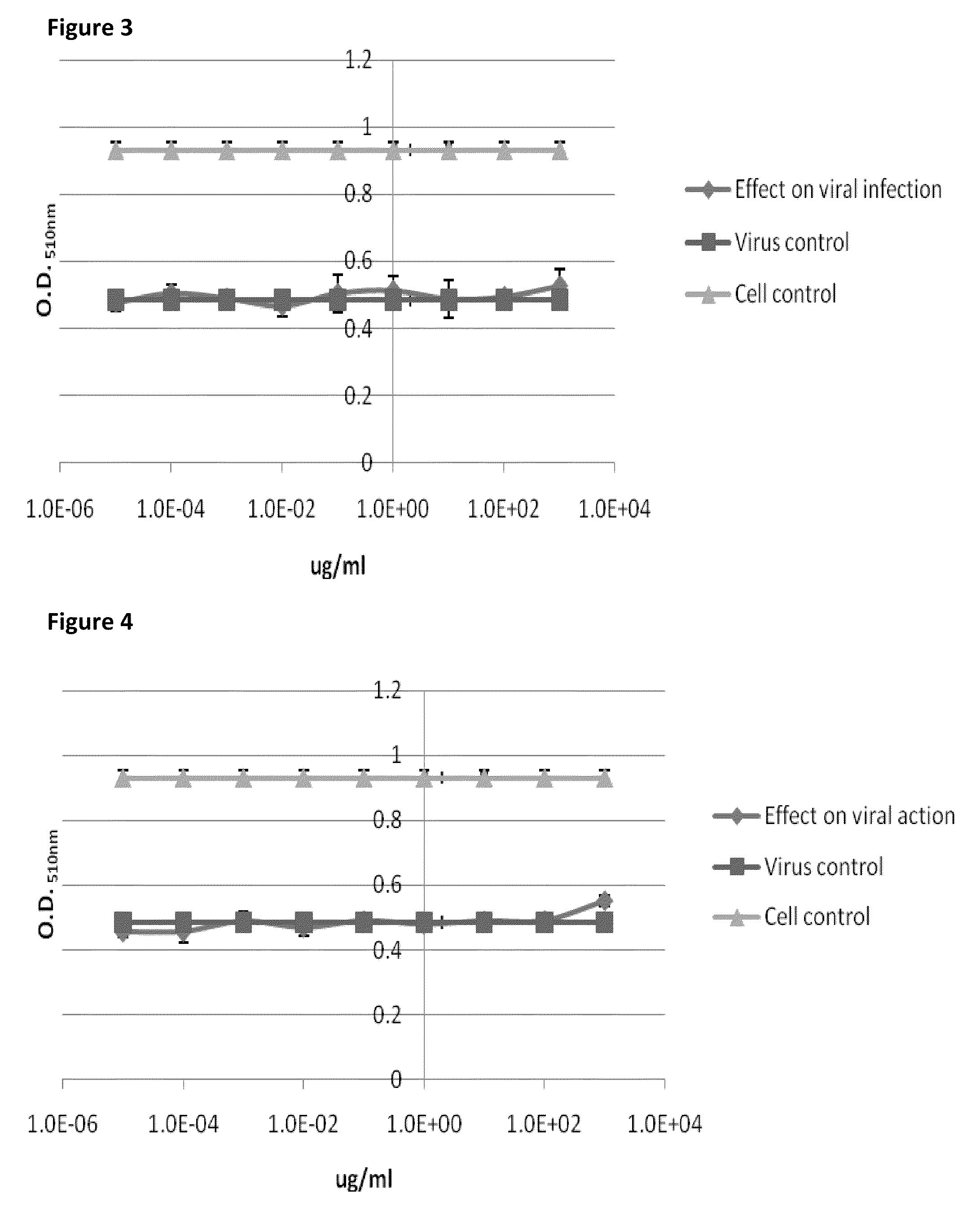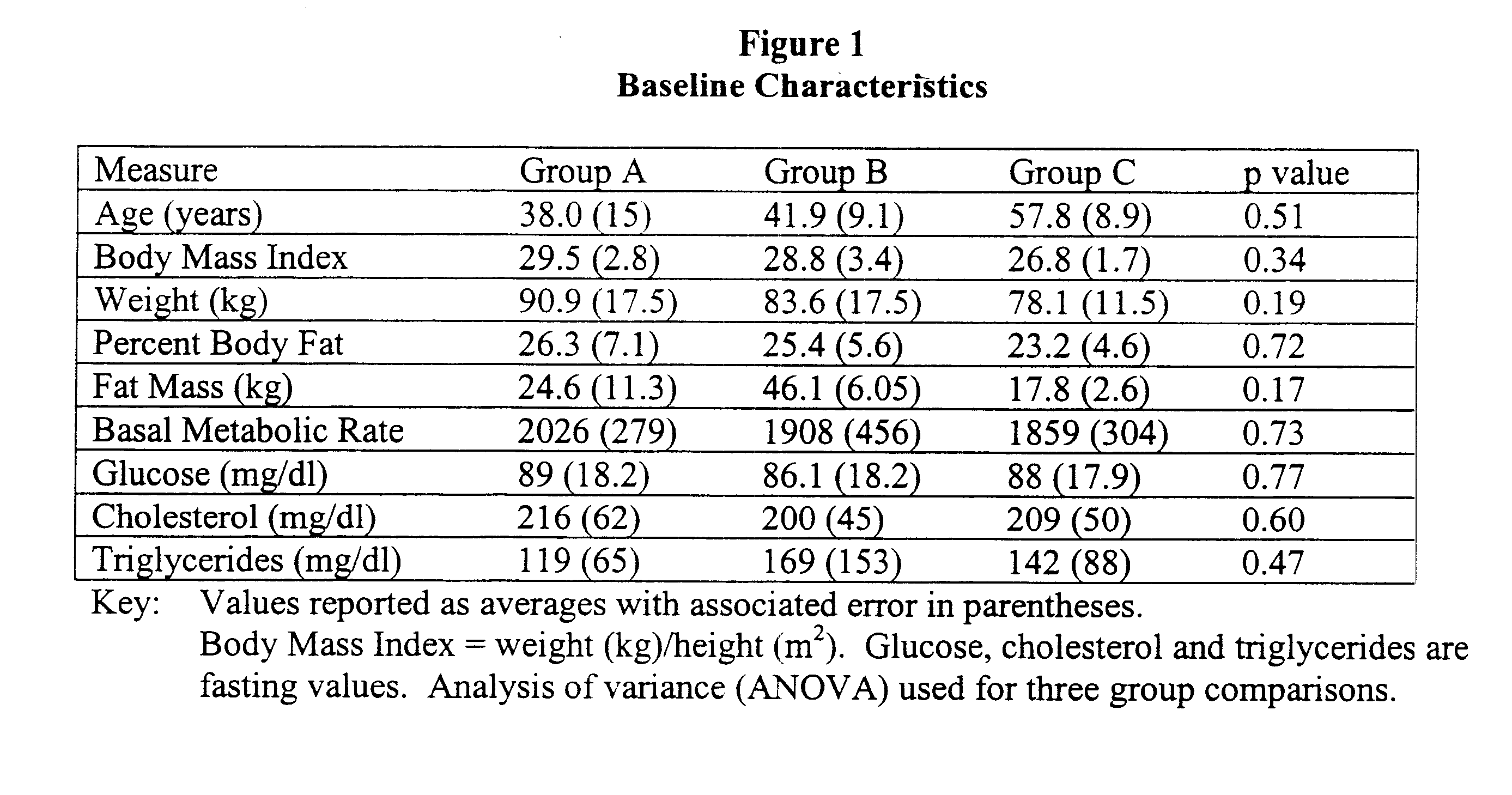Patents
Literature
95 results about "LBM - Lean body mass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Instead, the body fat percentage, which is the complement, is computed, and is typically 10–40%. The lean body mass (LBM) has been described as an index superior to total body weight for prescribing proper levels of medications and for assessing metabolic disorders, as body fat is less relevant for metabolism.
Methods for affecting body composition
InactiveUS20050197287A1Preserving lean body massReduce lossesHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhysiologyLBM - Lean body mass
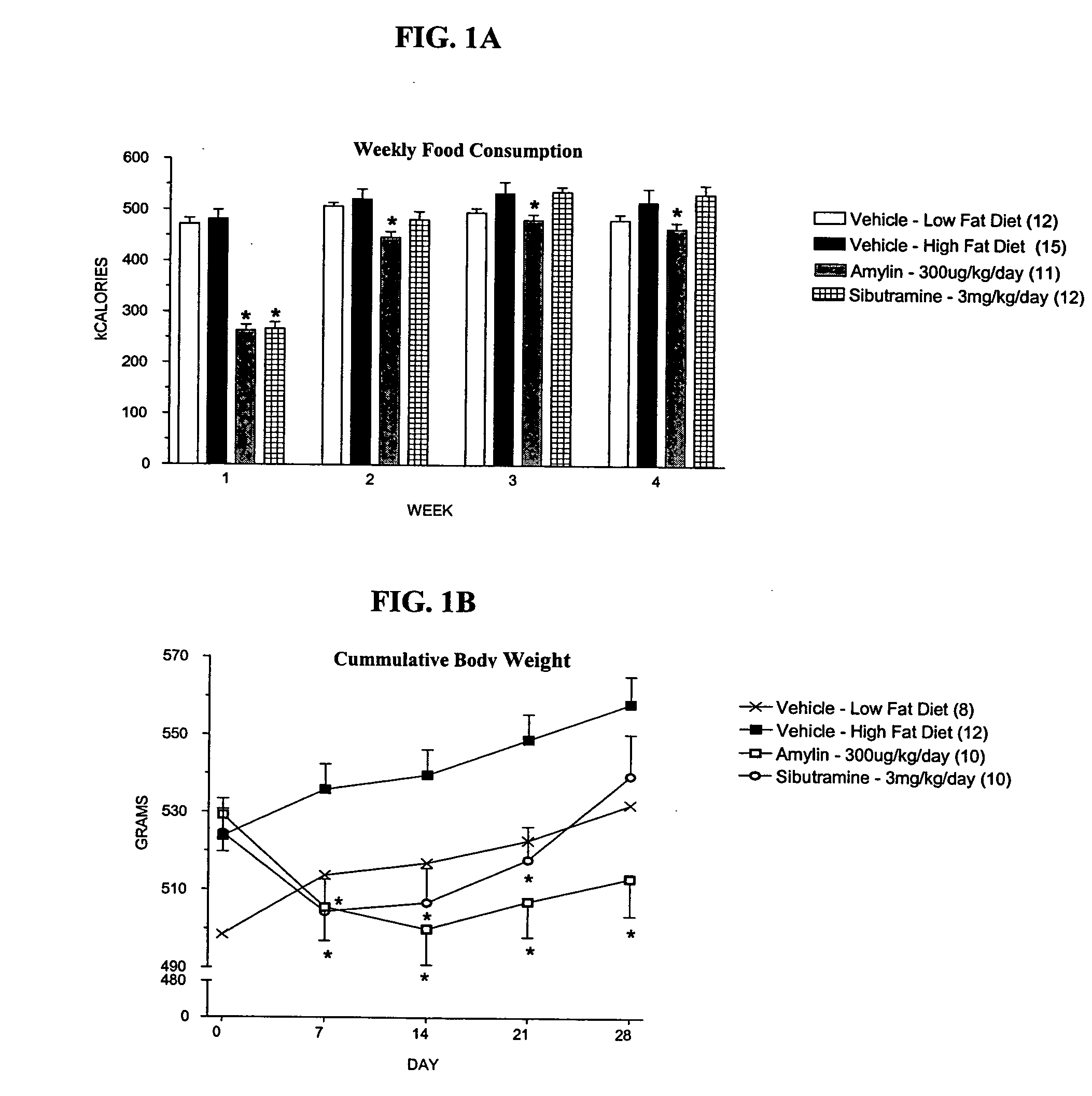
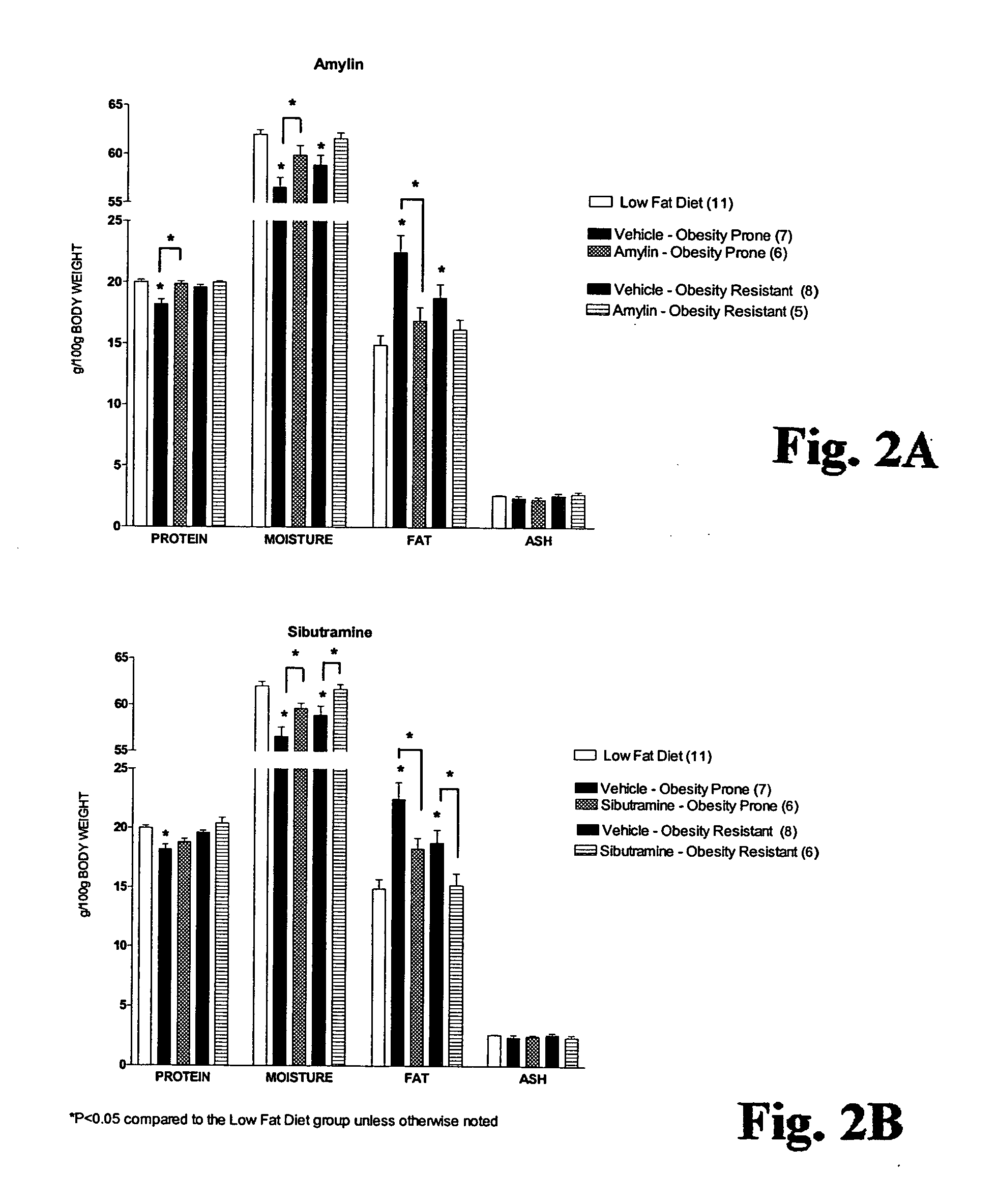
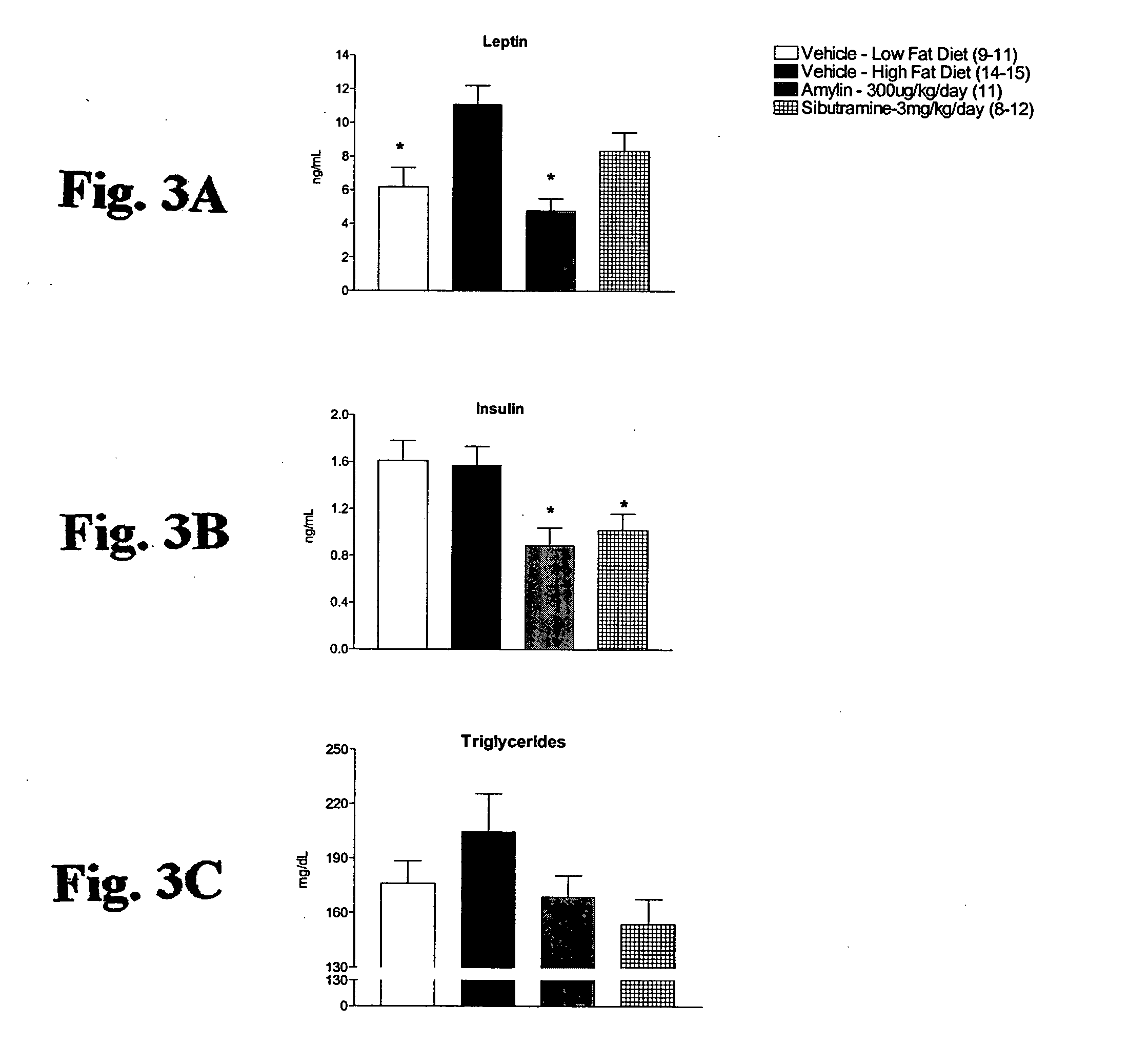
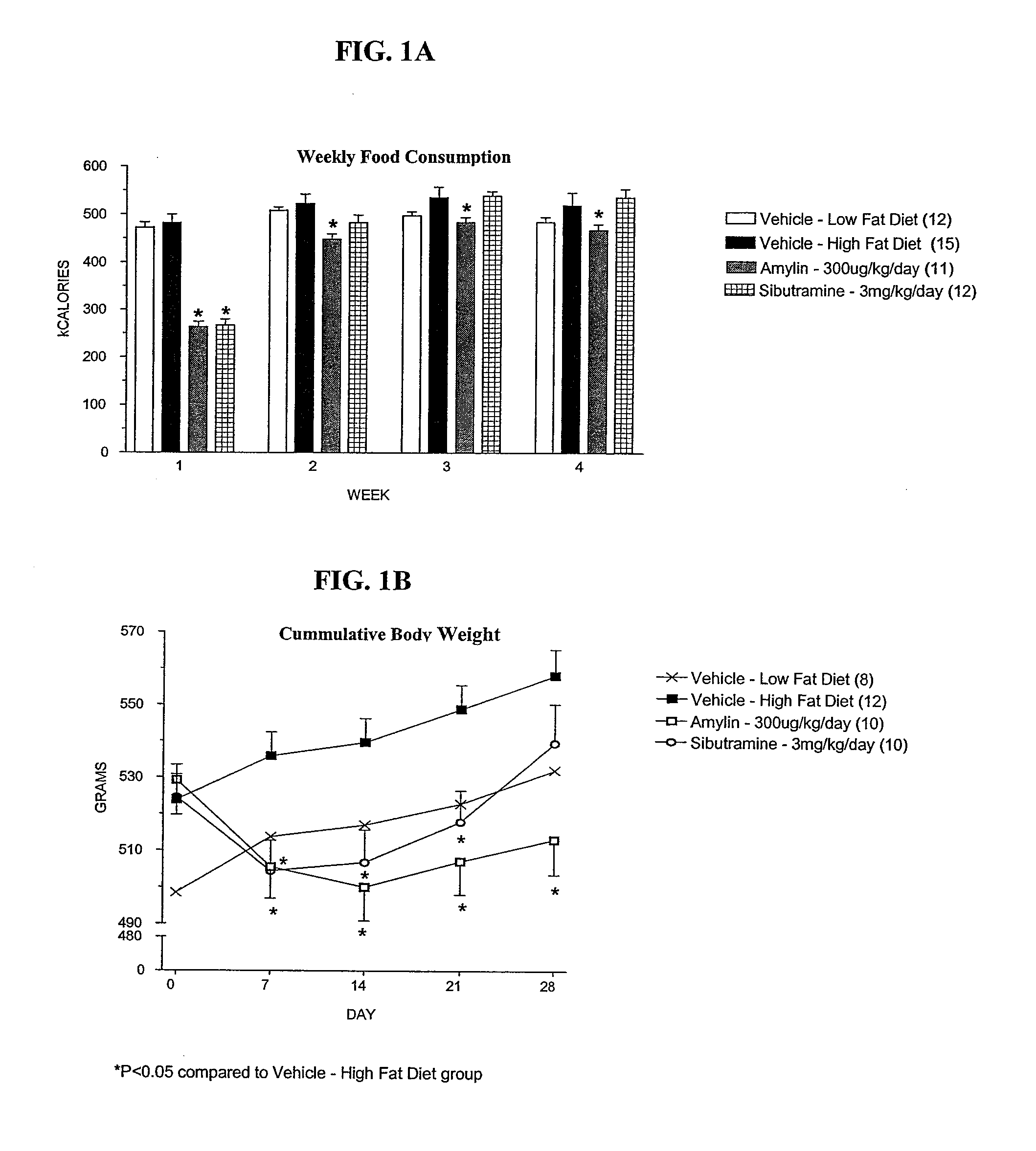
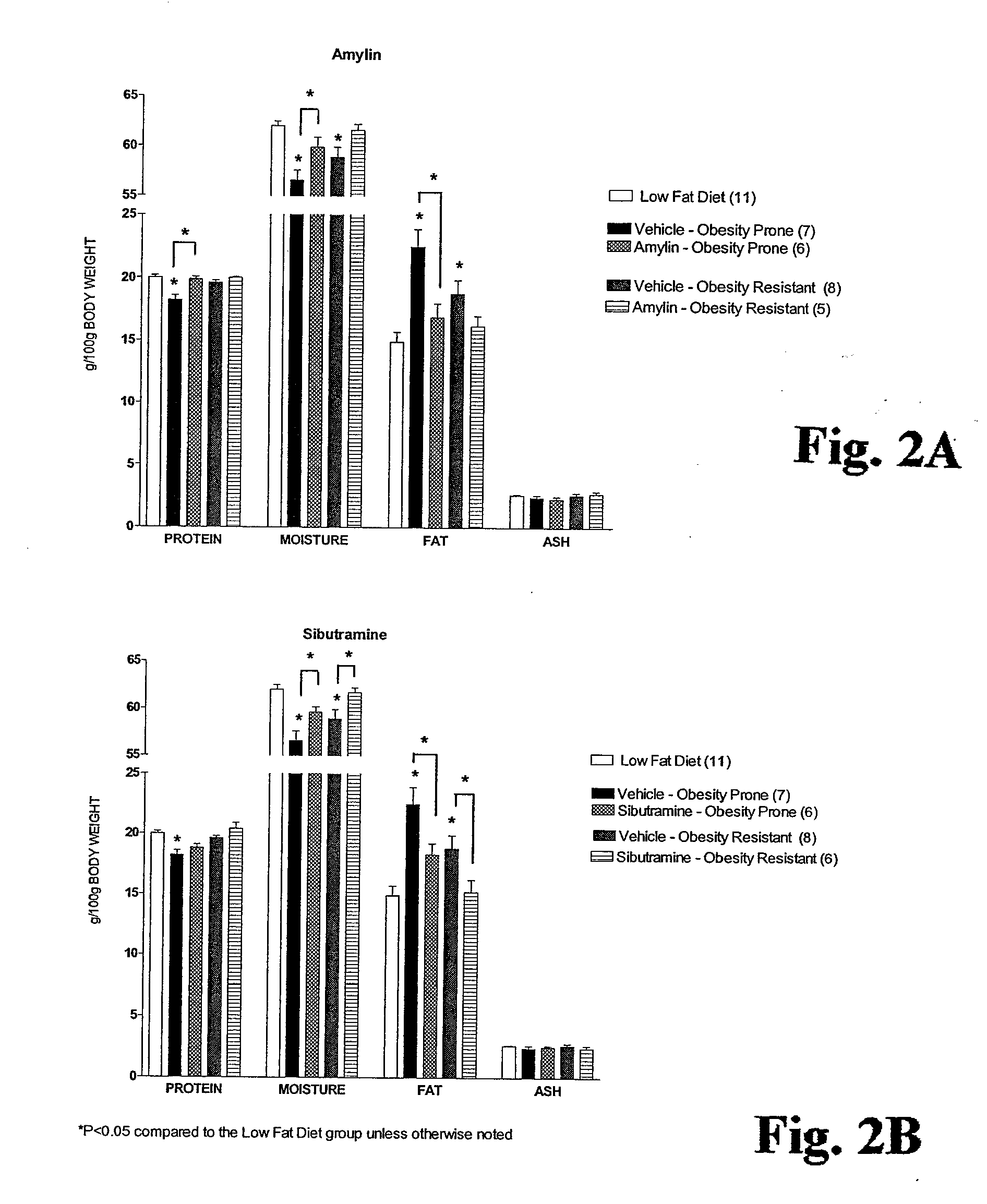
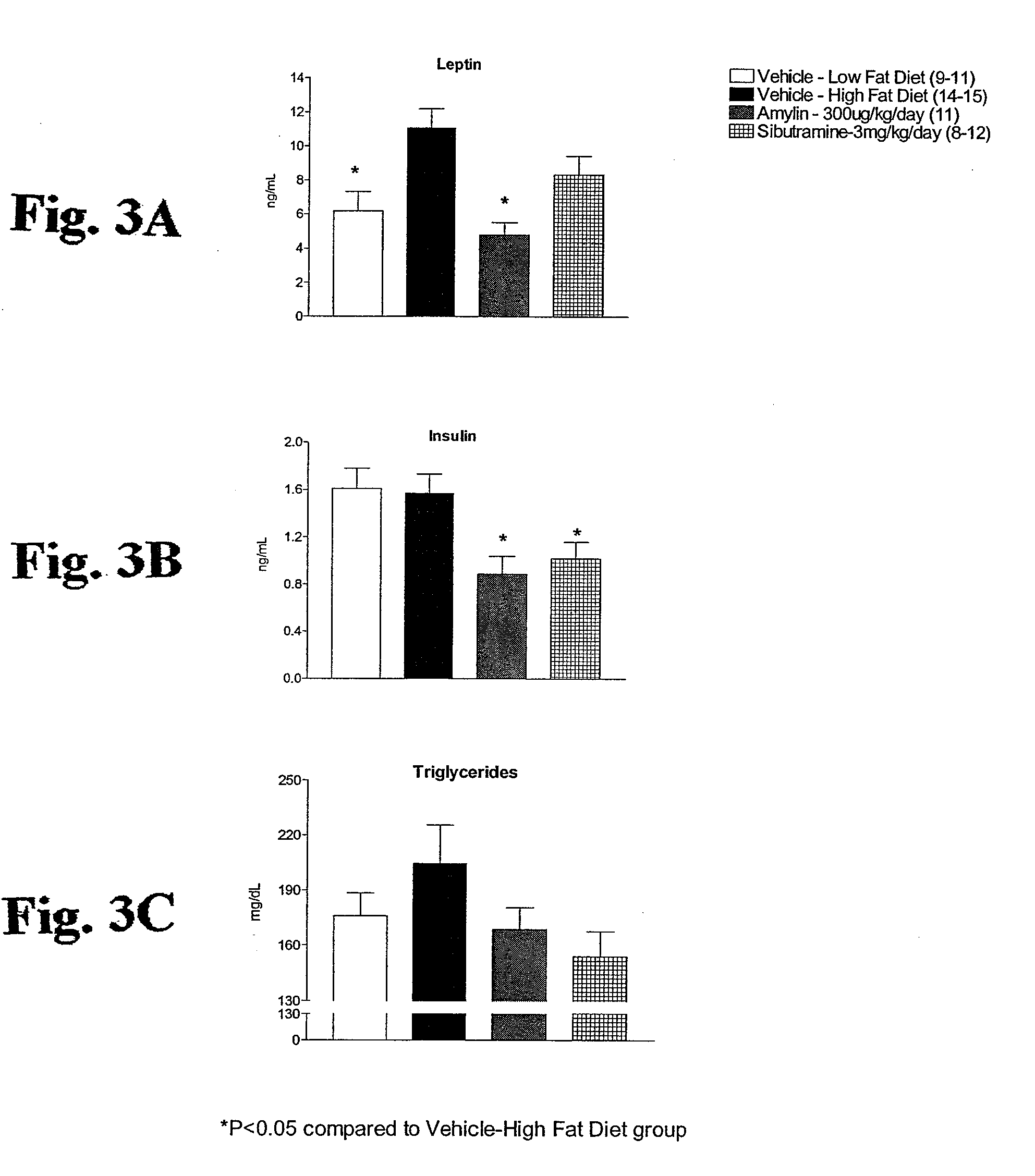
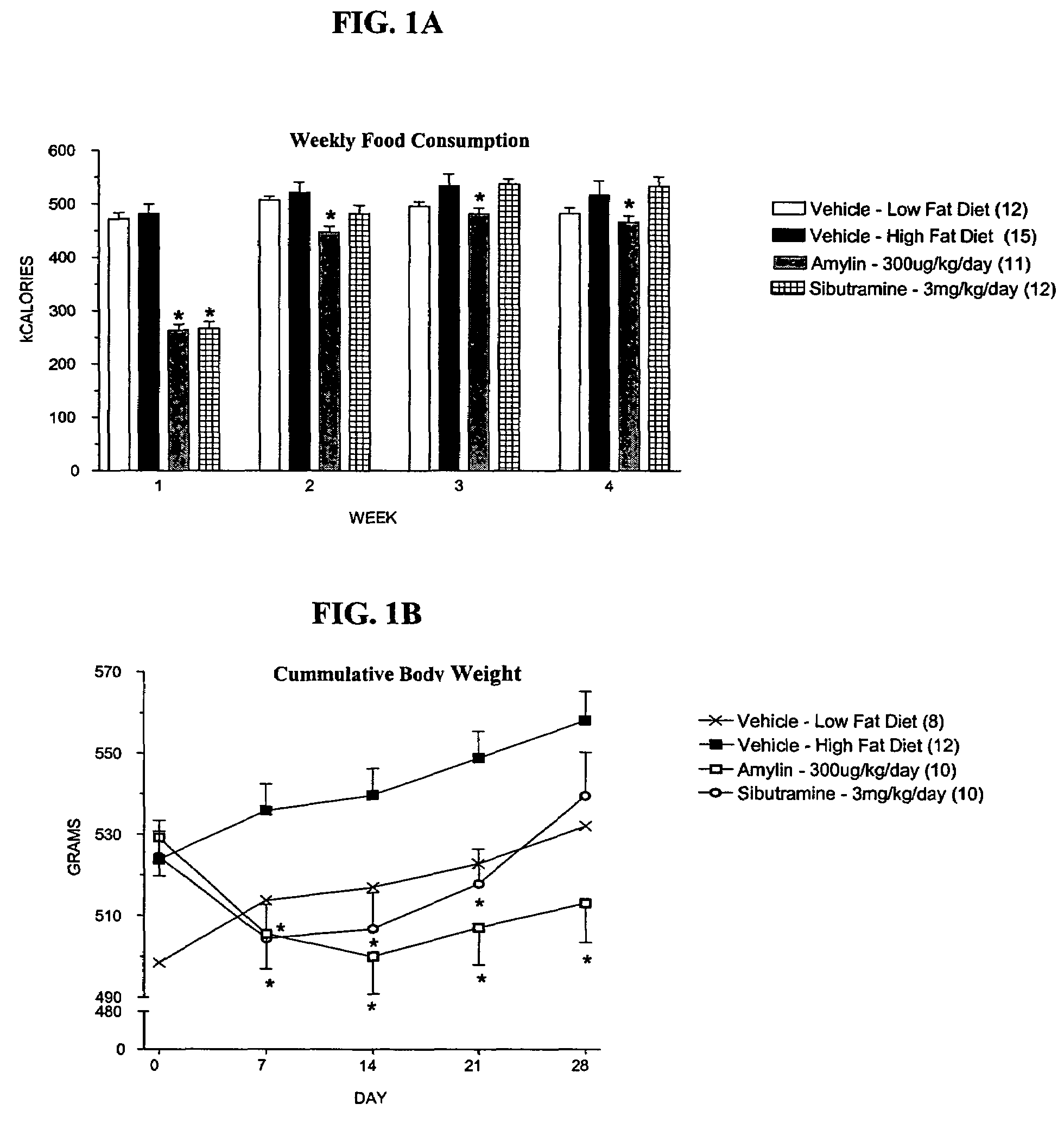
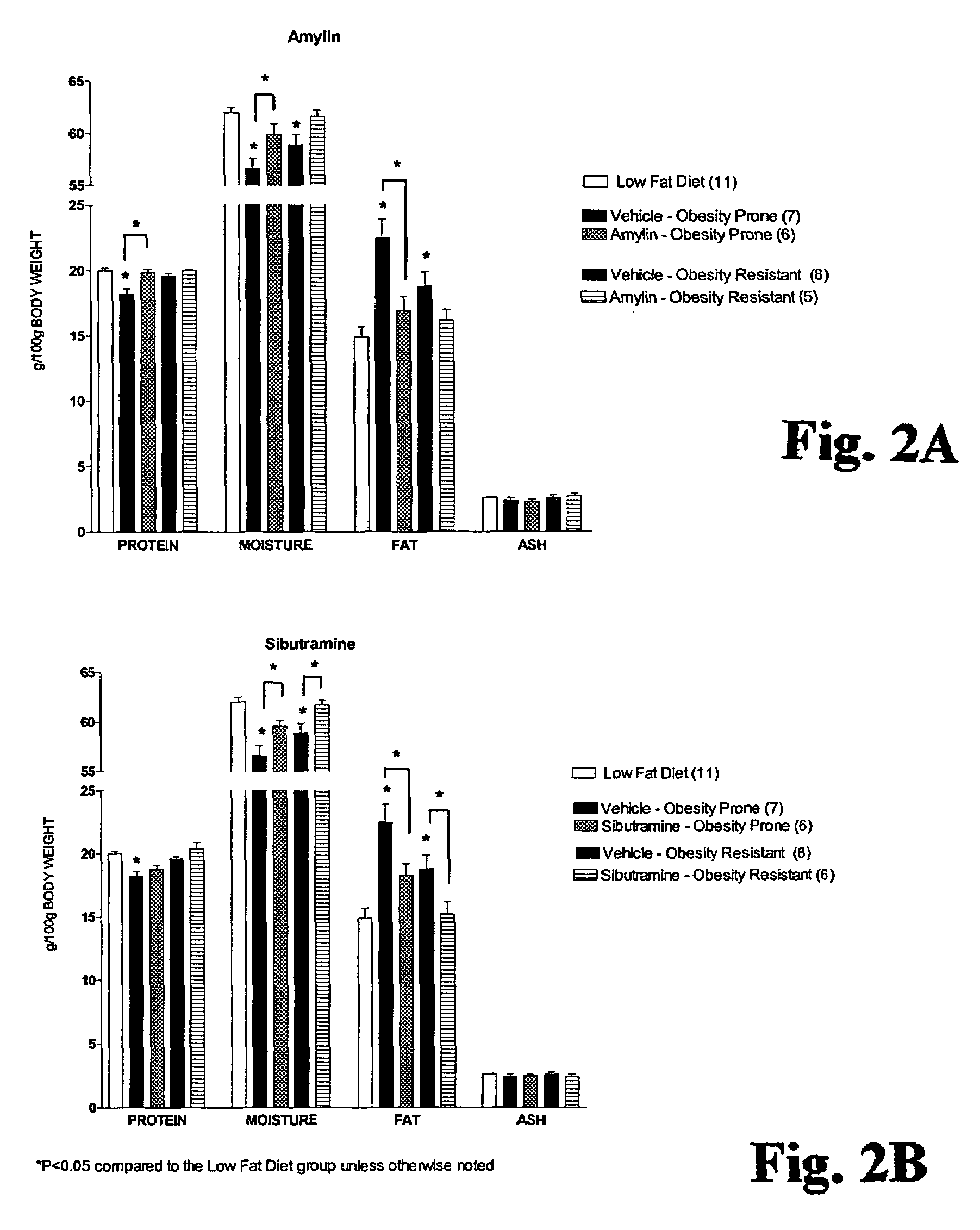
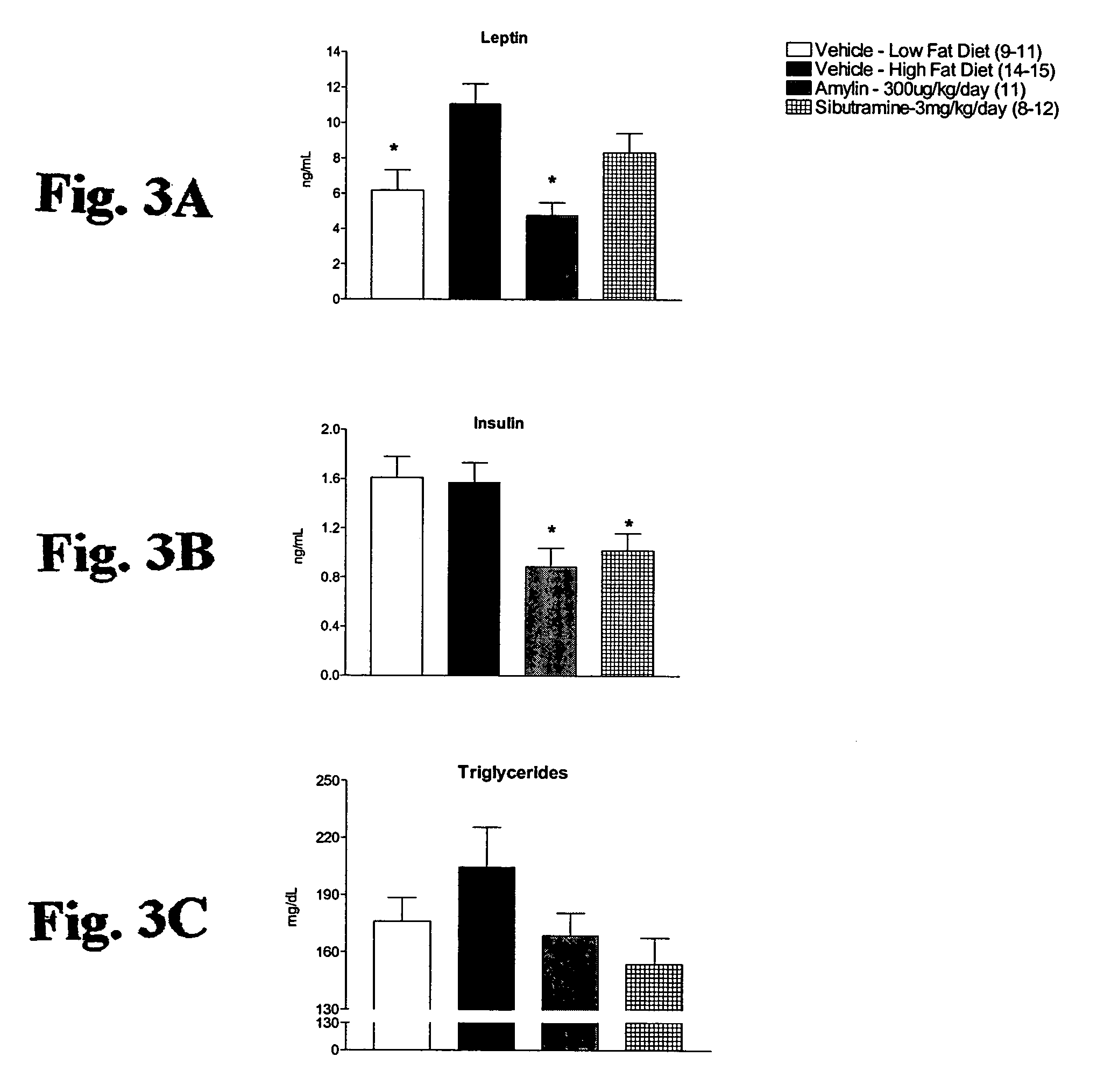
Methods for affecting body composition include the use of amylin or amylin agonist(s). Total body weight may be reduced, maintained or even increased; however, the body fat is reduced or body fat gain is prevented, while lean body mass is maintained or increased.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Compositions and methods for producing elevated and sustained ketosis
ActiveUS9138420B2Rapid and sustained elevationImprove the level ofHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSignificant elevationKetogenic diet
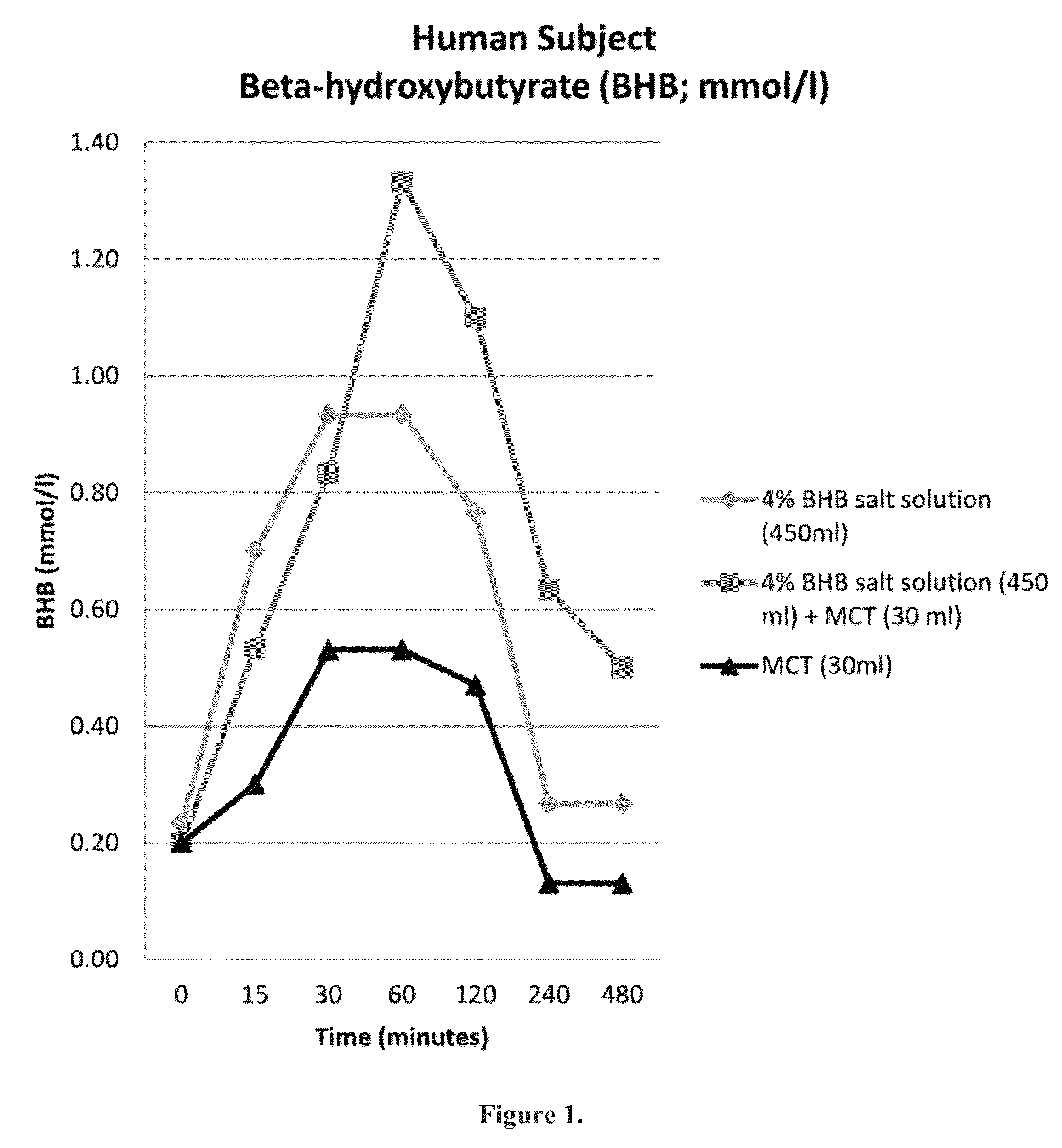
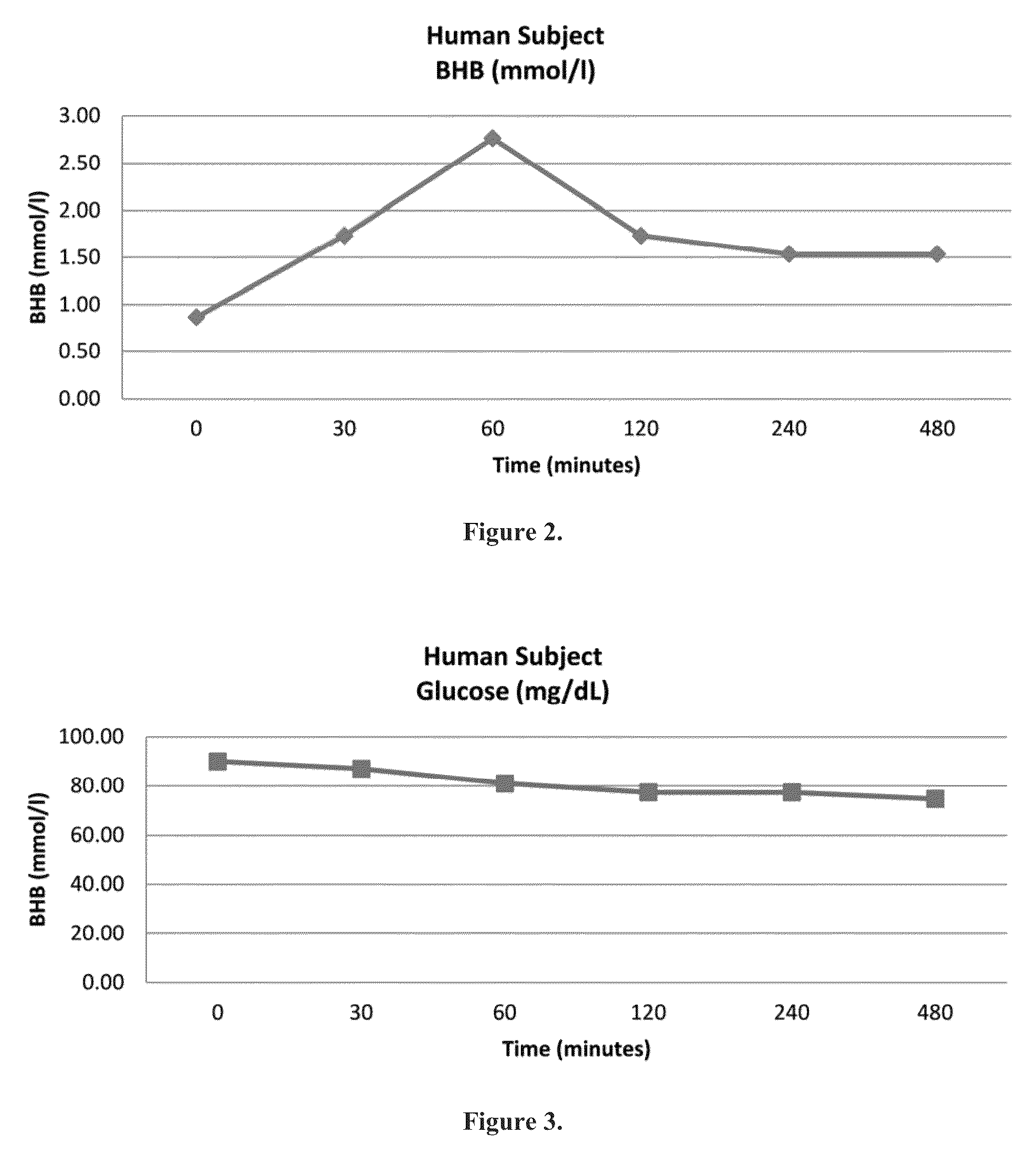
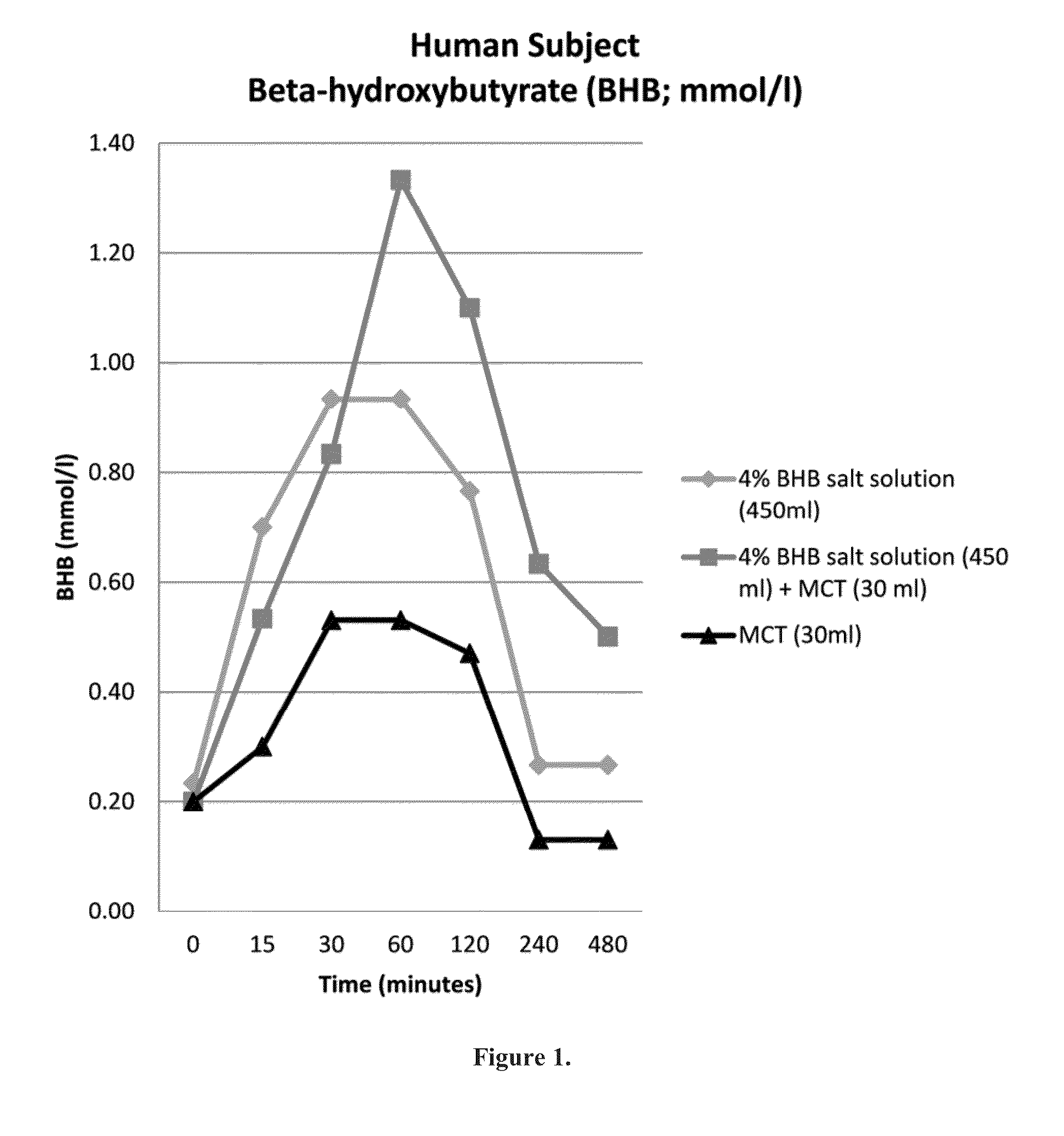
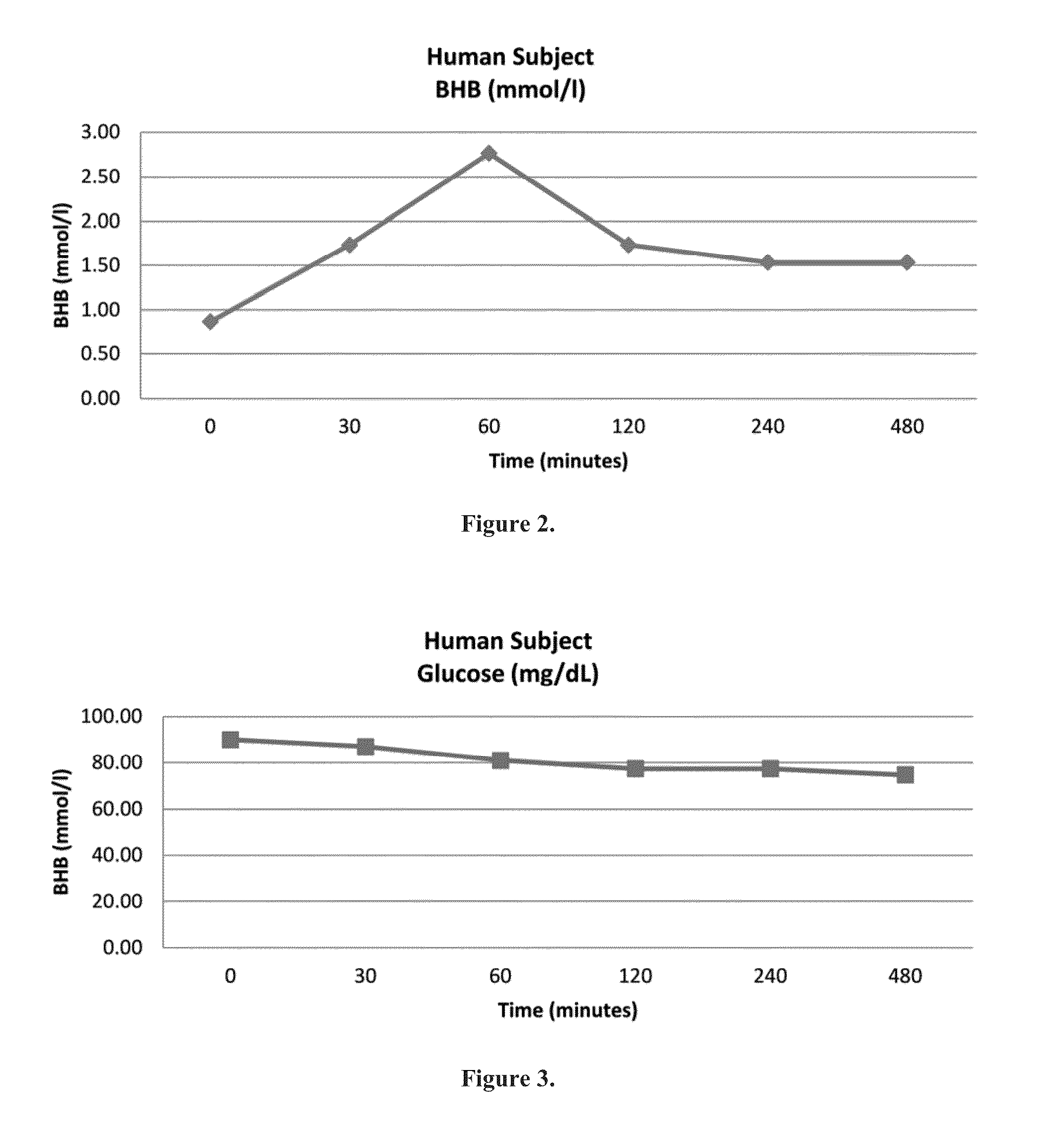
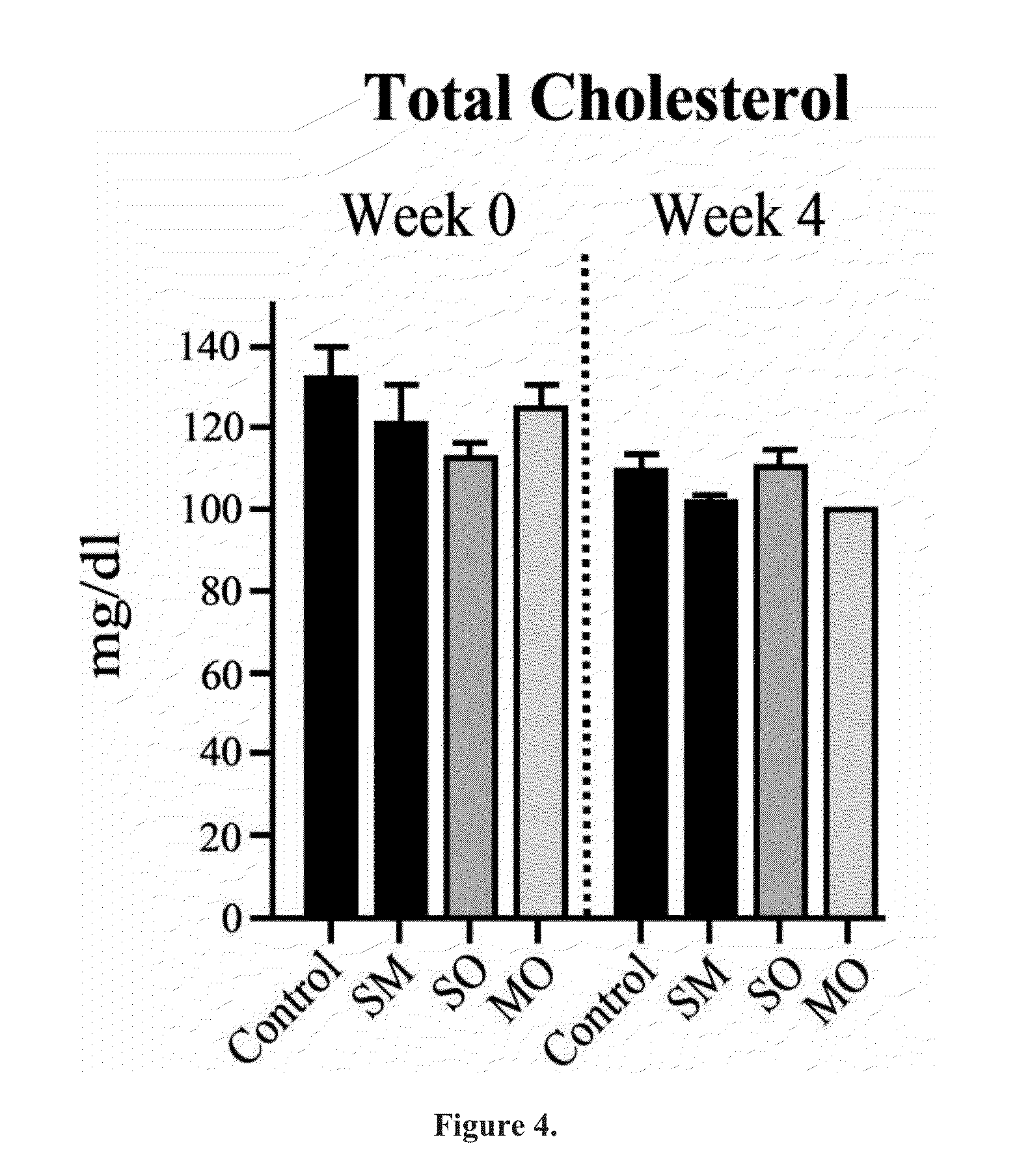
Beta-hydroxybutyrate mineral salts in combination with medium chain fatty acids or an ester thereof such as medium chain triglycerides were used to induce ketosis, achieving blood ketone levels of (2-7 mmol / L), with or without dietary restriction. The combination results in substantial improvements in metabolic biomarkers related to insulin resistance, diabetes, weight loss, and physical performance in a short period of time. Further, use of these supplements to achieve ketosis yields a significant elevation of blood ketones and reduction of blood glucose levels. Use of these substances does not adversely affect lipid profiles. By initiating rapid ketosis and accelerating the rate of ketoadaptation, this invention is useful for the avoidance of glucose withdrawal symptoms commonly experienced by individuals initiating a ketogenic diet, and minimizes the loss of lean body mass during dietary restriction.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Compositions and methods for glycogen synthesis
InactiveUS20050176827A1Function increaseIncrease insulin sensitivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCysteine thiolateTryptophan
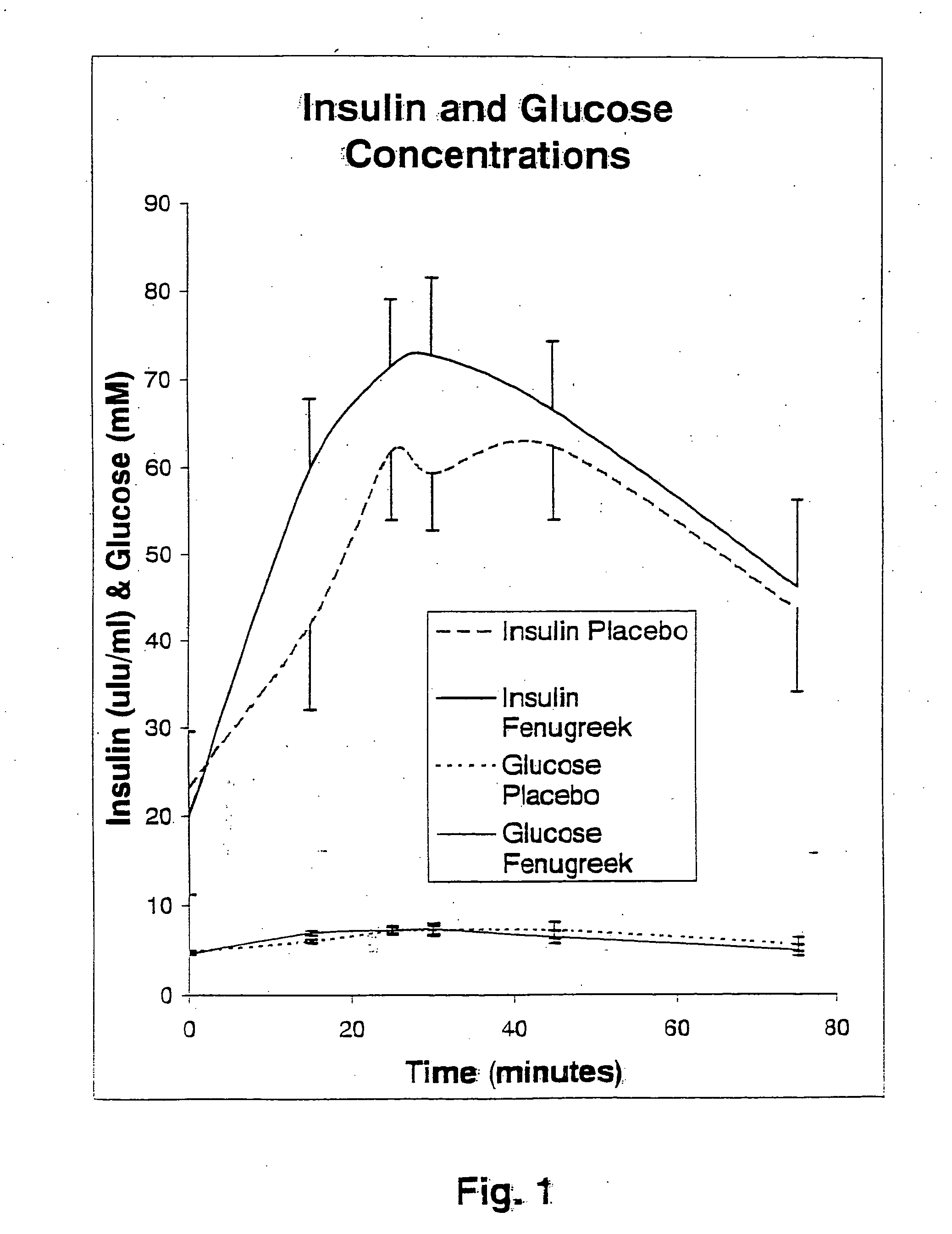
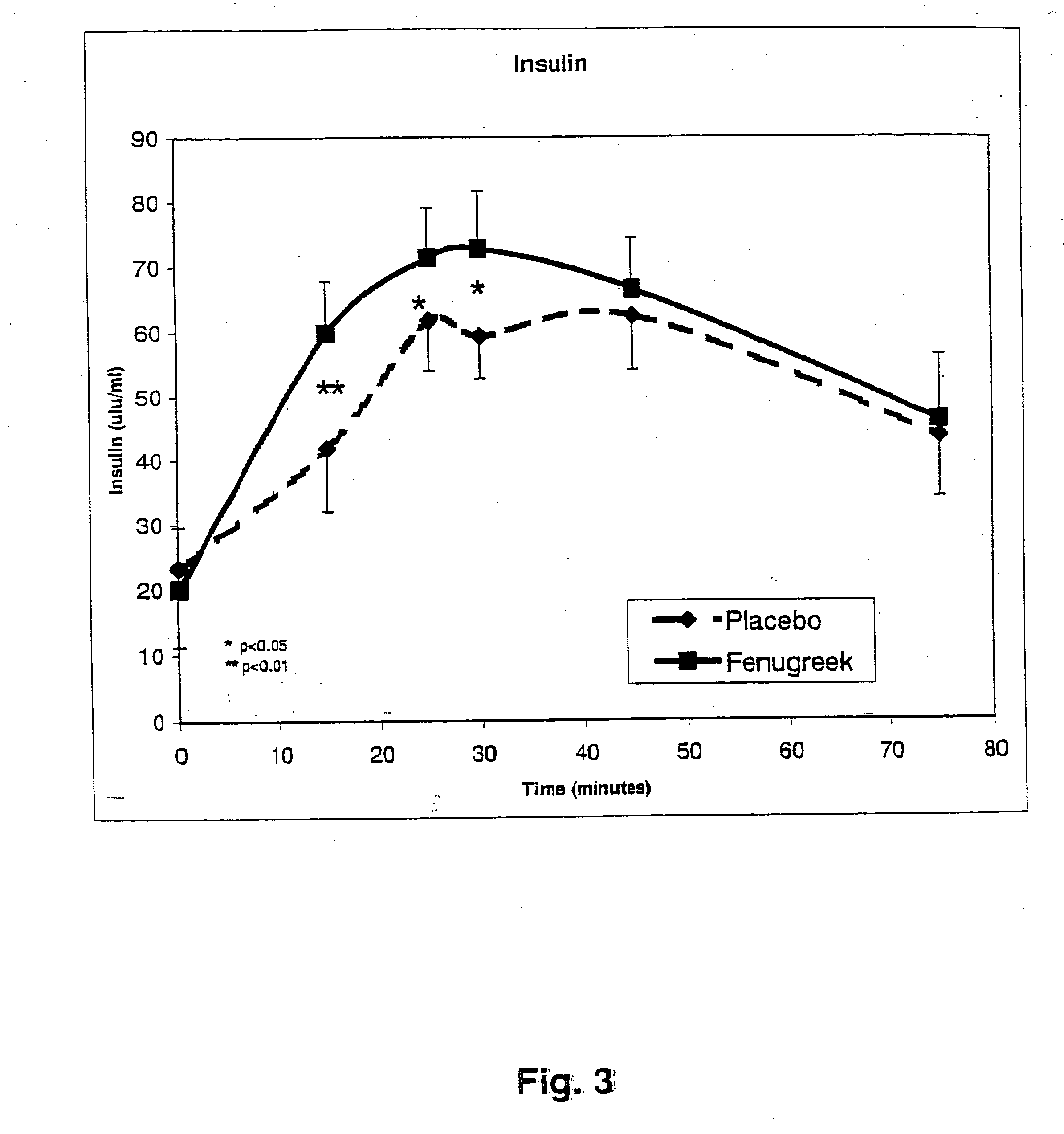
A composition of bio-active compounds and methods for facilitating and supporting the metabolism and transport of glucose and carbohydrates into muscle cells, promoting muscle function and growth, promoting glycogen synthesis, enhancing glucose disposal, stimulating pancreatic beta cells, promoting metabolic recovery, promoting muscle recovery, promoting lean body mass, and promoting fat burning. Preferably, the composition of bio-active compounds includes a combination of 4-hydroxyisoleucine with at least one amino acid selected from the group consisting of arginine, aspartate, threonine, serine, glutamate, proline, glycine, alanine, cysteine, valine, methionine, isoleucine, leucine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, ornithine, lysine, histidine, gamma-amino butyrate and tyrosine. In one presently preferred embodiment of the present invention, the combination is derived, isolated, and / or extracted from fenugreek seeds. Methods for using a novel composition of bio-active compounds from fenugreek seed for facilitating and supporting the metabolism and transport of glucose and carbohydrates into muscle cells, promoting muscle function and growth, promoting glycogen synthesis, enhancing glucose disposal, stimulating pancreatic beta cells, promoting metabolic recovery, promoting muscle recovery, promoting lean body mass, and promoting fat burning are also disclosed, wherein methods comprise the steps of: (1) providing an effective amount of a composition of bio-active compounds derived, isolated, and / or extracted from fenugreek seeds; and (2) administering the composition to a human or animal.
Owner:TSI INC
Methods for Affecting Body Composition
InactiveUS20080176804A1Reducing body fatPreventing body fat gainPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhysiologyWhole body
Methods for affecting body composition include the use of amylin or amylin agonist(s). Total body weight may be reduced, maintained or even increased; however, the body fat is reduced or body fat gain is prevented, while lean body mass is maintained or increased.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Compositions and methods for producing elevated and sustained ketosis
ActiveUS20140350105A1Rapid and sustained elevationImprove metabolic healthBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsKetoneSignificant elevation
Beta-hydroxybutyrate mineral salts in combination with medium chain fatty acids or an ester thereof such as medium chain triglycerides were used to induce ketosis, achieving blood ketone levels of (2-7 mmol / L), with or without dietary restriction. The combination results in substantial improvements in metabolic biomarkers related to insulin resistance, diabetes, weight loss, and physical performance in a short period of time. Further, use of these supplements to achieve ketosis yields a significant elevation of blood ketones and reduction of blood glucose levels. Use of these substances does not adversely affect lipid profiles. By initiating rapid ketosis and accelerating the rate of ketoadaptation, this invention is useful for the avoidance of glucose withdrawal symptoms commonly experienced by individuals initiating a ketogenic diet, and minimizes the loss of lean body mass during dietary restriction.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Composition and method for promoting internal health and external appearance
The present invention relates to a new composition comprising substances that promote DNA repair, reduce body fat levels and increase lean body mass and that decrease wrinkle appearance and / or improvement in skin surface. In some aspects, the composition of the present invention include resveratrol, forskohlin and astaxanthin. In another aspect the composition of the present invention further comprises carboxy alkyl ester. The present invention also relates to a method of promoting internal health and external appearance in a subject in need, said method comprising administering to the subject a composition that promotes DNA repair, reduces body fat levels and increases lean body mass and that decreases wrinkle appearance and / or improvement in skin surface.
Owner:NUVOCARE HEALTH SCI
Methods for affecting body composition
InactiveUS7399744B2Reducing body fatPreventing body fat gainHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhysiologyWhole body
Methods for affecting body composition include the use of amylin or amylin agonist(s). Total body weight may be reduced, maintained or even increased; however, the body fat is reduced or body fat gain is prevented, while lean body mass is maintained or increased.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Use Of Secretagogue For The Teatment Of Ghrelin Deficiency
InactiveUS20080171700A1Improve the level ofPrevents upregulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSleep patternsCvd risk
The present invention relates to the use of a growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of ghrelin deficiency, and / or undesirable symptoms associated therewith, in an individual at risk of acquiring partial or complete ghrelin deficiency resulting from a medical treatment and / or from a pathological condition. The present invention also relates to use of a secretagogue compound for the preparation of a medicament for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more of: loss of fat mass, loss of lean body mass, weight loss, cachexia, loss of appetite, immunological dysfunction, malnutrition, disrupted sleep pattern, sleepiness, reduction in intestinal absorption and / or intestinal mobility problems in an individual suffering from, or at risk of suffering from, ghrelin deficiency. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of a secretagogue, such as a ghrelin-like compound, for the production of a medicament for preventing weight increase in an individual either: a) being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state, or b) in remission from being converted from a hyperthyroidic state to euthyroid state.
Owner:GASTROTECH PHARMA AS
Method of increasing lean body mass and reducing body fat mass in infants
ActiveUS20070026049A1Increasing lean body massReduce the total massBiocidePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLBM - Lean body massBody weight measure
Disclosed is a method of increasing lean body mass and reducing fat body mass in infants, said method comprising administration to an infant, term or preterm, a nutritional formula comprising a source of DHA and ARA. It has been found that the administration of DHA and ARA, or a source thereof, in infants can increase lean body mass and reduce fat body mass, when compared to an unsupplemented control formula, without impacting the total overall growth of the infant. This method is especially useful in preterm infants.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
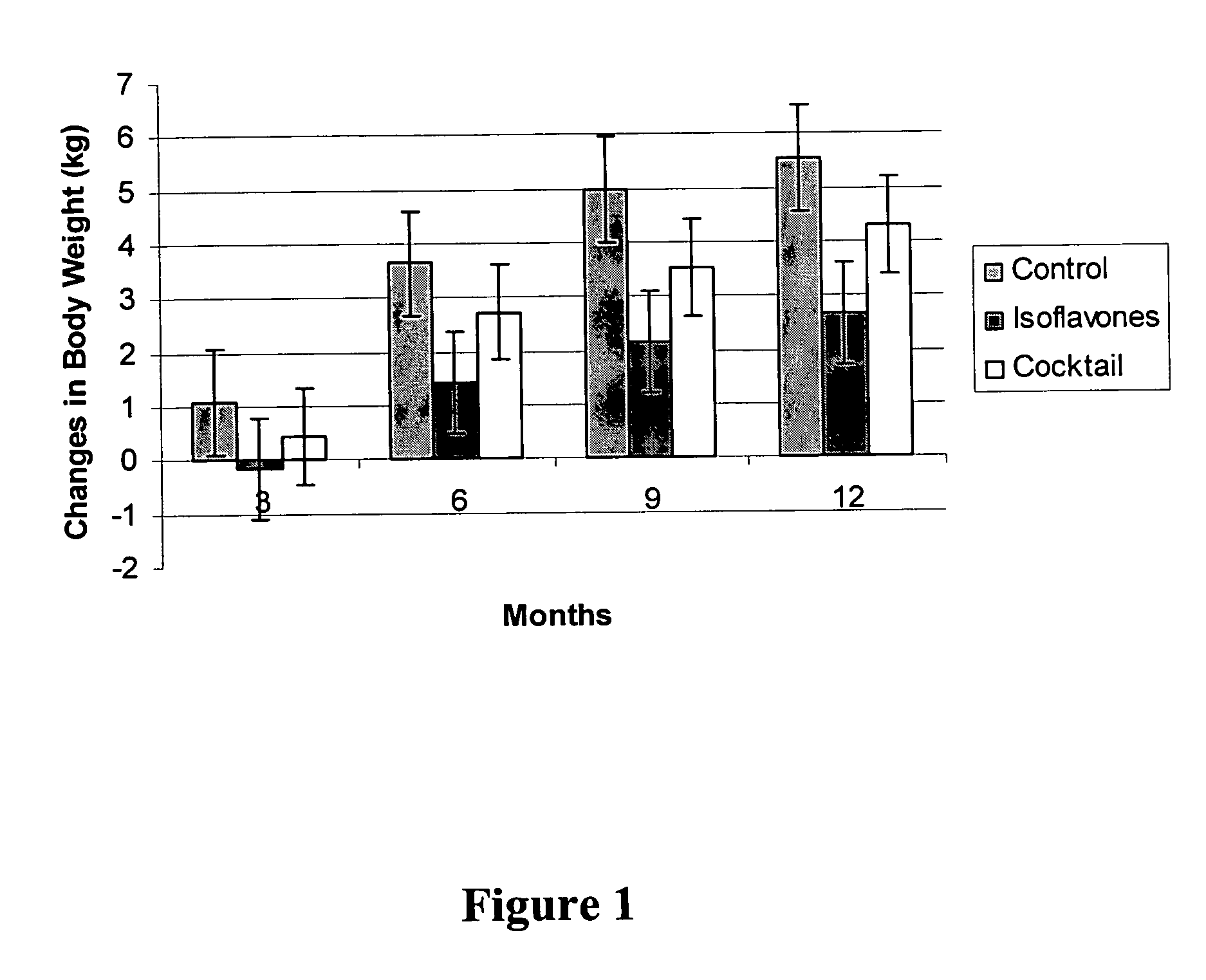
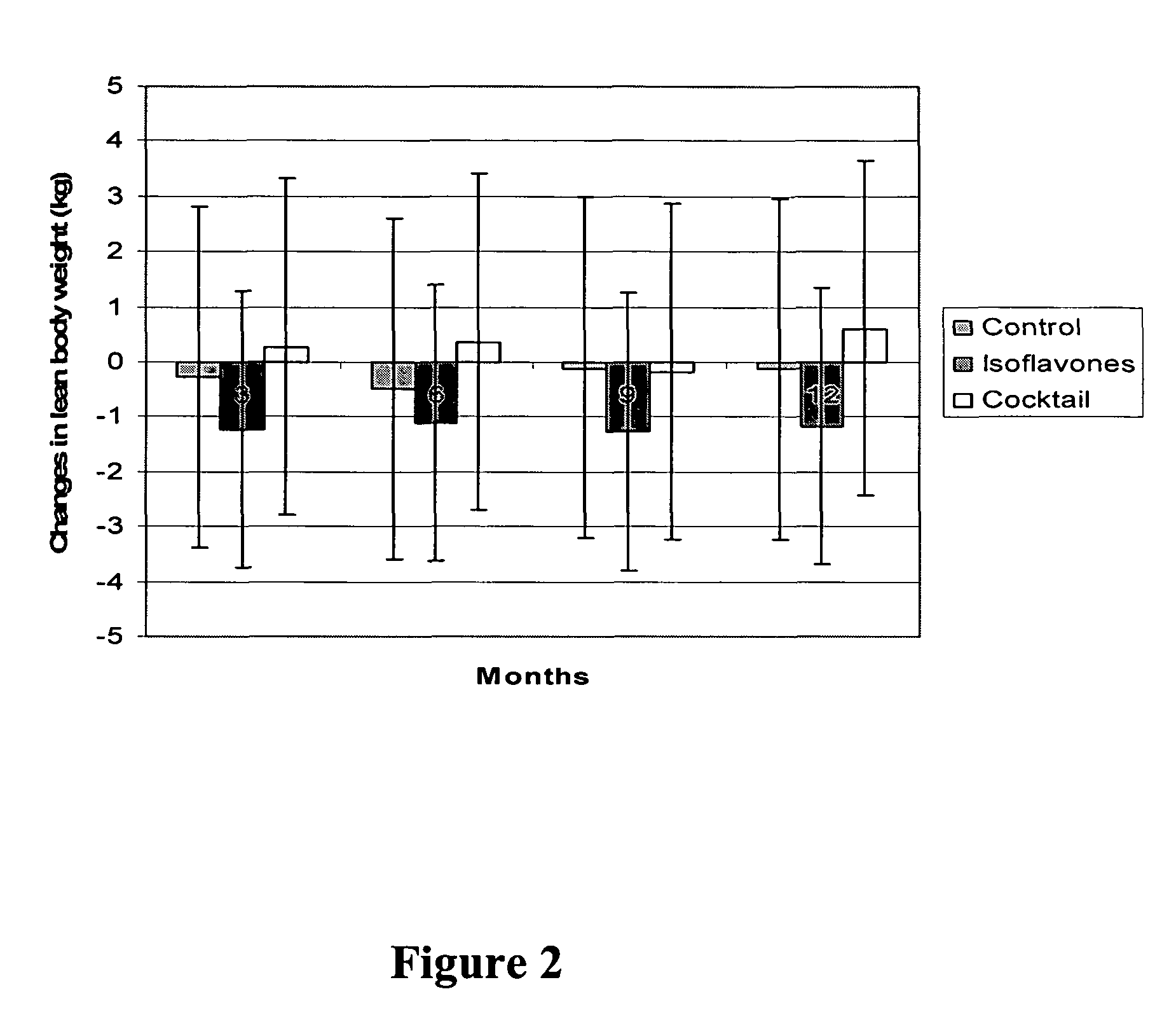
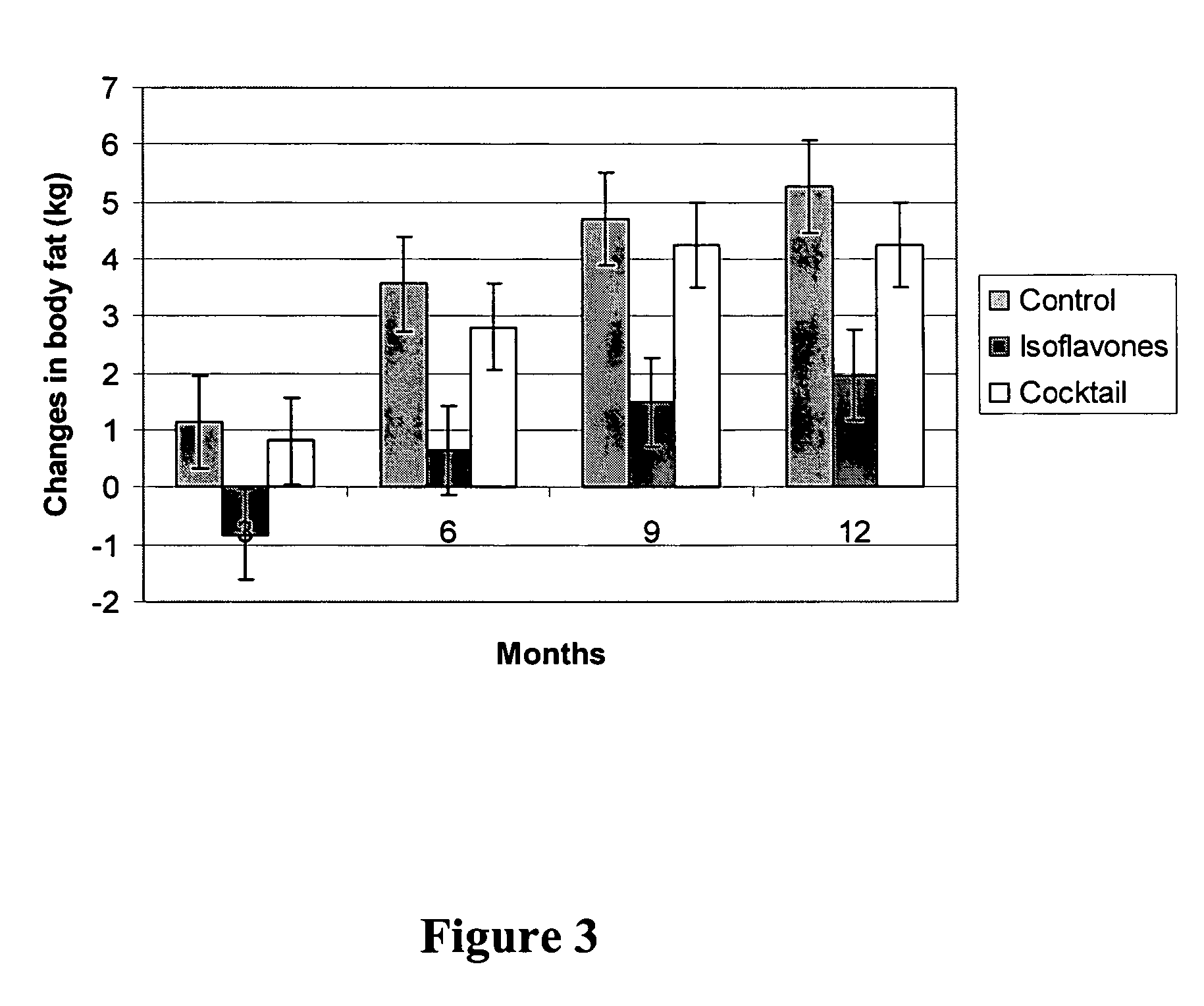
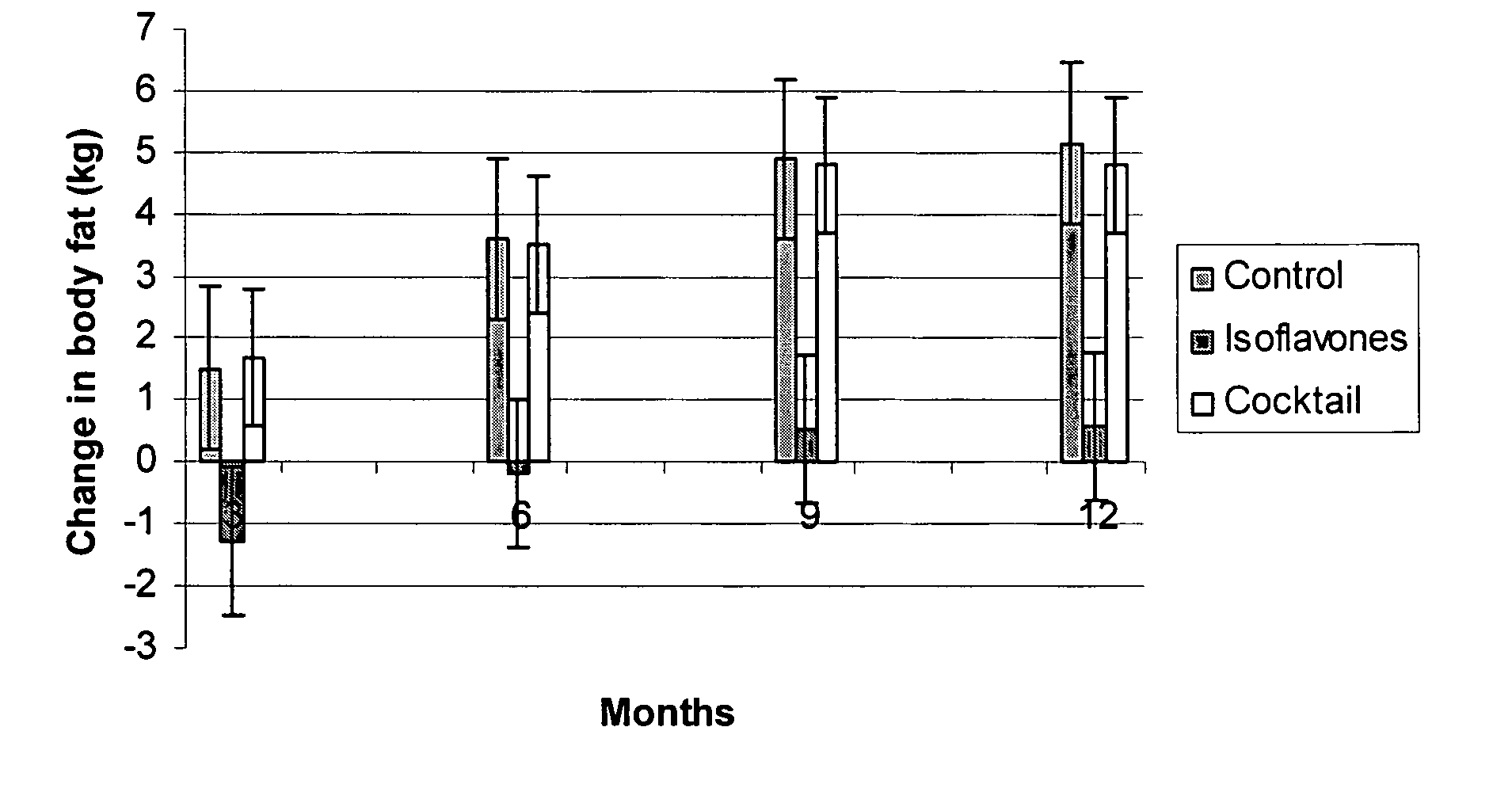
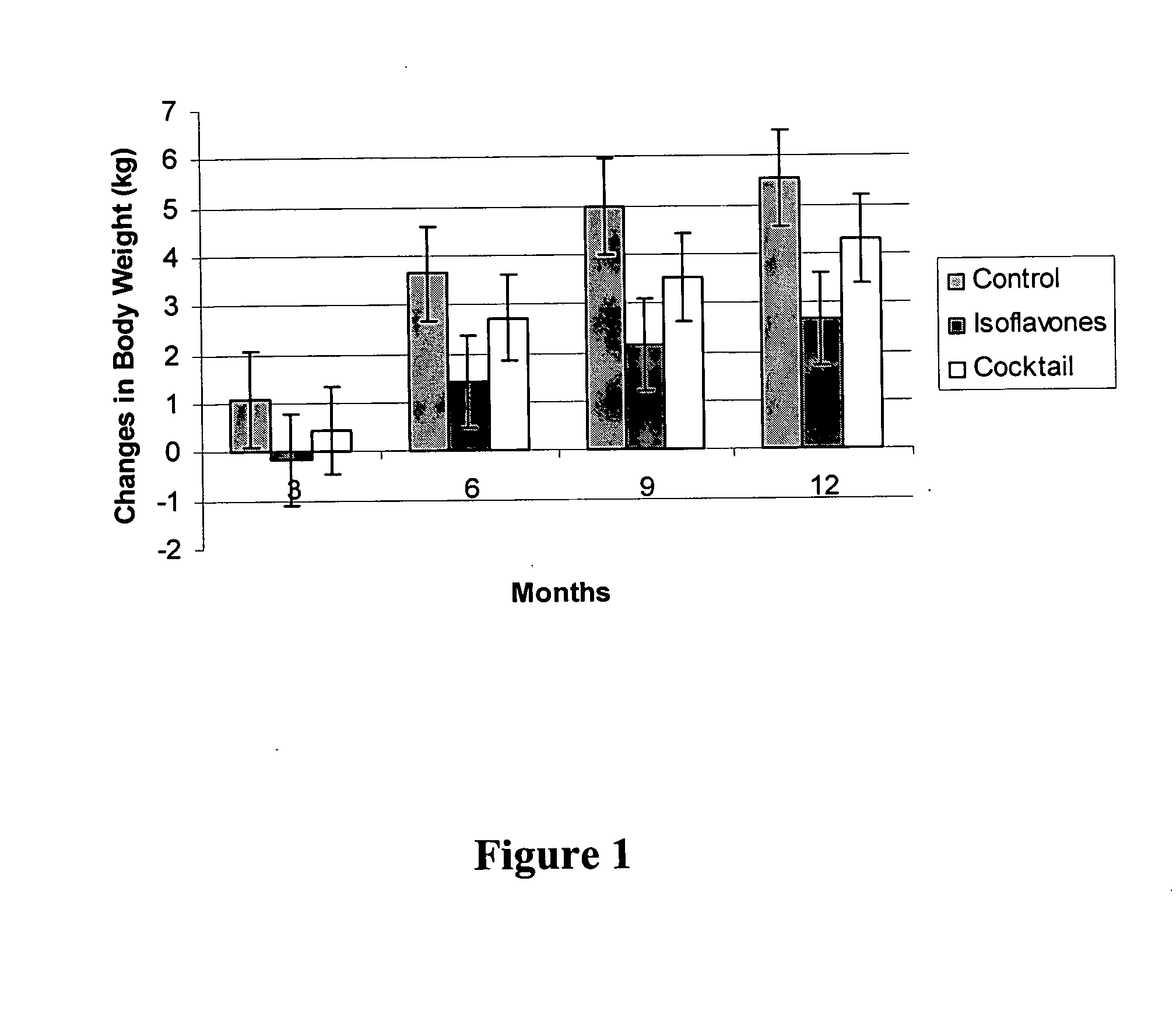
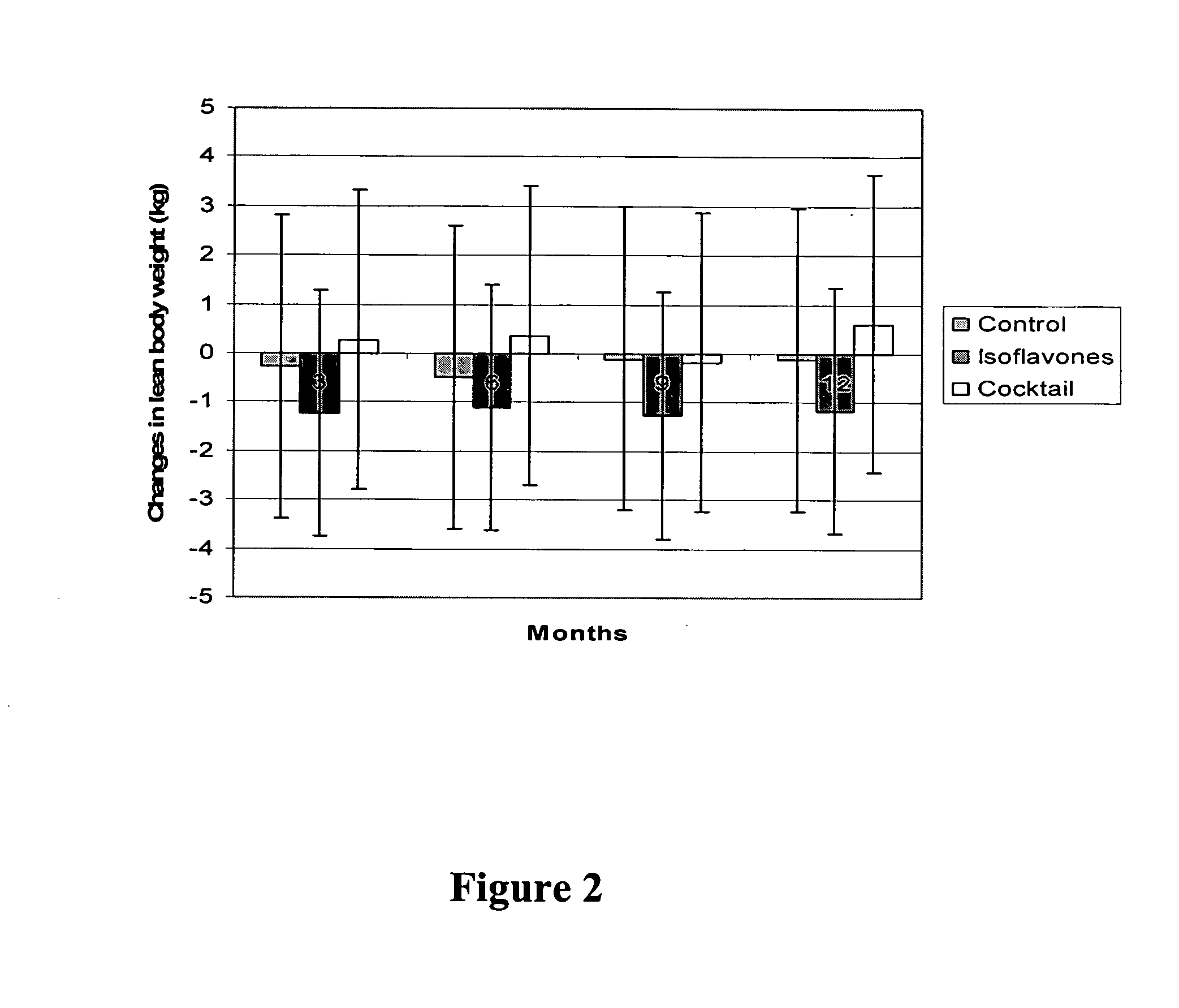
Isoflavone compositions for reducing accumulation of body fat in male mammals, and methods for their use
ActiveUS8226973B2Reduce fat accumulationEfficient reductionBiocideMetabolism disorderMetaboliteAnimal science
Edible compositions useful for weight management in male animals are disclosed. The compositions comprise one or more isoflavones or isoflavone metabolites and are particularly useful for reducing or preventing the accumulation of body fat. Also disclosed are methods useful for weight management in an animal utilizing compositions comprising one or more isoflavones. The compositions and methods are particularly useful for the reduction or prevention of body fat accumulation during periods of excess caloric intake, and preferably have a sparing effect on lean body mass.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Probiotic and prebiotic composition for forming lean body mass and application thereof
ActiveCN110151796AEffective regulationImprove immunityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseBody shape
The invention discloses a probiotic and prebiotic composition for forming lean body mass and application thereof, and relates to the field of biomedicine. The composition comprises probiotics such asbifidobacterium lactis, bifidobacterium longum, lactobacillus reuteri, lactobacillus rhamnosus, lactobacillus acidophilus, streptococcus thermophilus, bacillus coagulans and clostridium butyricum, anda prebiotic mixture is also added. By reasonably matching the components of the composition, the intestinal flora is effectively regulated, and the obesity is more efficiently and healthily relieved;for people with normal weight, the weight reduction effect is not obvious, but the body shape is more beautiful; meanwhile, the composition can effectively prevent hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and other diseases and improve the body immunity, is suitable for a wider range of people, and can be applied to food, pharmacy and healthy or natural product production.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIKANG BEIJING BIOTECH CO LTD
Dietary compositions and methods of enhancing lean body mass and exercise performance
InactiveUS20080233186A1Improve athletic abilityOrganic active ingredientsUrea derivatives preparationArgininePhysiology
Various compounds can be administered orally to humans or animals for the purpose of enhancing nitric oxide production. Enhancing nitric oxide production is beneficial for those looking to increase lean body mass or enhance exercise performance. Such administration can also be used for the purpose of enhancing nutrient transport for purposes of athletic performance and controlling bodyweight and body fat levels. L-Arginine and alpha amino n-Butryate work synergistically to enhance nitric oxide production and may further be coupled with either and / or a) an inhibitor of nitric oxide breakdown or b) a nitric oxide potentiators or other precursor and serve to accomplish this goal of enhance nitric oxide. The composition may be administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks.
Owner:IN INGREDIENTS
Compositions and methods of treating viral infections
ActiveUS20100190744A1Decreasing body fatQuality improvementBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsAstragalus polysaccharideSulfated polysaccharides
The present invention relates to the field of nutraceuticals, and in particular to nutraceuticals comprising sulfated polysaccharides, Astragalus polysaccharides, resveratrol, and combinations thereof. These compositions find use in inducing physiological responses such, decreasing body fat, increasing lean body mass, alleviating the symptoms of colds, preventing the onset of colds, increasing energy, increasing the feeling of well-being in subjects, and improving skin tone and appearance.
Owner:LIFE SCI NUTRITION AS
Compositions containing policosanol and chromium and/or chromium salts and their pharmaceutical uses
InactiveUS20060024383A1Increasing lean body massLower blood sugar levelsHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCoronary heart diseaseHypoglycemia
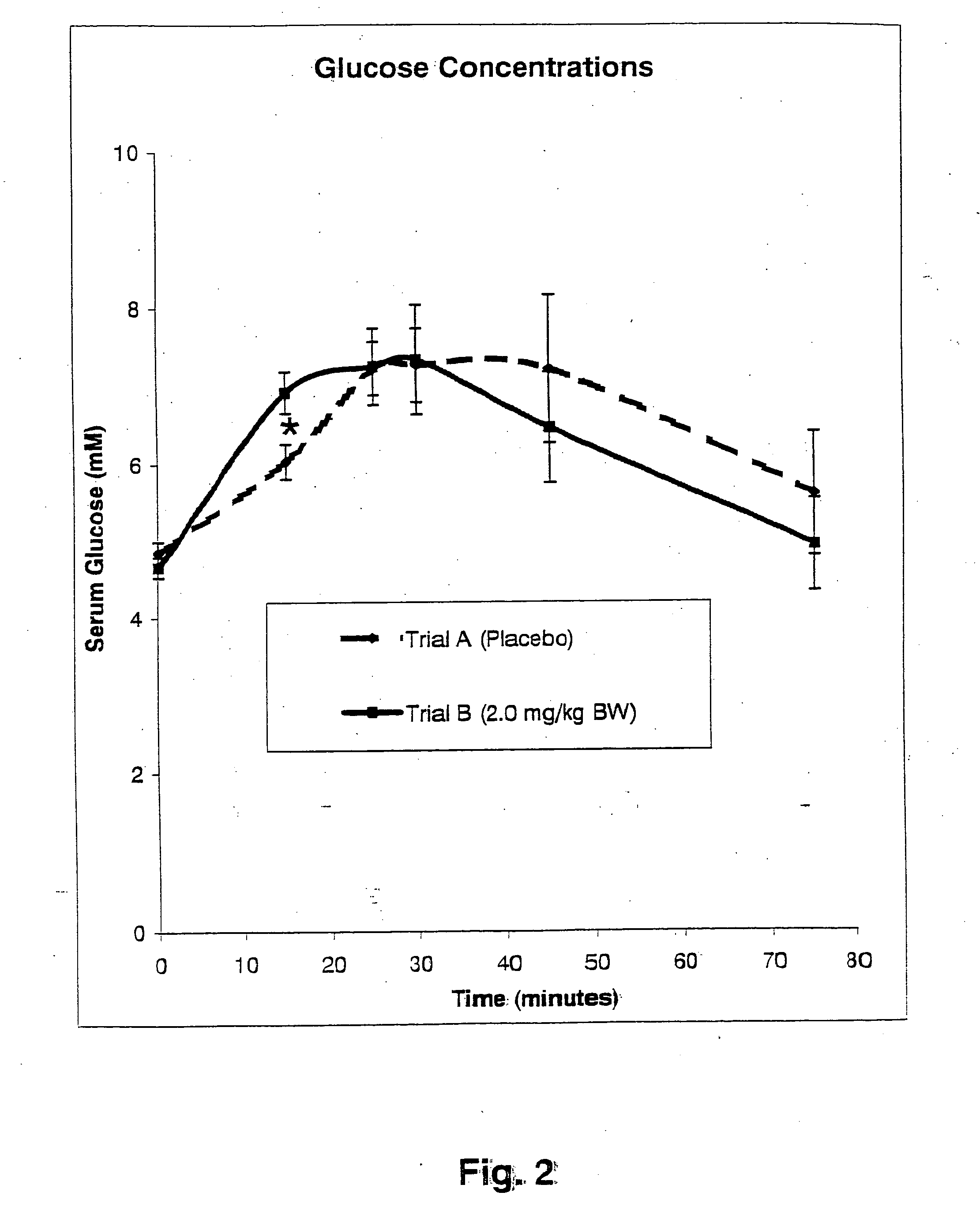
A composition is provided which contains policosanol and chromium and / or chromium salts and which may be used for treating, preventing and or reducing metabolic syndrome, hypercholesterolemia and hypoglycemia related diseases, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, LDL / HDL ratio, triglycerides, coronary heart disease (heart attacks and strokes), inflammation, deep-vein thrombosis, immunoregulatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, raised blood pressure, fatigue, premenstrual syndrome, anxiety, depression and / or neurodegenerative disorders, and / or raising HDL cholesterol and / or lean body mass in humans and animals. The method comprises administering policosanol and chromium and / or chromium salts which together effectively lower blood glucose levels and lower the LDL / HDL cholesterol ratio. Typically, the administered composition includes about 0.1-10:1 parts by weight of policosanol to chromium and / or chromium salts.
Owner:WYETH
Dietary supplement and method of using same
InactiveUS6576272B1Good for weight lossMaintaining and preserving lean body massBiocideStringersCitrus aurantium extractDietary supplement
Dietary supplements comprising Citrus aurantium extract and a methylxanthine, with or without St. John's wort extract and L-Phenylalanine for controlling weight wherein fat is lost and lean body mass preserved.
Owner:ISI BRANDS +11
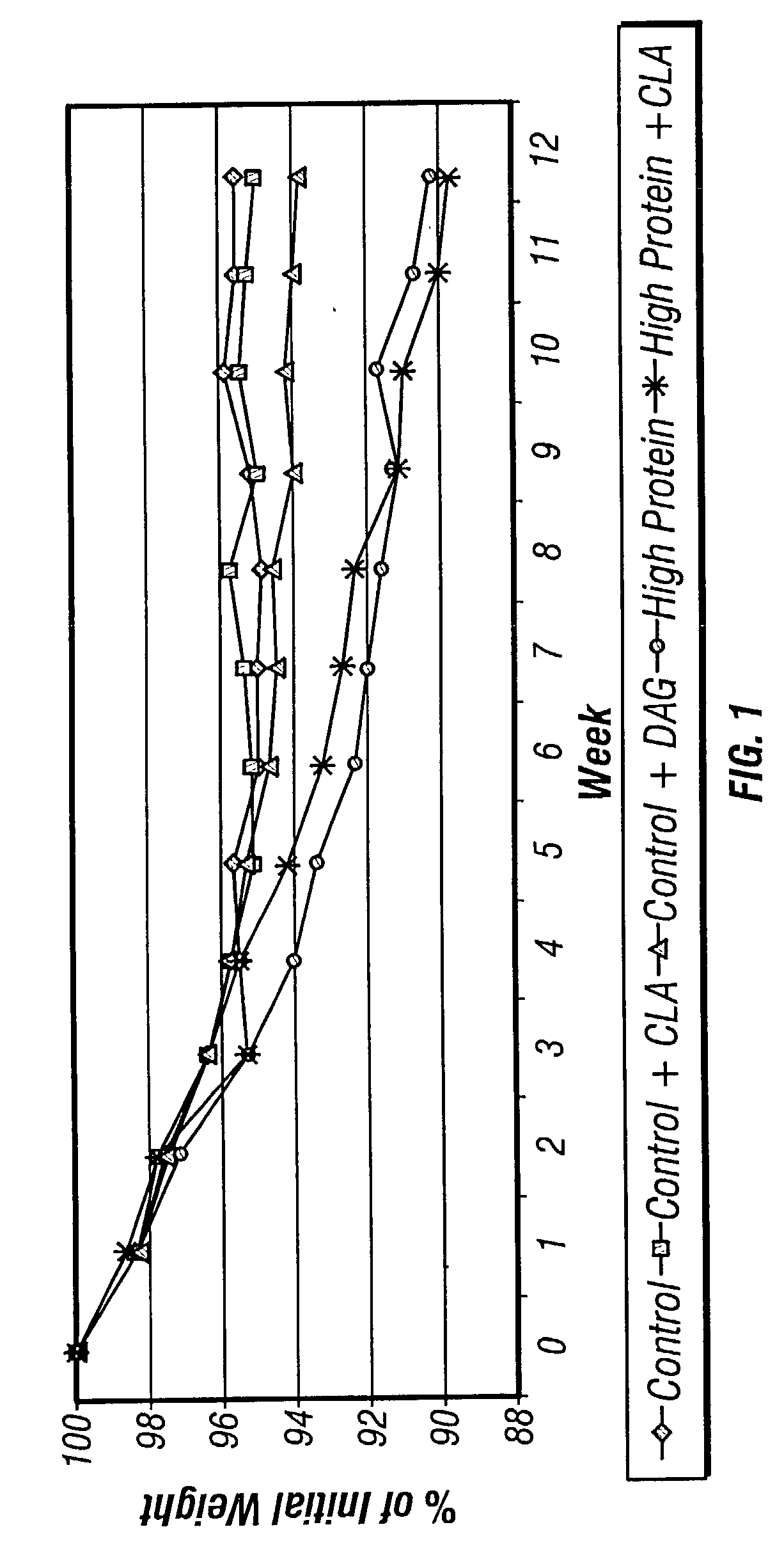
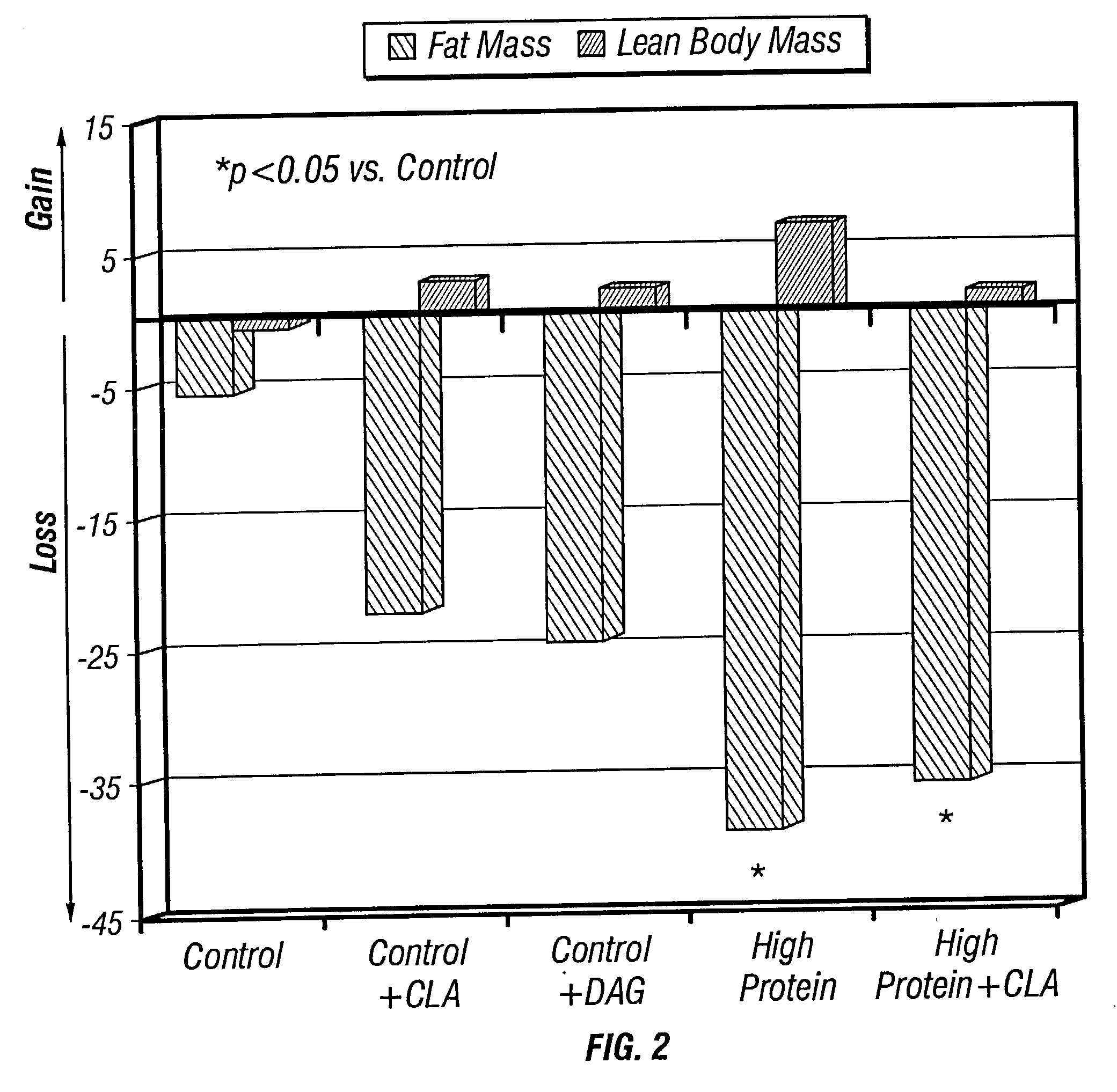
Gene expression profiles associated with lean phenotype and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110183870A1High in proteinIncrease exercisePeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMuscle tissueRegimen
Gene expression profiles associated with improved or maintained lean body mass or reduced body fat are disclosed. The gene expression profiles were determined in adipose, liver, and muscle tissue of animals subjected to lean-promoting regimens such as consumption of a high protein diet, ingestion of conjugated linolenic acid, and / or increased exercise. Methods of using such profiles for the identification of pharmaceutical substances, nutraceutical substances, dietary substances, or treatment regimens that modulate or contribute to desired phenotypes in animals are also disclosed
Owner:NESTEC SA
Sports nutritional supplement containing HMB
The invention relates to a sports nutritional supplement containing HMB. The sports nutritional supplement takes HMB as a main raw material, and also comprises phosphate and taurine; moreover, the supplement can be added with creatine. The supplement can effectively reduce the decomposition of protein (muscle) after a strenuous exercise, increase the lean body mass, obviously relieve the damage extent of muscular cells, resist the exercise fatigue and improve the athletic ability of an organism.
Owner:BEIJING COMPETITOR SPORTS SCI & TECH
Liquid pharmaceutical preparation comprising forskolin for promoting lean body mass
A liquid pharmaceutical preparation comprising forskolin in an amount of about 0.025 mg / ml to about 1 mg / ml of the liquid pharmaceutical preparation for promoting lean body mass in a human subject. Further, an effective amount of the liquid pharmaceutical preparation comprising forskolin is administered subcutaneously in the human subject.
Owner:ASHWORTH LANCE
Dietary compositions and methods of enhancing lean body mass and exercise performance
Various compounds can be administered orally to humans or animals for the purpose of enhancing nitric oxide production. Enhancing nitric oxide production is beneficial for those looking to increase lean body mass or enhance exercise performance. Such administration can also be used for the purpose of enhancing nutrient transport for purposes of athletic performance and controlling bodyweight and body fat levels. L-Arginine and alpha amino n-Butryate work synergistically to enhance nitric oxide production and may further be coupled with either and / or a) an inhibitor of nitric oxide breakdown or b) a nitric oxide potentiators or other precursor and serve to accomplish this goal of enhance nitric oxide. The composition may be administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks.
Owner:IN INGREDIENTS
Treatment or prevention of acute renal failure
InactiveUS6998404B2Increase urine outputLow creatinine levelBiocideAnimal repellantsVentricular tachycardiaCardiac monitoring
Adenosine receptor antagonists, especially aminophyllline, are used to treat or prevent acute renal failure. In the preferred embodiment, aminophylline is administered by infusion so that it does not exceed a serum theophylline level of 15-20 micrograms / ml, most preferably the aminophylline is administered to achieve a serum theophylline concentration of 3-10 micrograms / ml, with an infusion rate of 0.1-0.6 mg / kg IBW / hour (IBW=ideal body weight). The adenosine receptor antagonist can also be used to help sustain a kidney for transplant purposes. Preferably, aminophylline is loaded while the kidney is still part of the donor. A dose of aminophylline of 5 mg / kg lean body weight is infused into the donor over a 30-60 min period, with cardiac monitoring. The infusion dose is decreased in the event of supraventricular or ventricular tachycardias. The kidney is removed and placed in the standard “cold” bath, but containing aminophylline at a dose of 5-10 micrograms / ml (5-10 mg / l). The kidney is then transported to the recipient. The recipient is similarly preloaded with 5 mg / kg lean body mass aminophylline intravenously over 30-60 min with cardiac monitoring, with a constant infusion of 0.1-0.3 mg / kg lean body mass / hr continuing during the next 24 hours after the kidney is transplanted into the recipient.
Owner:GENOMED
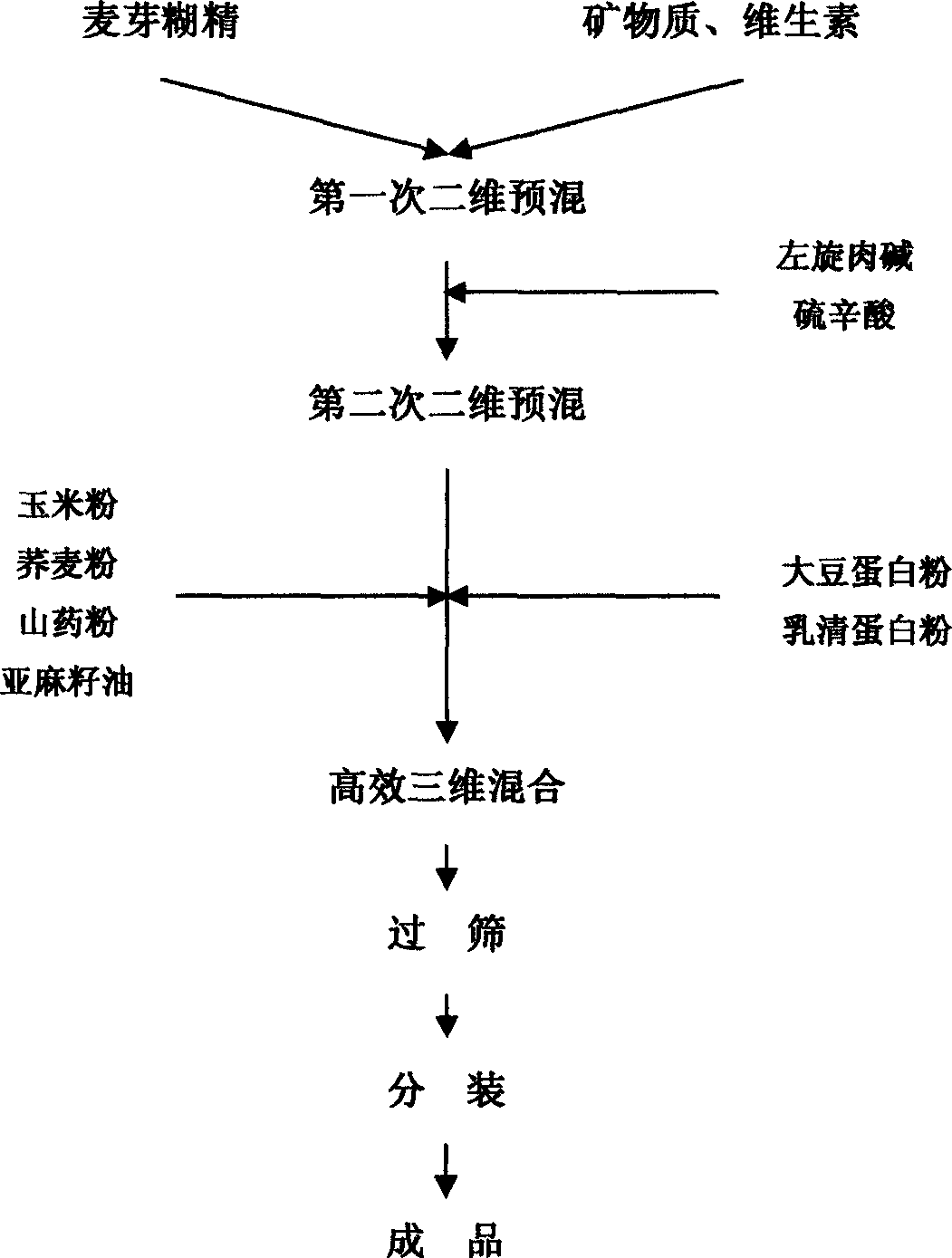
Enteral nutrition preparation for fat-burning intervention on metabolic syndrome and application thereof
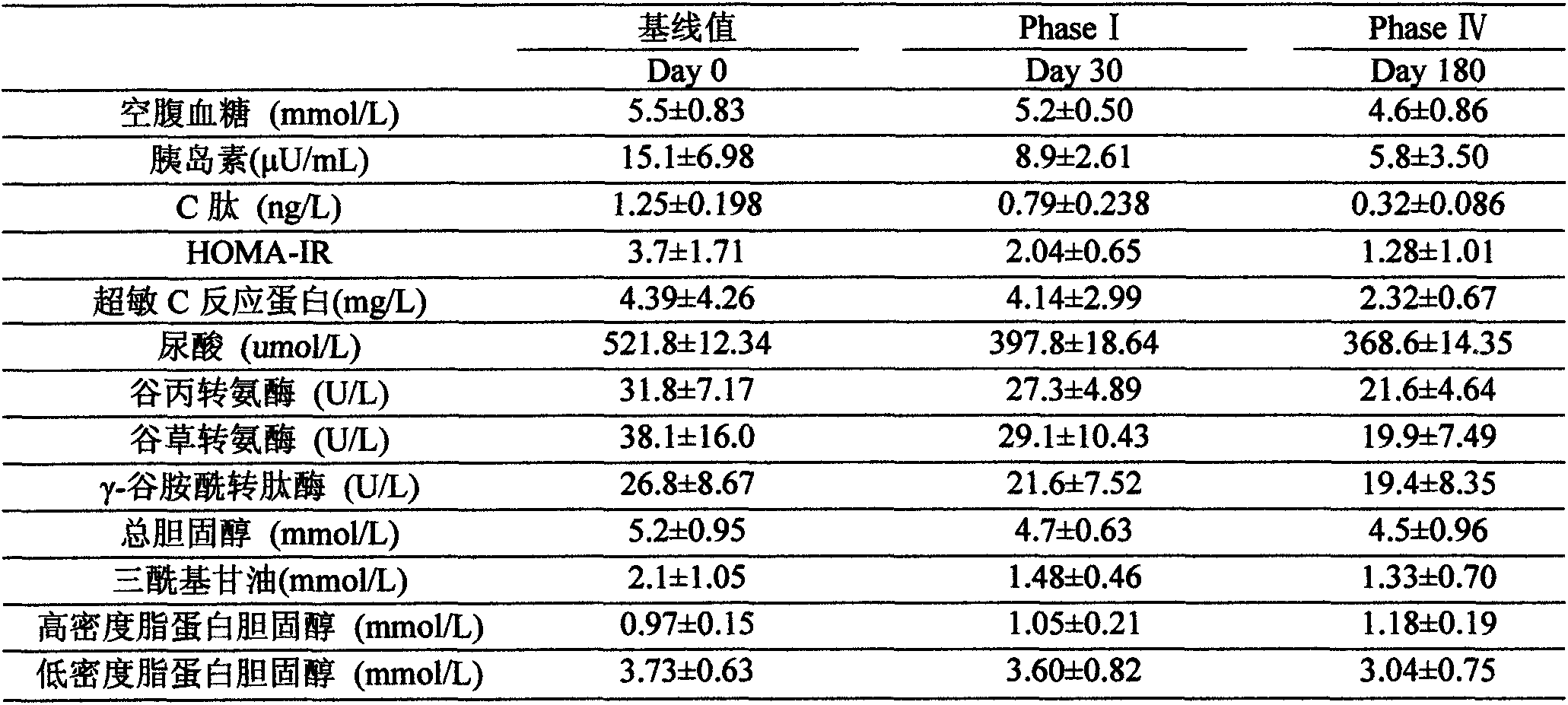
The invention relates to an enteral nutrition preparation for fat-burning intervention on metabolic syndrome and an application thereof. The preparation is prepared through mixing corns, Chinese yams, buckwheat, soy protein, whey protein, linseed oil, lipoic acid, L-carnitine, minerals, vitamins and other raw materials. The preparation is a special formula for the nutritional intervention on metabolic syndrome of the very low-calorie dietetic therapy, has the effects of promoting steatolysis, promoting weight loss, reducing blood pressure, blood glucose and blood fat, improving the insulin sensitivity and the liver function, and reducing the lean body mass loss, and achieves good prevention and supportive therapeutic efficacies for metabolic syndrome. The preparation can be used for the development of healthcare products and food aimed at promoting weight loss, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WEALTHCOME HEALTH PROD CO LTD
Preparation method of fat-fighting low-calorie full-nutrition meal replacement preparation
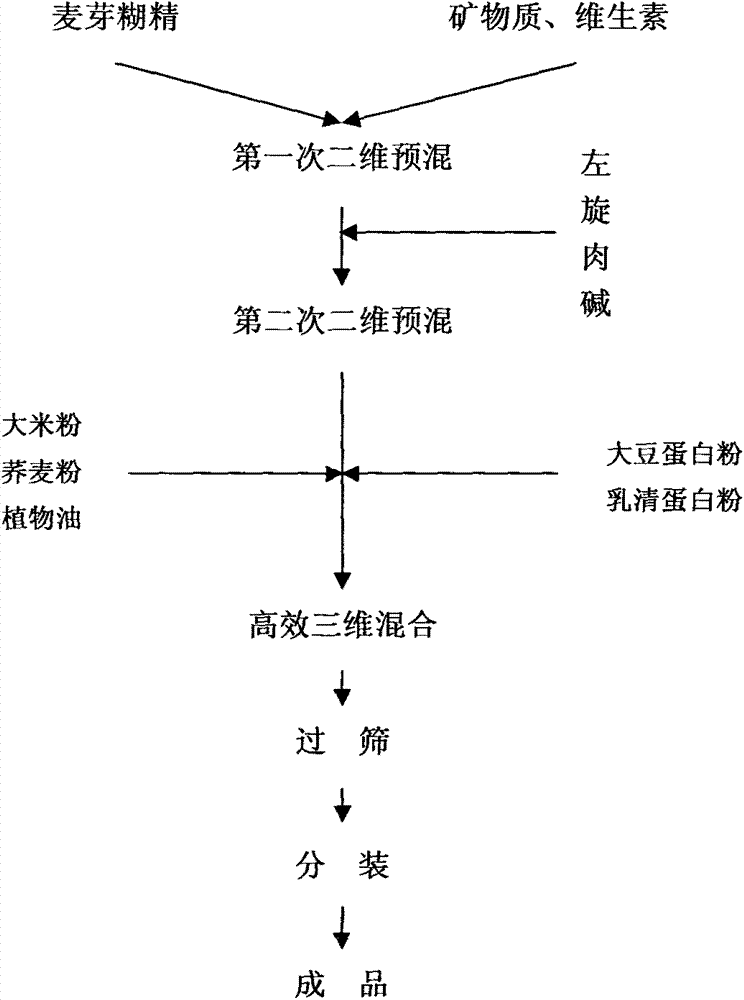
InactiveCN103494213APromote oxidationTo promote metabolismFood preparationCoronary heart diseaseWhey protein powder
The invention provides a preparation method of a fat-fighting low-calorie full-nutrition meal replacement preparation. The fat-fighting low-calorie full-nutrition meal replacement preparation is prepared from L-carnitine and common nutraceutical bulk pharmaceutical chemicals such as maltodextrin, rice meal, corn meal, soyabean protein powder, lactalbumin powder, sunflower seed oil, mineral substance mixtures, and vitamin mixtures, wherein the ratio of the L-carnitine is 1-6 percent. The L-carnitine has the function of improving the glucolipid metabolism, and an extremely-low-calorie high-protein diet has the functions of promoting the fat hydrolysis, lightening the hunger sensation, improving the lean body mass proportion and the like. Clinical and trial studies indicate that the fat-fighting low-calorie full-nutrition meal replacement preparation is accurate in treatment effect, is capable of rapidly reducing the weight within a short time, reducing the blood pressure, and improving the blood sugar, blood fat insulin sensitivity and liver functions, has a good prevention function on high blood pressure, diabetes and coronary heart disease, is capable of reducing adverse reaction in the dieting process and improving the tolerance of a human body to hunger, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Ketogenic nutritional compositions
ActiveUS20190191755A1Sustain metabolic ketosisEasy maintenanceFood ingredient functionsMuscle strengthLBM - Lean body mass
A nutritional composition comprises fat, protein and carbohydrate such that the fat provides from about 60 to about 90% of the total calories of the composition, the protein provides from about 10 to about 30% of the total calories of the composition, and the carbohydrate provides from about 0.1 to about 15% of the total calories of the composition, and the composition comprises from about 0.01 to about 10 wt % beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB). A method of achieving or sustaining metabolic ketosis in an individual comprises administering the nutritional composition to the individual. A method of maintaining lean body mass and muscle strength in an individual during dietary ketosis comprises administering the nutritional composition to the individual.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Aryloxy propanolamines for improving livestock production
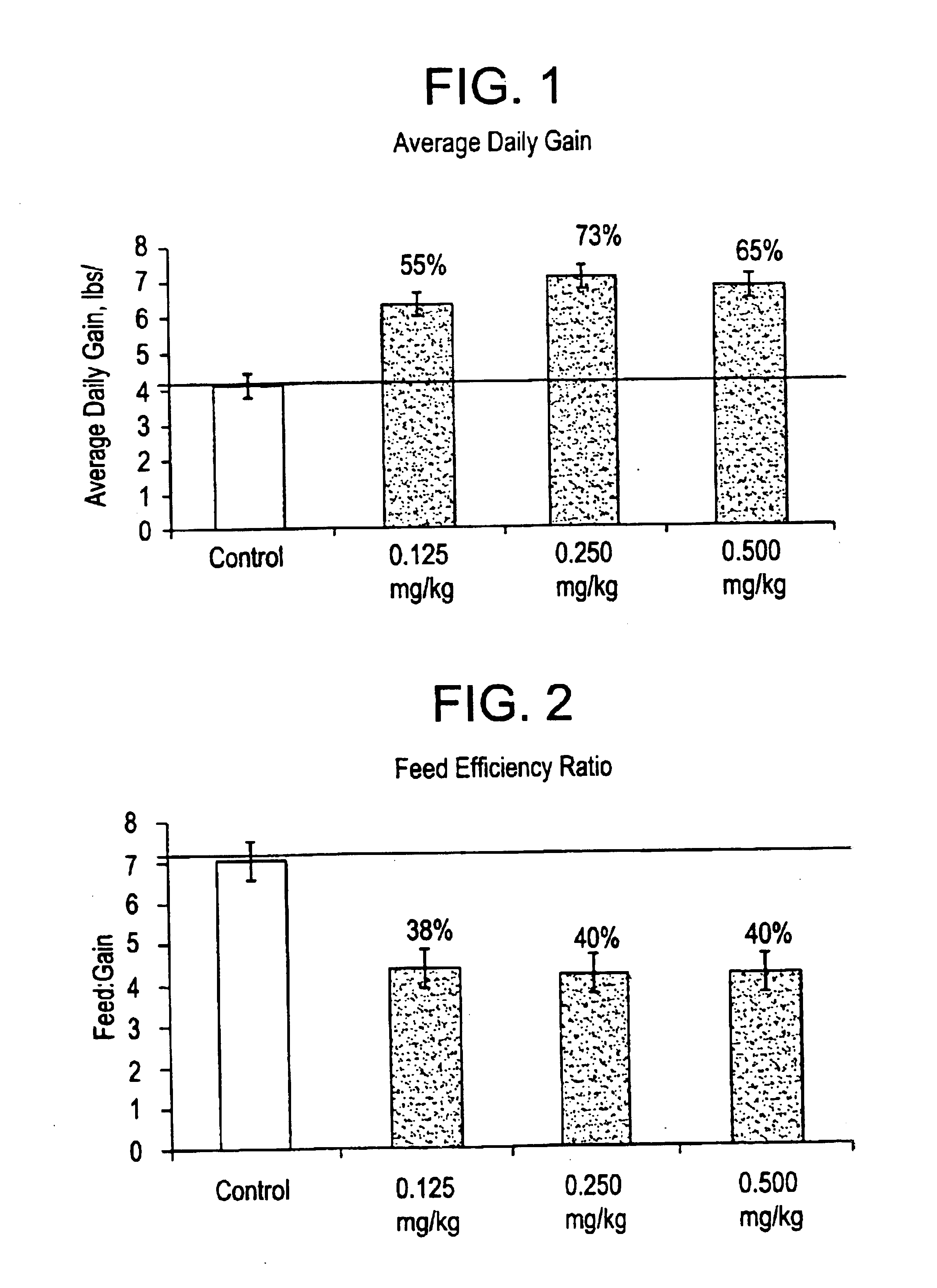
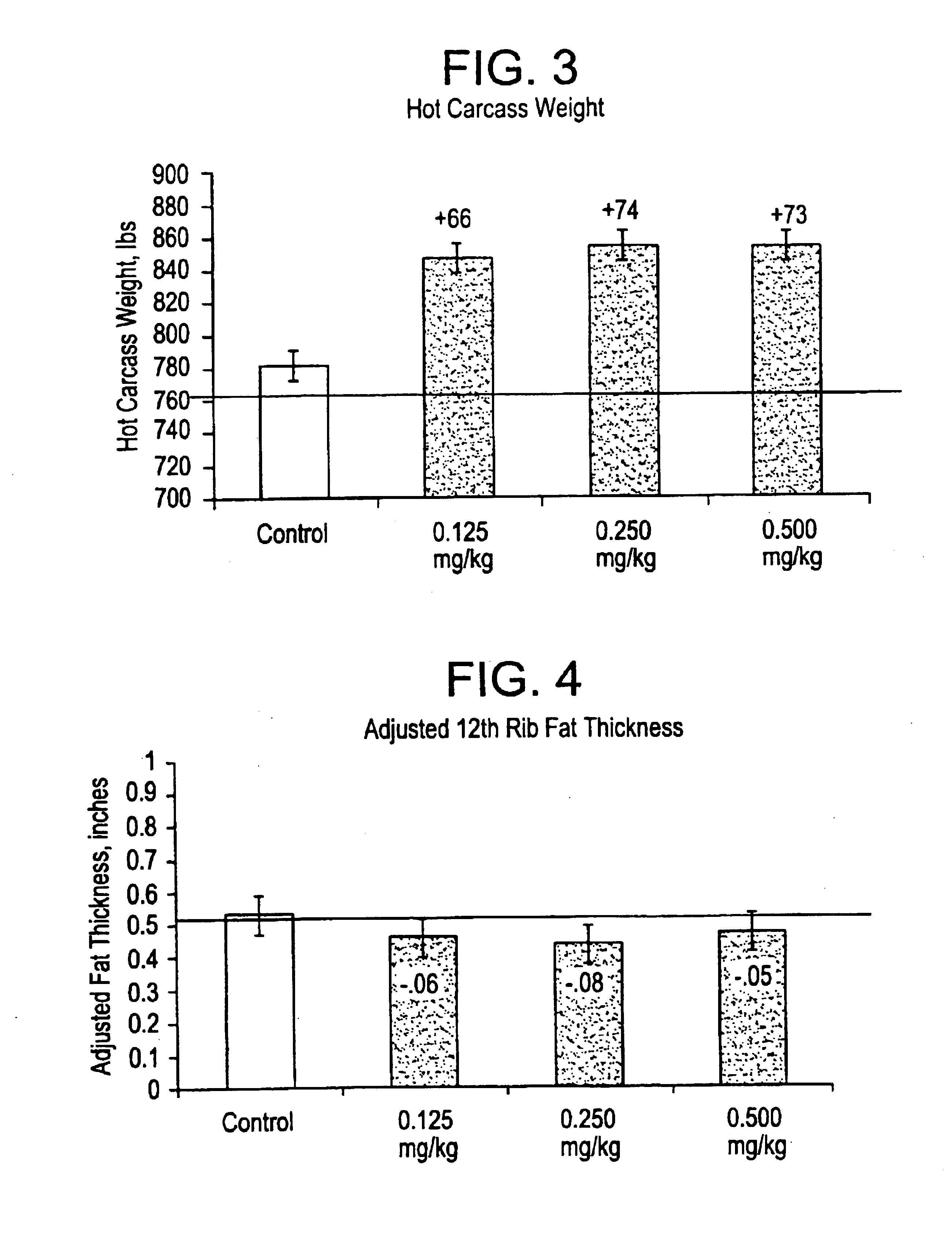
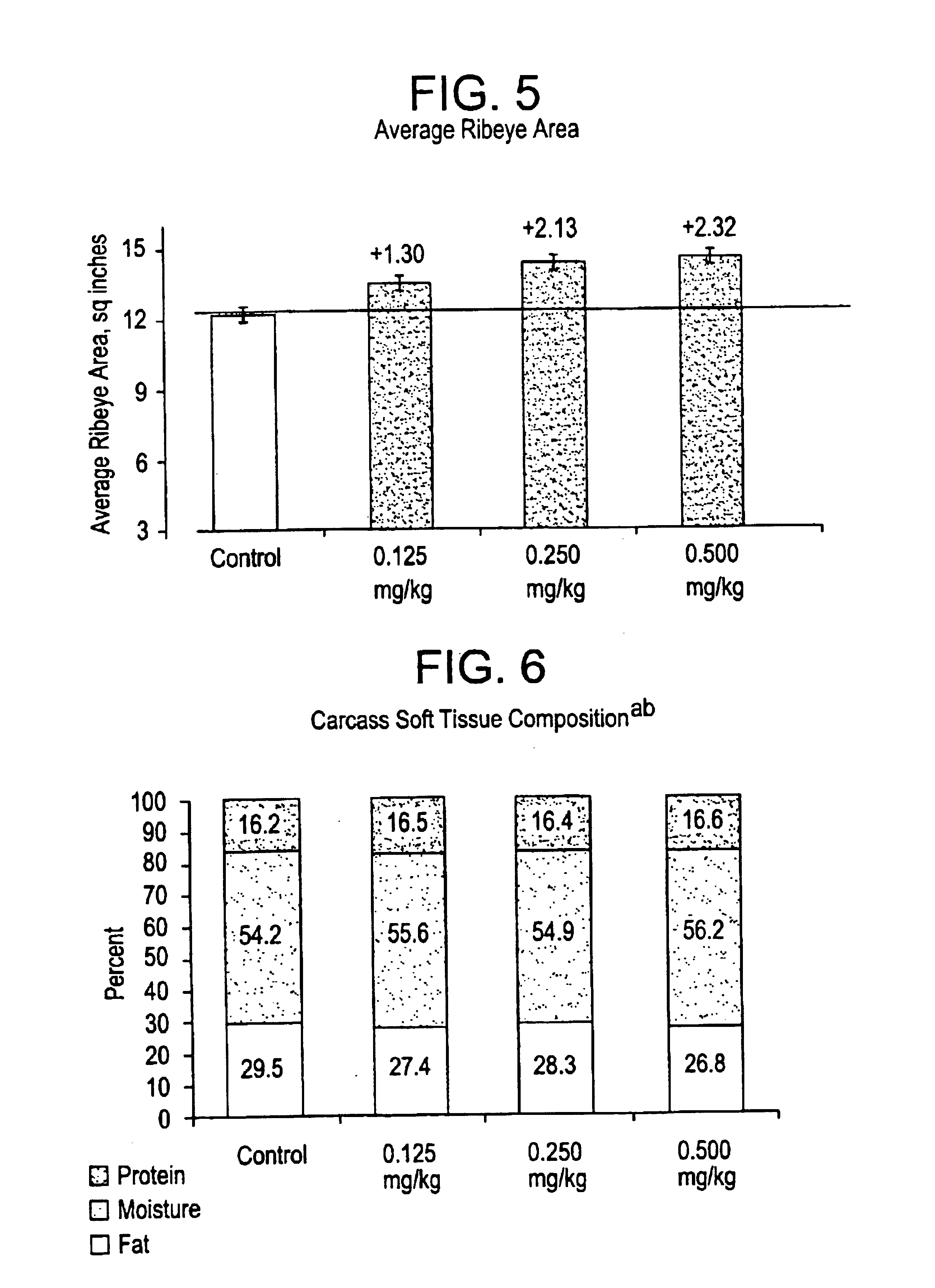
Disclosed is a compound represented by structural formula (I): R1 is a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group. R2 and R3 are independently —H, a C1-C4 straight chained or branched alkyl group. R4 and R5 are independently —H, a C1-C4 straight chained or branched alkyl group or, taken together with the nitrogen atom to which each is bonded, a non-aromatic heterocyclic ring. Ring A and Ring B are independently further substituted with zero, one or two substituents. Physiologically acceptable salts of structural formula shown above are also included. Also disclosed is a method promoting growth, efficiency of feed utilization and / or production of lean body mass in a livestock animal. The method comprises administering to the animal an effective amount of one or more compounds represented by the structural formula as shown or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:ELANCO US INC
Dietary supplements containing extracts of nelumbo and processes of using same
InactiveUS20100227007A1Improve athletic performanceImprove enduranceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInsulin signallingDietary supplement
Materials derived from Nelumbo are administered orally to humans or animals for the purpose of enhancing creatine transport into skeletal tissue and for purposes of enhancing lean body mass. Enhancing creatine transport through improved insulin signaling is a new method of depositing creatine and enhancing lean body mass. Such administration is also used for enhancing athletic performance and controlling bodyweight and body fat levels. More specifically, such administration is used for the purpose of enhancing creatine transport into excitable tissues such as skeletal muscle. The material is administered as extracts of Nelumbo and administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks.
Owner:IN INGREDIENTS
Supplement feed for sheep
InactiveCN103371280AHigh protein contentNormal digestive functionAnimal feeding stuffMaldevelopmentYoung sheep
The invention discloses a supplement feed for sheep, relates to supplement feeds for domestic animals, and belongs to a supplement compound premixed feed for winter and spring. The supplement feed is mainly prepared from the following materials by weight percentage: 78-85% of concentrated feed and 15-25% of green feed, wherein the concentrated feed comprises soybeans, bean cakes, corns, wheat bran, rice bran, calcium hydrophosphate, mountain flour and salt, and the green feed comprises alfalfa, highland barley and maize straws. The supplement feed for the sheep has the beneficial effects that a nitrogen-containing additive serves as supplement for pasture with insufficient protein level in winter and spring, so that the problems that the lamb grows slowly, has lean body mass and has low rate of survival, the young sheep is in maldevelopment, and the mature sheep has low productivity caused by nutrition reduction of the pasture in winter and spring in a traditional sheep feeding manner are solved.
Owner:袁宏
Methods for managing weight loss and body mass
ActiveUS8968804B2Increased energy expenditureAvoiding at least some of the undesirable animal behaviorsMetabolism disorderAnimal feeding stuffAnimal behaviorWeight-Loss Agents
The invention provides methods for promoting weight loss by an animal, promoting weight loss by an animal while preventing or minimizing loss of lean body mass by the animal, preventing a reduction in energy metabolism by an animal, reducing the risk of regaining weight by an animal after weight loss, and ameliorating undesirable animal behaviors associated with reduced caloric intake by intermittently feeding an animal a first diet containing calories that meet the animal's maintenance energy requirements and a second diet containing calories that do not meet the animal's maintenance energy requirements. In preferred embodiments, the described feeding pattern and diets are fed in conjunction with one or more weight loss agents.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Isoflavone compositions for reducing accumulation of body fat in male mammals, and methods for their use
ActiveUS20070110789A1Reduce fat accumulationEfficient reductionBiocideMetabolism disorderAnimal scienceMetabolite
Edible compositions useful for weight management in male animals are disclosed. The compositions comprise one or more isoflavones or isoflavone metabolites and are particularly useful for reducing or preventing the accumulation of body fat. Also disclosed are methods useful for weight management in an animal utilizing compositions comprising one or more isoflavones. The compositions and methods are particularly useful for the reduction or prevention of body fat accumulation during periods of excess caloric intake, and preferably have a sparing effect on lean body mass.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Weight management system for obese animals
ActiveUS20030138548A1Organic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsAnimal scienceSevere weight faltering
A diet system for promoting comprehensive weight management in companion animals. The diet system includes a stage I pet food product for promoting weight loss and building lean body mass and a stage II pet food product for maintaining the weight loss and the lean body mass.
Owner:MARS INC
Dietary compositions containing alpha amino n-butyrate and methods of enhancing lean body mass
InactiveUS20080242727A1Increase synthesisDecrease protein catabolismBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAlpha-Amino-N-Butyric Acid
A composition that may include branched chain amino acids, alpha amino n-Butyrate and / or alpha amino-n-valerate works synergistically to enhance lean body mass and prevent body mass breakdown. The composition may also be coupled with other agents to a) provide an increased level of amino acids and / or protein in the body's total pool or b) increase markers for protein translation or decrease markers of protein turnover. The composition may be administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks. Increasing lean body mass is import to athletes looking to enhance performance, in the event of certain muscle wasting diseases, and to the general population that loses muscle mass as it ages.
Owner:ROMERO TIM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com