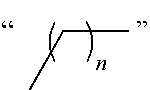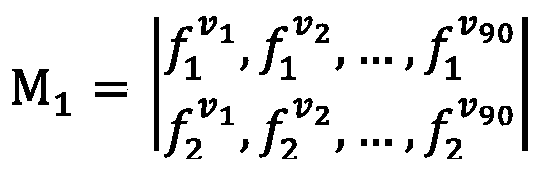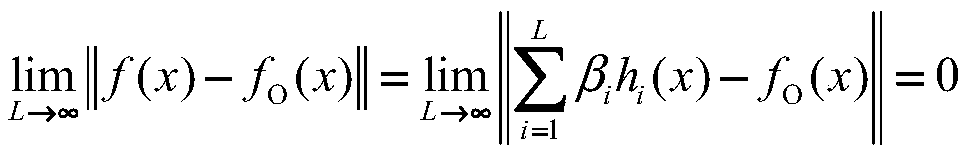Patents
Literature
287 results about "Brain network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
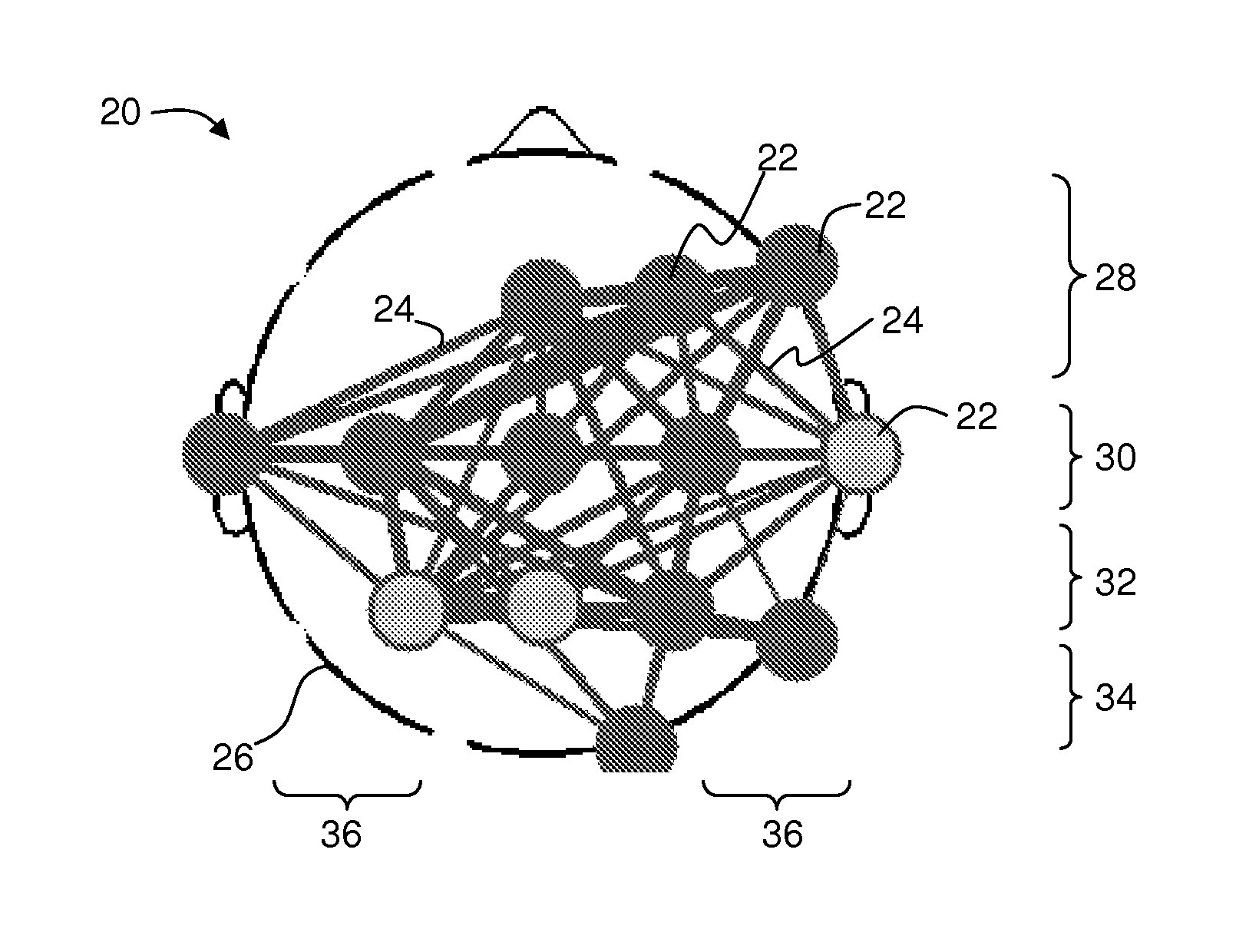
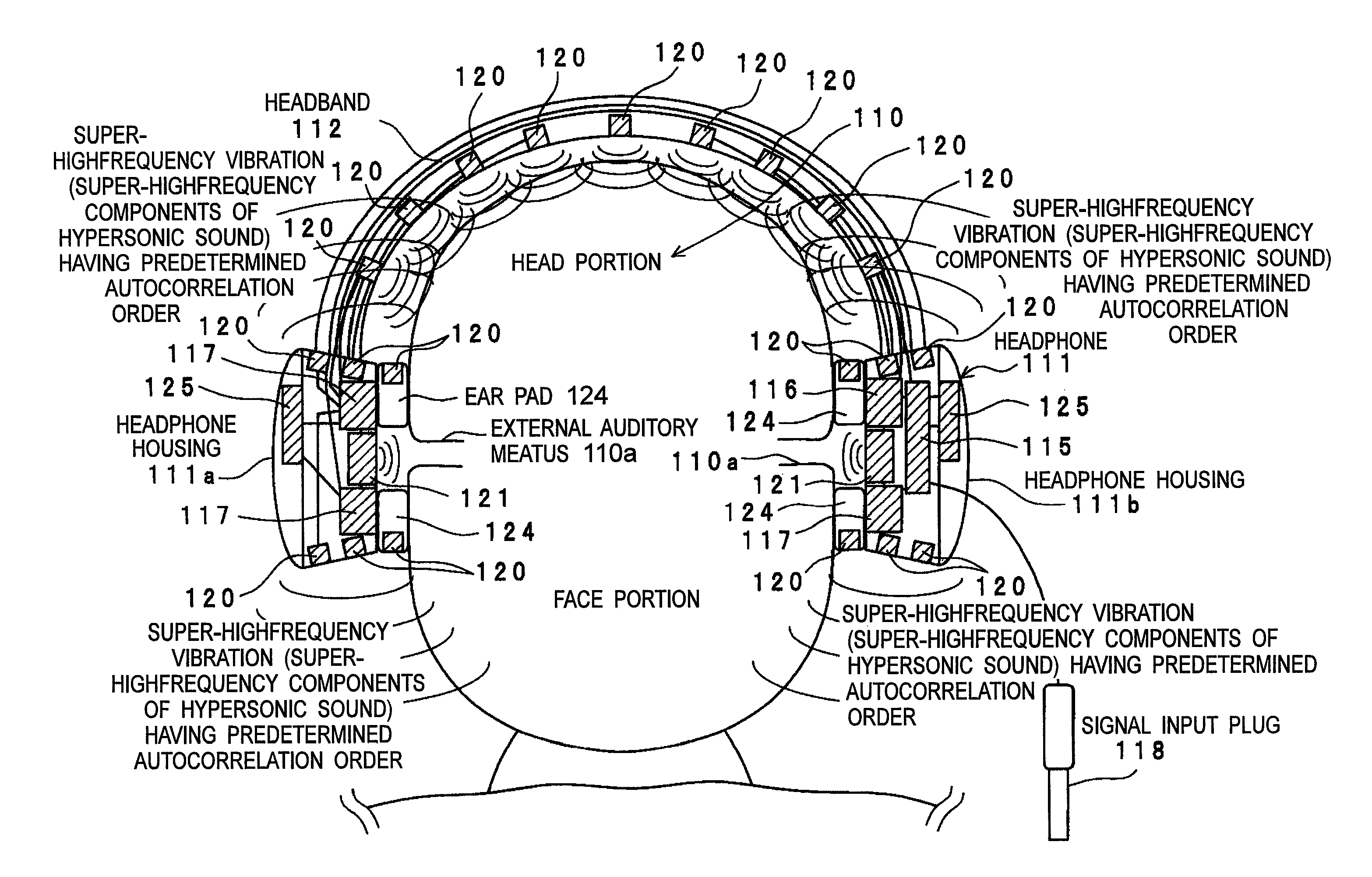
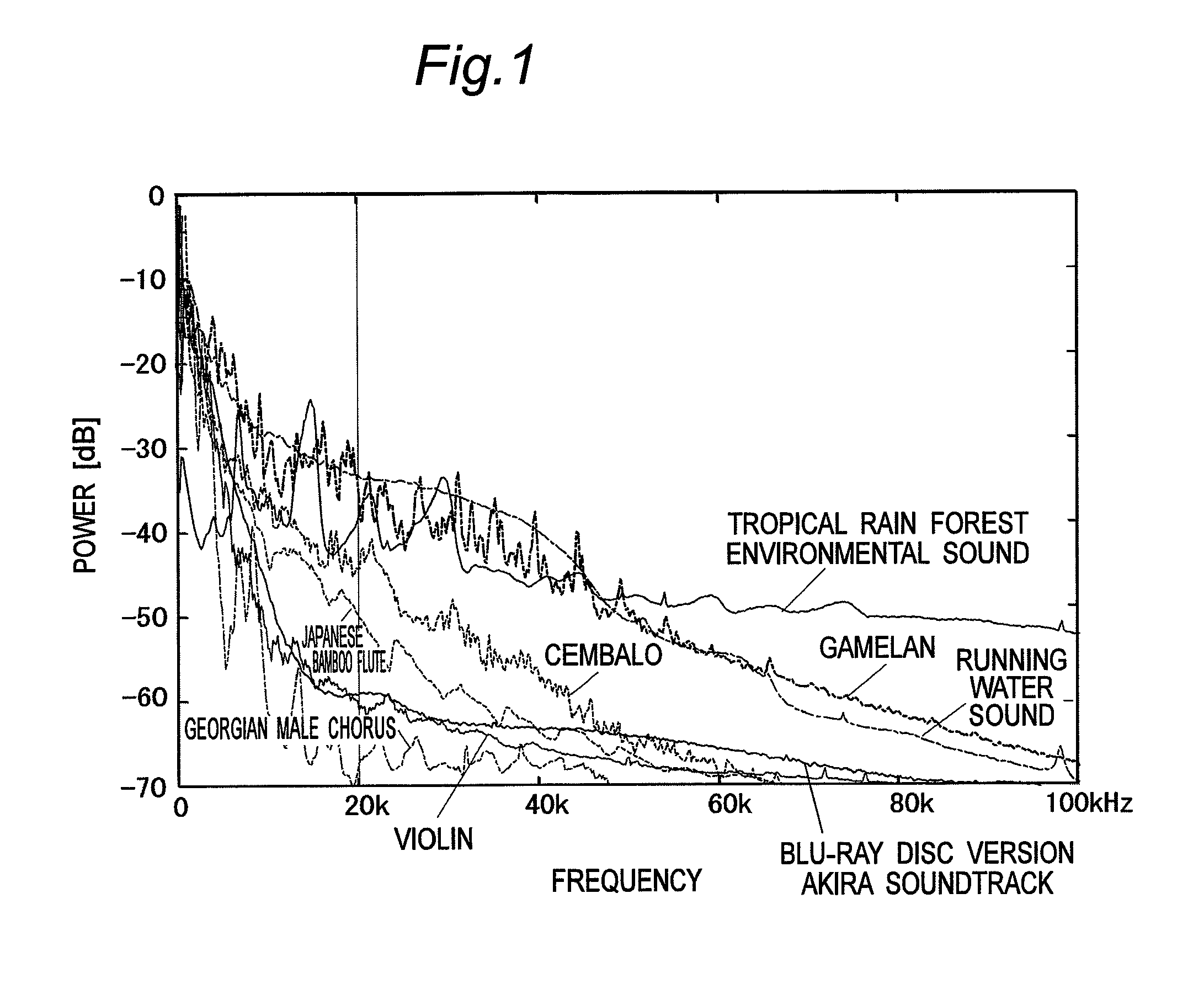
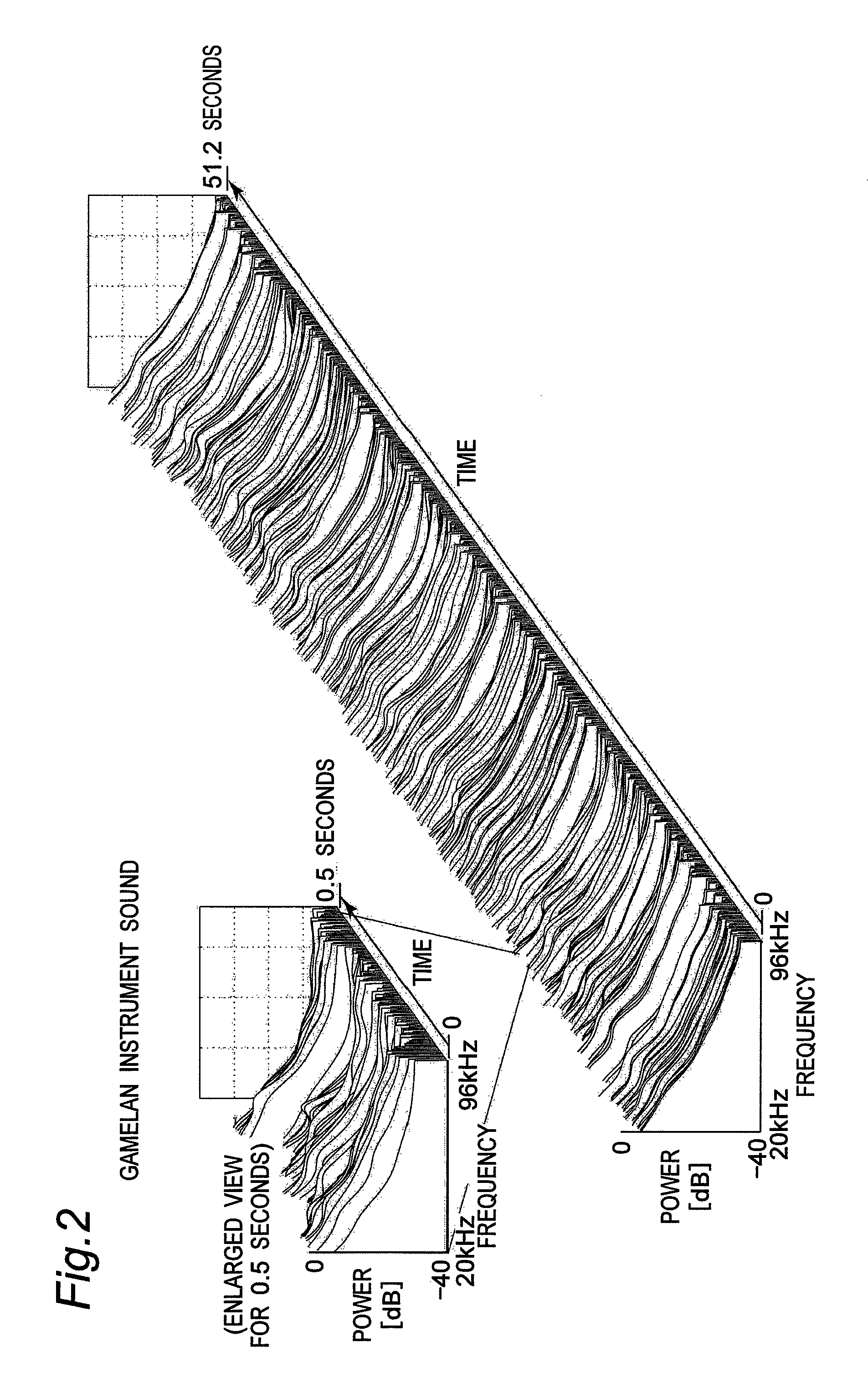
Vibration generating apparatus and method introducing hypersonic effect to activate fundamental brain network and heighten aesthetic sensibility
ActiveUS20110152729A1Discriminating vibrationPrevention of deterioration in brain activityUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesThalamusNeuron projection
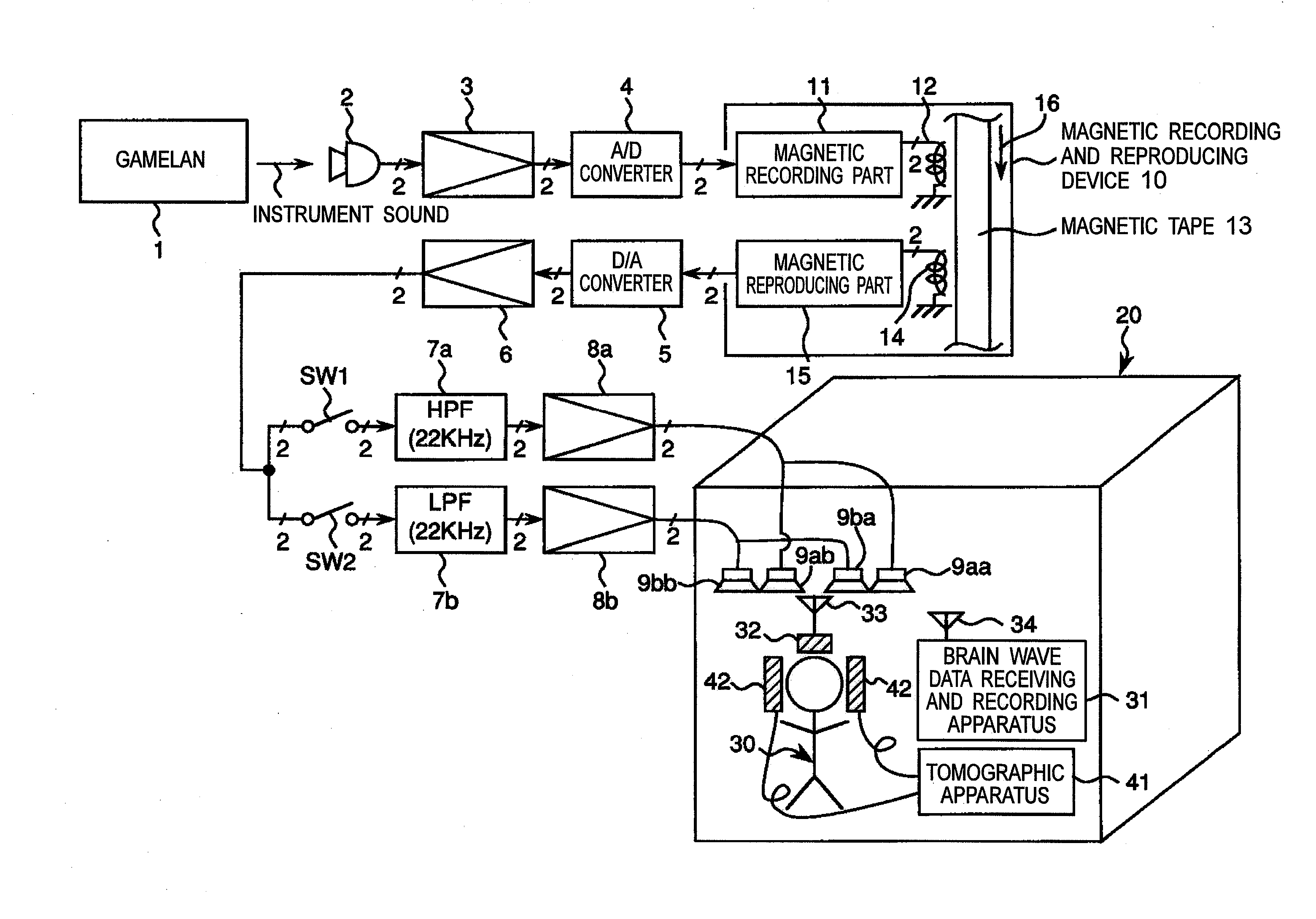
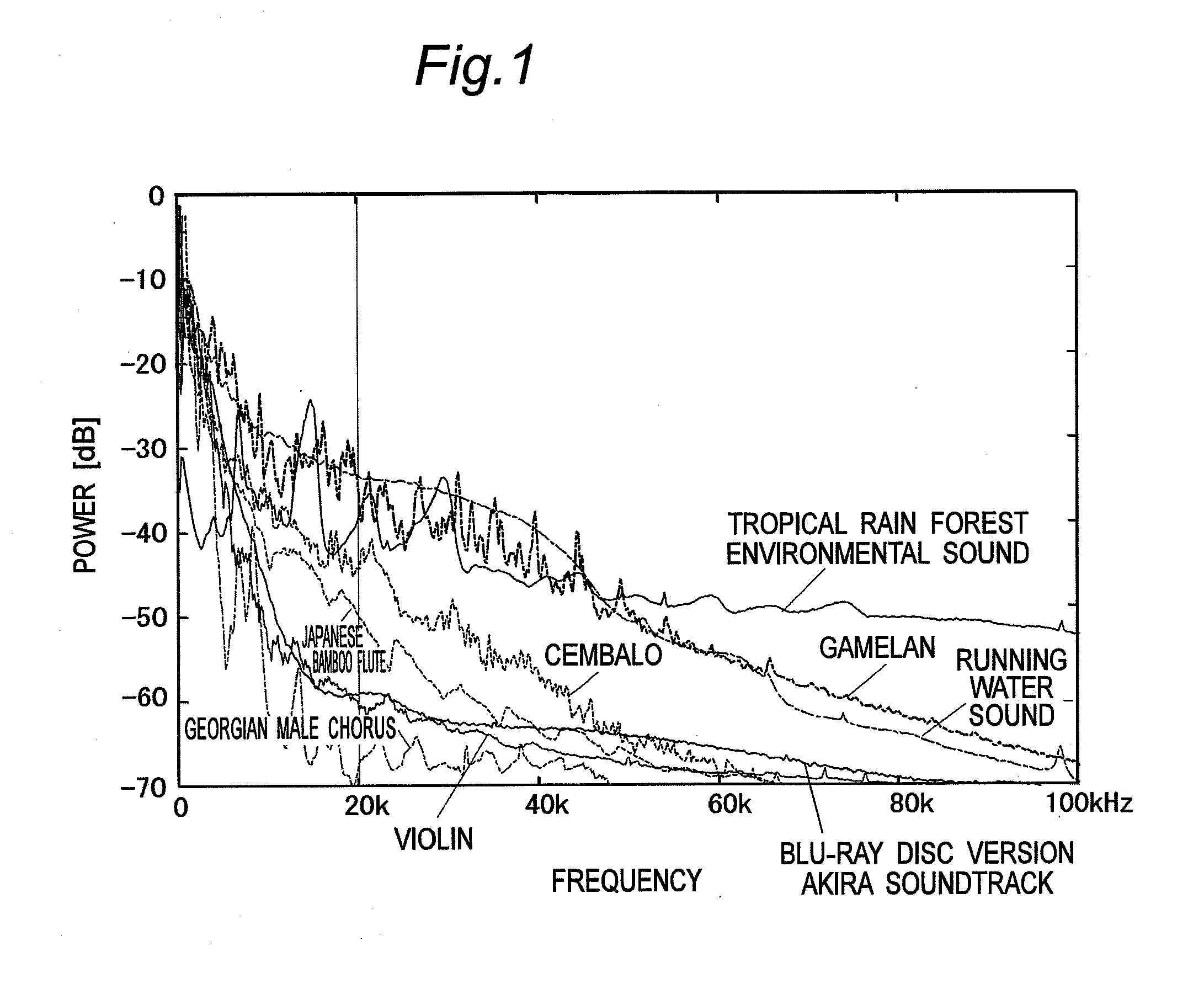
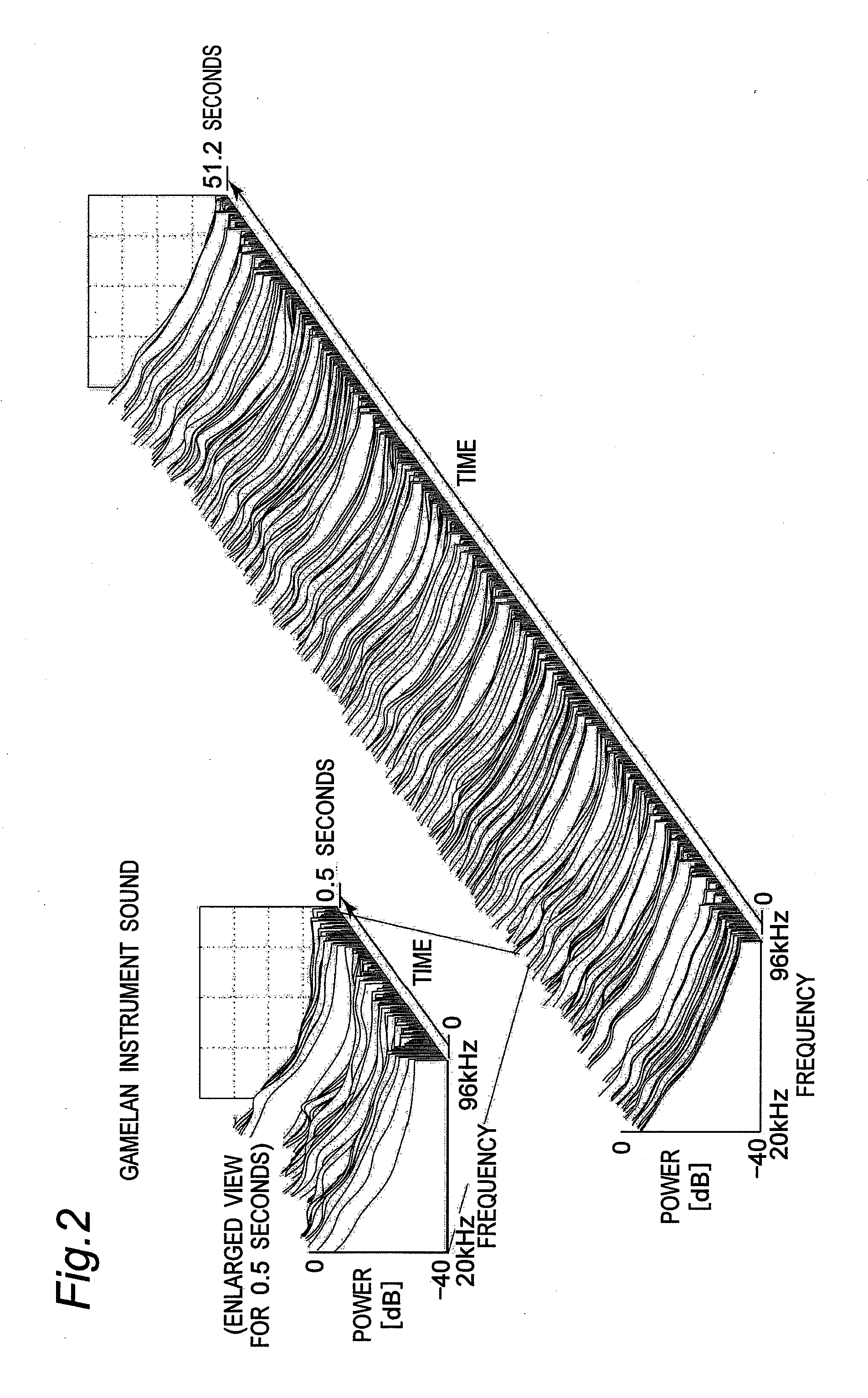
Means is provided for generating a vibration or a vibration signal, which contains audible range components that are vibration components in the audible frequency range and super-highfrequency components within a range exceeding the audible frequency range up to a predetermined maximum frequency, and which has an autocorrelation order represented by at least either one of a first property and a second property. By applying the vibration or an actual vibration generated from the vibration signal to a human being, a fundamental brain activation effect for activating the fundamental brain network system constituted of a fundamental brain including the brain stem, thalamus and hypothalamus that are regions to bear the fundamental function of the human being and the fundamental brain network of neuronal projection from the fundamental brain to various brain regions is introduced.
Owner:ACTION RES
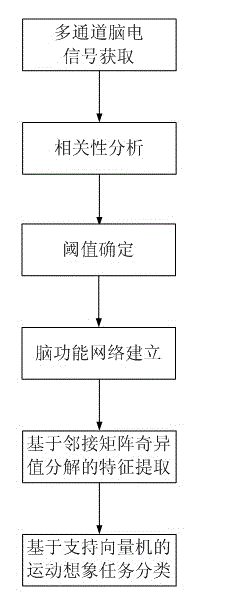
Electroencephalogram feature extracting method based on brain function network adjacent matrix decomposition
InactiveCN102722727AIgnore the relationshipIgnore coordinationCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix decompositionSingular value decomposition
The invention relates to an electroencephalogram feature extracting method based on brain function network adjacent matrix decomposition. The current motion image electroencephalogram signal feature extraction algorithm mostly focuses on partially activating the qualitative and quantitative analysis of brain areas, and ignores the interrelation of the bran areas and the overall coordination. In light of a brain function network, and on the basis of complex brain network theory based on atlas analysis, the method comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing the brain function network through a multi-channel motion image electroencephalogram signal, secondly, carrying out singular value decomposition on the network adjacent matrix, thirdly, identifying a group of feature parameters based on the singular value obtained by the decomposition for showing the feature vector of the electroencephalogram signal, and fourthly, inputting the feature vector into a classifier of a supporting vector machine to complete the classification and identification of various motion image tasks. The method has a wide application prospect in the identification of a motion image task in the field of brain-machine interfaces.
Owner:启东晟涵医疗科技有限公司
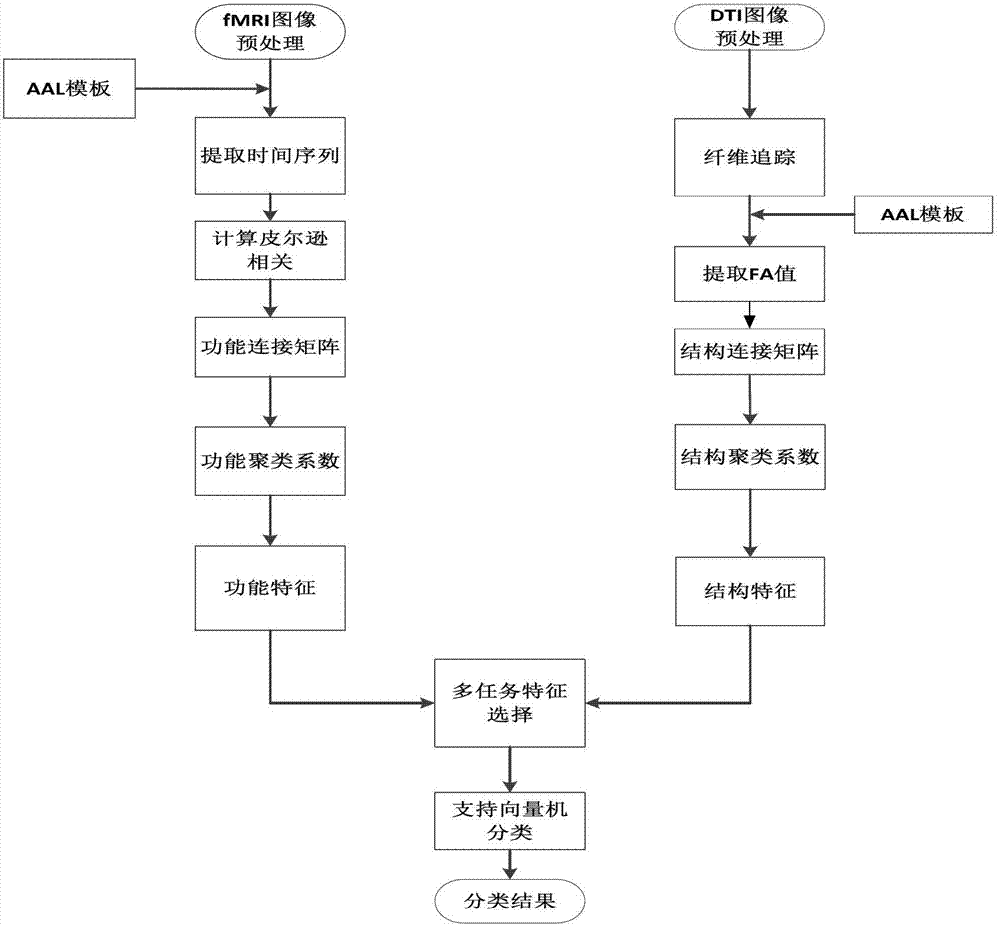
Multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on multi-task learning
InactiveCN103093087ACustomer Service RelevanceImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFiberDiagnostic Radiology Modality
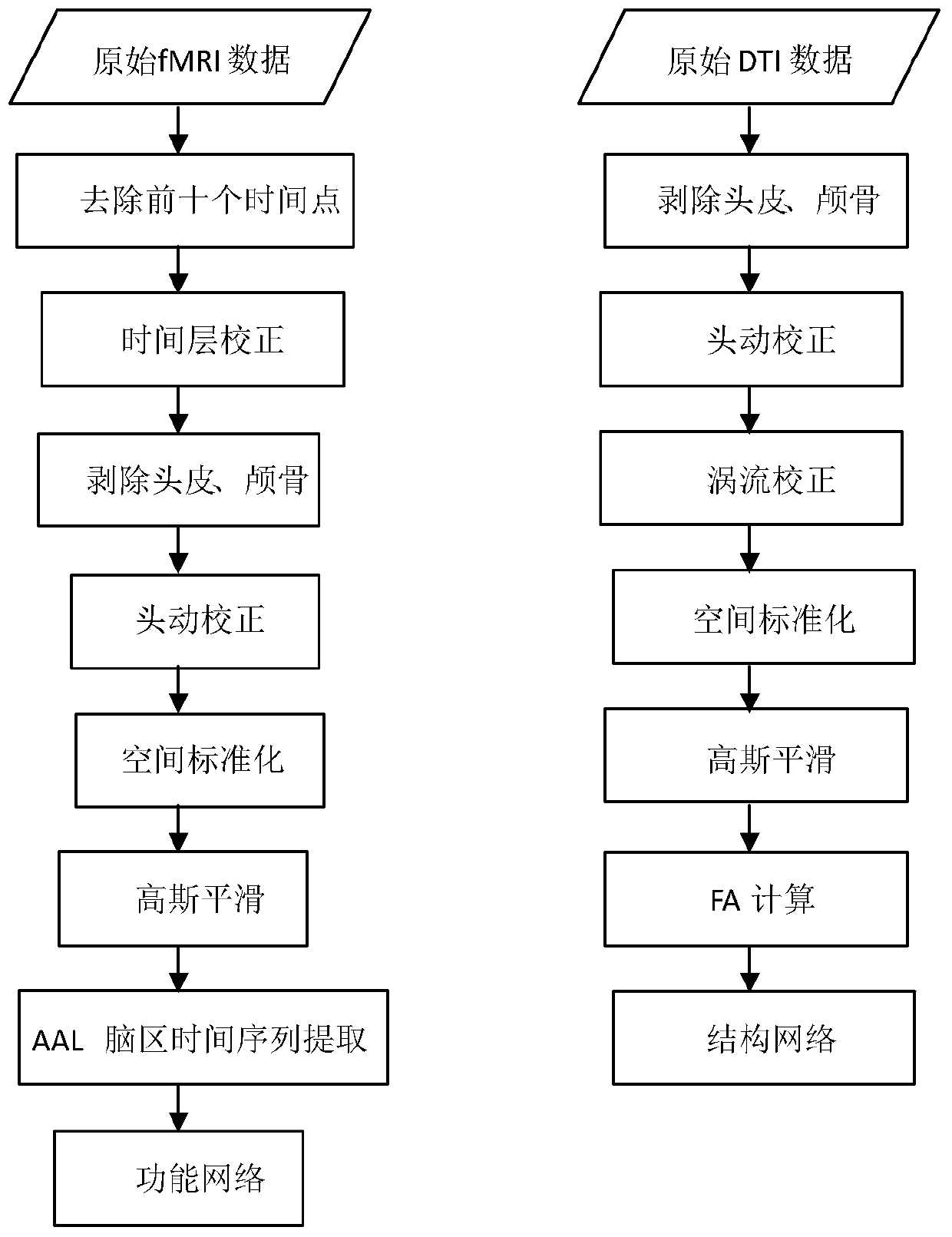
The invention discloses a multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on multi-task learning, and the multimodal brain network feature fusion method based on the multi-task learning includes the steps of preprocessing the obtained functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) images and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) images, registrating the preprocessed fMRI image to the standard AAL template, carrying out a fiber tracking for preprocessed DTI images, calculating fiber anisotropy (FA) value, and constructing structure connection matrix through the AAL template. Clustering coefficient of each brain area in a function connection matrix and the structure connection matrix is calculated to be regarded as function features and structure features. As two different tasks, the function features and the structure features assess an optimal feature set by solving the problem of multi-task learning optimization. The method uses information with multiple modalities complementing each other to learn simultaneously and to classify, improves the classification accuracy, solves the problems that a single task feature does not consider the correlation between features, and the fact that only one modality feature is used for pattern classification can bring to insufficient amount of information.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
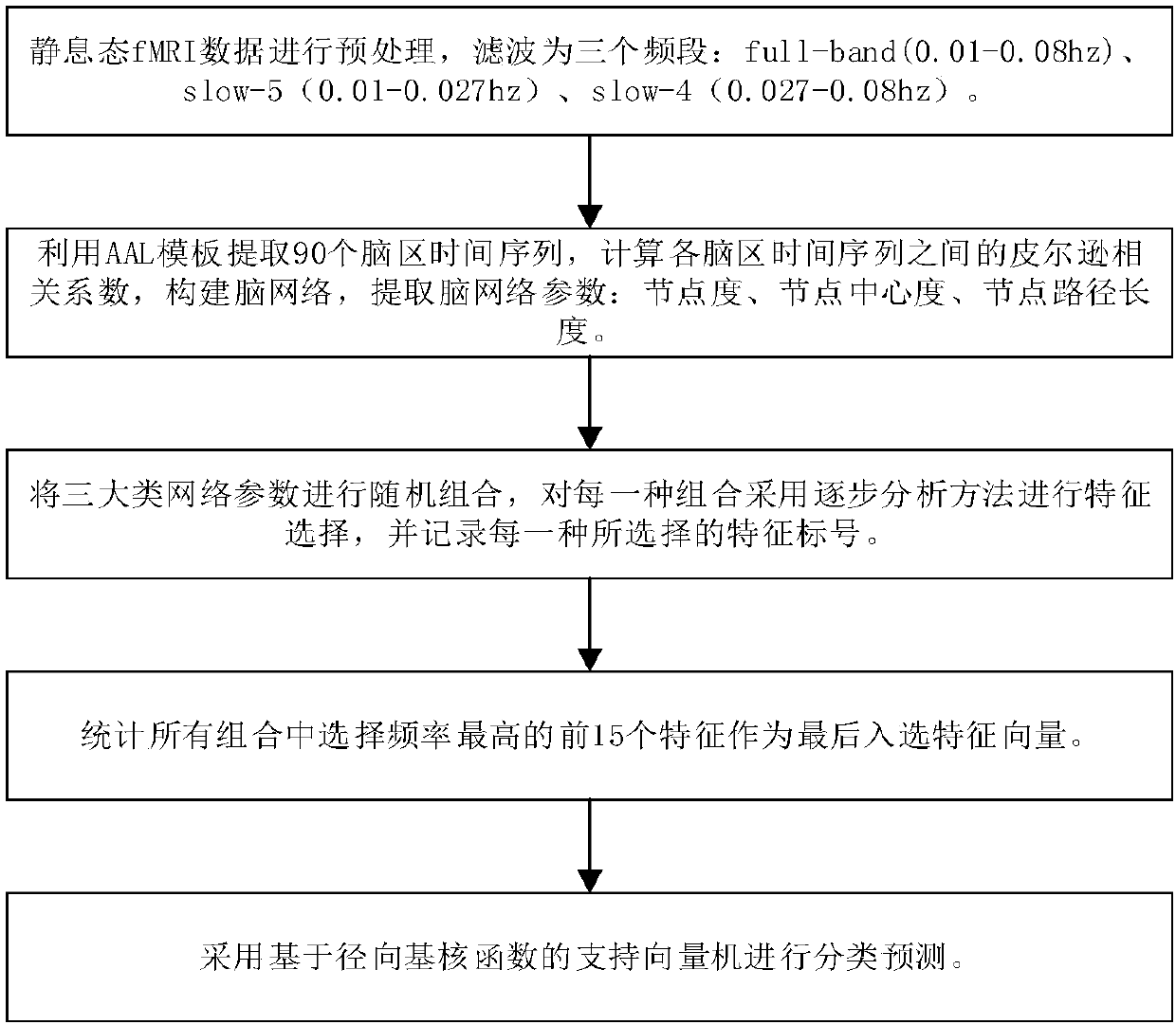
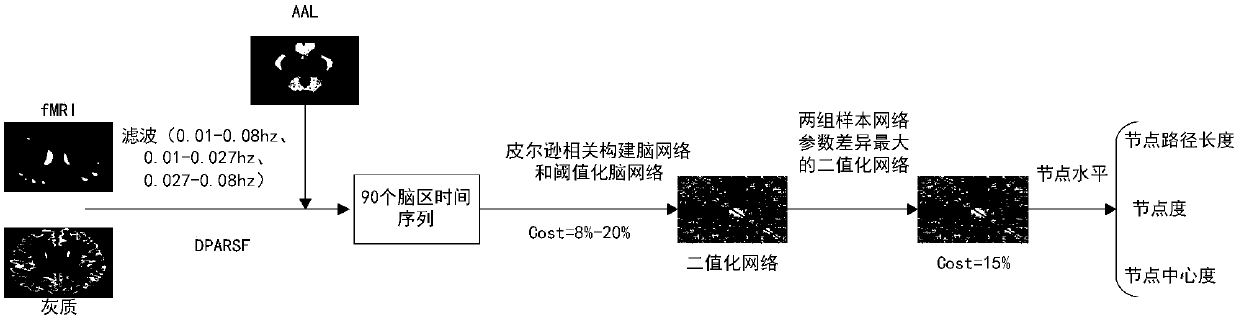
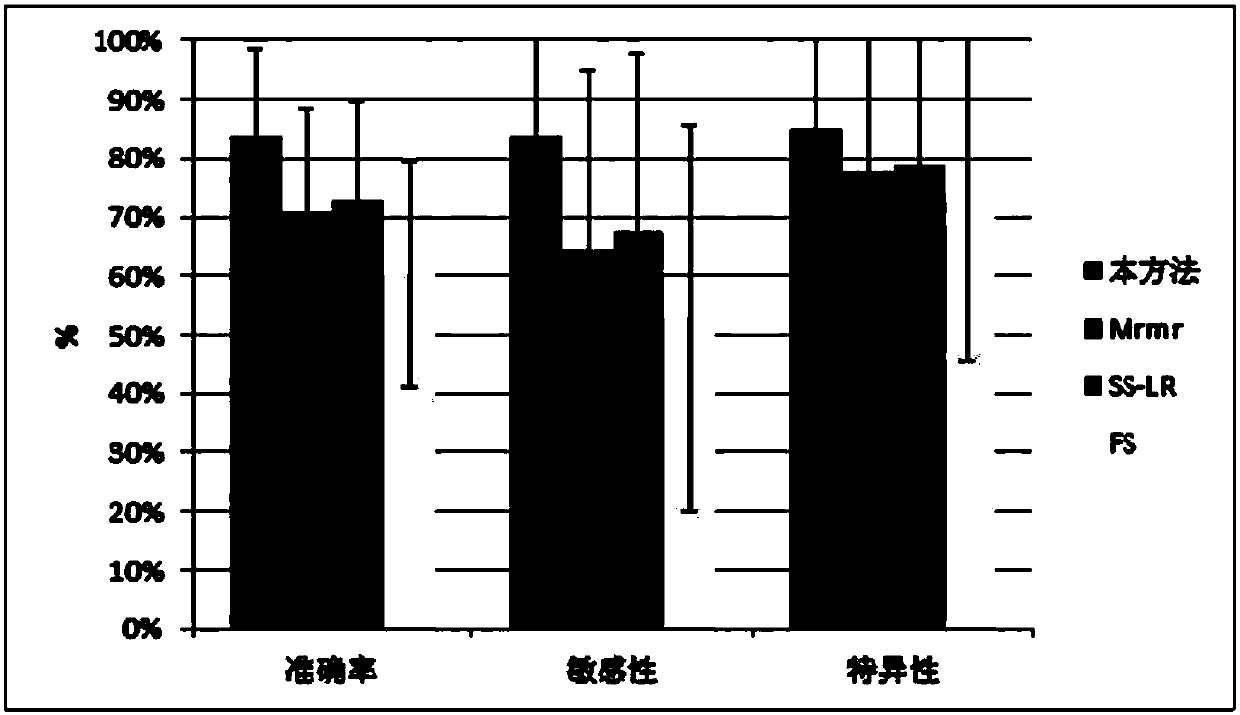
Early and late mild cognitive impairment classification method and device based on brain function network characteristics
ActiveCN107909117AImprove classification accuracyIncreased sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsCognitive disorder
The invention discloses an early and late mild cognitive impairment classification method and device based on brain function network characteristics and belongs to the medical image processing technology field. According to the method, firstly, sample data is pre-processed, multiple brain region time series are extracted, the brain function network is constructed by utilizing a correlation coefficient between the Pearson's correlation calculation brain area time series, and brain network parameters are calculated; secondly, the stepwise analysis method is utilized to extract characteristics, abinary classifier is trained, corresponding characteristic vectors are extracted from to-be-classified resting state functional magnetic resonance data and are inputted to the trained binary classifier, and the medical image classification result is acquired. Compared with a method in the prior art, the method is advantaged in that classification accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are better.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
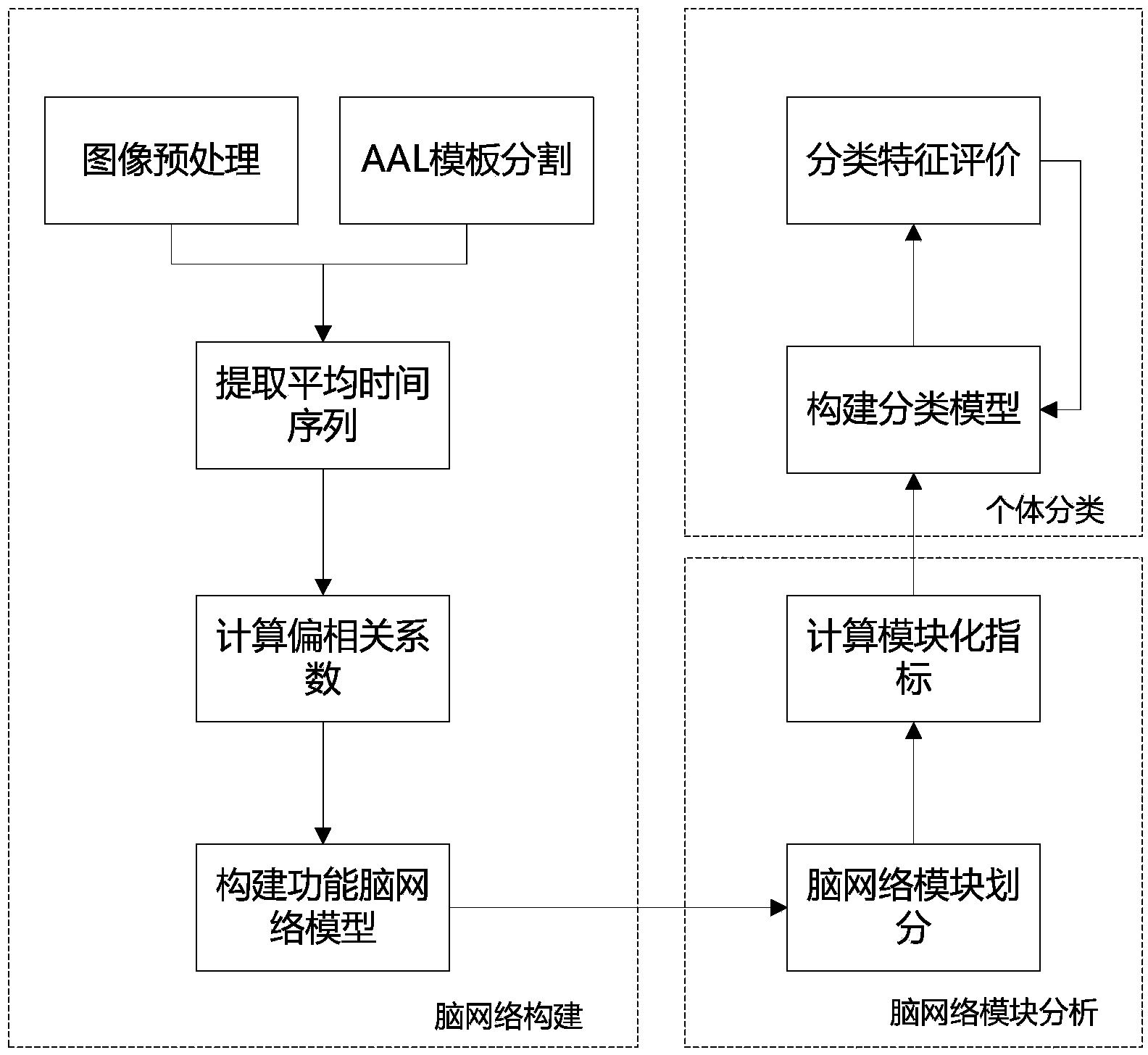
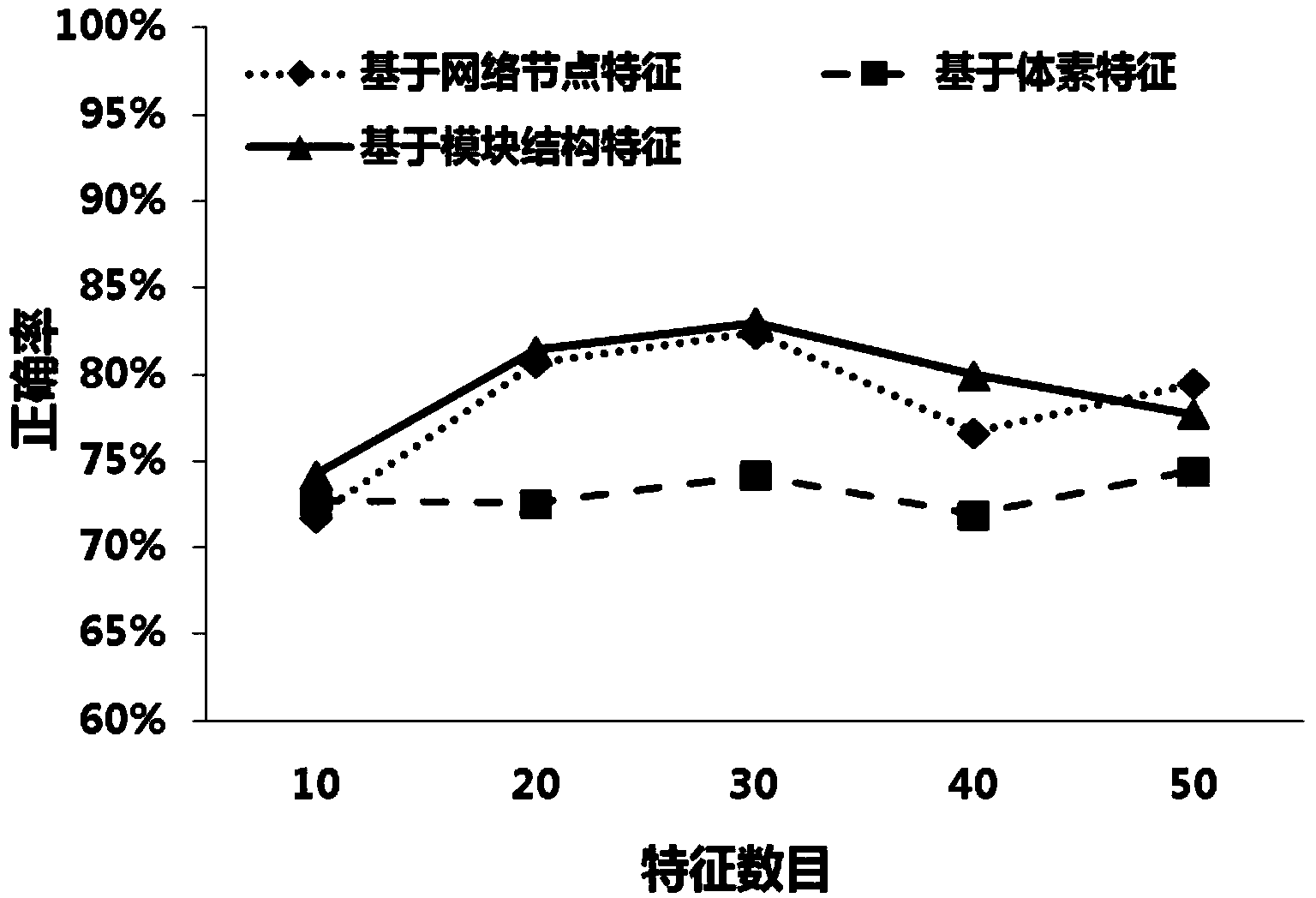
Functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on brain network modular structure characteristics
InactiveCN103886328AReflect the characteristics of the groupImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsClassification methodsBrain network
The invention discloses a functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on brain network modular structure characteristics. According to the functional magnetic resonance image data classification method based on the brain network modular structure characteristics, network local gathering characteristics are described from the perspective of a modular structure, network collectivization characteristics are reflected, the potential relation between the structure and the function in the network is reflected, the defect that according to a traditional classification method, description of brain local characteristics is poor is overcome, and data classification accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
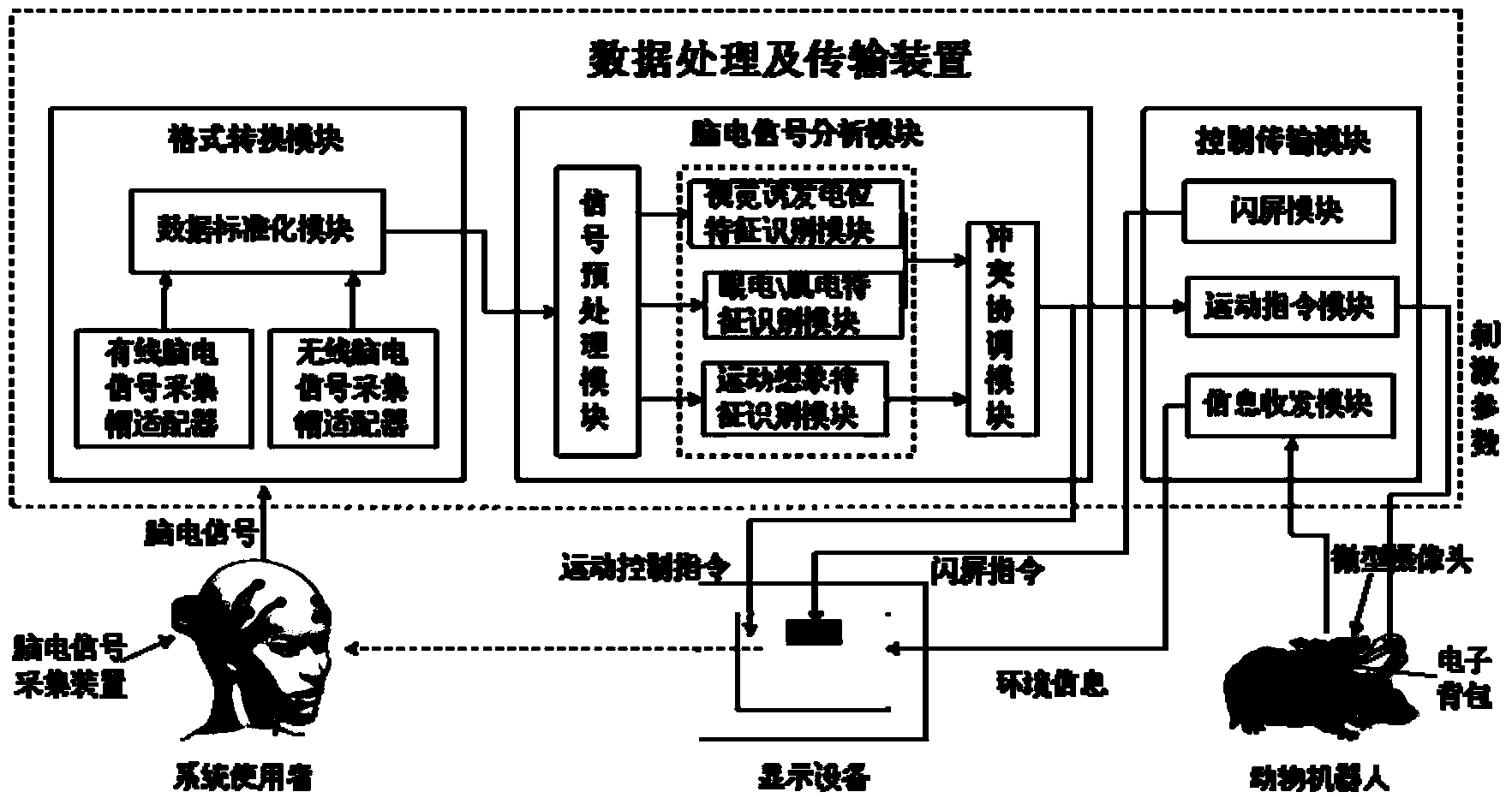
Brain-controlling animal robot system and brain-controlling method of animal robot
ActiveCN103885445AImprove real-time performanceImprove reliabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsRobotic systemsElectricity
The invention discloses a brain-controlling animal robot system and a brain-controlling method of an animal robot. A corresponding control instruction is generated by collecting brain electrical signals of the brain and processing the brain electrical signals, the corresponding control instruction is used for controlling the animal robot to move, and a brain-to-brain normal form of two mixed modes can effectively control the brain-to-brain animal robot. The brain-controlling animal robot system and the brain-controlling method of the animal robot adopt two control modes, namely the mixed control mode based on ocular electricity / myoelectricity characteristics and motion imagery characteristics of the brain electrical signals and the mixed control mode based on visual evoked potential characteristics and the motion imagery characteristics, select a proper control mode according to the state of a user, and largely improve the real-time performance and reliability of control. The brain-controlling animal robot system can be applied to the fields of unknown environment exploration, brain function mechanism research, brain-to-brain network communication, life assistance and entertainment for the disabled and the like.
Owner:浙江浙大西投脑机智能科技有限公司
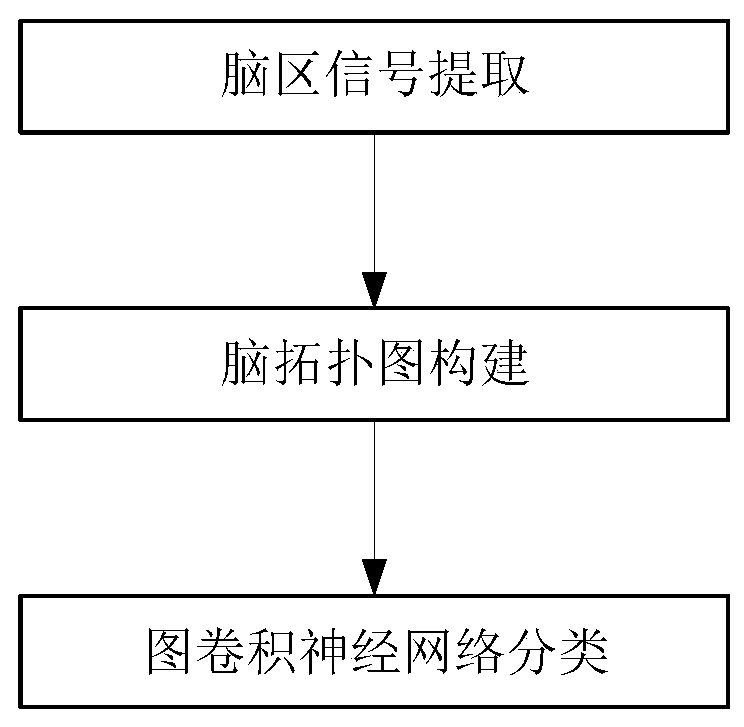
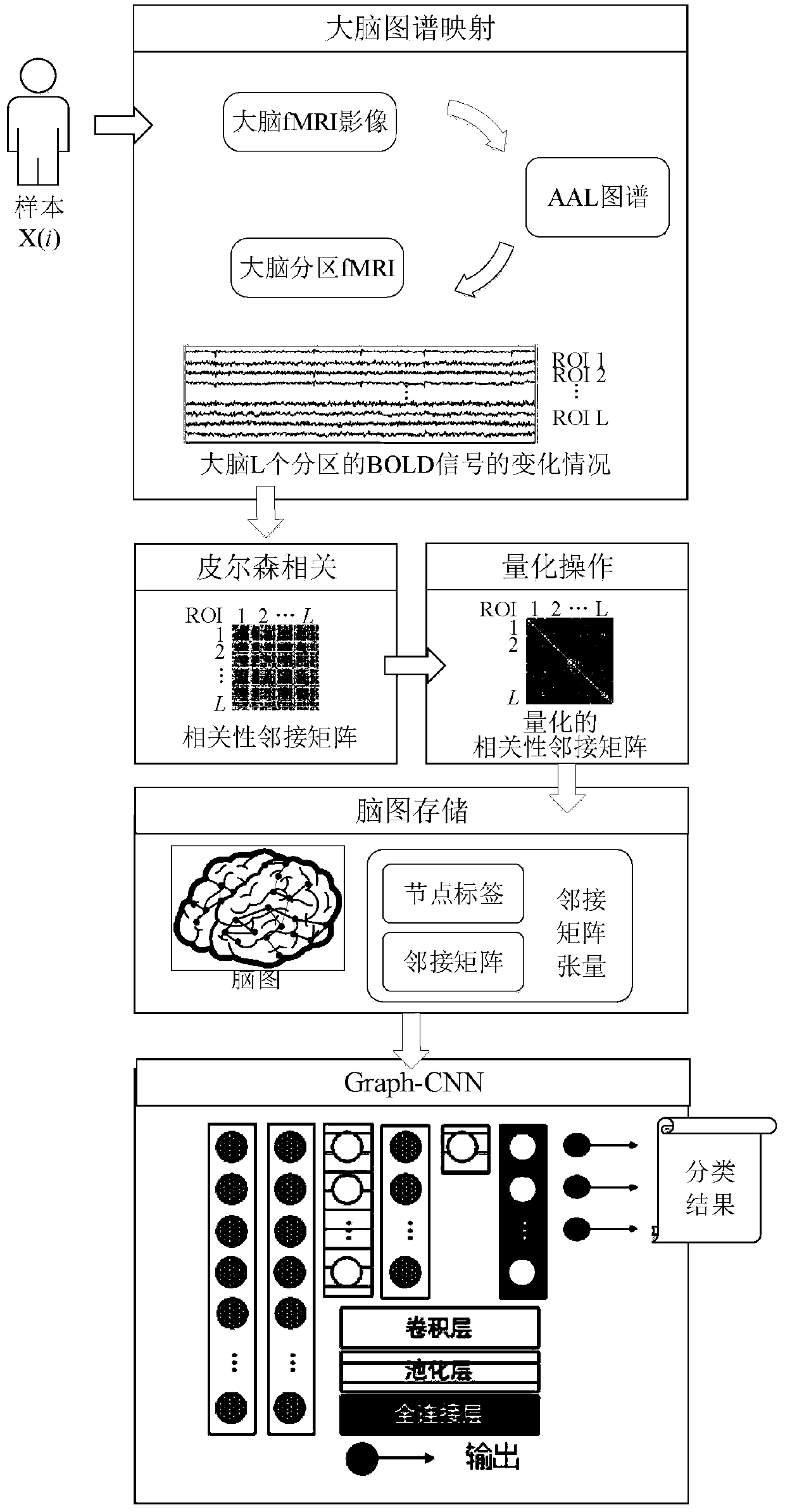
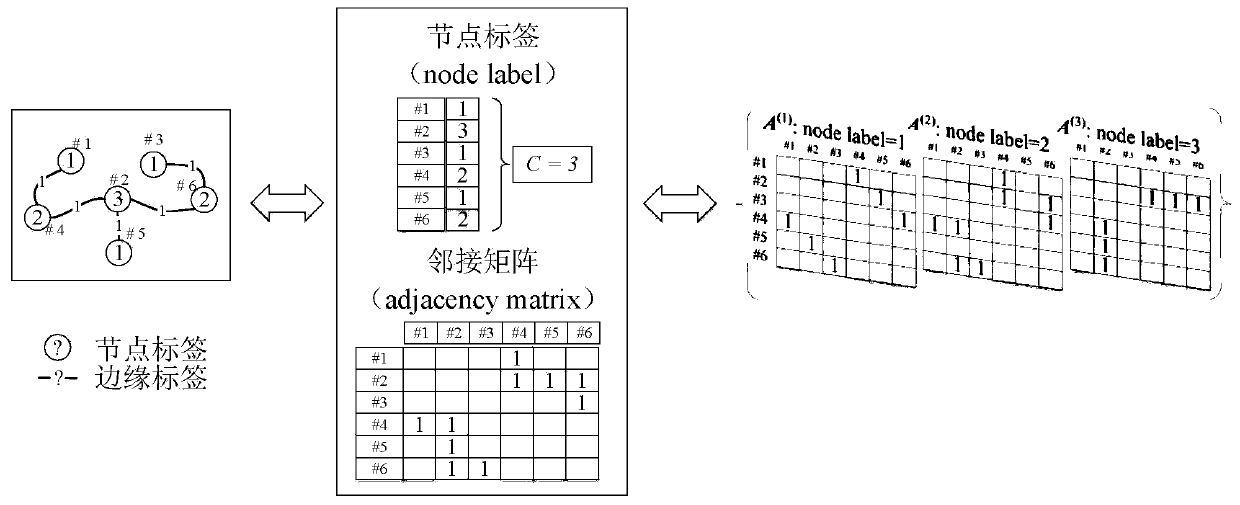
Brain network classification method based on graph convolutional neural network
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
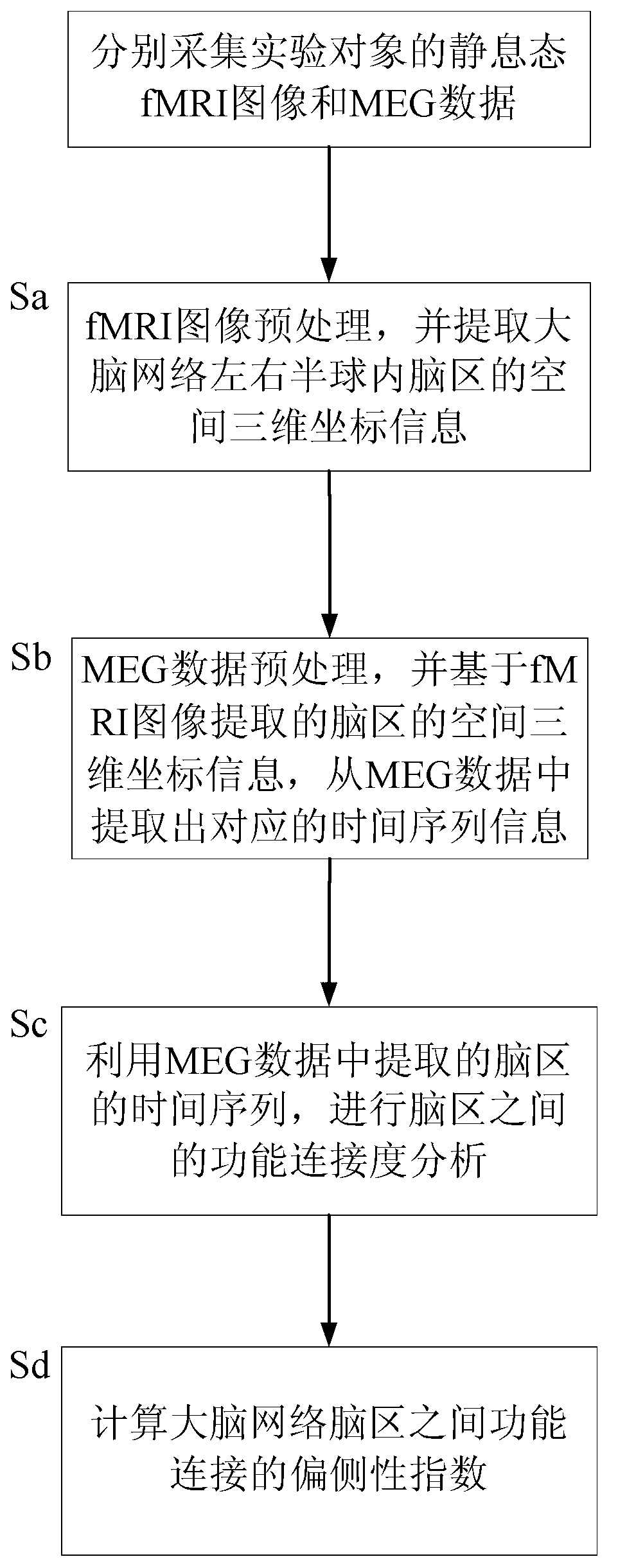
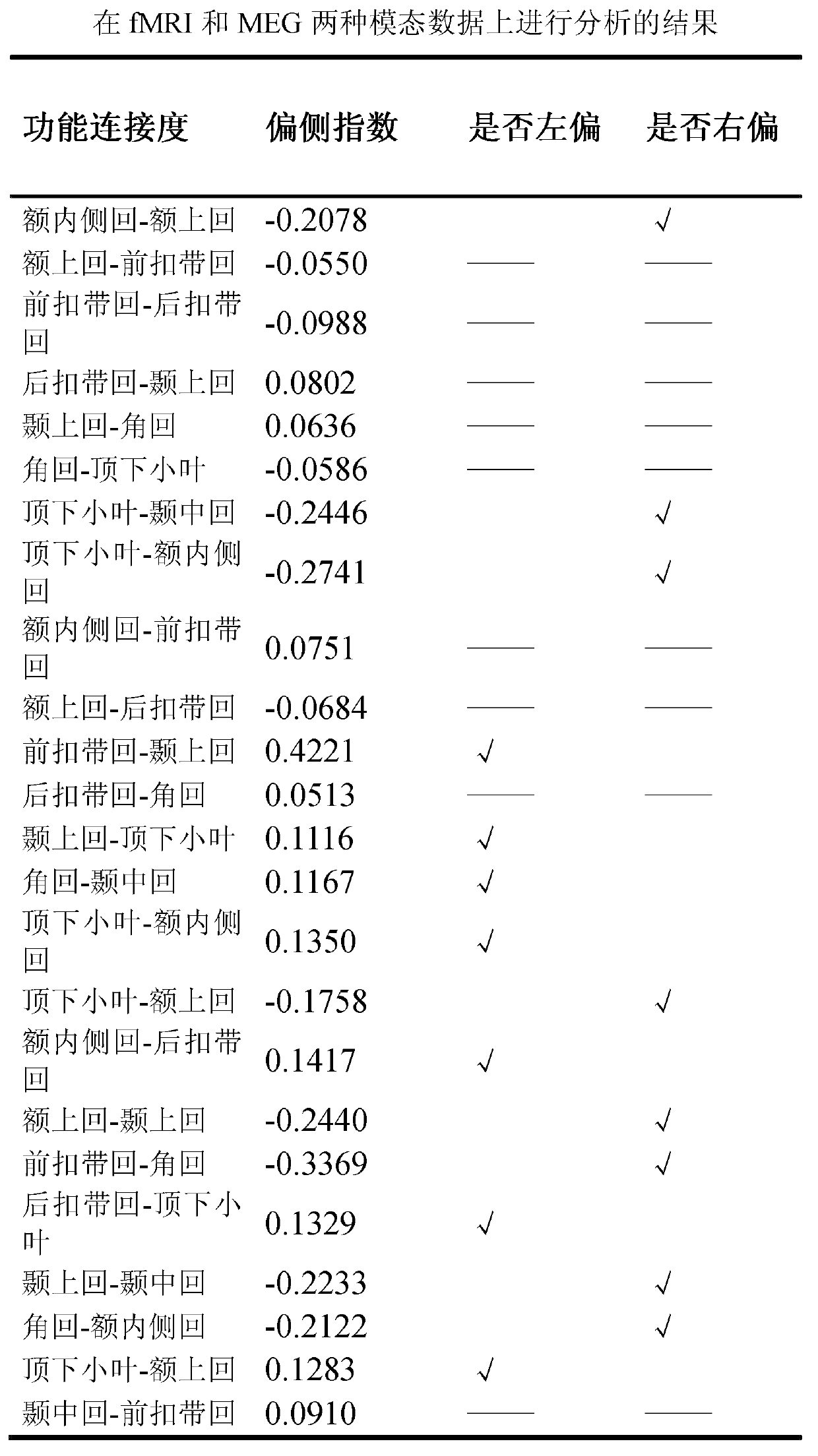
Method for detecting brain network function connectivity lateralization based on modality fusion
ActiveCN103345749ALaterality detectionImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFunctional connectivity
The invention relates to a method for detecting brain network function connectivity lateralization based on modality fusion. The method includes the steps that first, pretreatment is conducted on an fMRI image, and three-dimensional space coordinate information of brain areas inside a left hemisphere and a right hemisphere of a brain network is extracted; then, corresponding time series information is extracted from pretreated MEG data based on the three-dimensional space coordinate information of the brain areas extracted through the fMRI image; afterwards, the time series of the brain areas extracted from the MEG data can be used for analyzing the function connectivity between the brain areas; ultimately, the lateralization index of the function connectivity between the brain areas of the brain network is calculated. The method is an effective method for detecting the brain network function connectivity lateralization based on magnetic resonance and magnetoencephalogram modality fusion, and the method can detect the brain network function connectivity lateralization more completely and comprehensively compared with a traditional detection method which only uses the fMRI image.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
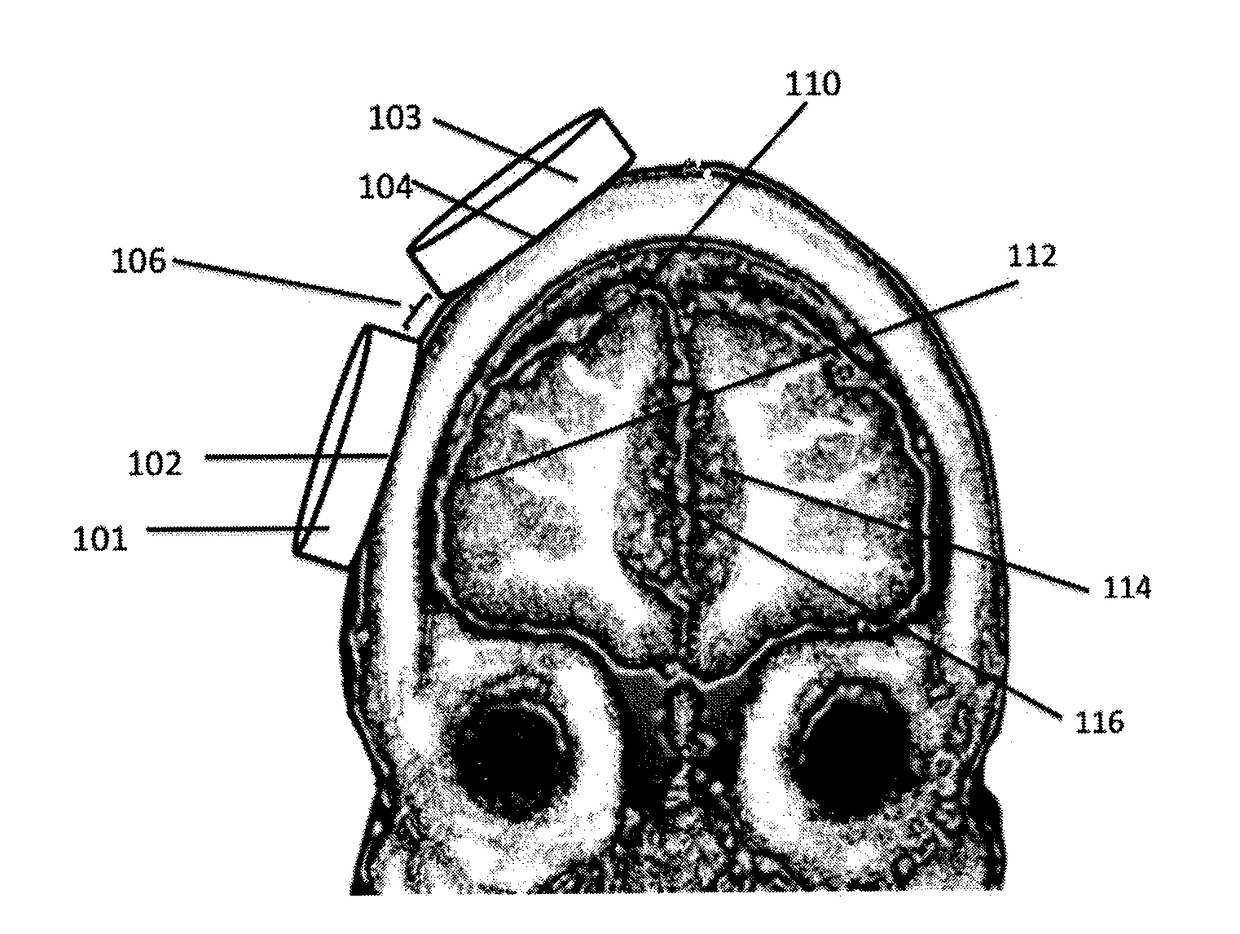
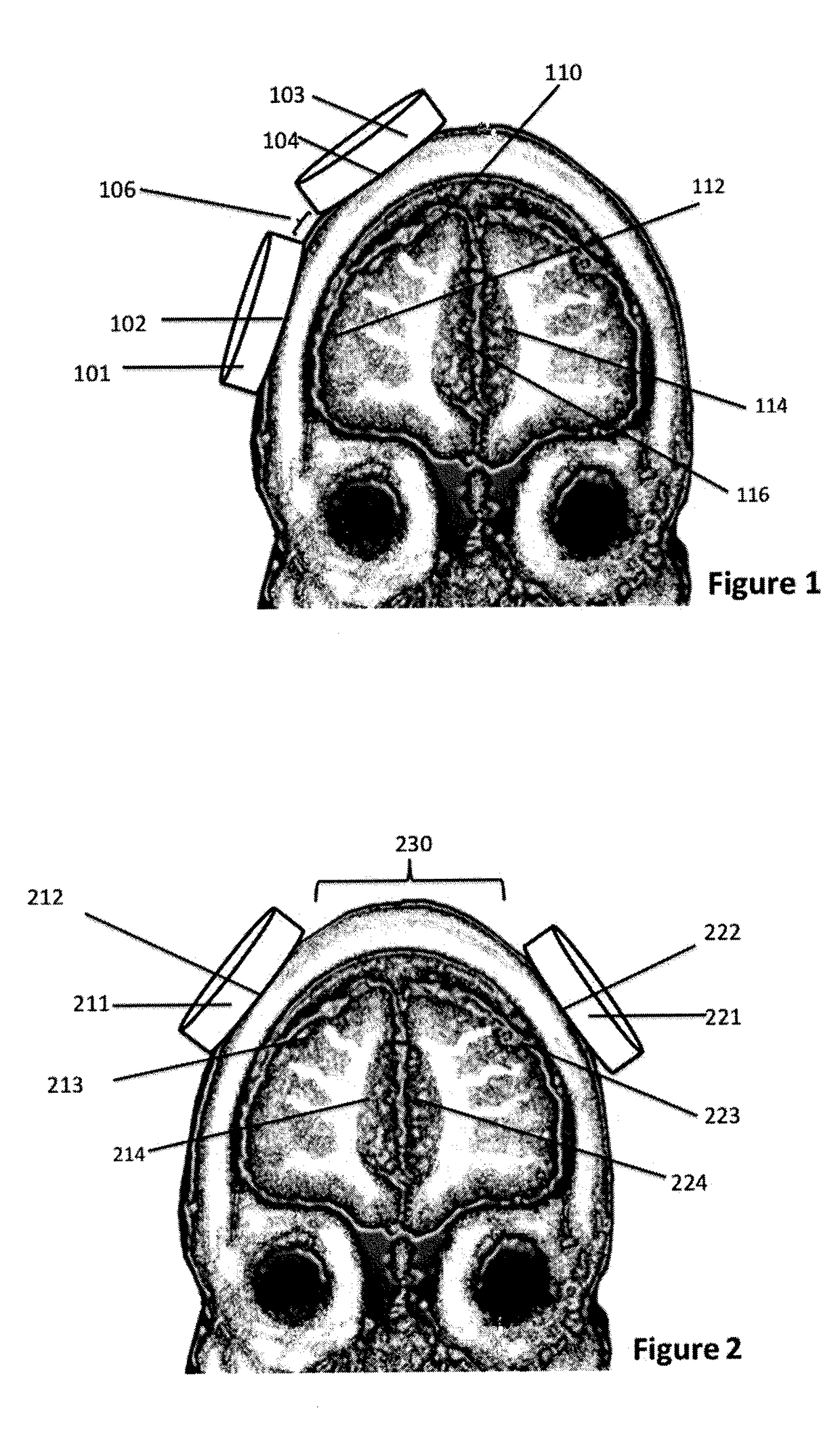
Control of spike-timing dependent brain network plasticity via multi-coil transcranial magnetic stimulation
InactiveUS20170106203A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNetwork connectionMedicine
Brain stimulation methods and devices in which at least two separate magnetic pulse sources with interposed space between them are placed over two distinct brain regions. The coils are pulsed at between 1 and 100 milliseconds apart (e.g., between 5 ms and 40 ms), thereby producing neuroplastic effects upon a third brain region that is network-connected to said first and second regions.
Owner:BRAINSWAY
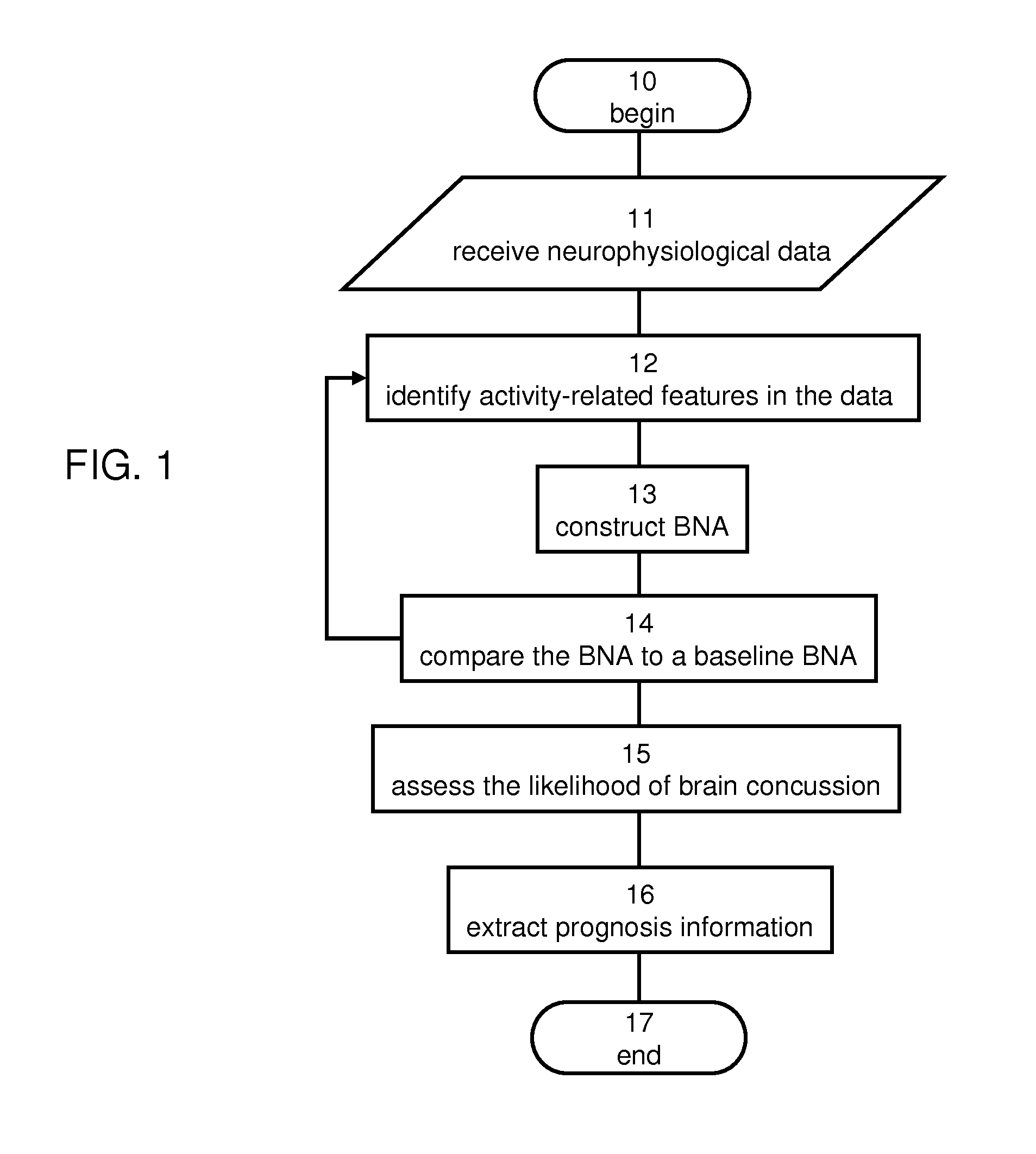
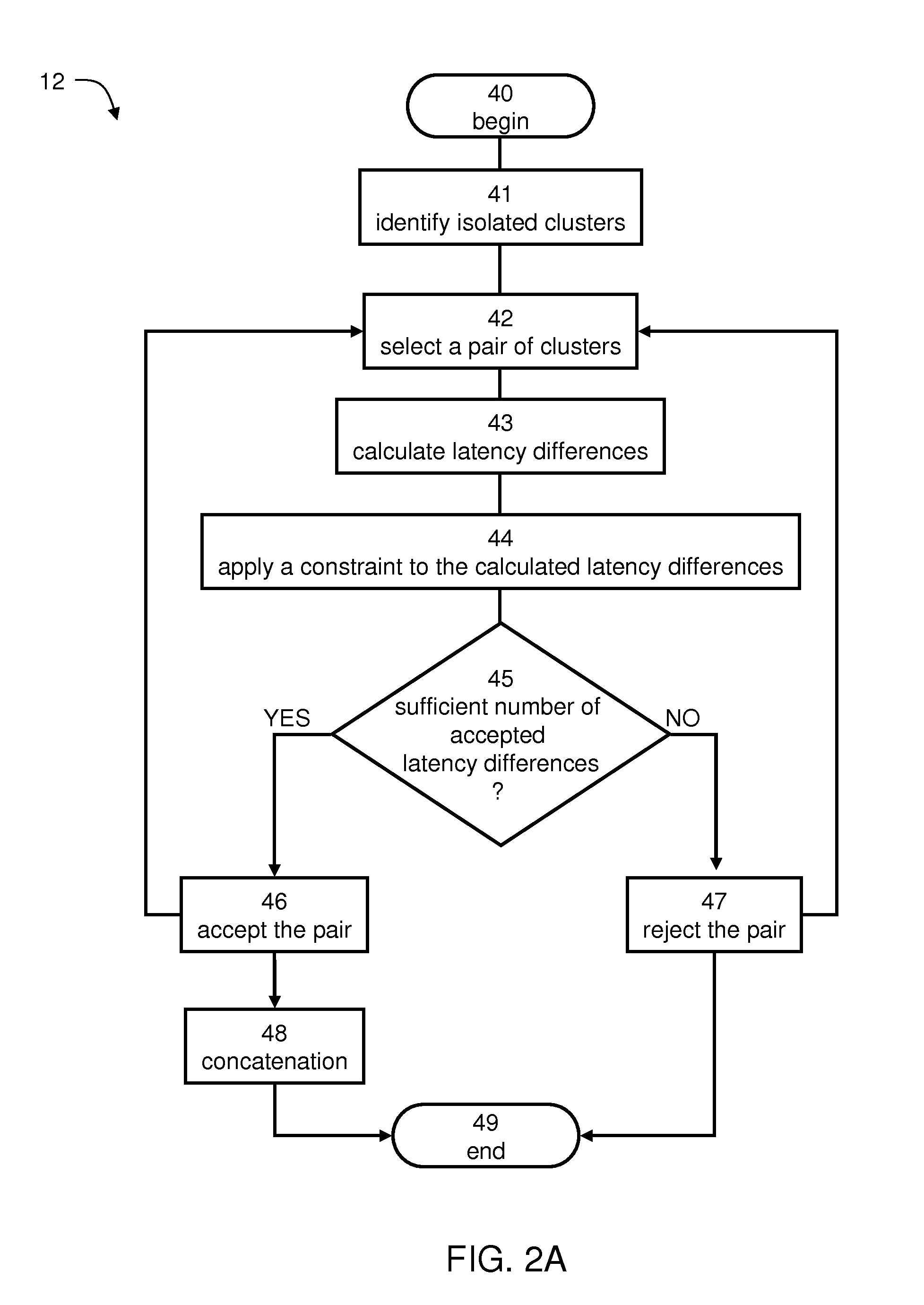
Method and system for estimating brain concussion
A method of estimating the likelihood of brain concussion from neurophysiological data acquired from the brain of the subject is disclosed. The method comprises: identifying activity-related features in the data; constructing a subject-specific brain network activity (BNA) pattern having a plurality of nodes, wherein each node represents a feature of the activity-related features, and each pair of nodes is assigned with a connectivity weight; calculating a BNA pattern similarity describing a comparison between the constructed BNA pattern and a baseline BNA pattern being specific to the subject; and assessing the likelihood of brain concussion responsively to the BNA pattern similarity.
Owner:ELMINDA LTD
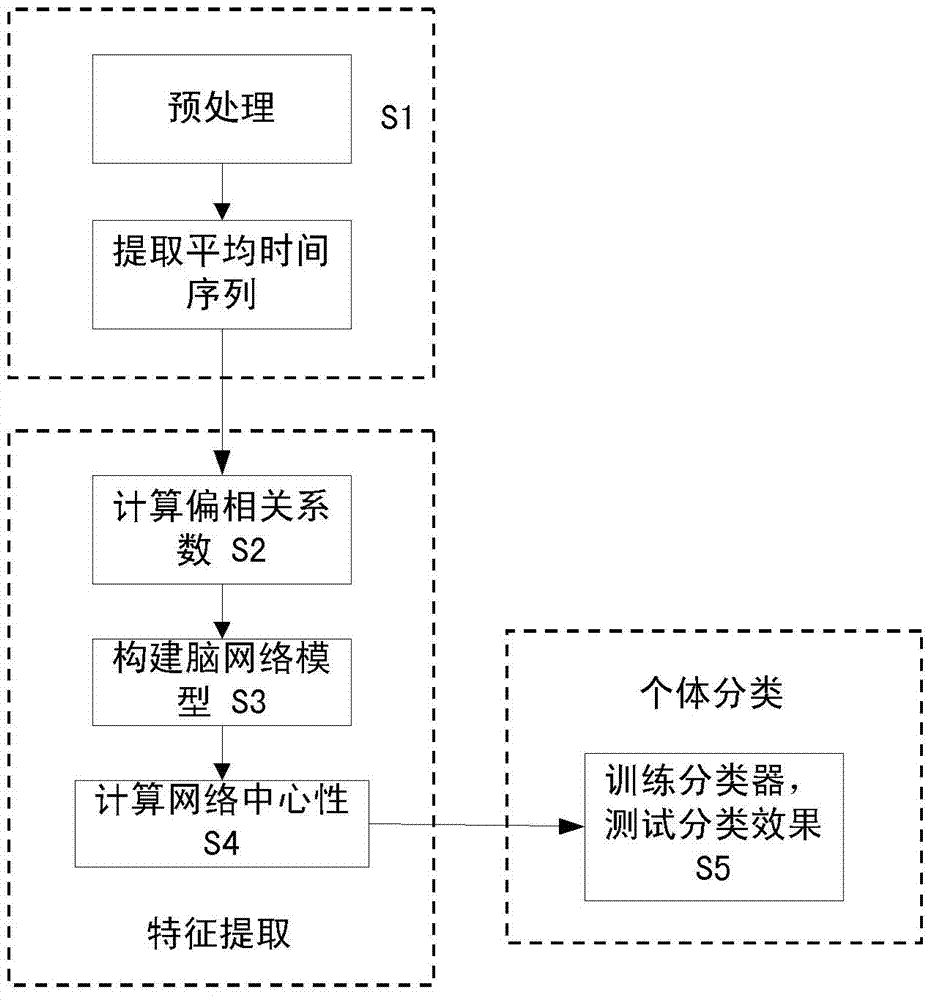
Brain function magnetic resonance image classification method based on network centrality
ActiveCN102855491AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpearman's rank correlation coefficientCorrelation coefficient
The invention discloses a brain function magnetic resonance image classification method based on network centrality. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing a brain function magnetic resonance image, performing brain region segmentation, and extracting an average time sequence of each brain region; calculating a partial correlation coefficient between each average time sequence, and obtaining a partial correlation coefficient matrix; performing binarization on the partial correlation coefficient matrix to obtain a brain network model; calculating the network centrality of each node in the network; and classifying the brain function magnetic resonance image by utilizing an adaptive improvement classifier, and checking the adaptive improvement classifier by employing a leave-one-out cross validation testing method. The brain function network is established by utilizing the brain function magnetic resonance image, the brain function magnetic resonance image is classified by utilizing the network topology information, and the brain function magnetic resonance image can be accurately classified.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for combining anatomical connectivity patterns and navigated brain stimulation
InactiveUS20130178693A1Complete and realistic viewImprove accuracyMedical imagingElectrotherapyMedicineDiagnostic information
When operating a brain stimulation device, it is critical to understand and control the network effects associated with the area being targeted for stimulation. The combined system and methods provided herein provides the operator with a real-time view of the brain network potentially affected by the stimulation. The system and method are capable of increasing the accuracy of diagnostic information. Additionally, disclosed herein are a system and method for combining navigated brain stimulation data and anatomical data with brain connectivity data for an individual.
Owner:NEXSTIM
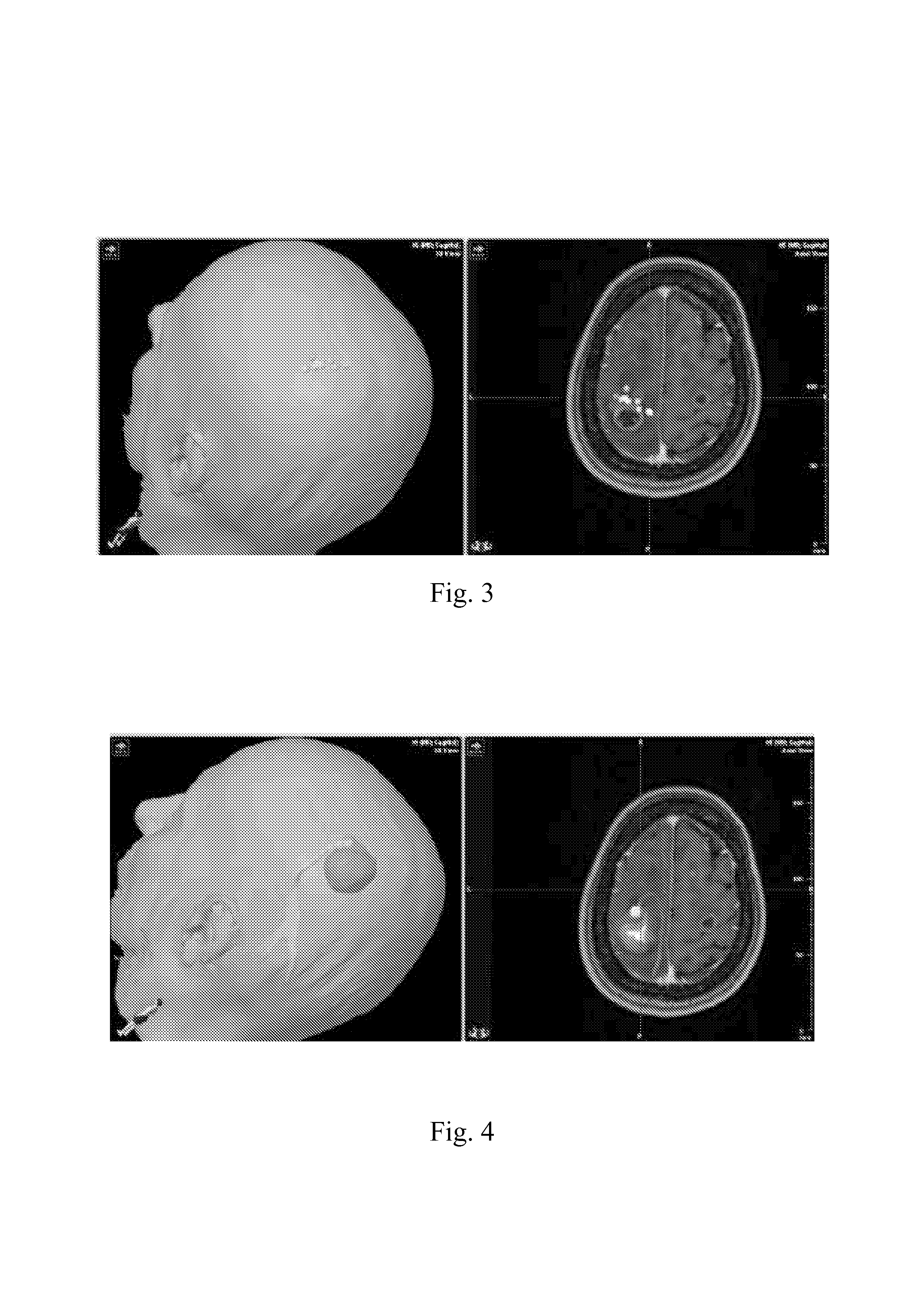
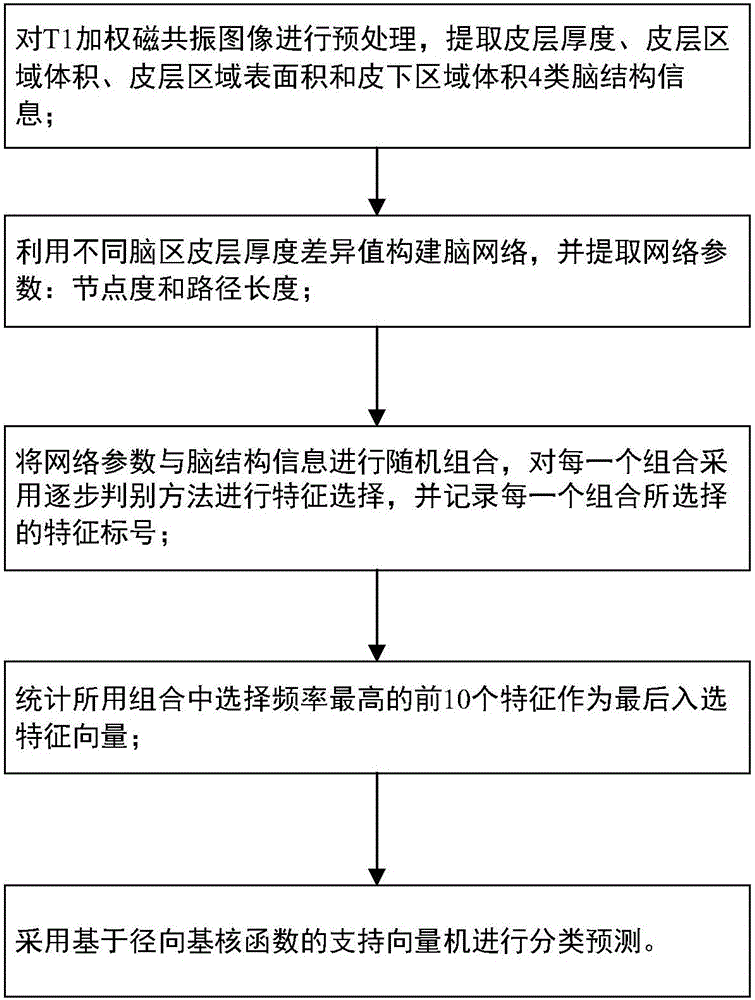
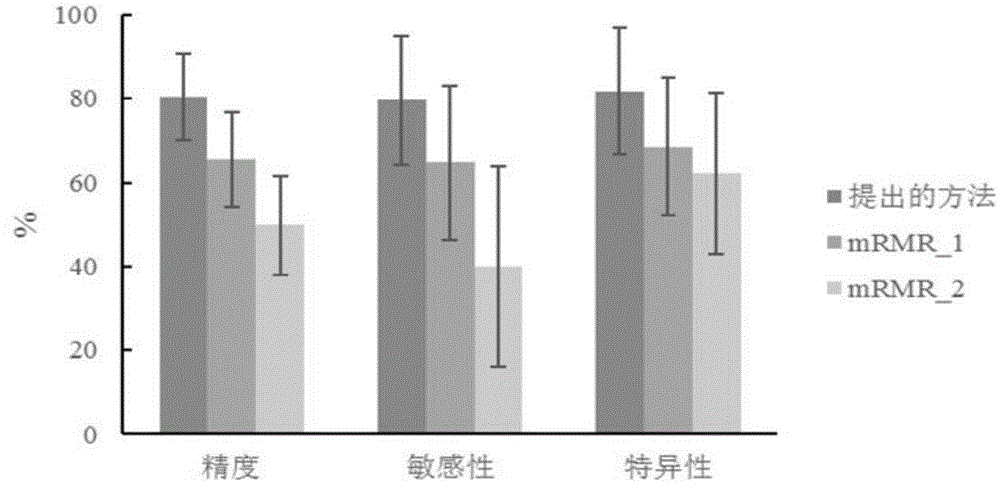
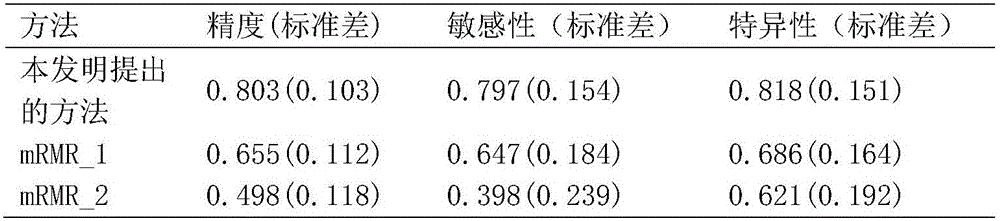
Mild cognitive impairment disease classifying method based on brain network and brain structure information
InactiveCN105726026AQuick and efficient selectionIncreased sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSupport vector machineClassification methods
The invention discloses a mild cognitive impairment disease classifying method based on a brain network and brain structure information, and belongs to the field of medical image disease classification. The method includes the steps that individual cortex characteristics are calculated first, and difference between individual cortices is calculated with a specific kernel function to construct the structural brain network; any number of parameter types are selected from network characteristics and original MRI data to be combined, characteristics are selected from each combined datum through a stepwise judgment method, and the top ten characteristics appearing the most frequently are used as classification characteristics; a support vector machine based on a radial basis function is adopted for classification. The interference on characteristic selection by different combining modes of the cortex characteristics and network characteristics is fully considered, and robustness and stationarity of characteristic selection are ensured. The characteristics with high sensitivity can be selected fast and effectively, and classification precision is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Vibration generating apparatus and method introducing hypersonic effect to activate fundamental brain network and heighten aesthetic sensibility
ActiveUS8167826B2Inhibit deteriorationImprove securityPublic address systemsChiropractic devicesThalamusBase function
Owner:ACTION RES
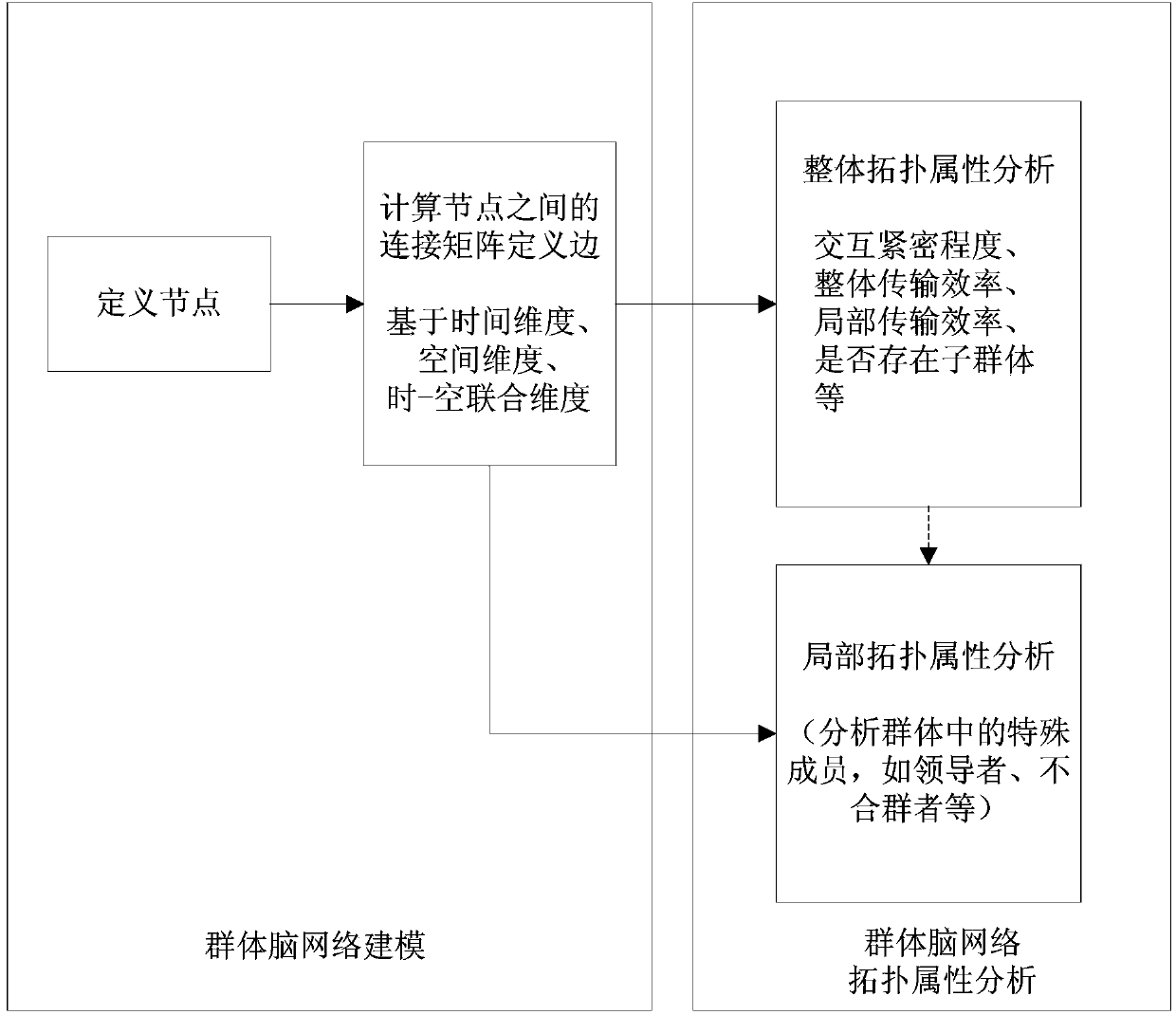
Modeling method and topological attribute analytical method for group brain network
ActiveCN104050394ABiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALModel method
The invention provides a modeling method for a group brain network. The modeling method comprises the following steps that (1), nodes of the group brain network are defined according to group brain imaging data; (2), connecting matrixes between the different nodes are calculated according to the nodes defined in the step (1) and adopted as edges; (3), a group brain network model is constructed according to the nodes defined in the step (1) and the edges defined in the step (2). Meanwhile, the invention provides a topological attribute analytical method for the group brain network. The topological attribute analytical method is achieved based on the modeling method for the group brain network. According to the modeling method and topological attribute analytical method for the group brain network, the interactive mode features of a studied group can be judged, and whether key members exist in the group or not is further analyzed. Therefore, group behaviors can be predicated by utilizing a group neural activity mode result.
Owner:北京超级袋鼠智能科技有限公司
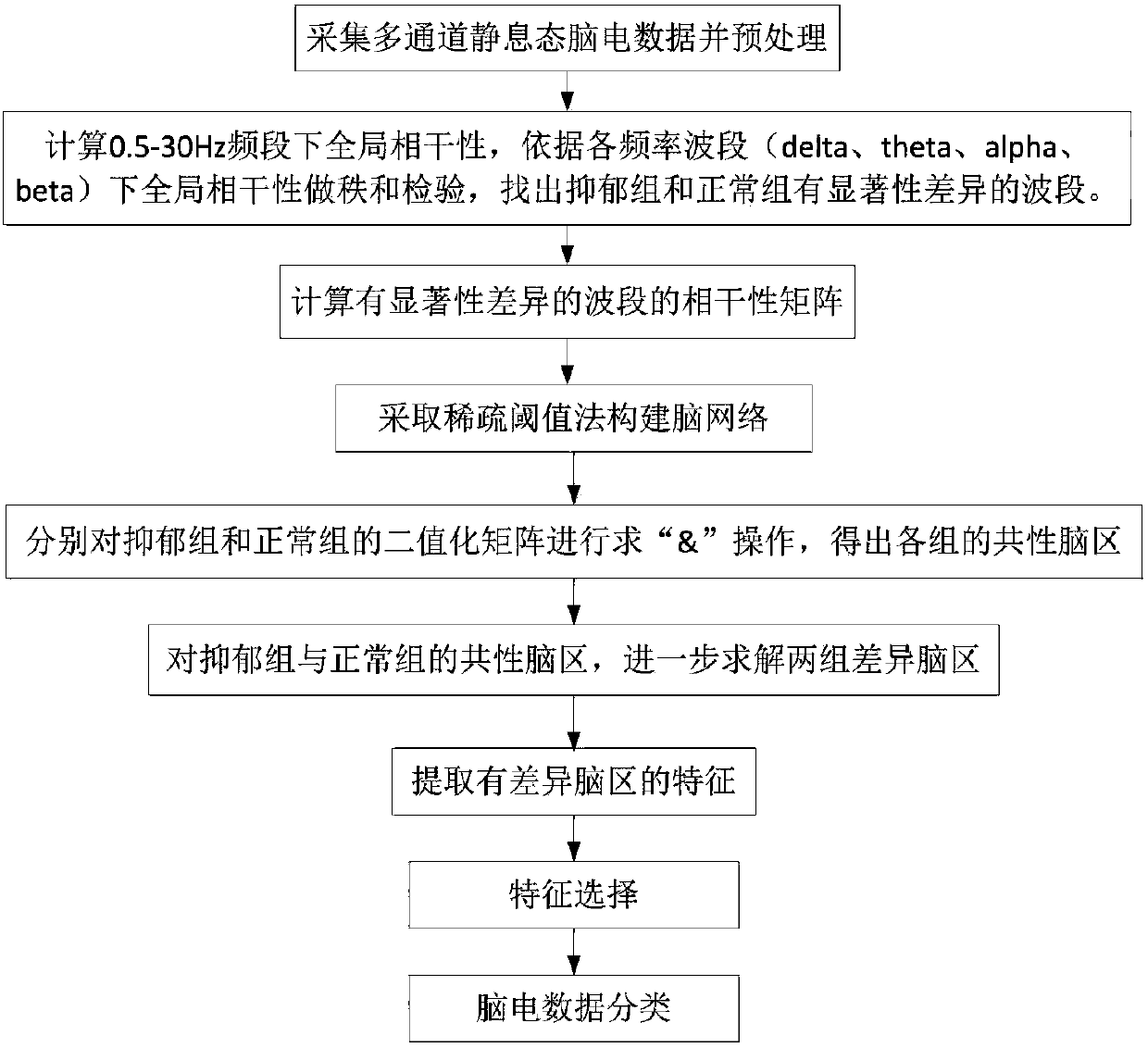
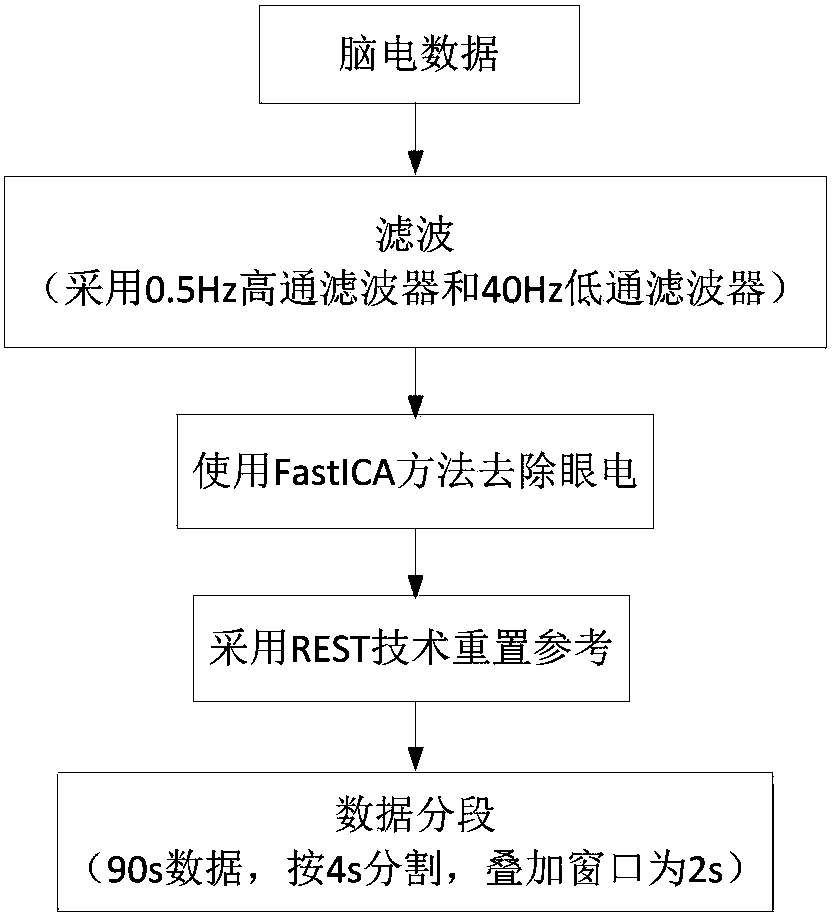
Depression recognition and analysis system based on resting state brain network
ActiveCN108427929ARealize Auxiliary DiagnosisRealize analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSensorsFunctional connectivityPersonalization
The invention provides a depression recognition and analysis system based on a resting state brain network. The depression recognition and analysis system comprises (a) a resting state electroencephalogram data acquisition and preprocessing module used for collecting resting state electroencephalogram data of subjects and preprocessing the collected resting state electroencephalogram data, (b) a brain network metric extraction module used for constructing a personalized brain network structure, respectively finding out common active brain regions of a depression group and a normal control group from the personalized brain network structure, finding out different brain regions based on the common active brain regions of the two groups and extracting brain network metrics, and (c) a classification recognition module used for conducting feature selection on the extracted brain network metrics and functional connection features and classifying the data of which features are already screened to achieve recognition of depression patients and normal subjects. The depression recognition and analysis system has the advantages that feature dimension is effectively reduced, calculation efficiency is improved, and depression recognition can be effectively achieved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
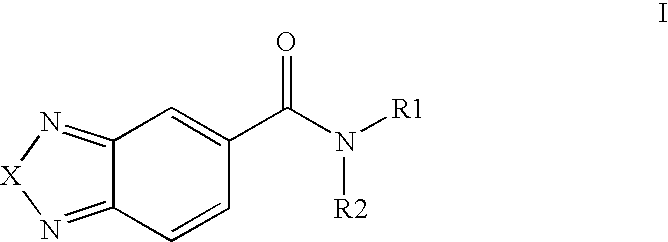
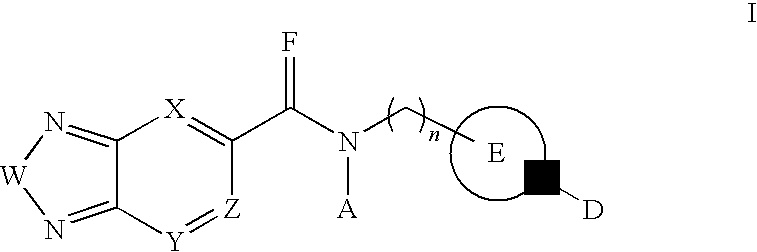
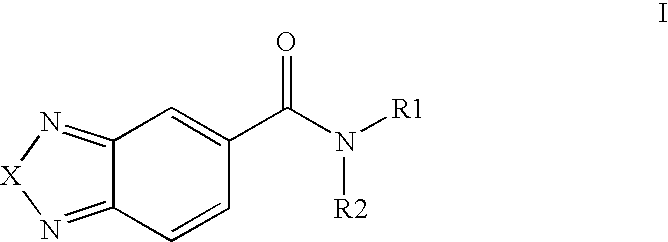
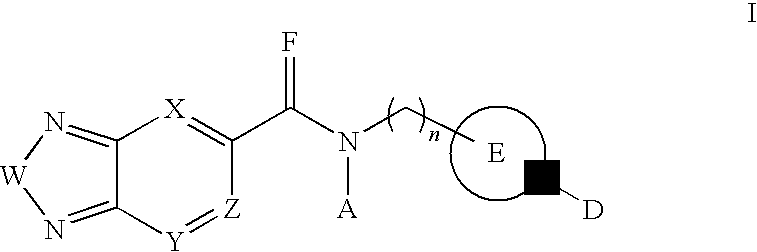
3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses
InactiveUS20100041647A1Improve responseFunction increaseBiocideNervous disorderMedicineBrain network
This invention relates to the prevention and treatment of cerebral insufficiency, including enhancement of receptor functioning in synapses in brain networks responsible for higher order behaviors. These brain networks are involved in cognitive abilities related to memory impairment, such as is observed in a variety of dementias and in imbalances in neuronal activity between different brain regions, as is suggested in disorders such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia and affective disorders. In a particular aspect, the present invention relates to compounds useful for treatment of such conditions, and methods of using these compounds for such treatment.
Owner:CORTEX PHARMA
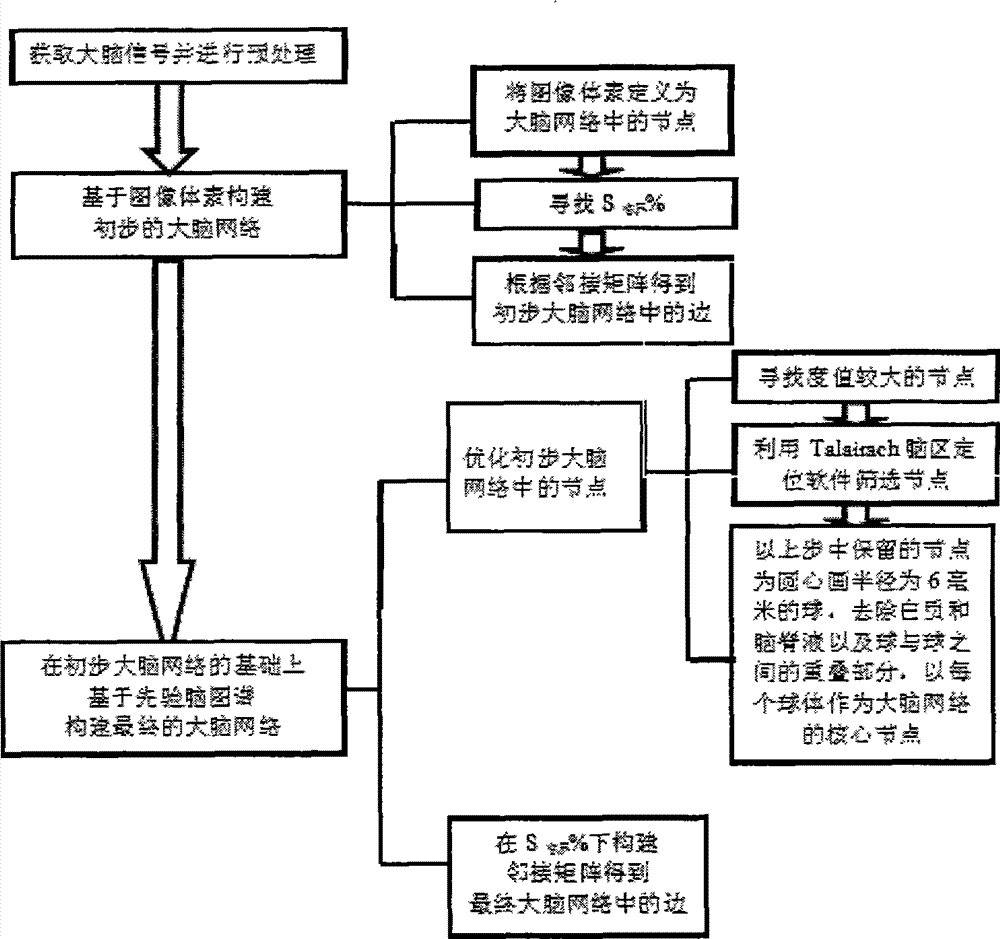
Image voxel and priori brain atlas division fused brain network construction method
InactiveCN103077298AOvercome deficienciesStrong visualizationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALVoxel
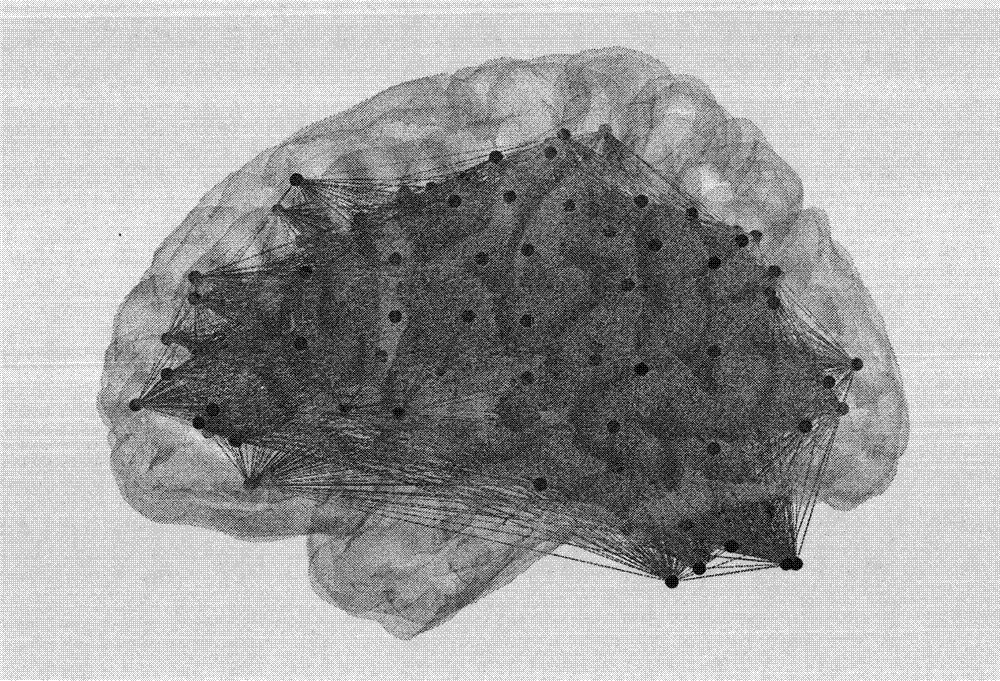
The invention provides an image voxel and priori brain atlas division fused brain network construction method to overcome defects of node selection methods in the conventional brain network construction method. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing functional magnetic resonance imaging data; constructing an initial brain network based on image voxels; and constructing a final brain network based on a priori brain atlas on the basis of the initial brain network. Two node selection methods in the prior art are fused, nodes with high degree values are searched on the basis of the image voxel, the nodes are screened by a Talairach encephalic region locating software on the basis of the priori brain atlas, the screened node is taken as a center of a circle to draw a sphere with the radius of 6 millimeters, the sphere is taken as a core node of the brain network, and the final brain network is determined according to the core node and sides of the obtained brain network. By the method, a brain functional network can be comprehensively and delicately described, the core node of the network is visualized in a brain space, and a function of observing a connecting mode between encephalic regions clearly is realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Di-substituted amides for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses
InactiveUS8013003B2Stable baselineIncrease amplitudeBiocideNervous disorderSIDS - Sudden infant death syndromeCentral sleep apnea
This invention relates to compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods for use in the prevention and treatment of cerebral insufficiency, including enhancement of receptor functioning in synapses in brain networks responsible for basic and higher order behaviors. These brain networks, which are involved in regulation of breathing, and cognitive abilities related to memory impairment, such as is observed in a variety of dementias, in imbalances in neuronal activity between different brain regions, as is suggested in disorders such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, respiratory depression, sleep apneas, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and affective or mood disorders, and in disorders wherein a deficiency in neurotrophic factors is implicated, as well as in disorders of respiration such as overdose of an alcohol, an opiate, an opioid, a barbiturate, an anesthetic, or a nerve toxin, or where the respiratory depression results form a medical condition such as central sleep apnea, stroke-induced central sleep apnea, obstructive sleep apnea, congenital hypoventilation syndrome, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, sudden infant death syndrome, Rett syndrome, spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury, Cheney-Stokes respiration, Ondines curse, Prader-Willi's syndrome and drowning. In a particular aspect, the invention relates to compounds useful for treatment of such conditions, and methods of using these compounds for such treatment.
Owner:CORTEX PHARMA INC
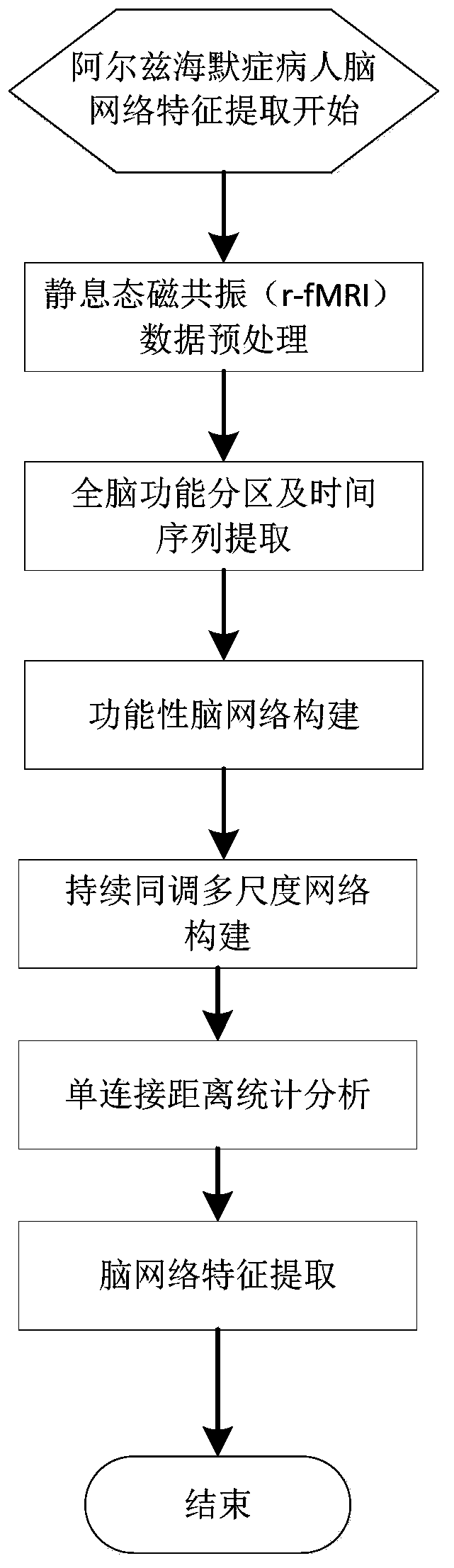
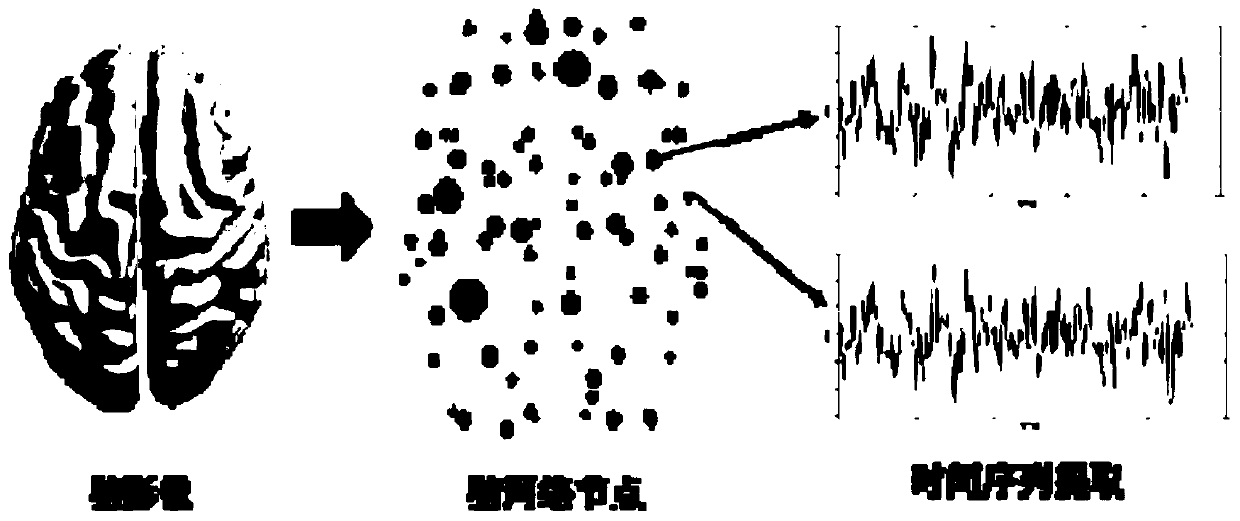
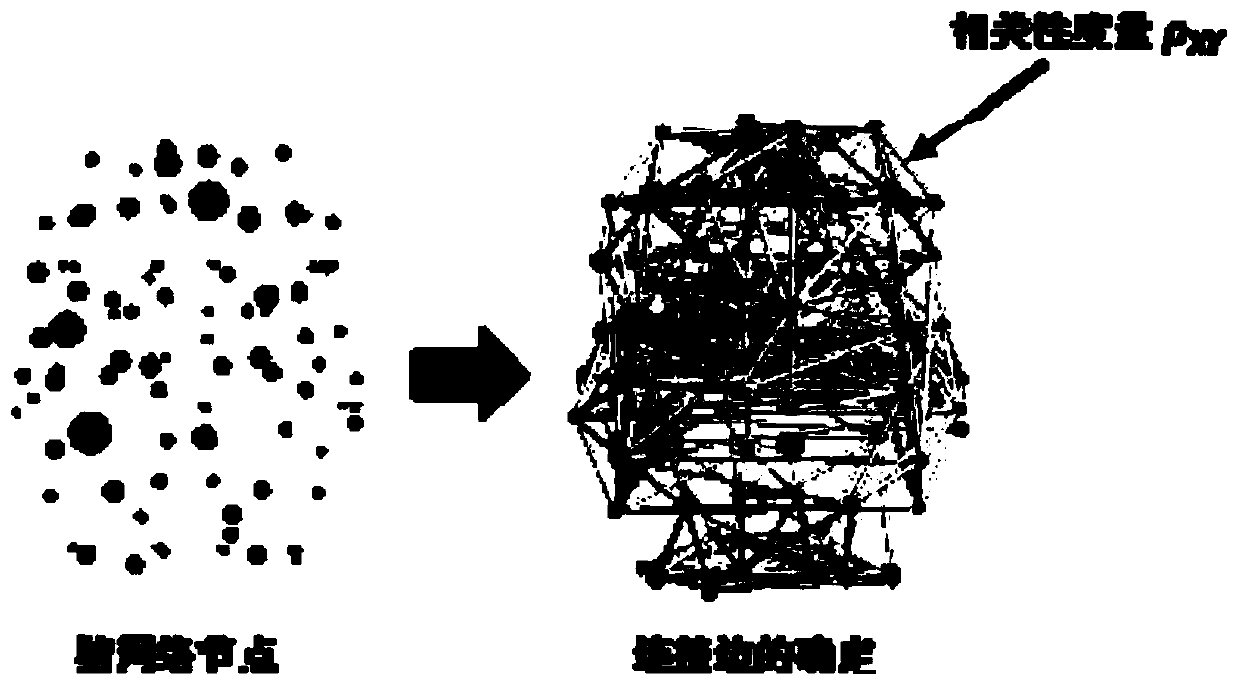
Alzheimer's disease brain network feature extraction method based on a continuous homology technology
ActiveCN109767435AAvoid Threshold Selection ProblemsLighten the computational burdenImage analysisDiseaseFeature extraction
The invention discloses an Alzheimer's disease brain network feature extraction method based on a continuous coherence technology, and belongs to the technical field of brain network analysis. According to the invention, through data preprocessing, brain network division, brain network construction, continuous coherent brain network filtering flow construction, continuous interval data statisticalanalysis and Alzheimer's disease brain network feature extraction, brain network feature extraction of a patient is realized. By constructing the multi-scale brain network with the variable thresholdvalue, the threshold value selection problem in a graph theory method is avoided, wherein the continuous feature discovery mechanism of the network complex flow can effectively reduce the calculationburden, and is an effective brain network analysis technology. The continuous homology theory is applied to the field of brain analysis of patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease, the brain mechanism is researched, the brain network connection characteristics of diseases are discovered, and the method is an innovative research idea and has important significance for early diagnosis, drug development and diagnosis and treatment scheme formulation of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Fatigue classification method for constructing brain function network and correlation vector machine based on generalized consistency
ActiveCN109770924AJudging driving fatigueImprove signal-to-noise ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringNODALMental state
The invention provides a fatigue classification method for constructing a brain function network and a correlation vector machine based on generalized consistency. Compared with the prior art, the method has higher reliability and accuracy, an effective fatigue classification network is constructed through information flowing direction and a causal relationship to classify connection characteristics of a brain network under different mental states, thereby effectively verifying results of topological structure research and improving the detection ability of driving fatigue. The fatigue classification method has the advantages that the brain network is constructed by using a generalized consistency algorithm method, the brain is regarded as a multi-regional cooperative network, informationcirculation direction and causal relationship between nodes of the brain are researched, topological structure changes of the brain network are analyzed under different mental states, the fatigue generation mechanism is disclosed, and a new perspective is provided for fatigue-related research; the correlation vector machine is used for classifying the connection characteristics, 90% or above classification accuracy can be achieved, the reliability of topological structure analysis is verified, and a new method is provided for fatigue detection.
Owner:WUYI UNIV
Weighted graph regularization sparse brain network construction method
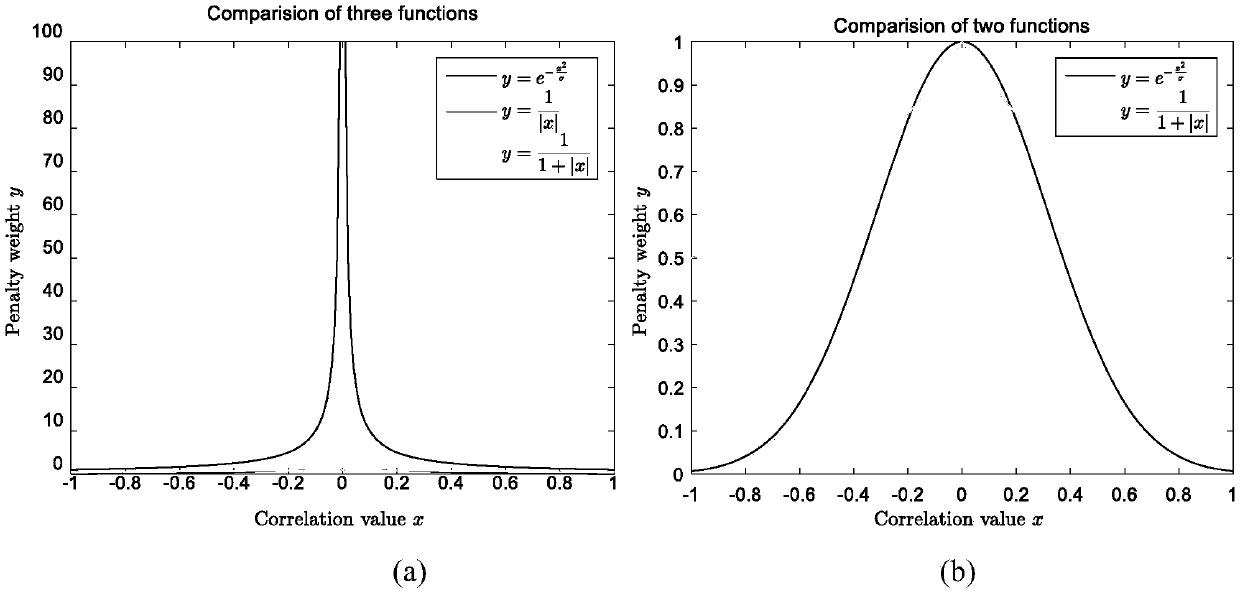
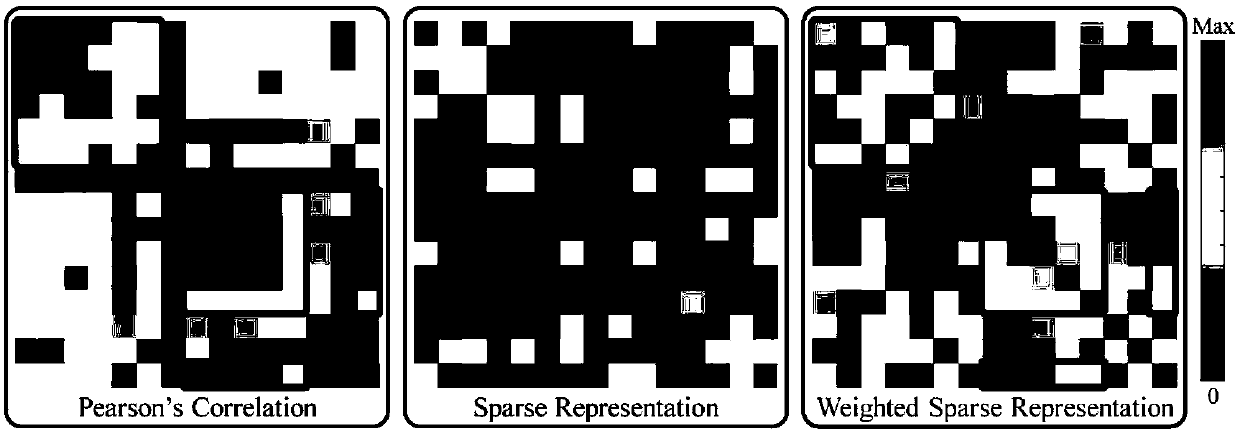
PendingCN109065128ASolve the problem that the solution does not convergeImprove classification accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFunctional connectivity
The invention discloses a weighted graph regularization sparse brain network construction method. According to the method, on the basis of analysis of keeping similar local manifold characteristics ofsimilar data in original data space after projection, constrained modeling is carried out on association between brain connection by using a graph regularization item; with consideration of correlation analysis, the similarity degree of essences in a time sequence signal sequence of a brain area can be measured, sparse modeling is constrained by using measured functional connection strength priorinformation, and a weighted sparse regularization item is established; and then combined modeling is carried out on the whole brain function network and a brain network with the biological significance is constructed. According to the invention, on the basis of integration of correlation analysis, sparsity and graph regularization constraint into the unified modeling frame, a brain function network is constructed effectively by utilizing the similarity and locality of functional magnetic resonance brain image data fully; and the method is also used for neurological disease identification andbiological marker analysis.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Method for extracting brain function network of individual based on analysis of multiple tested brain function data
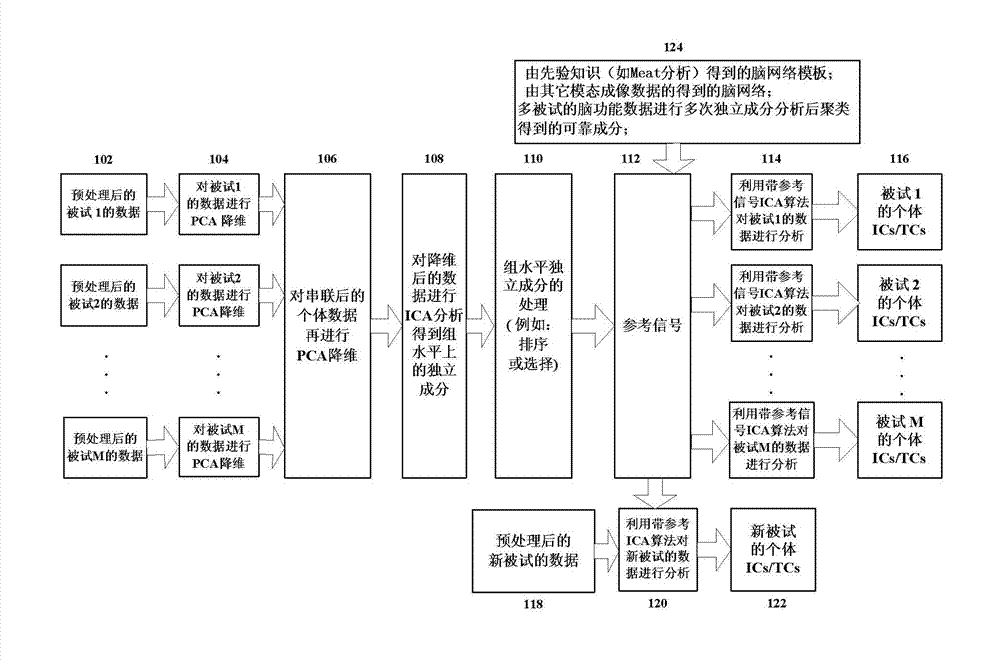
ActiveCN103034778AEasy to analyzeOvercoming the shortcomings of analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMeta-analysisFunction optimization
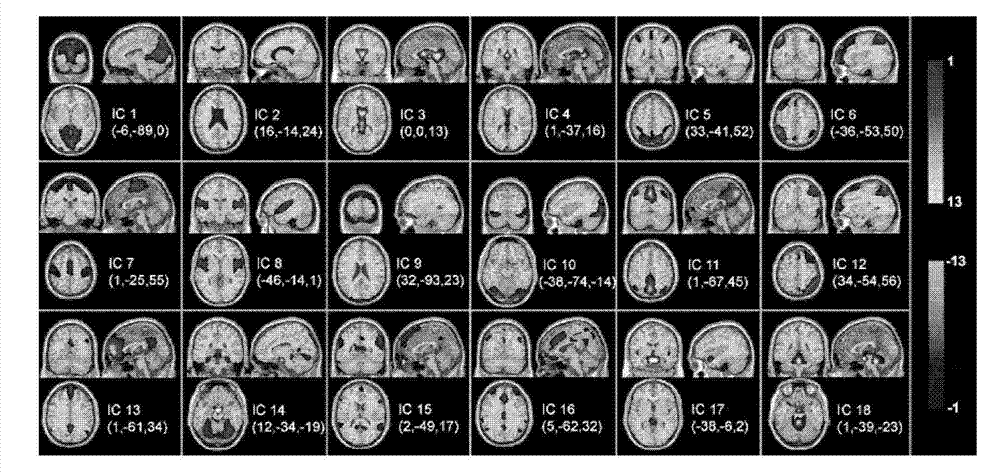
The invention discloses a method for extracting a brain function network of an individual based on the analysis of multiple tested brain function data. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating the tested independent components of the individual, having correspondence among the different tested, based on the tested brain function data of the individual; using a provided algorithm for analyzing the independent components with reference signals based on a multi-target function optimization framework, meanwhile, optimizing the correspondence between the tested independent components of the individual and the reference signals and the independence among the different tested components of the individual, wherein the reference signals are obtained by jointly analyzing the independent components of the tested brain function data of the individual, and can also be obtained from a brain network pattern and the like obtained through the brain network analysis or meta analysis of other modal imaging data; after the tested independent components of the individual are obtained, using a provided time sequence calculation method to calculate a time sequence corresponding to each independent component; and judging the obtained independent components to obtain a brain function network, wherein the time sequence corresponding to the independent component is an activating mode corresponding to the brain function network.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-modal magnetic resonance image data classification method based on minimal spanning tree
ActiveCN106548206AImprove classification accuracyRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsCorrelation coefficientImaging processing
The invention relates to a multi-modal magnetic resonance image data classification method based on a minimal spanning tree, belongs to image processing technologies, and solves the problem that a traditional magnetic resonance image data classification method is low in classification accuracy. The method is realized by the following steps that S1) a resting-modal function magnetic resonance image is pre-processed; S2) a Pearson's correlation coefficient between average time sequences of every two encephalic regions is calculated; S3) a magnetic resonance dispersion tensor imaging image is preprocessed; S4) the weights of every two encephalic regions are calculated; S5) a multi-modal minimal spanning tree brain network is constructed; S6) local attributes of the multi-modal minimal spanning tree brain network are calculated; S7) a classifier is constructed; and S8) the significance and redundancy of a selected characteristic in the classifier are quantified. The method is suitable for classification of magnetic resonance image data.
Owner:山西三川孪生数字科技有限公司
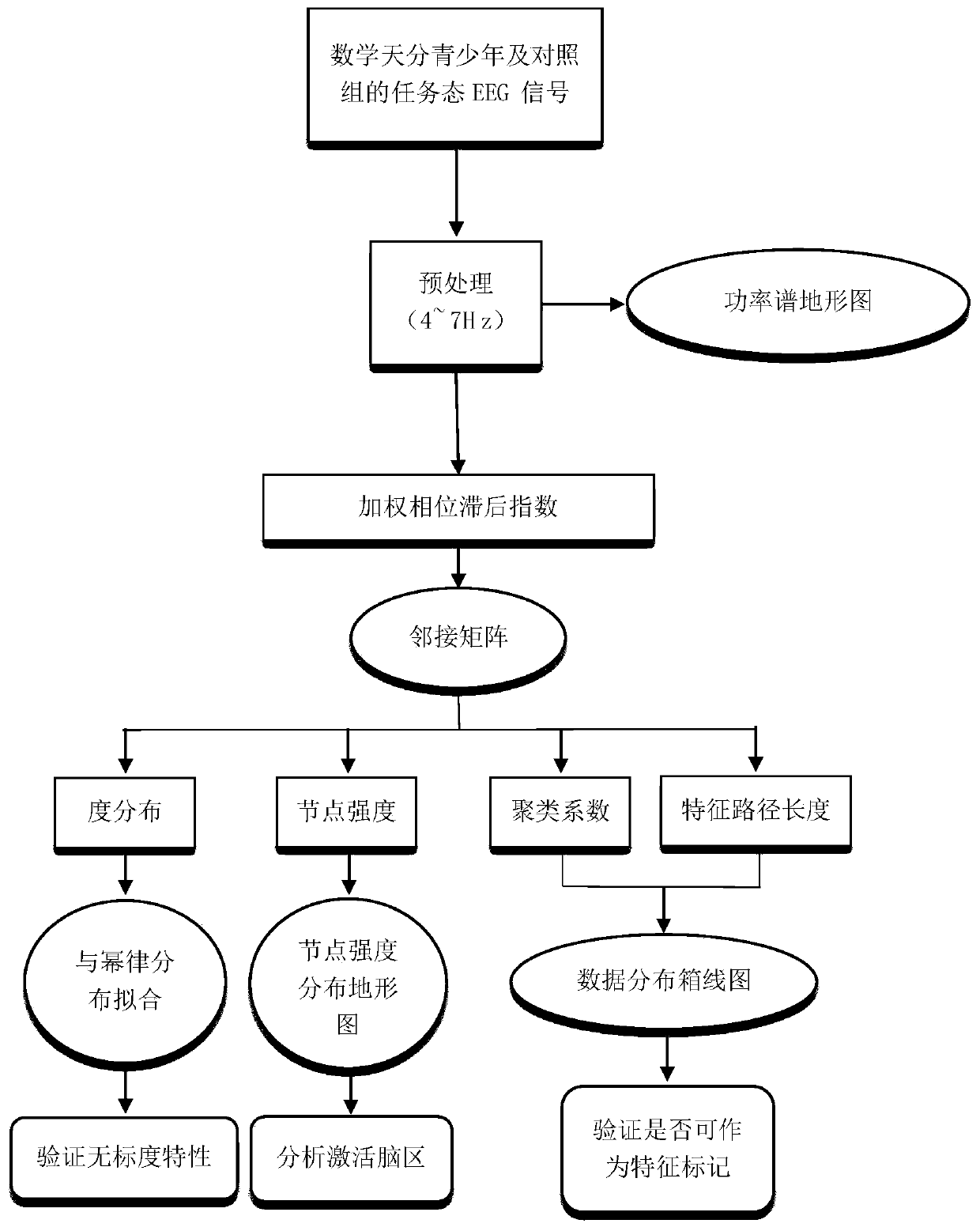
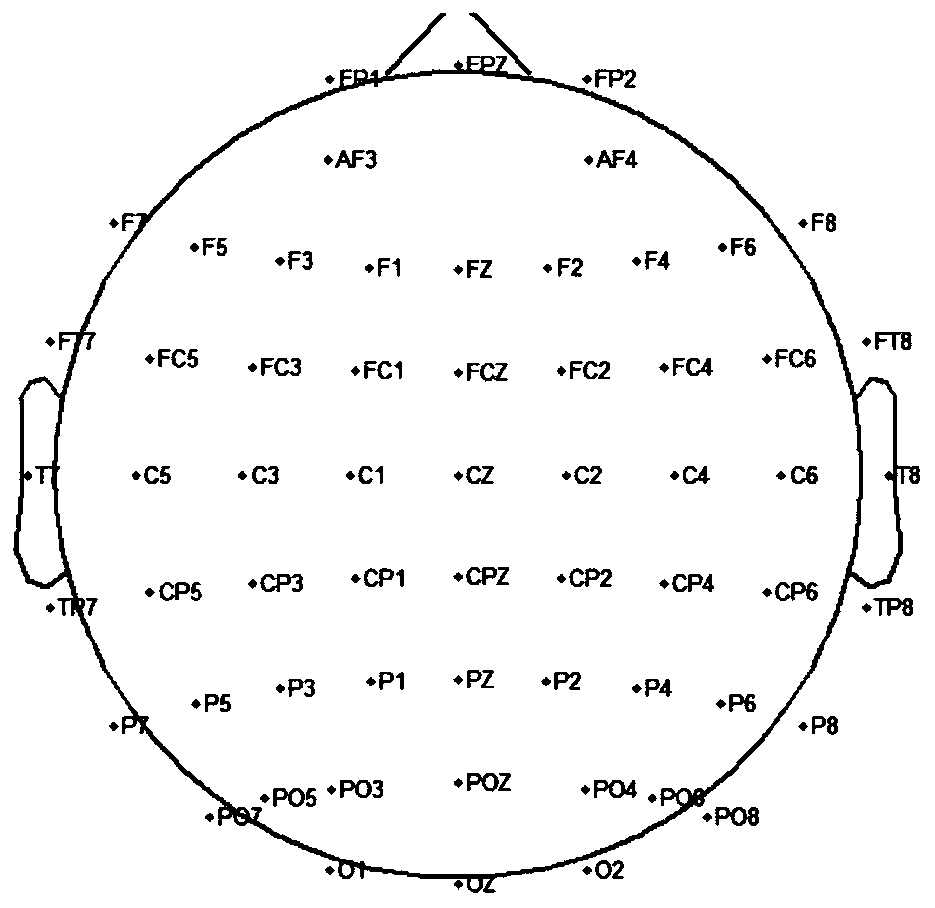
Mathematical talent teenager brain network analysis method based on weighted phase lag index
InactiveCN110859614AHigh sensitivityCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringFunctional connectivityAlgorithm
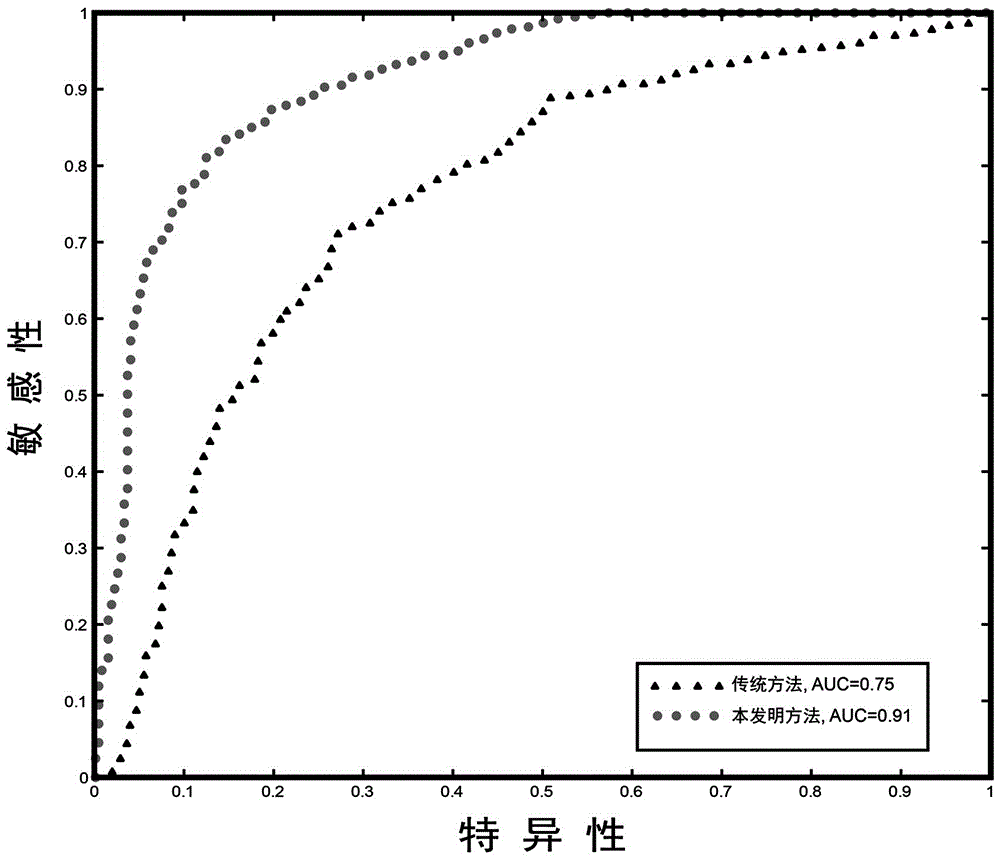
The invention discloses a mathematical talent teenager brain network analysis method based on a weighted phase lag index, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a phase synchronization network based on a task state EEG signal through employing an algorithm based on the weighted phase lag index, and converting the phase synchronization network into a functional connectivity network; and measuring the connection network by utilizing graph theory indexes, and describing connection network characteristics of the mathematical talent teenagers, including active brain regions and the graphtheory indexes. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the connection network characteristics of the mathematical exceptional teenagers are describedbased on the task state EEG signals, and the phase synchronization network is constructed by adopting the weighted phase lag index and is converted into the functional connection network, which reduces the probability of detecting false positives when the phase difference between volumetrically conducted noise sources is zero, and increases the sensitivity of detecting phase synchronization.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
method for detecting fMRI brain network dynamic co-variations
ActiveCN109522894ADifficult to solveEasy to exploreCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmResonance
The invention provides a method for detecting fMRI brain network dynamic covariations. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a sample; Firstly, constructing a brain functional networkby utilizing functional magnetic resonance data; according to a certain basis (factors such as age, disease course length, education degree and the like), different network matrixes are arranged in sequence;obtaining a cross-tested network matrix sequence; then, a sliding window method is used for researching a covariant relationship between ROI brain regions which cross a tested object; and obtaining a series of covariant matrixes, and depicting the difference of the brain interval collaborative activity modes under the trans-tested scale is by calculating mathematical indexes for describing covariant relationship variability or through statistical inspection, so that the interactive relationship between brain regions in the network can be better understood.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System for early detection and risk prediction of schizophrenia
ActiveCN110063732AImprove classification accuracyHigh sensitivitySensorsPsychotechnic devicesCrowdsCvd risk
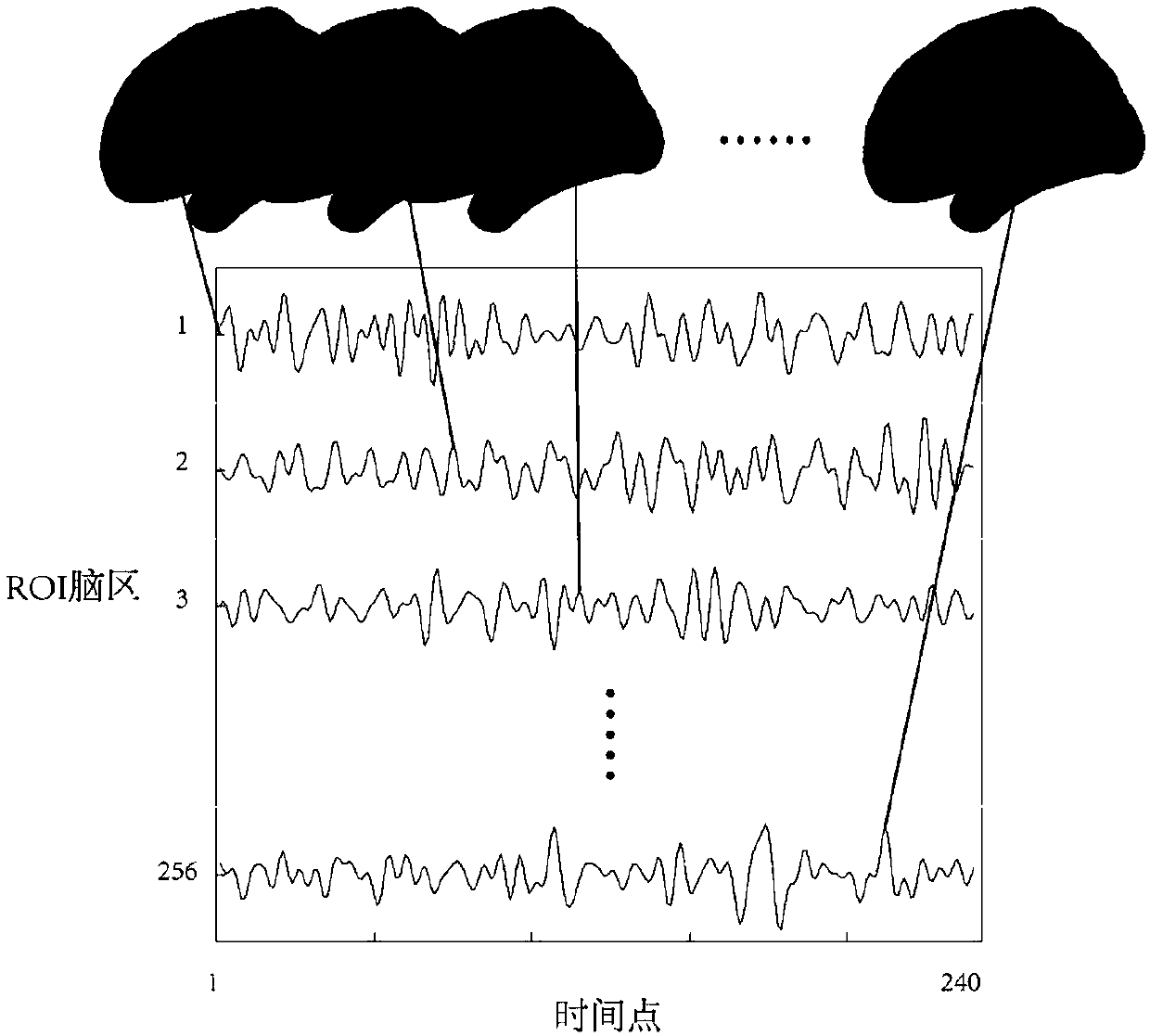
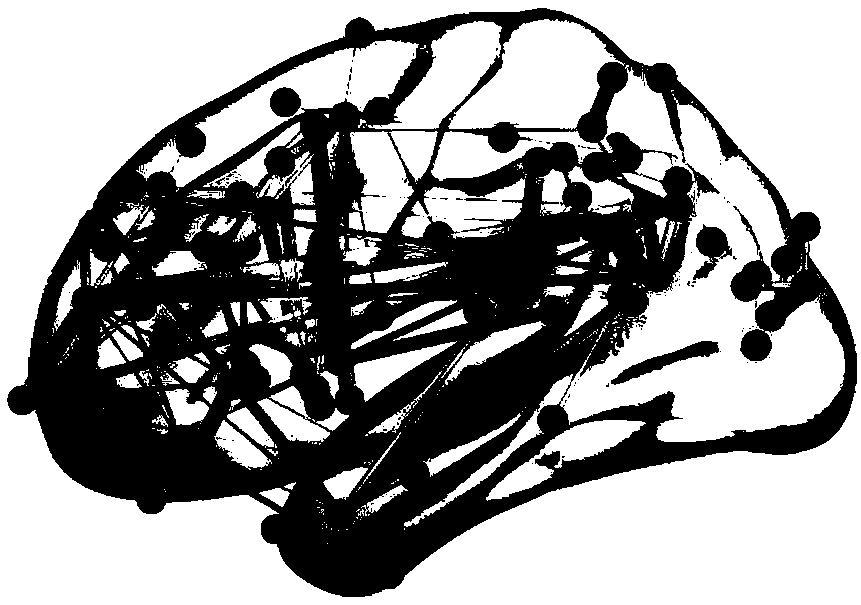
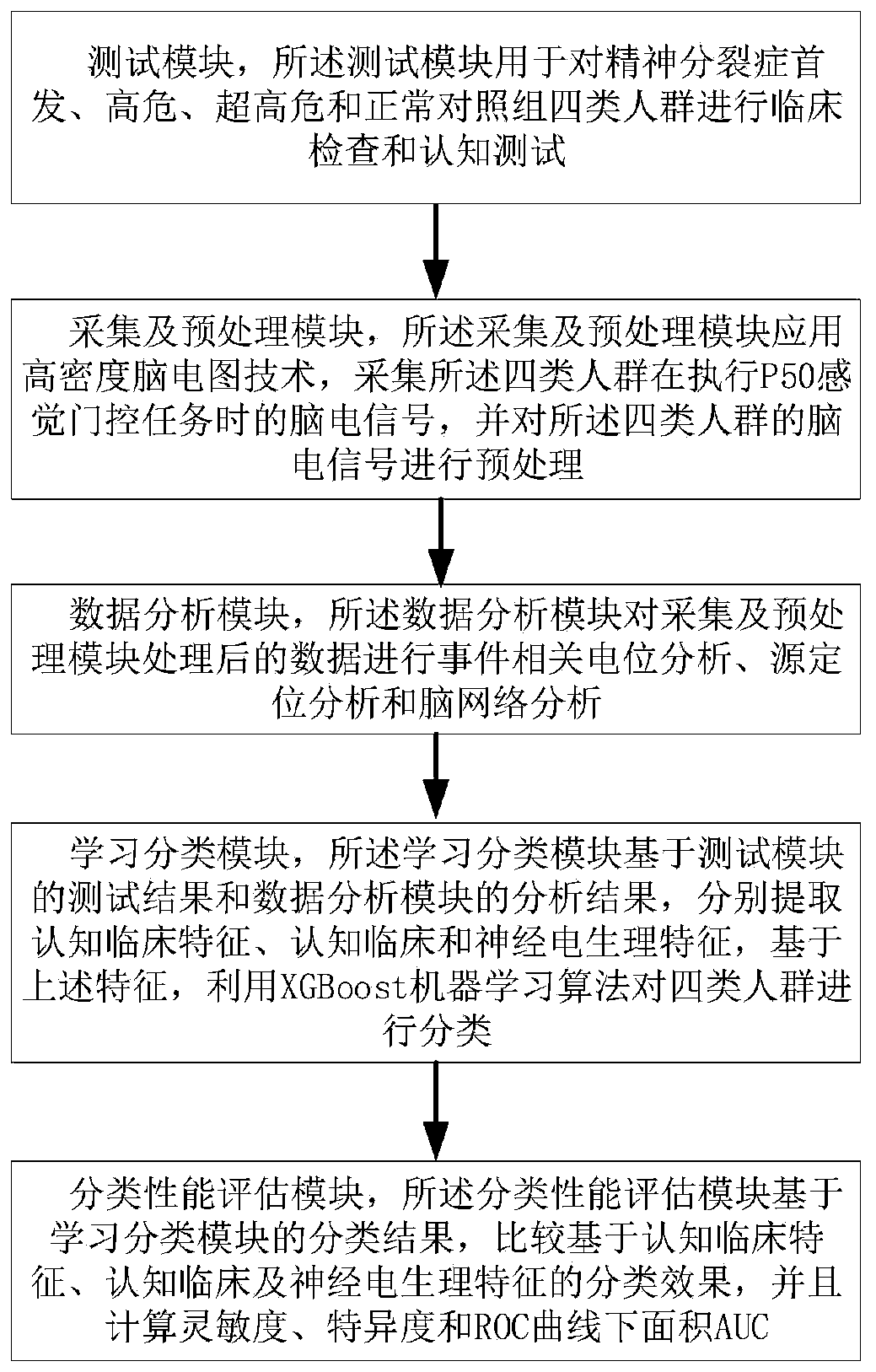
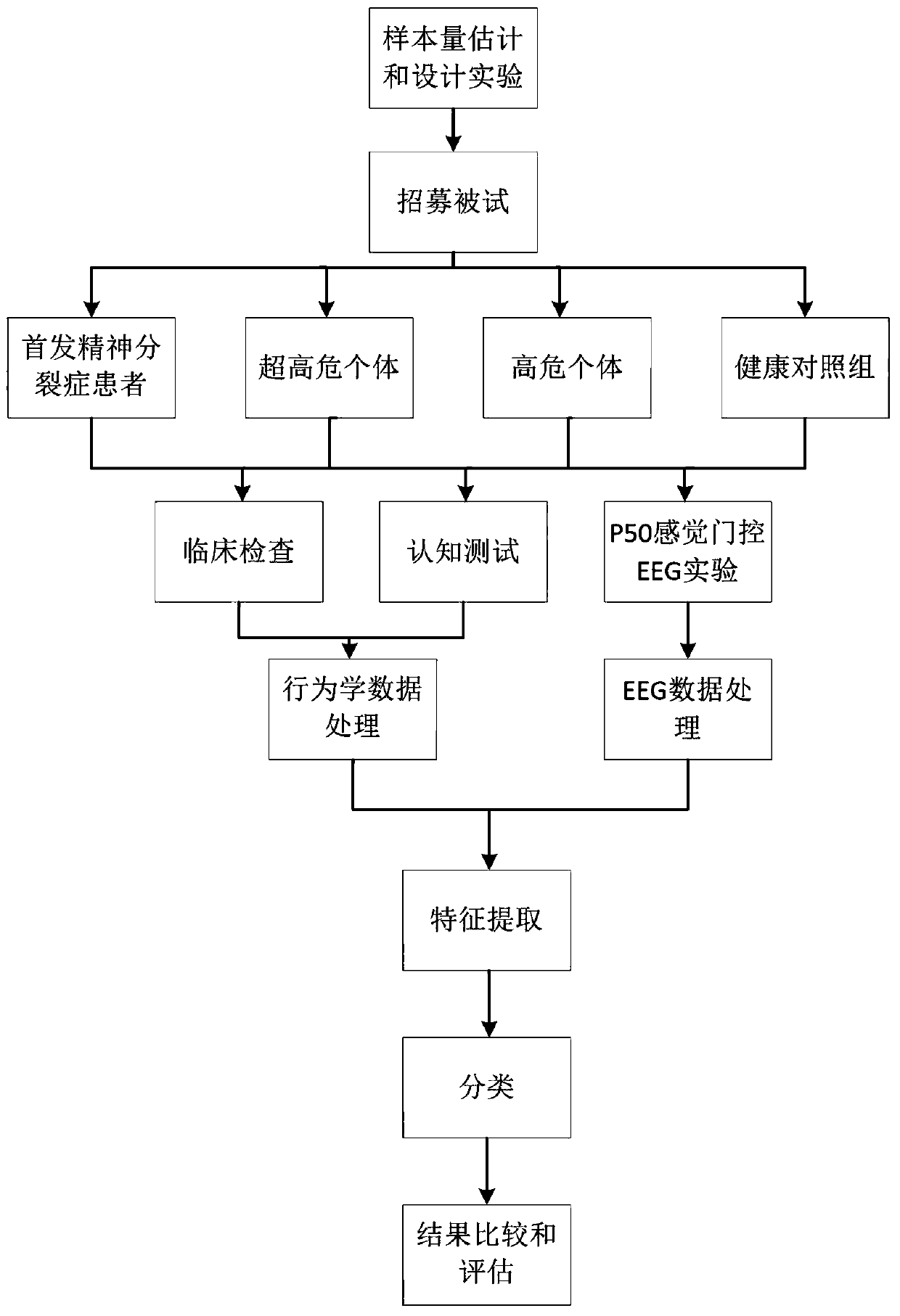
The invention discloses a system for early detection and risk prediction of schizophrenia. The technical problem that currently, it is hard to accurately and objectively carry out early detection andrisk prediction on schizophrenia can be solved. The system comprises a test module, a collecting and preprocessing module, a data analysis module, a learning classification module and a classificationperformance evaluation method. According to the system for early detection and risk prediction of the schizophrenia, high-risk individuals, ultra-high-risk individuals and initially-attacked people of the schizophrenia are subjected to quantitative and objective detection recognition and risk prediction by comprehensively utilizing cognitive tests, clinical detection, P50 sensory gating electrophysiological characteristics and an XGBoost(the Extreme Gradient Boosting) machine learning method; specifically, by combinedly using cognition, clinic and P50 sensory gating experiments, and adoptingsource location, brain networks, machine learning and other analysis methods, initially-attacked people, high-risk people, ultra-high-risk people and normal contrast people are classified, and the classification accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Di-substituted amides for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses
InactiveUS20100120764A1Stable baselineIncrease amplitudeBiocideNervous disorderSIDS - Sudden infant death syndromeCentral sleep apnea
This invention relates to compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods for use in the prevention and treatment of cerebral insufficiency, including enhancement of receptor functioning in synapses in brain networks responsible for basic and higher order behaviors. These brain networks, which are involved in regulation of breathing, and cognitive abilities related to memory impairment, such as is observed in a variety of dementias, in imbalances in neuronal activity between different brain regions, as is suggested in disorders such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, respiratory depression, sleep apneas, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and affective or mood disorders, and in disorders wherein a deficiency in neurotrophic factors is implicated, as well as in disorders of respiration such as overdose of an alcohol, an opiate, an opioid, a barbiturate, an anesthetic, or a nerve toxin, or where the respiratory depression results form a medical condition such as central sleep apnea, stroke-induced central sleep apnea, obstructive sleep apnea, congenital hypoventilation syndrome, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, sudden infant death syndrome, Rett syndrome, spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury, Cheney-Stokes respiration, Ondines curse, Prader-Willi's syndrome and drowning. In a particular aspect, the invention relates to compounds useful for treatment of such conditions, and methods of using these compounds for such treatment.
Owner:CORTEX PHARMA
Multi-modal brain image depression identification method and system based on graph node embedding
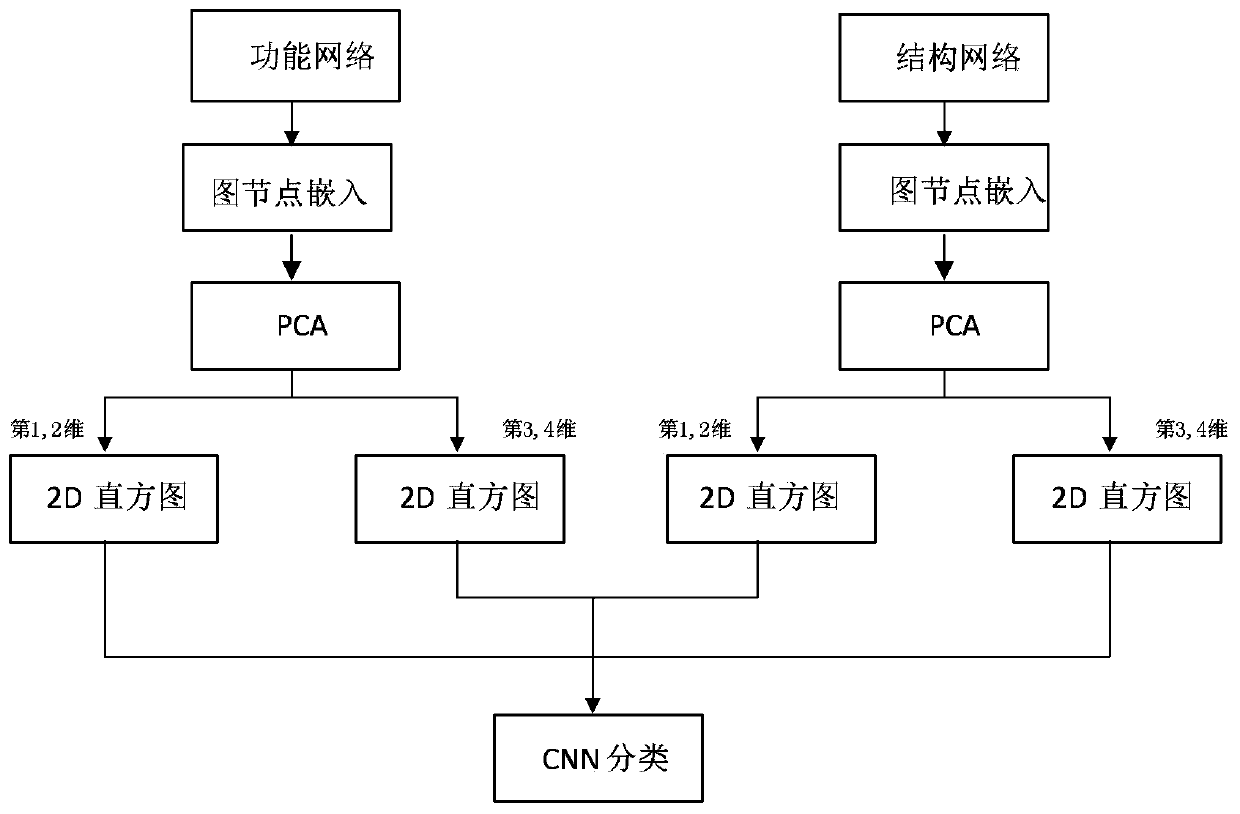
ActiveCN111127441AImprove recognition resultsImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging dataNeural network nn
The invention provides a multi-modal brain image depression identification method and system based on graph node embedding. Deep learning is applied to the depression recognition of a multi-modal brain image, and a bridge is built between a multi-modal brain network and a convolutional neural network (CNN) through graph node embedding, so that the CNN can be used for the depression recognition ofthe multi-modal brain image, and therefore, depression recognition accuracy is improved. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring the resting state fMRI and DTI image data of a depressive patient and a normal control group; 2) preprocessing the acquired fMRI and DTI image data; 3) respectively constructing a brain function network and a brain structure network according to the preprocessed fMRI and DTI image data to obtain a brain network adjacency matrix, and 4) adopting graph node embedding to express the adjacency matrix as an image, inputting the image into a convolutionalneural network for classifying the image, and establishing a classification model for identifying depressive patients and normal subjects.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
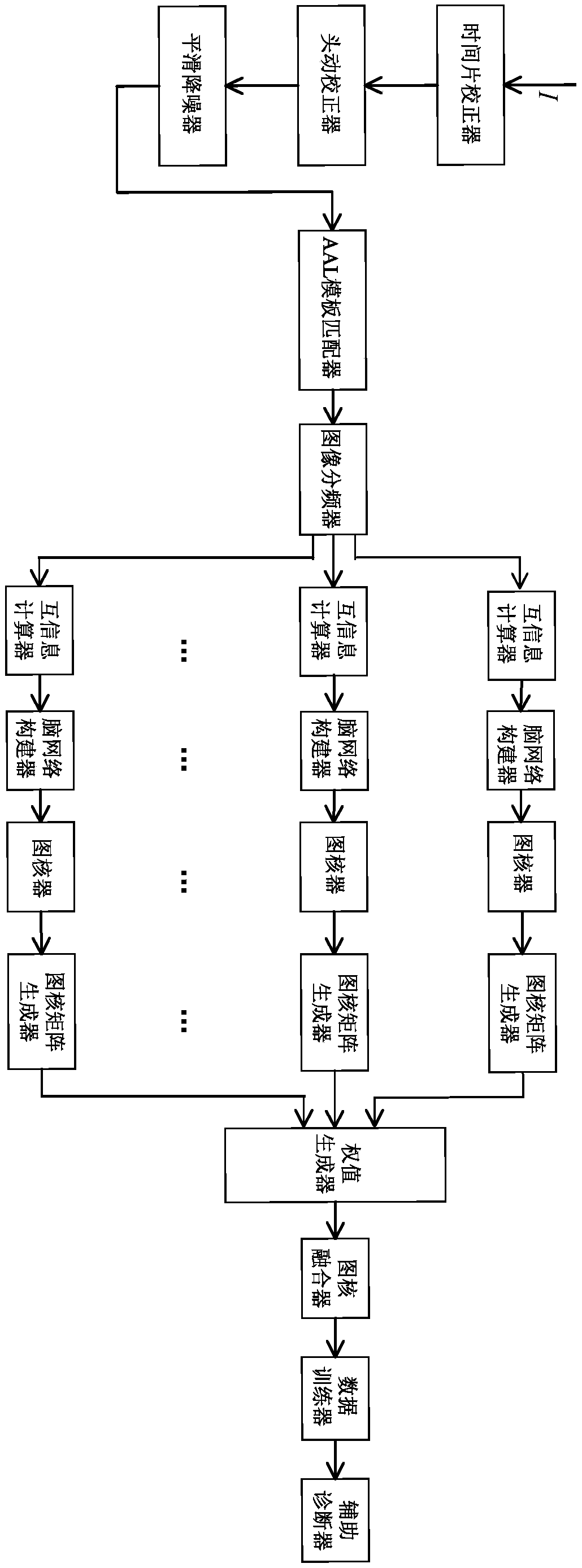
Alzheimer's disease auxiliary diagnosis device and method based on brain network multi-frequency fusion image core
ActiveCN109034263AOvercoming the Deficiency of Information DisparityGood effectReconstruction from projectionMedical automated diagnosisDiseaseLearning machine
The invention provides an auxiliary diagnosis device and a method for Alzheimer's disease of a brain network multi-frequency fusion map core, which relates to the technical field of computer-aided diagnosis. The device comprises an image preprocessing module, an image frequency dividing module, a graph kernel generation module, a graph kernel fusion module and an auxiliary diagnosis module. The image dividing module matches the fMRI image with the AAL template and divides the fMRI image. The image kernel generation module constructs a multi-frequency brain network for the divided image and forms a matrix. The graph kernel fusion module fuses all the graph kernels into one graph kernel. The auxiliary diagnostic module combines the fused graph kernel with the kernel limit learning machine torealize the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides a method for diagnosing by using the device. The brain network multi-frequency fusion image core auxiliary diagnosis device and method for Alzheimer's disease provided by the invention can sufficiently express the difference of brain activity information under multi-frequency bands, so that the signal information of the functional nuclear magnetic resonance image can be fully exerted.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
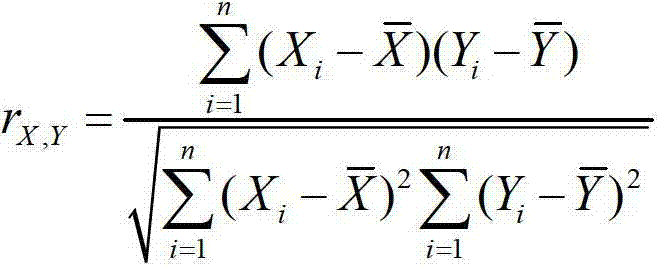
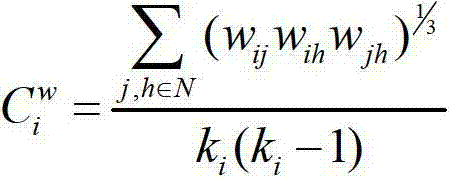
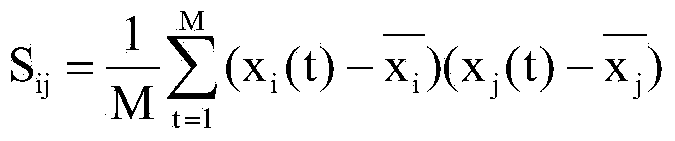
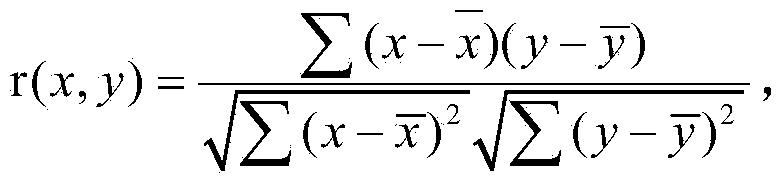
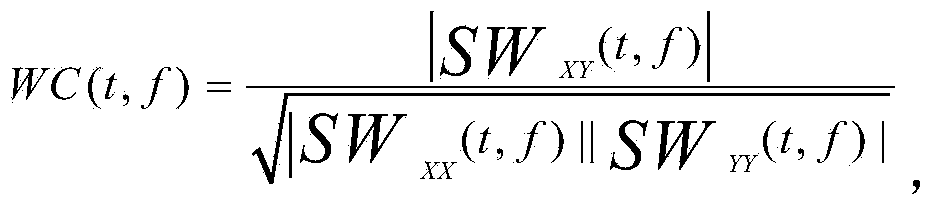
![3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses 3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/abe3f606-7941-4deb-9246-7db7234da7f3/US20100041647A1-20100218-C00001.png)
![3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses 3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/abe3f606-7941-4deb-9246-7db7234da7f3/US20100041647A1-20100218-C00002.png)
![3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses 3-Substituted-[1,2,3]-Benzotriazinone compounds for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/abe3f606-7941-4deb-9246-7db7234da7f3/US20100041647A1-20100218-C00003.png)