A block-chain hybrid consensus method based on DAG algorithm
A blockchain and consensus technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problems of inability to accurately judge whether synchronization is complete, inability to know when the transaction is valid, and uncertainty of transaction confirmation time, so as to improve transaction query efficiency, improve consensus efficiency, Improve the effect of trading TPS
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
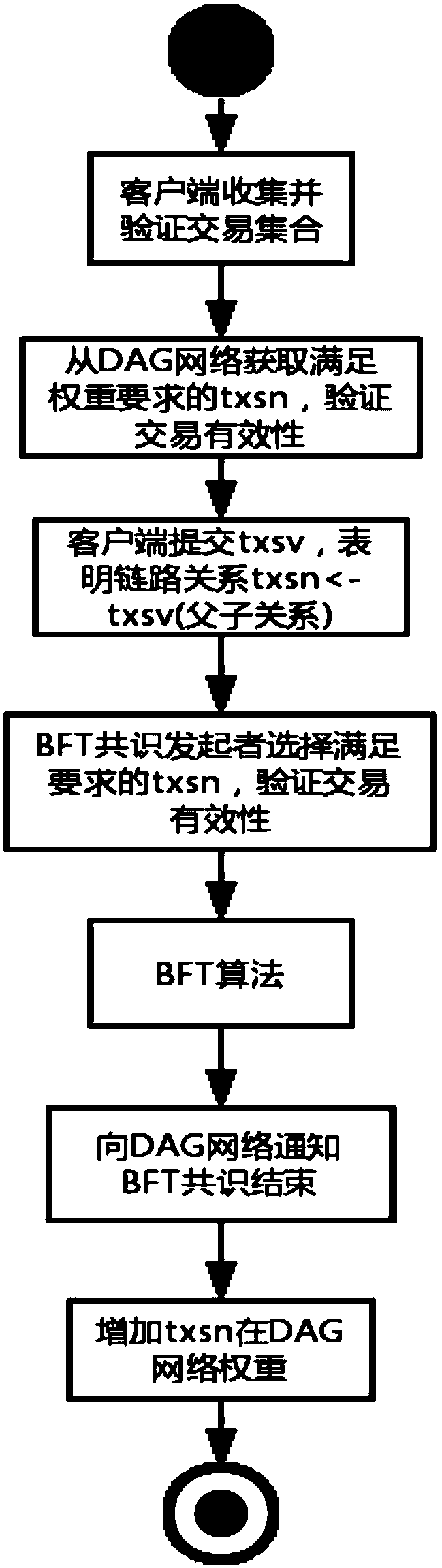
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, a blockchain hybrid consensus method based on the DAG algorithm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048] S1: The client receives a single transaction or transaction set within a period of time, the client verifies the validity of the transaction, and the verified transaction or transaction set is called txsv,
[0049] S2: Define the graph node of the DAG network as txsn, select two txsn whose weight is higher than the set value from the DAG network, and verify the transaction validity of the transaction sets of these two txsn.
[0050] S3: After the verification is passed, the client submits txsv to the DAG network and appends it to the end of the two txsn that passed the verification.
[0051] S4: The BFT consensus initiator randomly selects a txsn whose weight is higher than the set value from the DAG network, and the parent block of the txsn is successfully recorded on the blockchain by BFT, and the BFT consensus initiator verifies the v...
Embodiment 2
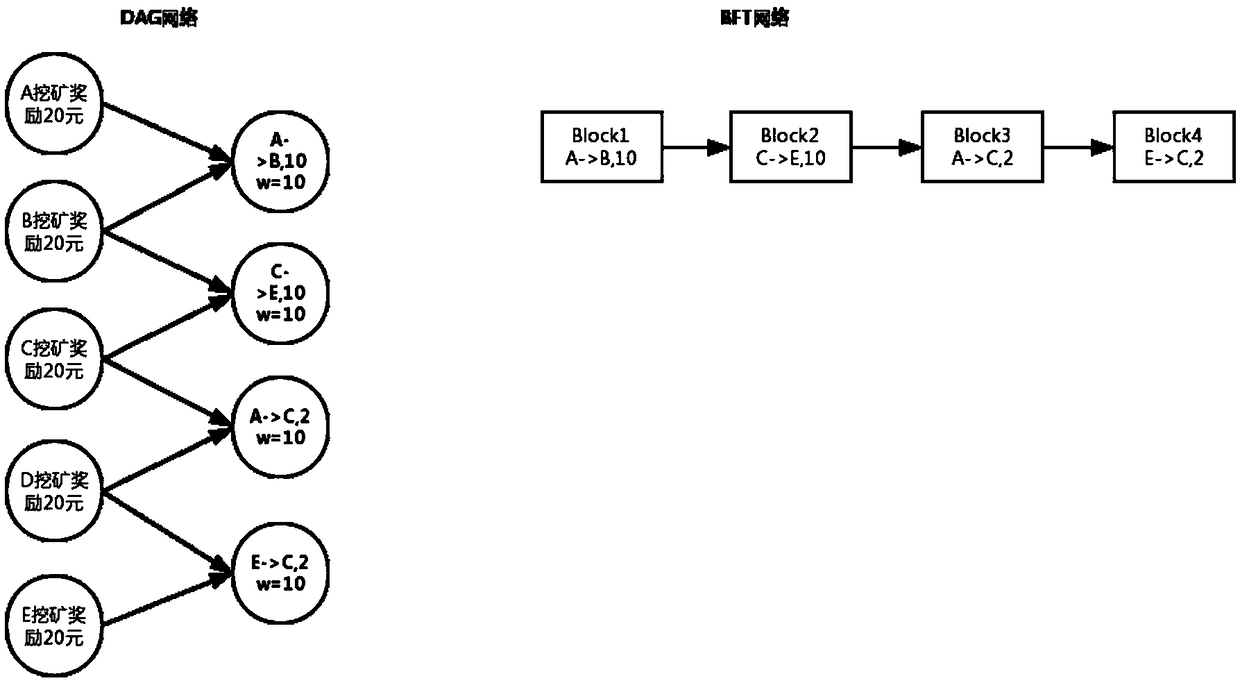
[0063] Such as Figure 7 As shown, in the case that other steps are the same as in the first embodiment, S4 adopts the PoS algorithm, that is, proof of rights and interests.
[0064] Suppose the total number of nodes in the whole network is: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
[0065] Assume that the Tokens owned by each node account are 10, 15, 100, 1, 50...
[0066] S41: Vote to select the proposer
[0067] Each node votes for each other according to its own Token number, and the number of votes each node can vote is the same as the Token it holds. Suppose A gets 180 votes, B: 20, C: 100, D: 33. Count the voting results within a certain period of time. A gets the highest number of votes, and A gets the proposal power;
[0068] S42: Block out
[0069] A packages the transactions it has received into blocks, and then broadcasts them to all nodes in the entire network. The whole network first identifies the identity of A, uses cryptography, performs each block, and comple...
Embodiment 3
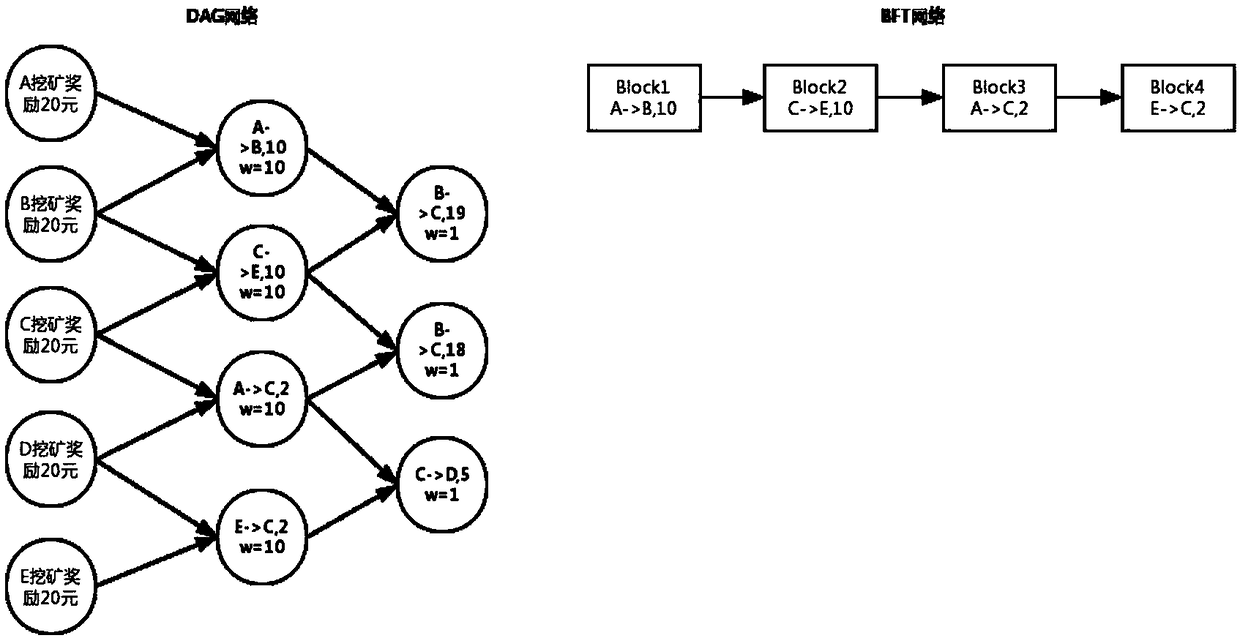
[0071] Such as Figure 8 As shown, in the case that other steps are the same as in Embodiment 1, S4 adopts the DPoS algorithm, that is, the delegated proof-of-stake algorithm;
[0072] Suppose the total number of nodes in the whole network is: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L
[0073] Assume that the Tokens owned by each node account are 10, 15, 100, 1, 50...
[0074] S41: Vote to select members of the consensus group
[0075] Each node conducts a comprehensive calculation based on its own Token number and the time it holds Token to obtain the voting value. Suppose A gets 180 votes, B: 20, C: 100, D: 33, E: 100, F: 20, G: 100, H: 33. According to the configuration requirements, four nodes with the highest votes are selected to form a consensus group, which are A:180, C:100, E:100, G:100;
[0076] S42: Proposer setting
[0077] Among the four selected members of the consensus group, set the proposer. The order of proposals can be selected according to round-robin or acc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com