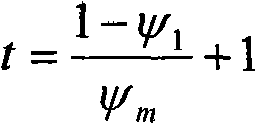Patents
Literature
157 results about "Fat mass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for selectively removing a body fat mass in human body
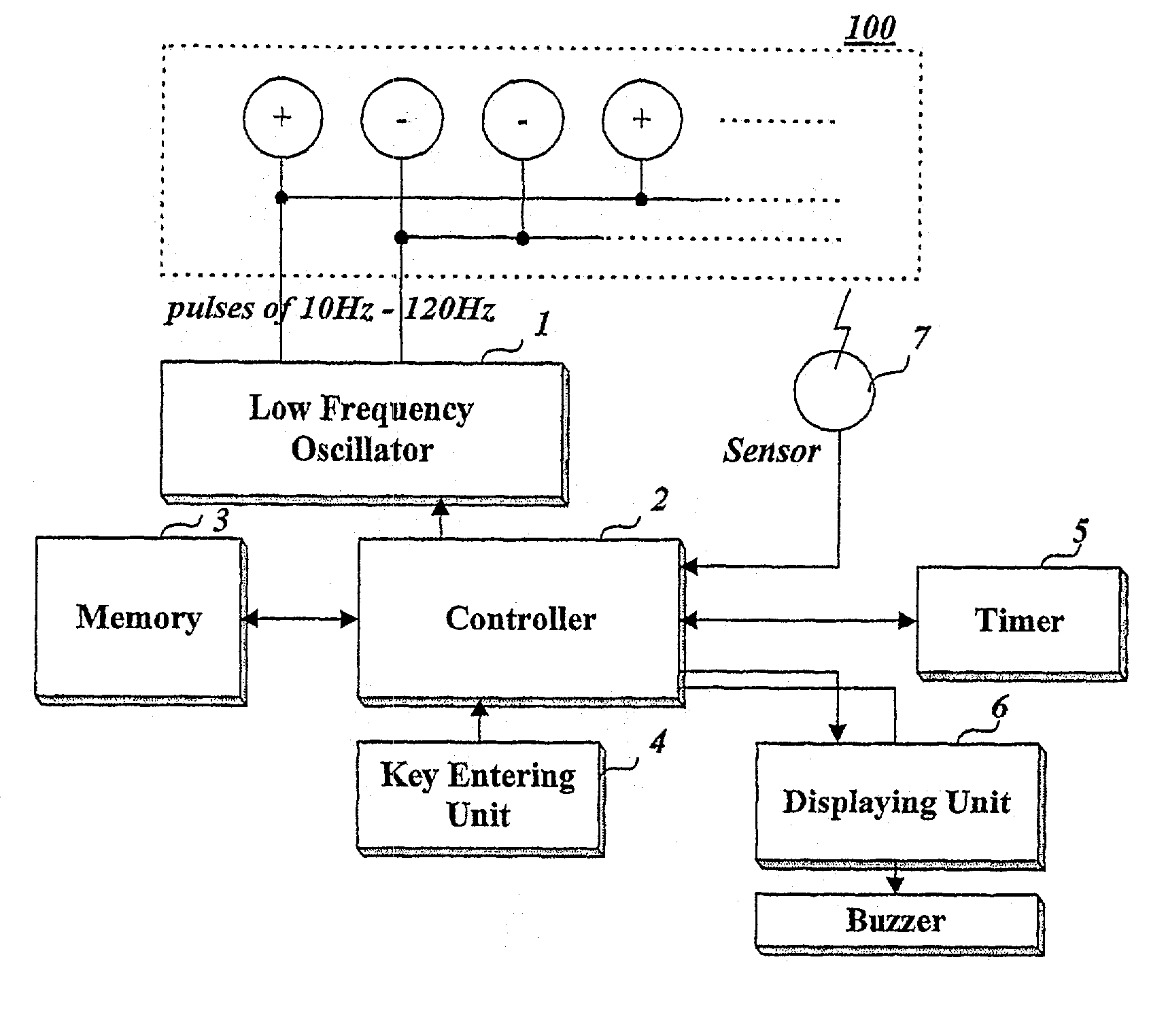
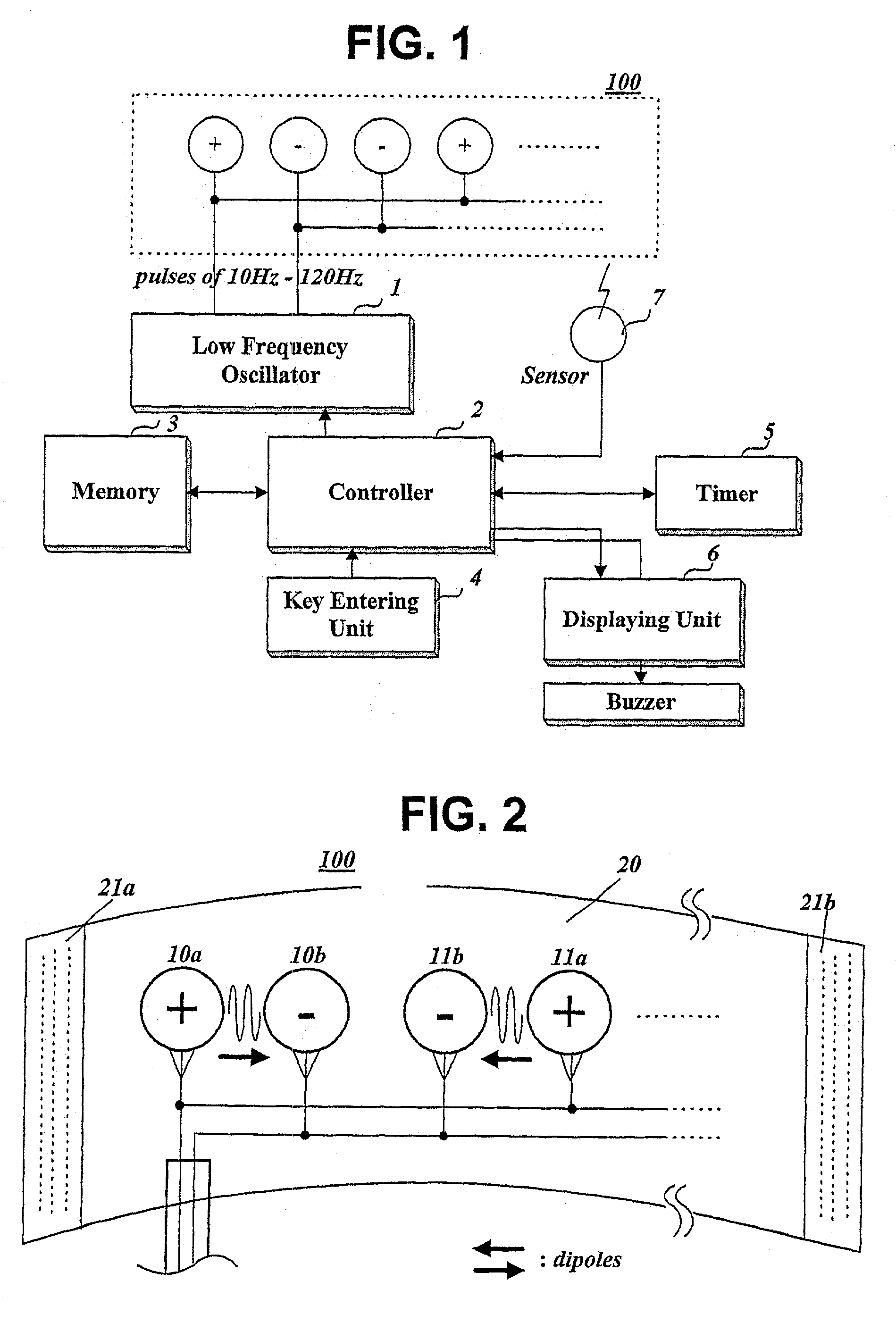
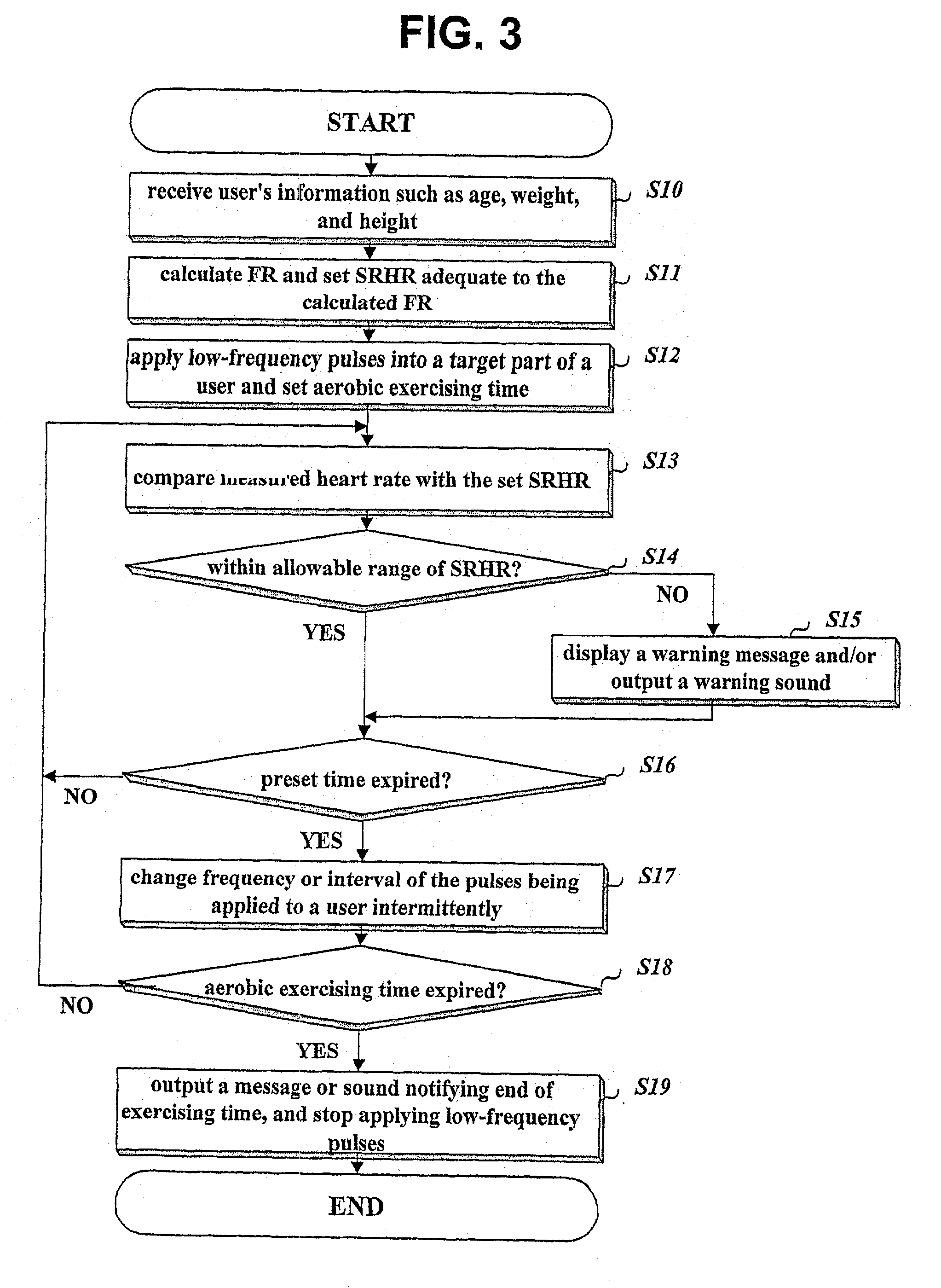
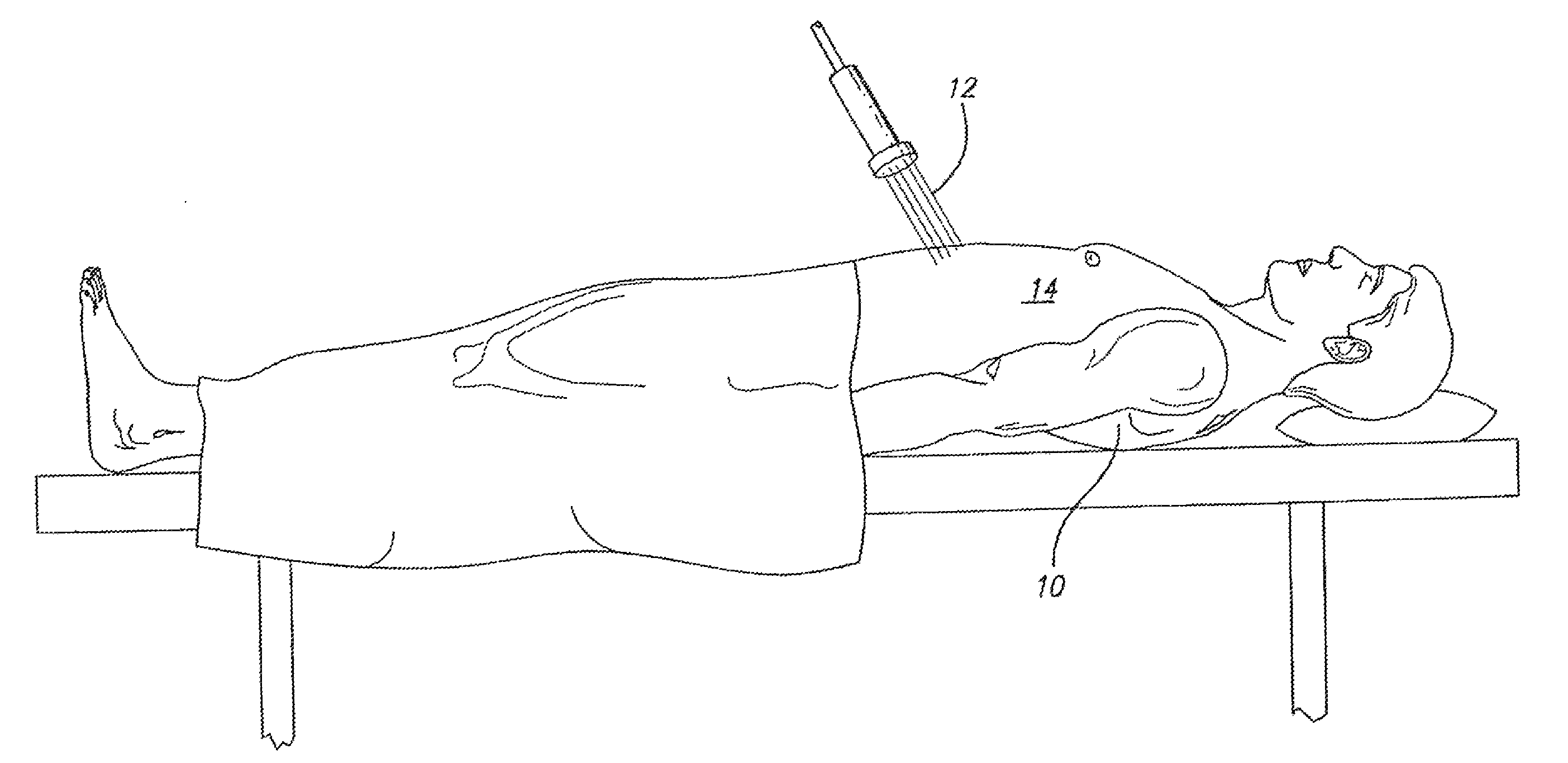
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for removing body fat. While an obesity patient or person wants to remove body fat built up in a certain part is conducting aerobic exercise such as running with attaching a surface-attaching type catheter on the fat part, the apparatus resolves and removes body fat by applying pulses, whose frequency is 10~120 Hz, through the catheter, and changes the exercising condition based upon his or her heart rate and standard heart rate, thereby conducting efficient removal of body fat.
Owner:SON YOUNG TAE
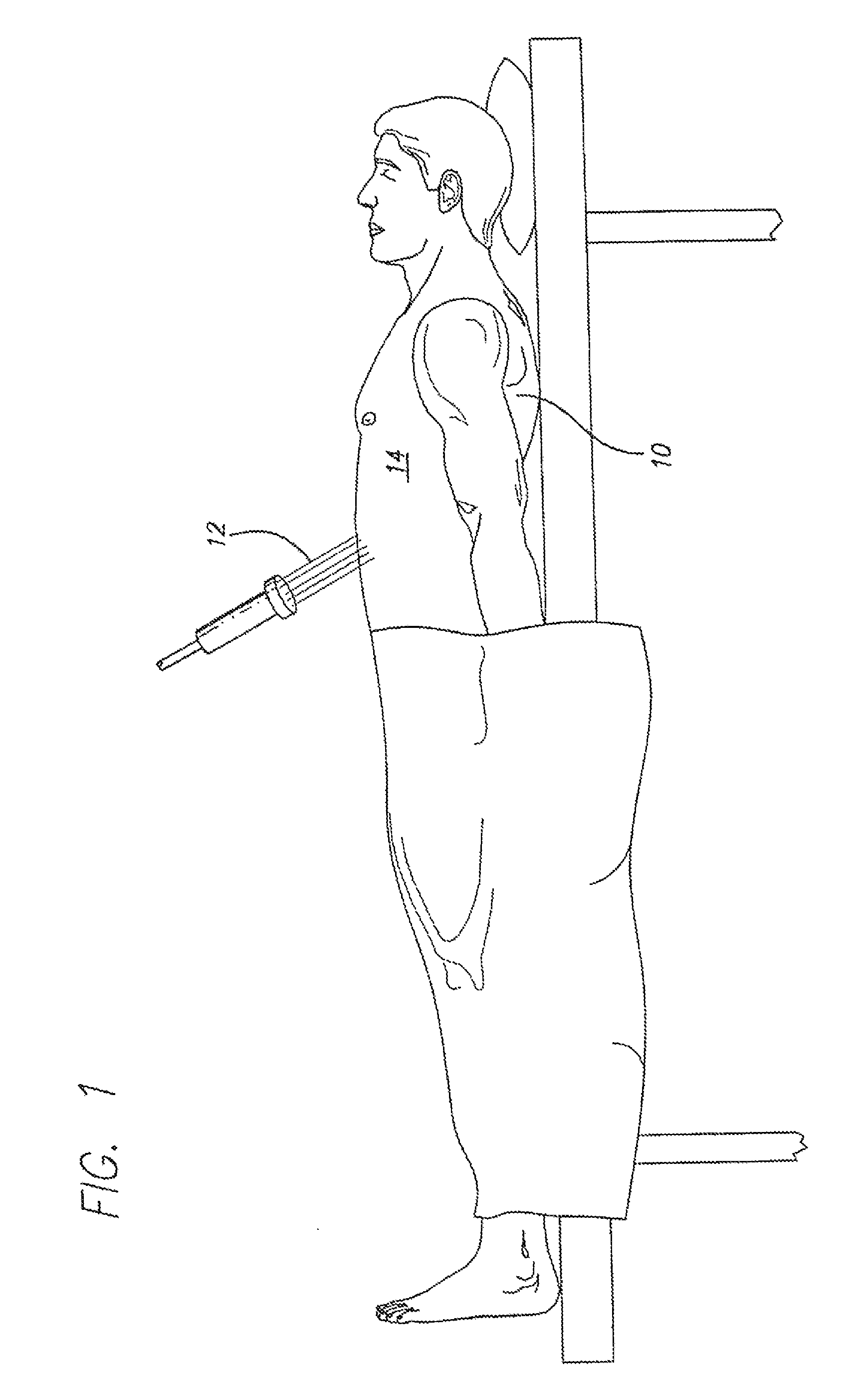
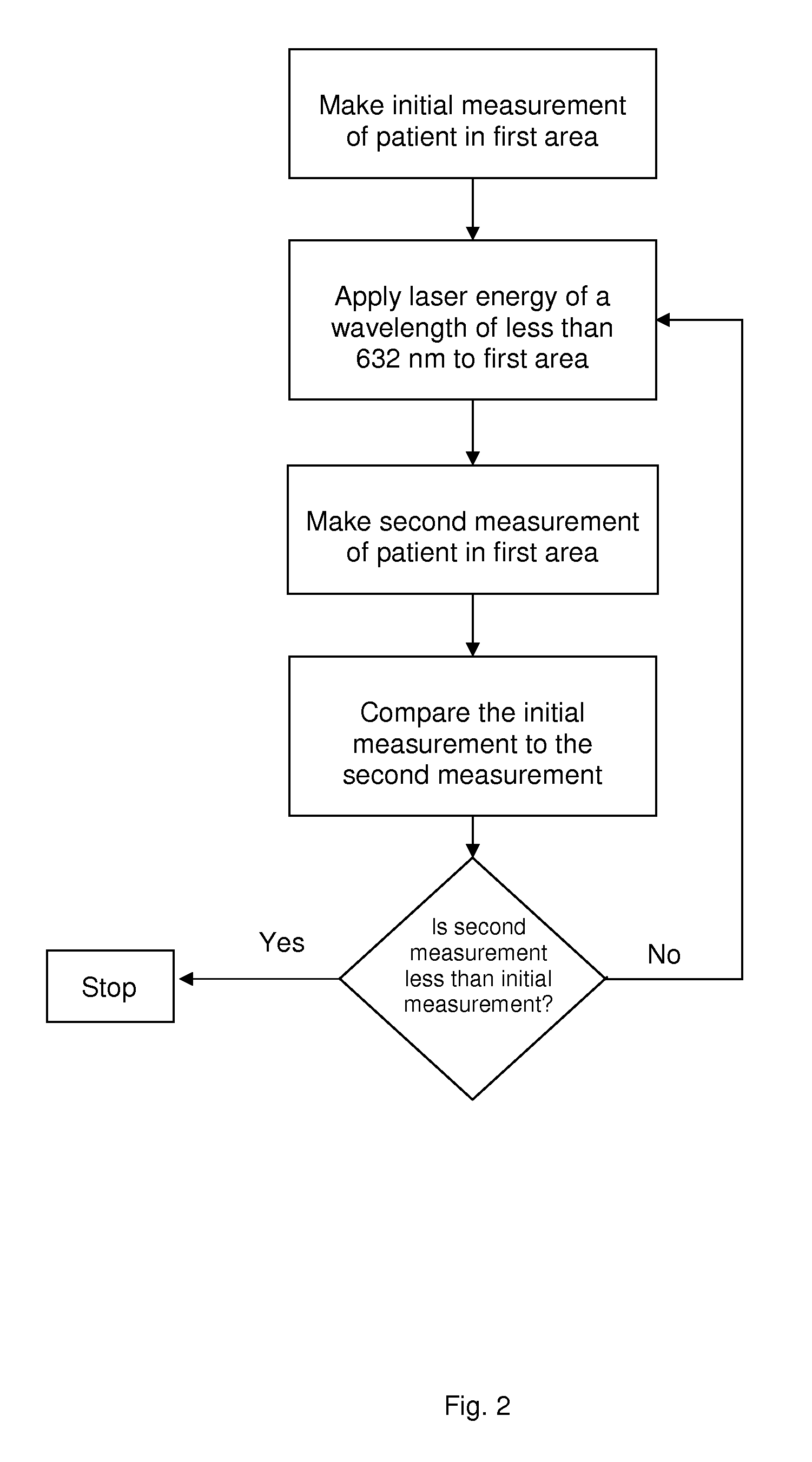
Non-invasive method for slimming a human body using laser energy of wavelengths shorter than 632 nm
A noninvasive method of slimming a patient's body by applying laser energy having a wavelength shorter than 632 nm externally through the skin of the patient. One or more areas of a patient's body, preferably the more fatty regions, such as the abdominal, buttock, lower back, thigh, bust or arm regions, is measured. Objective measurements are made of body criteria, including external dimension, percentage body fat, fat mass, or body mass. Sufficient laser energy, preferably in a range of 0.03-0.1 J / cm2, is applied to one or more of those areas to cause a reduction in the measurement in the lasered areas, as well as overall body slimming. The preferred embodiments use laser light at about 532 nm, 440 nm, or 405 nm. Preferably 18 mW or 25 mW laser diodes are used to apply laser energy at 0.03-0.1 J / cm2 for 15 minutes, every other day for 1-4 weeks, depending on the amount of slimming desired.
Owner:ERCHONIA CORP
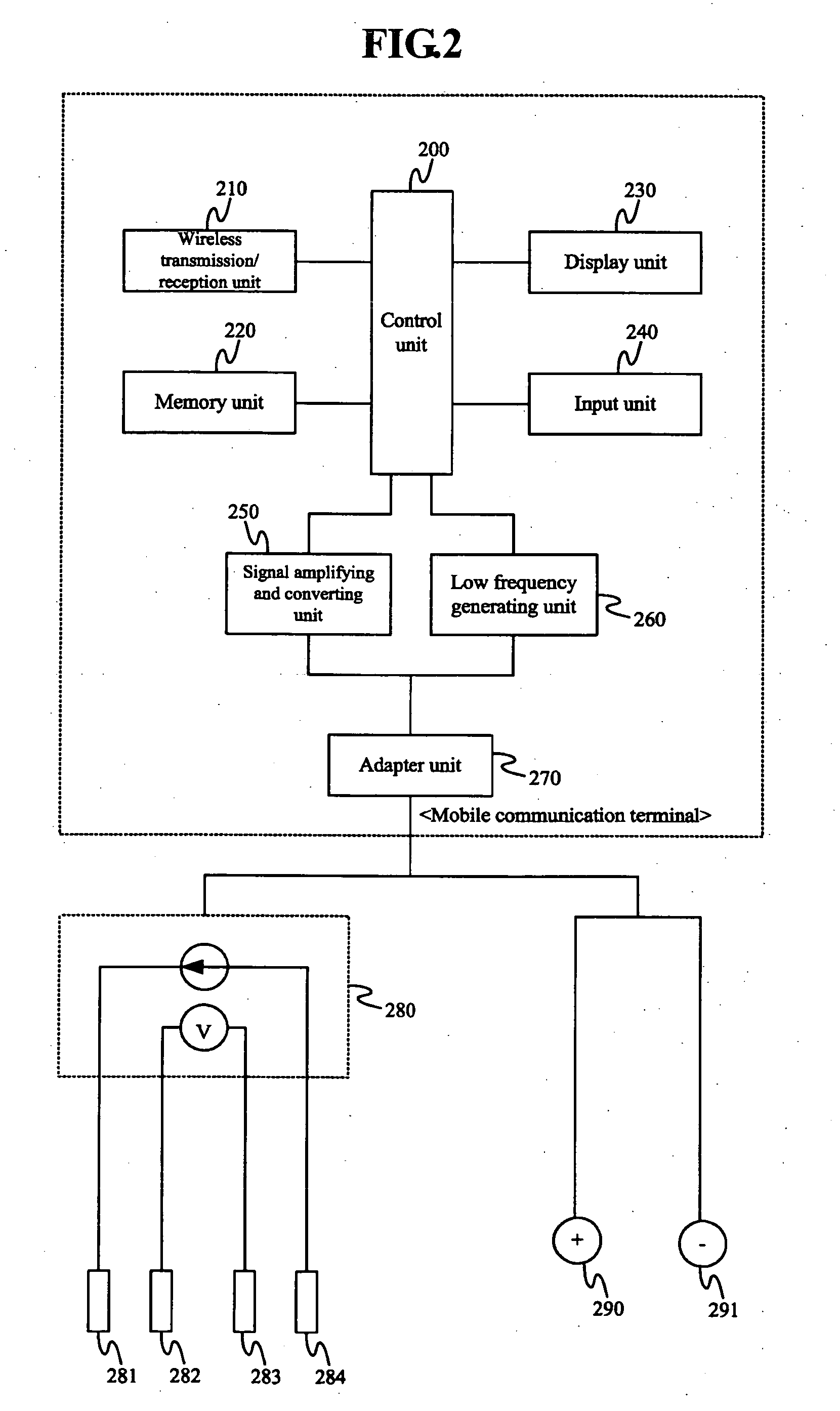
Management method of fat mass and management device of fat mass using mobile phone
InactiveUS20060129060A1Easy to carryEfficient managementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMemory bankEngineering
The present invention relates generally to an apparatus for managing the body fat of a human body and, more particularly, to a mobile communication terminal in which a body fat managing function is embedded, and an apparatus in which a body fat managing device is connected to a mobile communication terminal. The mobile communication terminal, in which a body fat managing function is embedded, includes a signal amplifying and converting unit for converting the measured value of body fat, a low frequency generating unit for generating low frequency waves, an input unit for receiving the body fat-related items, a display unit for displaying the measured value of the body fat, a memory unit for storing the measured value of the body fat, an adaptor unit connected to outside electrode lines, and a control unit for controlling the respective function units. Additionally, a body fat managing device, which is used while being connected to a mobile communication terminal, includes a signal amplifying and converting unit, a low frequency generating unit, an electrode unit and a conduction unit.
Owner:HEALTHPIA AMERICA
Sarms and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20100249228A1Increasing lean massReducing fat mass/percent fat massBiocideOrganic chemistryCarcass compositionReduced fat
This invention is directed to a feed composition and method of affecting the carcass composition by increasing the lean mass, reducing the fat mass, and / or reducing the percent fat mass comprising SARM compounds.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
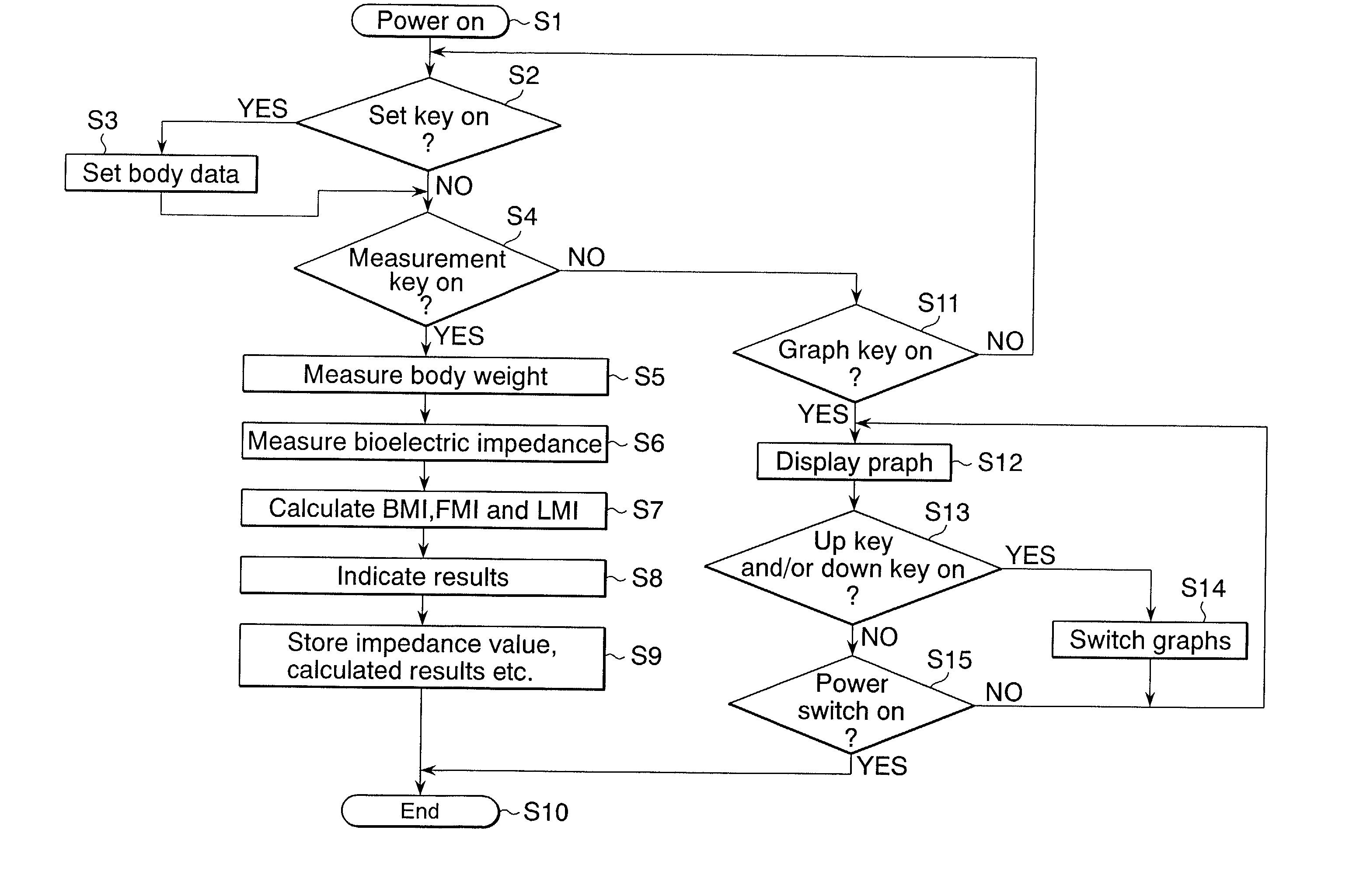
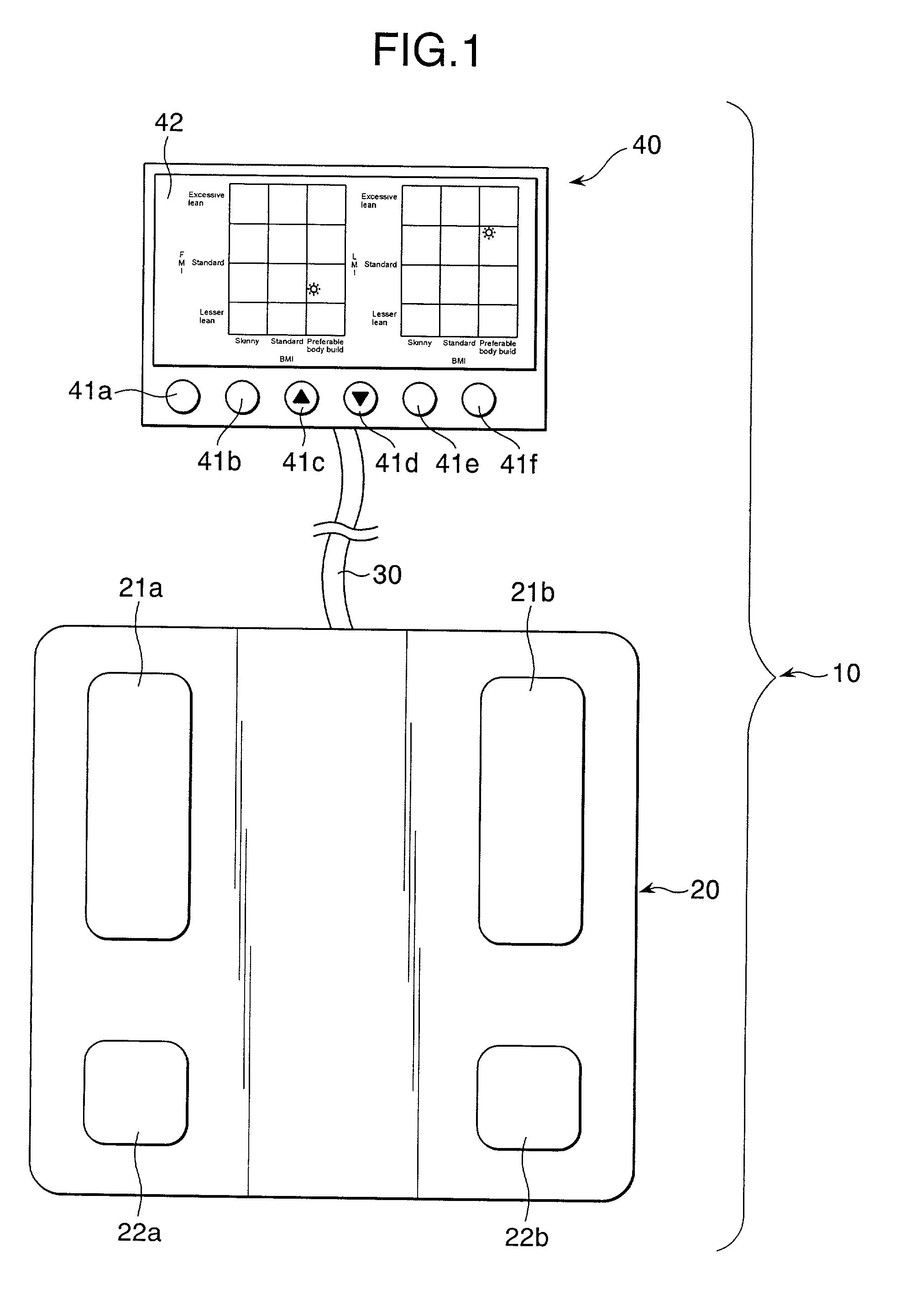
Body type determination apparatus
InactiveUS6539310B2Easy to understandReduce riskDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceMedicine
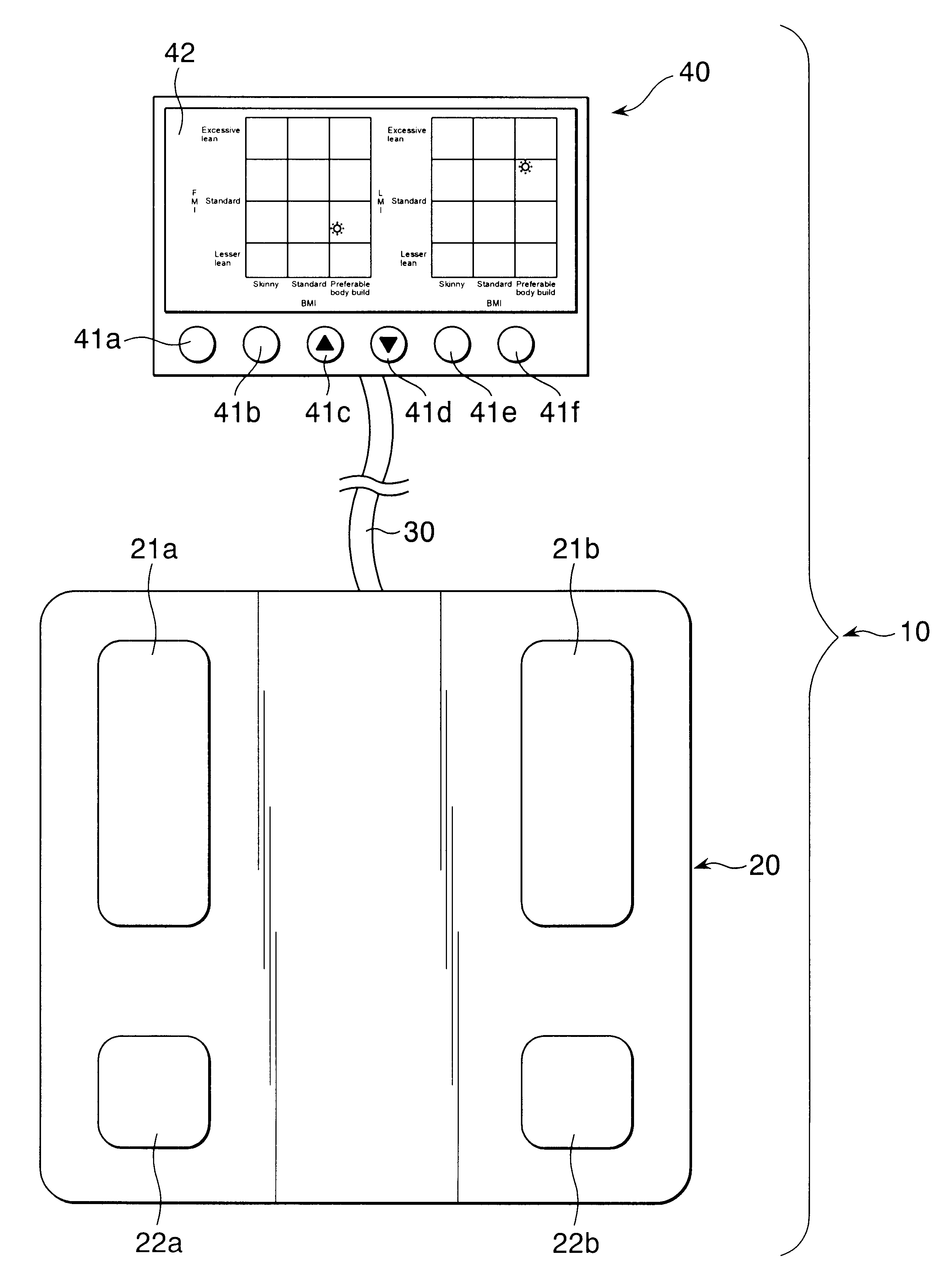
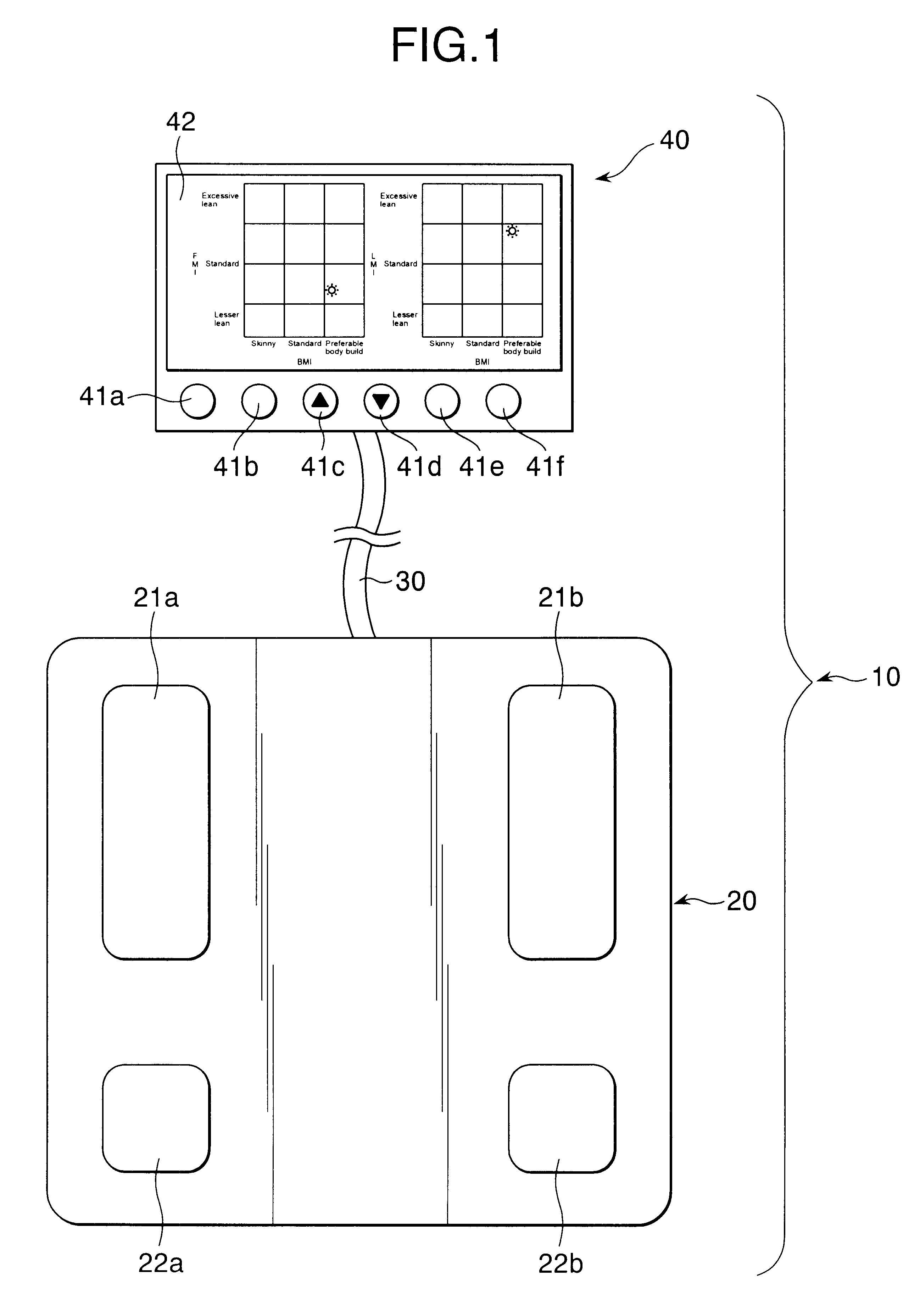
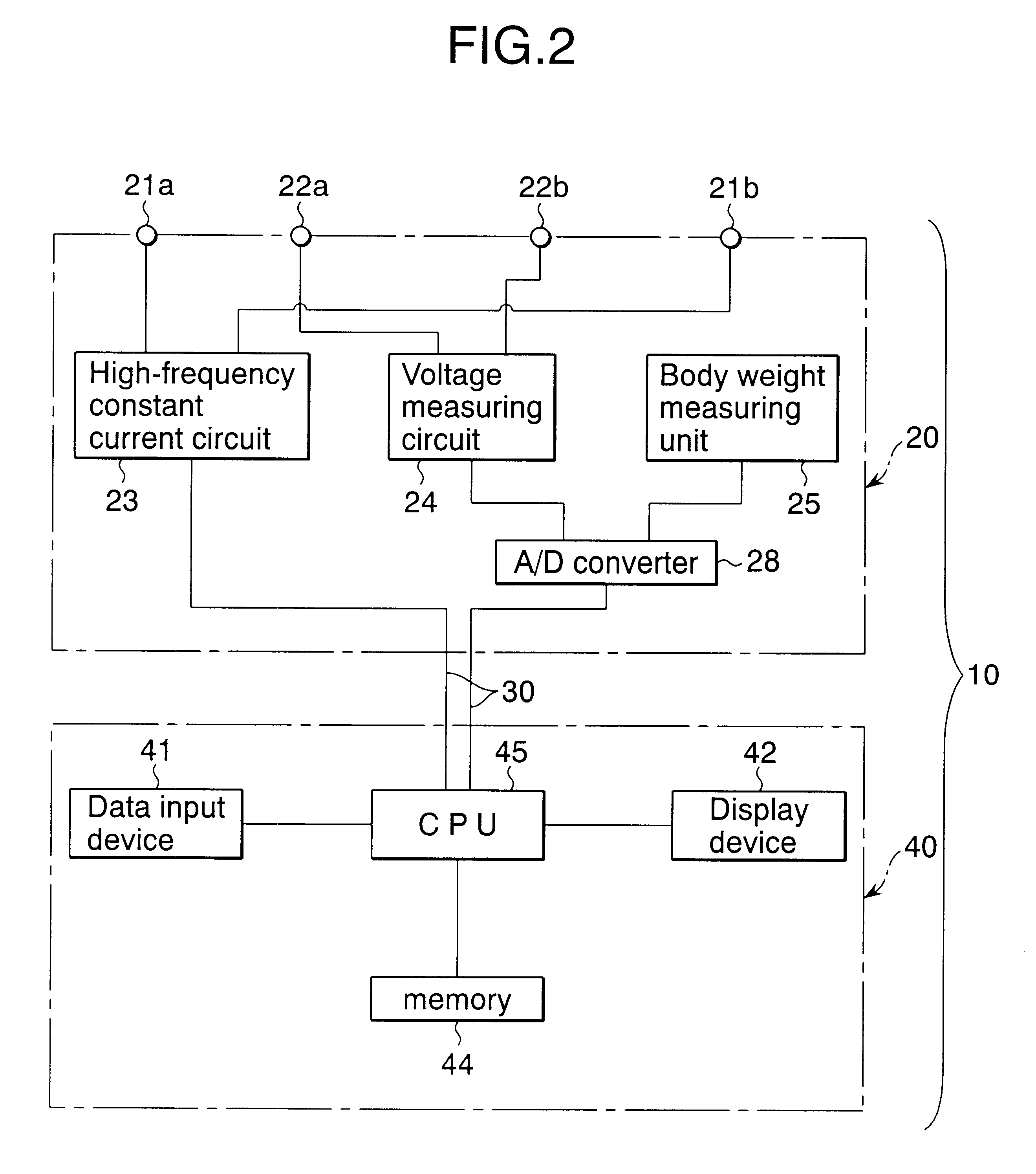
An object of the present invention is to provide an easy-understandable representation of fat tissue and lean tissue respectively occupying in a body constitution of a subject. Another object thereof is to help the subject determine which one of the fat tissue or the lean tissue is decreasing by weight reduction. A body type determination apparatus according to the present invention calculates an index of body fat mass, FMI (Fat Mass Index: fat mass / body height2), an index of lean mass, LMI (Lean Mass Index: lean mass / body height2), and a body build index, BMI (Body Mass Index: body weight / body height2) from entered body data and a measured bioelectric impedance, and further the apparatus displays a relationship between the BMI and the FMI and / or between the BMI and the LMI as a result of measurement by way of a graph and / or an illustration.
Owner:TANITA CORP
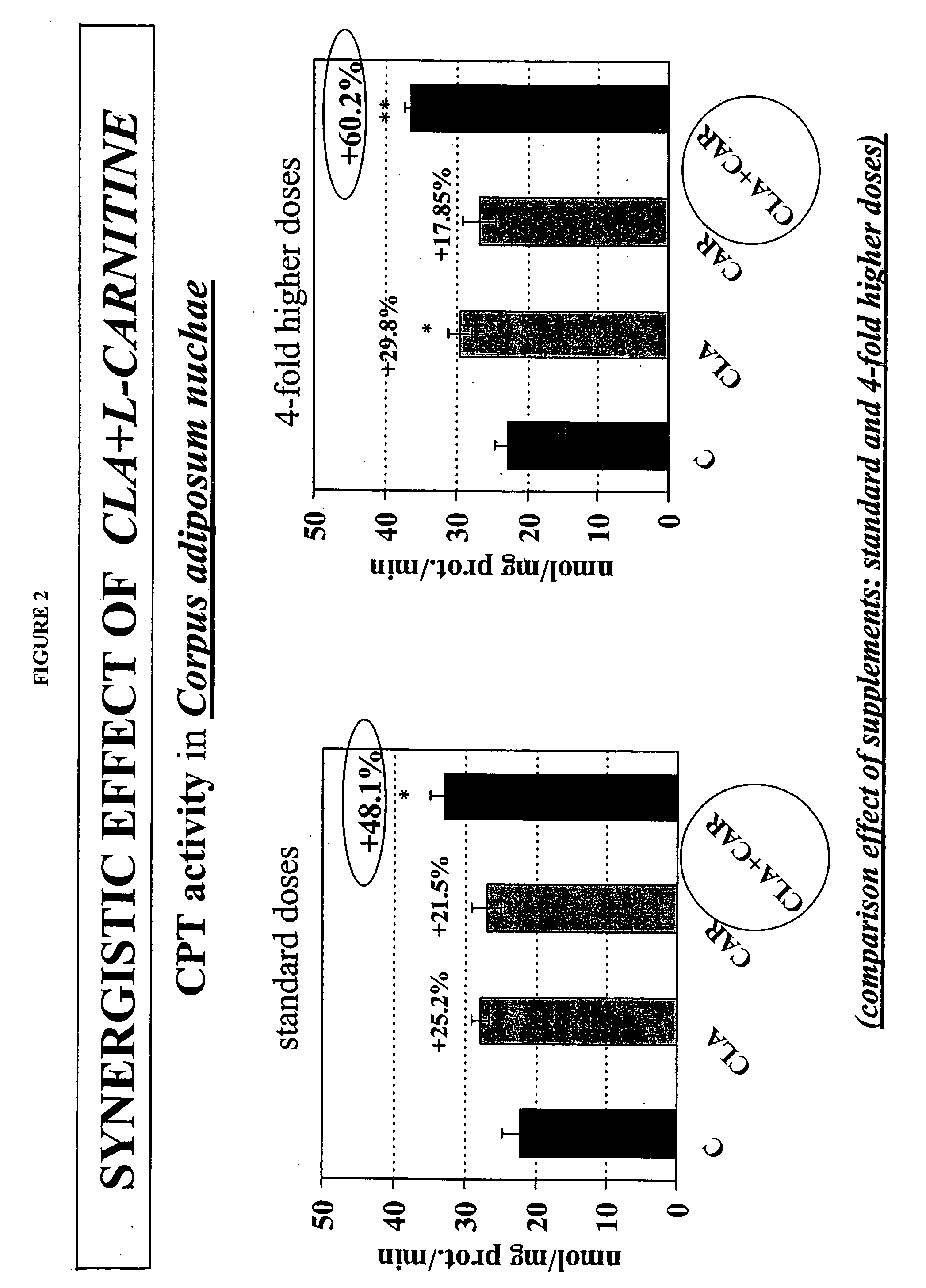
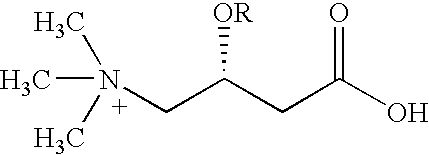
Synergistic conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and carnitine combination
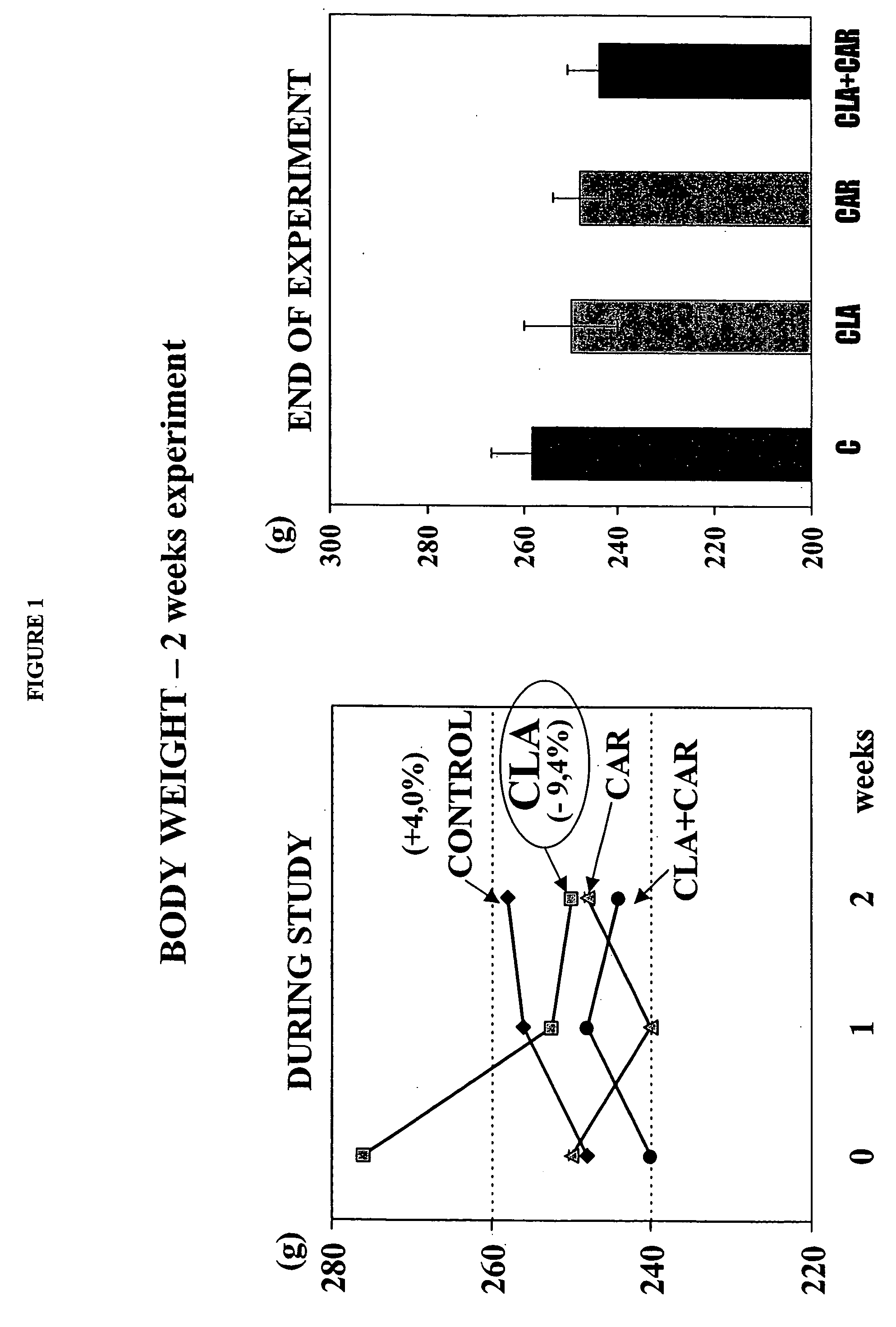
InactiveUS20060041017A1Improve impactImprove blood sugar levelsBiocideAnimal repellantsSecondary hyperlipidemiaBody weight
The present invention relates to the unexpected discovery that a combination of effective amounts of carnitine (in any form, as described in further detail herein) and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) administered to a patient in need thereof exhibits synergistic activity in treating obesity by reducing fat mass and overall weight as well as one or more of hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes (both diabetes mellitus I and II), metabolic syndrome (syndrome X), kidiney failure and high blood pressure, where those conditions exist.
Owner:QUTEN RES INST LLC
Body type determination apparatus
InactiveUS20020049546A1Easy to understandReduce riskDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceMedicine
An object of the present invention is to provide an easy-understandable representation of fat tissue and lean tissue respectively occupying in a body constitution of a subject. Another object thereof is to help the subject determine which one of the fat tissue or the lean tissue is decreasing by weight reduction. A body type determination apparatus according to the present invention calculates an index of body fat mass, FMI (Fat Mass Index: fat mass / body height2), an index of lean mass, LMI (Lean Mass Index: lean mass / body height2), and a body build index, BMI (Body Mass Index: body weight / body height2) from entered body data and a measured bioelectric impedance, and further the apparatus displays a relationship between the BMI and the FMI and / or between the BMI and the LMI as a result of measurement by way of a graph and / or an illustration.
Owner:TANITA CORP
Exercise aid device
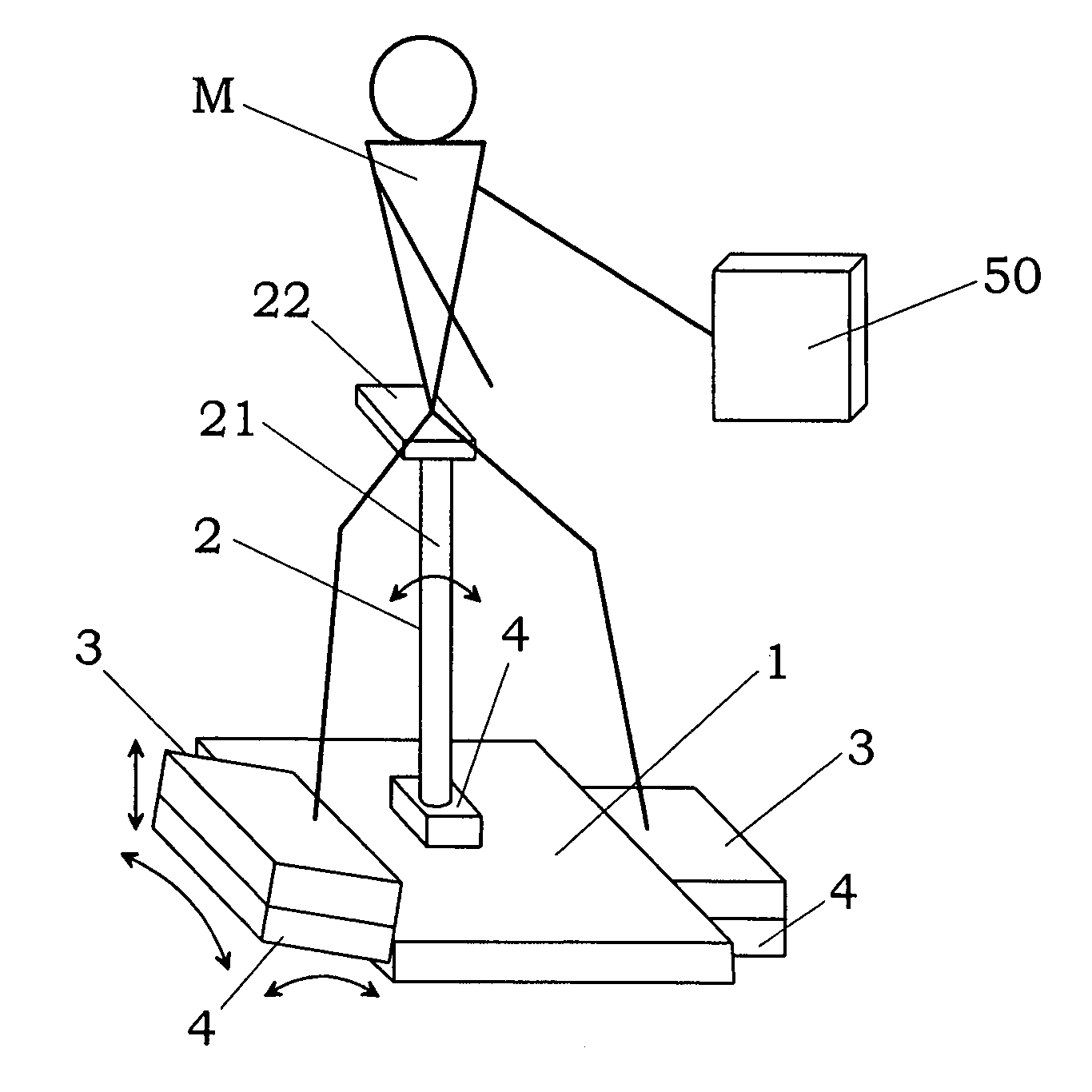
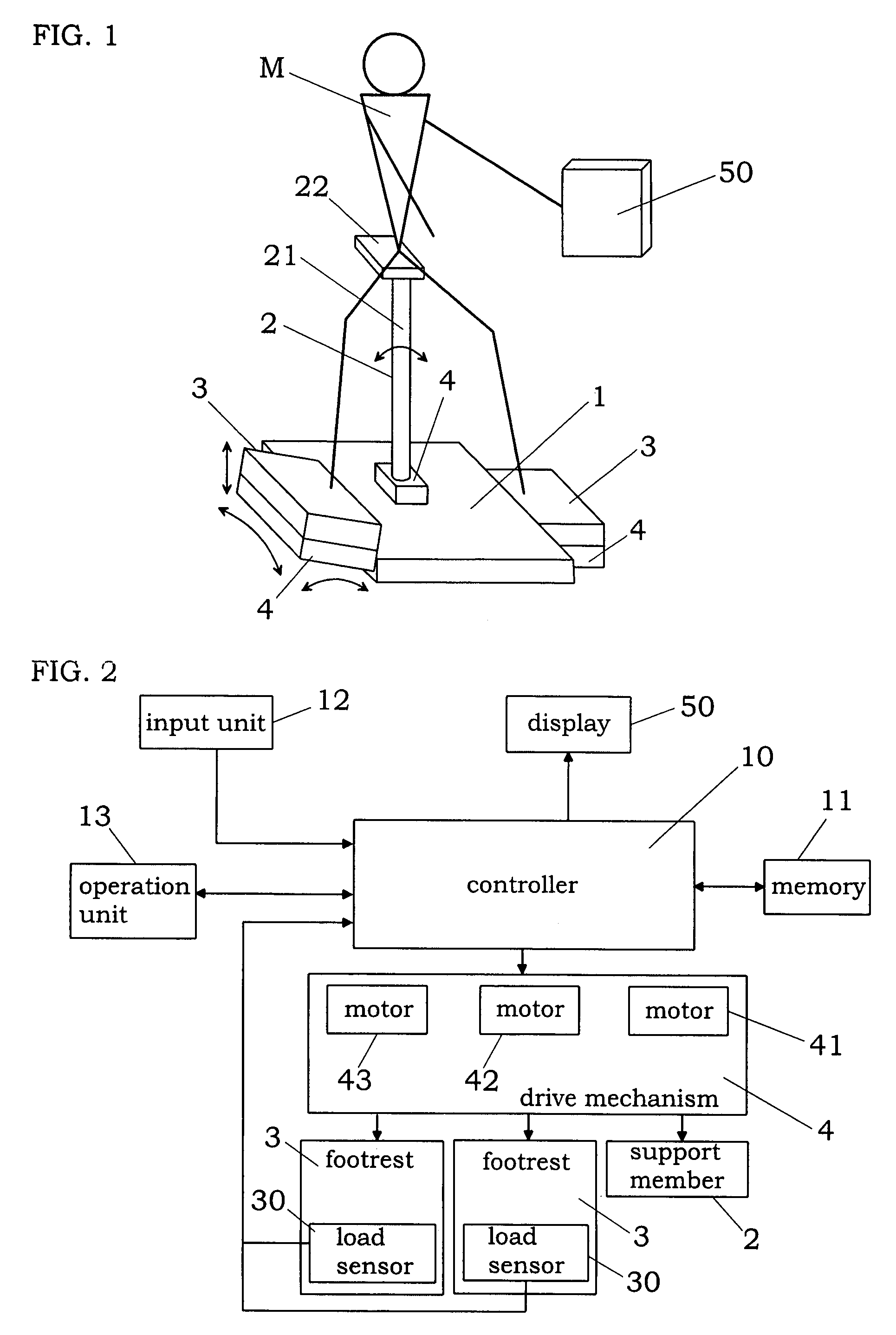
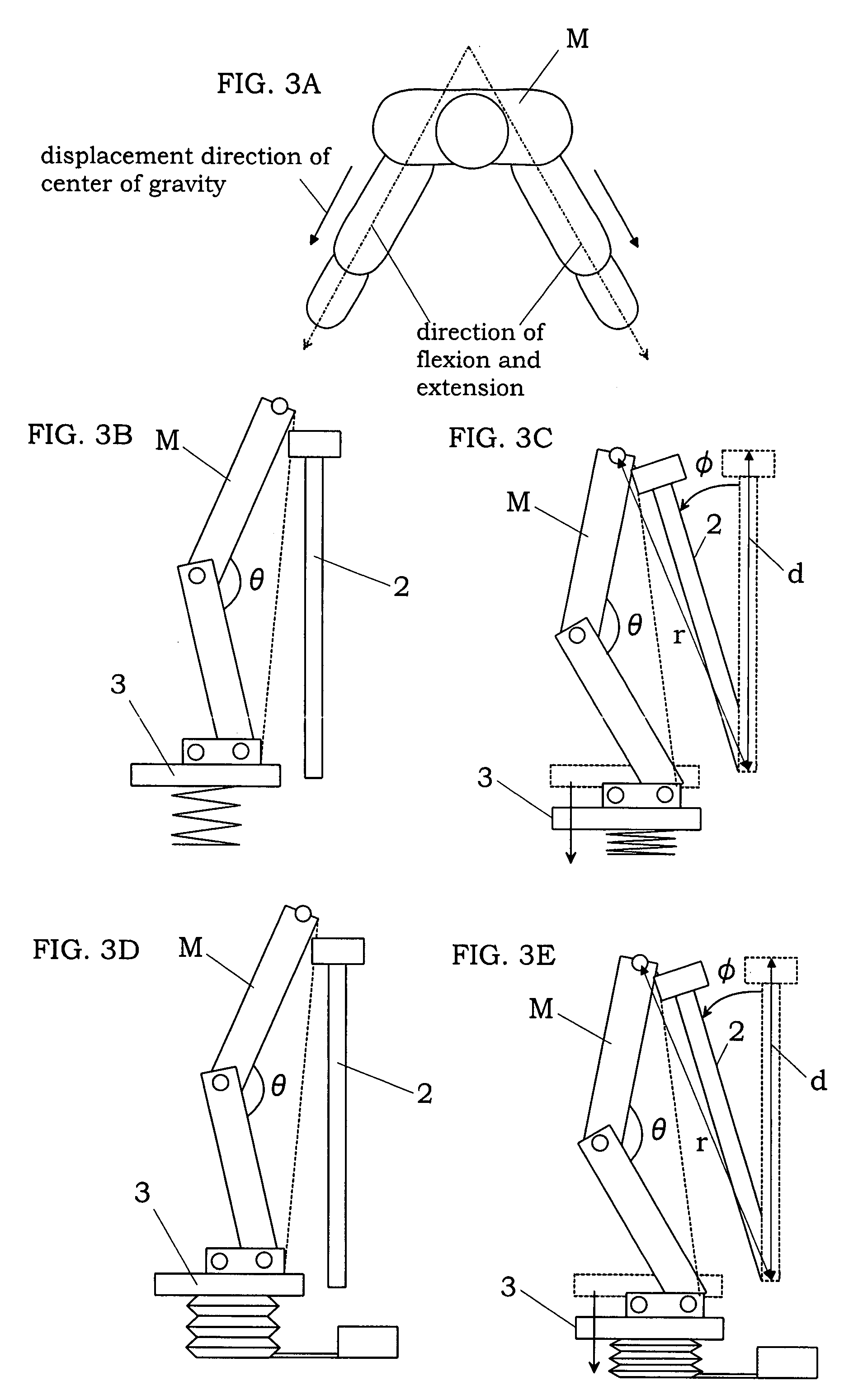
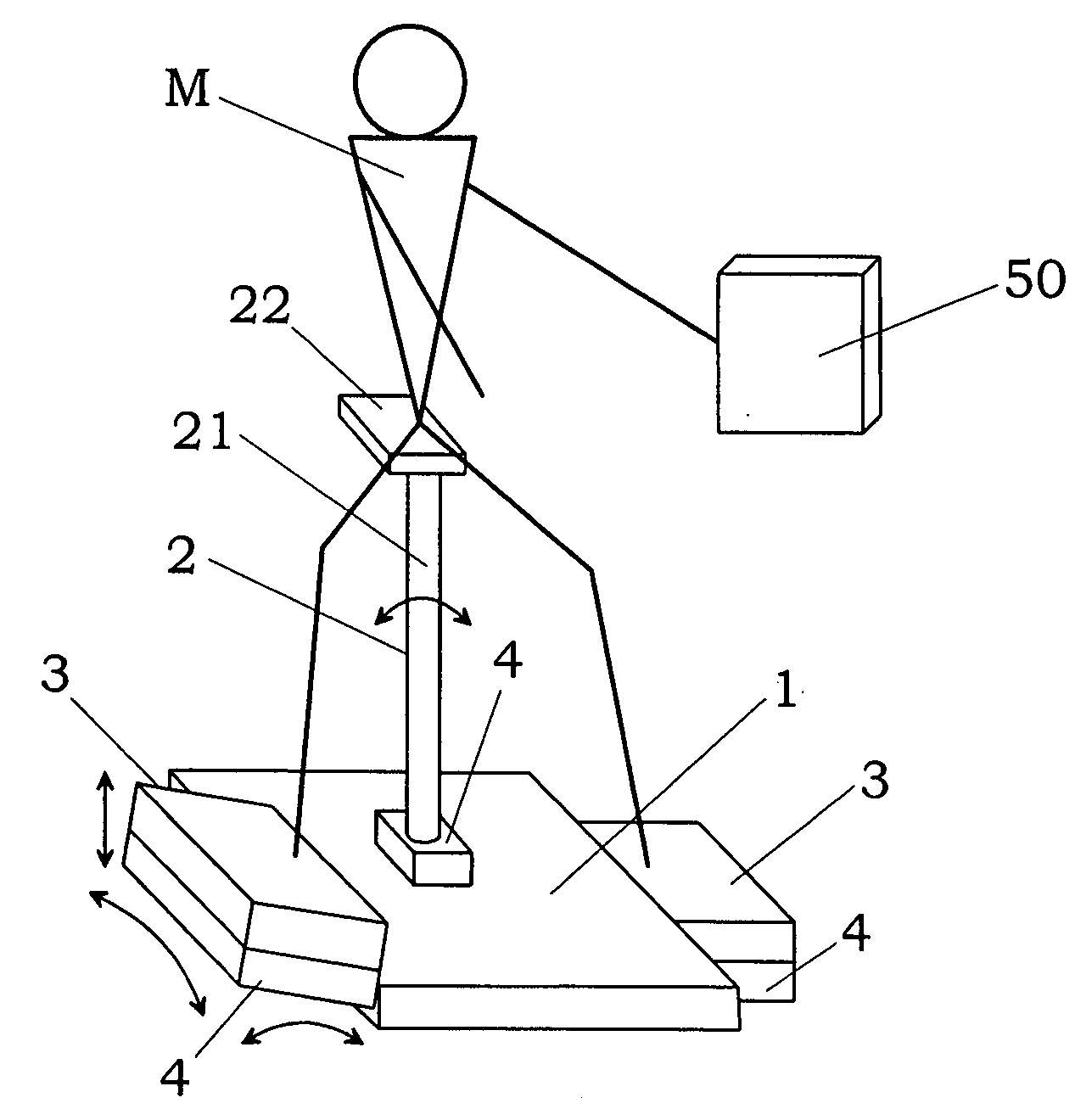
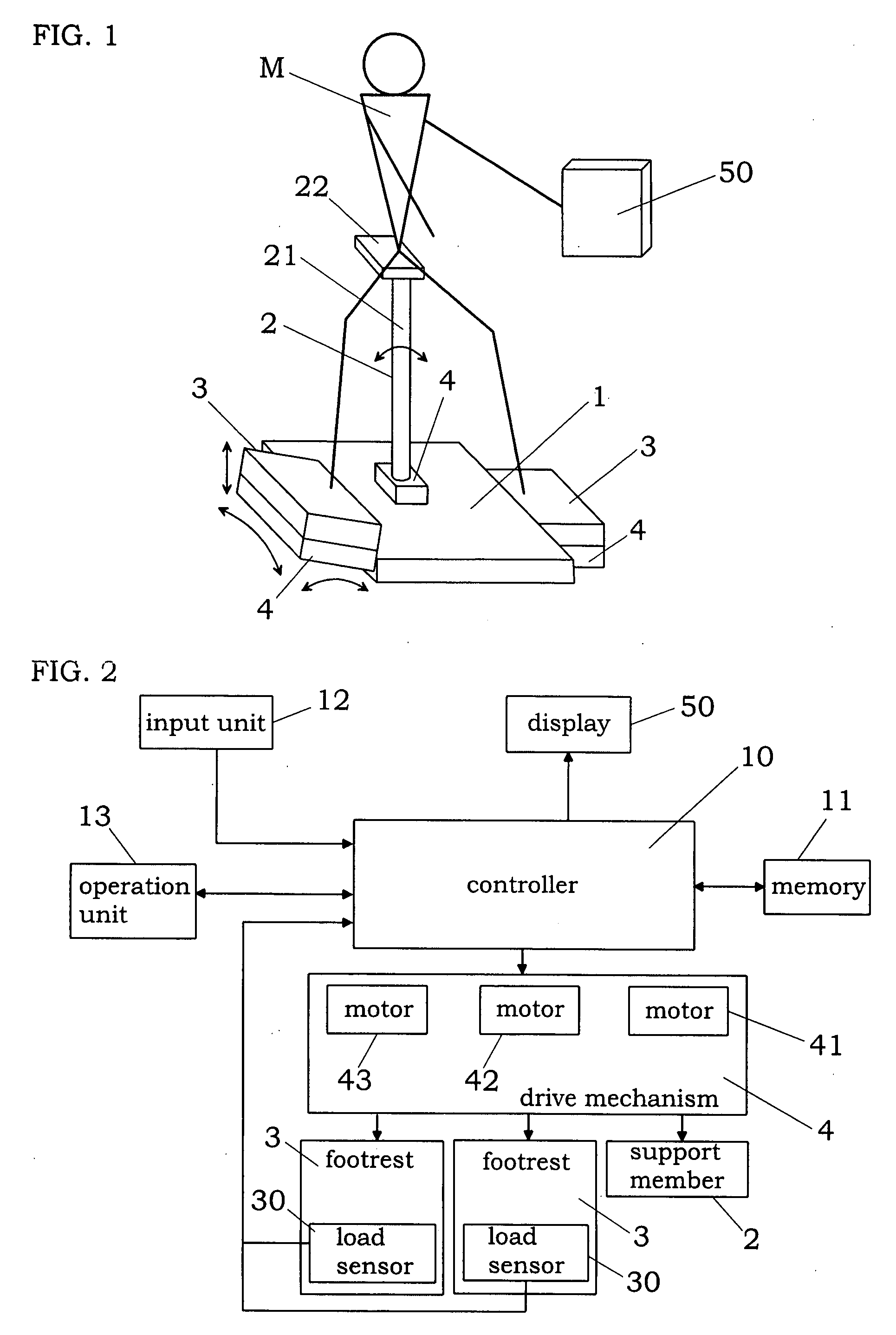
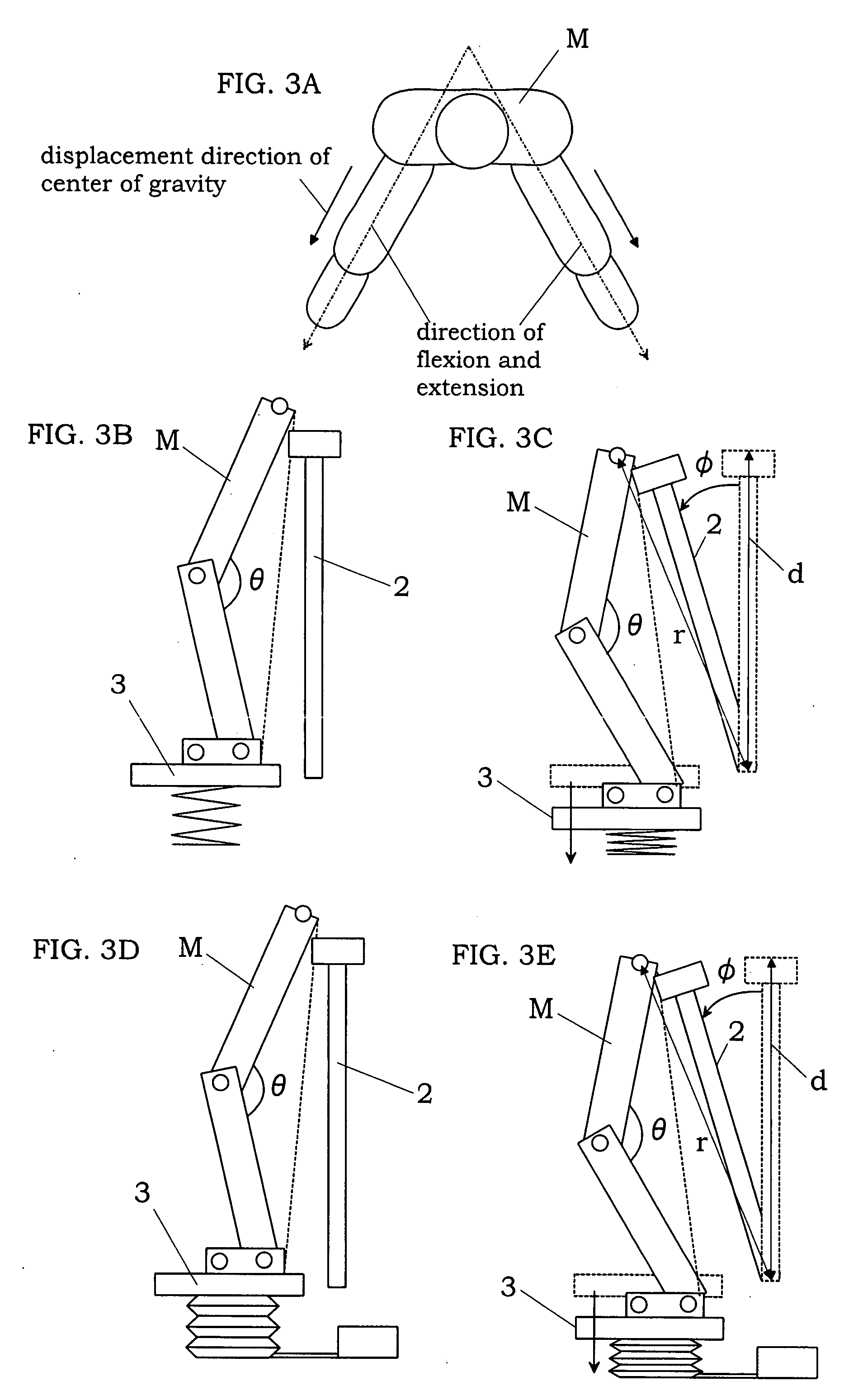
InactiveUS7942783B2Reduce the burden onEfficiently provideClubsPerson identificationTrochanter majorKnee Joint
An exercise aid device has a hip supporting member movable relative to a base, footrests movable relative to the base, drive means for driving the hip supporting member, body constitution estimating unit for estimating at least one of fat mass and muscle mass of a user, and a controller for the drive means. The controller controls the drive means such that a load acting on a femoral region by own weight of the user supported on the hip supporting member changes according to a relative positional displacement between the user's toe and trochanter major, the positional displacement is allowed in a direction of flexion and extension of knee joint of the user, and an angle of the knee joint is maintained substantially constant. In addition, since the controller controls the drive means by use of an output of the body constitution estimating unit, it is possible to provide an exercise with less burden to the knee joint and a suitable strength for the user.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Nuclear receptor binding agents
InactiveUS20100267767A1Increased energy expenditureReduce morbidityBiocideNervous disorderAdipogenesisInsulin resistance
The present invention relates to methods for prevention and / or treatment of metabolic disorders, post-menopausal obesity and conditions associated with high fat diet consumption including, obesity, body weight gain, fat mass formation, bone mineral content reduction, white adipose tissue weight gain, increased cholesterol levels, increased leptin levels, insulin resistance, type II diabetes, increased blood glucose levels, inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, fatty liver condition (accumulation of fat in the liver), decreased uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1) levels and increased lipogenesis.
Owner:GTX INCORPORATED
Use Of Secretagogue For The Teatment Of Ghrelin Deficiency
InactiveUS20080171700A1Improve the level ofPrevents upregulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSleep patternsCvd risk
The present invention relates to the use of a growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of ghrelin deficiency, and / or undesirable symptoms associated therewith, in an individual at risk of acquiring partial or complete ghrelin deficiency resulting from a medical treatment and / or from a pathological condition. The present invention also relates to use of a secretagogue compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more of: loss of fat mass, loss of lean body mass, weight loss, cachexia, loss of appetite, immunological dysfunction, malnutrition, disrupted sleep pattern, sleepiness, reduction in intestinal absorption and / or intestinal mobility problems in an individual suffering from, or at risk of suffering from, ghrelin deficiency. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of a secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the production of a medicament for preventing weight increase in an individual either: a) being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state, or b) in remission from being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state.
Owner:GASTROTECH PHARMA AS
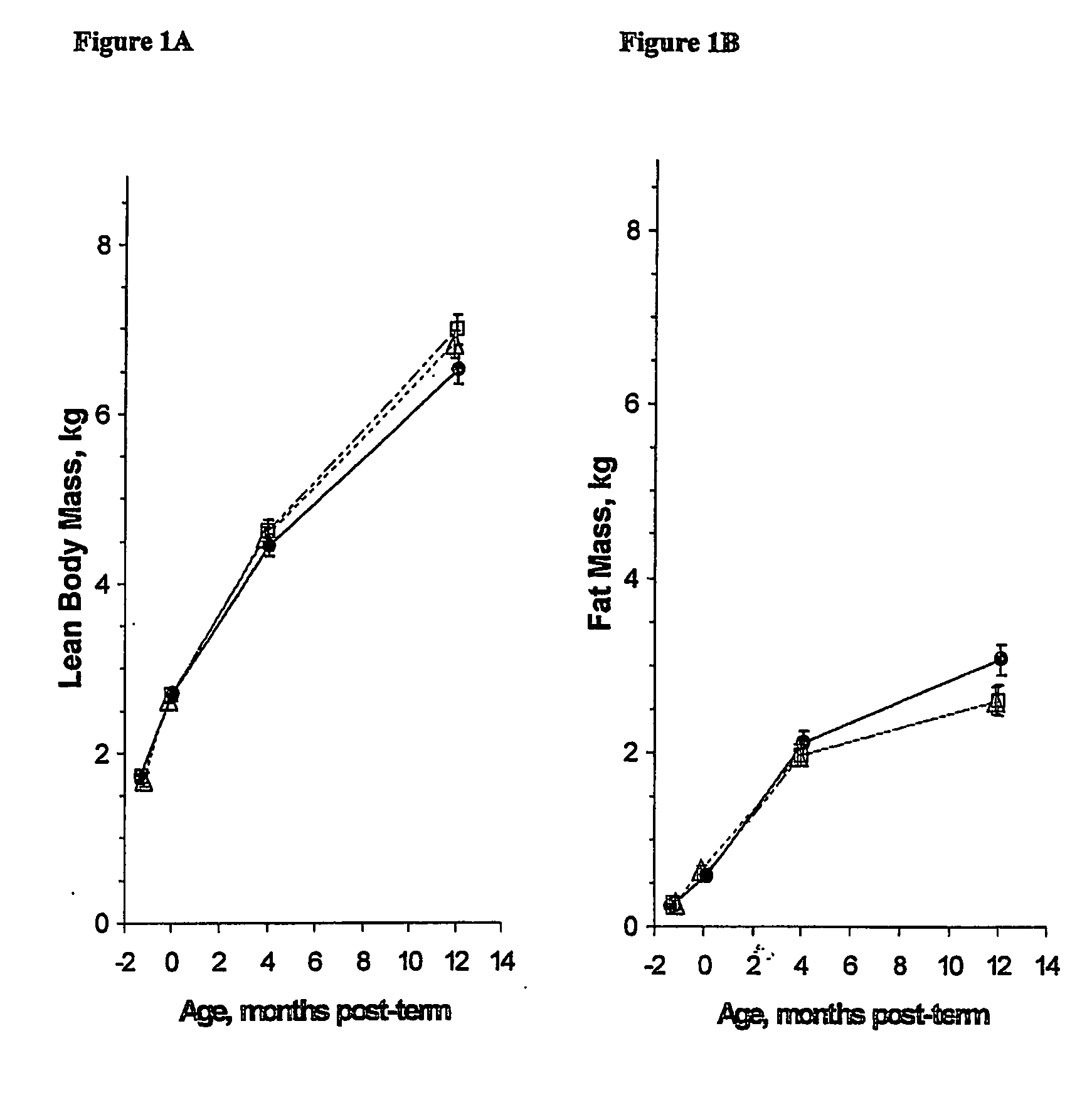
Method of increasing lean body mass and reducing body fat mass in infants
ActiveUS20070026049A1Increasing lean body massReduce the total massBiocidePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLBM - Lean body massBody weight measure
Disclosed is a method of increasing lean body mass and reducing fat body mass in infants, said method comprising administration to an infant, term or preterm, a nutritional formula comprising a source of DHA and ARA. It has been found that the administration of DHA and ARA, or a source thereof, in infants can increase lean body mass and reduce fat body mass, when compared to an unsupplemented control formula, without impacting the total overall growth of the infant. This method is especially useful in preterm infants.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
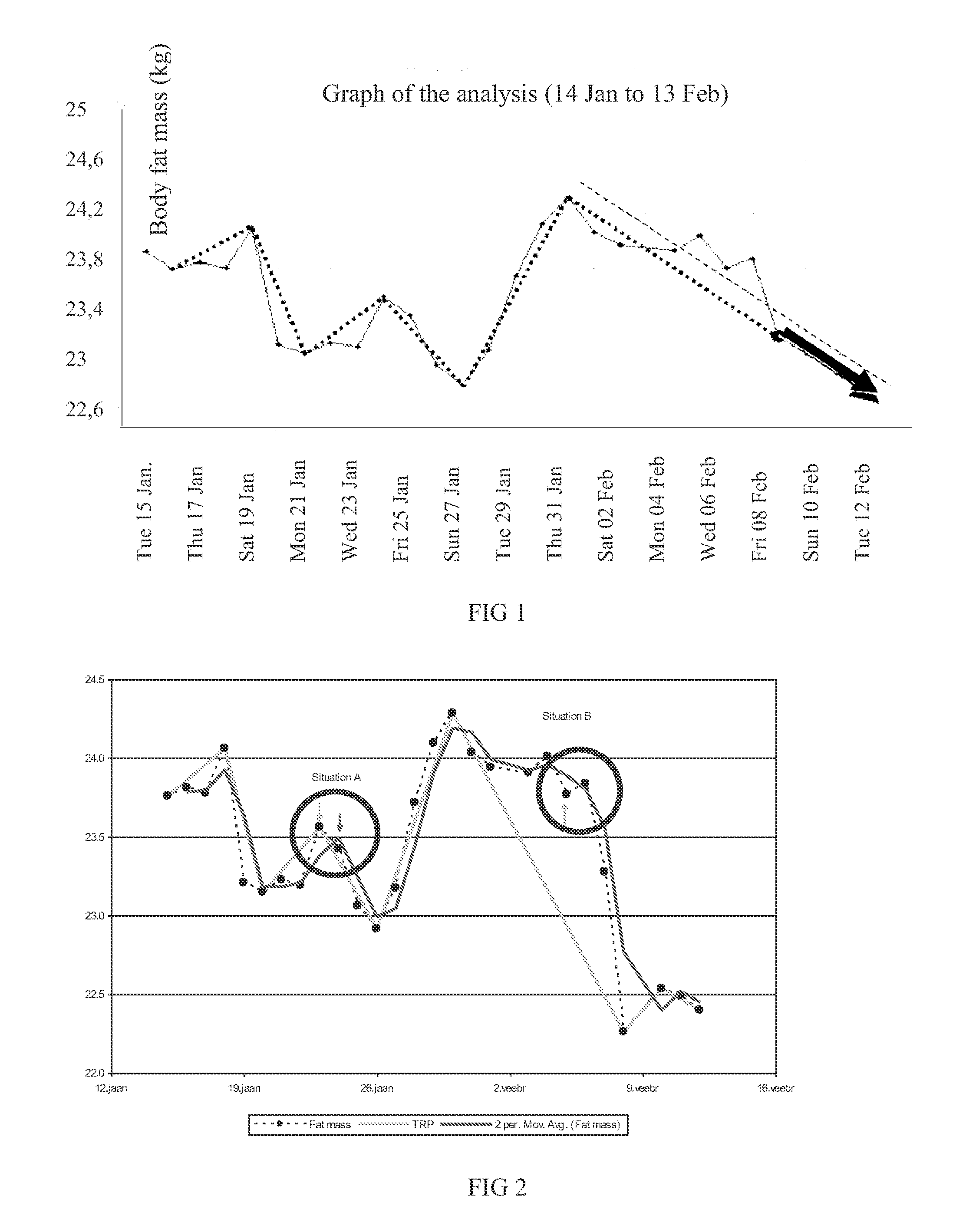
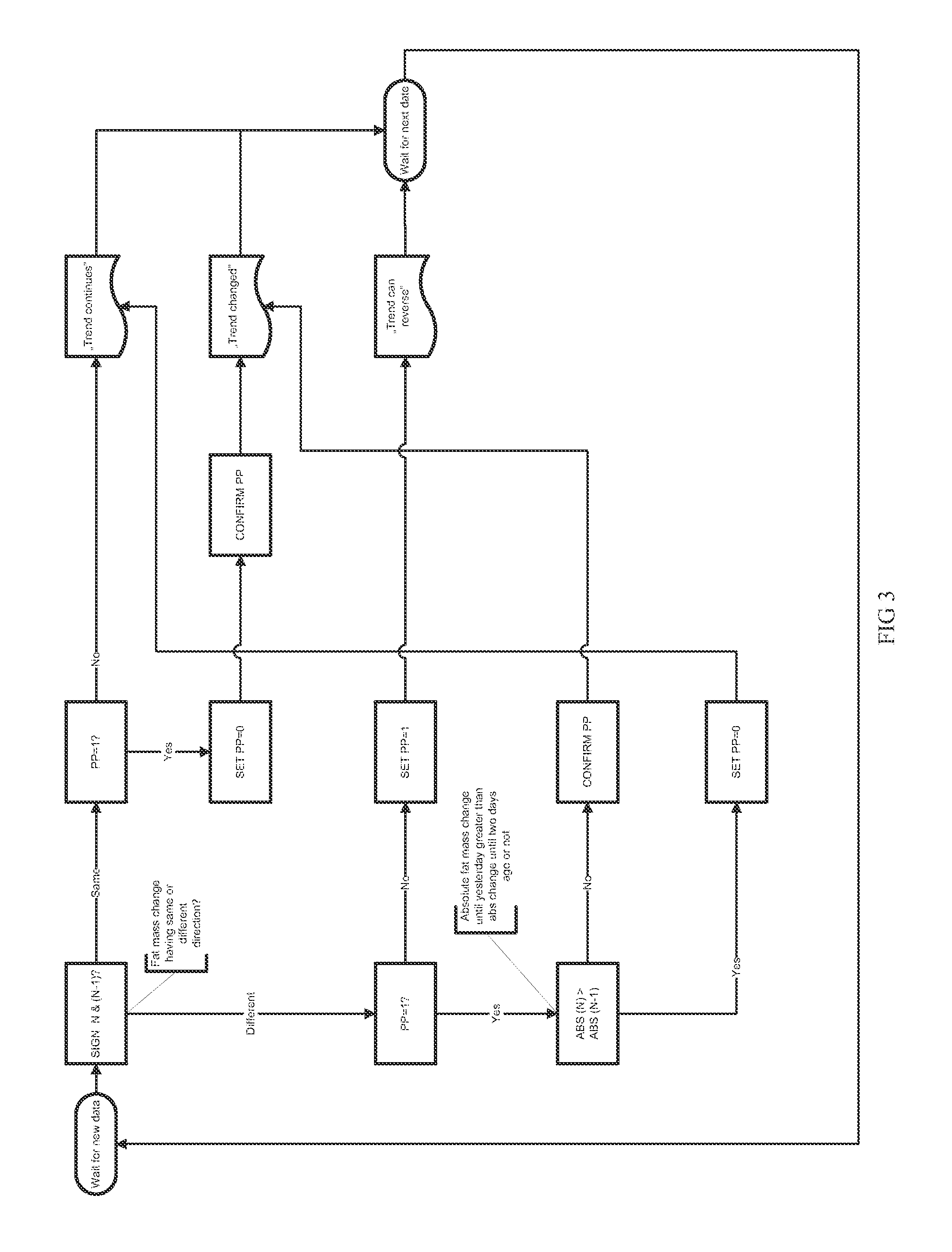
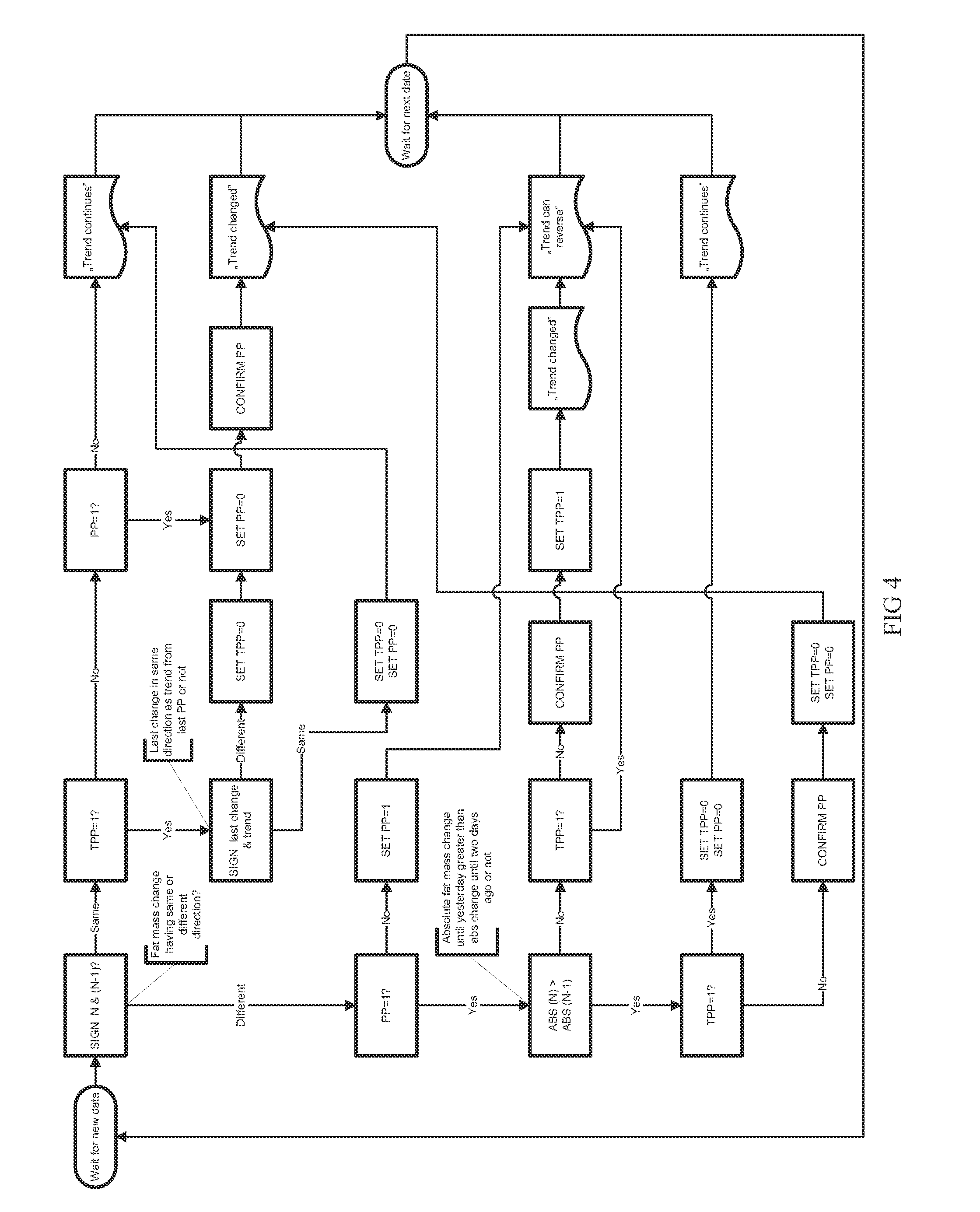
Method for monitoring an individual's fat metabolism state
ActiveUS20120065895A1Nutrition controlBiological testingEnergy balancingPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Method of monitoring energy consumption of an individual in an information system, comprised of periodically determining the energy balance of the individual by measuring body fat percentages (or body fat mass) at least at three consecutive moments of time and calculating change of body fat percentages (body fat mass) from two consecutive moments of time, and calculating the trends of the individual's energy balance from the changes of body fat percentages (body fat mass) and determining from the trend whether the individual is in the stage of burning or accumulating fat. The information system automatically generates recommendations for controlling energy balance based on the trends of changes of the energy balance.
Owner:SAUL INDREK
Exercise Aid Device
InactiveUS20080312040A1Reduce the burden onEfficiently provideClubsPerson identificationTrochanter majorKnee Joint
An exercise aid device has a hip supporting member movable relative to a base, footrests movable relative to the base, drive means for driving the hip supporting member, body constitution estimating unit for estimating at least one of fat mass and muscle mass of a user, and a controller for the drive means. The controller controls the drive means such that a load acting on a femoral region by own weight of the user supported on the hip supporting member changes according to a relative positional displacement between the user's toe and trochanter major, the positional displacement is allowed in a direction of flexion and extension of knee joint of the user, and an angle of the knee joint is maintained substantially constant. In addition, since the controller controls the drive means by use of an output of the body constitution estimating unit, it is possible to provide an exercise with less burden to the knee joint and a suitable strength for the user.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
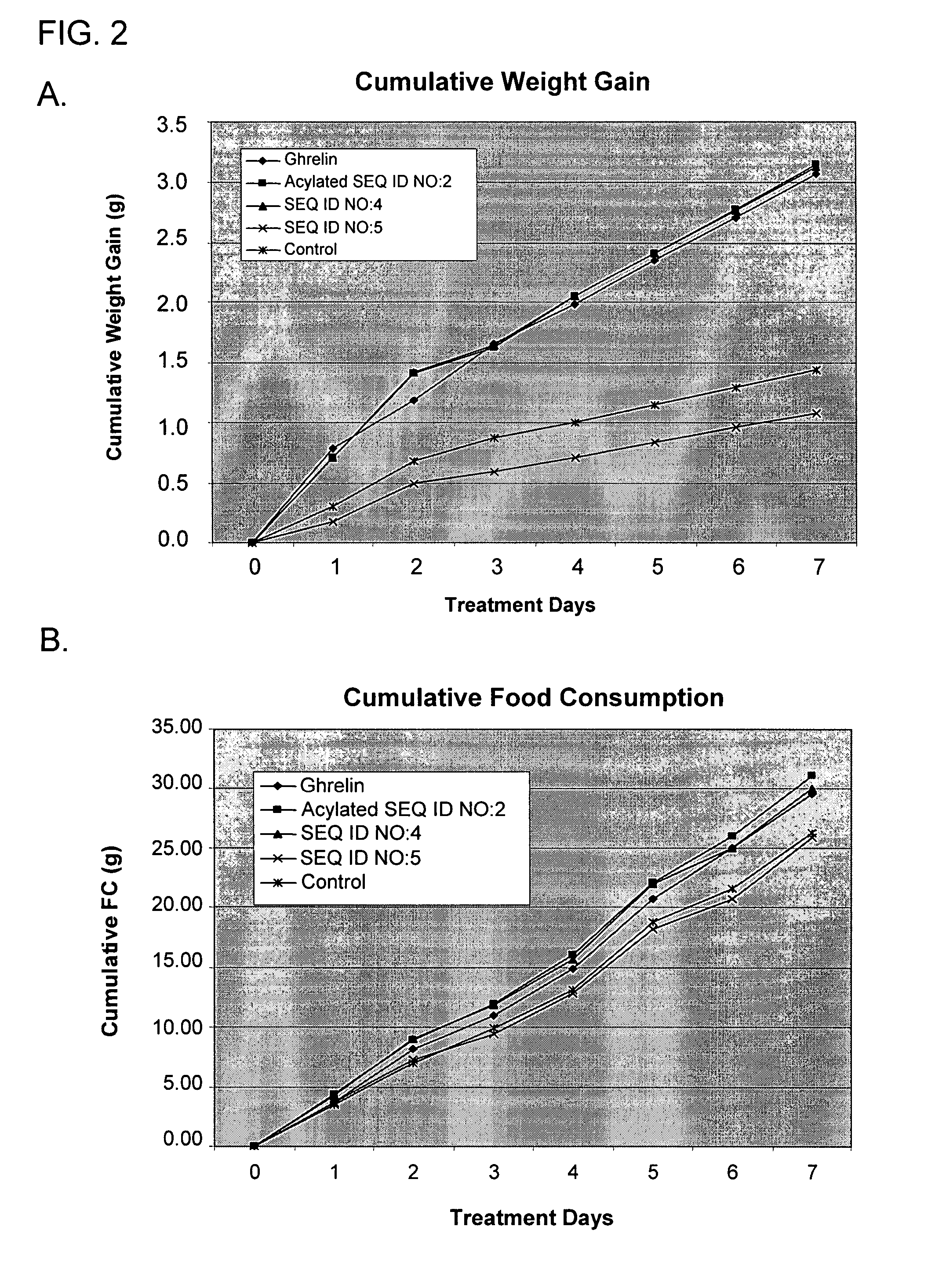
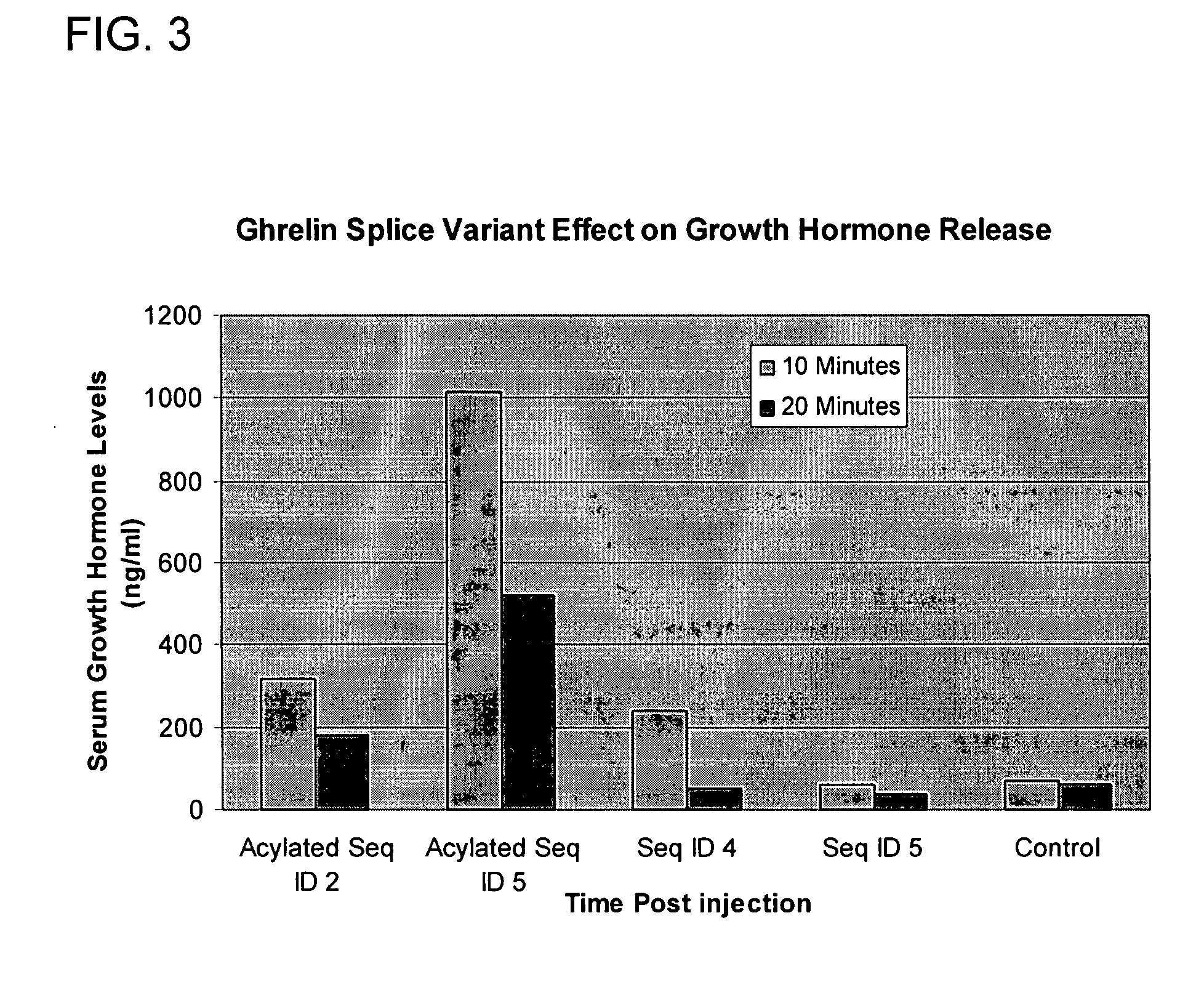
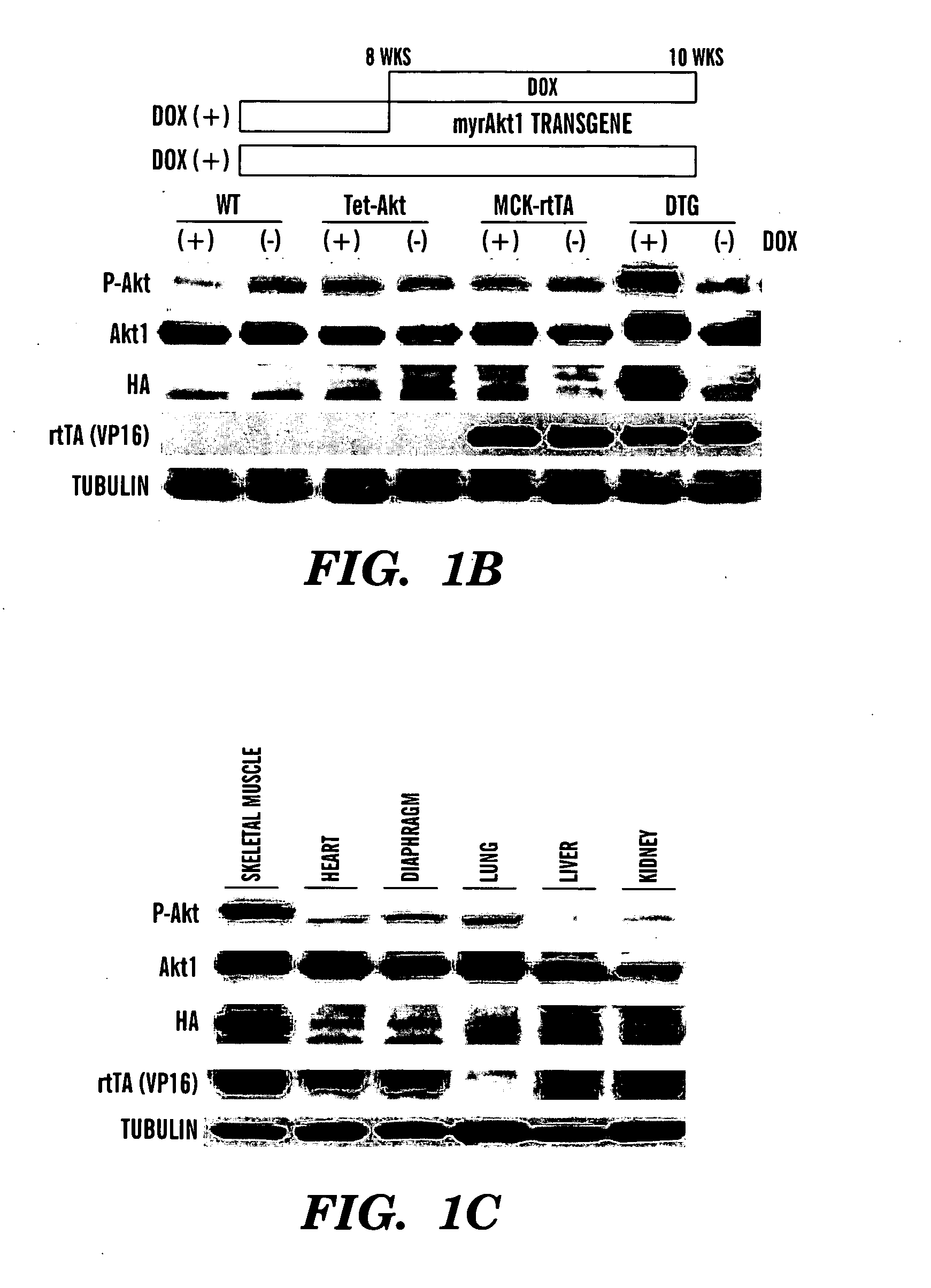
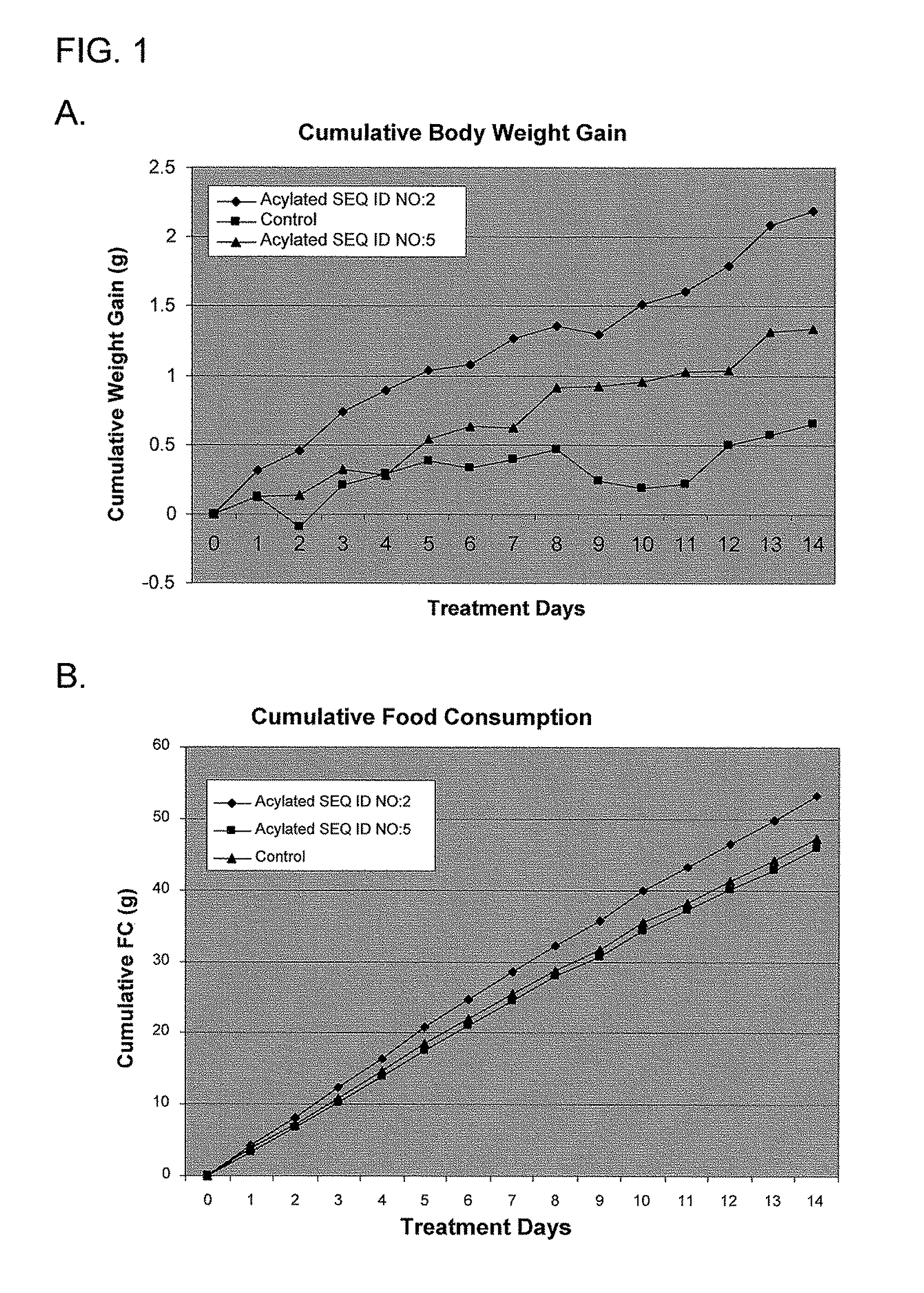
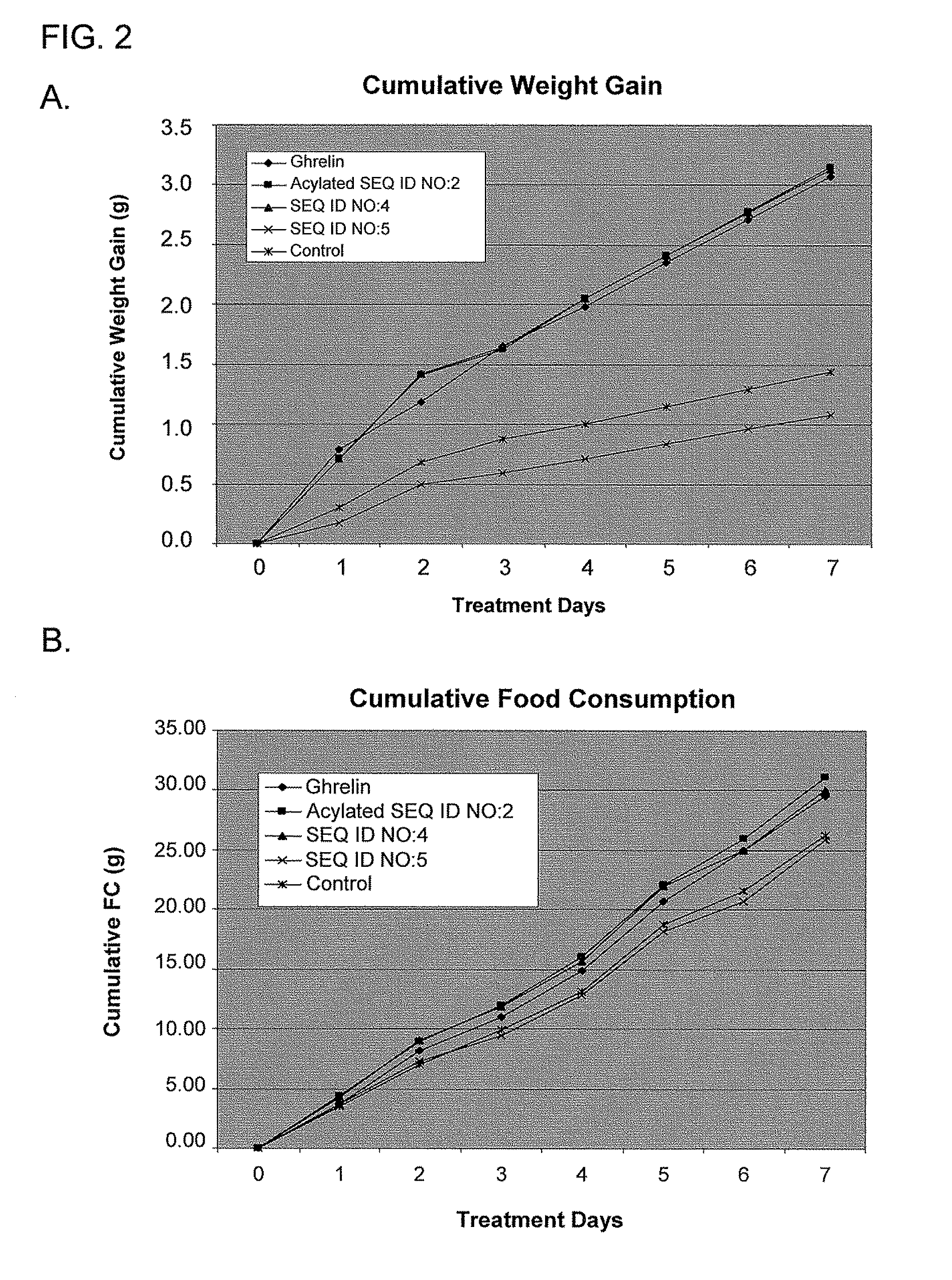
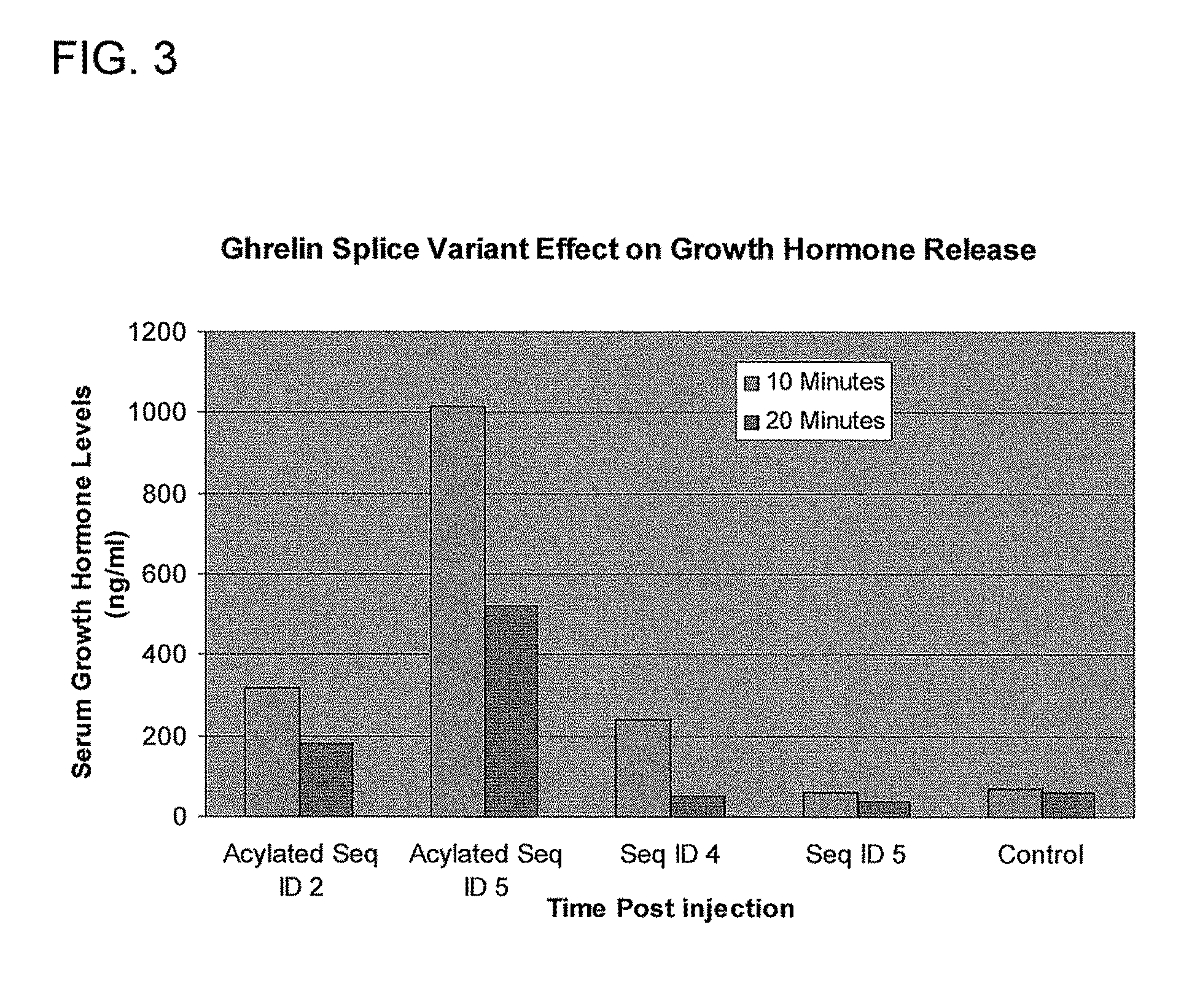
Use of ghrelin splice variant for treating cachexia and/or anorexia and/or anorexia-cachexia and/or malnutrition and/or lipodystrophy and/or muscle wasting and/or appetite-stimulation
The present disclosure relates, in one aspect, to use of ghrelin splice variant or an analogue thereof for the preparation of a medicament for one or more of: treatment and / or prevention of loss of body weight and body fat, prophylaxis or treatment of cachexia, stimulation of appetite, stimulation of food intake, stimulation of weight gain, or increasing body fat mass, or increasing body lean mass. Another aspect relates to the use of a ghrelin splice variant-like compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer cachexia in an individual in need of such treatment. Another aspect relates to the use of a ghrelin splice variant-like compound for the preparation of a medicament for prophylaxis or treatment of cachexia in an individual by administering a subcutaneous dosage of said medicament to the individual. A further aspect relates to the use of a ghrelin splice variant-like compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for the preparation of a medicament for stimulation of appetite in an individual by administering a subcutaneous dosage of said medicament to the individual. A further aspect relates to a number of new ghrelin splice variant-like compounds and uses thereof, as well as to pharmaceutical compositions and medical packaging comprising the new ghrelin splice variant-like compounds.
Owner:MINTZ LIAT
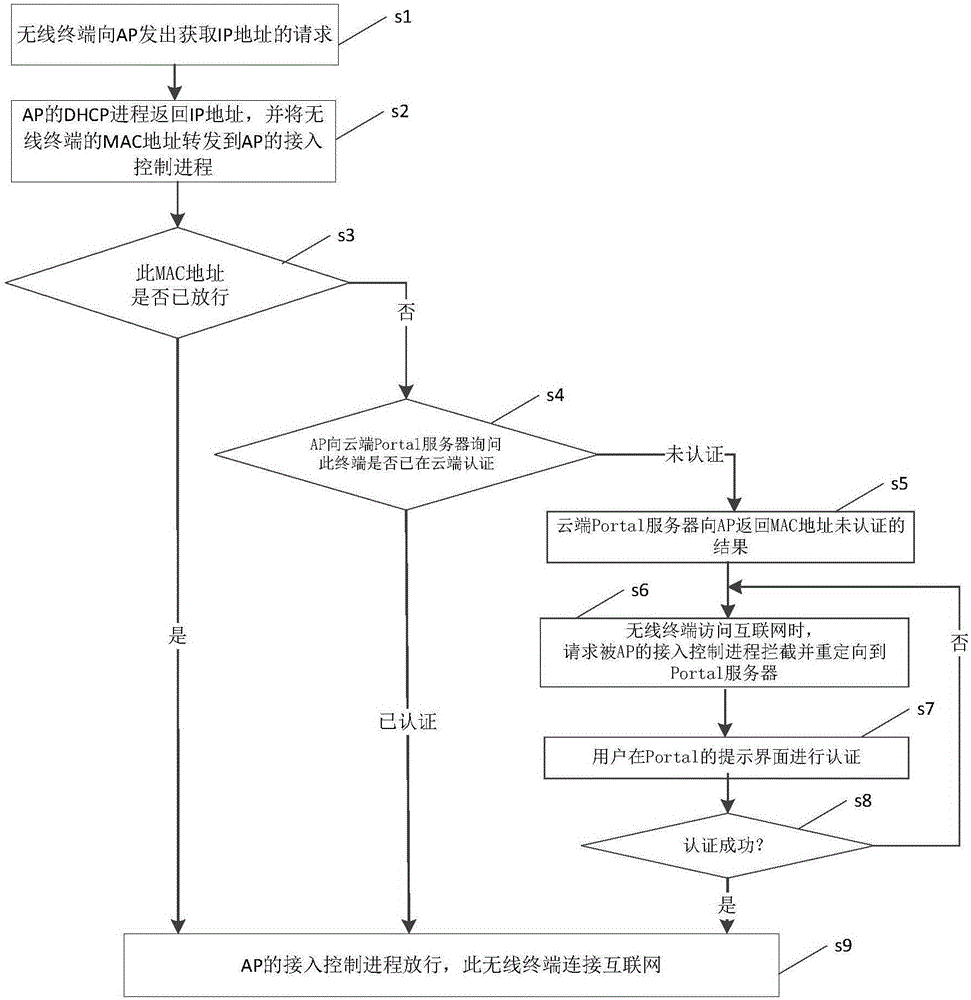
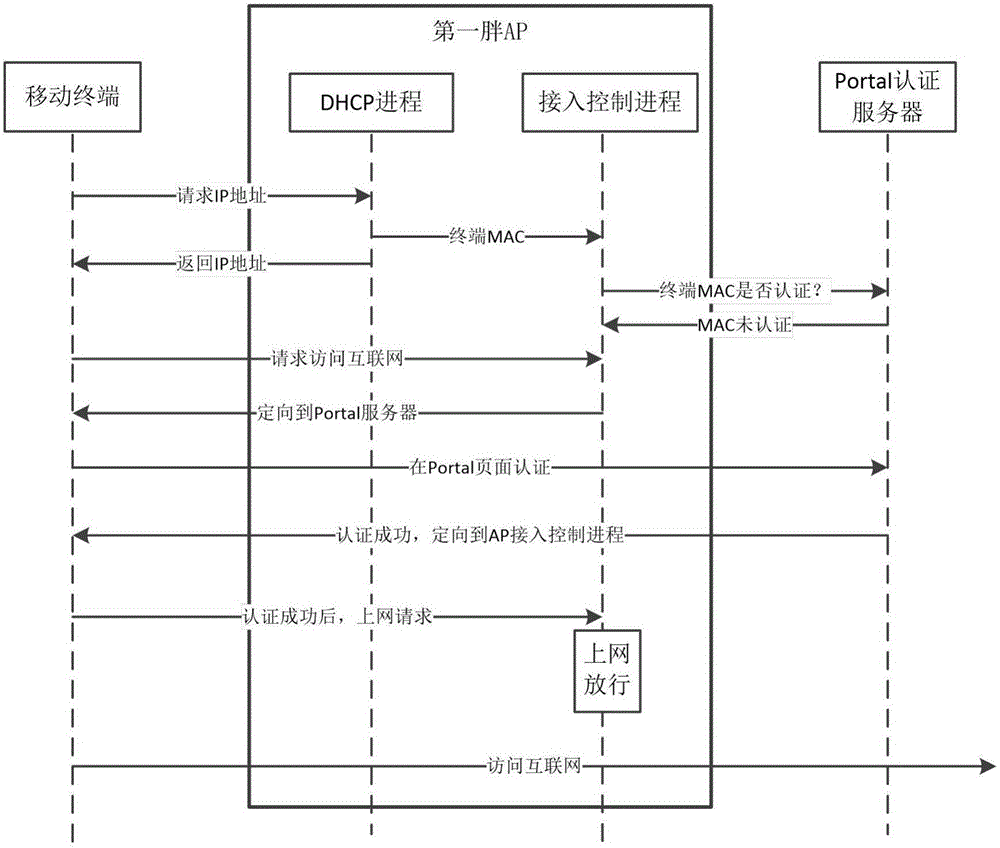
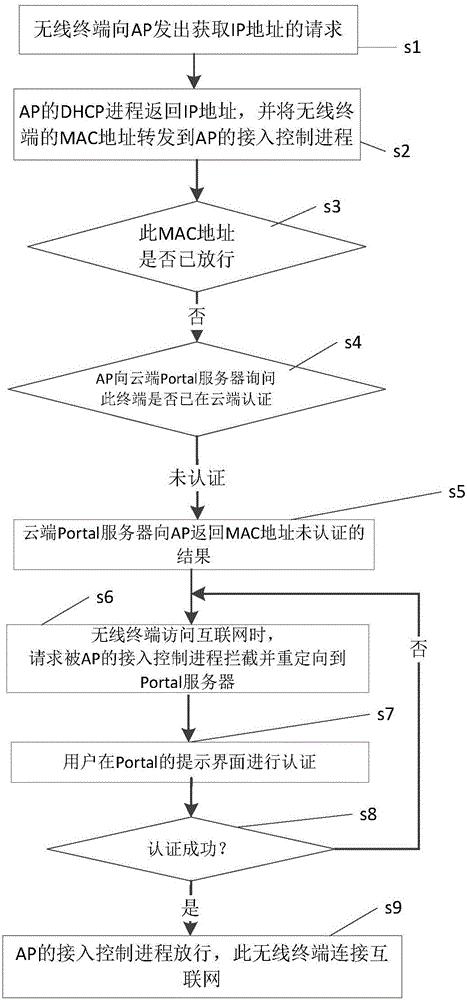
Method for wireless terminal networking based on fat APs and method for wandering among fat APs
The invention provides a method for wireless terminal networking based on a fat AP and a method for wandering among the fat APs. The networking method comprises the step that a wireless terminal requests obtaining of an IP address from a DHCP process of the fat AP; the DHCP process of the fat AP returns the IP and forwards an MAC address of the wireless terminal to an access control process; the access control process inquires a Portal server whether the MAC address of the wireless terminal passes authentication, and the access control process releases the wireless terminal and the wireless terminal can be connected to the Internet if the authentication is completed; if the authentication is not completed, the wireless terminal is then oriented to the Portal server for the authentication; if the wireless terminal passes the authentication, the access control process of the fat AP releases the wireless terminal, and the wireless terminal can be connected to the Internet; and if the wireless terminal does not pass the authentication, the access control process cannot release the wireless terminal, and the wireless terminal cannot be connected to the Internet. After the same terminal passes the authentication of the previous fat AP, the state of a Portal cloud terminal can be changed to completion of the authentication; the terminal does not need to pass the authentication of the next fat AP; and the wireless terminal can be connected and get access to the Internet without informing a user.
Owner:张胜利 +1
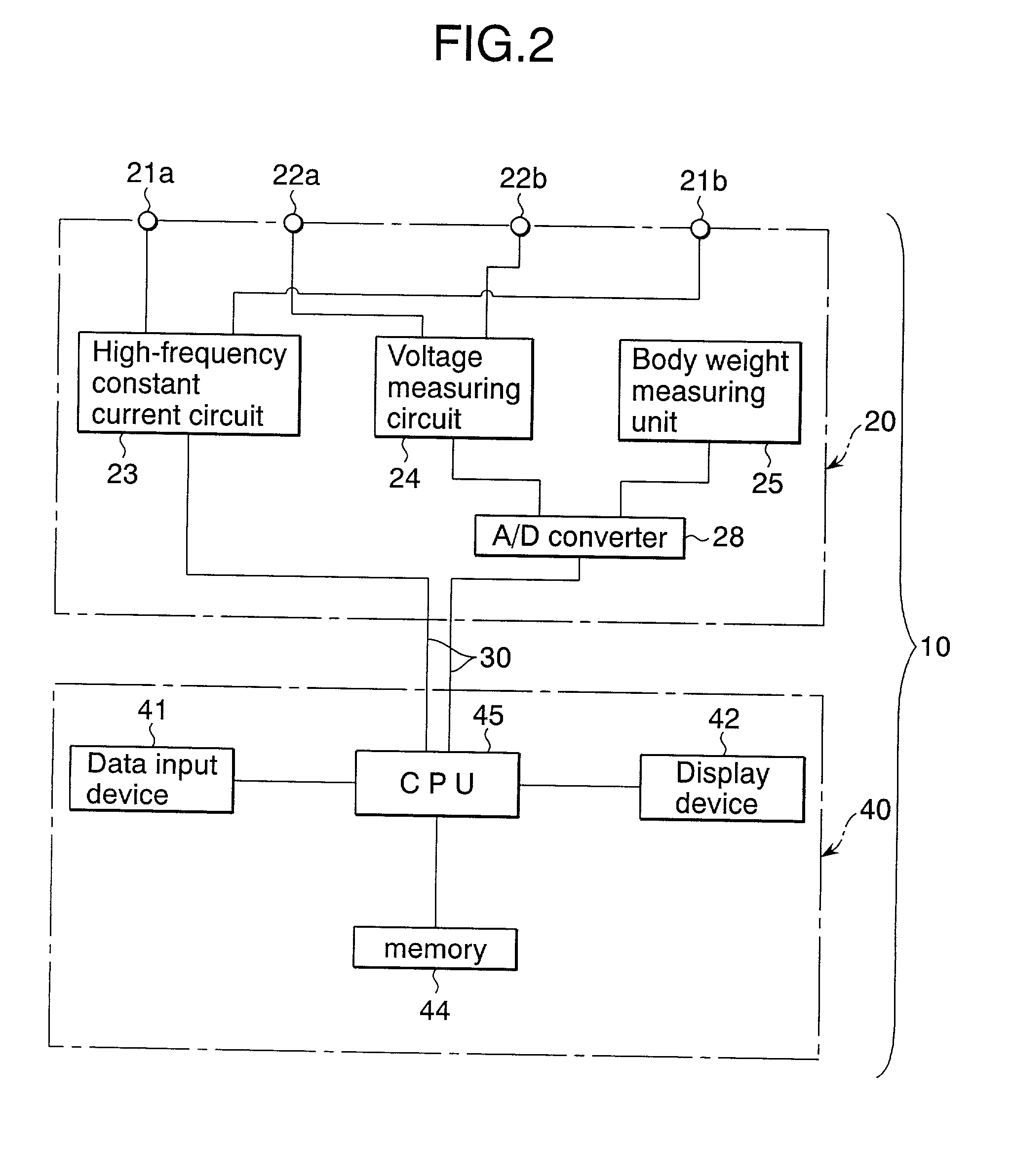
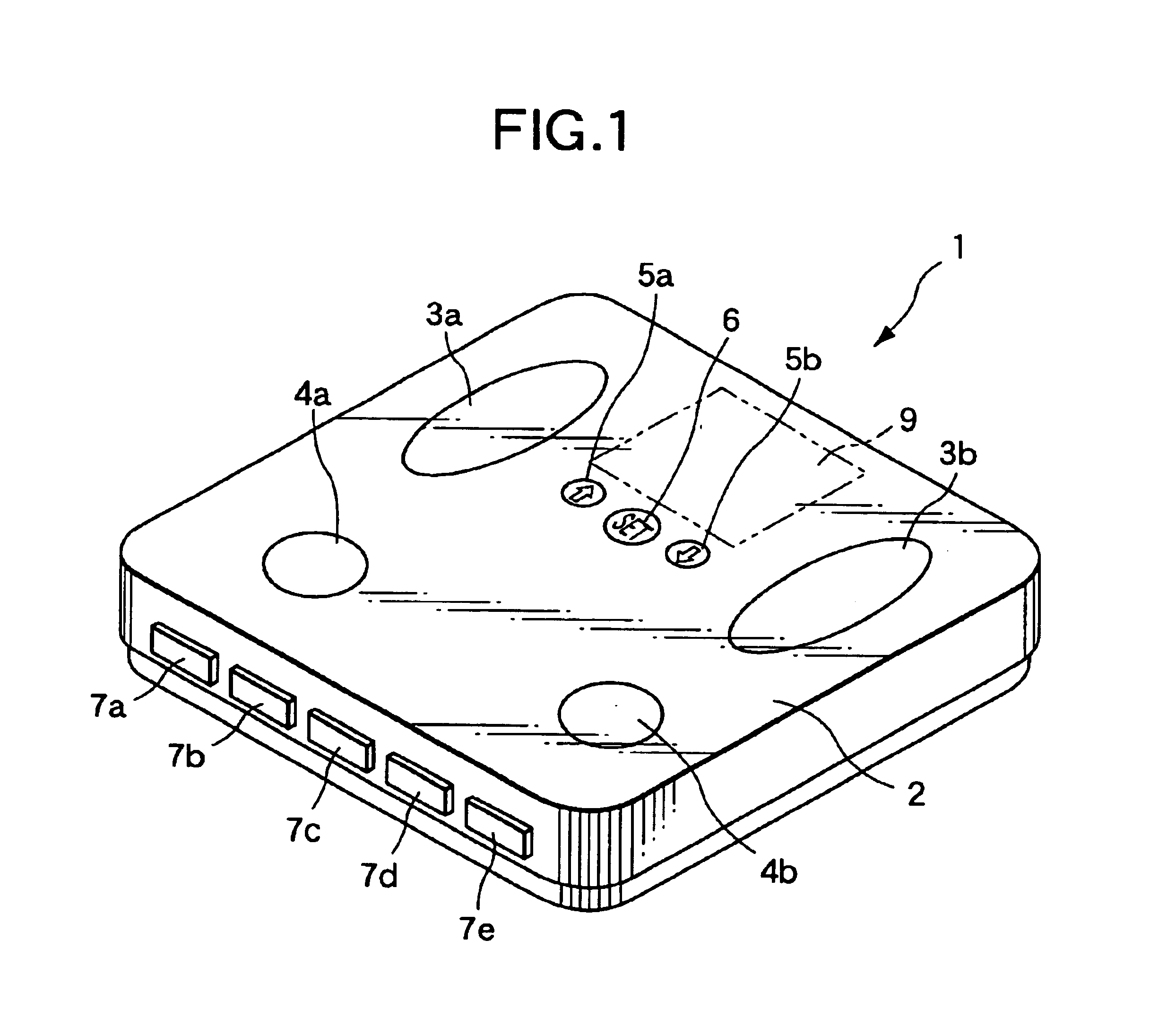
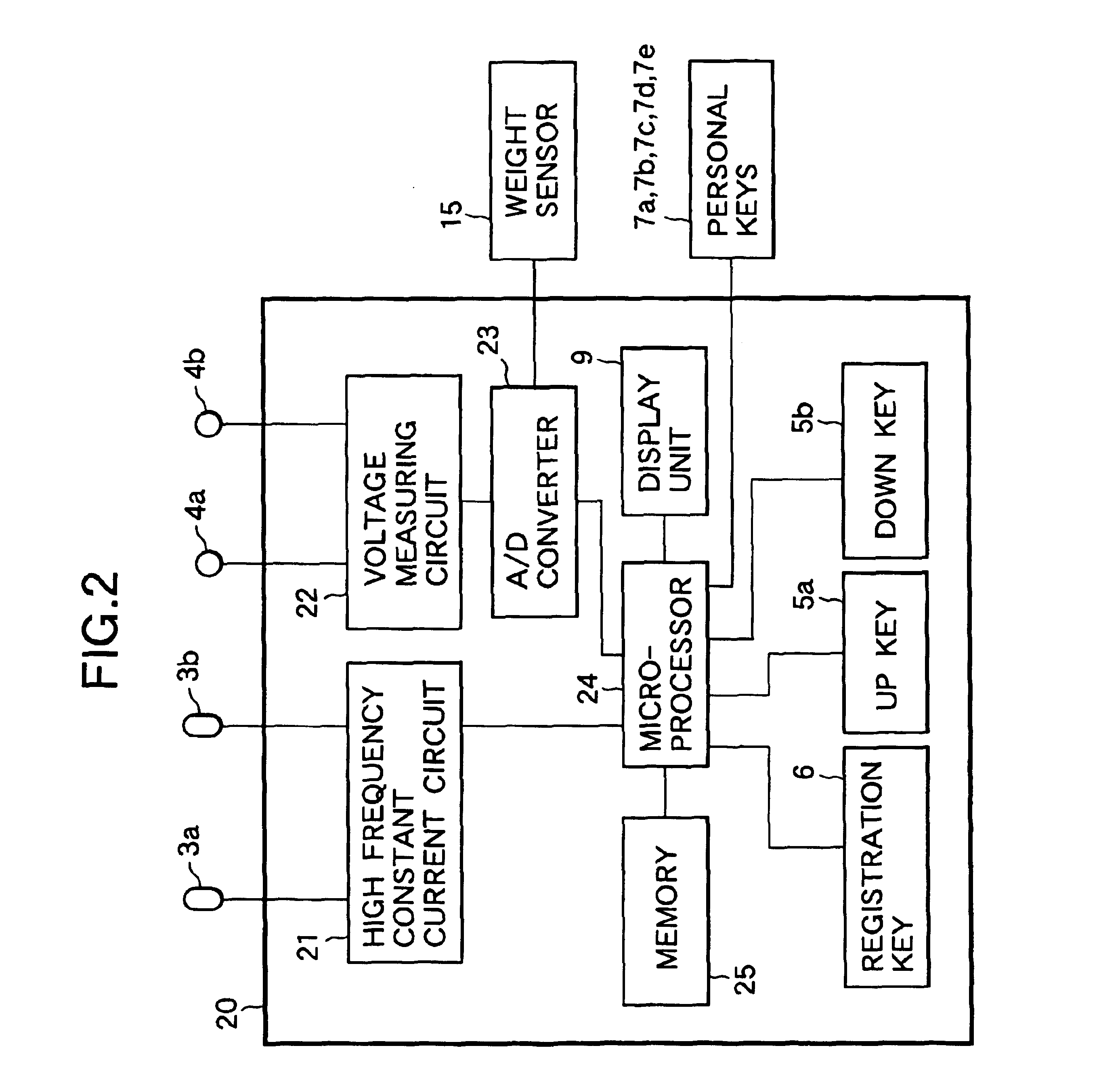
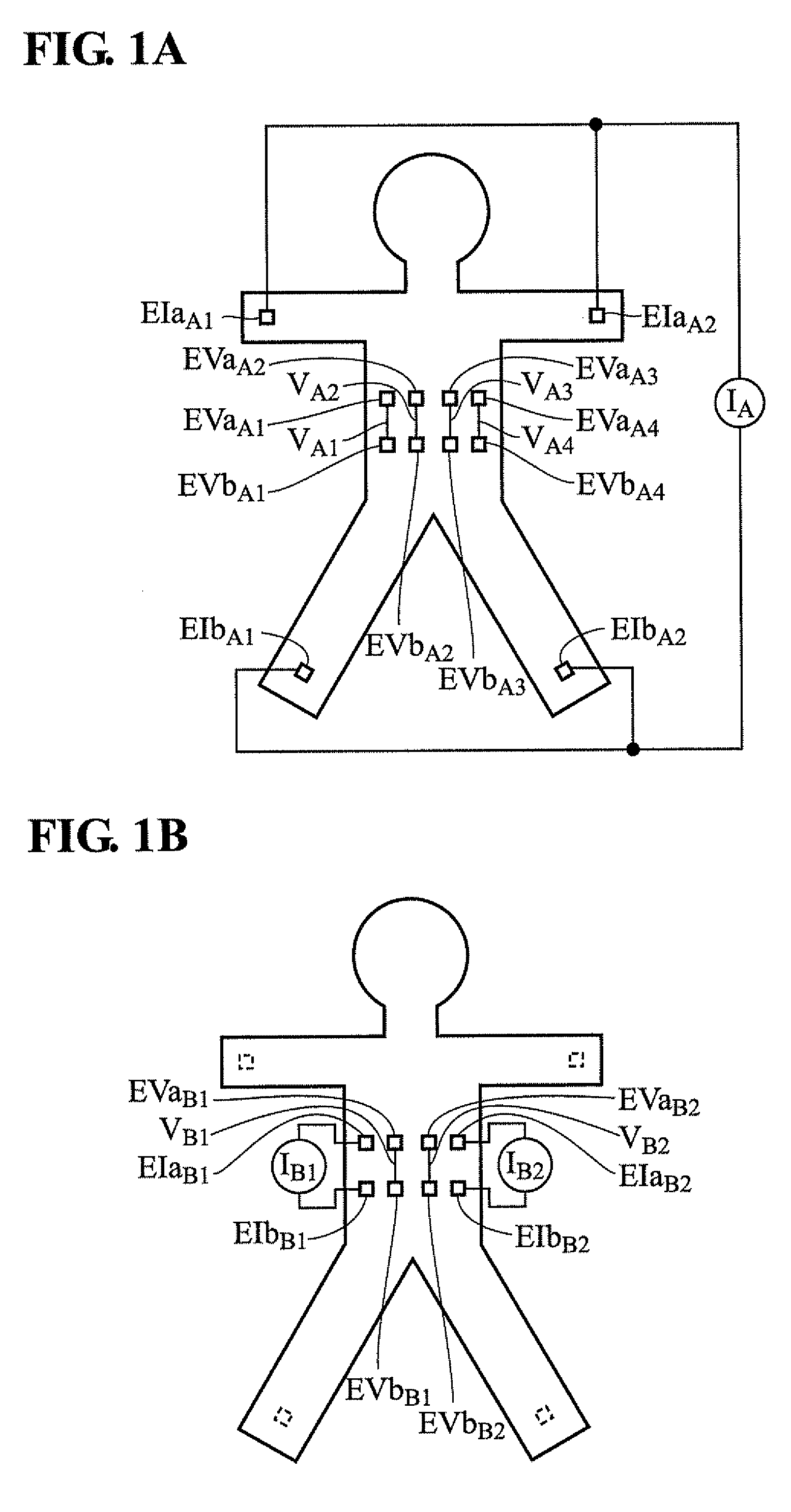
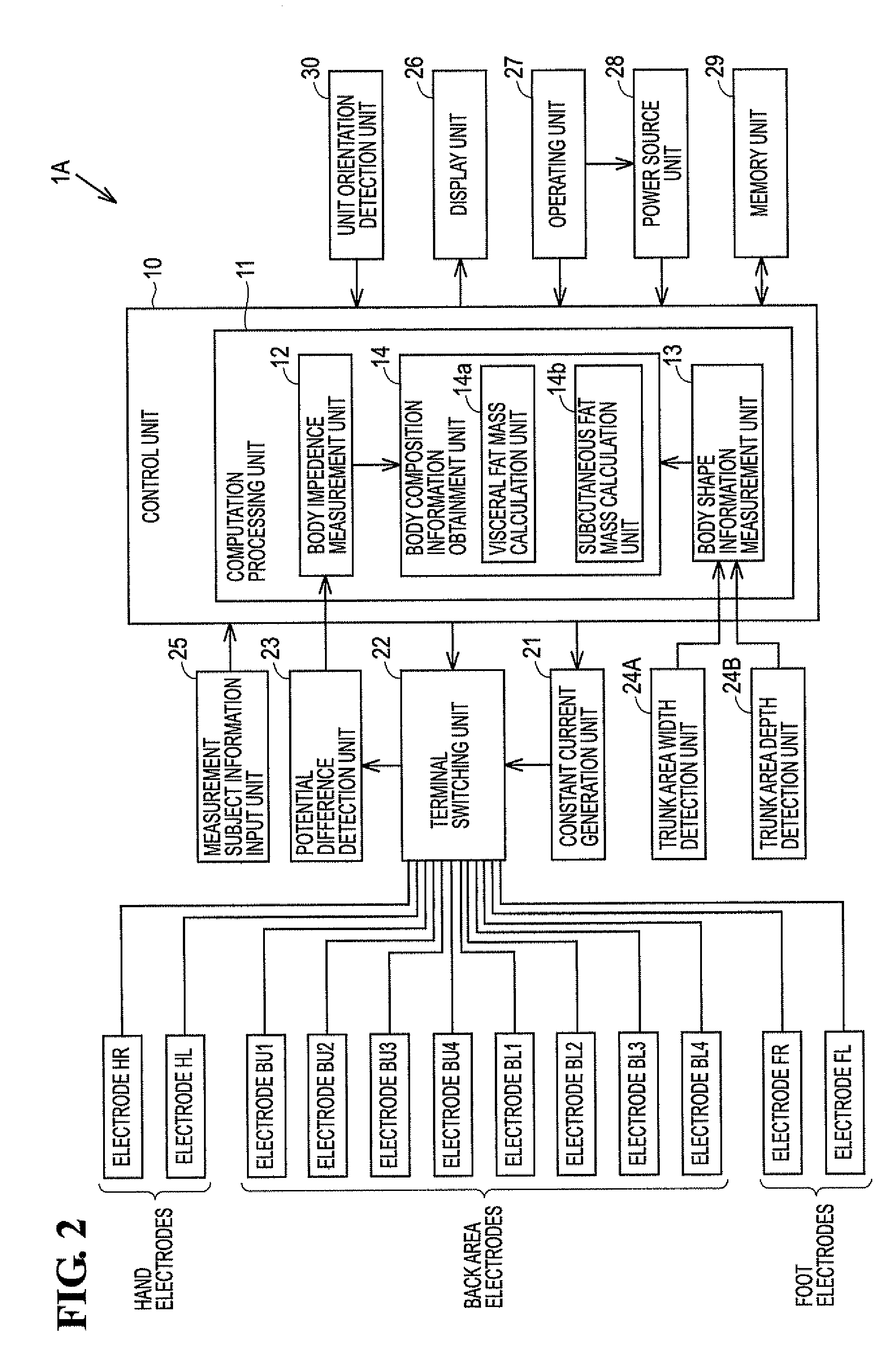
Fat mass measurement apparatus
A fat mass measurement apparatus includes an area detection unit that detects a predetermined position in a measurement subject's trunk area and detecting a predetermined area in the trunk area using the detected position; an electrode position setting unit that sets, on the body surface at the predetermined area detected by the area detection unit, a plurality of positions along the vertical direction of the trunk area for measuring the body impedance; an impedance measurement unit that measures the body impedance by bringing the impedance measurement electrodes into contact with each of the plurality of positions that have been set; and an abdominal area fat mass calculation unit that calculates a fat volume at the predetermined area based on the body impedances at each of the plurality of positions measured by the impedance measurement and the size of the trunk area at the predetermined area.
Owner:FUKUDA DENSHI CO LTD
An injectable decellularized fat-matrix microparticle and applications thereof in implants
InactiveCN106492288APromote regenerationPromote repairPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationTissue repairCell adhesion
An injectable decellularized fat-matrix microparticle and applications thereof in implants are disclosed. The microparticle is prepared by rinsing, disinfecting and rising fat mass, performing repeated freezing-thawing, cutting the fat mass into slices, soaking the slices, degreasing, decellularizing, performing freeze-drying, and performing low-temperature grinding. The microparticle can be cooperated with an implant auxiliary and adopted as an injectable decellularized fat-matrix microparticle implant. The microparticle has advantages of good biocompatibility, capability of promoting tissue regeneration, and the like. As the microparticle has a three-dimensional structure, the microparticle can be adopted as a support for supporting tissue and cell growth. Active components of the microparticle can induce and regulate cell adhesion, growth, proliferation and differentiation and can promote tissue repairing and regeneration. The implant can be adopted as a minimally invasive plastic injection implanting material, and the implant has a filling function and a tissue repairing function as the natural three-dimensional structure and a lot of the active components of fat are preserved.
Owner:广州昕生医学材料有限公司
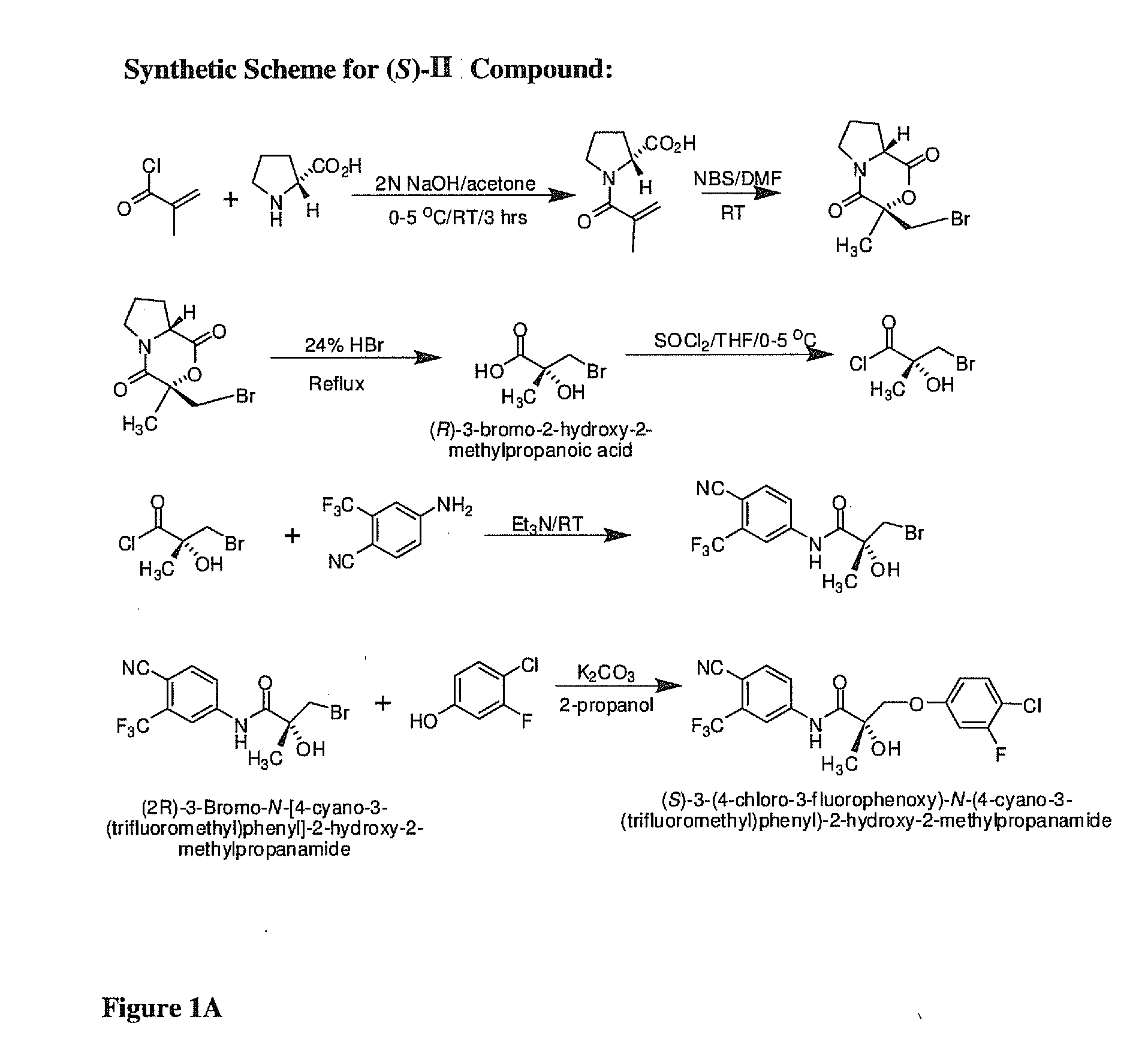
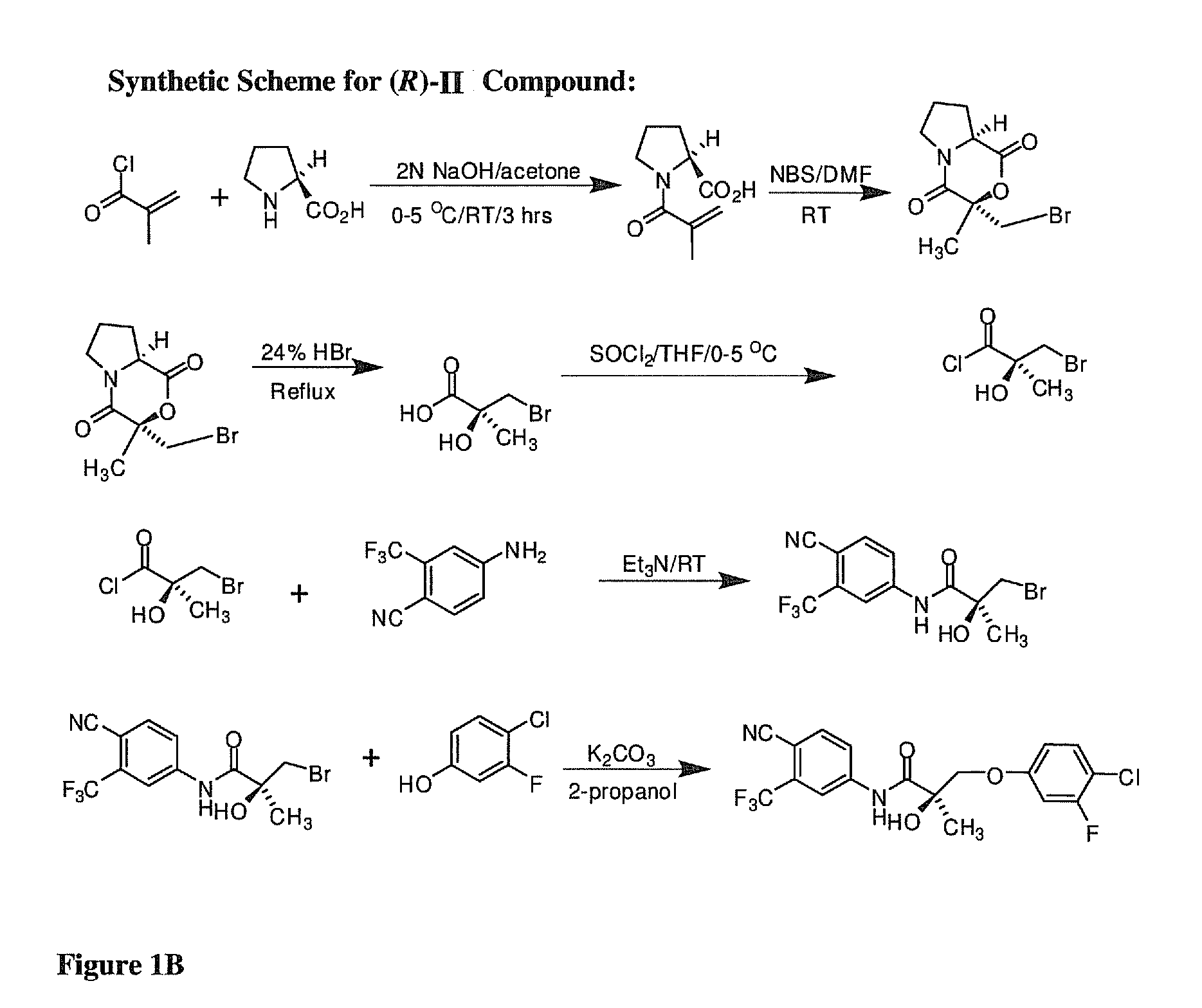
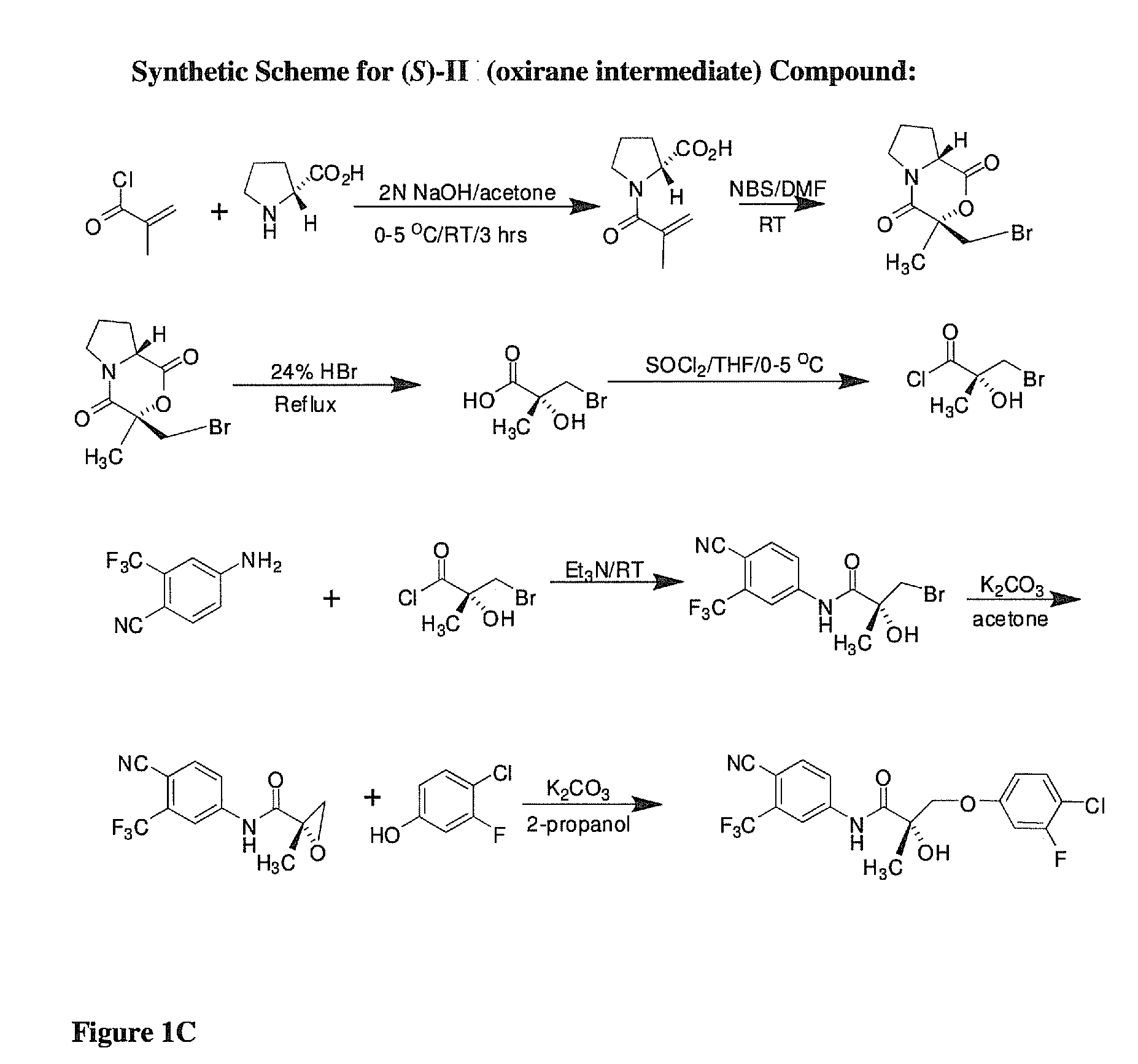
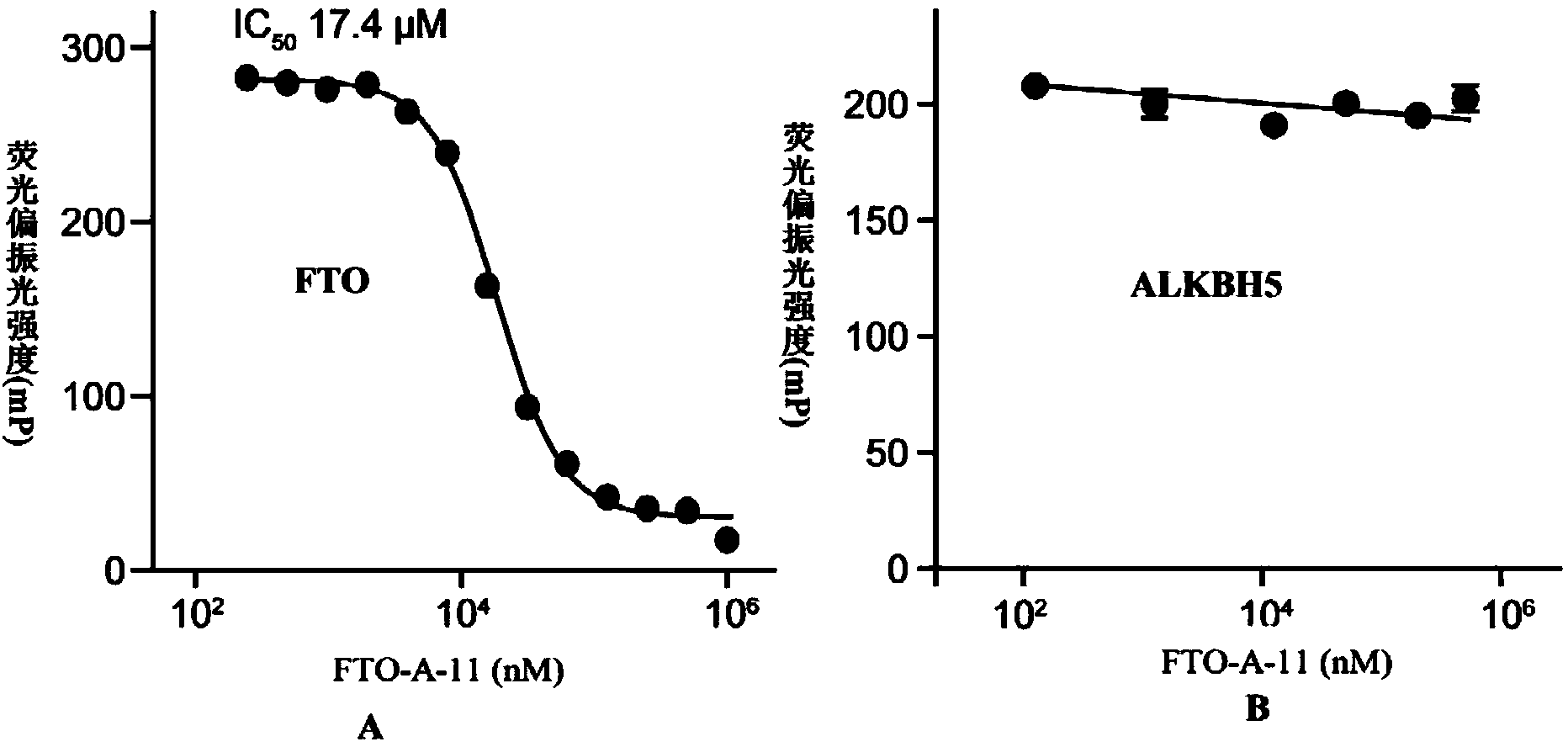
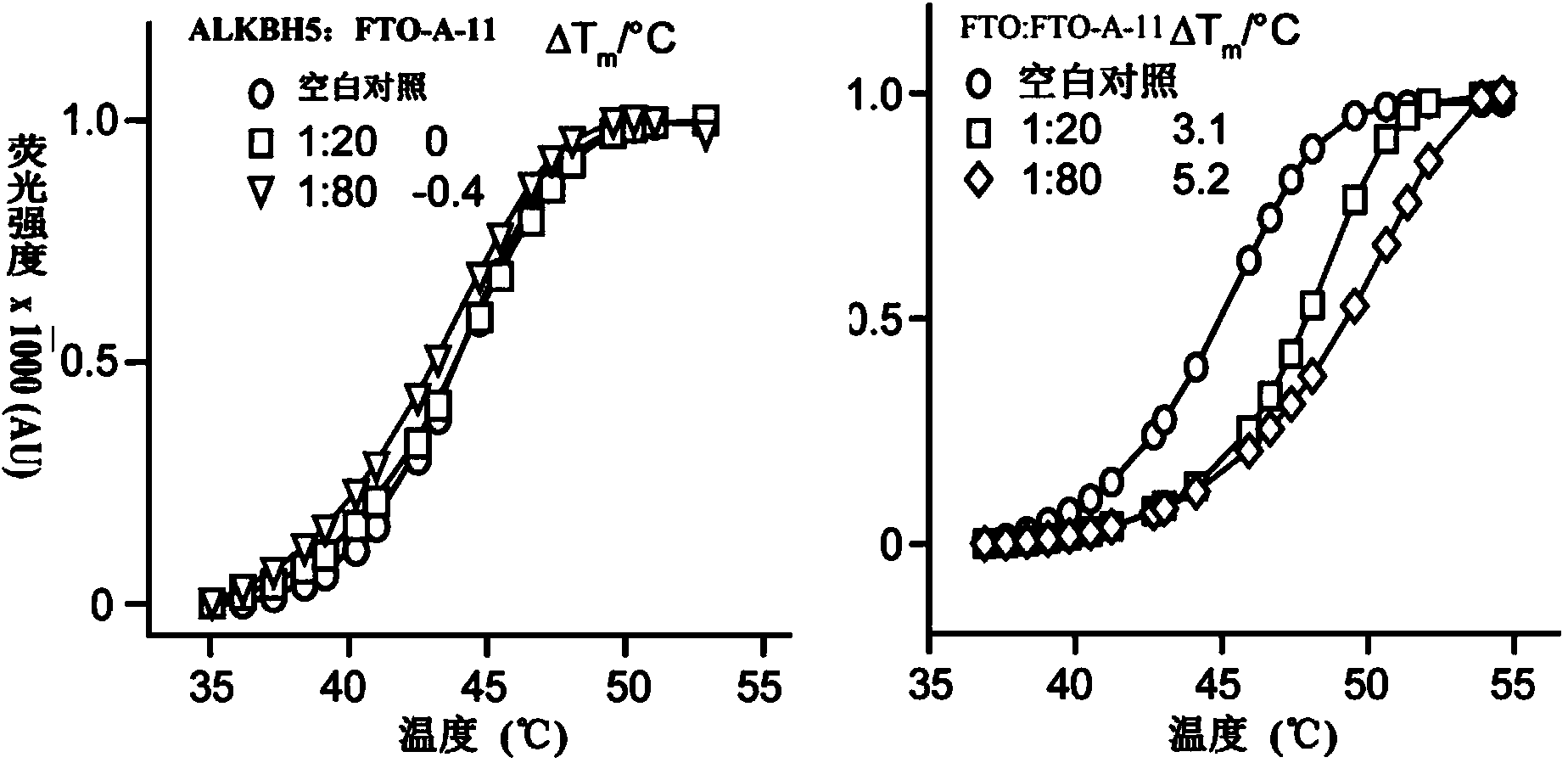
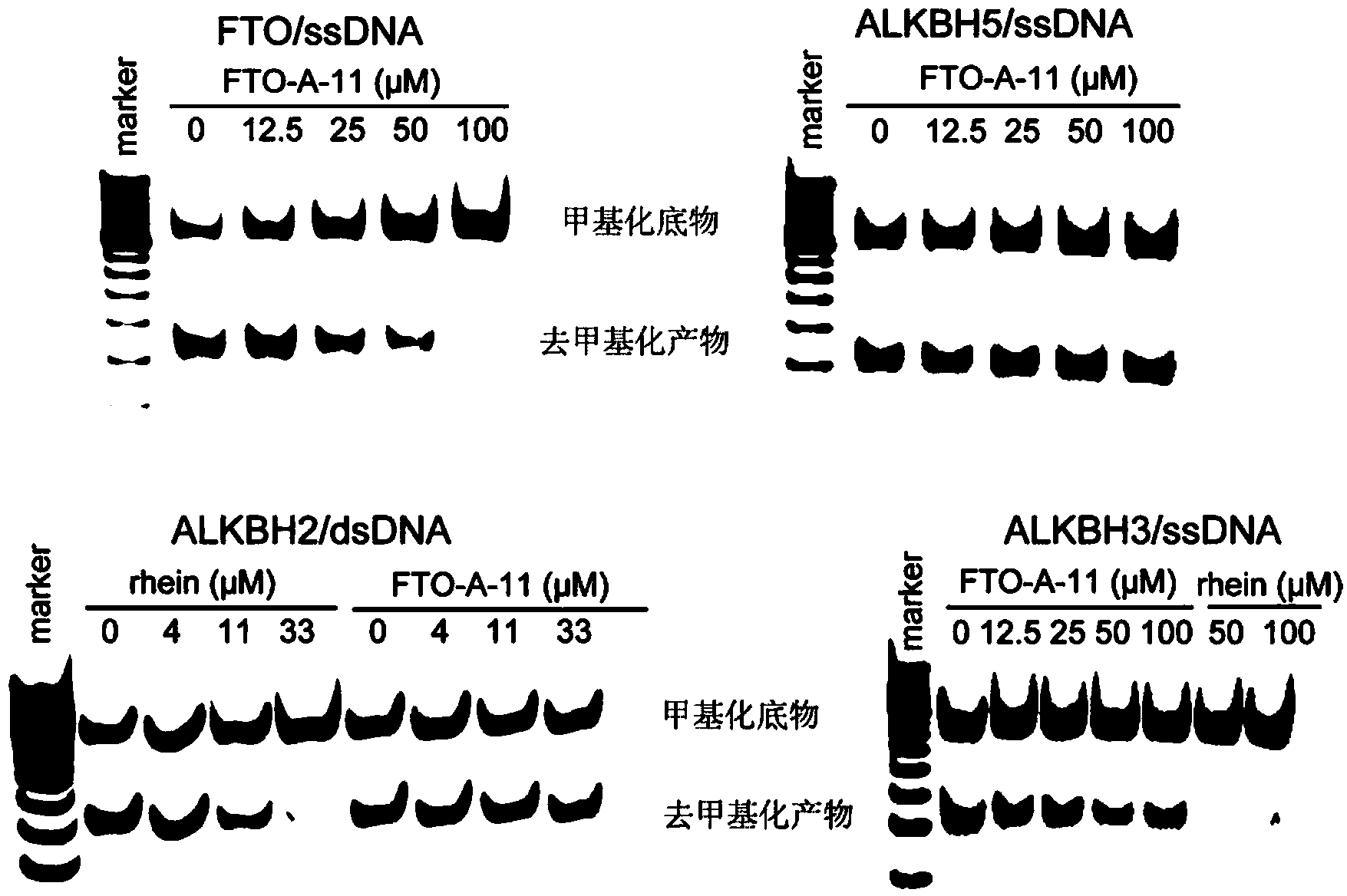
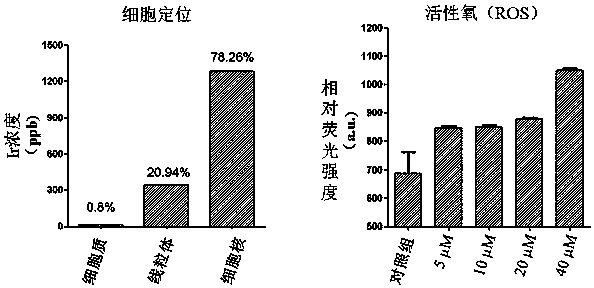
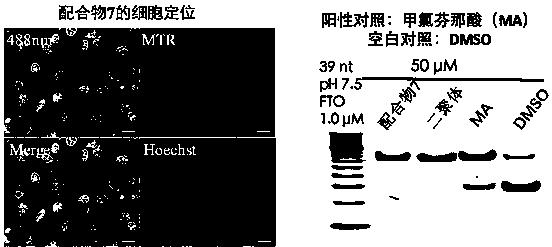
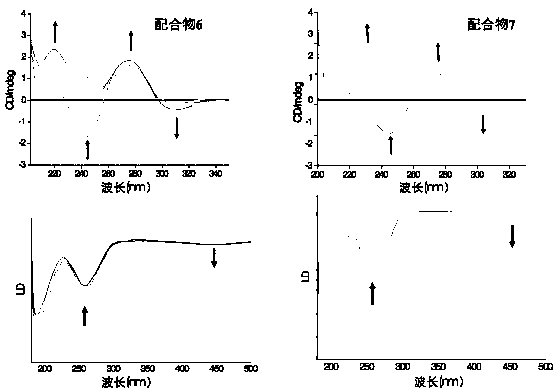
Use of 2-(substituted phenylamino) benzoic acid and ester compound thereof in preparation of FTO (Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Protein) inhibitor
The invention provides use of 2-(substituted phenylamino) benzoic acid and ester compound thereof in preparation of an FTO (Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Protein) inhibitor. The invention particularly discloses the use of 2-(substituted phenylamino)-benzoic acid and the ester compound and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof which are shown in the formula I in preparation of the FTO inhibitor or a pharmaceutical composition for treating FTO-related diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Purple sweet potato flaky pastry and making method thereof
InactiveCN104757085ATake advantage of the benefitsImprove developmentBakery productsCarrot juiceFlaky pastry
The invention relates to purple sweet potato flaky pastry and a making method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of food. The purple sweet potato flaky pastry comprises, by weight, 100-150 parts of high-gluten flour, 50-60 parts of low-gluten flour, 100-120 parts of lotus seeds, 10-25 parts of white granulated sugar, 20-40 parts of sweet osmanthus honey, 30-50 parts of peanut oil, 50-60 parts of carrot juice, 50-80 parts of purple sweet potatoes, 20-28 parts of pumpkins, 10-15 parts of bacon, 5-8 parts of dried blueberries, 6-9 parts of dried mango and 5-9 parts of walnut kernels. The purple sweet potato flaky pastry is nutrient, healthy, reasonable in match and easy and convenient to make, has a little of fat mass, can be eaten by people at ease, can be eaten as dessert and staple food and can resist cancer if being eaten by people for a long time, so that the effect of purple sweet potatoes is sufficiently utilized, and purple sweet potatoes can be better developed and utilized.
Owner:崔子扬
Method and system for estimating visceral fat area
Owner:TANITA CORP
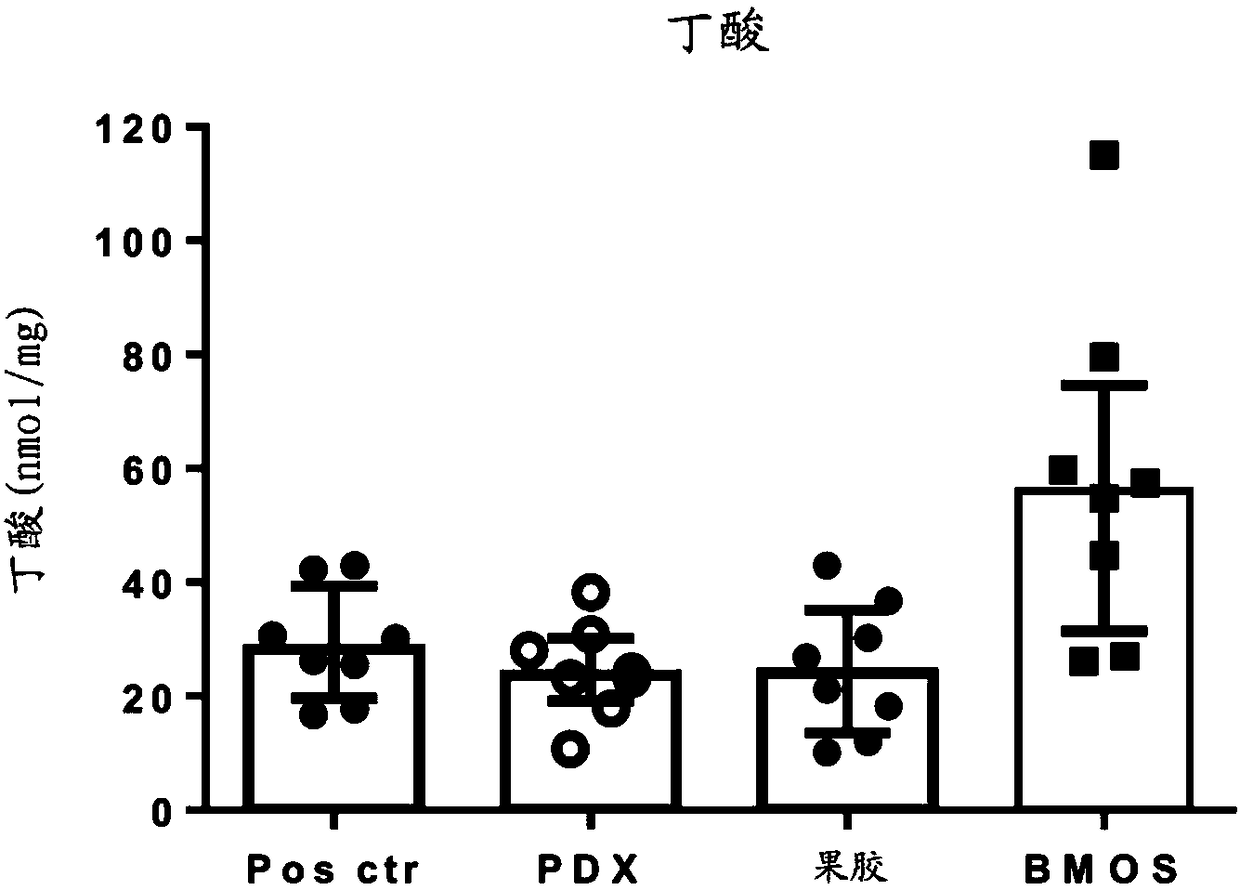
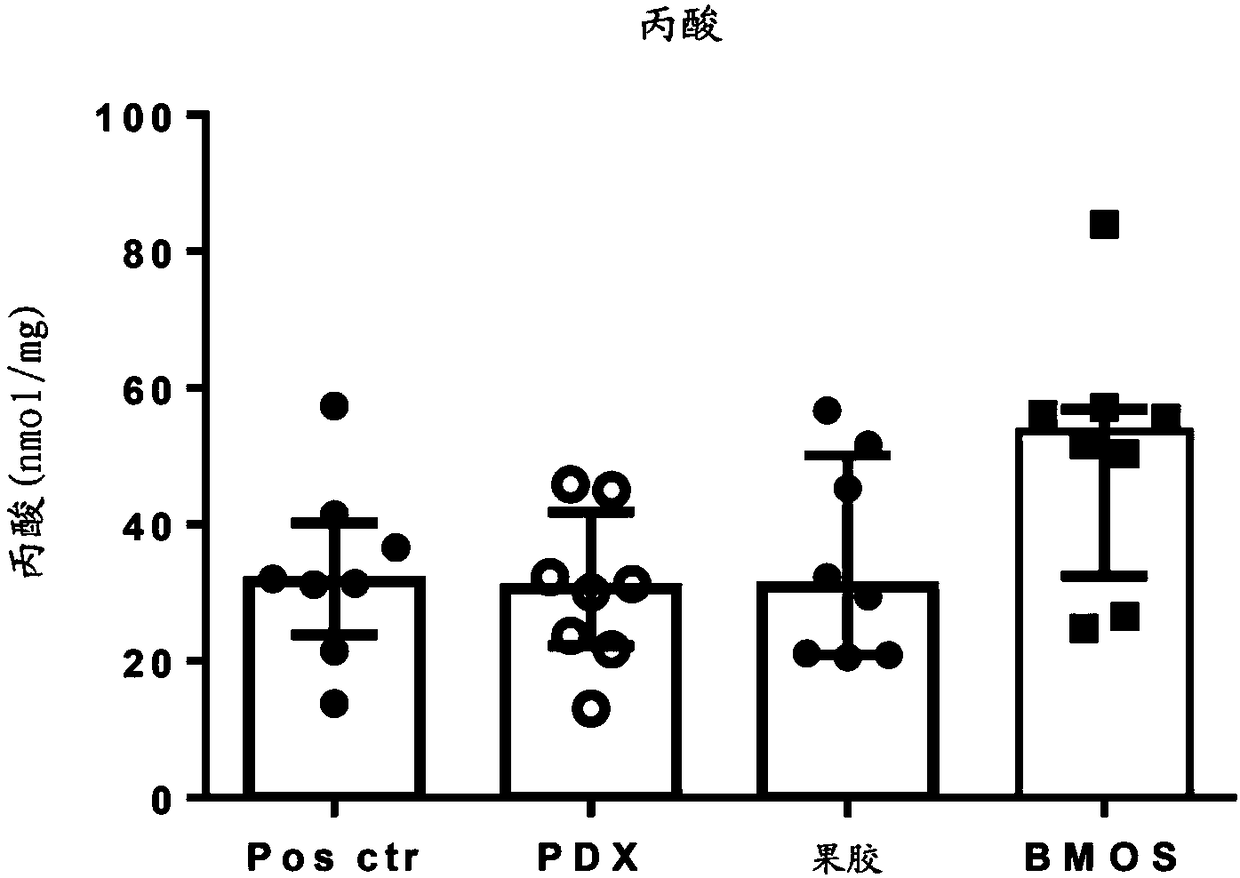
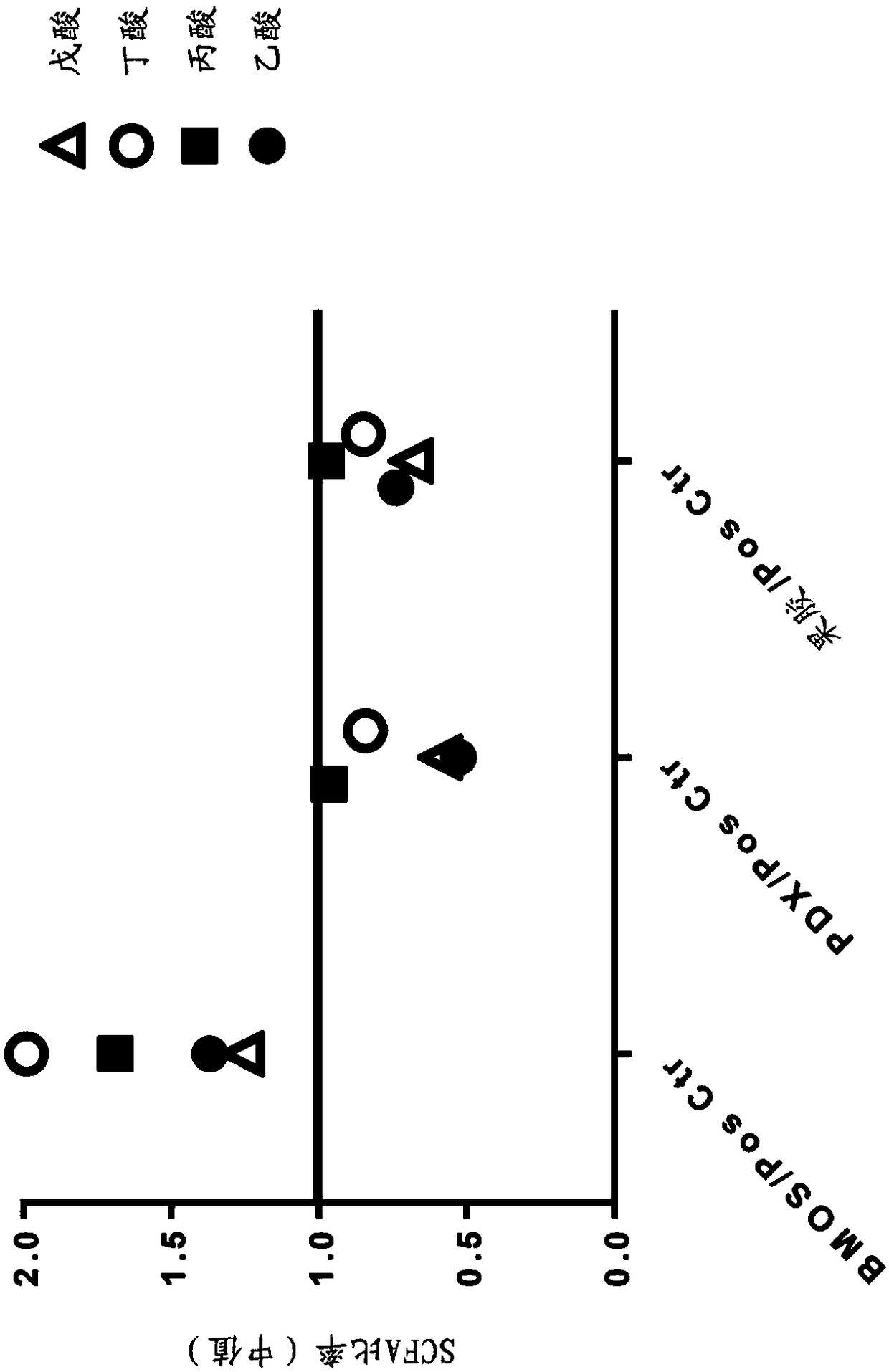
Compositions with specific oligosaccharides to prevent later in life obesity or related comorbidities, by increasing colonic scfa production and/or by increasing glp-1 secretion
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
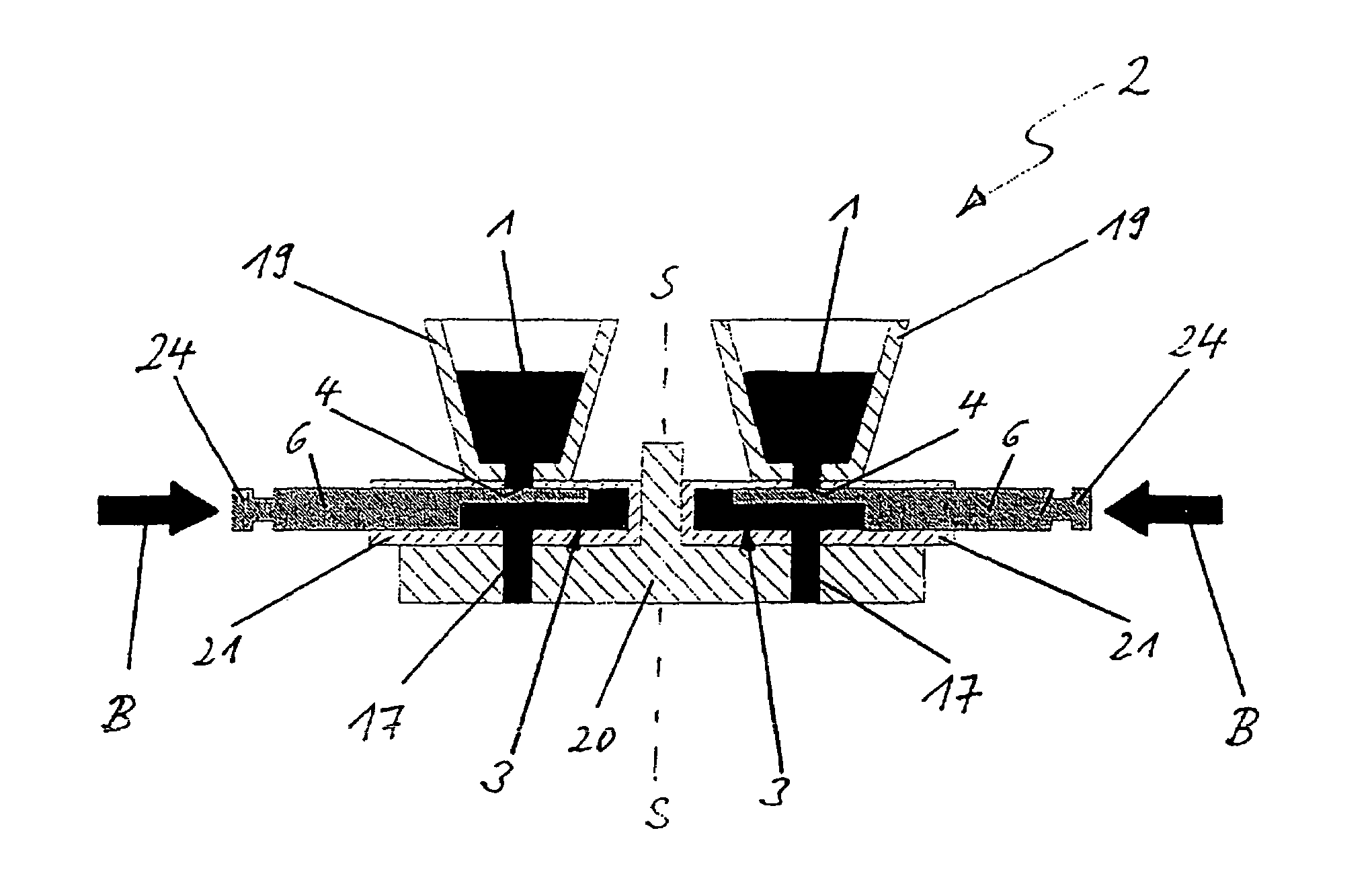
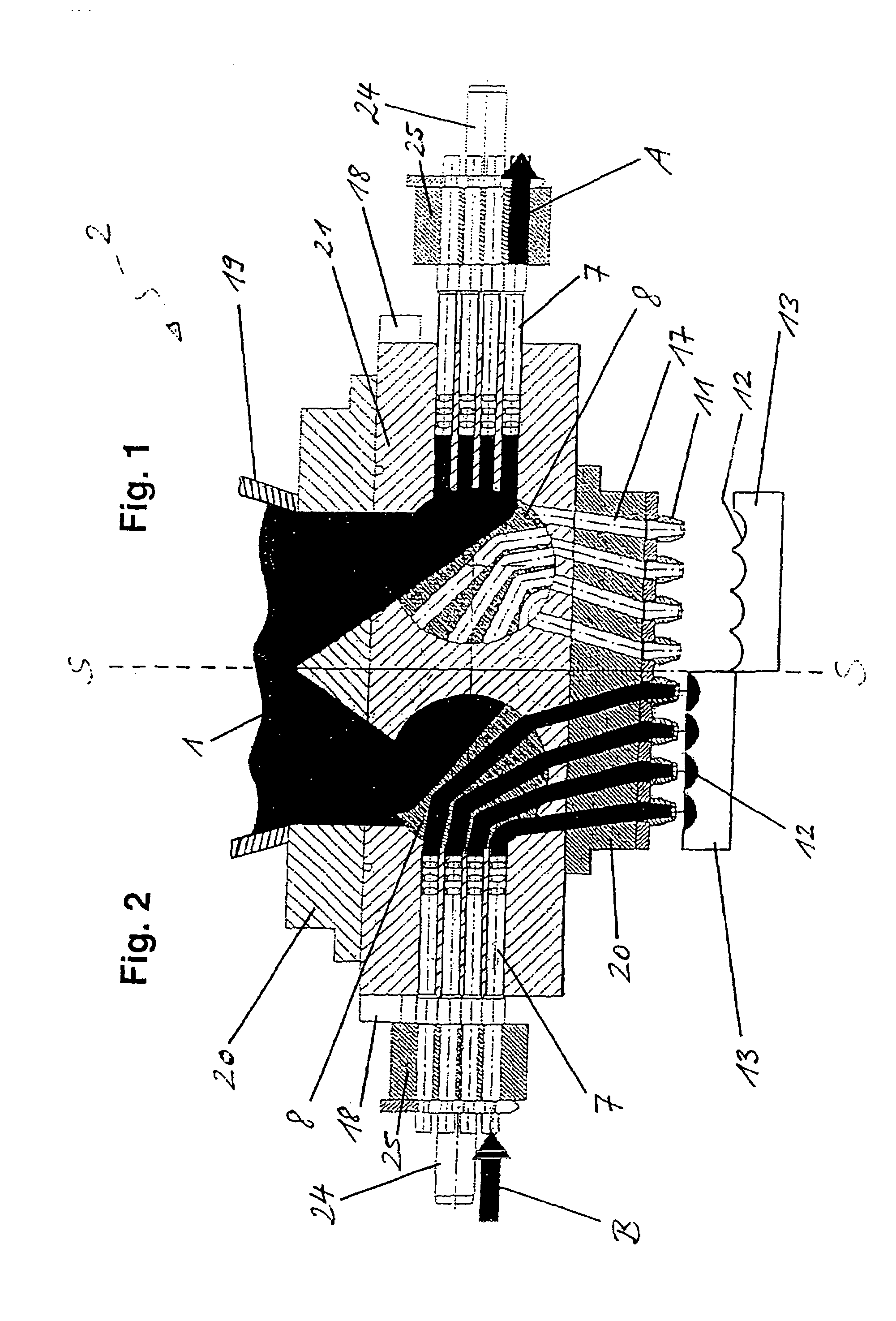
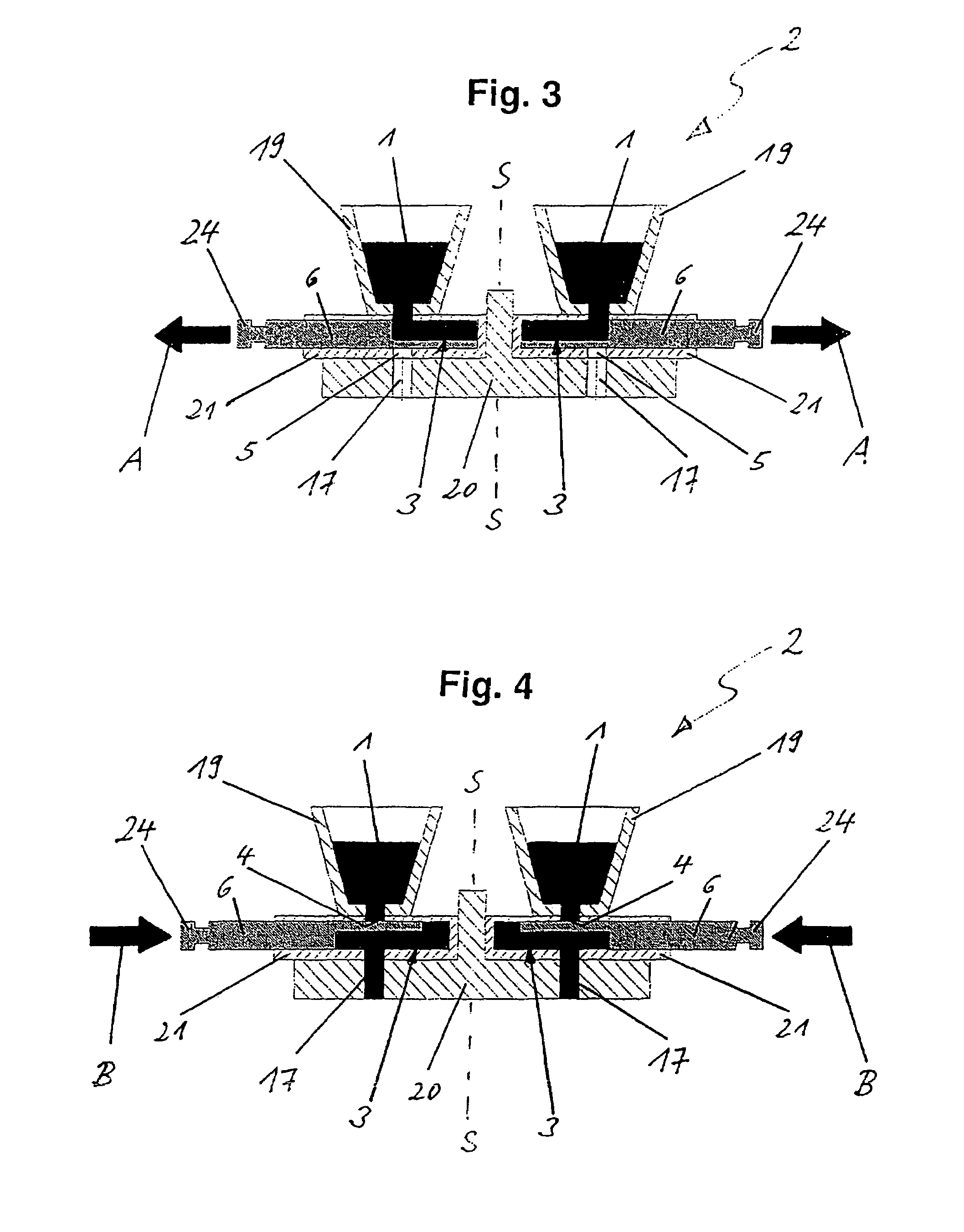
Device for processing an edible product
ActiveUS7618251B2Inadequate hygieneLow stiffnessFrozen sweetsConfectioneryProduct baseSpecific volume
The invention relates to a device for processing an edible product in the form a viscous to pasty mass (1), especially an edible product based on a fat mass, such as chocolate, or based on water, such as ice cream. Said device comprises a dosing unit (2) for the dosed delivery of a specific volume of the mass (1) to shaping units (13). The movement of the displacement element (6) determining the dosage volume is performed via servo drive (9) while an inlet (4) and an outlet (5) are closed and opened via servo drive or pneumatic drive, respectively. Preferably, the displacement element is embodied as a combined lifting / rotating plunger (6) which can perform a linear movement for a suctioning lift and a dosing lift while being able to perform a rotary movement for opening and closing the inlet (4) and the outlet (5), i.e. a valve function.
Owner:BUEHLER AG
Human mitochondrial dna polymorphisms, haplogroups, associations with physiological conditions, and genotyping arrays
InactiveUS20050123913A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotidePhosphorylation
This invention provides human mtDNA polymorphisms that are diagnostic of all the major human haplogroups and methods of diagnosing those haplogroups and selected subhaplogroups. This invention also provides methods for identifying evolutionarily significant mitochondrial DNA genes, nucleotide alleles, and amino acid alleles. Evolutionarily significant genes and alleles are identified using one or two populations of a single species. The process of identifying evolutionarily significant nucleotide alleles involves identifying evolutionarily significant genes and then evolutionarily significant nucleotide alleles in those genes, and identifying evolutionarily significant amino acid alleles involves identifying amino acids encoded by all nonsynonymous alleles. Synonymous codings of the nucleotide alleles encoding evolutionarily significant amino acid alleles of this invention are equivalent to the evolutionarily significant amino acid alleles disclosed herein and are included within the scope of this invention. Synonymous codings include alleles at neighboring nucleotide loci that are within the same codon. This invention also provides methods for associating haplogroups and evolutionarily significant nucleotide and amino acid alleles with predispositions to physiological conditions. Methods for diagnosing predisposition to LHON, and methods for diagnosing increased likelihood of developing blindness, centenaria, and increased longevity that are not dependent on the geographical location of the individual being diagnosed are provided herein. Diagnosis of an individual with a predisposition to an energy metabolism-related physiological condition is dependent on the geographic region of the individual. Physiological conditions diagnosable by the methods of this invention include healthy conditions and pathological conditions. Physiological conditions that are associated with haplogroups and with alleles provided by this invention include energetic imbalance, metabolic disease, abnormal energy metabolism, abnormal temperature regulation, abnormal oxidative phosphorylation, abnormal electron transport, obesity, amount of body fat, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
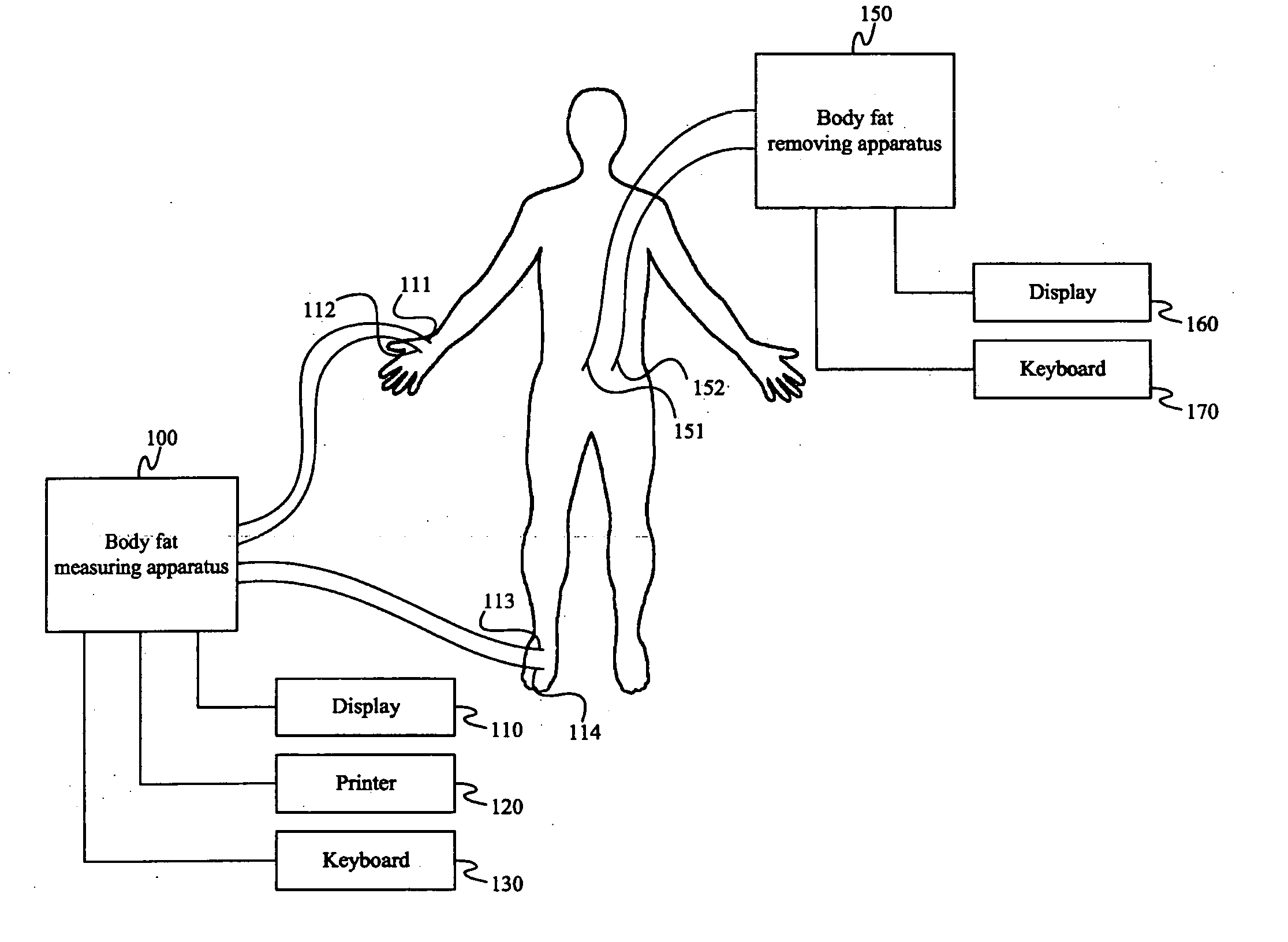
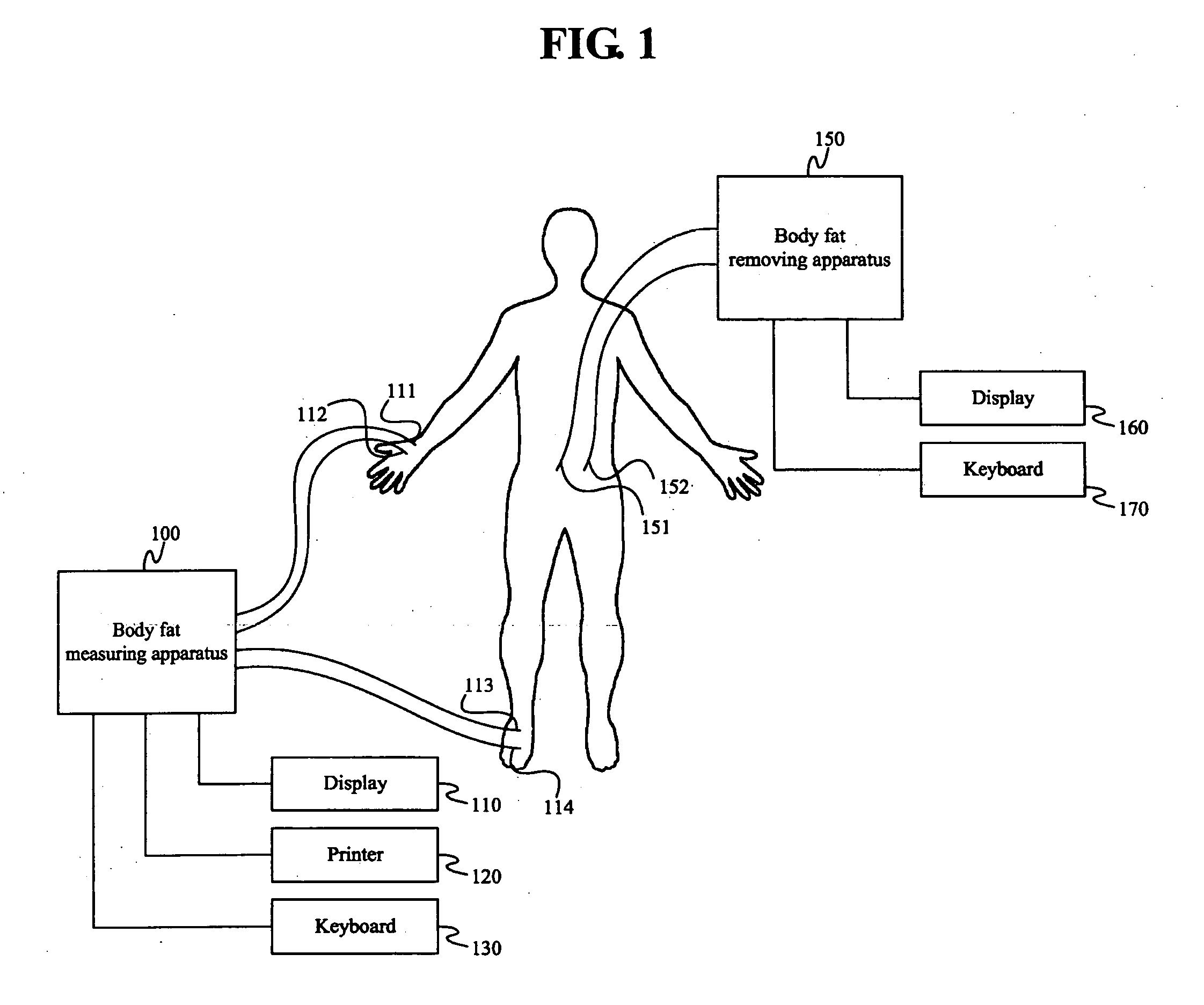
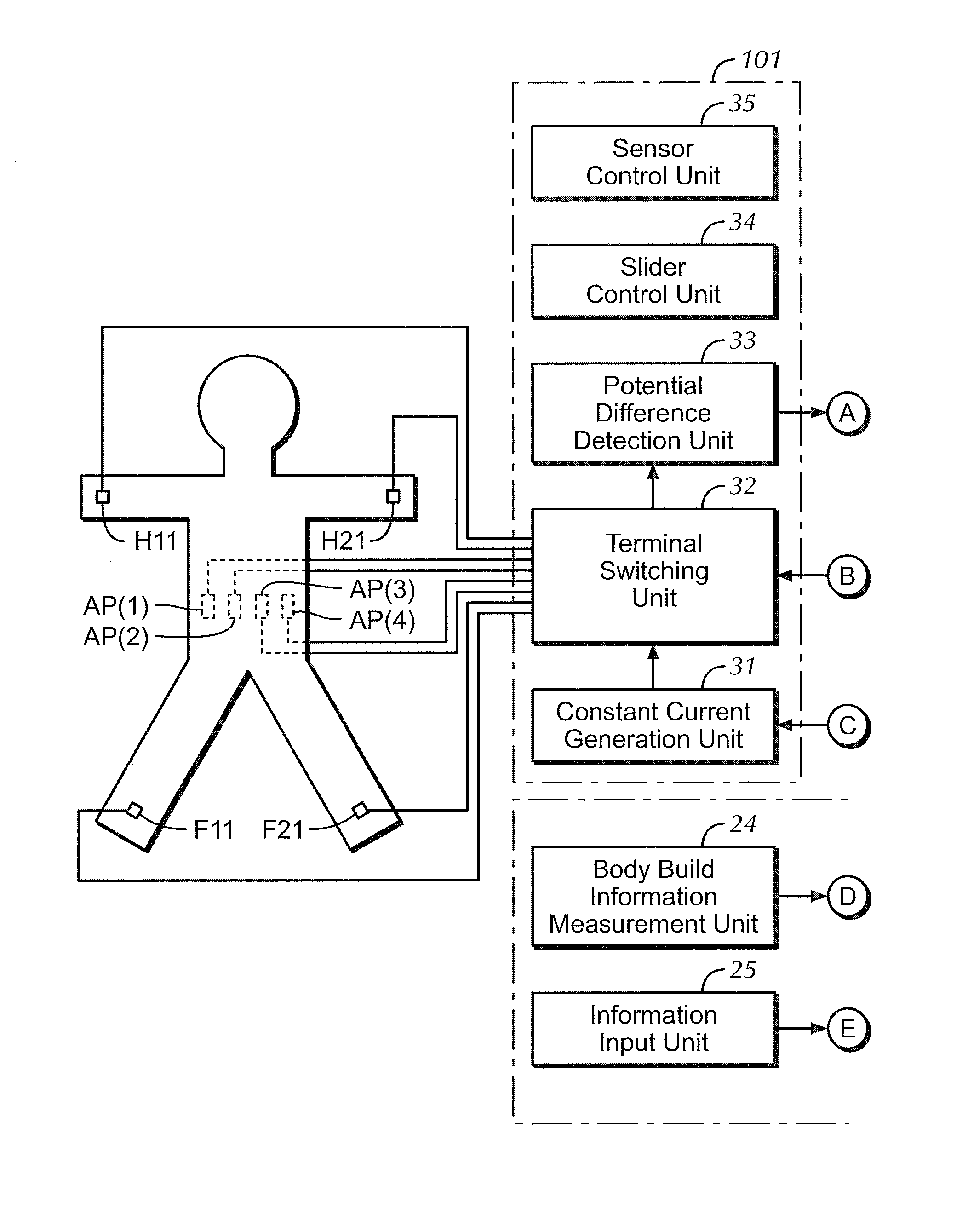
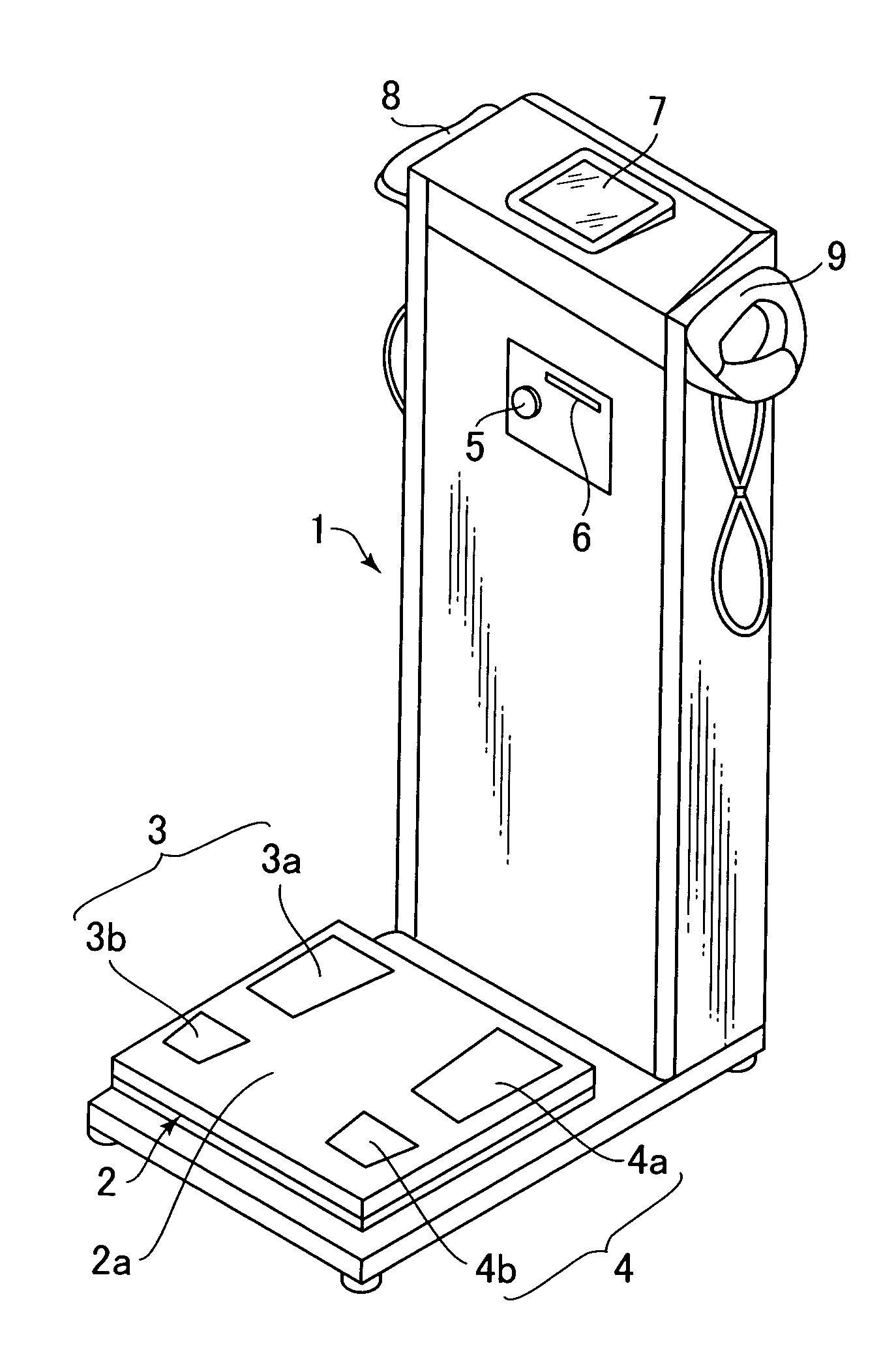
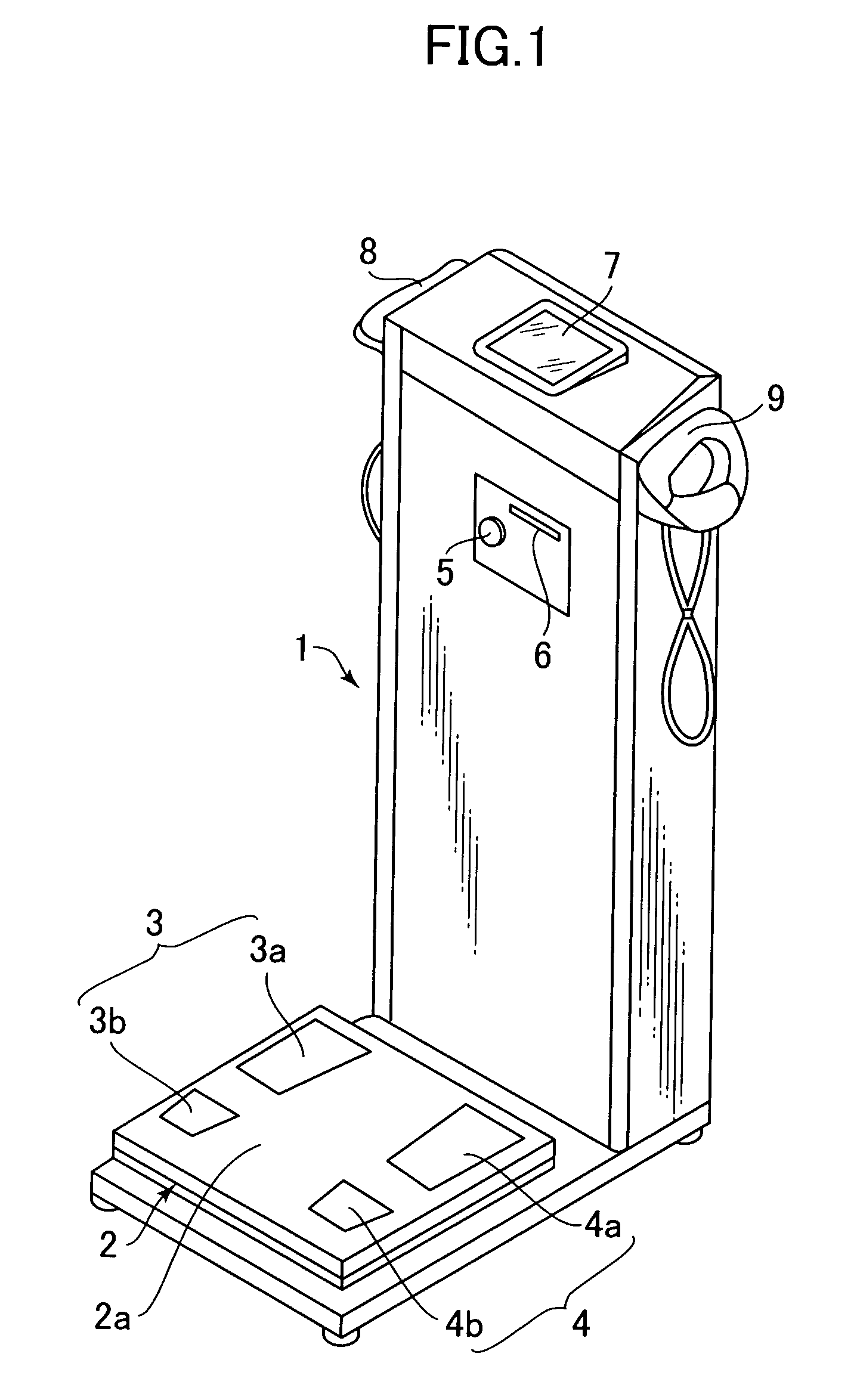
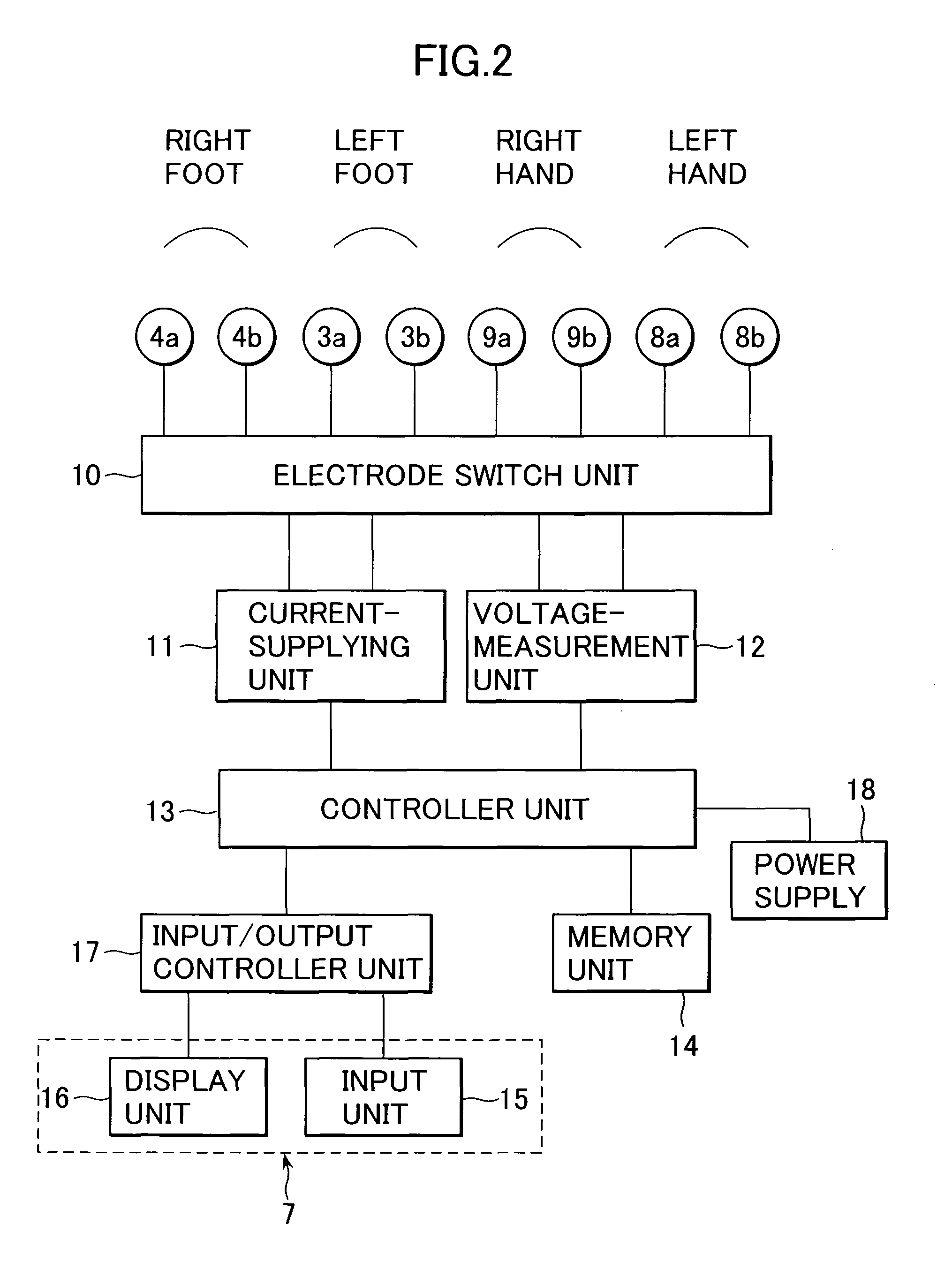
Body fat measurement device
A body fat measurement device includes hand electrodes that contact both hands, back area electrodes that contact the surface of a trunk area of the back, foot electrodes that contact both feet, a trunk area width detection unit for measuring the width and depth of the trunk area, a body impedance measurement unit that measures the body impedance of a body using the multiple electrodes and a body fat mass calculation unit that calculates a body fat mass based on the body impedance and the width and depth of the trunk area. The back area electrodes that make contact with the surface of the back of the trunk area are provided in a fitting unit in an exposed state, as well as the trunk area width detection unit. Accordingly, a body fat measurement device can measure a body fat mass easily and accurately in a household or the like.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Fat-mass film-coated slow-release fertilizer
The invention discloses a fat-mass film-coated slow-release fertilizer comprising a fertilizer core and a fertilizer core outer capsule. The capsule is an amine resin-montmorillonite composite film or a composite layer of the amine resin-montmorillonite composite film and a degradable polymer film and can be compounded with a sulfur film and / or a high-resistance permeable organic film layer with preferable thickness not more than 20um; high-resistance permeable organic matter can be also mixed in the amine resin-montmorillonite composite film; the mass fraction of the montmorillonite in the high-resistance permeable organic film layer is preferably not more than 50% and optimally 0.5-30%; the total thickness of the capsule is preferably not less than 30um; and the thickness of the sulfur film is preferably 0-50um. The capsule body of the fat-mass film-coated slow-release fertilizer is (basically) harmless to the environment, is a fertilizer constituent and has low cost and long release period.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for judgment of physical constitution and physical strength for person under test
ActiveUS7125386B2Excessive body weightSmall volumePerson identificationSensorsFat massPhysical strength
A method and an apparatus for judgment of physical constitution and physical strength for a person under test are described. The apparatus comprises a first input unit, a second input unit, and an arithmetic unit. According to the present invention the first input unit enters fat mass in a trunk of the person under test. The second input unit enters fat mass in lower limbs of the person under test. The arithmetic unit calculates Proportion Age based on the data entered from said first and second input units.
Owner:TANITA CORP
Methods to identify factors associated with muscle growth and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110191871A1Easy to implementOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCell based assaysAngiogenesis growth factor
The present invention relates to methods to identify factors associated with muscle growth, angiogenesis, obesity, insulin sensitivity body weight, fat mass, muscle mass and cardiovascular function. In particular, the methods of the present invention relates to assays to identify such factors using a transgenic animal model and / or a cell-based assay.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Use of ghrelin splice variant for treating cachexia and/or anorexia and/or anorexia-cachexia and/or malnutrition and/or lipodystrophy and/or muscle wasting and/or appetite-stimulation
The present disclosure relates, in one aspect, to use of ghrelin splice variant or an analogue thereof for the preparation of a medicament for one or more of: treatment and / or prevention of loss of body weight and body fat, prophylaxis or treatment of cachexia, stimulation of appetite, stimulation of food intake, stimulation of weight gain, or increasing body fat mass, or increasing body lean mass. Another aspect relates to the use of a ghrelin splice variant-like compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of cancer cachexia in an individual in need of such treatment. Another aspect relates to the use of a ghrelin splice variant-like compound for the preparation of a medicament for prophylaxis or treatment of cachexia in an individual by administering a subcutaneous dosage of said medicament to the individual. A further aspect relates to the use of a ghrelin splice variant-like compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for the preparation of a medicament for stimulation of appetite in an individual by administering a subcutaneous dosage of said medicament to the individual. A further aspect relates to a number of new ghrelin splice variant-like compounds and uses thereof, as well as to pharmaceutical compositions and medical packaging comprising the new ghrelin splice variant-like compounds.
Owner:MINTZ LIAT
Rhein specific group modified organic compound, aryl metal complex, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108530343AImprove cancer resistanceHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSimple Organic CompoundsAryl
The invention discloses a rhein specific group modified organic compound, an aryl metal complex, a preparation method and application thereof. Compared with rhein molecules, the organic compound and metal complex have better antitumor and antibacterial activity, and the metal complex also can induce nucleic acid configuration transformation. Specifically, the aryl metal dimer and the above-mentioned metal complex both have good FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) inhibitory activity, and are good FTO inhibitors. The invention also discloses a synthesis method of the organic compound and themetal complex thereof, and the method has the characteristics of simple technological process, easy operation, and high yield. Finally, the invention discloses application of the rhein group-containing organic compound, the metal complex and aromatic metal dimer thereof in preparation of FTO inhibitor drugs, FTO inhibitor drug components, weight-reducing drugs, weight-reducing drug components, anticancer drugs, anticancer drug components, antibacterial drugs and antibacterial drug components.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical Composition for Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes or Obesity Comprising a Compound that Inhibits Activity of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV, and other Antidiabetic or Antiobesity Agents as Active Ingredients
ActiveUS20110201624A1Enhance glucose tolerance effectInhibition of blood glucose levelPowder deliveryHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidaseGlucose polymers
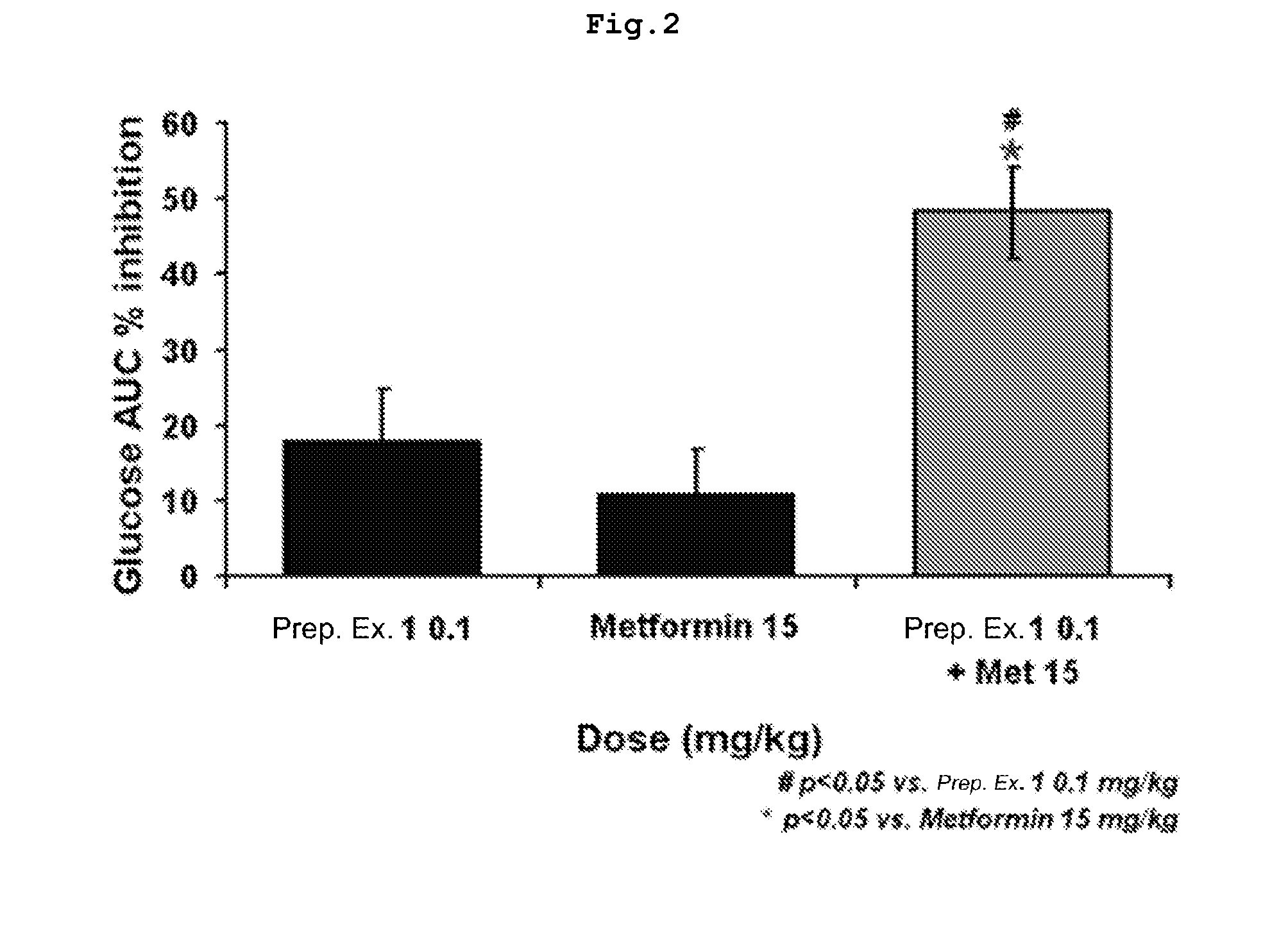
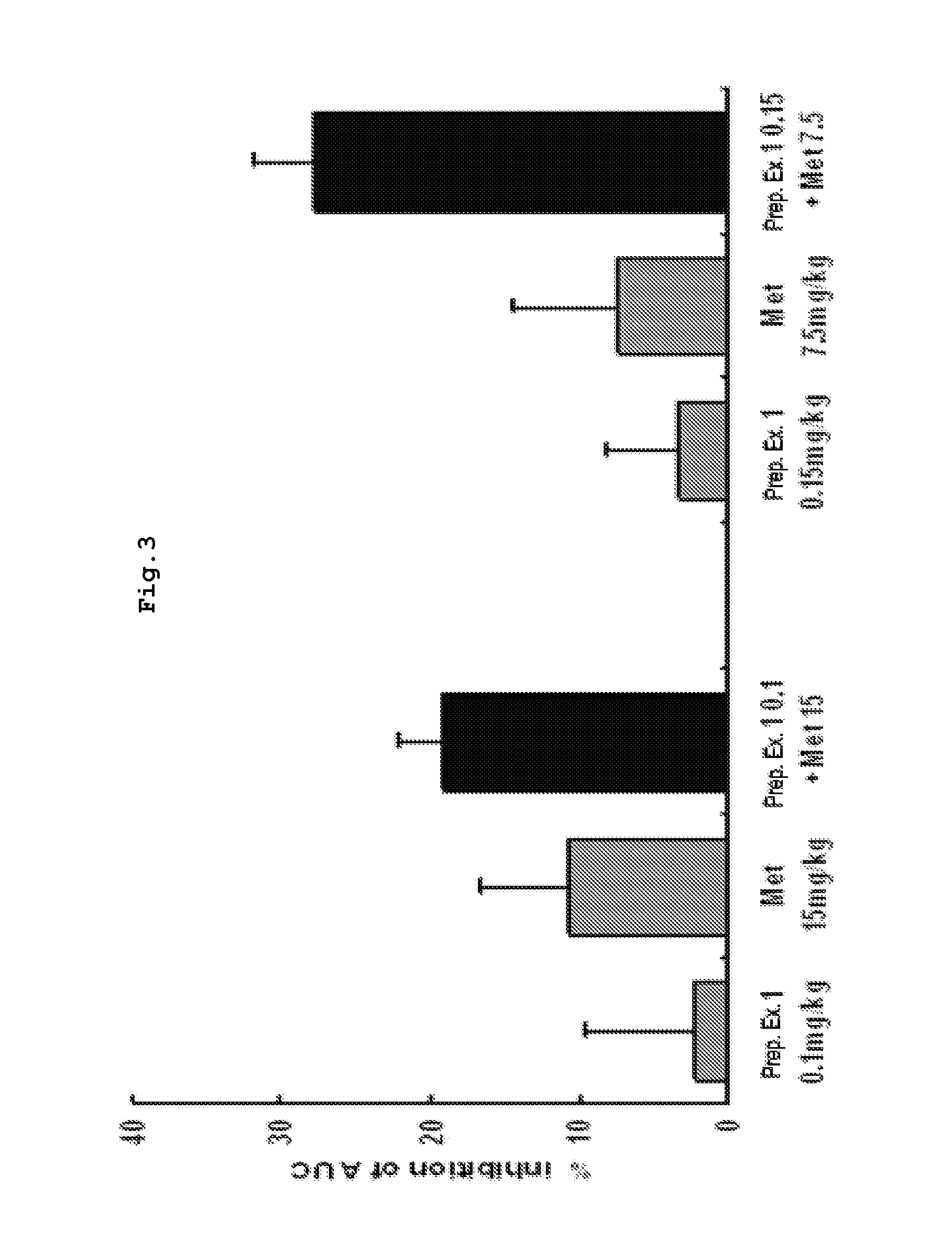
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention and treatment of diabetes or obesity comprising as active ingredients a compound which inhibits the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a hydrate thereof, or a solvate thereof, and one or more other antidiabetic or antiobesity agents. The pharmaceutical composition exhibits excellent glucose tolerance and may be useful in the prevention and treatment of diabetes, obesity, and the like by effectively inhibiting blood glucose levels and reducing fat mass.
Owner:DONG A PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com