Patents
Literature
50 results about "Acute stroke" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An acute stroke is a potentially life-threatening cerebrovascular event in which the brain is temporarily deprived of oxygen. Marked by a momentary disruption in blood flow, an acute stroke necessitates immediate medical attention and, if left untreated, may result in permanent disability or death.
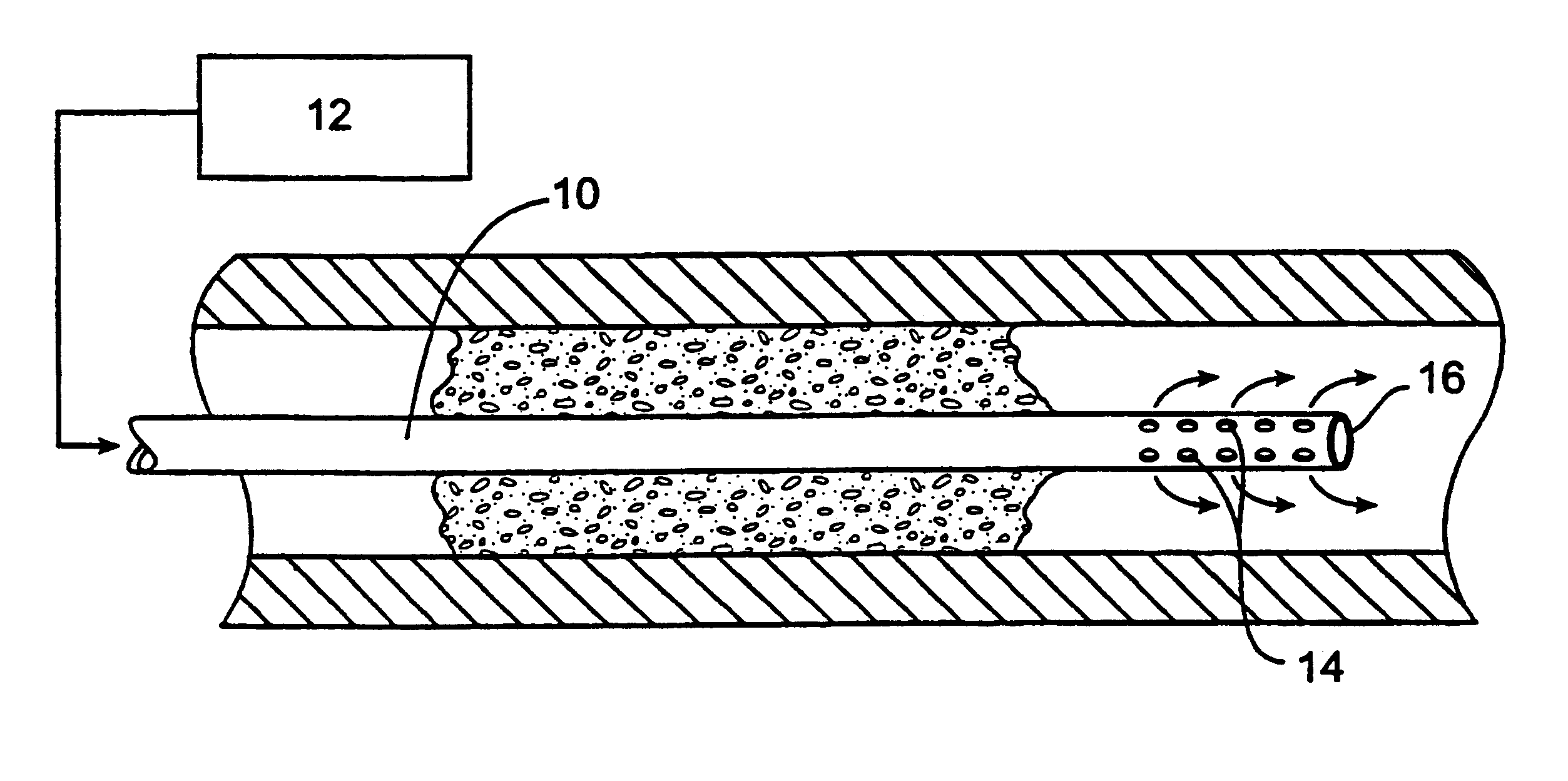
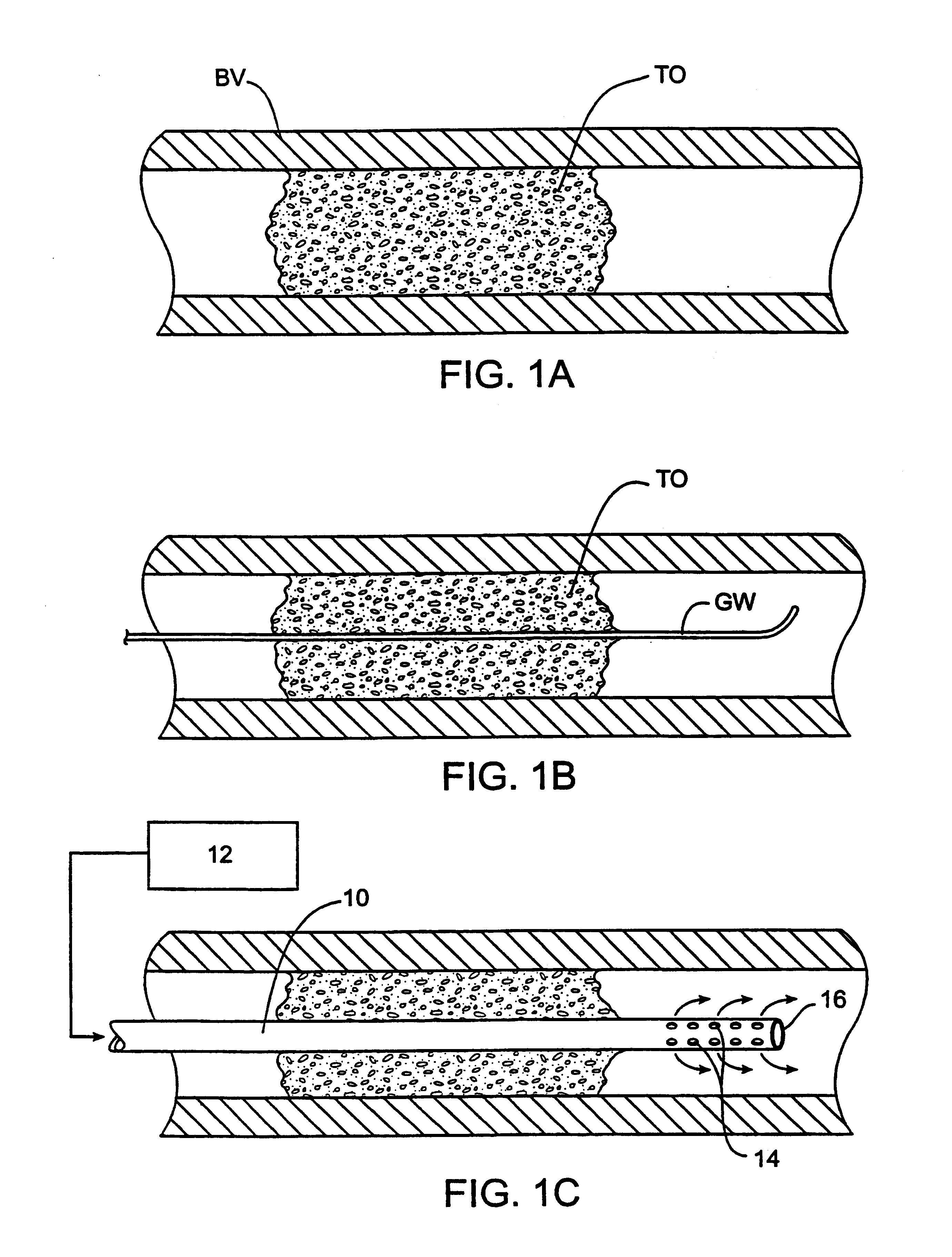
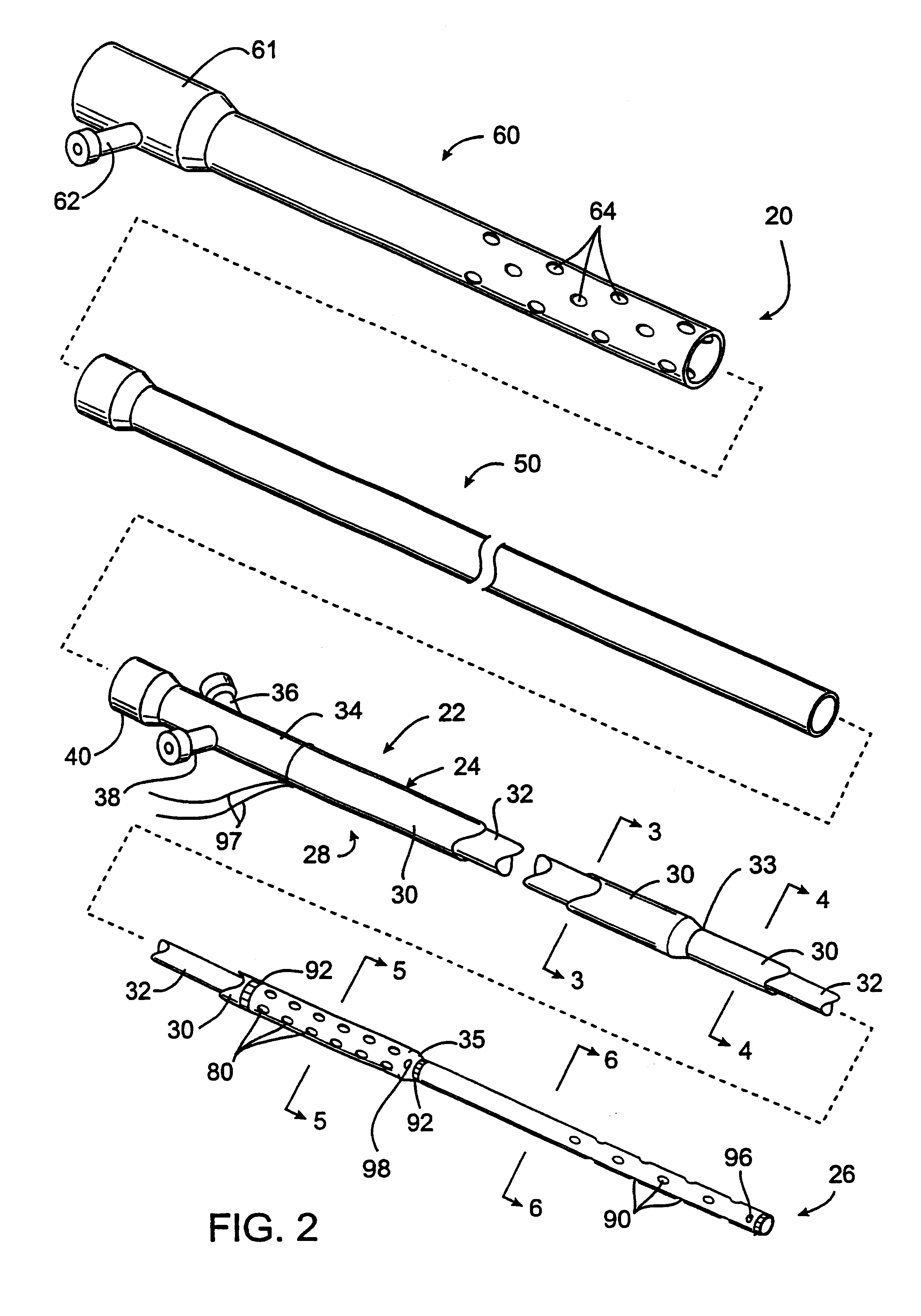
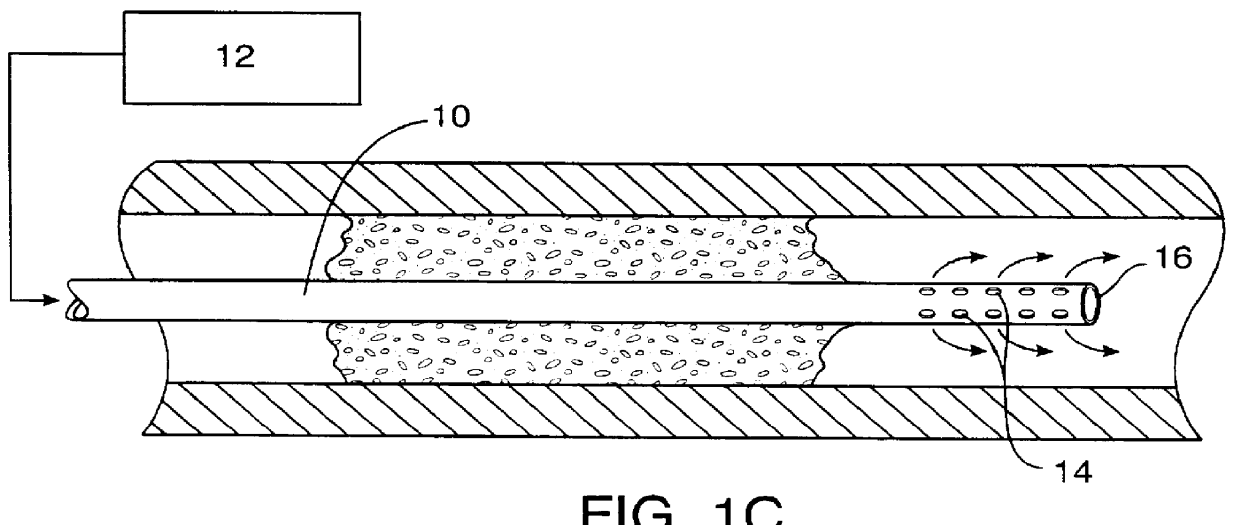
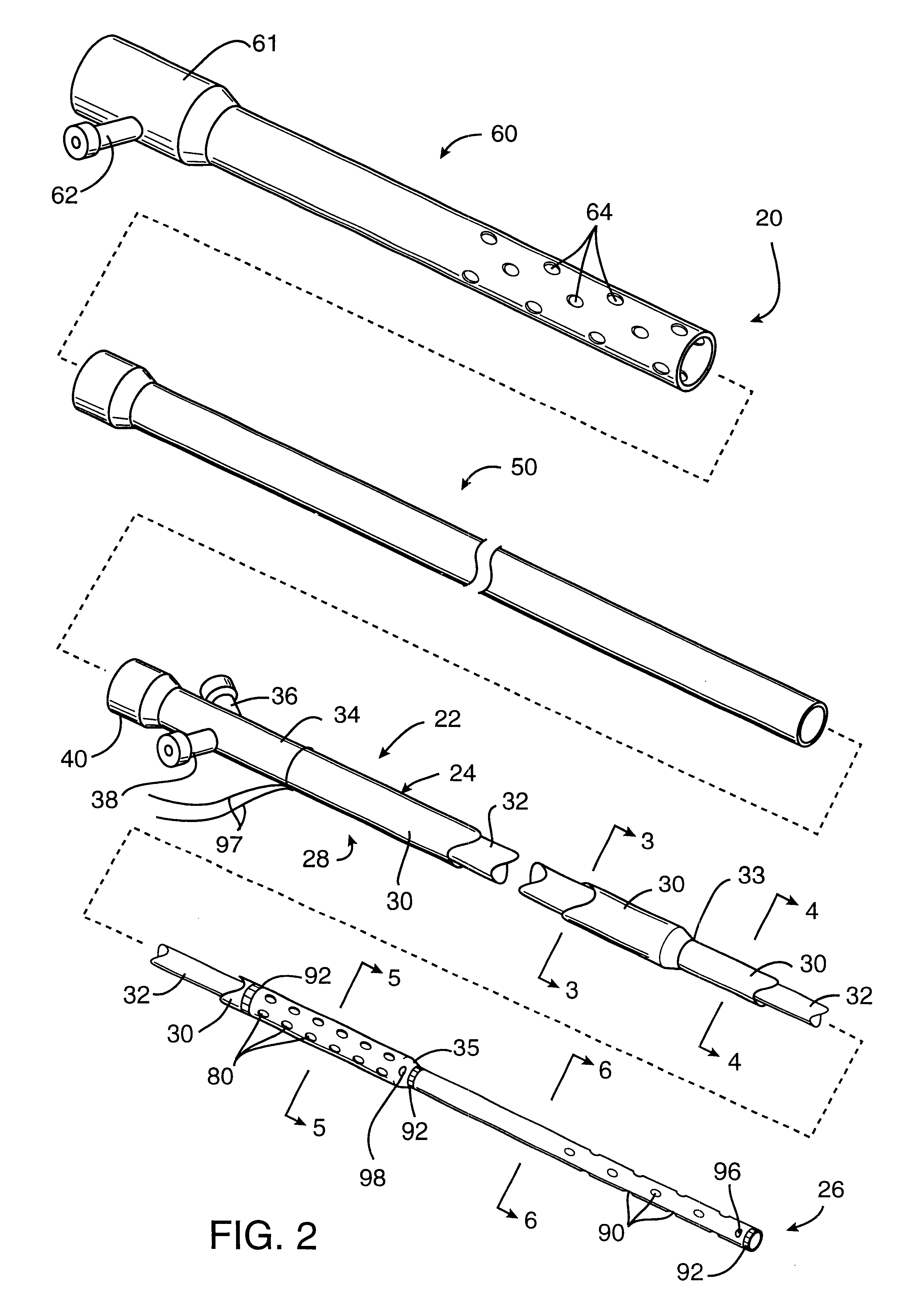
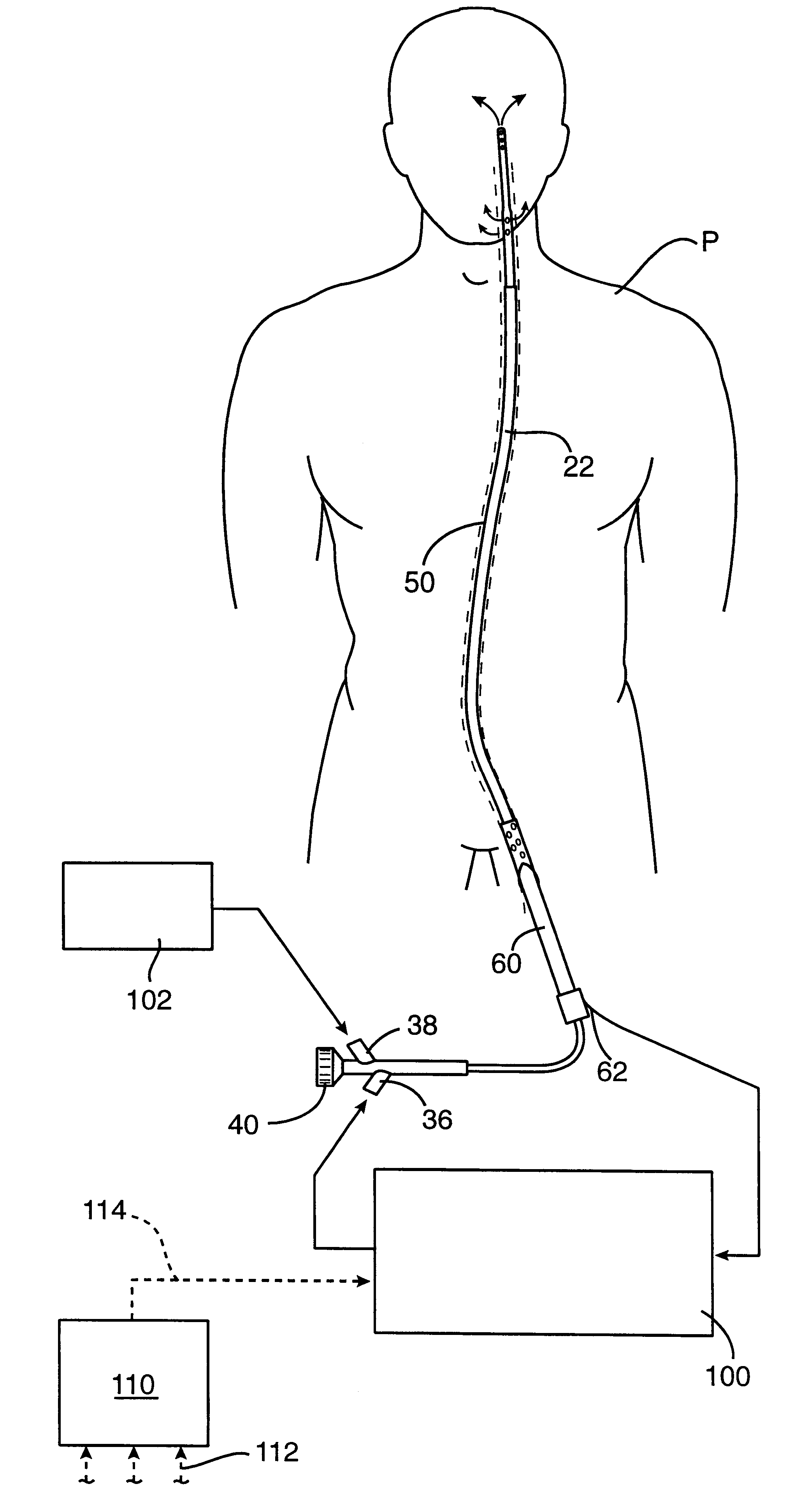
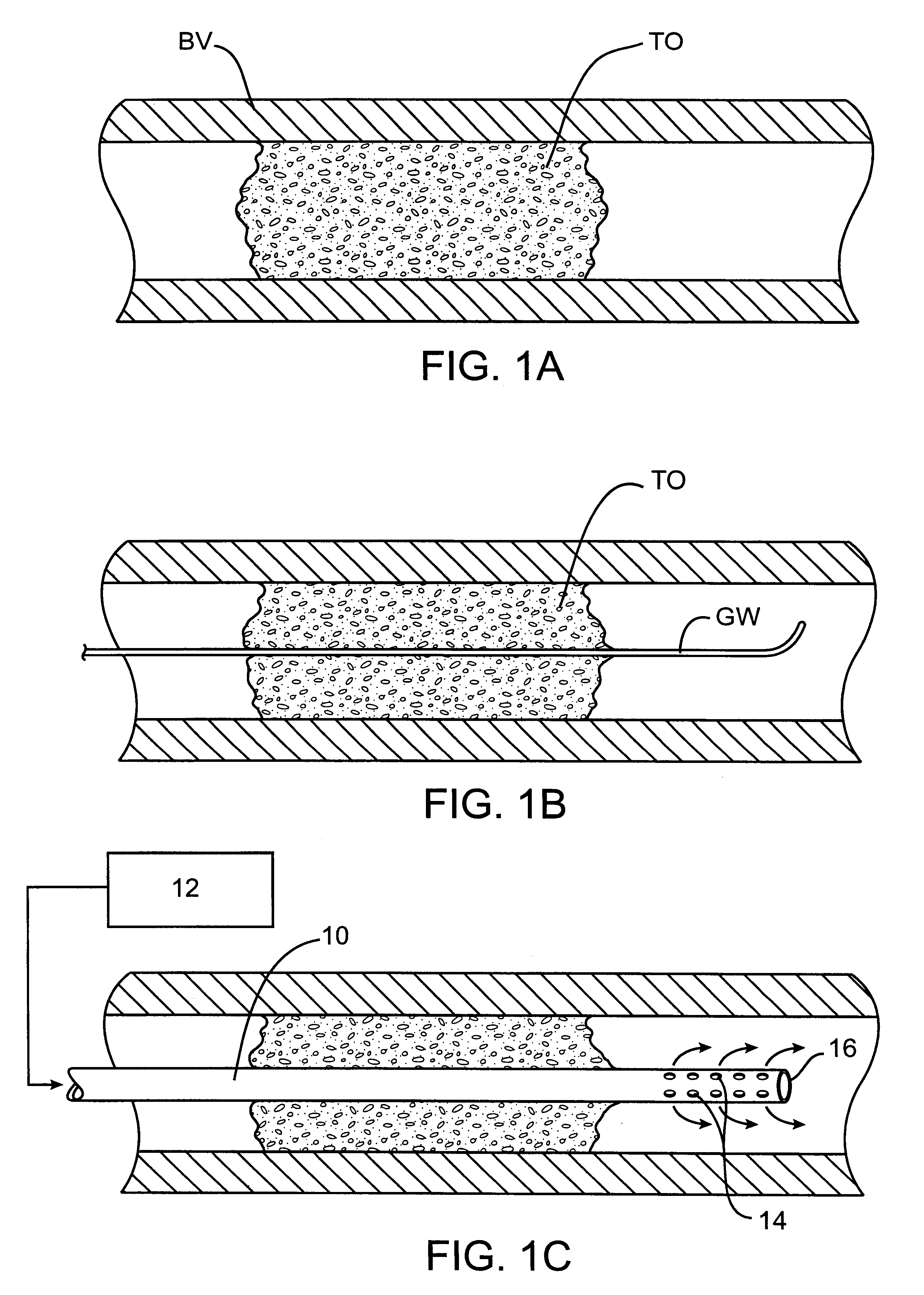
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
InactiveUS6295990B1Promote dissolution and removalMinimize and prevent ischemiaStentsBalloon catheterControl mannerDecreased mean arterial pressure
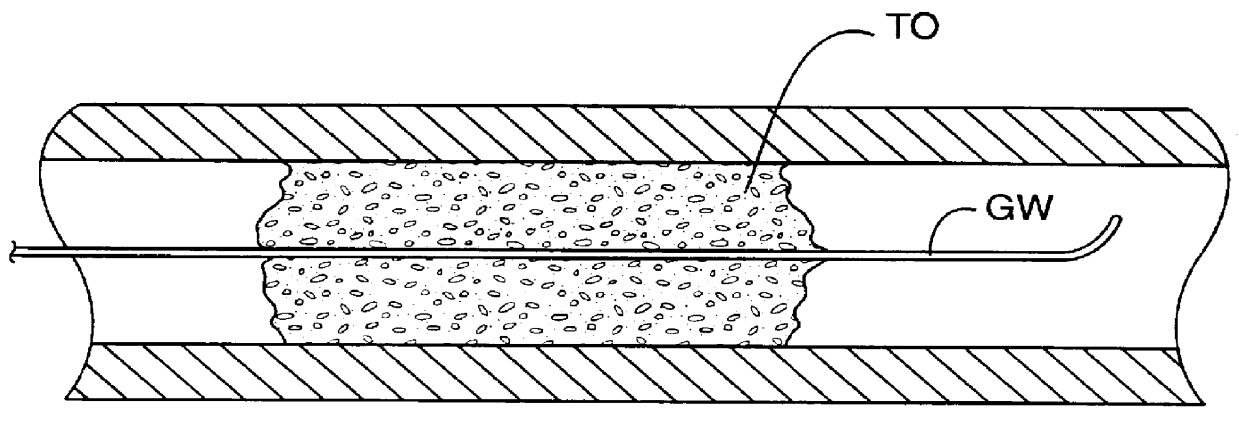
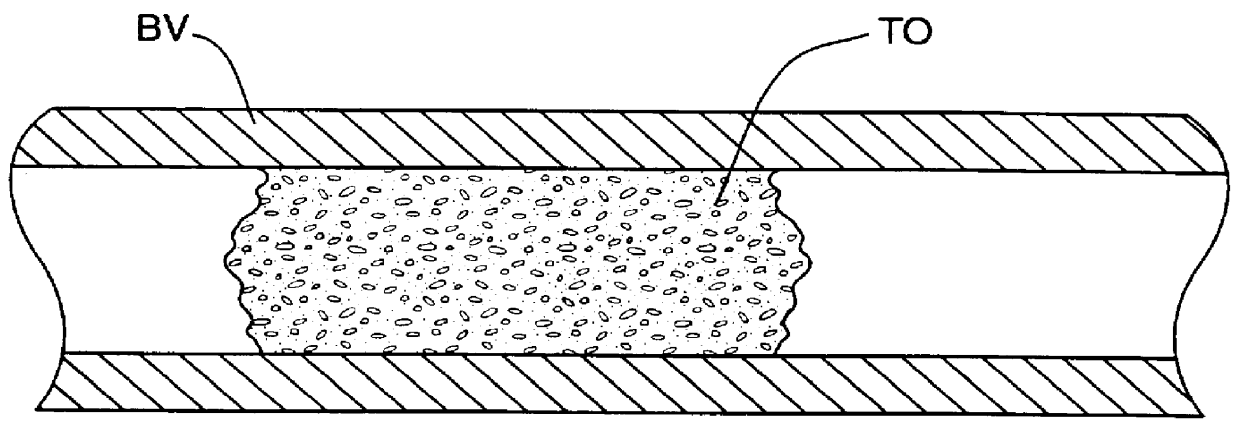
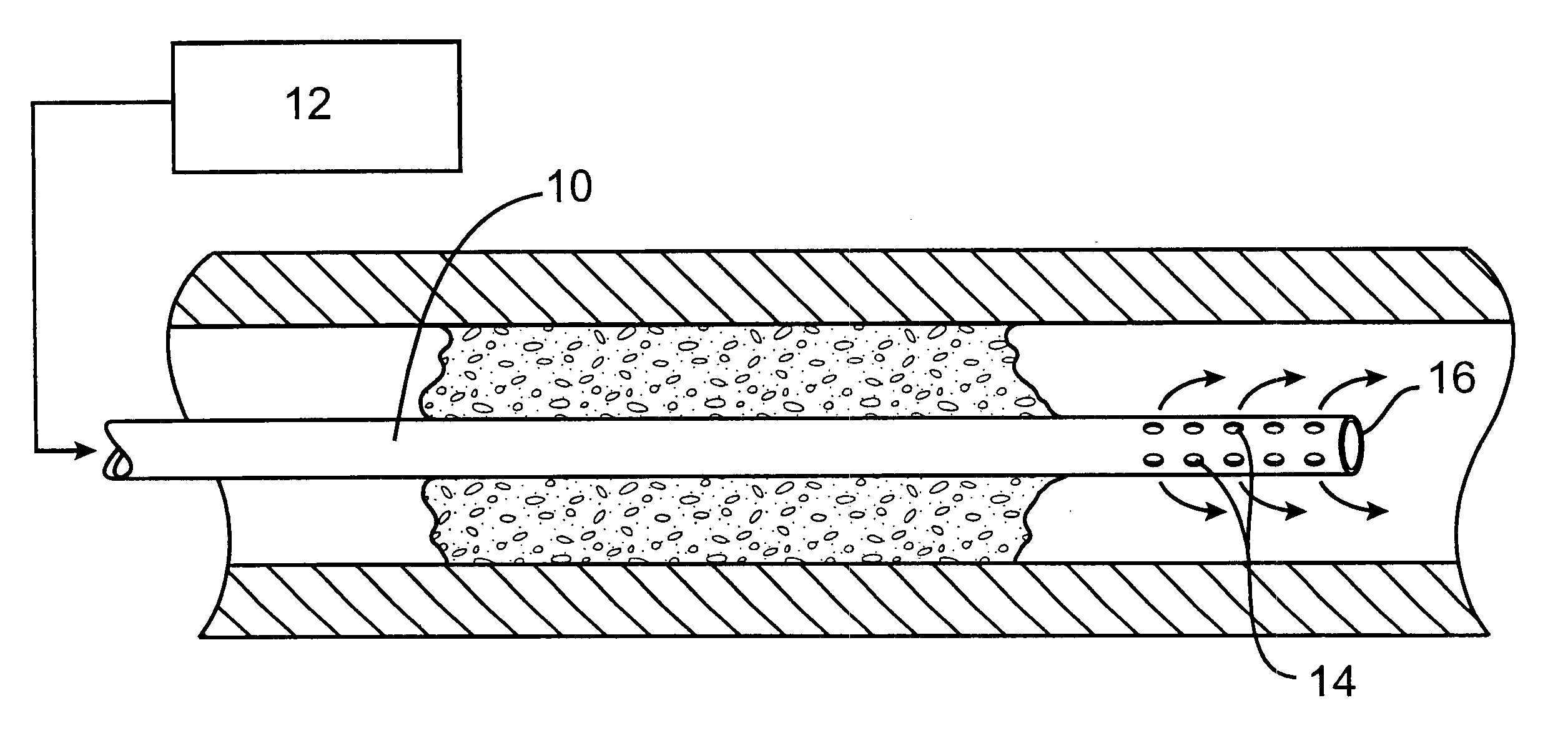
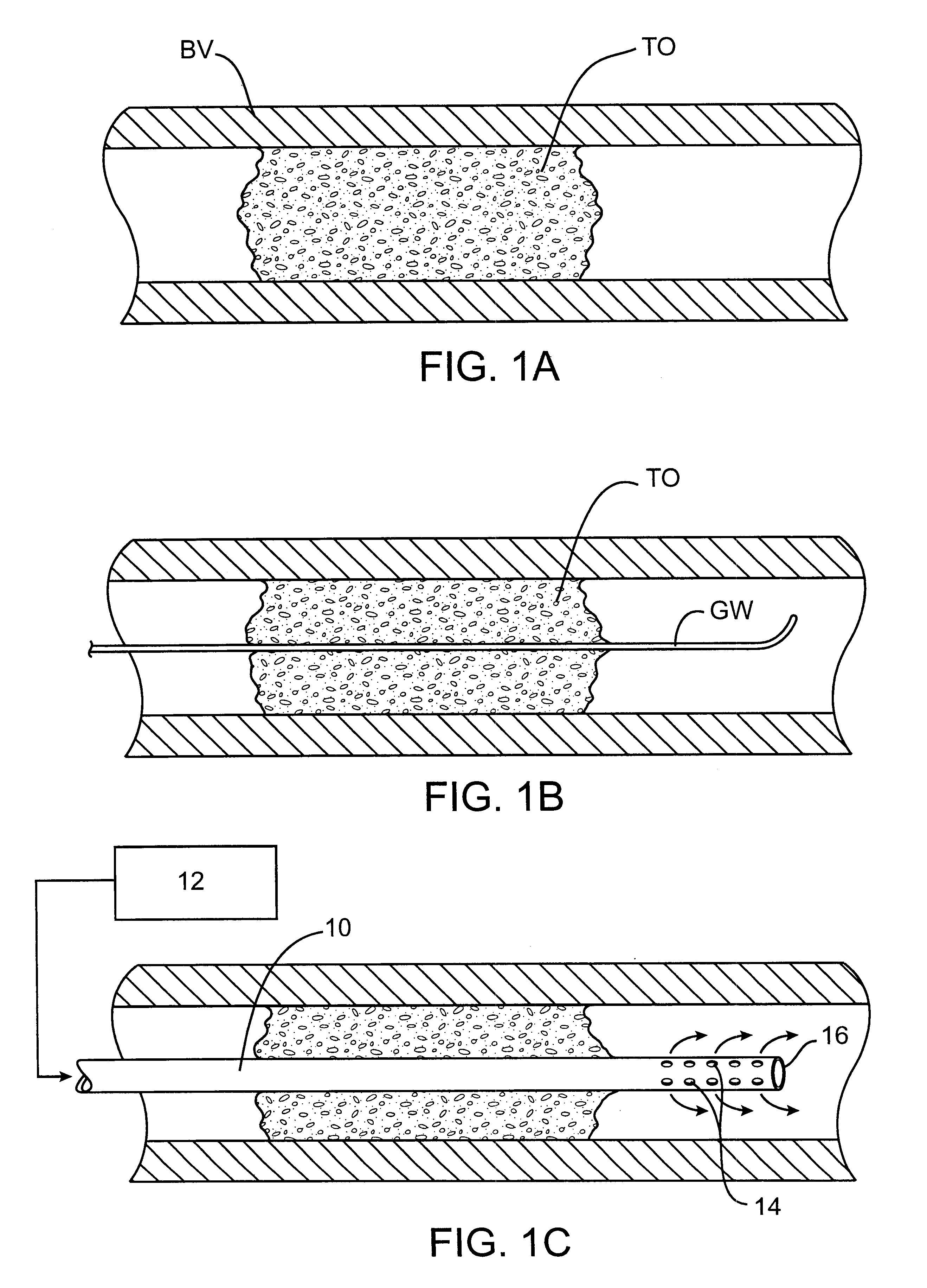
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit in a controlled manner, preferably at a controlled pressure below the arterial pressure, to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. In another aspect, interventional devices, such as stents or balloon catheters, are passed through the perfusion catheter to remove obstructions. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit or by employing mechanical means to remove the obstruction. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent irreversible damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
InactiveUS6435189B1Promote dissolution and removalMinimize and prevent ischemiaStentsBalloon catheterControl mannerDecreased mean arterial pressure
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit in a controlled manner, preferably at a controlled pressure below the arterial pressure, to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. In another aspect, interventional devices, such as stents or balloon catheters, are passed through the perfusion catheter to remove obstructions. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit or by employing mechanical means to remove the obstruction. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
InactiveUS6436087B1Promote dissolution and removalMinimize and prevent ischemiaStentsBalloon catheterControl mannerThrombus
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit in a controlled manner, preferably at a controlled pressure below the arterial pressure, to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. In another aspect, interventional devices, such as stents or balloon catheters, are passed through the perfusion catheter to remove obstructions. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit or by employing mechanical means to remove the obstruction. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Modulating Function of Neural Structures Near the Ear
ActiveUS20130150653A1Increase blood flowIncrease cerebral blood flowUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNervous systemModulation function
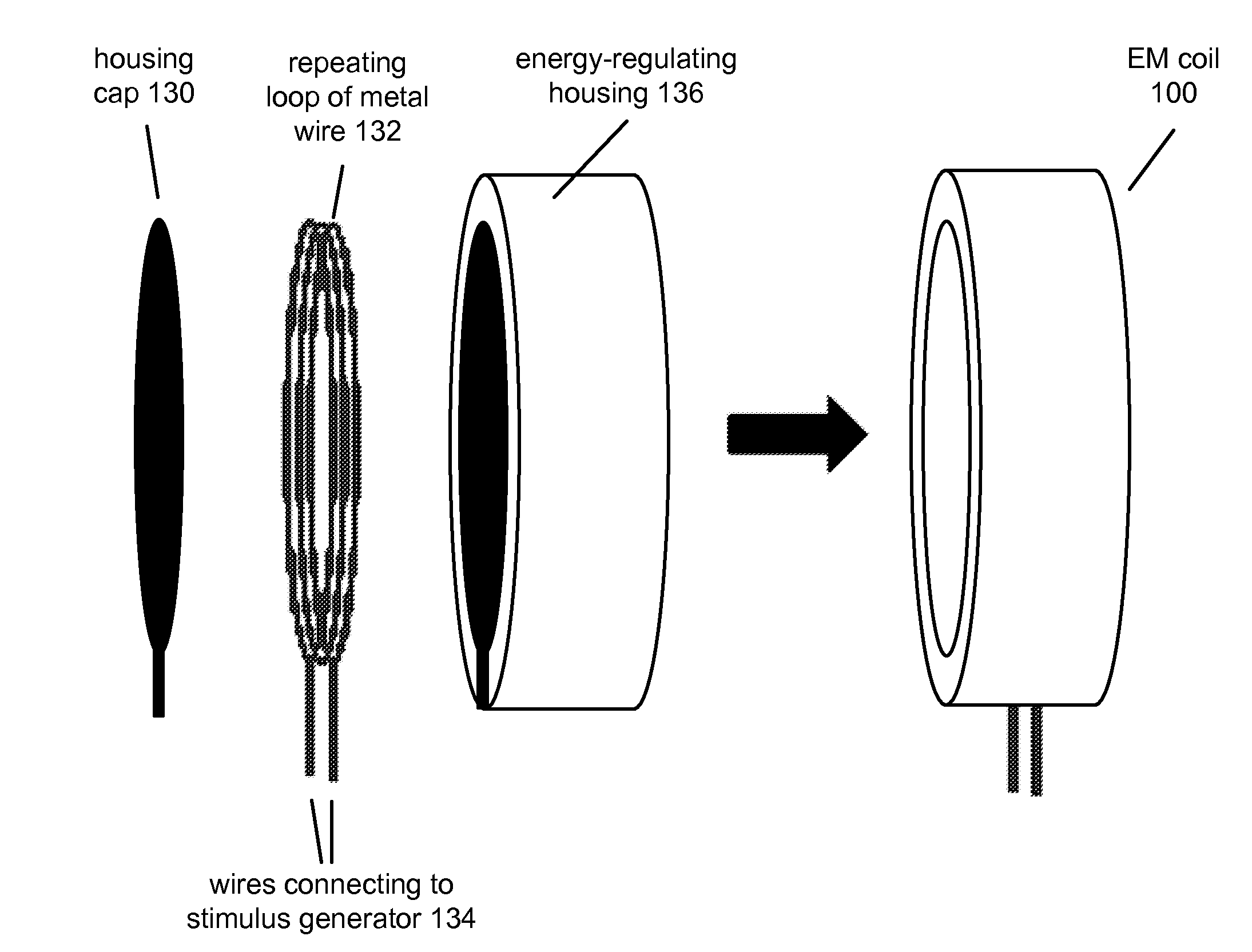
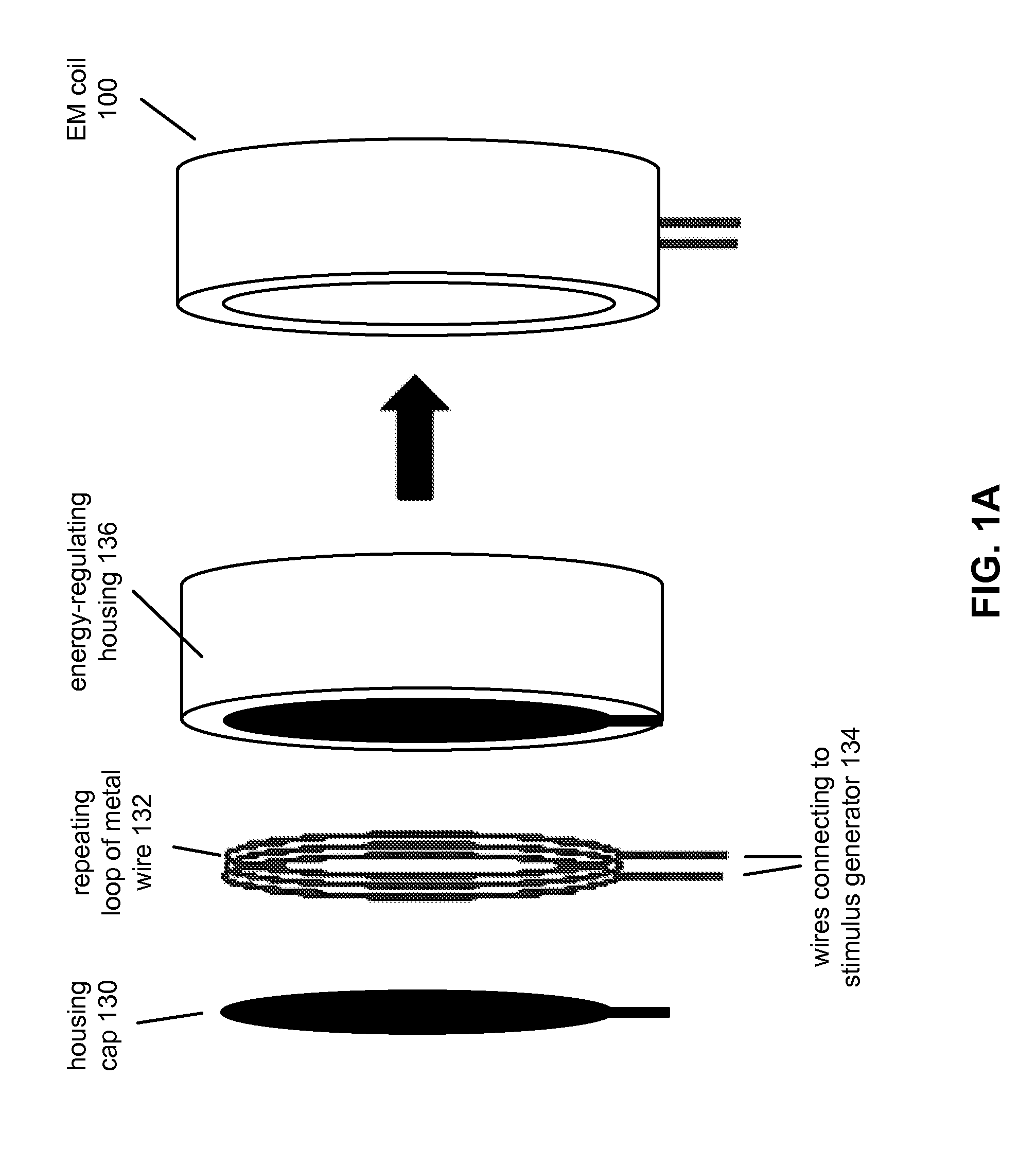
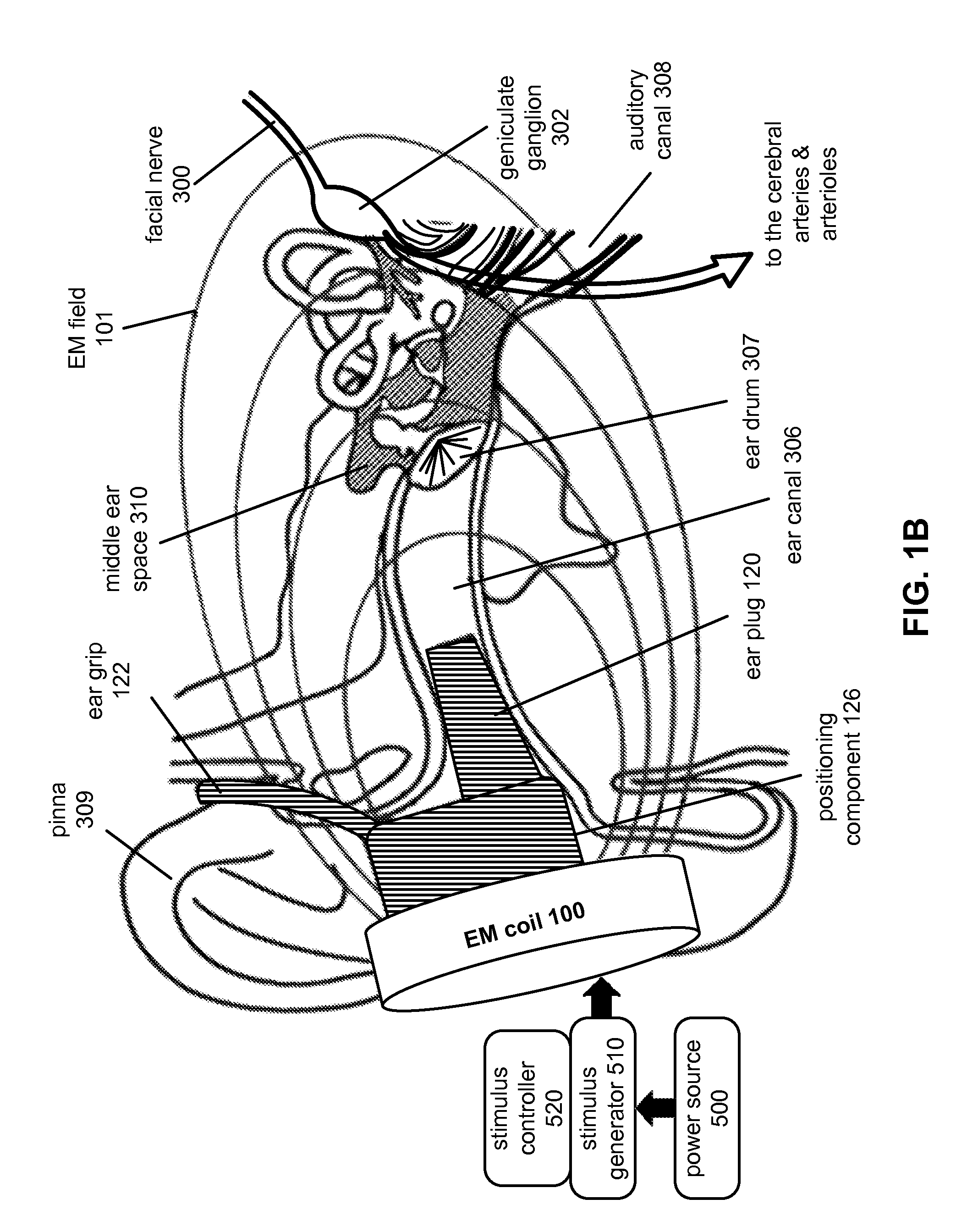
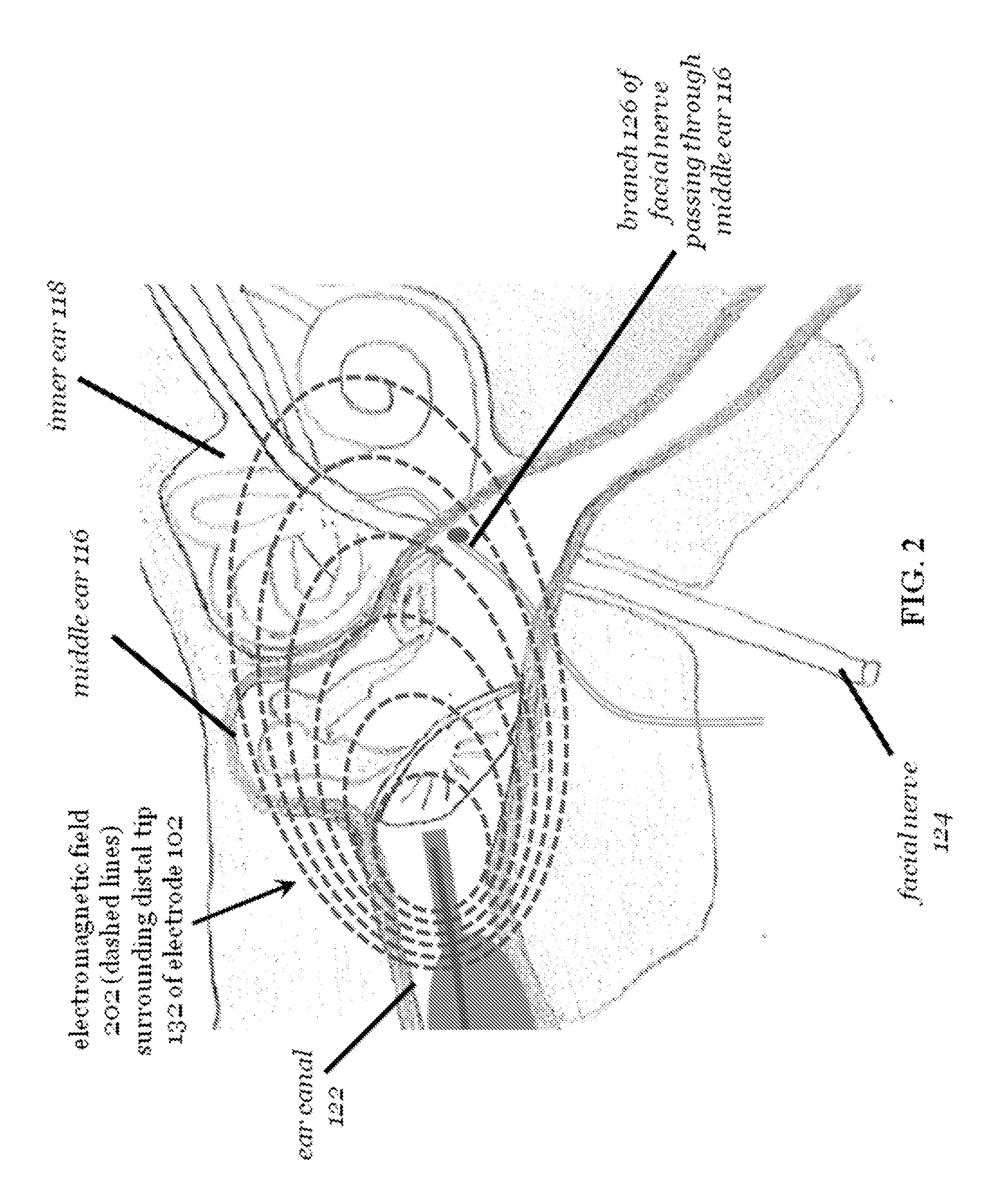
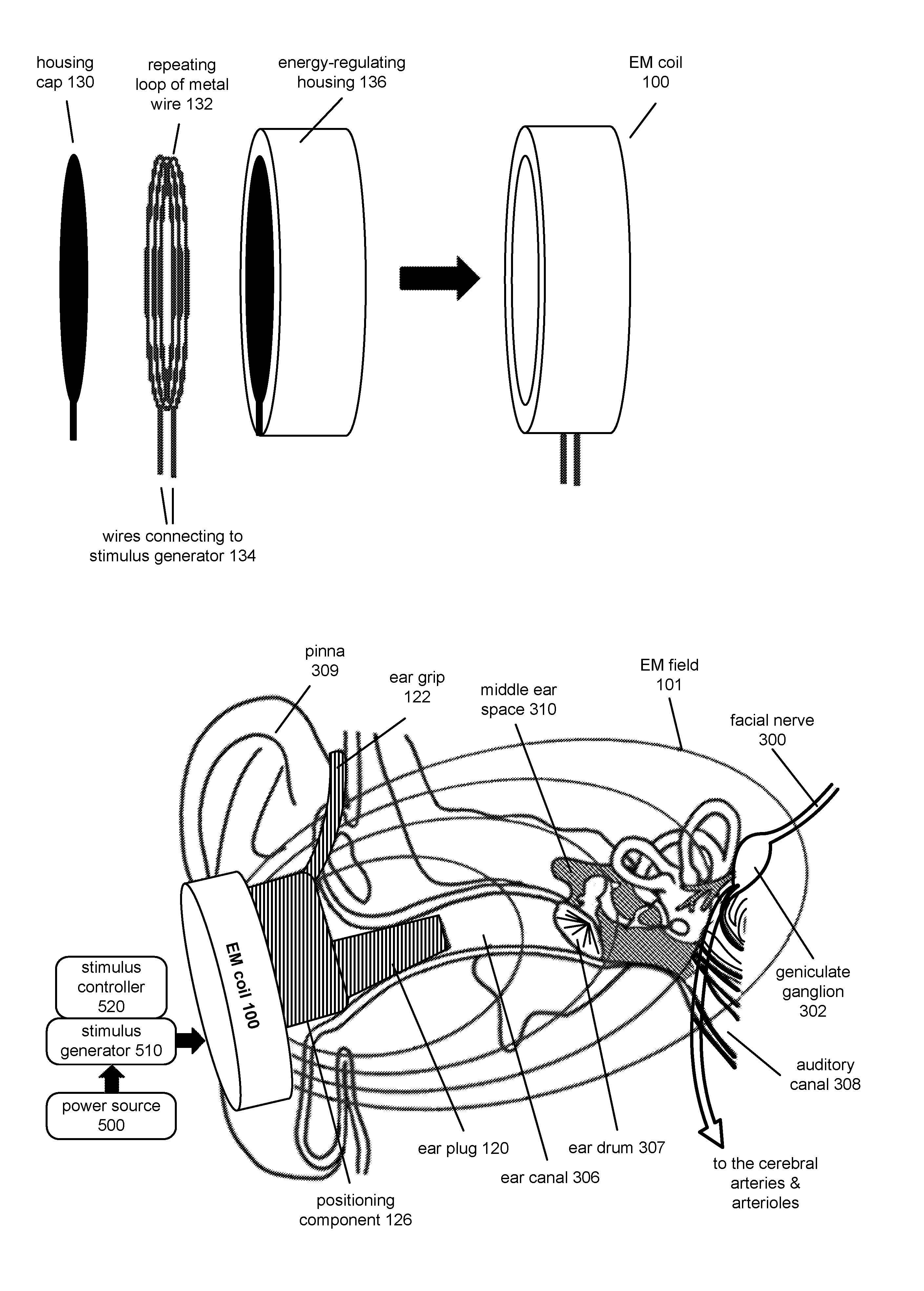
Stimulation of the facial nerve system (e.g., electrically, electromagnetically, etc.) in ischemic stroke patients will cause dilation of occluded arteries and dilation of surrounding arteries, allowing for blood flow to circumvent the obstruction and reach previously-deprived tissue. The device approaches the facial nerve and its branches in the vicinity of the ear. In use, the device can be inserted into the ear canal and / or placed in proximity to the ear in order to stimulate the facial nerve system non-invasively (e.g., using an electromagnetic field). The device can be used in the emergency treatment of acute stroke or chronically variations for long-term maintenance of blood flow to the brain and stroke prevention. Additional embodiments of the device may be adapted for use on different regions of the body.
Owner:NERVIVE
Method of stimulating fastigium nucleus to treat neurological disorders
ActiveUS7286879B2Increase blood flowInternal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseNervous system
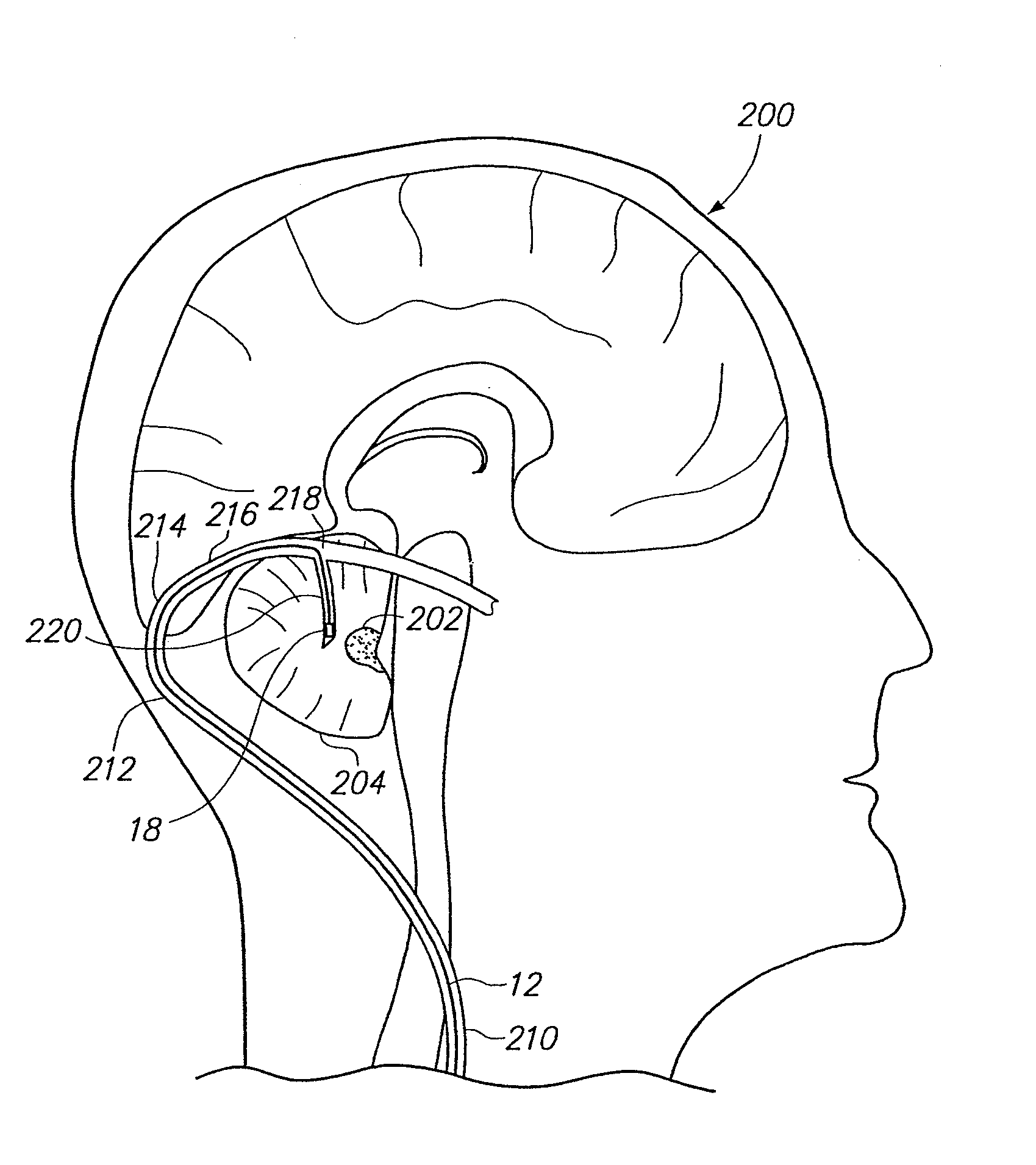
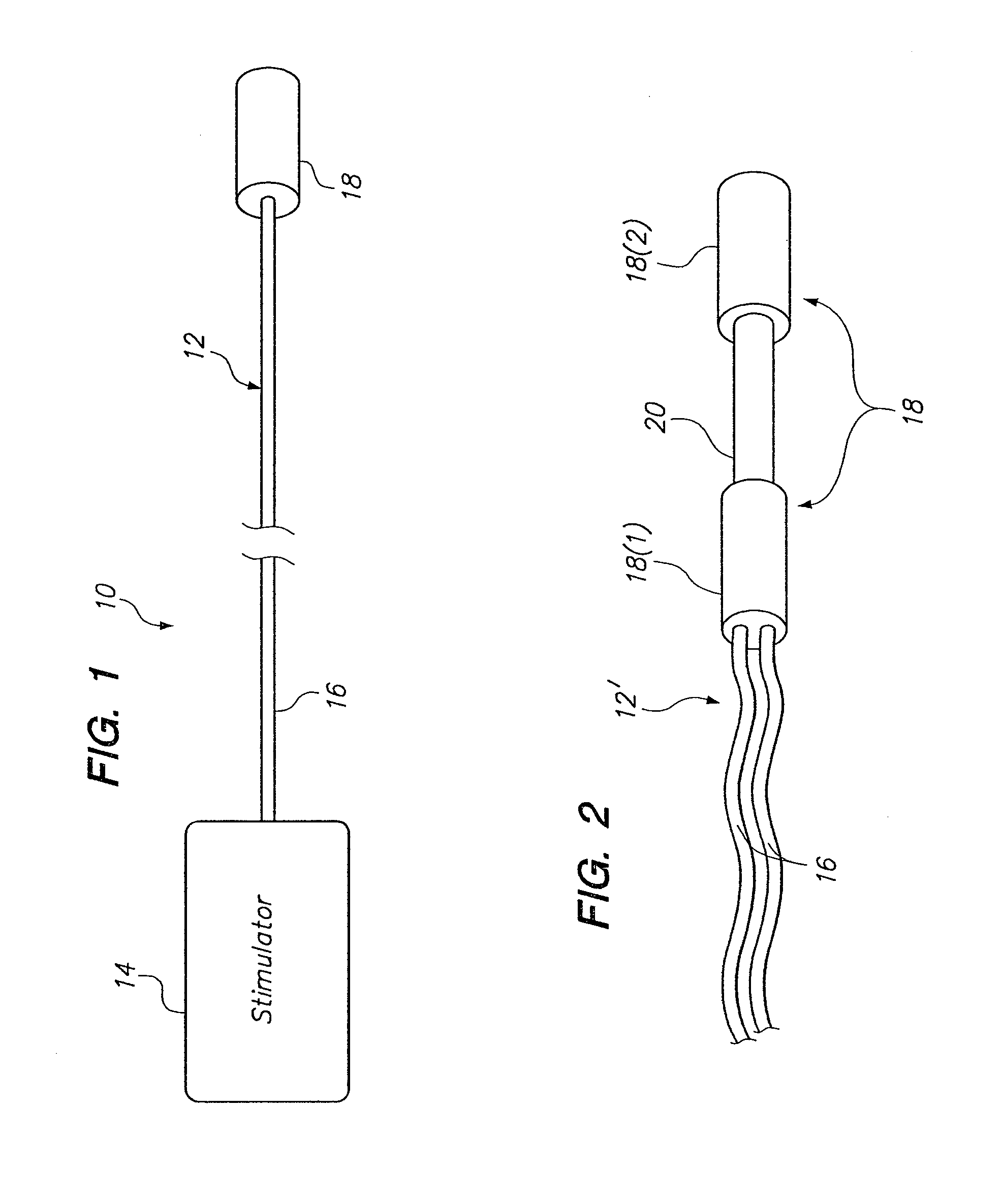
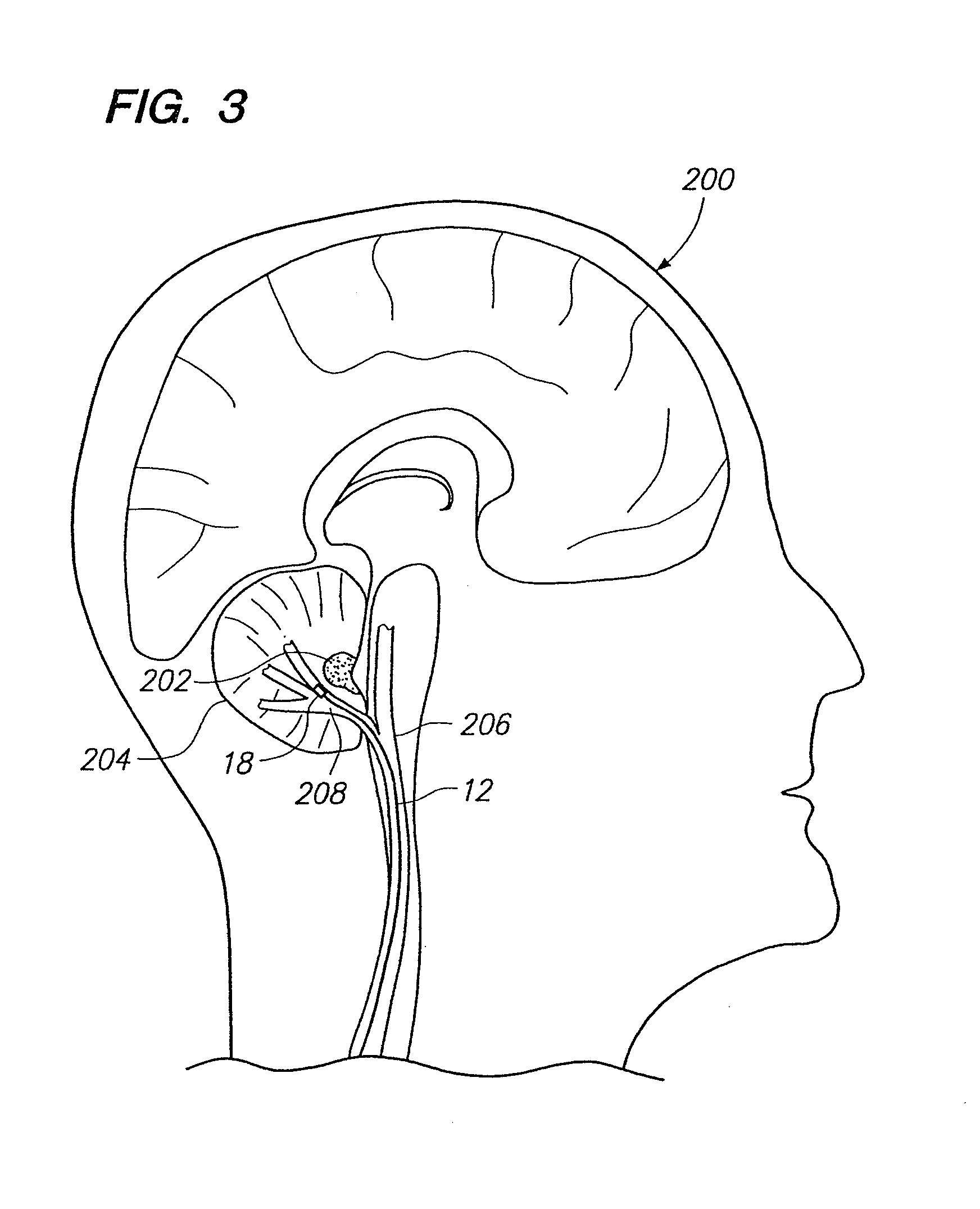
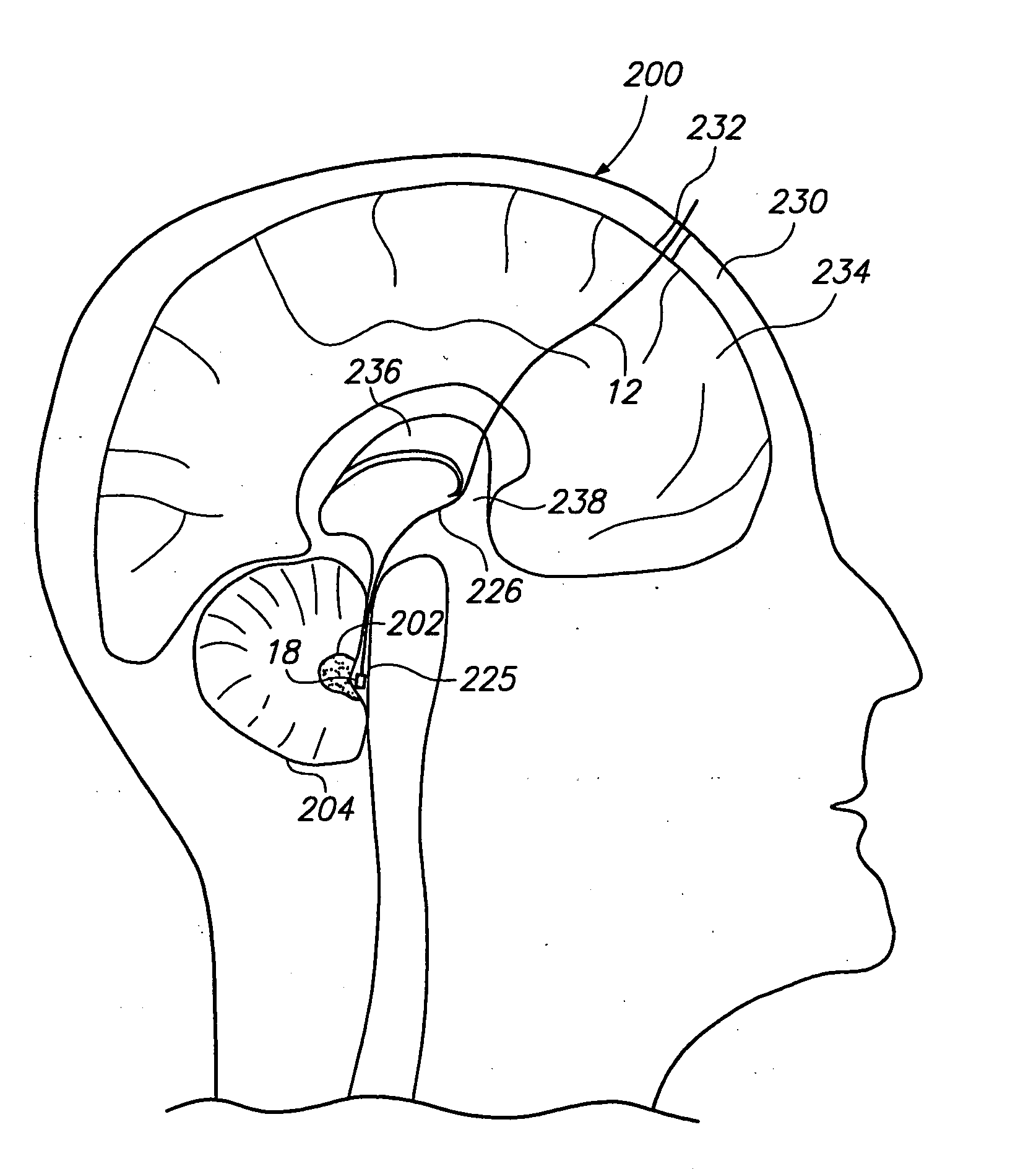
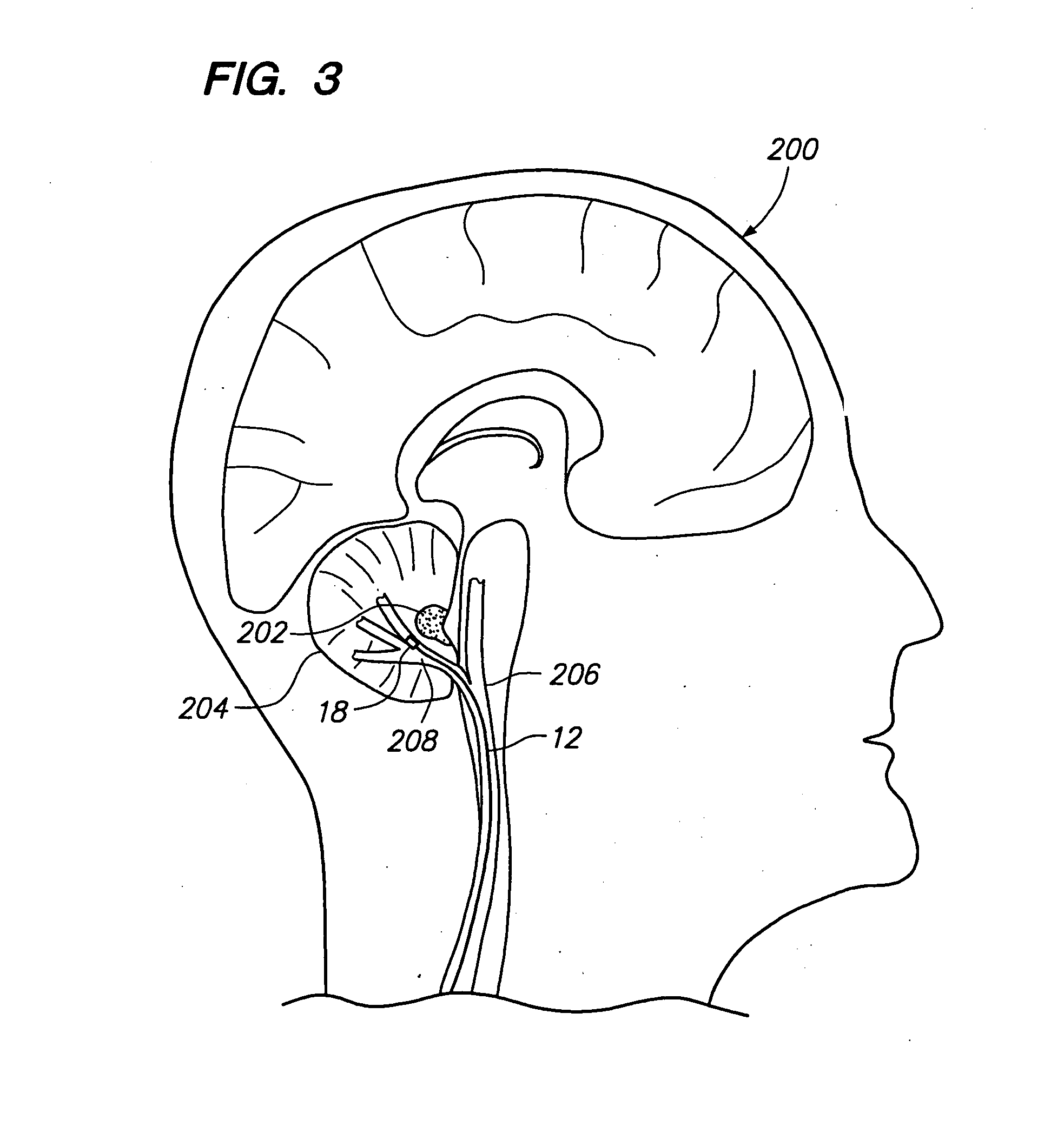
A method of treating a neurological disorder (such as acute stroke) in a patient is provided. The method comprises introducing an electrical stimulation lead within the patient's head, advancing the stimulation lead within an intracranial vascular body, such as a blood vessel or ventricle, placing the stimulation lead adjacent the fastigium nucleus of the patient's brain, and stimulating the fastigium nucleus with the stimulation lead to treat the neurological disorder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP +1
Helmet Apparatus and System with Carotid Collar Means On-Boarded
InactiveUS20160030001A1Quick cureSave brain cellMedical imagingHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSonificationEngineering
Apparatus for helmeting with carotid collars works in conjunction with a transcranial Doppler, phased array photoacoustic device to transmit a first energy to a region of interest at an internal site of a subject to produce an image and blood flow velocities of a region of interest by outputting an optical excitation energy to said region of interest and heating said region, causing a transient thermoelastic expansion and produce a wideband ultrasonic emission. Systems integrate and register the signals for use in, for example, acute stroke care.
Owner:STEIN STUART +1
Method and apparatus for treating acute stroke
The invention provides a method and system for introducing cool fluid to a targeted treatment site, such as, for example, a stroke-affected brain hemisphere. In one approach, the method generally includes introducing a catheter into a branch artery of the external carotid artery, and introducing fluid into the ipsilateral internal carotid artery. In one approach, a balloon is used to occlude the external carotid artery during introduction of the fluid into the internal carotid artery.
Owner:DOYLE AIDEN J
Method and apparatus for creating penumbra and infarct images
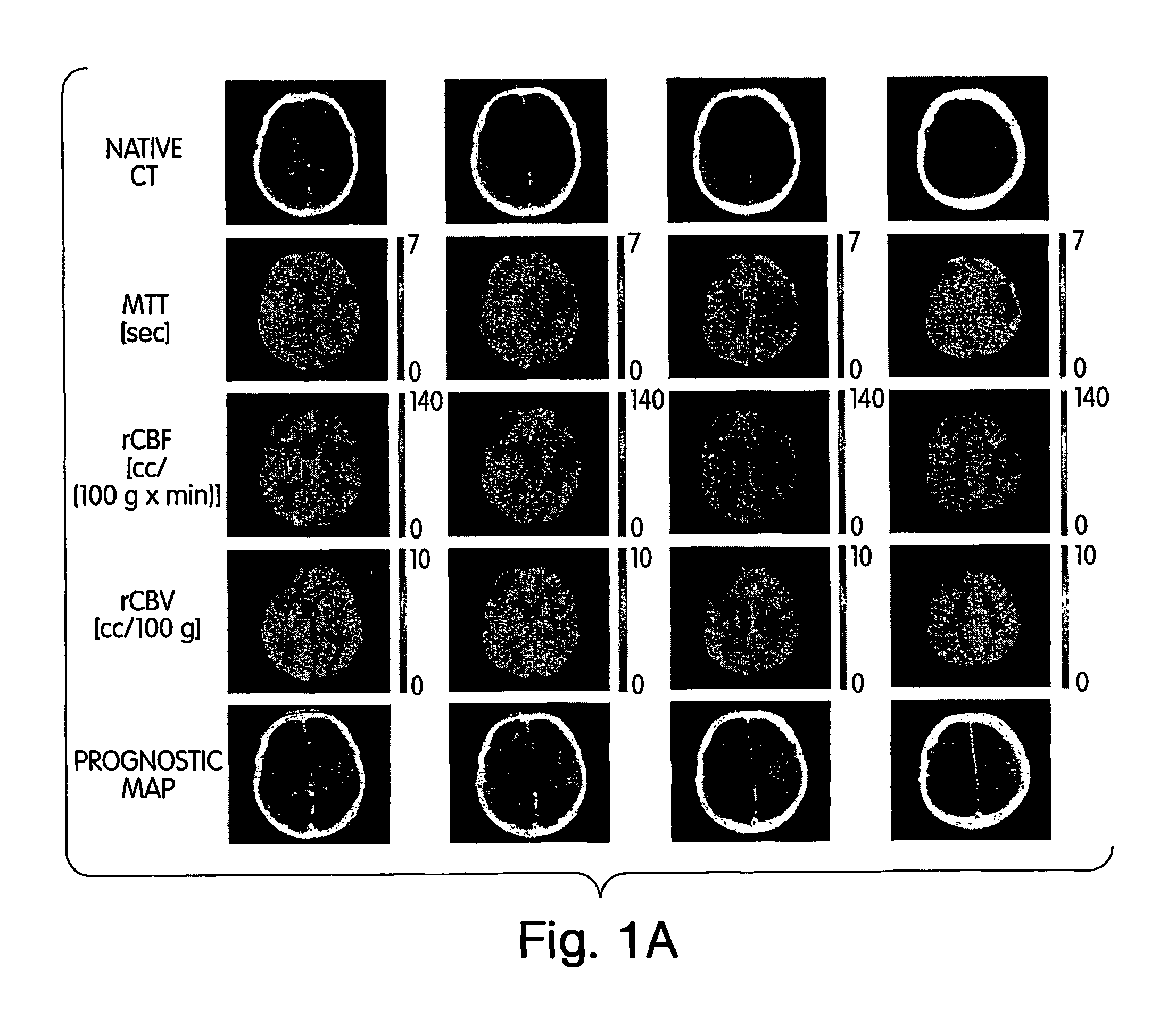
InactiveUS20020161292A1Computerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologyCerebral blood volume
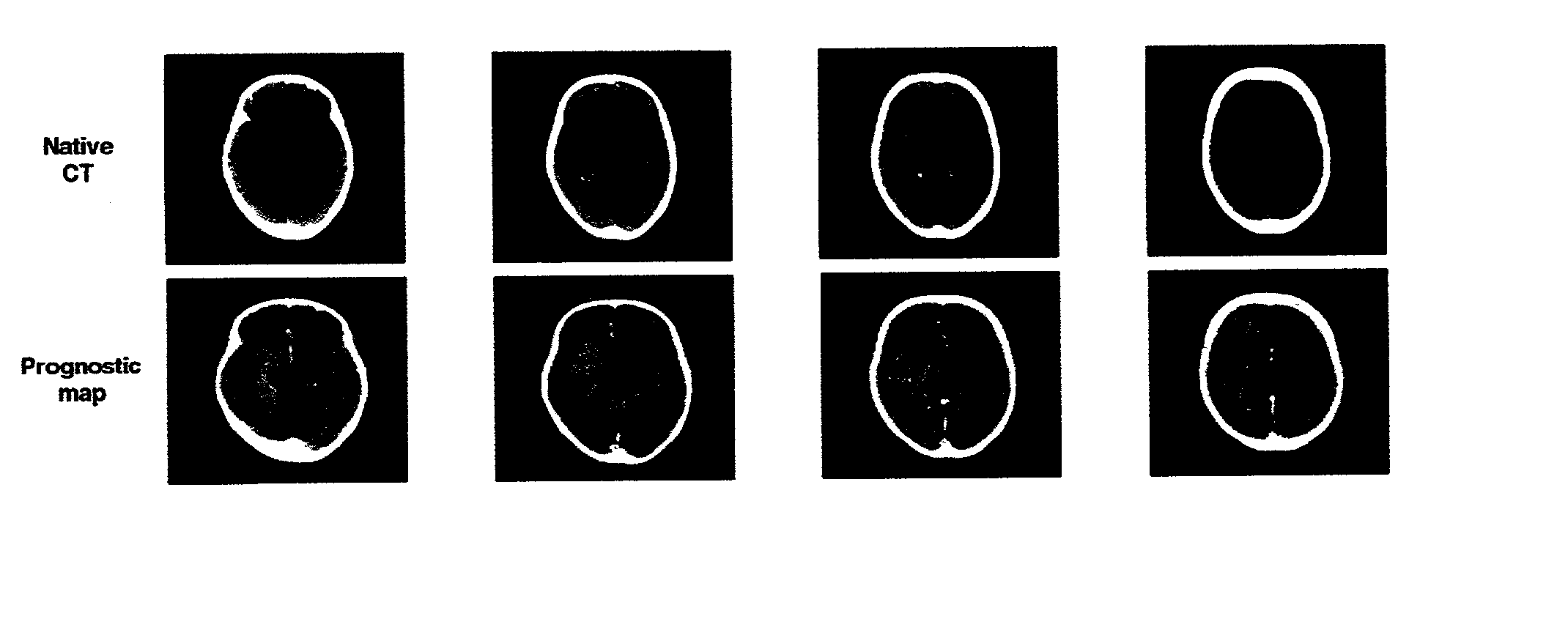
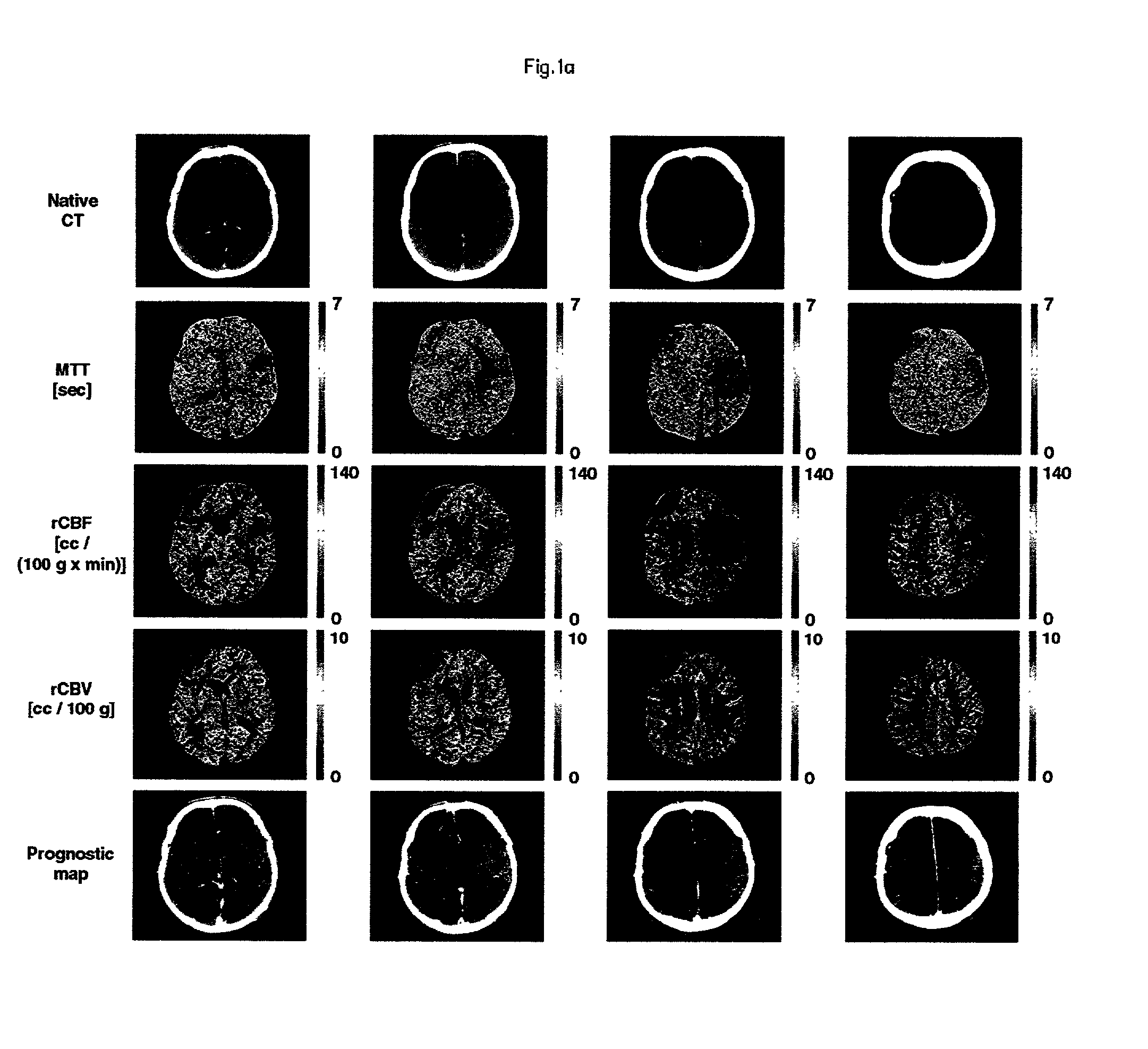
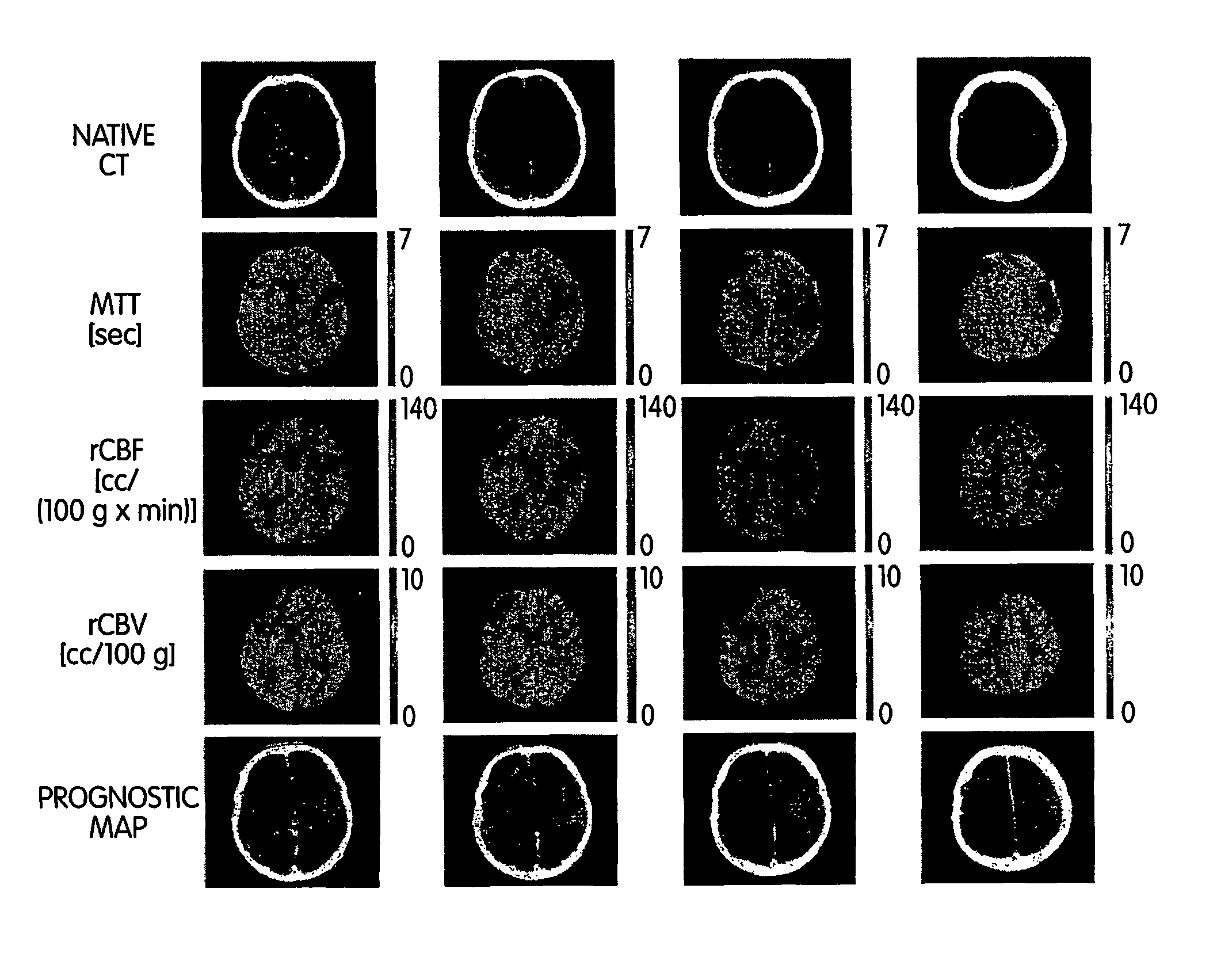
A method and apparatus for evaluating acute stroke patients and for determining whether a stroke patient will benefit from the use of thrombolysis therapy includes obtaining measurements of the cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume of the brain of a stroke patient, determining ischemic areas of the brain where the ischemic areas comprise the measurements of cerebral blood flow which are less than a first value and creating a penumbra-infarct map of the ischemic areas of the brain using the measurements. The infarct area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is less than a second value. The penumbra area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is greater than this second value. The method also includes determining a ratio of penumbra size to the total of penumbra size and infarct size. When the ratio is greater than a predetermined value, the stroke patient is a candidate for thrombolysis therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
Modulating function of the facial nerve system or related neural structures via the ear
ActiveUS20110270361A1Increase blood flowSpinal electrodesHead electrodesMiddle ear functionNerve structure
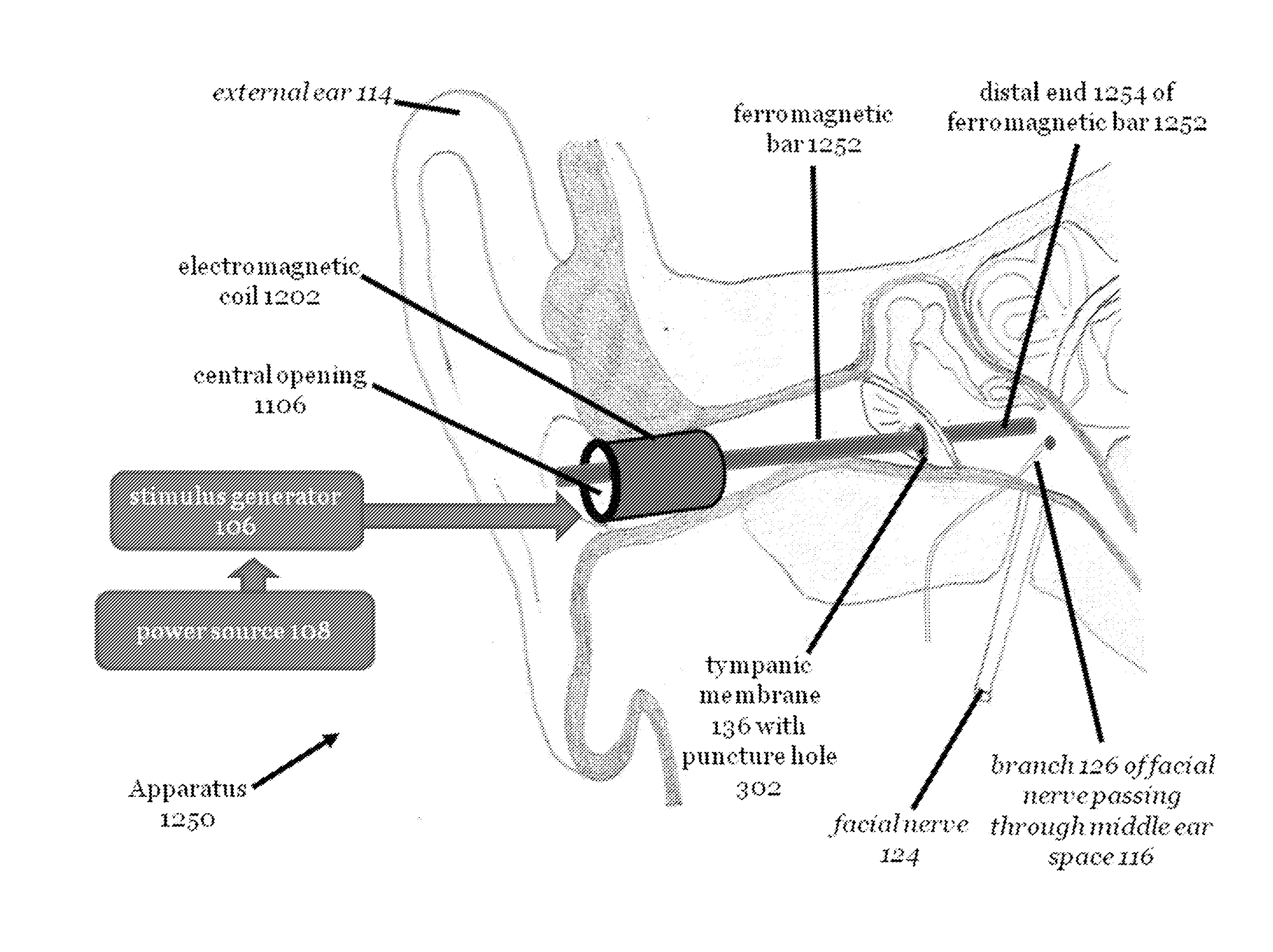
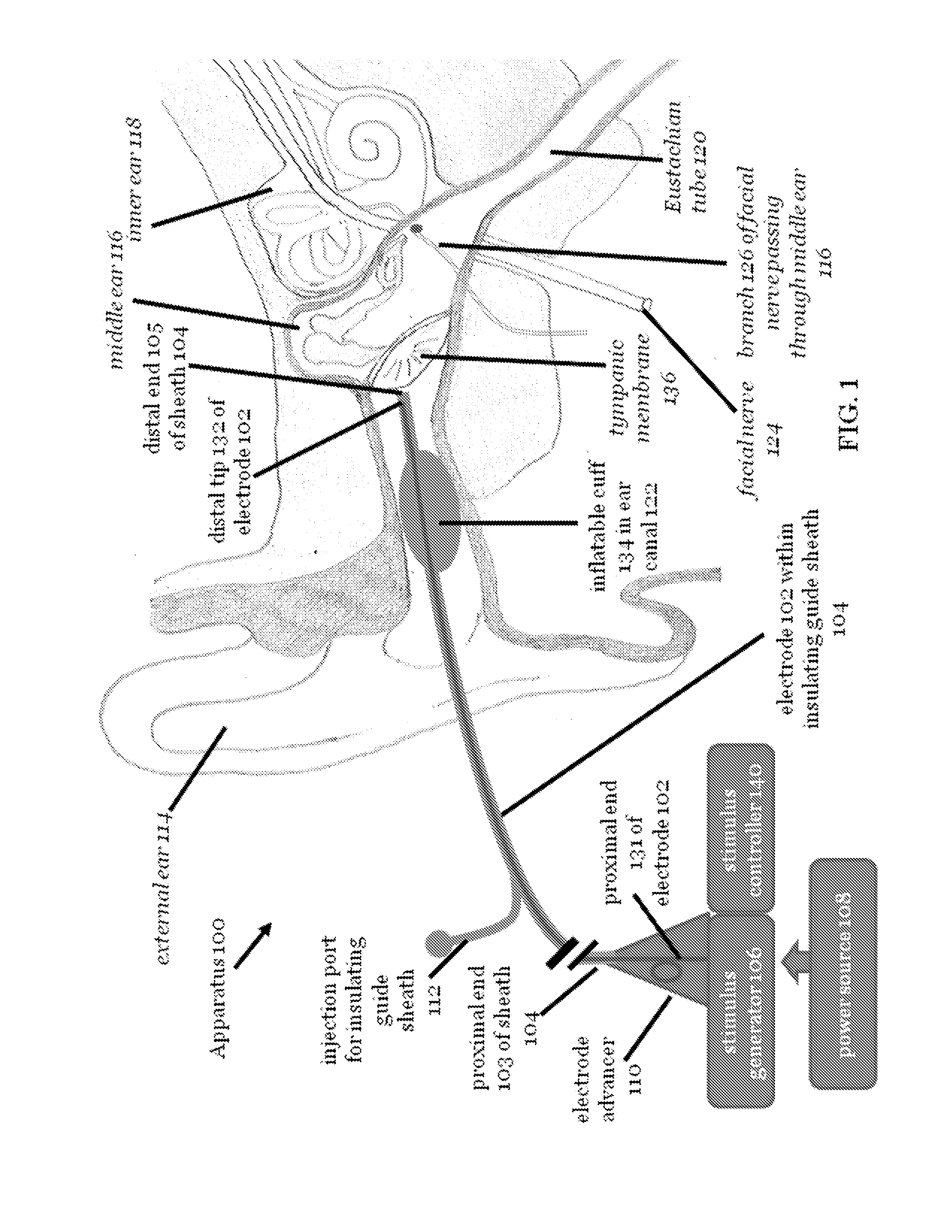
Stimulation of the facial nerve system (e.g., electrically, electromagnetically, etc.) in stroke patients will cause dilation of occluded arteries and dilation of surrounding arteries, allowing for blood flow to circumvent the obstruction and reach previously-deprived tissue. The device approaches the facial nerve and its branches in the vicinity of the ear. In use, the device can be inserted into the ear canal or placed in proximity to the ear in order to stimulate the facial nerve system without puncturing the tympanic membrane (e.g., using an electromagnetic field). The device can also be advanced into the middle ear through a puncture created in the tympanic membrane. Branches of the facial nerve in the middle ear can then be stimulated directly (e.g., by application of electrical current). The device can be used in the emergency treatment of acute stroke or as chronically-implanted / inserted variations for long-term maintenance of blood flow to the brain and stroke prevention
Owner:NERVIVE
Method of stimulating fastigium nucleus to treat neurological disorders
ActiveUS20060015152A1Increase blood flowElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseNervous system
A method of treating a neurological disorder (such as acute stroke) in a patient is provided. The method comprises introducing an electrical stimulation lead within the patient's head, advancing the stimulation lead within an intracranial vascular body, such as a blood vessel or ventricle, placing the stimulation lead adjacent the fastigium nucleus of the patient's brain, and stimulating the fastigium nucleus with the stimulation lead to treat the neurological disorder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP +1
Ct/mri integrated system for the diagnosis of acute strokes and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150208994A1Magnetic measurementsPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputed tomographyRisk stroke
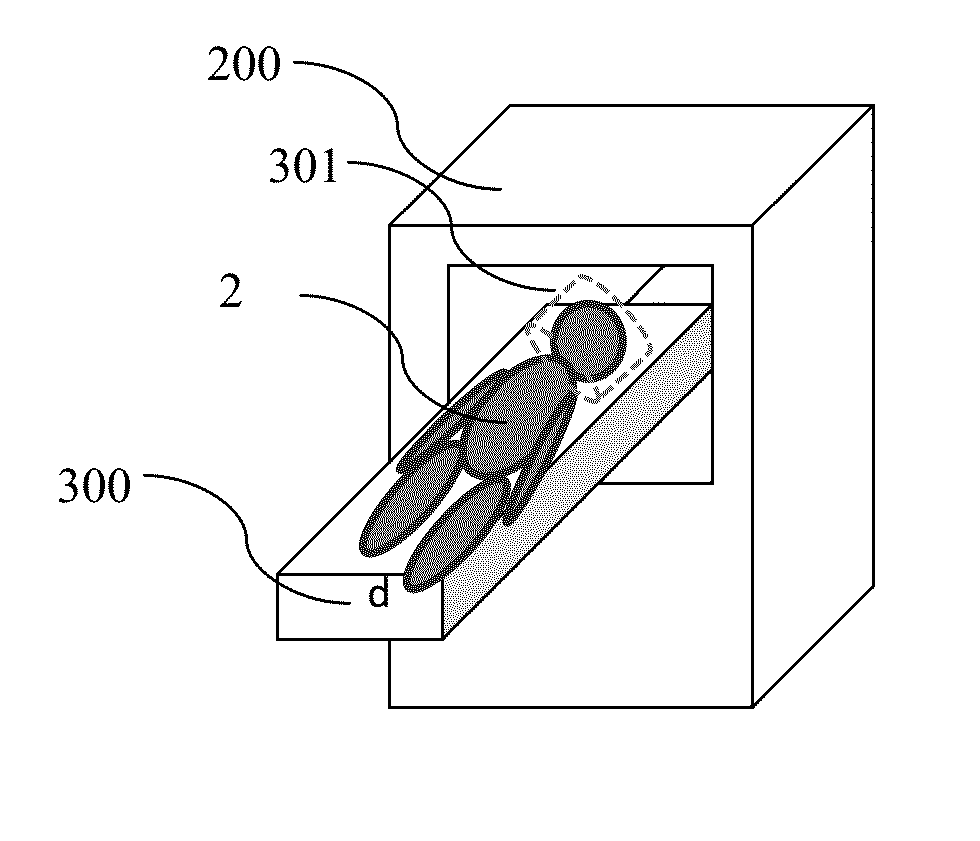
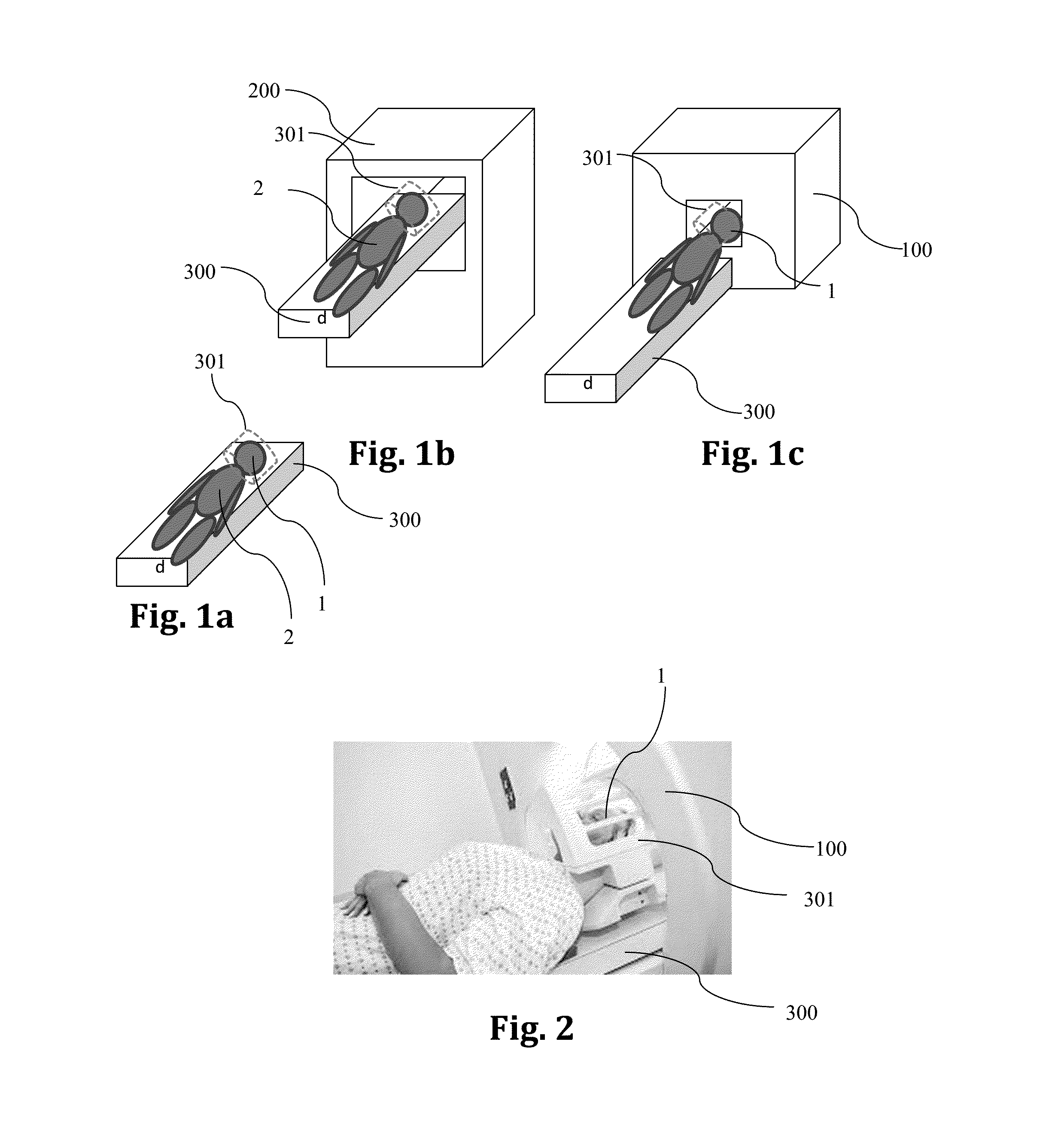
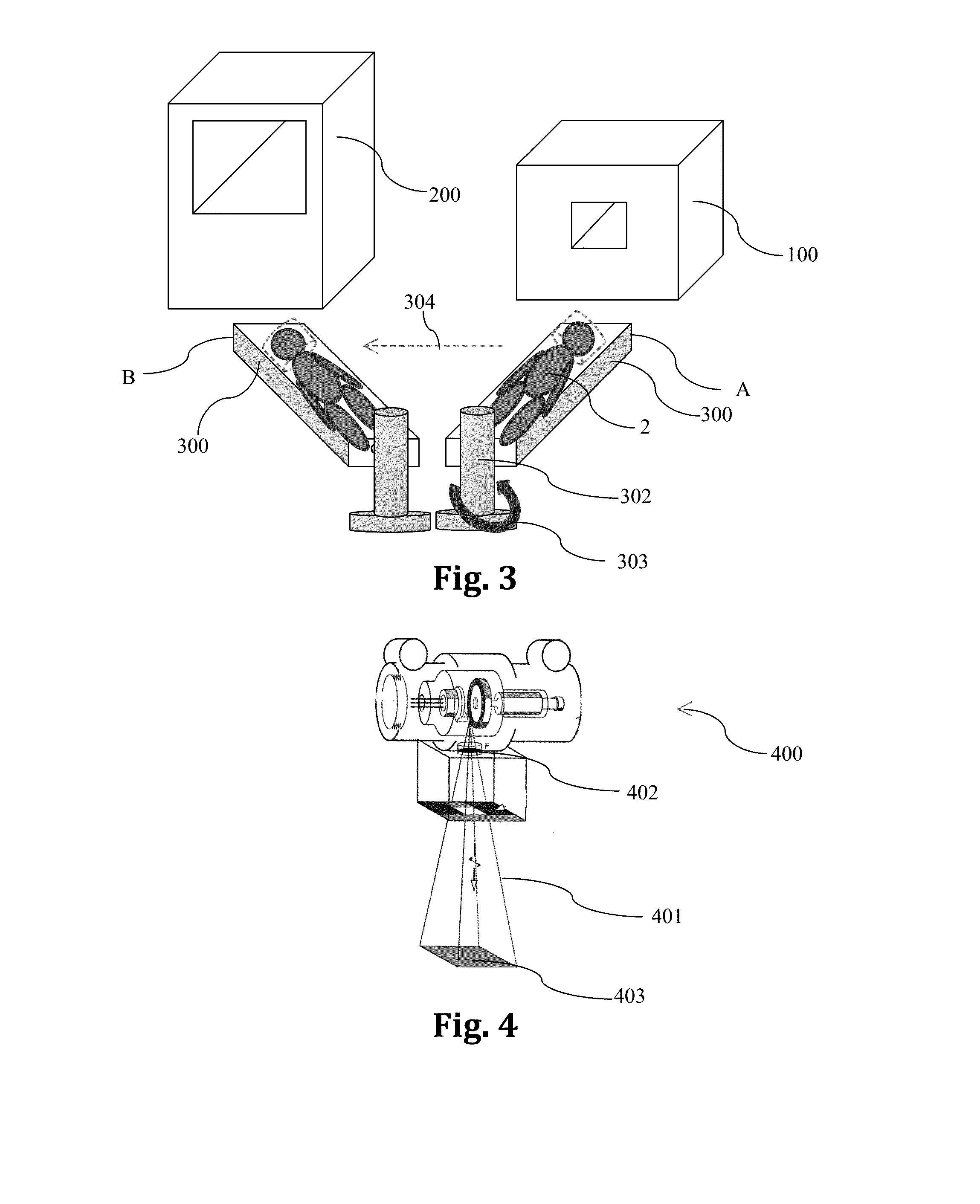
A dual modality CT / MRI integrated system for the diagnosis of acute strokes and treating a patient and methods thereof. The method includes: immobilizing a patient or a portion thereof to a support; accommodating the patient or portion thereof in a CT device; scanning the same; placing the patient or portion thereof within an MRI device and imaging the same such that the orientation of the patient or portion thereof in the CT scanning and the MRI imaging is identical or at least spatially (2D or 3D) retrievable.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
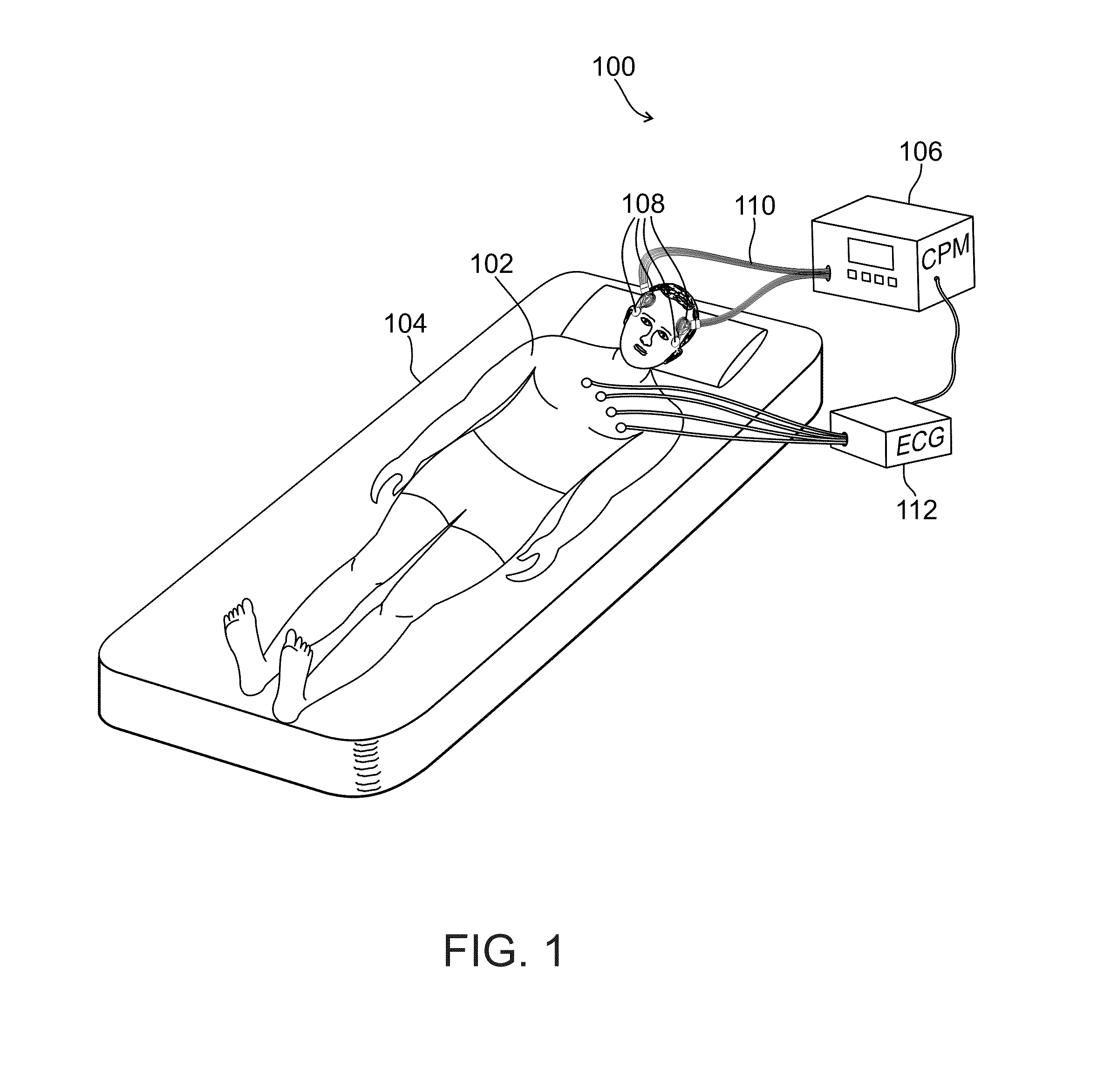
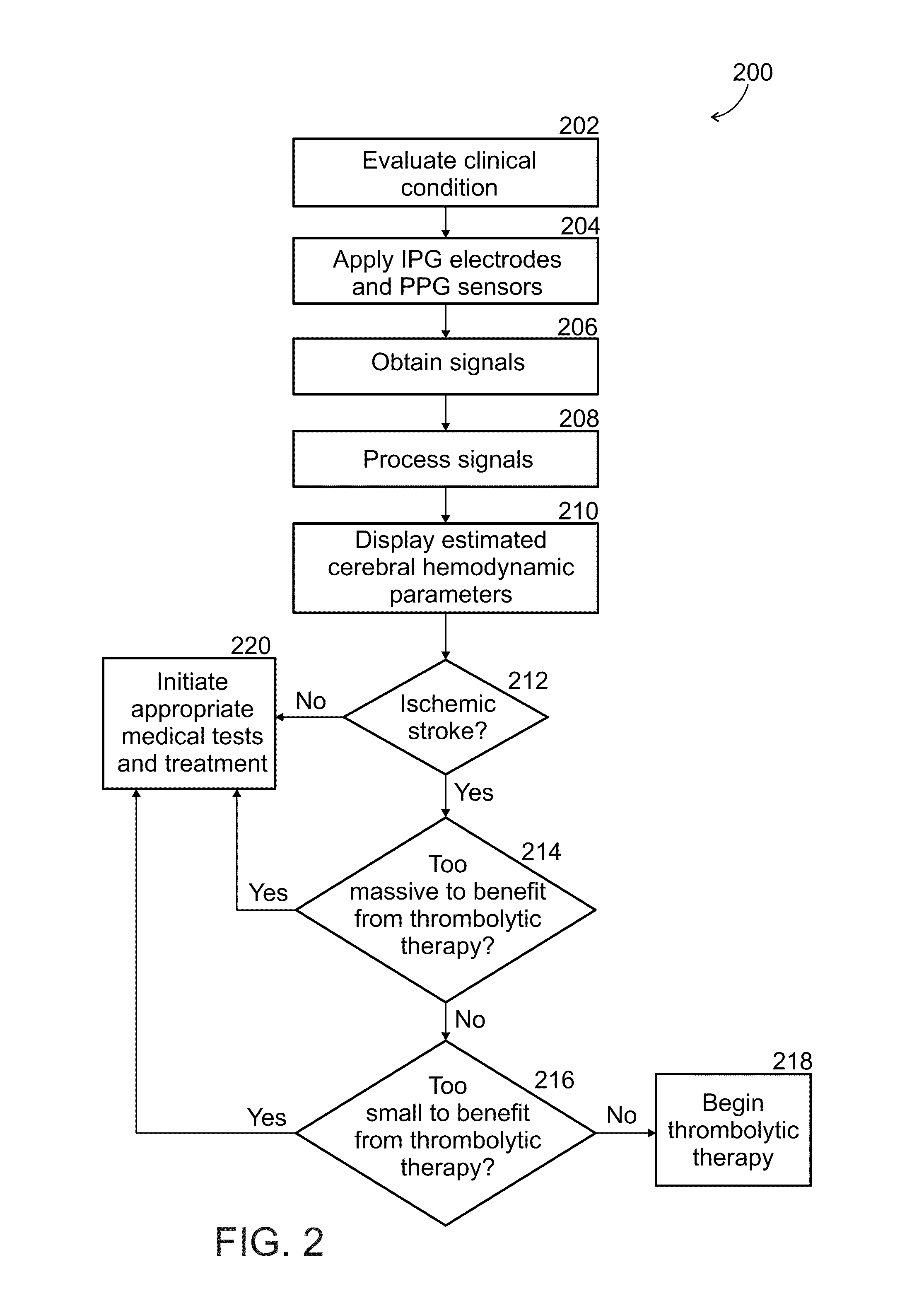
Diagnosis of acute strokes
A method of evaluating patients suspected of suffering from an acute stroke, the method comprising:a) obtaining signals of impedance plethysmography (IPG), photoplethysmography (PPG) or both, in the patient;b) processing the one or more signals to obtain one or more measures of cerebral hemodynamics of the patient; andc) applying a rule to match said measures to a disease indication or choice of therapy or both, for the patient.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
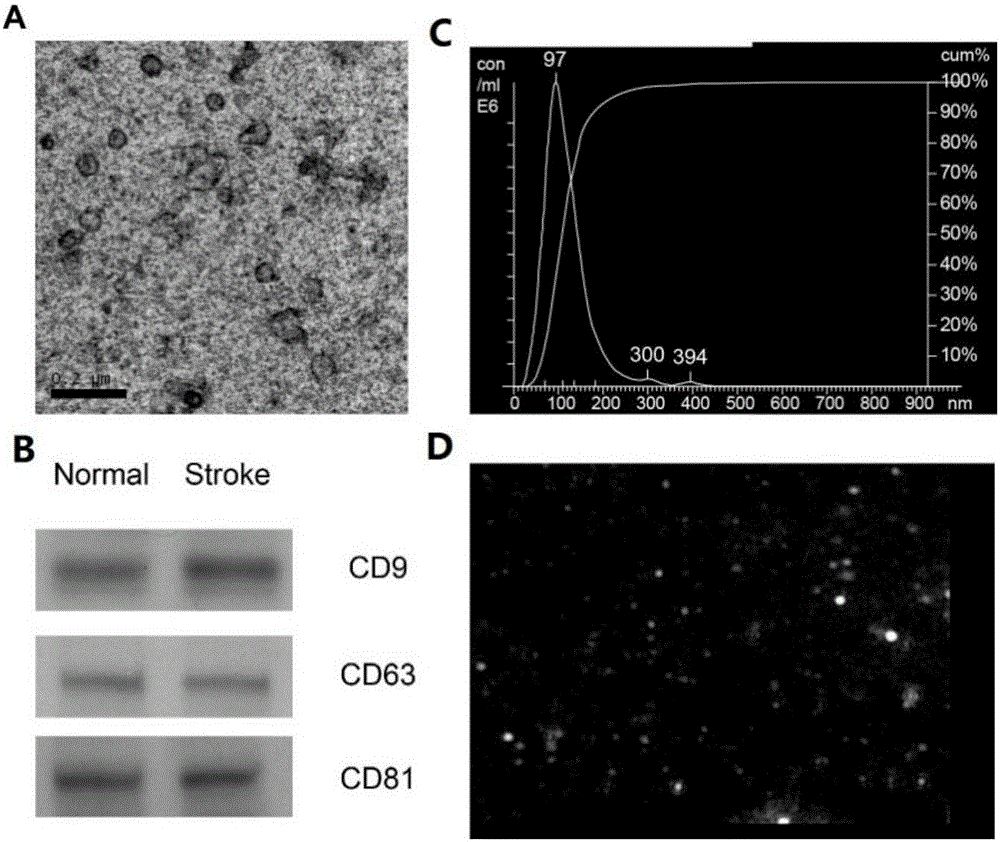
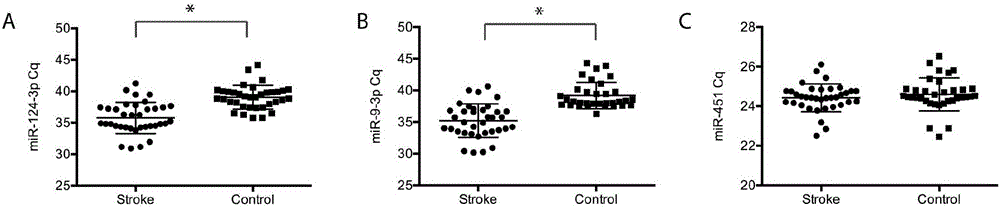
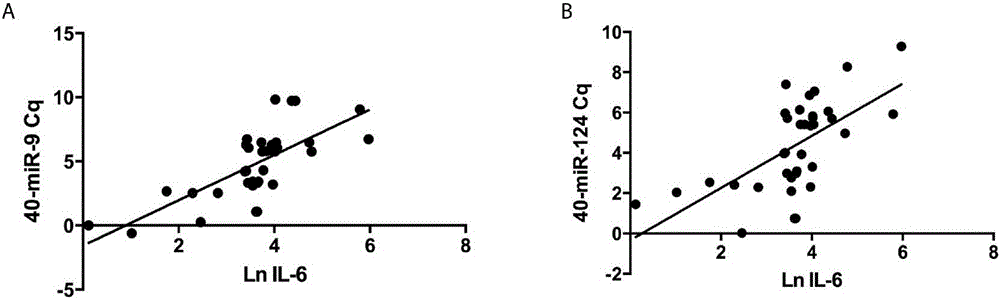
Application of serum exosomes miR-9-3p and miR-124-3p as diagnosis markers of acute cerebral infarction
ActiveCN105925677AAccurately reflectImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMir 124 3pSerum ige
The invention discloses an application of serum exosomes miR-9-3p and miR-124-3p as diagnosis markers of acute cerebral infarction, wherein sequences of the miR-9-3p and miR-124-3p are shown as AUAAAGCUAGAUAACCGAAAGU and UAAGGCACGCGGUGAAUGCC. The exosomes in serum are precipitated by virtue of a high-molecular polyme, and the expression and differences of the brain tissue specific miR-9-3p and miR-124-3p in serum exosomes of a patient with stroke and a healthy person are analyzed by virtue of a real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. In the case of acute stroke, the brain tissue specific miR-9-3p and miR-124-3p enter peripheral blood in the form of the exosomes, with a level obviously increased in comparison with a control group, and expression quantities are positively correlated to a degree of brain injury; therefore, the miR-9-3p and miR-124-3p can be used as the markers for judging cerebral ischemic injury and degree.
Owner:广州爱索达生物医药技术有限公司
Metabolic intervention with GLP-1 or its biologically active analogues to improve the function of the ischemic and reperfused brain
InactiveUSRE41288E1Promote insulin secretionIncreasing brain anabolismOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlycemicCvd risk
It has now been discovered that GLP-1 treatment after acute stroke or hemorrhage, preferably intravenous administration, can be an ideal treatment because it provides a means for optimizing insulin secretion, increasing brain anabolism, enhancing insulin effectiveness by suppressing glucagon, and maintaining euglycemia or mild hypoglycemia with no risk of severe hypoglycemia.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Method and system for mapping tissue status of acute stroke
ActiveUS20110229003A1Minimize impactMotion compensationImage enhancementImage analysisCerebral blood volumeIschemic lesion
The current invention provides a method of identifying a ischemic lesion. The method includes loading perfusion imaging data into an electronic memory element and deriving perfusion maps from the perfusion imaging data, where the perfusion maps include a cerebral blood volume (CBV) map and an arterial delay time (DT) map, which utilize arterial delay and dispersion effects. Ischemic pixels are determined from the perfusion imaging data, where the DT is greater than a predetermined first threshold value and the CBV is below a second threshold value and the infarct portion of the ischemic lesion is determined, where DT is greater than a predetermined third threshold value and / or the CBV is below a forth threshold value. A cluster analysis is applied to all of the determined ischemic lesion and infarct pixels and the penumbra is then determined, where mismatch regions between the ischemic lesion and the infarct core define the penumbra.
Owner:APOLLO MEDICAL IMAGING TECH
Method and apparatus for creating penumbra and infarct images
InactiveUS20040138549A1Character and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsRadiologyCerebral blood volume
A method and apparatus for evaluating acute stroke patients and for determining whether a stroke patient will benefit from the use of thrombolysis therapy includes obtaining measurements of the cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume of the brain of a stroke patient, determining ischemic areas of the brain where the ischemic areas comprise the measurements of cerebral blood flow which are less than a first value and creating a penumbra-infarct map of the ischemic areas of the brain using the measurements. The infarct area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is less than a second value. The penumbra area corresponds to the area of the brain where cerebral blood volume is greater than this second dvalue. The method also includes determining a ratio of penumbra size to the total of penumbra size and infarct size. When the ratio is greater than a predetermined value, the stroke patient is a candidate for thrombolysis therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
Modulating Function of Neural Structures Near the Ear
ActiveUS20160175605A1Increase blood flowIncrease cerebral blood flowUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNerve structureNervous system
Stimulation of the facial nerve system (e.g., electrically, electromagnetically, etc.) in ischemic stroke patients will cause dilation of occluded arteries and dilation of surrounding arteries, allowing for blood flow to circumvent the obstruction and reach previously-deprived tissue. The device approaches the facial nerve and its branches in the vicinity of the ear. In use, the device can be inserted into the ear canal and / or placed in proximity to the ear in order to stimulate the facial nerve system non-invasively (e.g., using an electromagnetic field). The device can be used in the emergency treatment of acute stroke or chronically variations for long-term maintenance of blood flow to the brain and stroke prevention. Additional embodiments of the device may be adapted for use on different regions of the body.
Owner:NERVIVE
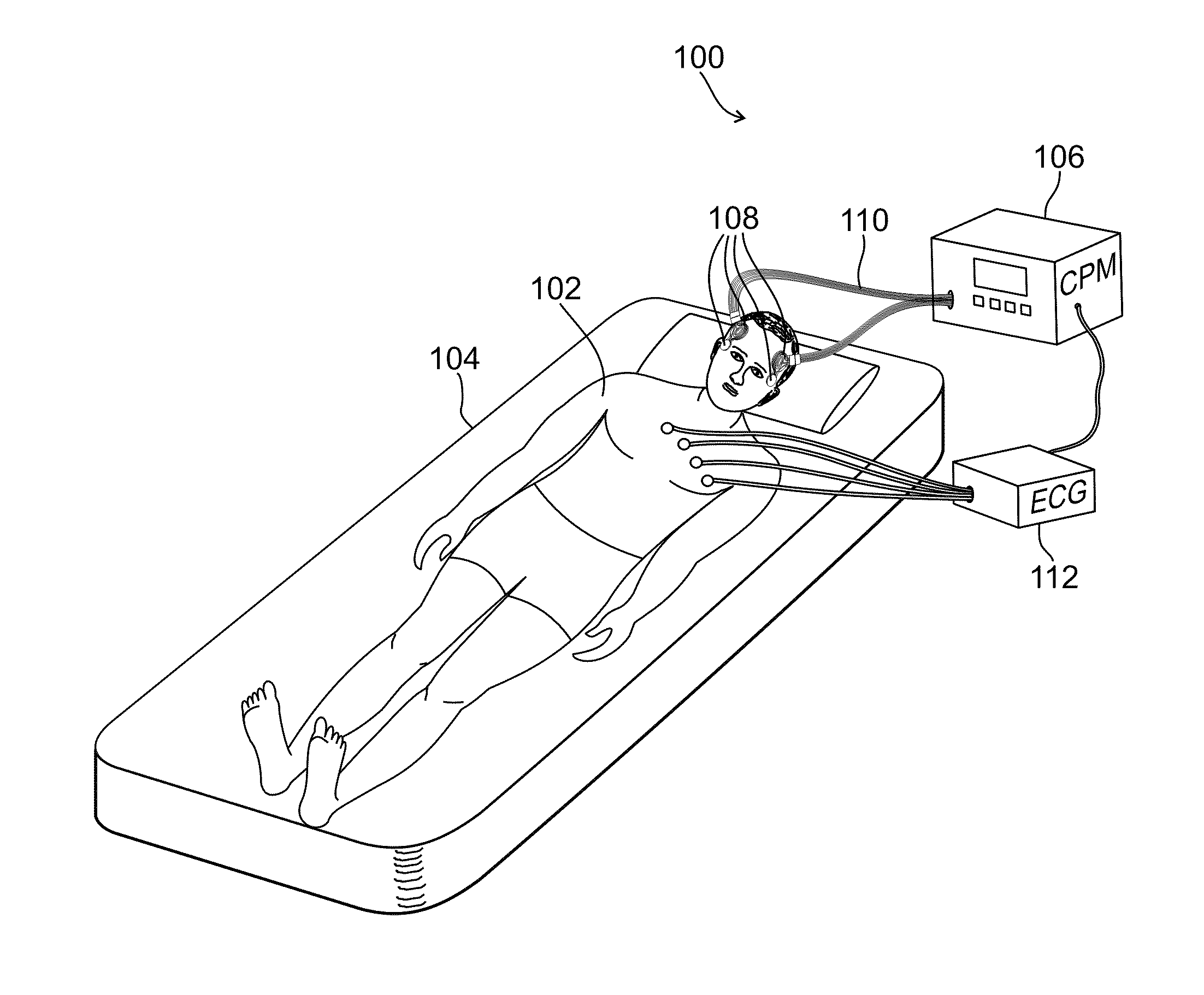
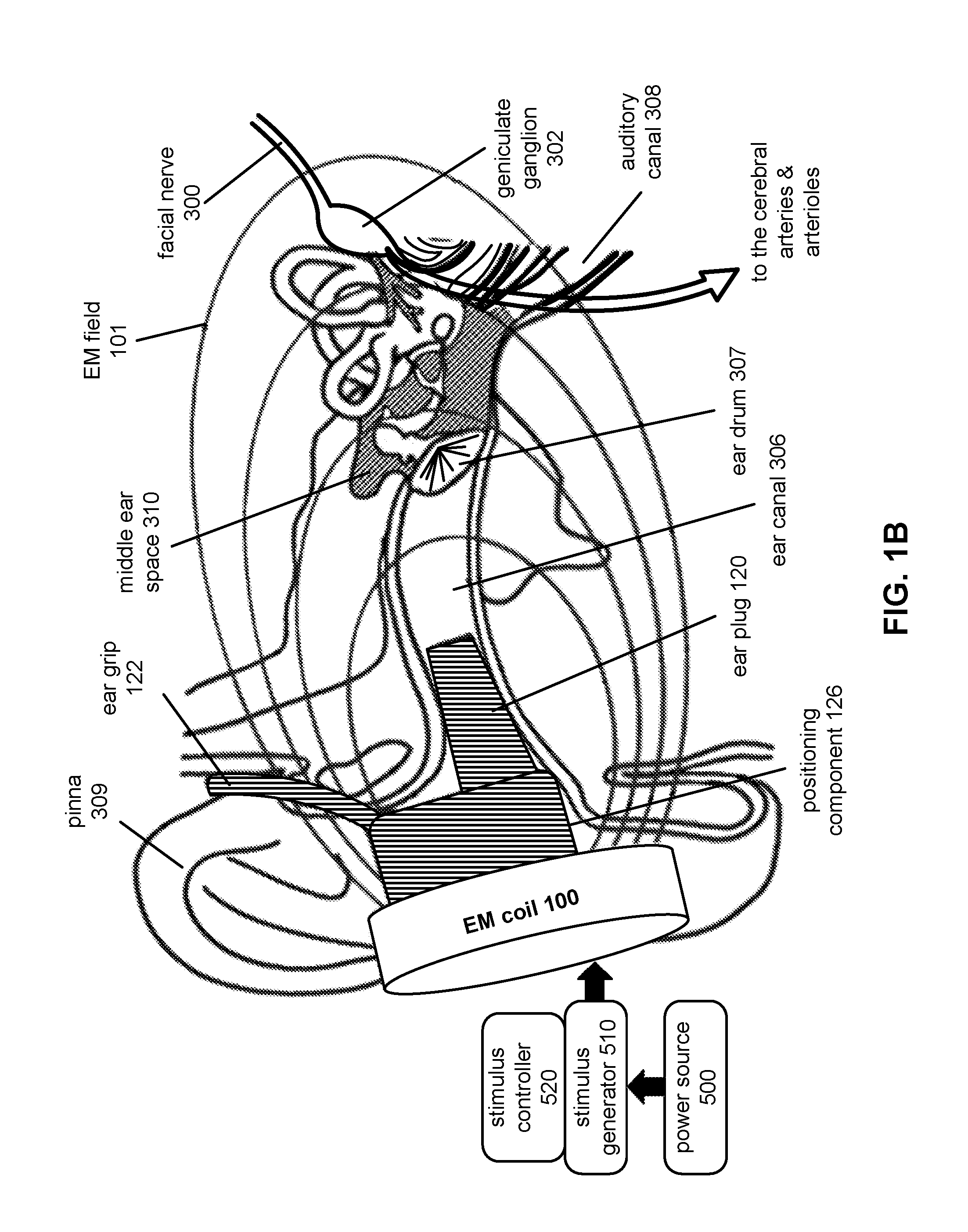
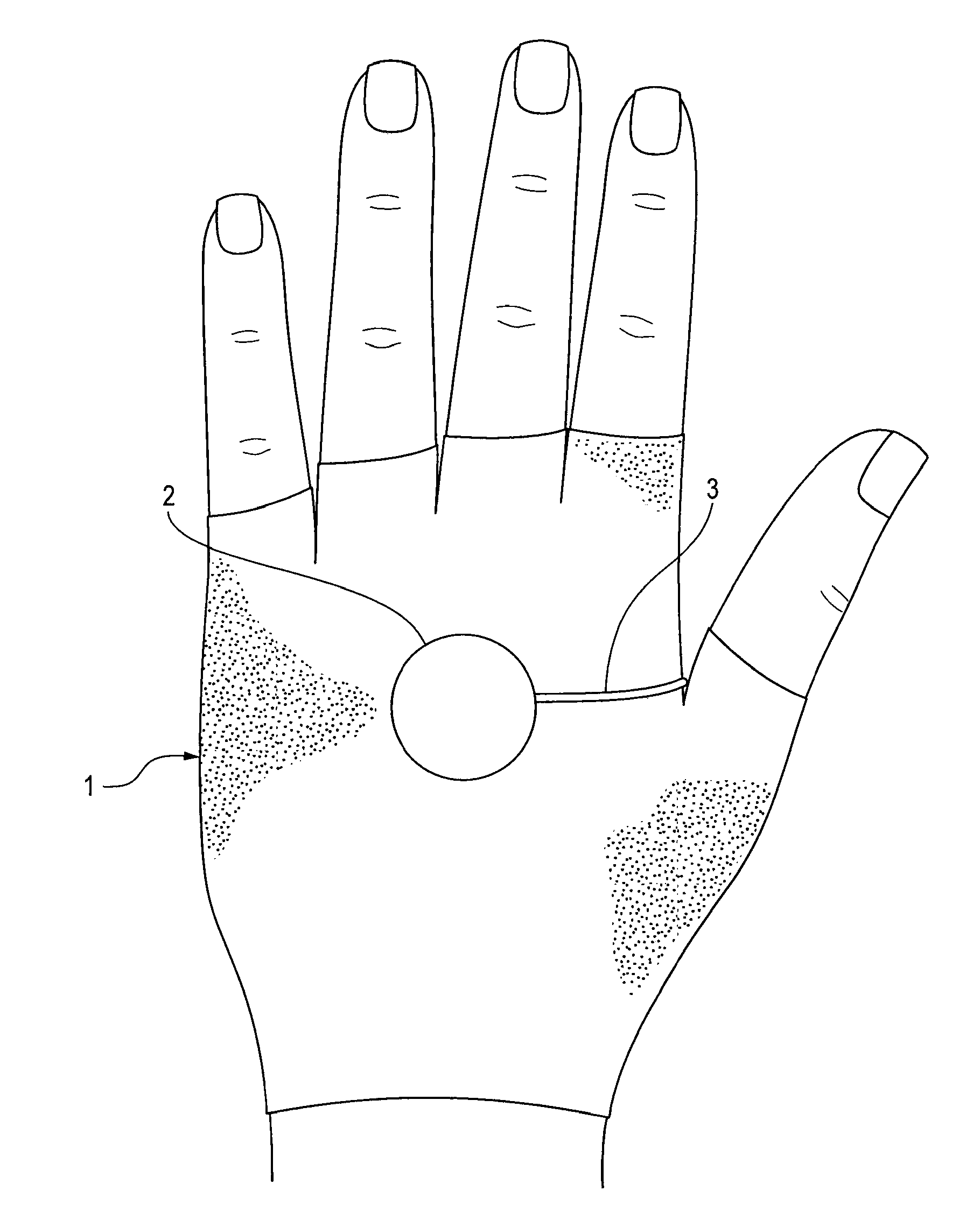
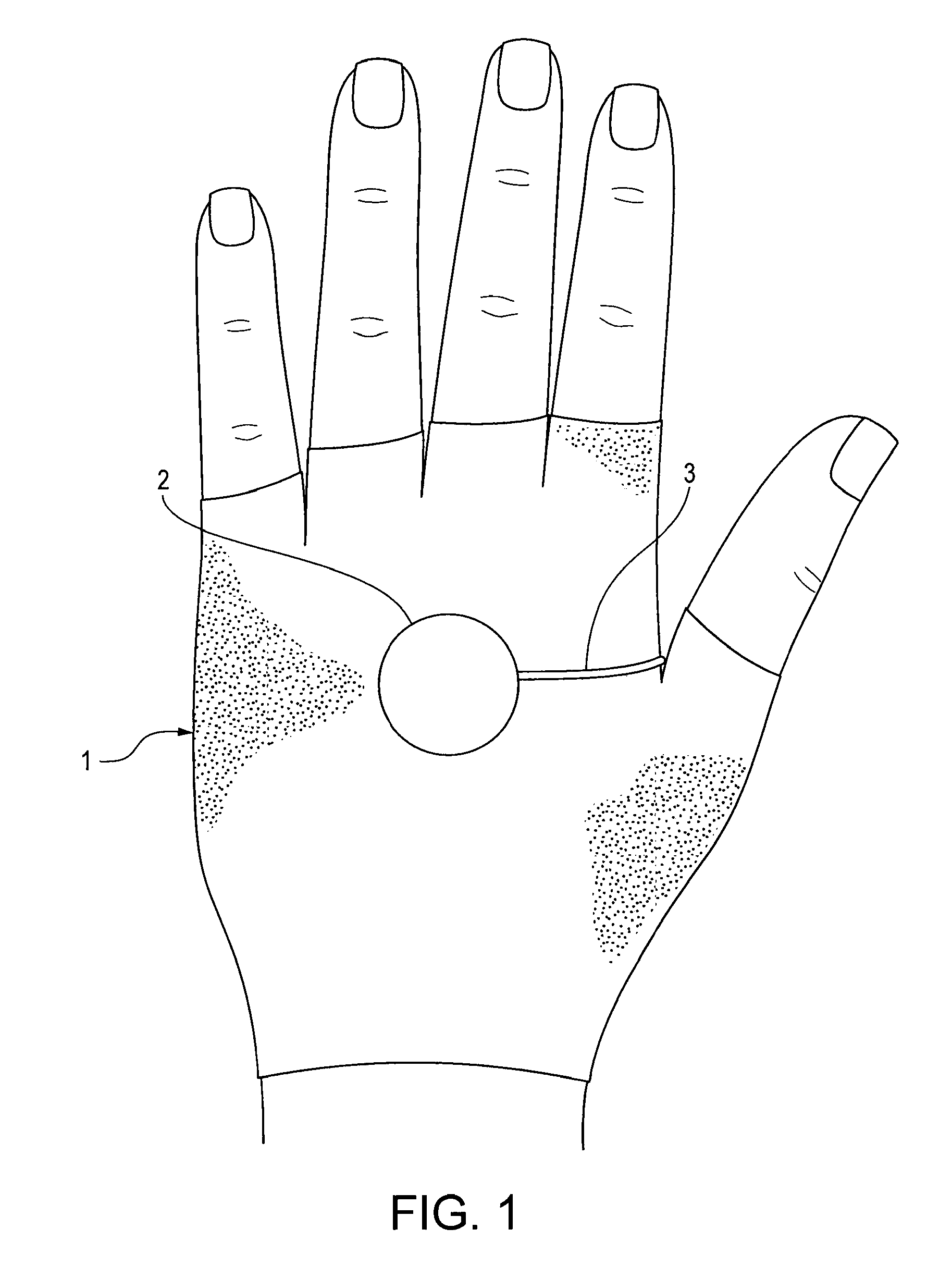
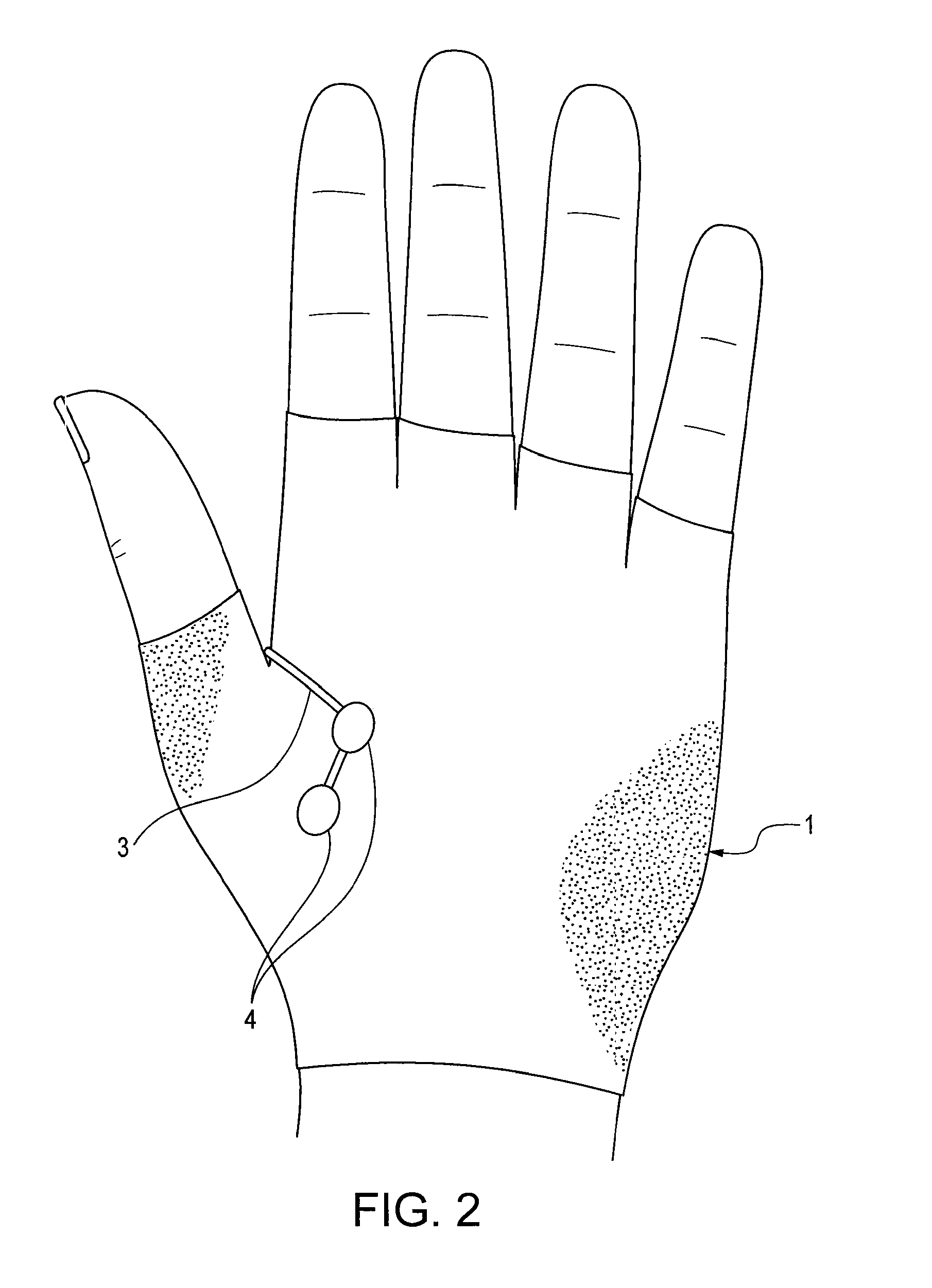
Sensors for detecting acute stroke and method of using same
A system and method for detecting stroke in an individual, and in particular a sleeping individual. The individual has sensors on a least one hand or wrist for detecting electrical and / or muscular activity. The sensors may be included in or on a glove or bracelet worn by the individual. The absence of electrical and / or muscular activity is indicative of a stroke, and when such absence is detected, an alert is raised. Absence of detecting electrical and / or muscular activity can be detected in only one hand and / or wrist to avoid false alarms from REM sleep which results in the absence of electrical and / or muscular activity in both hands.
Owner:PARODI JUAN +1
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating acute stroke and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101780227AImprove permeabilityImprove the quality of lifeNervous disorderUnknown materialsIntestinal structureSide effect
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating acute stroke and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine composition mainly comprises the following raw medicines: senna leaf, giant knotweed rhizome, artificial bovine calculus powder, concretio silicea bambusae and trichosanthes fruit seed. The traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention has the efficacy of dredging intestines and inducing resuscitation, is suitable for the symptoms of viscera and phlegm retention and viscera qi obstruction caused by the acute stroke, and is used for treating phlegm retention and viscera qi obstruction of yang and yin shutting syndromes of viscera caused by the stroke. The traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating patients suffering from acute stroke can improve clinical curative effect, reduce mortality and improve the life quality of patients; and the clinical application is safe without side effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG HOSPITAL OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
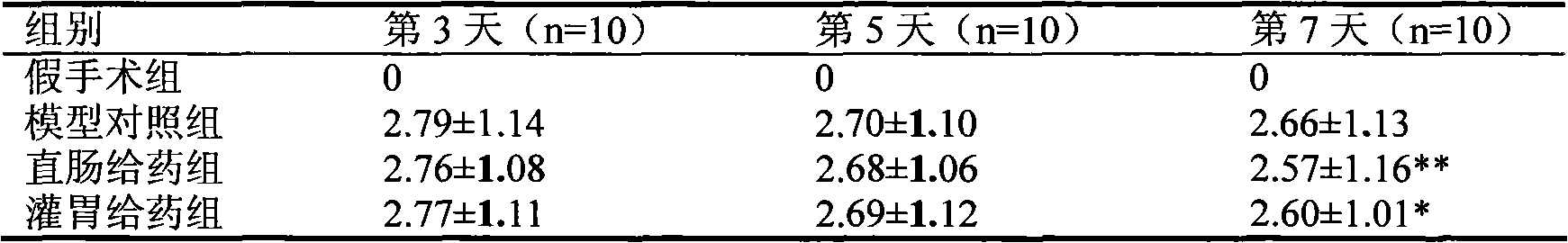
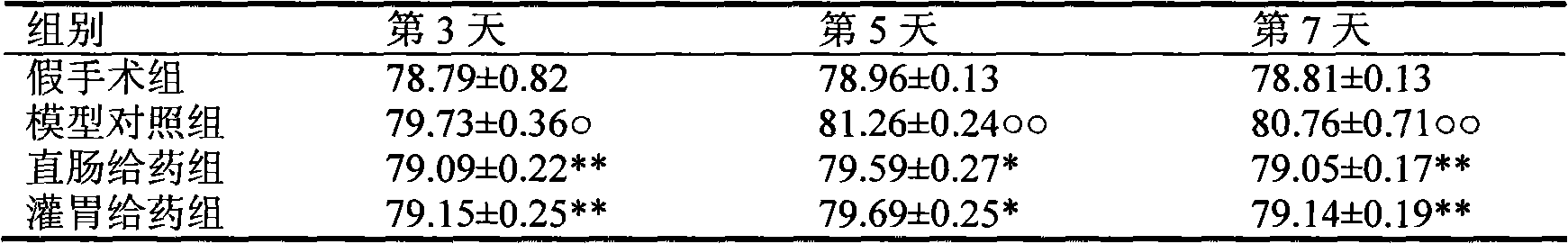
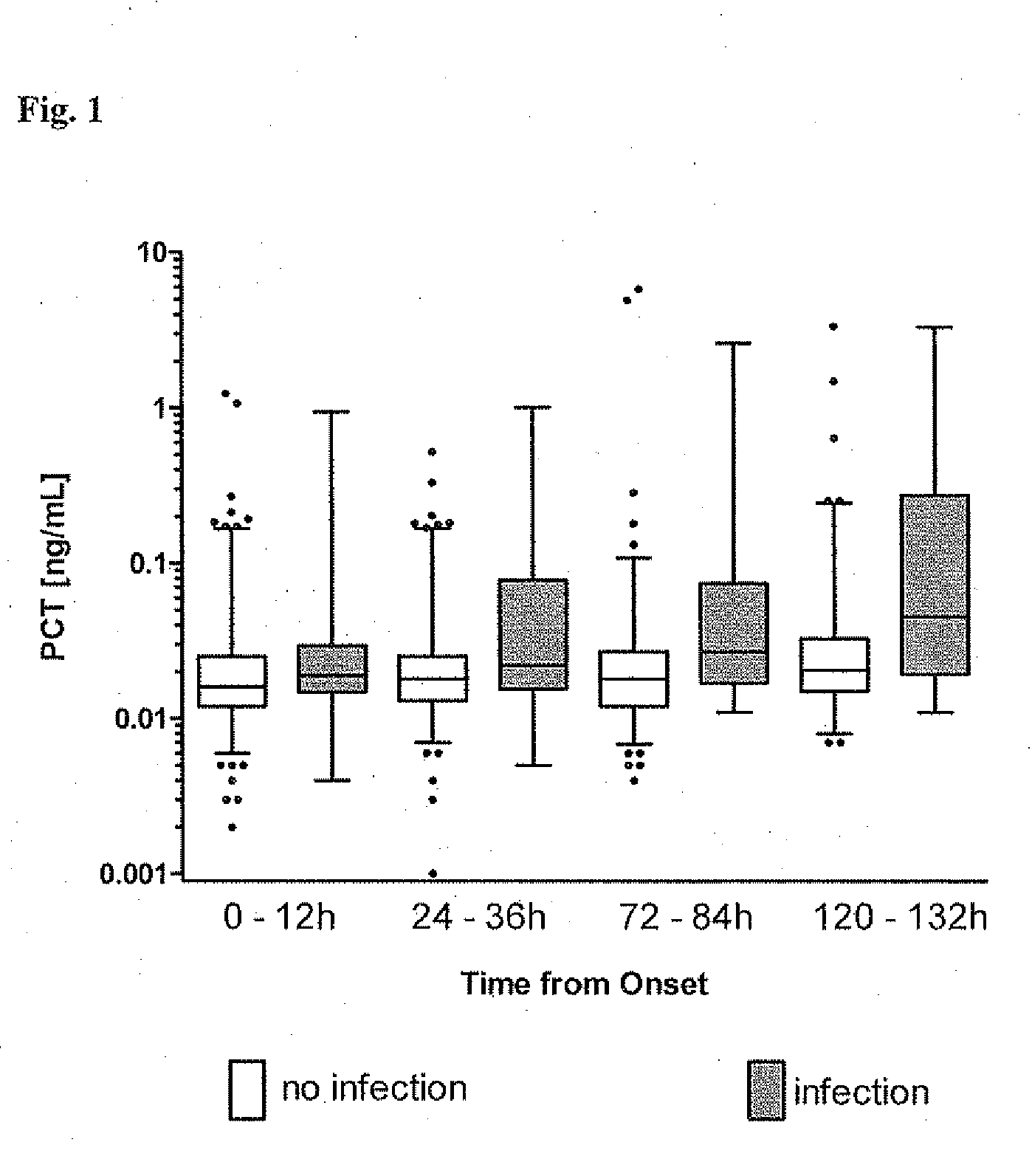
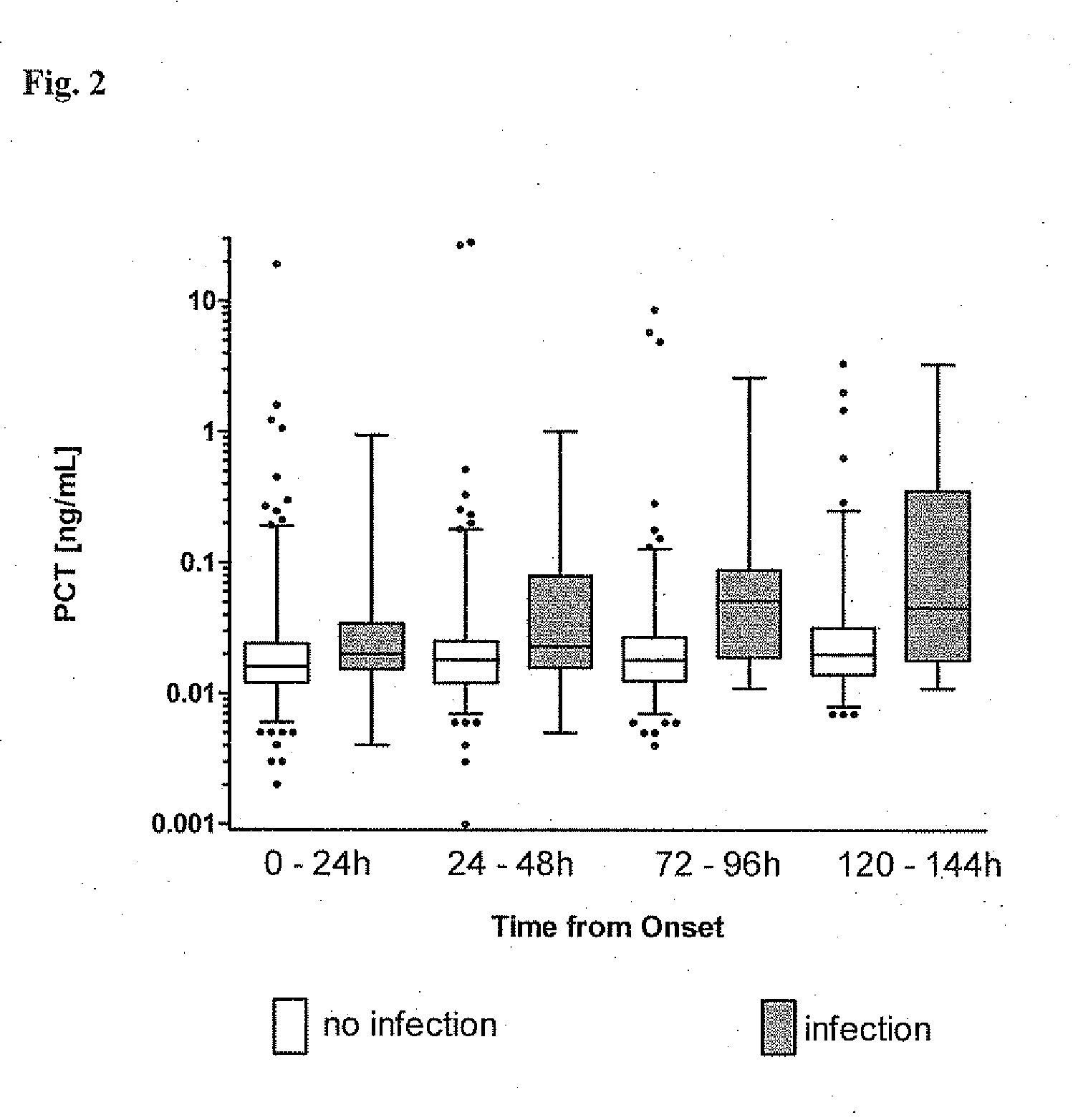
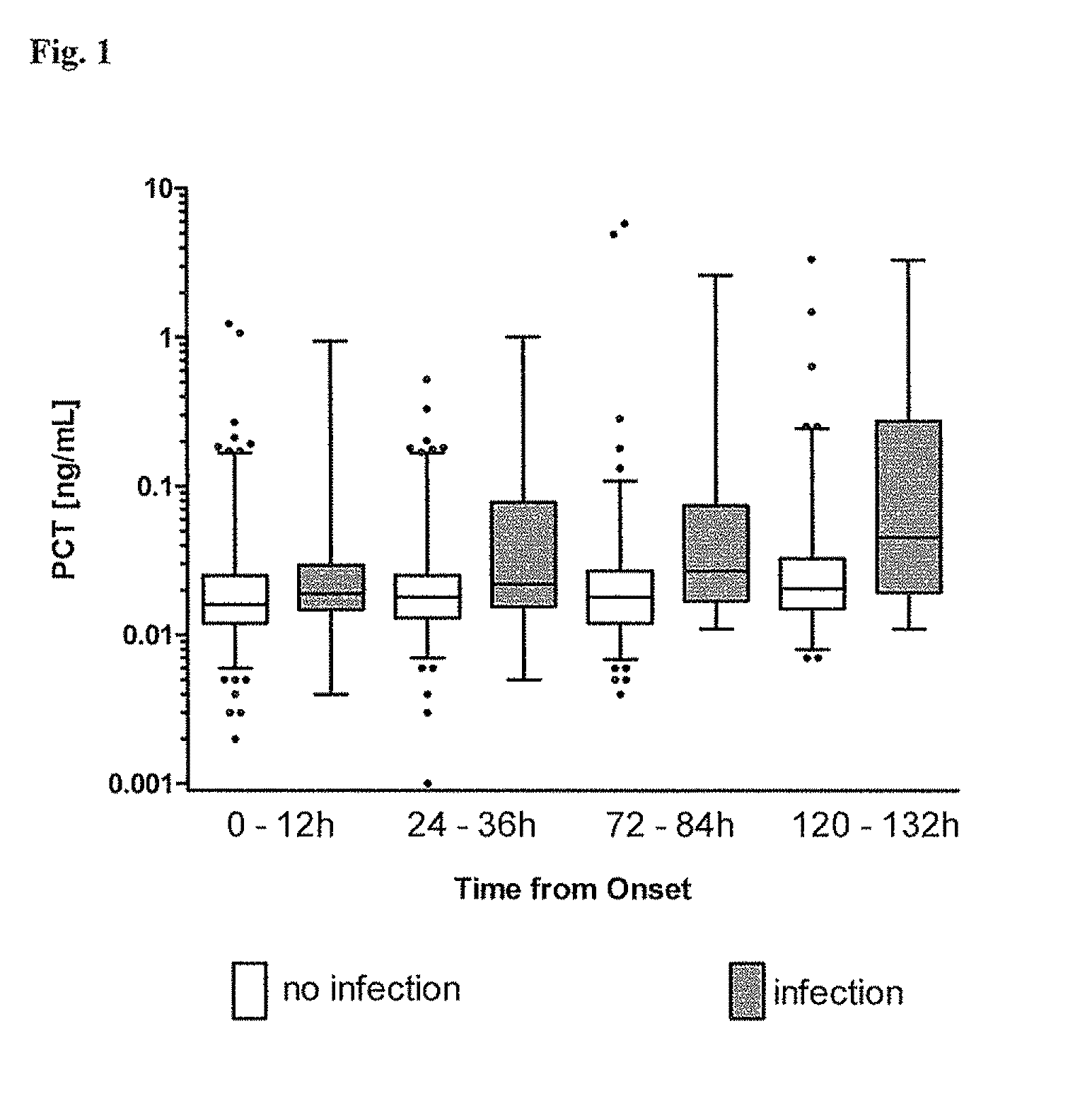
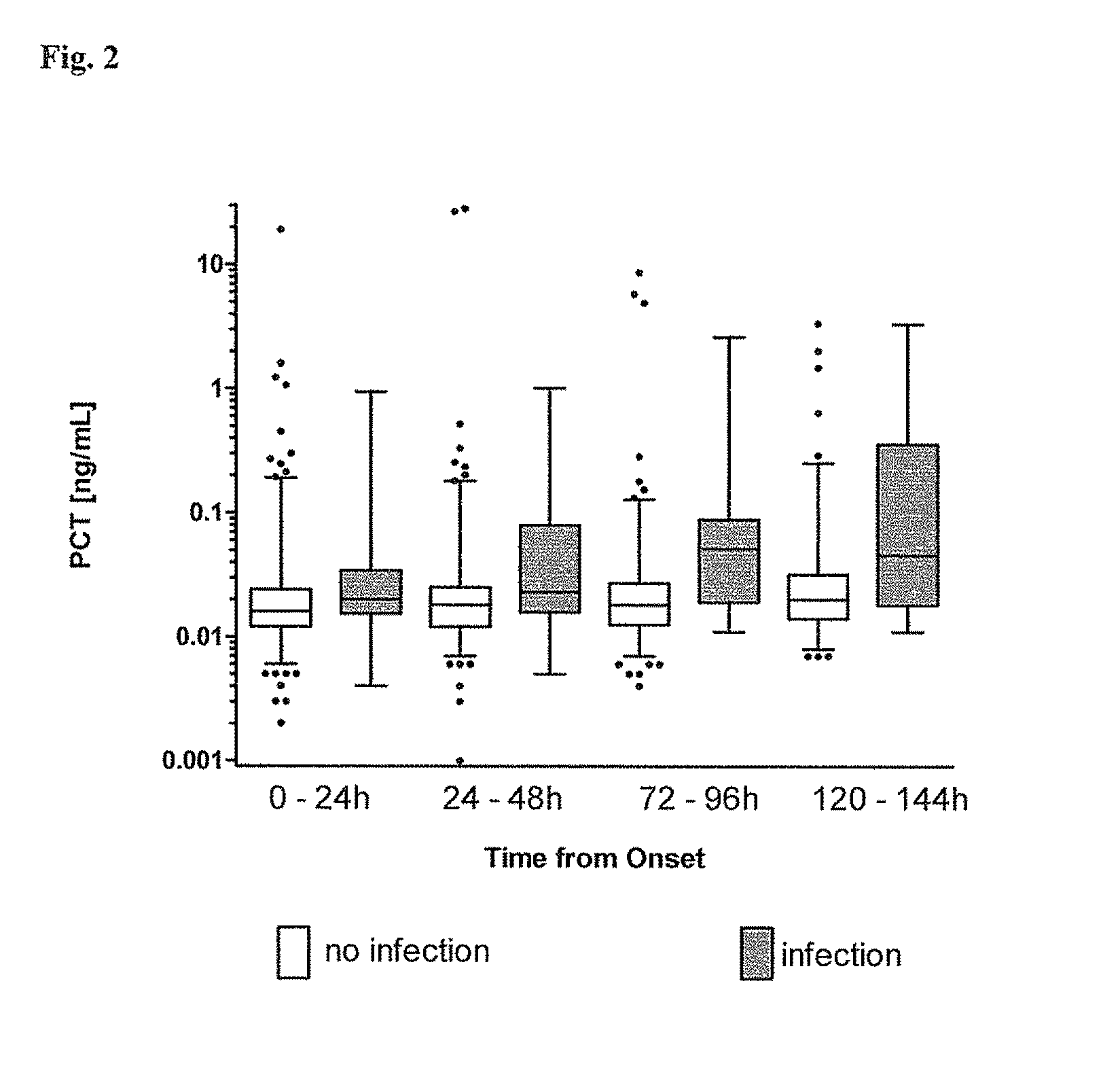
Procalcitonin for the diagnosis of bacterial infections and guidance of antibiotic treatment in patients with acute stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS20110086831A1Improve patient outcomesHigh sensitivityAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibioticsAcute ischemia
The present invention relates to an in vitro method for the diagnosis and treatment guidance of a bacterial infection in patients suffering from an acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, comprising the determination of the level of Procalcitonin (PCT) or a fragment thereof having at least 12 amino acid residues in a sample of a bodily fluid from said patient and the correlation of the determined level to the diagnosis of a bacterial infection in said patient.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
Methods and compositions for recovery from stroke
ActiveUS9427439B1Promote recoveryOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIschemic injuryNeurologic injury
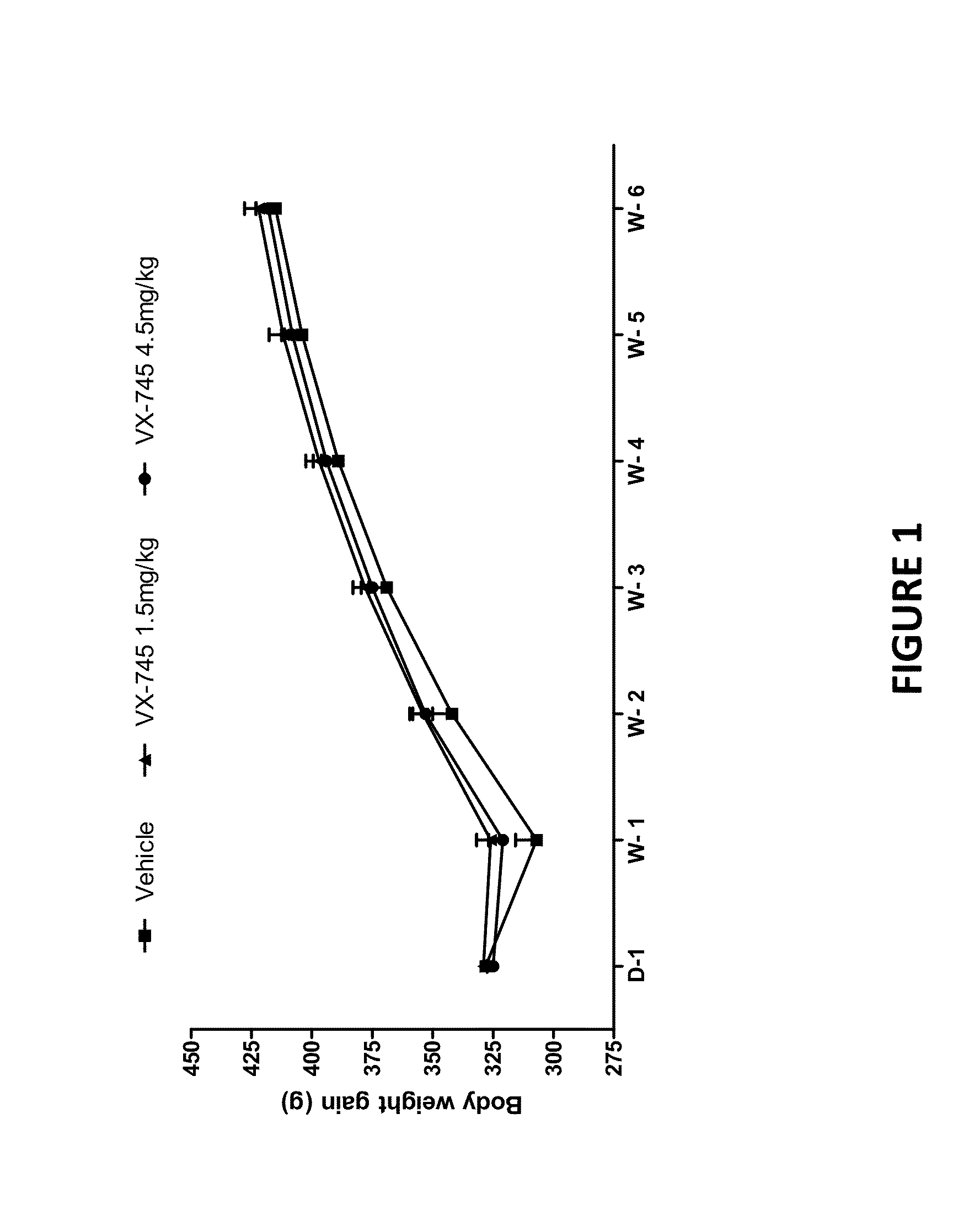
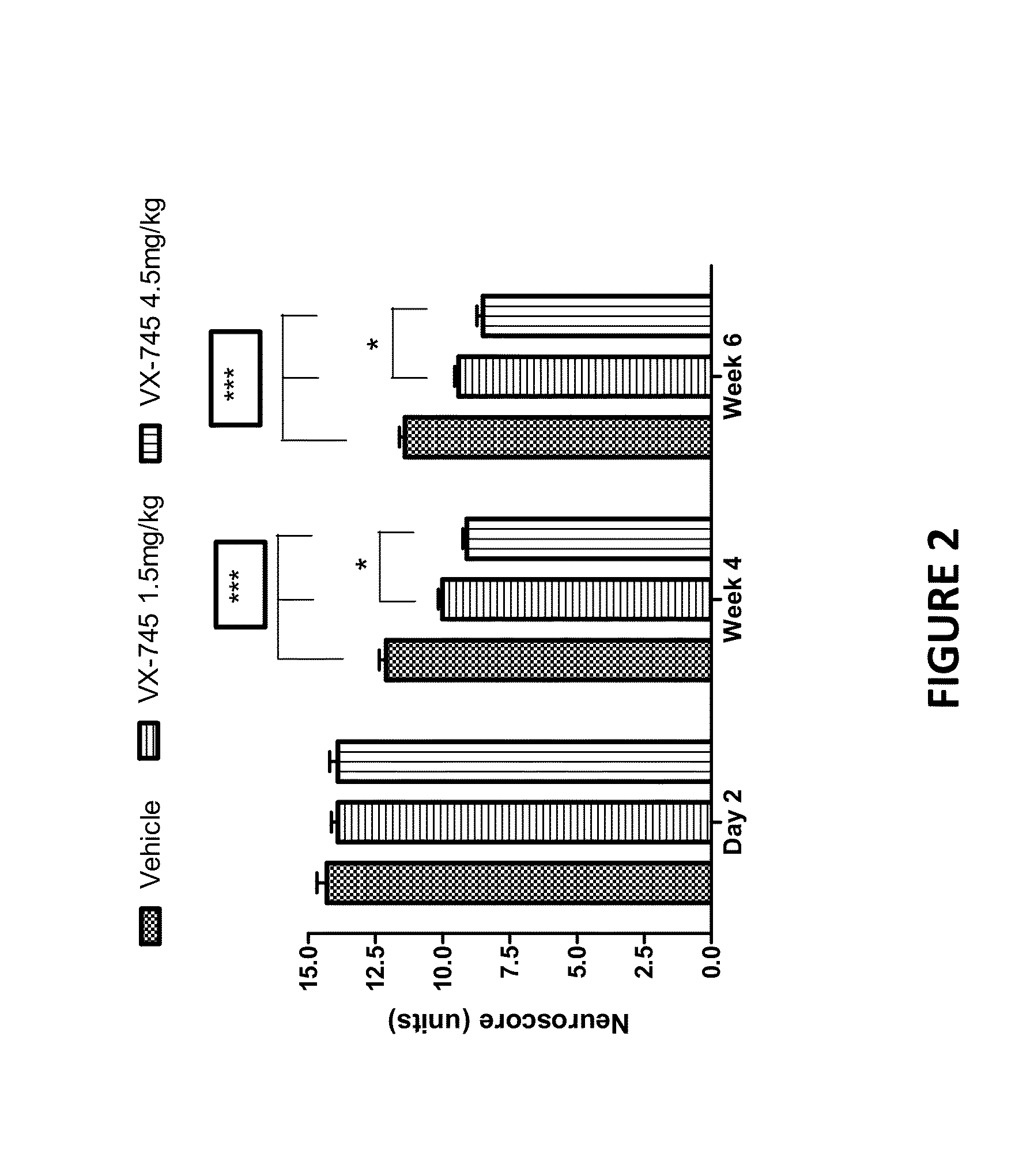
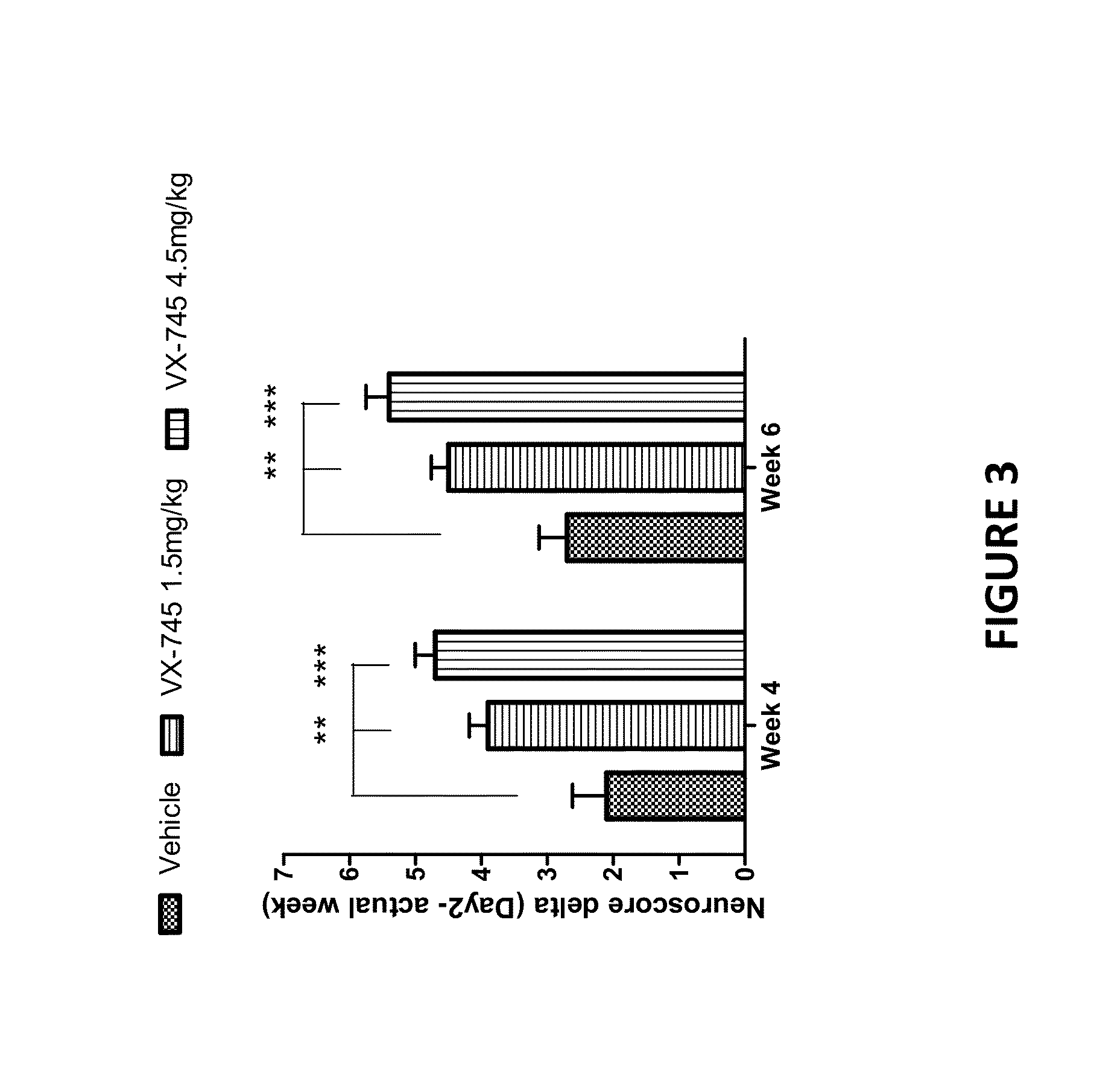
The present invention provides methods and compositions for promoting recovery of function from neurologic injury, such as ischemic injury caused by acute stroke.
Owner:EIP PHARMA
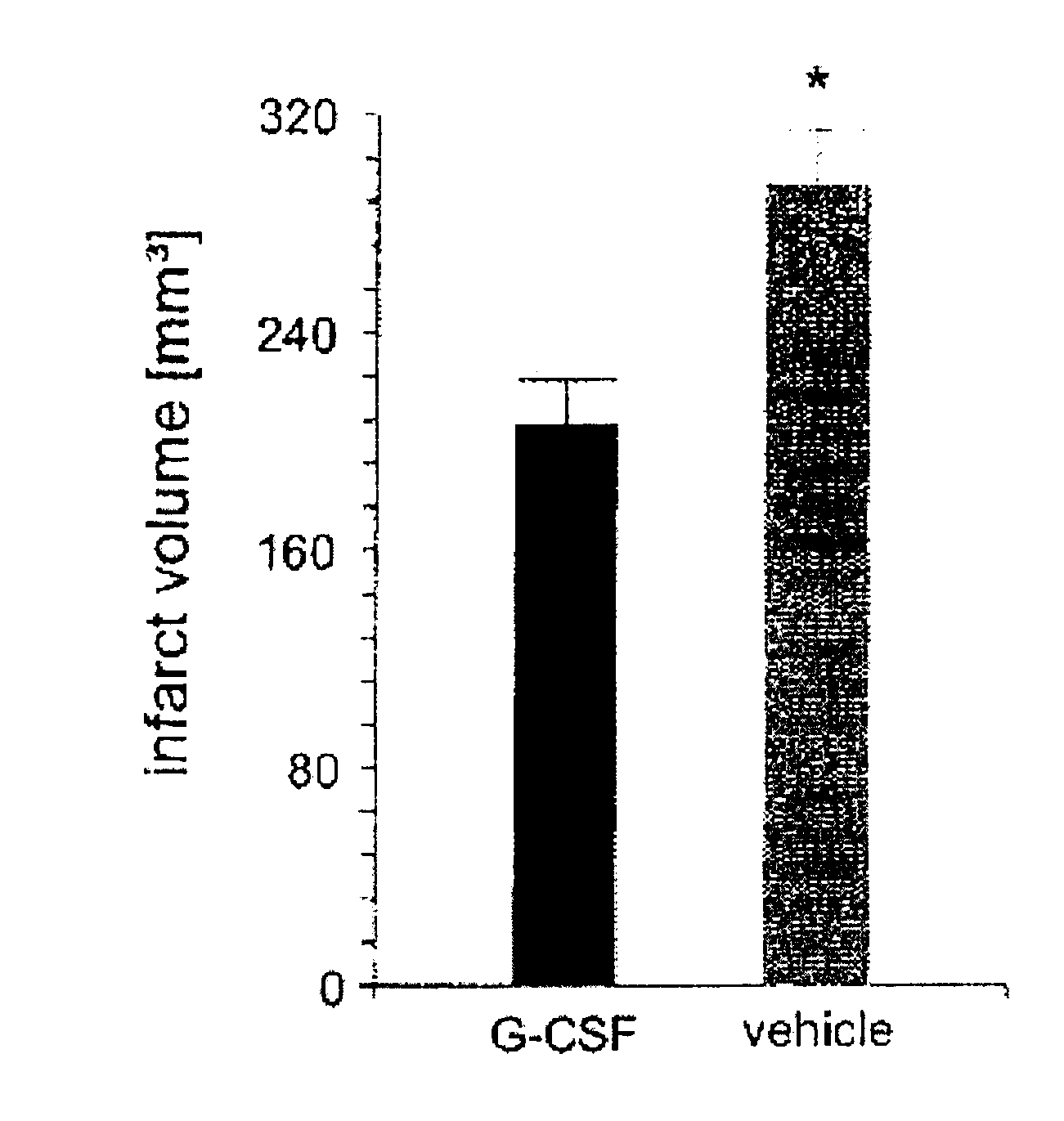
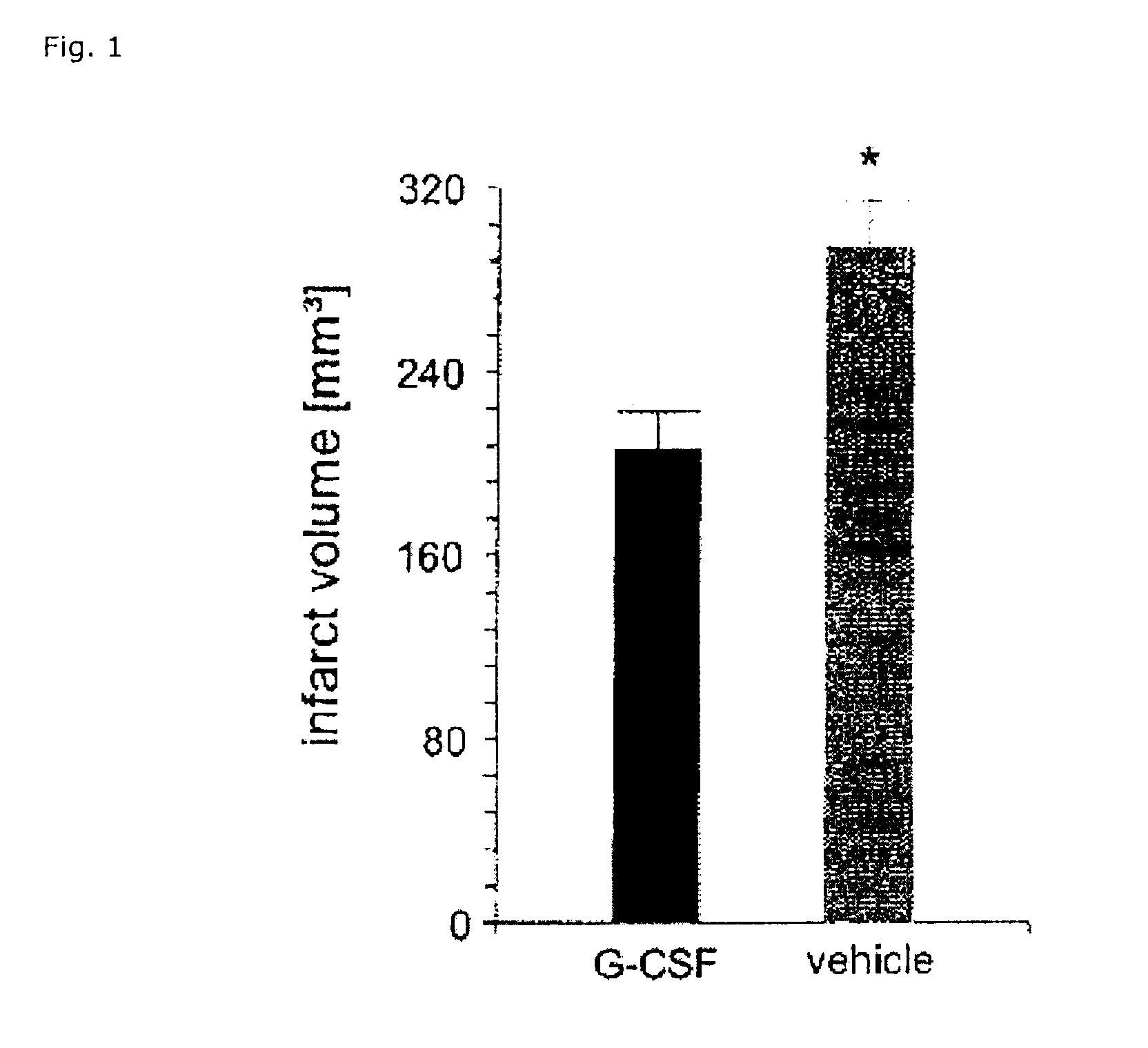
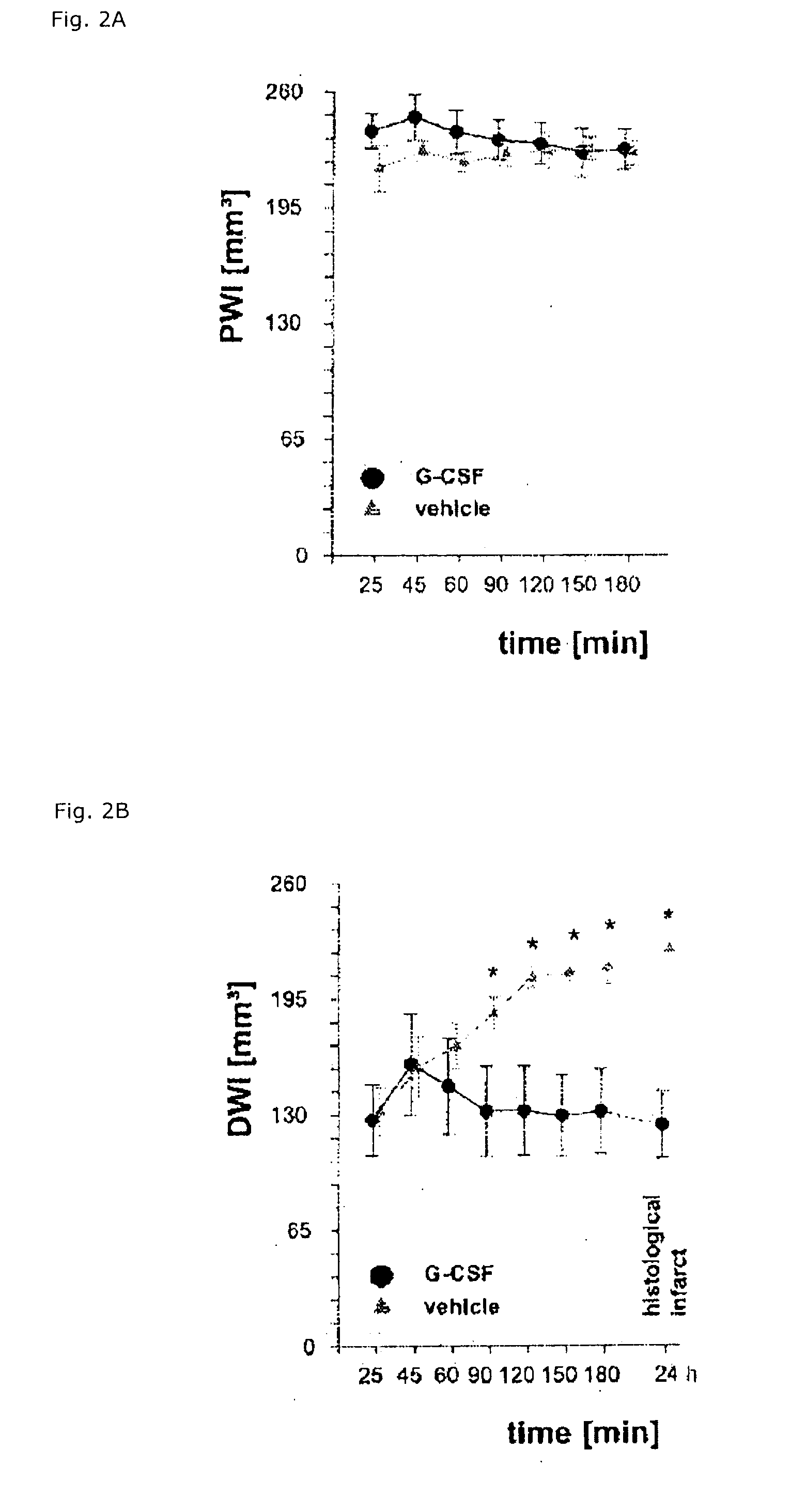
Use of g-csf for the extension of the therapeutic time-window of thrombolytic stroke therapy
InactiveUS20120070403A1Effective treatmentImprove clinical outcomesNervous disorderHydrolasesSide effectMedicine
The present invention relates to the use of G-CSF and derivatives thereof for extending the therapeutic window of subsequent thrombolytic treatment of acute stroke, and thereby, allowing the diagnostic examinations which are necessary prior to the thrombolytic treatment in order to avoid hemorrhagic and other severe adverse side effects of the thrombolysis.
Owner:SYGNIS BIOSCIENCE GMBH & CO KG
Procalcitonin for the diagnosis of bacterial infections and guidance of antibiotic treatment in patients with acute stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS8383332B2High sensitivityImprove patient outcomesAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibioticsAcute ischemia
The present invention relates to an in vitro method for the diagnosis and treatment guidance of a bacterial infection in patients suffering from an acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, comprising the determination of the level of Procalcitonin (PCT) or a fragment thereof having at least 12 amino acid residues in a sample of a bodily fluid from said patient and the correlation of the determined level to the diagnosis of a bacterial infection in said patient.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
Methods for diagnosis and monitoring of neurological disease by detection of an encephalotoxin
InactiveUS7344853B2Microbiological testing/measurementSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsHiv 1 associated dementiaDisease progression
Encephalotoxin produced by activated mononuclear phagocytes is present in individuals having neurological disease including neurodegenerative and neuro-inflammatory diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), HIV-1-associated dementia (HAD), Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Mild Cognitive Impairment, prion disease, minor cognitive / motor dysfunction, acute stroke, acute trauma, or neuro-AIDS. Biochemical detection of encephalotoxin according to the methods of the invention will allow diagnosis of neurological disease in early, presymptomatic stages, thereby allowing early intervention in disease progression as well as identification of subjects or populations at risk for developing neurodegenerative disease. The methods of the invention also provide a mechanism for monitoring progression and treatment of neurological disease.
Owner:JACOBUS PHARMA CO INC
Method and composition for enhancing the delivery of Anti-platelet drugs for the treatment of acute stroke
InactiveUS20150064238A1Reduce the probability of bindingReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSide effectHigh doses
Owner:LIN JEN CHENG
Balloon catheter for partially blocking blood flow
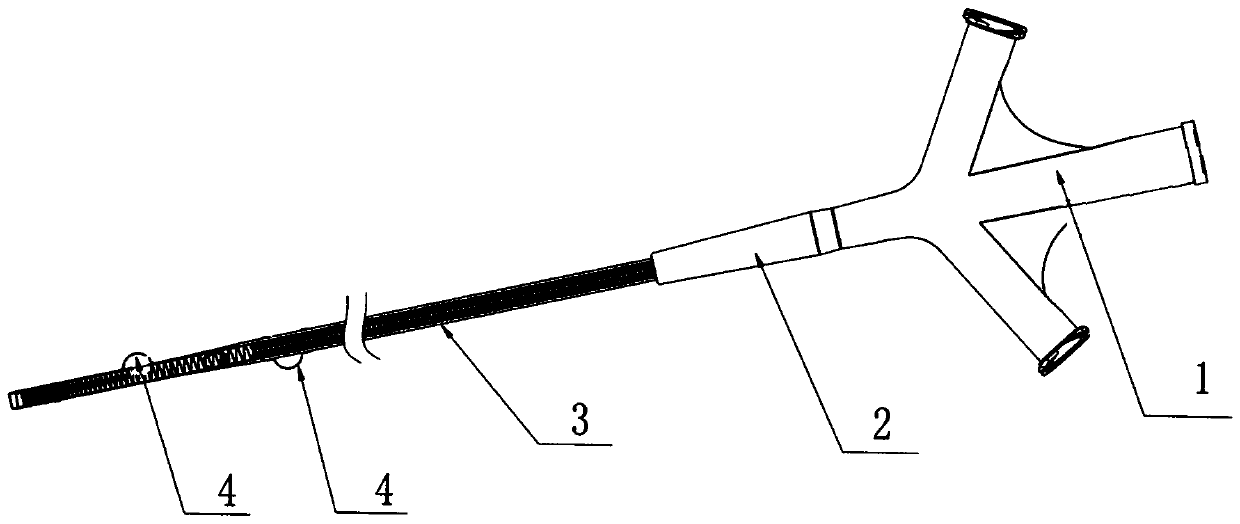
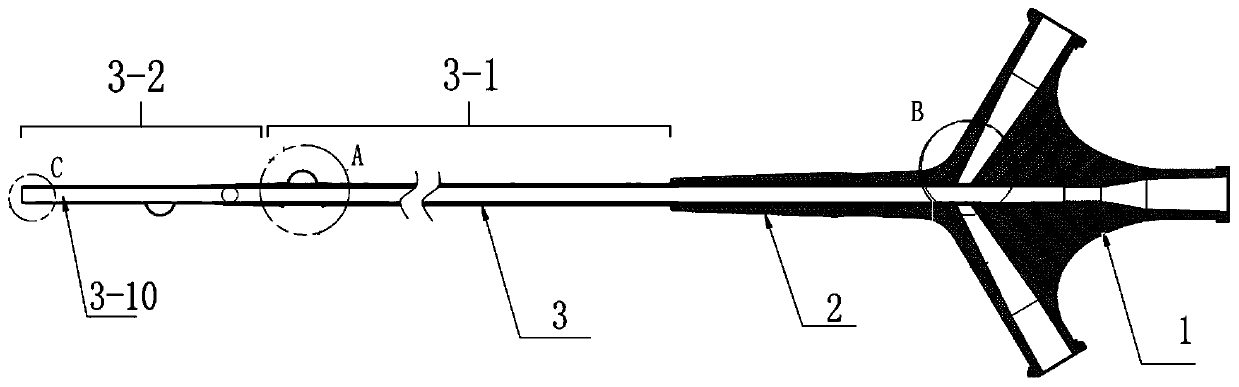
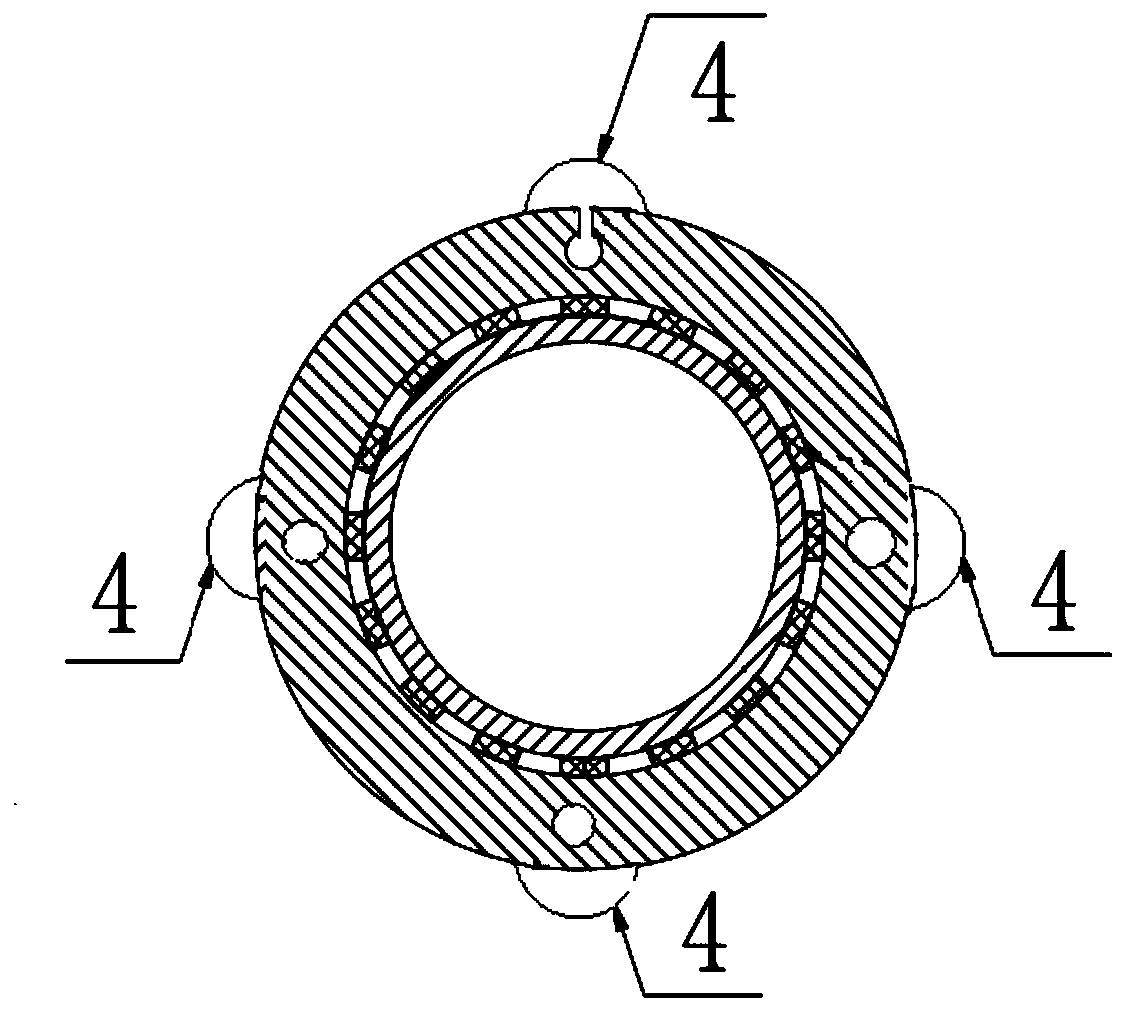
InactiveCN111228633APrevent thrombosisReduced perfusionBalloon catheterMedical devicesCatheter hubThrombus
The invention discloses a balloon catheter for partially blocking blood flow. The balloon catheter comprises a catheter seat and a catheter body mounted at the catheter seat, wherein a plurality of balloons are arranged on a far-end segment of the catheter body, a main hole channel and a plurality of side hole channels are formed in the catheter body, the main hole channel axially extends, and theside hole channels are isolated from another; and a main pipe and a plurality of side pipes are correspondingly arranged on the catheter seat, and the multiple side hole channels respectively communicate to different balloons and are used for respectively controlling inflation states of the multiple balloons. By inflating the multiple balloons, near-end blood vessels of a thrombus are effectivelysealed, blocked and protected to different degrees, so that early perfusion of a lot of blood flow is reduced after acute stroke is dredged, and reperfusion injury complications are reduced; by adjusting the inflation states of the multiple balloons, multi-level accurate adjustment of the sealing states of blood vessels is realized, so that accurate control of perfusion blood flow is realized, and functional recovery of the brain is promoted; and manifold auxiliary instruments do not need to be used, and blood flow retardant radiography evaluation, short-term pipe flushing and liquid perfusion during operations can be realized by virtue of the single instrument.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
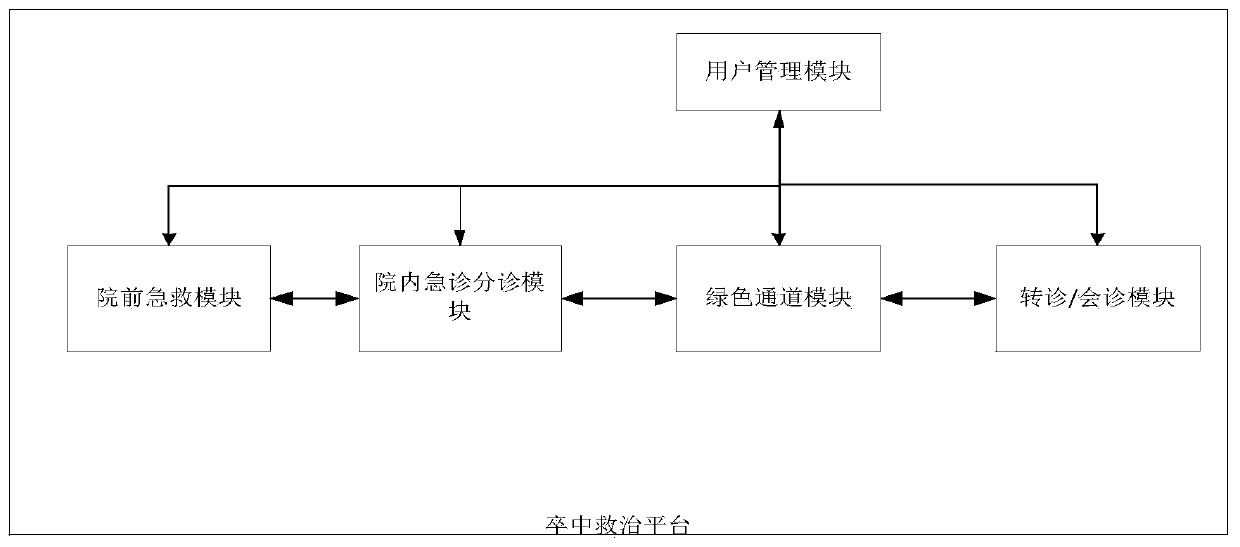
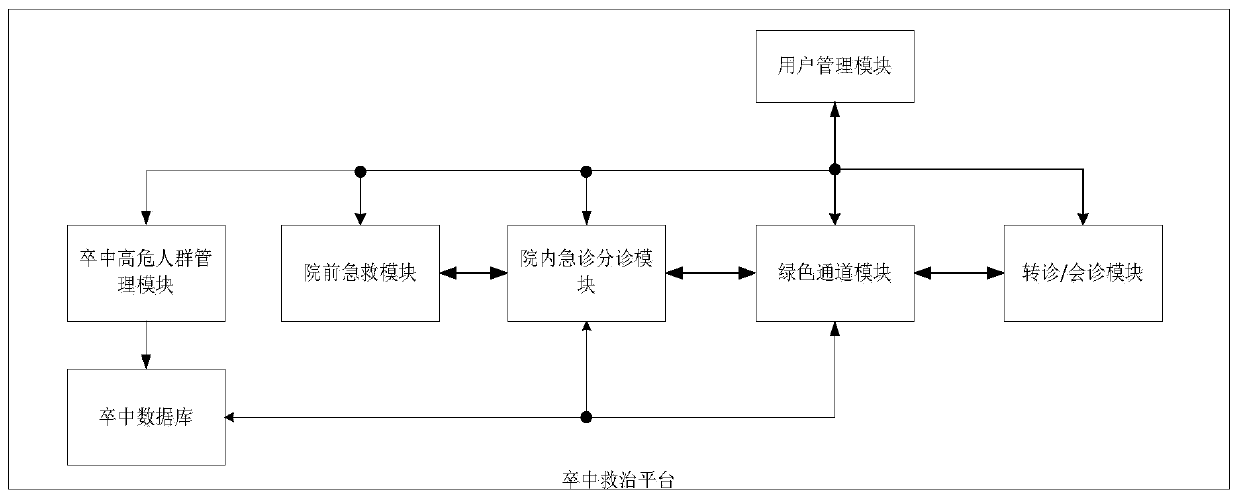
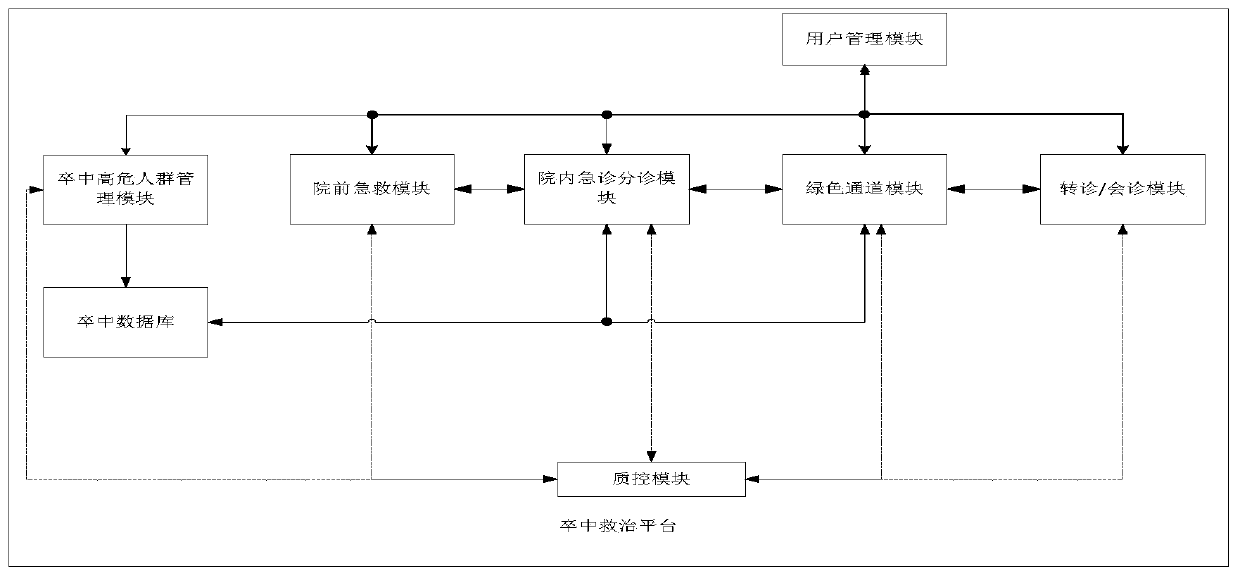
Stroke treatment network system and stroke treatment platform
PendingCN111199791ARealize synchronous sharingReduce delaysHealth-index calculationHealthcare resources and facilitiesStroke treatmentPhysical therapy
The invention discloses a stroke treatment network system and a stroke treatment platform. A stroke treatment platform is constructed, the information expressway for acute stroke treatment is built before the hospital, so that seamless joint of pre-hospital first aid and in-hospital first aid, no arrival of a patient and first arrival of information are achieved, delay in the stroke hospital is reduced, acute stroke treatment time is gained, and thus the treatment efficiency of the acute stroke patient is improved. A three-in-one cerebral stroke treatment network integrating pre-hospital first aid, in-hospital diagnosis and treatment and post-hospital follow-up visit is built based on the stroke treatment platform, so that the pre-hospital stroke treatment process is standardized and unblocked, the treatment time is shortened, the treatment efficiency is improved, and the fatality rate and disability rate of stroke attack are practically reduced.
Owner:重庆携心科技股份有限公司
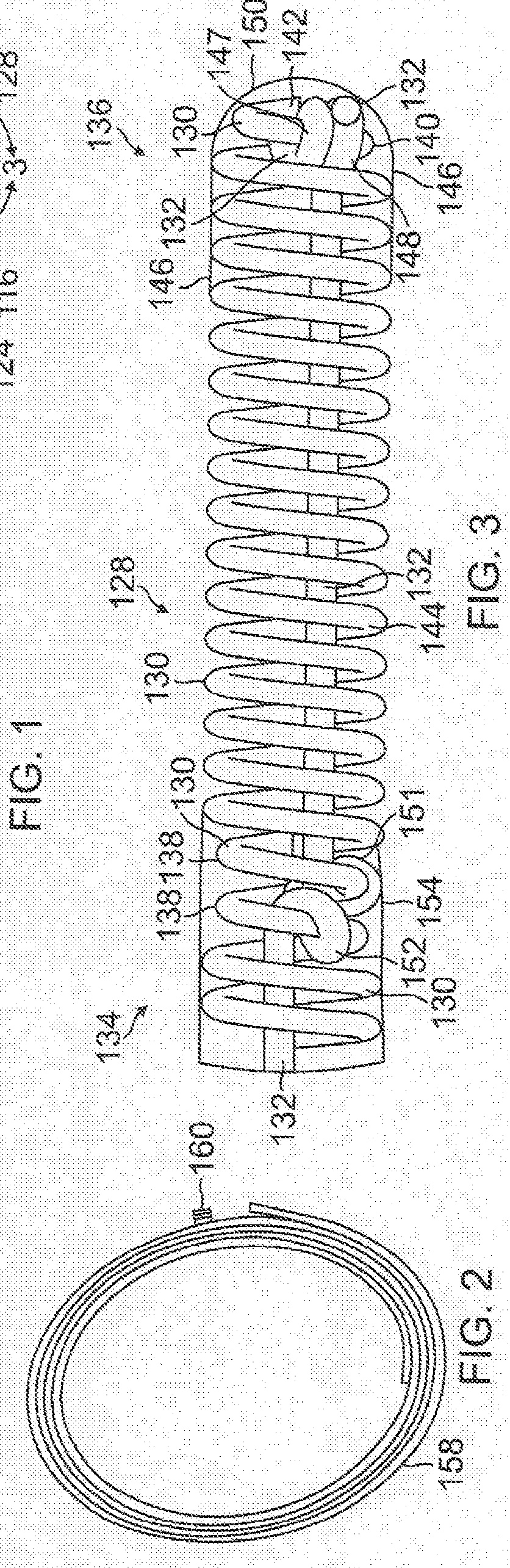
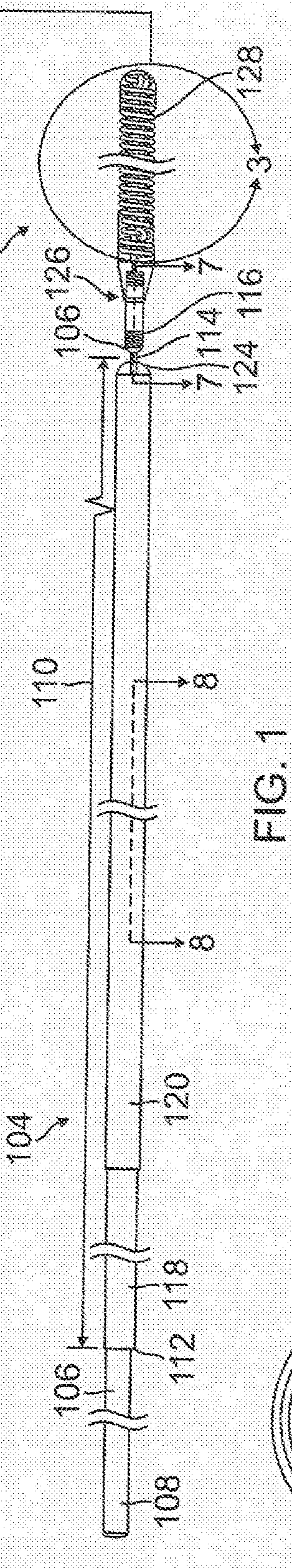
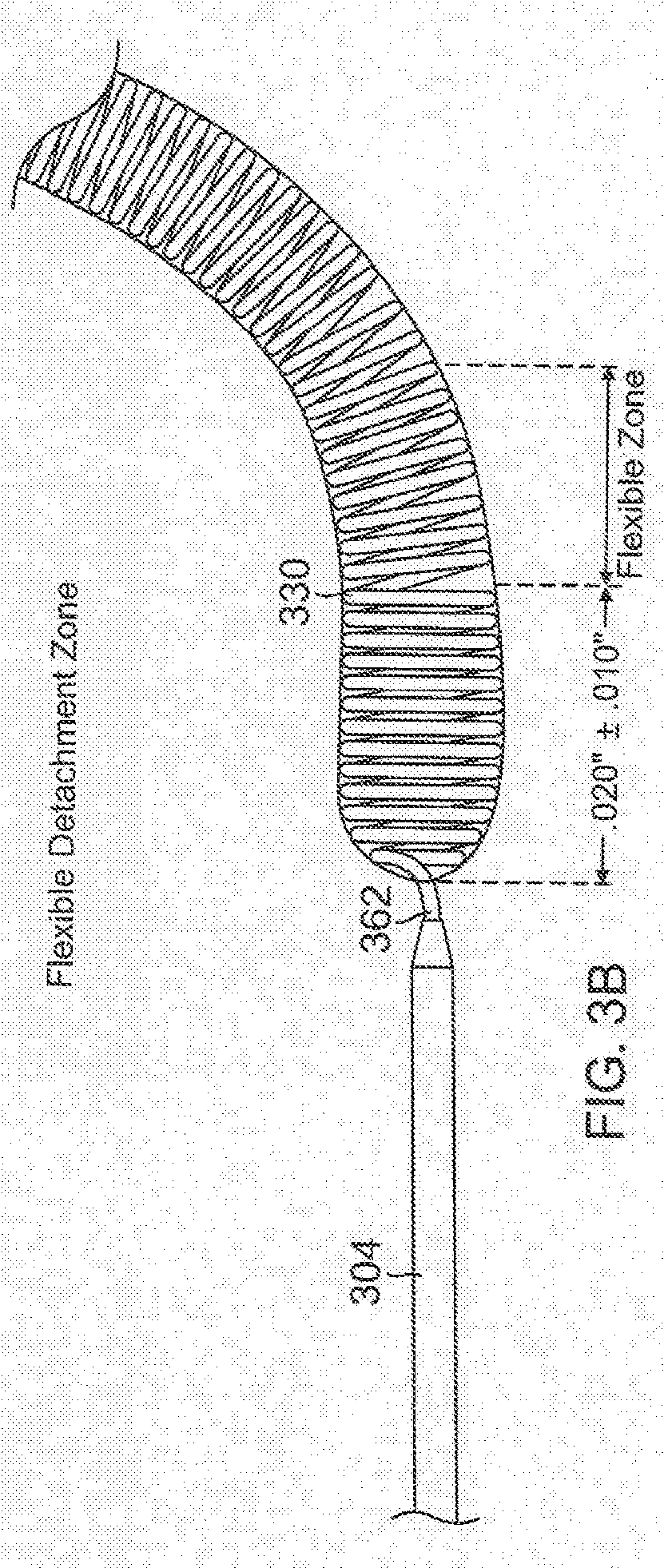
Vascular Implant System and Processes with Flexible Detachment Zones
Vascular issues are addressed with systems, devices, and methods for delivering implants with accurate and ready detachability, along other features, for addressing, for example, acute stroke issues with due alacrity.
Owner:BALT LLC
Metabolic intervention with GLP-1 or its biologically active analygues to improve the function of the ischemic and reperfused brain
InactiveCN1376072AImprove utilizationPromotes anabolismOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLow glucoseBrain hemorrhage
Owner:AMYLIN PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com