Patents
Literature
103results about How to "Preventing number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
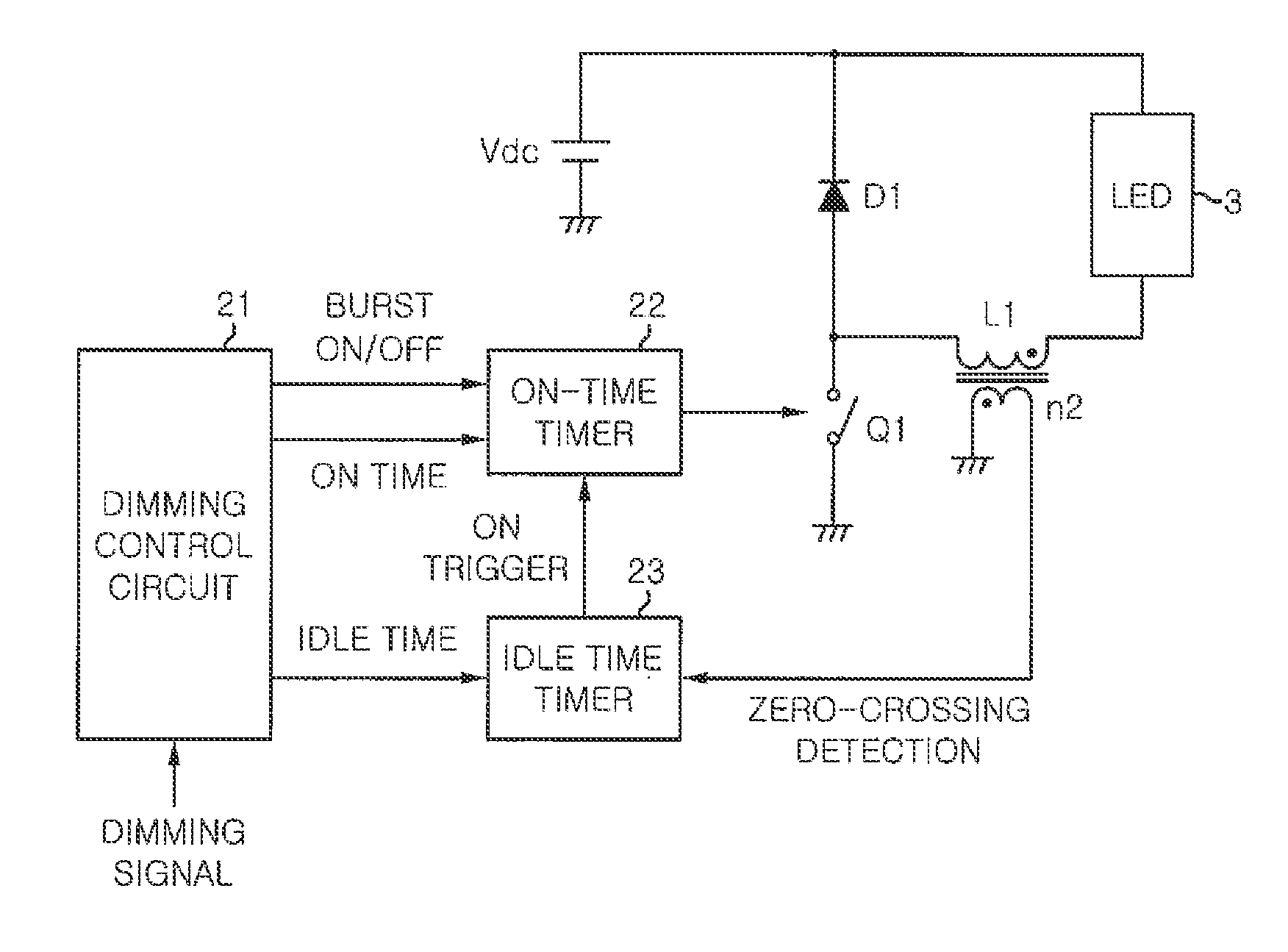
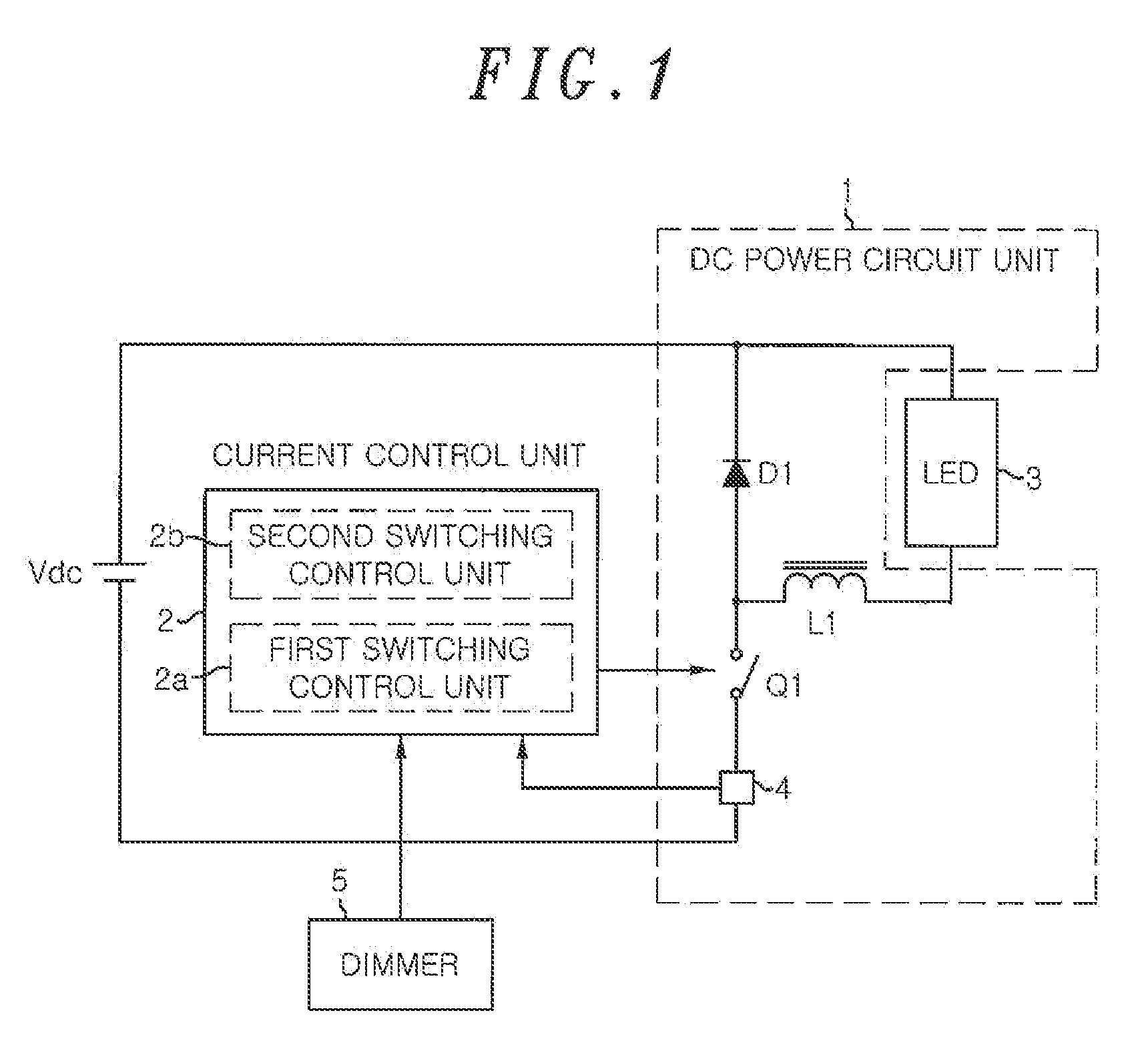
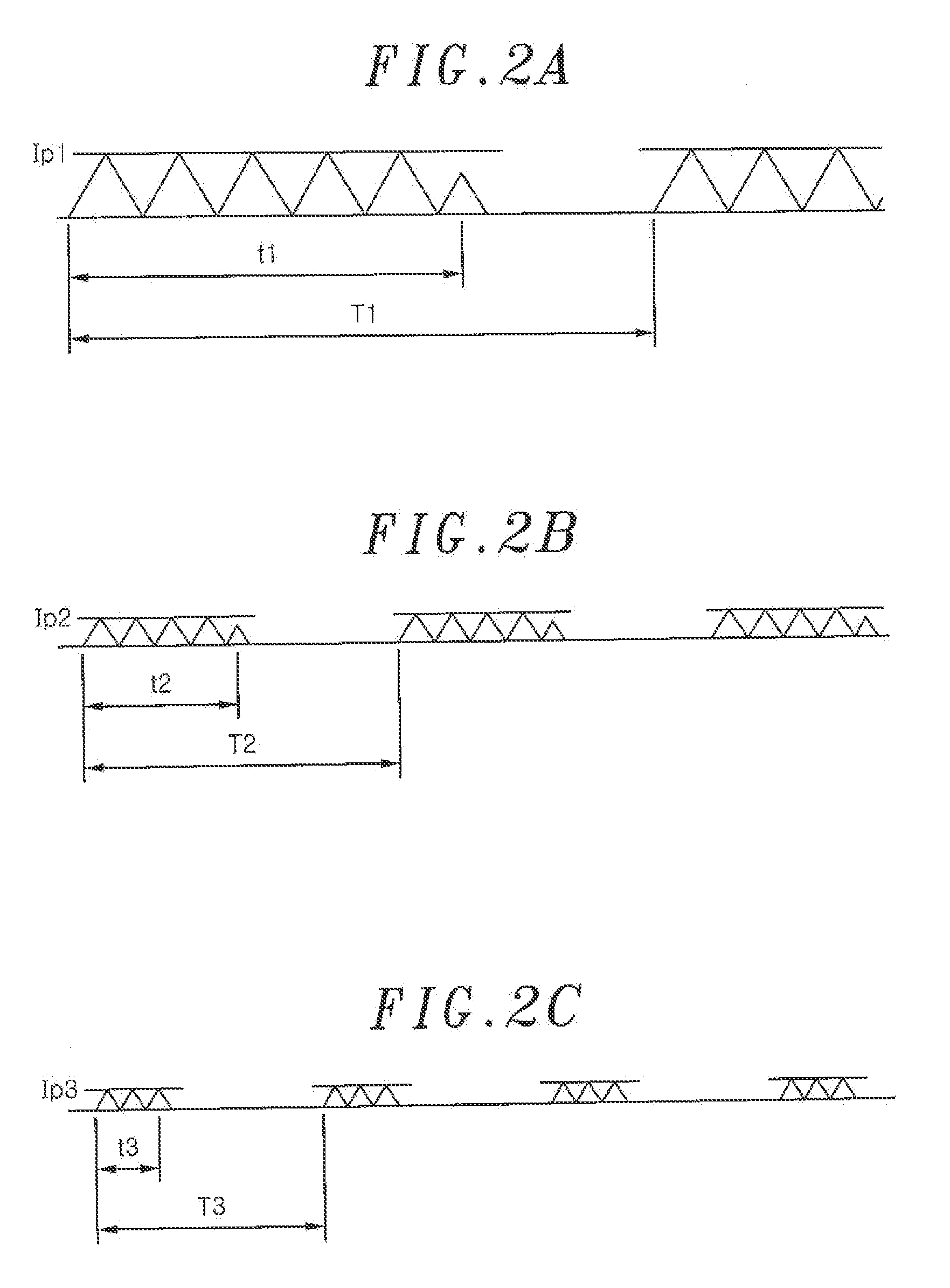
Lighting device for solid-state light source and illumination apparatus using same
ActiveUS20120286686A1Resolution of be ensureReduce numberElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-statePower circuits
A lighting device for lighting a solid-state light source includes: a DC power circuit unit for converting a power of an input DC power source using a switching element and flowing a current through a solid-state light source; and a control unit for performing a first switching control in which the switching element is turned on / off at a first high frequency and a second switching control in which an ON / OFF operation of the switching element is intermittently stopped at a second frequency lower than the first frequency of the first switching control. When the current flowing through the solid-state light source is changed, the second frequency is varied.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High-speed data transmission in a digital mobile communication system
InactiveUS6148209AReduce data transfer rateLow data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile communication systemsMobile station
A data transmission in a digital mobile communication system employing a so-called multi-channel access technique, in which one or more traffic channels may be allocated to a mobile station for data transmission in accordance with the data transfer rate required by the application using the mobile station. Upon establishing a data call, the mobile station indicates to the mobile communication network the maximum and optionally the minimum requirements for the user data transfer rate. The mobile communication network assigns the mobile station for a data call a channel configuration consisting of one or more traffic channels in connection with call set-up or handover, the channel configuration depending on the resources currently available in the mobile communication network and enabling performance of the data channel, which is not lower than the minimum requirement and not higher than the maximum requirement.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
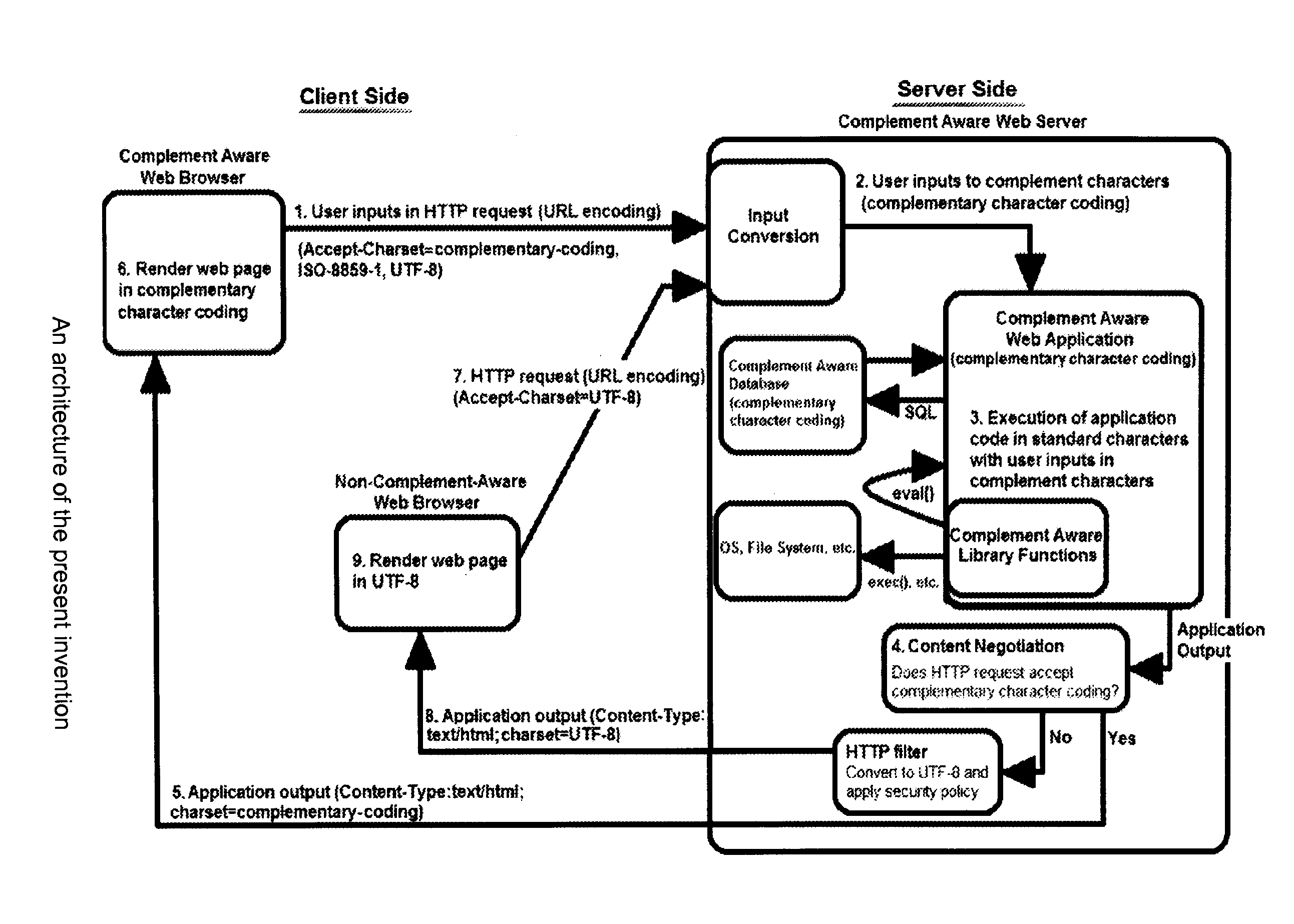
Complementary Character Encoding for Preventing Input Injection in Web Applications
InactiveUS20110252475A1Reduce overheadPreventing executionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSQL injectionLexical analysis
Method to prevent the effect of web application injection attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS), which are major threats to the security of the Internet. Method using complementary character coding, a new approach to character level dynamic tainting, which allows efficient and precise taint propagation across the boundaries of server components, and also between servers and clients over HTTP. In this approach, each character has two encodings, which can be used to distinguish trusted and untrusted data. Small modifications to the lexical analyzers in components such as the application code interpreter, the database management system, and (optionally) the web browser allow them to become complement aware components, capable of using this alternative character coding scheme to enforce security policies aimed at preventing injection attacks, while continuing to function normally in other respects. This approach overcomes some weaknesses of previous dynamic tainting approaches by offering a precise protection against persistent cross-site scripting attacks, as taint information is maintained when data is passed to a database and later retrieved by the application program. The technique is effective on a group of vulnerable benchmarks and has low overhead.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Collective printed circuit board
ActiveUS20120081864A1High yieldNumberSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPrinted circuit boardSemiconductor components
There is provided a collective printed circuit board including a plurality of printed circuit boards each having a mounting unit on which a semiconductor element is mounted at an upper-surface central portion, and a frame having a plurality of through holes having sizes to surround the mounting portion. Upper-surface peripheral edge portions of the printed circuit boards and a through-hole peripheral portion of the frame are bonded to each other such that the mounting units are exposed from the through holes.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Frame Relay Device
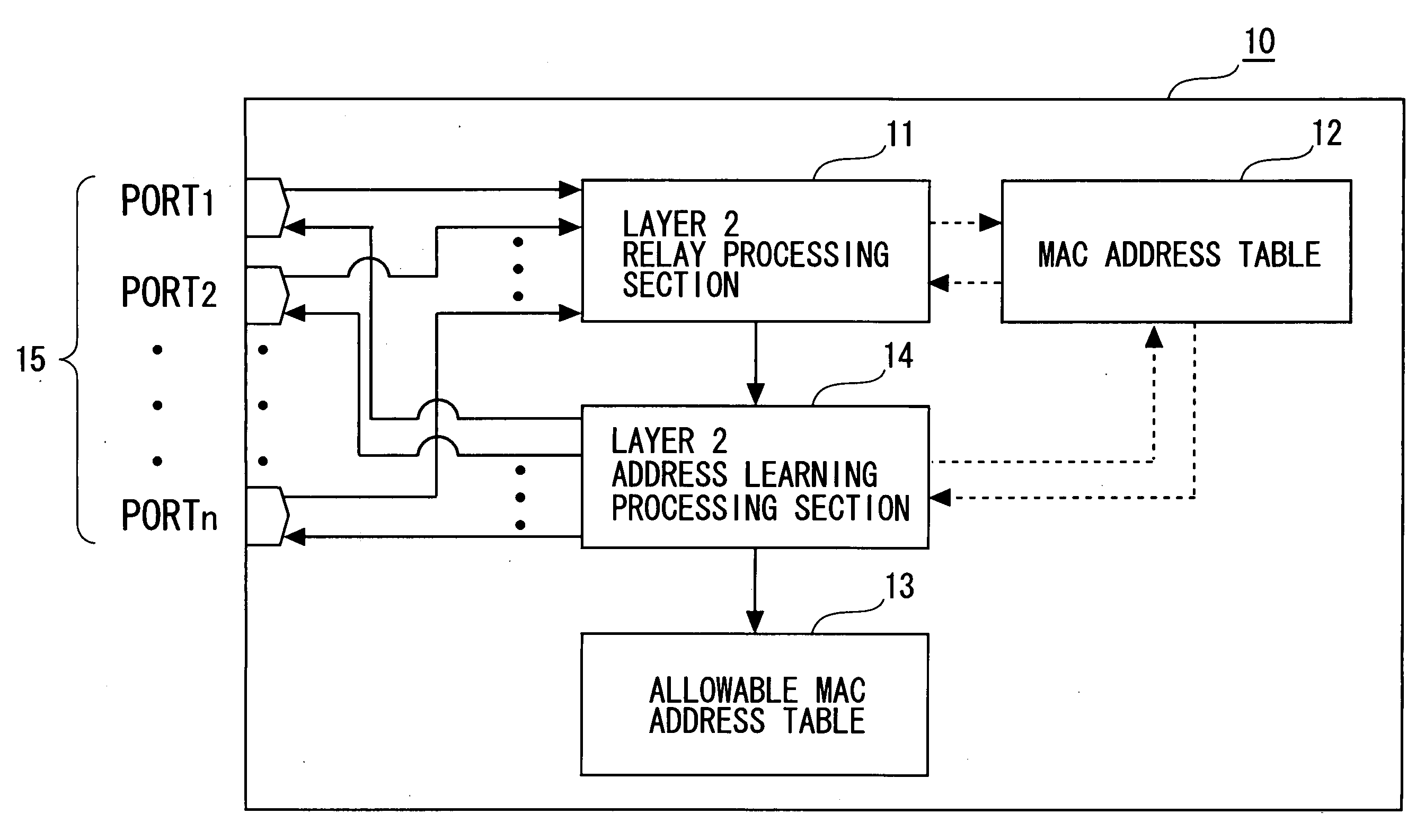
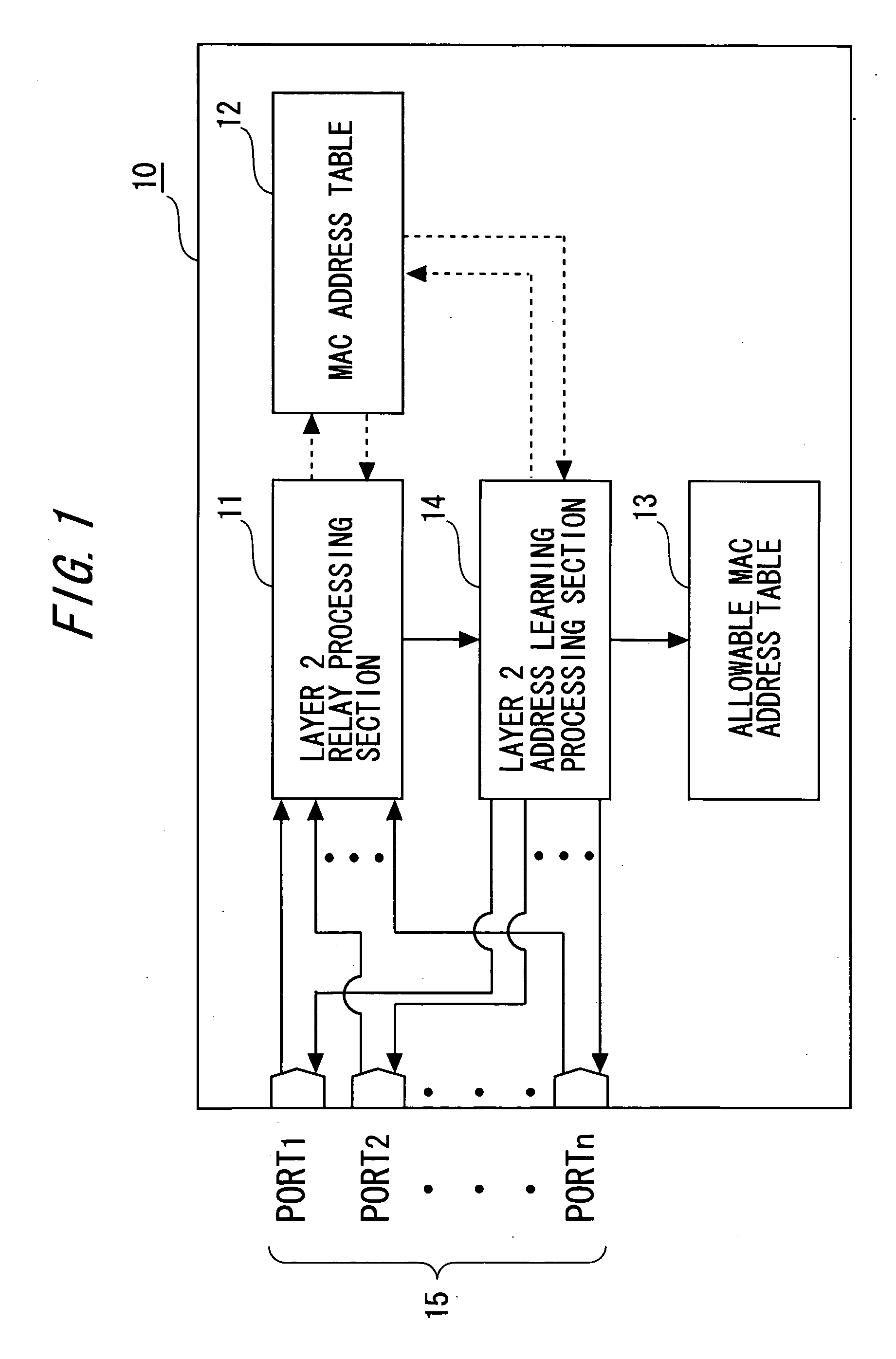
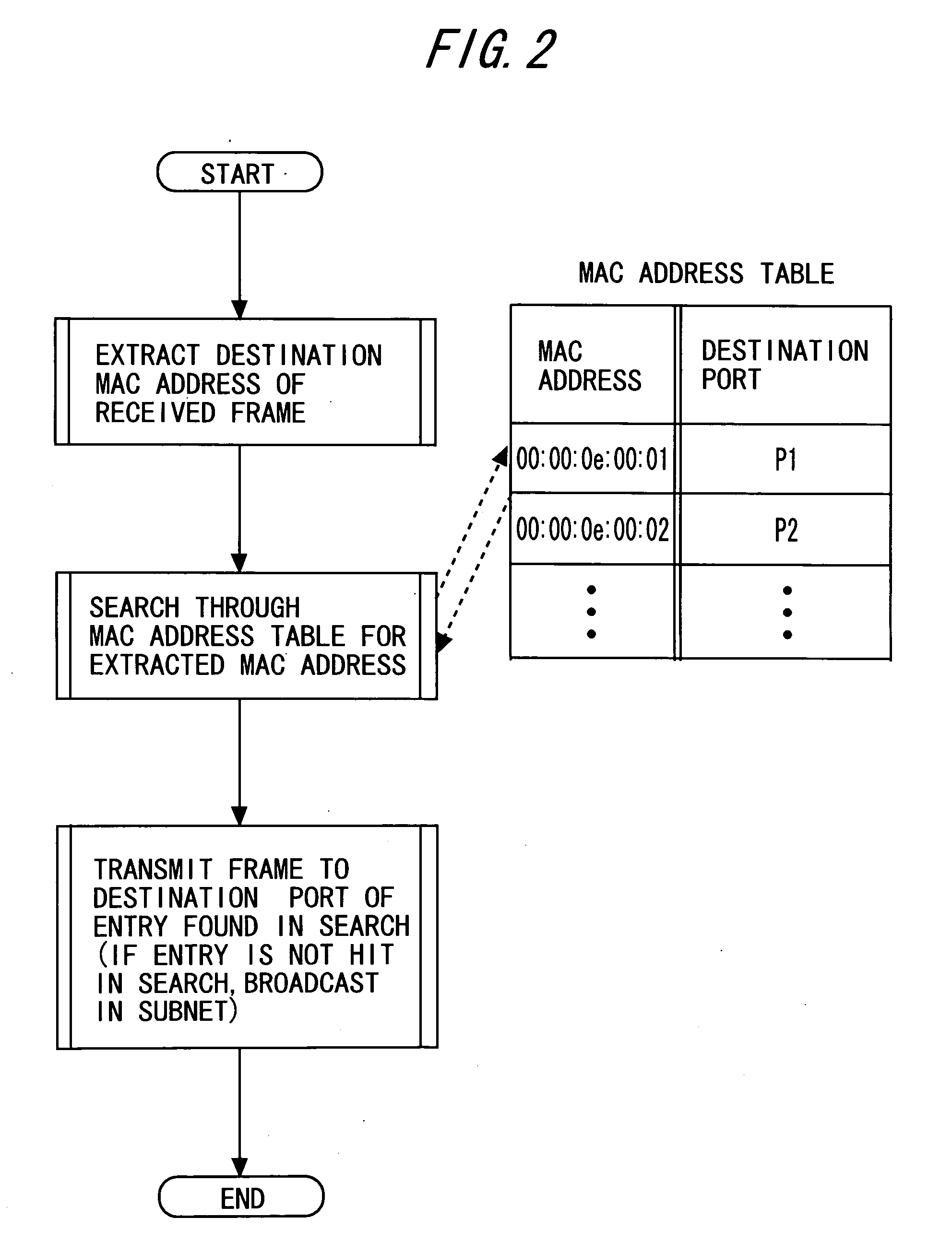
InactiveUS20080250496A1Preventing numberMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareFrame Relay
A frame relay device includes a table where an entry containing a combination of an MAC address and an IP address is registered to be used in the frame relay processing of a local device. Moreover, the frame relay device includes judgment means for searching the table by the transmission origin MAC address and the transmission origin IP address contained in the frame received and judging whether the combination of the transmission origin addresses is registered as a relay object in the layer 3. Furthermore, the frame relay device includes layer 3 relay processing means for performing layer 3 relay processing only for the frame which has been judged to contain the combination of the transmission origin addresses as a relay object.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Image processing apparatus and personal information management program
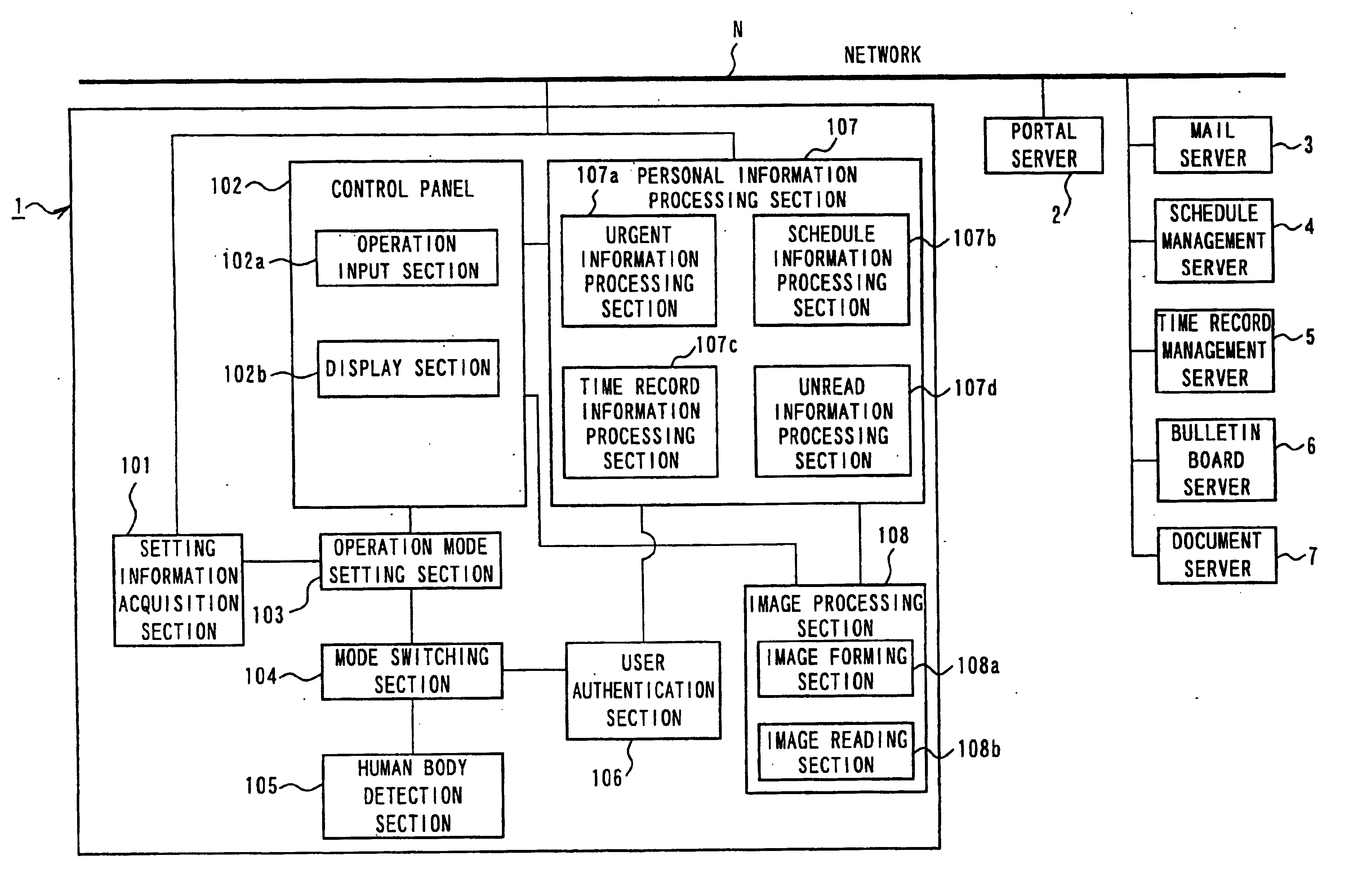
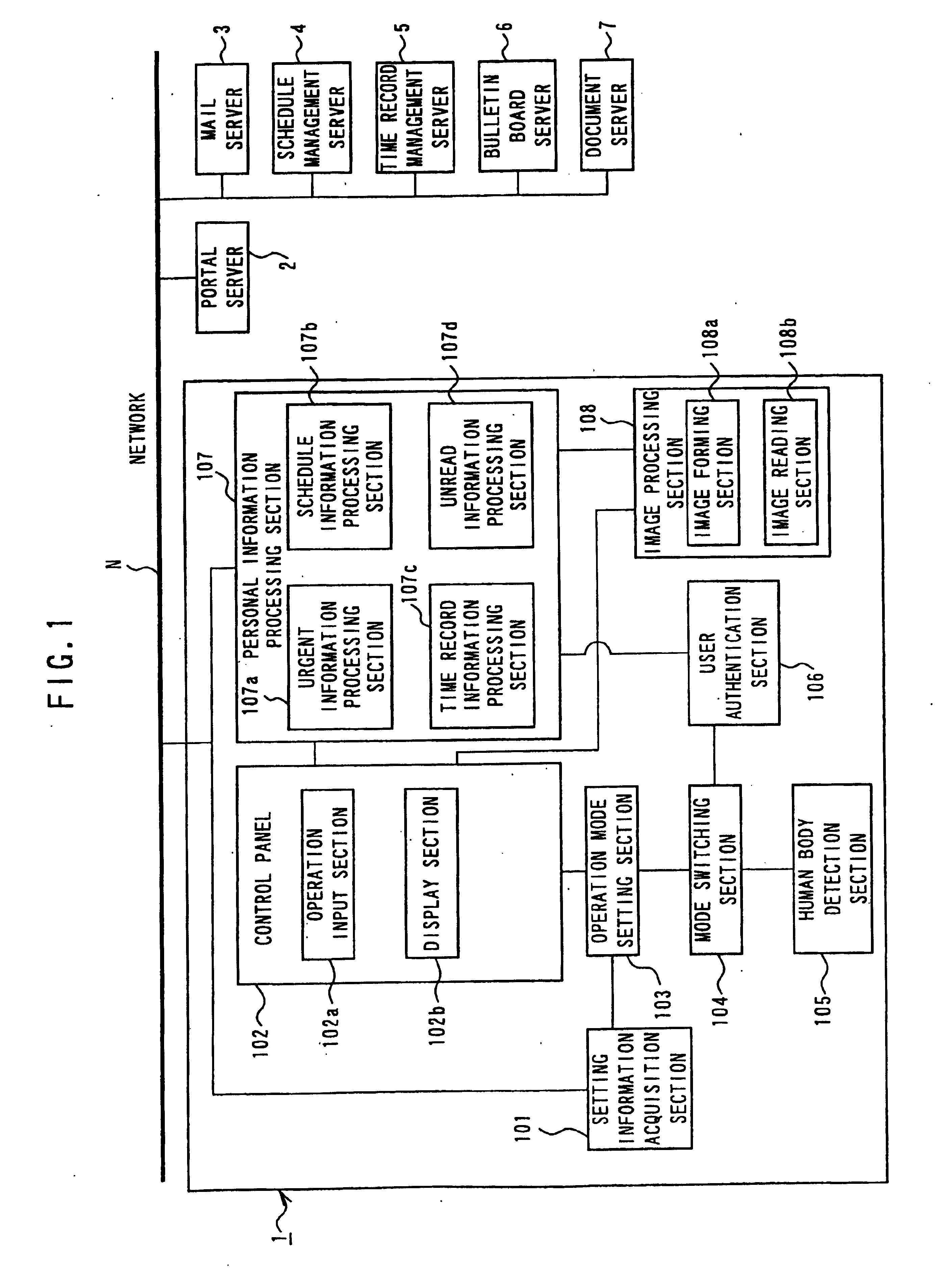
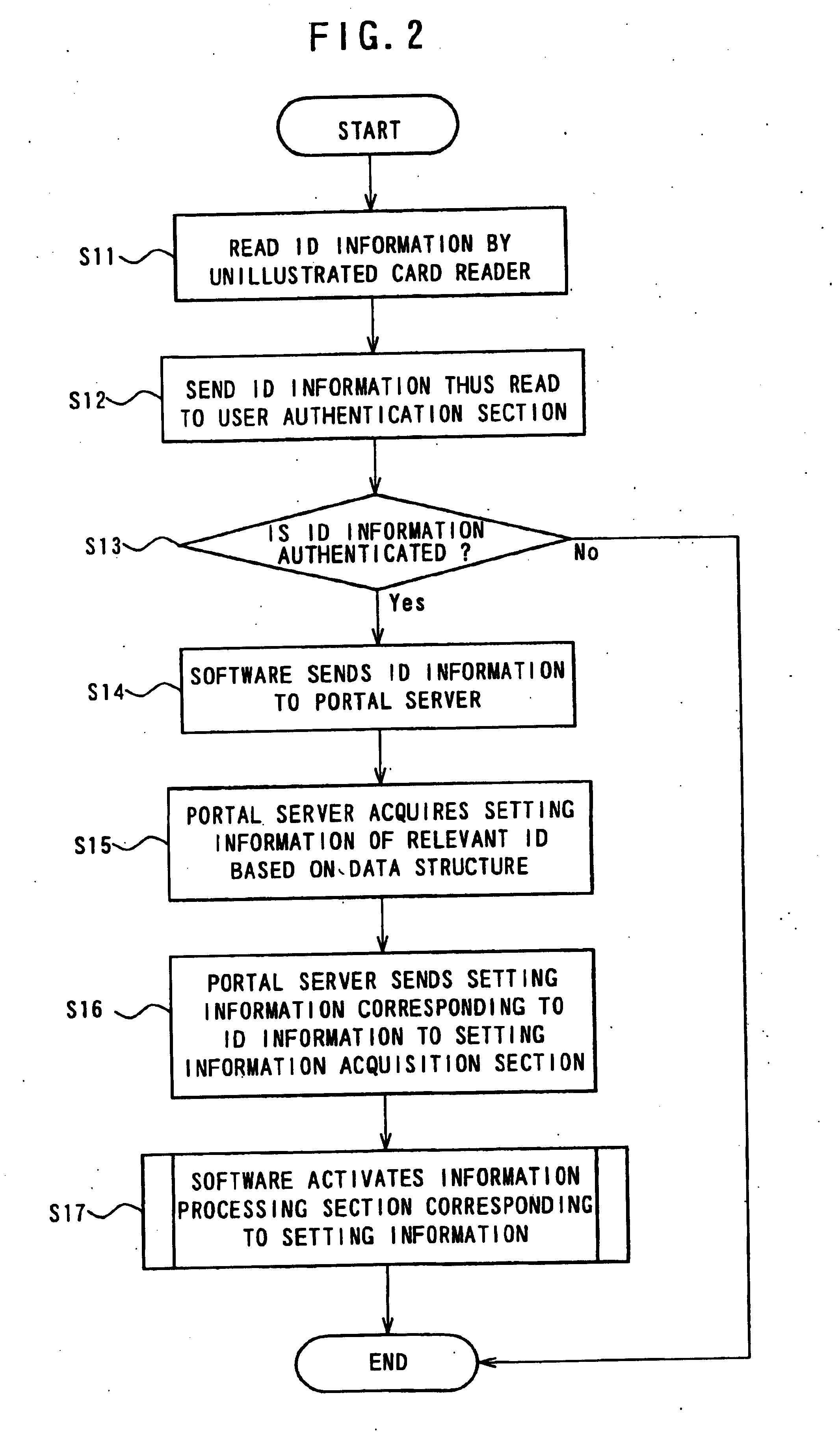
InactiveUS20050204144A1Prevent leakagePreventing numberUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsUser authenticationInternet privacy
An image processing apparatus and a personal information management program are provided in which each user is permitted to perform the processing of user's own personal information while preventing leakage of user's personal information without disturbing the use of the apparatus by an infinite number of users to any substantial extent. The apparatus includes a user authentication section that acquires ID information to identify each user from among a plurality of users, and performs user authentication based on the ID information; an operation mode setting section that can selectively set, as an operation mode that sets a work environment for operation inputs, between an personal operation mode to permit each user to operate individually and a public operation mode to permit an indefinite number of users to operate; and a mode switching section that, when a user is authenticated in the user authentication section, switches the operation mode from the public operation mode into the personal operation mode for the authenticated user.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Power source apparatus
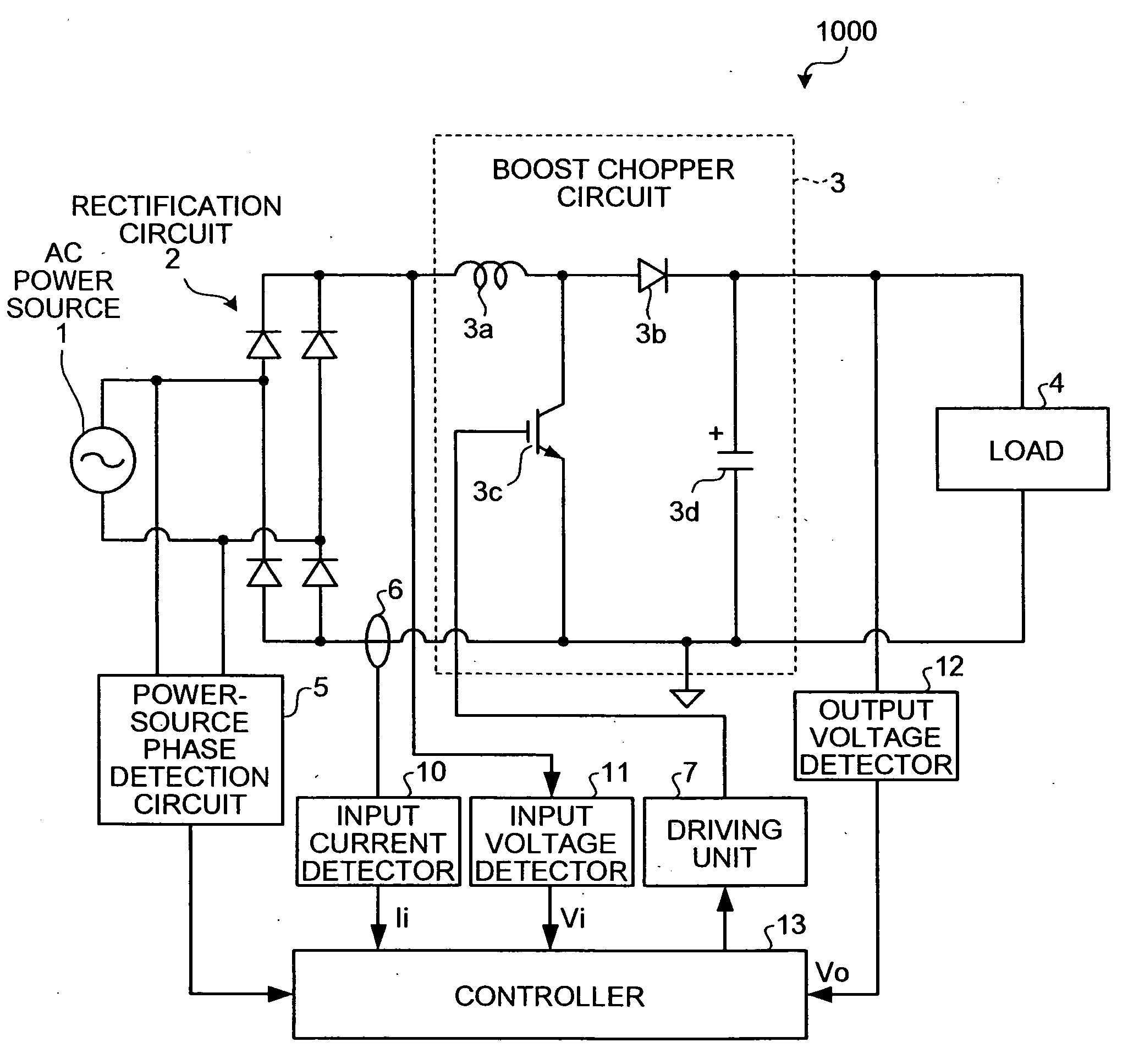
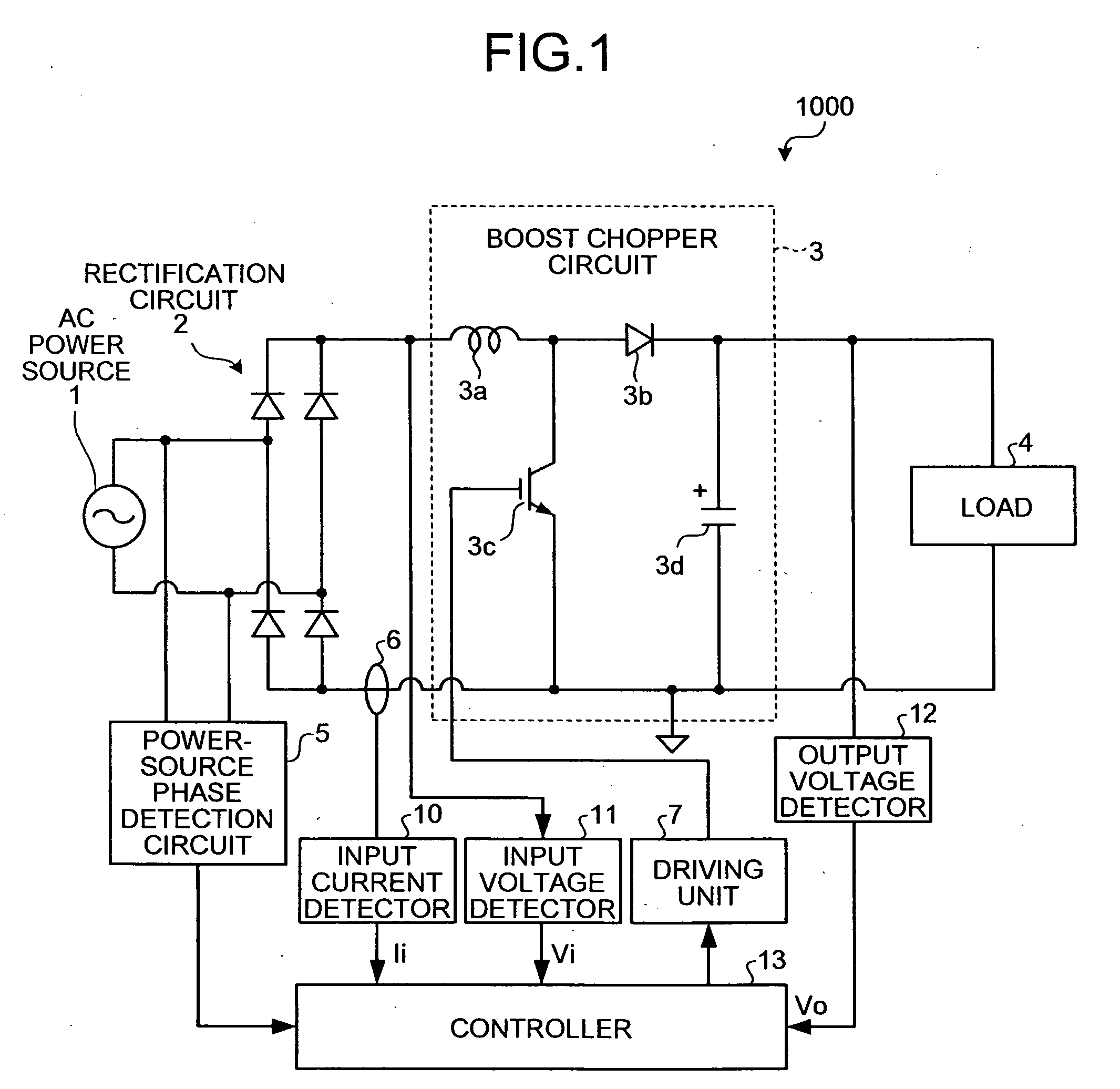
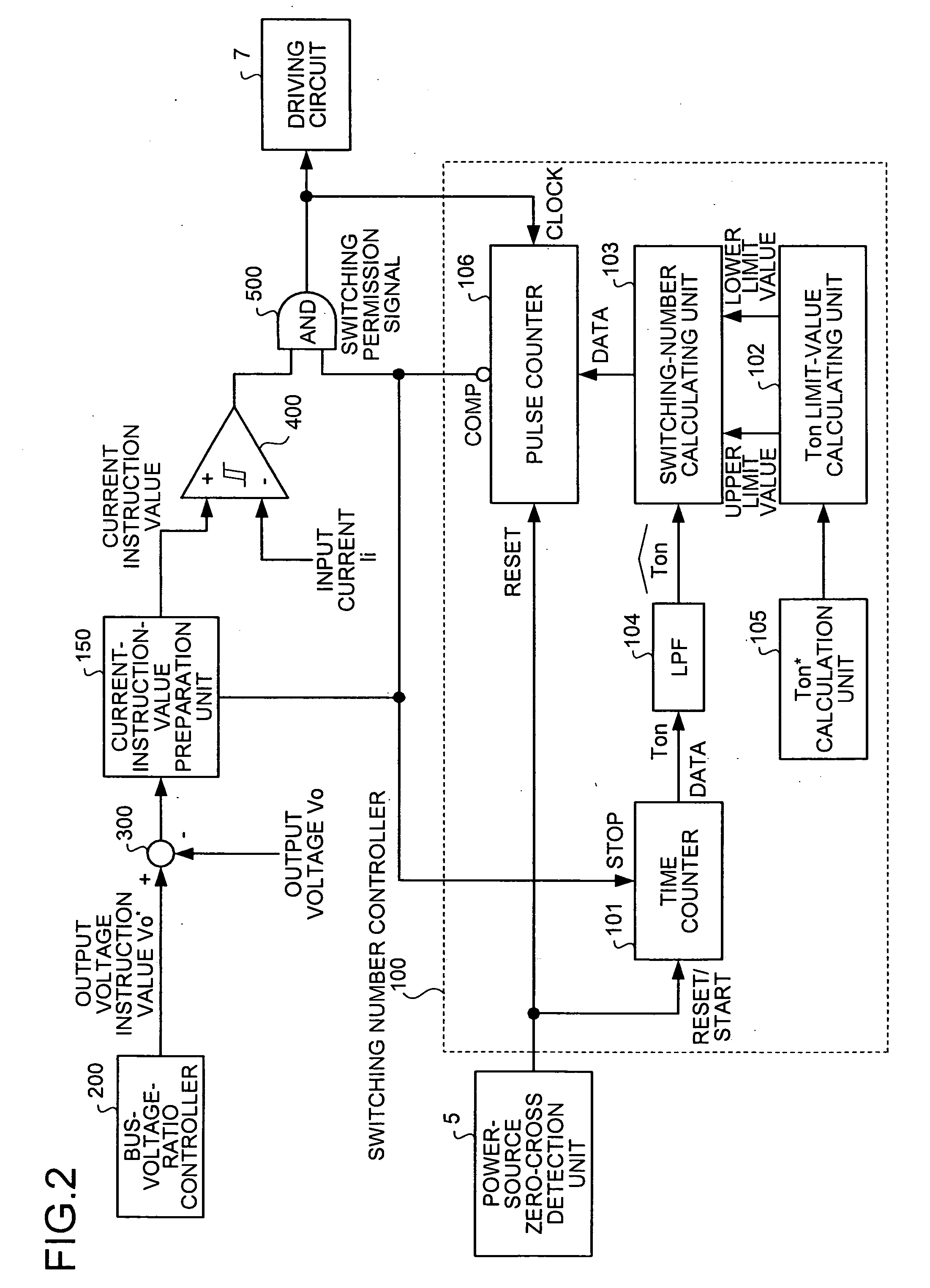
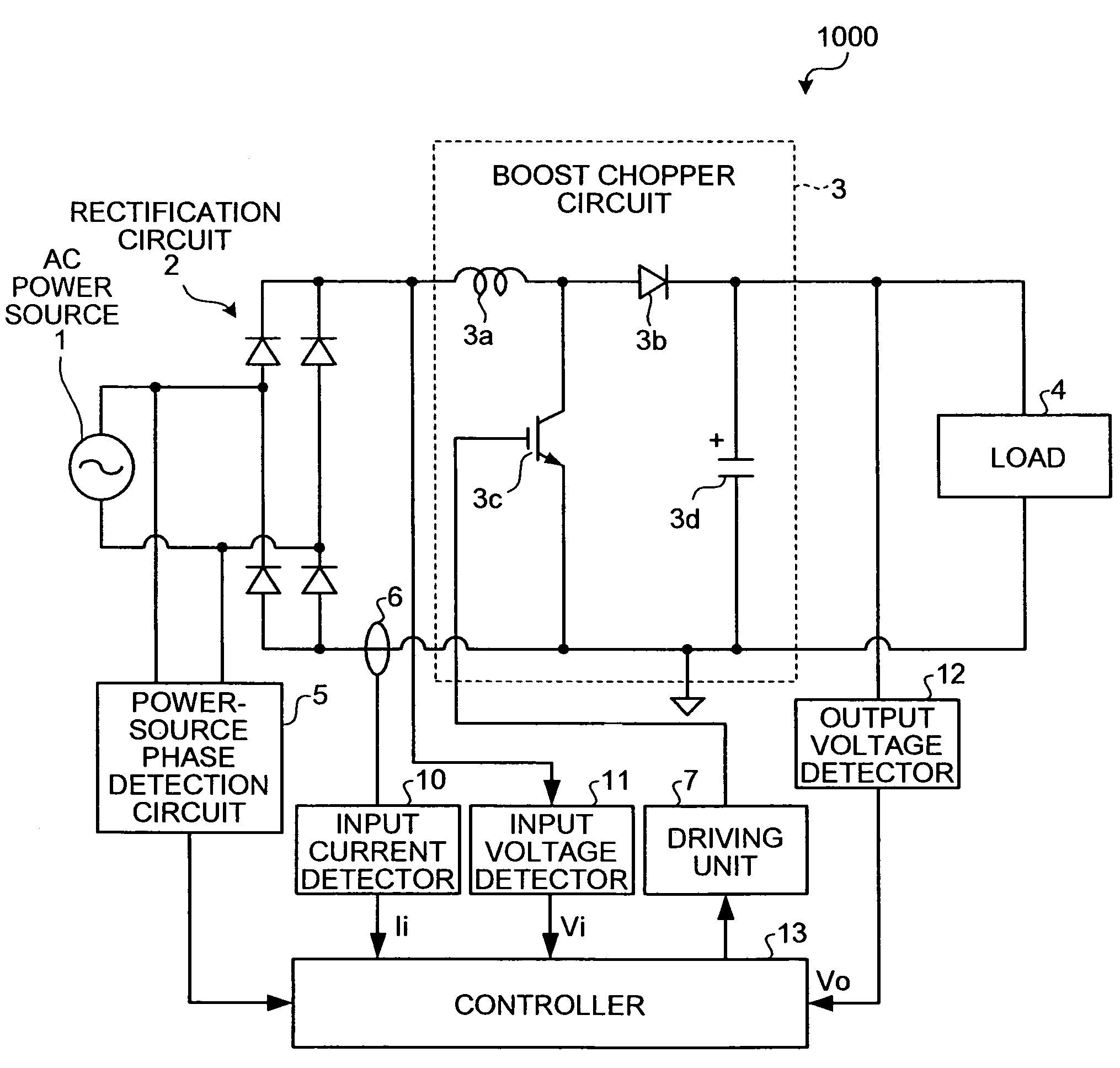
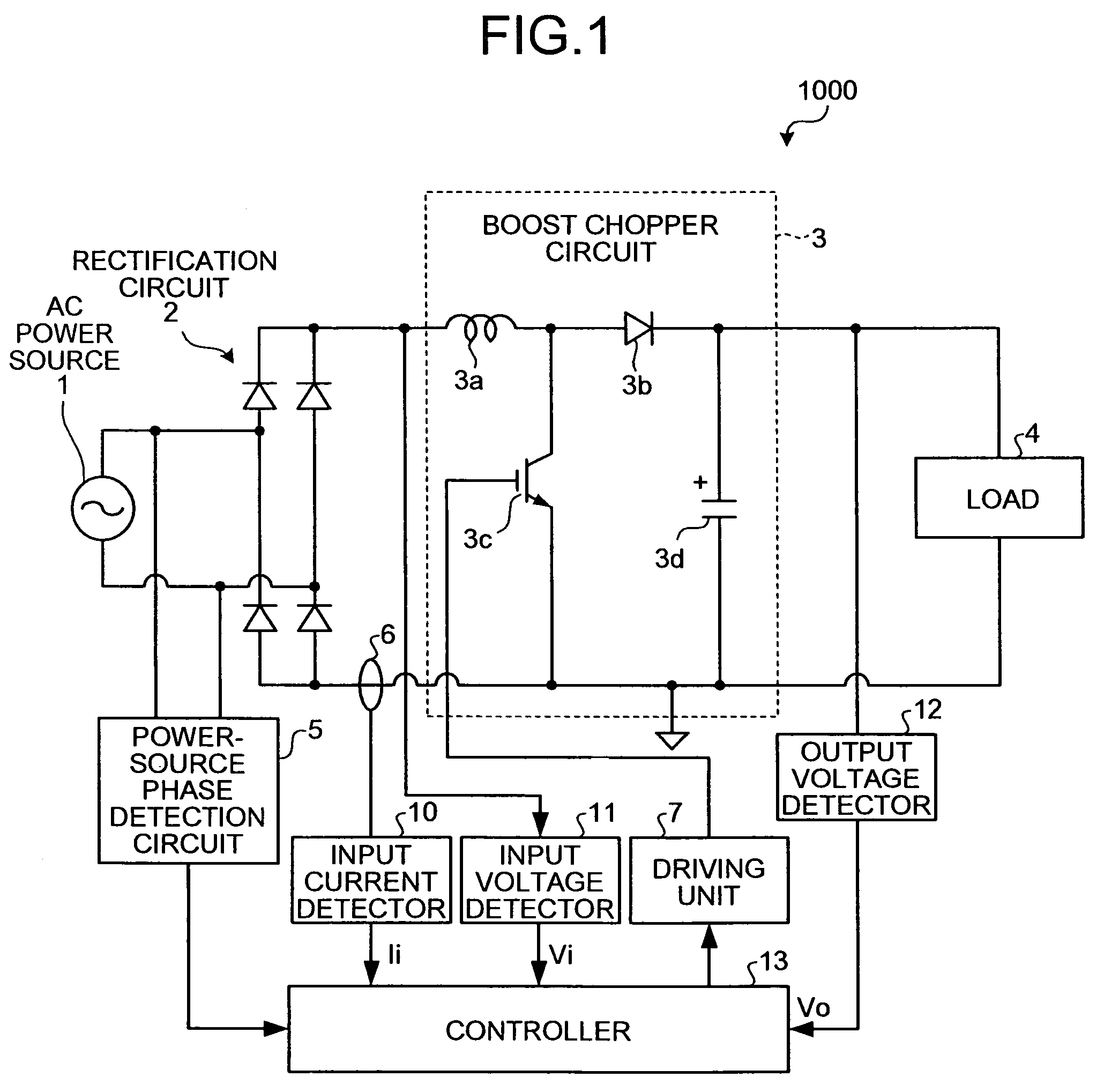
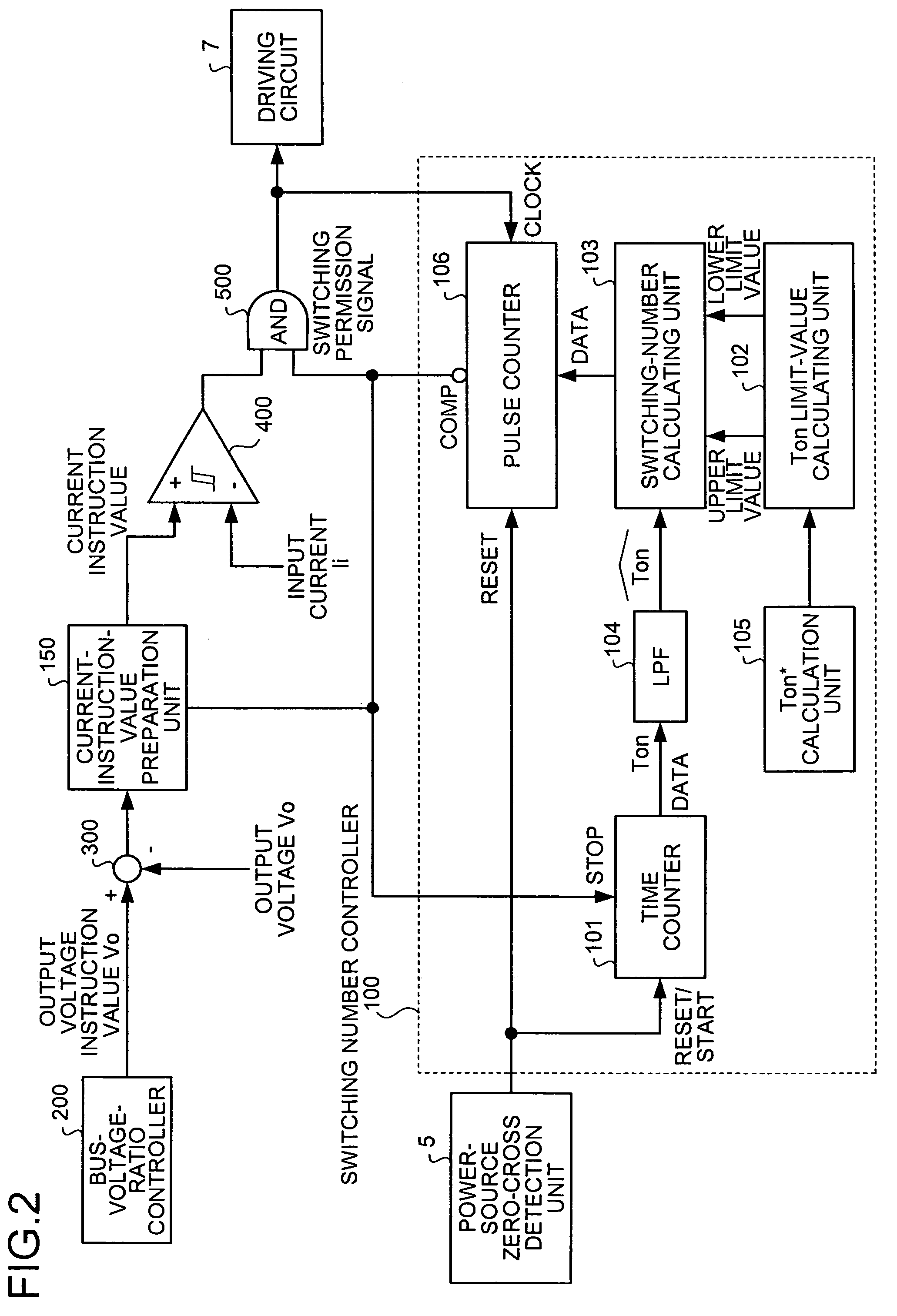
ActiveUS20070103947A1Solve problemsImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionBoost chopperHarmonic
A boost chopper circuit converts AC power to DC voltage and supplies the DC voltage to a load. The boost chopper circuit includes a switching element and a reactor. A controller ON / OFF controls the switching element based on a comparison result in an interval of the former half of a half cycle of the AC power between a detected input current by a input current detector and a current instruction value of a modeling waveform obtained by reducing a harmonic component of a predetermined order from the current waveform.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Method and Apparatus for Detecting RF Field Strength
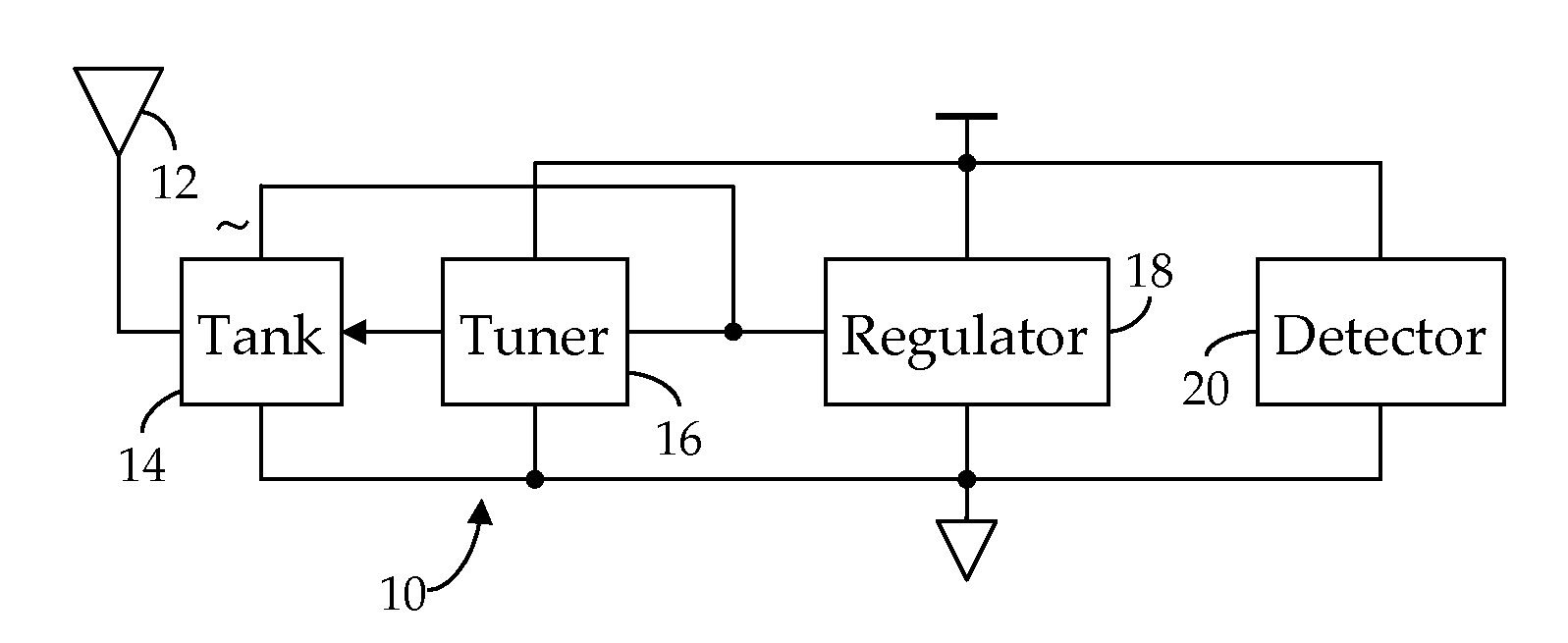
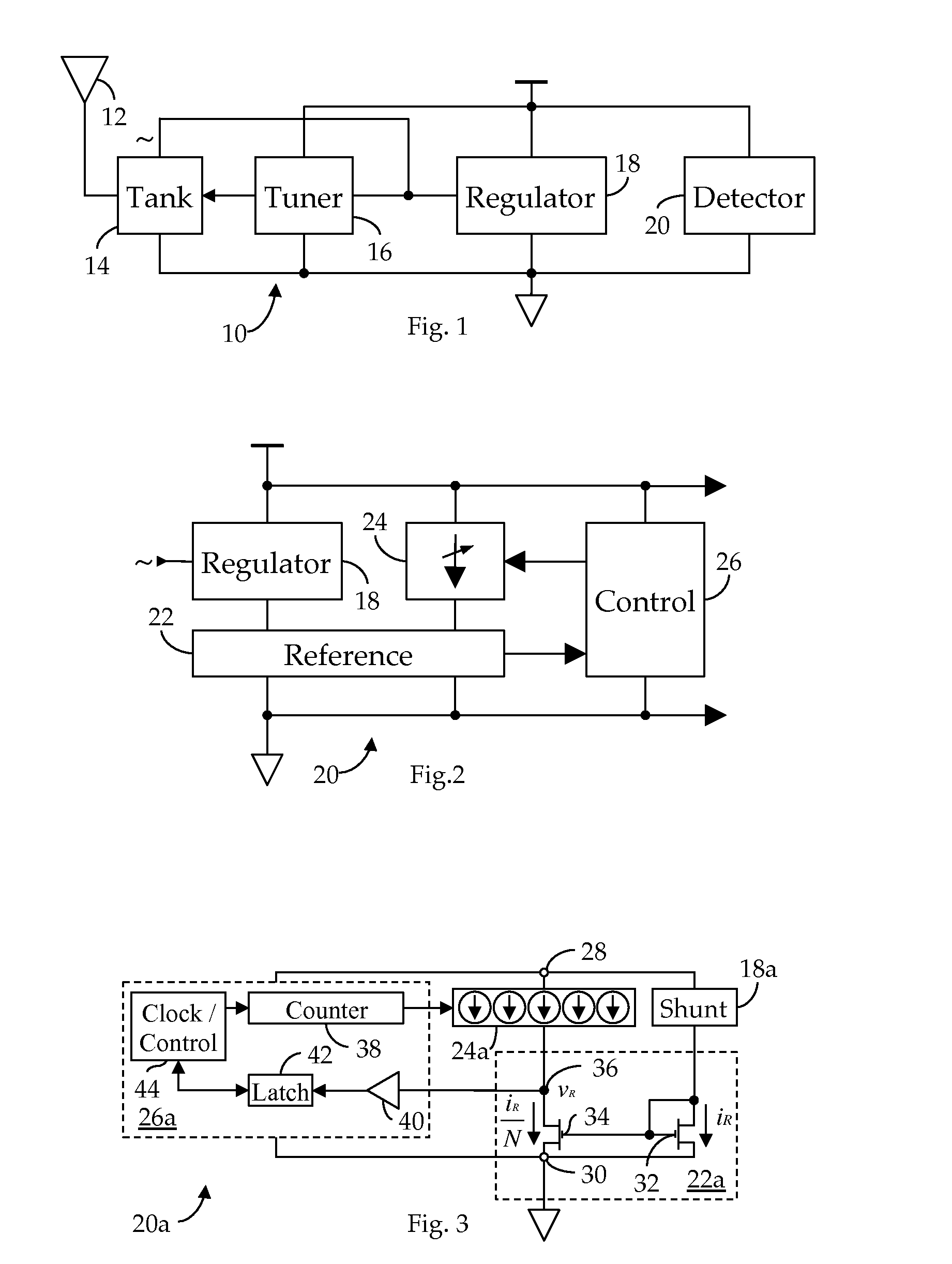
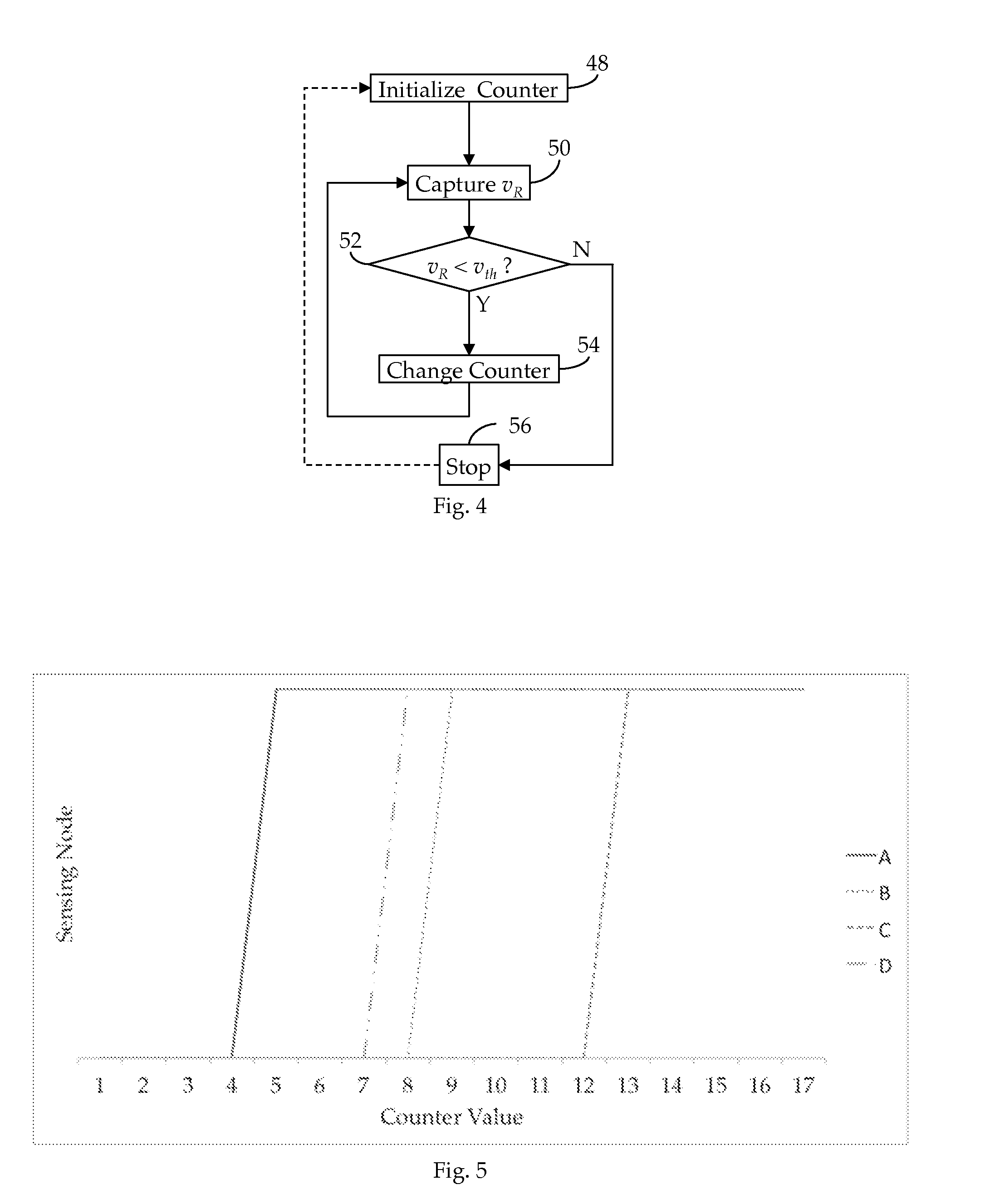
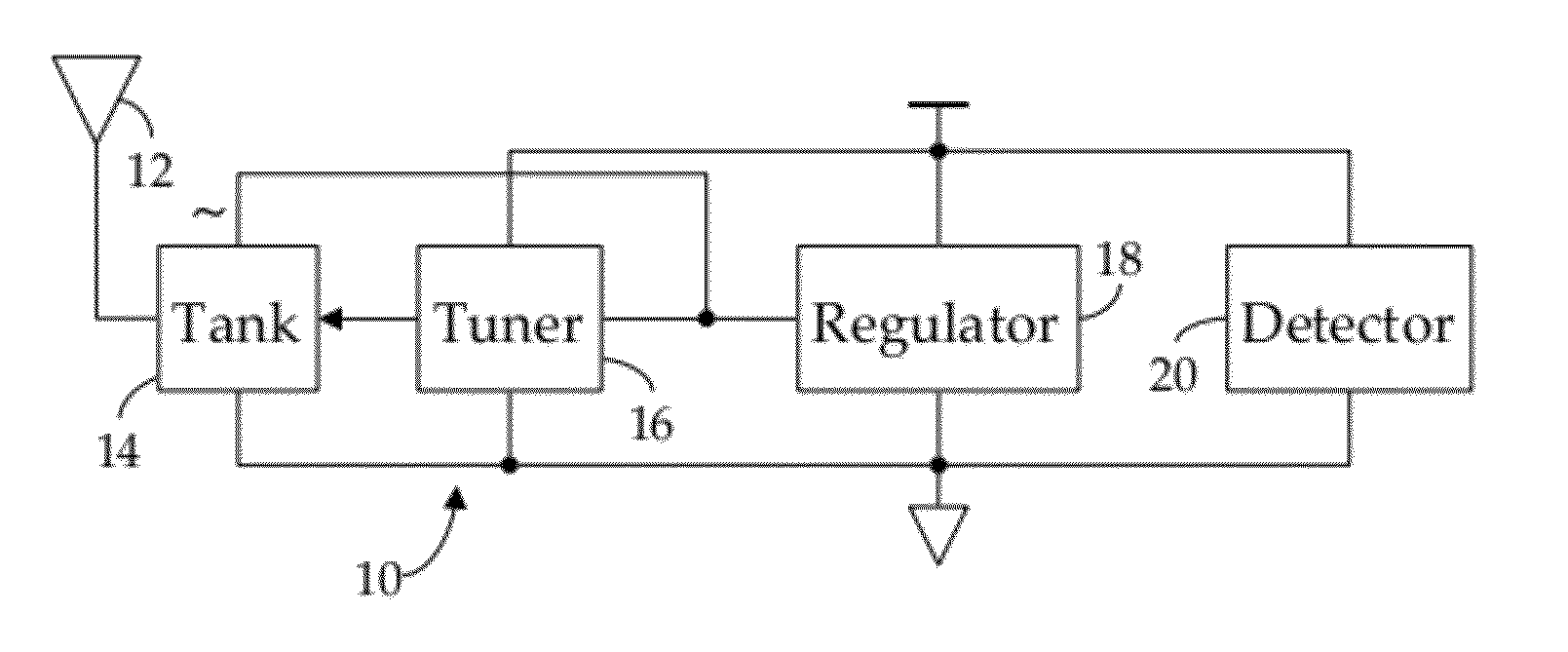
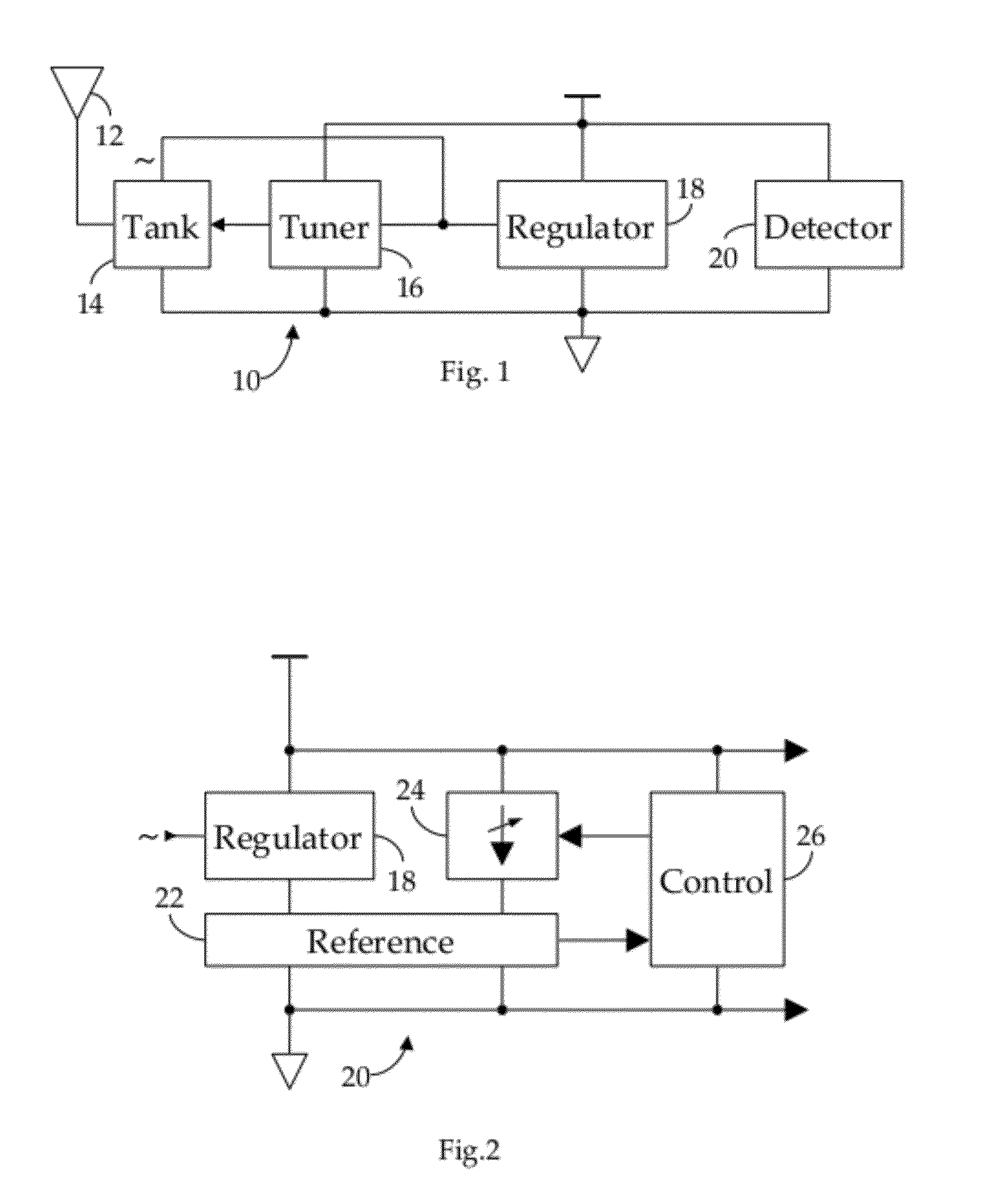
ActiveUS20110300808A1Preventing numberMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionEngineeringRf field
A method and apparatus for detecting RF field strength. A field strength reference generator develops a field strength reference current as a function of a field strength of a received RF signal; and a field strength quantizer develops a digital field-strength value indicative of the field strength reference current. In one embodiment, detected field strength is used to dynamically vary the impedance of a tank circuit whereby, over time, induced current is maximized.
Owner:RFMICRON
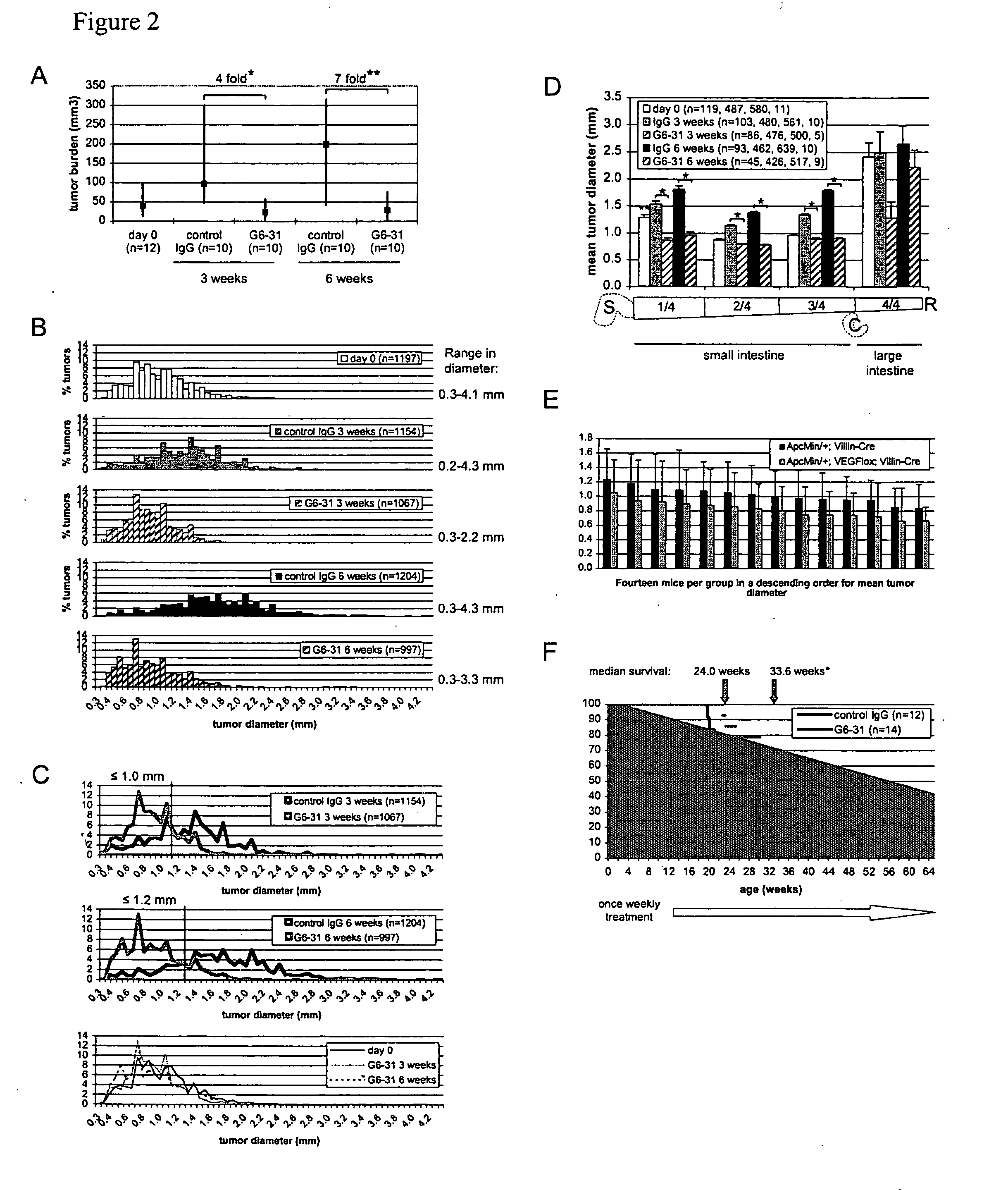
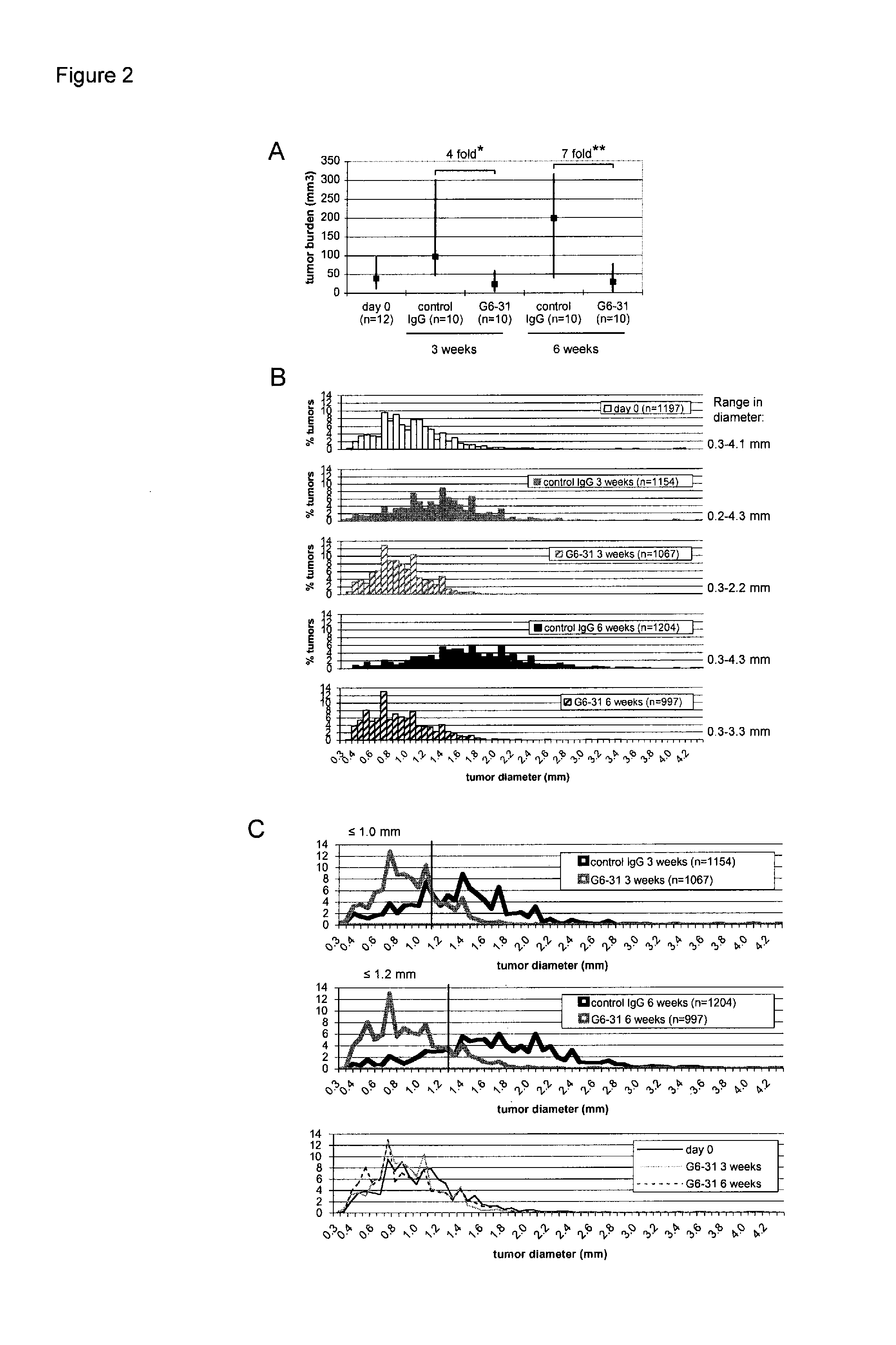
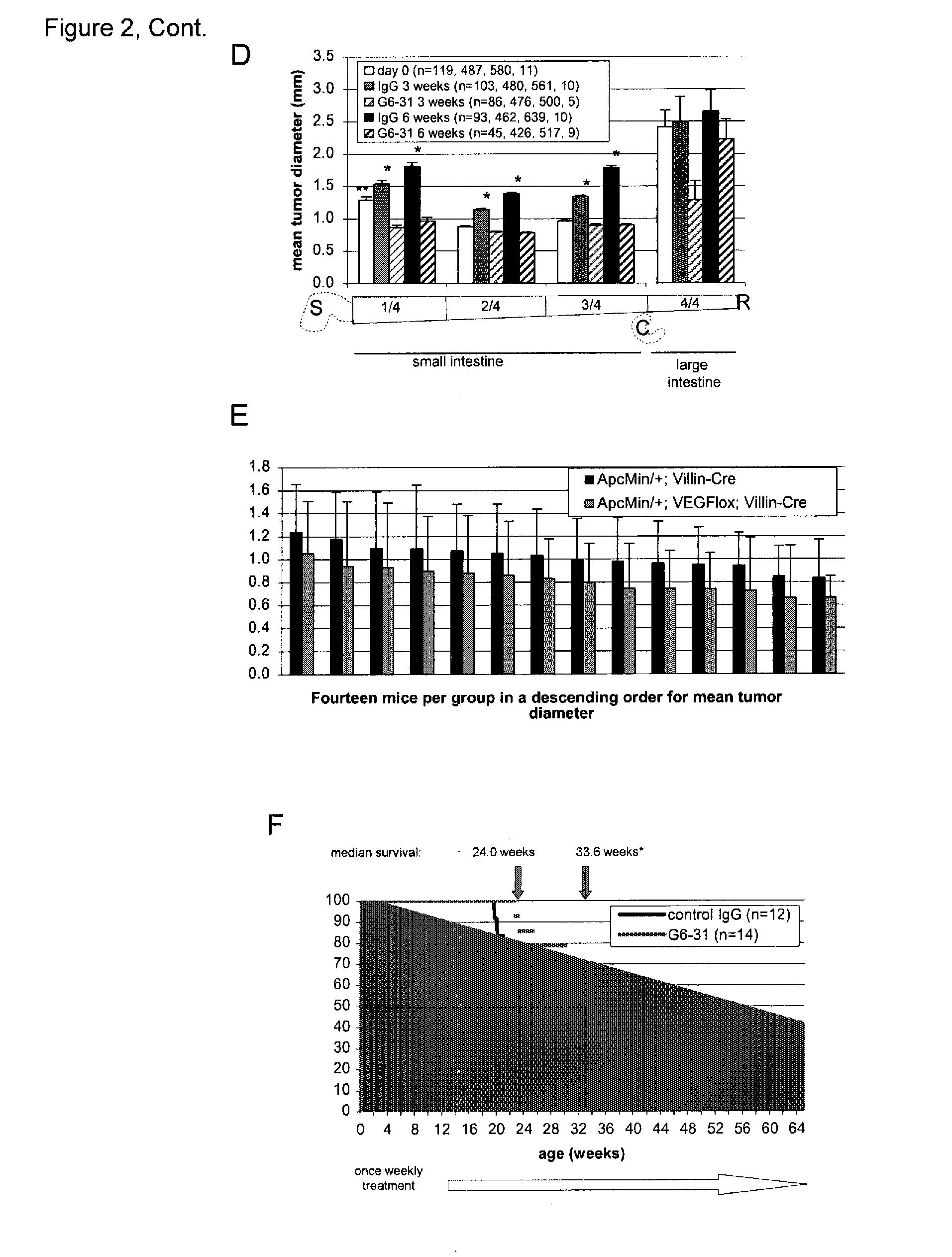
VEGF-specific antagonists for adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy and the treatment of early stage tumors
InactiveUS20080248033A1Reduce and prevent likelihoodPrevent relapseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsStaging tumorsStage tumor
Disclosed herein are methods of treating benign, pre-cancerous, or non-metastatic tumors using an anti-VEGF-specific antagonist. Also disclosed are methods of treating a subject at risk of developing benign, pre-cancerous, or non-metastatic tumors using an anti-VEGF-specific antagonist. Also disclosed are methods of treating or preventing recurrence of a tumor using an anti-VEGF-specific antagonist as well as use of VEGF-specific antagonists in neoadjuvant and adjuvant cancer therapy.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Roll-To-Roll Production of RFID Tags
ActiveUS20120217311A1Preventing numberResonant circuit detailsRecord carriers used with machinesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A method and apparatus for manufacturing thin RFID tags adapted to be mounted proximate an interfering substance, such as metal or liquid. Each tag comprises: a web substrate having a predetermined thickness; an antenna attached to the substrate; and an RFID integrated circuit connected to the antenna, the RFID integrated circuit comprising a tank circuit adapted to be tuned in response to an RF signal after the tag has been mounted proximate the interfering substance. In one embodiment, the tag is manufactured using roll-to-roll manufacturing technology.
Owner:RFMICRON
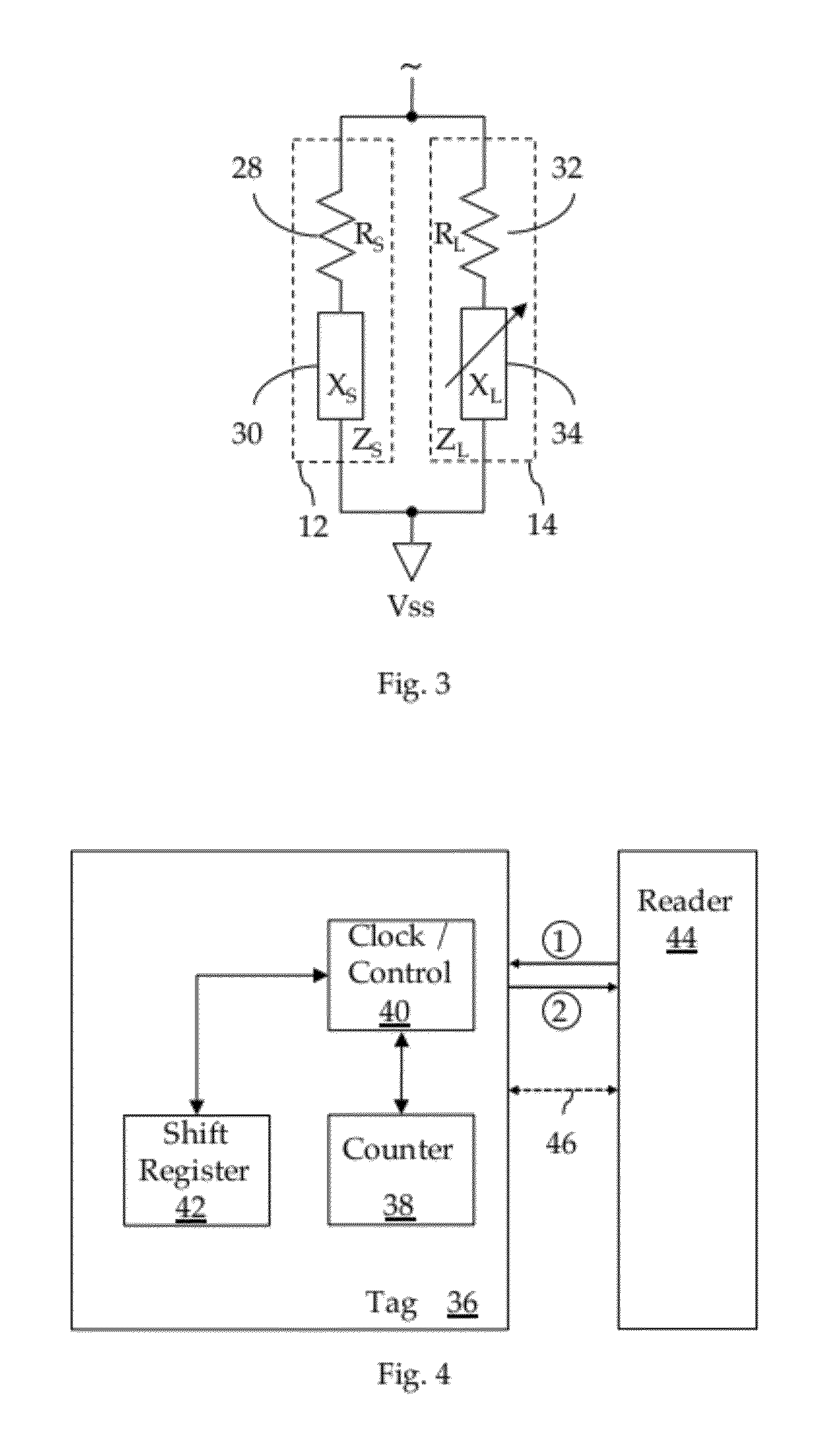
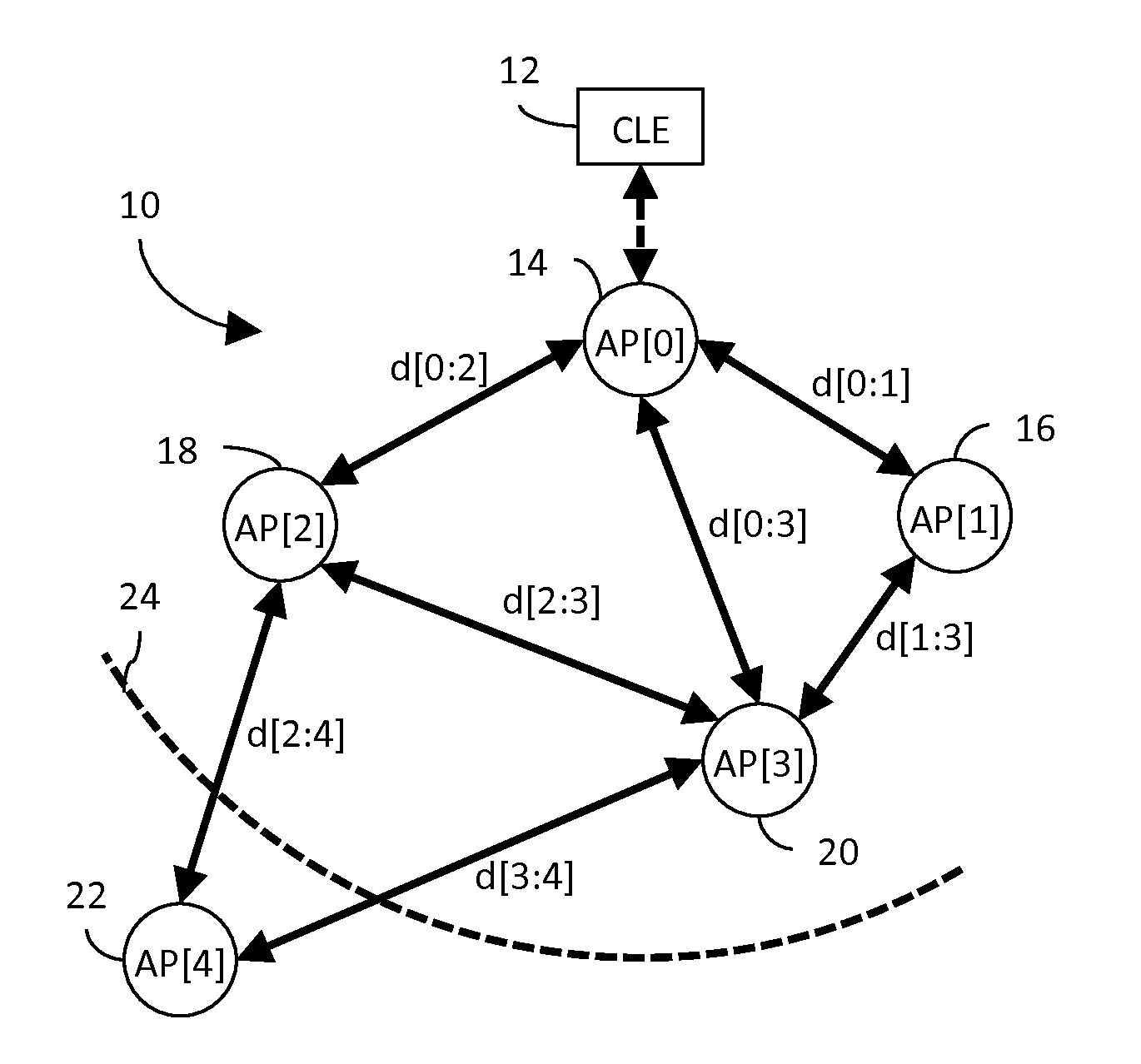
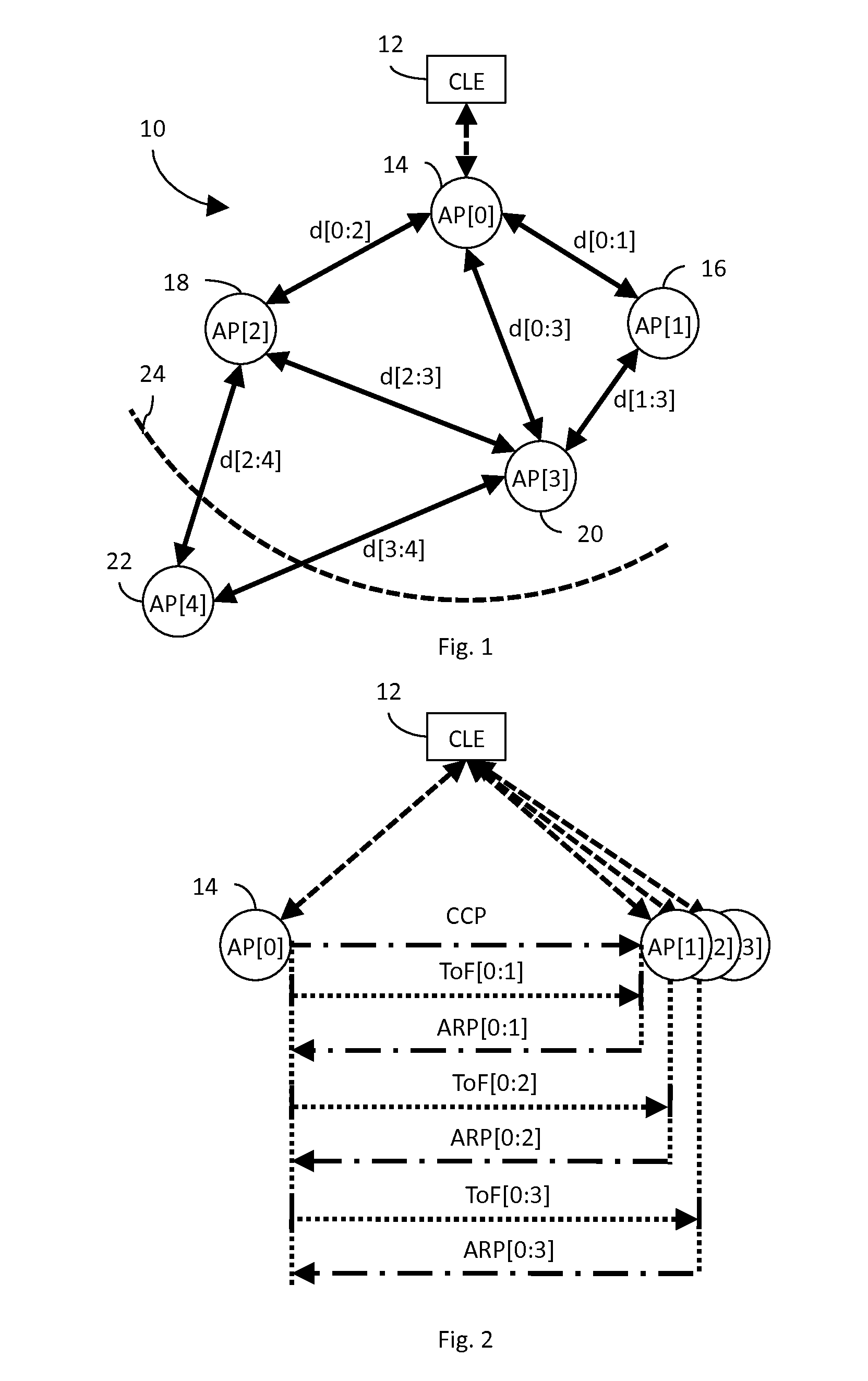
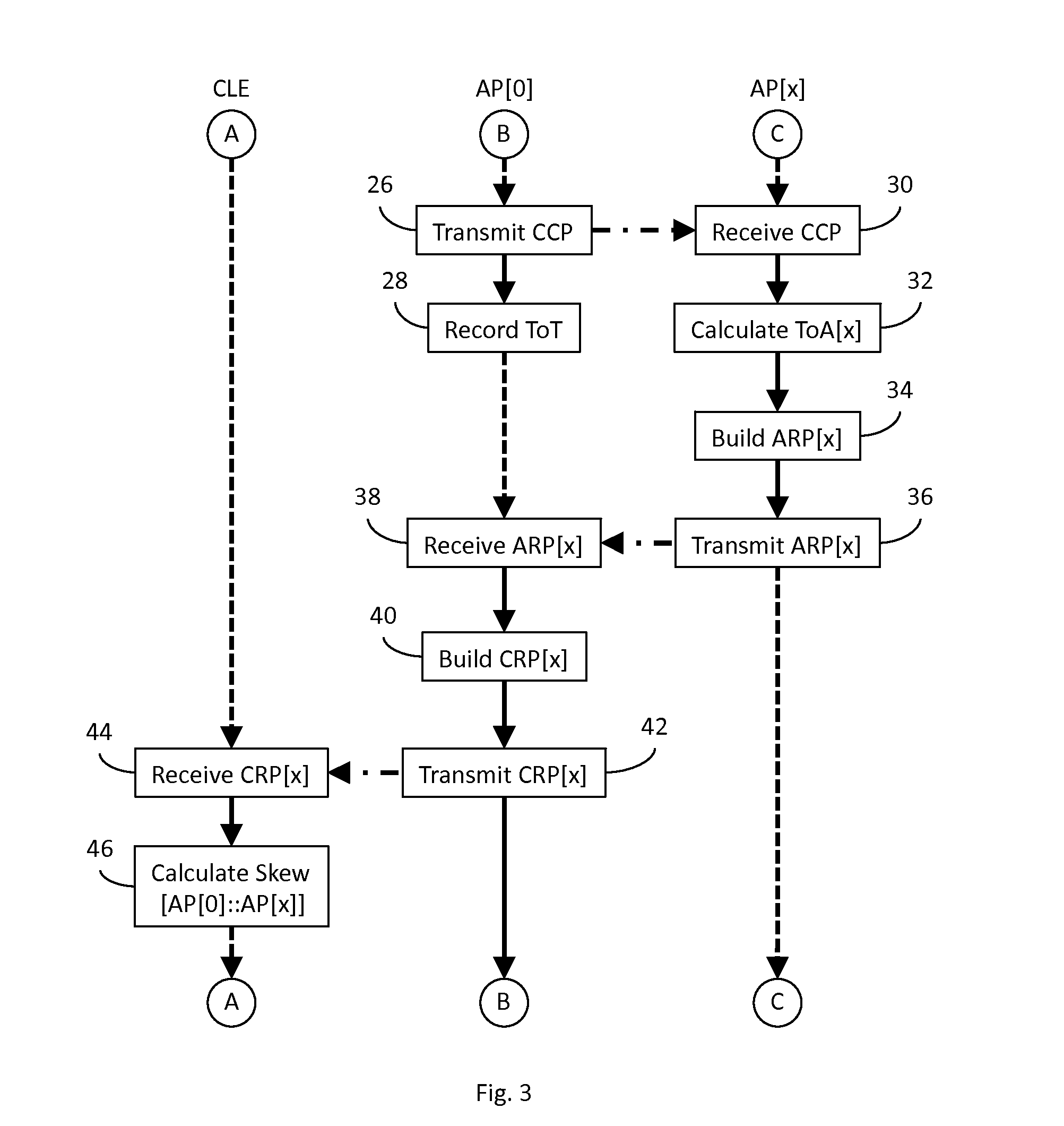
Wireless access point clock synchronization system
InactiveUS20120120874A1Preventing numberSynchronisation arrangementWireless commuication servicesUltra-widebandWireless access point
In an ultra-wideband (“UWB”) network, a central location engine (“CLE”) coordinates operation of an anchor access point (“AP”), AP[0], and a plurality of non-anchor AP[x]s. A clock calibration packet (“CCP”) transmission method and related apparatus facilitate normalization of CCP time references reported to the CLE by all APs. Implementing a digital phase locked loop (“DPLL”) in the CLE facilitates clock normalization. Implementing a DPLL in at least the non-anchor AP[x]s facilitates local clock synchronization, and may improve network efficiency by reducing clock synchronization traffic.
Owner:DECAWAVE
Processor with prefetch function
InactiveUS20090106499A1Improve processor performanceAmount of hardware is restrained being increasedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl unitInformation storage
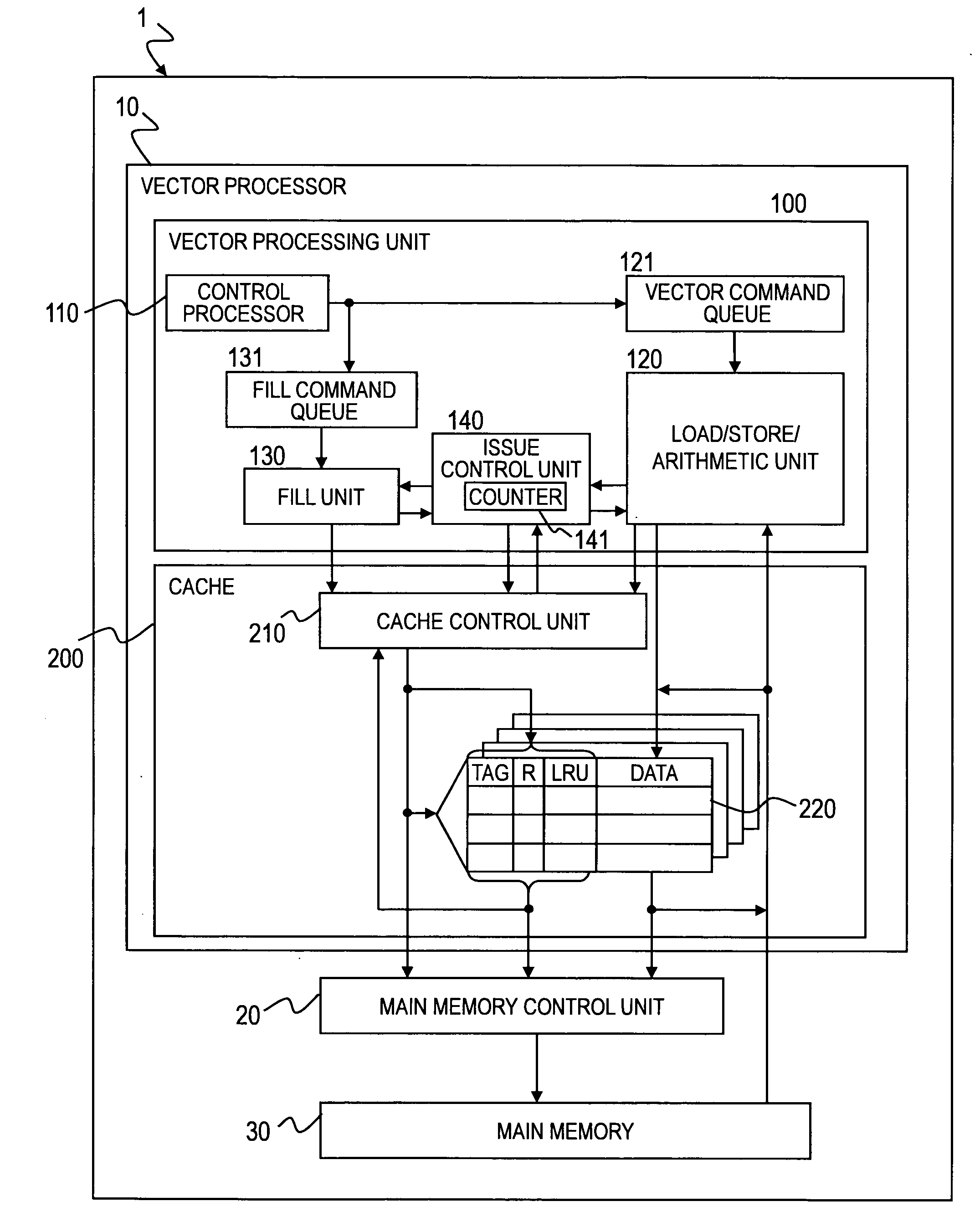
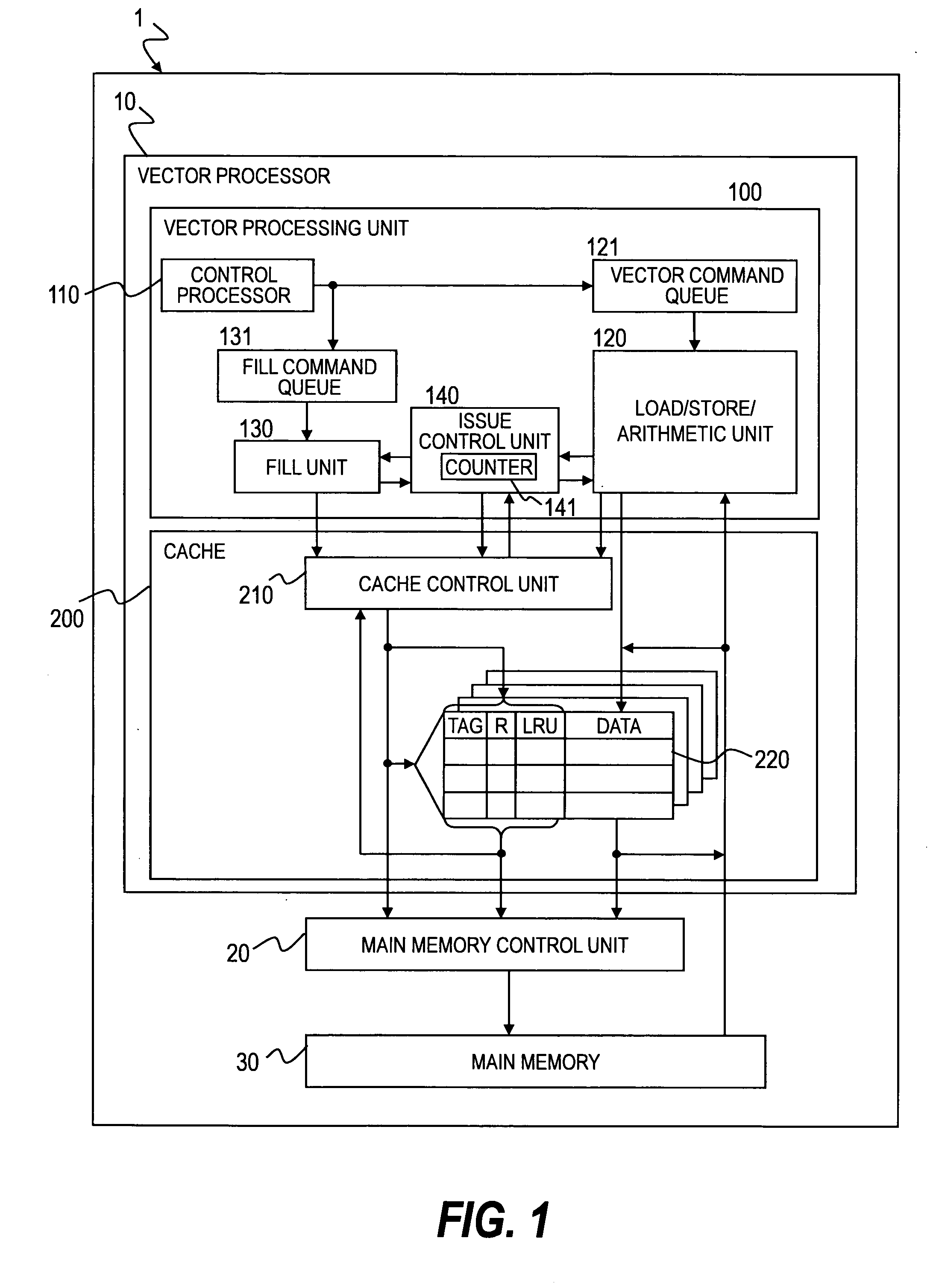
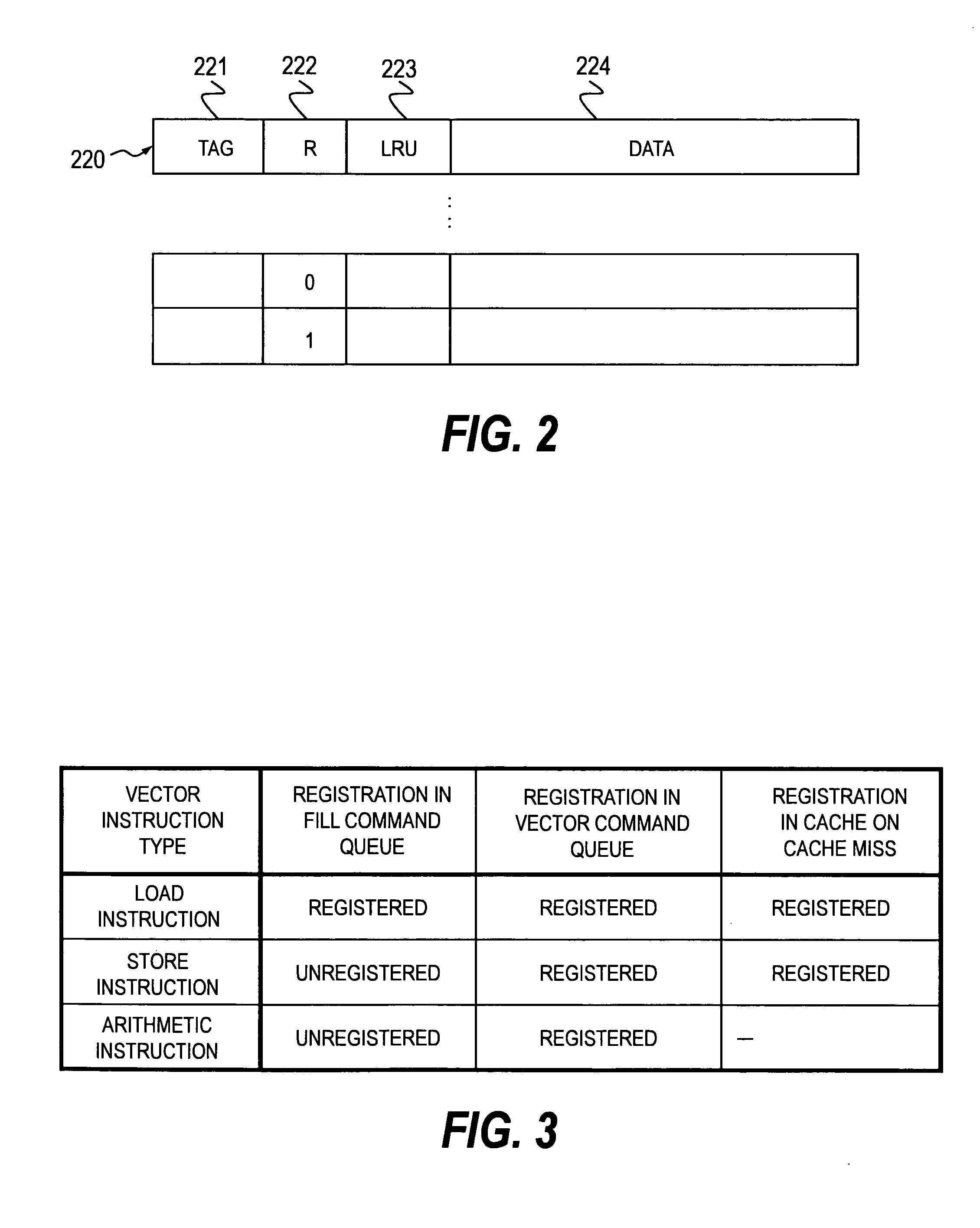
Non-speculatively prefetched data is prevented from being discarded from a cache memory before being accessed. In a cache memory including a cache control unit for reading data from a main memory into the cache memory and registering the data in the cache memory upon reception of a fill request from a processor and for accessing the data in the cache memory upon reception of a memory instruction from the processor, a cache line of the cache memory includes a registration information storage unit for storing information indicating whether the registered data is written into the cache line in response to the fill request and whether the registered data is accessed by the memory instruction. The cache control unit sets information in the registration information storage unit for performing a prefetch based on the fill request and resets the information for accessing the cache line based on the memory instruction.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical add-drop apparatus and method
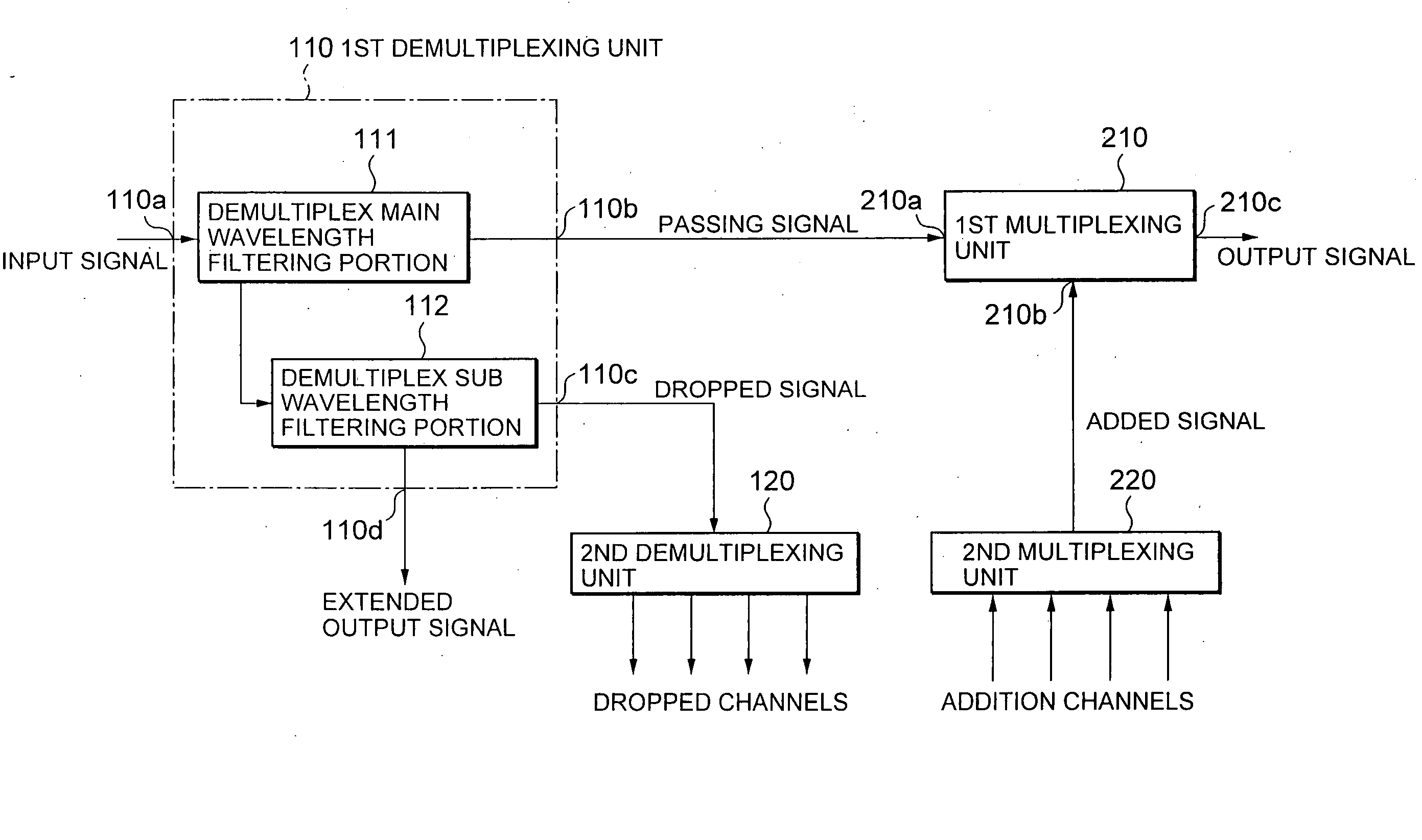
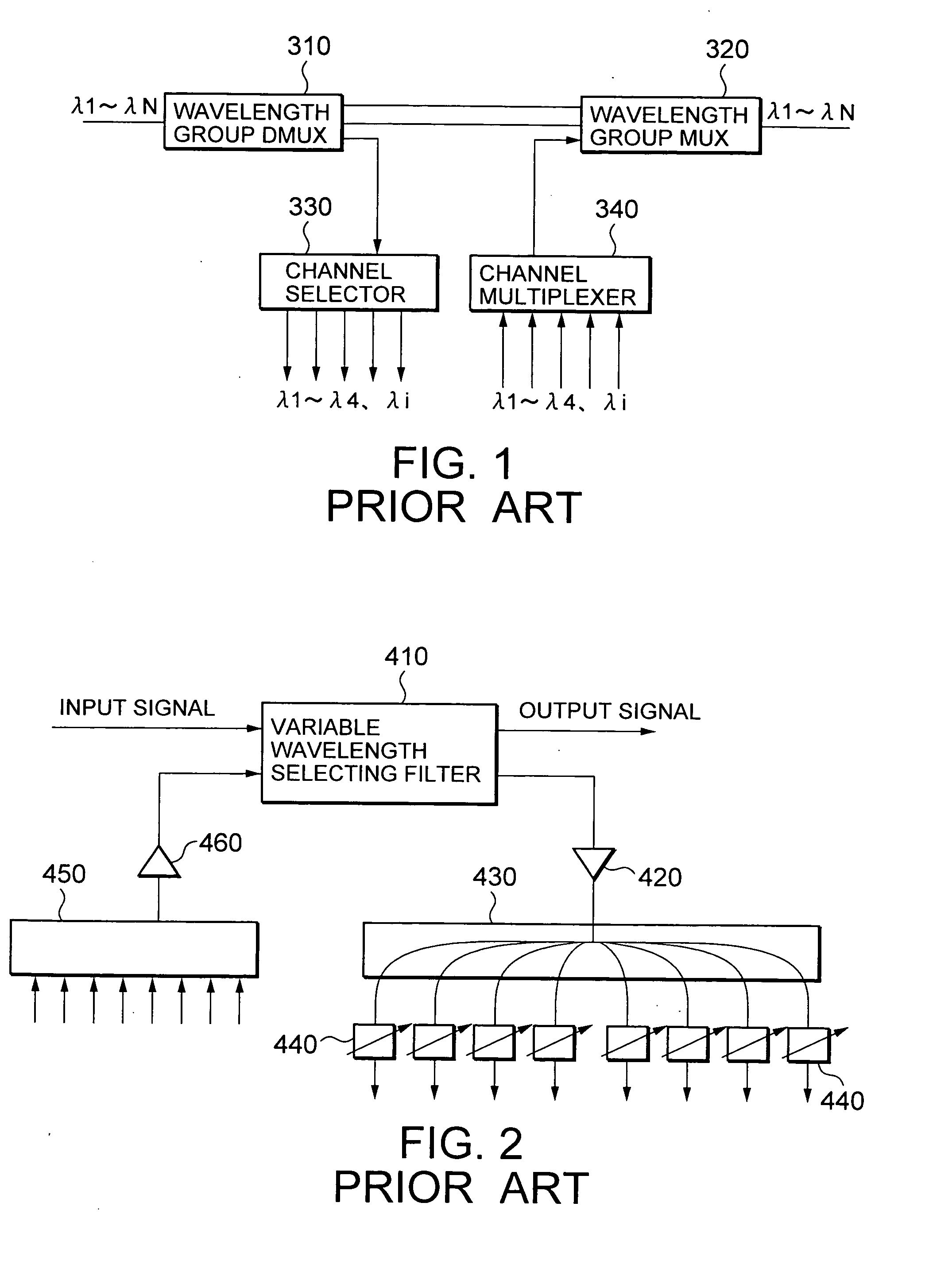
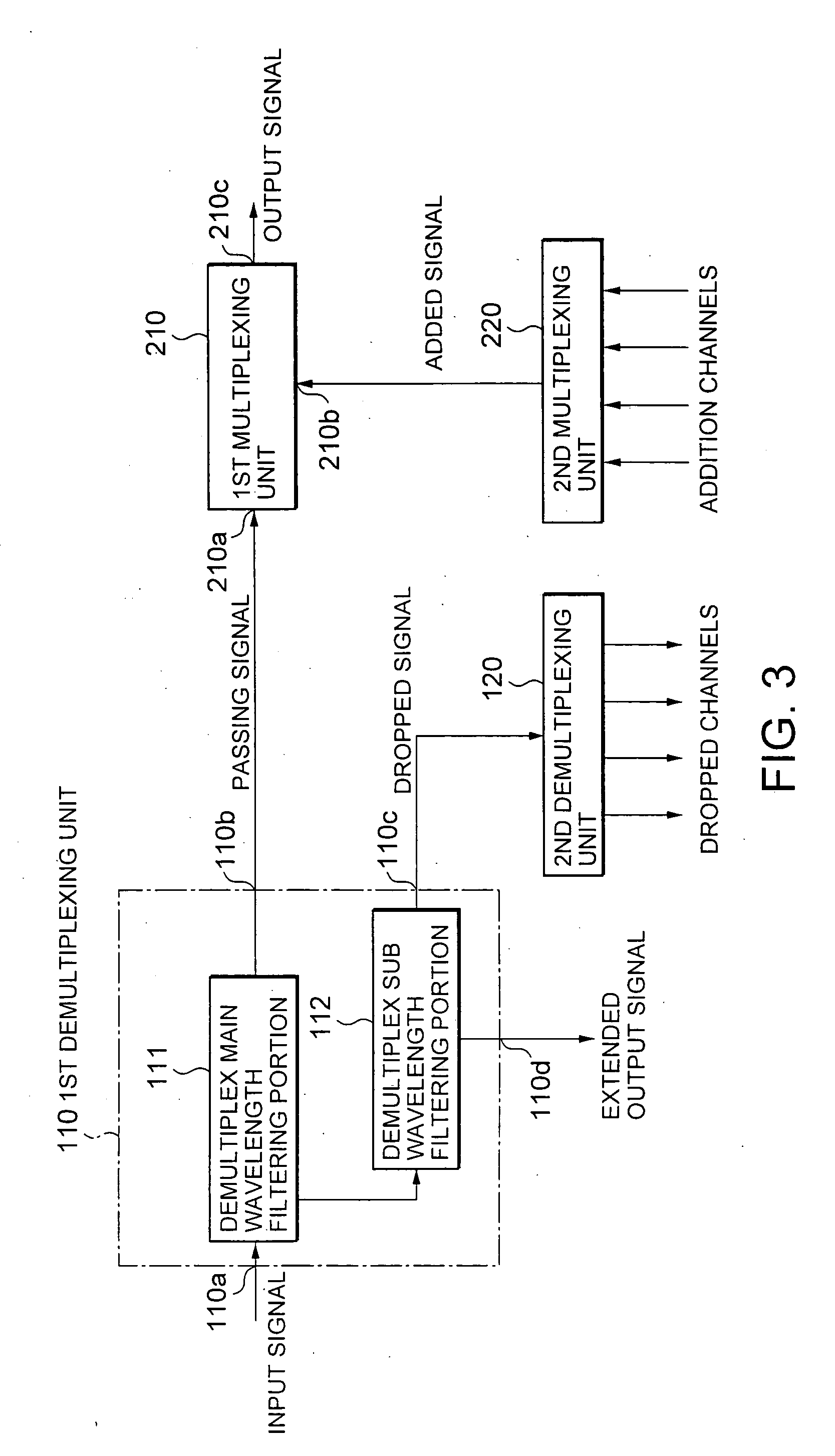
InactiveUS20050013615A1Reduce five filterReduce in quantityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsLength waveSignal multiplexing
A wavelength variable filter (111) separates an input signal into a passing signal and an intermediate output signal. A wavelength variable filter (112) separates the intermediate output signal into a dropped signal and an extended output signal. An interleaver (120) separates the dropped signal into individual dropped channels. An intrerleaver (220A) multiplexes a plurality of addition channels into an added signal. A wavelength variable filter (212) multiplexes the added signal and an extended input signal to produce an intermediate input signal. A wavelength variable filter (211) multiplexes the passing signal and the intermediate input signal into an output signal. A wavelength setting portion (100) sets a wavelength of each wavelength variable filter in accordance with operation of an operator.
Owner:NEC CORP
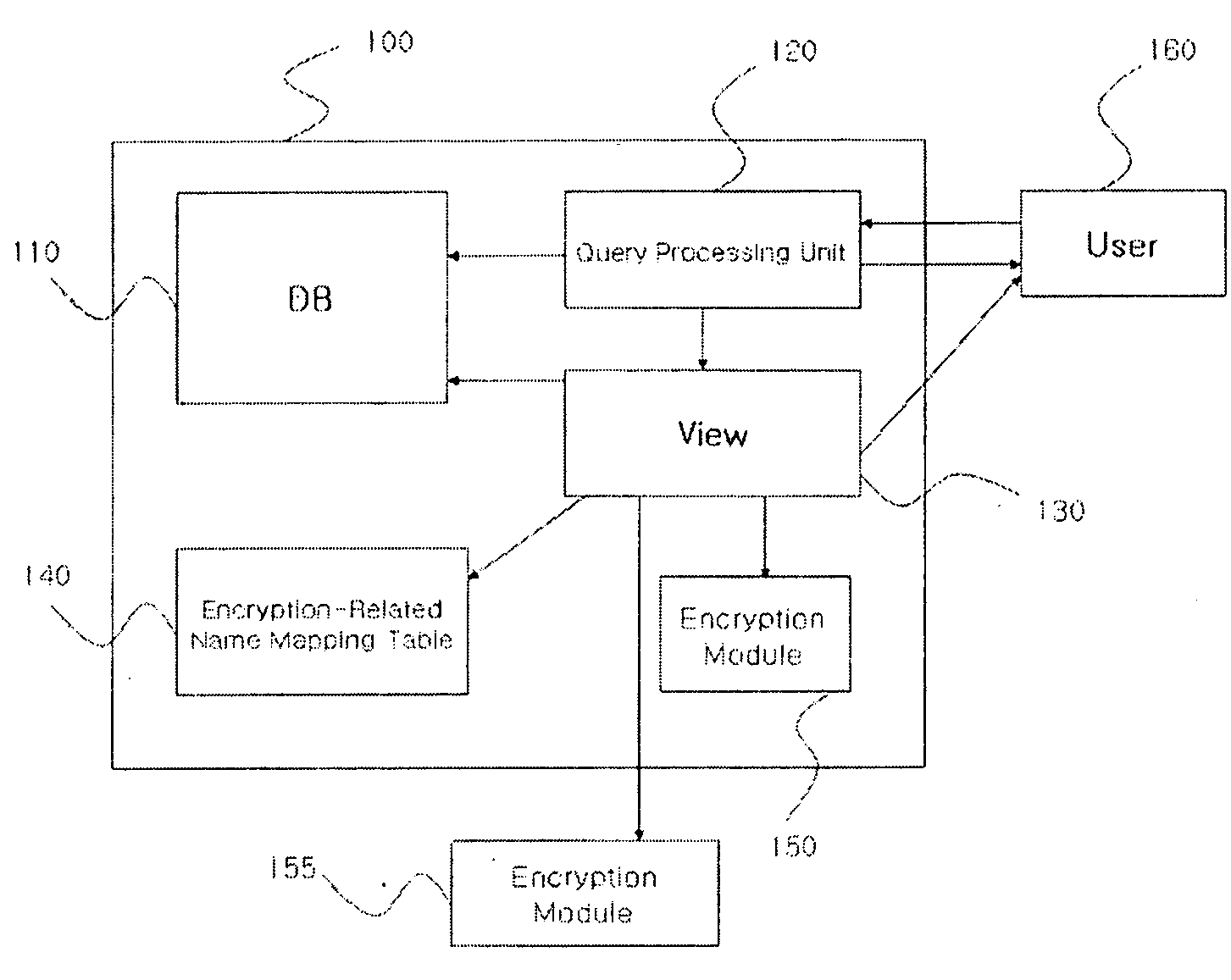
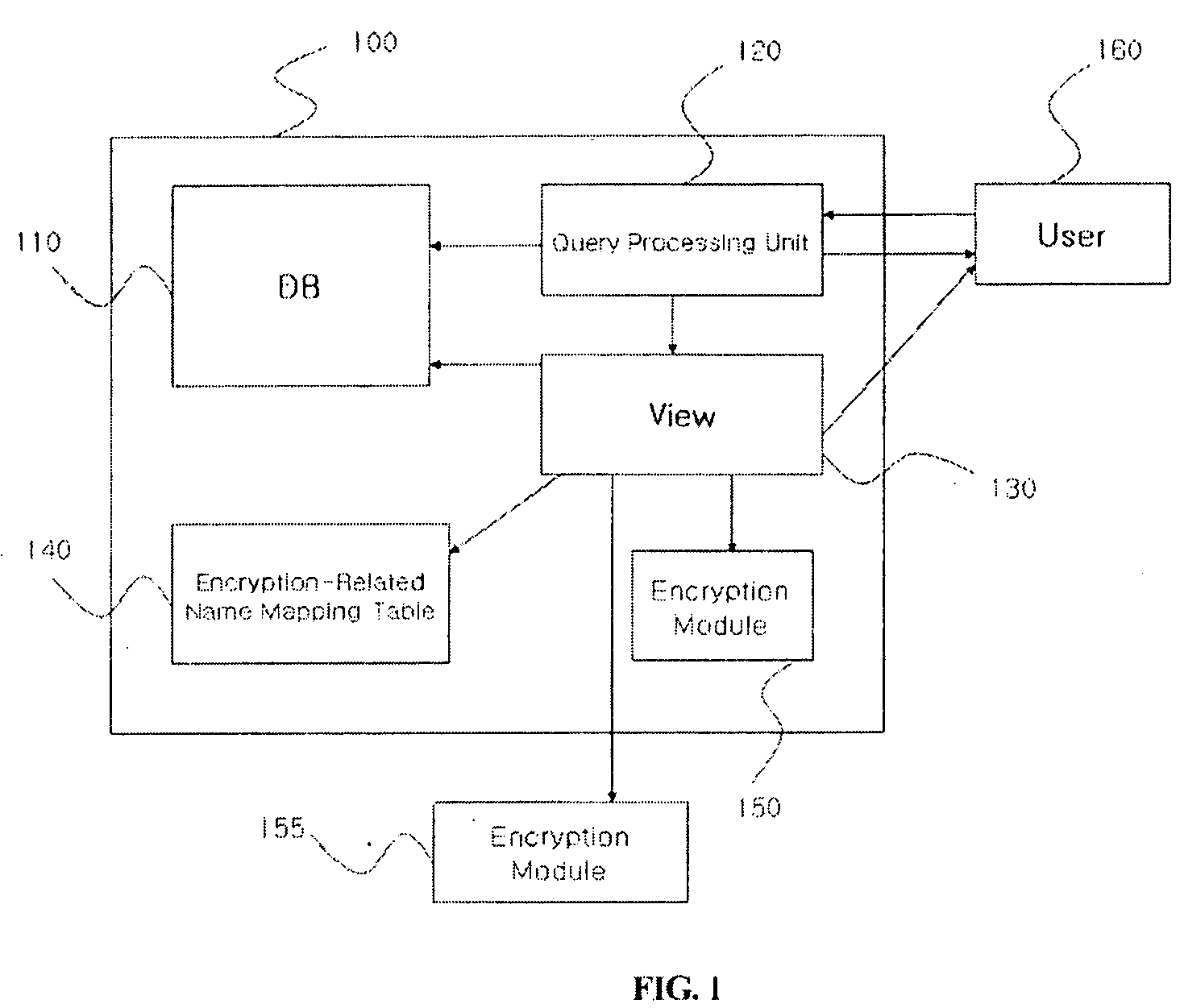
Query processing system and method for database with encrypted column by query encryption transformation
ActiveUS20090100033A1Improve encryptionOvercome slowdownDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsQuery transformationEncryption
Query processing system and method by query transformation transform a user request query based on an original DB structure, destined to a DBMS of a DB with some columns encrypted, into a query based on an encrypted DB structure so that the DBMS processes the query. The query is processed irrespective of whether or not the query includes an encryption-related item, and query-processing performance is remarkably improved.
Owner:PENTA SECURITY SYST
Power source apparatus
ActiveUS7580272B2Improve power factorPreventing numberAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionBoost chopperHarmonic
A boost chopper circuit converts AC power to DC voltage and supplies the DC voltage to a load. The boost chopper circuit includes a switching element and a reactor. A controller ON / OFF controls the switching element based on a comparison result in an interval of the former half of a half cycle of the AC power between a detected input current by a input current detector and a current instruction value of a modeling waveform obtained by reducing a harmonic component of a predetermined order from the current waveform.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Sheet stacking apparatus and image forming apparatus
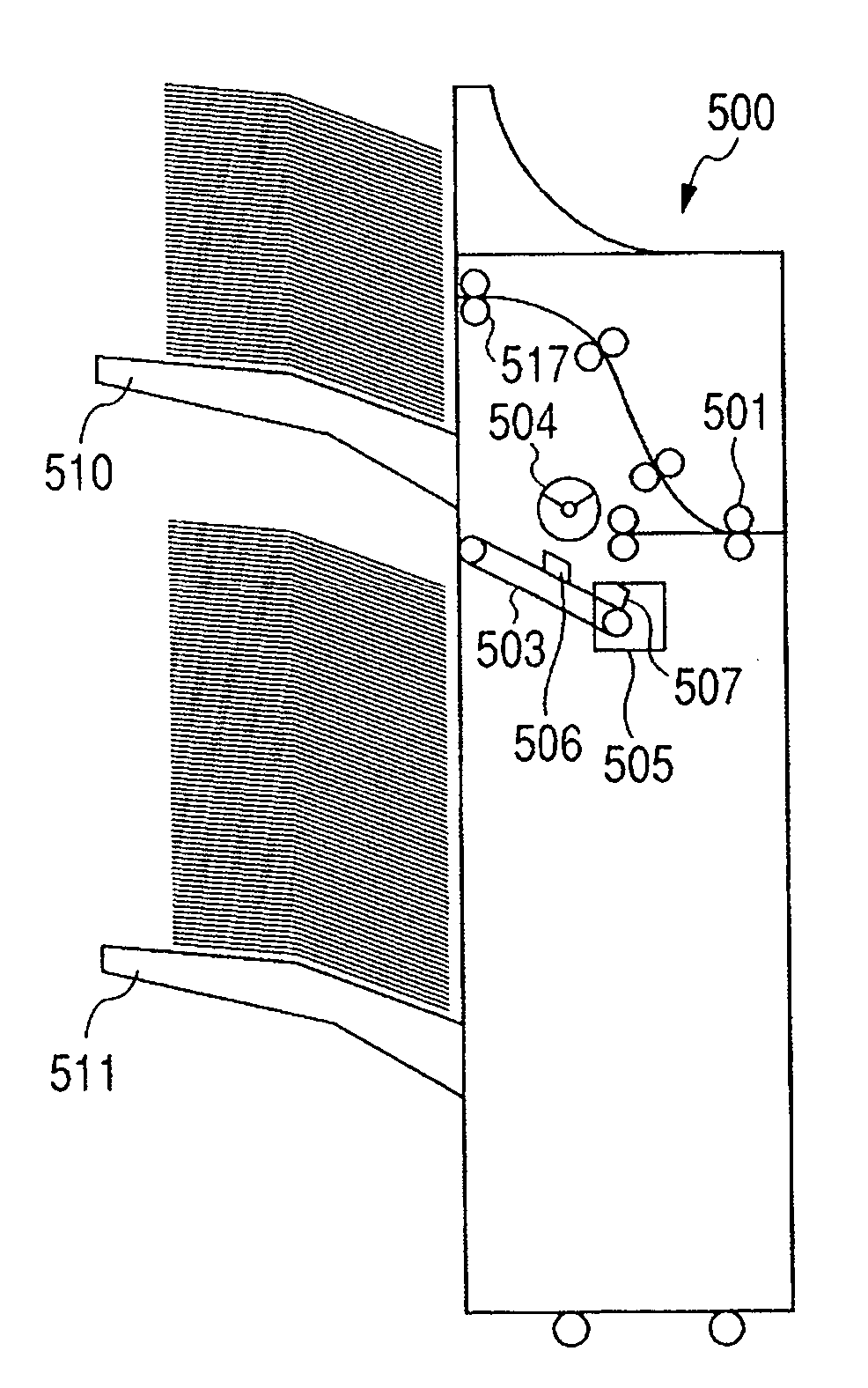
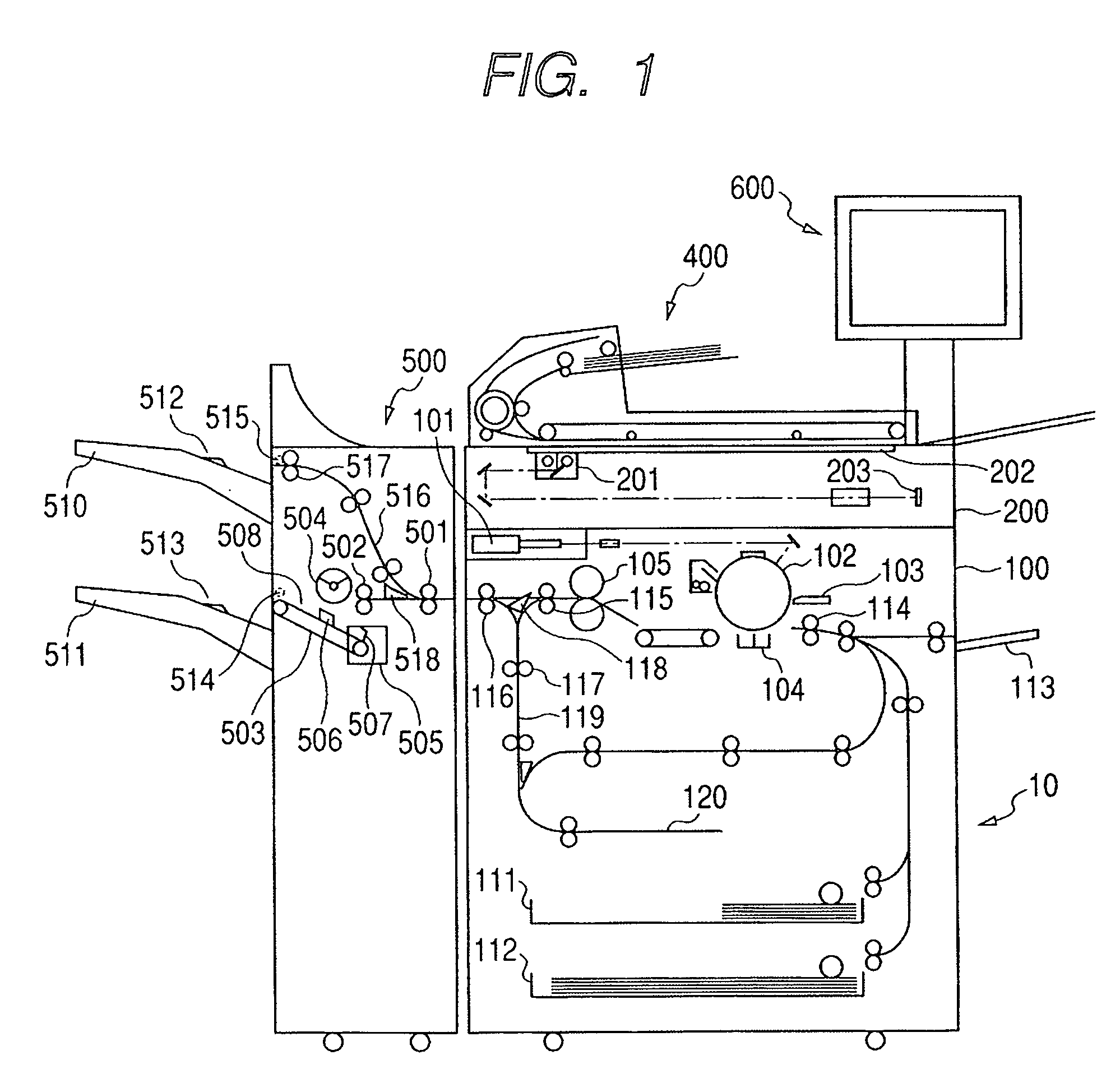
InactiveUS20060261543A1Decrease temporary numberPreventing numberFunction indicatorsPile receiversPaper sheetElectrical and Electronics engineering
A sheet stacking apparatus has a stack tray which can move so that a sheet stack surface keeps a constant position from a discharge outlet and which is a finisher capable of using the stack tray by switching it. When stacking the maximum number of sheets to be stacked on the stack tray and preventing stacking of sheets on the stack tray up to the maximum number of sheets to be stacked and the number of sheets stacked on the stack tray reaches a predetermined number of sheets to be stacked which does not prevent up to the maximum number of sheets from being stacked on the stack tray, stacking of sheets on the stack tray is temporarily prohibited to stack sheets by switching to the stack tray. Thereby, all sheet stack trays can stack up to the maximum number of sheets to be stacked, decrease of the number of stacked sheets is prevented in the whole sheet stacking apparatus and the number of temporal interruptions of a job is decreased.
Owner:CANON KK
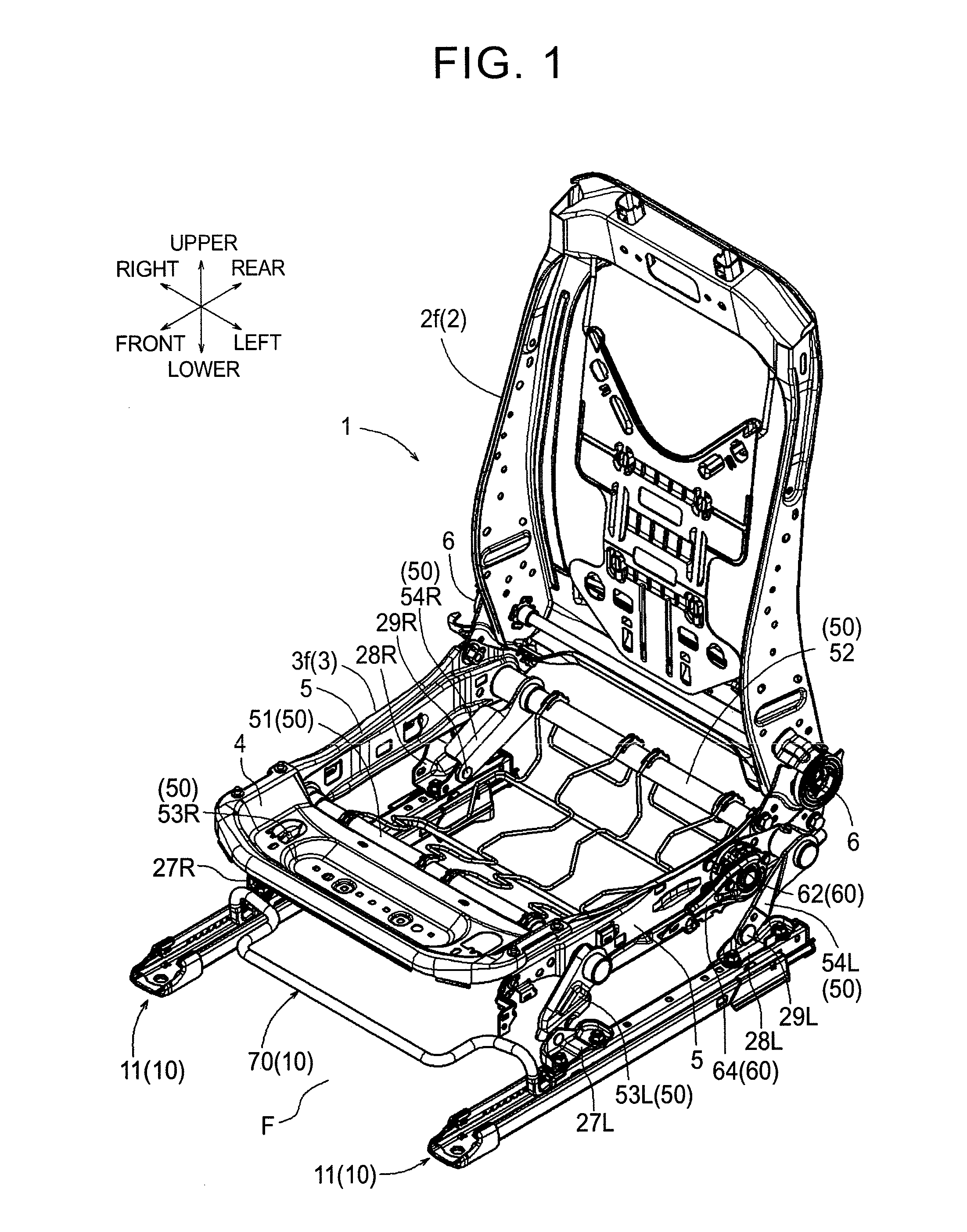
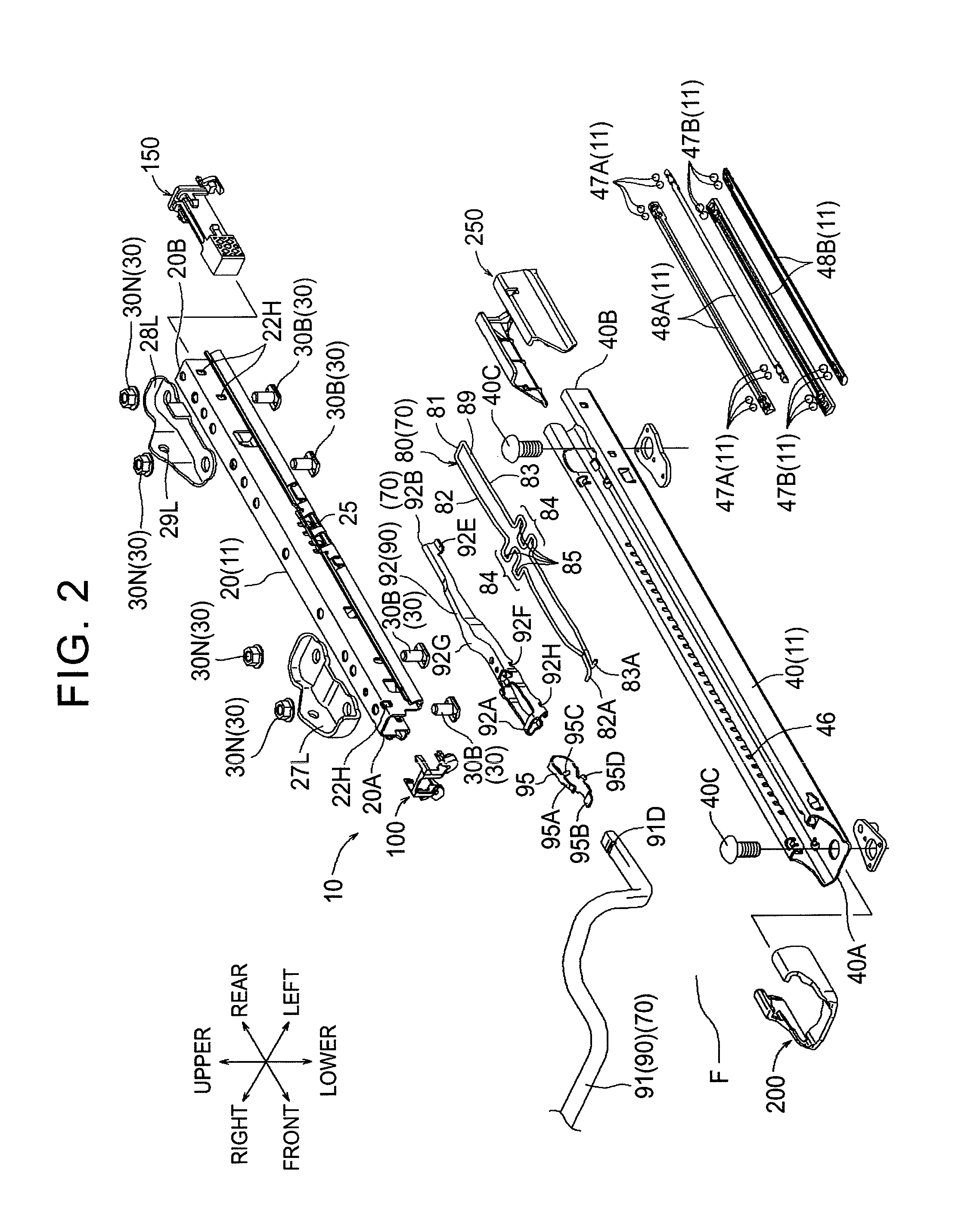
Vehicle seat
ActiveUS20150090853A1Avoid deformationProtect the endStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK +2
Use Of Secretagogue For The Teatment Of Ghrelin Deficiency
InactiveUS20080171700A1Improve the level ofPrevents upregulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSleep patternsCvd risk
The present invention relates to the use of a growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of ghrelin deficiency, and / or undesirable symptoms associated therewith, in an individual at risk of acquiring partial or complete ghrelin deficiency resulting from a medical treatment and / or from a pathological condition. The present invention also relates to use of a secretagogue compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more of: loss of fat mass, loss of lean body mass, weight loss, cachexia, loss of appetite, immunological dysfunction, malnutrition, disrupted sleep pattern, sleepiness, reduction in intestinal absorption and / or intestinal mobility problems in an individual suffering from, or at risk of suffering from, ghrelin deficiency. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of a secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the production of a medicament for preventing weight increase in an individual either: a) being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state, or b) in remission from being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state.
Owner:GASTROTECH PHARMA AS
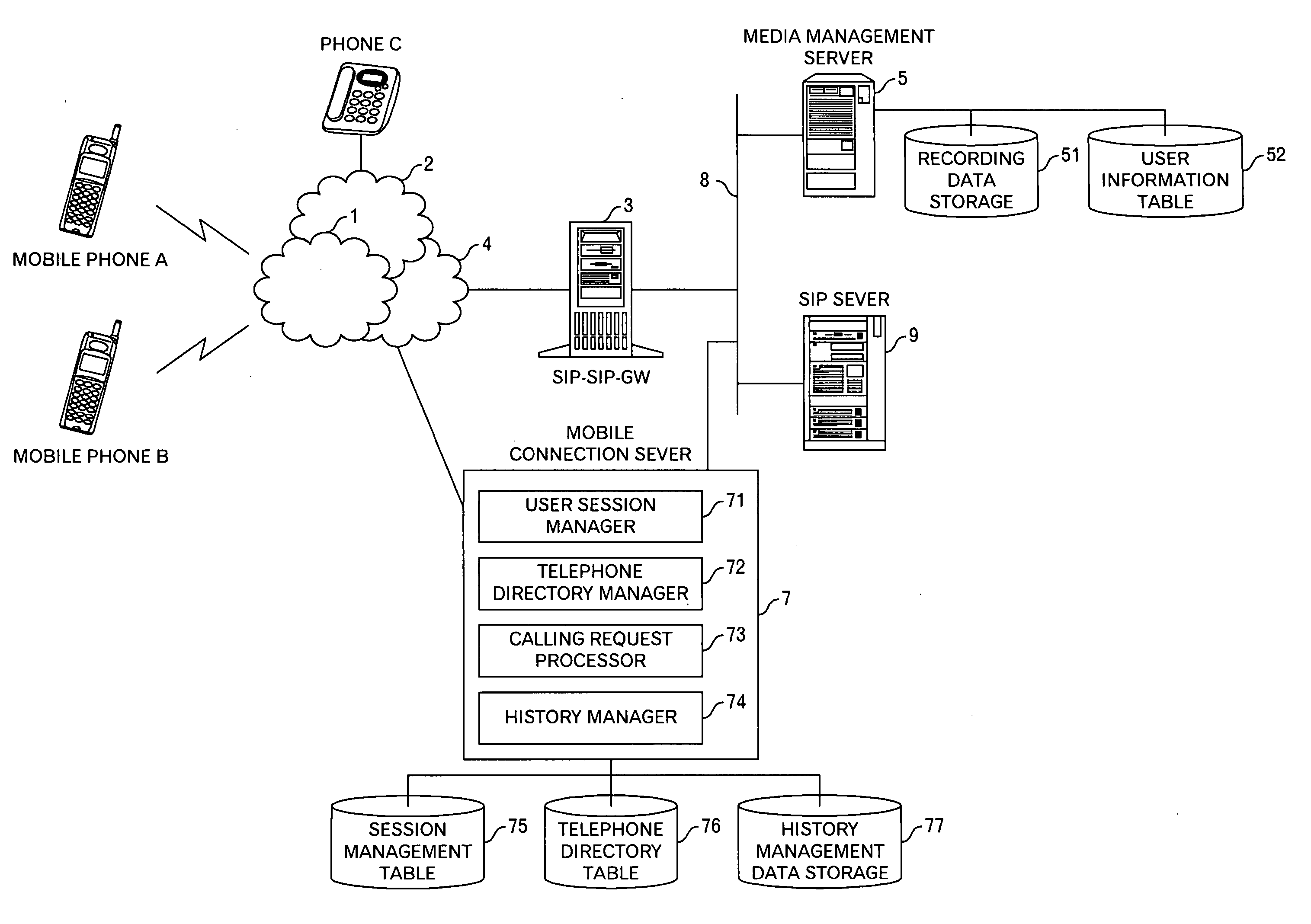
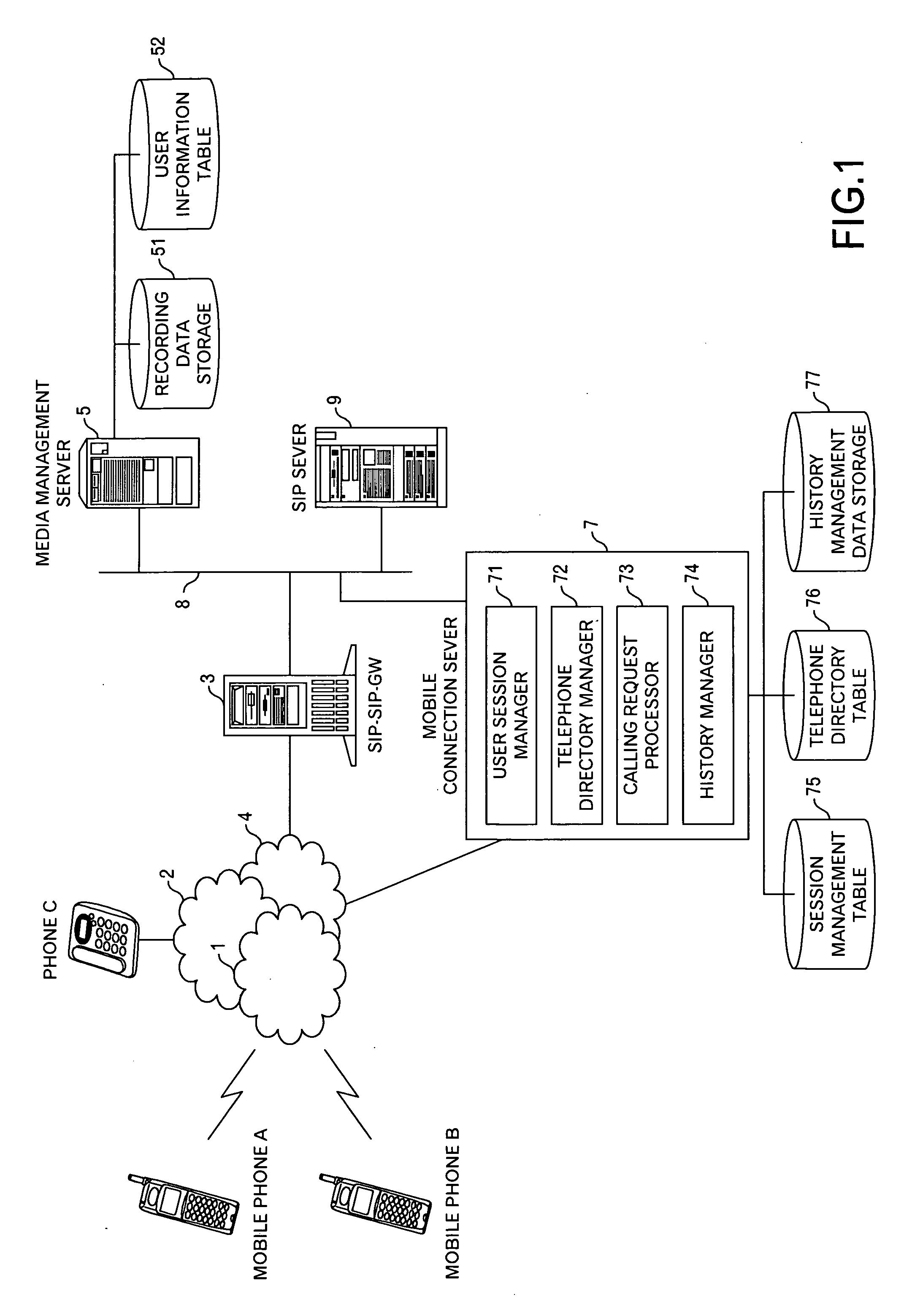
Information processing method and system for preventing leakage of information from mobile phone
InactiveUS20070123224A1Prevent leakageImprove usabilityInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersInformation processingVoice communication
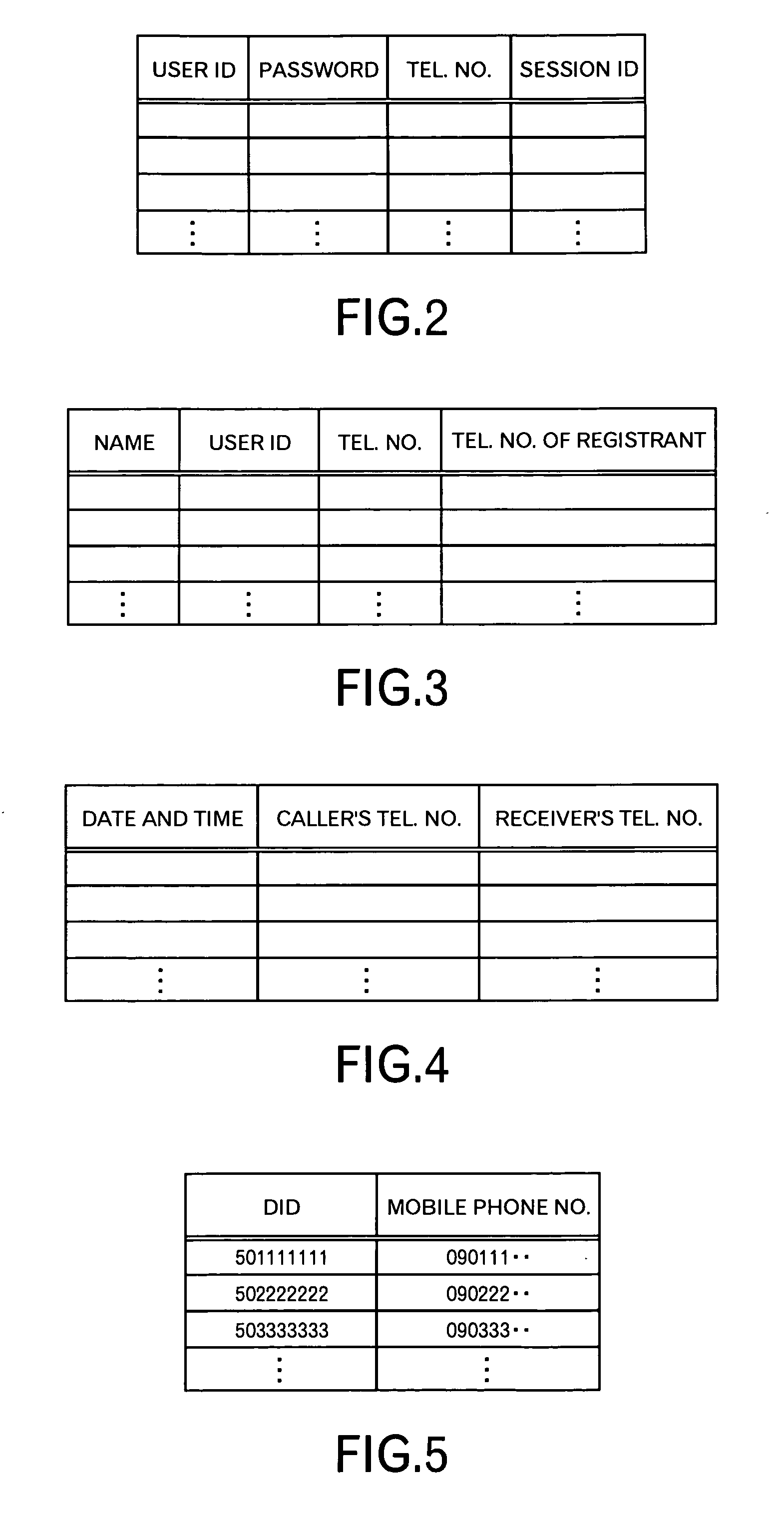
This invention is to provide a technology for preventing information from being leaked from a mobile phone. For this purpose, this invention includes: receiving a request for data to select a calling destination from a first mobile phone capable of executing voice communication and data communication; identifying calling destination candidates registered in a data storage in association with a user of the first mobile phone by identification information other than telephone numbers of the calling destination candidates; and transmitting data to specify and select anyone of the identified calling destination candidates by the identification information other than the telephone numbers of the calling destination candidates, to the first mobile phone. Because the telephone number of the client is not sent to the mobile phone, the leakage of the client information is prevented, even if the mobile phone is stolen.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor memory device
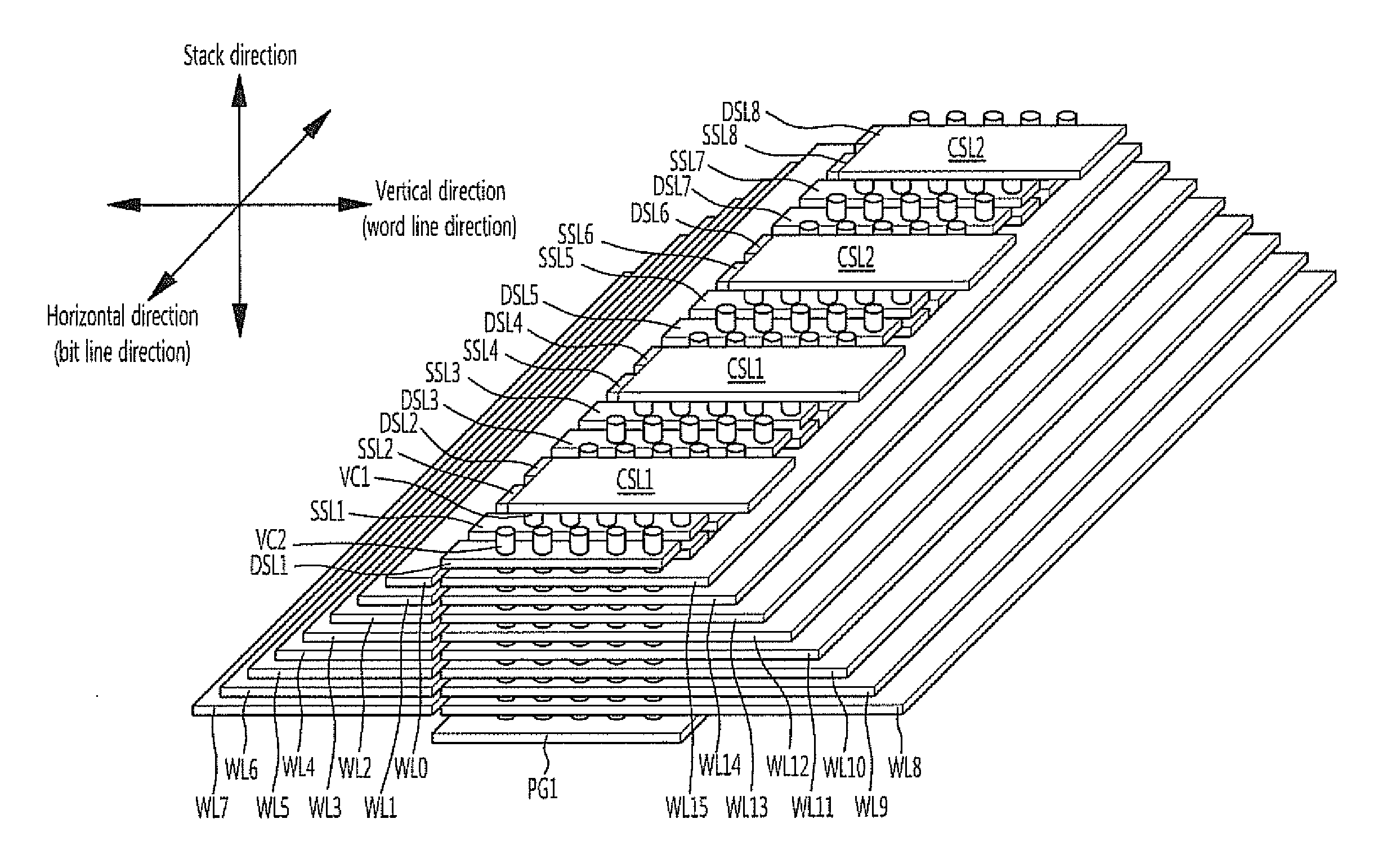
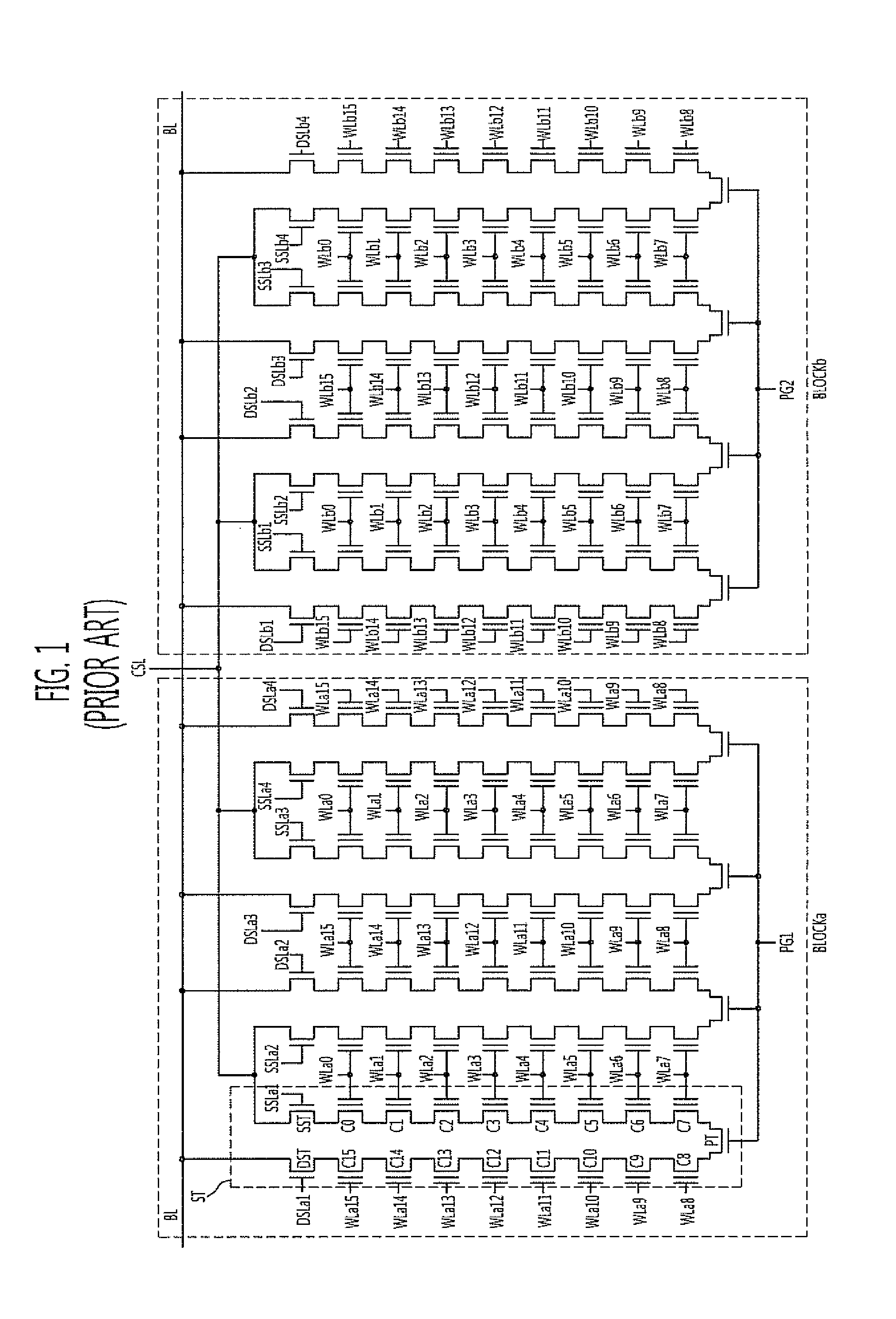
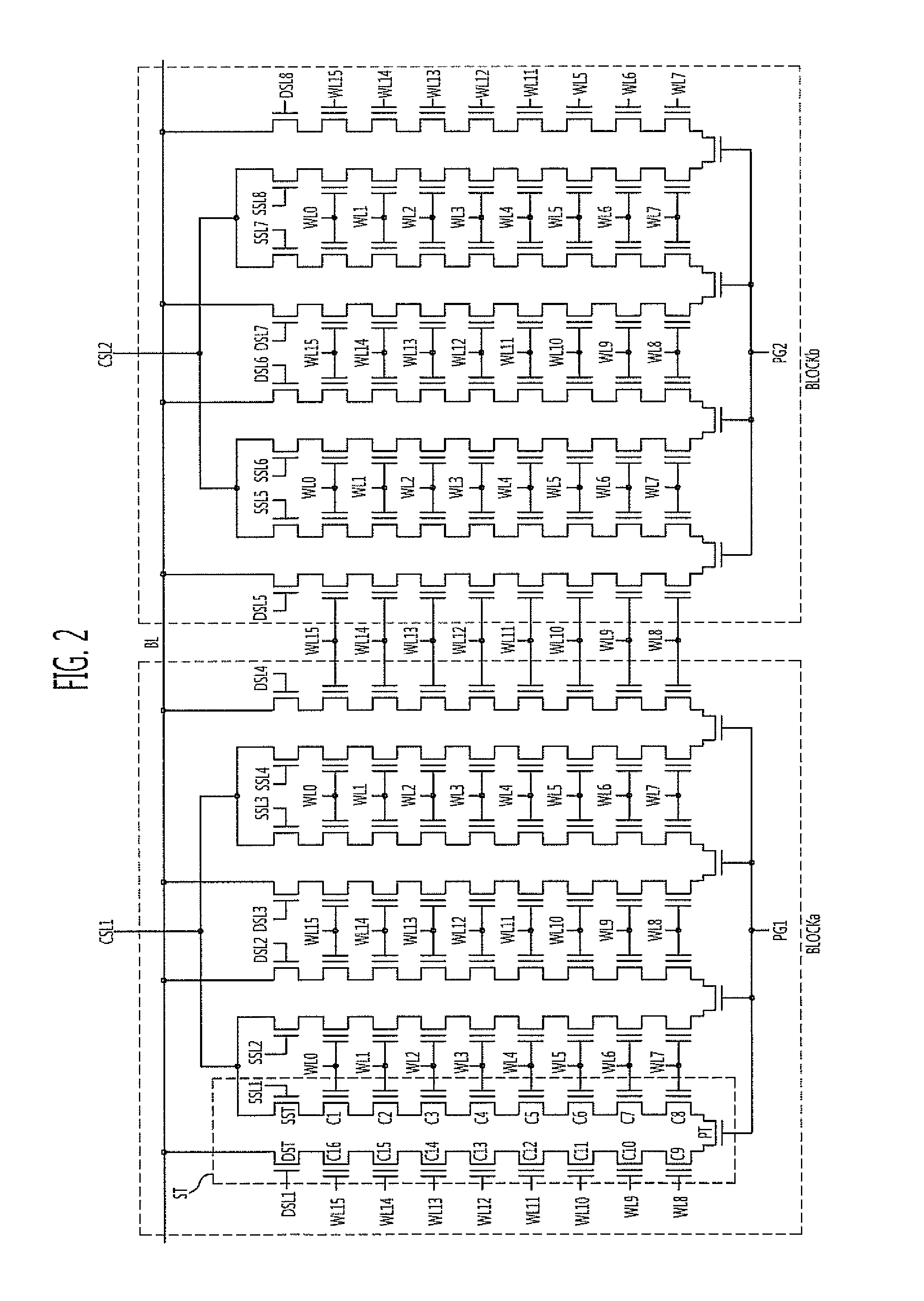
ActiveUS20120314514A1Highly integratedPreventing numberTransistorSolid-state devicesVertical channelComputer science
A semiconductor memory device includes word lines stacked over a substrate having a plurality of memory block regions, select lines arranged over the word lines, vertical channel layers formed to penetrate through the select lines and the word lines and extending to the substrate, and a charge trap layer disposed between the word lines and the vertical channel layers, wherein the stacked word lines are separated by memory block groups that each include two or more memory block regions.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Complementary character encoding for preventing input injection in web applications
InactiveUS8615804B2Appropriate treatmentImprove efficiencyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSQL injectionLexical analysis
Method to prevent the effect of web application injection attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS), which are major threats to the security of the Internet. Method using complementary character coding, a new approach to character level dynamic tainting, which allows efficient and precise taint propagation across the boundaries of server components, and also between servers and clients over HTTP. In this approach, each character has two encodings, which can be used to distinguish trusted and untrusted data. Small modifications to the lexical analyzers in components such as the application code interpreter, the database management system, and (optionally) the web browser allow them to become complement aware components, capable of using this alternative character coding scheme to enforce security policies aimed at preventing injection attacks, while continuing to function normally in other respects. This approach overcomes some weaknesses of previous dynamic tainting approaches by offering a precise protection against persistent cross-site scripting attacks, as taint information is maintained when data is passed to a database and later retrieved by the application program. The technique is effective on a group of vulnerable benchmarks and has low overhead.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
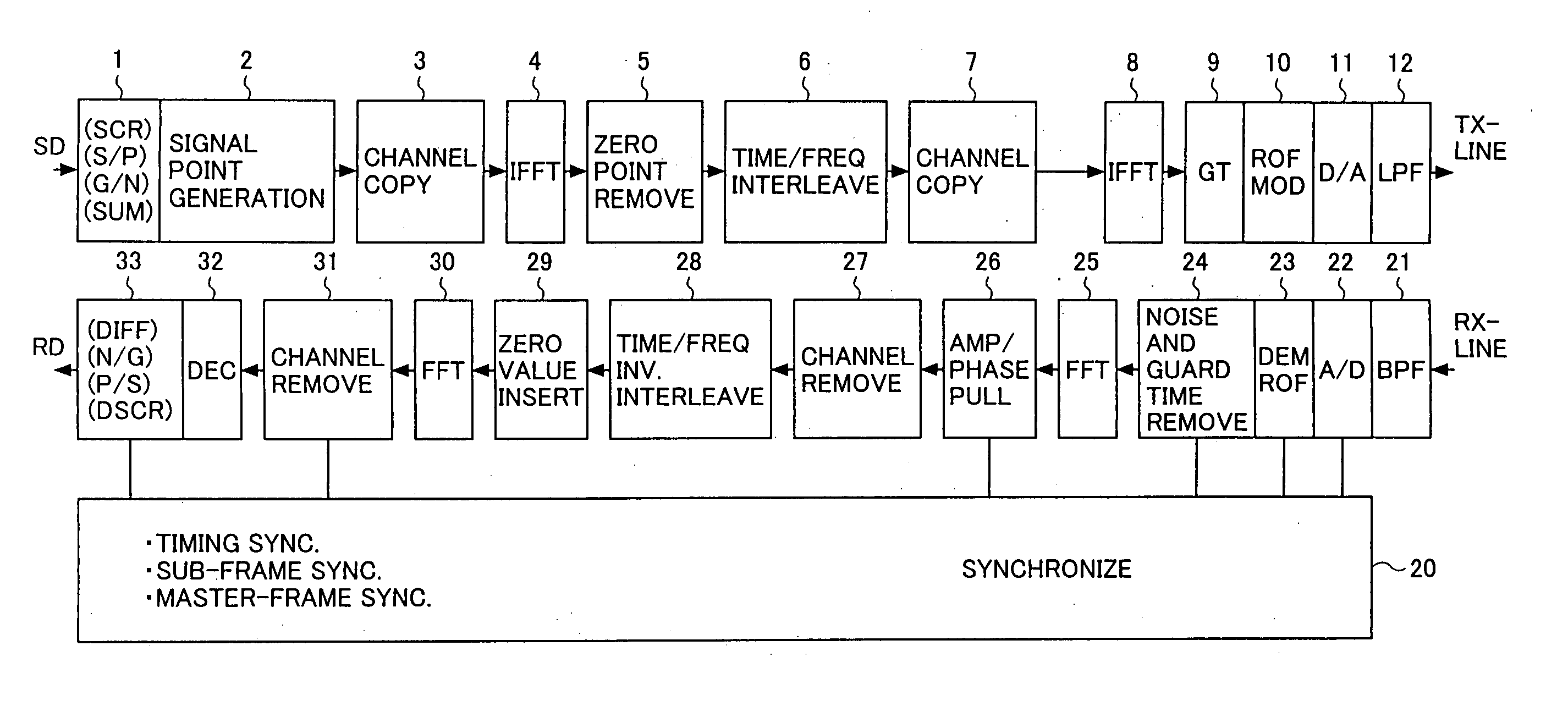
Data transmission method and data transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20070009061A1Reduce in quantityReduce signal noiseSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsComputer hardwareData transmission
A data transmission method comprises the steps of: a) performing two-dimensional interleaving along a time axis and along a frequency axis; b) transmitting the thus-obtained data by a multi-carrier transmission form; and c) producing, by channel copy operation, data which is short for the number of channels required for fast inverse Fourier transform performed antecedent and subsequent to said step a).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
DC to DC convertor
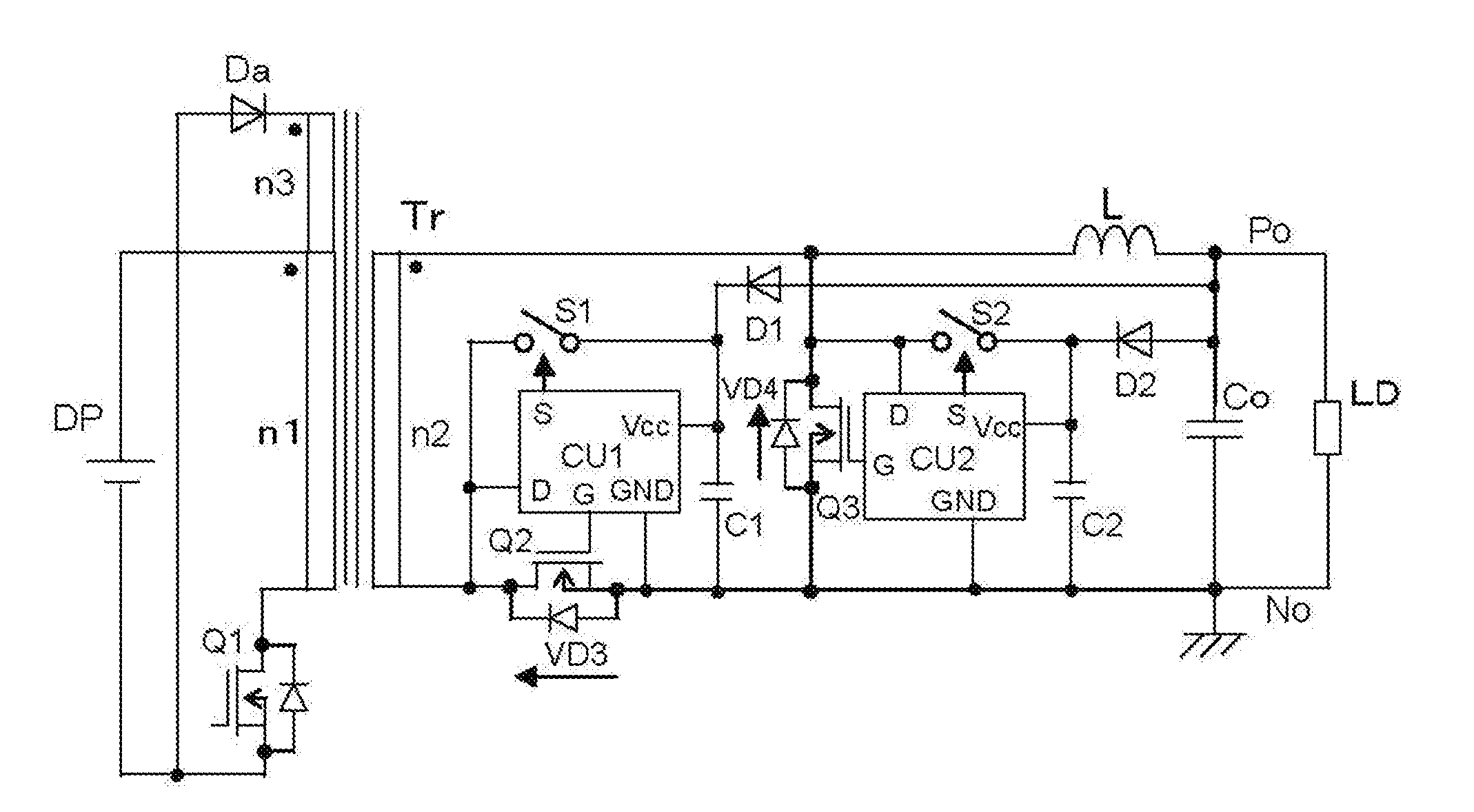
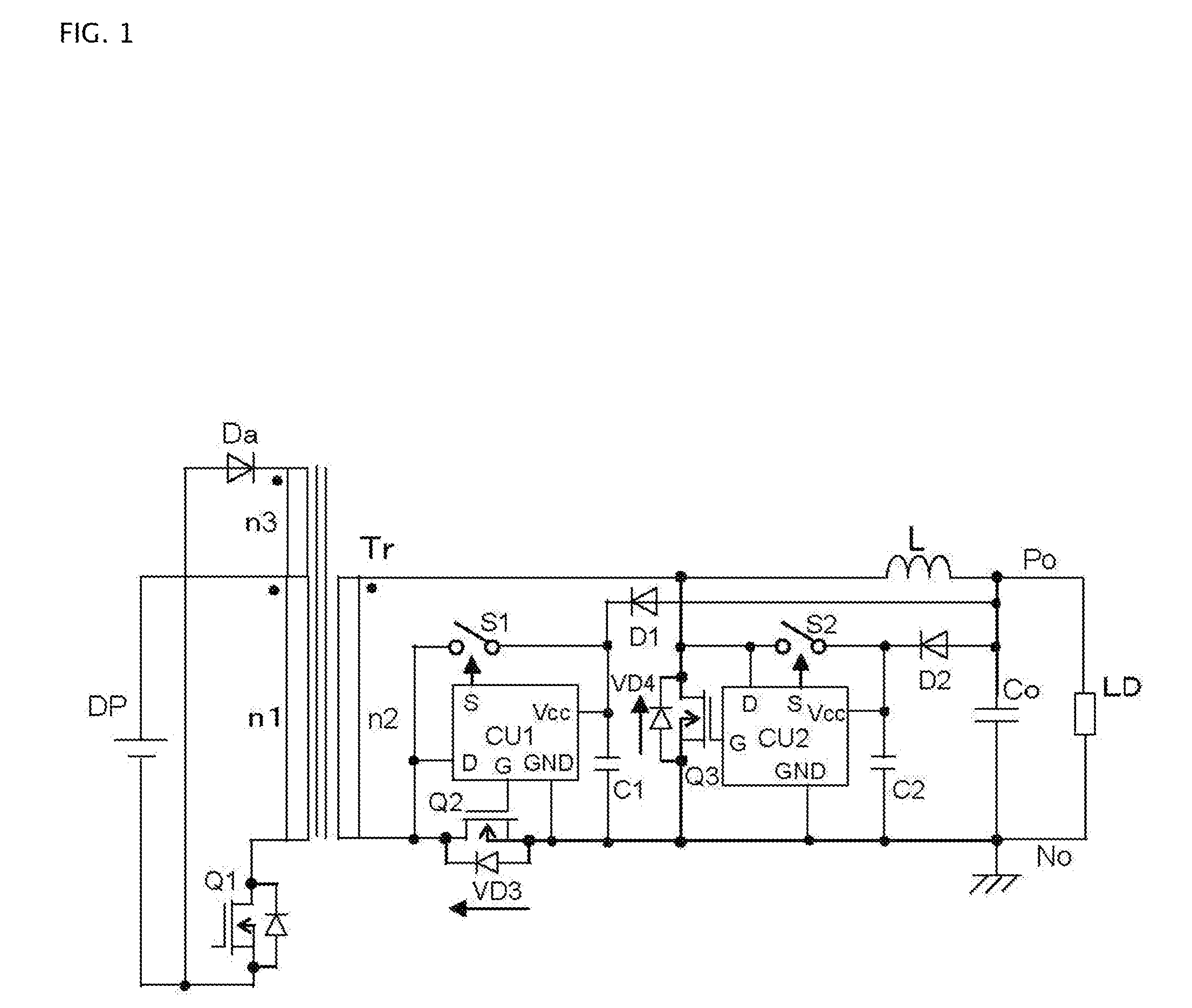
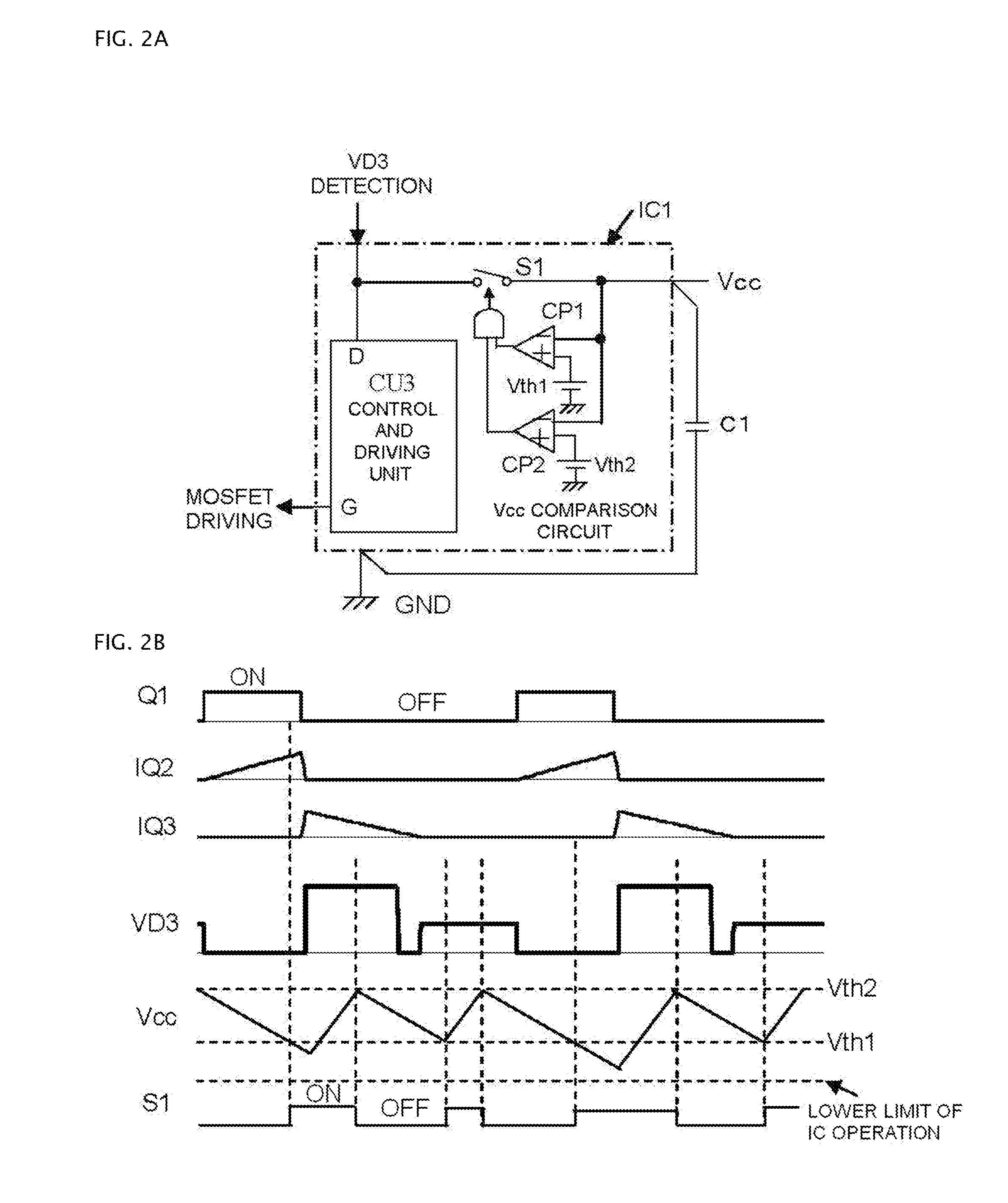
ActiveUS20130107582A1Low power lossReduce power consumptionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMOSFETDC-to-DC converter
A DC to DC converter can include a reverse-blocking semiconductor switch that makes a synchronously rectifying MOSFET become parallel-connected with a capacitor that is connected to a power supply of a controller IC for a conventionally used synchronously rectifying circuit. The reverse-blocking semiconductor switch can be driven either by signals for adjusting a voltage of the capacitor within a permitted range of voltage of the power supply of the controller circuit, or by signals that are determined by a signal obtained from voltage across the MOSFET and the signals for adjusting a voltage of the capacitor within a permitted range of voltage of the power supply of the controller circuit.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Methods and infrastructure for performing repetitive data protection and a corresponding restore of data
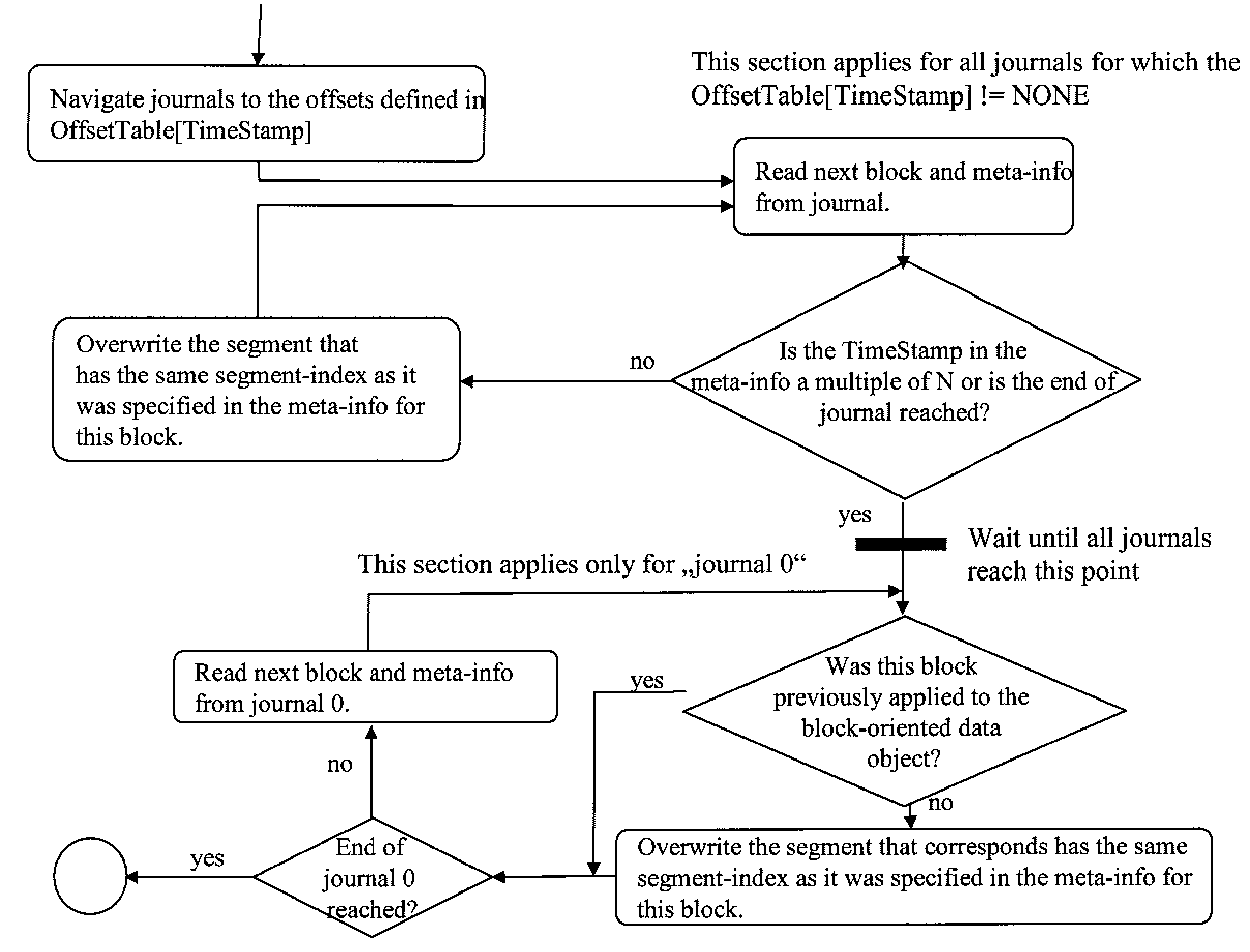
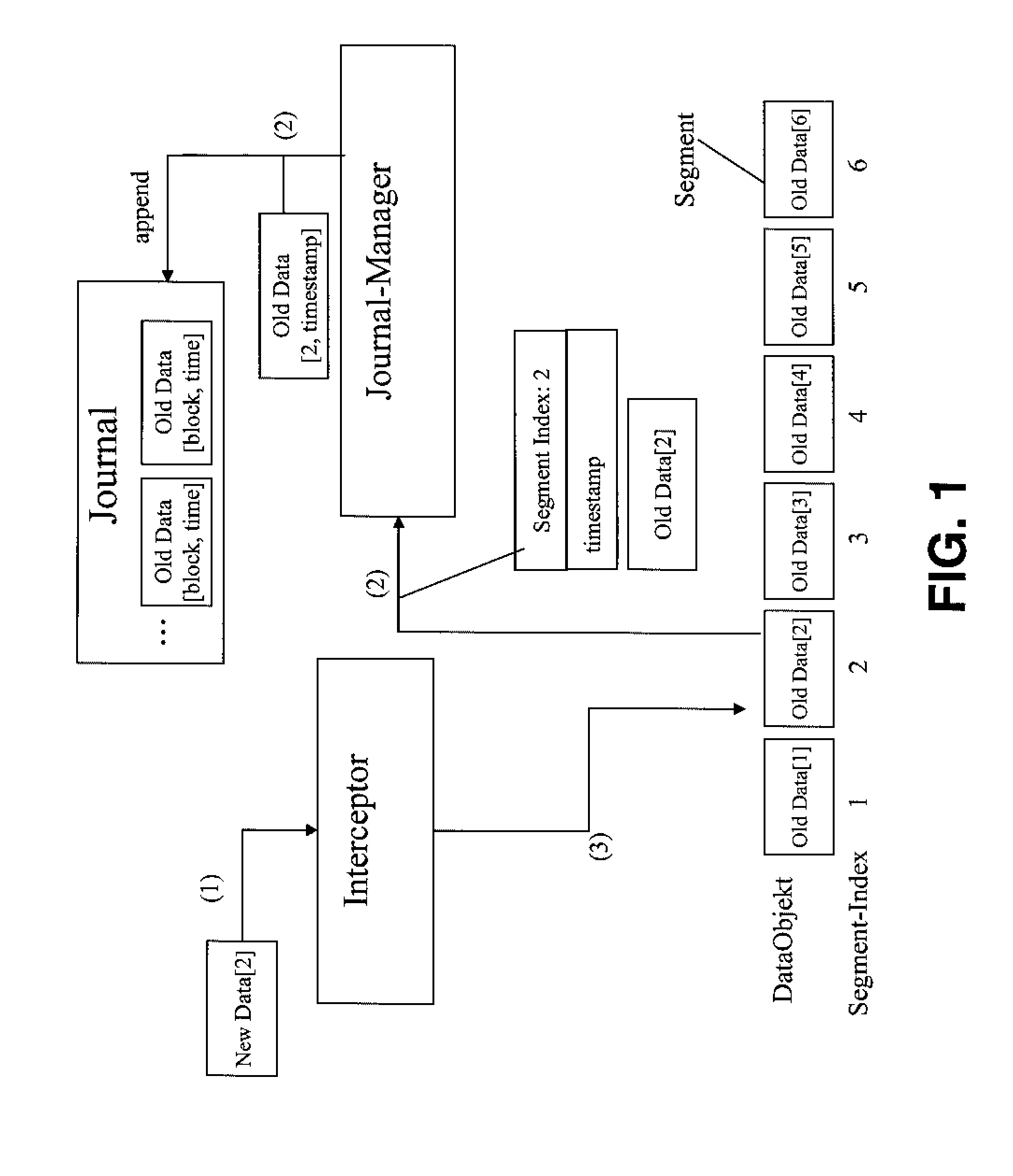
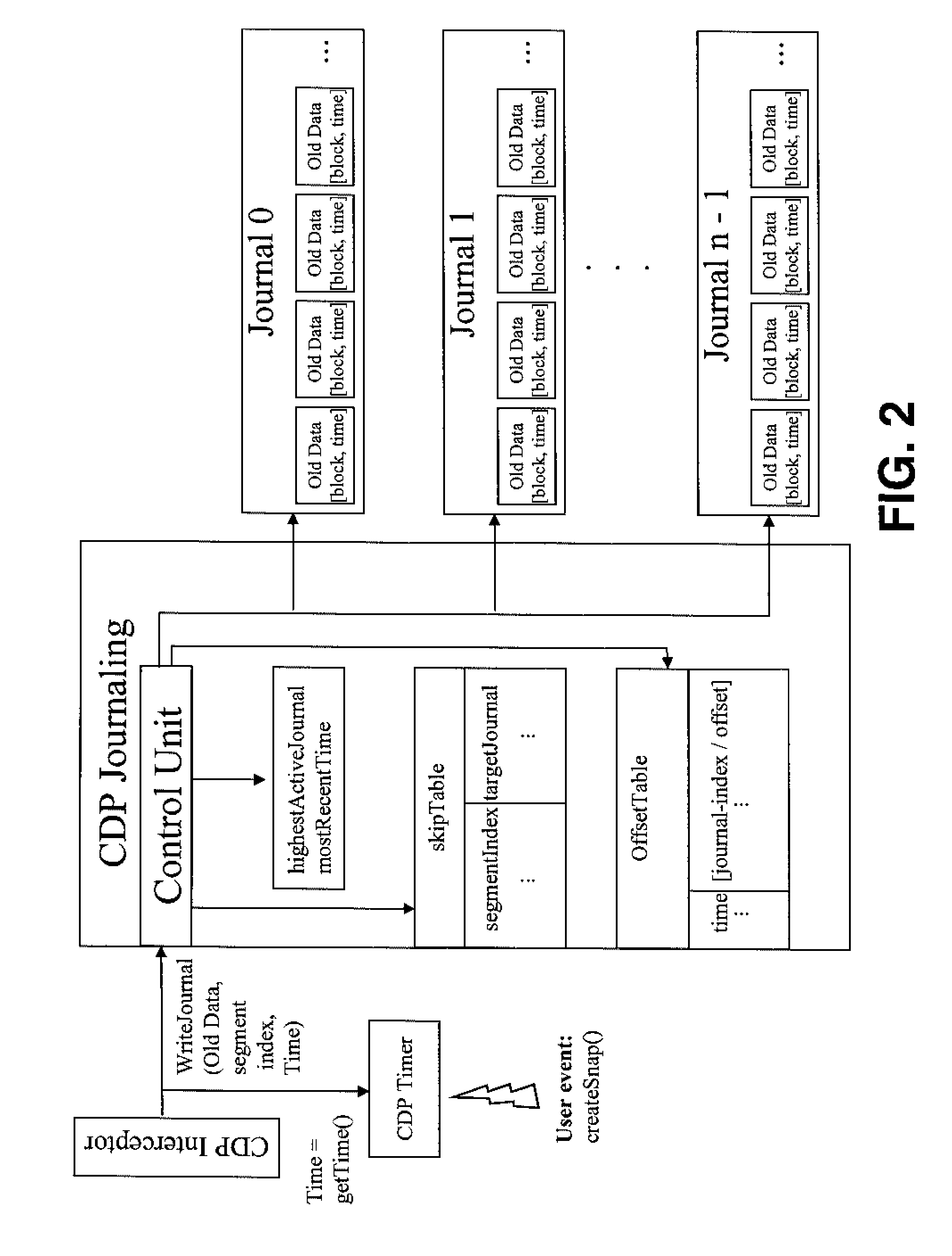
InactiveUS20080162840A1Improve performancePreventing numberError detection/correctionMemory systemsTimestampSystem recovery
According to the present invention methods and an infrastructure are provided for performing repetitive data protection and a corresponding restore of data for block oriented data objects comprising several indexed segments.For implementing the invention, timestamps tk are set by a time k; and only the first data modification of a segment is recorded, after a timestamp tk has been set, by storing the old data contents of said segment together with the segment index i an said timestamp tk as undo-log block in a journal, first, before overwriting said segment with the modified new data. The main idea of the invention is that the undo-log blocks of the segments are distributed to N journals jn, wherein N>1 and n=0, . . . , N-1, such thata) at time tn+(m·N) (0≦n<N) at most m+1 undo-log blocks corresponding to the same segment are recorded in the journal j0,b) during the time interval [tk+(m·N), t(m+1)·N) no duplicates are recorded in the union of journals j0, . . . jk, (0≦k<N), andc) an undo-log block is written to journal jn+(m·N) (0<n<N) if and only if the corresponding segment was modified in time interval [t(n-1)+(m·N), tn+(m·N)) for the last time before the current modification;wherein m=0, 1, . . . ∞ and wherein the timestamps t(m·N) represent consecutive reset points.Then, only journals j0, . . . , jk are needed for a point in time restore of time rk+(m·N) and all changes that were written after t(m+1)·N located in journal j0. Thus, the present invention allows to reduce the amount of data that needs to be read from the journals in order to recover the system to a given point in time.
Owner:IBM CORP
User authentication device and electric commerce system using the device
InactiveUS20020013900A1Preventing numberDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationEngineeringUser authentication
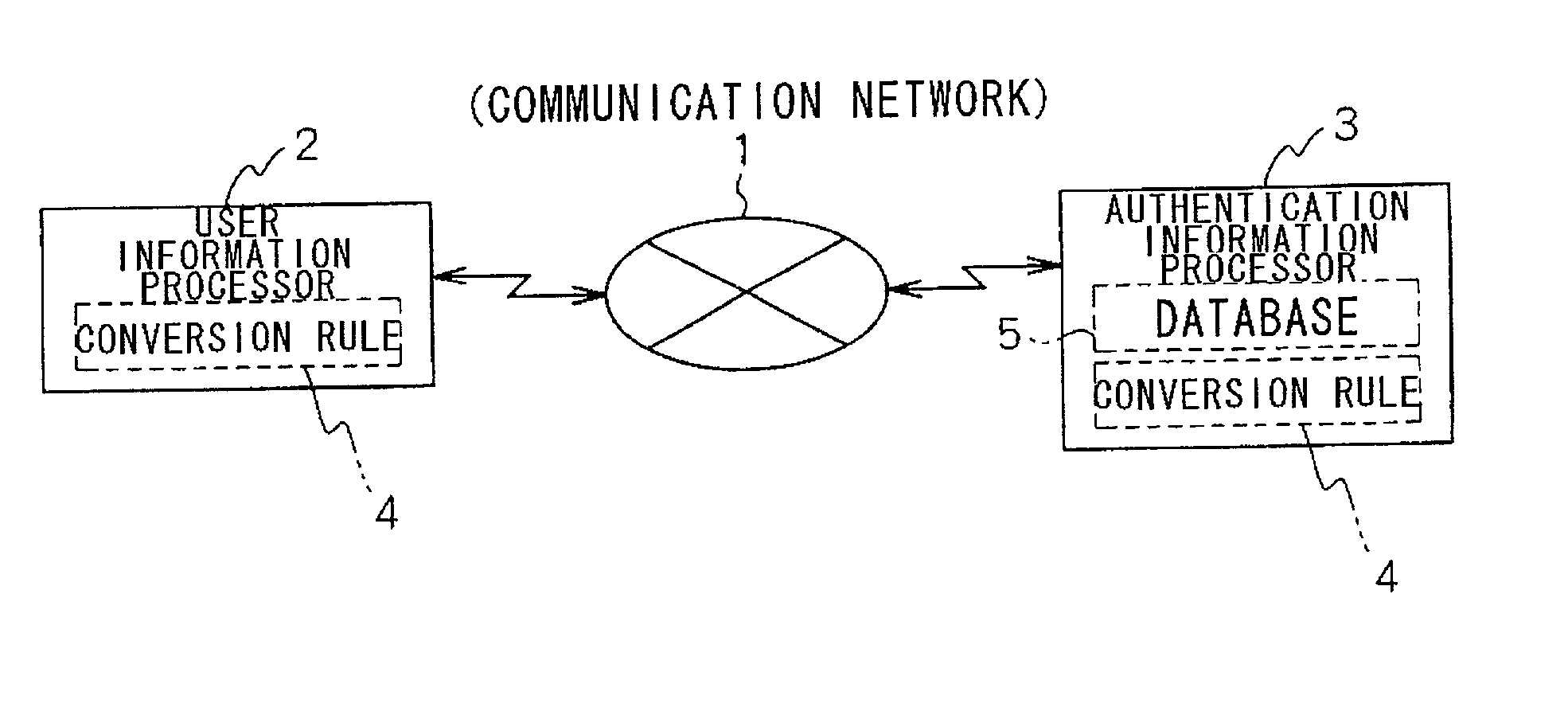
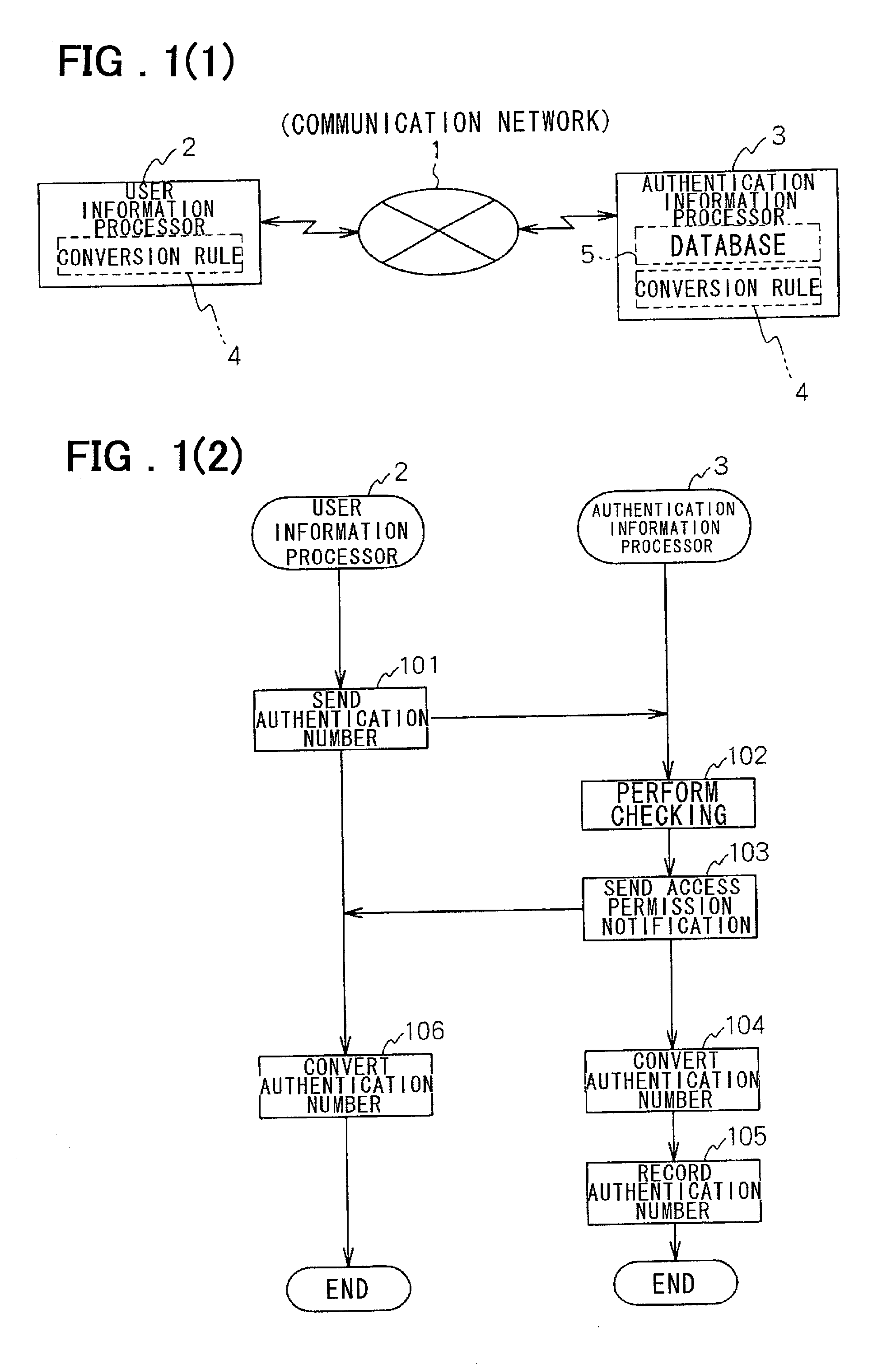
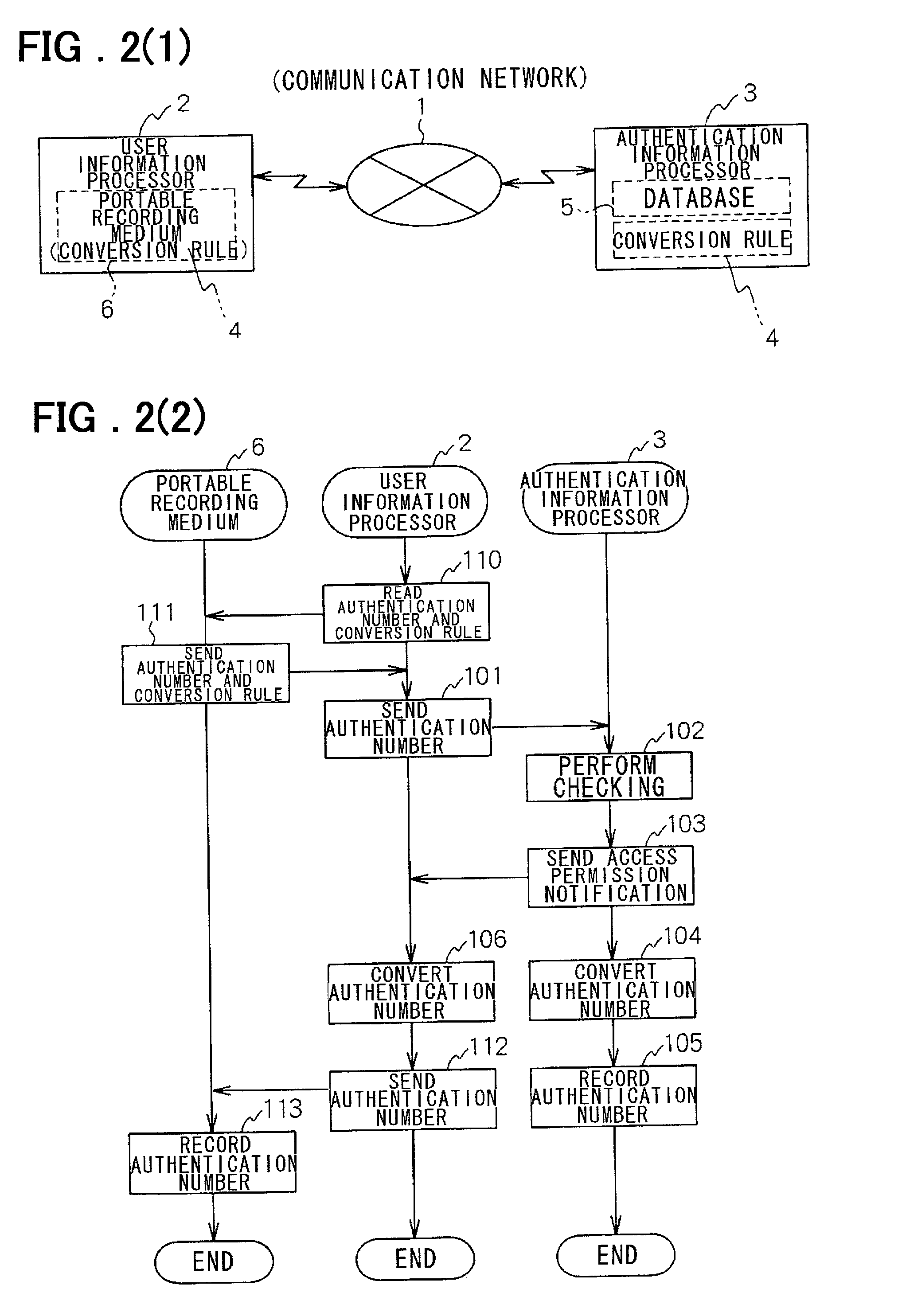
A user information processor 2 comprises a function unit for sending a first authentication number to an authentication information processor 3 and a function unit for converting the first authentication number to a second authentication number using a conversion rule 4 in response to an access permission notification from the authentication information processor 3 and for using the second authentication number as a new first authentication number. The authentication information processor 3 comprises a function unit for making a check in response to the first authentication number, a function unit for sending the access permission notification to the user information processor if a user is authenticated as valid, and a function unit for converting the first authentication number to the second authentication number using the same conversion rule as the conversion rule 4 and for recording the second authentication number into a database 5 as a new first authentication number.
Owner:NEC CORP
Vegf-specific antagonists for adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy and the treatment of early stage tumors
InactiveUS20110052576A1Reduce the burden onSmall sizeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsStaging tumorsAdjuvant
Disclosed herein are methods of treating benign, pre-cancerous, or non-metastatic tumors using an anti-VEGF-specific antagonist. Also disclosed are methods of treating a subject at risk of developing benign, pre-cancerous, or non-metastatic tumors using an anti-VEGF-specific antagonist. Also disclosed are methods of treating or preventing recurrence of a tumor using an anti-VEGF-specific antagonist as well as use of VEGF-specific antagonists in neoadjuvant and adjuvant cancer therapy.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Appliance Immersion Cooling System
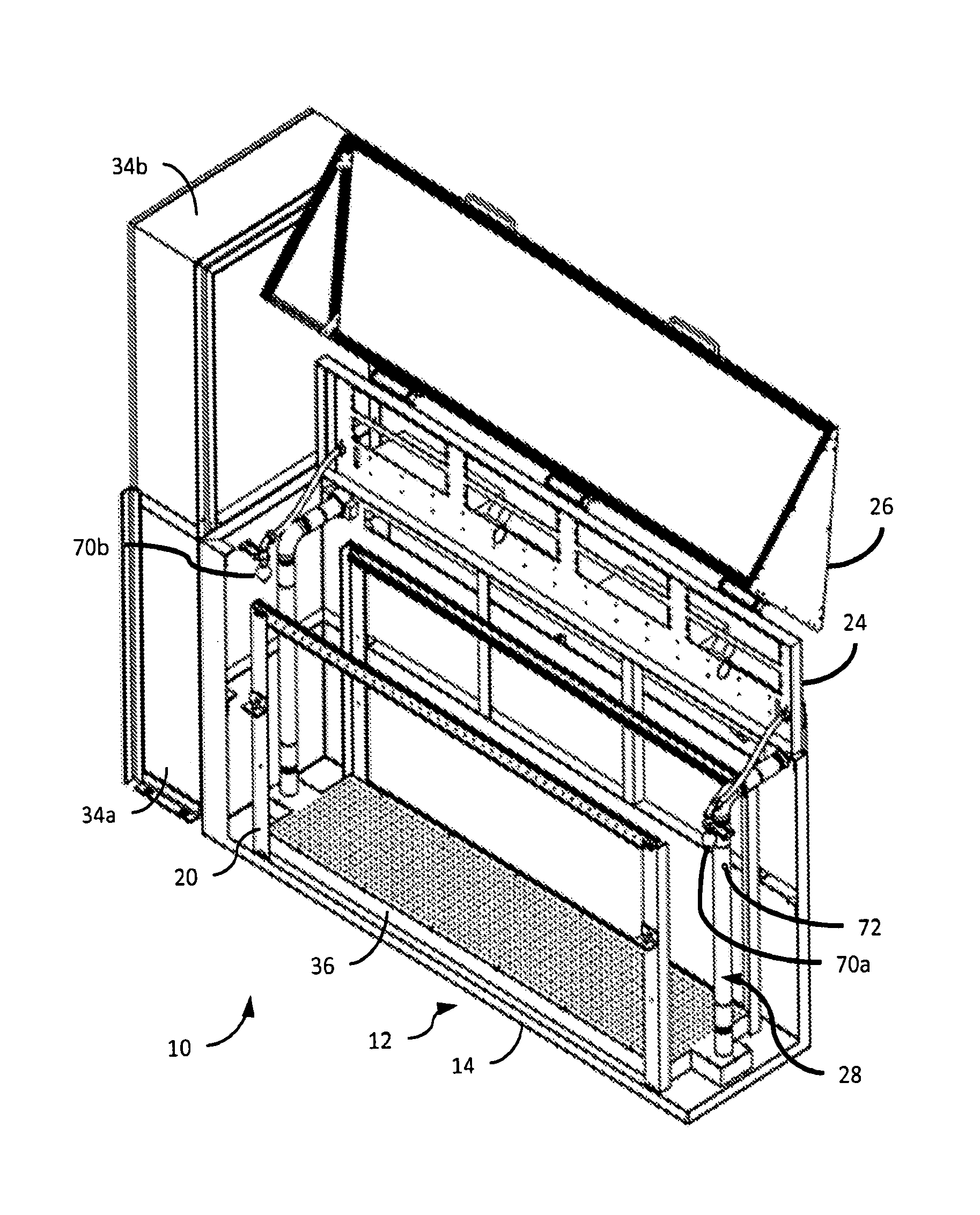
ActiveUS20150181762A1Preventing numberSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIndirect heat exchangersDielectricEngineering
A appliance immersion tank system comprising: a generally rectangular tank adapted to immerse in a dielectric fluid a plurality of appliances, each in a respective appliance slot distributed vertically along, and extending transverse to, the long axis of the tank; a primary circulation facility adapted to circulate the dielectric fluid through the tank; a secondary fluid circulation facility adapted to extract heat from the dielectric fluid circulating in the primary circulation facility, and to dissipate to the environment the heat so extracted; and a control facility adapted to coordinate the operation of the primary and secondary fluid circulation facilities as a function of the temperature of the dielectric fluid in the tank. A plenum, positioned adjacent the bottom of the tank, is adapted to dispense the dielectric fluid substantially uniformly upwardly through each appliance slot. A weir, integrated horizontally into a long wall of the tank, is adapted to facilitate substantially uniform recovery of the dielectric fluid flowing through each appliance slot. All active and most passive components of both the primary and secondary fluid circulation facilities, and the control facility are fully redundant, and are adapted automatically to operate in a fail-soft mode.
Owner:MIDAS GREEN TECH
Methods and systems for assignment of user data blocks for transmission over a network
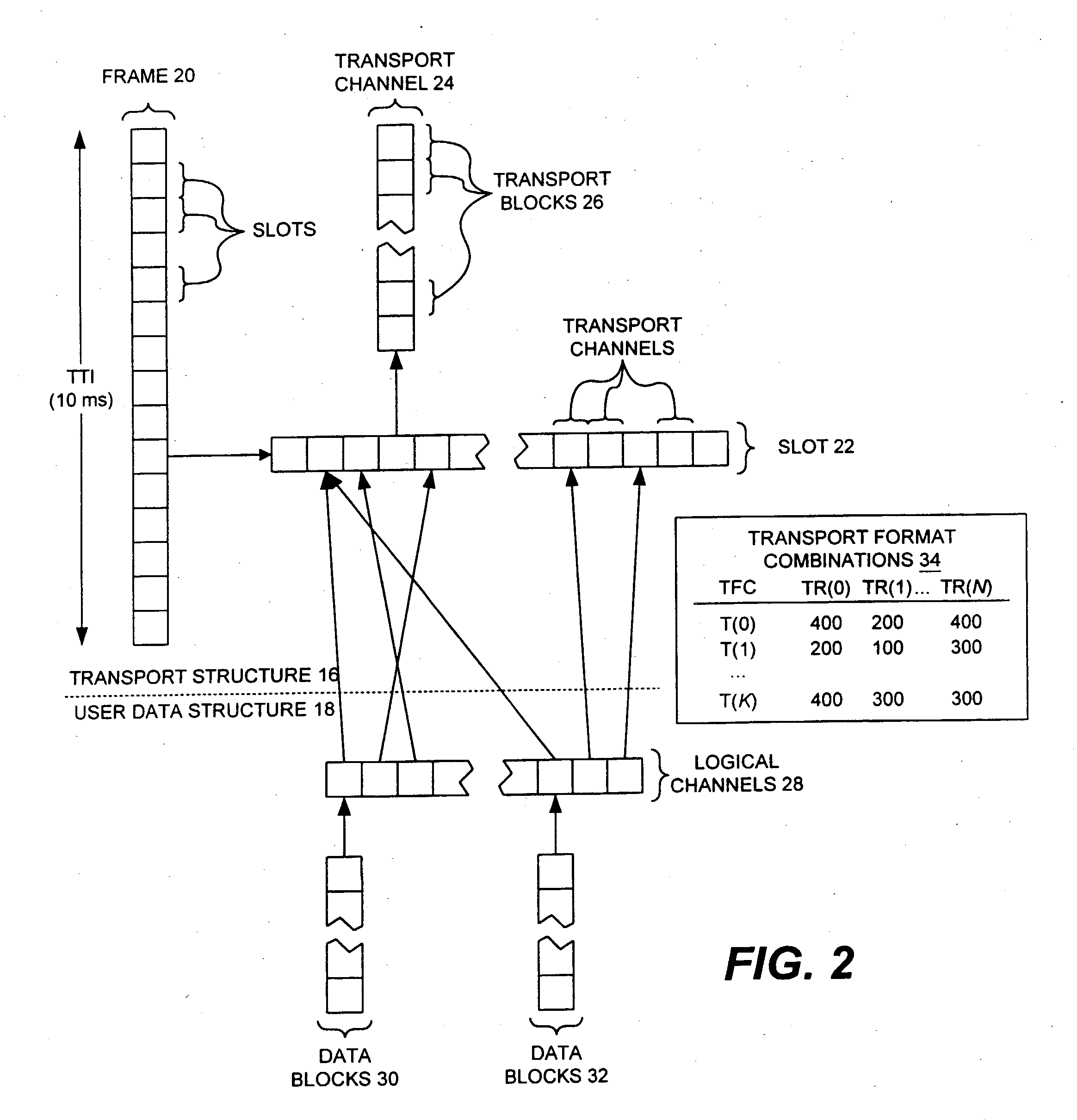
InactiveUS20040254974A1Preventing numberIncrease in sizeMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless communicationReal-time computingTransport format
A user data assignment apparatus and computer implemented techniques for assigning user data blocks to resources in a network for transmission of the user data in the network. According to one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a memory region comprising a selection module and a processing unit communicatively coupled to the memory region. The processing unit is configured to execute instructions from the selection module, the instructions including: a priority loop module configured to sequentially focus user data to be operated on to user data with a particular priority; a transport format combination iteration module configured to execute within the priority loop module and to iterate through a plurality of transport format combinations; and a transfer channel module configured to execute within the transport format combination iteration module and to compute transport occupancy information corresponding to assignments of user data to particular transport format combinations.
Owner:ARGUIN COMM
Thin film transistor, array substrate and method for fabricating the same, and display device
ActiveUS20150303222A1Avoid performance degradationEnsure performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerDisplay device
A thin film transistor, an array substrate and a method for fabricating the array substrate, and a display device are disclosed. The thin film transistor comprises a gate electrode, a gate insulation layer, a semiconductor active layer, a source electrode, a drain electrode and a protection layer provided on a base substrate, and comprises: a first transparent electrode provided between the source electrode and the semiconductor active layer, corresponding to the source electrode and in direct contact with the source electrode; a second transparent electrode provided between the drain electrode and the semiconductor active layer, corresponding to the drain electrode and in direct contact with the drain electrode, the first transparent electrode is in contact with the semiconductor active layer through a first via provided in the protection layer, the second transparent electrode is in contact with the semiconductor active layer through a second via provided in the protection layer.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Method and formulation for the extraction of nucleic acids from any complex starting materials
ActiveUS20090011469A1Preventing numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcoholElution
The invention relates to a universal and greatly simplified method as well as a composition for isolating nucleic acids from different starting materials containing nucleic acids. The composition contains at least one buffer solution for proteolytically solubilizing biological samples, the buffer containing no chaotropic or antichaotropic component, at least one alcoholic component and / or a detergent, a solid phase, and a wash and elution buffer.
Owner:AJ INNUSCREEN GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com