Patents
Literature
195 results about "Embolic Protection Devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vascular filters or occlusive devices that provide mechanical protection of the distal end organ from blood clots or EMBOLISM-causing debri dislodged during ENDOVASCULAR PROCEDURES.
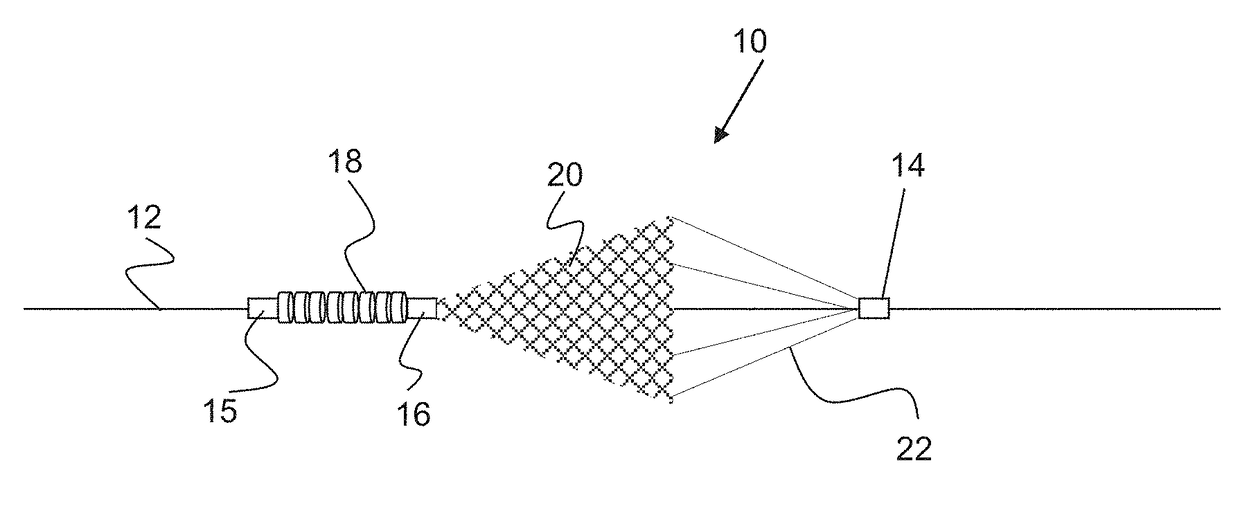
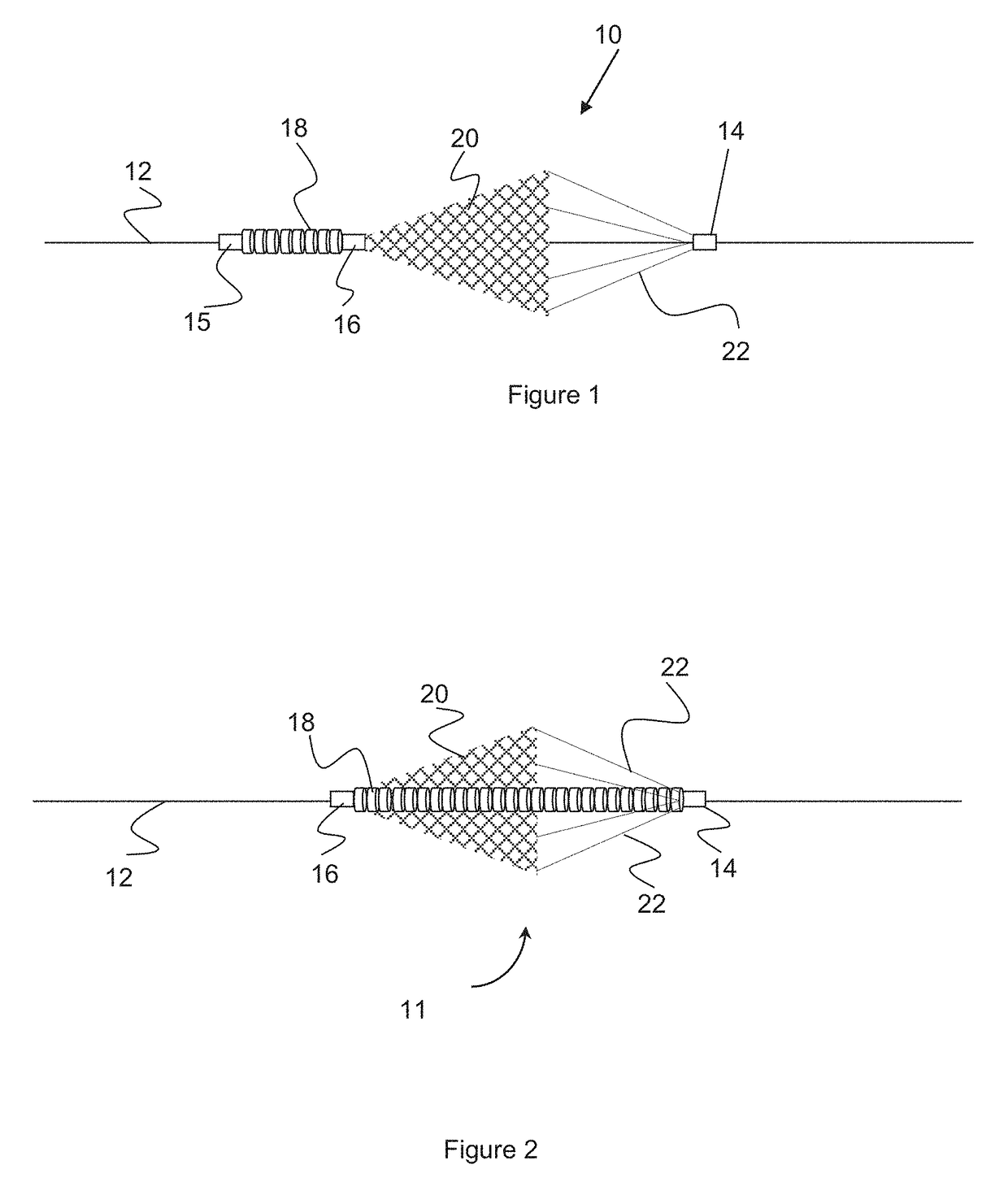
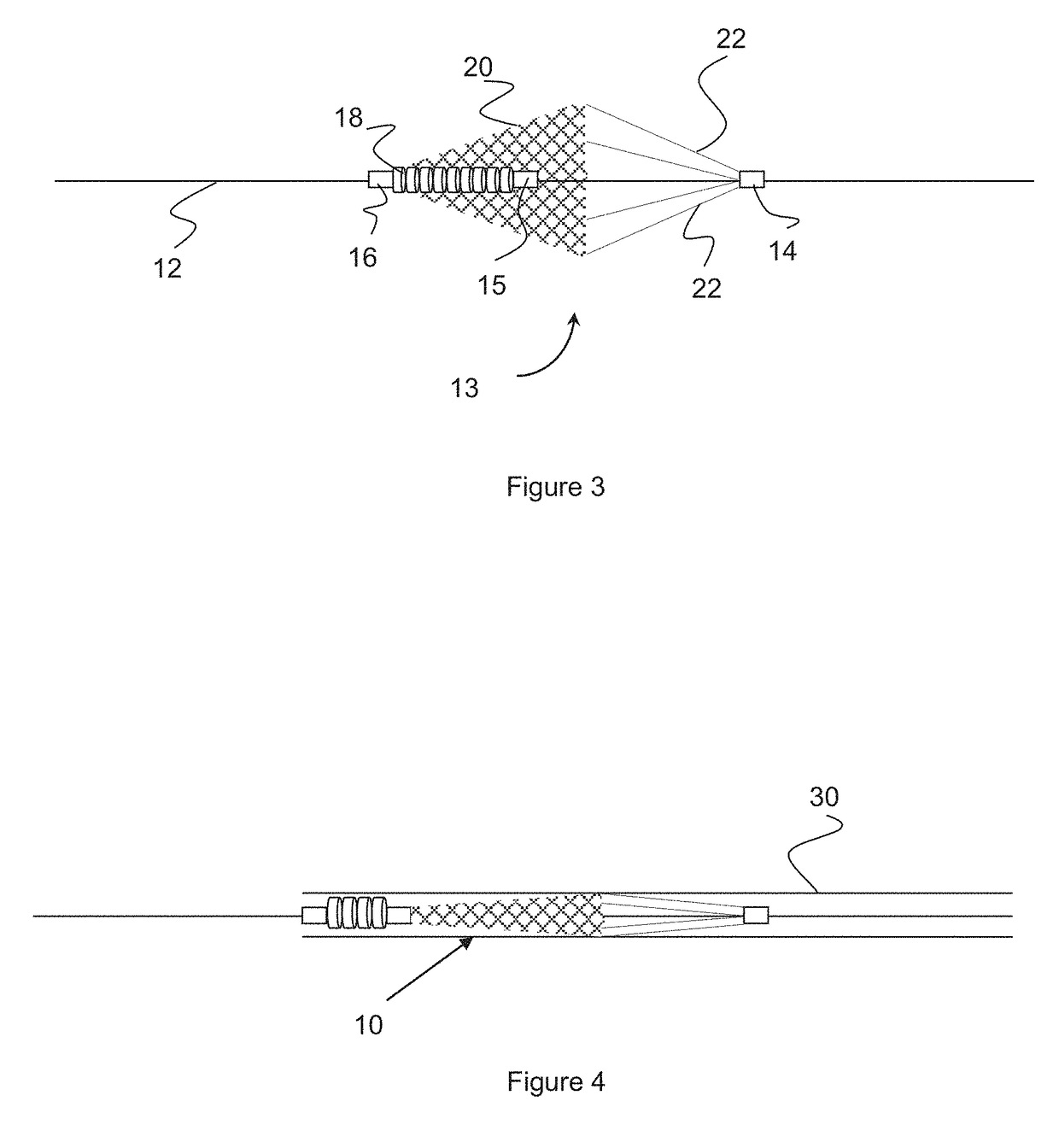
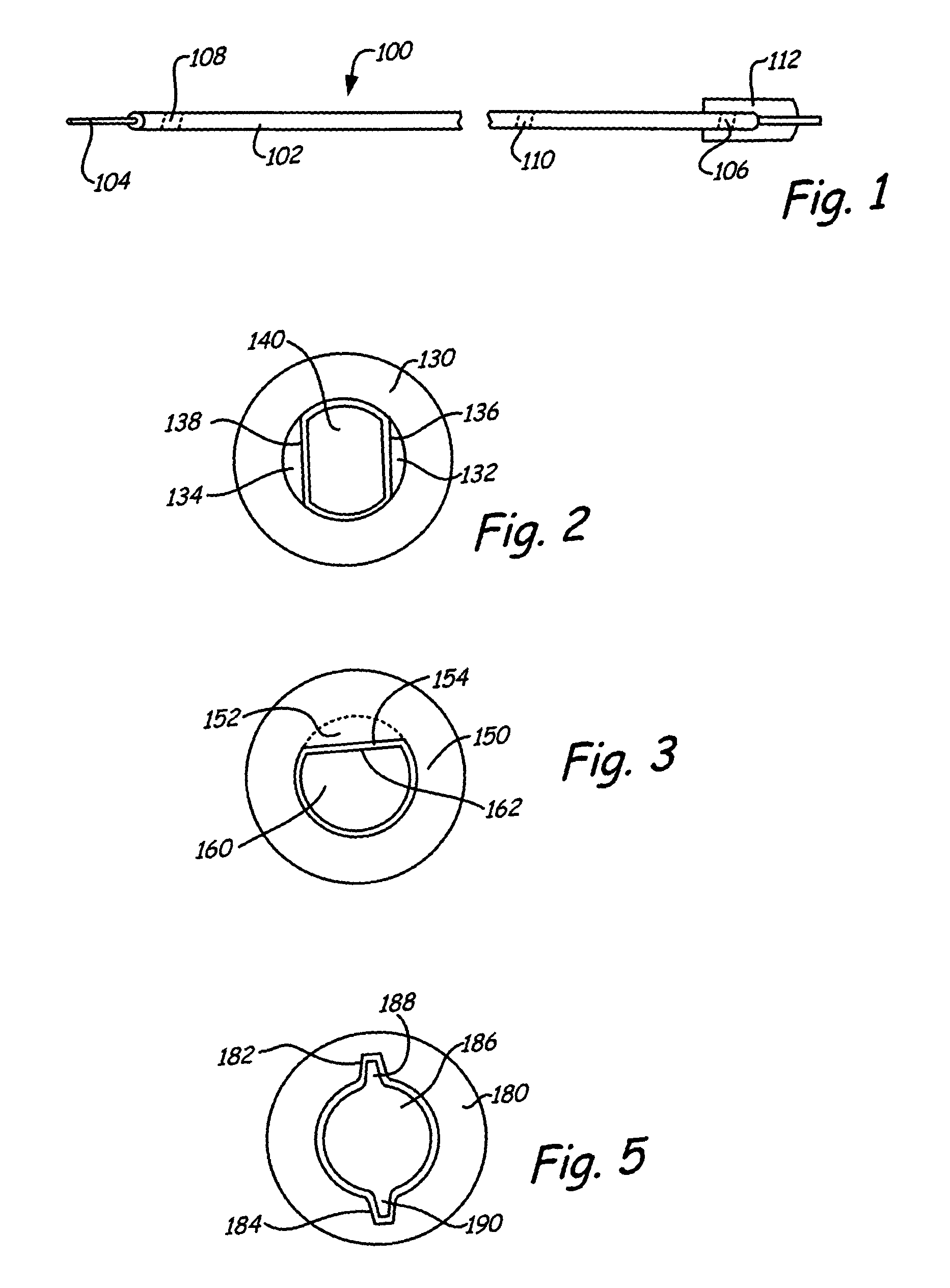
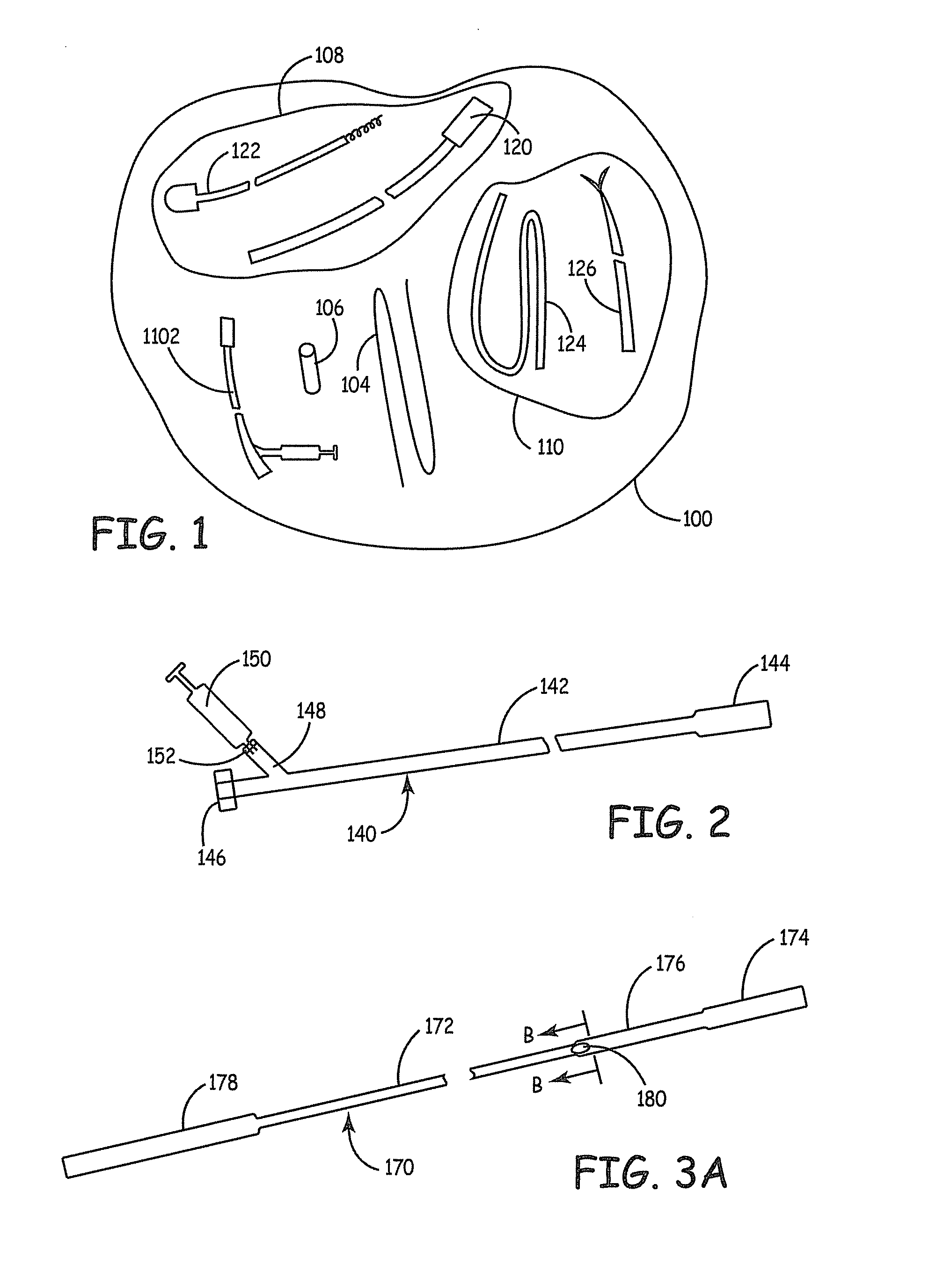
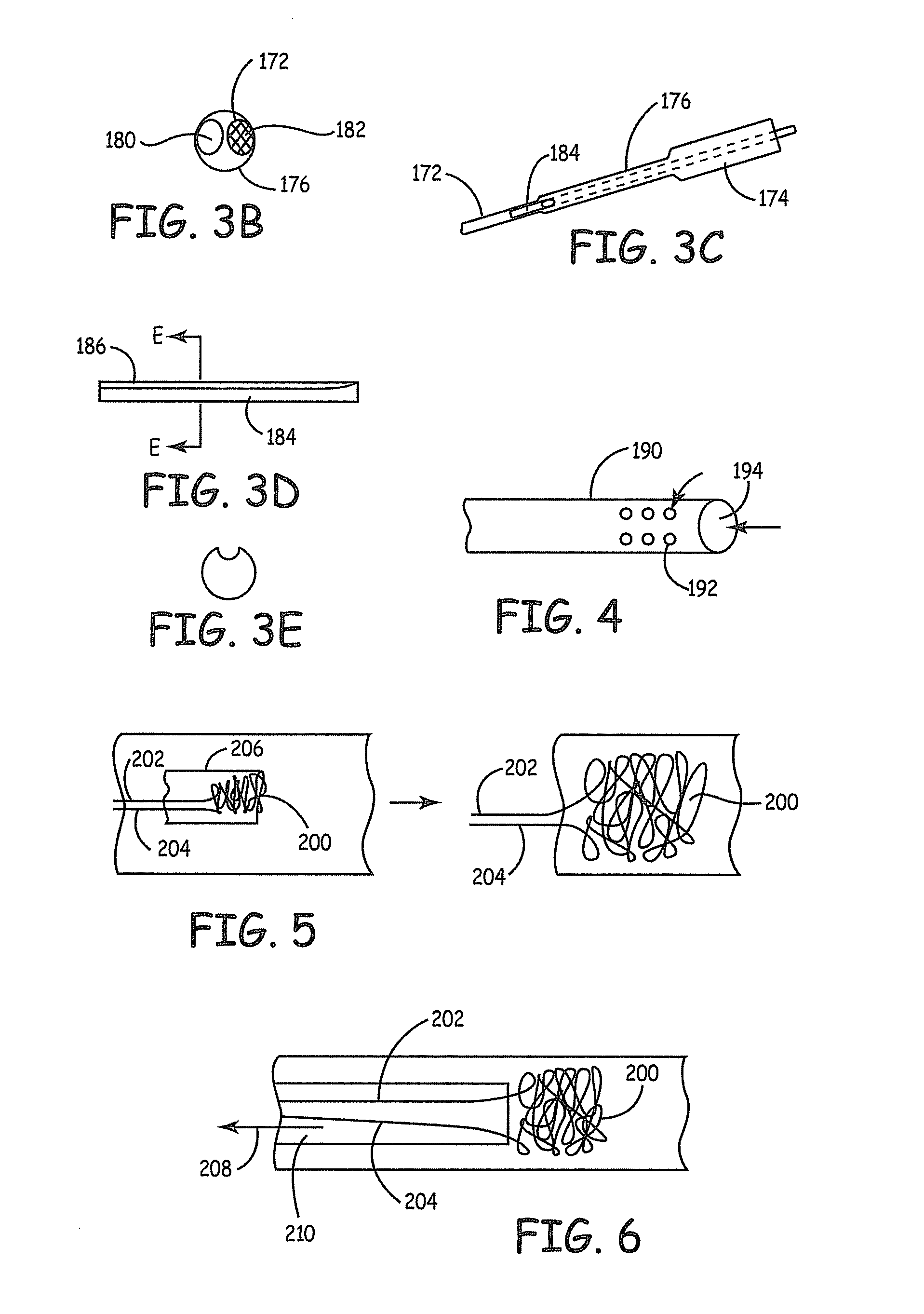
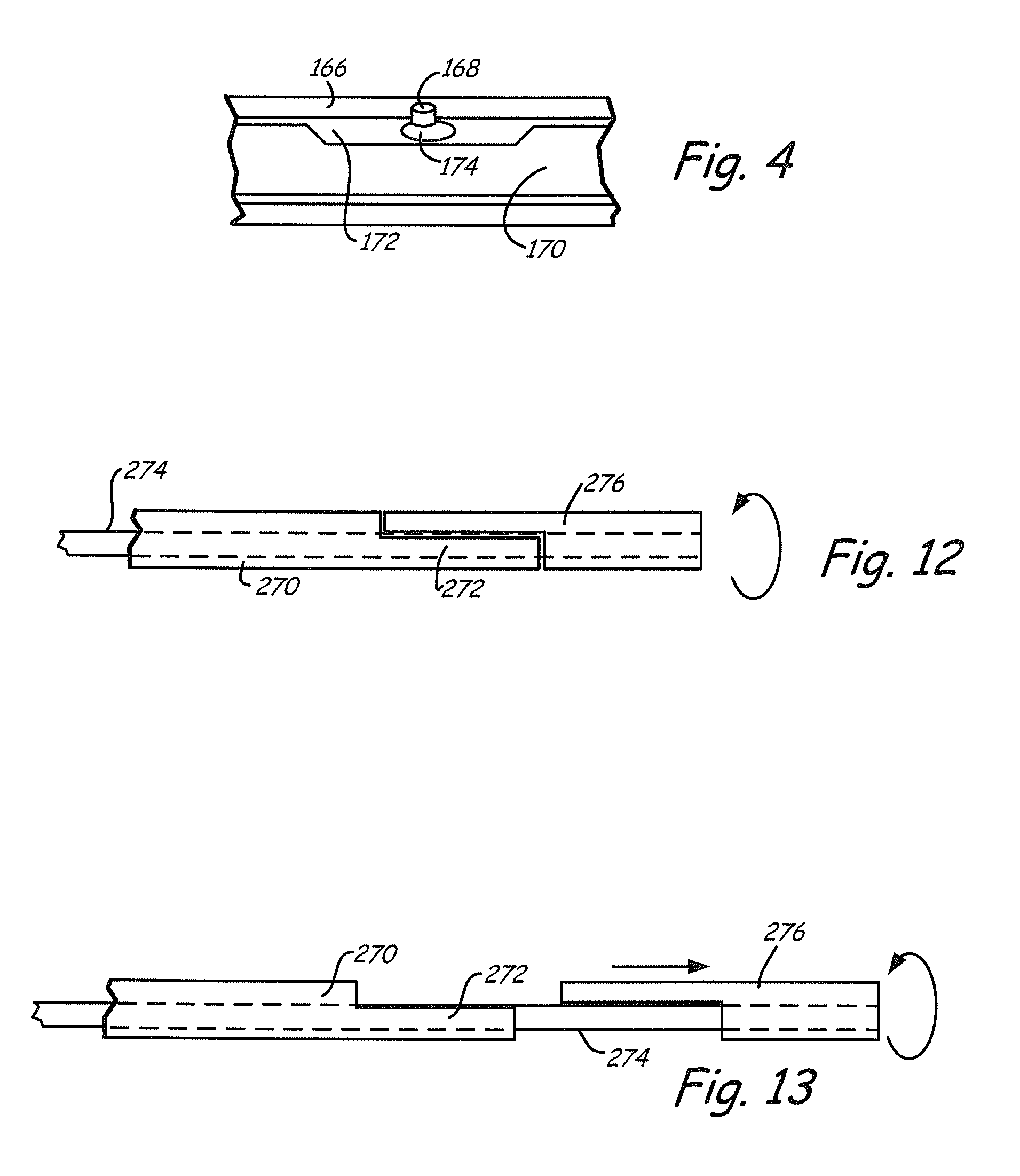
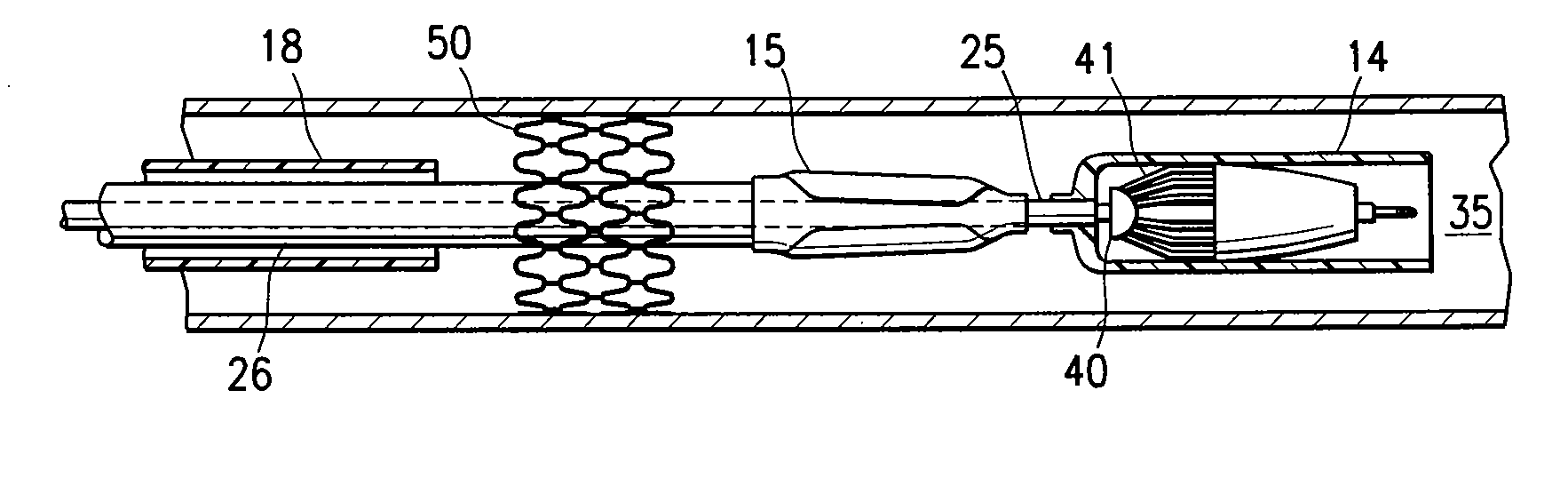
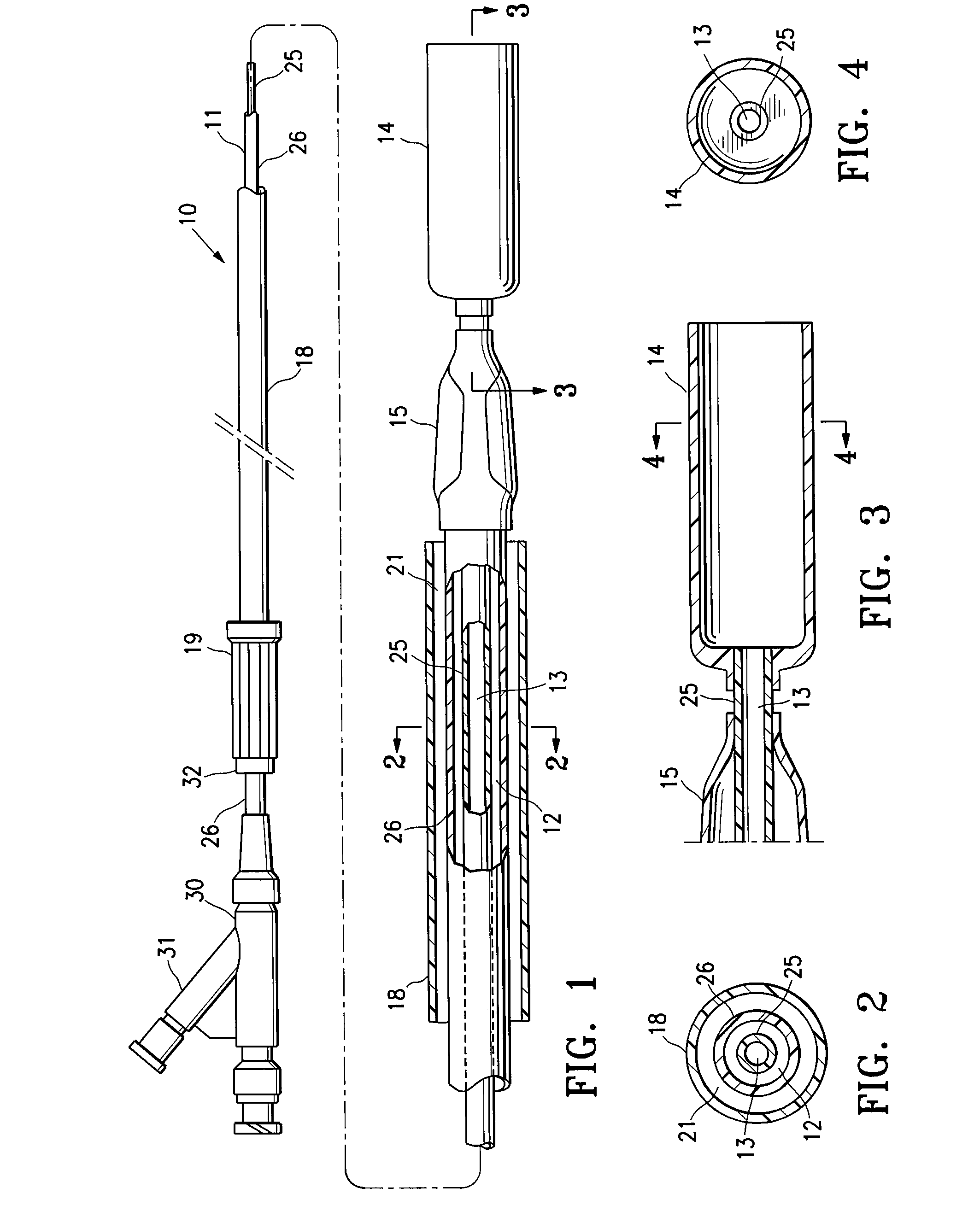
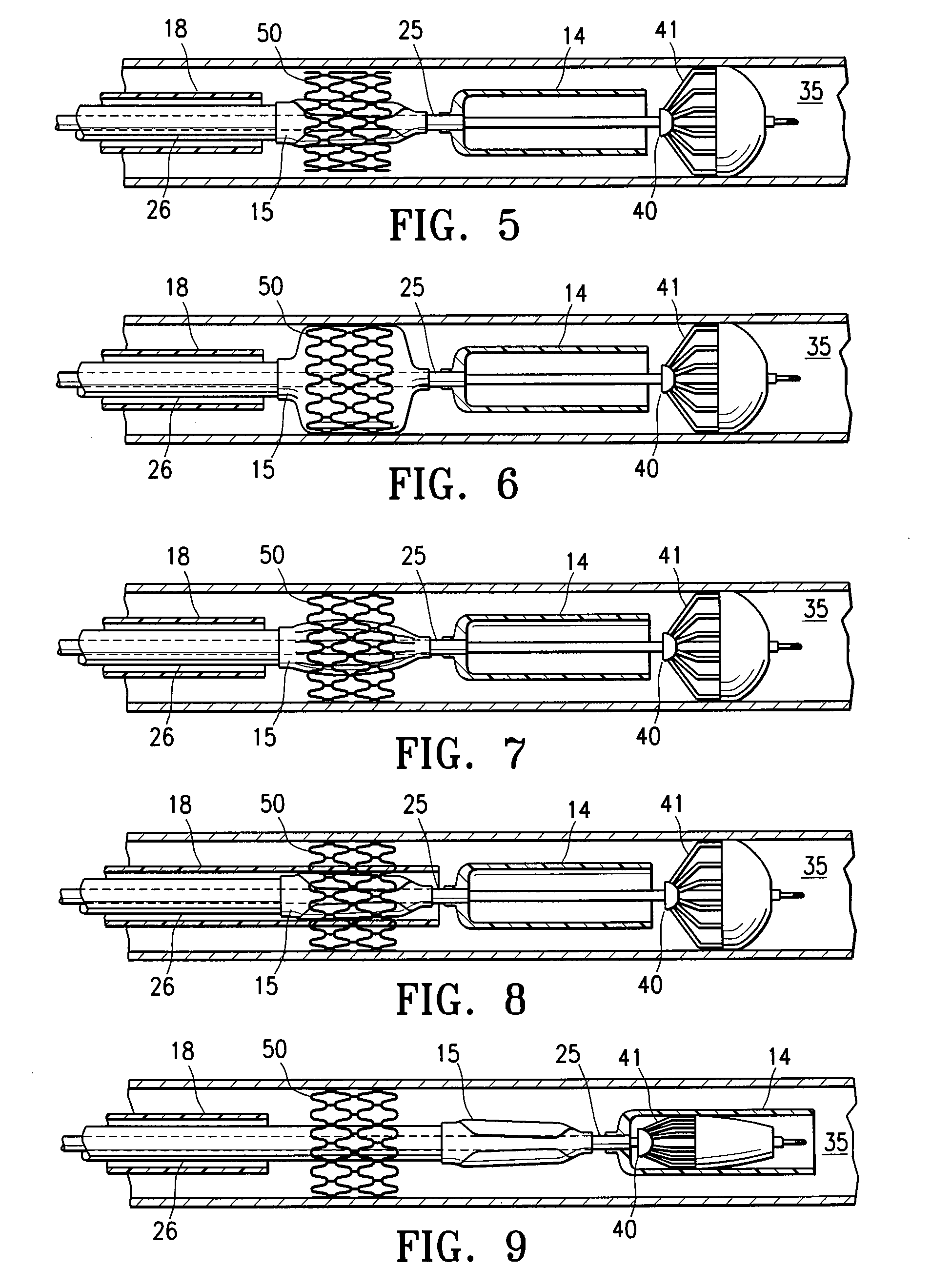
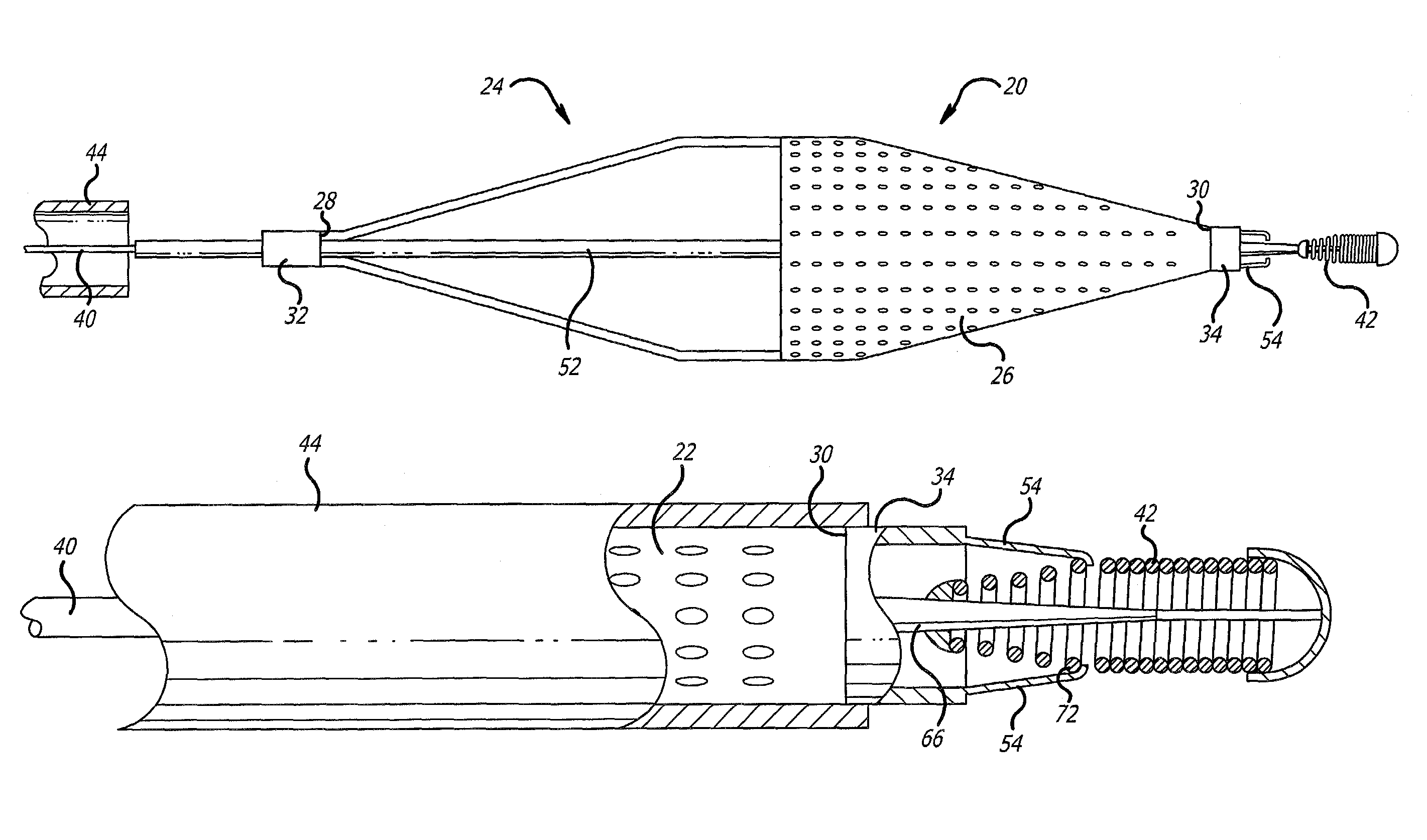
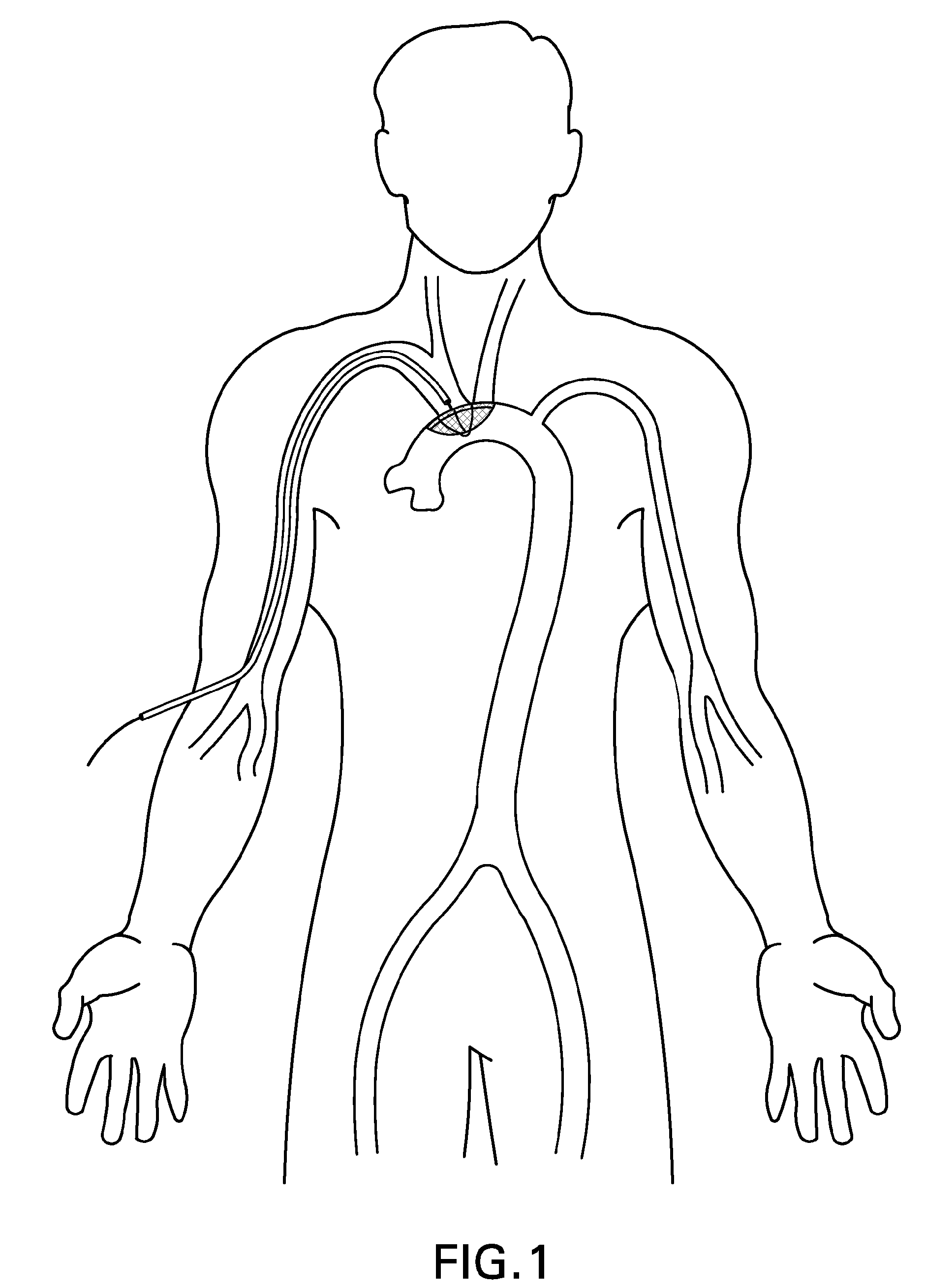
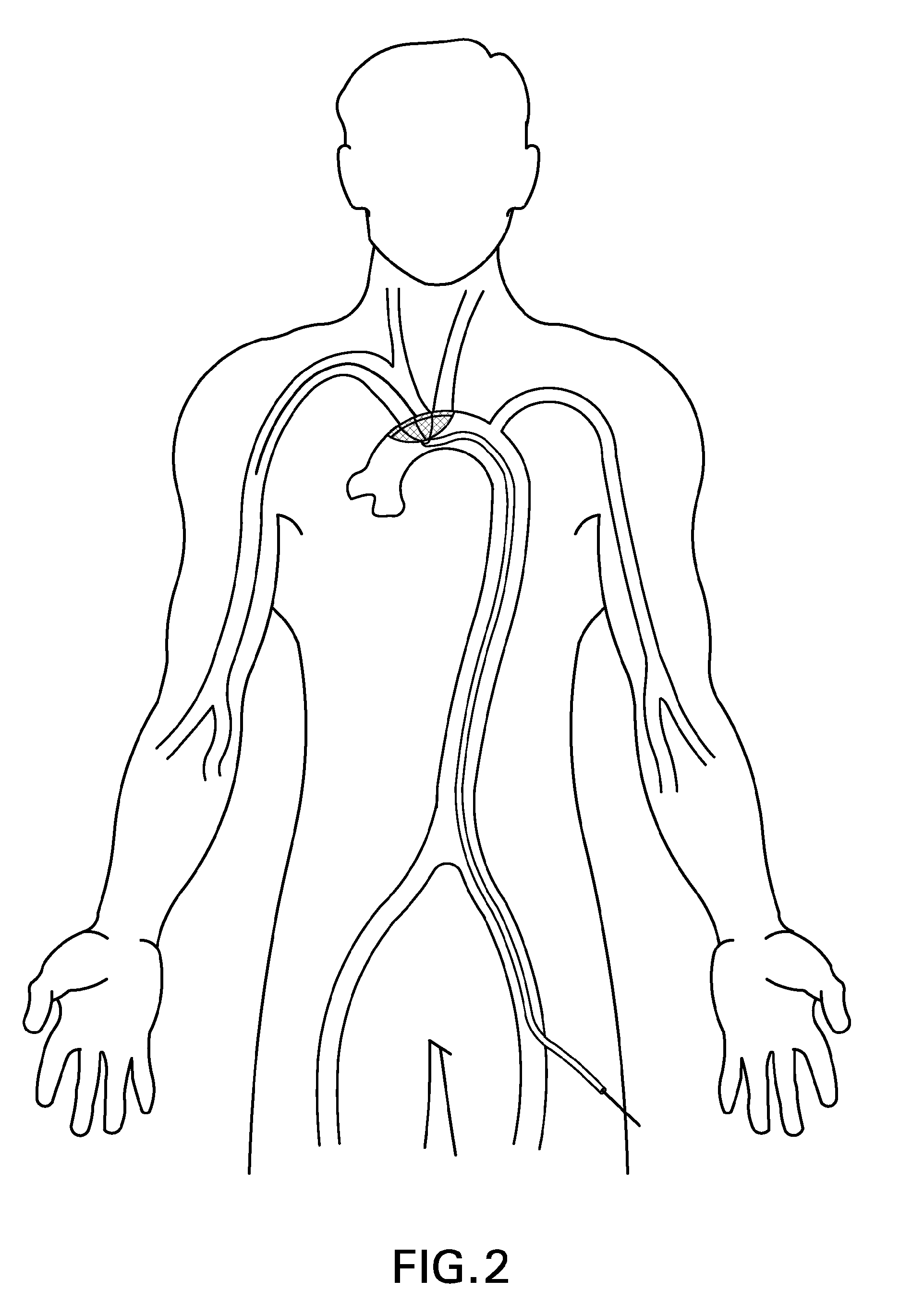
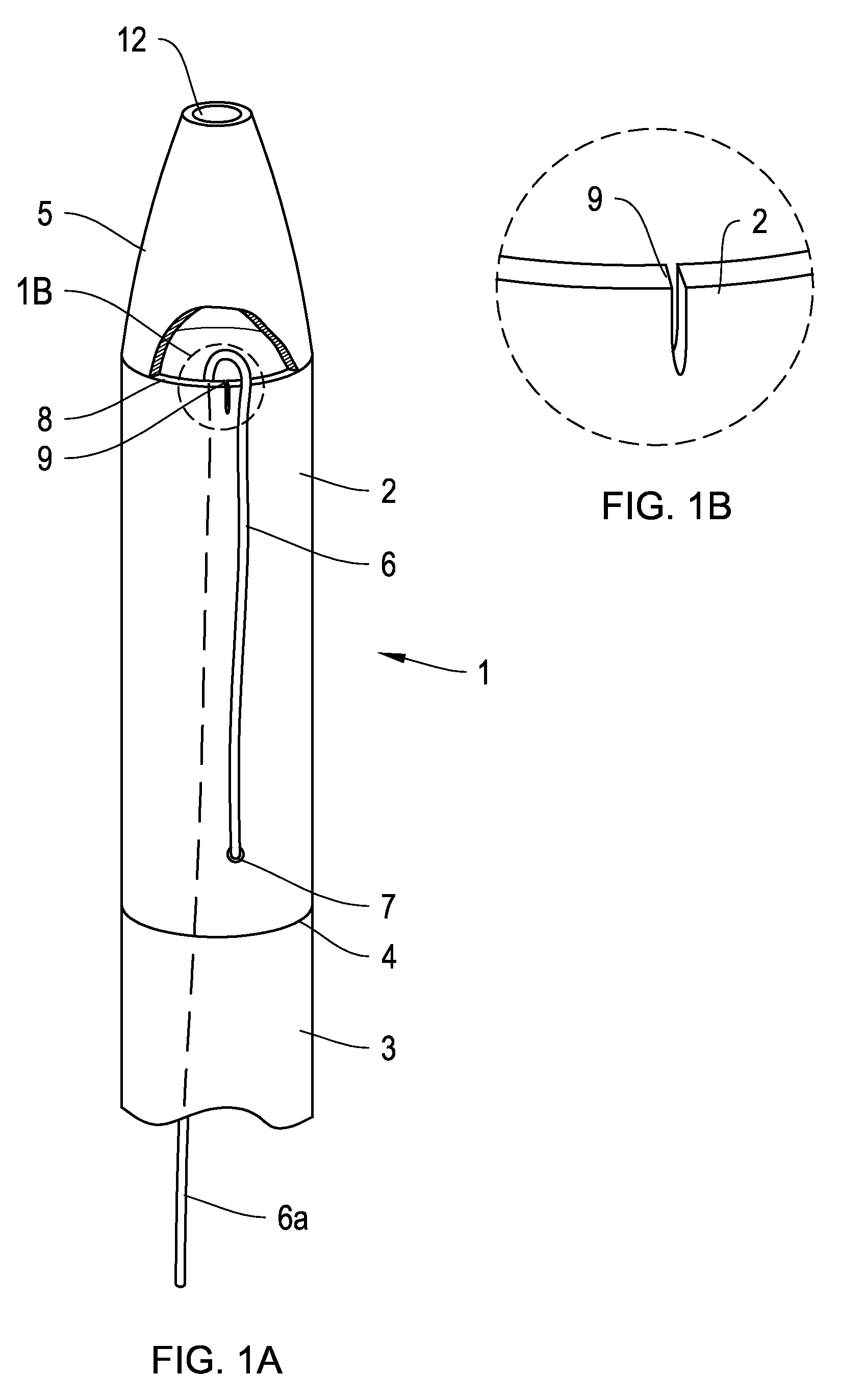
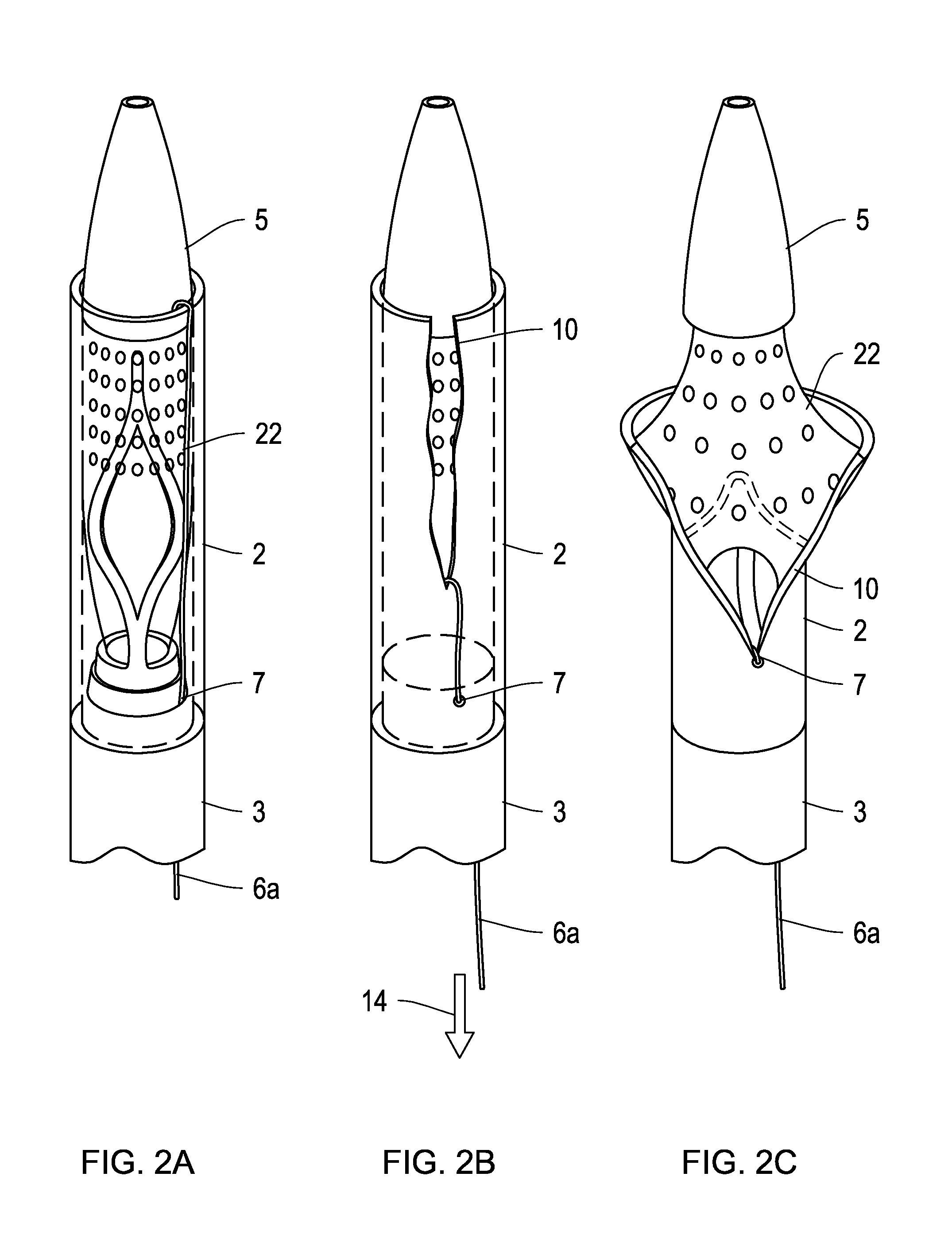
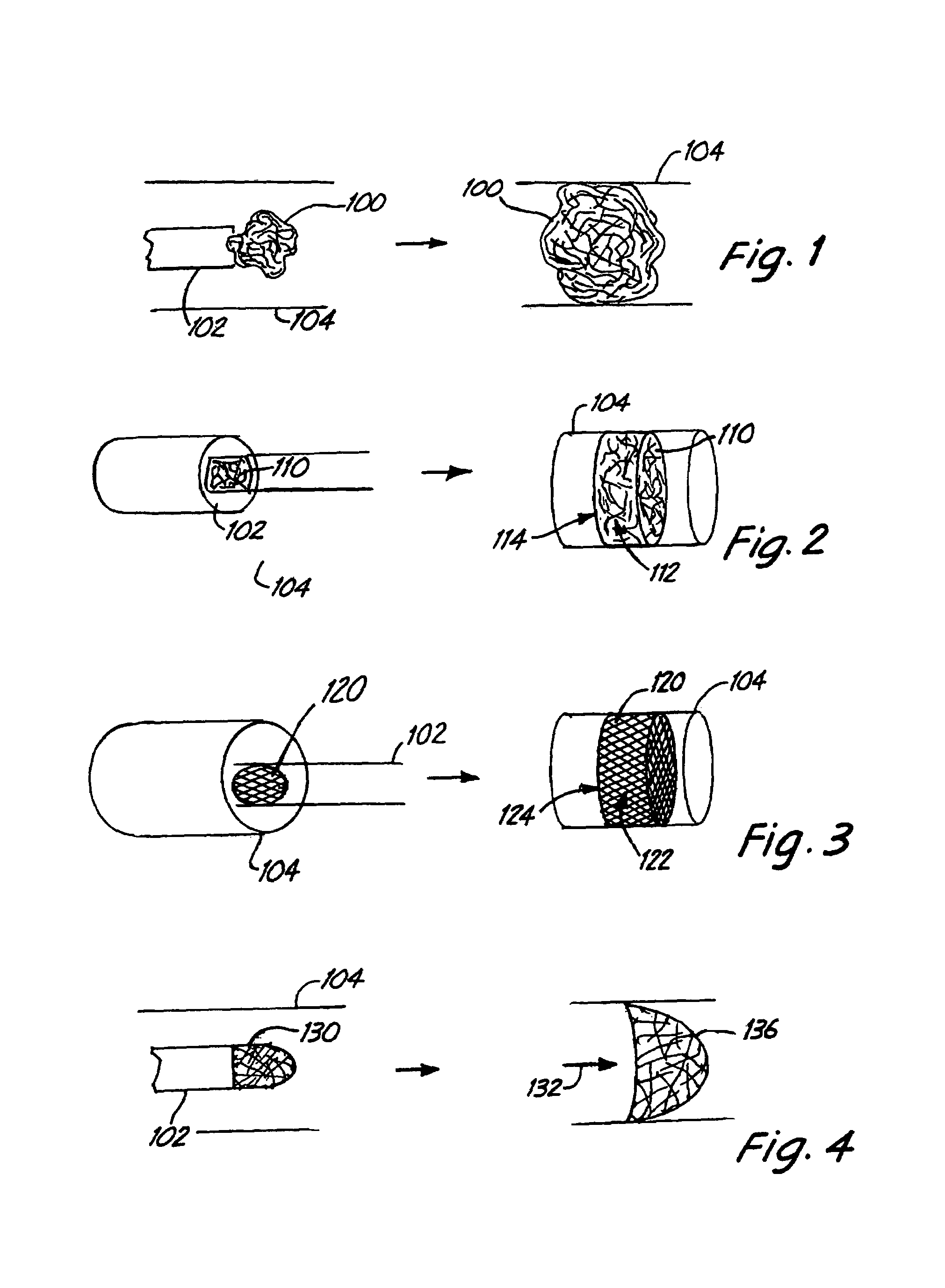
Apparatus and methods for intravascular embolic protection
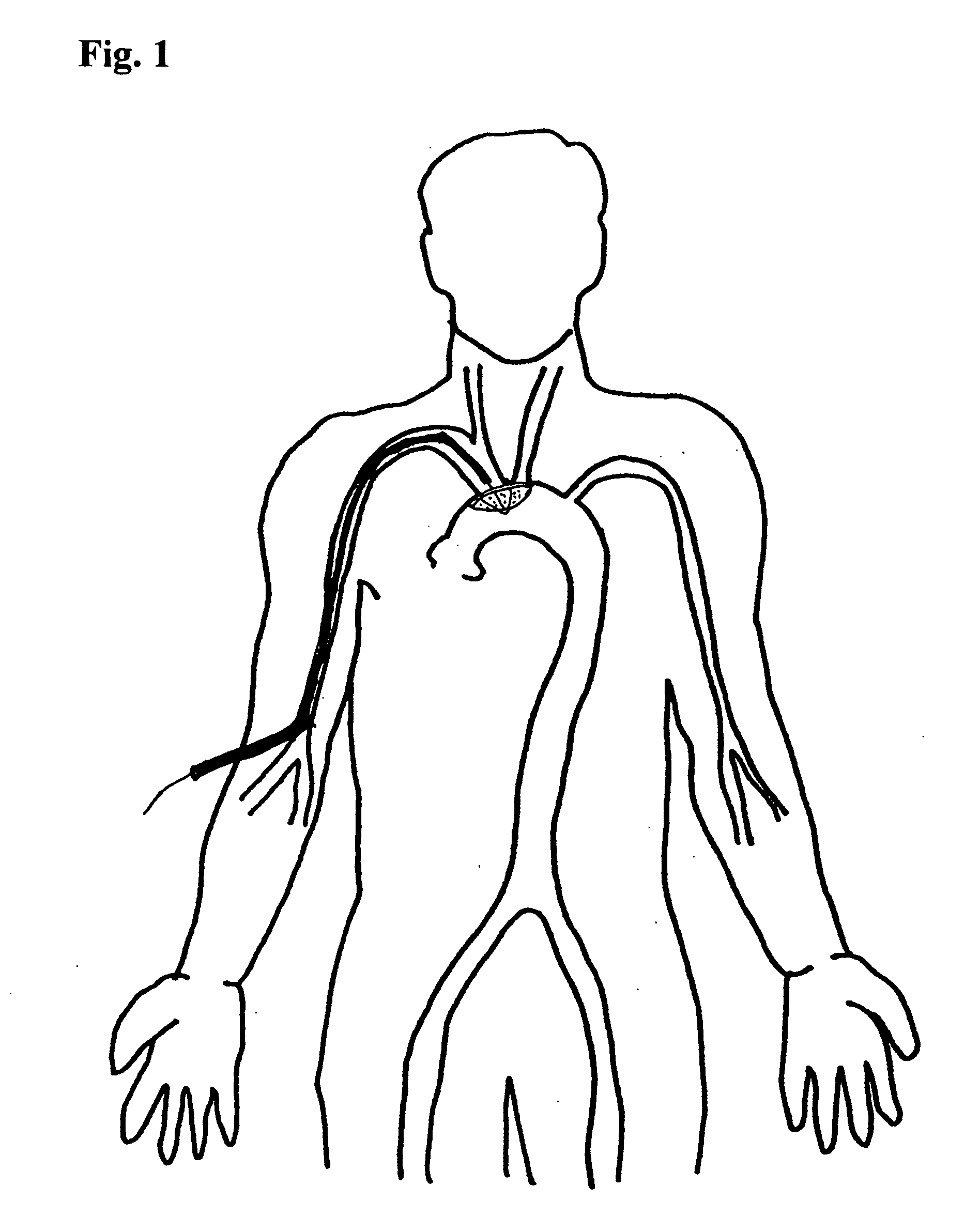
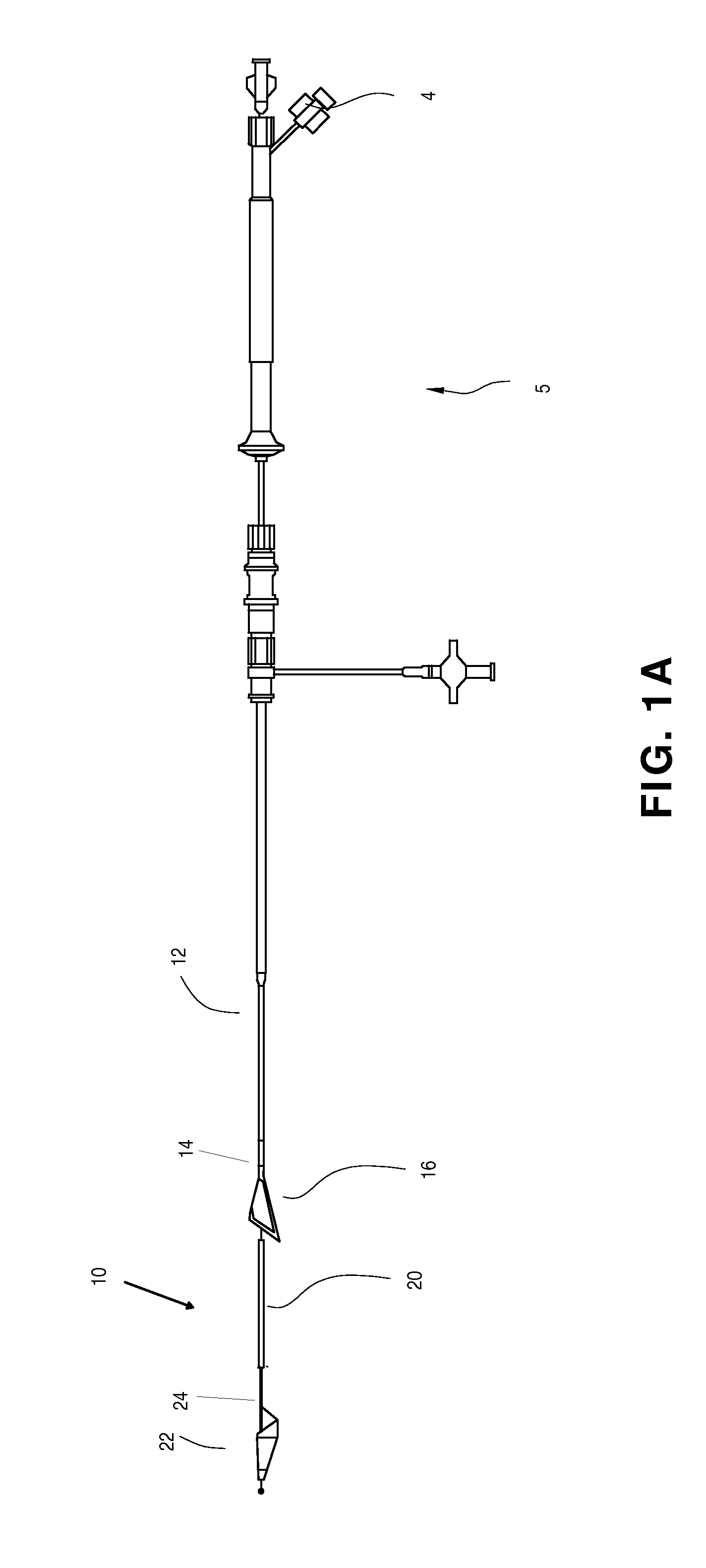
The present invention provides intravascular embolic protection apparatus including a blood filter element having an accommodating passageway adapted to permit passage of a procedure device therethrough and to substantially seal against passage of particles between the embolic protection apparatus and the procedure device by accommodating to a size and shape of the procedure device. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method of performing an endovascular procedure on a patient including the steps of delivering an embolic protection apparatus to a location within a vascular lumen of the patient; passing a procedure device through an accommodating passageway of the apparatus, the accommodating passageway accommodating to a size and shape of the procedure device; performing the endovascular procedure; and removing the procedure device from the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
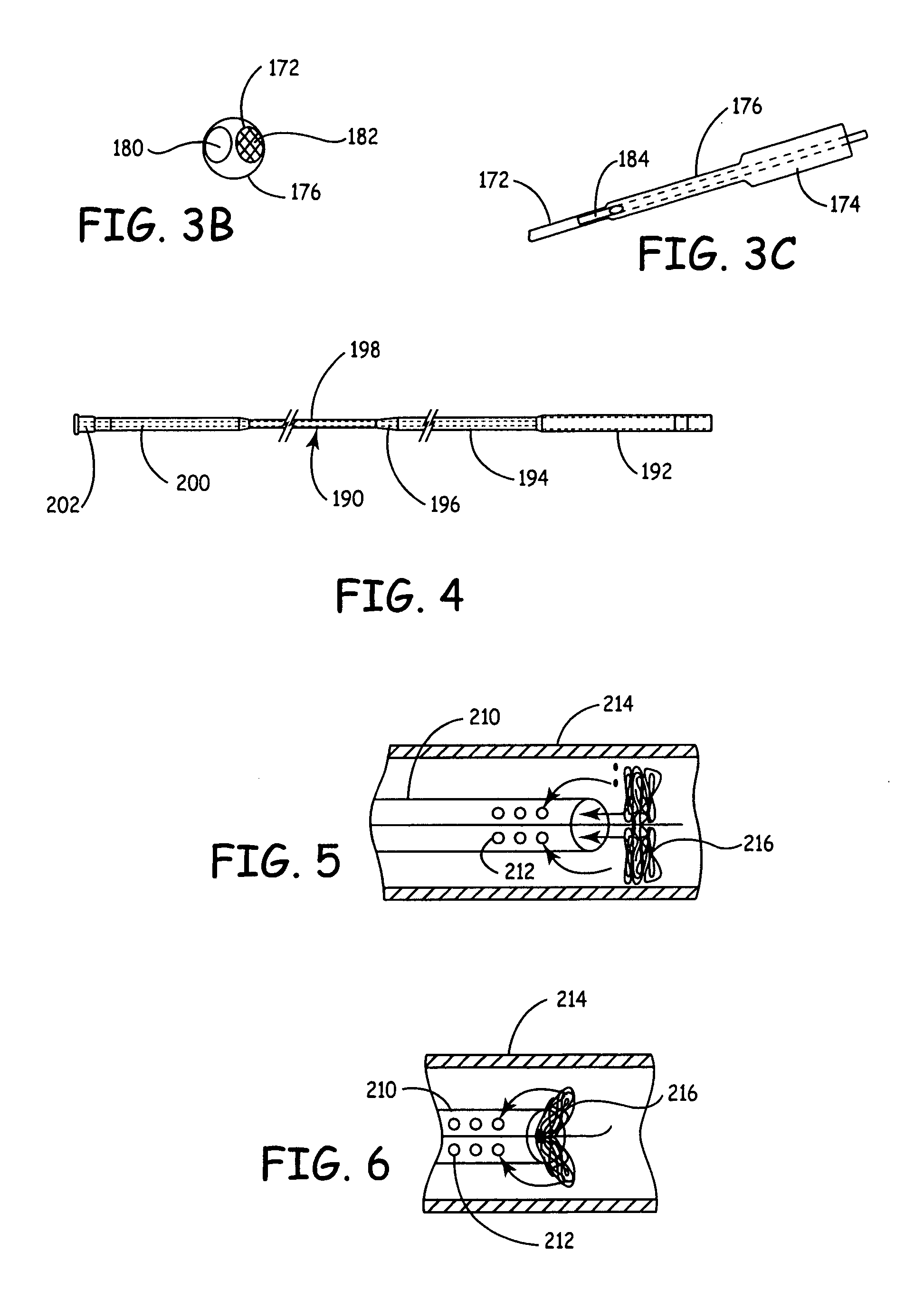
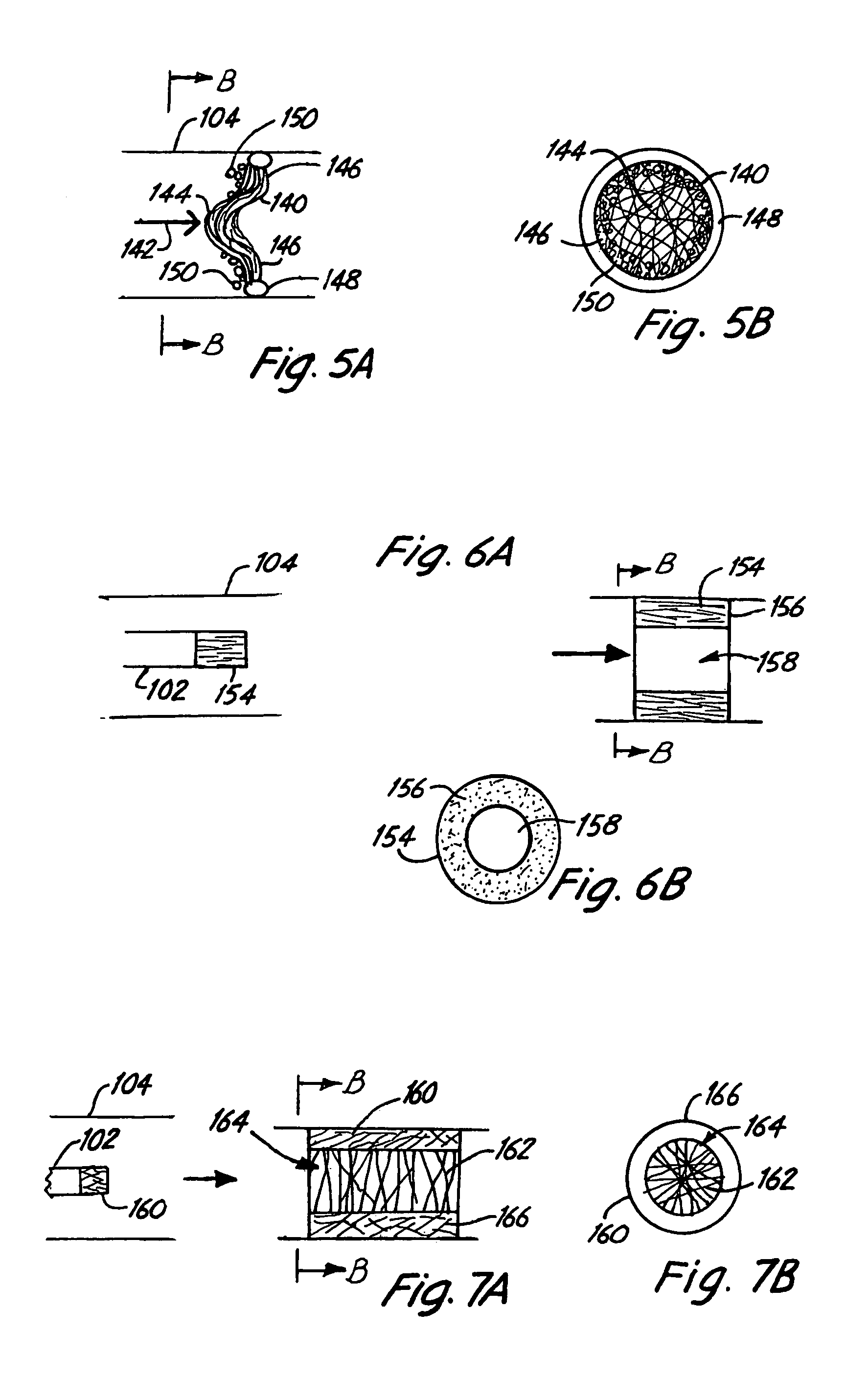
Fiber based embolism protection device
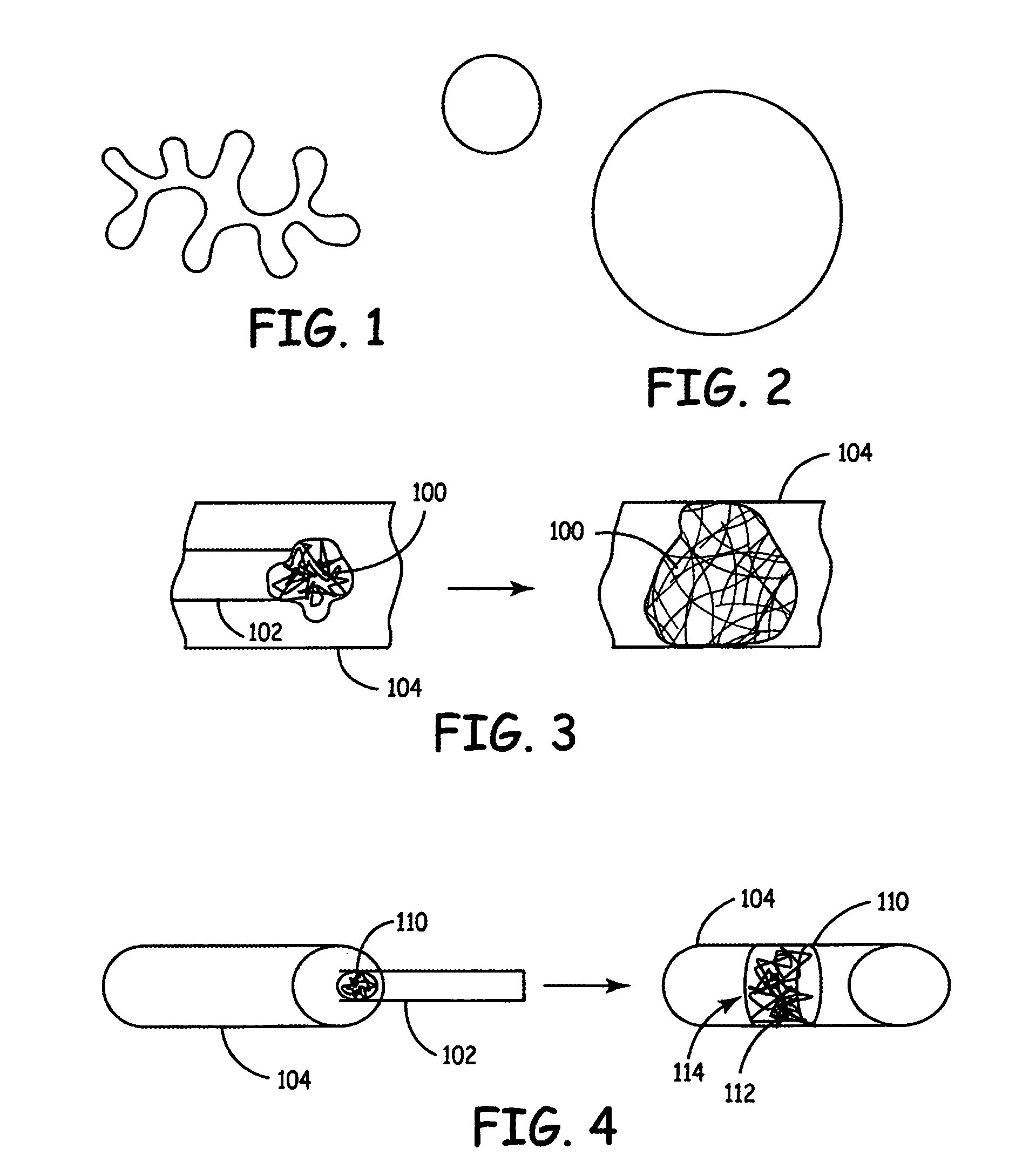
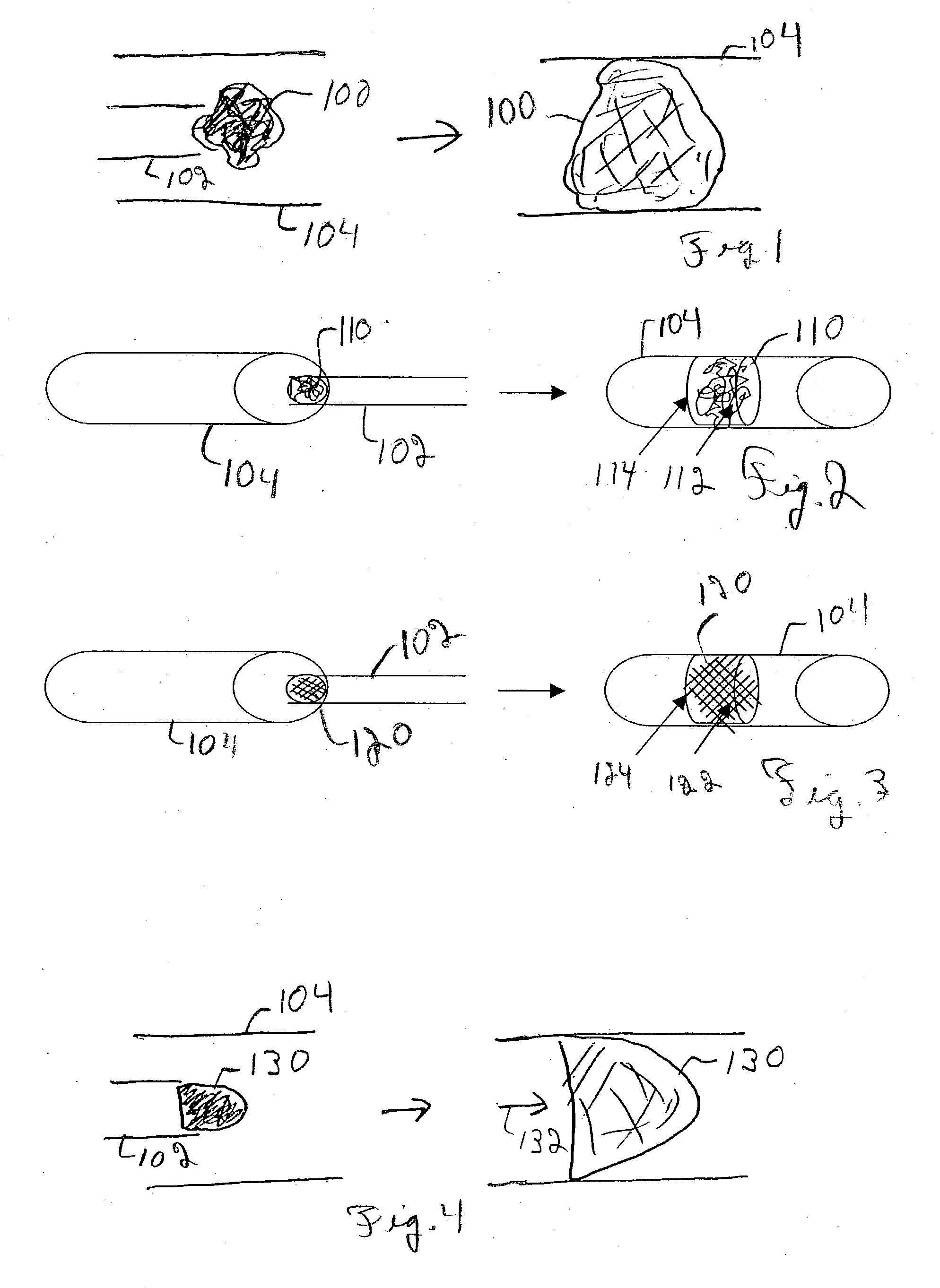
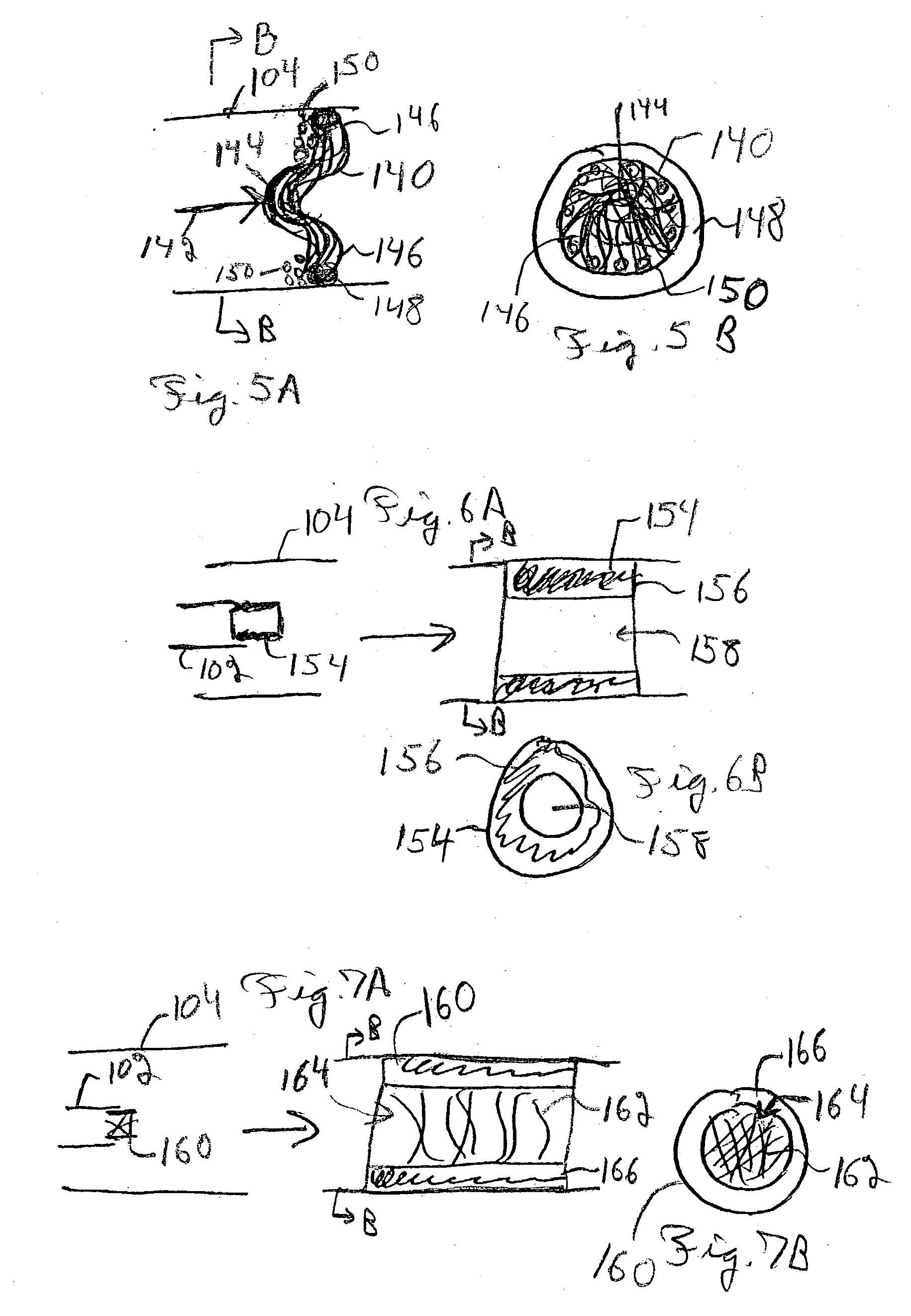
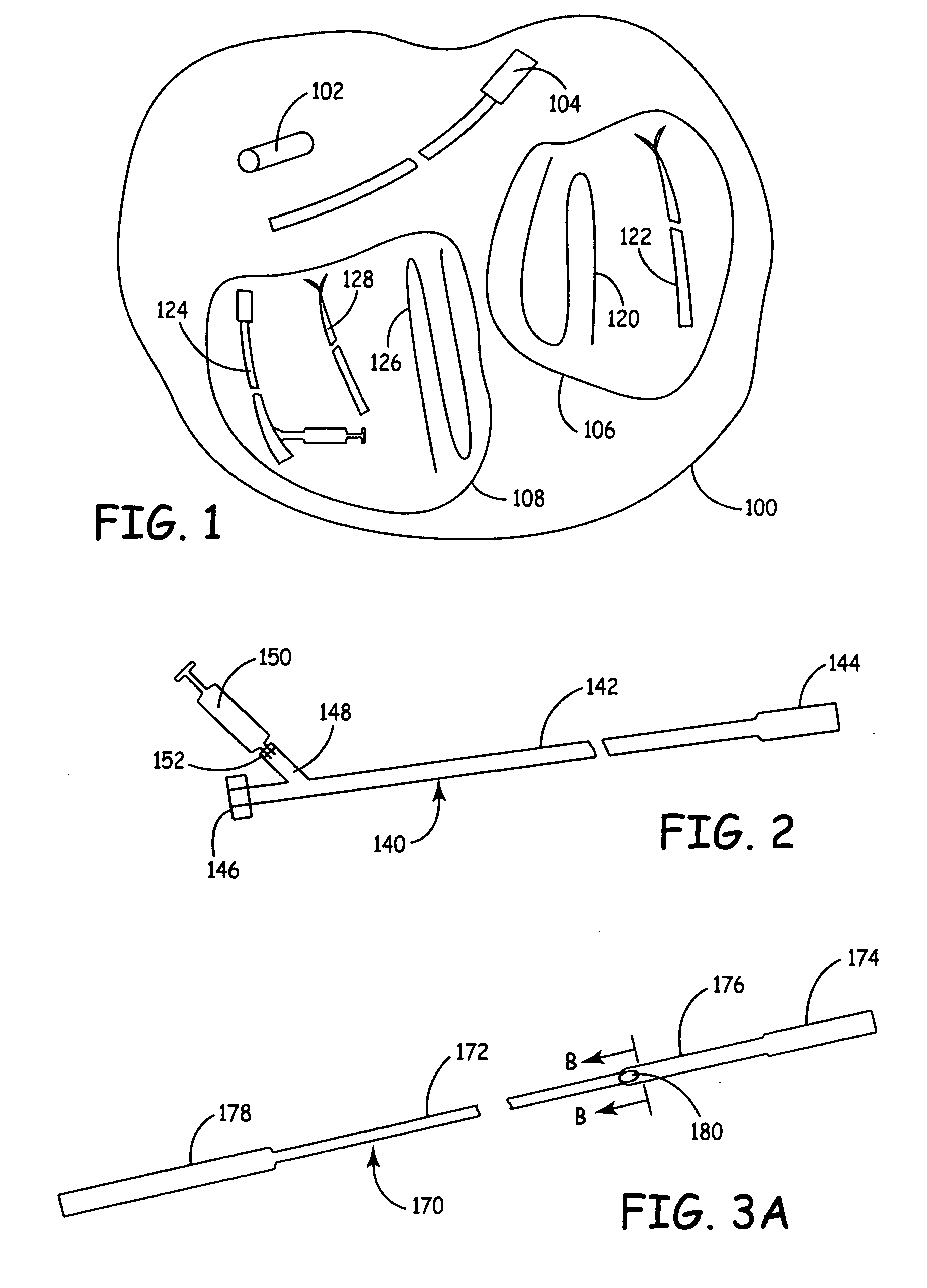
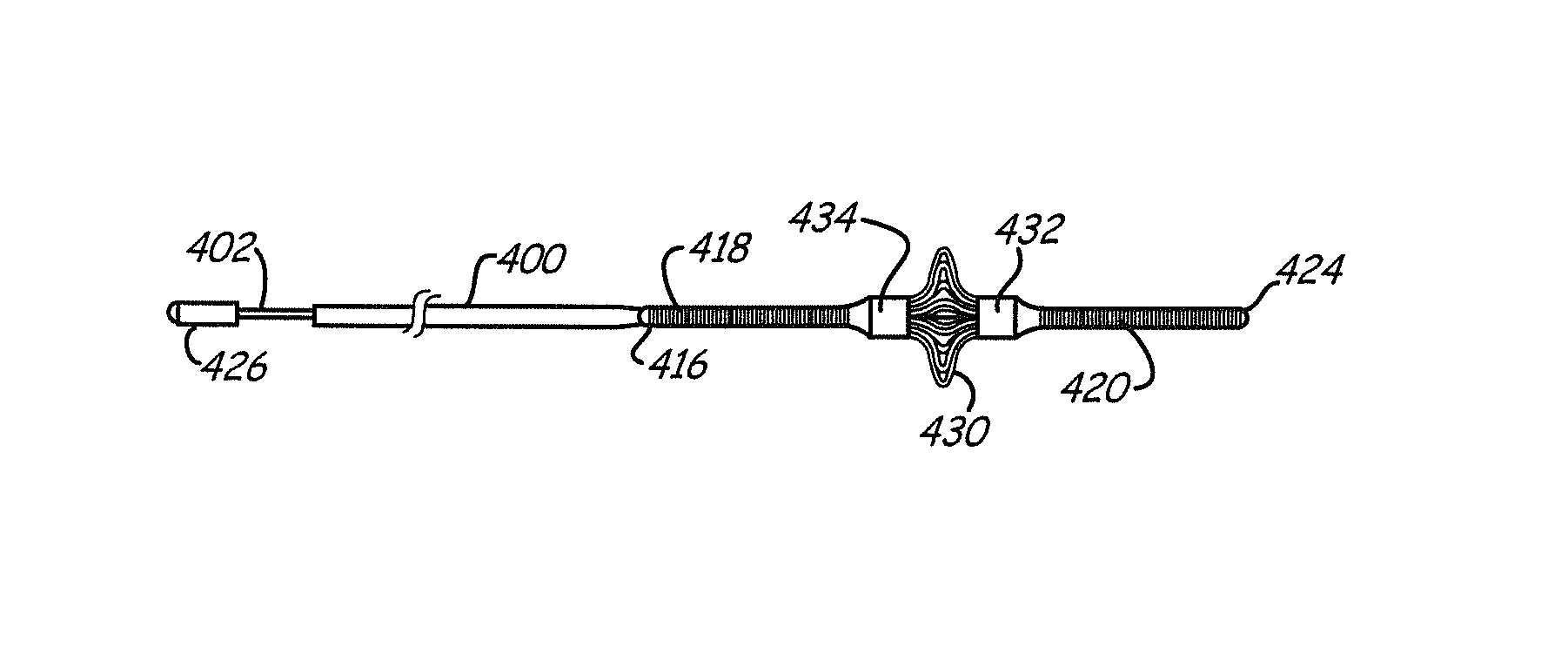
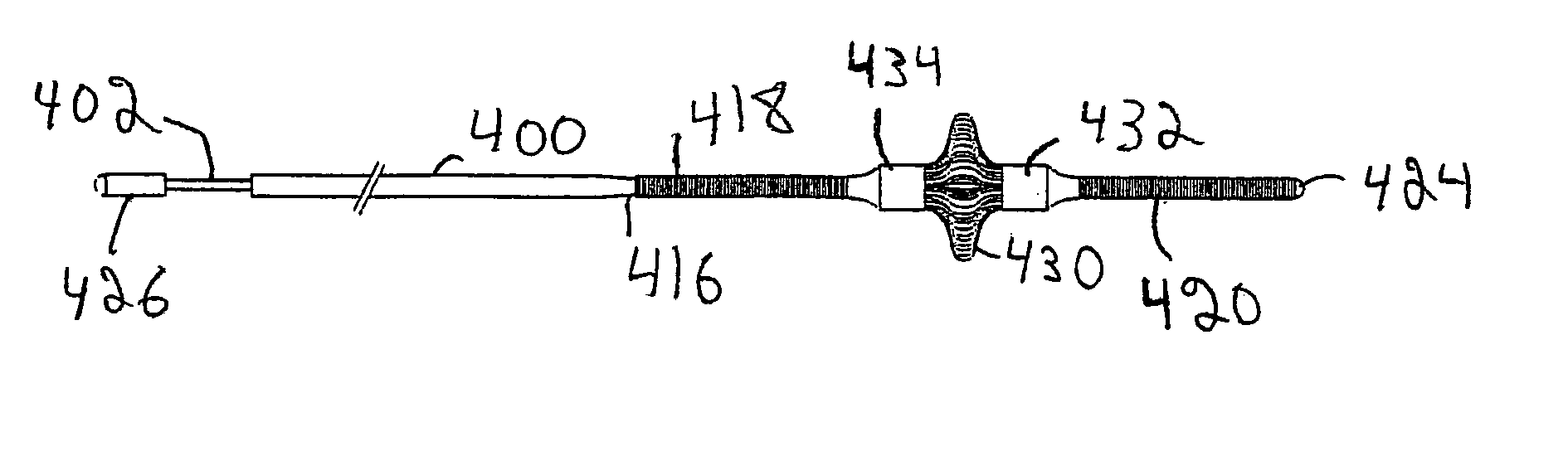
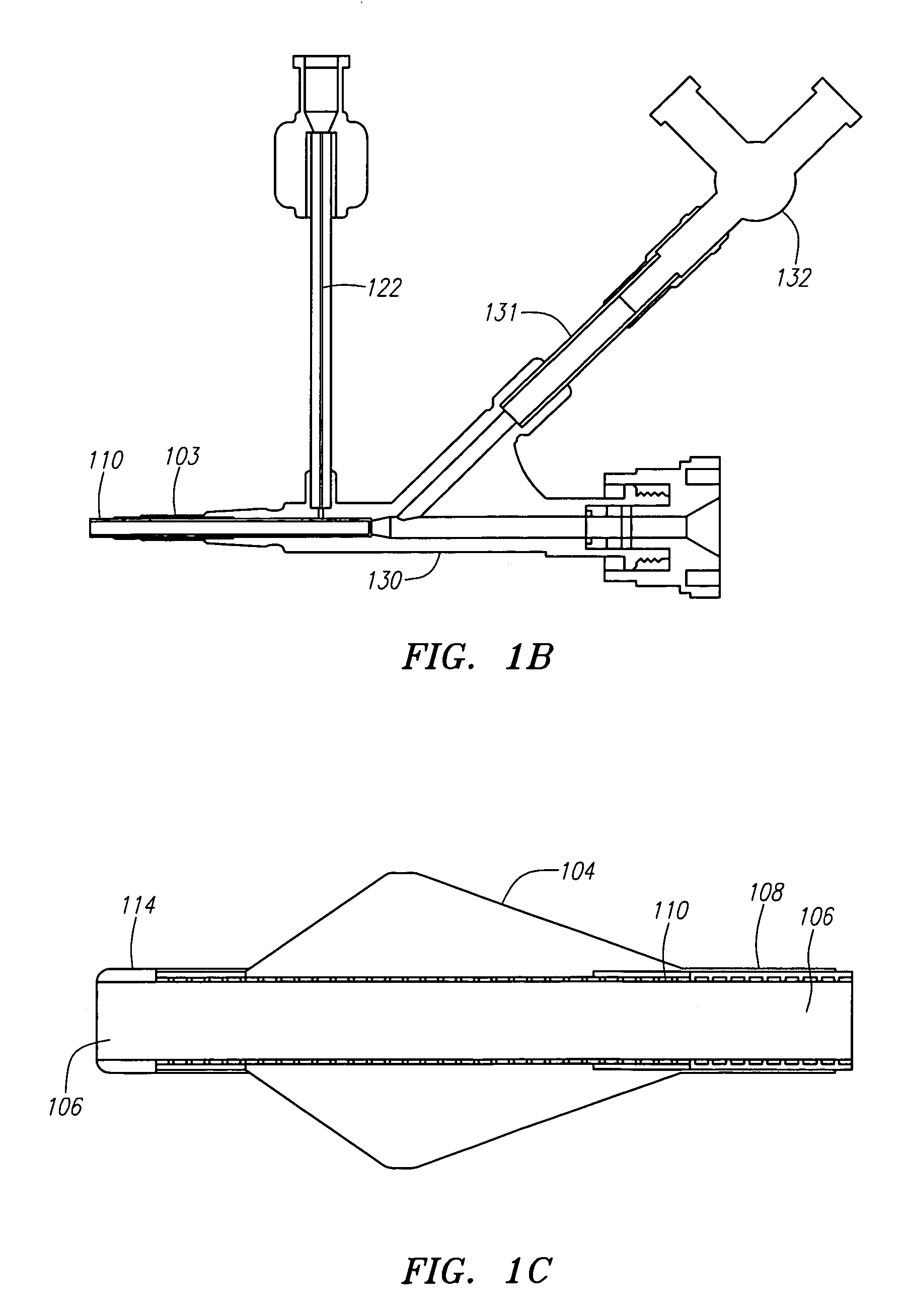
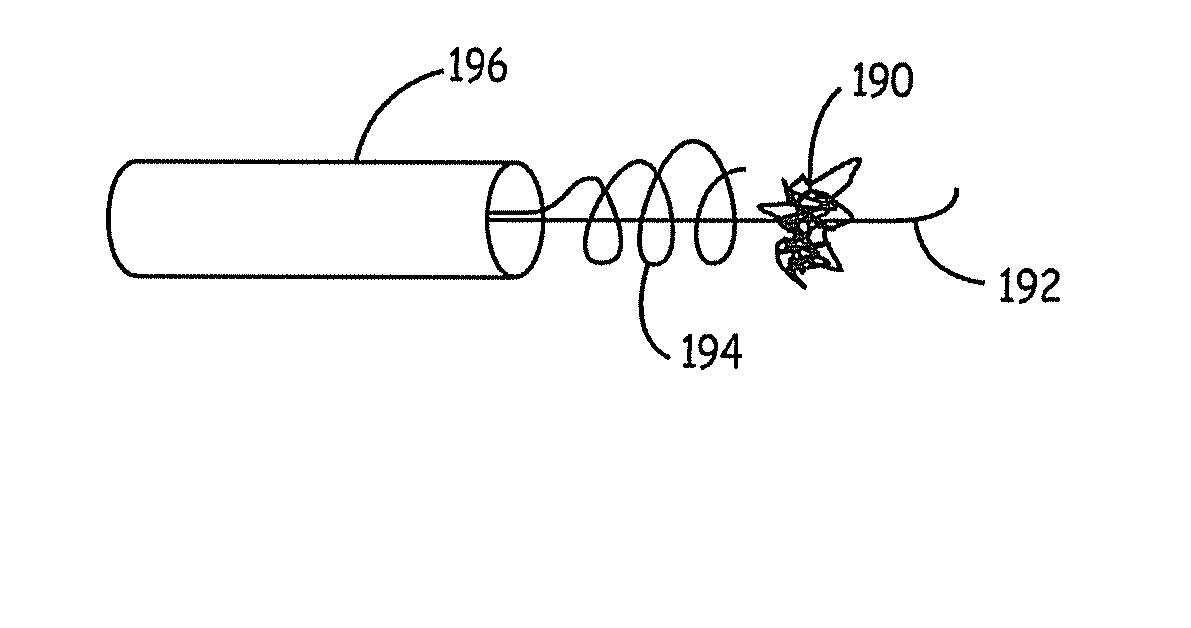
Improved embolism protection devices comprises fibers that can have one configuration for delivery of the device and a second configuration in which the device is deployed for filtering of flow within a vessel. In some embodiments, the fibers can be connected to a fiber support, which is connected to an actuating element. The actuating element controls the transition from the delivery configuration to the deployed configuration. The embolism protection device can comprise a guidewire. The fibers can be attached at one end to a fiber support structure and at another end to the guidewire. A hypotube can be attached to the proximal end of the fibers while the guidewire is attached at the distal end of the fibers with the guidewire extending within a central channel of the hypotube. The hypotube can be used to guide the delivery of treatment structures, such as a balloon and / or a stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Embolic protection device and method of use
There is disclosed a blood debris deflector for preventing embolization during a surgical procedure, and methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
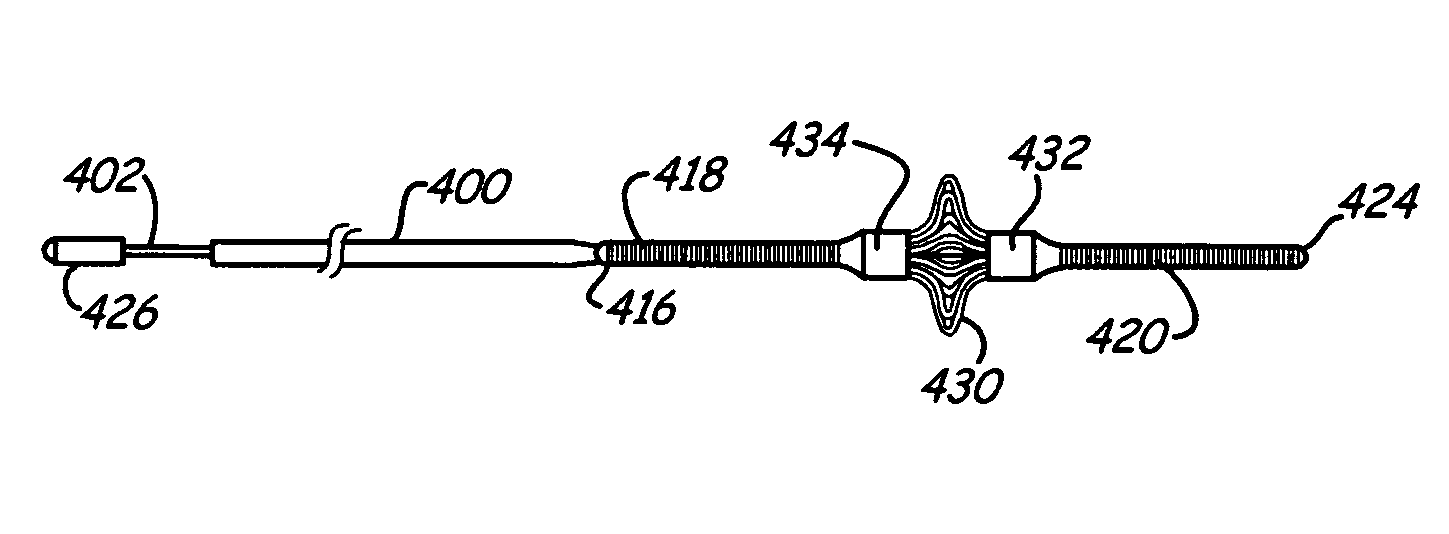
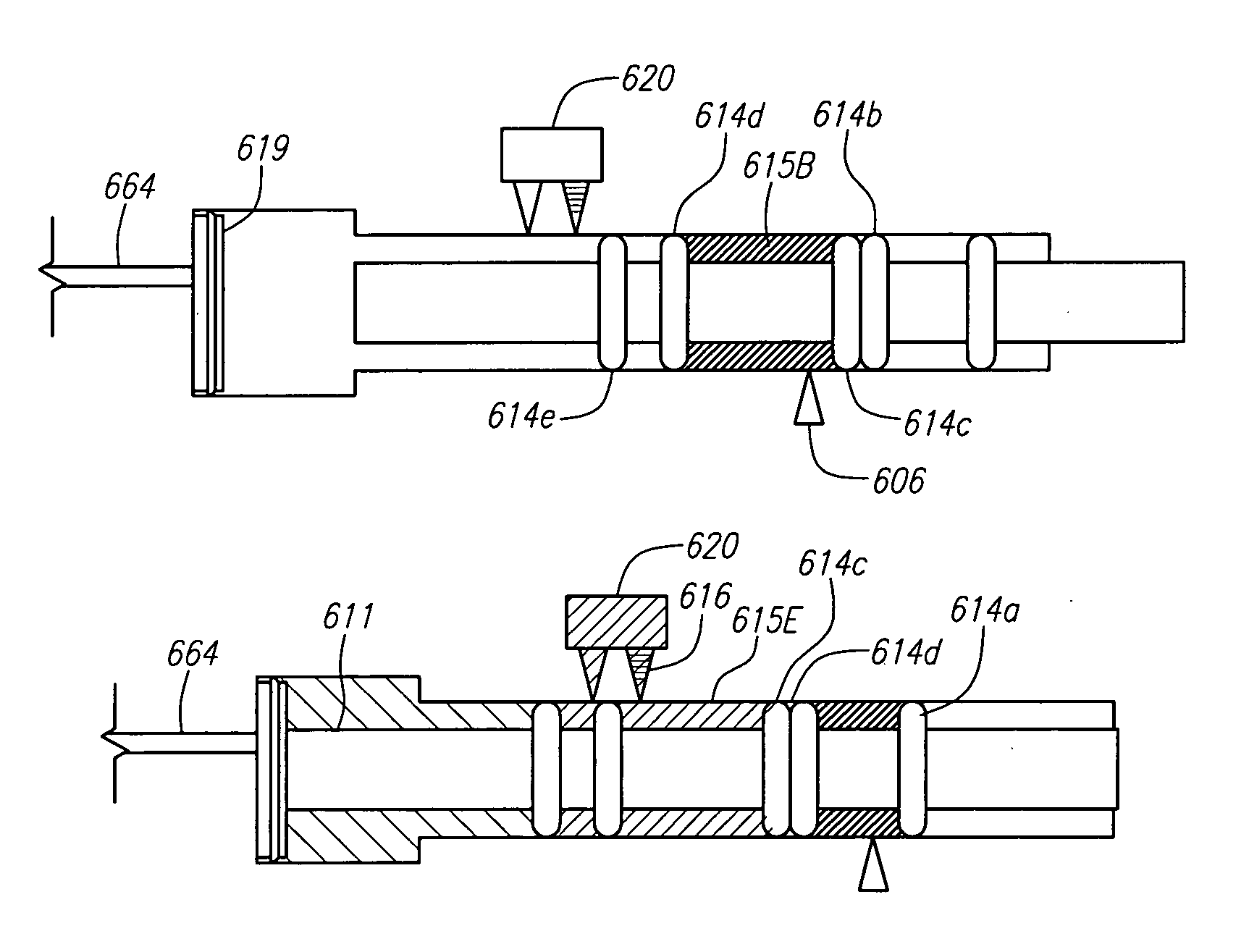
Steerable device having a corewire within a tube and combination with a functional medical component
An integrated guiding device has a tube and a corewire within the tube and a torque coupler. The torque coupler can couple the rotational motion of the tube with the rotational motion of the corewire. The wire can be moved longitudinally at least some amount relative to the tube. The device can further comprise a functional medical structure, such as an embolism protection structure. The device can be used in medical procedures, such as less invasive procedures within the cardiovascular system. Improved fiber based embolism protection devices comprise fiber bundles that are twisted prior to delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
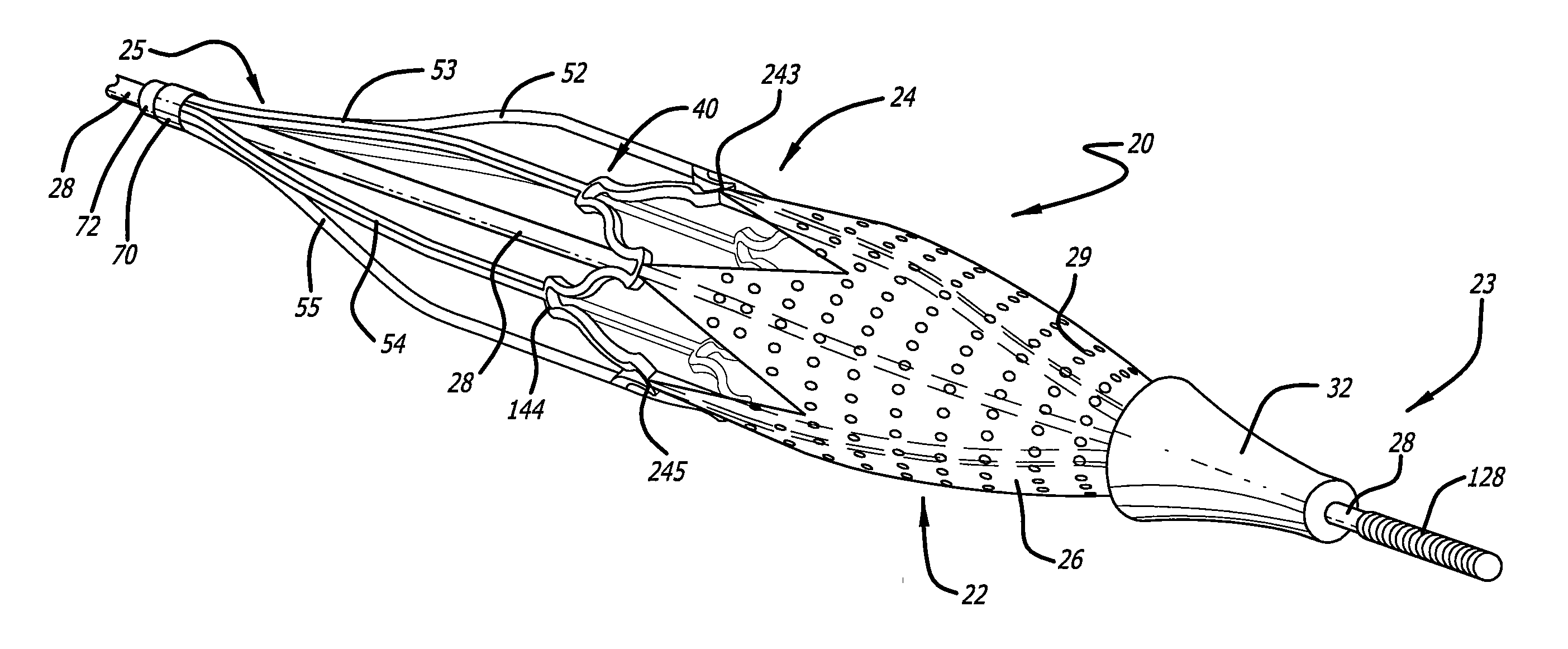
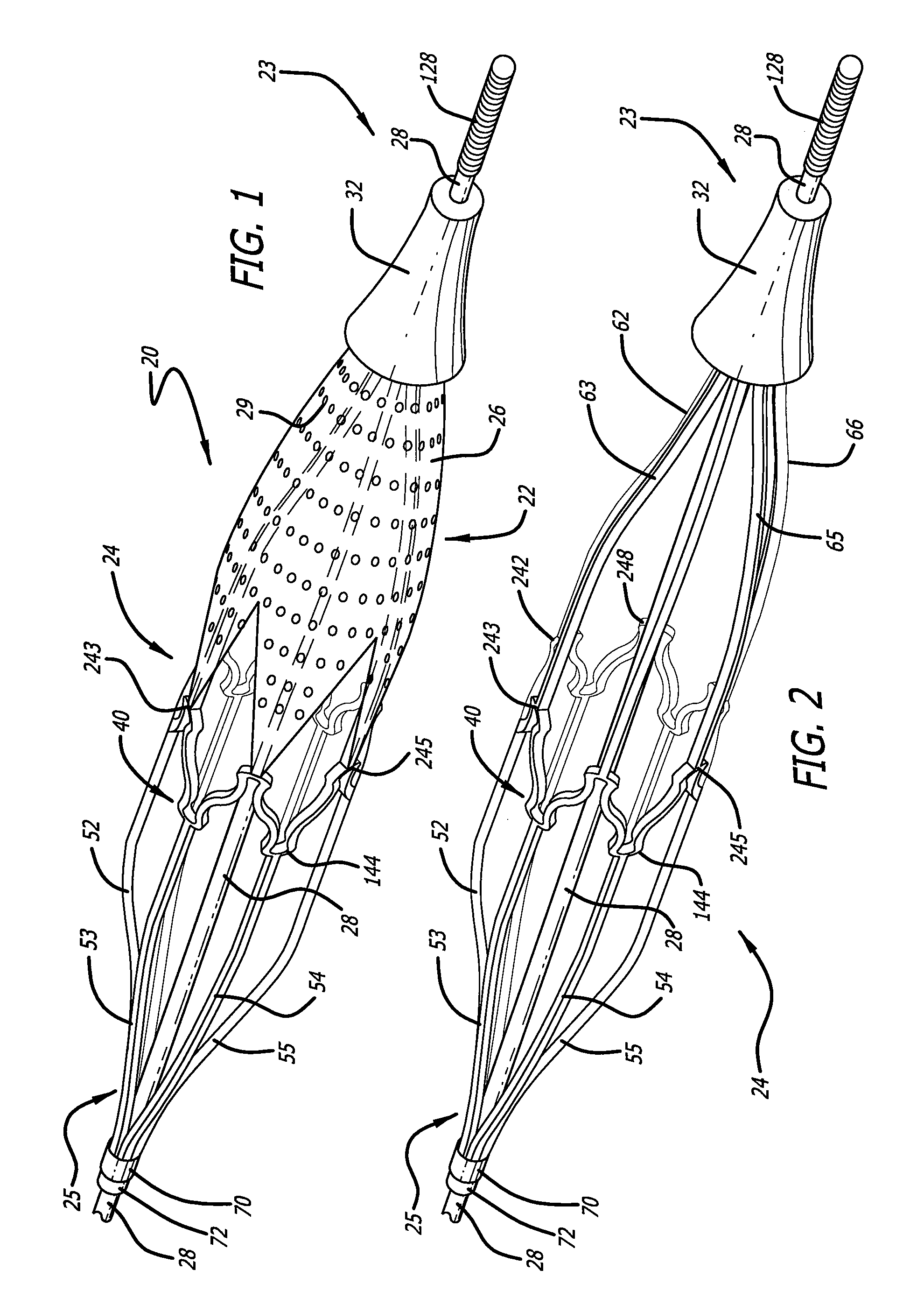
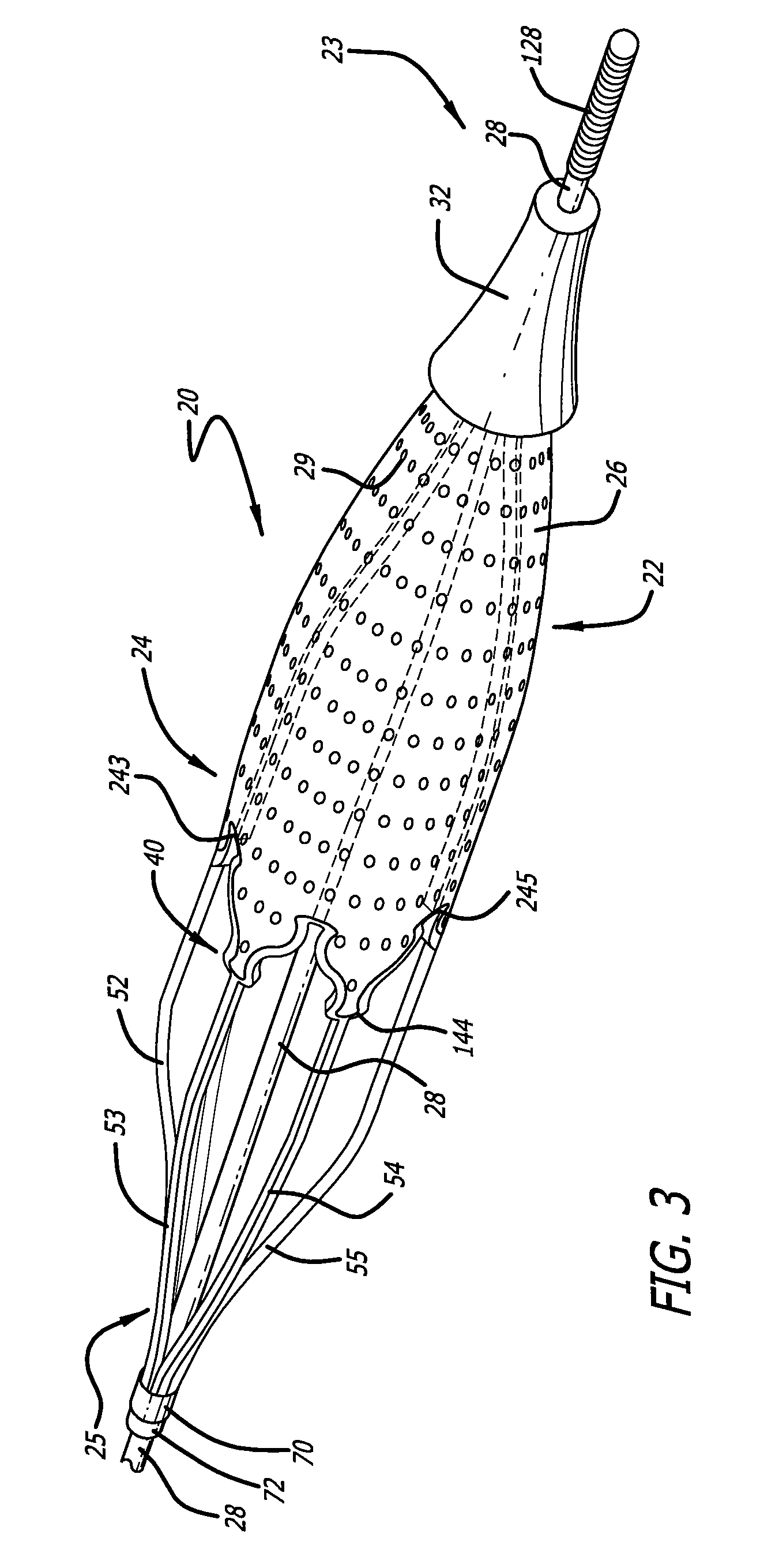
Embolic protection device
An embolic protection device includes an expandable and contractible filter that can be supported by one or more struts. The struts can be connected to the filter or interwoven into the filter, so as to assist in the expansion and contraction of the filter. In one embodiment, the proximal ends of the struts connect to a joint that is fixed in position relative to a delivery wire, while the distal end of the filter connect to a joint that slides relative to the delivery wire.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Embolism protection devices
InactiveUS20040093015A1Reduce adverse effectsDilatorsTissue regenerationEmbolic Protection DevicesActive agent
Embolism protection devices can be formed with a biocompatible expandable polymer that can expand upon release within a patient's vessel. Upon release, the structure can be configured to filter flow through the vessel. The material of the embolism protection devices can release one or more biologically active agents, such as a thrombolitic agent, including, for example, tPA. Alternatively or additionally, the embolism protection device can be connected to a tether that elutes one or more biologically active agents.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Emboli filter export system
ActiveUS20050277976A1Reducing platelet aggregationMeaningful long-term clinical benefitSurgeryDilatorsDistal portionEmbolic Protection Devices
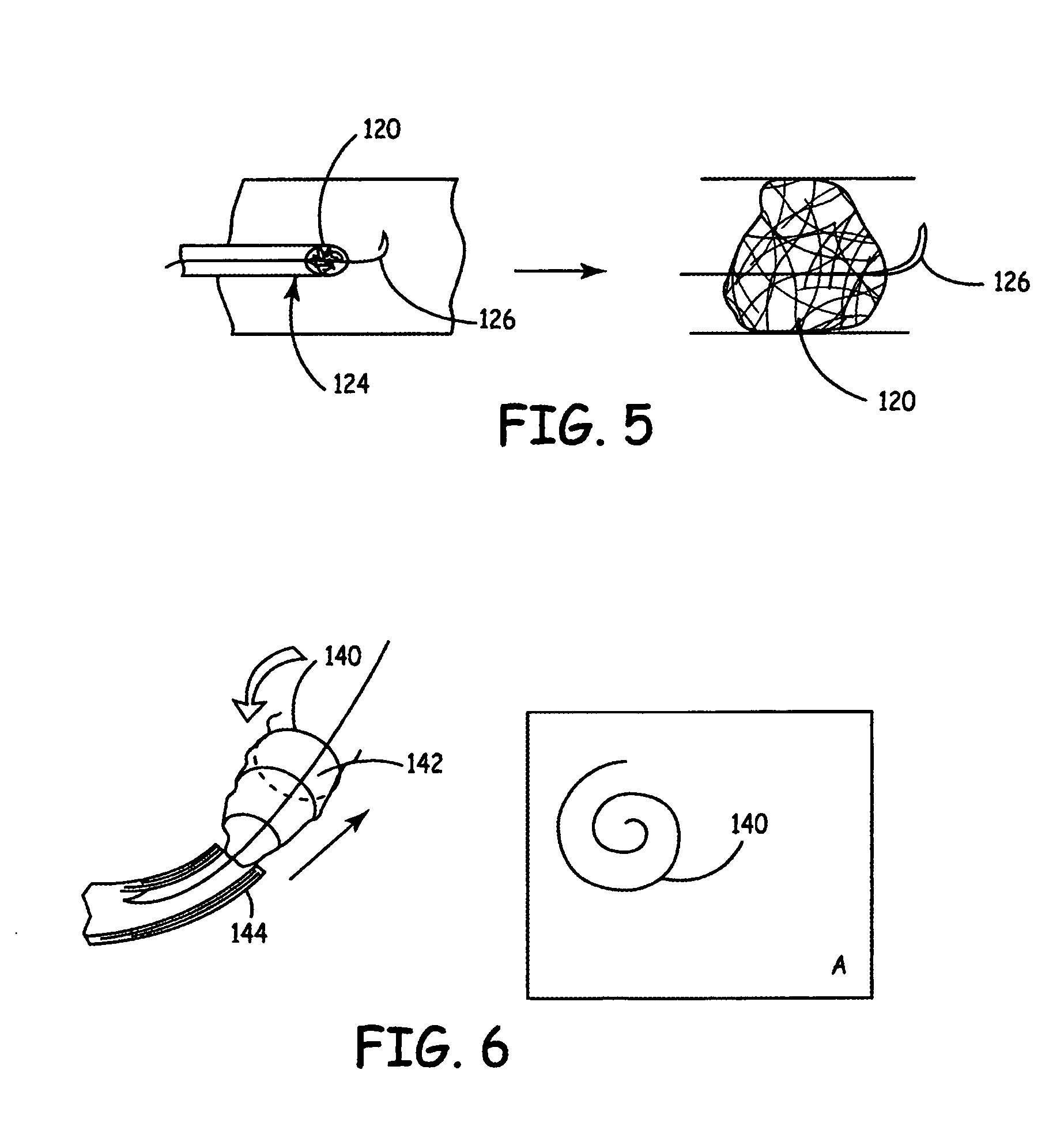
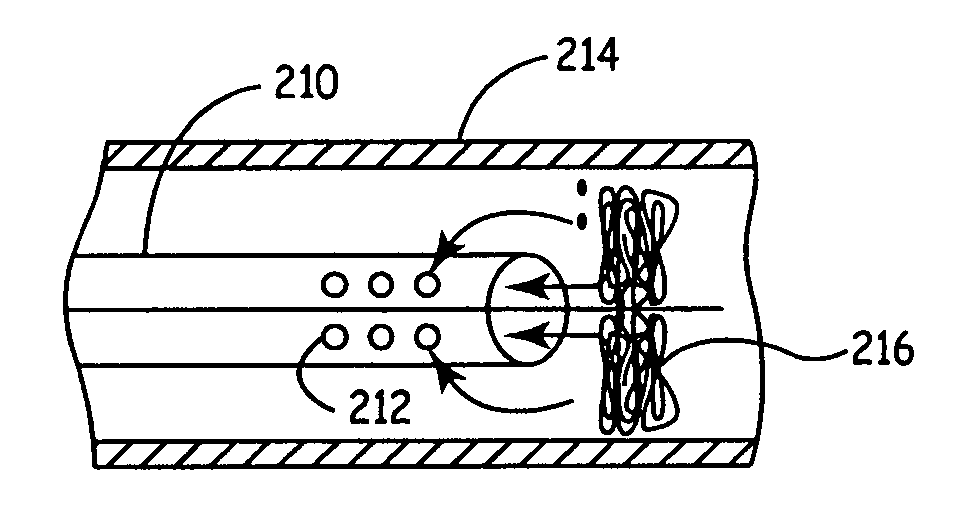
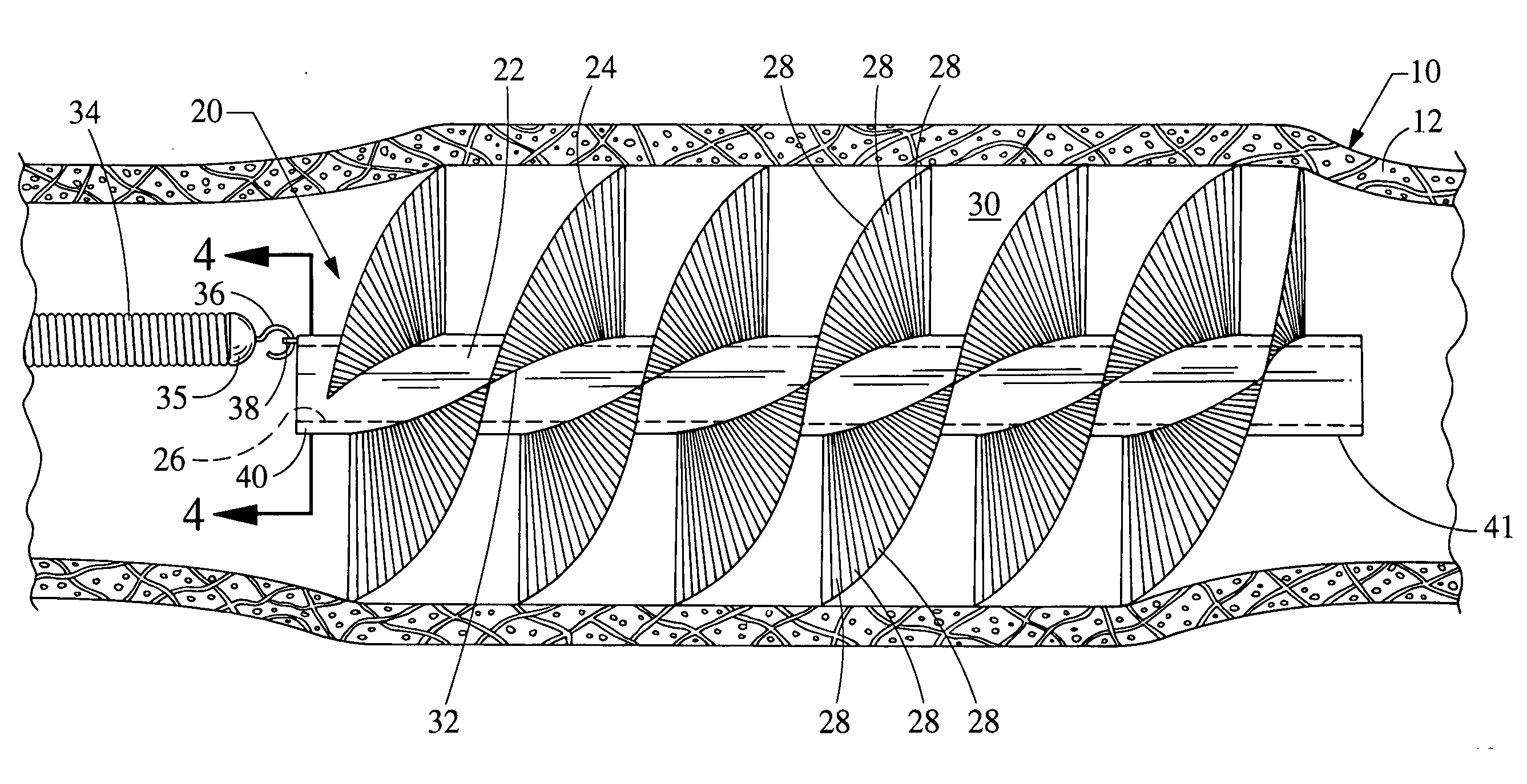
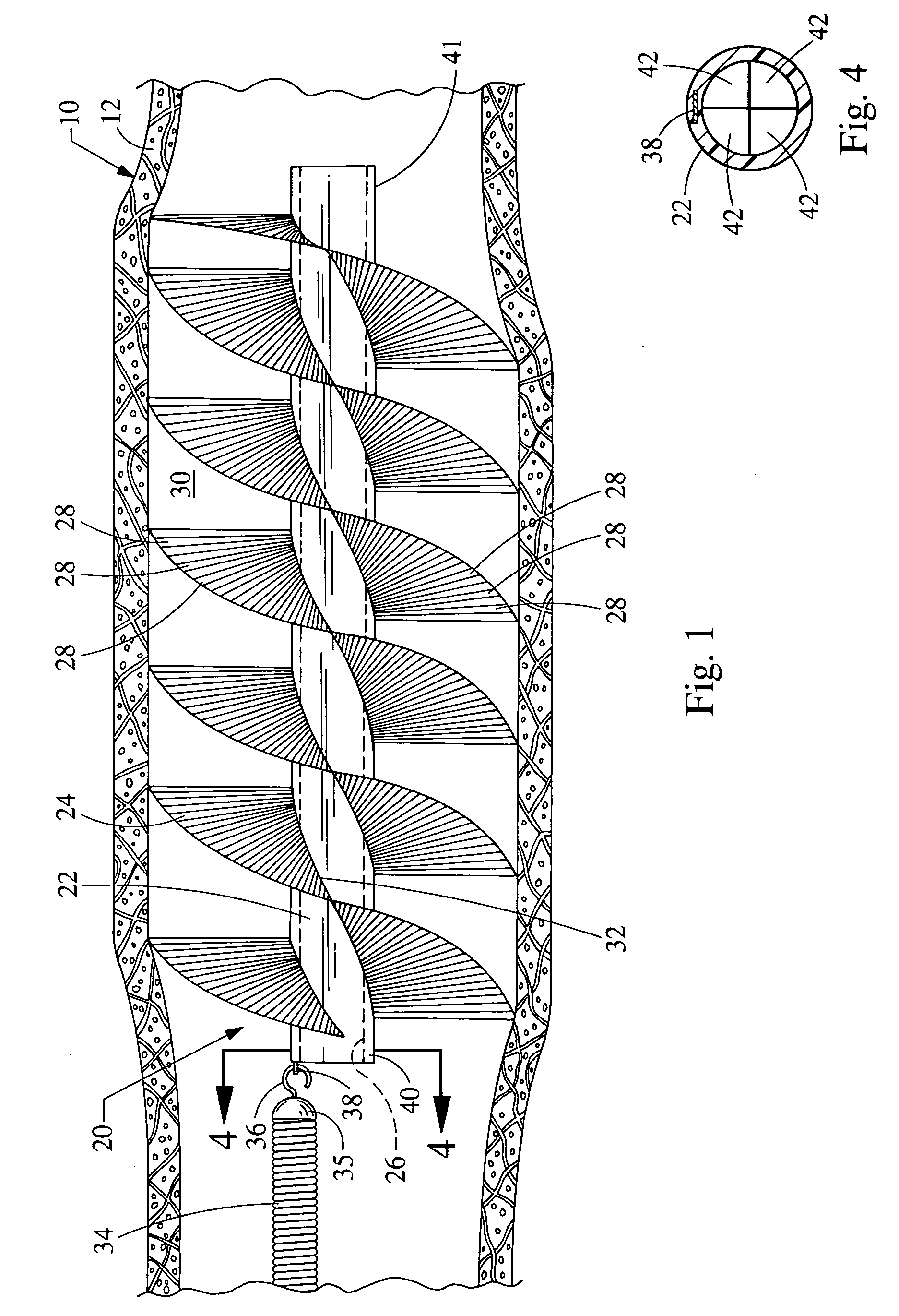
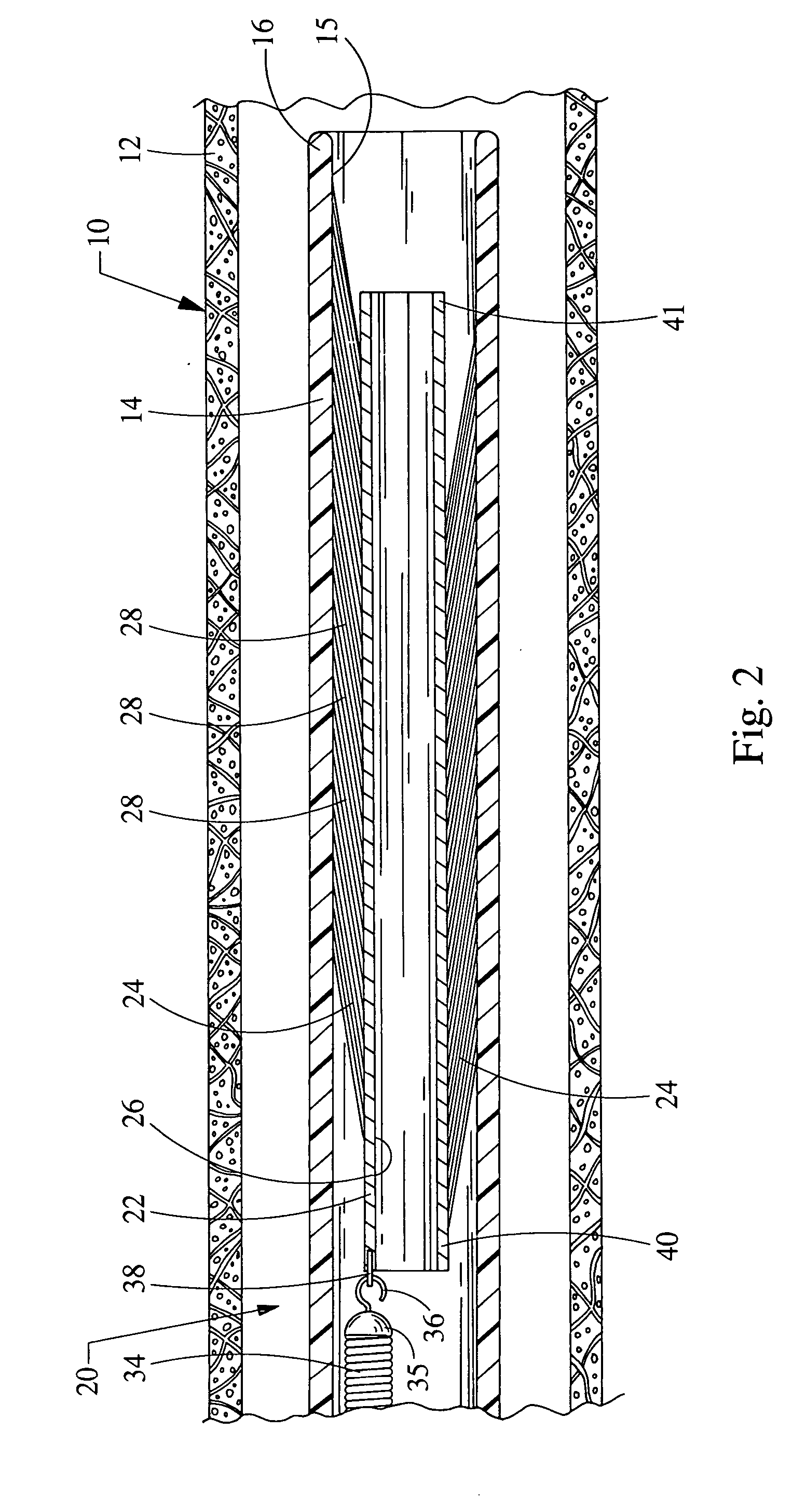
Methods for the removal of an embolism protection device use aspiration during the drawing of the embolism protection device into the catheter. Generally, the embolism protection device comprises a three dimensional filtering matrix that provides improved filtering without blocking the flow through the patient's vessel. In some embodiments, the embolism protection device can be actuated between a deployed configuration and a removal configuration with a reduced area across the cross section of the vessel lumen. The embolism protection device in the removal configuration can be drawn within the aspiration catheter. The aspiration catheter can have a distal portion with an expanded compartment with an average diameter at least about 20 percent larger than the average diameter of the shaft of the catheter within about 10 centimeters of the expanded compartment. In a rapid exchange version, the rapid exchange segment can have a length of at least about 10 centimeters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Steerable device having a corewire within a tube and combination with a functional medical component
An integrated guiding device has a tube and a corewire within the tube and a torque coupler. The torque coupler can couple the rotational motion of the tube with the rotational motion of the corewire. The wire can be moved longitudinally at least some amount relative to the tube. The device can further comprise a functional medical structure, such as an embolism protection structure. The device can be used in medical procedures, such as less invasive procedures within the cardiovascular system. Improved fiber based embolism protection devices comprise fiber bundles that are twisted prior to delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
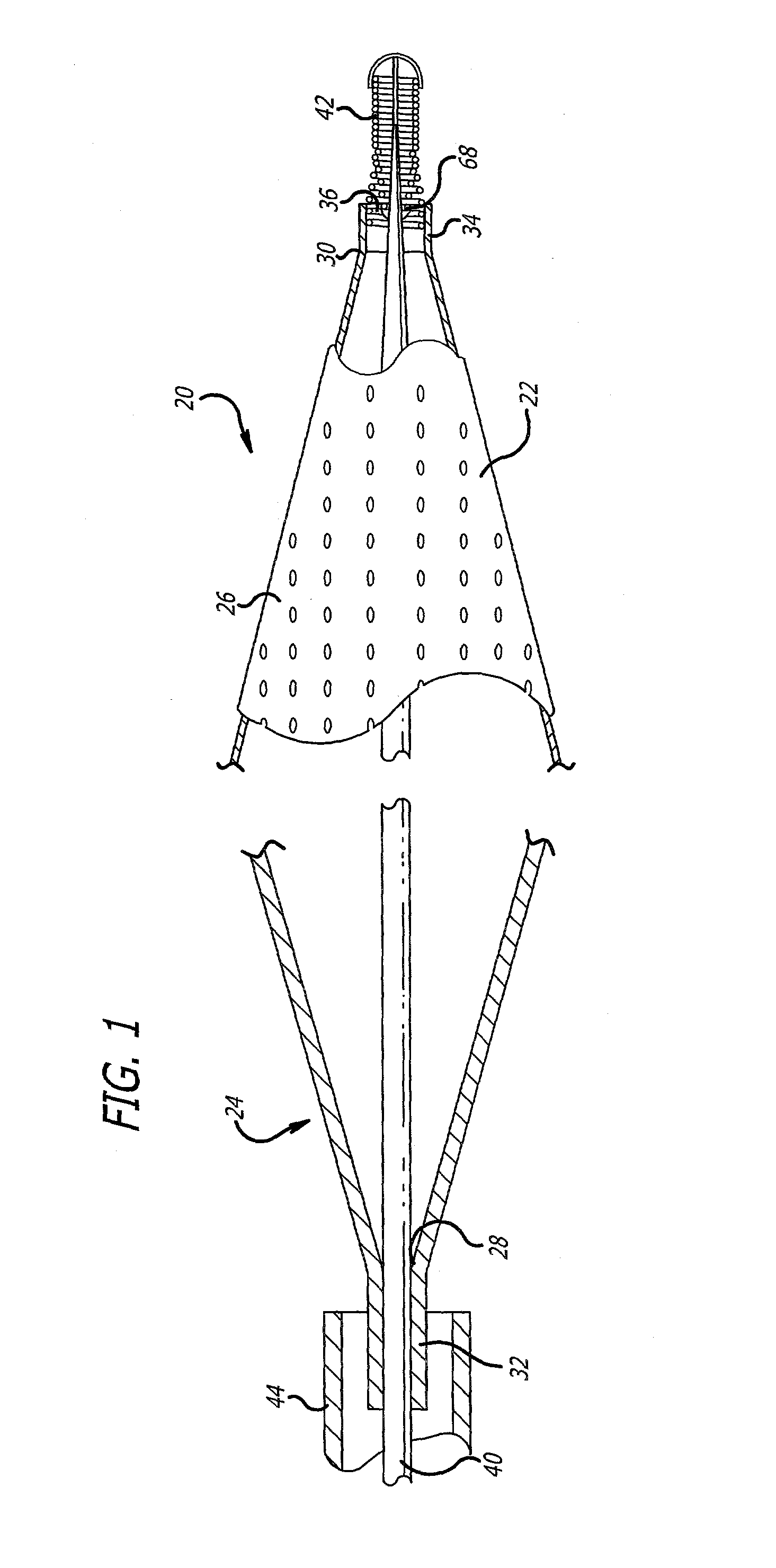
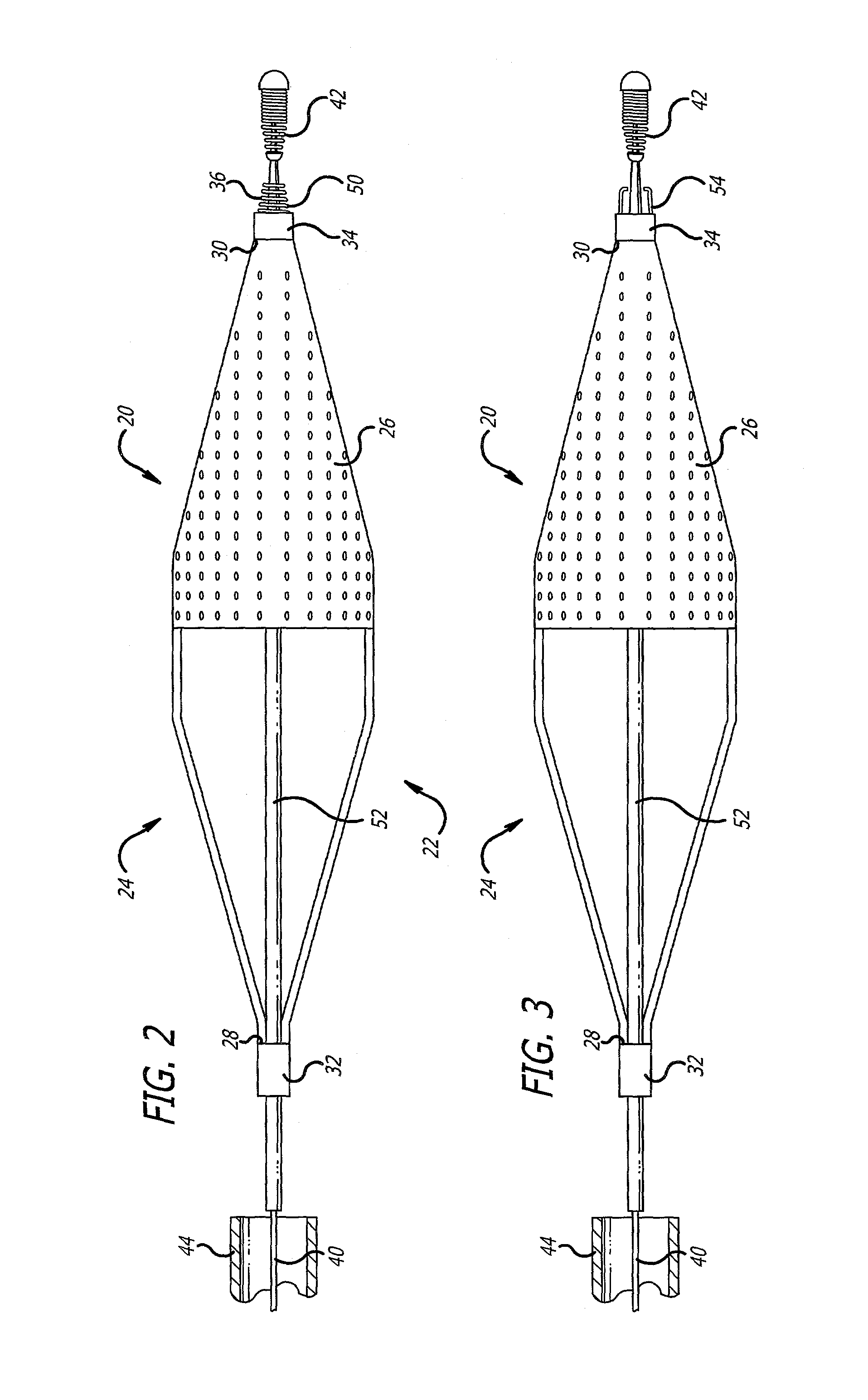
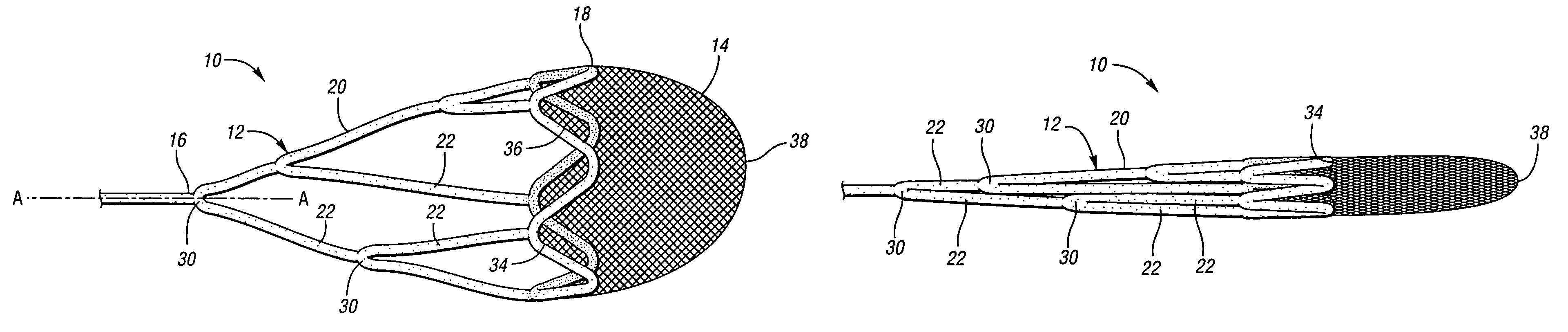
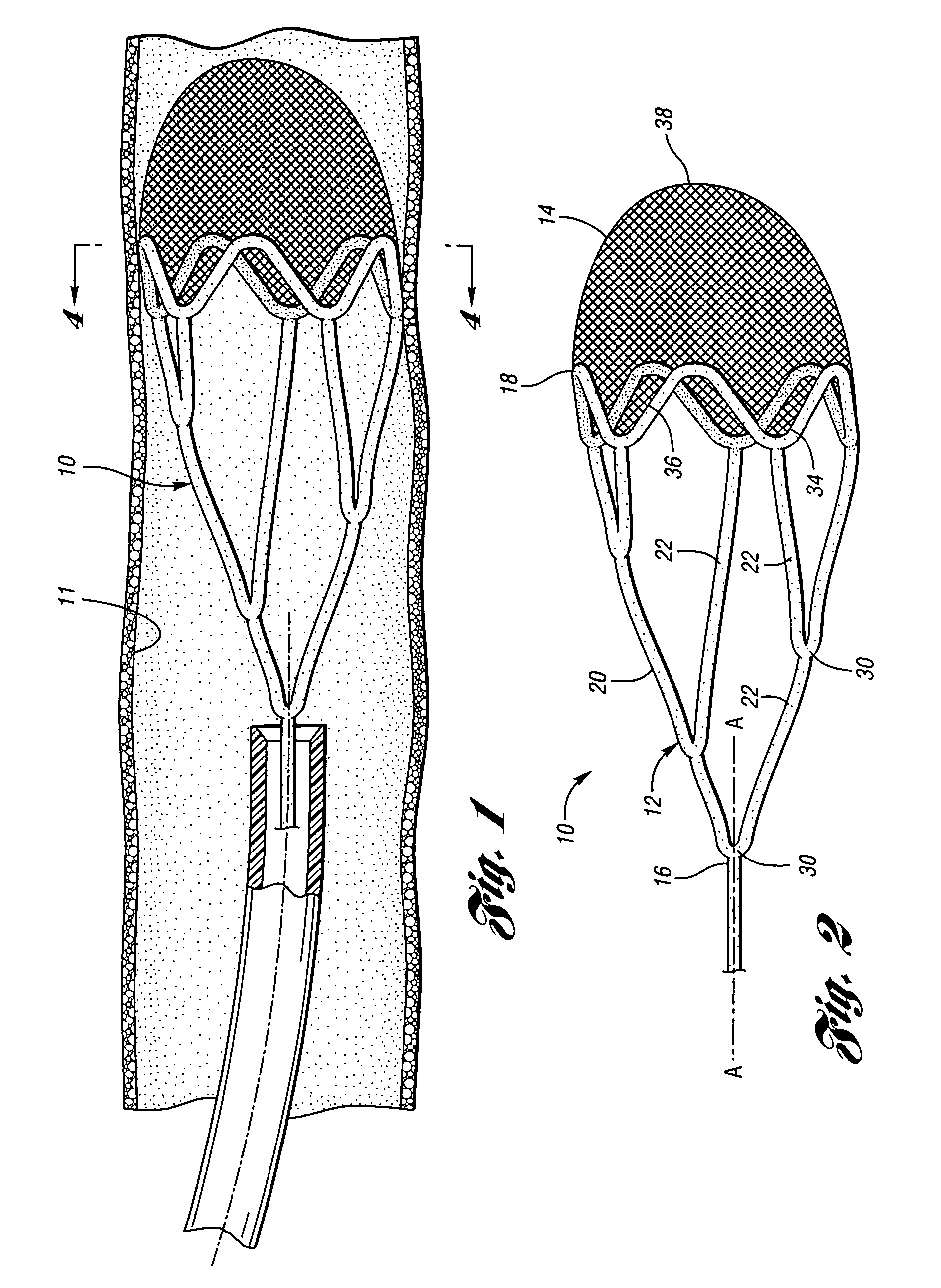
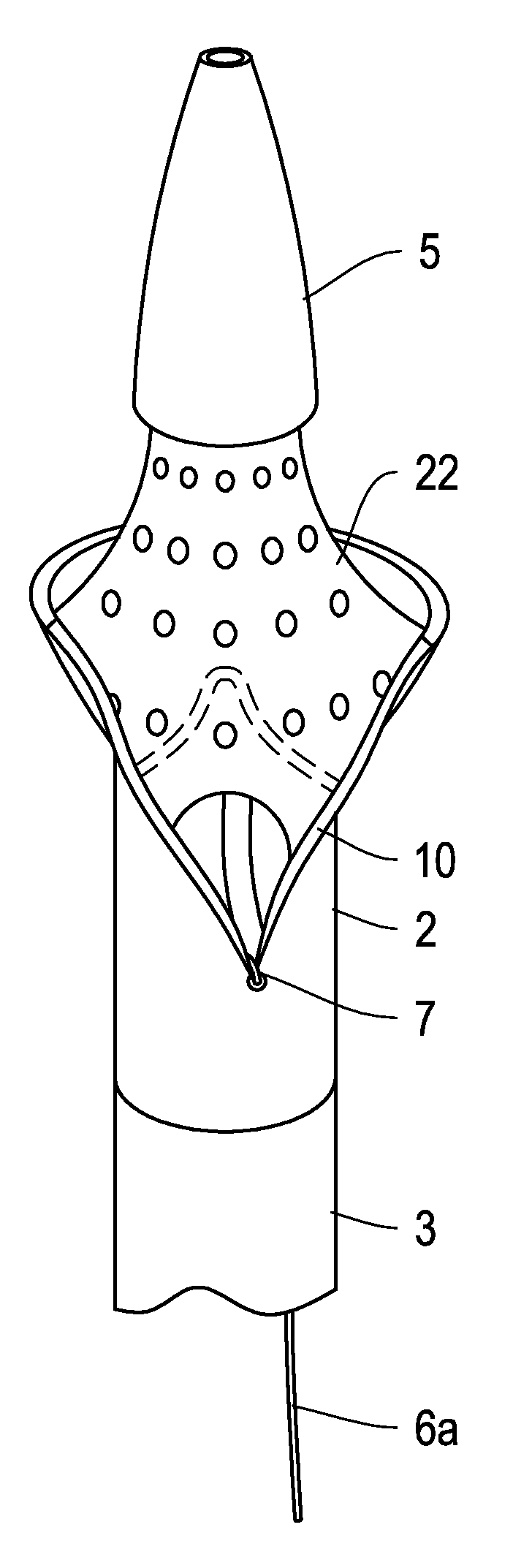
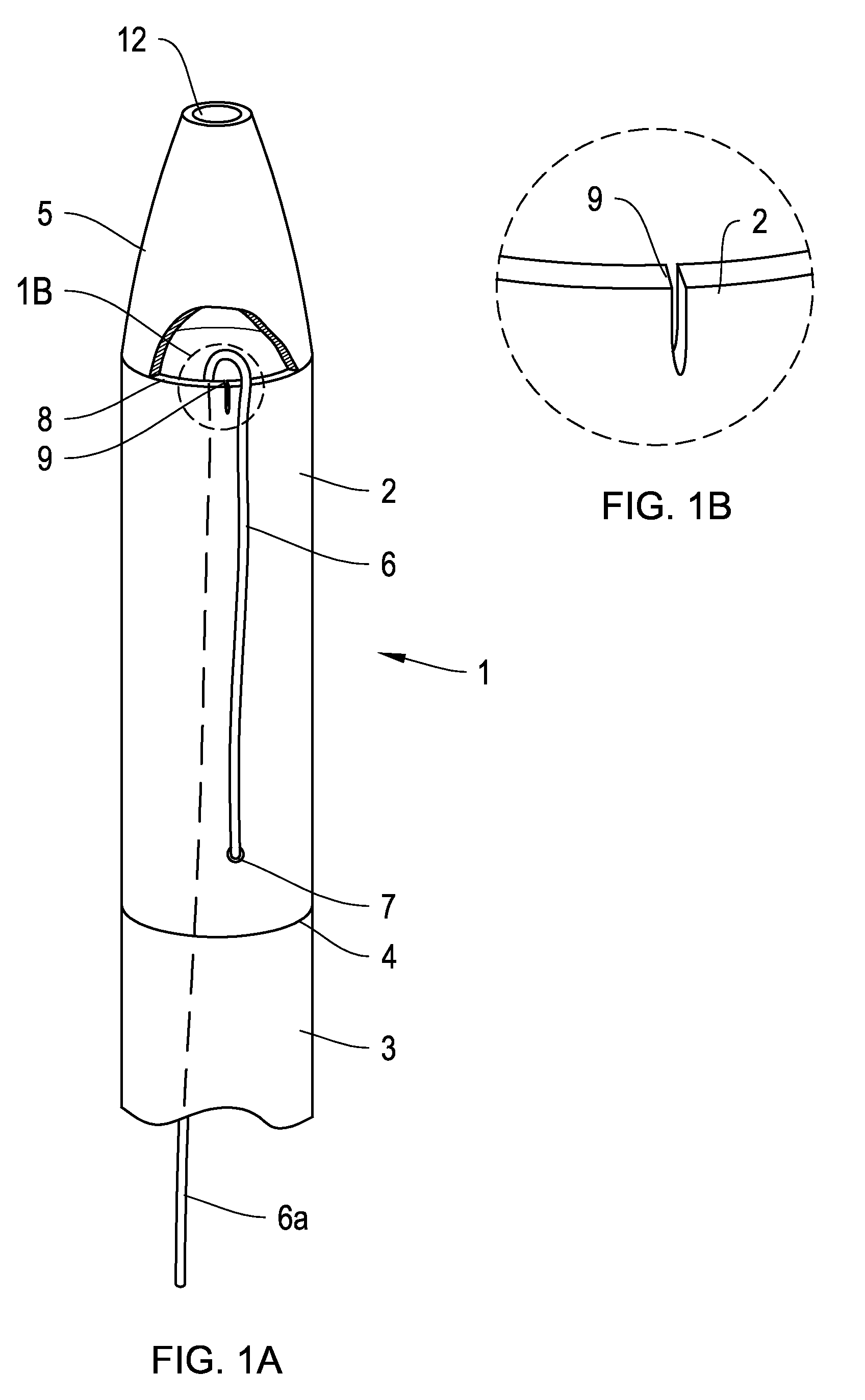
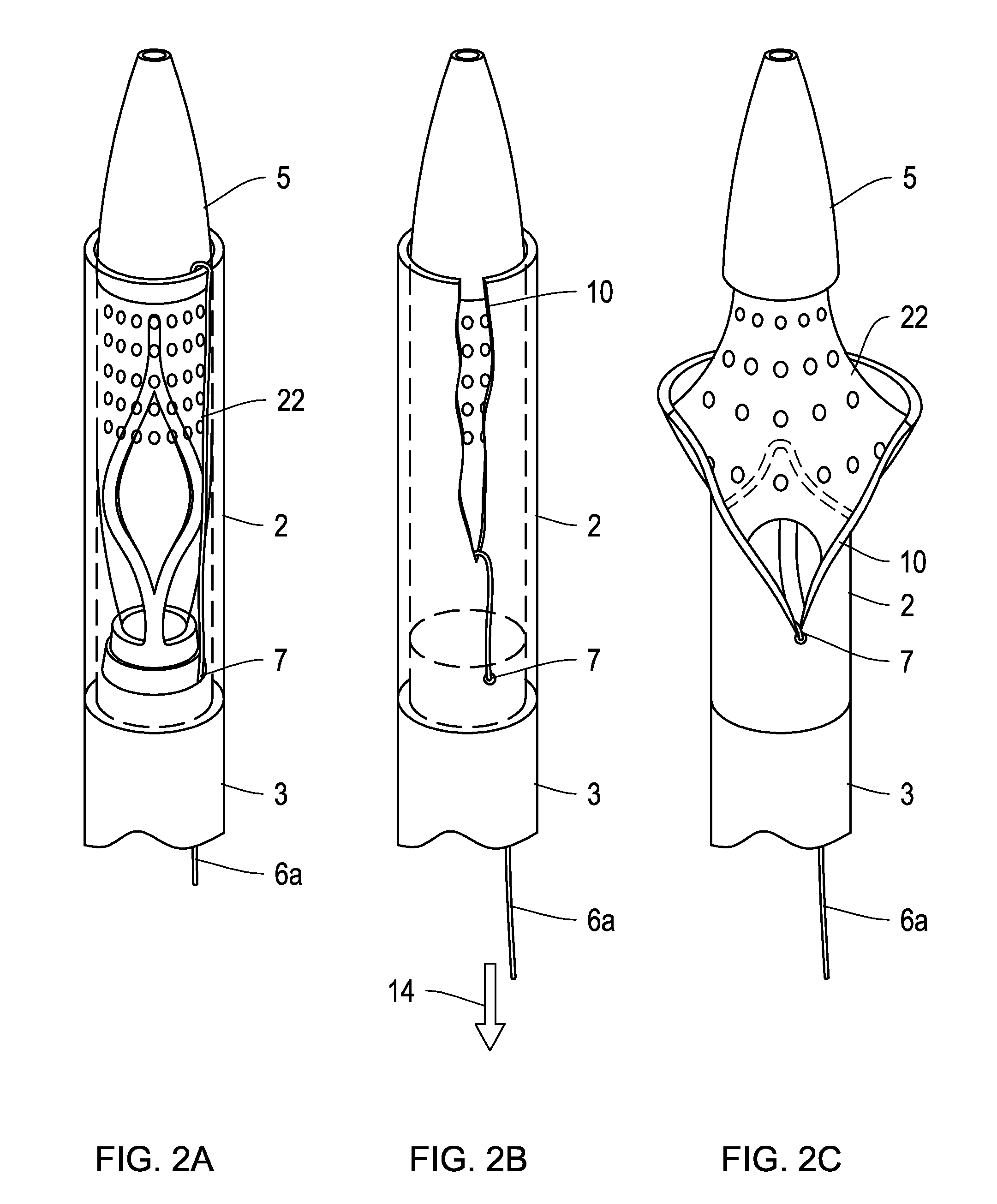
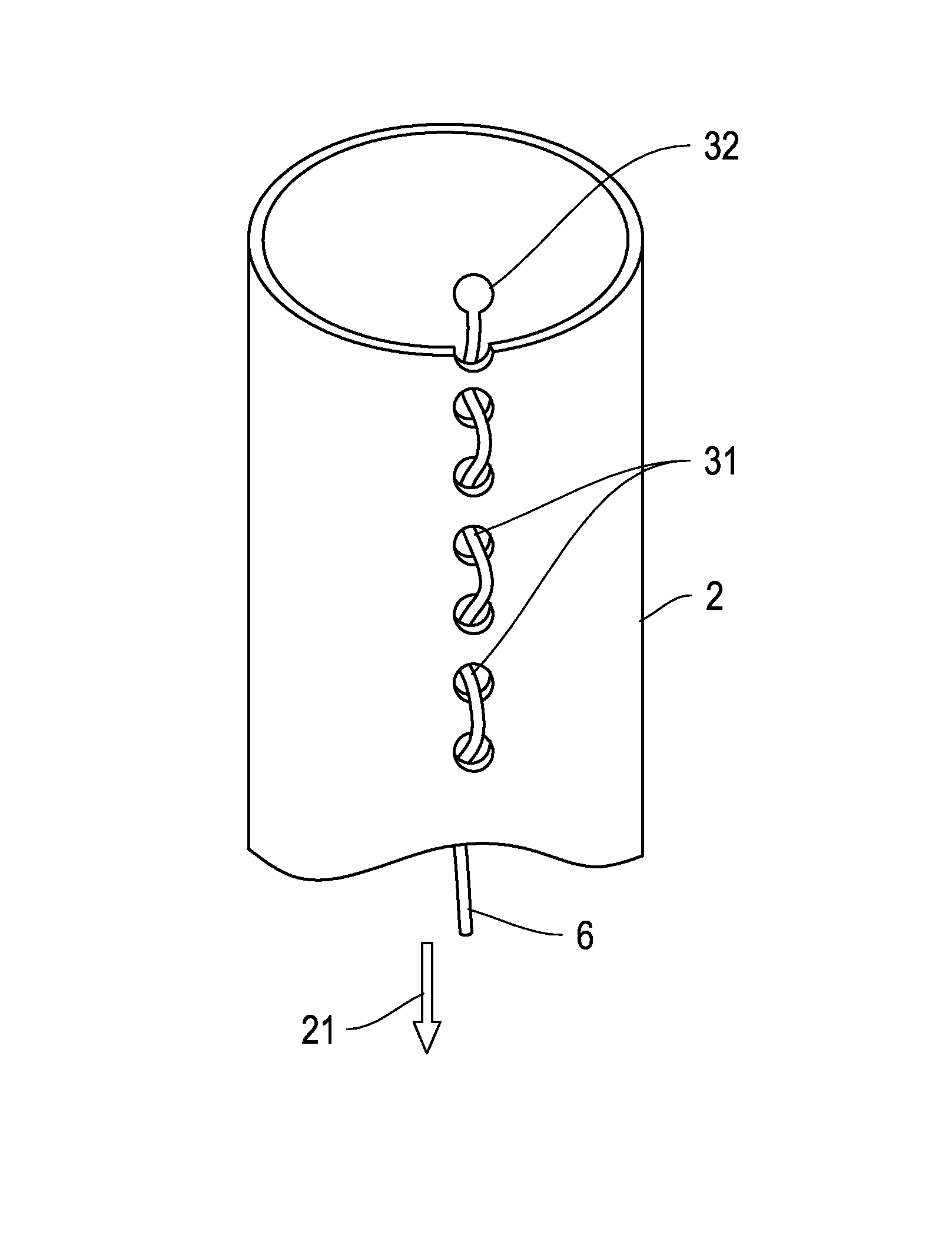
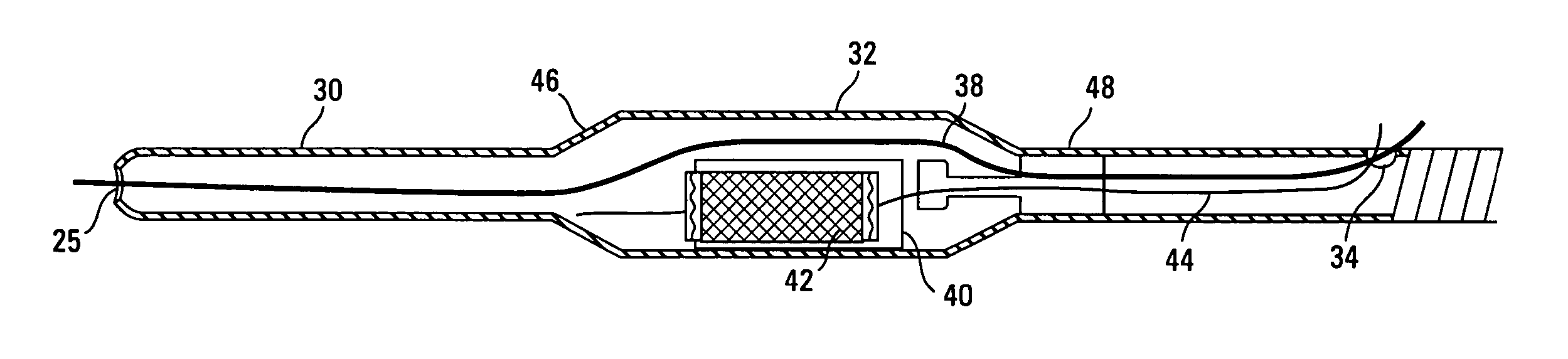
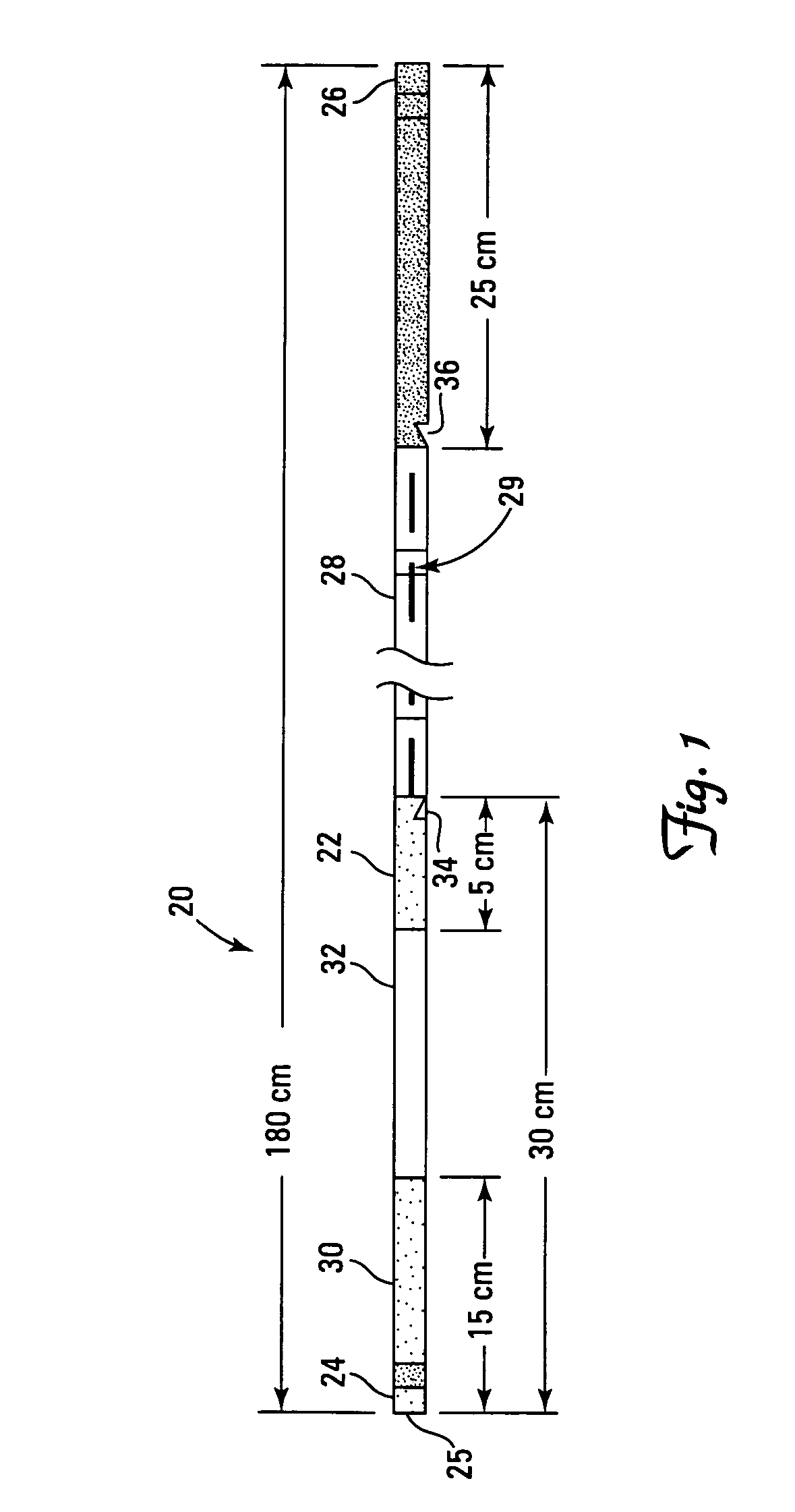
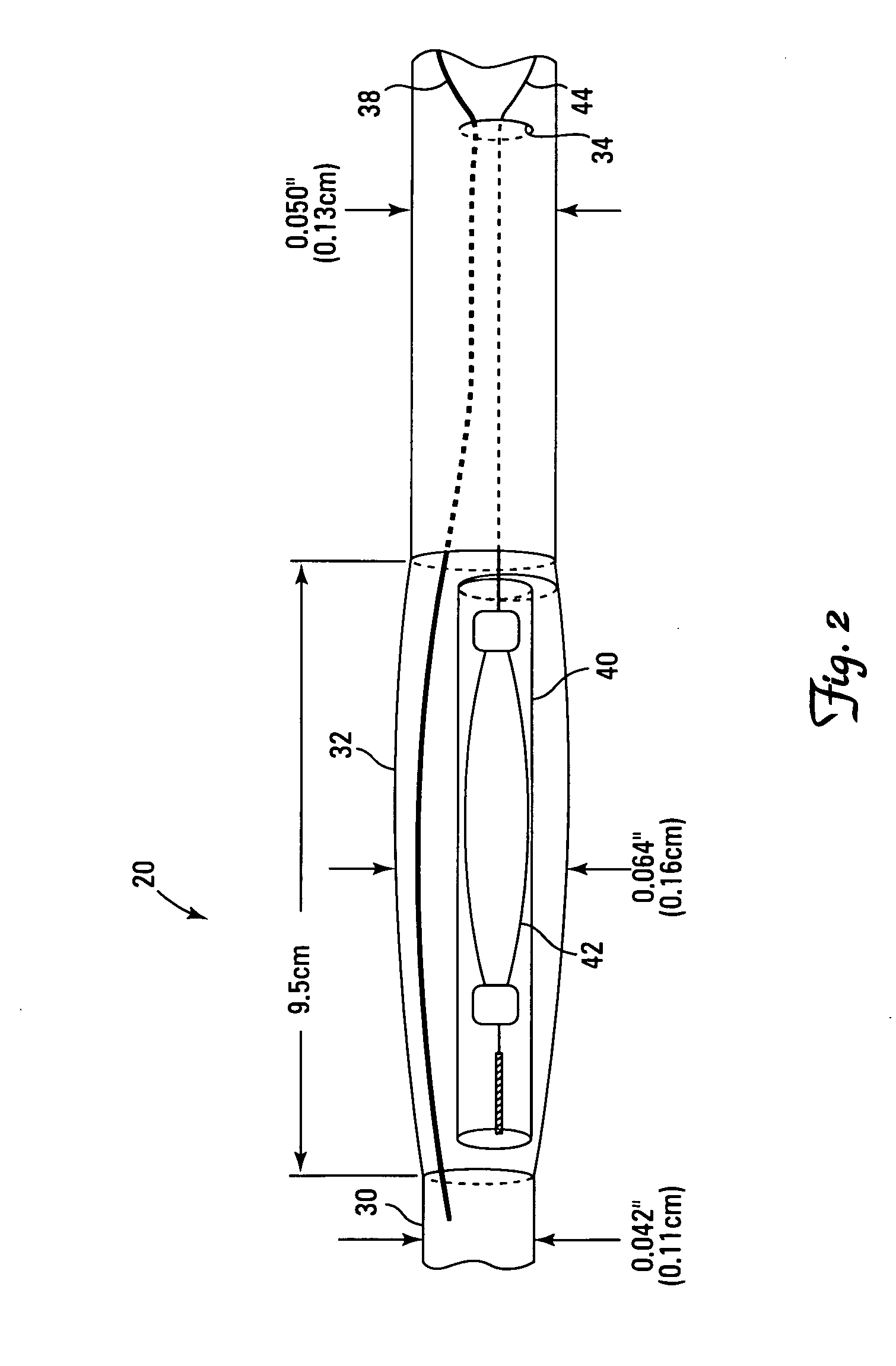
Embolic protection device
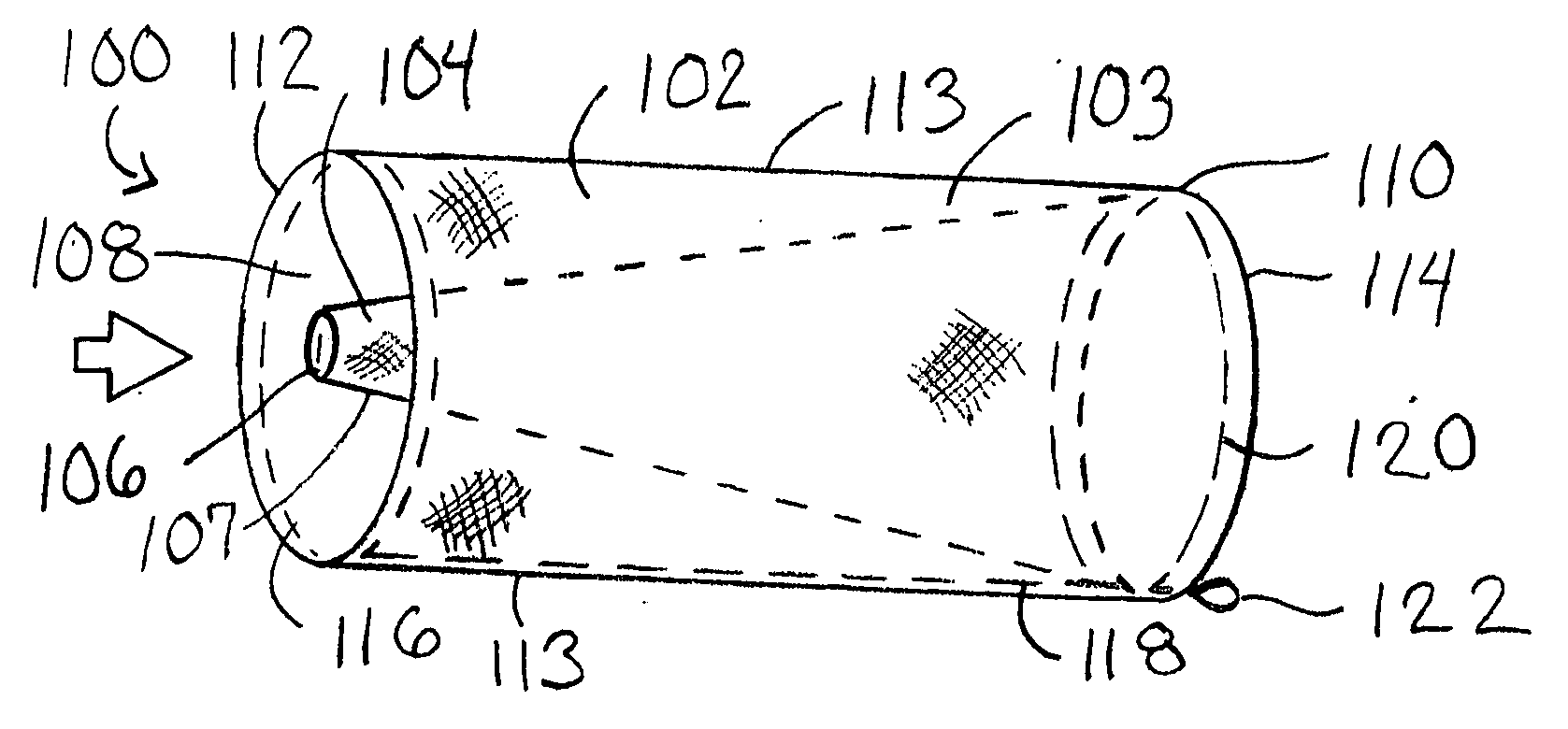
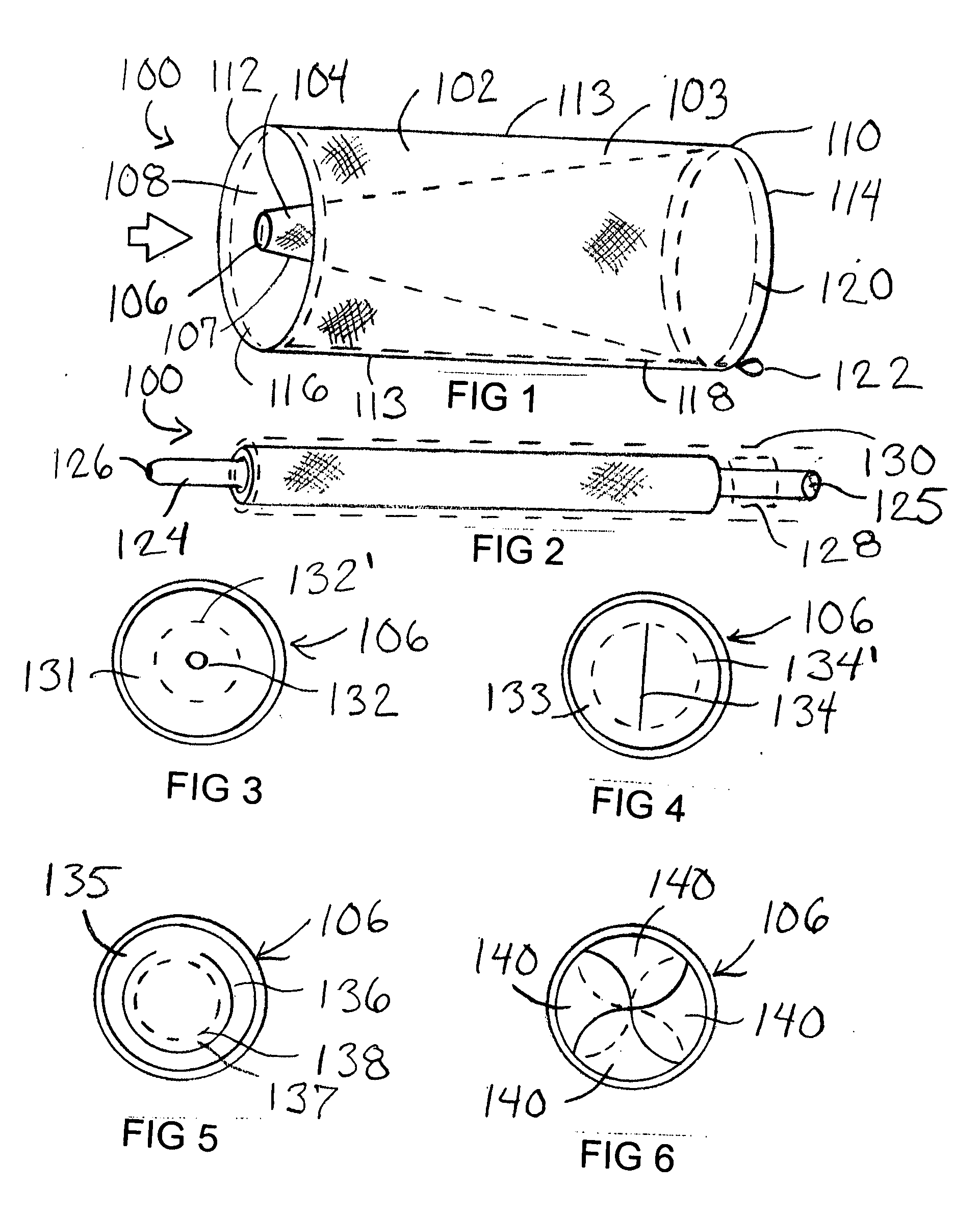
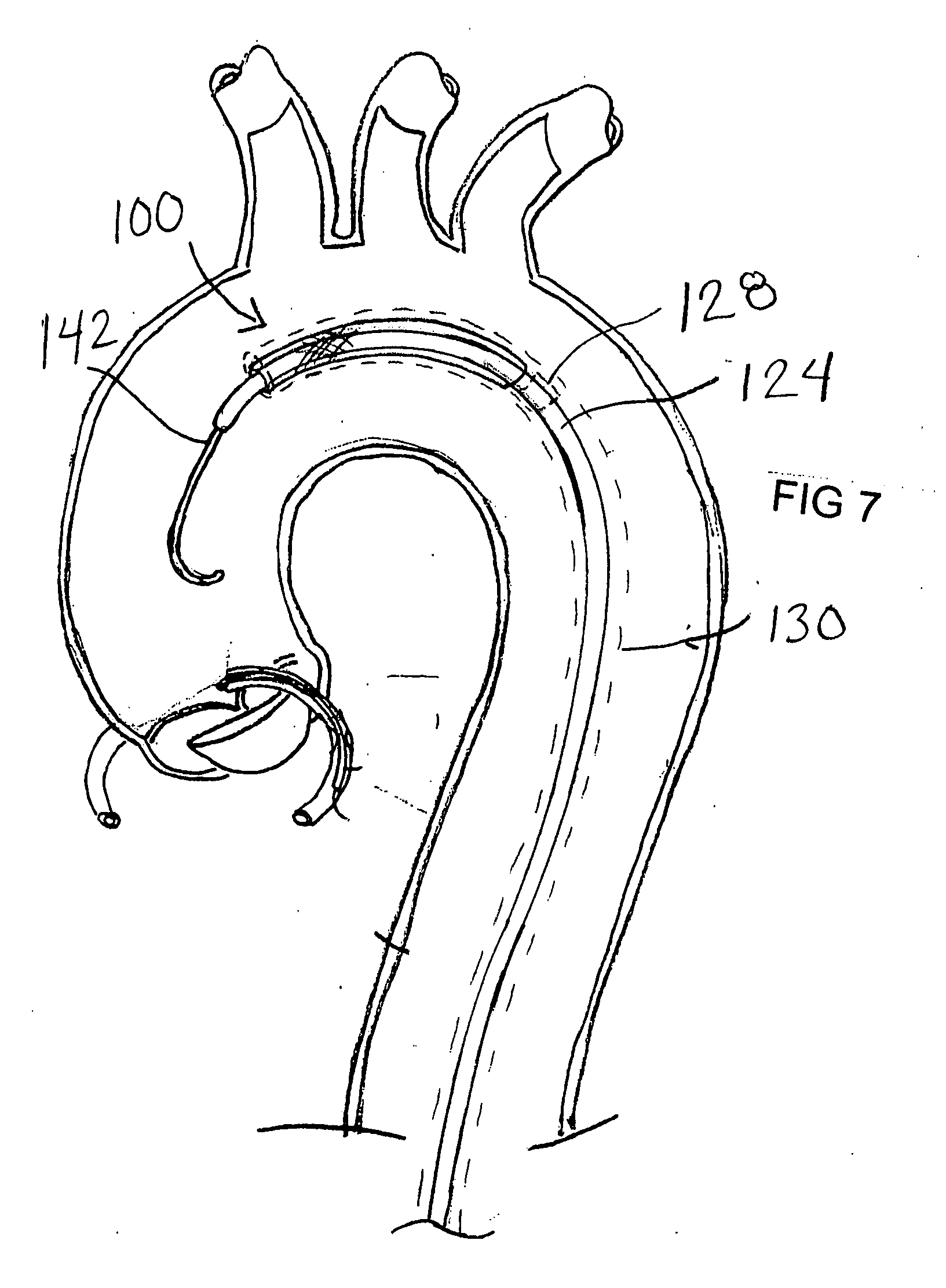
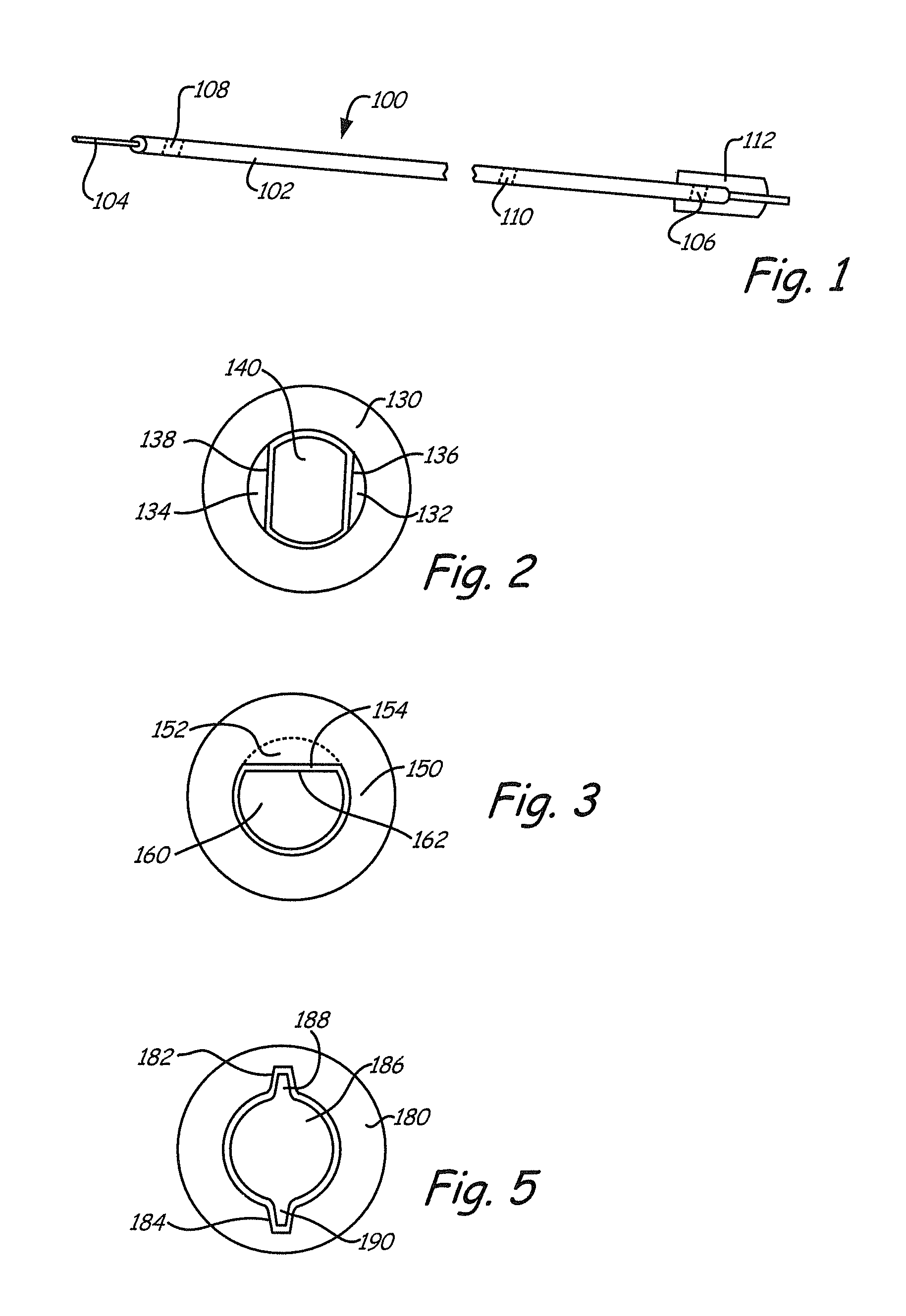
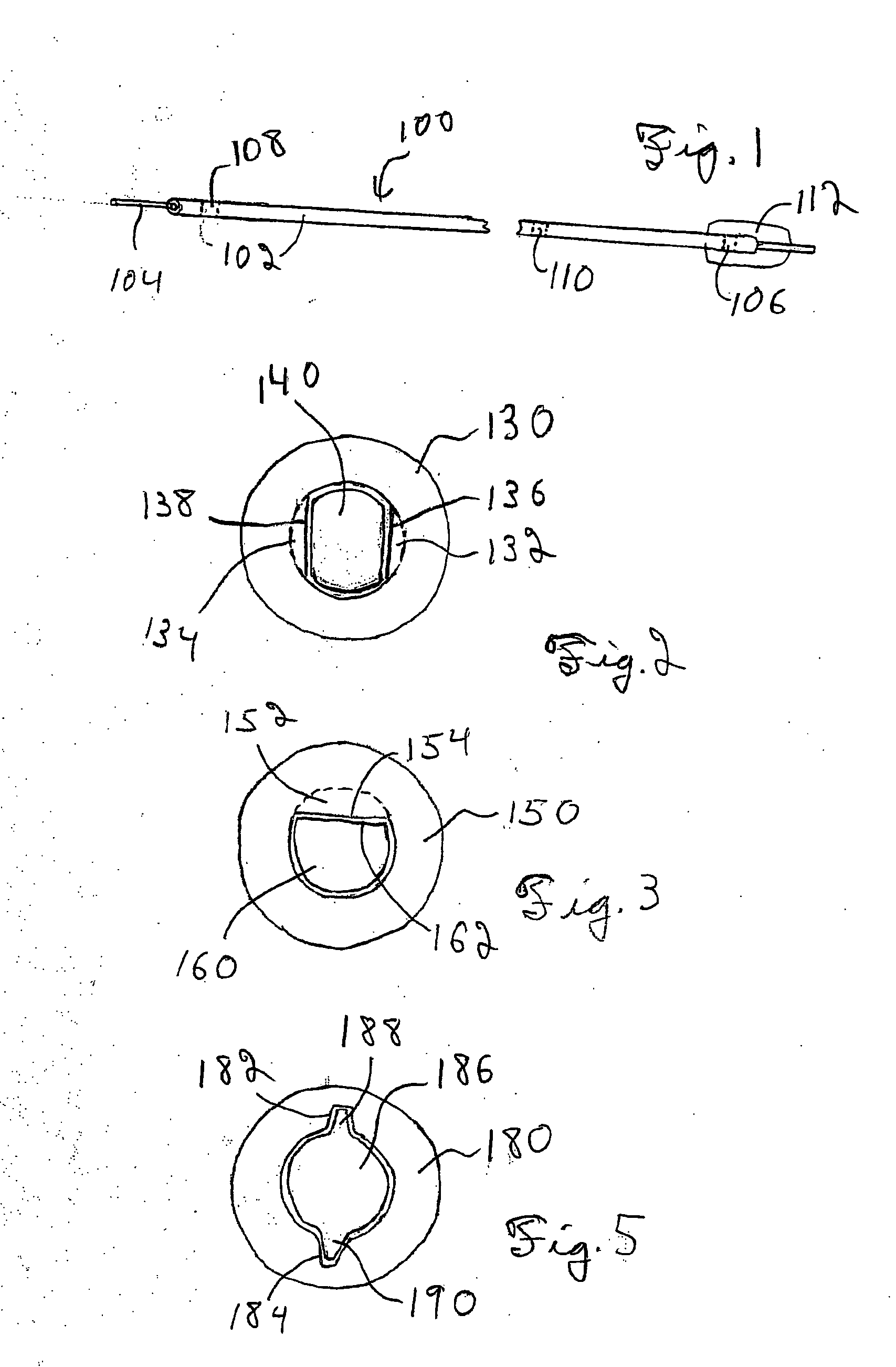
An embolic protection device for use in a patient's blood vessel, such as the aorta, has an approximately cylindrical outer structure made of a filter mesh material and an approximately conical inner structure also made of a filter mesh material. On the downstream end of the embolic protection device, the wider end of the conical inner structure is joined to the cylindrical outer structure. The upstream end of the embolic protection device is open for blood to flow between the conical inner structure and the cylindrical outer structure. The space between the conical inner structure and the cylindrical outer structure defines a collection chamber for captured emboli. The narrow upstream end of the conical inner structure has a catheter port with a resilient seal that is sized for passage of a catheter shaft. The filter mesh material may be self-supporting or it may be supported on a resilient-framework or an inflatable framework.
Owner:EMBOLINE
Tracking aspiration catheter
In general, aspiration catheters have a suction device, a proximal portion and a shaft with a proximal end and a distal end. Improvements in the aspiration catheter design provide for improved tracking and / or reduced chance of snagging during delivery of the aspiration catheter. In some embodiments, the tip of the shaft has a curve relative to the neutral orientation of the remaining portions of the shaft. In other embodiments, the aspiration catheter further comprises a tracking portion that has a guide lumen. A guide structure can extend through the guide lumen to limit the motion of the tip of the catheter relative to the guide structure during delivery of the aspiration catheter within a patient's vessel. In further embodiments, the aspiration catheter comprises a deflection structure having a tether and a bumper. Improved methods for using the aspiration catheter to recover an embolism protection device are described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
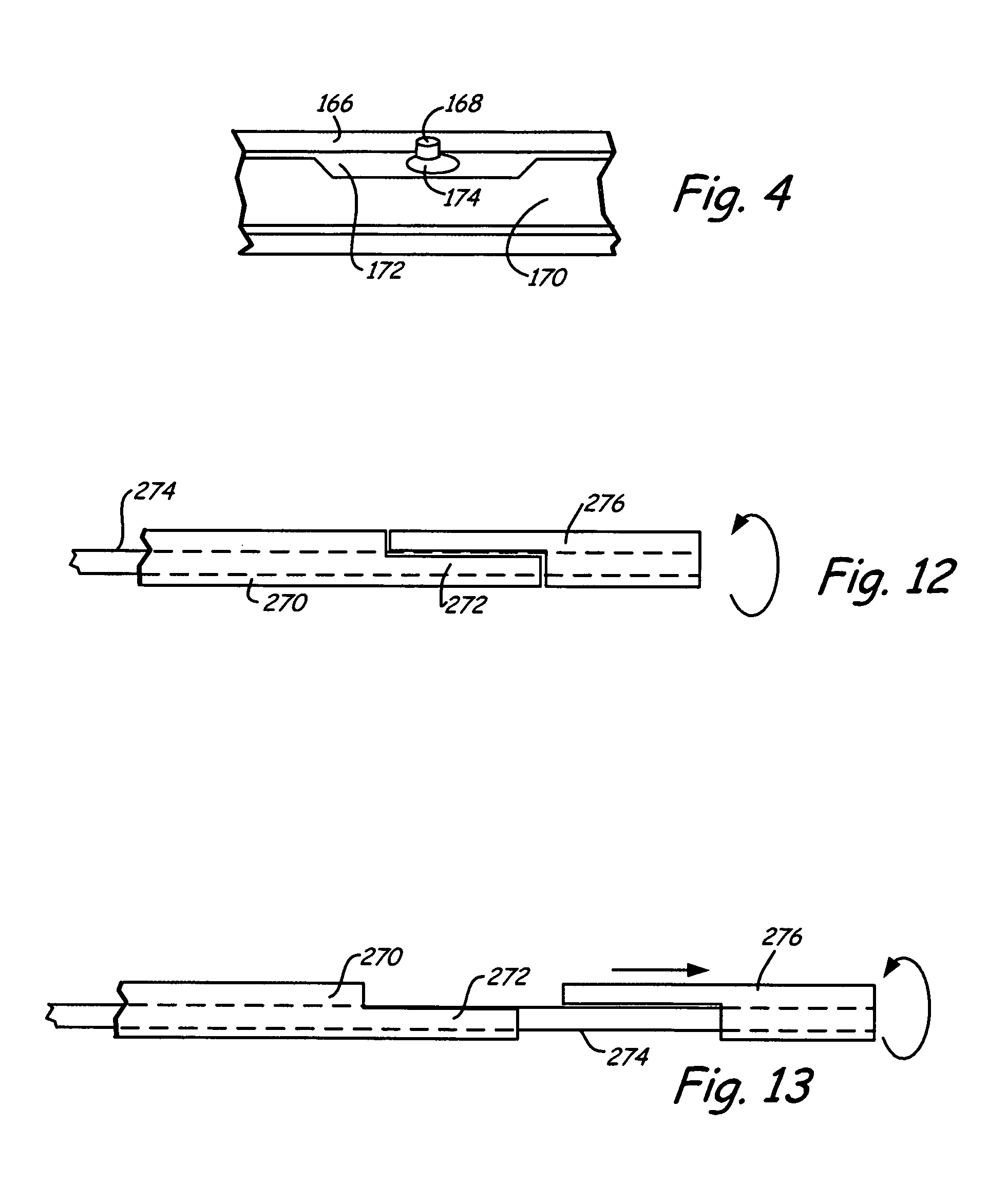
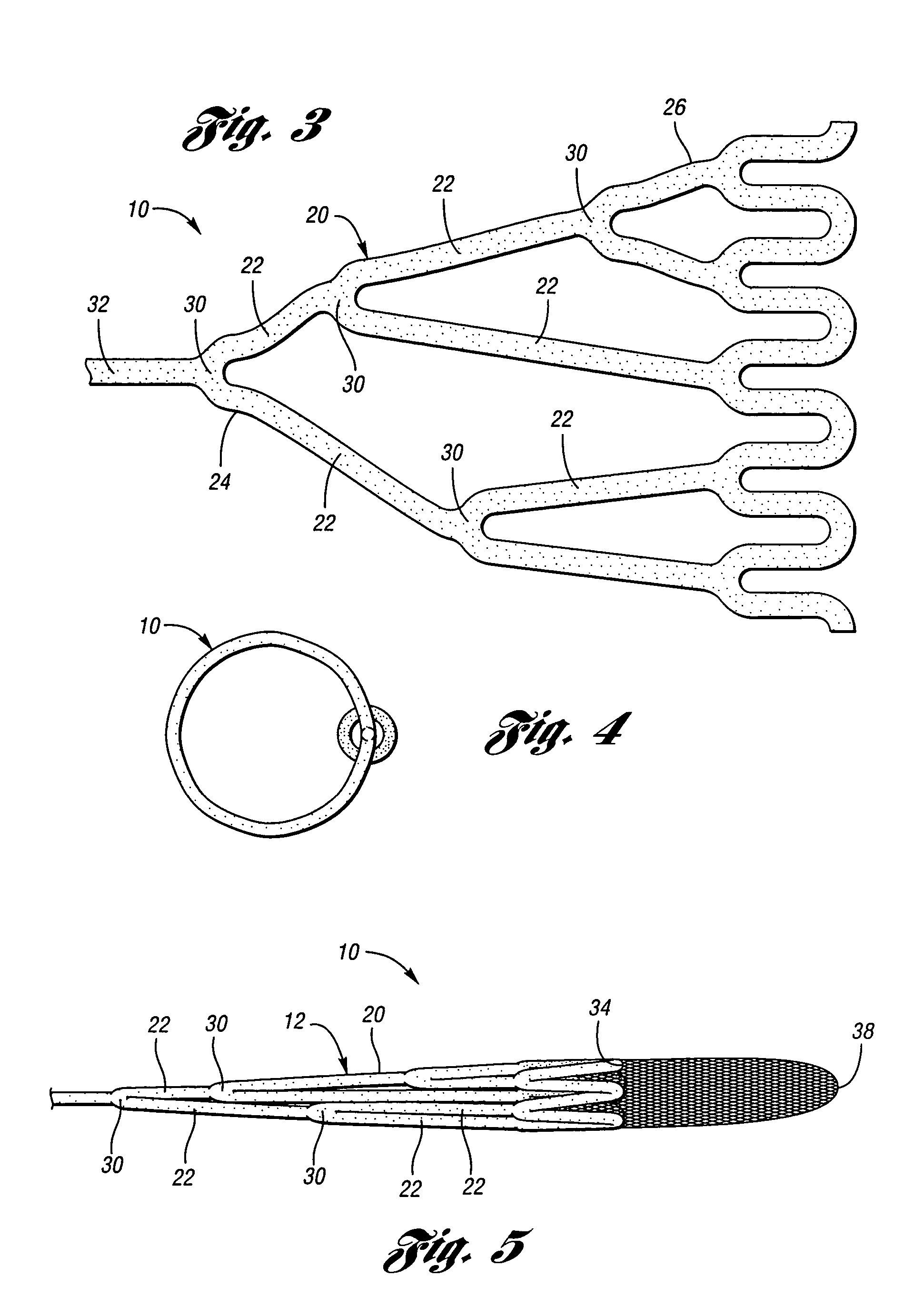
Support frame for an embolic protection device
InactiveUS6964672B2Reduce the overall diameterEasy to deploySurgeryDilatorsEmbolic Protection DevicesEngineering
An embolic protection device comprises a collapsible filter body and a filter support for the filter body. The filter support comprises a support frame defined by at least two wire segments having terminations. The terminations of adjacent segments are fixed relative to one another and extend generally parallel in a bifilar manner for enhanced trackability and flexibility.
Owner:SALVIAC
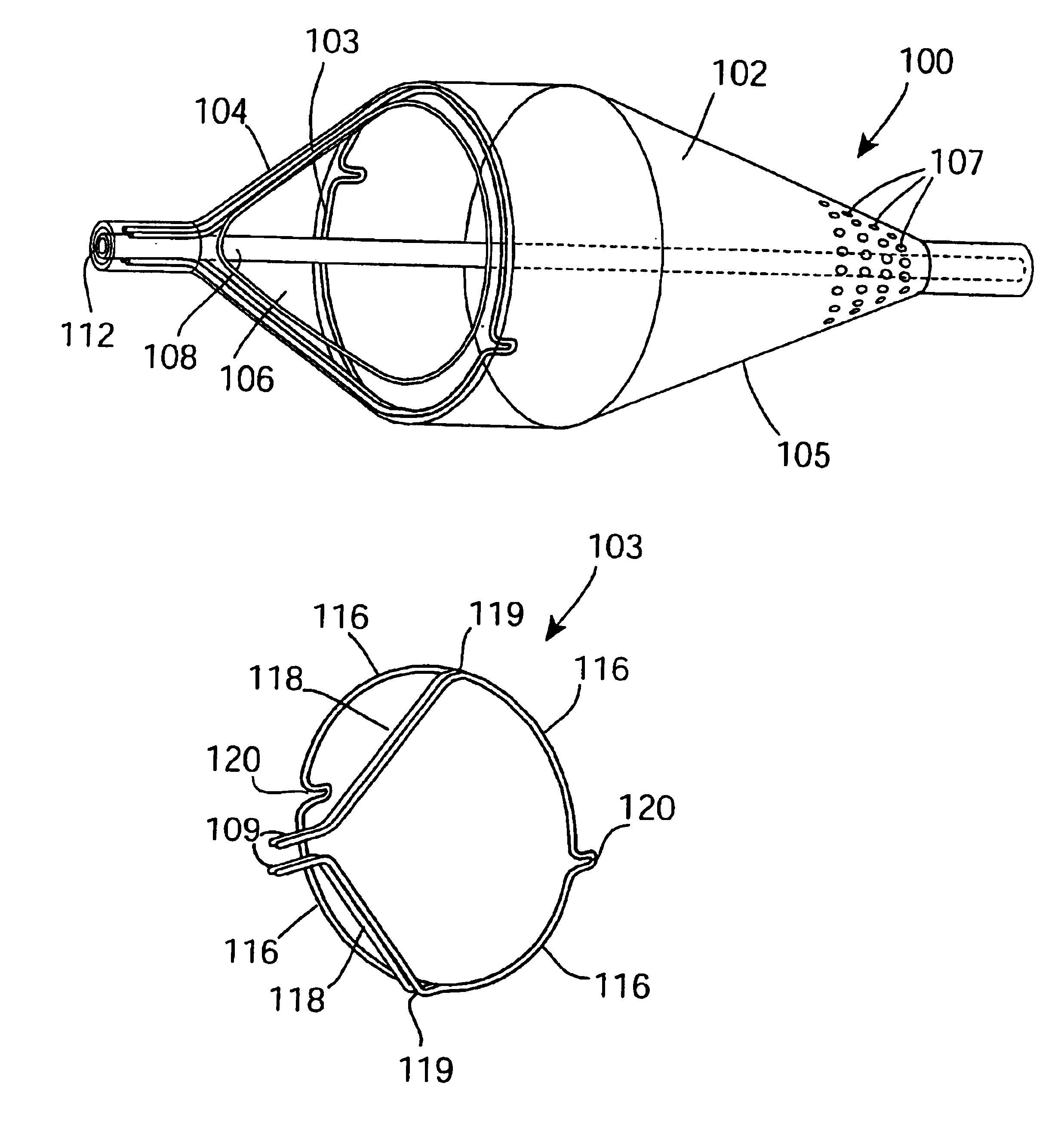
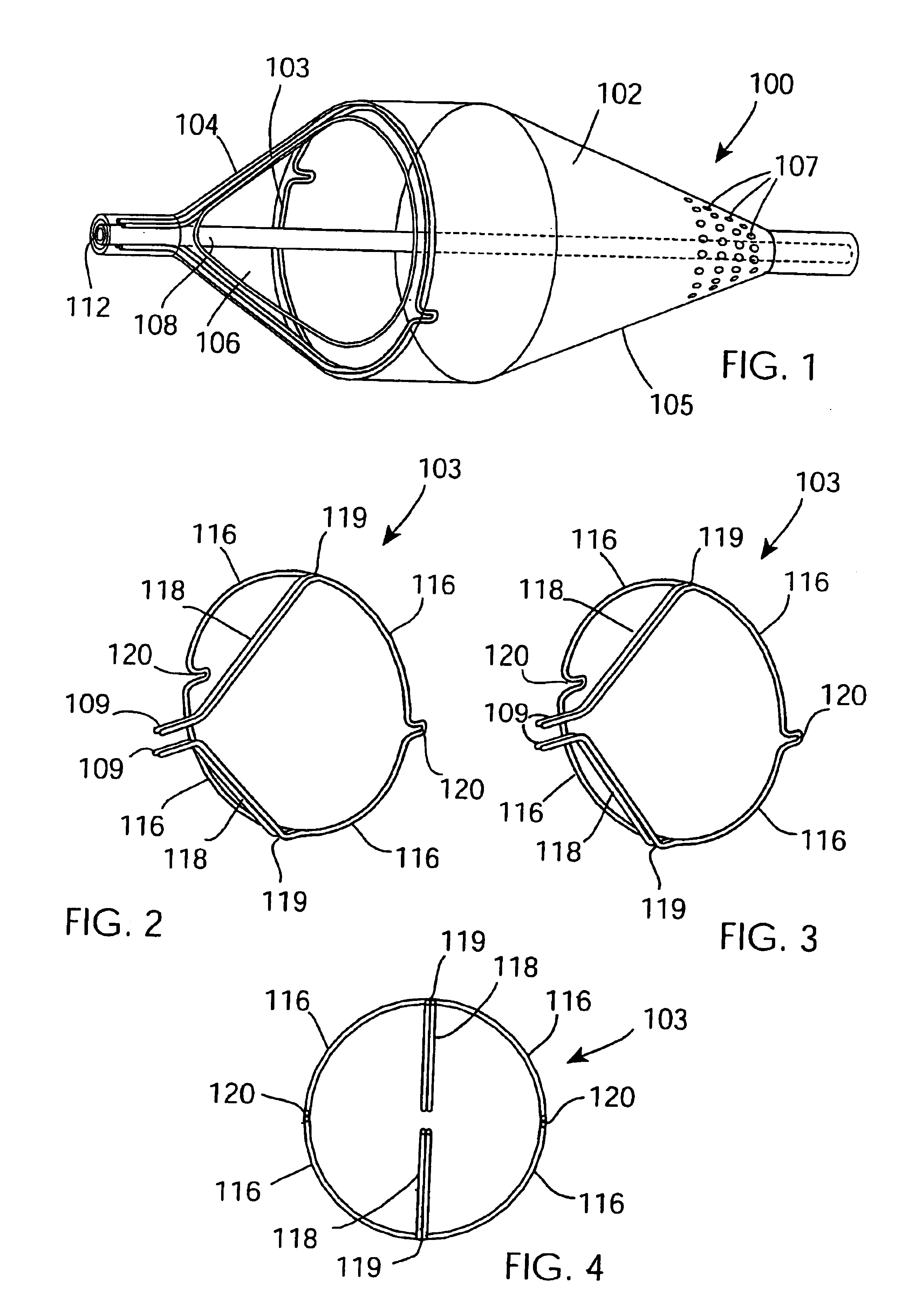
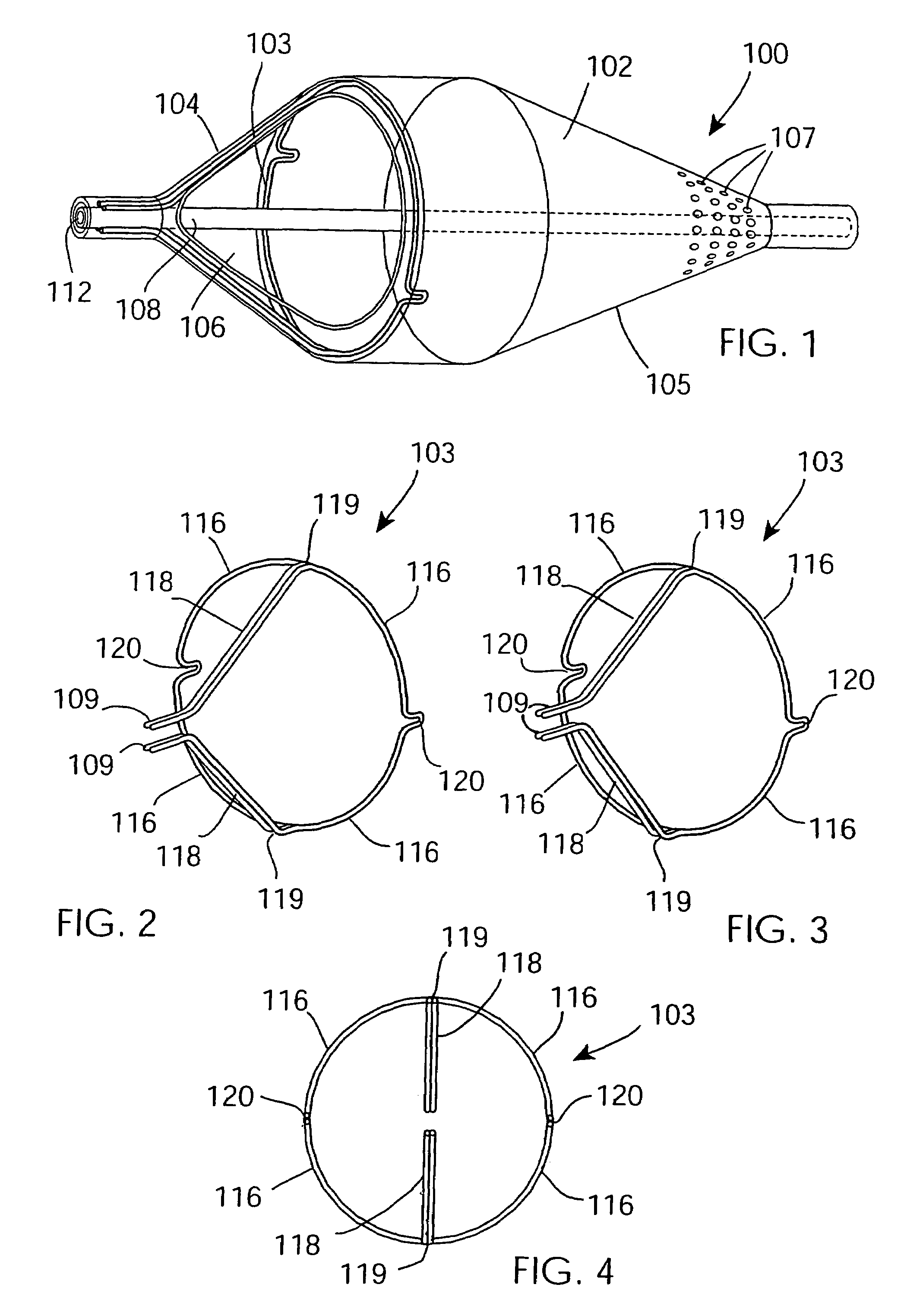
Support frame for an embolic protection device
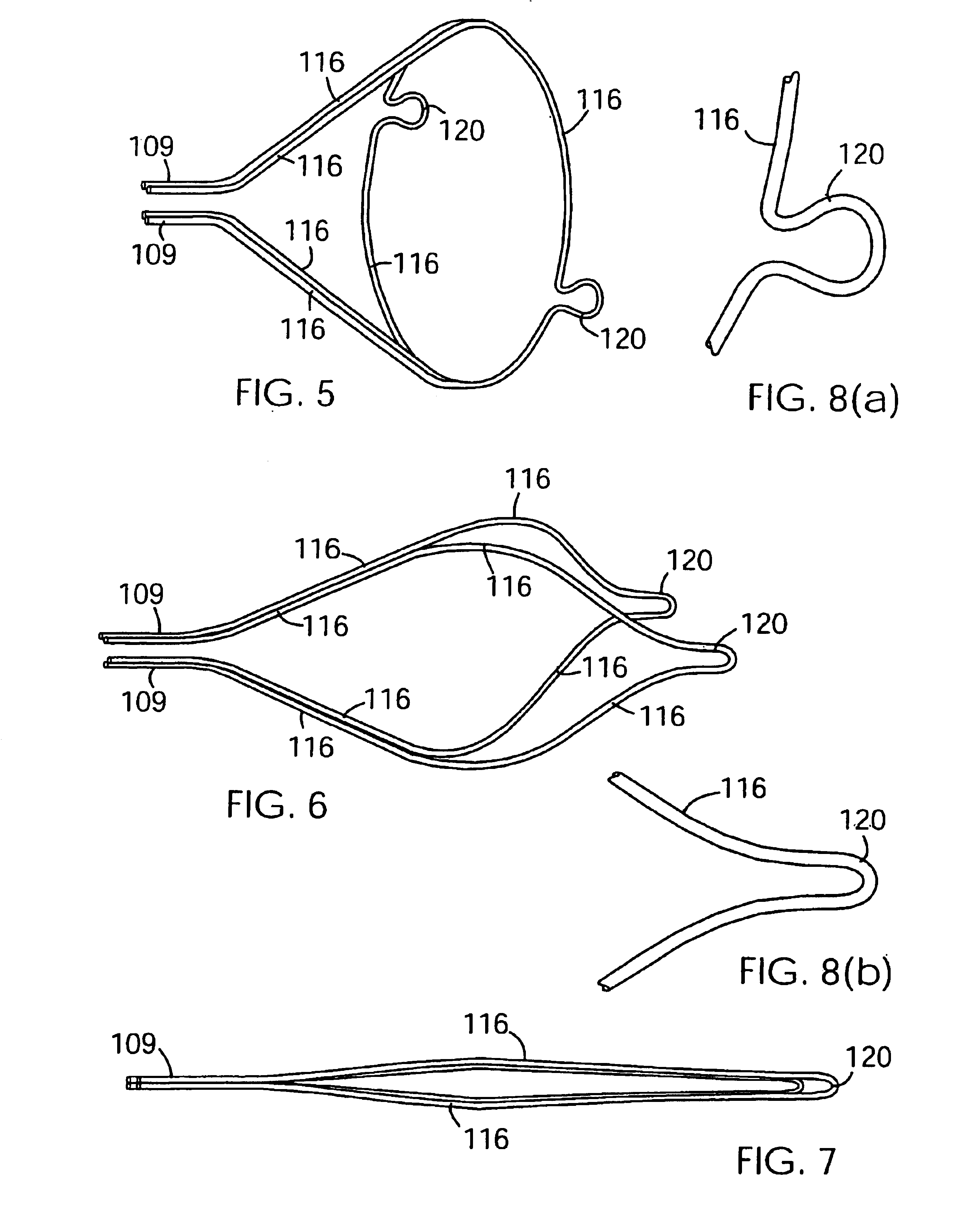
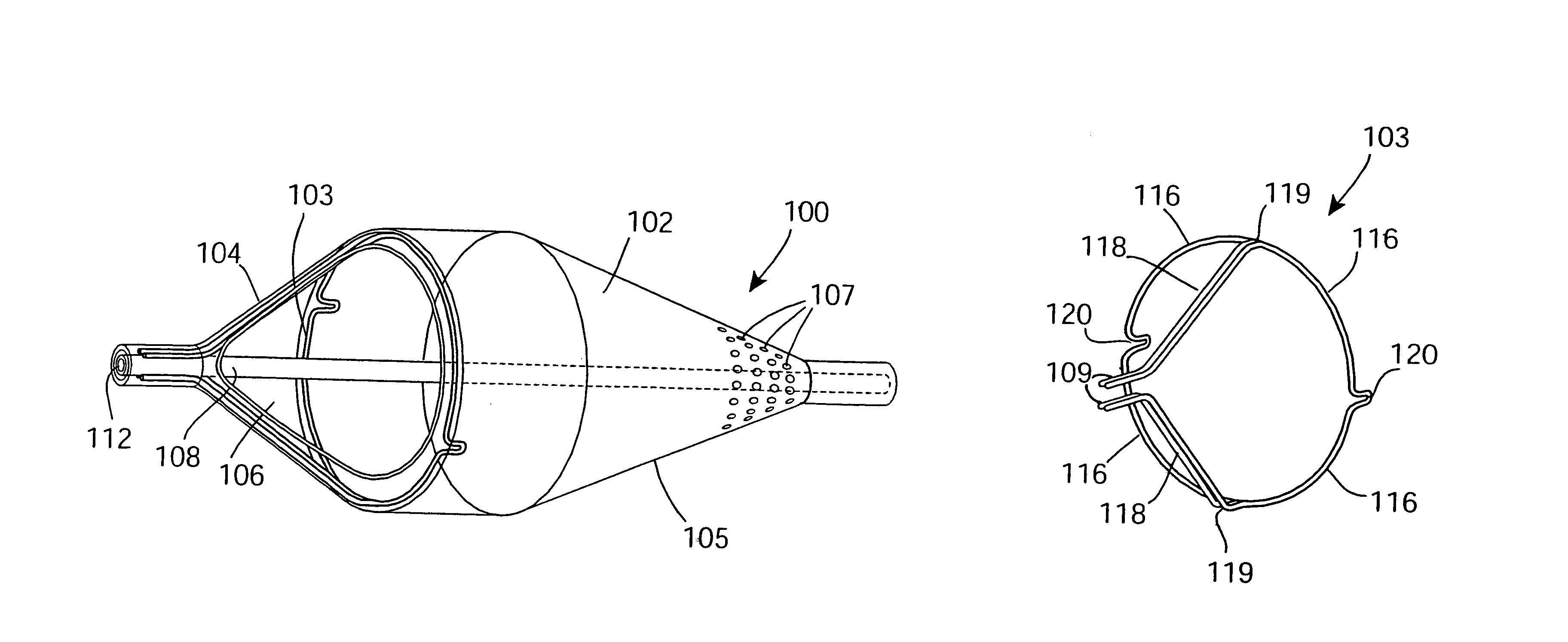
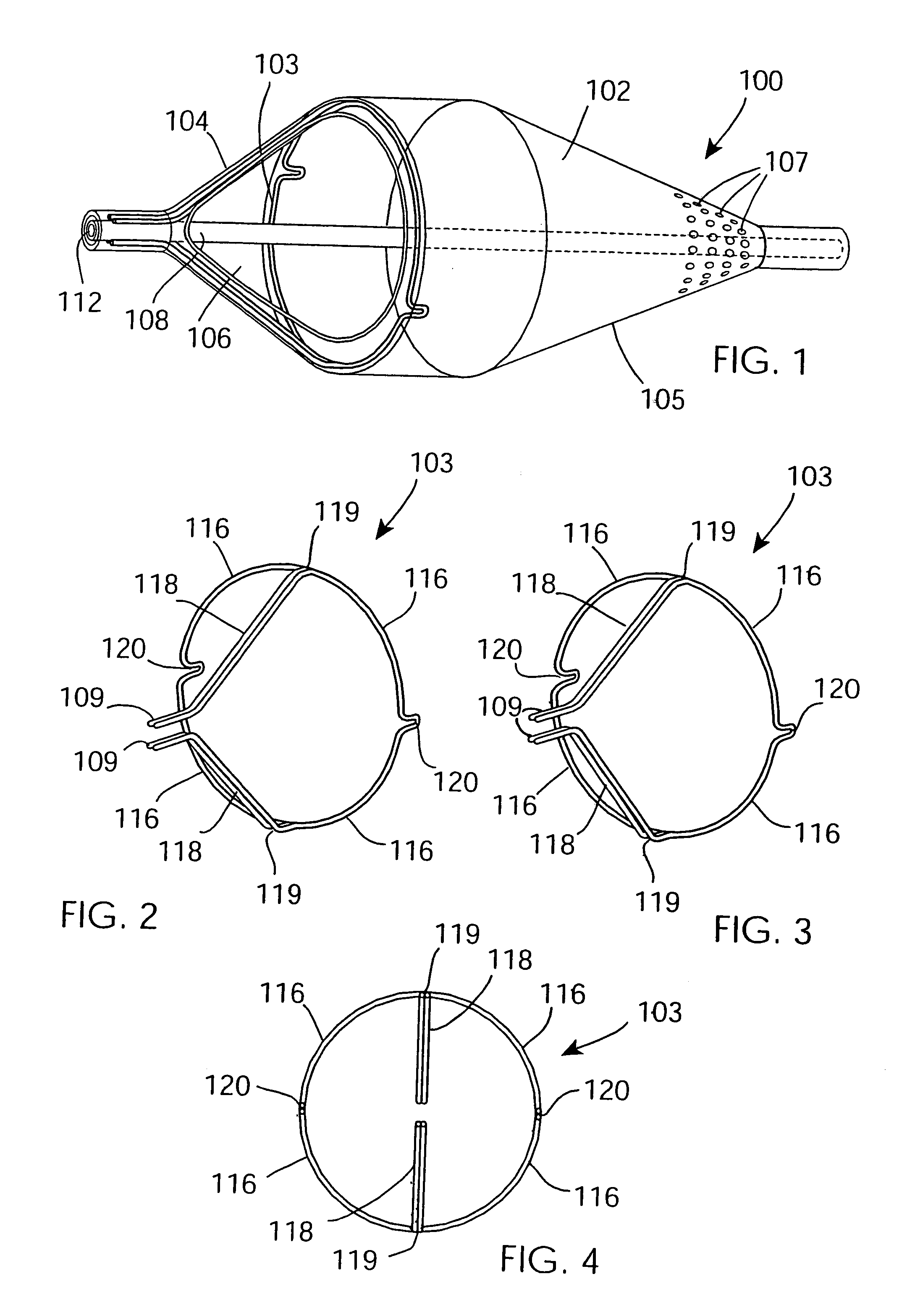
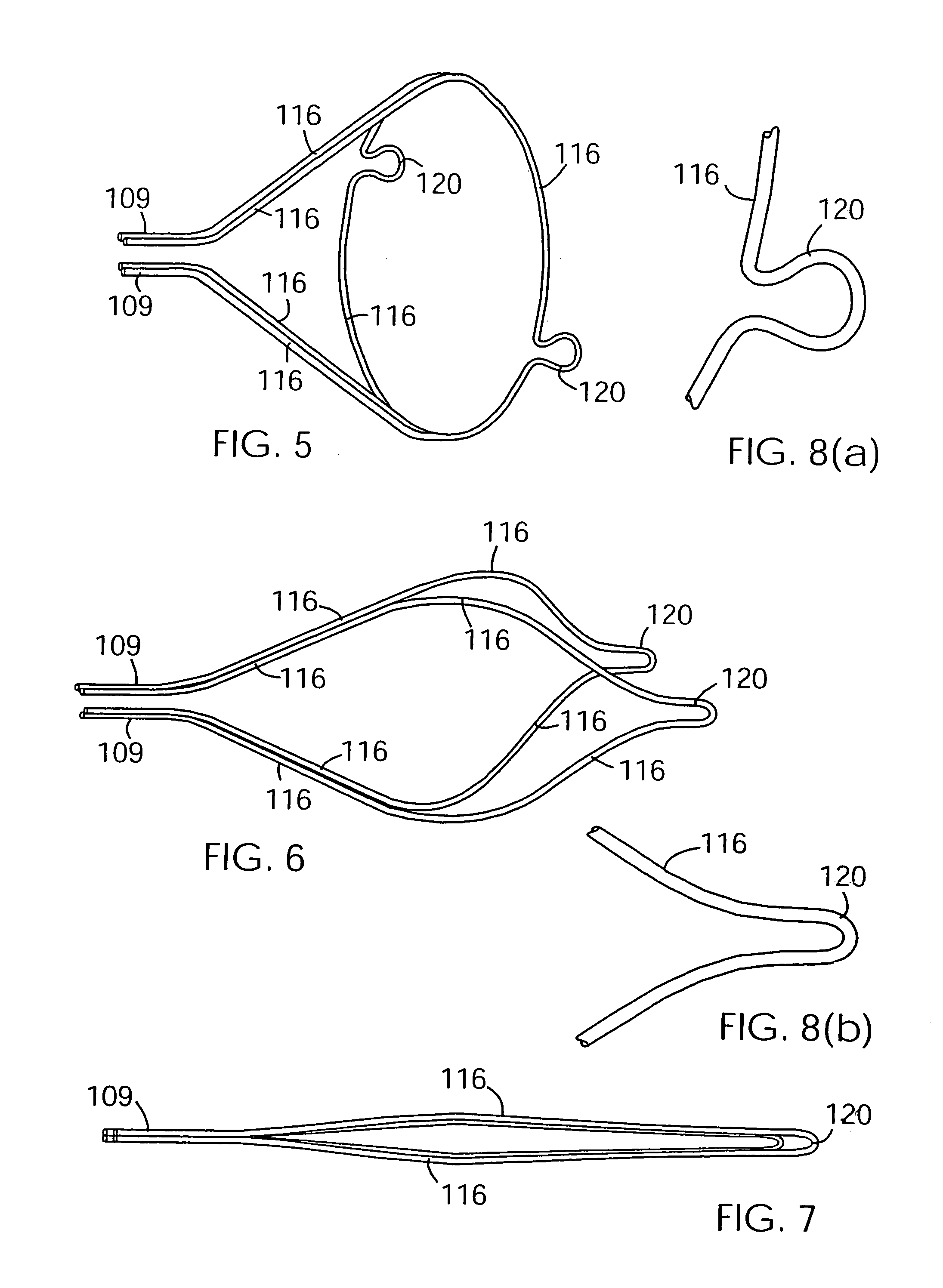
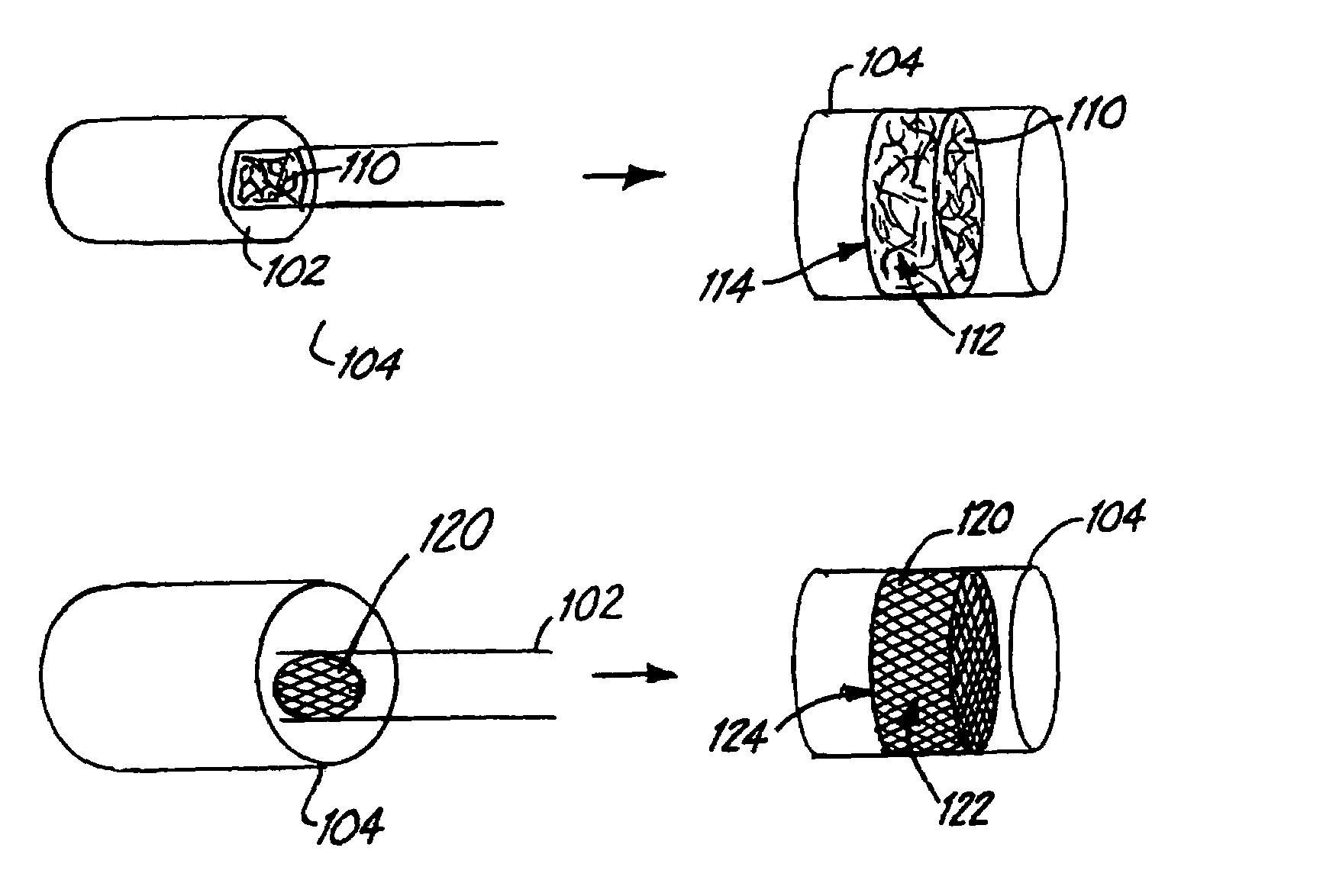
InactiveUS7037320B2Good flexibilitySlow its advancementSurgeryDilatorsEmbolic Protection DevicesMechanical engineering
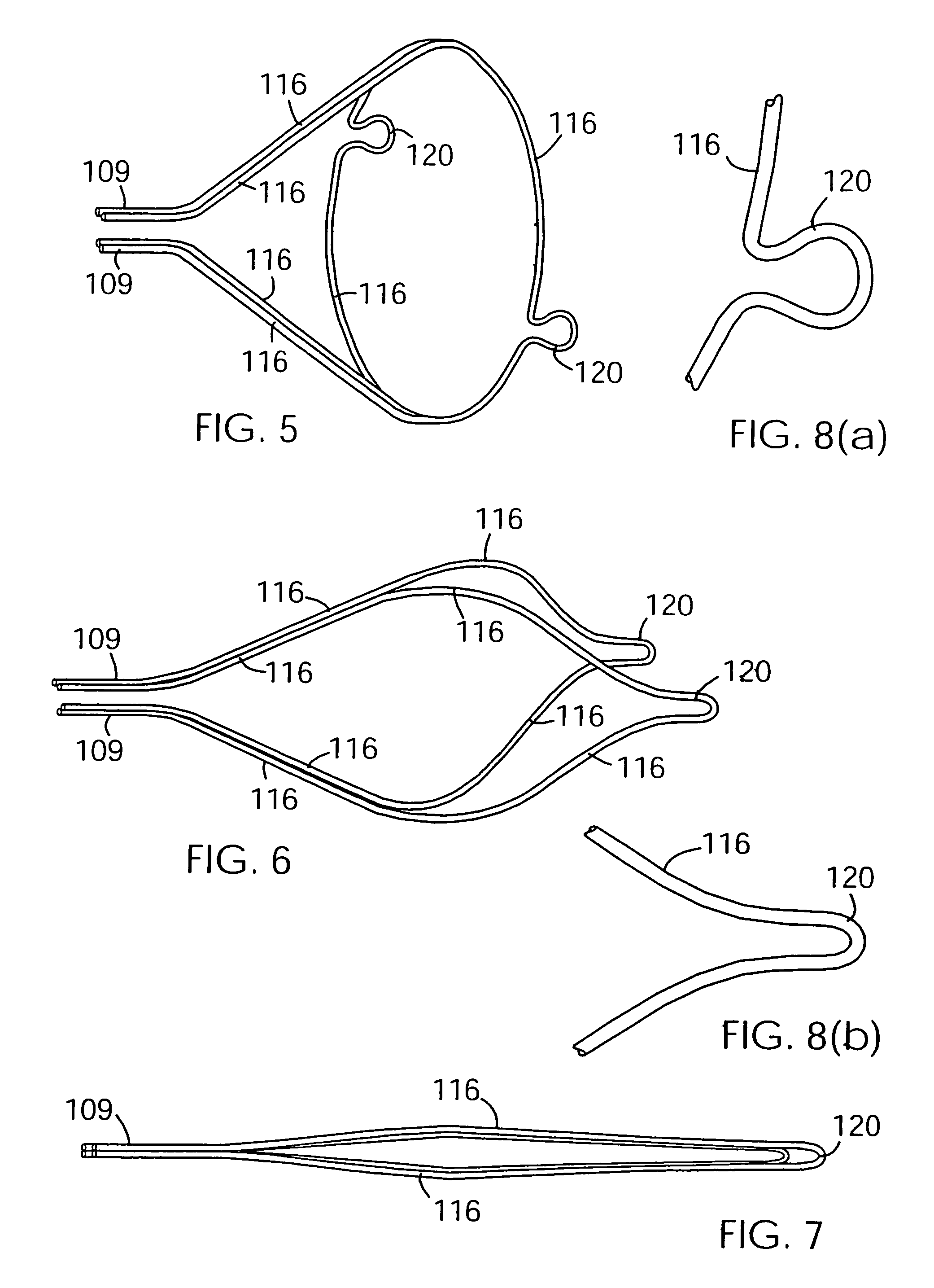
A support 103 for an embolic protection device comprises round wires 116 which may form one or more support hoops for a filter body. The circumferential hoop formed by the wires 116 ensures that in the expanded position, the filter body 102 will be supported by the support frame 103 in circumferential apposition with the interior wall of the vasculature. The wires 116 may have a strain distributing linkage element in the form of a loop 120 in. The loop 120 acts as a diameter or circumference adjuster allowing an embolic protection device to adapt to different vessel contours and sizes whilst maintaining apposition with the vessel wall. The strain relieving geometry of the loops enhances the compliance of the bend points without creating a weakened hinge point, thus ensuring that there is no discontinuity in the circumferential seal against the vessel wall.
Owner:SALVIAC
Embolic protection device with open cell design
InactiveUS20090024157A1Increase flexibilityOvercome deficienciesDiagnosticsSurgeryEmbolic Protection DevicesLanding zone
A cage and sleeve assembly for an embolic filtering device used to filter embolic particles from a body vessel has a strut assembly that is movable between an unexpanded position and an expanded position. The struts are configured to form a cage having an open cell design. The open cell design provides a filter cage with increased radial flexibility that also increases the contact with a vessel wall while reducing the landing zone length. Such an open cell design may have one or more rings that are not connected together at each vertex, and may be constructed from one ring. The sleeve assembly of the embolic filtering device may be joined to the filter cage at each vertex of the open cell or along the periphery of the open cell.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Embolic protection device for protecting the cerebral vasculature
ActiveUS20120172915A1Improve the level ofAvoiding and minimizingHeart valvesSurgeryParticulatesEmbolic Protection Devices
Single filter and multi-filter endolumenal methods and systems for filtering fluids within the body. In some embodiments a blood filtering system captures and removes particulates dislodged or generated during a surgical procedure and circulating in a patient's vasculature. In some embodiments a filter system protects the cerebral vasculature during a cardiac valve repair or replacement procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Steerable device having a corewire within a tube and combination with a functional medical component
An integrated guiding device has a tube and a corewire within the tube and a torque coupler. The torque coupler can couple the rotational motion of the tube with the rotational motion of the corewire. The wire can be moved longitudinally at least some amount relative to the tube. The device can further comprise a functional medical structure, such as an embolism protection structure. The device can be used in medical procedures, such as less invasive procedures within the cardiovascular system. Improved fiber based embolism protection devices comprise fiber bundles that are twisted prior to delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Radiopaque distal embolic protection device
InactiveUS20060030878A1Precise positioningSmall sizeSurgeryDilatorsDistal portionEmbolic Protection Devices
The present invention is a radiopaque distal embolic protection device for use in a lumen of a patient's body, such as a blood vessel. The protection device has an expandable and retractable filter attached to a distal portion of a guidewire. At least a portion of the filter has a radiopaque coating for viewing under fluoroscopy during use. The radiopaque coating allows the operator to ensure that the periphery of the filter has fully engaged the wall of a blood vessel and to take appropriate measures in recovery of the protection device after capture of emboli and particulate matter.
Owner:EV3
Balloon catheter having a regrooming sheath and method for collapsing an expanded medical device
InactiveUS20080140003A1Low profileFacilitate maneuveringStentsBalloon catheterEmbolic Protection DevicesMedicine
A method of using a balloon catheter to perform a medical procedure at a treatment site in a patient's body lumen and to recover an expanded device, such as an embolic protection device, which is adjacent to the treatment site in the body lumen. The inflated balloon is deflated and regroomed to a low profile configuration in the body lumen, and the balloon catheter is advanced distally from the treatment site to collapse the expanded device (e.g., embolic protection filter) within the balloon catheter. The balloon catheter has a recovery distal tip for collapsing an expanded device, and has a regrooming sheath member configured to slidably receive the deflated balloon therein to regroom the balloon.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Guide wire with embolic filtering attachment
A separate deliverable embolic protection device filter that attaches to a helical coil at a distal end of a conventional guide, for use in a blood vessel when an interventional procedure is being performed to capture any embolic material which may be created and released into the bloodstream during the procedure. The device includes a filter assembly with a proximal end and a distal end, and a guide wire connector attached to the distal end of the filter assembly. The guide wire connector is able to couple with the helical coil of the guide wire. A restraining sheath placed over the filter assembly in a coaxial arrangement maintains the filter assembly in a collapsed position and delivers the filter assembly separately to the helical coil of the guide wire, and then the guide wire connector is joined to the helical coil. Alternatively, the guide wire can include a rotatable coil section forming a portion of the distal tip coil on the guide wire which is adapted to be coupled to the filter assembly. This arrangement allows the filter assembly to be rotatably mounted onto the guide wire.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
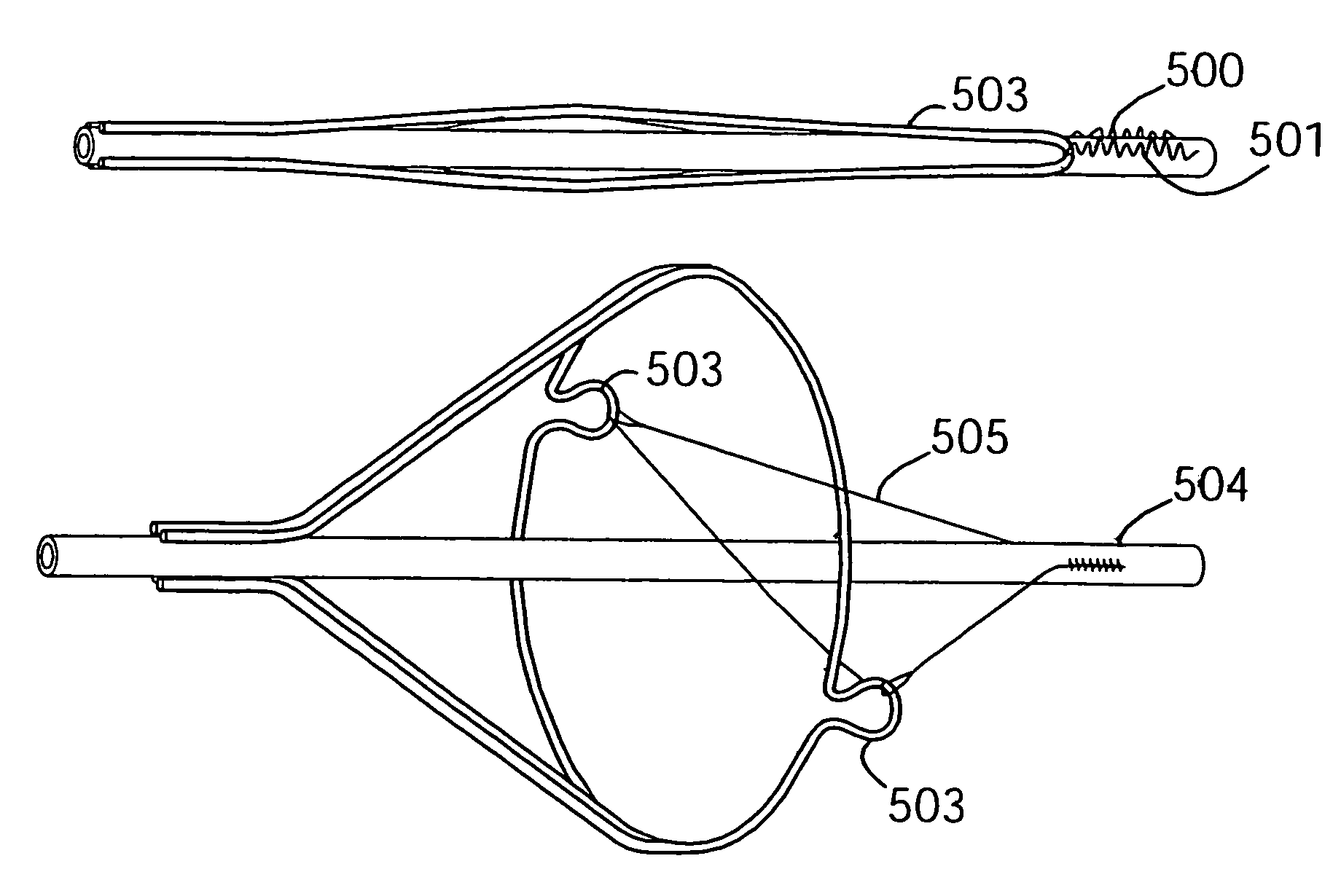
Support frame for an embolic protection device
InactiveUS7014647B2Good flexibilitySlow its advancementSurgeryDilatorsTetheringEmbolic Protection Devices
An embolic protection device has a support frame incorporating tethering features for connecting the support frame distally and / or proximally and / or intermediately to a carrier. Tethers may also be used additionally or alternatively for connecting various elements of a support frame. The tethers may be used to connect a support hoop 503 to a tubular member 504. The tethers provide added safety and stability to the frame without any increase in the length of the device when wrapped down for delivery.
Owner:SALVIAC
Embolic protection device
An embolic protection device generally includes an elongated hub and at least one projection. The projection defines a tortuous pathway between the hub and the vessel wall to prevent emboli from following the pathway and passing beyond the device. The tortuous pathway is structured to permit the bodily fluid to follow the pathway and pass beyond the device.
Owner:COOK INC
Steerable device having a corewire within a tube and combination with a functional medical component
An integrated guiding device has a tube and a corewire within the tube and a torque coupler. The torque coupler can couple the rotational motion of the tube with the rotational motion of the corewire. The wire can be moved longitudinally at least some amount relative to the tube. The device can further comprise a functional medical structure, such as an embolism protection structure. The device can be used in medical procedures, such as less invasive procedures within the cardiovascular system. Improved fiber based embolism protection devices comprise fiber bundles that are twisted prior to delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
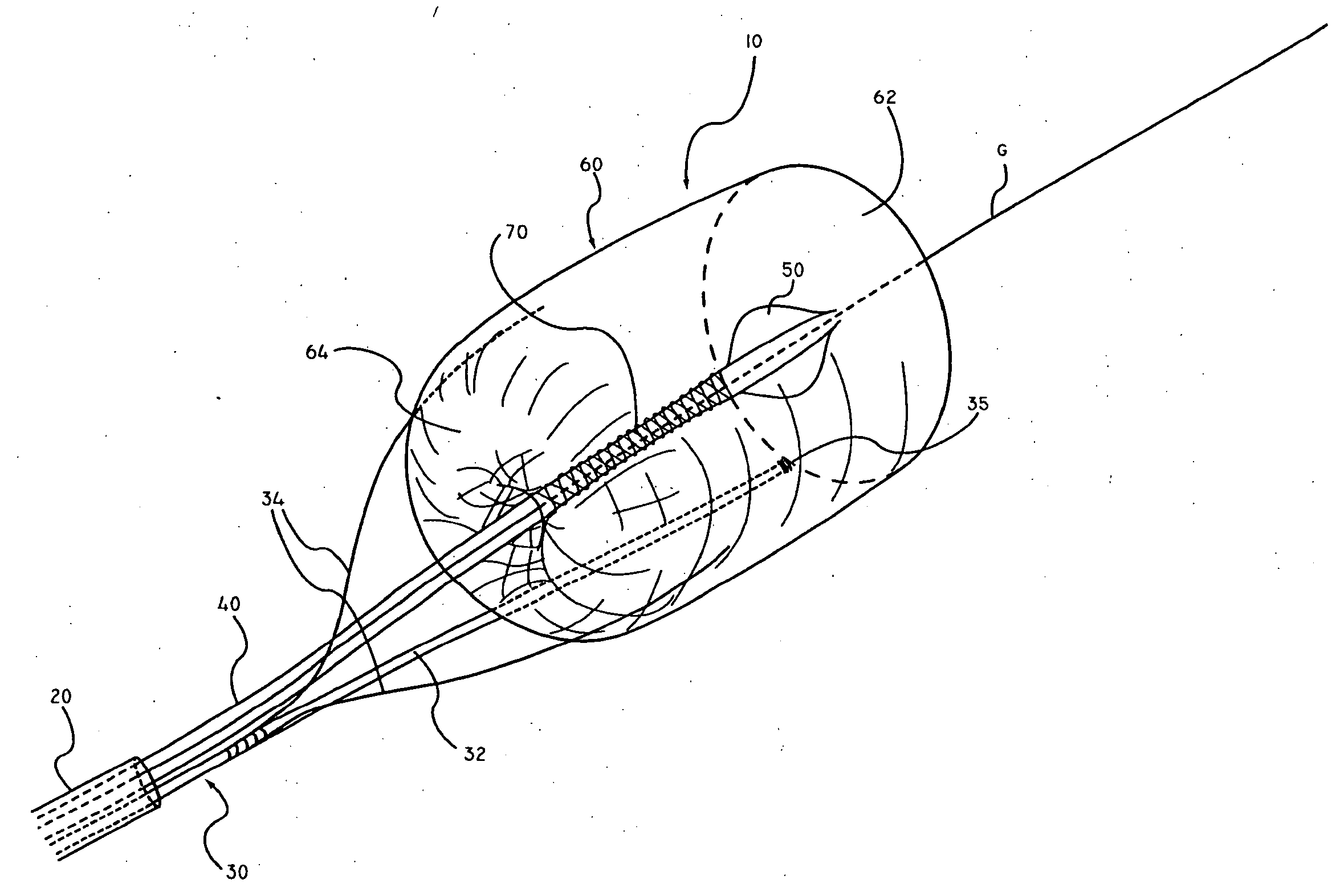
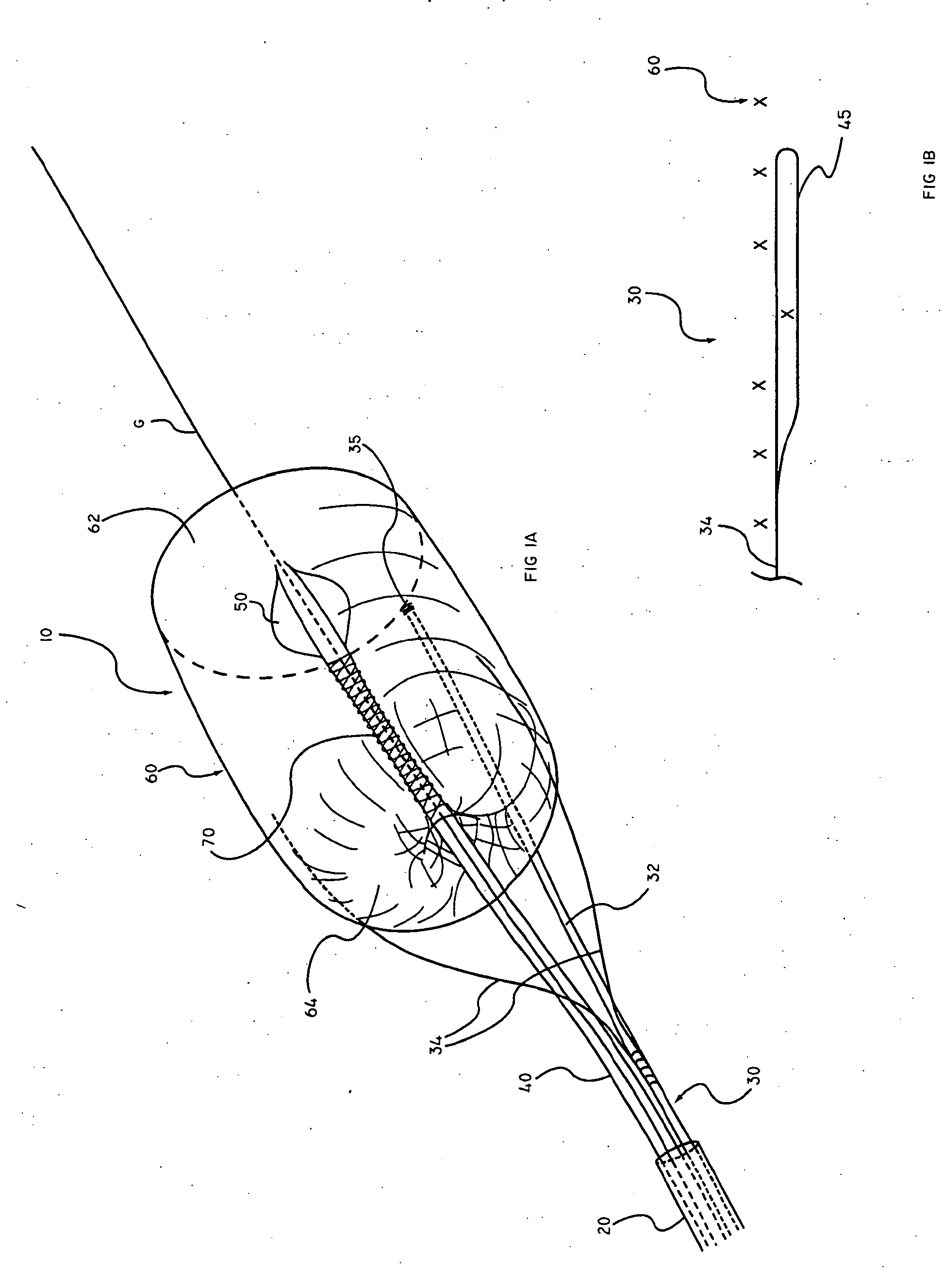
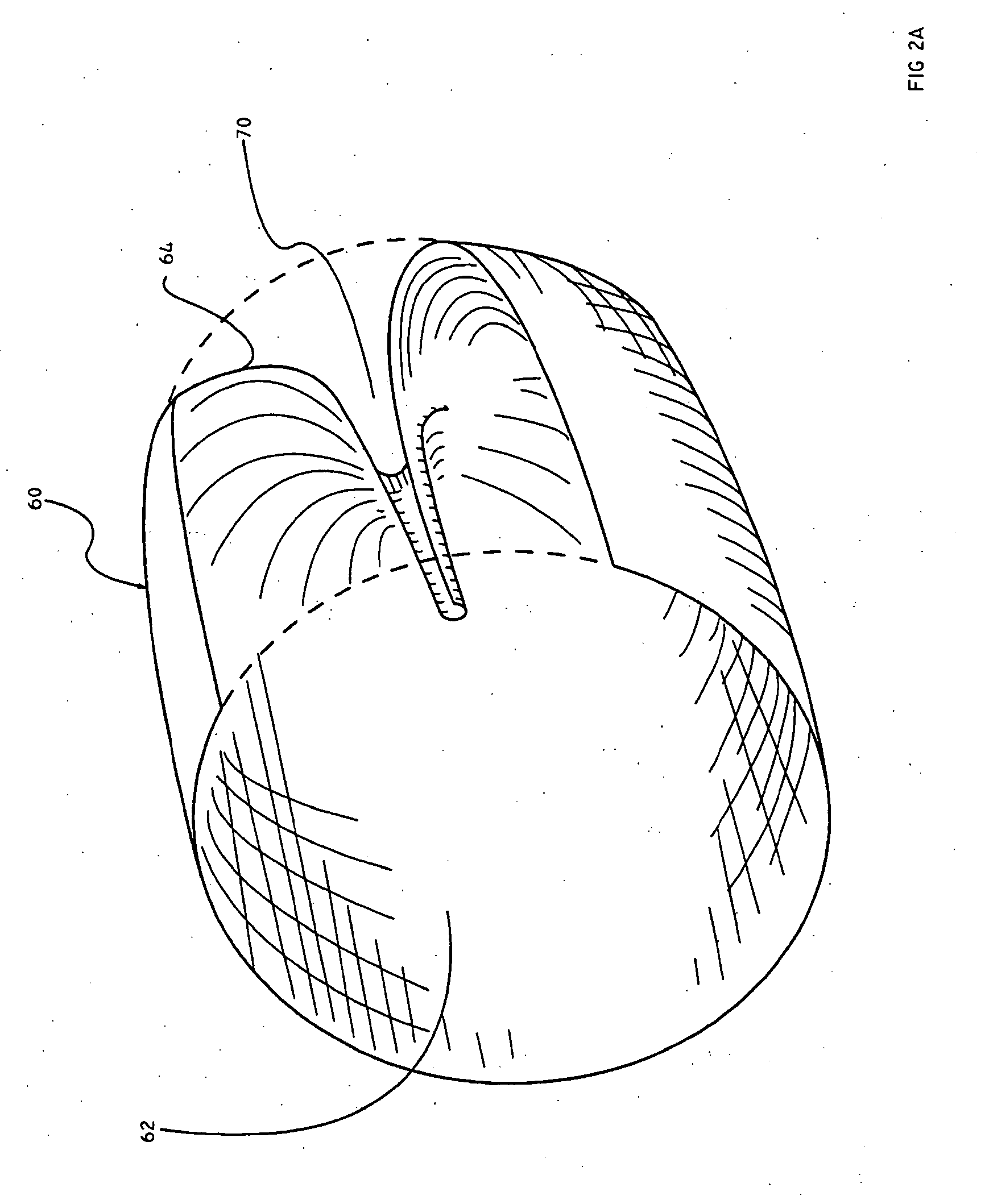
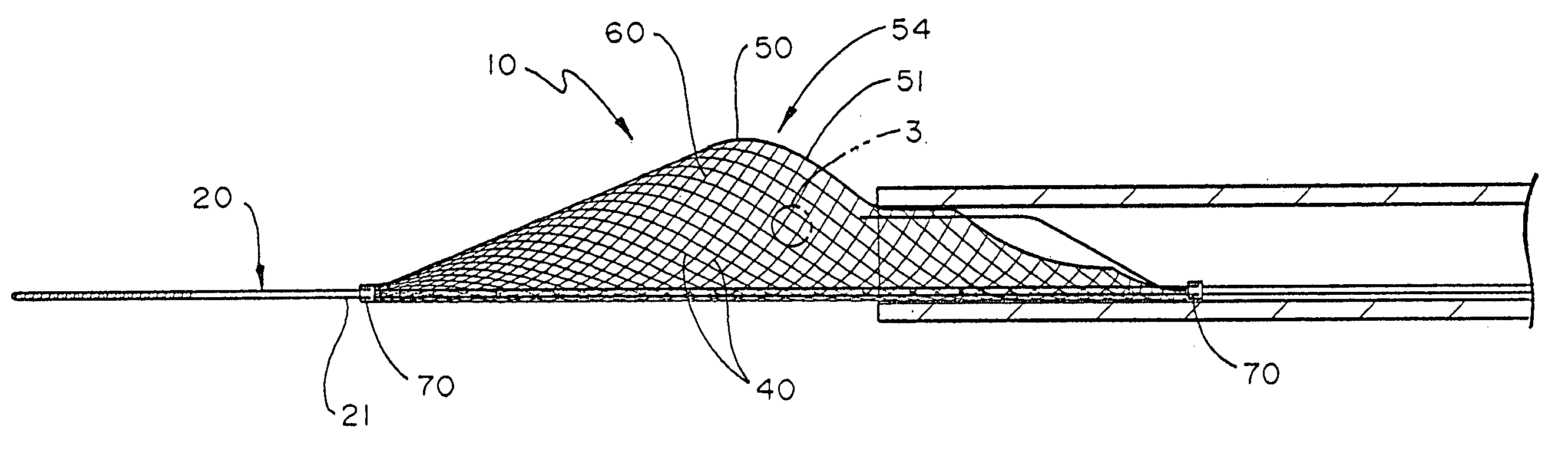
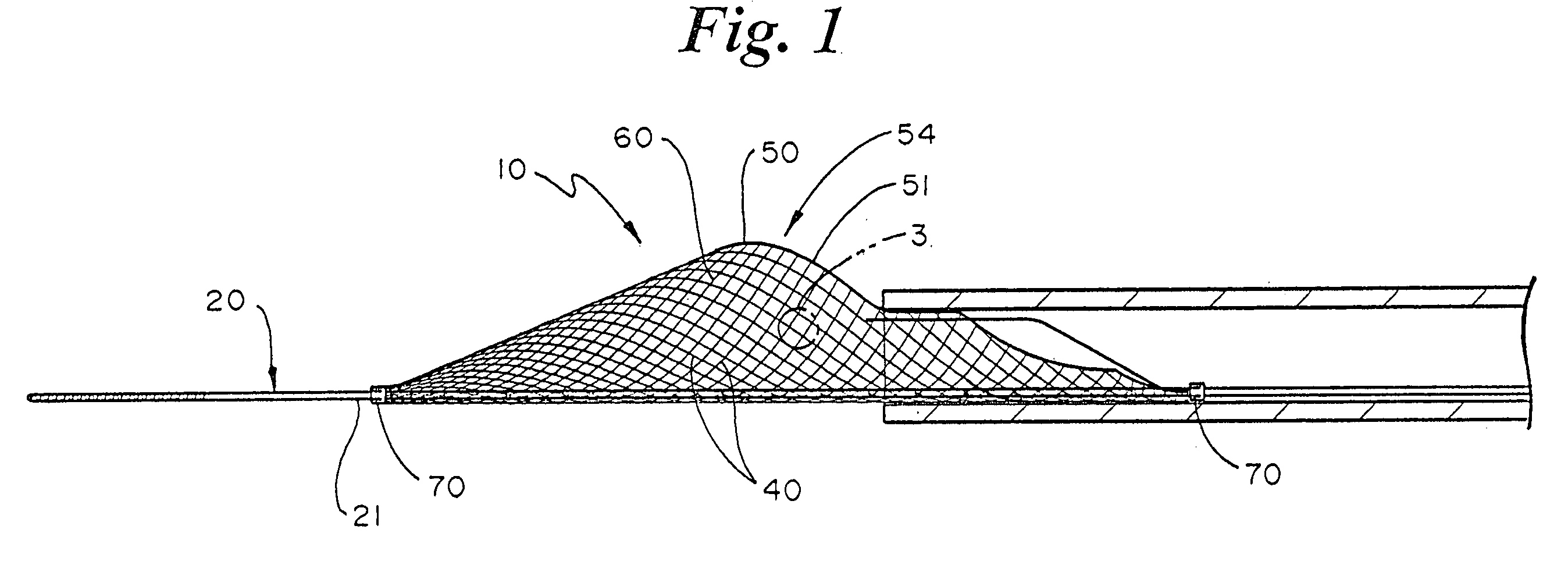
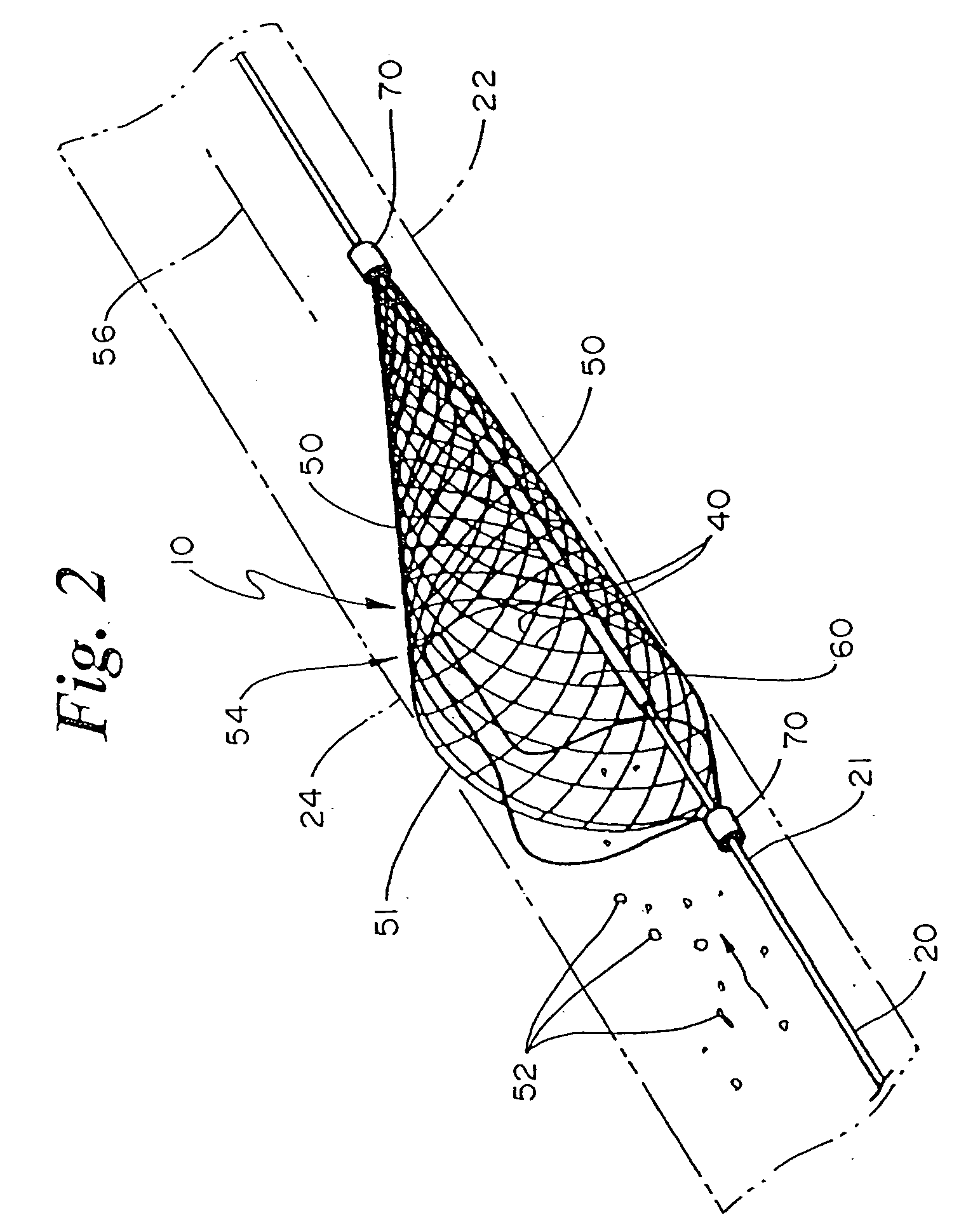
Embolic Protection Device and Method of Use
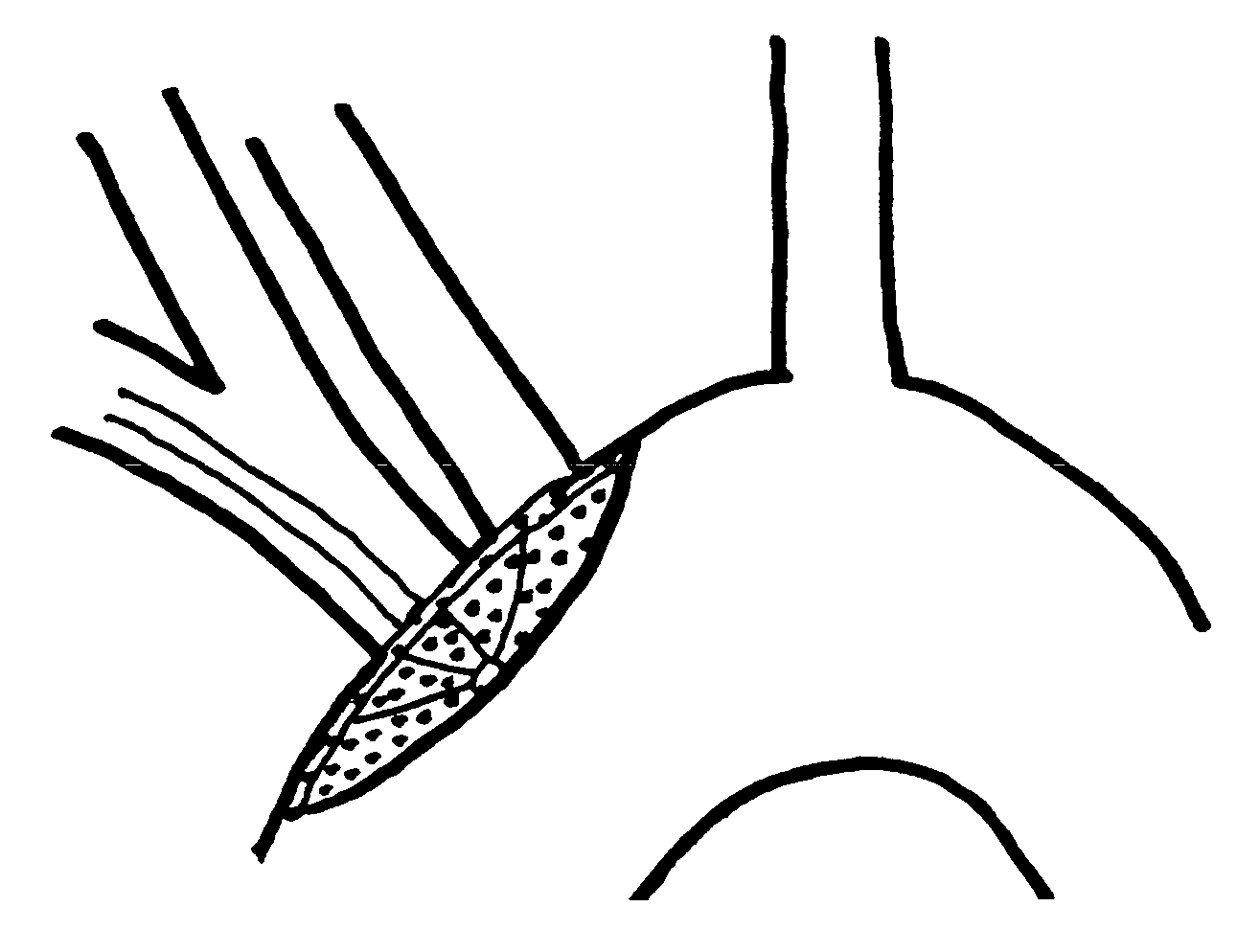
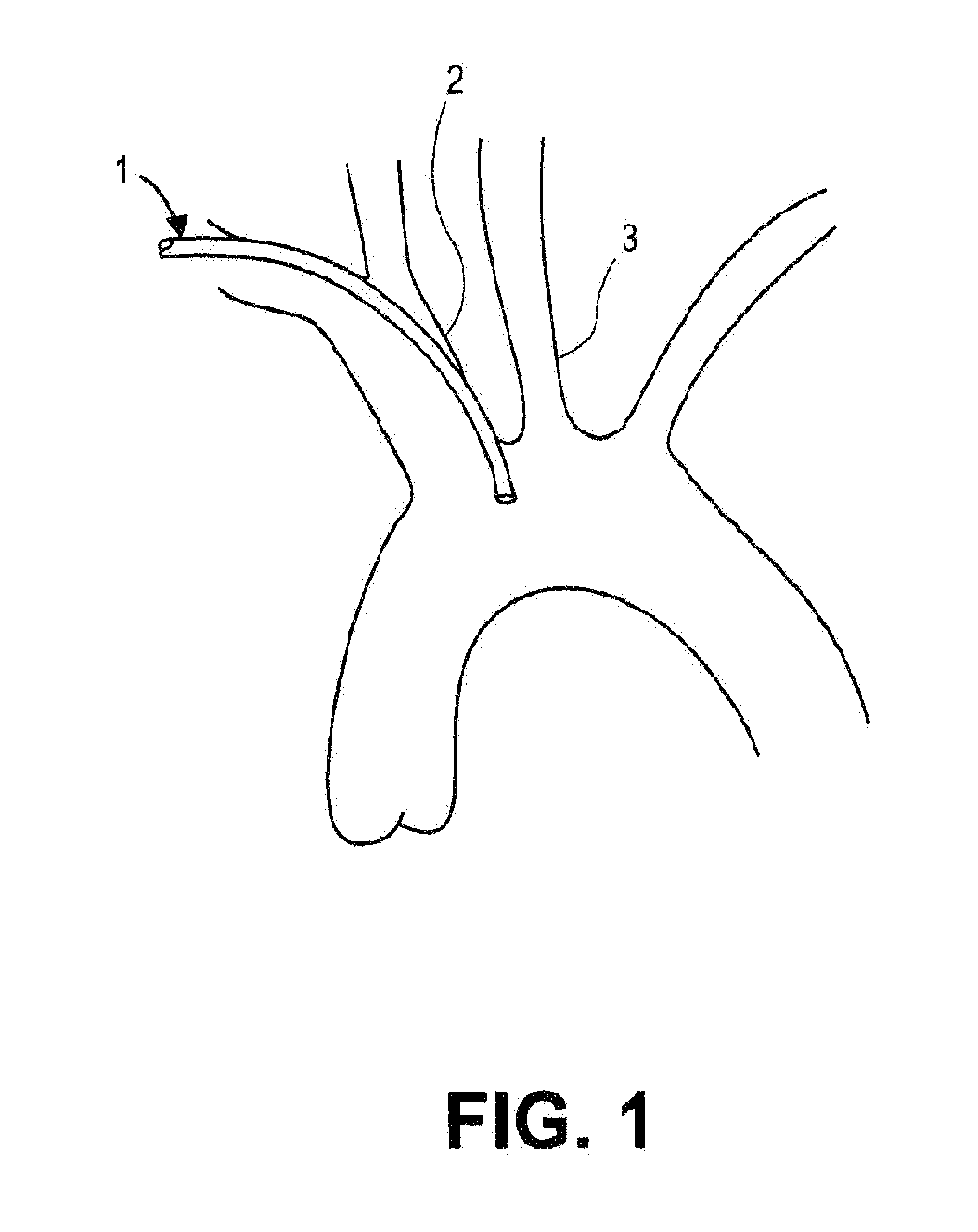
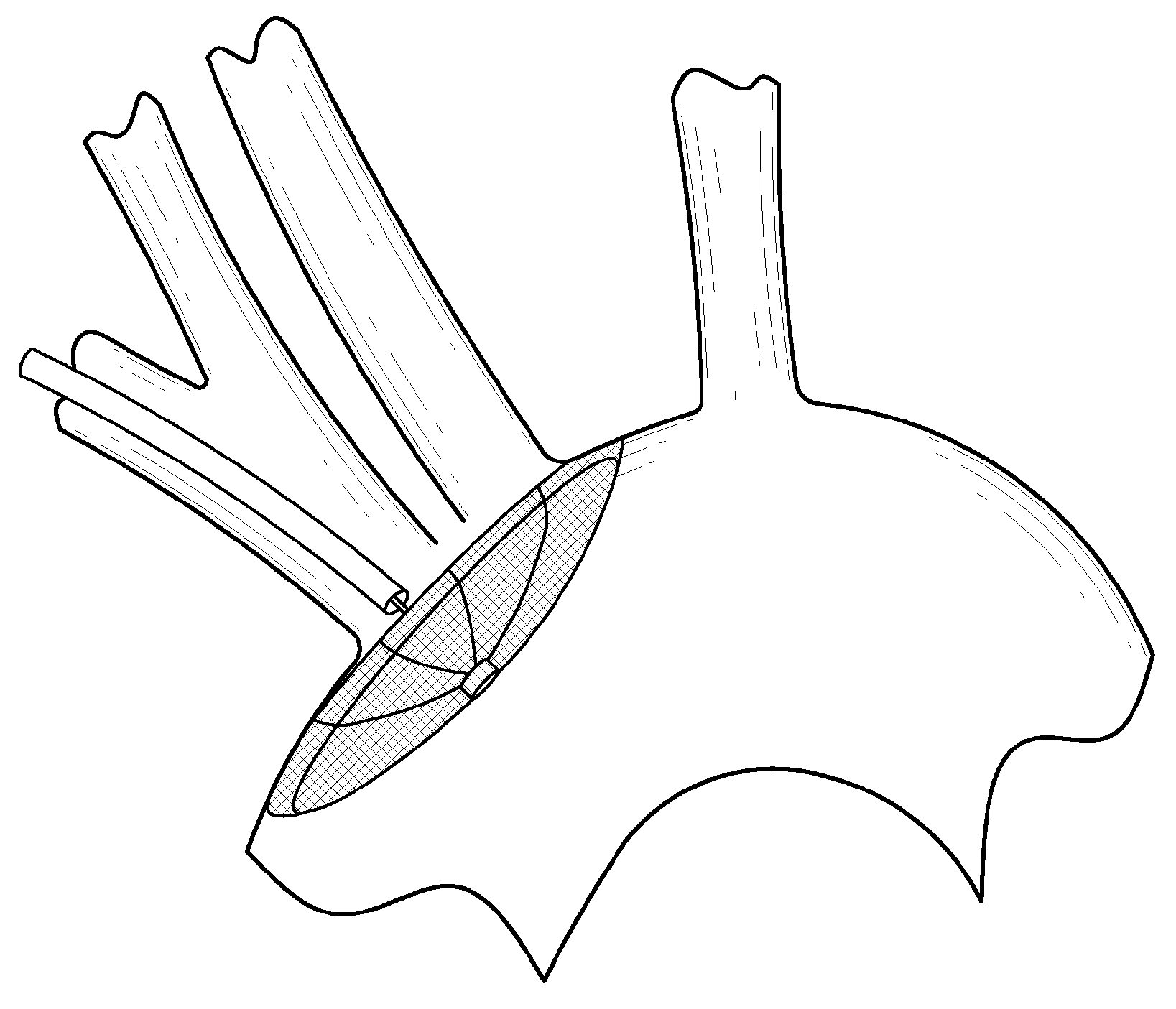
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (greater than 100 microns in the preferred embodiment) from entering either the right or left carotid arteries by deflecting emboli downstream in the blood flow. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The device has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the device.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG +1
Embolic protection device having a reticulated body with staggered struts
ActiveUS7850708B2Minimizes restricted flowEasy retrievalSurgeryDilatorsStenotic lesionEmbolic Protection Devices
An embolic protection device for capturing emboli during treatment of a stenotic lesion in a body vessel is disclosed. The device comprises a basket and a filter attached to the basket. The basket has a deployed state and an undeployed state. The basket includes a reticulated body having an outer diameter. The reticulated body includes a plurality of struts connected together in a singly staggered configuration distally along a longitudinal axis to a distal end. The plurality of struts of the reticulated body is configured to fold along the longitudinal axis. The basket has a proximal stem proximally extending from the body. The filter portion has a lip attached to the distal end defining an opening of the filter portion when the basket is in the deployed state for capturing emboli. The filter portion extends from the lip to a filter end.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
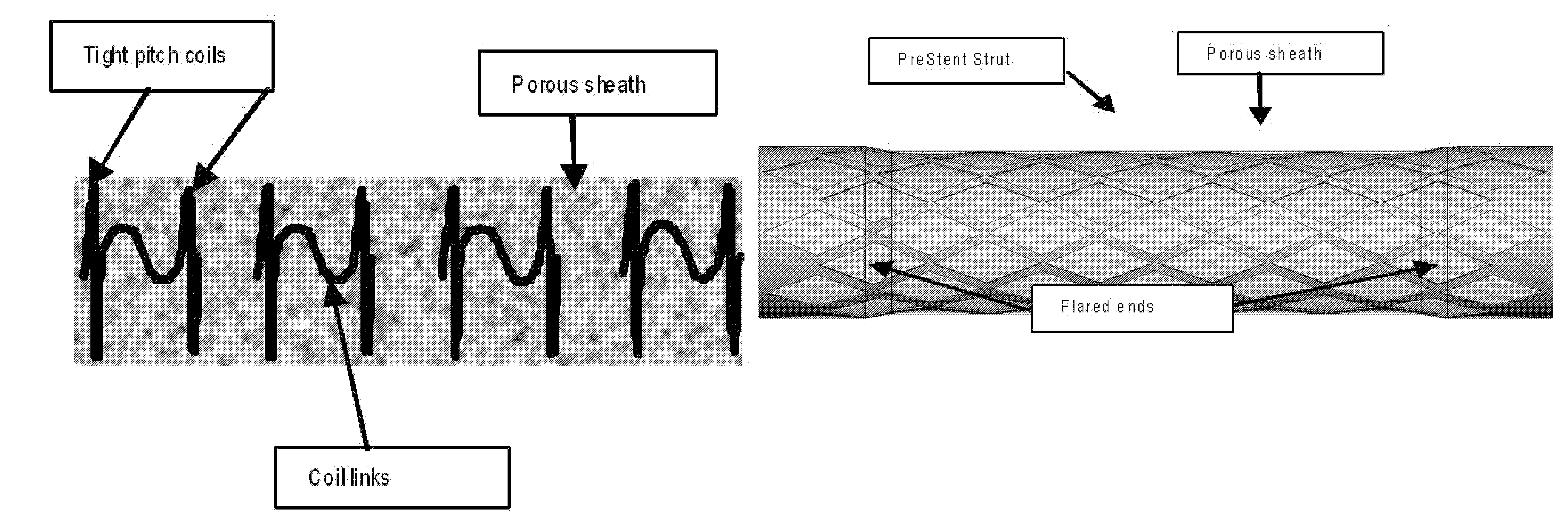
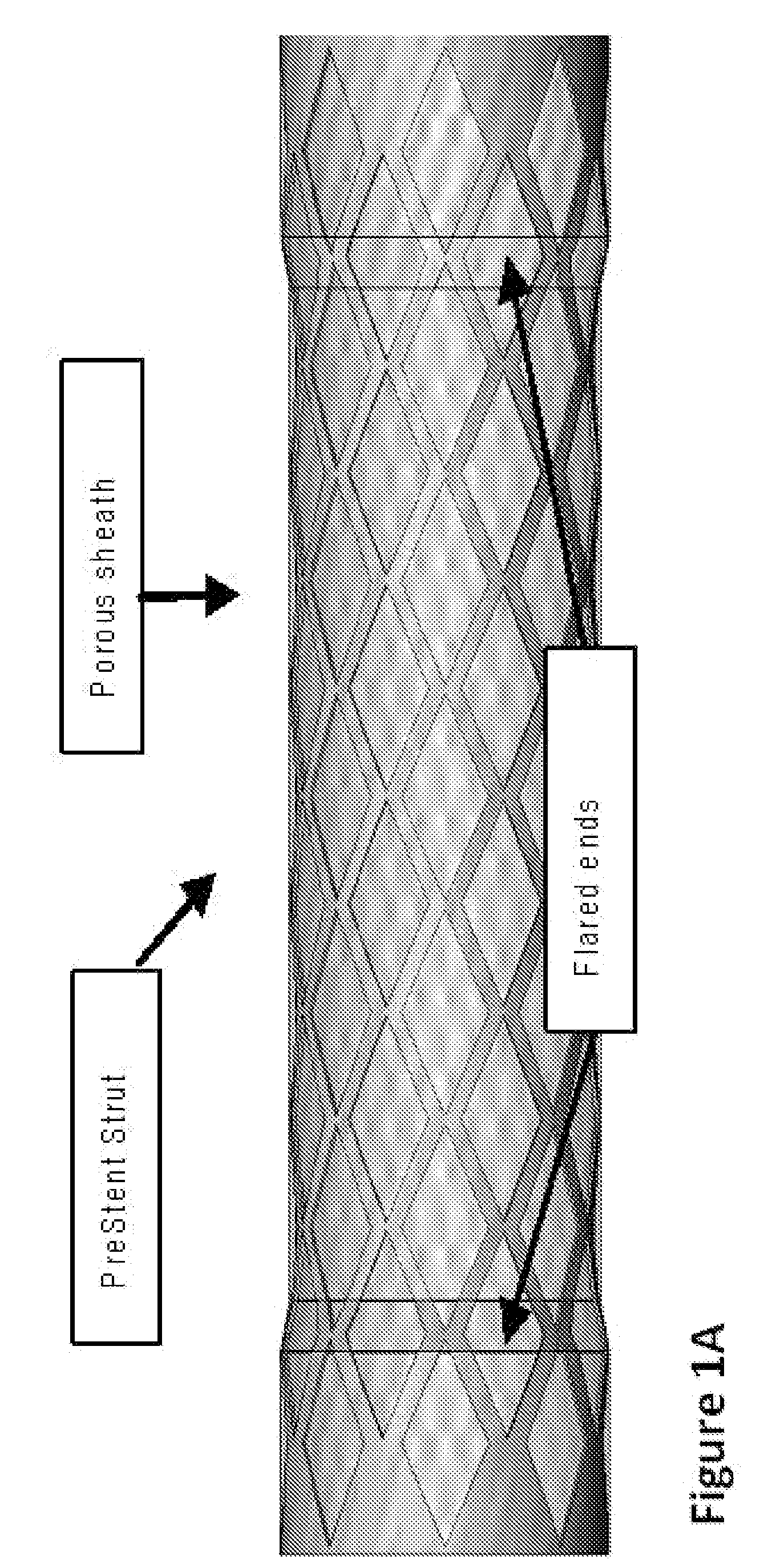
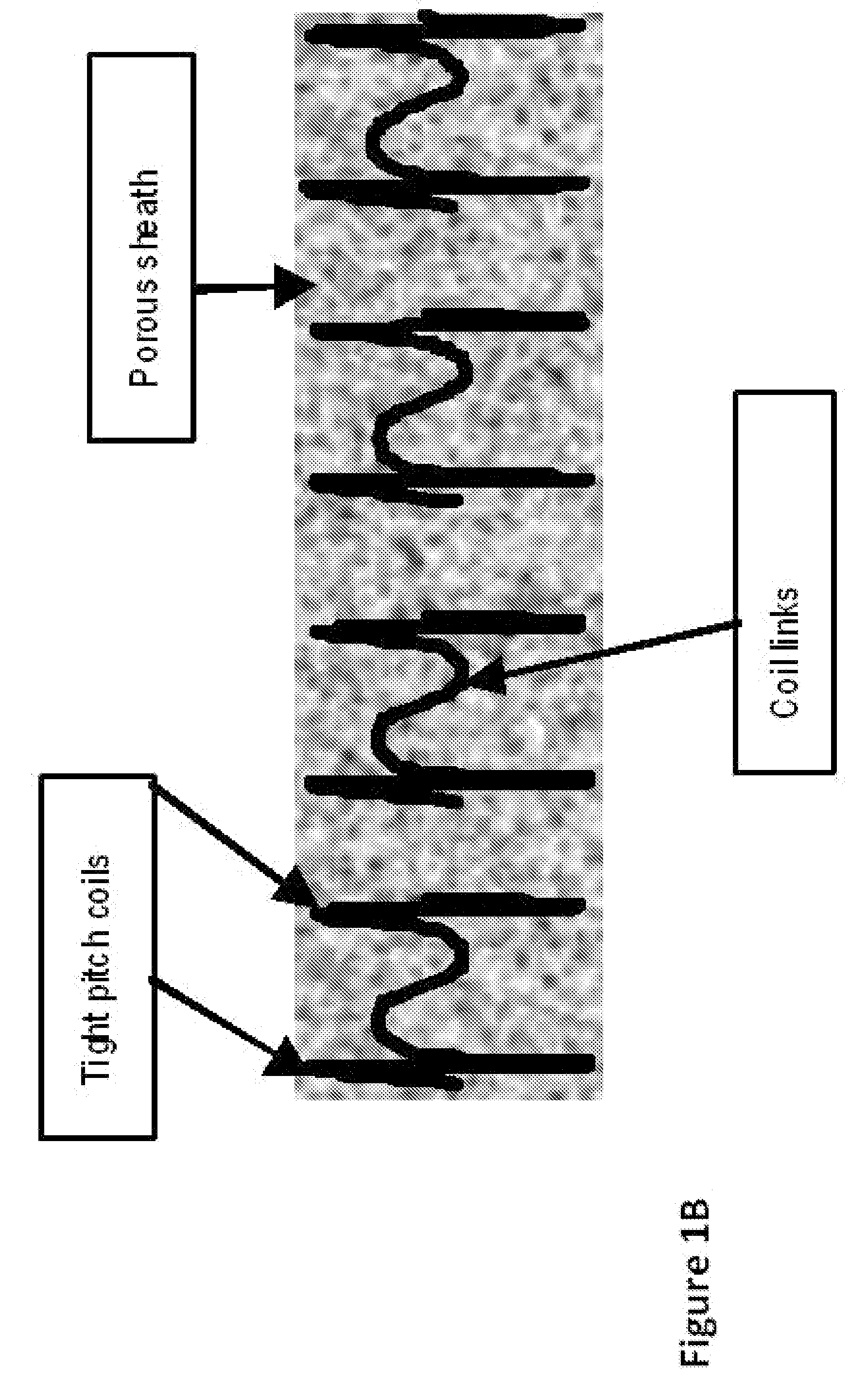
Embolic protection devices and methods
InactiveUS20090043330A1Facilitate safe insertionImprove securityStentsDiagnosticsSupporting systemEmbolic Protection Devices
The present invention provides a PreStent comprising a sheath and frame designed for preparing a vessel passageway for the subsequent delivery of a stent. The PreStent can be self-expanding or balloon-expandable. Also provided is a supporting system for delivering the PreStent safely. The supporting system includes a delivery catheter, one or more occlusion balloon, optionally one or more dilation balloon, and a retention sheath for the self-expanding type of PreStent. The PreStent of the present invention is flexible for use with a variety of stent and guidewire models such that it can easily be incorporated with existing devices to improve stenting procedures.
Owner:SPECIALIZED VASCULAR TECH
Delivery catheter with constraining sheath and methods of deploying medical devices into a body lumen
ActiveUS20090254169A1Easy to tearFacilitate and control tearingGuide needlesStentsPull forceInsertion stent
A delivery catheter includes a constraining sheath coupled to a distal end of the catheter, and a medical device, such as an embolic protection device (EPD) or a stent, constrained by the sheath. A wire may extend proximally from the constraining sheath and be coupled thereto. A proximal pulling force on the wire causes the wire to tear the constraining sheath, thereby releasing the medical device from a constrained configuration to an expanded configuration.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Delivery catheter with constraining sheath and methods of deploying medical devices into a body lumen
ActiveUS8545544B2Facilitate and control tearingStentsGuide needlesEmbolic Protection DevicesInsertion stent
A delivery catheter includes a constraining sheath coupled to a distal end of the catheter, and a medical device, such as an embolic protection device (EPD) or a stent, constrained by the sheath. A wire may extend proximally from the constraining sheath and be coupled thereto. A proximal pulling force on the wire causes the wire to tear the constraining sheath, thereby releasing the medical device from a constrained configuration to an expanded configuration.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Embolic protection device and methods of use
An evacuation sheath assembly and method of reducing or removing a blockage within a vessel without permitting embolization of particulate matter is provided. The evacuation sheath assembly includes a first elongate tubular member, having proximal and distal ends and a main lumen configured to be placed in fluid communication with a blood vessel. An expandable member is provided on a distal portion of the tubular member and is configured to form a seal with the blood vessel. The evacuation assembly further includes a second elongate tubular member having proximal and distal ends and an inflation lumen configured to be placed in fluid communication with the expandable member and a gas inflator. The gas inflator includes a high pressure gas source and a mechanism for regulating the pressure of the gas delivered by the gas inflator. The gas inflator is configured to be placed in fluid communication with the proximal end of the inflation lumen in order to provide a regulated pressure gas source for inflating the expandable member. A method of treatment of a blood vessel using the evacuation sheath assembly includes advancing the evacuation sheath assembly into the blood vessel through a guide catheter. The expandable member is inflated to provide form a seal between the blood vessel and the guide catheter and a vacuum is applied to the main lumen of the first elongate tubular member to cause retrograde blood flow and carry fluid into the main lumen of the evacuation sheath assembly.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Fiber based embolism protection device
ActiveUS20080109088A1Additive manufacturing apparatusBalloon catheterFiberEmbolic Protection Devices
Improved embolism protection devices comprises fibers that can have one configuration for delivery of the device and a second configuration in which the device is deployed for filtering of flow within a vessel. In some embodiments, the fibers can be connected to a fiber support, which is connected to an actuating element. The actuating element controls the transition from the delivery configuration to the deployed configuration. The embolism protection device can comprise a guidewire. The fibers can be attached at one end to a fiber support structure and at another end to the guidewire. A hypotube can be attached to the proximal end of the fibers while the guidewire is attached at the distal end of the fibers with the guidewire extending within a central channel of the hypotube. The hypotube can be used to guide the delivery of treatment structures, such as a balloon and / or a stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
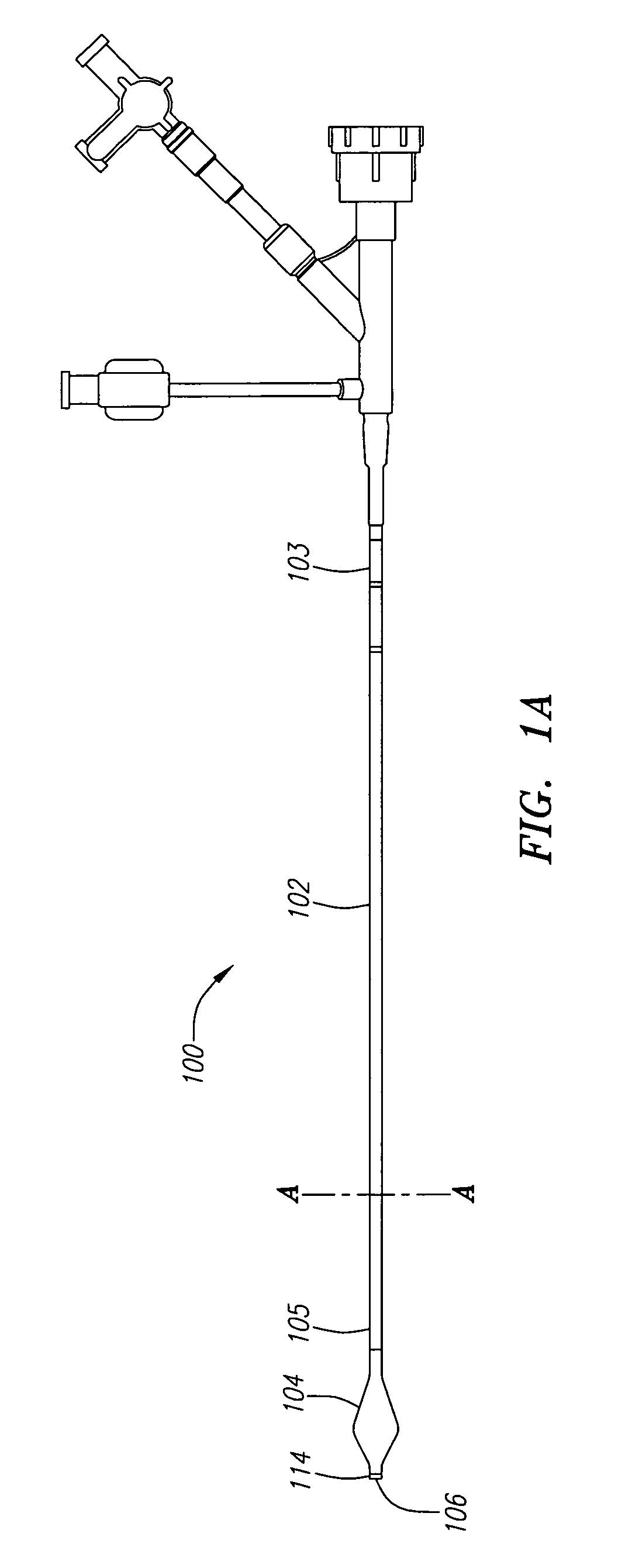
Rapid exchange catheters and embolic protection devices
A catheter comprising a housing portion defining an interior cavity and the housing portion comprising a housing member having an interior space dimensioned for housing an indwelling medical device. The elongated member comprises a lumen extending at least from an exit port to a distal port, the housing member is disposed within the lumen, and the lumen is dimensioned in the housing portion to receive a guidewire outside of the interior space of the housing member. A medical device for filtering emboli from blood flowing in a blood vessel of patient comprising an elongate support member and an elongate side branch member connected to the elongate support member. The filter element is attached to the elongate side branch member by a proximal filter element slider, and the elongate side branch member is adapted to maintain the filter element centered in the vessel.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Embolism protection devices
Embolism protection devices can be formed with a biocompatible expandable polymer that can expand upon release within a patient's vessel. Upon release, the structure can be configured to filter flow through the vessel. The material of the embolism protection devices can release one or more biologically active agents, such as a thrombolitic agent, including, for example, tPA. Alternatively or additionally, the embolism protection device can be connected to a tether that elutes one or more biologically active agents.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com