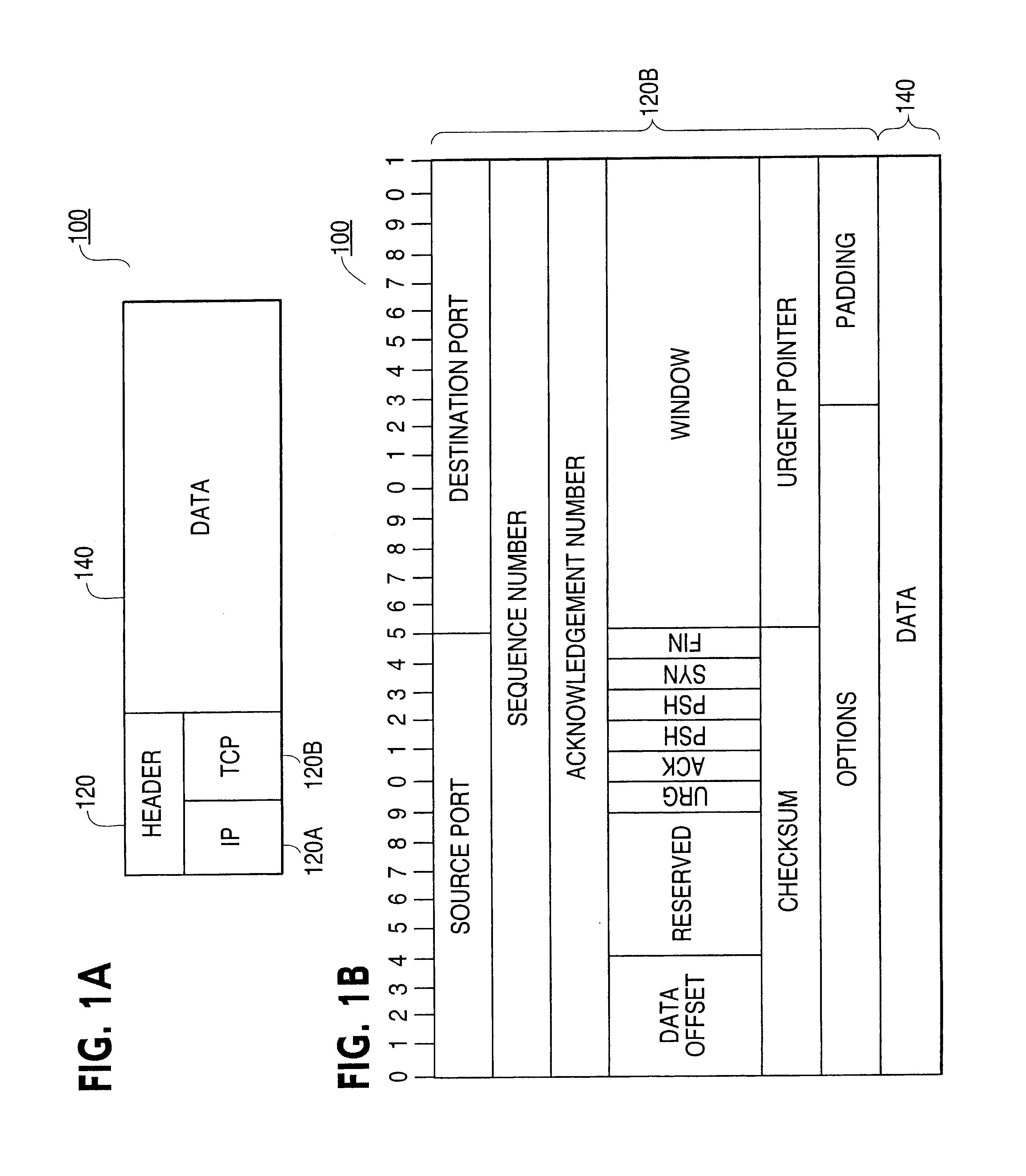
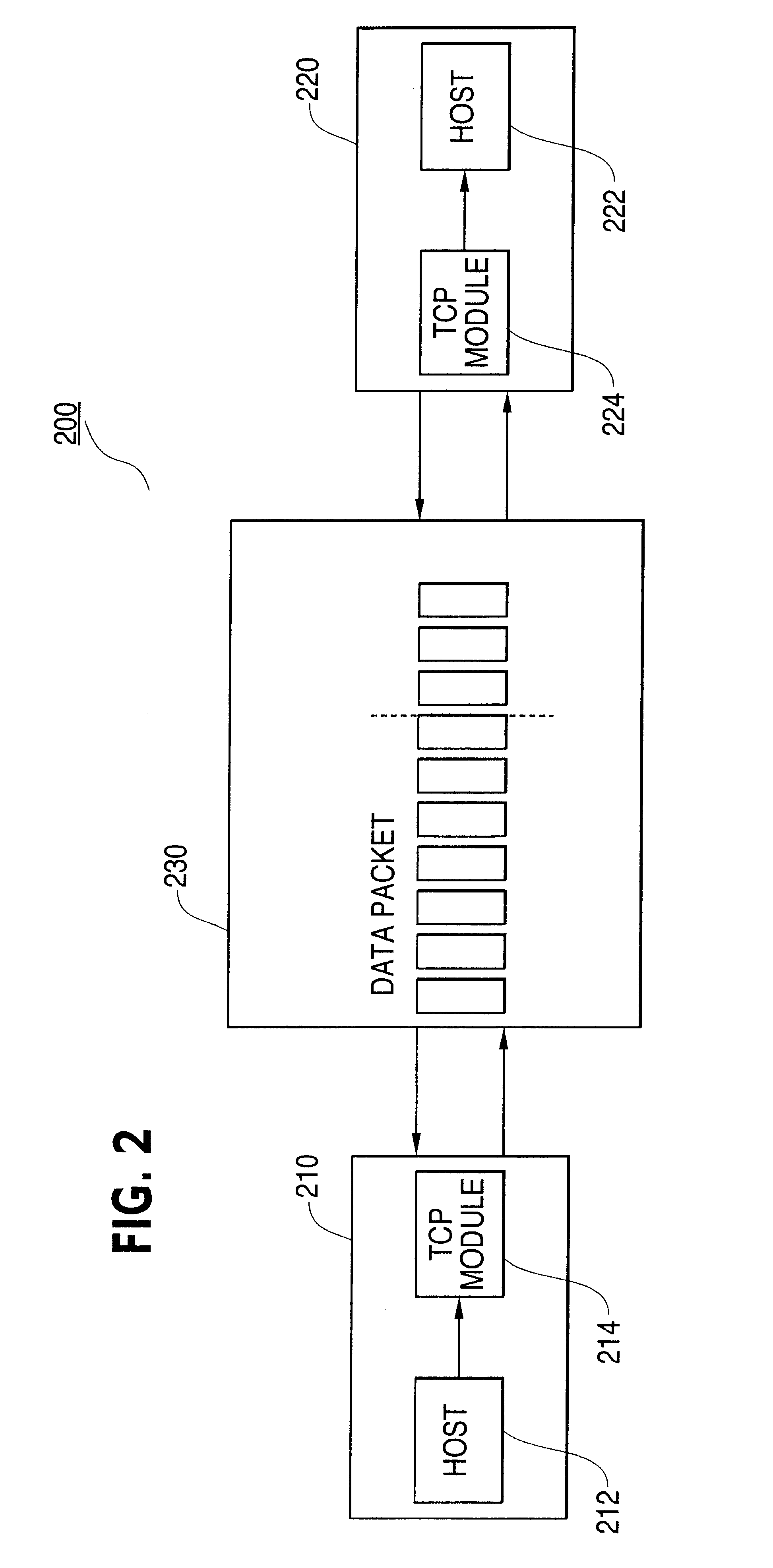
Patents
Literature
3505 results about "Network congestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
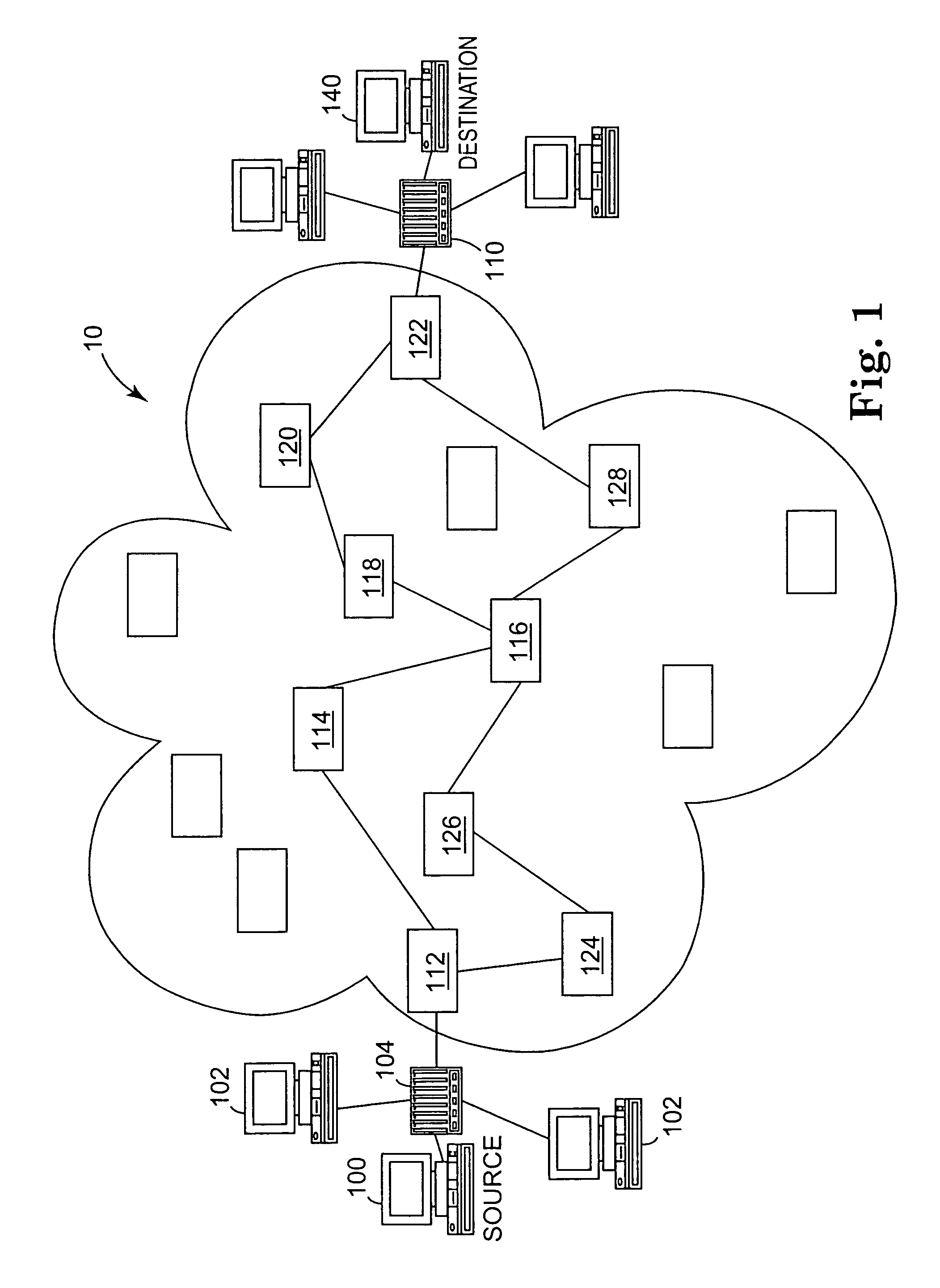
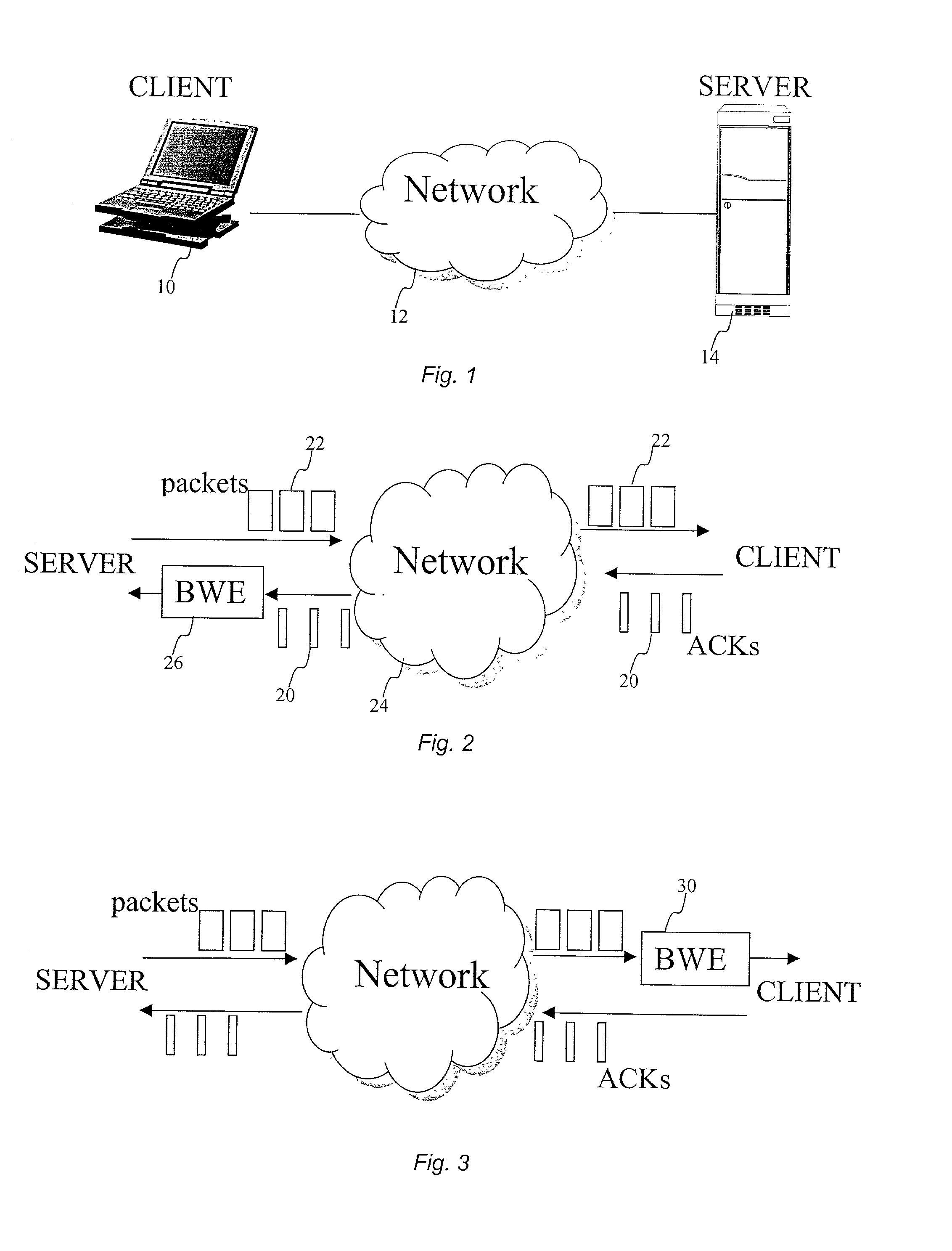
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A consequence of congestion is that an incremental increase in offered load leads either only to a small increase or even a decrease in network throughput.
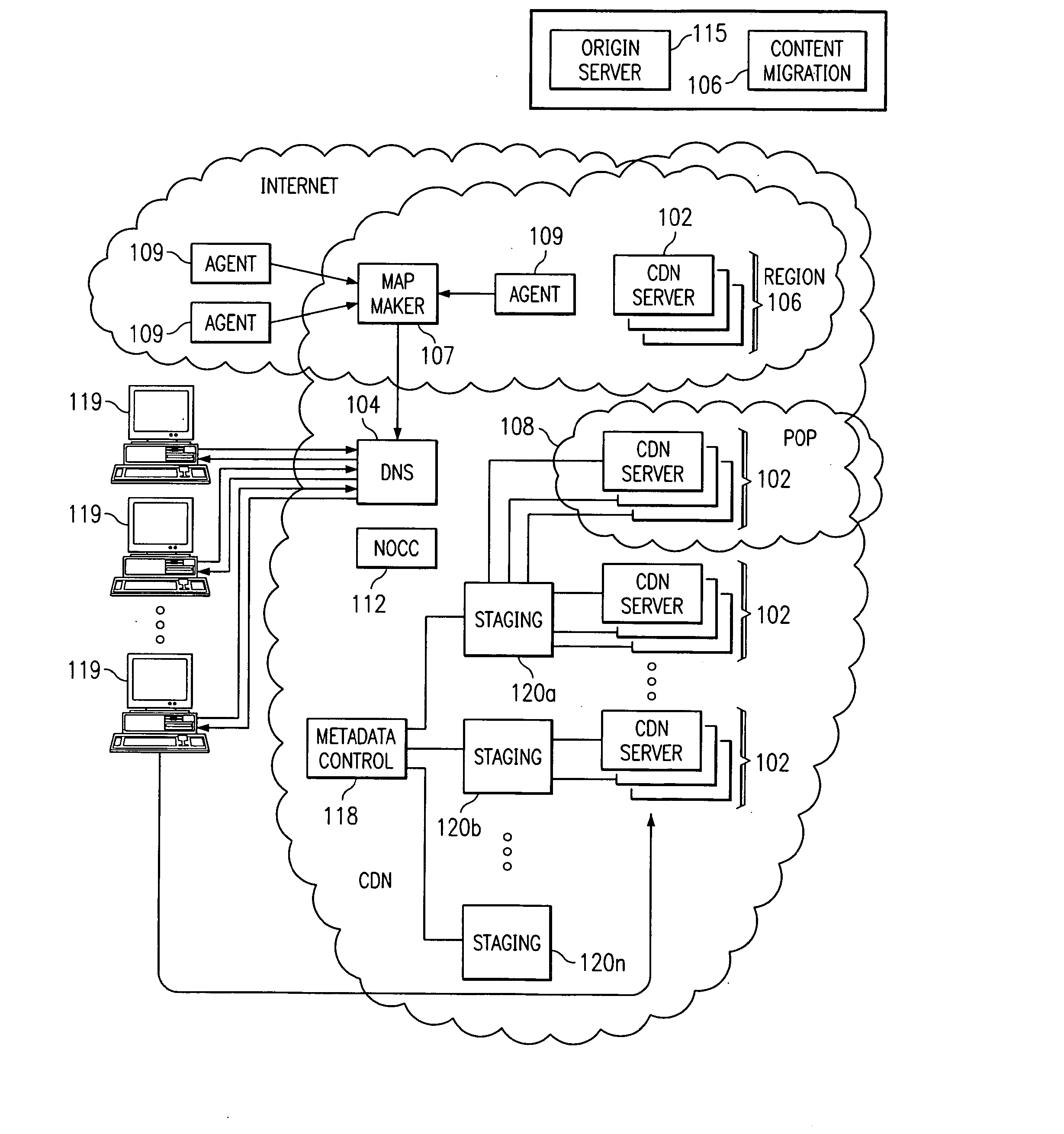
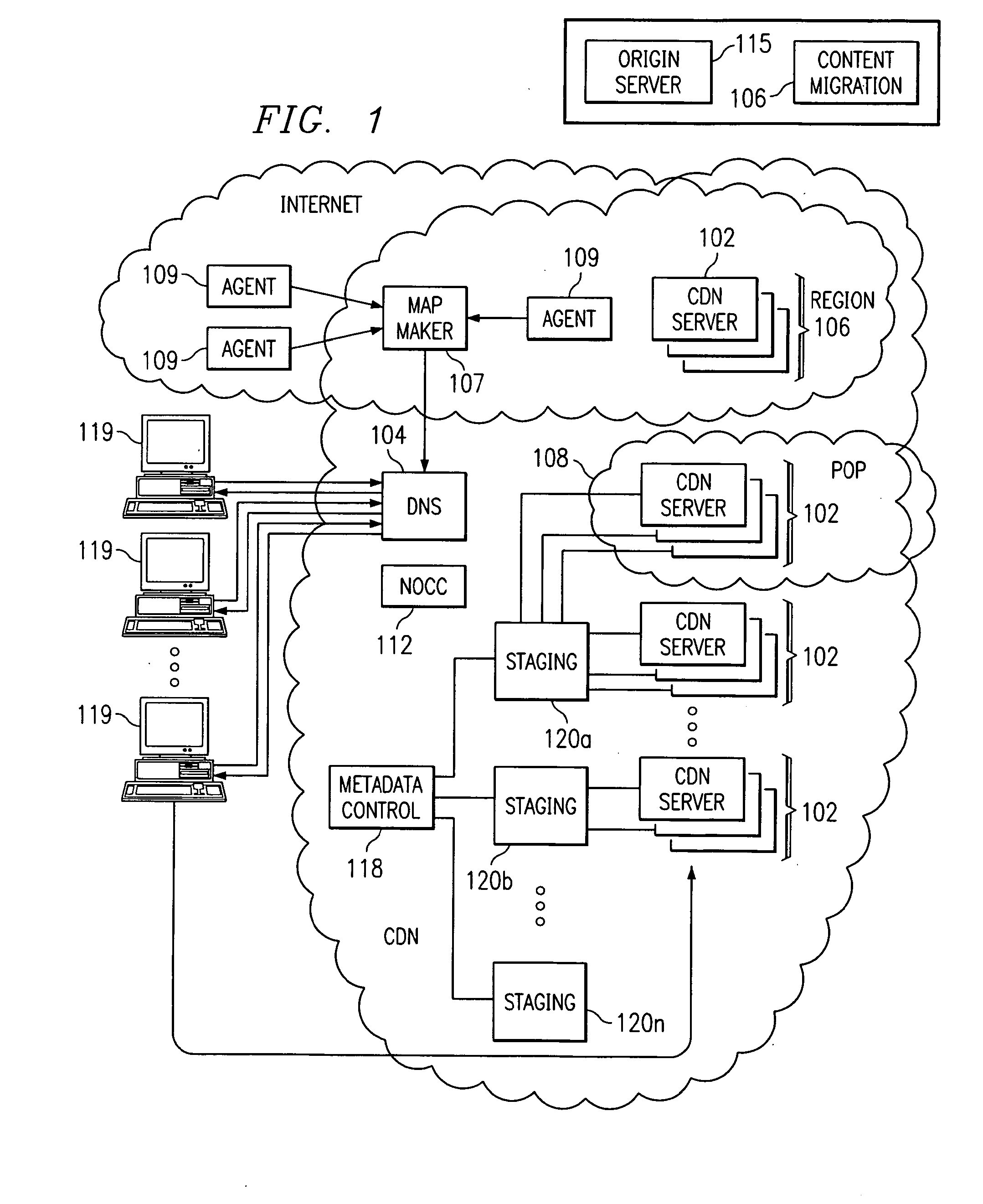
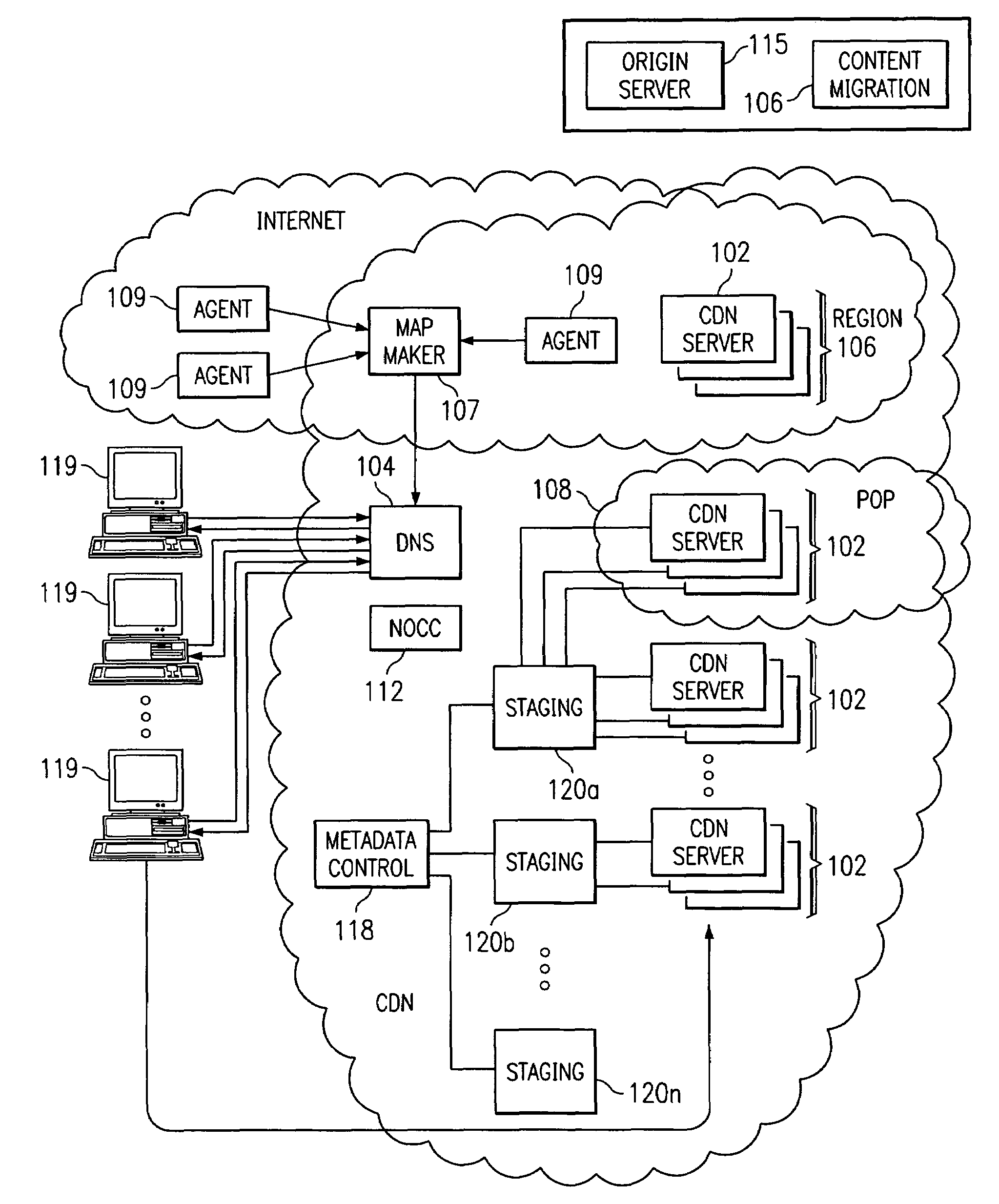
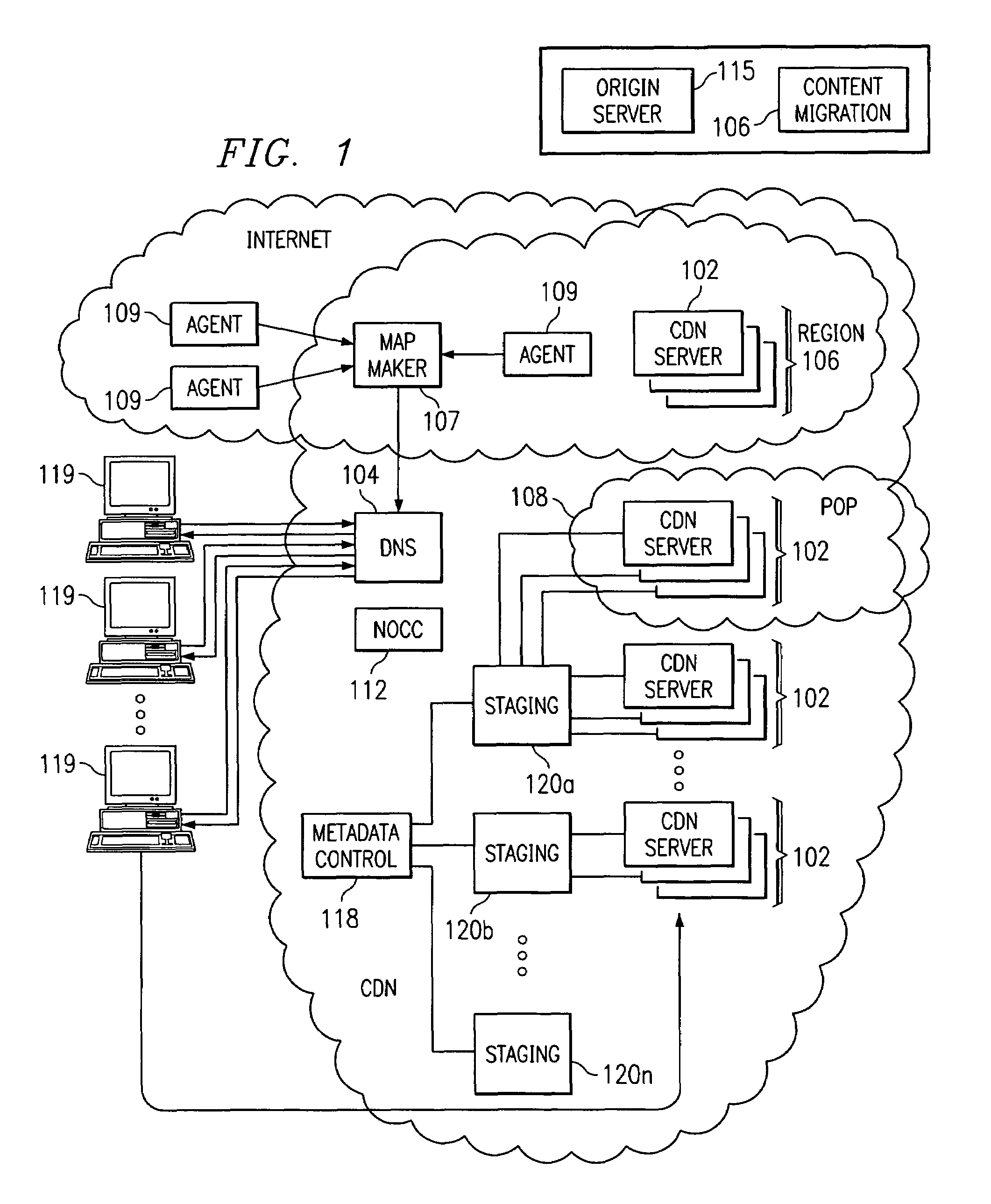
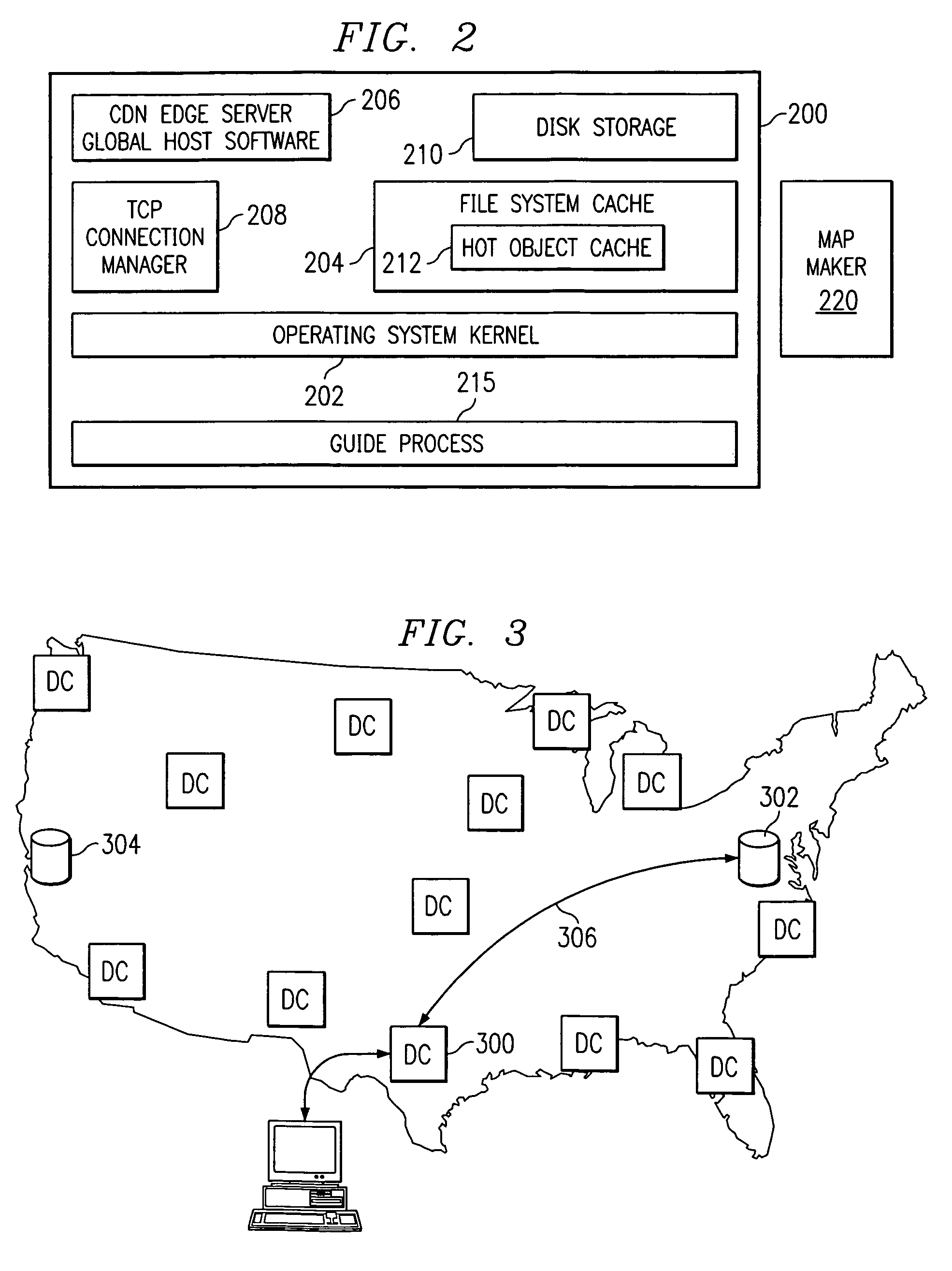
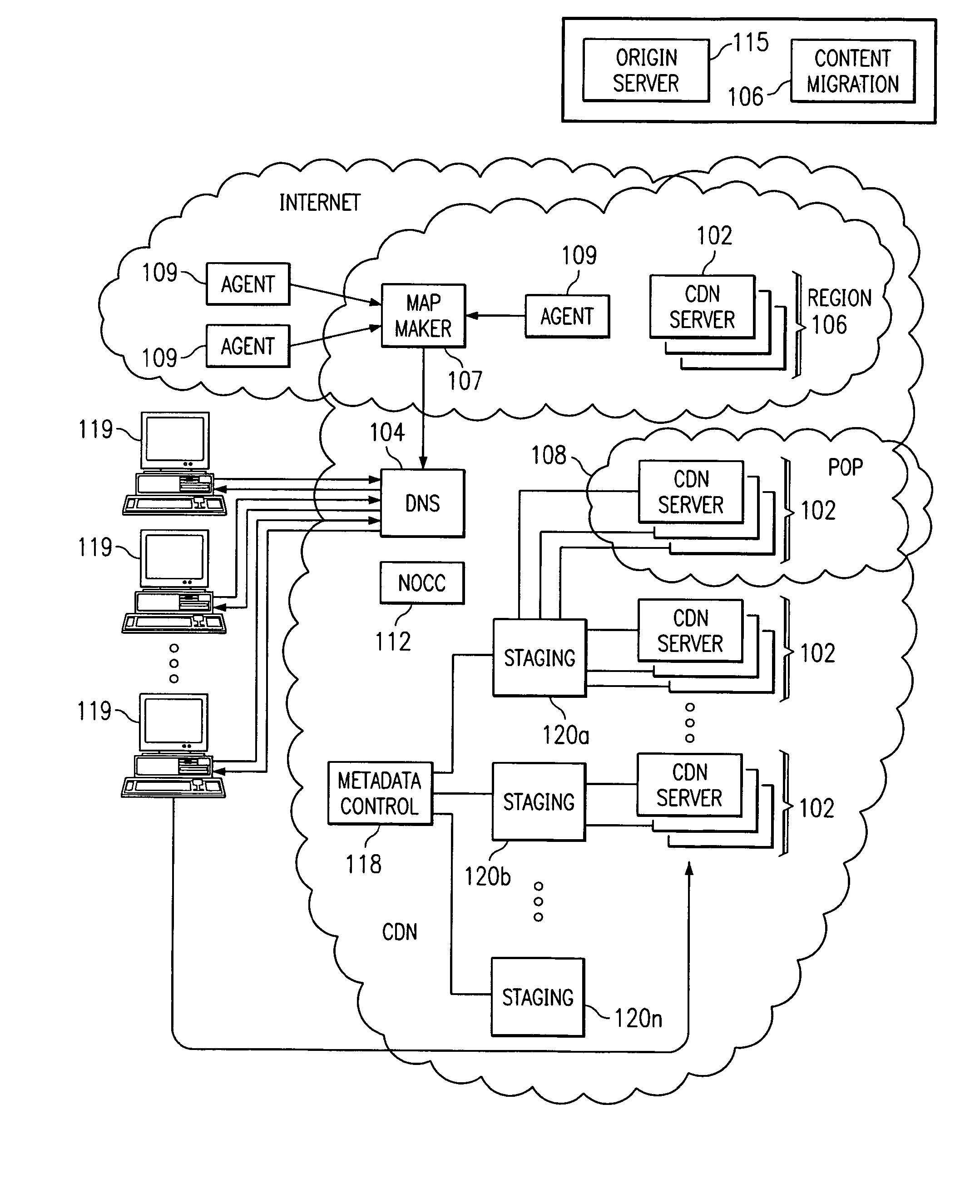
Optimal route selection in a content delivery network
InactiveUS20080008089A1Improve speed and reliabilityRetrieve content (cacheableError preventionTransmission systemsFile area networkPeer-to-peer
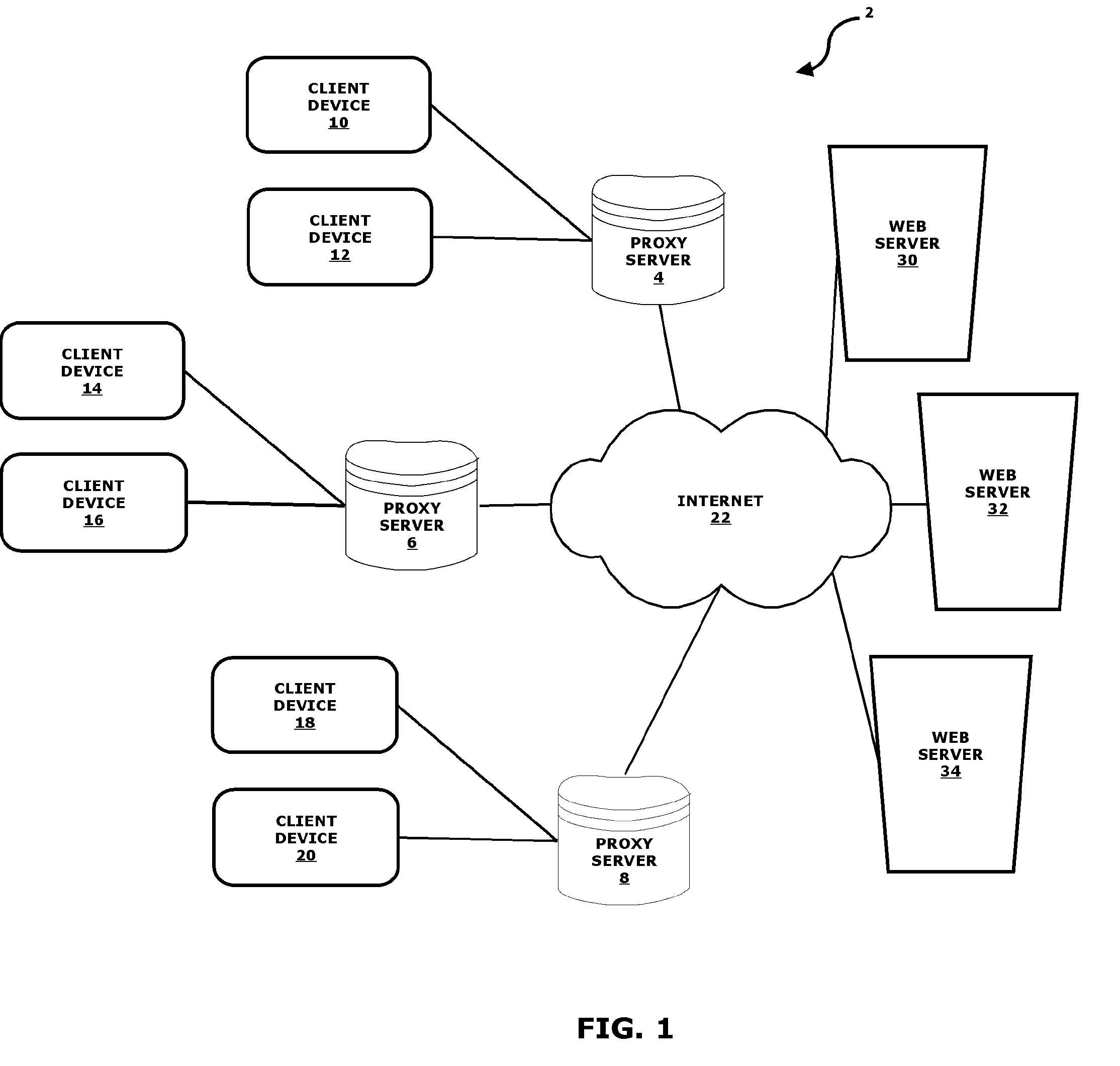
A routing mechanism, service or system operable in a distributed networking environment. One preferred environment is a content delivery network (CDN) wherein the present invention provides improved connectivity back to an origin server, especially for HTTP traffic. In a CDN, edge servers are typically organized into regions, with each region comprising a set of content servers that preferably operate in a peer-to-peer manner and share data across a common backbone such as a local area network (LAN). The inventive routing technique enables an edge server operating within a given CDN region to retrieve content (cacheable, non-cacheable and the like) from an origin server more efficiently by selectively routing through the CDN's own nodes, thereby avoiding network congestion and hot spots. The invention enables an edge server to fetch content from an origin server through an intermediate CDN server or, more generally, enables an edge server within a given first region to fetch content from the origin server through an intermediate CDN region.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Optimal route selection in a content delivery network
ActiveUS7274658B2Improve speed and reliabilityRetrieve content (cacheableError preventionTransmission systemsFile area networkPeer-to-peer
A routing mechanism, service or system operable in a distributed networking environment. One preferred environment is a content delivery network (CDN) wherein the present invention provides improved connectivity back to an origin server, especially for HTTP traffic. In a CDN, edge servers are typically organized into regions, with each region comprising a set of content servers that preferably operate in a peer-to-peer manner and share data across a common backbone such as a local area network (LAN). The inventive routing technique enables an edge server operating within a given CDN region to retrieve content (cacheable, non-cacheable and the like) from an origin server more efficiently by selectively routing through the CDN's own nodes, thereby avoiding network congestion and hot spots. The invention enables an edge server to fetch content from an origin server through an intermediate CDN server or, more generally, enables an edge server within a given first region to fetch content from the origin server through an intermediate CDN region. As used herein, this routing through an intermediate server, node or region is sometimes referred to as “tunneling.”
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
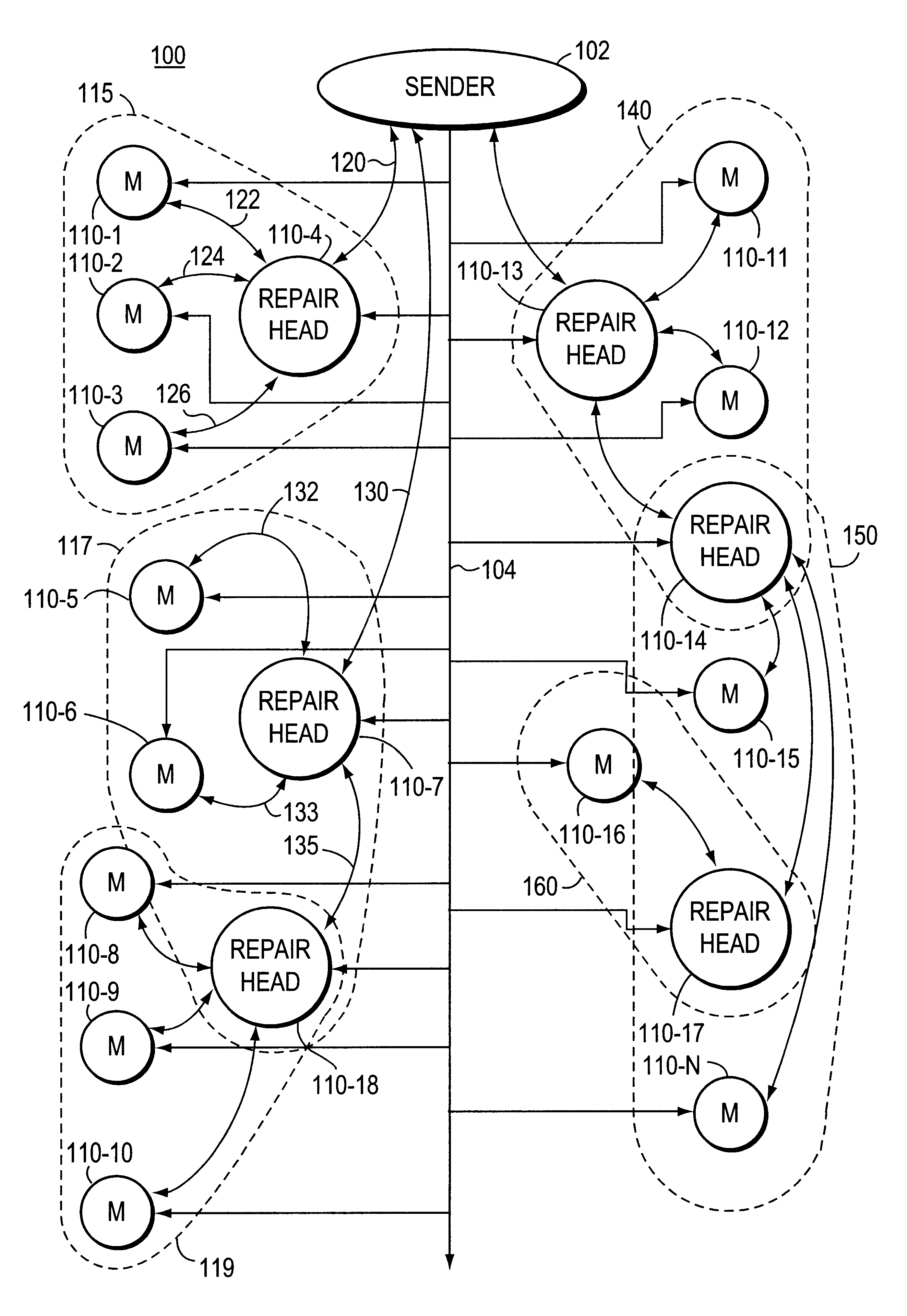
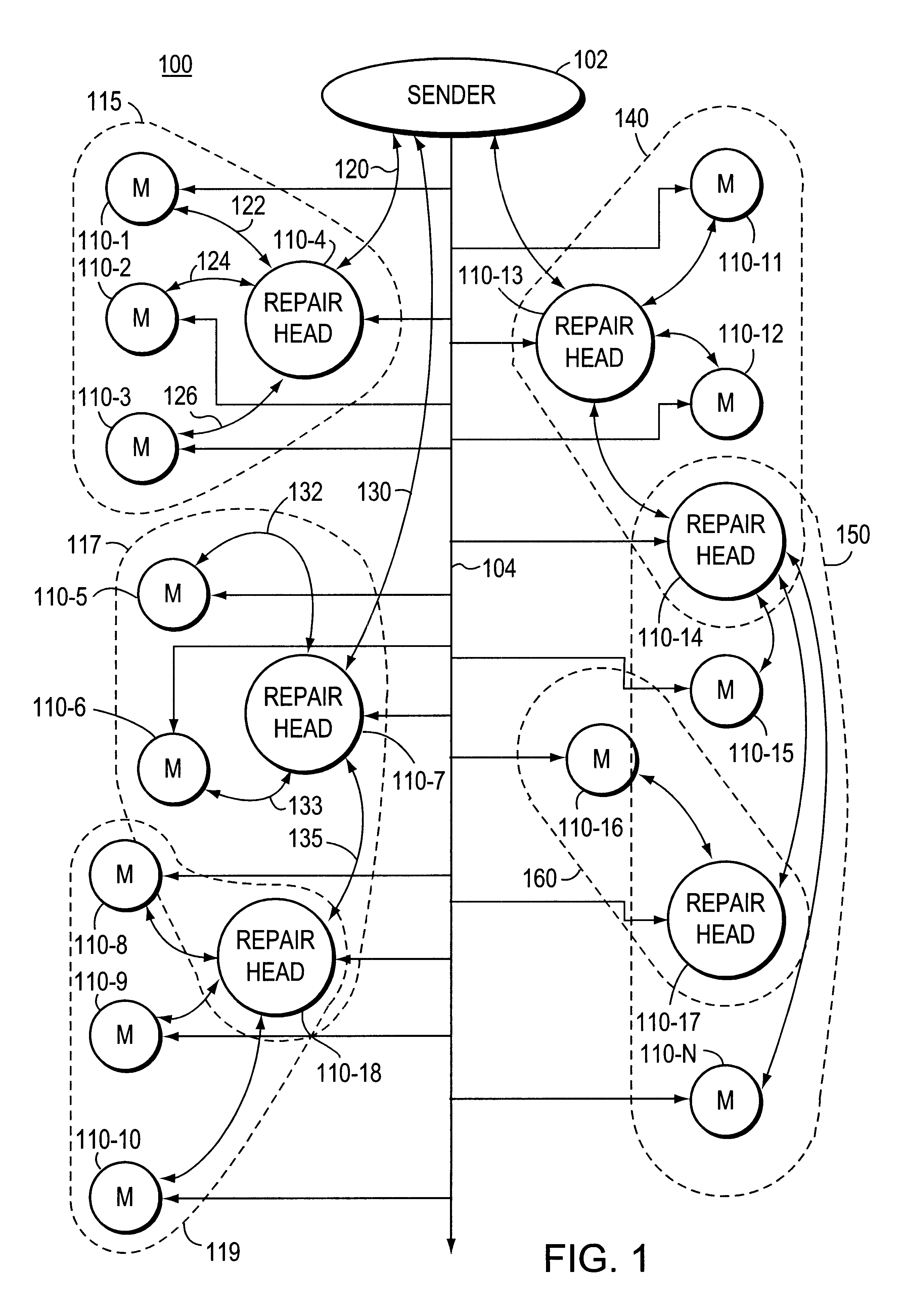
Multiple ACK windows providing congestion control in reliable multicast protocol
InactiveUS6505253B1Special service provision for substationFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsReliable multicast
A multicast repair tree is established, the repair tree having one sender station and a plurality of repair head stations. A repair head station has an affiliated group of member stations. A repair head station retransmits a lost message to its affiliated group of member stations upon receipt from a member station of a NACK message indicating that the selected message was not received. Acknowledgment windows (ACK windows) are established in a member station for transmission of ACK or NACK message by the member station. A number of messages transmitted by the sender station during a transmission window is established. Also a same size of ACK window is established in the receiving stations, with a slot in the ACK window corresponding to each message transmitted by the repair head station. Each receiving station is assigned a slot in the ACK window during which time that receiving station transmits its ACK or NACK messages. Thus the ACK window slots assigned to receiver stations for transmission of ACK / NACK windows are staggered so that different receiver stations transmit their ACKNACK messages at different times. The slot for a particular receiver station to use may be assigned by a random process.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
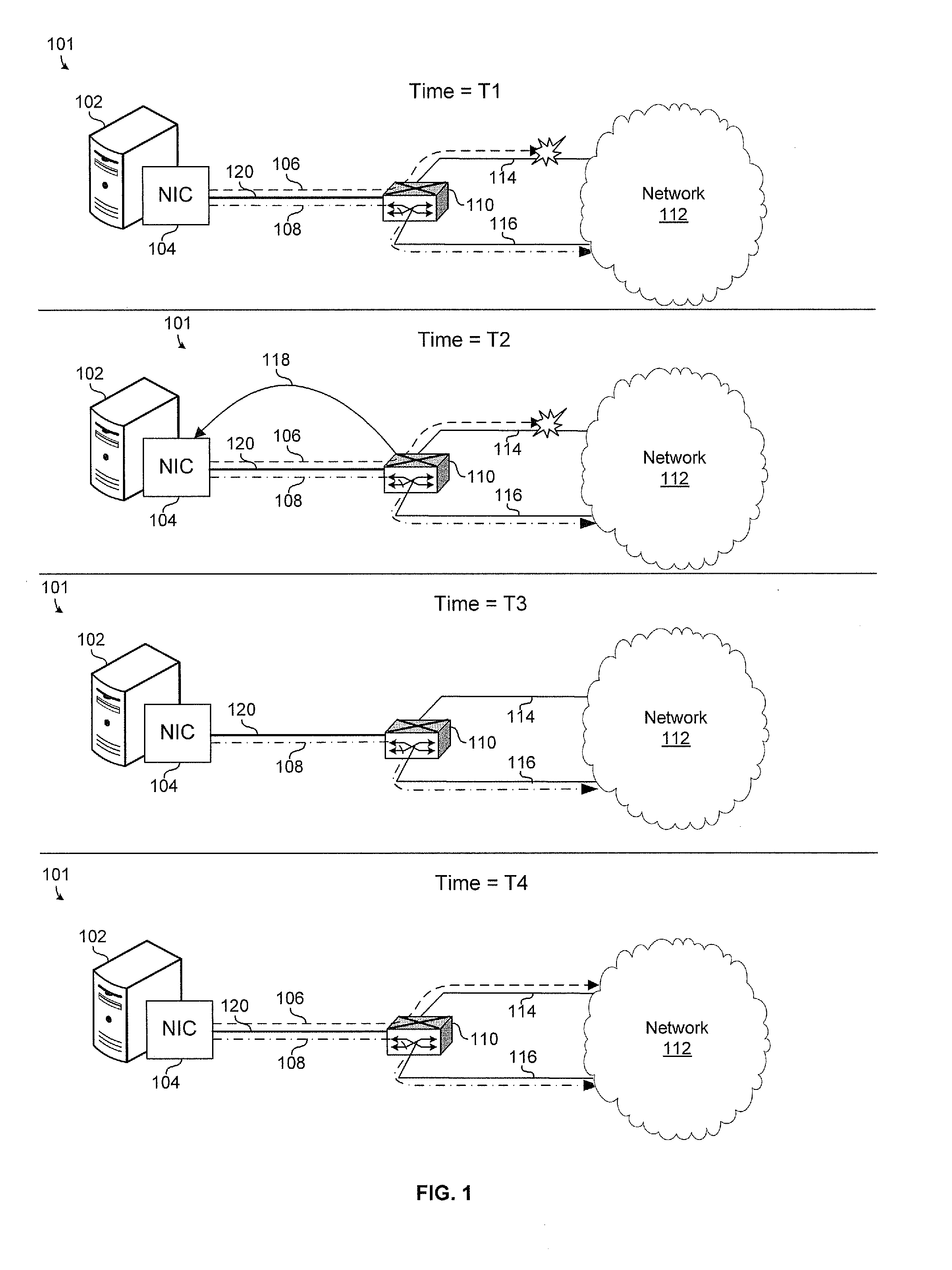
Method and apparatus to avoid network congestion
ActiveUS7675857B1Avoid network congestionError preventionTransmission systemsDistributed computingNetwork congestion
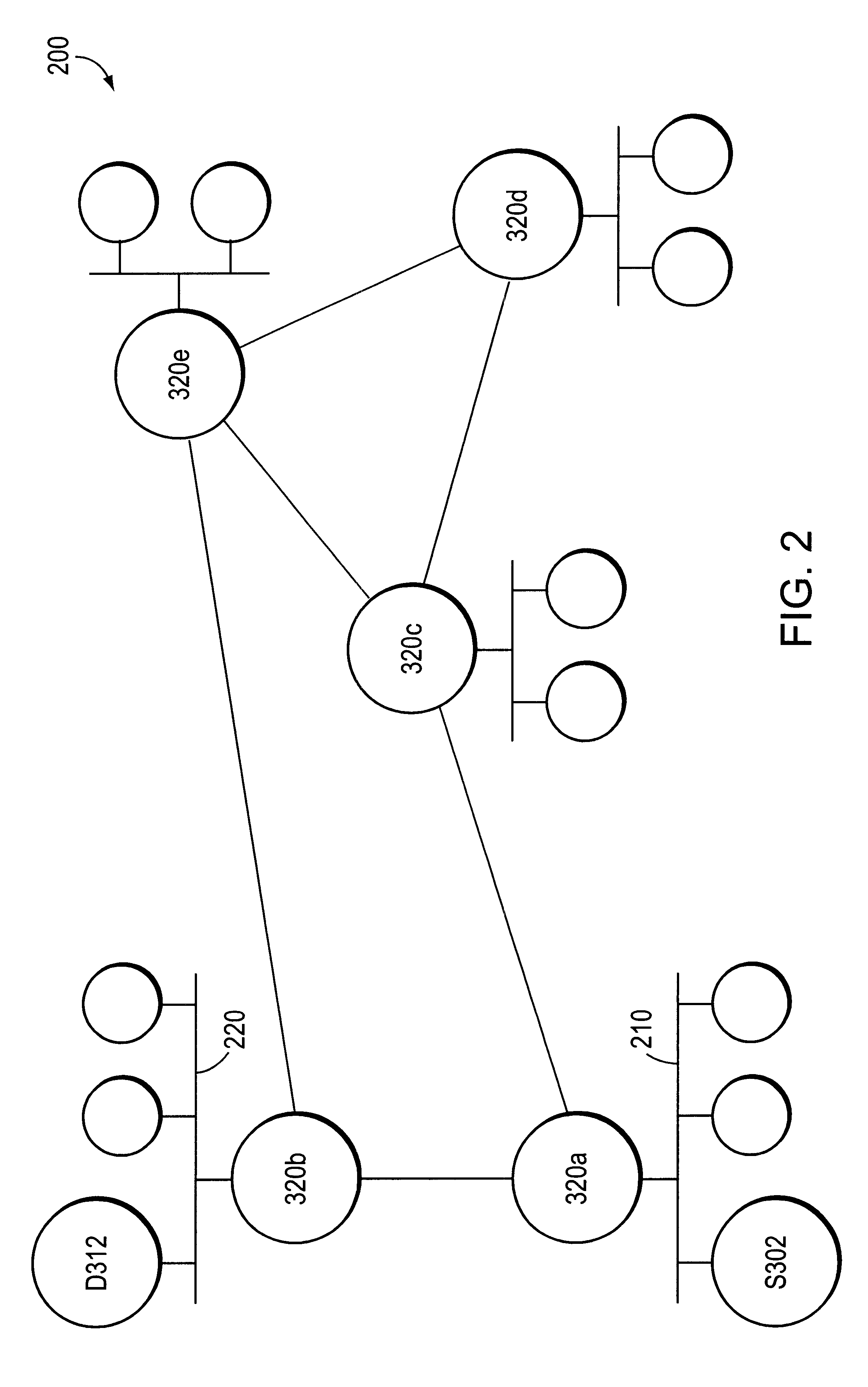
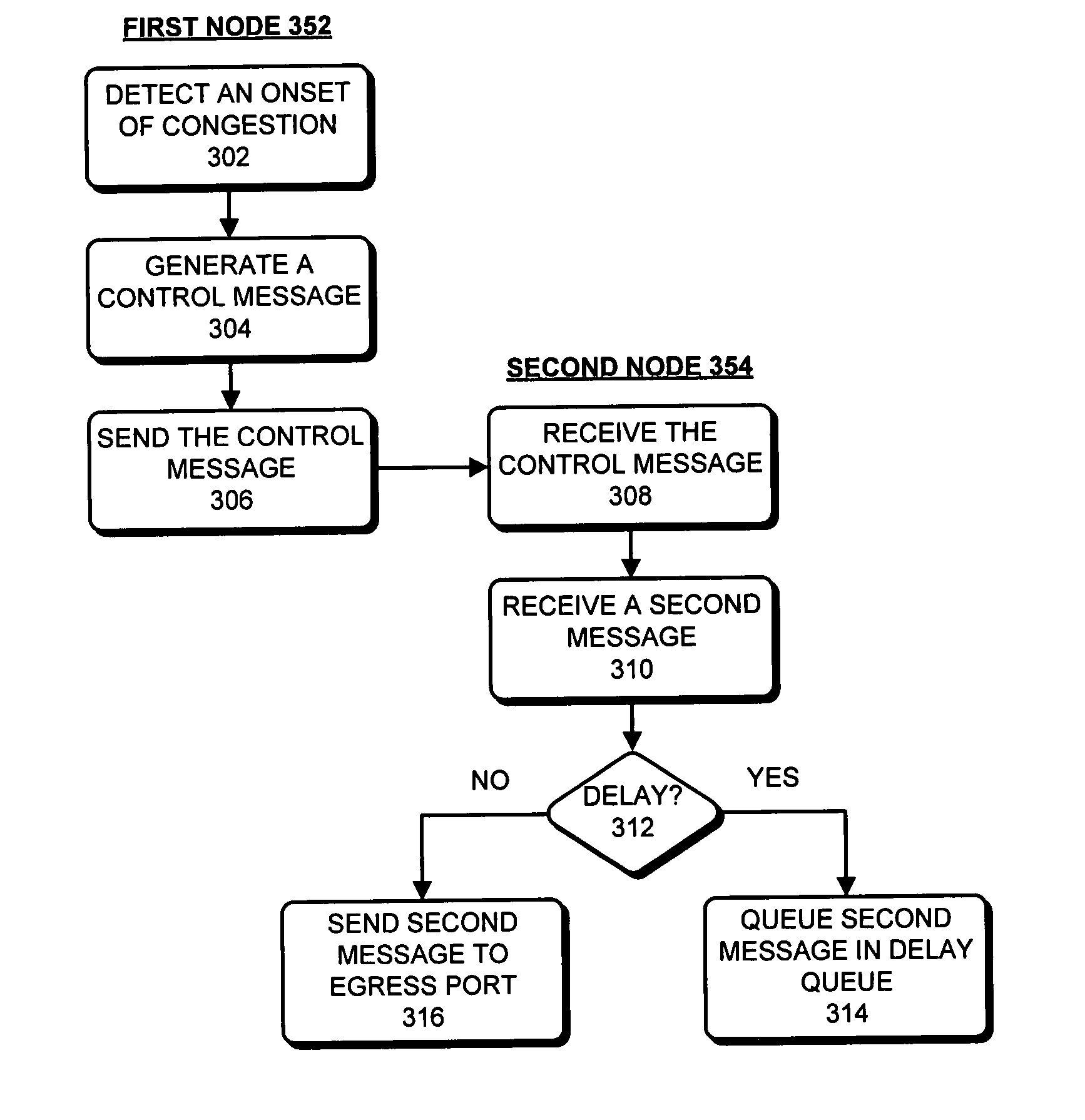
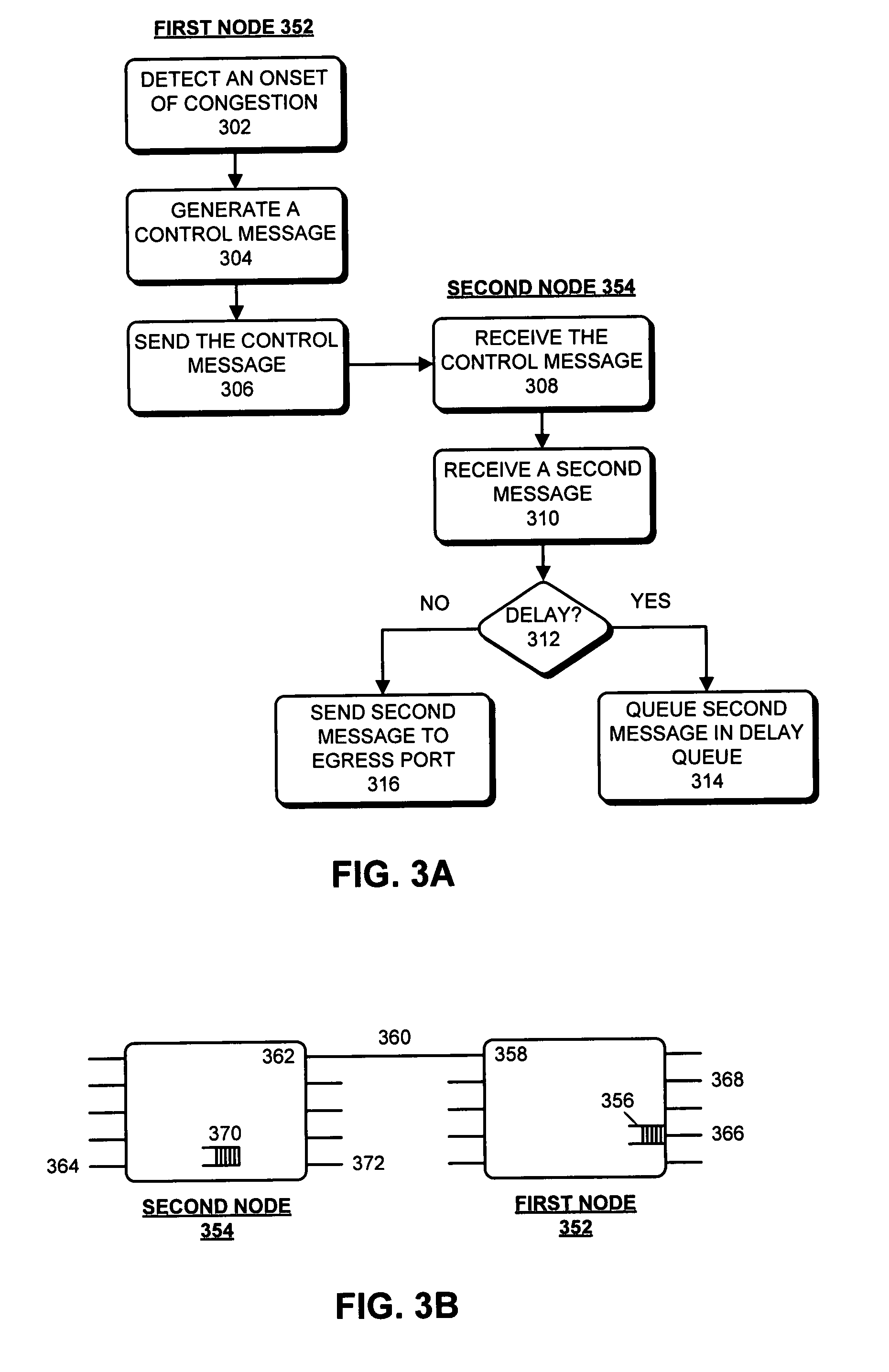
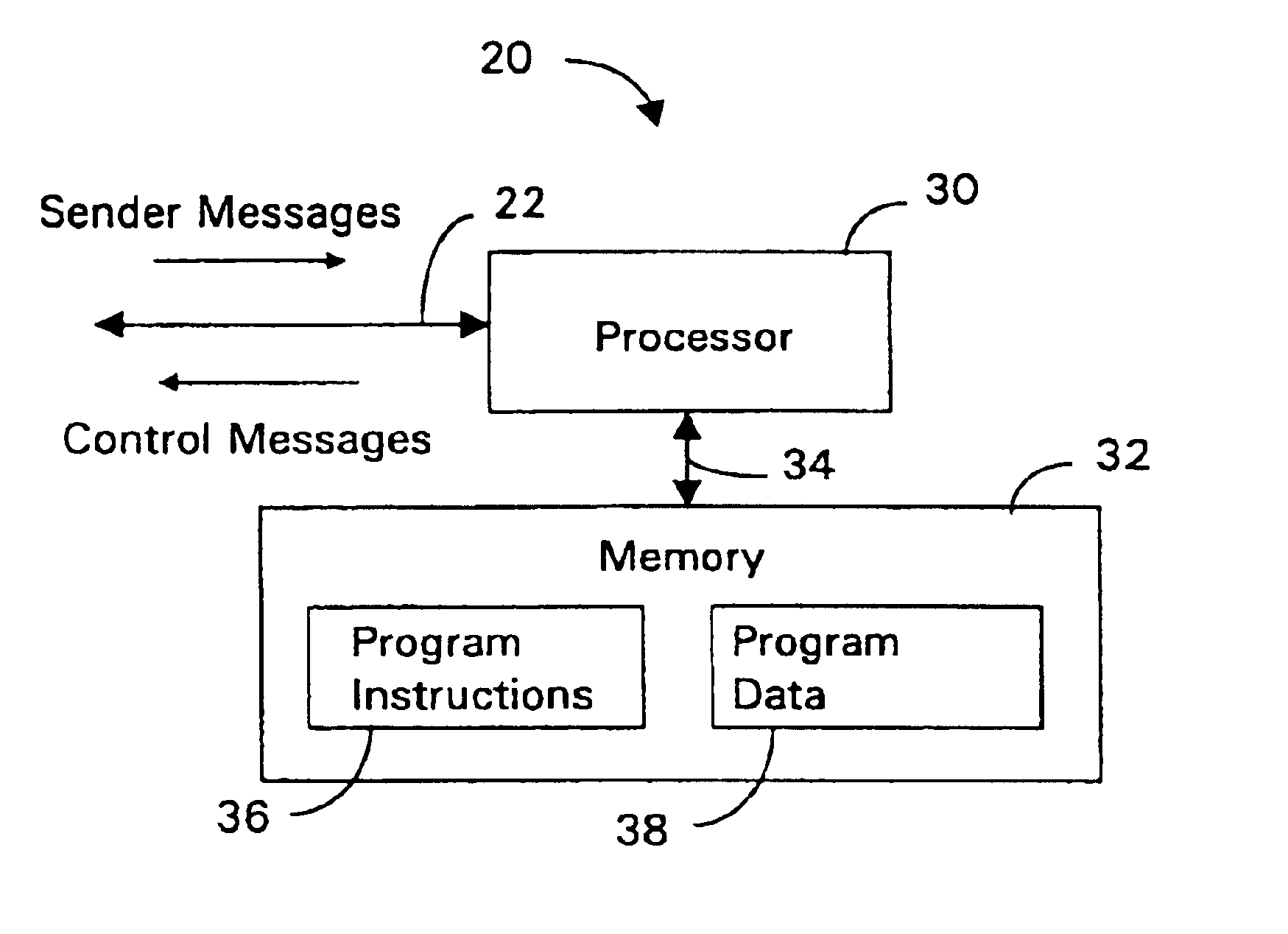
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that avoids network congestion. During operation, the system can detect an onset of congestion in a first queue at a first node. Next, the first node can generate a first control-message, wherein the first control-message contains a congestion-point identifier which is associated with the first queue. The first node can then send the first control-message to a second node, which can cause the second node to delay sending a second message to the first node, wherein the second message is expected to be routed through the first queue at the first node. Next, the second node may propagate the control-message to a third node which may cause the third node to delay sending a third message to the second node, wherein the third message is expected to be routed through the first queue at the first node.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
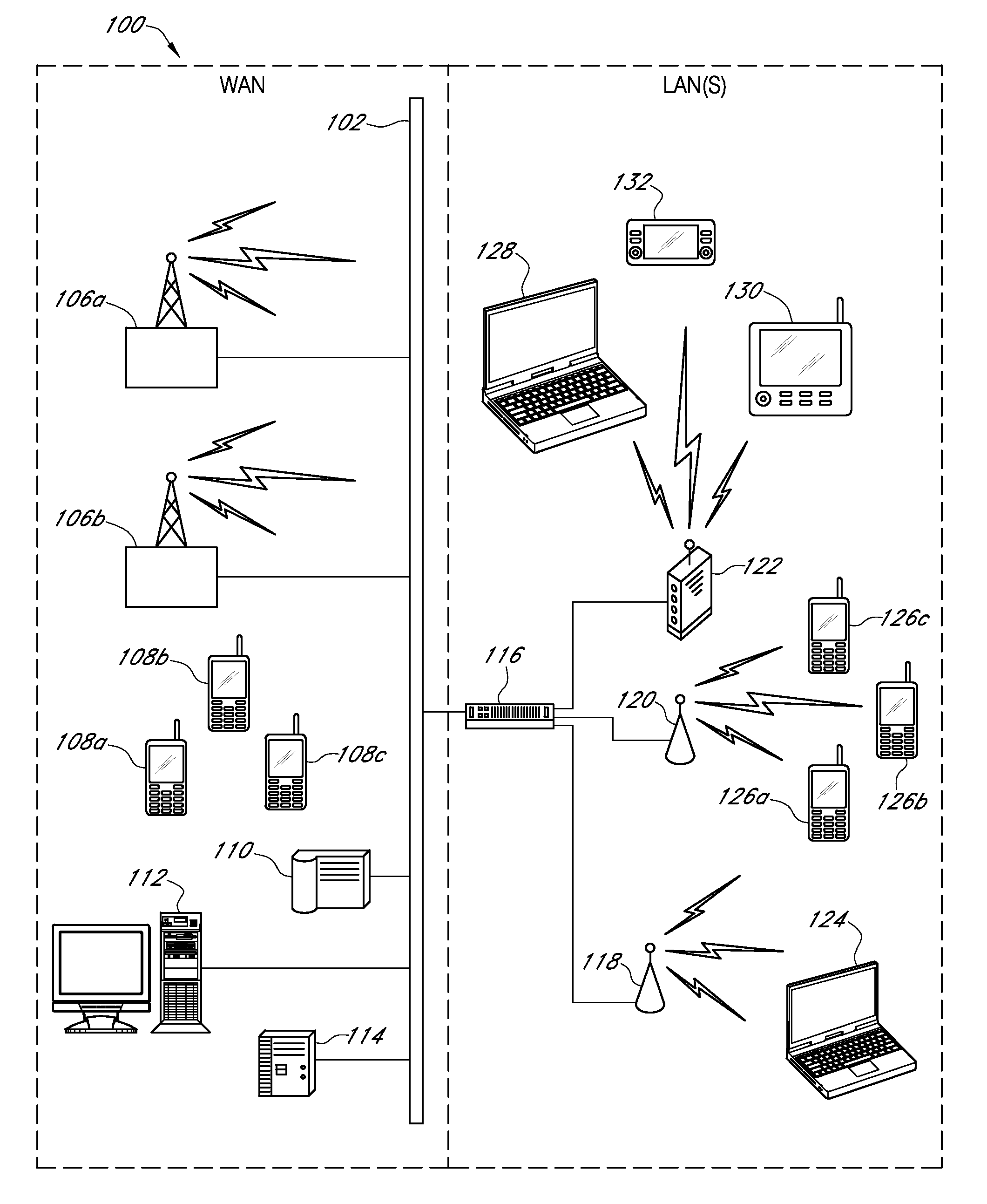
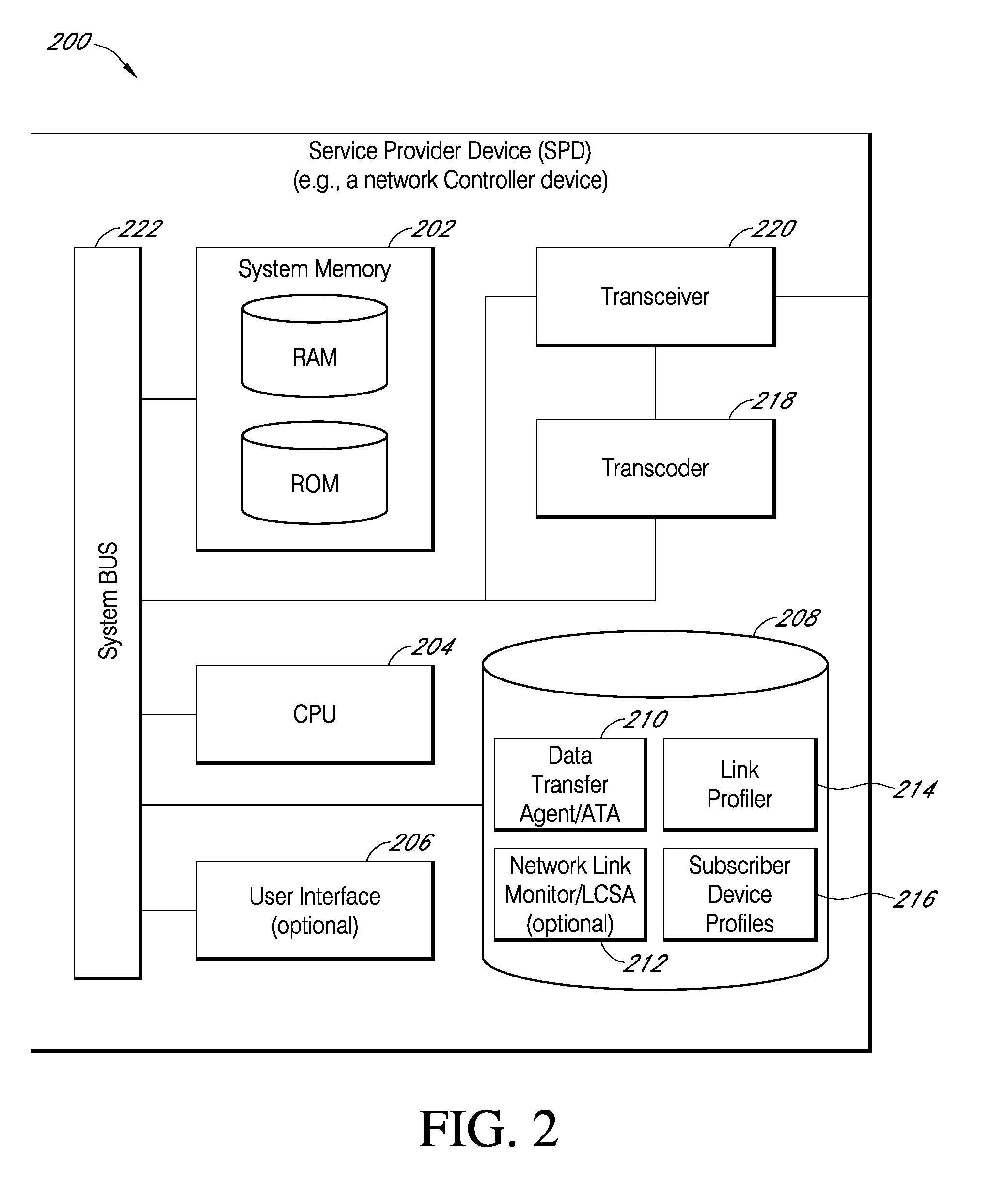
Systems and methods for enhanced data delivery based on real time analysis of network communications quality and traffic
ActiveUS8019886B2Network traffic/resource managementInformation formatDigital dataReal time analysis
A system for improving digital data content delivery based on real time analysis of one or more network communications states. The networked computing system may include a network service provider device, a user equipment, a network link monitor, a data transfer agent, and a data communications network facilitating data communications amongst all devices of the networked computing system. The networked computing system may be configured to: detect at least one network communications metric, determine a network communications state associated with diminished communications throughput based on the detected at least one network communications metric, and then select an optimal rate for a data content transfer based on the determined network communications state. The network communications state may relate to either a state of network congestion or a state of reduced regional radio communications quality.
Owner:OPANGA NETWORKS
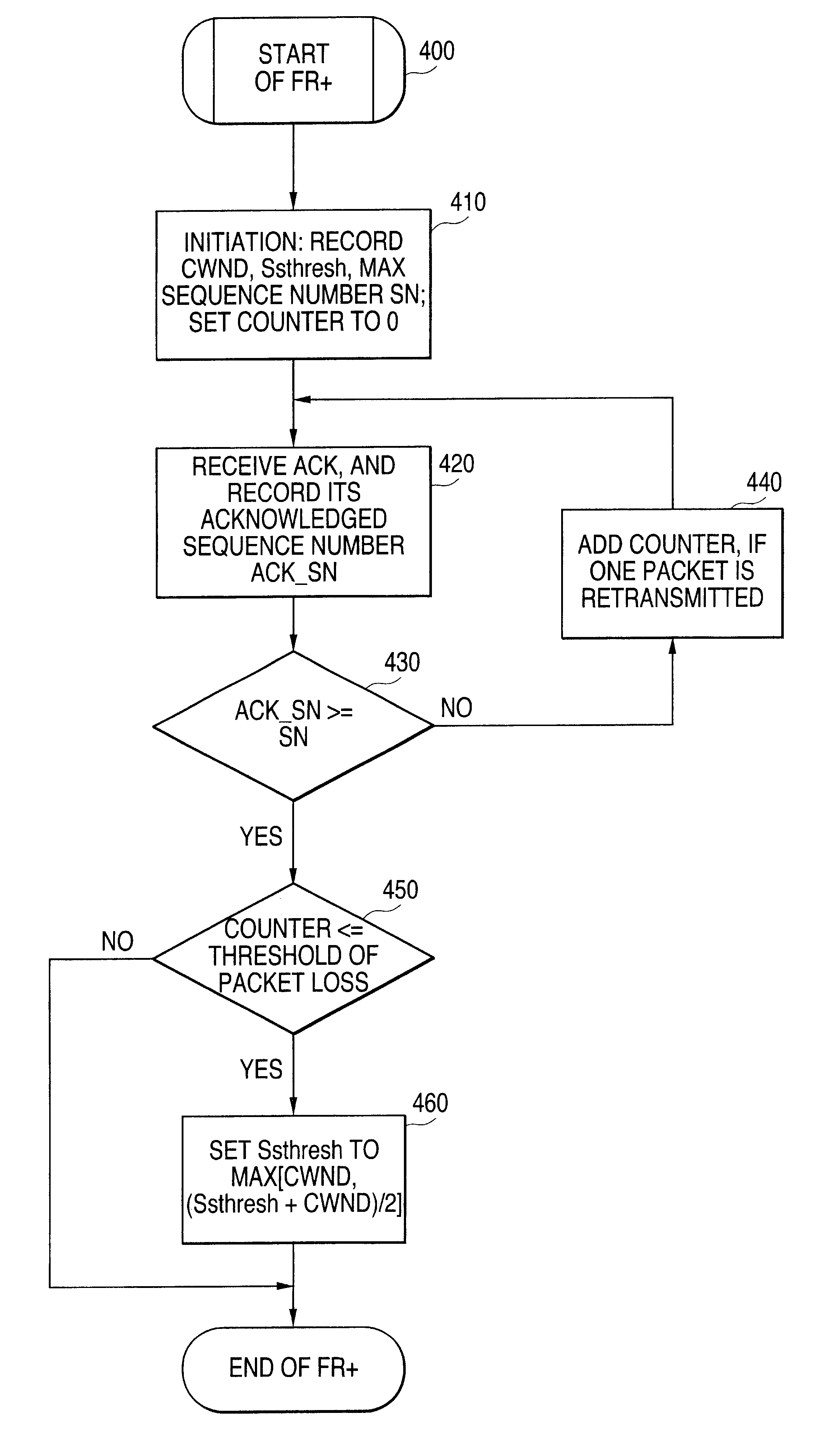
Performance enhancement of transmission control protocol (TCP) for wireless network applications
InactiveUS6757248B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementPerformance enhancementData stream
A new Fast Recovery Plus (FR+) mechanism, and associated method, for wireless and / or mobile network applications to control data flow and avoid network congestion in a TCP / IP packet-switched network.
Owner:NOKIA INTERNET COMM
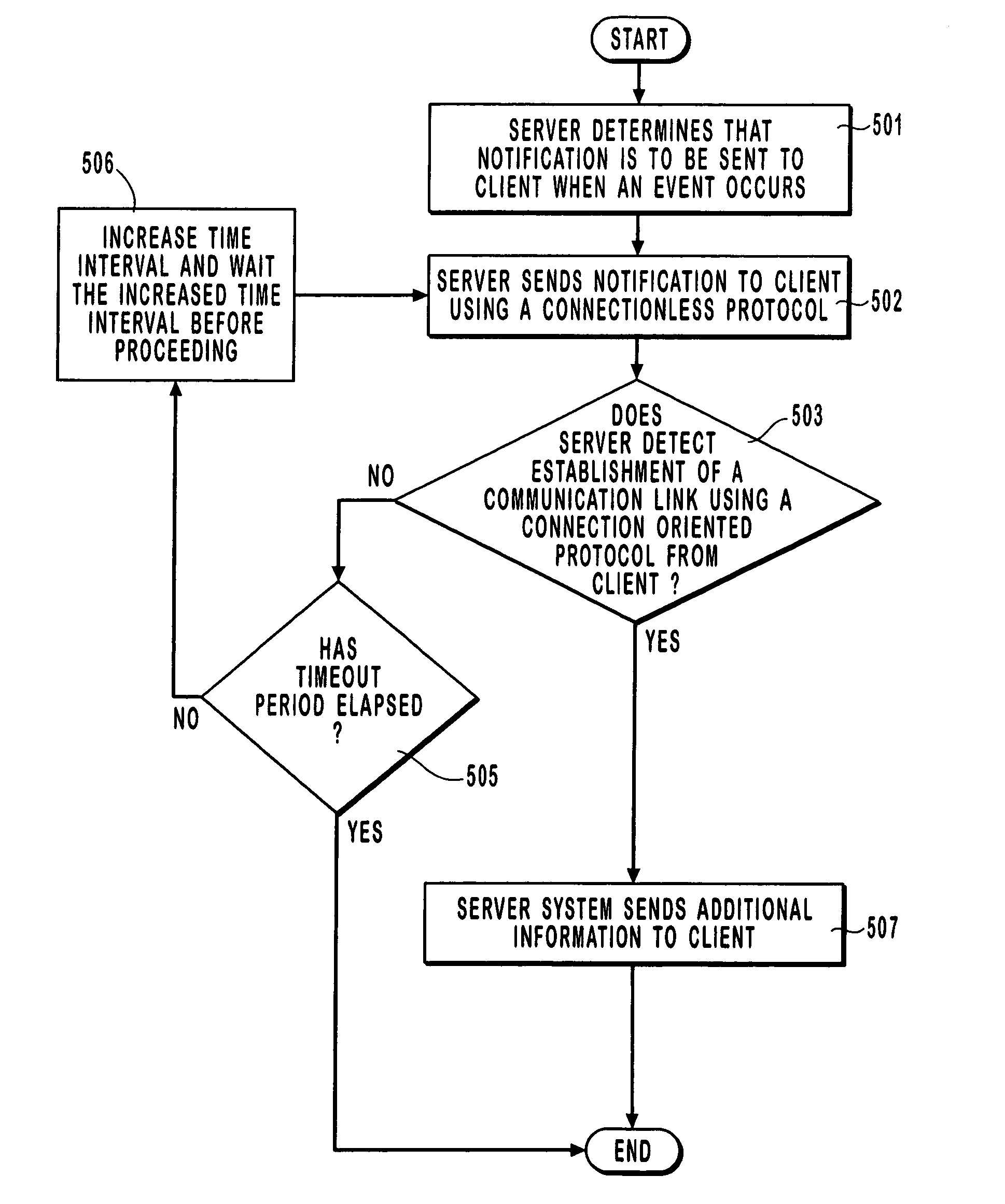
Efficiently sending event notifications over a computer network
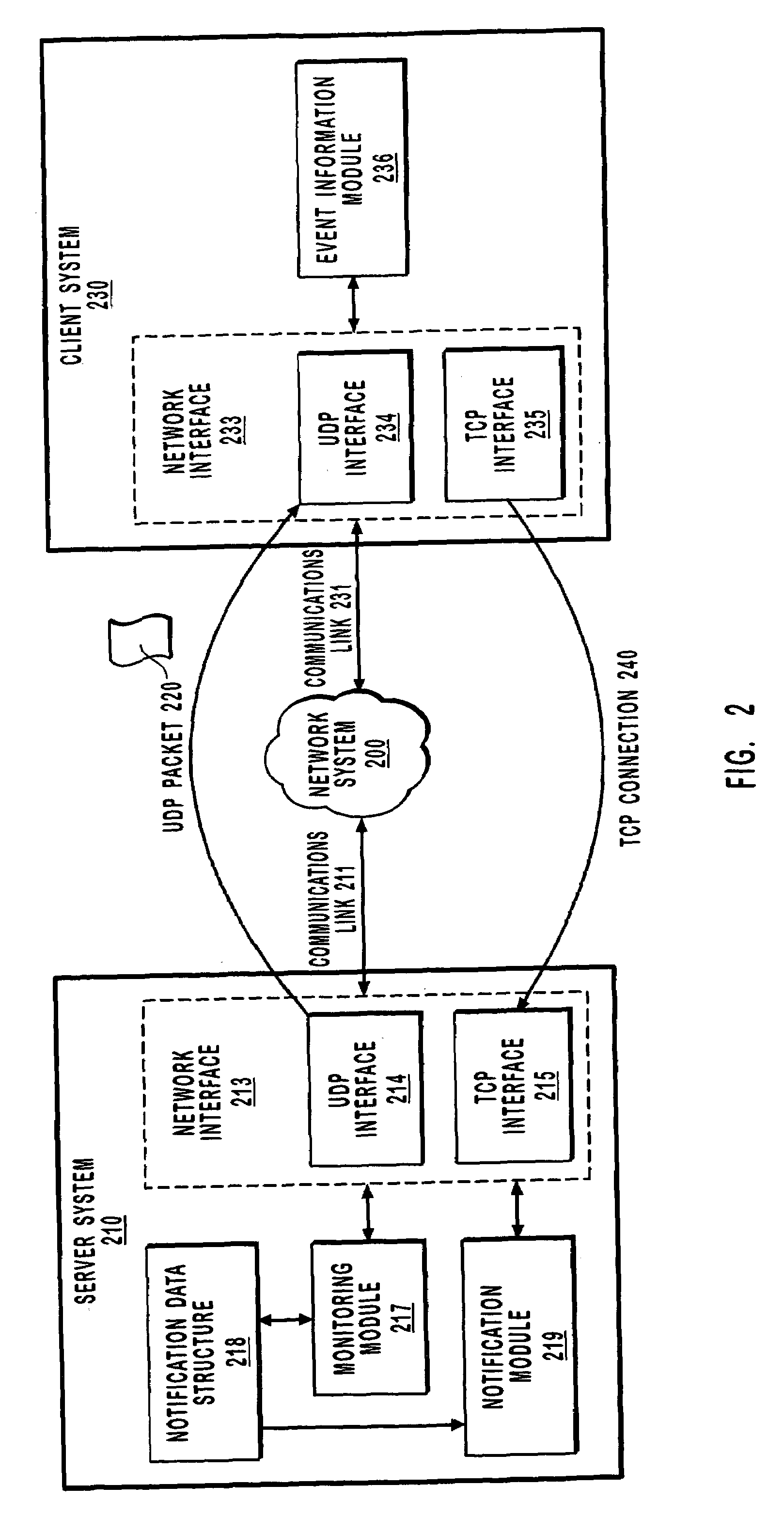
InactiveUS6999992B1Reduce data volumeEliminate overheadMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication softwareClient-side
A method for efficiently sending notifications over a network. A client system requests to be notified when an event occurs. A server system receives the requests and monitors for the occurrence of the event. When the event occurs a single packet using a connectionless protocol (such as User Datagram Protocol) is sent to the client to notify the client of the occurrence of the event. Using a connectionless protocol to send notification reduces the overall amount of data on the network and thus reduces network congestion and the processing capacity of the server and client. When the client system receives notification an attempt to establish a connection using as connection-oriented protocol is executed. Additional data associated with the occurrence of the event is transferred over the connection. The server may repeatedly send notification using a connectionless protocol until a connection using a connection-oriented protocol is established. The server may send notification that notifies the client of the occurrence of multiple events simultaneously within a single packet. The server may also notify multiple applications of the occurrence of an event using a single notification.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Communication system with content-based data compression
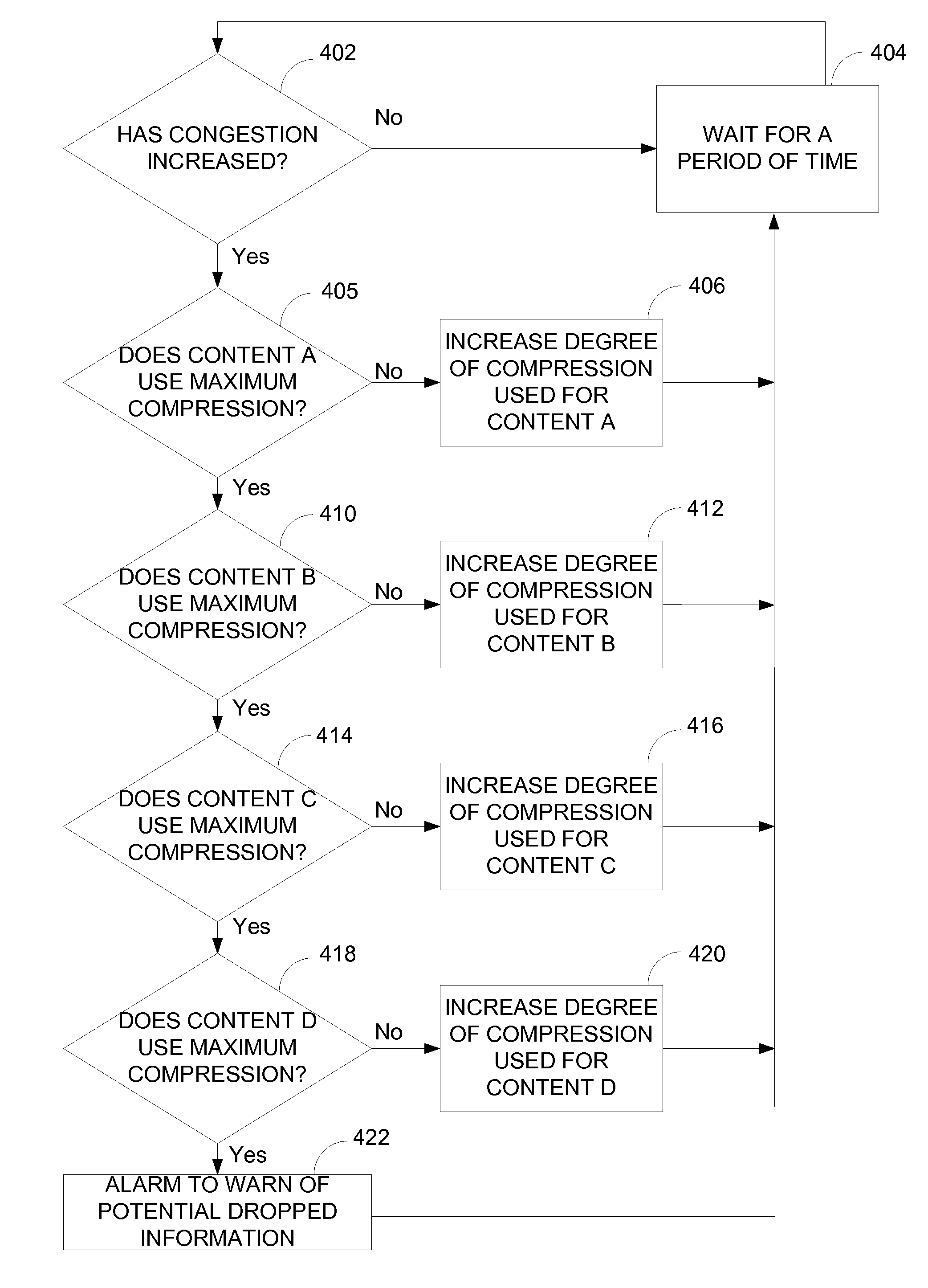
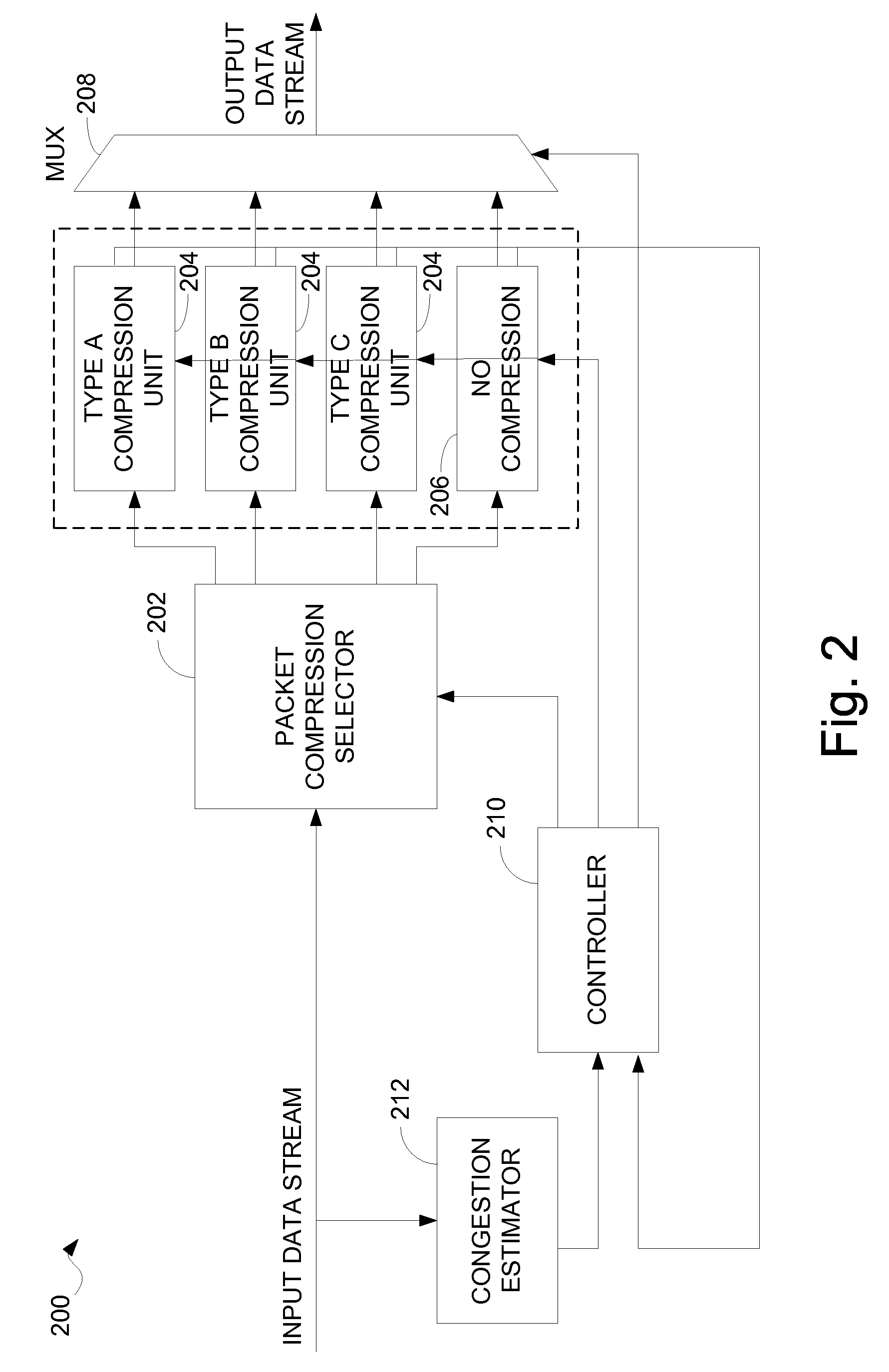
InactiveUS7069342B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData compressionCommunications system
Methods and apparatus for dynamically adapting the degree of compression used in compressing data based upon the type of contents contained within a packet are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an apparatus that forwards data across a digital communications network includes a compression switch, a compression system, and an output interface. The compression switch receives the data, determines a content type associated with the data by examining the data, and assigns a compression level to the data in response to the determined content type. The compression system is arranged to compress the data based upon the compression level, while the output interface forwards the compressed data across the network. In one embodiment, the apparatus also includes a network congestion estimator that determines a level of network congestion.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Congestion control method for a packet-switched network
InactiveUS7369498B1Increase profitError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket loss
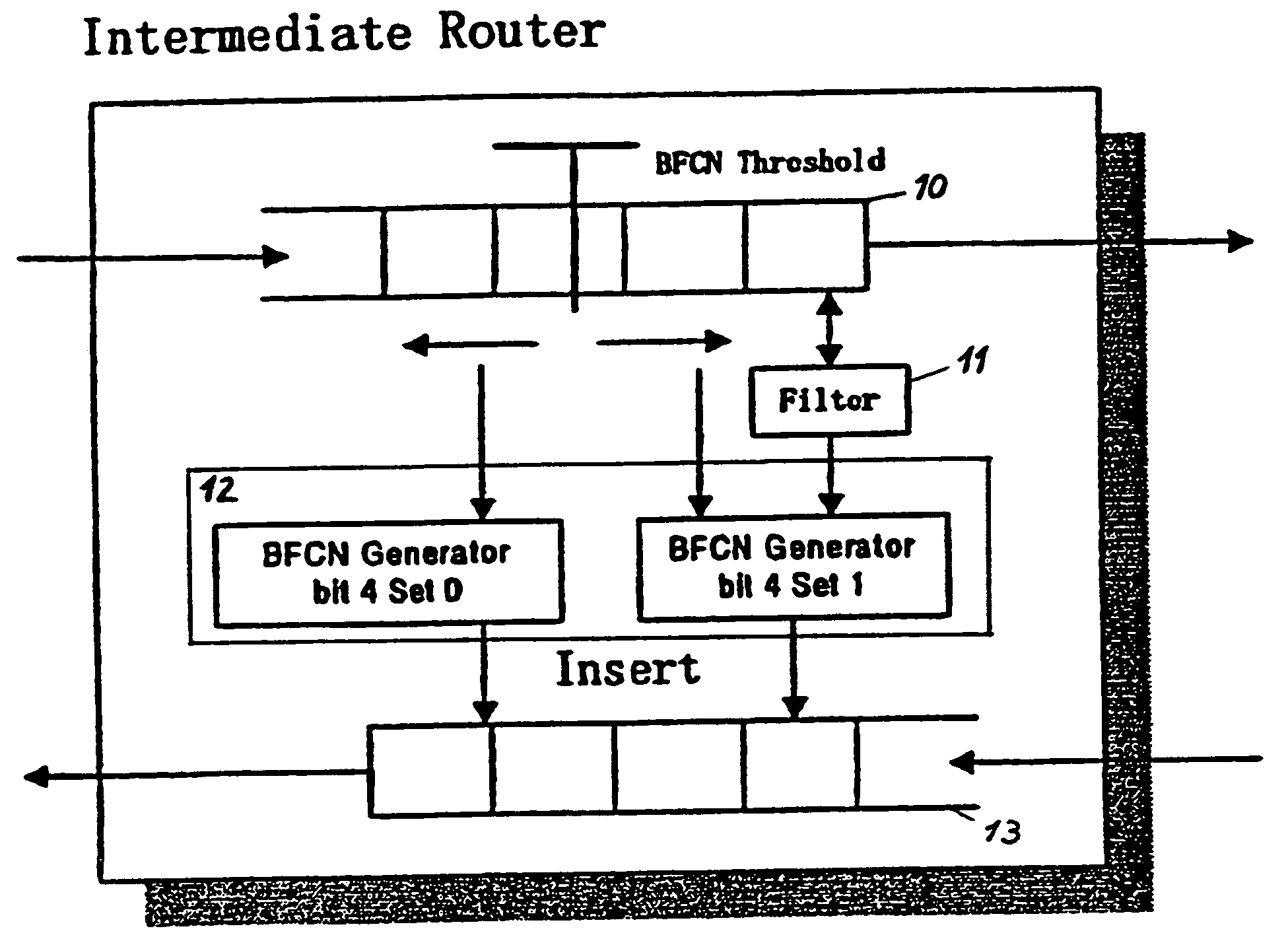
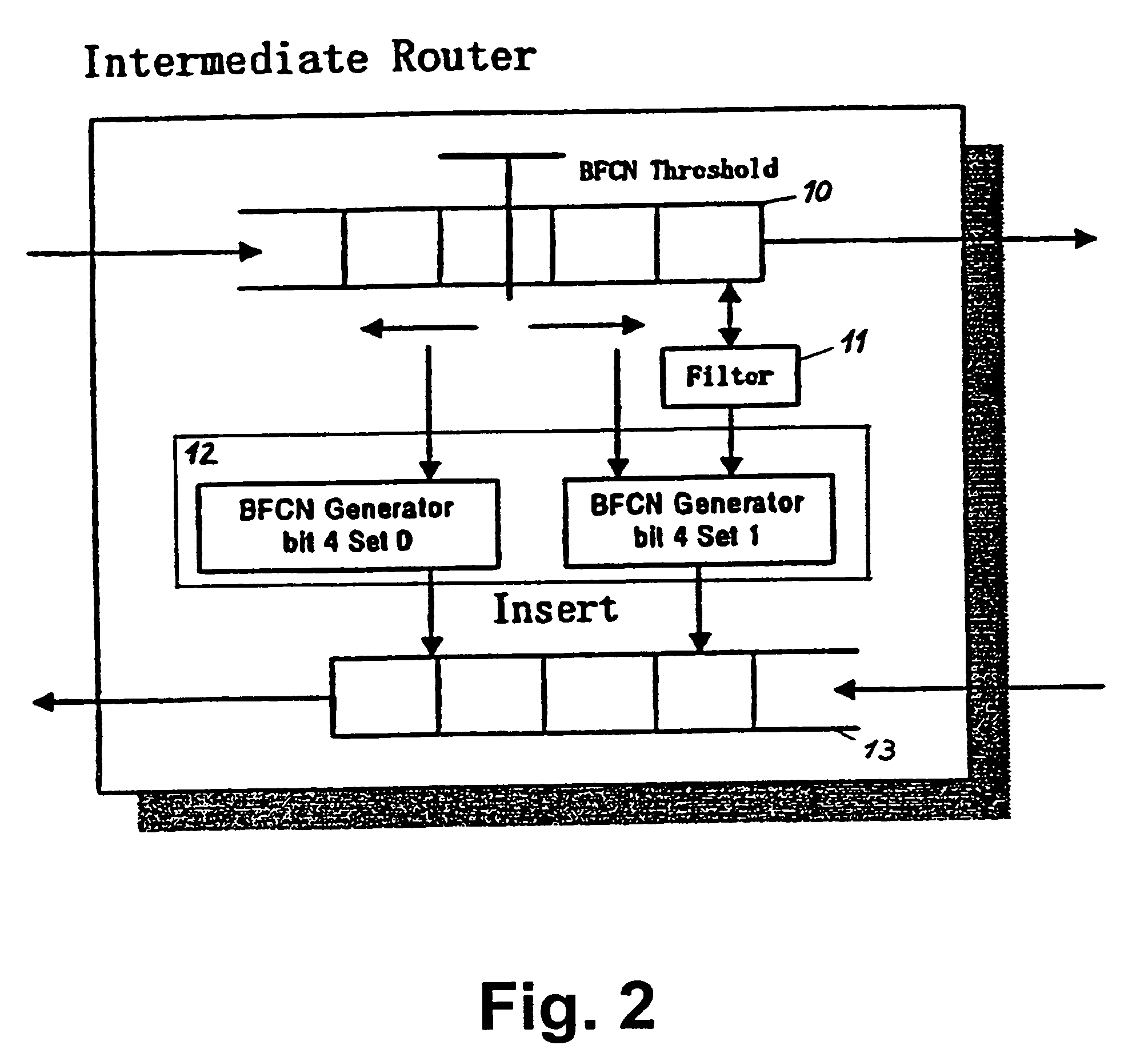
The present invention relates to a method and network for controlling congestion in a packet-switched network, comprising traffic sources, traffic destinations and network nodes, wherein a packet queue length in a network node is determined and a congestion notification is transmitted back towards the source address of an incoming data packet received at the network node, if the detected packet queue length exceeds a predetermined threshold. Then, congestion control is performed at a predetermined intermediate network node in response to the receipt of the congestion notification. Thereby, burts of source traffic can be constrained and unnecessary packet losses can be avoided already at an intermediate access node and within the network. The congestion notification message generated due to an incipient congestion is immediately routed back according to its source address. As a result, control delay time is shortened, such that buffer size requirements and number of congestion notification messages are reduced.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
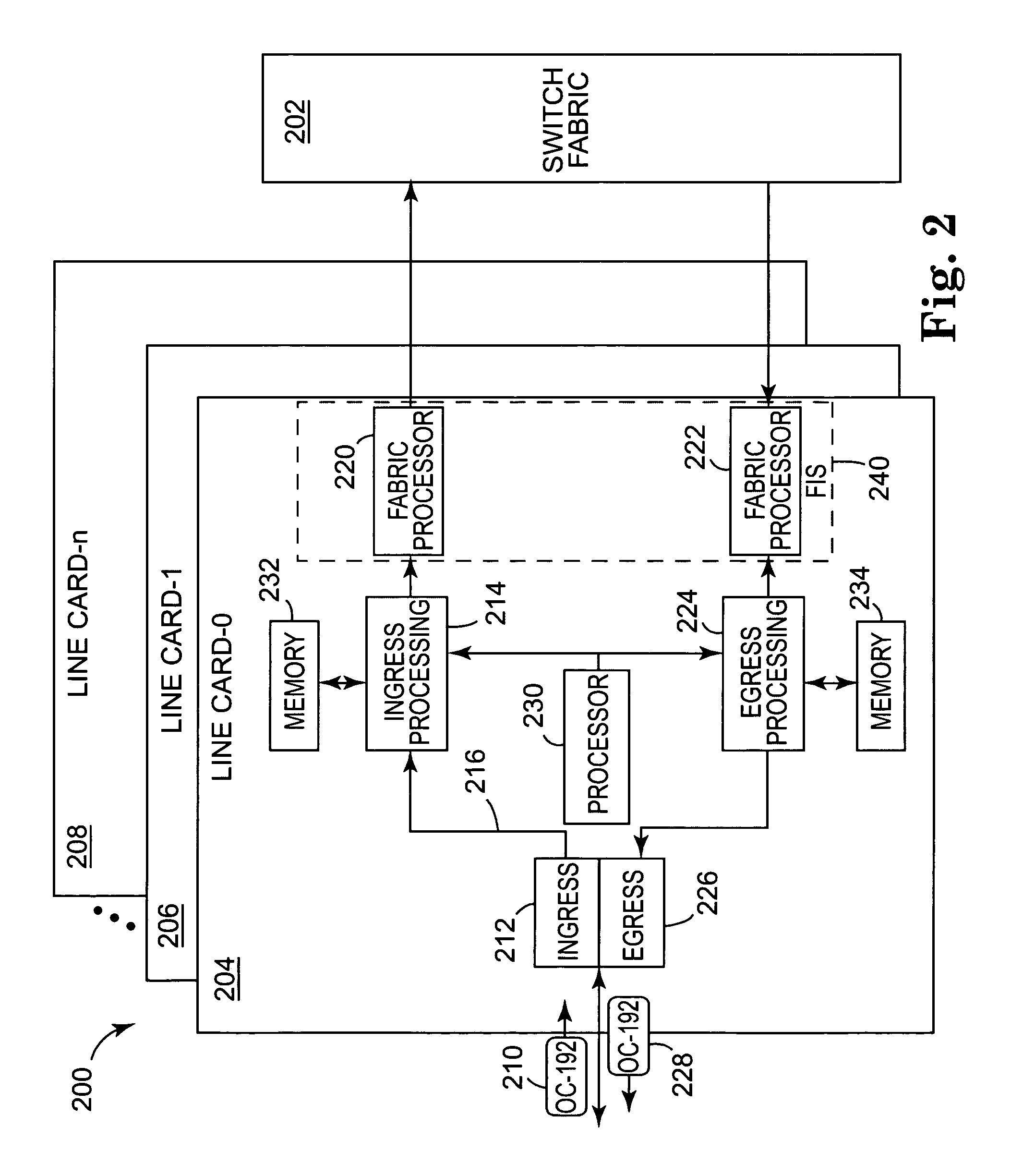
Multi-service queuing method and apparatus that provides exhaustive arbitration, load balancing, and support for rapid port failover
InactiveUS7151744B2Efficient multicastingEasy to handleError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityFailover
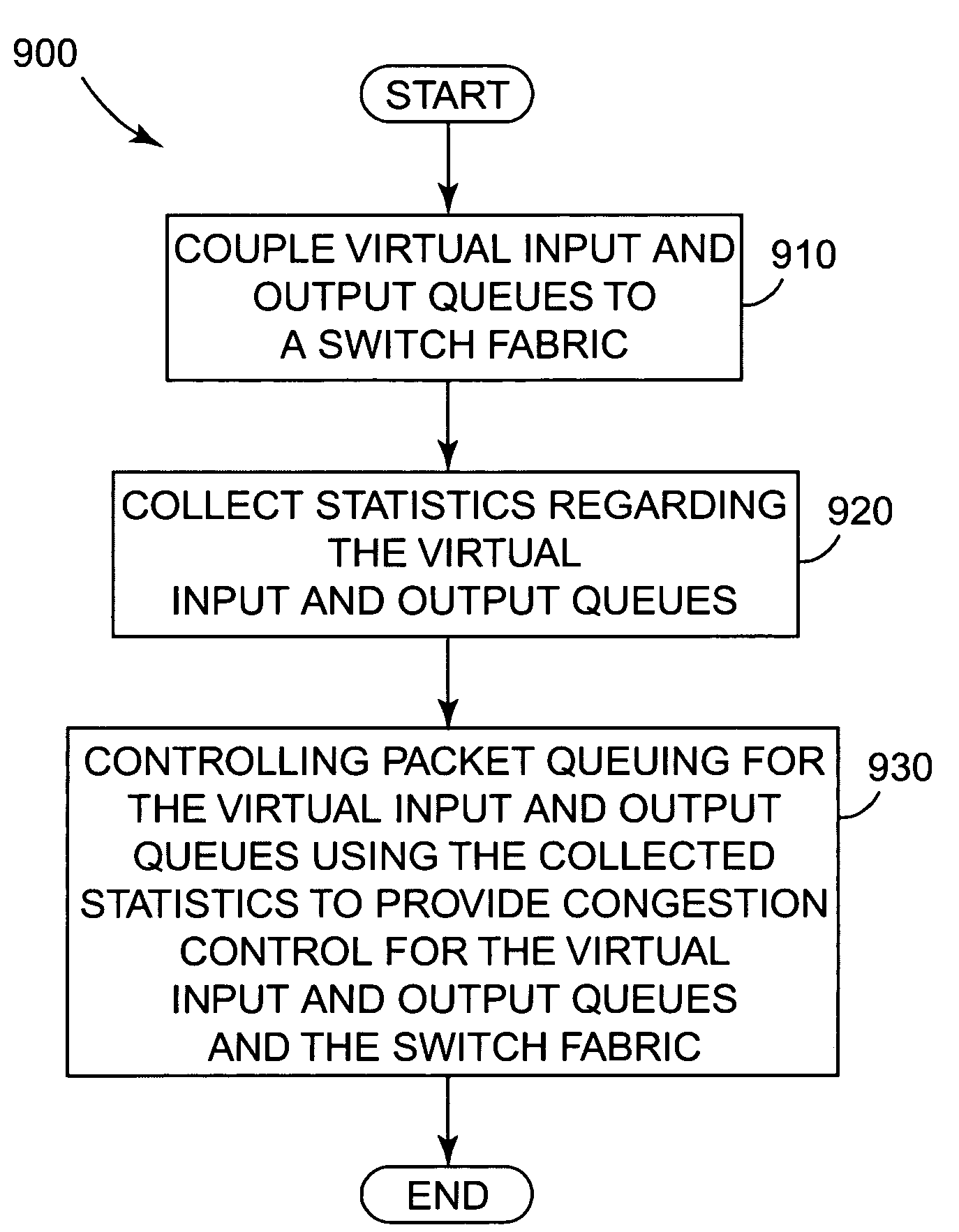
The present invention provides a multi-service queuing method and apparatus that provides exhaustive arbitration, load balancing, and support for rapid port failover. Routers and switches according to the present invention can instantaneously direct the flow of traffic to another port should there be a failure on a link, efficiently handle multicast traffic and provide multiple service classes. The fabric interface interfaces the switch fabric with the ingress and egress functions provided at a network node and provides virtual input and output queuing with backpressure feedback, redundancy for high availability applications, and packet segmentation and reassembly into variable length cells. The user configures fixed and variable-length cells. Virtual input and output queues are coupled to a switch fabric. Statistics regarding the virtual input and output queues are collected and packet queuing for the virtual input and output queues is controlled using the collected statistic to provide congestion control for the virtual input and output queues and the switch fabric.
Owner:RPX CORP
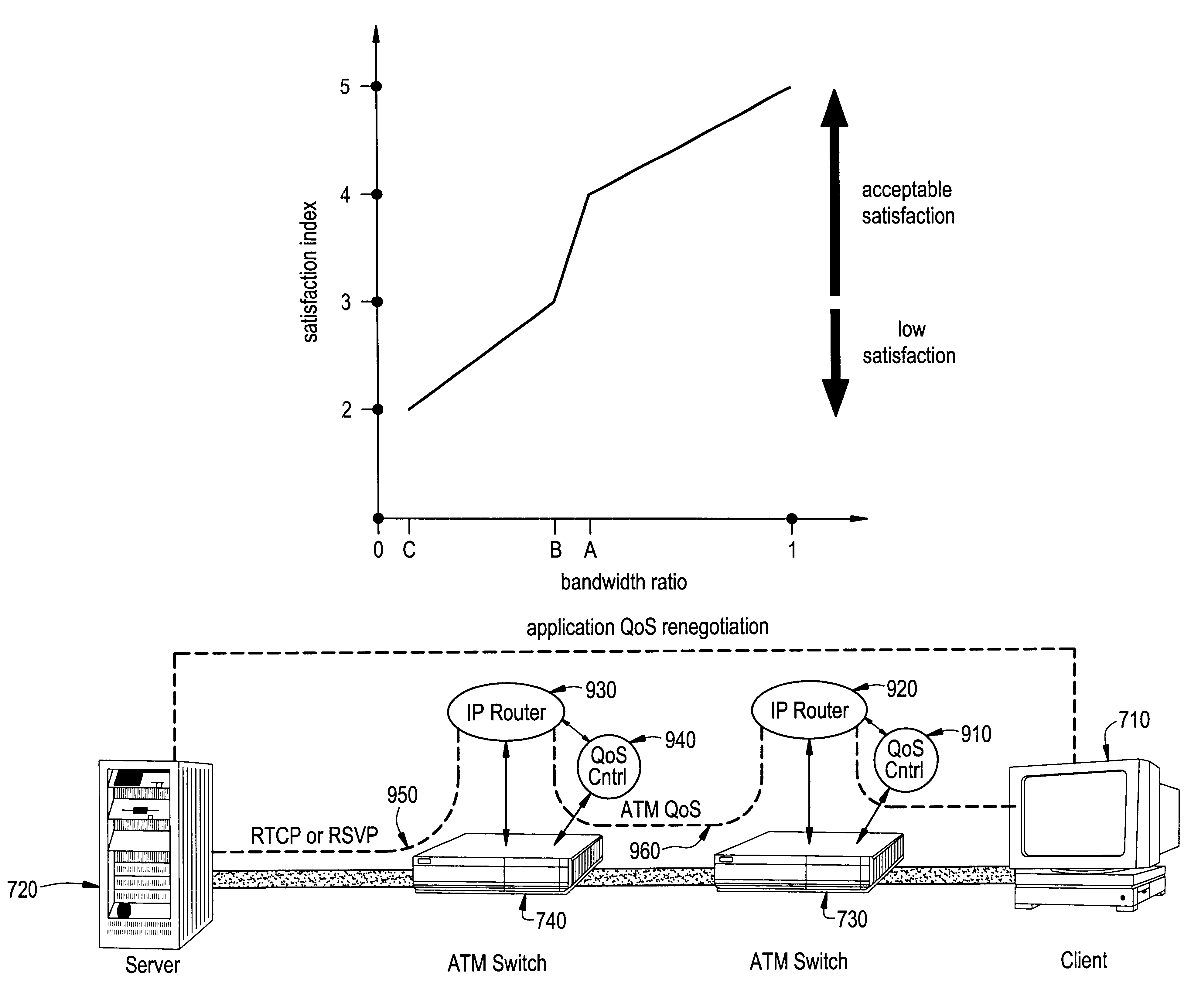
Dynamic network bandwidth allocation for multimedia applications with soft quality-of-service requirements
InactiveUS6404738B1Lower connection costsLow costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationService level requirement
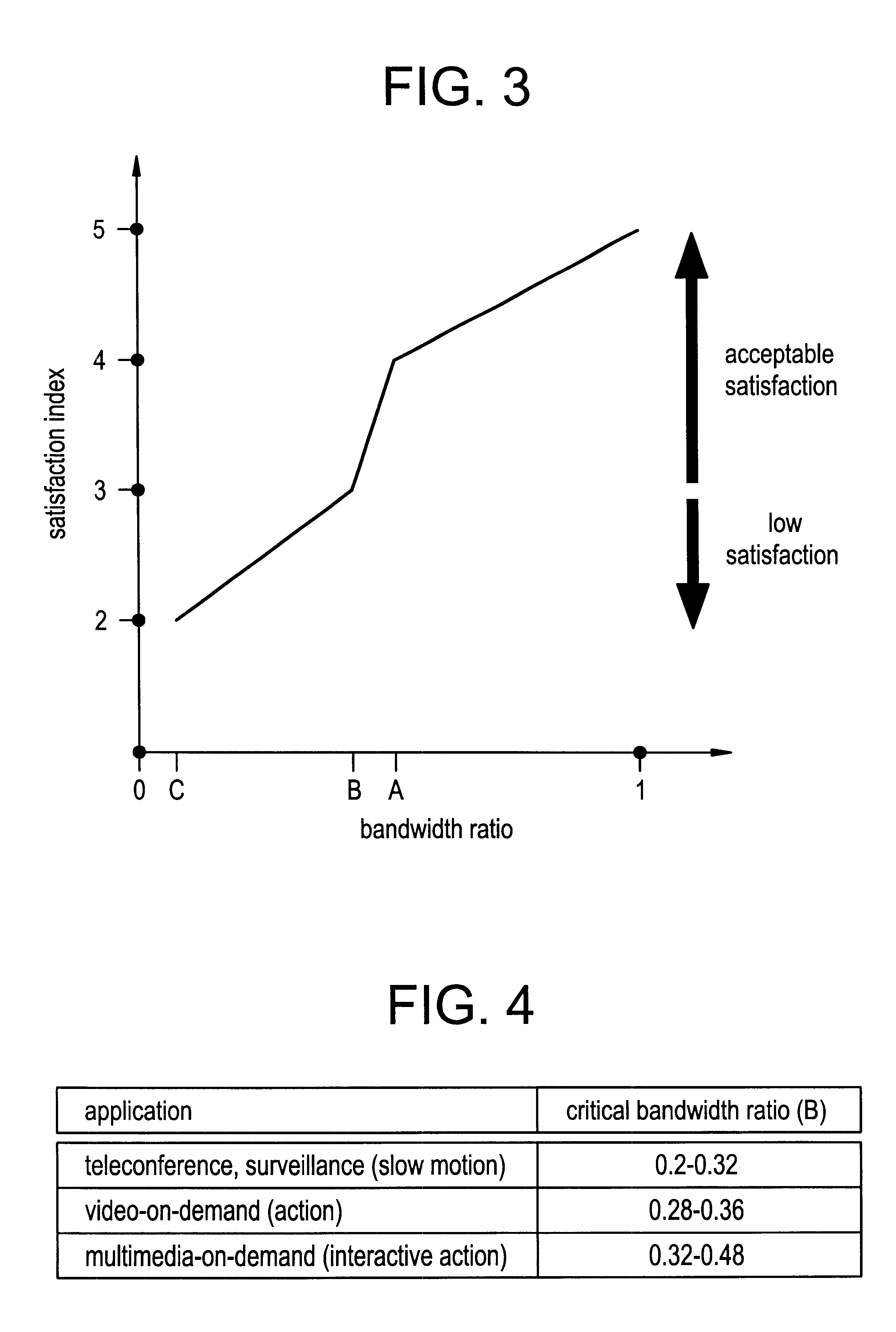
A new concept of soft quality-of-service (soft-QoS) is developed that bridges the gap between the efficient provision of network-level QoS and the requirements of multimedia applications. Soft-QoS is defined by a satisfaction index (a number that rates users' perceptual quality) and a softness profile (a function that captures the robustness of multimedia applications to network congestion). Another aspect of this invention is a bandwidth allocation scheme for multimedia applications with soft-QoS requirements is presented. The implementation of the bandwidth allocation scheme on a network element realizes a soft-QoS controller. The controller uses the connections' softness profiles to compute a bandwidth allocation that maximizes the minimum satisfaction index of active connections.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and system for mobile IP home agent redundancy by using home agent control nodes for managing multiple home agents
InactiveUS7080151B1Reduce failed callImprove user satisfactionMultiprogramming arrangementsCommmunication supplementary servicesComputer networkMulticast network
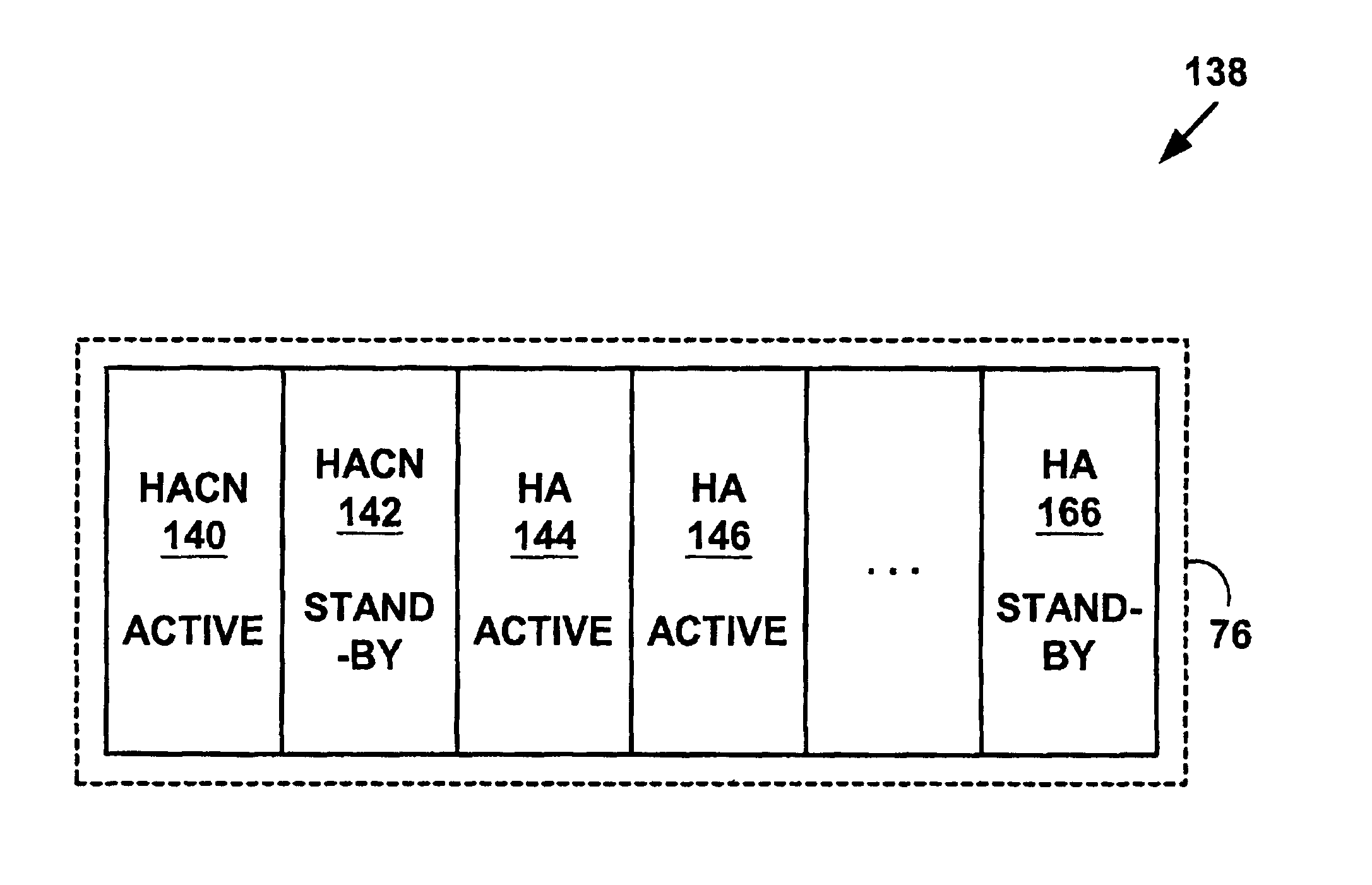
A method and system for Mobile Internet Protocol (IP) device redundancy. As mobile devices roam away from a home network and change a connective status, mobility binding records are sent to a multicast network address on the home network. The multicast network address multicasts the mobility binding records to other active Mobile IP home agent control nodes, standby home agent control nodes and standby home agents on the home network. The method and system allows standby home agent control nodes or standby home agents to be transparently switched for active home agent control nodes or active home agents that fail without downloading or uploading large numbers of mobility binding records after a failure. The method and system may also help reduce failed calls (e.g., data sessions including Voice over IP (VoIP), H.323, etc.), network congestion and improve user satisfaction in Mobile IP systems.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
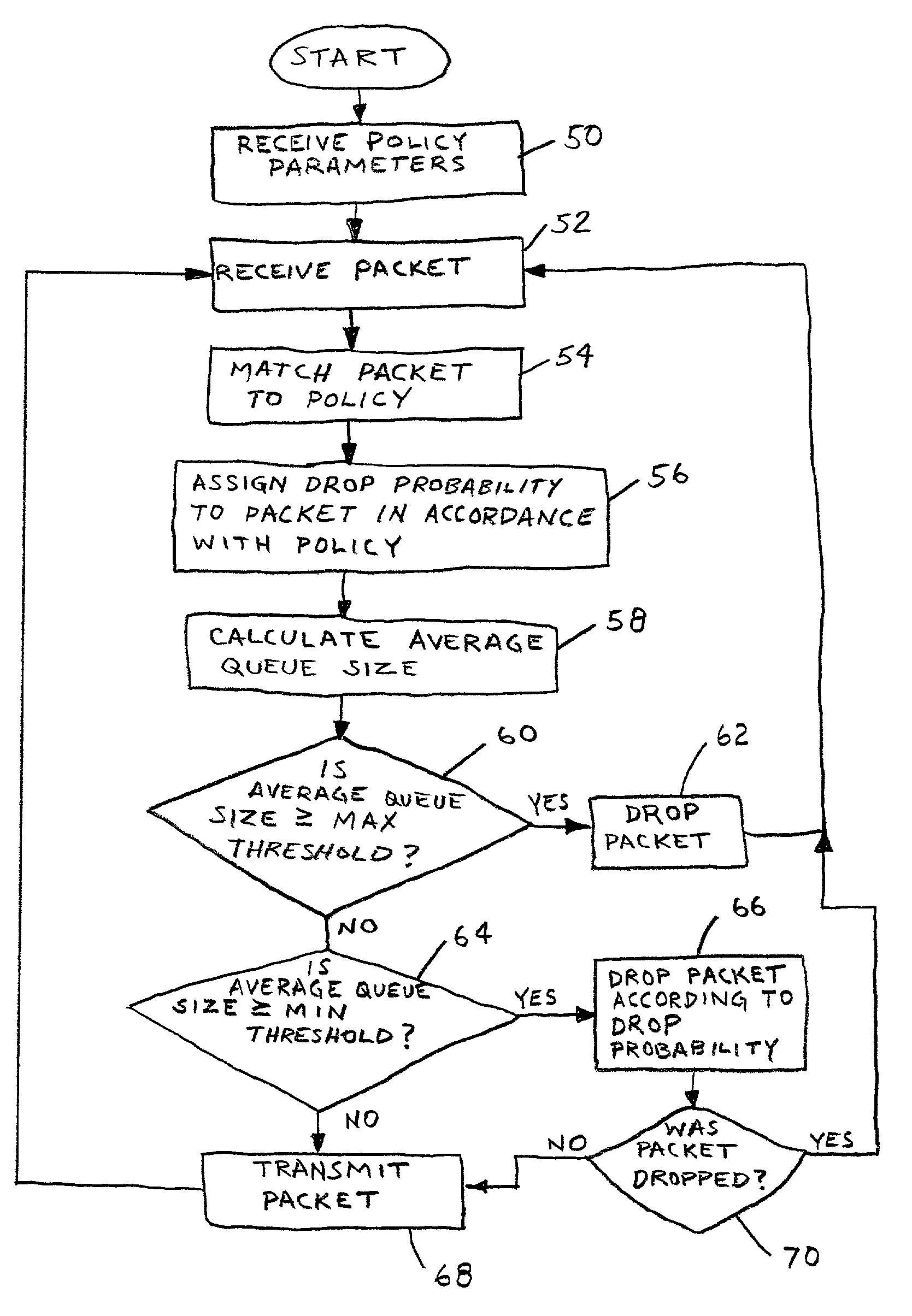
Policy-based weighted random early detection method for avoiding congestion in internet traffic
InactiveUS6996062B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityRandom early detection
A method and apparatus for avoiding network congestion. An exemplary packet forwarding device may apply policy rules to incoming packets to assign relative drop probabilities to the packets based on the priority of the packets. In times of network congestion, packets may be selectively dropped according to their associated drop probability.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
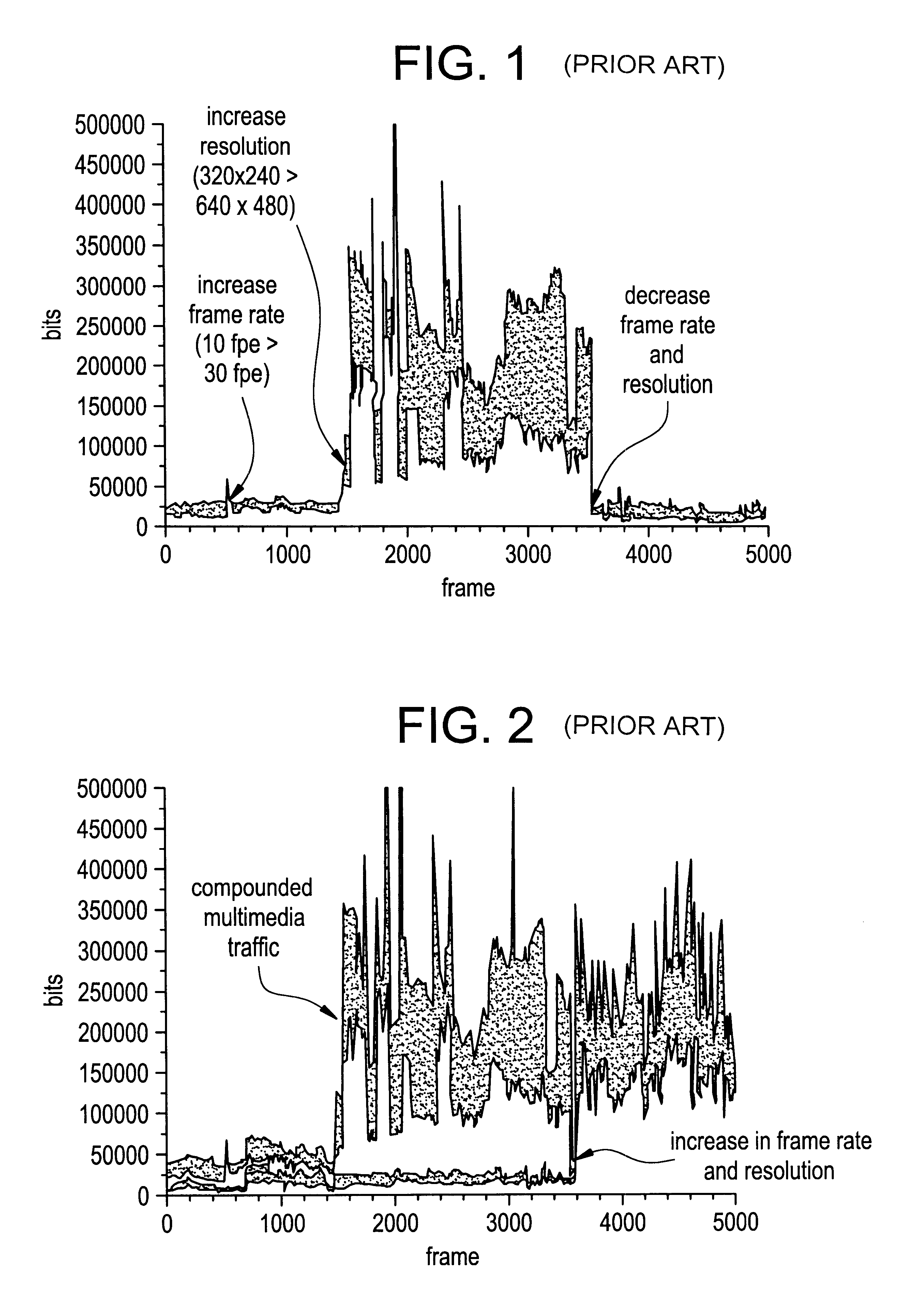
System and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data employing a limited number of supported coding bit rates
InactiveUS20060165166A1Maximize qualityStable and high qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningStreaming dataNatural variation
A system and process for controlling the coding bit rate of streaming media data is presented where a server streams data that exhibits one of a number of coding bit rates supported by the server. Initially, the server chooses the coding bit rate. However, after this startup period, the client provides coding bit rate requests. The server transmits the streaming media data at the most appropriate supported coding bit rate closest to the rate requested. The coding bit rates requested are those estimated to provide a high quality playback of the streaming data while still keeping a decoder buffer of the client filled to a desired level. A leaky bucket model is incorporated so that the changes in buffer duration due to natural variation in the instantaneous coding bit rate are not mistaken for changes in buffer duration due to network congestion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
User and content aware object-based data stream transmission methods and arrangements
InactiveUS7093028B1Quality improvementImprove interactivityMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksObject basedData stream
A scalable video transmission scheme is provided in which client interaction and video content itself are taken into consideration during transmission. Methods and arrangements are provided to prioritize / classify different types of information according to their importance and to packetize or otherwise arrange the prioritized information in a manner such that lower priority information may be dropped during transmission. Thus, when network congestion occurs or there is not enough network bandwidth to transmit all of the prioritized information about an object, some (e.g., lower priority) information may be dropped at the server or at an intermediate network node to reduce the bit rate. Thus, when the server transmits multiple video objects over a channel of limited bandwidth capacity, the bit rate allocated to each object can be adjusted according to several factors, such as, e.g., information importance and client interaction.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for flow control
InactiveUS20020136163A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityData stream
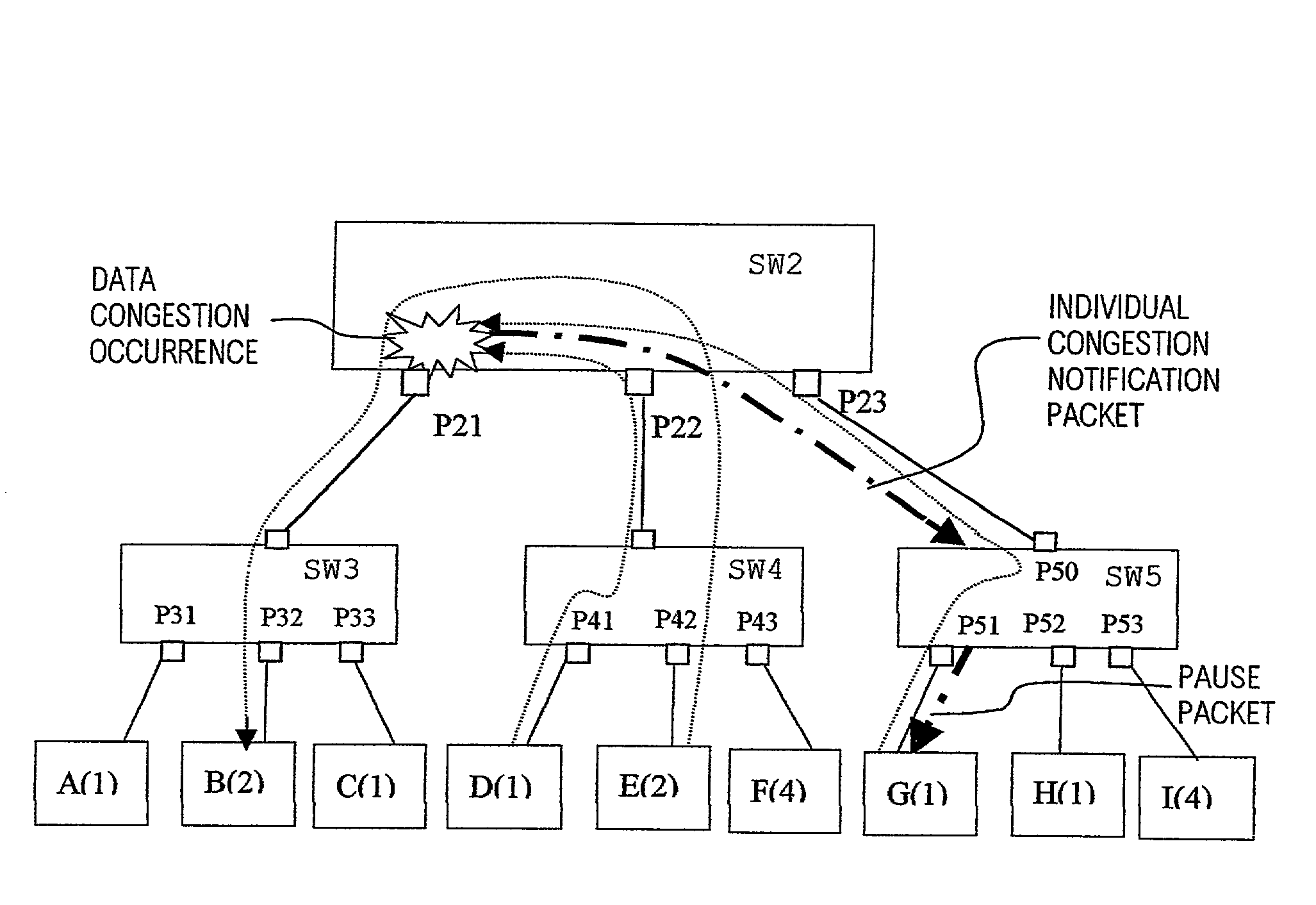
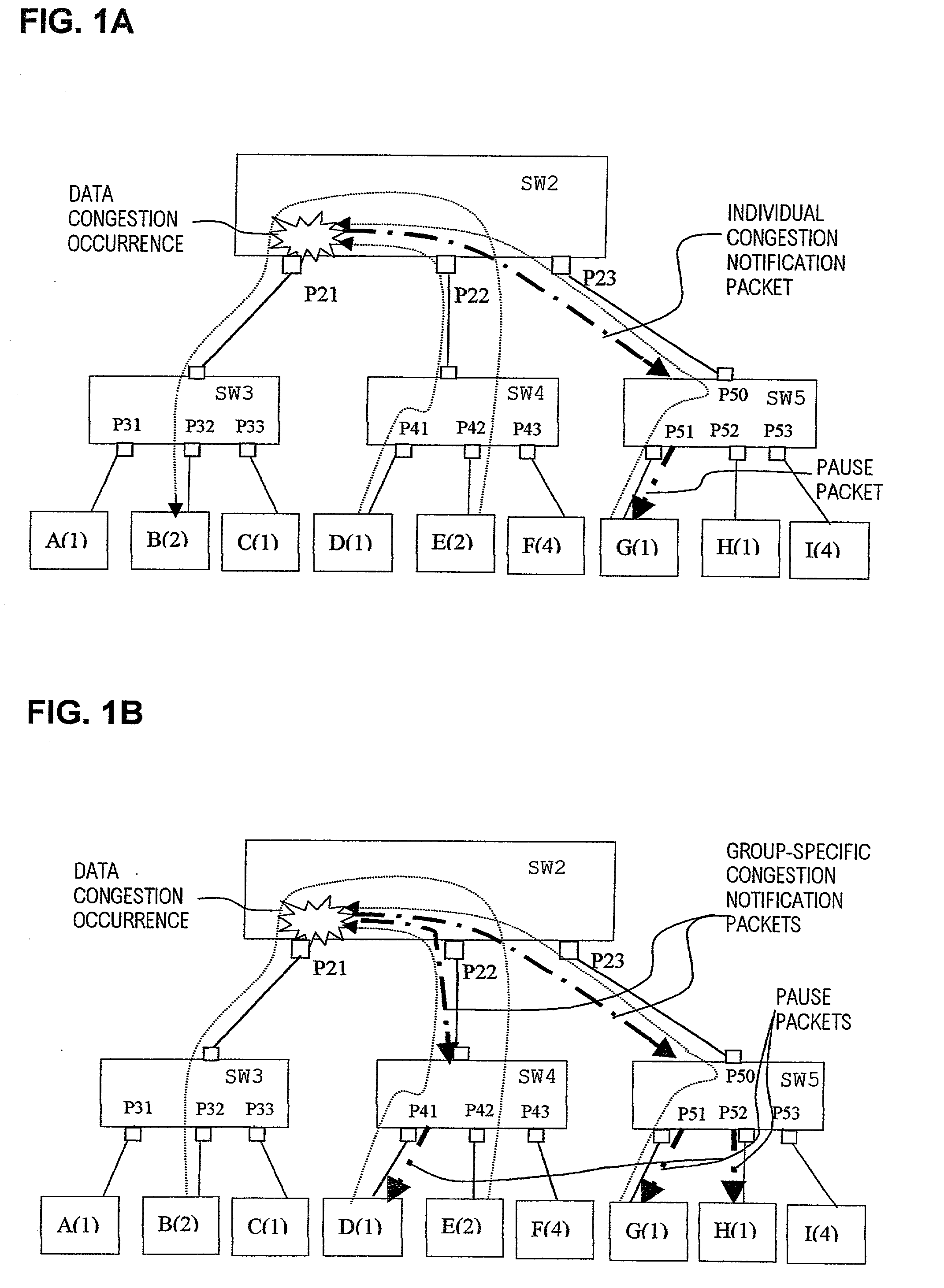
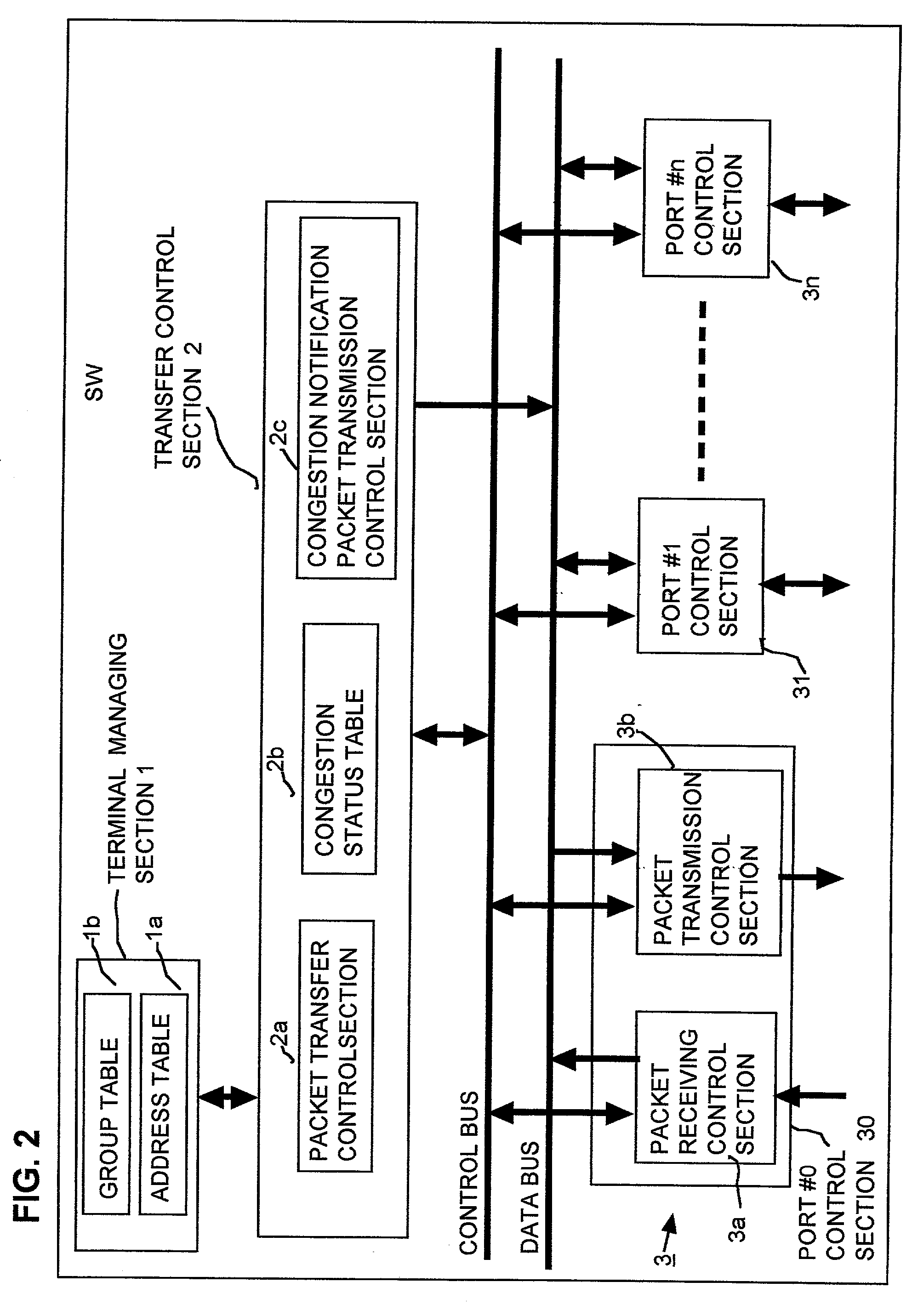
In flow control apparatus formed of a network of switching hubs in a hierarchy configuration for performing data packet transfer within each of a plurality of respectively separate groups of terminals, based on use of group identifiers contained in the data packets, occurrence of congestion of the output section of a port of a switching hub is judged respectively separately for each of the terminal groups, and one or more congestion notification packets for effecting a pause in data packet transmission are generated and transmitted from that switching hub, directed only to one or more terminals of a group relating to the congestion. As a result, the effects of port congestion and of congestion control operations are limited to the terminal group concerned. Congestion can be judged for a terminal group based on a level of utilization of a port output buffer that is used only by that group, or based on a rate of flow of data from that group into a port output buffer which is used in common for all terminal groups, and congestion notification packets may be transmitted from a single port or from a plurality of ports of a switching hub, in accordance with the detected degree of congestion.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
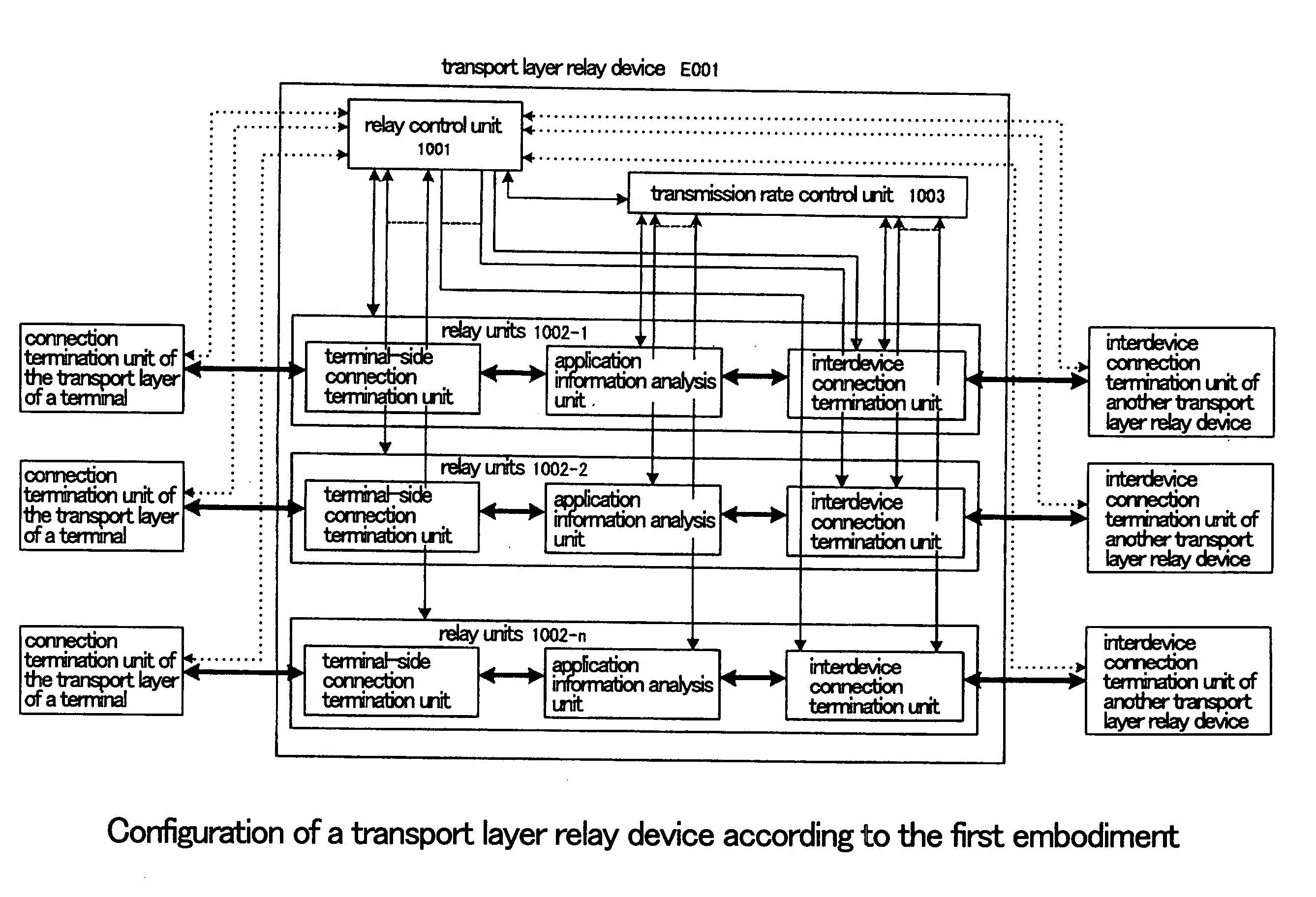
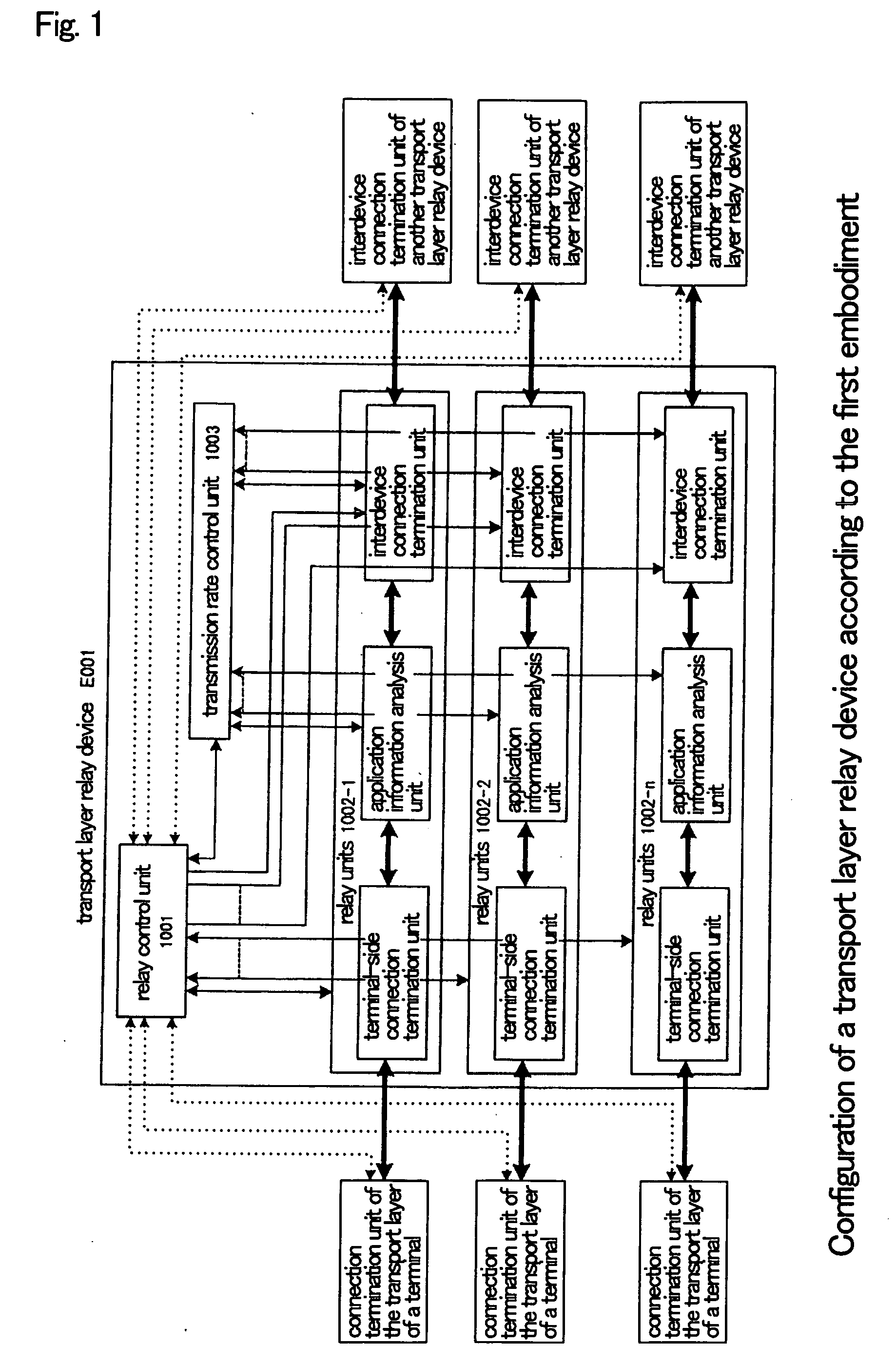
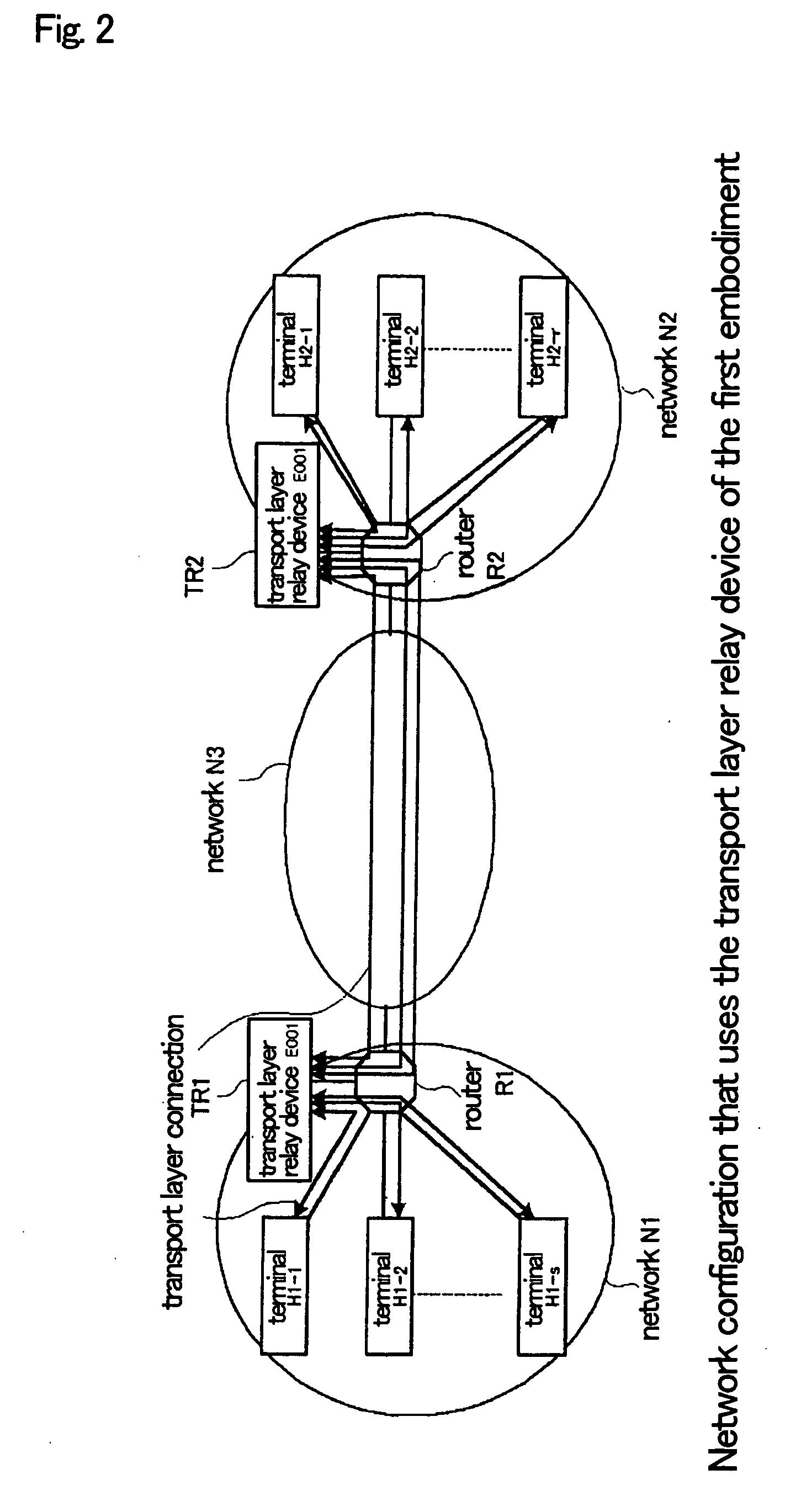
Transport layer relay method, transport layer relay device, and program
ActiveUS20070008883A1Low costRedistribute bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsTransport layerEngineering
Relay units (1002-1-1002-n) terminate a plurality of transport layer connections from terminals in a transport layer and relay each of these connections to other transport layer connections (relay connections). A transmission rate control unit (1003) determines the total transmission rate of the relay connections according to the number of connections that are being relayed and network congestion conditions such that a desired effective rate is obtained, and moreover, allots the total transmission rate as transmission rates to each of relay units (1002-1-1002-n) in accordance with the results of the analysis of information of the applications being carried on the transport layer connections during relay.
Owner:NEC CORP
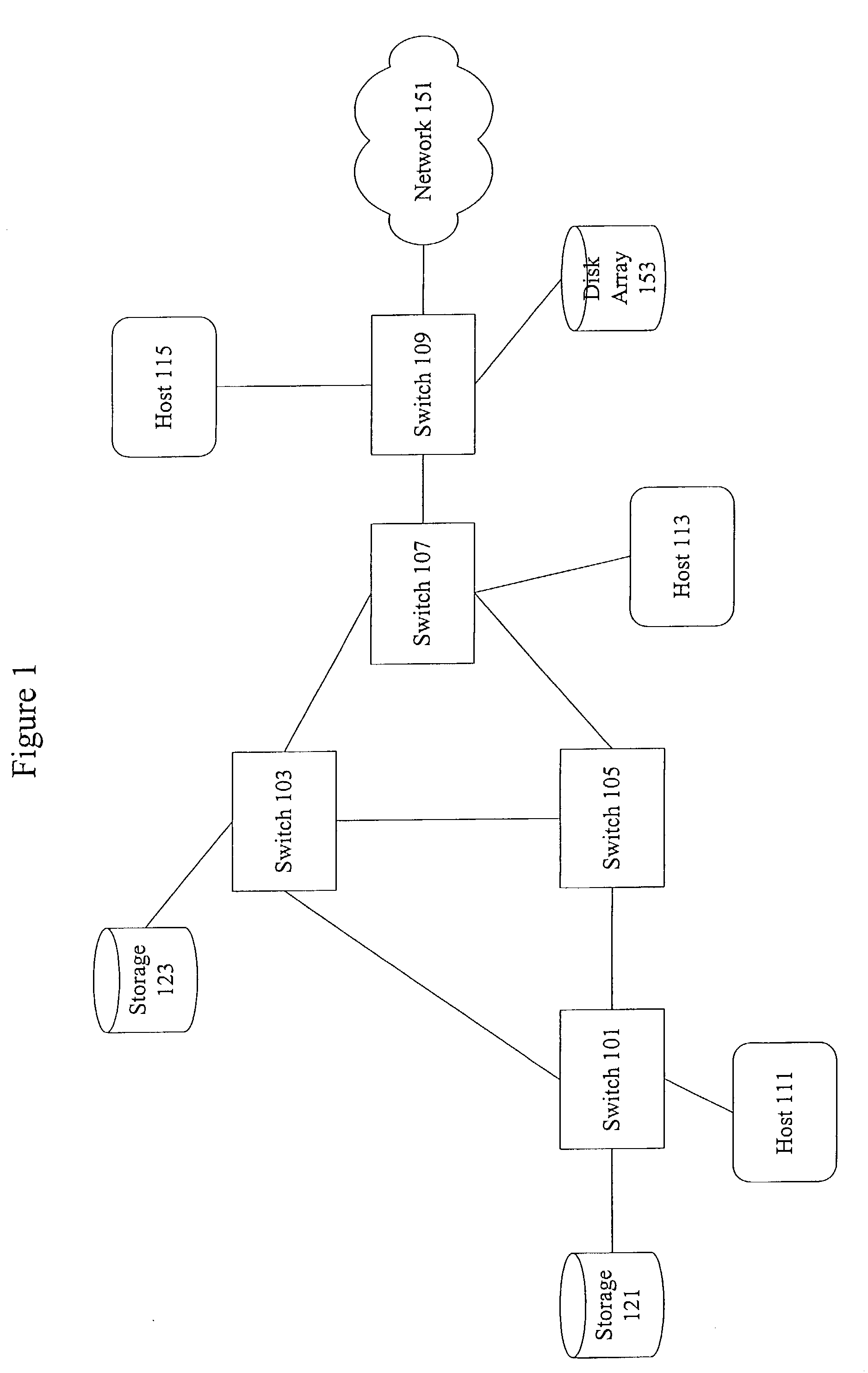
Method and system for congestion management in a fibre channel network
ActiveUS20090116381A1Facilitates congestion managementAvoid network congestionMultiplex system selection arrangementsEnergy efficient ICTFiberChannel network
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates congestion management in a Fibre Channel (FC) network. During operation, the system determines a threshold data rate on an outgoing link coupled to an FC switch. The system further determines the number of sources that send data to the outgoing link and an aggregate arrival rate of data for the outgoing link. Next, the system determines an injection data rate for a respective source based on the threshold data rate on the outgoing link, the number of sources transmitting data to the outgoing link, and the aggregate arrival data rate for the outgoing link. Subsequently, the system communicates the injection data rate to the source, thereby allowing the source to throttle its data injection in the FC network to prevent network congestion.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
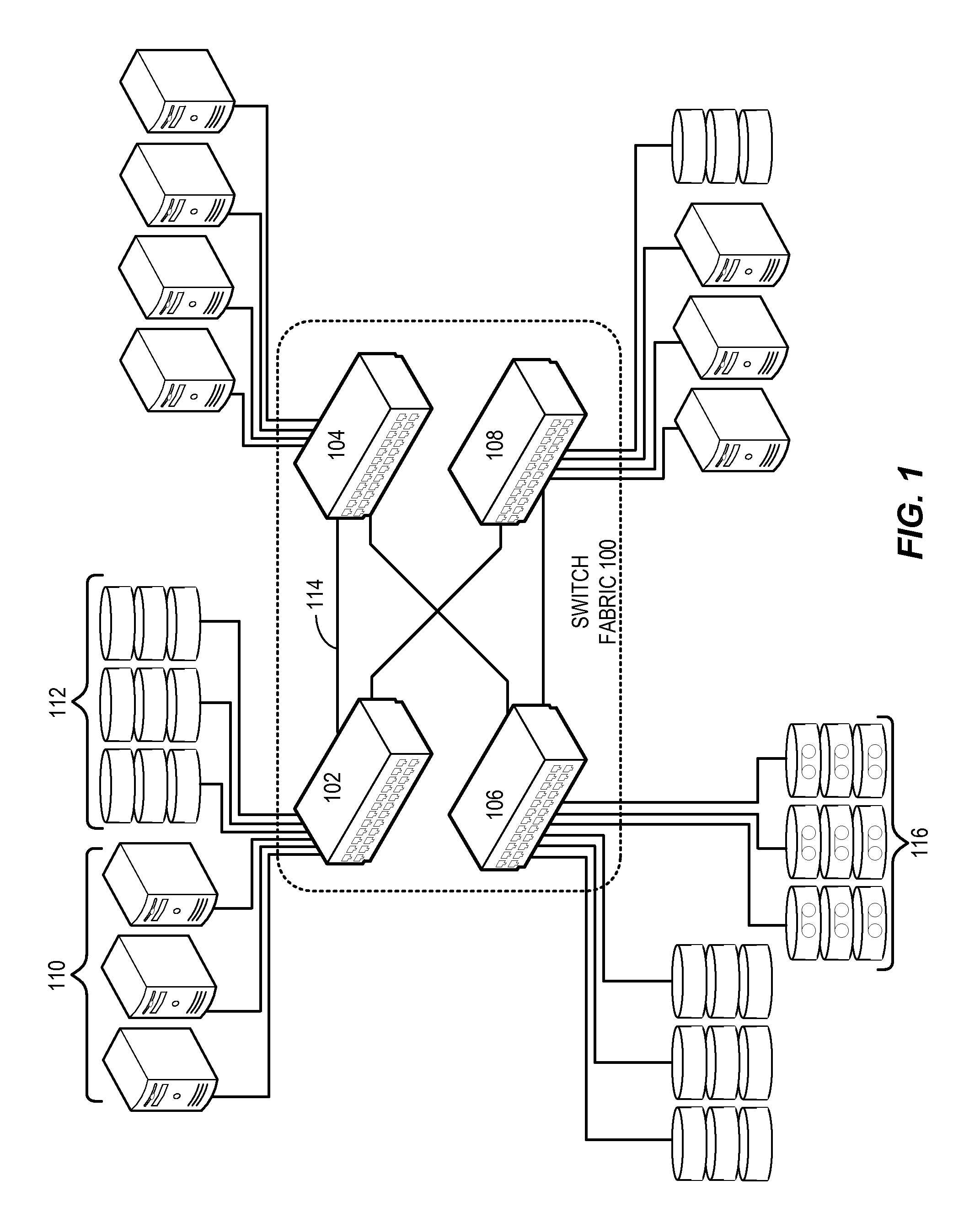
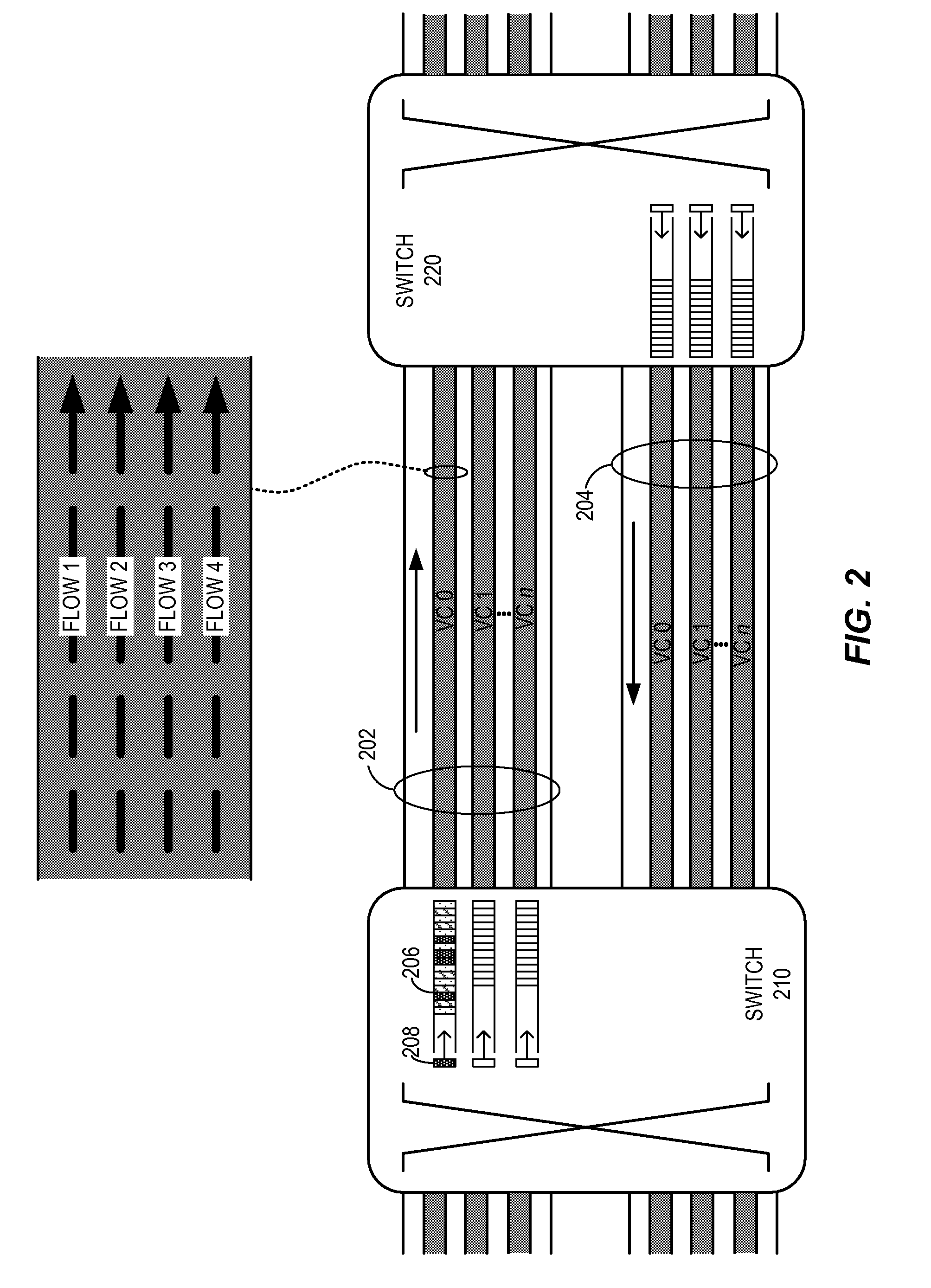
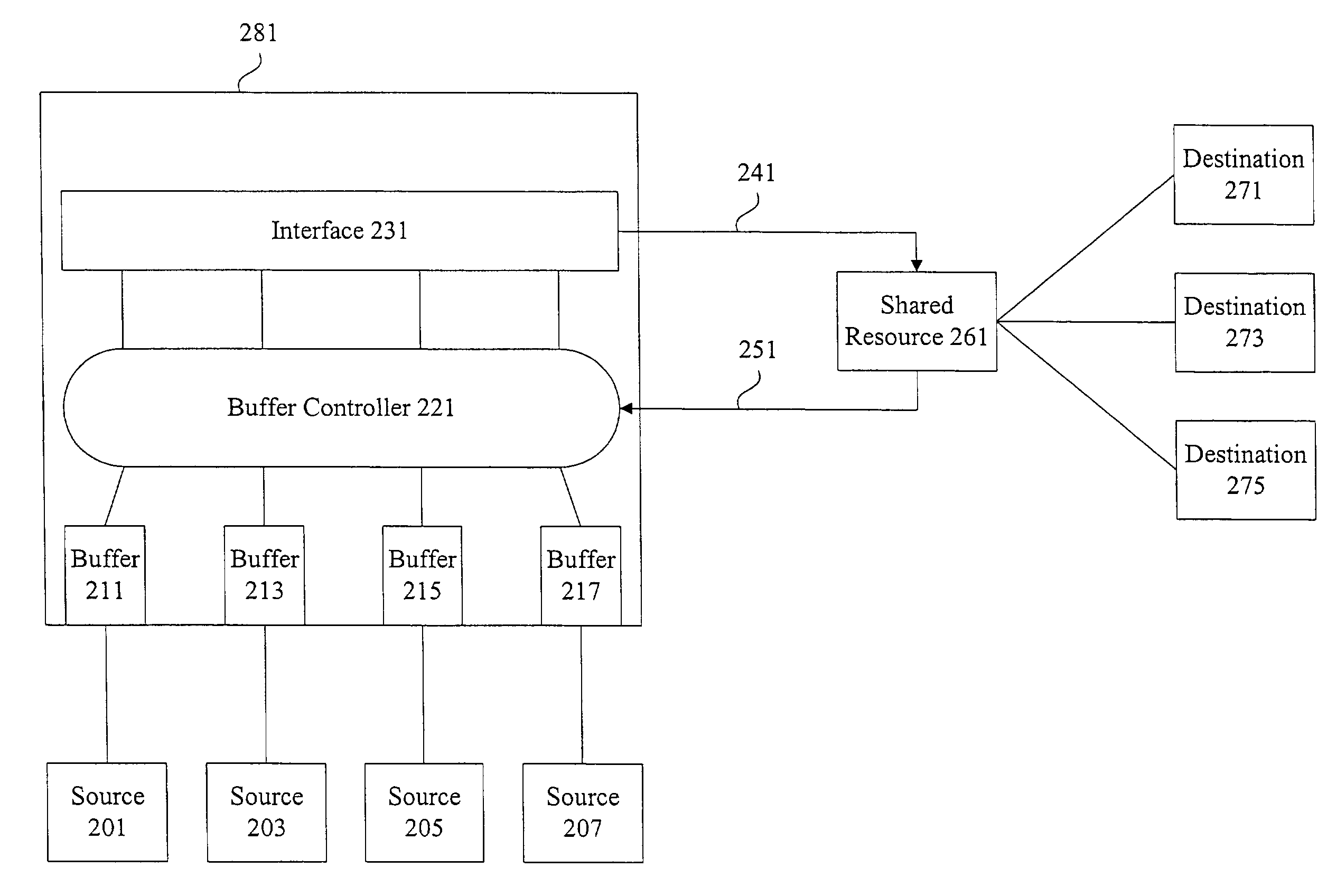
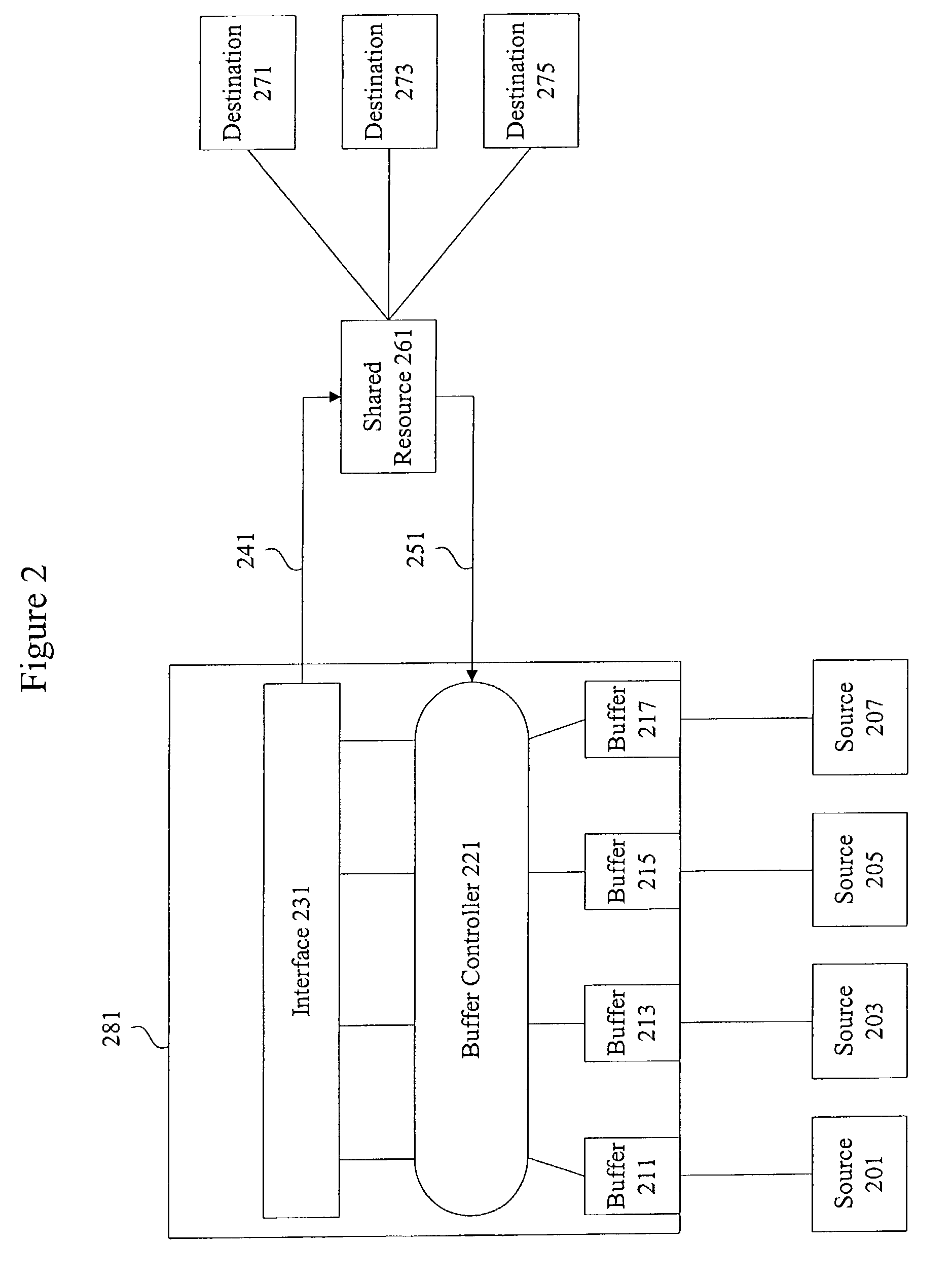
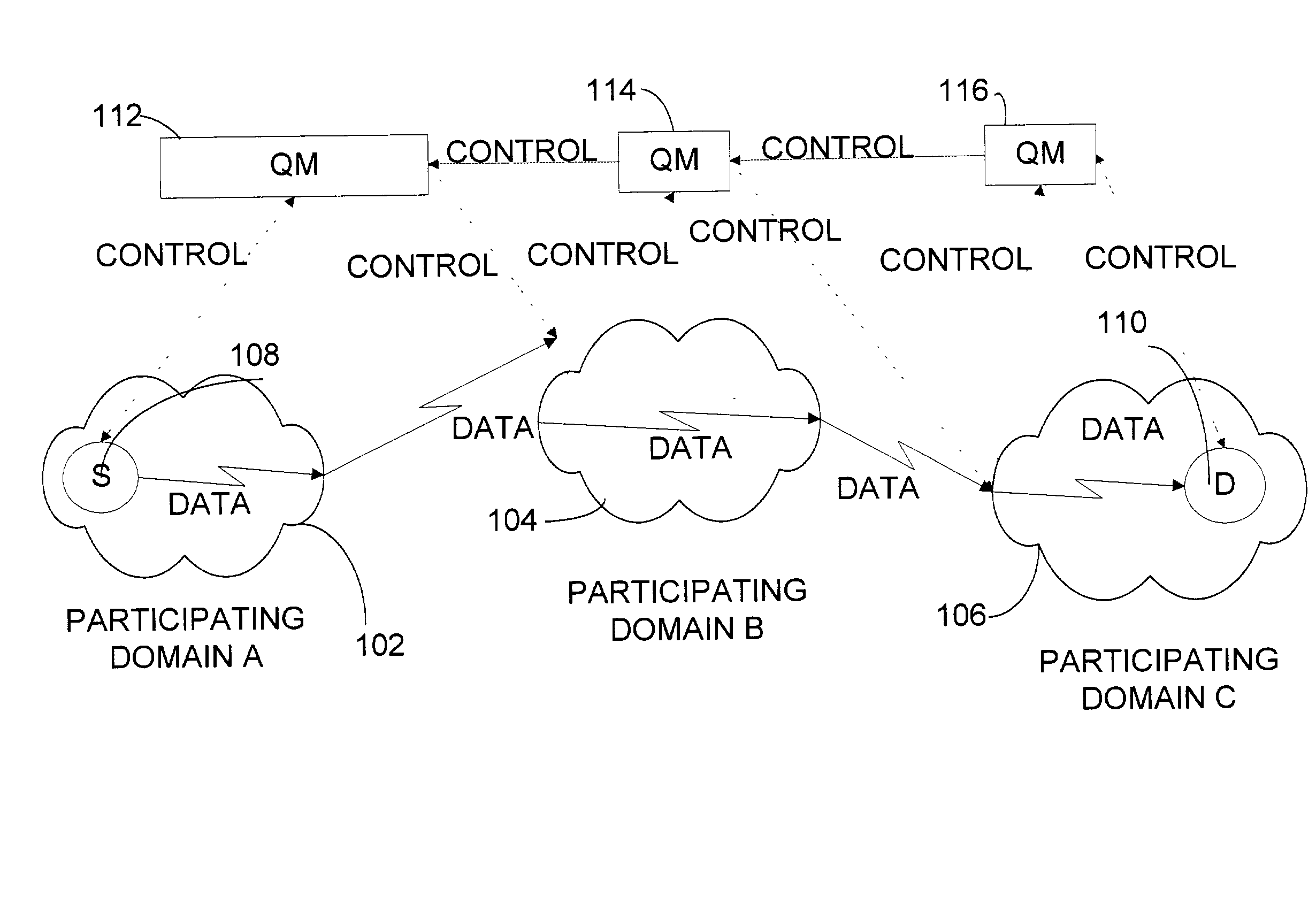
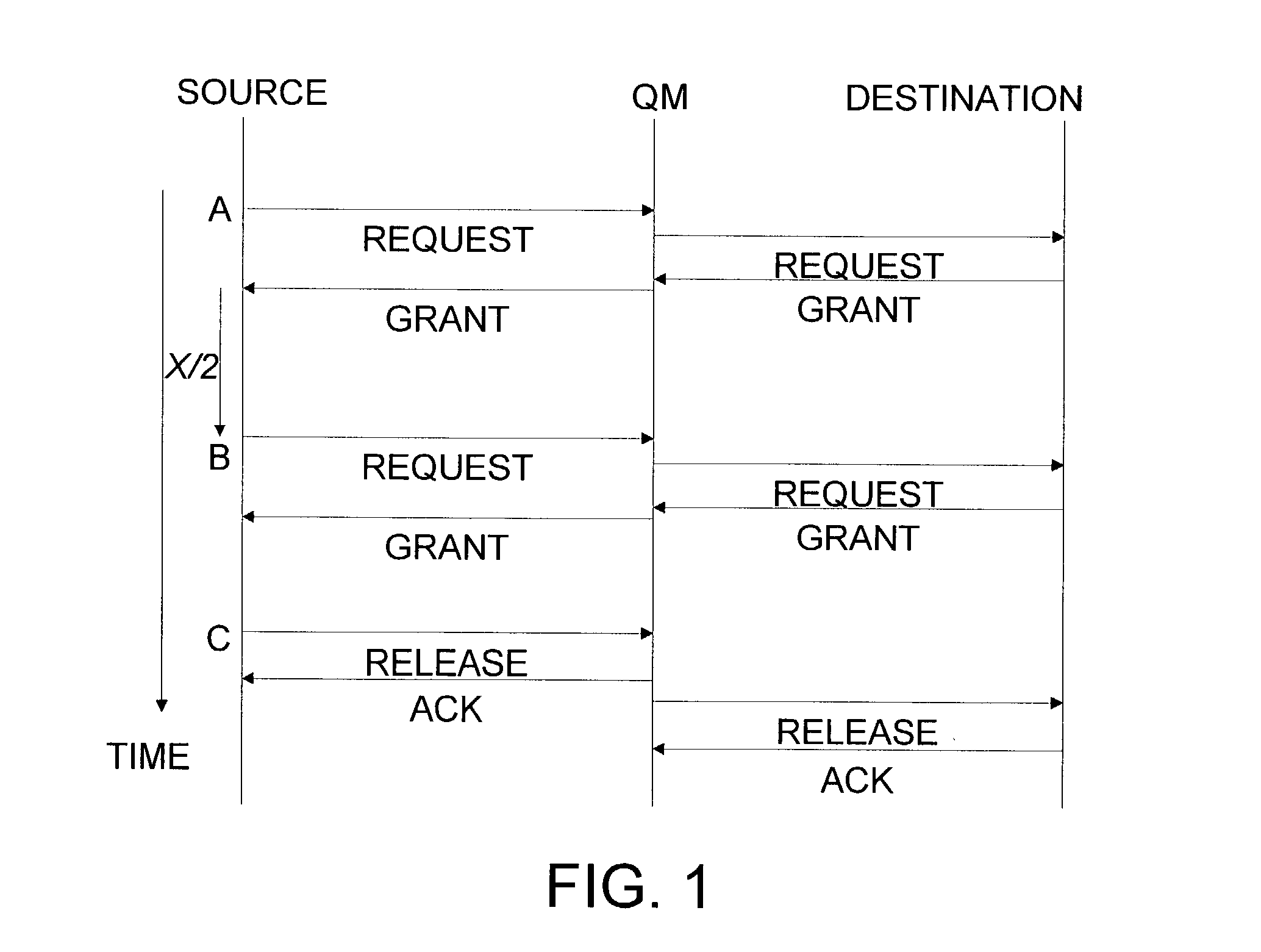
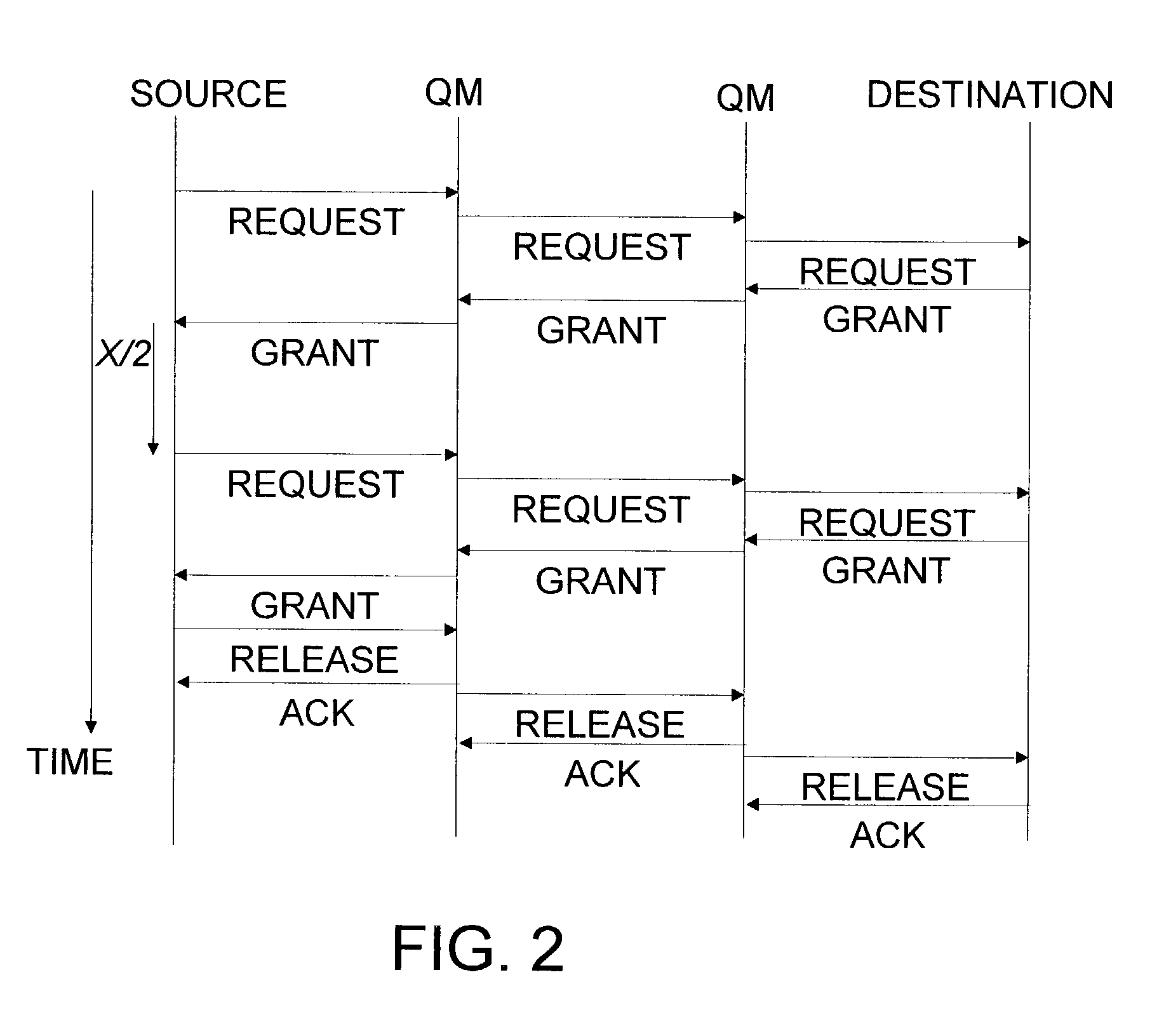
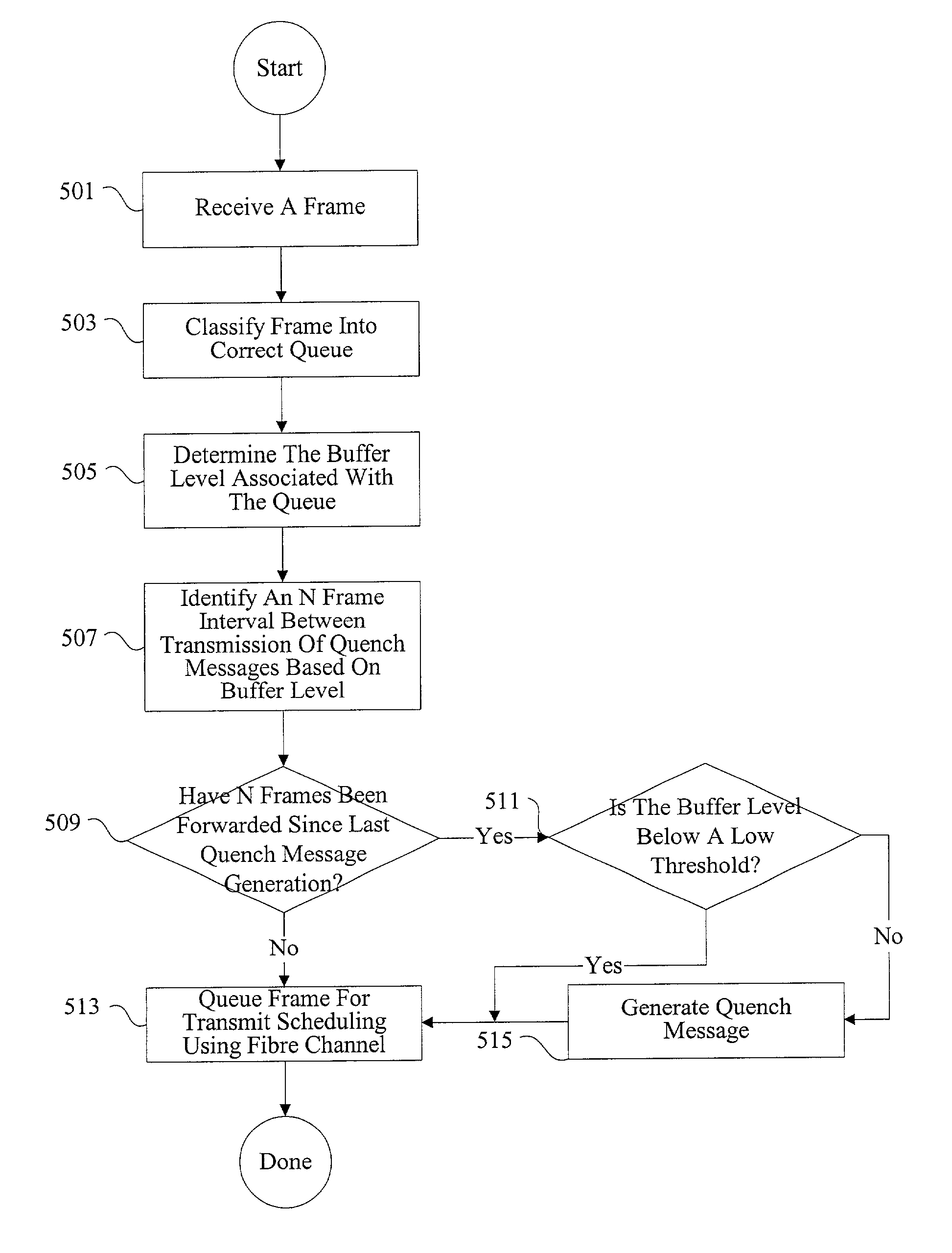
Methods and apparatus for network congestion control
Methods and apparatus are provided for controlling congestion in a network such as a fiber channel network. Techniques are provided for detecting congestion at a shared resource such as a network node. When a controller sends data to a shared resource, the delay between sending the data and receiving a credit is measured. If the delay is significant, it is assumed that the path towards the destination associated with the data is congested and subsequent traffic from the port associated with the data is blocked.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for providing faster and more efficient data communication
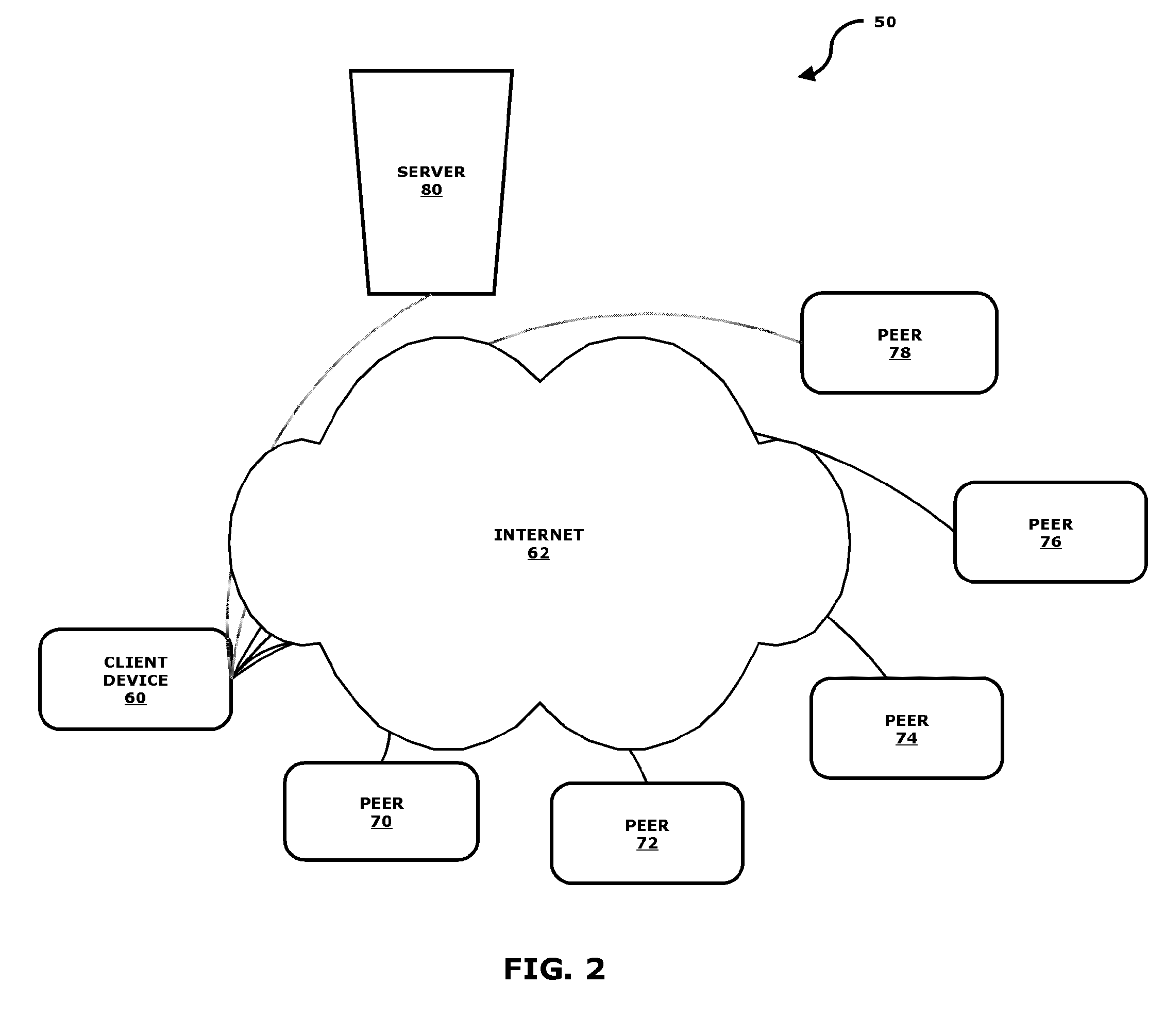
A system designed for increasing network communication speed for users, while lowering network congestion for content owners and ISPs. The system employs network elements including an acceleration server, clients, agents, and peers, where communication requests generated by applications are intercepted by the client on the same machine. The IP address of the server in the communication request is transmitted to the acceleration server, which provides a list of agents to use for this IP address. The communication request is sent to the agents. One or more of the agents respond with a list of peers that have previously seen some or all of the content which is the response to this request (after checking whether this data is still valid). The client then downloads the data from these peers in parts and in parallel, thereby speeding up the Web transfer, releasing congestion from the Web by fetching the information from multiple sources, and relieving traffic from Web servers by offloading the data transfers from them to nearby peers.
Owner:BRIGHT DATA LTD
Method and system for providing a mobile IP network with non-path dependent intra domain quality of service
InactiveUS7269657B1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsDomain nameQuality of service
A system and method for providing quality of service (QoS) service over a mobile IP network with dynamic domains, multiple or distributed QoS managers per domain and / or with network congestion feedback being used to establish an estimated total domain bandwidth which is used for regulating access to a domain.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
System and method for providing faster and more efficient data communication
ActiveUS20110087733A1Faster and efficient data communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionClient agentIp address
A system designed for increasing network communication speed for users, while lowering network congestion for content owners and ISPs. The system employs network elements including an acceleration server, clients, agents, and peers, where communication requests generated by applications are intercepted by the client on the same machine. The IP address of the server in the communication request is transmitted to the acceleration server, which provides a list of agents to use for this IP address. The communication request is sent to the agents. One or more of the agents respond with a list of peers that have previously seen some or all of the content which is the response to this request (after checking whether this data is still valid). The client then downloads the data from these peers in parts and in parallel, thereby speeding up the Web transfer, releasing congestion from the Web by fetching the information from multiple sources, and relieving traffic from Web servers by offloading the data transfers from them to nearby peers.
Owner:BRIGHT DATA LTD
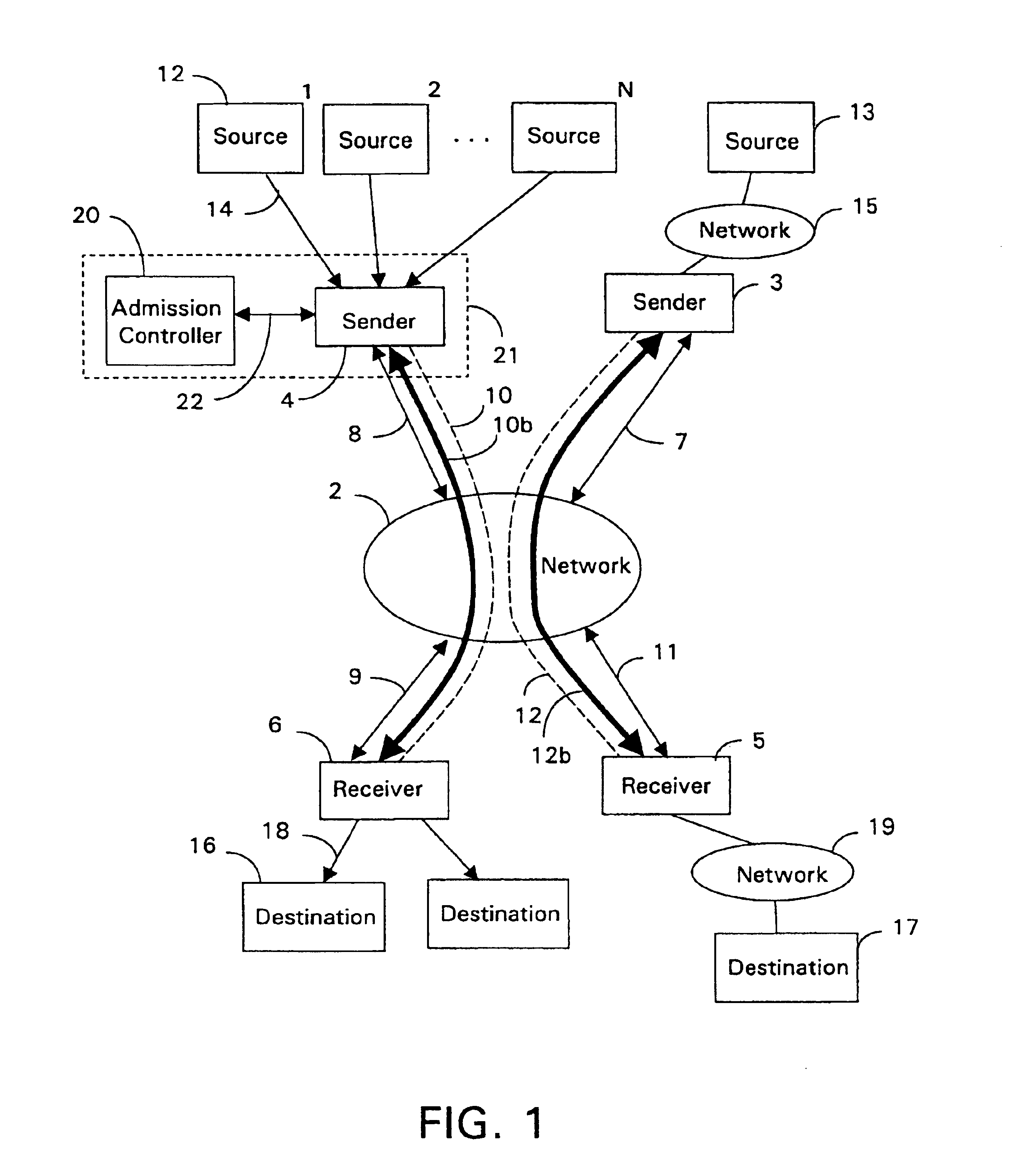
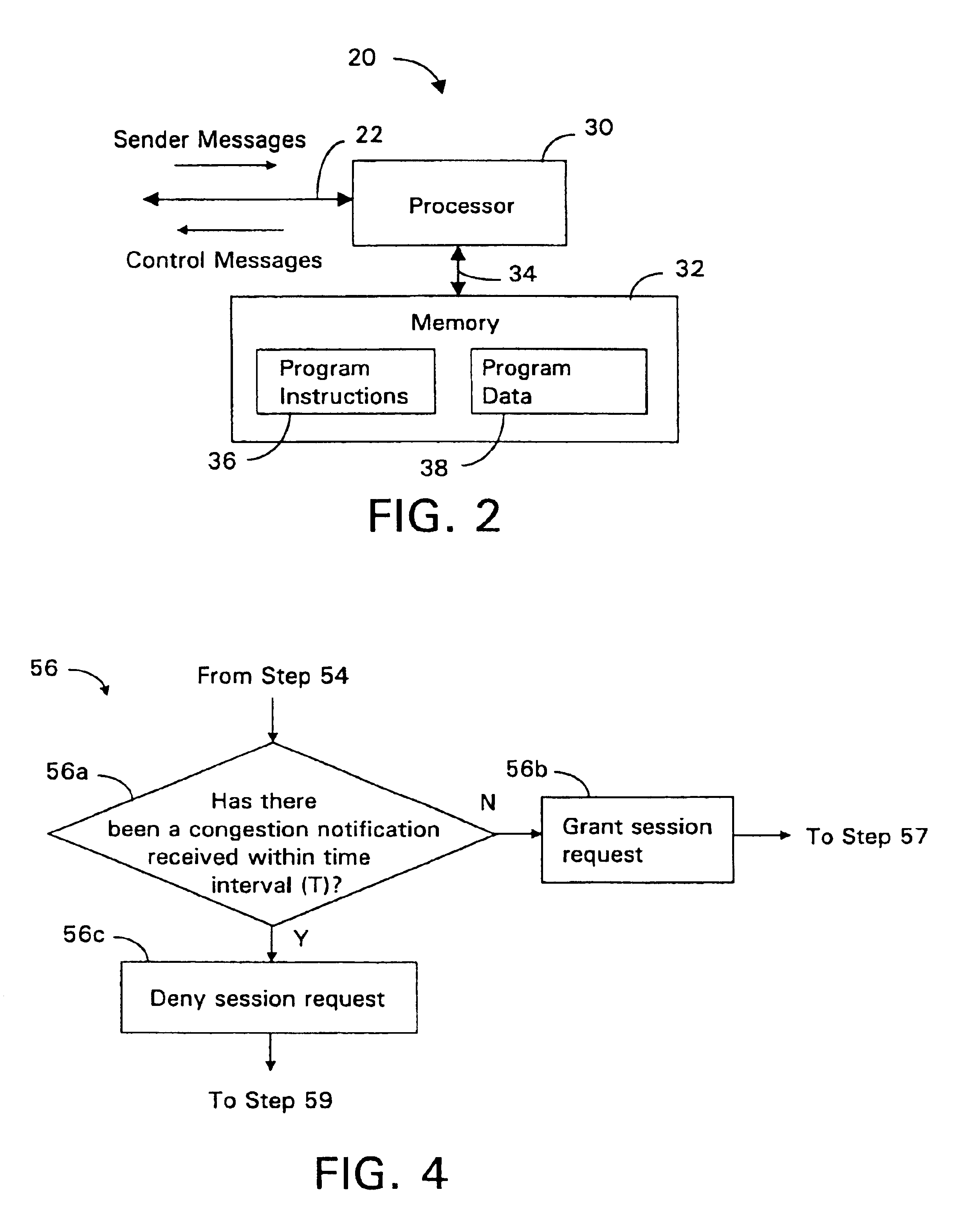
Admission control for aggregate data flows based on a threshold adjusted according to the frequency of traffic congestion notification
InactiveUS6839767B1Guaranteed bandwidthExacerbating congestion condition is avoidedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData stream
An admission controller and its method of operation for controlling admission of data flows into an aggregate data flow are described. Admitted data flows are aggregated into an aggregate data flow for transmission by a router, for example, over a data network. The aggregate data flow typically follows a pre-established path through the network; for example a multi-protocol label switched (MPLS) path. The path has minimum and maximum bandwidth limits assigned to it. The admission controller controls admission of new data flows into the aggregate data flow by granting or denying new session requests for the new data flows. Congestion notifications received from the network and bandwidth limits of the path are considered in determining whether to grant or deny a new session request. In this way, the admission controller provides elastic sharing of network bandwidth among data flows without exacerbating network congestion and while remaining within the path's bandwidth limits. The data flows may include transaction oriented traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
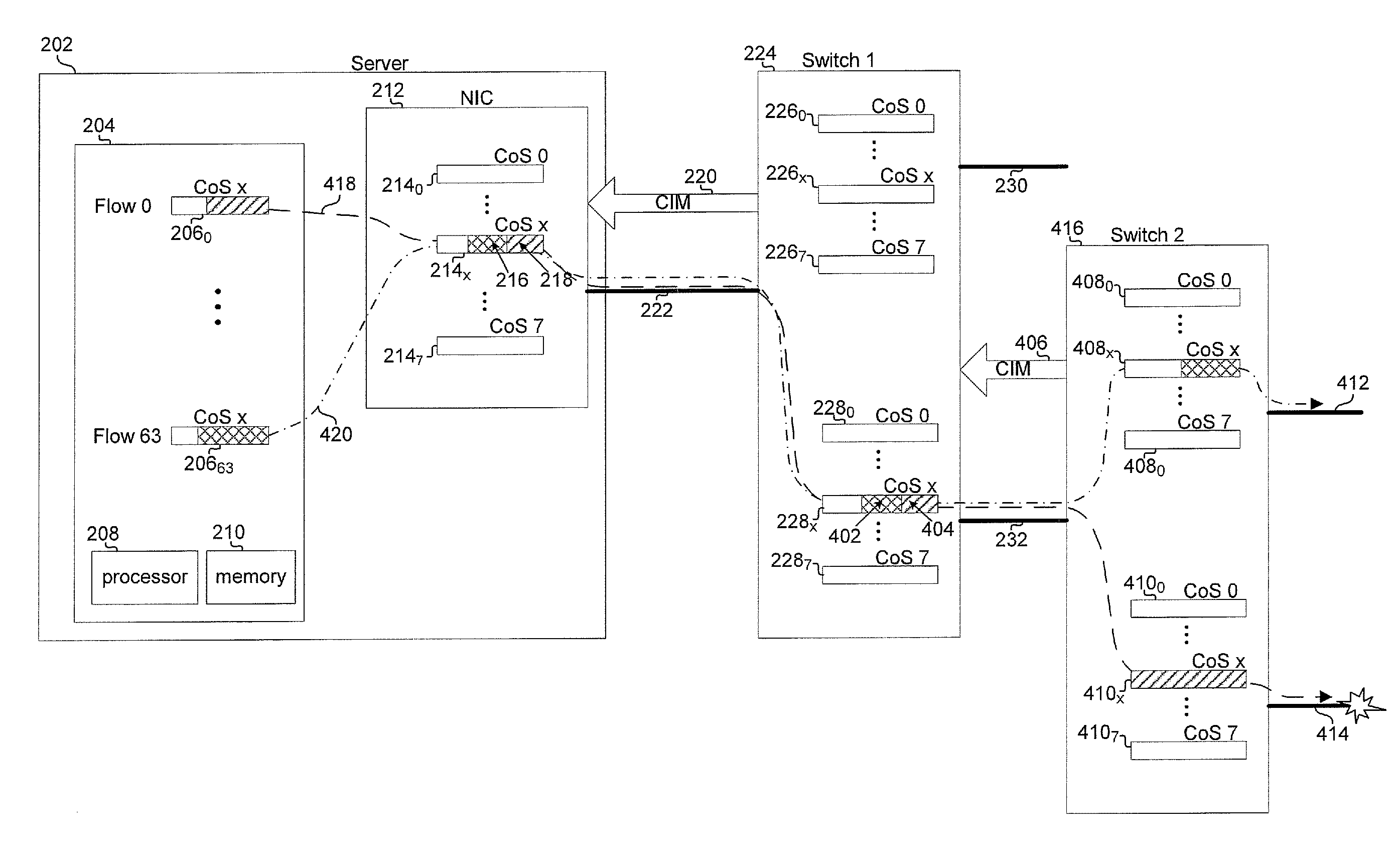
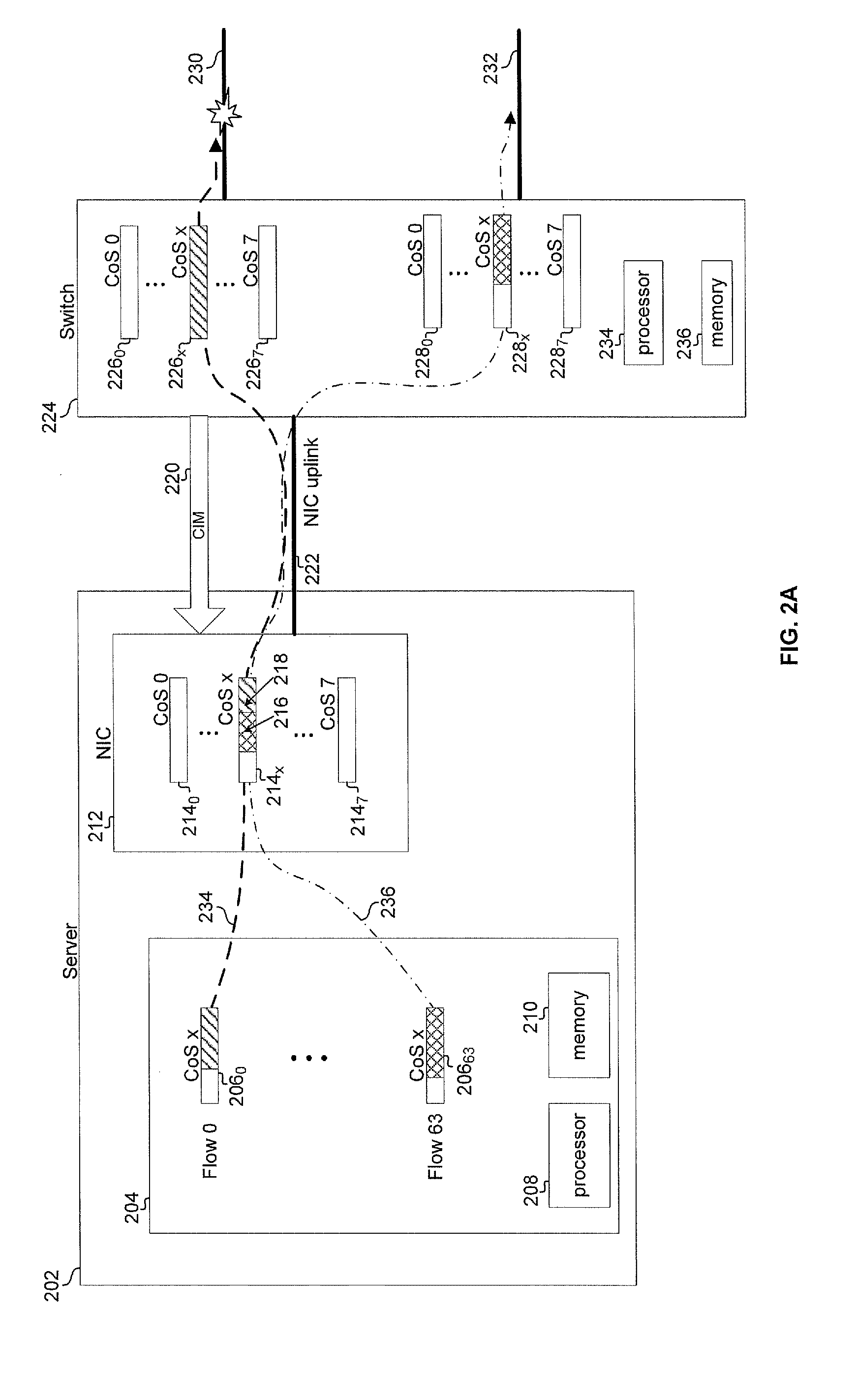
Method and system for path based network congestion management
InactiveUS20090300209A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionForward algorithmData stream
Aspects of a method and system for path based network congestion management are provided. In this regard, an indication of conditions, such as congestion, in a network may be utilized to determine which data flows may be affected by congestion in a network. A path table may be maintained to associate conditions in the network with flows affected by the conditions. Flows which are determined as being affected by a condition may be paused or flagged and transmission of data belonging to those flows may be deferred. Flows affected by a condition such as congestion may be identified based on a class of service with which they are associated. Transmission of one or more of the plurality of flows may be scheduled based on the determination. The determination may be based on one or both of a forwarding table and a forwarding algorithm of the downstream network device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Optimal route selection in a content delivery network
InactiveUS7929429B2Improve speed and reliabilityRetrieve content (cacheableError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEdge serverDistributed computing
A routing mechanism, service or system operable in a distributed networking environment. One preferred environment is a content delivery network (CDN) wherein the present invention provides improved connectivity back to an origin server, especially for HTTP traffic. In a CDN, edge servers are typically organized into regions, with each region comprising a set of content servers that preferably operate in a peer-to-peer manner and share data across a common backbone such as a local area network (LAN). The inventive routing technique enables an edge server operating within a given CDN region to retrieve content (cacheable, non-cacheable and the like) from an origin server more efficiently by selectively routing through the CDN's own nodes, thereby avoiding network congestion and hot spots. The invention enables an edge server to fetch content from an origin server through an intermediate CDN server or, more generally, enables an edge server within a given first region to fetch content from the origin server through an intermediate CDN region.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
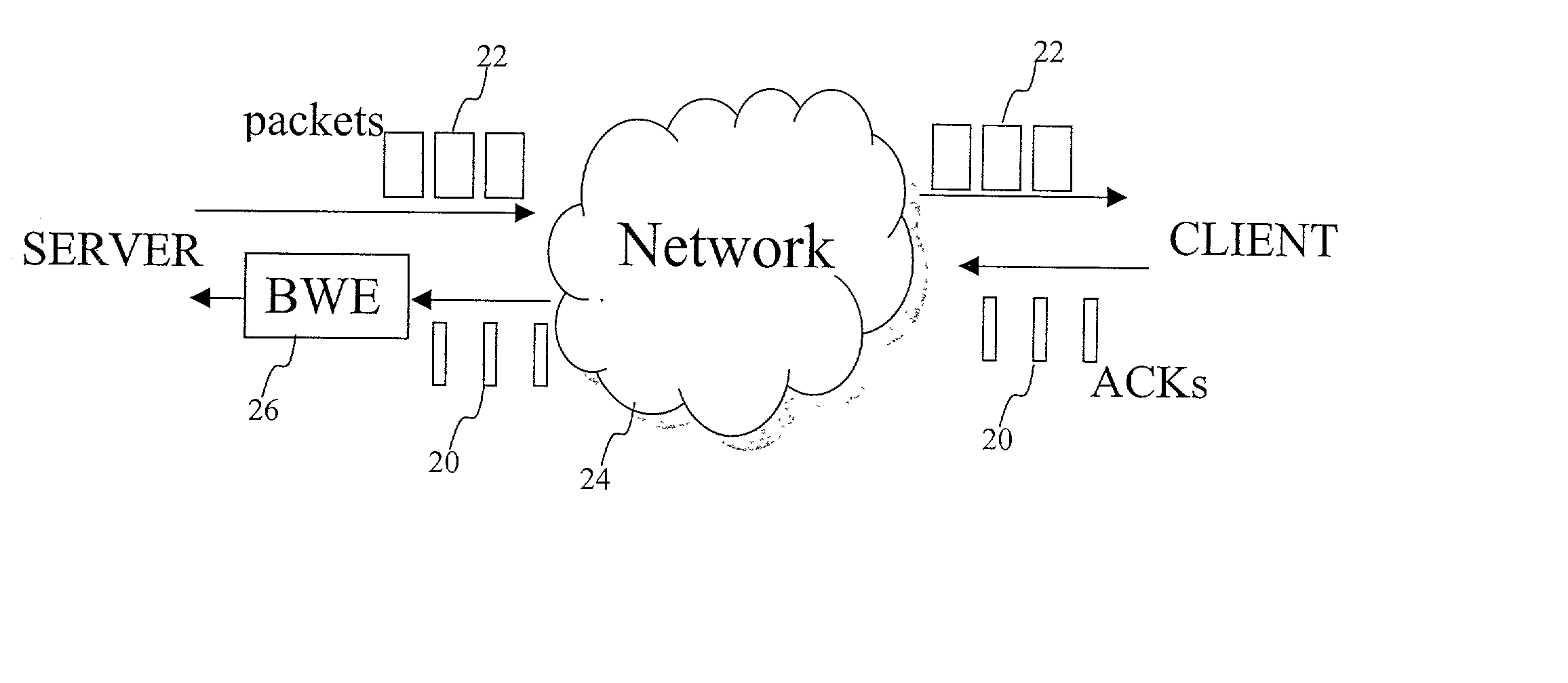
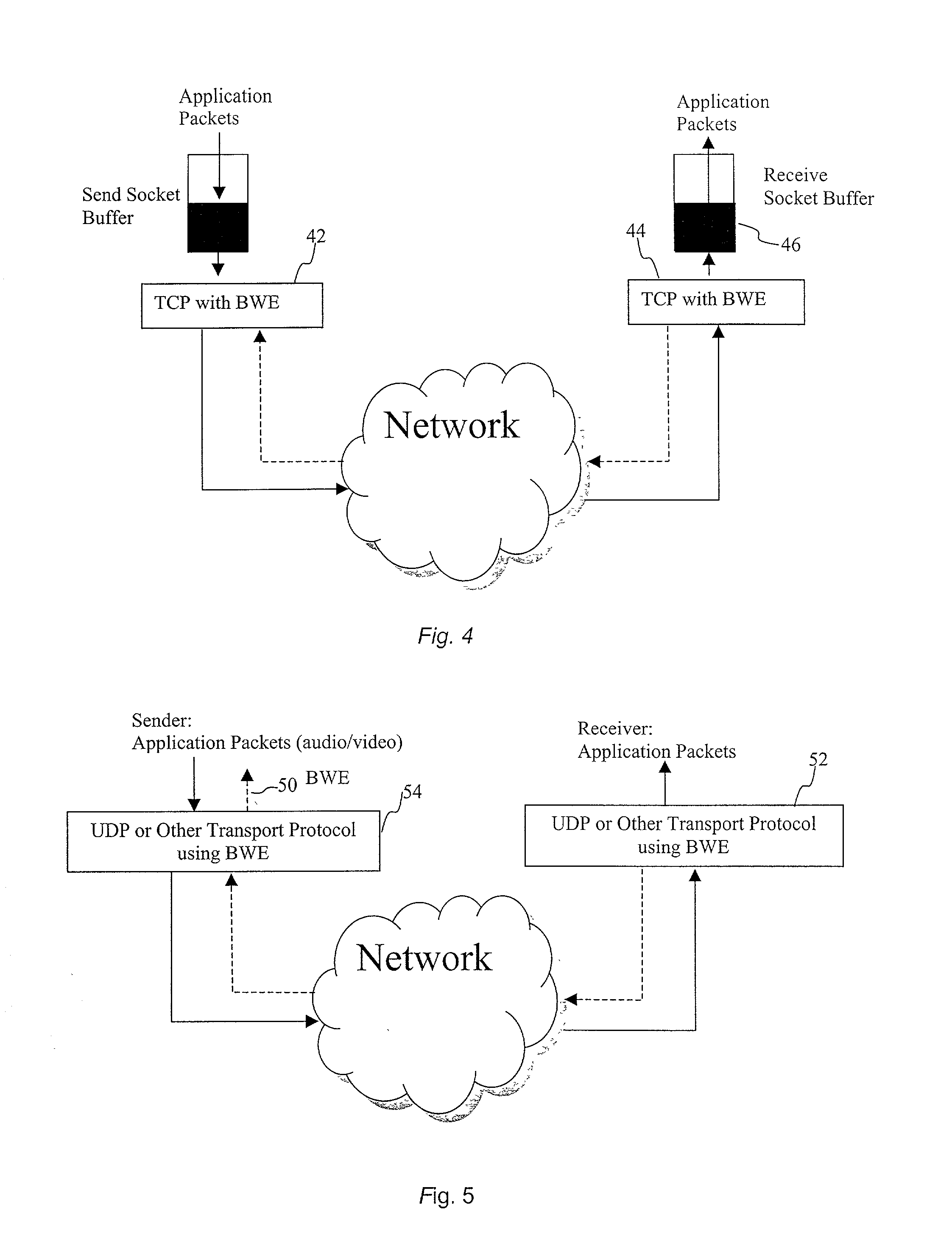
End-to end bandwidth estimation for congestion control in packet switching networks
InactiveUS20020085587A1Improve network bandwidth utilizationImprove fairnessEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityPacket-switching node
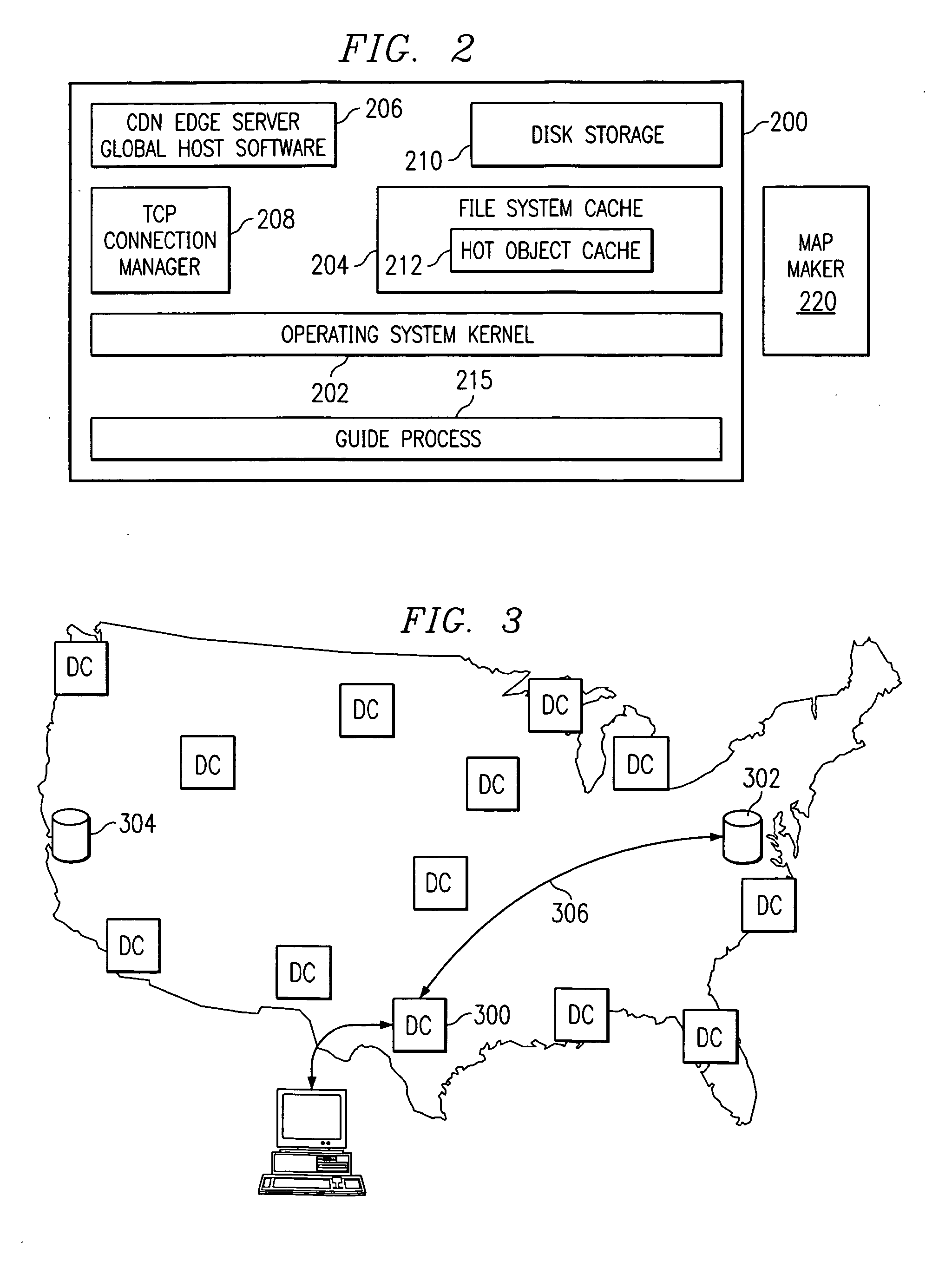
The invention herein described consists of an algorithm, which performs an end-to-end estimation of the bandwidth available in an end-to-end connection established between a server and a client via a packet switching network such as the Internet Protocol Network (IP). This algorithm is used to properly regulate the input rate at the send side. Typical applications are delivering best effort traffic over TCP, or audio and video traffic over RTP / UDP. The invention is particularly effective over wireless Internet and can be used in a content delivery system to dynamically choose the best server between a set of servers to satisfy the request of a client, or to select the best route in a content deliver or global hosting system.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
Controlling network congestion using a biased packet discard policy for congestion control and encoded session packets: methods, systems, and program products
ActiveUS7042841B2Increase bitrateNetwork degradationError preventionTransmission systemsControl systemNetwork congestion control
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Congestion control for internet protocol storage
InactiveUS20010032269A1Energy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworked systemThroughput
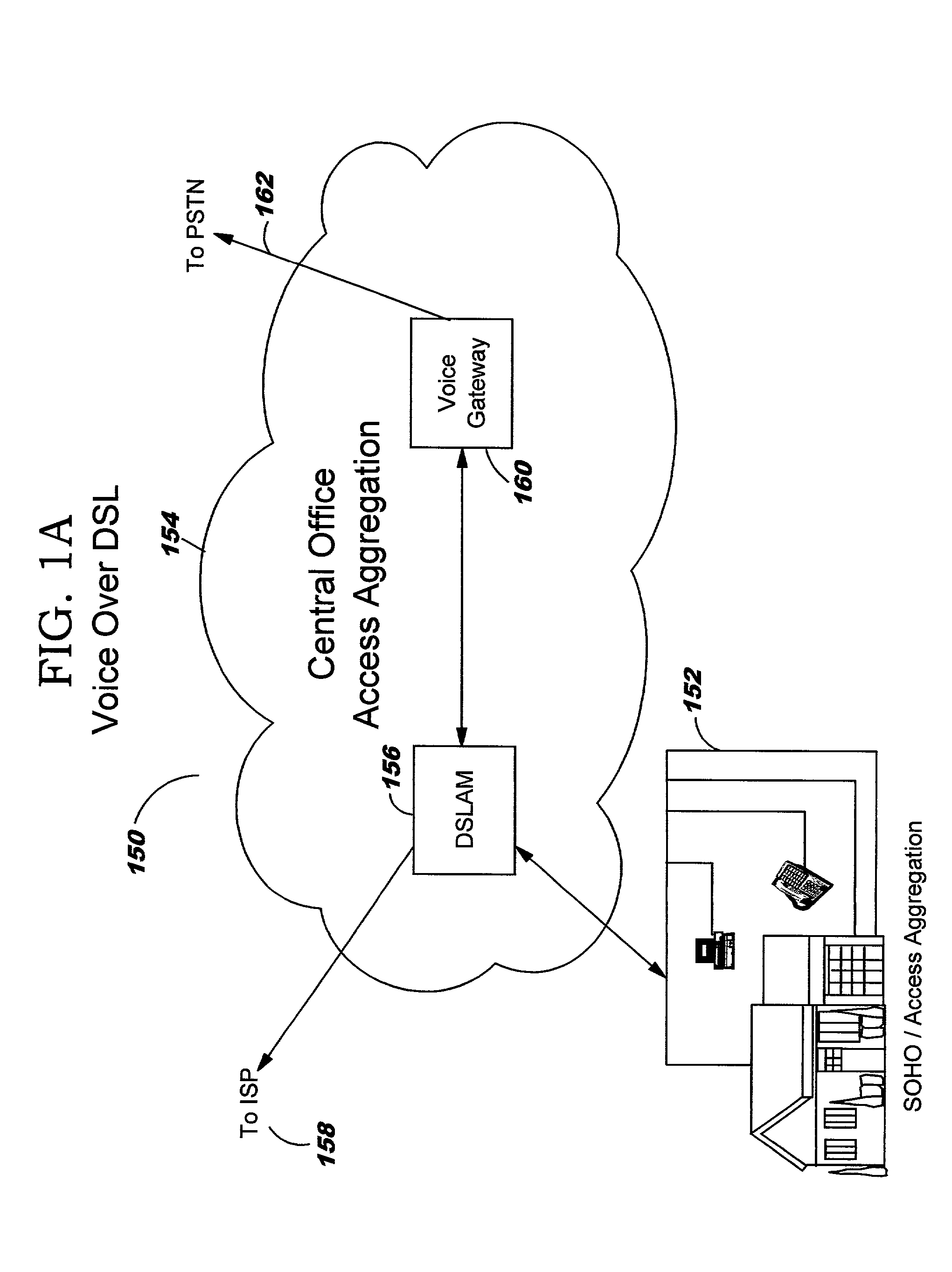
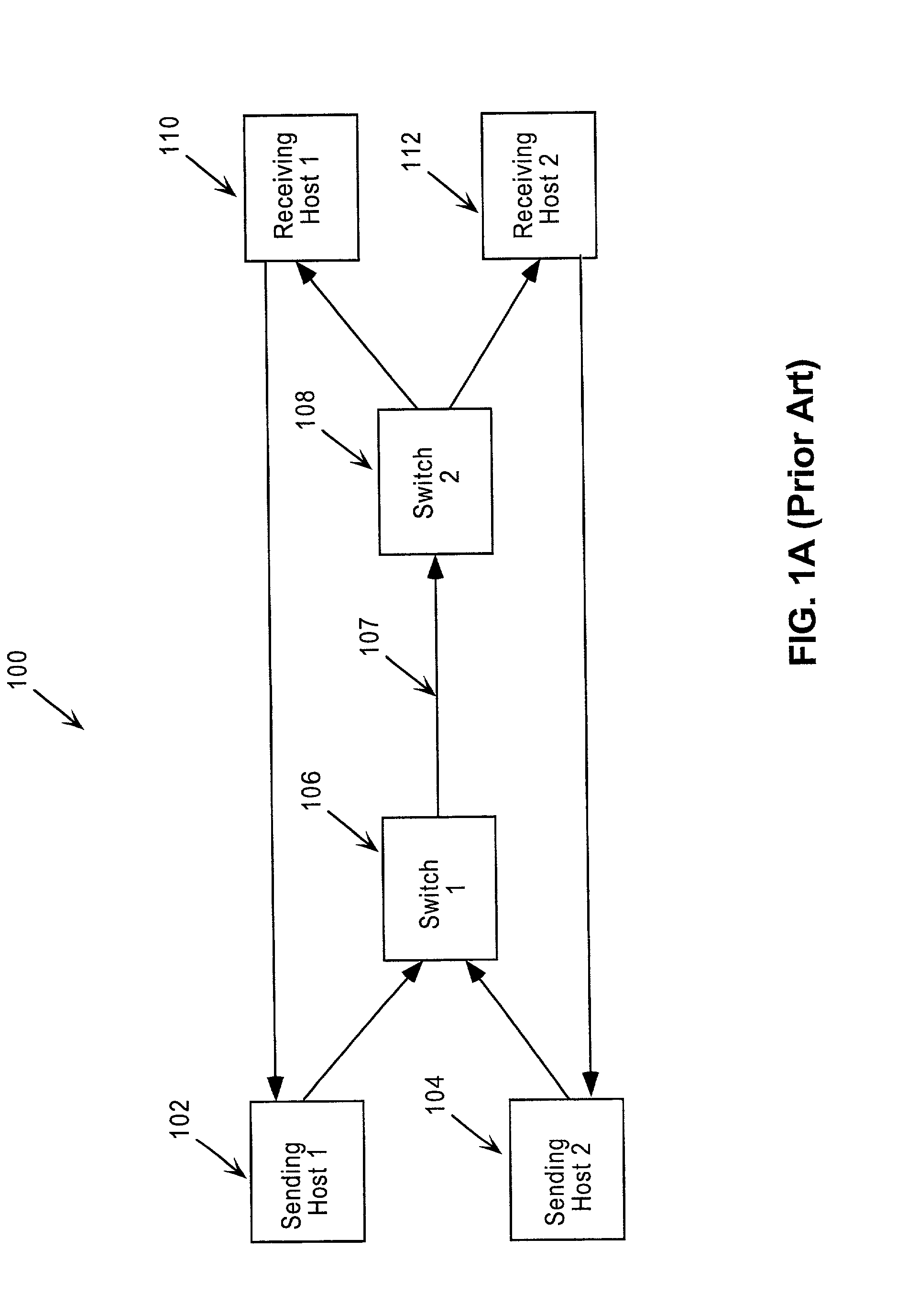
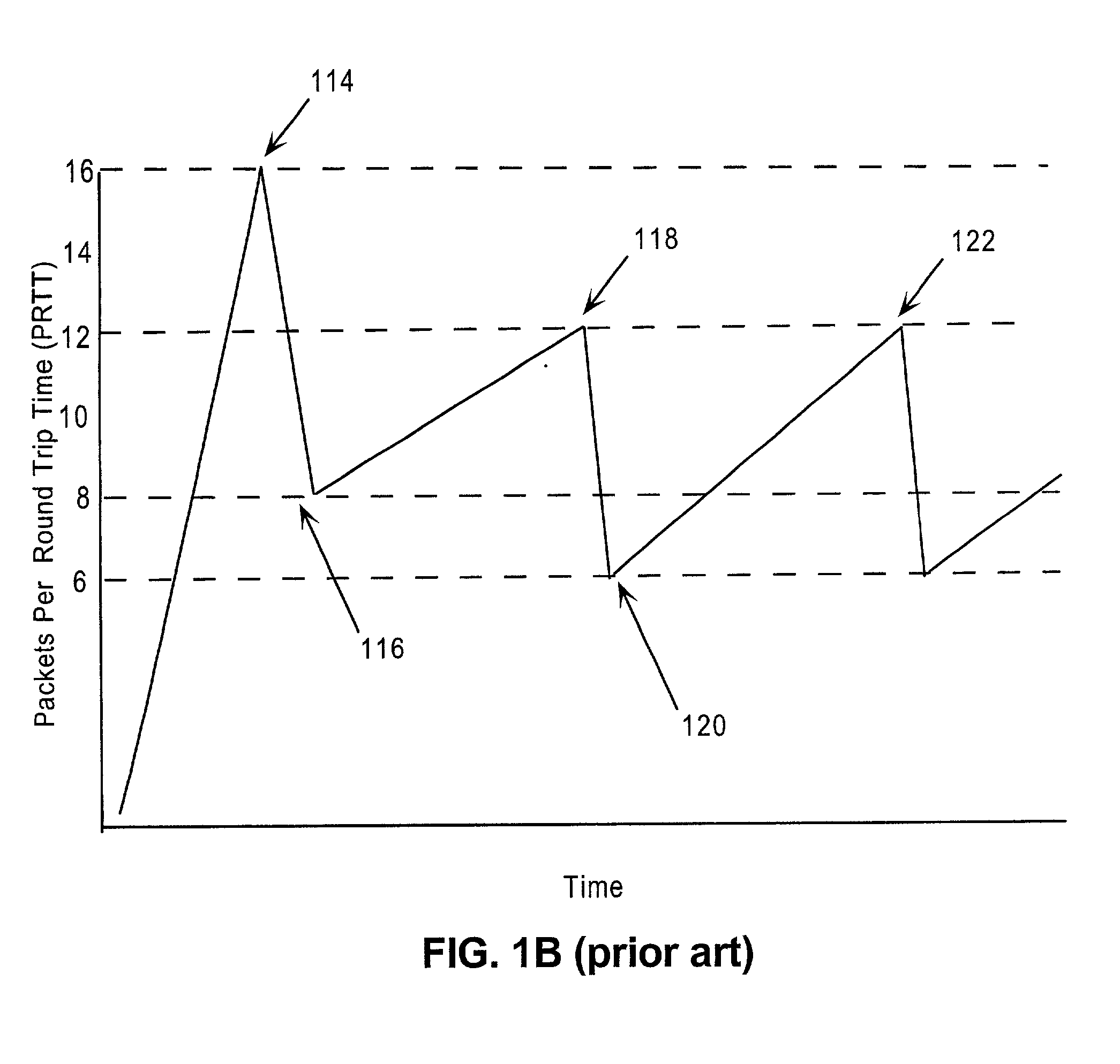
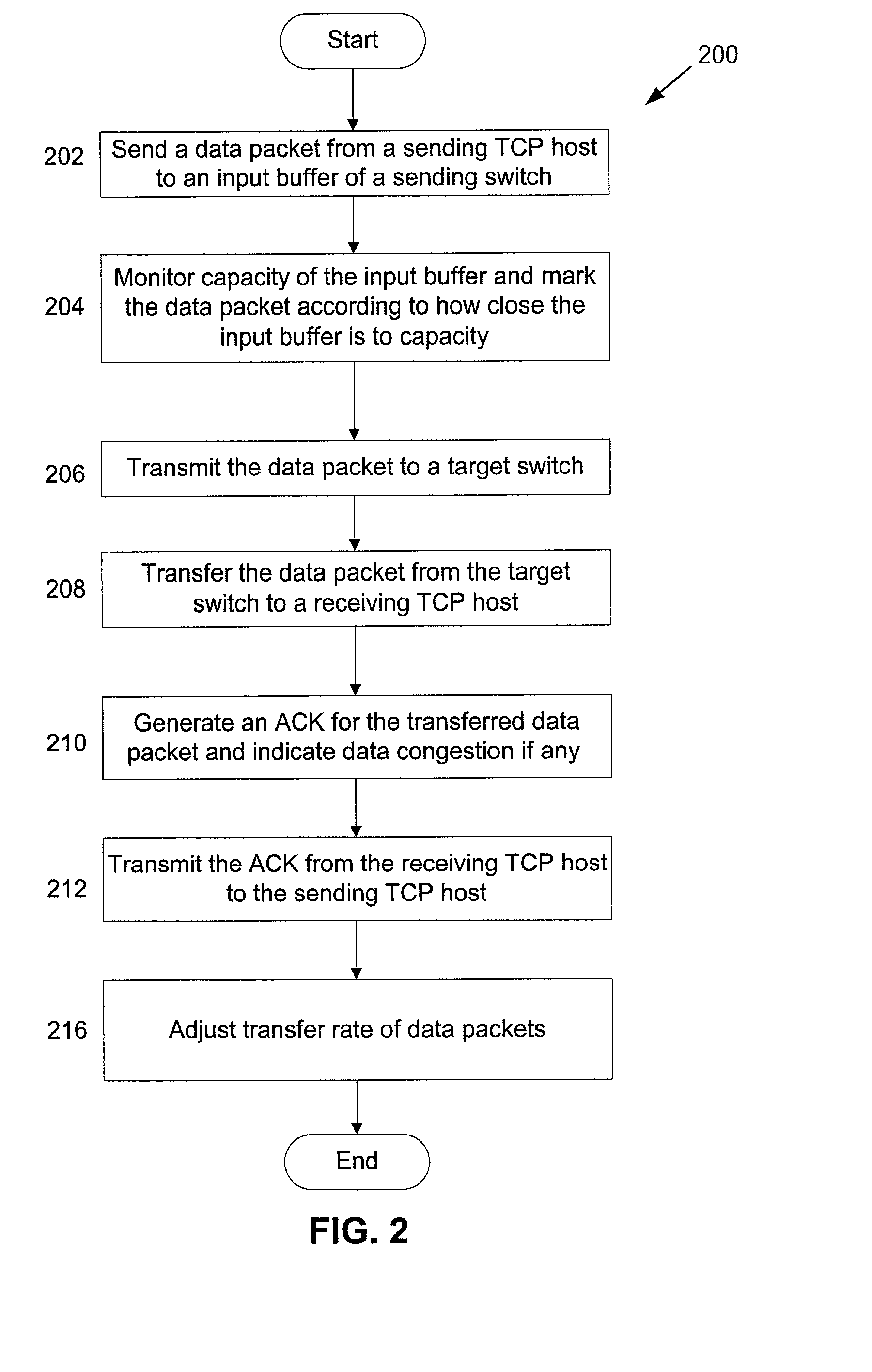
A network system for actively controlling congestion to optimize throughput is provided. The network system includes a sending host which is configured to send packet traffic at a set rate. The network system also includes a sending switch for receiving the packet traffic. The sending switch includes an input buffer for receiving the packet traffic at the set rate where the input buffer is actively monitored to ascertain a capacity level. The sending switch also includes code for setting a probability factor that is correlated to the capacity level where the probability factor increases as the capacity level increases and decreases as the capacity level decreases. The sending switch also has code for randomly generating a value where the value is indicative of whether packets being sent by the sending switch are to be marked with a congestion indicator. The sending switch also includes transmit code that forwards the packet traffic out of the sending switch where the packet traffic includes one of marked packets and unmarked packets. The network system also has a receiving end which is the recipient of the packet traffic and also generates acknowledgment packets back to the sending host where the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator when receiving marked packets and are not marked with the congestion indicator when receiving unmarked packets. In another example, the sending host is configured to monitor the acknowledgment packets and to adjust the set rate based on whether the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator. In a further example, the set rate is decreased every time one of the marked packets is detected and increased when no marked packets are detected per round trip time (PRTT).
Owner:ADAPTEC +1
Methods and apparatus for network congestion control
Methods and apparatus are provided for controlling congestion in a network such as a fibre channel network. Techniques are provided for characterizing traffic flow at a congested network node. The congested network node can generate various instructions such as quench messages to control traffic flow towards the congested network node. The quench messages can optionally include information about the characteristics of the congestion. The instructions are distributed to other nodes in the network. The other network nodes can interpret the instructions and control traffic flow towards the congested node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
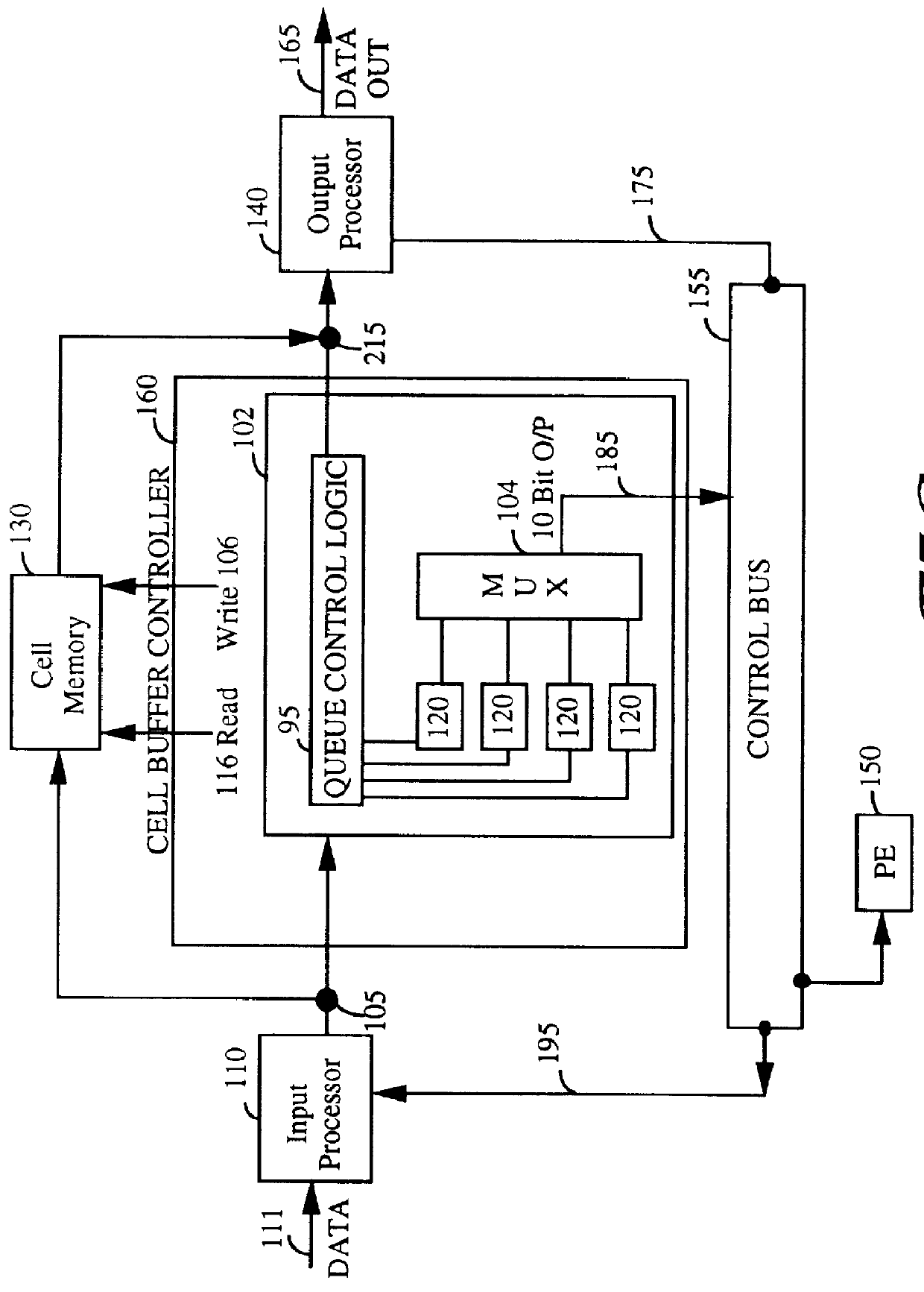
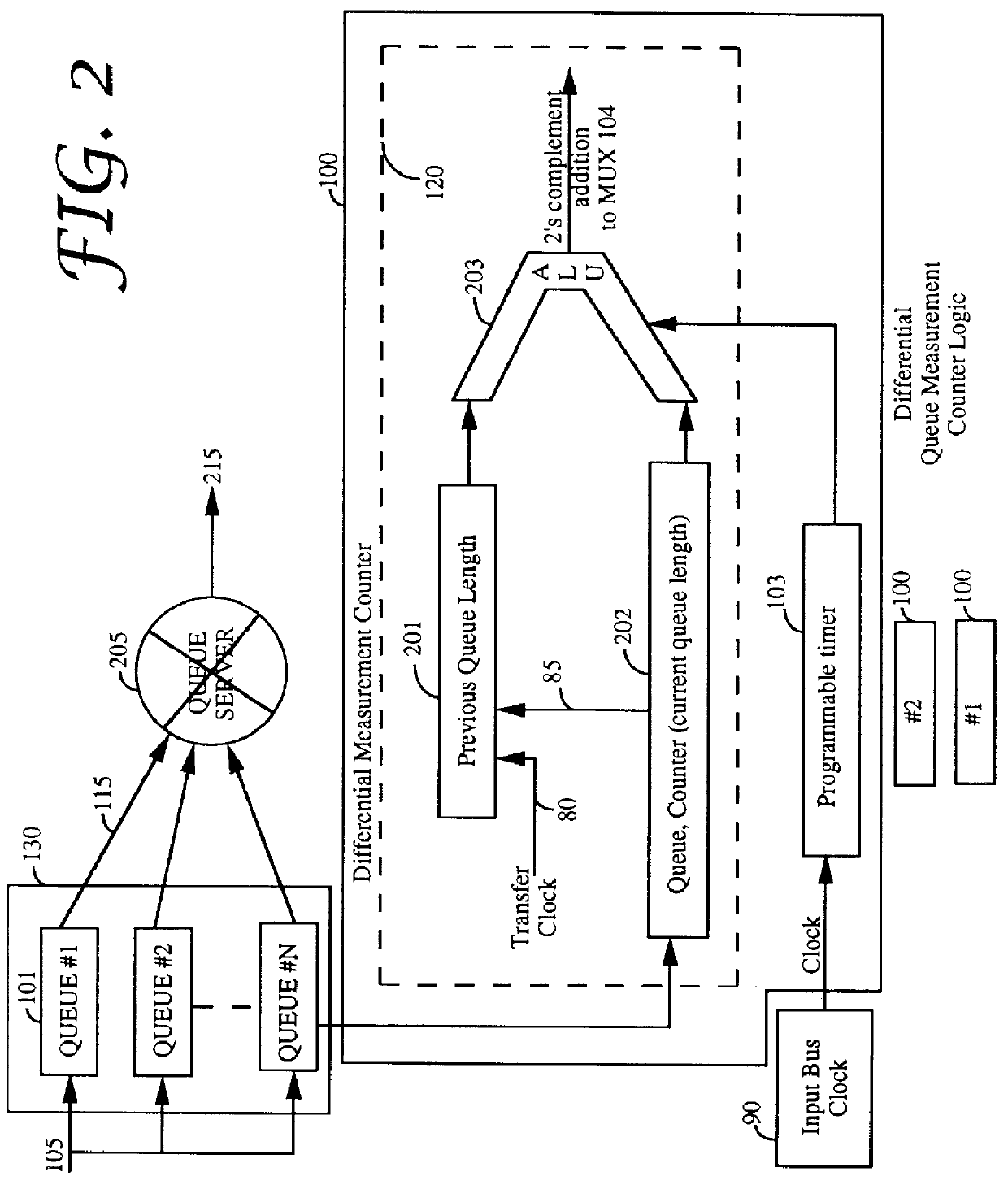
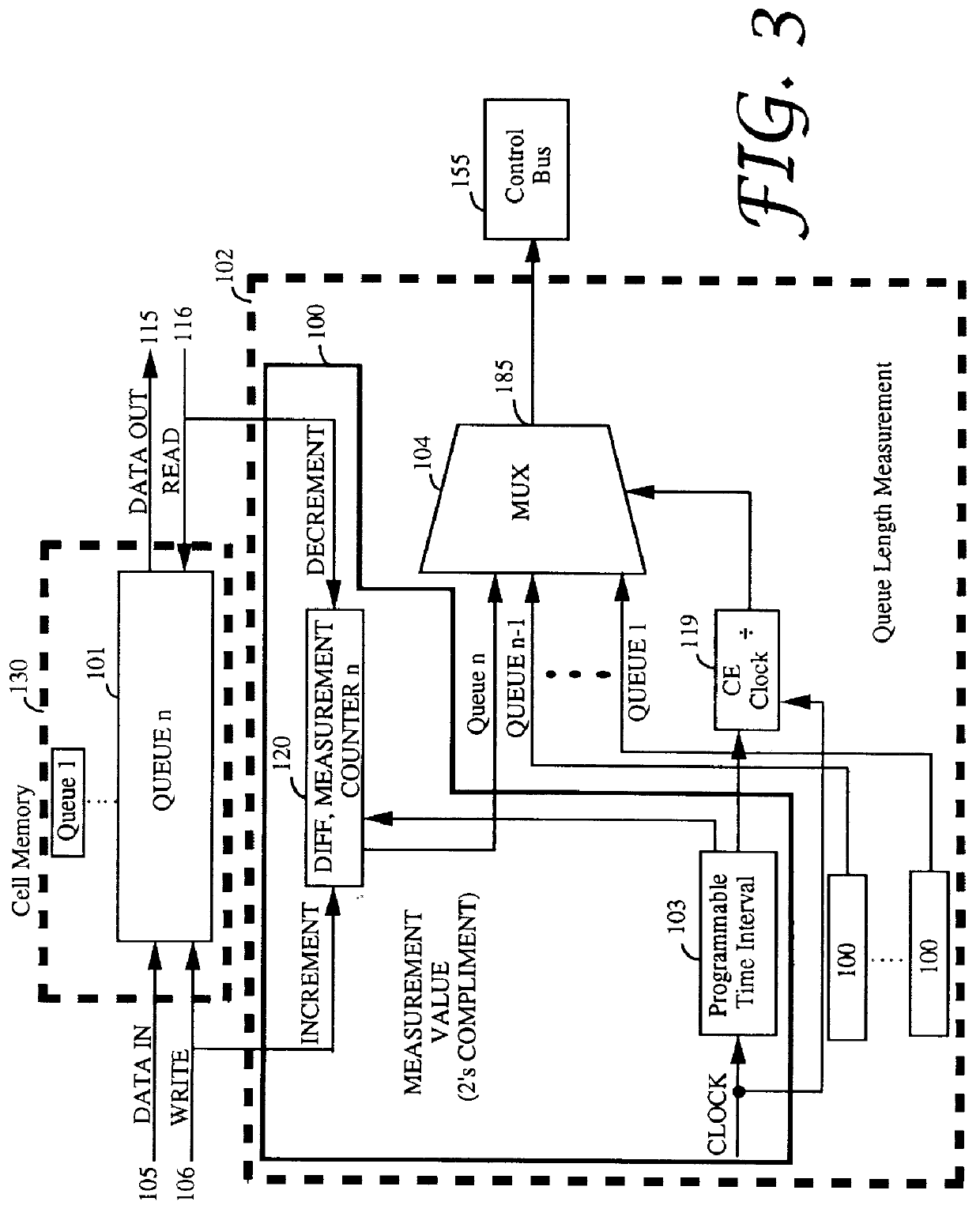
Closed loop congestion control using a queue measurement system
A queue length measurement device that is comprised of a number of queues that are capable of holding data cells. A differential counter is coupled to each queue. The counter is incremented when a cell is written into the queue and decremented when a cell is read from the queue. An interval measurement device, coupled to the differential counter, generates a pulse to reset the counter at fixed intervals equivalent to n cells time (where n is the maximum number of cells the queue counter can measure). A multiplexer is coupled to the multiple differential counters. A transfer control circuit coupled to the interval measurement device selects the appropriate queue measurement to be output from the multiplexer to the other switch elements. A system and methodology provide for queue flow statistics and closed loop control of cell flow into the queue. A congestion control system is provided comprising a queue (having an input and an output, and capable of storing and outputting a plurality of data cells), an input processor (for coupling a plurality of data cells to the queue input), an output processor, an interval measurement device (generating a pulse at predetermined intervals), and differential queue length generation logic. The output processor, couples to the queue output, for receiving a plurality of data cells from the queue, which generates a queue change in size signal in response to determining for each of the predefined intervals of the difference between a present and a previous queue length.
Owner:WHITTAKER COMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com