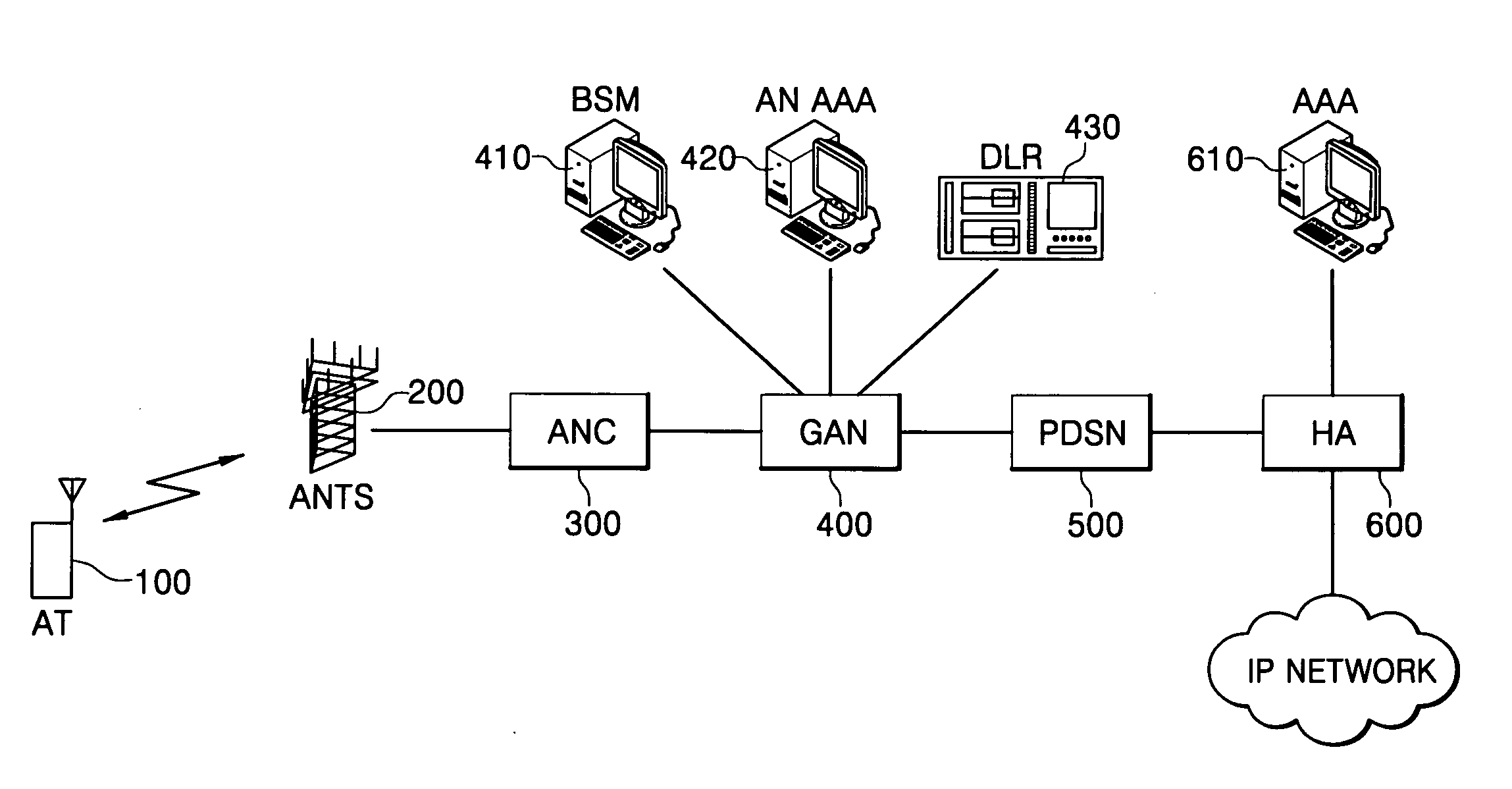
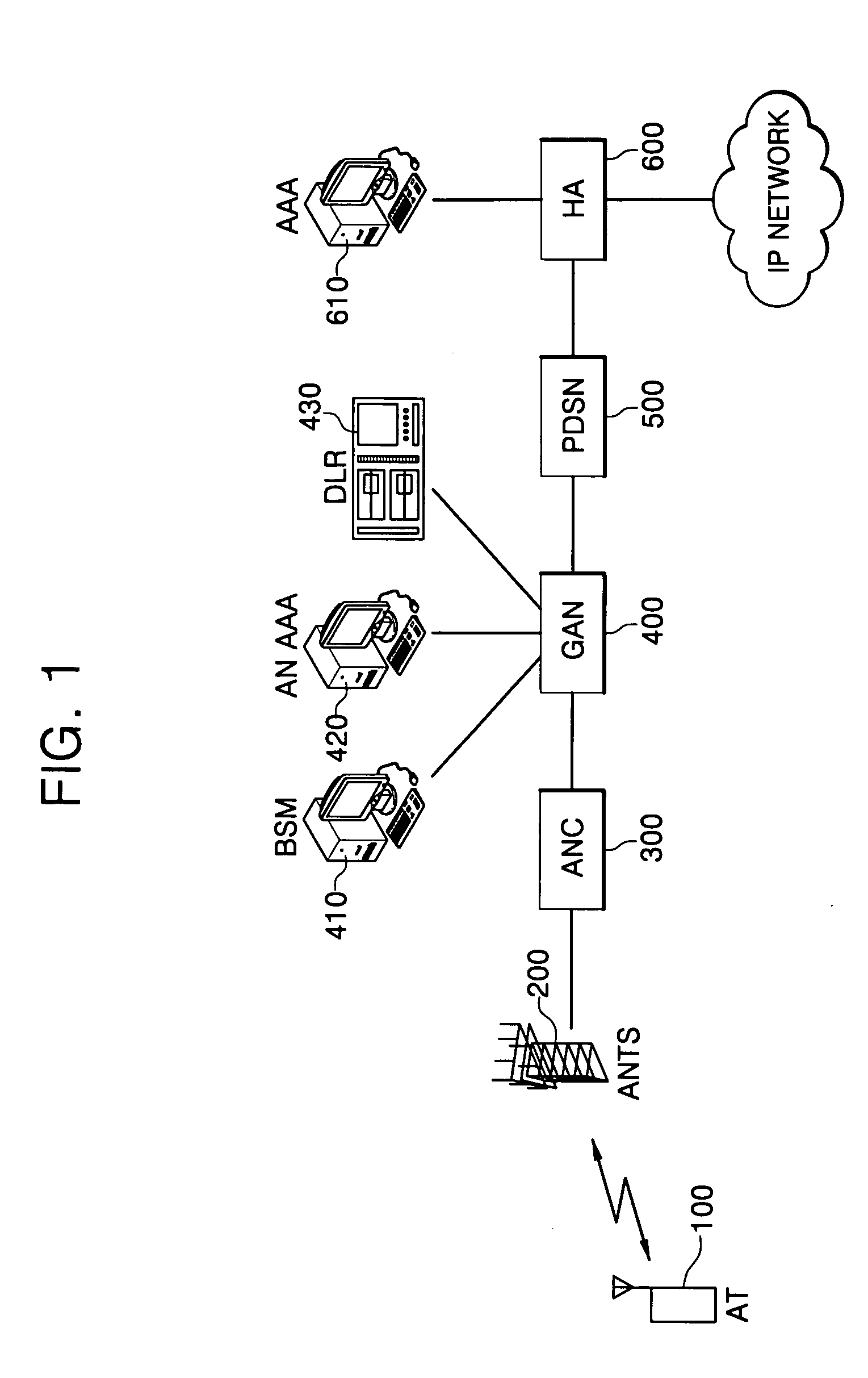
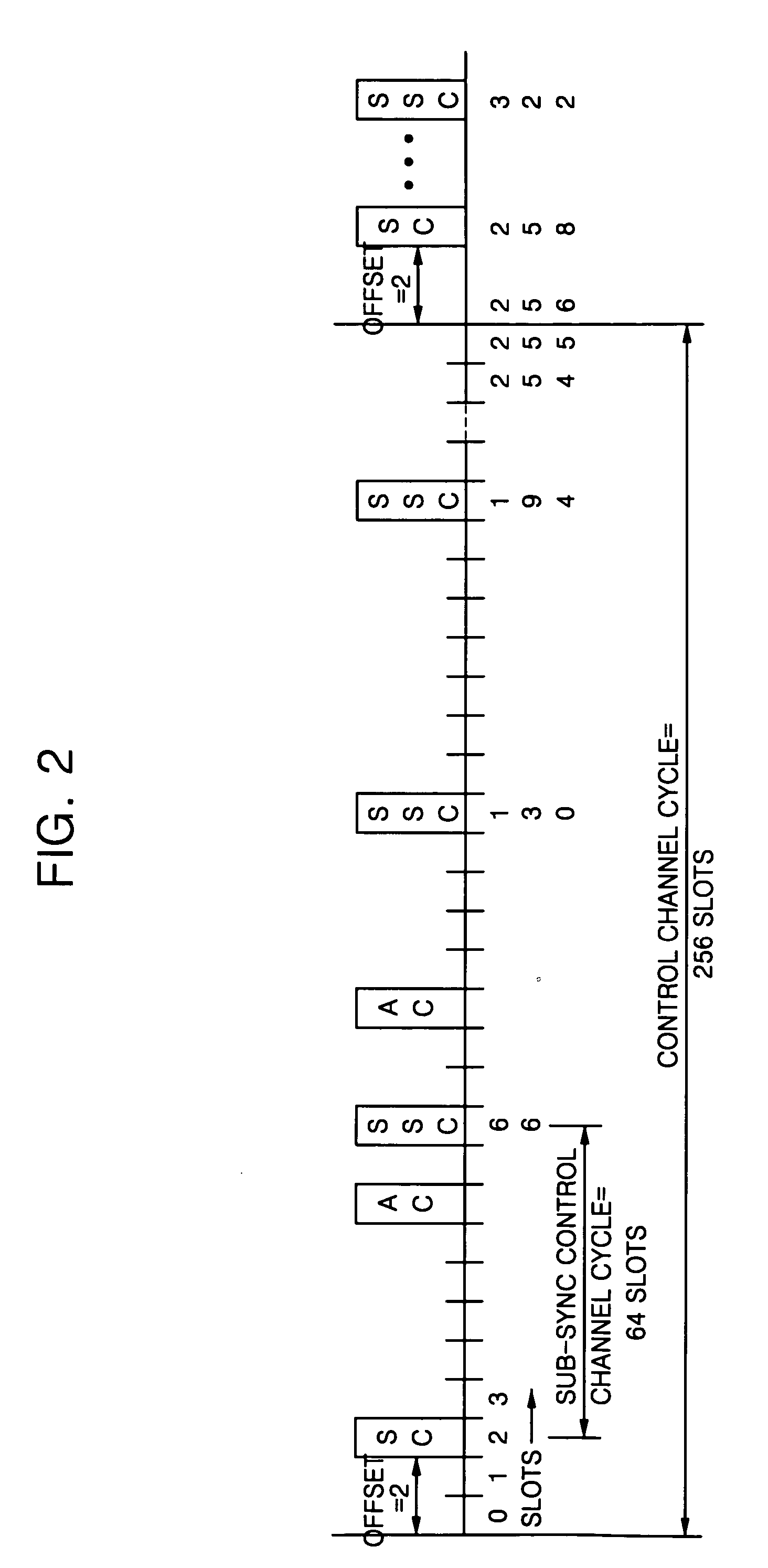
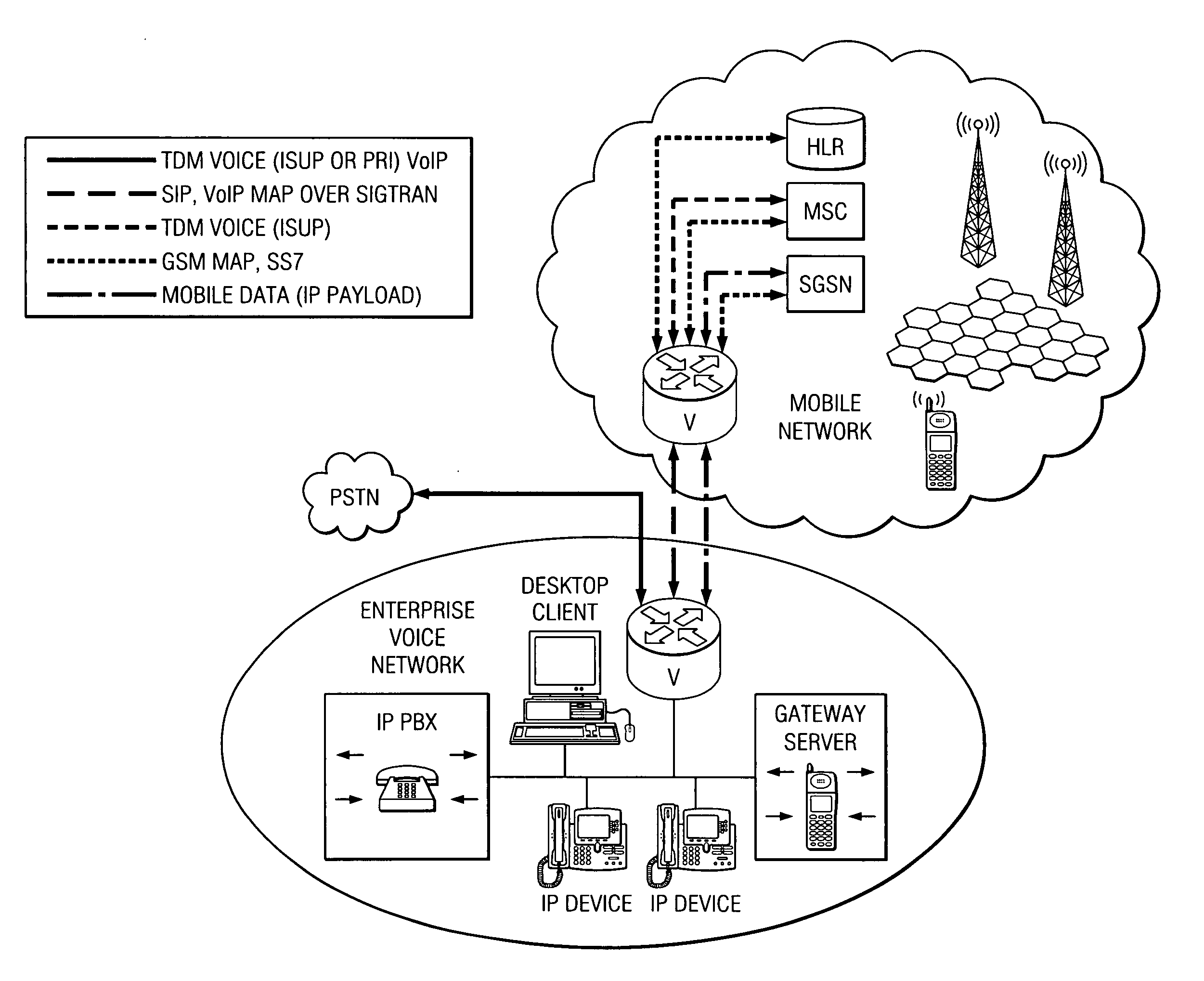
Patents
Literature
2417 results about "Call control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
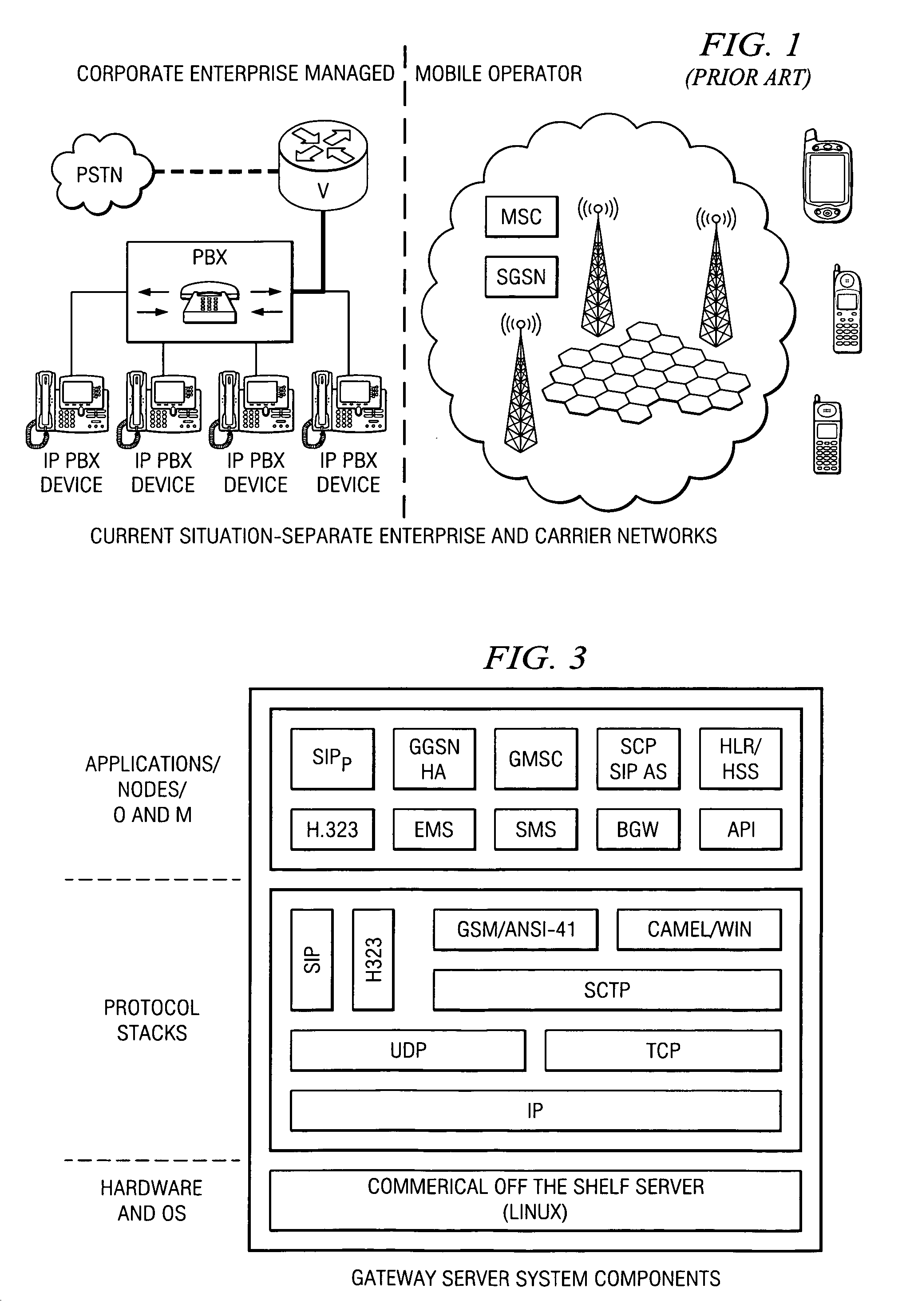
In telephony, call control refers to the software within a telephone switch that supplies its central function. Call control decodes addressing information and routes telephone calls from one end point to another. It also creates the features that can be used to adapt standard switch operation to the needs of users. These are called supplementary services and are commonly invoked by a Vertical service code. Examples include "Call Waiting", "Call Forward on Busy" etc.
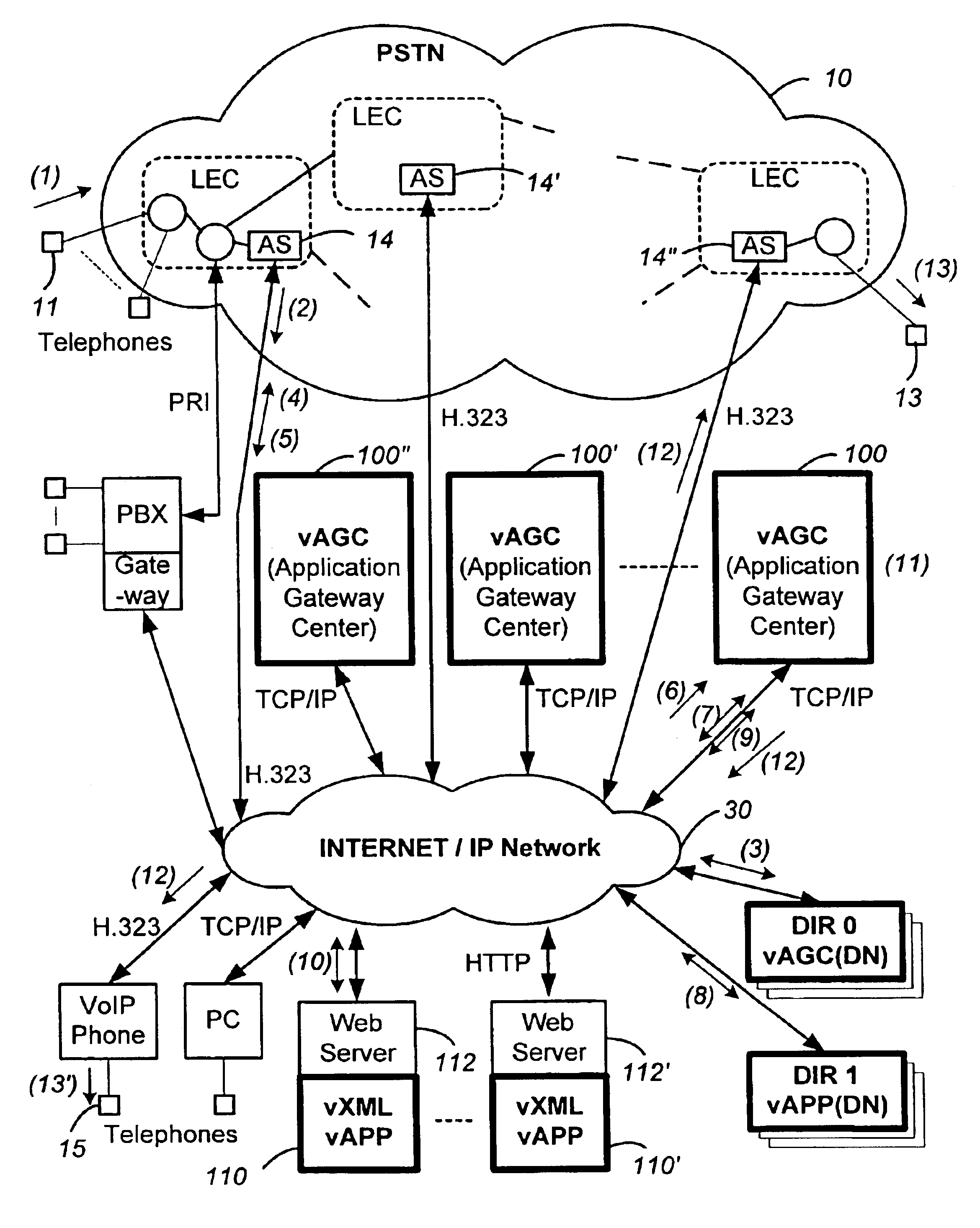
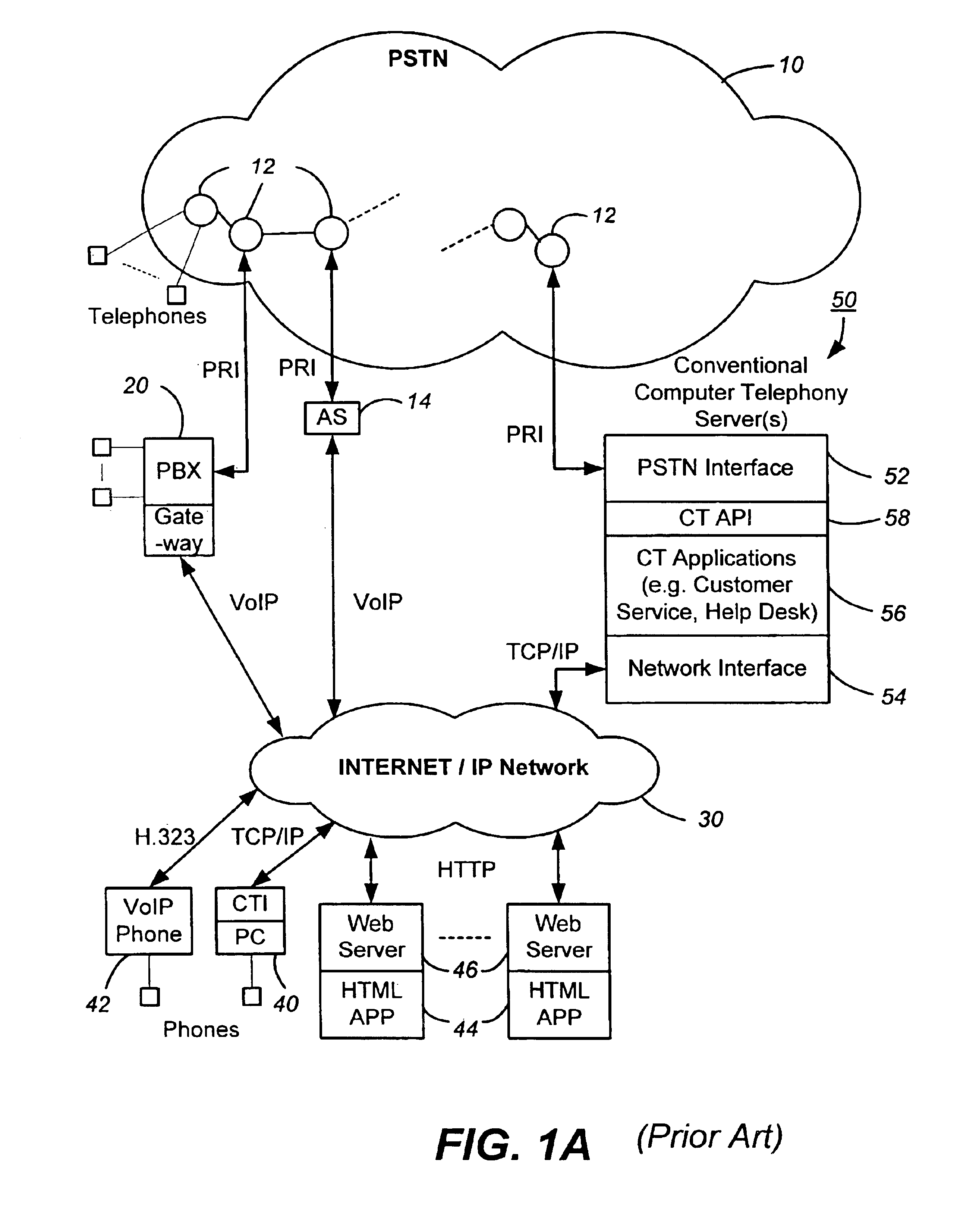
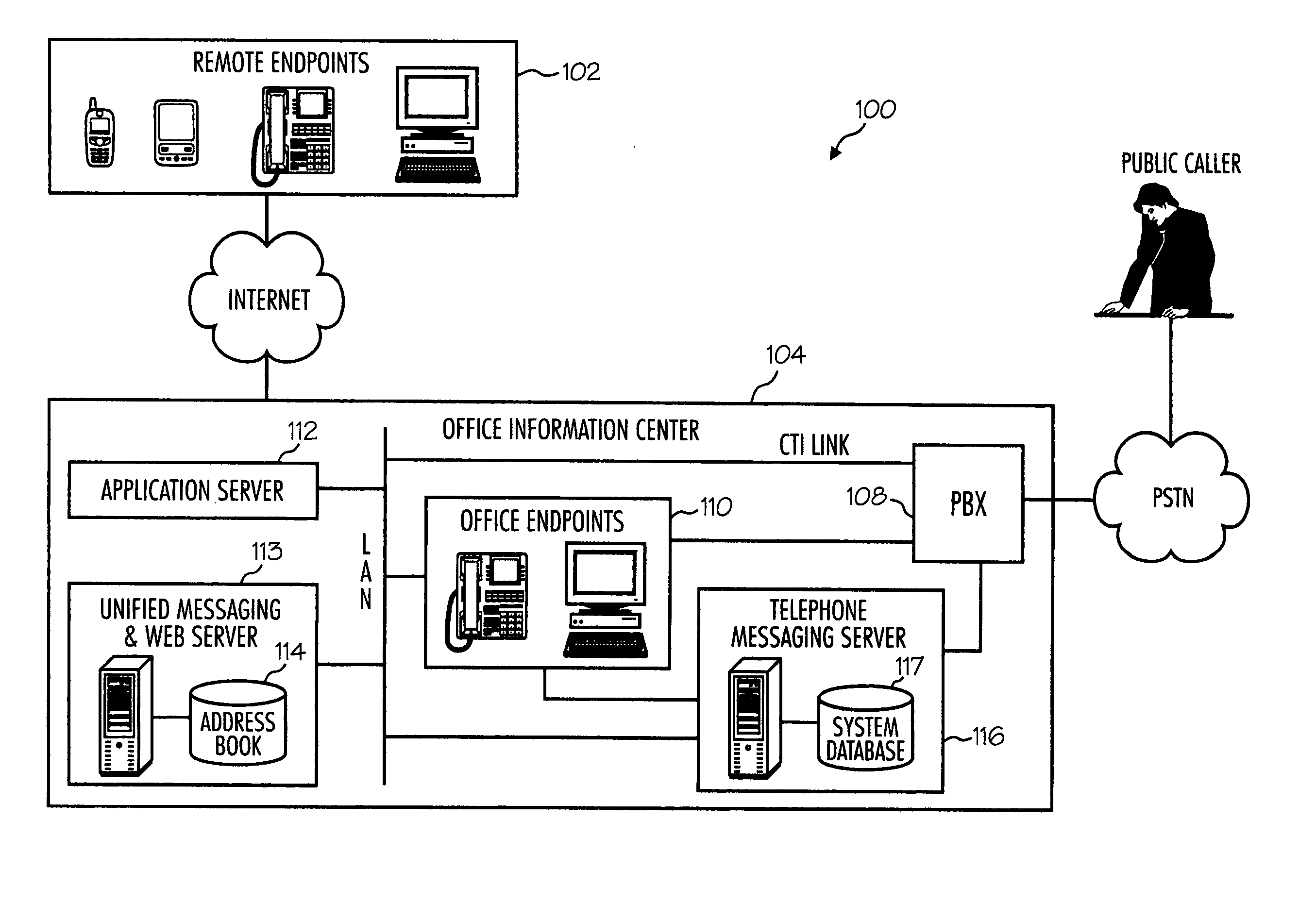
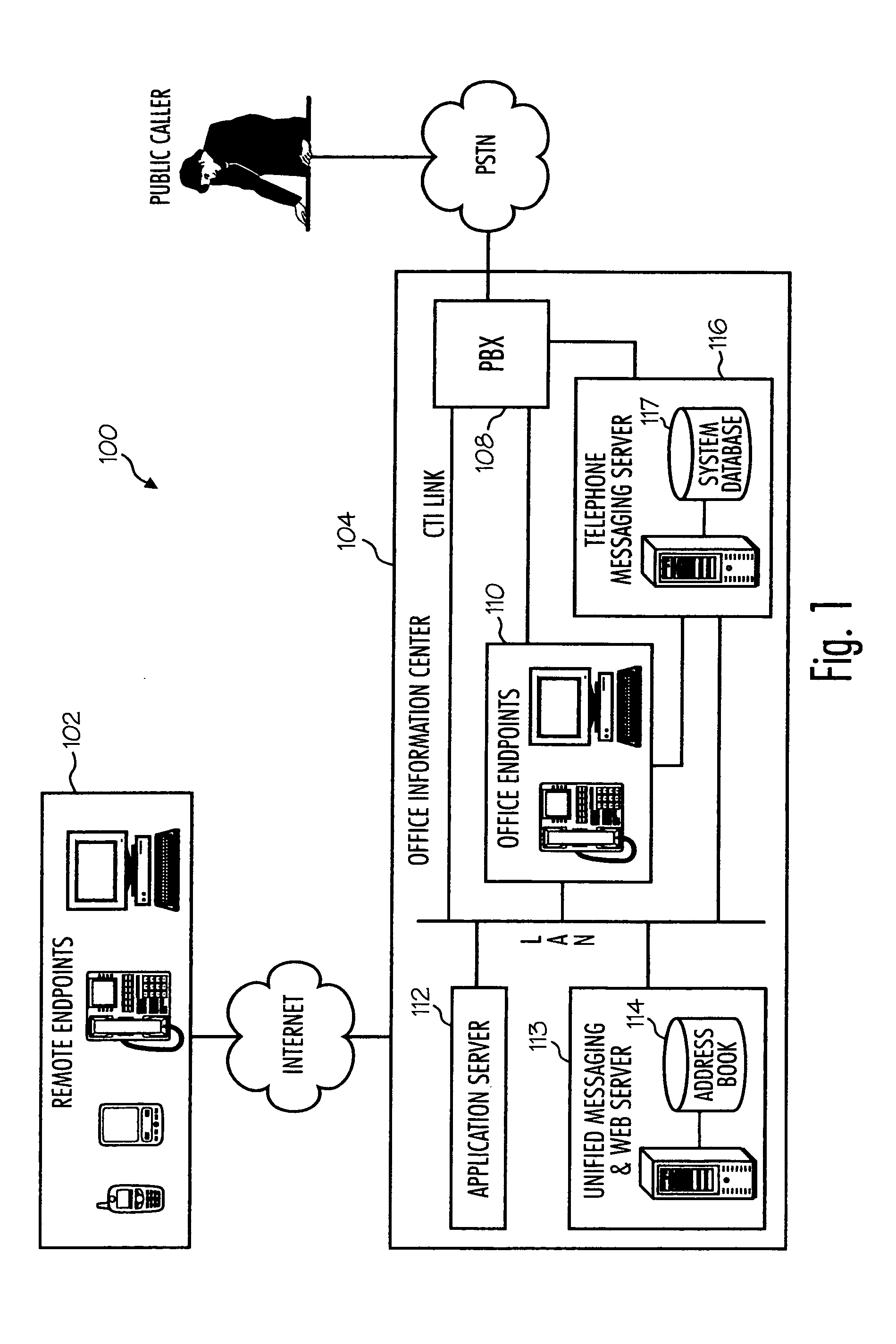
Networked computer telephony system driven by web-based applications
InactiveUS6922411B1Improve developmentEasy to deploySpecial service for subscribersData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceThe Internet
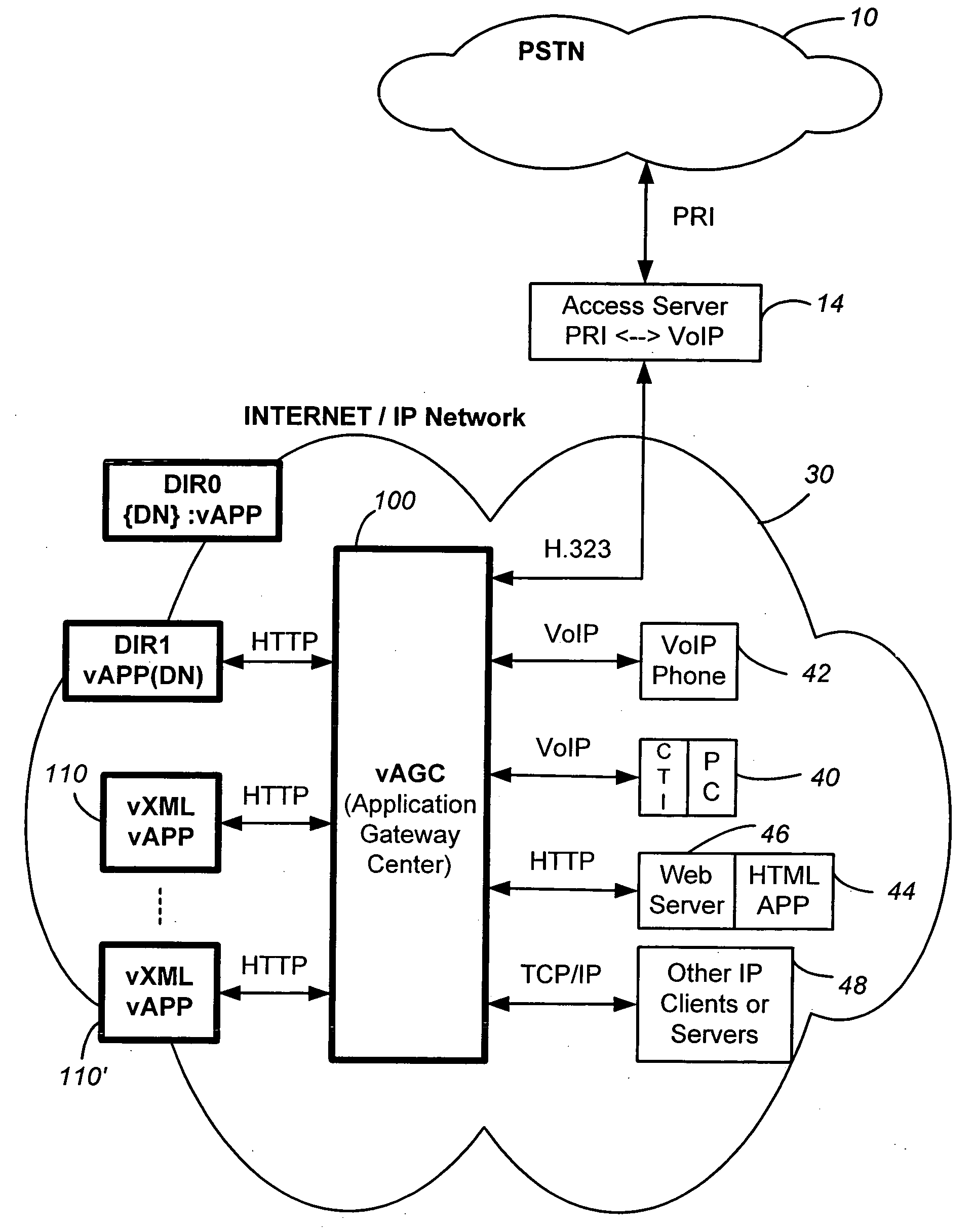
A networked telephony system and method allow users to deploy on the Internet computer telephony applications associated with designated telephone numbers. The telephony application is easily created by a user in XML (Extensible Markup Language) with predefined telephony XML tags and easily deployed on a website. The telephony XML tags include those for call control and media manipulation. A call to anyone of these designated telephone numbers may originate from anyone of the networked telephone system such as the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone System), a wireless network, or the Internet. The call is received by an application gateway center (AGC) installed on the Internet. Analogous to a web browser, the AGC provides facility for retrieving the associated XML application from its website and processing the call accordingly. The architecture and design of the system allow for reliability, high quality-of-service, easy scalability and the ability to incorporate additional telephony hardware and software and protocols.
Owner:ALVARIA INC
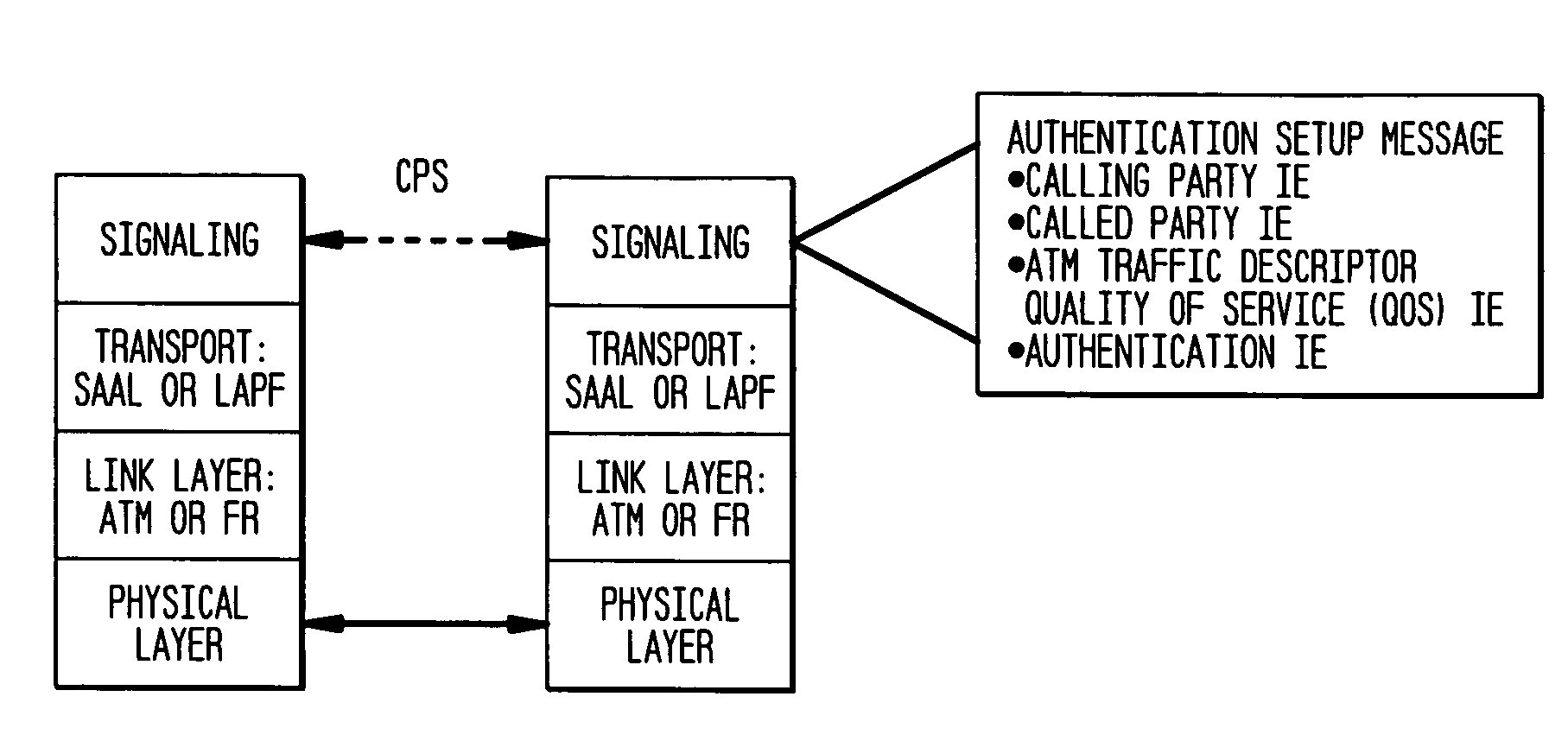
Authentication mechanisms for call control message integrity and origin verification
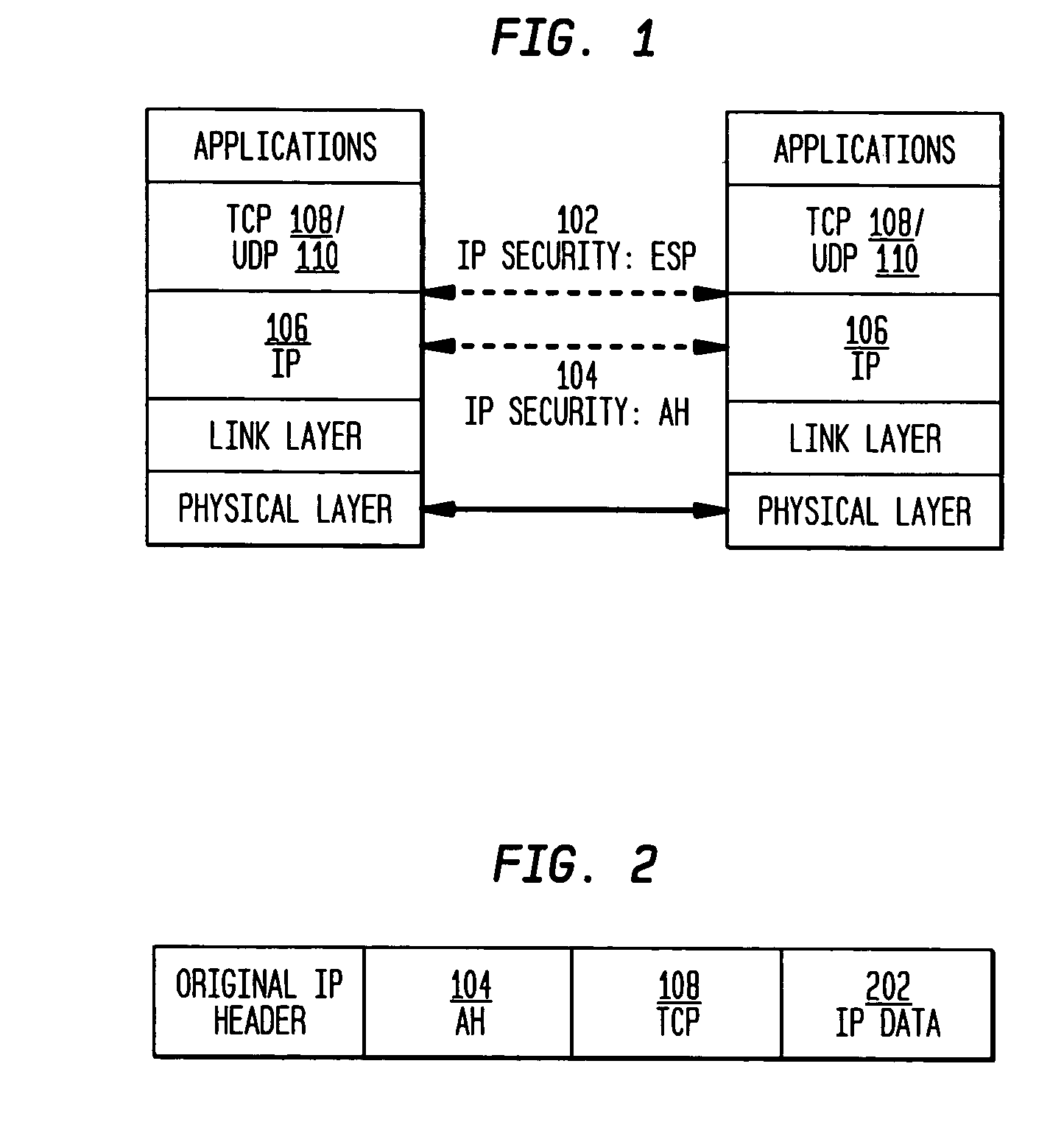
The present invention incorporates methodologies developed in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Protocol Security (IPSEC) Working Group into asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and frame relay (FR) signaling to provide message integrity and origin authentication. In one implementation the invention provides a virtual private network (VPN) infrastructure with call control message integrity, origin verification, and transit network filtering. The invention utilizes a set of control plane messages based on the IPSEC authentication header (AH) methodology to provide these security mechanisms for ATM and FR network switching equipment and signaling protocols. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
System and method for secure web-based mobile phone parental controls
InactiveUS20060293057A1Unwanted useGraded-service arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWeb siteSelf limiting
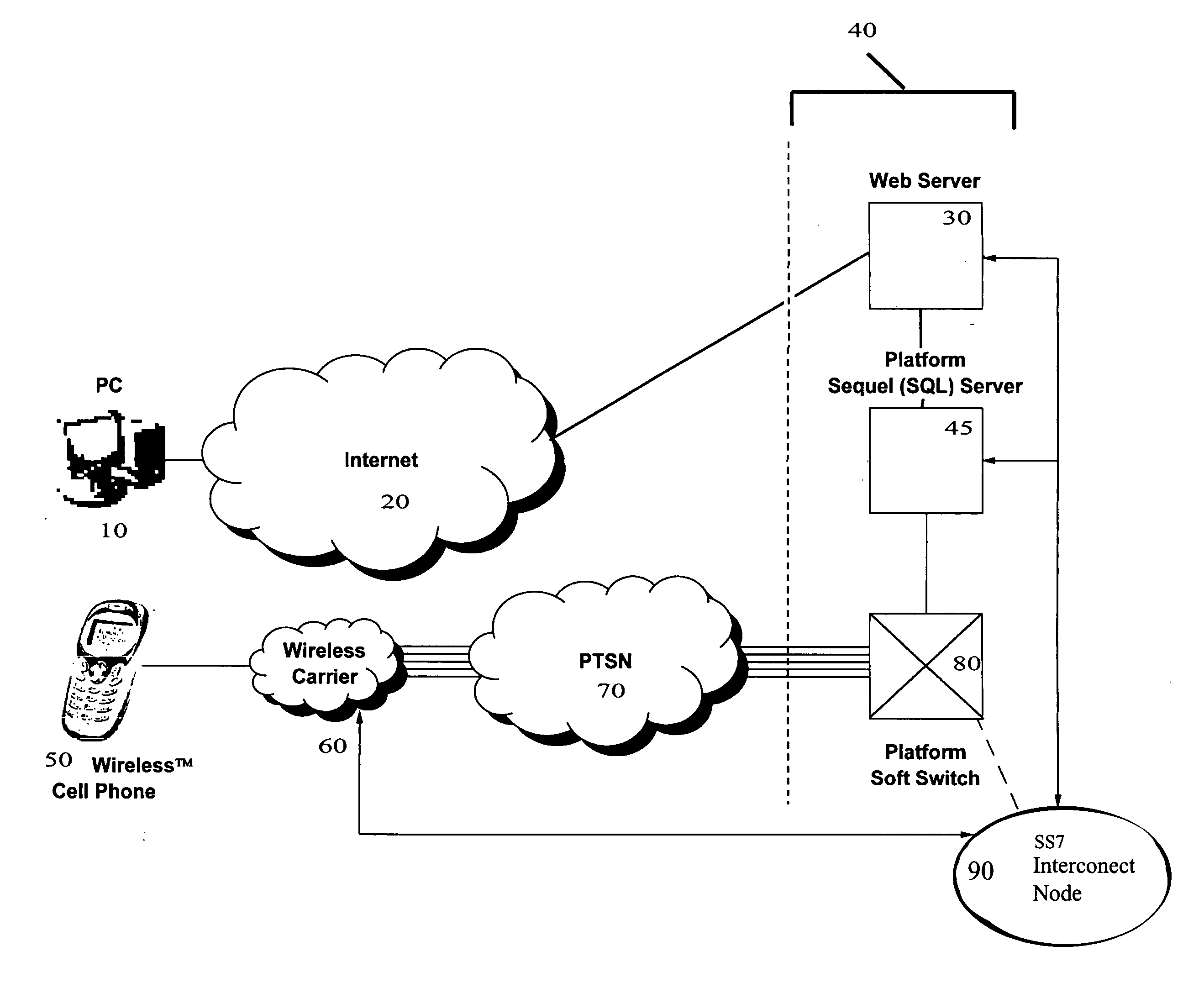
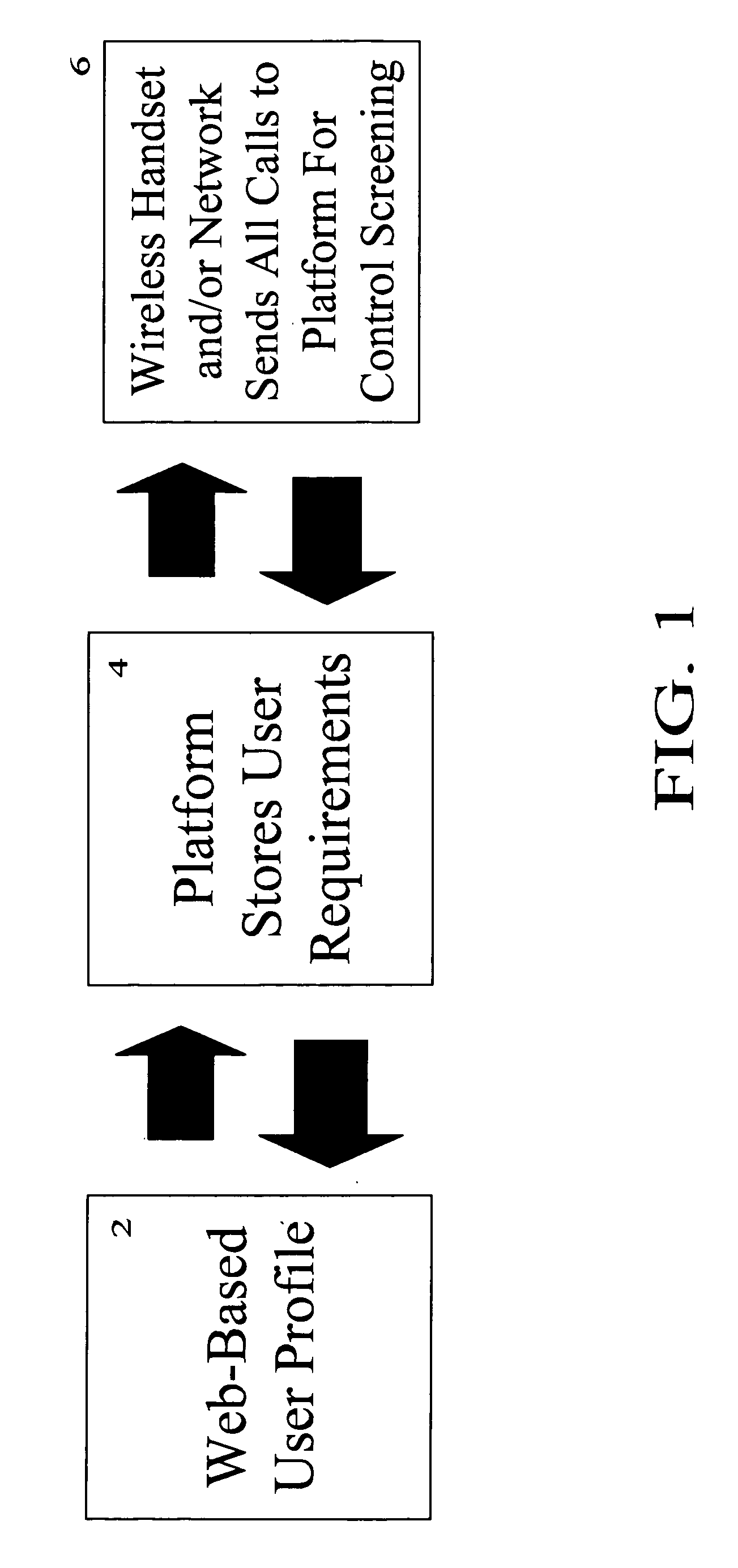
A wireless system and method for implementing call controls (such as parental controls) for wireless telephones via a call-intercept platform (including a soft switch and / or an SS7 interconnection node, and SQL database), and a conventional mobile phone that makes and receives all outgoing calls through the call intercept platform. The call intercept platform includes secure web server to provide a secure website point of entry for allowing parents to specify a ruleset of parental controls that is stored in the SQL database. Every outgoing call from the mobile phone is routed into the call-intercept platform, which logs the call, crosschecks the mobile phone and outgoing call number against the stored ruleset for that phone / user, and selectively screens te calls. Incoming calls are automatically forwarded from the wireless carrier to the call intercept platform and are logged, cross-checked and selectively screened. The secure web portal allows parents and guardians or other individuals who desire to self-limit call usage to thoroughly manage their dependent's or their own phone, inclusive of viewing calls, activating and deactivating controls, customizing controls, as well as purchasing prepaid minutes and managing their accounts.
Owner:CLOSECALL AMERICA
Networked computer telephony system driven by web-based applications
InactiveUS20050240659A1Easy development and deploymentLow costSpecial service for subscribersData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceWeb browser
A networked telephony system and method allow users to deploy on the Internet computer telephony applications associated with designated telephone numbers. The telephony application is easily created by a user in XML (Extensible Markup Language) with predefined telephony XML tags and easily deployed on a website. The telephony XML tags include those for call control and media manipulation. A call to anyone of these designated telephone numbers may originate from anyone of the networked telephone system such as the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone System), a wireless network, or the Internet. The call is received by an application gateway center (AGC) installed on the Internet. Analogous to a web browser, the AGC provides facility for retrieving the associated XML application from its website and processing the call accordingly. The architecture and design of the system allow for reliability, high quality-of-service, easy scalability and the ability to incorporate additional telephony hardware and software and protocols.
Owner:ALVARIA INC
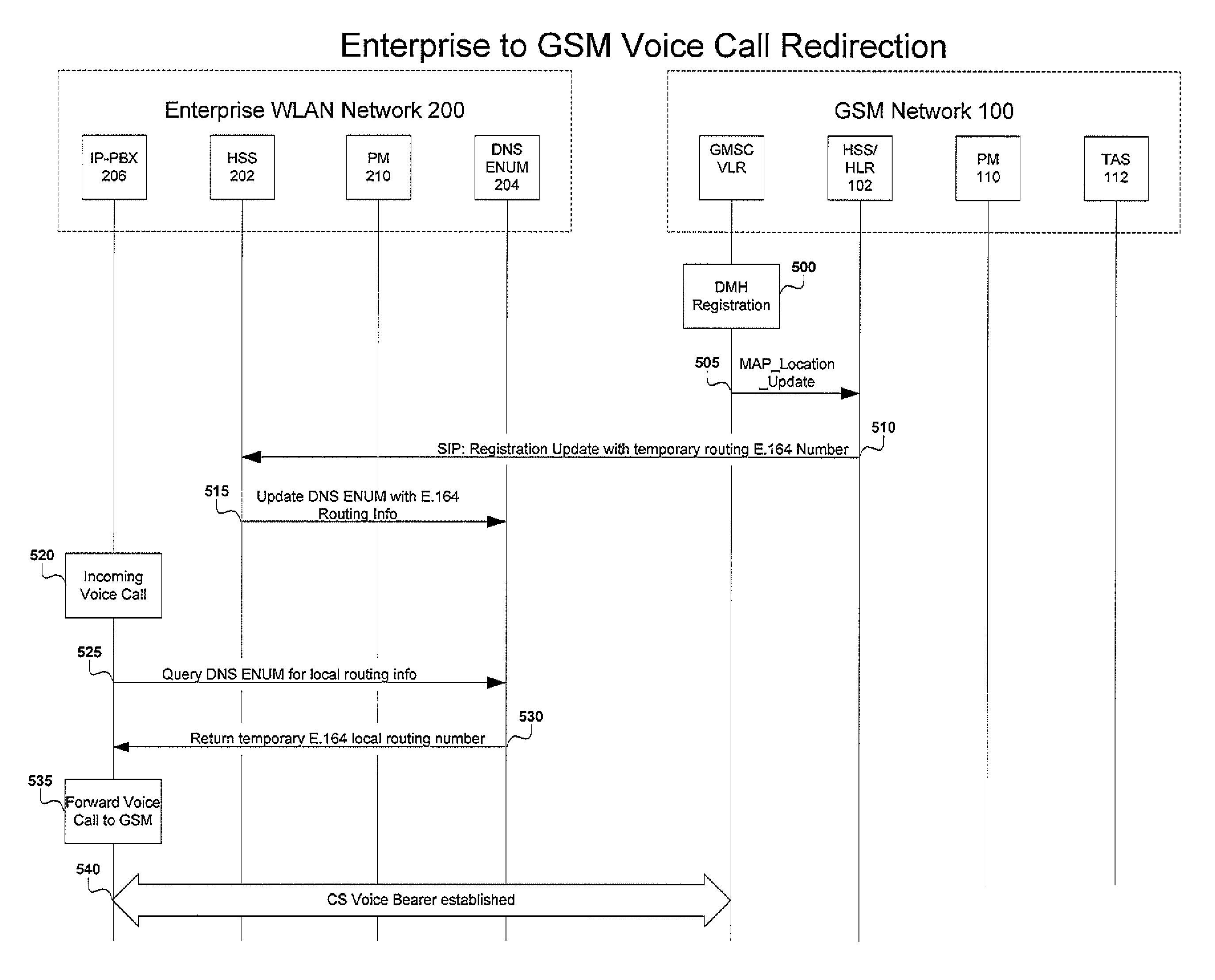
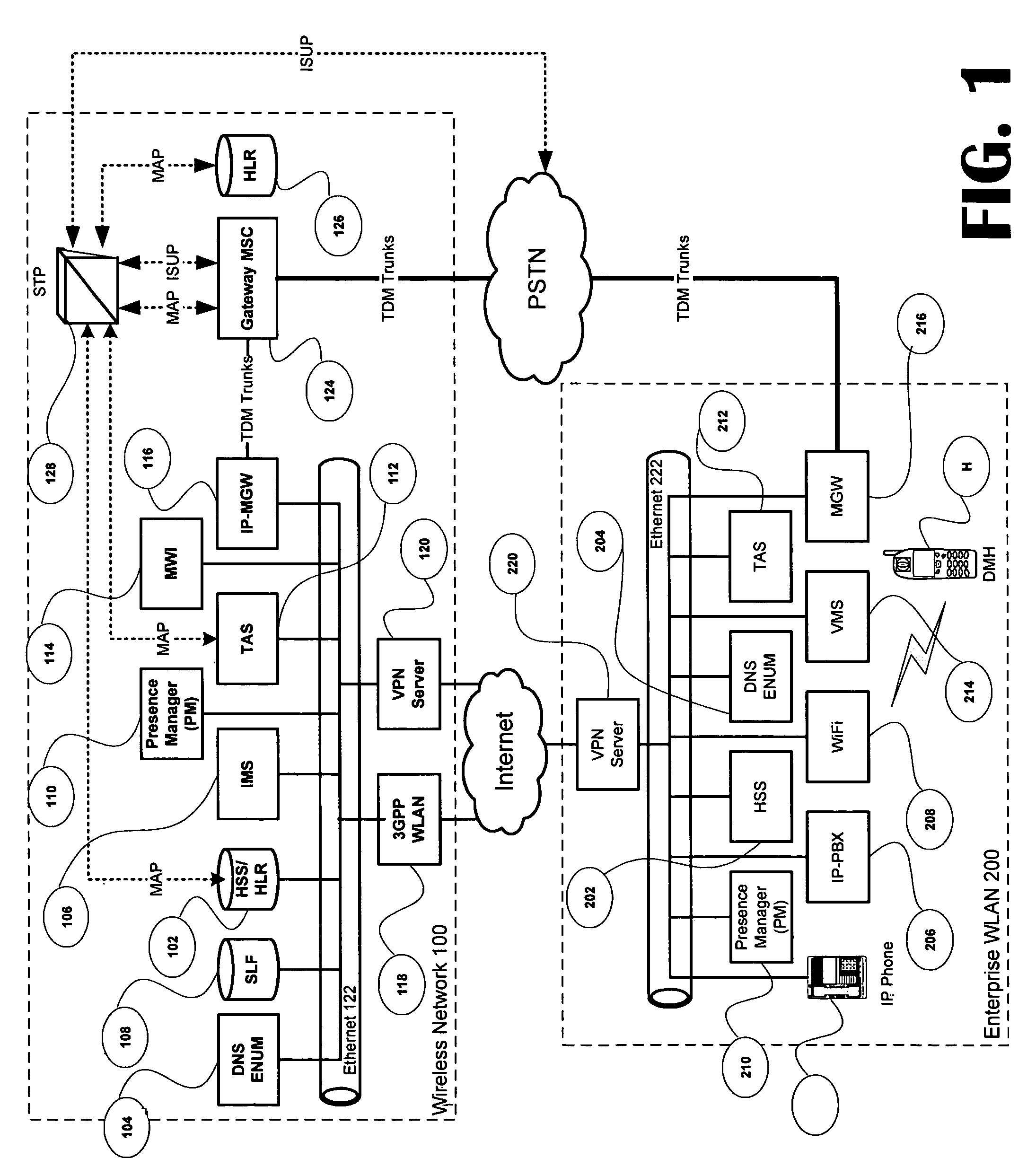
Voice call redirection for enterprise hosted dual mode service
ActiveUS7664495B1Network topologiesCommmunication supplementary servicesDevice registerSpecific function
Systems and methods provide a single E.164 number for voice and data call redirection and telephony services such as caller identification, regardless of in which type of network a dual mode mobile device operates. When the dual mode device registers and is active in a GSM network, temporary routing and status updates are triggered and resultant information is maintained in both networks. A mobile terminated call is routed through an enterprise WLAN with call control within the enterprise being handled by SIP or H.323 signaling, and the call is redirected to the mobile device in the GSM network, where call control is assumed by the SS7 network. Services are provided using the protocols native to the active network, and the single E.164 is used consistently along with or lieu of the temporary routing information for subscriber identity specific functions, such as caller identification and voice mail.
Owner:MITEL NETWORKS INC +1
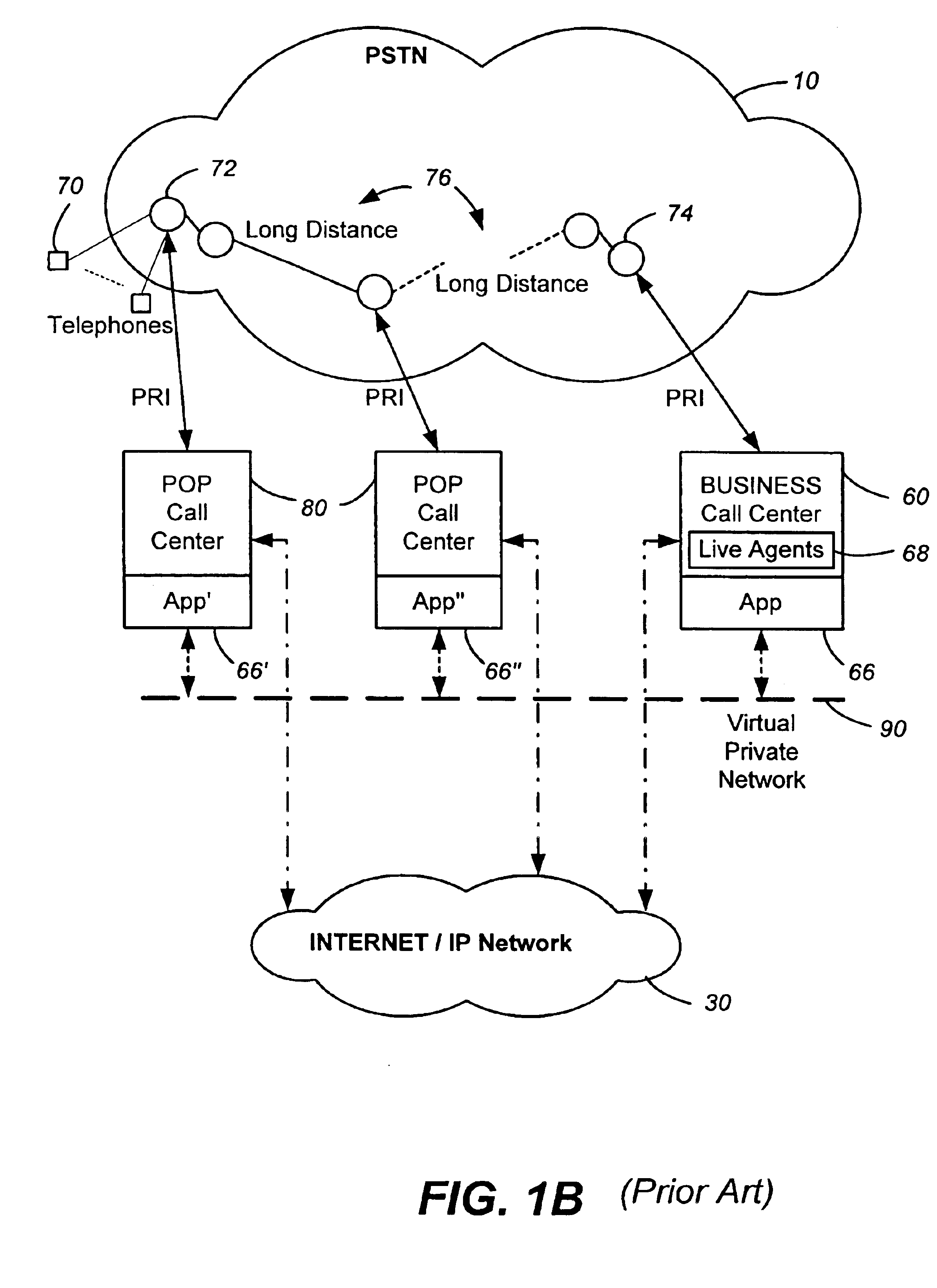
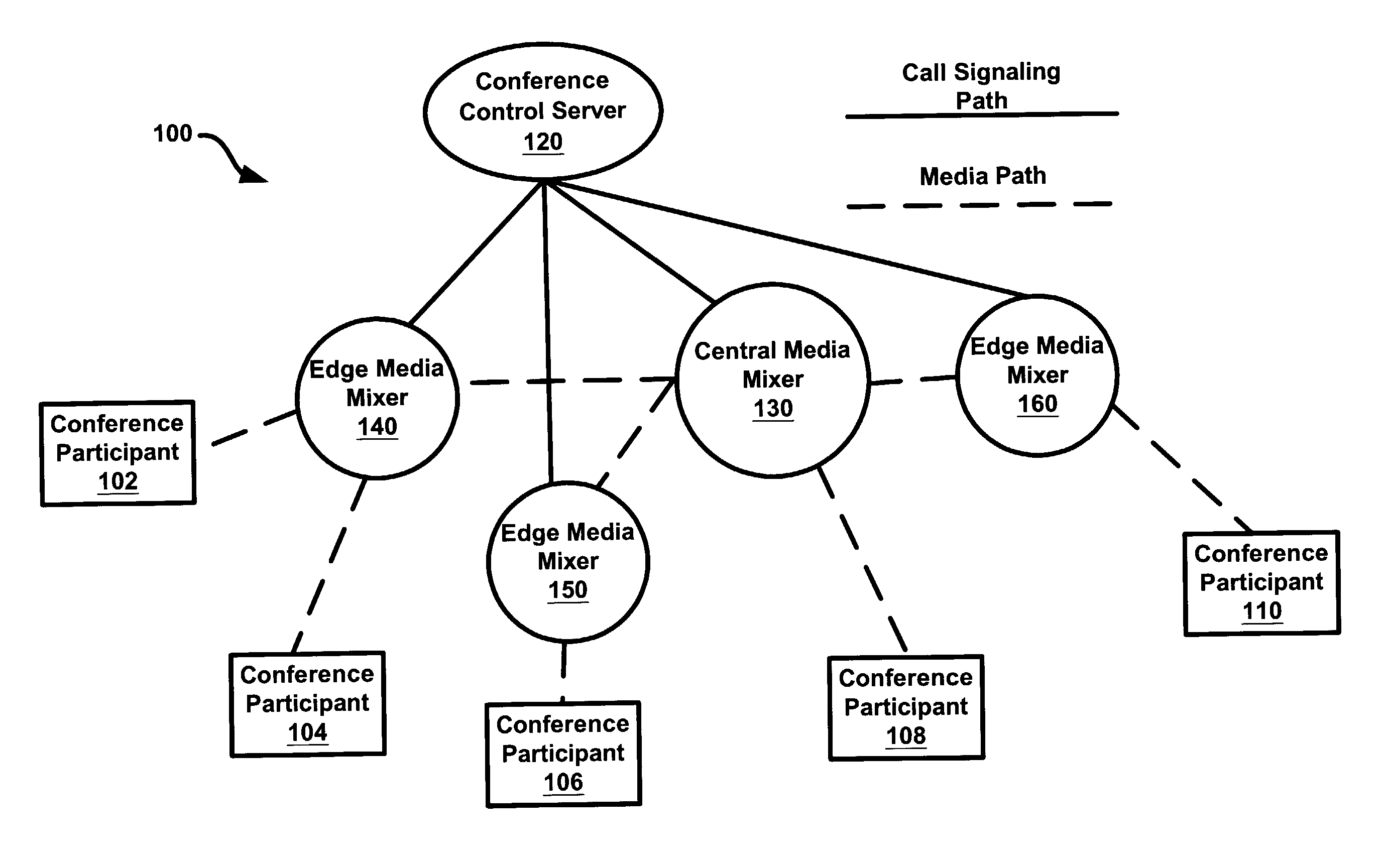
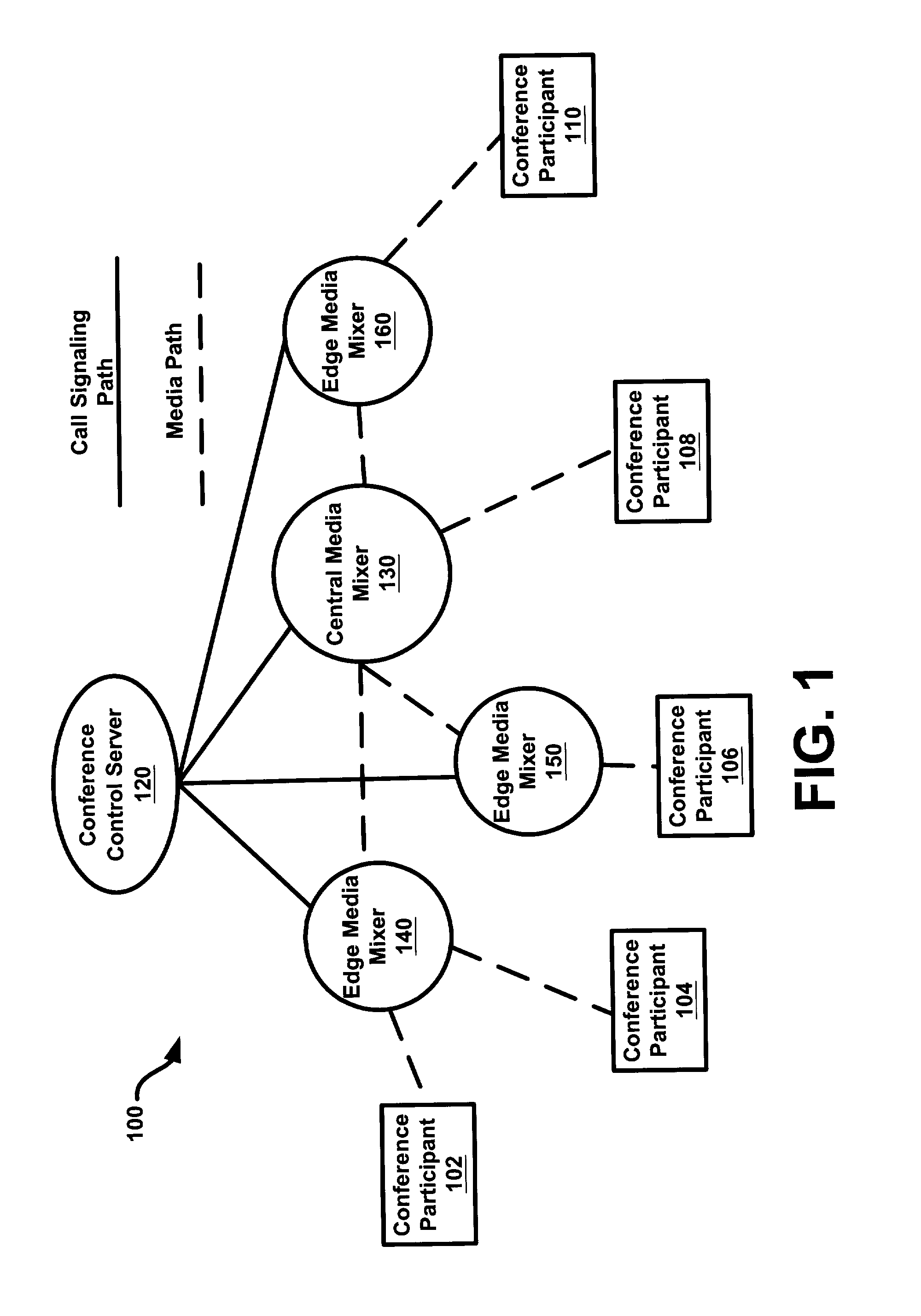
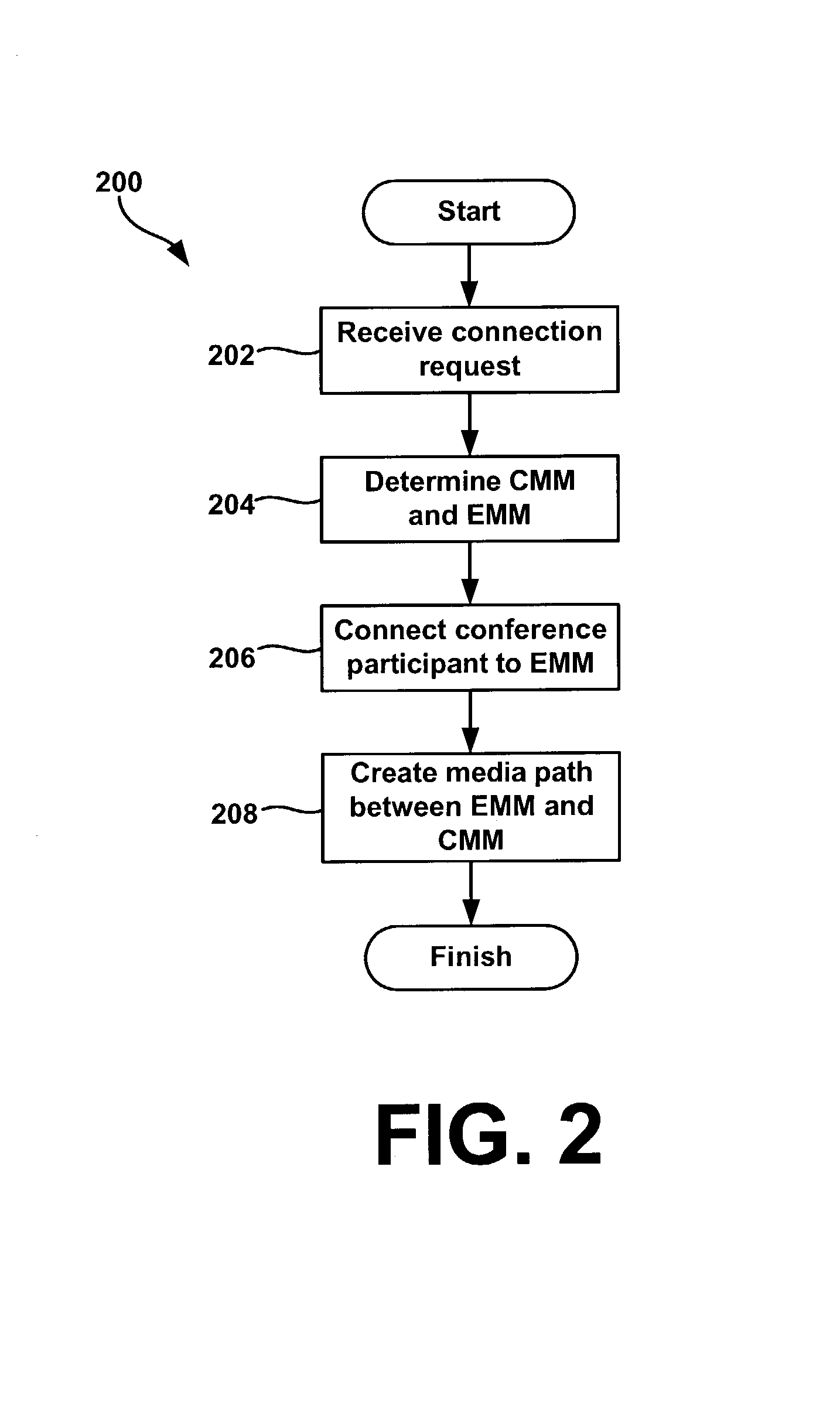
System and method for large capacity conference calls
ActiveUS7298834B1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsConference controlHuman–computer interaction
A system and method for teleconferencing using multiple media mixers is provided. In an exemplary embodiment, a conferencing system may include a conference control server in communication with a central media mixer (CMM) and one or more edge media mixers (EMM). The conference control server may create a media path that connects the CMM and the EMM(s) via a call-control protocol. Additionally, conference participants may communicate with one another by connecting to the CMM and / or the EMM.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Multi-protocol wireless communication apparatus and method
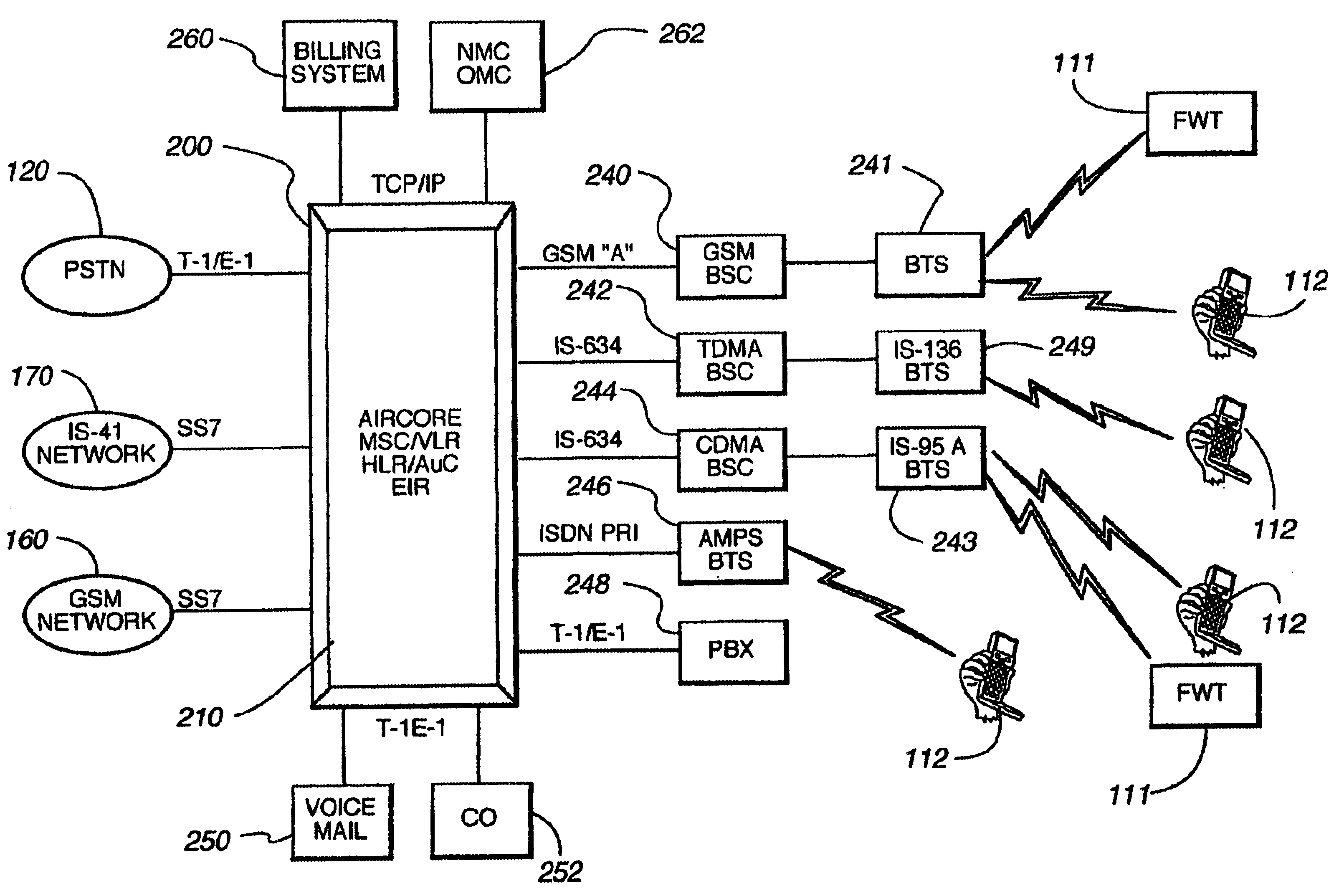
InactiveUS6912230B1Easy to updateEasy accessTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentMulti protocolUser interface
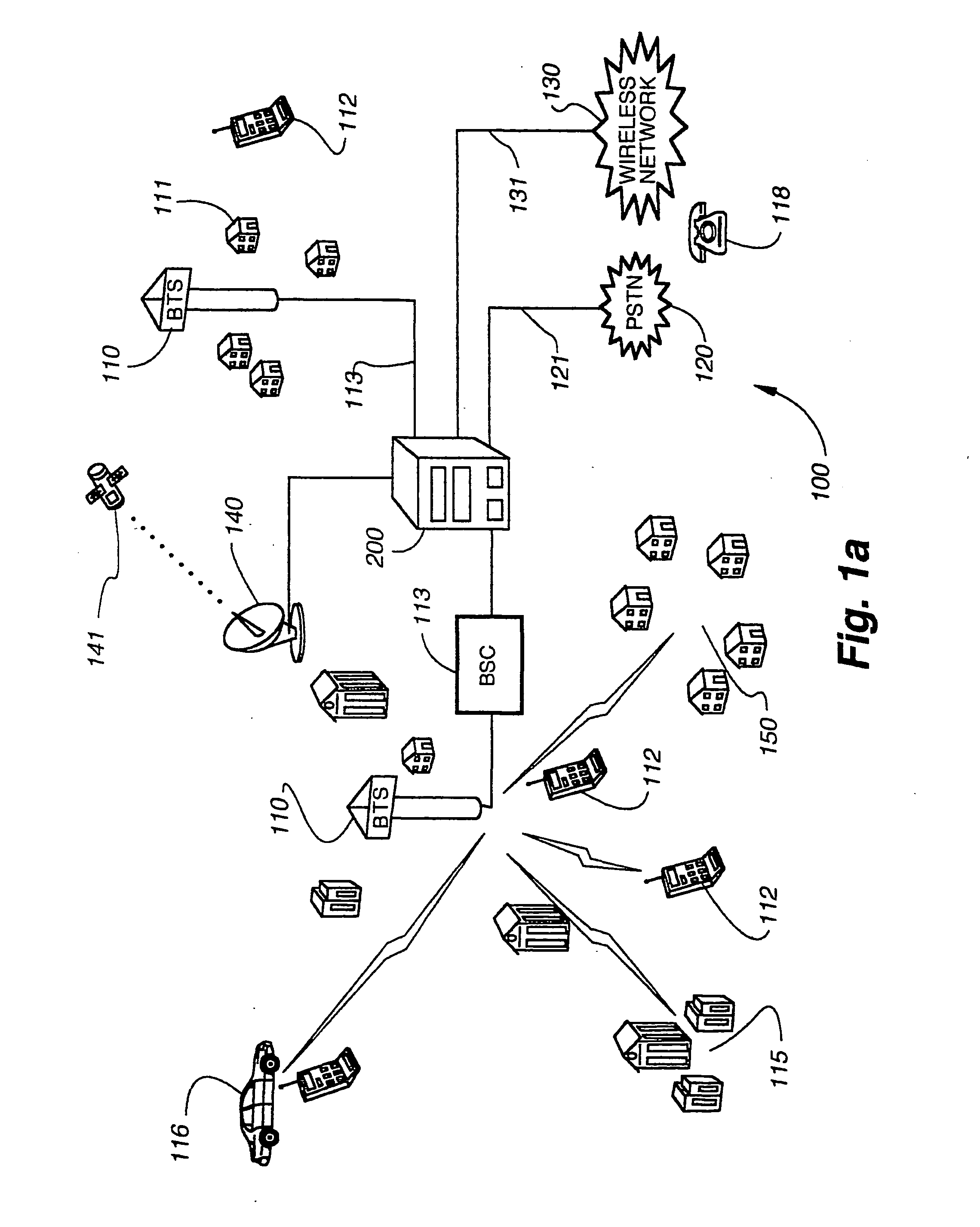
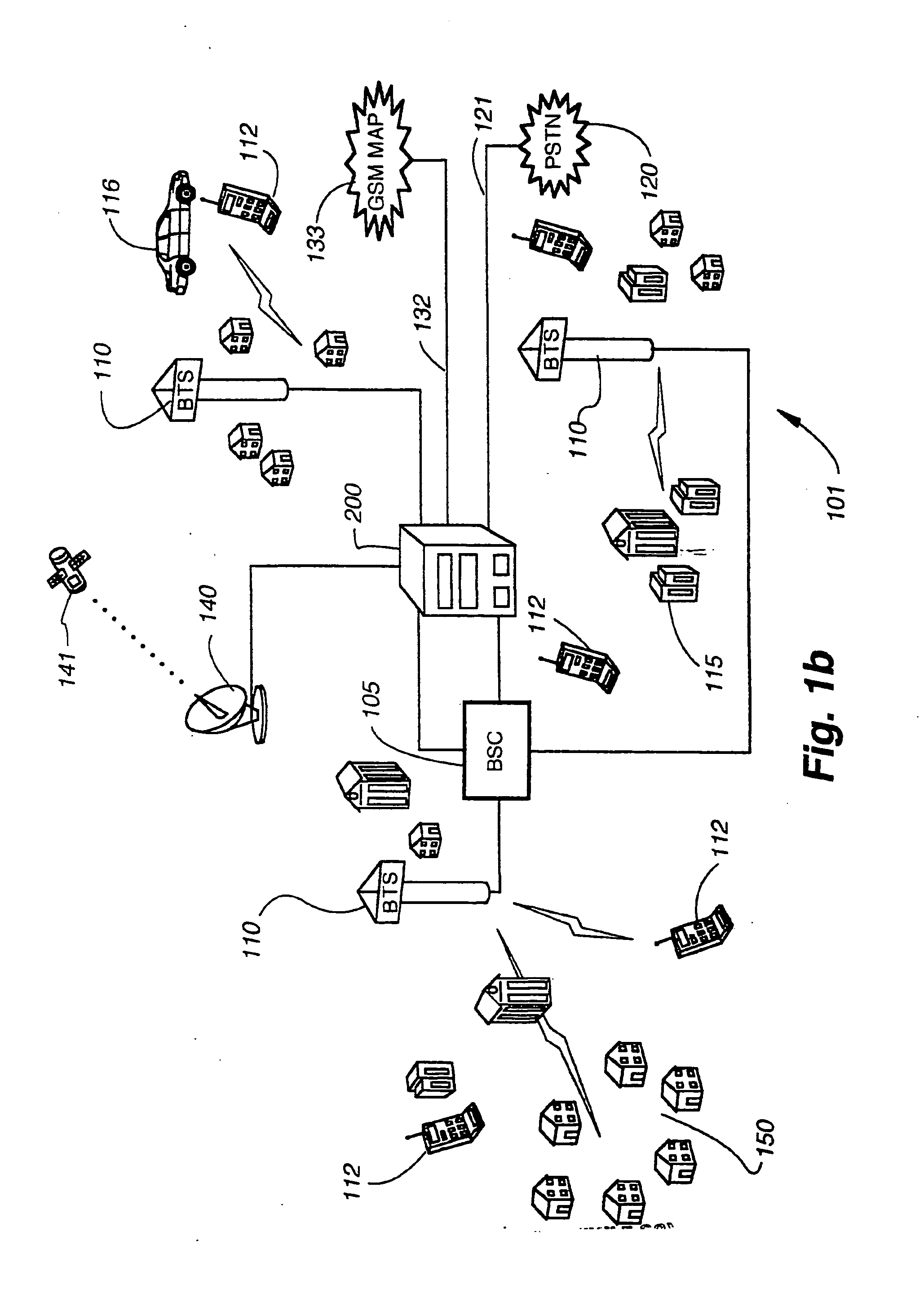
A scalable, multi-protocol mobile switching center in a wireless communications network provides communications control for digital and analog wireless communications devices including devices that operate according to GSM and IS-41 standards. The hardware and software architecture of the switching center is designed so that processing that is unique to a particular protocol is performed at the lowest possible level, and remaining processing can use generic procedures. The switching center incorporates a home location register and visitor location register that are used in conjunction with software applications to determine the protocol of mobile communications devices using the wireless communications network. The mobile switching center can be used to provide a large scale distributed wireless network or a small scale wireless network. The switching center can also be used as an adjunct to a private branch exchange to provide in-building wireless services and call control. Graphical user interfaces make the wireless communications network easy to maintain.
Owner:TECORE INC
Enabling quality voice communications from web page call control
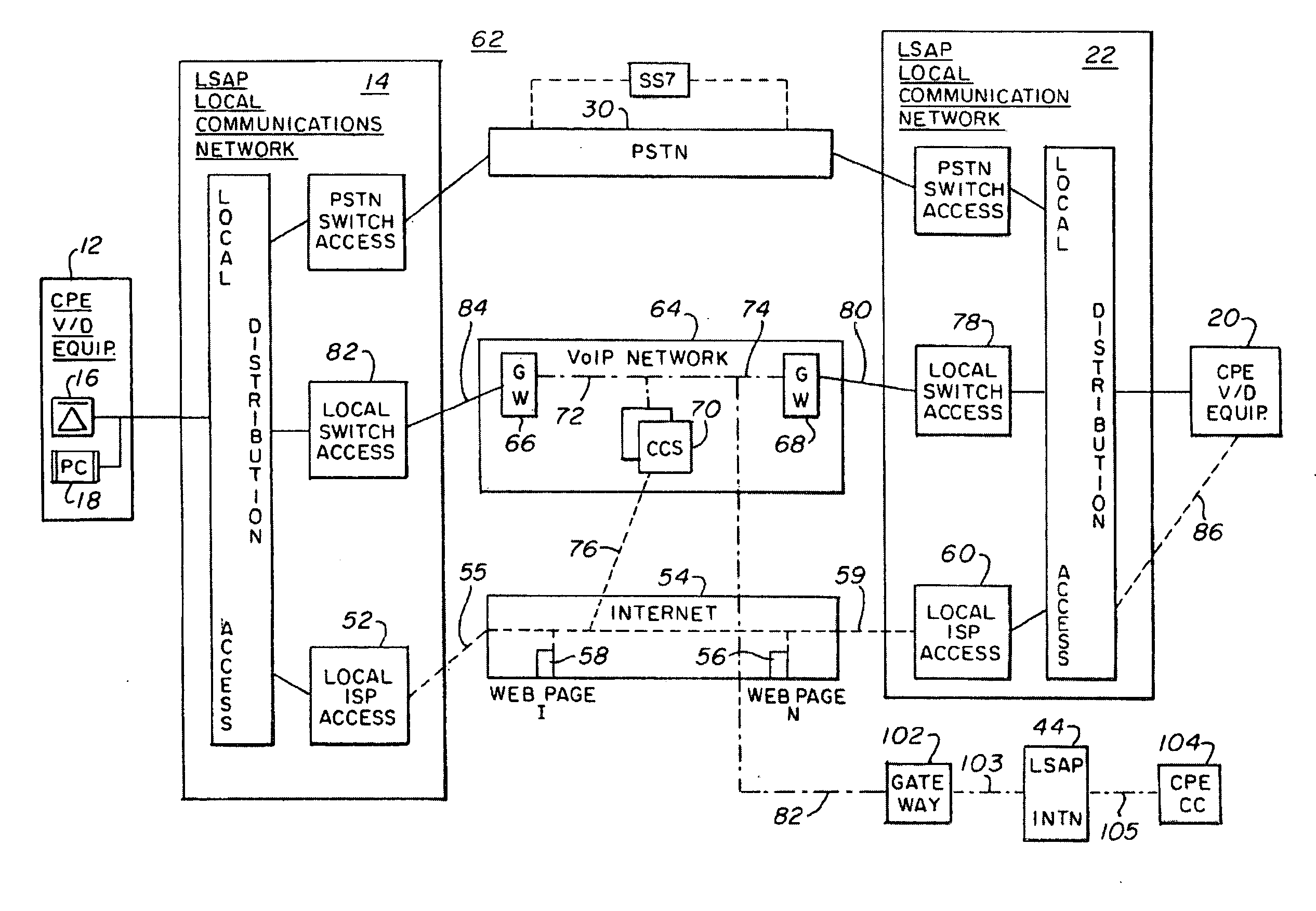
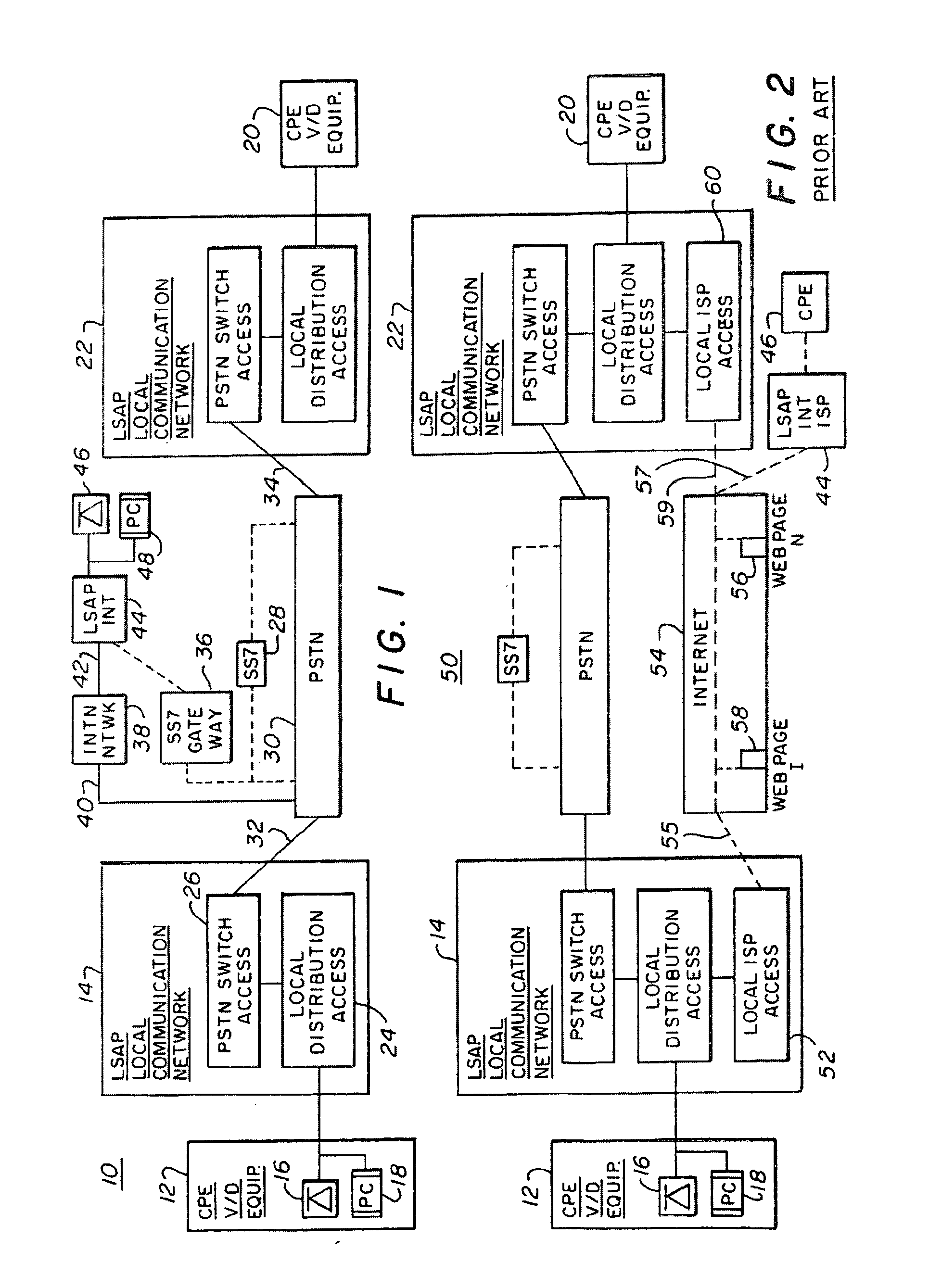
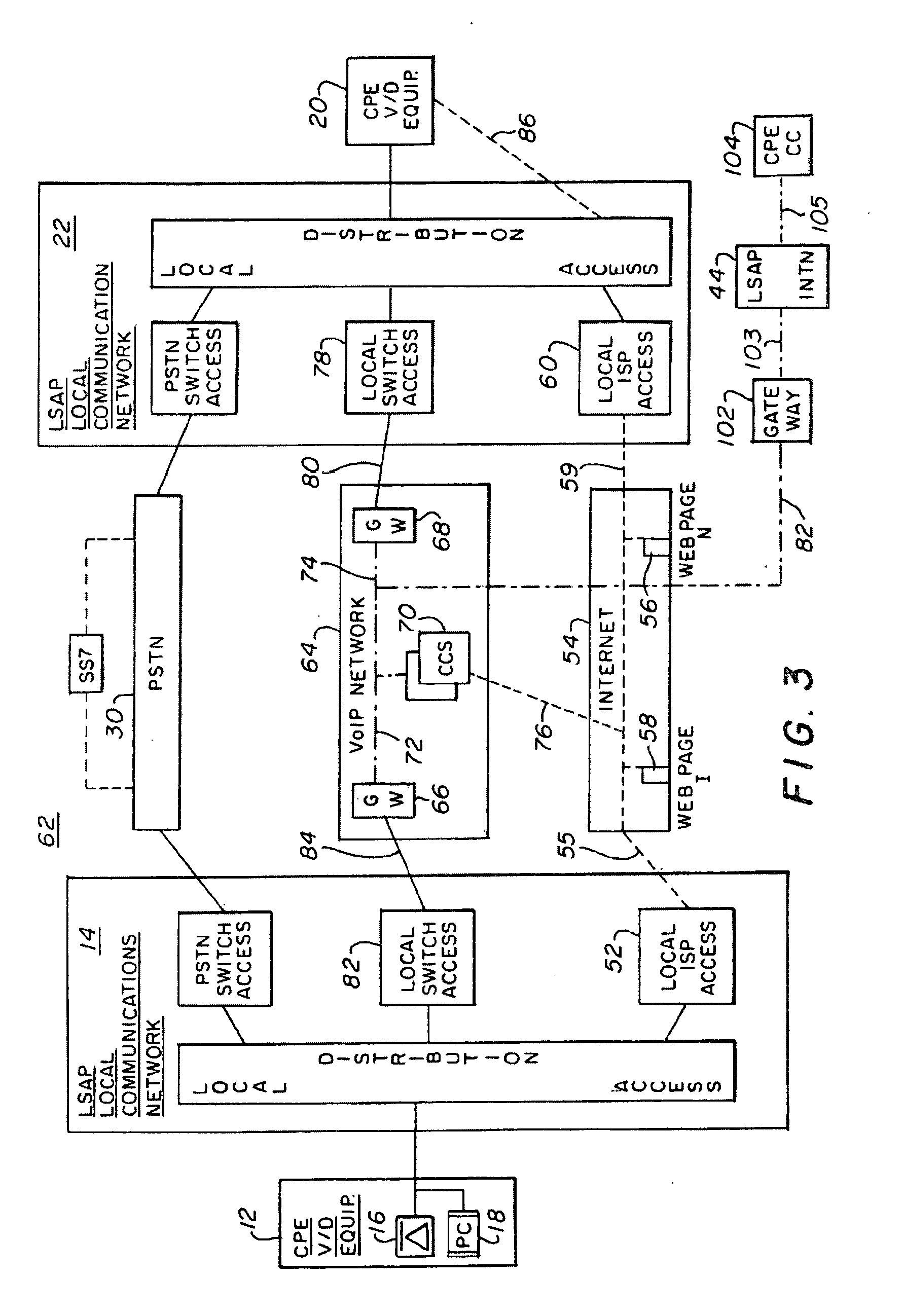
InactiveUS20050265322A1Add featureEnhance network call queuingFrequency-division multiplex detailsSpecial service for subscribersCarrier gradeVoice communication
A system and method of bypassing the regulated portion of the Public Switching Telephone Network (PSTN) to establish carrier-grade voice transmissions and / or IP data communications between an Internet Calling Person having a first telephone and a first PC coupled to a first Local Service Access Provider (LSAP) and an Internet Called Party having a second telephone and a second PC coupled to a second different Local Service Access Provider (LSAP).
Owner:RPX CORP
System and method for controlling congestion between response messages responsive to a group call page in a mobile communication system
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Call flow system and method use in legacy telecommunication system
ActiveUS20070206568A1Data switching by path configurationElectrical componentsNetwork connectionCarrier signal
A method of operating a network server, such as a mobile application gateway, connect devices on a cellular or carrier network with individual networks, such as enterprise voice and data networks or residential networks. The effects of the present invention are far reaching in terms of transferring effective call control from the cellular network into the control of the individual network, such as the enterprise, and enabling new business models for the purchase of cellular service from a public cellular carrier by an enterprise.
Owner:TANGO NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for functional architecture of voice-over-IP SIP network border element
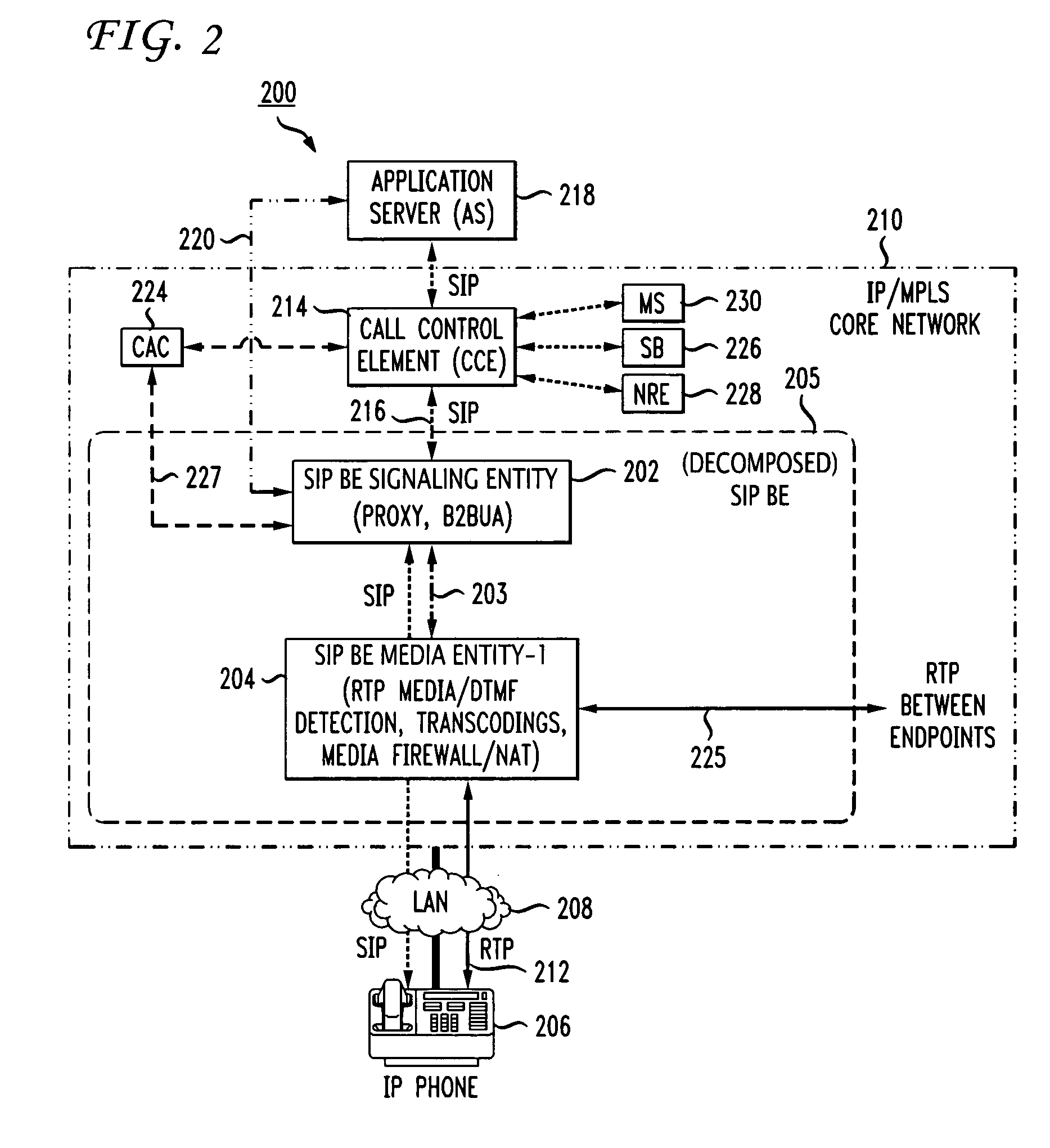
InactiveUS20050083912A1Improve system efficiencyImproves cost advantageMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationScalable systemDecomposition
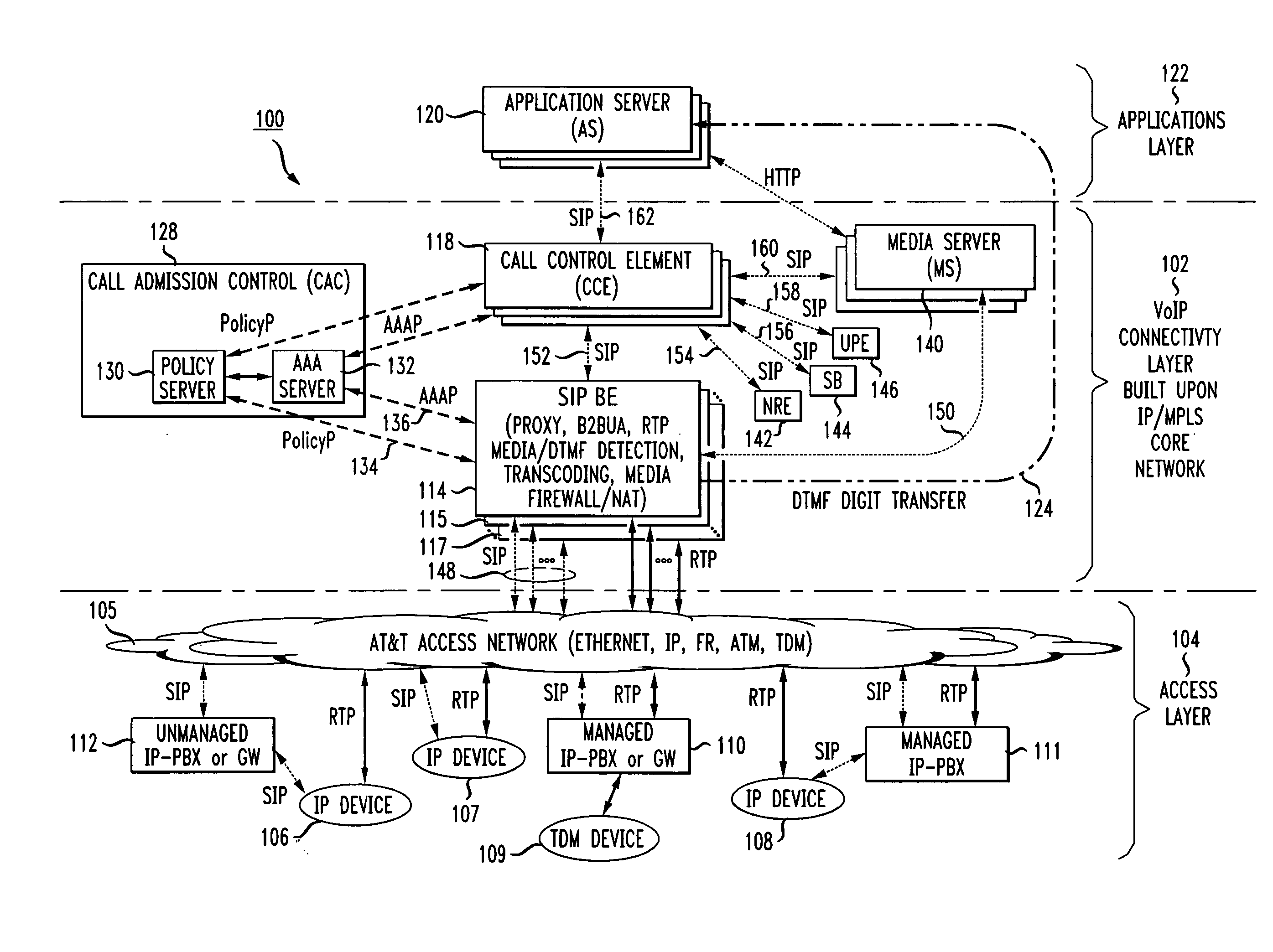
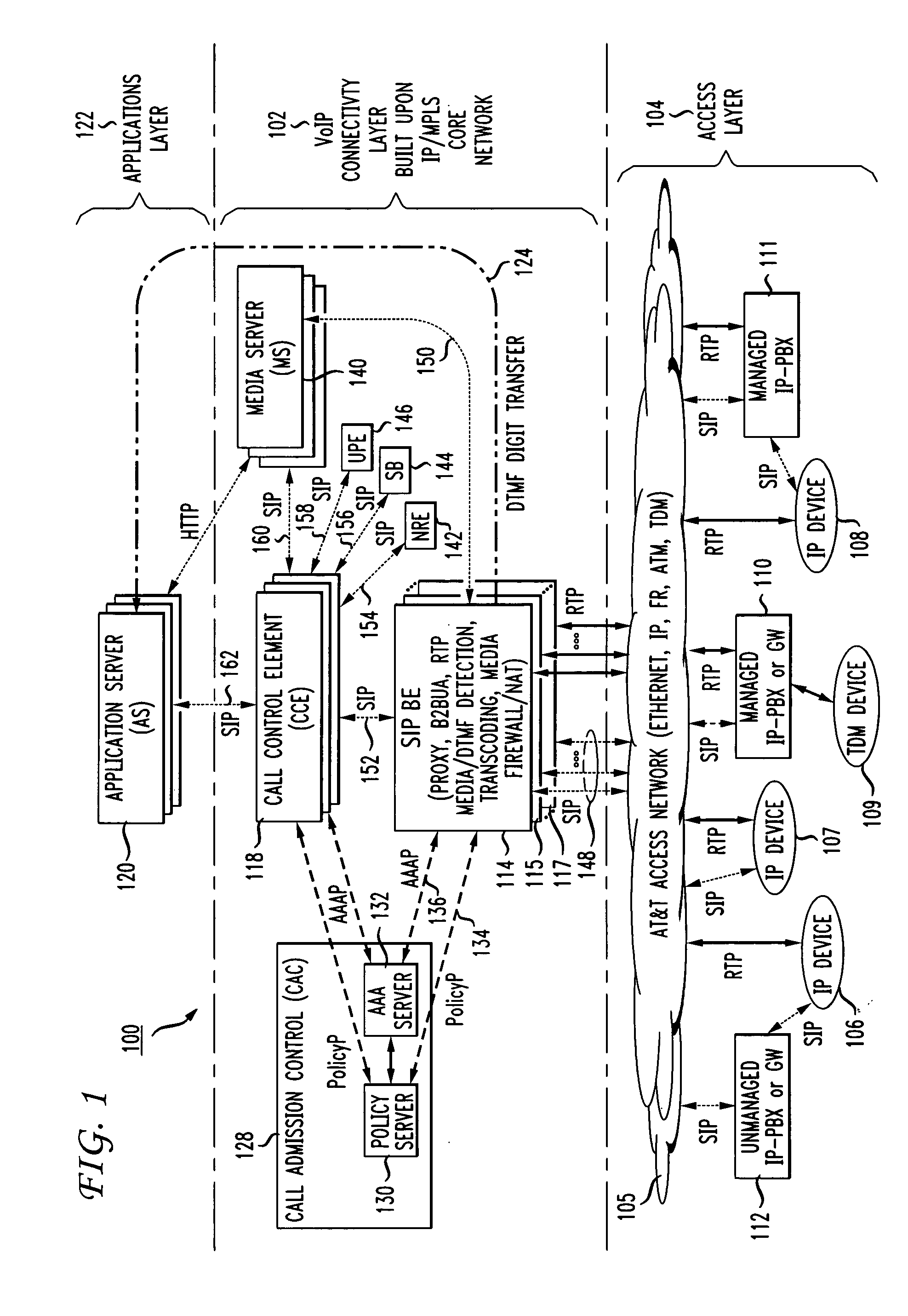
In order to provide a single common cost-efficient architecture for real time communication services for audio, video, and data over internet protocol, a voice over internet protocol (VoIP) system and architecture is provided by placing border elements (BEs) at the interface boundaries between the access network the user devices use and the VoIP infrastructure. The BEs use SIP protocol as the access call control protocol over any access networking technologies, for example, IP, Ethernet, ATM, and FR, and provides all services transparently to the end users that use SIP-enabled devices. To enable a scalable system, the SIP BEs are decomposed into separate communicating entities that make the SIP BE scalable and provide new capabilities not previously available by a self-contained SIP BE. Further, multiple levels of decomposition of a SIP BE can be provided by the present invention supporting a flexible and scalable SIP BE design that further improves system efficiencies and cost advantages as compared to use of single integrated border or edge elements. Further, a scalable SIP BE, made up of a plurality of physical entities for optimization of a large scale design, acts as a single integrated functional entity to logically execute a set of functions at the border of a VoIP infrastructure.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
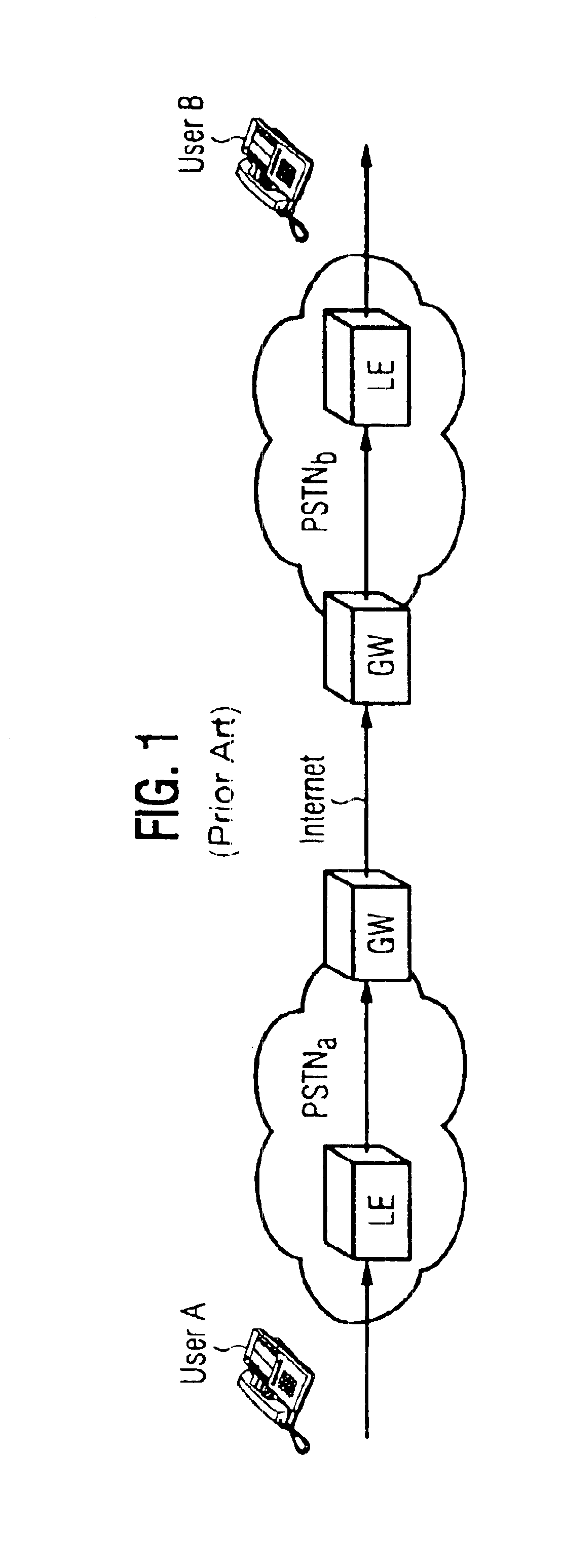
System and method for implementing multimedia calls across a private network boundary
ActiveUS20070140267A1Integrity guaranteedData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesInformation processingPrivate network
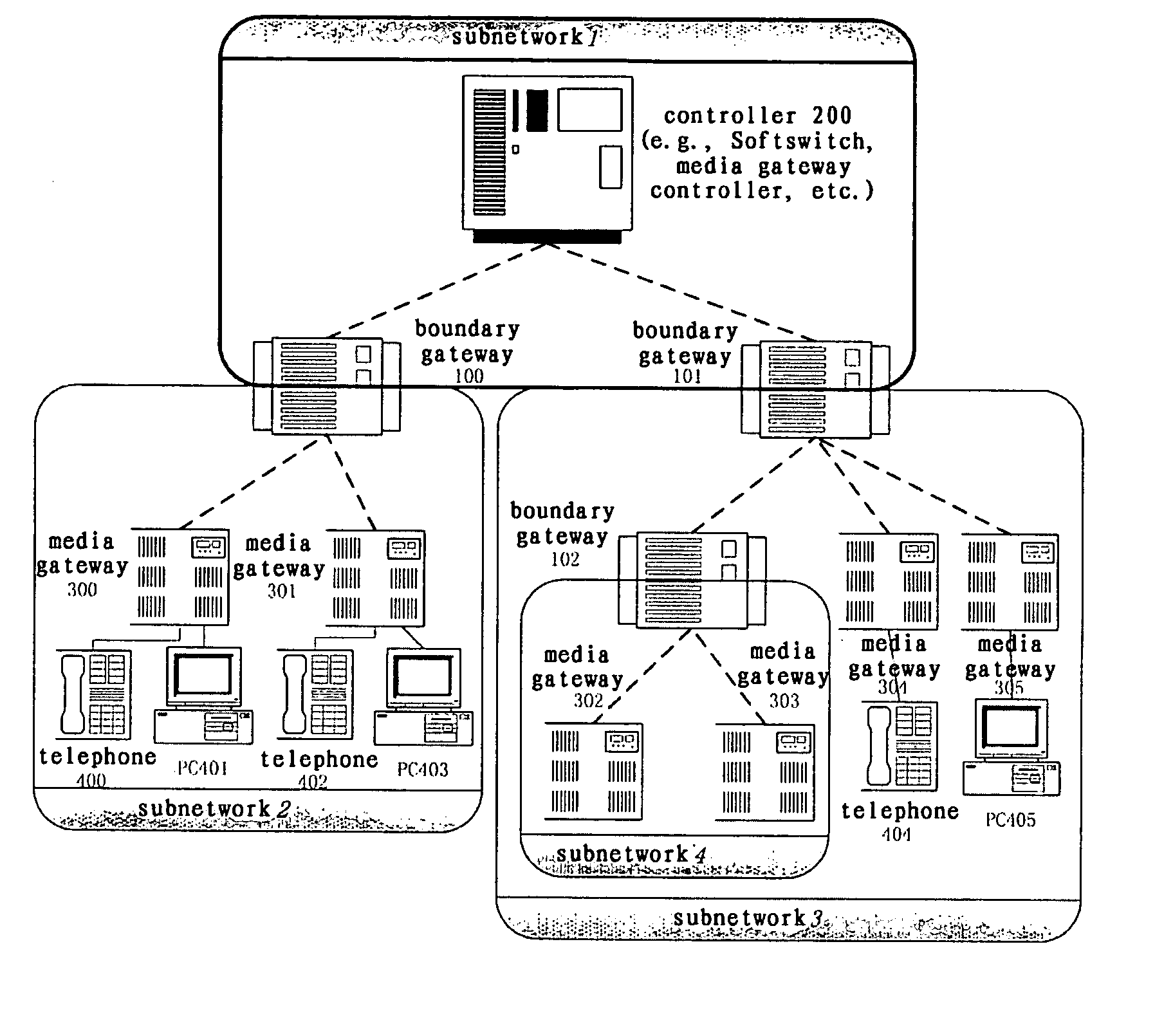
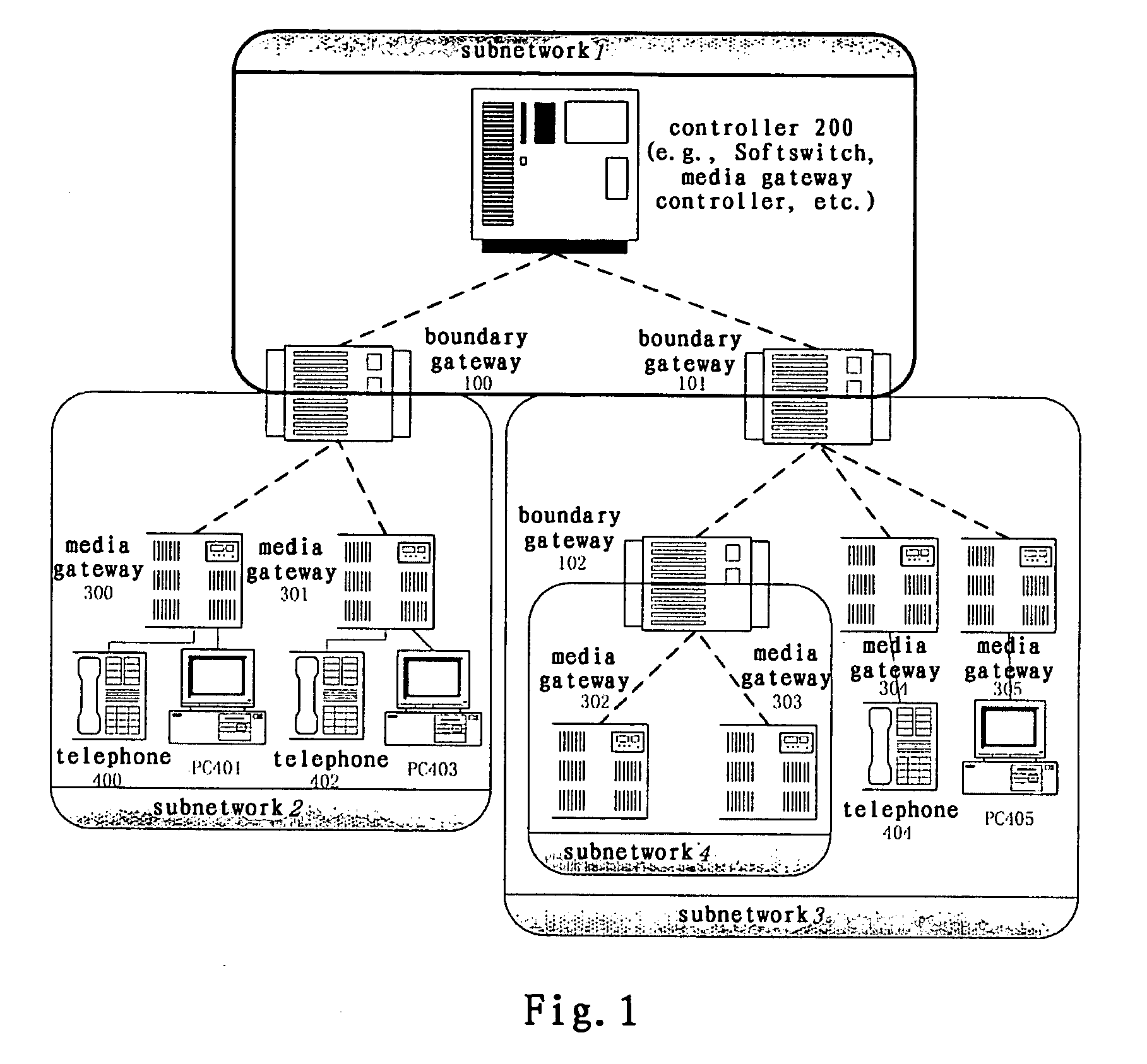
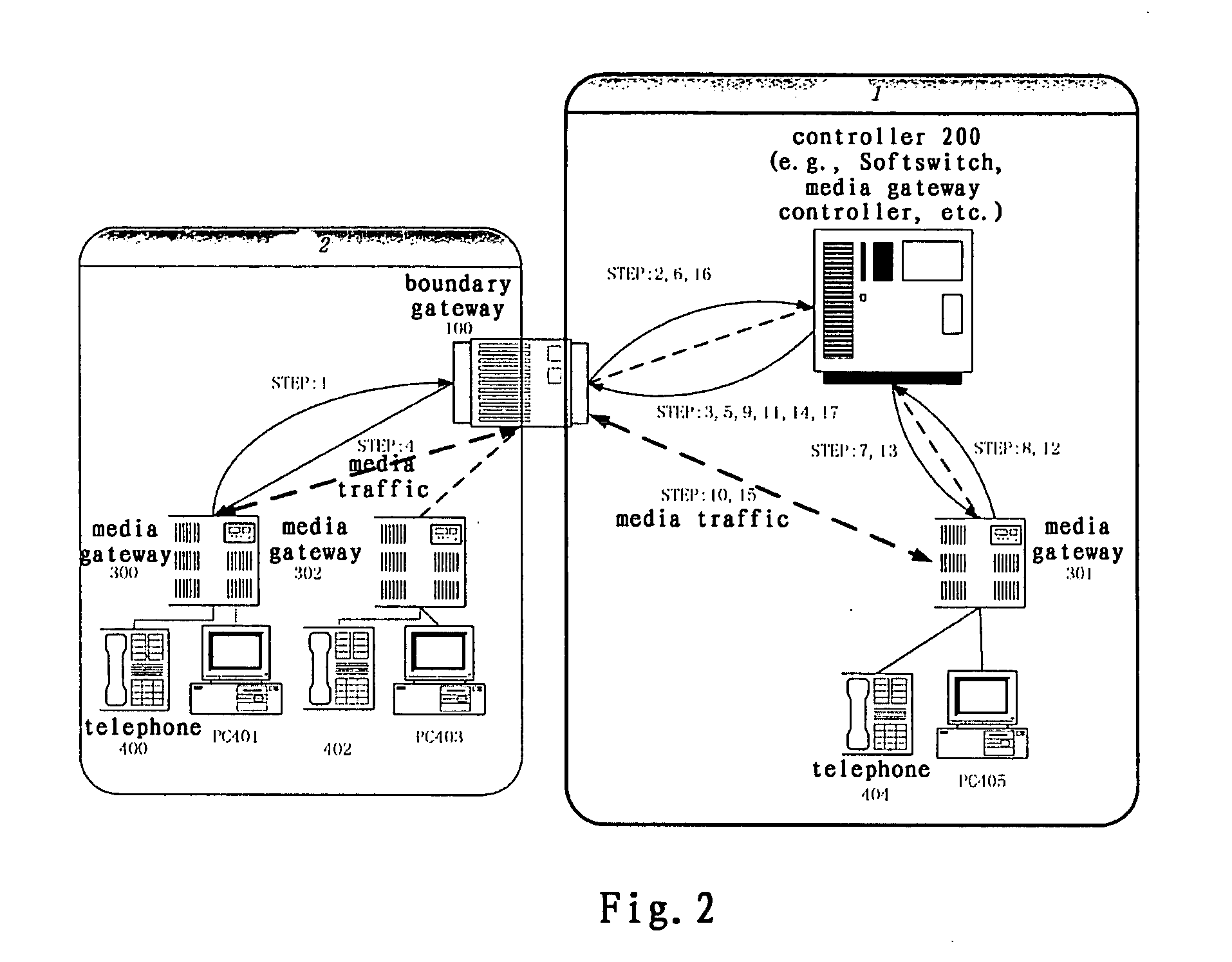
A system and method of the present invention for implementing multimedia calls across a private network boundary is provided, the system comprising a public network and at least one private network, and at least the following hardware components: at least one media gateway for connecting with multimedia terminals of various protocols; at least one boundary gateway for connecting the private network and the public network and performing the translation of a private network address and a public network address between each other, wherein each boundary gateway is provide with an unique subnetwork ID to correspond to the private network connected therewith; a call controller for establishing calls and controlling service logics, in which is recorded the correspondence relationship information of all said boundary gateways and the subnetwork IDs; wherein, the call controller processes a call concerning a private network according to the subnetwork ID information. The system and method of the present invention is simple to implement, has high efficiency and wide application range; saves the boundary gateway resources, does not modify the signaling content and retain its integrity; is applicable to the media gateways of various protocols, and has a high adaptability.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Dynamically switched and static multiple video streams for a multimedia conference
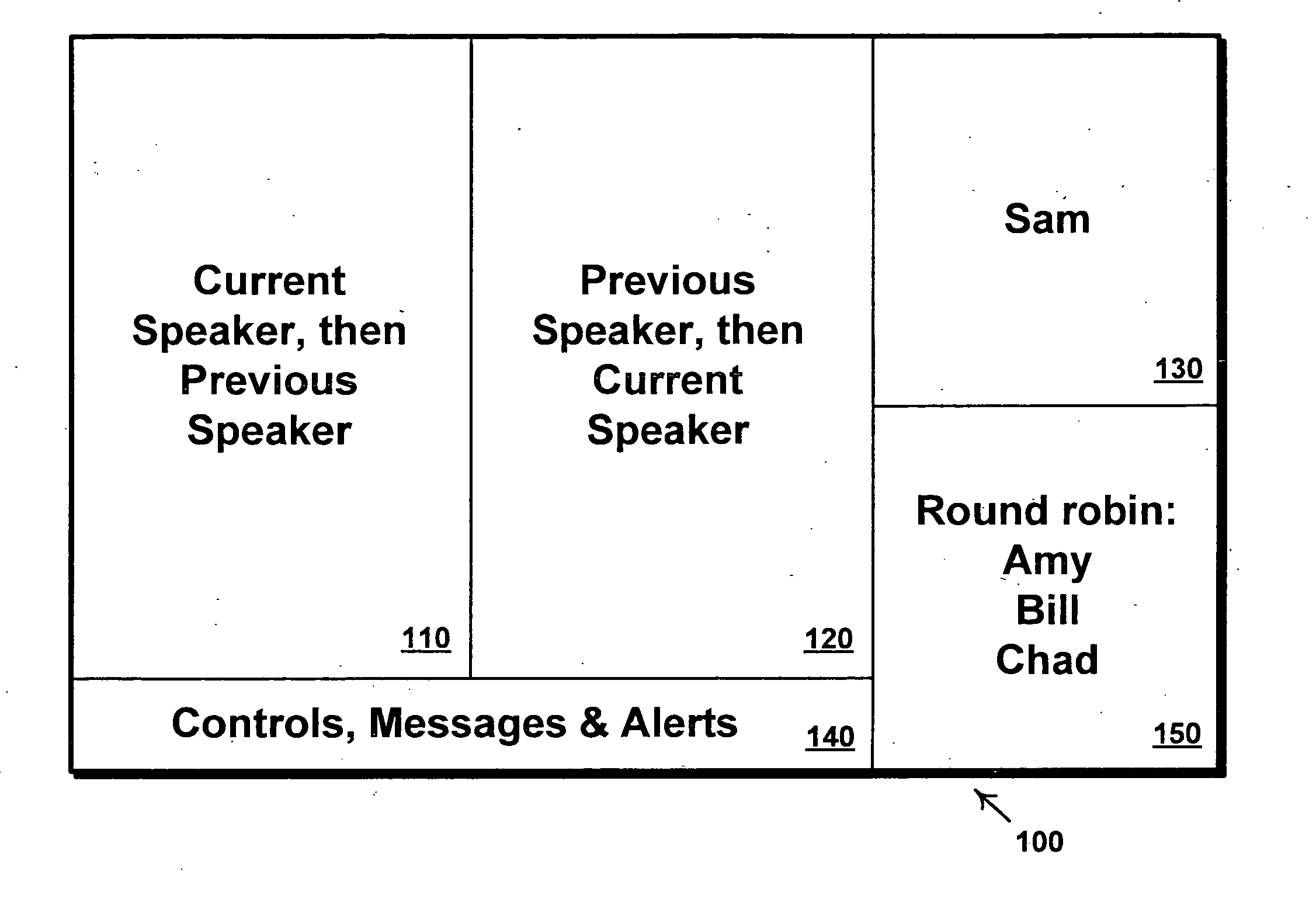
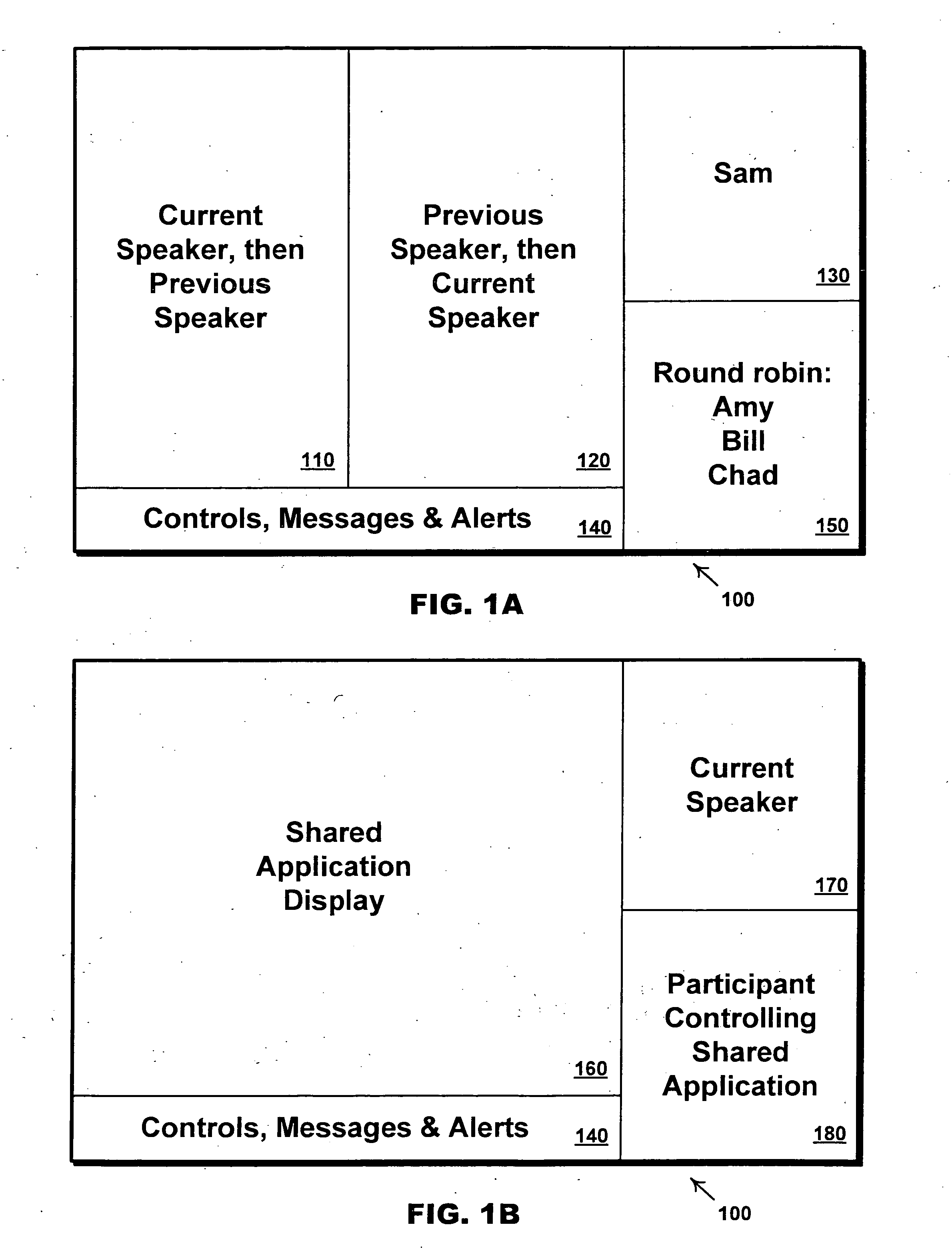
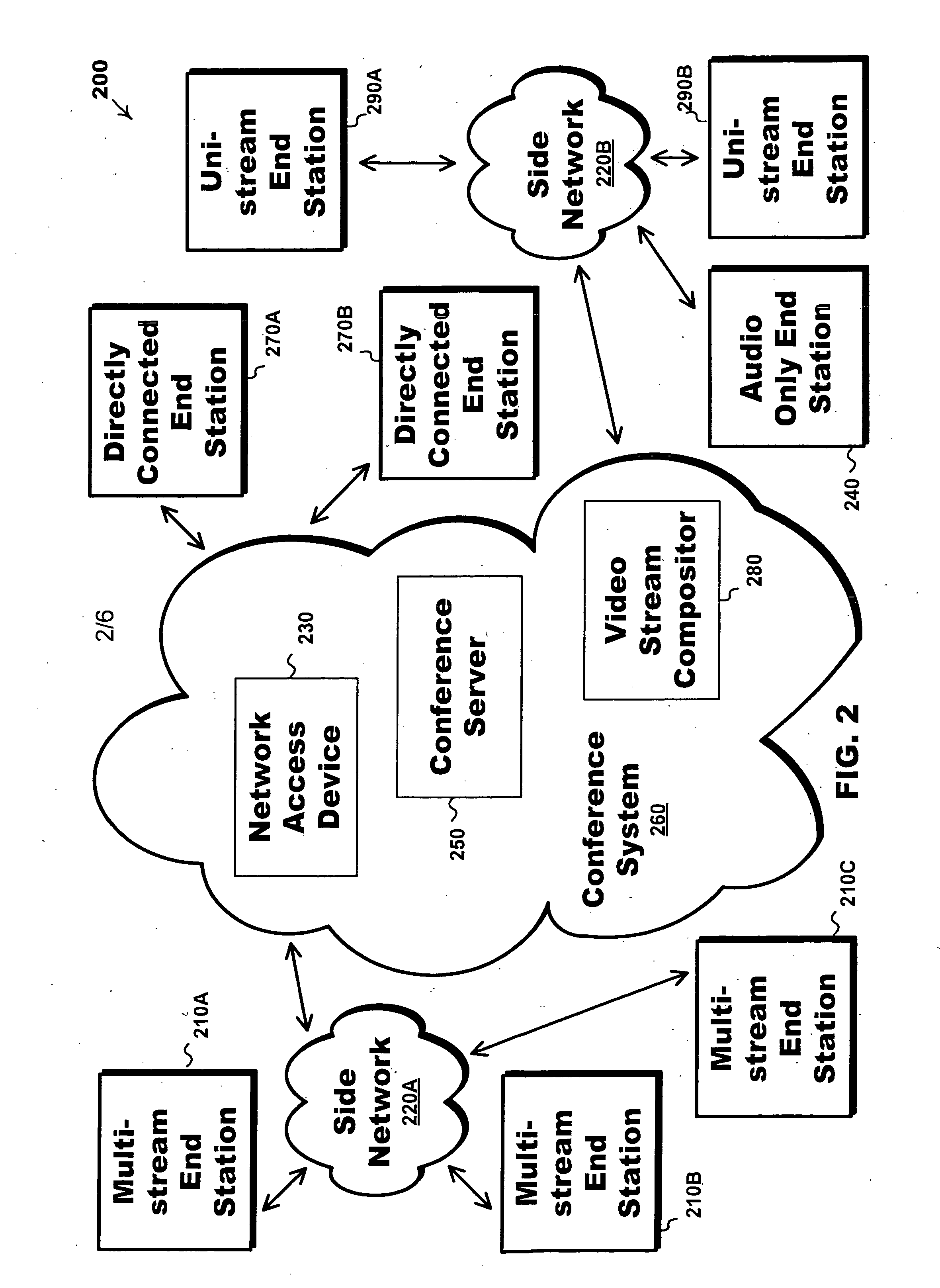
An end station for a videoconference / multimedia conference is disclosed, where the end station requests, receives and displays multiple video streams. Call control messages request video streams with specified video policies. A static policy specifies a constant source video stream, e.g., a participant. A dynamic policy dynamically maps various source streams to a requested stream and shows, for example, the current speaker, or a round robin of participants. A network access device, e.g., a media switch or a video composition system, mediates between the multi-stream end station and the core conference system. Multi-stream endpoints need not handle the complexity of directly receiving video according to a potentially wide variety of call control protocols, formats, and bit-rates. Multi-stream endpoints decentralize compositing video streams, which increases functional flexibility and reduces the need for centralized equipment.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mobile application gateway for connecting devices on a cellular network with individual enterprise and data networks
ActiveUS20070206563A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsNetwork connectionNetwork architecture
A mobile application gateway for connecting devices on a cellular network with individual networks, such as enterprise voice and data networks and / or residential networks. The effects of the present invention are far reaching in terms of transferring effective call control from the cellular network into the control of the individual network such as the enterprise, and enabling new business models for the purchase of cellular service from a public cellular carrier by an enterprise. The invention may consist of a primarily of core network and services components based on the IMS network architecture, and is backward compatible to support legacy systems in place in current telecom and data networks.
Owner:TANGO NETWORKS
Wireless base station device
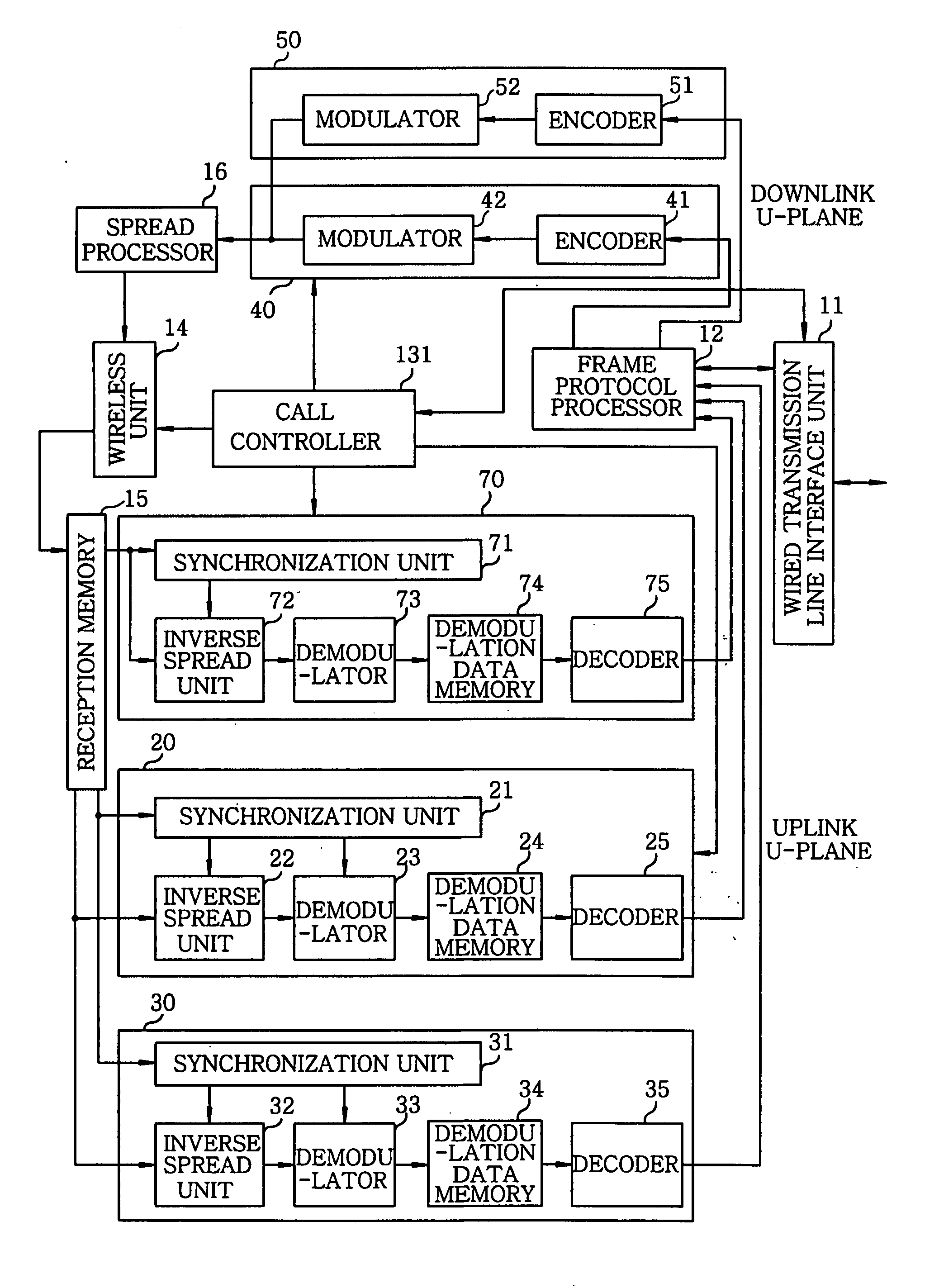
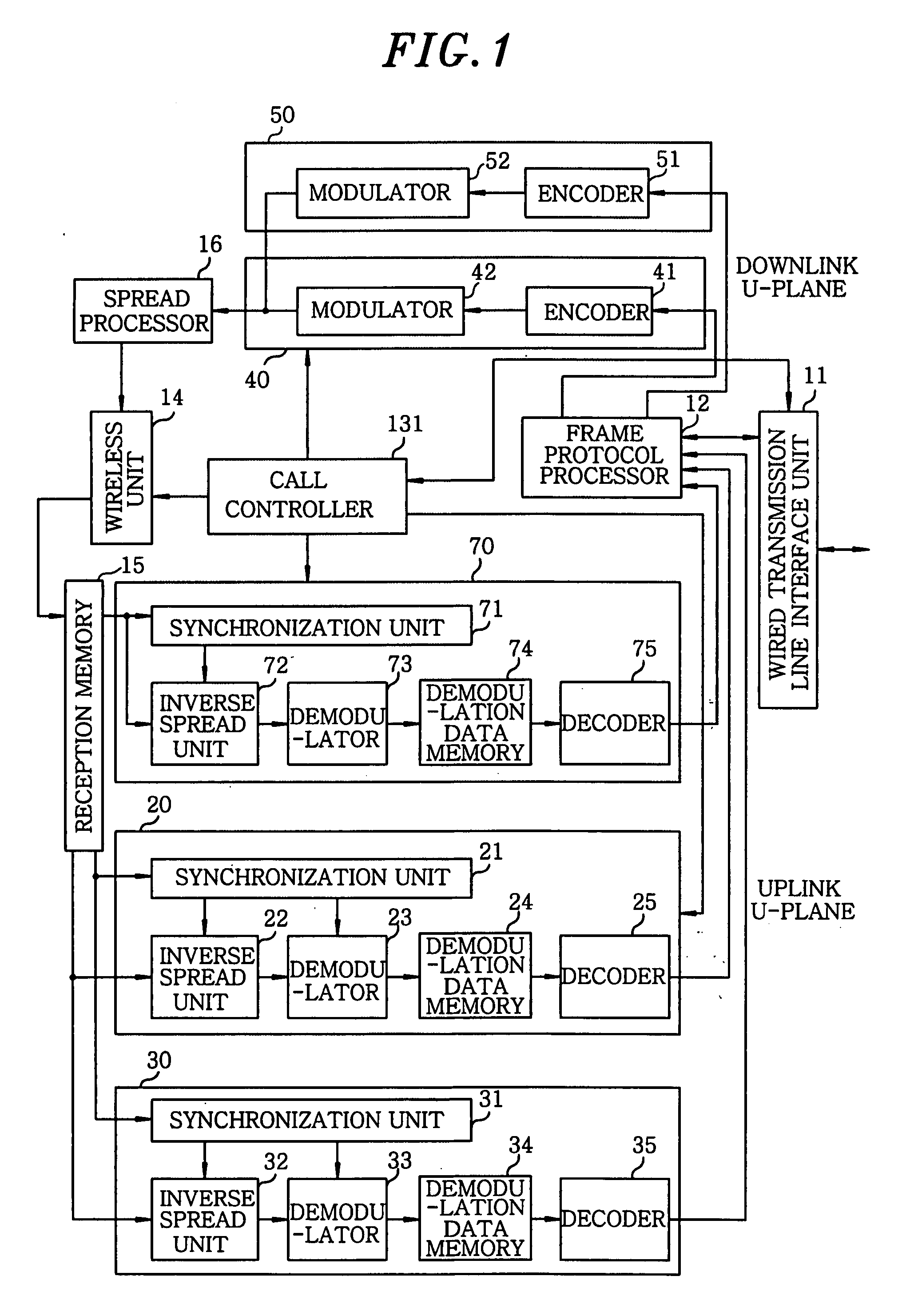
InactiveUS20070287501A1Efficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower managementFrequency spectrumProtocol processing
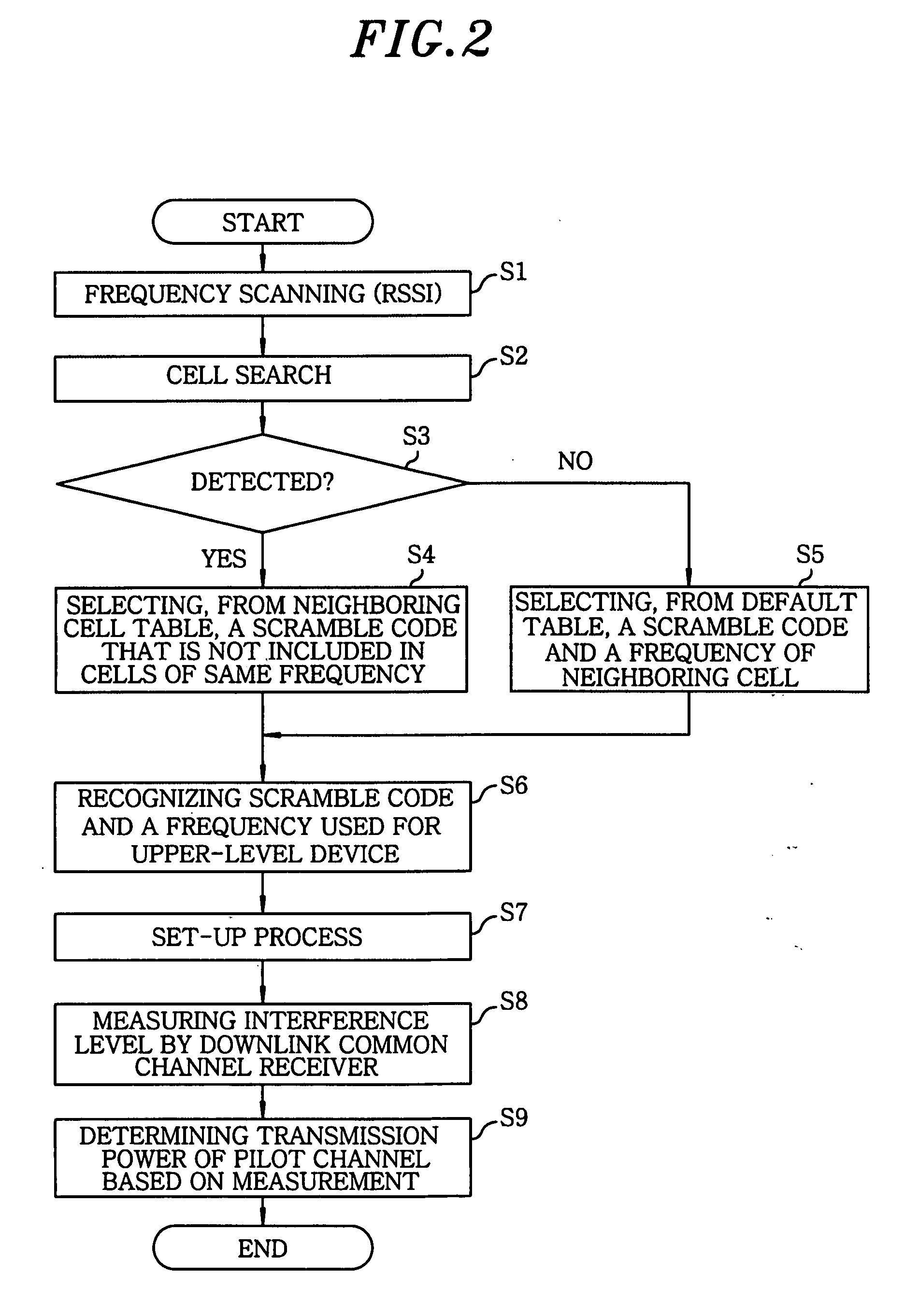
A wireless base station device includes a wireless unit for performing wireless communications with a mobile station; a reception memory unit for storing therein reception spectrum spread data as reception data; a baseband reception unit for processing and decoding the reception data stored in the reception memory unit; a common downlink channel reception unit for receiving a downlink signal of other base station devices; a frame protocol processing unit for converting a transmission channel format; a baseband transmission unit for outputting encoded data; a spread processing unit for outputting spread-modulated data to the wireless unit; and a call controller for controlling an allocation of processing resources. Parameters including a spreading code and a transmission power required for installing the wireless base station device are automatically set by operating the common downlink channel reception unit to detect notification information and signal levels of neighboring base station devices.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
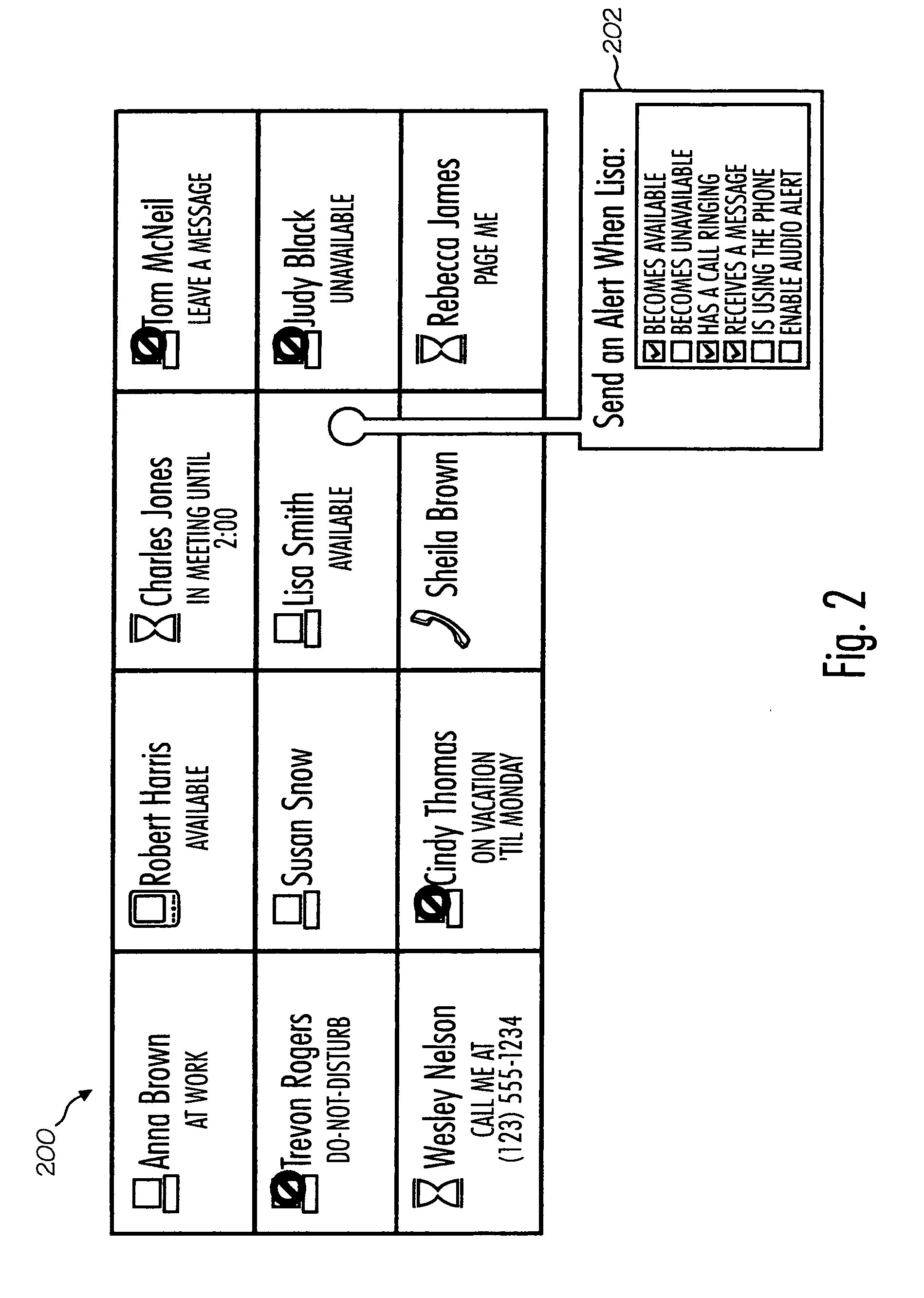
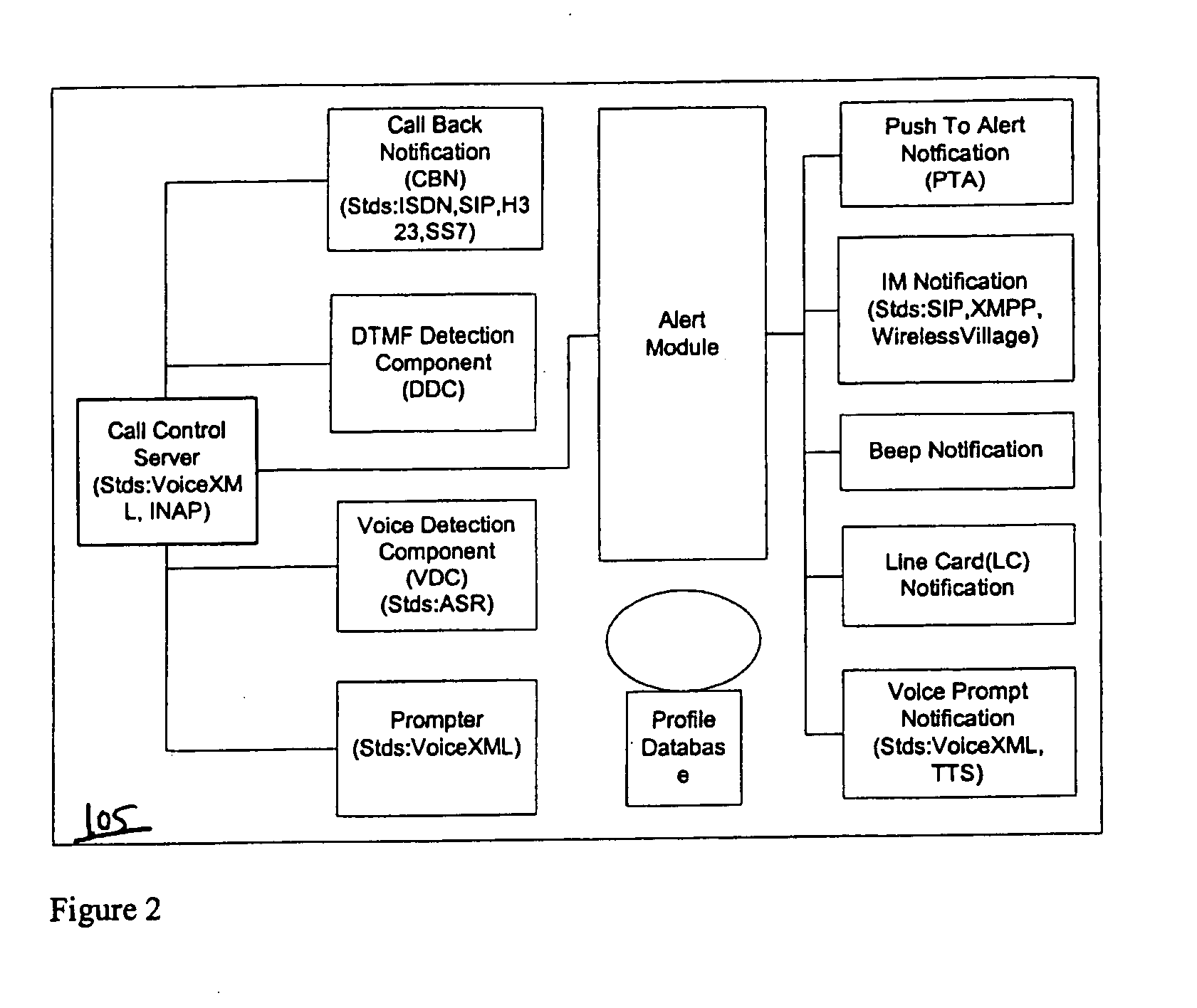
Endpoint status notification system
ActiveUS20050108348A1Interconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersAddress bookCall control
The endpoint status notification system includes an address book of network user's names and their associated endpoints. A user selects a personal list of contacts from the address book and receives an instant message alert upon every occurrence of a reportable event for one of the contacts on the list. Alerts are informational status messages pertaining to the contact and are delivered unbeknownst to the contact. Preferably, alerts are popup windows displayed for a preset amount of time, however audible alerts are available in lieu of or in combination with the popups. Reportable events are selected by the user for each of the contacts on the list and may differ from contact to contact. Simultaneous with the alert, the user may be provided a call-control option related to the reportable event and pertaining to the contact. If selected, the call-control option causes a telecommunication function to immediately occur.
Owner:MITEL DELAWARE INC
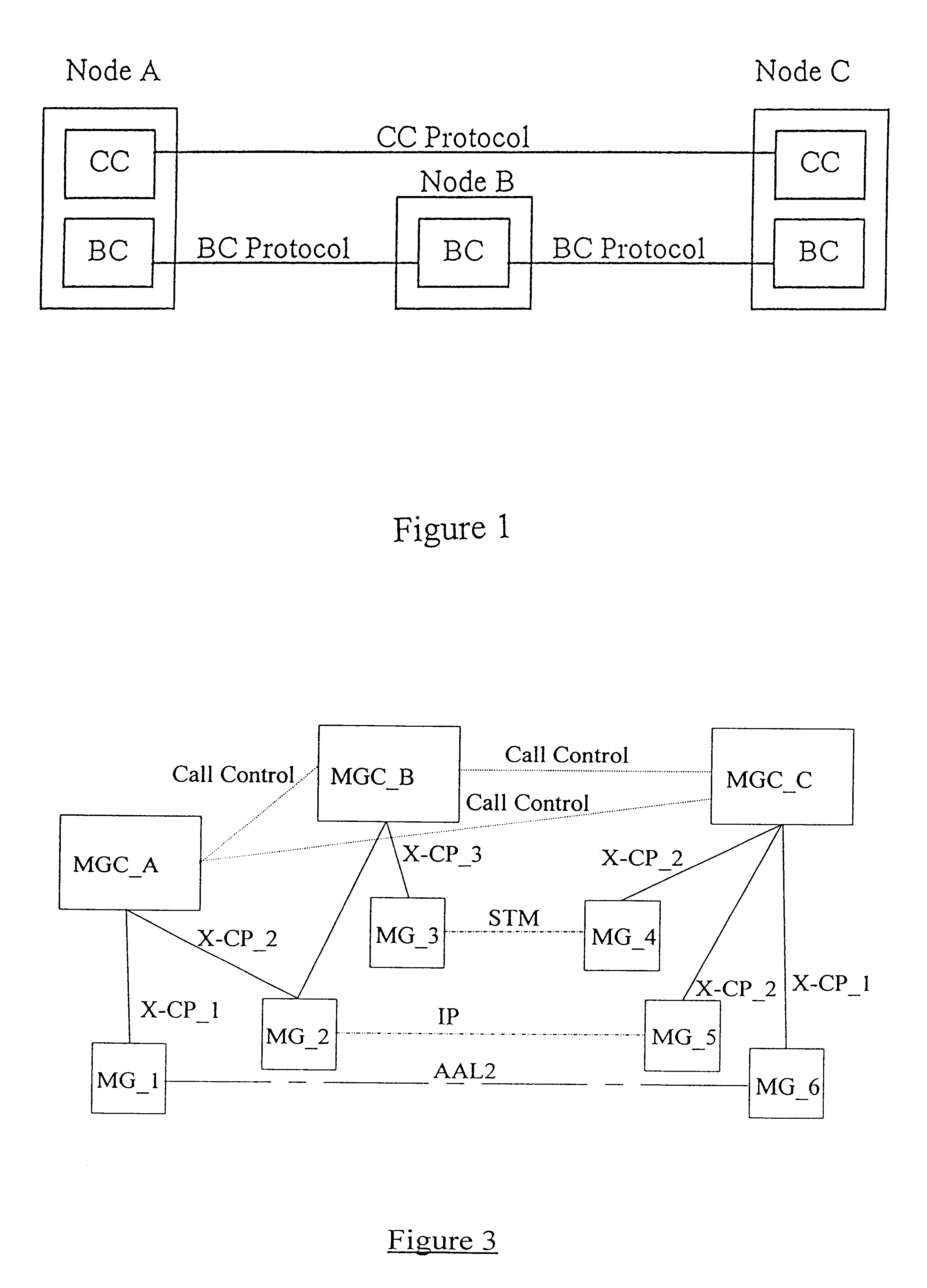
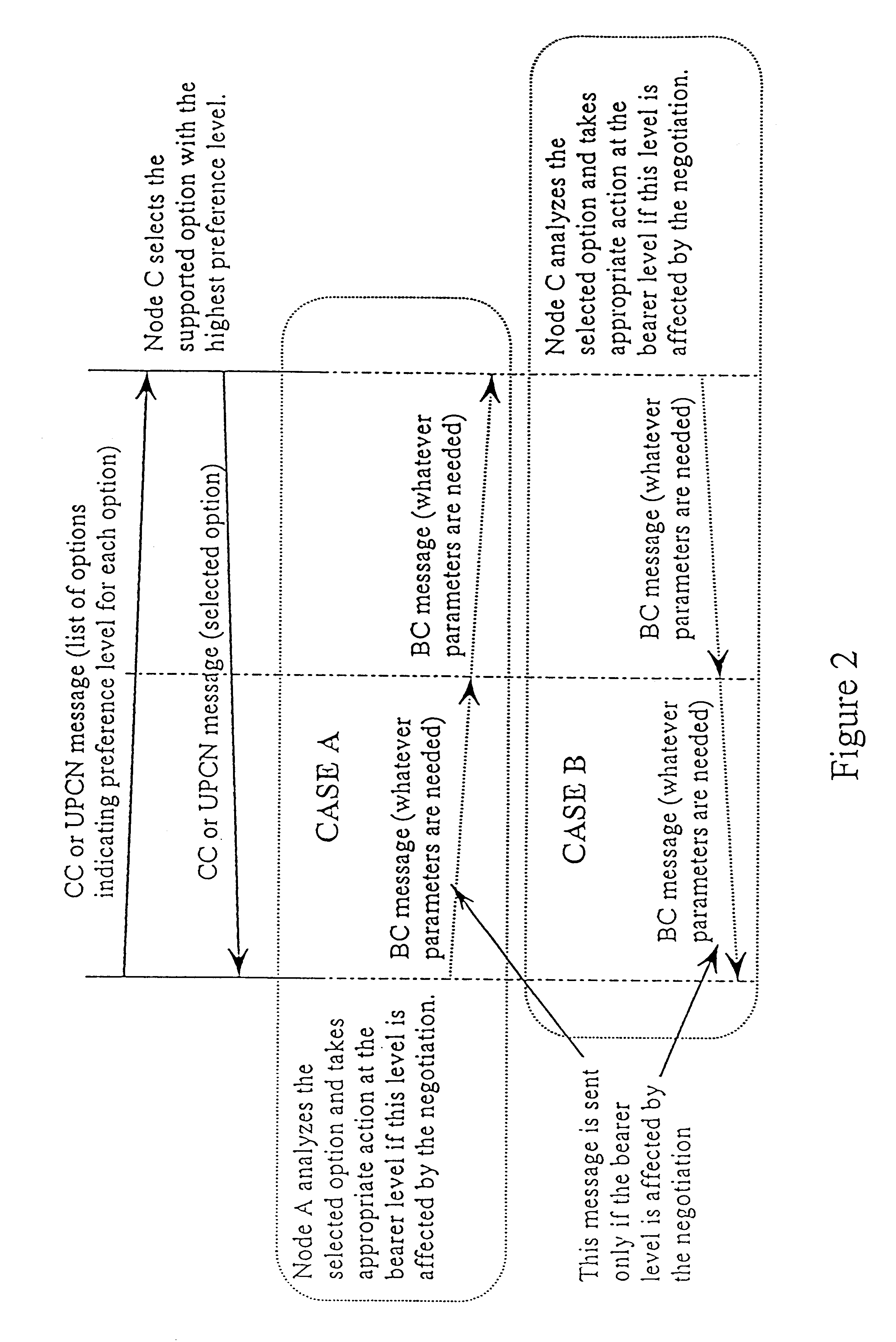
Capability negotiation in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6671367B1Smooth transferNetwork traffic/resource managementSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsTelecommunications linkCall control
A method of negotiating a call capability between signalling points in a telecommunications system. The method comprises sending a capability preference or prioritised list of preferences from an originating signalling point to a terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point, at the Call Control level. A capability acceptance is returned from the terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point to the originating signalling point at the Call Control level, if the terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point accepts a preference sent by the originating signalling point.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
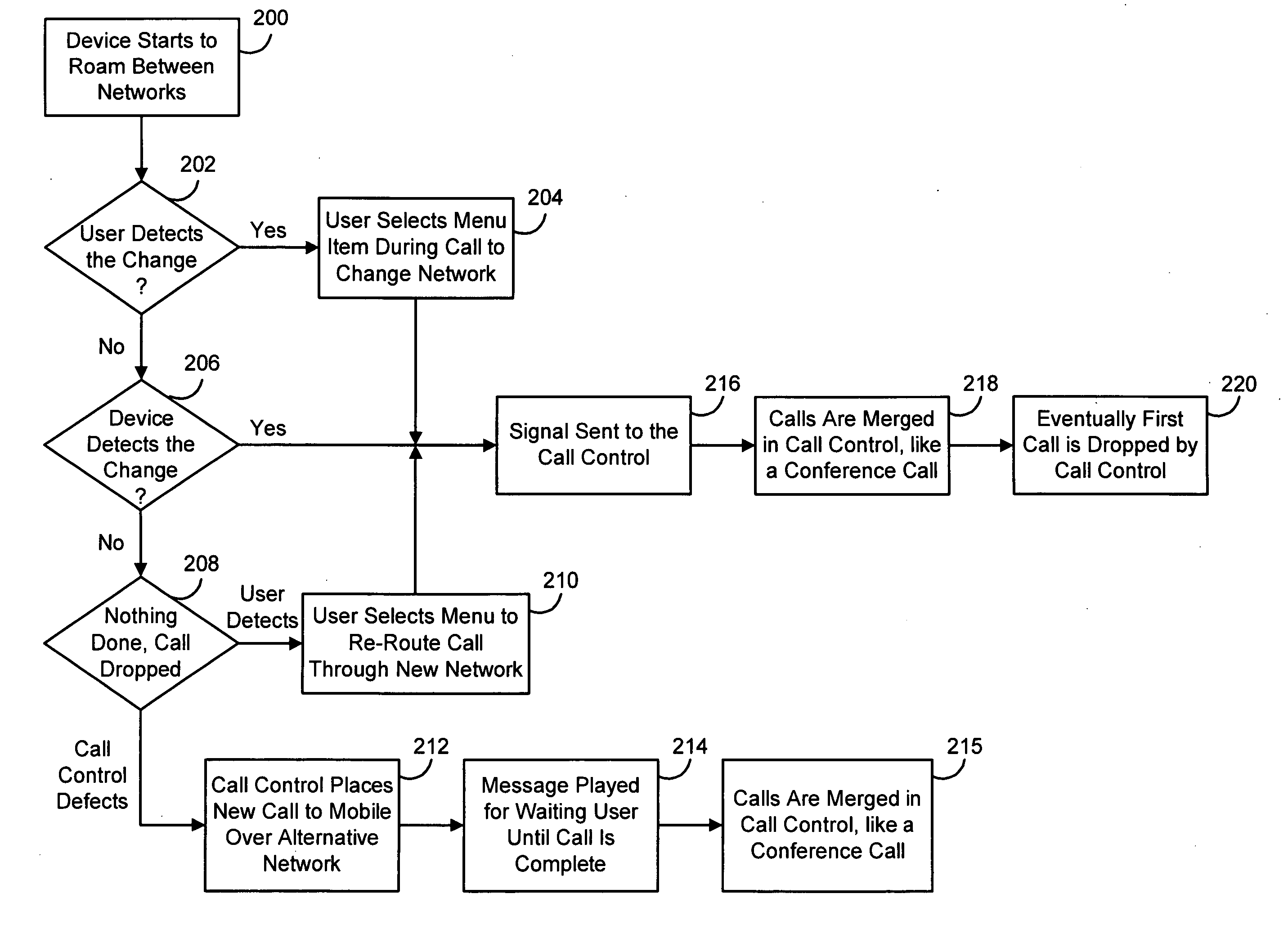
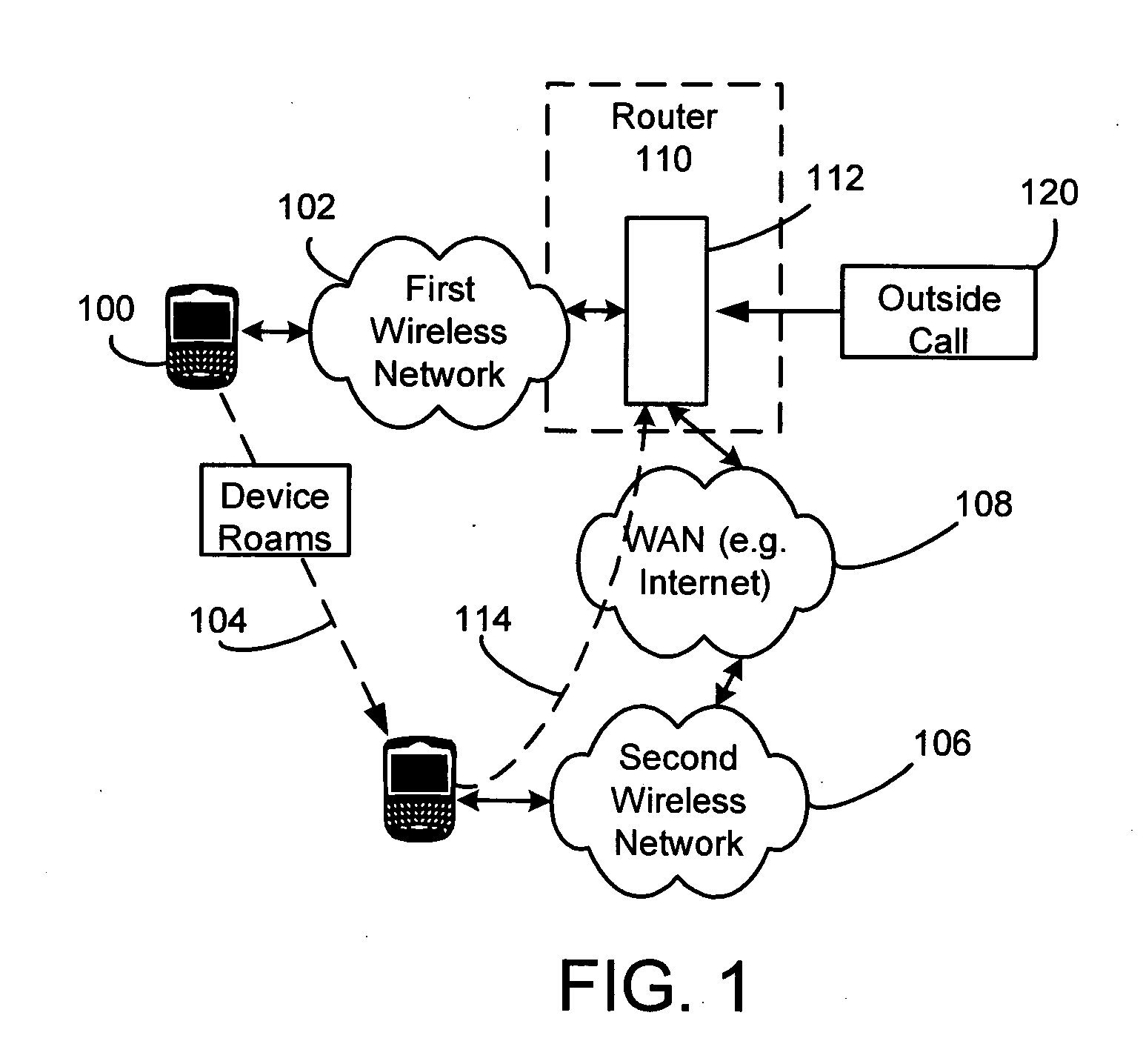
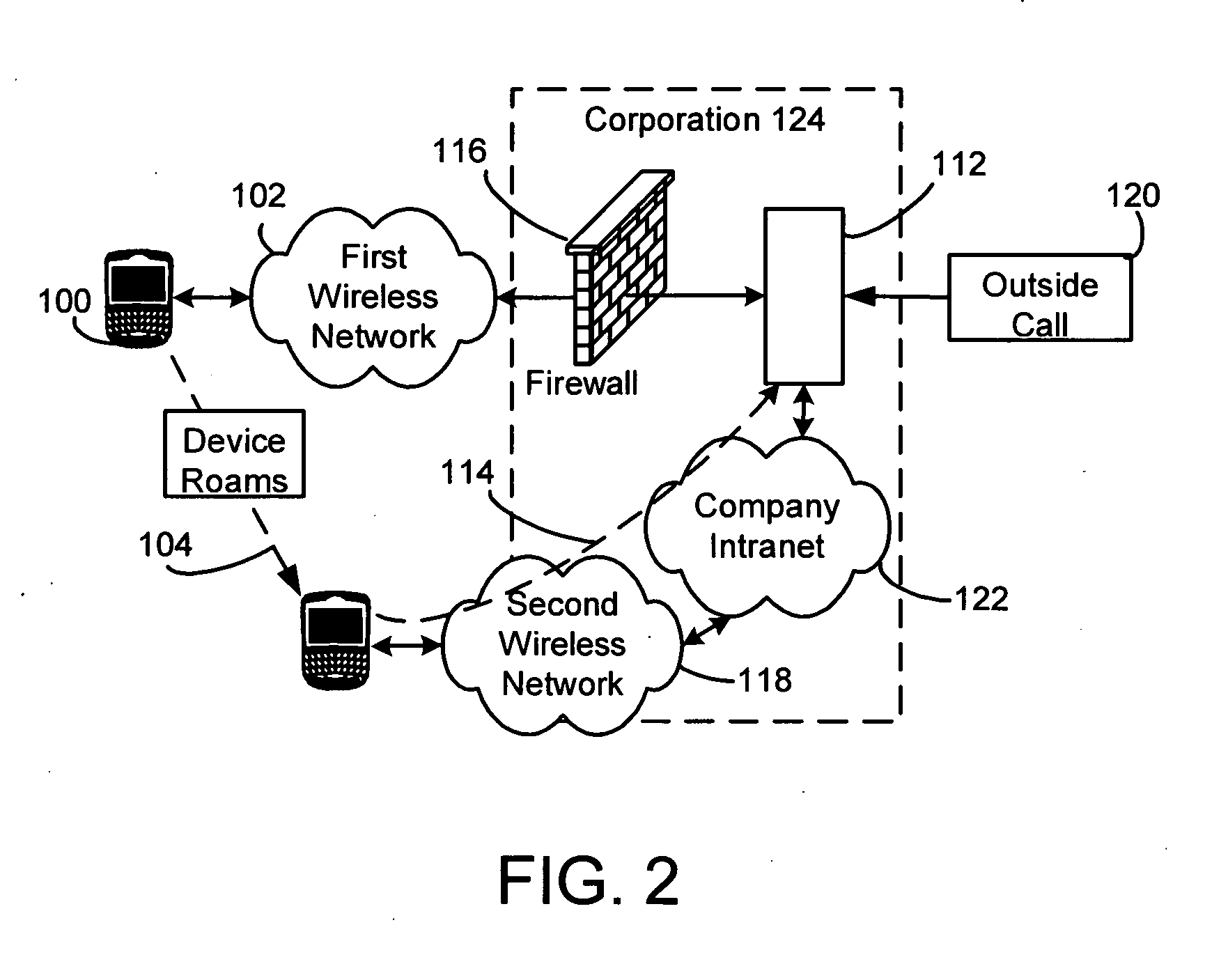
Seamless call switching in a dual mode environment
ActiveUS20050159153A1Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless transceiverTransceiver
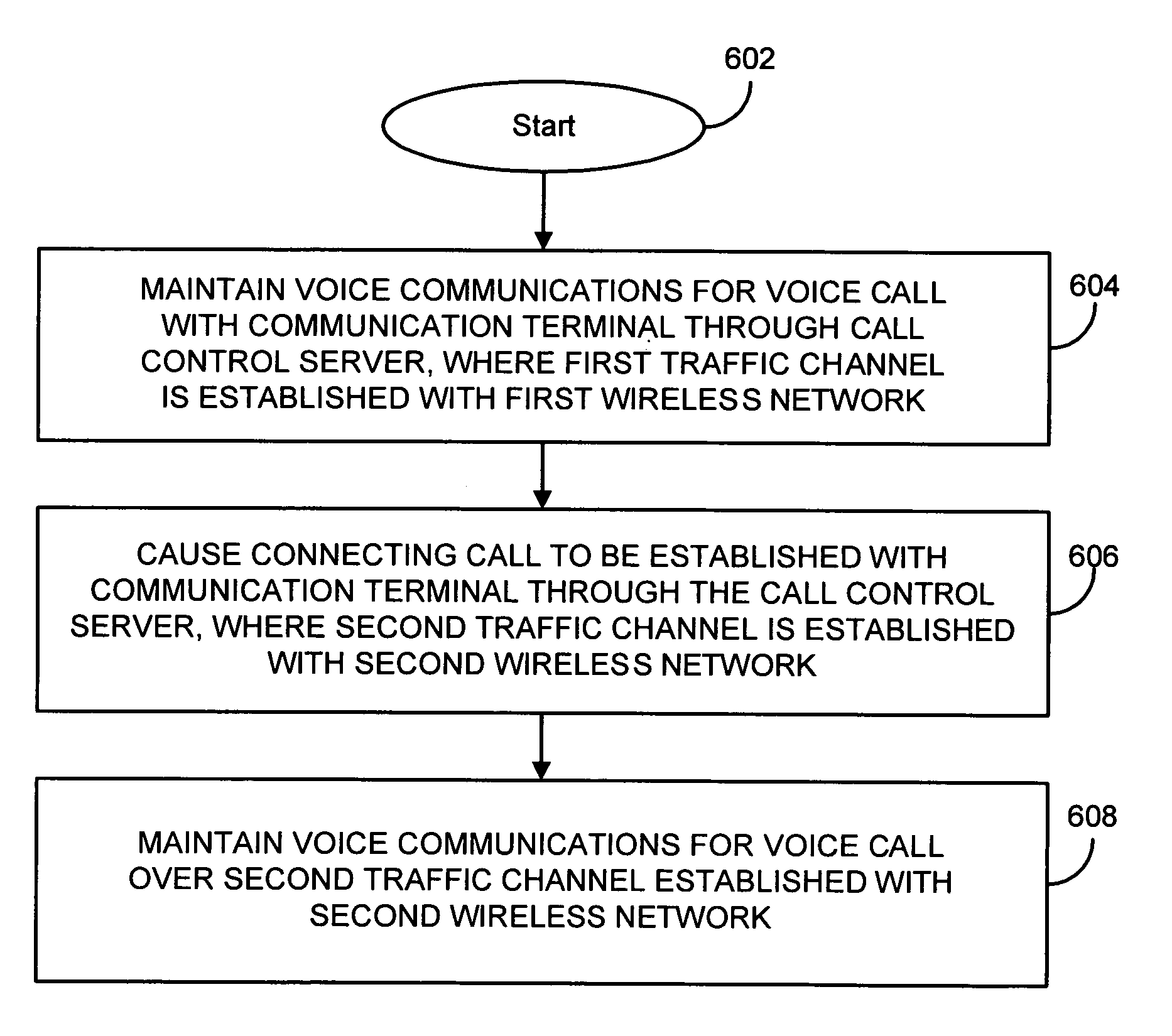
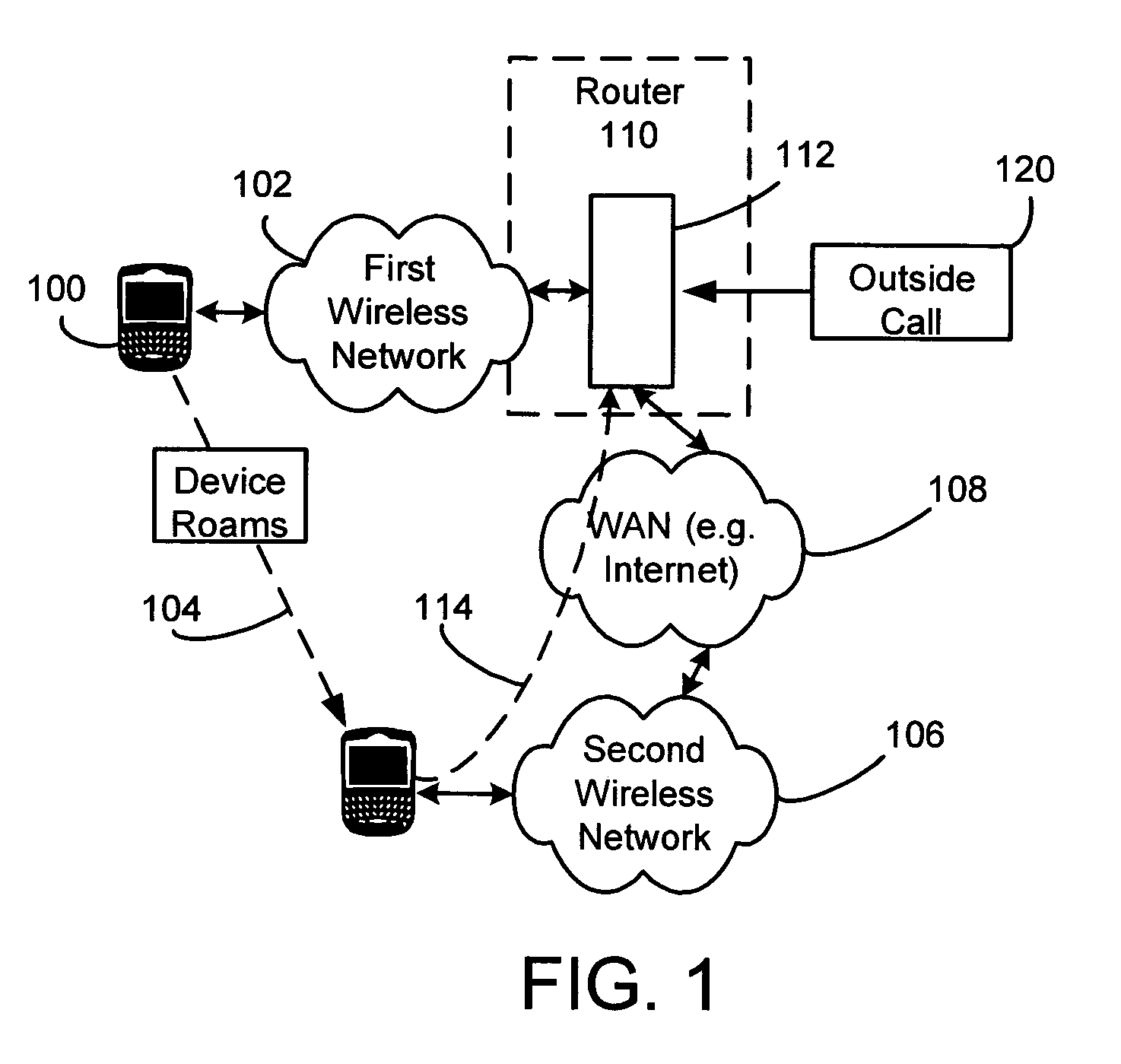
Methods and apparatus for providing a seamless switching of voice calls between different wireless networks are disclosed. In one illustrative example, a mobile communication device has a processor and one or more wireless transceivers coupled to the processor. The one or more wireless transceivers include a first transceiver portion operative in accordance with a first wireless network (e.g. a GSM / GPRS cellular network) and a second transceiver portion operative in accordance with a second wireless network (e.g. an 802.11 wireless network). A voice call is maintained between the mobile device and a communication terminal through call control equipment. The processor of the mobile device is operative to maintain voice communications for the voice call over a traffic channel established between the mobile device and the first wireless network using the first transceiver portion; cause a connecting call to be established with the communication terminal through the call control equipment in response to a predetermined condition, where the connecting call involves a traffic channel established between the second wireless network and the mobile device using the second transceiver portion; and after the connecting call is established, maintain voice communications for the voice call over the traffic channel established between the second wireless network and the mobile device.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Conversational bearer negotiation
InactiveUS20040249887A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersAccess networkCommunications system
A method of setting up a session between peer user terminals of a communication system, said session extending at least in part across a circuit switched access network. The method comprises transporting signalling to initiate said session between at least one of the peer user terminals and said communication system via an IP based packet switched access network using a call control protocol which is also used for setting up end-to-end packet switched sessions, and subsequently establishing said session based upon said signalling.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Communication network with a collection gateway and method for providing surveillance services
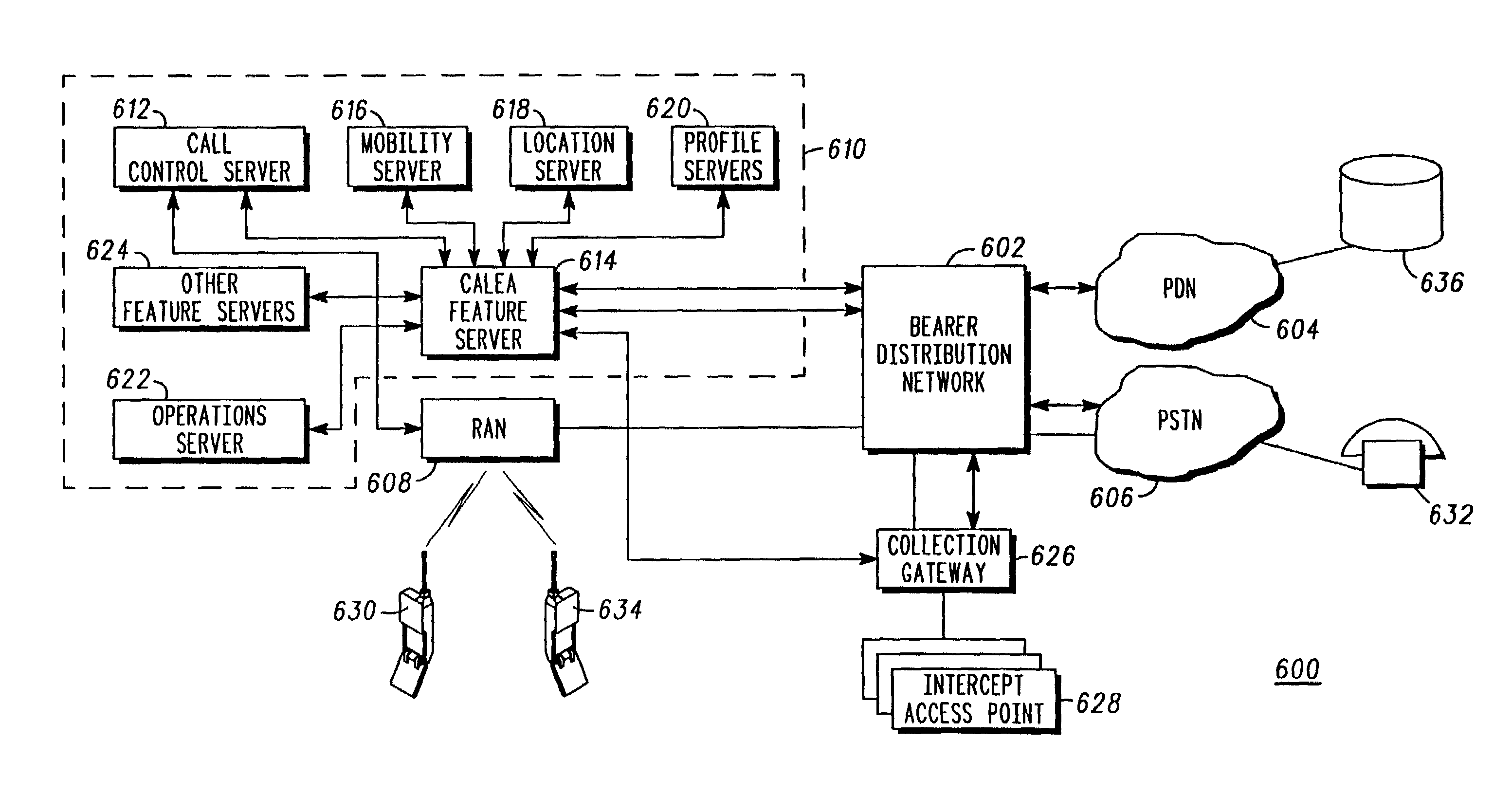
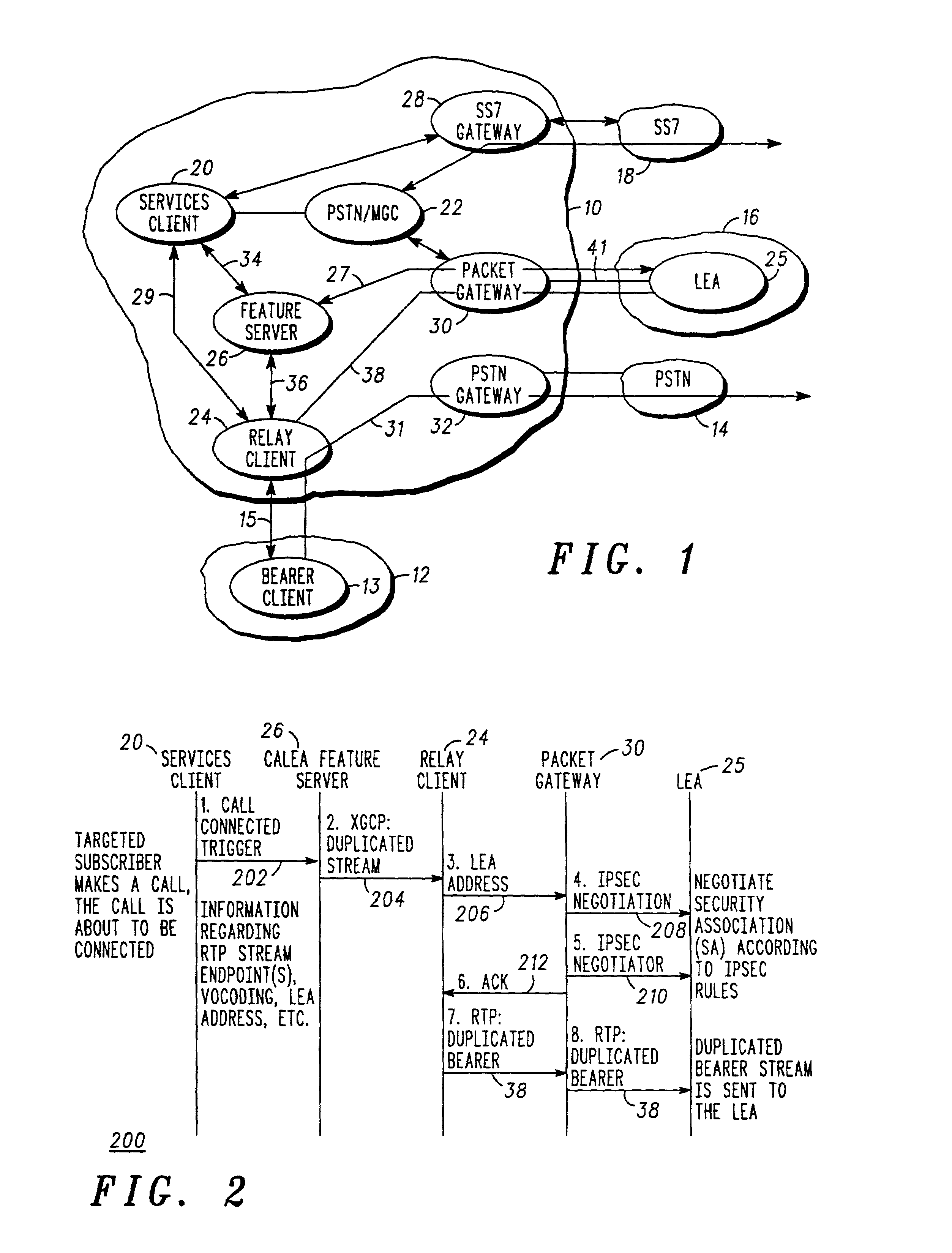
ActiveUS7006508B2Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsData switching by path configurationCommunication surveillanceCall control
A communication network (10) utilized for providing communications between a first party and a second party includes a surveillance server (26) within a core network (10) to provide communication surveillance capability. The core network (10) may be a packet data network, and the surveillance server (26) is operable responsive to trigger information to establish communications surveillance. Communication surveillance may be established by creating duplicate bearer packets of those data packets carrying the communicated data between the parties, creating duplicate control packets of those data packets carrying in-band or out-of-band call control information between the parties and within the packet data network, and / or various combinations thereof. The duplicate bearer packets and the duplicate control packets are routed to appropriate authorized law enforcement agencies for providing surveillance.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
System and method for communications in a multi-platform environment
ActiveUS20060019655A1Improve mobilityImprove responsivenessMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationRadio networksMulti platform
A radio networking system includes at least a first communication port operable to facilitate communication between the radio networking system and a first communication platform. The system further includes at least a second communication port operable to facilitate communication between the radio networking system and a second communication platform. Additionally, a call control software module is operable to automatically and intelligently switch an incoming call from the first communication platform to the second communication platform which is controlled by a processor operable to execute the call control software module according to the information contained in a system configuration database. The call control software module further manages the configuration of call connections and conferencing services and supports real time user control of desired communication services.
Owner:RADIONET CORP
Multi-protocol wireless communication apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050190789A1Eliminate needEasy to updateTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentGraphicsCOLA (software architecture)
A scalable, multi-protocol mobile switching center in a wireless communications network provides communications control for digital and analog wireless communications devices including devices that operate according to GSM and IS-41 standards. The hardware and software architecture of the switching center is designed so that processing that is unique to a particular protocol is performed at the lowest possible level, and remaining processing can use generic procedures. The switching center incorporates a home location register and visitor location register that are used in conjunction with software applications to determine the protocol of mobile communications devices using the wireless communications network. The mobile switching center can be used to provide a large scale distributed wireless network or a small scale wireless network. The switching center can also be used as an adjunct to a private branch exchange to provide in-building wireless services and call control. Graphical user interfaces make the wireless communications network easy to maintain.
Owner:TECORE INC
Seamless call switching in a dual mode environment
Methods and apparatus for providing a seamless switching of voice calls between different wireless networks are disclosed. In one illustrative example, a mobile communication device has a processor and one or more wireless transceivers coupled to the processor. The one or more wireless transceivers include a first transceiver portion operative in accordance with a first wireless network (e.g. a GSM / GPRS cellular network) and a second transceiver portion operative in accordance with a second wireless network (e.g. an 802.11 wireless network). A voice call is maintained between the mobile device and a communication terminal through call control equipment. The processor of the mobile device is operative to maintain voice communications for the voice call over a traffic channel established between the mobile device and the first wireless network using the first transceiver portion; cause a connecting call to be established with the communication terminal through the call control equipment in response to a predetermined condition, where the connecting call involves a traffic channel established between the second wireless network and the mobile device using the second transceiver portion; and after the connecting call is established, maintain voice communications for the voice call over the traffic channel established between the second wireless network and the mobile device.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
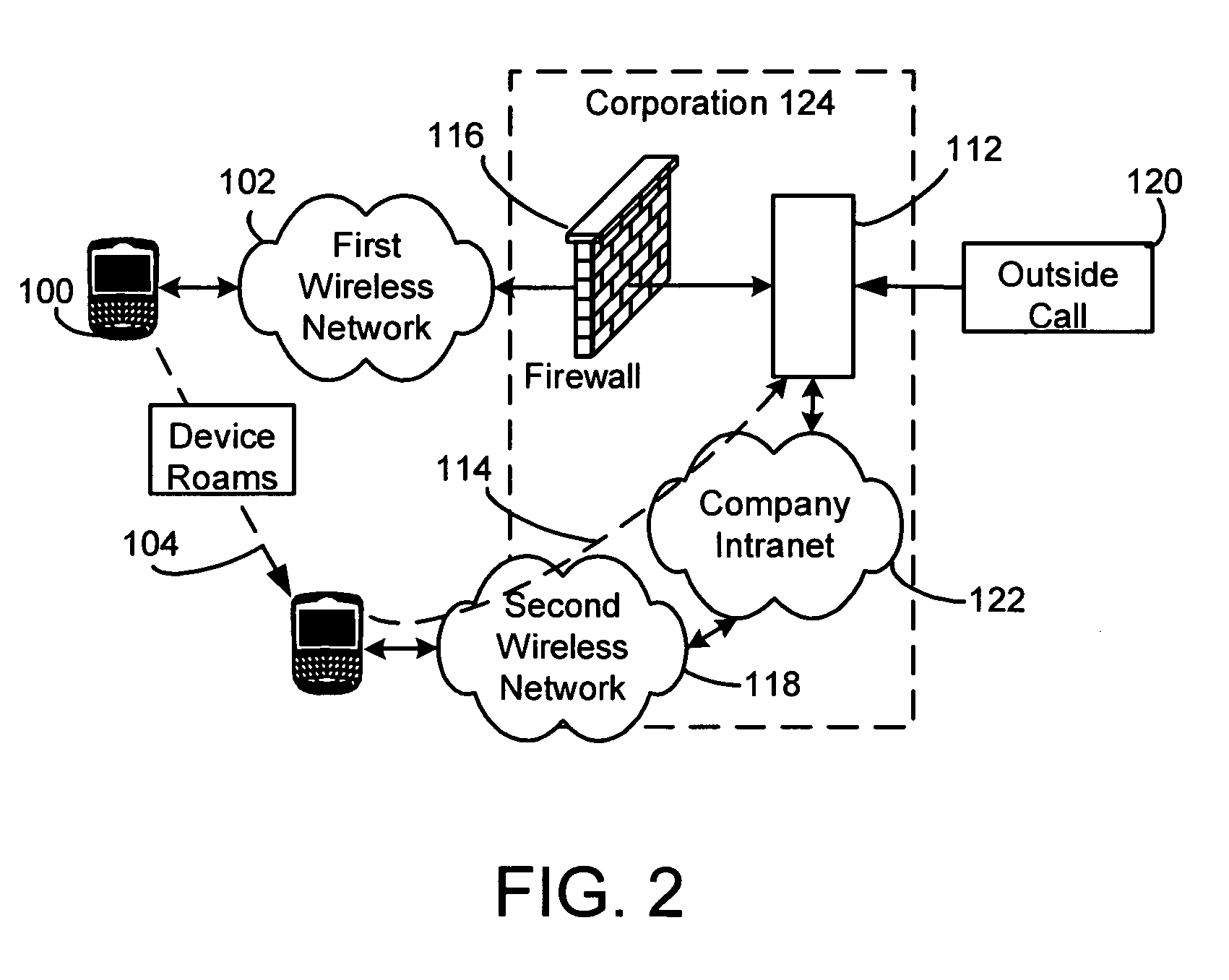
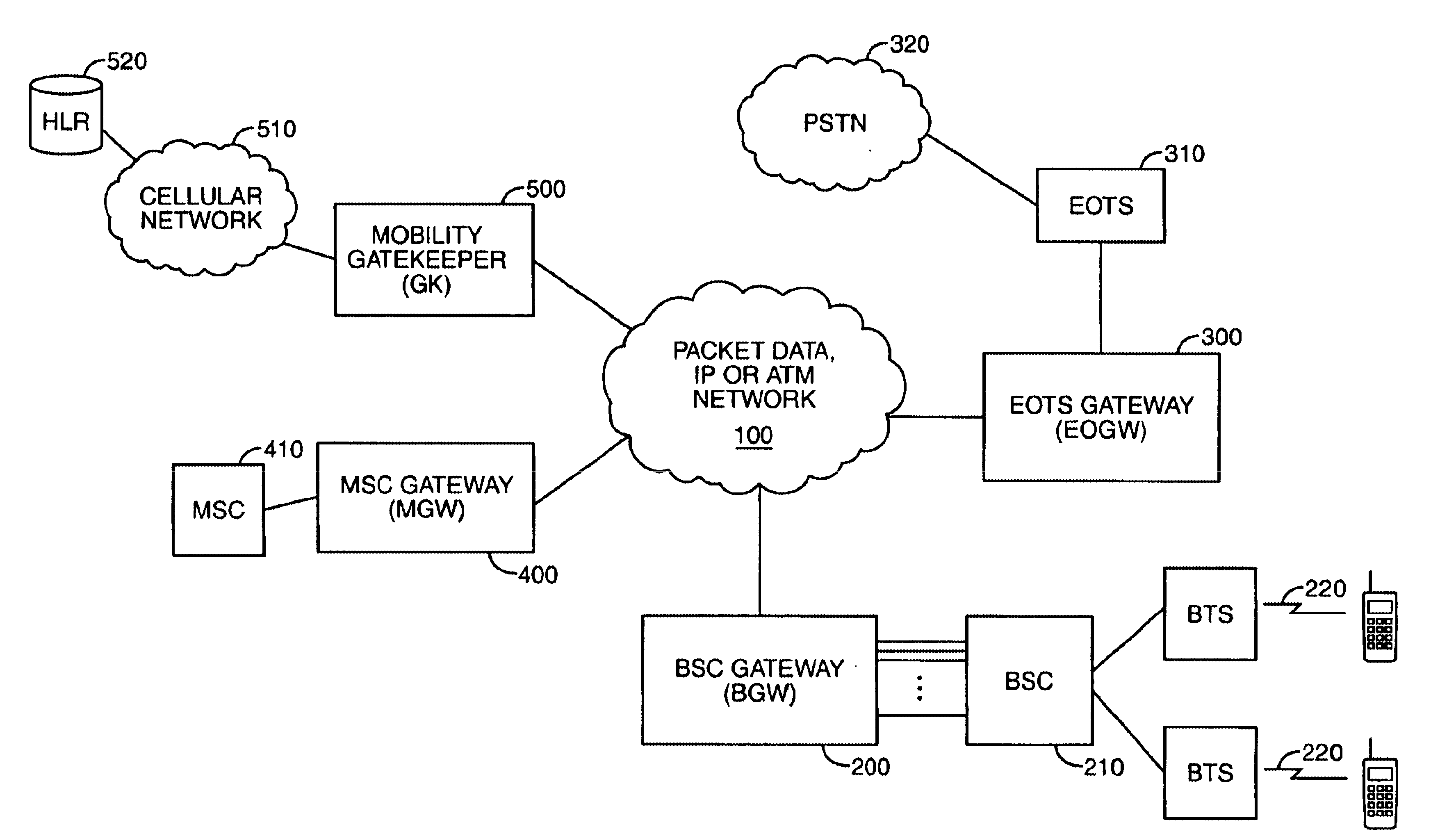
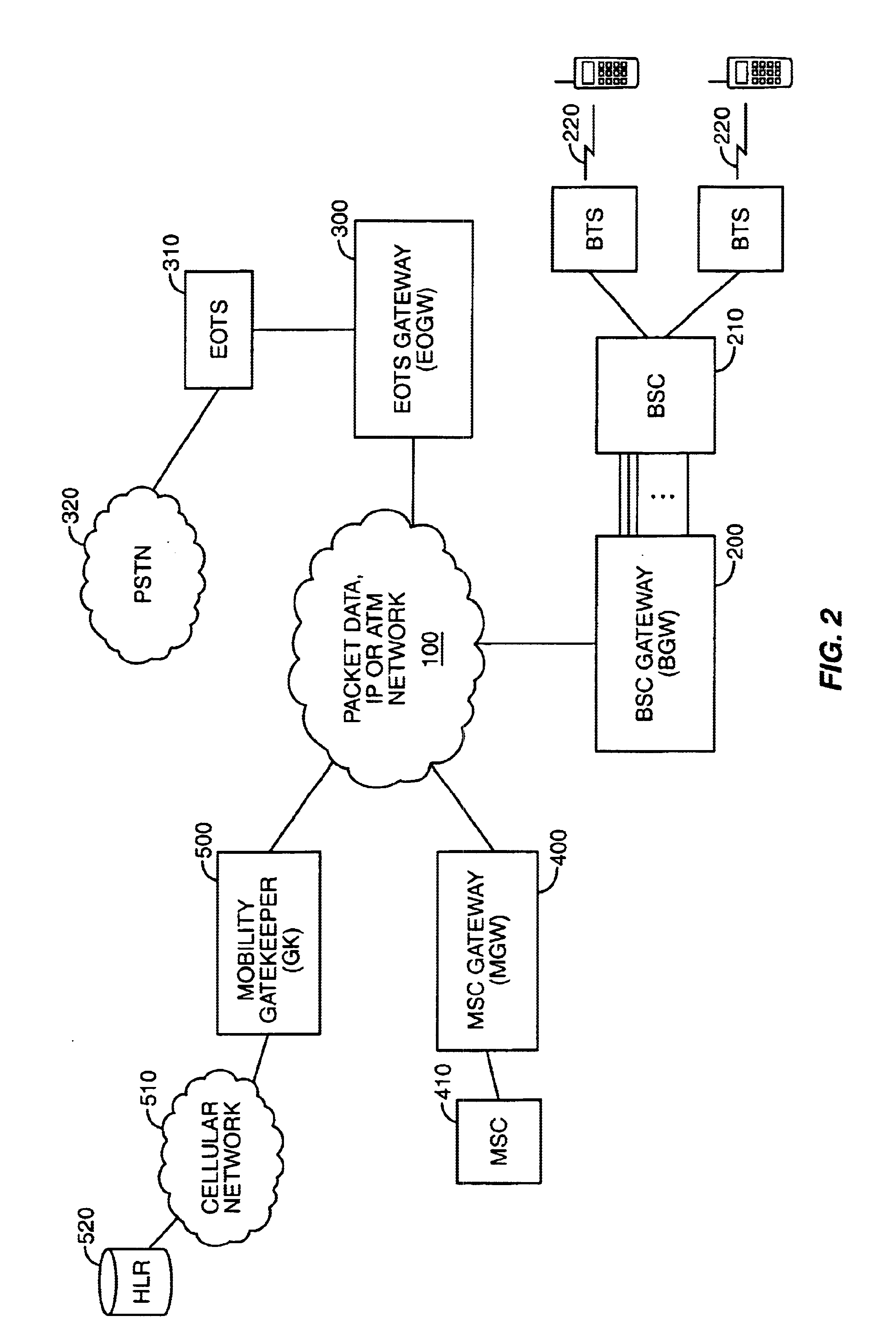
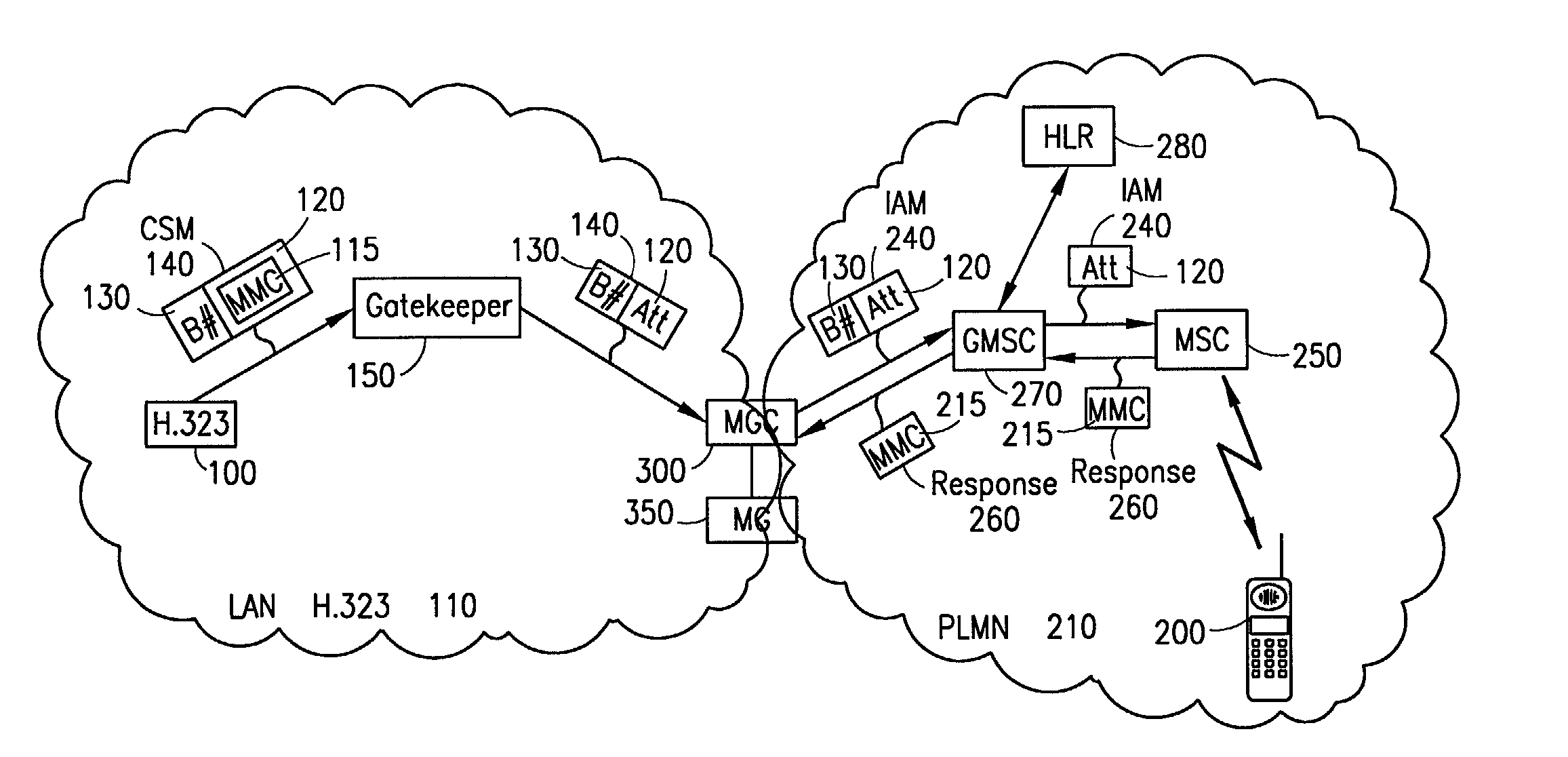
System, method, and computer program product for connectivity of wireless base station to PSTN via an IP data network
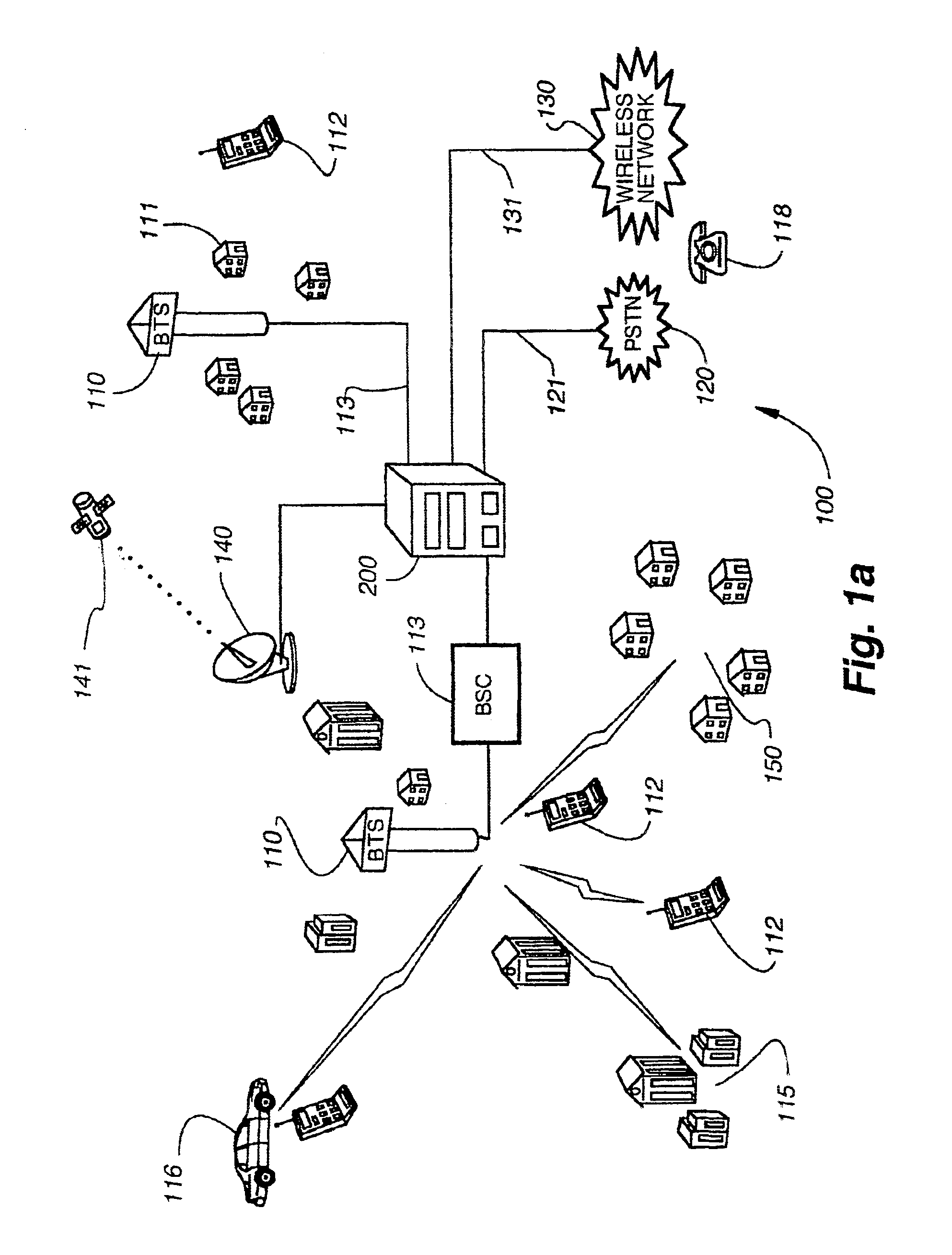
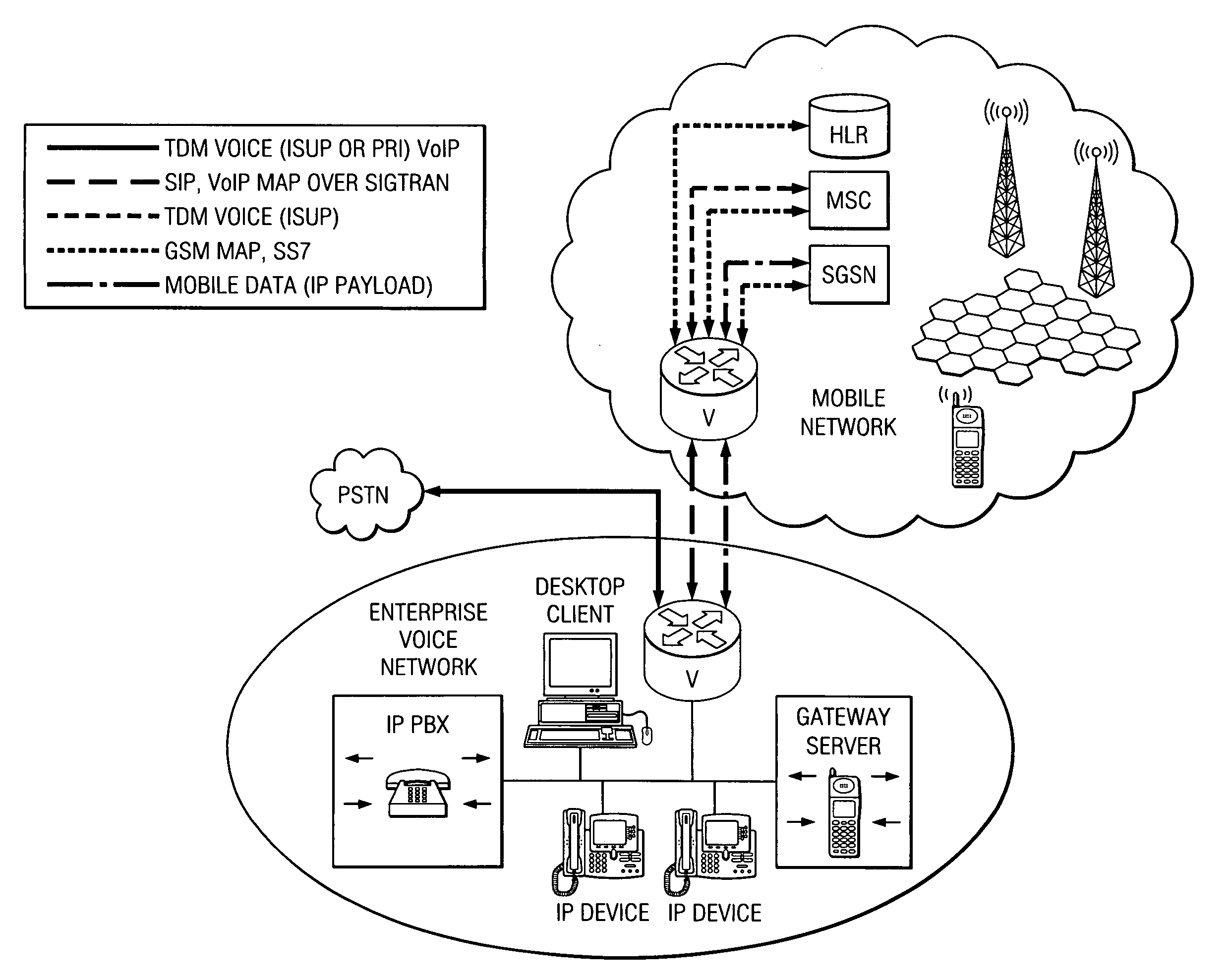
InactiveUS6888803B1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCable telephonySystem call
A system for providing wireline telephone services to wireless subscribers utilizing a packet data network 100. The system includes a base station controller (BSC) 210 a base station controller gateway (BGW) 200 for providing client based services to mobile subscribers and providing protocol mapping between a mobile protocol and a packet data network protocol. The system further comprises a mobility gatekeeper (GK) 500 for managing network mobility services for each wireless call including the establishment of a call control path and a speech path between said base station controller and a serving end office telephone point. The system also comprises a end office gateway (EOGW) 300 for providing protocol conversion between the packet data network protocol and the end office point data protocol such that a wireless subscriber has access to all wireline services provided by the end office point. A mobile switching center (MSC) 410 and mobile switching center gateway (MGW) 400 are included to facilitate inter-system call handoffs into an existing circuit-switched wireless telephony network.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Call control method and apparatus
InactiveCN101500041AImprove performanceImprove completenessSpecial service for subscribersTelephone sets with user guidance/featuresNetworked systemTerminal equipment
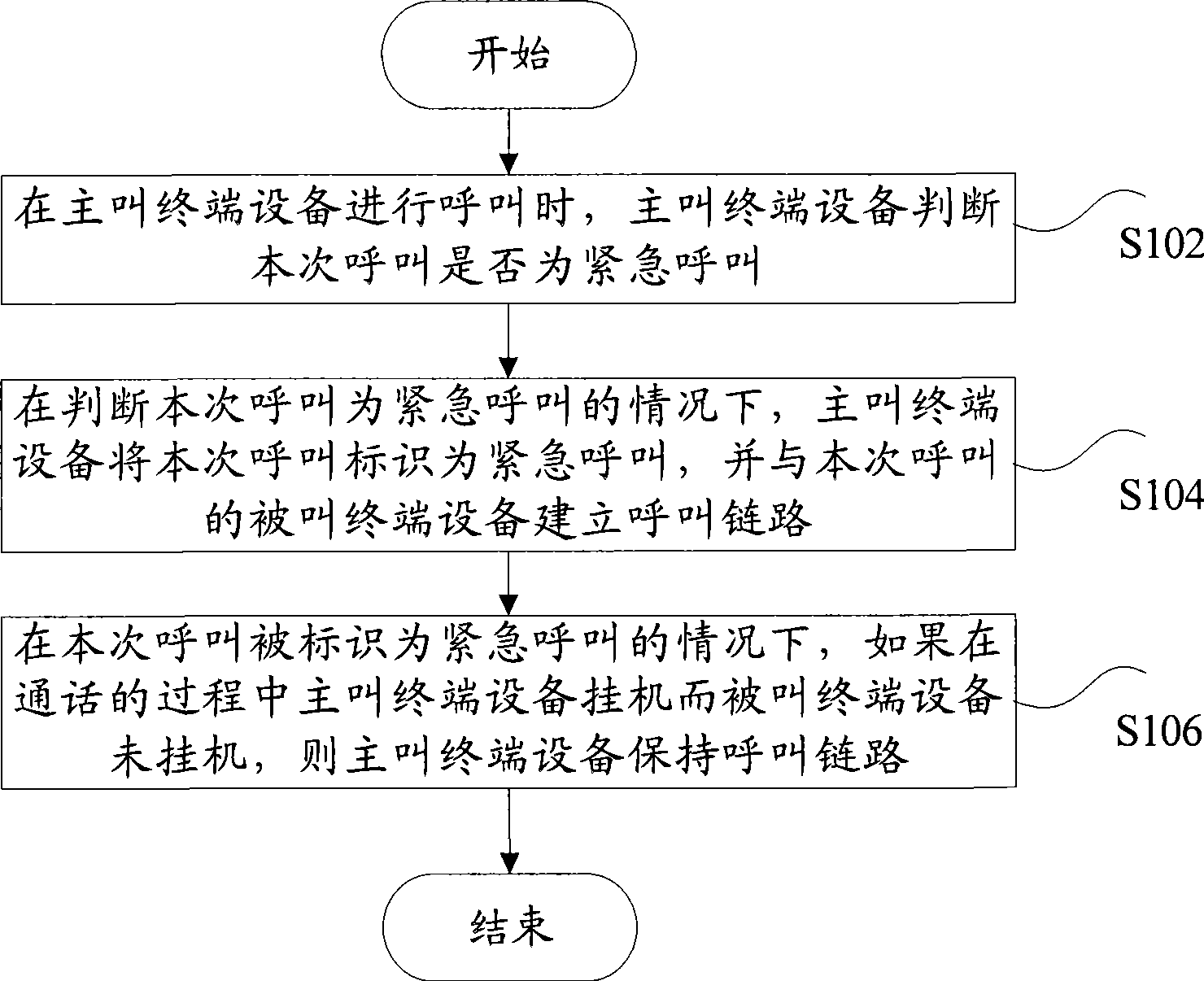
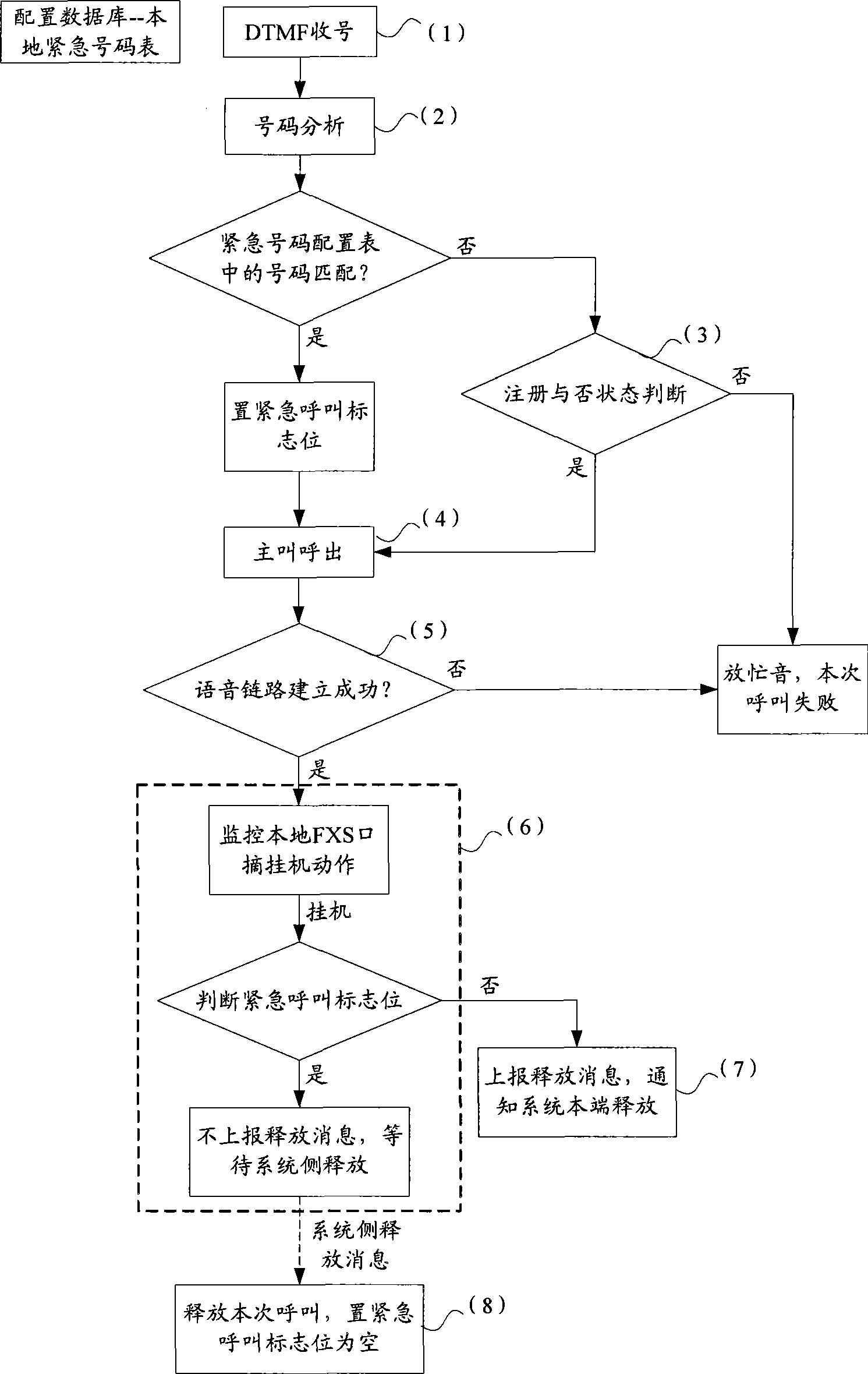
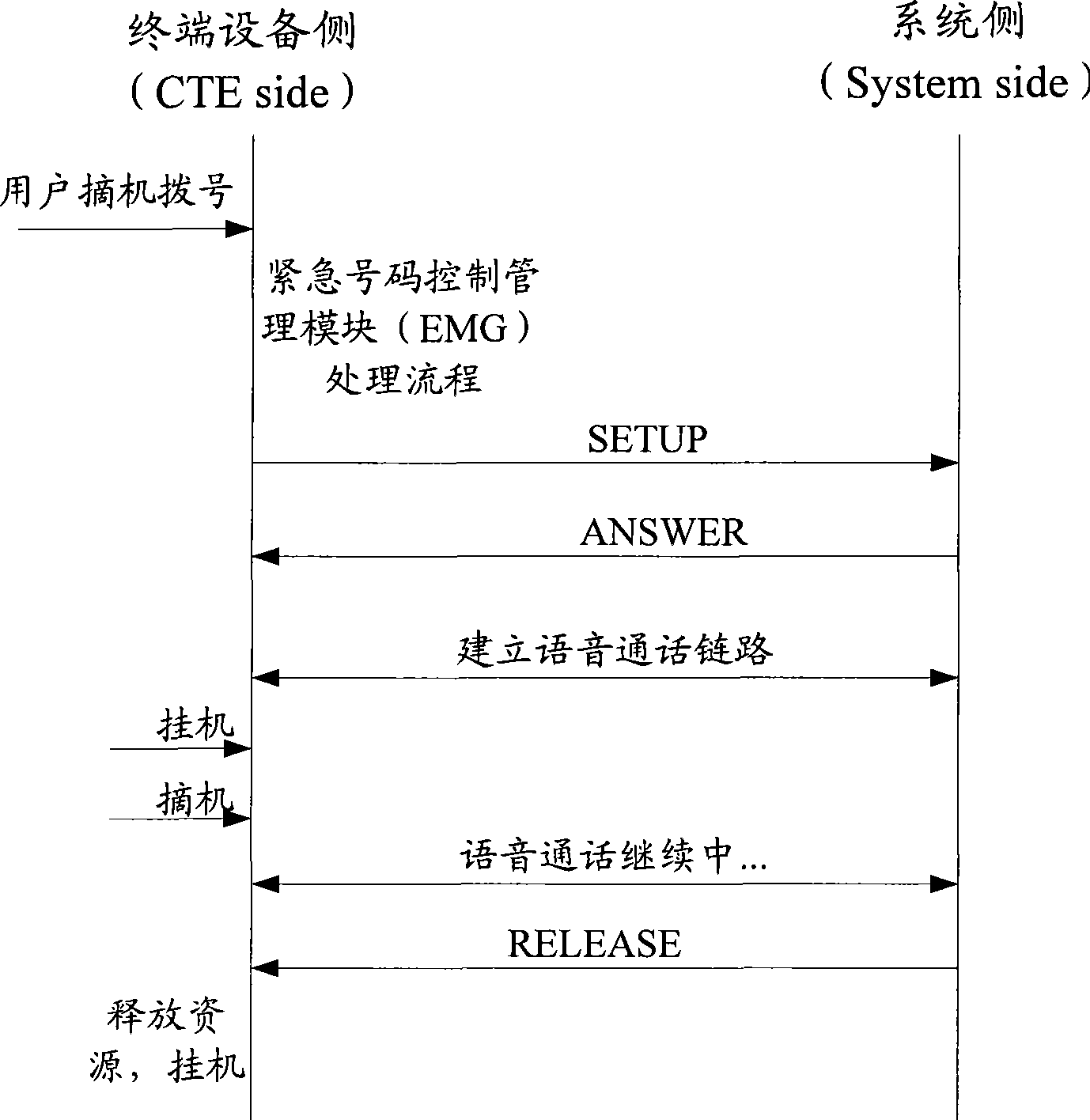
The invention discloses a call control method, which comprises step S102, when calling terminal equipment calls, the calling terminal equipment judges whether the calling is emergent or not; step S104, under the situation of judging the calling is emergent, the calling terminal equipment labels the calling as emergent calling, and establishes a call link with the called terminal equipment of the calling; and step S106, under the situation of labeling the calling is emergent, if the calling terminal equipment hangs off whereas the called terminal equipment does not hang off in the talking process, the calling terminal equipment maintains the call link. Furthermore, the invention also discloses a call control device. The invention effectively protects the emergent call speech link, reduces time waste caused by abnormal hanging off, reduces the dependency of communication terminal equipment CTE on network system side equipment, improves the adaptability of the system, and improves the performance and intelligent degree of the terminal equipment in a real sense.
Owner:ZTE CORP
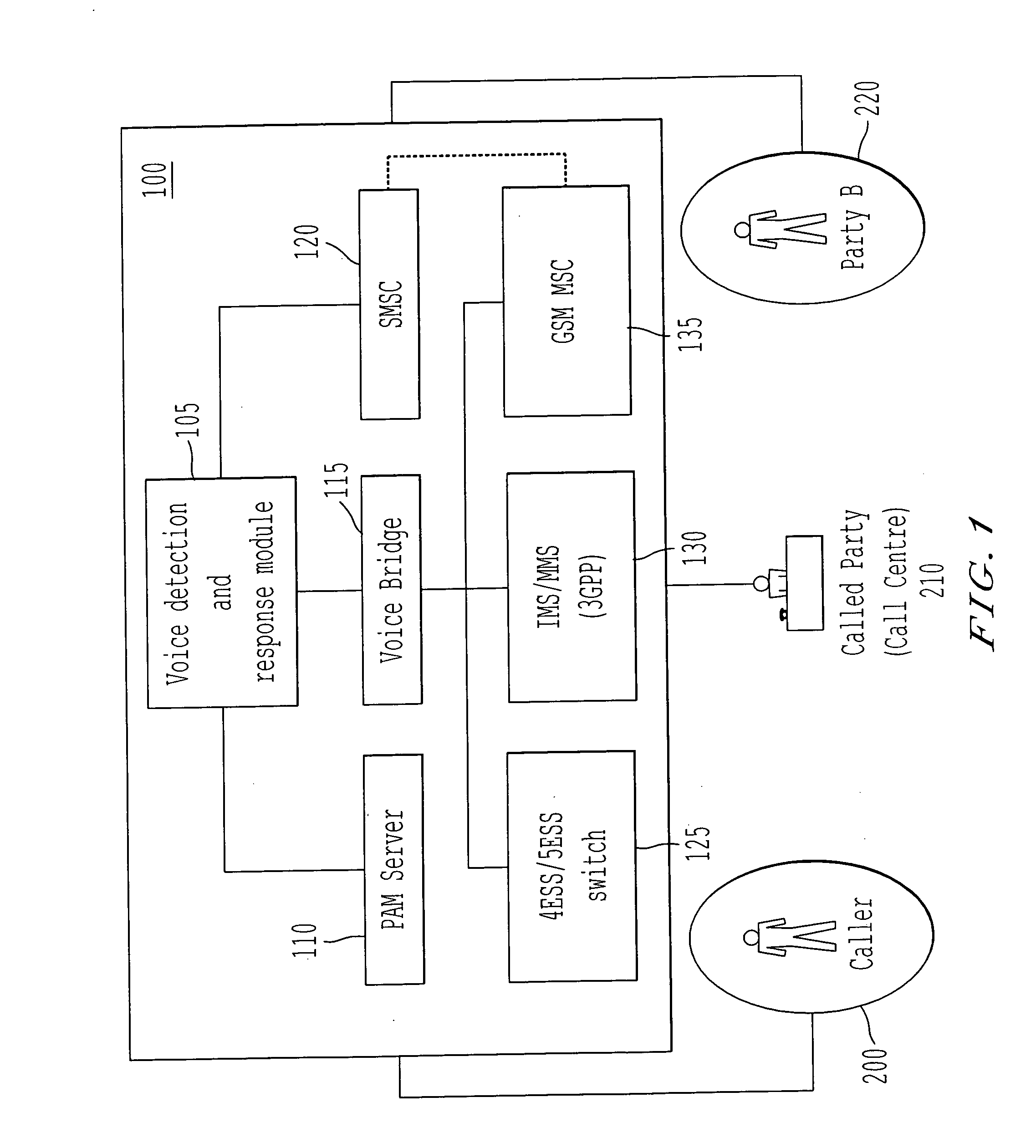
Method and system for alerting call participant of a change in a call hold status
A method and system for controlling a connection between a calling party and a called party. When a call is placed on hold, detection services are utilized to determine when the call changes from being “on hold” to being active. The call control system can then contact the caller to inform the caller of the change in the status of the call. Such contacts can be either in-band or out-of-band. If the caller is unable to respond to the change in call status, the called party can leave a message for the caller.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
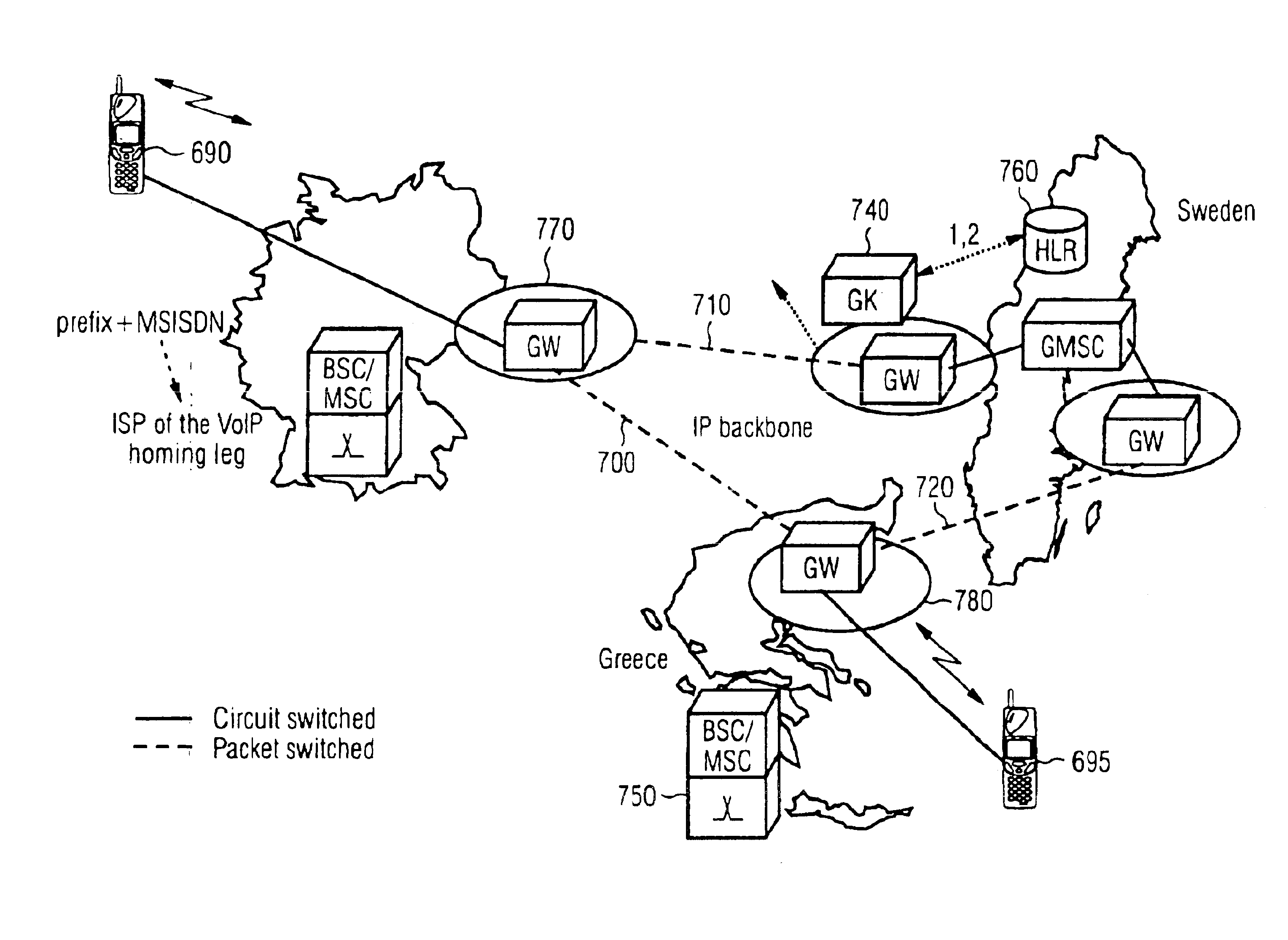
Methods and systems for call routing and codec negotiation in hybrid voice/data/internet/wireless systems
InactiveUS6856612B1Minimize delayMinimize the numberInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsThe InternetTranscoding
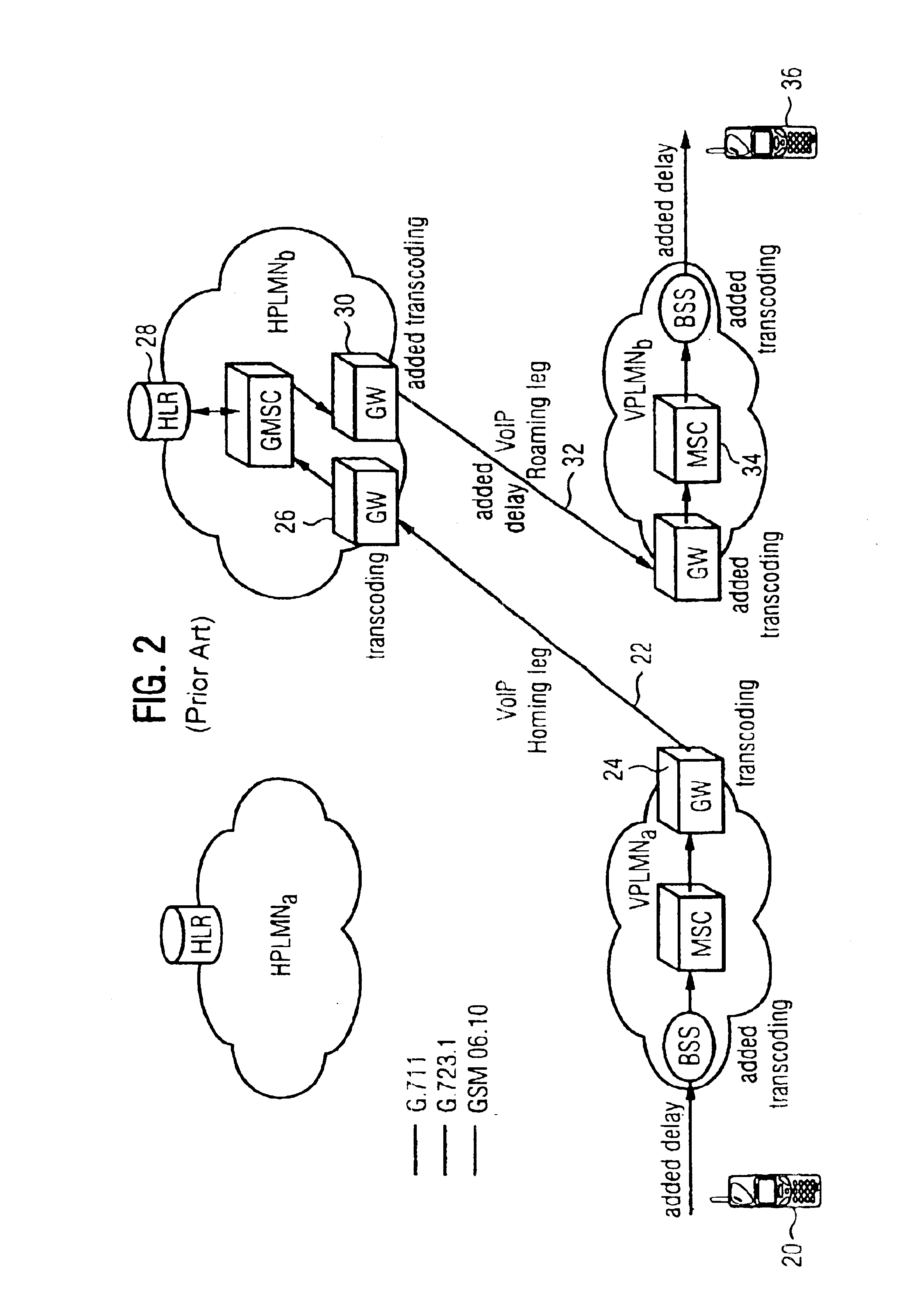
A method and system for communicating information includes evaluation regarding routing of calls performed at a call control point in an ITSP and / or wireless network. A PIC identity associated with another party's preferences is acquired and sent to the call control point. The PIC identity identifies the type of the carrier network (e.g., circuit switched or VoIP) and is used to make further routing decisions. If a circuit-switched carrier is identified, the IP homing leg is terminated at the voice gateway in the recipient's HPLMN and information is sent over to the GMSC where normal, circuit-switched routing procedures. If a VoIP carrier is identified then the called user's roaming number is retrieved from the HLR, and the call is further routed directly over the IP domain towards a voice gateway at the visited network minimizing the number of transcodings. Additional transcoding steps can be avoided if a single encoding is agreed upon according to “tandem free operation” (TFO). Combining inband signaling through the telephony exchanges and out-of-band signaling in the IP network it is possible to achieve, for a mobile subscriber, one encoding and one decoding of a voice.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Communications network and method having accessible directory of user profile data
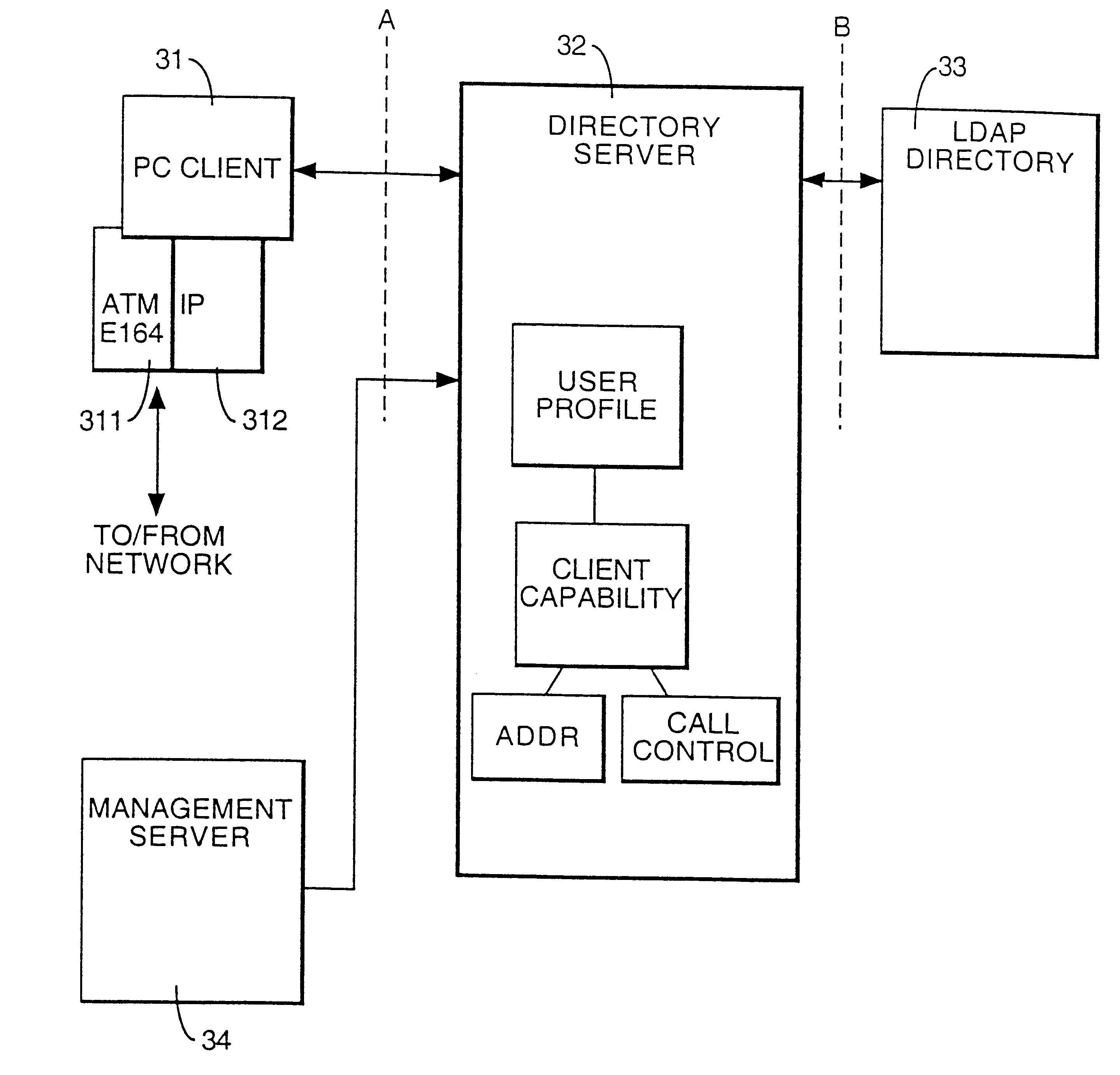
InactiveUS6694375B1Multiple digital computer combinationsAutomatic exchangesUser profileCall control
In a communications network, each of a number of users registers user profile data in a directory. The directory is available to other users. The user profile data includes identifiers for one or more of a plurality of call control protocols. Prior to establishing a call, a user retrieves user profile data for the called party from the directory. The call is then established using a call control protocol which was identified in the relevant user profile.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
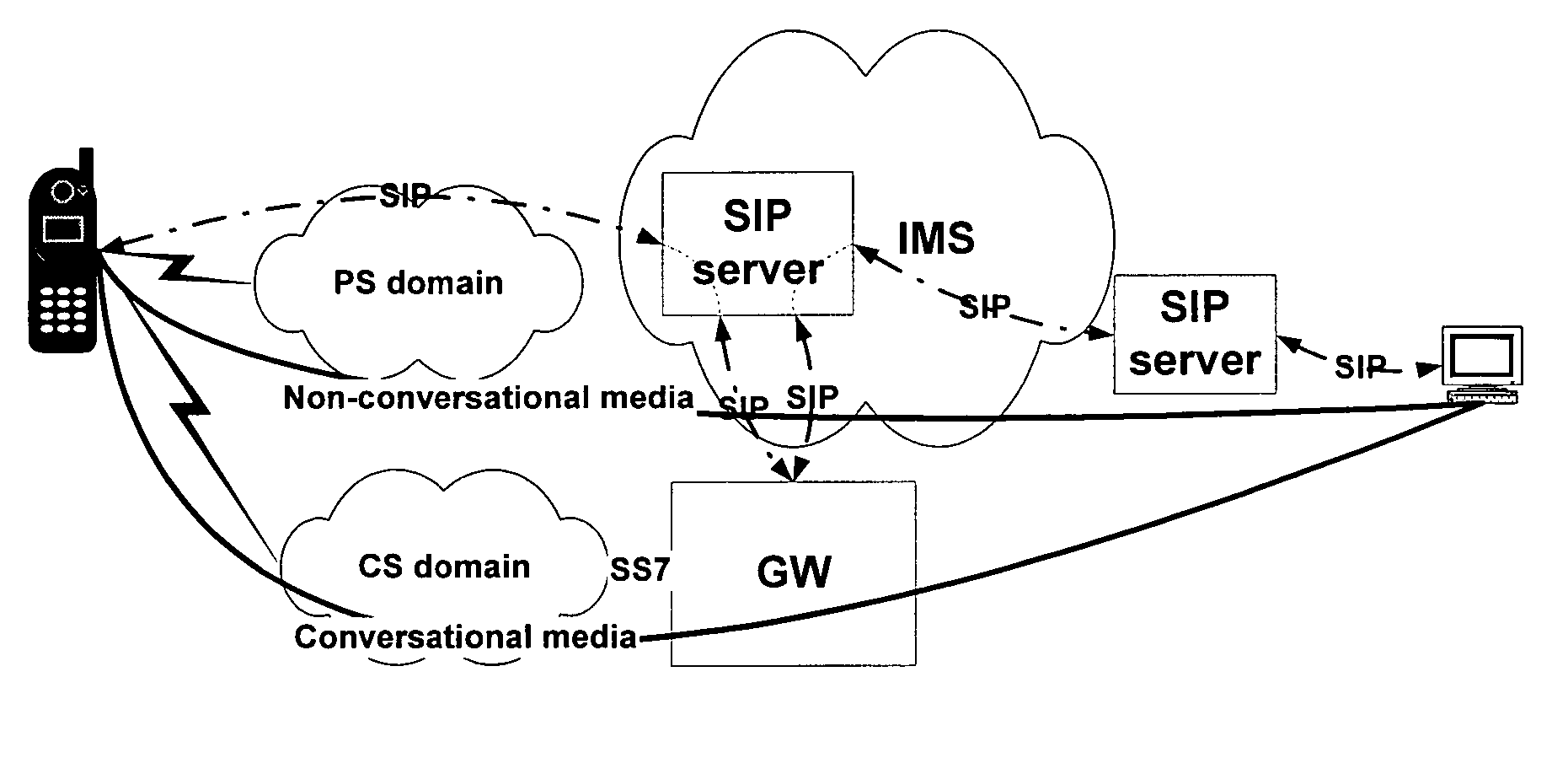
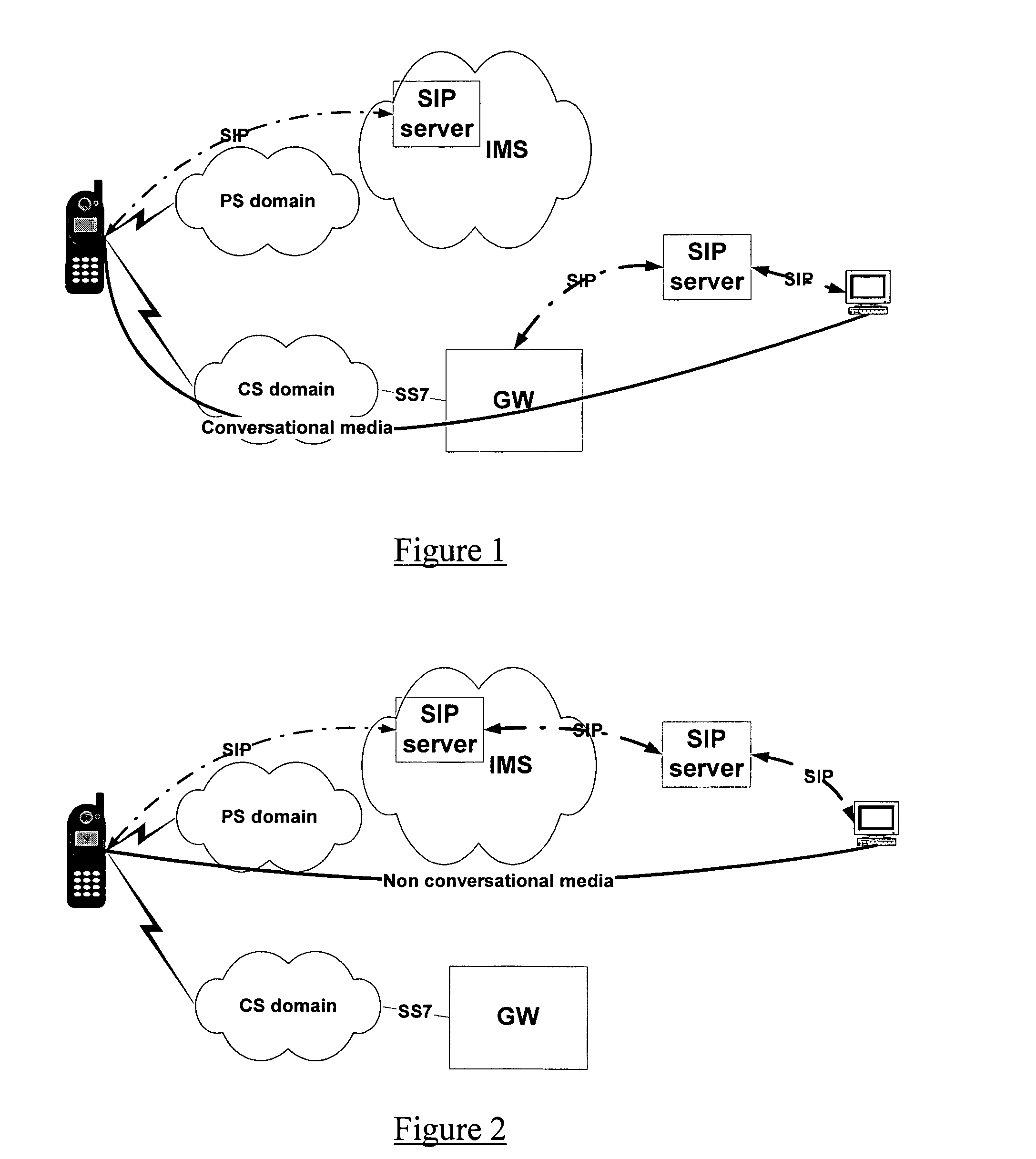
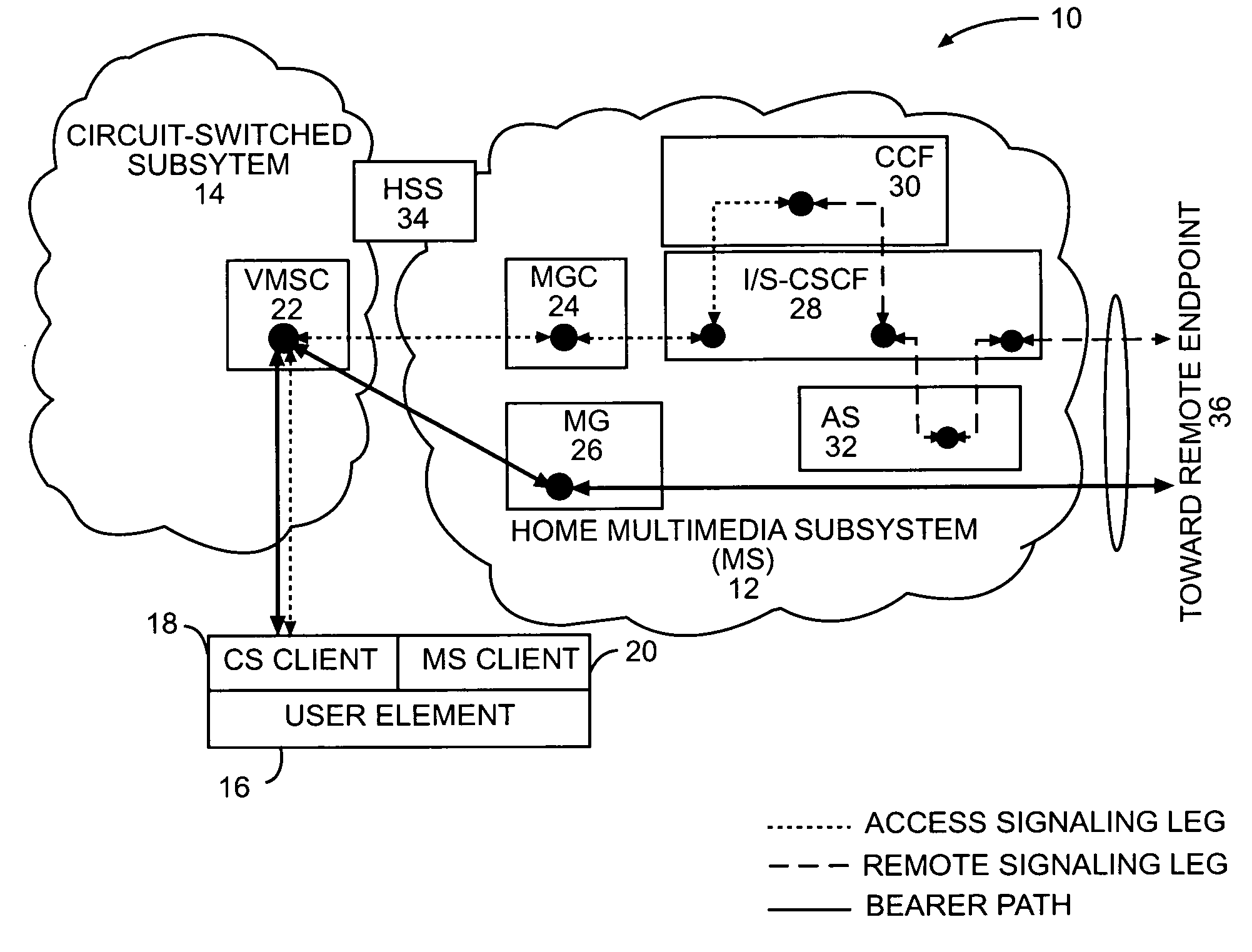
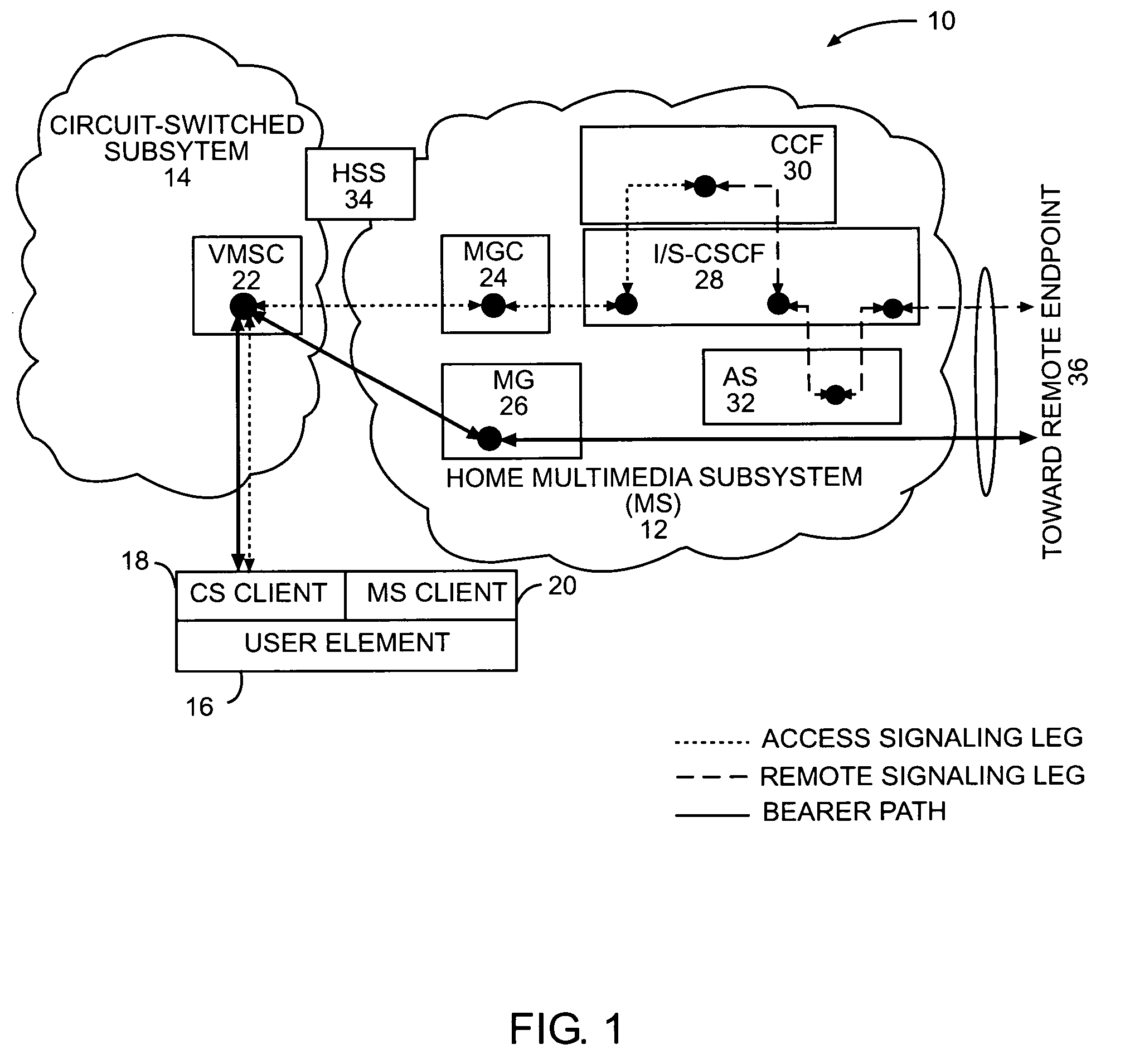
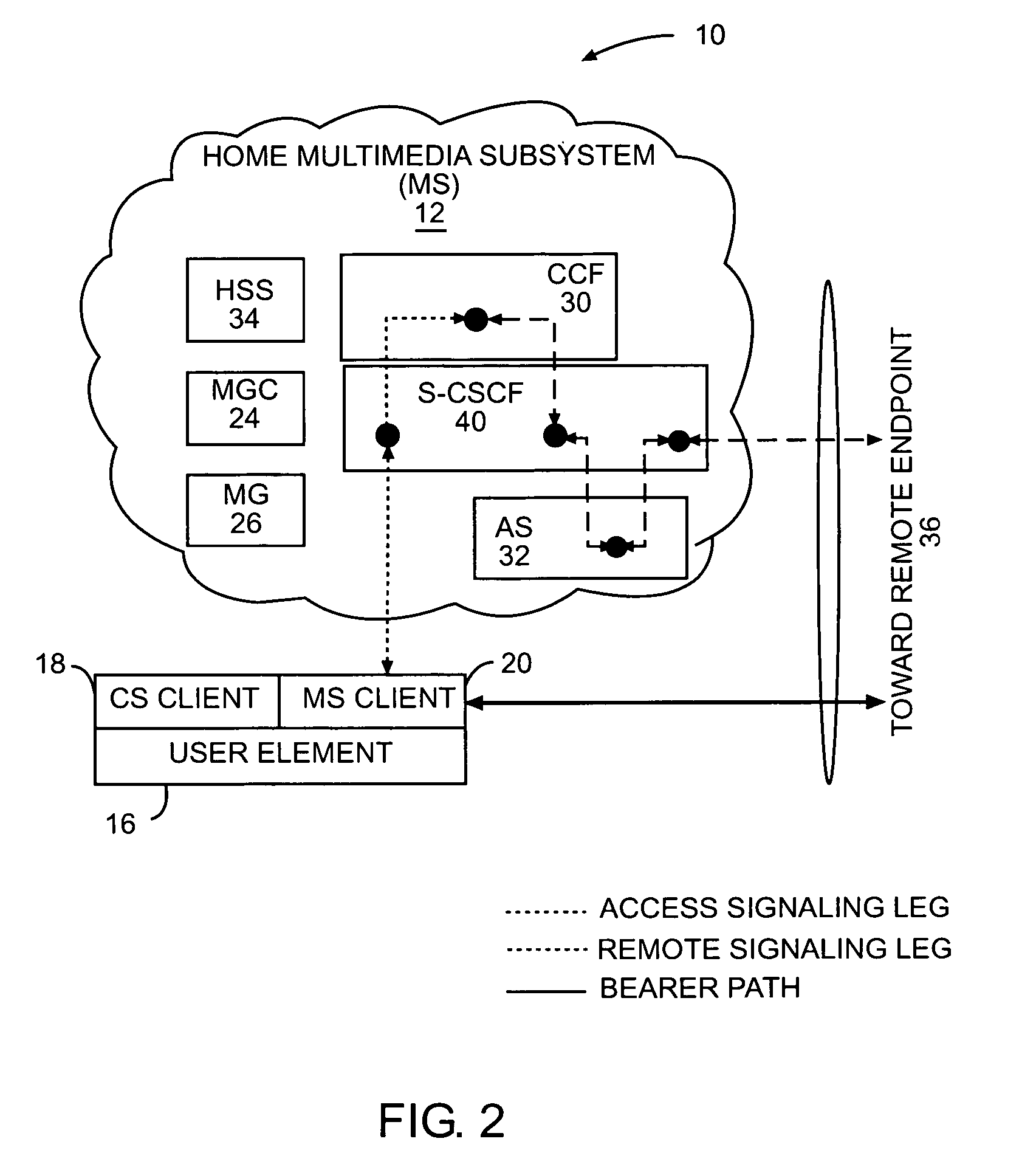
Circuit-switched and multimedia subsystem voice continuity
ActiveUS20060209805A1Low costData switching by path configurationHybrid transportService controlThe Internet
The present invention moves service control, including call control, for a user element from a cellular network to a multimedia subsystem (MS), such as the Internet Protocol (IP) Multimedia Subsystem (IMS). Call control is provided by the MS irrespective of whether the user element is using cellular or WLAN access for the call. Call control for originating and terminating calls in the CS or MS as well as transferring calls between a circuit-switched subsystem (CS) and MS is anchored at a continuity control function (CCF) in the MS. All call signaling for the call is passed through the CCF. The CCF is a service provided in the user element's home MS and anchors the user element's active CS calls and MS sessions to enable active roaming across the CS and MS.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
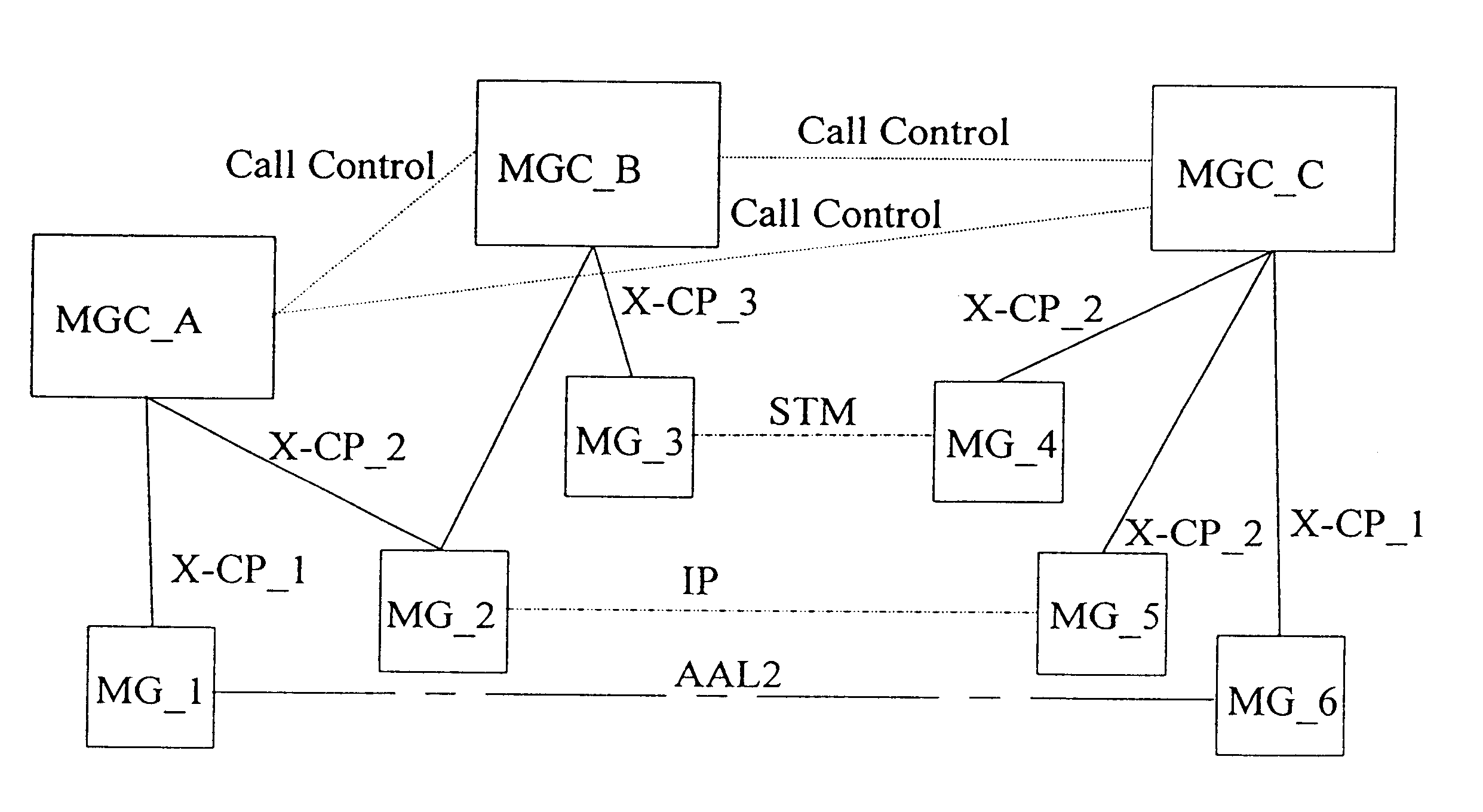
System and method for negotiation of multi-media capabilities across networks
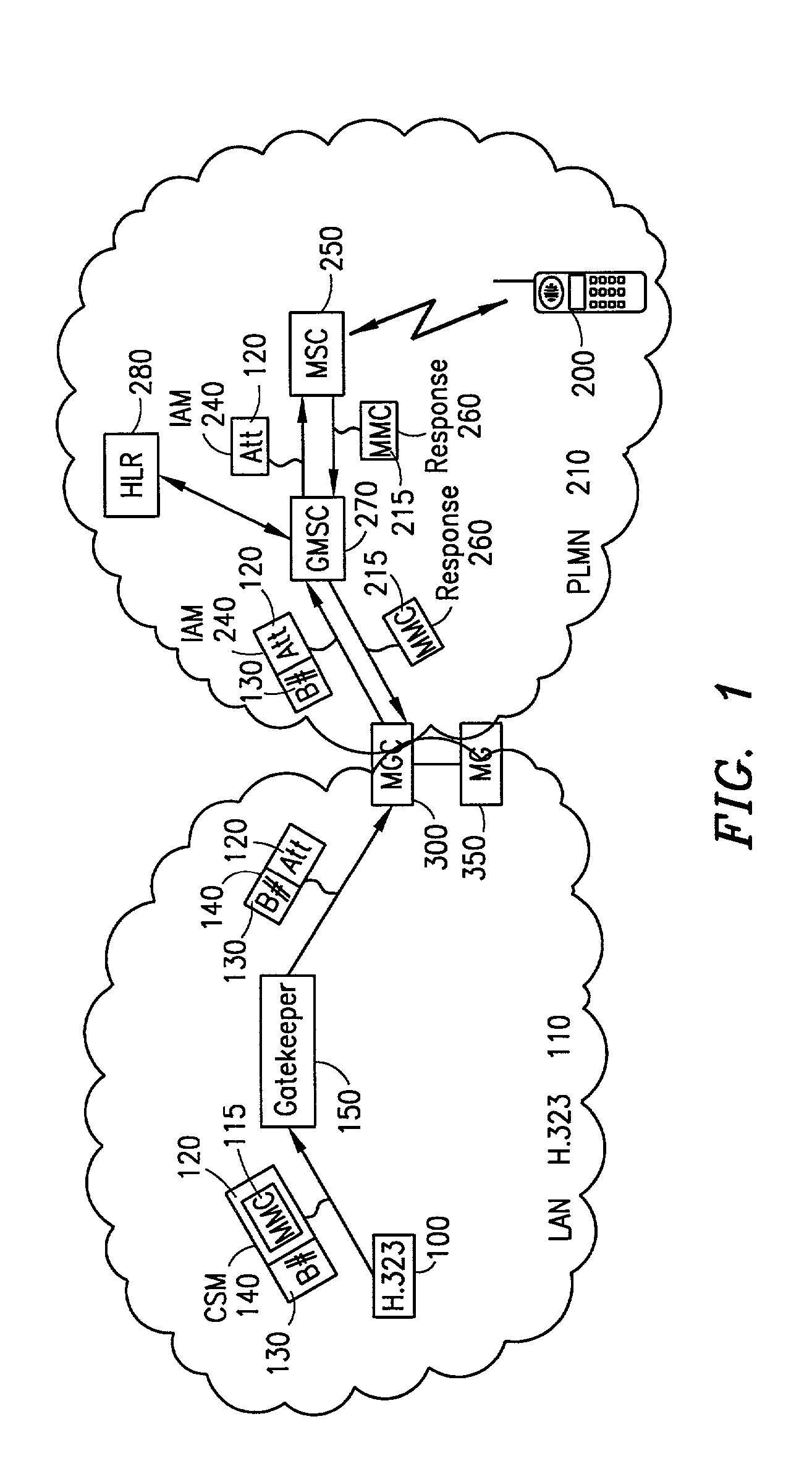
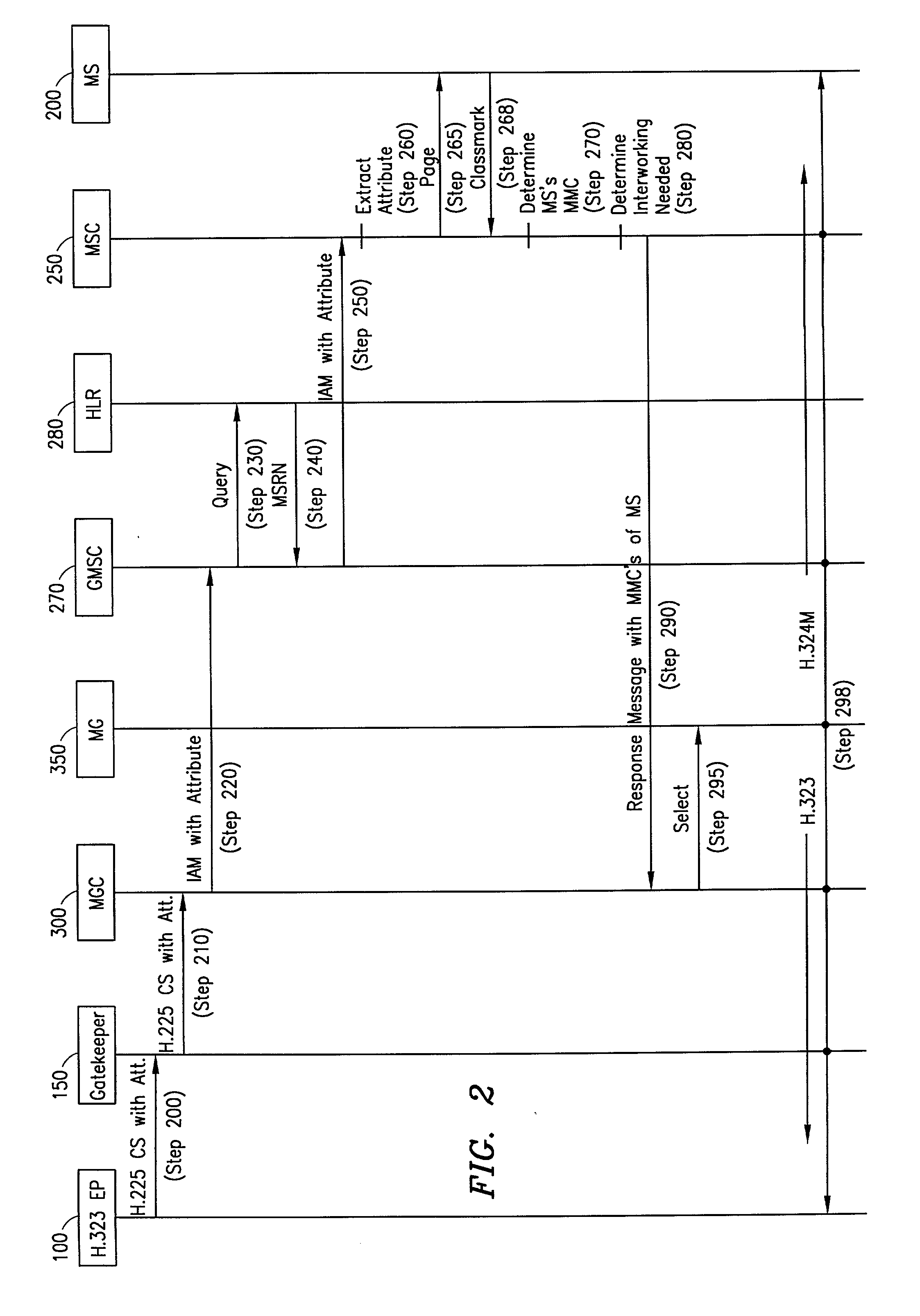
A telecommunications system and method is disclosed for converting between networks for multi-media purposes by adding an attribute to the call control protocol to indicate the multi-media coding of the calling subscriber. This attribute is used to negotiate the multi-media coding between the different nodes involved in a call. Based on the negotiation, various Media Gateways (MG) can be selected to perform the necessary interworking.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com