Patents
Literature
202 results about "Frame Relay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
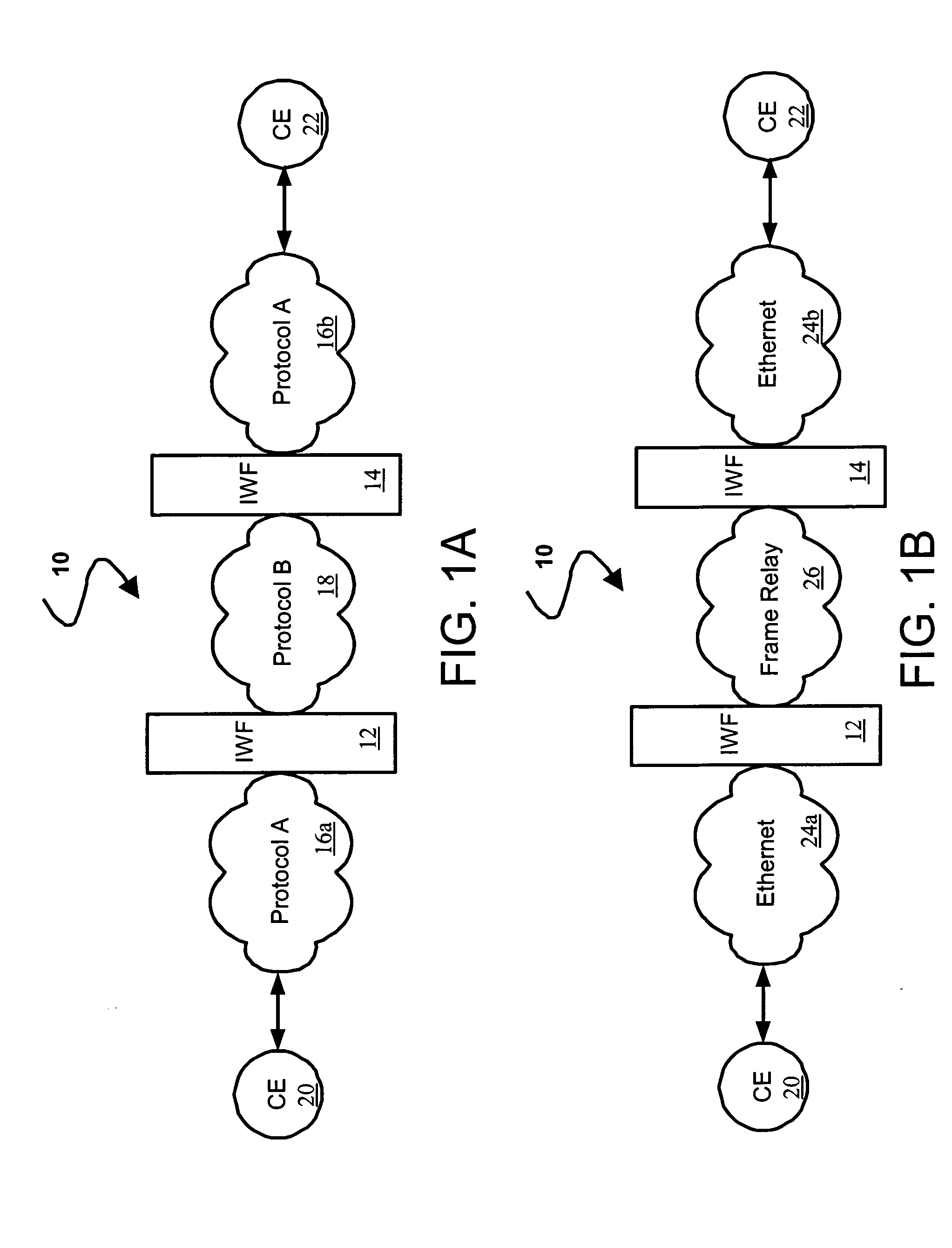
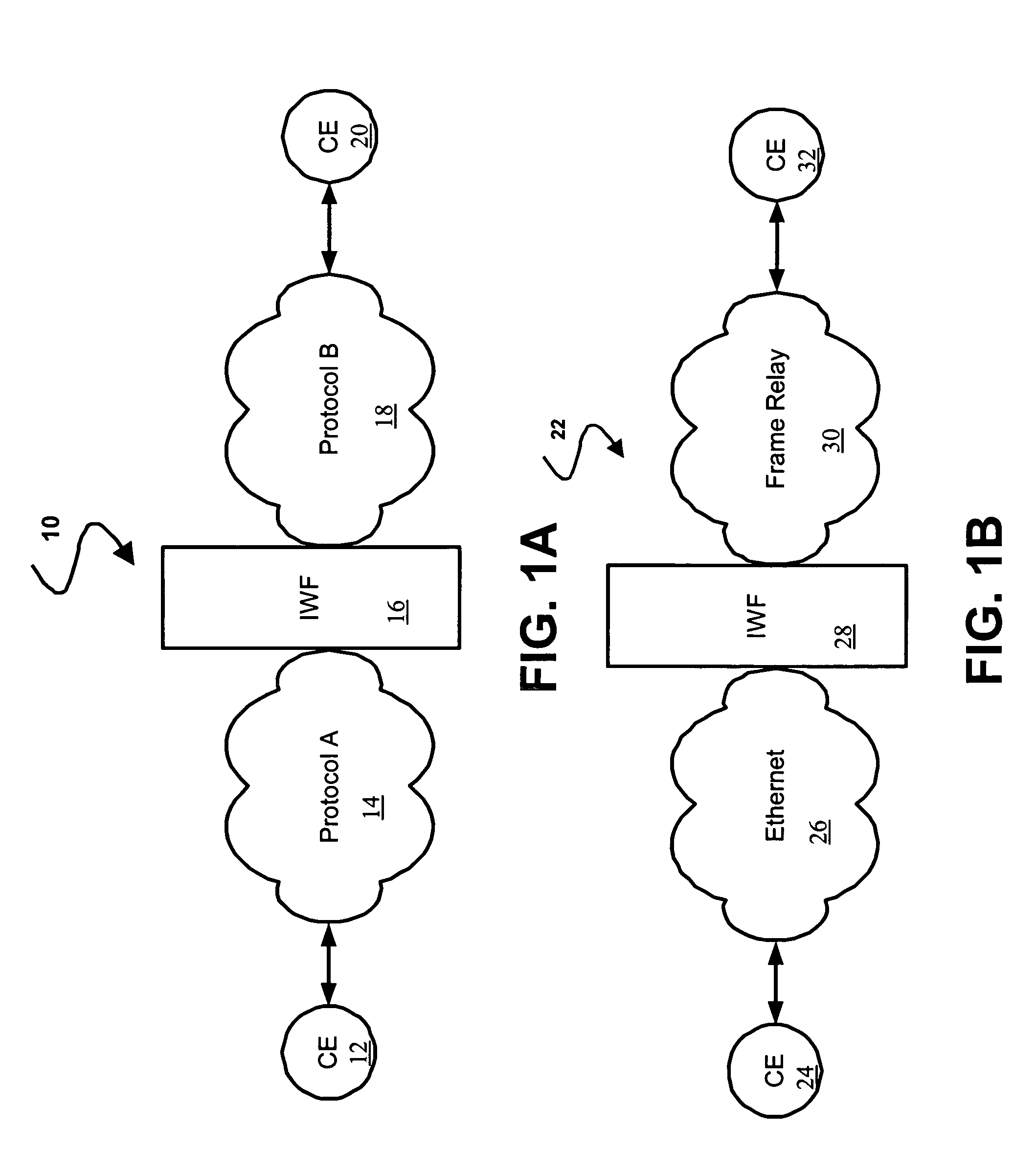
Frame Relay is a standardized wide area network technology that specifies the physical and data link layers of digital telecommunications channels using a packet switching methodology. Originally designed for transport across Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) infrastructure, it may be used today in the context of many other network interfaces.
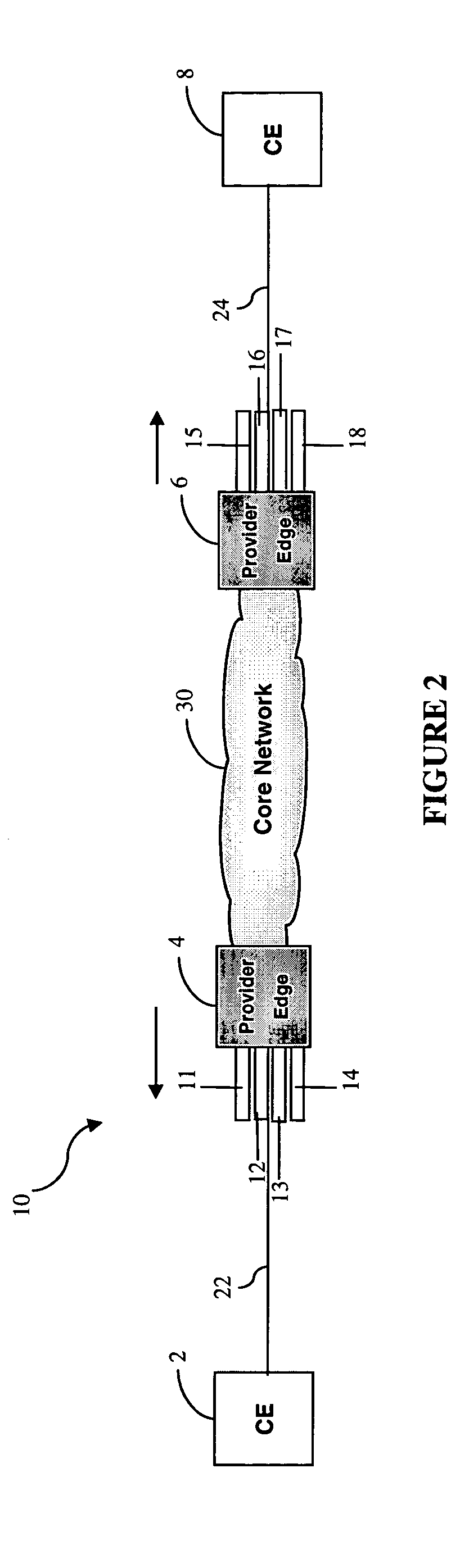
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
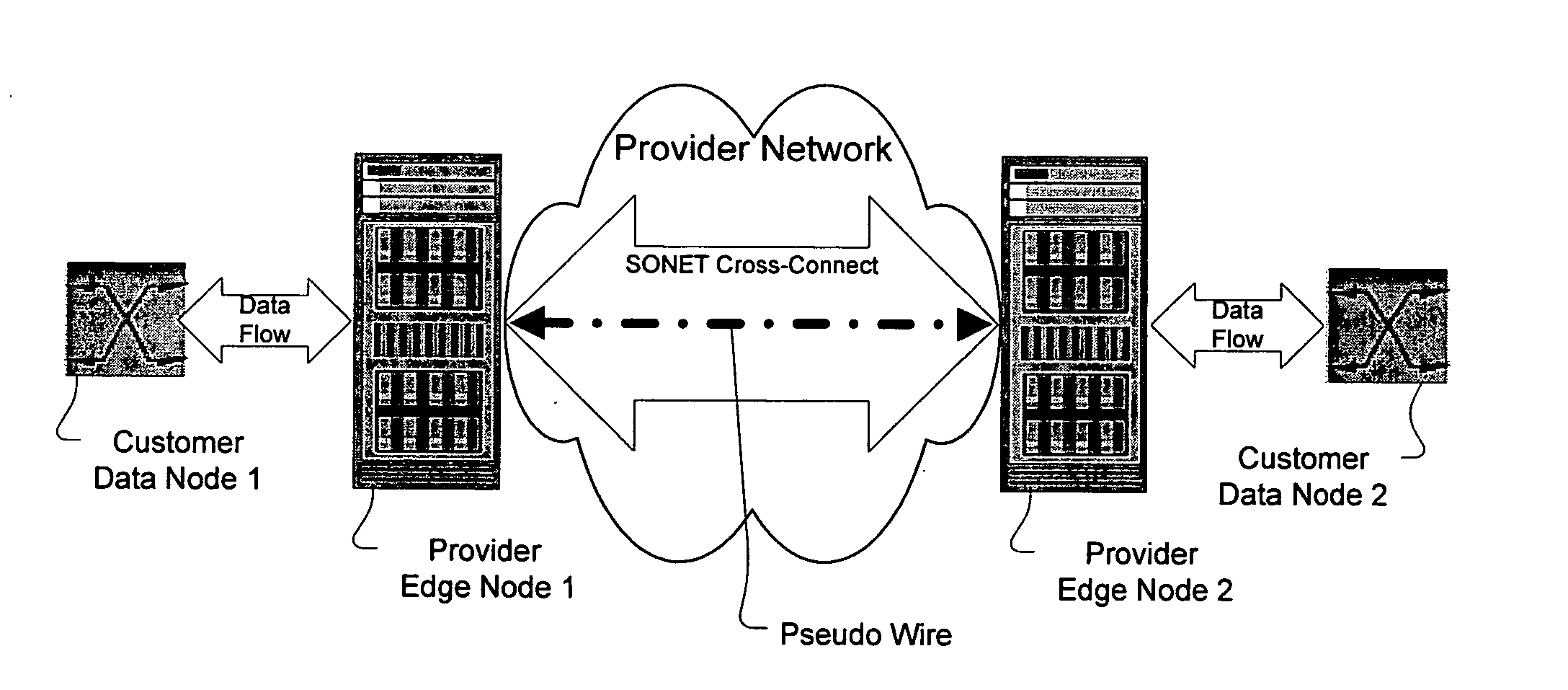
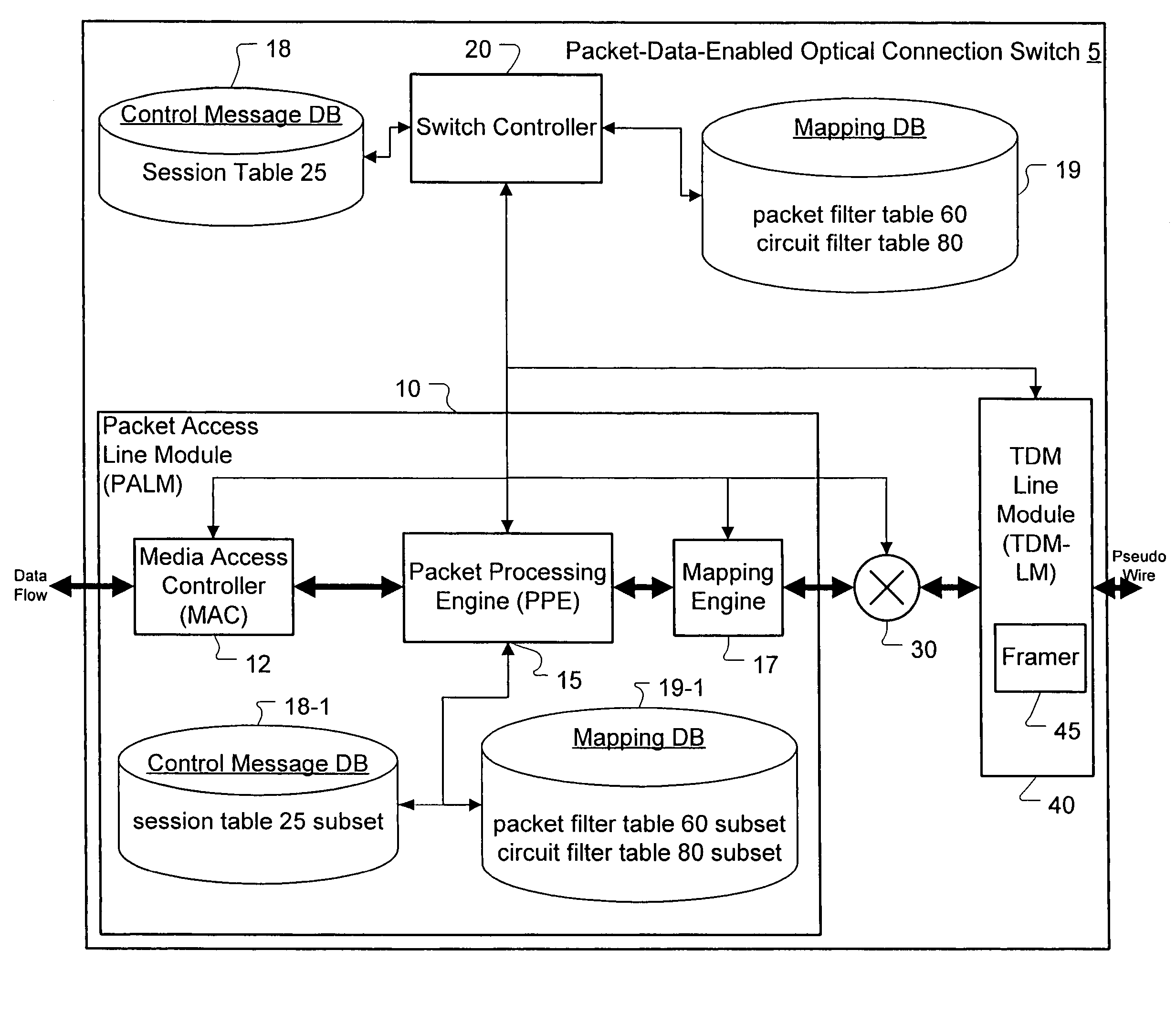
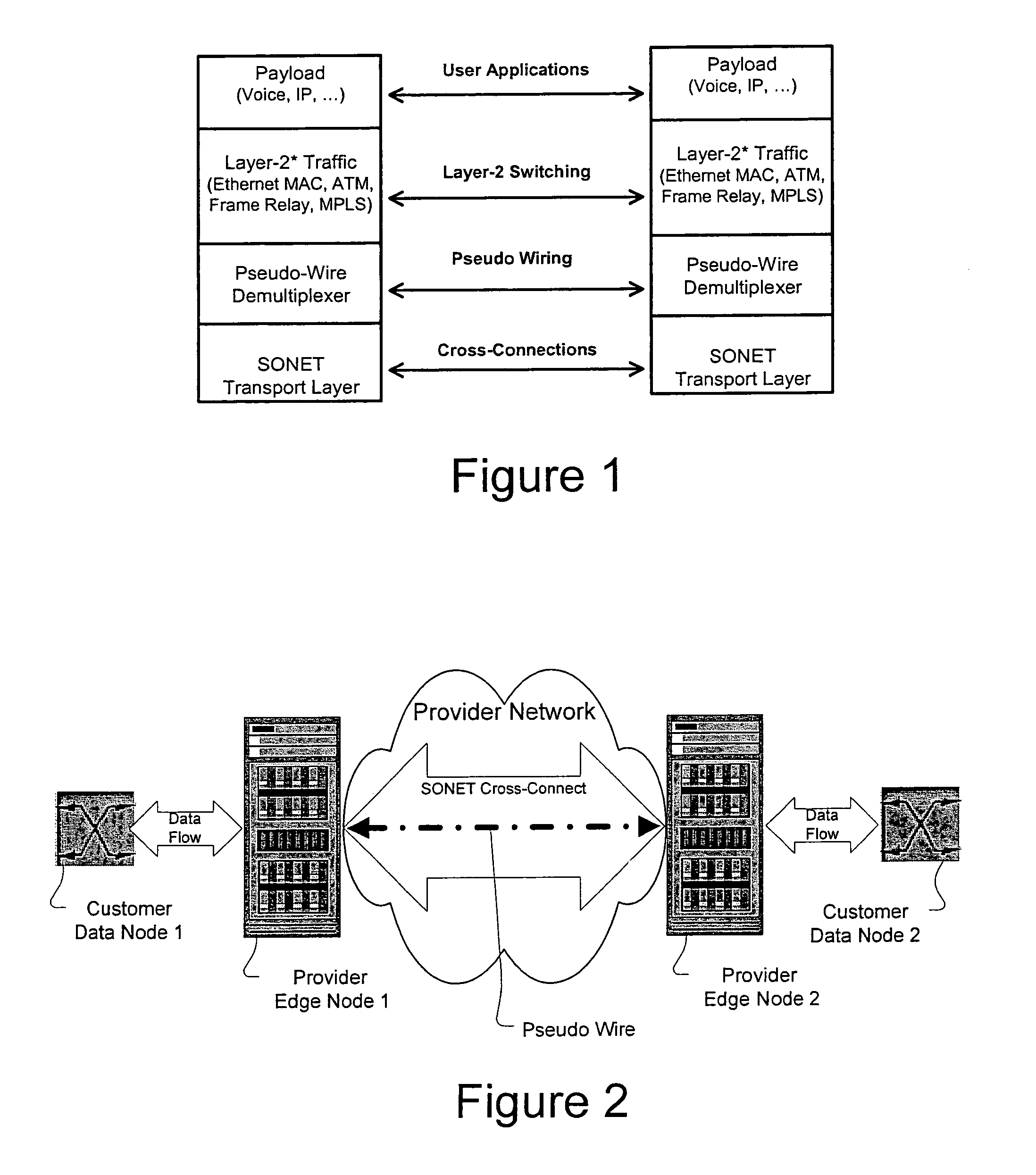
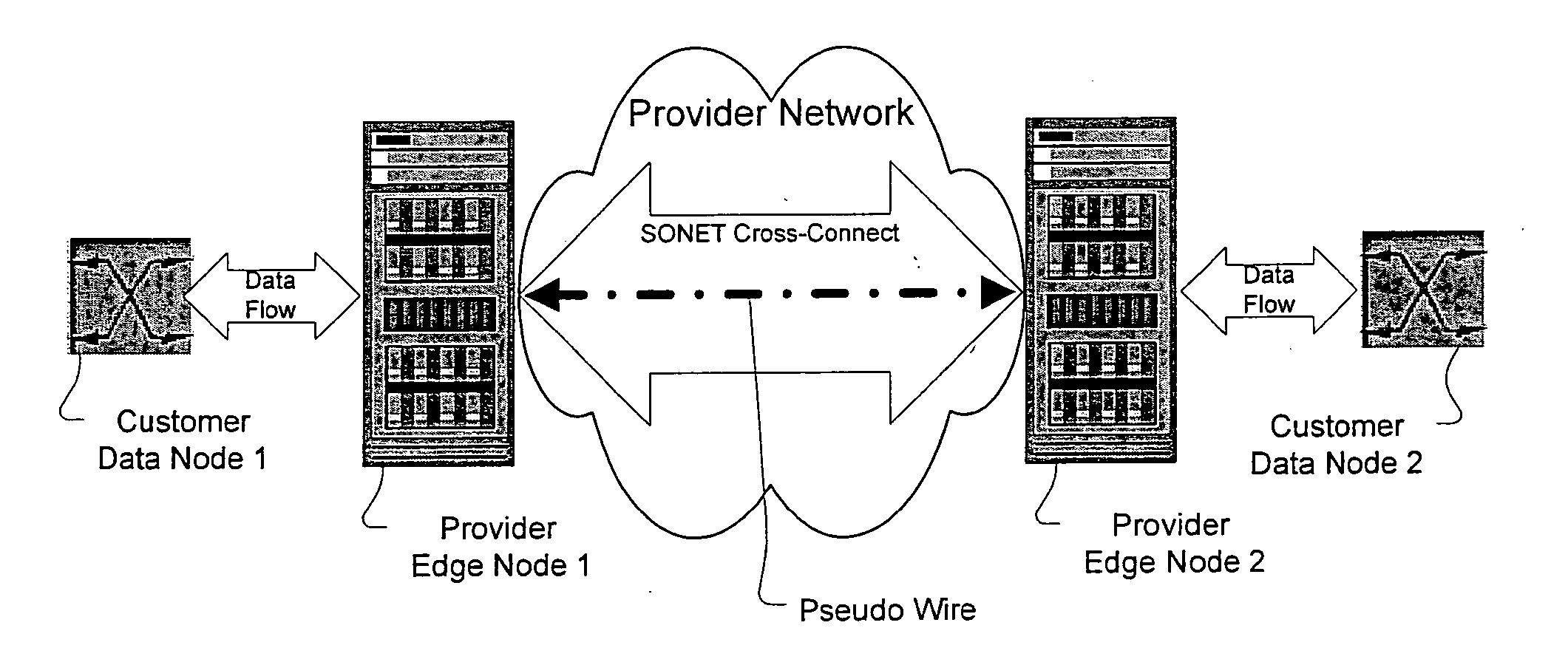
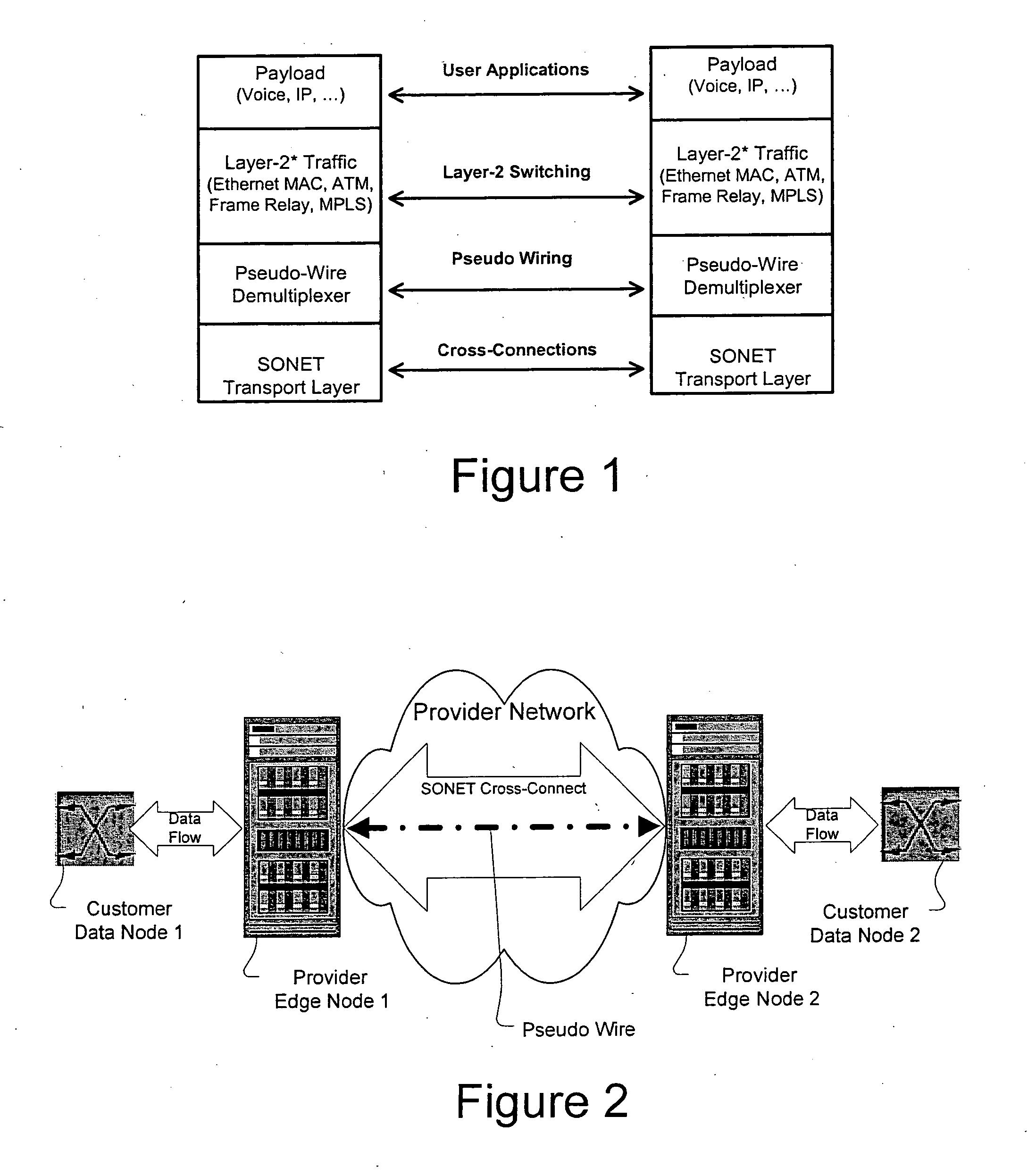
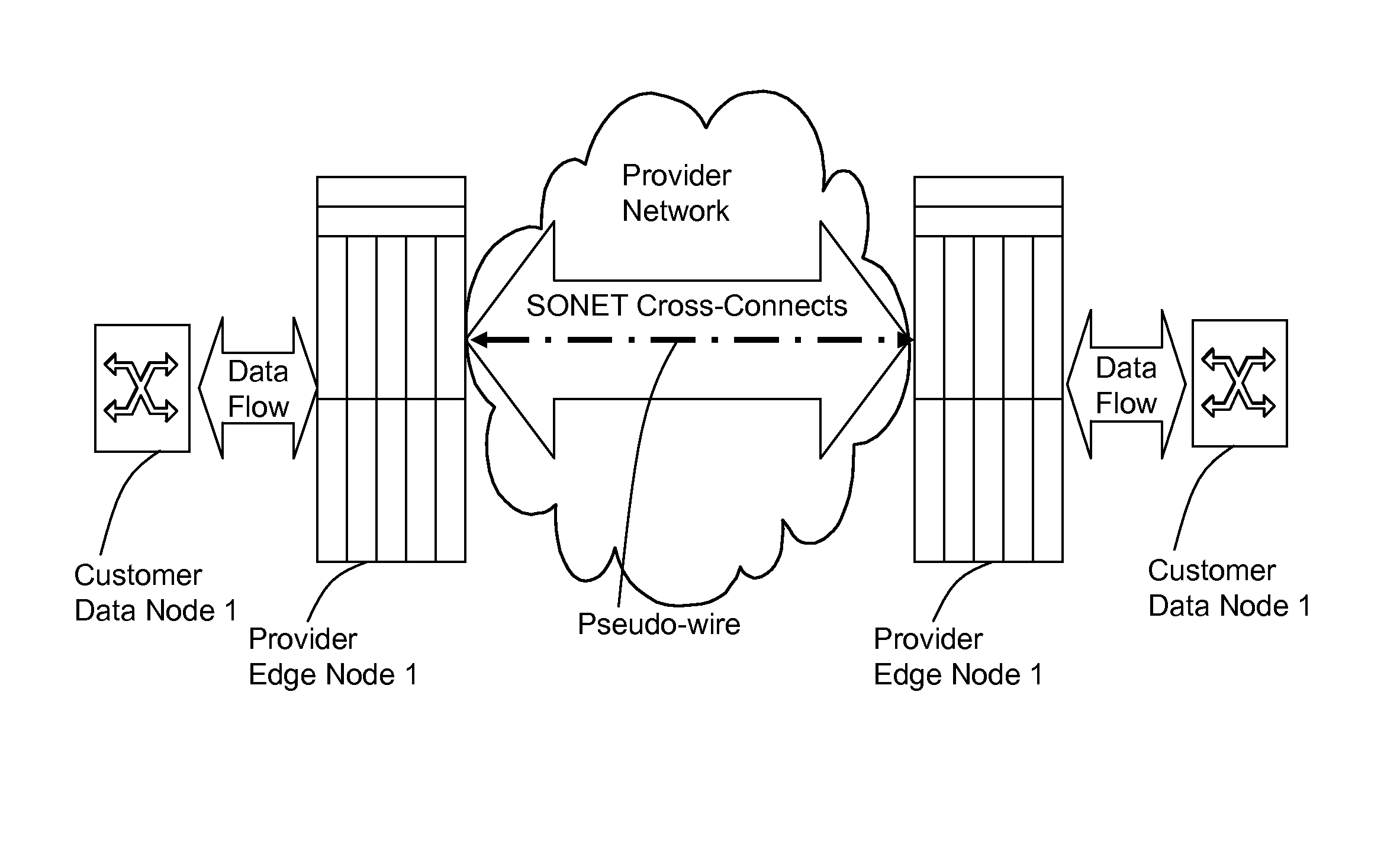
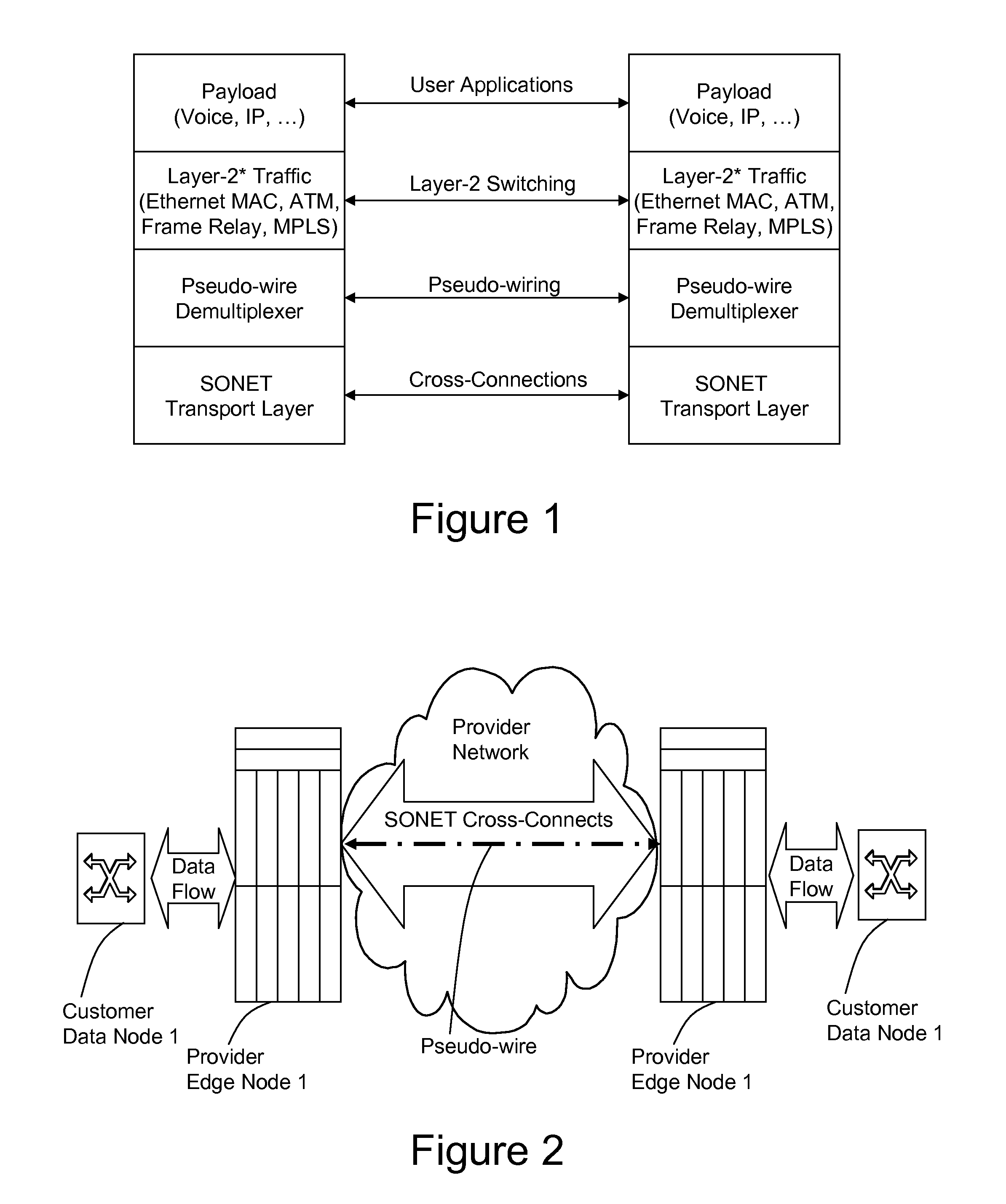
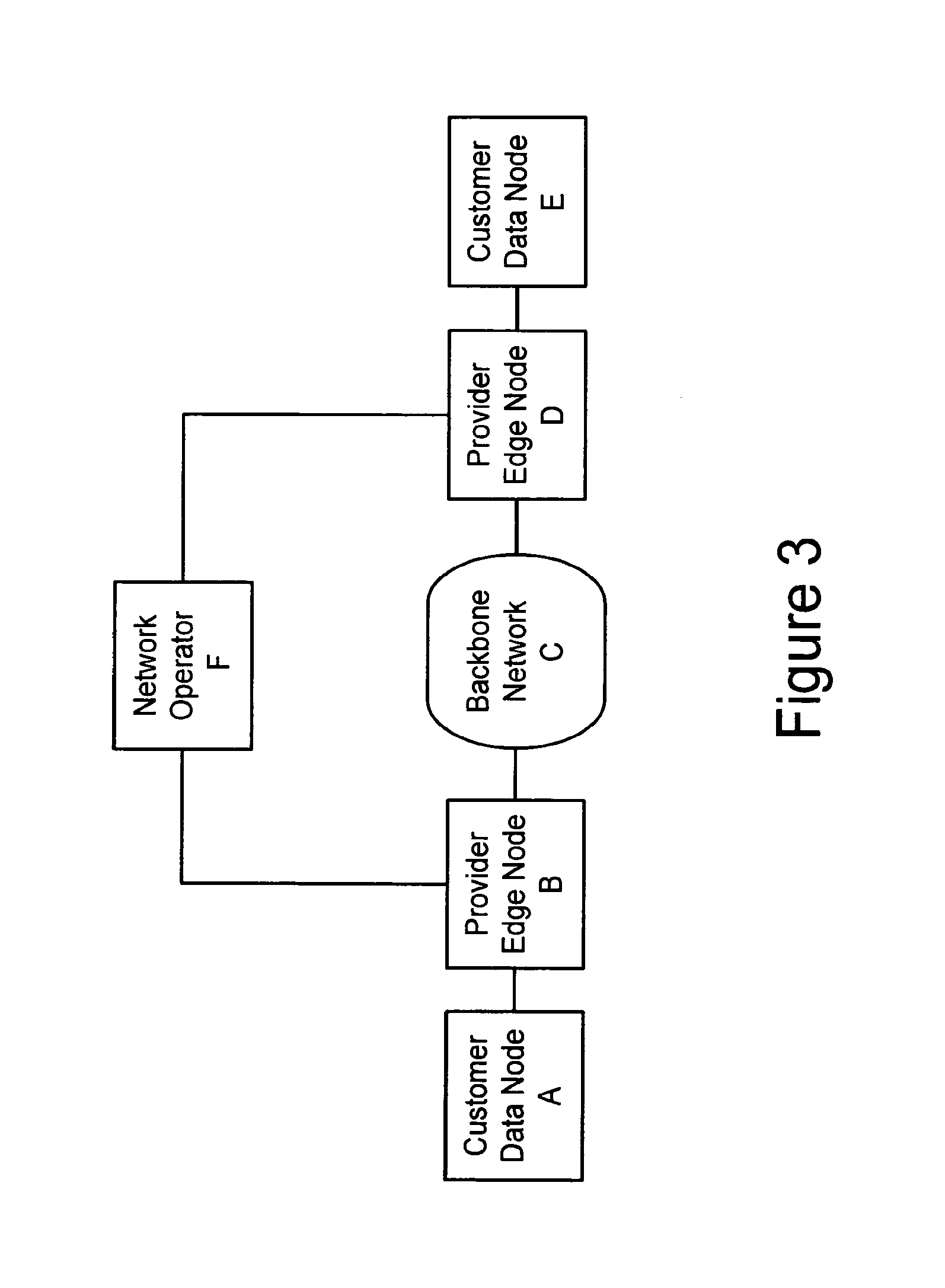
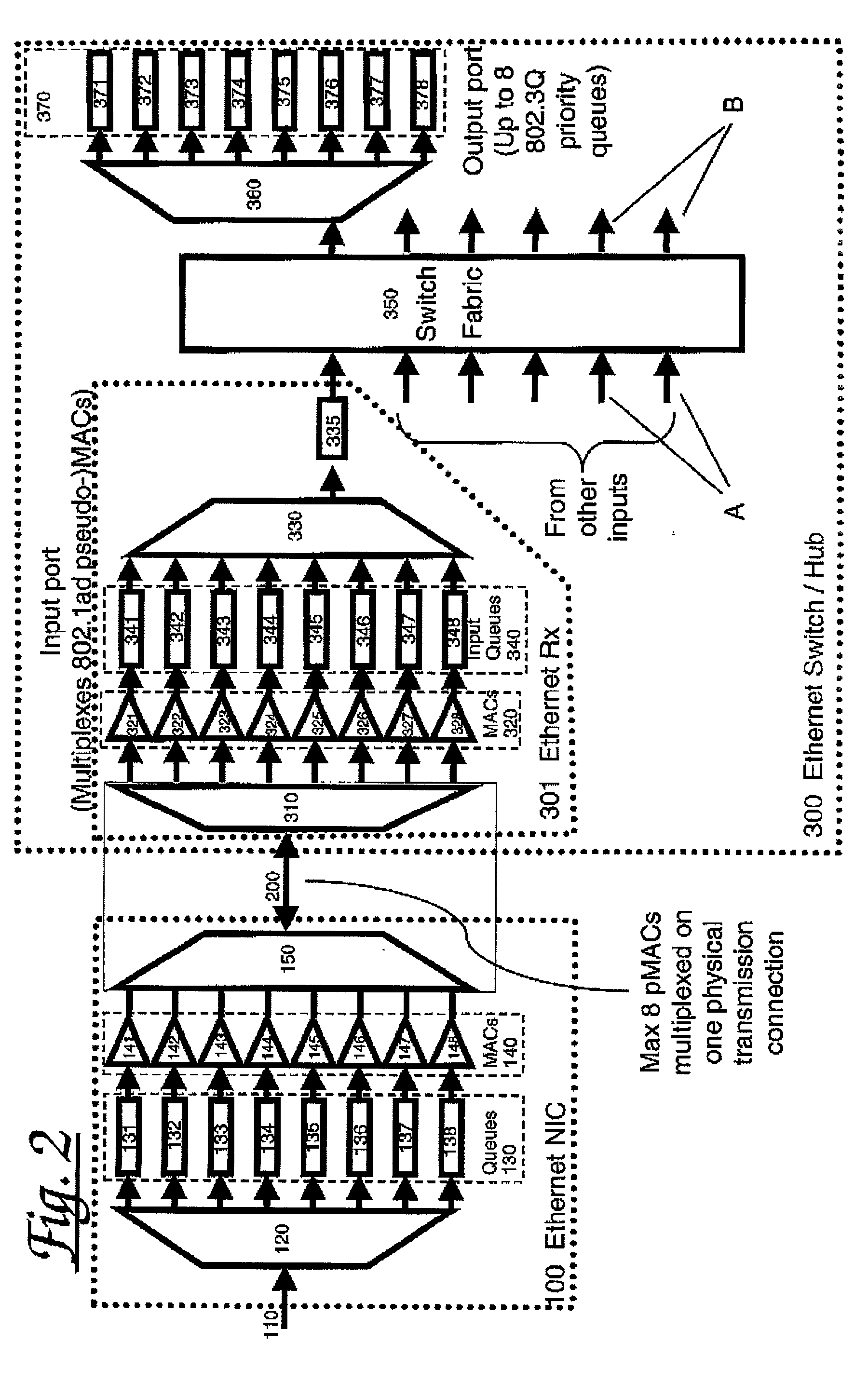
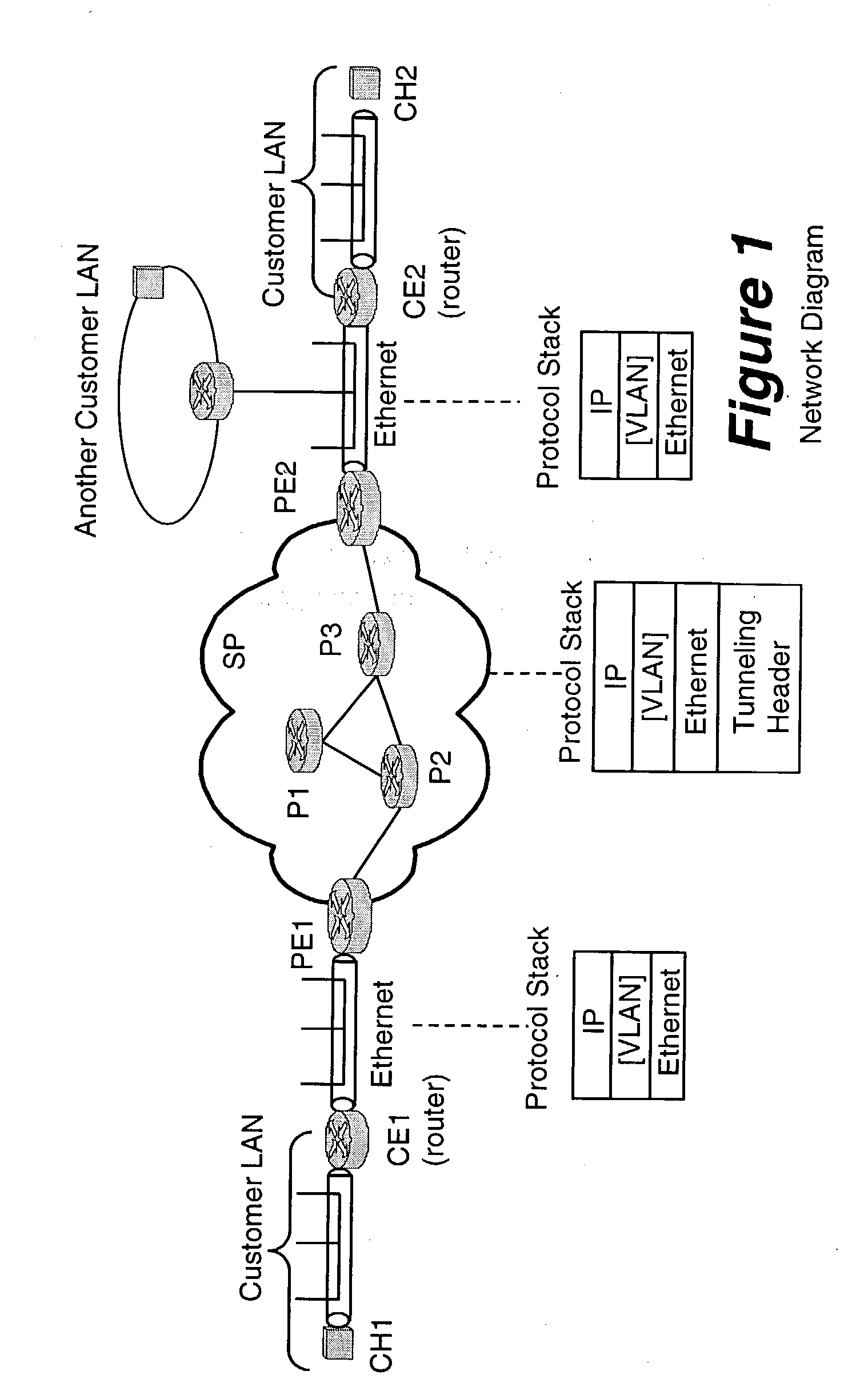
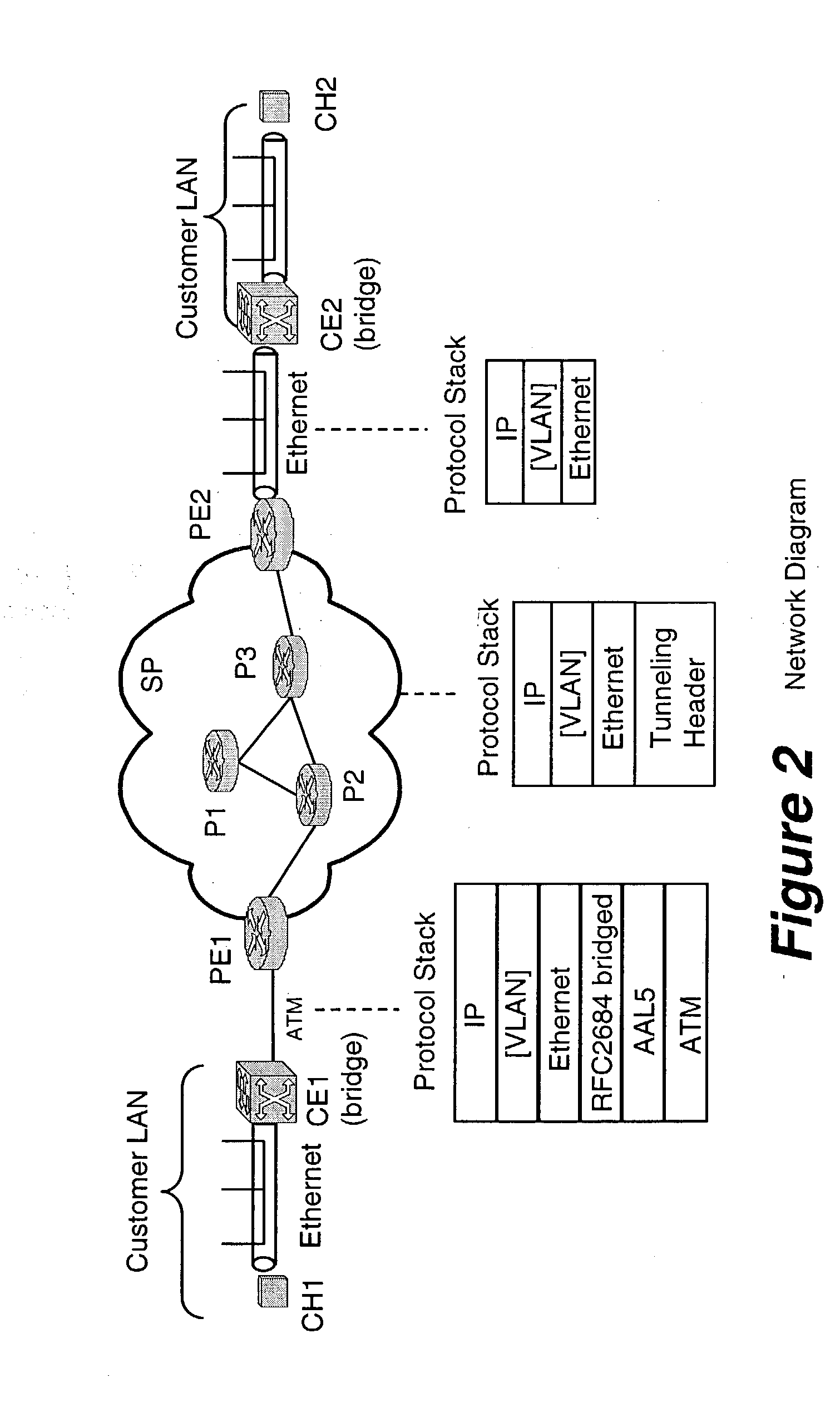
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
Authentication mechanisms for call control message integrity and origin verification
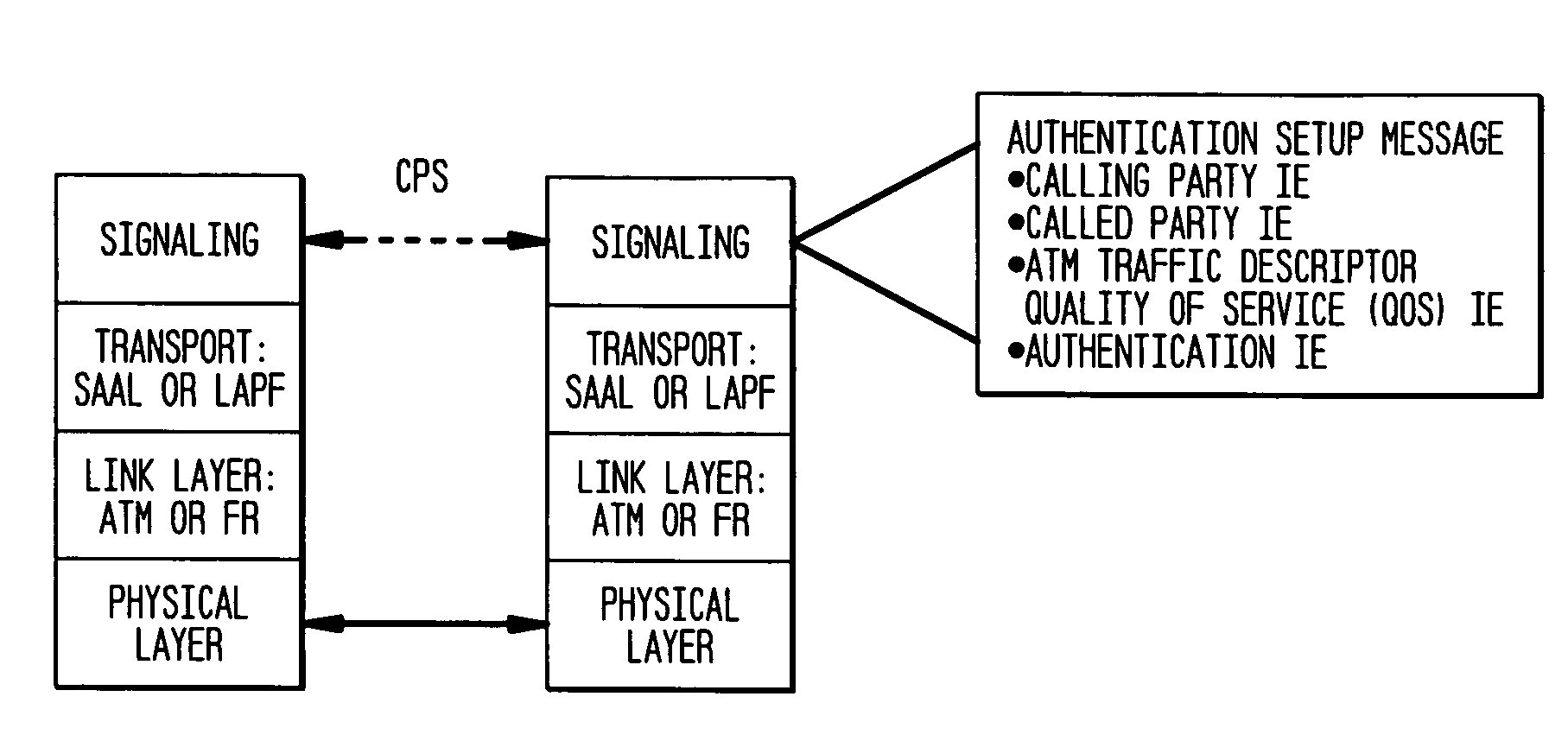
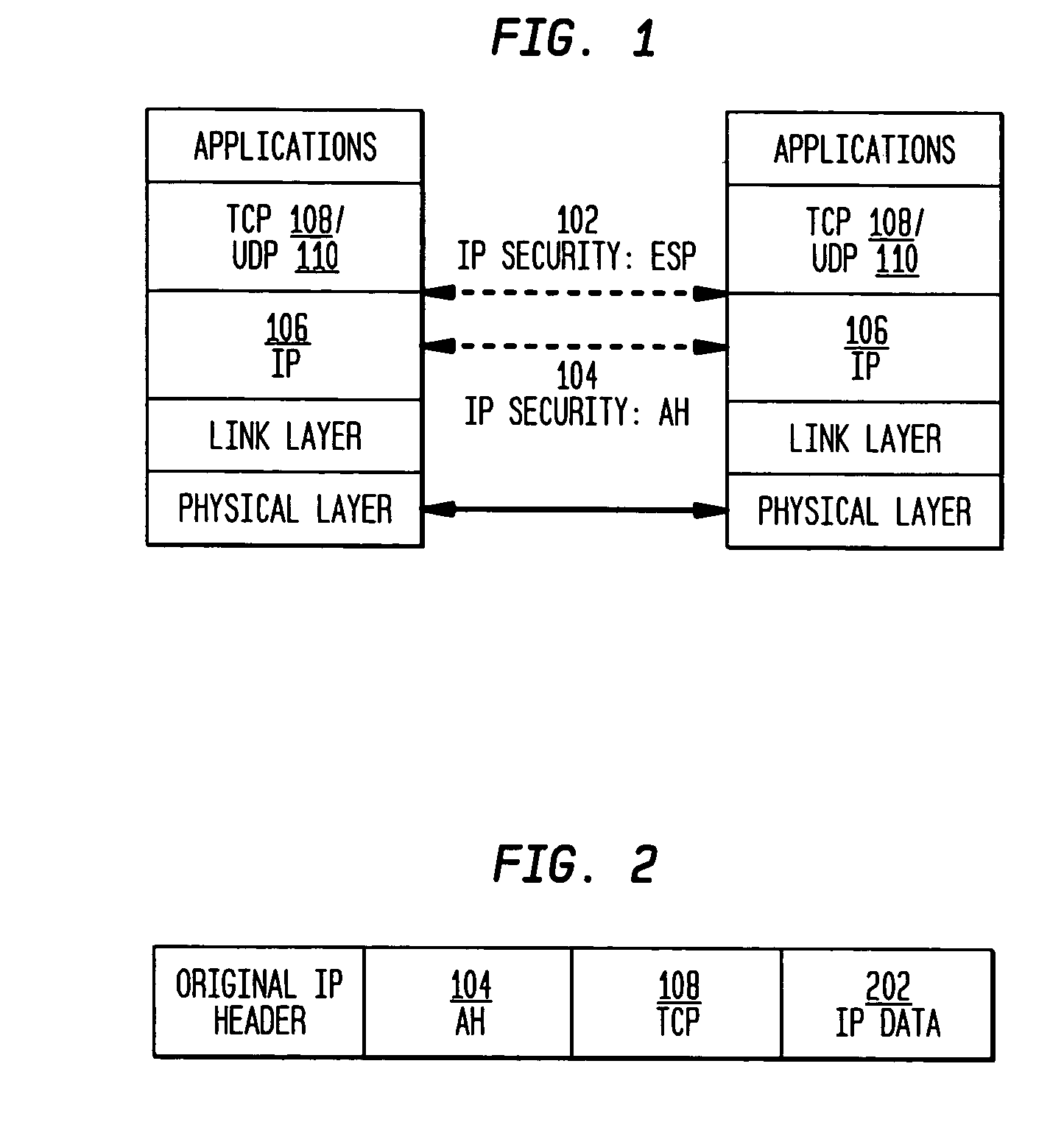
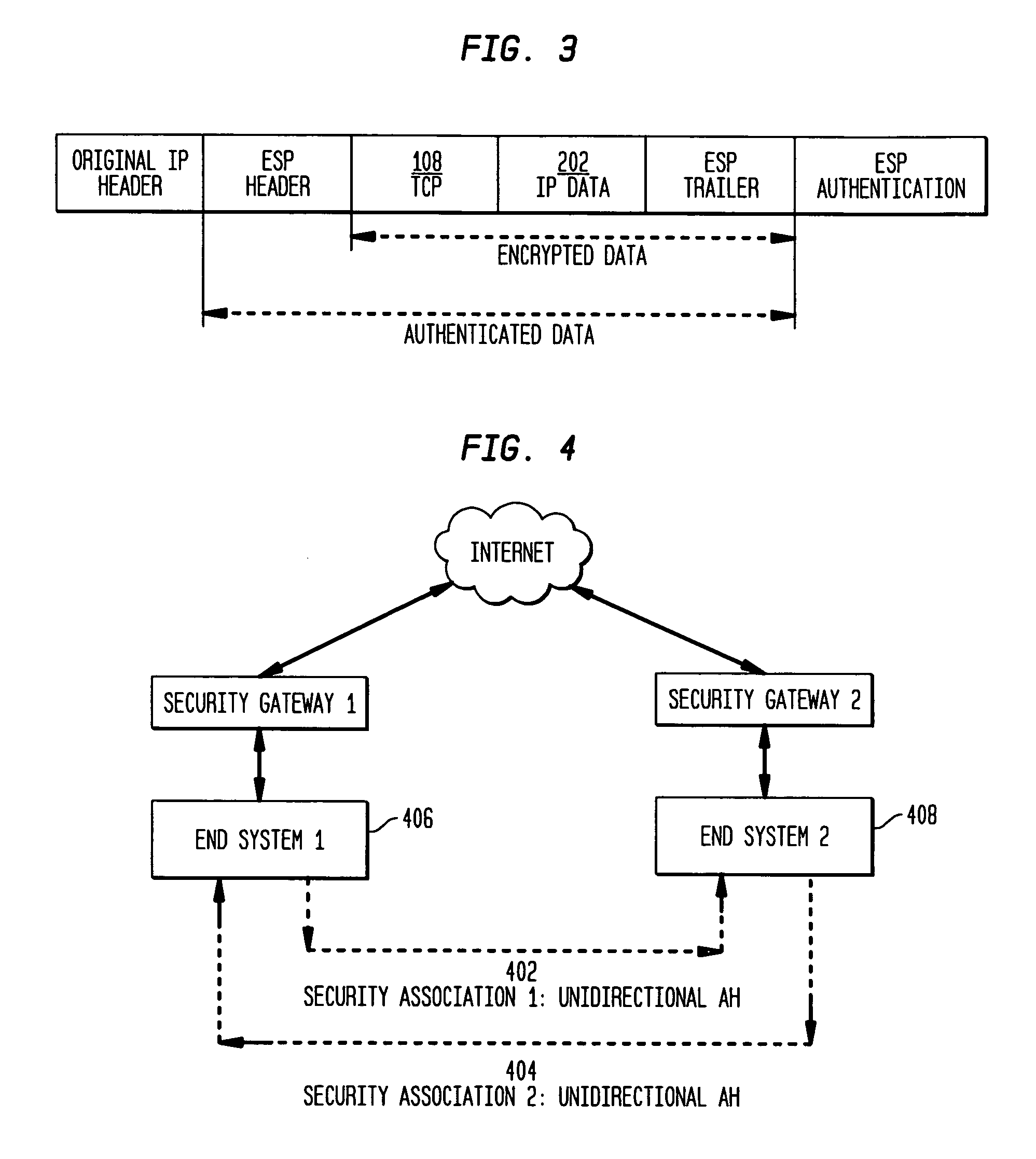
The present invention incorporates methodologies developed in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Protocol Security (IPSEC) Working Group into asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and frame relay (FR) signaling to provide message integrity and origin authentication. In one implementation the invention provides a virtual private network (VPN) infrastructure with call control message integrity, origin verification, and transit network filtering. The invention utilizes a set of control plane messages based on the IPSEC authentication header (AH) methodology to provide these security mechanisms for ATM and FR network switching equipment and signaling protocols. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
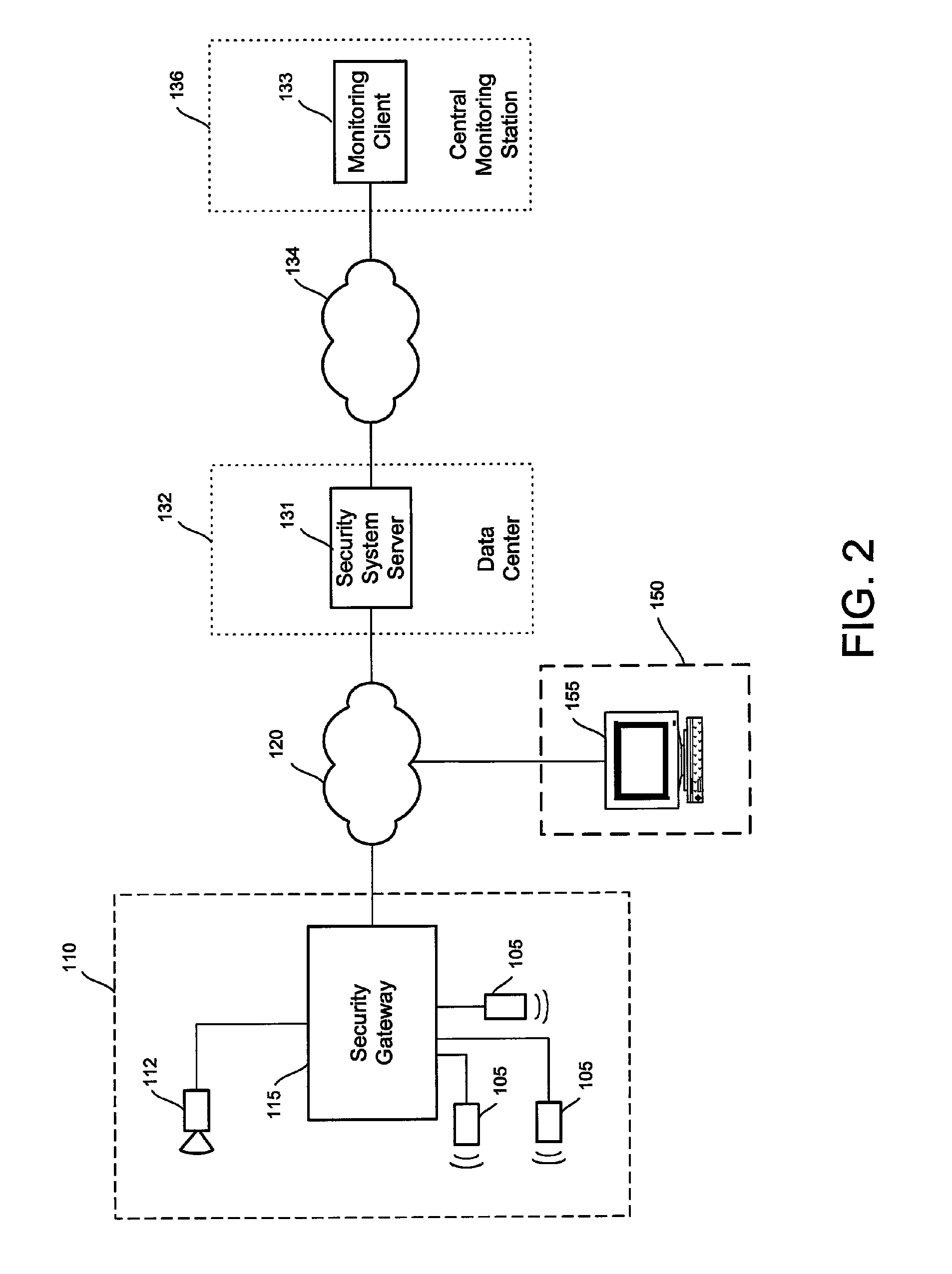
Video security system
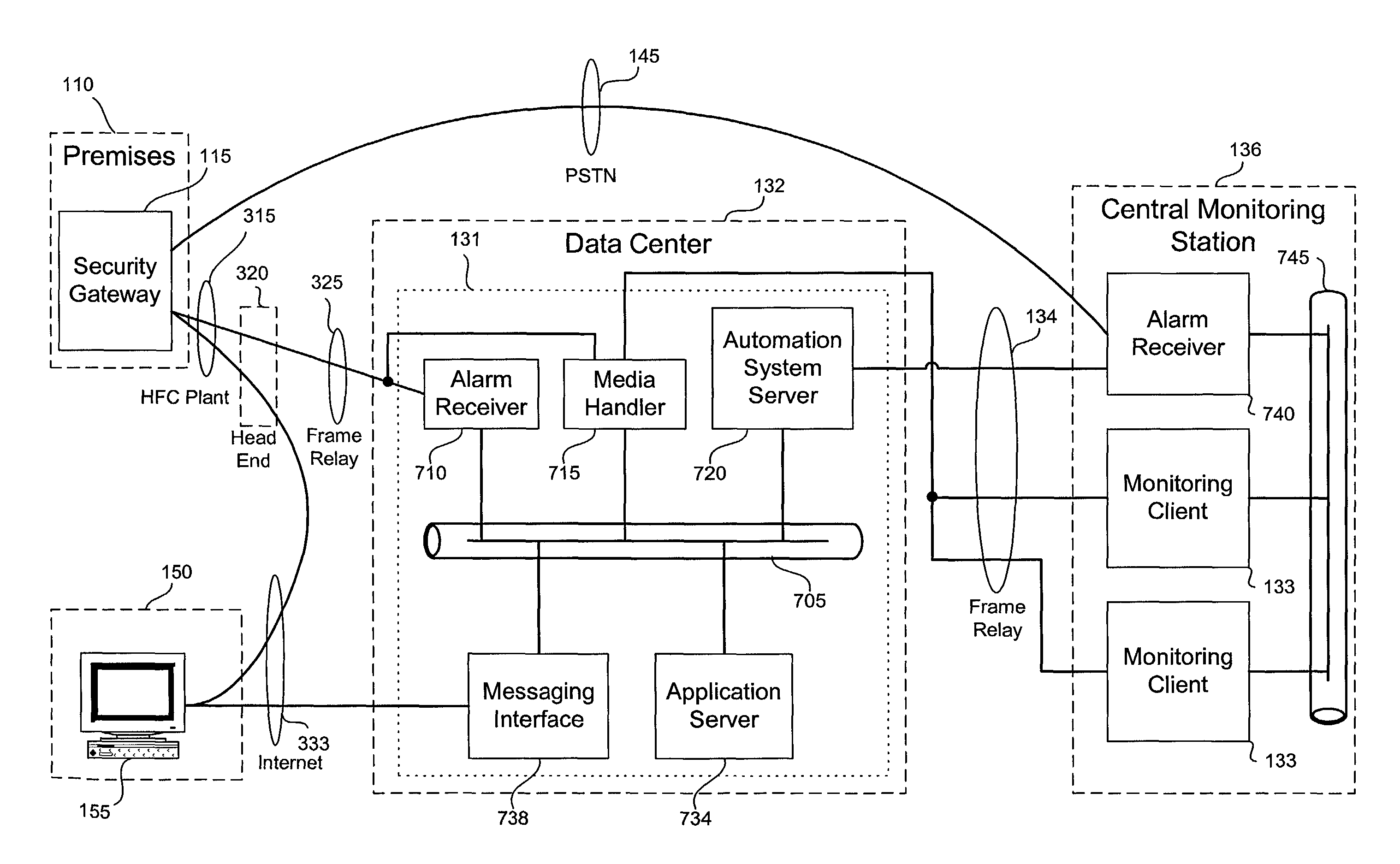
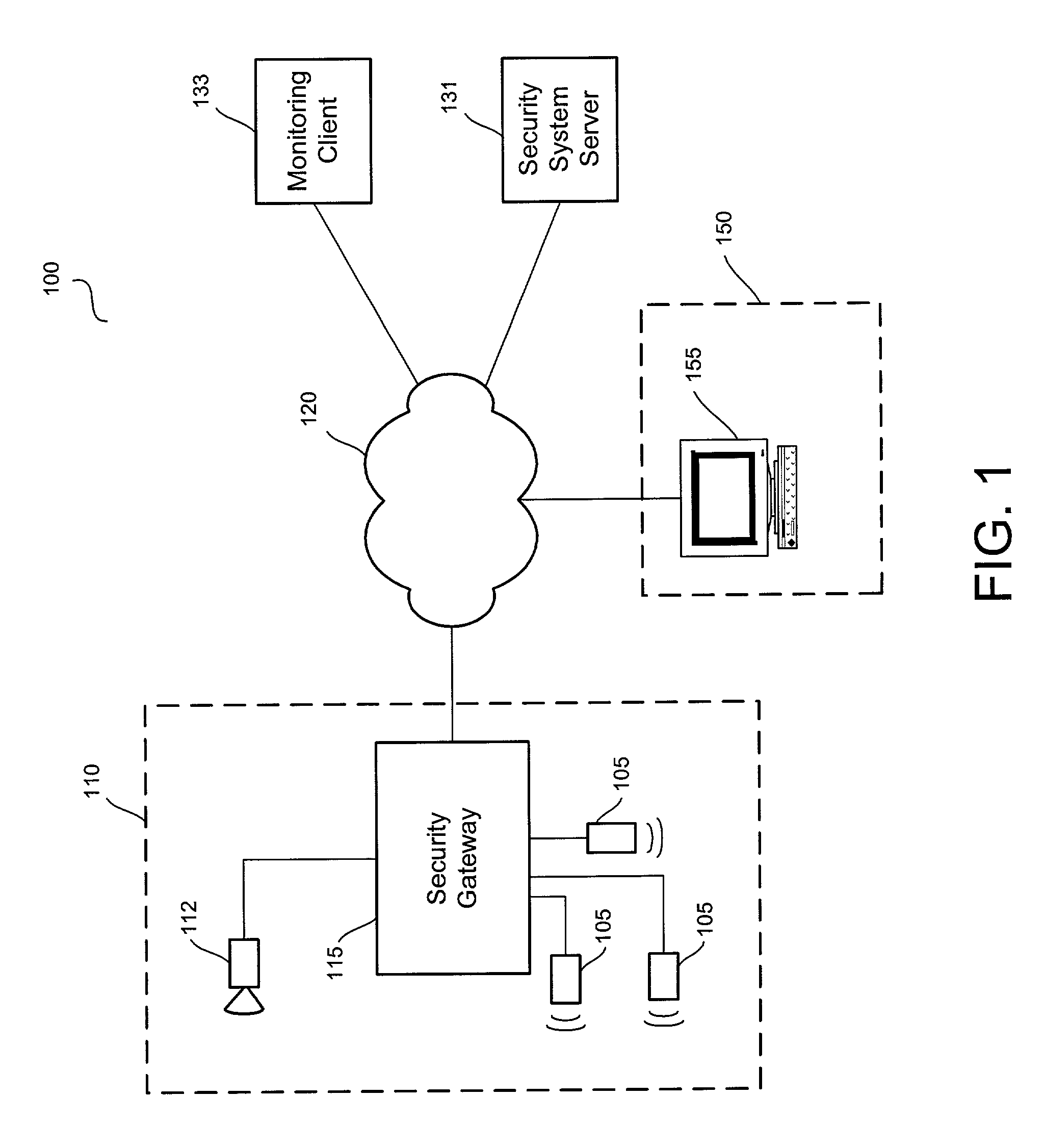
A video security system for the remote verification and monitoring of conditions surrounding an alarm signal. A security gateway at the monitored premises detects alarm conditions and transmits information and video relating to the alarm condition to personnel at a central monitoring station in substantially real time for verification. Various embodiments of the system transmit alarm information to the central monitoring station through hybrid-fiber coaxial, DSL, fiber-optic, high-speed fixed wireless and mobile communications networks. The security system may include secondary alarm notification from the security gateway to the central monitoring station via a second network, such as IP, Ethernet, Internet, frame relay, public switched telephone, wireless, and mobile communications networks.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
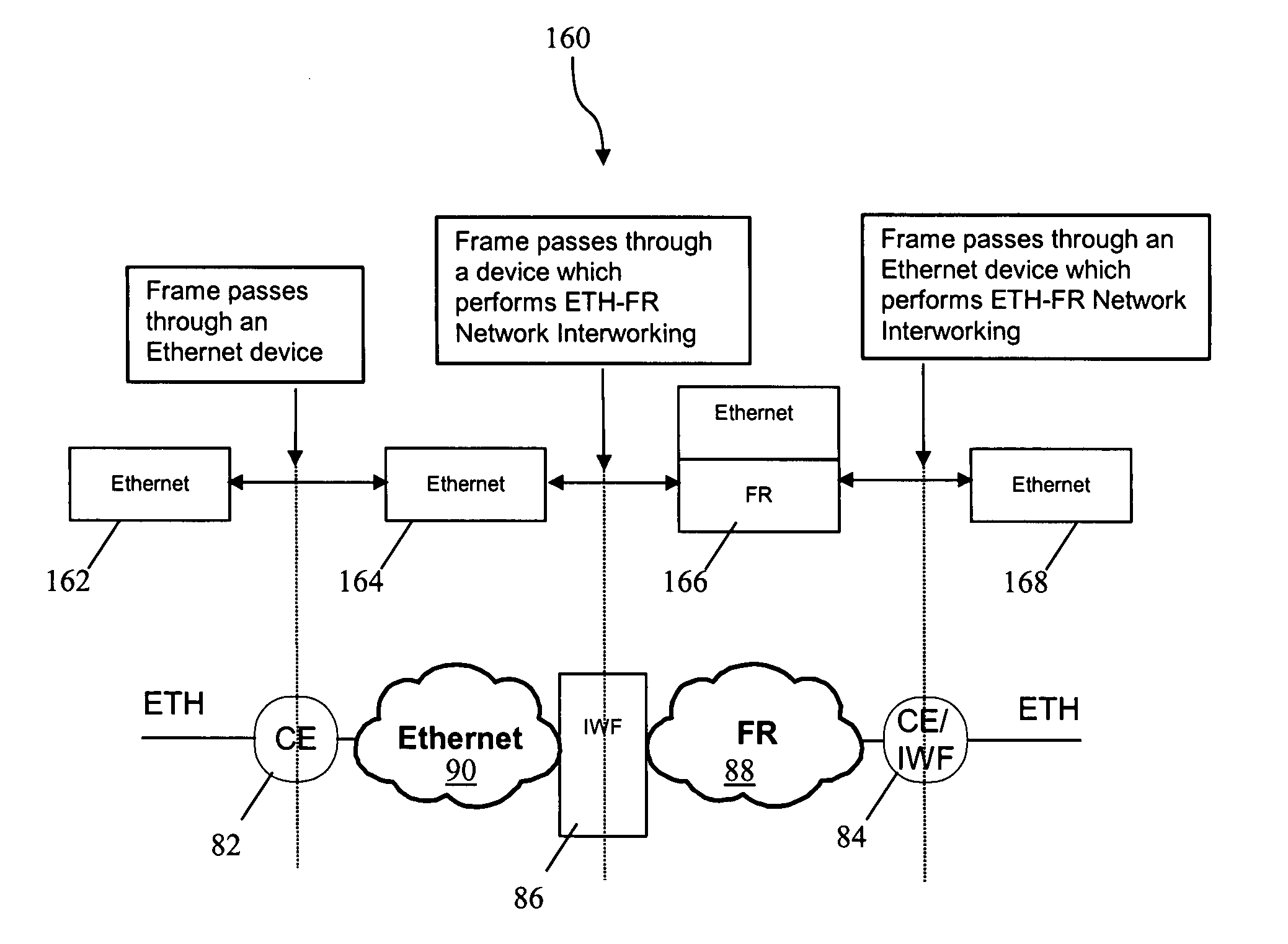
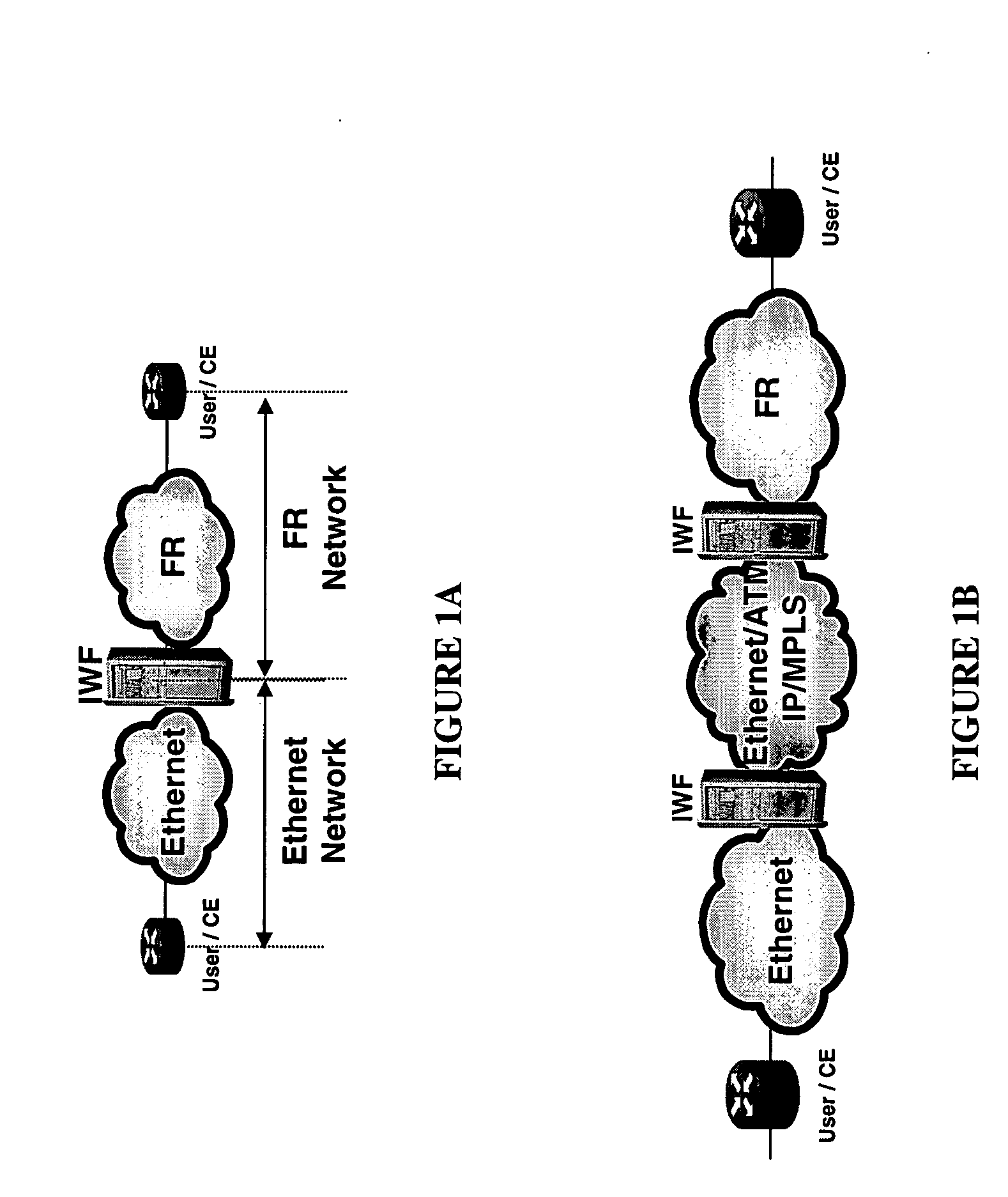
Method and system for ethernet and frame relay network interworking
InactiveUS20050157751A1Different level of performanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFrame RelayEthernet frame
A method and system for interworking between an Ethernet communication network and a frame relay network, in which a first network interface is operable to communicate with the Ethernet communication network using an Ethernet communication protocol. A second network interface is operable to communicate with the frame relay communication network using a frame relay protocol. A processing unit is in communication with the first network interface and the second network interface, in which the processing unit encapsulates frames received from the Ethernet network into frame relay frames, decapsulates frames received from the frame relay network to recover Ethernet frames and maps parameters corresponding to the received one of the frame relay and Ethernet frames into the other of the frame relay and Ethernet frames, the mapped parameters including connection configuration control plane information and data plane parameters corresponding to individual frames.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for transporting packet data over an optical network
ActiveUS6985488B2Time-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsFrame RelayTransport layer
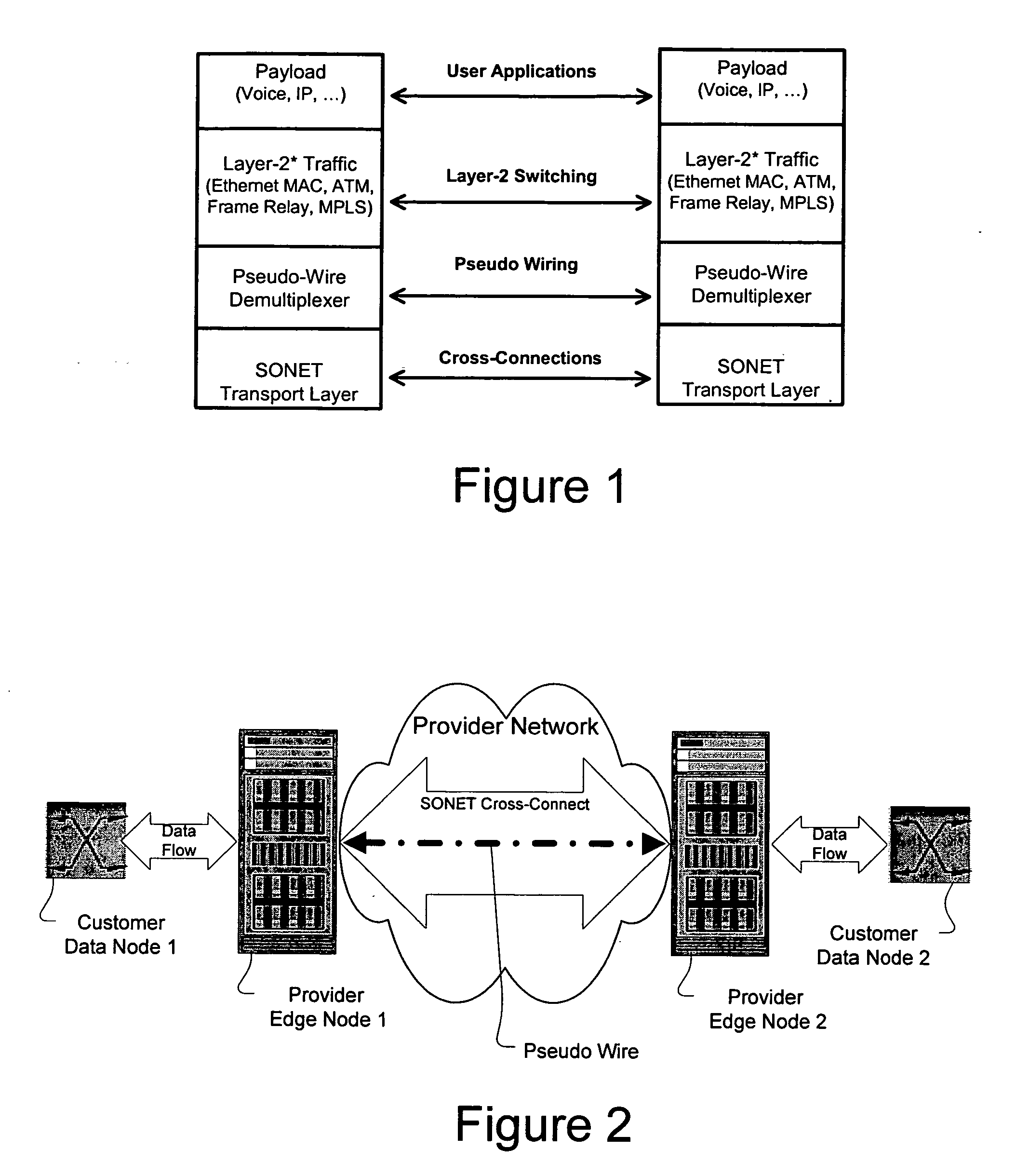
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over SONET, SDH, or OTN transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes “pseudo-wires” between, for example, SONET switches and directly on top of the SONET layer. The method may implement MPLS signaling protocols on traditional SONET switches for the purpose of aggregating layer-2 frames from the transport network edges, while the transport network itself is independent from IP and MPLS routing. This approach provides a number of advantages to the network carriers in terms of operation and equipment expense reduction. To enable the transport network to be independent from IP and MPLS, and avoid subsequent IP control message processing inside the networks, an edge-to-edge “tunneling” mechanism is designed to transmit control messages as a part of the SONET (or SDH or OTN) frame payload.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for transporting packet data over an optical network
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over SONET, SDH, or OTN transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, SONET switches and directly on top of the SONET layer. The method may implement MPLS signaling protocols on traditional SONET switches for the purpose of aggregating layer-2 frames from the transport network edges, while the transport network itself is independent from IP and MPLS routing. This approach provides a number of advantages to the network carriers in terms of operation and equipment expense reduction. To enable the transport network to be independent from IP and MPLS, and avoid subsequent IP control message processing inside the networks, an edge-to-edge "tunneling" mechanism is designed to transmit control messages as a part of the SONET (or SDH or OTN) frame payload.
Owner:CIENA
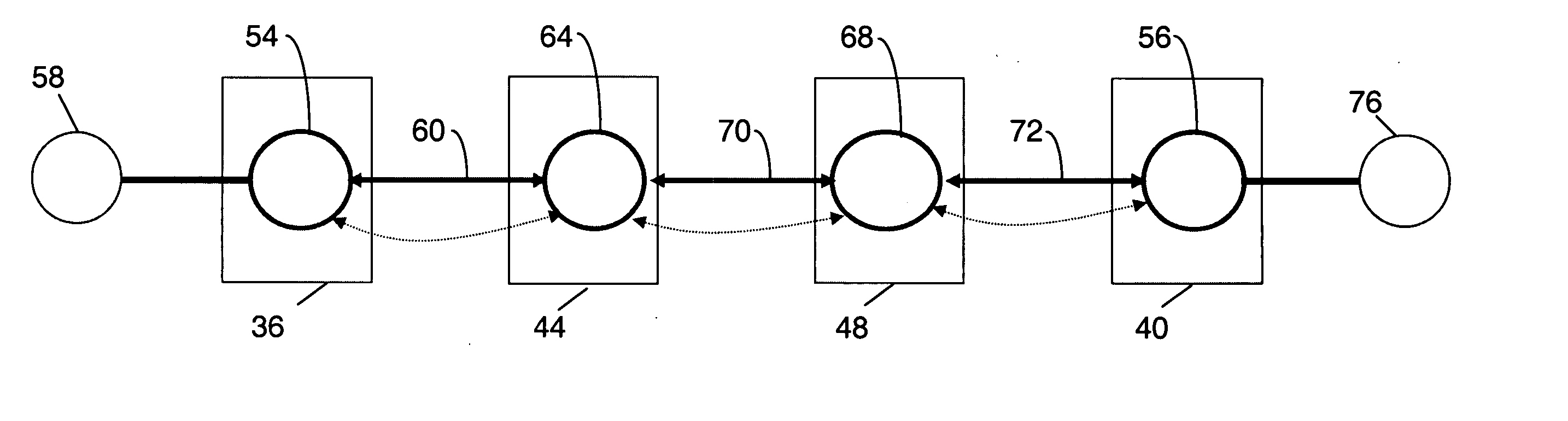
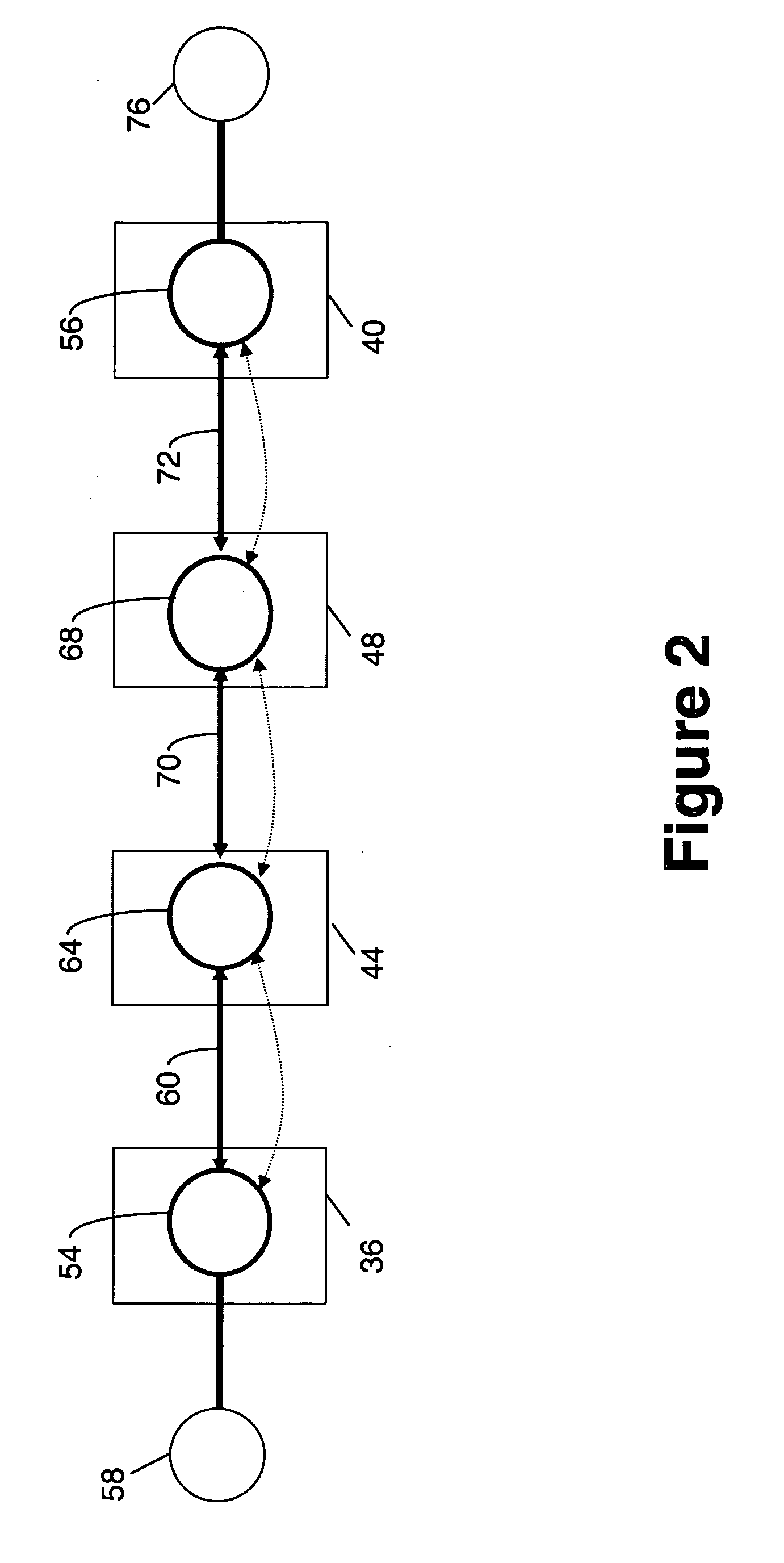
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes “pseudo-wires” between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
Multimedia network appliances for security and surveillance applications
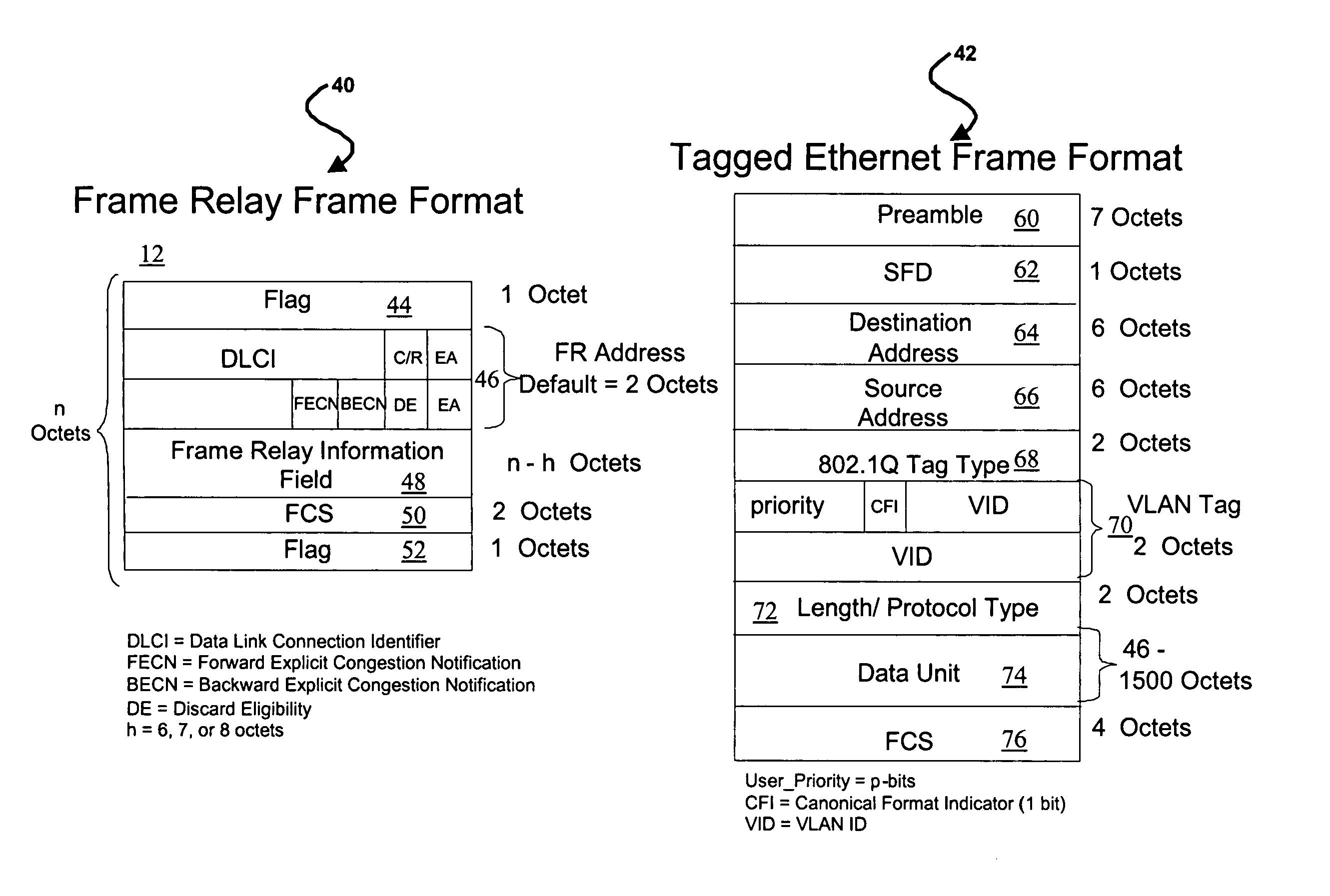
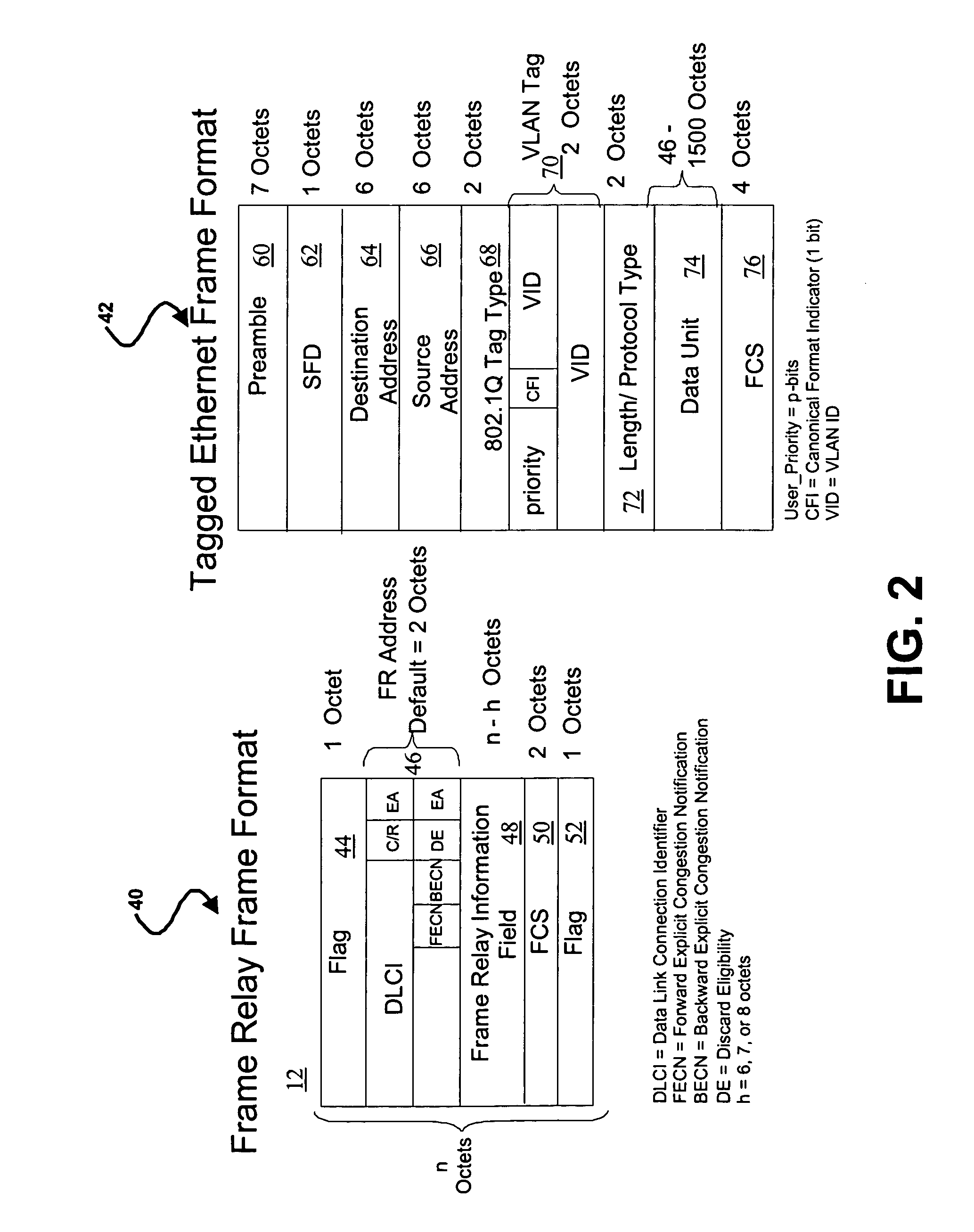
ActiveUS7228429B2Improve functionalityStable supportComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsMotion detectorGeolocation
Network appliances for use in combination with a network based full service, multi-media surveillance system provide a wide range of monitoring techniques utilizing digital network architecture. The appliances may be connected to the surveillance system for transmitting event data, video and / or image monitoring information, audio signals and other data over significant distances using digital data transmission over networks such as a local area network (LAN), a wireless LAN (WLAN), a wide area network such as the Internet for other networks, permitting remote manual and / or automatic assessment and response. The wireless LAN connectivity permits local distribution of sensor information audio, video and image data with relatively high bandwidth without requirement of a license and without relying on a common carrier and the fees associated therewith. The surveillance system may be interfaced with a WAN (wide area network) such as frame relay or the Internet for providing a worldwide, low cost surveillance system with virtually unlimited geographic application. Multiple sensors and appliances may be accommodated, as required. The topology of the network will be established by the geographic situation of the specific installation. Appropriate firewalls may be set up as desired to protect unauthorized access to the system or collected data. The server based system permits a security provider to have access to the appliance, related sensor and surveillance data or to configure or reconfigure the system from any station on the Intranet or Internet. The use of power supplied over LAN wiring to various configurations of security network appliances provides an important simplification and cost reduction of the installation of various alarm and security system devices, such as card readers and scanners, audible devices, strobe enunciators, keypads, motion detectors, and the like. The use of networked sensors in the form of network appliances allows various servers and monitors to share common sensors, further reducing installation costs and greatly increased flexibility.
Owner:PR NEWSWIRE
Apparatus and method for multihop MPLS/IP/ATM/frame relay/ethernet pseudo-wire
InactiveUS20050147104A1Eliminates end to end signallingEliminates end to end encapsulation negotiationNetworks interconnectionFrame RelayPseudo-wire
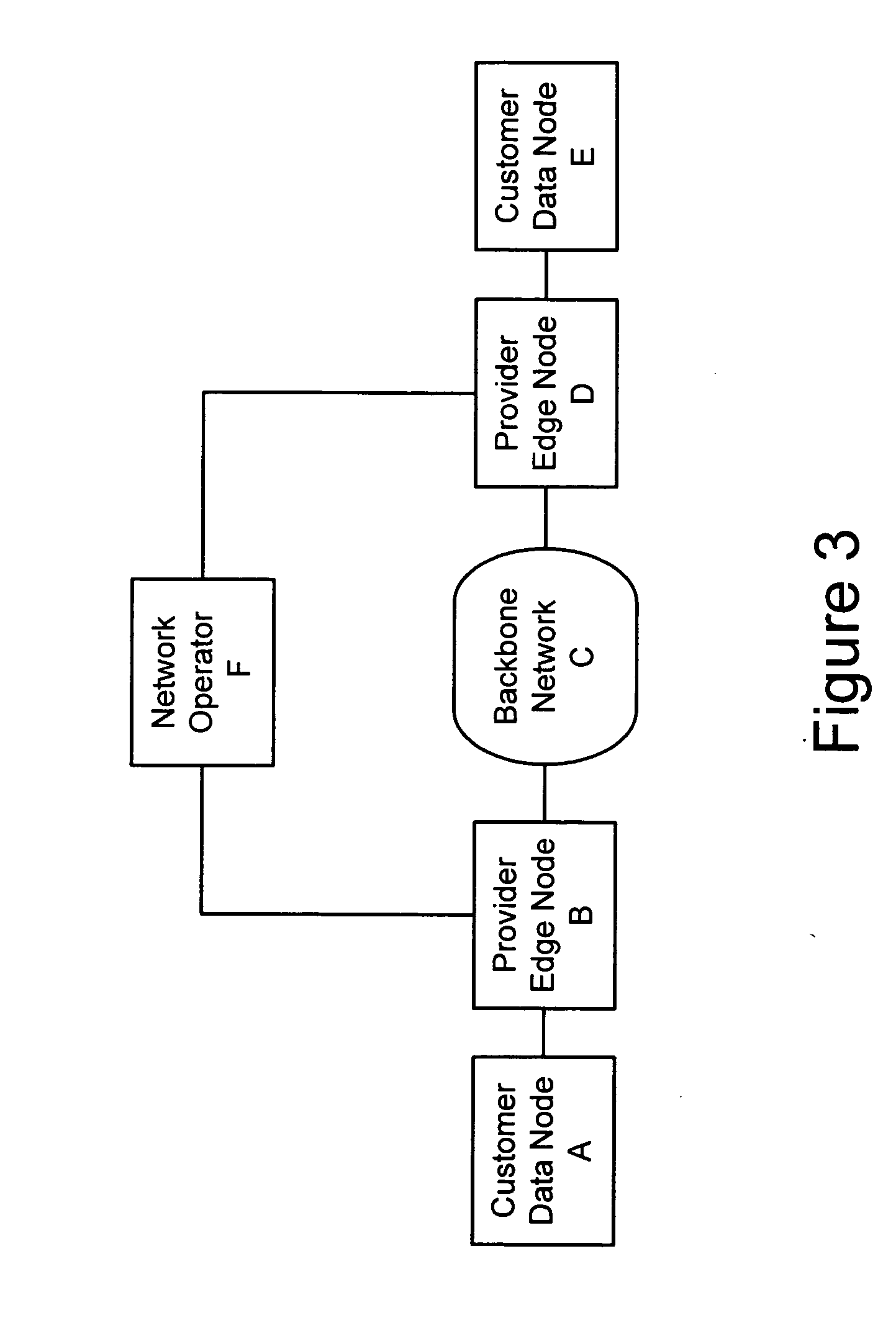
An apparatus for emulating a layer-2 service over at least one network is disclosed. The apparatus includes a signal transmission path. Two provider edge devices are located at opposite ends of the signal transmission path. A provider device is located along the signal transmission path, and this provider device divides the signal transmission path into segments. One of the provider edge devices includes code for adding a demultiplexing header onto data units prior to the data units being transmitted along the signal transmission path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
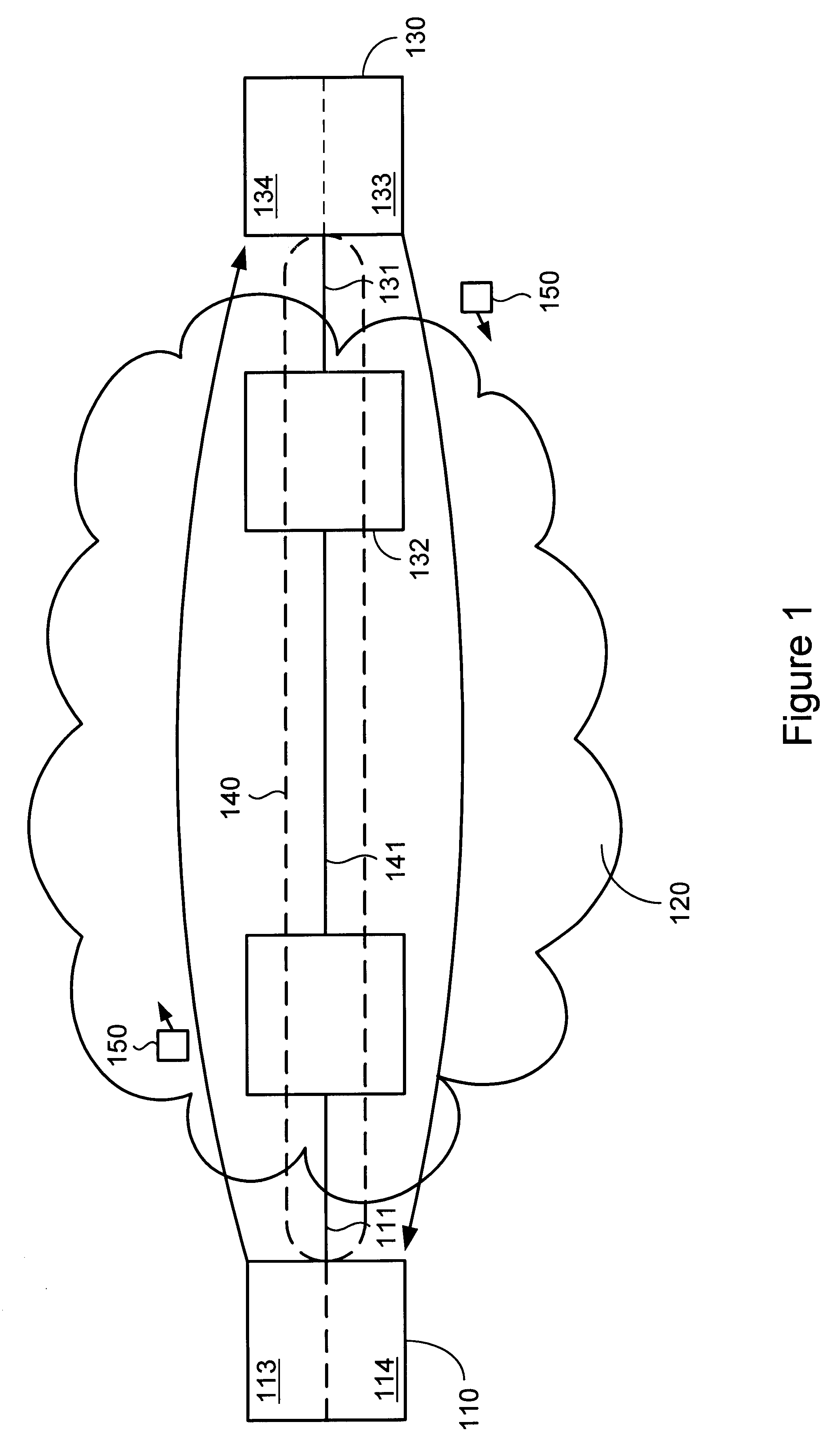
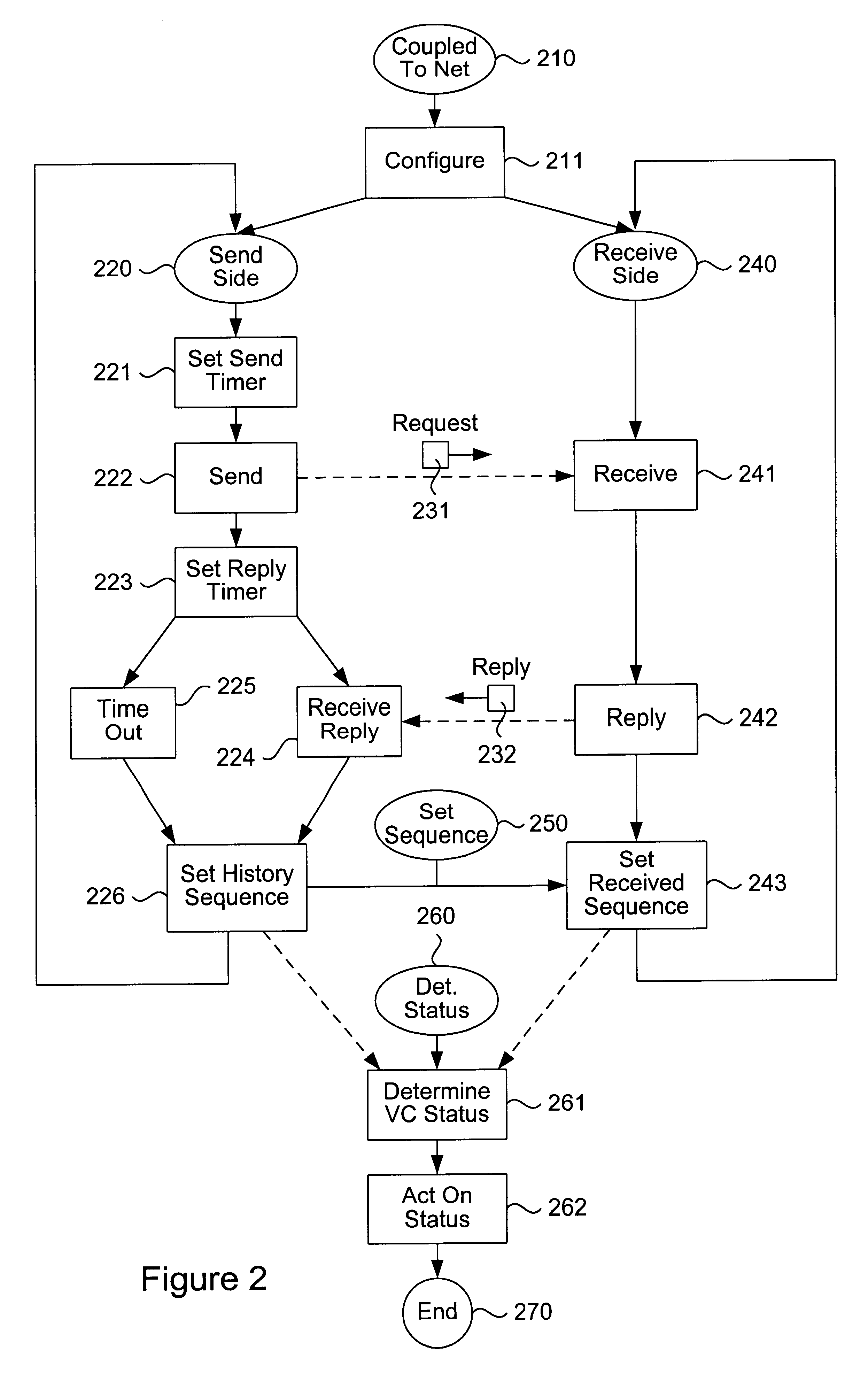
End-to-end bidirectional keep-alive using virtual circuits
The invention provides a method and system for sending and receiving end-to-end bidirectional keep-alive messages using virtual circuits. Nodes coupled to a network, such as a frame relay network, periodically exchange link-layer "keep-alive" messages which indicate information regarding configuration and status of the virtual circuit, as well as information regarding congestion at sending nodes. Nodes respond to received keep-alive messages, or to timed-out failure to receive keep-alive messages, with follow-on actions, such as attempting to reconnect when a virtual circuit fails. Keep-alive messages may be propagated across multiple networks of either similar or different architecture. Keep-alive messages include sent and received sequence numbers, thus providing receiving nodes with a technique for determining if any keep-alive messages have been lost. Keep-alive messages can also include information regarding configuration of the virtual circuit, status of the virtual circuit (including counts of recent keep-alive message failure or success), and congestion at the sending node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Flow control and quality of service provision for frame relay protocols
InactiveUS20030185249A1Energy efficient ICTChannel dividing arrangementsTraffic capacityQuality of service
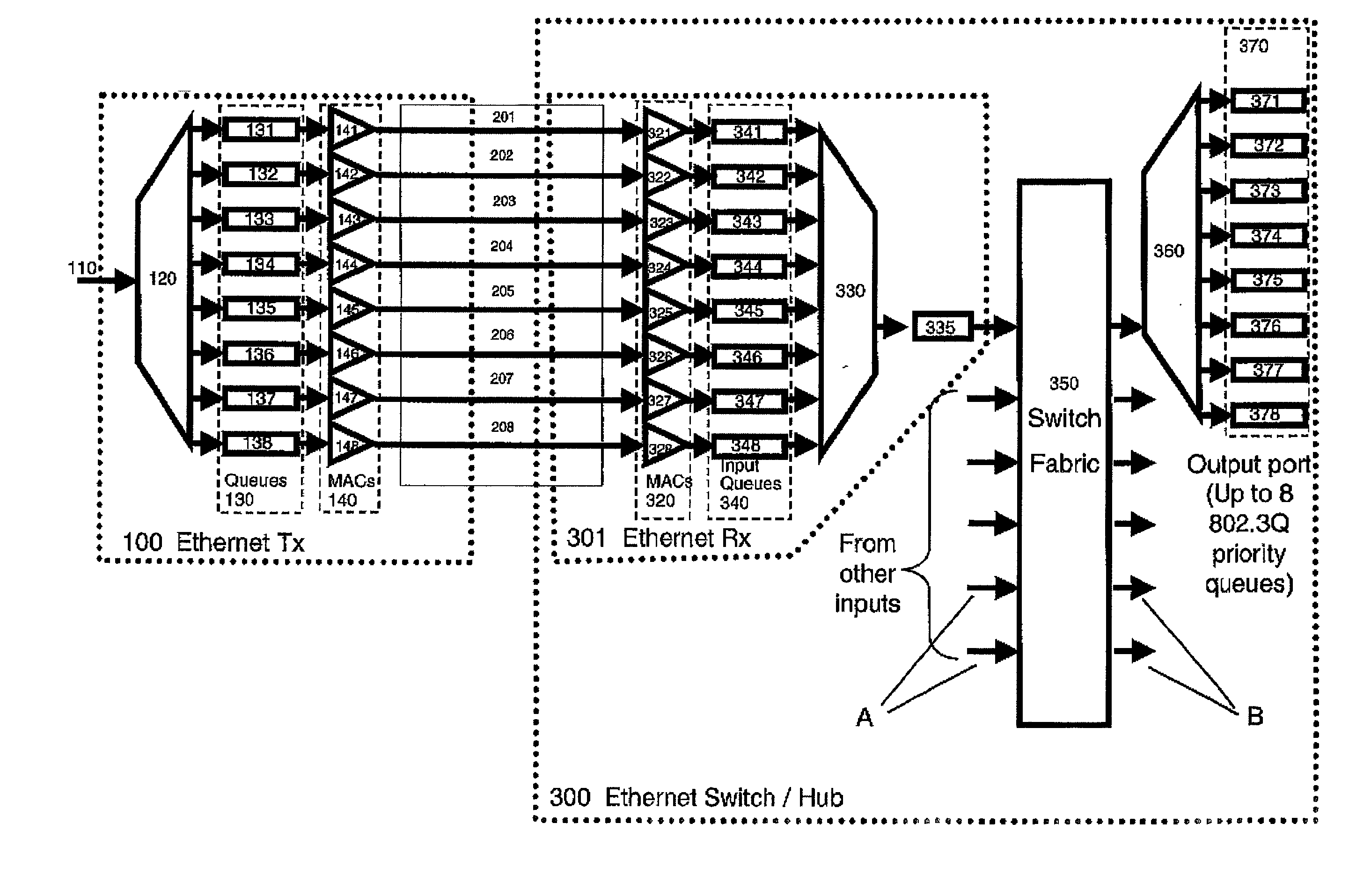
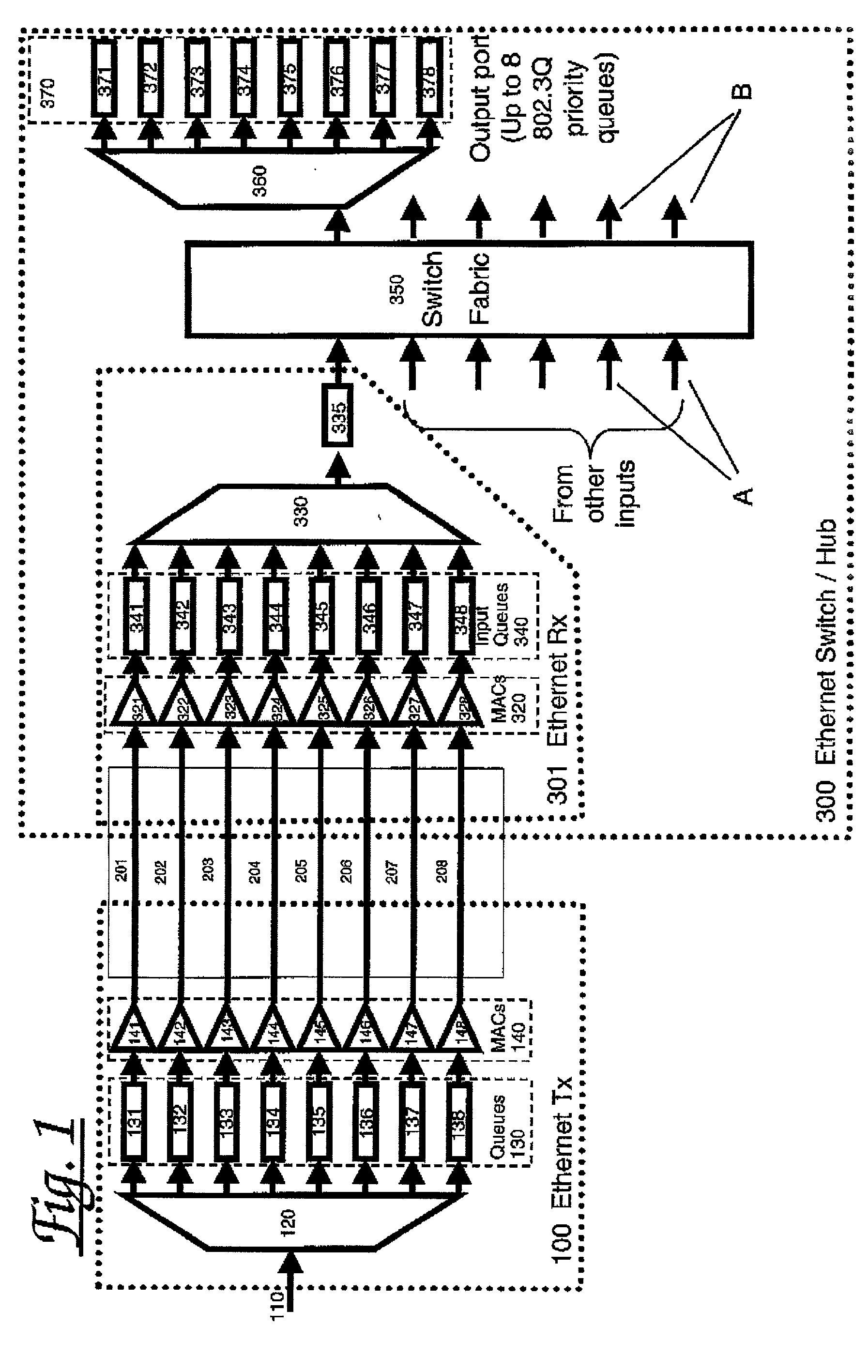
Apparatus and method for providing controlled Quality of Service over Ethernet-like links. Prioritised frames are allocated to transmission queues responsive to their priorities. Each queue has an associated subsidiary Ethernet MAC which transmits frames from its queue subject to a scheduler which selects from the set of MAC's according to a pre-determined algorithm. The multiple logical paths between corresponding pairs of transmitter and receiver subsidiary MAC's are preferably multiplexed over a single physical channel. If congestion occurs at the receiver, then Ethernet PAUSE frames may be sent back to the transmitter, directed to specific subsidiary MAC's-typically those with lower priority-to suspend transmission from the corresponding queue for a time period indicated in the PAUSE frame. In this way back pressure flow control may be applied selectively to so that large amounts of low priority traffic do not cause unnecessary delays to higher priority traffic.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Method and system for protecting frame relay traffic over SONET rings
A frame relay (FR) protection method generates an OAM frame to other nodes upon detecting a defect on a SONET ring. The protection frame comprises a type of failure and a location of failure. A node that detected the defect transmits the protection frame to other nodes about the location of the failure and the type failure. Protection tables are provided for switching a working fiber link to a protection fiber link. A protection switching provides a method re-establish FR traffic in spite of a detected failure on a SONET ring.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for telecommunications using internet protocol
InactiveUS6788675B1Network traffic/resource managementSpeech analysisInternet protocol suiteTelecommunications network
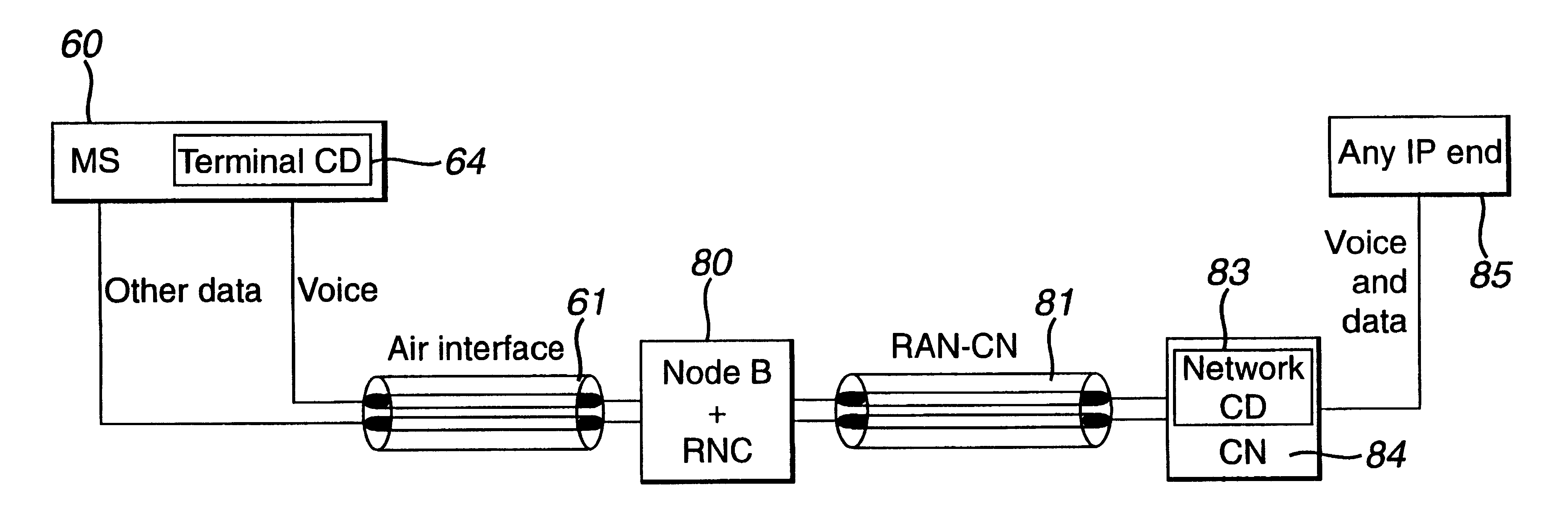
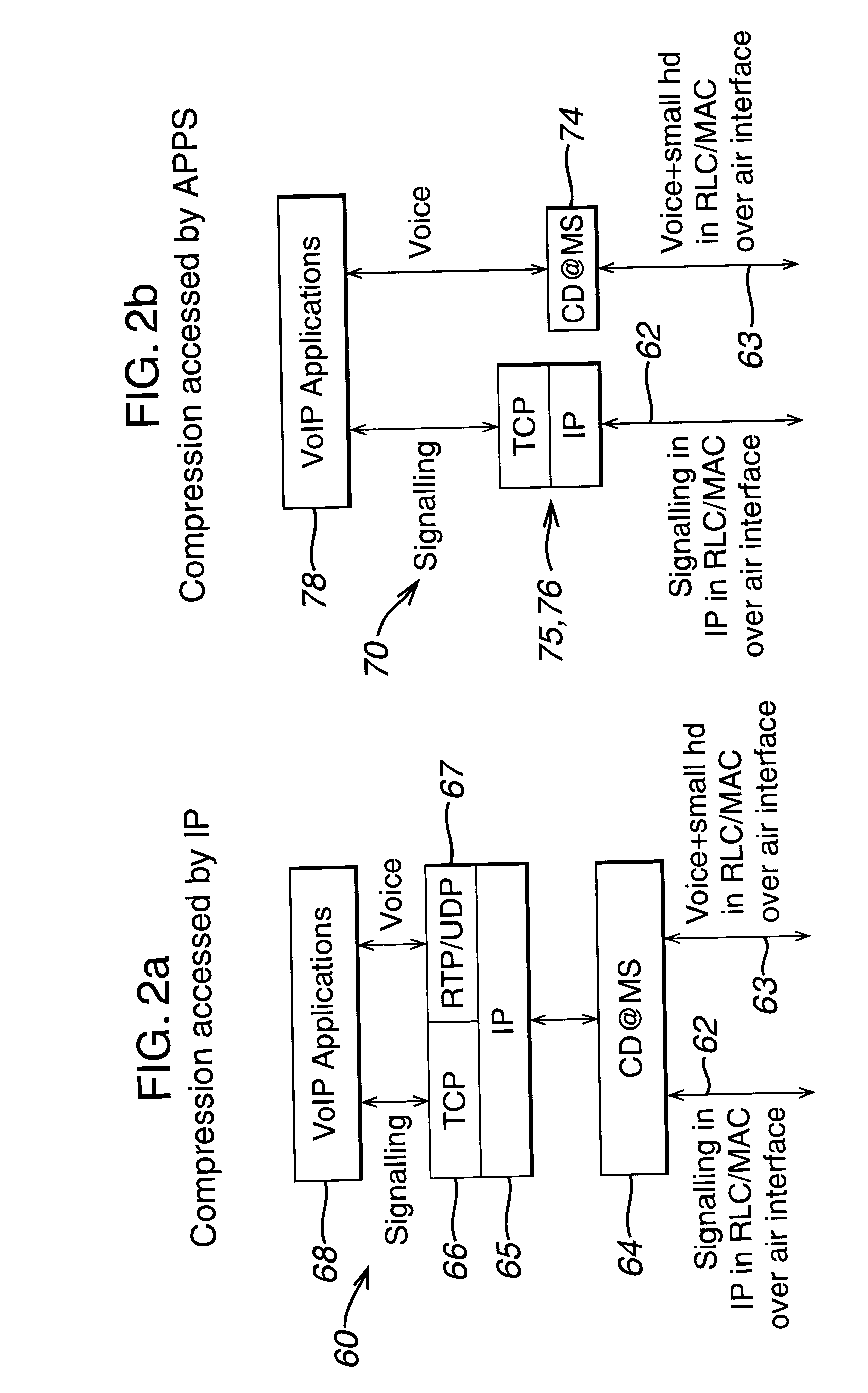
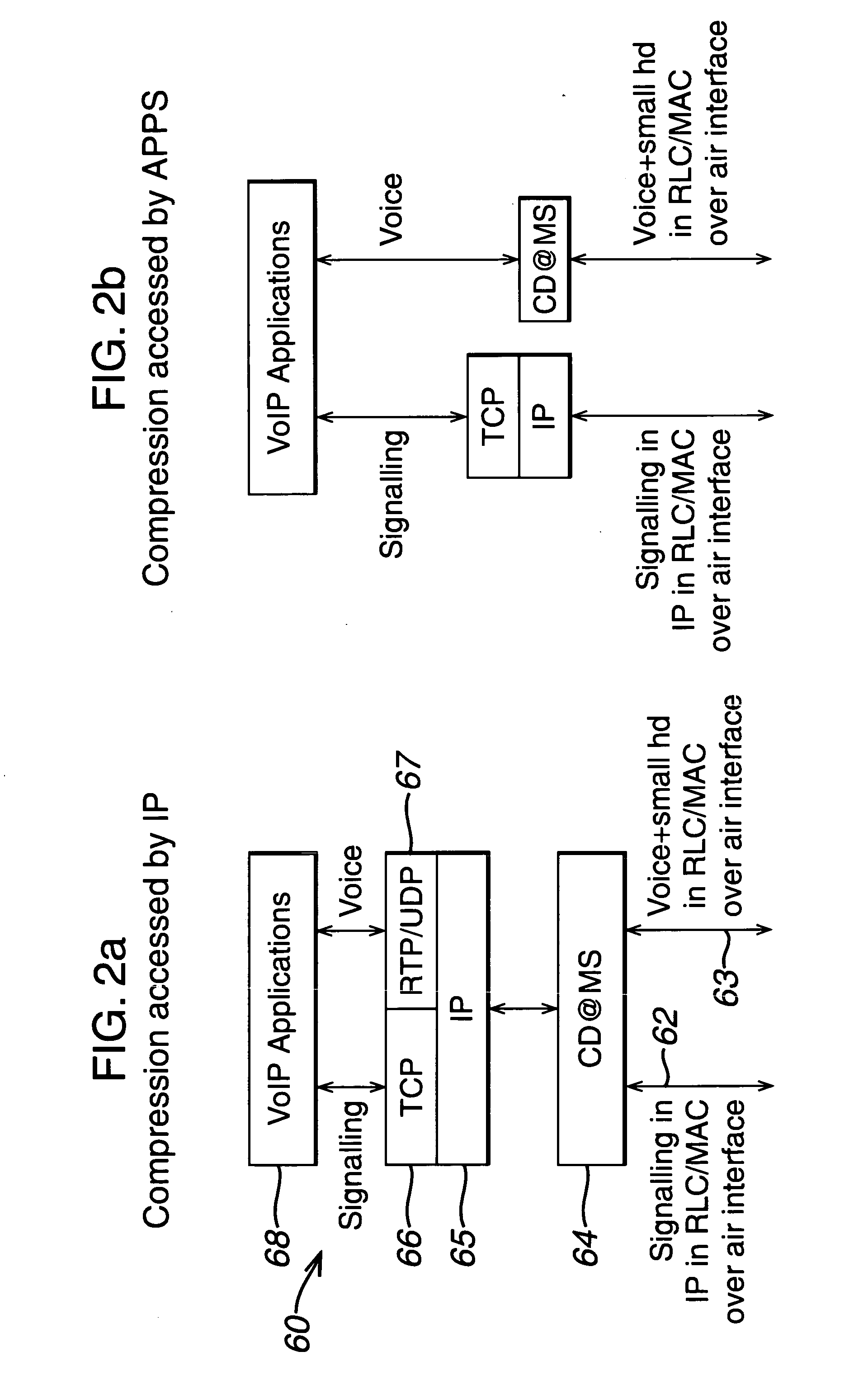
In a wireless packet switching telecommunications network, voice services are provided by having a compressor / decompressor in each mobile station to provide each voice packet with a compressed header. Voice data and signalling data are sent separately and in different data formats to the air interface. The compressed header may be an M bit and a cyclically reset timeclick_number, which is decompressed by use of a wallclock which counts reset cycles to reinstate the voice packet headers. Alternatively, RTP agents are provided at the compression and decompression points, and voice packets are sent without headers over a "high quality" network such as a frame relay or ATM network. Compression state of a voice packet header can be established by sending call set-up information over an out-of-band channel between compression points in a mobile station and in die network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Apparatus and method for providing a network termination point
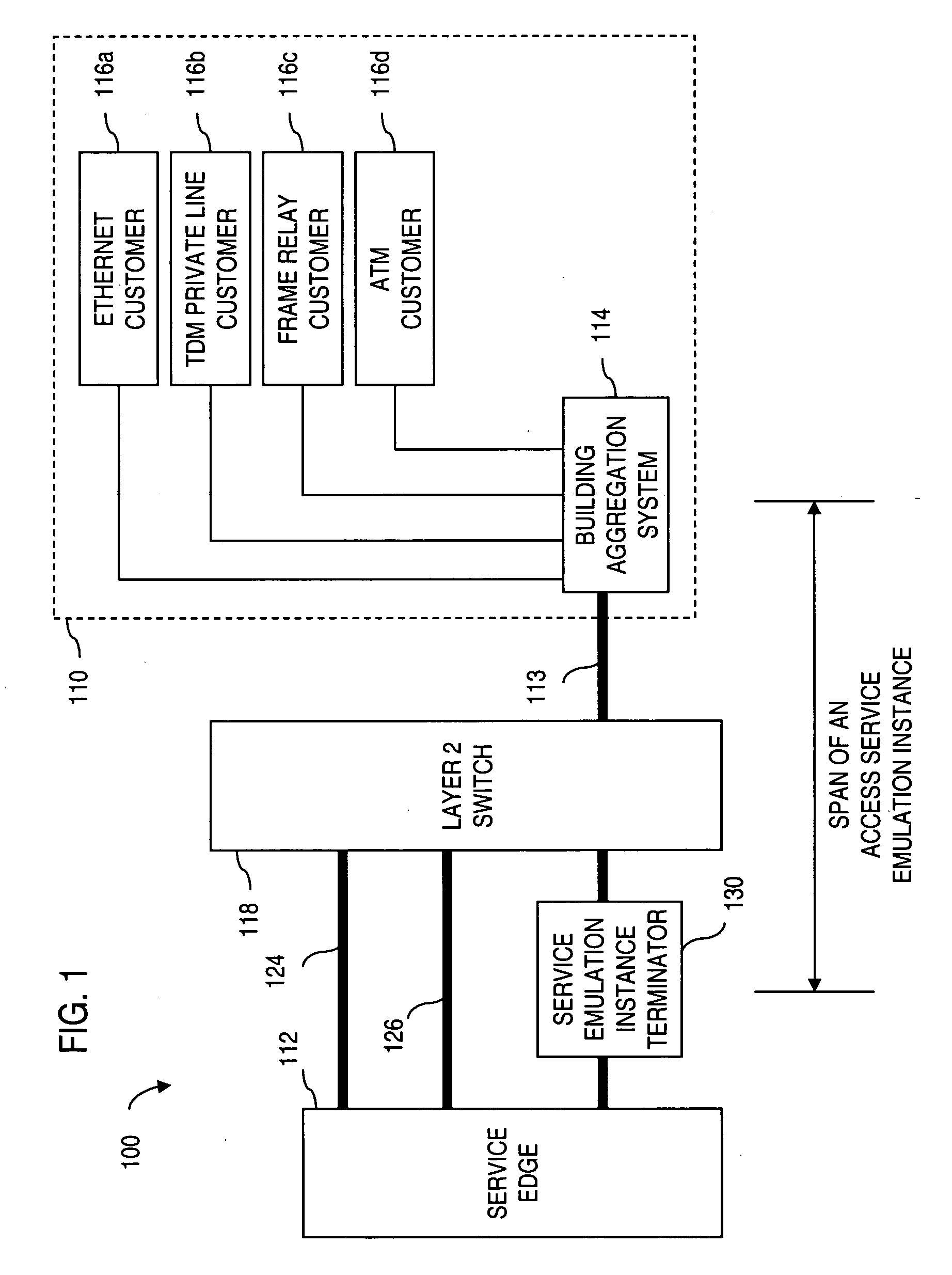
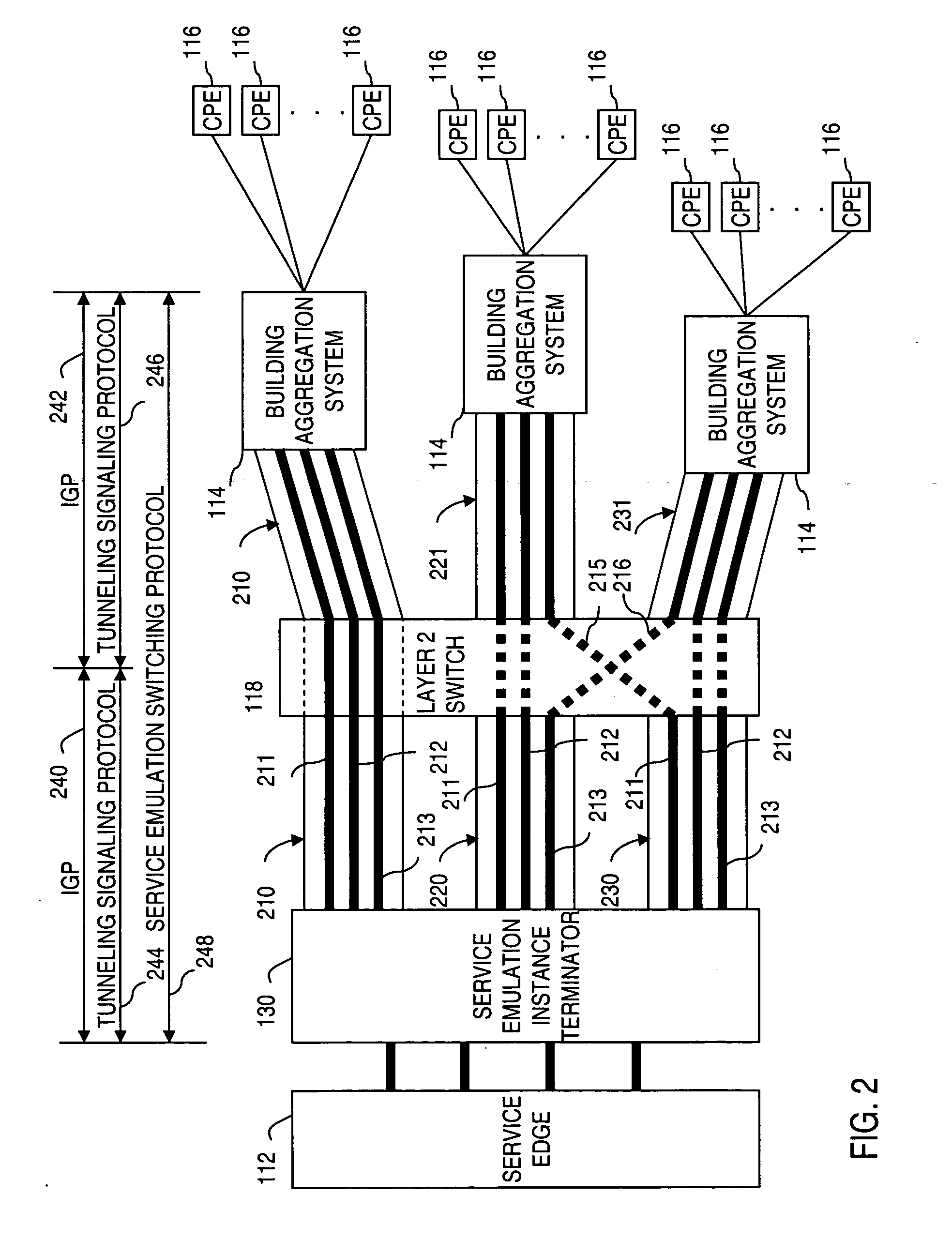
ActiveUS20050238049A1Efficient executionTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityAccess network
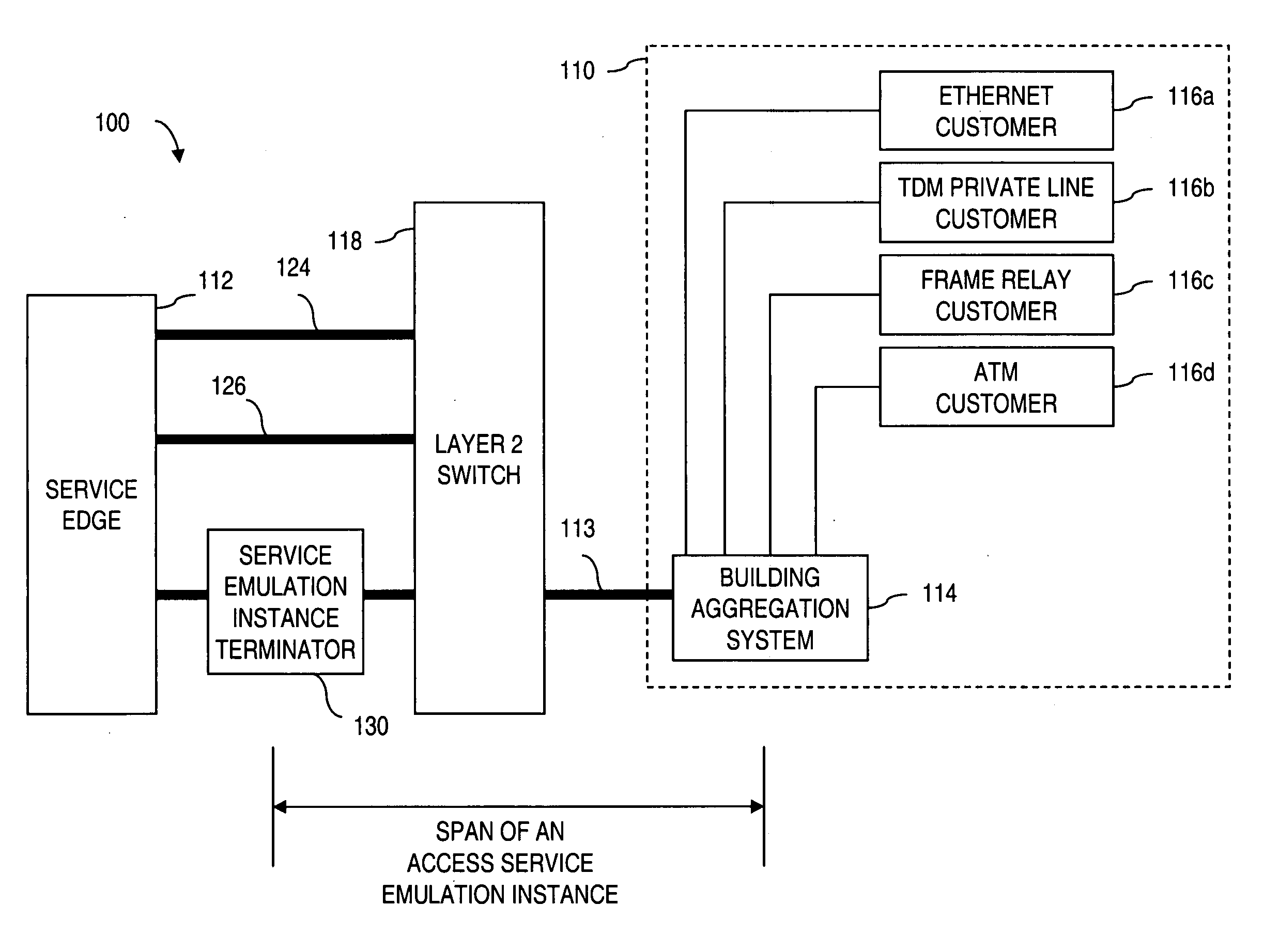
Apparatus and method for providing a termination point for service emulation instances in an access network is provided. In an embodiment, the service emulation instances are implemented utilizing, for example, pseudowires. Communications to and from the access network are aggregated and transmitted via one or more pseudowires to a service emulation instance terminator. The service emulation instance terminator converts the traffic to its native form and, if necessary, converts the traffic to a different type of format or service. The service emulation instance terminator then frames the traffic for the appropriate type of service and transmits the traffic to the service edge. Traffic received from the service is removed prepended with a pseudowire label and aggregated with other traffic. The aggregated traffic is transmitted to the customer via the access network. If necessary, an interworking function may convert the traffic from one type of service to another type of service. Further, functionalities of equipment such as frame relay switching or Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching may be realized in the service emulation instance terminator.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Method and apparatus for encapsulating services for transportation over metallic physical mediums
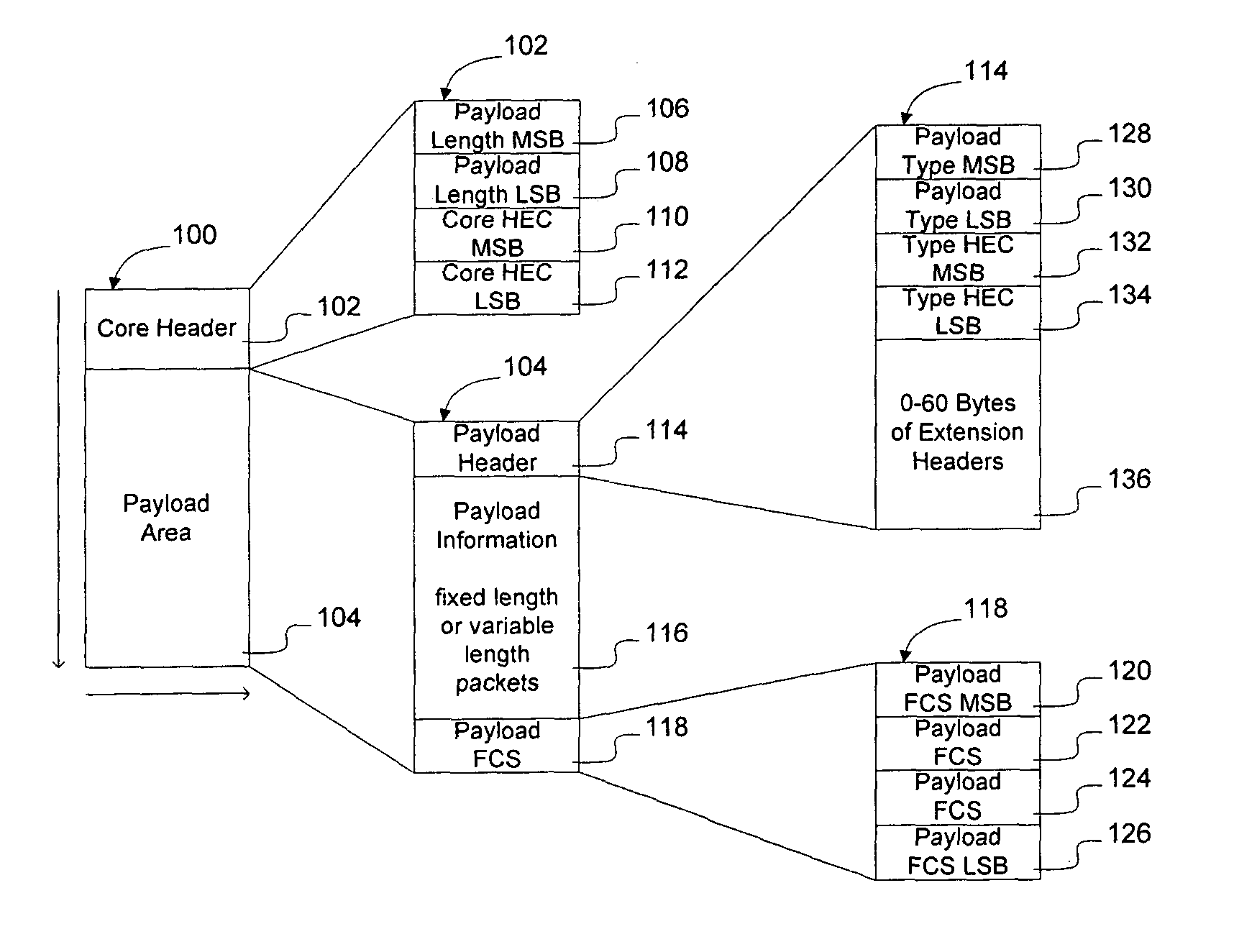
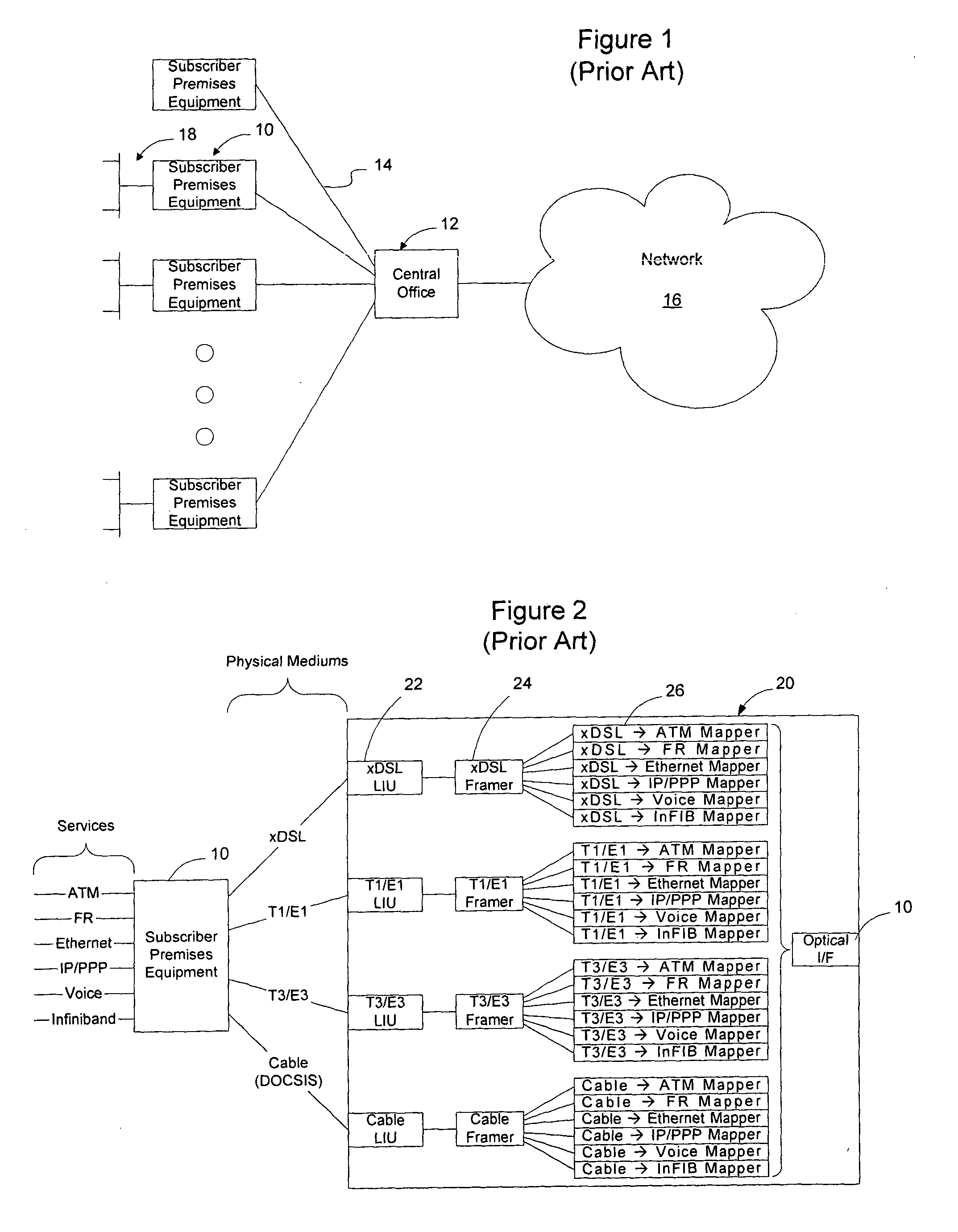
InactiveUS20050053064A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce complexityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFrame RelayPhysical layer
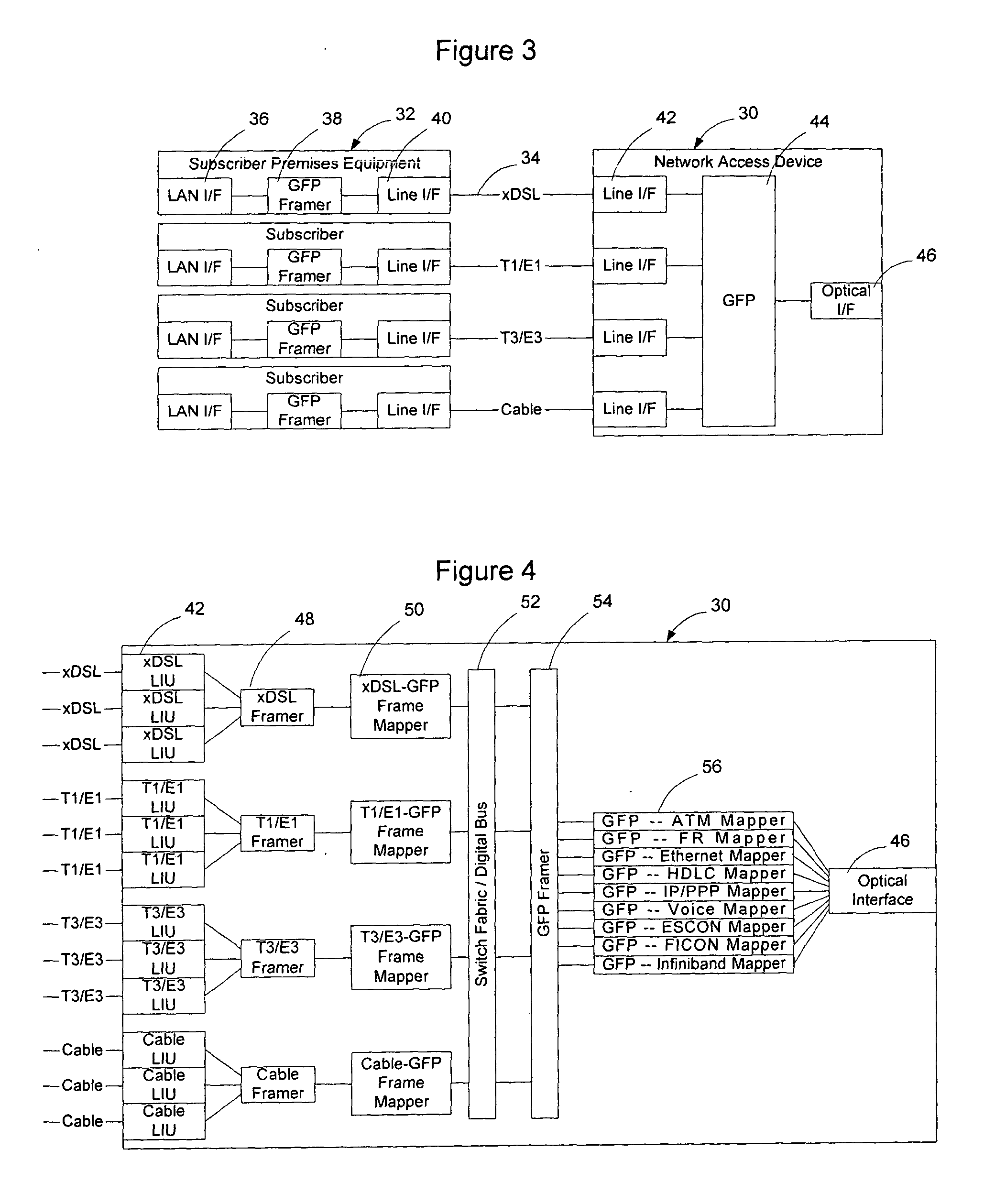
A network element employing a universal mapper enables multiple services to be mapped onto a physical medium (metallic link with a particular physical layer protocol) so that the number of service mappers, and hence the complexity of the network element, may be reduced, the cost of provisioning the device may be reduced, and new services may be deployed, such as Ethernet over T1. The universal mapper may be configured to generate frames for transmission over multiple physical mediums utilizing a protocol known as Generic Framing Procedure (GFP). Using this embodiment, services such as ATM, Frame Relay, Ethernet, IP / PPP, Voice, and Infiniband may be transported in GFP frames over metallic links operating using xDSL, T1 / E1, T3 / E3, or cable access technologies by utilizing a single GFP framer and a single set of service mappers.
Owner:INT LICENSE EXCHANGE OF AMERICA LLC
Method and system for retrieving link management interface status for a logical port
InactiveUS7209452B2Reduce equipment costsReduce personnel costsError preventionTransmission systemsFrame RelayIntegration testing
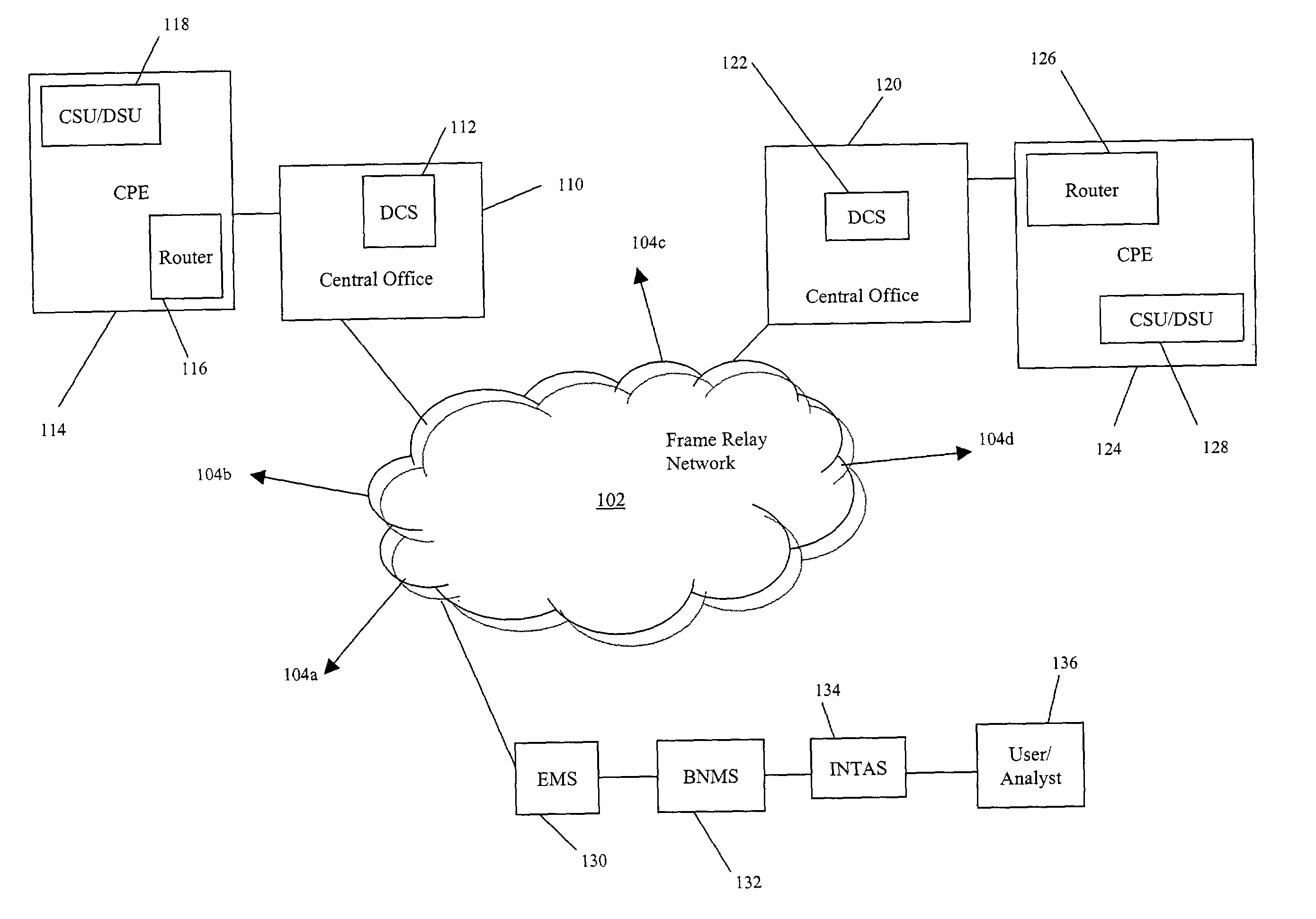
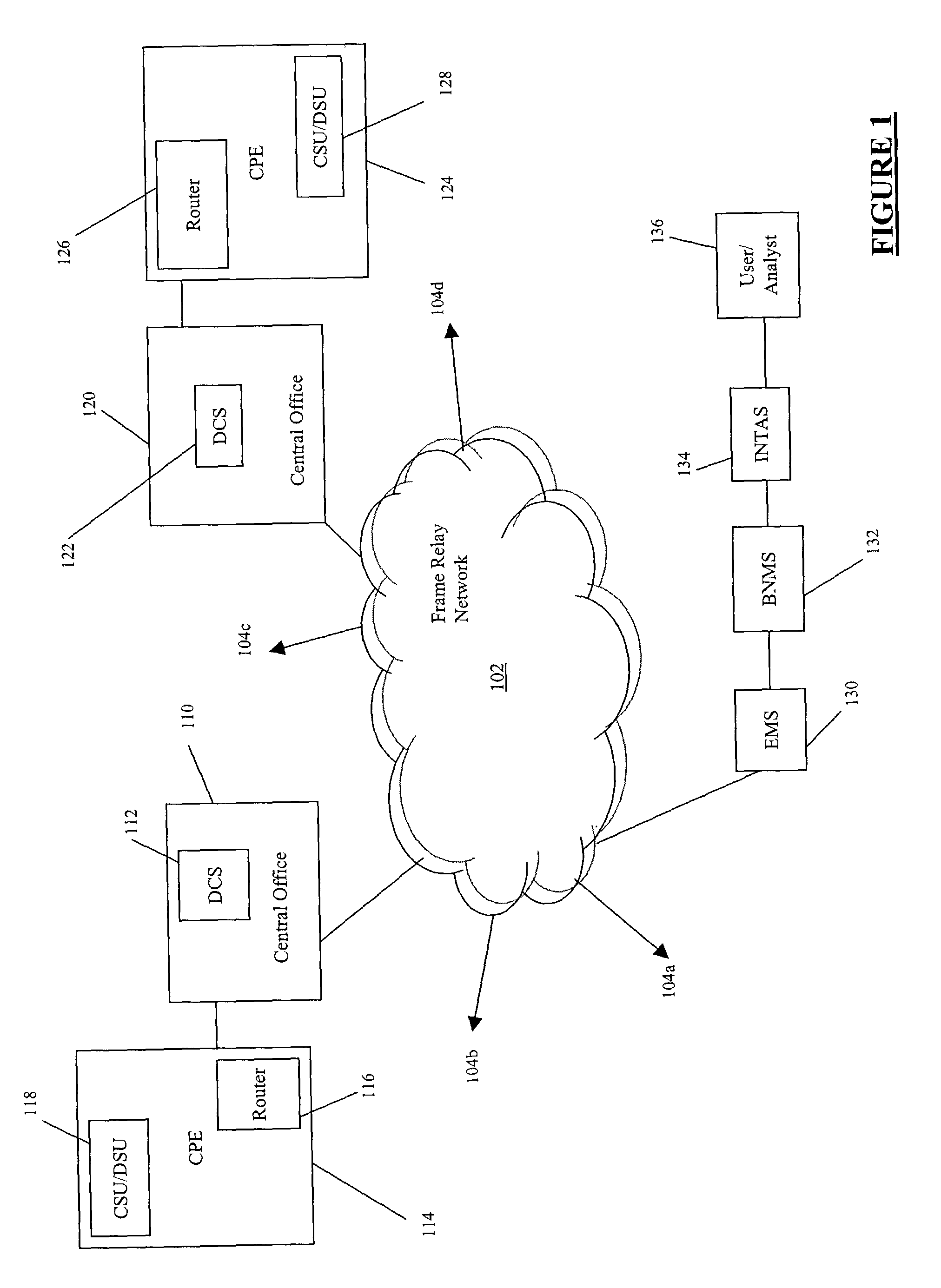
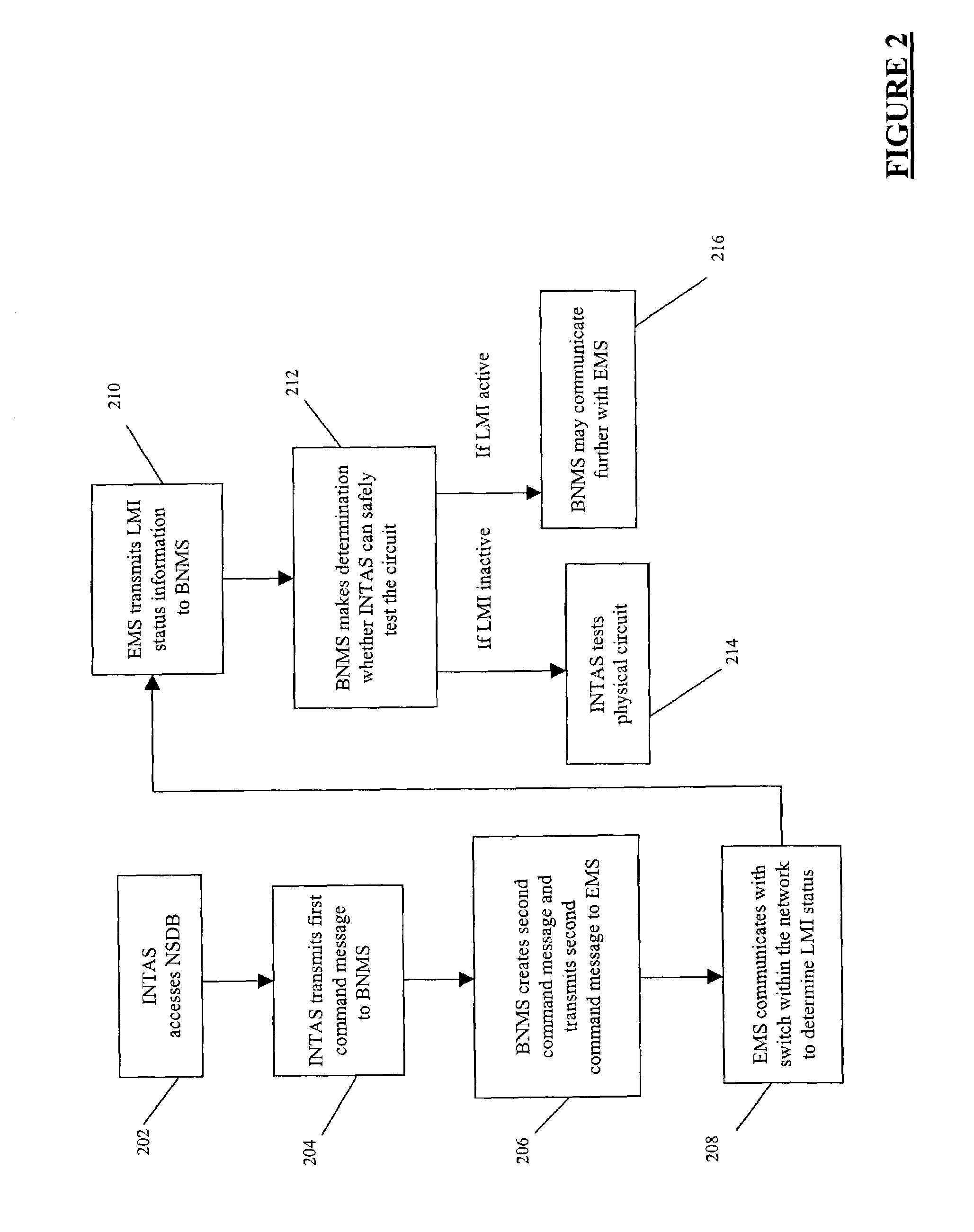
Systems and methods for obtaining logical layer information in a frame relay and / or asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network are described. In an exemplary embodiment, a physical layer test system, such as an integrated testing and analysis system, communicates with a broadband network management system, which in turn communicates with an element management system for a frame relay and / or ATM network.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
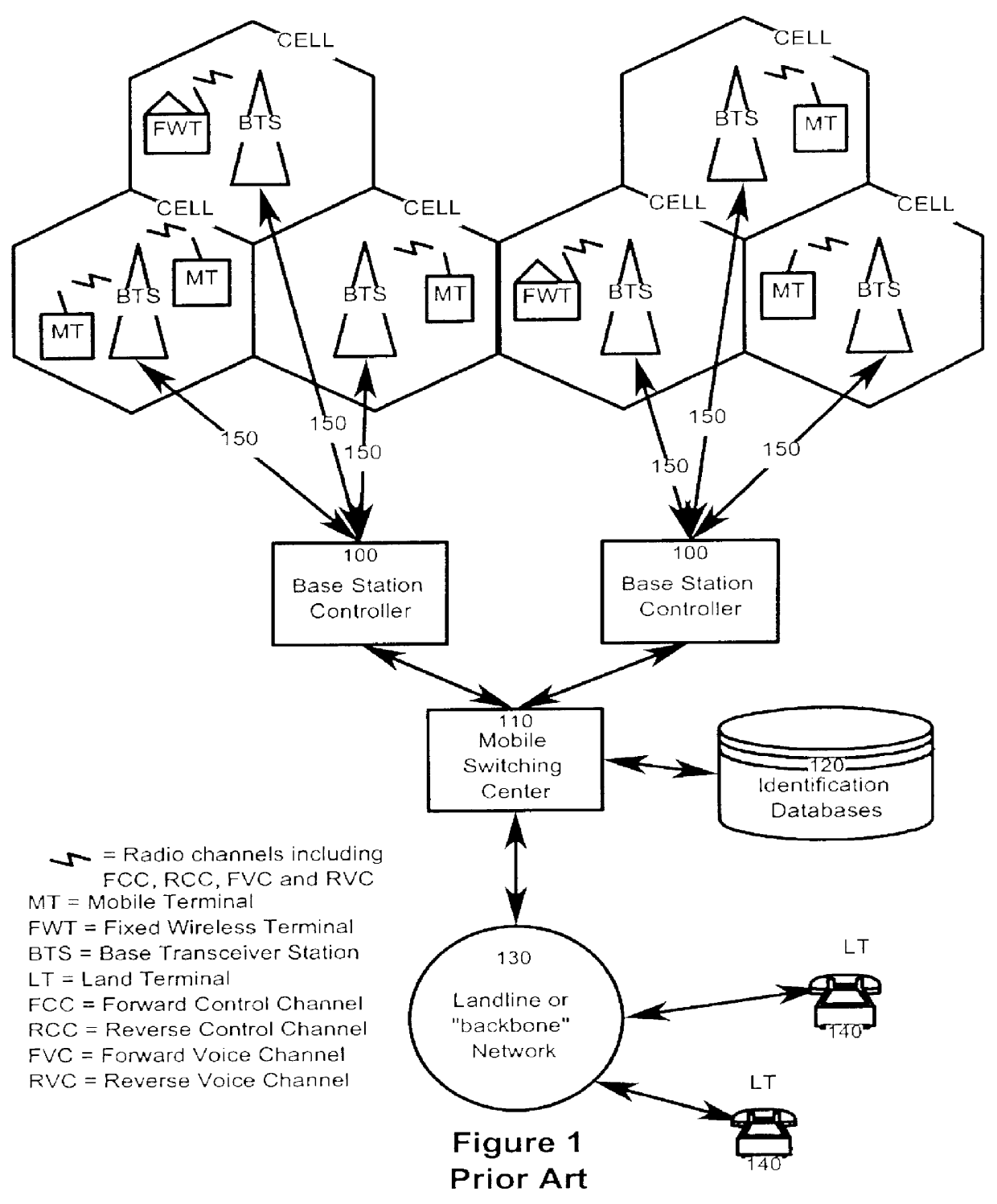
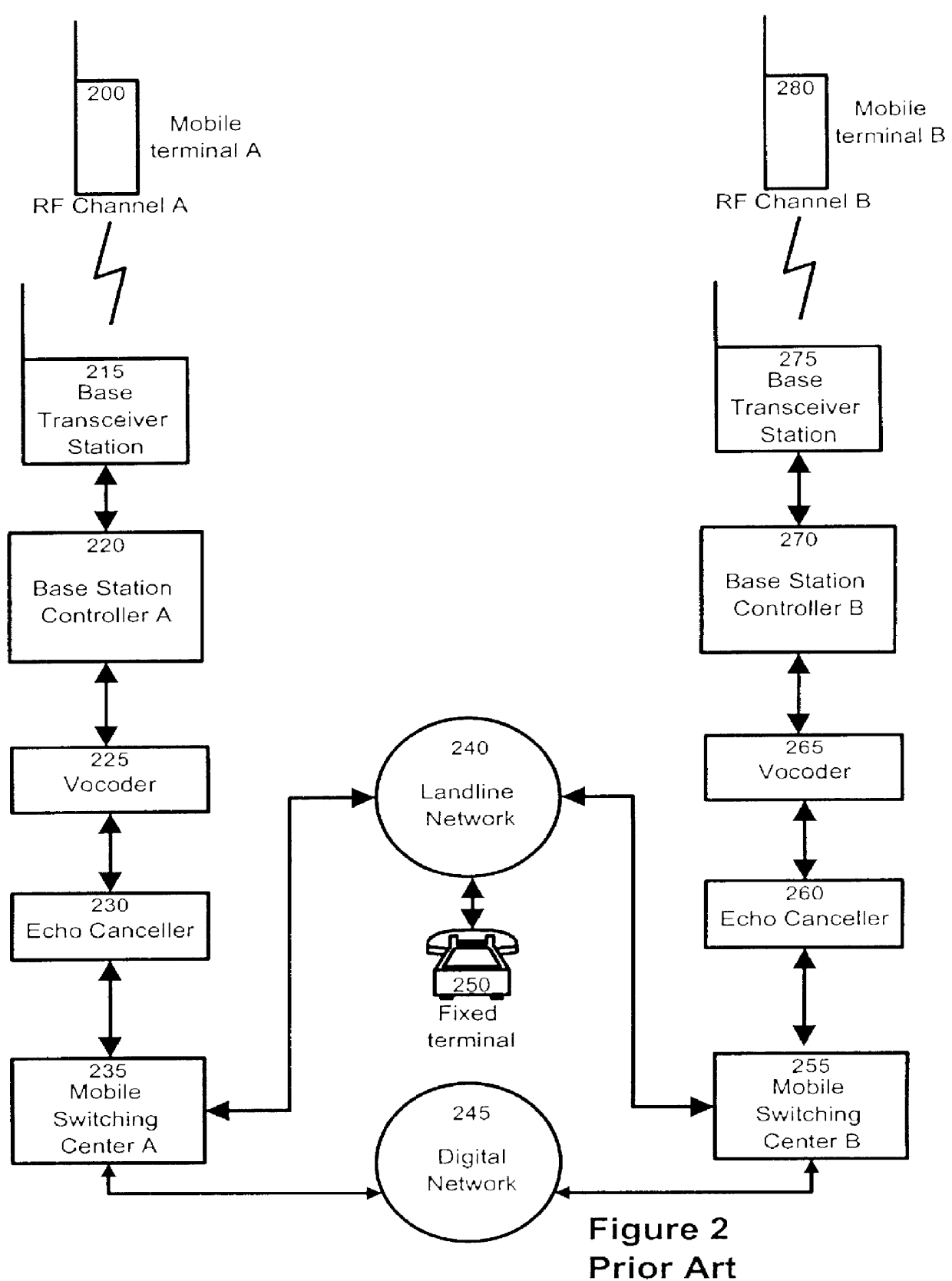
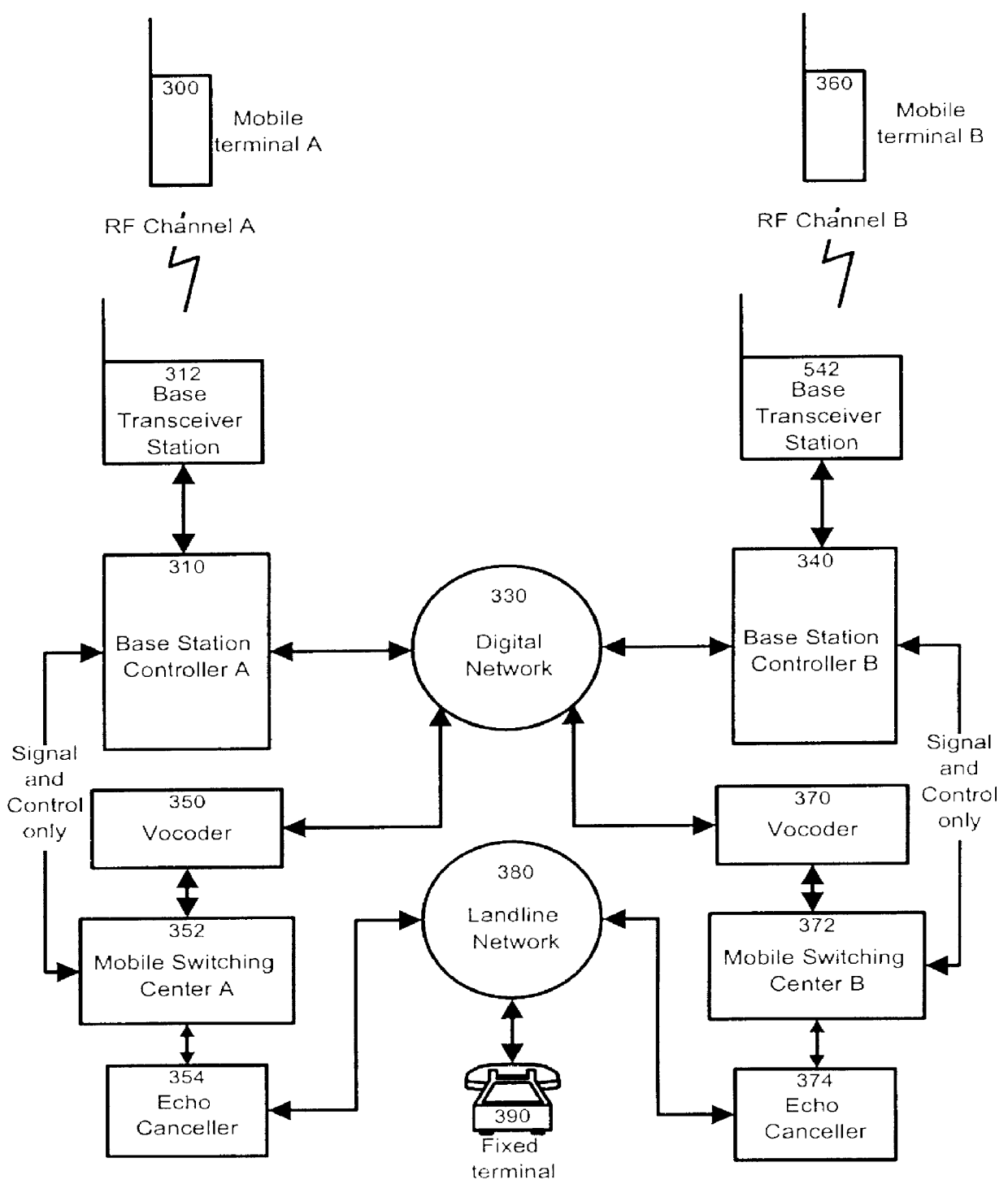
Cellular communication network with vocoder sharing feature
InactiveUS6138022AReduce the possibilityPrevent degradationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrame RelayNetwork architecture
The present invention provides a novel system and a method for improving the voice quality of wireless-to-wireless calls or wireless-to-fixed terminal calls, while permitting a more efficient utilization of network resources. In a first aspect, the invention provides a communication system including a plurality of base stations connected to one another through a digital network (such as TDM, frame relay or ATM). Also, a plurality of vocoder channels, separate from the individual base stations, provide a data flow path from the base stations to wireline terminals first through the digital network via a Mobile Switching Center and finally through a landline network. In a wireless-to-wireless call, the compressed audio signal travels from one base station to another without undergoing any de-compression / compression. This avoids undesirable vocoder tandeming known to degrade voice quality. If the call is identified as being of a wireless-to-wireline terminal nature, the data is directed to a vocoder channel for decompression into PCM samples. The samples are then transmitted to the fixed terminal through the landline network. The main advantage of this network architecture is that fewer vocoders are required by comparison to prior art systems, therefore fewer costs are incurred. In addition, voice quality is improved.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
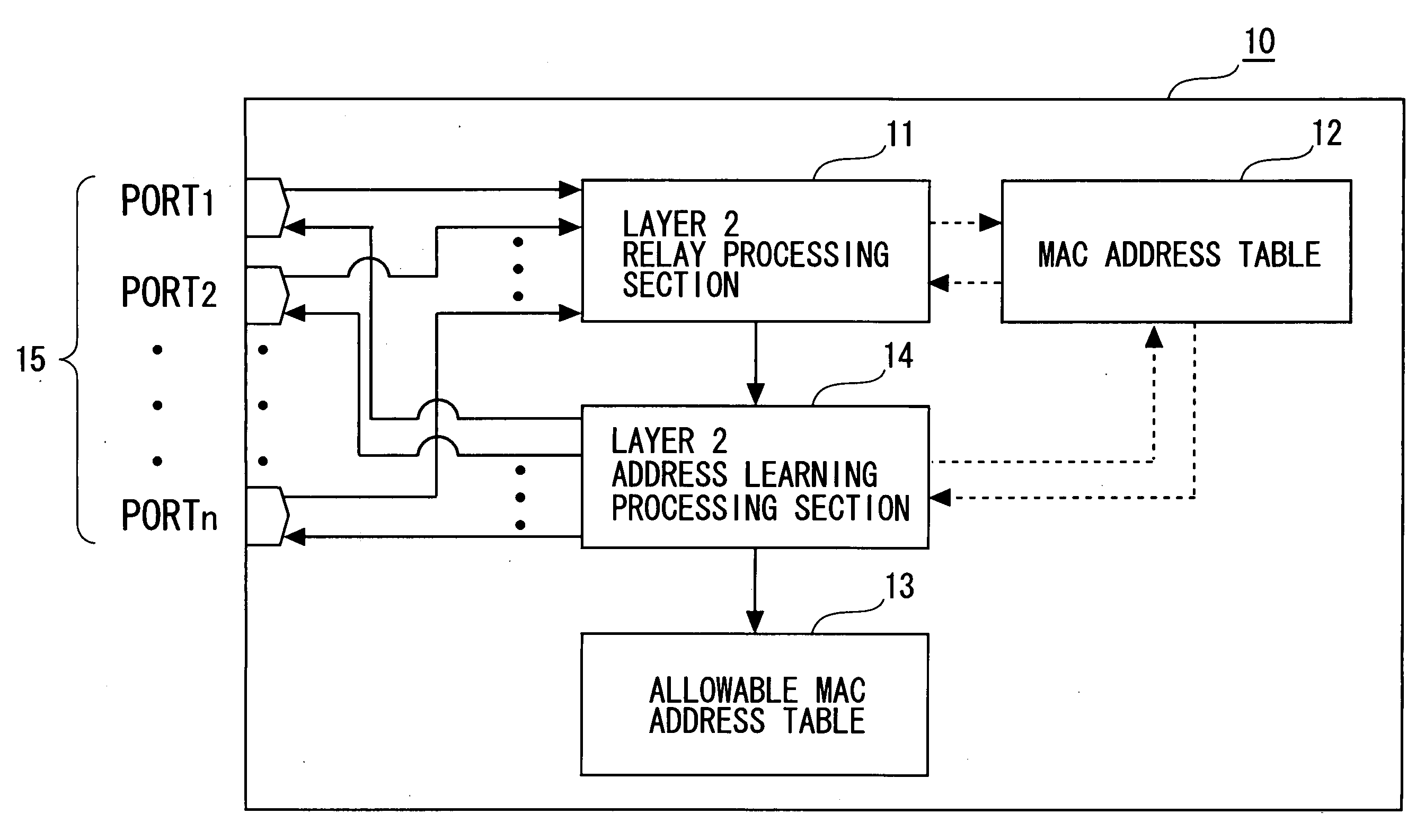
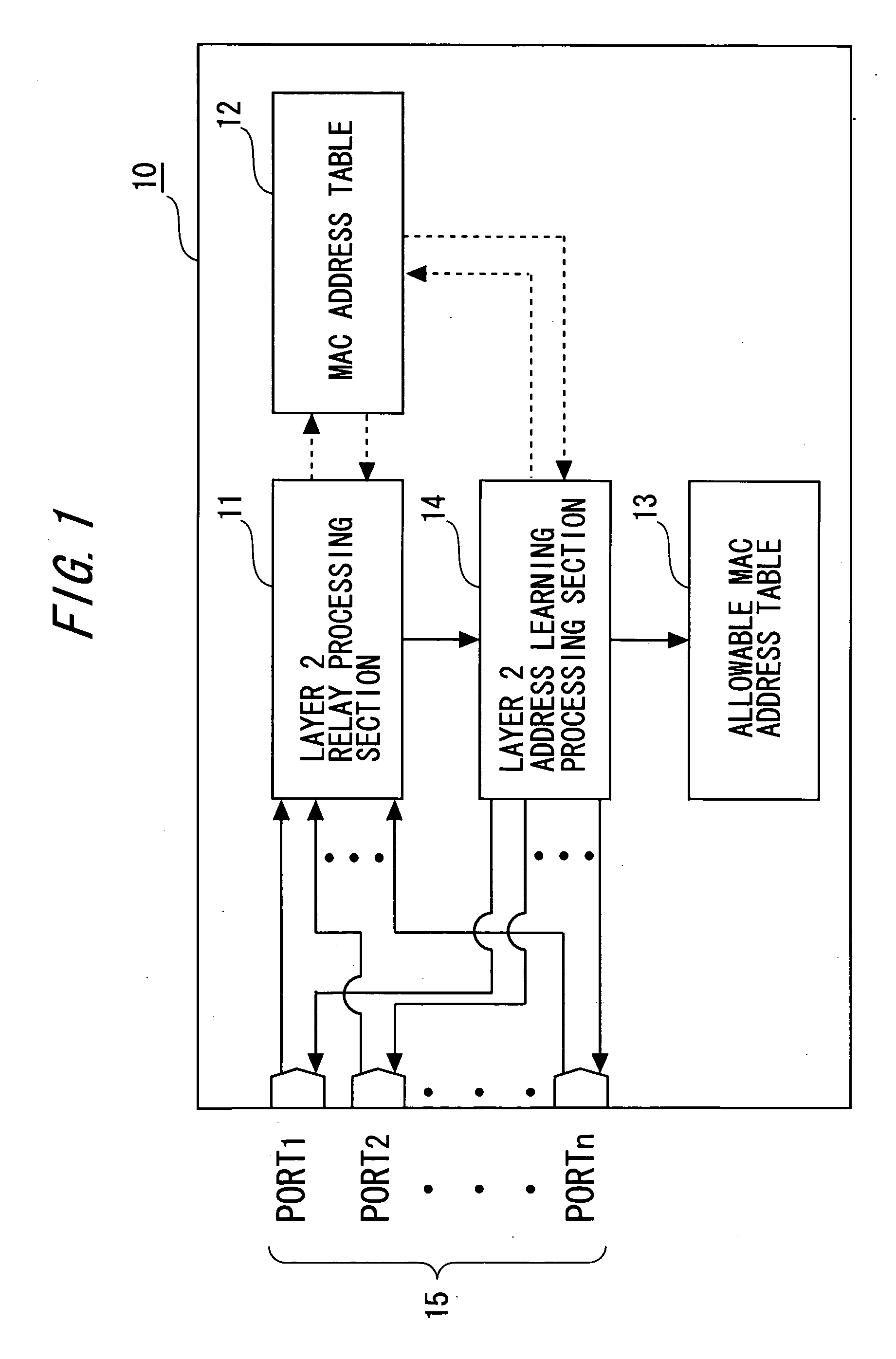
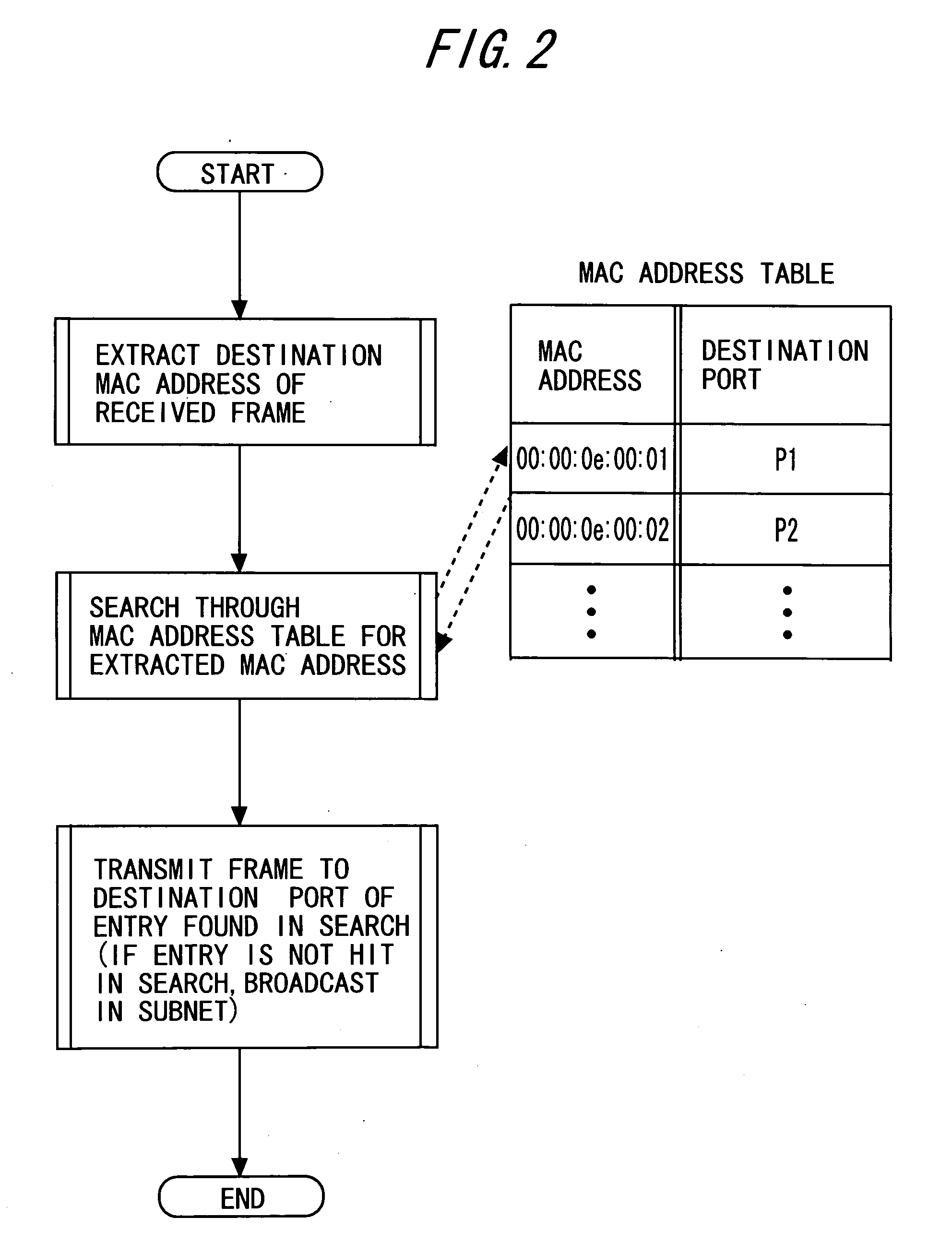
Frame Relay Device
InactiveUS20080250496A1Preventing numberMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareFrame Relay
A frame relay device includes a table where an entry containing a combination of an MAC address and an IP address is registered to be used in the frame relay processing of a local device. Moreover, the frame relay device includes judgment means for searching the table by the transmission origin MAC address and the transmission origin IP address contained in the frame received and judging whether the combination of the transmission origin addresses is registered as a relay object in the layer 3. Furthermore, the frame relay device includes layer 3 relay processing means for performing layer 3 relay processing only for the frame which has been judged to contain the combination of the transmission origin addresses as a relay object.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for telecommunications using internet protocol
InactiveUS20040095939A1Network traffic/resource managementSpeech analysisInternet protocol suiteFrame Relay
In a wireless packet switching telecommunications network, voice services are provided by having a compressor / decompressor in each mobile station to provide each voice packet with a compressed header. Voice data and signalling data are sent separately and in different data formats to the air interface. The compressed header may be an M bit and a cyclically reset timeclick_number, which is decompressed by use of a wallclock which counts reset cycles to reinstate the voice packet headers. Alternatively, RTP agents are provided at the compression and decompression points, and voice packets are sent without headers over a "high quality" network such as a frame relay or ATM network. Compression state of a voice packet header can be established by sending call setup information over an out-of-band channel between compression points in a mobile station and in the network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
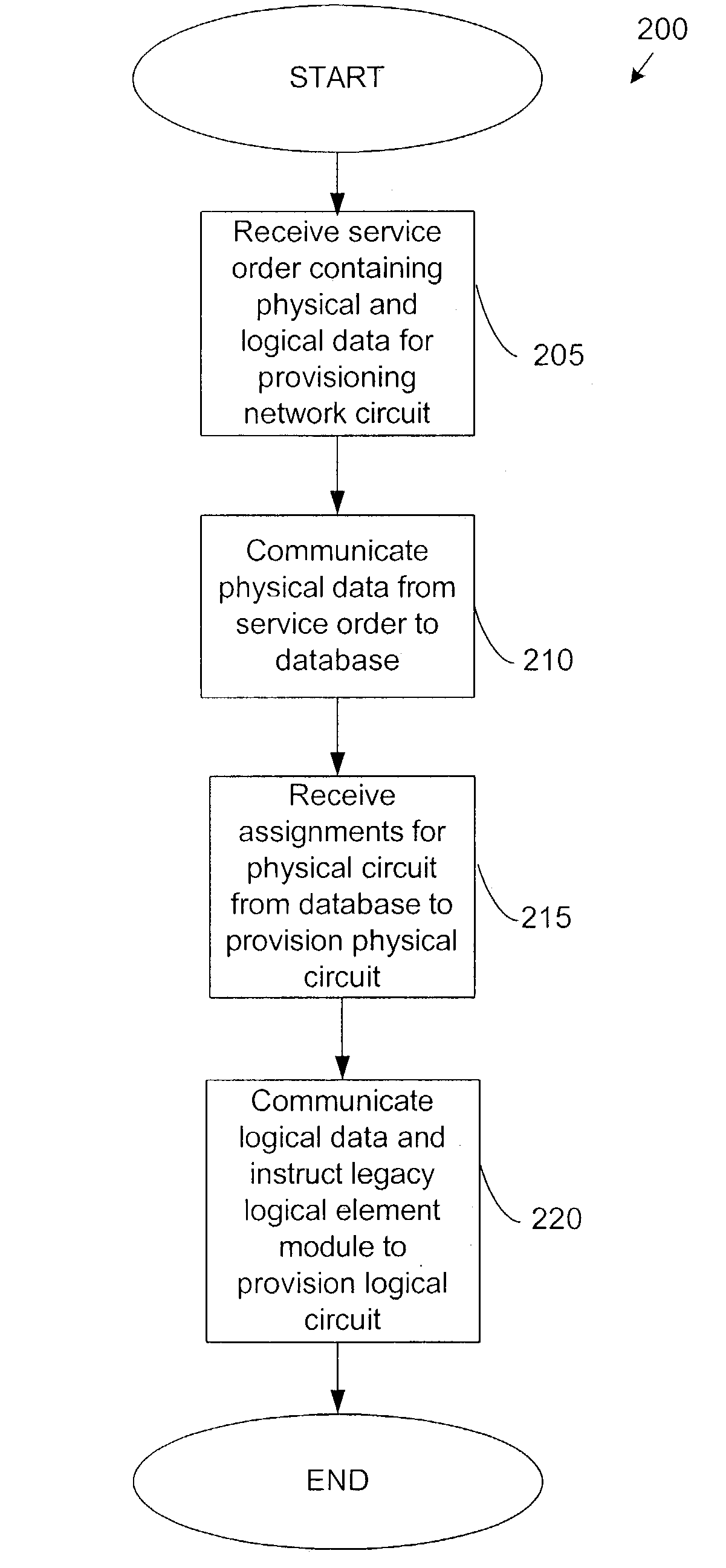
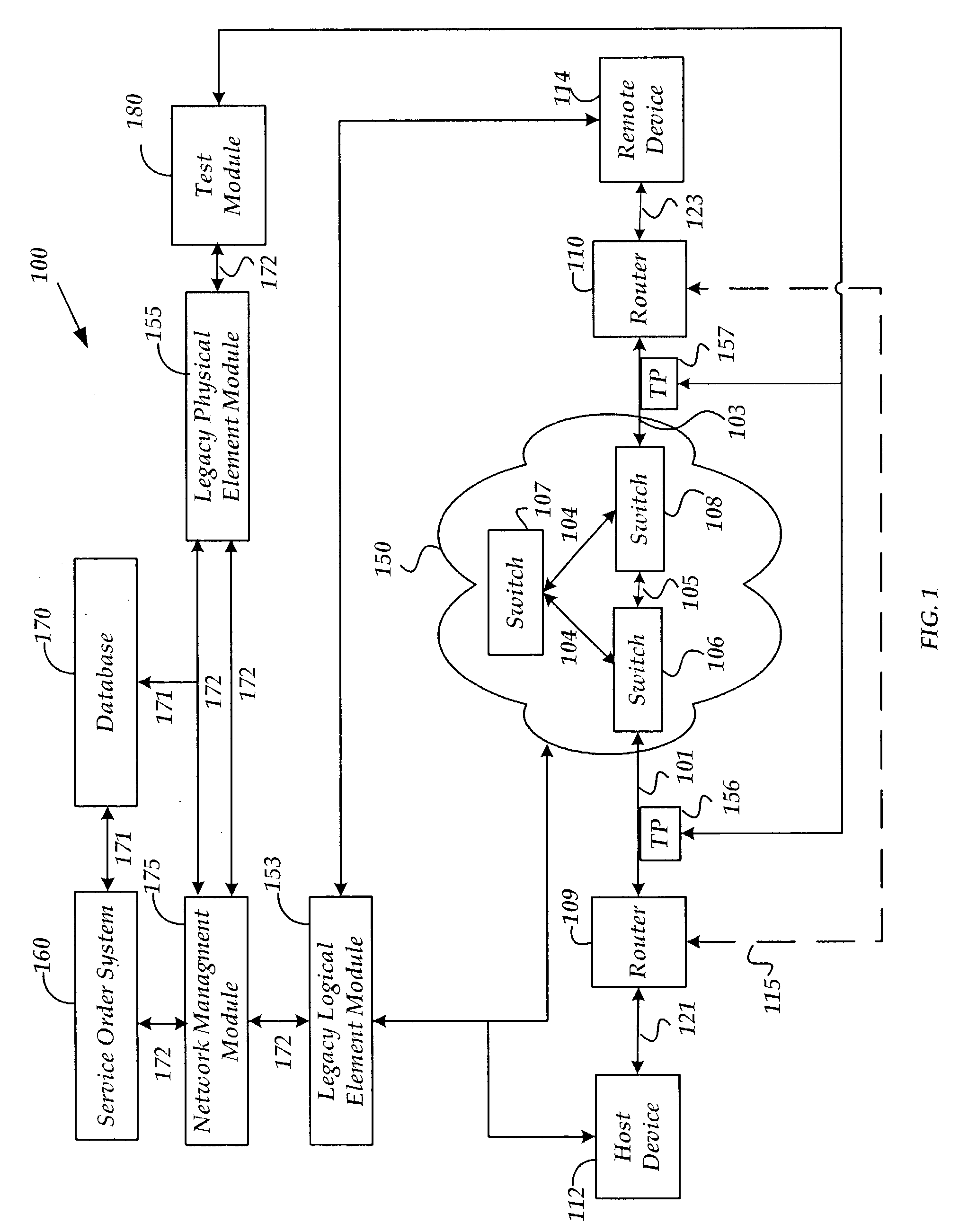
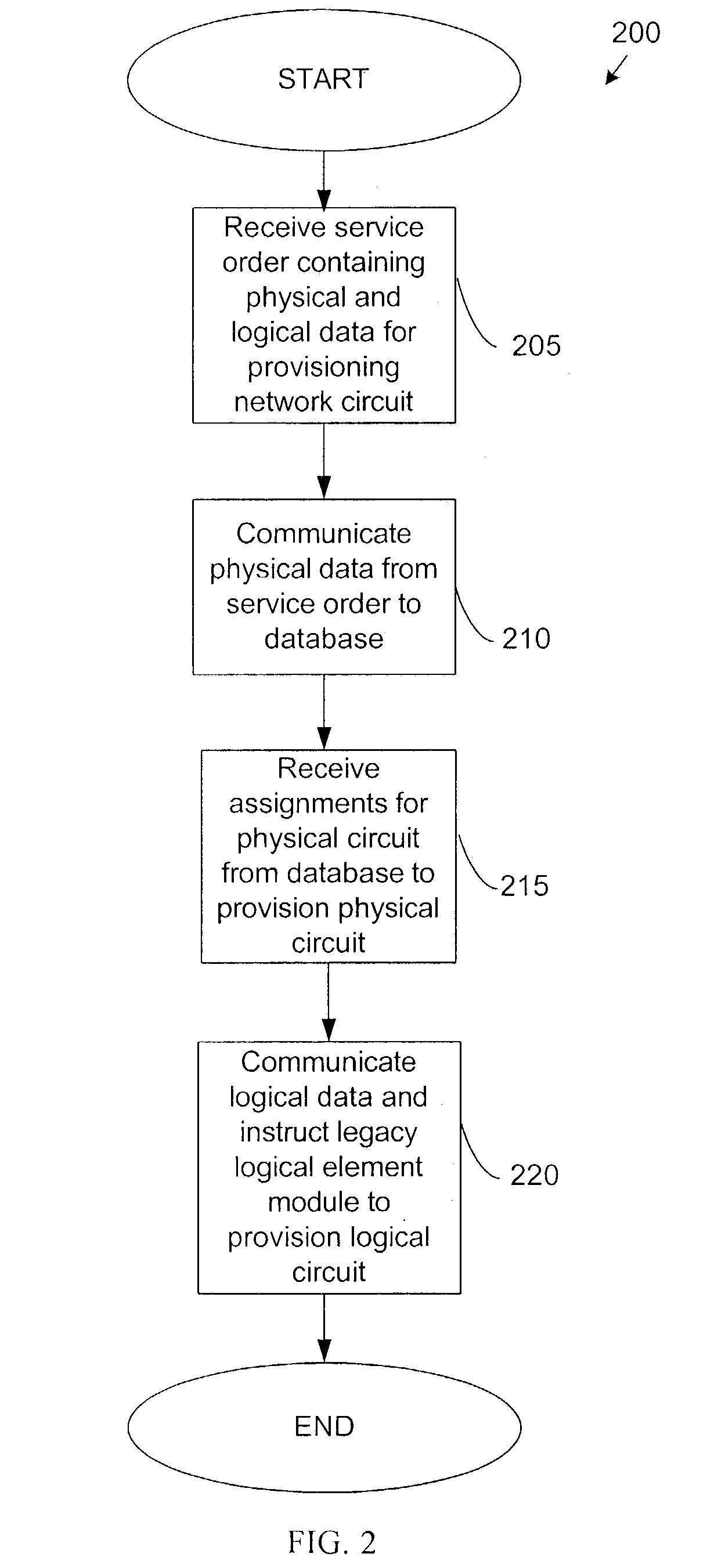
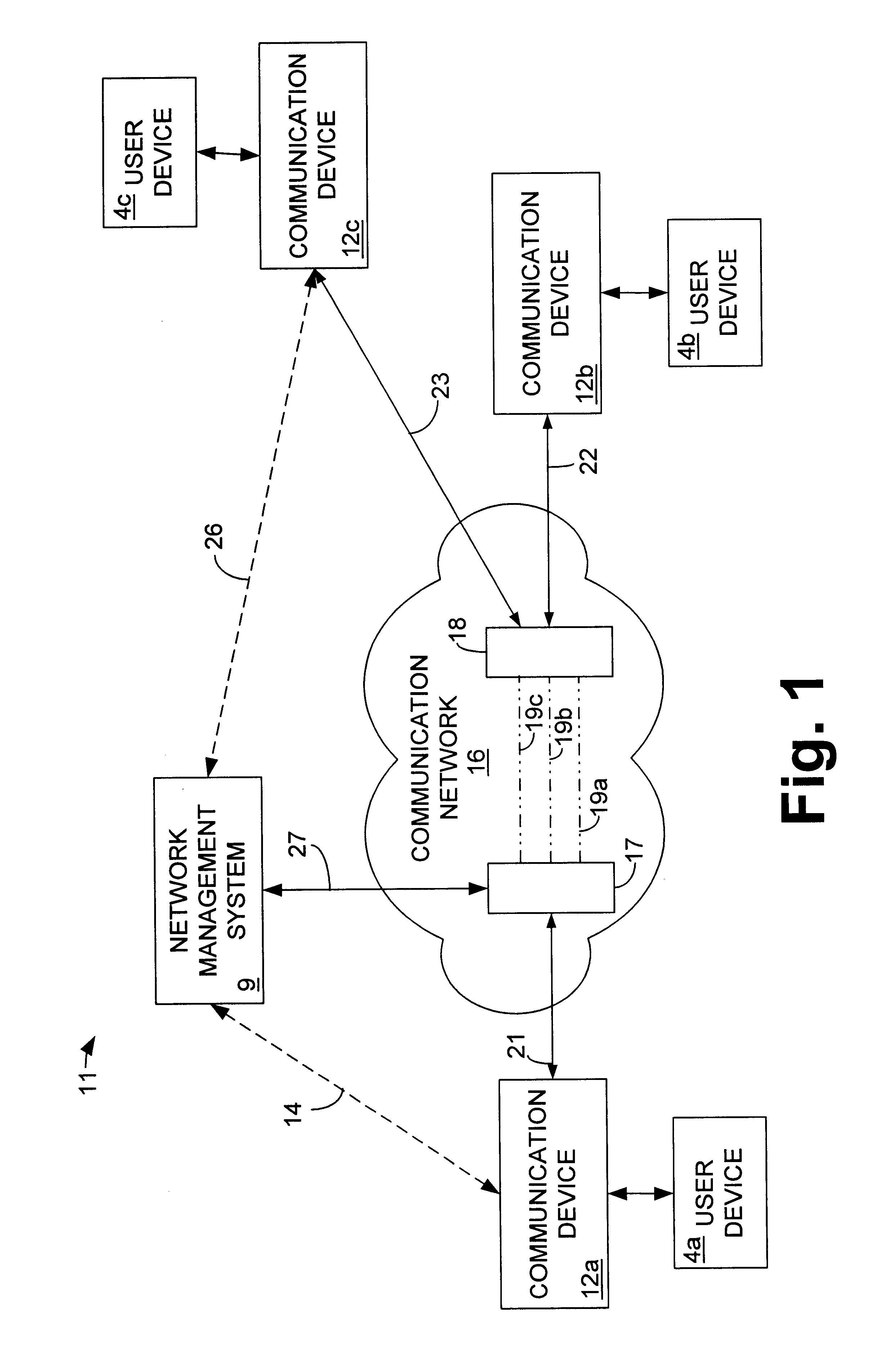
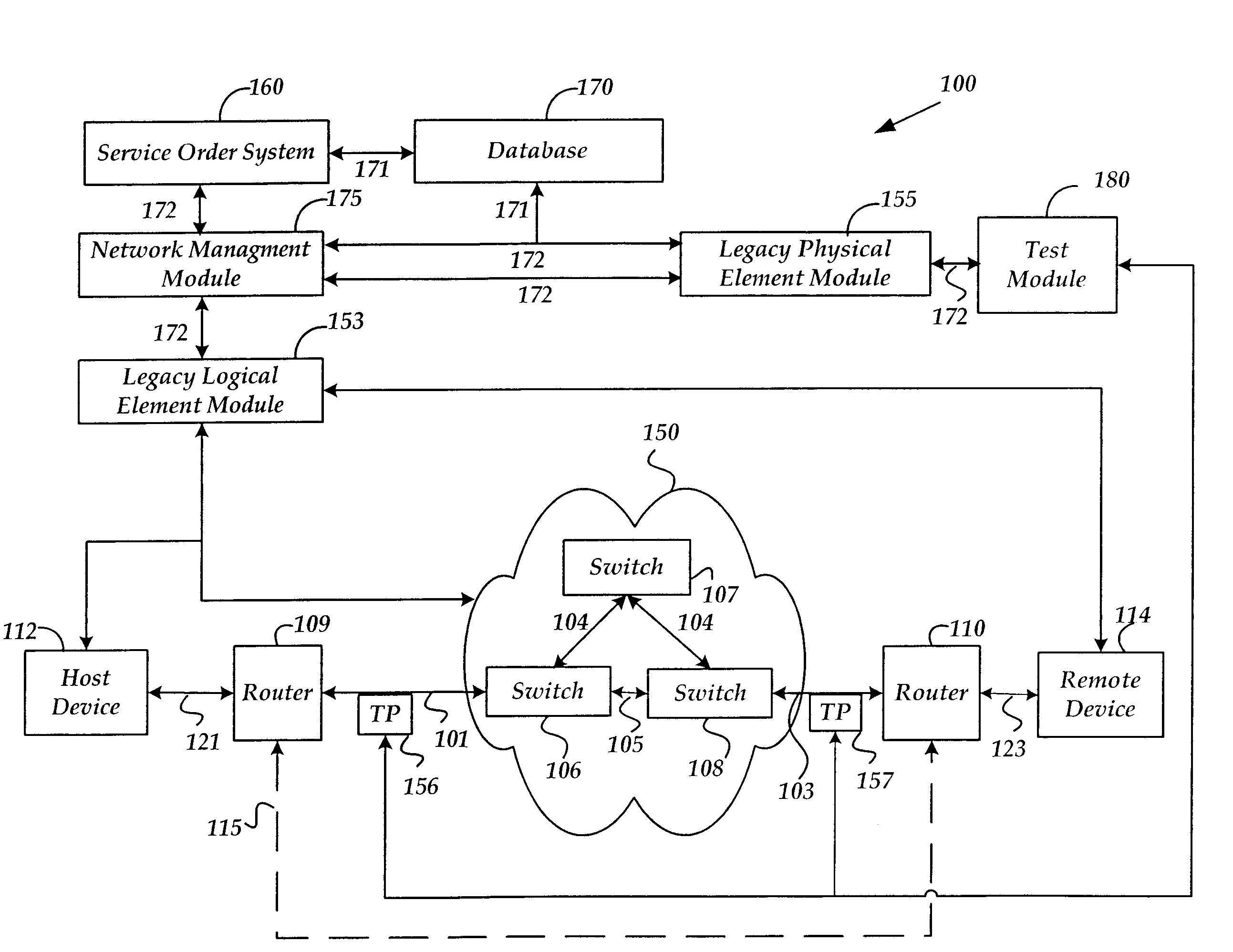
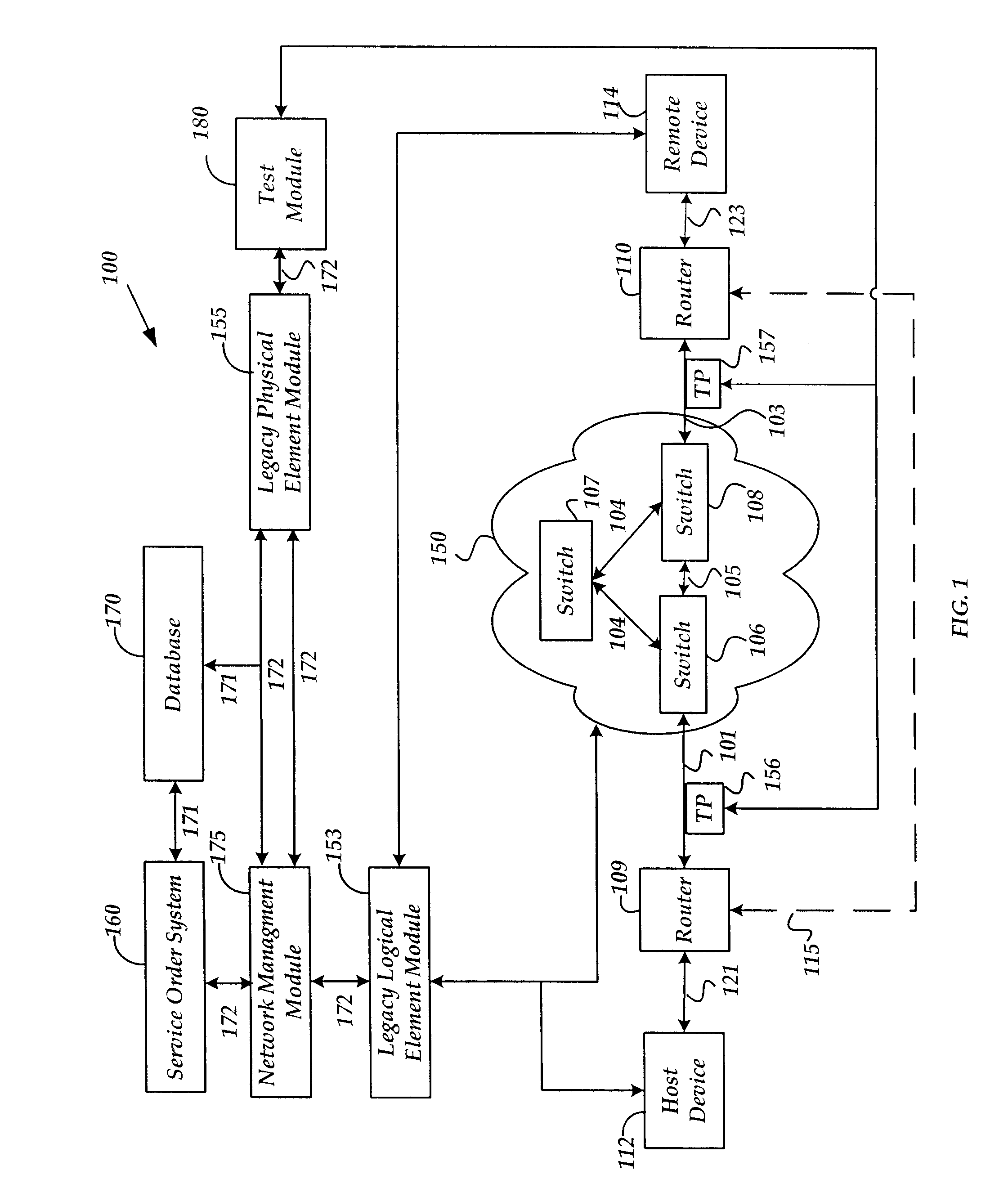
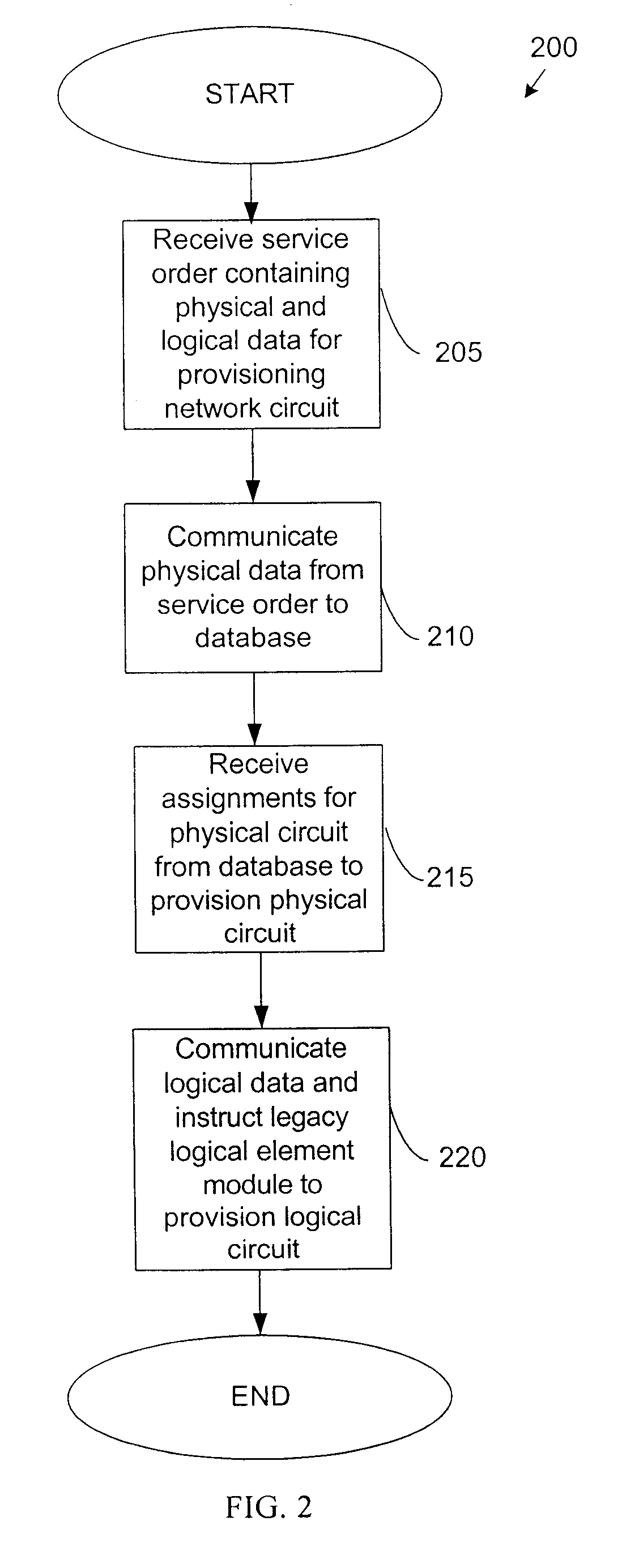
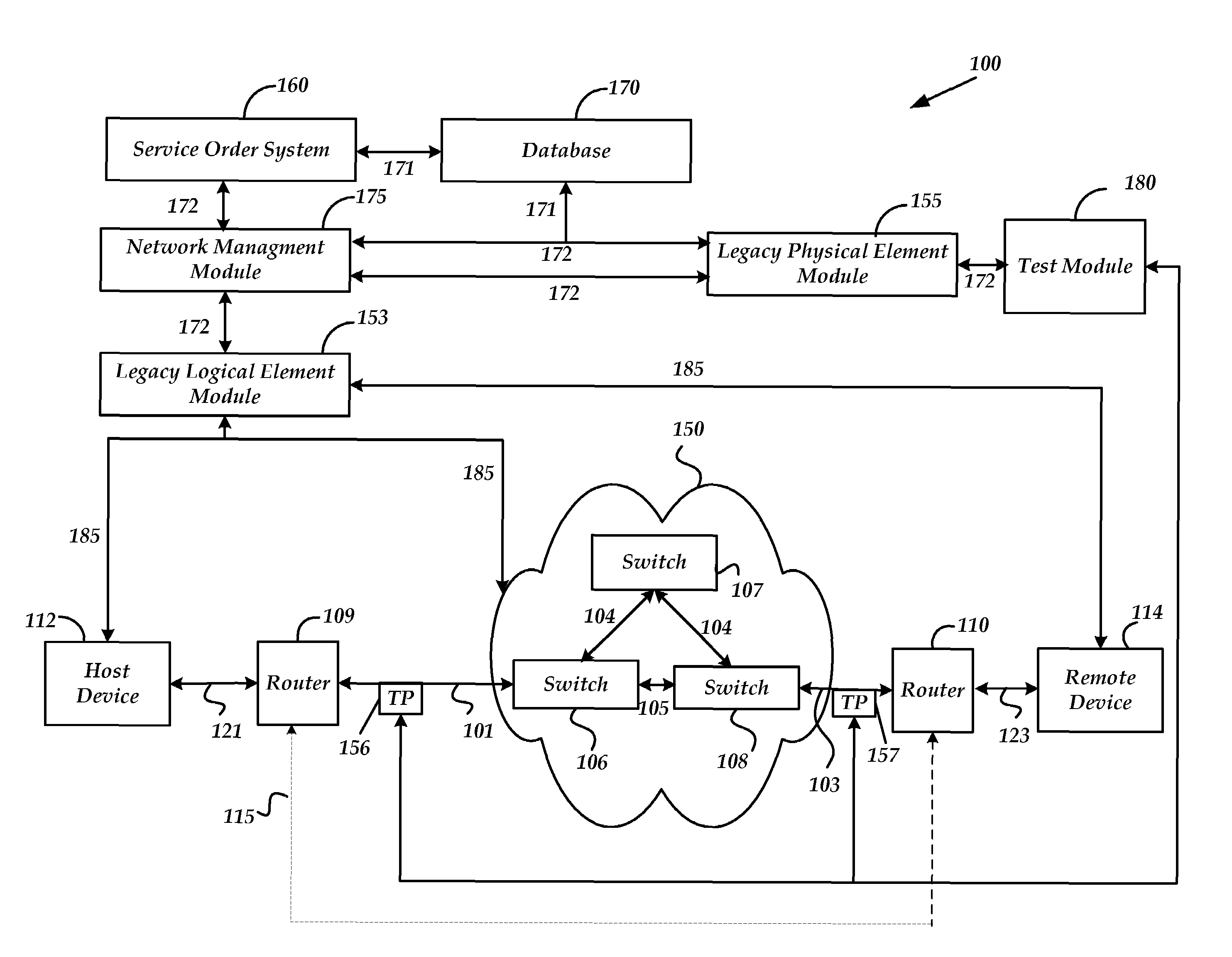
Method and system for provisioning and maintaining a circuit in a data network
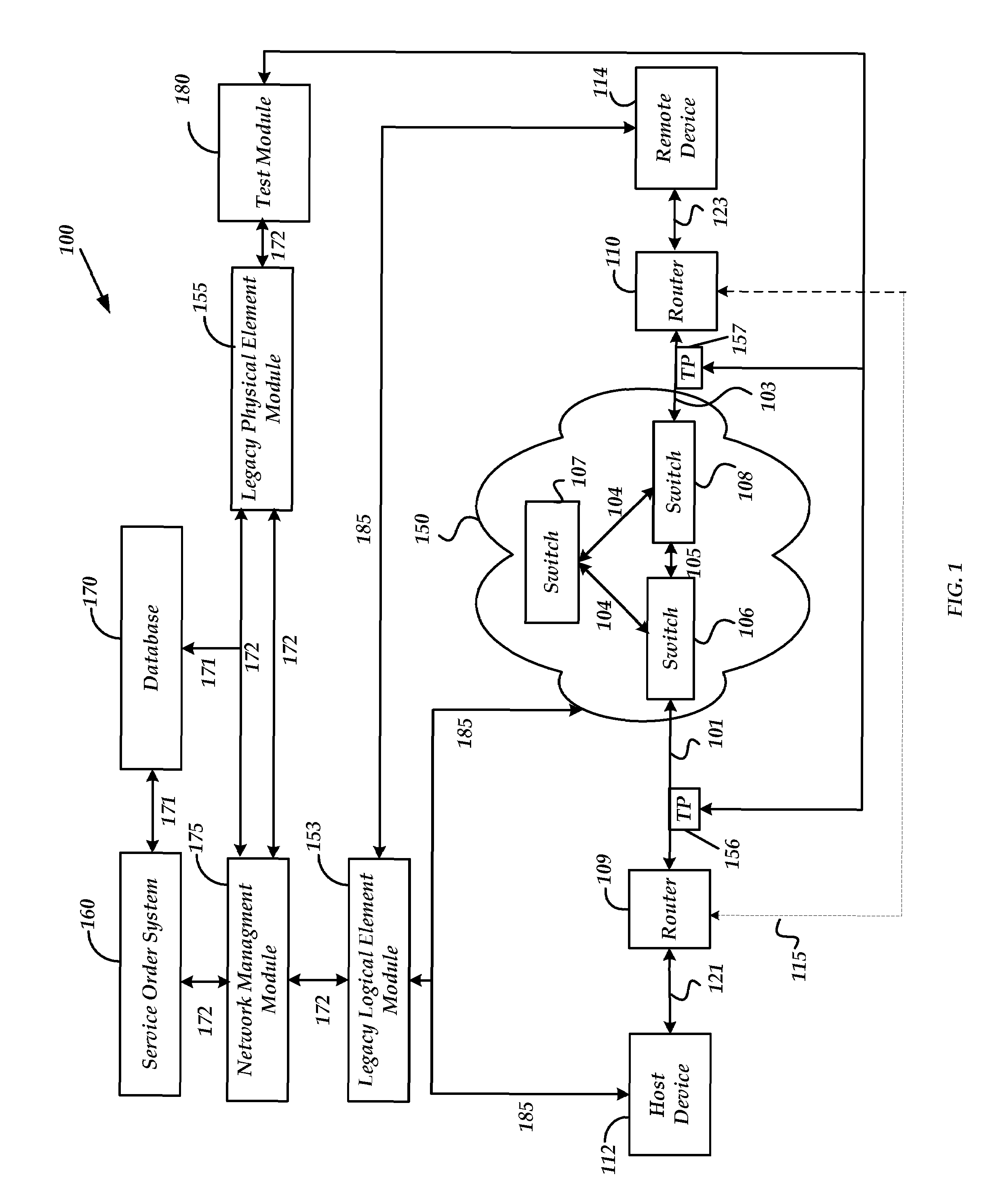
A method and system are provided for provisioning a circuit in a data network without manual intervention. A network management module receives an order for provisioning the circuit and then, based on the order, transmits a request to a legacy logical element module to configure a logical circuit in one or more network devices in the network. The network device may be a switch. The circuit may be a frame relay circuit or an ATM circuit. A method and system are also provided for maintaining a network circuit in a data network. The network circuit includes both a logical circuit and a physical circuit. A legacy physical element module sends a request for logical circuit data to a legacy logical element module through a network management module in communication with the legacy physical element module and the legacy physical element module. Based on the request, the legacy logical element module retrieves the logical circuit data from one or more network devices in the network and transmits the data to the legacy physical element module through the network management module. Upon receiving the logical circuit data, the legacy physical element module troubleshoots the physical circuit to maintain the network circuit.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Address resolution in IP interworking layer 2 point-to-point connections
InactiveUS20040202199A1Time-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolFrame Relay
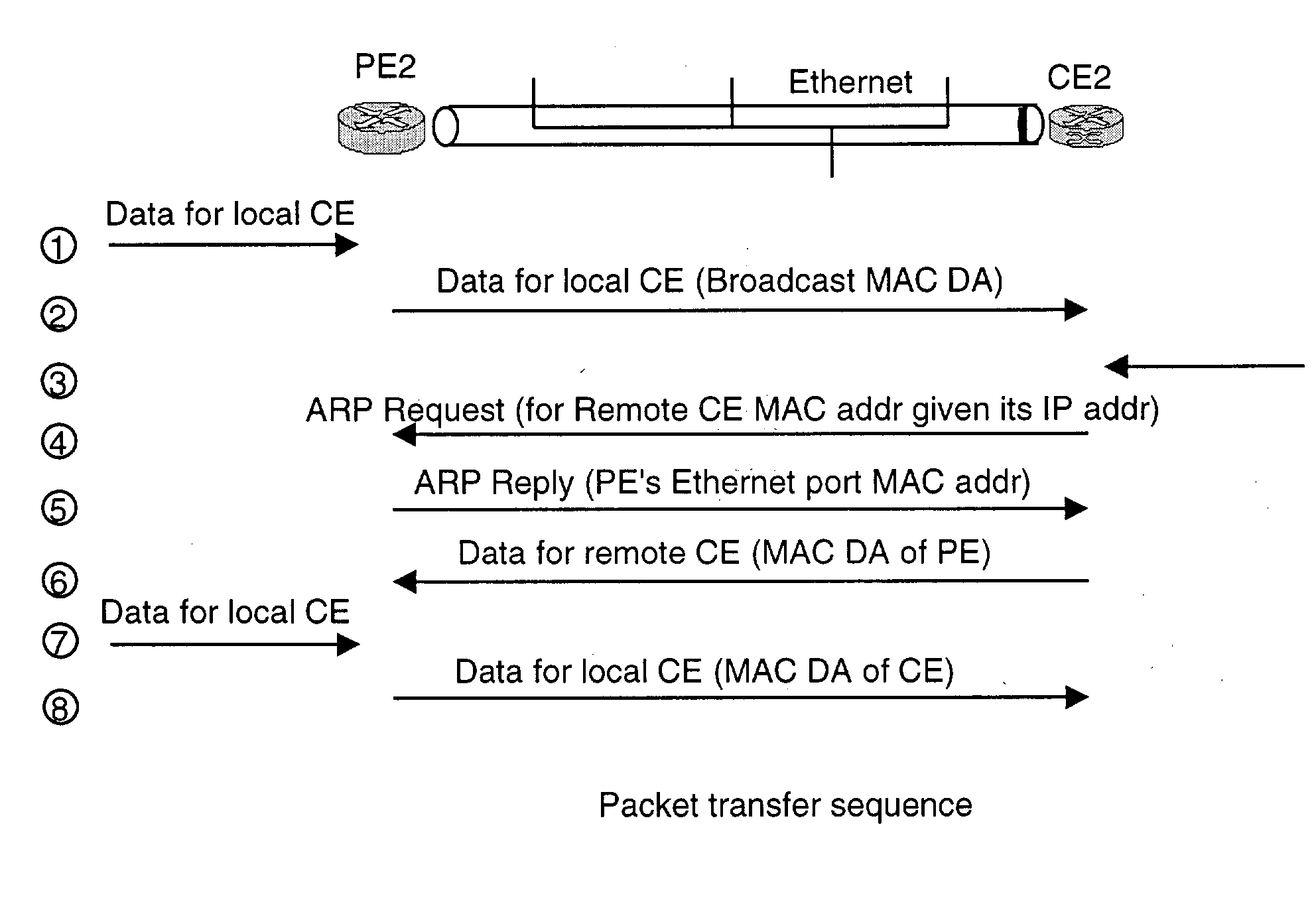
A heterogeneous point-to-point links involves different technologies at it two ends, e.g., Ethernet at one end and ATM or Frame Relay at the other end. If two IP systems are connected via a heterogeneous point-to-point link, each may be using different address learning techniques. It is up to the Provider Edge devices to make these different techniques inter-work. A novel provider edge device and procedures that the edge device it to perform for forwarding packets properly are described. According to the invention, the provider edge device uses a broadcast address to forward the packet in one direction toward a customer edge device. In another direction, the provider edge device responds to an ARP request from the customer edge device with its own MAC address so that it can receive a packet from the customer edge device.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
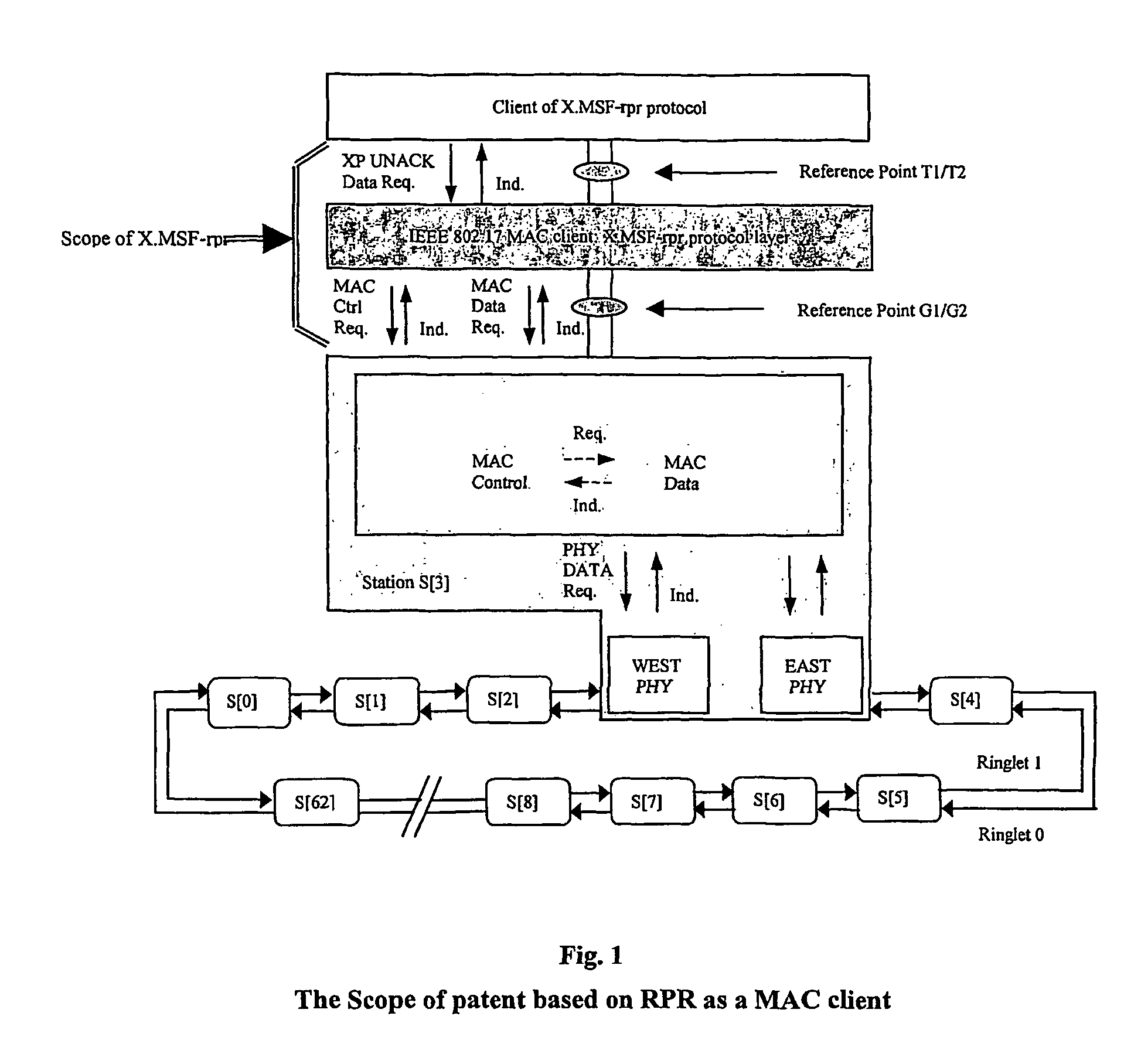
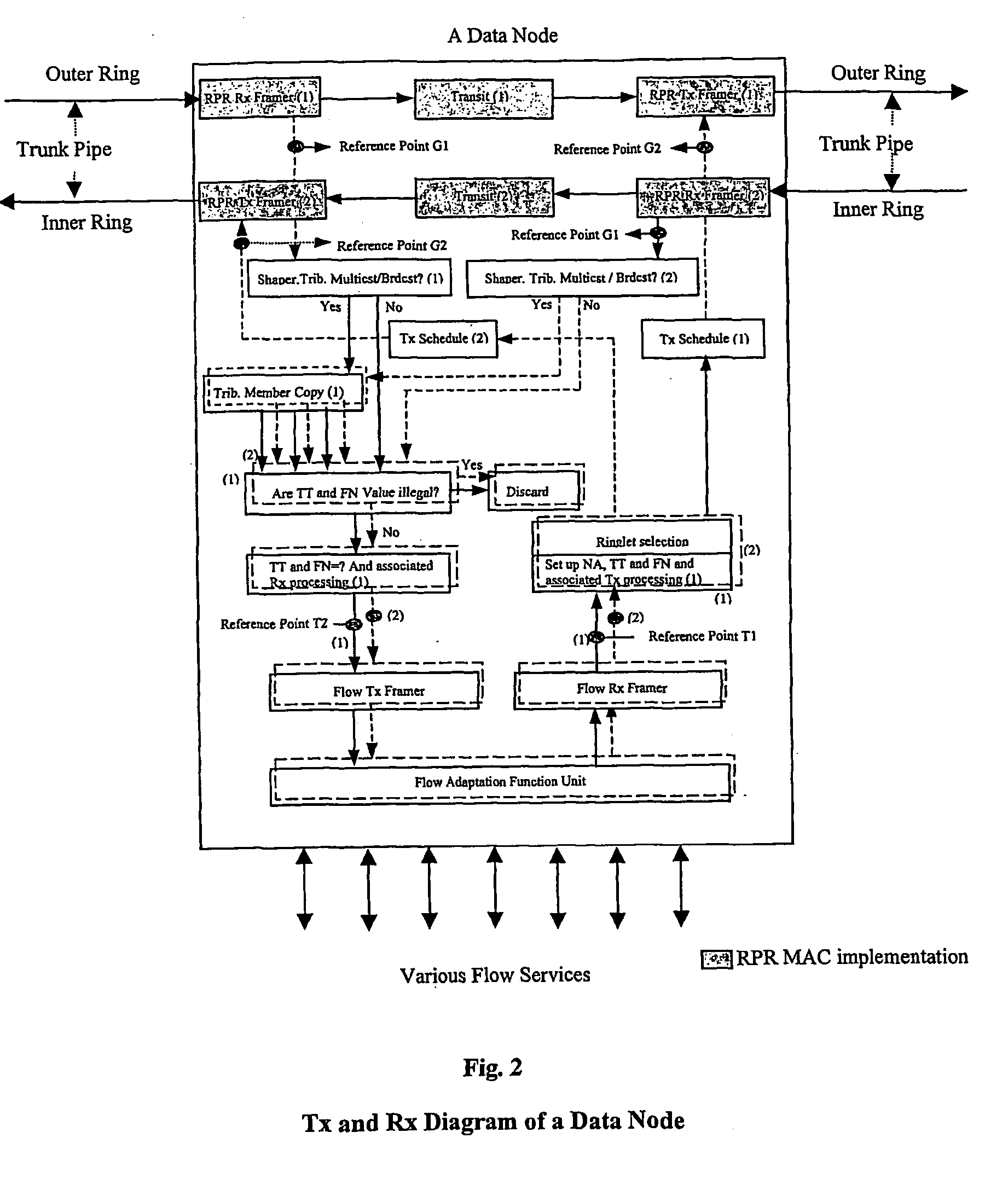
Implementation method on multi-service flow over rpr and apparatus therefor
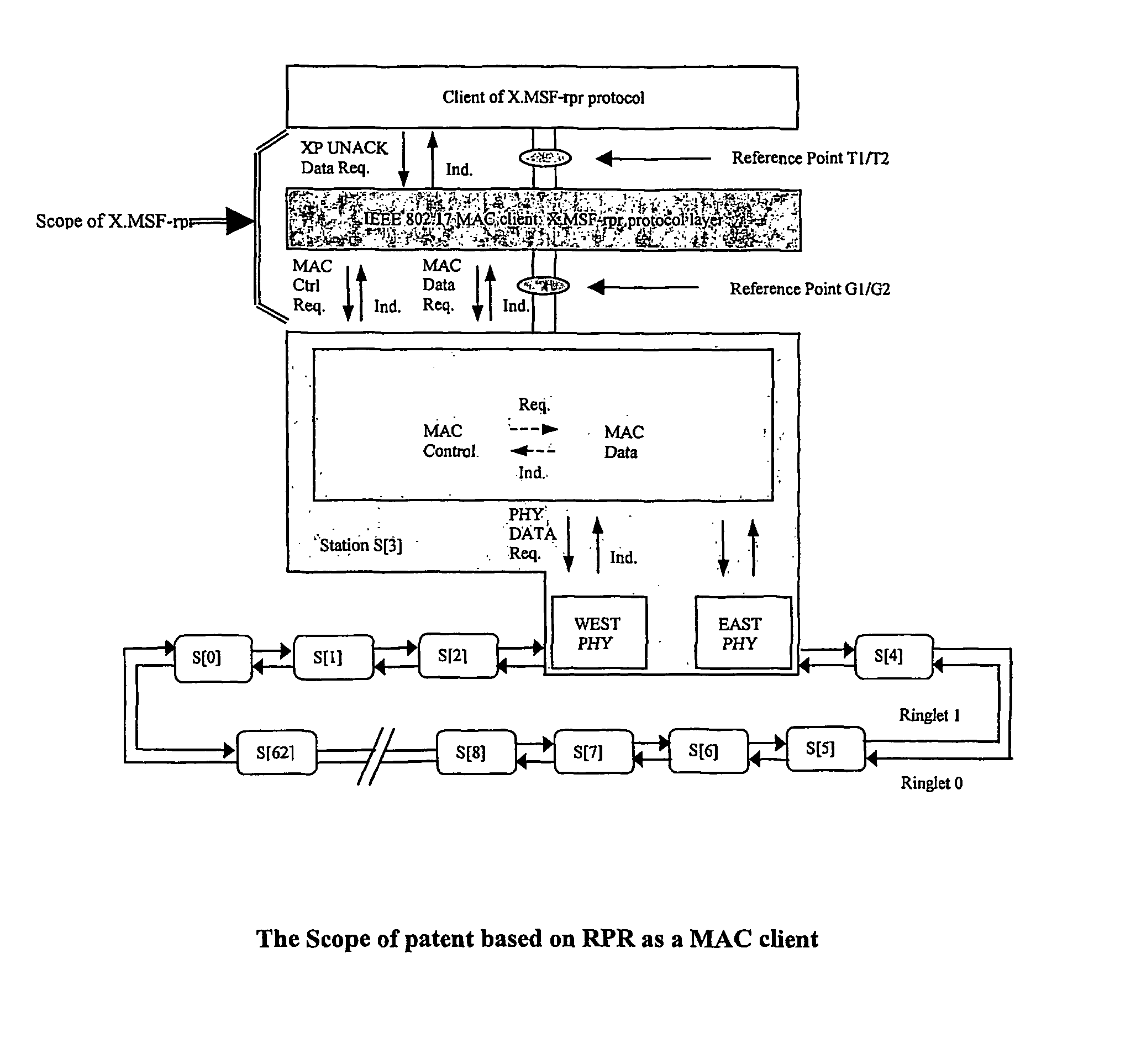
ActiveUS20060007854A1Simplify accounting mechanismMaintenance work is reducedSpecial service provision for substationLaser detailsService flowFrame Relay
This technology handles Multiple Services Flow (MSF) Based on RPR and a way of multi-service flow over RPR. MSF is defined to work at the client RPR MAC layer and uses Fairness of RPR MAC to support services of Class A, Class B and Class C. MSF is used in configurations where flow based service is managed from provisioning. Architecturally, the link and broadcast topologies are supported also. The features of flow (Service, just like Ethernet, Frame Relay and G.702 etc) based 1+1, 1:1 and 1:N protection within 50 ms, flow (or Service flow) based BW management with symmetry and asymmetry, flow based multicast and Frame Sequence Number for Performance Monitoring of flow are highlighted in this patent.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
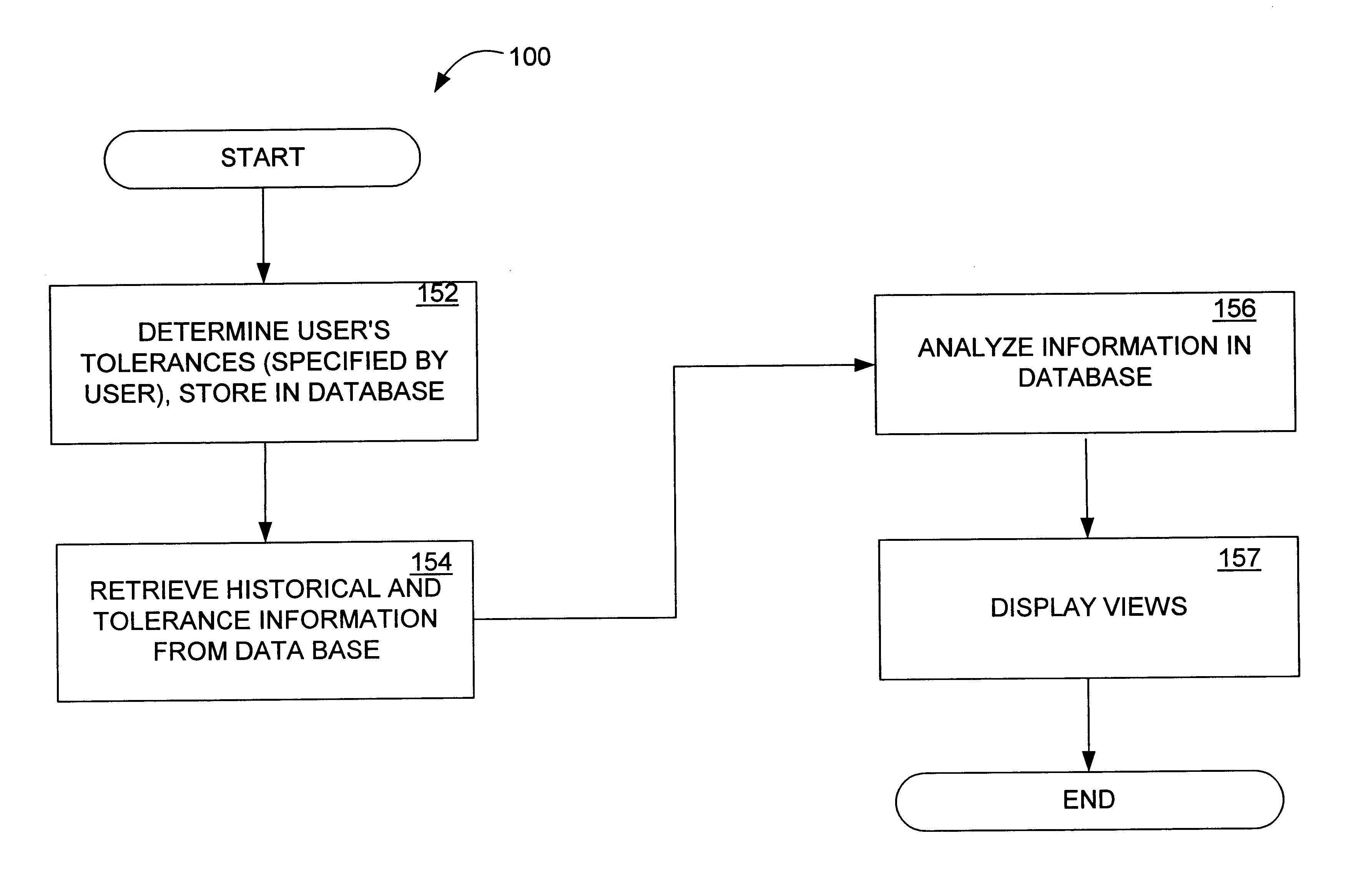
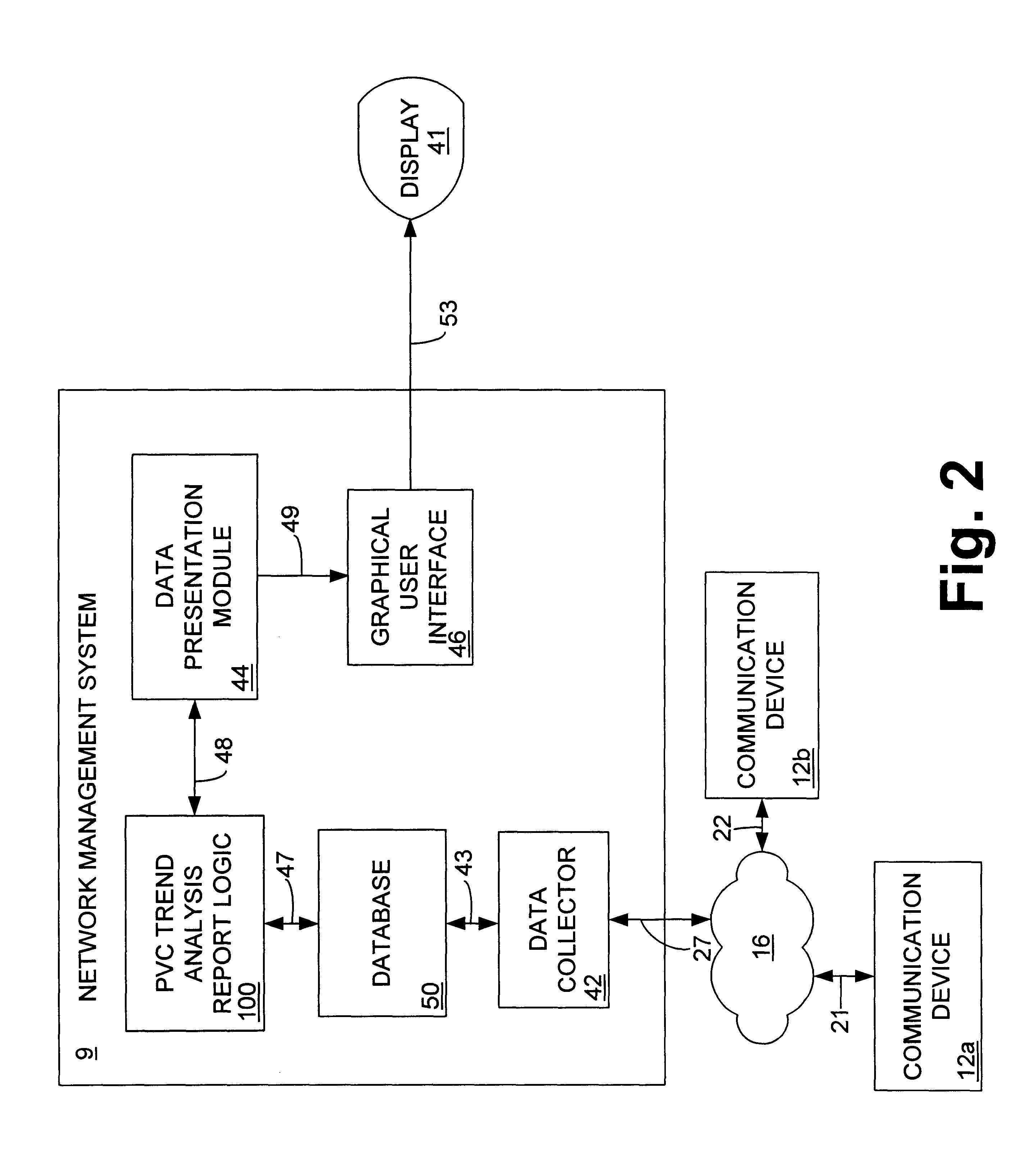
System and method for automatically determining recommended committed information rate in a frame relay network
InactiveUS6912575B1Automatically determineTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsCommitted information rate
A system and method are disclosed for using tolerances obtained from a user together with historical information about a communication network to analyze the network's performance and to calculate and recommend a specific change to the committed information rate (CIR) over a given frame relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC). The historical information, which is collected by a network management system connected to at least two communication devices in a communication network, relates to various performance parameters, which may include the total data transmitted, received and dropped above and within the original CIR, and the burstiness of the data. The historical information is automatically analyzed in view of the user's designated tolerances to determine the network's data transmission performance, and a forward-looking recommendation of an optimum CIR is made, based on the analysis. The results of the analysis and the recommended change to the CIR are displayed to the user in a graphical format.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and system for provisioning and maintaining a circuit in a data network
A method and system are provided for provisioning a circuit in a data network without manual intervention. A network management module receives an order for provisioning the circuit and then, based on the order, transmits a request to a legacy logical element module to configure a logical circuit in one or more network devices in the network. The network device may be a switch. The circuit may be a frame relay circuit or an ATM circuit. A method and system are also provided for maintaining a network circuit in a data network. The network circuit includes both a logical circuit and a physical circuit. A legacy physical element module sends a request for logical circuit data to a legacy logical element module through a network management module in communication with the legacy physical element module and the legacy physical element module. Based on the request, the legacy logical element module retrieves the logical circuit data from one or more network devices in the network and transmits the data to the legacy physical element module through the network management module. Upon receiving the logical circuit data, the legacy physical element module troubleshoots the physical circuit to maintain the network circuit.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P +1
Relay apparatus for encrypting and relaying a frame
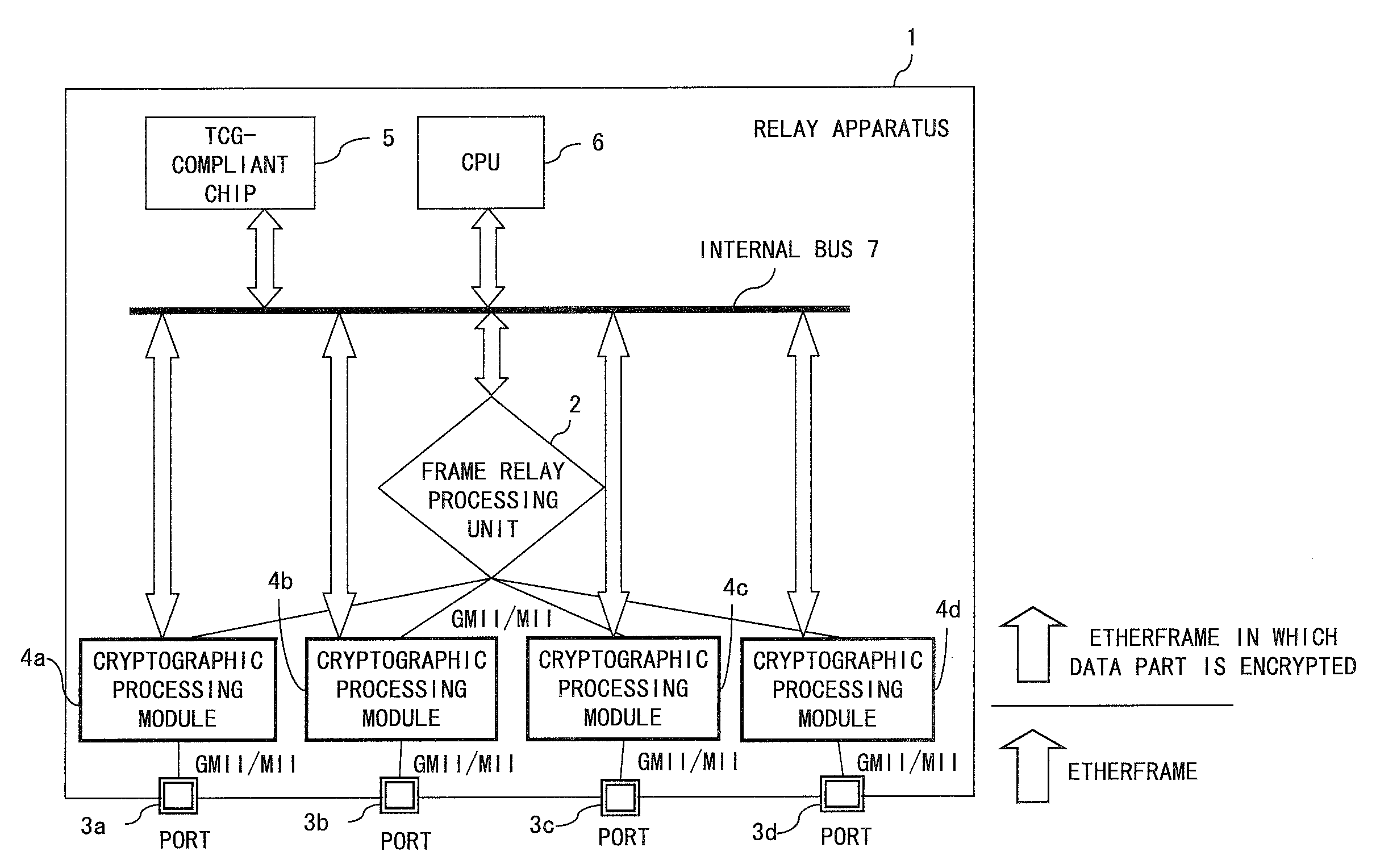
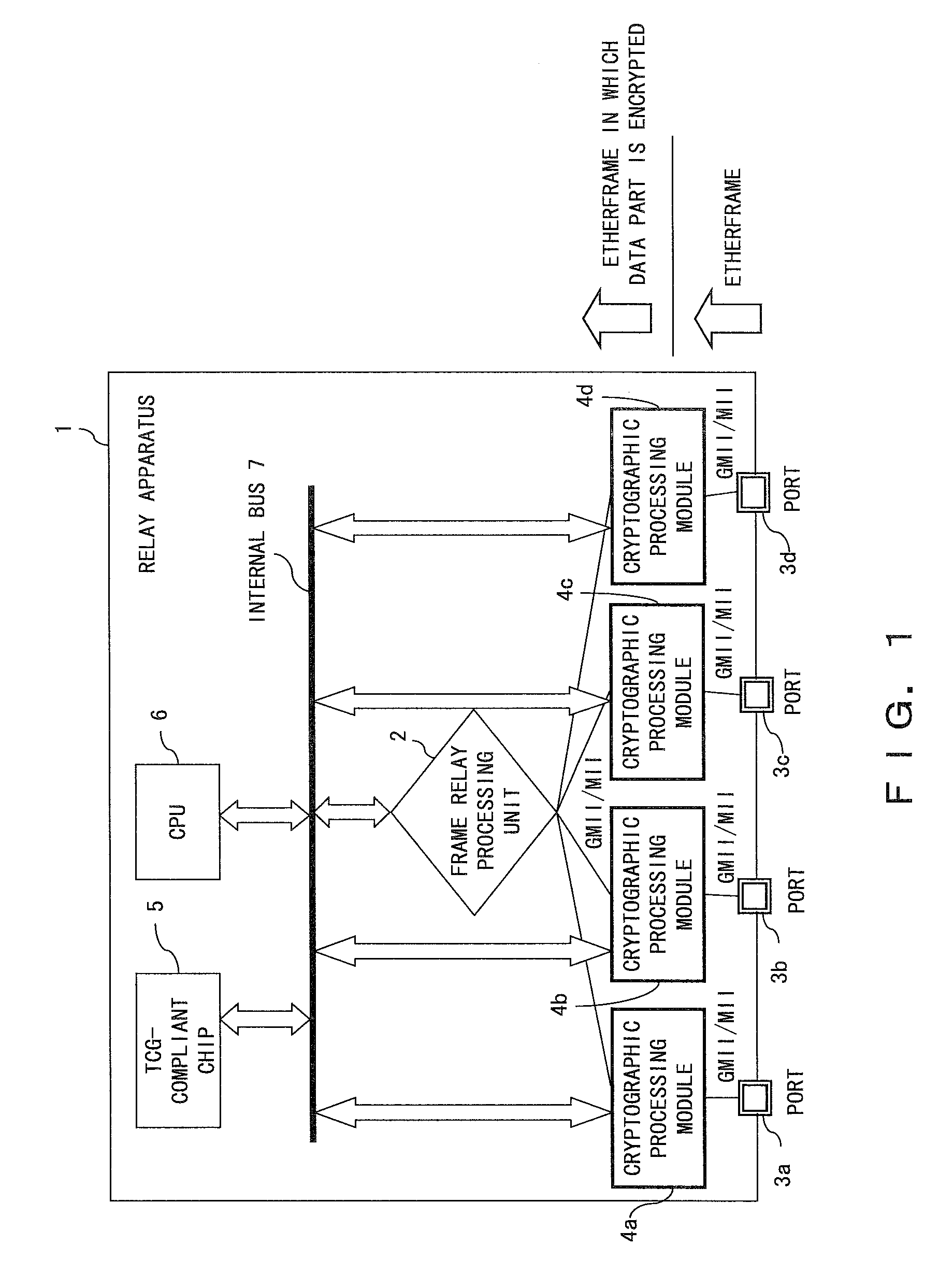
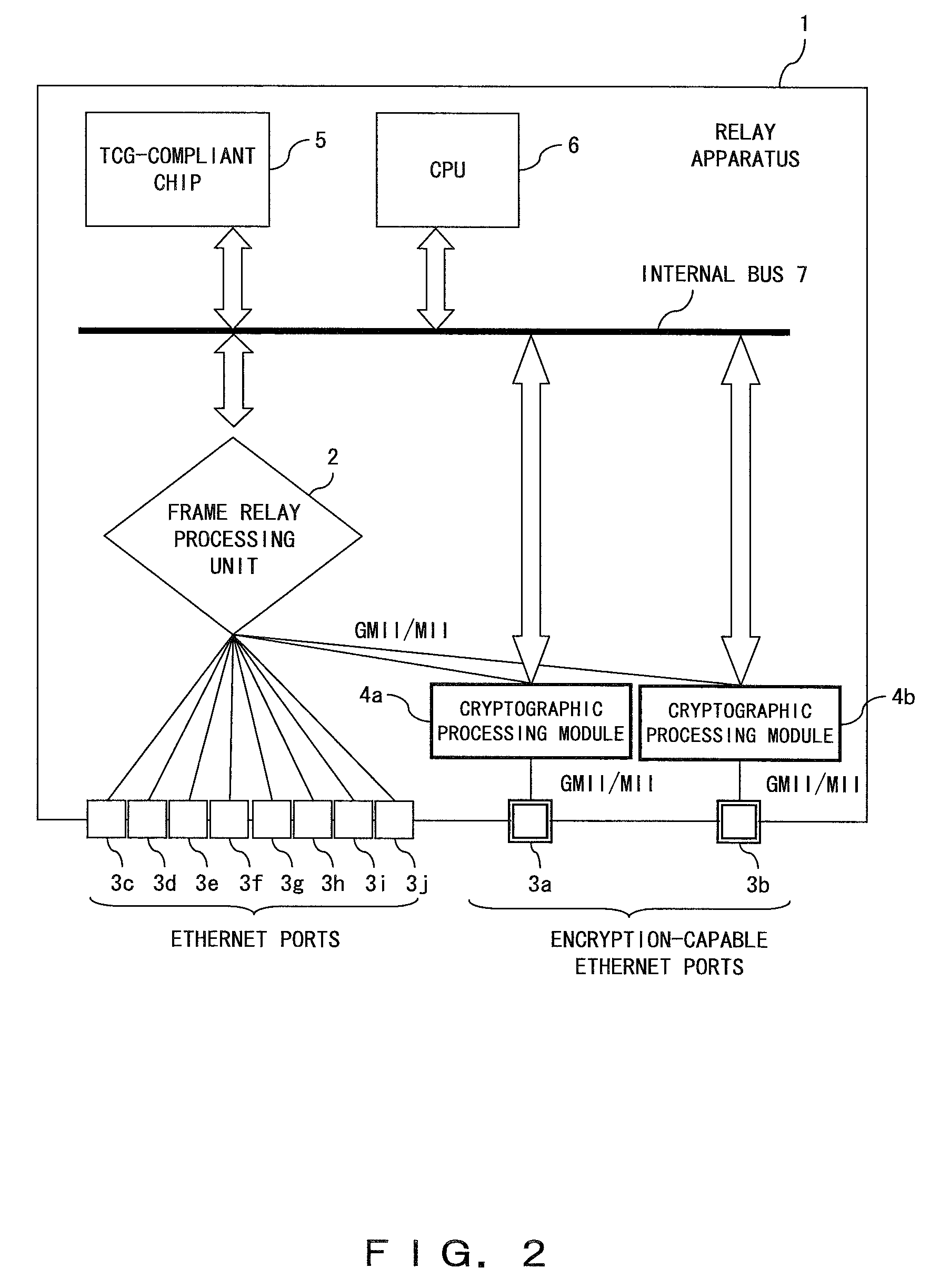
InactiveUS20080052533A1Simple configurationIncrease speedMultiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationGeneral purposeFrame Relay
A relay apparatus comprises a frame relay processing unit for relaying a frame, a plurality of ports for sending and receiving the frame to and from the outside, and a cryptographic processing module corresponding to each of the ports. Each cryptographic processing module is connected to the corresponding port and to the frame relay processing unit by means of general-purpose interfaces such as MII. The cryptographic processing module performs the encryption process and decryption process so that the frame relay processing unit can concentrate on the relay process and the relay speed is not subject to degradation. Also, the cryptographic processing module can generate a different cryptographic key for each frame without requiring dynamic exchange of key information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
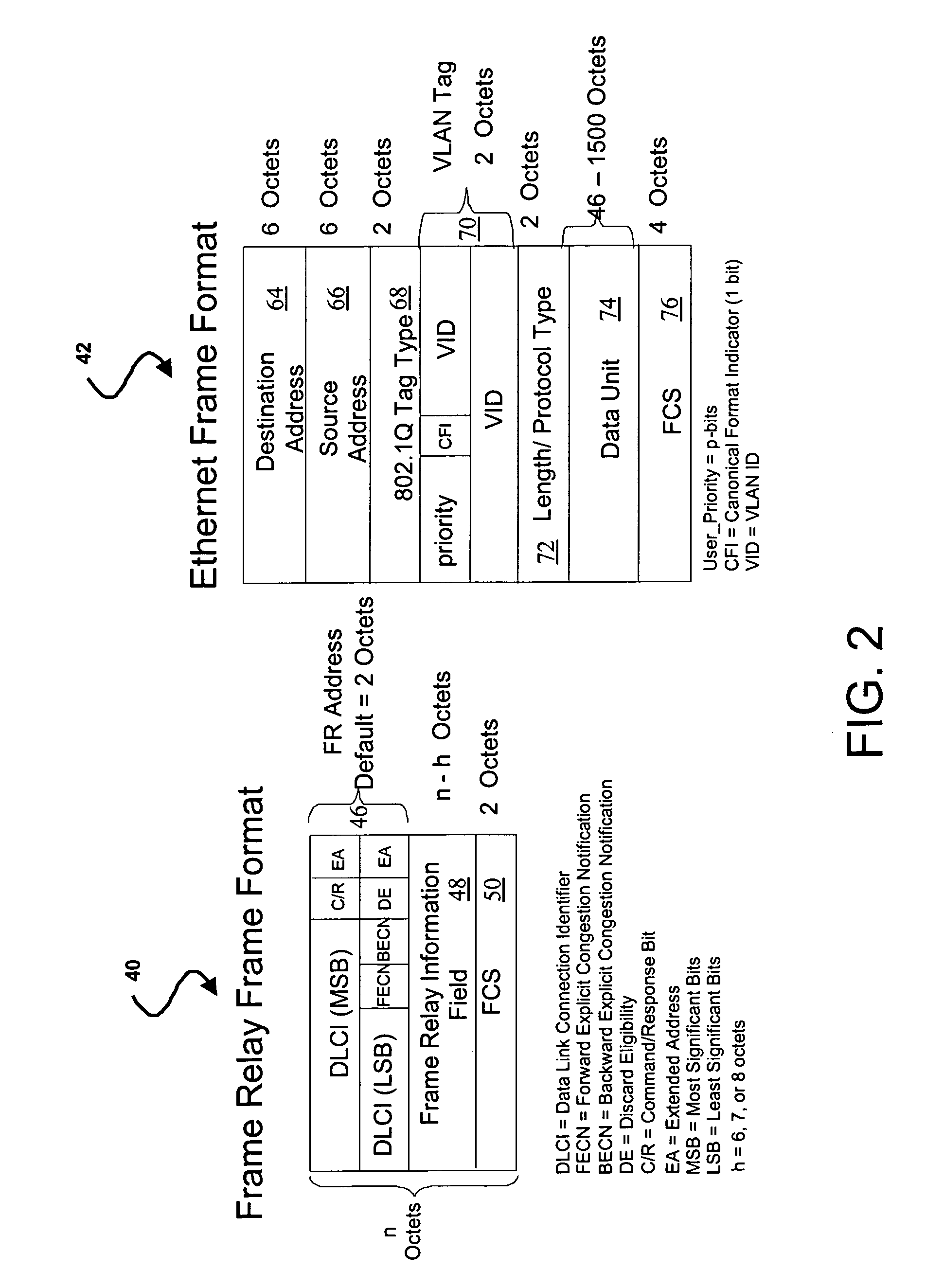
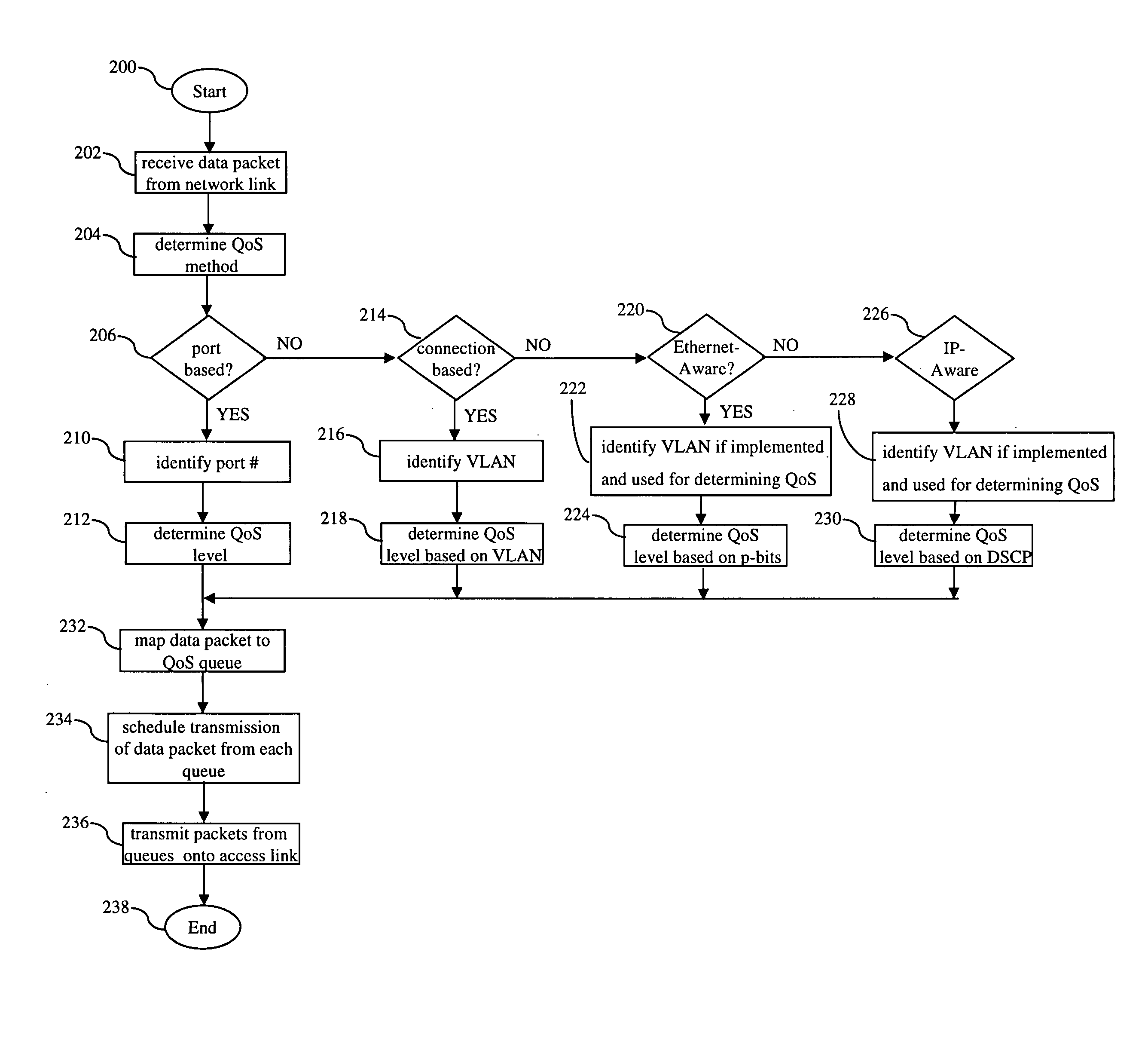
Ethernet to frame relay interworking with multiple quality of service levels
ActiveUS20050144327A1Easy to operateMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionQuality of serviceFrame Relay
A method of supporting multiple quality of service (QoS) levels for data being transmitted between two networking devices, such as customer equipment (CE), that use Ethernet and Frame Relay (FR). The method supports multiple QoS services in a network where a first CE is connected to a first edge device (interworking unit) using the Ethernet protocol and a second CE is connected to a second edge device using the FR protocol. The edge devices may be directly connected together or they may be connected through a network backbone using any generally accepted network protocol. The first CE may be connected to the first edge device using a single Ethernet port, multiple Ethernet ports, a single virtual local area network (VLAN), or multiple VLAN's. The second CE is connected to an edge device using a single data link connection (DLC), or multiple DLC's. The method ensures QoS for data transmitted between the first and the second CE via the Ethernet protocol to the FR protocol and vice versa.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
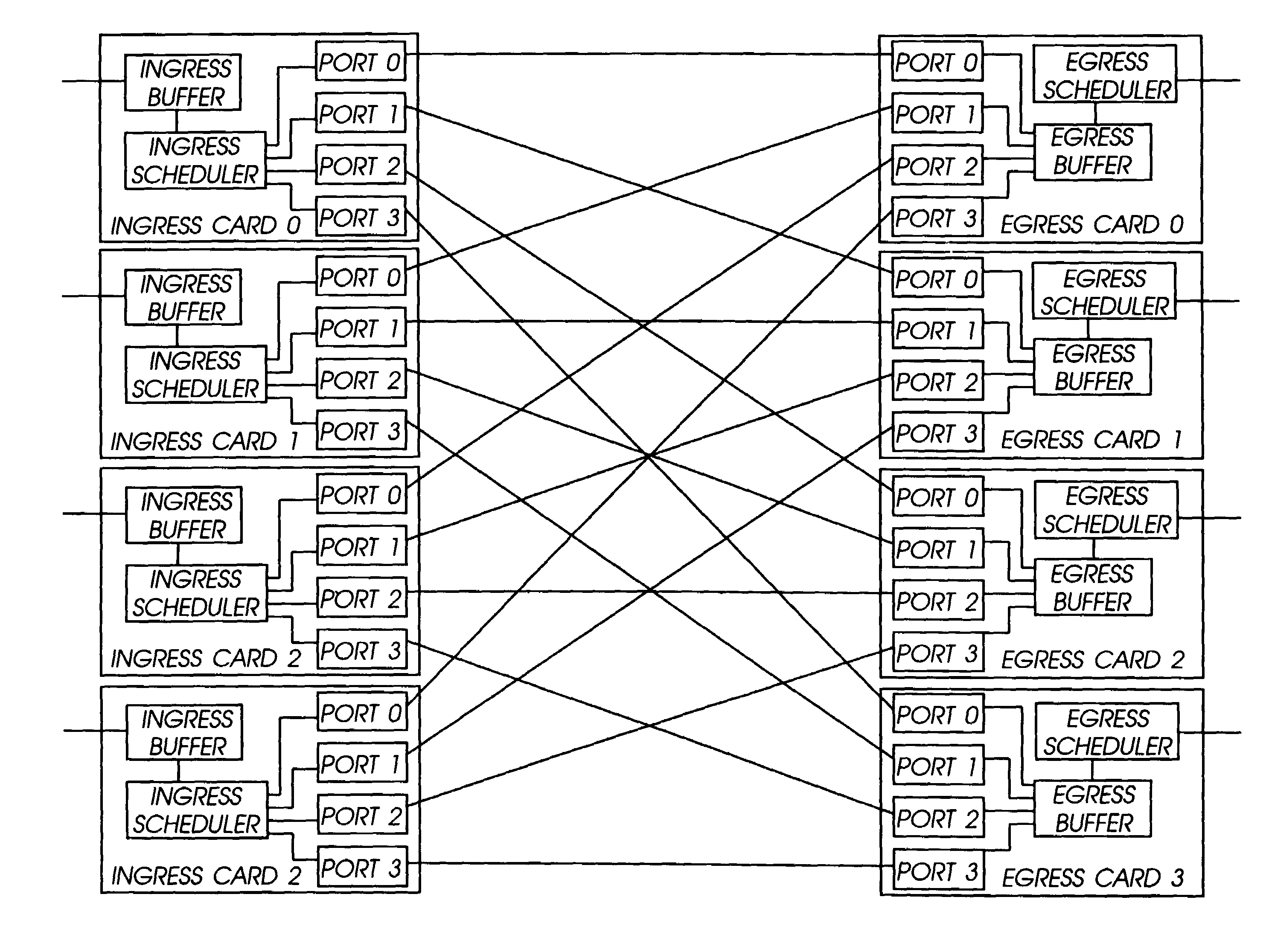
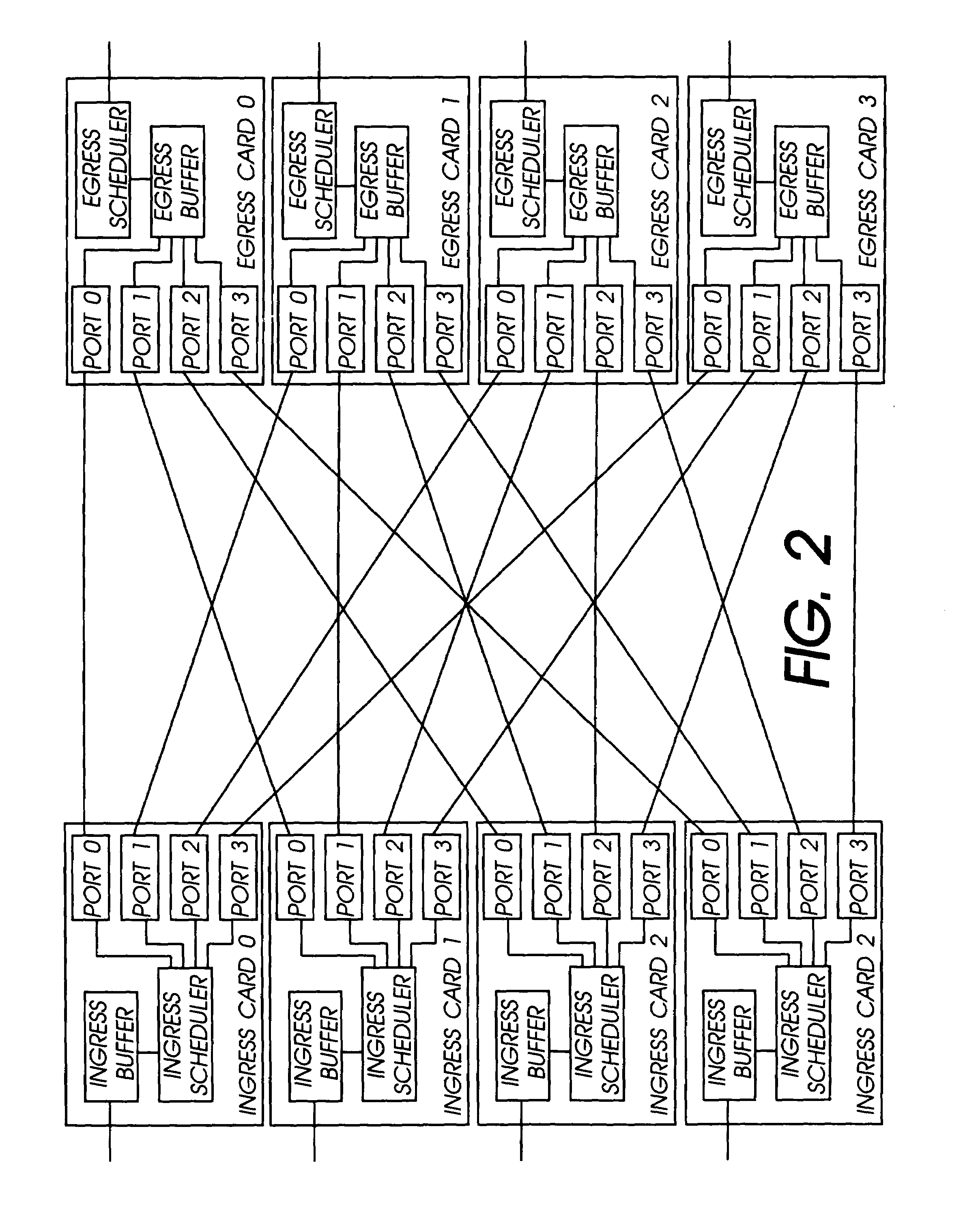
Distributed control of data flow in a network switch
The network switch described herein provides a cell / packet switching architecture that switches between line interface cards across a meshed backplane. In one embodiment, the switching can be accomplished at, or near, line speed in a protocol independent manner. The protocol independent switching provides support for various applications including Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching, Internet Protocol (IP) switching, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) switching, Ethernet switching and frame relay switching. The architecture allows the network switch to provision service on a per port basis. In one embodiment, the network switch provides a non-blocking topology with both input and output queuing and per flow queuing at both ingress and egress. Per flow flow-control can be provided between ingress and egress scheduling. Strict priority, round robin, weighted round robin and earliest deadline first scheduling can be provided.
Owner:FORCE10
Method and system for frame relay and Ethernet service interworking
InactiveUS20050157750A1Different level of performanceMore bandwidth efficientTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFrame RelayProcessing element
A method and system for interworking between an Ethernet communication network and a frame relay network, in which a first network interface is operable to communicate with the Ethernet communication network using an Ethernet communication protocol. A second network interface is operable to communicate with the frame relay communication network using a frame relay protocol. A processing unit is in communication with the first network interface and the second network interface, in which the processing unit terminates frames received from a one of the frame relay communication network and the Ethernet communication network and maps parameters corresponding to the received one of the frame relay and Ethernet frames into the other of the frame relay and Ethernet frames. The mapped parameters include circuit configuration control plane information and data plane parameters corresponding to individual frames.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Apparatus and method for providing seamless service between a cellular network and wireless local area network for a mobile user
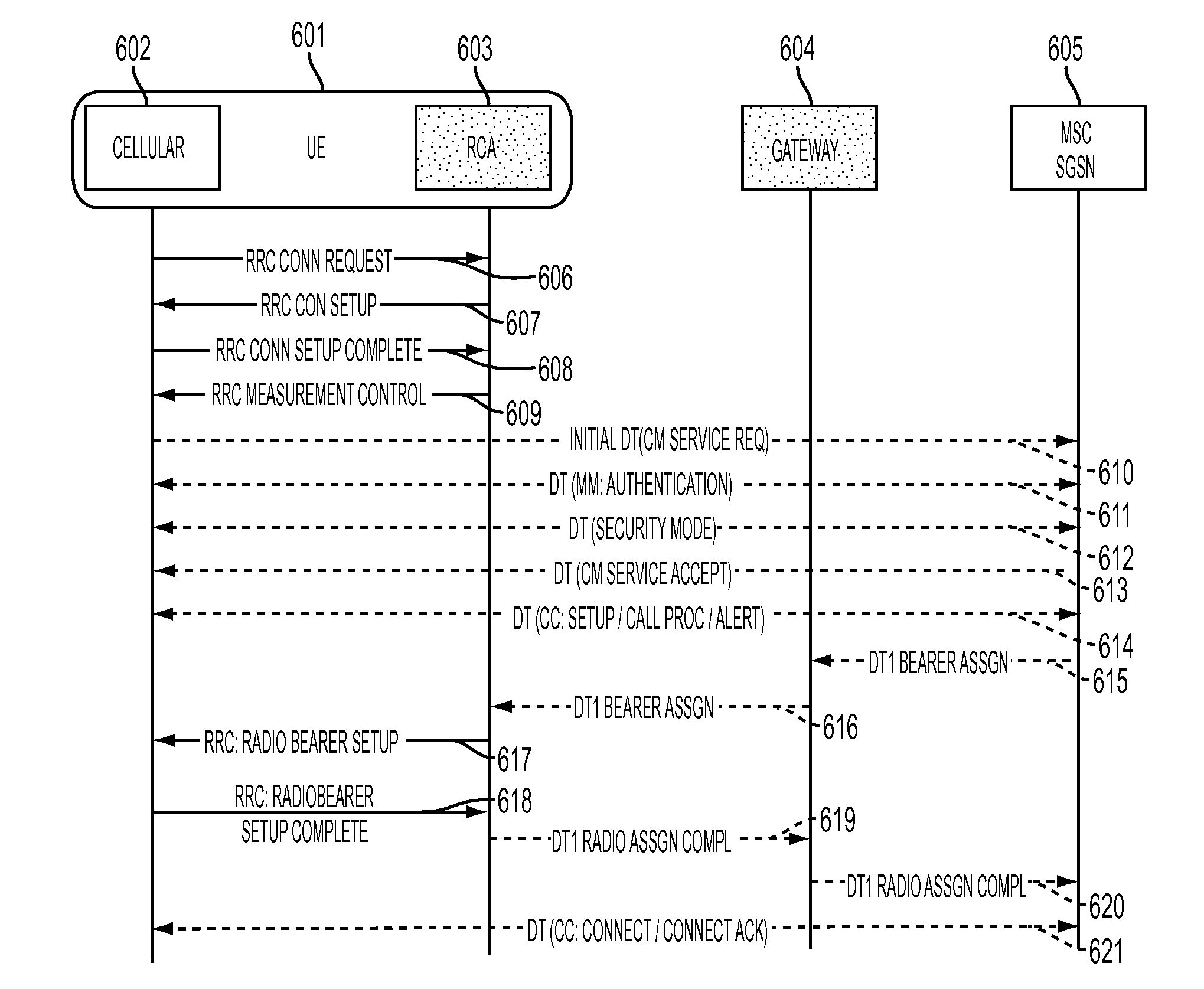
InactiveUS20130029639A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsGeneral Packet Radio ServiceFrame Relay
A wireless communication system including a cellular network and a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) providing cellular network services via the WLAN is provided. The system includes a Radio Access Network (RAN) providing the cellular network, a WLAN Access Point (AP) providing the WLAN, a Mobile Switching Center / General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Support Node (MSC / GSN) providing a connection to a core network, a gateway connecting the WLAN AP to the MSC / GSN, and a User Equipment (UE) accessing both the cellular network provided by the RAN and the WLAN provided by the WLAN AP, the UE including a cellular communications unit including a cellular network protocol interface, a Frame Relay Switch (FRS), and a cellular modem, and a WLAN communications unit including a WLAN modem and a Radio Control Agent (RCA), wherein the RCA provides a communications tunnel between the cellular communications unit and a gateway of the WLAN.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for obtaining logical performance data for a circuit in a data network
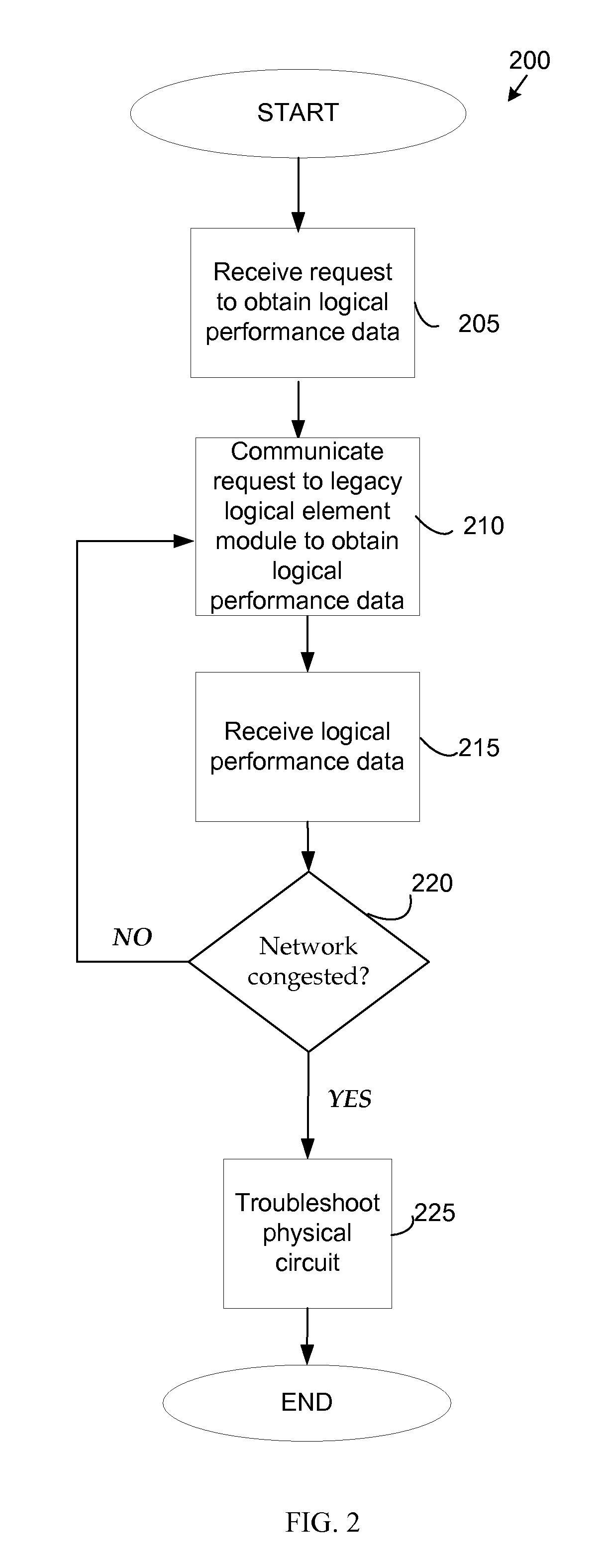
A method and system are provided for obtaining logical performance data for a network circuit in a data network. The network circuit includes both a logical circuit and a physical circuit. A legacy physical element module sends a request for logical performance data to a logical element module through a network management module in communication with the legacy physical element module and the legacy physical element module. Based on the request, the logical element module retrieves the logical performance data from one or more network devices in the network and transmits the data to the legacy physical element module through the network management module. Upon receiving the logical performance data, the legacy physical element module uses the performance data to troubleshoot the physical circuit. The network device may be a switch. The circuit may be a frame relay circuit or an ATM circuit.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com