Patents
Literature
57 results about "Random early detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
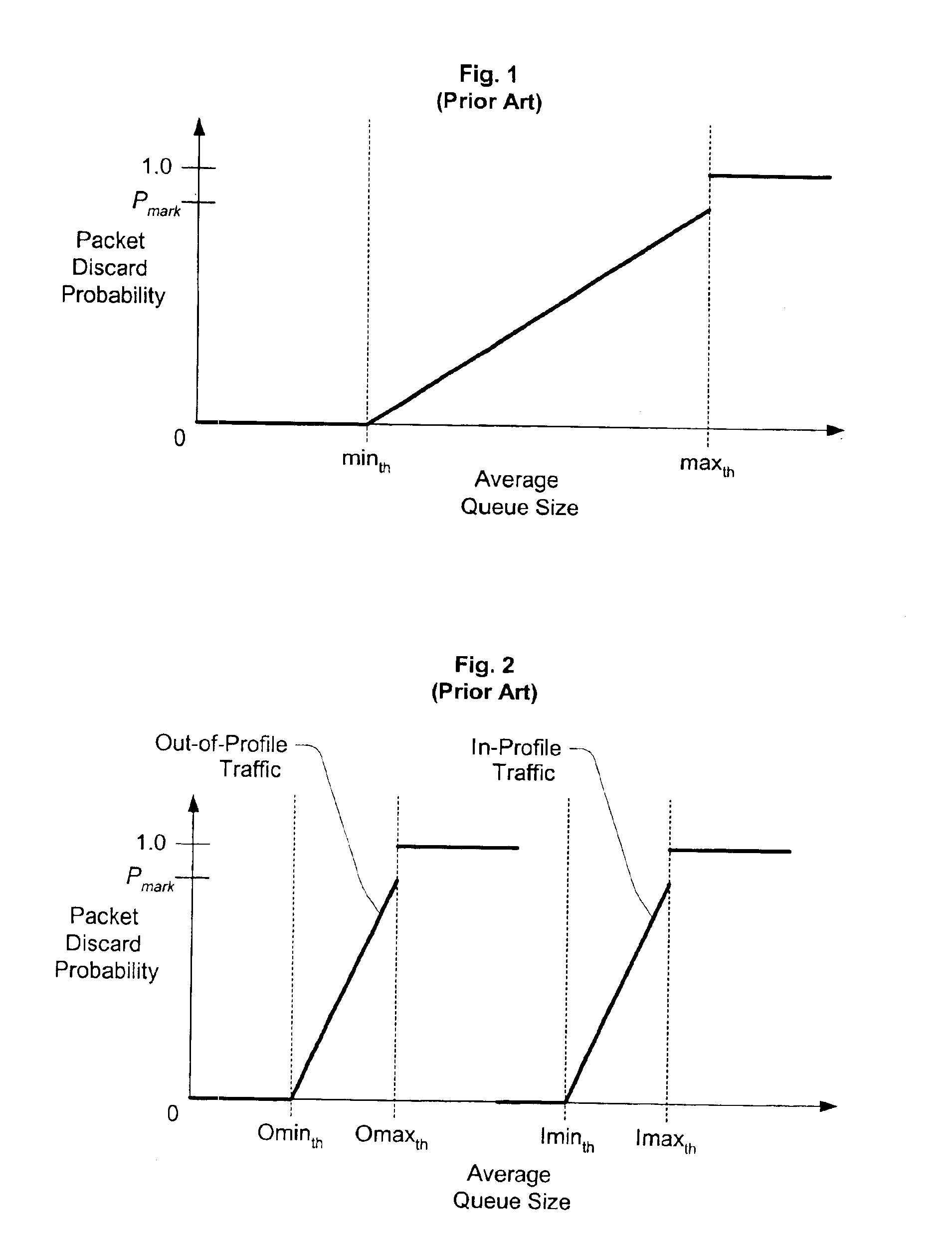
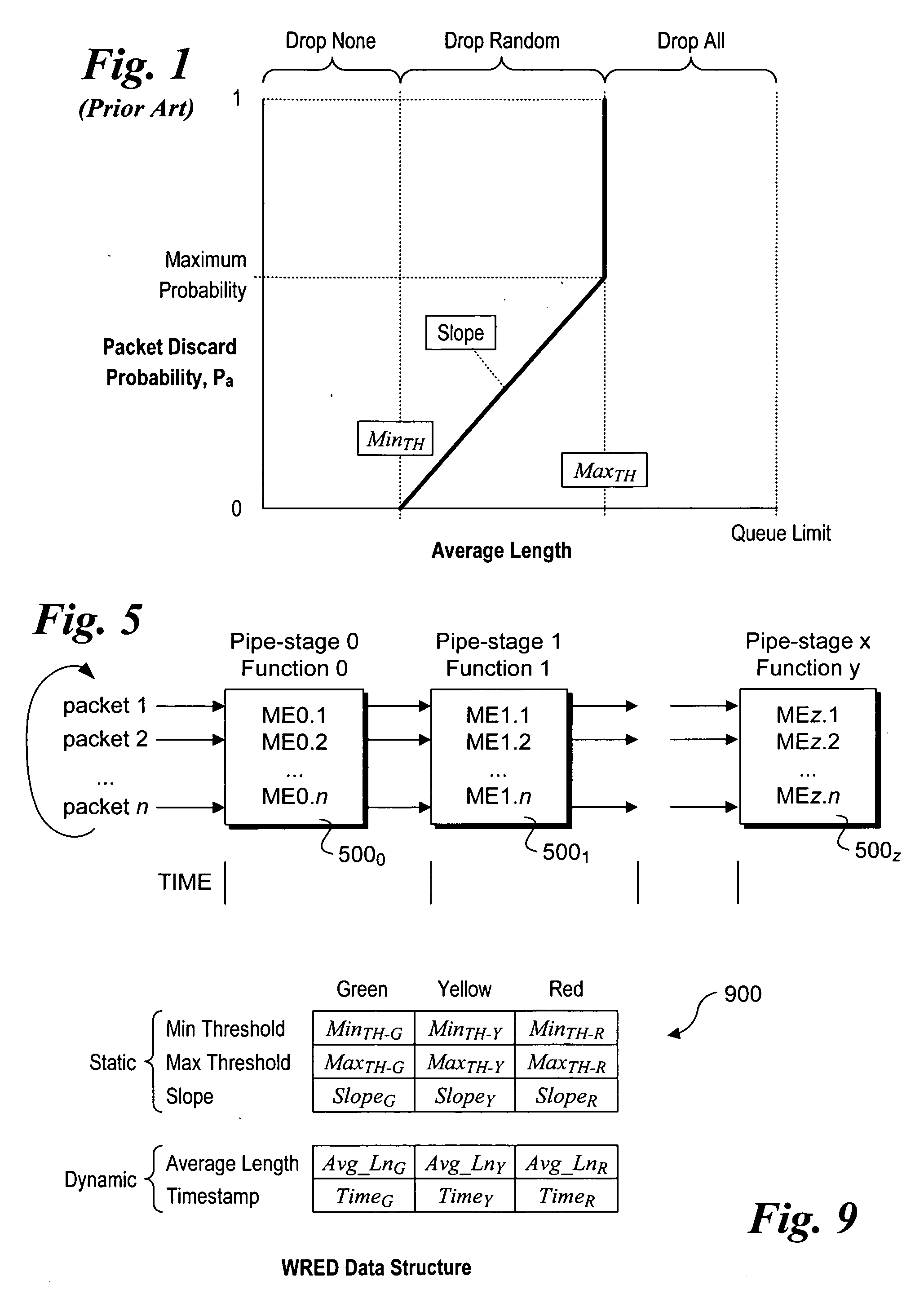
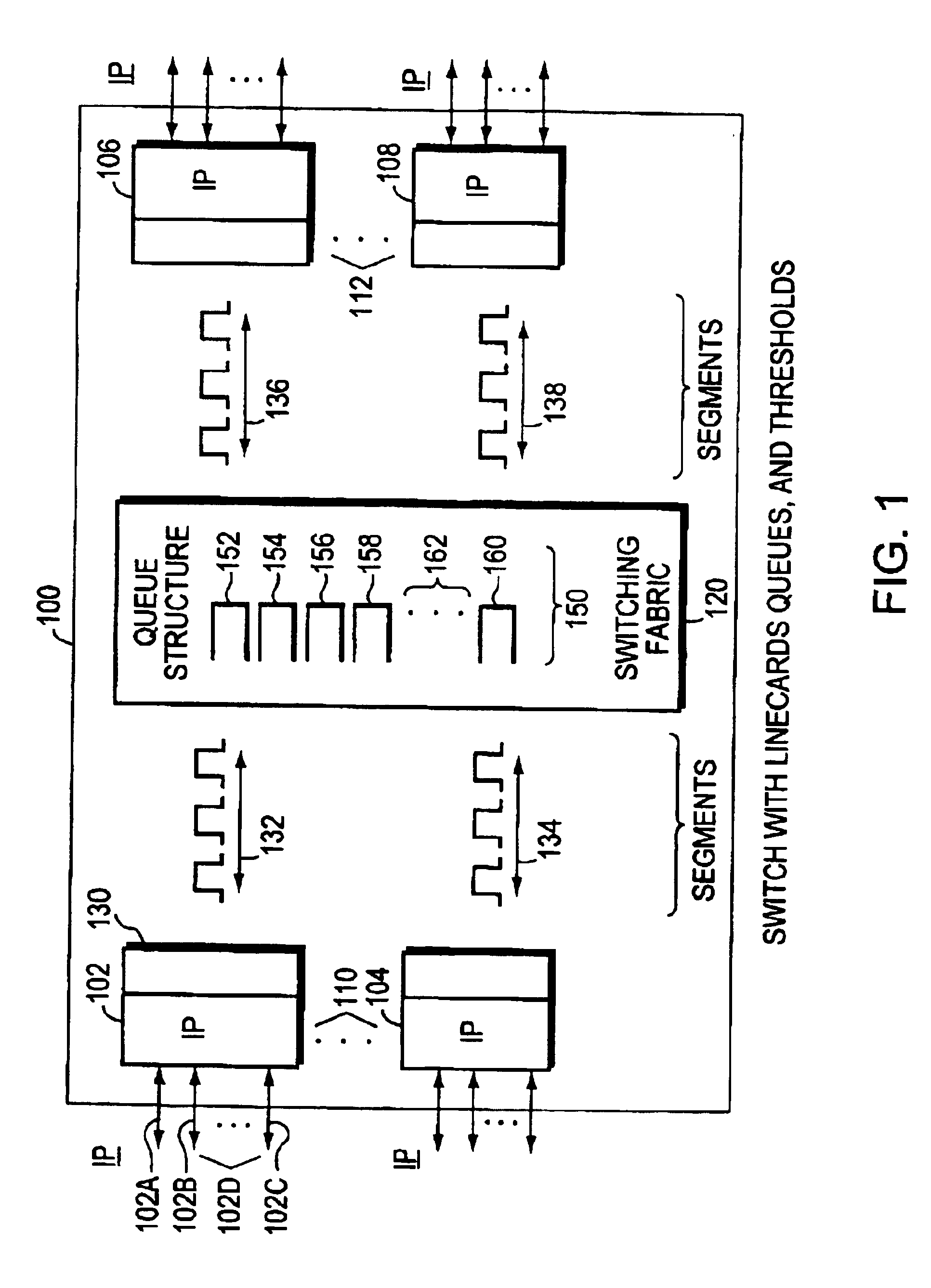
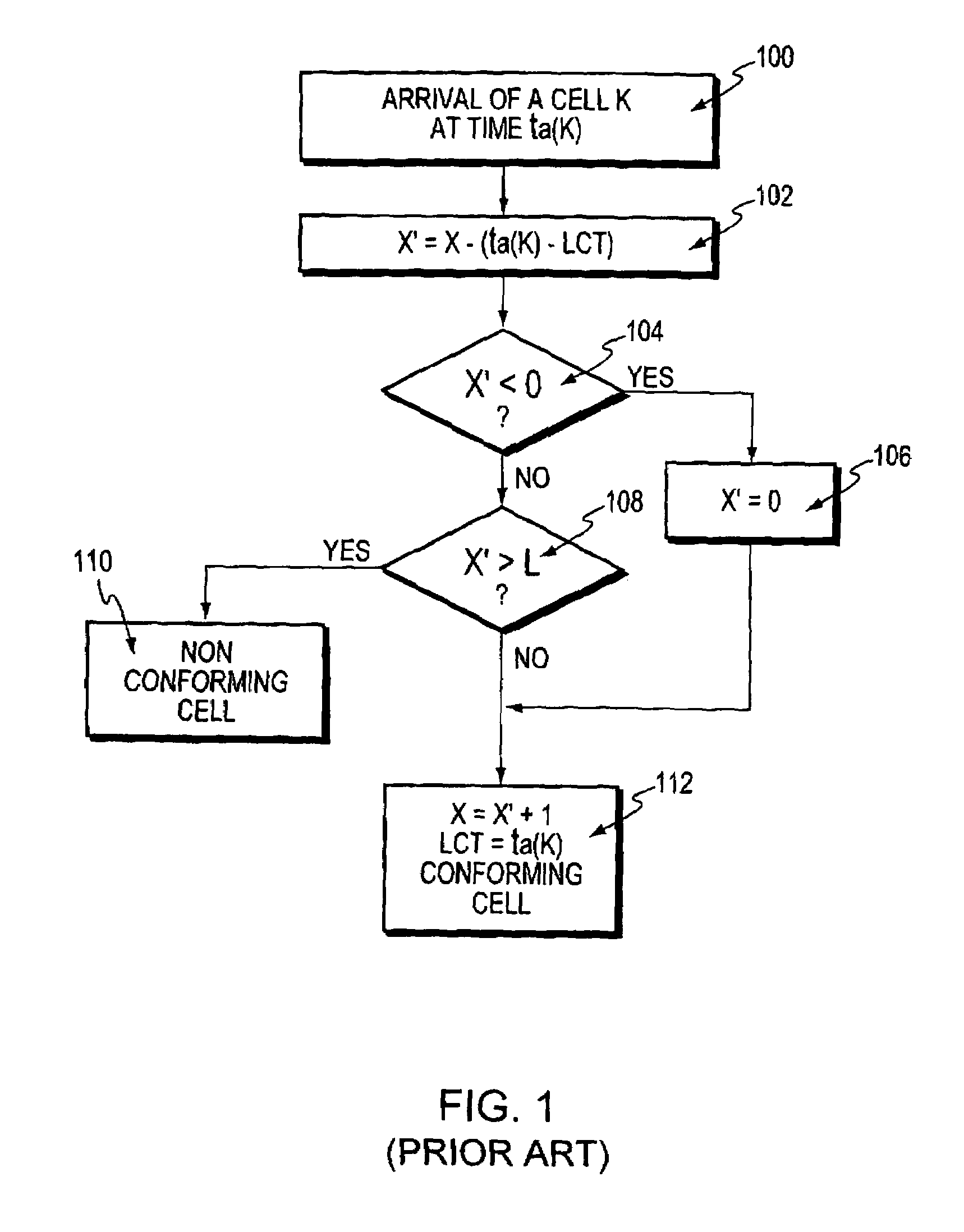
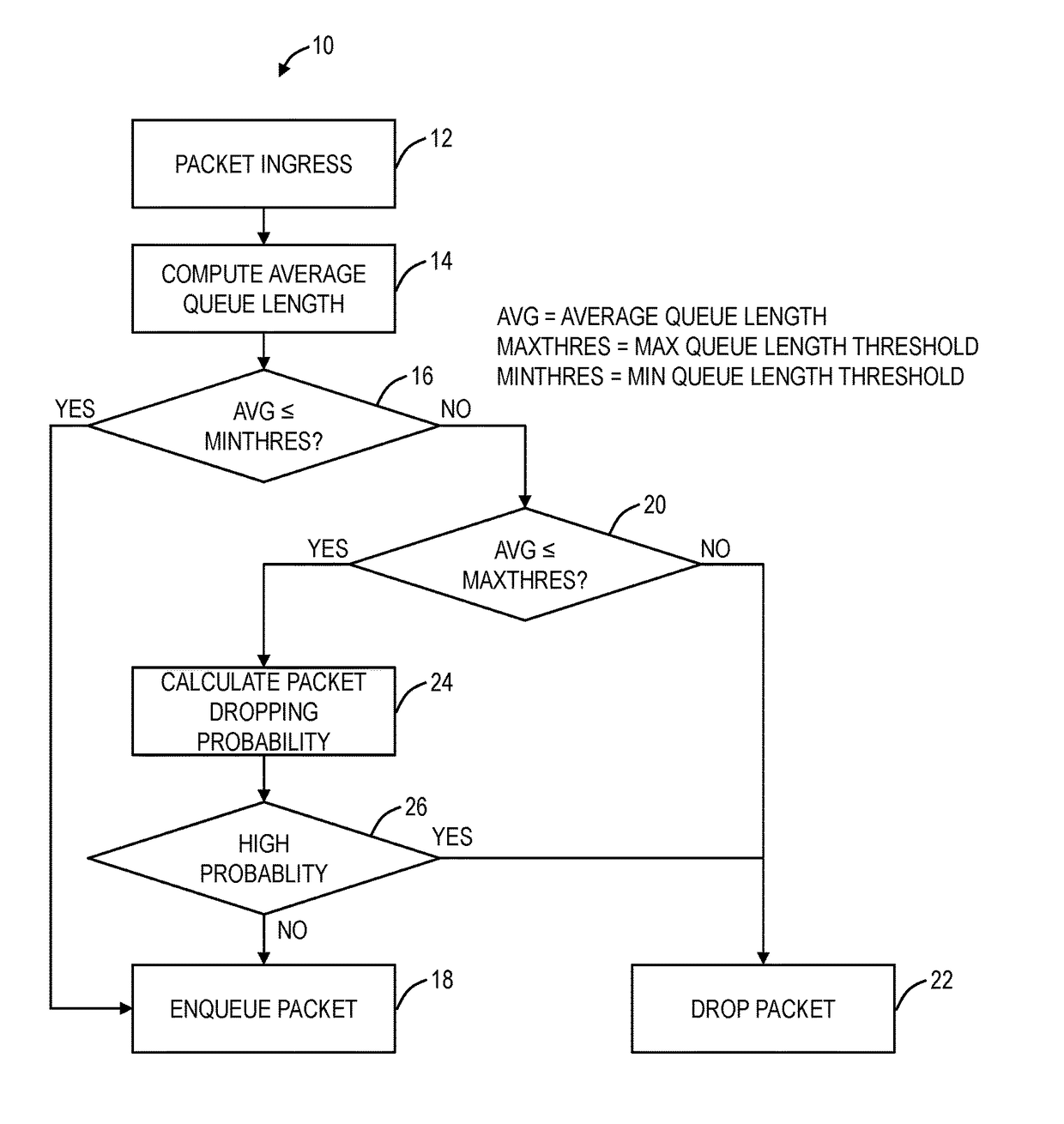
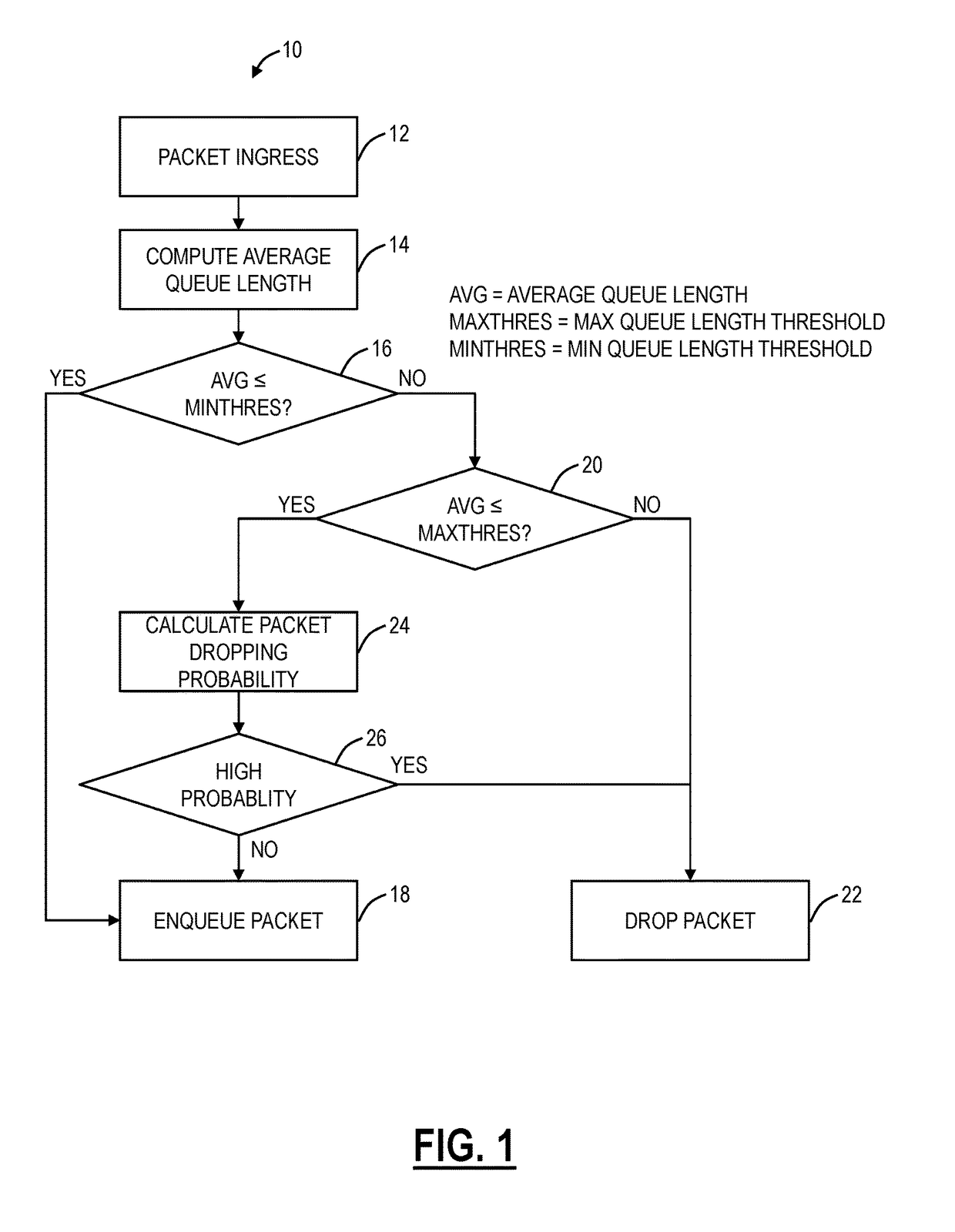
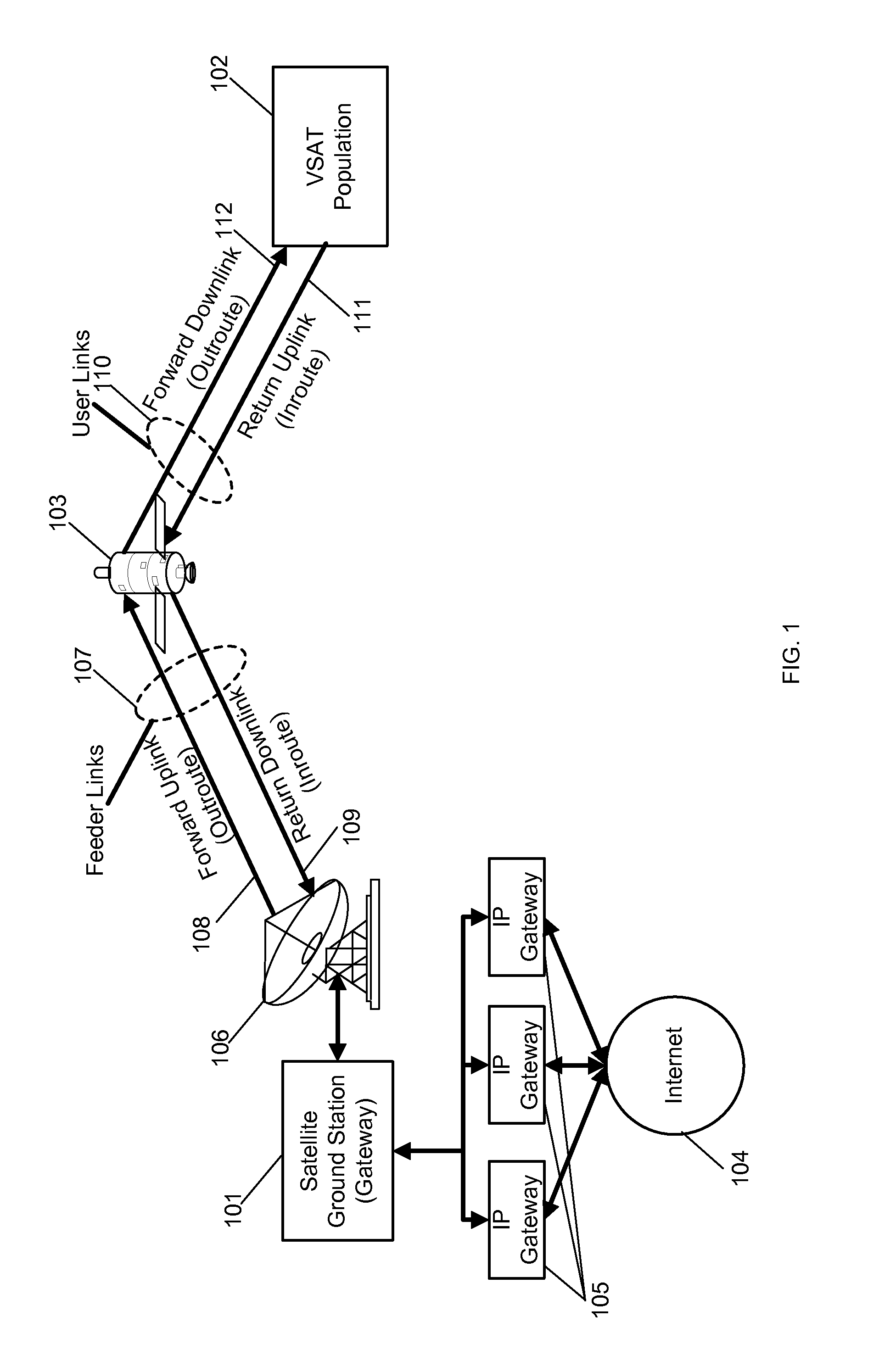
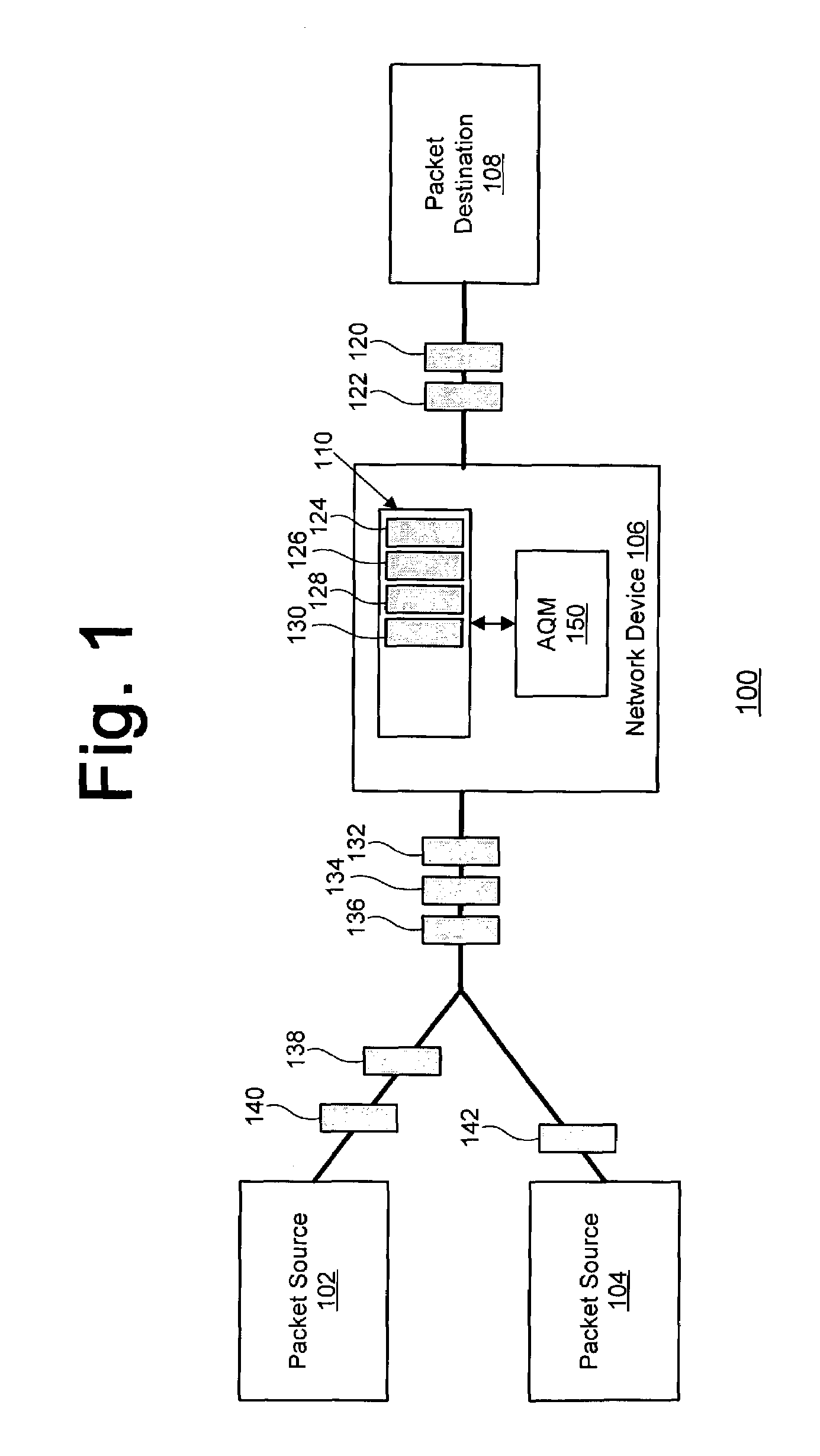
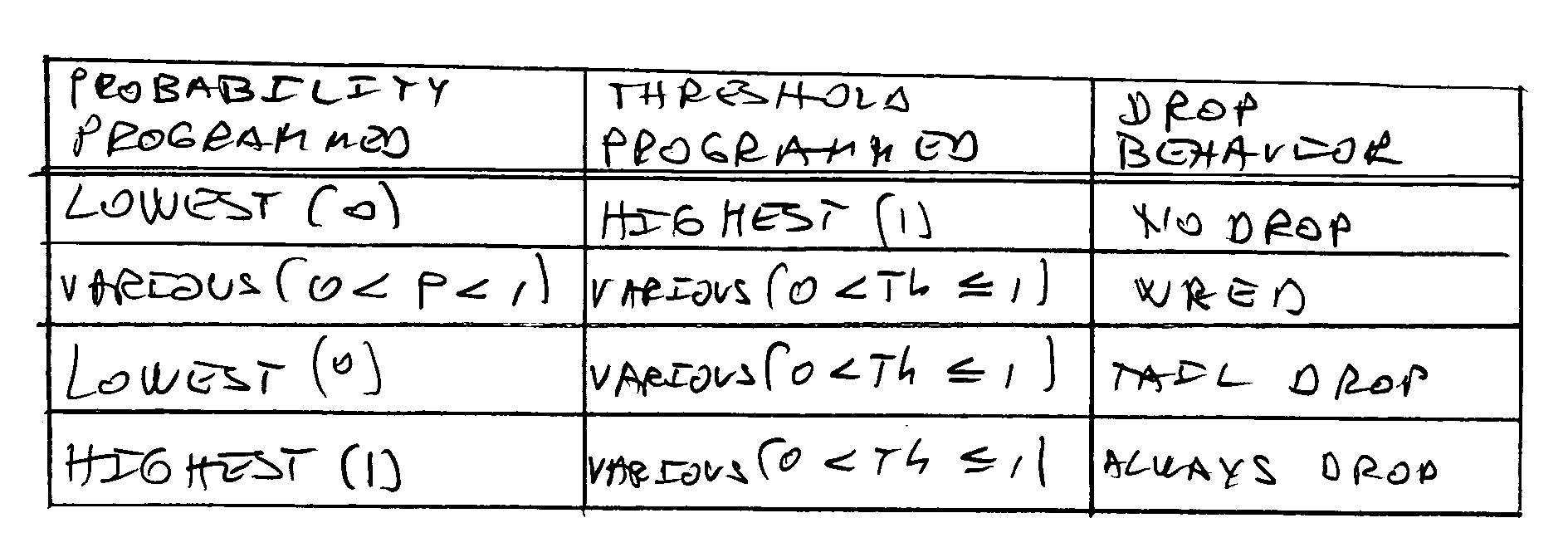
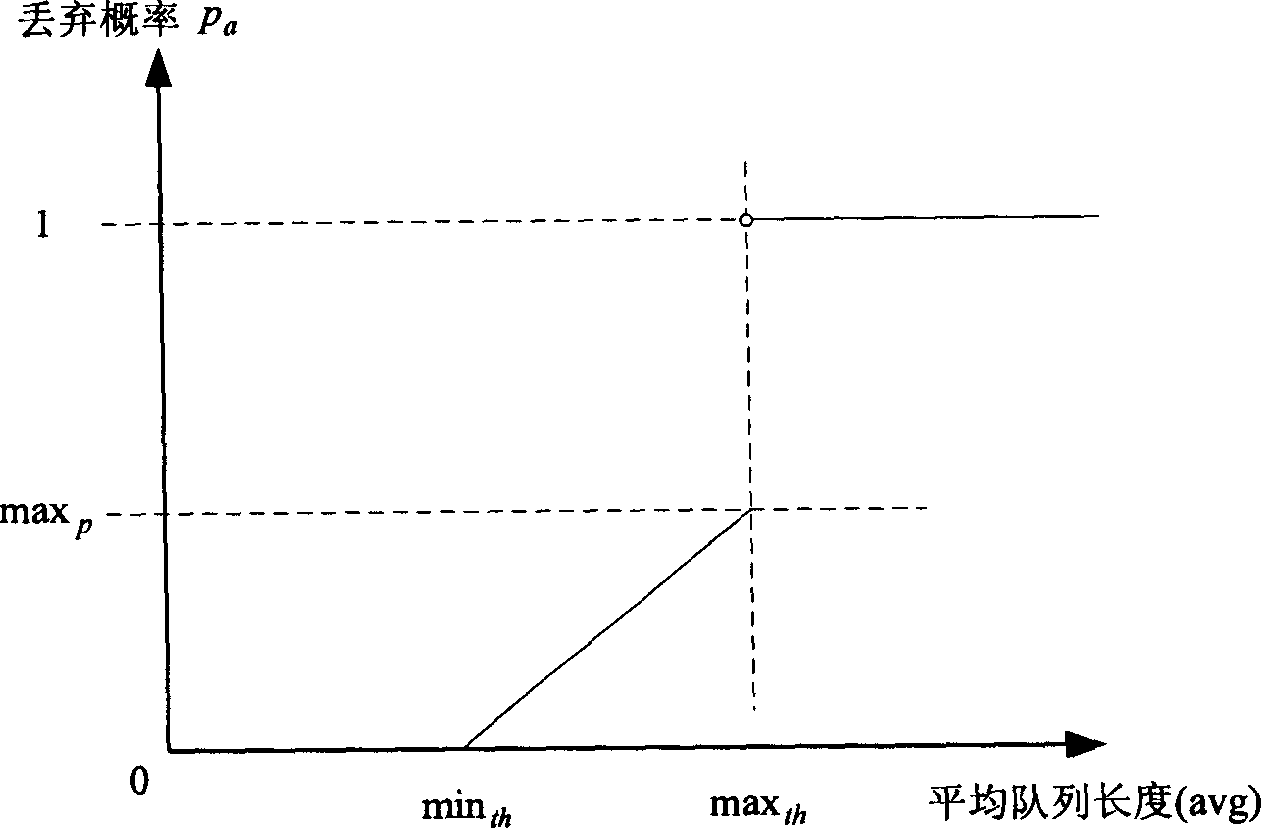
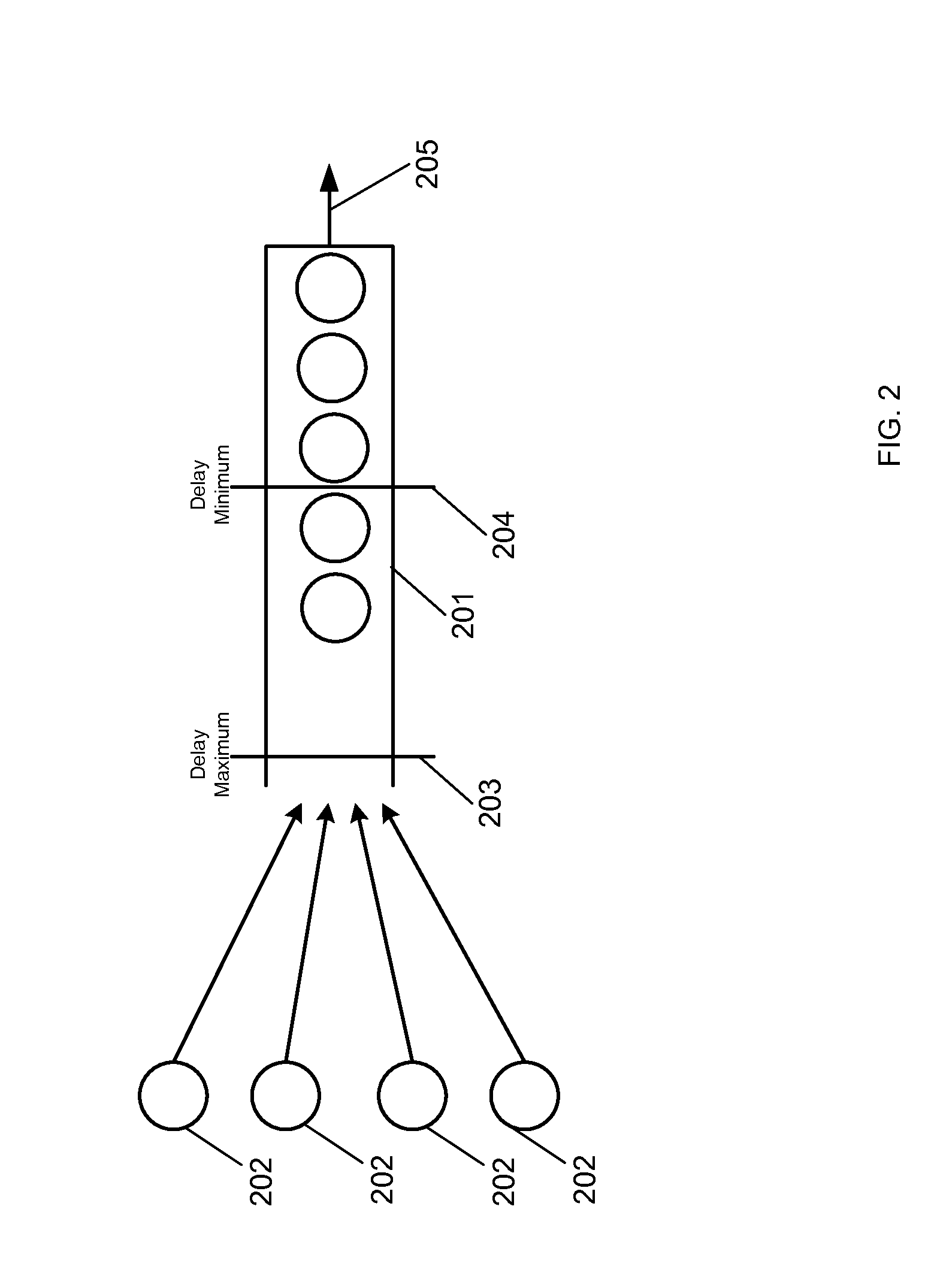
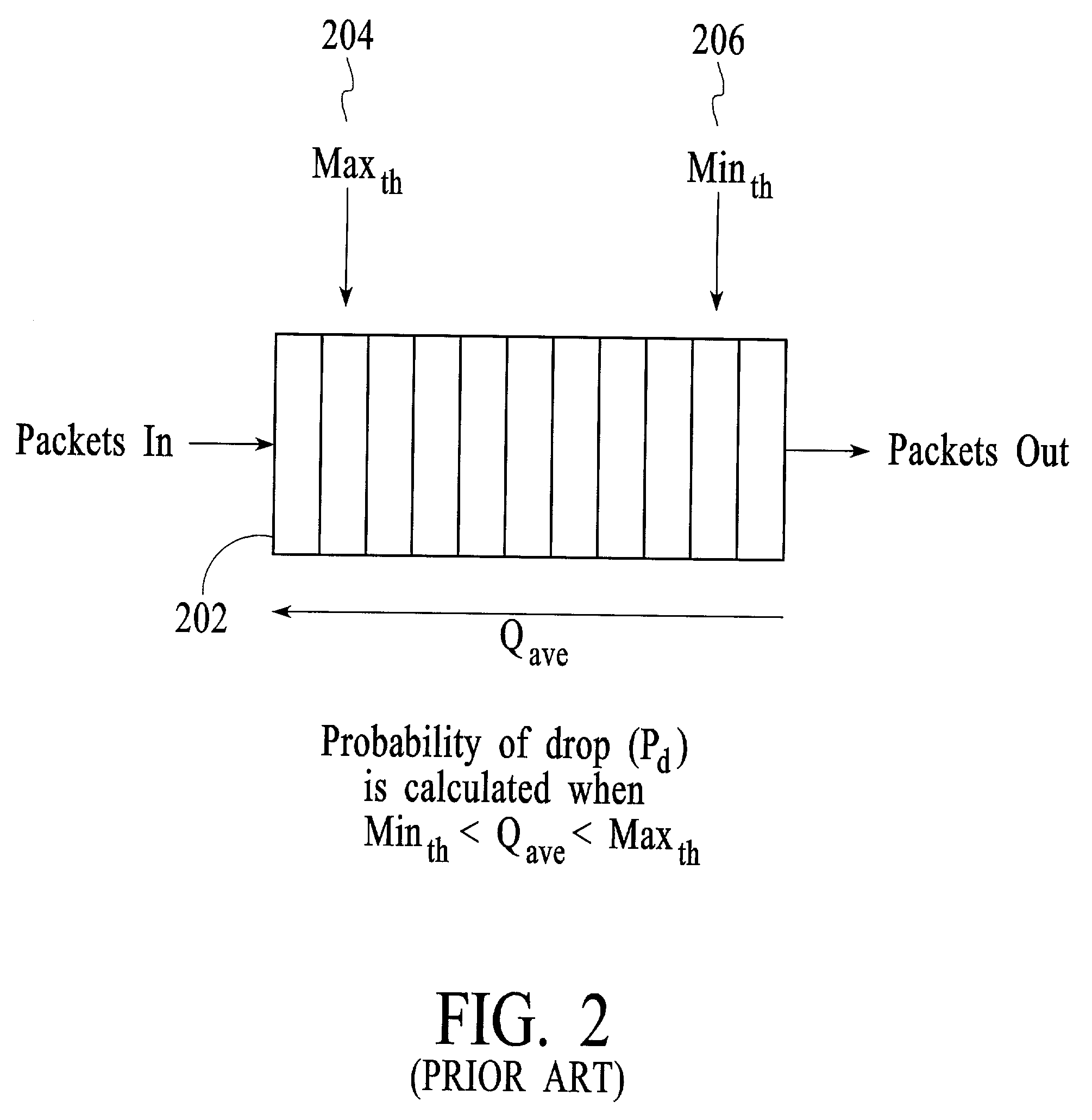
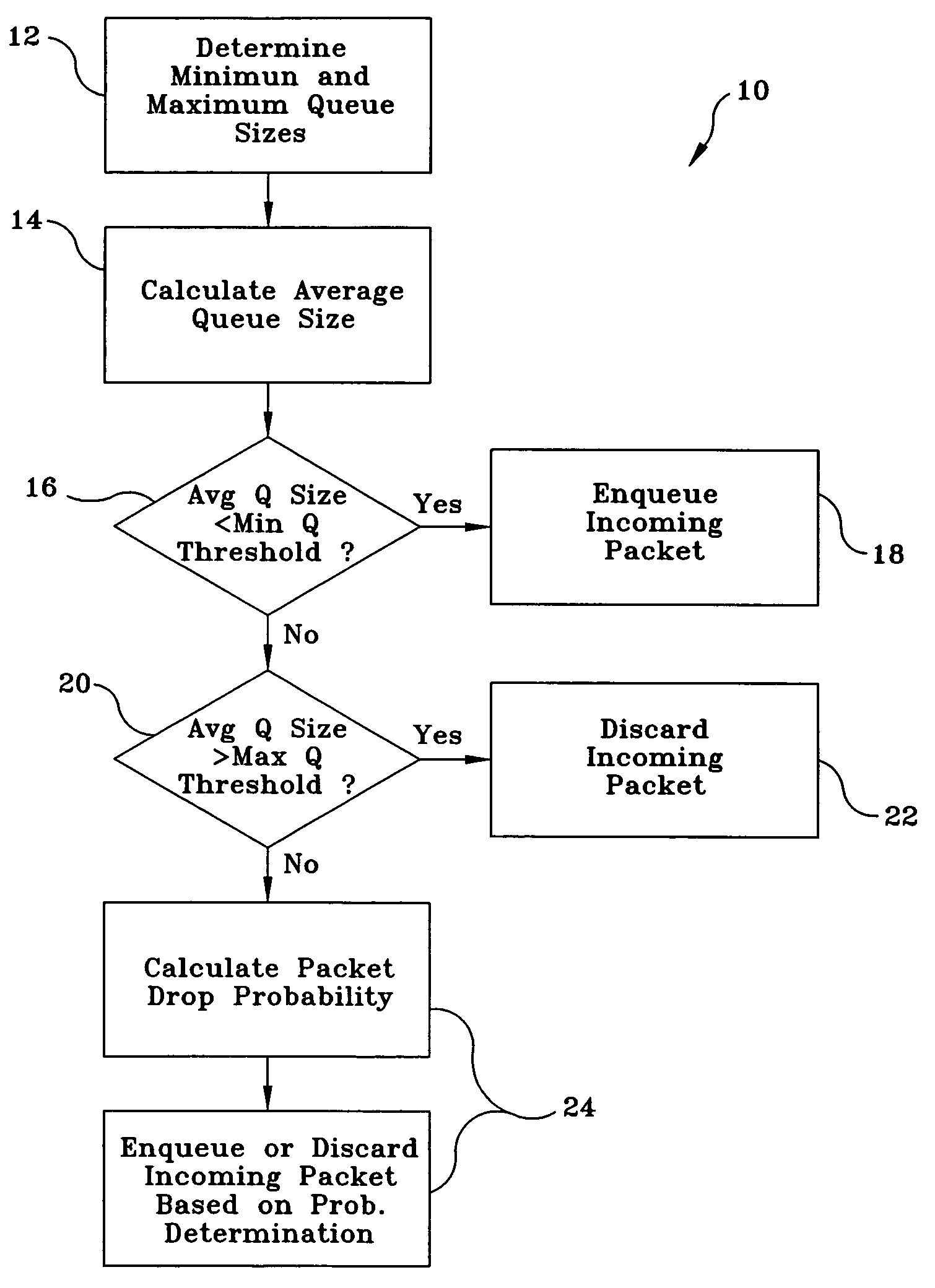
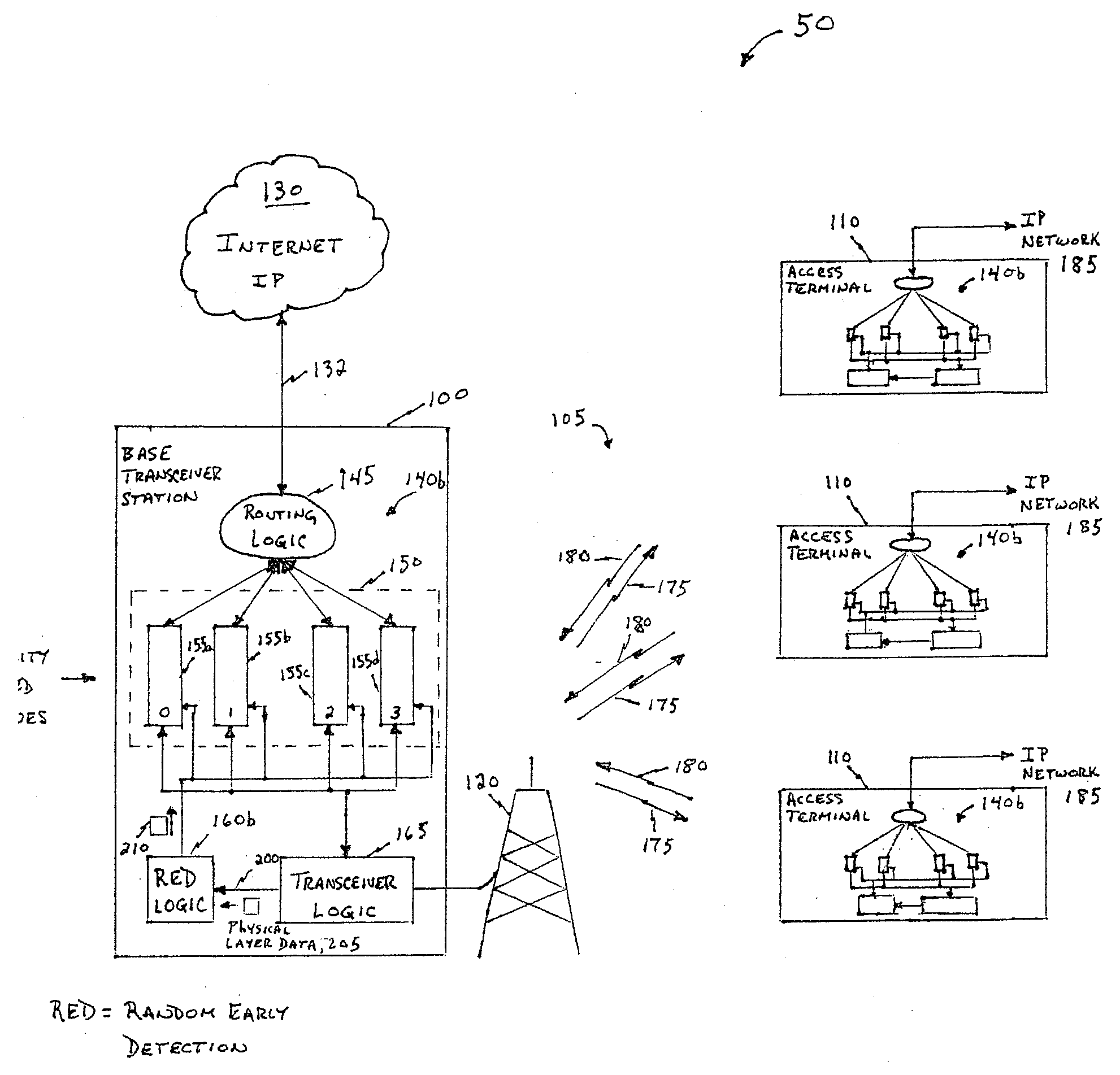
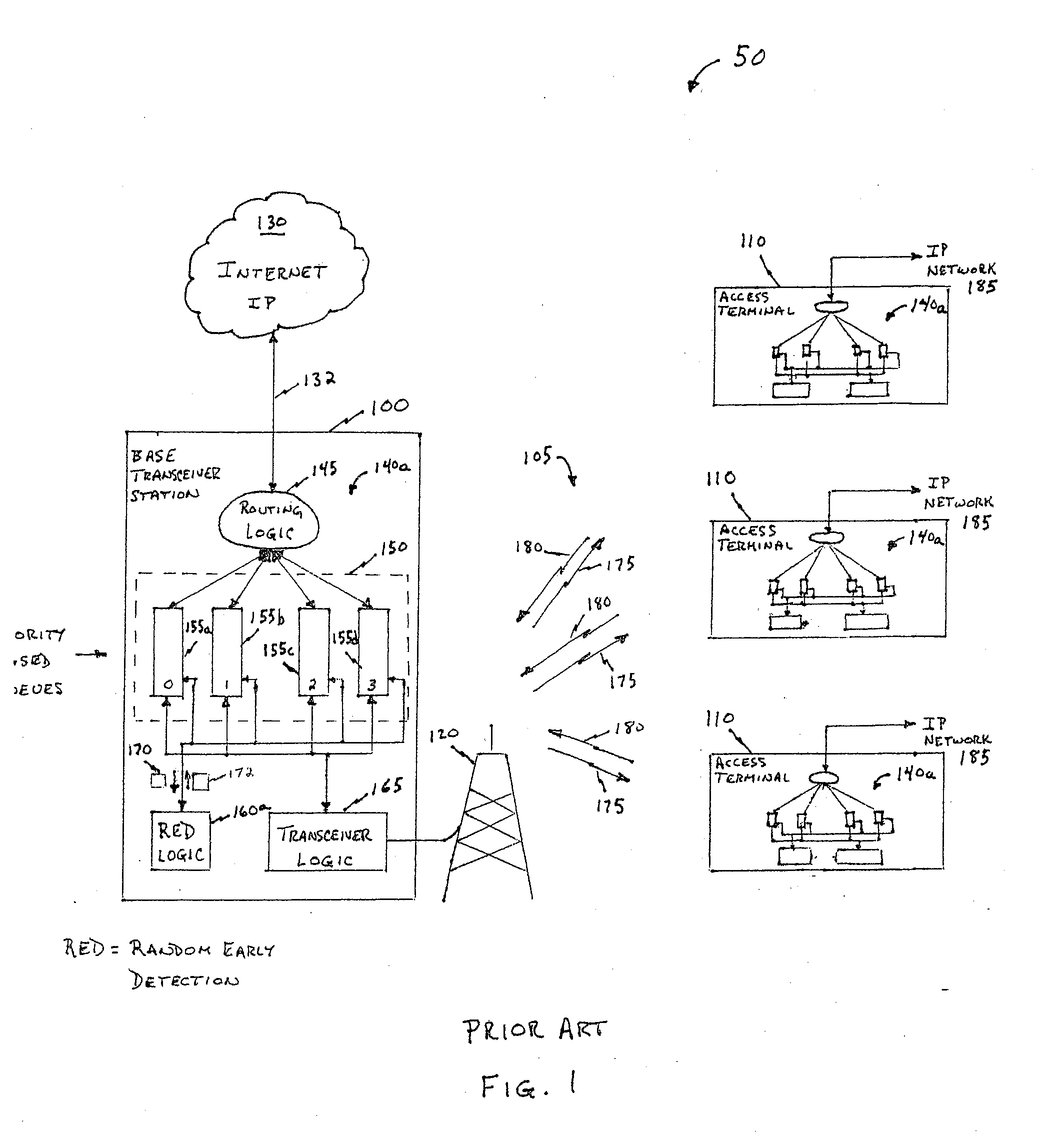
Random early detection (RED), also known as random early discard or random early drop is a queuing discipline for a network scheduler suited for congestion avoidance. In the conventional tail drop algorithm, a router or other network component buffers as many packets as it can, and simply drops the ones it cannot buffer. If buffers are constantly full, the network is congested. Tail drop distributes buffer space unfairly among traffic flows. Tail drop can also lead to TCP global synchronization as all TCP connections "hold back" simultaneously, and then step forward simultaneously. Networks become under-utilized and flooded—alternately, in waves.
Policy-based weighted random early detection method for avoiding congestion in internet traffic
InactiveUS6996062B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityRandom early detection
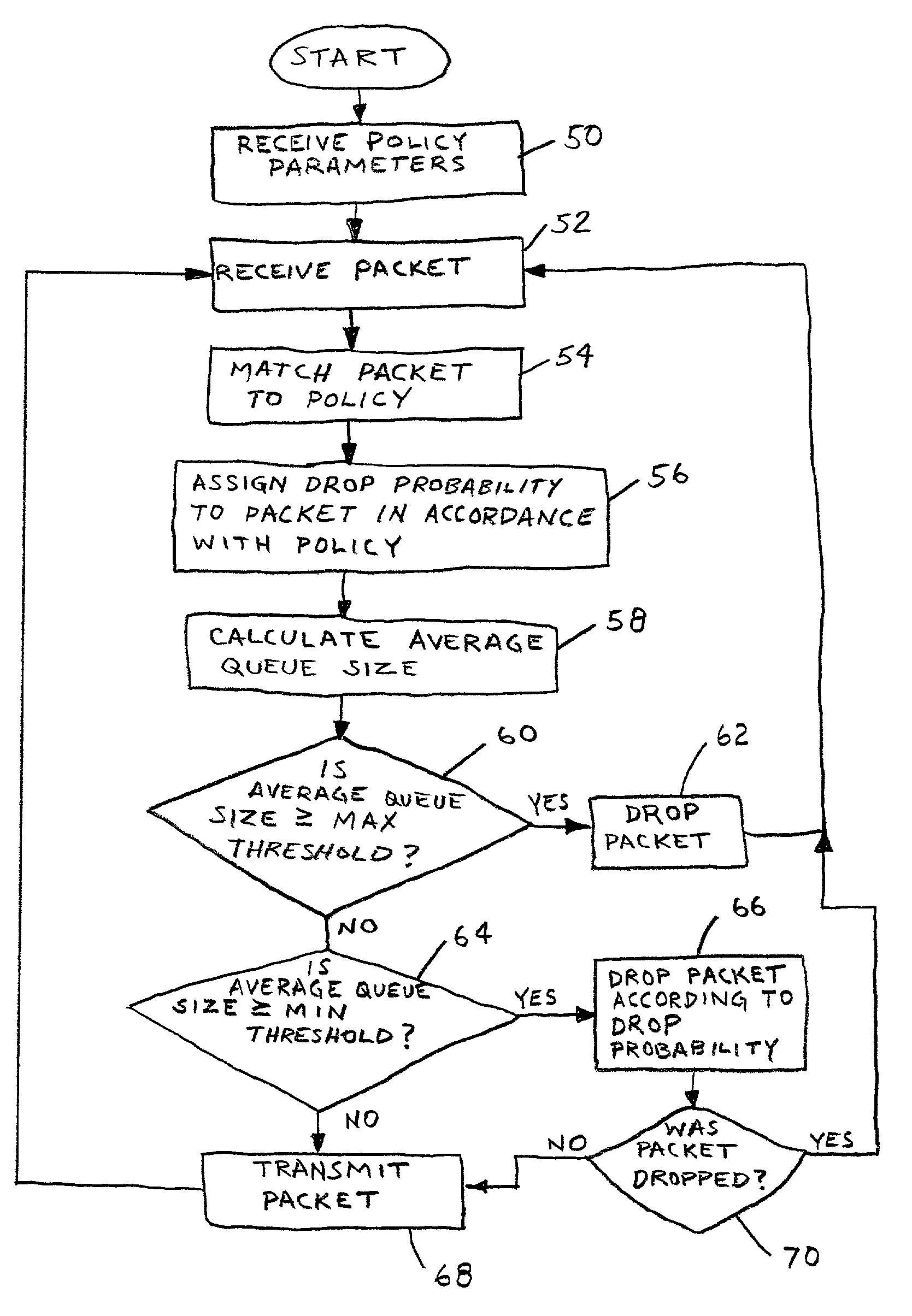
A method and apparatus for avoiding network congestion. An exemplary packet forwarding device may apply policy rules to incoming packets to assign relative drop probabilities to the packets based on the priority of the packets. In times of network congestion, packets may be selectively dropped according to their associated drop probability.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Congestion avoidance profiles in a packet switching system
InactiveUS6904015B1Low costImprove approachError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRandom early detectionConfigfs
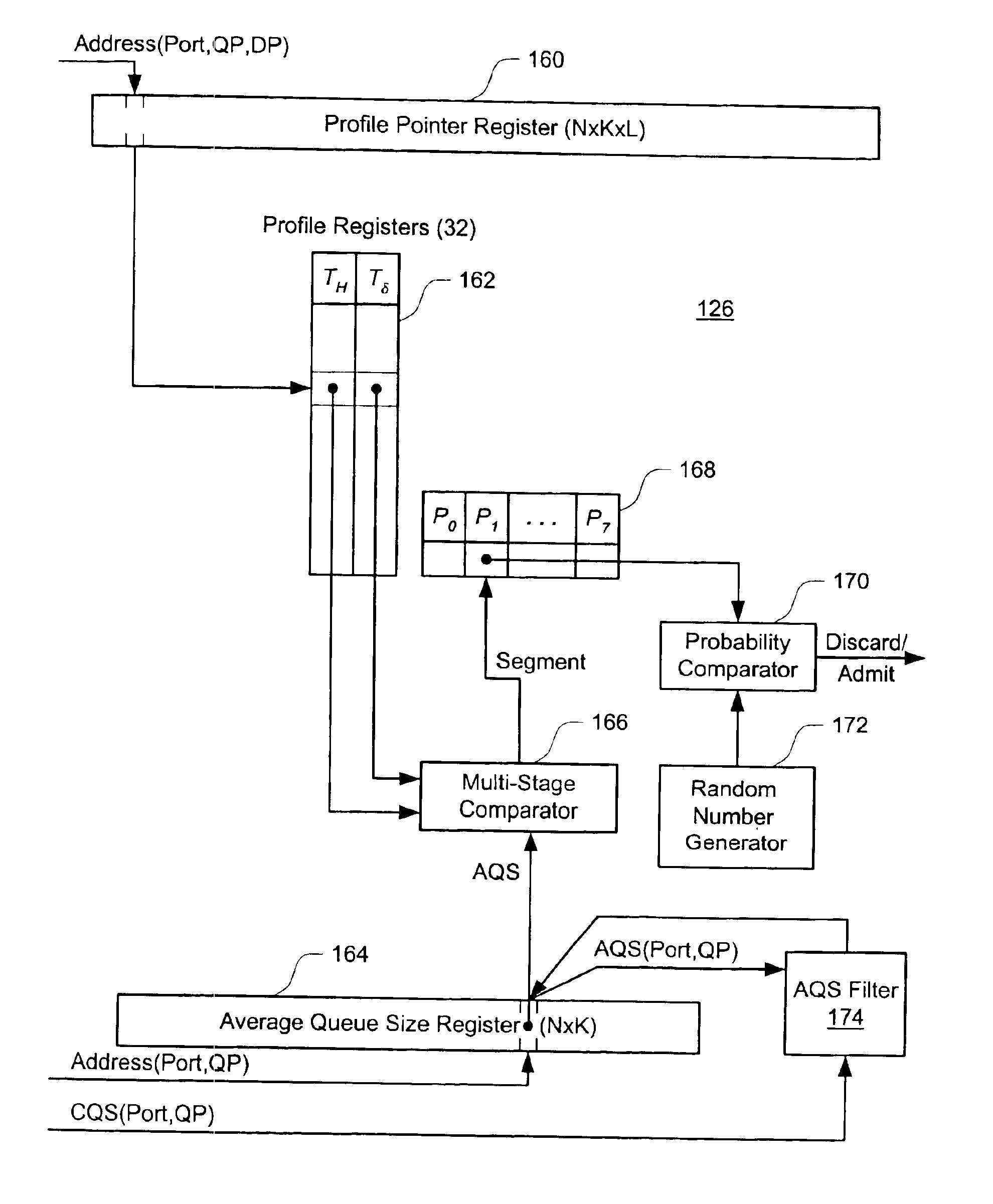
Methods and apparatus for an improvement on Random Early Detection (RED) router congestion avoidance are disclosed. A traffic conditioner stores a drop probability profile as a collection of configurable profile segments. A multi-stage comparator compares an average queue size (AQS) for a packet queue to the segments, and determines which segment the AQS lies within. This segment is keyed to a corresponding drop probability, which is used to make a packet discard / admit decision for a packet.In a preferred implementation, this computational core is surrounded by a set of registers, allowing it to serve multiple packet queues and packets with different discard priorities. Each queue and discard priority can be keyed to a drop probability profile selected from a pool of such profiles. This provides a highly-configurable, inexpensive, and fast RED solution for a high-performance router.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Method and apparatus to implement a very efficient random early detection algorithm in the forwarding path
InactiveUS20070070907A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRandom early detectionDistributed computing
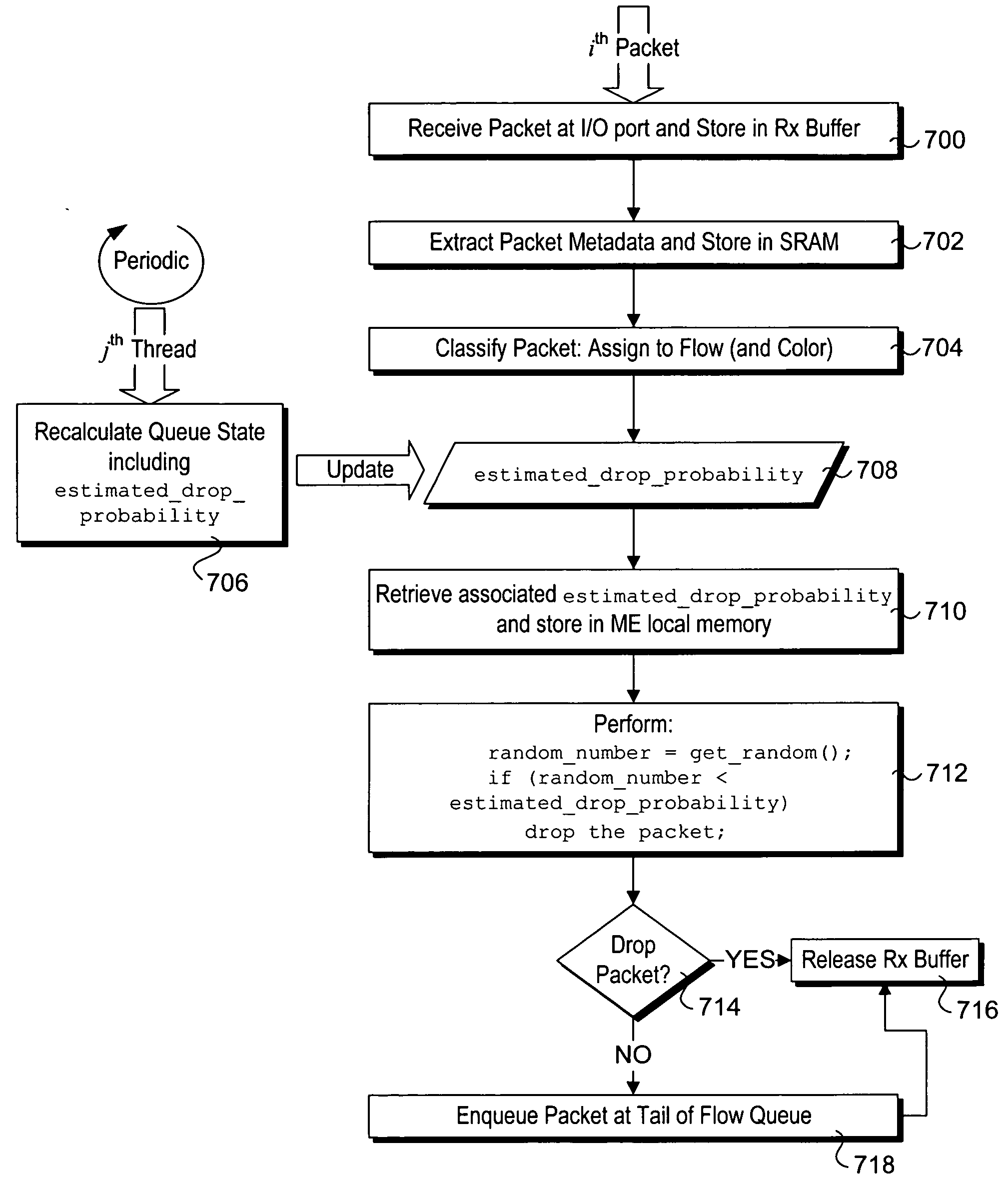
A method and apparatus for implementing a very efficient random early detection algorithm in the forwarding path of a network device. Under one embodiment of the method flows are associated with corresponding Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) drop profile parameters, and a flow queue is allocated to each of multiple flows. Estimated drop probability values are repeatedly generated for the flow queues based on existing flow queue state data in combination with WRED drop profile parameters. In parallel, various packet forwarding operations are performed, including packet classification, which assigns a packet to a flow queue for enqueing. In conjunction with this, a determination is made to whether to enqueue the packet in the flow queue or drop it by comparing the estimated drop probability value for the flow queue with a random number that is generated in the forwarding path.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Random early detection (RED) algorithm using marked segments to detect congestion in a computer network
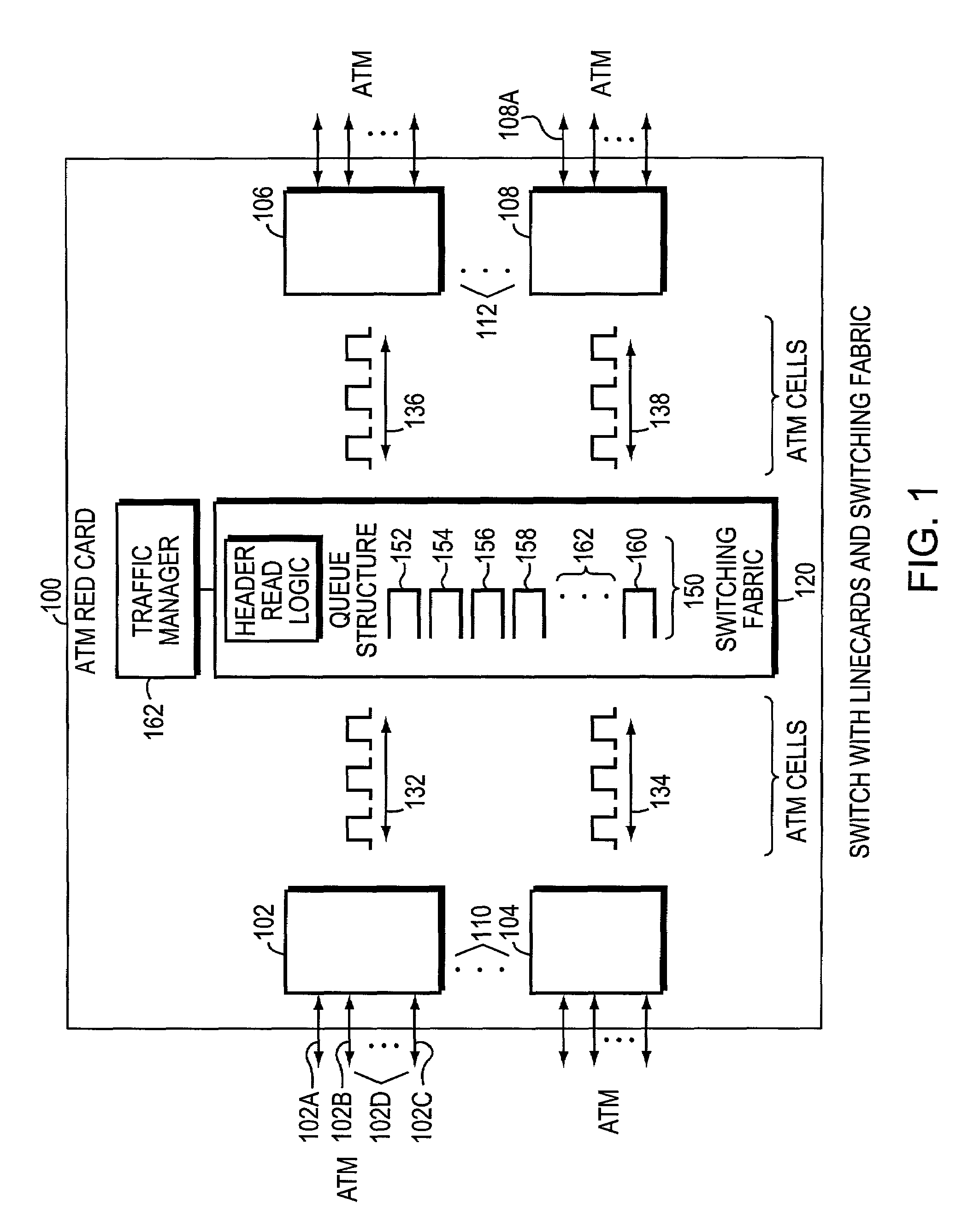
InactiveUS6888824B1Smooth changeEasy to handleMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexAtm switchingRandom early detection
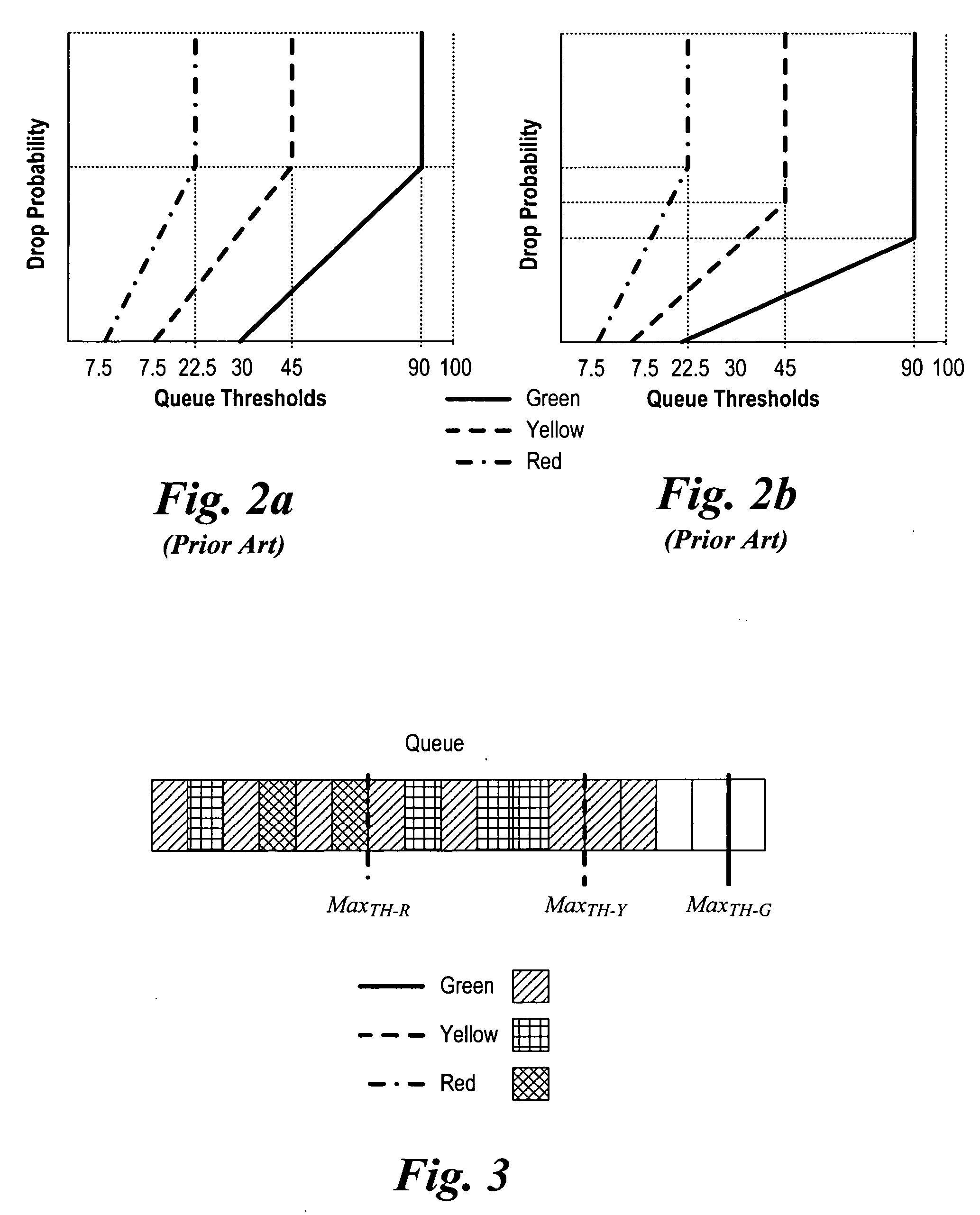
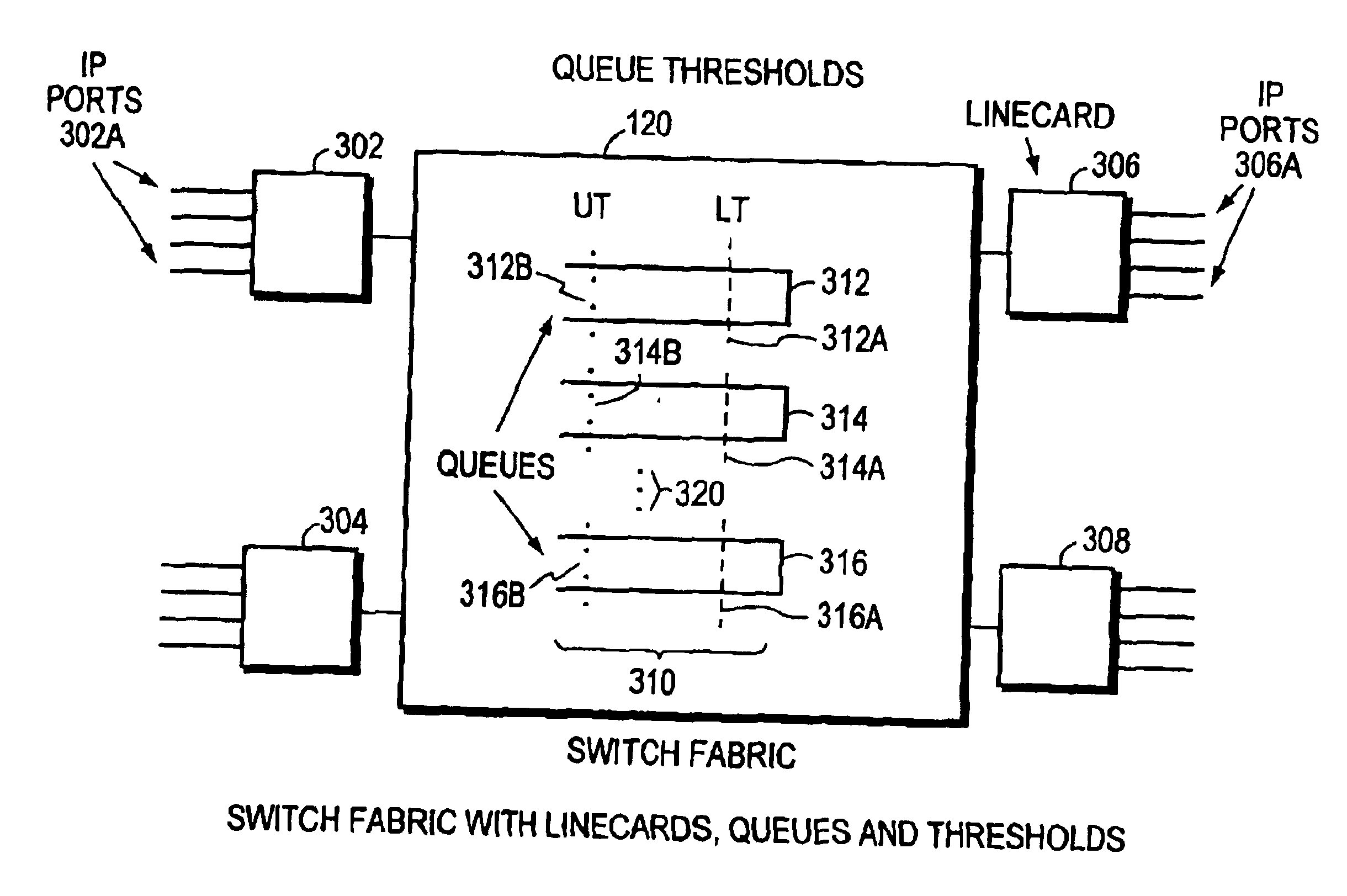
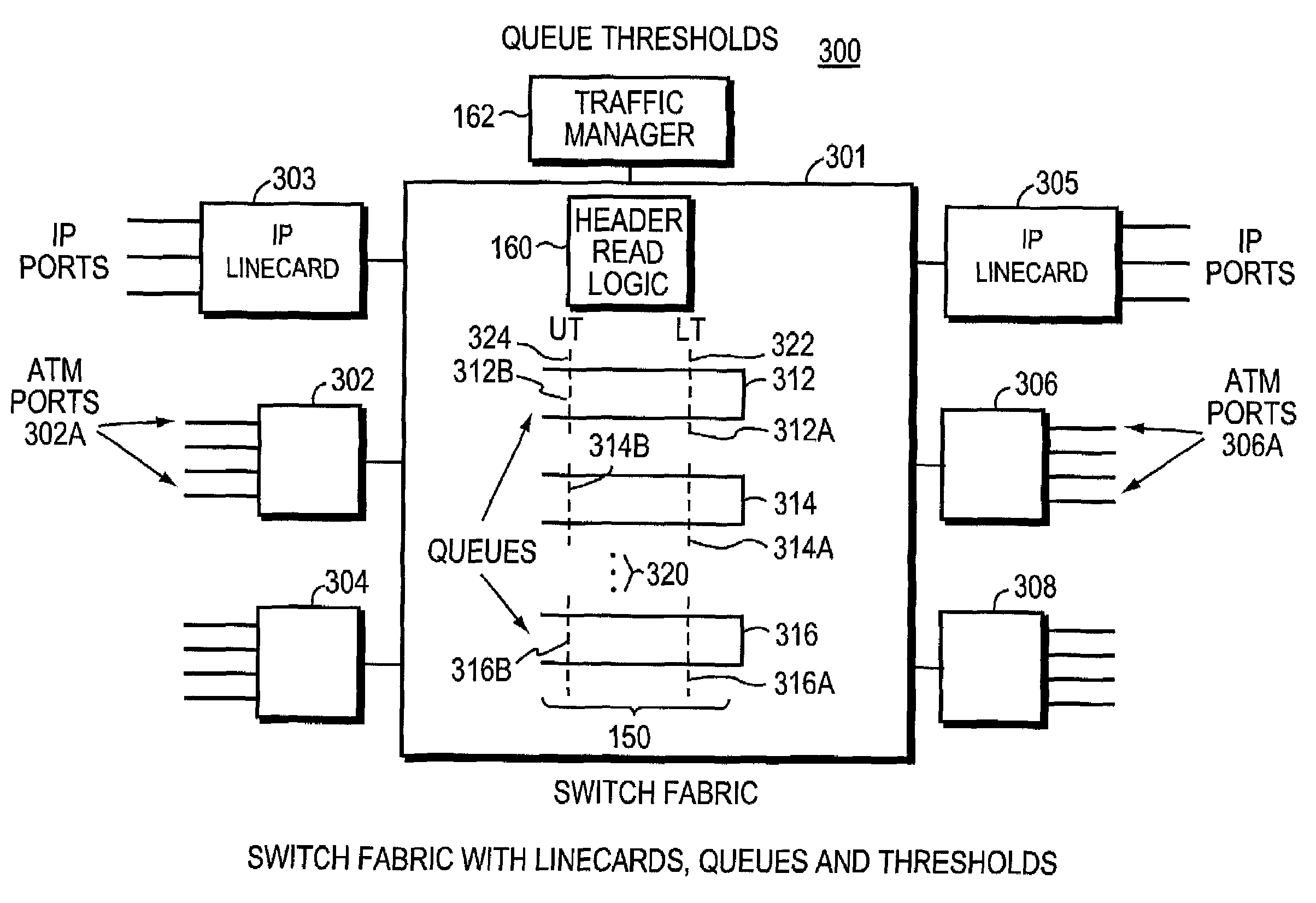
The invention is to use the ability of a switching fabric to set a congestion indicator bit in a segment if any queue through which the segment passes is filled above a lower threshold. The output linecard monitors the field of the congestion indicator bit as it receives segments from the switching fabric. The output linecard periodically calculates the ratio of segments having the congestion bit set to all segments routed to a particular port. The periodically calculated ratio is used as an input parameter to a Random Early Detection (RED) algorithm. The RED algorithm selects a packet for the output linecard to drop, by use of a random selection method. The destination computer then does not receive the packet. The random selection of packets to drop has the effect of helping to prevent undesirable network synchronization of transmission of replacement packets. With adaptive source computers, the network device then does not reach a congested state, thereby maintaining optimum throughput for the computer network. When an ATM switching fabric is used with ATM cells for the segments, then the Explicit Forward Congestion Indication Field (EFCI bit) of a data cell is used to mark a data cell which has passed through a queue which is filled above a lower threshold level. Data cells arriving at the output line card with the EFCI bit set are then counted, and this count is used in the periodic calculation of the ratio used as input to the RED algorithm.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method of detecting non-responsive network flows
InactiveUS6934256B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRandom early detectionReal-time computing
A network device identifies a non-adaptive flow as follows. The network device drops packets on a random basis using a Random Early Detection (RED) algorithm. A classifier reads indicia of a selected flow from at least one field of a header of a packet received by the network device. The network device calculates a drop interval for packets of the selected flow dropped by the RED algorithm, in response to a time at which the packets were dropped. The network device then applies a statistical test to drop intervals of a plurality of flows in order to identify the non-adaptive flow.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Random early detection policer using randomization of packet drops
InactiveUS7149187B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsRandom early detectionRandomization
A Random Early Detection (RED) policer in accordance with the invention does not tail-drop arriving packets as being non-conforming. For instance, because the RED policer uses a running estimate such as an exponential weighted moving average (EWMA), for example, it allows the policer to absorb traffic bursts. The policer uses randomization in choosing which packets to drop; with this method, the probability of dropping a packet from a particular sending node is roughly proportional to the node's bandwidth share, hence the packets of different flows are fairly dropped.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
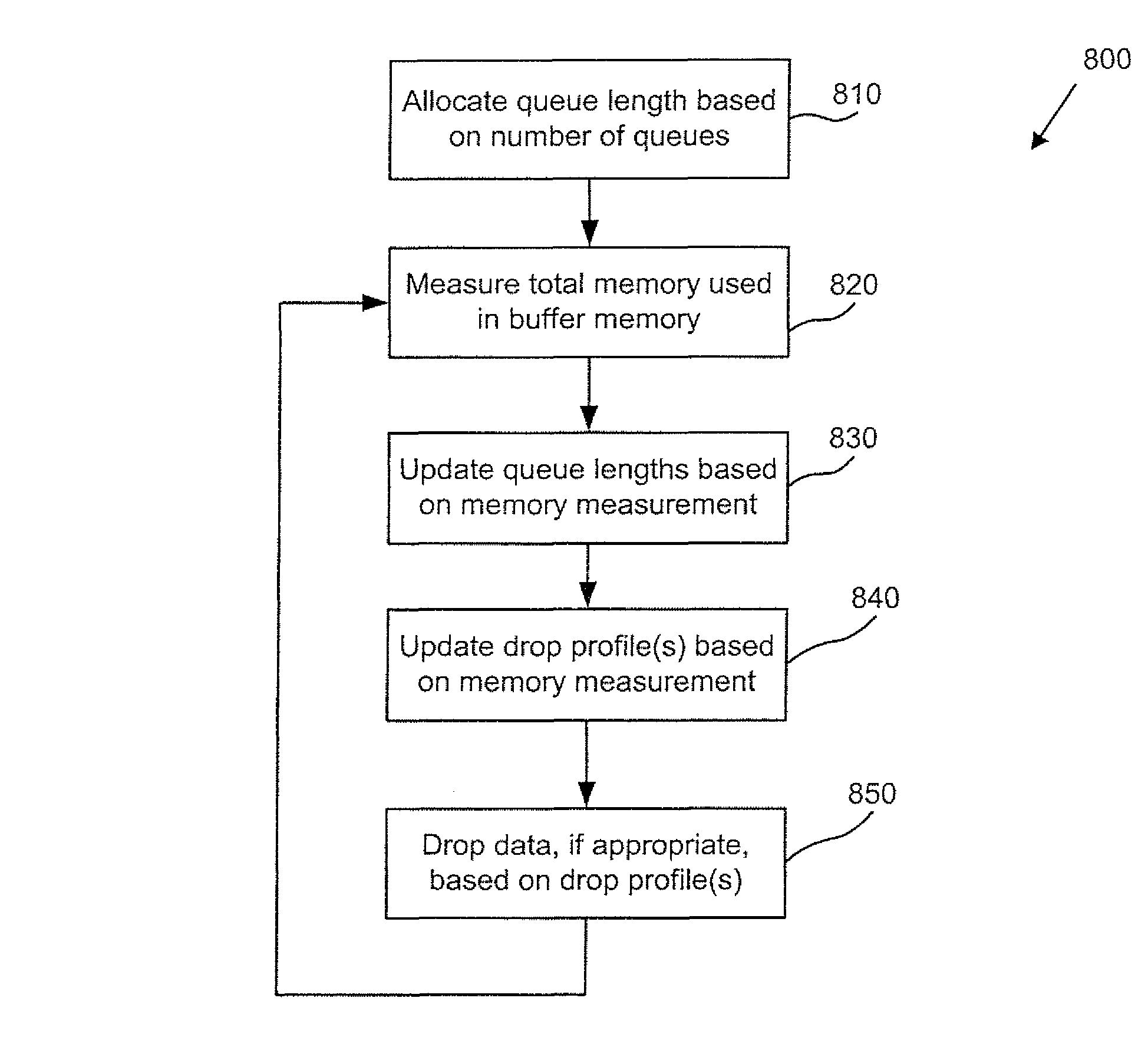
Dynamic queue threshold extensions to random early detection
ActiveUS7369500B1Efficiently process and bufferError preventionTransmission systemsRandom early detectionParallel computing
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method of detecting non-responsive network flows
InactiveUS20050226149A1Error preventionTransmission systemsRandom early detectionReal-time computing
A network device identifies a non-adaptive flow as follows. The network device drops packets on a random basis using a Random Early Detection (RED) algorithm. A classifier reads indicia of a flow from at least one field of a header of a packet received by the network device. The network device calculates a drop interval for packets of the flow dropped by the RED algorithm, in response to a time at which the packets were dropped. The network device then applies a statistical test to drop intervals of a plurality of flows in order to identify the non-adaptive flow.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
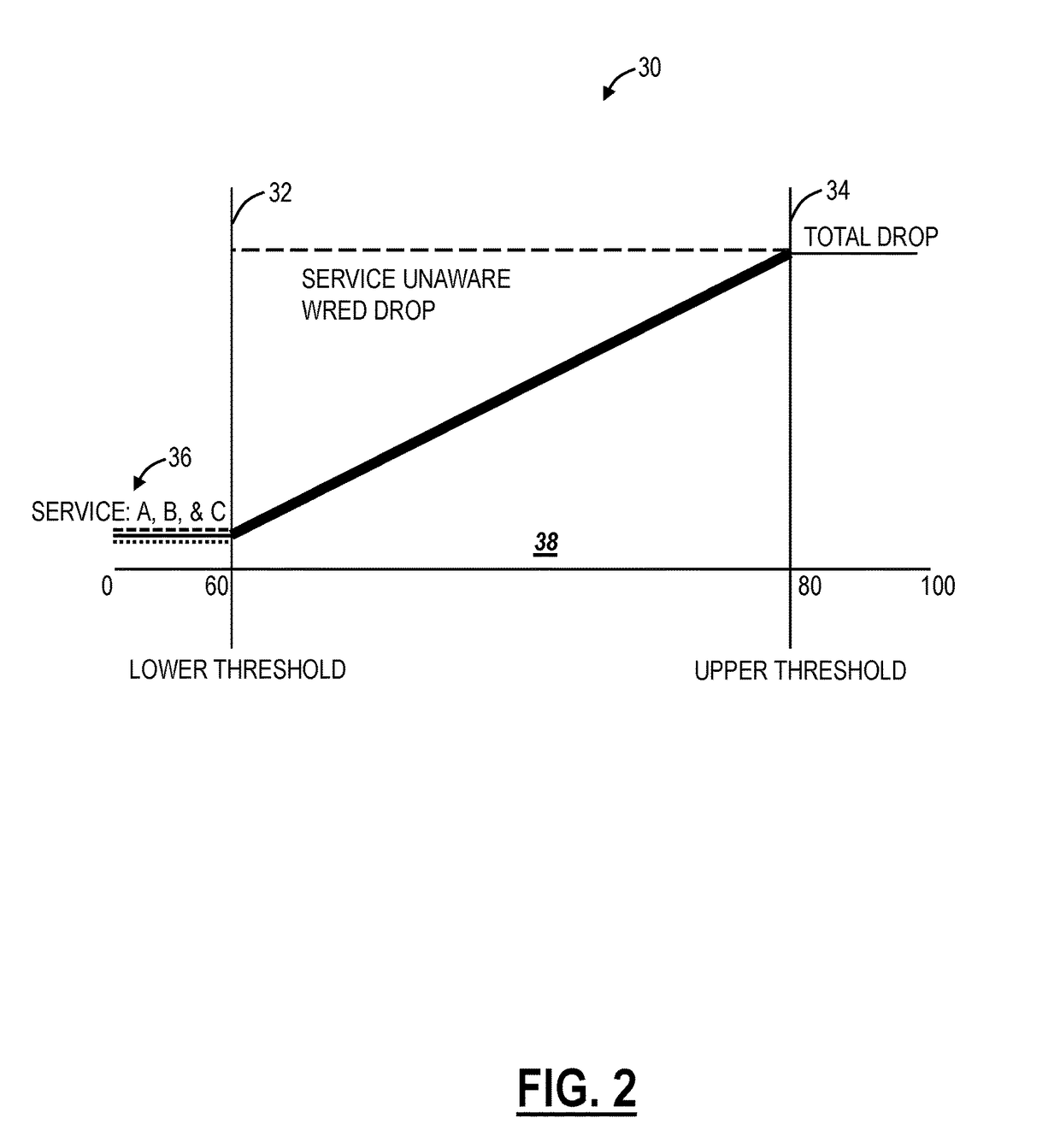
Per queue per service differentiation for dropping packets in weighted random early detection
Systems and methods for per service differentiation for congestion avoidance through dropping packets based on service priority include receiving an ingress packet; responsive to no congestion, providing the ingress packet to a queue of one or more queues; and, responsive to congestion, during a congestion window, one of providing the ingress packet to the queue and dropping the packet based on a packet dropping capability and service priority of a service associated with the packet.
Owner:CIENA
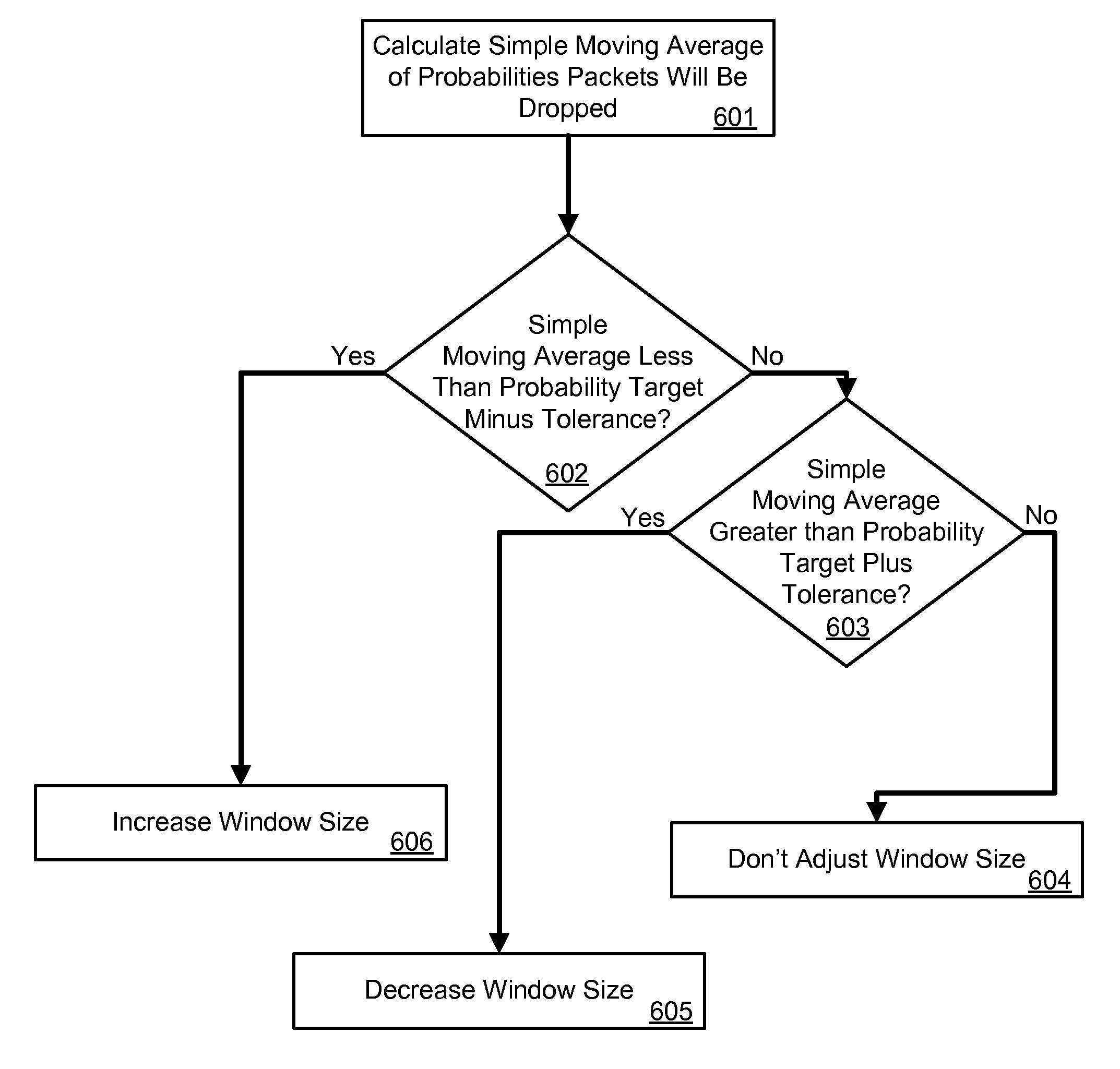
Method and system for controlling TCP traffic with random early detection and window size adjustments
ActiveUS20130136000A1Reduce window sizeIncrease window sizeError preventionTransmission systemsMoving averageTraffic capacity
A method for controlling data traffic with random early detection and window size adjustments including performing random early detection on incoming data packets, calculating a simple moving average of packet dropping probabilities for the data packets as calculated when performing random early detection, decreasing an advertised window size if the simple moving average is greater than a probability target plus a tolerance factor, increasing the advertised window size if the simple moving average is less than the probability target minus a tolerance factor, and not adjusting the window size if the simple moving average is not greater than a probability target plus a tolerance factor and not less than a probability target minus a tolerance factor.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
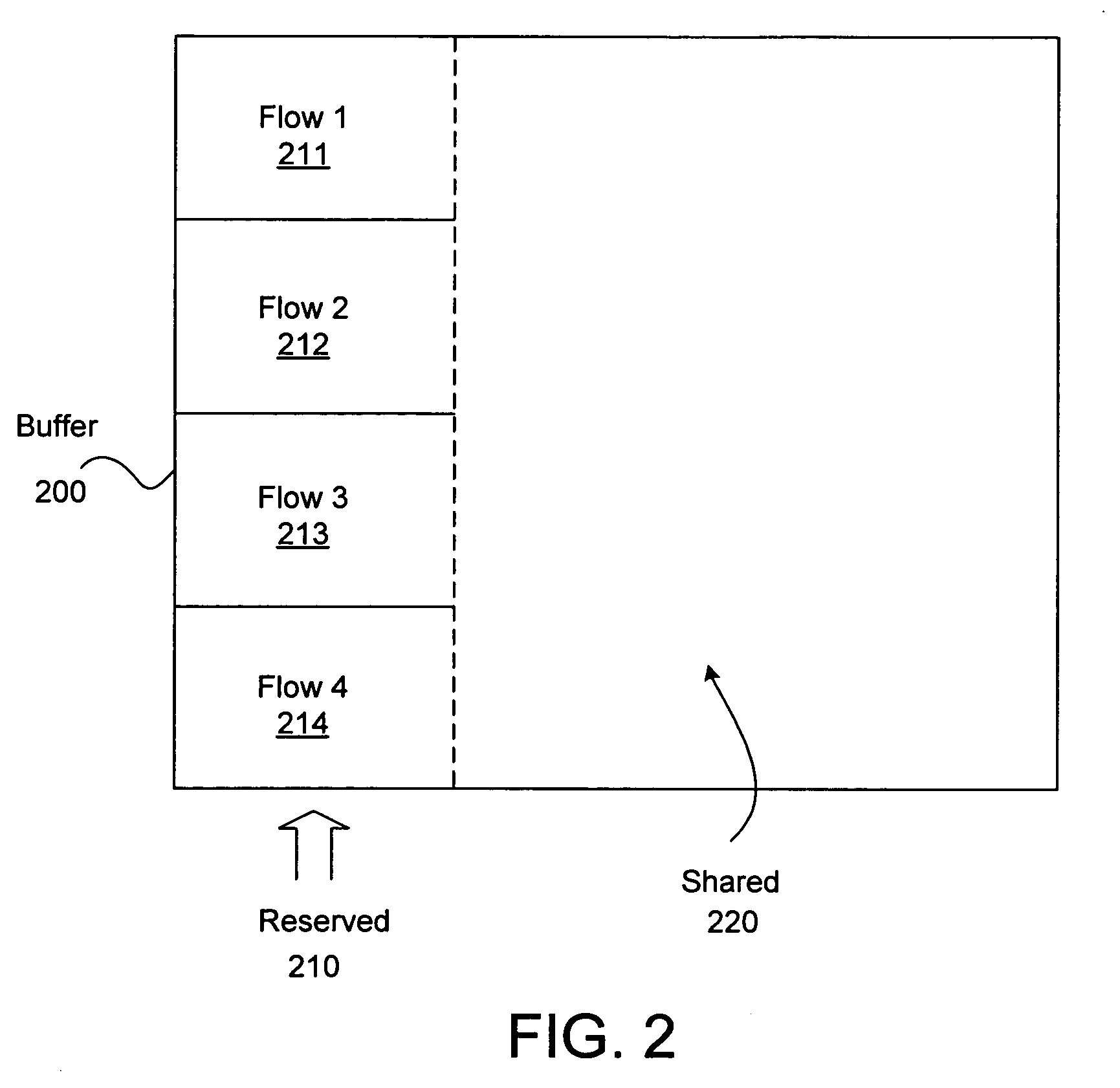
Approximation of the weighted random early detection buffer admittance algorithm
InactiveUS6856596B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRandom early detectionComputer science
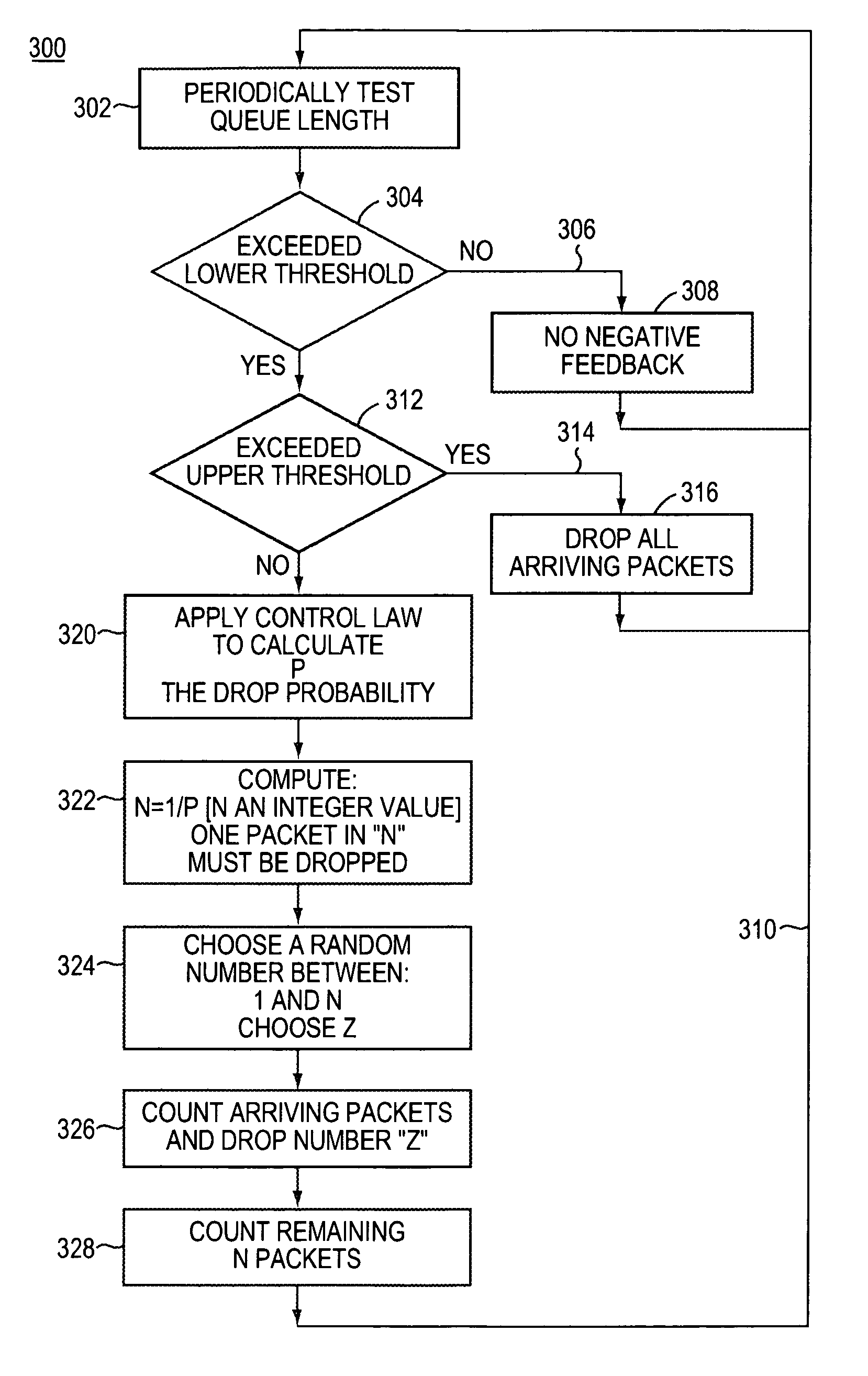
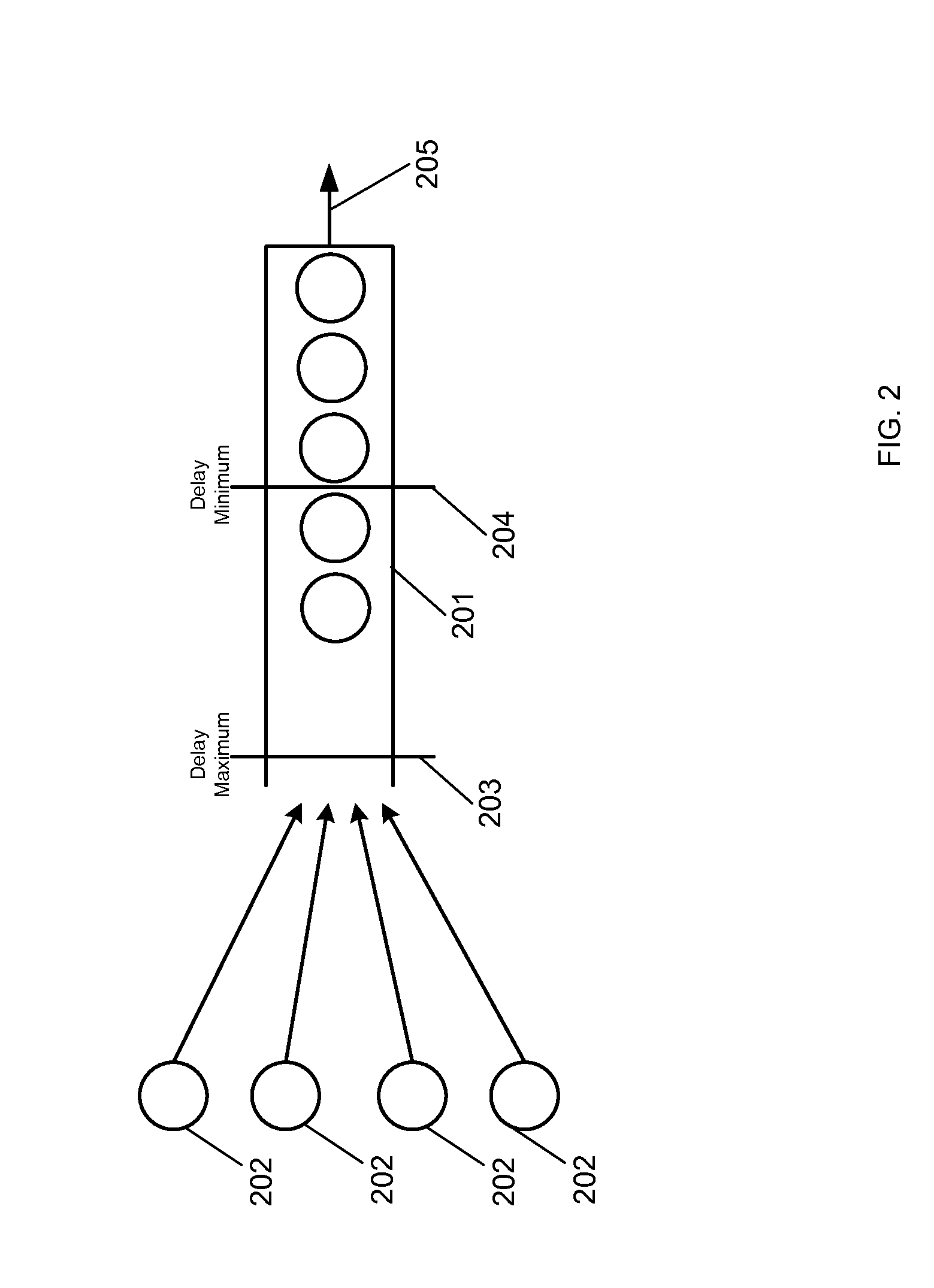
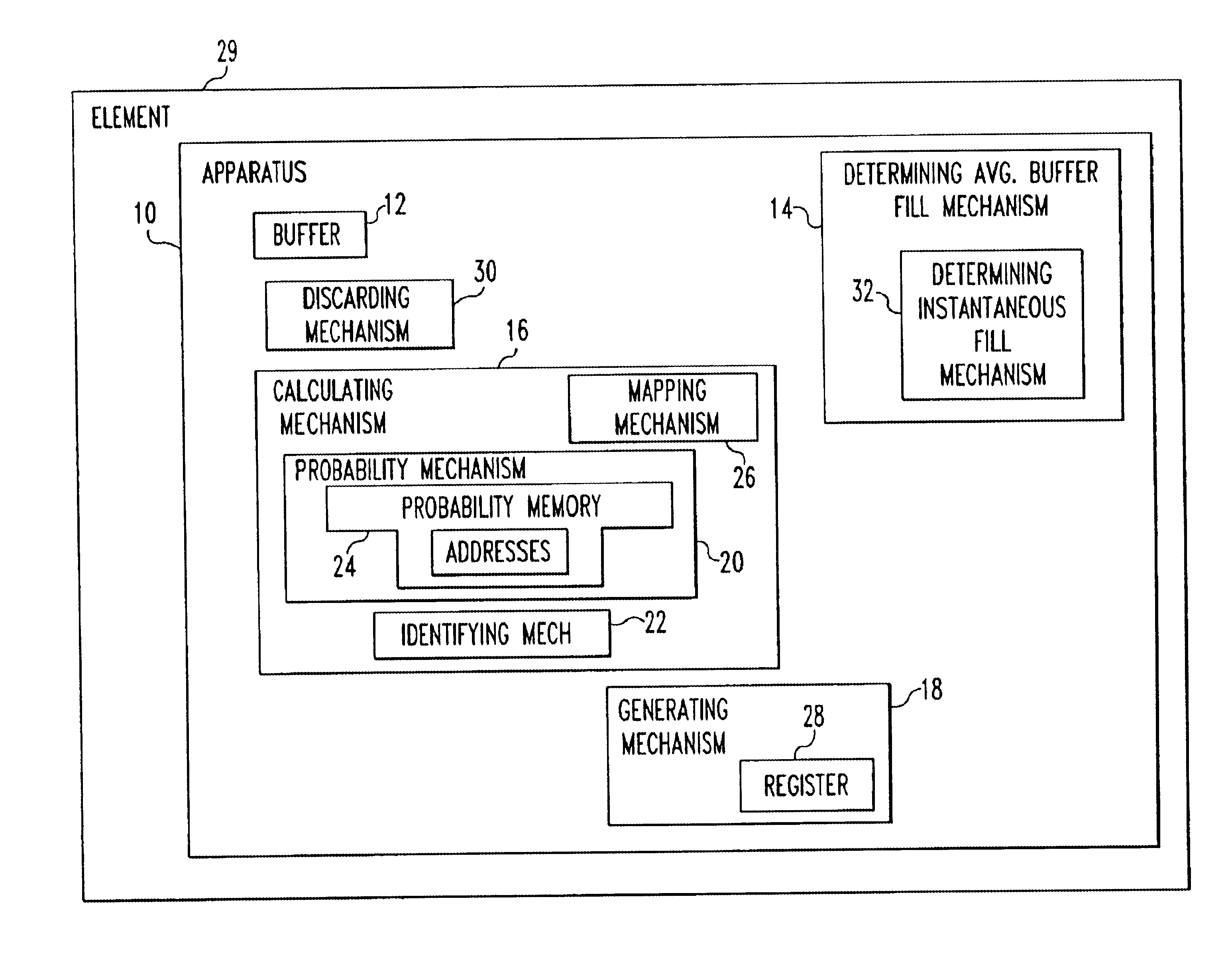
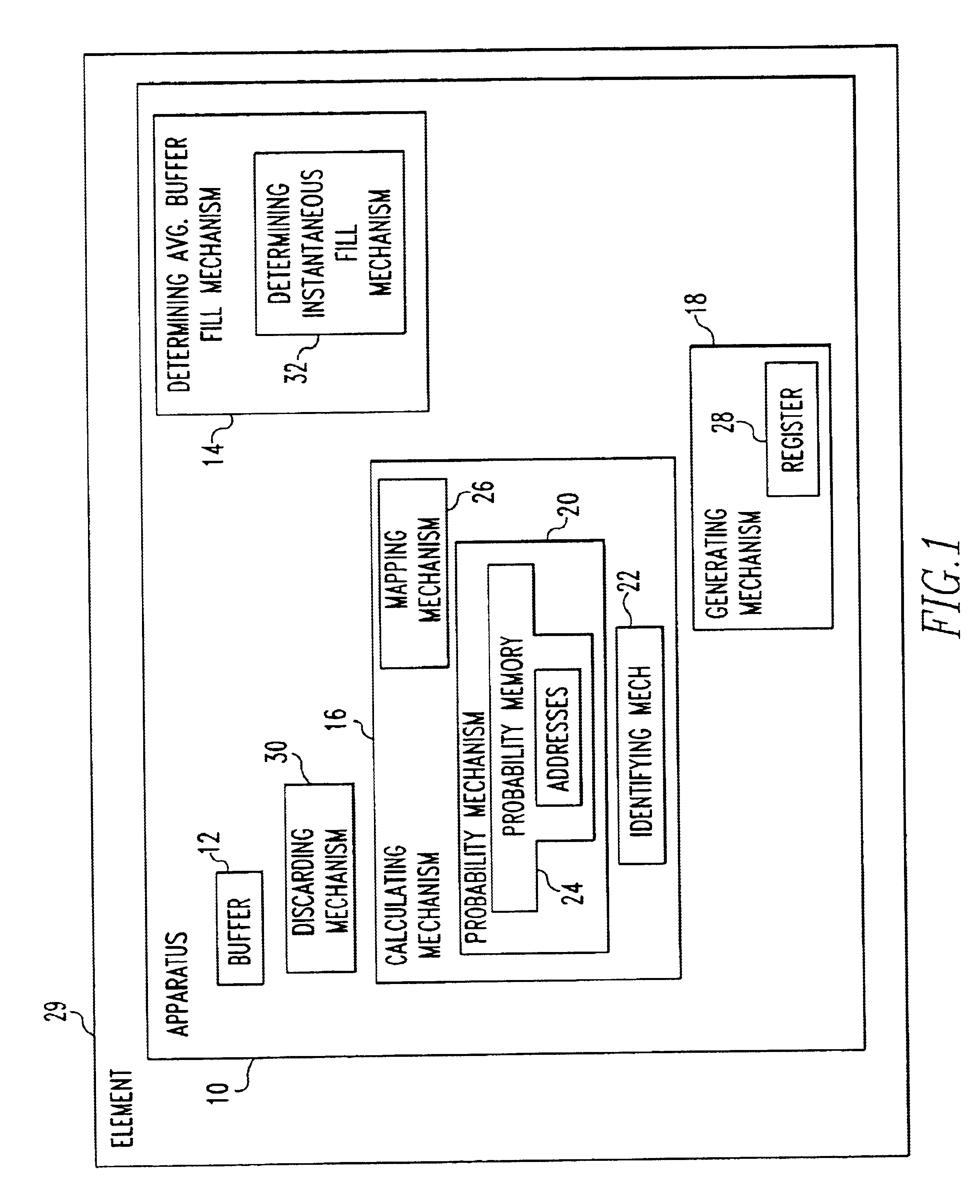
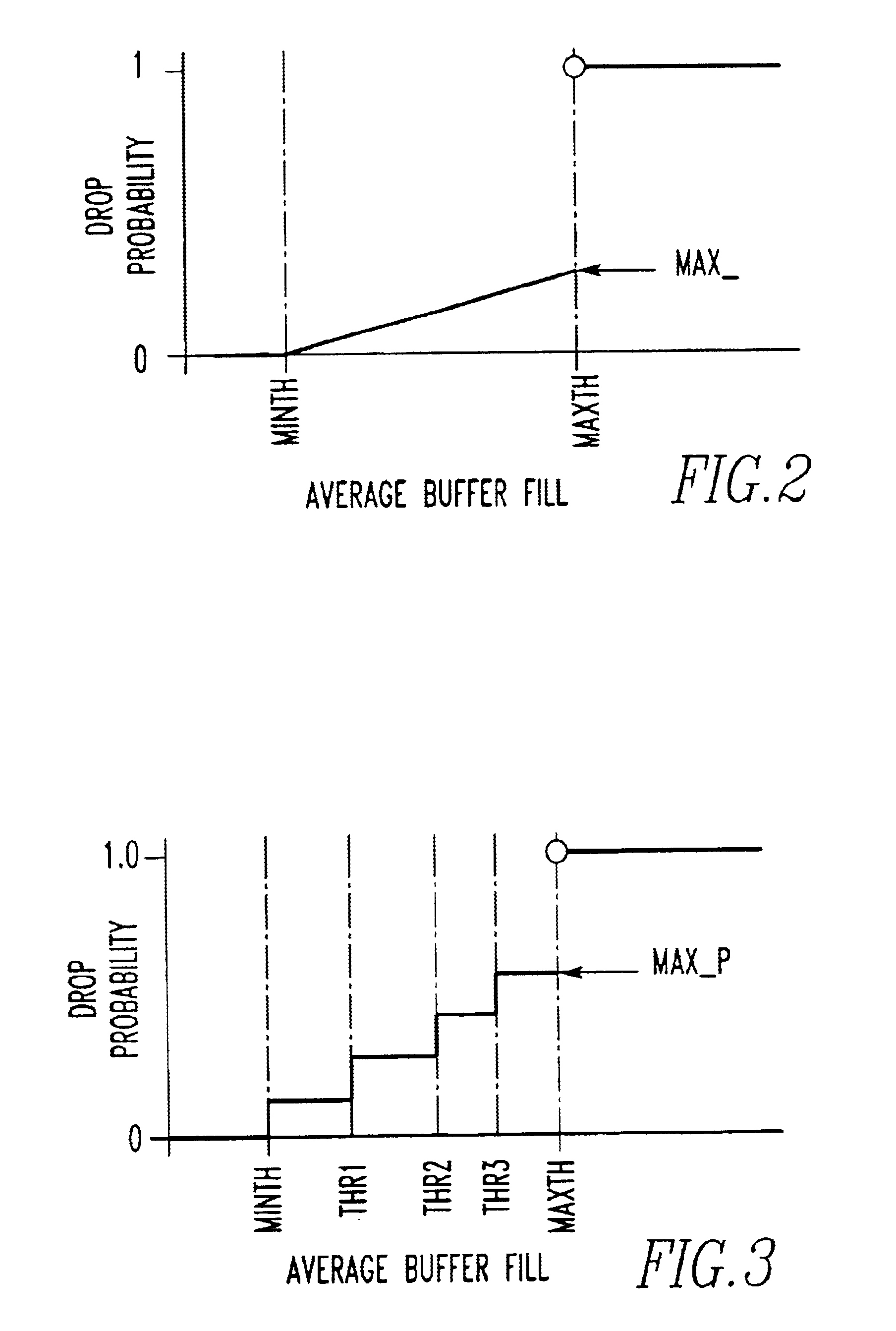
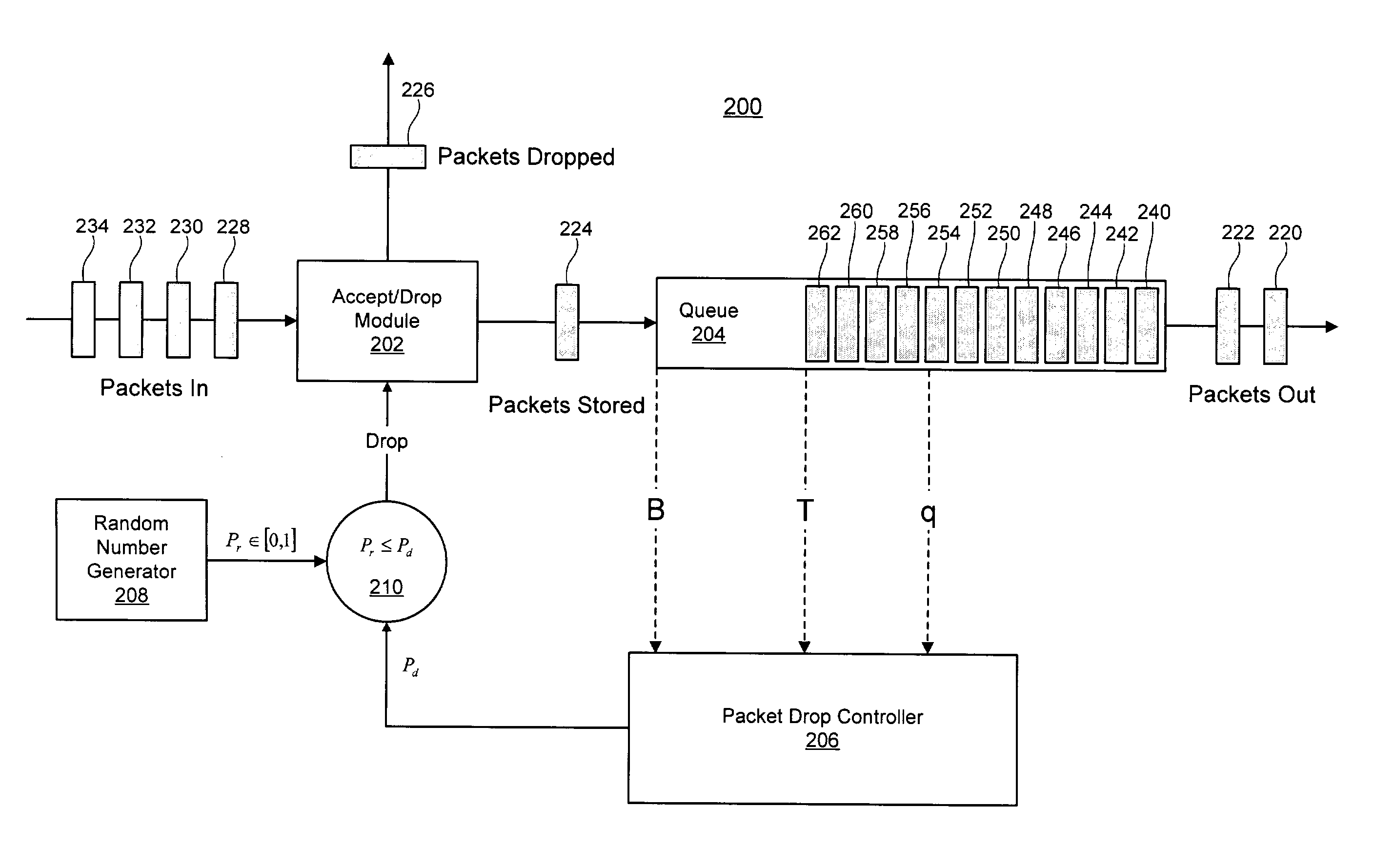
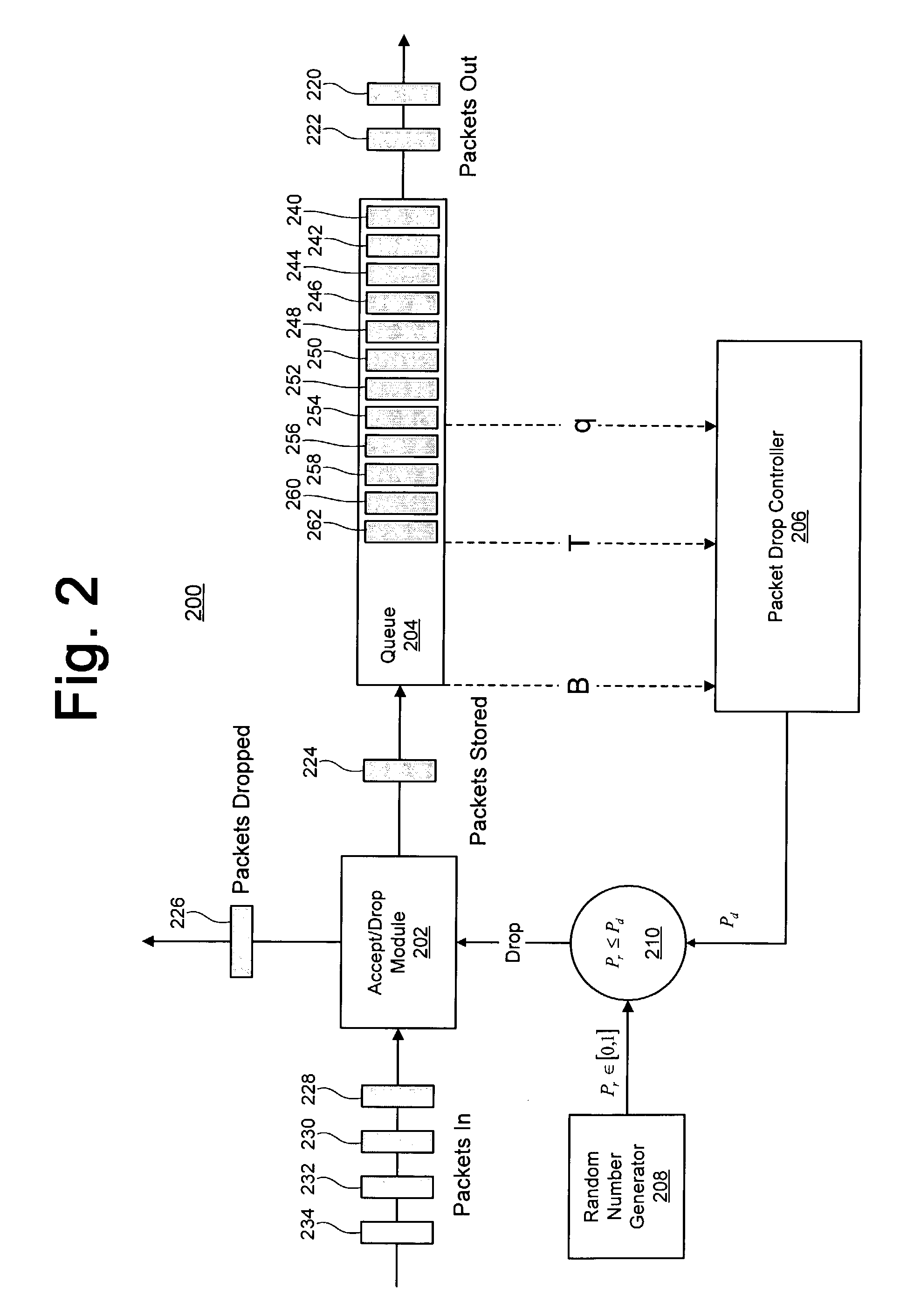
An apparatus for storing a packet including a buffer in which packets are stored. The apparatus includes a mechanism for determining an average buffer fill of the buffer, where the average buffer fill is an average fill state of the buffer. The determining mechanism is connected to the buffer. The apparatus includes a mechanism for calculating a drop probability associated with the packet which identify is the probability the packet will be dropped from a the buffer. The apparatus includes a mechanism for generating a random number. The apparatus includes a mechanism for discarding the packet from the elements if the drop probability is greater in than the random number. A method for access control.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Constant gain controller for active queue management
InactiveUS7336672B1Constant gainData switching by path configurationRandom early detectionDynamic models
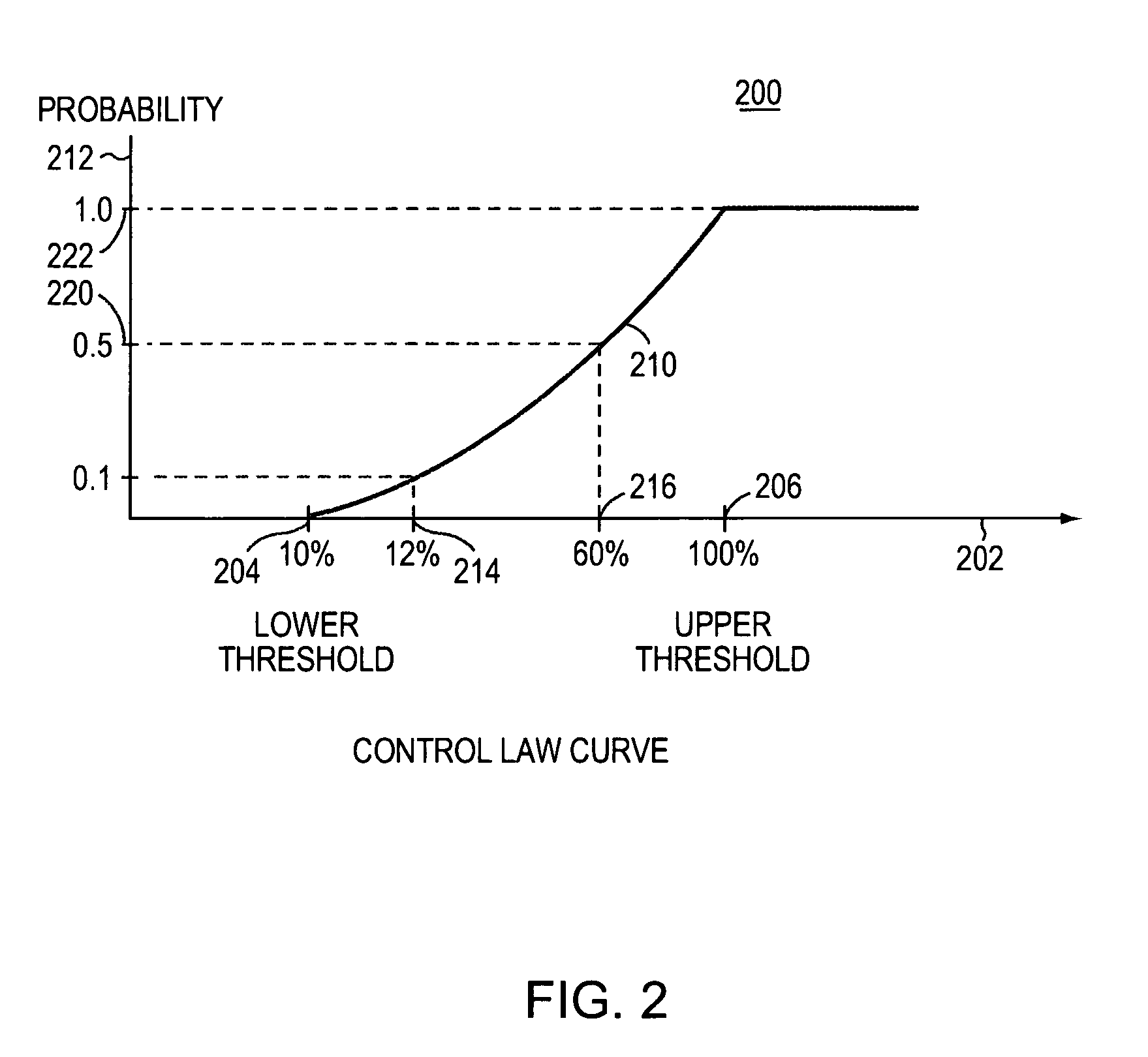
Various techniques for queue management based on random early detection (RED) are disclosed herein. In particular, a method for generating a drop probability for an incoming packet in a device having a queue to buffer packets between segments of a network is provided. The method comprises determining, upon receipt of an incoming packet, a size of the queue and determining an error based at least in part on a difference between the queue size and a threshold. The method further comprises determining a drop probability for the incoming packet based at least in part on the error and a constant gain factor. The constant gain factor may be based at least in part on a linearized second order dynamic model of the network.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
Device and method for managing oversubsription in a network
InactiveUS20060045009A1Error preventionTransmission systemsDeficit round robinRandom early detection
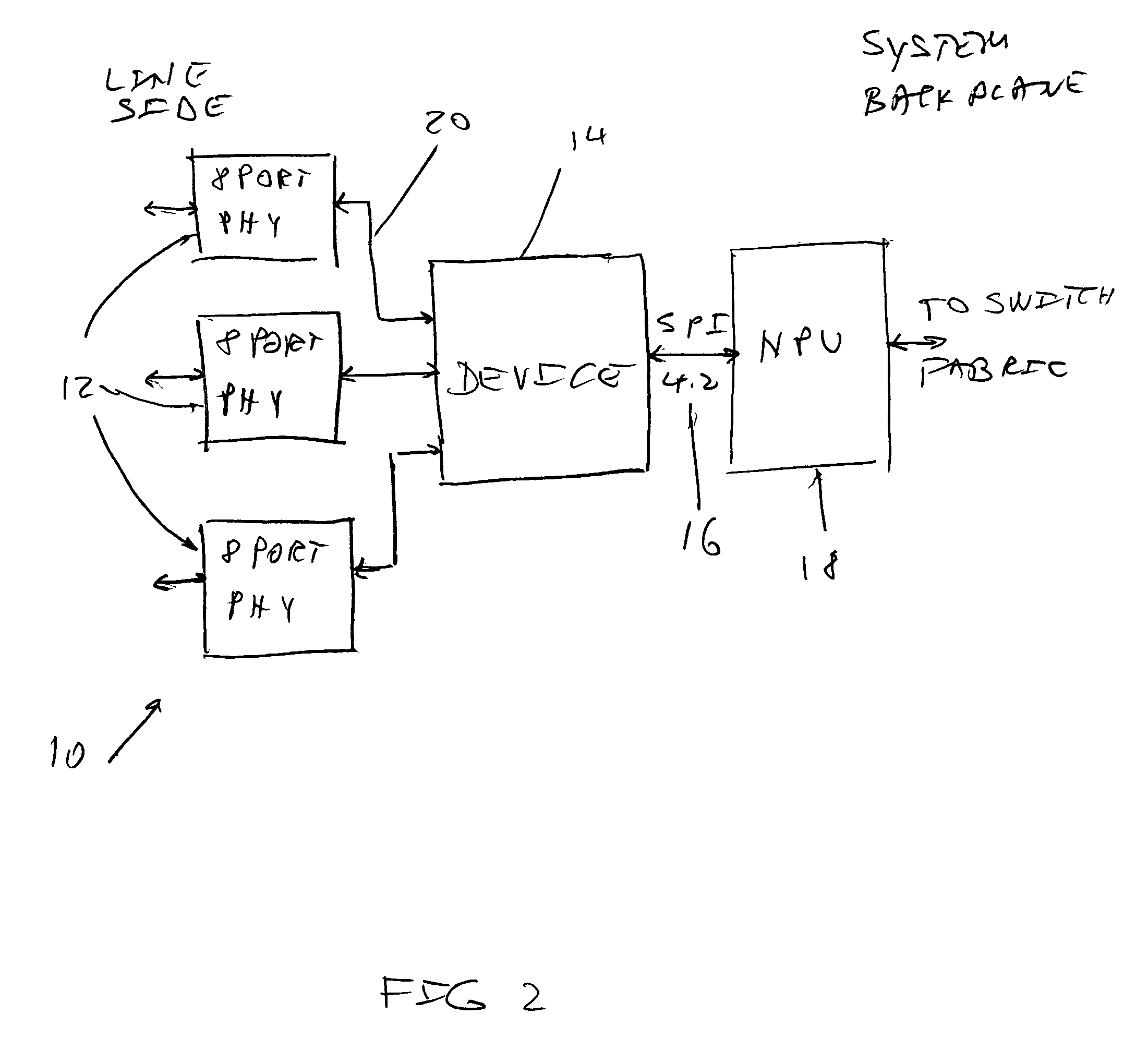
A device and a method for aggregating and managing large quantities of data are disclosed. The received data are prioritized into high and low priority queues. The device receive memory is partitioned into 1 Kilo byte (1 KB) blocks which are further divided into free list and allocation list. The low priority queues occupy between 1 and 48 blocks and the high priority queues occupy between 1 and 32 blocks. The incoming data are further subjected to Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) process that controls congestion before it occurs by dropping some of the queues. The stored data are read using Modified Deficit Round Robin (MDRR) approach The transmit memory operates with 240 1 KB blocks and the data is transmitted out via an SPI 4.2 or similar device.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK AS AGENT
Random early detection algorithm using an indicator bit to detect congestion in a computer network
InactiveUS7218608B1Smooth changeEasy to handleError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityRandom early detection
A switching fabric sets a congestion indicator bit (EFCI bit) in an ATM cell if any queue through which the ATM cell passes is filled above a lower threshold. A Traffic Manager monitors the field of the EFCI bit as cells arrive at an output port of the switching fabric. The traffic manager periodically calculates the ratio of ATM cells having the EFCI congestion bit set to all ATM cells routed to a particular output port. The periodically calculated ratio is used as an input parameter to a Random Early Detection (RED) algorithm. The RED algorithm selects a cell for the switch fabric to drop, by use of a random selection method. The destination computer then does not receive the packet since cells forming part of the packet have been discarded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Jamming control method and device
InactiveCN101272314AReduce loadReduce resource utilizationData switching networksRandom early detectionResource utilization
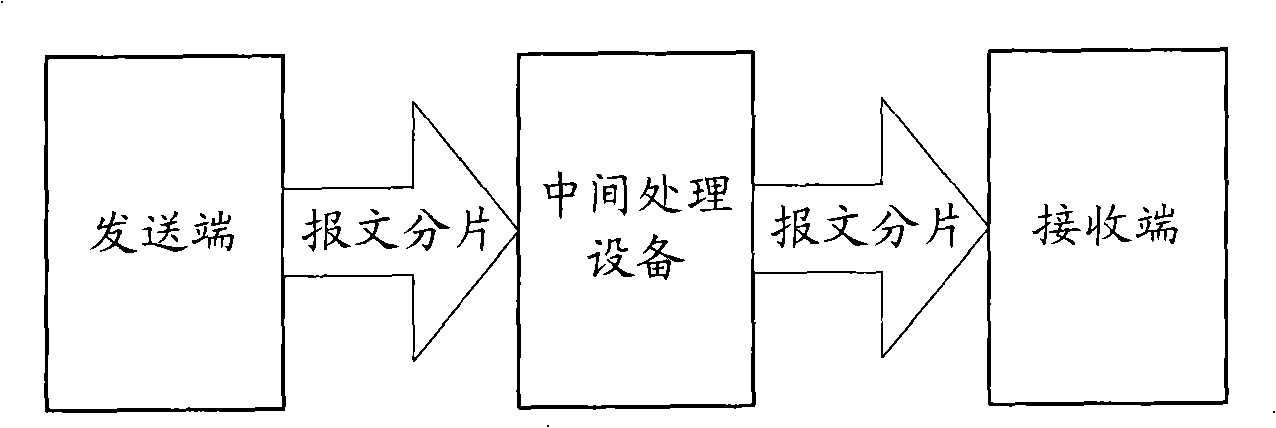
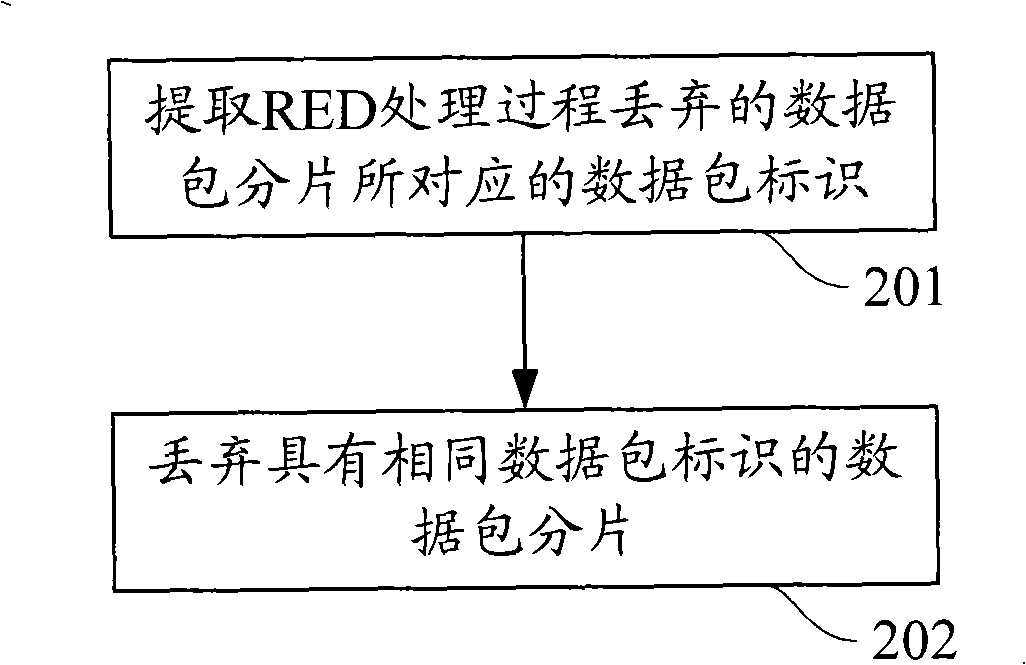
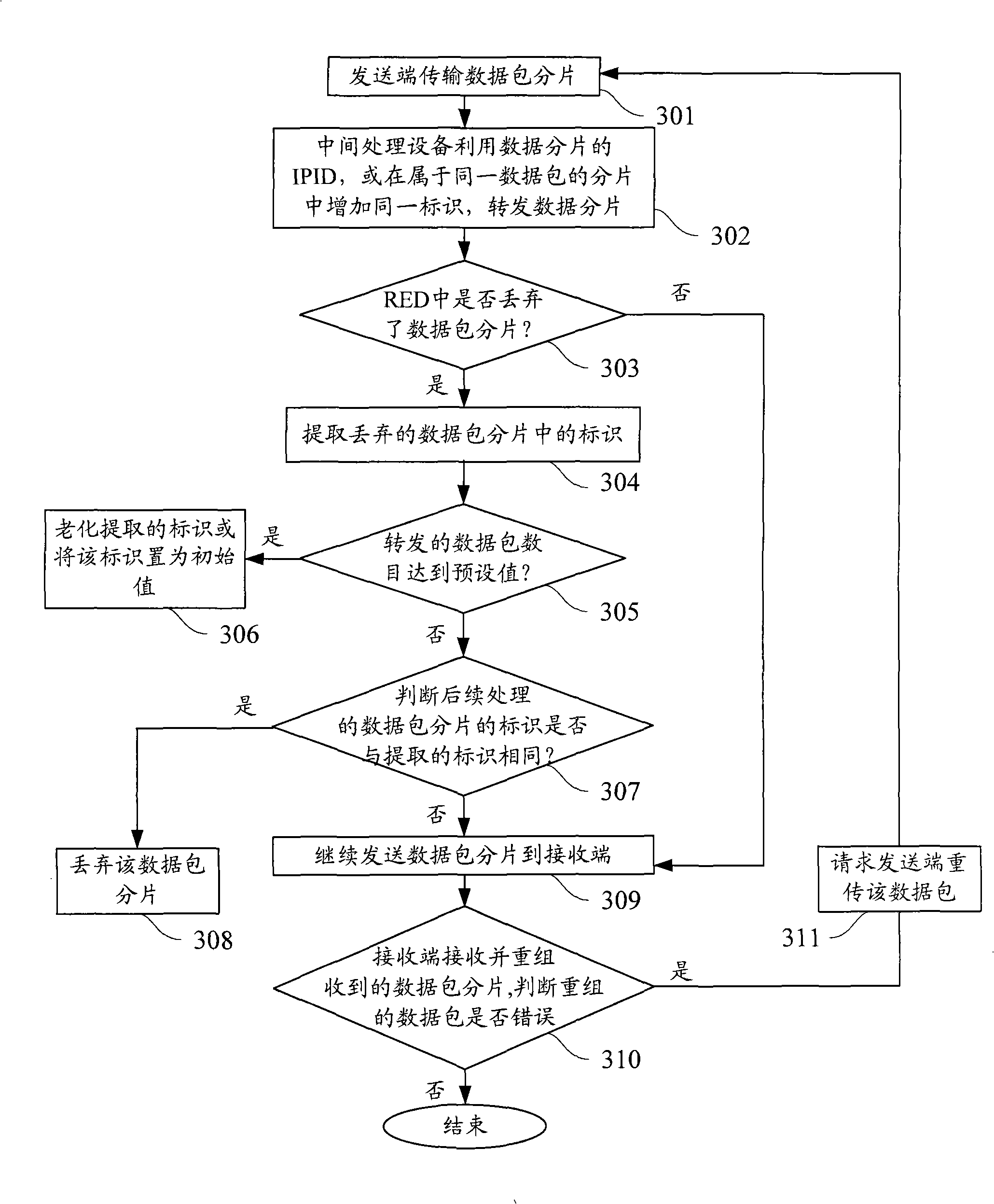
The invention discloses a congestion controlling method which is applied to a network technique field and comprises: packet identifiers that are corresponding to the packet slicing which is discarded in the process of random early testing and processing are extracted; the packet slicing with the same packet identifier is discarded. Internetwork protocol identifiers can be taken as the packet identifiers or adding identifiers; internetwork protocol identifiers or adding identifiers which are corresponding to the packet slicing which is discarded in the process of random early testing and processing are extracted; the extracted identifiers are compared with identifiers of subsequent packet slicing and if the identifiers are the same, the packet slicing are discarded, and if not, are retransmitted continuously. A receiving end receives and reorganizes the received packet slicing and when the reorganization goes wrong, retransmission is requested. The invention also discloses a congestion controlling device. The utilization of the invention can discard the useless relevant packet slicing in advance, thus alleviating the load of network devices, reducing the resource utilization rate, saving bandwidth and further ensuring high effectively carrying out other sessions without discarding packets.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
AQM (Active Queue Management) system and method based on generalized PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) random early detection algorithm
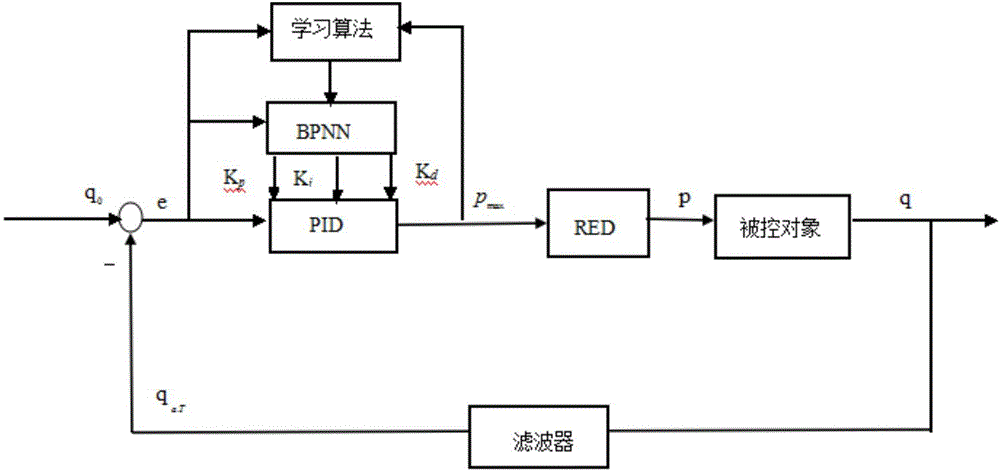
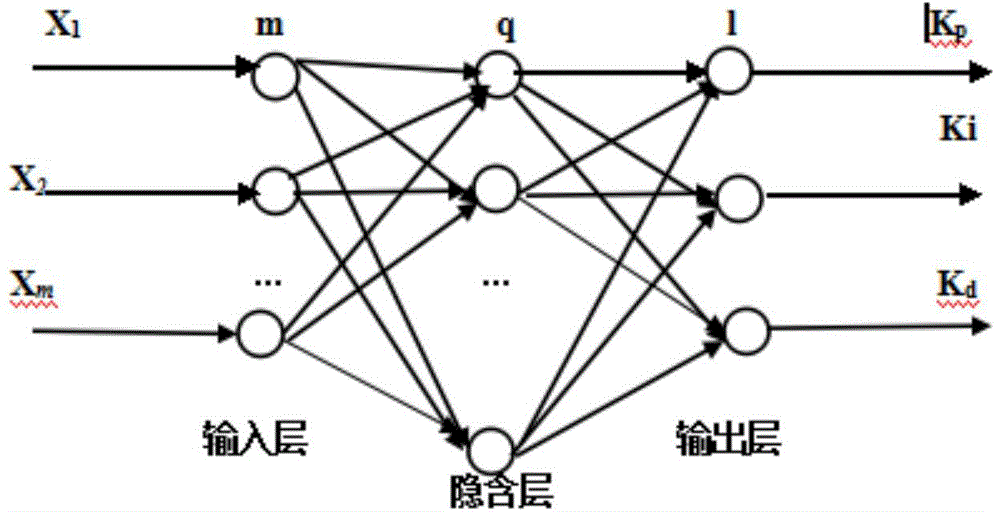
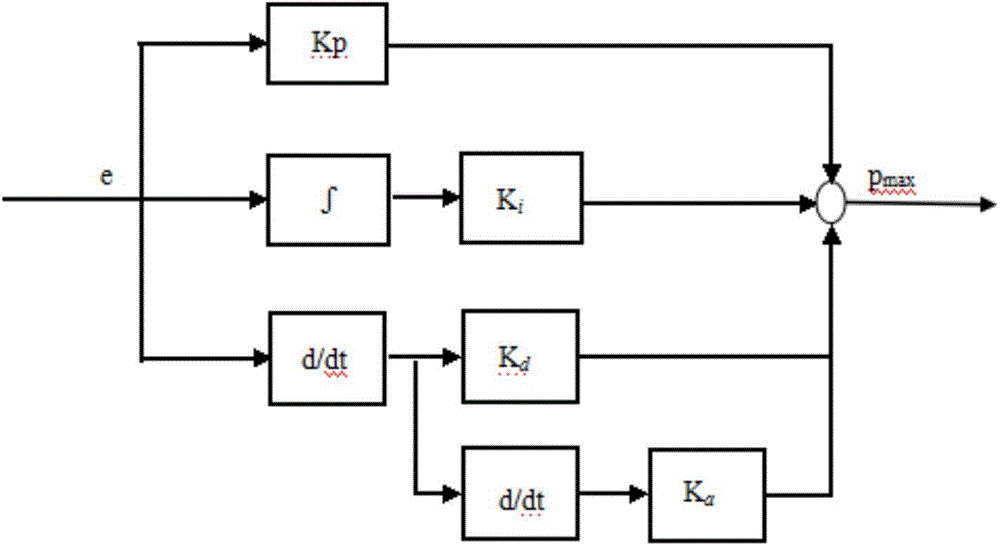
ActiveCN104486248AMeet the dynamic performanceImprove throughputData switching networksCurrent loadProportion integration differentiation
The invention discloses an AQM (Active Queue Management) system and an AQM method based on a generalized PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) random early detection algorithm. The system comprises a BP neural network module, a generalized PID control module and a random early detection module, wherein the BP neural network can be used for finding out parameters under a certain optimal control law by self learning; the generalized PID control module is used for performing proportion, integration and differentiation operations on regulated own parameters and stabilizing the queue length under different network loads at a corresponding fixed value; the random early detection module is used for acquiring the fixed value as a maximum dropping probability and generating a dropping probability suitable for a current load by self-regulation; a controlled object gives a corresponding response according to the dropping probability, so that the queue length in a router can be stabilized at an expected value. Therefore, the utilization rate of network resources is increased and the average time delay of a network can be reduced.
Owner:南京华睿智光信息科技研究院有限公司
Sharing cache dynamic threshold early drop device for supporting multi queue
InactiveCN1777147AAdaptableImprove cache utilizationData switching networksRandom early detectionPacket loss
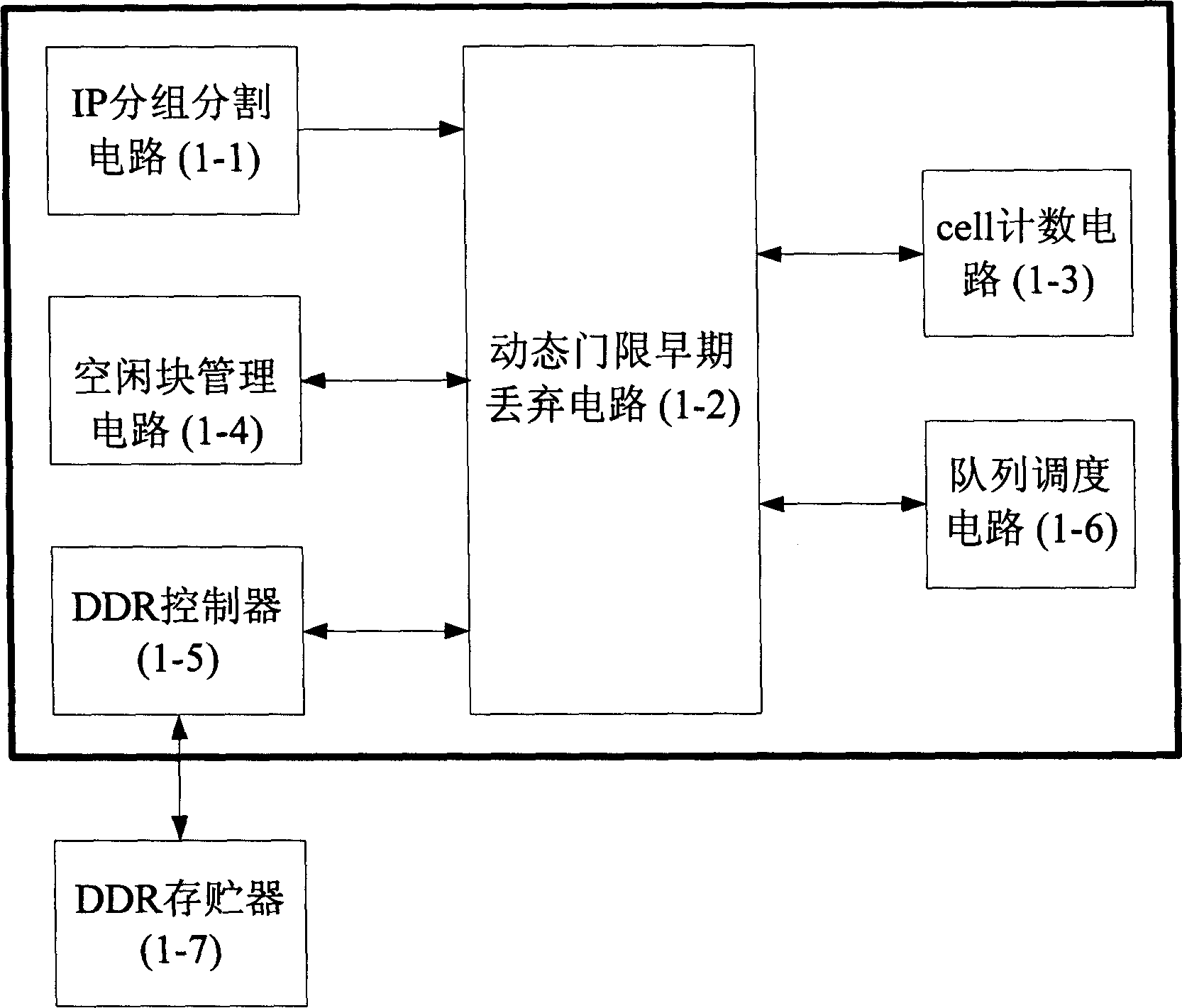
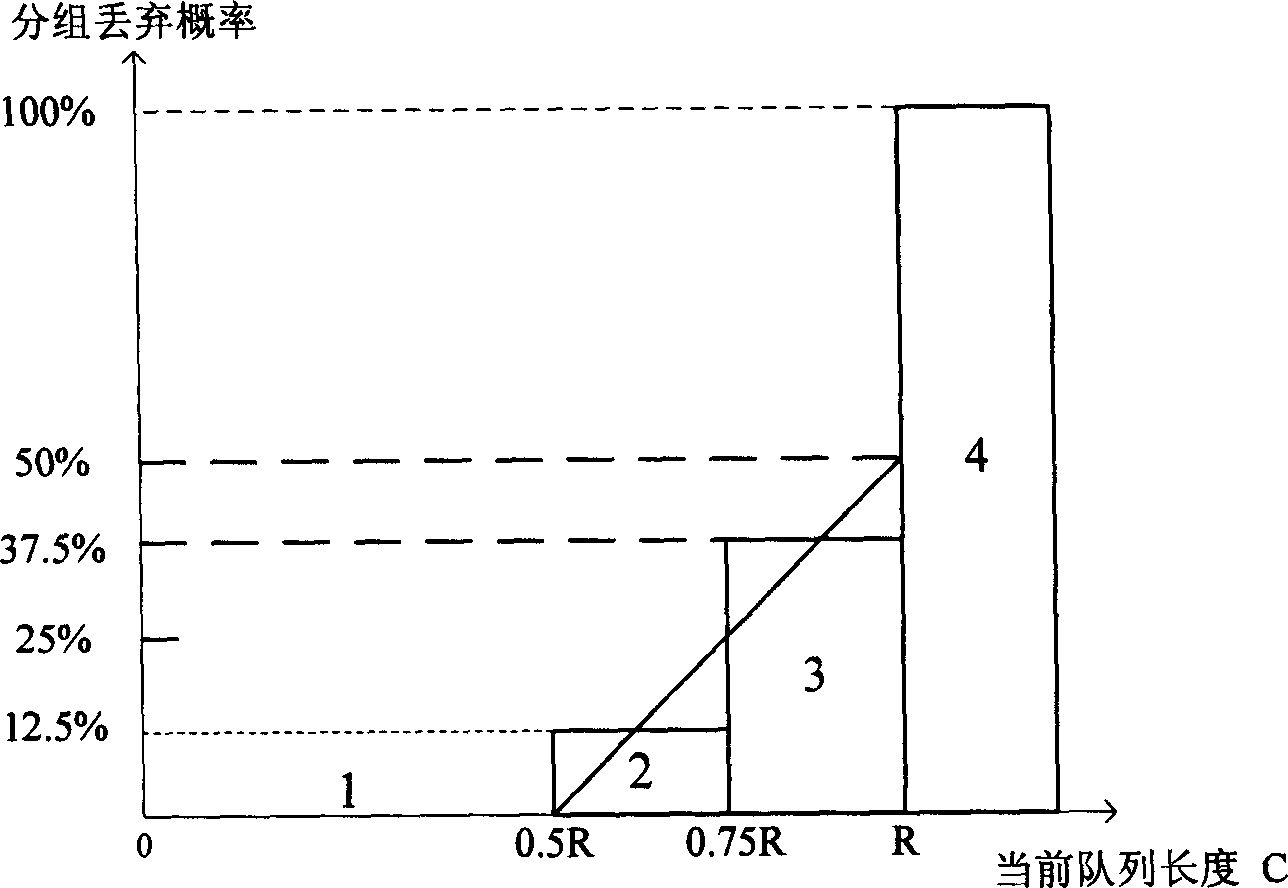
Belonging to IP technical area, the invention is realized on a piece of field programmable gate array (FPGA). Characters of the invention are that the device includes IP grouping circuit, early discarding circuit with dynamic threshold, cell counting circuit, idle block management circuit, DDR controller, queue dispatch circuit, storage outside DDR. Based on average queue size of each current active queue and average queue size in whole shared buffer area, the invention adjusts parameters of random early detection (RED) algorithm to put forward dynamic threshold early discarding method of supporting multiple queues and sharing buffer. The method keeps both advantages of mechanism of RED and dynamic threshold. It is good for realization in FPGA to use cascaded discarding curve approximation. Features are: smaller rate of packet loss, higher use ratio of buffer, and a compromise of fairness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
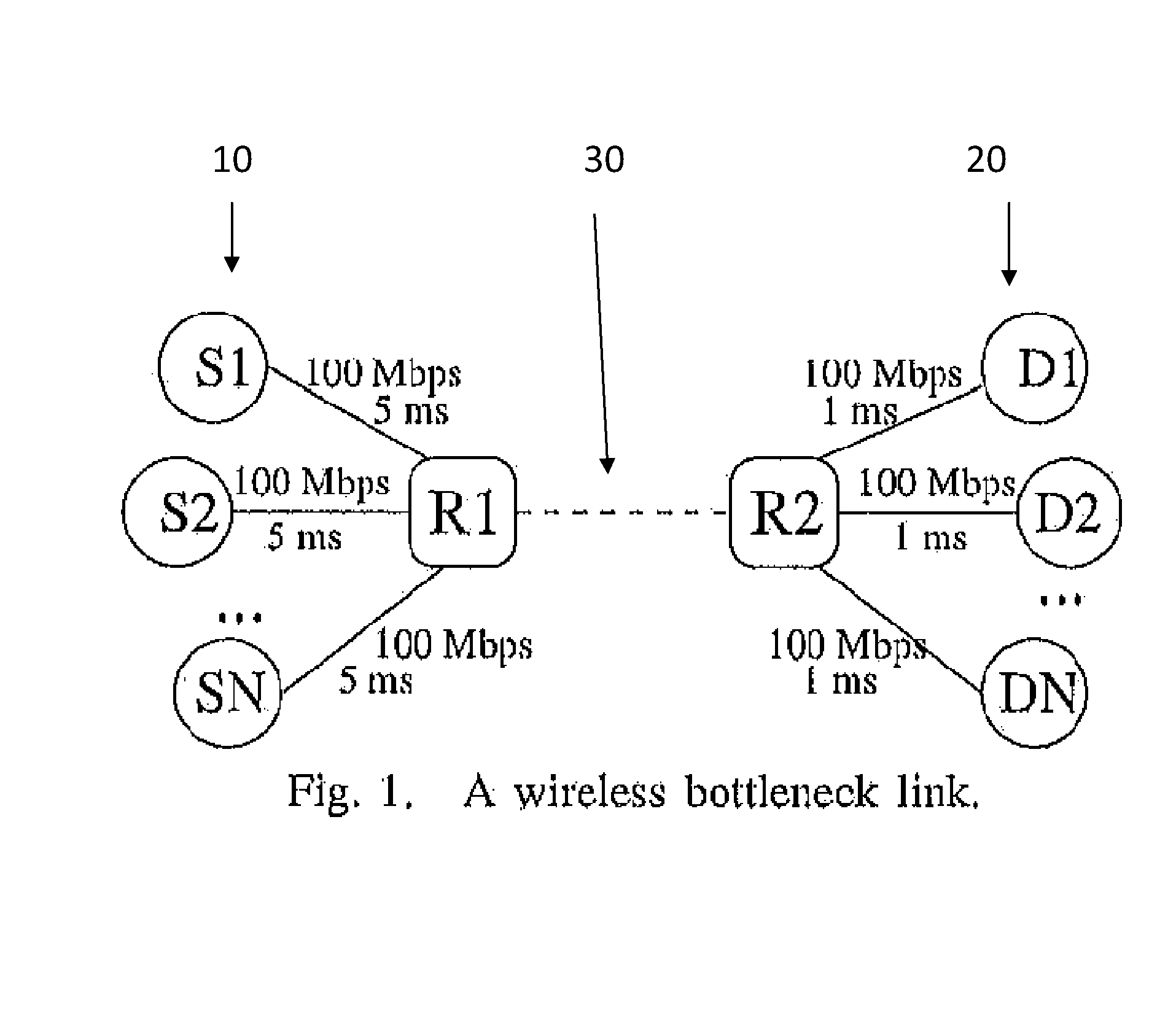
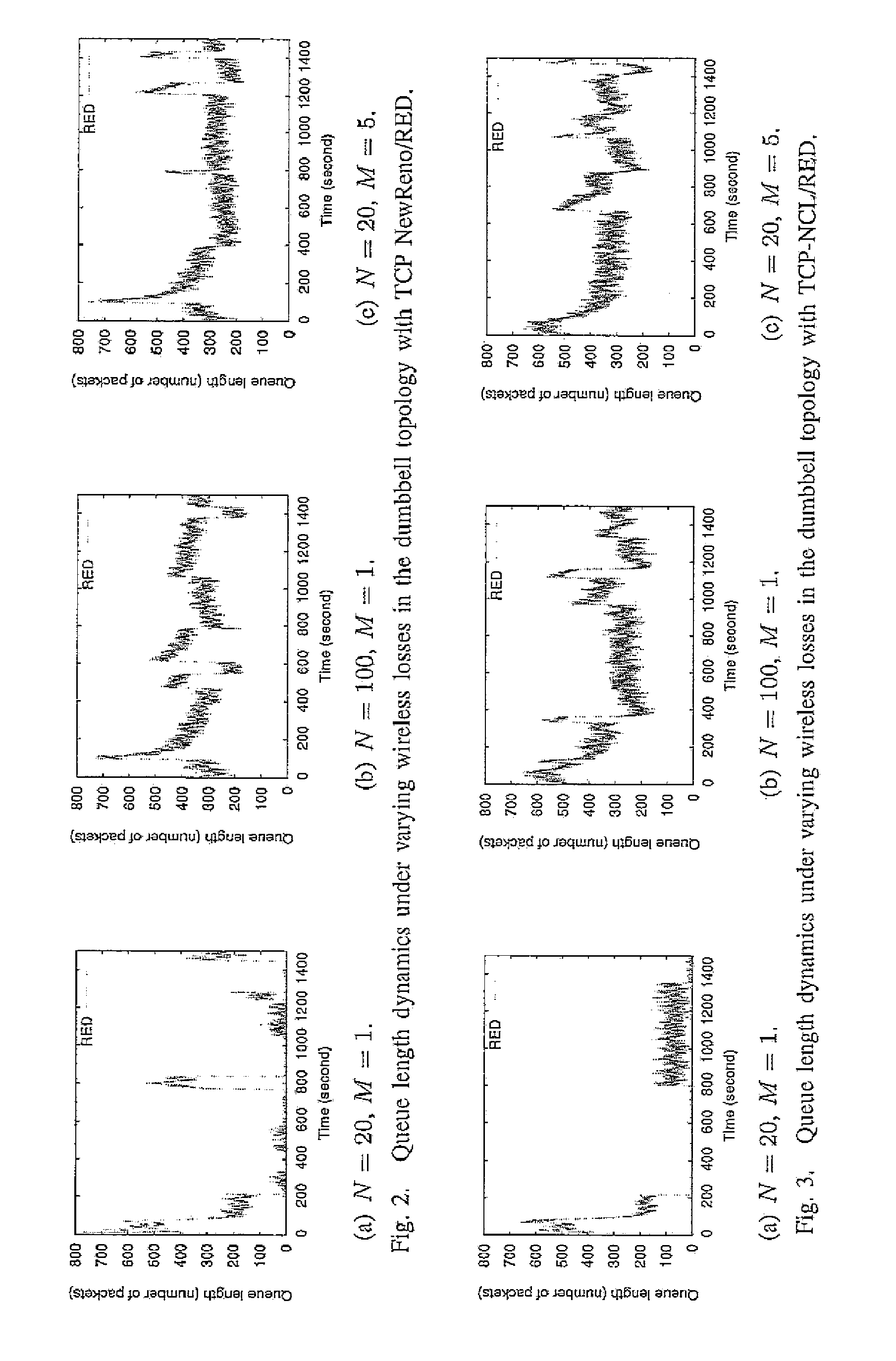
Enhancing aqm to combat wireless losses
ActiveUS20130322247A1Stabilizing backlogReduce decreaseError preventionTransmission systemsRandom early detectionIntegral controller
In order to maintain a small, stable backlog at an internet router buffer, active queue management (AQM) algorithms drop packets probabilistically at the onset of congestion. This causes Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) data flow rates to reduce. However, wireless losses may be misinterpreted as congestive losses and induce spurious reductions in flow rates. A prior art AQM with random early detection (RED), fails to maintain a stable backlog under time-varying wireless losses. However, the present invention can resolve the problem and provide a robust tracking of the backlog to a preset reference level by applying a control-theoretic vehicle, Internal Model principle, to realize such tracking. An integral controller (IC) is used as an embodiment of the principle that is robust against time-varying wireless losses under various network scenarios.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method and system for controlling TCP traffic with random early detection and window size adjustments
A method for controlling data traffic with random early detection and window size adjustments including performing random early detection on incoming data packets, calculating a simple moving average of packet dropping probabilities for the data packets as calculated when performing random early detection, decreasing an advertised window size if the simple moving average is greater than a probability target plus a tolerance factor, increasing the advertised window size if the simple moving average is less than the probability target minus a tolerance factor, and not adjusting the window size if the simple moving average is not greater than a probability target plus a tolerance factor and not less than a probability target minus a tolerance factor.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Controlling the flow of packets within a network node utilizing random early detection
A method and system for controlling the flow of packets within a network node is disclosed. The method comprises receiving packets that are intended for a queue, classifying each of packets into at least one of a plurality of traffic classes and applying class-specific random early detection to each of said packets. The system comprises a classification engine configured to classify packets into one of a plurality of traffic classes, class-specific random early detection (RED) logic configured to apply class-specific RED to each of said packets that have been classified by said classification engine; and a queue for queuing any of said packets that are not dropped in response to application of said class-specific RED.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Compartment congestion controlling means for router with changing load
InactiveCN101286929AReduce discard rateImprove throughputData switching networksLoss rateRandom early detection
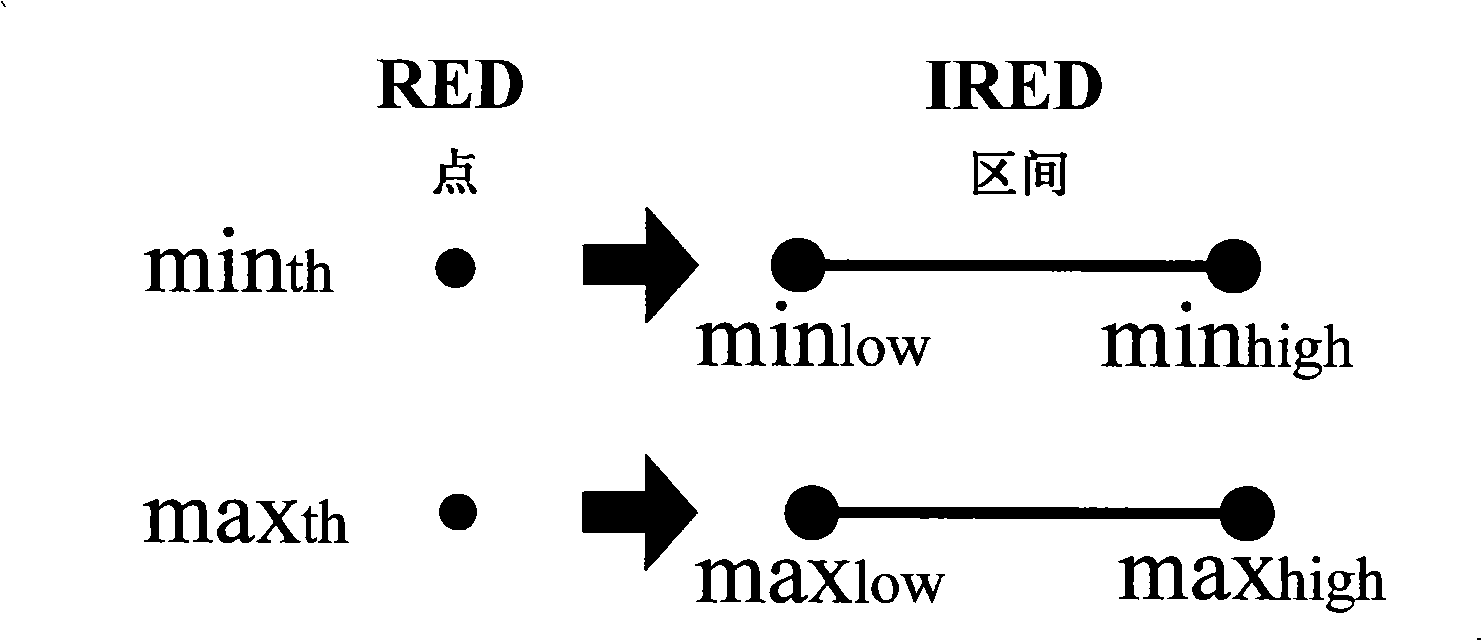
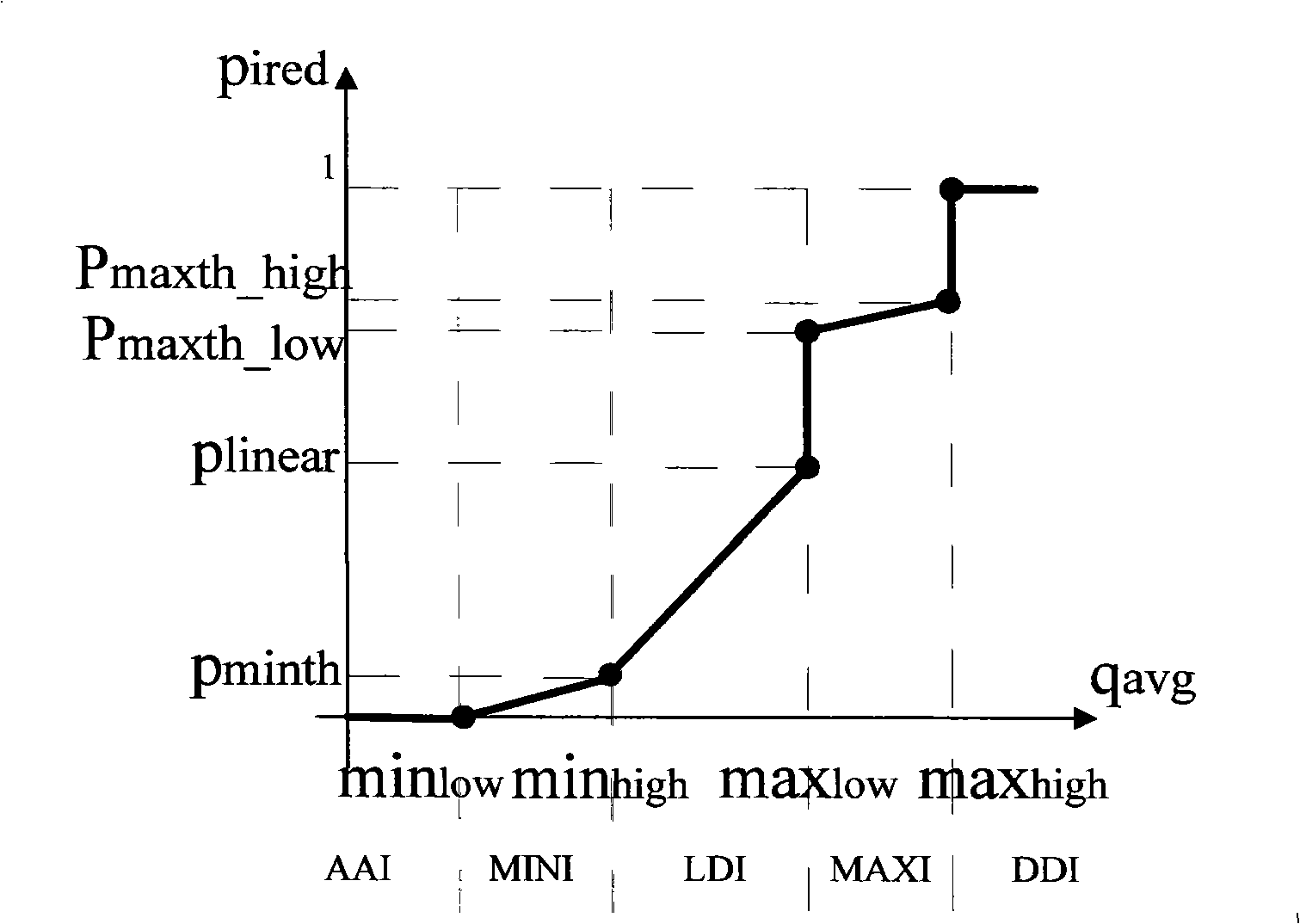
The invention relates to an interval type congestion control method for routers based on changeable load, which overcomes the over sensitivity of the existing RED(Random Early Detection) method to parameter setting and network environment and improves the threshold value in an RED from a point to an interval so as to obtain a new interval type RED method, namely, IRED (Interval Random Early Detection) algorithm, which obtains more strong robustness and better control under the load changeable network environment. Compared with the RED method, the performance of the system can be obviously improved by applying the method of the invention to carry out congestion control for routers, which leads to the decrease of loss rate of data packets, improvement of throughput of a network system and enhancement of stability. The method of the invention is a convenient and practical interval type congestion control method for the routers based on changeable load with excellent performance.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Single cycle weighted random early detection circuit and method
ActiveUS7286550B2Efficient packetOptimizing packet deliveryError preventionTransmission systemsRandom early detectionThe Internet
A system and method is provided for traffic management and regulation in a packet-based communication network, the system and method facilitating proactive, discriminating congestion control on a per flow basis of packets traversing the Internet via use of a Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) algorithm that monitors the incoming packet queue and optimizes enqueuing or discard of incoming packets to stabilize queue length and promote efficient packet processing. During optimized discard conditions, the system and method discern a relative priority among incoming packets, distribute packets with a relatively high priority and discard packets with a relatively low priority. Additionally, packet traffic are policed and discarded according to packet type, quantity or other predetermined criteria. The present invention performs in periodic mode, demand mode or both, and can be implemented as a hardware solution, a software solution, or a combination thereof.
Owner:IDT CANADA
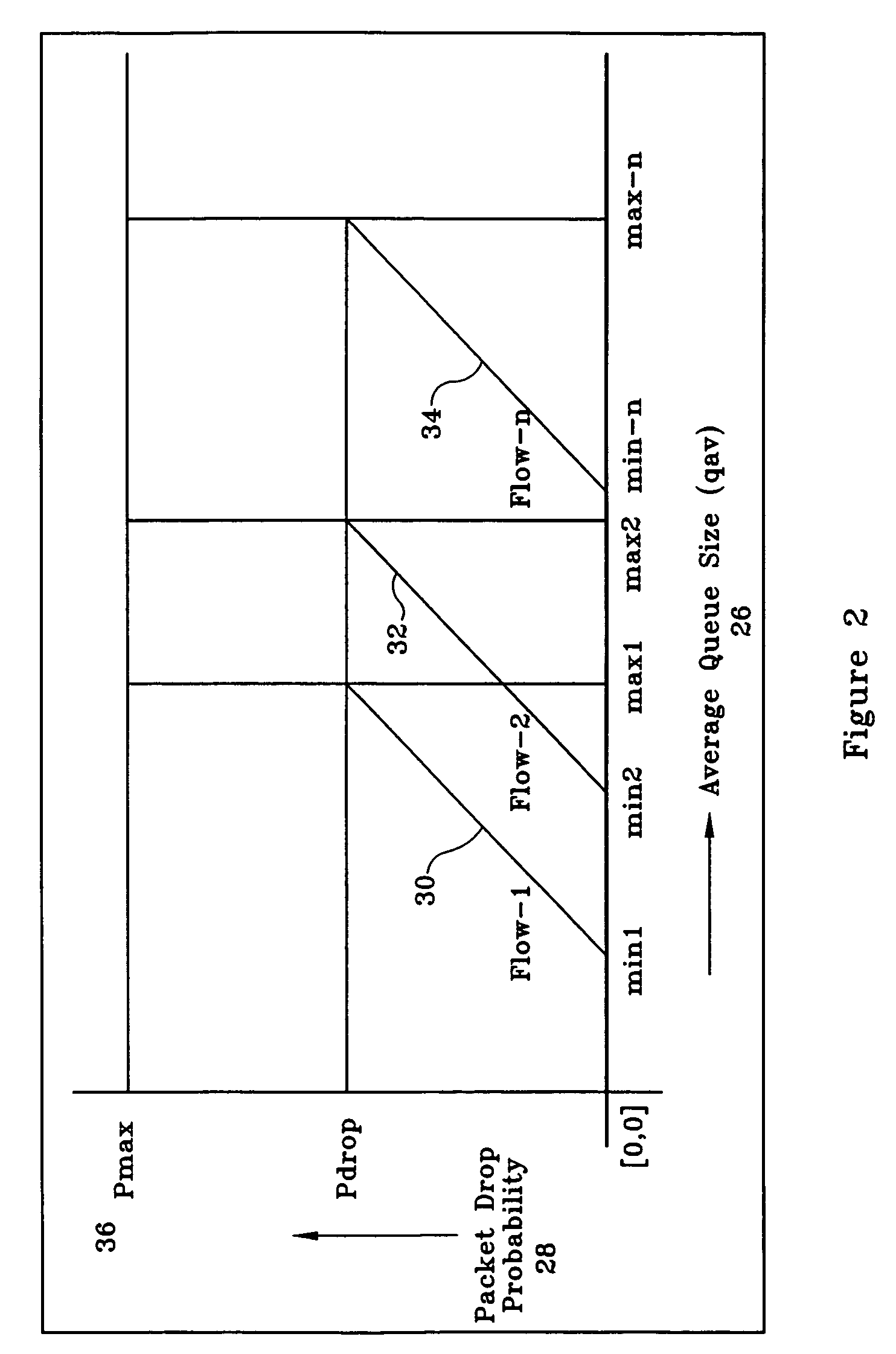
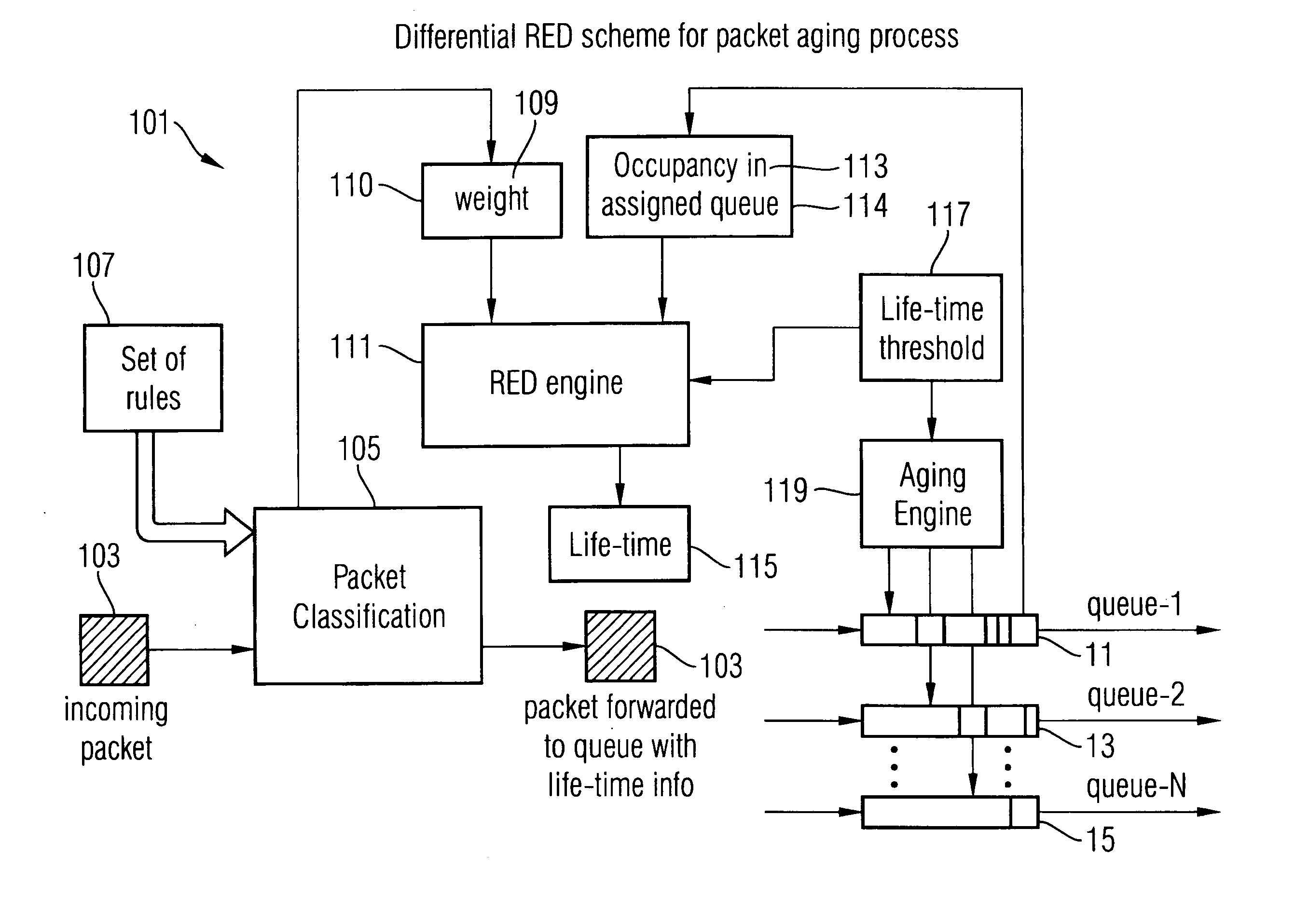
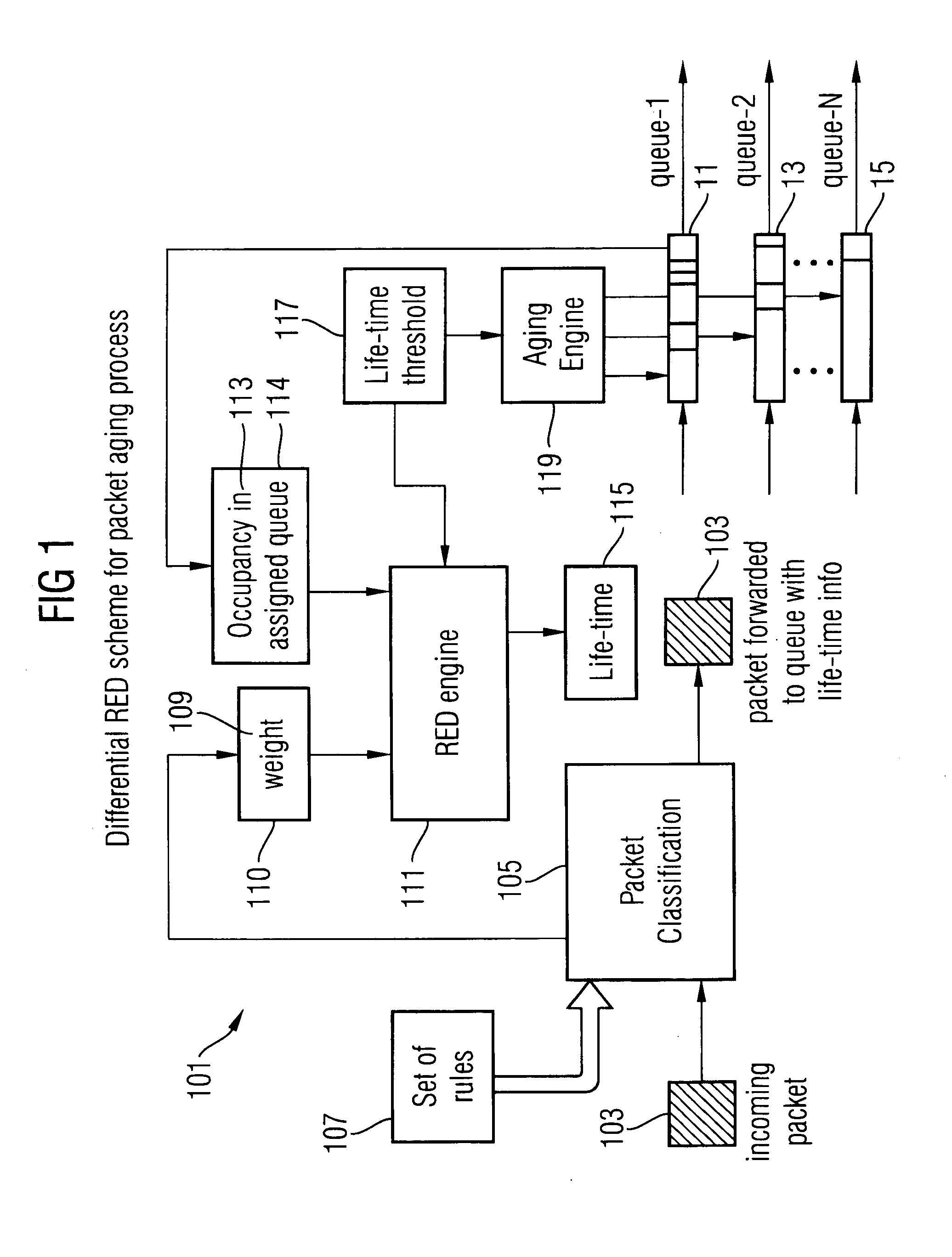
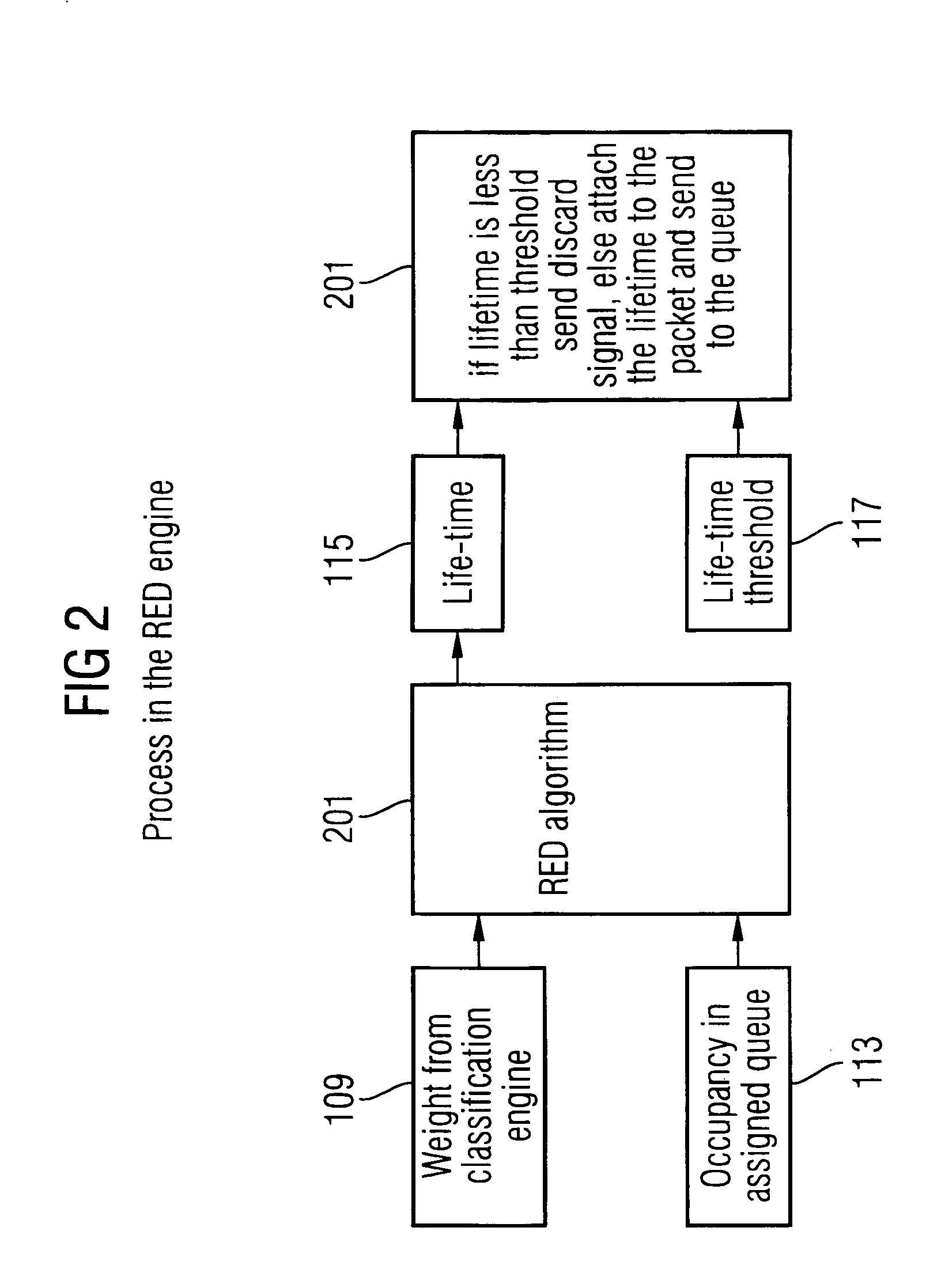
Random early detect and differential packet aging flow control in switch queues
InactiveUS20050149563A1Avoid congestionExacerbate network congestionData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsRandom early detectionNetwork packet
Flow control is provided for a packet switch. An incoming packet is classified according to its priority based on predefined rules to produce a weight value based on the priority of the packet. A lifetime value associated with the packet is produced based on the weight value and the queue occupancy in a queue to which the packet is assigned. The packet is discarded if its associated lifetime value is less than or equal to a threshold value. Otherwise the packet and associated lifetime value are sent to the queue. The lifetime value is periodically changed and compared to a threshold value. The packet is removed from the queue when its lifetime value reaches the threshold value.
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
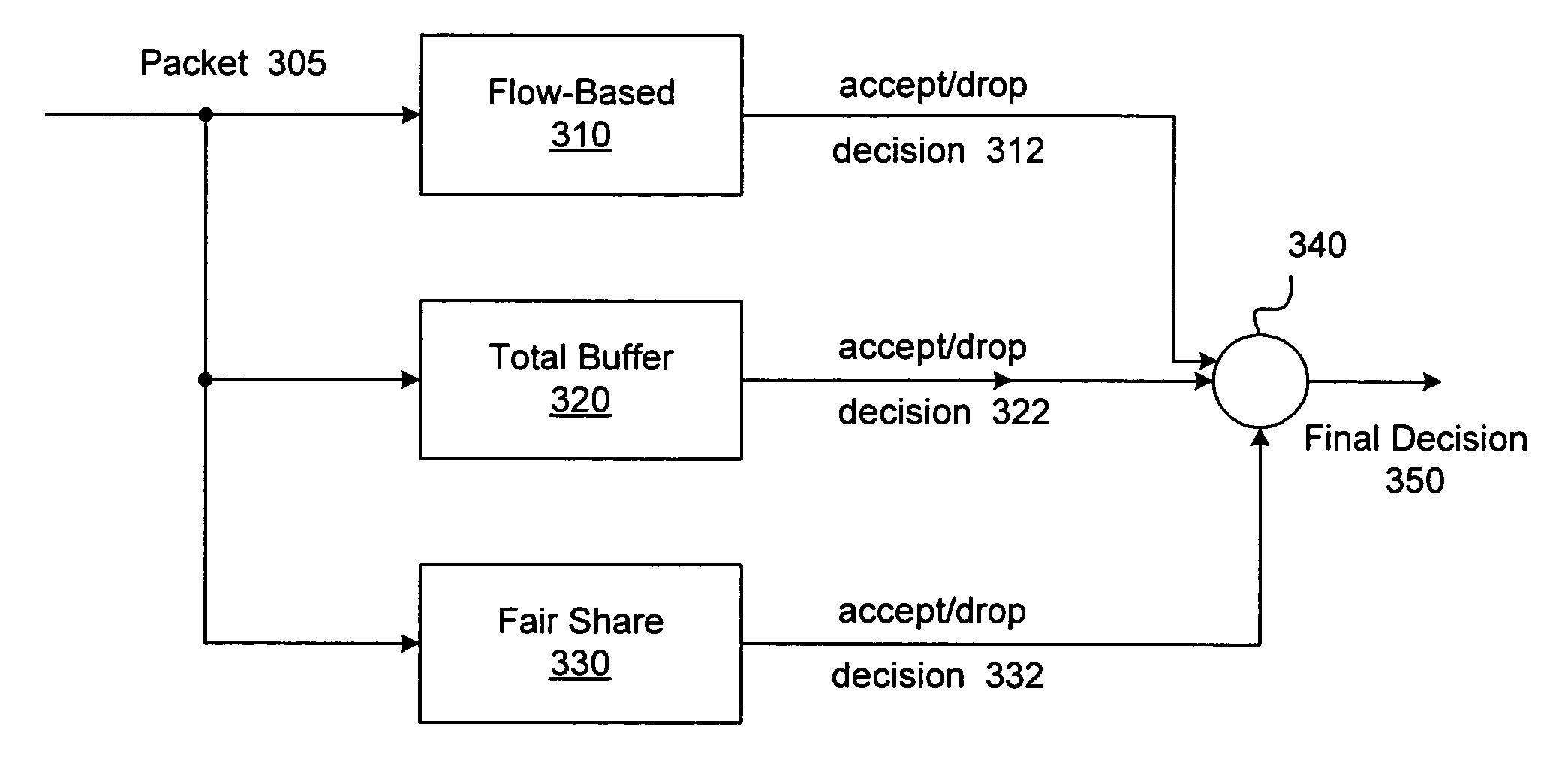
Mechanism for managing access to resources in a heterogeneous data redirection device
InactiveUS7944829B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRandom early detectionNetwork packet
A system and method for policing of access to resources in a heterogeneous data redirection device is disclosed. The invention utilizes Random Early Detection to determine whether or not a given packet should be dropped or accepted into the resource. The invention uses a combination of different metrics each of which utilizes a different version of RED. Schemes can include a Per-Flow Weighted RED metric, a Global RED metric and a Fair Share Pool metric, where shared resource allocation is dependent dynamically upon the number of users at the time a packet requests access. These metrics can be combined in variety of ways to yield a final drop or accept decision for an incoming packet so that it does not access resources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
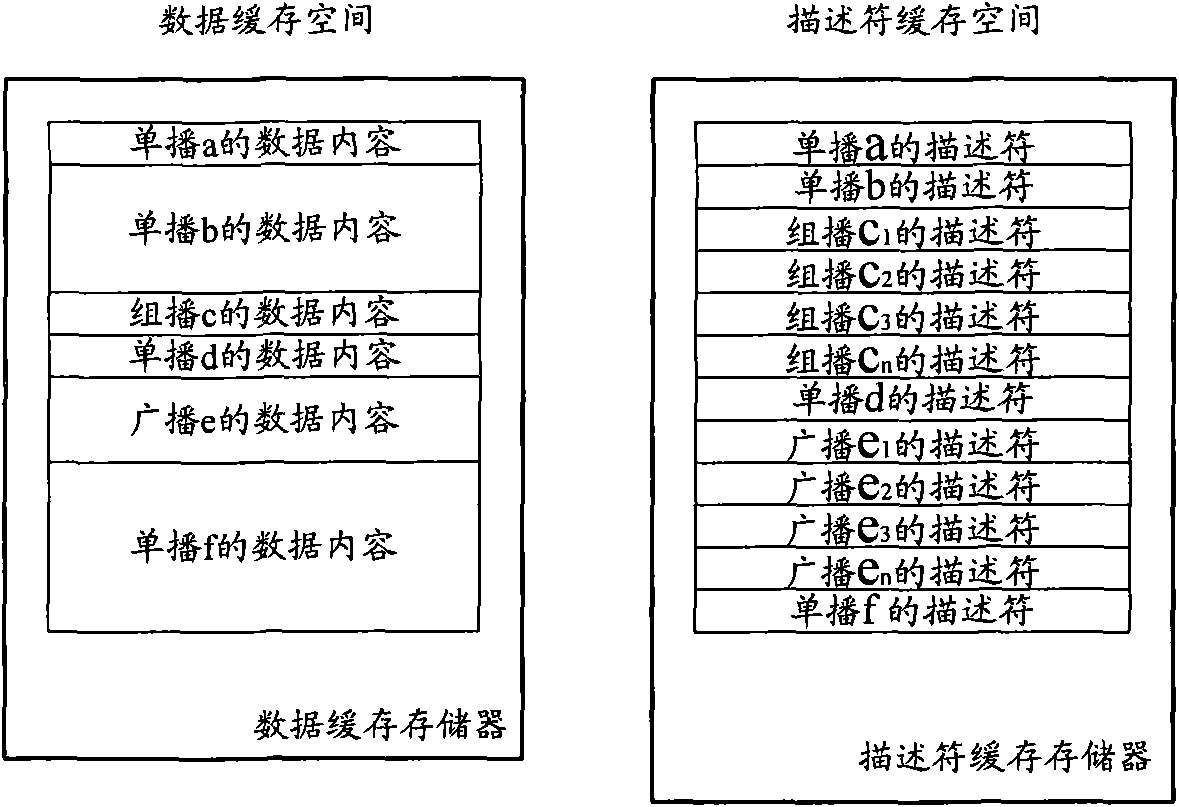
Random early detection method and device for data flow management
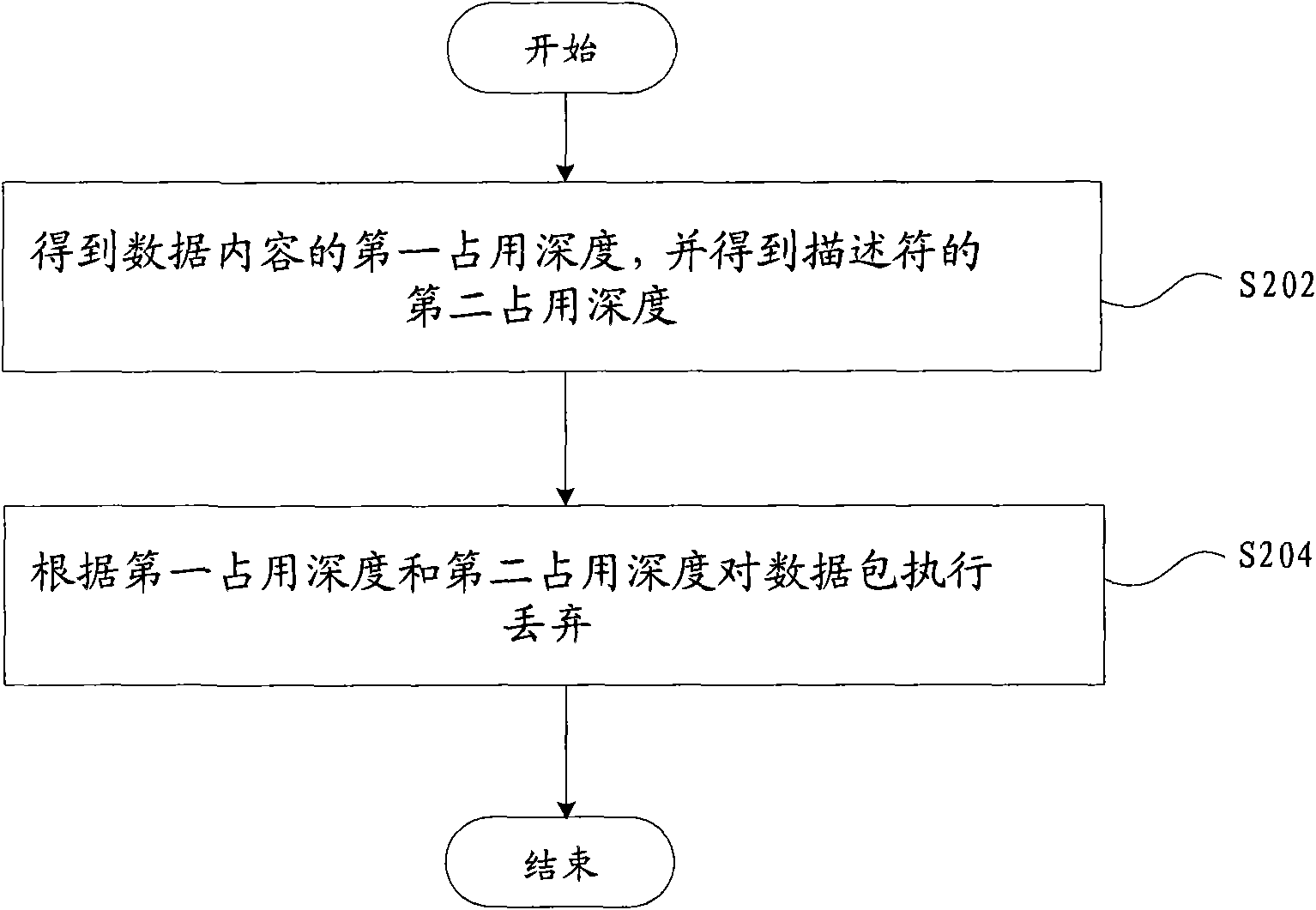
ActiveCN101938404AQuality improvementAvoid continuous packet lossData switching networksRandom early detectionNetwork packet
The invention discloses a random early detection method and a random early detection device for data flow management. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring first occupation depth of data content according to first length of the data content of a data packet which is to be input to a data cache space of a flow management chip, and current occupation depth of the data cache space; acquiring second occupation depth of a descriptor according to second length of the descriptor of the data packet and the current occupation depth of a descriptor cache space; and detecting the data packet according to the first occupation depth and the second occupation depth. The method and the device avoid a great amount of continuous detection caused by overflow of the descriptor cache space and achieve a technical effect of improving network quality.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Dynamic queue threshold extensions to random early detection
ActiveUS7990868B1Efficiently process and bufferError preventionTransmission systemsRandom early detectionParallel computing
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Packet loss method in LTE and LTE-A system based on RED algorithm
InactiveCN102801502AReduce queuing delayImprove adaptabilityError preventionRandom early detectionPacket loss
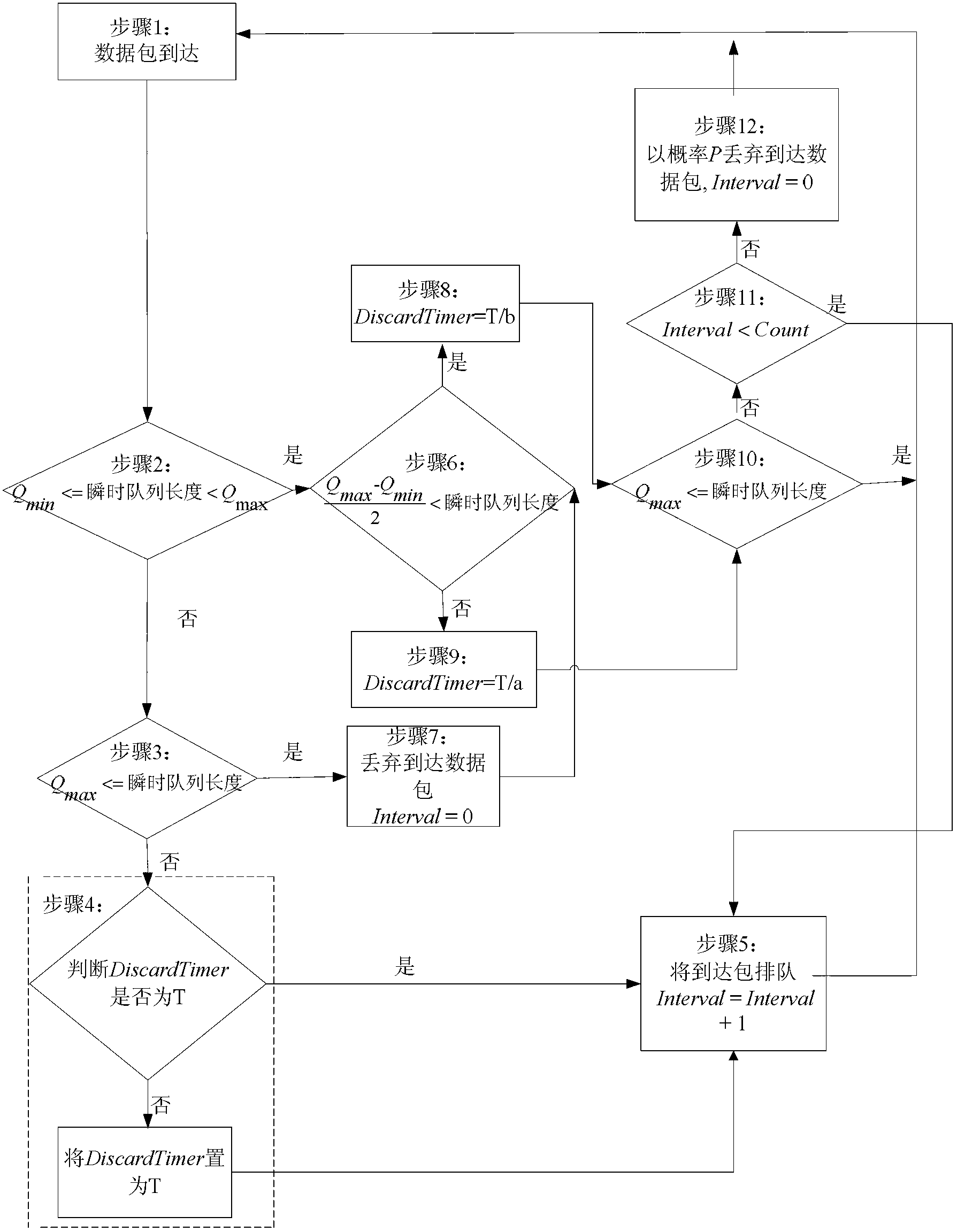
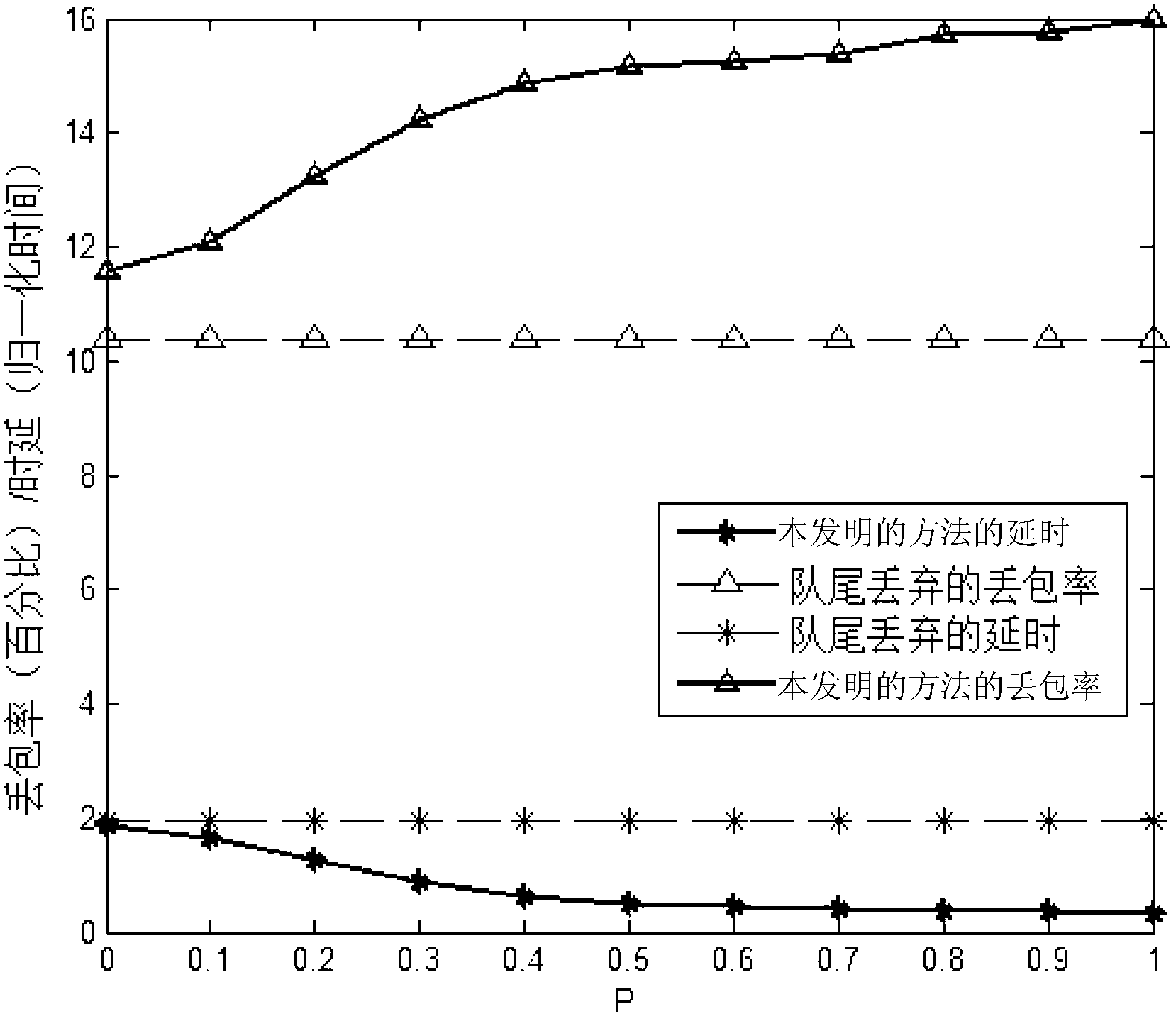
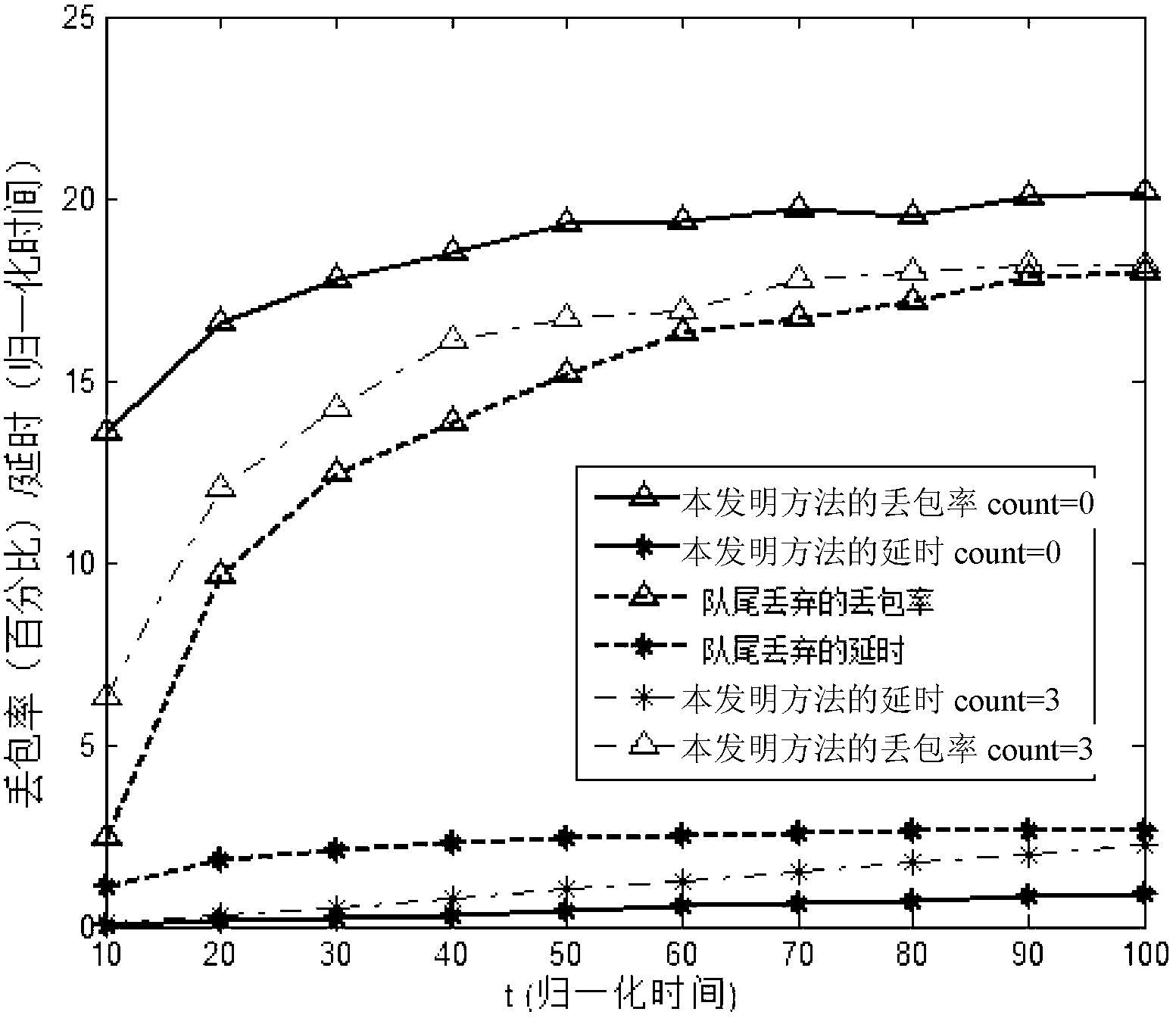
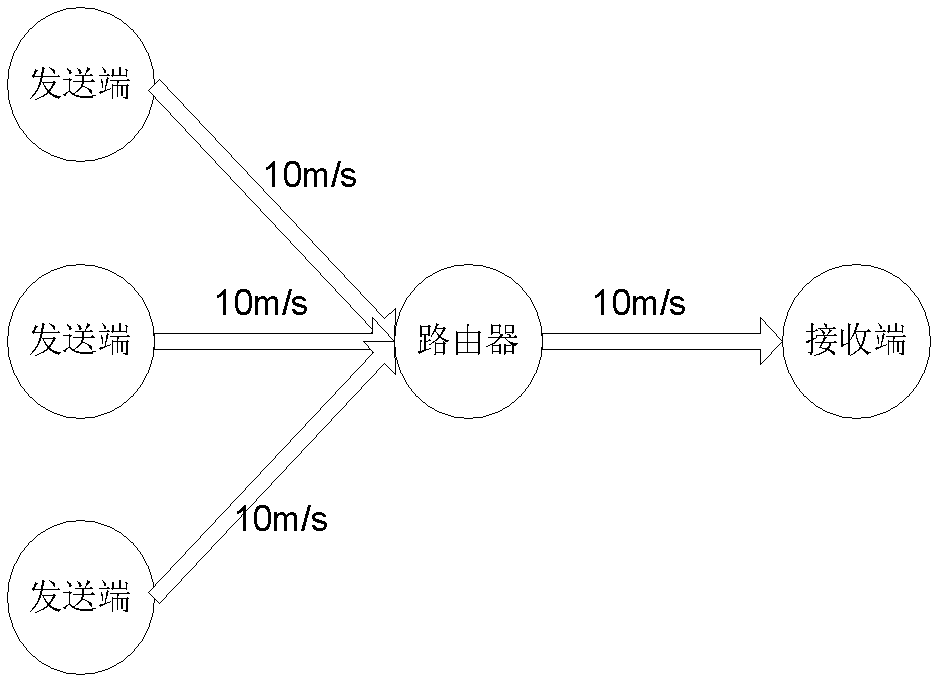
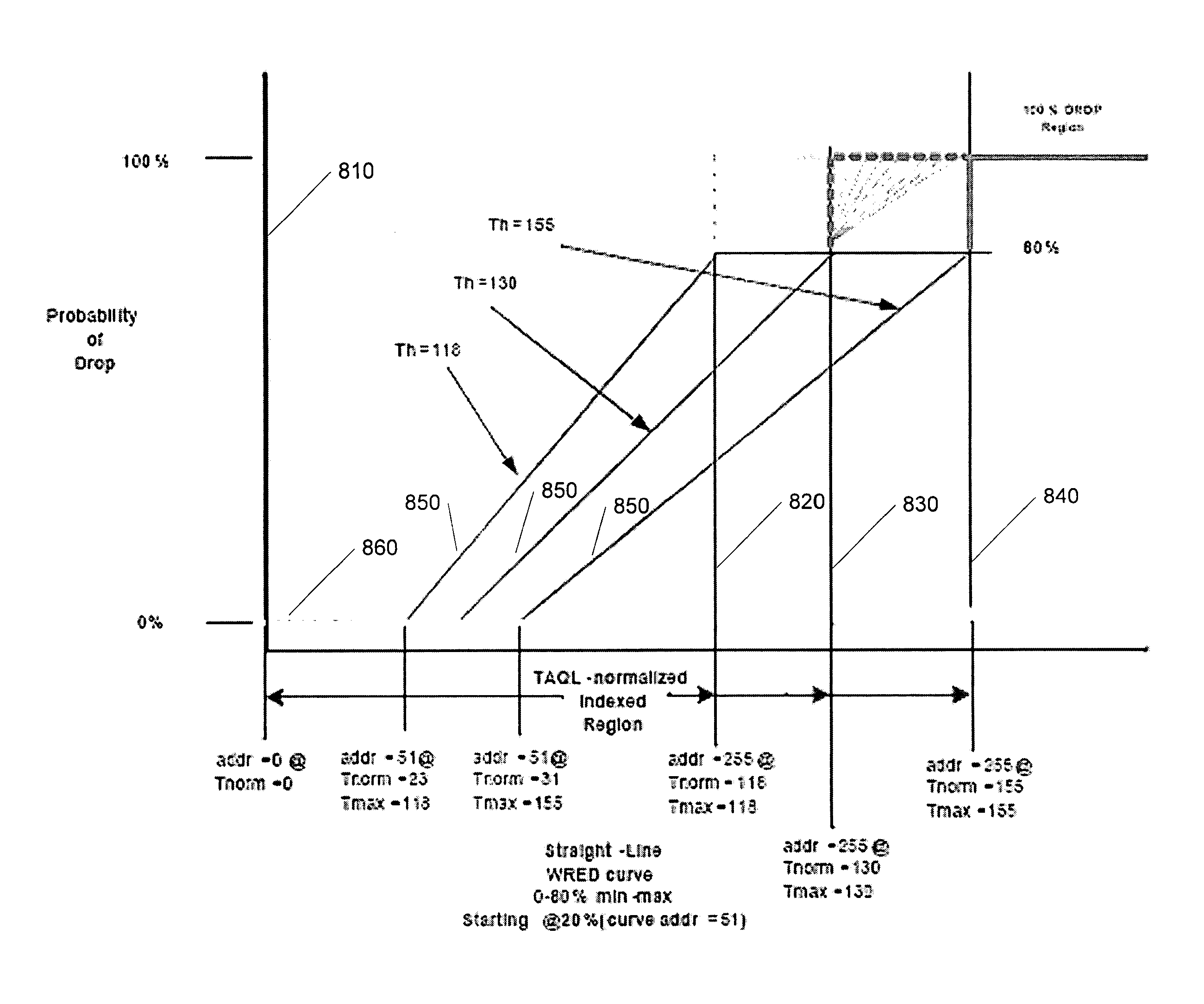
The invention discloses a packet loss method in a long term evolution (LTE) system and a long term evolution-advanced (LTE-A) system based on an RED (Random Early Detection) algorithm, relates to a packet loss method, and aims to solve the delay problem of long waiting of delay sensitive data flow in a radio link control (RLC) layer buffer of the LTE system and the LTE-A system caused by congestion and even buffer overflow. The packet loss is controlled and implemented by changing the set value of a discard timer in the LTE system and the LTE-A system and comparing an instantaneous queue length in the buffer with a minimal threshold Qmin and a maximal threshold Qmax. The randomness of a probability P ensures the randomness and fairness of the packet loss, and is favorable for the algorithm to avoid continuous packet loss. The method provided by the invention is used for implementing the packet loss in the LTE system and the LTE-A system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Nomadic application-oriented network congestion control method
InactiveCN102325082AGuaranteed stabilityCongestion suppressionData switching networksRandom early detectionOriginal data
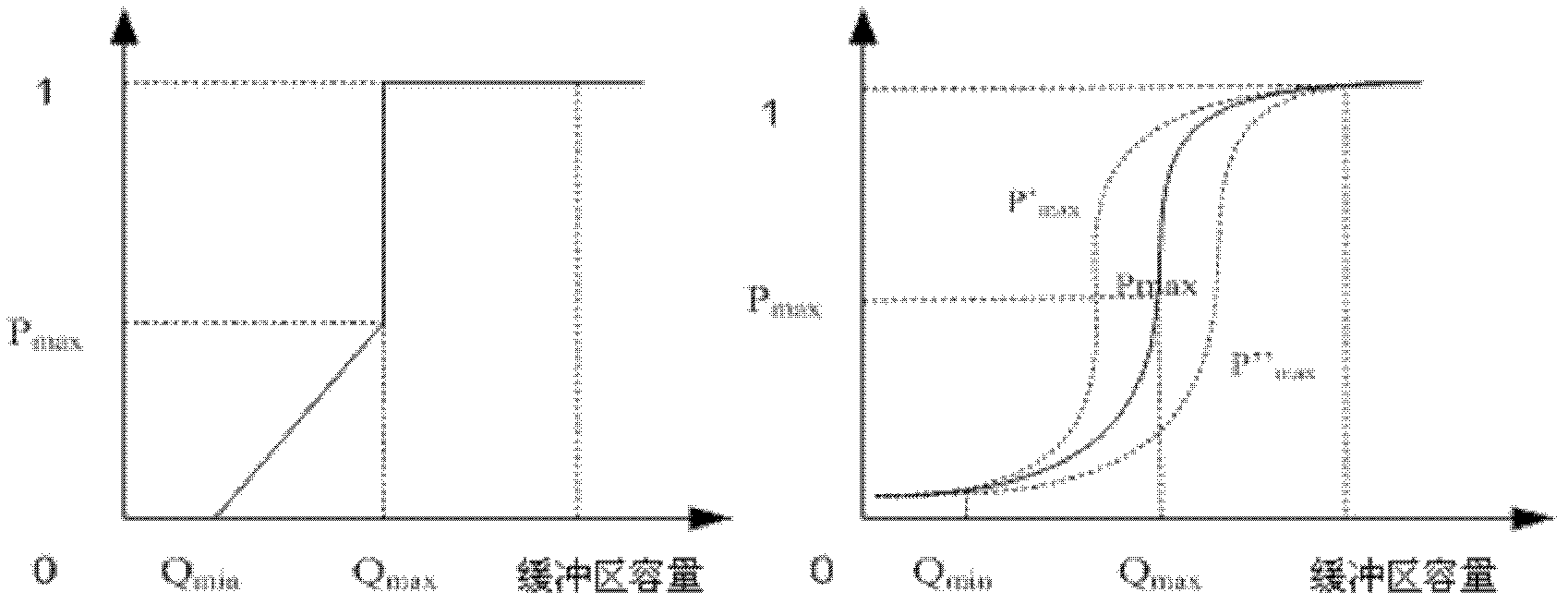
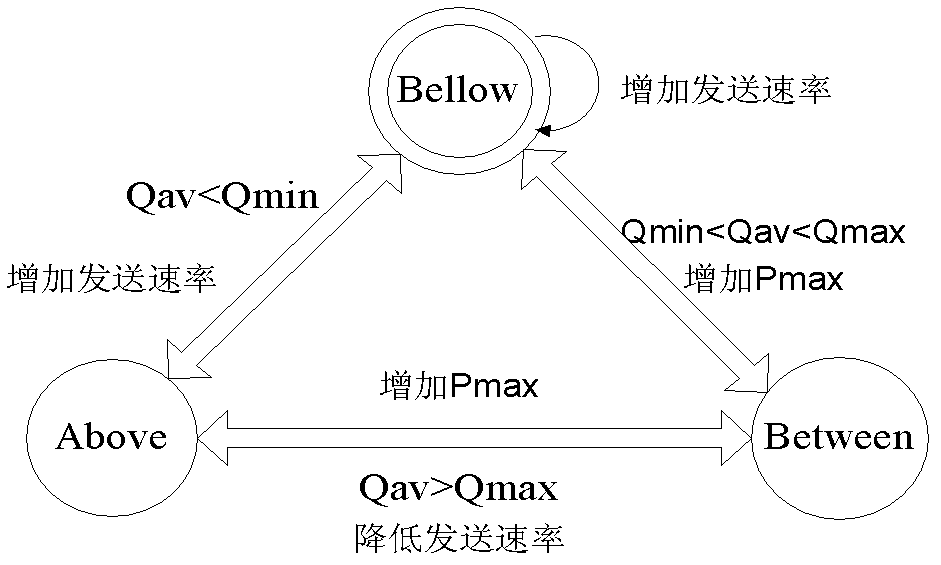
The invention relates to a nomadic-application-oriented network congestion control method. The network congestion adaptive method provides a congestion adaptive control algorithm based on up semi-normal distribution-DARED (distributed adaptive random early detection). According to the DARED algorithm, the corresponding congestion control is performed by improving an original data packet discarding probability function curve, namely adjusting an existing linear discarding straight line of an RED (random early detection) algorithm to a smooth curve, and dividing into different network states according to the queue length. The DARED is characterized in that a real-time dynamic parameter Pmax is introduced on the basis of the traditional RED algorithm, the stability of a queue is kept and the controllability of network congestion is increased. Correspondingly, in the aspect of a nomadic application system, when applied to the aspect of a multimedia seamless migration system, the congestion control algorithm realizes the seamless migration strategy under different architectures, namely the migration strategy under a B / S (browser / server) architecture, the migration strategy under a P2P (peer-to-peer) architecture and the migration strategy under a C / S (client / server) architecture. By adopting the nomadic application-oriented network congestion control method, the continuity, the rapidity, the smoothness and the correctness of media migration can be effectively ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Pseudo-relative mode wred/tail drop mechanism
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Random early detection over wireless links
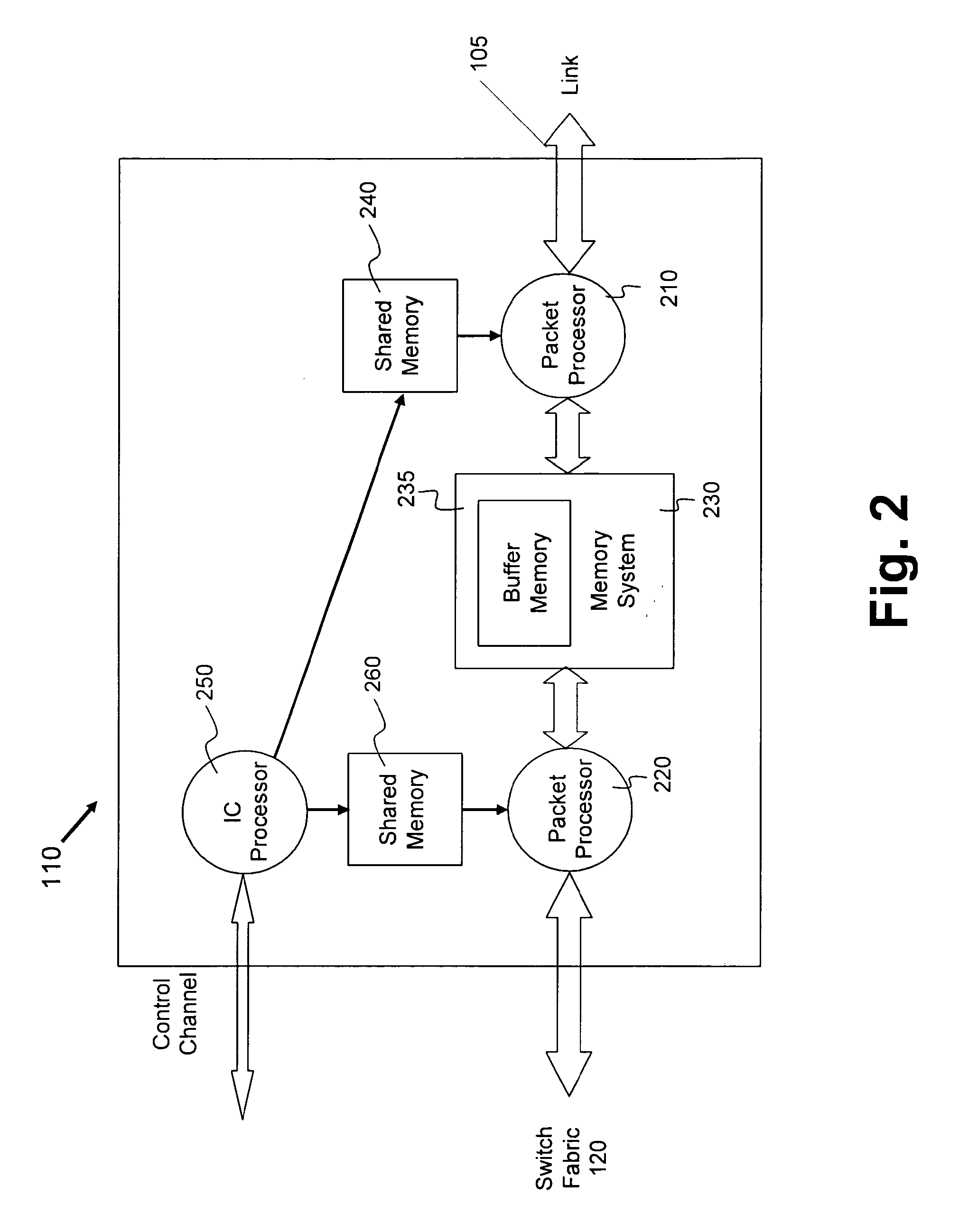
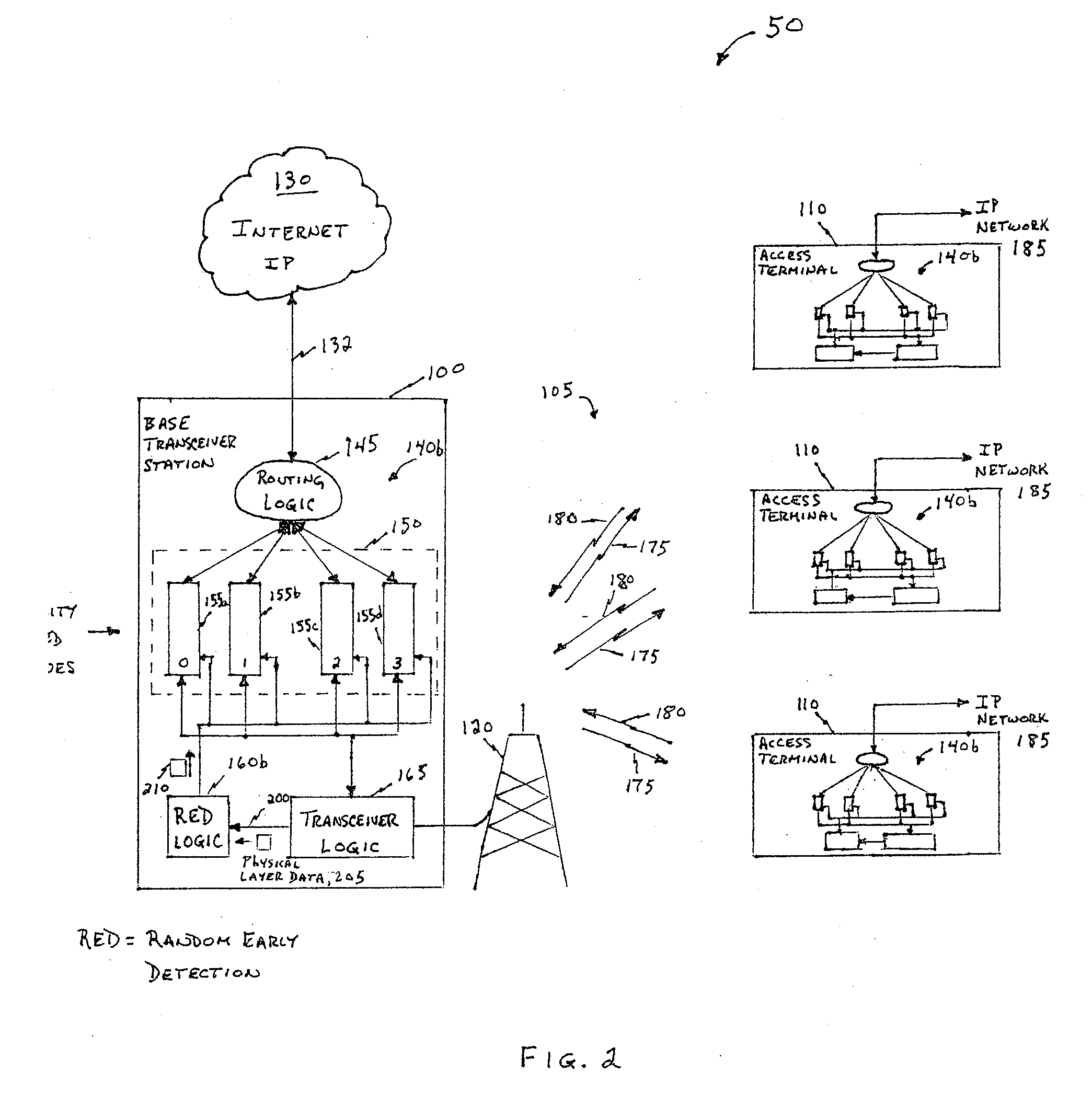
InactiveUS20090232002A1Error preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications linkRandom early detection
Random early detection (RED) controlled loss (i.e., discarding data packets) is determined as a function of change in processing gain assigned by a resource management system in a data network having a communications link between first and second network nodes. Rather than triggering RED controlled loss as a function of buffer levels, triggering is determined as a function of change in processing gain caused by, for example, a change in code rate, modulation technique, error (e.g., bit error rate or frame error rate), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) or carrier-to-interference (C / I) level, or a number of traffic code channels or TDMA slots assigned to the nodes. In a wireless data network, this technique may be deployed in a base station or access terminal. A tight coupling between the physical layer and link layer is provided using this technique.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com