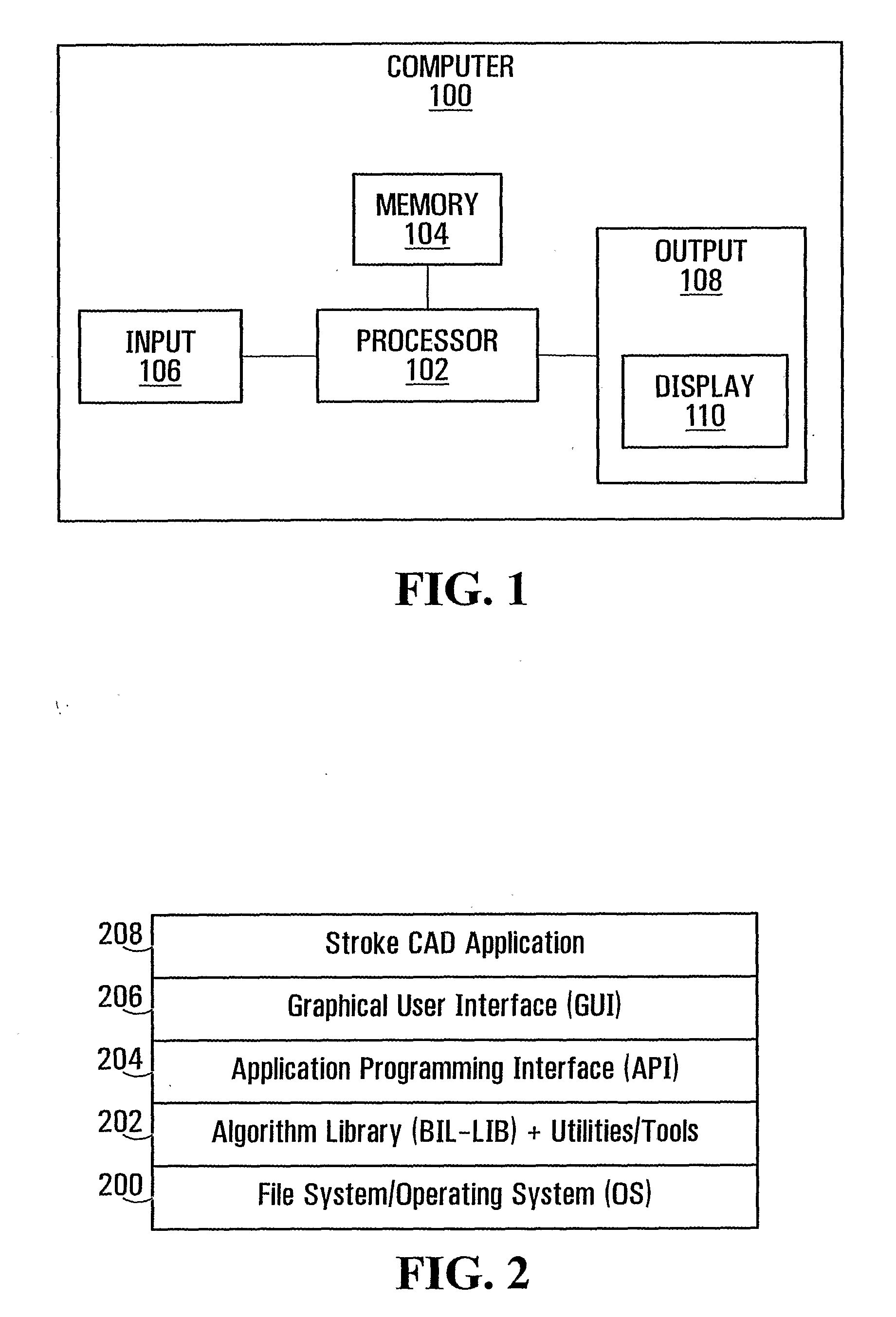
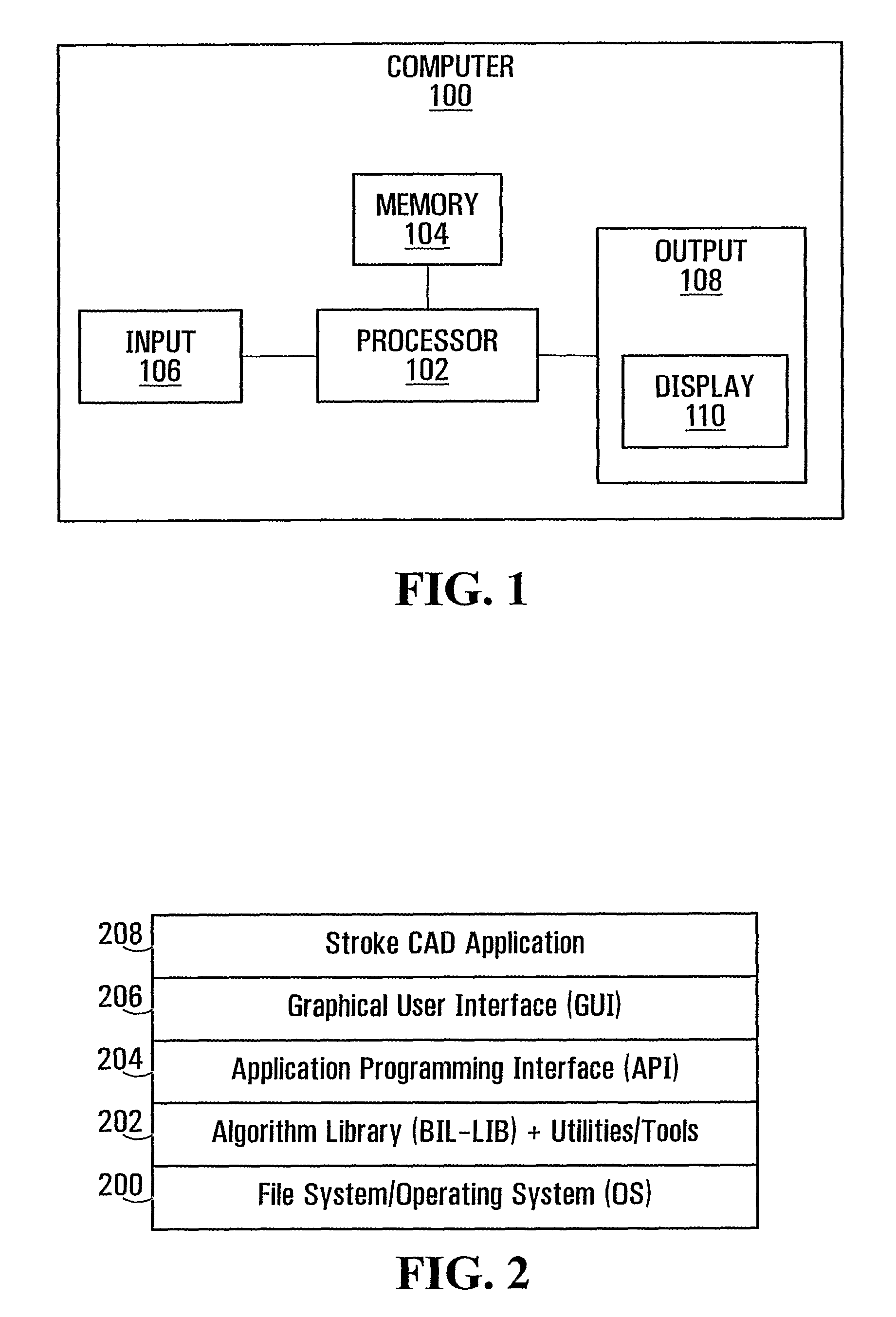
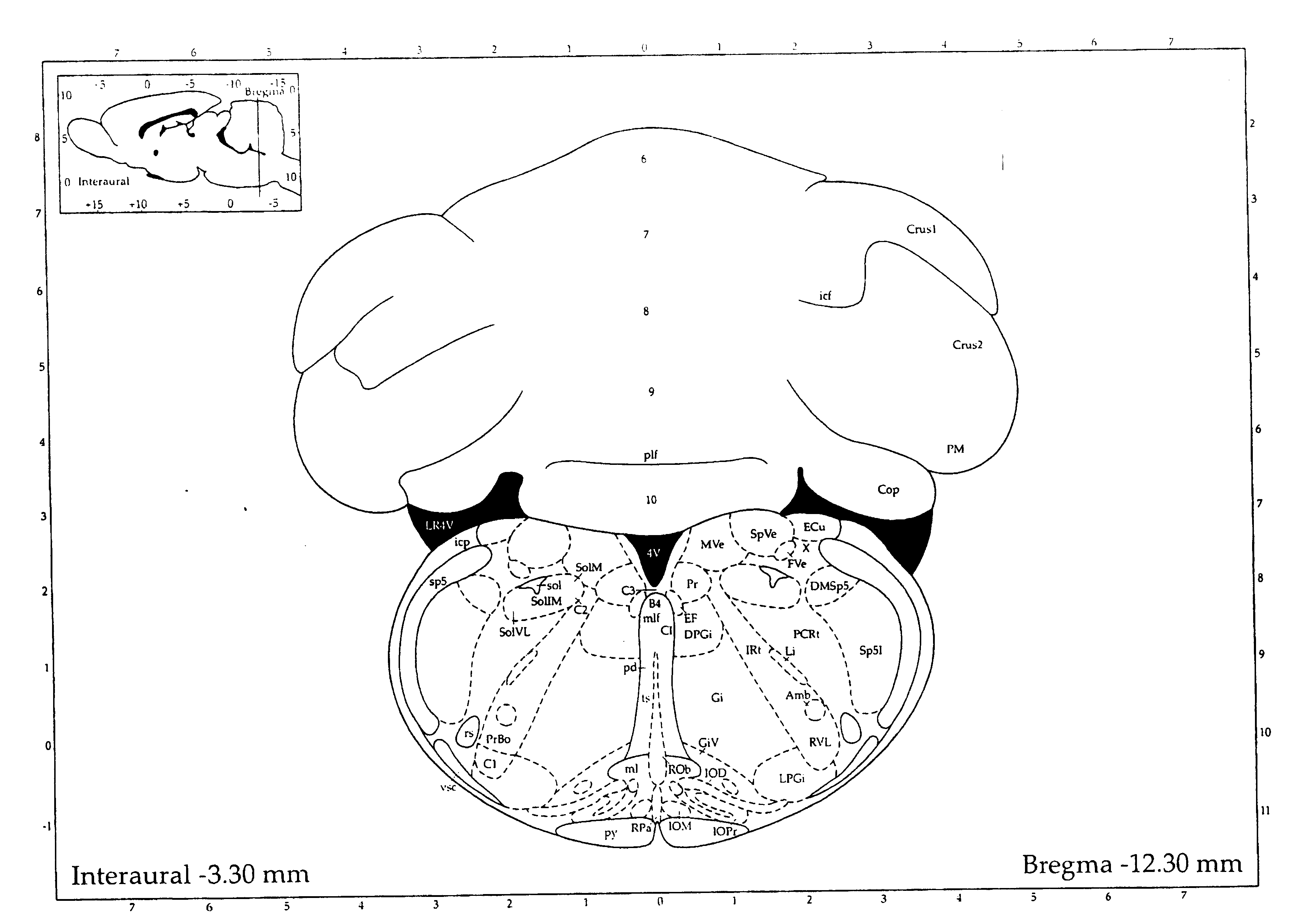
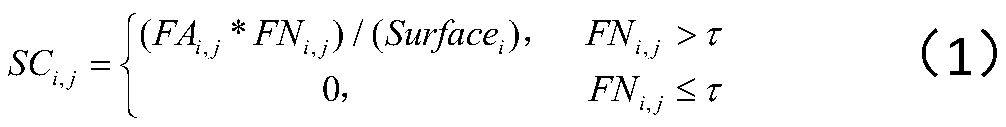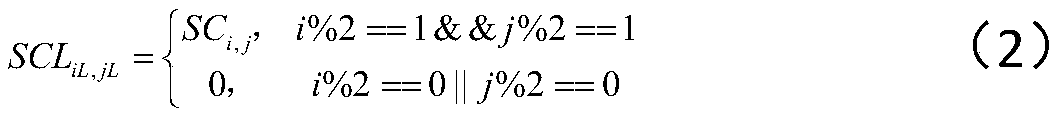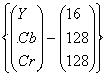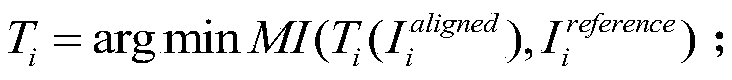Patents
Literature
51 results about "Brain atlas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
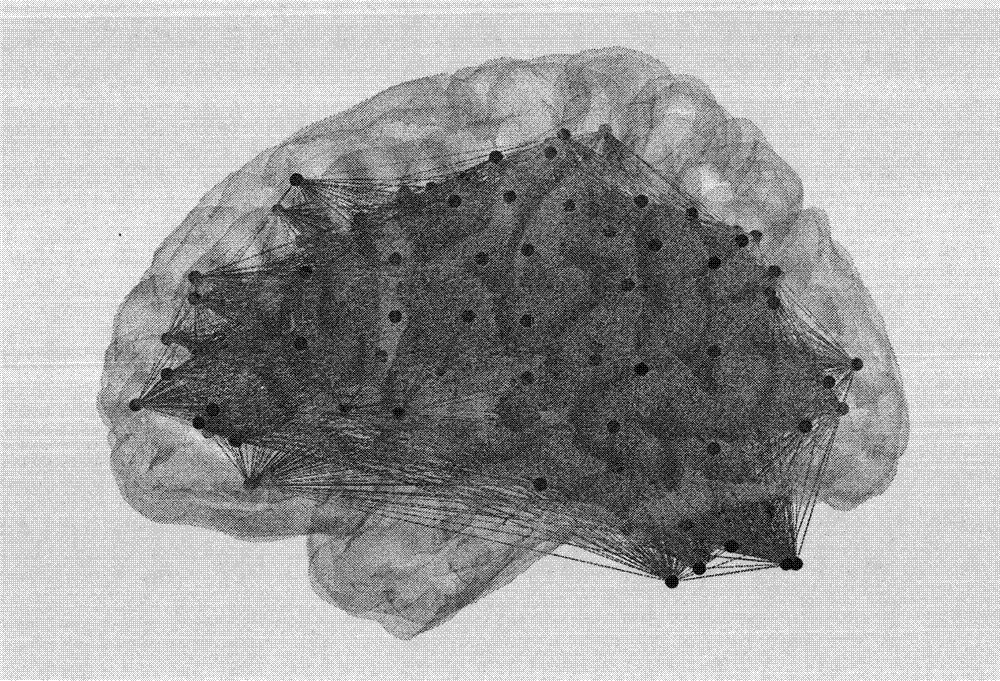
A brain atlas is composed of serial sections along different anatomical planes of the healthy or diseased developing or adult animal or human brain where each relevant brain structure is assigned a number of coordinates to define its outline or volume. Brain atlases are contiguous, comprehensive results of visual brain mapping and may include anatomical, genetical or functional features.
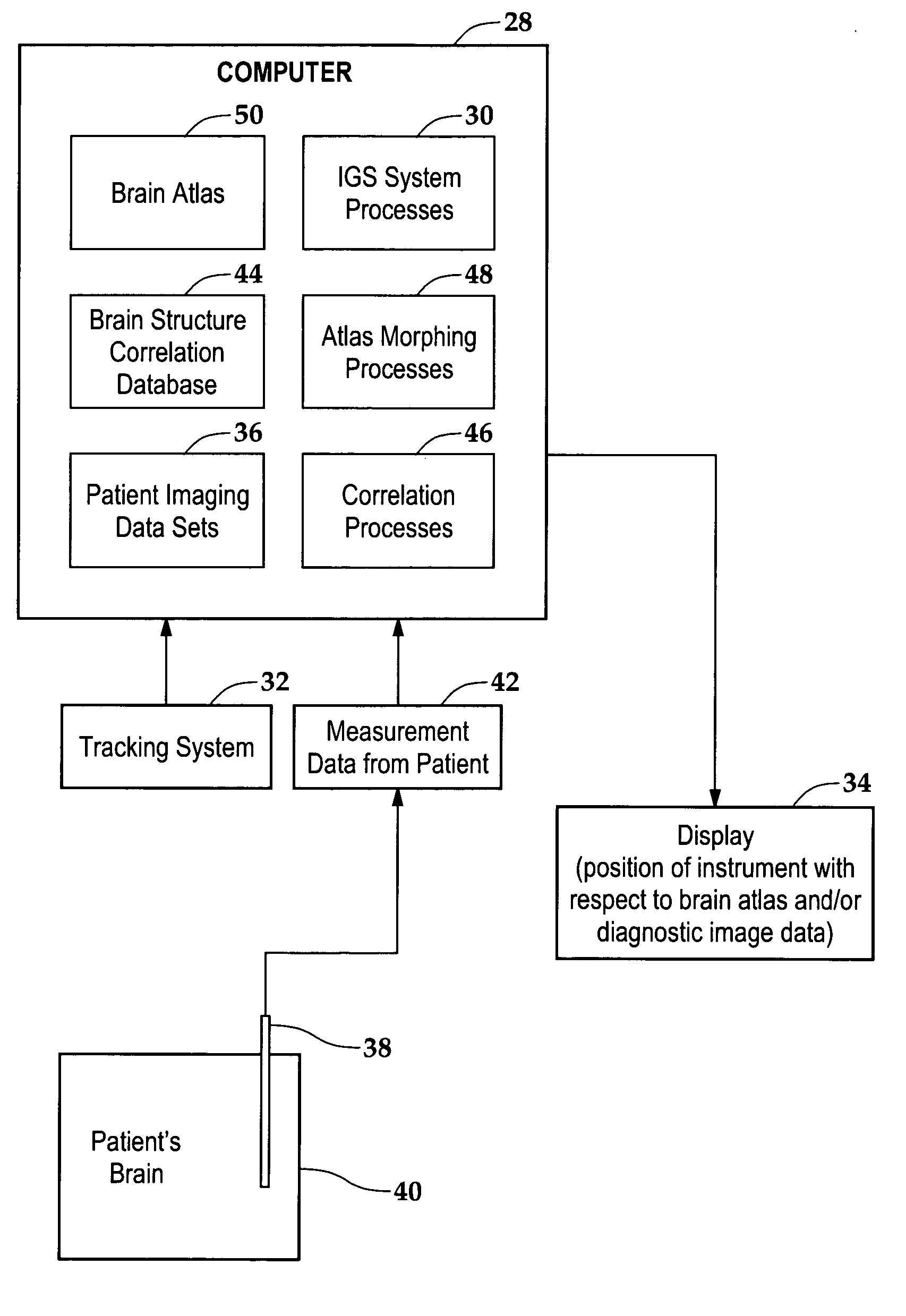
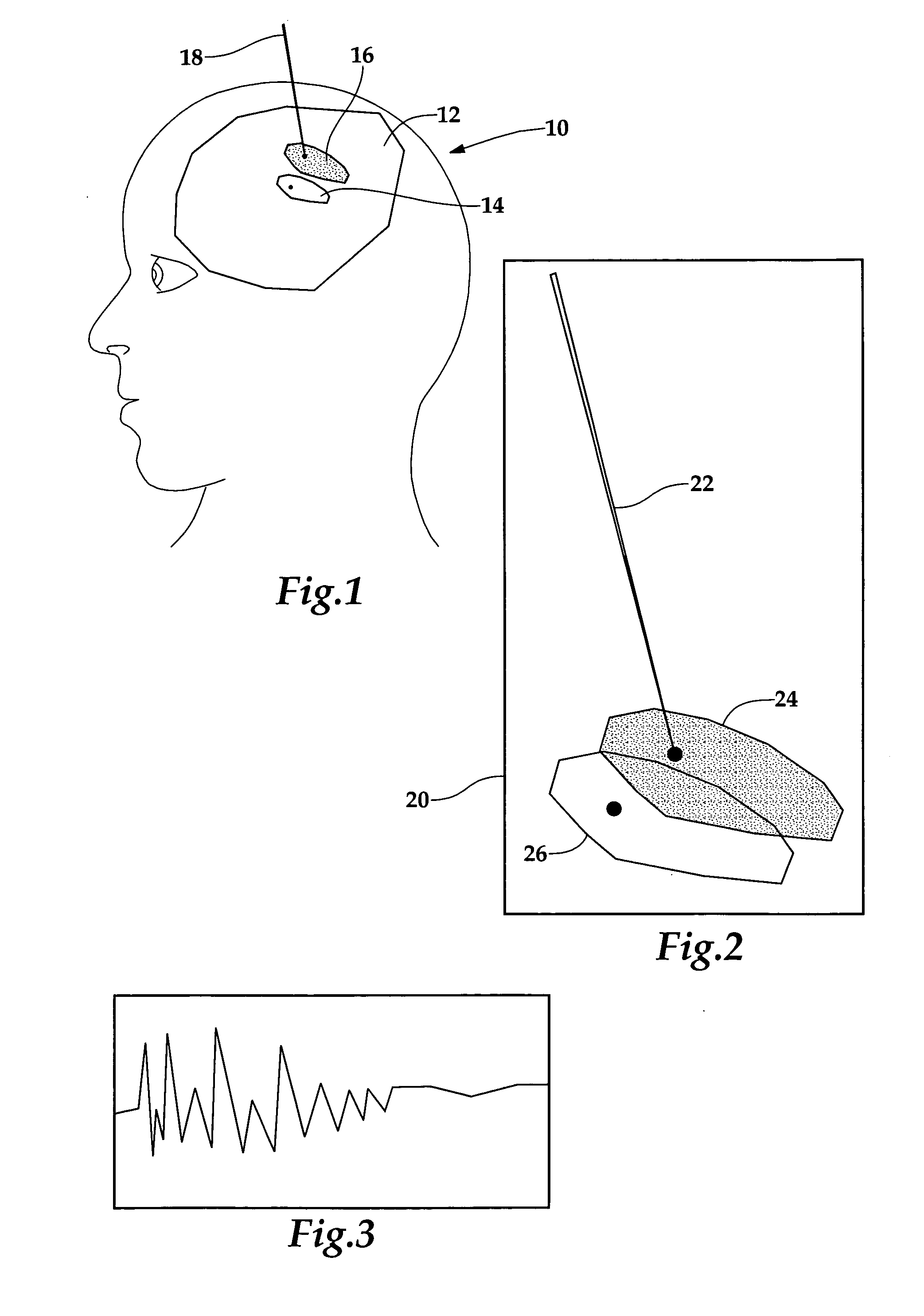
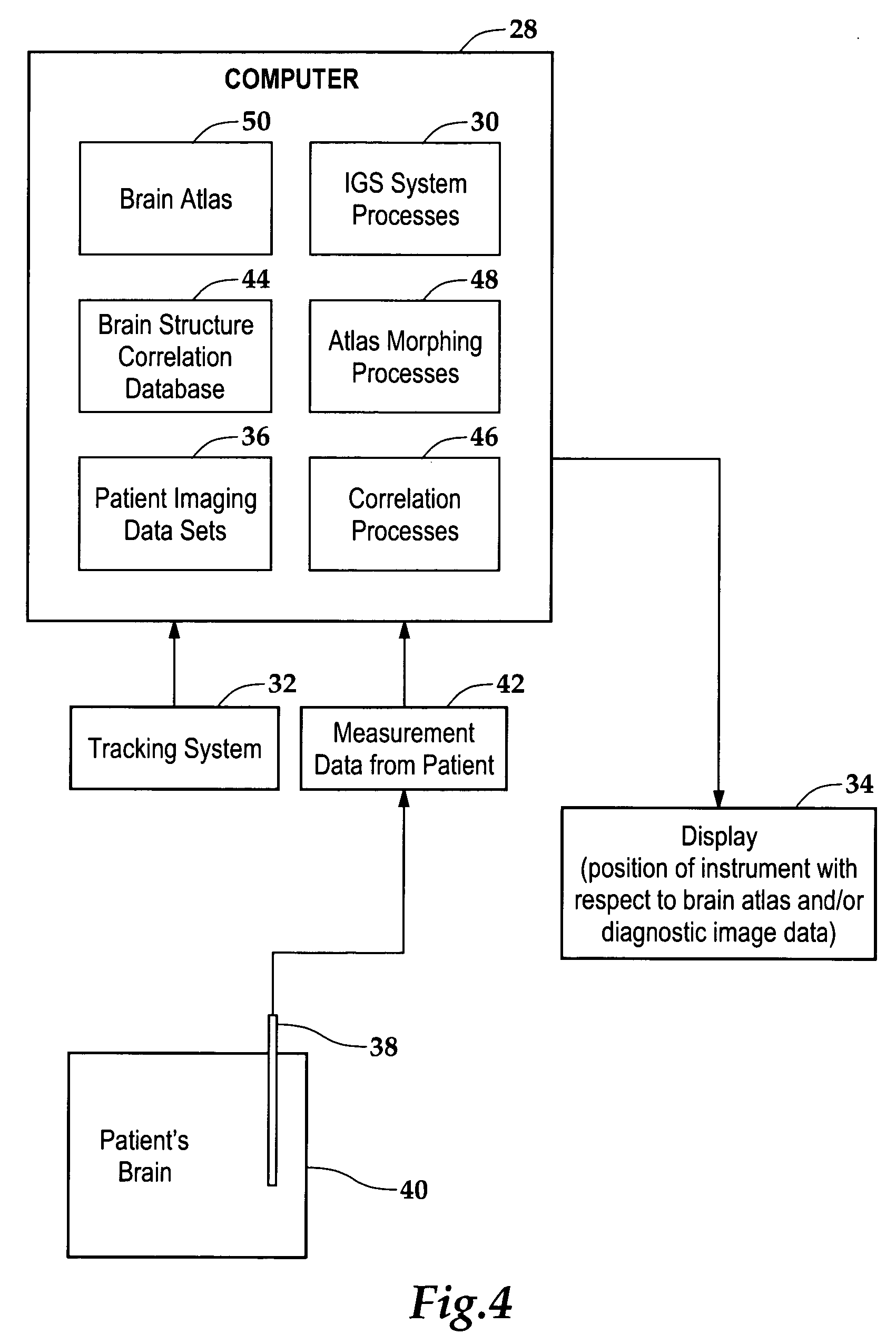
Neurosurgery targeting and delivery system for brain structures
InactiveUS20050171558A1Avoid excessive errorAccurate placementDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsData setMedicine
Morphing or fitting a brain atlas to a diagnostic image data set of the patient, or to a patient registered to the brain atlas, is enhanced using measurements of one or more physical characteristics of the brain taken with the aid of an instrument as it is being inserted into the brain. The measurements are then compared against known physical characteristics of certain brain structures, thus permitting correlation of the measured physical characteristic to a brain structure. The brain atlas then may be morphed or deformed so that the identified brain structure in the atlas is at or near the position at which the measurement was taken, as known from the tracked position of the instrument.
Owner:ABOVITZ RONY +3
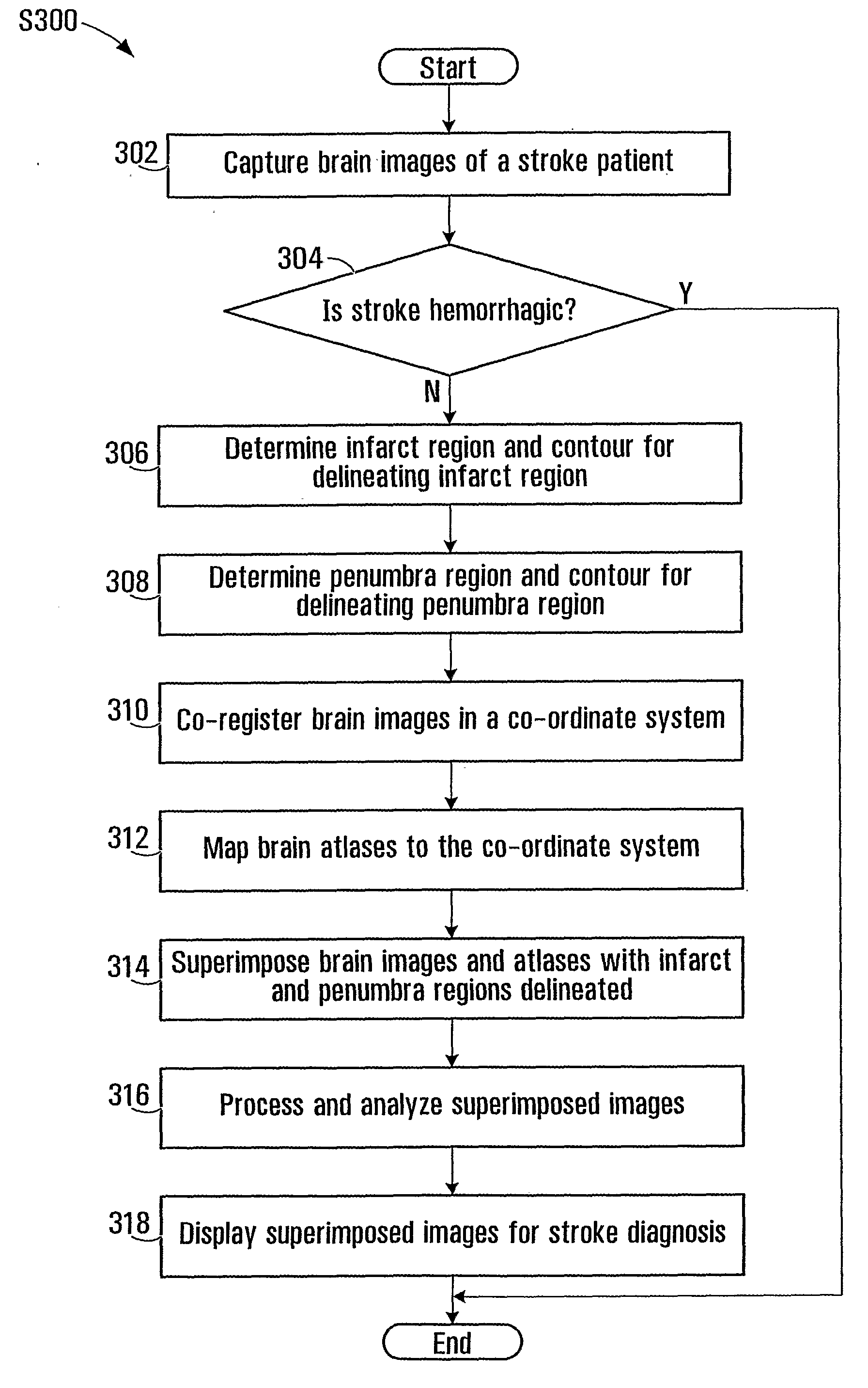
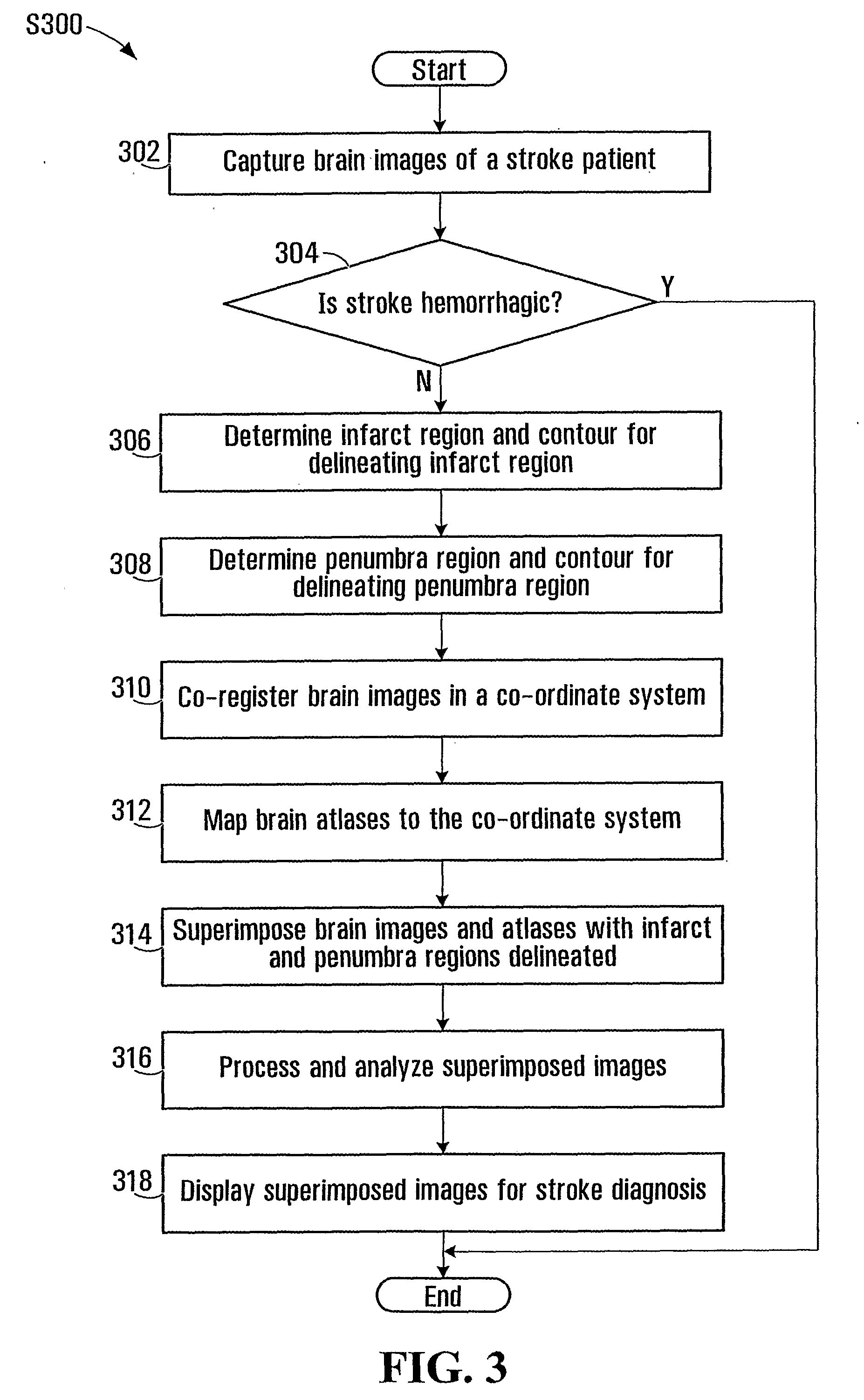
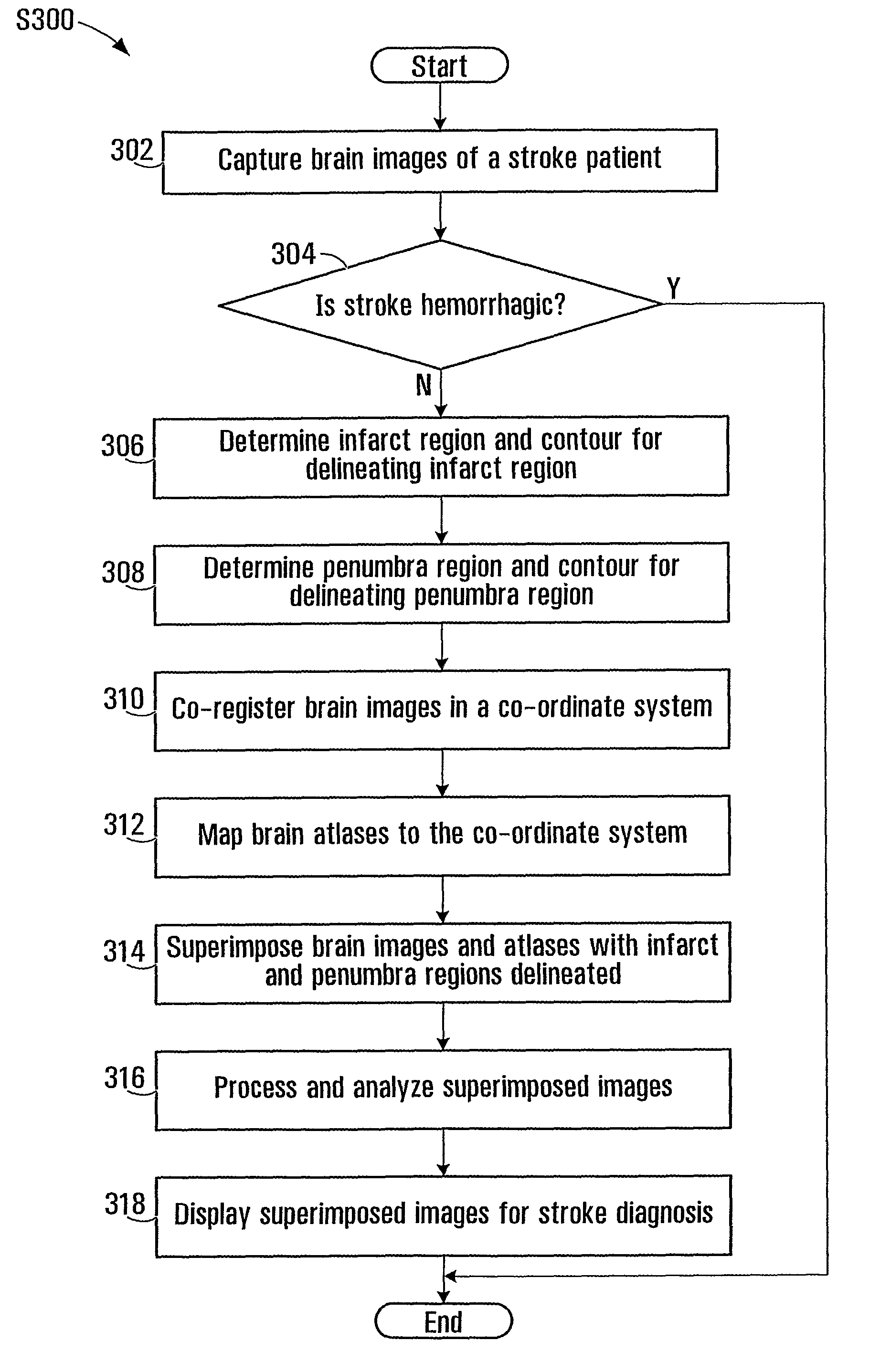
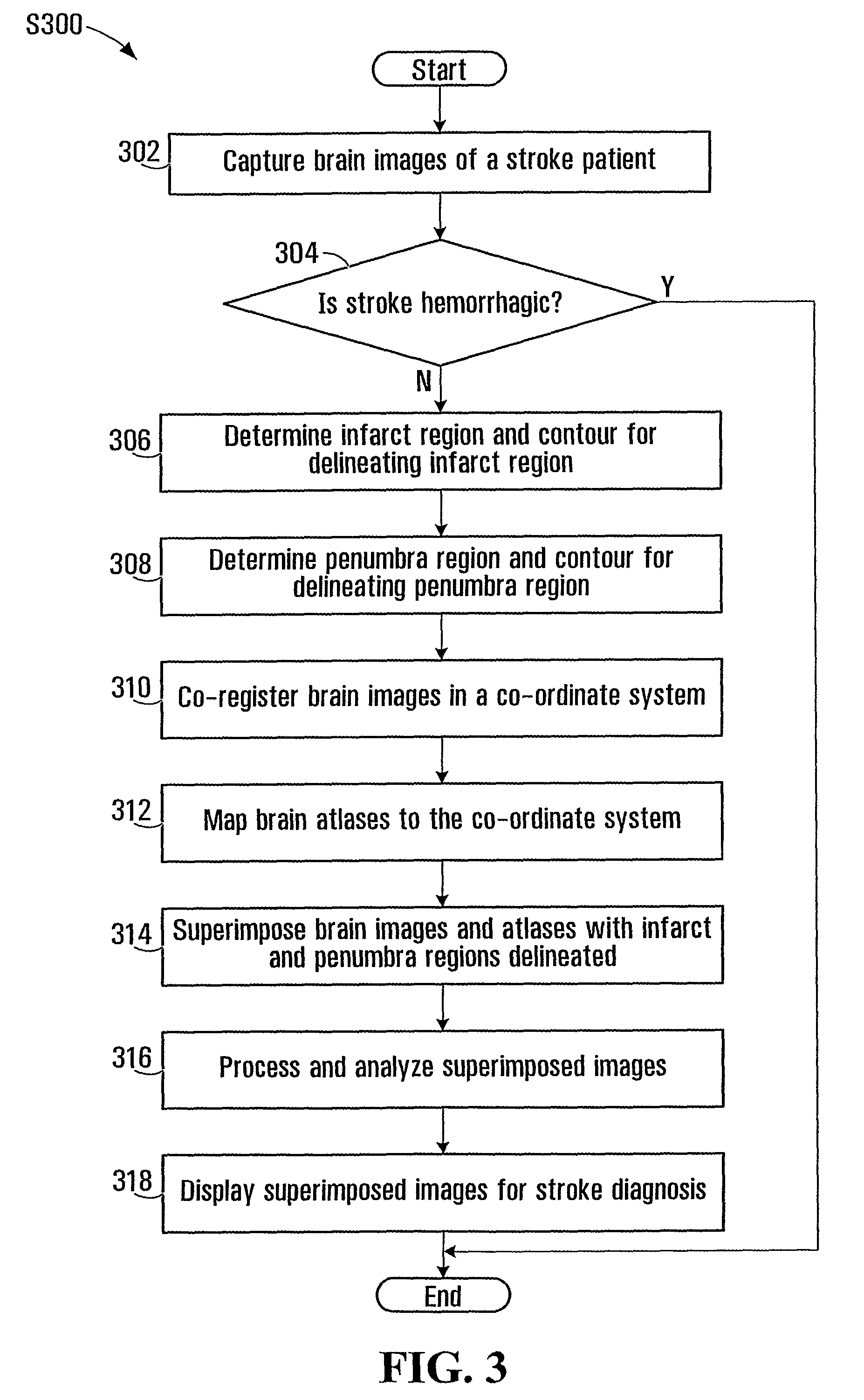
Superimposing brain atlas images and brain images with delineation of infarct and penumbra for stroke diagnosis
InactiveUS20090034812A1Conveniently identifiedConveniently visualizedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresRisk stroke
Brain images are processed and analyzed with the aid of a computer for stroke diagnosis or therapeutic decision making, where multiple stroke-related images are superimposed. The superimposed images include brain images that have infarct and penumbra regions, and patient-specific brain atlas images. The infarct and penumbra regions are determined and delineated on the superimposed images. Each patient-specific brain atlas image may be formed by mapping a pre-existing brain atlas to a co-ordinate system in which the brain images are co-registered. A brain atlas may depict brain structures such as anatomy structures, blood supply territories (BST), or cerebral vasculature. The superimposed images may be used to determine any overlap between a particular brain structure and the infarct and penumbra regions.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
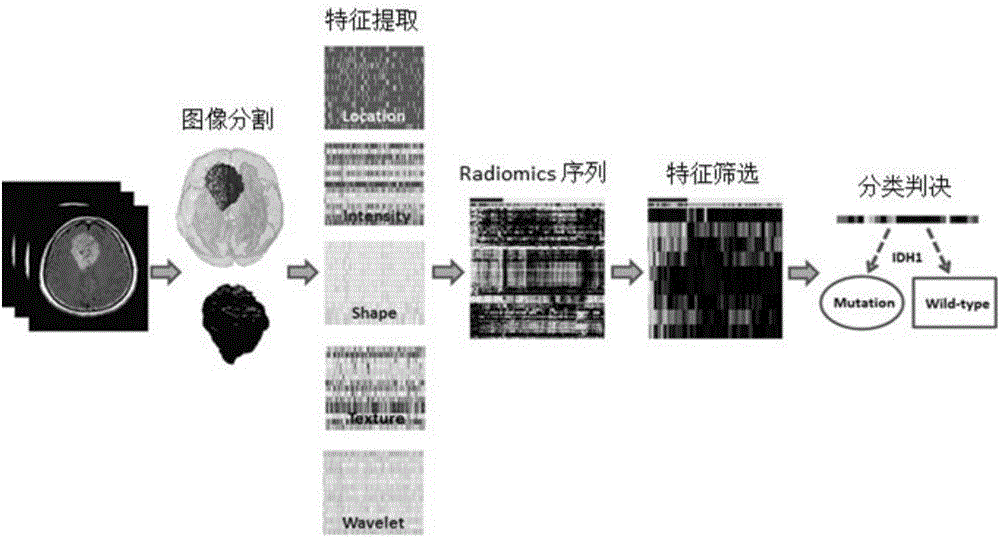
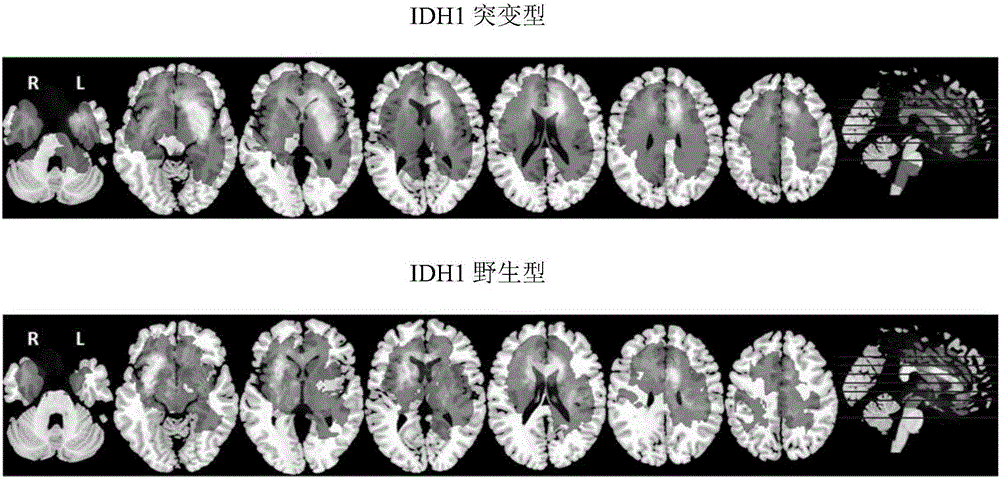
Brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and prediction system based on radiomics
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer-aided diagnosis, and specifically relates to a brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and a prediction system based on radiomics. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image automatic segmentation method based on a convolution neural network; registering a tumor obtained from segmentation to a standard brain atlas, and acquiring 116 position features of tumor distribution; getting 21 gray features, 15 shape features and 39 texture features through calculation; carrying out three-dimensional wavelet decomposition on the gray features and the texture features to get 480 wavelet features of eight sub-bands; acquiring 671 high-throughput features from the three-dimensional T2-Flair magnetic resonance image of each case; using a feature screening strategy combining p-value screening and a genetic algorithm to get 110 features highly associated with IDH1; and using a support vector machine and an AdaBoost classifier to get a classification of which the IDH1 prediction accuracy is 80%. As a novel method of radiomics, the method provides a nondestructive prediction scheme of important molecular markers for clinical diagnosis of gliomas.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
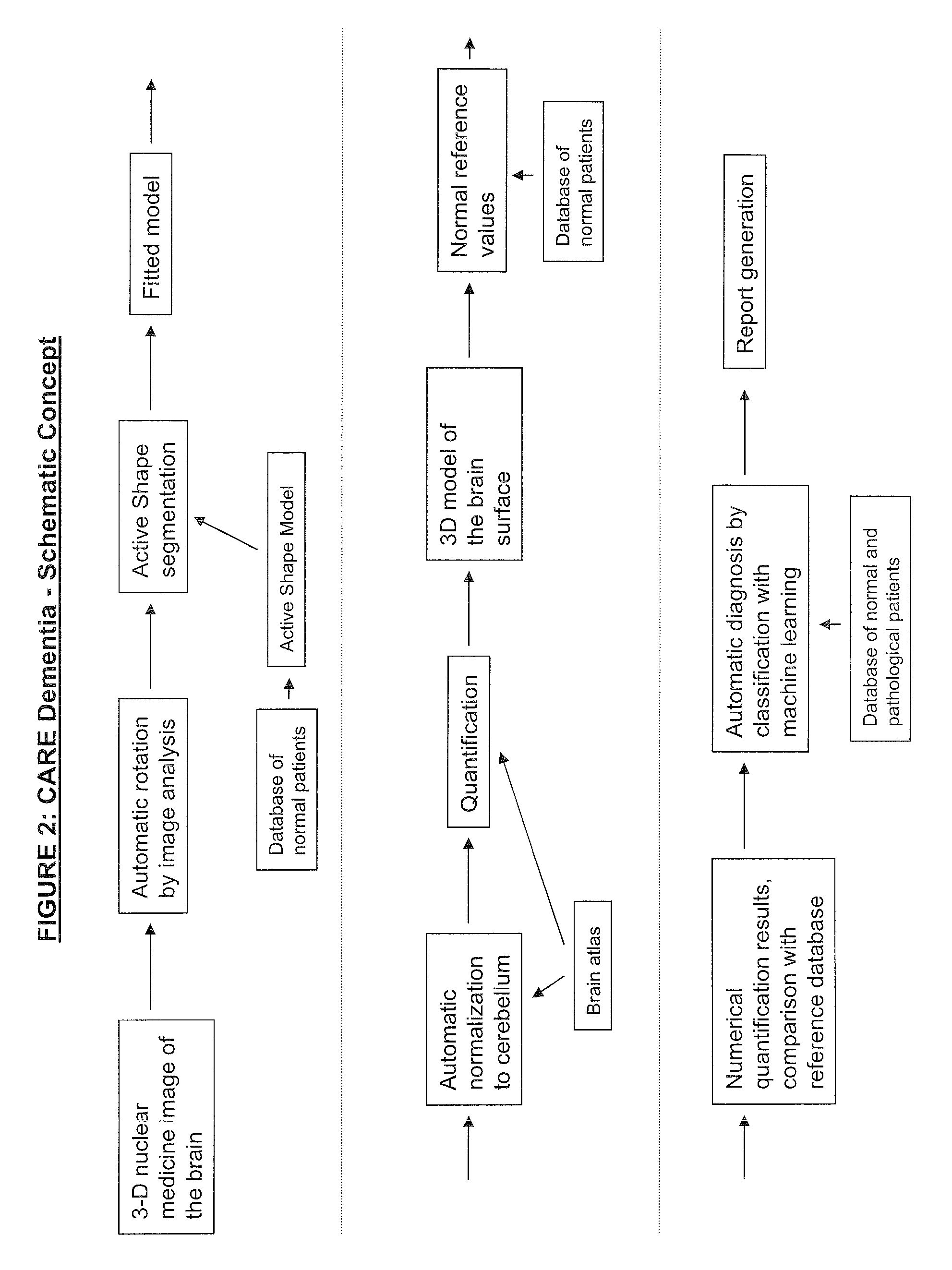
Automatic interpretation of 3-d medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS20100067761A1Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
Superimposing brain atlas images and brain images with delineation of infarct and penumbra for stroke diagnosis
InactiveUS8019142B2Conveniently identifiedConveniently visualizedImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresMedicine
Brain images are processed and analyzed with the aid of a computer for stroke diagnosis or therapeutic decision making, where multiple stroke-related images are superimposed. The superimposed images include brain images that have infarct and penumbra regions, and patient-specific brain atlas images. The infarct and penumbra regions are determined and delineated on the superimposed images. Each patient-specific brain atlas image may be formed by mapping a pre-existing brain atlas to a co-ordinate system in which the brain images are co-registered. A brain atlas may depict brain structures such as anatomy structures, blood supply territories (BST), or cerebral vasculature. The superimposed images may be used to determine any overlap between a particular brain structure and the infarct and penumbra regions.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
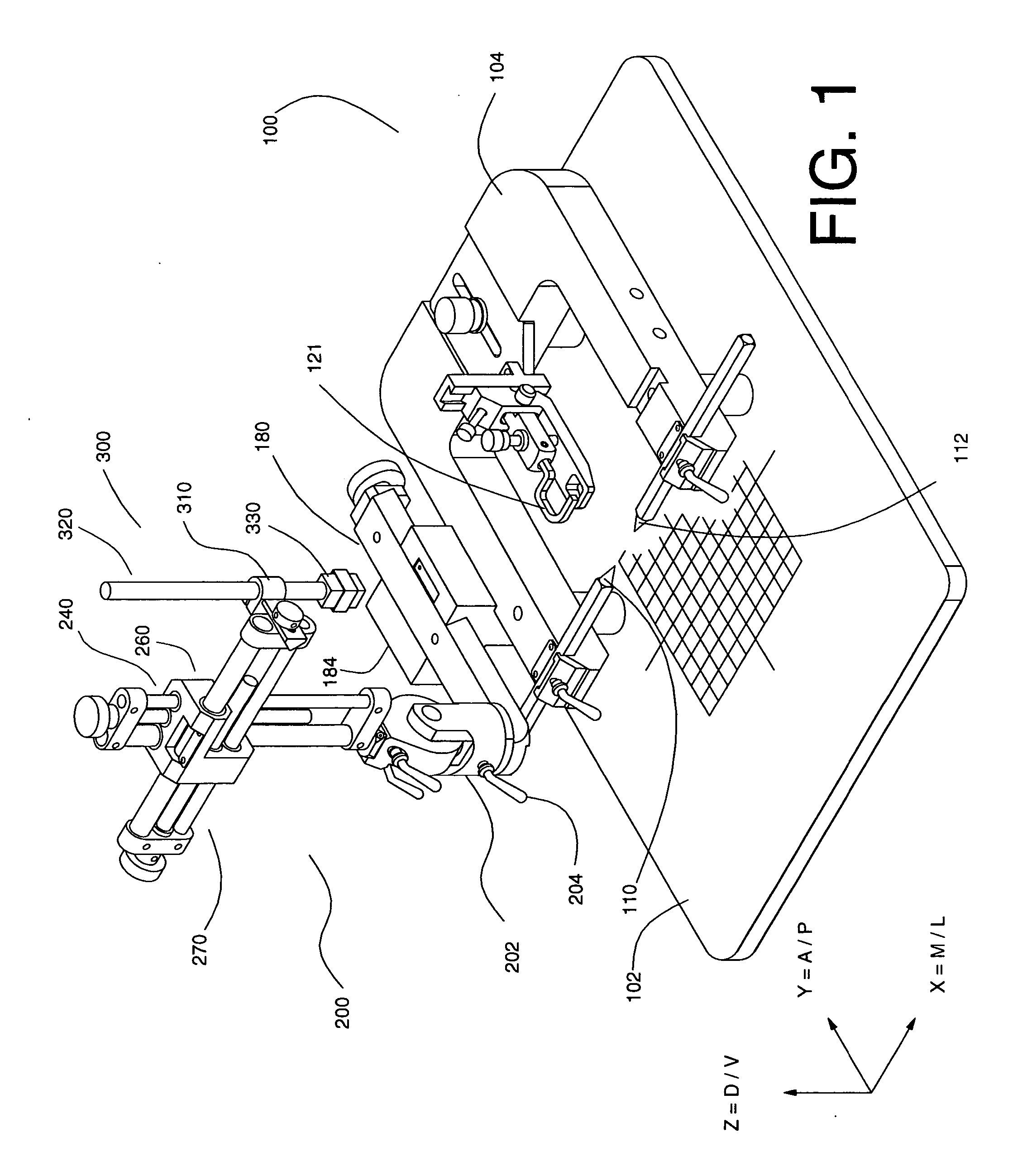
Digital stereotaxic manipulator with interfaces for use with computerized brain atlases
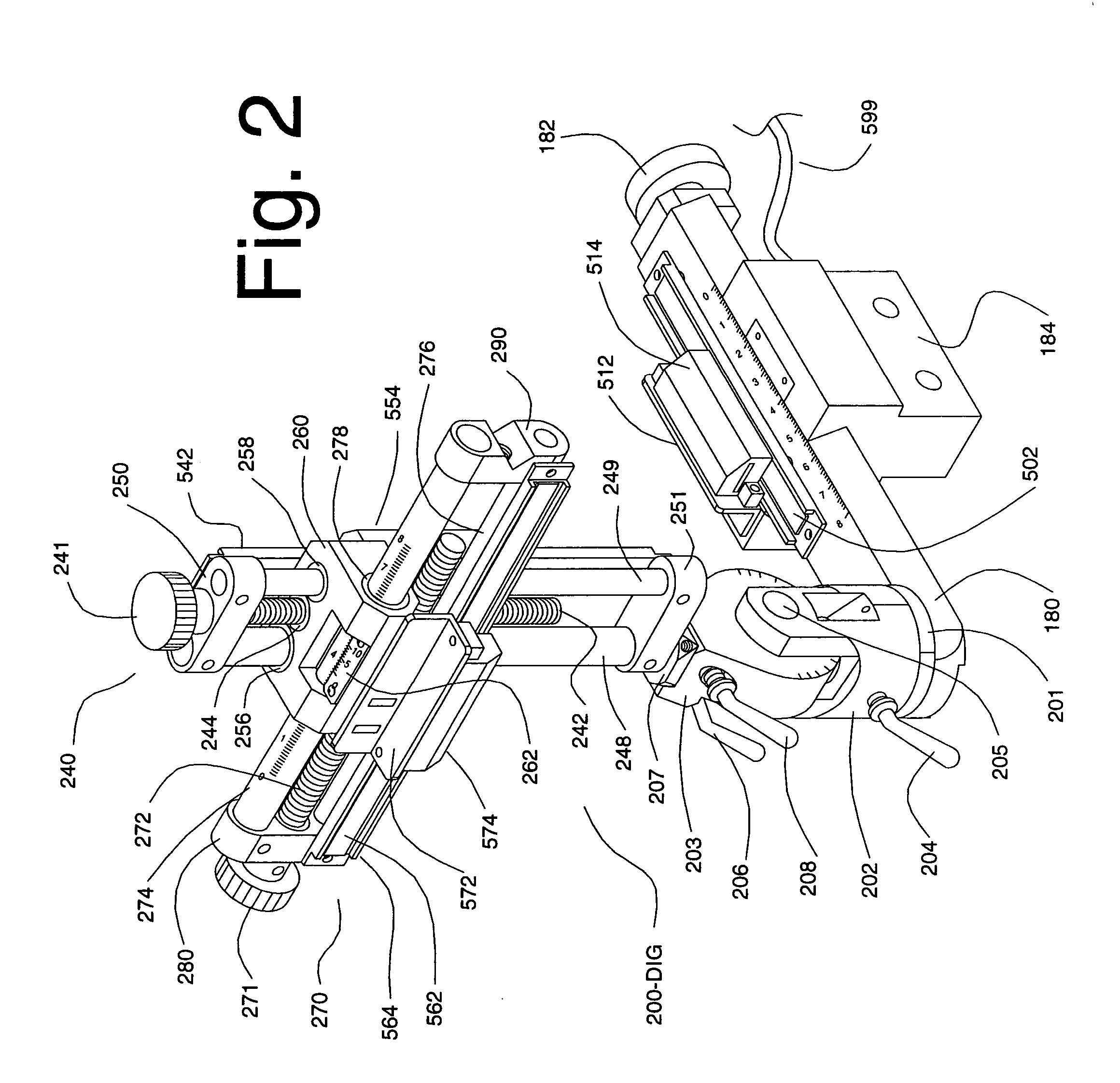
InactiveUS20060052689A1Least possible damageClear locationSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer monitorImage resolution
A system is disclosed that allows stereotaxic procedures being performed on lab animals to interact, on a “live” or “real-time” basis, with information that has been compiled in stereotaxic brain atlases. For example, during an invasive procedure, a researcher can see, on a cross-sectional brain map displayed on a full-sized computer monitor, the location and travel of an instrument tip, indicated by means such as a bright blinking cursor or icon. If desired, important brain structures (such as major nerve bundles) can been prominently labeled and / or colored, to clearly indicate their locations, and help the researcher ensure that they are avoided. This system can be provided by coupling a digital stereotaxic manipulator to a dedicated controller with touch-screen capability, and coupling the PLC processor to a computer having a monitor screen that is large enough to display a brain map with good resolution. Alternately, the digital stereotaxic manipulator can be coupled directly to a computer, via an interface card or other device.
Owner:SCOUTEN CHARLES W +2
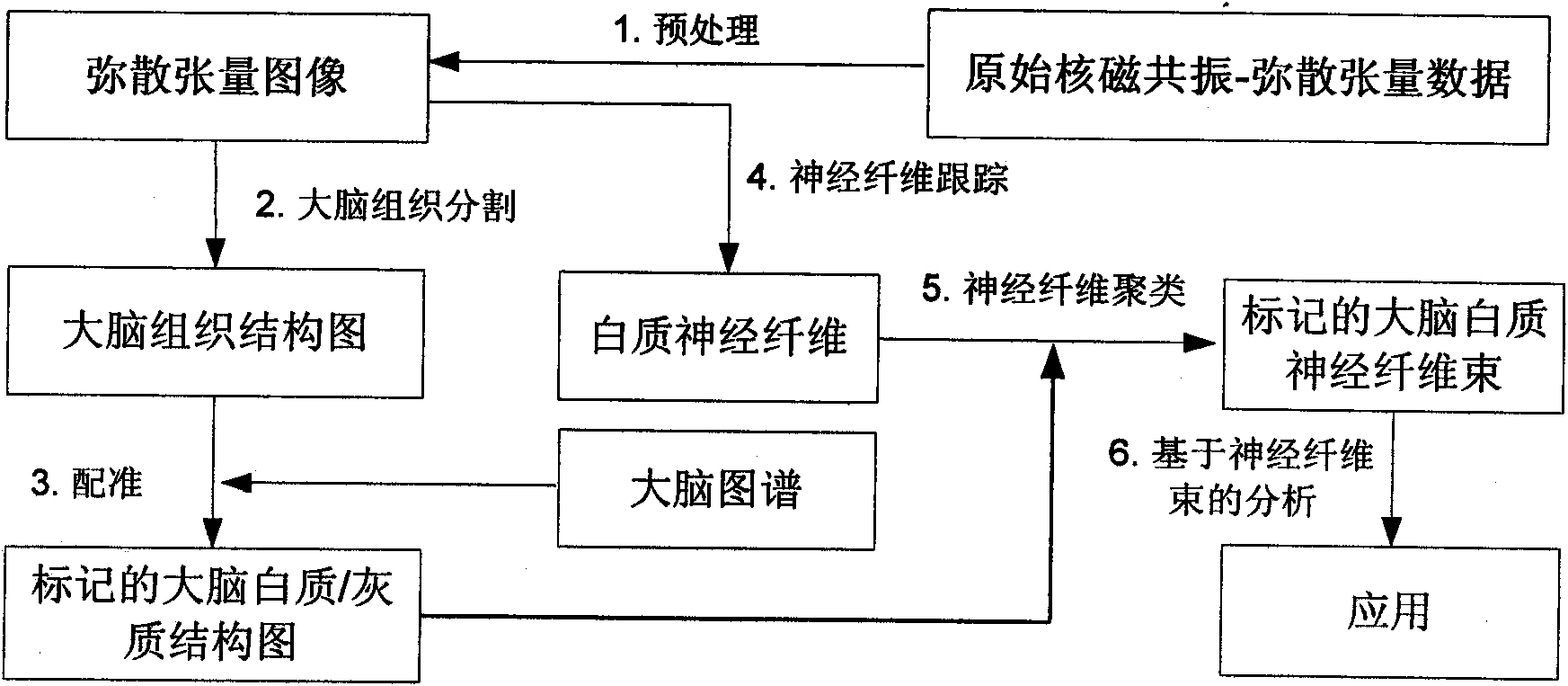
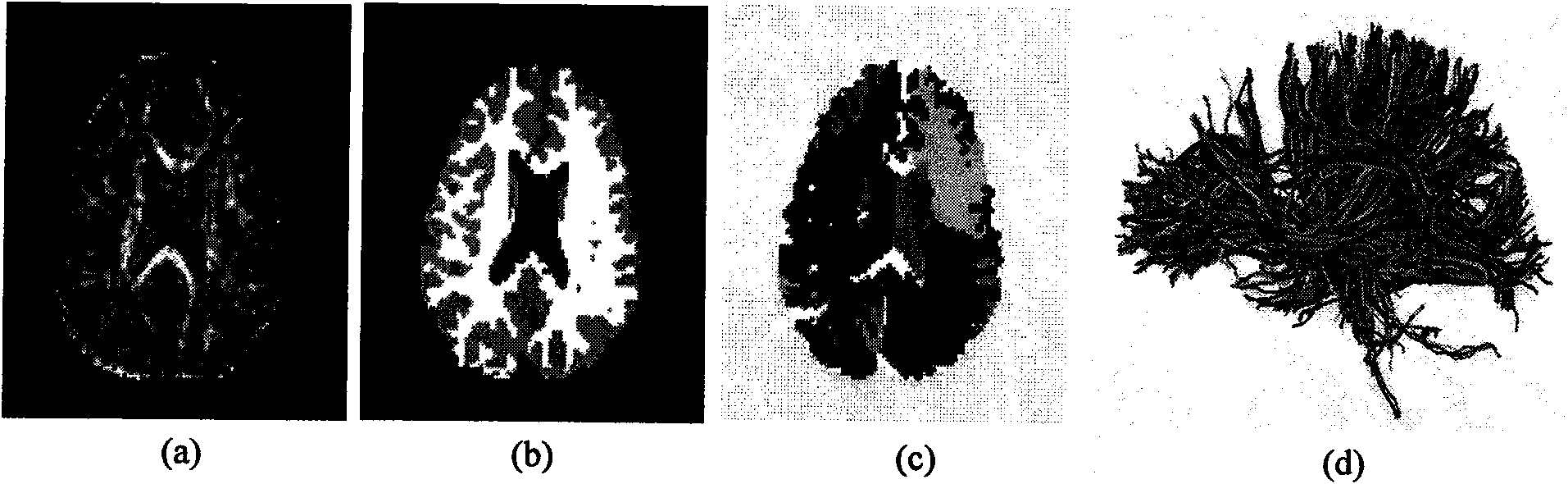
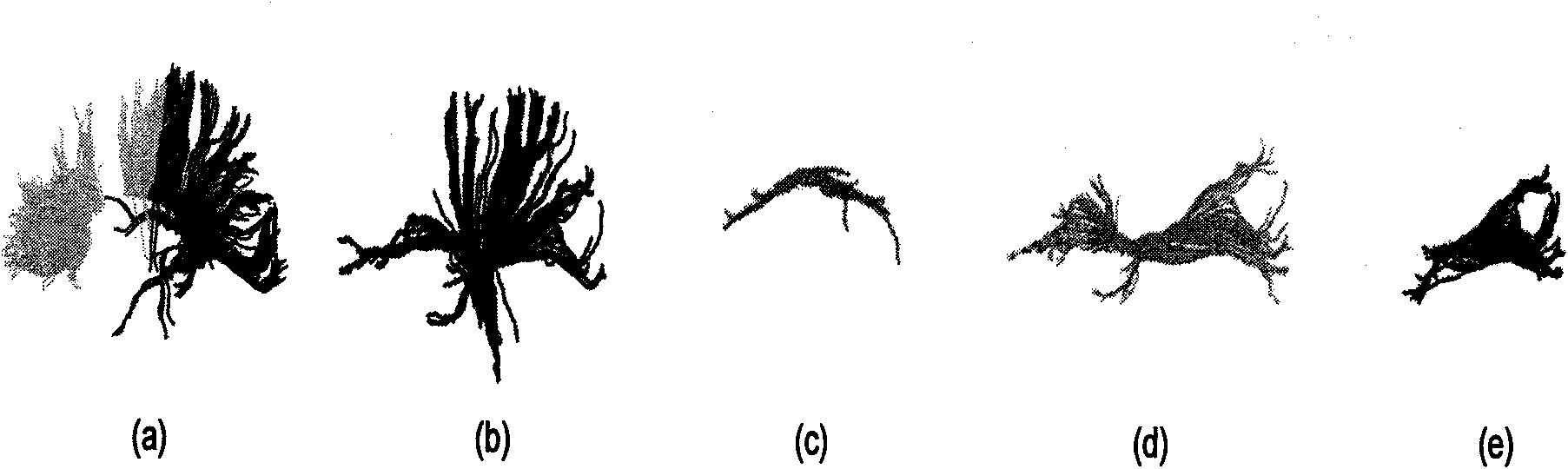
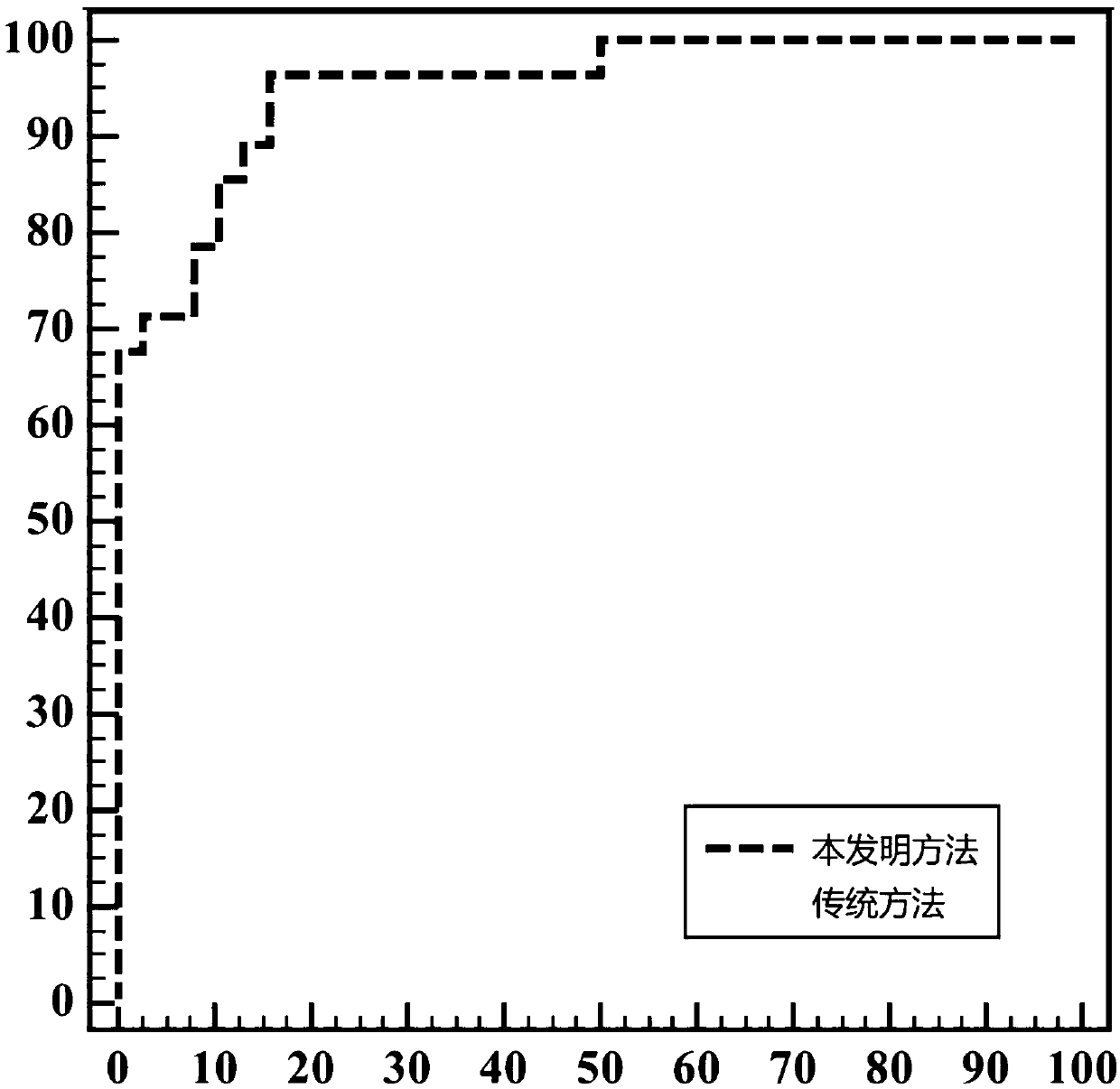
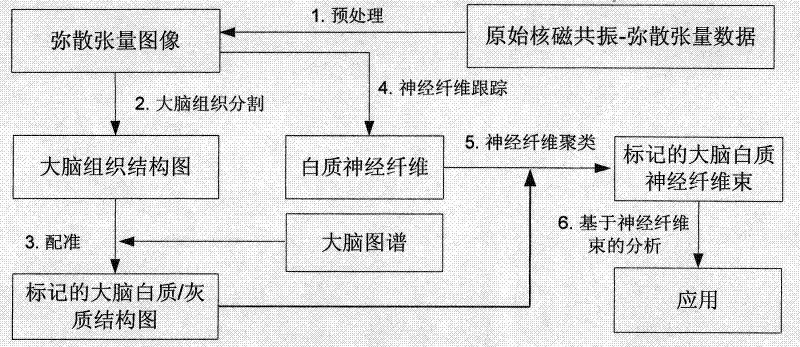
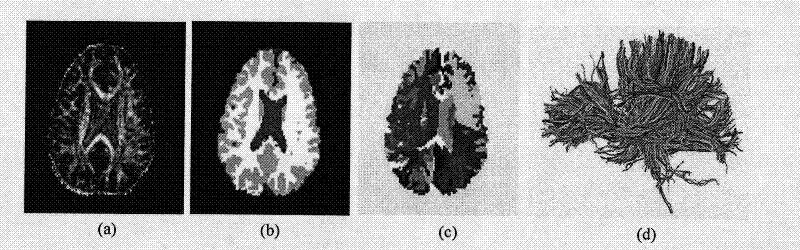
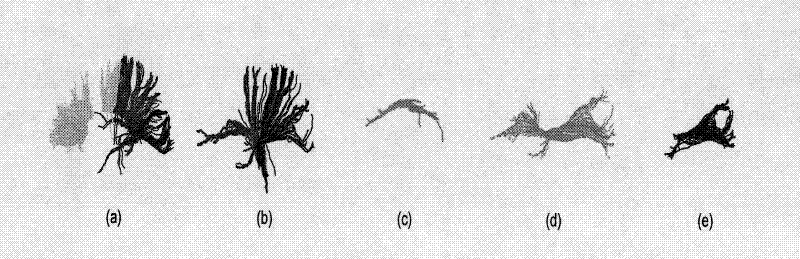
Mixed brain white matter nerve fiber automatic cluster and marking method
ActiveCN101650827AStable extractionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh dimensionalConductor Coil
The invention relates to a mixed brain white matter nerve fiber automatic cluster and a marking method. The marking method is characterized in that: firstly, using a high dimensional elastic registration method to match a standard brain atlas to a single brain space, thereby being capable of dividing a single brain into 104 anatomical regions with structural information; secondly, using differentnerve fiber bundles to extract and mark 15 nerve fiber bundles according to the characteristics of different brain anatomical regions; thirdly, to other 4 nerve fiber bundles which can not be extracted by the above method due to strong winding between the 4 nerve fiber bundles and the nerve fiber bundles at the periphery thereof, using a method combing Kernel-PCA and Fuzzyc-mean and based on similarity measurement to automatically carry out clustering analysis; and at last, using an identification method based on characteristics to mark the result of clustering analysis. By the above method, 19 main white matter nerve fiber bundles of the brain can be extracted and marked automatically.
Owner:南通曙光新能源装备有限公司 +1
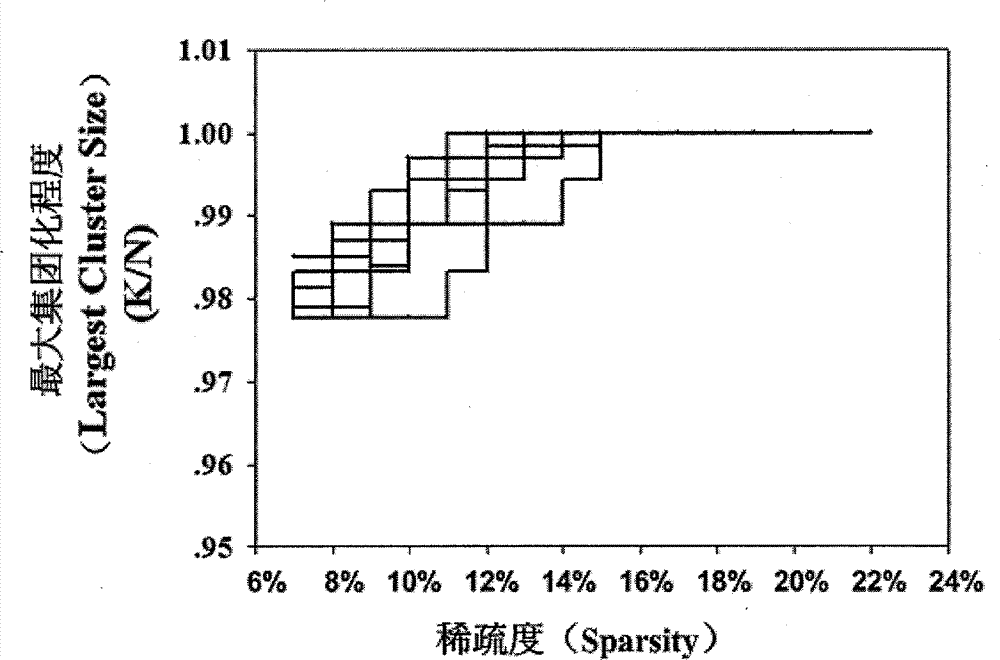
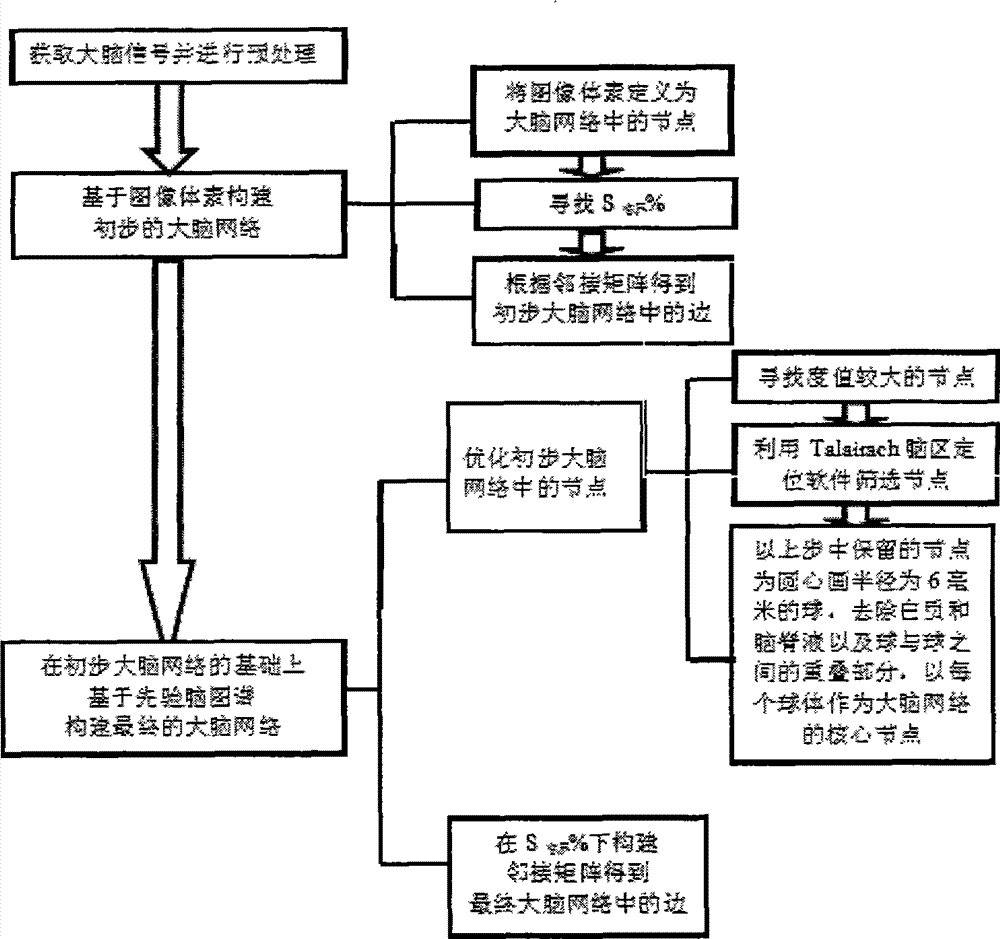
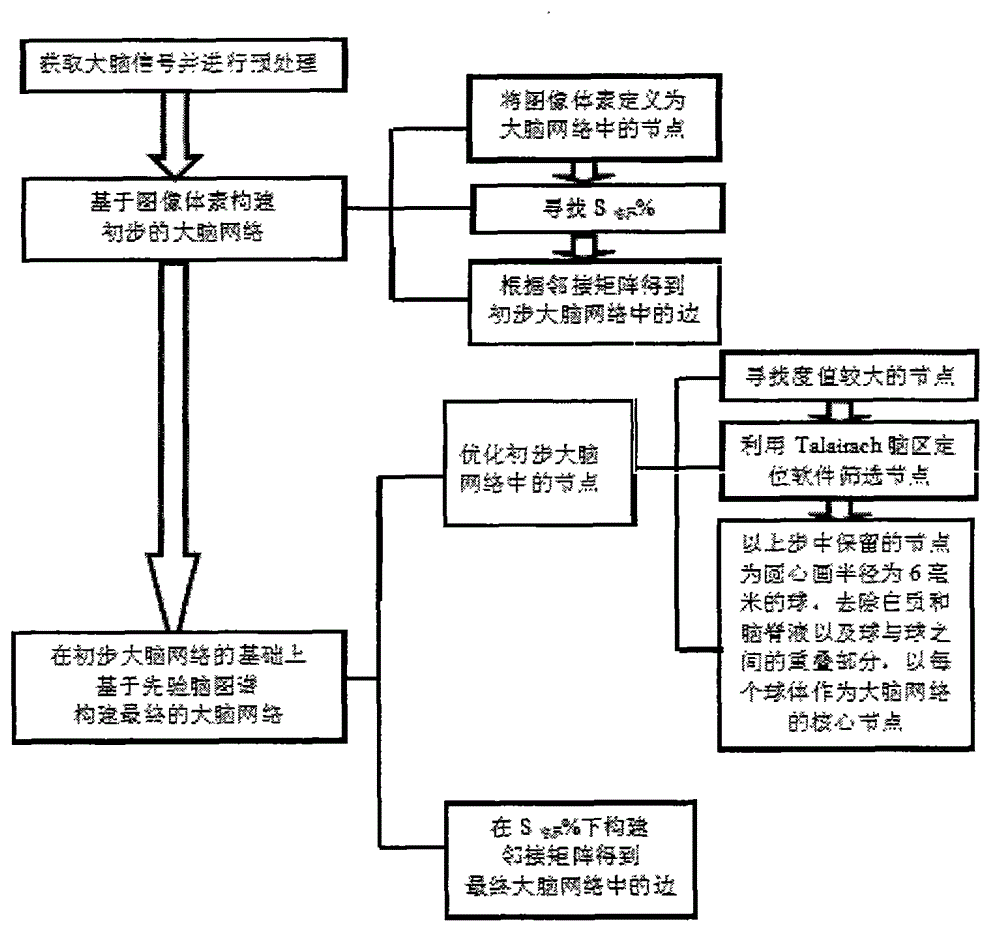
Image voxel and priori brain atlas division fused brain network construction method
InactiveCN103077298AOvercome deficienciesStrong visualizationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALVoxel
The invention provides an image voxel and priori brain atlas division fused brain network construction method to overcome defects of node selection methods in the conventional brain network construction method. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing functional magnetic resonance imaging data; constructing an initial brain network based on image voxels; and constructing a final brain network based on a priori brain atlas on the basis of the initial brain network. Two node selection methods in the prior art are fused, nodes with high degree values are searched on the basis of the image voxel, the nodes are screened by a Talairach encephalic region locating software on the basis of the priori brain atlas, the screened node is taken as a center of a circle to draw a sphere with the radius of 6 millimeters, the sphere is taken as a core node of the brain network, and the final brain network is determined according to the core node and sides of the obtained brain network. By the method, a brain functional network can be comprehensively and delicately described, the core node of the network is visualized in a brain space, and a function of observing a connecting mode between encephalic regions clearly is realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
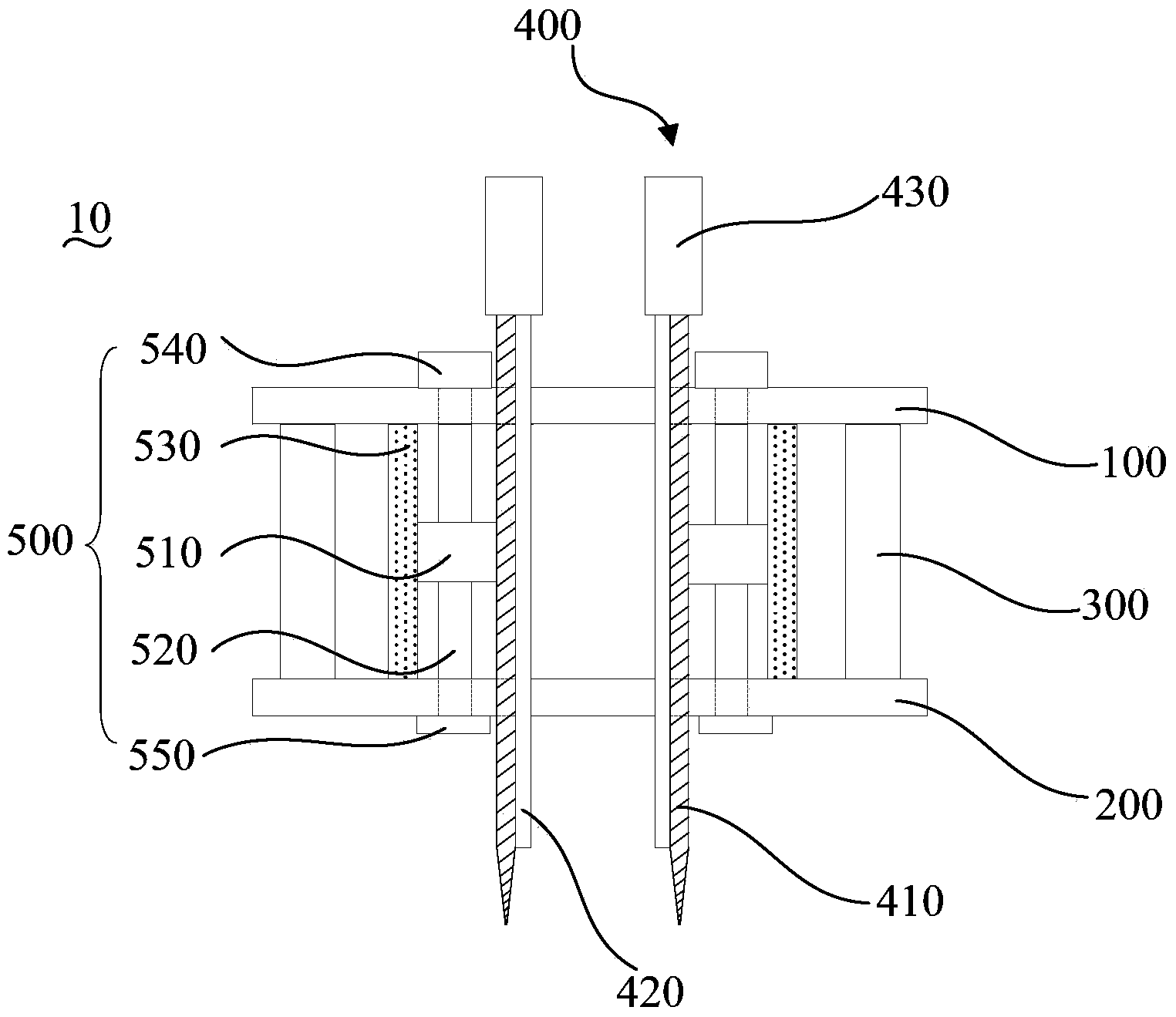
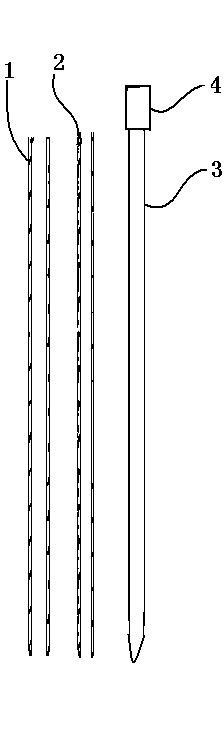
Electrophysiology recording device
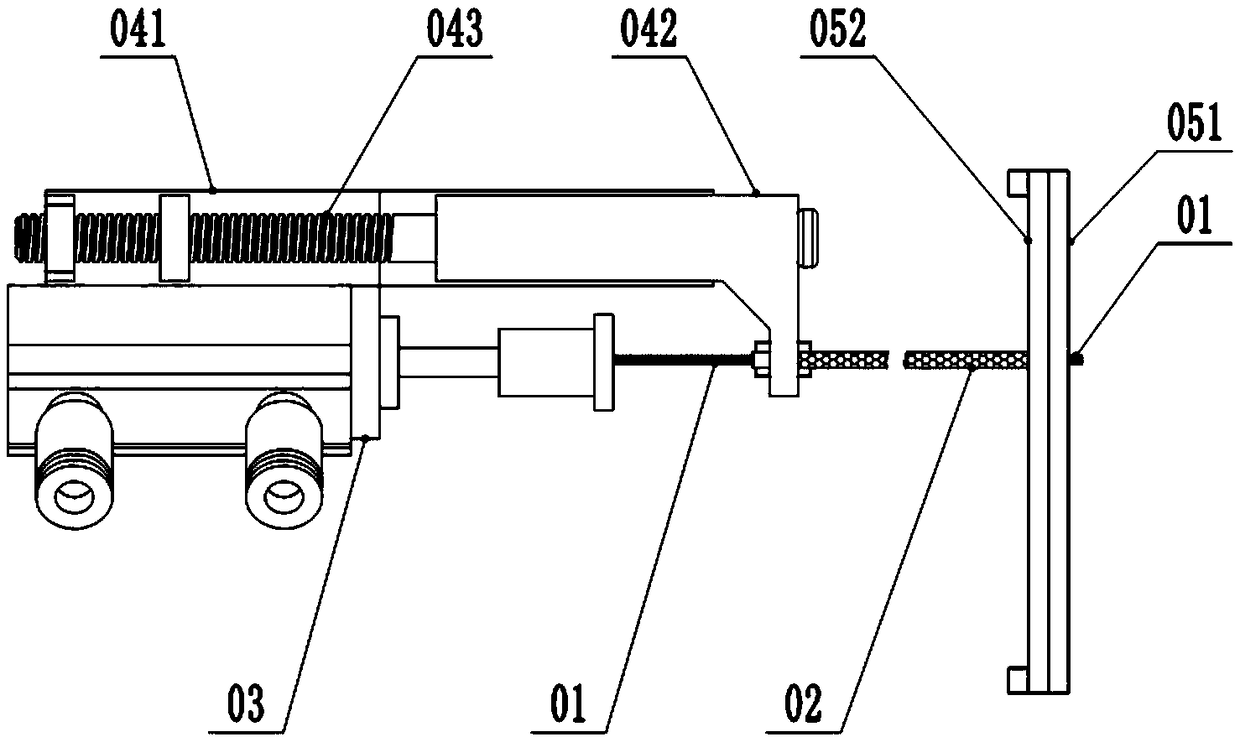
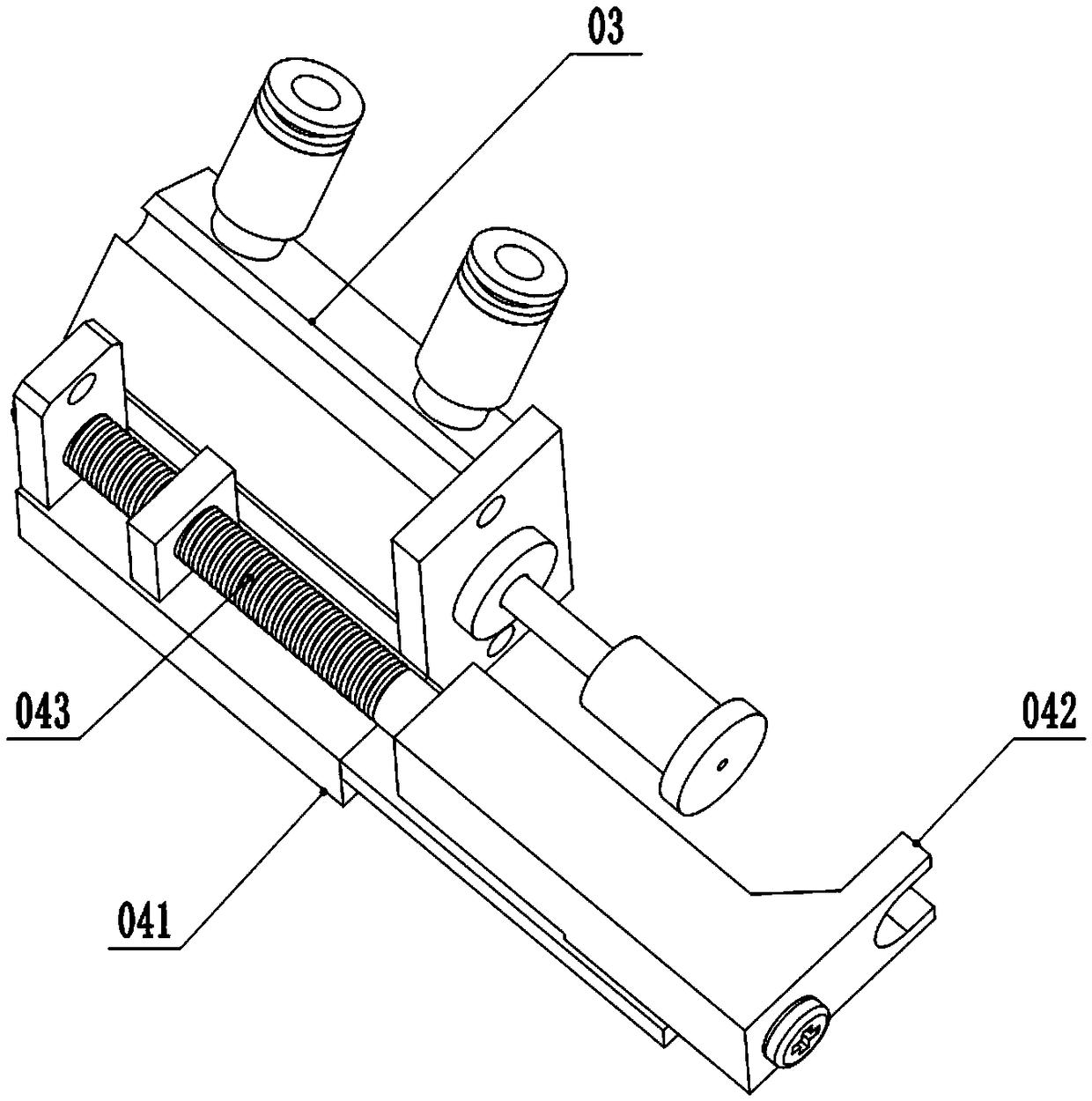
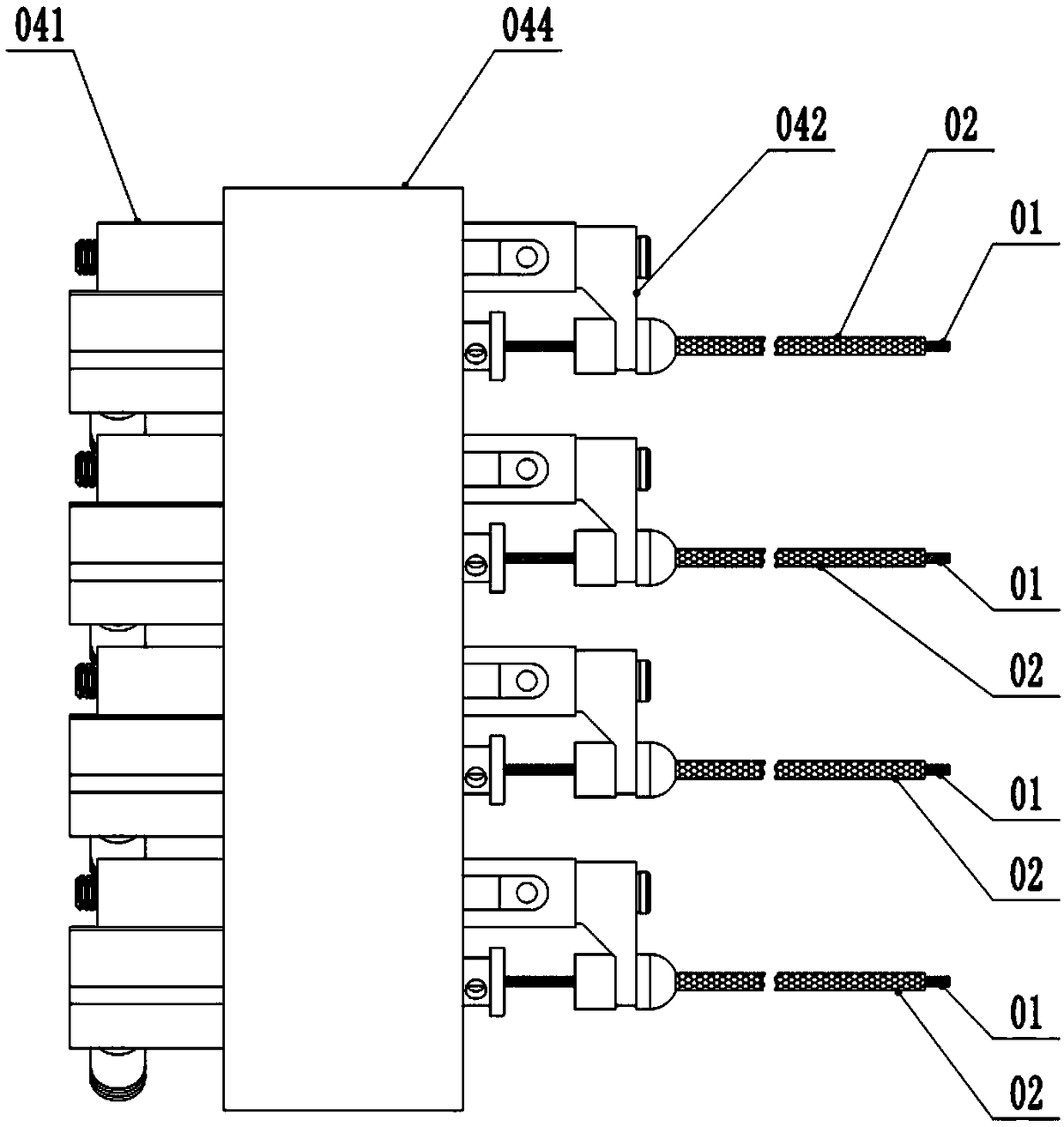
The invention relates to an electrophysiology recording device which is used for simultaneously recording electrophysiological signals of multiple brain regions of a laboratory animal. Through holes with the same number as the brain regions of the to-be-recorded electrophysiological signals are formed in a positioning plate; the through holes distributed in the positioning plate correspond to the to-be-recorded brain regions determined by a brain atlas of the laboratory animal one to one; recording electrodes run through the positioning plate by virtue of the through holes; the parts, positioned in the through holes, of the recording electrodes are butted with the positioning plate. According to the electrophysiology recording device, multiple recording electrodes can be simultaneously transplanted into multiple brain regions so as to record the electrophysiological signals of the multiple brain regions.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
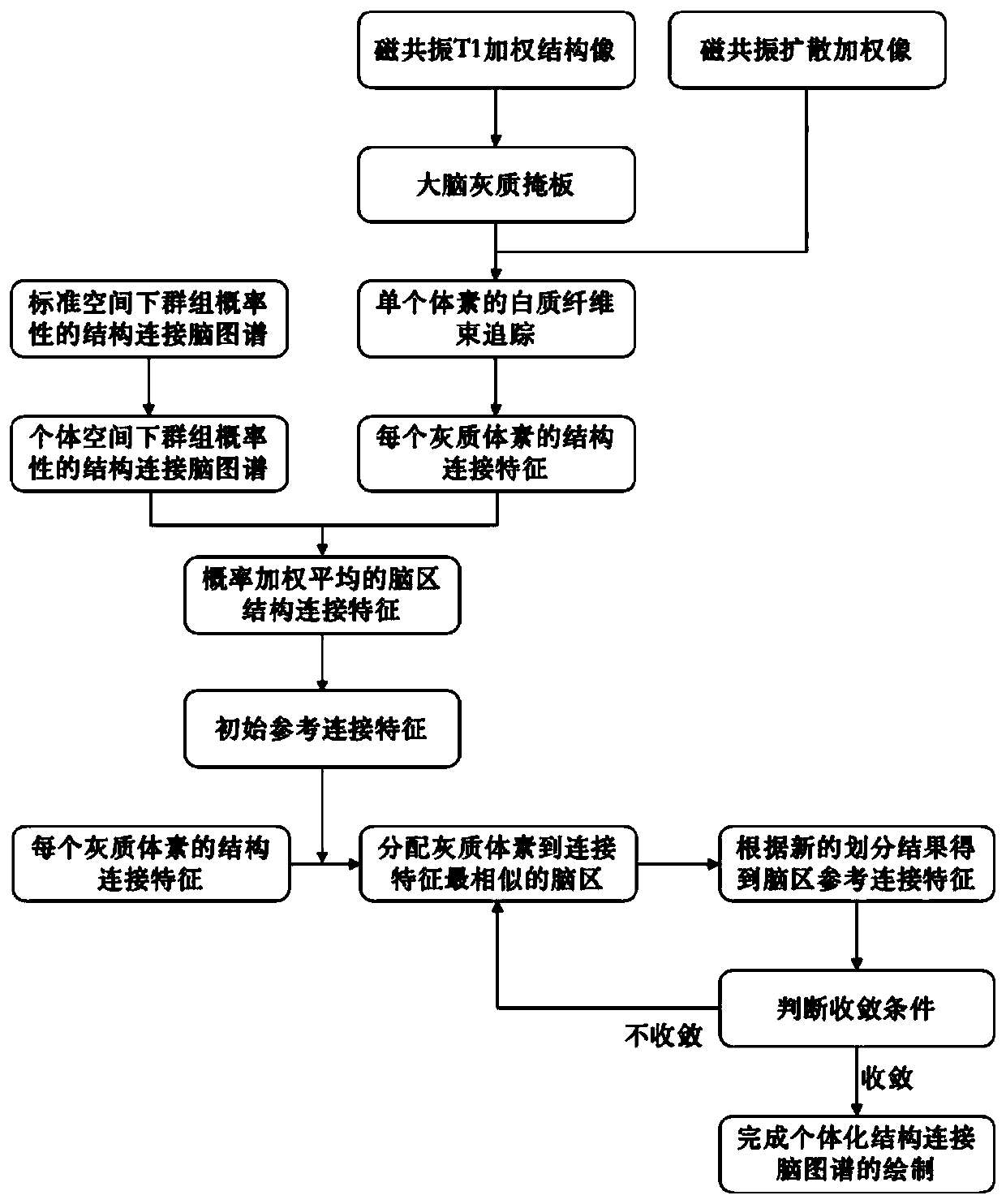
Individualized structure connection brain atlas drawing method based on diffusion magnetic resonance imaging fiber bundle tracking technology
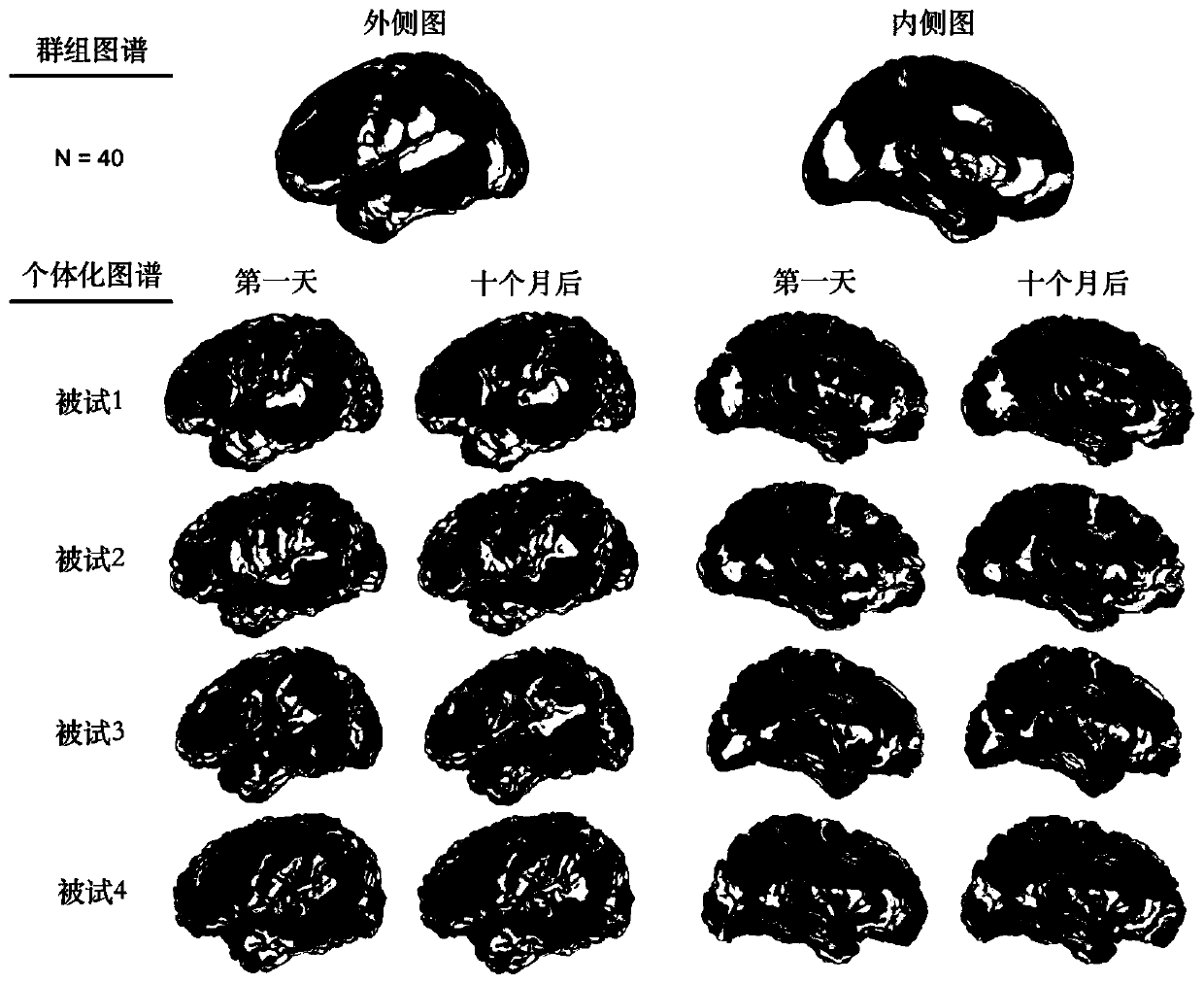
The invention provides an individualized structure connection brain atlas drawing method based on a diffusion magnetic resonance imaging fiber bundle tracking technology. A group probabilistic brain atlas based on cerebral cortex structure connection is used as a priori starting point, and iterative optimization is performed at the individual brain level according to the structure connection information of the local cortex of the individual brain so as to generate a spatial division mode of the individualized brain region. The method is suitable for drawing and analyzing the individualized brain atlas by utilizing diffusion magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Individual-characteristic-based transcranial brain atlas generation method, navigation method, and navigation system
ActiveUS20190320966A1High coverage accuracyIncreased sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisScalpNavigation system
The present invention discloses an individual-level transcranial brain atlas generation method, where invisible intracerebral atlas information may be projected onto a visible scalp surface, so that an operational space and an effective space that are originally separated are fused together. For the problem of applying a transcranial brain atlas to guidance of individual placement of a transcranial device, the present invention further provides an individual-characteristic-based transcranial brain atlas generation method and navigation system. An experimental result indicates that, the present invention can be used to effectively improve coverage accuracy of a near-infrared measurement optrode in a brain region of interest, and consistency between measurement locations on upper cortexes of different persons, thereby improving sensibility of detecting a task-induced brain activity by using a near-infrared technology.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Brain slice image region division method and device
ActiveCN110555835AFully automatic area divisionZoning FastImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionImage registration
The invention relates to a brain slice image region division method and device, and belongs to the technical field of image registration. The method comprises the steps of acquiring multiple groups ofimages wherein each group of images comprises an original image to be subjected to region division and a gray scale and color standard brain atlas corresponding to the original image; performing affine transformation on the gray scale and color standard brain atlas to obtain a gray scale and color standard brain atlas after affine transformation; respectively carrying out feature extraction on the original image and the affine-transformed gray scale standard brain atlas to obtain a single-mode original image and a single-mode gray scale standard brain atlas; taking the single-mode original image and the single-mode gray scale standard brain atlas as training samples, and training a registration network; inputting the color standard brain map after affine transformation into a trained registration network to obtain a registered color standard brain map; and fusing with an original image to complete region division. Full-automatic and rapid region division of the multi-modal brain sliceimage is realized, the operation is simple and convenient, and the region division is accurate.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
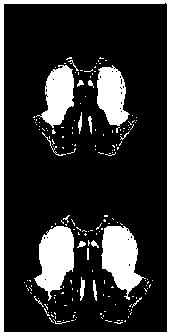
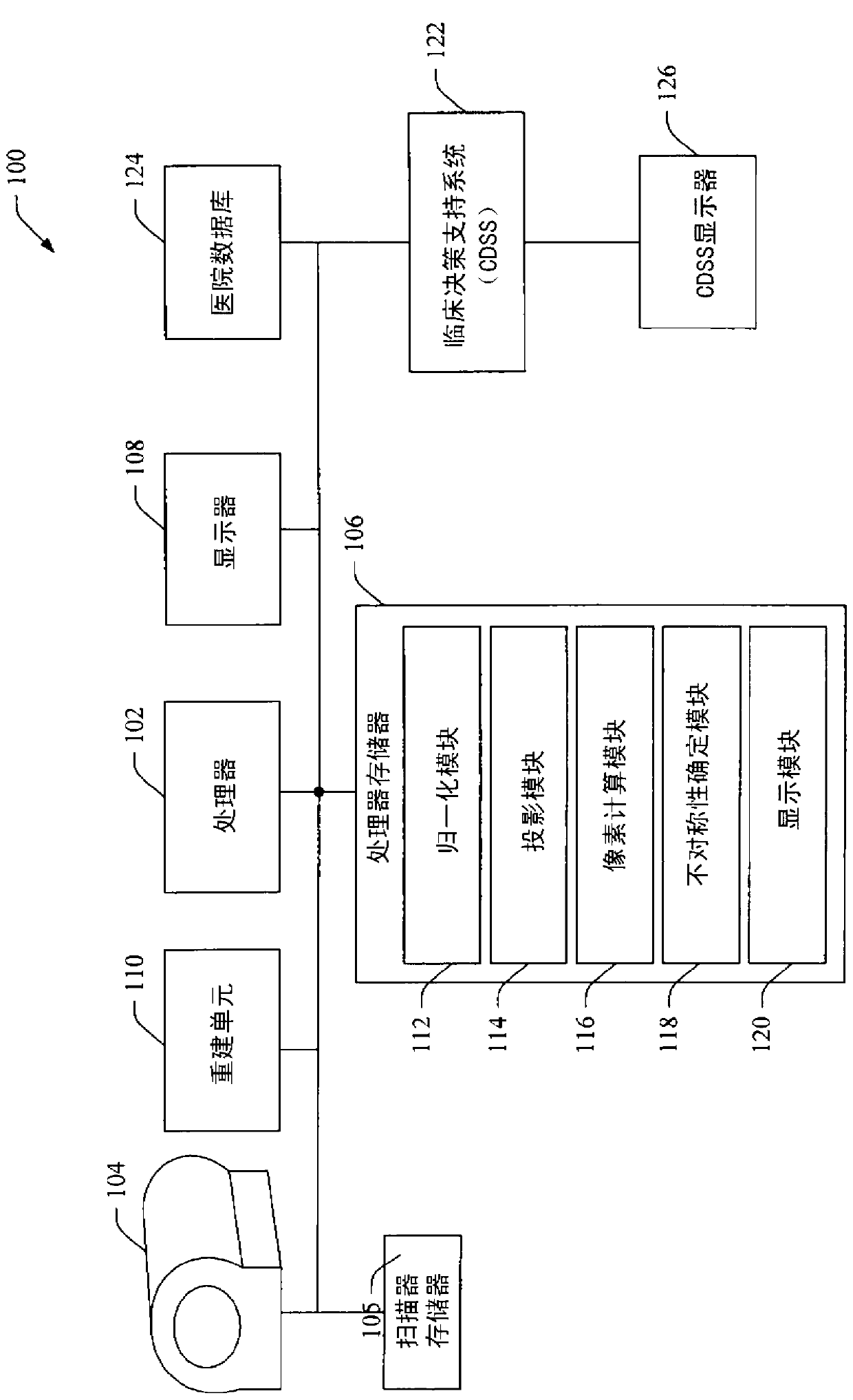
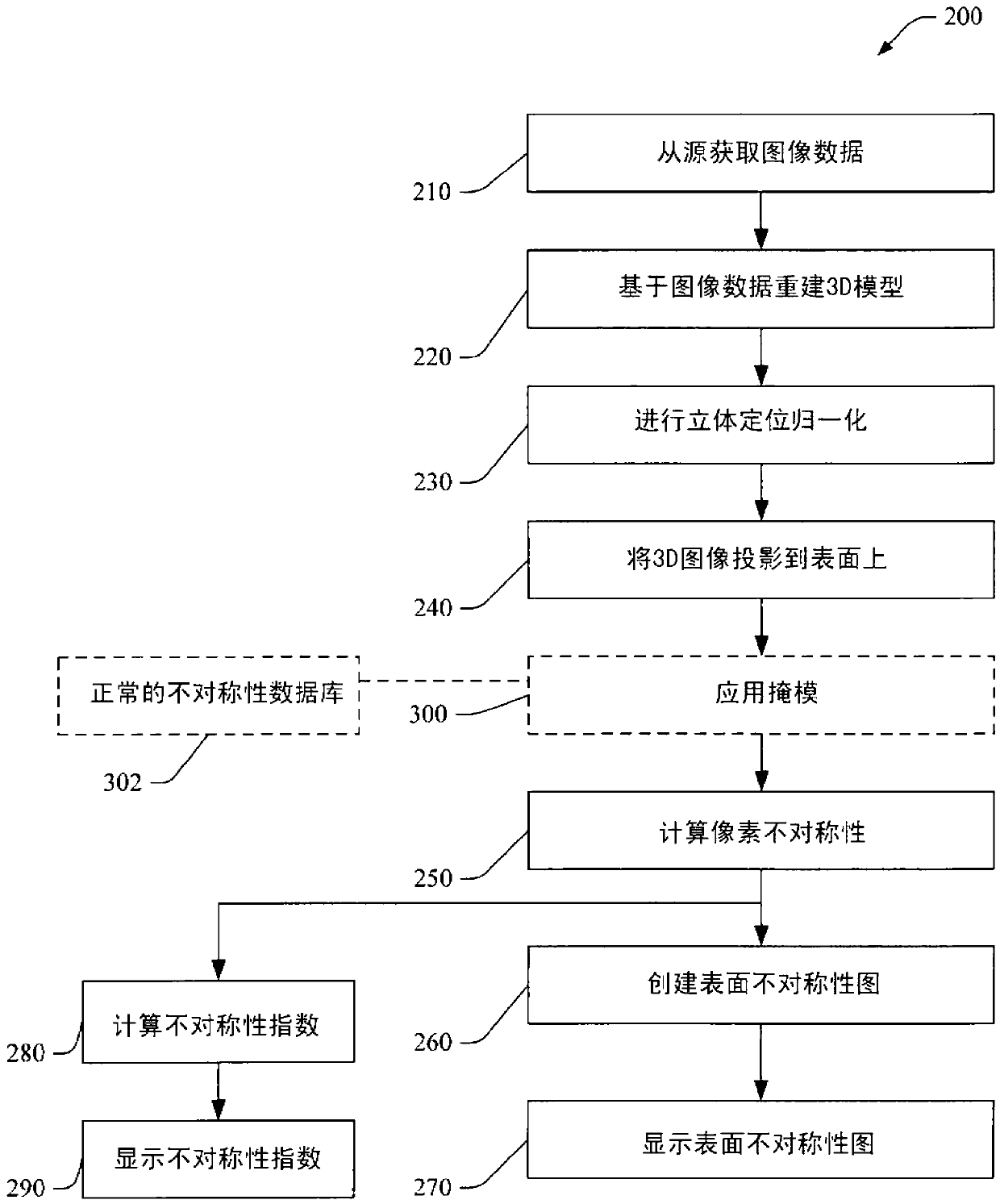
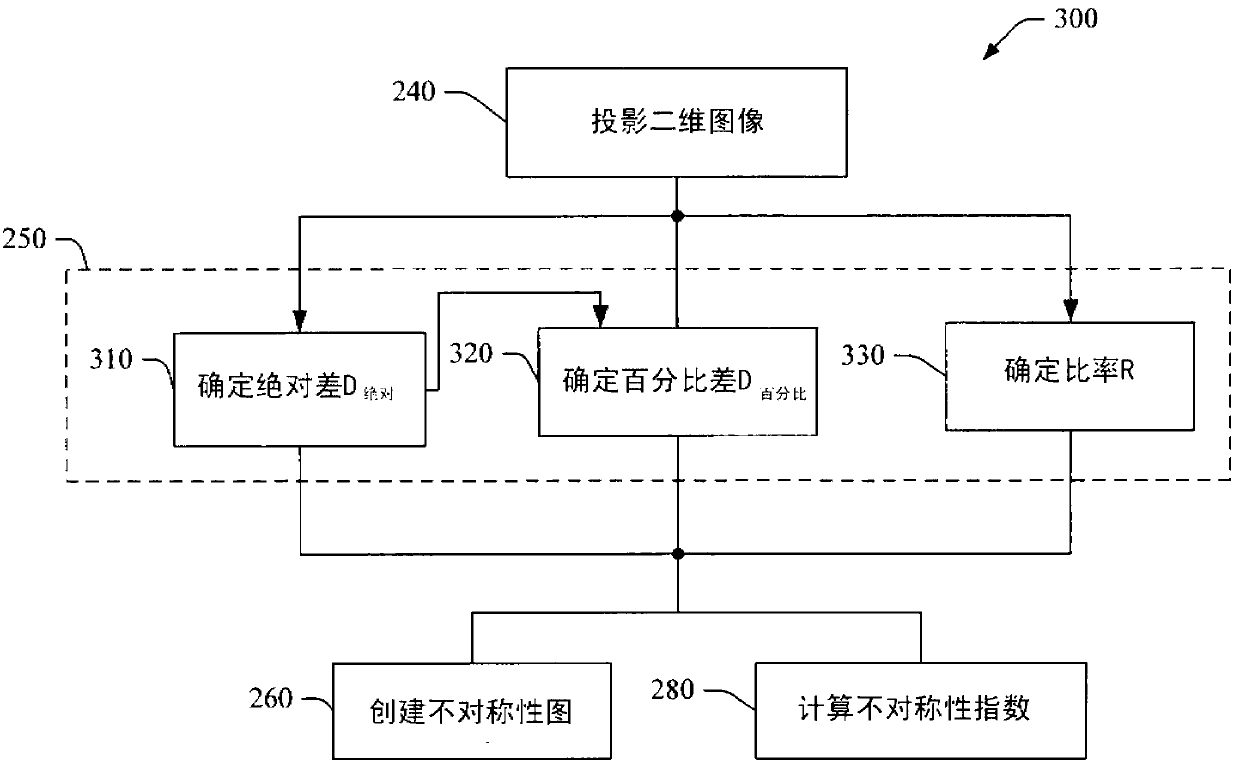
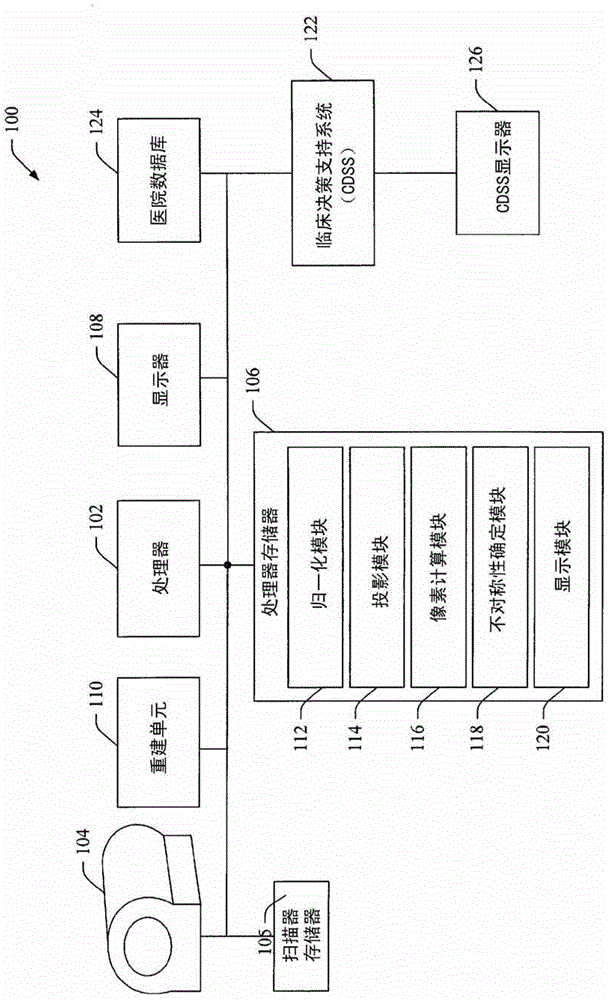
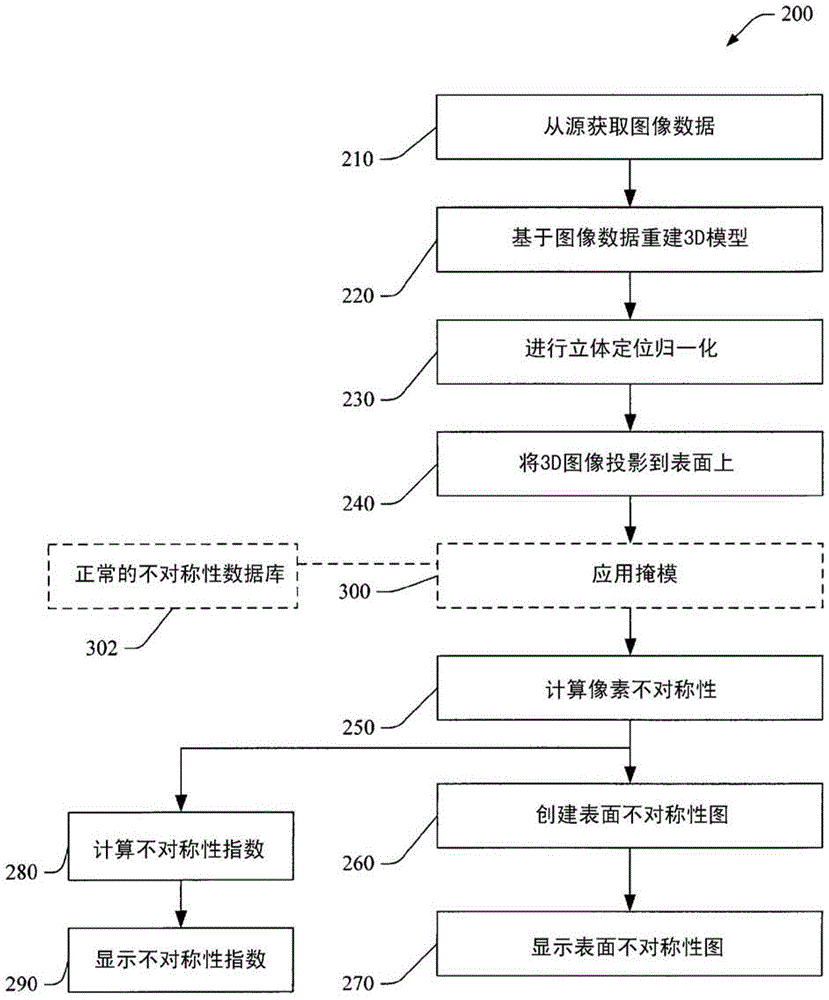
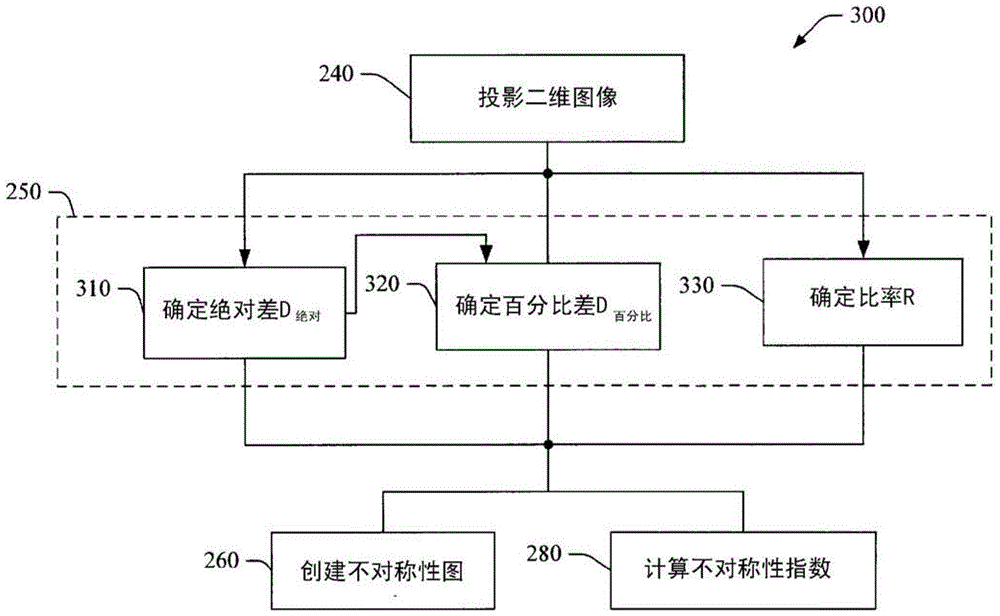
Automatic quantification of asymmetry
An apparatus detects asymmetry in an object, such as a brain. The apparatus includes a processor programmed to fit a three-dimensional image of the object to a preselected shape, such as a standard brain atlas. The processor projects the three- dimensional image of the object to a two-dimensional surface image. The processor compares corresponding mirror image symmetric voxel pairs on the left and right sides of the surface image. The processor generates at least one of an asymmetry map and an asymmetry index based on the deviations in the pixel pairs. The processor can also mask, before the comparison, pixels of the surface image which are asymmetric in a normal brain.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for localizing implanted intracranial electrode
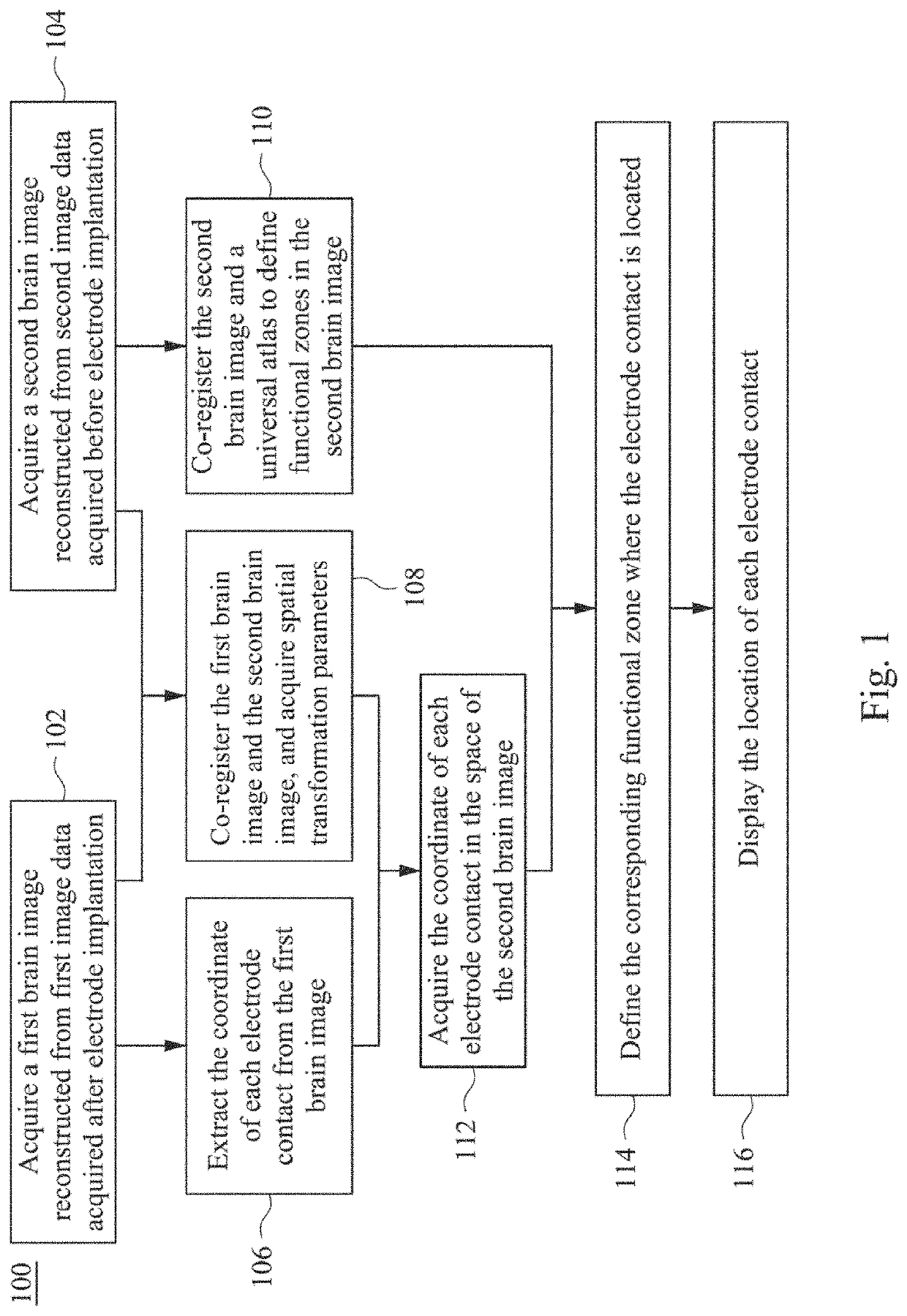
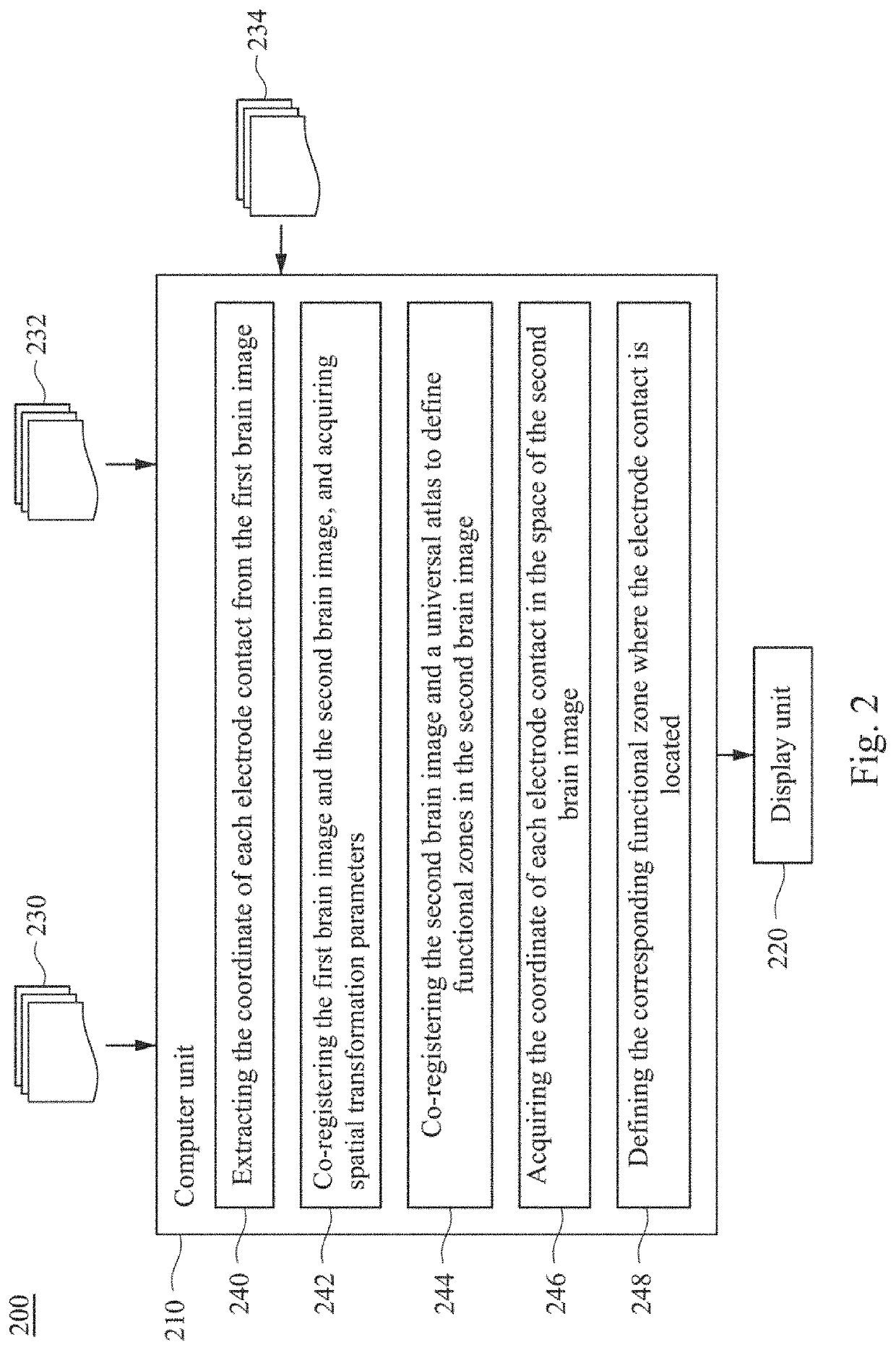
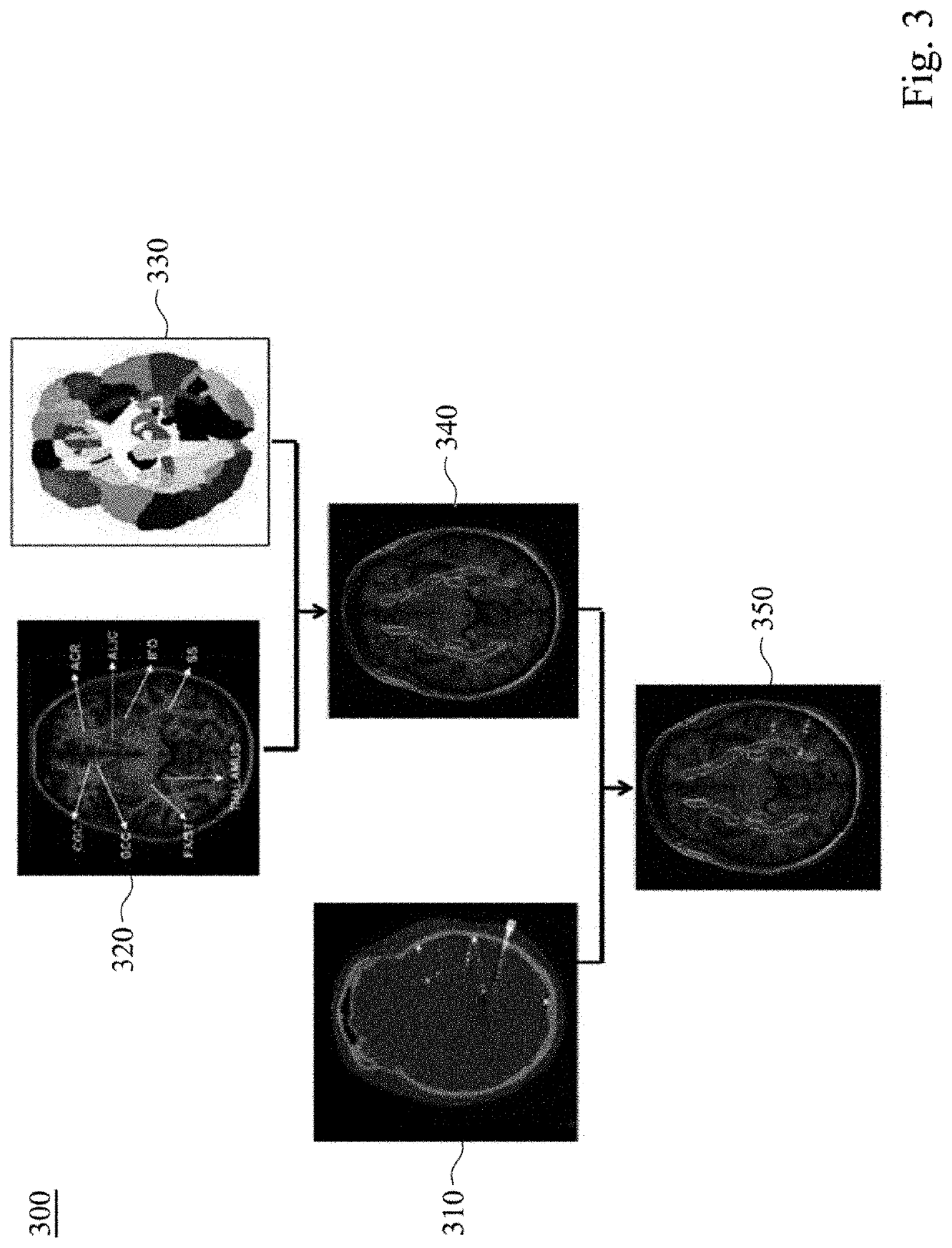
A method for localizing an intracranial electrode in a subject's brain is provided. The intracranial electrode has at least one electrode contact. The method includes: acquiring a first brain image reconstructed from first image data acquired after electrode-implantation; acquiring a second brain image reconstructed from second image data acquired before the electrode-implantation; co-registering the first brain image and the second brain image to acquire spatial transformation parameters; extracting a first coordinate of the electrode contact from the first brain image; converting the first coordinate into a second coordinate in the second brain image by using the spatial transformation parameters; co-registering the second brain image and a universal brain atlas to define functional zones in the second brain image; and defining a corresponding functional zone where the second coordinate is located. Another alternative method and a system for localizing an intracranial electrode are also provided herein.
Owner:NAT YANG MING CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Image-driven brain atlas construction method and device, equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112735570AReduce false positive rateAvoid heterogeneityMedical imagesNeural learning methodsRadiologyBrain section
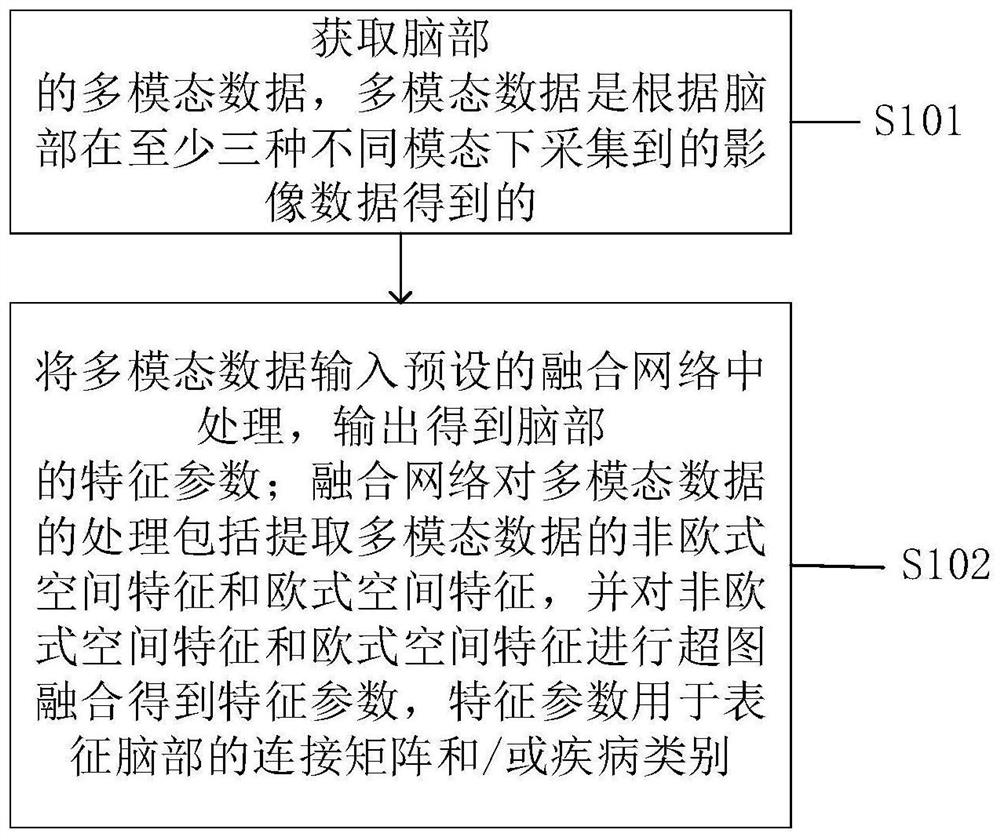
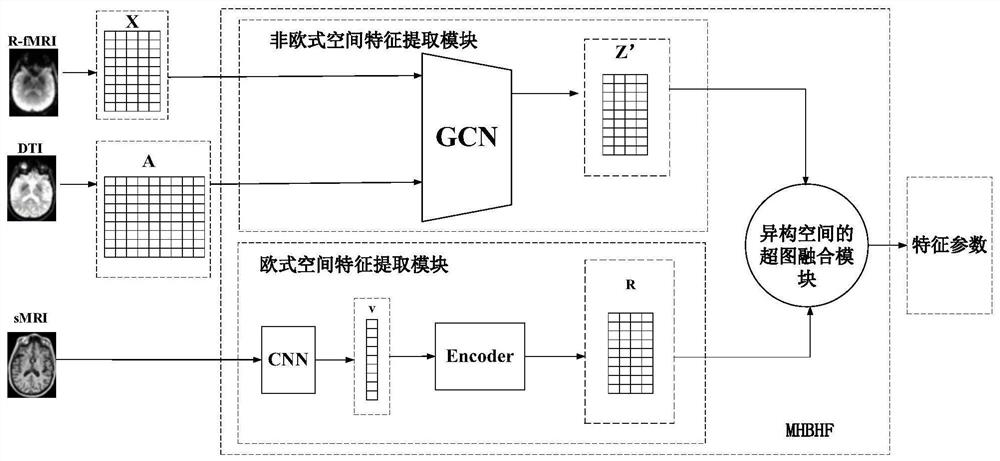
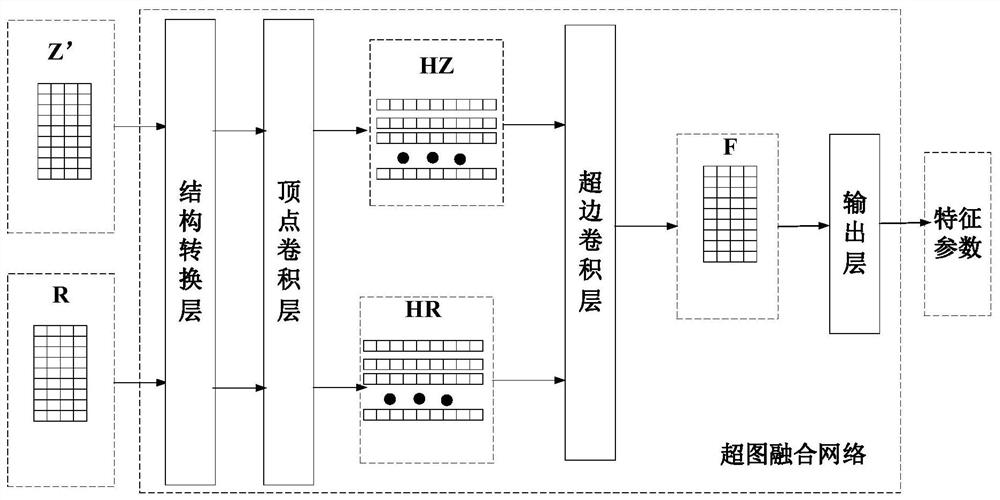
The invention is applicable to the technical field of medical images, and provides an image-driven brain atlas construction method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining multi-modal data of a to-be-predicted brain, wherein the multi-modal data is obtained according to image data collected by the brain in at least three different modes; inputting the multi-modal data into a preset fusion network for processing, and outputting to obtain characteristic parameters of the brain; the processing of the multi-modal data by the fusion network comprises the steps of extracting non-Euclidean spatial features and Euclidean spatial features of the multi-modal data, and performing hypergraph fusion on the non-Euclidean spatial features and the Euclidean spatial features to obtain feature parameters which are used for representing a brain connection matrix and / or a disease category of the brain. FEatures of different spaces are mapped into a hypergraph data structure for hypergraph fusion, possible isomerism among the features of the different spaces is avoided, and therefore complementary fusion features among the multi-modal data are obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Laterality detection method of brain structure network based on module connection
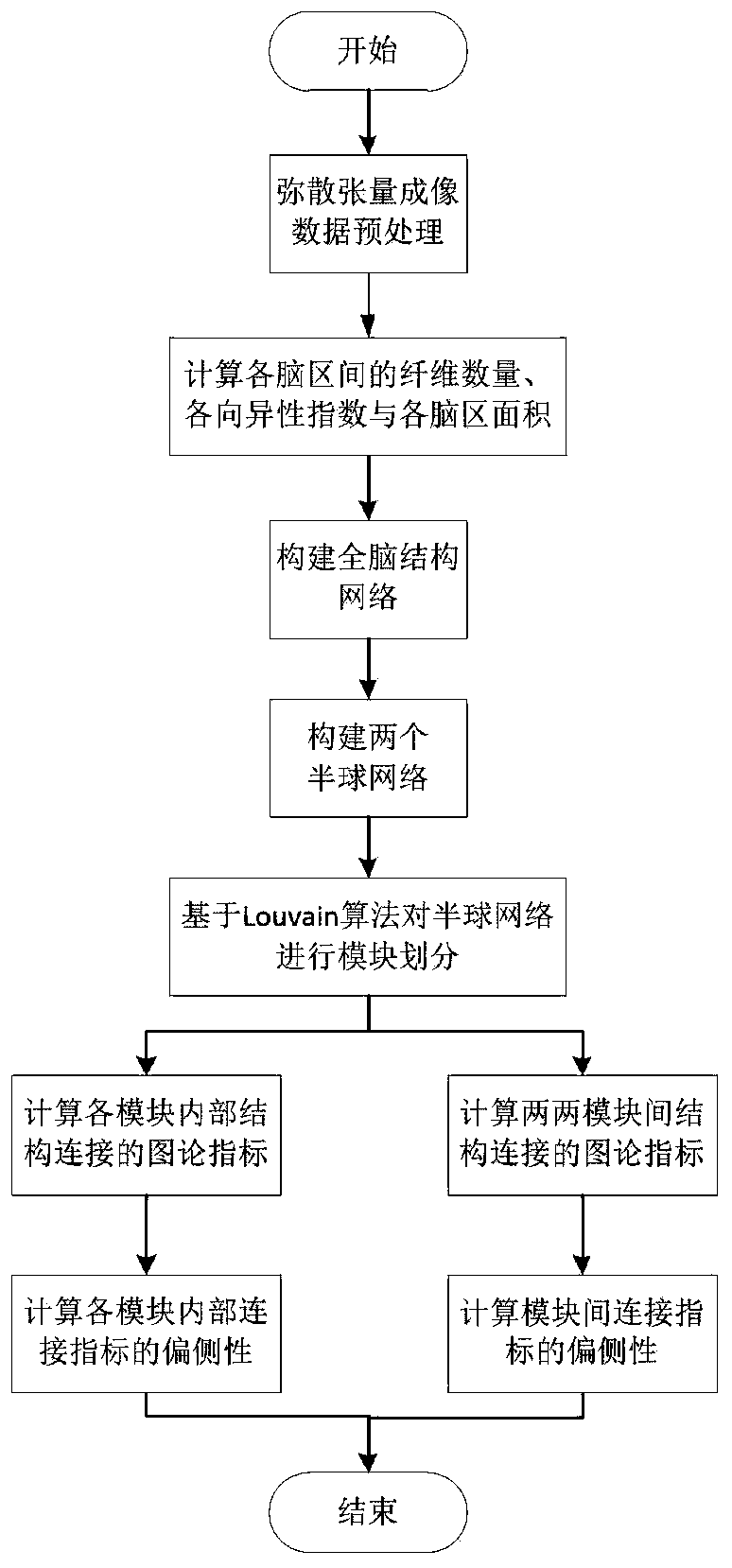
ActiveCN111340821AEfficient miningExcavate accuratelyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFiber bundle
The invention discloses a laterality detection method for a brain structure network based on module connection, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the preprocessing of a diffusion tensor image, and carrying out the region segmentation of the preprocessed diffusion tensor image according to a selected standardized brain atlas; adopting a deterministic fiber bundle tracking algorithm; reconstructing fibers of the whole brain on the basis of tracking end conditions, and calculating the number of fiber bundles and partial anisotropy indexes of every two brain regions and the superficial area of each brain region to obtain a fiber bundle number matrix FN, a partial anisotropy index matrix FA and a brain region superficial area matrix Surface of the brain regions. Compared with a traditional laterality detection method, the laterality detection method of the brain structure network based on module connection has the advantages that the modularity and the laterality ofthe network are fused, the laterality of local network indexes of the brain can be mined more effectively and accurately, and certain help is provided for exploring a brain working mechanism.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Tactile stimulation device and tactile brain atlas measuring system
PendingCN109106370AAlleviate the technical issue of applying less precisionIncrease stiffnessDiagnostics using pressureCatheterCatheterHaptic sensation
The invention provides a tactile stimulation device and a tactile brain atlas measuring system, which relate to the technical field of a functional brain atlas measuring device. The haptic stimulationdevice comprises a stimulation assembly, a driving end fixing member and a terminal fixing member. The stimulation assembly comprises a telescopic driving member, a catheter and a guide wire. One endof the catheter is connected with the driving end fixing part and the other end is connected with the terminal fixing part; the guide wire penetrates into the catheter; the telescopic drive member isconnected to the first end of the guide wire for driving the guide wire to move relative to the catheter so that the second end of the guide wire extends outwardly or retracts inwardly from the catheter. By the tactile stimulation device provided by the invention, the technical problems of slow response speed and low application precision of the tactile stimulation site existing in the device forapplying the tactile stimulation in the prior art are alleviated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
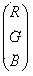
Segmenting method of gecko brain atlas processed through hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining
InactiveCN104318574ADistinguish clearlyNo interferenceImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEosin
The invention relates to a segmenting method of a gecko brain atlas processed through hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. Aimed at color features of tissues on the brain atlas shot by a Microscope or a digital camera, the segmenting method based on an YCbCr space is provided. According to the segmenting method of the gecko brain atlas processed through the HE staining, firstly, the color of the atlas is converted from an RGB space into the YCbCr space, then the brain atlas is segmented according to distribution differences of components Cb and components Cr in different regions of the atlas, and finally the different tissues in the atlas are completely segmented. The segmenting method provides a more convenient condition for researches on the brain structures of geckos and corresponding biobots.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Method for establishing animal model for senile dementia, special liquid medicine and dosing device
InactiveCN103284980ATypical behaviorTypical pathological symptomsHydroxy compound active ingredientsMedical devicesSterile environmentSenile dementia
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Continuous brain slice image three-dimensional registration method based on shape constraint
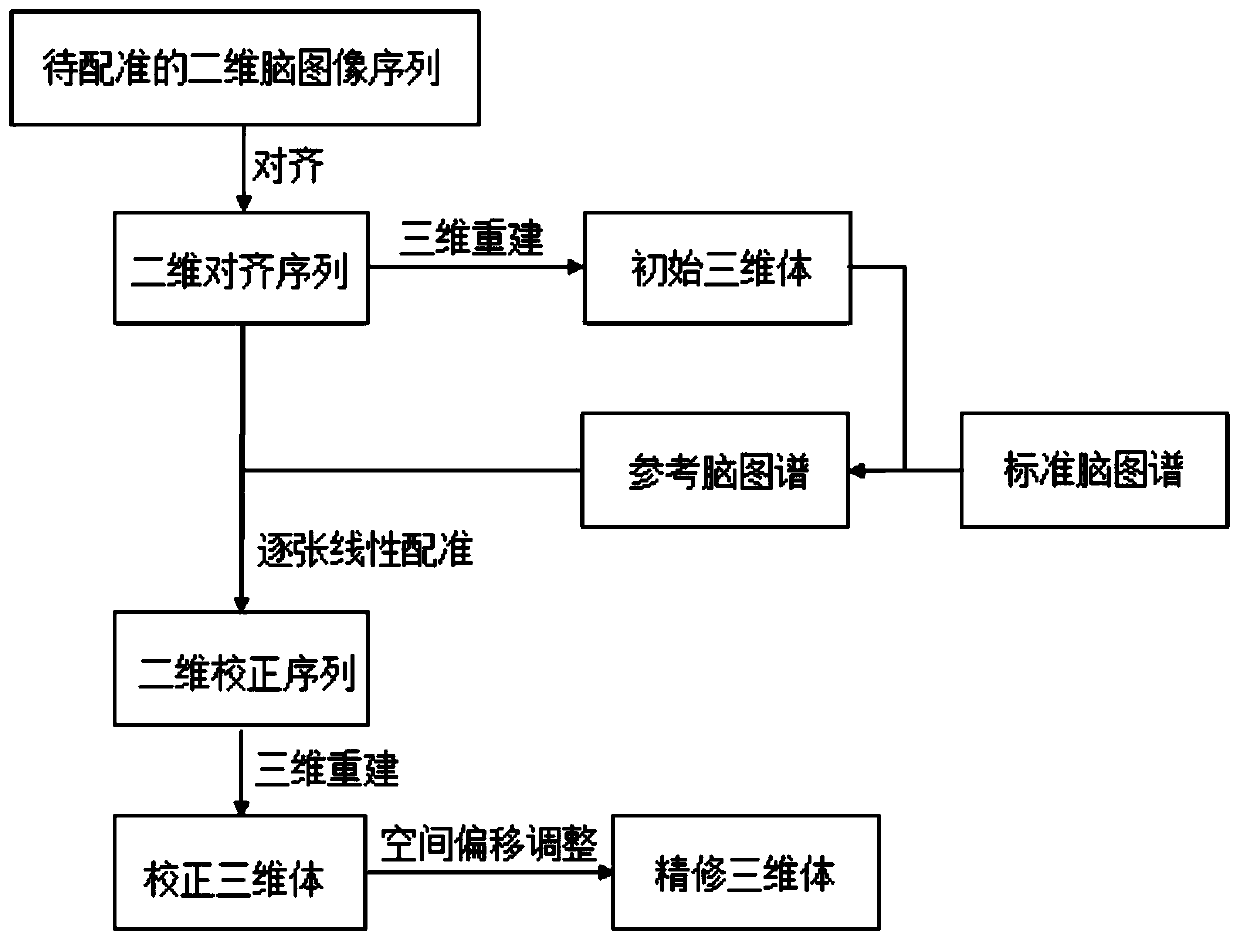
ActiveCN110782488ASolve the problem of axial offsetShape fitsImage enhancementImage analysisSequence reconstructionNuclear medicine
The invention provides a continuous brain slice image three-dimensional registration method based on shape constraint, and relates to the technical field of image registration. The method comprises the following steps: S1, aligning a to-be-registered two-dimensional brain image sequence to obtain a two-dimensional alignment sequence, and reconstructing the two-dimensional alignment sequence into an initial three-dimensional body; S2, linearly registering the standard brain atlas to the initial three-dimensional body to obtain a reference brain atlas, registering pictures of the two-dimensionalalignment sequence to tangent planes of corresponding positions in the reference brain atlas one by one to obtain a two-dimensional correction sequence, and reconstructing a corrected three-dimensional body; and S3, obtaining reverse deformation parameters of each pixel point in the corrected three-dimensional body, and performing spatial offset adjustment on the corrected three-dimensional bodyaccording to the reverse deformation parameters to obtain a refined three-dimensional body. The reference brain atlas is used as a constraint condition of the global shape, so that the correct shape of the real brain tissue is introduced into correction three-dimensional body reconstruction, and the problem of axial offset caused by lack of a spatial position relationship and global shape information in the prior art is solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic resonance image classification method based on an independent component high-order uncertain brain network
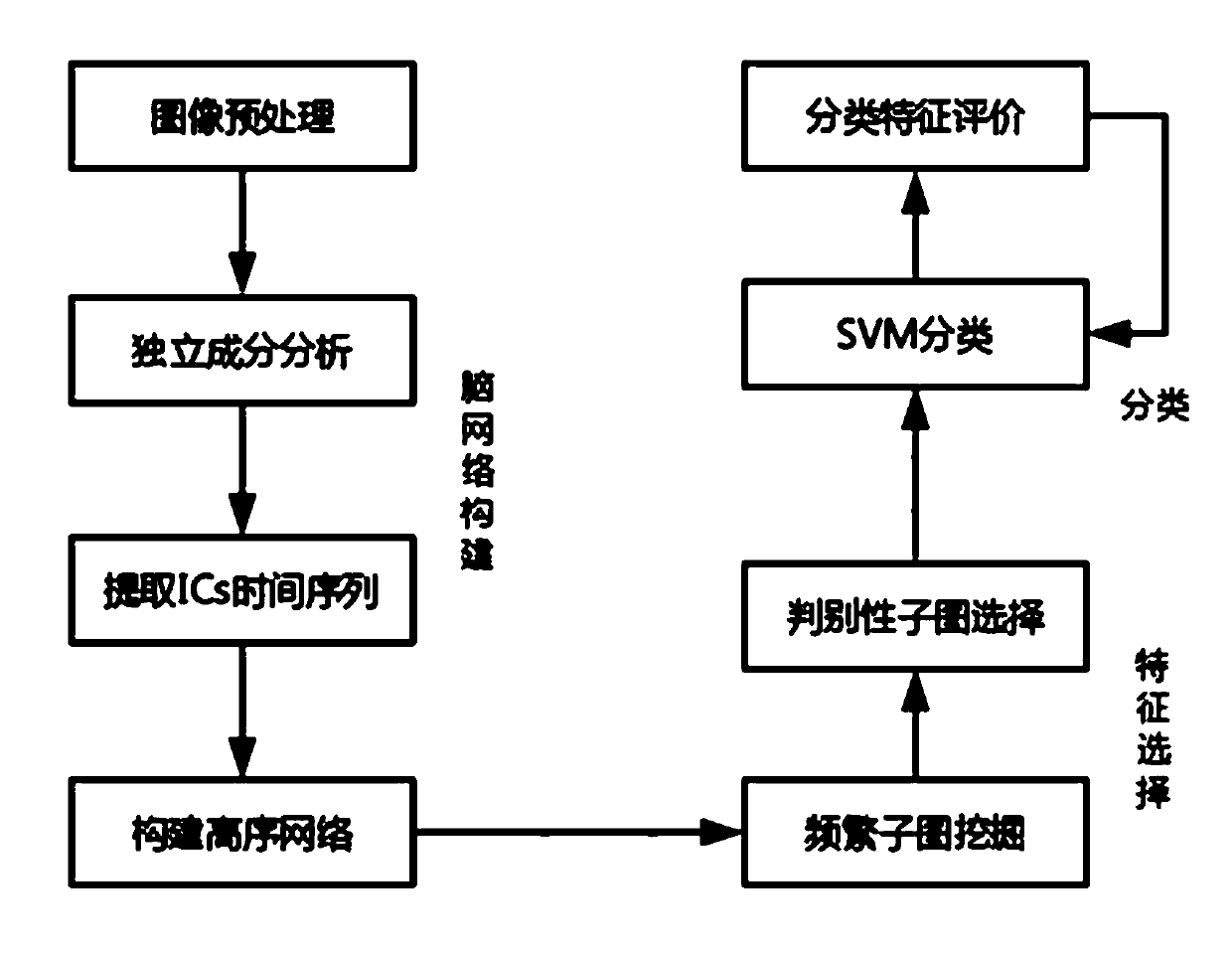
ActiveCN108846407AImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFunctional connectivityImaging processing
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance image classification method based on an independent component high-order uncertain brain network and relates to the image processing technology. The methodcomprises the steps of extracting a default network independent component by using independent component analysis, then a high-order functional connection network is constructed on the time series ofthe independent component by using a time window sliding method, a frequent subgraph mining and feature selection method based on a weighted graph is used, and the classification and recognition arecarried out with a discriminant subgraph as a feature. The method does not rely on a priori brain atlas template, time-varying characteristics in a scanning time are fully considered, the frequent subgraph mining is applied to the weighted graph, and more advanced and more complex interaction between brain regions is showed. The problem of the low accuracy of a traditional magnetic resonance imagedata classification method is solved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for establishing non-human primate animal model of parkinson disease by lateral ventricle administration of MPP<+>
InactiveCN103340859ATypical behavioral symptomsBasic physical condition is goodHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSide effectIodide
A method for establishing a non-human primate animal model of parkinson disease by lateral ventricle administration of MPP<+> belongs to the biomedical technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a lateral ventricle administration device; 2, according to a monkey brain atlas and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging data, acquiring a positioning coordinate of a lateral ventricle; 3, inserting a catheter into a lateral ventricle administration position through a monkey stereotaxic instrument, and beginning to administrate the drug after 5-8 days after the animal recovers; injecting a physiological saline solution containing MPP<+> into the lateral ventricle by an injector connected with the tail end of an administration pipe, with the MPP<+> concentration of 0.5-0.7 mg / mL and each administration dosage of 0.1-0.3 mL; carrying out administration one time every 48-72 hours, and after administration for 30-60 days, establishing the non-human primate animal model of the parkinson disease. The method employs a new administration mode that the MPP<+> (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium iodide) drug is directly injected into the lateral ventricle of the animal for modeling. With lateral ventricle injection, MPP<+> can perform whole brain circulation together with cerebrospinal fluid to specifically damage dopamine neurons in a brain and cause symptoms of the parkinson disease, and can furthest avoid toxic and side effects of the drug on a periphery.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A hybrid approach for automatic clustering and labeling of neuronal fibers in white matter of the brain
ActiveCN101650827BStable extractionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve fiber bundleFiber bundle
The invention relates to a method for automatic clustering and labeling of mixed brain white matter nerve fibers, which is characterized in that: firstly, a standard brain atlas is matched to a single brain space by using a high-dimensional elastic registration method, so that a single brain can be divided into 104 anatomical regions with structural information; then use different nerve fiber bundles to extract and mark 15 kinds of nerve fiber bundles through the characteristics of different brain anatomical regions; for the other 4 kinds, the above-mentioned ones cannot be used because they are strongly entangled with peripheral nerve fiber bundles The nerve fiber bundles extracted by the method are automatically clustered and analyzed by using the method based on the similarity measure combined with Kernel-PCA and Fuzzyc-mean. Finally, a feature-based identification method is used to mark the results of the cluster analysis . Through the above method, the 19 main white matter nerve fiber bundles of the brain can be automatically extracted and labeled.
Owner:南通曙光新能源装备有限公司 +1
Brain image classification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114241240AAuxiliary diagnosisThe analysis result is accurateCharacter and pattern recognitionSensorsPrediction probabilityClassification methods
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Brain Network Construction Method Fused with Image Voxels and Prior Brain Atlas Partitioning
InactiveCN103077298BOvercome deficienciesStrong visualizationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALVoxel
The invention provides an image voxel and priori brain atlas division fused brain network construction method to overcome defects of node selection methods in the conventional brain network construction method. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing functional magnetic resonance imaging data; constructing an initial brain network based on image voxels; and constructing a final brain network based on a priori brain atlas on the basis of the initial brain network. Two node selection methods in the prior art are fused, nodes with high degree values are searched on the basis of the image voxel, the nodes are screened by a Talairach encephalic region locating software on the basis of the priori brain atlas, the screened node is taken as a center of a circle to draw a sphere with the radius of 6 millimeters, the sphere is taken as a core node of the brain network, and the final brain network is determined according to the core node and sides of the obtained brain network. By the method, a brain functional network can be comprehensively and delicately described, the core node of the network is visualized in a brain space, and a function of observing a connecting mode between encephalic regions clearly is realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
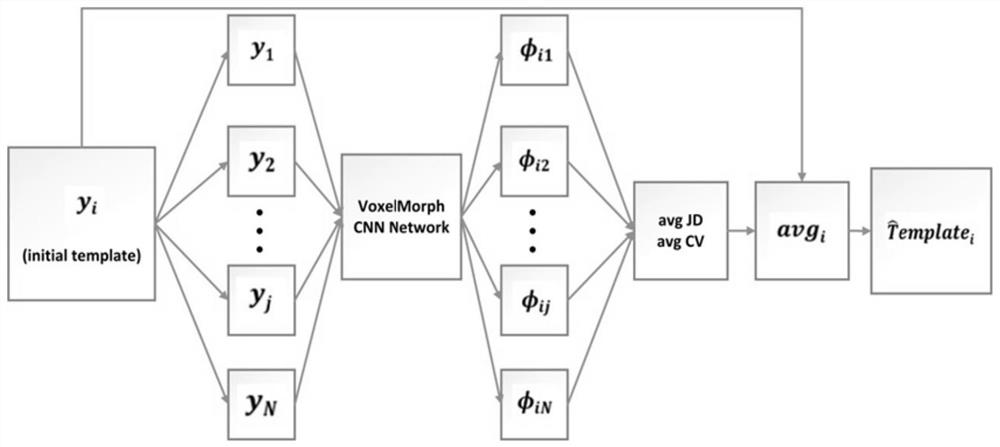
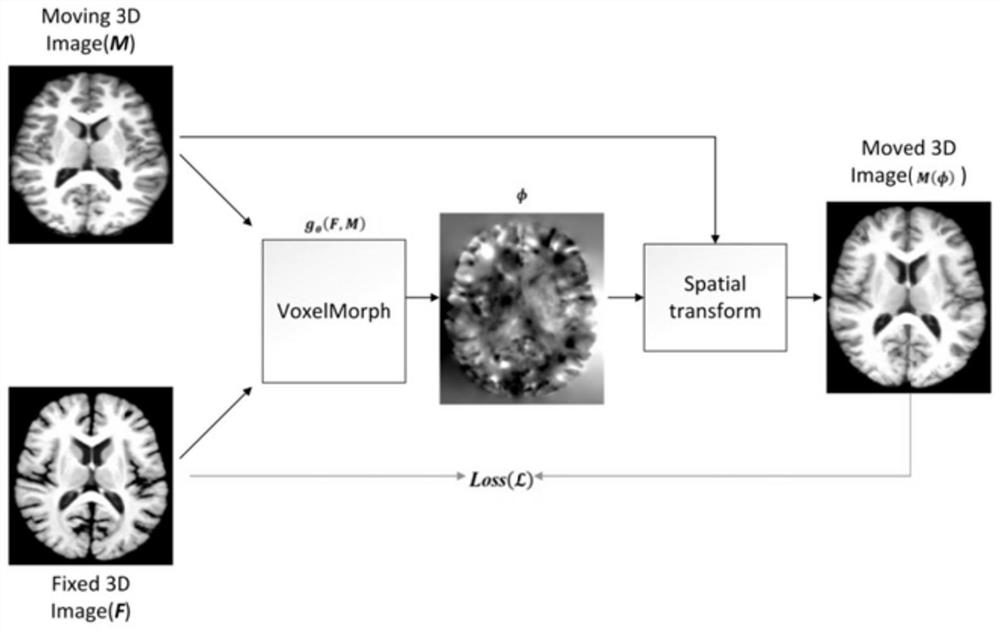
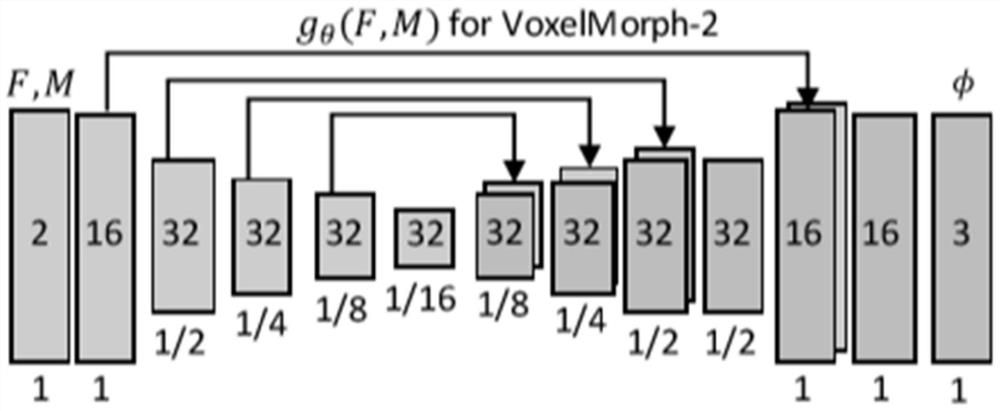
Method for constructing brain atlas based on differential geometry technology
The invention discloses a method for constructing a brain map based on a differential geometry technology. The method comprises the following steps: for N volume data sets, sequentially taking any one yi as an initial template, and registering the yi to all N yjs based on a convolutional neural network framework to obtain each registration domain phi; calculating an average domain of each registration domain phi through an average transform domain to obtain N average domains avg; and enabling the average domain to act on yi to obtain a new template, so when the average domain of the N temporary templates meets a set target, N template images are obtained, and the N template images are used as fixed images during registration. According to the method, better performance can be achieved in construction of brain MRI atlas, and a standard template is provided for disease diagnosis of doctors.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for identifying brain region position of fresh and live in-vitro tissue
PendingCN111887813AHigh-precision identificationAvoid differencesDiagnostics using tomographySensorsImage extractionRadiology
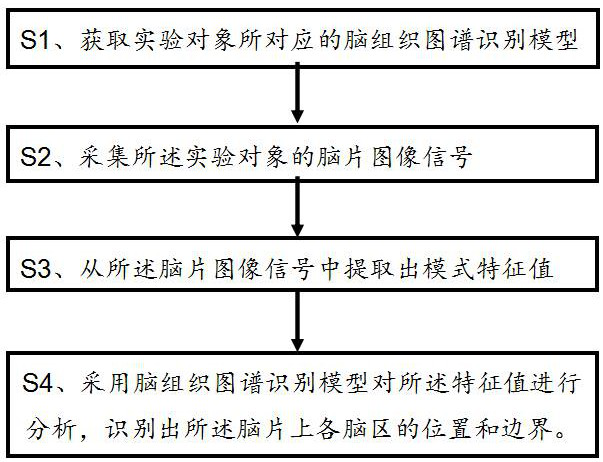
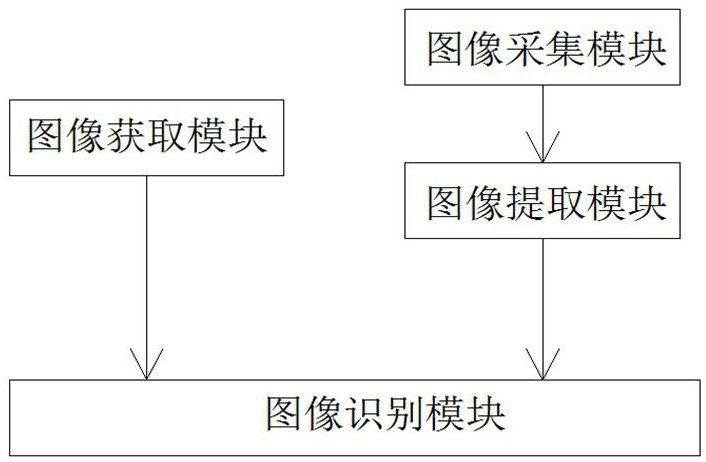
The invention discloses a method for identifying a brain region position of fresh and live in-vitro brain tissue. The method comprises the following steps: S1. obtaining a brain tissue atlas identification model corresponding to an experimental object from a brain atlas model library according to the experimental object where the fresh and live in-vitro brain tissue is derived; S2. acquiring brainslice image signals of the fresh and live in-vitro brain tissue; S3. extracting an eigen value of the brain slice image signals from the brain slice image signals; and S4. analyzing the extracted eigen value by adopting the brain tissue atlas identification model, so as to identify a brain atlas corresponding to a brain slice image of the fresh and live in-vitro brain tissue and identify variousbrain regions on the brain slice image. The invention discloses a device for identifying the brain region position of the fresh and live in-vitro brain tissue. The device comprises an image obtainingmodule, an image acquisition module, an image extraction module and an image identification module. According to the method and the device, the transformation to that a brain region structure of an in-vitro fresh and live brain tissue slice is observed, identified and labeled by machines from that the brain region structure of the in-vitro fresh and live brain tissue slice is observed and identified manually can be achieved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
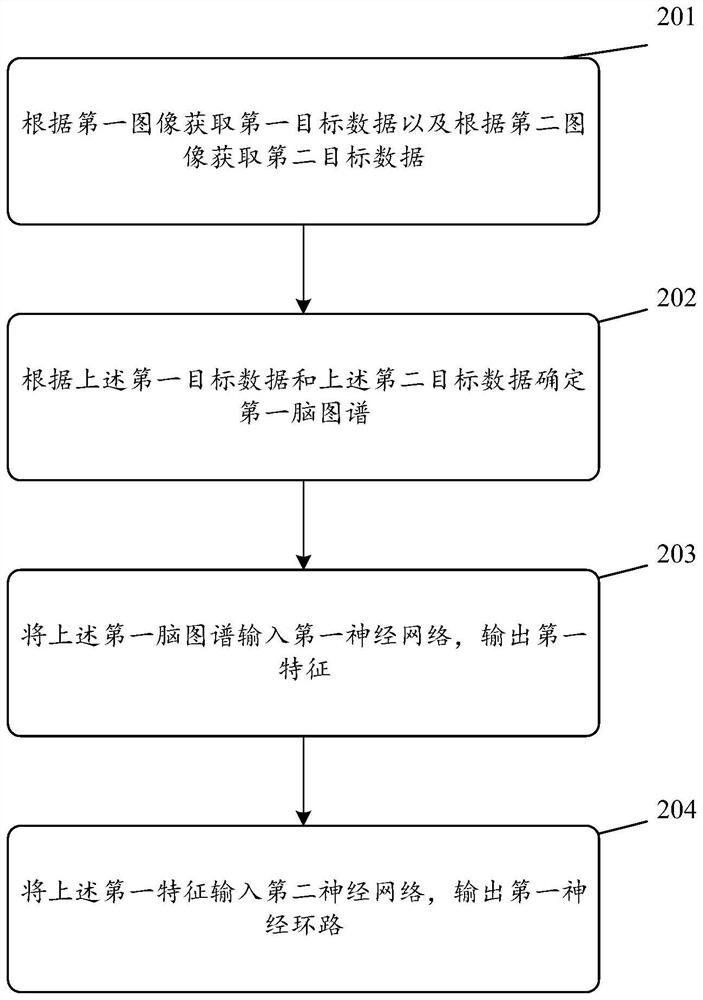
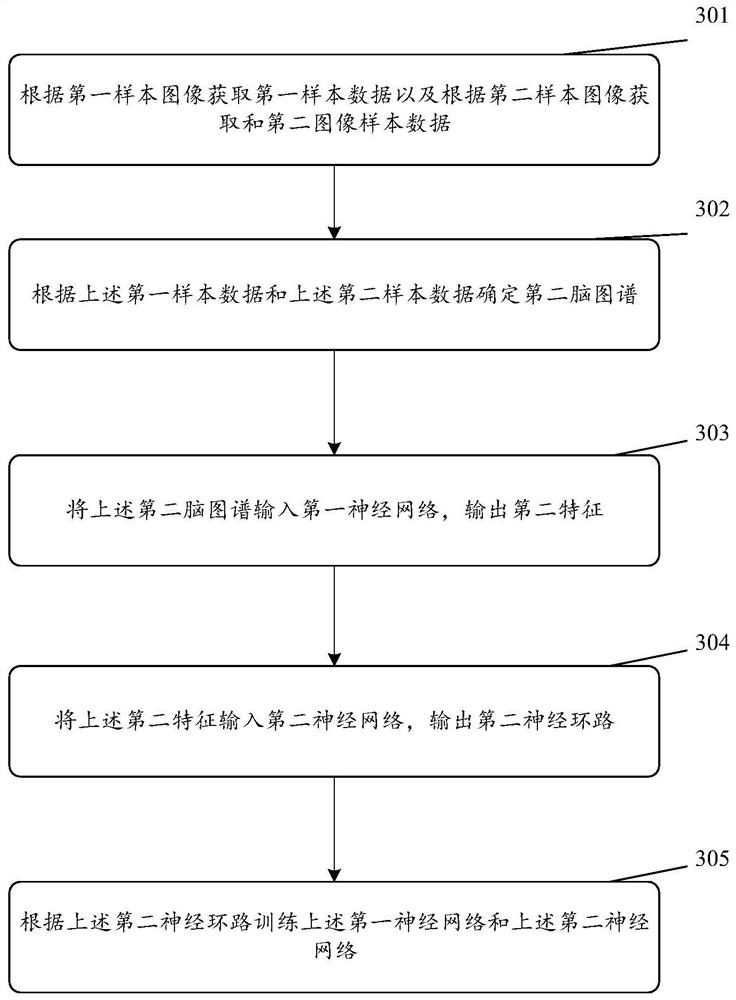
Brain map construction and neural circuit detection method and related products
The embodiment of the invention provides a brain map construction and neural circuit detection method and a related product. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring first target data according to a first image and acquiring second target data according to a second image; determining a first brain map according to the first target data and the second target data, wherein the first brain map is used for representing a relationship between the first target data and the second target data; inputting the first brain map into a first neural network, and outputting a first feature which is used for representing a high-order topological feature of the first brain map; the first feature is input into a second neural network, a first neural circuit is output, the second neural network is used for decoupling the areas in the first brain atlas, the first neural circuit is used for representing the connection relation between the areas of the first brain atlas, and the purpose of detecting the neural circuit can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
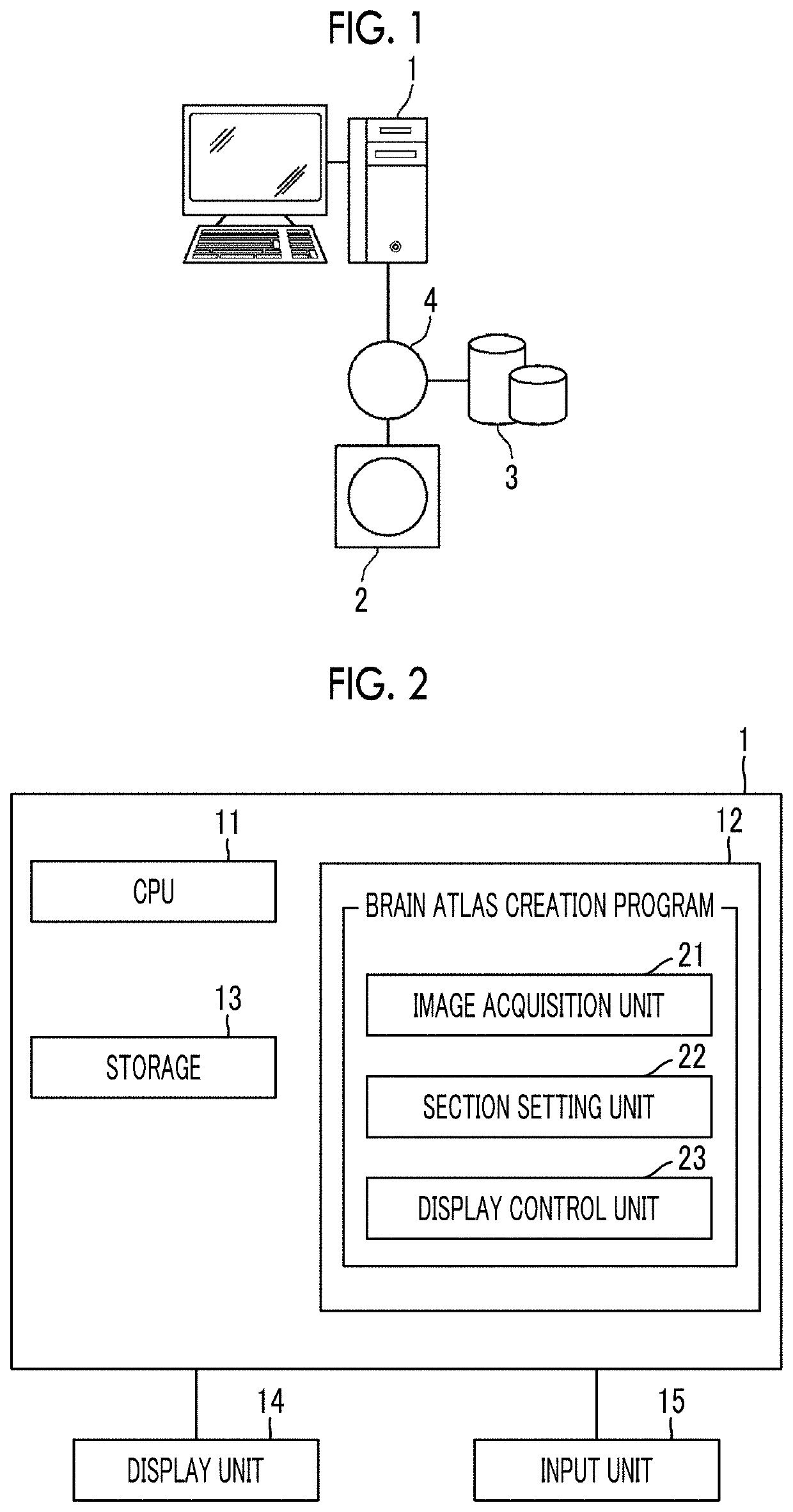
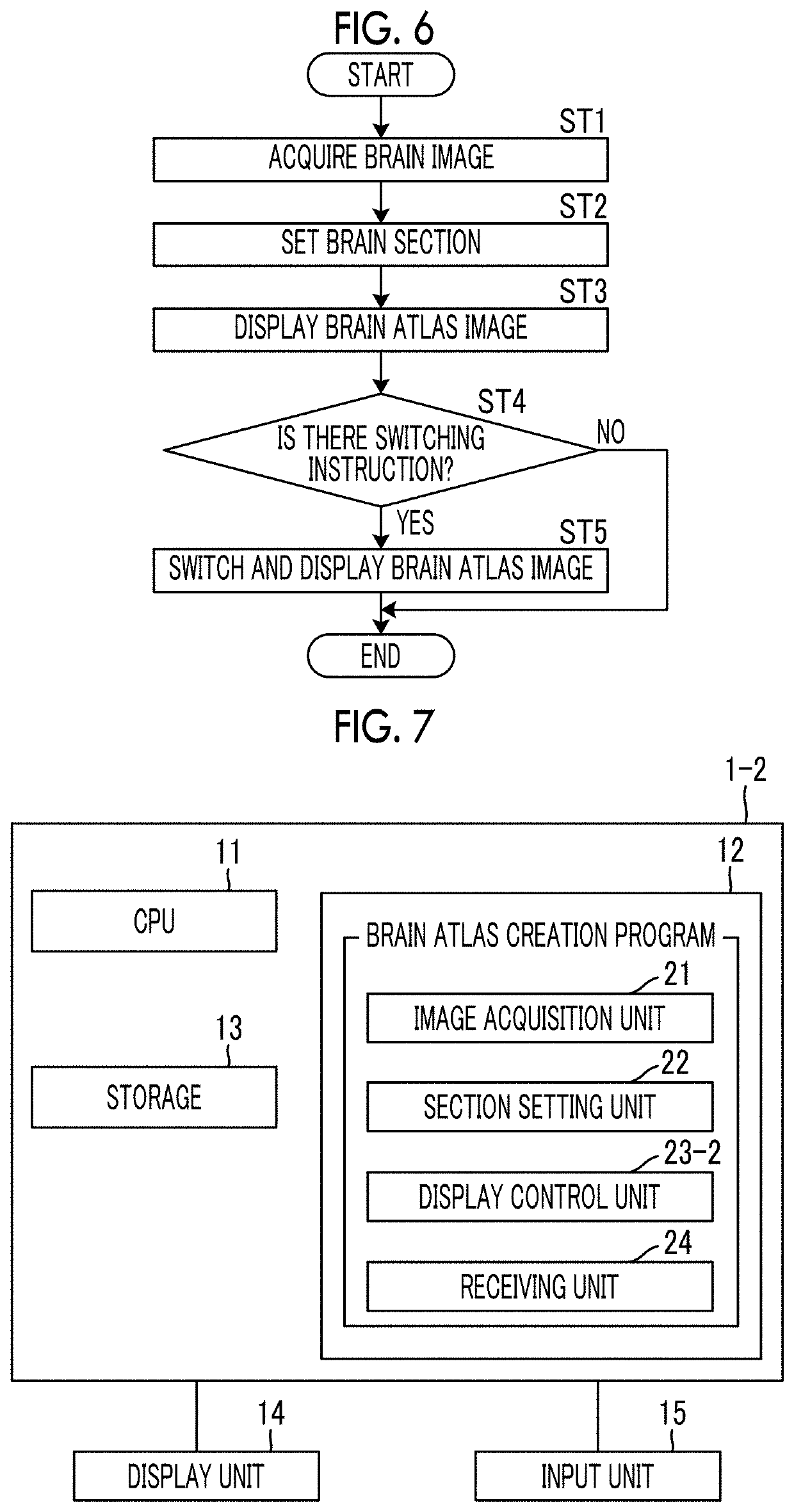
Brain atlas creation apparatus, brain atlas creation method, and brain atlas creation program
The brain atlas creation apparatus includes: an image acquisition unit that acquires a brain image; a section setting unit that classifies a brain area in the brain image acquired by the image acquisition unit into a plurality of layers from a major category which is a higher layer to a minor category which is a lower layer and sets a brain section for each category; and a display control unit that performs control to switch the brain image for each category classified by the section setting unit and to display the brain image on a display unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Automatic quantification of asymmetry
A device for detecting asymmetry in an object such as a brain. The device includes a processor programmed to fit the three-dimensional image of the subject to a preselected shape, such as a standard brain atlas. The processor projects the three-dimensional image of the object onto a two-dimensional surface image. The processor compares corresponding mirror-symmetric voxel pairs on the left and right sides of the surface image. The processor generates at least one of an asymmetry map and an asymmetry index based on deviations in the voxel pairs. The processor may also mask pixels of the surface image that are asymmetric in a normal brain prior to the comparing.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com