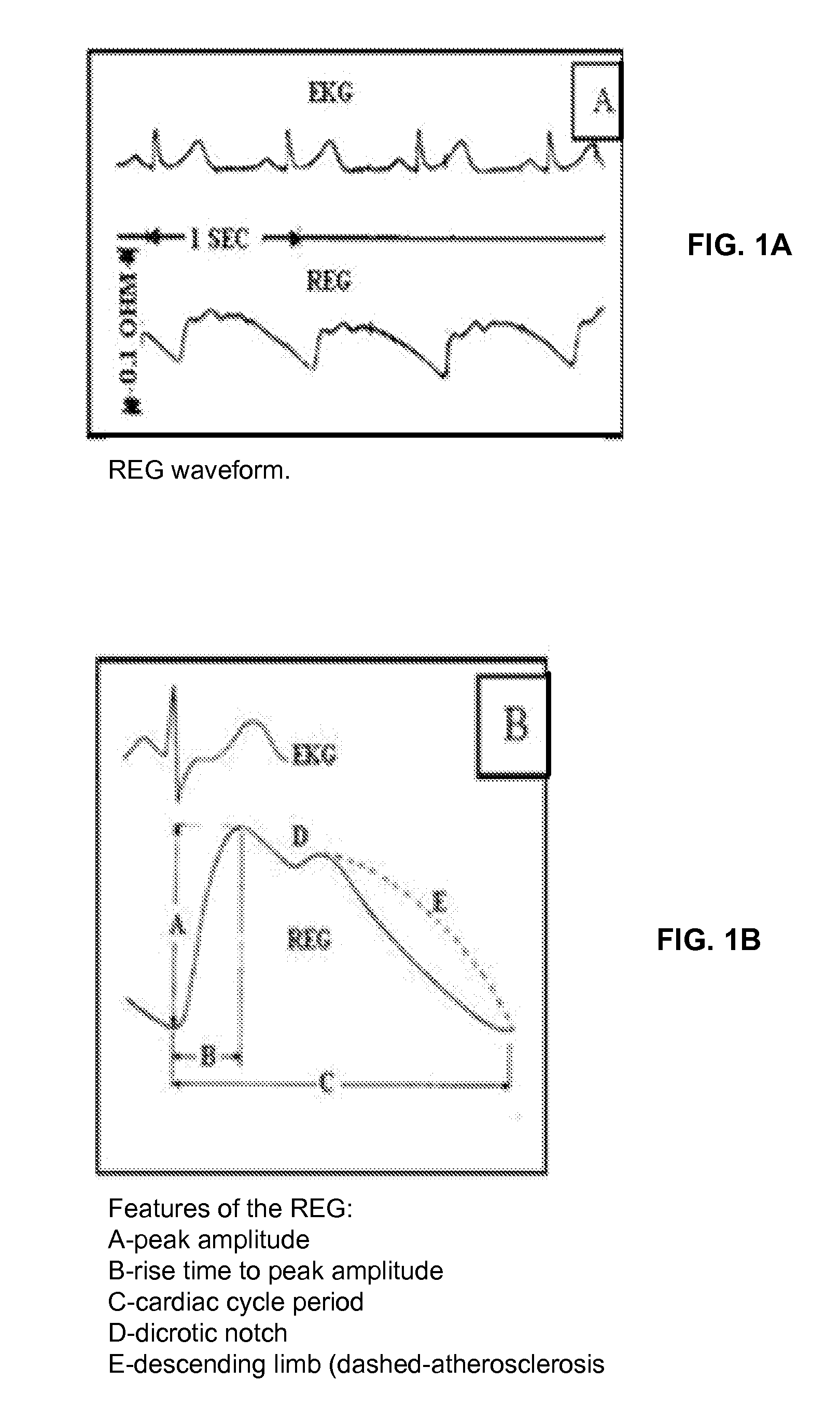
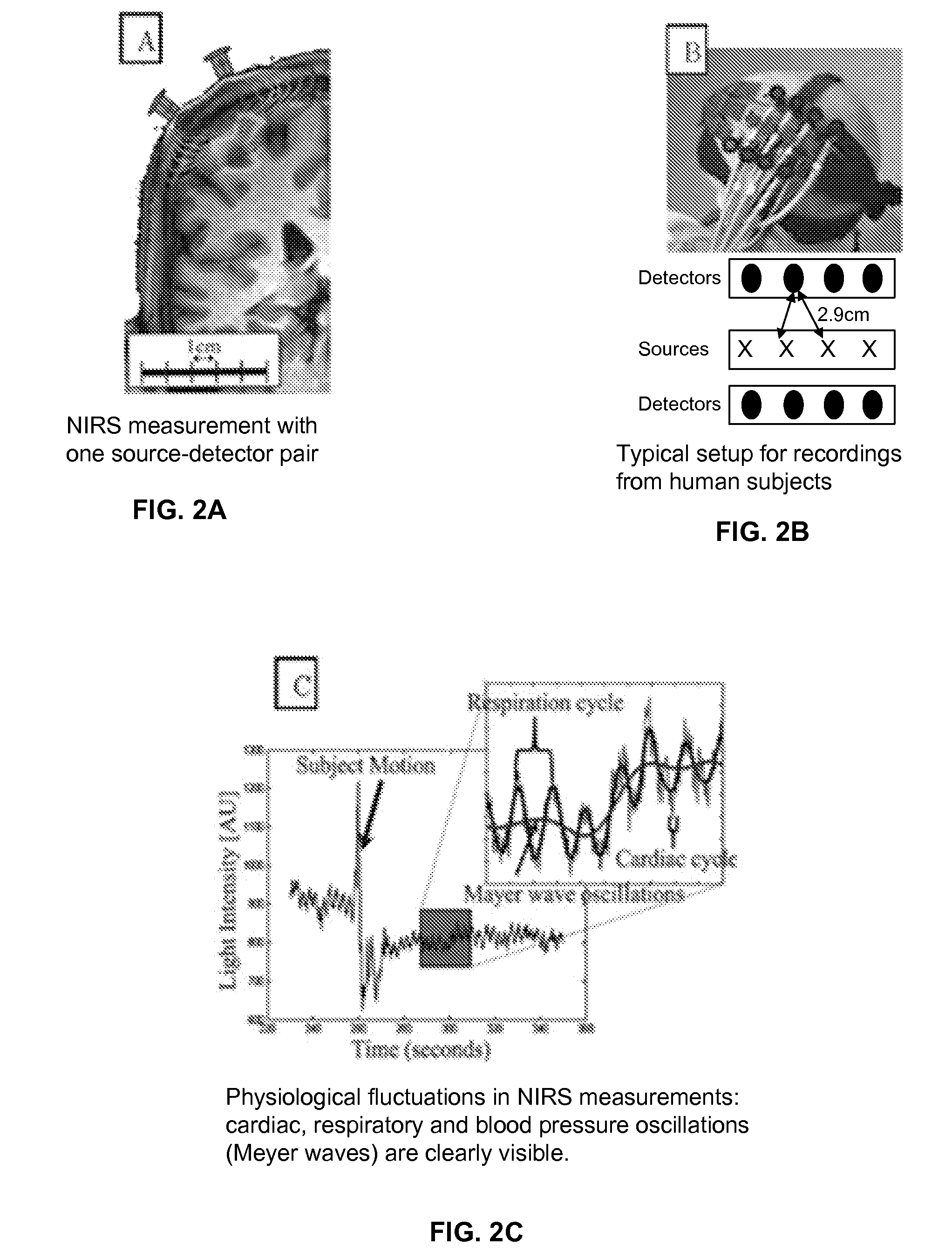
A method and apparatus for assessment of hemodynamic and functional state of the brain is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus includes non-invasive measurement of intracranial pressure, assessment of the brain's electrical activity, and measurement of cerebral blood flow. In some embodiments, the method and apparatus include measuring the volume change in the intracranial vessels with a near-infrared spectroscopy or other optical method, measuring the volume change in the intracranial vessels with rheoencephalography or other electrical method, and measuring the brain's electrical activity using electroencephalography.
Owner:ADVANCED BRAIN MONITORING
Regulation of cerebral blood flow by temperature change-induced vasodilatation
InactiveUS6942686B1Increase cerebral blood flowTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingVascular dilatationRight internal carotid artery
A method for enhancing cerebral blood flow in a patient. The patient's baseline cerebral blood flow is measured. An artery of the patient is cooled or warmed to produce vasodilatation of the artery. The artery is typically one or more of the left or right common carotid artery, left or right internal carotid artery, left or right middle cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery, left or right vertebral artery, or basilar artery. Vasodilatation enhances cerebral blood flow. The enhanced cerebral blood flow is measured after cooling or warming the artery. The enhanced cerebral blood flow is compared to the baseline cerebral blood flow. Cooling or warming is then adjusted as needed to achieve a desired enhancement in cerebral blood flow. Devices for cooling and warming are also described.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Enhancement of cerebral blood flow by electrical nerve stimulation
InactiveUS7340298B1Increase cerebral blood flowElectrotherapySubarachnoid spaceCerebral blood volume
A method for increasing cerebral blood flow in a patient. A electrical stimulating device is provided. The electrical stimulating device is applied to the patient at a region adjacent the cervical sympathetic chain, the brain stem, the head, or the sympathetic nervous system. The electrical stimulating device is applied by any route selected from transcutaneous, subcutaneous, and subarachnoid. The electrical stimulating device is activated to stimulate or inhibit nerve impulses of the cervical sympathetic chain, thereby producing vasodilation in the cerebral vasculature, thereby increasing cerebral blood flow. Devices for increasing cerebral blood flow in a patient are also described.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Seizure therapy and suppression using an implantable device
A system and method for detecting neurological conditions, including periods of high ictal activity and periods of low ictal activity, uses a relatively low-power central processing unit in connection with signal processing circuitry to identify characteristics of an electrographic signal received from a patient's brain. Cerebral blood flow may also be monitored. Observed characteristics are used to drive targeted responsive therapy and suppressive responsive therapy, or the modulation of cerebral blood flow, to prevent or terminate imminent seizures and to reduce the likelihood of future seizures.
Owner:NEUROPACE
Method and apparatus for creating penumbra and infarct images
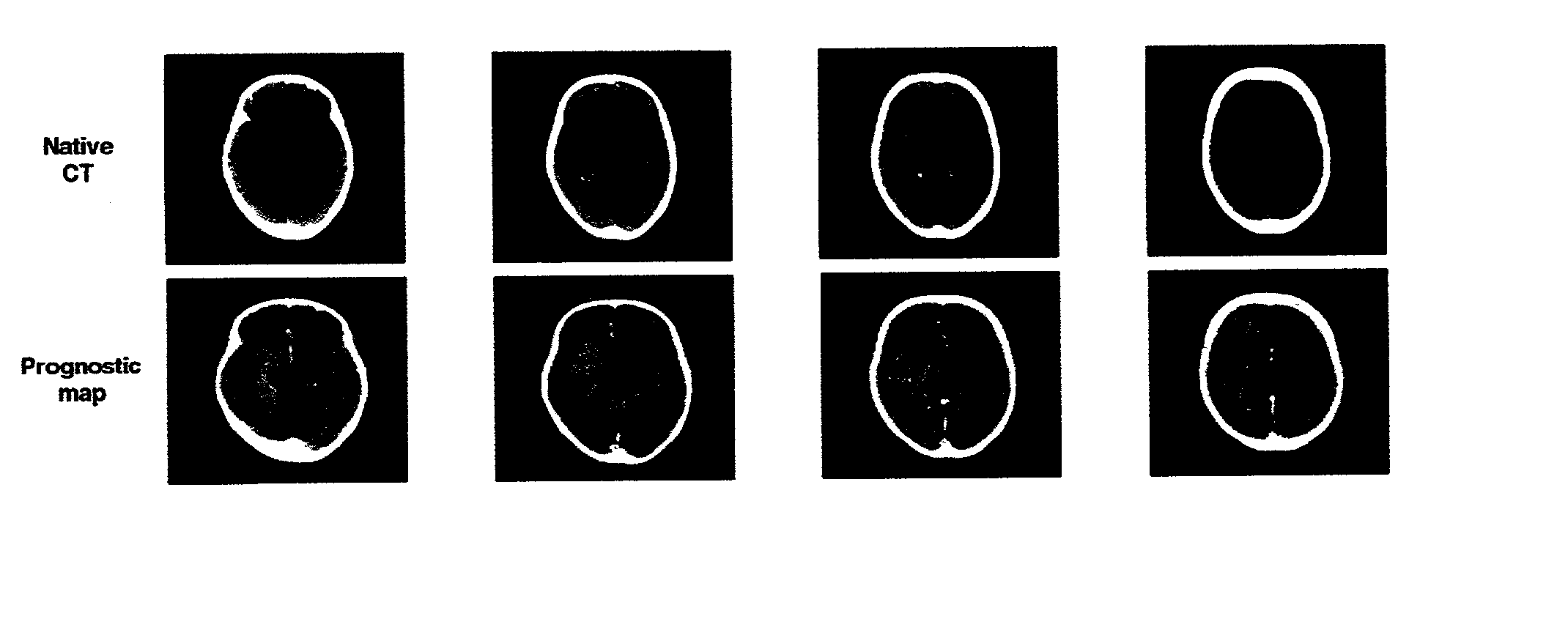
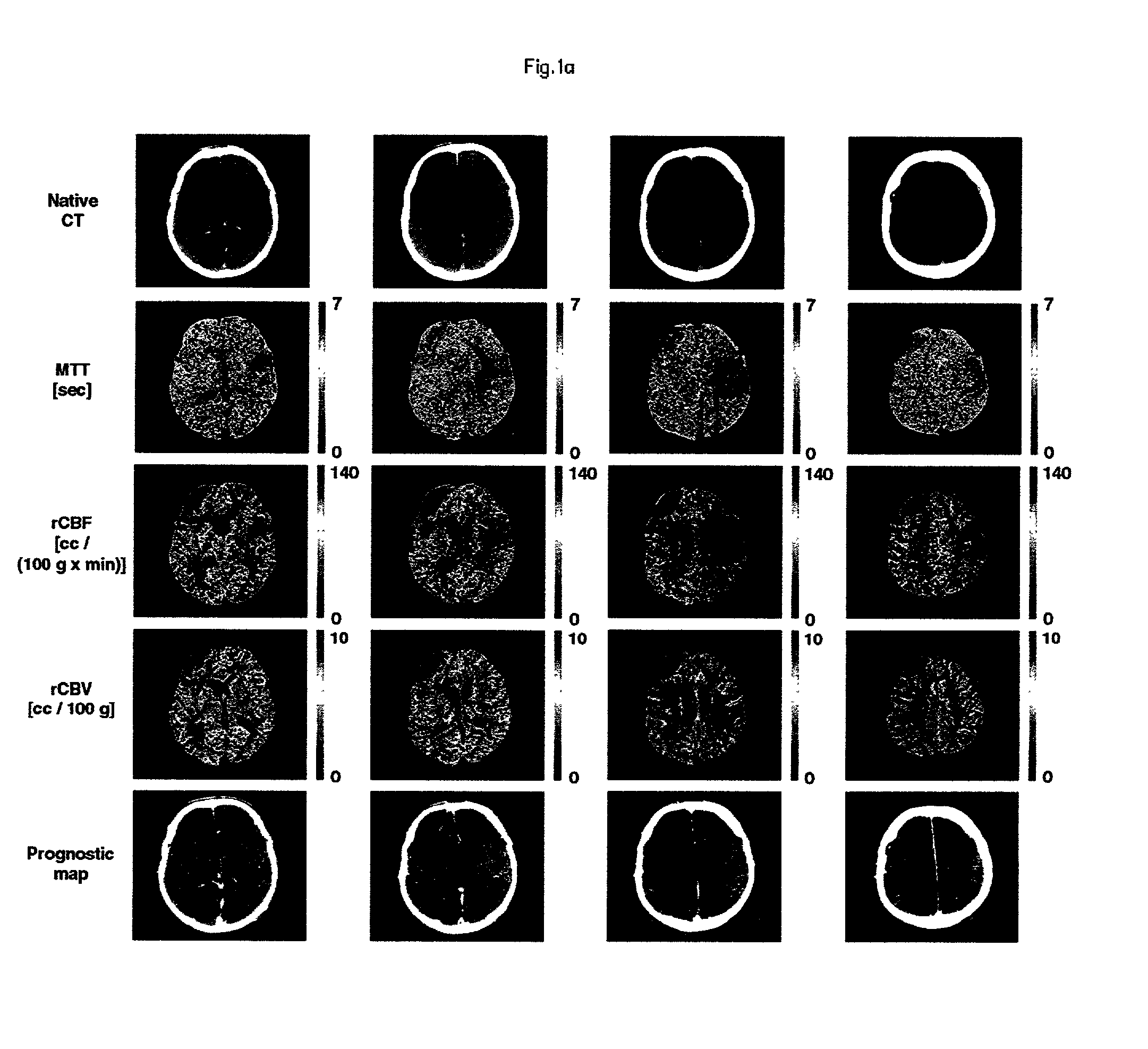
InactiveUS20020161292A1Computerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologyCerebral blood volume
A method and apparatus for evaluating acute stroke patients and for determining whether a stroke patient will benefit from the use of thrombolysis therapy includes obtaining measurements of the cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume of the brain of a stroke patient, determining ischemic areas of the brain where the ischemic areas comprise the measurements of cerebral blood flow which are less than a first value and creating a penumbra-infarct map of the ischemic areas of the brain using the measurements. The infarct area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is less than a second value. The penumbra area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is greater than this second value. The method also includes determining a ratio of penumbra size to the total of penumbra size and infarct size. When the ratio is greater than a predetermined value, the stroke patient is a candidate for thrombolysis therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
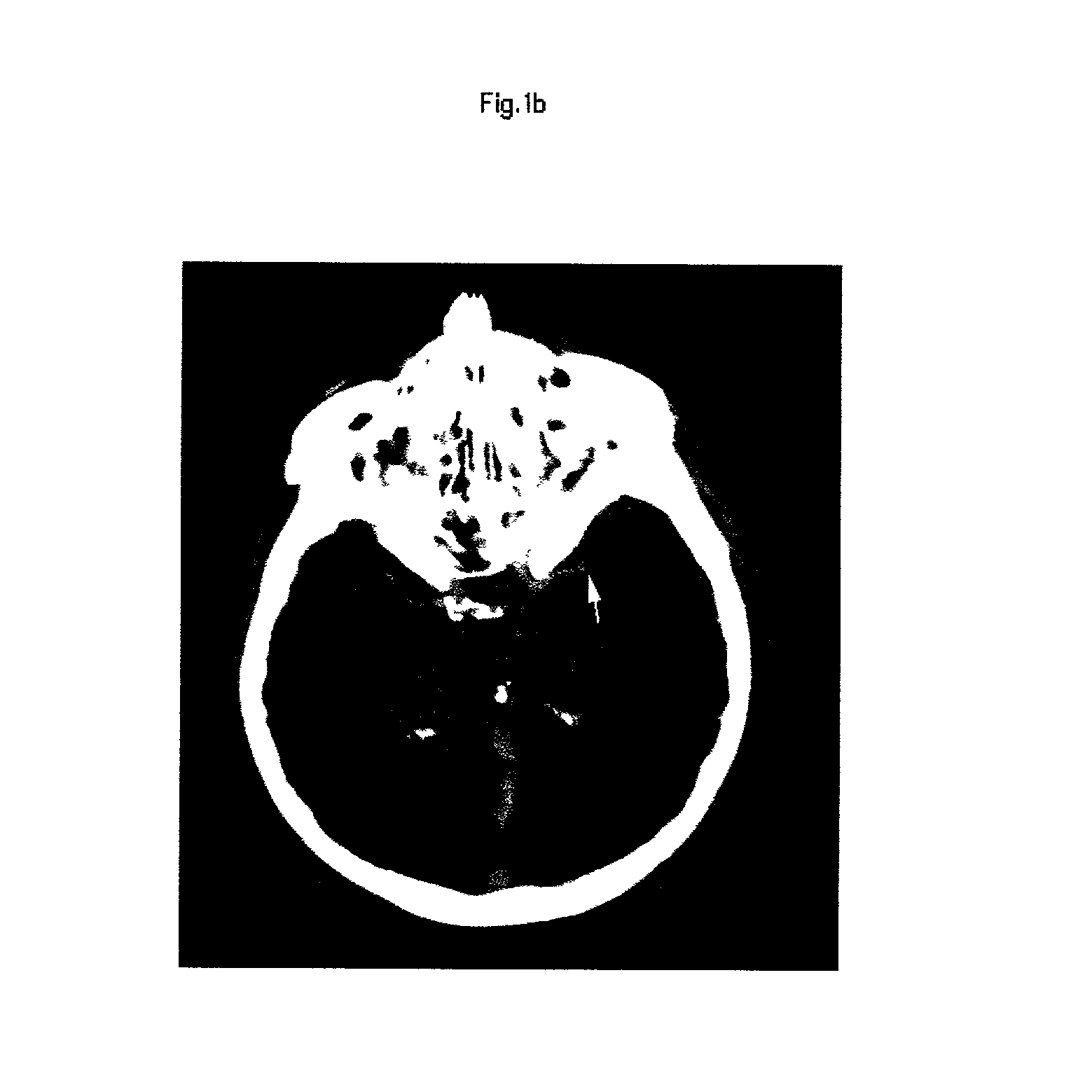
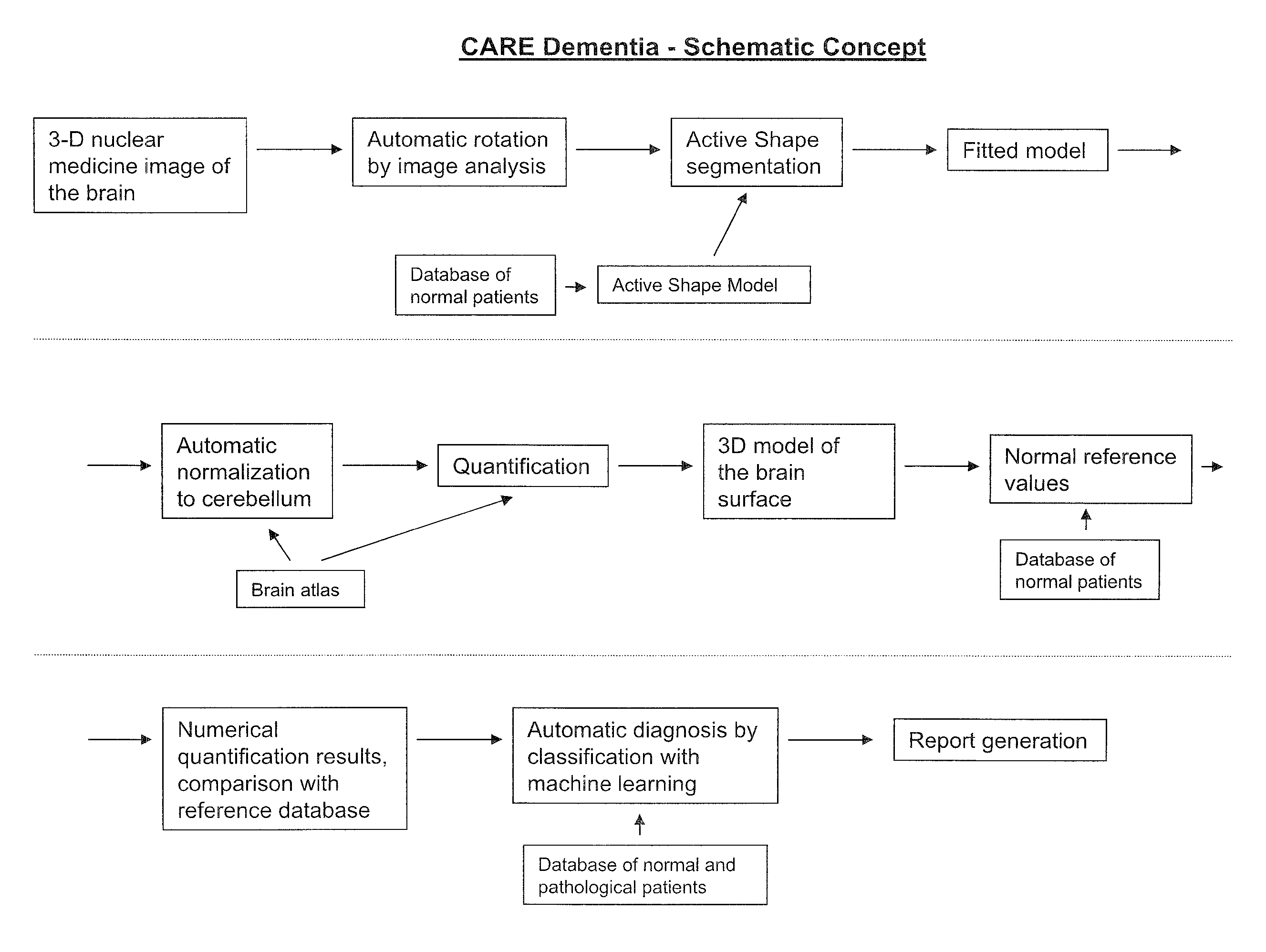
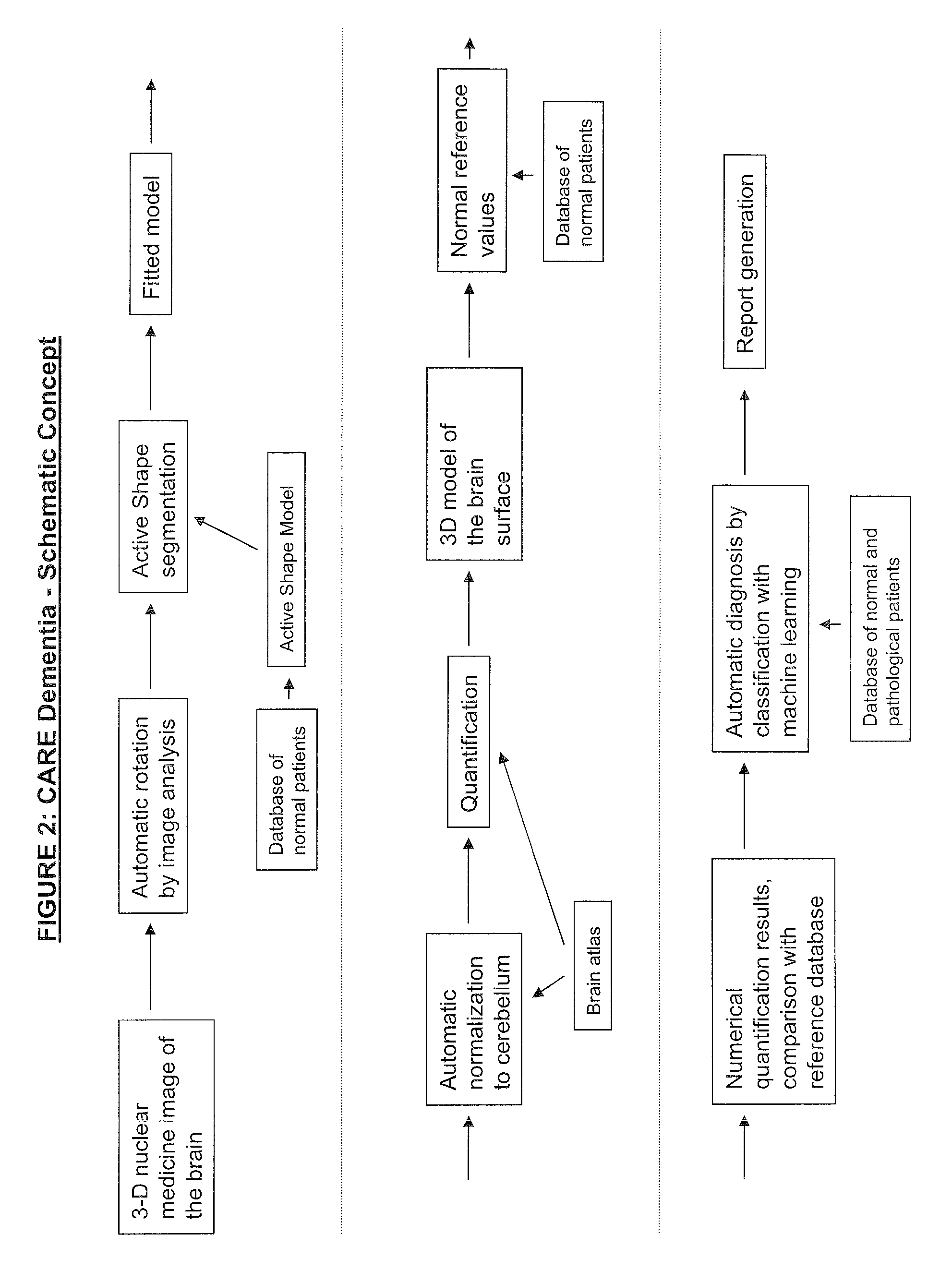
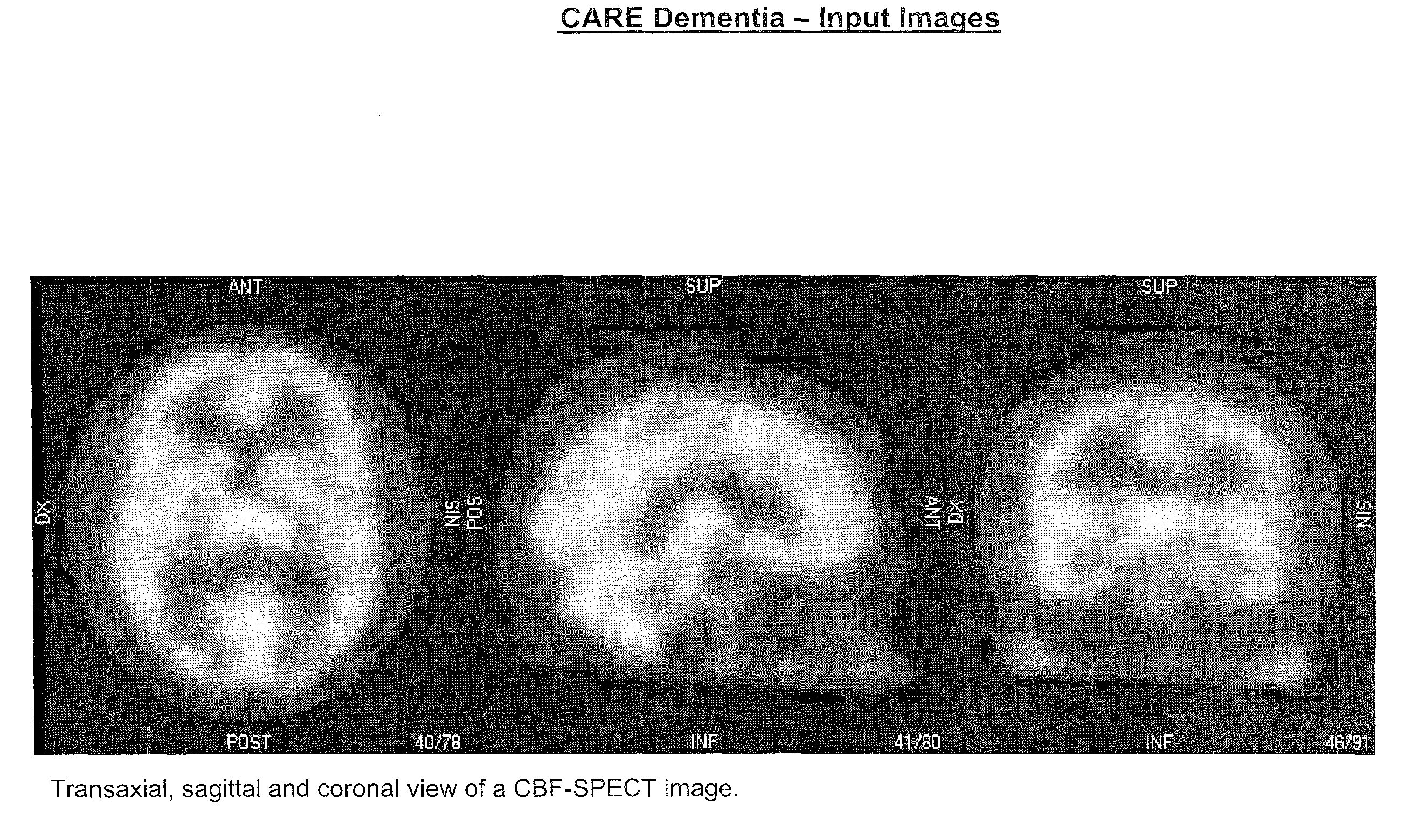
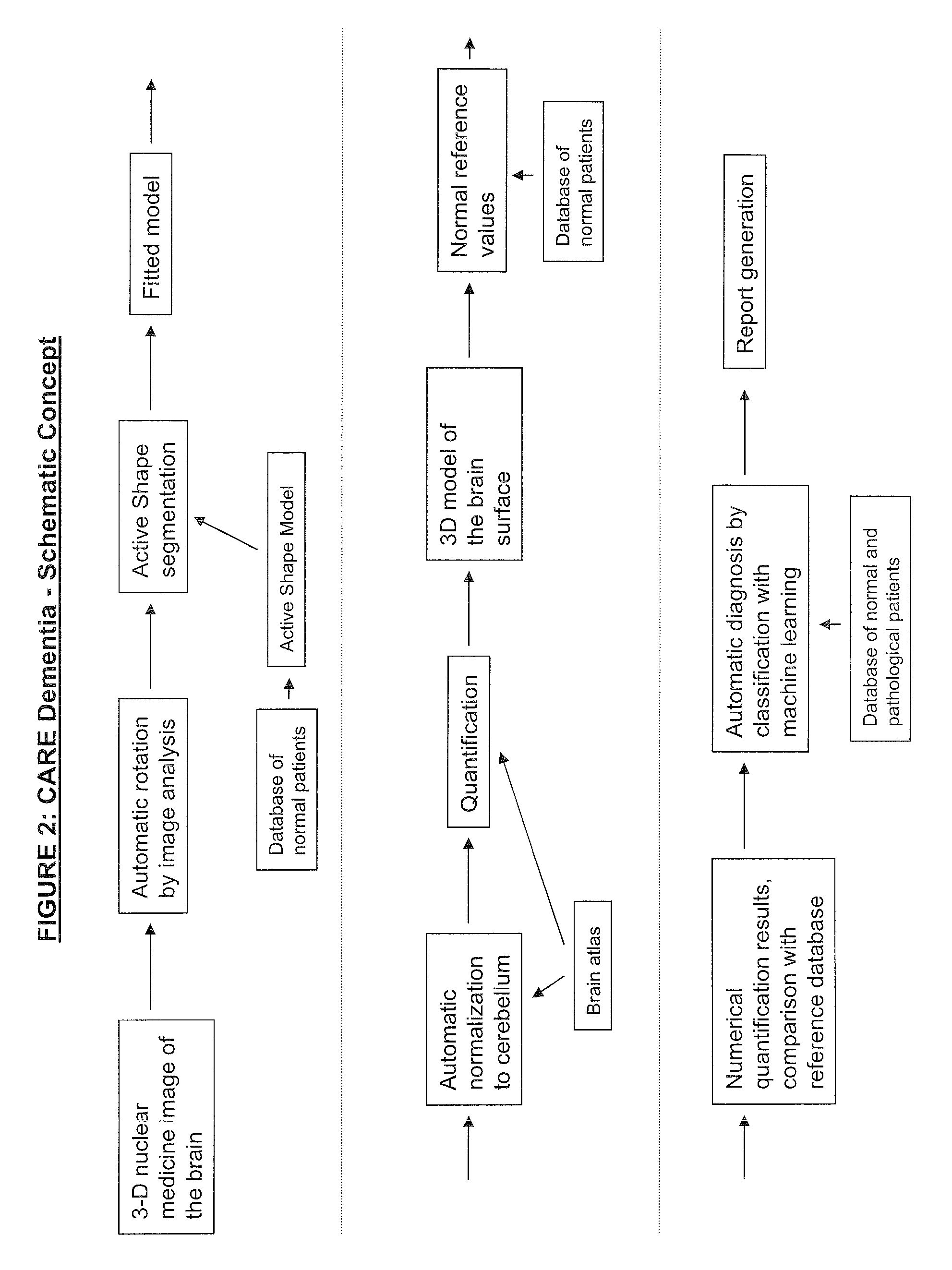
Automatic interpretation of 3-D medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS8199985B2Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
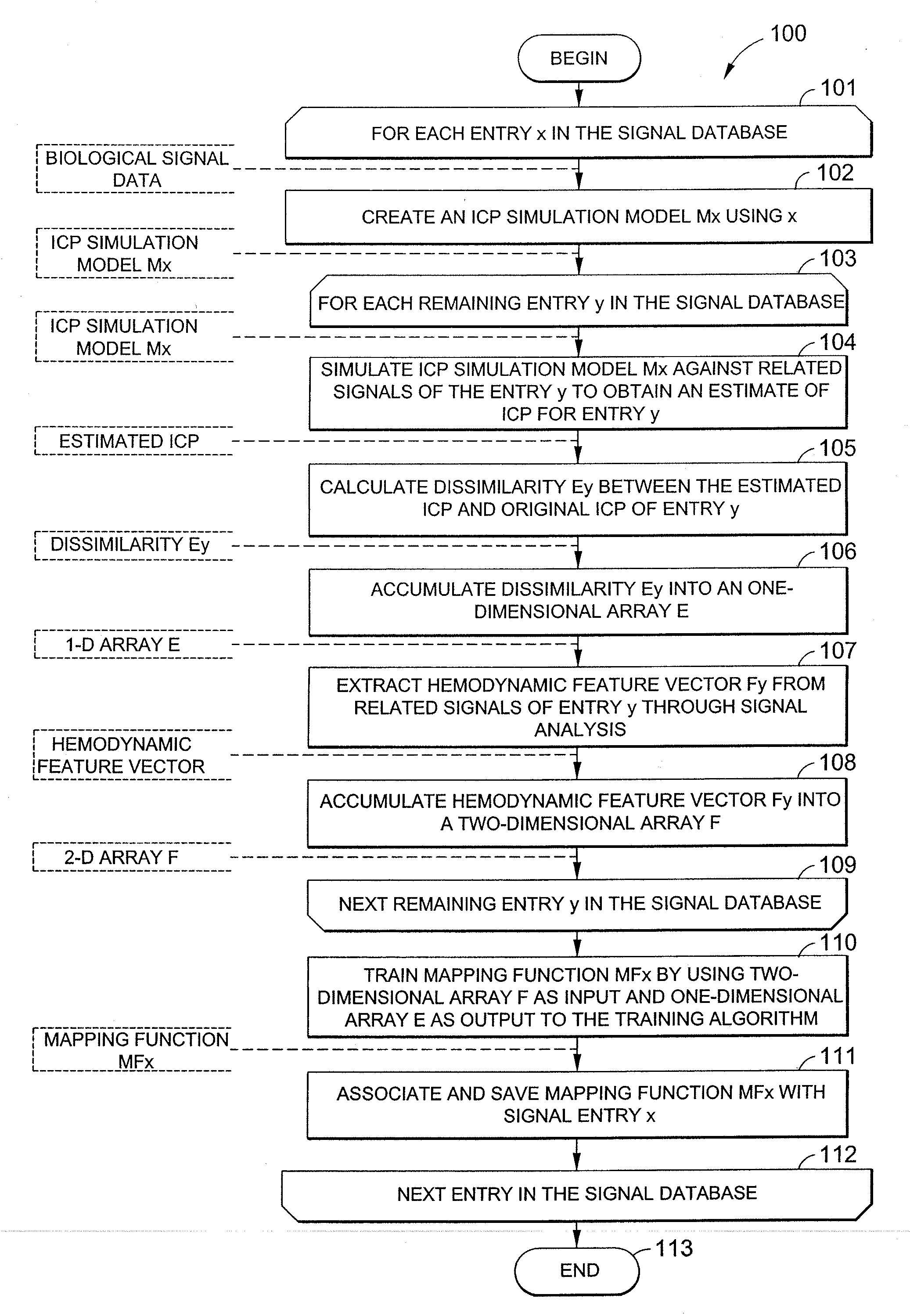
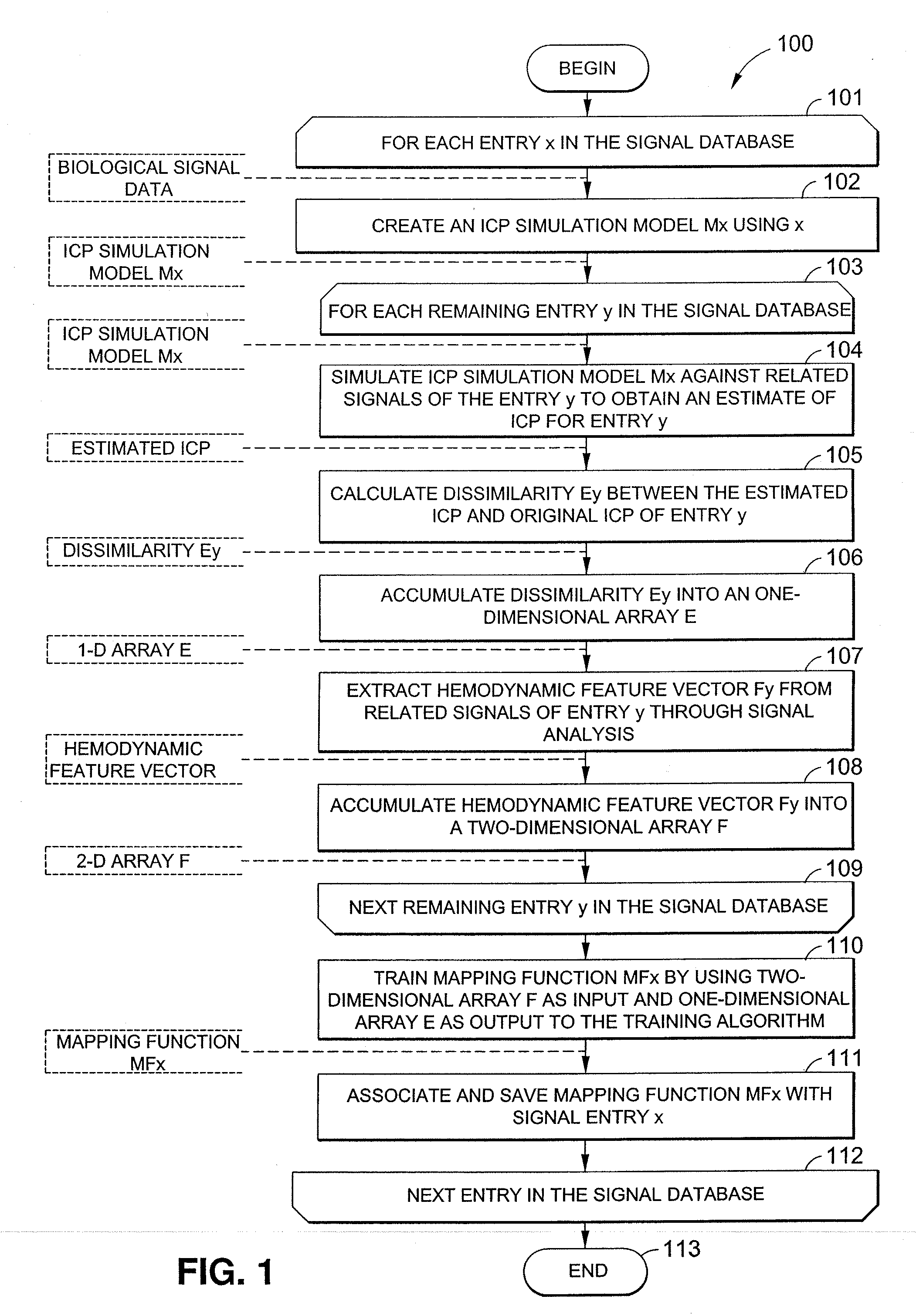
Data mining system for noninvasive intracranial pressure assessment
Systems and methods are described for noninvasively assessing an intracranial pressure of a patient. Some embodiments include providing a simulation model with a measured arterial blood pressure of the patient. Some embodiments further include providing the simulation model with a measured cerebral blood flow velocity of the patient. The simulation model correlates arterial blood pressure values, cerebral blood flow velocity values, and intracranial pressure values. Some embodiments further includes determining an intracranial pressure of the patient based on the simulation model. Some embodiments further includes creating an output data set indicative of the determined intracranial pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modulation and analysis of cerebral perfusion in epilepsy and other neurological disorders
Owner:NEUROPACE
Automatic interpretation of 3-d medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS20100067761A1Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
Medical oscillating compliance devices and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090177279A1Improve efficiencyStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
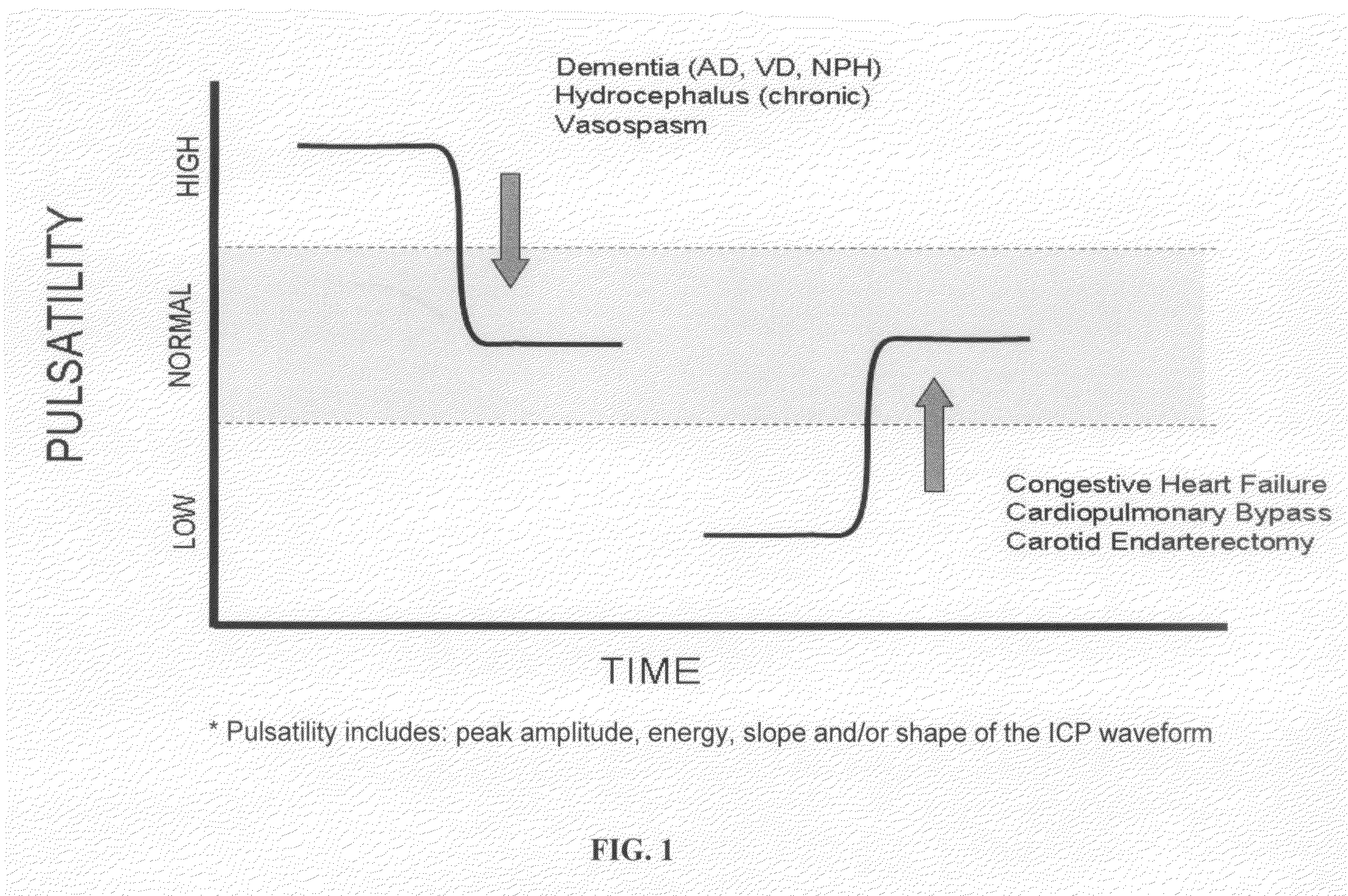
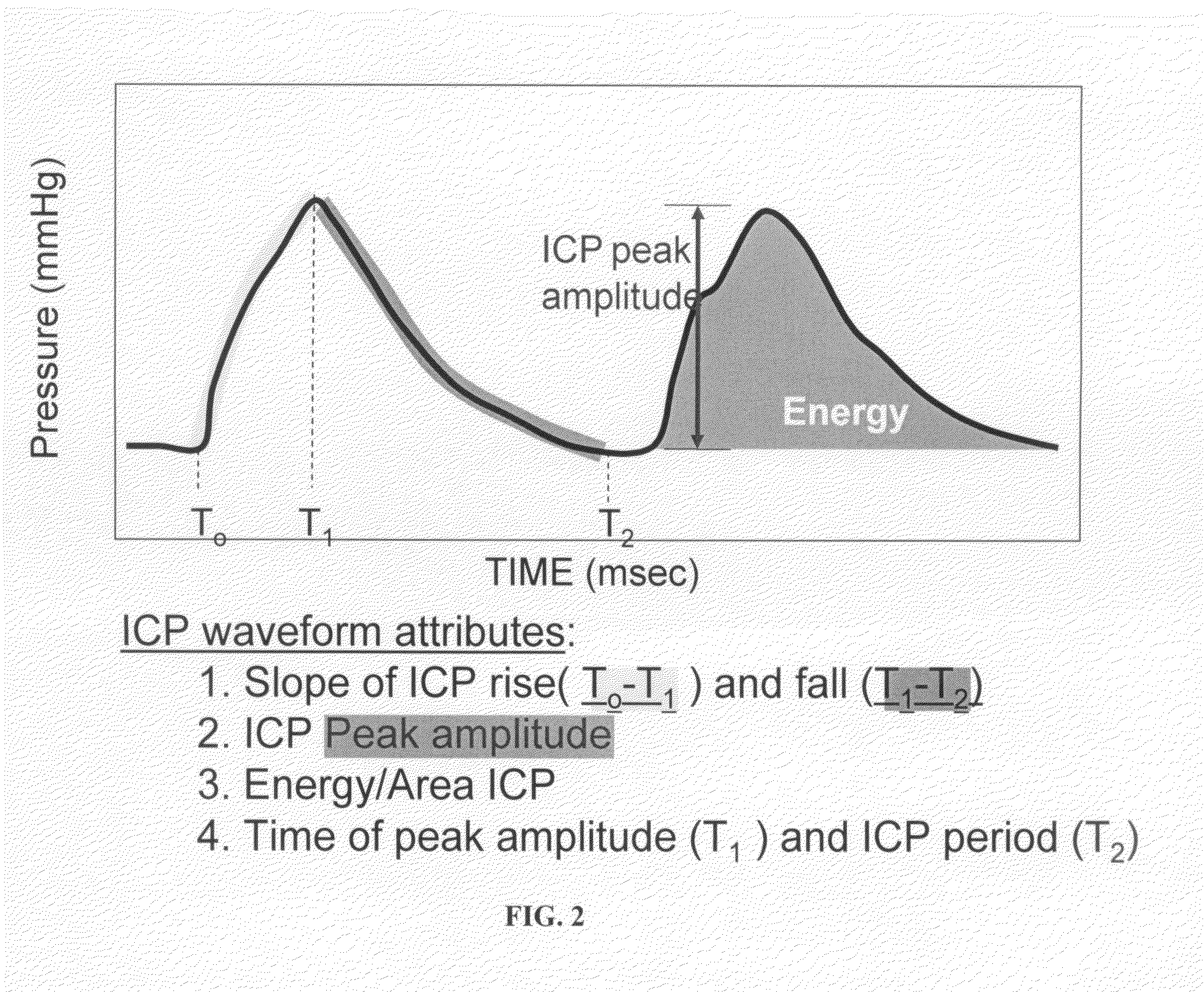
The present invention relates to devices and systems that alter intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform by oscillating the contraction and expansion of a compressible composition within the cranial or spinal cavities such that they increase intracranial capacity. The contraction and expansion of the compressible composition in the oscillating compliance devices can be due to an individual's intracranial pressure, the result of the expansion and compression of a reservoir which is mediated by the contractility of the heart or driven by a pump gaited to a biorhythm. The invention also relates to methods for protecting an individual's brain from abnormal arterial pulsations and for altering an individual's cerebral blood flow using the devices and systems of the invention. The oscillating compliance devices can be used to treat several diseases and / or conditions characterized by altered / abnormal intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform, including hydrocephalus, stroke, dementia and migraine headaches, vasospasms, congestive heart failure, cardiopulmonary bypass or carotid endarterectomy.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Long-term SPG stimulation therapy for prevention of vascular dementia
ActiveUS7860569B2Reduce riskReduce development riskSpinal electrodesHead electrodesDeep petrosal nerveMedicine
A method is provided that includes identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from vascular dementia (VaD). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of development of the VaD is reduced by applying electrical stimulation to a site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve; and configuring the stimulation to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
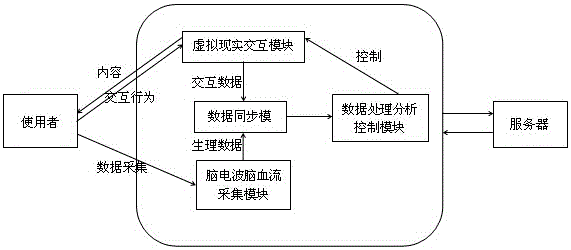
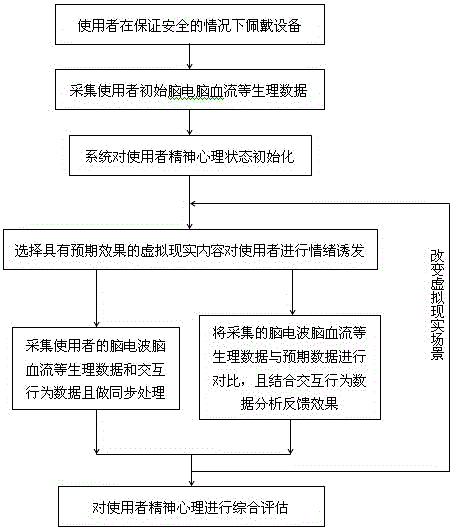
Mental and psychological assessment method based on VR interaction and brain wave and cerebral blood flow monitoring
ActiveCN105893780AReduce subjectivityDiagnosis and treatment normsInput/output for user-computer interactionHealth-index calculationUser needsFeedback effect
The invention discloses a mental and psychological assessment method based on VR interaction and brain wave and cerebral blood flow monitoring, and relates to the field of medical treatment. The method comprises three parts of a user specific emotion elicitation link based on virtual-real interaction technology, a user psychological data analysis link based on brain wave and cerebral blood flow data real-time monitoring, and a user mental and psychological assessment link. According to the method, according to the doctor or user needs and on the premise of ensuring safety, a virtual-real module is used for providing virtual-real contents of different forms for the user to elicit the specific emotion fluctuation of the user, and brain wave, cerebral blood flow and other psychological data of the user is subjected to comparative analysis with the expected data, so that the feedback effect of the user observing the virtual-real contents is analyzed and obtained, and the mental and psychological assessment of the user is performed by combining with the feedback effect of the user observing a series of virtual-real contents with specific emotion elicitation effects.
Owner:广州博微智能科技有限公司
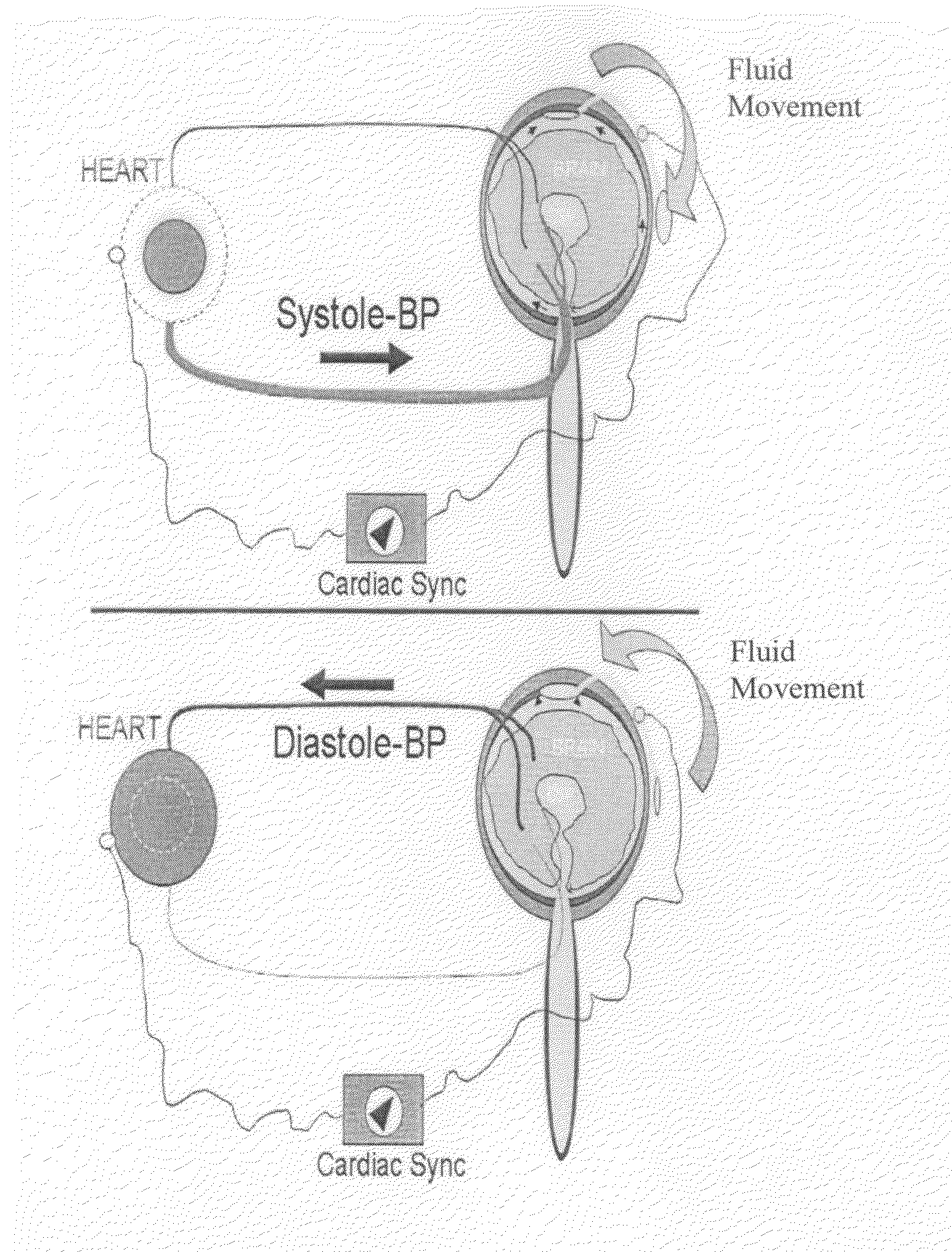
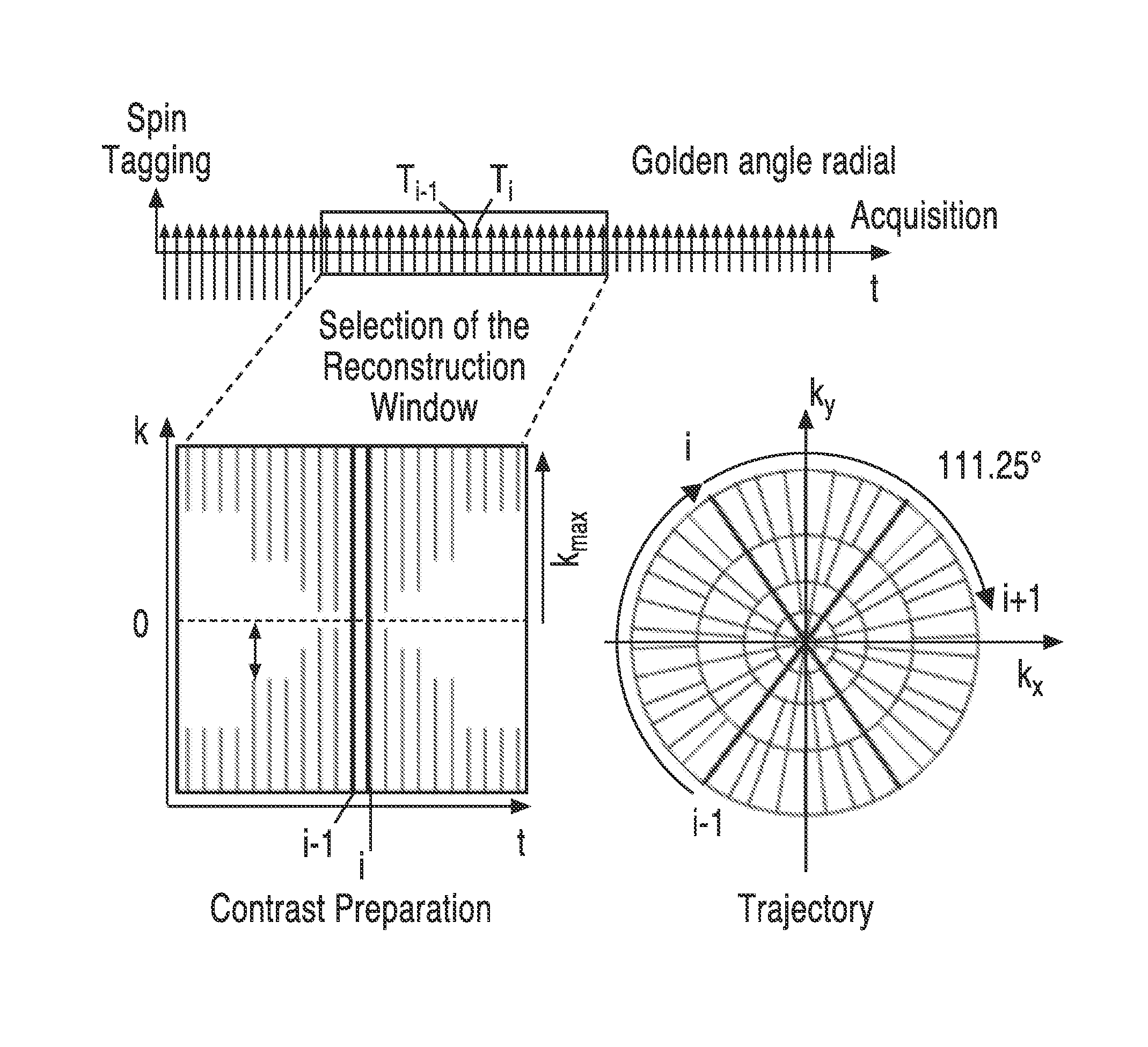
Noninvasive 4-d time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography
ActiveUS20150327783A1High degree of efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsSystoleCardiac cycle
A method for non-contrast enhanced 4D time resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using arterial spin labeling of blood water as an endogenous tracer and a multiphase balanced steady state free precession readout is presented. Imaging can be accelerated with dynamic golden angle radial acquisitions and k-space weighted imaging contrast (KWIC) image reconstruction and it can be used with parallel imaging techniques. Quantitative tracer kinetic models can be formed allowing cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow and mean transit time to be estimated. Vascular compliance can also be assessed using 4D dMRA by synchronizing dMRA acquisitions with the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
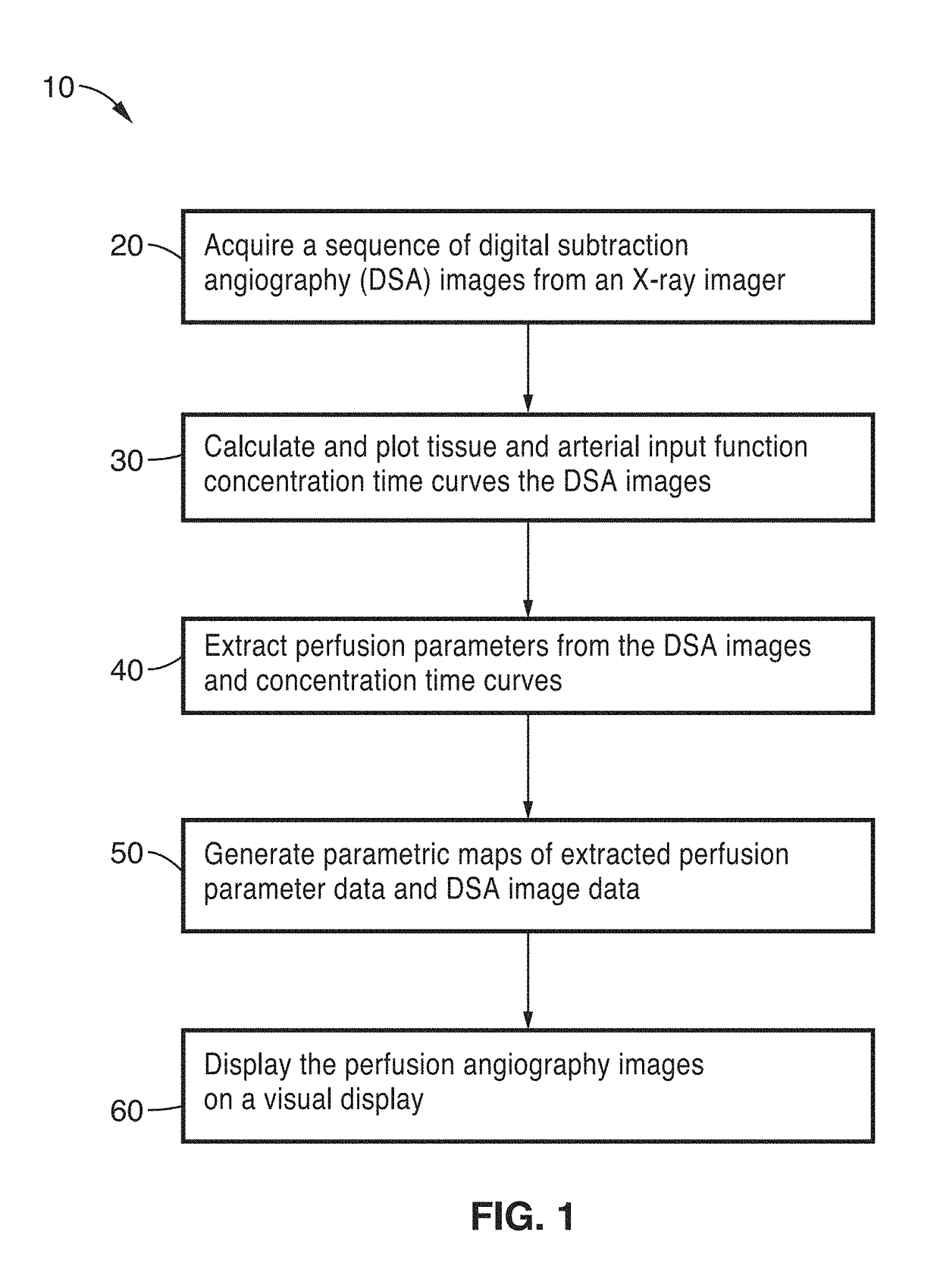
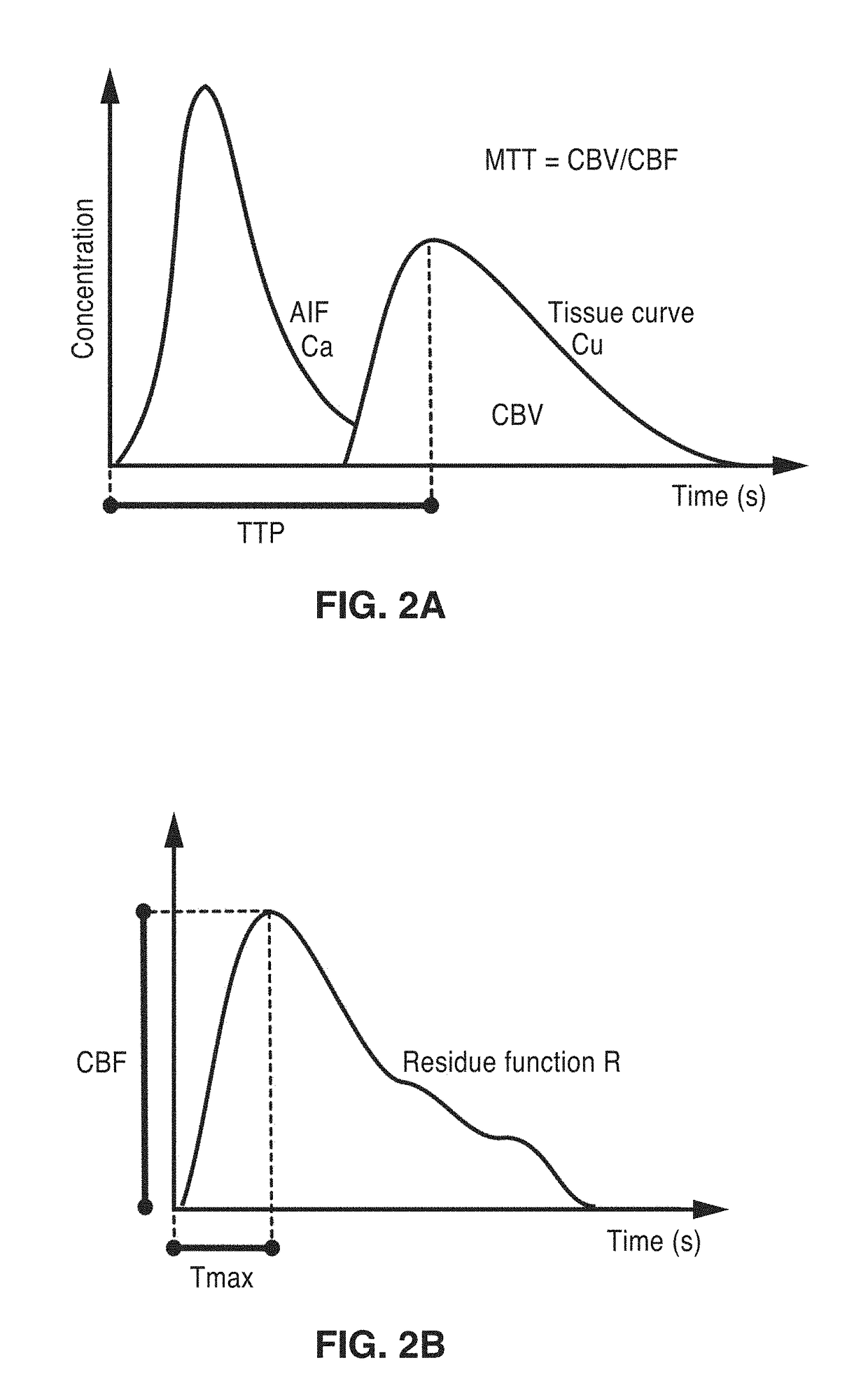
Perfusion digital subtraction angiography
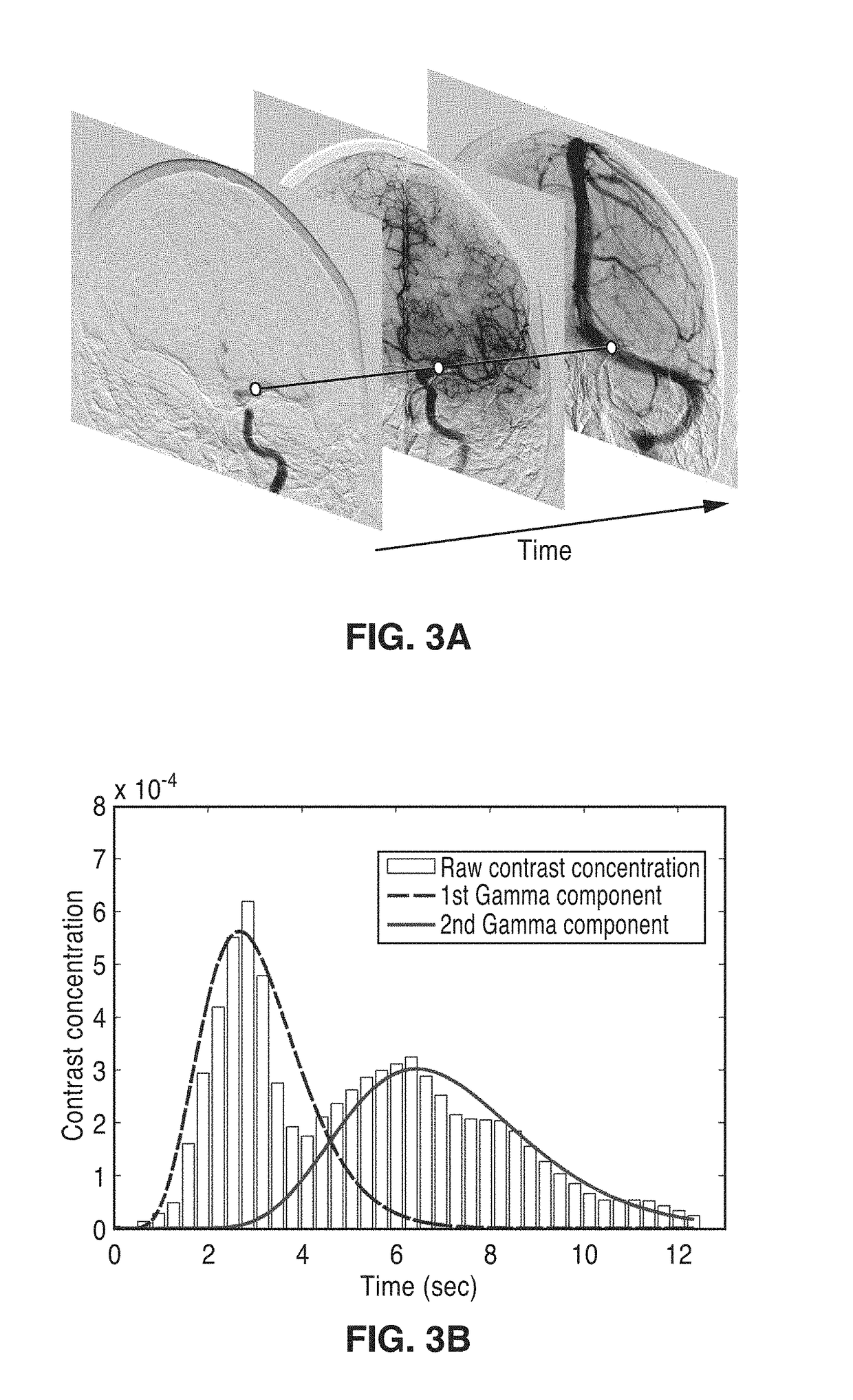
ActiveUS20190015061A1Improve patient outcomesSustain viabilityImage enhancementImage analysisTime density curveVolumetric Mass Density
An apparatus and methodological framework are provided, named perfusion angiography, for the quantitative analysis and visualization of blood flow parameters from DSA images. The parameters, including cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV), mean transit time (MTT), time-to-peak (TTP), and Tmax, are computed using a bolus tracking method based on the deconvolution of time-density curves on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Individual contrast concentration curves of overlapping vessels can be delineated with multivariate Gamma fitting. The extracted parameters are each transformed into parametric maps of the target that can be color coded with different colors to represent parameter values within a particular set range. Side by side parametric maps with corresponding DSA images allow expert evaluation and condition diagnosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and equipment for transcranial cerebral blood flow high-resolution imaging
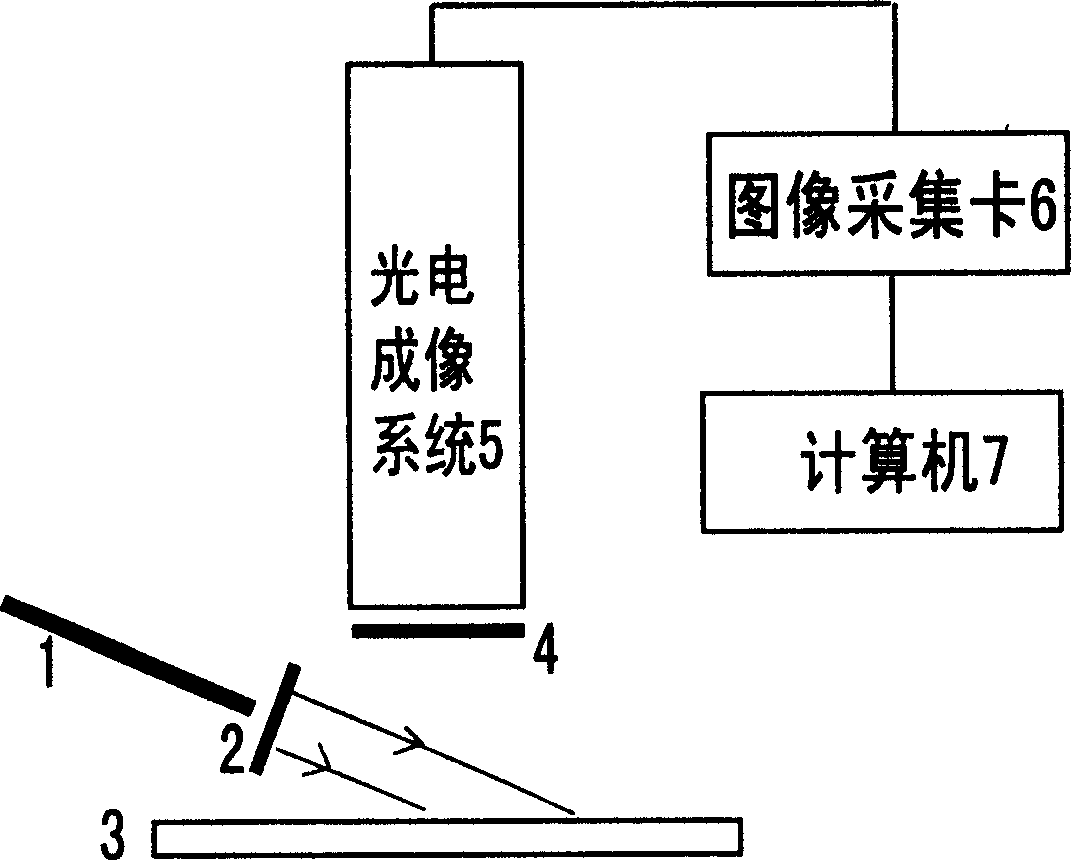
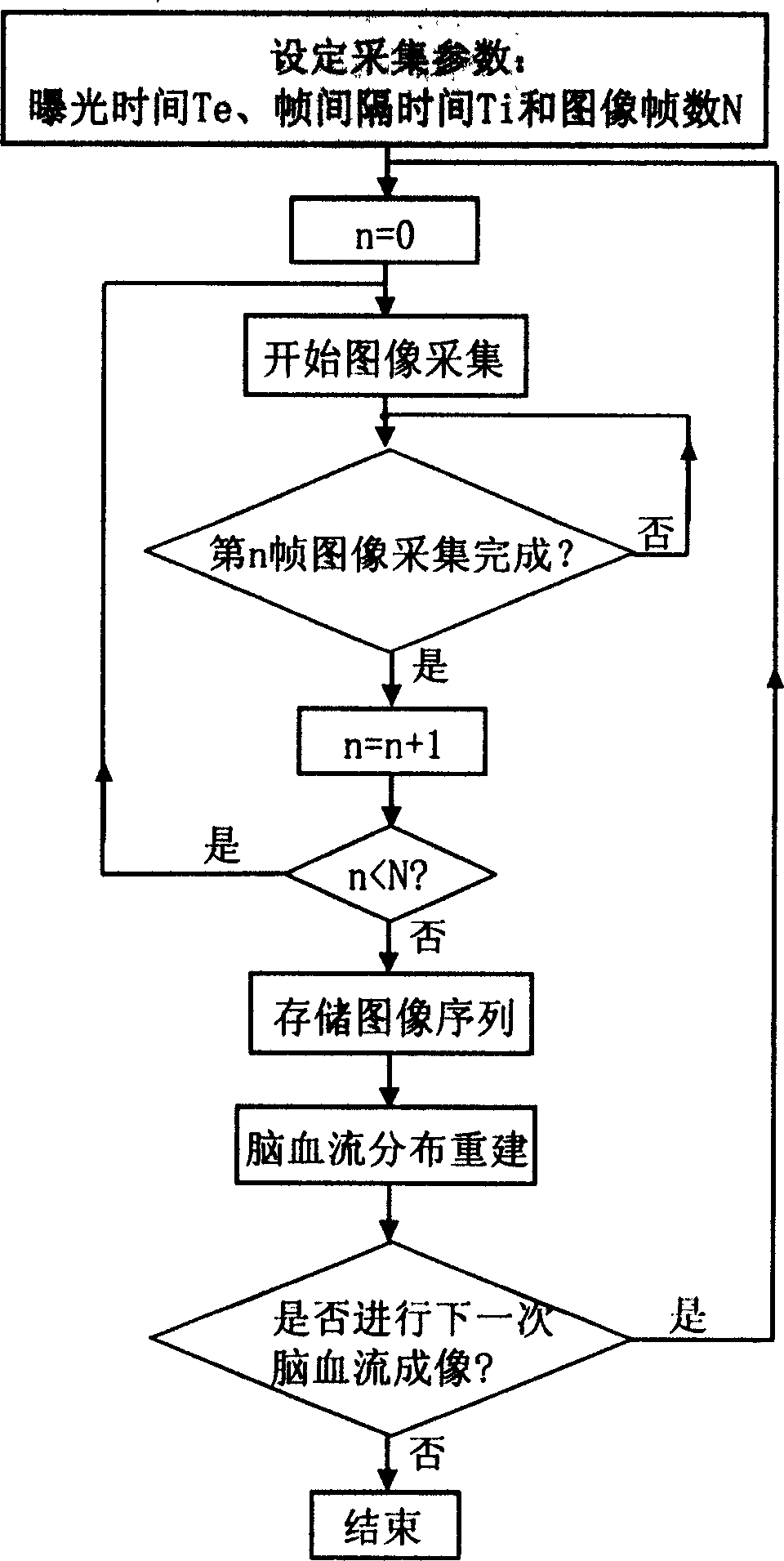
InactiveCN1792323AImprove spatial resolutionImage data processing detailsBlood flow measurementHigh resolution imagingPolarizer
A high-definition imaging method for the craniocerebral blood flow includes such steps as irradiating the near infrared collimated laser beam onto an object to be tested, continuously taking several frames of reflected laser speckle image at intervals, calculating the time contrast of light intensity variation with time for each pixel, calculating the speed of its cerebral blood flow, and using it as grayscale to configure the 2D speed distribution chart of cerebral blood flow. Its apparatus is composed of laser device, two polarizers, bench, photoelectric imaging system and computer.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for Quantitative Diagnosis of Cerebrovascular, Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases via Computation of a CO2 Vasomotor Reactivity Index based on a Nonlinear Predictive Model
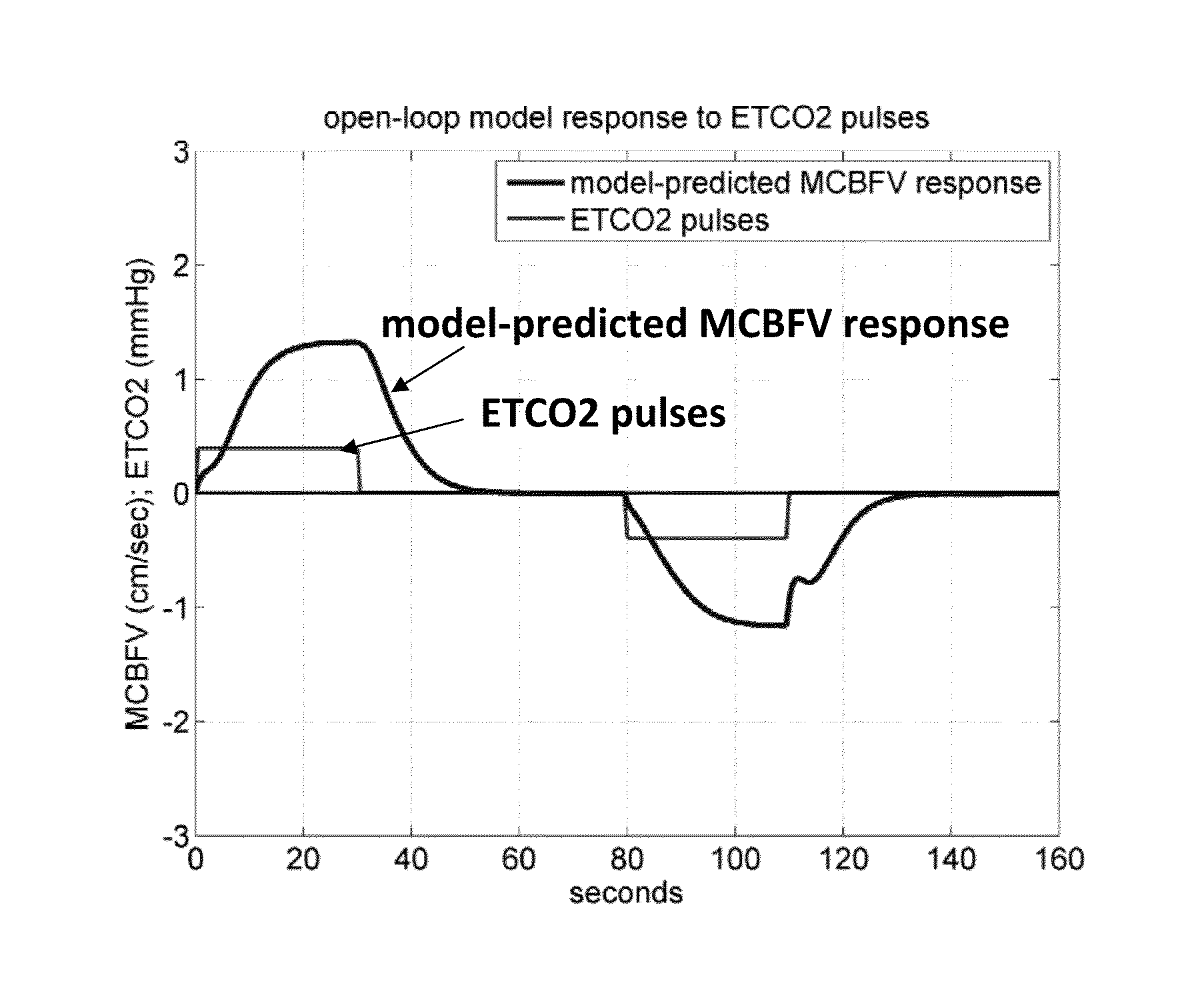
InactiveUS20140278285A1Sensitive and reliableMedical simulationHealth-index calculationComputational modelComputer aid
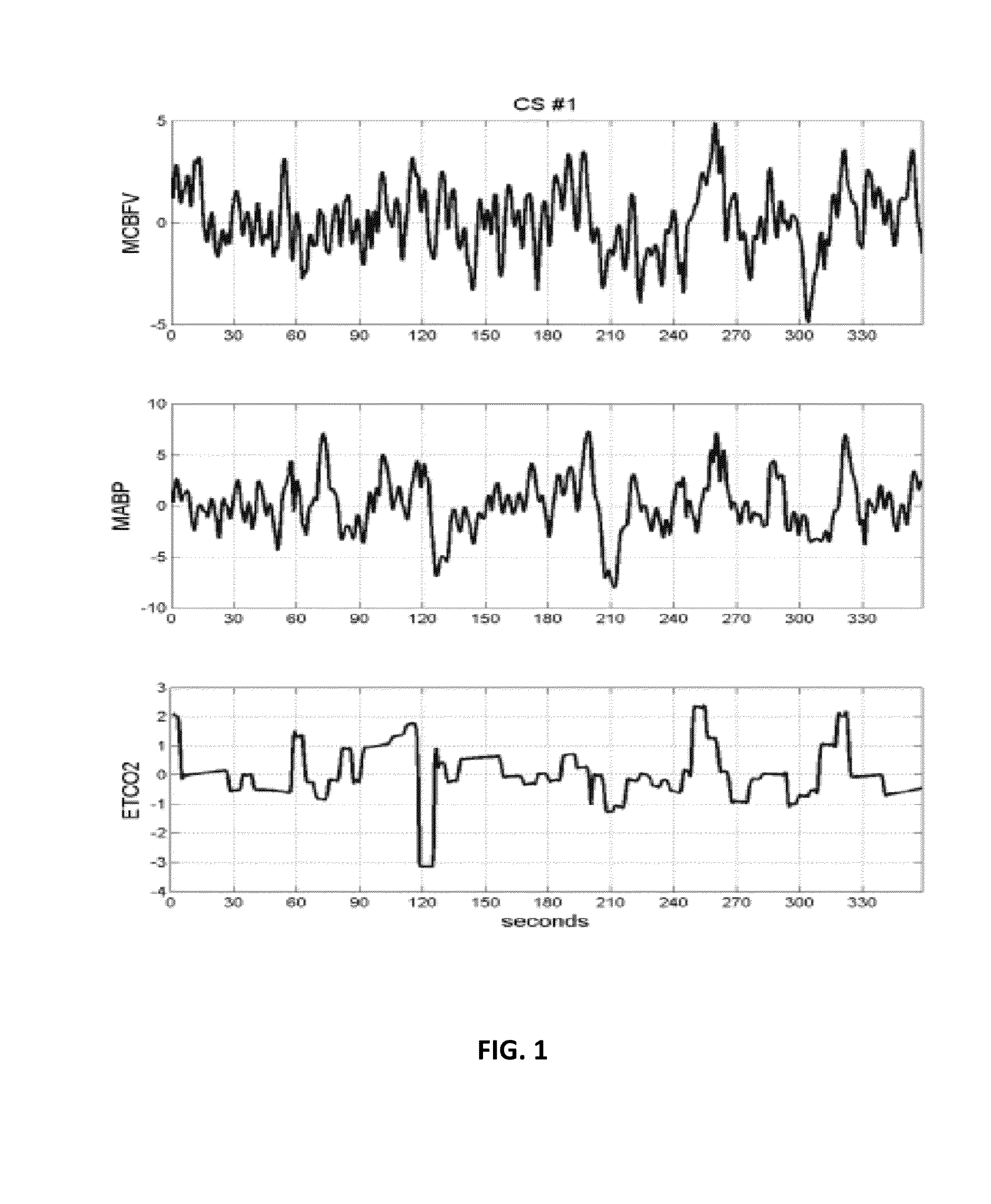
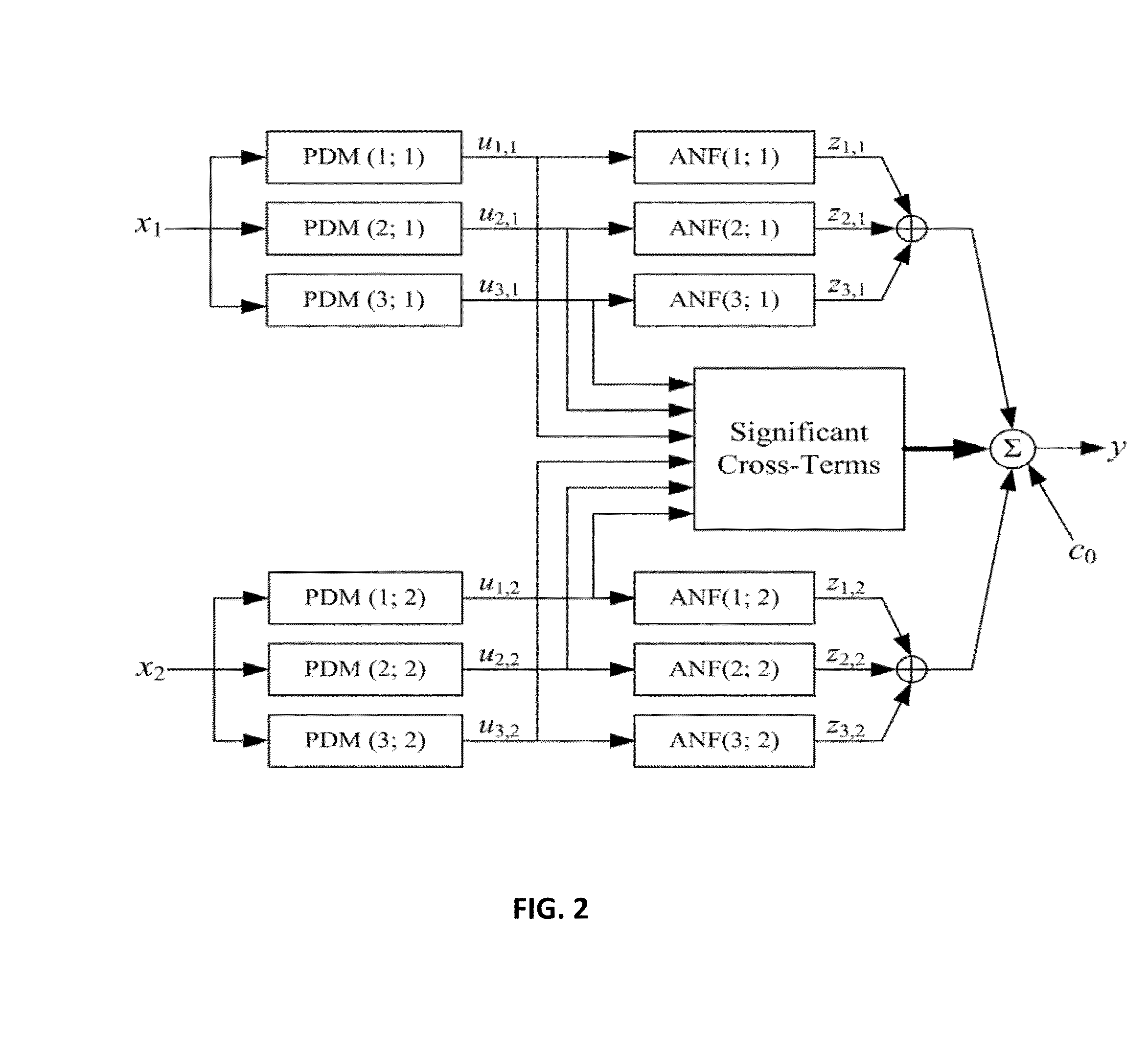
The present invention relates generally to a method for computer-aided quantitative diagnosis of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's, vascular dementia, mild cognitive impairment, transient ischemia, stroke etc.) via a vasomotor reactivity index (VMRI) which is computed on the basis of a computational model of the dynamic nonlinear inter-relationships between beat-to-beat time-series measurements of cerebral blood flow velocity, arterial blood pressure and end-tidal CO2. This model is obtained by means of a method pioneered by the inventors and may incorporate additional physiological measurements from human subjects. Its purpose is to provide useful information to physicians involved in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases with a significant neurovascular component by offering quantitative means of assessment of the effects of the disease or medication on cerebral vasomotor reactivity. Initial results from clinical data have corroborated the diagnostic potential of this approach.
Owner:MARMARELIS VASILIS Z +2
Embolic deflection device
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com