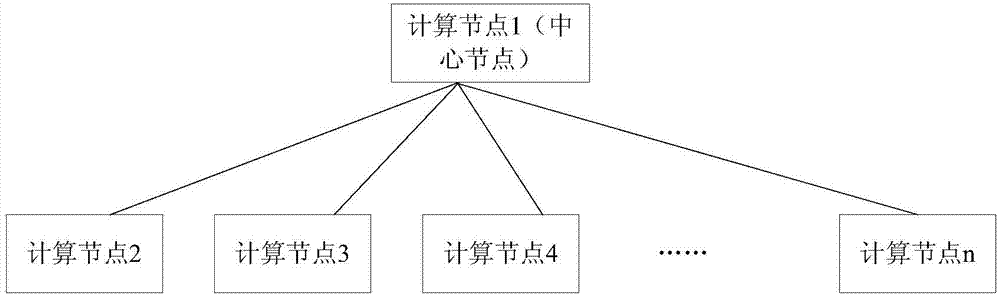
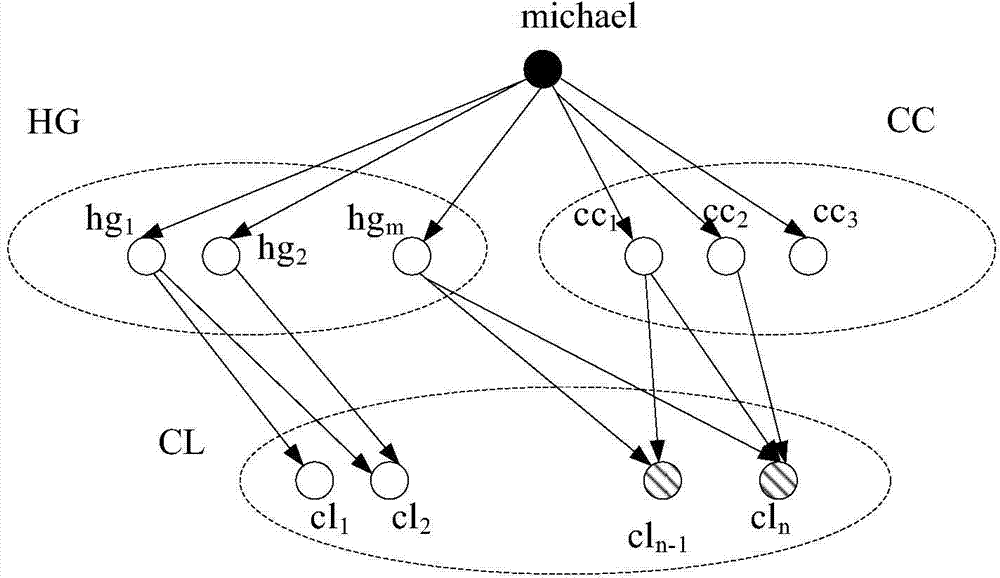
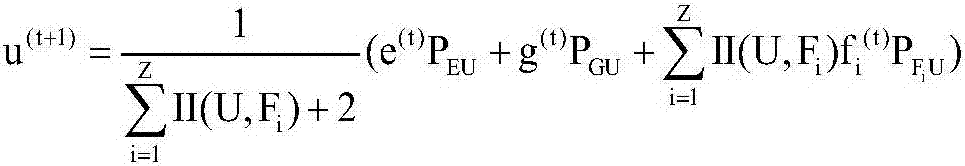Patents
Literature
404 results about "Graph Node" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The node graph architecture often allows grouping of nodes inside other group nodes. This hides complexity inside of the group nodes, and limits their coupling with other nodes outside the group. This leads to a hierarchy where smaller graphs are embedded in group nodes.
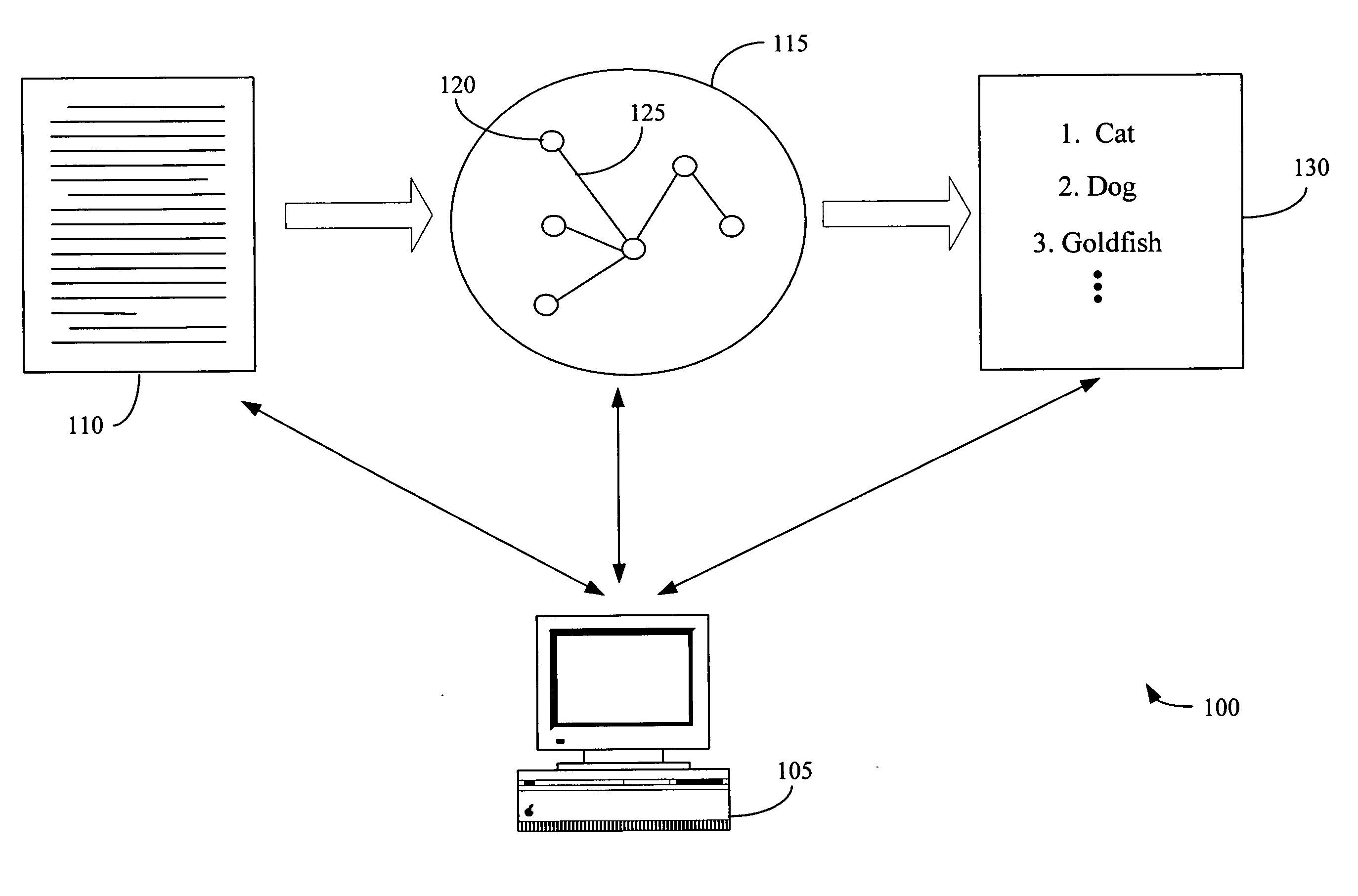
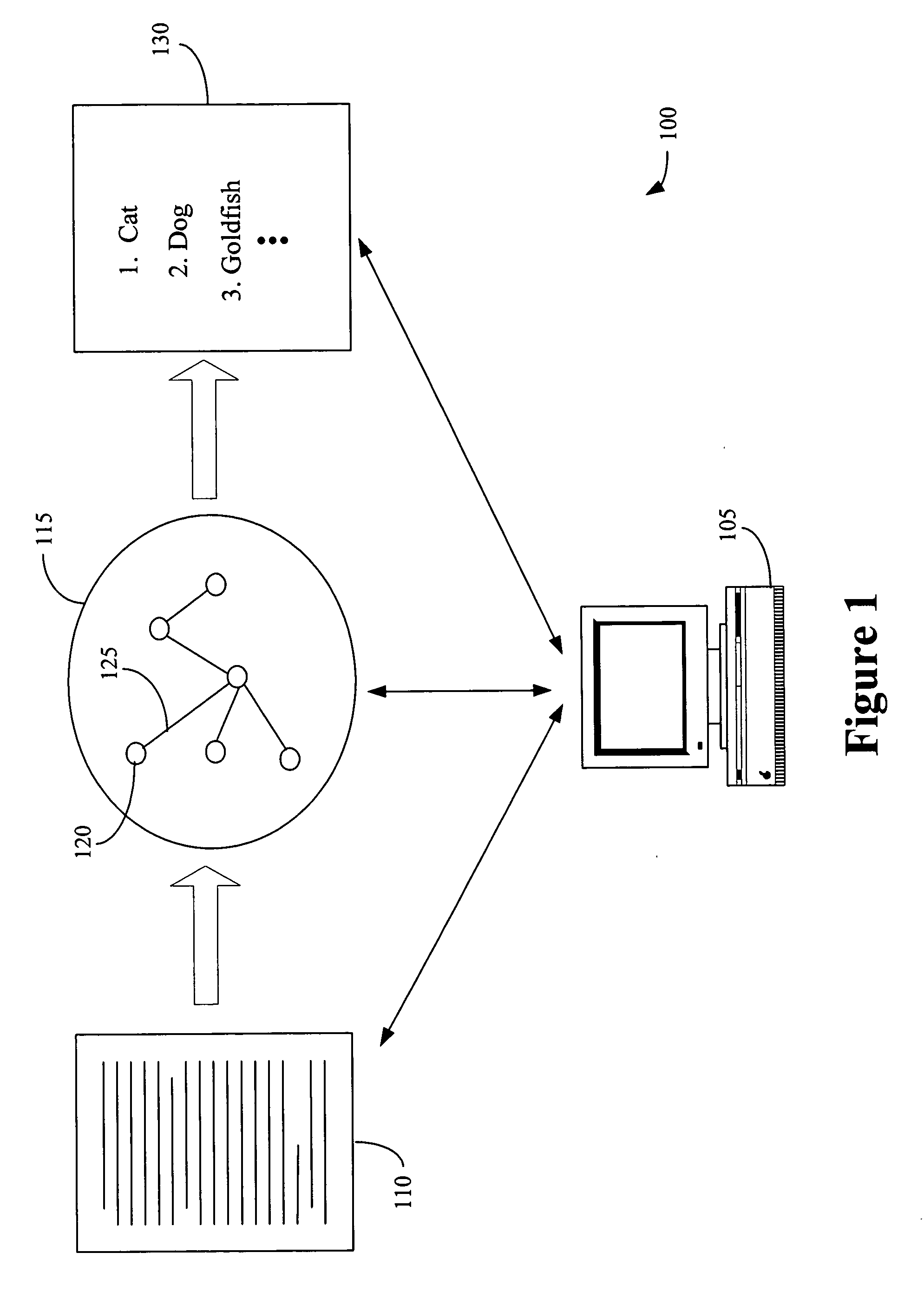
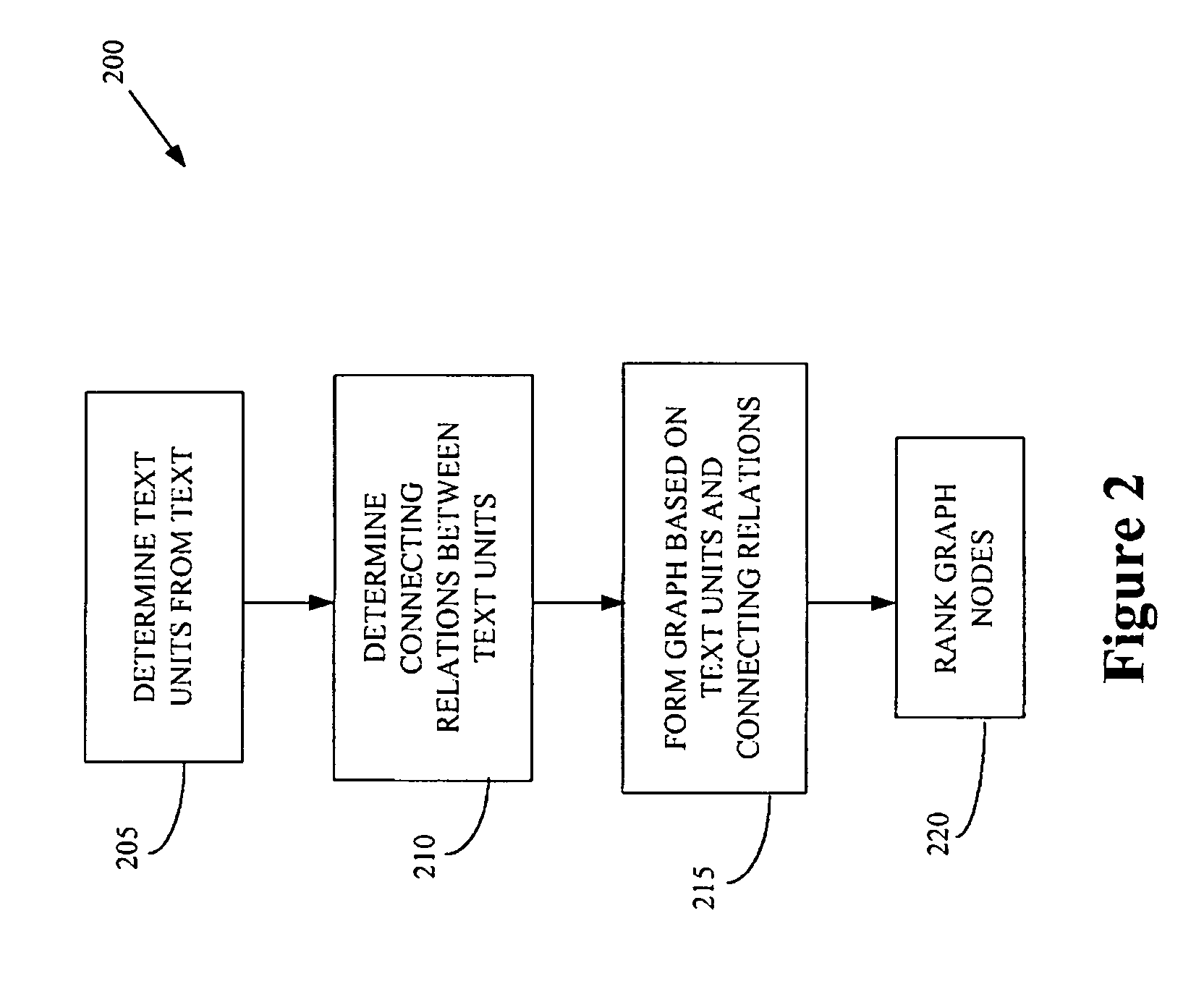
Graph-based ranking algorithms for text processing
InactiveUS20050278325A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisGraphicsWord-sense disambiguation
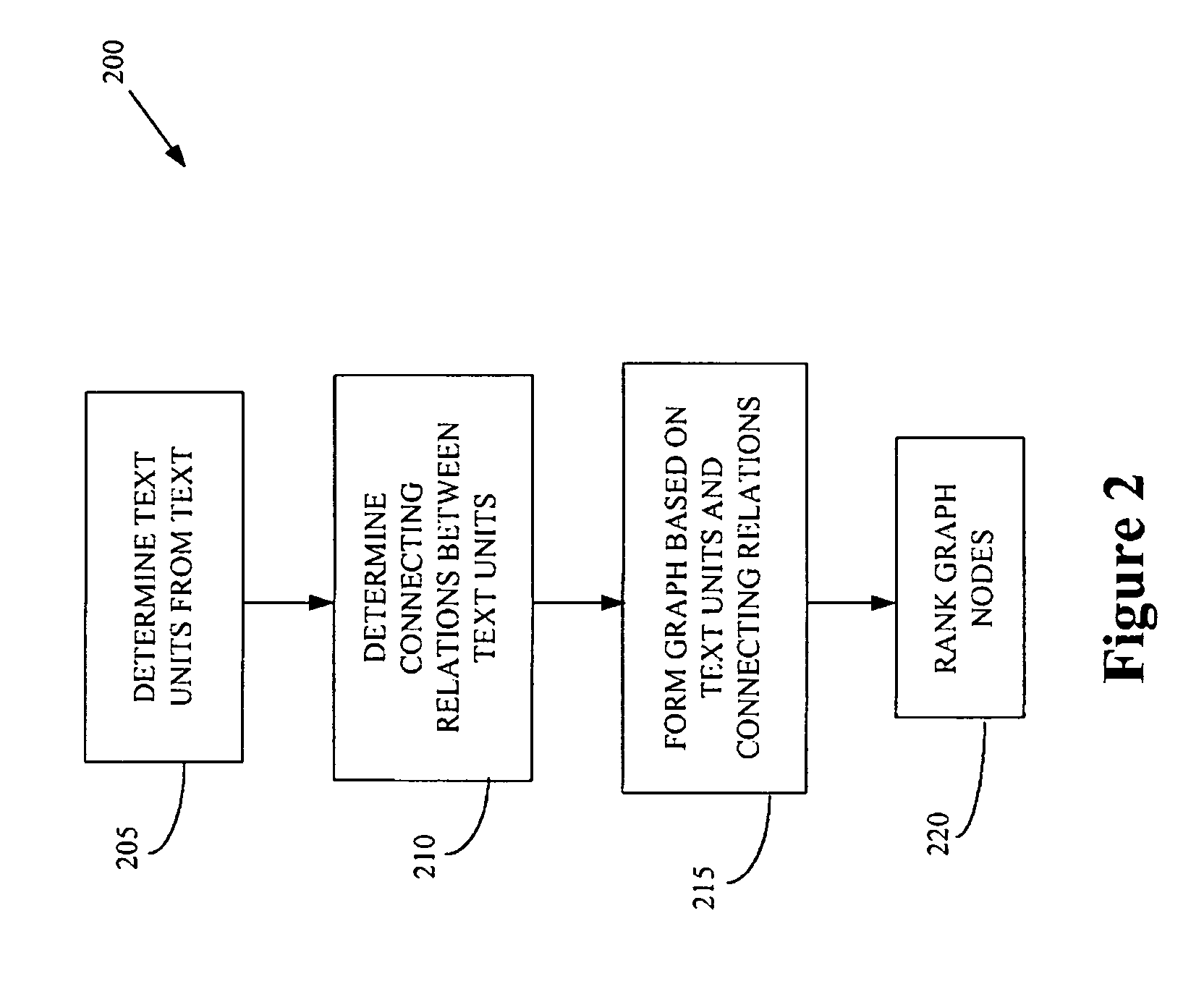
The present invention provides a method of processing at least one natural language text using a graph. The method includes determining a plurality of text units based upon the natural language text, associating the plurality of text units with a plurality of graph nodes, and determining at least one connecting relation between at least two of the plurality of text units. The method also includes associating the at least one connecting relation with at least one graph edge connecting at least two of the plurality of graph nodes and determining a plurality of rankings associated with the plurality of graph nodes based upon the at least one graph edge. The method can also include a graphical visualization of at least one important text unit in a natural language text or collection of texts. Methods for word sense disambiguation, keyword extraction, and sentence extraction are also provided.
Owner:NORTH TEXAS UNIV OF
Spectral kernels for learning machines
InactiveUS6944602B2Reduce computing costLow costKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature vector
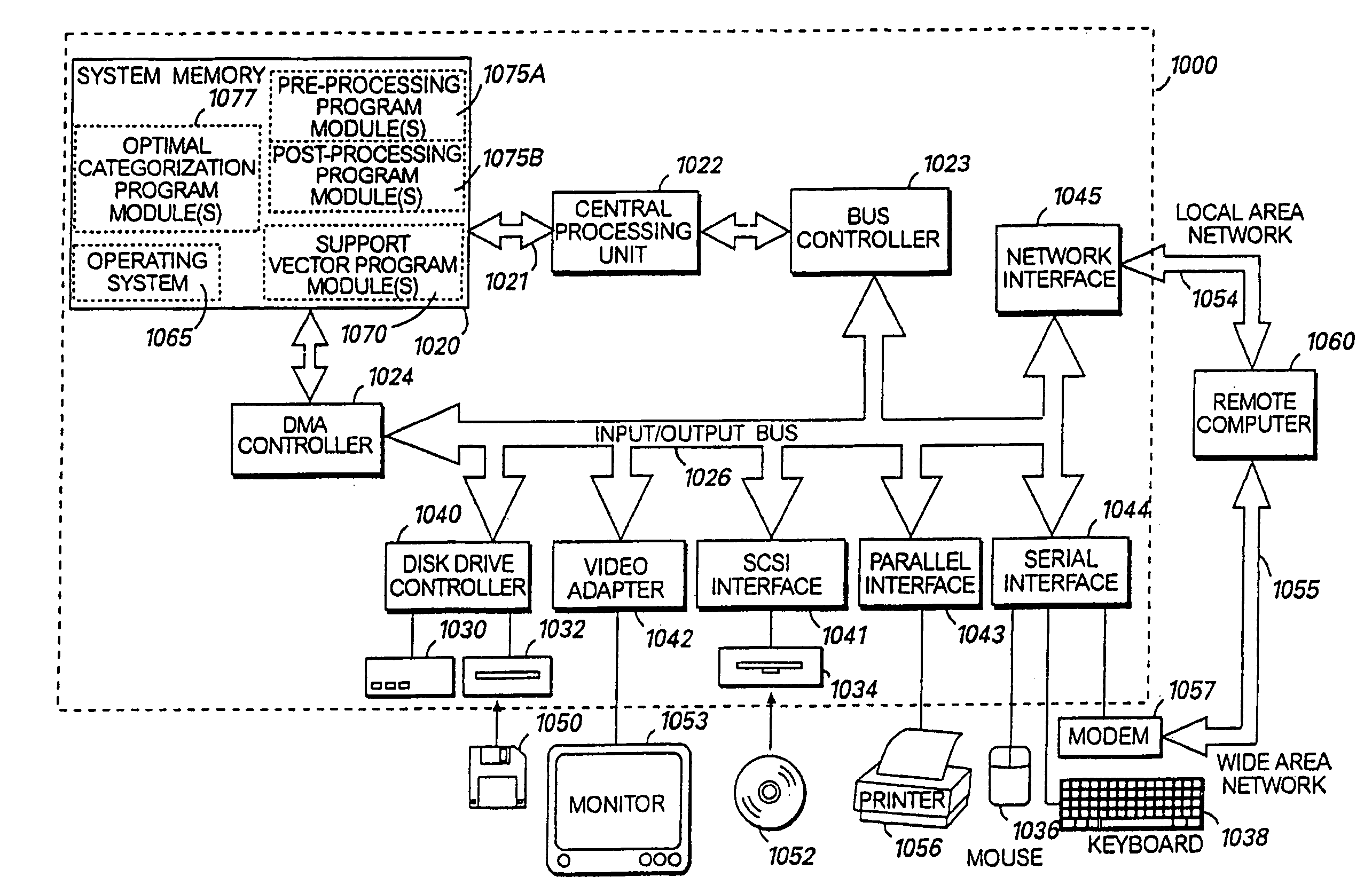
The spectral kernel machine combines kernel functions and spectral graph theory for solving problems of machine learning. The data points in the dataset are placed in the form of a matrix known as a kernel matrix, or Gram matrix, containing all pairwise kernels between the data points. The dataset is regarded as nodes of a fully connected graph. A weight equal to the kernel between the two nodes is assigned to each edge of the graph. The adjacency matrix of the graph is equivalent to the kernel matrix, also known as the Gram matrix. The eigenvectors and their corresponding eigenvalues provide information about the properties of the graph, and thus, the dataset. The second eigenvector can be thresholded to approximate the class assignment of graph nodes. Eigenvectors of the kernel matrix may be used to assign unlabeled data to clusters, merge information from labeled and unlabeled data by transduction, provide model selection information for other kernels, detect novelties or anomalies and / or clean data, and perform supervised learning tasks such as classification.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Graph-based ranking algorithms for text processing
InactiveUS7809548B2Digital data information retrievalSemantic analysisGraphicsWord-sense disambiguation
The present invention provides a method of processing at least one natural language text using a graph. The method includes determining a plurality of text units based upon the natural language text, associating the plurality of text units with a plurality of graph nodes, and determining at least one connecting relation between at least two of the plurality of text units. The method also includes associating the at least one connecting relation with at least one graph edge connecting at least two of the plurality of graph nodes and determining a plurality of rankings associated with the plurality of graph nodes based upon the at least one graph edge. The method can also include a graphical visualization of at least one important text unit in a natural language text or collection of texts. Methods for word sense disambiguation, keyword extraction, and sentence extraction are also provided.
Owner:NORTH TEXAS UNIV OF
Spectral kernels for learning machines
InactiveUS20060074821A1Low costEasy to spotKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature vector
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Pivoting from a graph of semantic similarity of documents to a derivative graph of relationships between entities mentioned in the documents
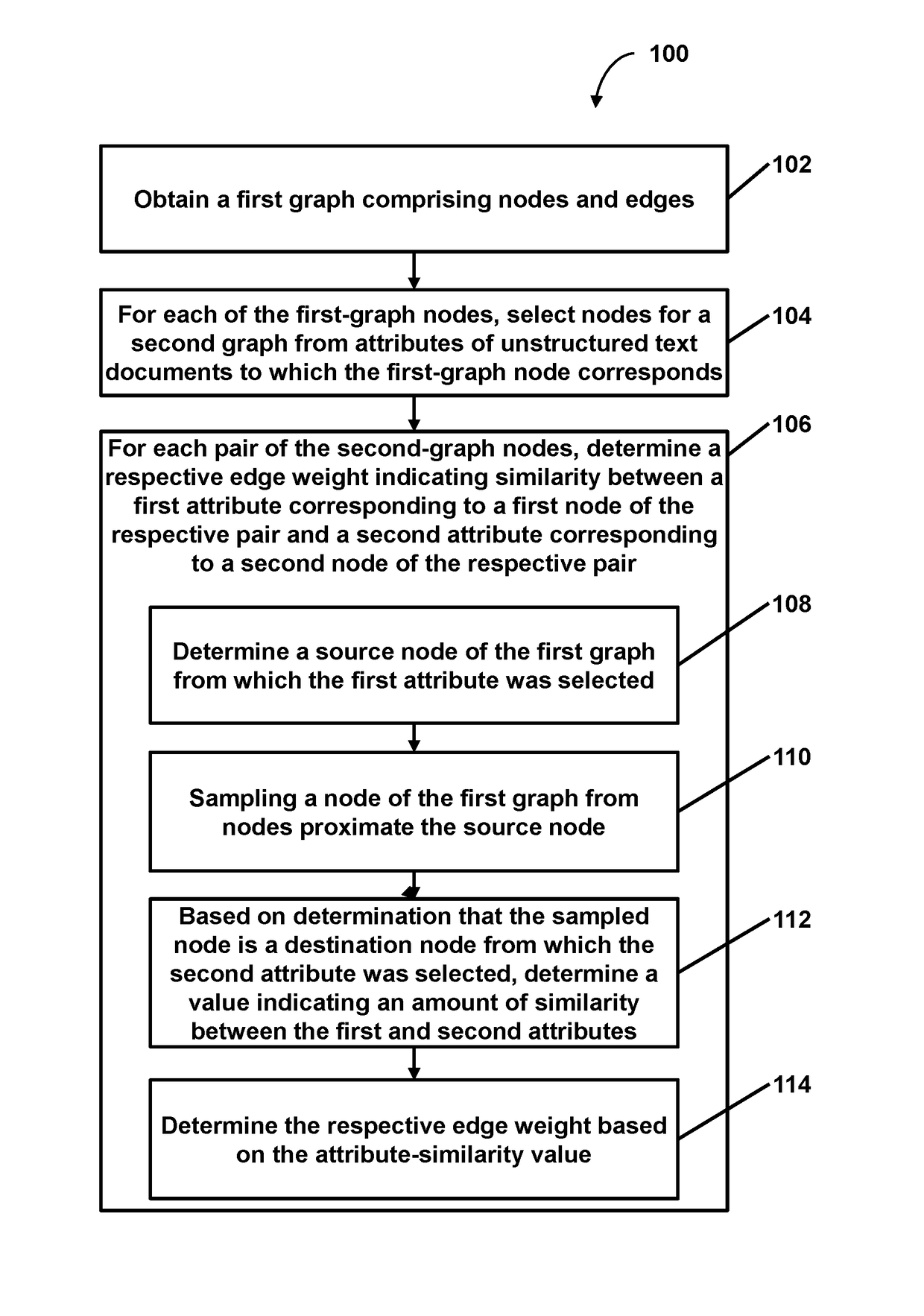
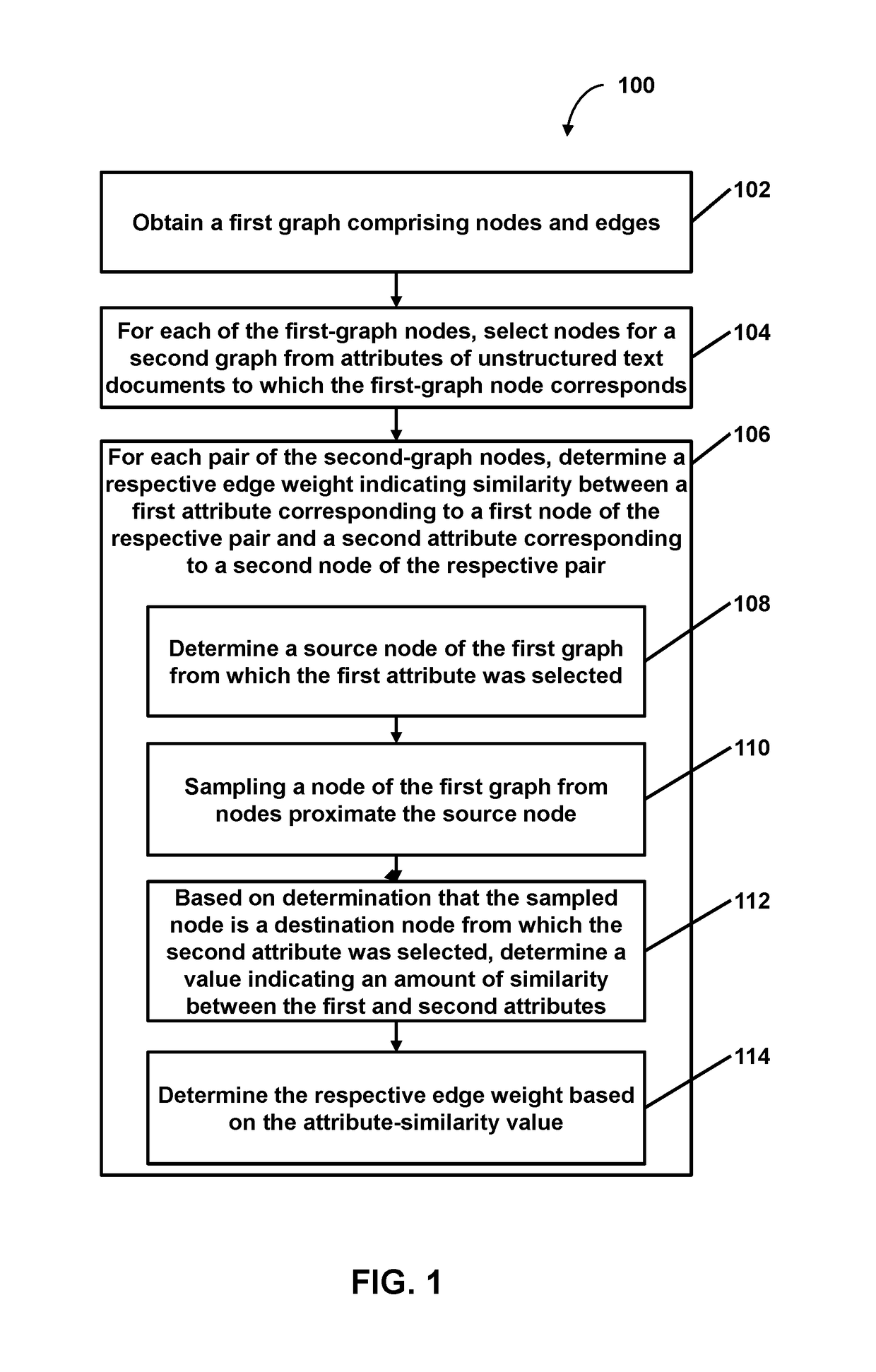
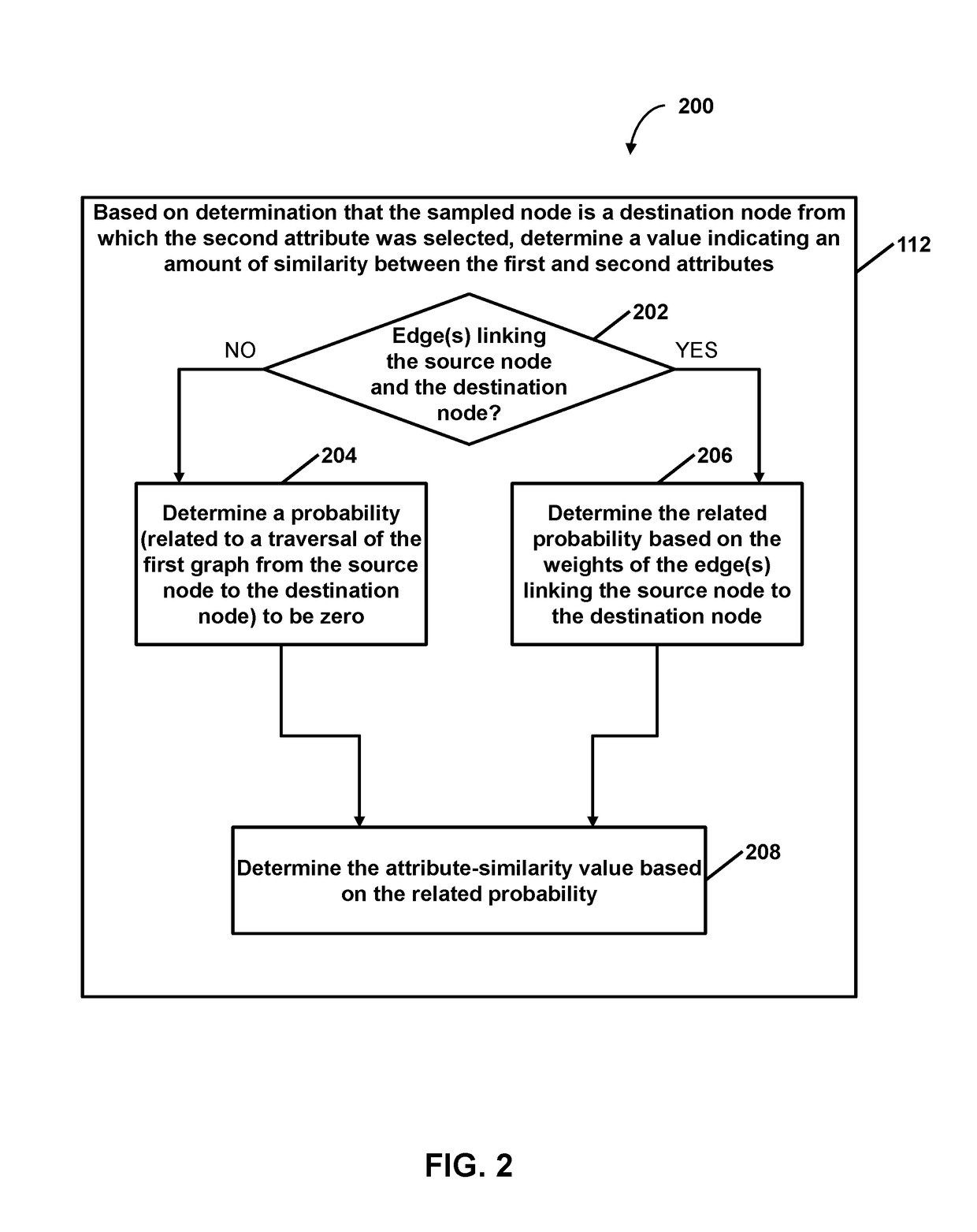
Provided is a process including: obtaining a first graph comprising nodes and edges, each of the first-graph edges linking two of the first-graph nodes and denoting semantic similarity of unstructured text in documents corresponding to the two linked first-graph nodes; for each of the first-graph nodes, selecting nodes for a second graph from attributes of the unstructured text documents to which the first-graph node corresponds, wherein the attributes are entities mentioned in the unstructured text documents, and wherein each of the second-graph nodes corresponds to a respective selected attribute; and for each pair of the second-graph nodes, determining a respective edge weight indicating similarity between a first entity corresponding to a first node of the respective pair and a second entity corresponding to a second node of the respective pair.
Owner:QUID LLC
Determining the importance of data items and their characteristics using centrality measures
InactiveUS20120278261A1Avoid expensiveAvoids non-parallelizable operationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsNODALPath length
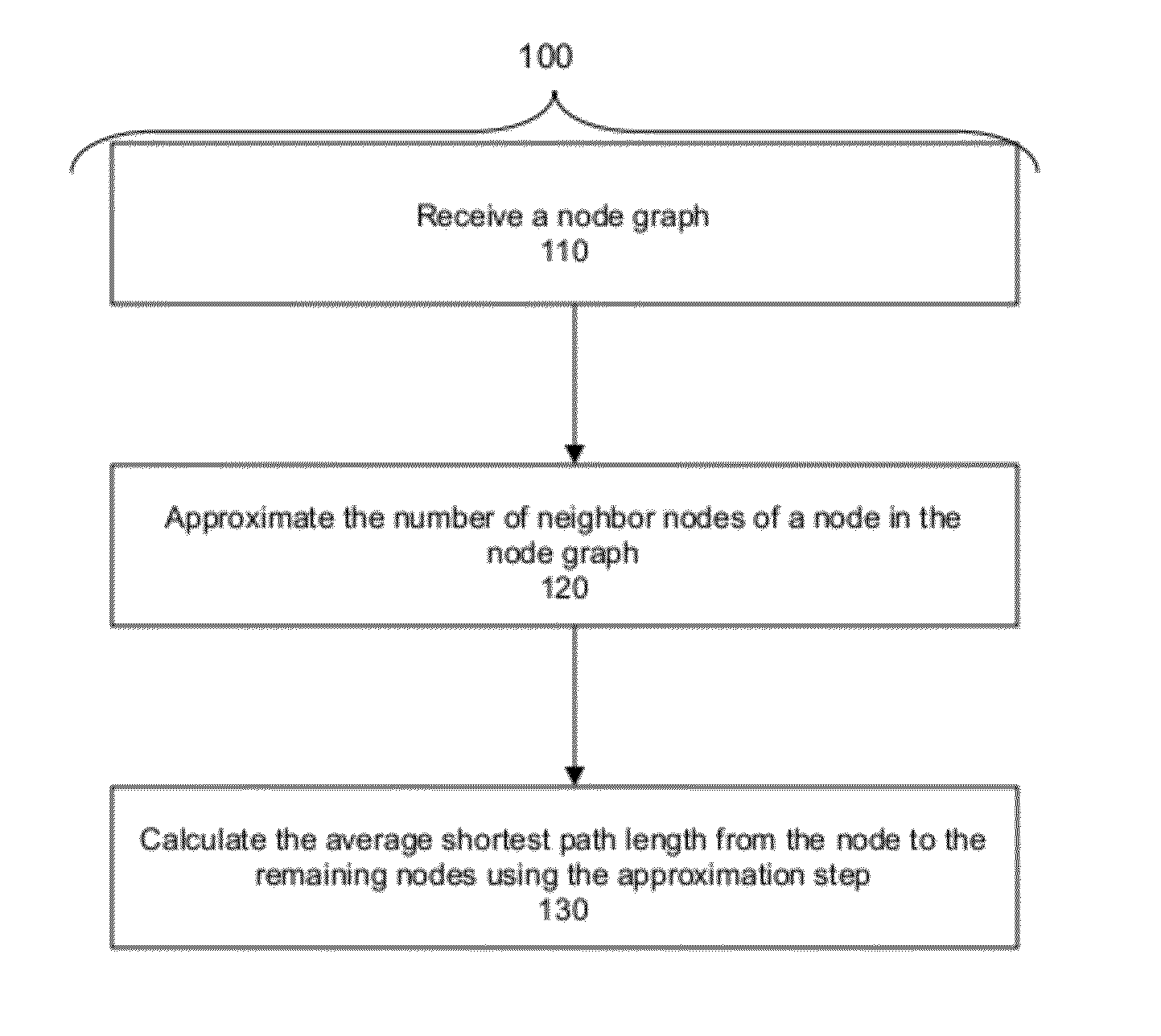
Computer-implemented methods, systems, and articles of manufacture for determining the importance of a data item. A method includes: (a) receiving a node graph; (b) approximating a number of neighbor nodes of a node; and (c) calculating a average shortest path length of the node to the remaining nodes using the approximation step, where this calculation demonstrates the importance of a data item represented by the node. Another method includes: (a) receiving a node graph; (b) building a decomposed line graph of the node graph; (c) calculating stationary probabilities of incident edges of a node graph node in the decomposed line graph, and (d) calculating a summation of the stationary probabilities of the incident edges associated with the node, where the summation demonstrates the importance of a data item represented by the node. Both methods have at least one step carried out using a computer device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Link-based classification of graph nodes
InactiveUS20090132561A1Website content managementSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmGraph Node
A method of labeling unlabeled nodes in a graph that represents objects that have an explicit structure between them. A computing device can use a labeling engine to labeled nodes in a graph that are labeled and can identify an unlabeled node in the graph that is structurally associated with the labeled nodes. The labeling engine can label the unlabeled node with the label of the labeled node based on the structural association between the unlabeled node and the labeled node.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
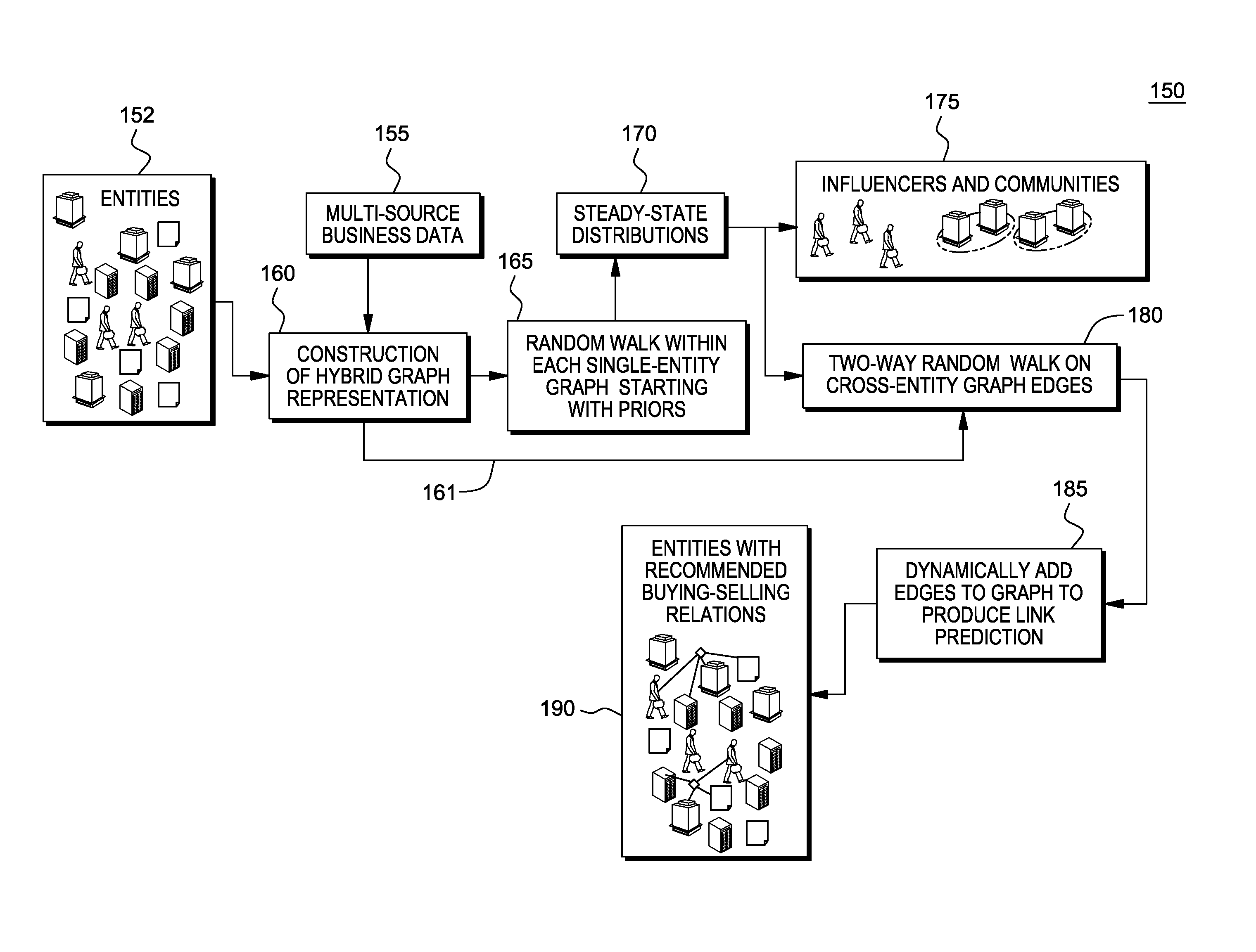
Predictive and descriptive analysis on relations graphs with heterogeneous entities
InactiveUS20140317033A1Avoid information lossMathematical modelsDigital computer detailsRelation graphGraphics
A system, method and computer program product provides a random walk model with heterogeneous graphs to leverage multiple source data and accomplish prediction tasks. The system and method components include: 1) A heterogeneous graph formulation including heterogeneous instances of abstract objects as graph nodes and multiple relations as edges connecting those nodes. The different types of relations, such as client-vendor relation and client-product relation, are often quantified as the weights of edges connecting those entities; 2) To accomplish prediction tasks with such information, launching a multi-stage random walk model over the heterogeneous graph. The random walk within a subgraph with homogenous nodes usually produces the relevance between entities of the same type. The random walk across different type of nodes provides the prediction of decisions, such as a client purchasing a product.
Owner:IBM CORP
Graph node multi-tag classification method based on depth learning
InactiveCN106997474AWith characteristicsHas the effect of dimensionality reductionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsFeature vectorMulti-label classification
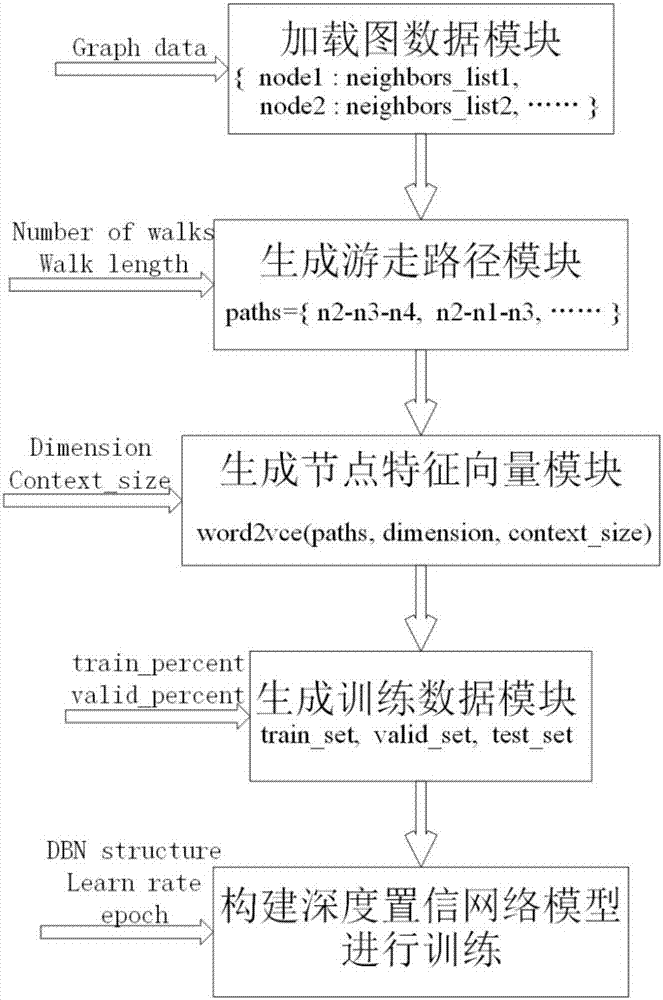
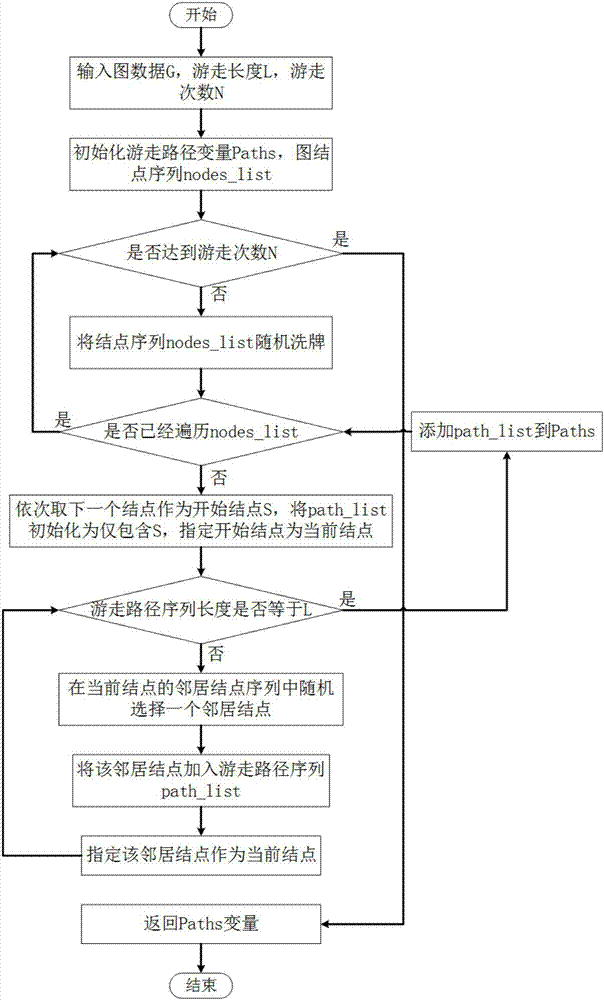
The invention discloses a graph node multi-tag classification method based on depth learning. The method comprises the steps that a graph data module is loaded, and graph data are analyzed and stored in the form of a dictionary; a walk path module is generated to complete random walk in the graph data, and a generated walk path is returned; a node eigenvector module is generated, and the walk path returned by the previous step, the specified vector representing dimension and the context window size are used as input to call a word2vec algorithm to calculate the eigenvector representation of each graph node; a training data module is generated, and nodes of a certain percentage are randomly selected from all graph nodes as training node data; for each node, the eigenvector and the tag sequence corresponding to the node are taken to form a two-tuple set as a training sample; and finally, a depth confidence network model is built. The graph node multi-tag classification algorithm proposed by the invention has higher correct rate than a traditional multi-tag classification algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Feedback-based prioritized cognitive analysis
ActiveUS20180367549A1Easy to analyzeDigital data information retrievalMachine learningEvent dataGraph Node
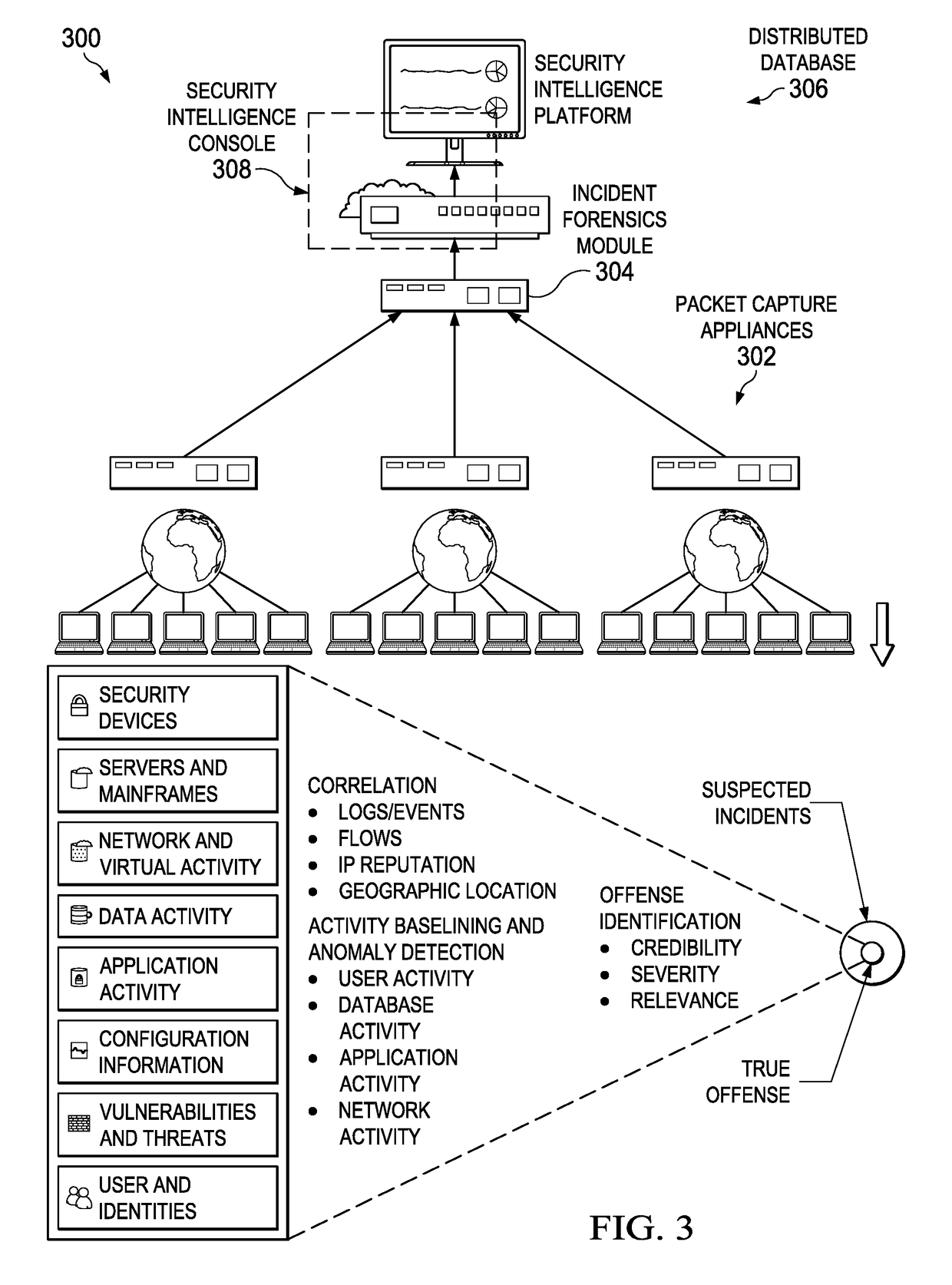
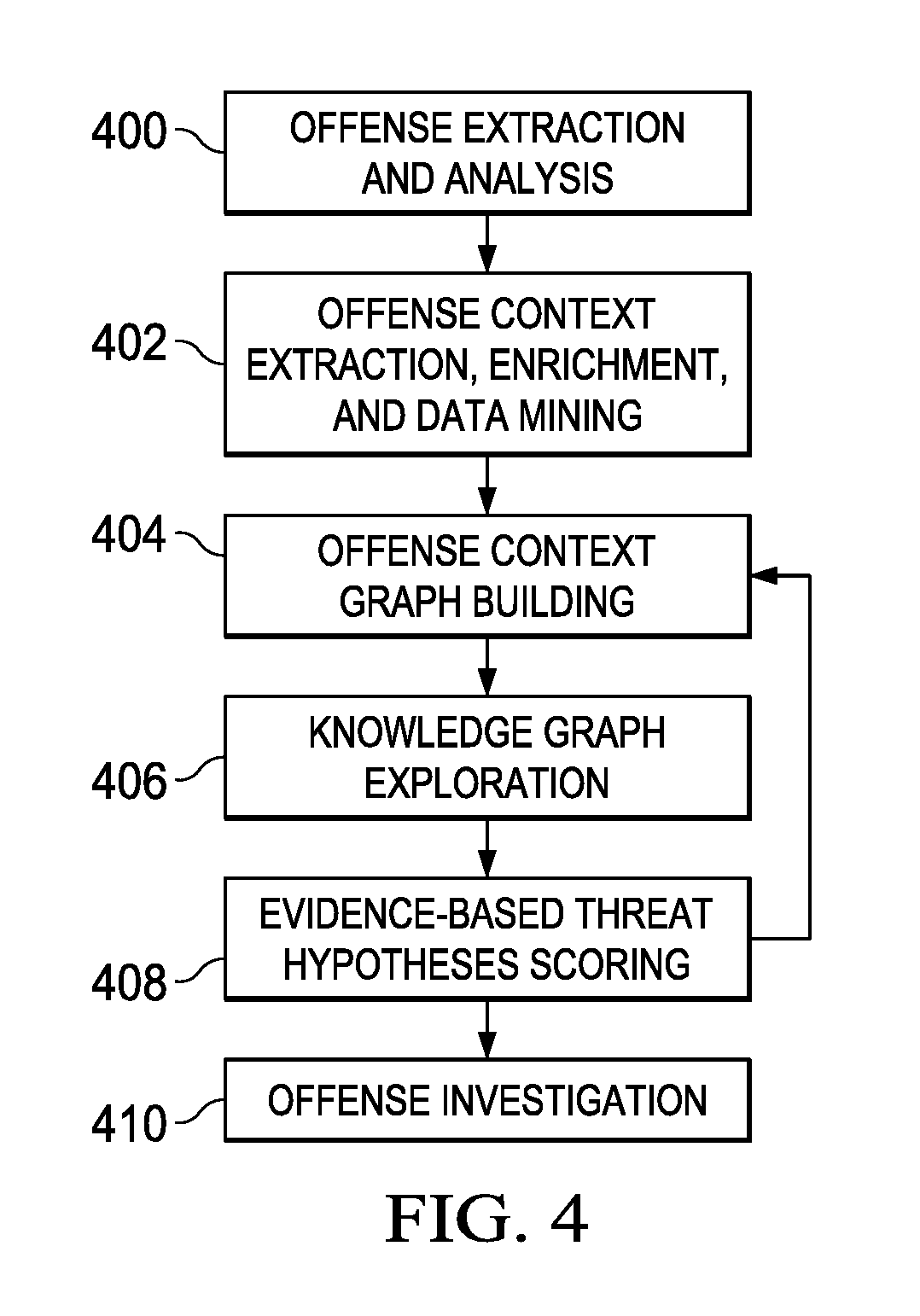
An automated method for processing security event data in association with a cybersecurity knowledge graph having nodes and edges. It begins by receiving from a security system (e.g., a SIEM) information representing an offense. An offense context graph is built. Thereafter, and to enhance the offense context graph, given nodes and edges of the knowledge graph are prioritized for traversal based on an encoding captured from a security analyst workflow. This prioritization is defined in a set of weights associated to the graph nodes and edges, and these weights may be derived using machine learning. The offense context graph is then refined by traversing the nodes and edges of the knowledge graph according to a prioritization tailored at least in part by the encoding. In addition to using security analyst workflow to augment generation of weights, preferably the machine learning system provides recommendations back to the security analysts to thereby influence their workflow.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microeconomic mechanism for distributed indexing
ActiveUS20060026117A1Profit maximizationImprove performanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRouting decisionLoad Shedding
A distributed index for discovering distributed data sources and computing resources based on predicates on attributes is provided. Proposed is a non-altruistic scheme for indexing distributed data, in which nodes are provided with incentives to cooperate in the referencing of data and the routing of search requests for indexed data. Indexed data is mapped to a dynamic routing graph, in which nodes earn credits each time they route a search request. Participatory nodes along a search request traversal continually modify local routing decisions in a manner necessary to maximize profit. Thus, routing paths as a whole are able to dynamically adapt to changing query workloads and access patterns. Dynamic adaptation also occurs by automatic load-balancing of recipients of frequently routed searches, known as “hot spots”, for frequently request data, “hot items”, as a result of an incentive to replicate the indexing strategy of a more profitable node.
Owner:SAP AG
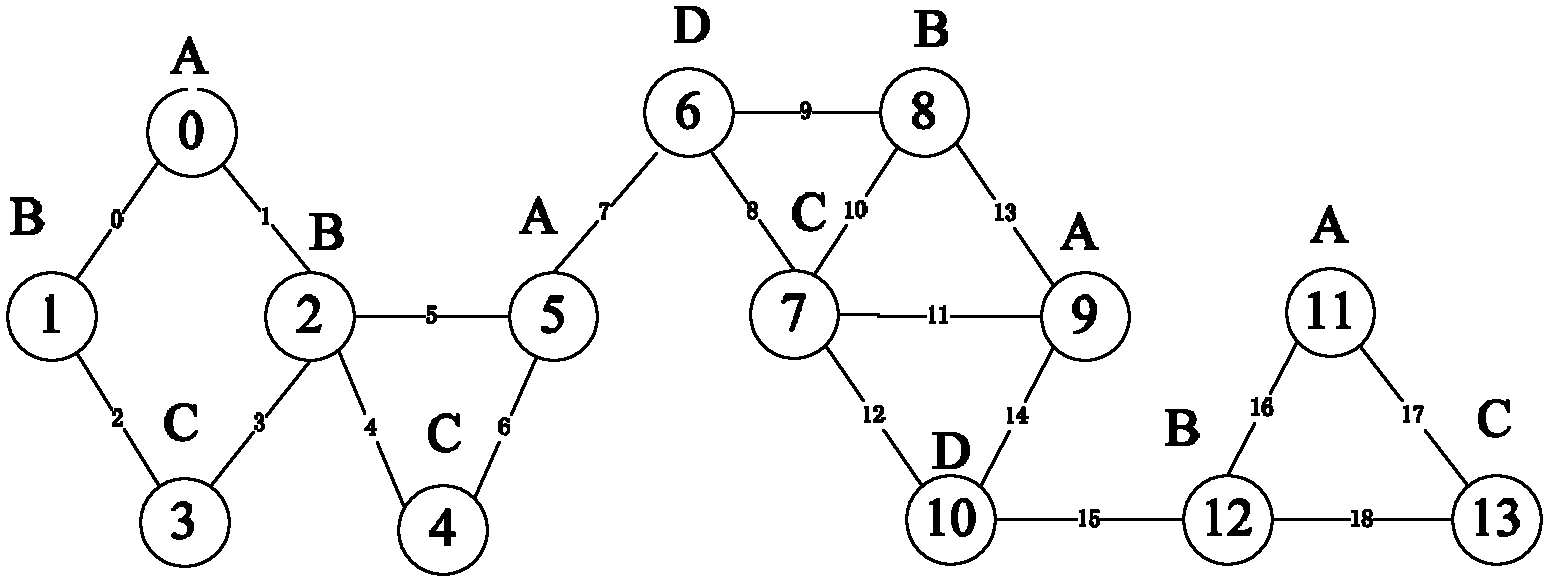
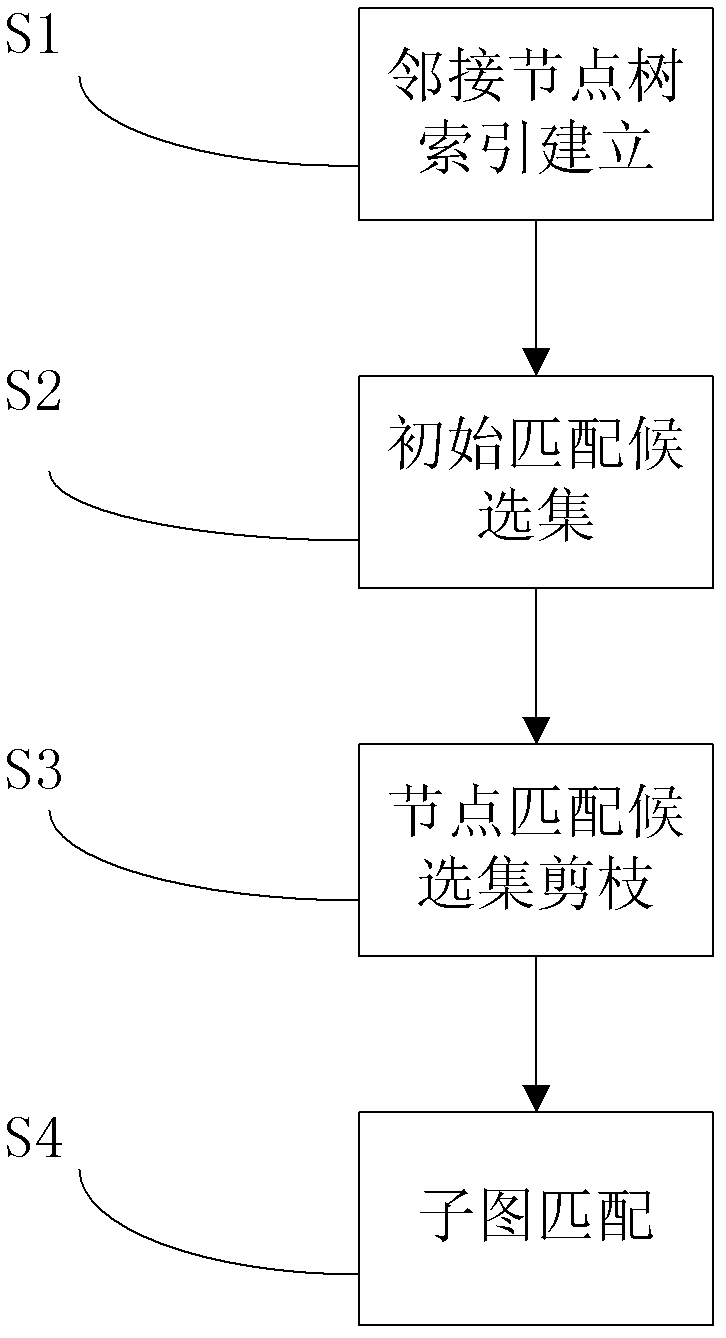
A network graph index method based on adjacent node trees
The invention discloses a subgraph query method in a large scale network graph based on adjacent node trees. The invention uses the adjacent relation of nodes to form index trees, and uses the adjacent node trees as an index characteristic of the large scale network graph to realize the query process of the subgraph. First, a graphic label list, a layer by layer tag list, and an edge list are established according to the adjacent relation of the graph nodes, and adjacent node tree index is constructed based on the lists; secondly, the nodes matching candidate set are obtained through decomposing the query graph to the adjacent node tree sets and tailoring the candidate nodes by utilizing the established adjacent node tree index; and finally, by employing the strategy of covering the query graph with the adjacent node tree sets, a subgraph query result is obtained based on the node matching method. The method uses the adjacent relation to realize effective filtering of the candidate nodes and rapid covering of the query graph, and is capable of supporting rapid query of the subgraph in the large scale network graph.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Simultaneous Power and Timing Optimization in Integrated Circuits by Performing Discrete Actions on Circuit Components
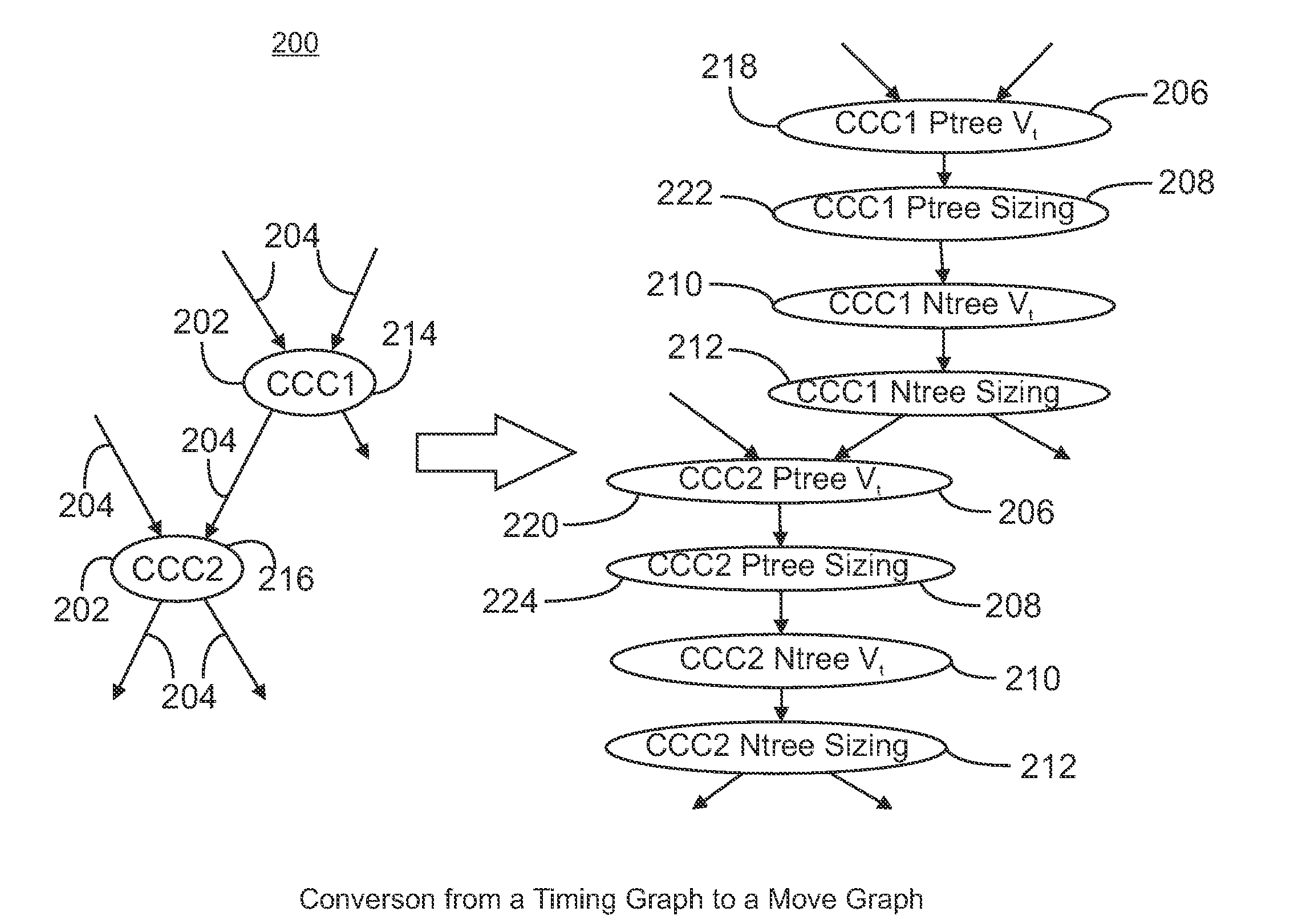
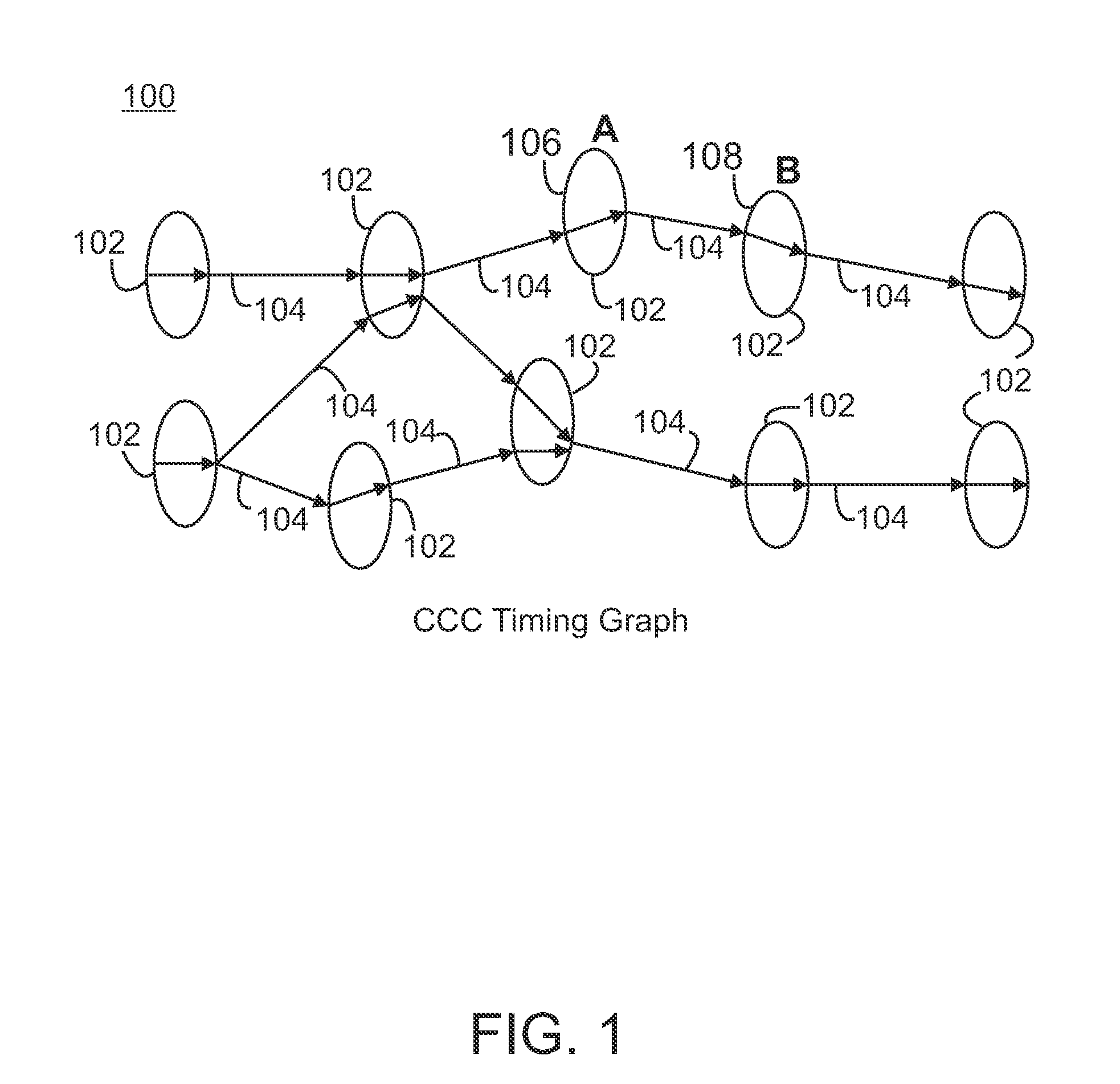
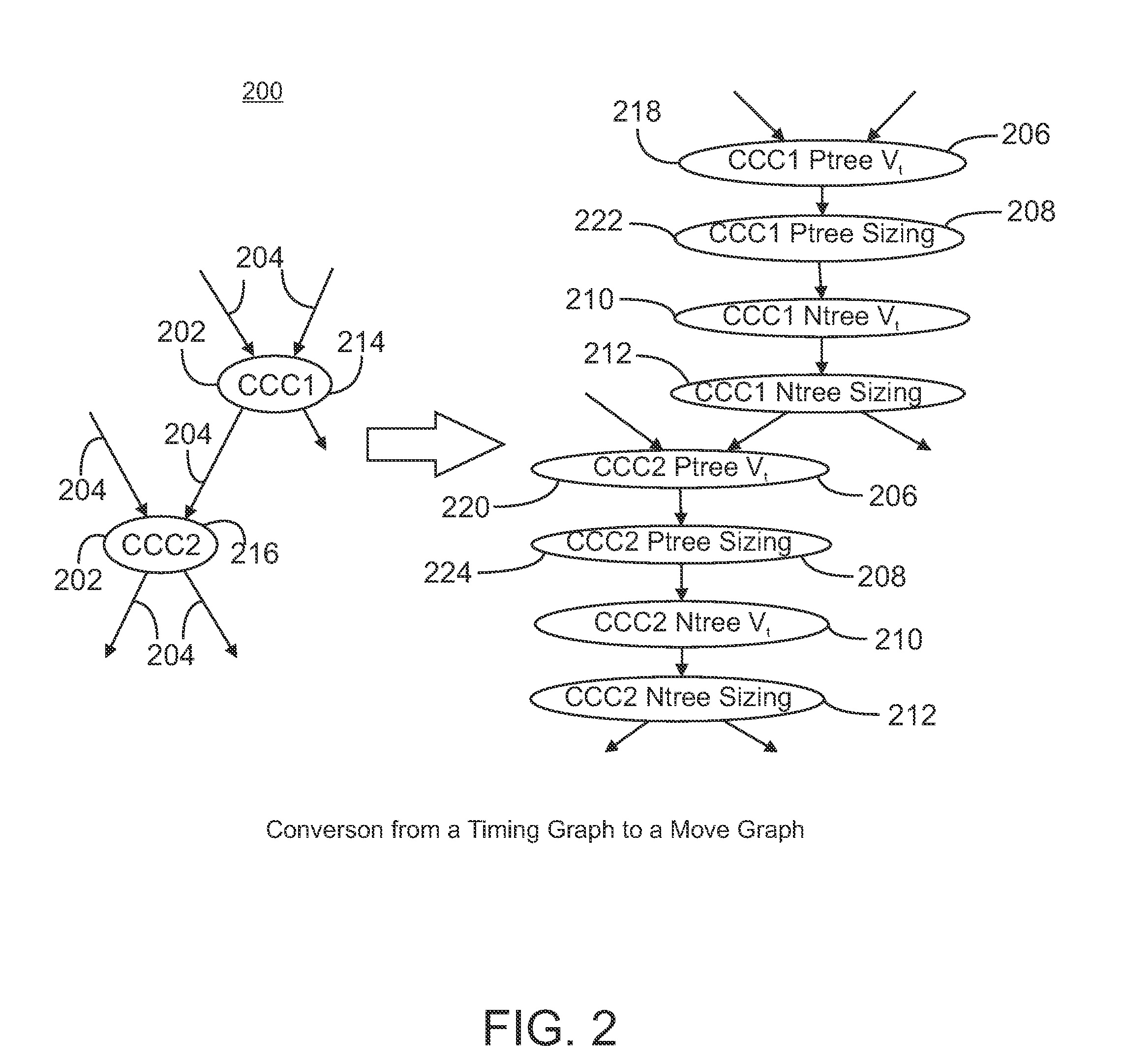
ActiveUS20090055780A1Less computation timePromote resultsComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGraph NodeDirect path
A graph-based iterative method is provided for selecting component modifications in an integrated circuit design that reduce the power consumption to a minimum while still meeting timing constraints. Channel-connected components are represented as nodes in a timing graph and edges in the timing graph represent directed paths. From the timing graph, a move graph is constructed containing a plurality of move nodes. Each move node represents a change to one of the components in one of the timing graph nodes. A given timing graph node can result in a plurality of move nodes. Move nodes can be merged into group nodes, and both the move nodes and group nodes are assigned a weight based on the change in power and timing effects of the associated components changes. These weights are used to select move nodes or group nodes. In general, a set of move or group nodes is selected representing the maximum cumulative weight and the components changes associated with the nodes in the set are performed on the integrated circuit design. Moves that cause timing violations are reversed. The node weights are updated following components changes and the selection of node sets is repeated iteratively until the power consumption converges to a minimum.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
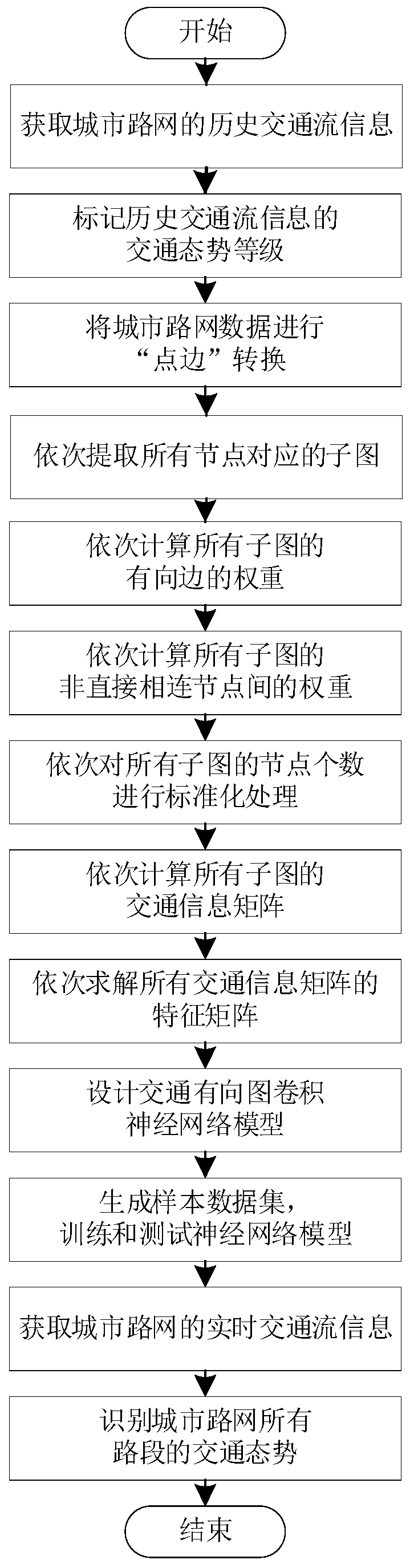
Urban traffic situation identification method based on directed graph convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111540198AImprove universalitySimple processDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionDirected graphRoad networks
The invention discloses an urban traffic situation identification method based on a directed graph convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the traffic situation classification of historical traffic flow information, converting an urban road network into a directed graph according to a point-edge conversion rule, and extracting a corresponding sub-graph; then, calculating the weight of a directed edge and the weight between non-directly connected nodes, standardizing the number of nodes of the subgraph, and calculating a traffic information matrix and a feature matrix of the subgraph; finally, designing a traffic directed graph convolutional neural network model, performing training and testing, using the model for classifying real-time traffic flow information to identify the real-time traffic situation of all road sections. According to the method, the incidence relation between directed road sections of different levels and different grades under the hybrid road network is fully considered, a unified standardized model input and traffic situation recognition model is designed, and good universality is achieved; moreover, the method has the characteristics of simple process, easiness in calculation, easiness in programming realization and the like, and can be suitable for complex urban road networks.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Chinese integrated entity linking method based on graph model
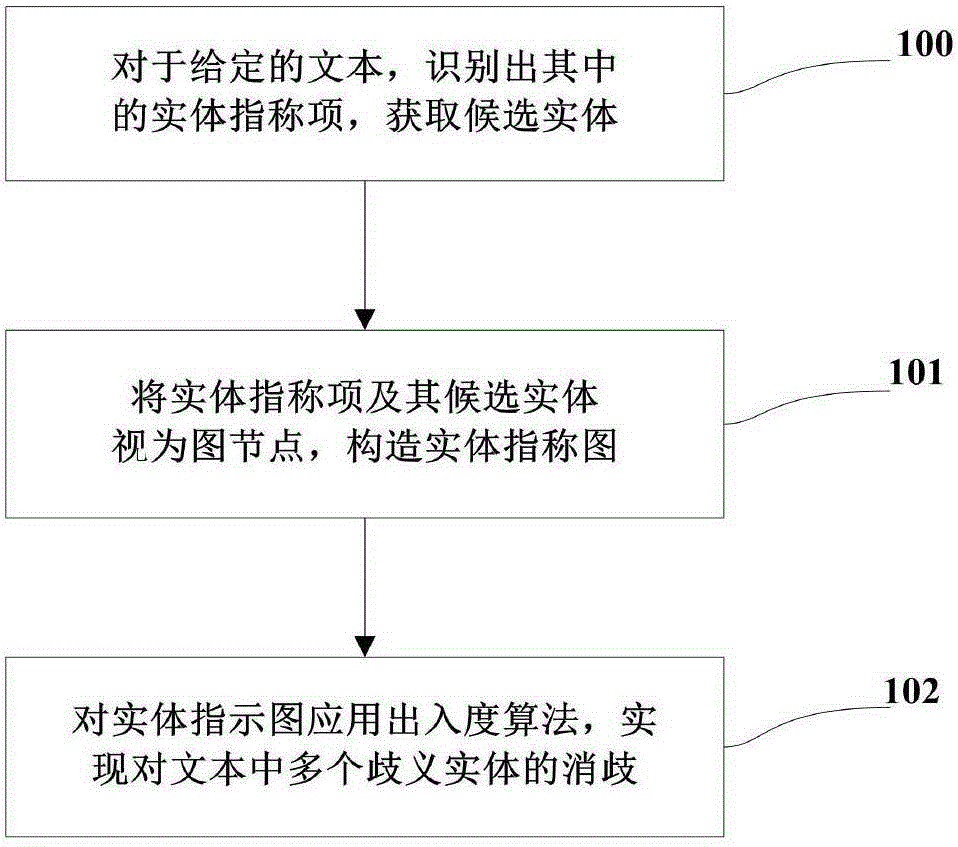
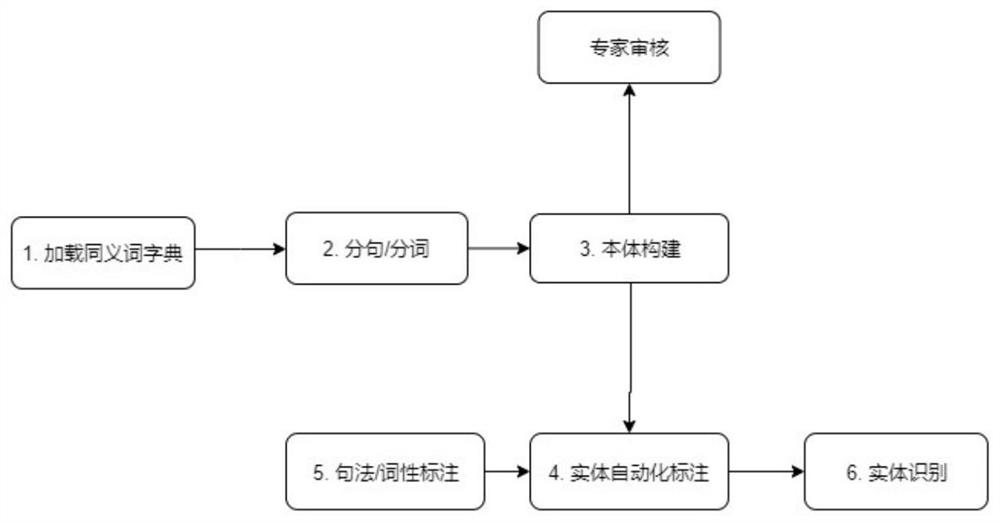
InactiveCN105183770AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsEntity linkingNODAL
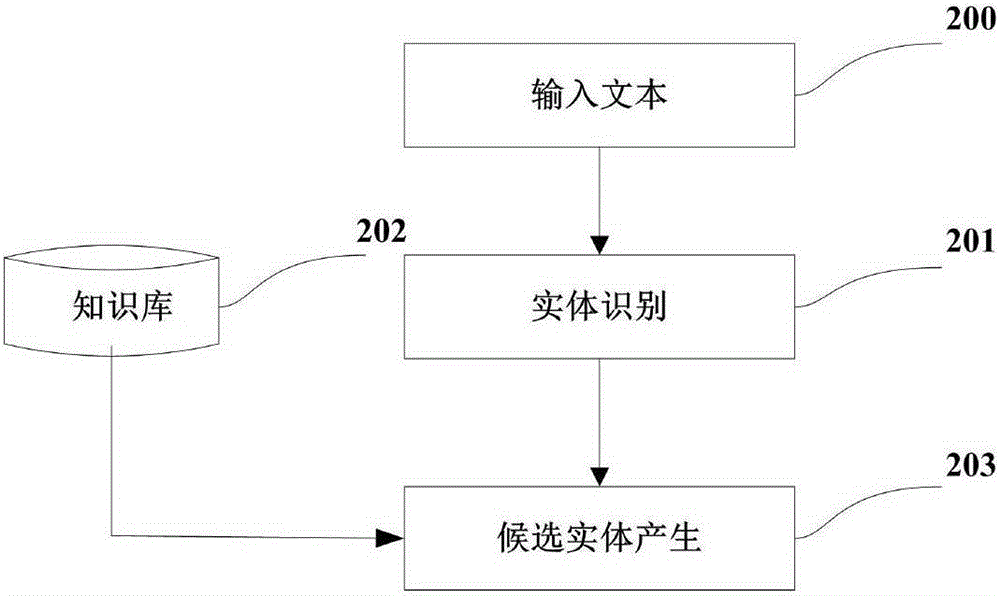
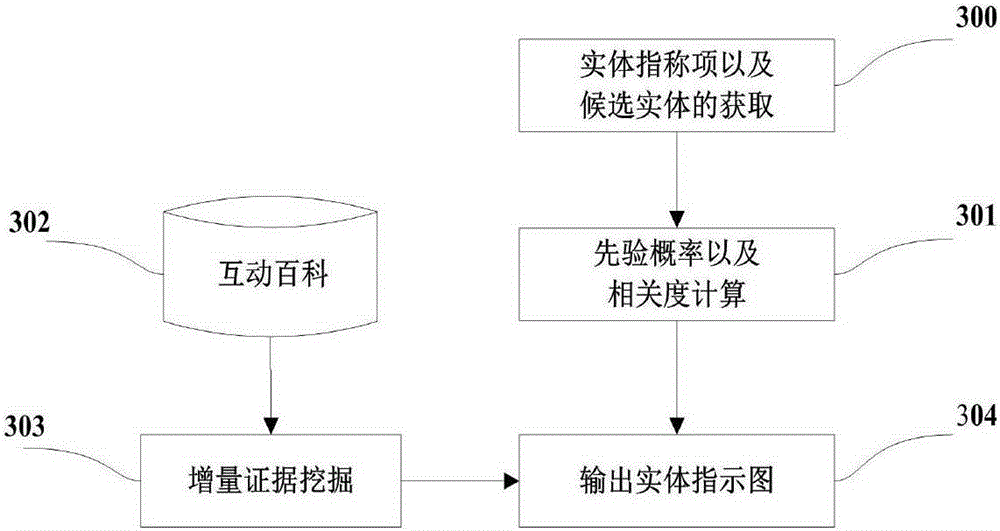
The present invention discloses a Chinese integrated entity linking method based on a graph model. An ambiguous entity in a text can be mapped into a specific entity in a real world, in order to provide aid for knowledge base expansion, information extraction and search engines. The method mainly comprises three parts of generating a candidate entity, constructing an entity indicator diagram, and disambiguating an integrated entity. For a given text, an entity referent item therein is recognized to obtain the candidate entity. The entity referent item and the candidate entity thereof are regarded as graph nodes to construct an entity referent graph. An in-degree and out-degree algorithm is applied to the entity indicator diagram for implementing disambiguation of multiple ambiguous entities in the text. The present invention does not depend on the knowledge base completely in the establishment of the entity indicator diagram, and also can implement incremental evidence mining to find evidence on an encyclopedia webpage. Dependence path analysis is employed to find the possibly related entity referent item. When the dependence path sizes of two entity referent items are within a set range, the two entity referent items are regarded as the possibly related entity referent items. Further, whether their candidate entities have relations in the real world is determined, so that the efficiency of disambiguation is greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Graph data searching method and device
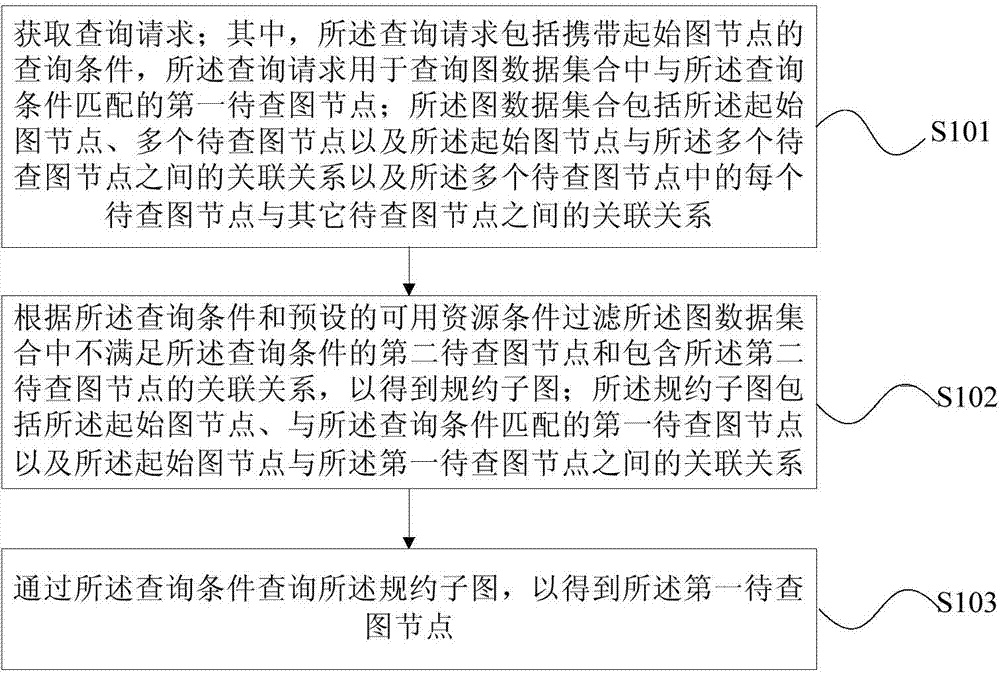
ActiveCN104504003AAvoid invalid searchesSave time resourcesWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsData setAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a graph data searching method and device. The method comprises the following steps that inquiry requests are obtained, wherein the inquiry requests include inquiry conditions carrying starting graph nodes, and the inquiry requests are used for inquiring first graph nodes to be inquired matched with the inquiry conditions in an inquiry graph data set; the association relationship including the second graph nodes to be inquired and the second graph nodes to be inquired not meeting the inquiry conditions in the graph data set are filtered according to the inquiry condition and the preset available resource condition, so that a stipulation sub graph is obtained; the stipulation sub graph includes initial graph nodes, the first graph nodes to be inquired matched with the inquiry condition and the association relationship between the initial graph nodes and the first graph nodes to be inquired; the stipulation sub graph is inquired through the inquiry conditions to obtain the first graph nodes to be inquired. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the graph data searching efficiency is improved, and in addition, memory resources and time resource of a computer are saved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Predictive and descriptive analysis on relations graphs with heterogeneous entities
InactiveUS9195941B2Avoid information lossProbabilistic networksKnowledge representationNODALRelation graph
Owner:IBM CORP
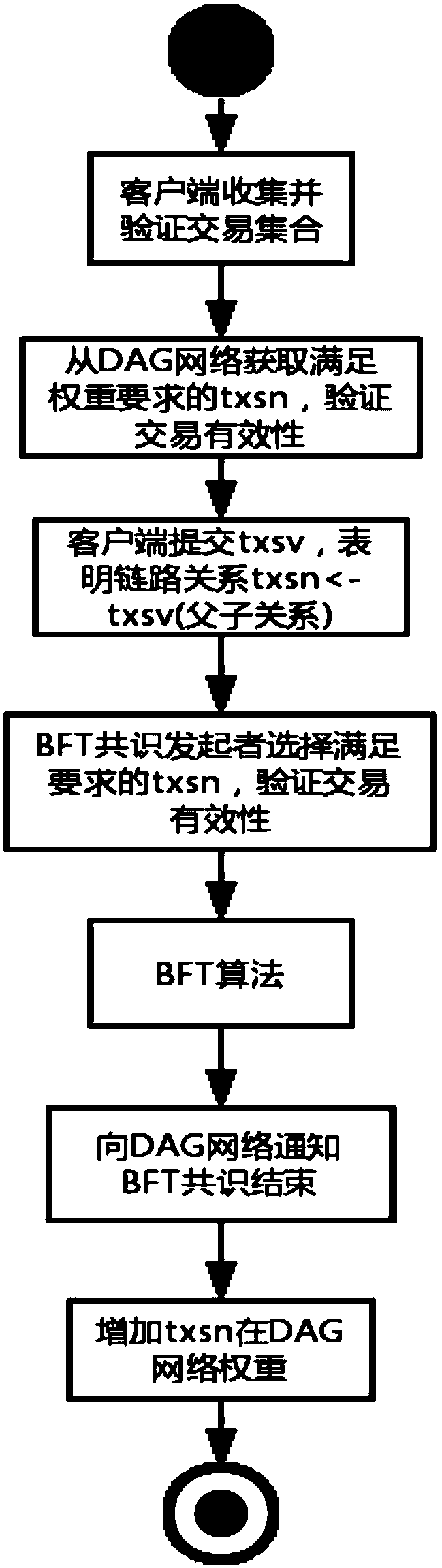
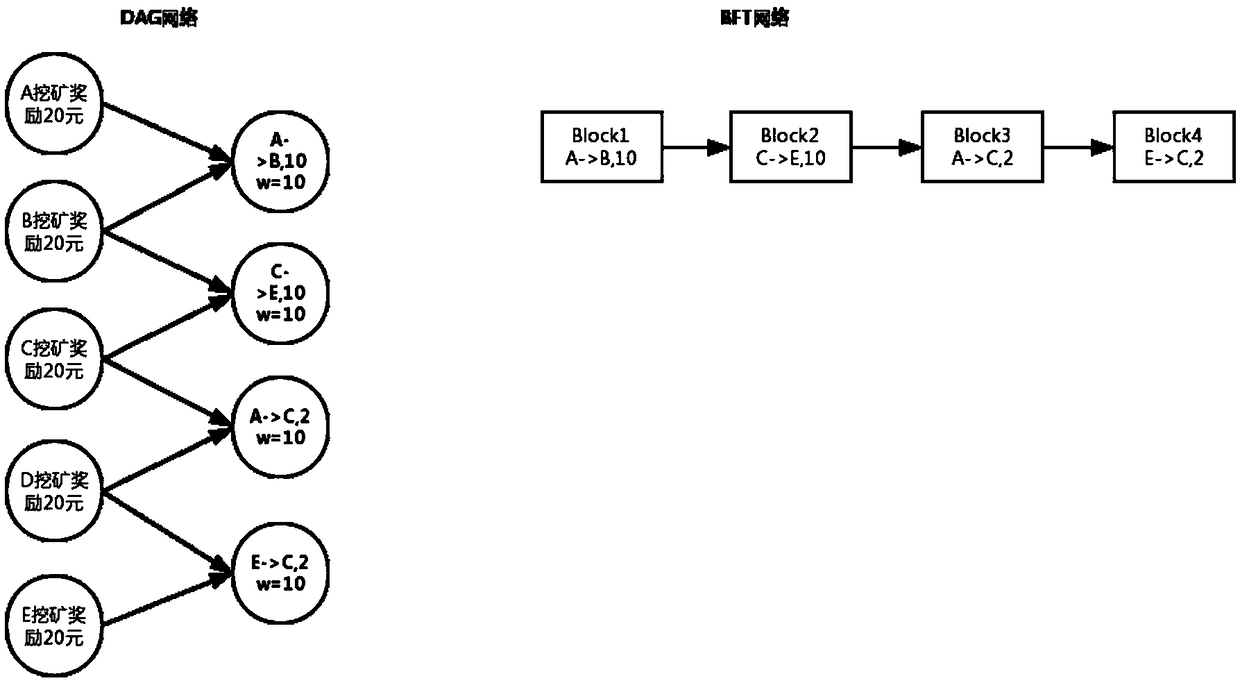
A block-chain hybrid consensus method based on DAG algorithm
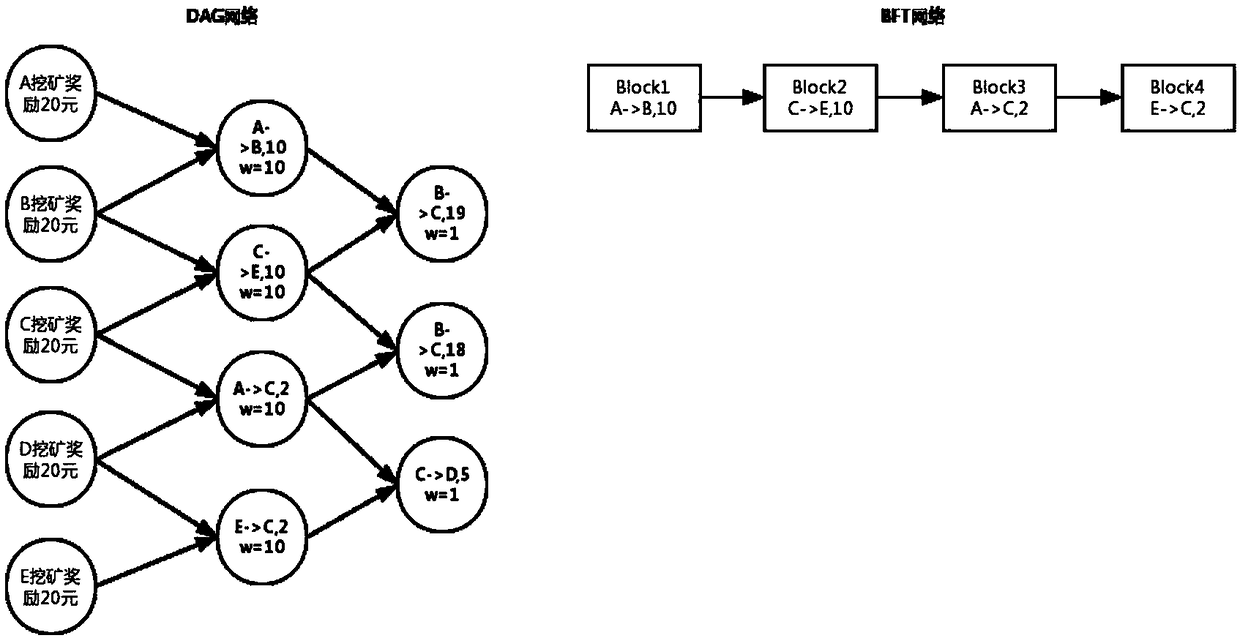
InactiveCN109214795AImprove consensus efficiencyRelieve stressFinancePayment circuitsGraph NodeClient-side
A block chain hybrid consensus method based on DAG algorithm comprises the following steps: 1.a client collects and verifies transactions or transaction sets; 2, selecting at least two graph nodes whose weight is high than that set value from the DAG network, verifying the transaction validity of the graph nodes or the transaction set, and proceed to the next step after the verification; 3, the client end submits a transaction or a transaction set to the DAG network; Step 4, adopting a second consensus algorithm different from the DAG consensus algorithm to carry out deterministic consensus; 5, the consensus initiator sends a graph node consensus completion message to the DAG network; Step 6: increasing the weight of the graph node in the DAG network.
Owner:北京物链互联科技有限公司
Dynamic graph convolution traffic speed prediction method
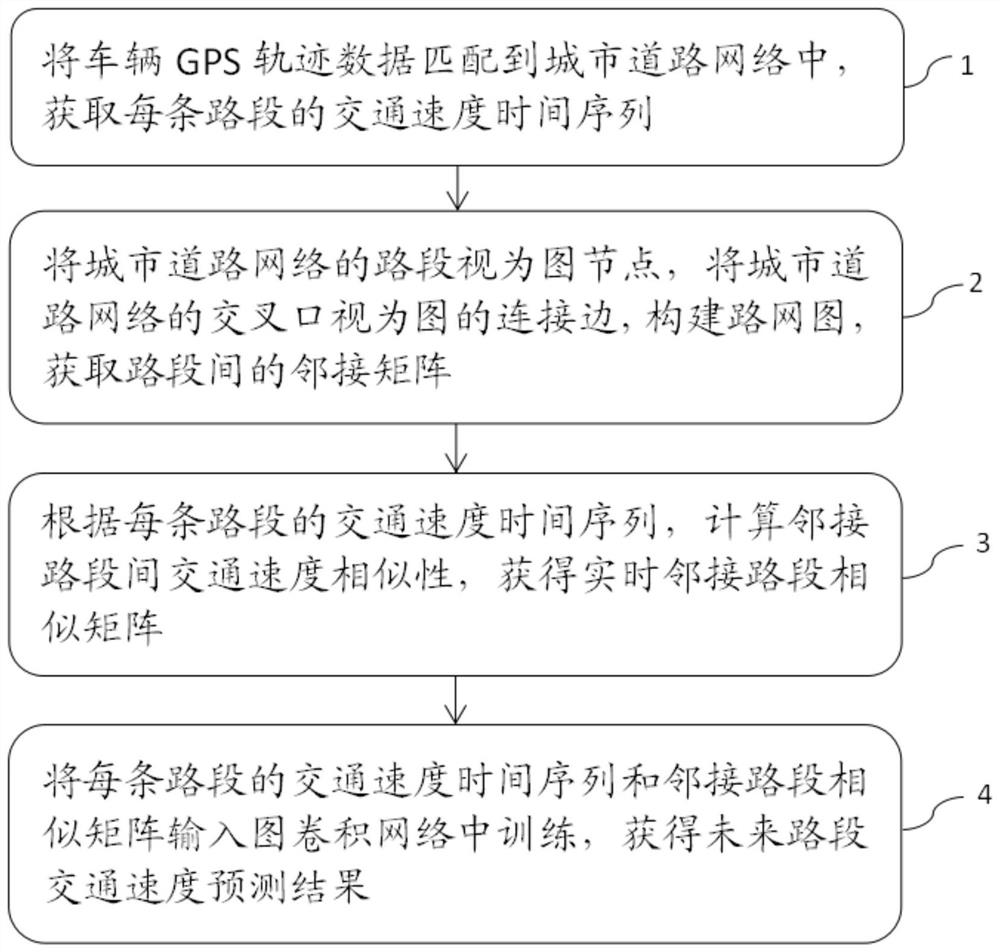
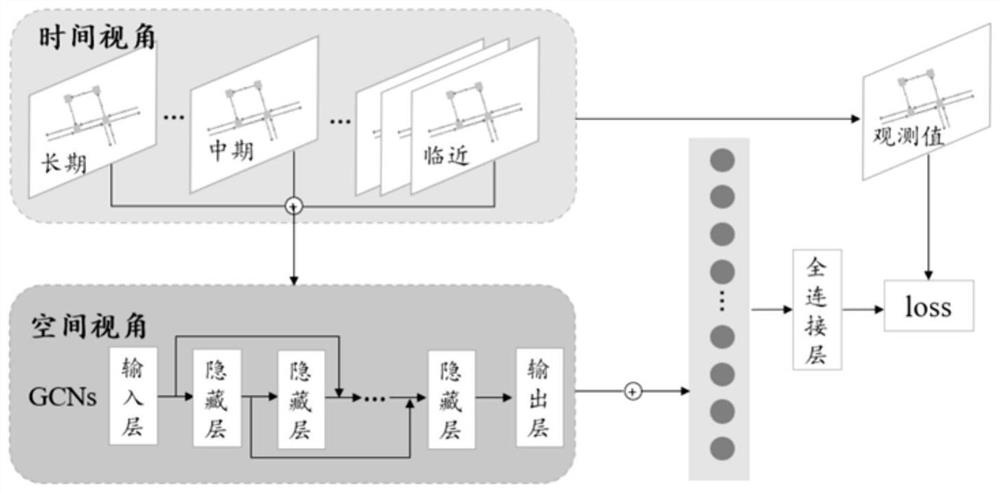
InactiveCN111696355ACaptures space-time dependenciesEnsure travel safetyDetection of traffic movementForecastingSimulationRoad networks
The invention provides a dynamic graph convolution traffic speed prediction method which comprises the steps: step 1, matching vehicle GPS trajectory data into an urban road network, and obtaining a traffic speed time sequence of each road section; step 2, regarding road sections of the urban road network as graph nodes, regarding intersections of the urban road network as connecting edges of a graph, constructing a road network graph, and obtaining an adjacent matrix between the road sections; step 3, calculating the traffic speed similarity between adjacent road sections according to the traffic speed time sequence of each road section, and obtaining a real-time adjacent road section similarity matrix; and step 4, inputting the traffic speed time sequence of each road section and the adjacent road section similarity matrix into a graph convolution network for training to obtain a future road section traffic speed prediction result. According to the invention, spatial dependence and time dependence between road sections can be learned in real time, the change rule of the traffic speed can be captured, the speed of future urban roads can be predicted more accurately, and the methodcan be applied to intelligent traffic and smart city construction.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Story albums
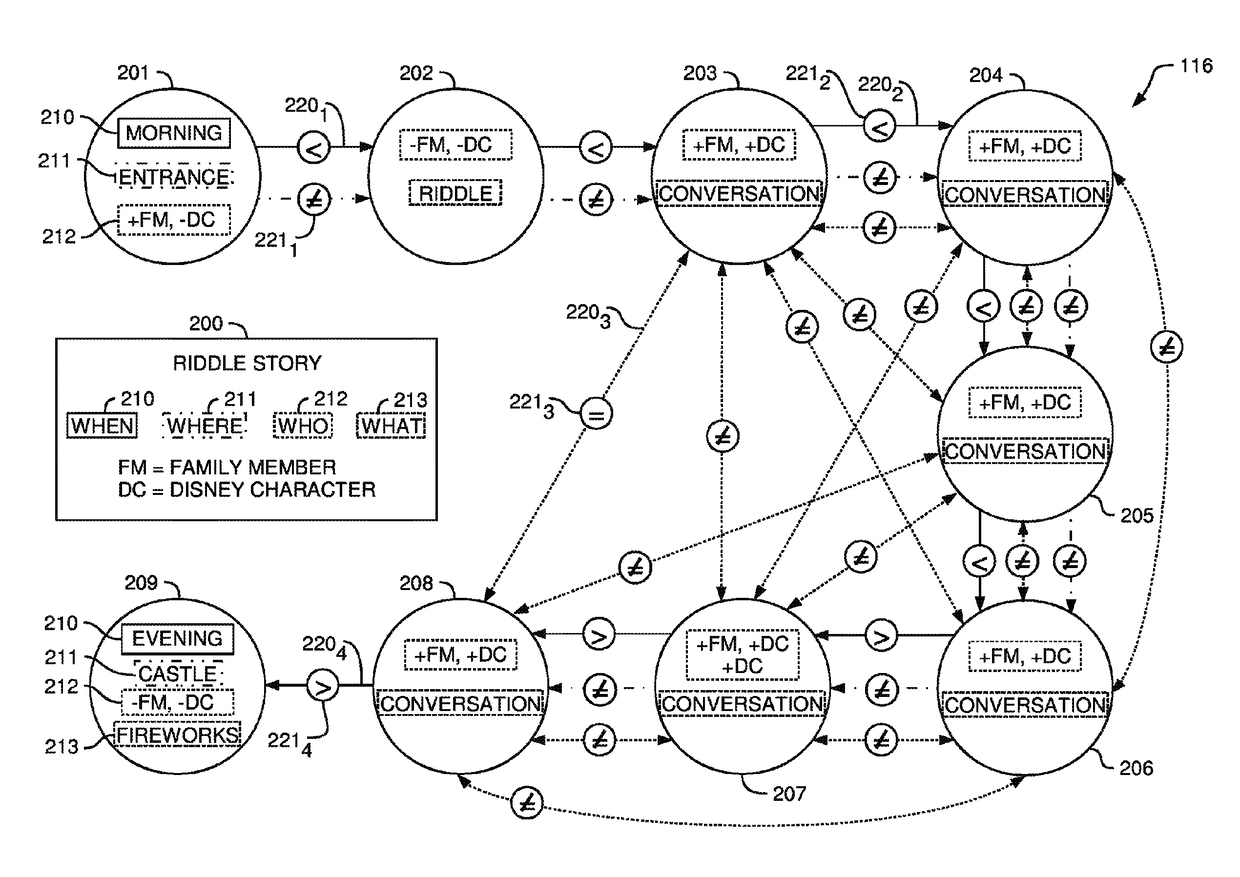
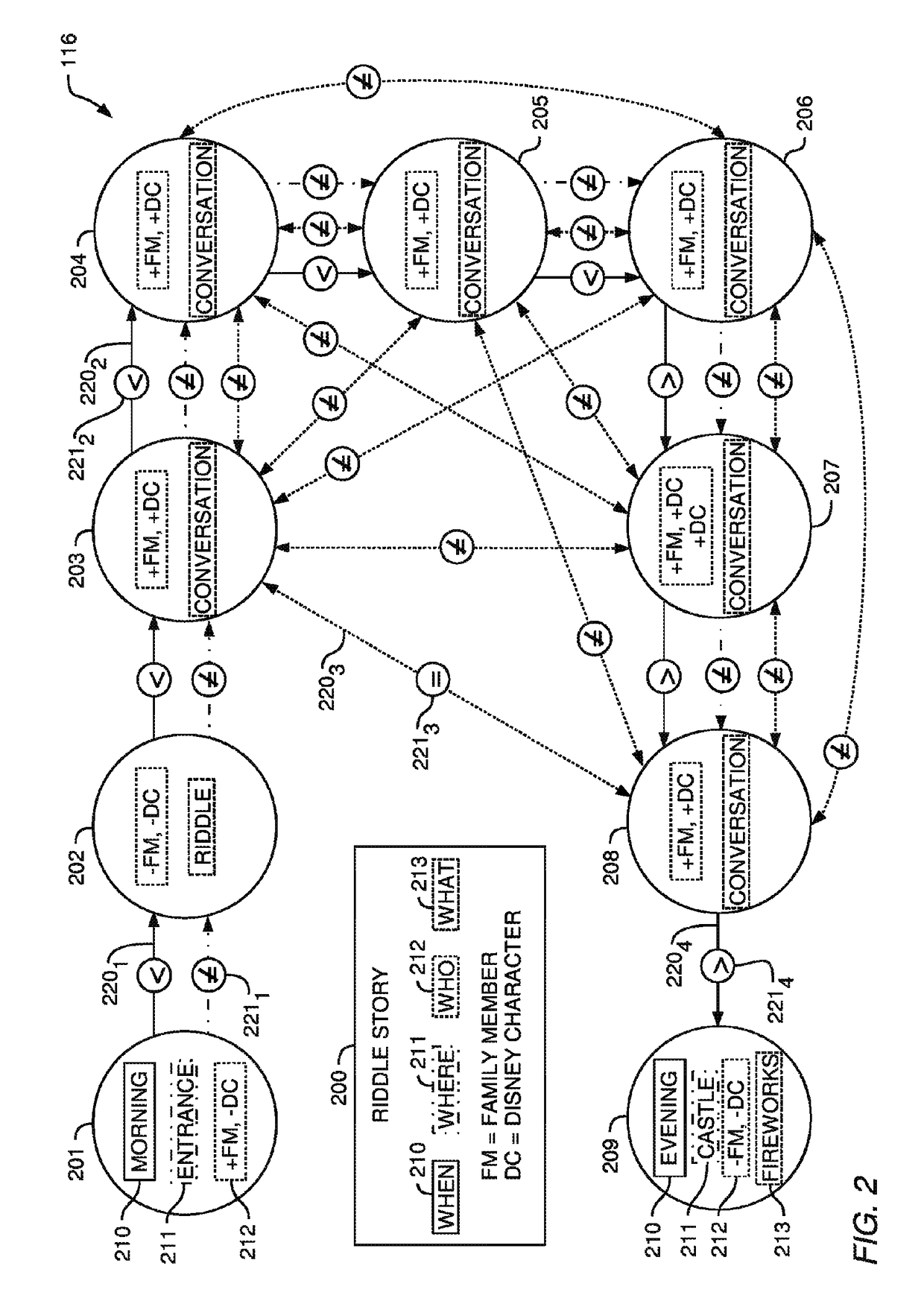
Systems, methods, and computer program products to perform an operation comprising assigning each of a plurality of nodes of a graph to a distinct image, of a plurality of images, wherein the graph represents a story, wherein each node corresponds to a respective element of the story, wherein each node comprises: (i) an attribute and (ii) a text of the respective element of the story, wherein the plurality of graph nodes are assigned based on a set of attributes of each of the plurality of images and the attribute of each node, and generating a visual depiction of the story, wherein the visual depiction comprises an ordered representation of each of the distinct images and the text of each respective element of the story.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Method and apparatus for processing virtual private cloud
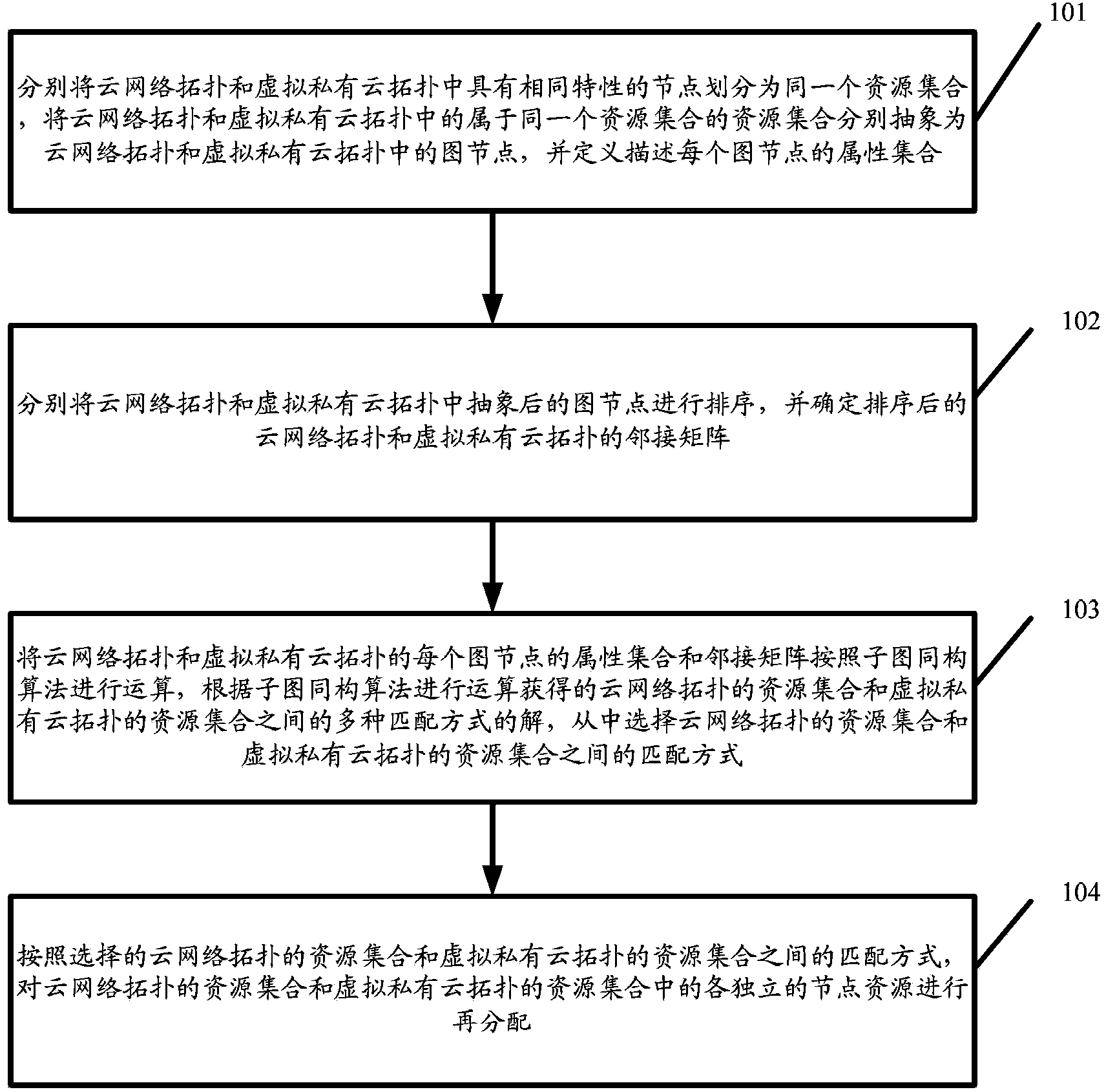
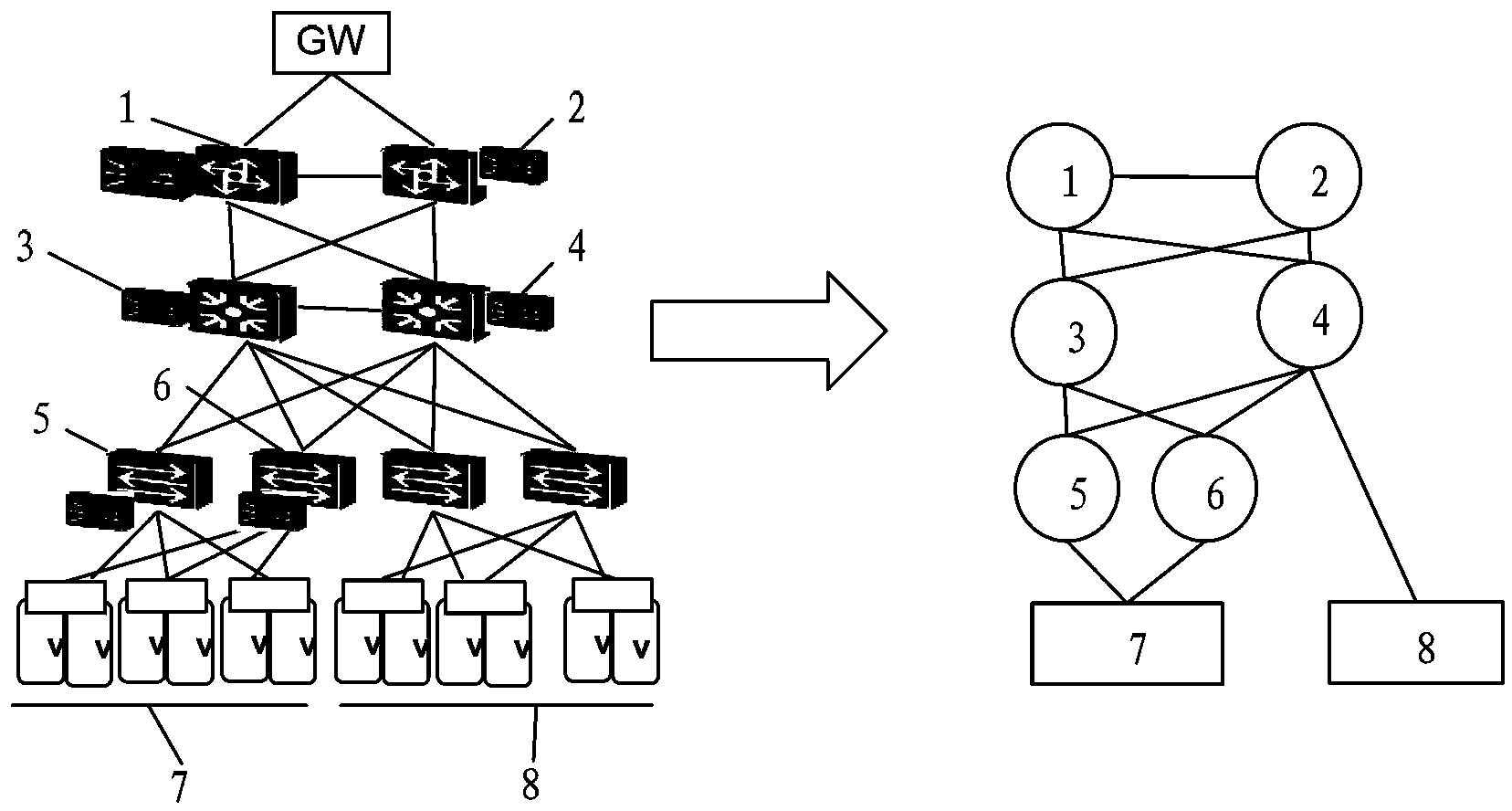
InactiveCN103516733ASmall scaleReduce computational complexityTransmissionGraph NodeMatching methods
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
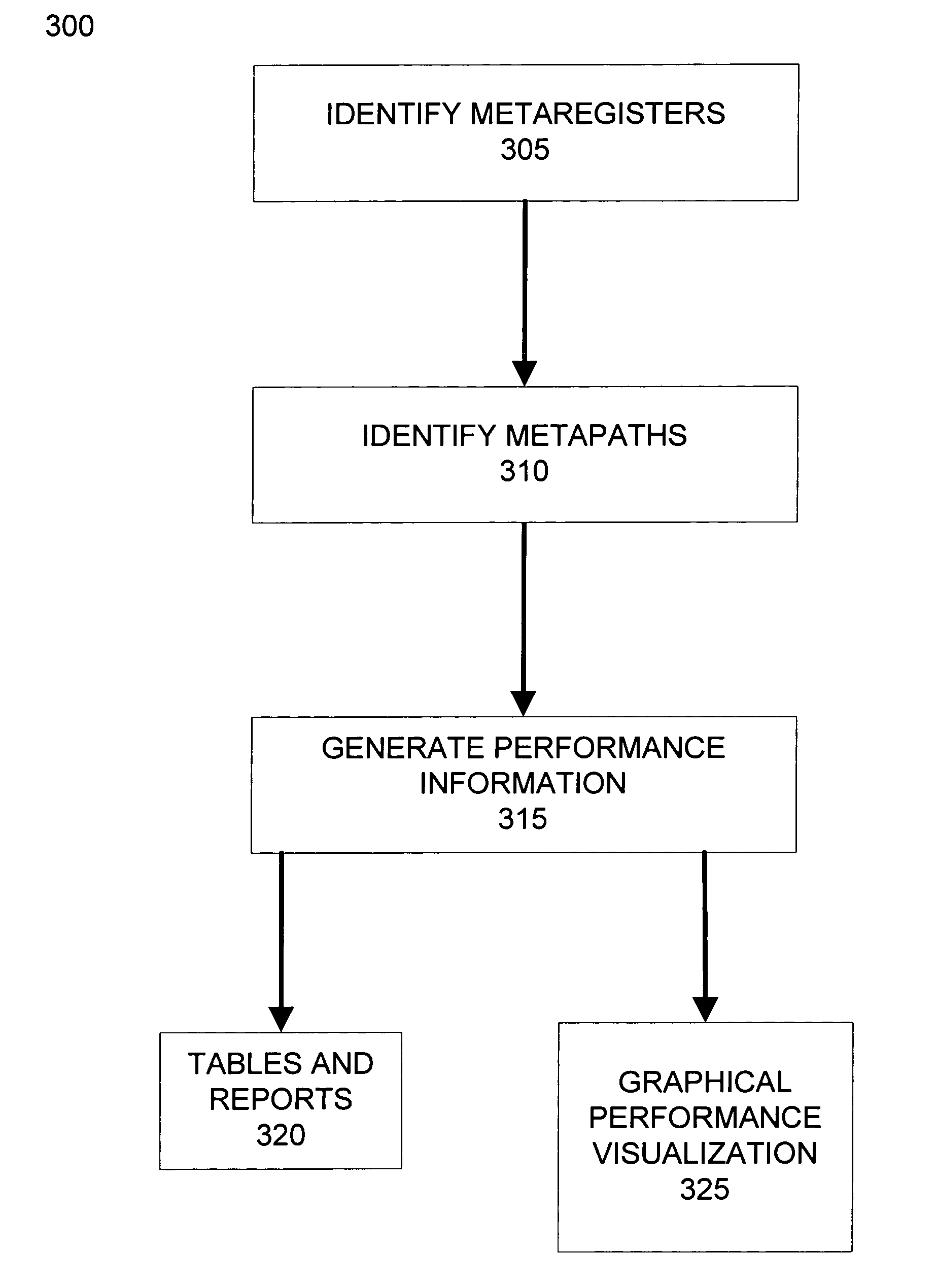
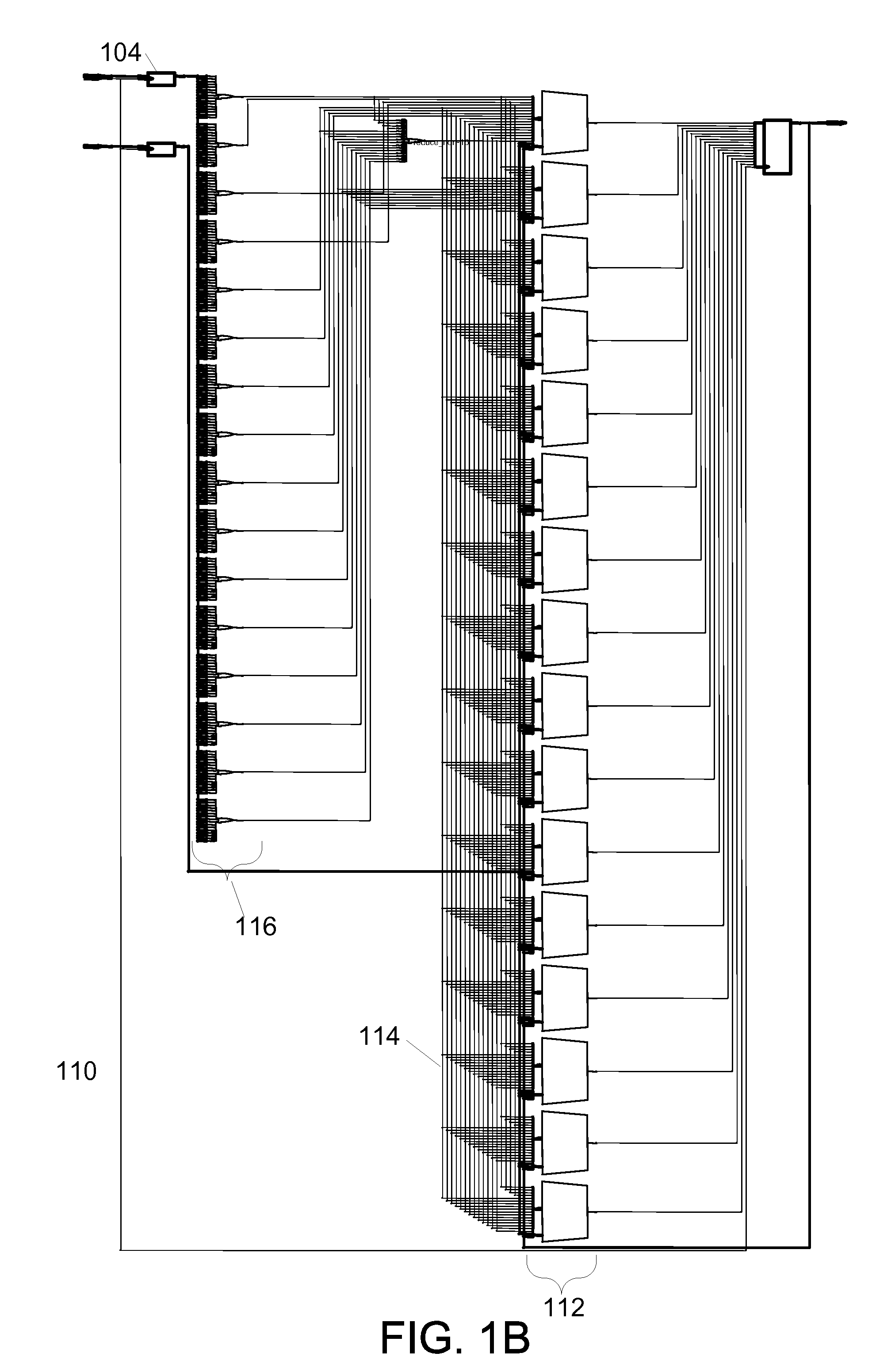
Performance visualization system
InactiveUS7784008B1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designGraphicsUser input
A visualization displays user designs and performance information at different levels of detail. Related register bits are combined into a metaregister and displayed as a graph node. The set of paths and associated combinatorial logic between two or more metaregisters are collapsed into a metapath and displayed as a graph connection. The set of paths associated with a metapath can be selectively revealed in response to user input. Metapaths can be annotated with performance information of its associated paths, such as timing, area, and power consumption information. The annotated performance information can represent performance information of one or more paths or aggregate attributes of the set of paths. Paths associated with control signals and finite state machines can be identified and displayed as separate graph connections.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method and device for determining diagram node vectors in relational network diagram
PendingCN110032665AImprove accuracyOther databases indexingSpecial data processing applicationsNODALEuclidean vector
The embodiment of the invention provides a computer-executed method for determining node vectors in a relational network diagram, the relational network diagram comprises N nodes and the connection edges between the nodes, and the N nodes comprise any first node. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, obtaining the adjacency information of the relational network diagram for recordinga connection relation between the nodes in the relational network diagram; then, according to the adjacency information, determining N first association degrees corresponding to the first node and the N nodes, wherein a first correlation degree between the first node and a second node in the N nodes is related to a path from the first node to the second node through the connection edges within apredetermined number K; then, based on the N first association degrees, determining a second association degree between the first node and each node, and obtaining N second association degrees; and then, constructing N-dimensional data at least based on the N second correlation degrees; and then, carrying out dimension reduction processing on the N-dimensional data to obtain a node vector of the first node.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
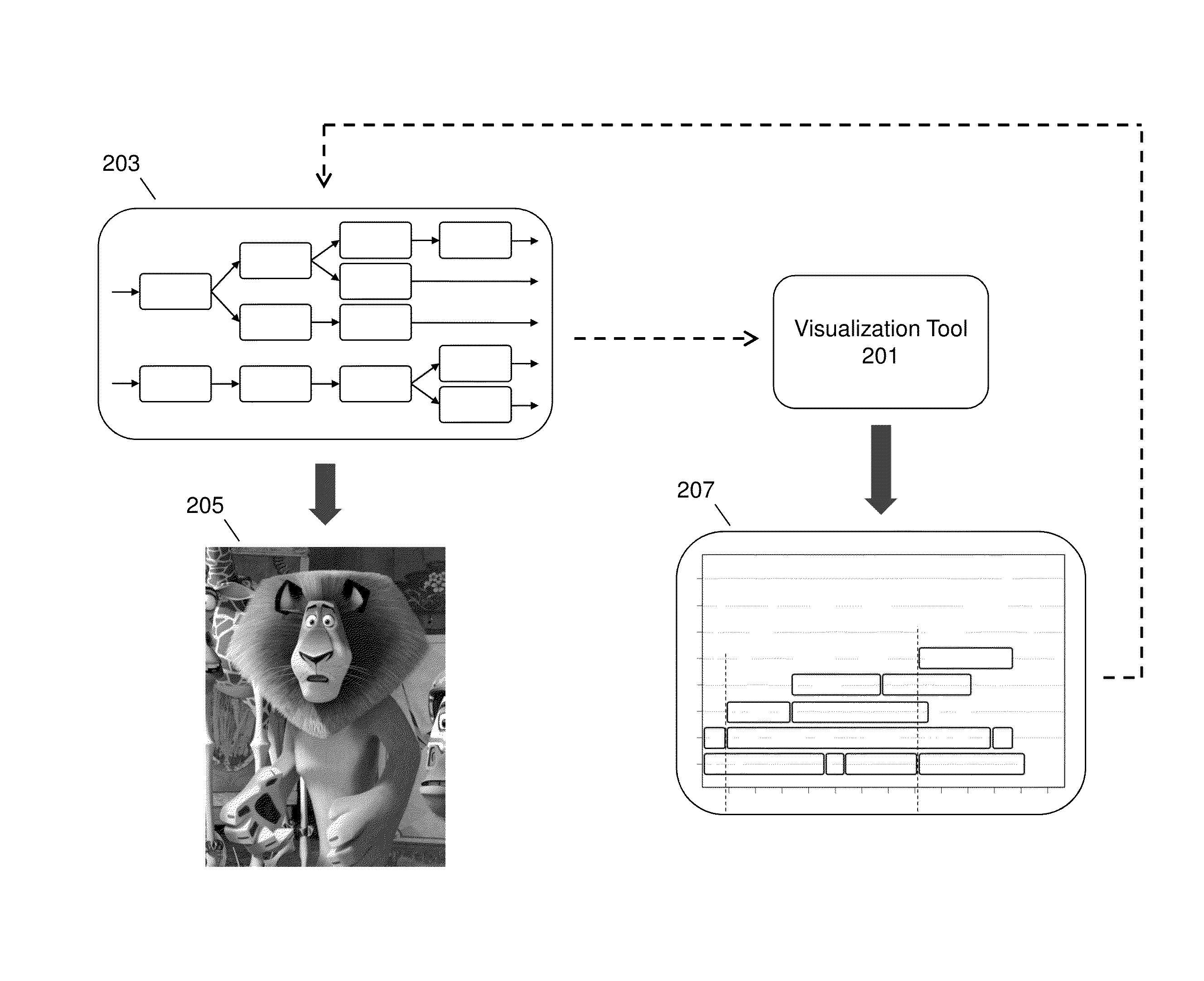
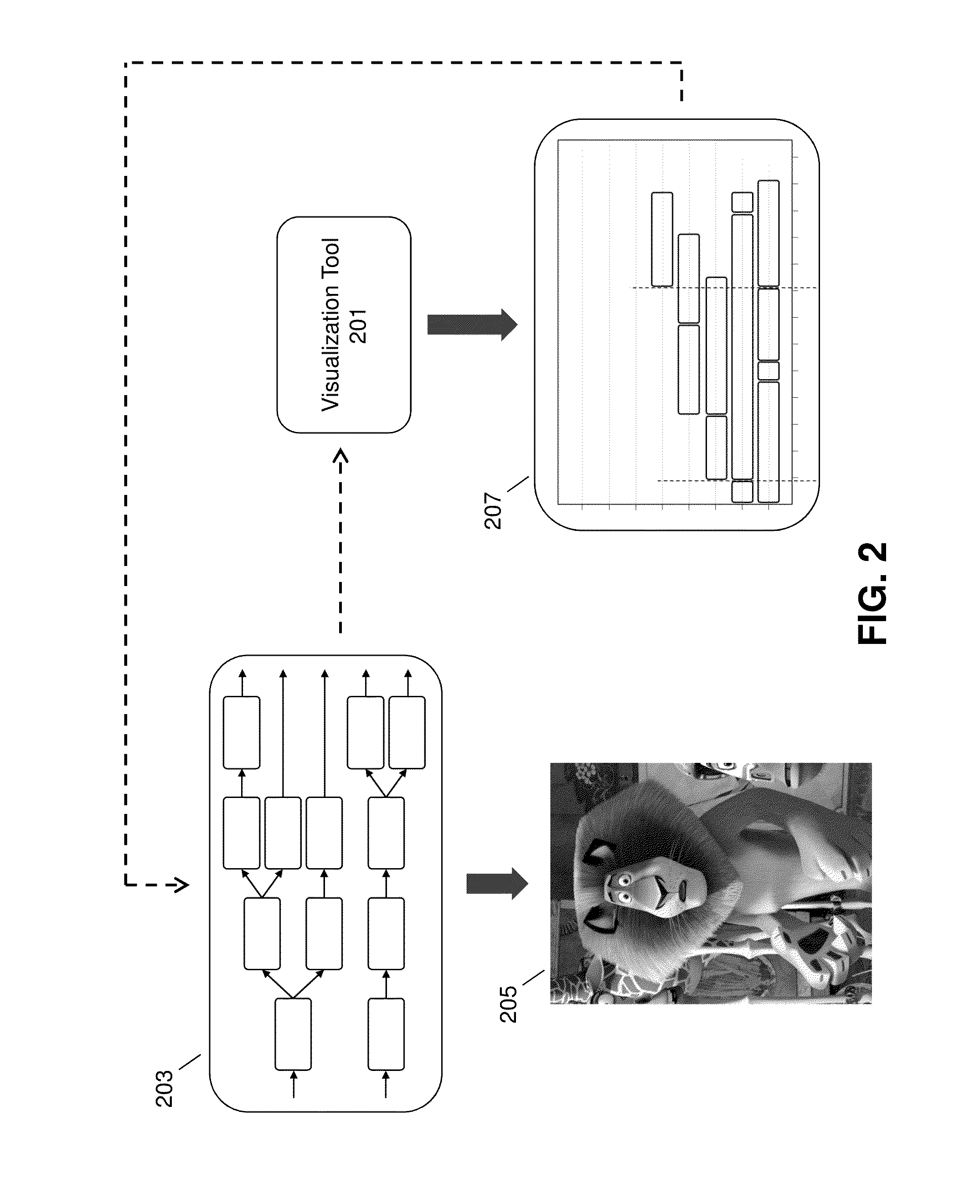
Visualization tool for parallel dependency graph evaluation
Systems and processes providing a tool for visualizing parallel dependency graph evaluation in computer animation are provided. Runtime evaluation data of a parallel dependency graph may be collected, including the start time and stop time for each node in the graph. The visualization tool may process the data to generate performance visualizations as well as other analysis features. Performance visualizations may illustrate the level of concurrency over time during parallel dependency graph evaluation. Performance visualizations may be generated by graphing node blocks according to node start time and stop time as well as the level of concurrency at a given time to illustrate parallelism. Performance visualizations may enable character technical directors, character riggers, programmers, and other users to evaluate how well parallelism is expressed in parallel dependency graphs in computer animation.
Owner:DREAMWORKS ANIMATION LLC
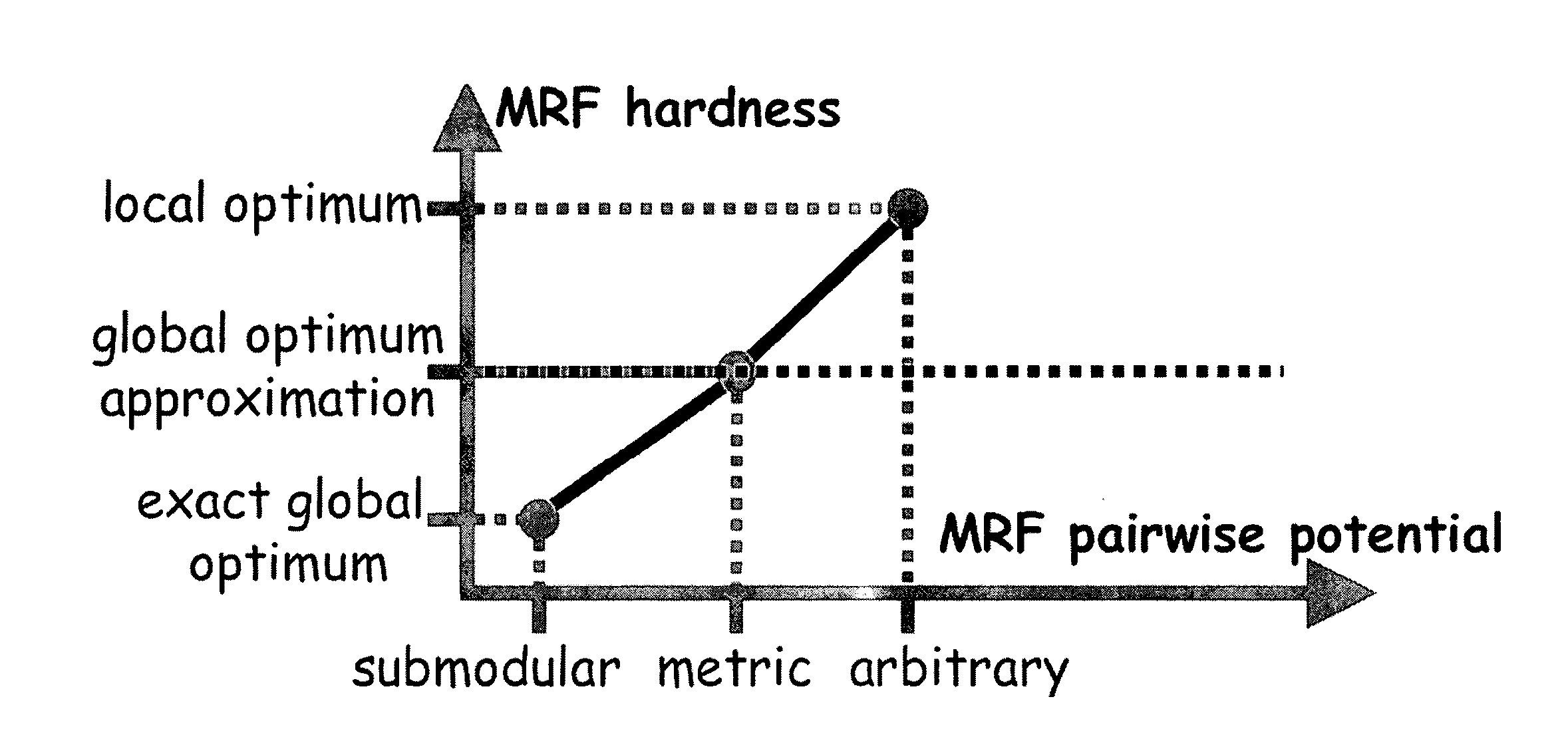
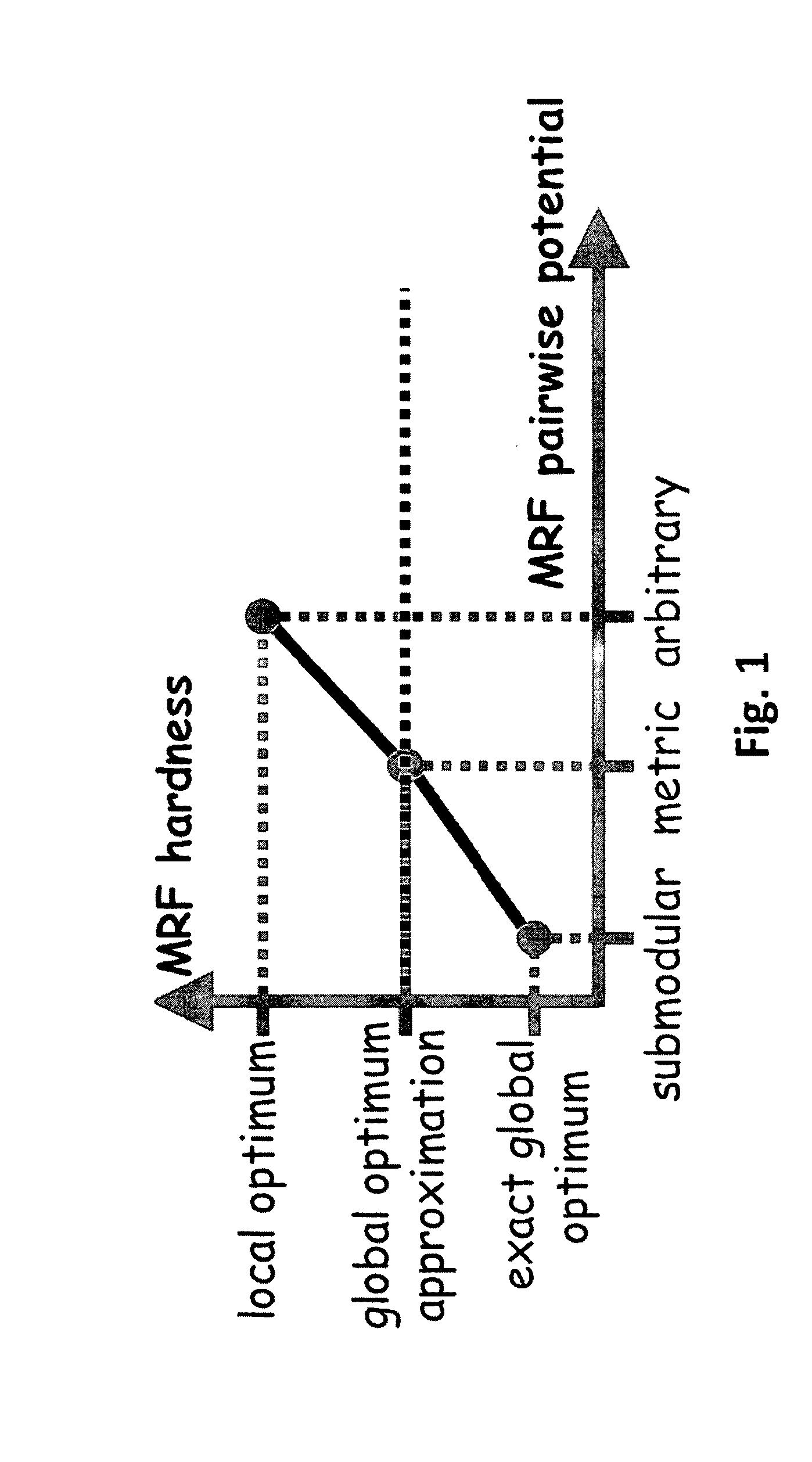
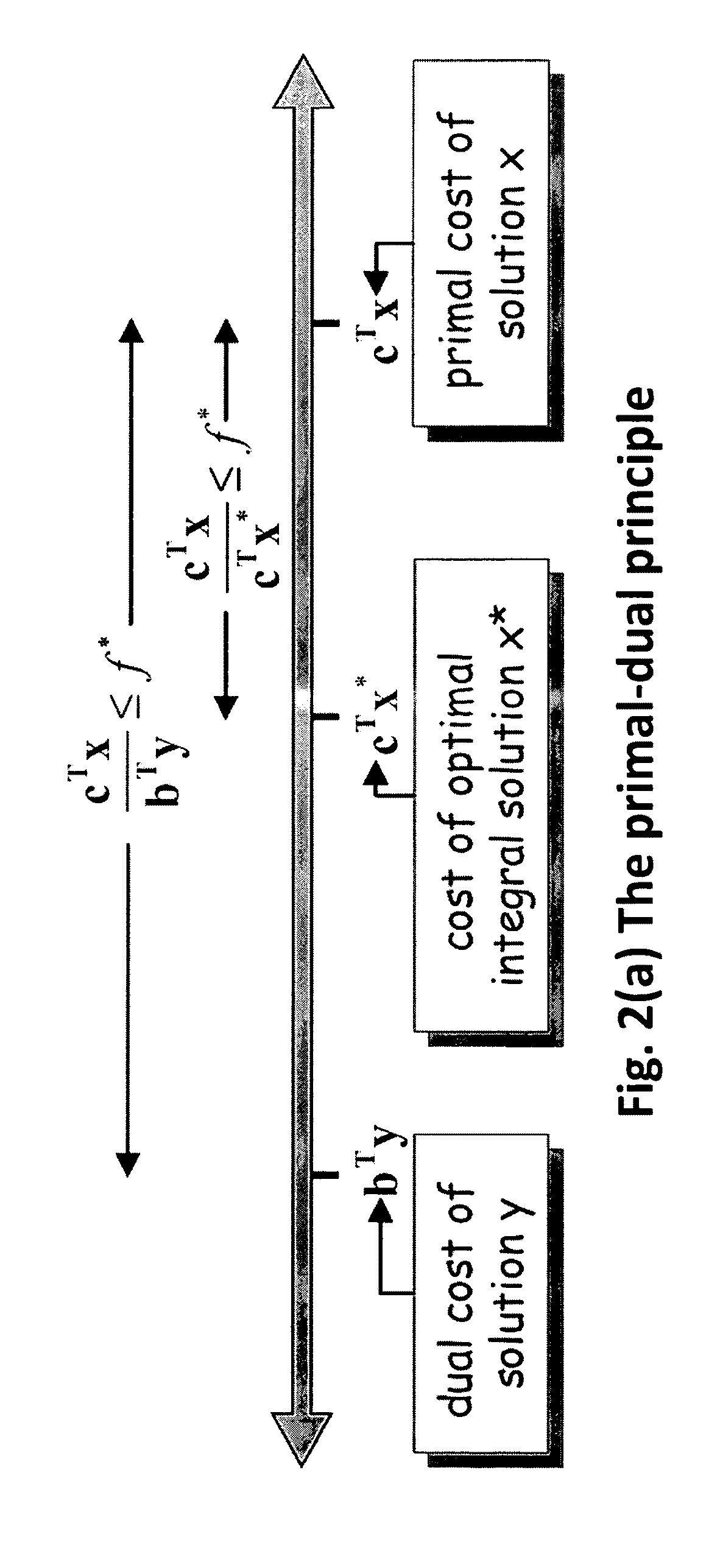
System and Method for Optimizing Single and Dynamic Markov Random Fields with Primal Dual Strategies
ActiveUS20090252416A1Not compromise efficiencyImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsAlgorithm
A method for determining an optimal labeling of pixels in computer vision includes modeling an image by a graph having interior nodes and edges where each image point p is associated with a graph node, each pair of nearest neighbor points p, q is connected by a graph edge, each graph node p is associated with a singleton potential c(p), and each graph edge is associated with a pairwise potential function d(p,q). A label is randomly assigned to each point to initialize unary variables including an indicator function that indicates which label is assigned to which point and dual variables including height variables associated with each node p and label a, and balance variables associated with each edge (p,q) and label a. For each label, a new label c is selected, a capacitated graph is constructed and solved. The label selection divides the image into disjoint regions.
Owner:CENTSUPELEC
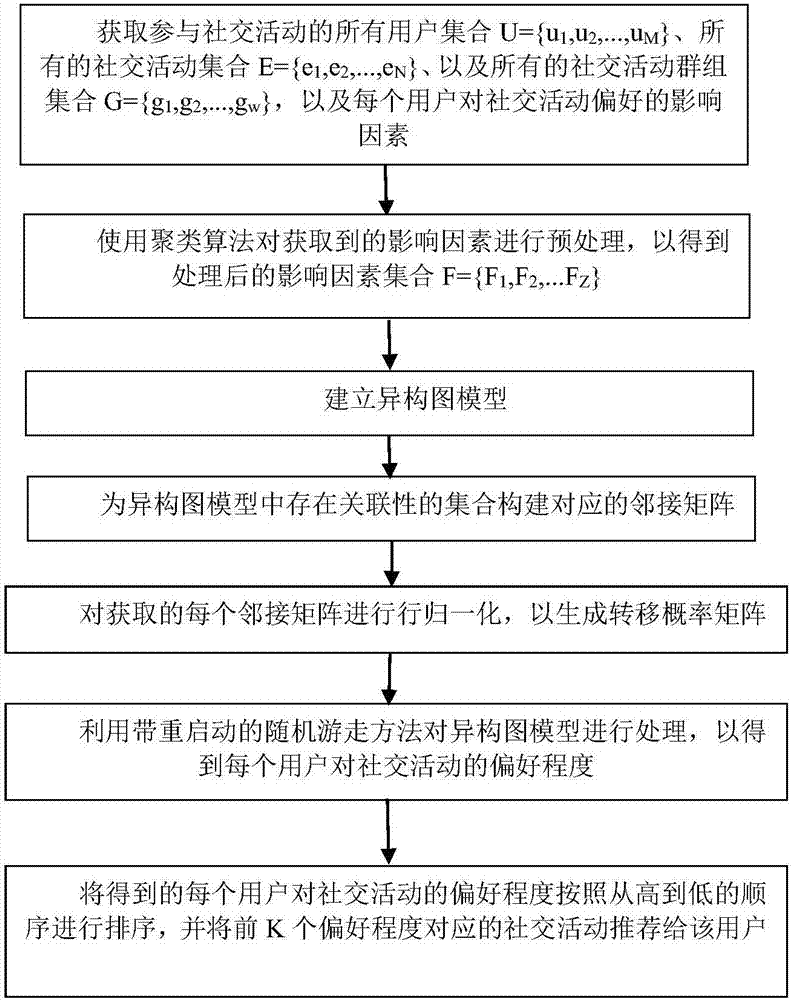
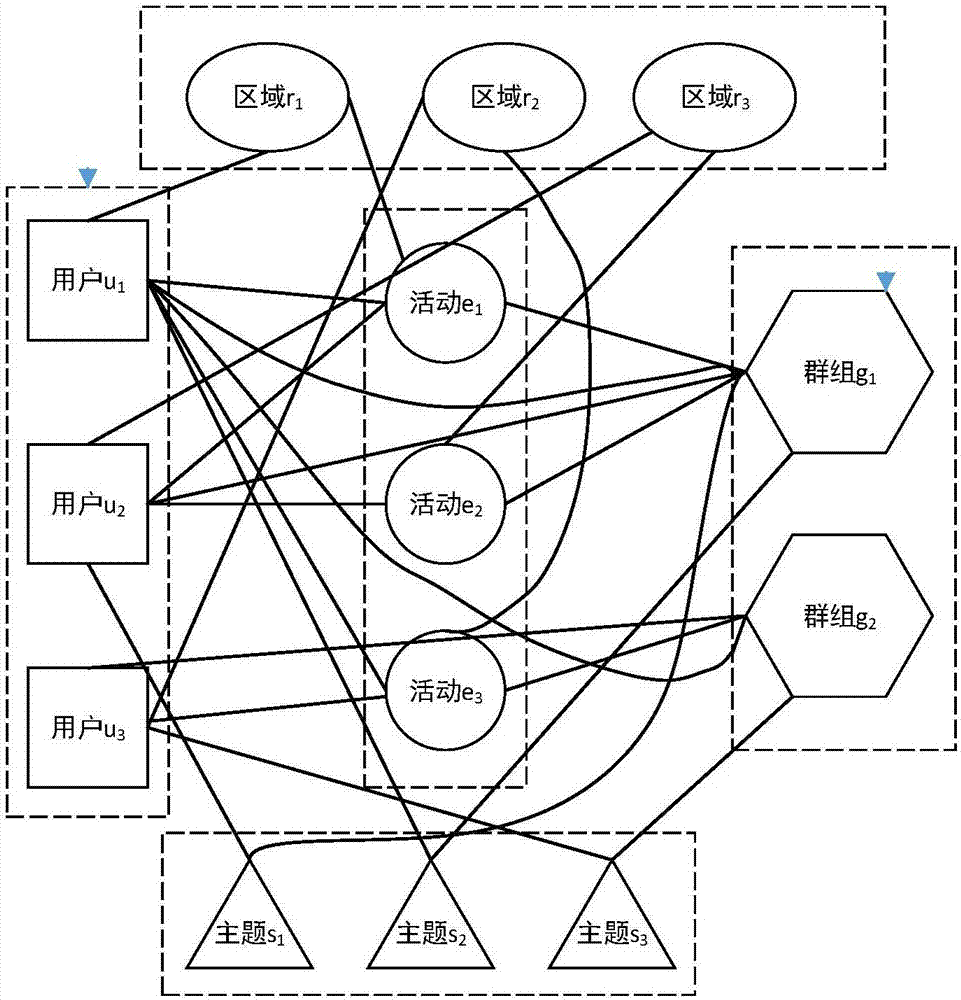
Social activity recommendation method based on heterogeneous graph model
InactiveCN106980659AMitigating adverse effects of steady-state probability distributionsSolve the real problemData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsComputational problemFeature Dimension
The invention discloses a social activity recommendation method based on a heterogeneous graph model. The method comprises the steps that an offline social activity is recommended to a user based on the hobby and interest, social relation, position preference, historical behaviors, etc. of the user, and a user distribution scheme is adjusted adaptively according to the scale of the activity. The heterogeneous graph model is the core of the technology, and construction of the heterogeneous graph model mainly comprises the steps of influence factor discrimination, feature dimension reduction, heterogeneous graph node selection, node connection establishment and "virtual connection" establishment for hanging nodes. After the graph model is established, a recommendation problem is transformed into a node adjacency calculation problem in the graph model from a similarity calculation problem between the user and the activity. In a graph network, user nodes and activity nodes are connected directly or indirectly through edges, the nodes in close connection have higher relevancy, candidate activities are arranged according to a descending order according to the relevancy between the user nodes and all the activity nodes, and therefore K users with the highest values are selected to form a user recommendation list.
Owner:EZHOU INST OF IND TECH HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method to model vehicular communication networks as random geometric graphs
A method for generating mathematical analysis of a communication protocol in a vehicular communications network. The method defines features of a vehicular network, which may include a graph of a street map within a geographic area. A random geometric graph with a plurality of parameters is generated. A plurality of communications protocols on the vehicular network are defined. A communication protocol over the random geometric graph is redefined. A communication protocol's basic properties and associated features on the random geometric graph are analyzed. Results of the analysis are generated. The results of the analysis based on the random geometric graph's parameters are translated into results based on the vehicular network features. The random geometric graph with the parameters are displayed. The parameters may include: a number of graph nodes; and a probability that any two nodes are communicably connected being expressed as a function of the vehicular network features.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Domain knowledge pushing method based on knowledge graph
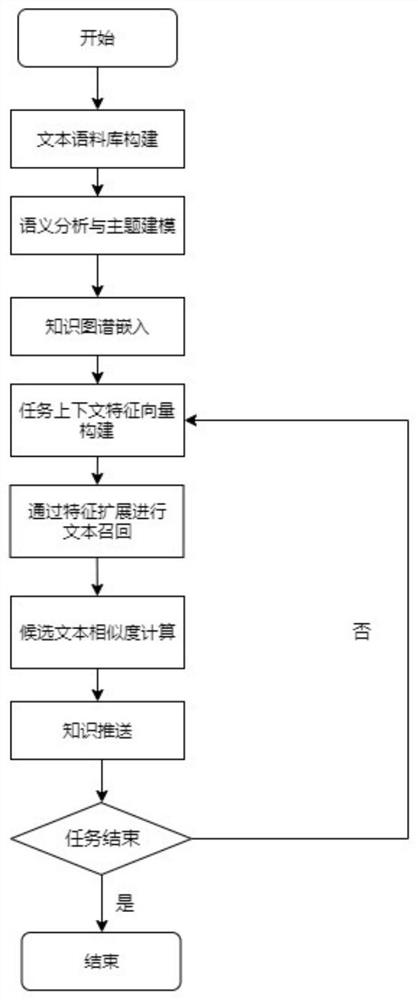
ActiveCN112699246AIncrease diversityActive Capture AttributesNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceGraph Node
The invention discloses a domain knowledge pushing method based on a knowledge graph. The domain knowledge pushing method comprises the steps of collecting domain knowledge texts to construct a text knowledge base; performing semantic analysis and topic modeling on the knowledge base text; obtaining semantic distribution vectors of the nodes through domain knowledge graph embedding; establishing task context features according to the user task description and the task theme; performing entity alignment according to domain entities in the task description and the knowledge graph, performing feature extension based on graph node paths and graph node semantic distribution features, and performing task associated knowledge recall; performing text similarity calculation on the recalled text and the user task text to obtain candidate text scores; and pushing the sorting result text to the user according to the score. The text matching degree and the user experience of domain knowledge pushing are improved through node associated knowledge of the knowledge graph and a graph embedding technology.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
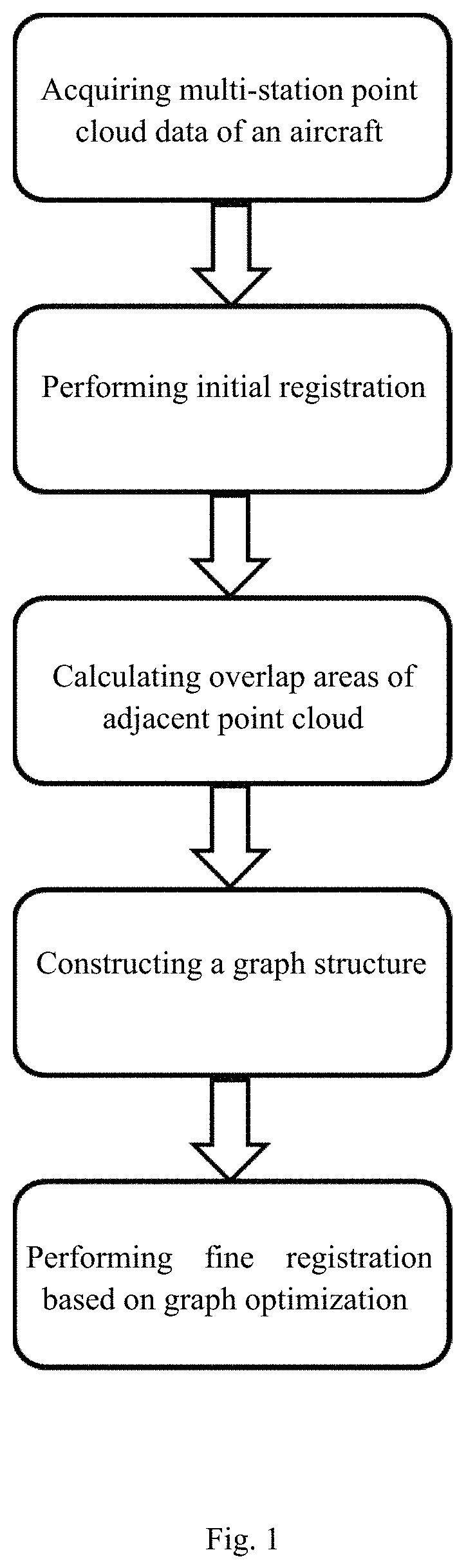
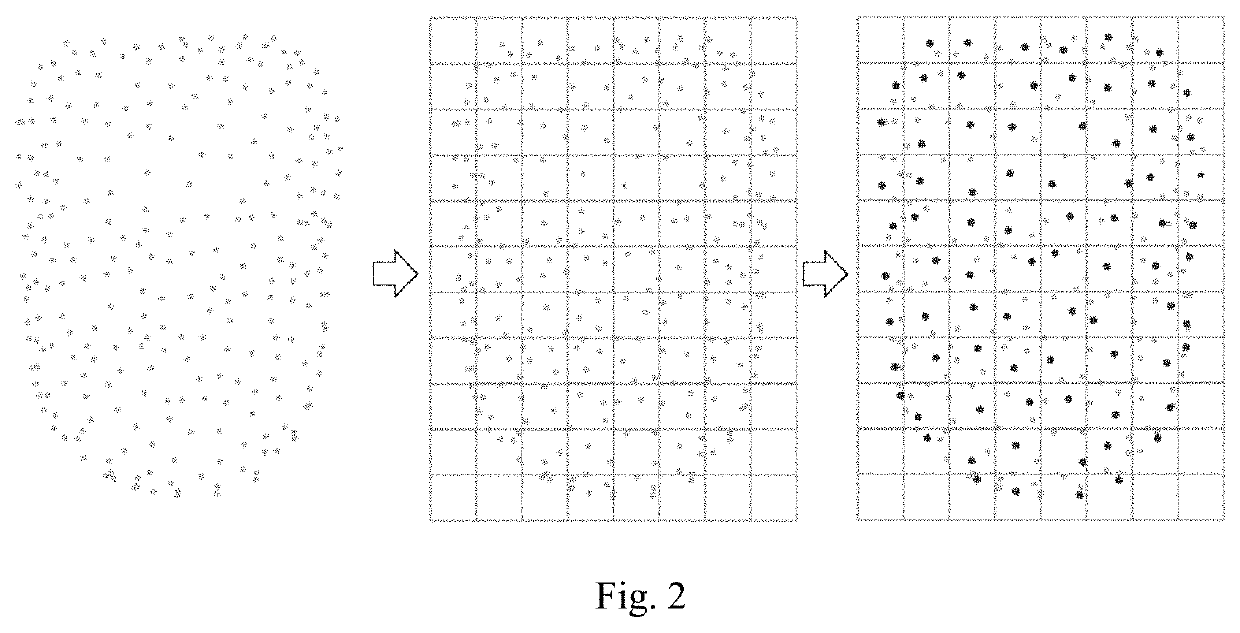
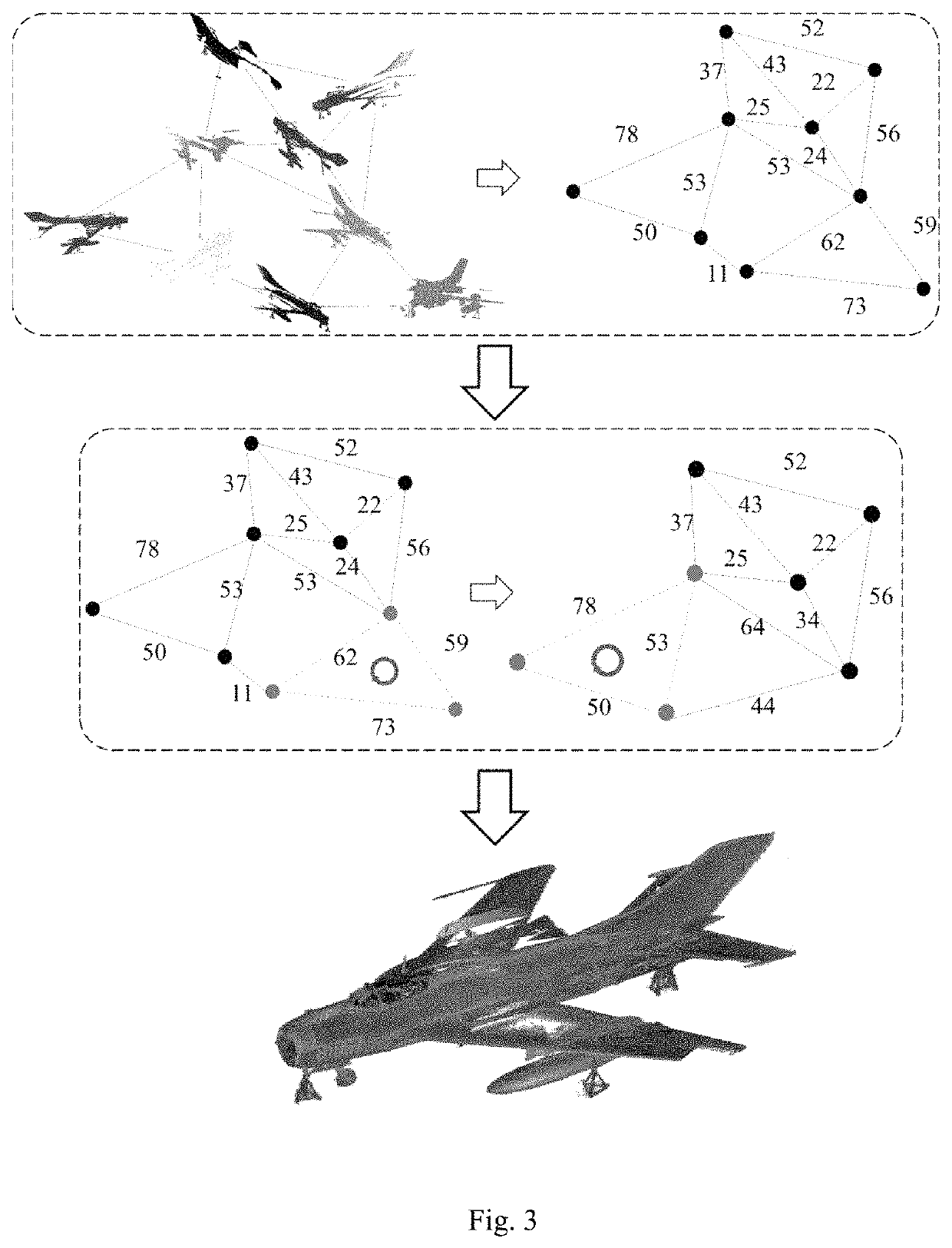
Multi-station scanning global point cloud registration method based on graph optimization
ActiveUS11037346B1Improve registration efficiencyEnsure processing accuracyImage enhancementDrawing from basic elementsPoint cloudAlgorithm
Disclosed a multi-station scanning global point cloud registration method based on graph optimization, including acquiring multi-station original three-dimensional point cloud data; based on initial registration of targets, completing initial registration of point cloud data at adjacent stations by virtue of the target at each angle of view; calculating a point cloud overlap area at adjacent angles of view, and calculating areas of overlap regions of adjacent point cloud by a gridded sampling method; constructing a fine registration graph structure, and constructing a fine registration graph by taking point cloud data of each station as a node of the graph and taking an overlap area of the point cloud data of adjacent stations as a side of adjacent nodes of the graph structure; and based on loop closure fine registration based on graph optimization, gradually completing point cloud fine registration of the whole aircraft according to a specific closure sequence.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Graph processing method and device
ActiveCN103713725AReduce energy consumptionReduced redraw processingPower supply for data processingImage data processing detailsGraphicsAlgorithm
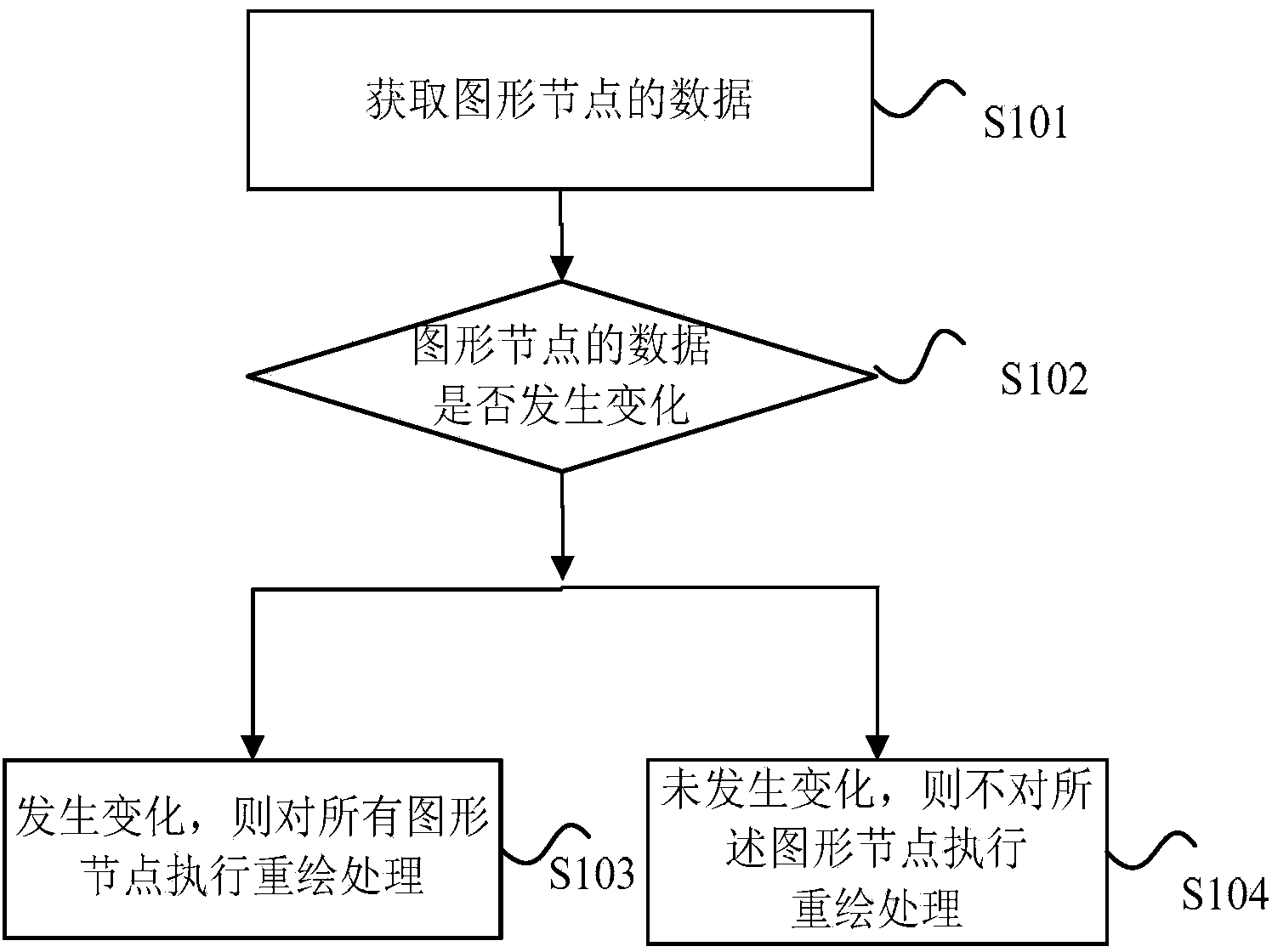
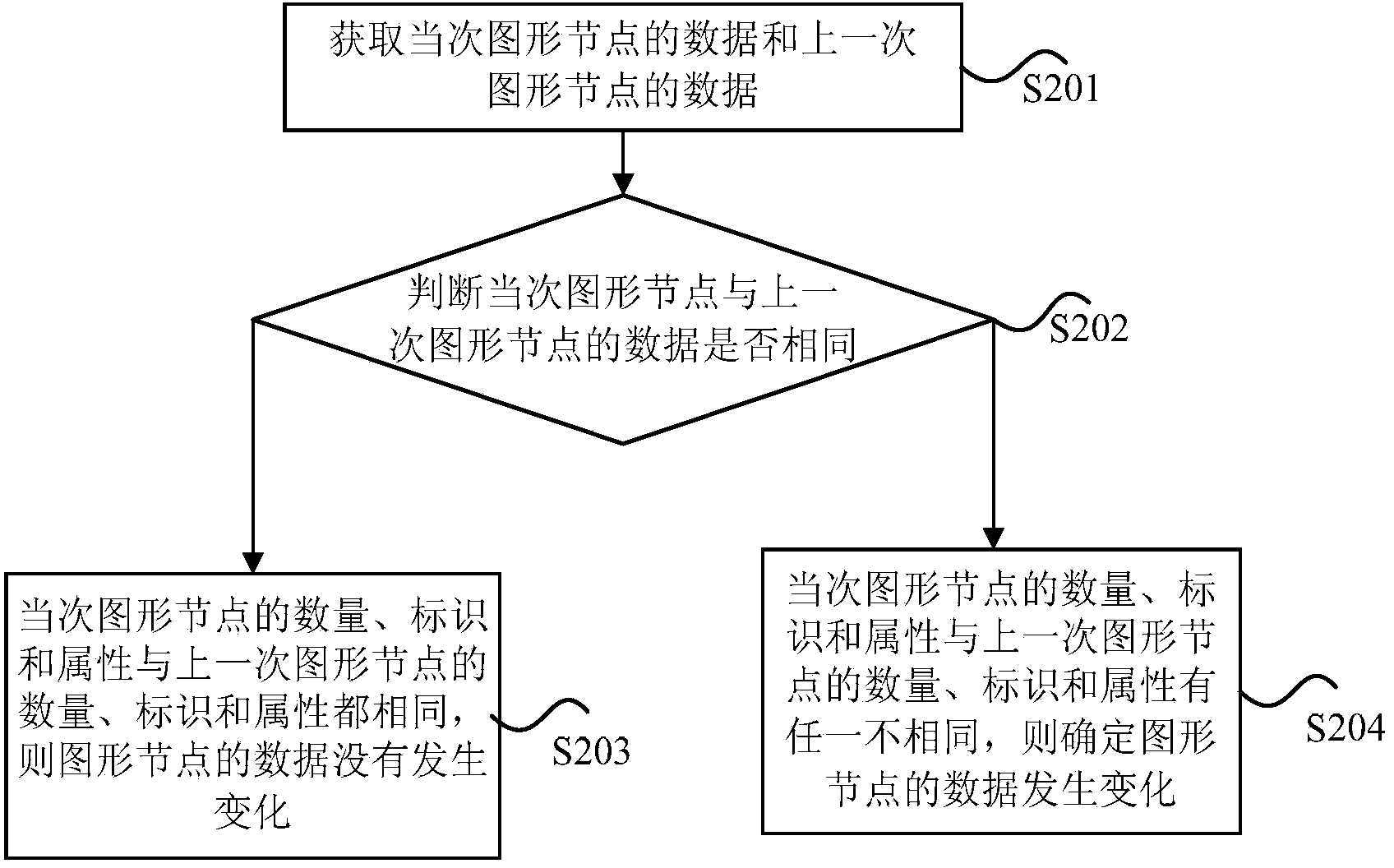
The invention discloses a graph processing method and device. The graph processing method comprises the steps of obtaining data of graph nodes; judging whether the data of the graph nodes change or not; if it is determined that the data of the graph nodes change, conducting redrawing processing on all the graph nodes; if it is determined that the data of the graph nodes do not change, not conducting the redrawing processing on the graph nodes. According to the graph processing method and device, the problem that CPU consumption is larger when the graph redrawing processing is carried out in the prior art is solved, and the effect that the CPU consumption is reduced when graph redrawing is carried out is achieved.
Owner:ALIBABA (CHINA) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com