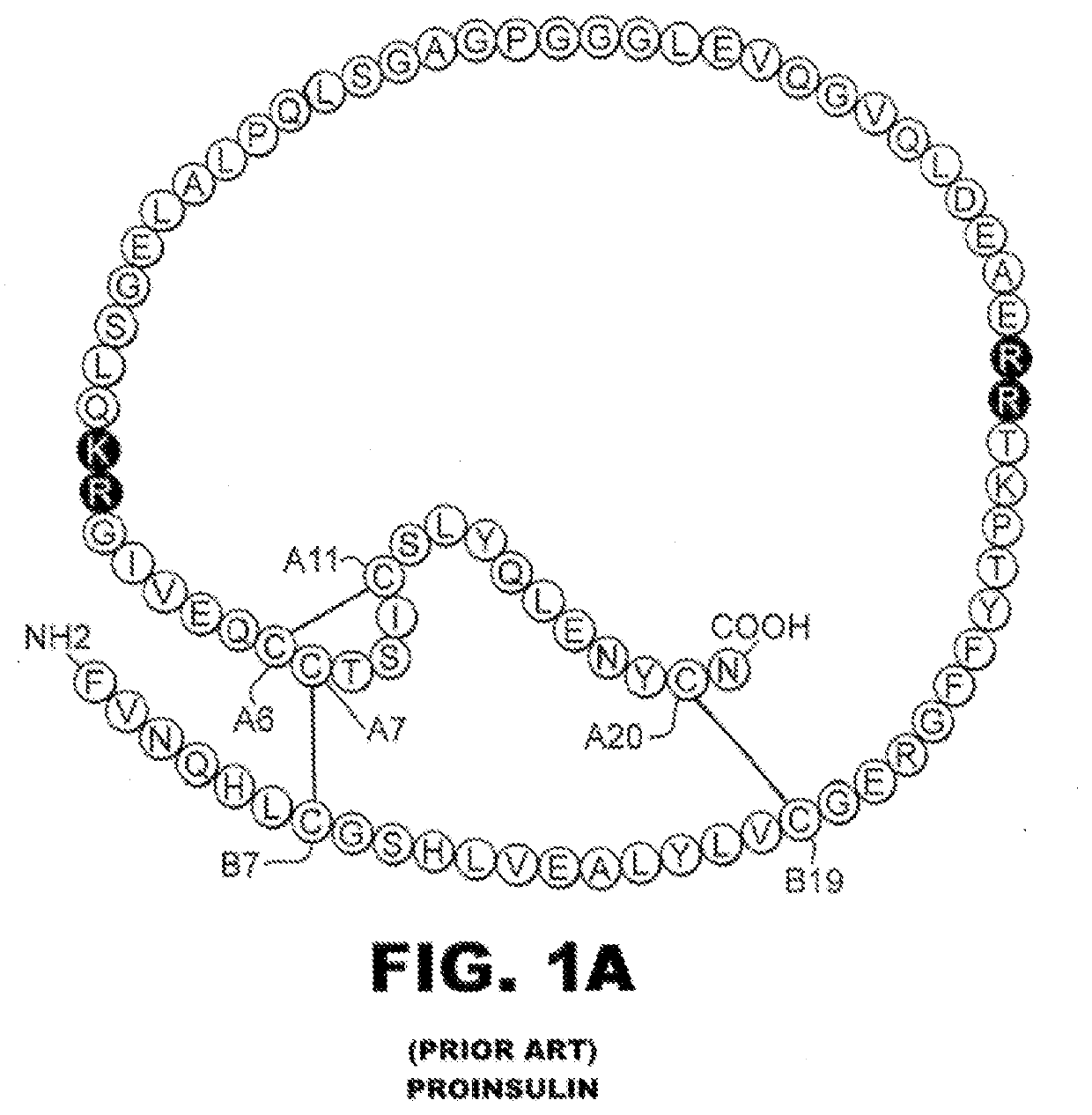
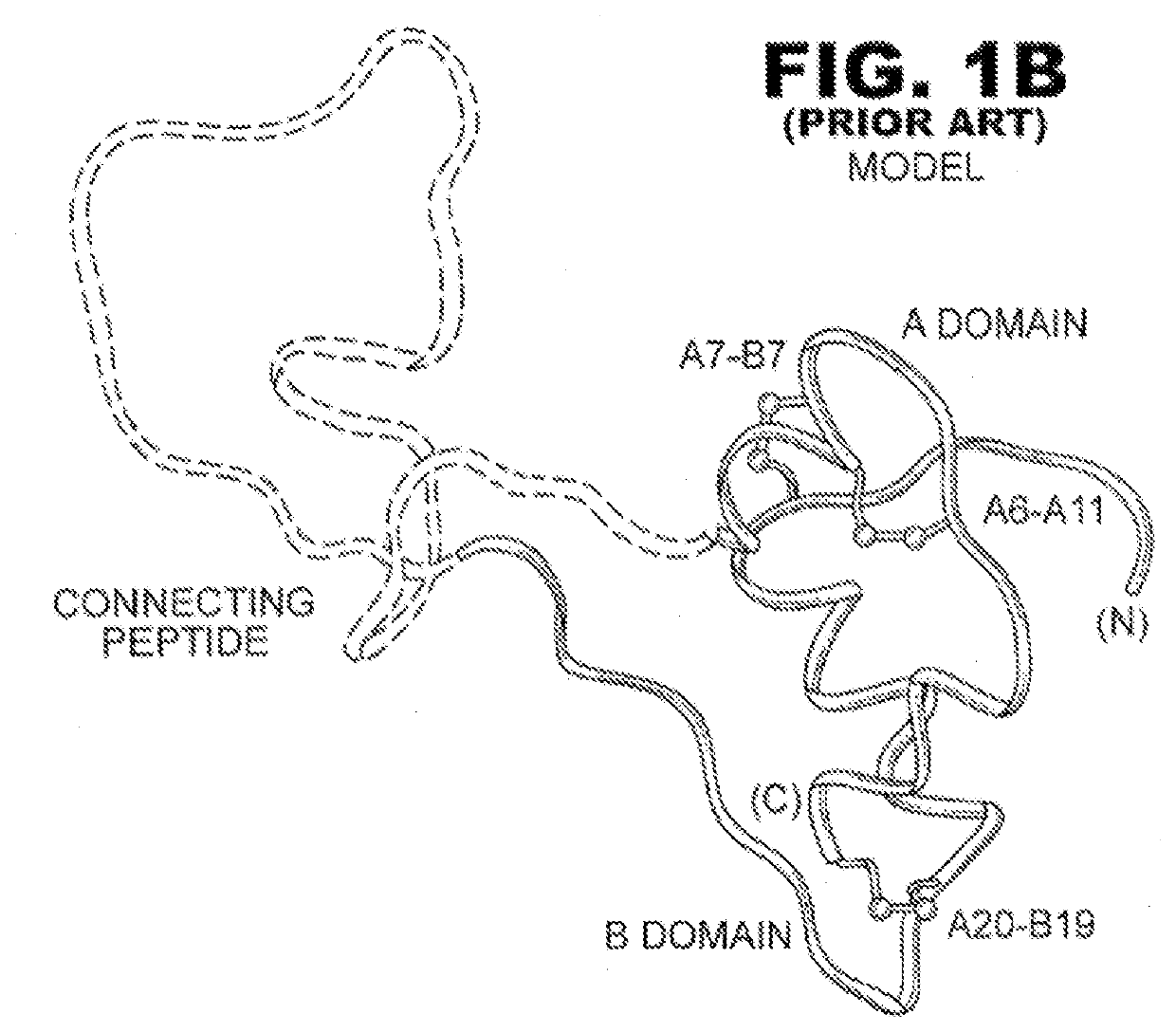
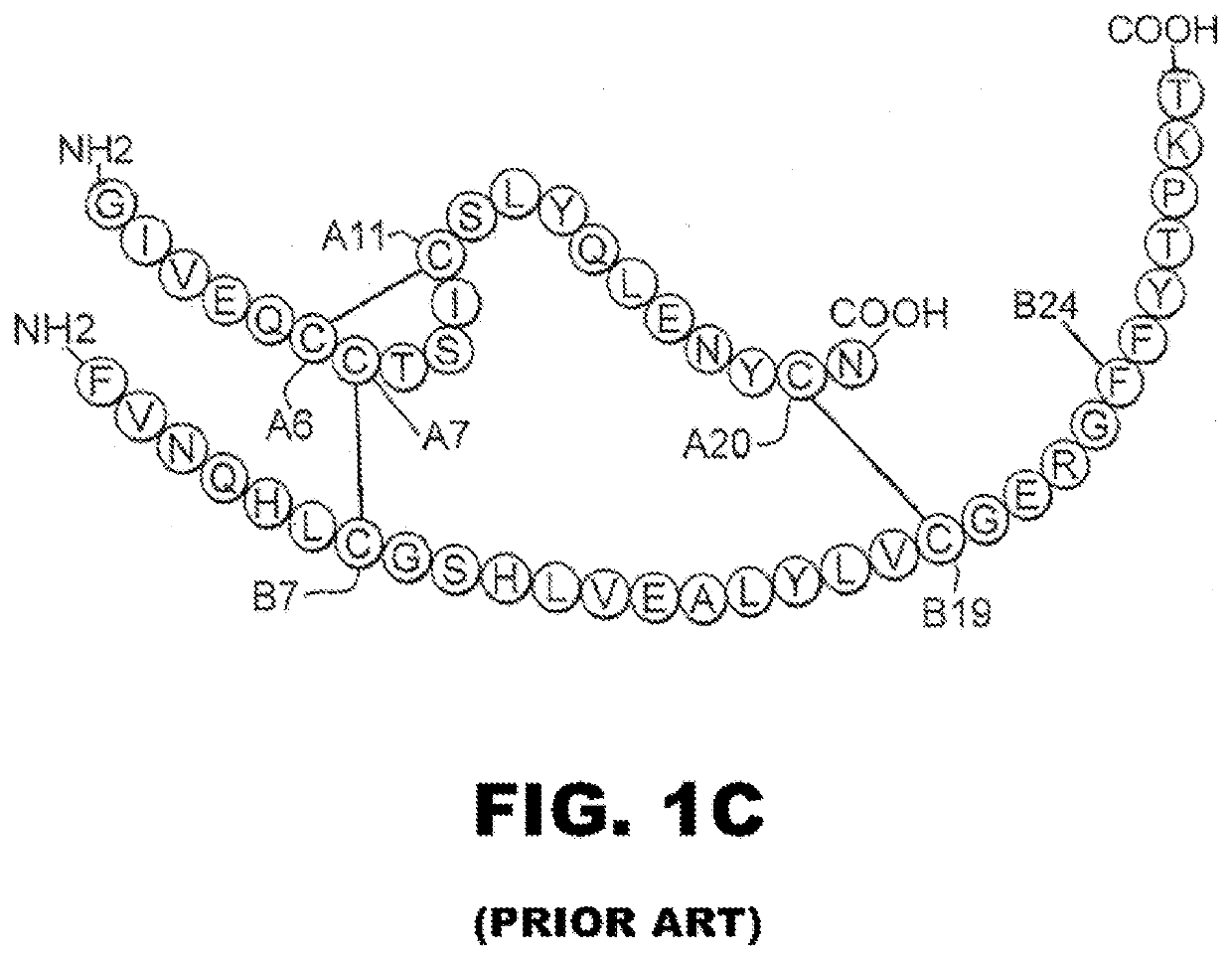
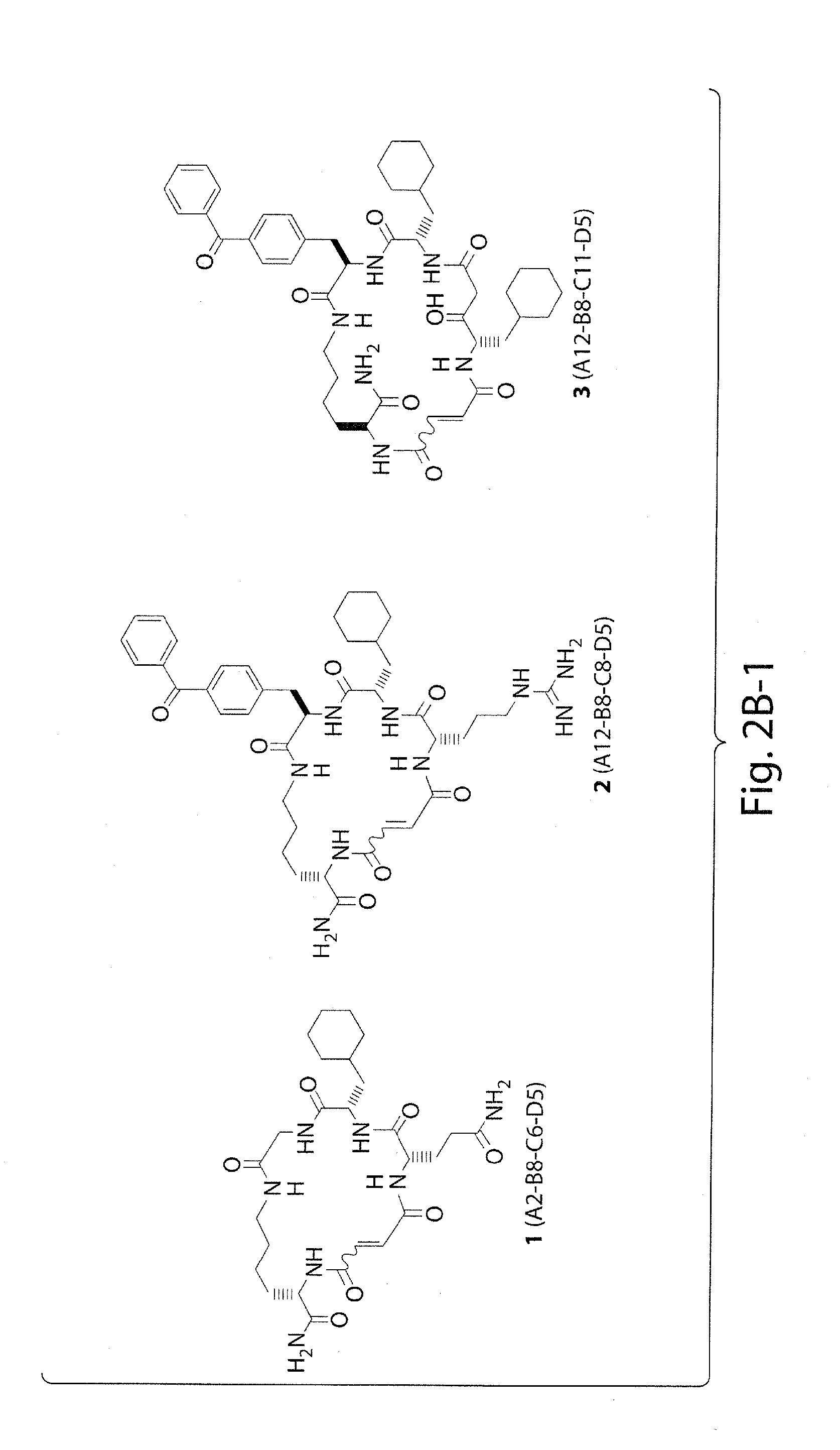
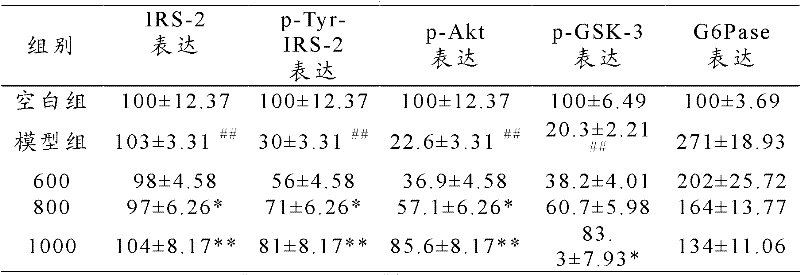
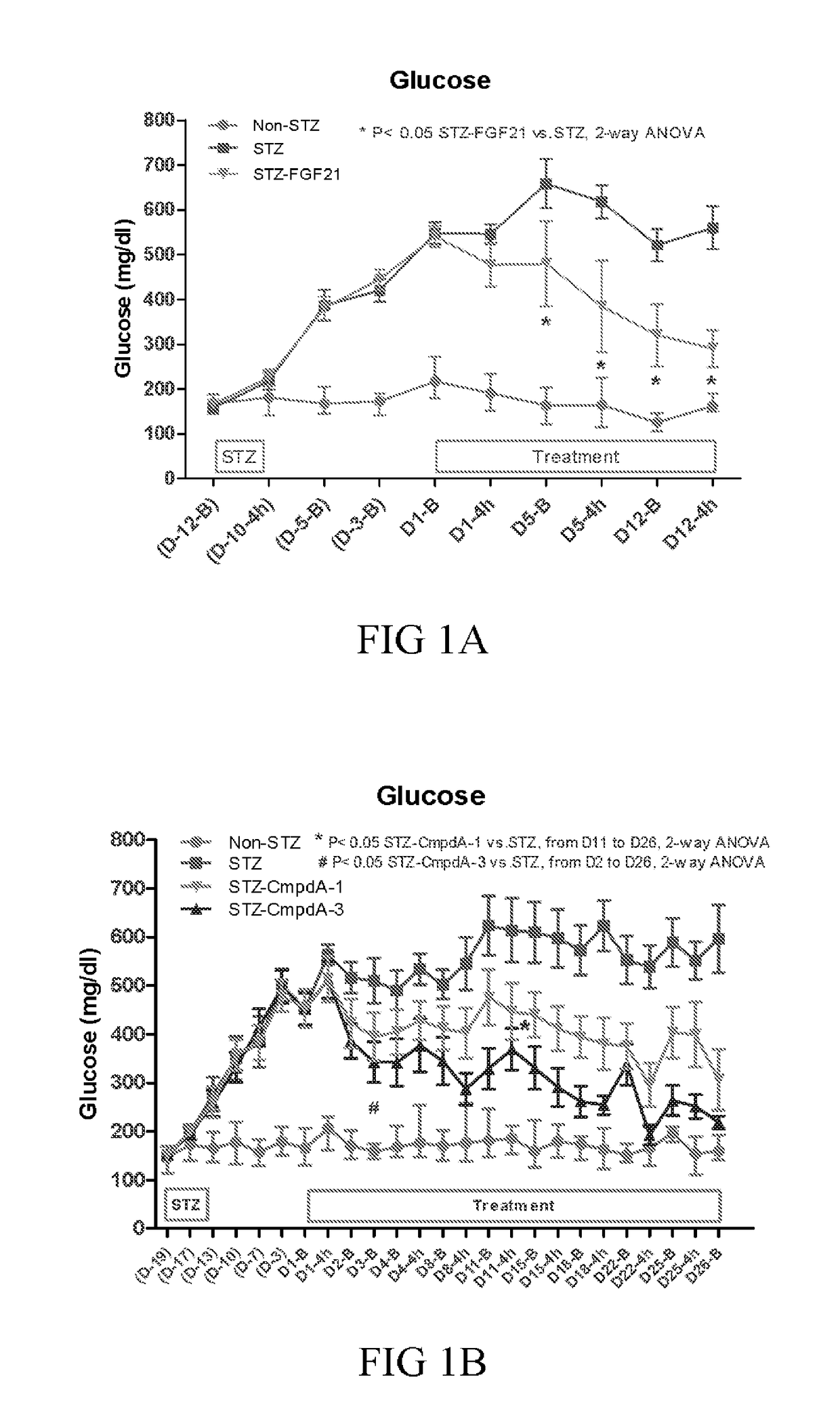
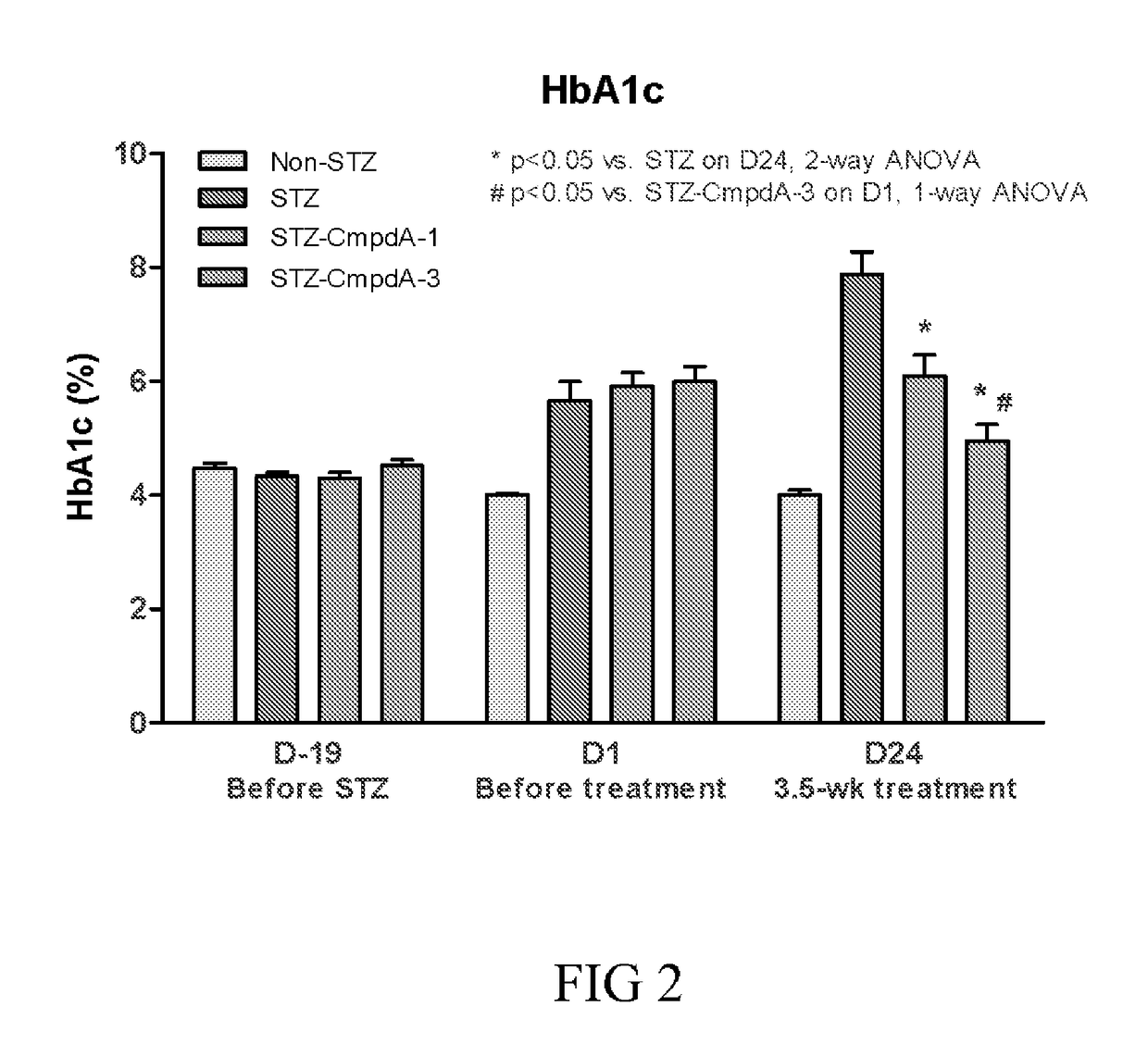
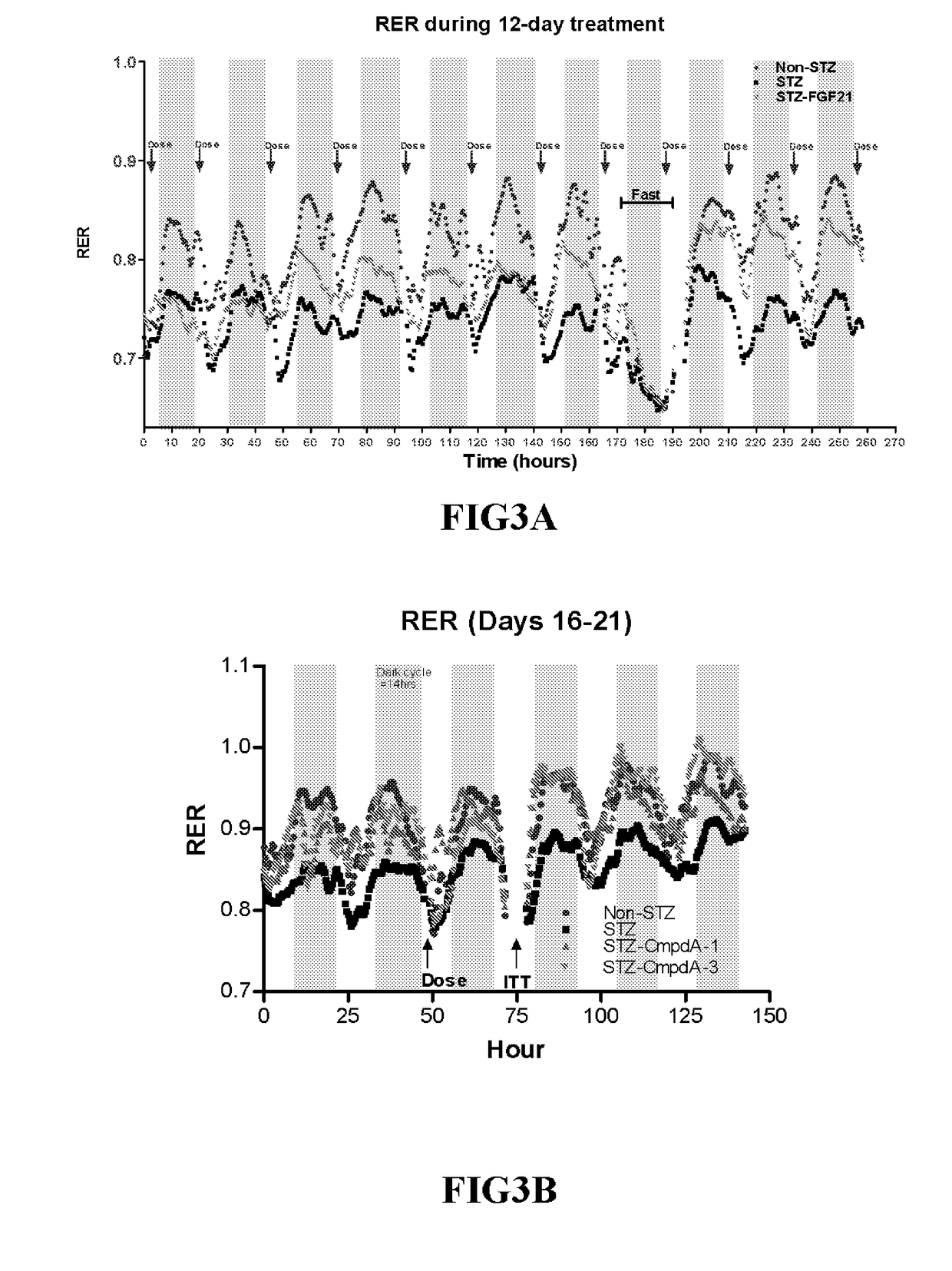
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Insulin signalling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
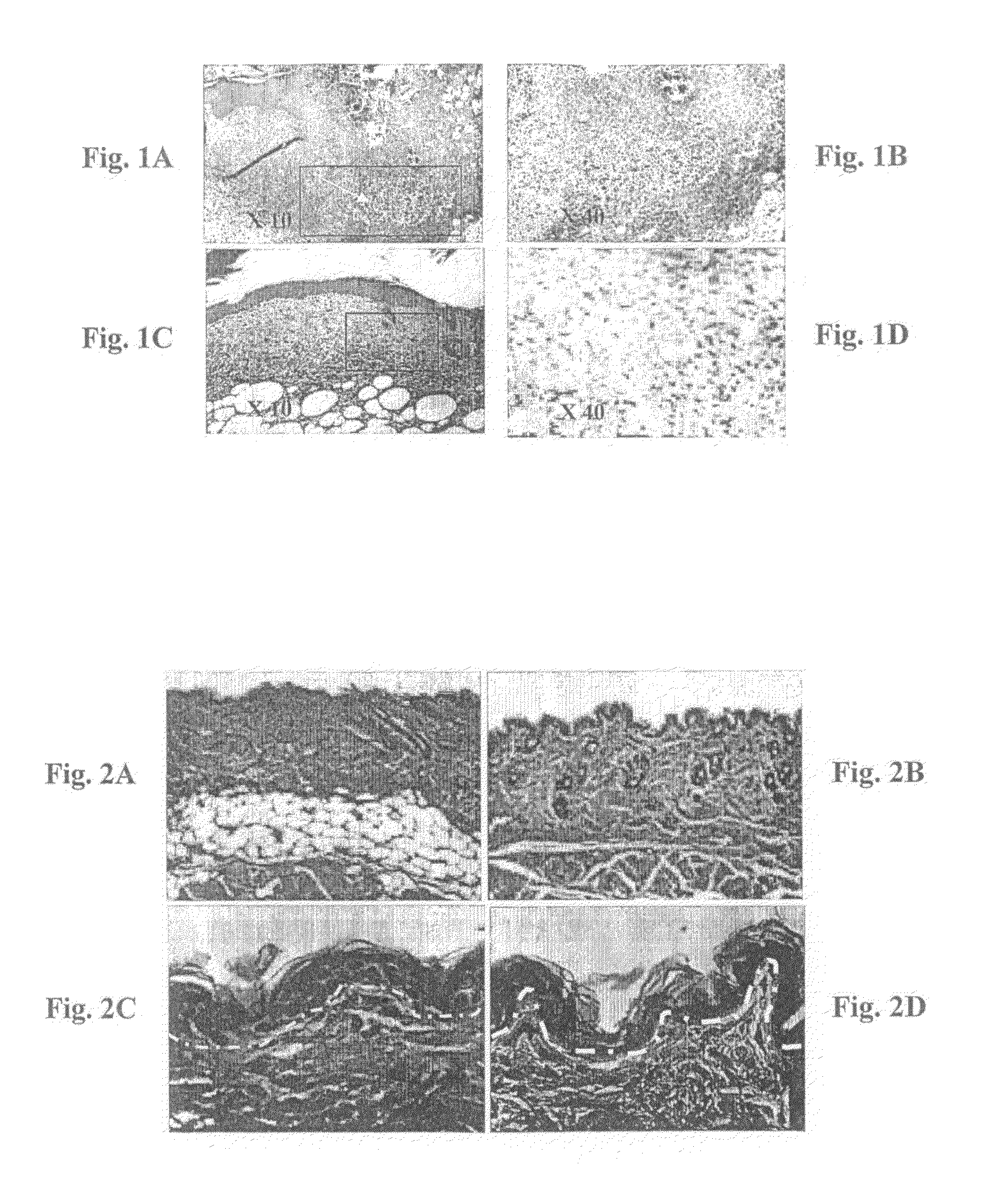
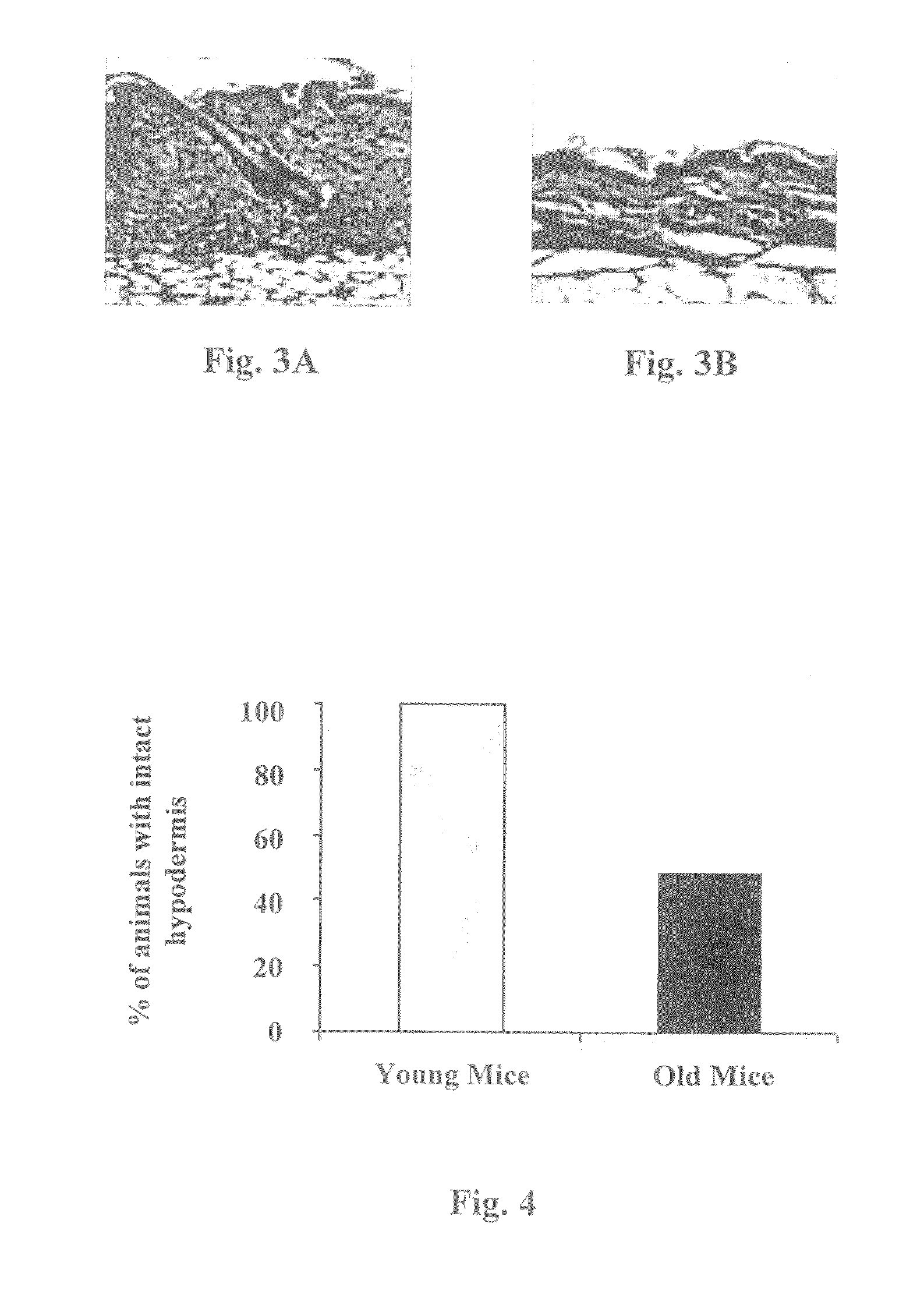
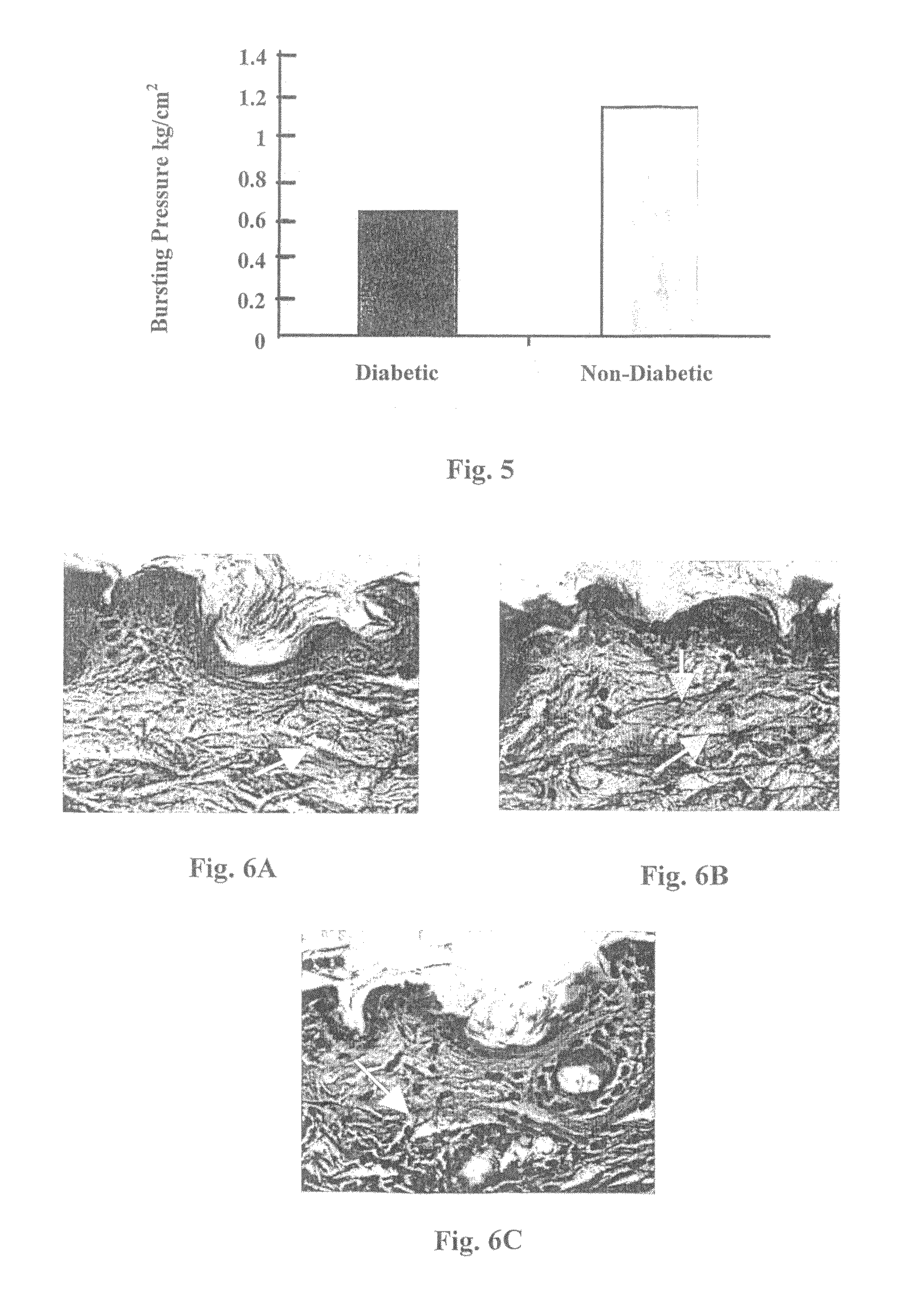
Method and compositions for prevention and treatment of diabetic and aged skin
ActiveUS8367606B2Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiabetes mellitusSubcutaneous adipose tissue
Method and compositions are provided for treating or preventing a skin pathology or disorder associated with diabetes and / or aging, by topical administration of at least one agent capable of restoring an impaired physiological condition of the skin associated with said skin pathology or disorder. Examples of such agents include PKC modulating agents, various adipokines and insulin signaling related molecules. In particular, restoration of the subcutaneous adipose tissue can overcome many of the diabetic skin pathologies and aging skin disorders and conditions.
Owner:HEALOR LTD
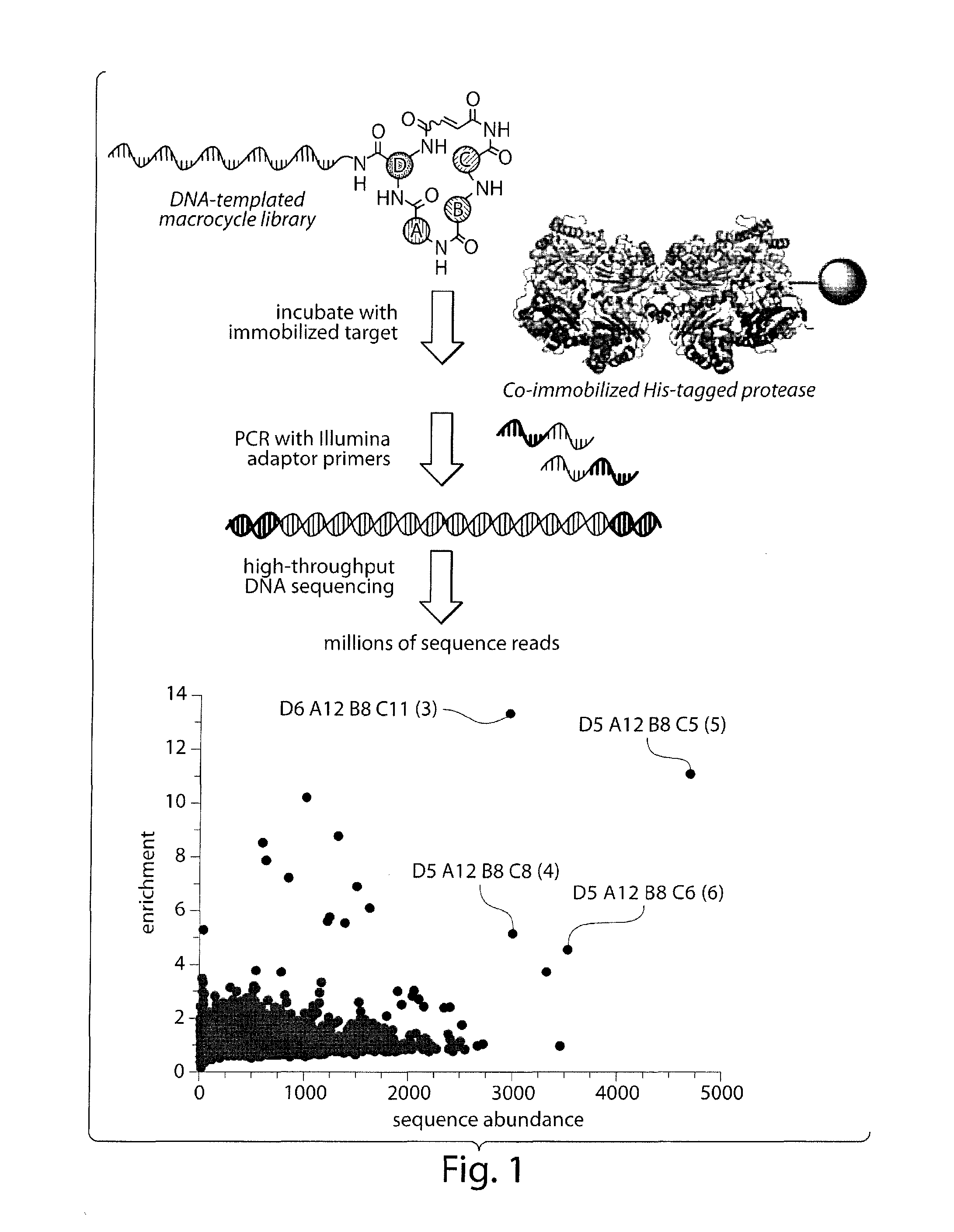
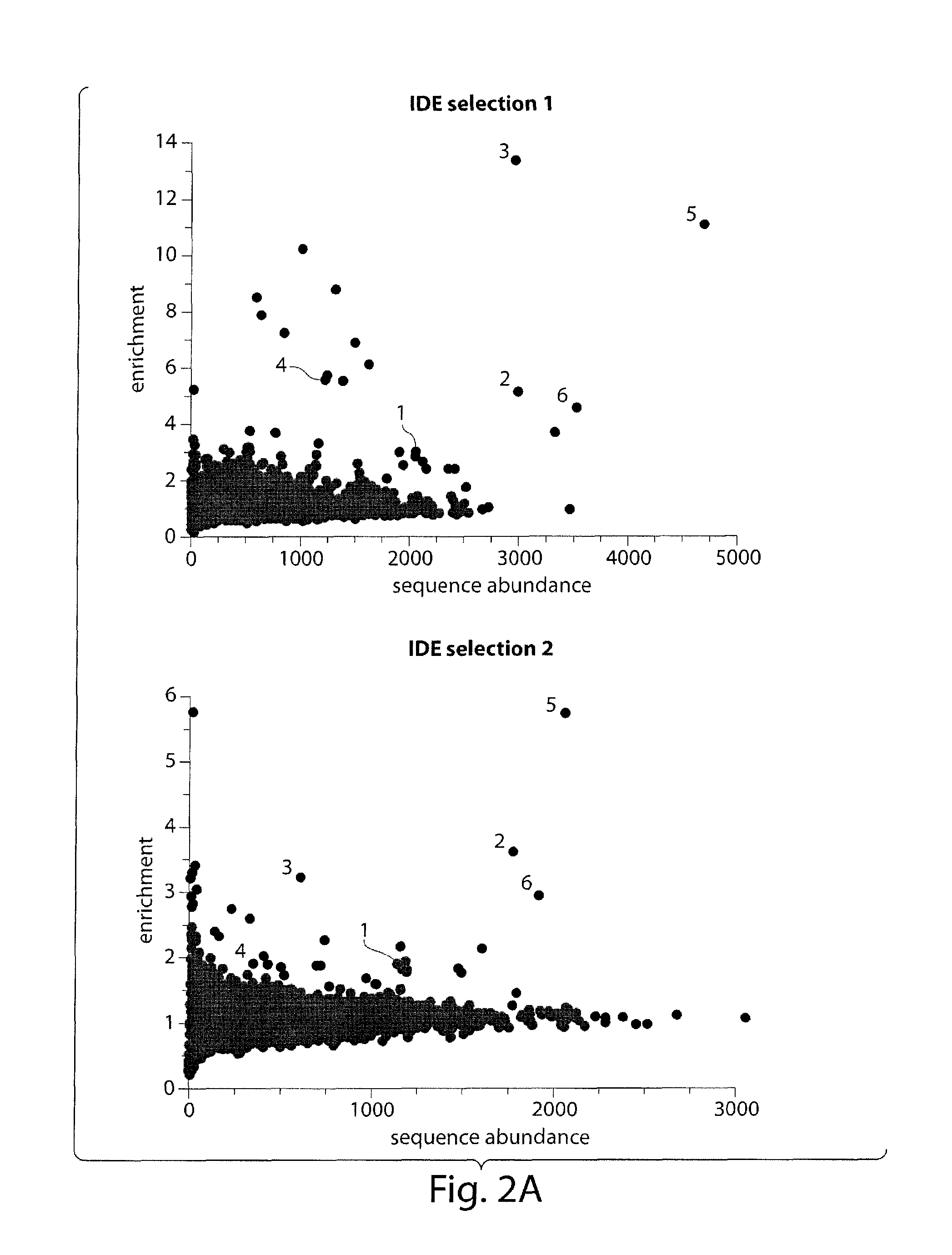
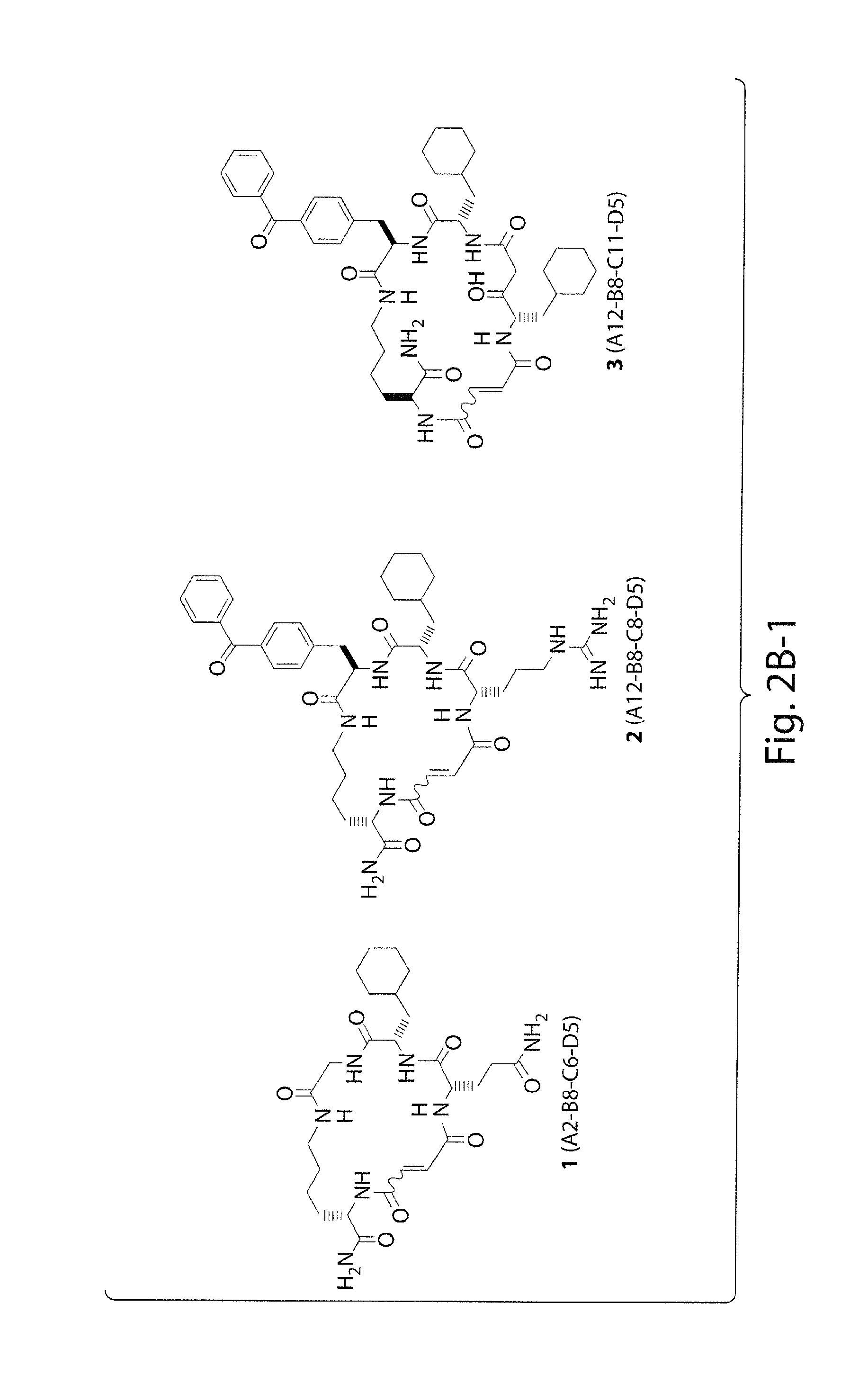
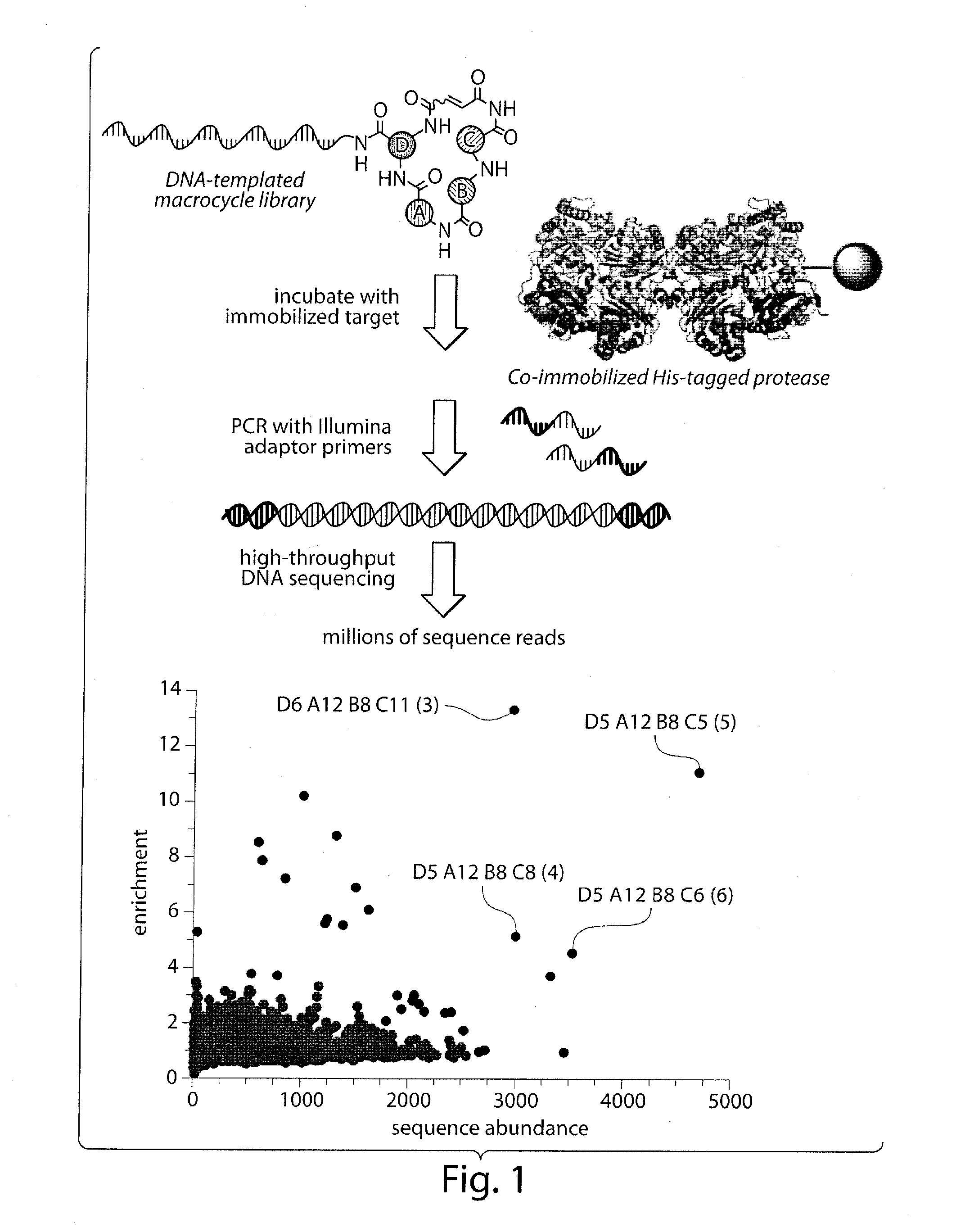
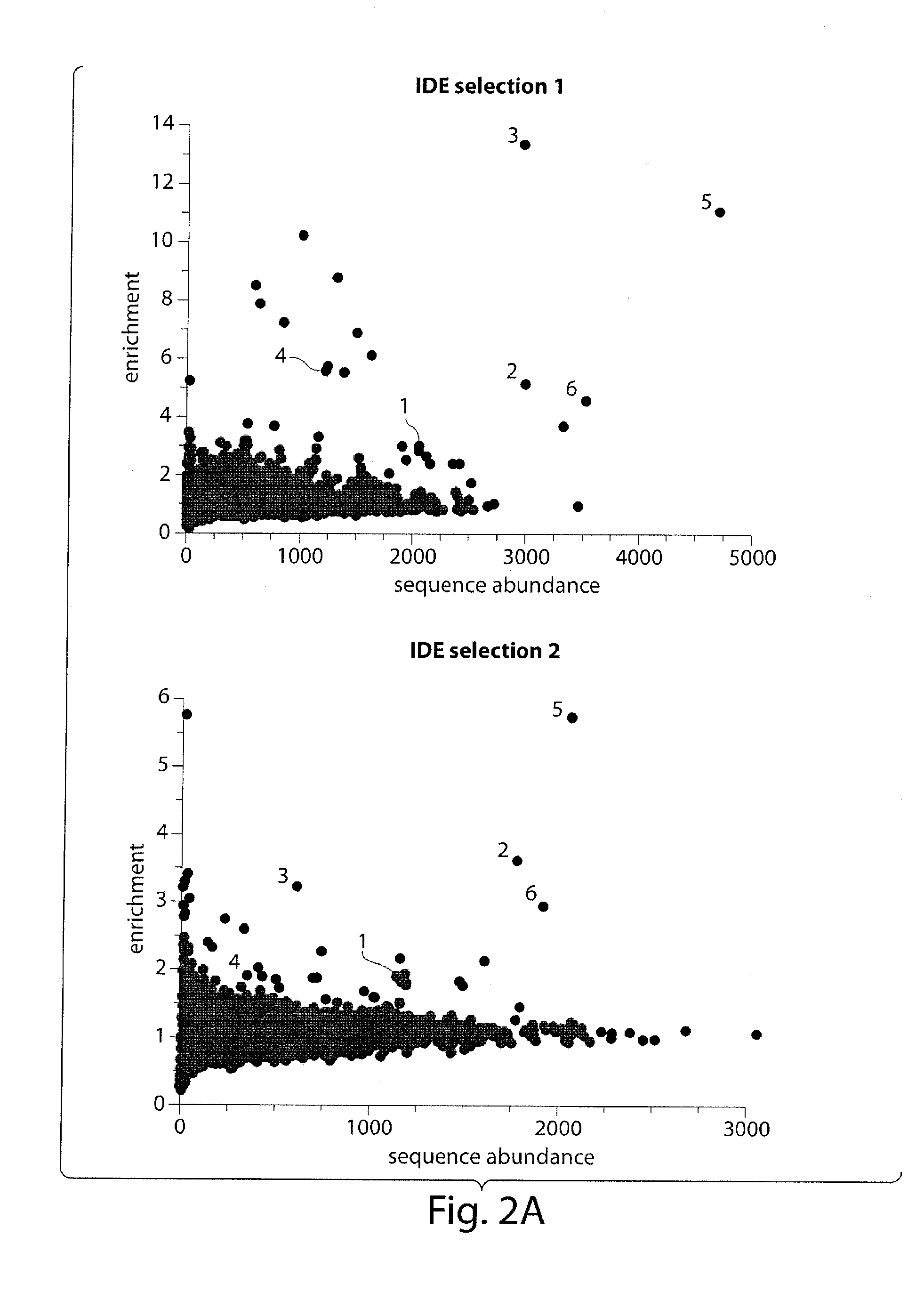
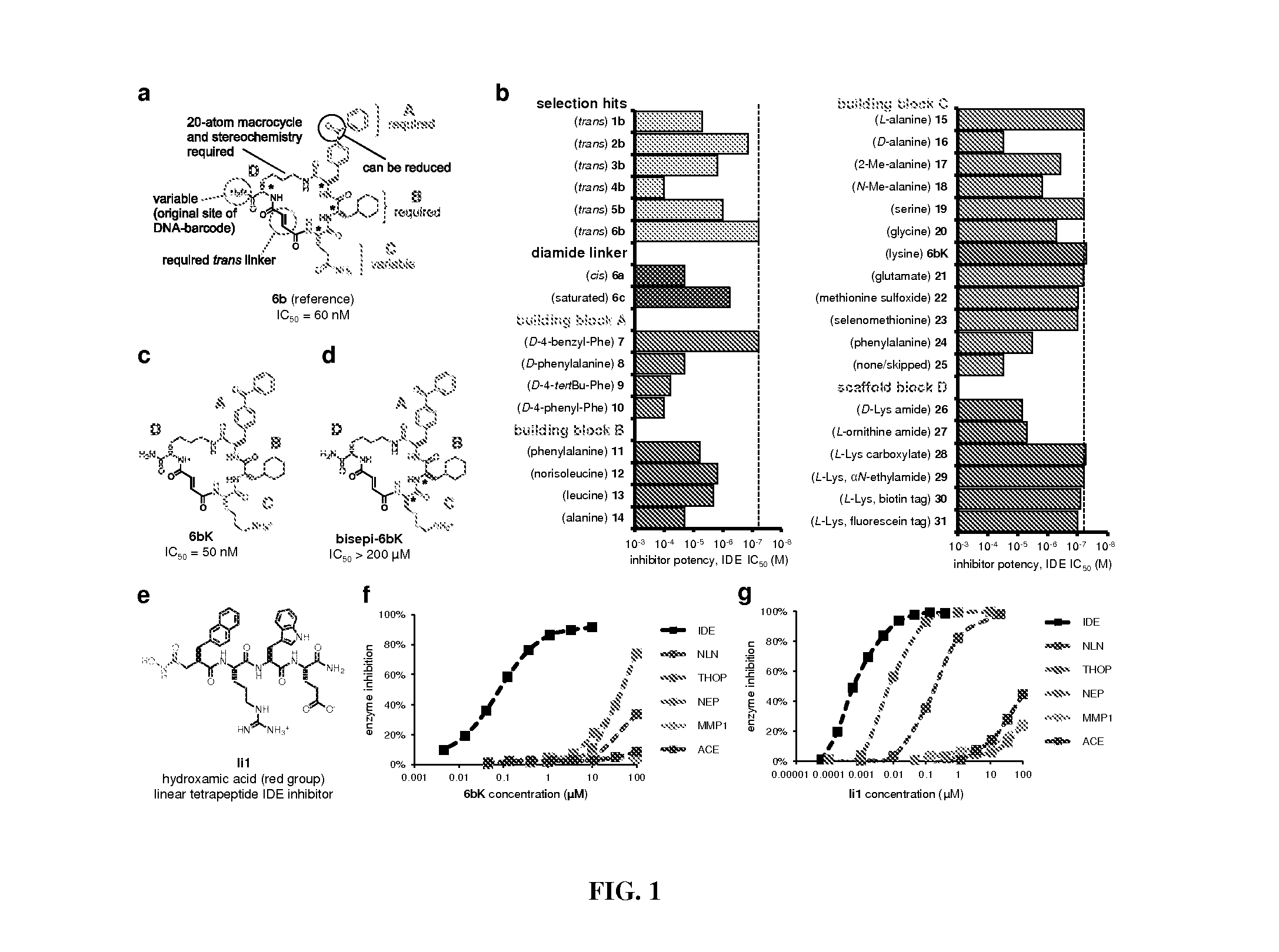
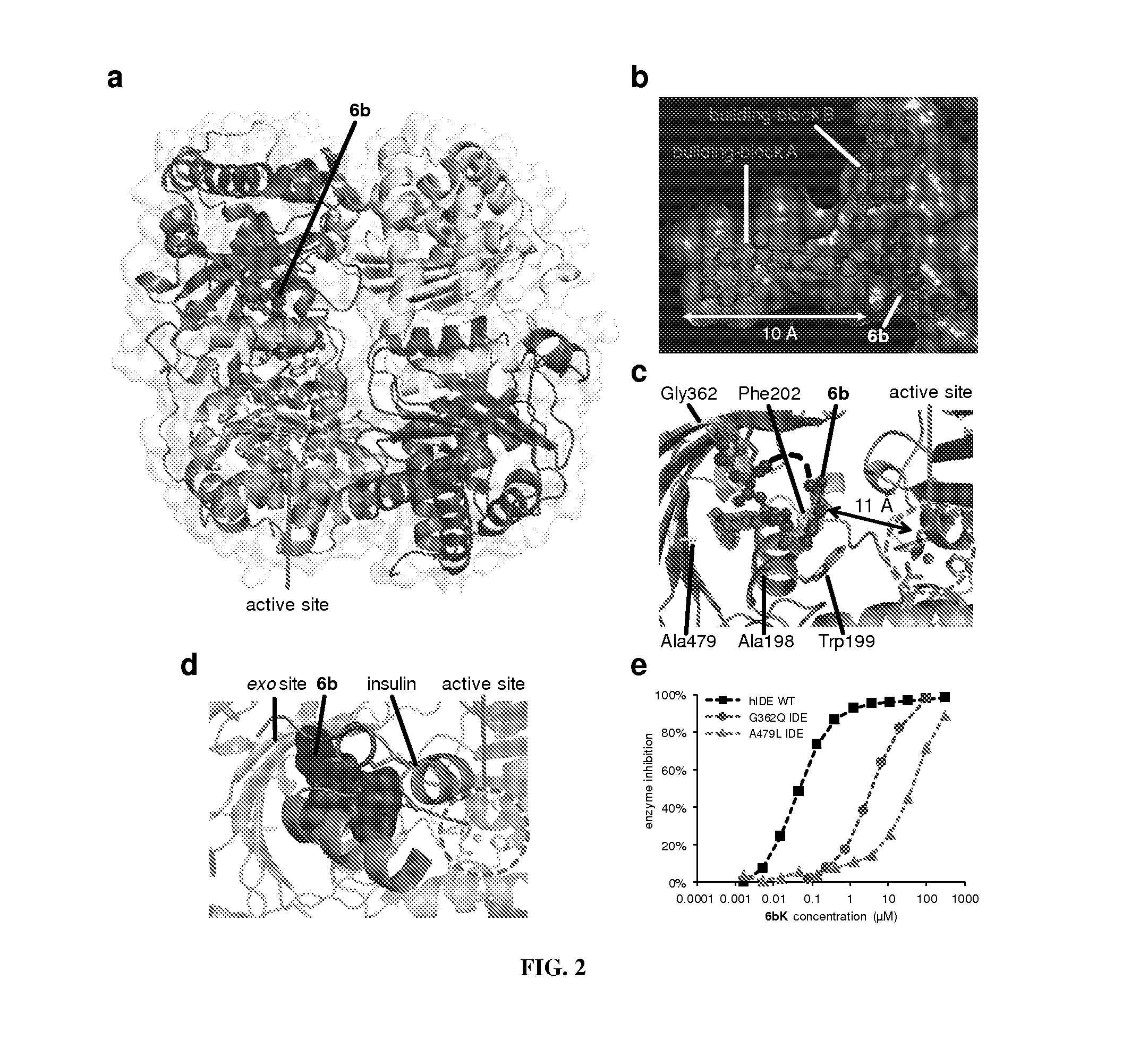
Macrocyclic insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS9243038B2Decrease entropic costLimited accessOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin-degrading enzymeInsulin signalling
Macrocyclic compounds that specifically inhibit insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) are provided. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, hydrates, stereoisomers, polymorphs, tautomers, isotopically enriched forms, and prodrugs of the macrocyclic IDE inhibitors are also described. Pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. In vivo and in vitro methods of using the IDE inhibitor, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the IDE inhibitor, for example, for the inhibition of IDE in a subject exhibiting aberrant IDE activity, impaired insulin signaling, or insulin resistance, for example, a subject having diabetes, are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
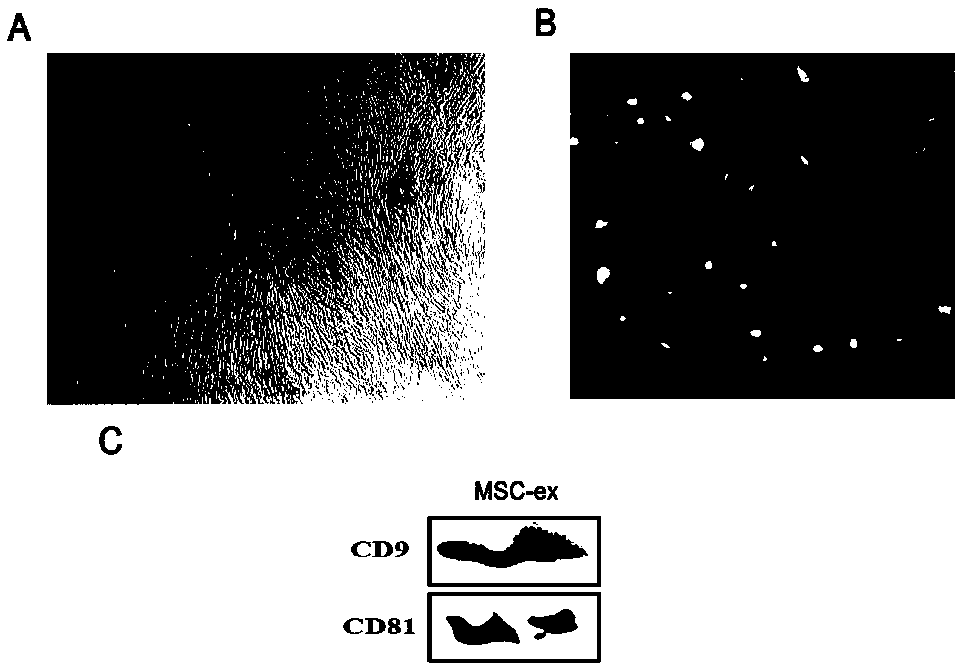
Separation and purification method of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome and application of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome
ActiveCN108103017AHigh protein purityGood repeatabilityMetabolism disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSucrosePurification methods
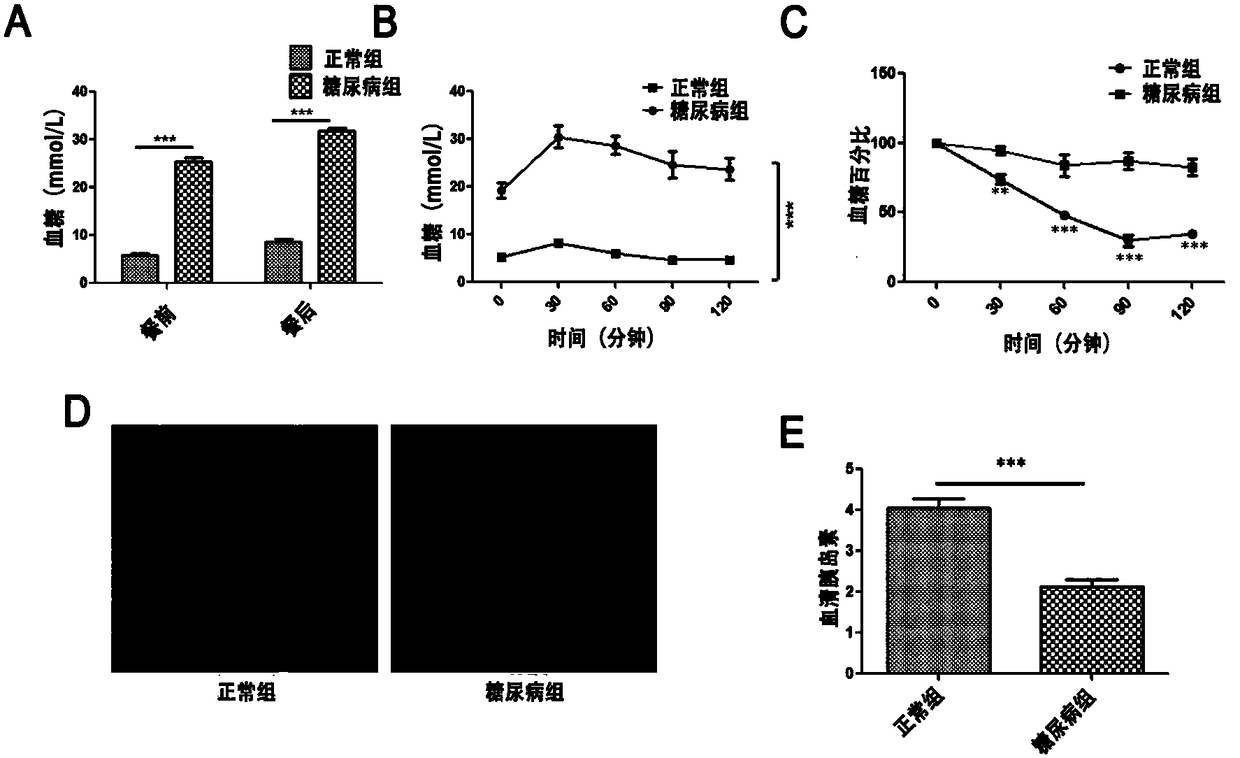
The invention provides a separation and purification method of a human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome and an application of the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome provided by the invention is prepared by cultivating human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via aserum-free medium, collecting supernatant liquid, implementing centrifuging as well as ultra-filtration and concentration, transferring a concentrated solution onto a 30% sucrose-heavy water densitypad and implementing further purification through sucrose density centrifuging, so that the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome is obtained. According to the separation and purificationmethod that the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome is obtained through separation and purification, immunoreactivity is effectively reduced, and a controllable dosage when the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome is used is guaranteed. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome, by improving a degree of activating an insulin signaling pathway of a type IIdiabetes animal model, can inhibit composition and decomposition of hepatic glycogen, so that glucose metabolism homeostasis can be achieved; and meanwhile, the sensitivity of the type II diabetes animal model to insulin and an insulin secretion function of pancreatic [beta] cells can be improved and a blood glucose concentration can be reduced, so that the application of the human umbilical cordmesenchymal stem cell exosome to the preparation of medicines for treating type II diabetes can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and compositions for prevention and treatment of diabetic and aged skin
ActiveUS20110021422A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiabetes mellitusSubcutaneous adipose tissue
Method and compositions are provided for treating or preventing a skin pathology or disorder associated with diabetes and / or aging, by topical administration of at least one agent capable of restoring an impaired physiological condition of the skin associated with said skin pathology or disorder. Examples of such agents include PKC modulating agents, various adipokines and insulin signaling related molecules. In particular, restoration of the subcutaneous adipose tissue can overcome many of the diabetic skin pathologies and aging skin disorders and conditions.
Owner:HEALOR LTD
Single-chain insulin analogues stabilized by a fourth disulfide bridge
ActiveUS20200140517A1Unfavorable effectReduces conformational fluctuationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDisulfide bondingDiabetes mellitus
A single-chain insulin analogue comprises a B-chain insulin polypeptide connected to an A-chain insulin polypeptide by a C-domain polypeptide. The B-chain insulin polypeptide contains a Cysteine substitution at position B4. The A-chain insulin polypeptide contains a Cysteine substitution at position A10. The C-domain polypeptide is 4 to 11 amino acids long. The analogue mitigates the unfavorable activity of this 4th disulfide bridge in conventional two-chain insulin analogues resulting in a duration of insulin signaling similar to that of wild-type insulin. A method of treating a patient with diabetes mellitus comprises the administration of a physiologically effective amount of the protein or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient. Use of a single-chain insulin analogue of the present invention in an insulin delivery device (such as a pump or pen) or as part of a high-temperature polymer-melt manufacturing process.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Fucoidan sulfate and application of low-molecular-weight fucoidan sulfate in preparation of metabolic syndrome resistant medicines and health products
InactiveCN104586878ASmall molecular weightEasy to transportOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderNatural productFucoidan
The invention provides fucoidan sulfate and an application of low-molecular-weight fucoidan sulfate in preparation of metabolic syndrome resistant medicines and health products. By adopting fucoidan sulfate, insulin signaling pathways can be relatively well improved, gluconeogenesis can be inhibited, the glycogen synthesis quantity can be increased, the glucose absorption of the skeletal muscles can be promoted, and insulin resistance can be effectively improved. Fucoidan sulfate can be taken as a natural product or medicine to be used for preventing and treating insulin resistance and metabolic syndromes; and fucoidan sulfate is sourced from marine algae, has the advantages of rich resources, easiness in industrialization and high safety, and has wide market and application prospects on the aspects of preventing and treating the metabolic syndromes. Fucoidan sulfate and the application provided by the invention can be used for providing reference significance and enlightenments for high-value applications of the marine algae.
Owner:MARINE BIOMEDICAL RES INST OF QINGDAO CO LTD
Compositions and Methods for Treating Disease
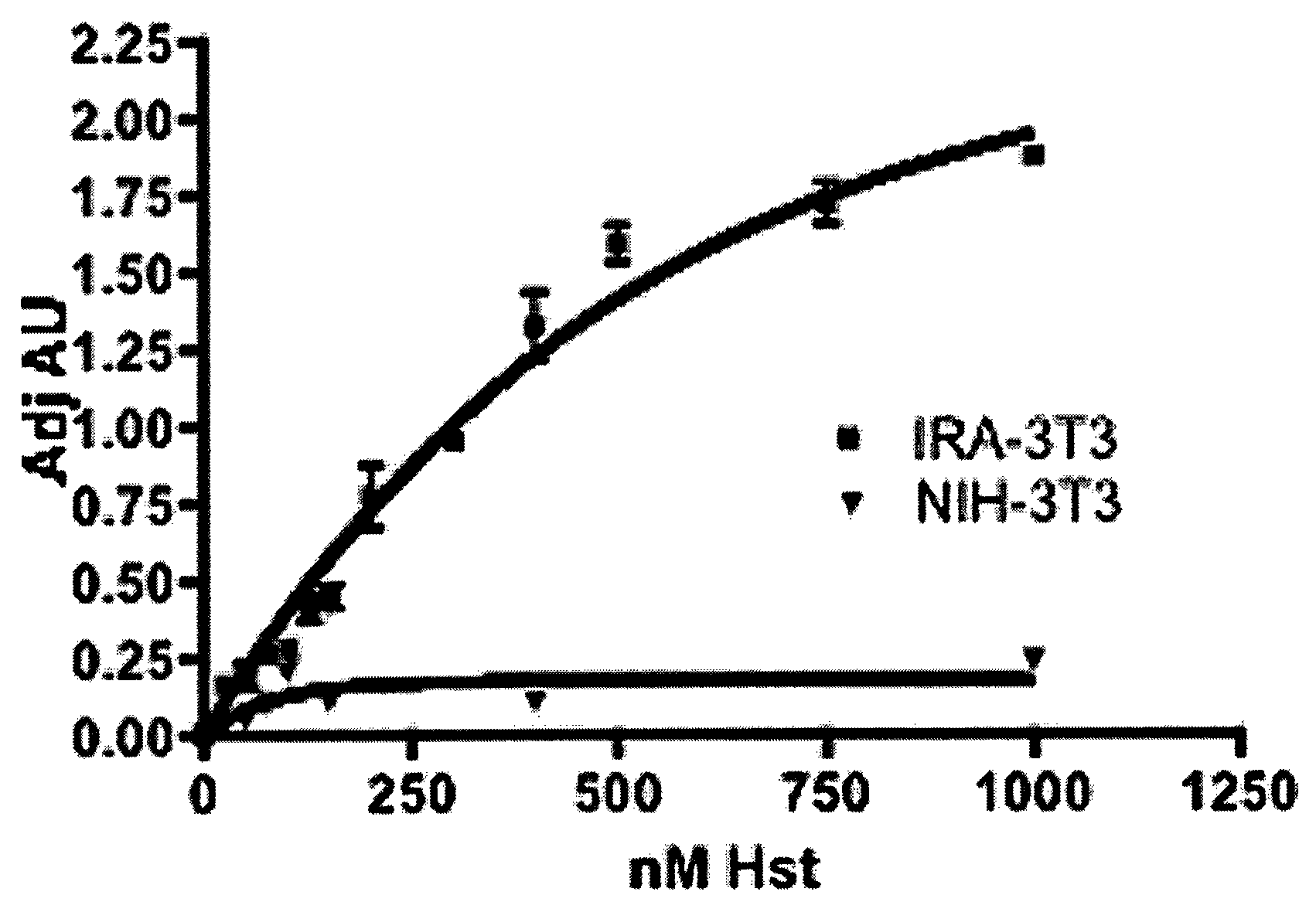
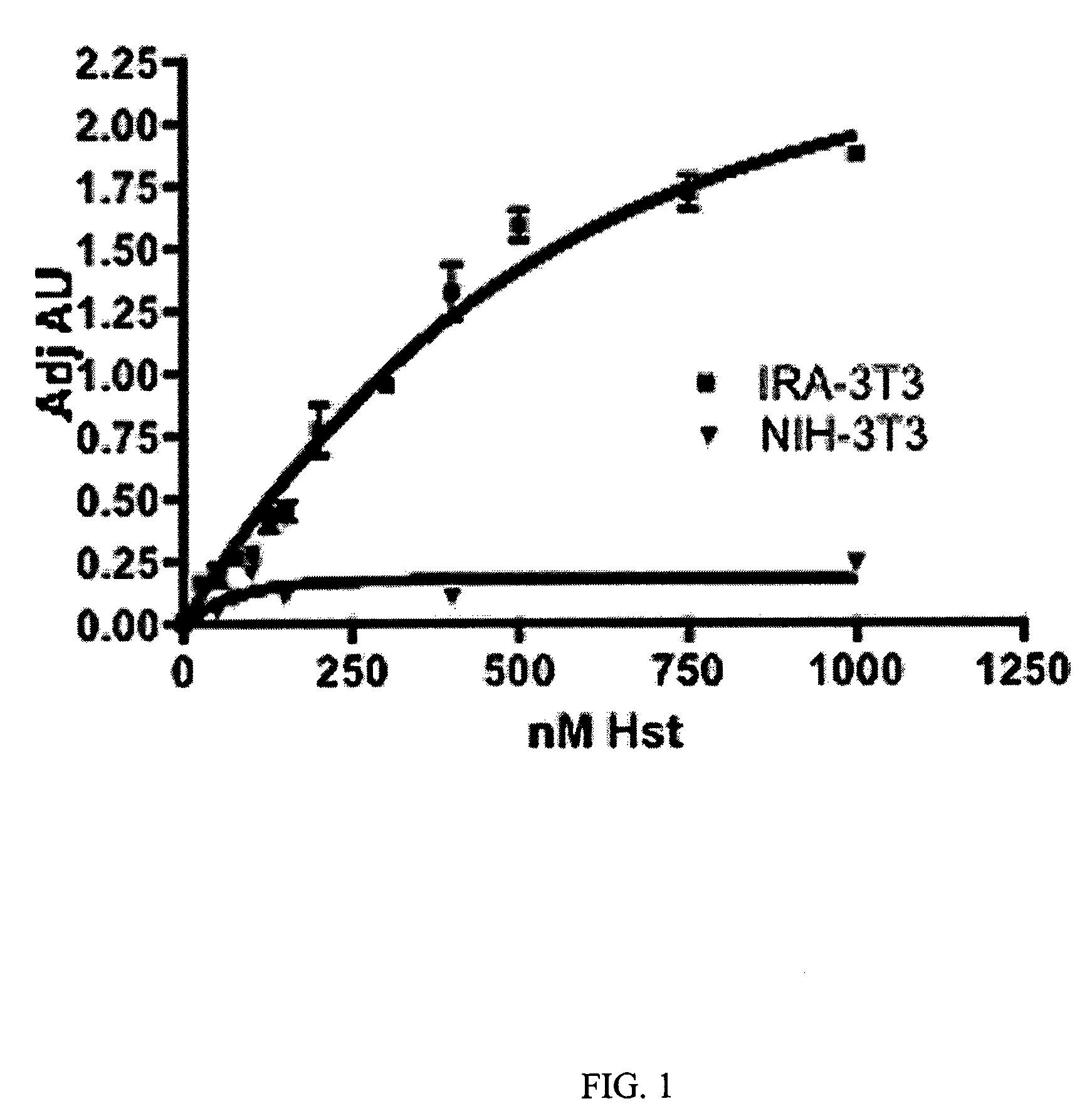
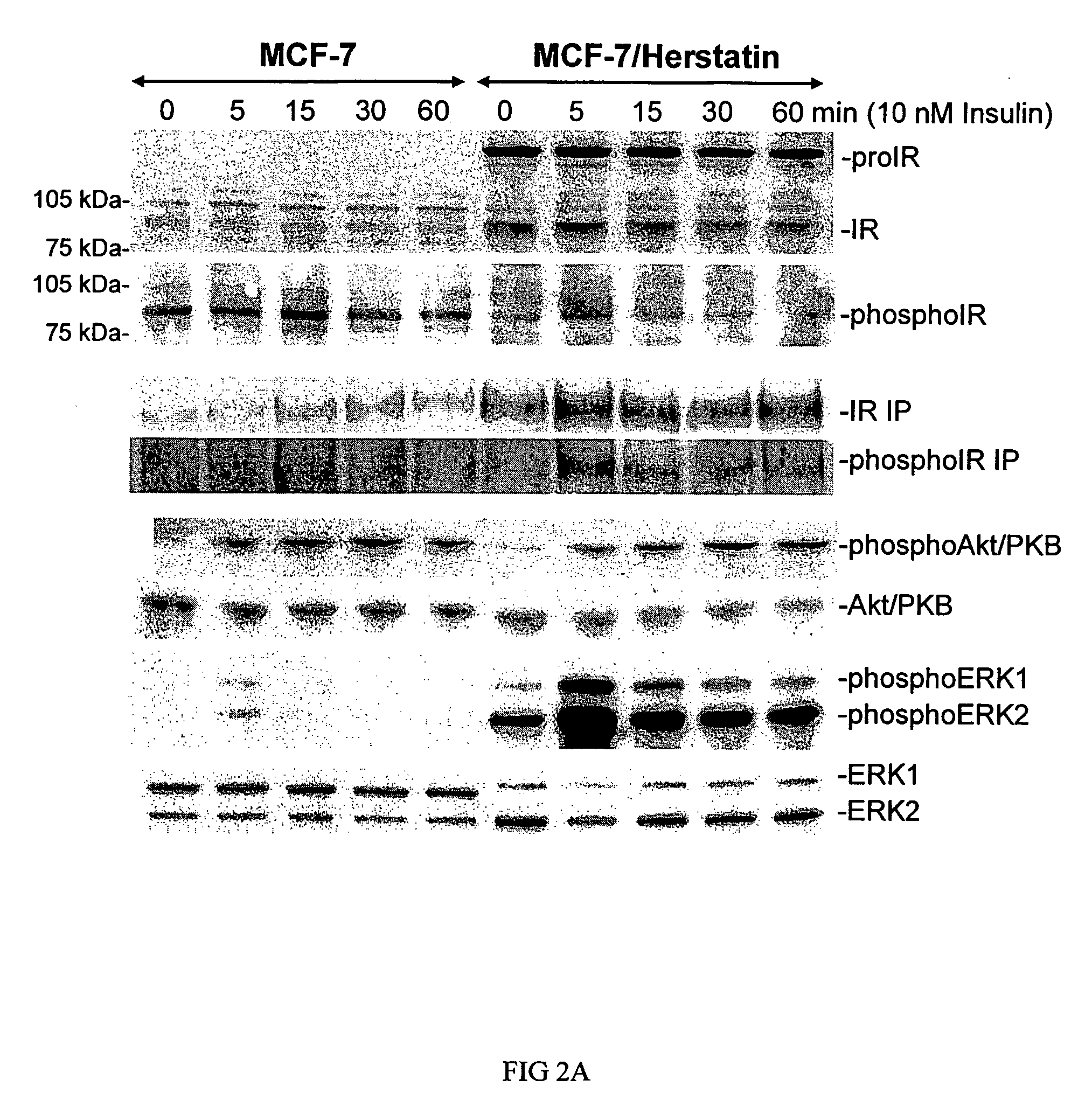
InactiveUS20080206231A1Significant positive effectIncreasing IR-mediated ERK pathway activationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiabetic heartDyslipidemia
The present invention discloses for the first time that the insulin receptor (IR) is a target of Herstatin, which modulates IR and IR-mediated intracellular signaling. In preferred aspects, Herstatin binds at nM concentrations to cell-surface IR, up-regulates basal IR expression by several-fold, induces the accumulation of pro-IR, and stimulates insulin activation of the ERK pathway. Moreover, these changes in insulin signaling are accompanied by alterations in IGF-IR expression, IRS-2 levels, and the serine phosphorylation state of both IRS-1 and IRS-2. Preferred aspects provide novel therapeutic methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of conditions associated with altered IR expression or IR-mediated signaling, including but not limited to insulin resistance syndrome, pre-diabetic conditions, metabolic syndrome, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, cardiac disease, diabetes-associated vascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes-associated lipid metabolism disorders (dyslipidemia), obesity, critical illness, neurodegenerative disorders, and combinations thereof, and cancer.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Selenium-rich bifidobacterium longum as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109486715AIncrease weightLower blood sugar levelsBacteriaMetabolism disorderCreatinine riseDiabetes model
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly discloses selenium-rich bifidobacterium longum as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The selenium-rich bifidobacterium longum prepared by virtue of the preparation method can be applied to the preparation drugs or foods for delaying the progress of diabetes mellitus and particularly can be applied to the preparation of the drugs or the foods for improving the physical signs and metabolism conditions of diabetes mellitus, the insulin signal pathways of a diabetes mellitus model, the pathological change of livers, pancreas and kidneys of patients with diabetes mellitus and the levels of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen of diabetes mellitus and preventing renal complications or renal function damage of diabetes mellitus.
Owner:JIANGSU TARGET BIOMEDICINE RES INST +1
Macrocyclic insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140213515A1Decrease entropic costLimited accessOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin-degrading enzymeInsulin signalling
Macrocyclic compounds that specifically inhibit insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) are provided. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, hydrates, stereoisomers, polymorphs, tautomers, isotopically enriched forms, and prodrugs of the macrocyclic IDE inhibitors are also described. Pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. In vivo and in vitro methods of using the IDE inhibitor, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the IDE inhibitor, for example, for the inhibition of IDE in a subject exhibiting aberrant IDE activity, impaired insulin signaling, or insulin resistance, for example, a subject having diabetes, are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Dietary supplements containing extracts of nelumbo and processes of using same
InactiveUS20100227007A1Improve athletic performanceImprove enduranceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInsulin signallingDietary supplement
Materials derived from Nelumbo are administered orally to humans or animals for the purpose of enhancing creatine transport into skeletal tissue and for purposes of enhancing lean body mass. Enhancing creatine transport through improved insulin signaling is a new method of depositing creatine and enhancing lean body mass. Such administration is also used for enhancing athletic performance and controlling bodyweight and body fat levels. More specifically, such administration is used for the purpose of enhancing creatine transport into excitable tissues such as skeletal muscle. The material is administered as extracts of Nelumbo and administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks.
Owner:IN INGREDIENTS
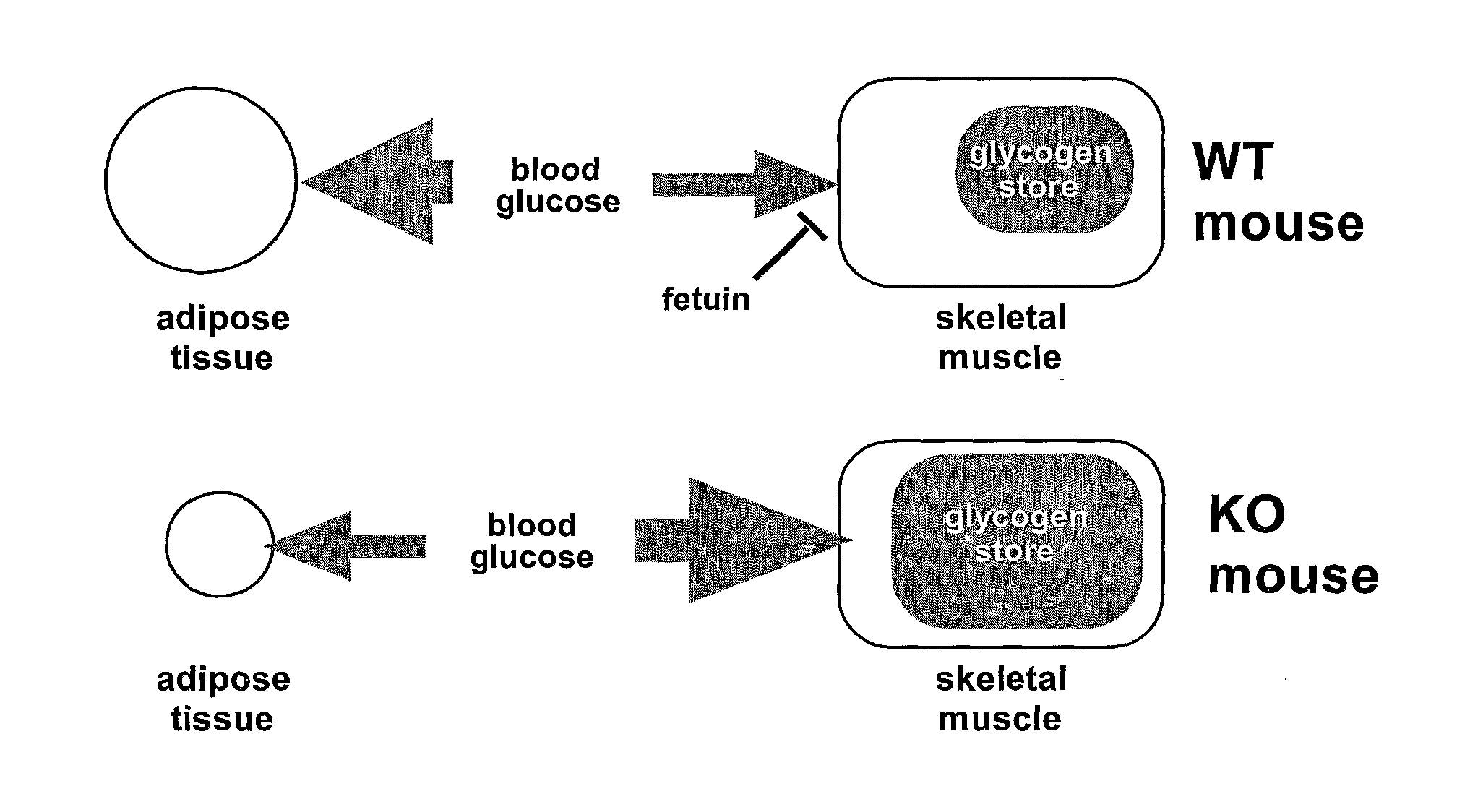
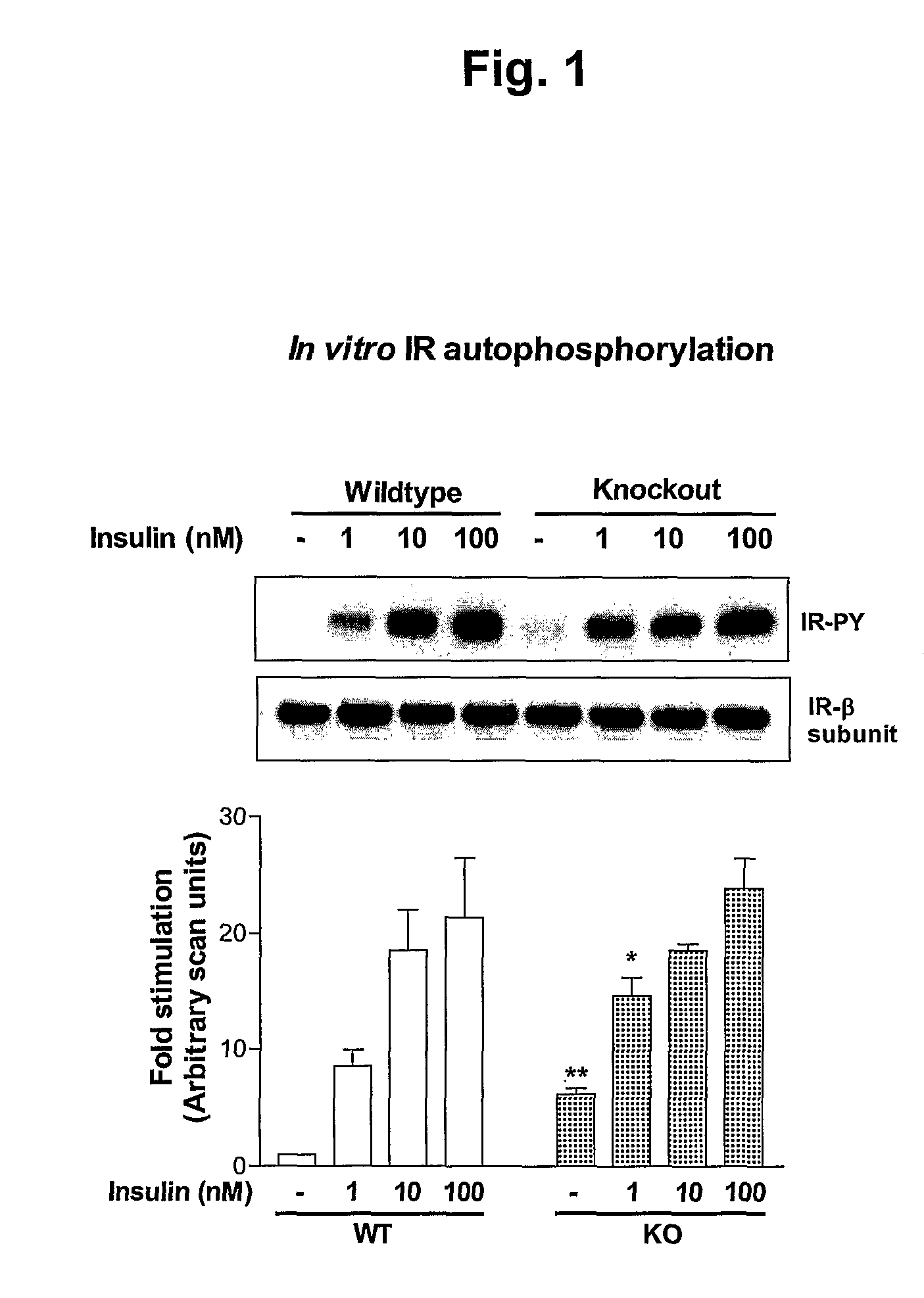
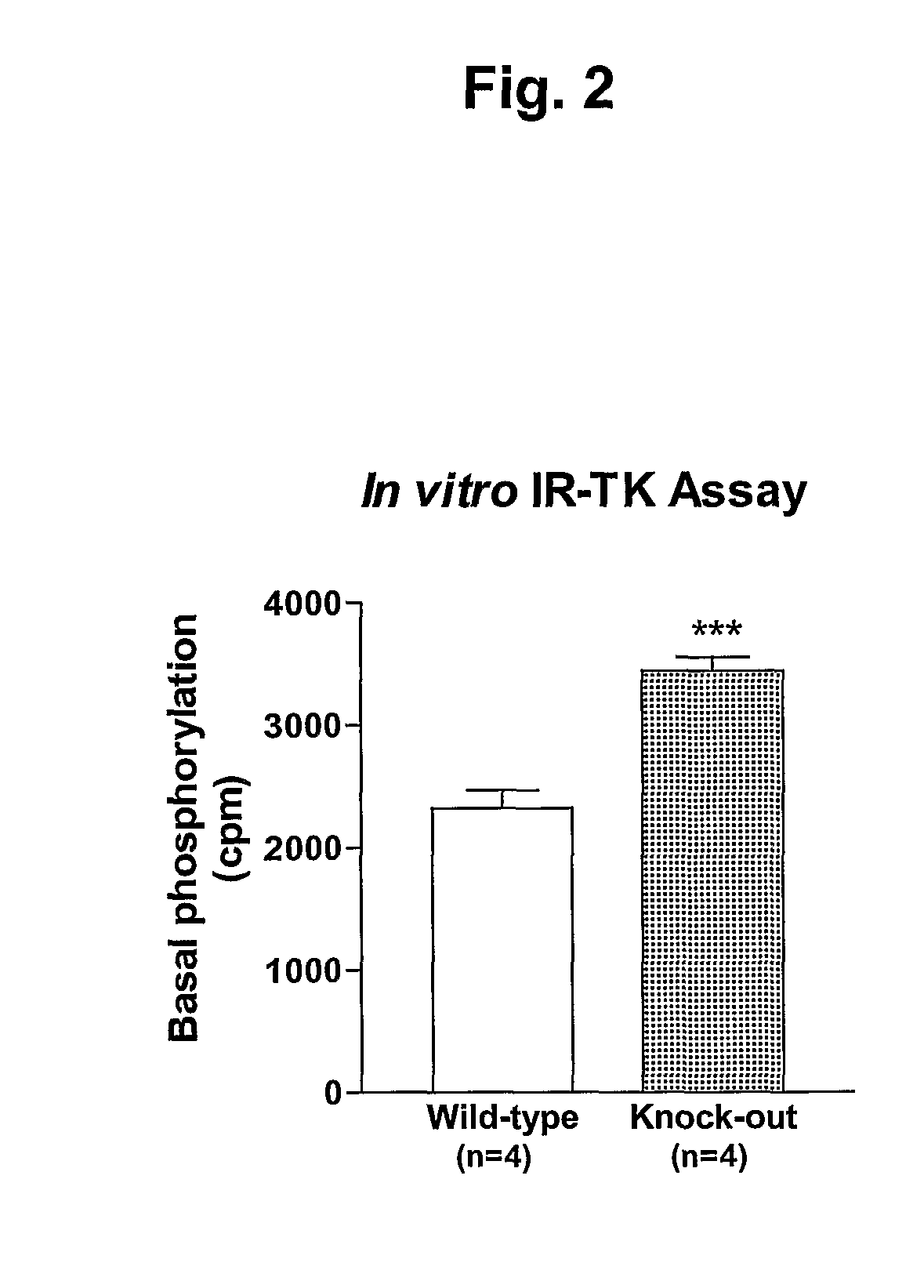
Inhibition of alpha-2 hs glycoprotein (AHSG/fetuin) in obesity and insulin control of glucose homeostasis
InactiveUS20080050372A1Reduce the amount requiredIncreased basalPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAlpha-2-HS-glycoproteinAnti-CEA Antibody
α2-Heremans Schmid Glycoprotein (AHSG) inhibits insulin-induced autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor (IR) and IR-tyroskine kinase (TK) activity; genetic ablation of the Ahsg gene enhances insulin signal transduction and increase whole-body insulin sensitivity. Therefor, AHSG and its gene(s) are useful targets for agents that inhibit the development or progression of Type II diabetes or any disease or disorder associated with increased insulin resistance. Provided herein is a method for inhibiting the biological activity of AHSG protein in a cell using compounds that inhibit phosphorylation of AHSG. Also disclosed is a method of augmenting the phosphorylation or IR-TK activity in a liver or muscle cell by providing a compound that lowers the amount of active AHSG or inhibits the biological activity of AHSG. Such effects may be achieved by delivering an antisense nucleic acid construct that hybridizes with AHSG encoding DNA. This invention includes a method (a) treating a subject that is susceptible to, or suffers from, obesity and insulin resistance or (b) increasing insulin sensitivity, and thereby preventing or treating insulin resistance in the subject. The method comprises lowering the amount of active AHSG or inhibiting the biological activity of AHSG in the subject, preferably in liver or muscle, by using AHSG antisense constructs or an anti-AHSG antibody. In a subject eating a high fat diet, the effect on body weight gain and / or insulin resistance is diminished, and total body fat content is lowered, by lowering the amount of active AHSG or inhibiting the action of the AHSG in the subject using the agents noted above.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
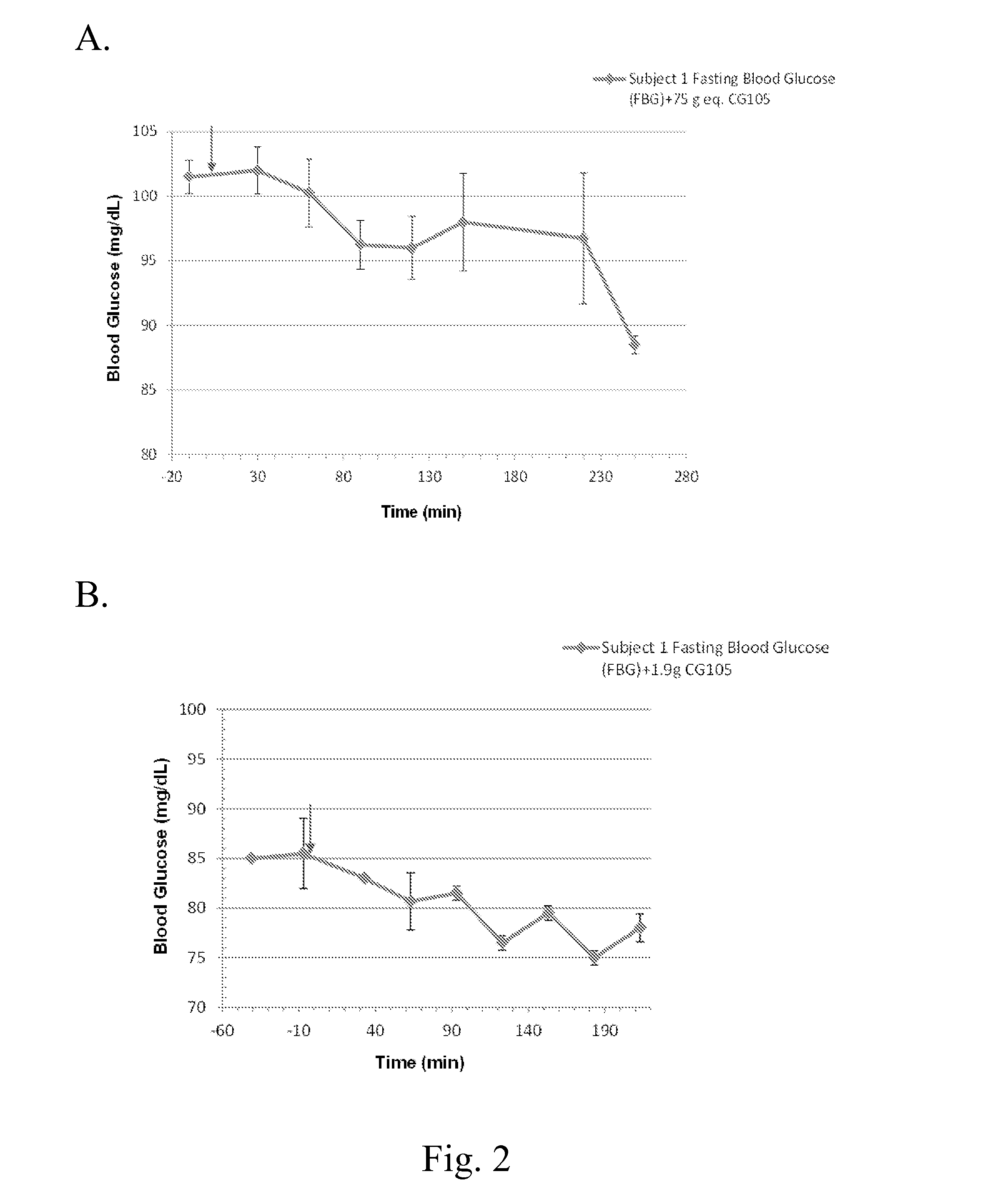
Method and composition for increasing insulin sensibility
InactiveCN101176786AIncreased sensitivityHigh biosecurityHydroxy compound active ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseInsulin signalling
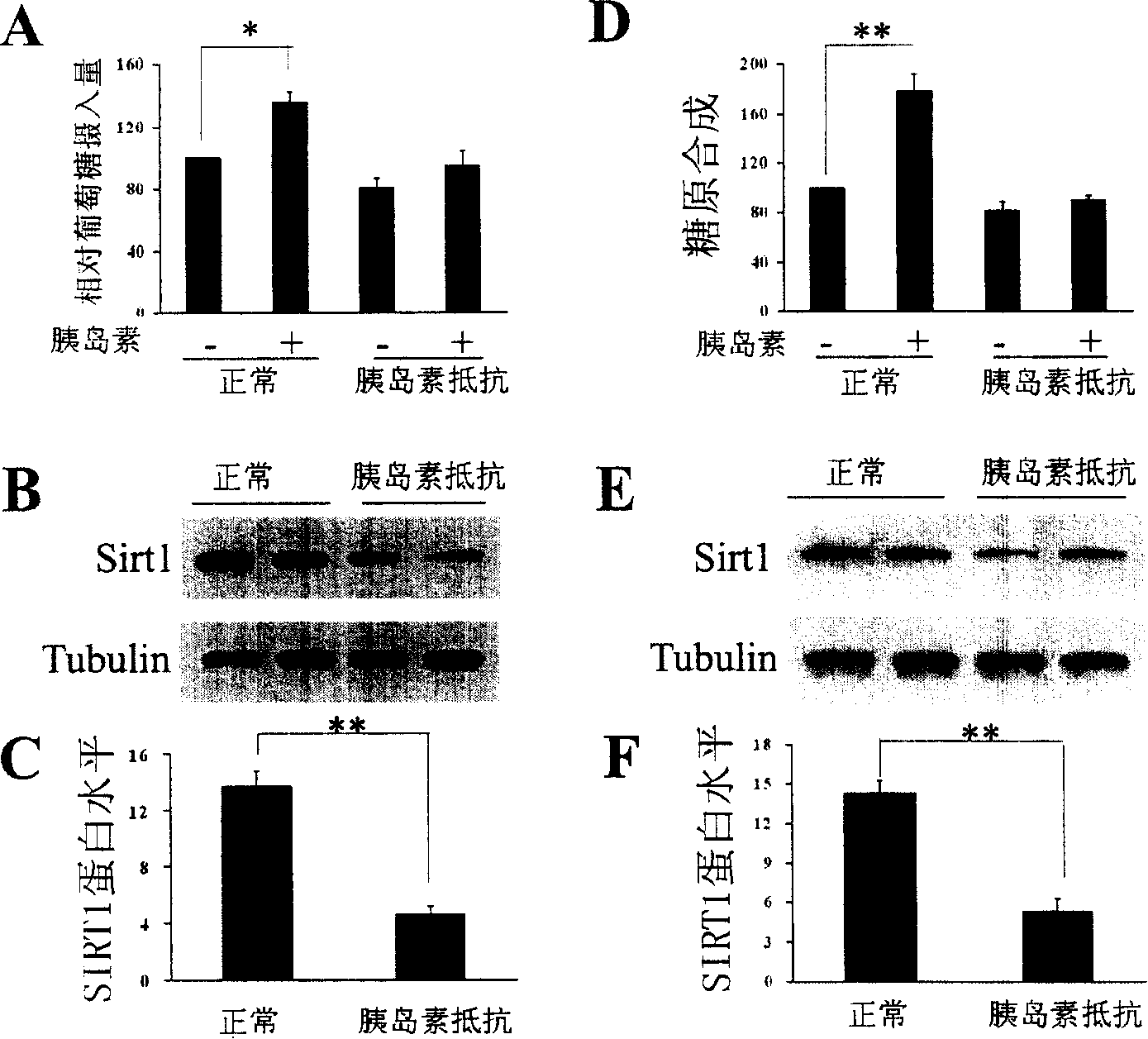
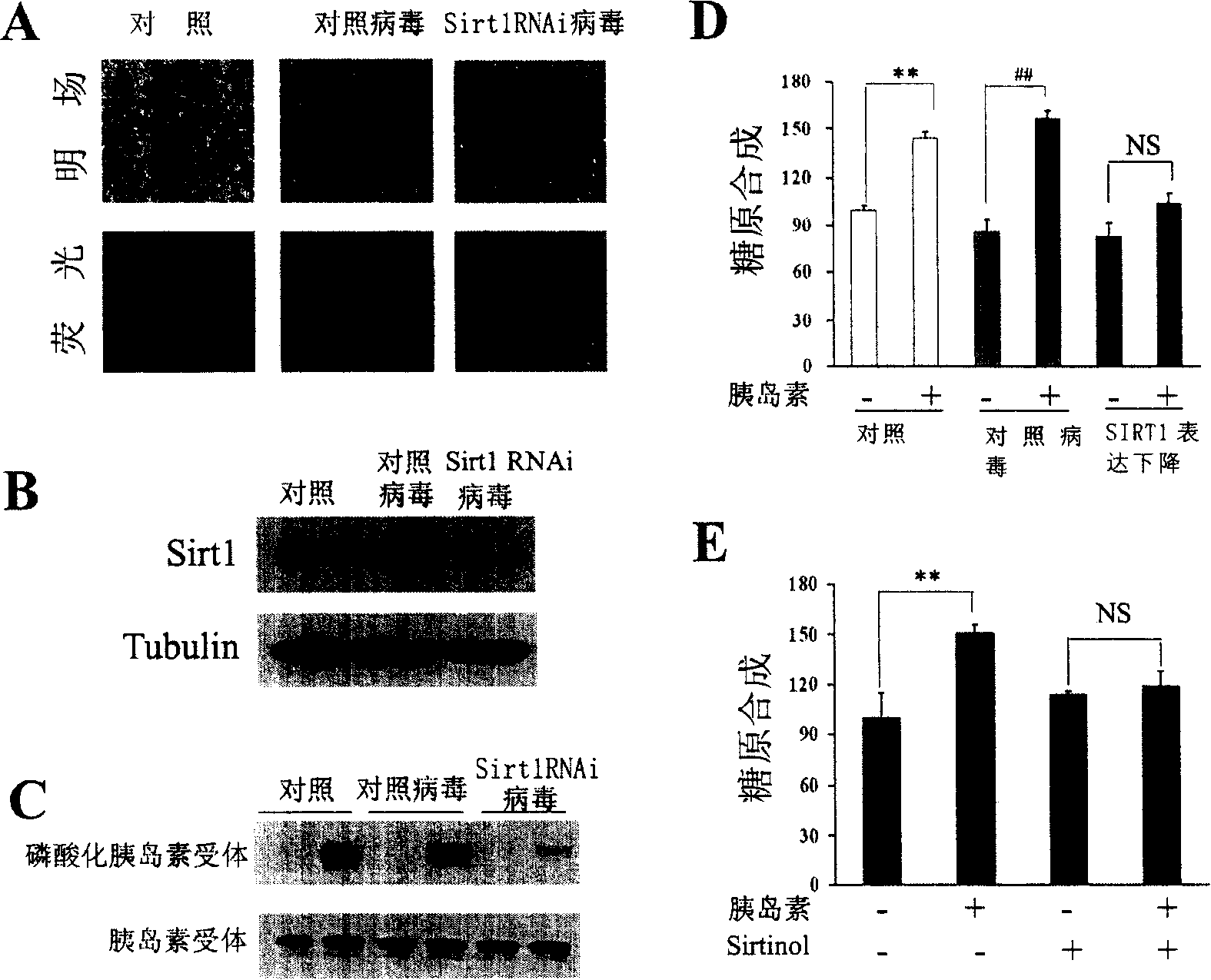
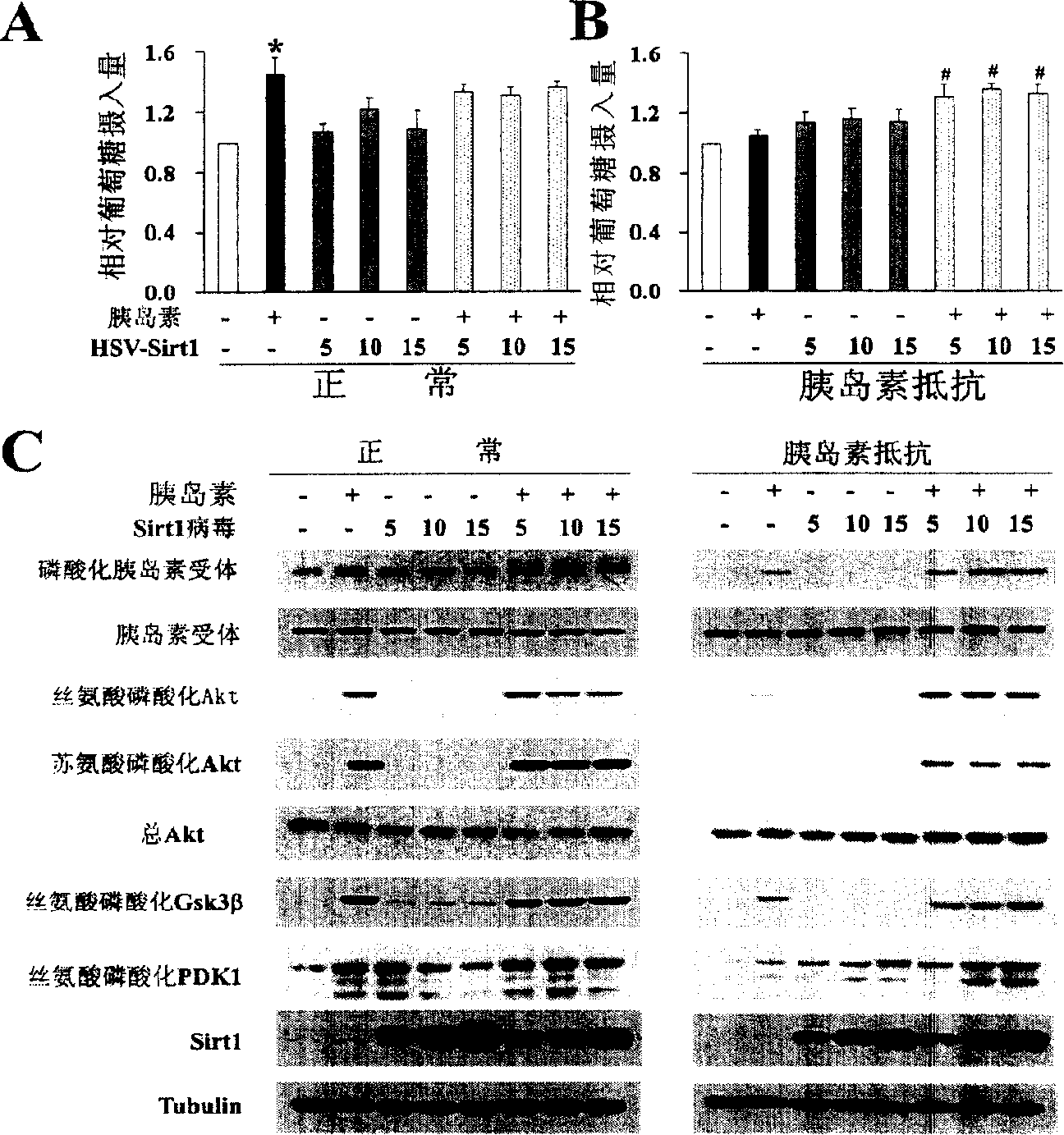
The present invention provides a use of SIRT1 protein or agonists or up-regulators thereof for manufacturing a composition which can increase insulin sensitivity. SIRT1 can be used to increase insulin sensitivity by down-regulating expression of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, a negative regulator of insulin action.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
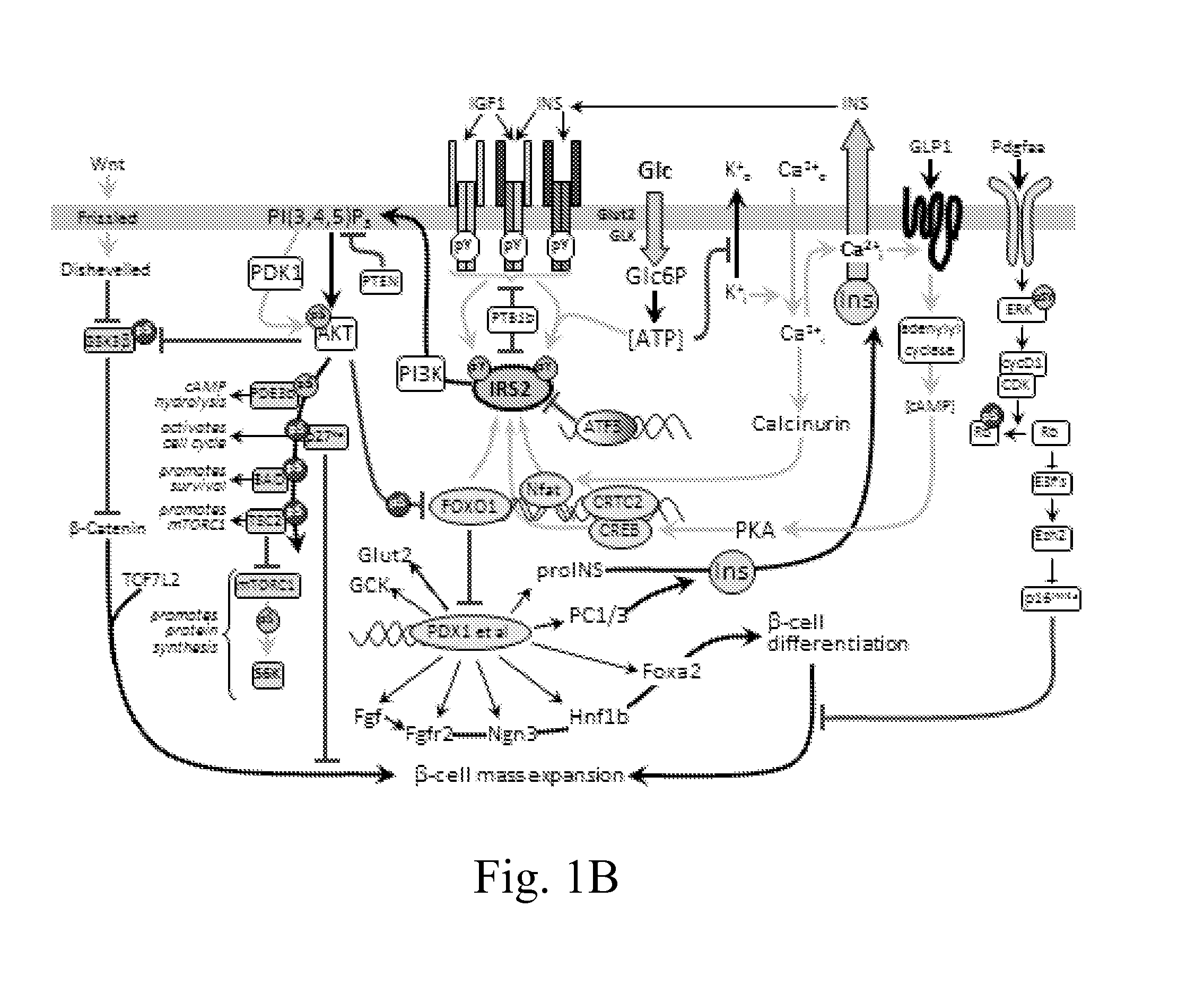
Methods of differentiating stem cells into liver cell lineages
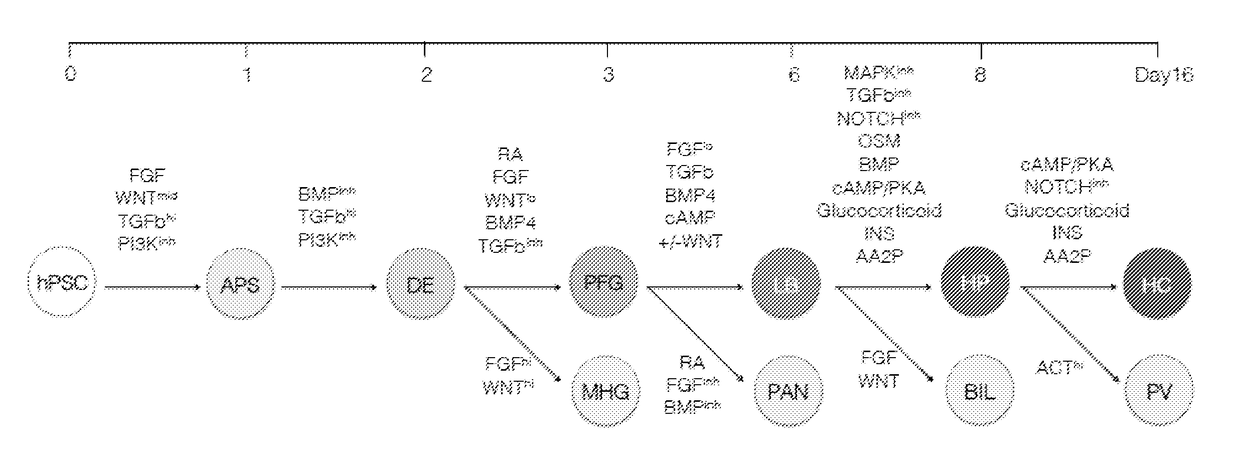
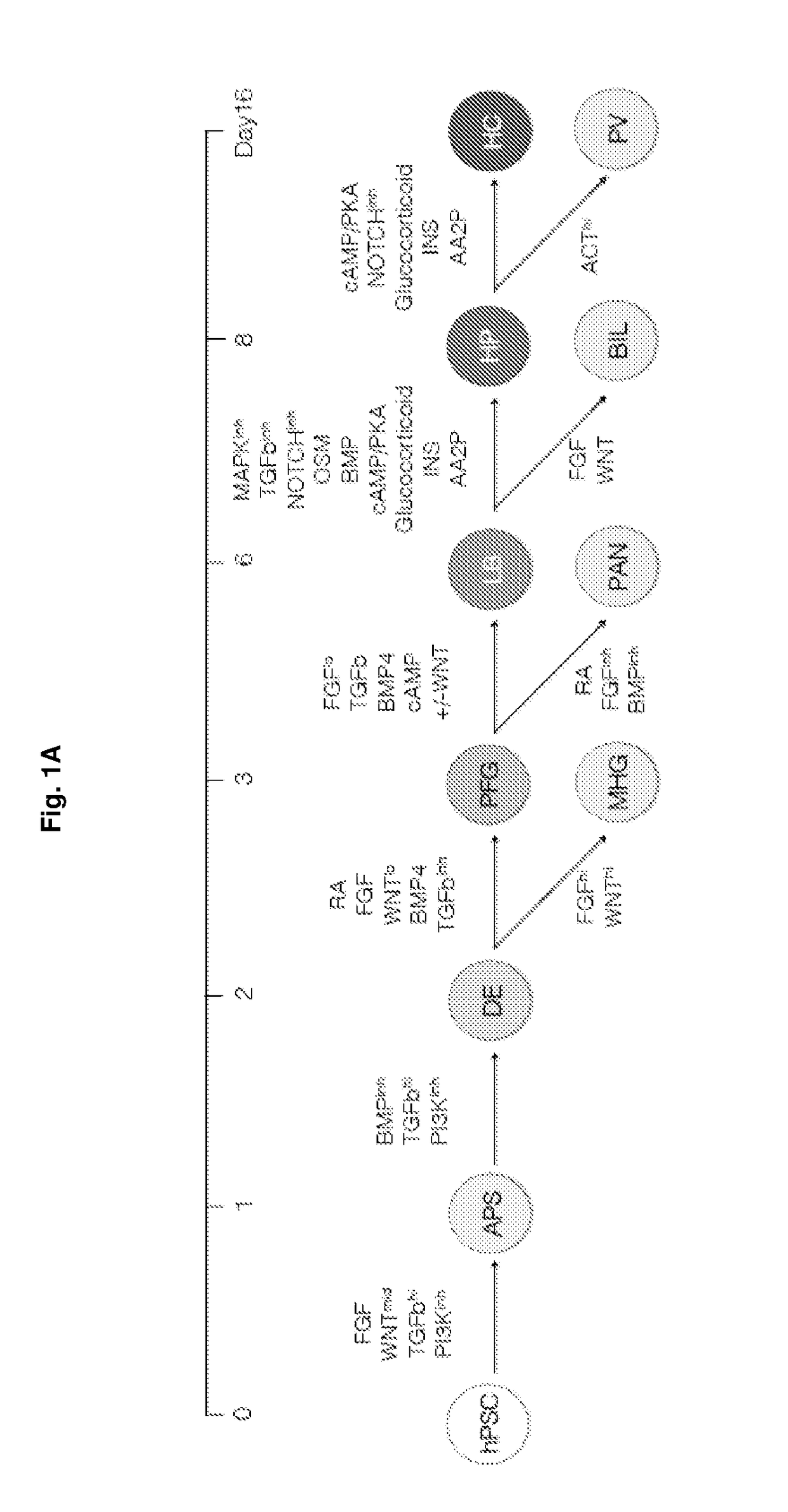
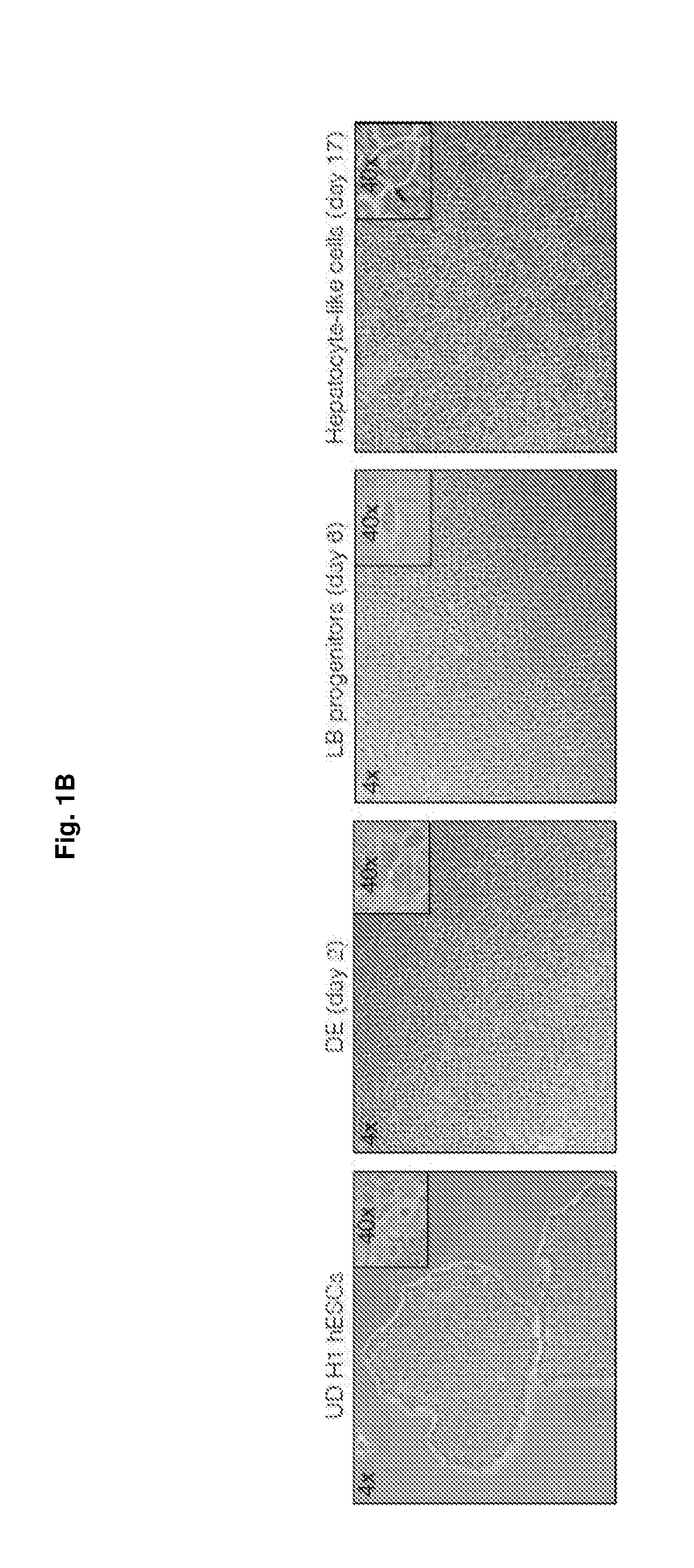
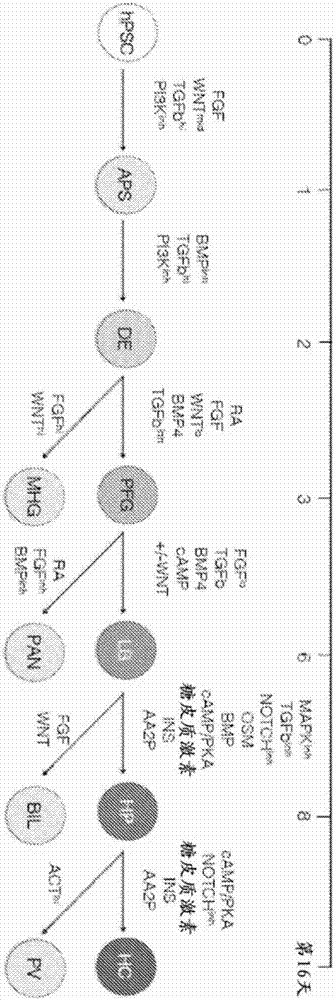
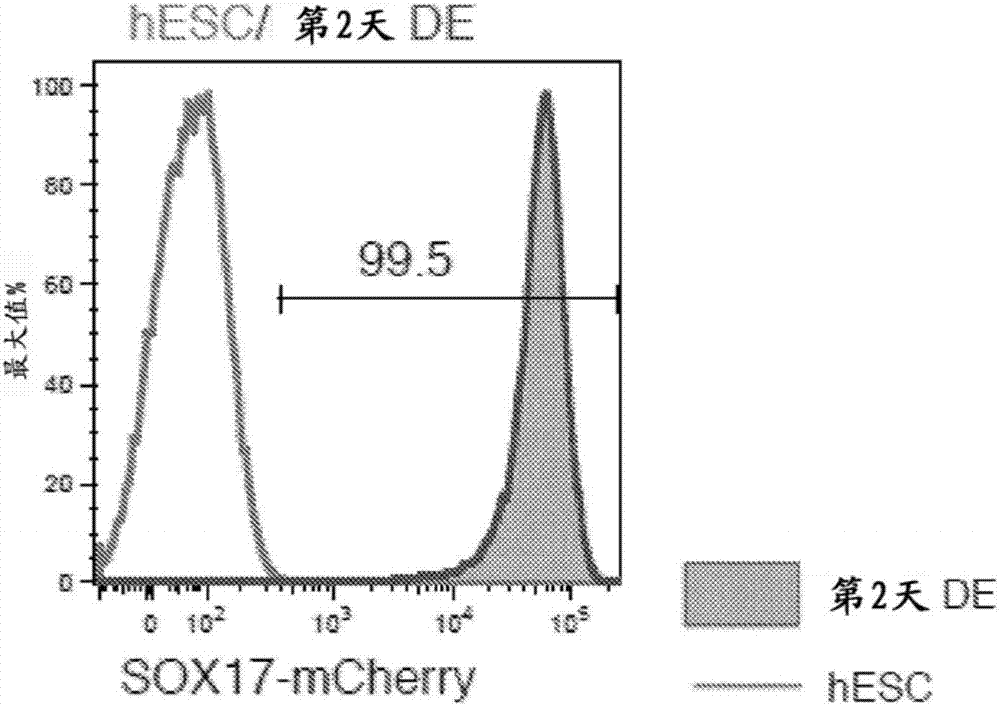
The present disclosure provides methods and kits for the differentiation of stem cells into relevant liver cell lineages, as well as methods of using the relevant liver cell lineages in screening for a cellular response, a phenotype and in the treatment of a condition. In one embodiment, stem cells are first differentiated into cells of the definitive endoderm lineage, which are differentiated into posterior foregut (PFG) lineage cells by one or more of retinoic acid activators and / or one or more inhibitors of transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ). An additional embodiment provides a method for the differentiation of posterior foregut lineage cells into liver bud progenitors (LB) by one or more activators of TGFβ signalling, and / or one or more modulators of Wnt signalling, and / or one or more activators of cyclic AMP / PKA signaling; and a further embodiment provides a method for the differentiation of liver bud progenitors into hepatic progenitors by one or more inhibitors of TGFβ signalling and / or fibroblast growth factor (FGF) inhibitors and / or one or more Notch inhibitors. Another embodiment discloses the differentiation of hepatic progenitors into hepatocyte-like cells or perivenous hepatocyte-like cells by one or more of Notch inhibitors and / or activators of glucocorticoid signalling and / or one or more activators of insulin signalling and / or one or more of ascorbic acid signalling activators and / or additional factors. Methods and kits for maintaining LB in self renewal state, hepatocyte-like cells in perivenous or periportal state, as well as surface markers for LB and mid / hindgut (MHG) cells are also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
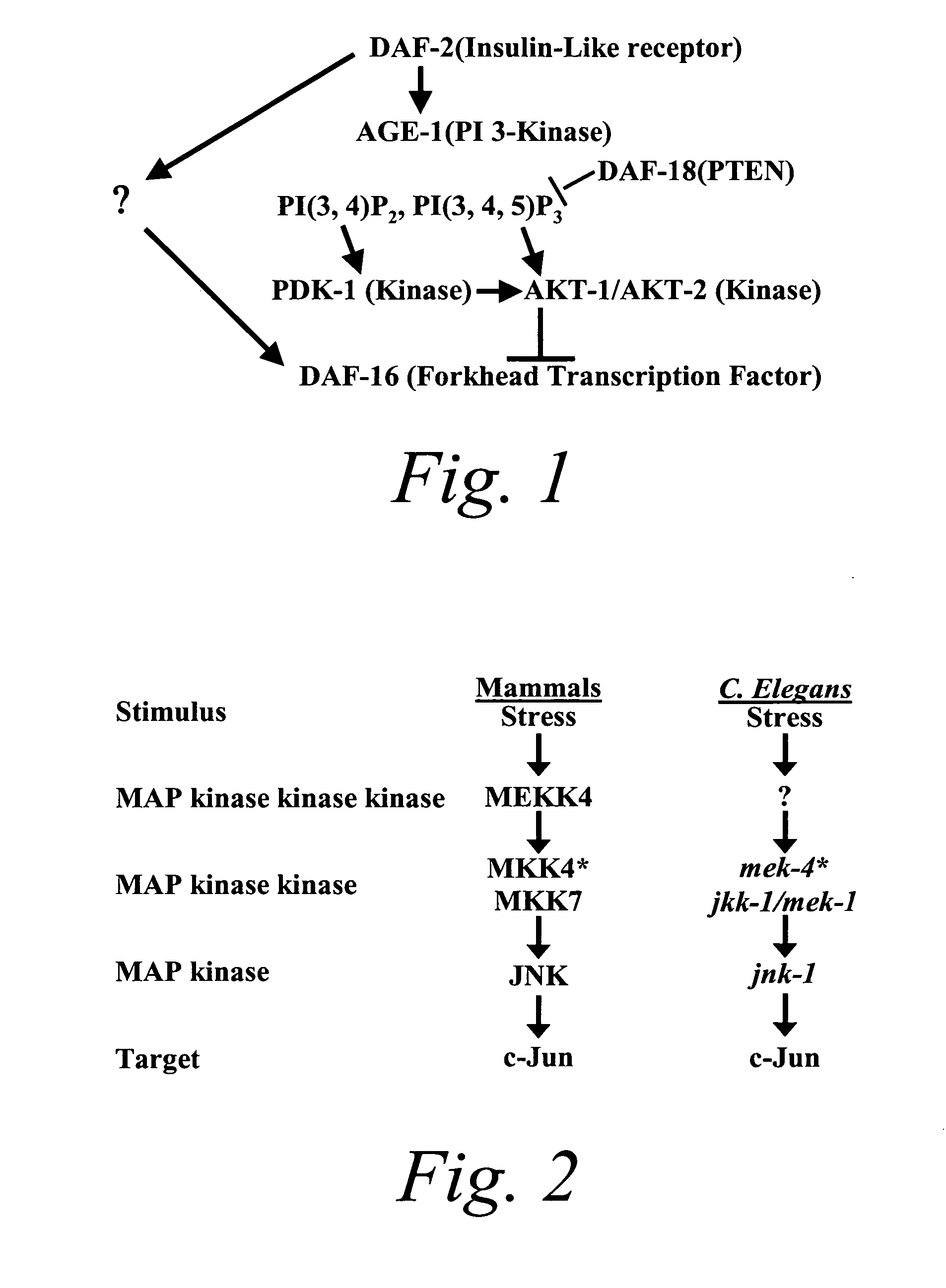
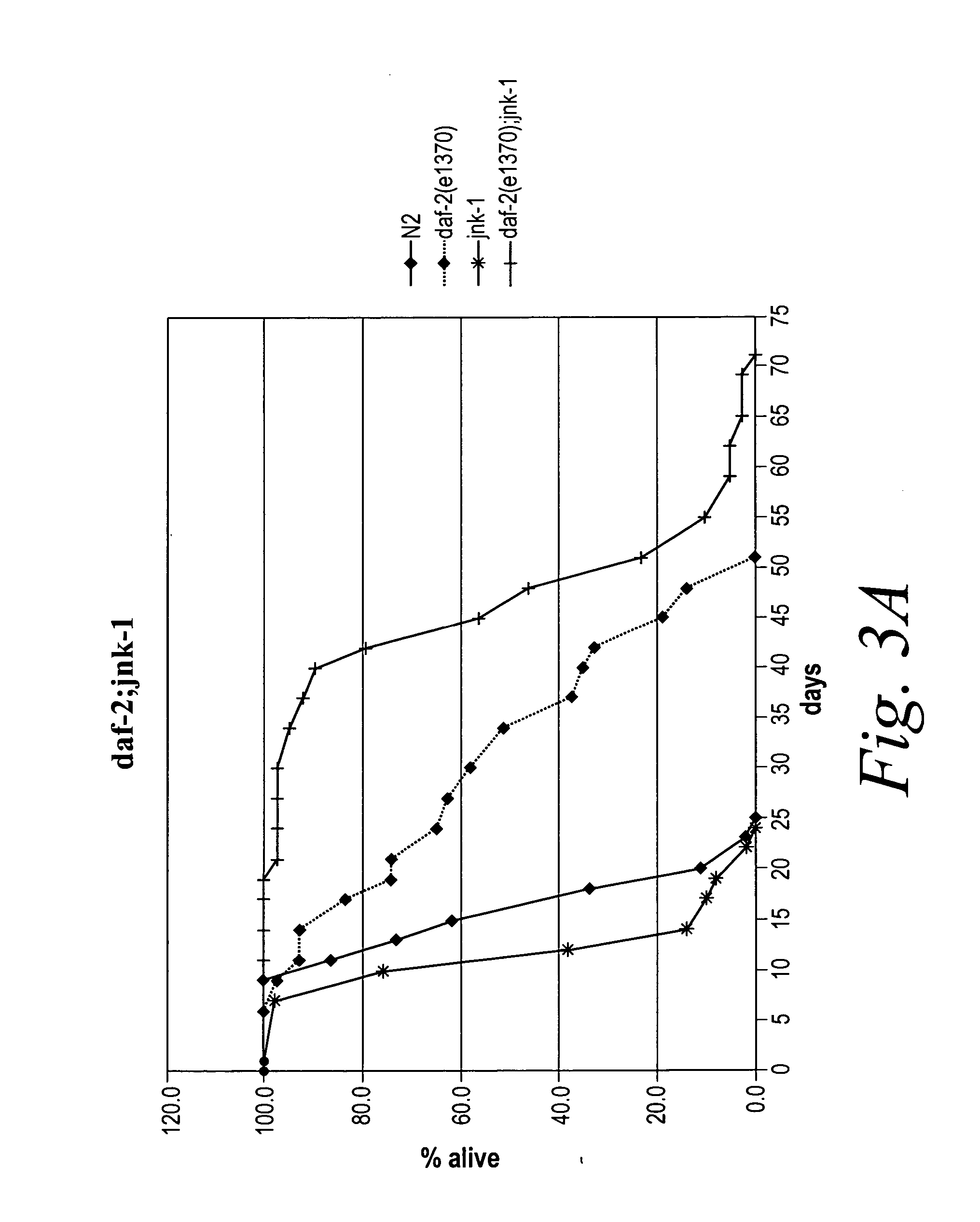
Methods of identifying longevity modulators and therapeutic methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060272039A1Extend your lifeReduced lifespanPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiological bodyInsulin signalling
The present invention is based at least in part on the discovery of a role for the JNK signaling pathway in longevity. In particular, the present inventors have shown that overexpression of c-jun N-terminal kinase 1 (jnk-1) extends lifespan and that said extended lifespan is associated with DAF-16 phosphorylation by JNK-1 and the consequent DAF-16 localization to the nucleus. Accordingly, the present invention features methods of identifying modulators of longevity in assays featuring organisms and / or cells having a JNK signaling pathway and, optionally, an IR signaling pathway. Also featured is an in vitro method of identifying an agent capable of enhancing longevity featuring an assay composition having a JNK signaling pathway molecule and insulin signaling pathway molecule. Further featured are therapeutic methods for the use of JNK signaling pathway modulators to enhance longevity, to prevent or reduce obesity and to prevent or treat type II diabetes.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
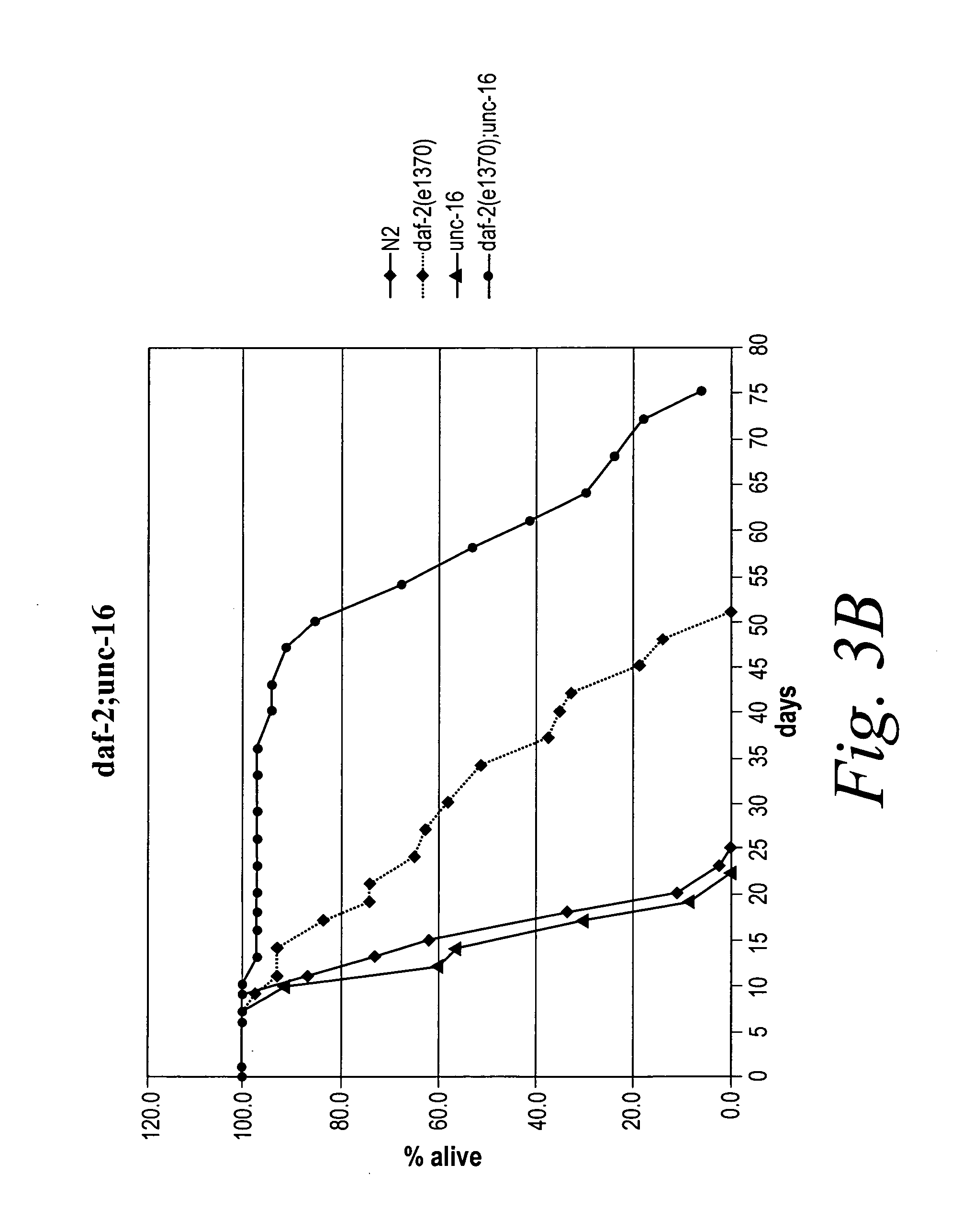
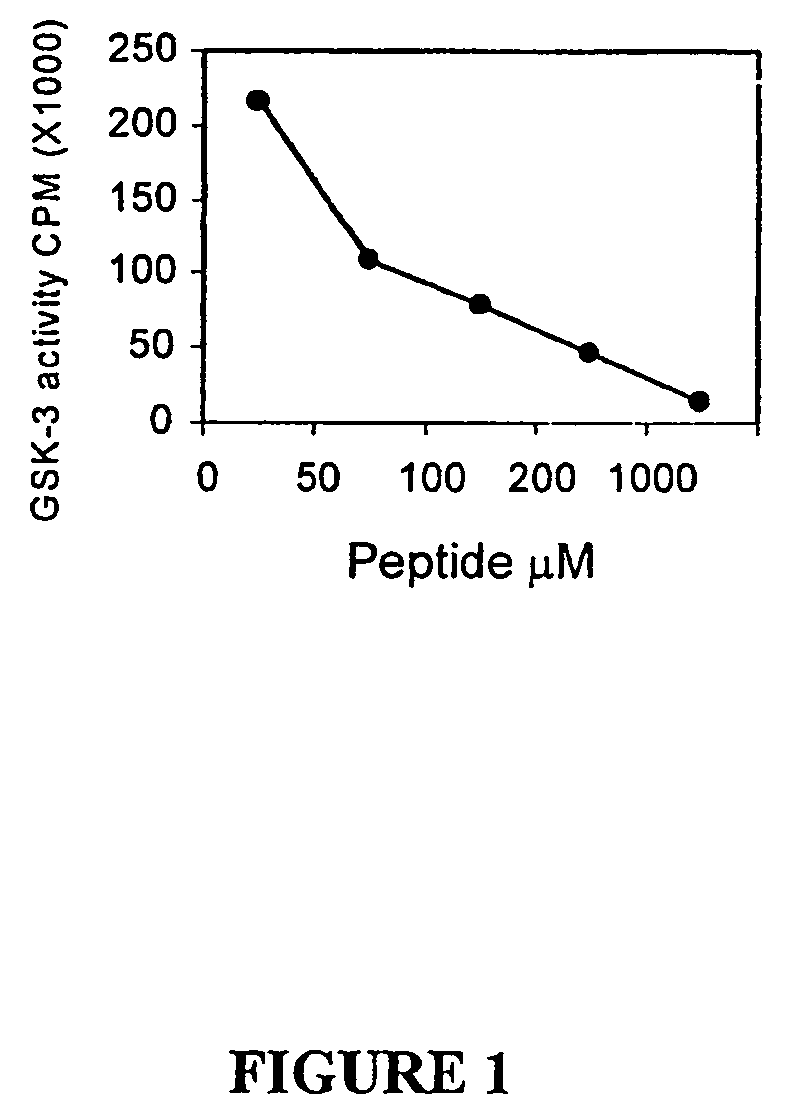
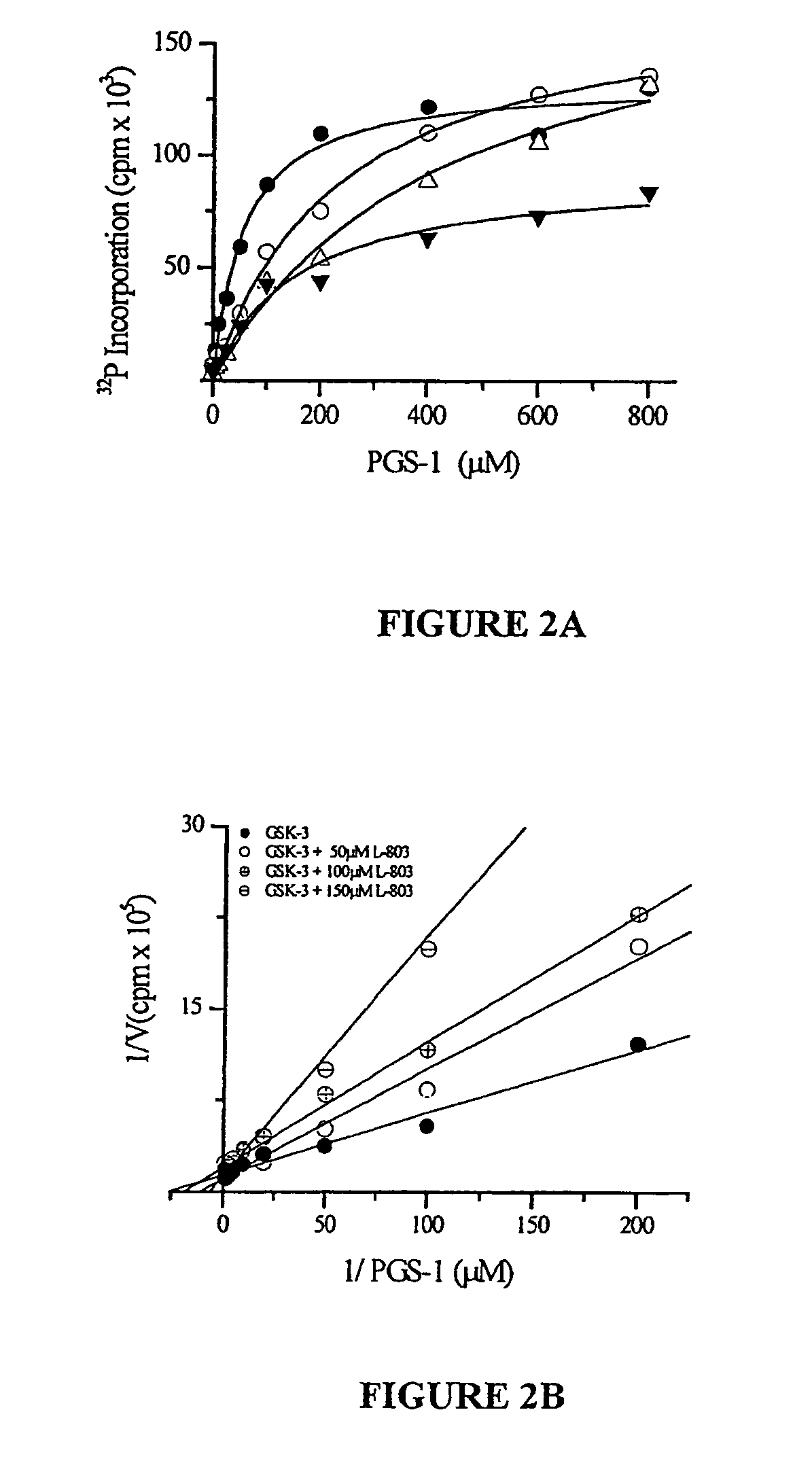
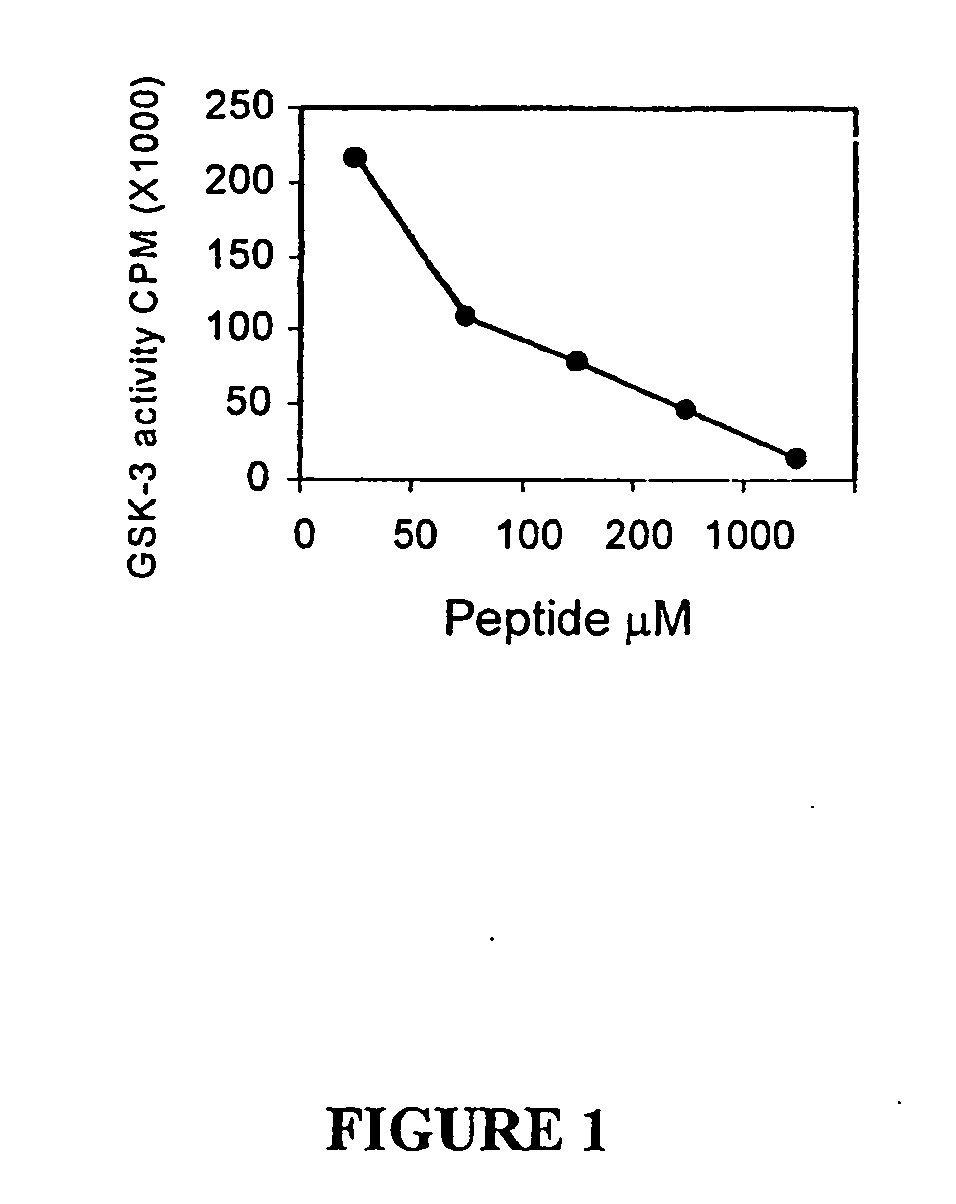
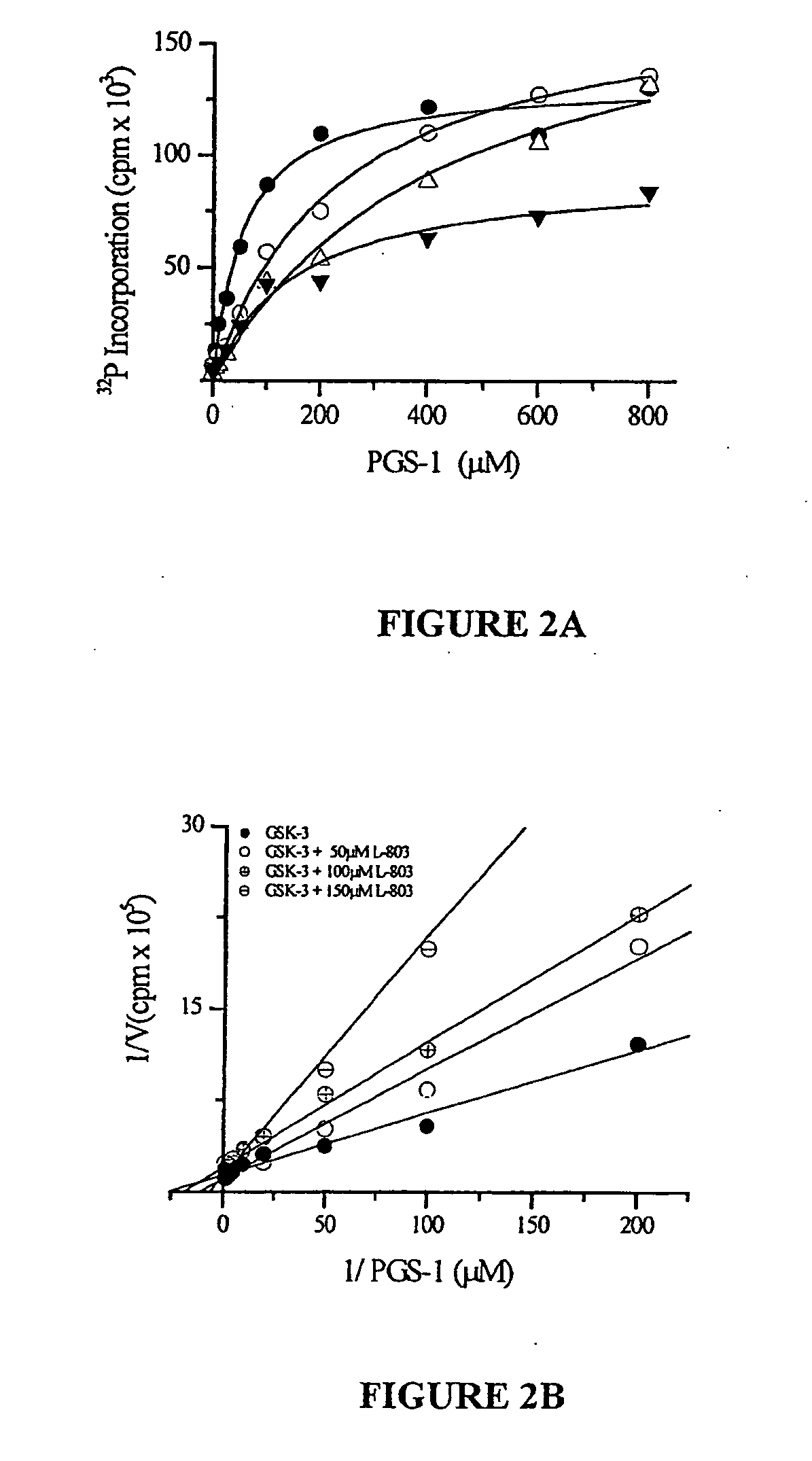
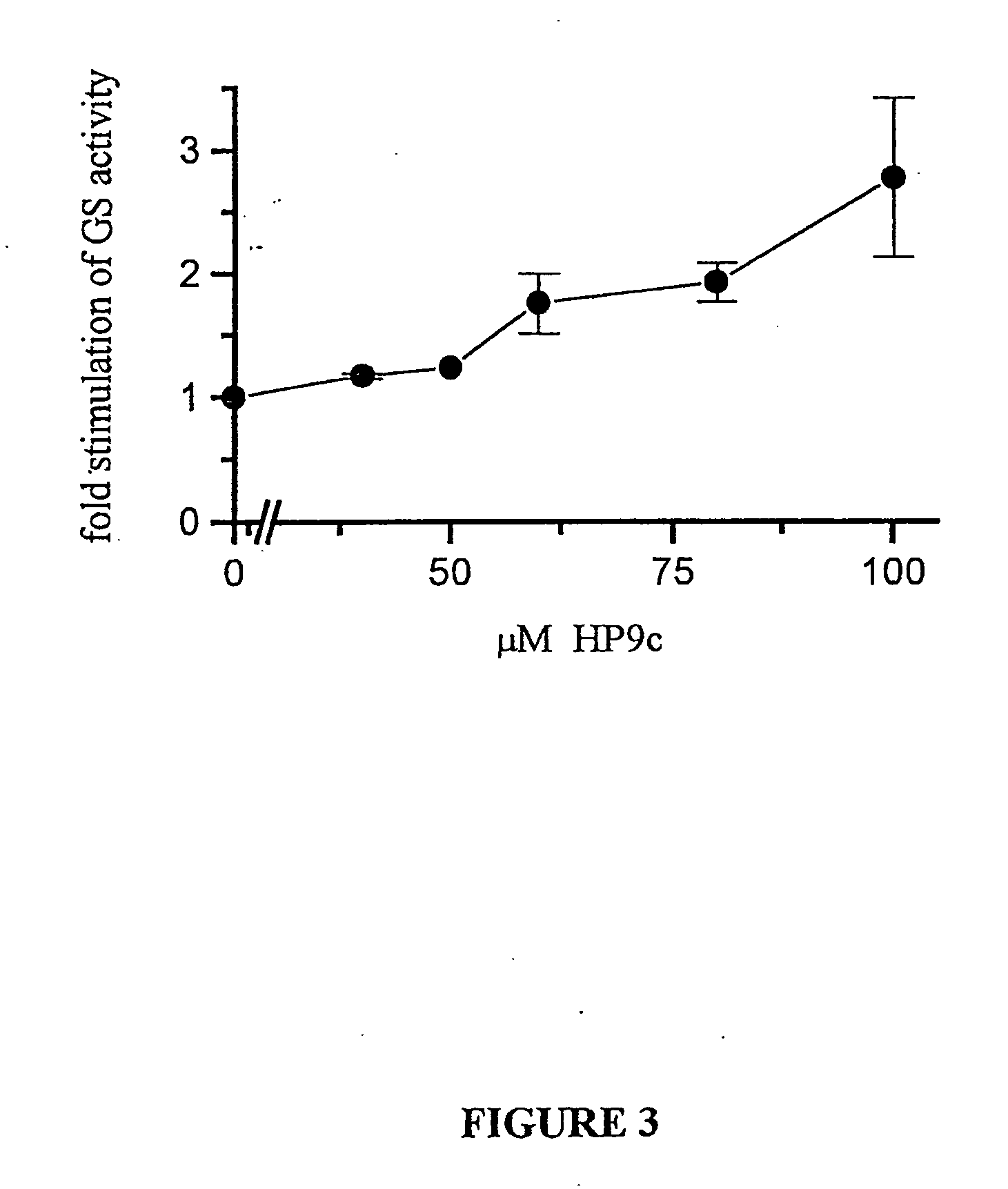
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors
Peptide inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) having an amino acid sequence motif of XZXXXS(p)X, wherein S(p)=phosphorylated serine or phosphorylated threonine, X=any amino acid, and Z=any amino acid except serine or threonine. These inhibitors, which are about 7 to 20 amino acids long, are specific for GSK-3 and strongly inhibit the enzyme with an IC50 of about 150 μM. Also provided are methods of treating biological conditions mediated by GSK-3 activity, such as potentiating insulin signaling in a subject, treating or preventing type 2 diabetes in a patient, and treating Alzheimer's Disease by administering peptide inhibitors. Compositions of these peptide inhibitors and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers are also provided, as is a method for identifying inhibitors of GSK-3. The invention further relates to a computer-assisted method of structure based drug design of GSK-3 inhibitors using a three-dimensional structure of a peptide substrate of GSK-3.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
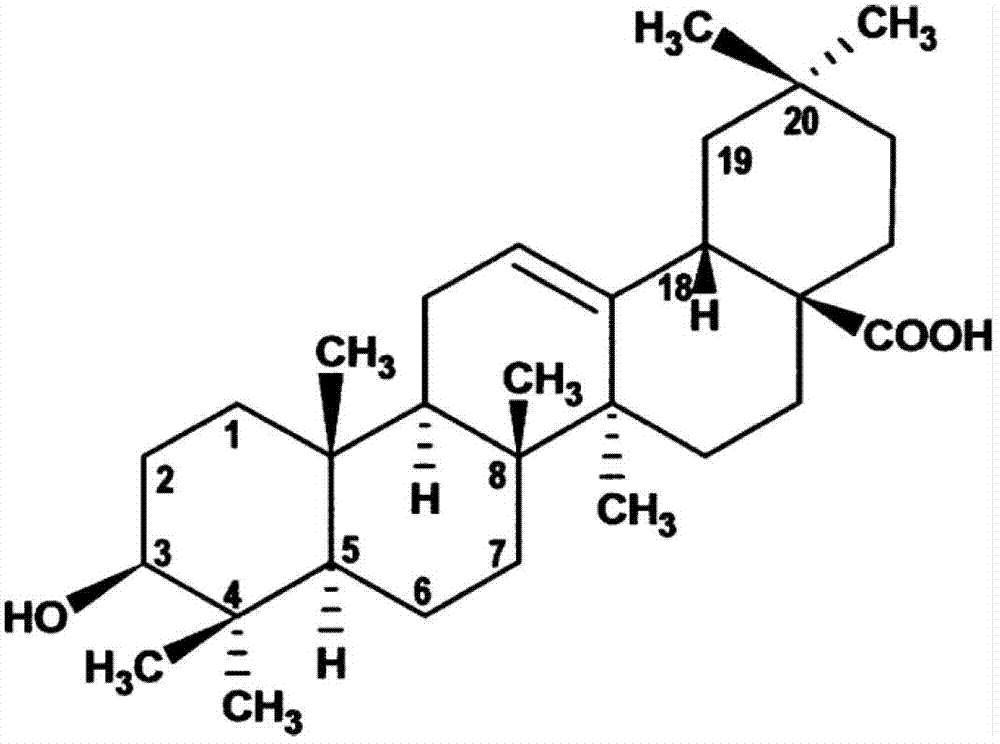
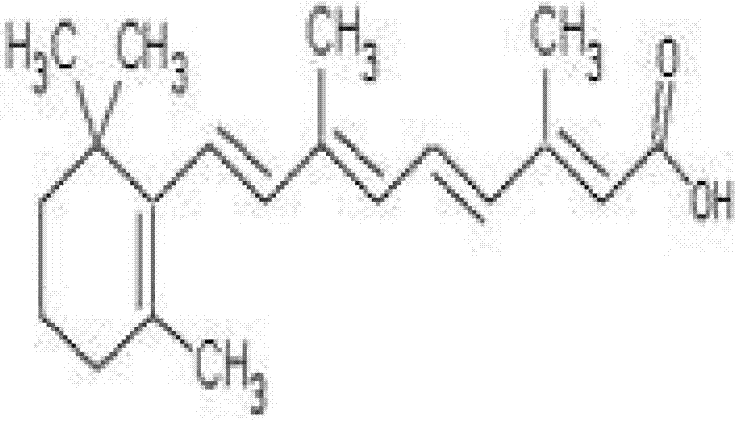
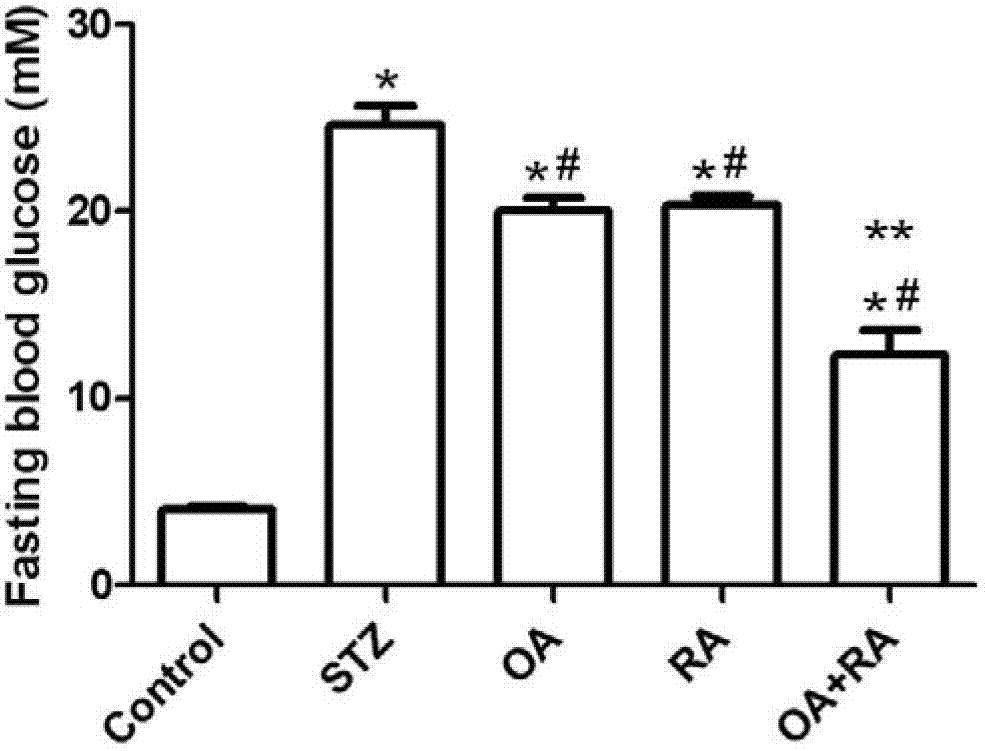
Application of oleanolic acid and retinoic acid pharmaceutical composition to medicament for treating insulin resistance and diabetes
InactiveCN102764262AReduce B phosphorylation levelsLower blood sugarHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetabolism disorderIntraperitoneal routeDiabrezide
The invention discloses application of an oleanolic acid and retinoic acid pharmaceutical composition to medicament for treating insulin resistance and diabetes. Intraperitoneal injection of the oleanolic acid and retinoic acid pharmaceutical composition to diabetic animal can significantly lower the blood glucose level; and addition of the oleanolic acid and retinoic acid pharmaceutical composition in culture solution for culturing liver cells can significantly promote transmission of an insulin signal. Therefore, the oleanolic acid and retinoic acid pharmaceutical composition can be applied to medicaments for treating diabetes, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome closely related to insulin resistance.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
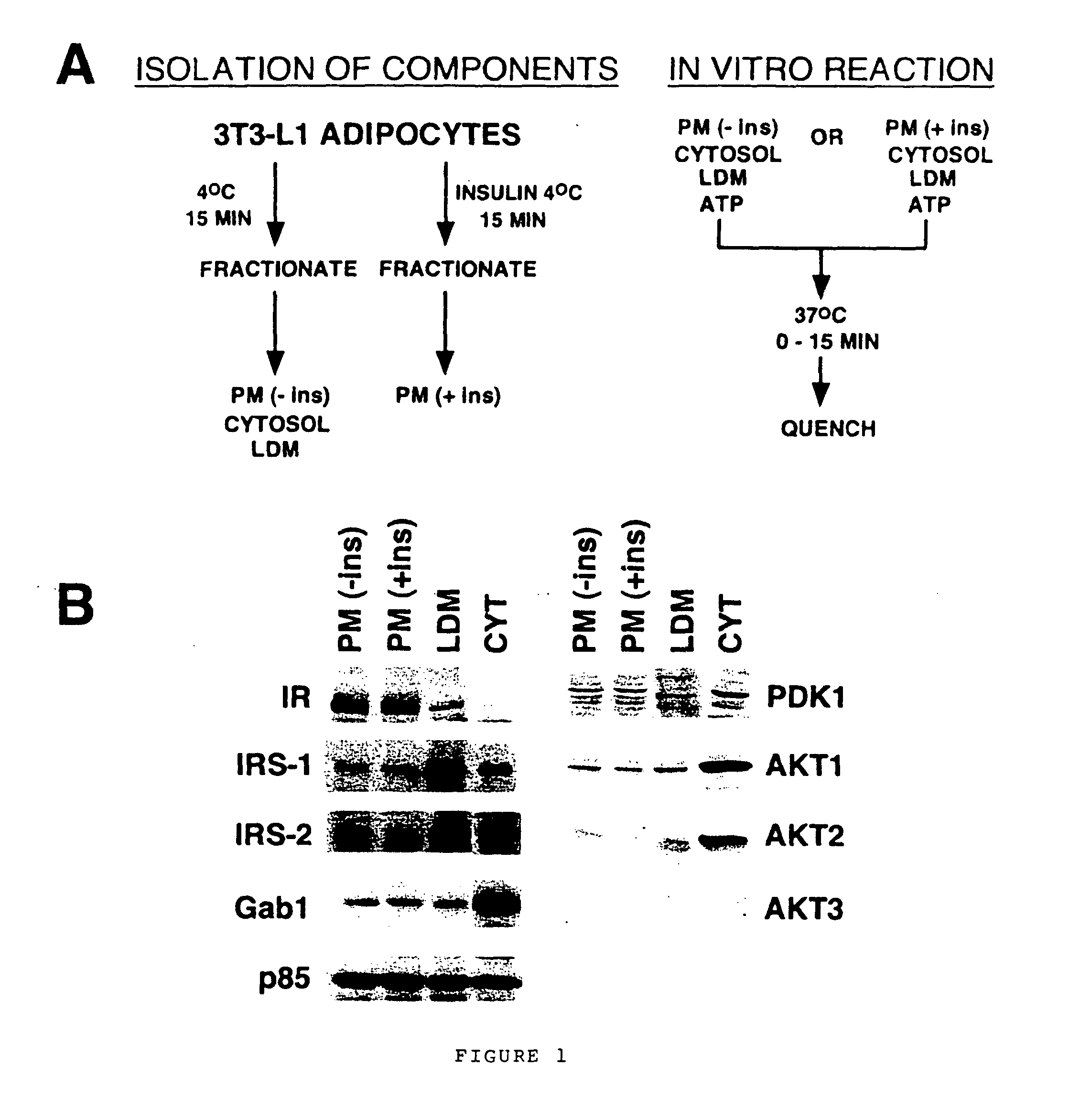
Cell-free assay for insulin signaling
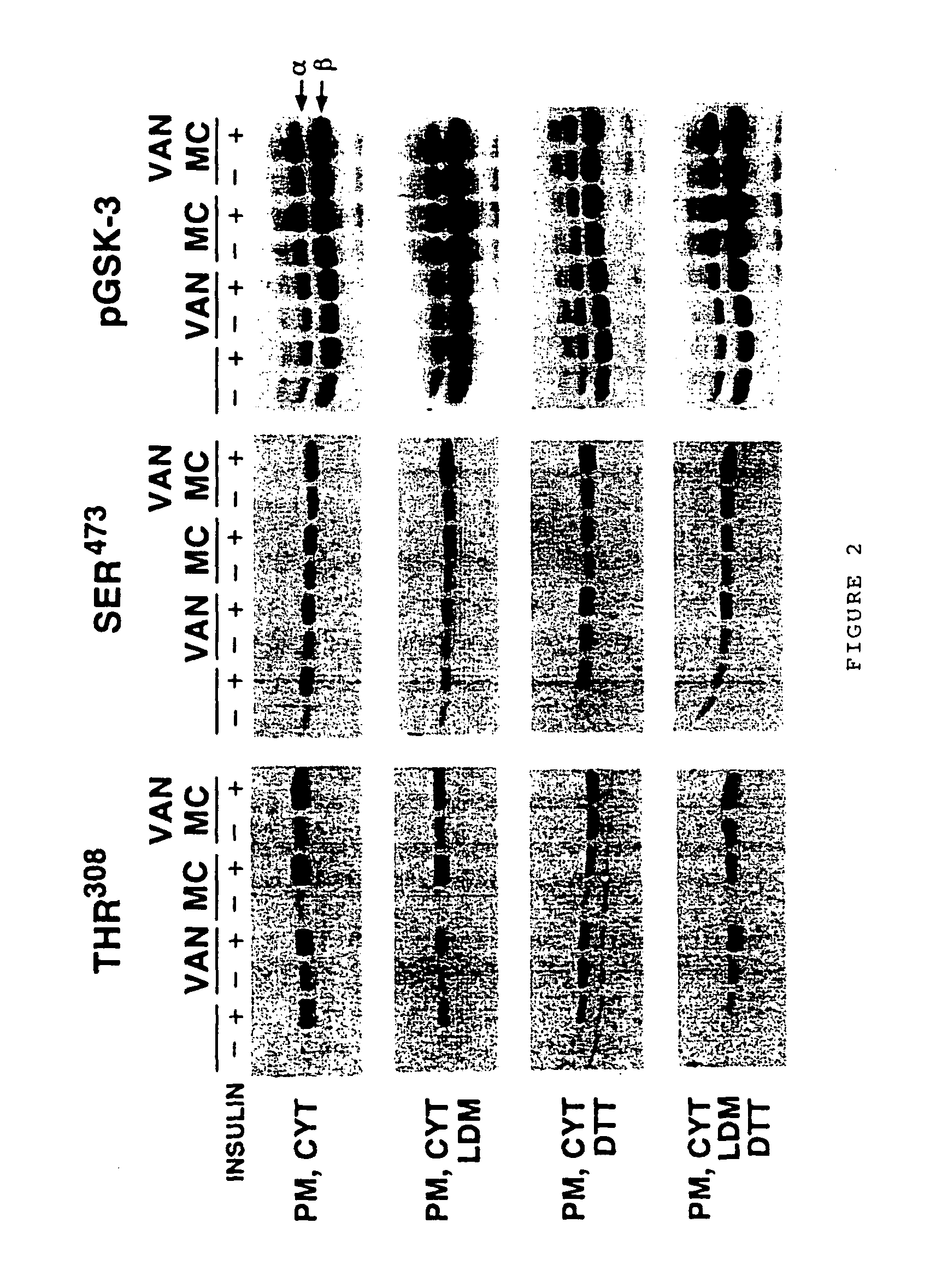
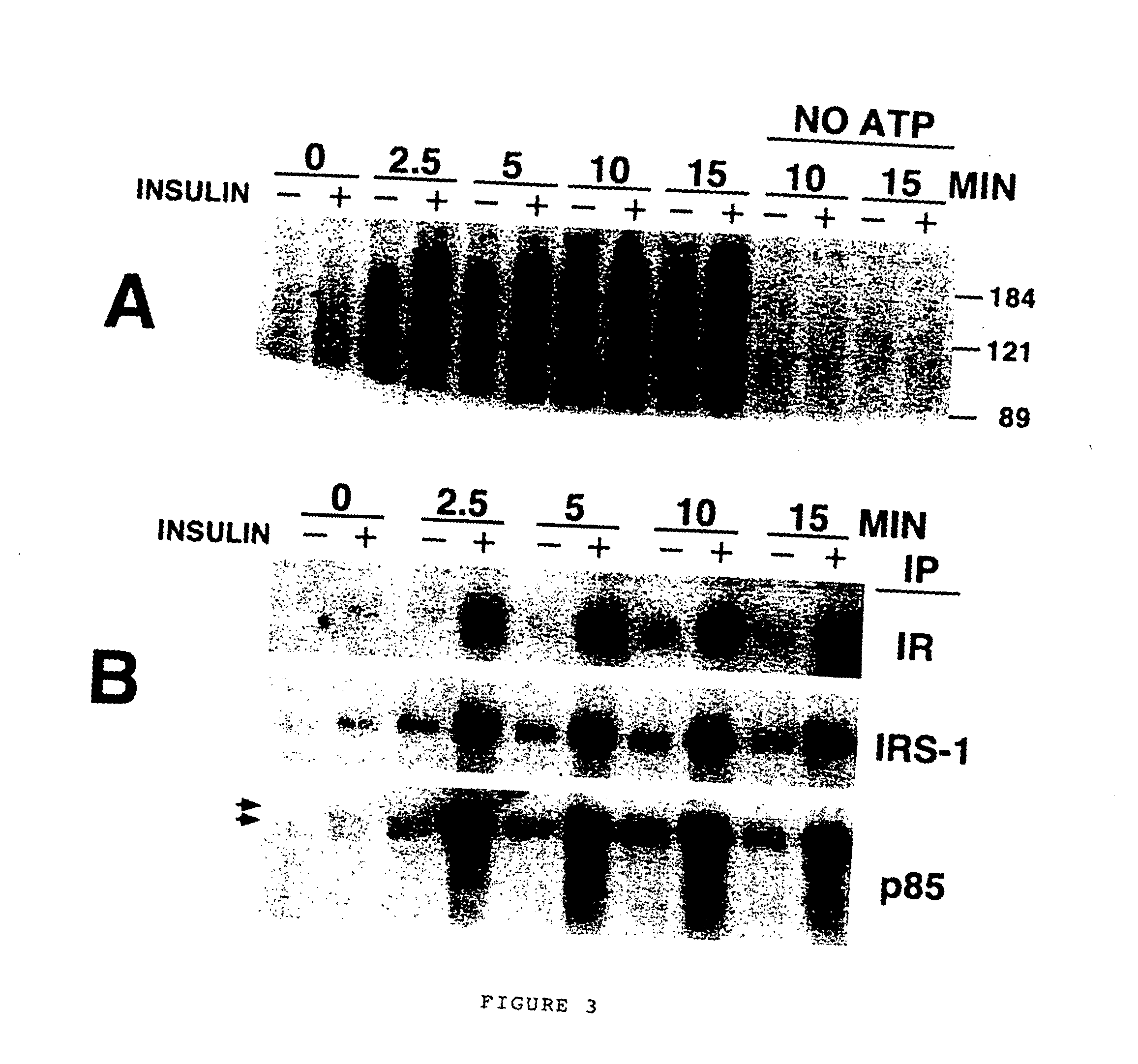
A cell-free assay system, which reconstitutes components of the phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase-mediated insulin signaling pathway including phosphatidylinositol phosphate dependent kinase-2 (“PDK2”). Alternatively, a in vitro method for phosphorylating a protein kinase B on Serine 473 or Serine 474. The invention relates generally to an in vitro method of phosphorylating a protein kinase B (“PKB” or “Akt”), to an in vitro method of assessing insulin action, and to an in vitro method of identifying an agent or process that modulates insulin signaling or any cellular activity regulated or influenced by PKB, including cell growth, mitosis, apoptosis, fuel metabolism, and oncogenic transformation. Such an agent or process may be useful in treating insulin resistance, diabetes, obesity, cancer, and a number of other diseases.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Application of health-care drinking liquid containing deep seawater in preparation of medicaments or health-care products for preventing or treating metabolic syndrome
ActiveCN102652757ANo toxicityImprove securityMetabolism disorderInorganic active ingredientsHigh concentrationInsulin signalling
The invention provides application of health-care drinking liquid containing deep seawater in preparation of medicaments or health-care products for preventing or treating metabolic syndrome. The health-care drinking liquid comprises liquid A and liquid B, wherein the liquid A is fresh water; and the liquid B is high-concentration concentrate obtained by reduced pressure concentration of concentrated water separated from the deep seawater through a reverse osmosis device, and the hardness range of the liquid B is 200 to 1000ppm. The health-care drinking liquid can regulate the insulin signaling channel in vitro level and improve the resistance of insulin so as to prevent the metabolic syndrome. The health-care drinking liquid prepared from the deep seawater has the advantages of rich resources, easiness in industrialization and the like, and has broad market and application prospect on the aspect of preventing and treating the metabolic syndrome.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Methods of treating metabolic disorders associated with lipodystrophies and defects in insulin production or signaling
InactiveUS20170065678A1Good biological propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDyslipidemiaCritically ill
The invention relates to the identification of new therapeutic methods for the FGF21 polypeptide or protein, or mutants, variants, and fusions thereof, for instance, in treating metabolic diseases associated defects in insulin signaling (e.g. insulin receptor mutation disorders (INSR disorders) and / or autoimmune insulin receptor disorders (Type B insulin Resistance)), defects in insulin production such as type 1 diabetes mellitus, mixed dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and other metabolic disorders, and various lipodystrophies such as HIV-HAART induced partial-lipodystrophy, and in reducing the mortality and morbidity of critically ill patients.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Plant extracts with Anti-diabetic and other useful activities
PendingUS20160022752A1Therapeutically effectiveRemarkable effectCompound screeningBiocideDiseaseInsulin-like growth factor
This invention relates to plant extracts containing nutritionally beneficial or medicinally active compounds. Some of these extracts, or the purified compounds contained therein, may be used for the nutritional support, prevention, treatment, or possible cure of various metabolic and other diseases and disorders in human beings and animals, including type 1 and type 2 diabetes, by regulating insulin signaling. This regulatory effect may include modulations of the levels and / or activity of the Insulin Receptor (IR), the Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) Receptor, and / or the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS) proteins in cells and tissues in the body.
Owner:HOUSEY PHARMA RES LAB L L C
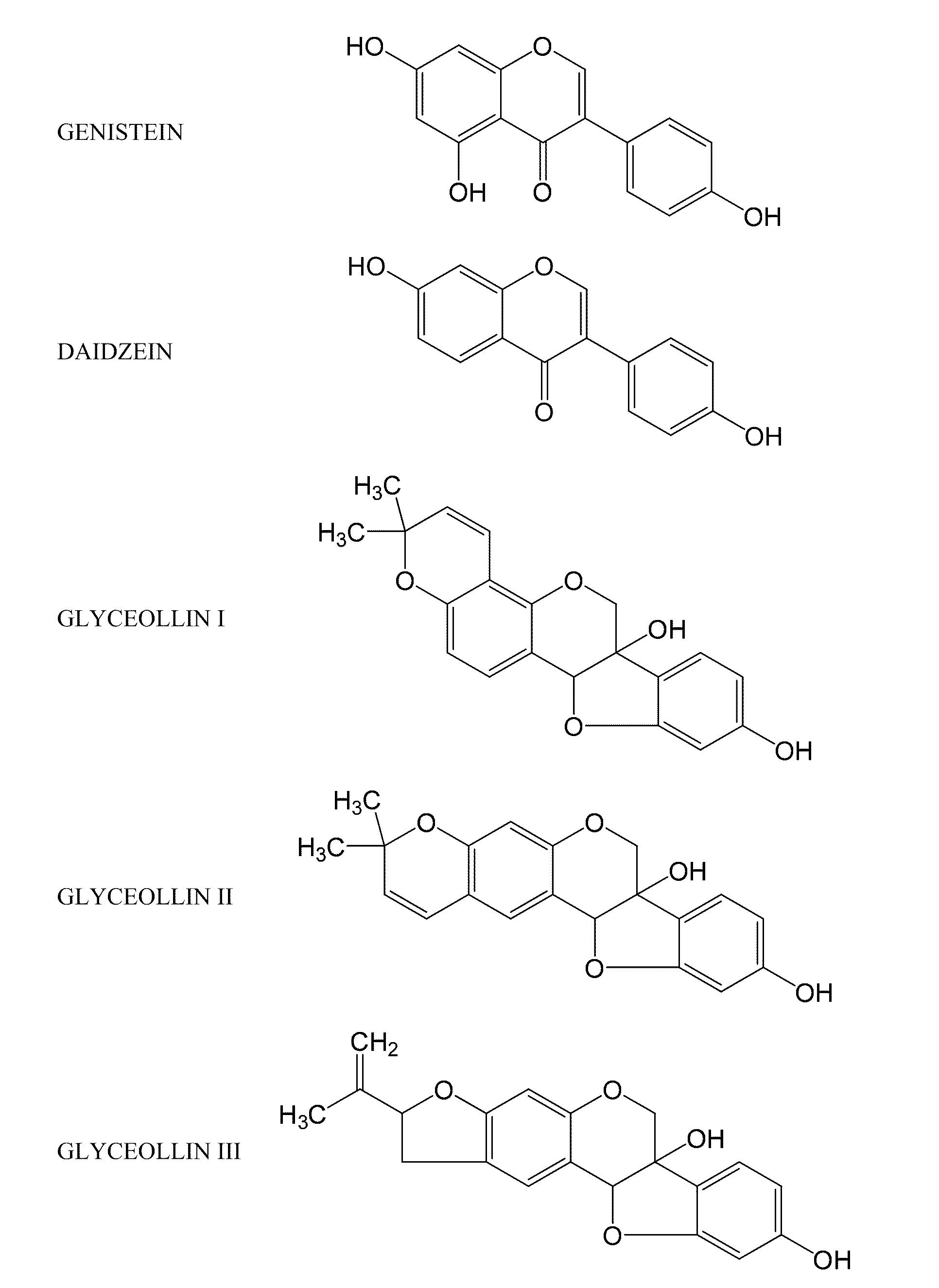
Compositions and Methods for Treating Obesity and Diabetes
ActiveUS20110237505A1Preventing and minimizing obesityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixCholesterol
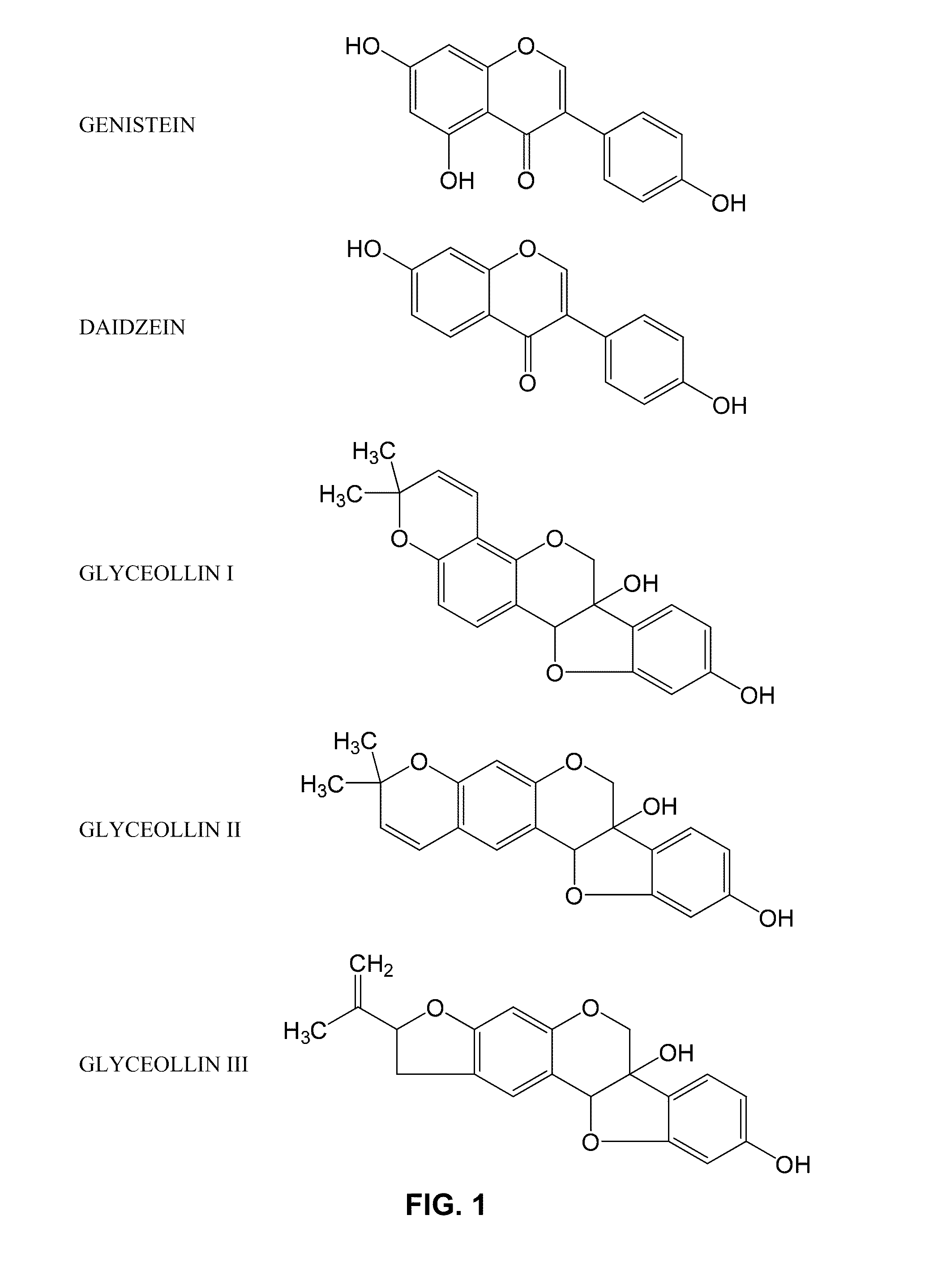
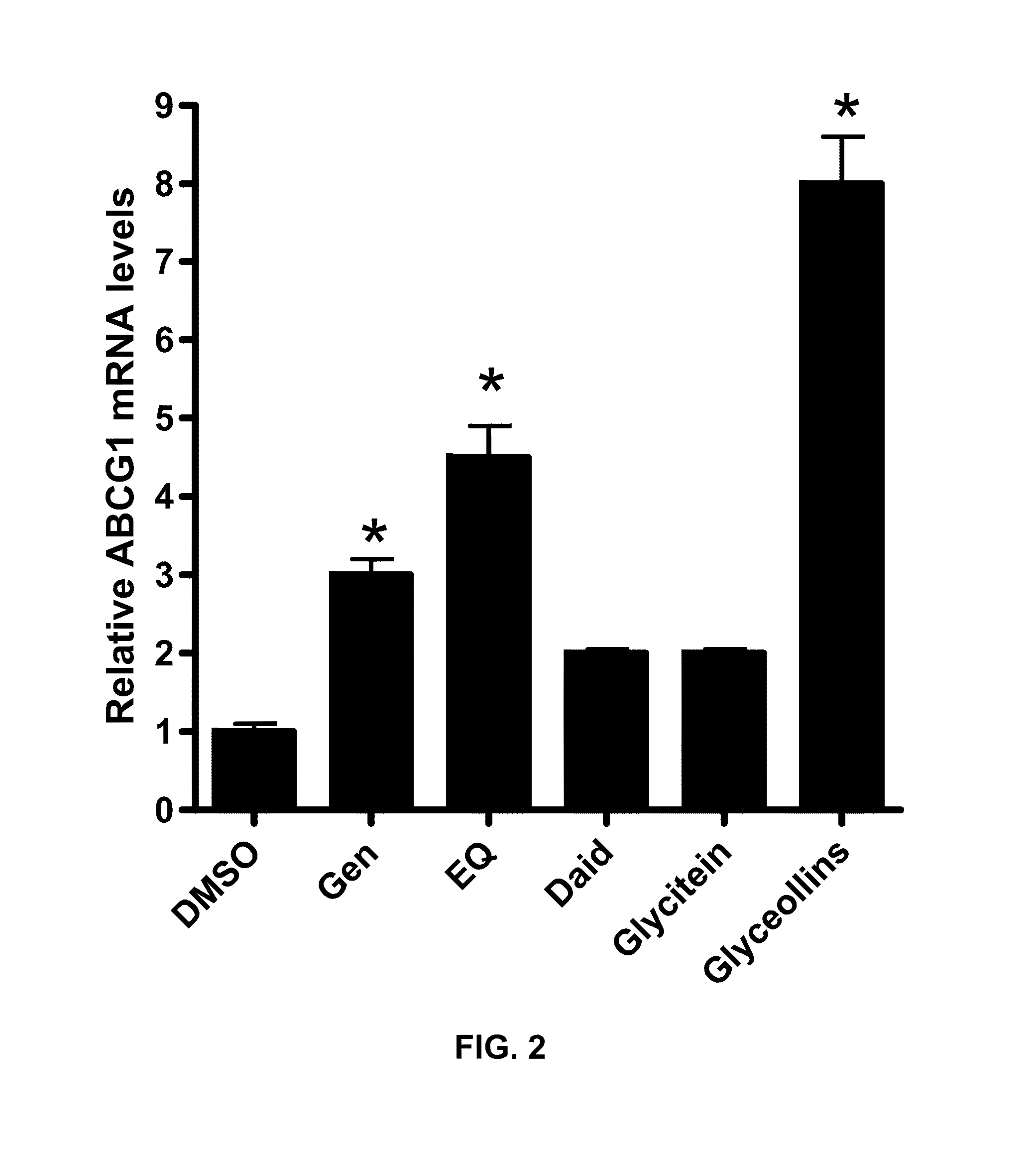
Disclosed are methods of modulating the expression of genes linked to adipocytokine signaling, carbohydrate metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, arachidonic acid metabolism, PPAR signaling, insulin signaling, lipid metabolism, extracellular matrix (ECM)-receptor interaction, or combinations thereof, methods of treating hyperlipidemia, obesity, excessive cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, diabetes, or combinations thereof, and methods of stimulating glucose uptake in an animal in need thereof, comprising administering a composition comprising at least one isolated glyceollin to said animal.
Owner:MICROBIOME THERAPEUTICS LLC +1
Application of miRNA-378 in treatment of fatty liver
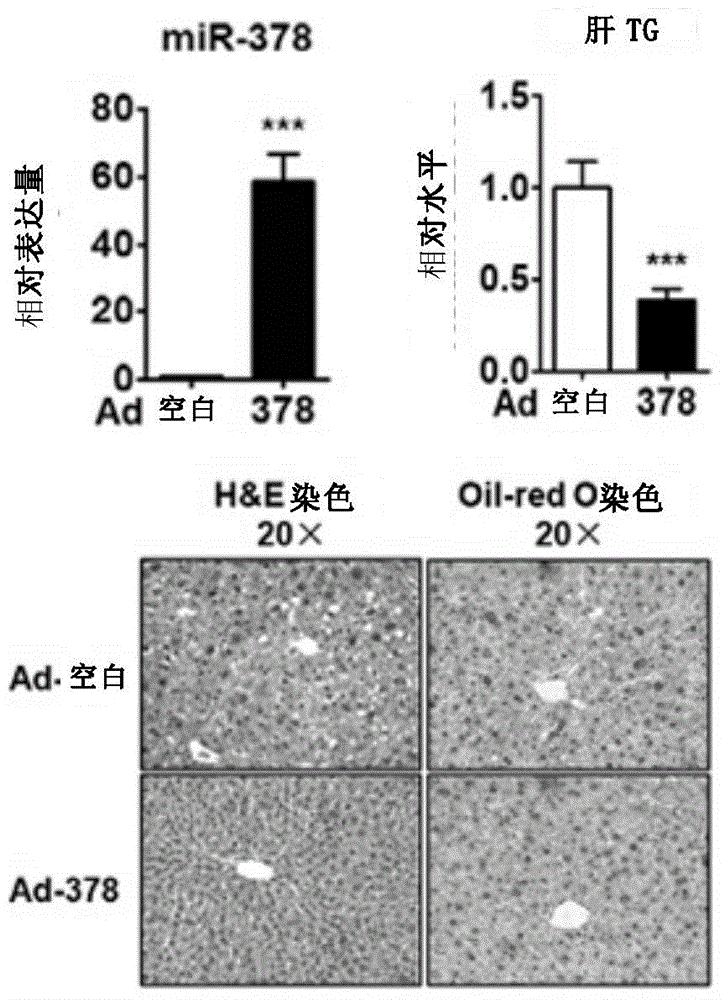
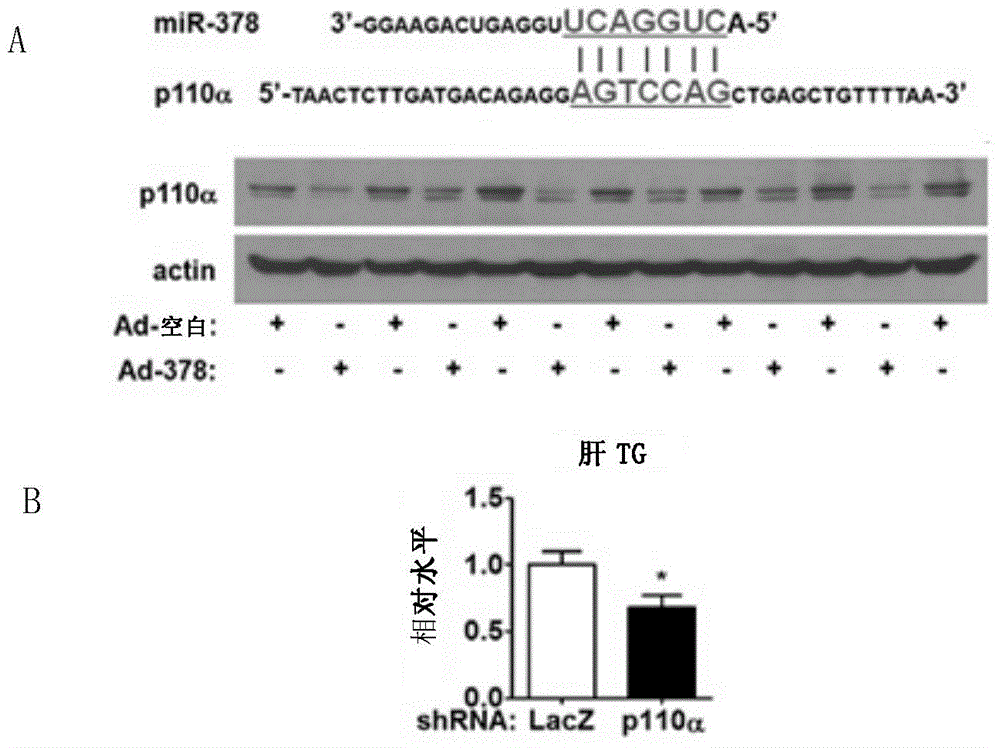
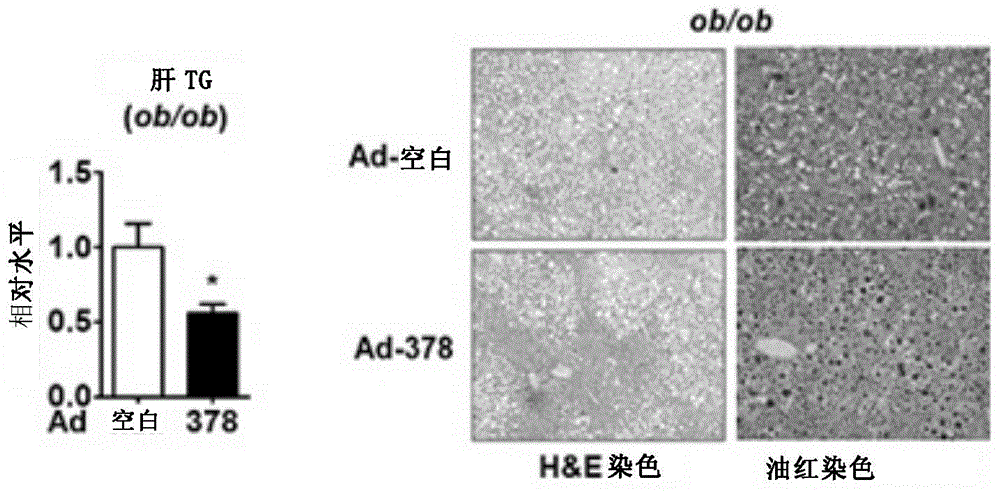
ActiveCN105617399ALower triglyceride levelsMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsFatty liverInsulin signalling
The present invention discloses application of miRNA-378 in treatment of fatty liver. In particular, the miRNA-378 in liver is confirmed to be an insulin signal pathway regulating core element. When the miR-378 is overexpressed in mouse liver, mouse lipid metabolism steady state is enhanced, and is mainly shown as decreased liver TG content, wherein the miR-378 can perform functions through inhibition of insulin signal pathway key protein p110 alpha, so that inhibition of the expression of the p110 alpha by the overexpression of the miR-378 in the liver can be a new therapeutic strategy for liver lipid accumulation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of differentiating stem cells into liver cell lineages
The invention discloses methods of differentiating stem cells into liver cell lineages. The present disclosure provides methods and kits for the differentiation of stem cells into relevant Iiver cell lineages, as well as methods of using the relevant Iiver cell lineages in screening for a cellular response, a phenotype and in the treatment of a condition. In one embodiment, stem cells are first differentiated into cells of the definitive endoderm lineage, which are differentiated into posterior foregut (PFG) lineage cells by one or more of retinoic acid activators and / or one or more inhibitors of transforming growth factor-[beta] (TGF[beta]). An additional embodiment provides a method for the differentiation of posterior foregut lineage cells into Iiver bud progenitors (LB) by one or more activators of TGF[beta] signalling, and / or one or more modulators of Wnt signalling, and / or one or more activators of cyclic AMP / PKA signaling; and a further embodiment provides a method for the differentiation of Iiver bud progenitors into hepatic progenitors by one or more inhibitors of TGF[beta] signalling and / or fibroblast growth factor (FGF) inhibitors and / or one or more Notch inhibitors. Another embodiment discloses the differentiation of hepatic progenitors into hepatocyte-like cells or perivenous hepatocyte-like cells by one or more of Notch inhibitors and / or activators of glucocorticoid signalling and / or one or more activators of insulin signalling and / or one or more of ascorbic acid signalling activators and / or additional factors. Methods and kits for maintaining LB in self renewal state, hepatocyte-like cells in perivenous or periportal state, as well as surface markers for LB and mid / hindgut (MHG) cells are also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Novel medicine use of indirubin derivates
InactiveCN101081222AOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin dependent diabetesInsulin signalling
The present invention relates to the medicinal use of indirubin derivative, and is especially the application of indirubin derivative in preparing medicine for treating non-insulin dependent diabetes. Pharmacodynamic experiment shows that the indirubin derivative has the function of affecting the activity of PI3K component in insulin signal conducting passage, and can activate Akt and inhibit mTOR to promote the transfer of insulin signal and sensitize the peripheral tissue in utilizing insulin. The indirubin derivative is hopeful in developing medicine acting on insulin resistance to treat type II diabetes. The indirubin derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable supplementary material may be prepared into tablet, capsule or other oral preparation.
Owner:安徽九鼎医药科技有限公司
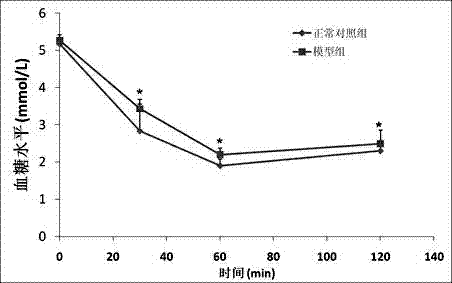
Method for constructing insulin resistance animal model
InactiveCN102228700AModeling method is simpleHigh molding ratePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological testingPhysiologyStatistical analysis
The invention relates to a method for constructing an insulin resistance animal model. A Sprague Dawley rat is injected with glucose oxidase (400U / kg weight) through tail vein injection to induce to generate insulin resistance. The statistical analysis of ghlcose tolerance and insulin tolerance and the detection of insulin signal transduction prove that the glucose oxidase constructed insulin resistance animal model is feasible, and can serve as a research model for insulin resistance, the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and a medicine function mechanism. Compared with the conventional model constructing technology, the method has the advantages of simple modeling method, high modeling efficiency, low cost, short period, high repeatability and the like.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Assay for insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) inhibitors
InactiveUS20160282364A1Improve glucose toleranceSlower gastric emptyingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionInsulin-degrading enzymeInsulin signalling
IDE-binding probes and assays for the identification of IDE-binding and IDE-inhibiting compounds are provided. Pharmaceutical compositions of macrocyclic IDE inhibitors are also provided, including compositions in which such IDE inhibitors are combined with an additional therapeutic agent. Methods of using IDE inhibitors for transiently inhibiting IDE in a subject in need thereof, for example, for the transient inhibition of IDE in a subject exhibiting aberrant IDE activity, impaired isulin signaling, or insulin resistance, for example, a subject having diabetes, are also provided. Methods of using IDE inhibitors for transiently modulating heart rate and / or blood pressure in a subject are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Polypeptide of protein p140 and DNAs encoding it
The present invention is related to a novel protein p140 polypeptide which is a key protein involved in the signal transmission system of insulin; method for preparation of it; DNA encoding the said polypeptide; vector derived the said DNA; host cells transformed the said vector; antibody of the said polypeptide; pharmaceutical composition containing the said peptide or antibody; method for the prevention and / or treatment of diabetes, which is characterized by tyrosine phosphorylation of the said protein p140; agent for the prevention and / or treatment for the currently said the prevention and / or treatment method; agent for the prevention and / or treatment of diabetes, which is characterized by containing a compound which can tyrosine phosphorylation of protein p140, as active ingredient and the screening methods of the said prevention and / or treatment agent.Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein p140 is an essential step in the induction of hypoglycemia by glucose uptake. Method and agent of prevention and / or treatment based on tyrosine phosphorylation of protein p140 in the present invention is not only improve the diabetes-derived hyperglycemic conditions but are also useful for the treatment and / or prevention of diabetes, especially non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM).
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors
Peptide inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) having an amino acid sequence motif of XZXXXS(p)X, wherein S(p)=phosphorylated serine or phosphorylated threonine, X=any amino acid, and Z=any amino acid except serine or threonine. These inhibitors, which are about 7 to 20 amino acids long, are specific for GSK-3 and strongly inhibit the enzyme with an IC50 of about 150 μM. Also provided are methods of treating biological conditions mediated by GSK-3 activity, such as potentiating insulin signaling in a subject, treating or preventing type 2 diabetes in a patient, and treating Alzheimer's Disease by administering peptide inhibitors. Compositions of these peptide inhibitors and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers are also provided, as is a method for identifying inhibitors of GSK-3. The invention further relates to a computer-assisted method of structure based drug design of GSK-3 inhibitors using a three-dimensional structure of a peptide substrate of GSK-3.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
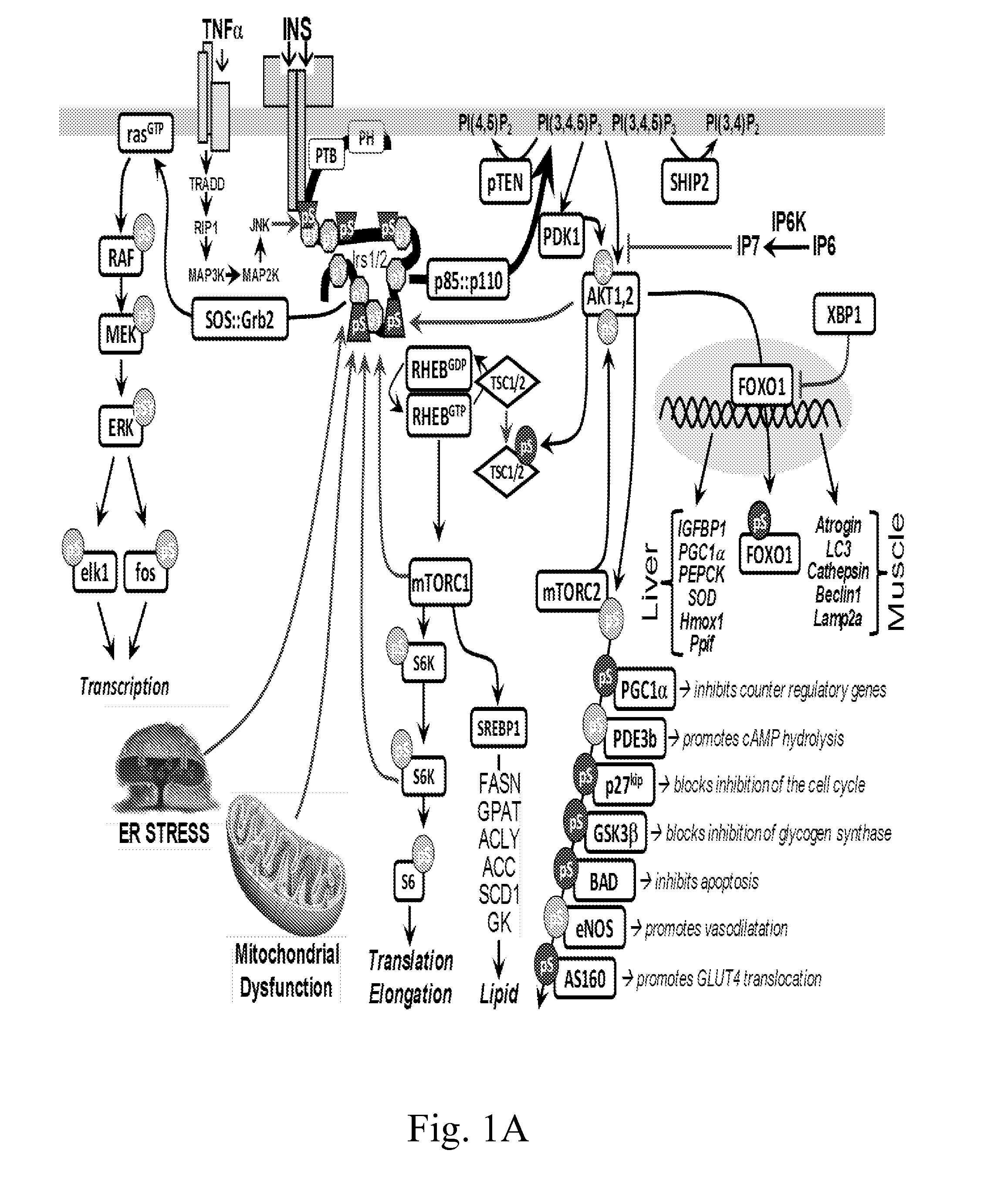
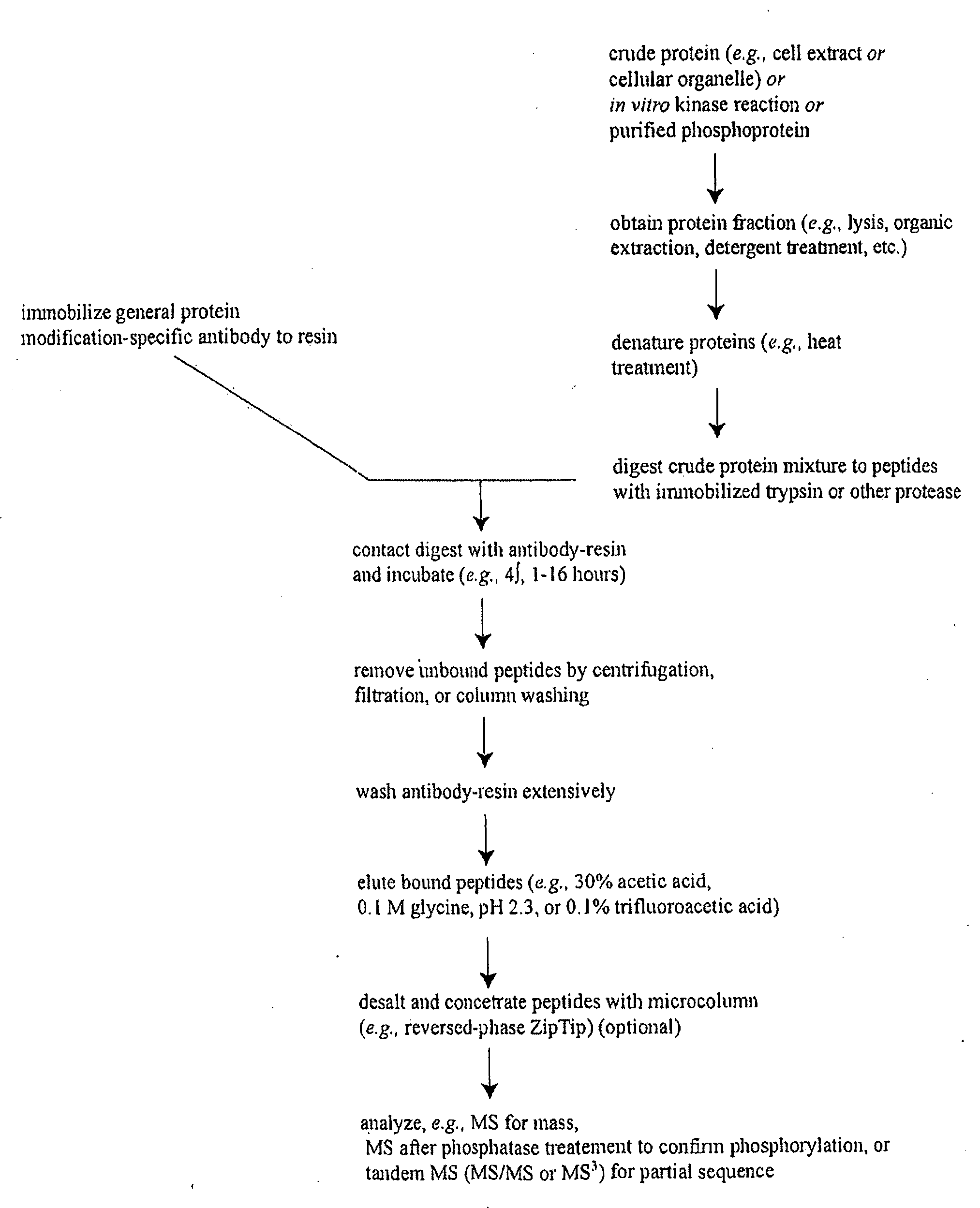
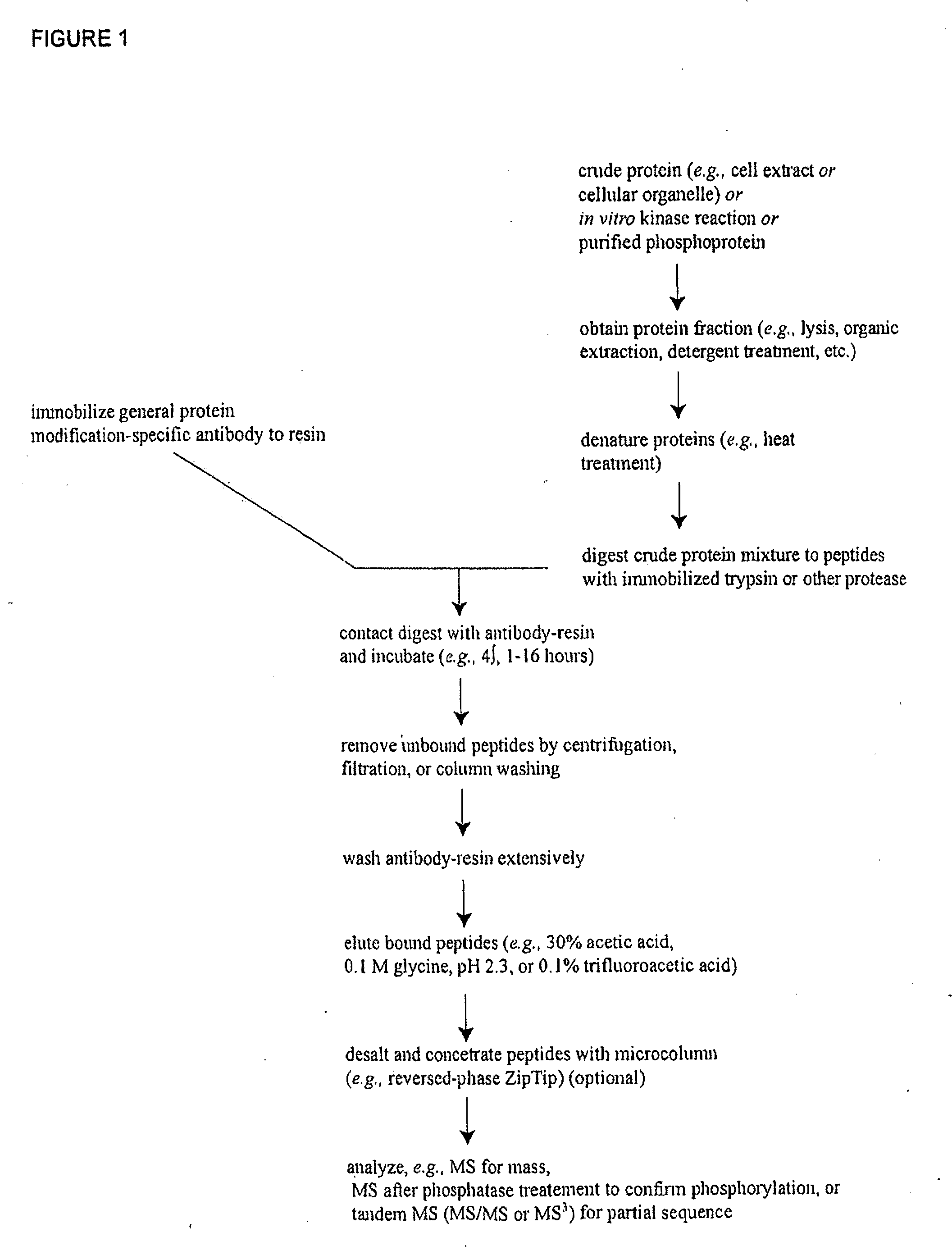
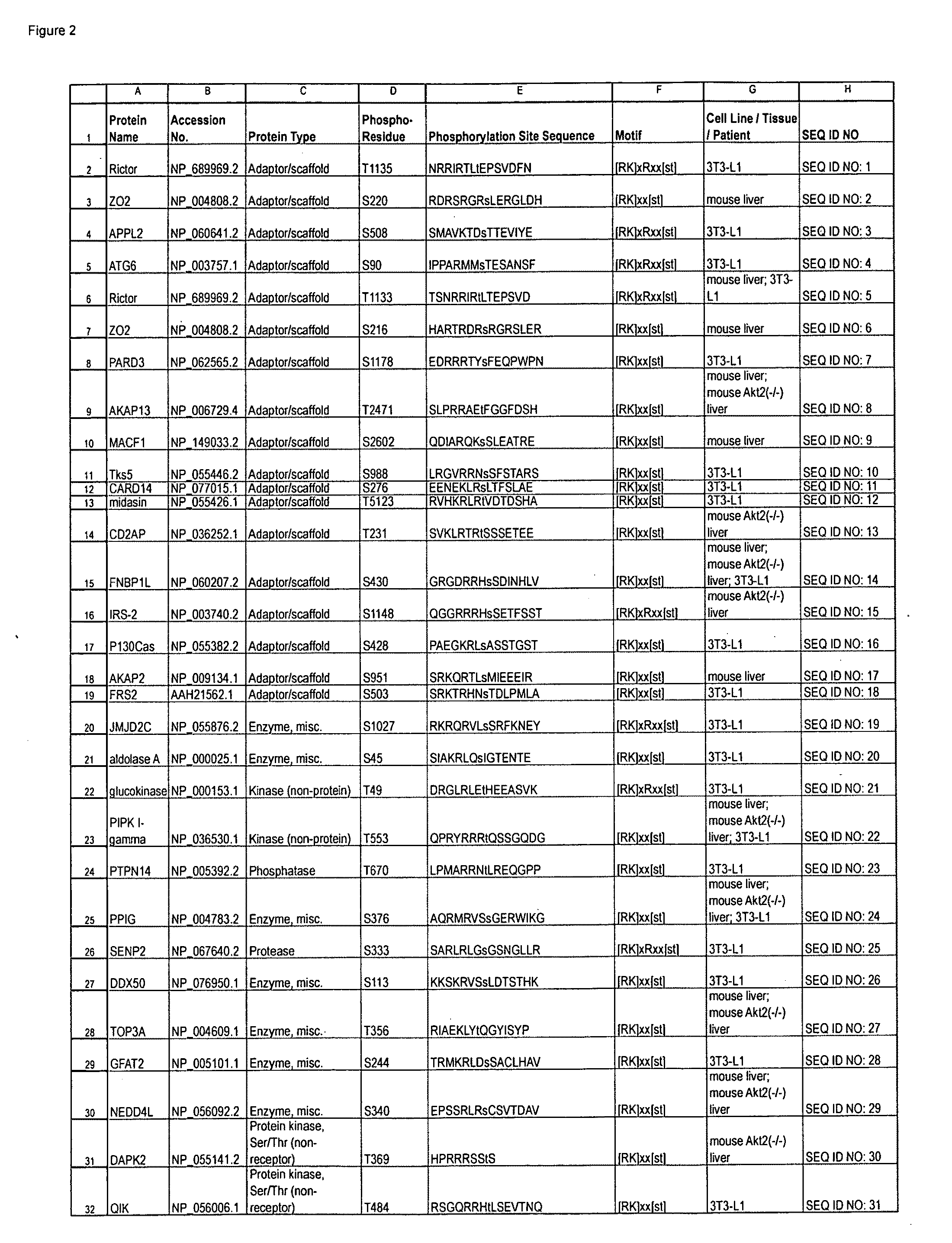
Protein phosphorylation by basophilic serine/threonine kinases in insulin signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090203043A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisInsulin signallingThreonine
The invention discloses 142 novel phosphorylation sites identified in insulin signaling pathways, peptides (including AQUA peptides) comprising a phosphorylation site of the invention, antibodies specifically bind to a novel phosphorylation site of the invention, and diagnostic and therapeutic uses of the above.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Dietary supplements containing extracts of Nelumbo and processes of using same
InactiveUS8613959B2Promote absorptionHigh gainBiocideOrganic active ingredientsInsulin signallingDietary supplement
Materials derived from Nelumbo are administered orally to humans or animals for the purpose of enhancing creatine transport into skeletal tissue and for purposes of enhancing lean body mass. Enhancing creatine transport through improved insulin signaling is a new method of depositing creatine and enhancing lean body mass. Such administration is also used for enhancing athletic performance and controlling bodyweight and body fat levels. More specifically, such administration is used for the purpose of enhancing creatine transport into excitable tissues such as skeletal muscle. The material is administered as extracts of Nelumbo and administered in a variety of ways including capsules, tablets, powdered beverages, bars, gels or drinks.
Owner:IN INGREDIENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com