Patents
Literature
70 results about "Atm switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
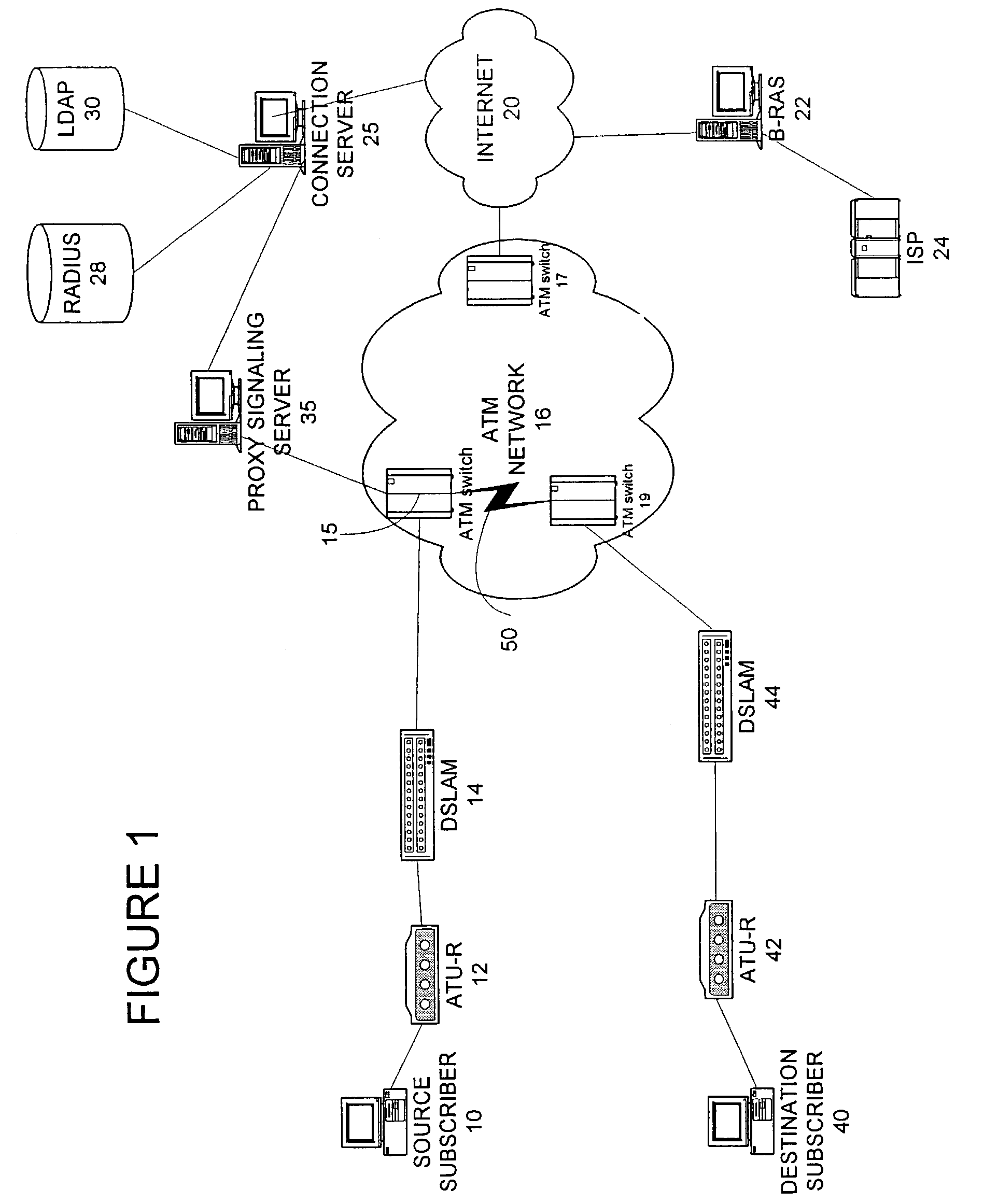
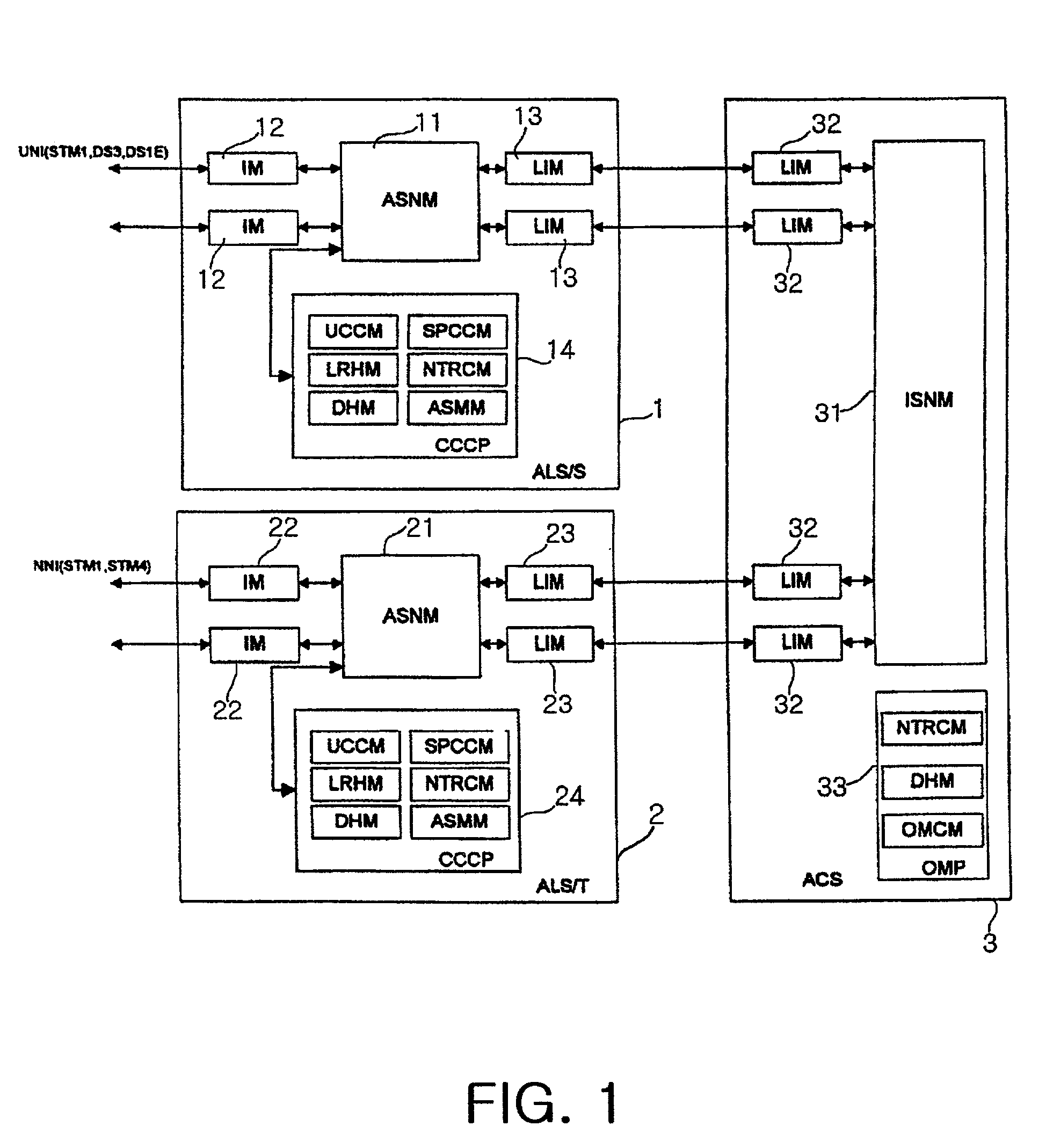
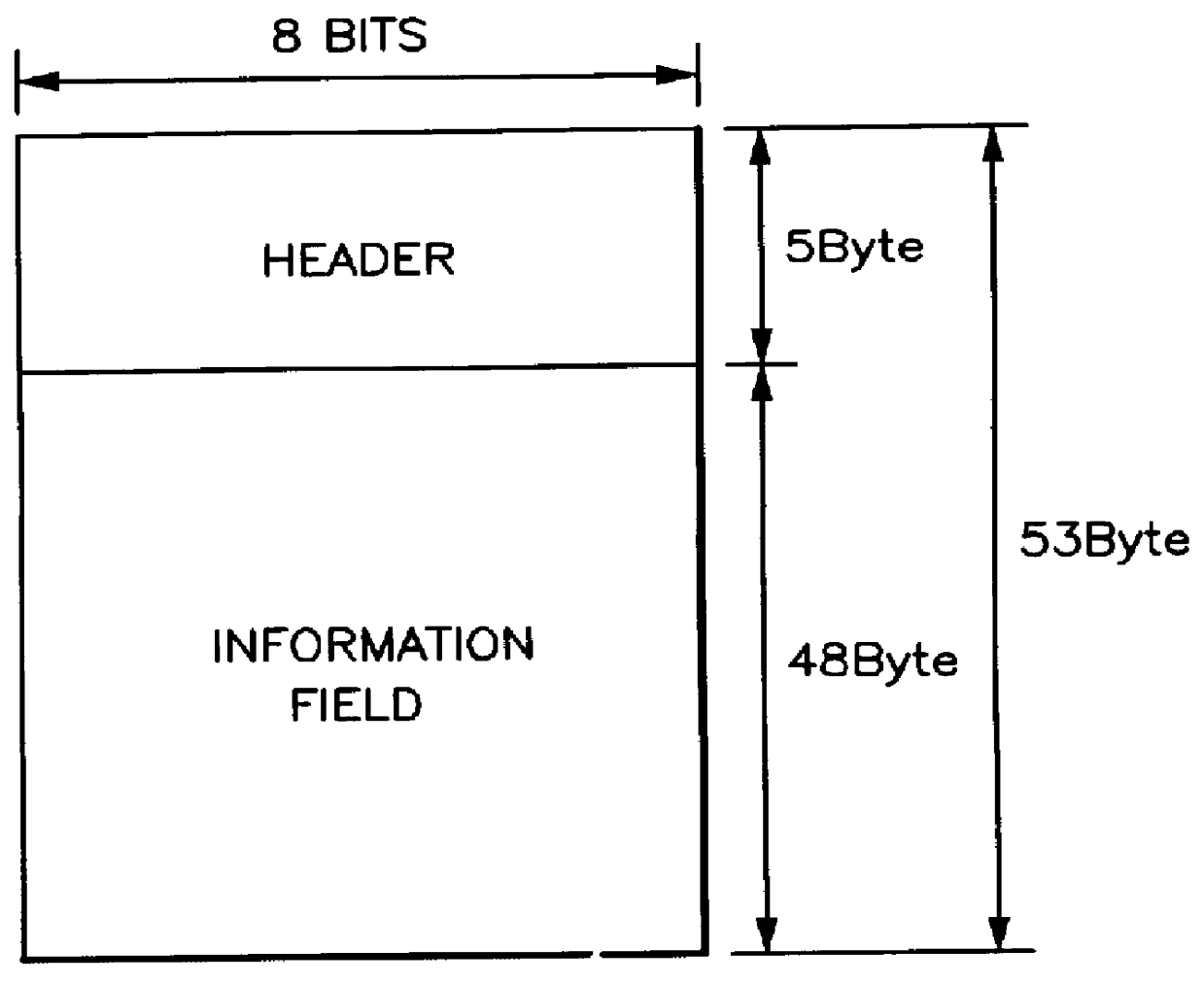
ATM switching. ATM Switching is also known as fast packet switching. ATM switching node transports cells from the incoming links to outgoing links using the routing information contained in the cell header and information stored at each switching node using connection set-up procedure.
System architecture for and method of processing packets and/or cells in a common switch
InactiveUS6259699B1Without impacting performance aspectPromote resultsData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsAtm switchingQos management
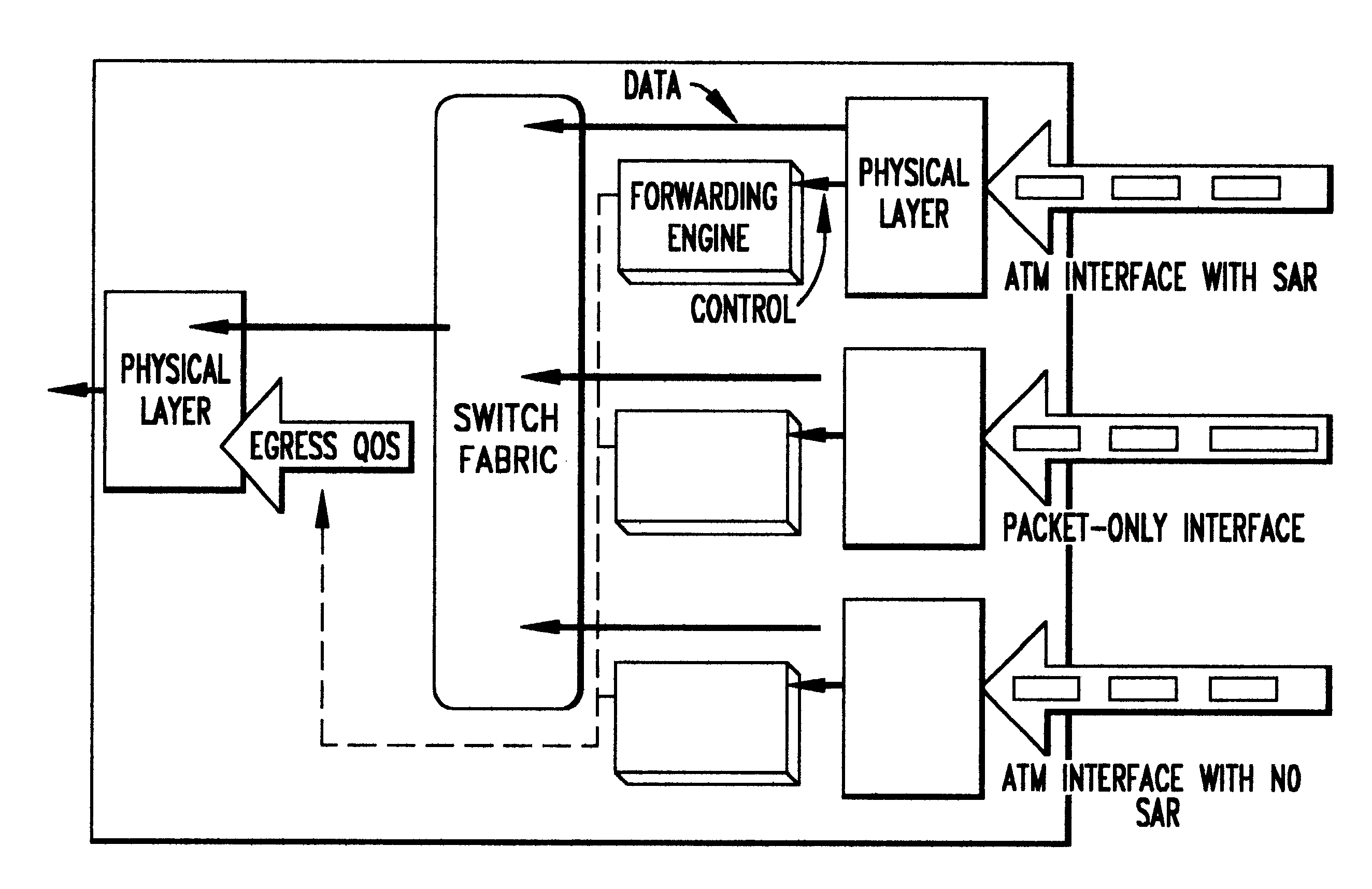
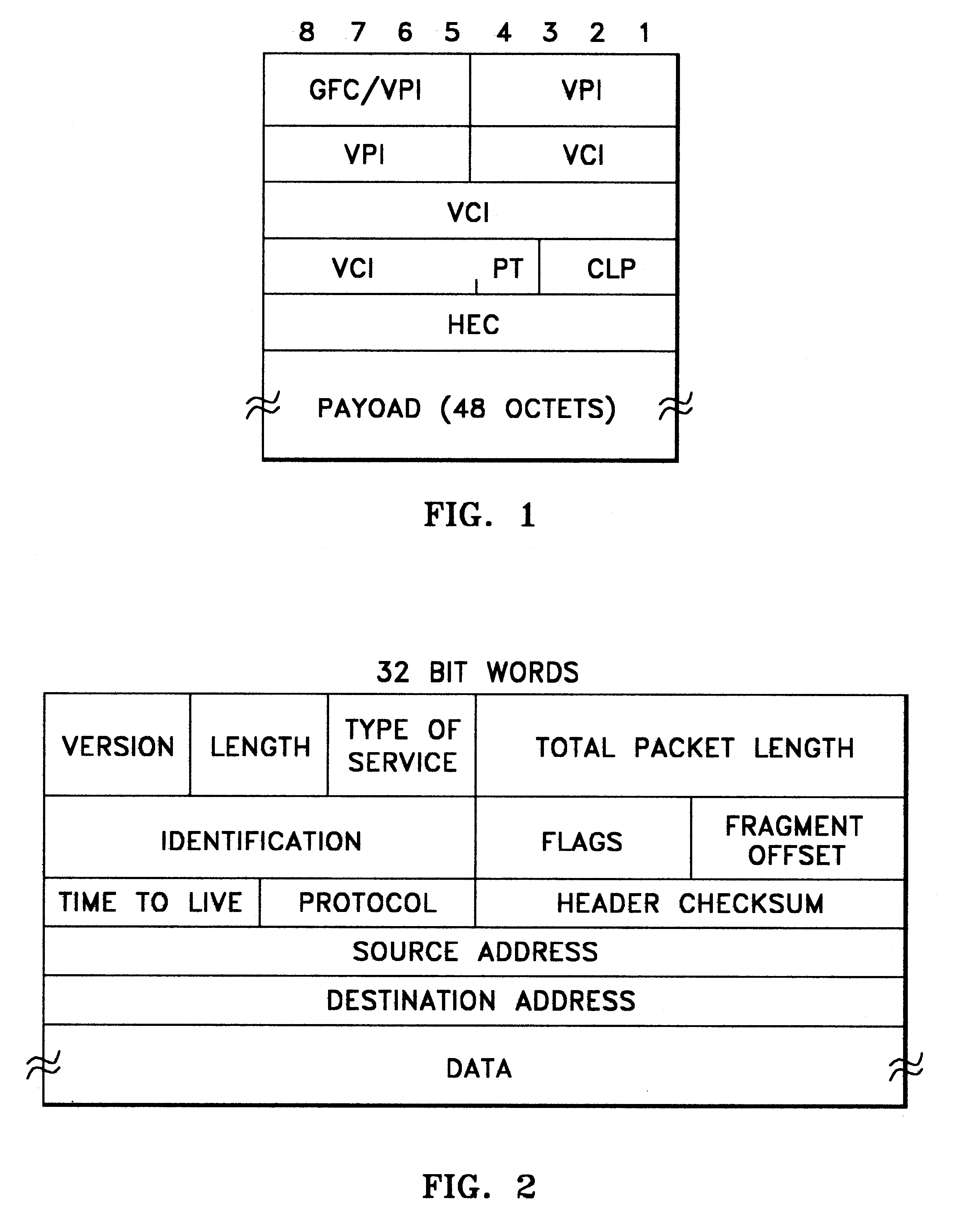
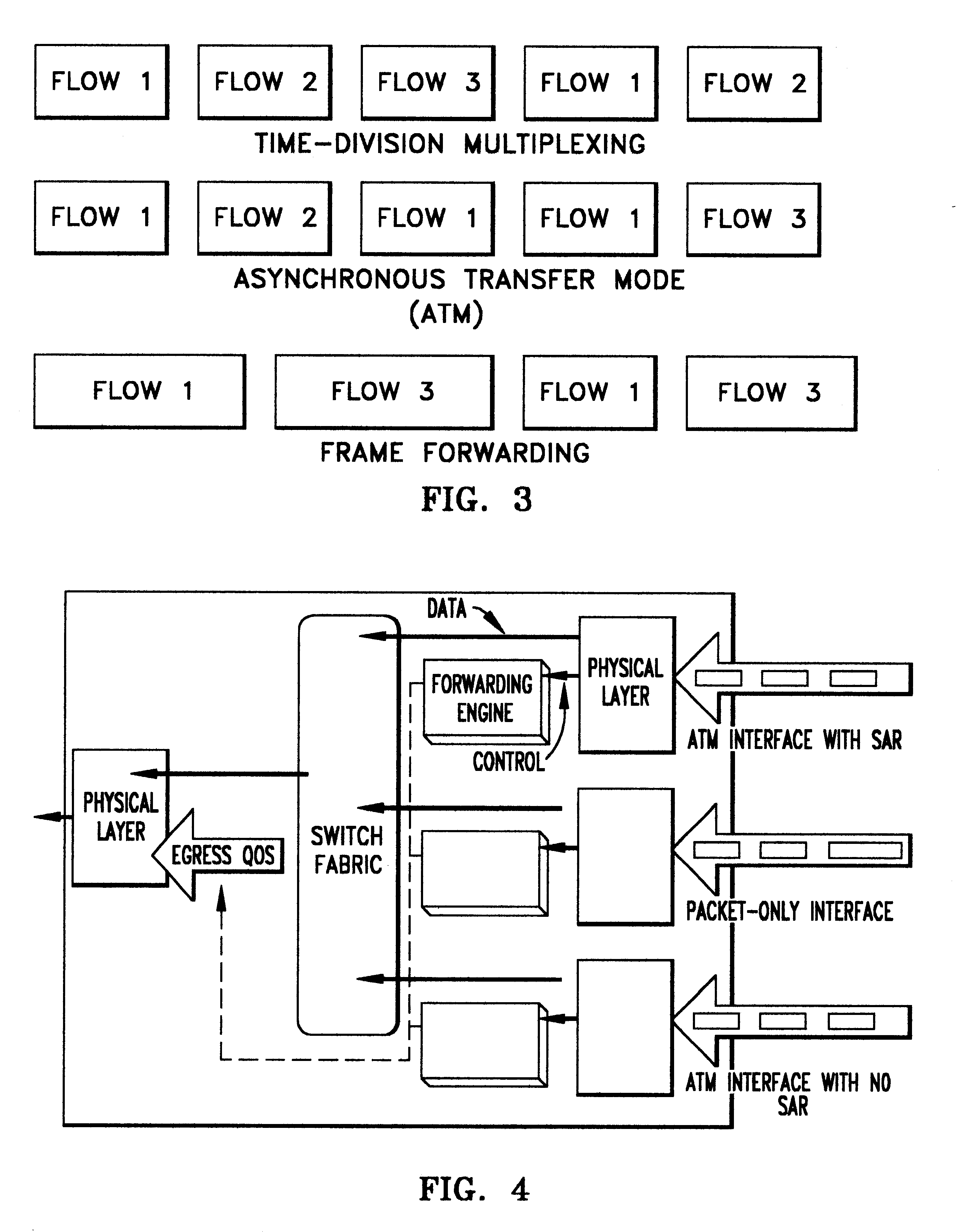
A novel networking architecture and technique for transmitting both cells and packets or frames across a common switch fabric, effected, at least in part, by utilizing a common set of algorithms for the forwarding engine (the ingress side) and a common set of algorithms for the QoS management (the egress part) that are provided for each I / O module to process packet / cell information without impacting the correct operation of ATM switching and without transforming packets into cells for transfer across the switch fabric.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Multi-channel support for virtual private networks in a packet to ATM cell cable system
InactiveUS6917614B1Avoid compromiseExtension of timeBroadband local area networksFrequency-division multiplexQuality of serviceScheduling function
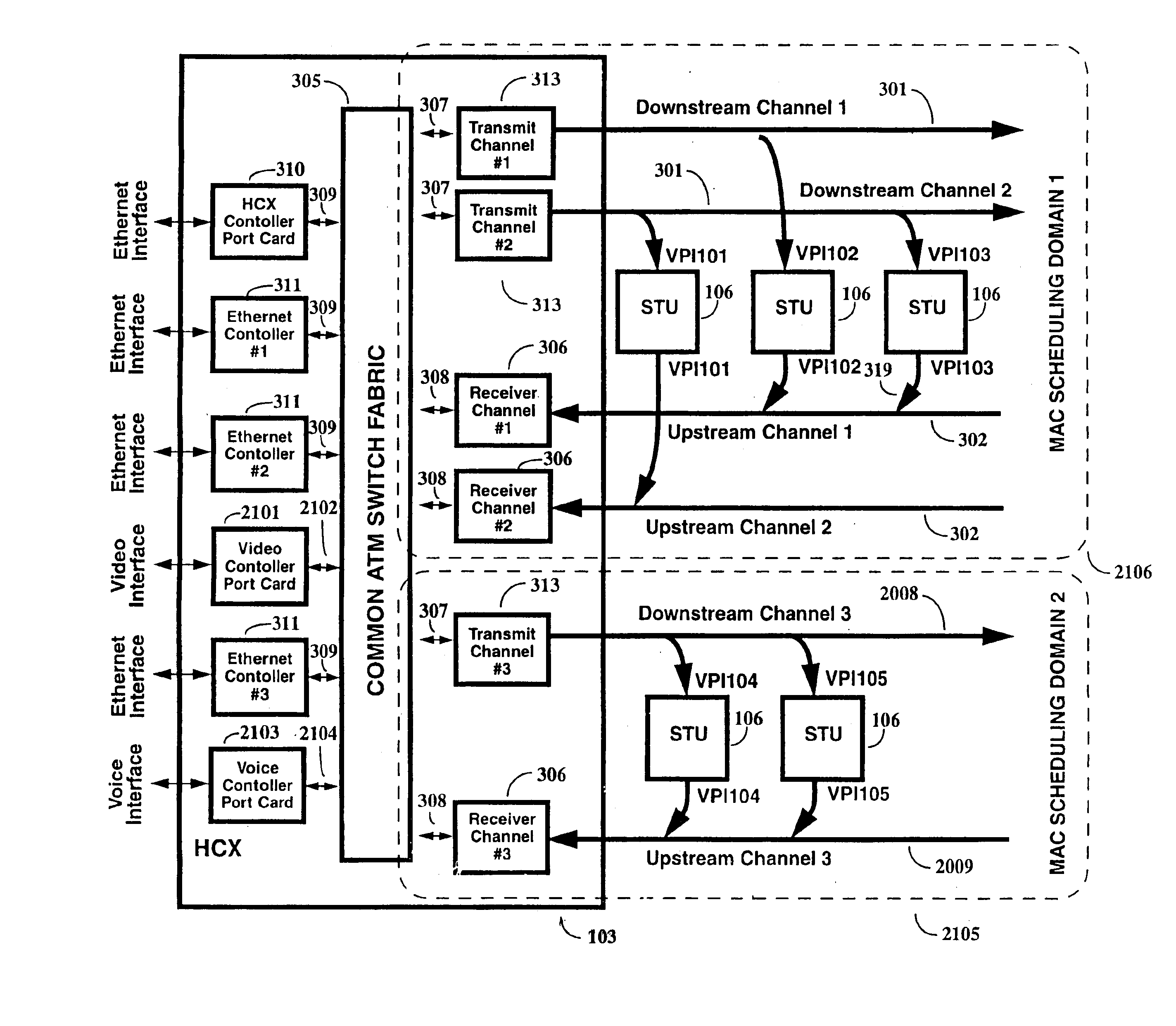
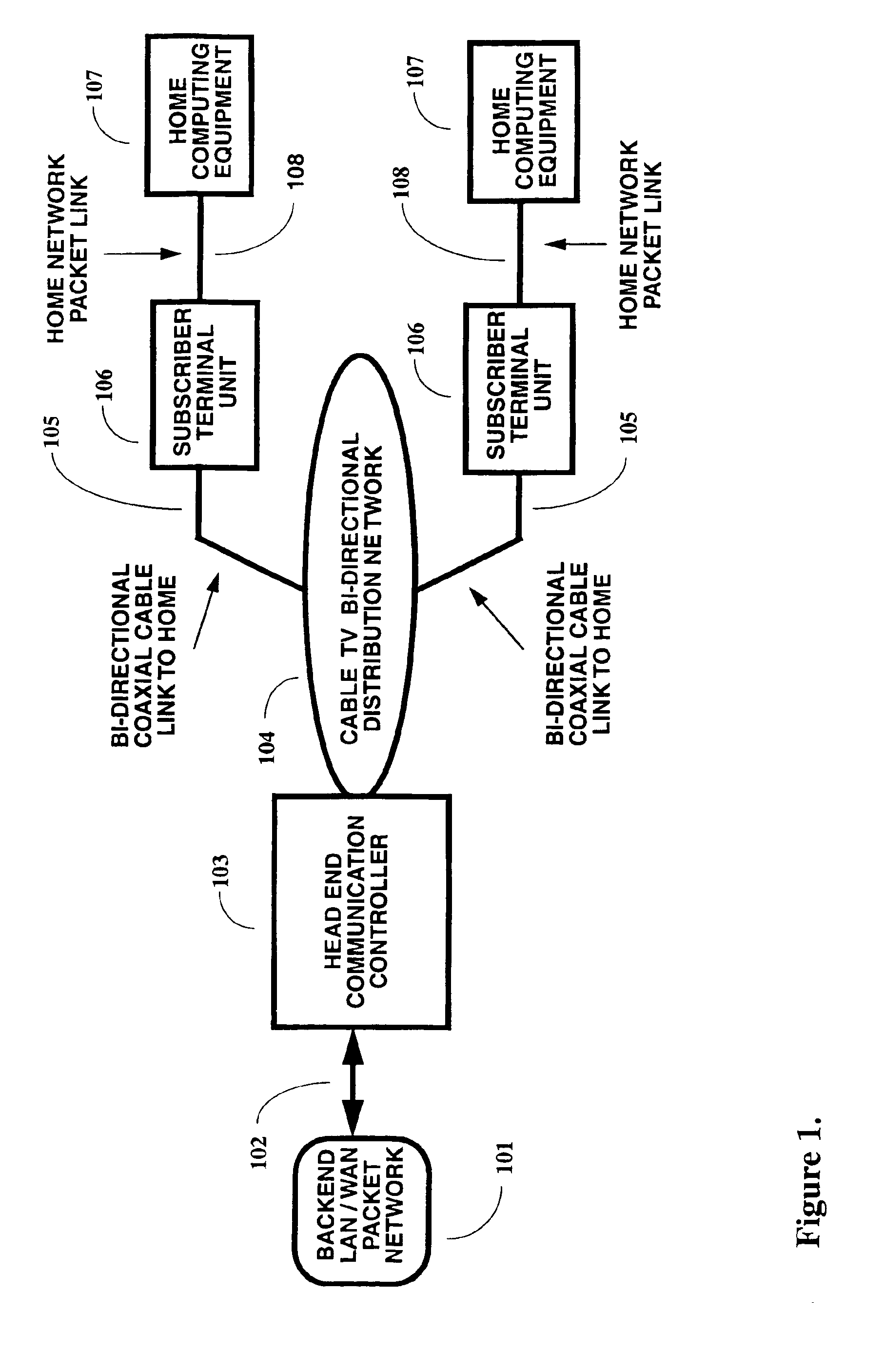
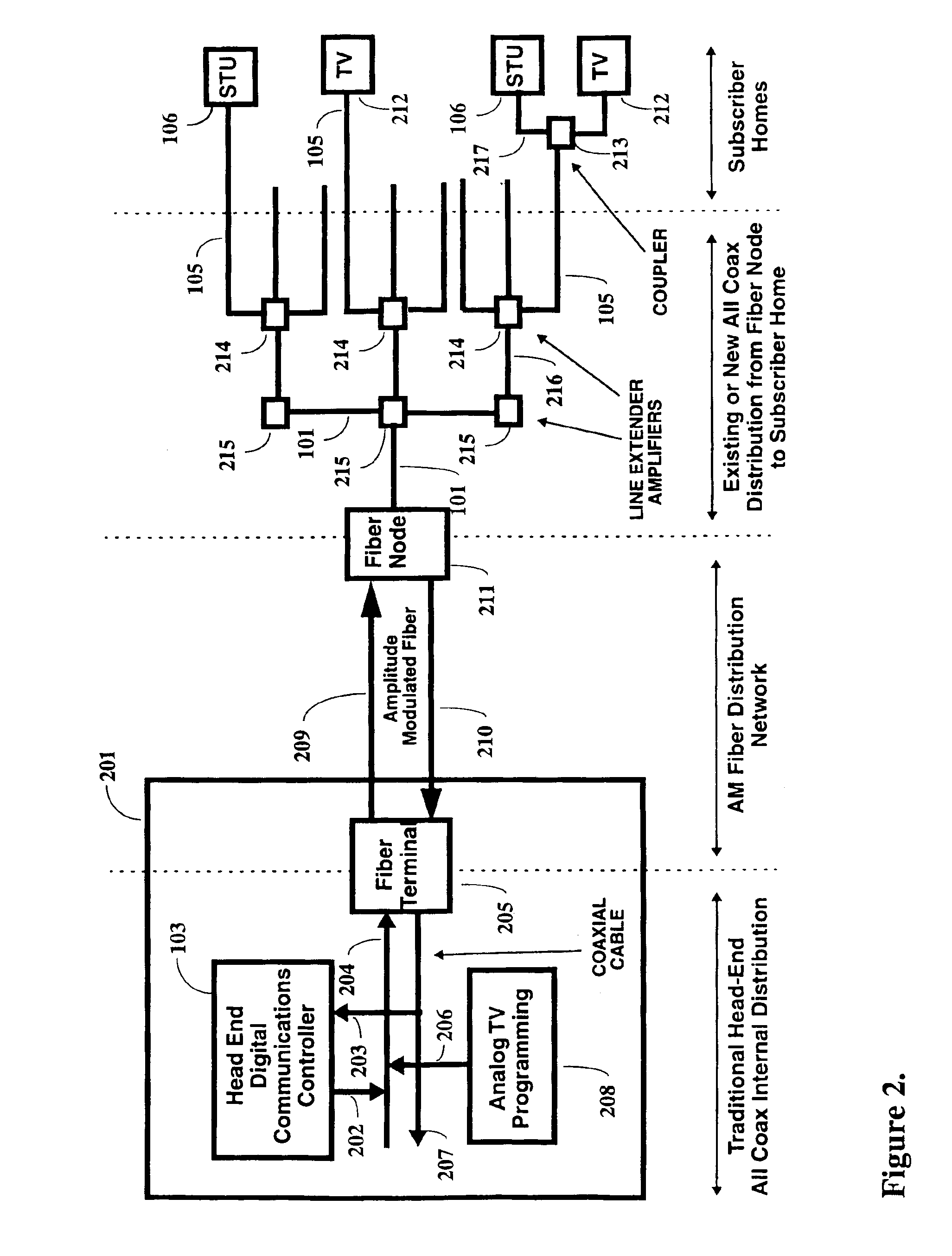
A two-way cable network offering high-speed broadband communications delivered via virtual private networks over a multi-channel shared media system. Bi-directional transmission of packet to ATM cell based communications is established between a head end communication controller and a number of subscriber terminal units, whereby individual cells are prioritized and routed according to a virtual connection. Virtual connections are organized to support multiple virtual private networks in a shared media CATV system. The virtual private network to which a particular STU belongs is user selectable and has the flexibility of handling multi up / downstream channels with different MAC domains. The present invention can also handle non-ATM MAC domains via the same common ATM switch. To overcome the limited number of addresses inherent to common ATM switches, a mapping / remapping function is implemented in the port cards. Furthermore, downstream as well as upstream traffic are filtered at each STU. In one embodiment, information pertaining to downstream traffic is used to implement predictive scheduling in order to improve the timing associated with the request / grant cycle. In another embodiment, a user has the ability to select a quality of service that best suits the needs of the current application. In a further embodiment, the scheduling function is associated with each of the receivers in order to provide improved scalability.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
ATM architecture and switching element
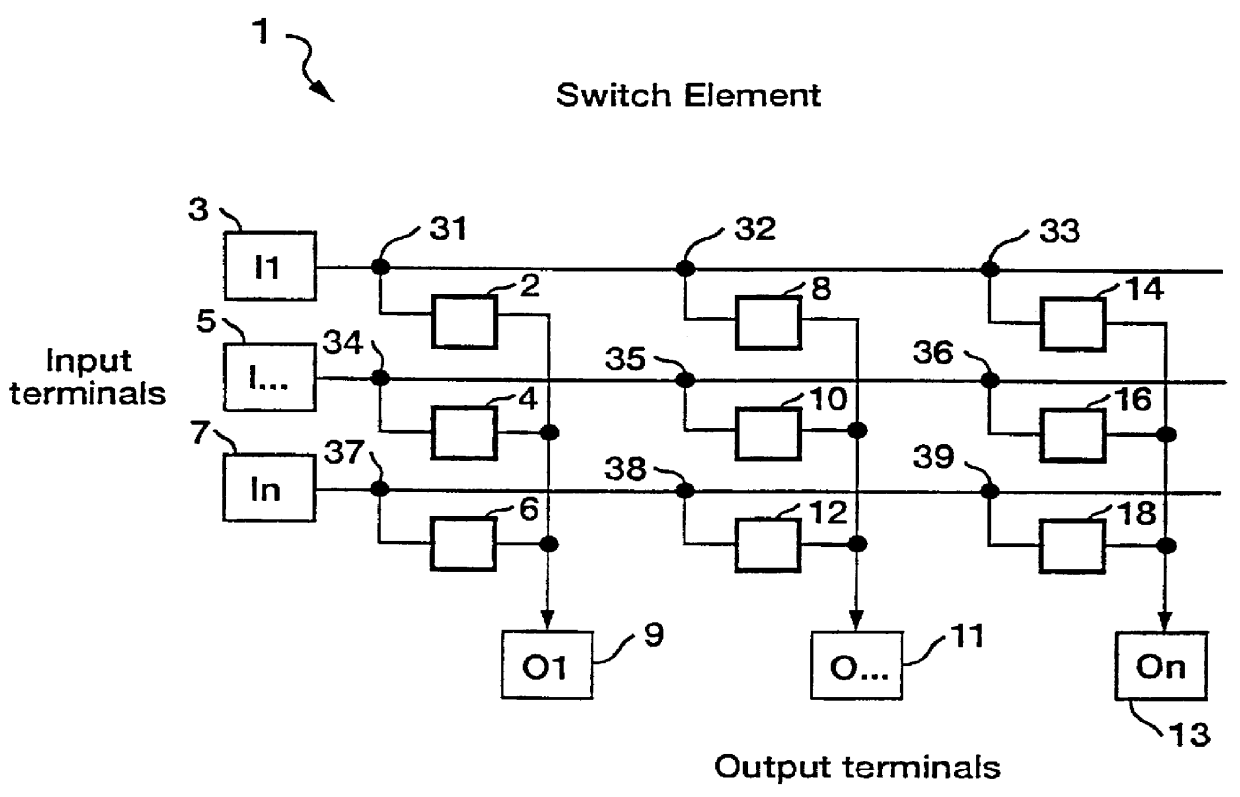
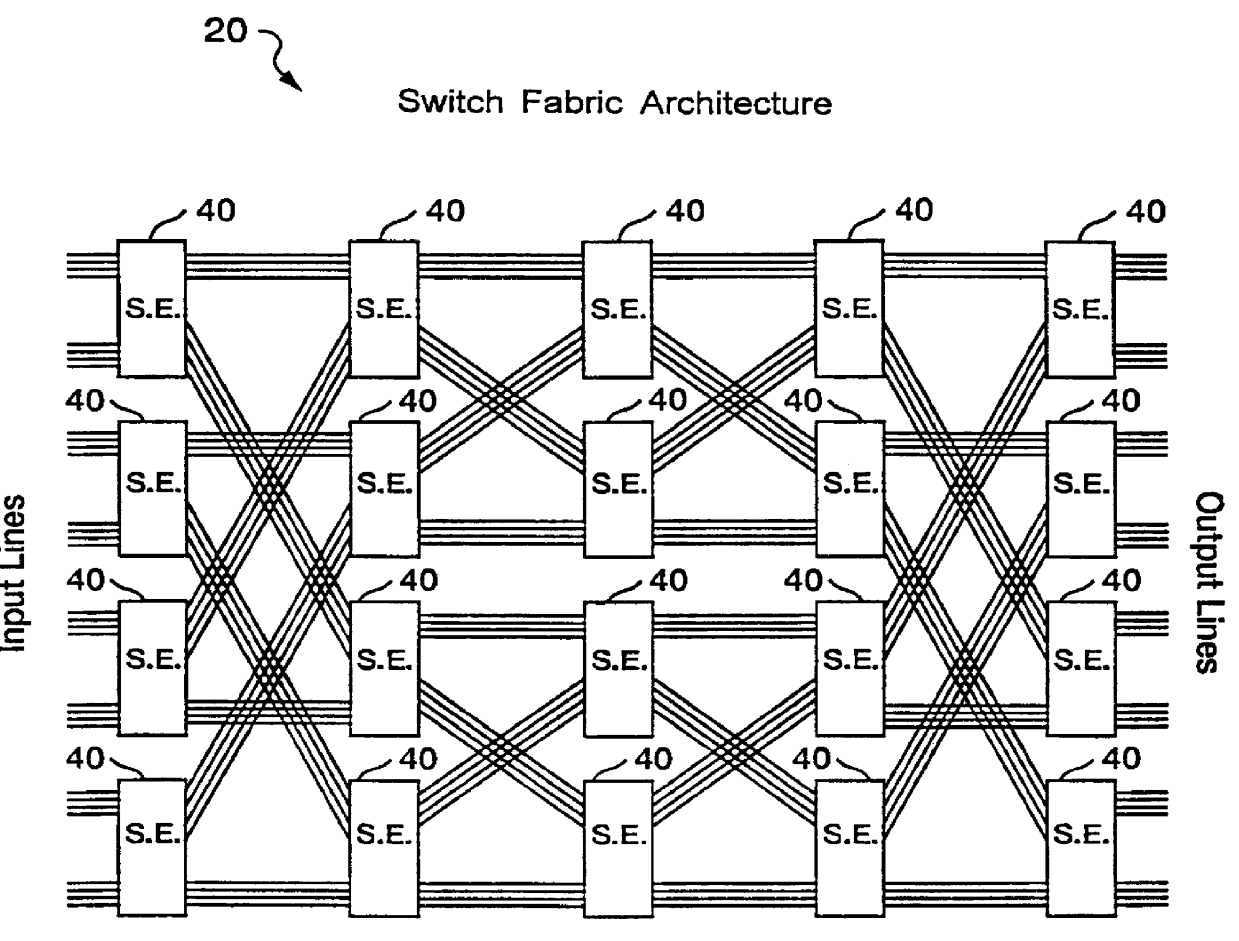
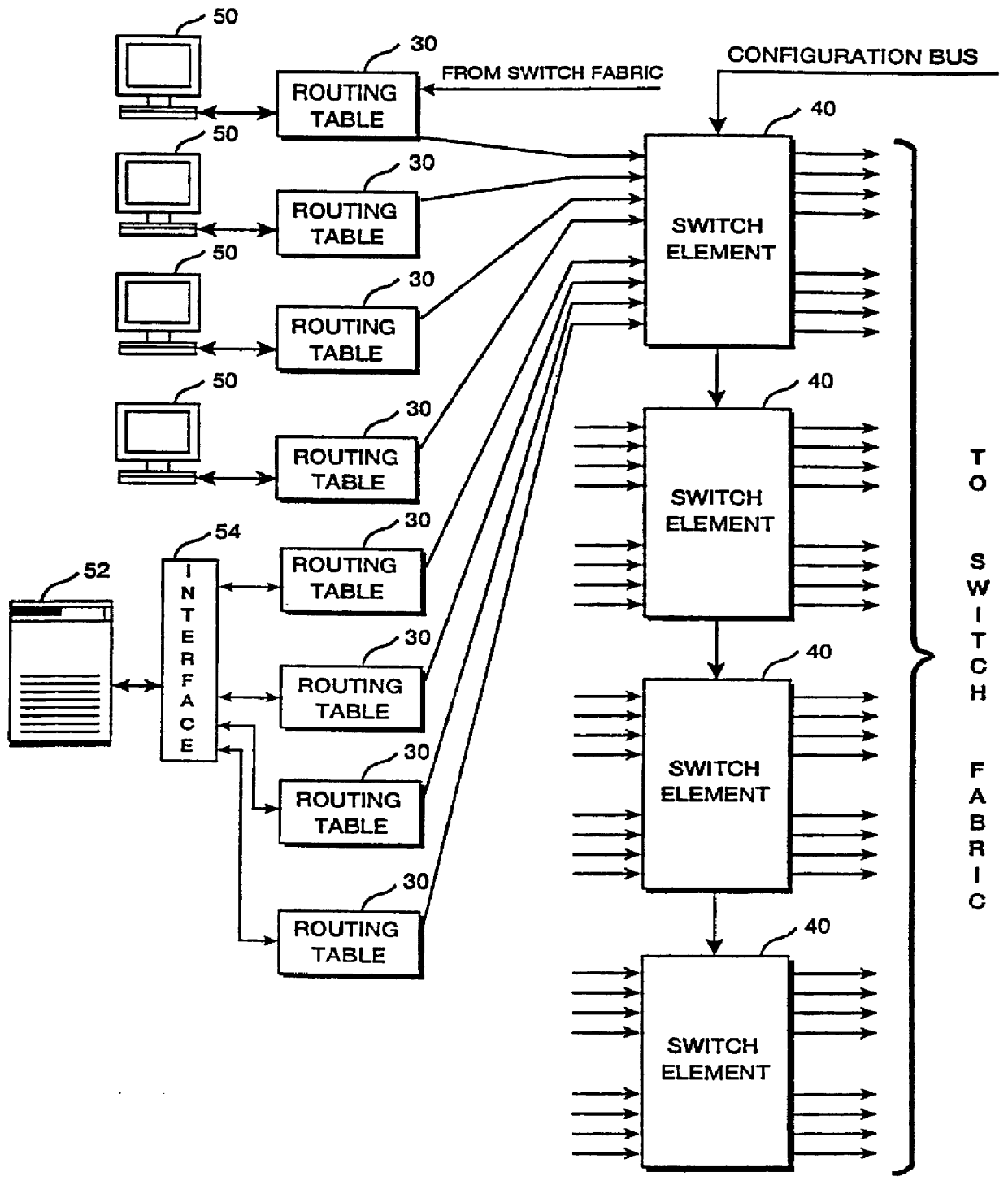
An ATM switching system architecture of a switch fabric-type is built of, a plurality of ATM switch element circuits and routing table circuits for each physical connection to / from the switch fabric. A shared pool of memory is employed to eliminate the need to provide memory at every crosspoint. Each routing table maintains a marked interrupt linked list for storing information about which ones of its virtual channels are experiencing congestion. This linked list is available to a processor in the external workstation to alert the processor when a congestion condition exists in one of the virtual channels. The switch element circuit typically has up to eight 4-bit-wide nibble inputs and eight 4-bit-wide nibble outputs and is capable of connecting cells received at any of its inputs to any of its outputs, based on the information in a routing tag uniquely associated with each cell.
Owner:PMC SEIRRA
ATM switching architecture for a wireless telecommunications network
InactiveUS6240078B1Solve insufficient bandwidthAvoid problemsConnection managementData switching by path configurationAtm switchingTelecommunications network
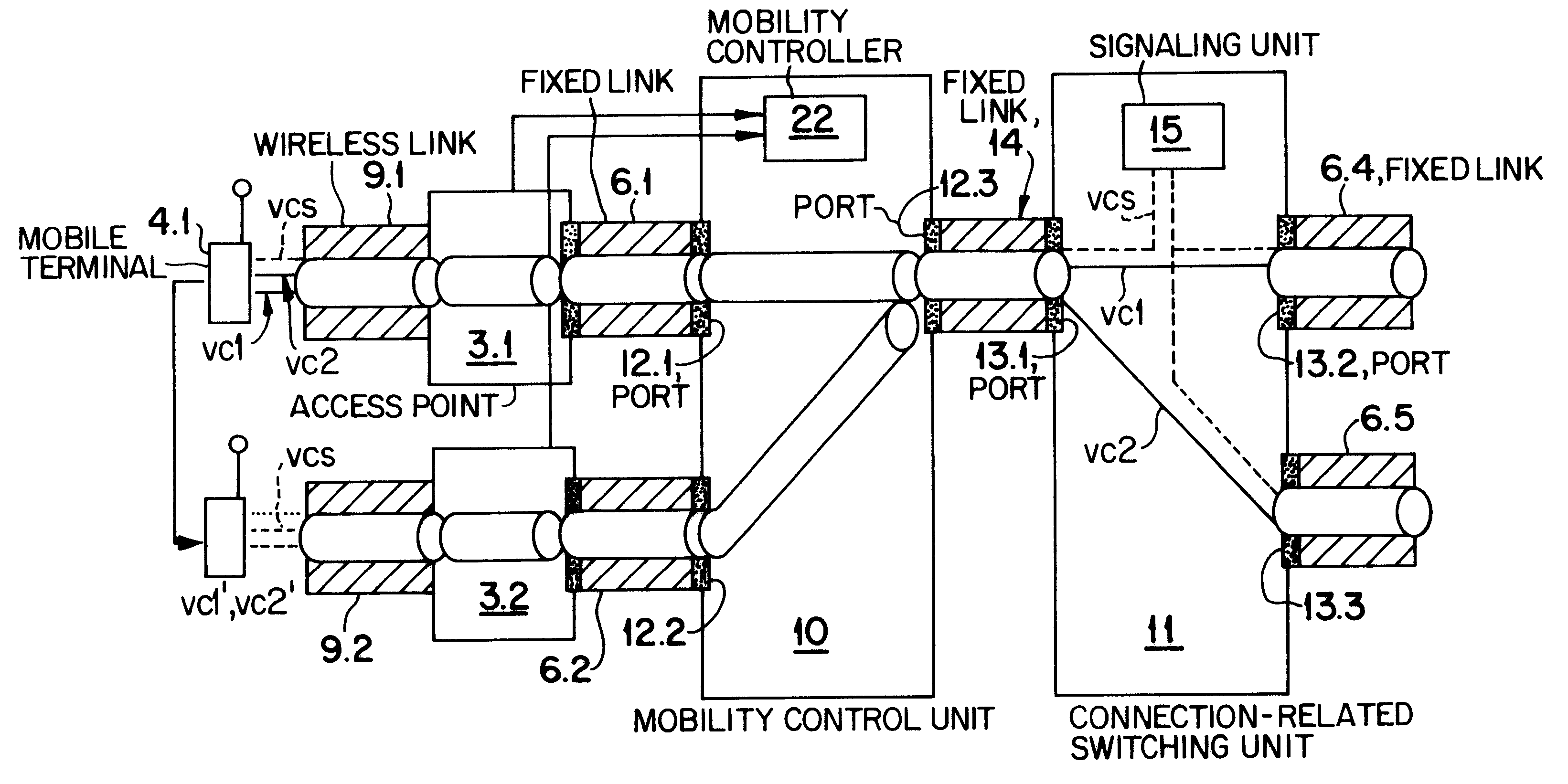
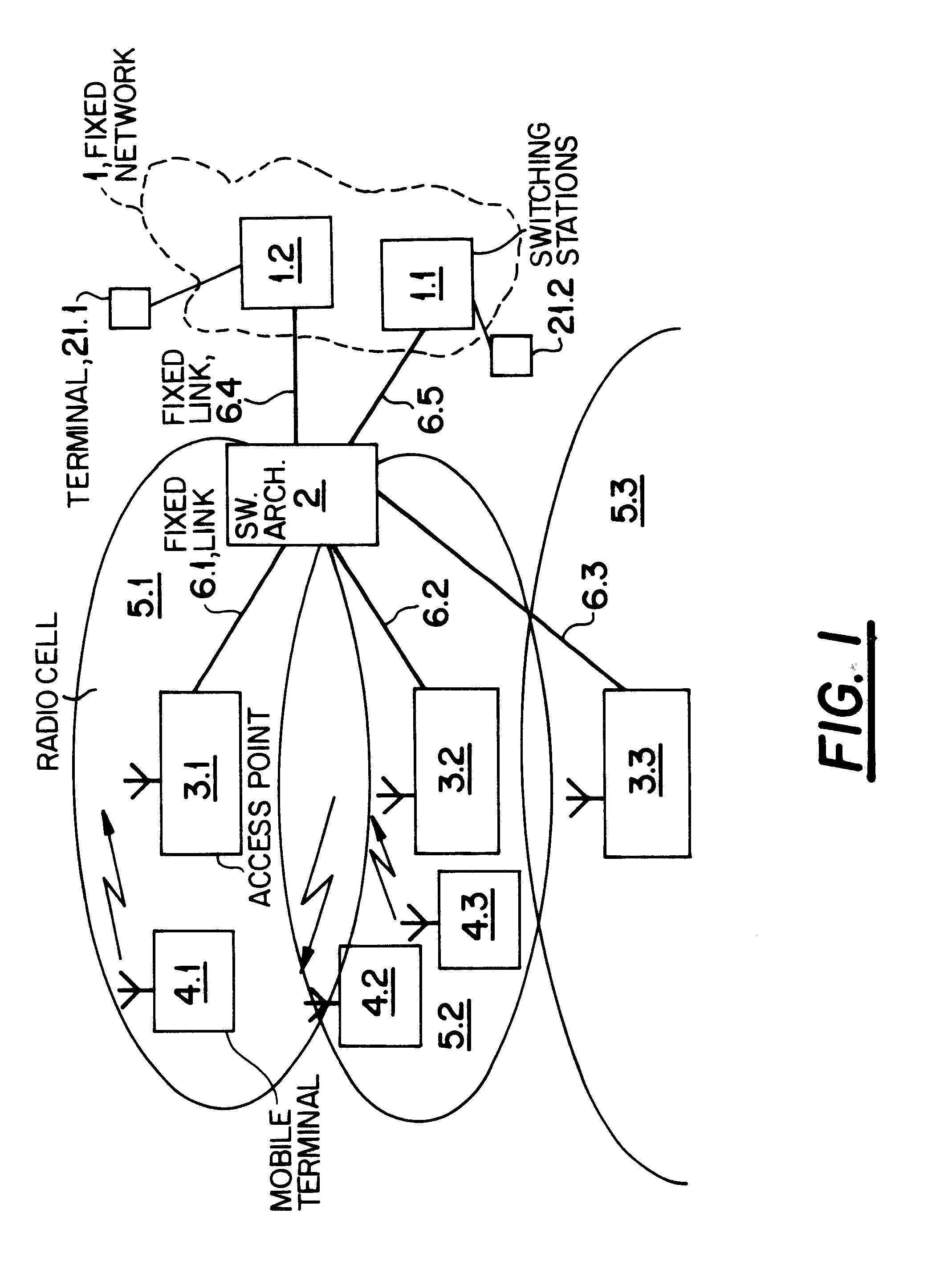
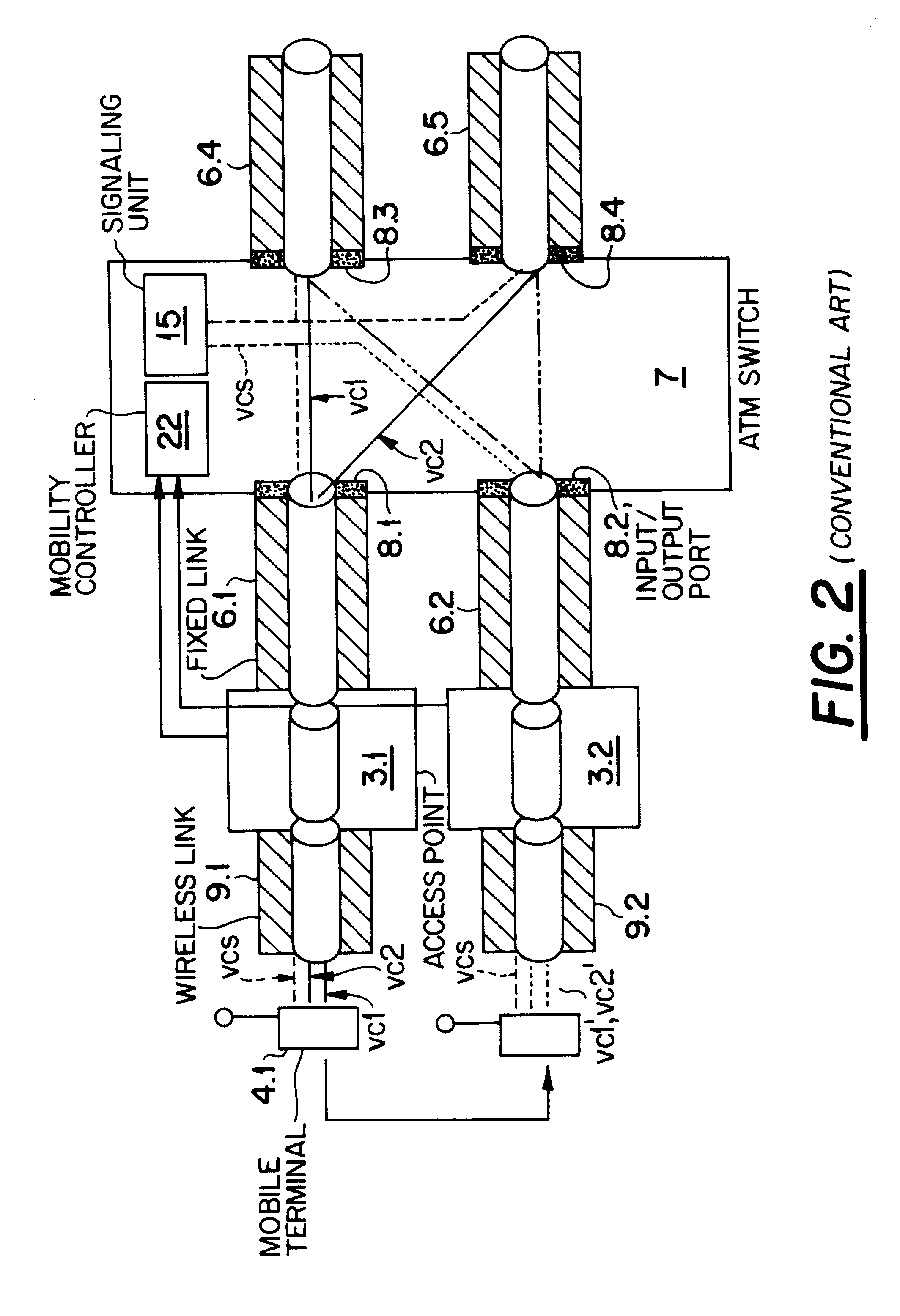
An ATM switching architecture for a wireless telecommunications network includes two separate units having different functionality. The first unit performs mobility control, wherein a virtual path which contains all virtual channels of a mobile terminal is switched from a first port associated with a first access point, to a second port connected to a first port of the second unit. The second unit performs a switching operation, wherein the virtual channels of the mobile terminal are distributed from the first port of the second unit to different destination ports of the second unit. In one embodiment, the two units may be dedicated hardware components, and in another embodiment, one single hardware component is functionally separated into two separate units connected by a loopback link.
Owner:NEC CORP
Random early detection (RED) algorithm using marked segments to detect congestion in a computer network
InactiveUS6888824B1Smooth changeEasy to handleMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexAtm switchingRandom early detection
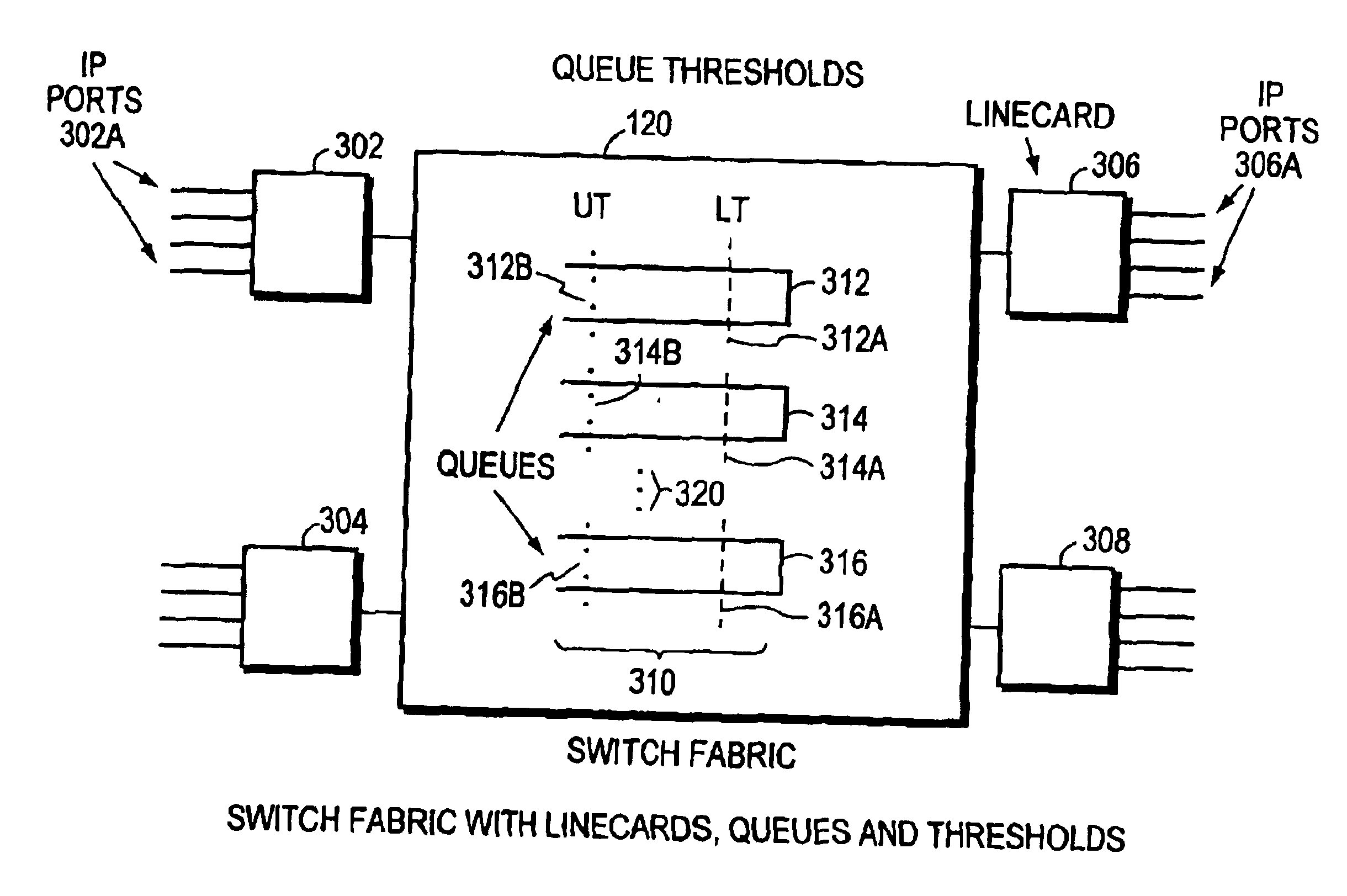
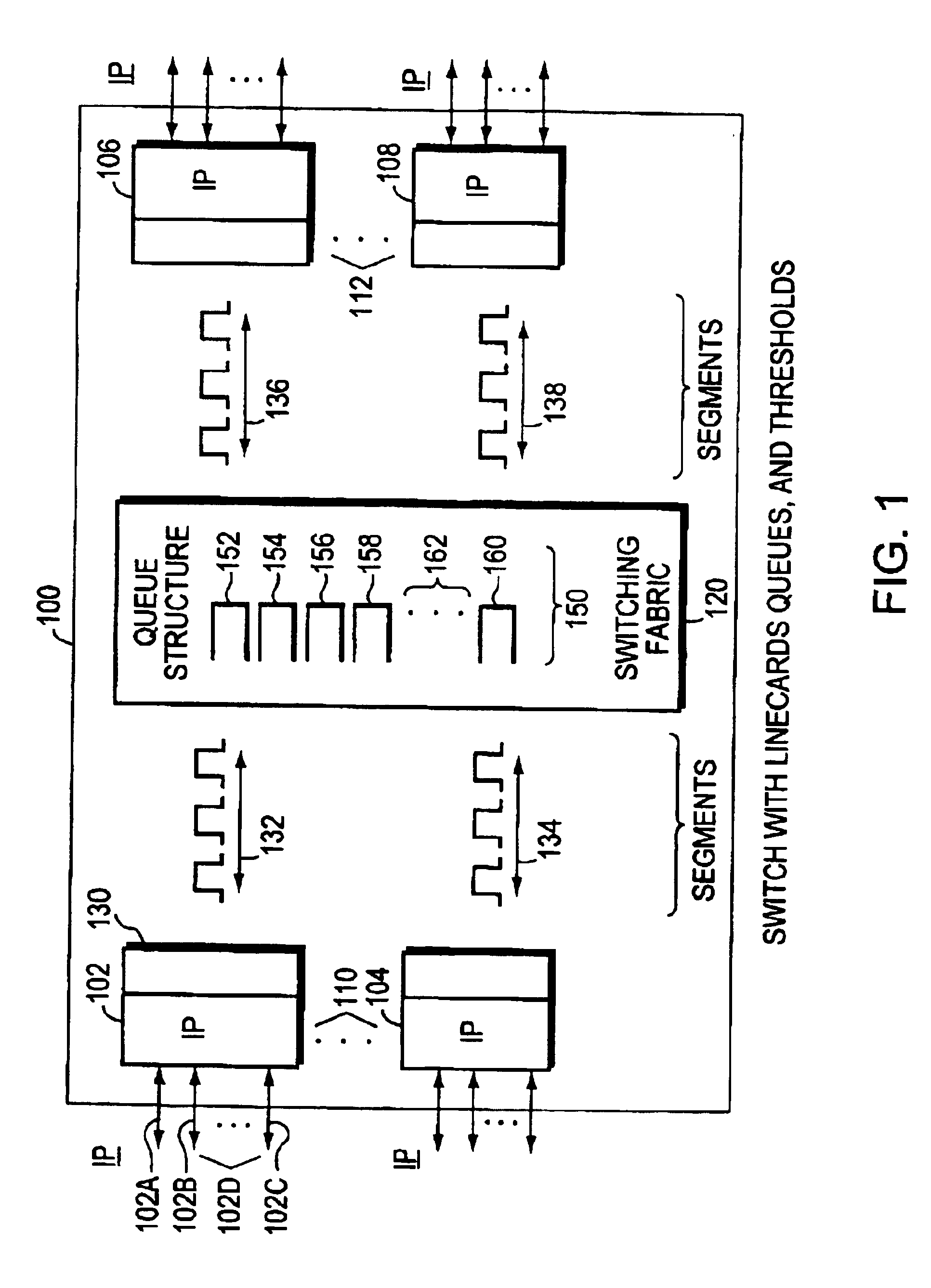
The invention is to use the ability of a switching fabric to set a congestion indicator bit in a segment if any queue through which the segment passes is filled above a lower threshold. The output linecard monitors the field of the congestion indicator bit as it receives segments from the switching fabric. The output linecard periodically calculates the ratio of segments having the congestion bit set to all segments routed to a particular port. The periodically calculated ratio is used as an input parameter to a Random Early Detection (RED) algorithm. The RED algorithm selects a packet for the output linecard to drop, by use of a random selection method. The destination computer then does not receive the packet. The random selection of packets to drop has the effect of helping to prevent undesirable network synchronization of transmission of replacement packets. With adaptive source computers, the network device then does not reach a congested state, thereby maintaining optimum throughput for the computer network. When an ATM switching fabric is used with ATM cells for the segments, then the Explicit Forward Congestion Indication Field (EFCI bit) of a data cell is used to mark a data cell which has passed through a queue which is filled above a lower threshold level. Data cells arriving at the output line card with the EFCI bit set are then counted, and this count is used in the periodic calculation of the ratio used as input to the RED algorithm.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
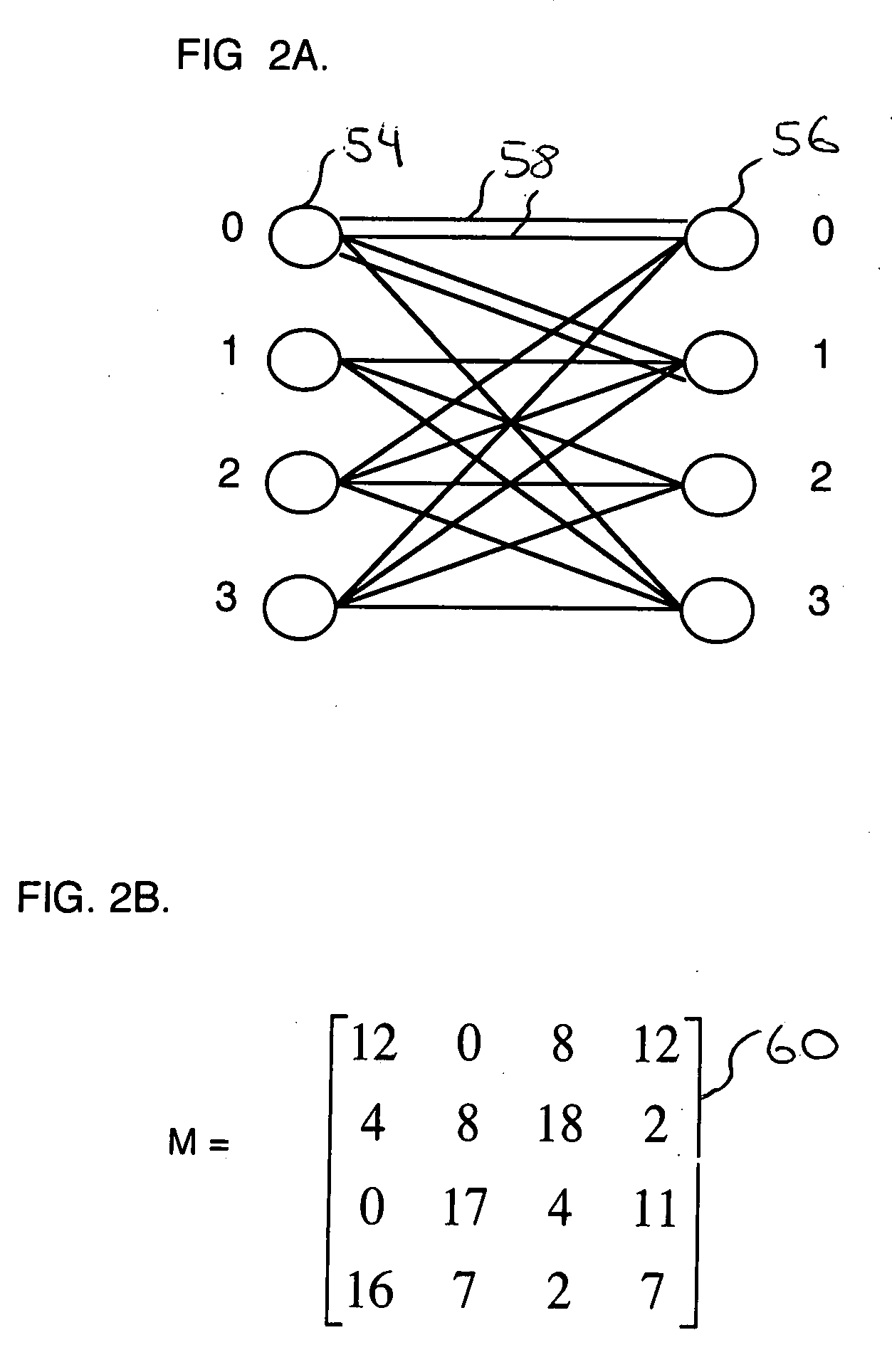
Method and apparatus to schedule packets through a crossbar switch with delay guarantees
ActiveUS20070280261A1Minimize delay jitterMeet bandwidth requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCrossbar switchDifferentiated services
A method for scheduling cell transmissions through a switch with rate and delay guarantees and with low jitter is proposed. The method applies to a classic input-buffered N×N crossbar switch without speedup. The time axis is divided into frames each containing F time-slots. An N×N traffic rate matrix specifies a quantized guaranteed traffic rate from each input port to each output port. The traffic rate matrix is transformed into a permutation with NF elements which is decomposed into F permutations of N elements using a recursive and fair decomposition method. Each permutation is used to configure the crossbar switch for one time-slot within a frame of size F time-slots, and all F permutations result in a Frame Schedule. In the frame schedule, the expected Inter-Departure Time (IDT) between cells in a flow equals the Ideal IDT and the delay jitter is bounded and small. For fixed frame size F, an individual flow can often be scheduled in O(logN) steps, while a complete reconfiguration requires O(NlogN) steps when implemented in a serial processor. An RSVP or Differentiated Services-like algorithm can be used to reserve bandwidth and buffer space in an IP-router, an ATM switch or MPLS switch during a connection setup phase, and the proposed method can be used to schedule traffic in each router or switch. Best-effort traffic can be scheduled using any existing dynamic scheduling algorithm to fill the remaining unused switch capacity within each Frame. The scheduling algorithm also supports multicast traffic.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED HENRYK
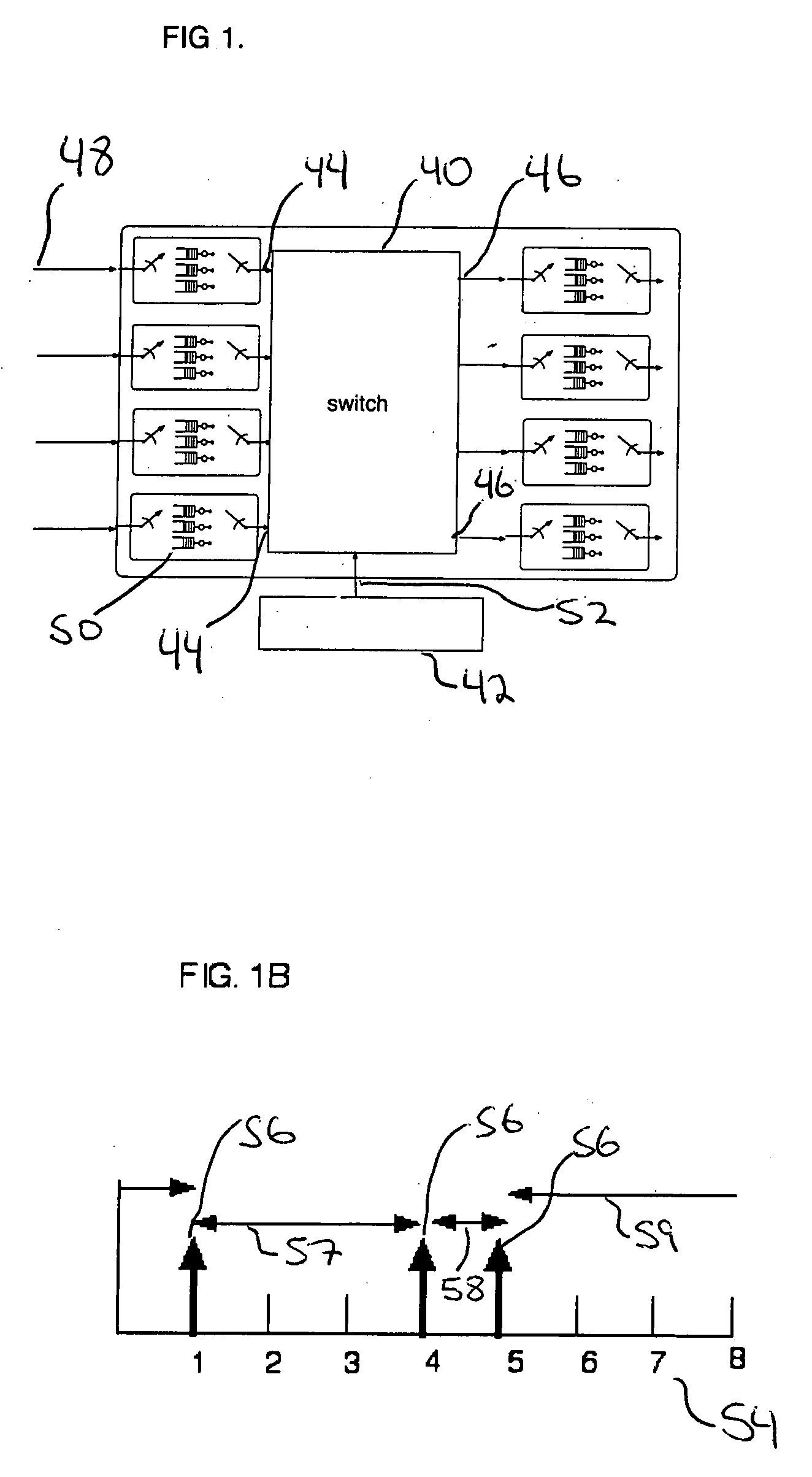
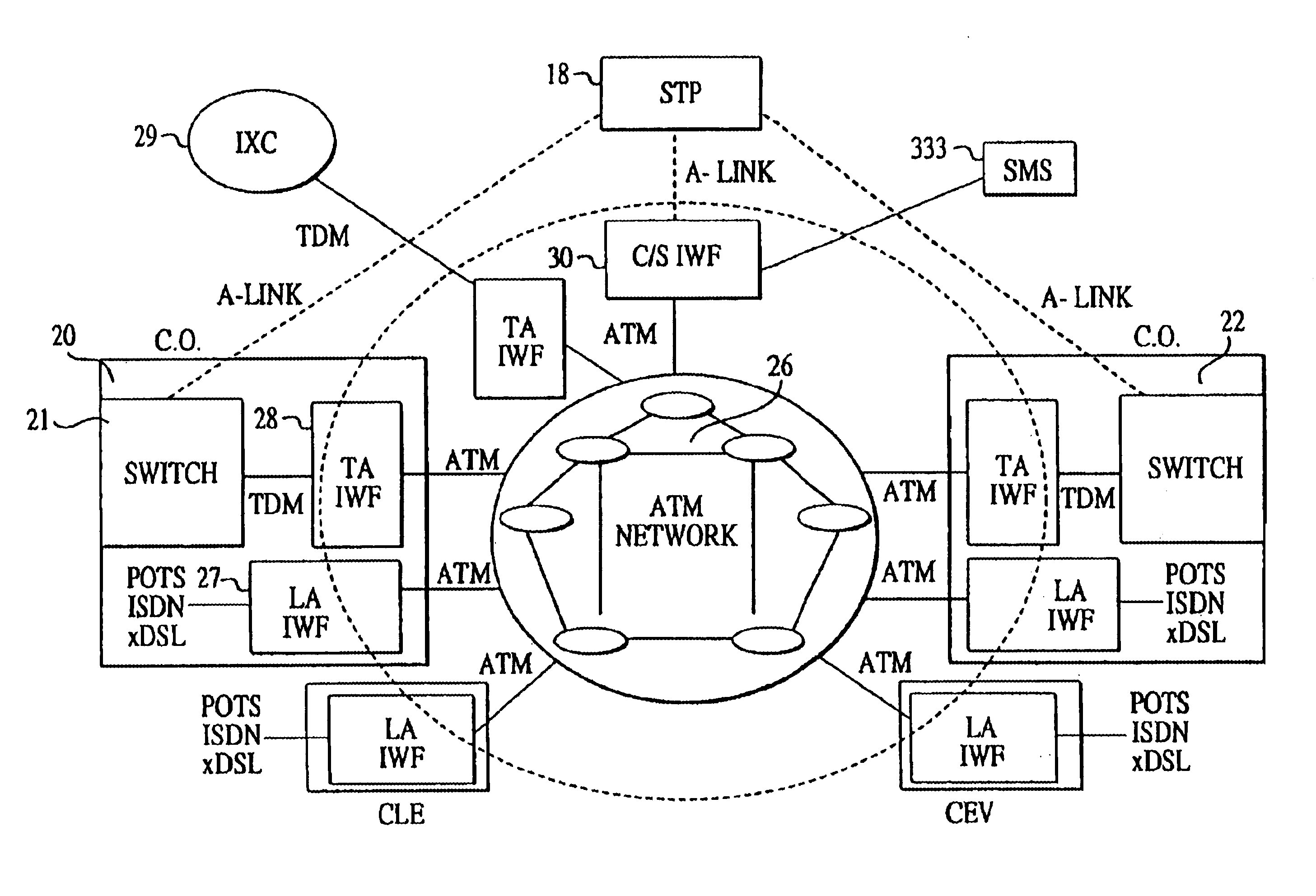
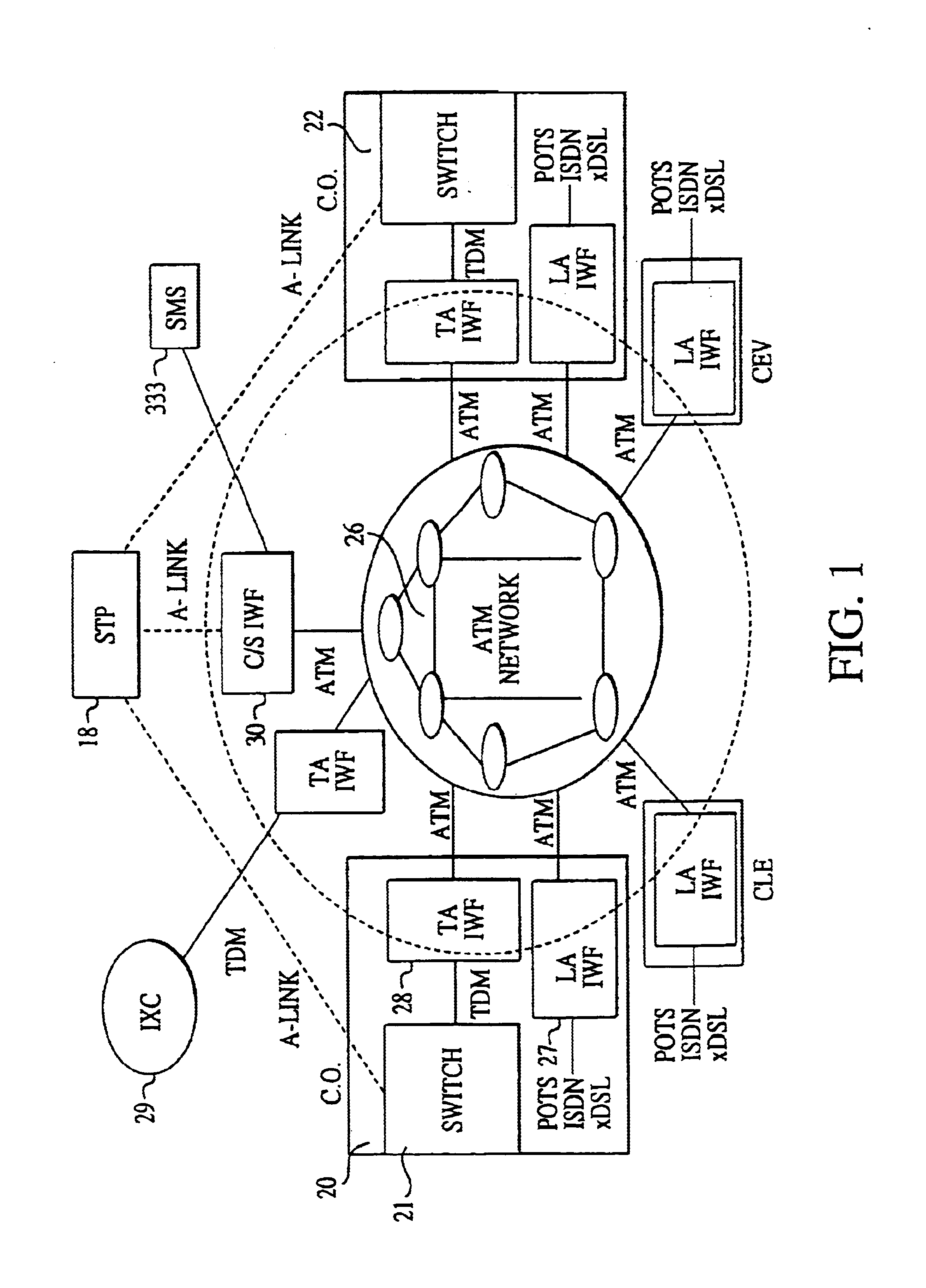
ATM-based distributed network switching system
InactiveUS6765903B1Multiplex communicationData switching by path configurationAtm switchingBroadband
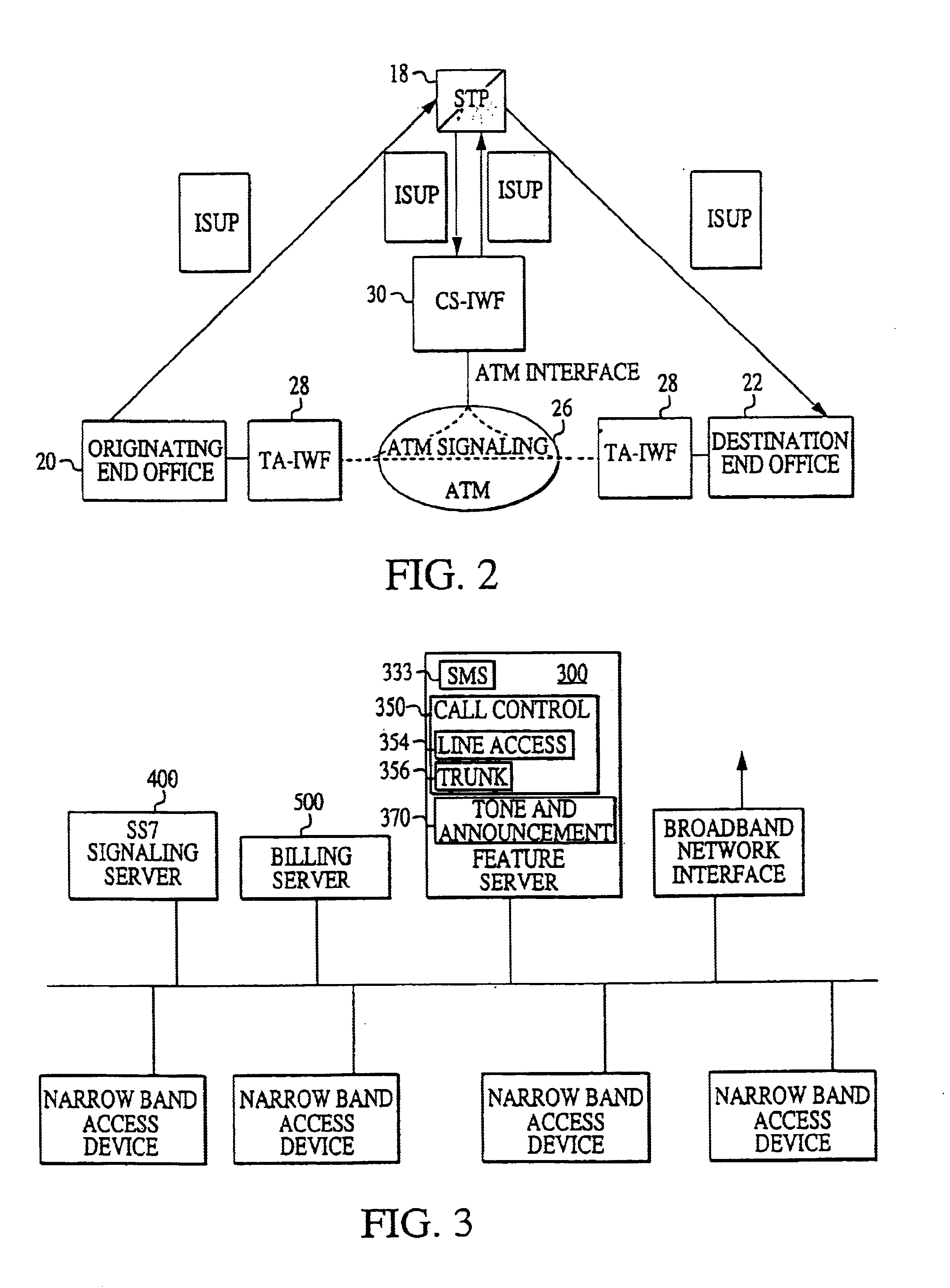
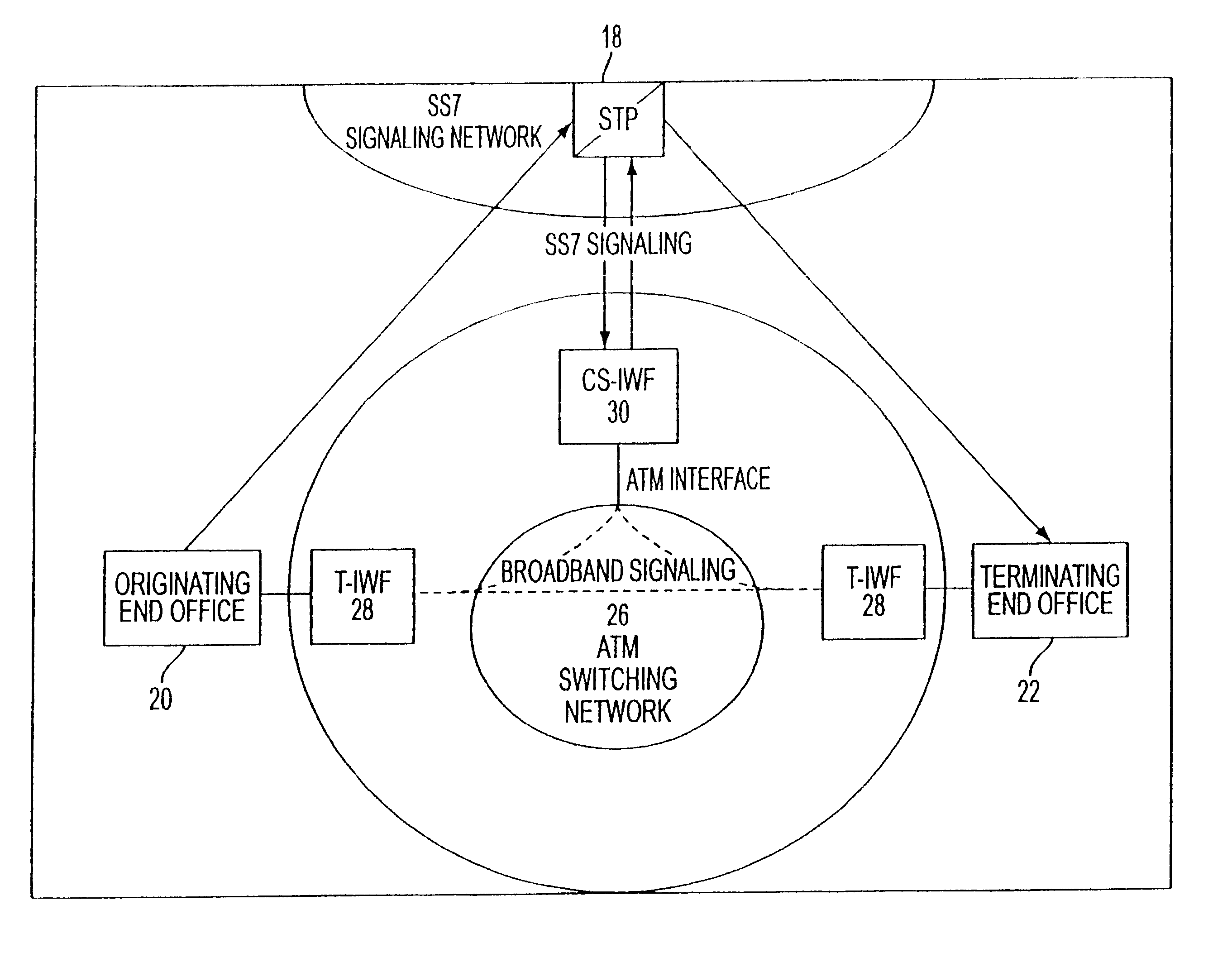
An Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)-based distributed network switching system includes an ATM switching network that dynamically sets up individual switched virtual connections. The system also includes multiple access interworking function (A-IWF) devices each operating as a gateway that enables customer premises devices to directly interface into the distributed ATM switching fabric. The system further includes a centralized control and signaling interworking function (CS-IWF) device that performs call control functions and administrative functions and is adapted to interface narrowband and broadband signaling for call processing and control within the ATM switching network. The CS-IWF device may be a server farm.
Owner:AT&T LABS
ATM-based distributed virtual tandem switching system
InactiveUS6389011B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAtm switchingBroadband
An Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)-based distributed virtual tandem switching system is provided in which a network of ATM-based devices is combined to create a distributed virtual tandem switch. The system includes an ATM switching network that dynamically sets up individual switched virtual connections. The system also includes a trunk interworking function (T-IWF) device and a centralized control and signaling interworking function (CS-IWF) device. The trunk interworking function device converts end office voice trunks from TDM channels to ATM cells by employing a structured circuit emulation service. The centralized control and signaling interworking function device performs call control functions and interfaces narrowband signaling and broadband signaling for call processing and control within the ATM switching network. Consequently, the ATM based distributed virtual tandem switching system replaces a standard tandem switch in the PSTN.
Owner:SBC TECH RESOURCES
IP multicast services over ATM multicast
InactiveUS6931005B1Reduce congestionGood serviceNetworks interconnectionTime-division multiplexing selectionAtm switchingTraffic capacity
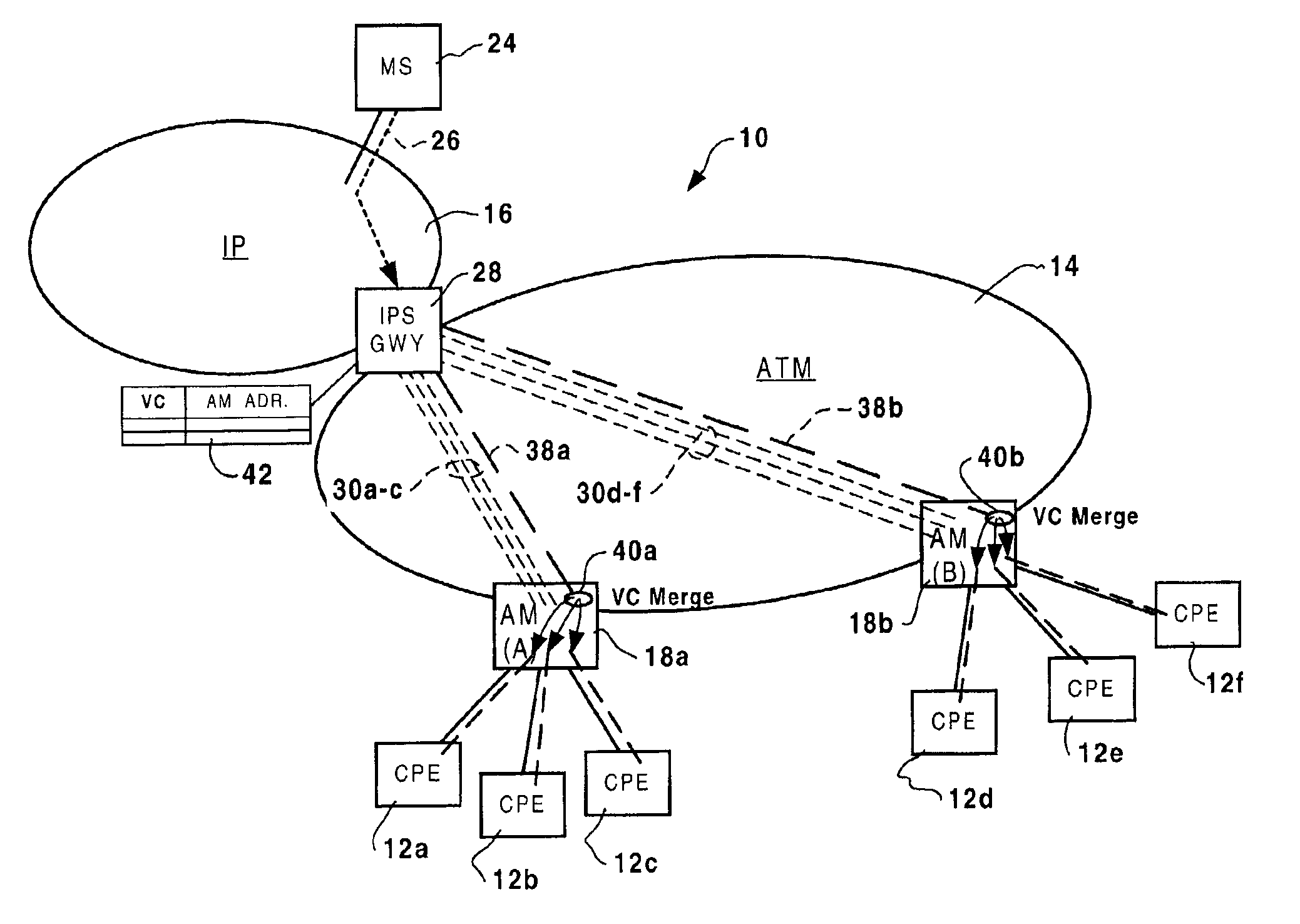
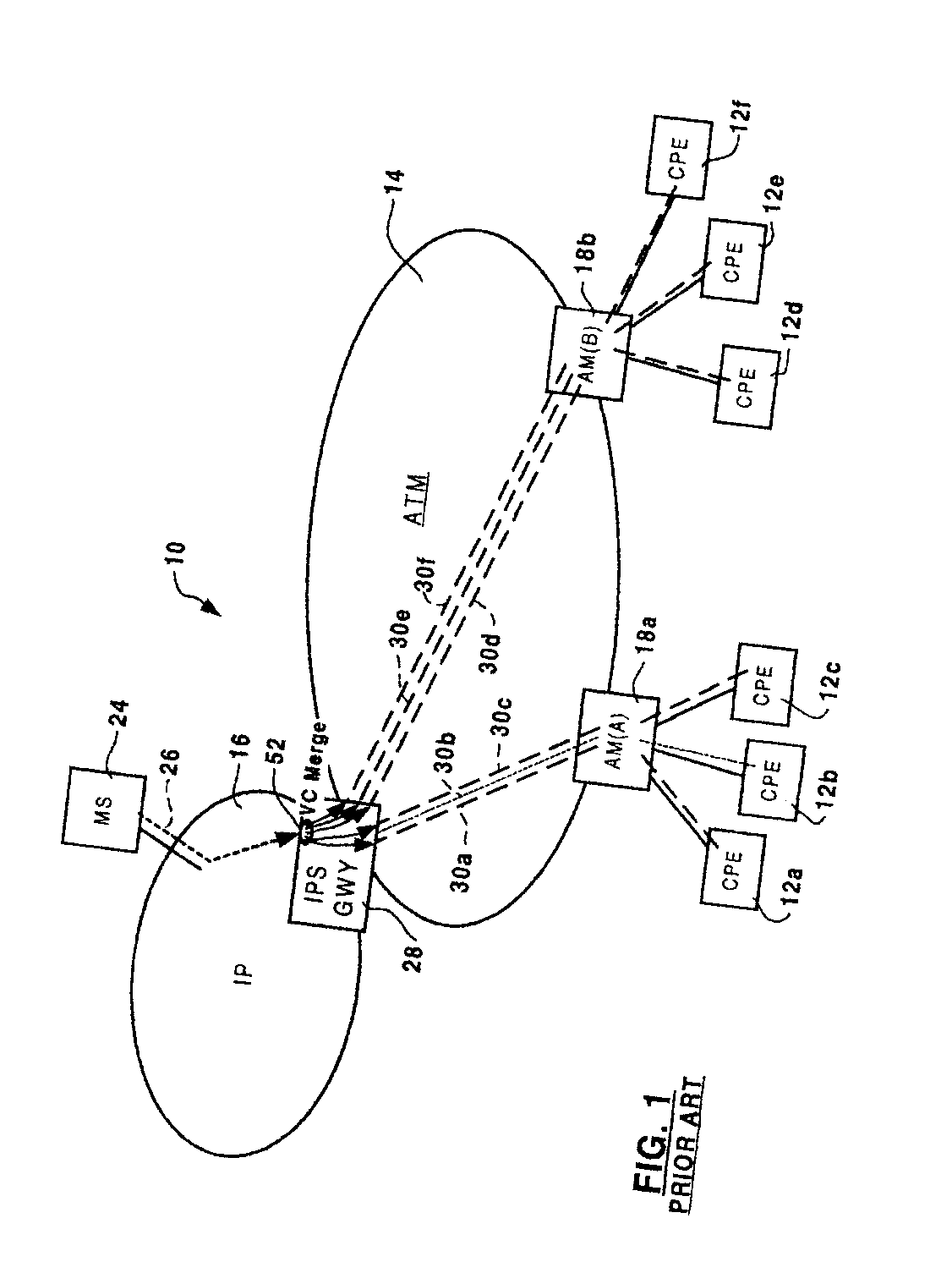
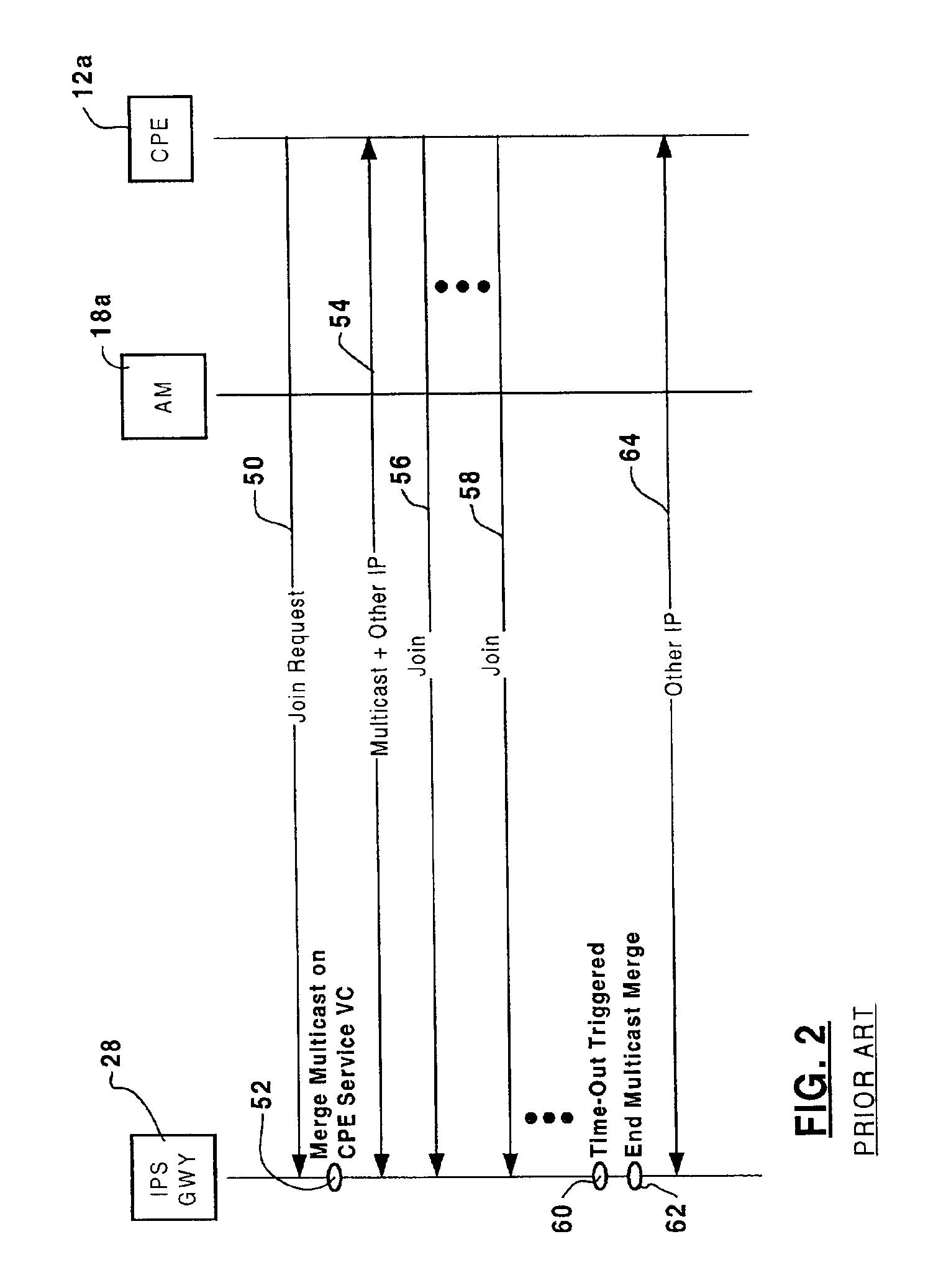
A method and apparatus for reducing bandwidth usage in an ATM switching network by controlling bandwidth used for IP multicasting through the switching network. Bandwidth usage is controlled by modifying ingress and access modules, such as IP service gateways and access modules that terminate branches of a multicast tree. If a join request is received at an IP service gateway from a sink node served by an access module, the IP service gateway instructs the access module to graft a leaf to the branch to join the sink node to the tree and to merge the multicast packets with other IP packets for the sink node. Consequently, only one connection carrying the multicast traffic is required between the IP service gateway and the access module. Bandwidth usage in the ATM switching network is thereby controlled, and bandwidth usage in service access trunks connecting the access modules to the ATM switching network is reduced.
Owner:AVAYA INC
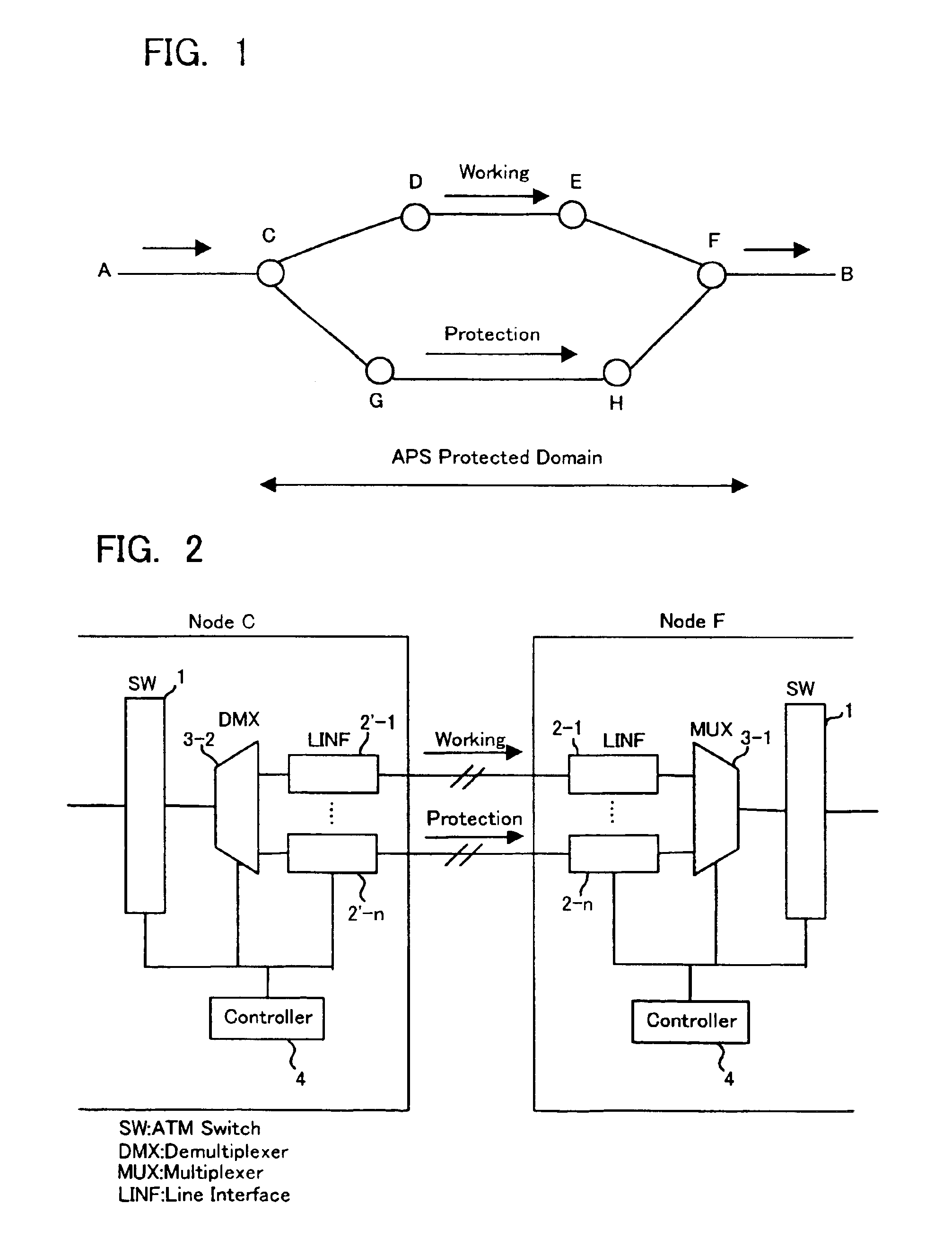
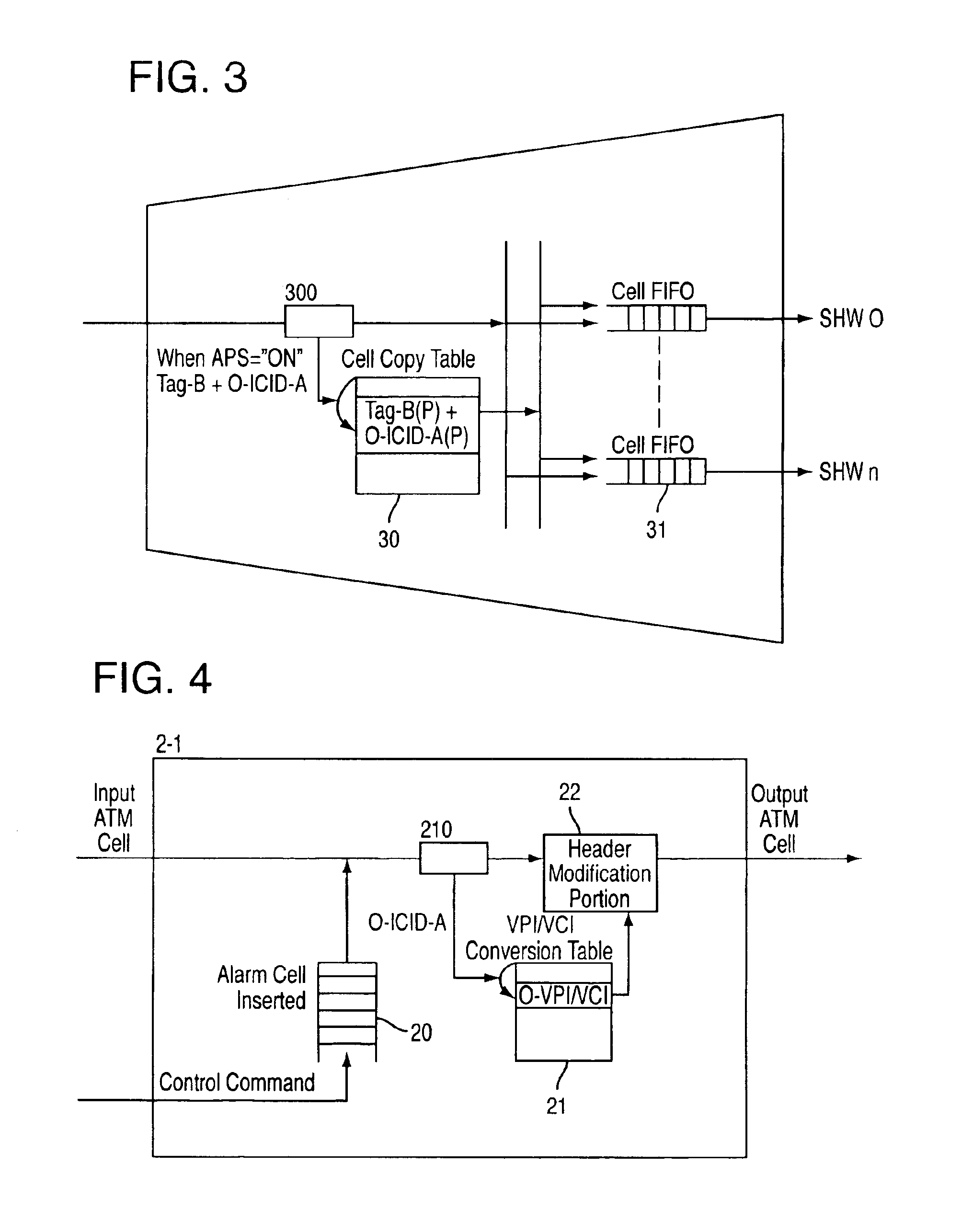
ATM switching system and method for switchover between working channel and protection channel in an ATM network
InactiveUS6856594B1Simple and efficient mannerError preventionTransmission systemsAtm switchingTelecommunications
A method and system including ATM switching equipment provided for switching between a working channel and a protection channel in an ATM network. The method and system include the following processes: In each cell for transmission providing an indication of whether the cell belongs connection currently in a working state via a working channel; cells are duplicated on each connection basis; the duplicated cells are transmitted simultaneously on both a working channel and a protection channel; and valid cells are selected from received cells according to the indication in each cell indicating whether the relevant connection is currently in a working state.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
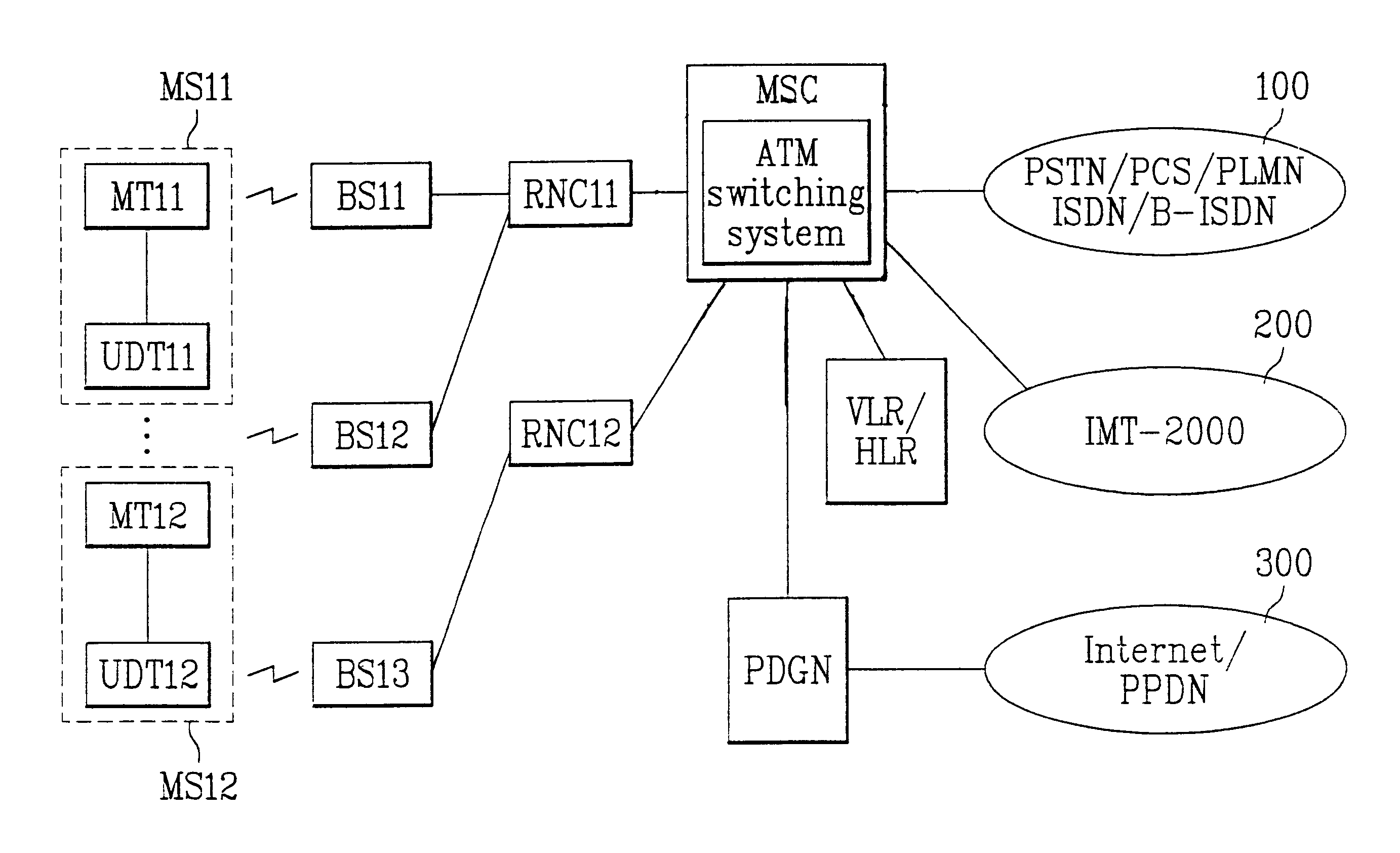
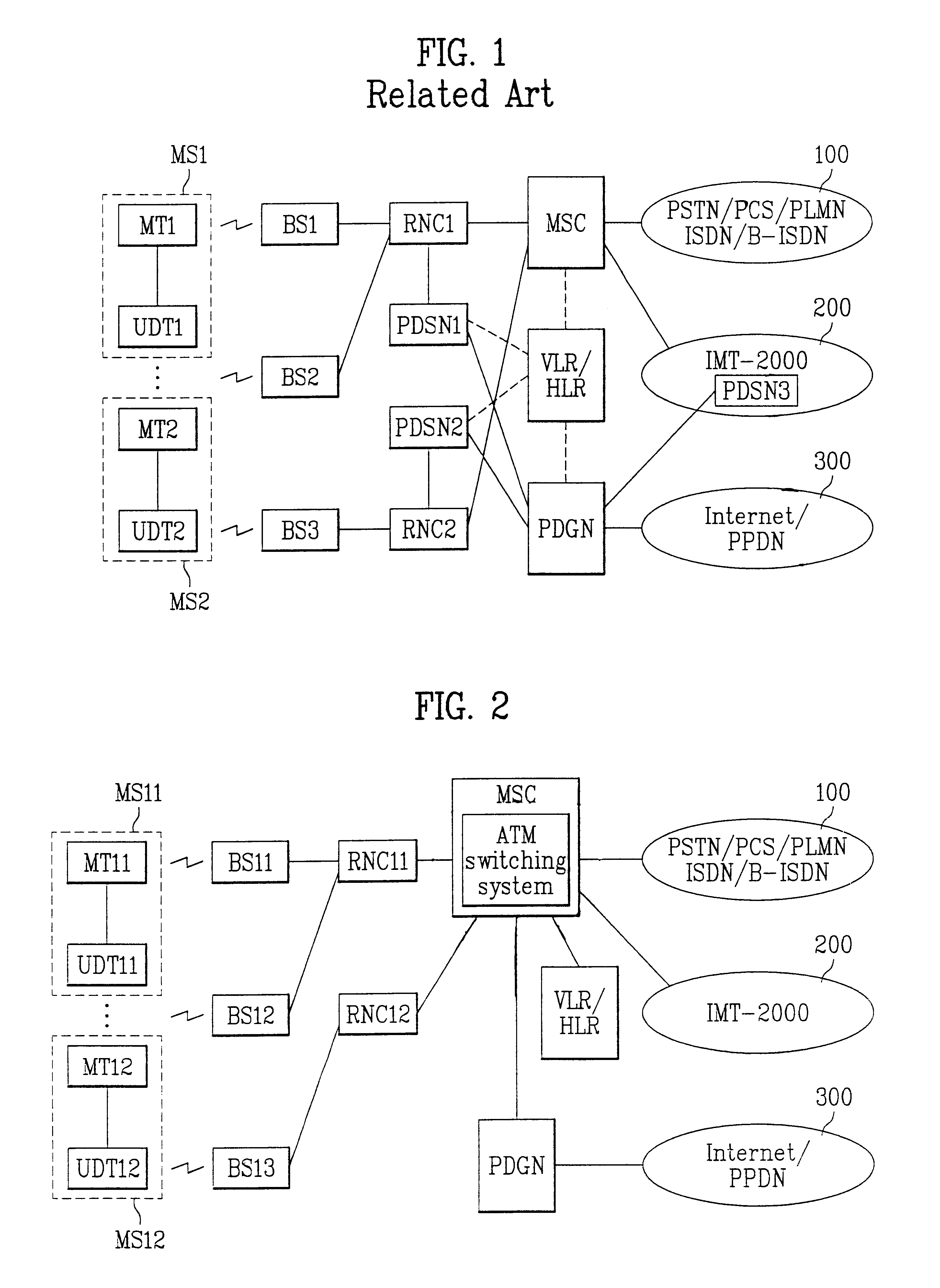
Architecture of mobile communication systems network and method for transmitting packet data using the same
InactiveUS6876634B1Minimize signalingIncrease contactNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexAtm switchingRadio networks
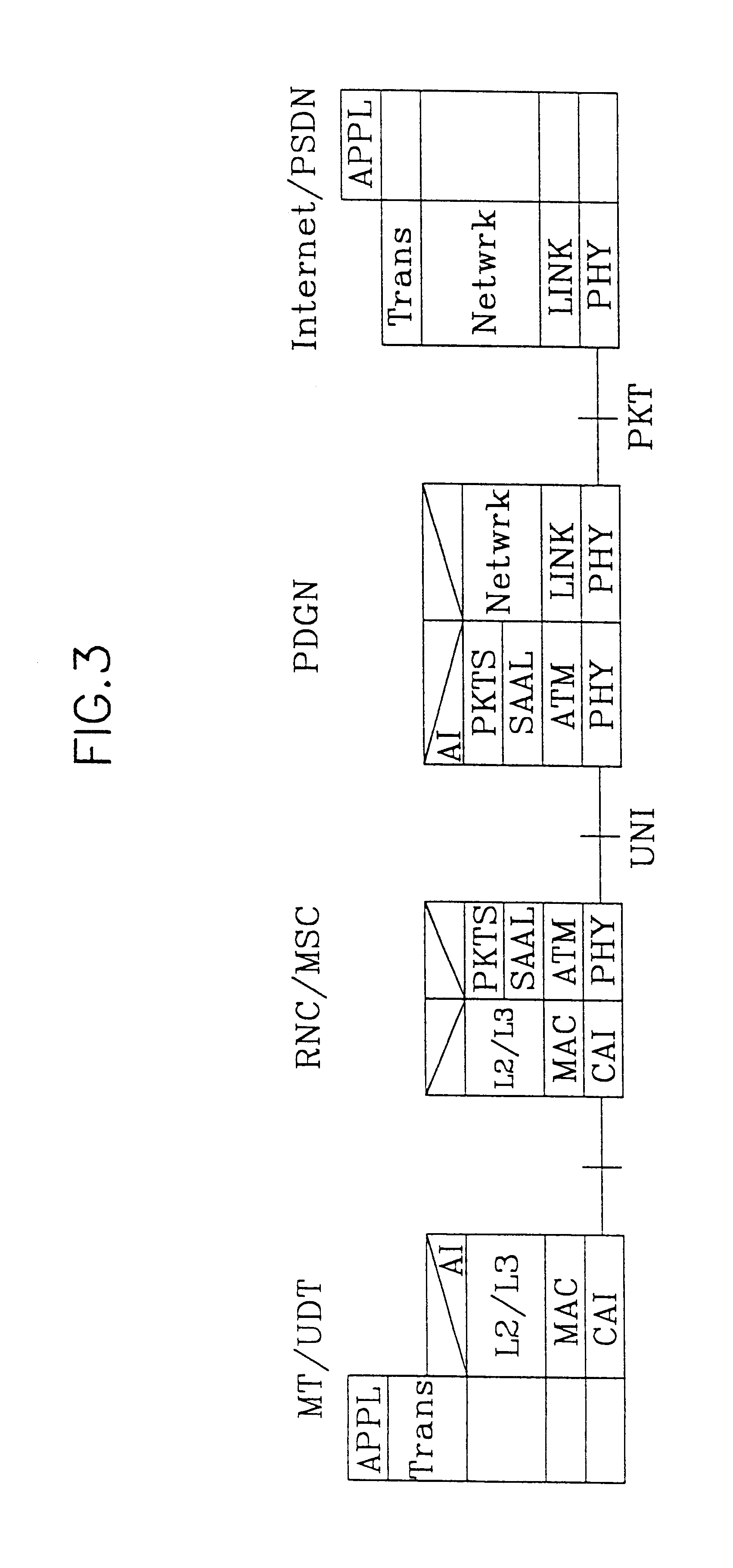
Architecture of a mobile communication system network and method for transmitting a packet data using the same, which can minimize required signal links and interlocking lines, the architecture including a plurality of radio network controllers each connected to a plurality of base stations in a cell or a sector to which the network controller pertains for separating a packet data service path from a circuit data service path when a particular mobile station is matched to this core network, at least one mobile switching center connected to the plurality of radio network controllers in a region of the mobile switching center by an ATM switching system for routing an originating call from the mobile station or a terminating call to the mobile station, a VLR / HLR(Visitor location register / home location register) connected to the mobile switching center for managing mobility of the mobile stations, and at least one PDGN(Packet data gateway node) for routing a packet data provided from either the mobile switching center or an external network according to a terminating call side identification number.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Traffic rate controller in a packet switching network
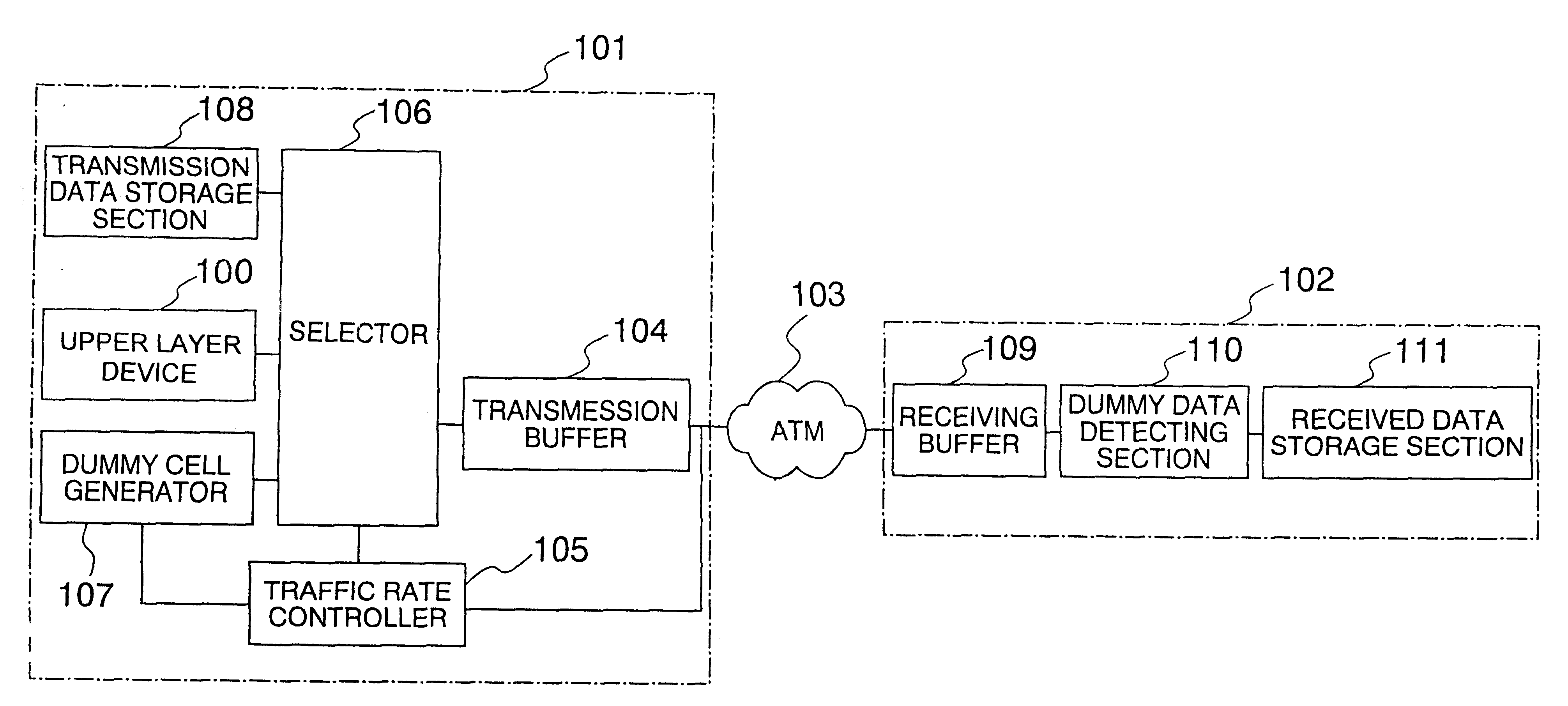
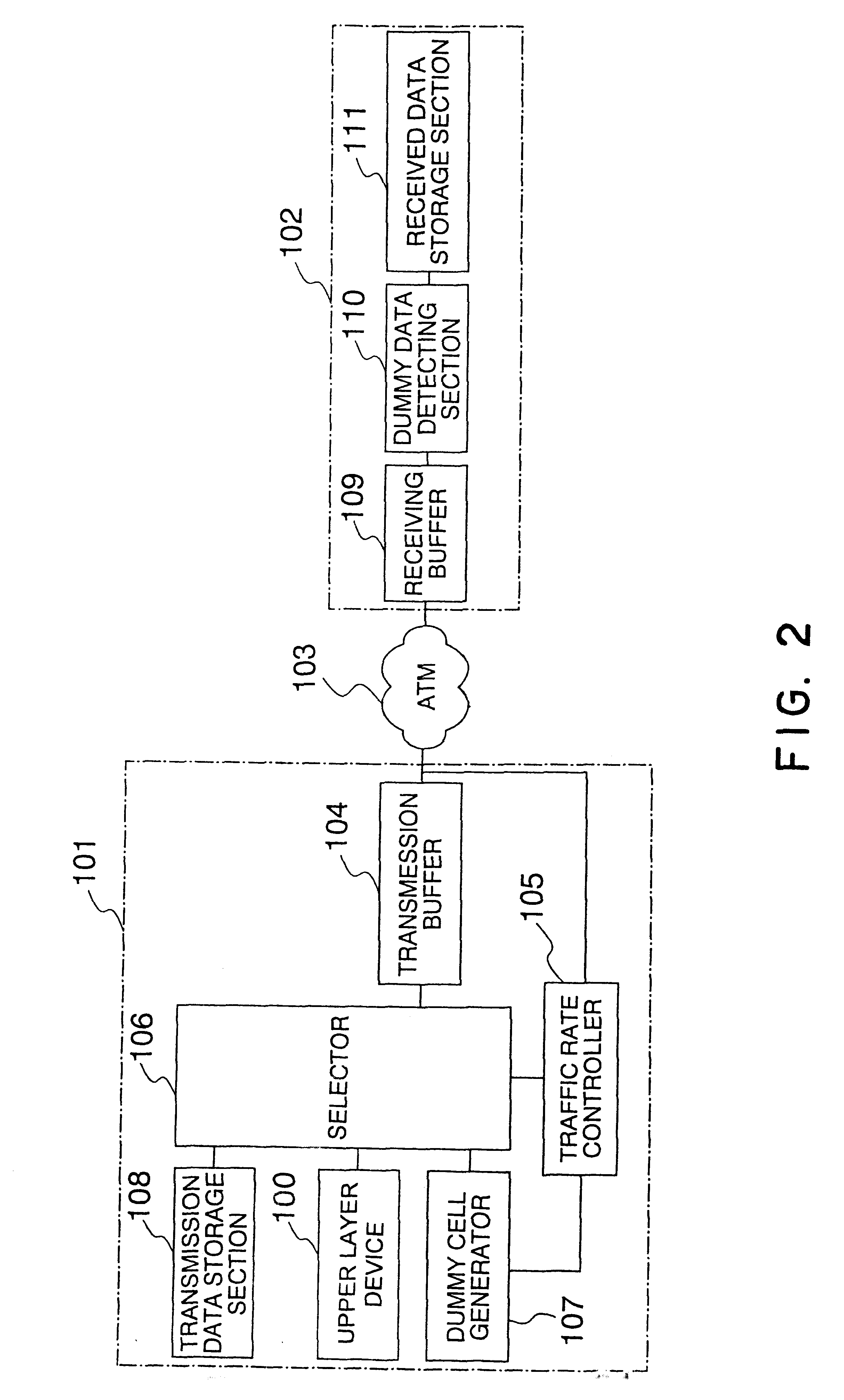
A packet switching network includes a transmitting station, an ATM switching system and a receiving station. The transmitting station has a traffic rate controller for controlling the traffic rate based on the congestion in the ATM switching system as well as the data cells stored in the transmission data storage section for receiving data for transmission. The traffic rate controller controls the number of transmitted cells between adjacent forward resource management (FRM cells, thereby avoiding a reduction in the traffic rate during data transmission which is caused by lack of available data for transmission supplied to the transmission station.
Owner:NEC CORP
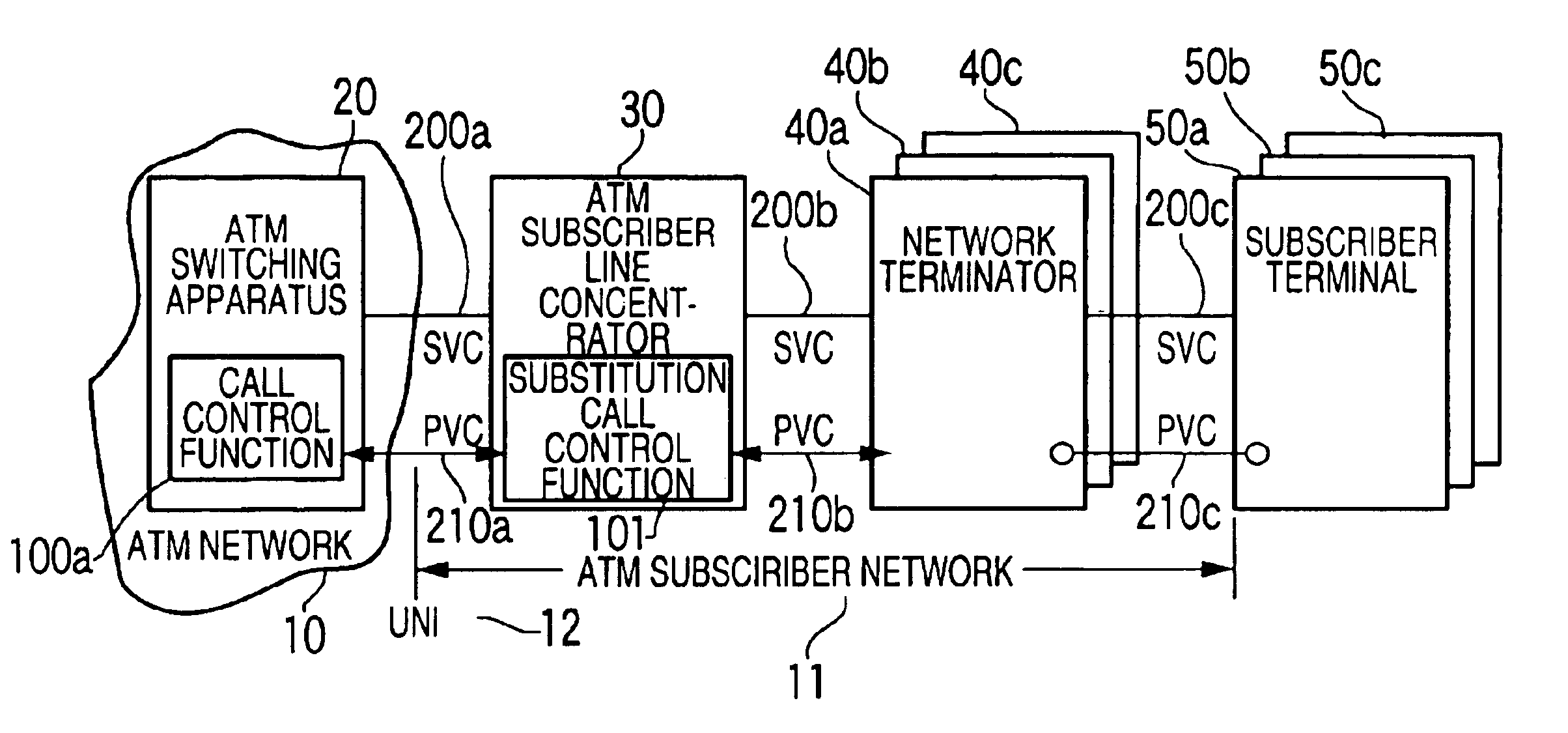
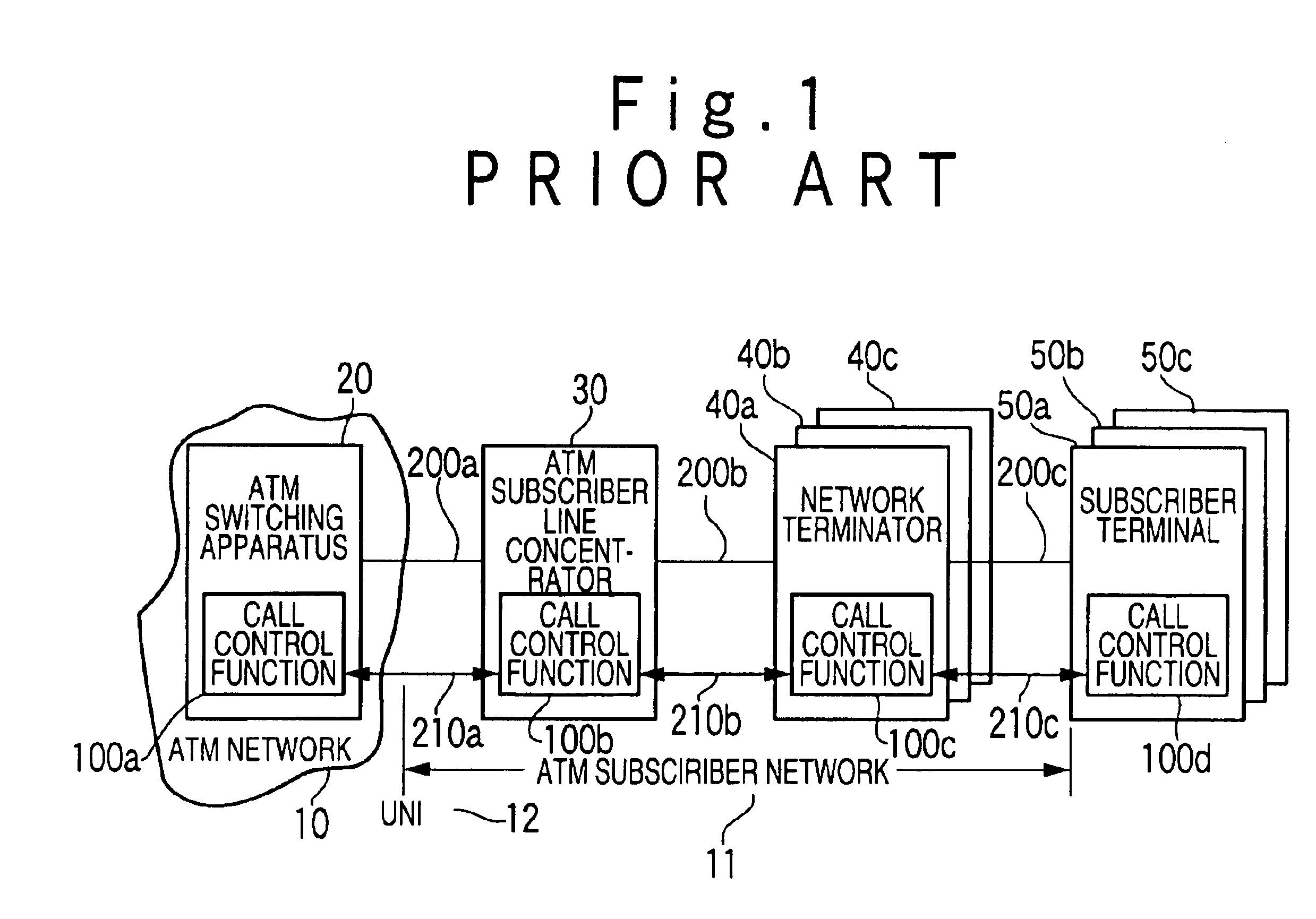
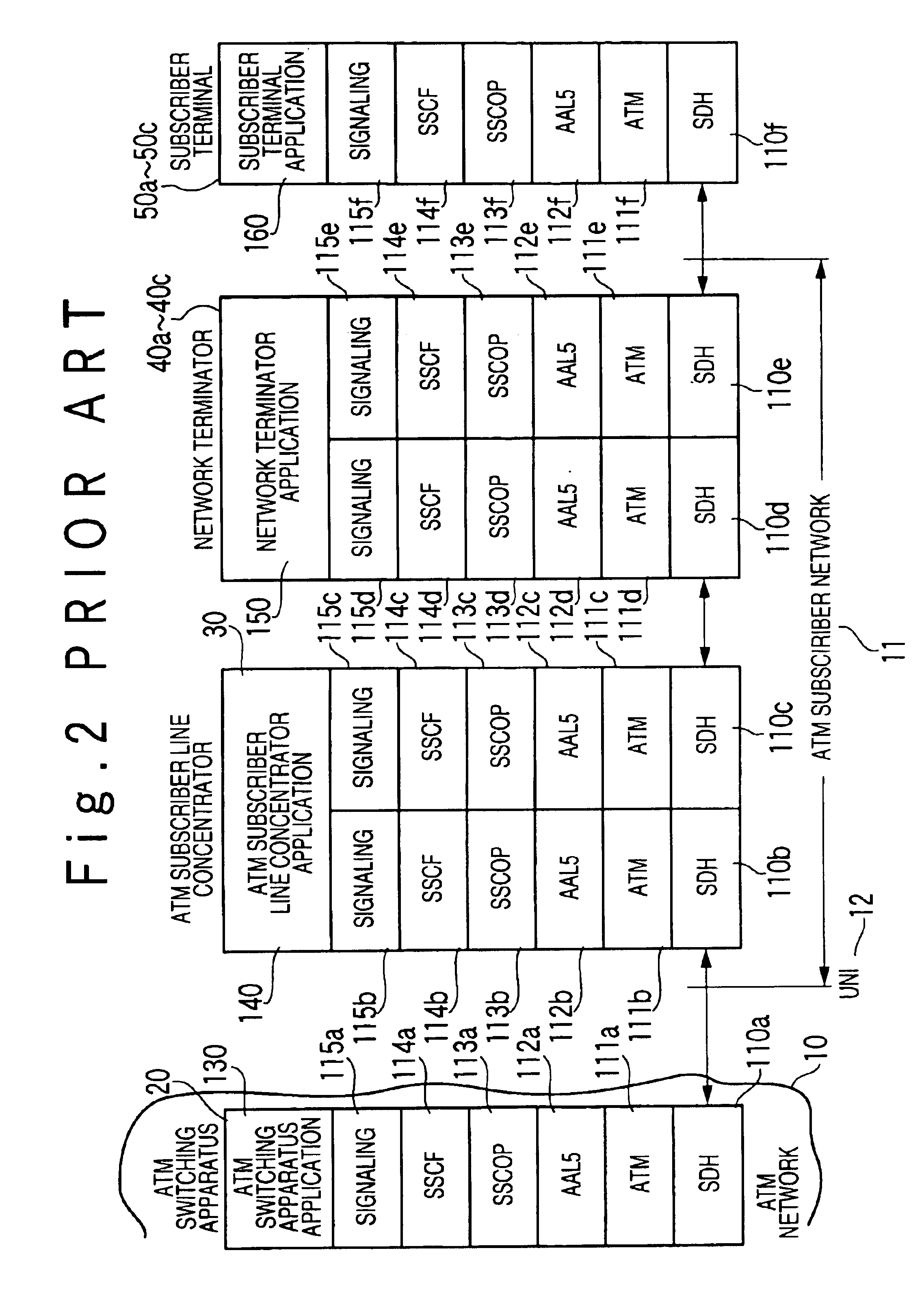
Substitution call control system in ATM communication network
InactiveUS6859457B1Low costImprove maintainabilityData switching by path configurationCircuit switching systemsAtm switchingNetwork termination
A substitution call control system includes an ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) subscriber network of an ATM communication network. The ATM subscriber network includes a plurality of network terminators respectively connected with a plurality of subscriber terminals, and an ATM subscriber line concentrator, which accommodates VCs (Virtual Connection) to the plurality of network terminators, and is connected with a ATM switching apparatus of the ATM network through a UNI (User-Network Interface). The ATM subscriber line concentrator includes a substitution call control function to substitute for the plurality of network terminators and the subscriber terminals for a call control.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
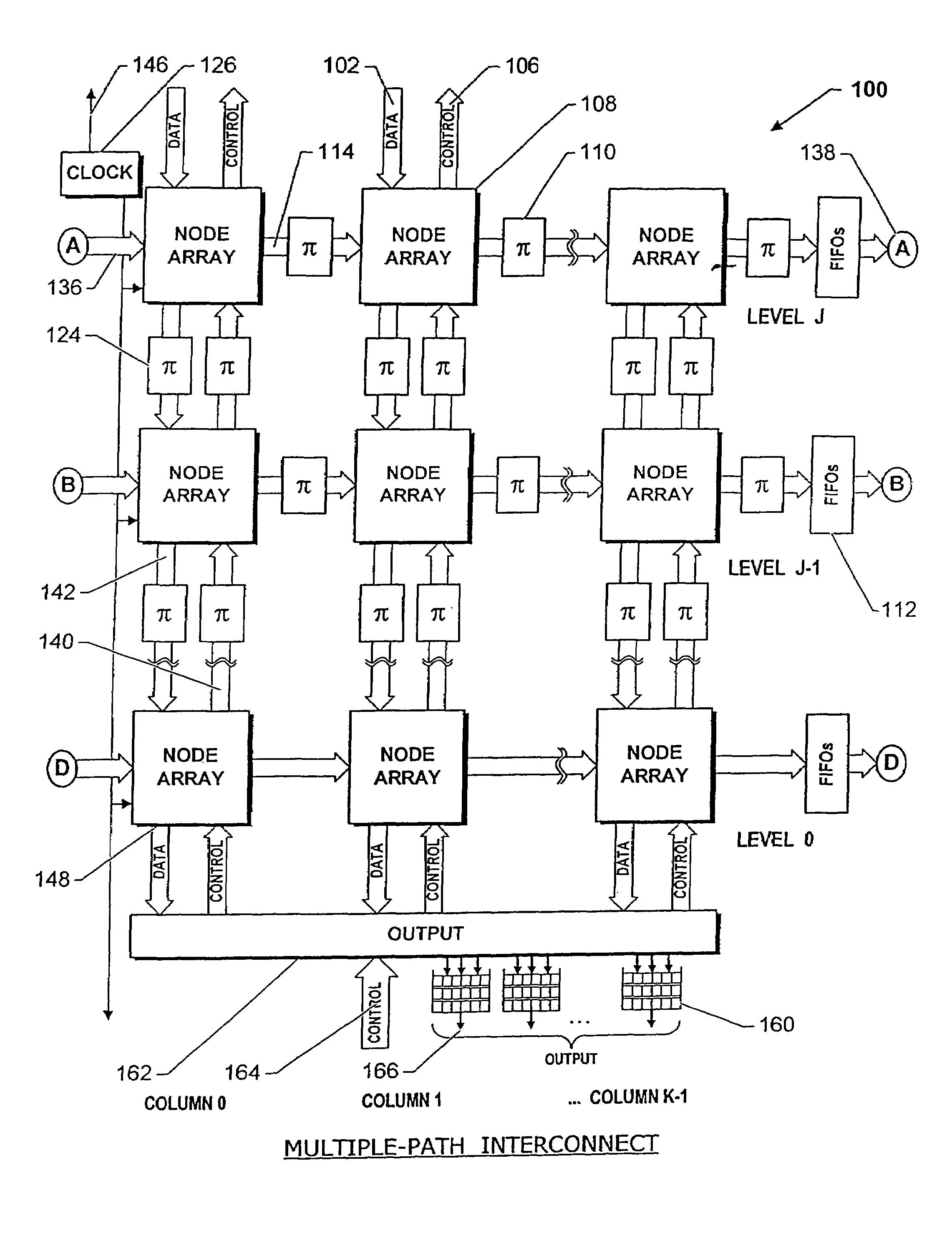
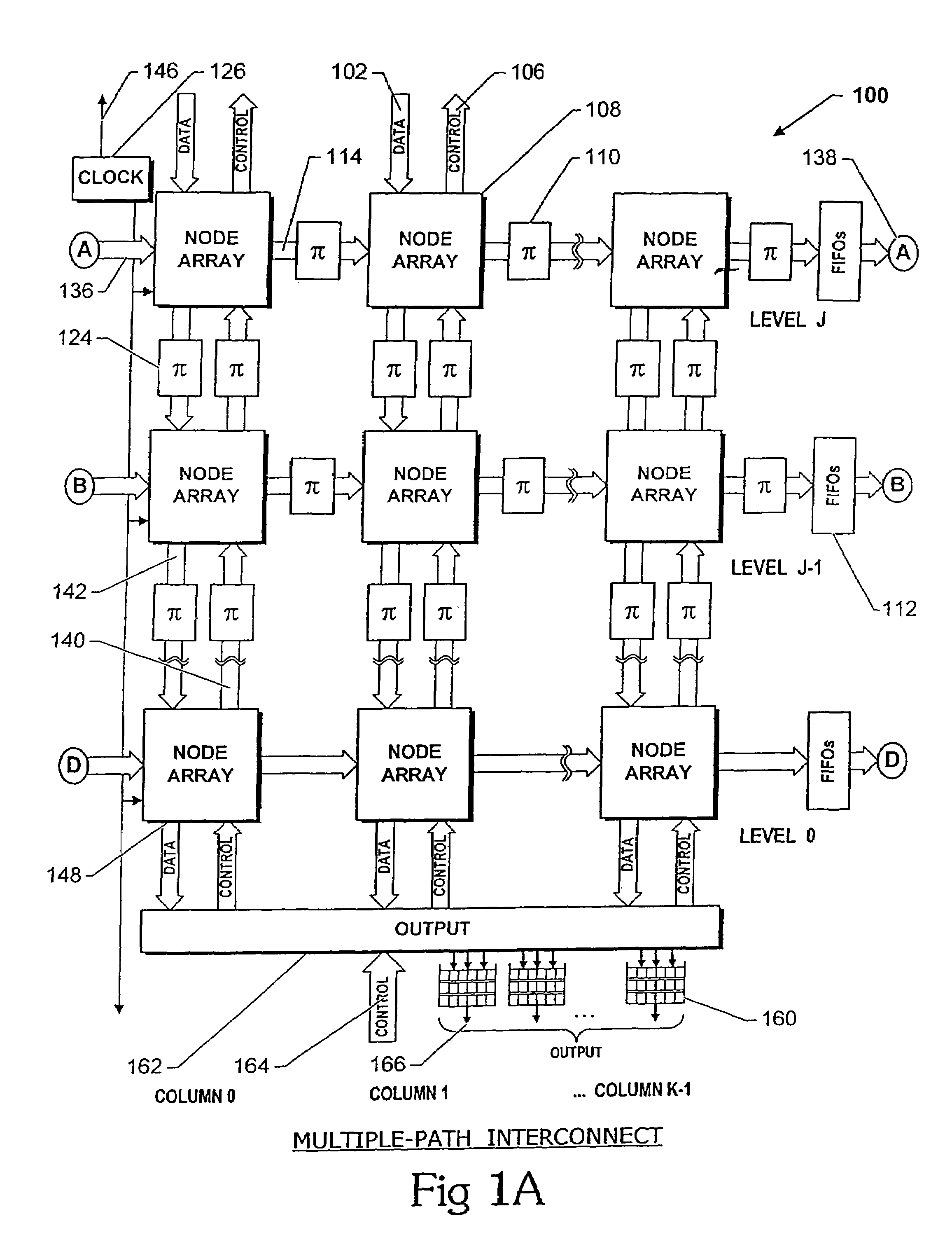
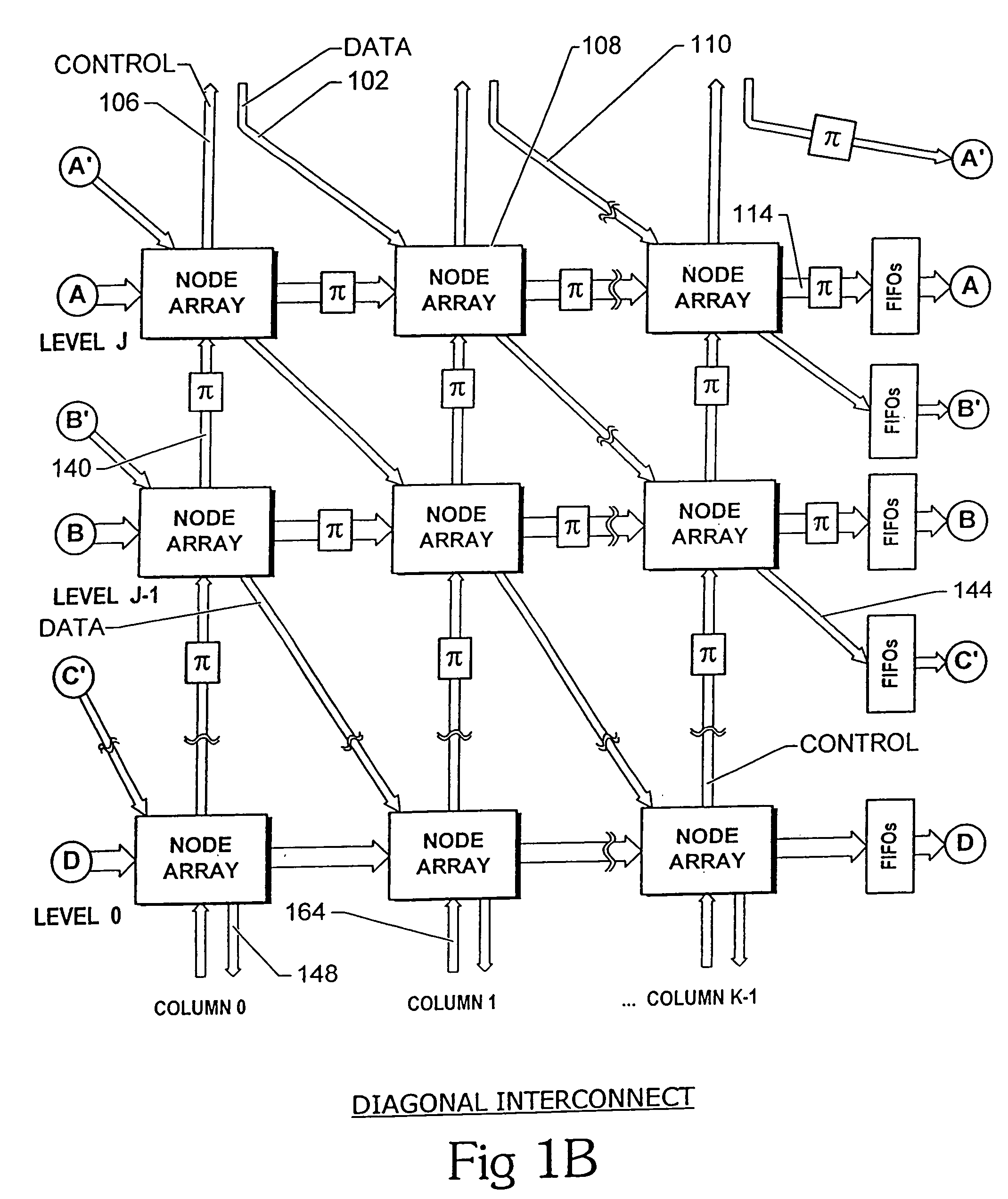
Multiple-path wormhole interconnect
InactiveUS7382775B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsSupercomputerWorkstation
Owner:INTERACTIC HLDG LLC
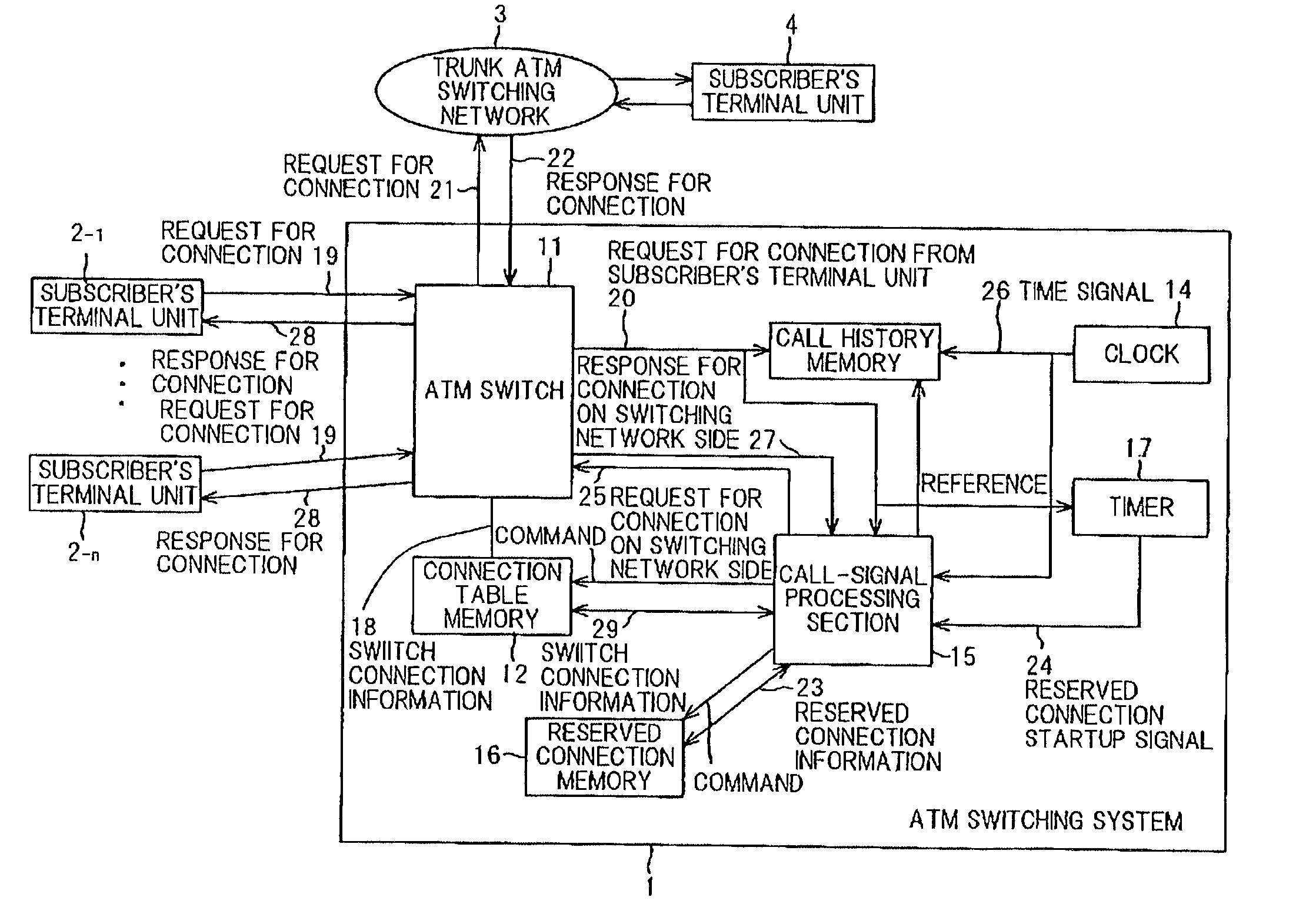
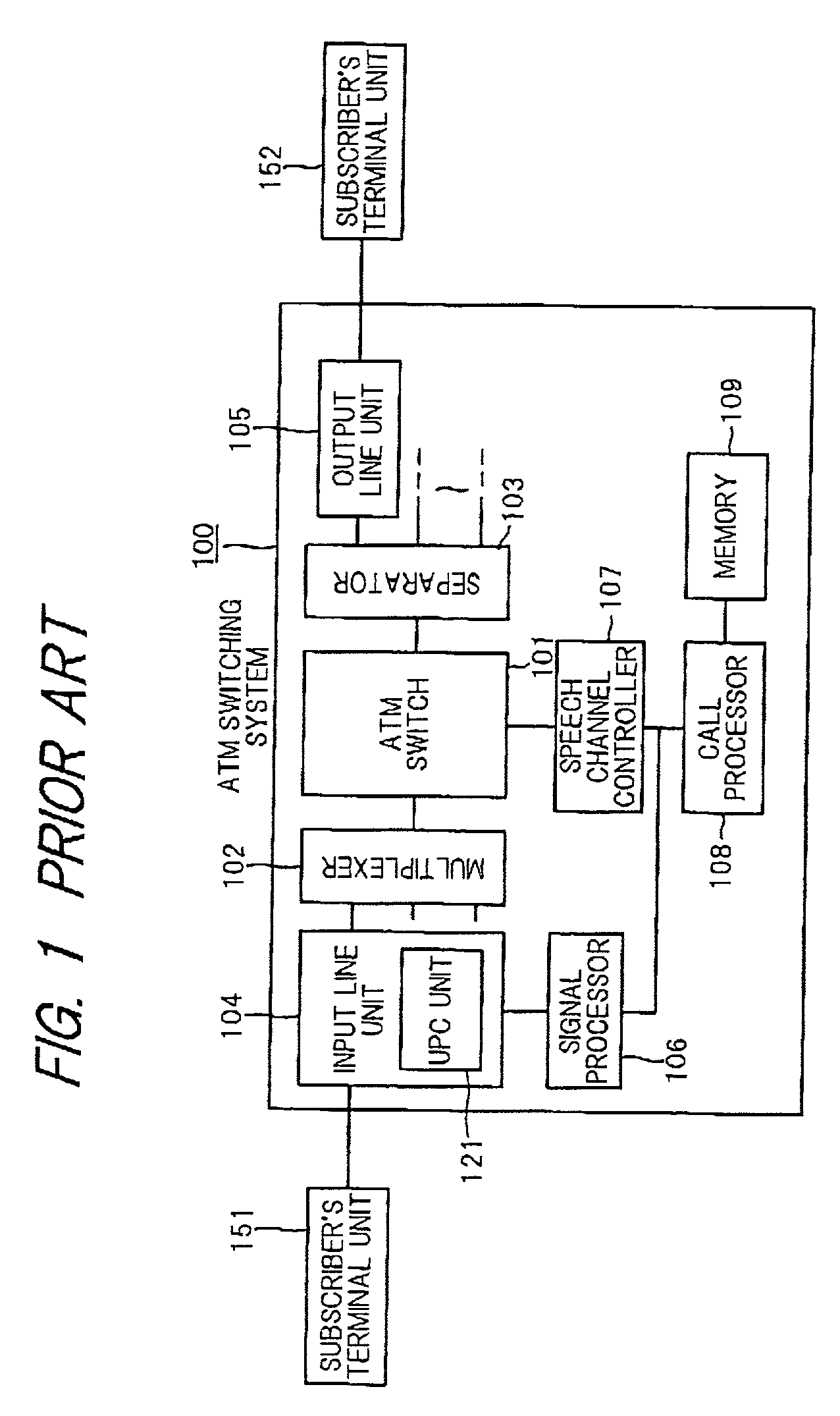
Asynchronous transfer mode switching system
ActiveUS6961308B2Short response timeReduce load concentrationError preventionTransmission systemsAtm switchingTelecommunications
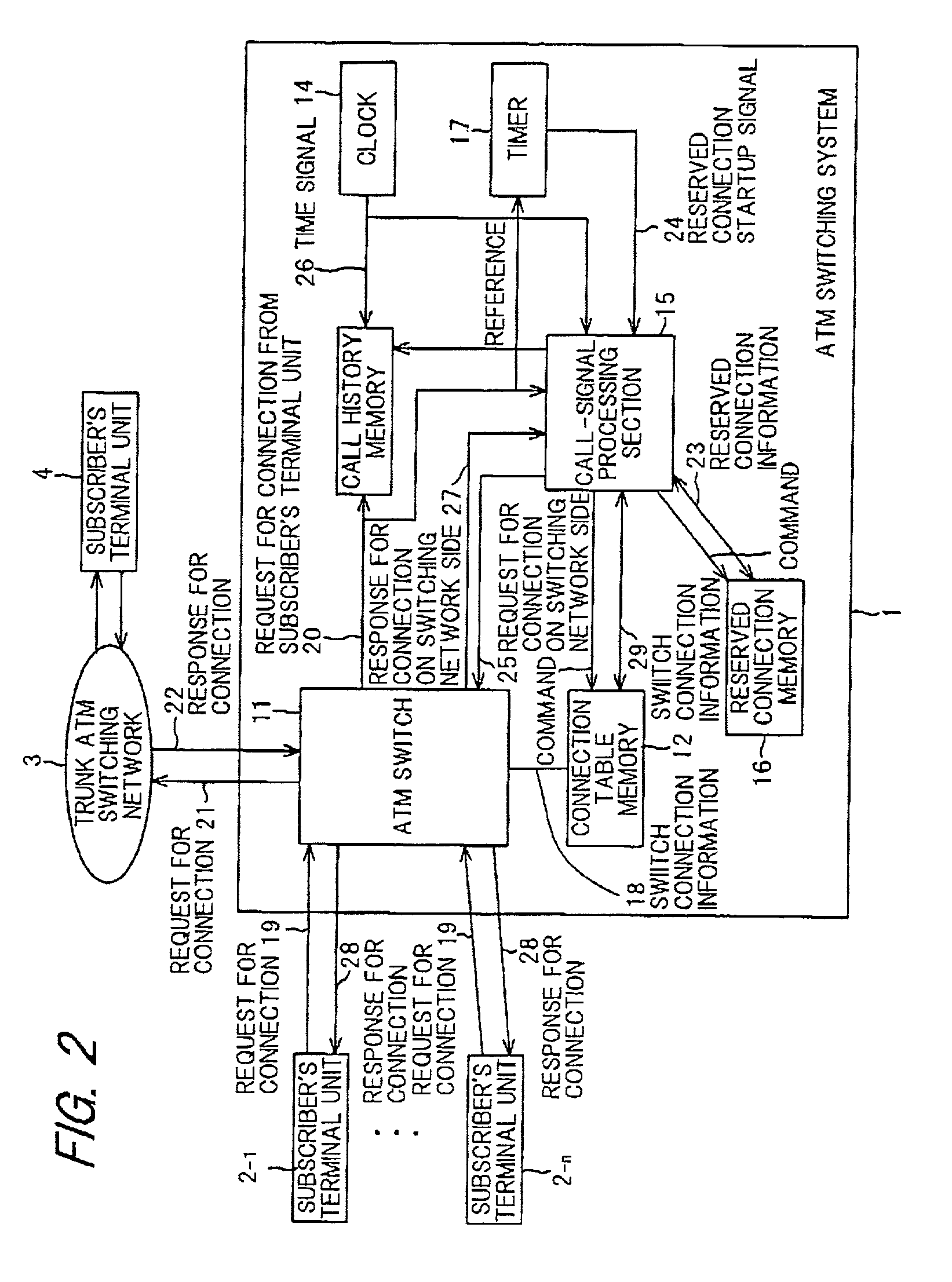
An ATM switching system 1 is provided with an ATM switch 11, a reserved connection memory 12 for storing reserved connection information, a call history memory 13 for maintaining call histories of requests for connection from subscriber's terminal units 2−1 to 2−n, and a call-signal processing section 15. The call-signal processing section 15 generates a request for connection with respect to a trunk ATM switching network 3 by the use of the call histories in the call history memory 13 in the case where no call was issued from the subscriber's terminal units, and stores response results thereof in the reserved connection memory 16. Thereafter, when there was a call from the subscriber's terminal units 2−1 to 2−n, and contents of the request for connection thereof are the same as the reserved connection information, which has been stored in the reserved connection memory 16, processing for connection is executed by the use of the reserved connection information. As a result, an ATM switching system by which response becomes possible in even the case where a large amount of calls are issued at the same time, besides reduction in cost can also be attained is provided.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Data packet re-sequencer
InactiveUS6434148B1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsRe sequencingAtm switching
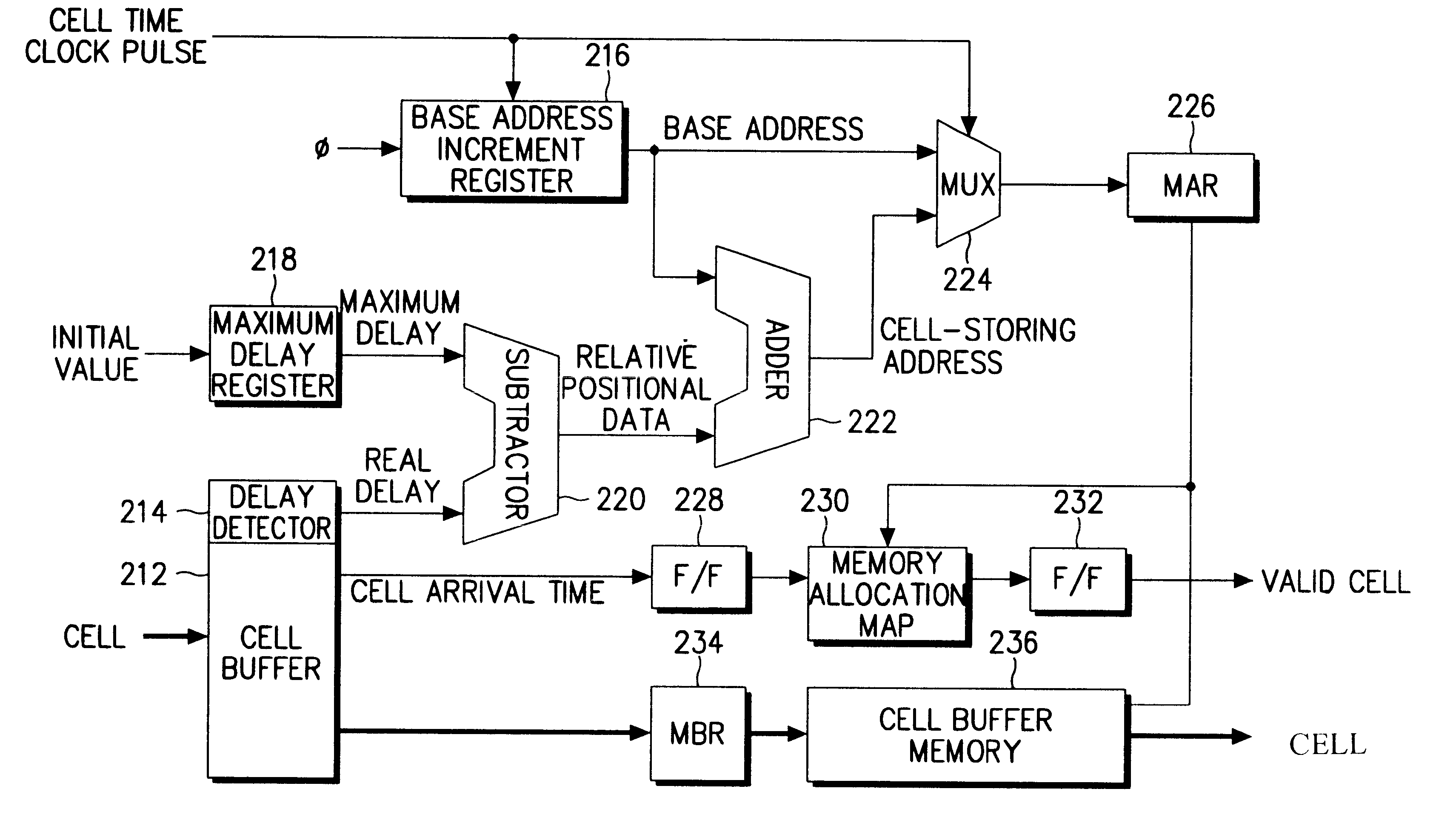
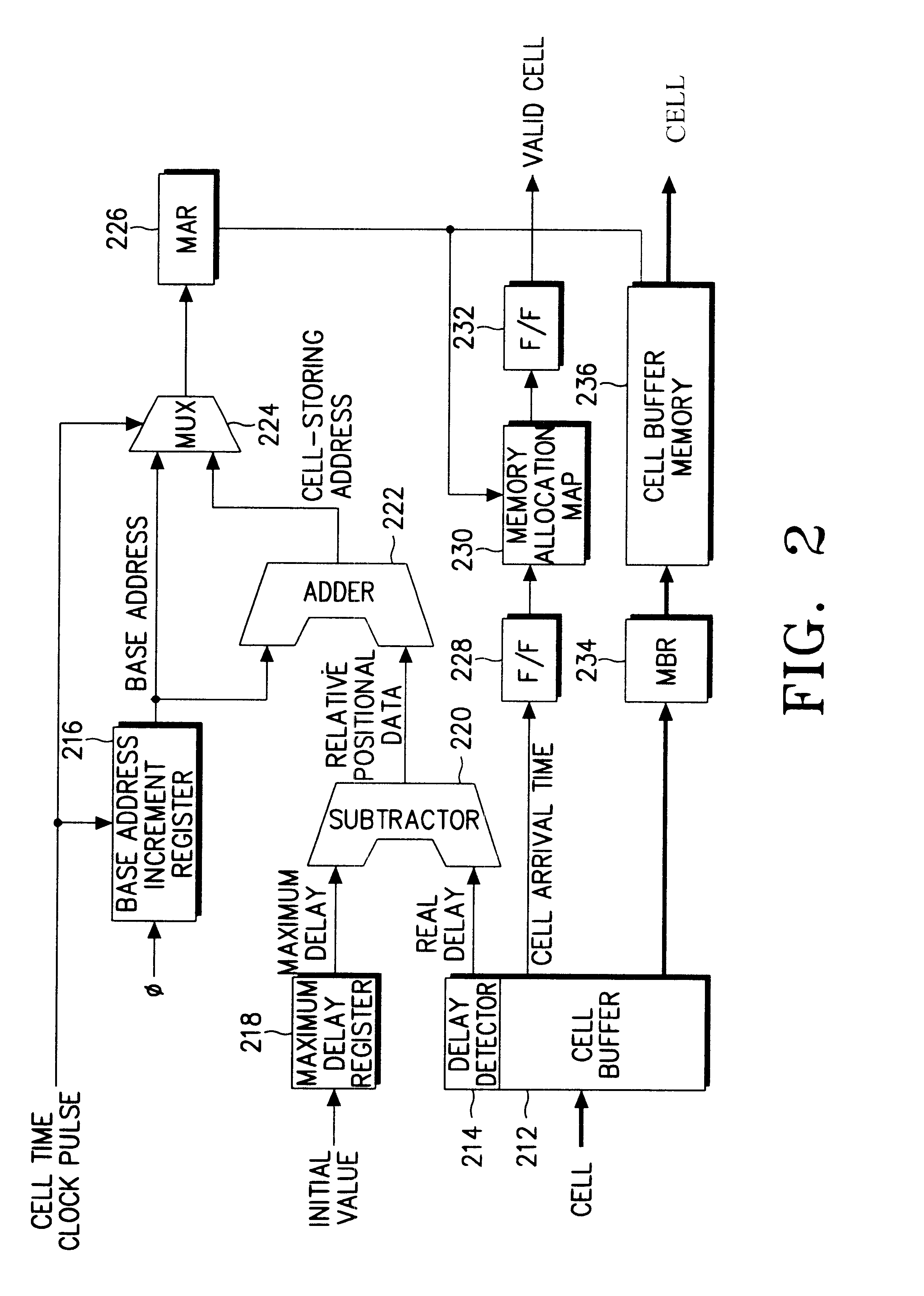
A cell re-sequencer for re-sequencing the cells switched by an ATM switching system, comprises a maximum delay register for setting the maximum delay value by initialization to output the maximum delay value according to internal clock pulses, a base address increment register for increasing the initial value of the initialization set as a base address one by one according to cell time clock pulses, a delay detector for detecting the real delay of a cell from its header, a cell storing address generator for adding the base address to the delay difference between the maximum delay and real delay to generate a cell storing address, a multiplexer for multiplexing the base address and cell storing address according to the cell time clock pulses, and a memory address register for temporarily storing the output of the multiplexer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus using in-band type access system
InactiveUS6970428B1Drawback can be obviatedIncrease flexibilityError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityAtm switching
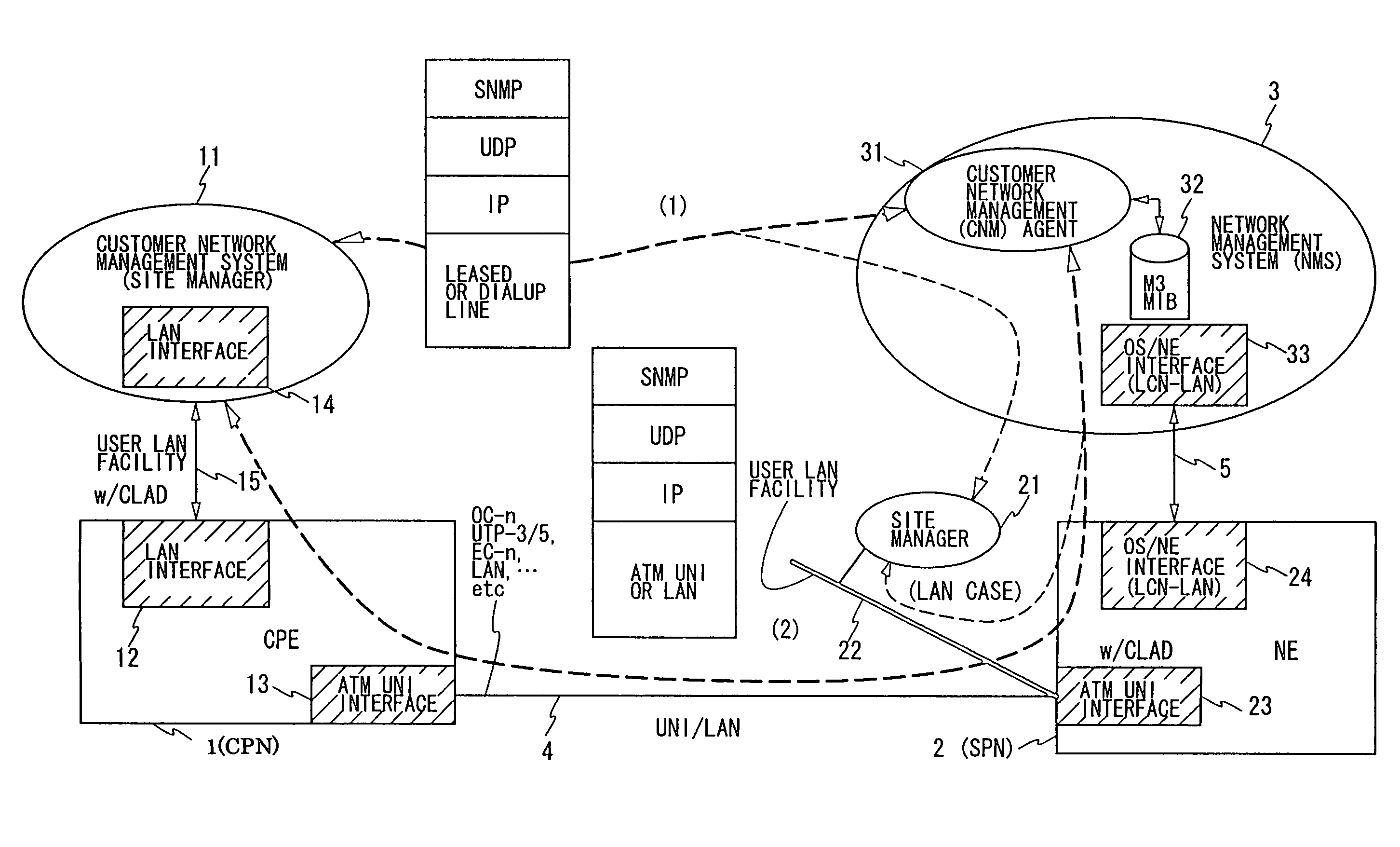
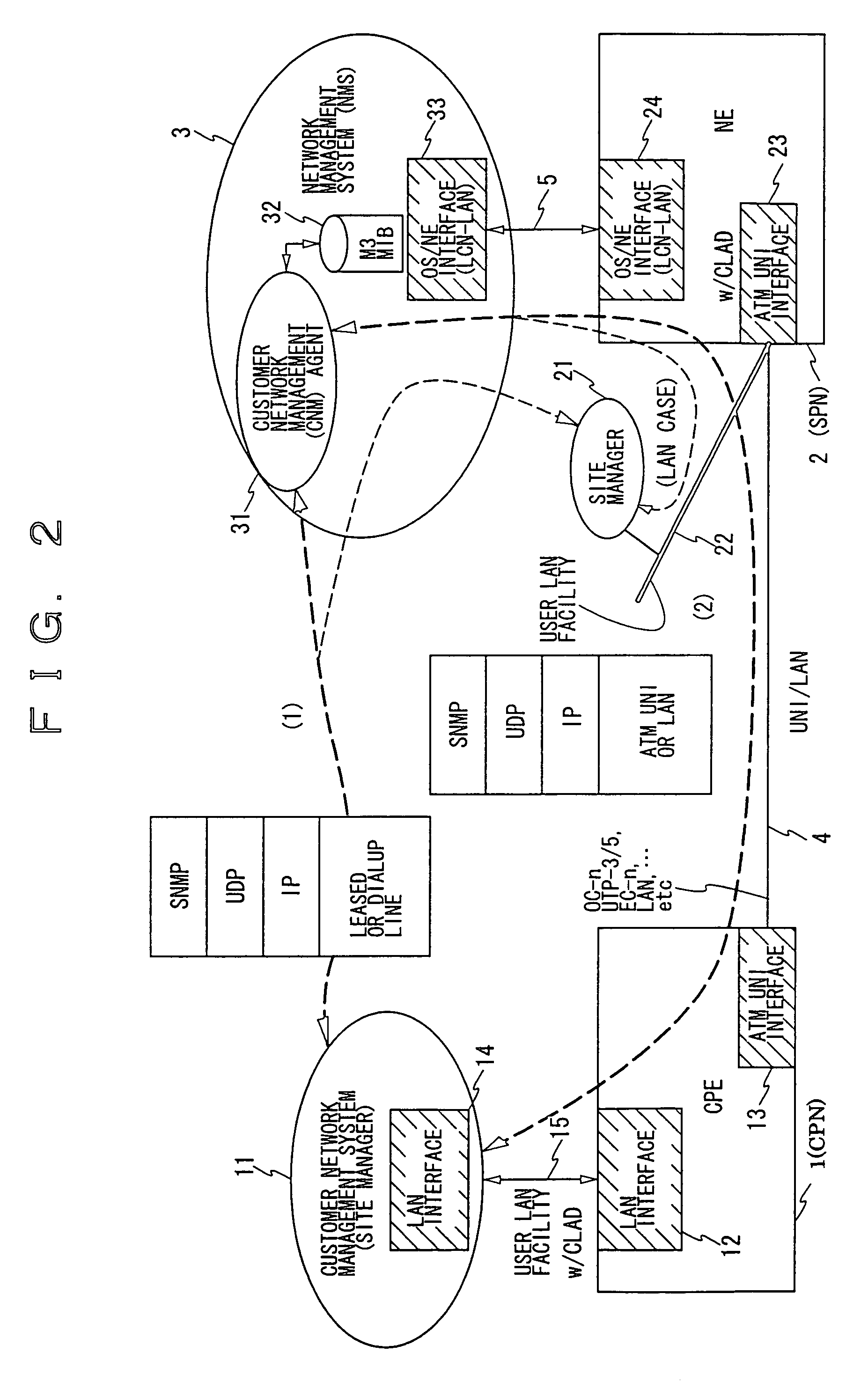
A transmission apparatus includes a part which sets a resource management information path based on a given network management protocol onto PVC logically set traffic defined in ATM switching so that a customer network management agent process and a user network management system can communicate with each other.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Extended virtual user-to-network interface with ATM network
An SVC is established via an ATM switch port, which includes multiple virtual paths (VPs), by associating multiple virtual user-to-network interfaces (UNIs) to each of the VPs. Each of the VPs includes multiple virtual circuit (VC) ranges, each of which corresponds to a different virtual UNI. Each VC range includes at least one VC for control and at least one VC for data transfer. Associating the virtual UNIs to each of the VPs includes mapping each virtual UNI to a corresponding VC range within a VP based on a virtual path index (VPI) / virtual channel index (VCI) of the virtual UNI initially received by the ATM switch port.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
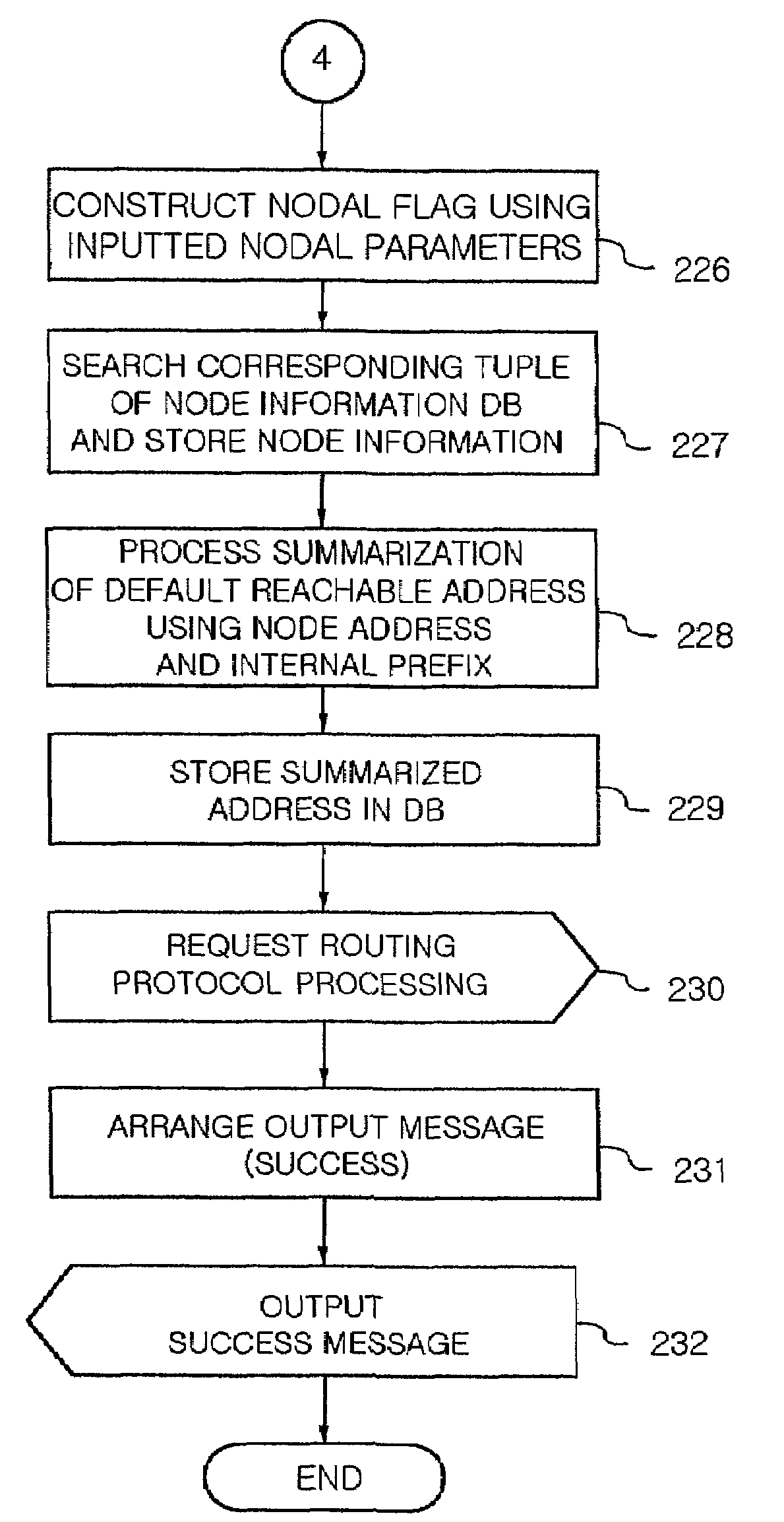
Method for summarizing default address of PNNI lowest level node in ATM switching system
ActiveUS7065085B2Reduce overheadEasy to useData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionAtm switchingEnd system
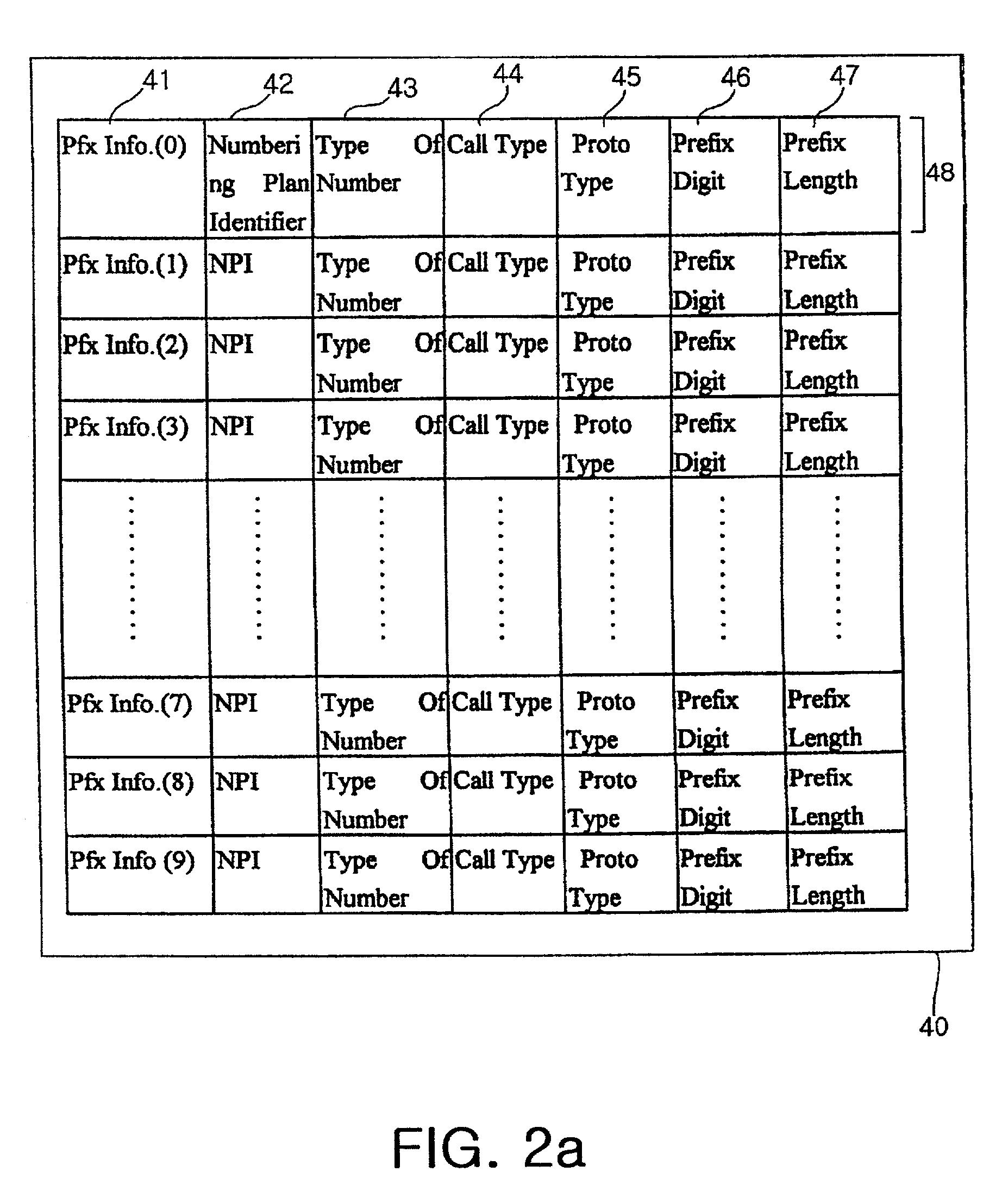
Disclosed herein is a method for summarizing a default address of a PNNI (Private Network-Network Interface) lowest level node in an ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) switching system. In the method, first, a database for storing prefix information, node information and reachable address information is constructed. Parameters inputted for creating an internal prefix is arranged to be adaptable to the system, a prefix information is generated by checking the validation and address system of the parameters inputted for creating the internal prefix, and the prefix information is registered in the prefix information database. An ATM end system address is generated by checking the validation and address system of parameters inputted for creating the node information. The node address of the node information is summarized up to the bit length of the internal prefix and the summarization of a default reachable address is performed by defining the internal prefix as the default reachable summarization address.
Owner:KT CORP
Header conversion technique in ATM switch
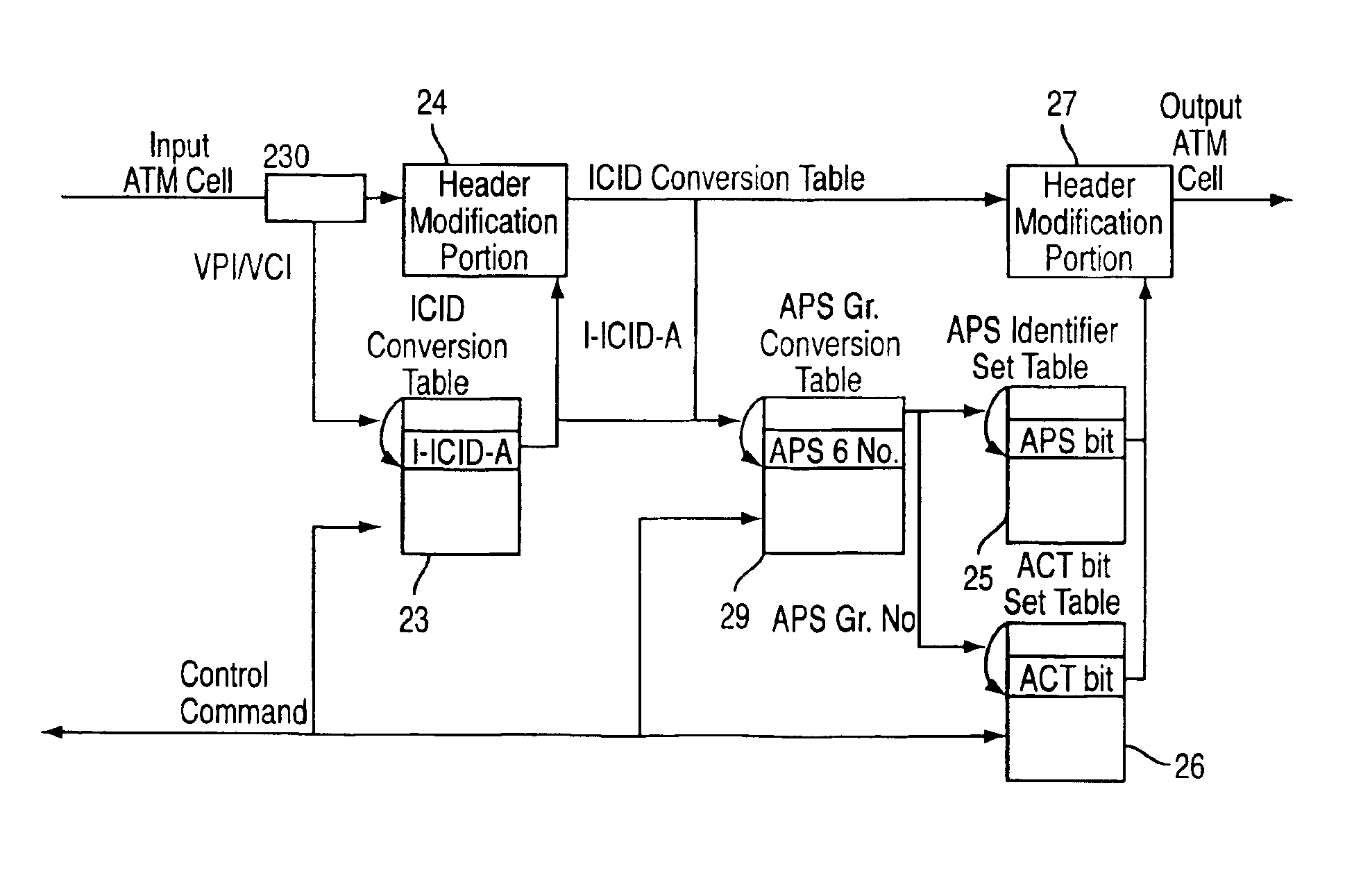
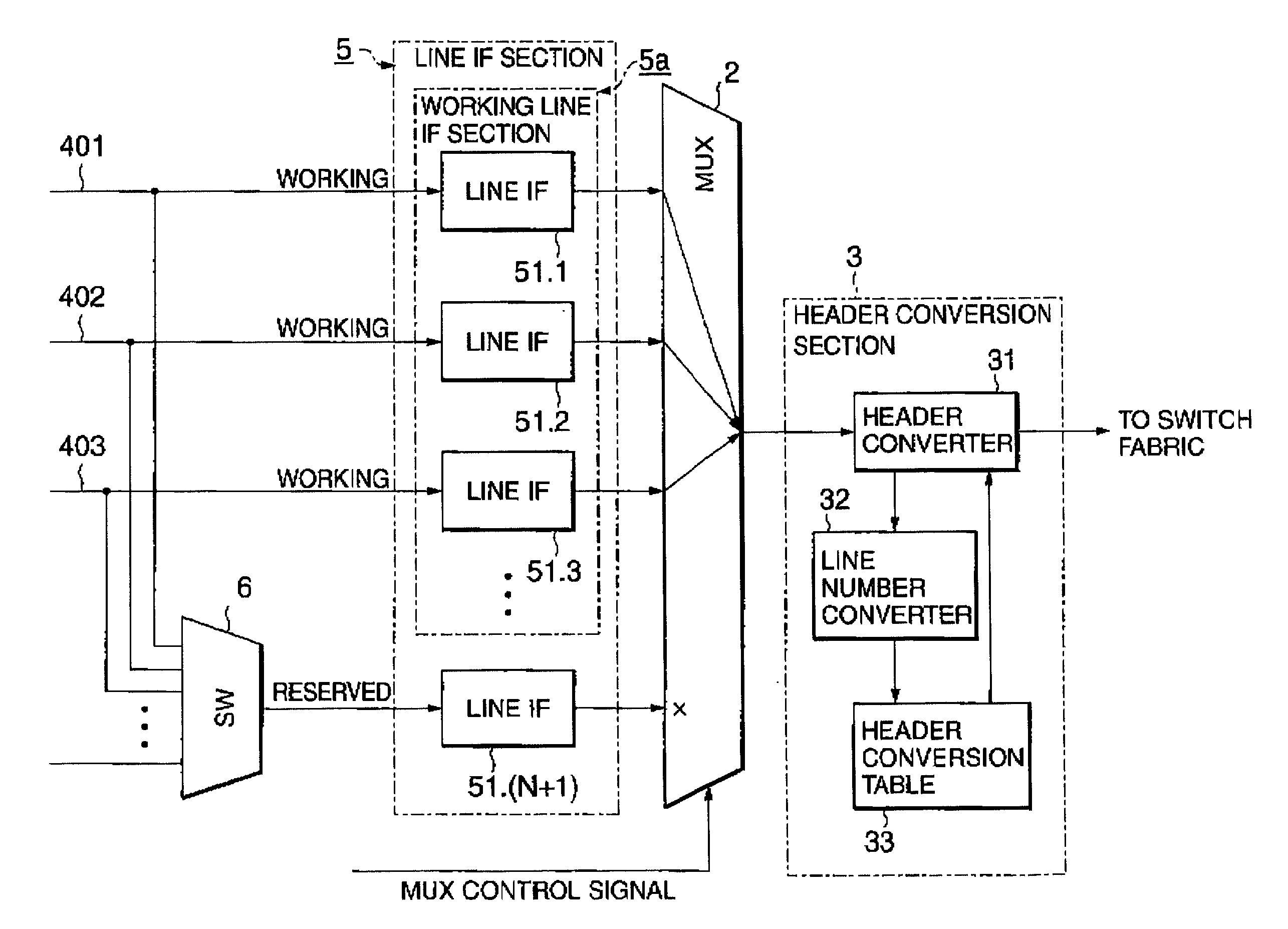
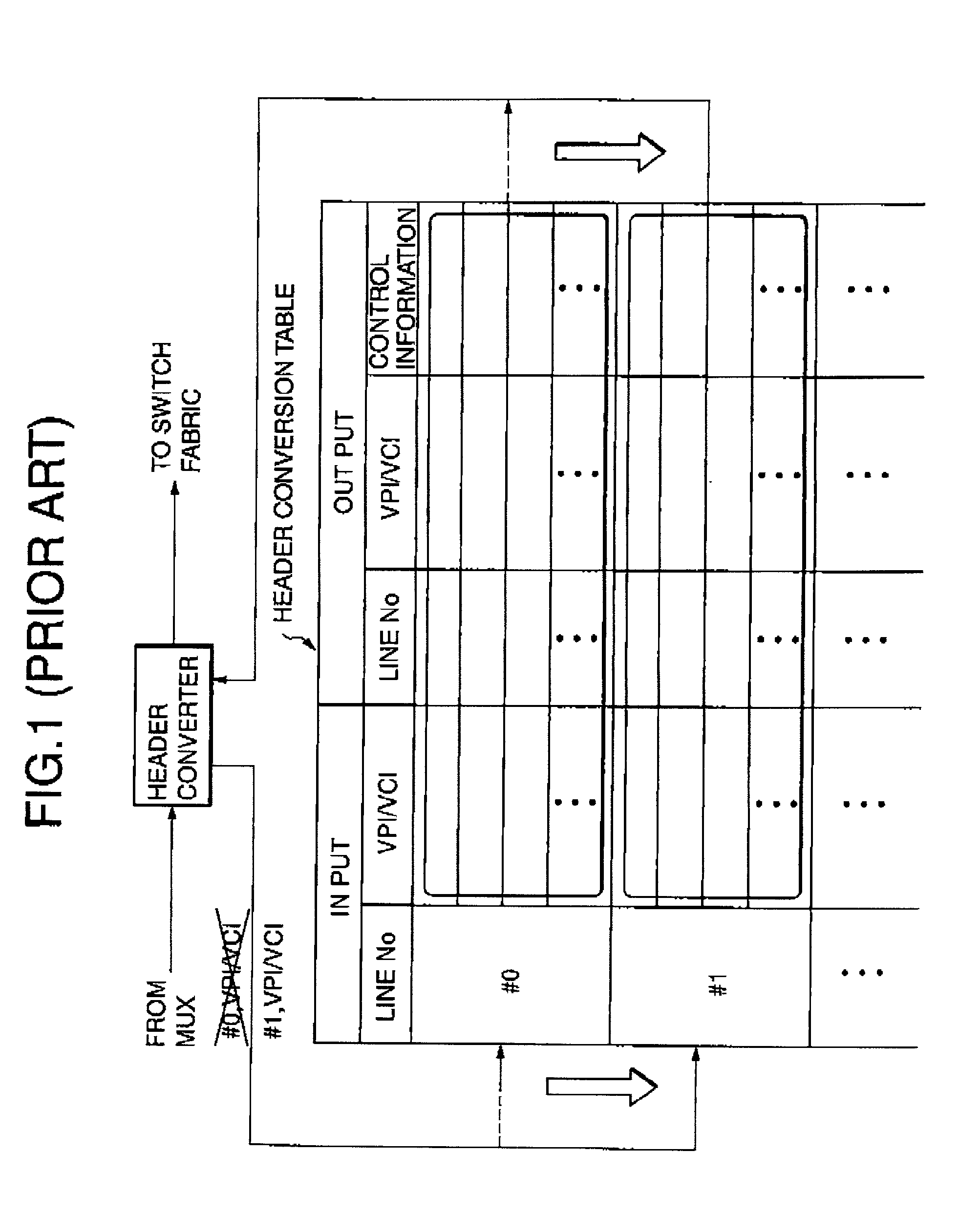
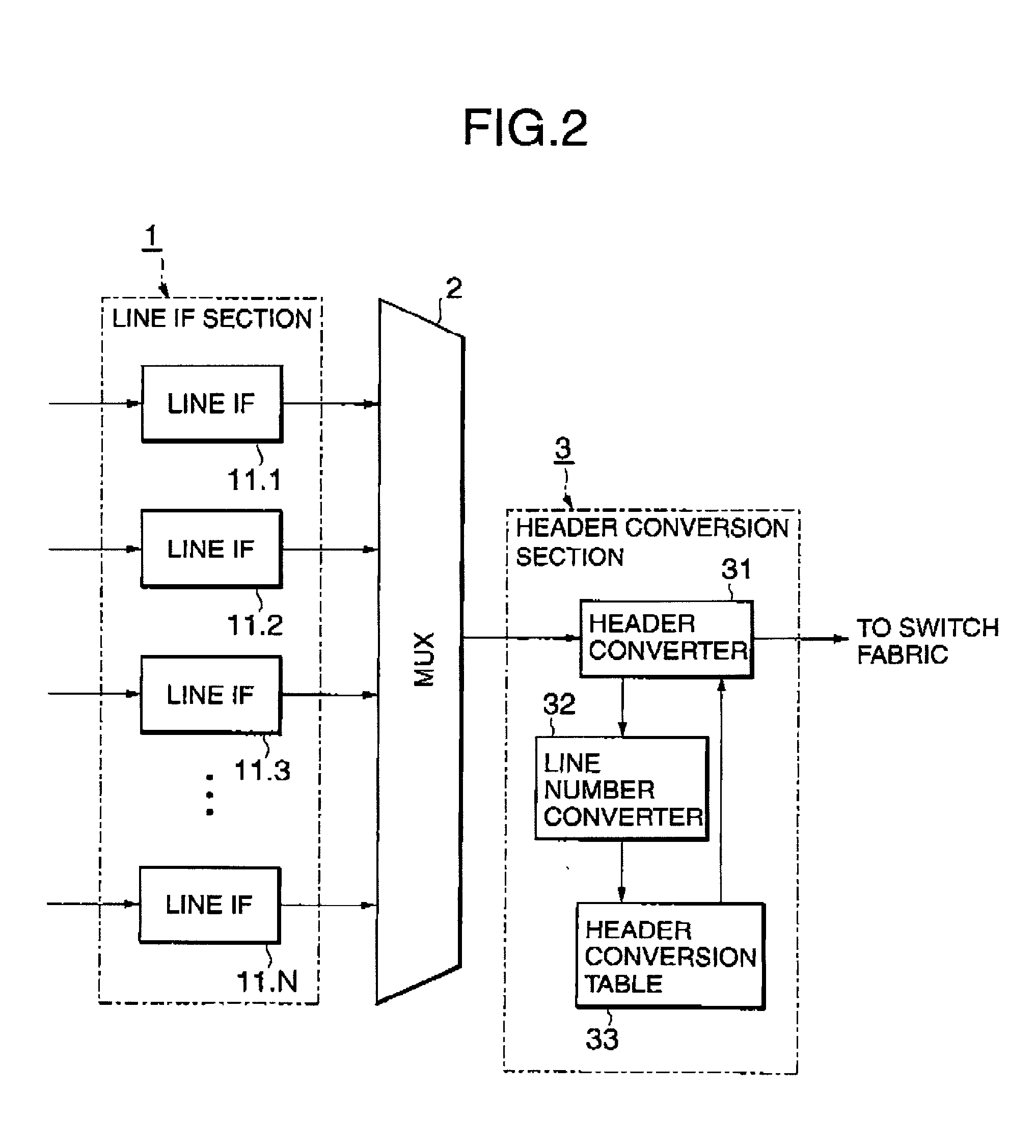
InactiveUS7058013B2Reduce the amount requiredEliminate needError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAtm switchingComputer hardware
A header conversion device allowing reduced amount of hardware and memory and high-speed line switching is disclosed. In an ATM switching device having redundant incoming line systems, a header conversion table stores a set of header conversion information for one of the redundant incoming line systems. A header converter converts the header of an ATM cell received from each of the redundant incoming line systems by referring the same set of header conversion information.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Large-scale service-rate regulators for ATM switching
Techniques of service-rate controls in ATM switches are described, and apparatus for their implementation are devised. The techniques fall in two categories: frequency domain controls, and time-domain controls. The regulators control the service rate on a per-class basis or on a per-connection basis. Some class regulators operate at very high speeds of the order of several gigabits per second and cover a medium number of classes, 32 for example. Other regulators operate at high speeds of the order of several-hundred megabits per second, and cover a very large number of classes, e.g., 10000. A compound regulator which combines both types of regulators is also described. The compound regulators extend the range of controllable classes considerably, covering some 200,000 classes. The main advantages of the regulators of the invention are simplicity, robustness, and high performance.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
System and method for cross connecting an ATM network and a telecommunication switch
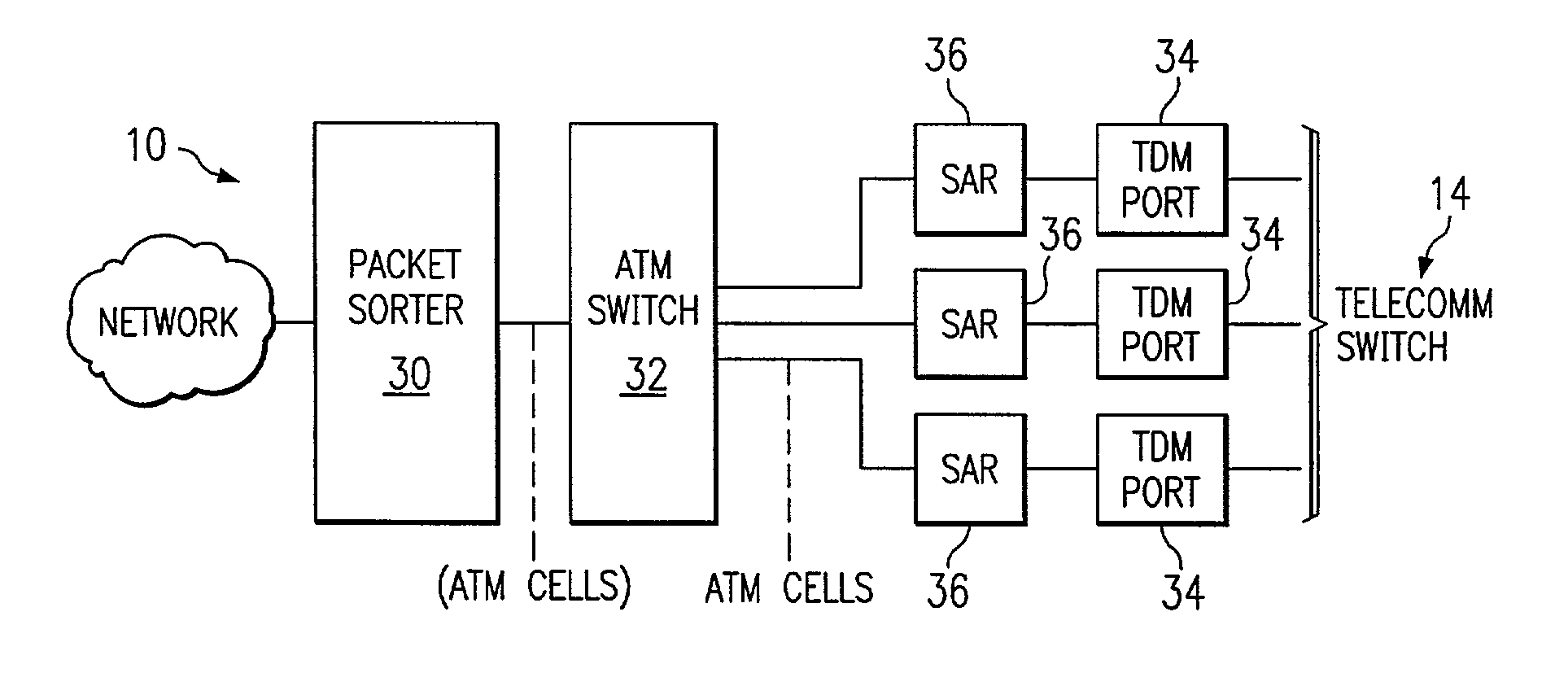
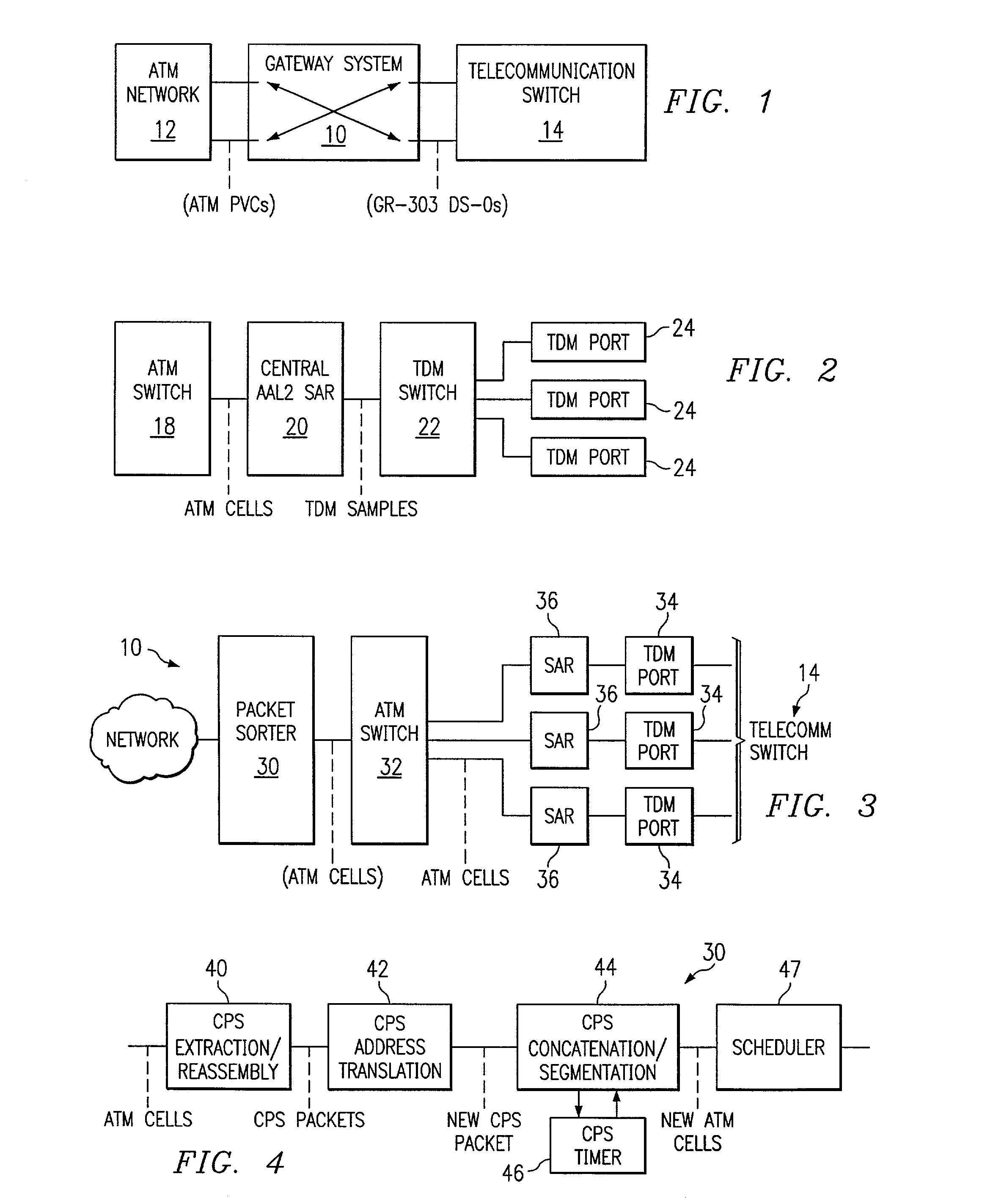
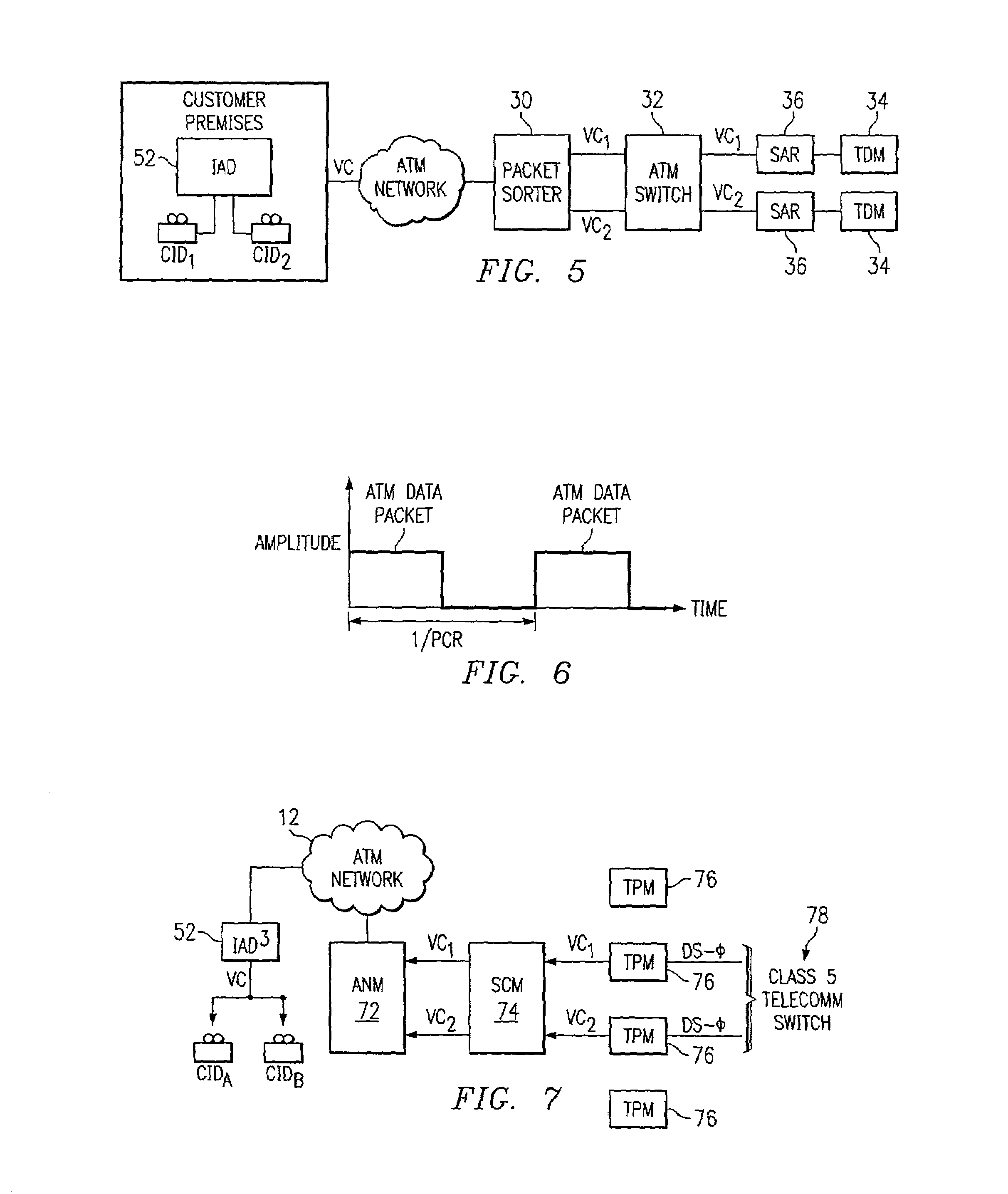
ActiveUS7120153B1Eliminate the problemSimplification of gateway SAR implementationData switching by path configurationAtm switchingComputer network
A method for cross connecting an ATM network and a telecommunication switch includes receiving ATM cells from the ATM network at a packet sorter and extracting data packets comprising address data and payload data from the ATM cells. Translated addresses are generated based on the address data, and new data packets are created based on the payload data and the translated addresses to create new ATM cells with the new data packets. The new ATM cells are scheduled to be transmitted from the packet sorter to an ATM switch in compliance with an ATM service contract. The new ATM cells are forwarded from the ATM switch to at least one distributed SAR, which converts the new ATM cells into TDM signals and transmits the TDM signals from to the telecommunication switch via at least one TDM port.
Owner:GENBAND US LLC
Apparatus and method for configuring multicasting network in asynchronous transfer mode switching system
InactiveUS6788679B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexAtm switchingMulticast network
The present invention relates to a multicasting network apparatus and method for an ATM switching system having a banyan network and a route network which includes a header encoder part for generating a header, a boolean splitter network for copying a cell routed from the banyan network to thereby transmit the same to a route network. The boolean splitter network includes a plurality of boolean splitters, each of the boolean splitters includes the step of dividing the destination addresses of a cell into an upper group and a lower group and selecting an active port to thereby route the same. As described above, any extra translation table is not required owing to a cell copying operation according to the present invention, whereby the number of hardware components can be reduced, and an expansion can be easily performed.
Owner:LG INFORMATION & COMM LTD
ATM switching apparatus applicable to short cell
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Telephone service system in a asynchronous transfer mode private network
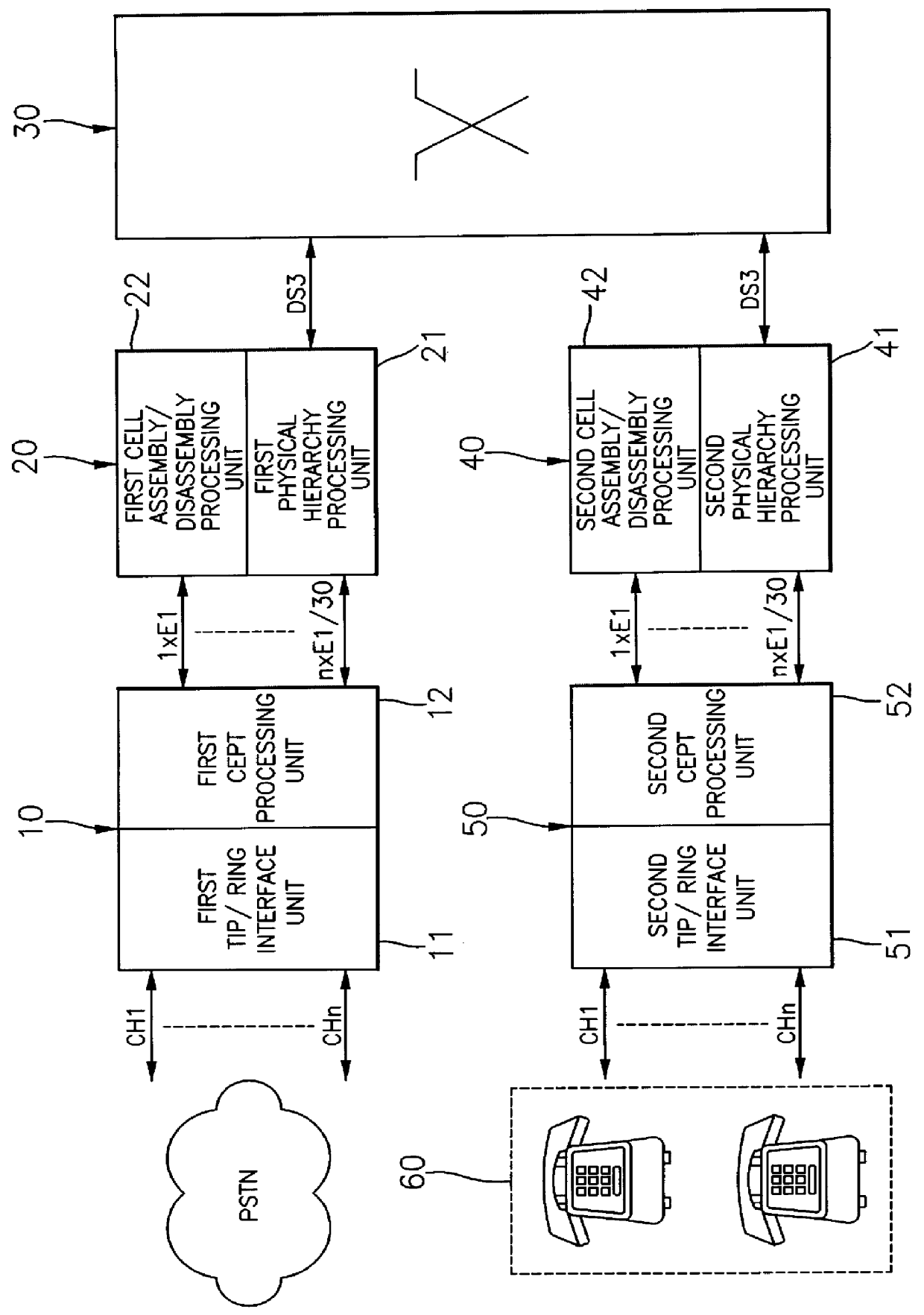
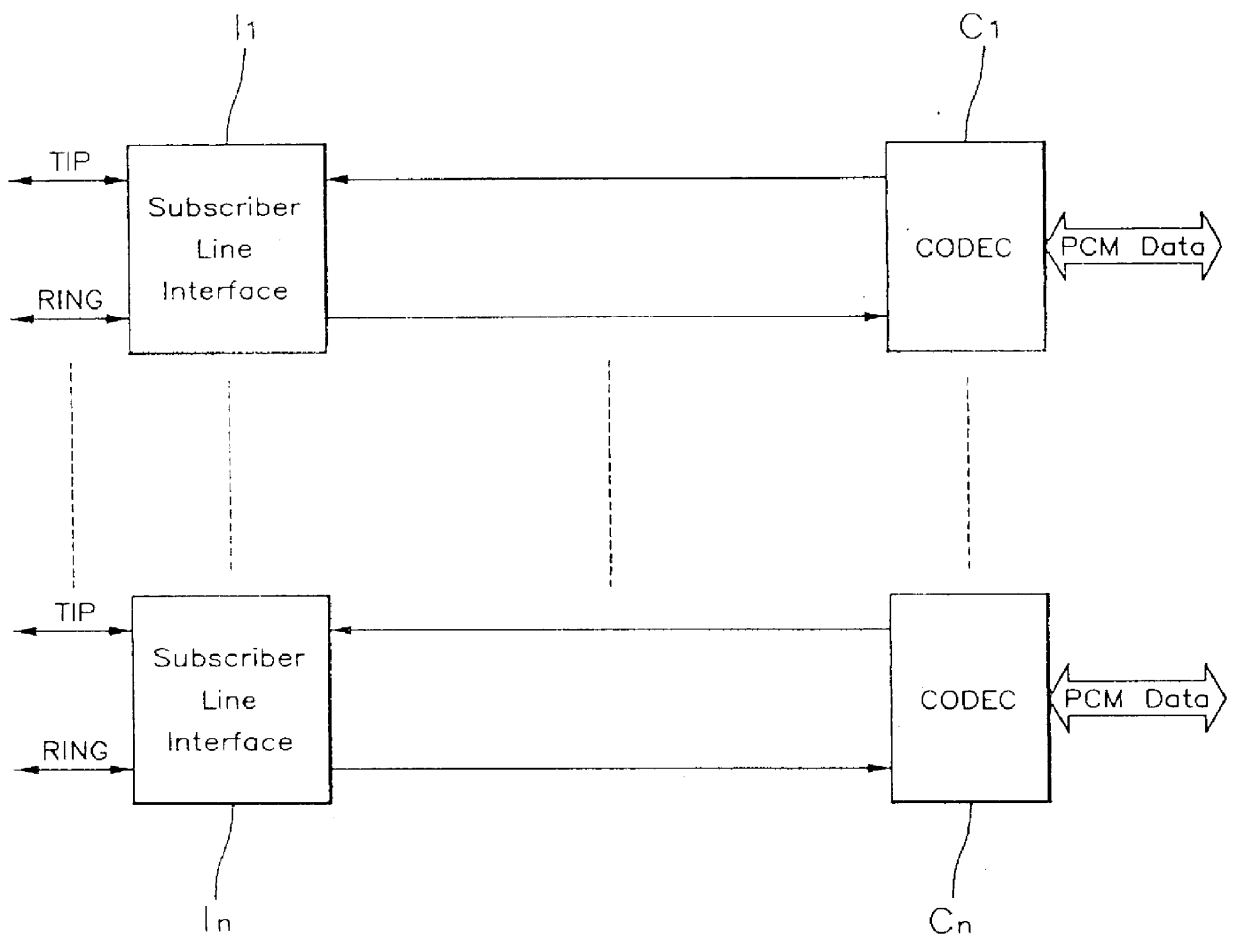
A telephone service system in an ATM private network, includes: a PSTN interface unit for performing PCM with an analog telephone signal transmitted from a channel in a PSTN, converting the modulated data into a CEPT frame before sending it to a subscriber, performing the PCM with CEPT frame data, from a subscriber, and converting the modulated data into an analog telephone signal, before forwarding it to the PSTN; a first ATM cell processing unit for converting the CEPT frame data from the PSTN interface unit into an ATM cell, converting an ATM cell from a subscriber into CEPT frame data, and sending it to the PSTN interface unit; an ATM switching unit for switching the ATM cell from the first ATM processing unit to the subscriber, and switching the ATM cell from the subscriber to the PSTN; a second ATM processing unit for converting the ATM cell from the ATM switching unit into CEPT frame data before sending it to the subscriber, and converting the CEPT frame data from the subscriber into an ATM cell before sending it to the ATM switching unit; and a subscriber line interface unit for converting the CEPT frame data from the second ATM processing unit into an analog telephone signal before sending it to a relevant subscriber, performing the PCM with the analog telephone signal from the subscriber, and converting the PCM data into CEPT frame data.
Owner:USRCOM KOREA
Switching system for telecommunication networks
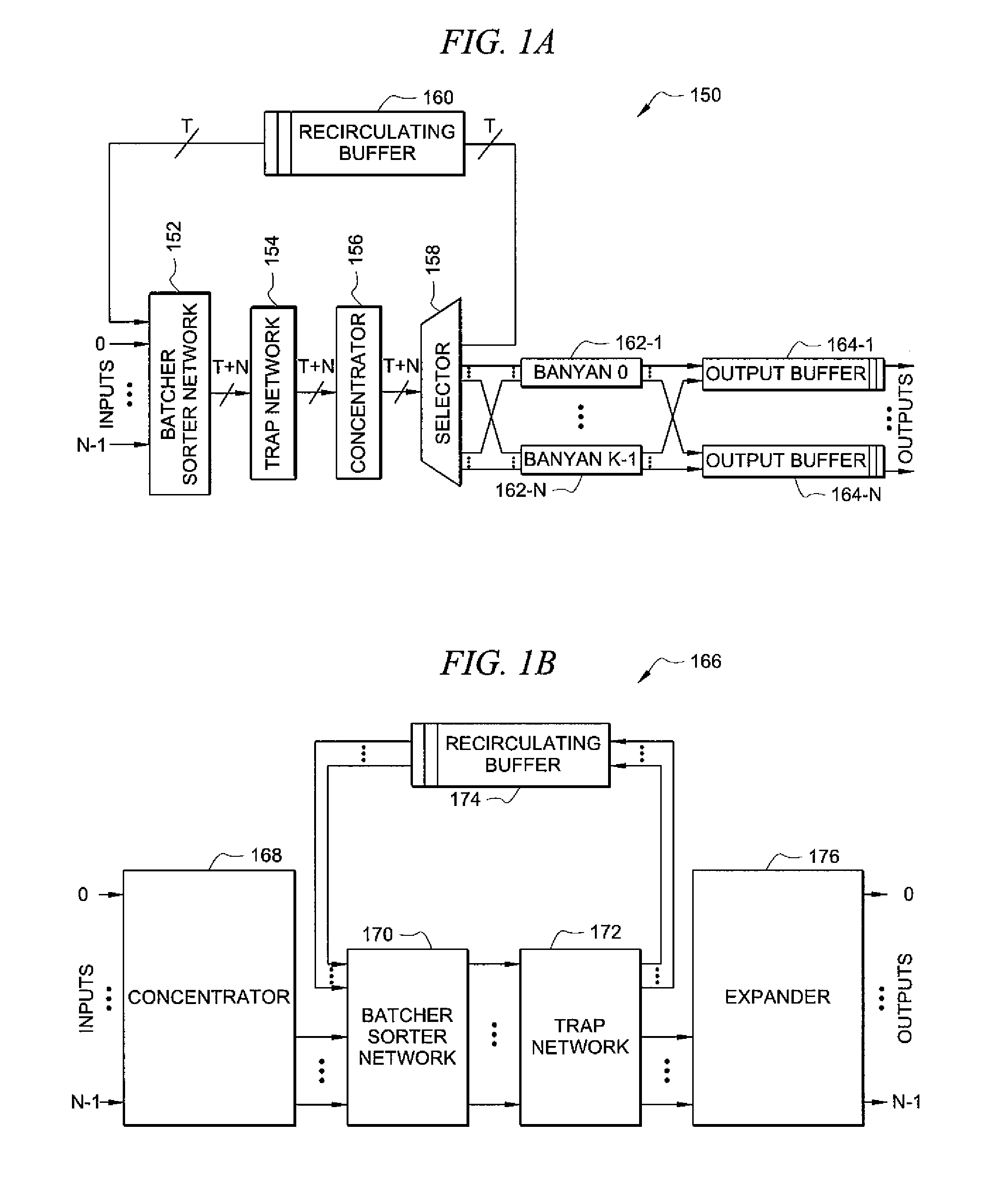
InactiveUS7336612B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAtm switchingTelecommunications network
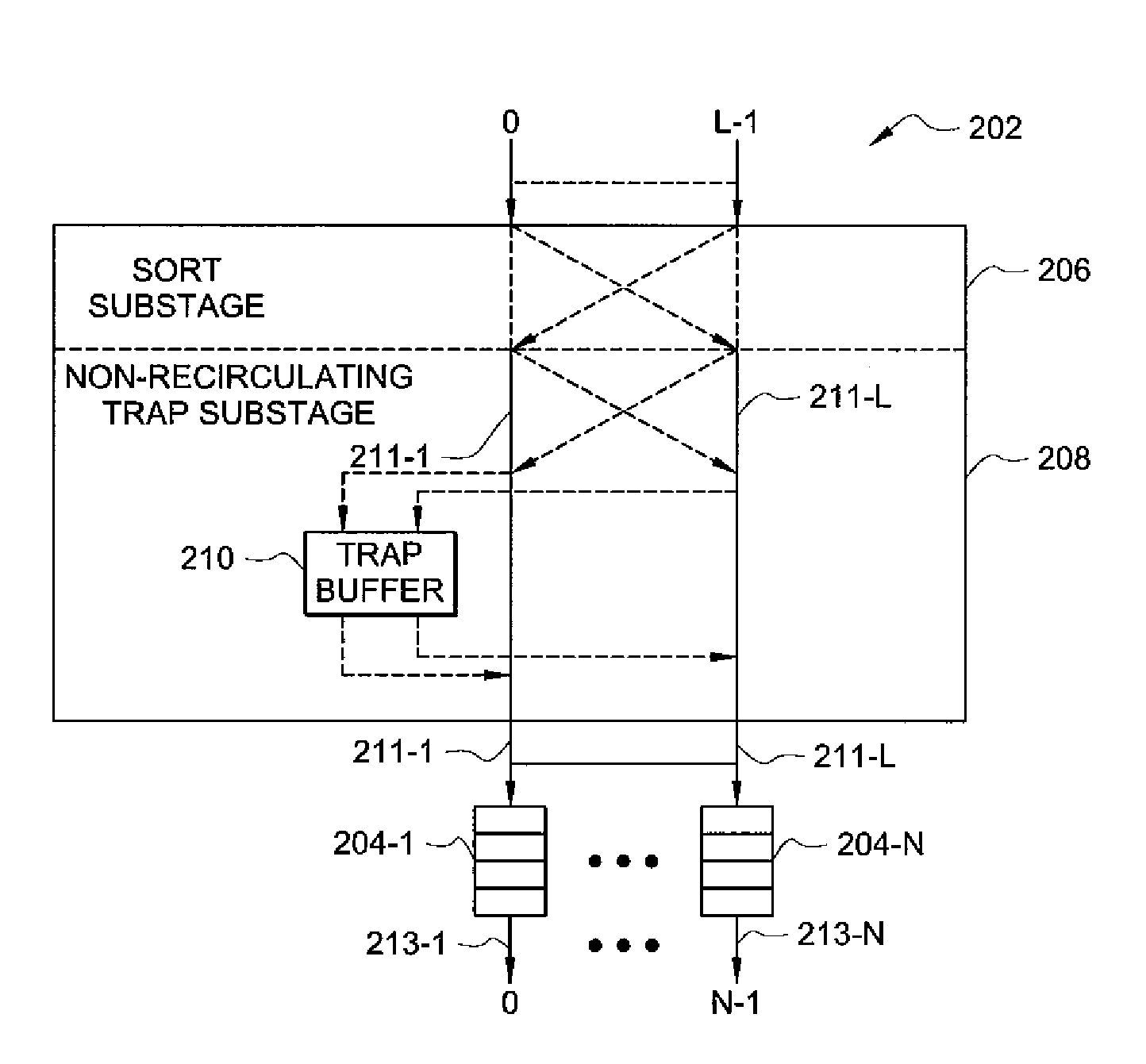
The present invention is directed to a high performance broadband ATM switching system comprised of concentrator, non-recirculating sort-trap and queuing stages. The concentrator stage concentrates cells entering the switch by discarding idle inputs thereto. Cells arriving at the non-recirculating sort-trap stage during a time slot are sorted based upon destination address and priority. Cells having a unique address for the time slot are placed in a corresponding output queue while cells having non-unique destination addresses are re-routed to a trap buffer which ages the cell until a subsequent time slot in which the destination address is unique.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
Method for sub-port multicasting in an ATM switching system
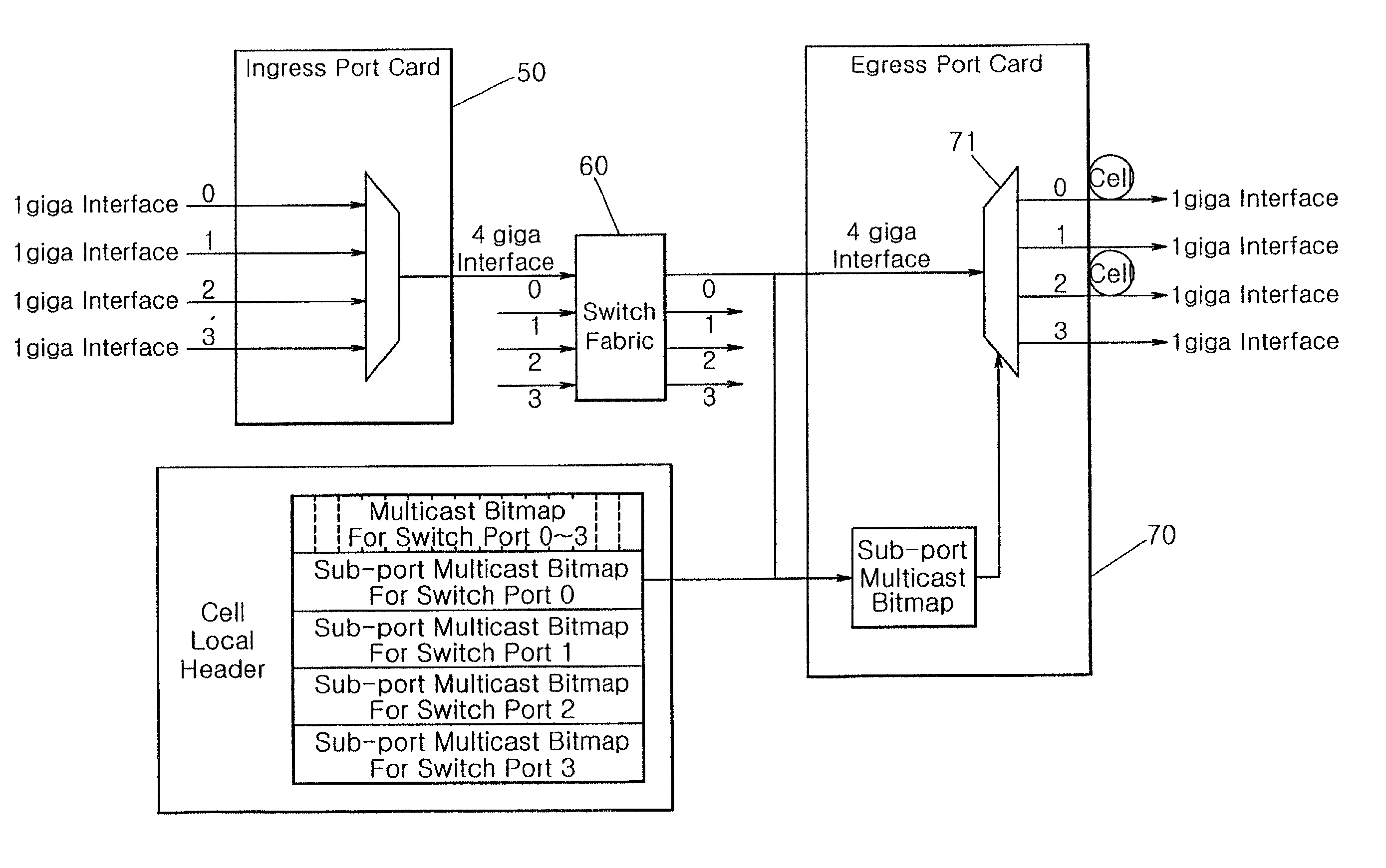
InactiveUS7400619B2Eliminate the causeSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationAtm switchingComputer network
A method for sub-port multicasting in an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching system, including inserting multicast fan-out port information for sub-ports of each of a plurality of switch ports into a multicast cell at an ingress port card, transmitting the multicast cell to an egress port card, reading the multicast fan-out port information from the multicast cell at the egress port card, and performing multicasting for the sub-ports corresponding to the multicast fan-out port information.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Apparatus for analyzing performance of traffic in asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switch and method thereof, and ATM switching system employing the same
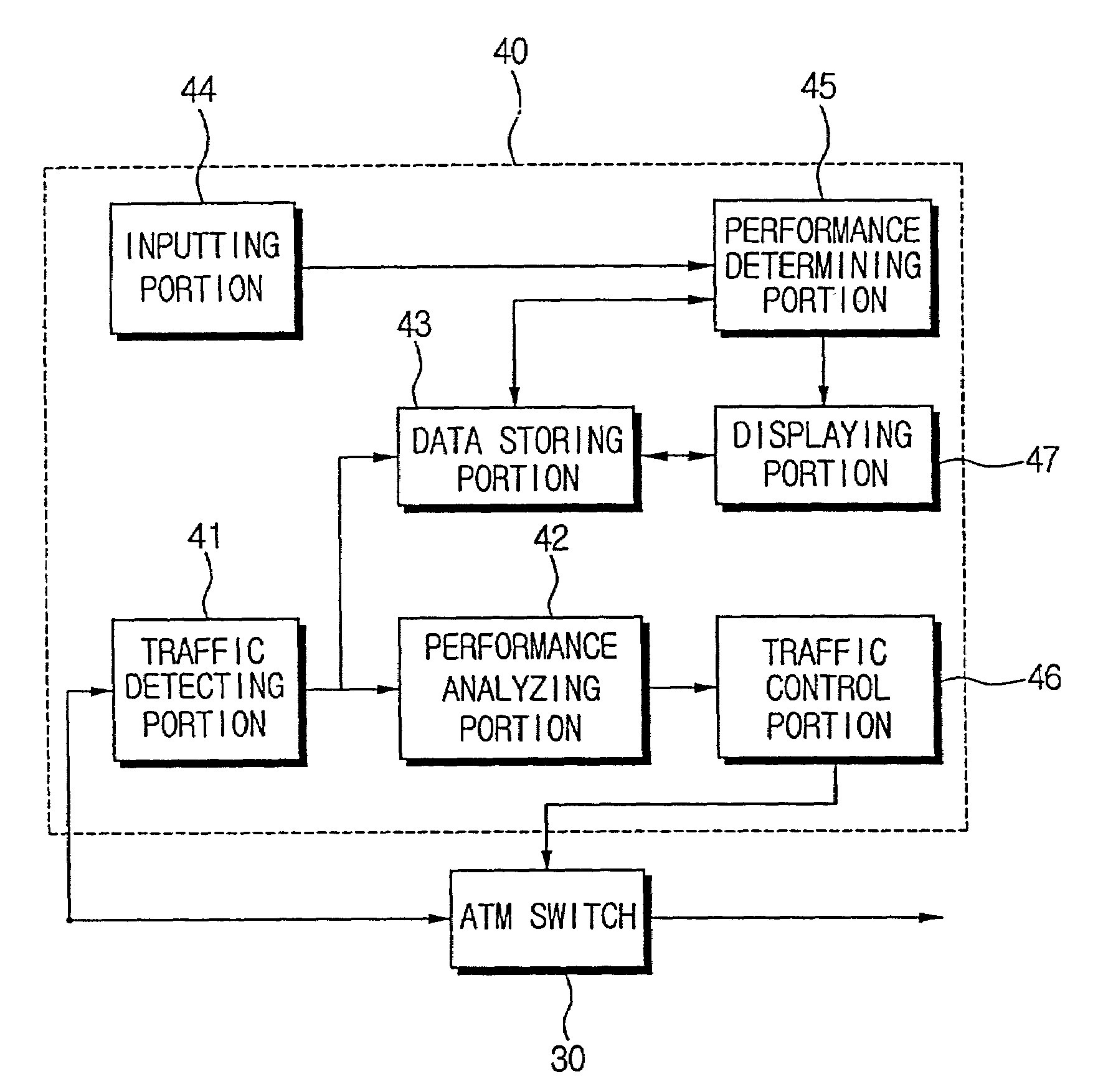
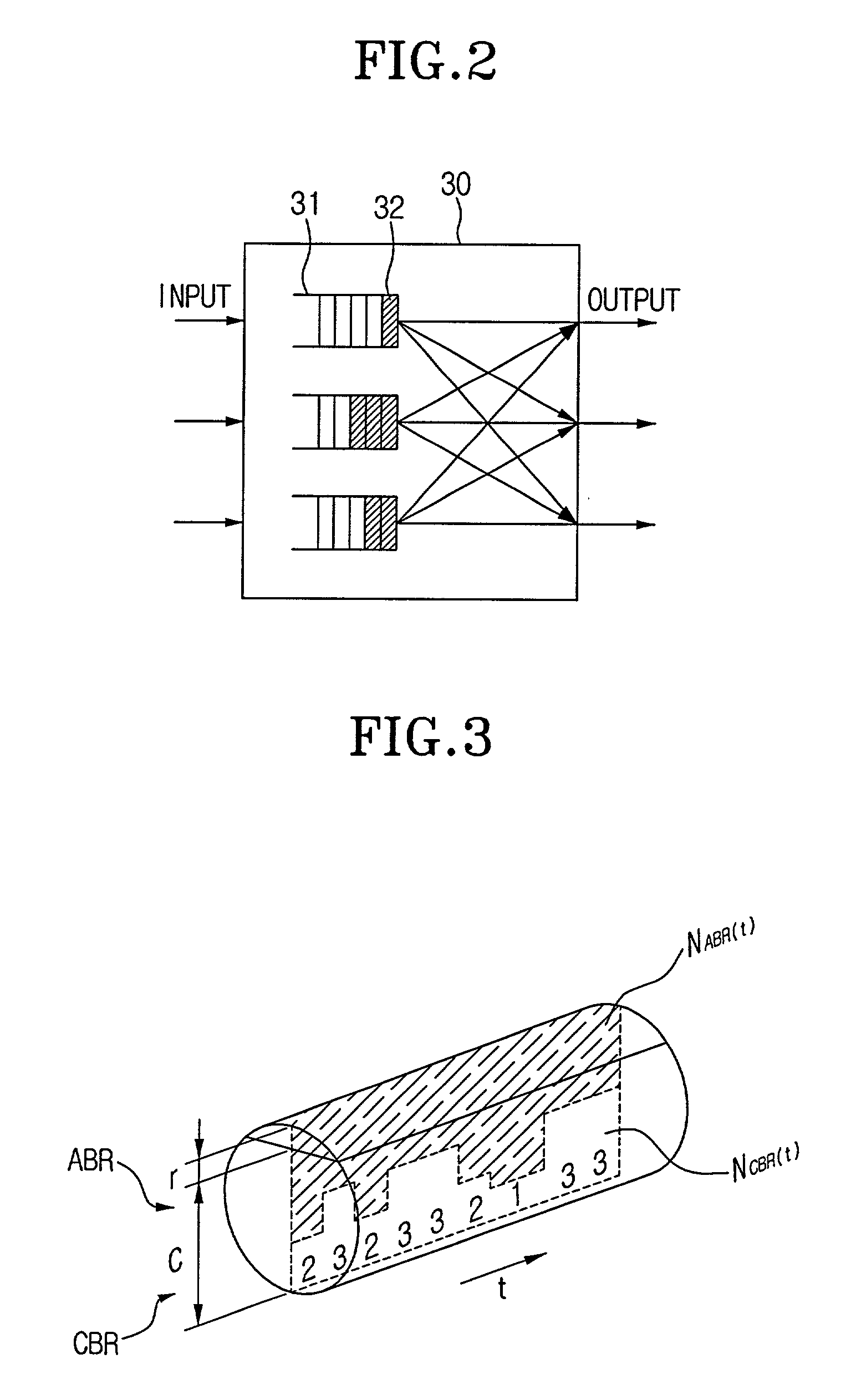
An apparatus and method for analyzing the performance of an ATM switch, and an ATM switching system employing the same. The apparatus includes a traffic detecting portion for detecting traffic of constant bit rate connection type data and available bit rate connection type data input to the ATM switch installed in a communication network for processing a data circuit switching, and a performance analyzing portion for calculating a performance of processing the constant bit rate connection type data and the available bit rate connection type data according to information related to the detected traffic of the constant bit rate connection type data and the available bit rate connection type data. According to the apparatus and method, and an ATM switching system employing the same, performance of the ATM switch can be analyzed and the analyzed result can be used in designing the ATM switch.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
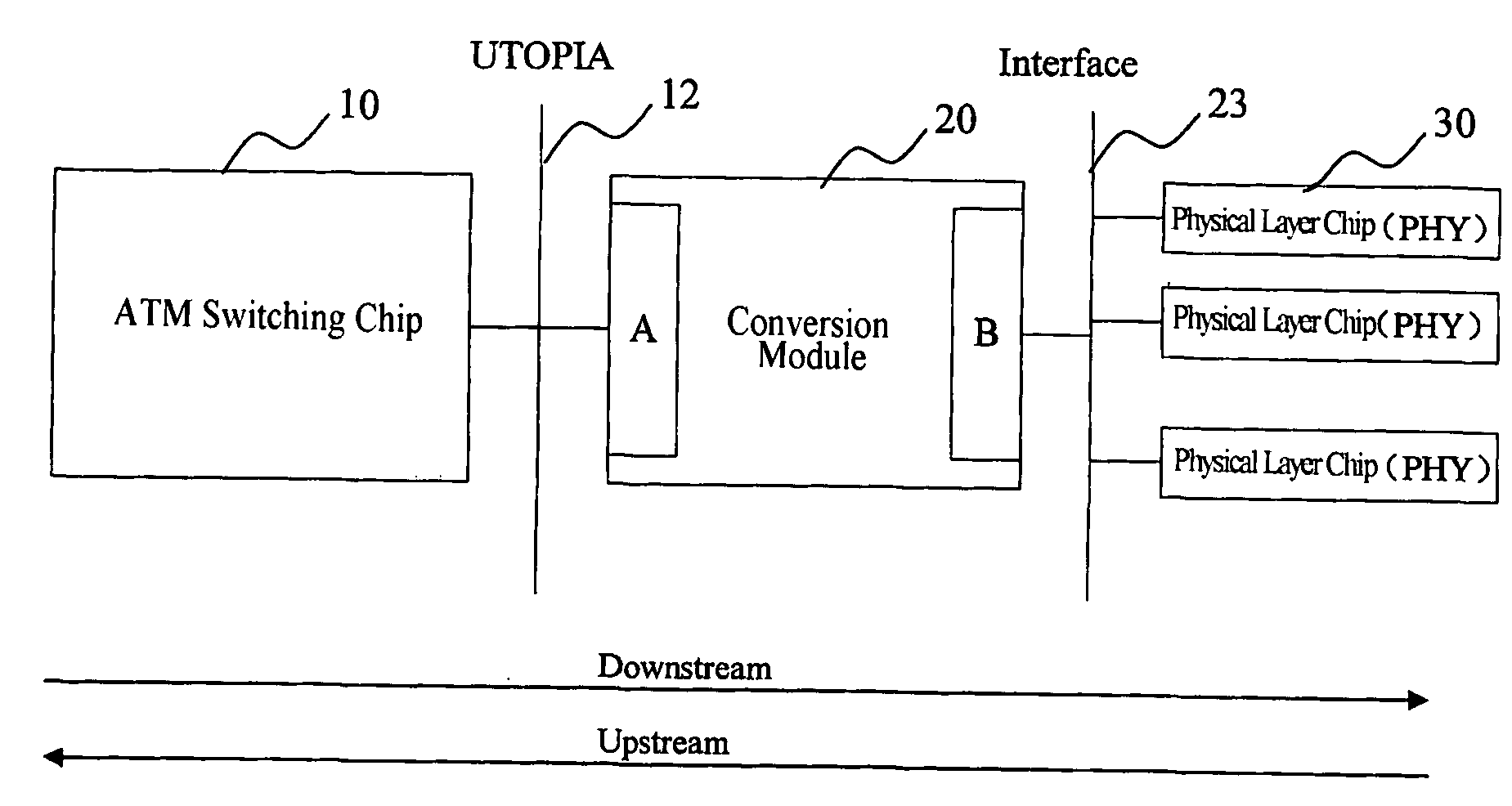
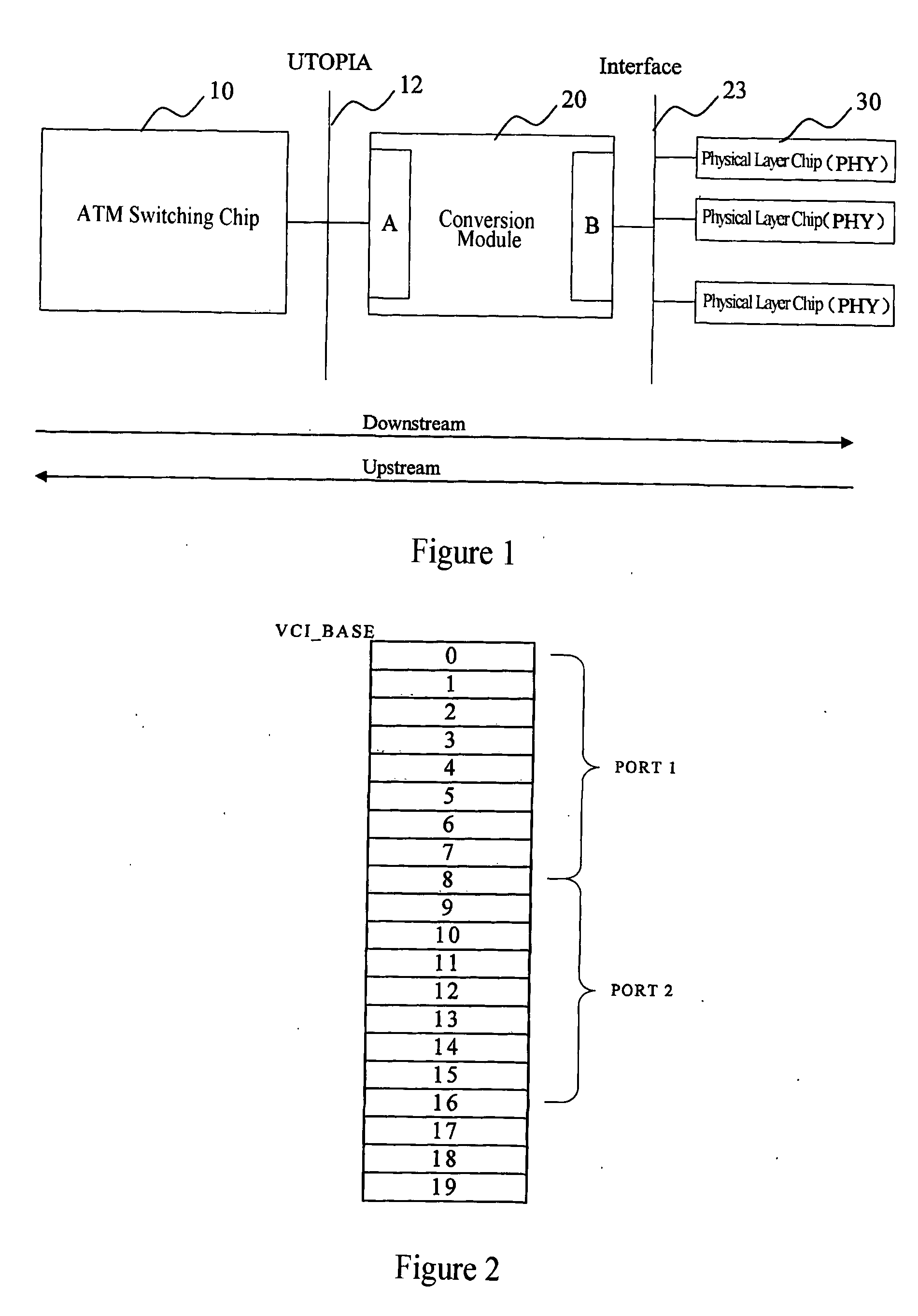
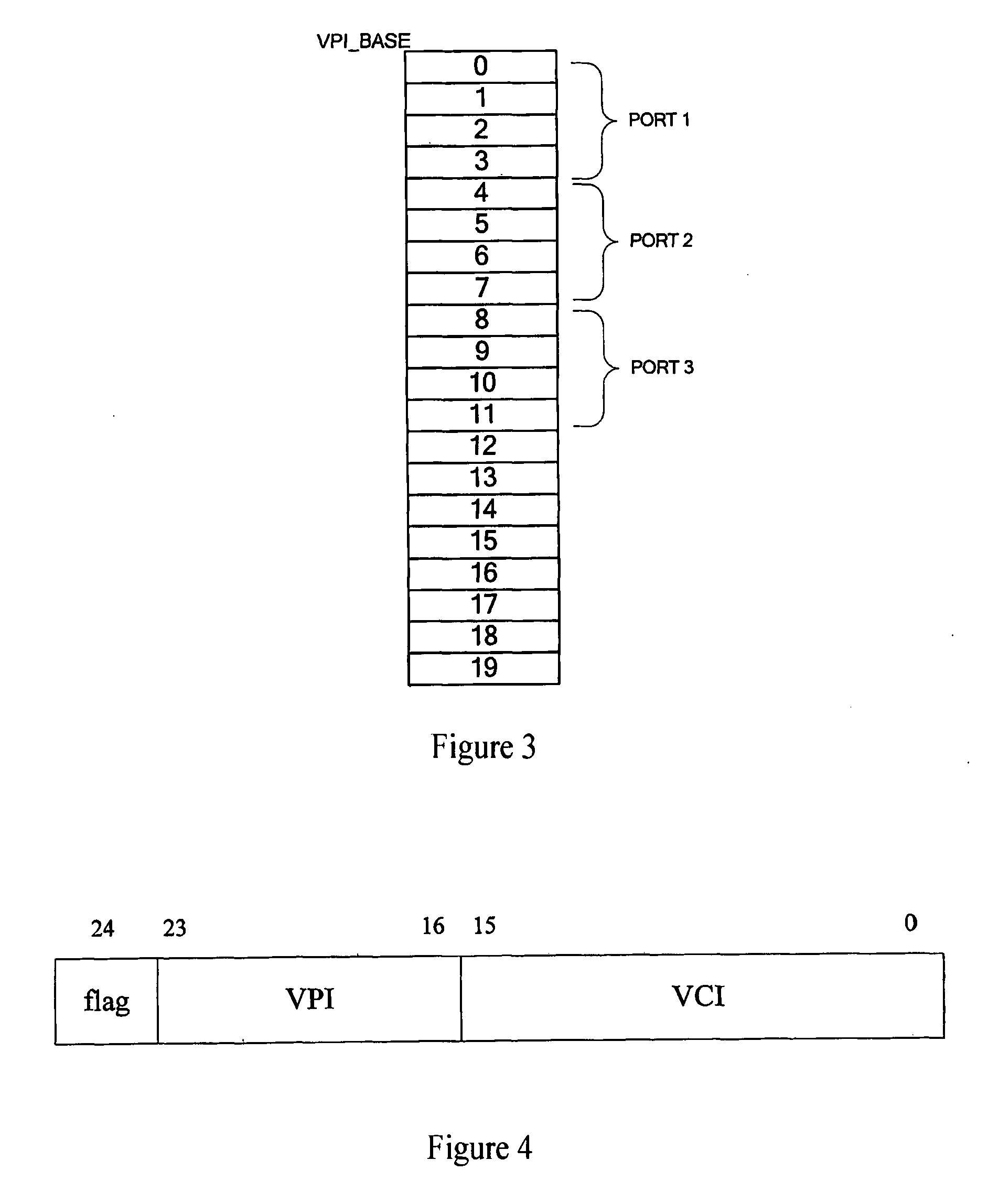
System of Extending Address on Atm Universal Test Operation Interface Bus and the Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090010266A1Improve application flexibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationAtm switchingEmbedded system
The system of this invention for extending address on UTOPIA and the method thereof can extend the single PHY on the ATM switching chip bus to many PHY ports easily without increasing too much cost, and thus increase the application flexibility of corresponding ATM switching chips. Evidently, there would be still many other embodiments of the invention, the people skilled in the art can make a variety of corresponding changes and transformations in accordance with the invention without departing from its spirit and essential, but these corresponding changes and transformations should also be in the protection range of the claims of this invention.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Concentrator type ATM switch for an ATM switching system
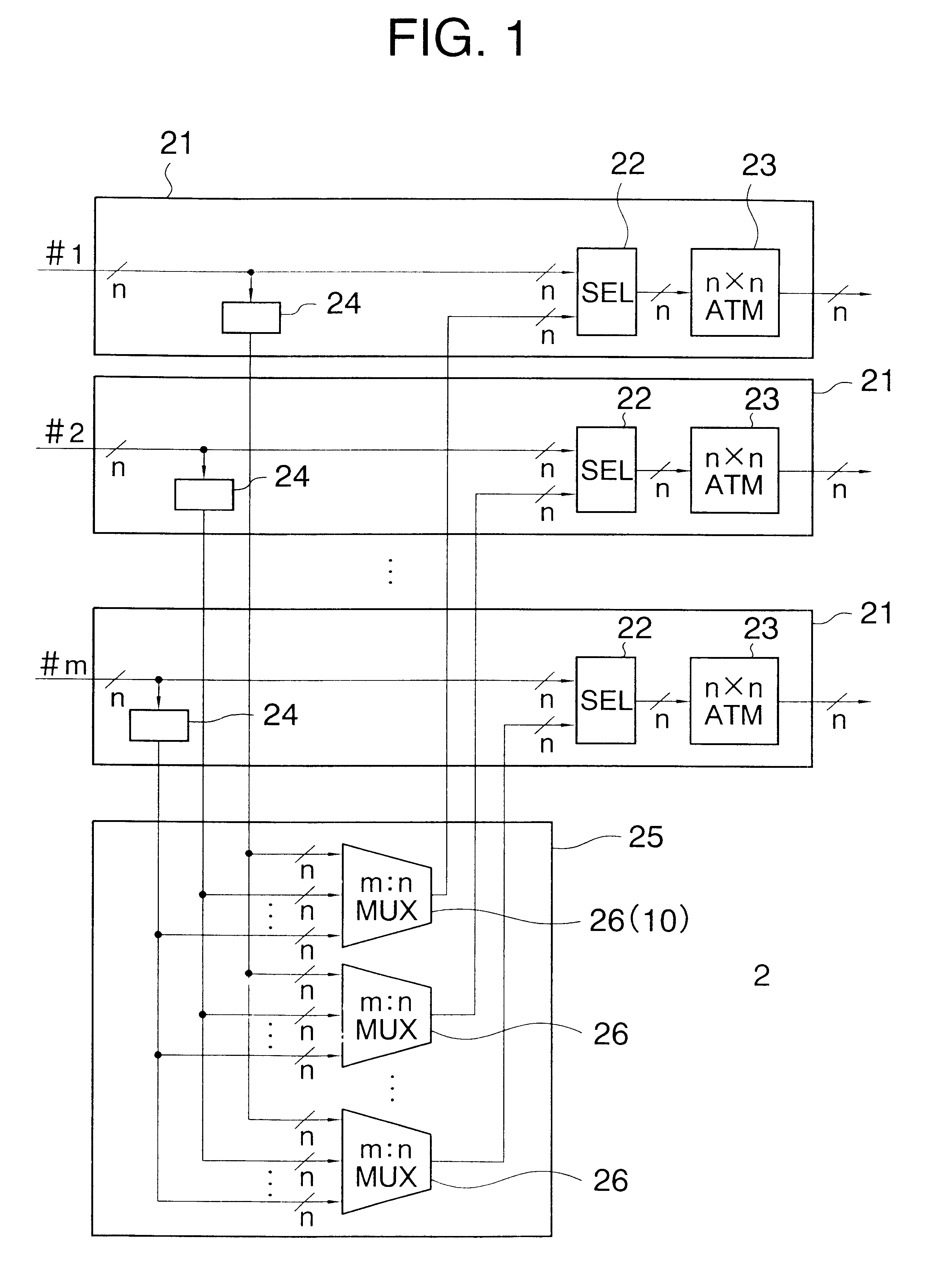
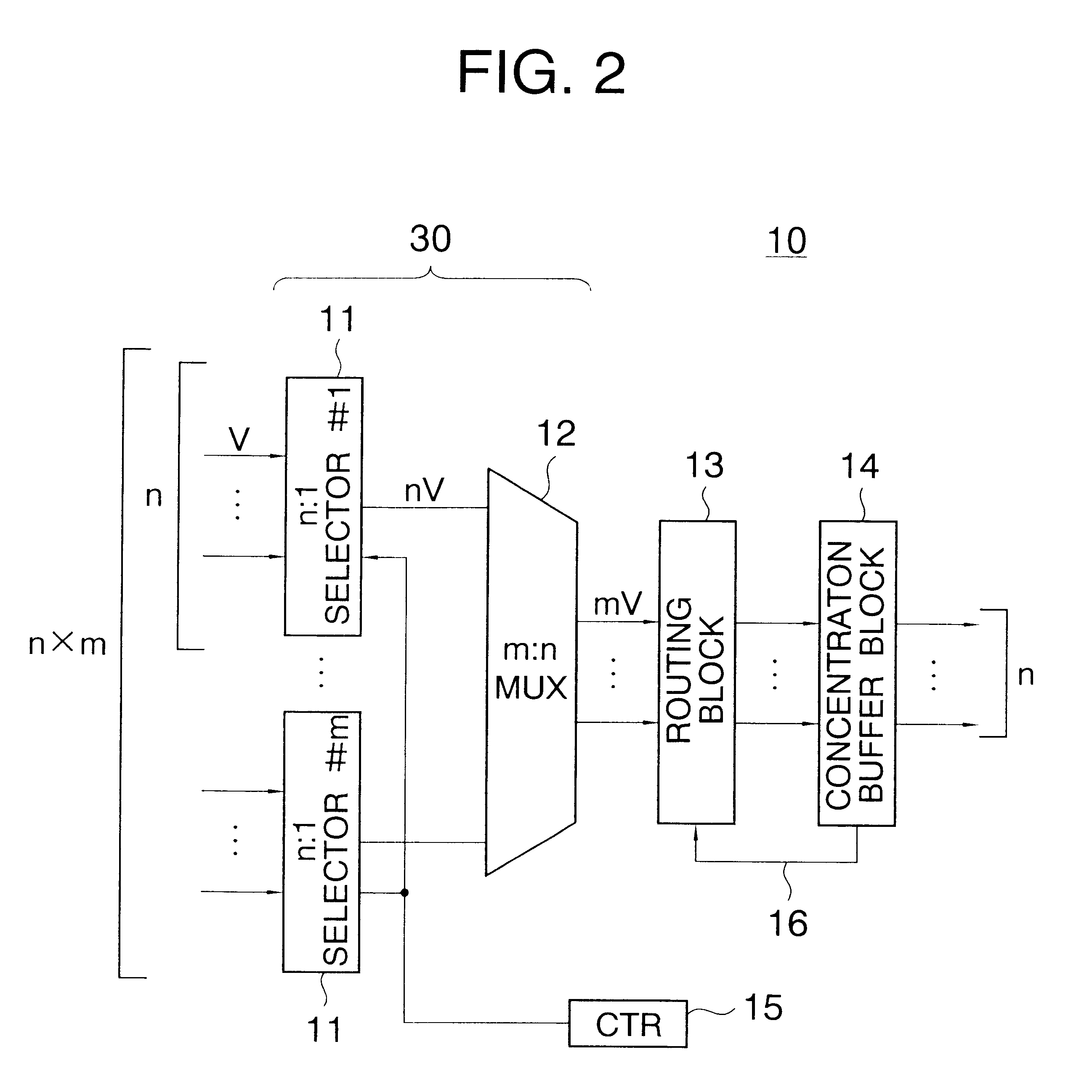
InactiveUS6580714B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAtm switchingMultiplexing
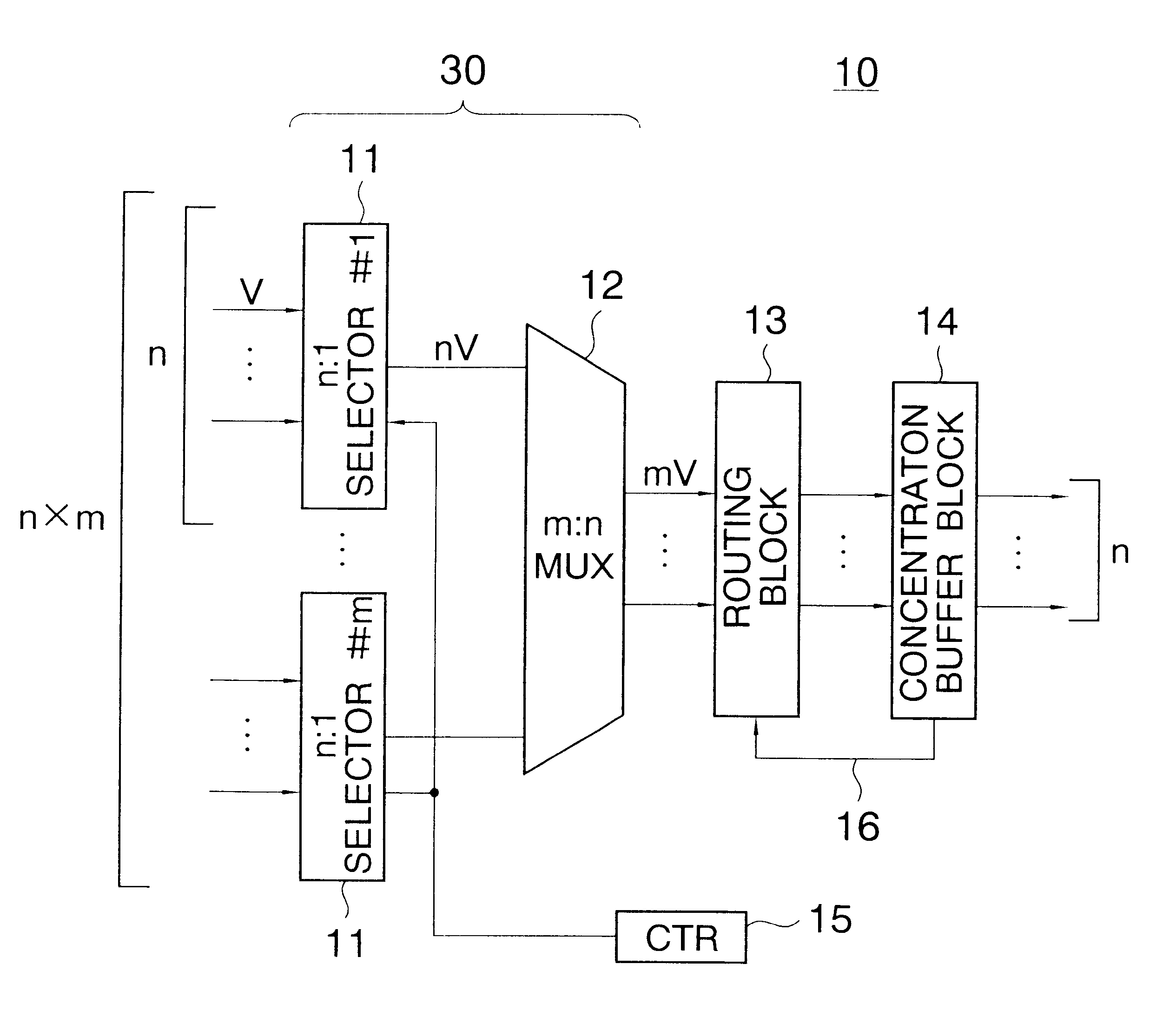
An ATM switching system includes a plurality of (m) small-scale nxn ATM switch modules, and a coupling module for coupling the ATM switch modules to one another to implement a large-scale ATM switching system. The coupling module includes m concentrators corresponding to the m ATM switch modules. Each concentrator has a multiplexing block for multiplexing mxn signal sequences into n signal sequences, concentration buffer block including a nxn banyan network for specifying one of ATM switch modules for each effective cell based on a destination signal and a plurality of buffers. The concentrator operates at slow transfer rate in a large-scale ATM system so that the performance of the concentrator does not restrict the scale of the ATM system.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com