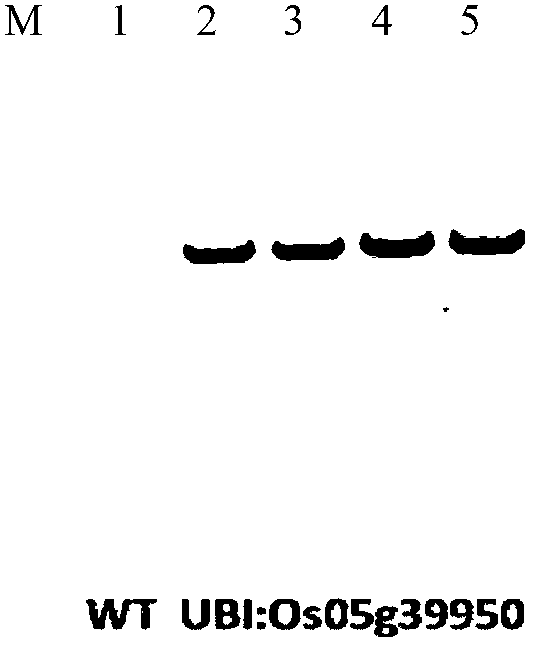Patents
Literature
121 results about "Sequence motif" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and has, or is conjectured to have, a biological significance. For proteins, a sequence motif is distinguished from a structural motif, a motif formed by the three-dimensional arrangement of amino acids which may not be adjacent.
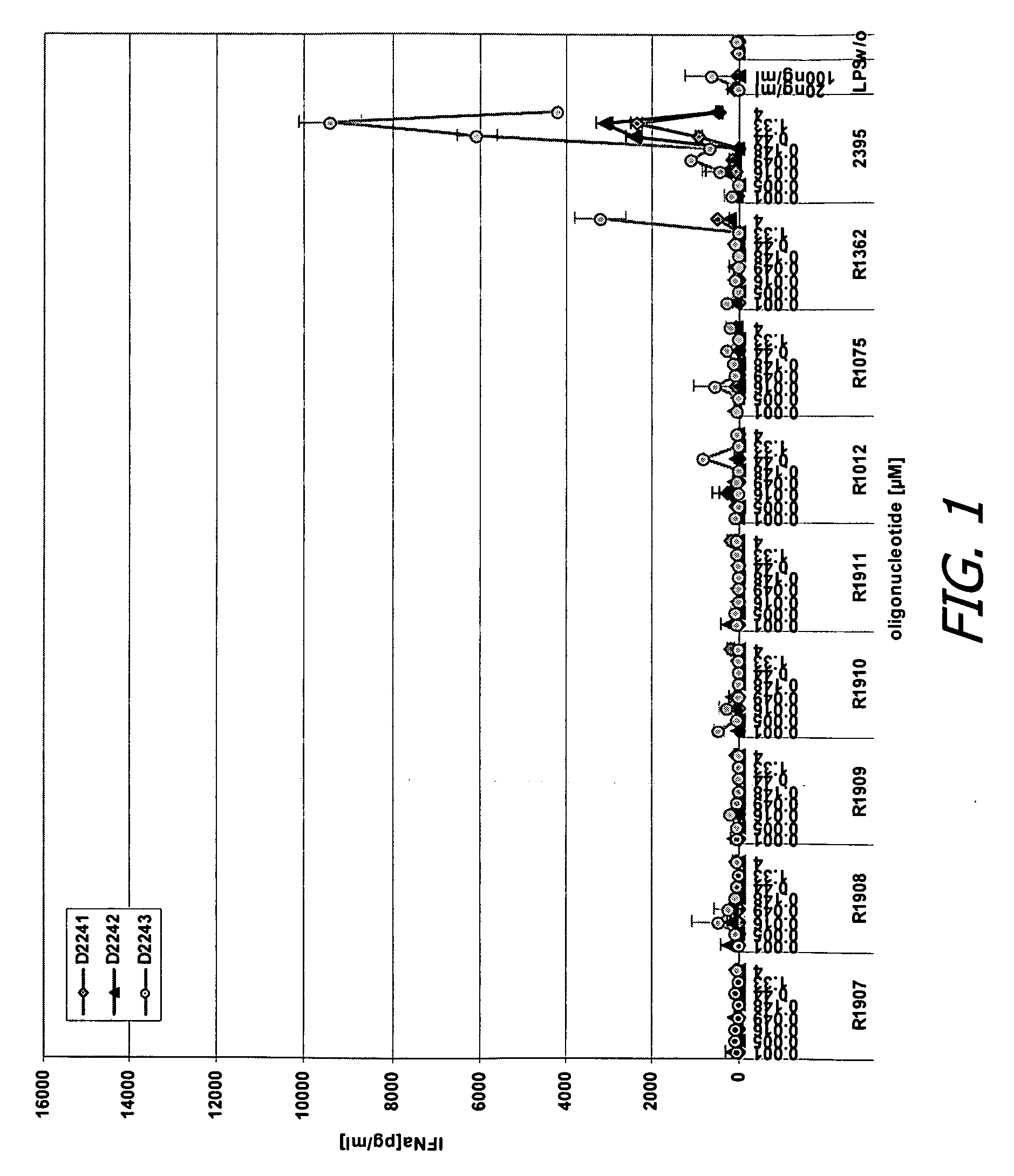
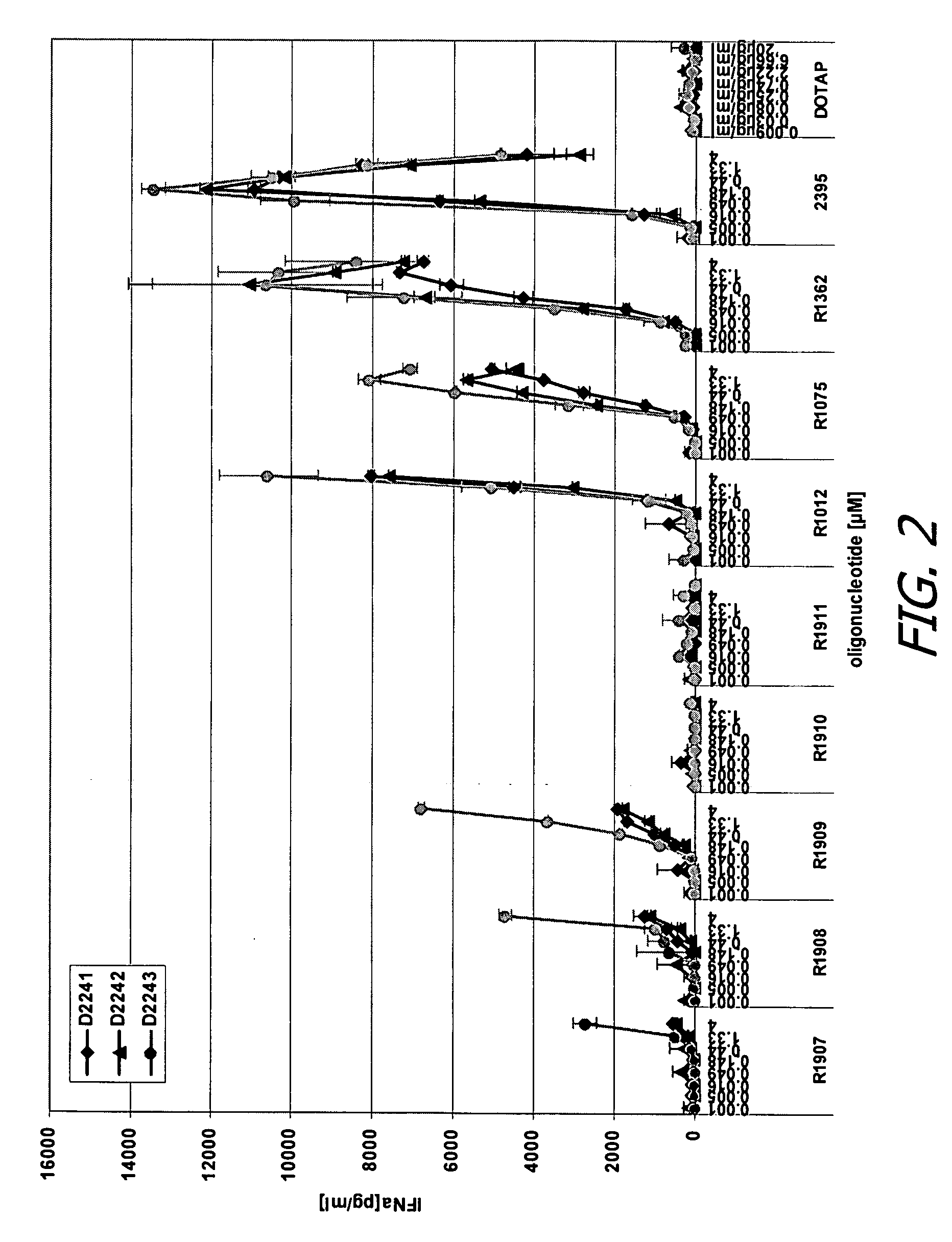
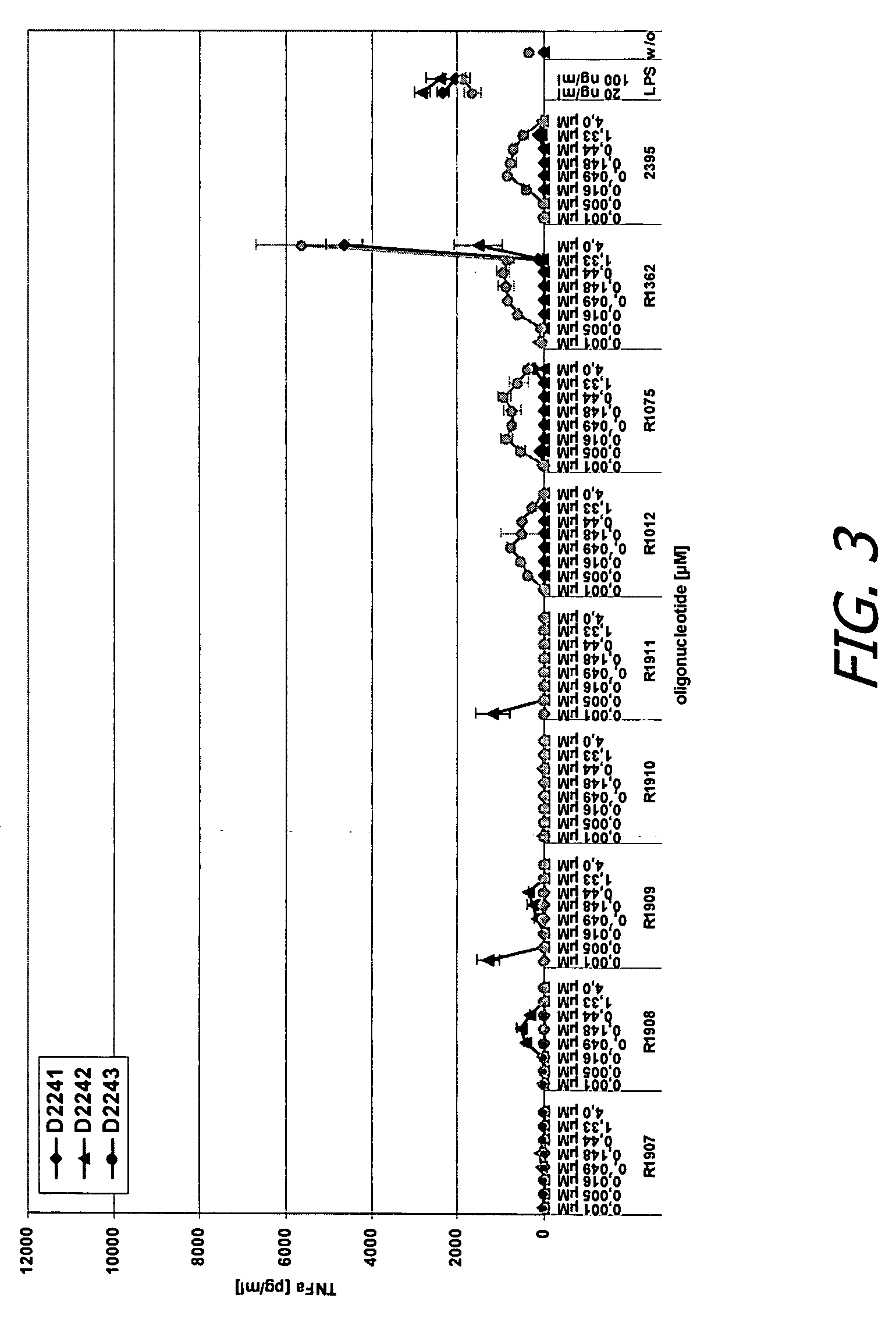
Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs with enhanced immunostimulatory activity
The invention provides immunostimulatory compositions and methods for their use. In particular, the immunostimulatory compositions of the invention include RNA-like polymers that incorporate an immunostimulatory sequence motif and at least one chemical modification to confer improved stability against nuclease degradation and improved activity. Specific modifications involving phosphate linkages, nucleotide analogs, and combinations thereof are provided. Compositions of the invention optionally include an antigen and can be used to stimulate an immune response. Also provided are compositions and methods useful for treating a subject having an infection, a cancer, an allergic condition, or asthma. Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs of the invention are believed to stimulate Toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR8.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GRP INC +1
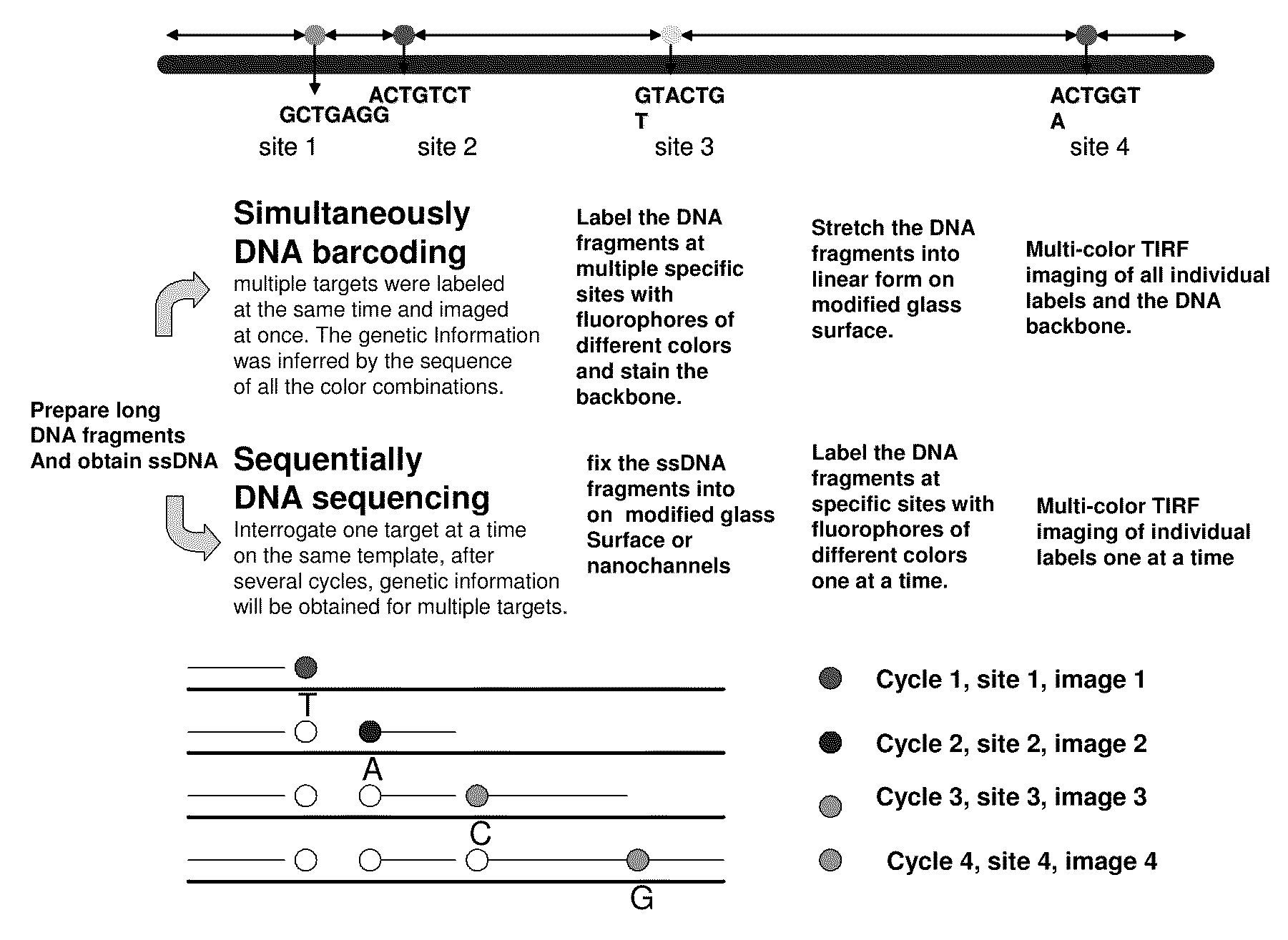
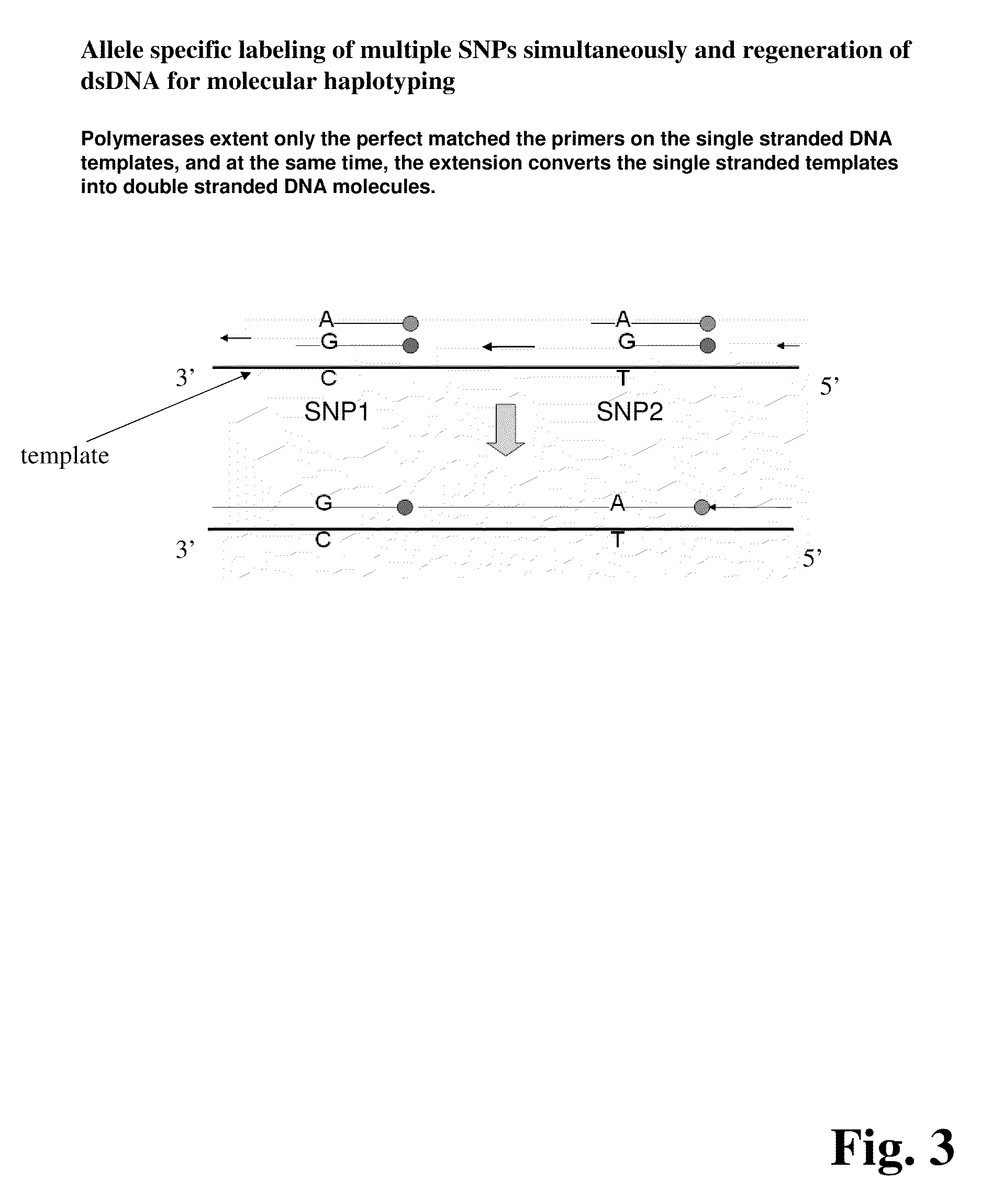
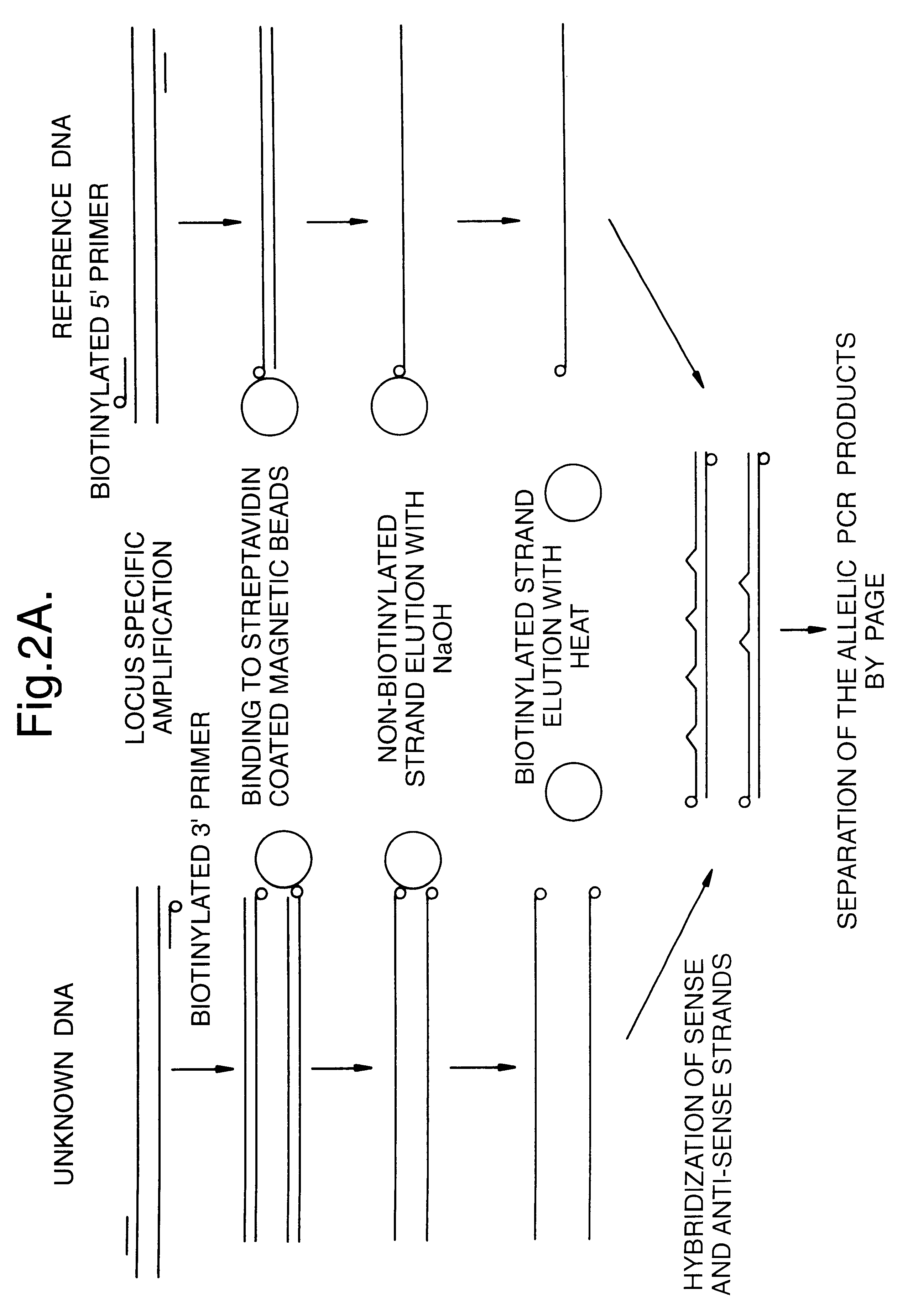
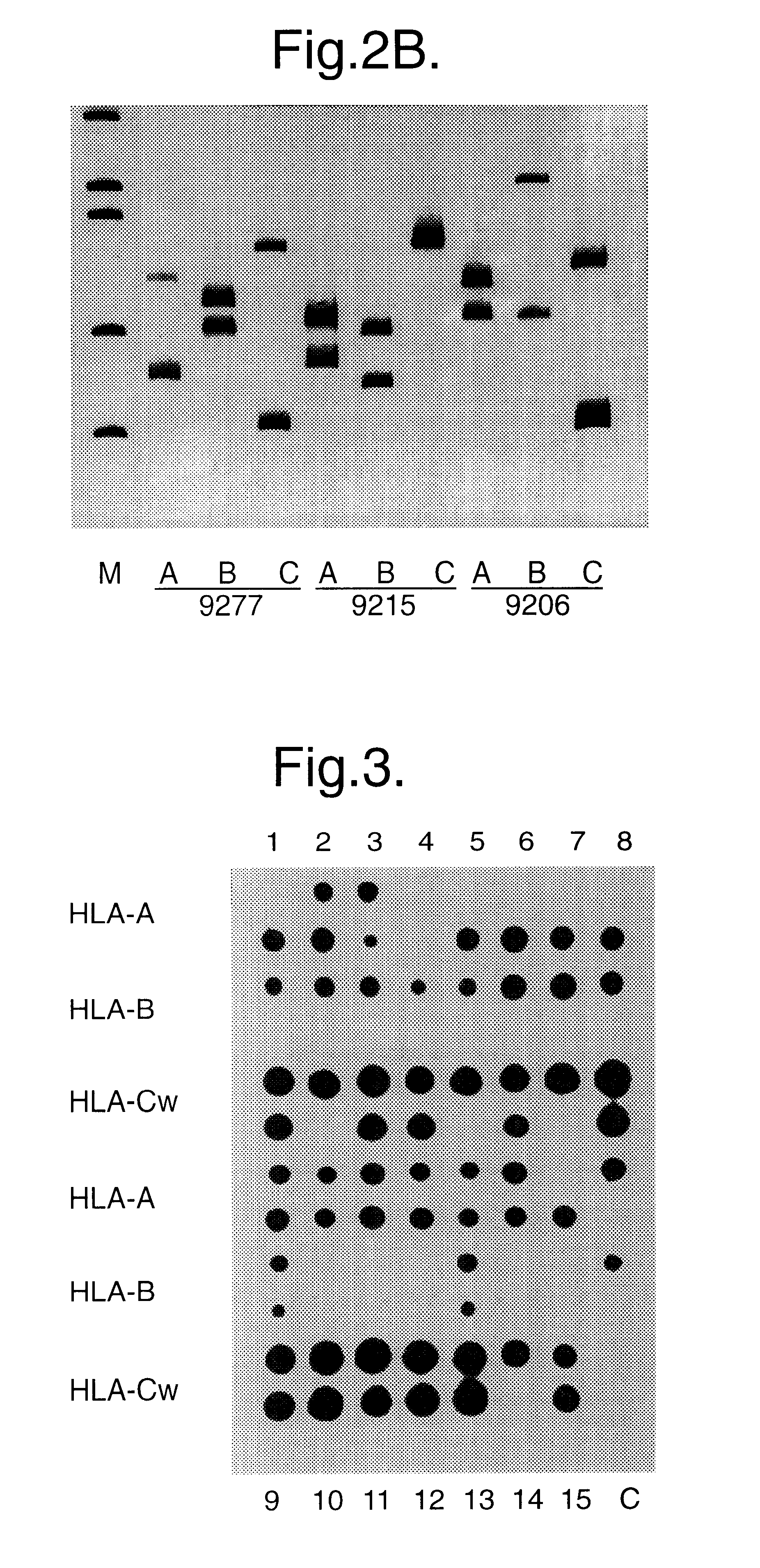
Methods for determining genetic haplotypes and DNA mapping
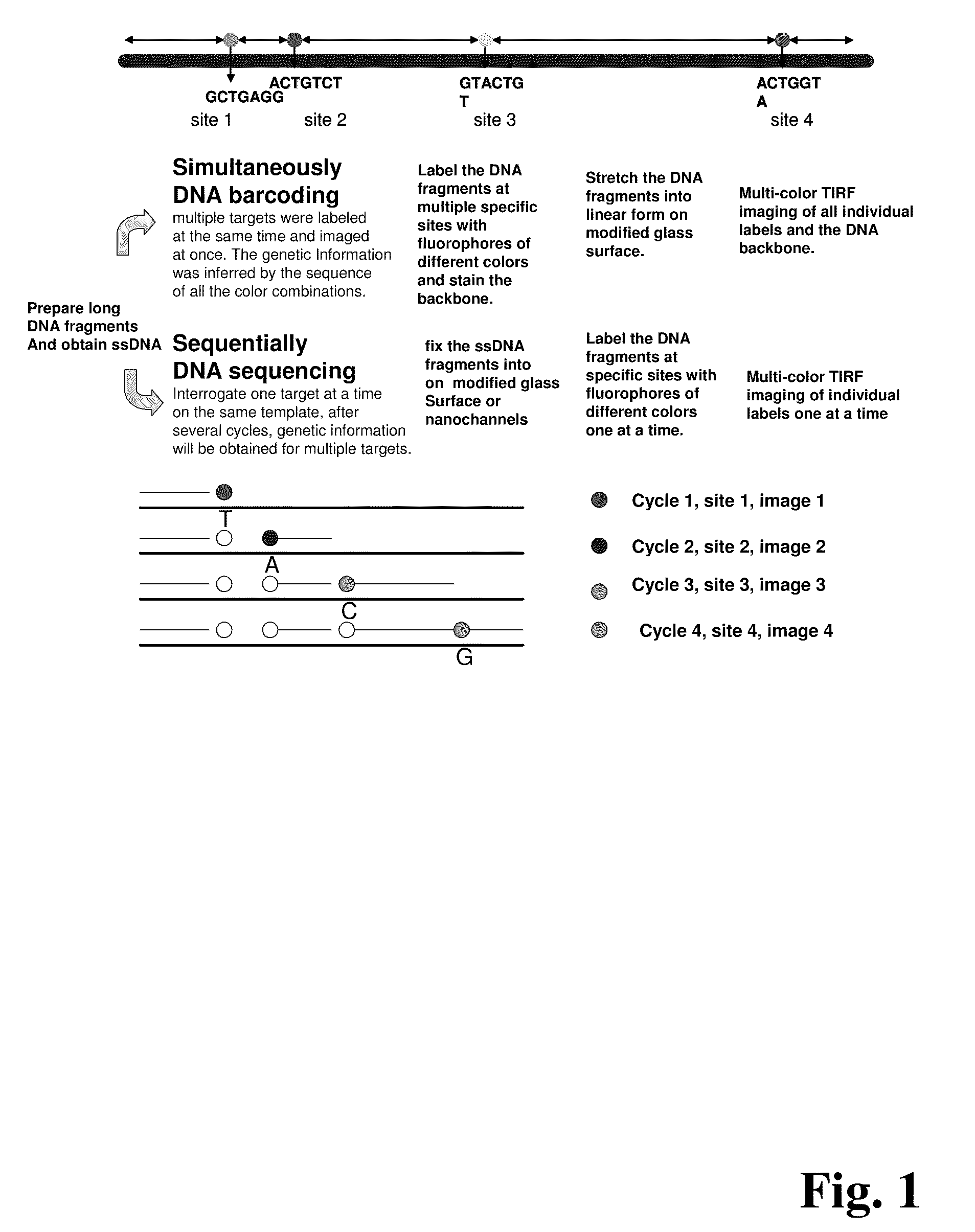
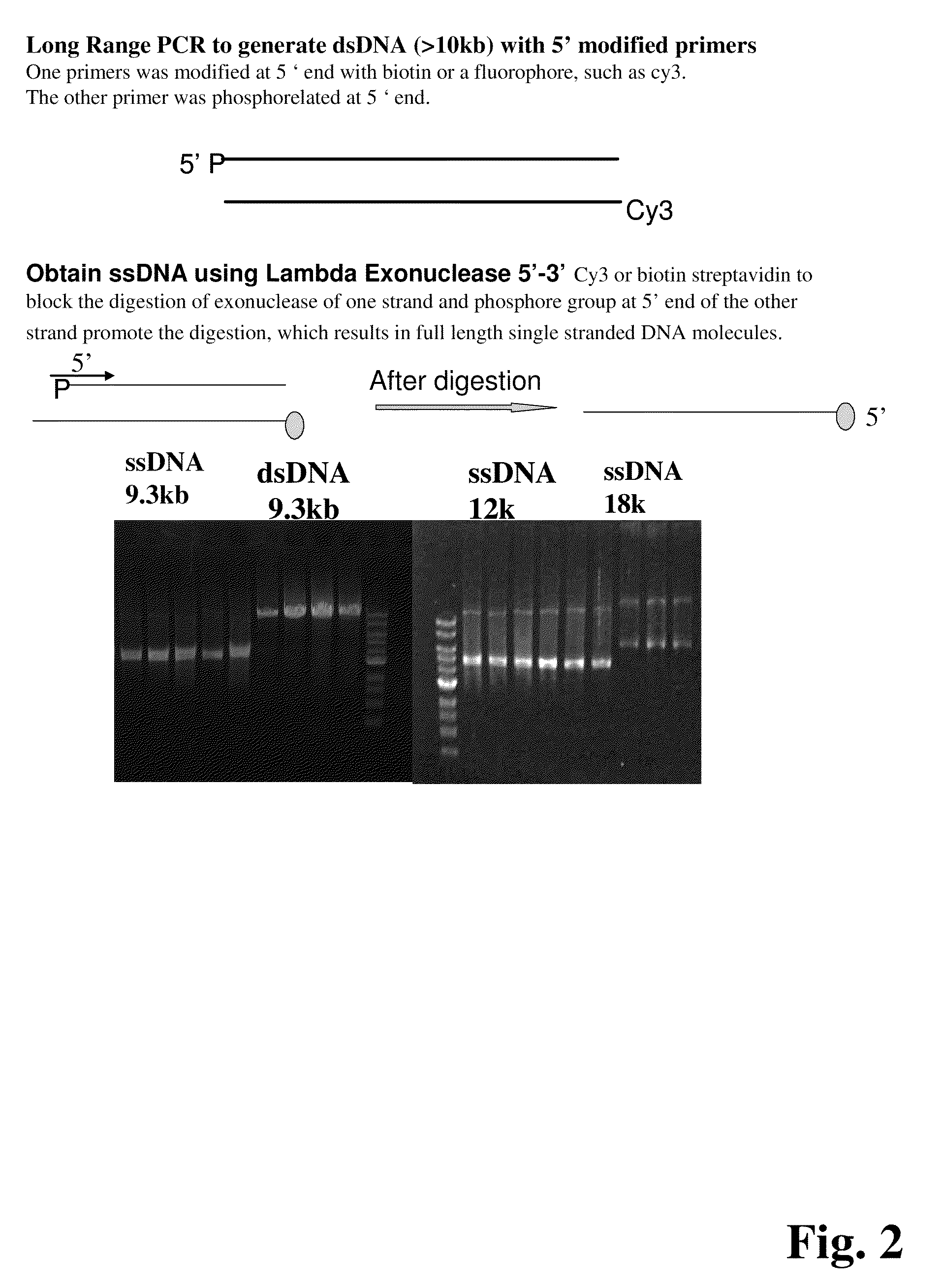
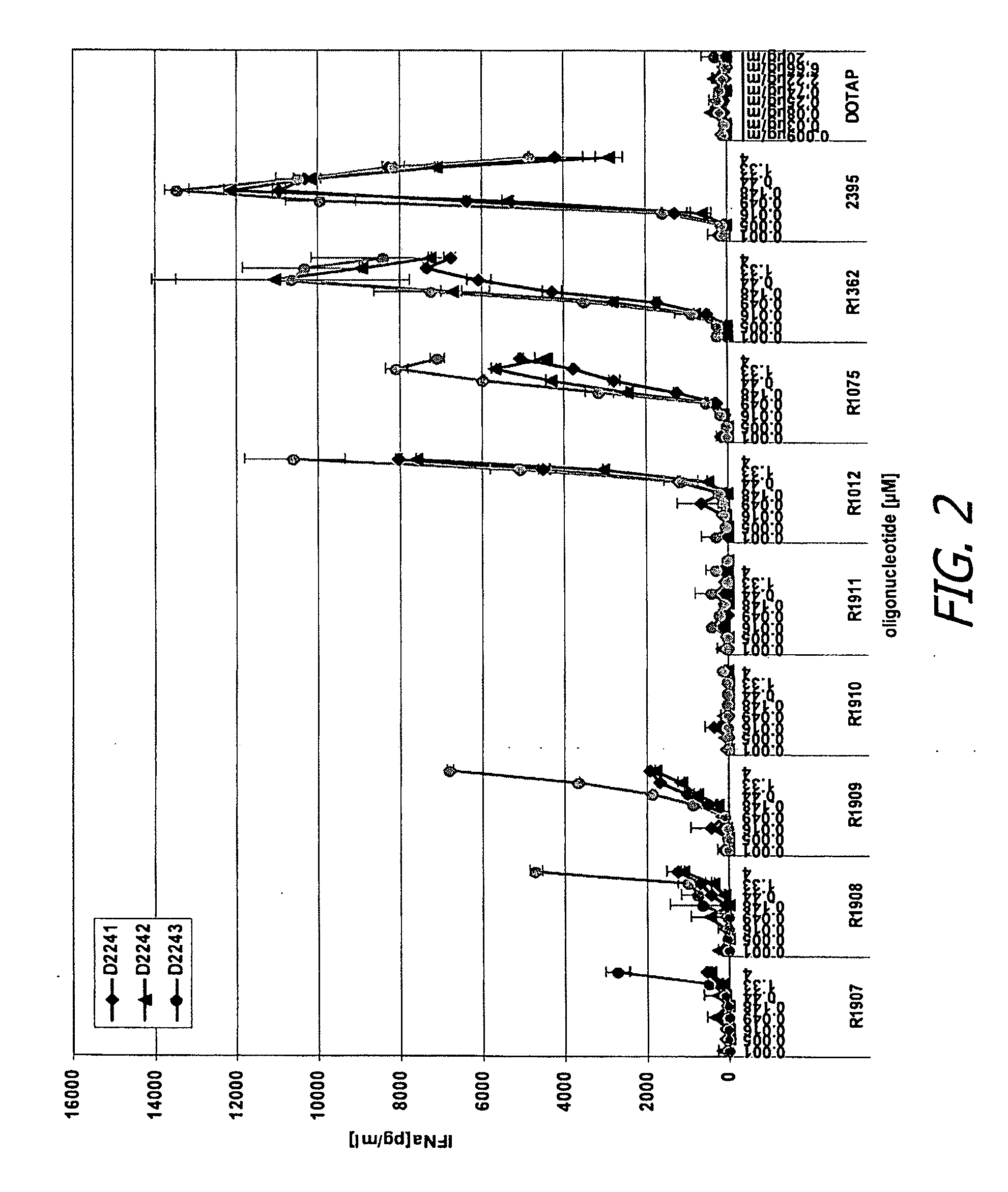
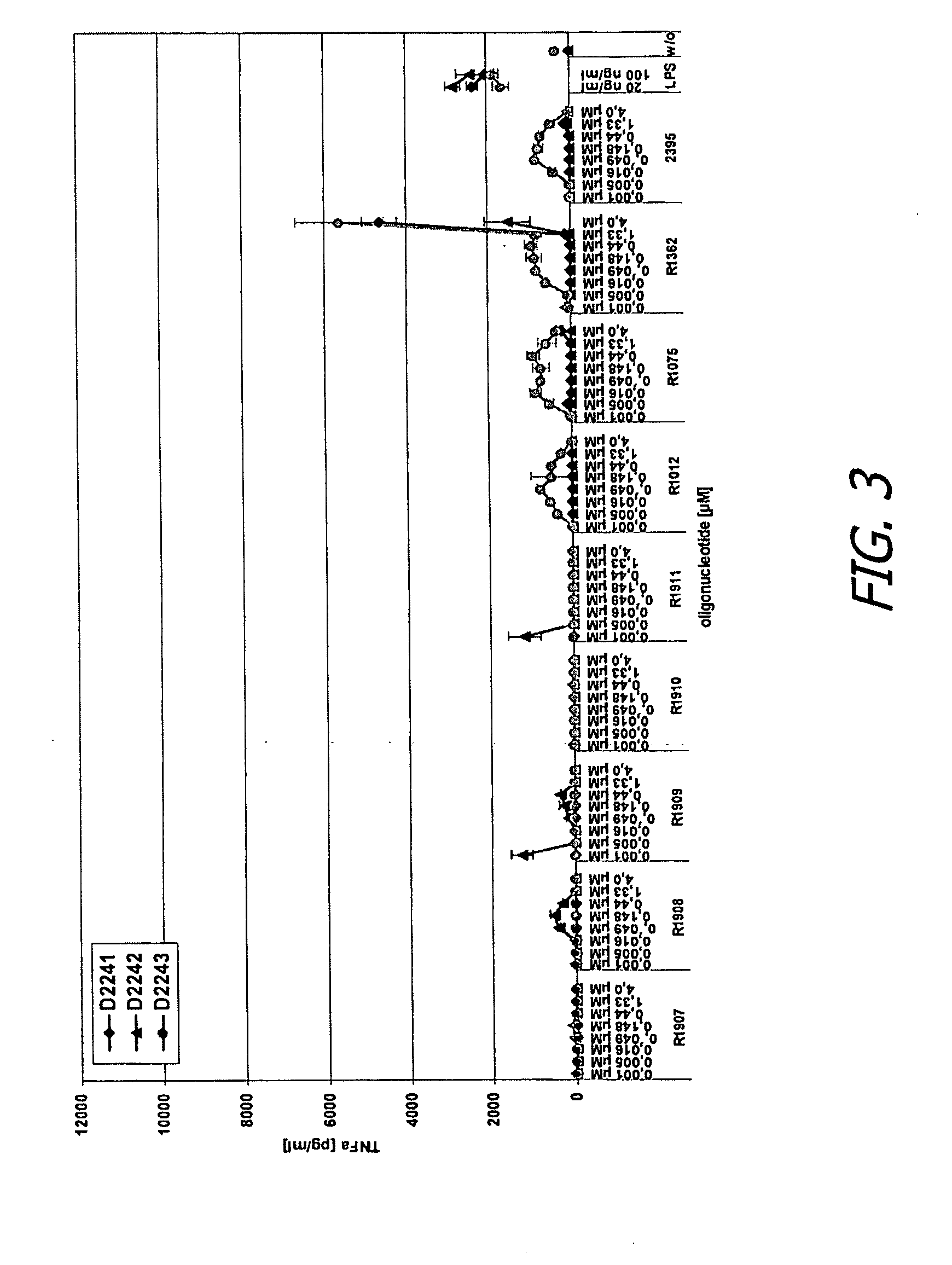
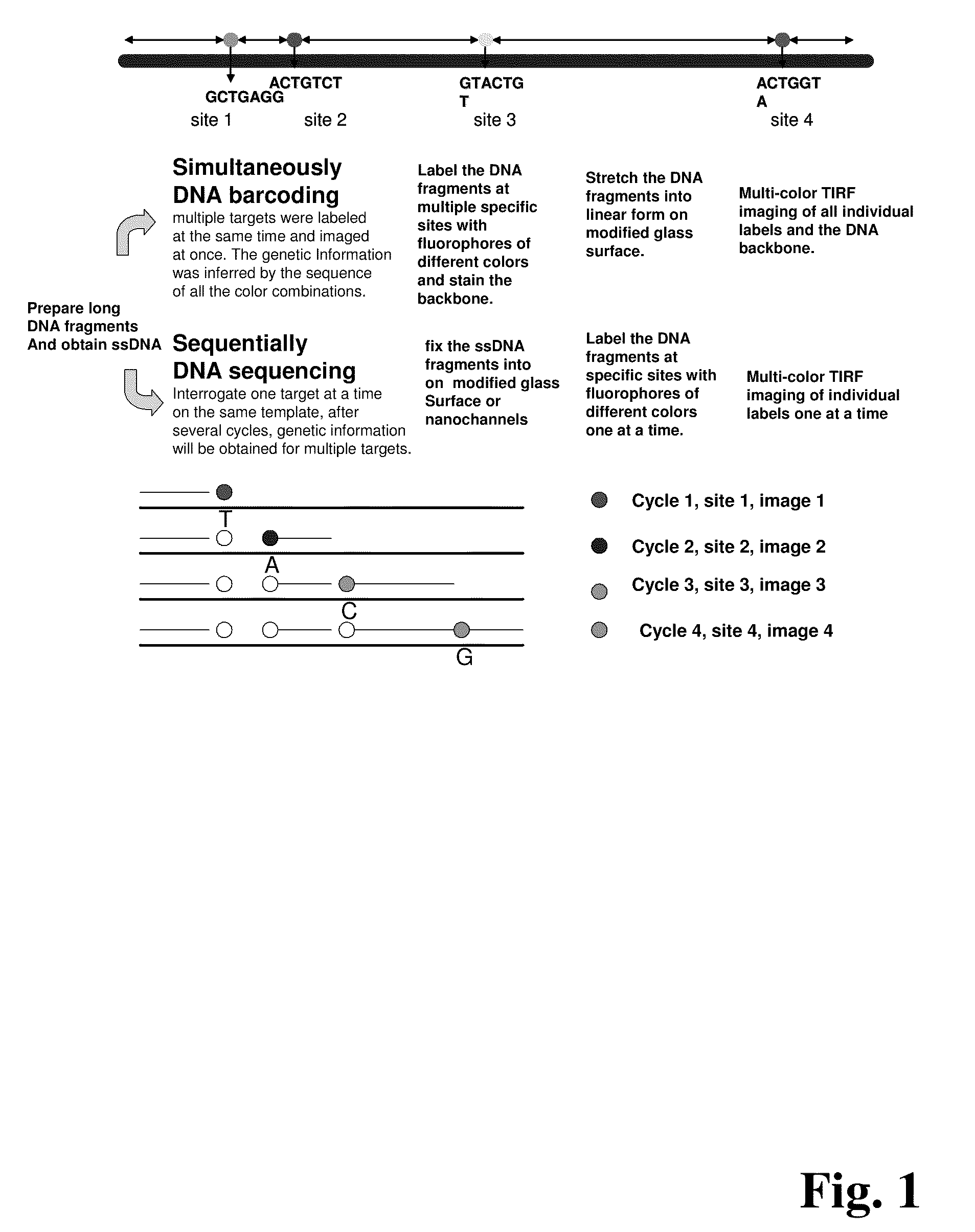
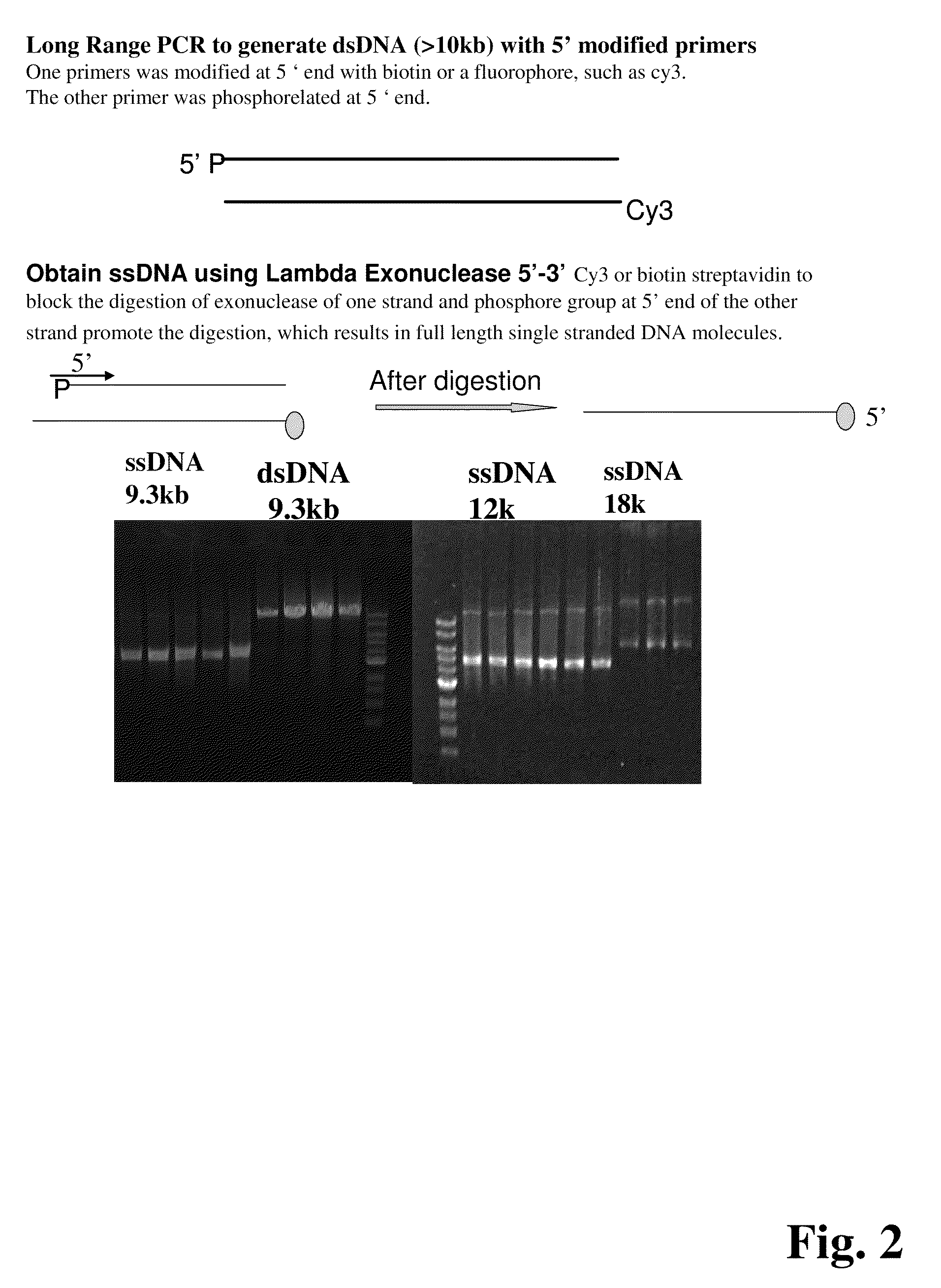
ActiveUS20090155780A1Improve labeling efficiencyStable labelingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDirect imagingDNA barcoding
Improved methods of genetic haplotyping and DNA sequencing and mapping, including methods for making amplified ssDNA, methods for allele determination, and a DNA barcoding strategy based on direct imaging of individual DNA molecules and localization of multiple sequence motifs or polymorphic sites on a single DNA molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Biomolecule partition motifs and uses thereof
The invention provides amino acid sequence motifs (e.g., biomolecule partition motifs) that can direct targeting of intracellular polypeptides to and through membranes, including cell surface membranes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for identifying sequence motifs, and applications thereof
InactiveUS20090208955A1Reduce in quantityIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBinding siteInstability
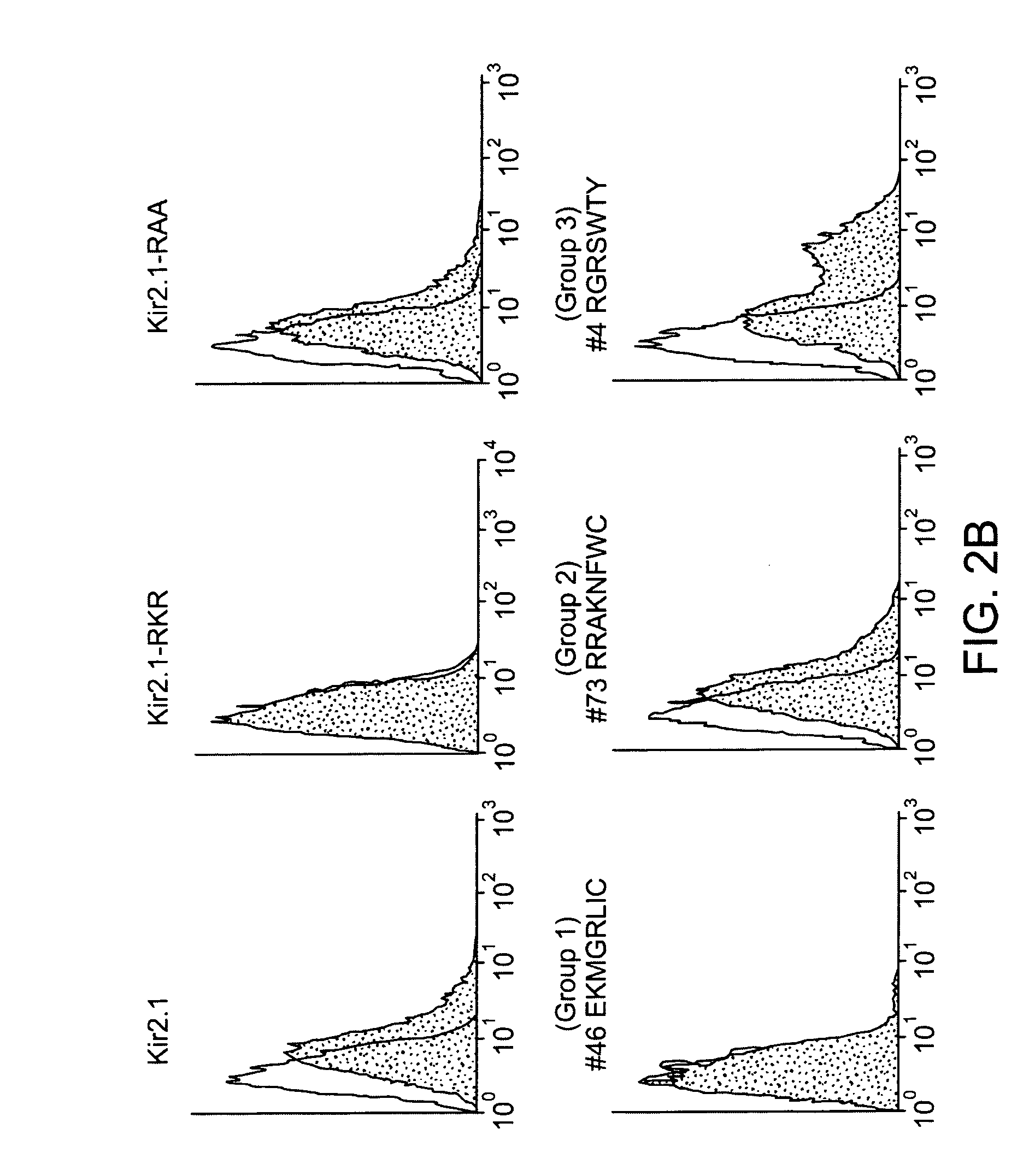
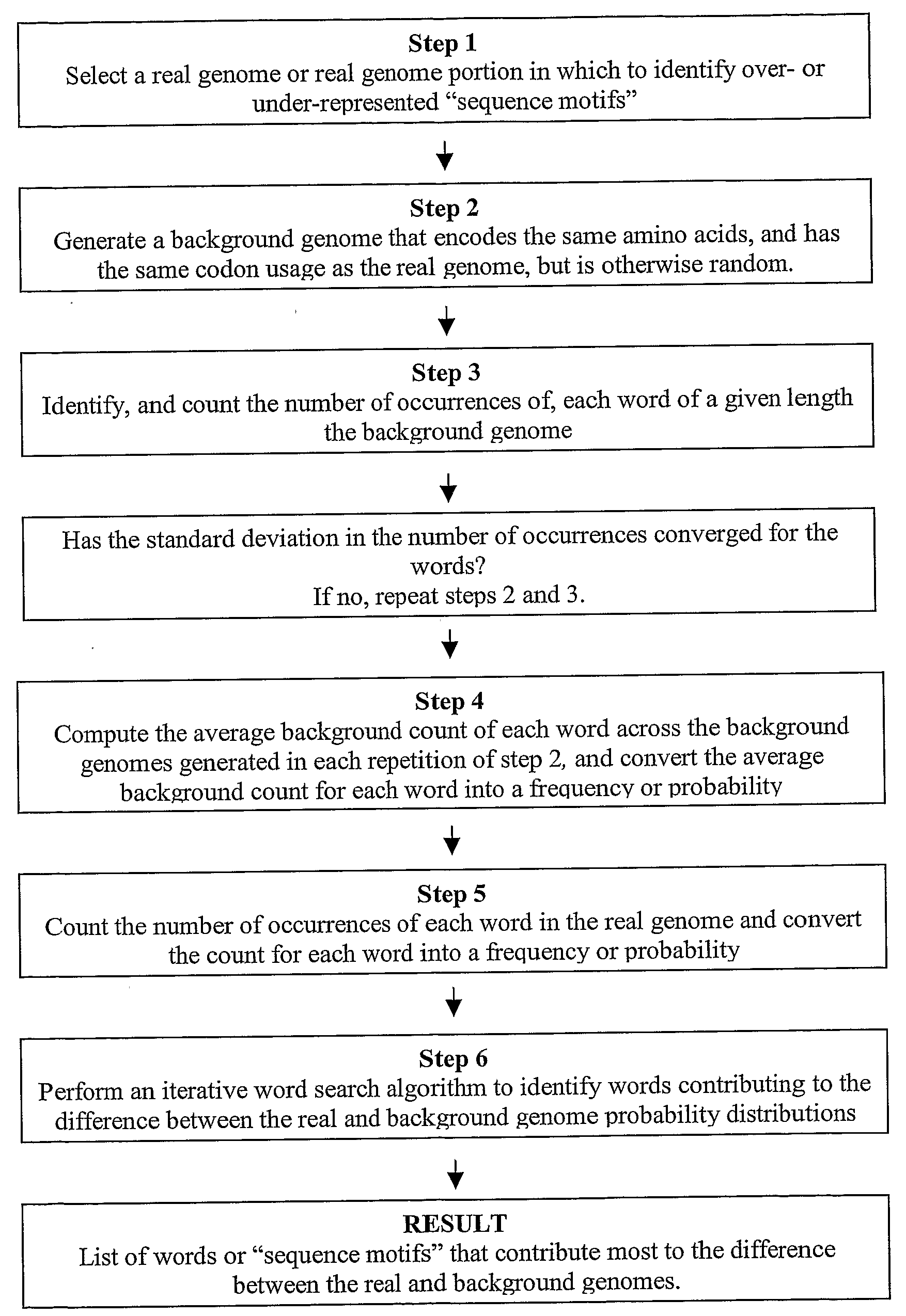
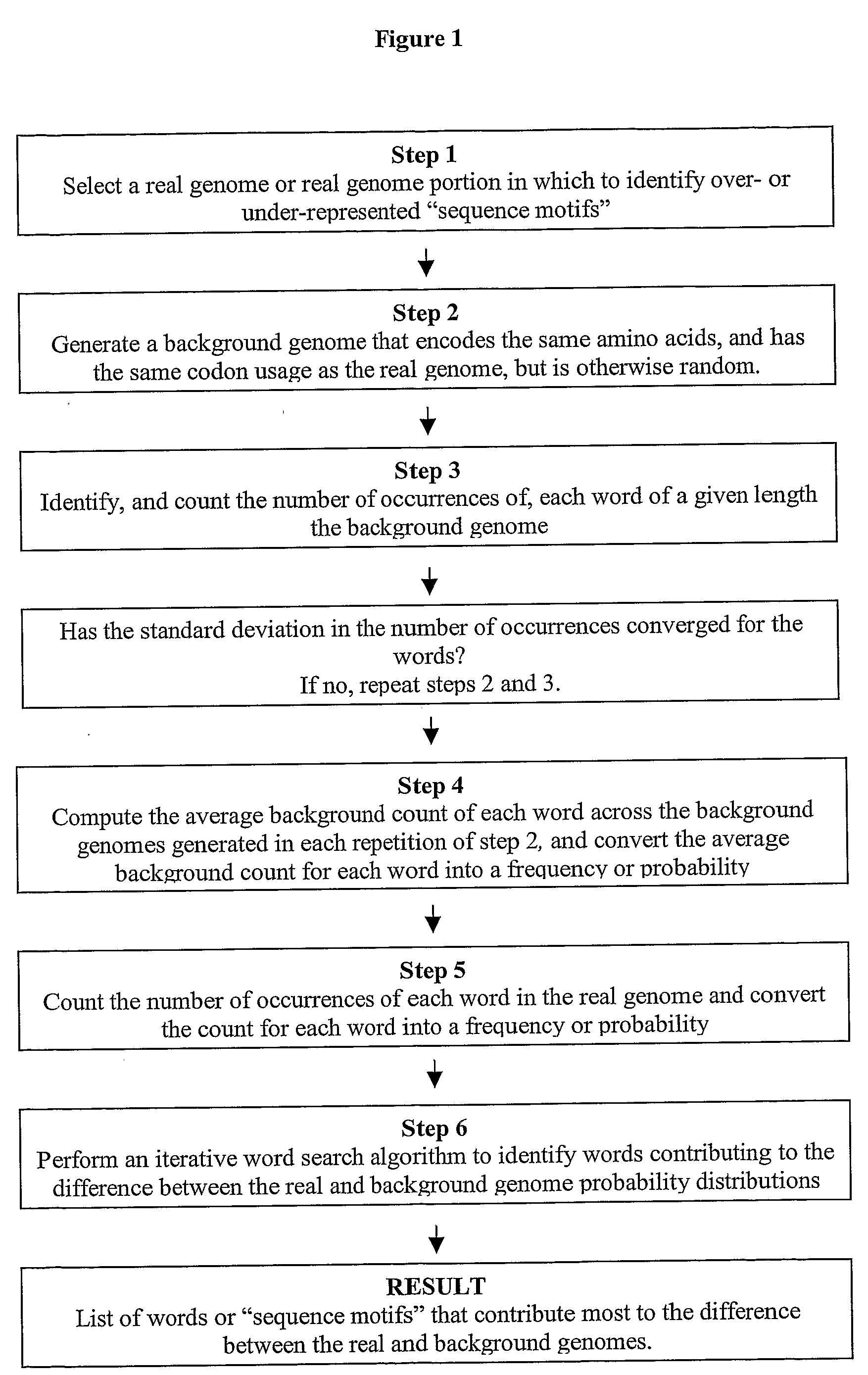
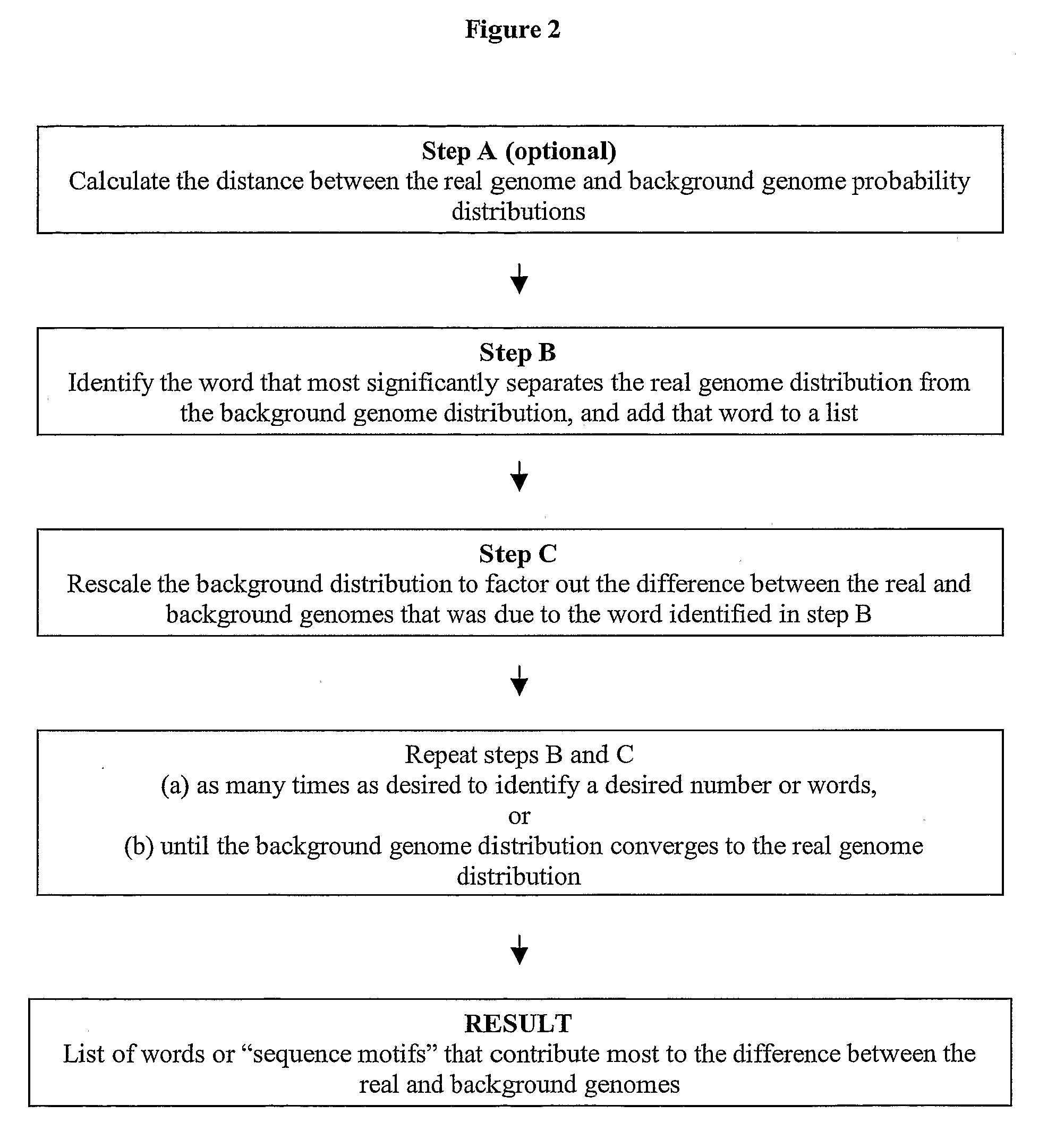
The present invention relates to methods and algorithms that can be used to identify sequence motifs that are either under- or over-represented in a given nucleotide sequence as compared to the frequency of those sequences that would be expected to occur by chance, or that are either under- or over-represented as compared to the frequency of those sequences that occur in other nucleotide sequences, and to methods of scoring sequences based on the occurrence of these sequence motifs. Such sequence motifs may be biologically significant, for example they may constitute transcription factor binding sites, mRNA stability / instability signals, epigenetic signals, and the like. The methods of the invention can also be used, inter alia, to classify sequences or organisms in terms of their phylogenetic relationships, or to identify the likely host of a pathogenic organism. The methods of the present invention can also be used to optimize expression of proteins.
Owner:INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY
Multilayer films, coatings, and microcapsules comprising polypeptides
ActiveUS20070077276A1Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyPolyelectrolyte
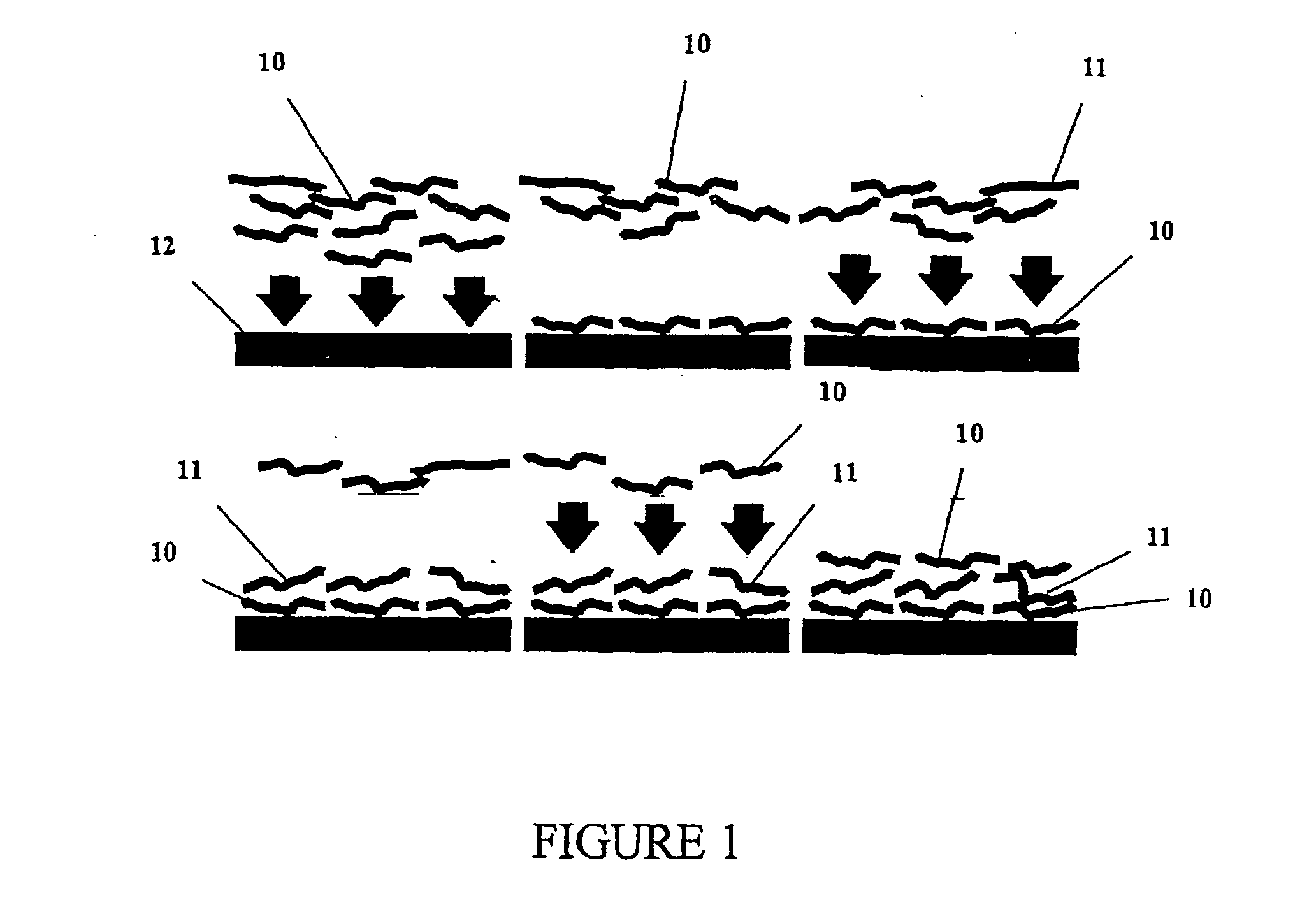
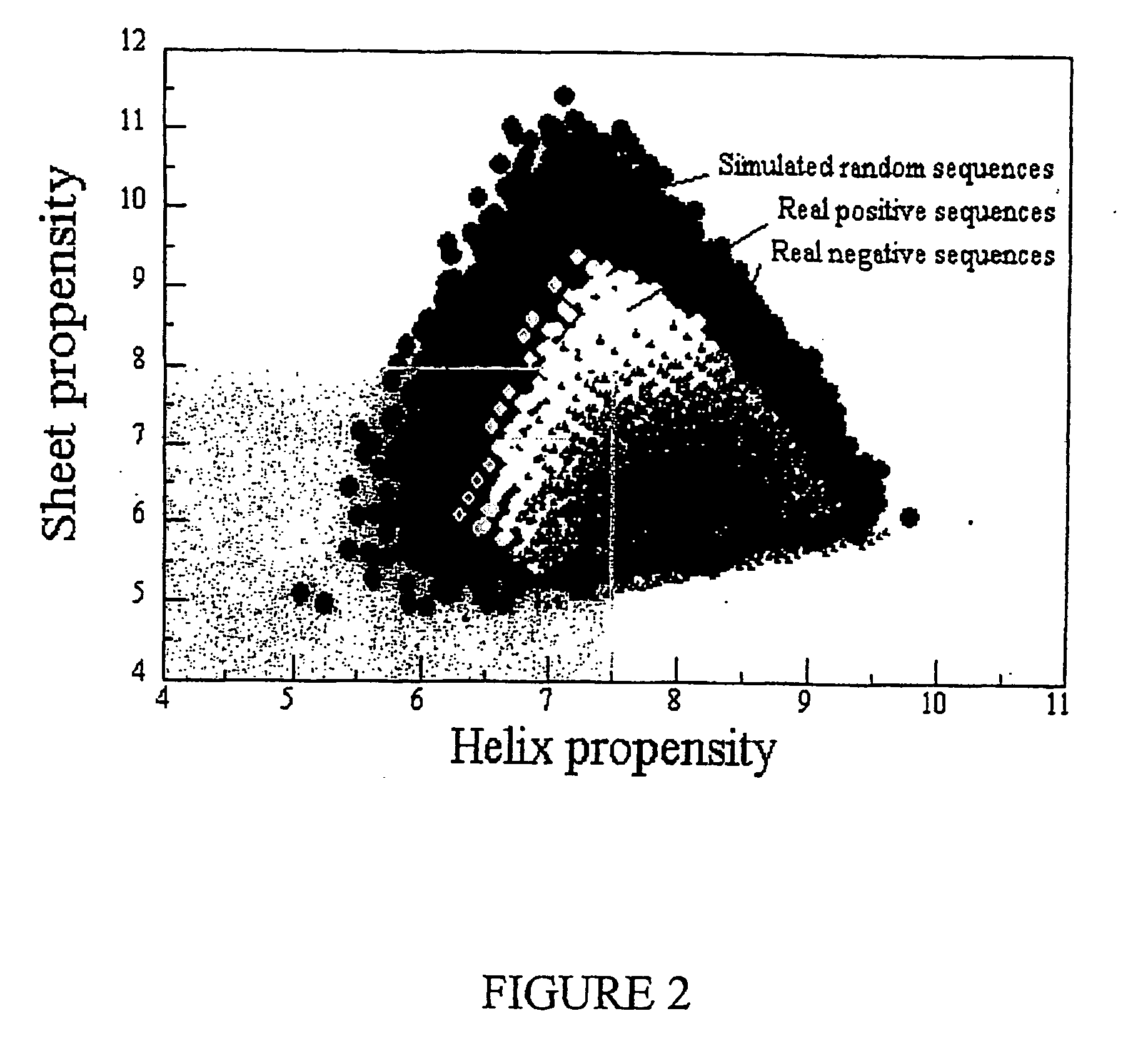
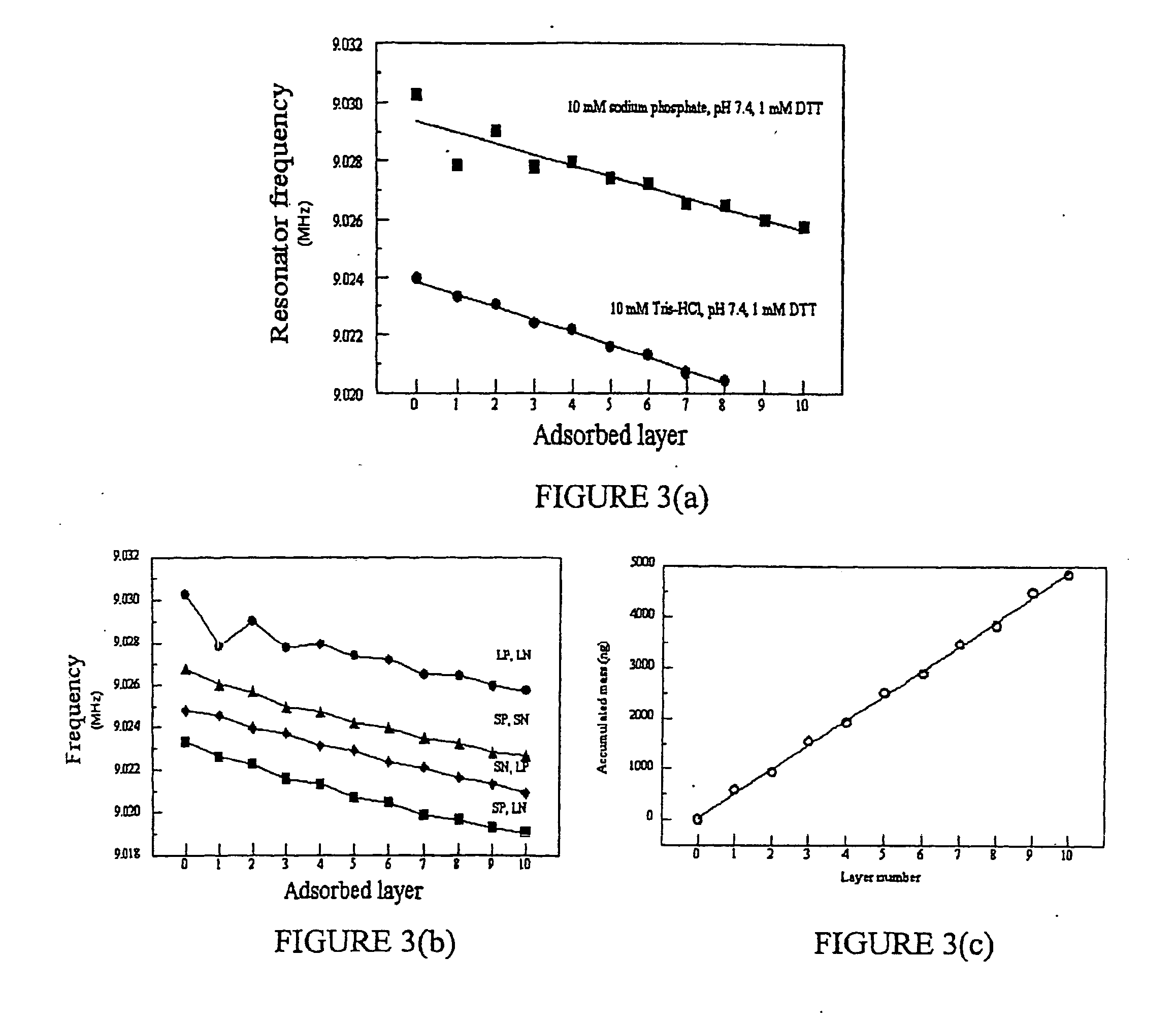
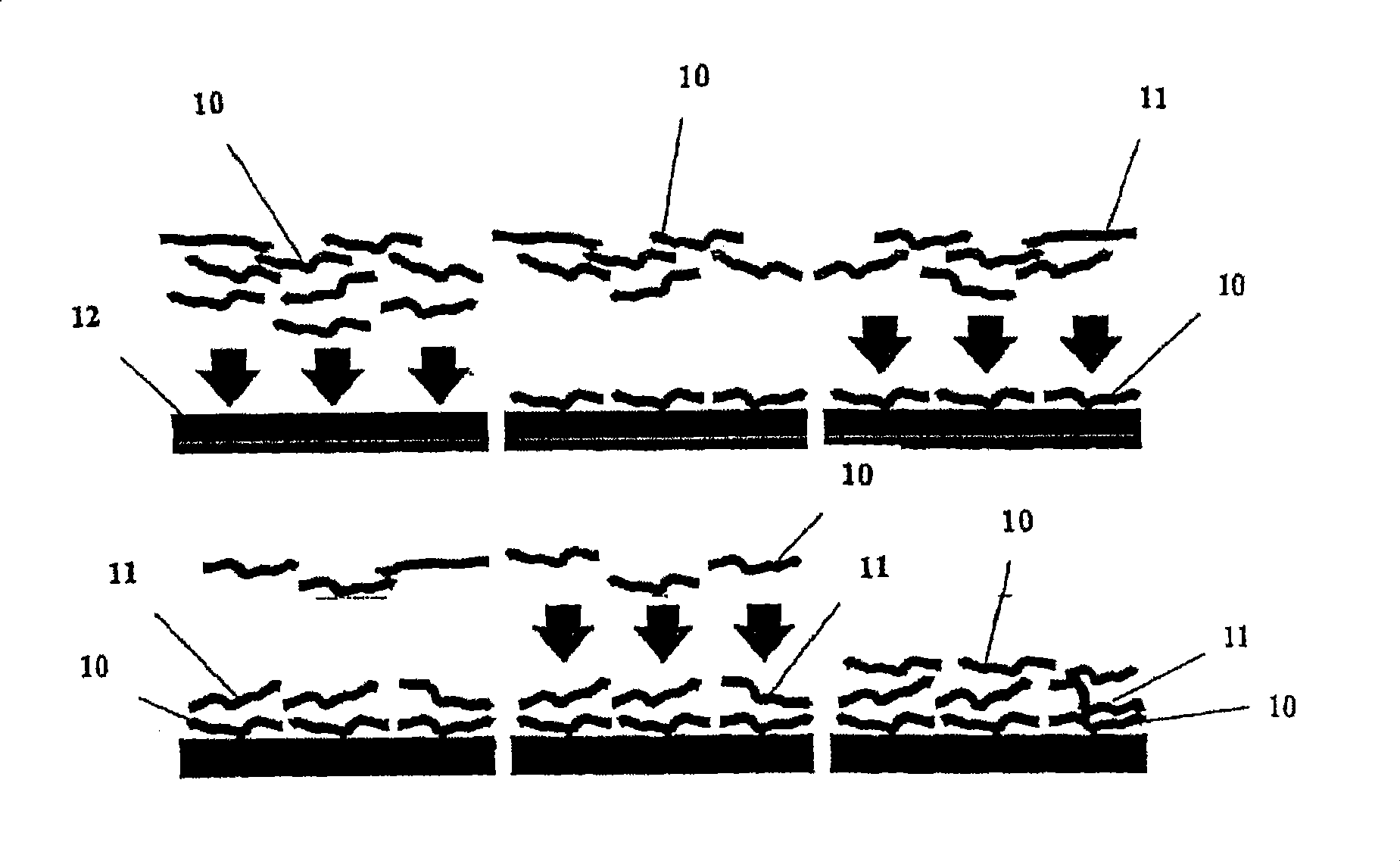
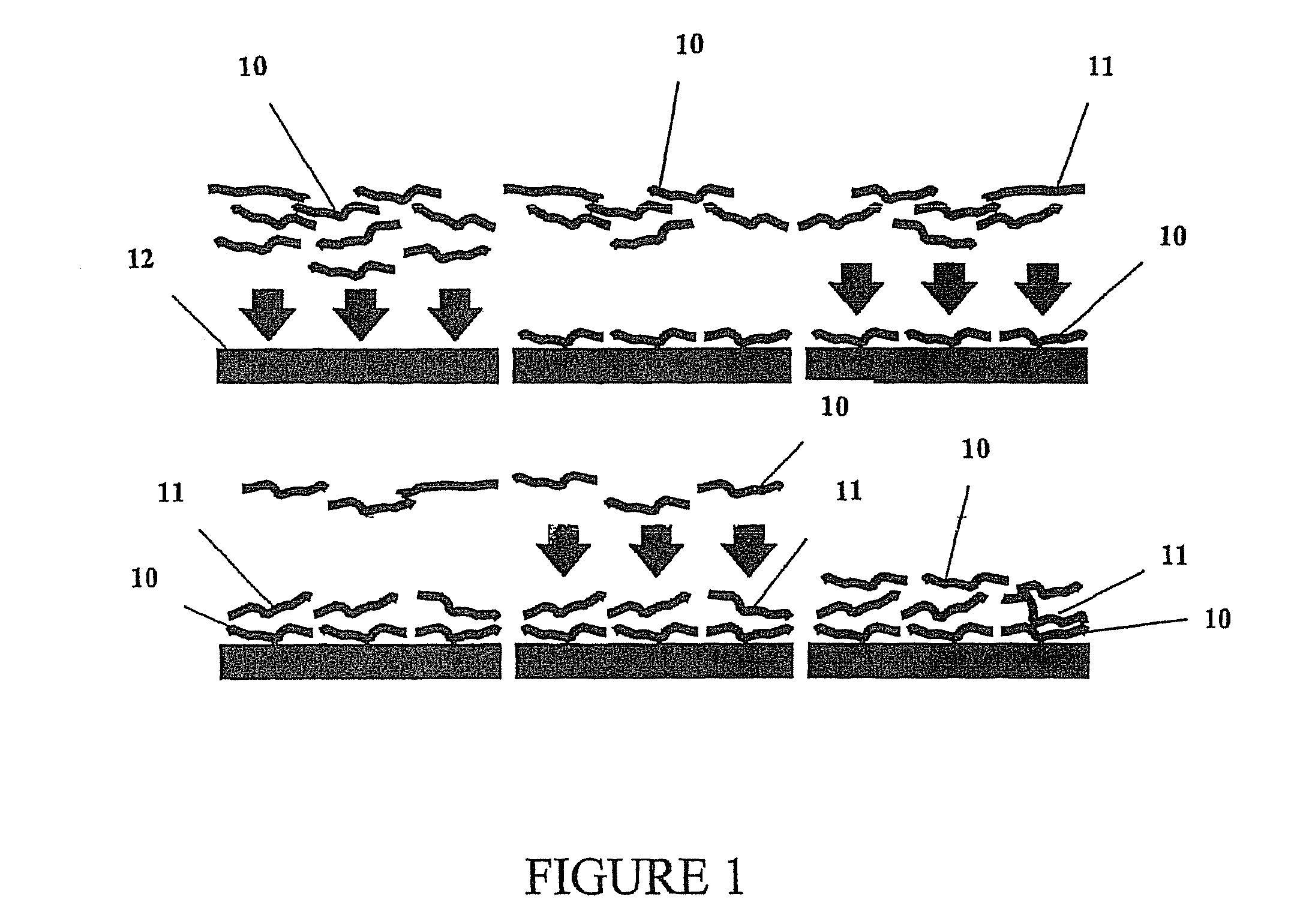
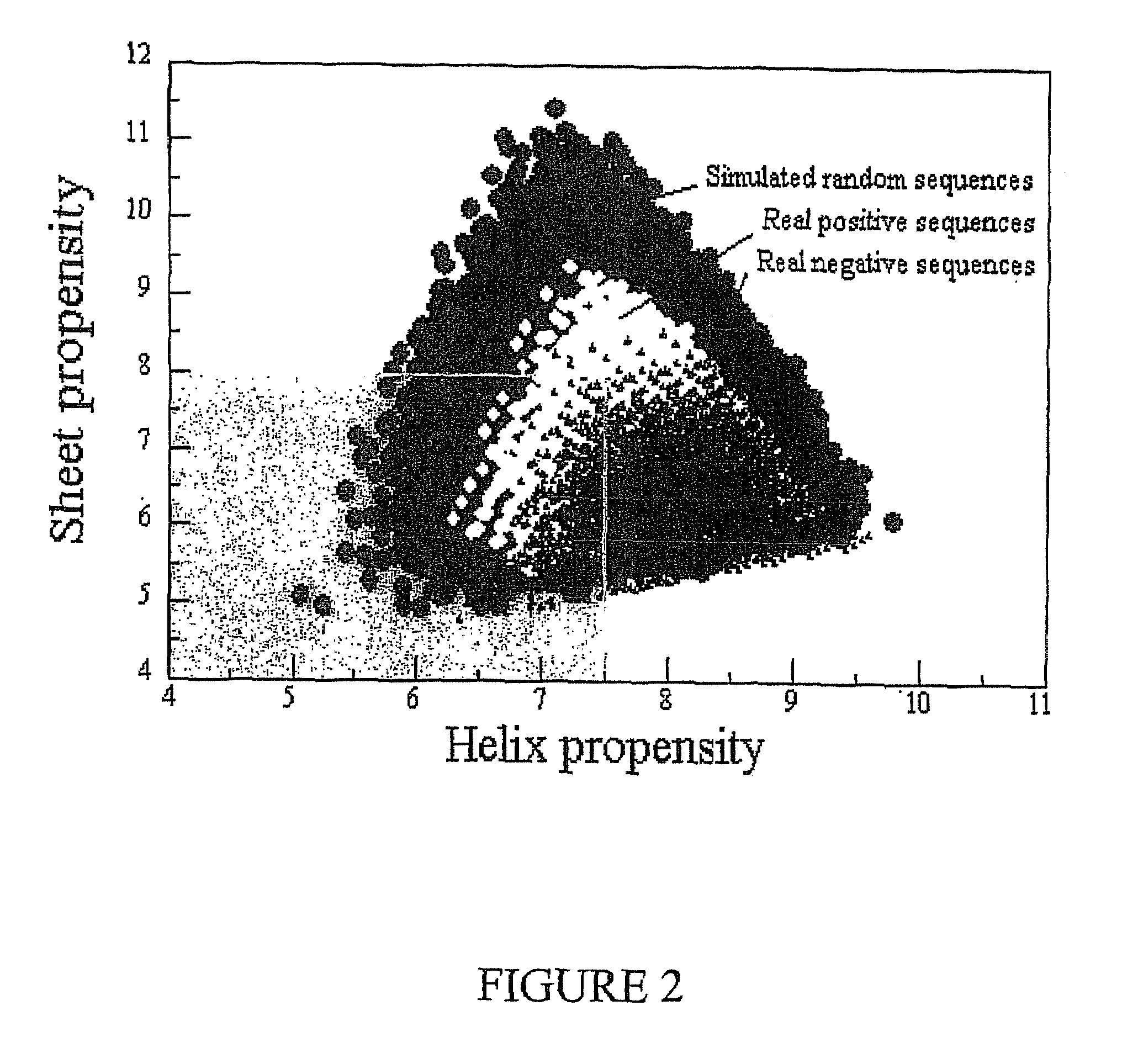
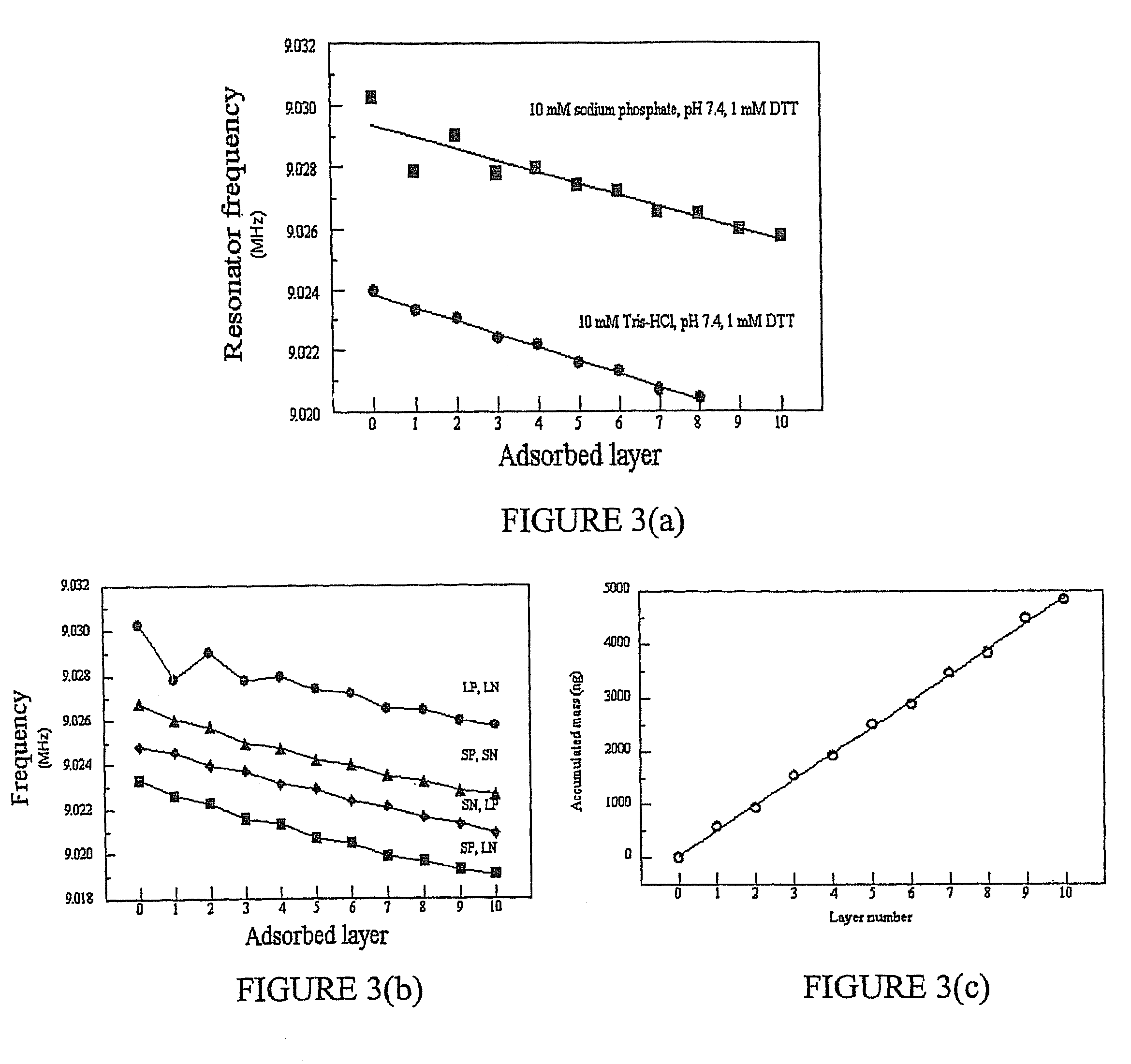
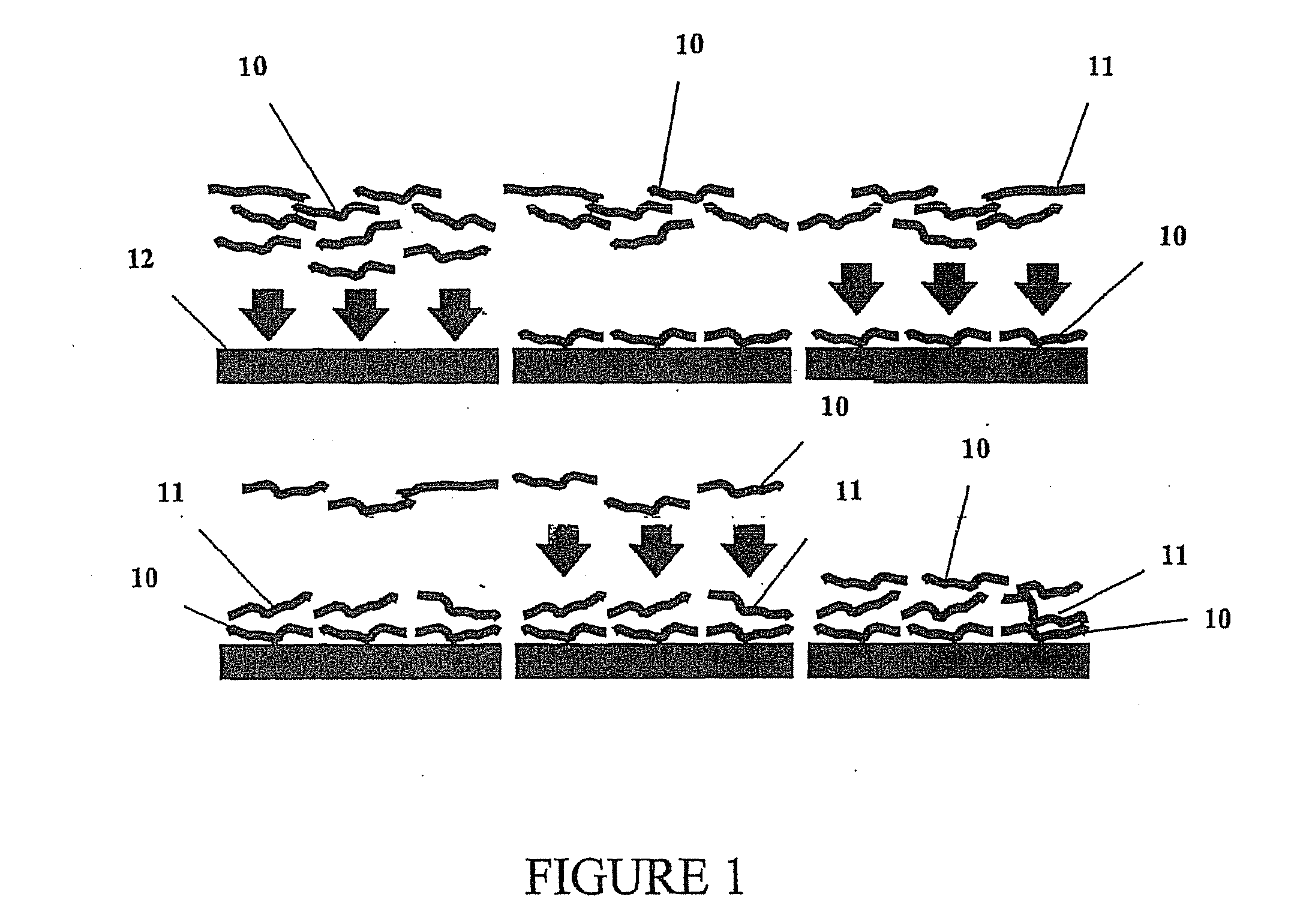
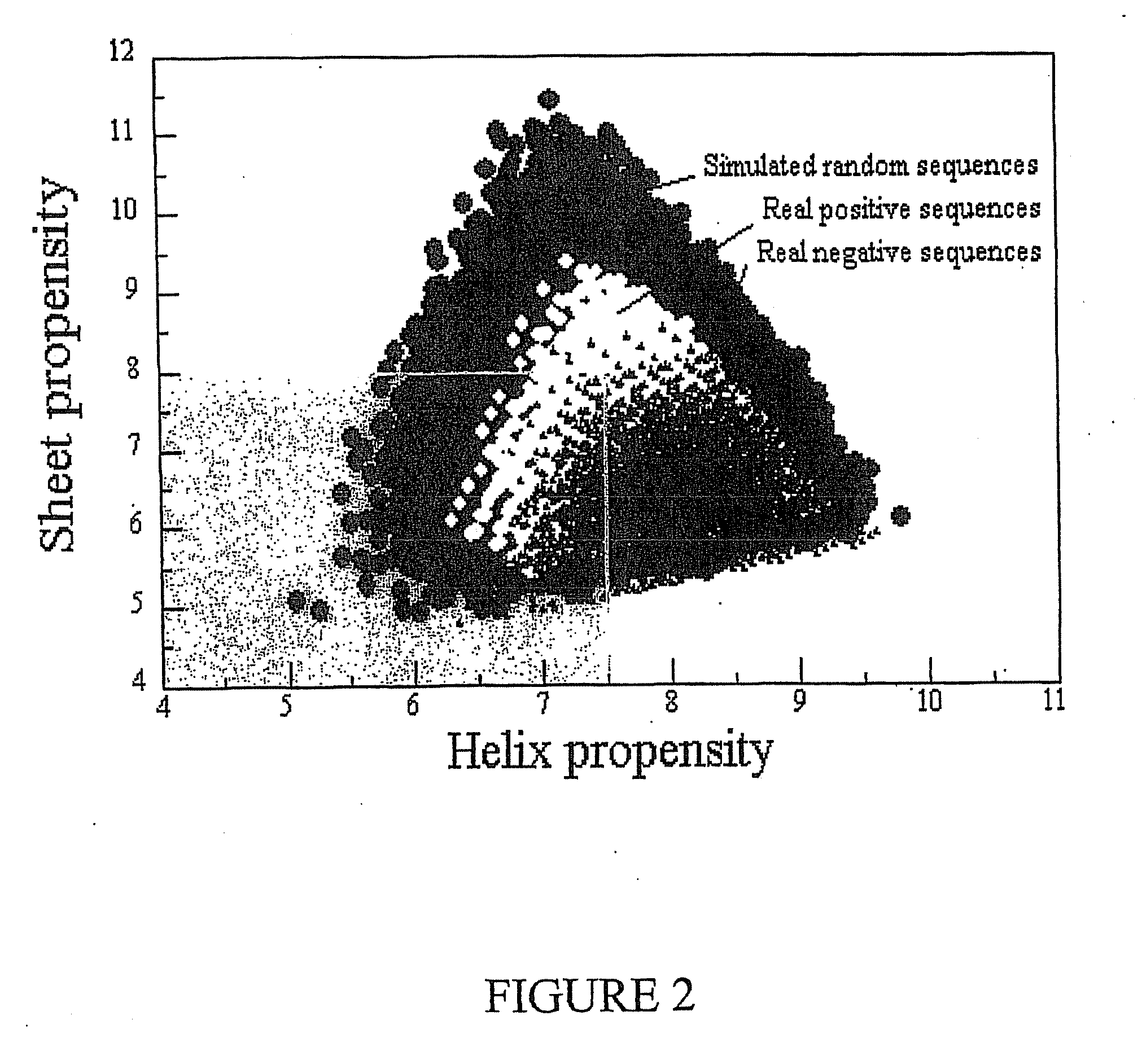
Disclosed herein is a multilayer film comprising two or more layers of polyelectrolytes, wherein adjacent layers comprise oppositely charged polyelectrolytes. A first layer polyelectrolye comprises a composite polypeptide comprising one or more surface adsorption regions covalently linked to one or more functional regions forming a single polypeptide chain. The surface adsorption regions comprise one or more amino acid sequence motifs consisting of 5 to 15 amino acid residues. The one or more functional regions comprise 3 to about 250 amino acid residues.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
Method
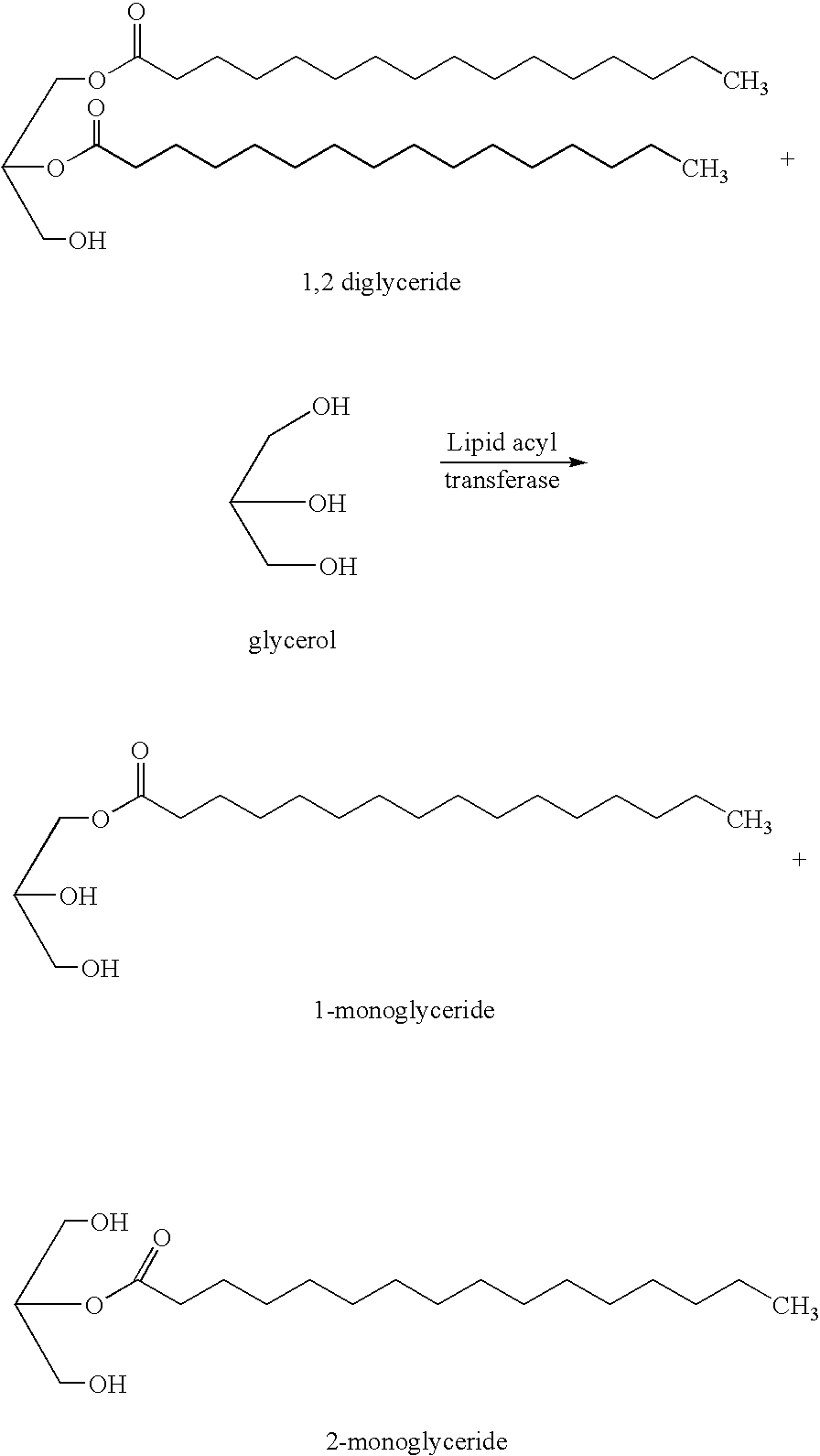
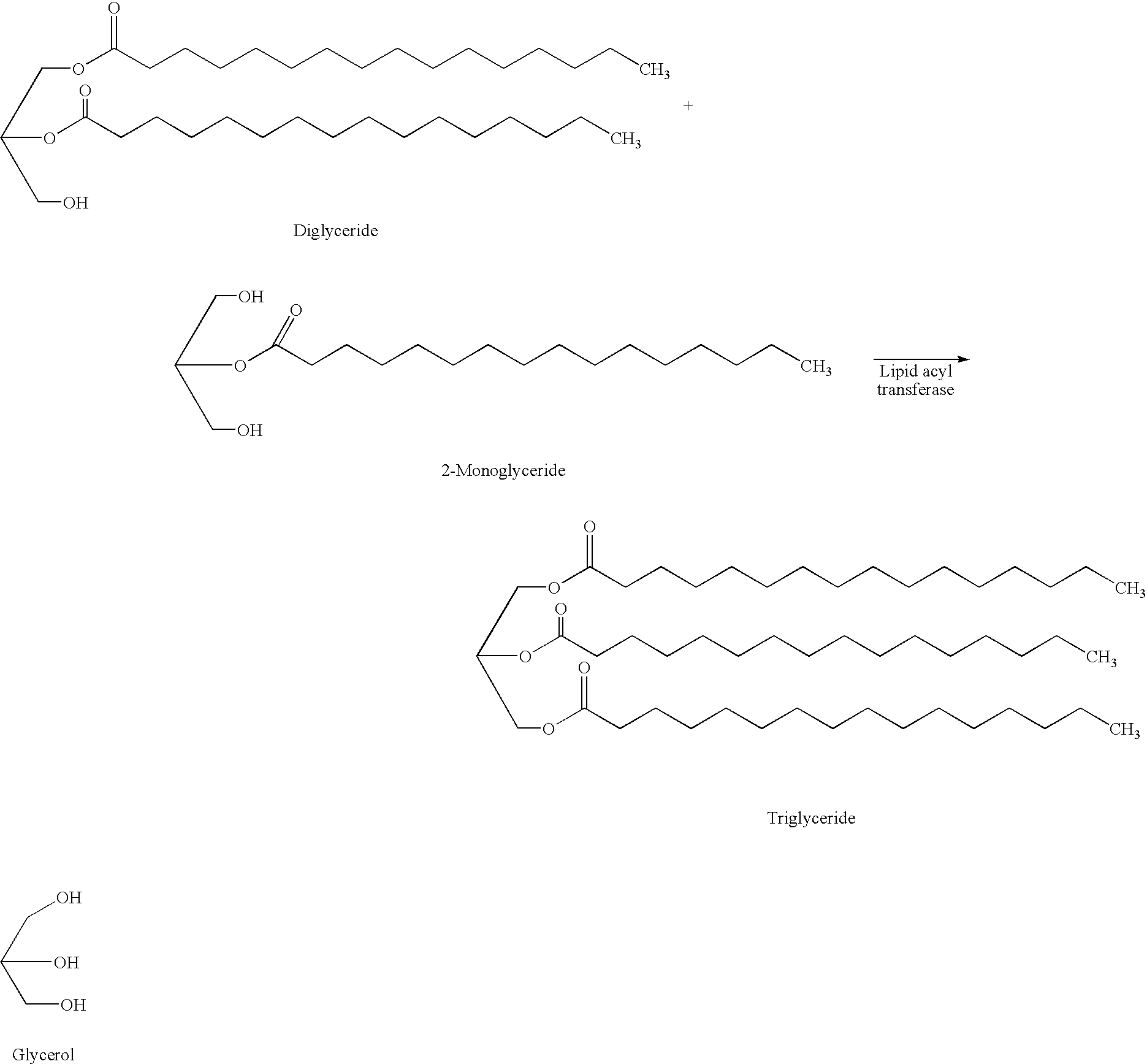
The present invention relates to a method of reducing and / or removing diglyceride from an edible oil, comprising a) admixing an edible oil with an acyl acceptor substrate and a diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase, wherein the diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase is characterized as an enzyme which in an edible oil is capable of transferring an acyl group from a diglyceride to glycerol. Preferably, the diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase comprises the amino acid sequence motif GDSX, wherein X is one or more of the following amino acid residues L, A, V, I, F, Y, H, Q, T, N, M or S. Furthermore the present invention relates to the use of a diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase characterized as an enzyme which in an edible oil is capable of transferring an acyl group from a diglyceride to glycerol, in the manufacture of an edible oil, for reducing and / or removing (preferably selectively reducing and / or removing) diglyceride from said edible oil and to the use of said enzyme in the manufacture of a foodstuff comprising an edible oil for improving the crystallization properties of said foodstuff.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Multilayer films, coatings, and microcapsules comprising polypeptides
InactiveUS7544770B2Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyPolyelectrolyte
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
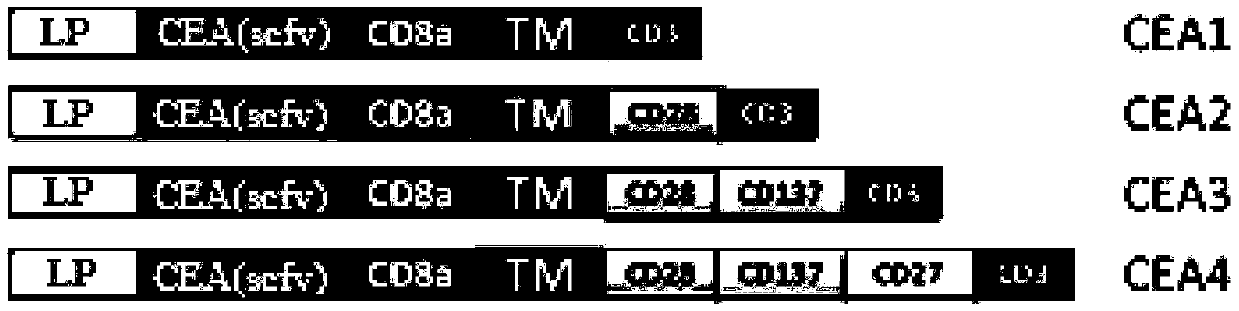
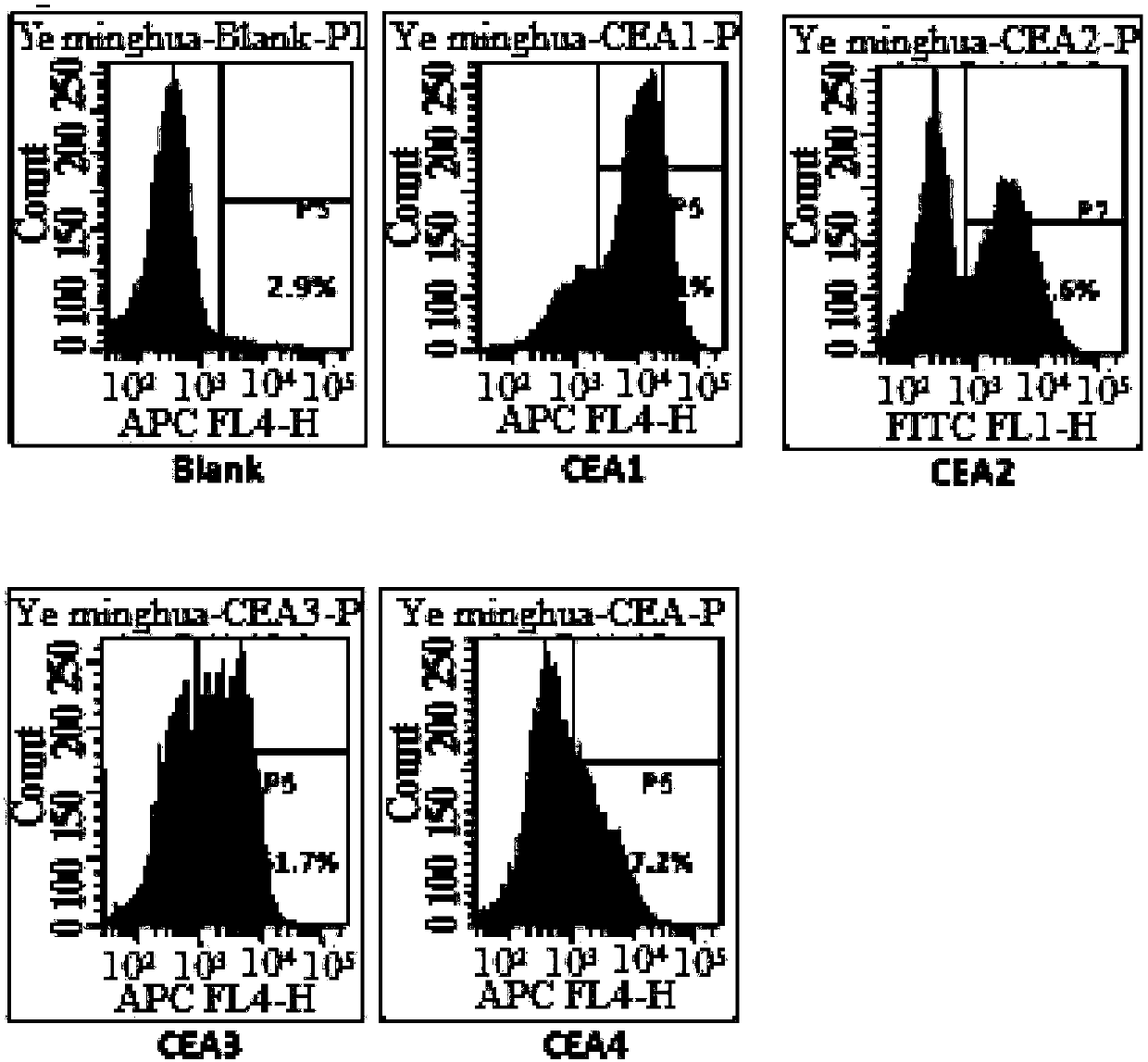
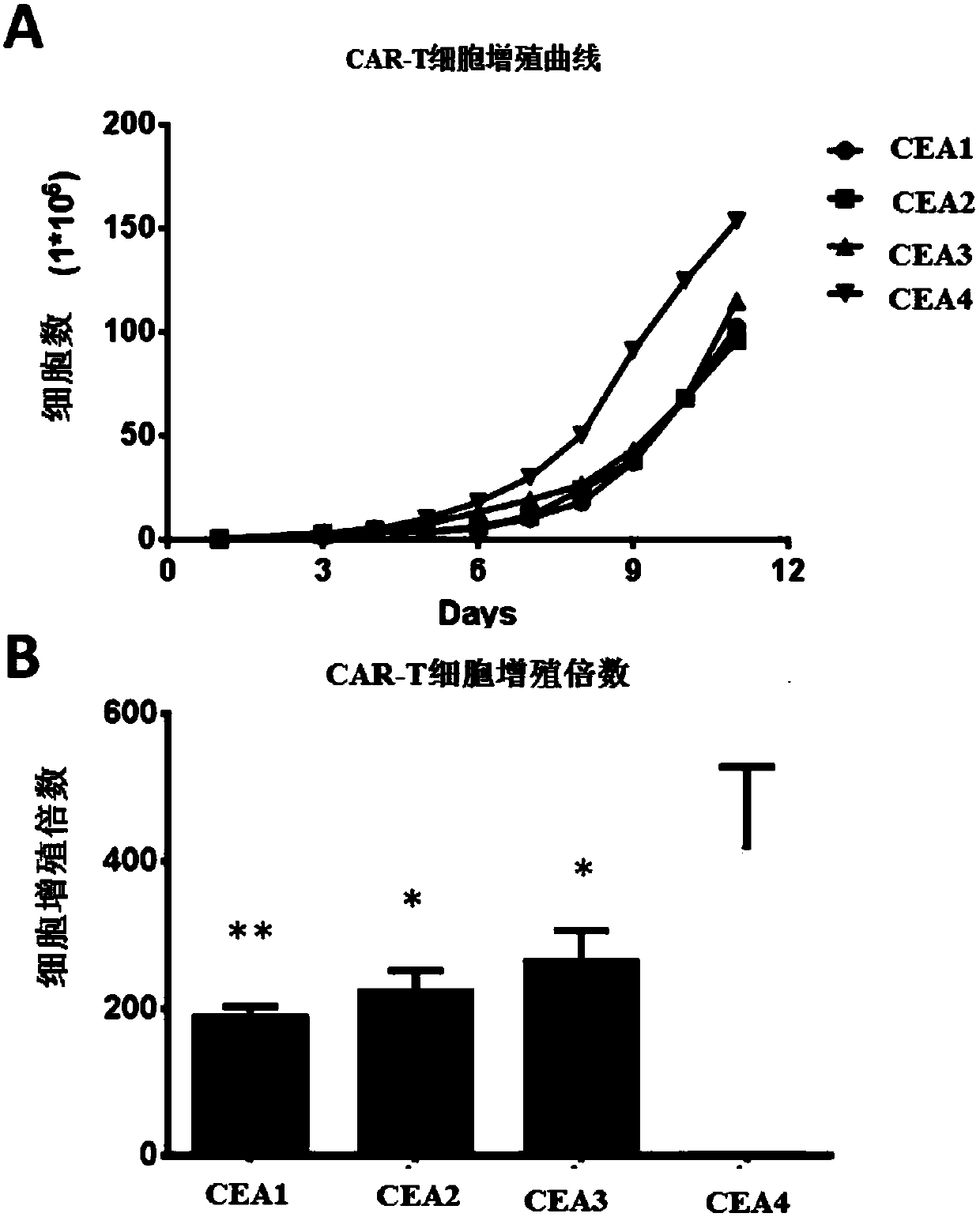
Chimeric antigen receptor containing CD27 intracellular domain, lentiviral vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105949325AHave the ability to bind antigenEfficient killingMammal material medical ingredientsNucleic acid vectorAntigenSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a chimeric antigen receptor containing a CD27 intracellular domain, a lentiviral vector and application thereof. The immune receptor tyrosine activation sequence motif of the chimeric antigen receptor containing CD27 intracellular domain contains CD27molecule intracellular signal domain and T cell costimulatory signal molecules. The CD27molecule intracellular signal domain is connected with costimulatory signals related to T cell activation, so that the in-vitro proliferation and apoptosis effect of T cells can be obviously enhanced, and the ratio of young sample Tscm cells (CD45RA+CD62L+) with in vivo therapeutic action and central memory cells (CD45RO+CD62L+) in CAR-T cells is increased; expression of IL-10 factors capable of restraining immunization is reduced, an obvious effect of improving the CAR-T (T cell chimeric antigen receptor) cellular therapy effect is achieved, and a new idea and a new selection are provided for the field of CAR-T cellular therapy.
Owner:CHONGQING PRECISION BIOTECH CO LTD
Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs with enhanced immunostimulatory activity
The invention provides immunostimulatory compositions and methods for their use. In particular, the immunostimulatory compositions of the invention include RNA-like polymers that incorporate an immunostimulatory sequence motif and at least one chemical modification to confer improved stability against nuclease degradation and improved activity. Specific modifications involving phosphate linkages, nucleotide analogs, and combinations thereof are provided. Compositions of the invention optionally include an antigen and can be used to stimulate an immune response. Also provided are compositions and methods useful for treating a subject having an infection, a cancer, an to allergic condition, or asthma. Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs of the invention are believed to stimulate Toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR8.
Owner:ZOTTIS BELGIUM
Methods for determining genetic haplotypes and DNA mapping
ActiveUS7771944B2Improve labeling efficiencyStable labelingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDirect imagingHaplotype
Improved methods of genetic haplotyping and DNA sequencing and mapping, including methods for making amplified ssDNA, methods for allele determination, and a DNA barcoding strategy based on direct imaging of individual DNA molecules and localization of multiple sequence motifs or polymorphic sites on a single DNA molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Calcium phosphopeptide complexes
InactiveUS7312193B2Prevent demineralisationInhibition formationAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseDietary supplement
Phosphopeptides containing the Ser(P) cluster sequence motif Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Ser(P)-Glu-Glu- can stabilize their own weight in amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) [Ca3(PO4)1.87(HPO4)0.2xH2O] and amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP) [Ca8(PO4)5F x H2O]. The amorphous phases stabilised by the phosphopeptides are an excellent delivery vehicle to co-localise Ca, F, and phosphate at the tooth surface in a slow-release amorphous form producing superior anticaries efficacy. These amorphous phases stabilised by the phosphopeptides also have utility as dietary supplements to increase calcium bioavailability and to help prevent diseases associated with calcium deficiencies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
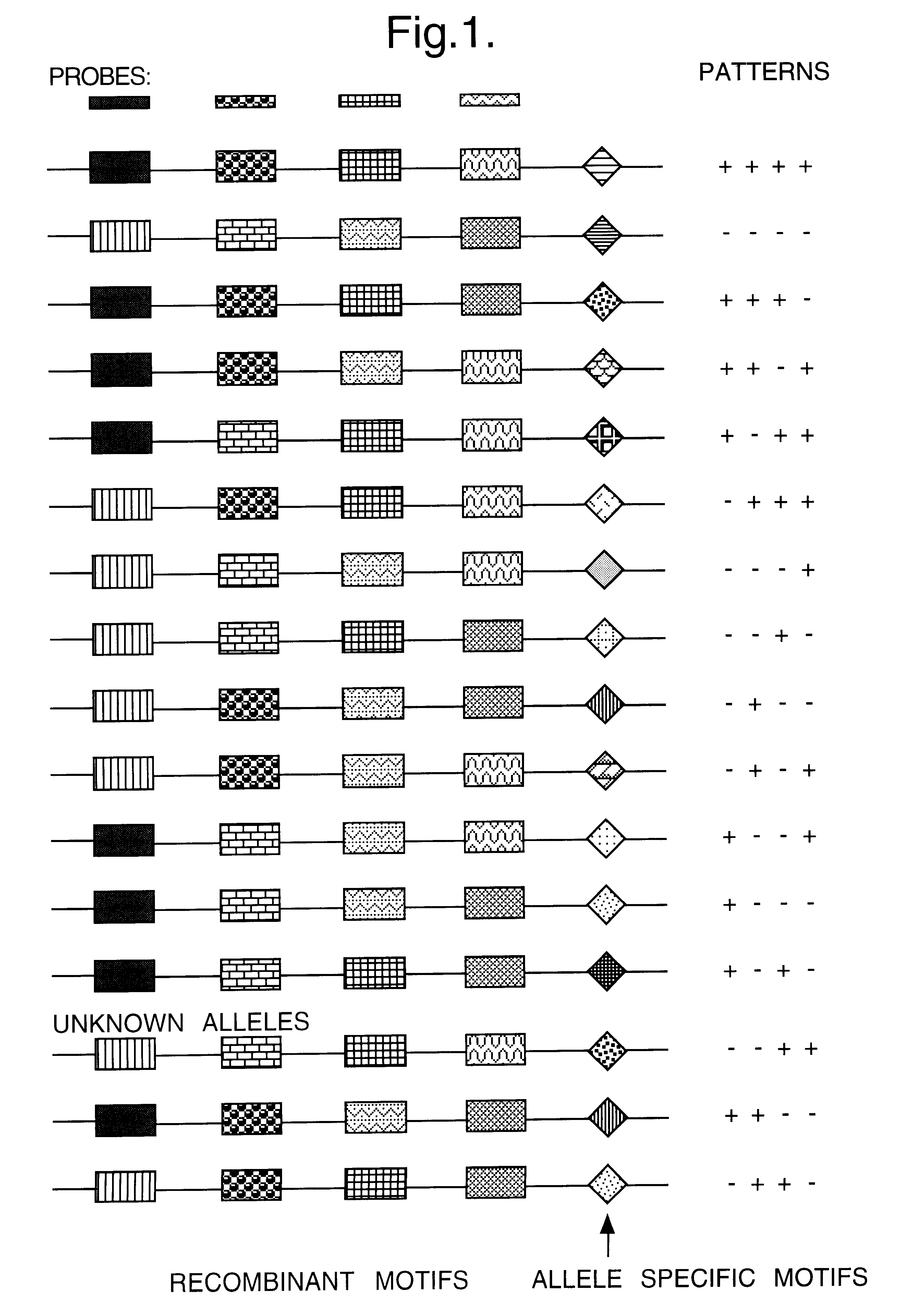
Method for identifying an unknown allele
The invention provides a method for identifying an unknown allele of a polyallelic gene, which method comprises (i) contacting the unknown allele with a panel of probes, each of which recognises a sequence motif that is present in some alleles of the polyallelic gene but not in others; (ii) observing which probes recognise the unknown allele so as to obtain a fingerprint of the unknown allele; and (iii) comparing the fingerprint with fingerprints of known alleles. The use of a panel of probes which each recognises a different motif allows identification of which motifs are present in the unknown allele. The alleles of the polyallelic gene each have a unique combination of motifs and so identification of this combination (or "fingerprint") leads to identification of the unknown allele.
Owner:ANTHONY NOLAN BONE MARROW TRUST
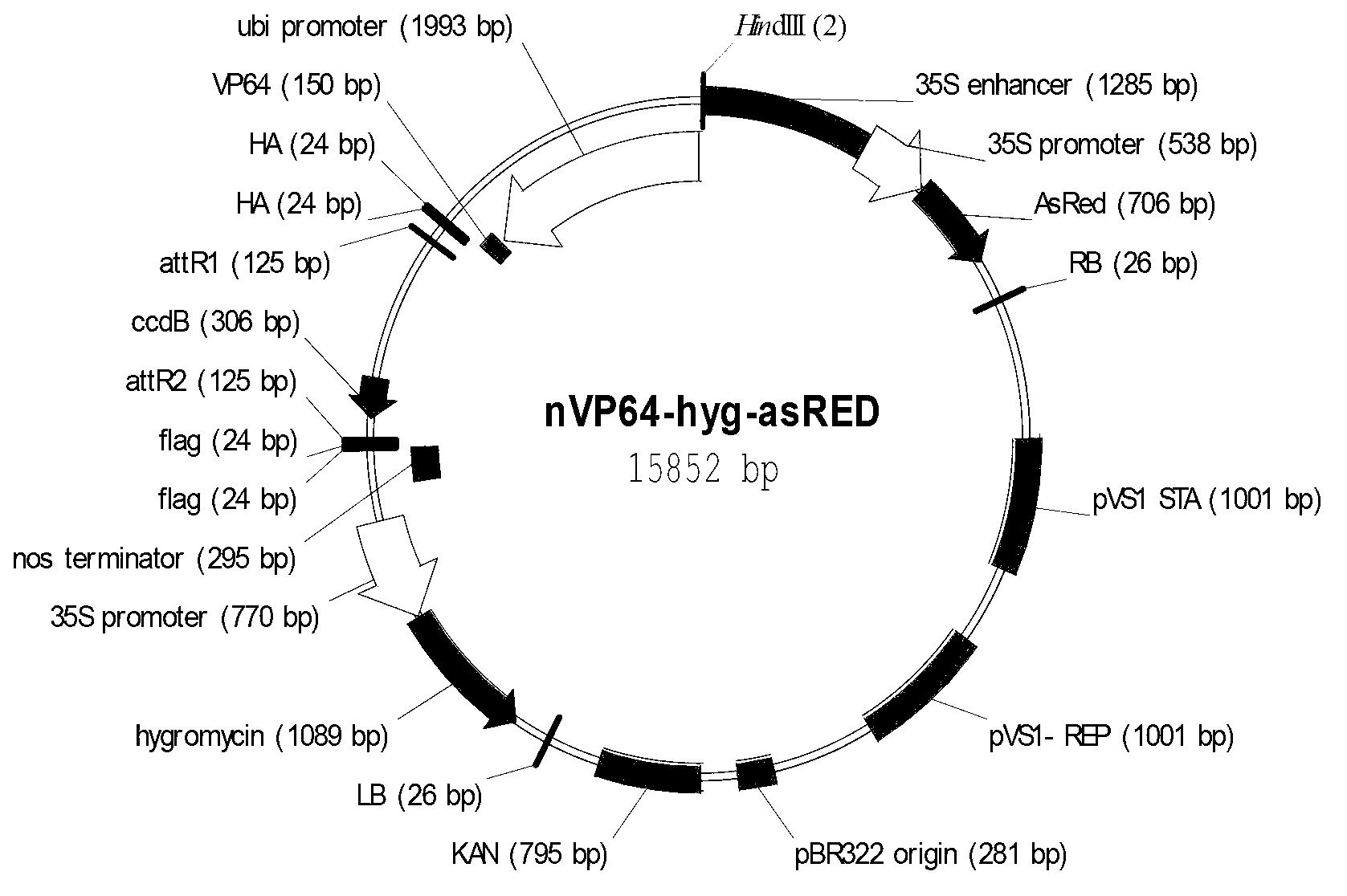
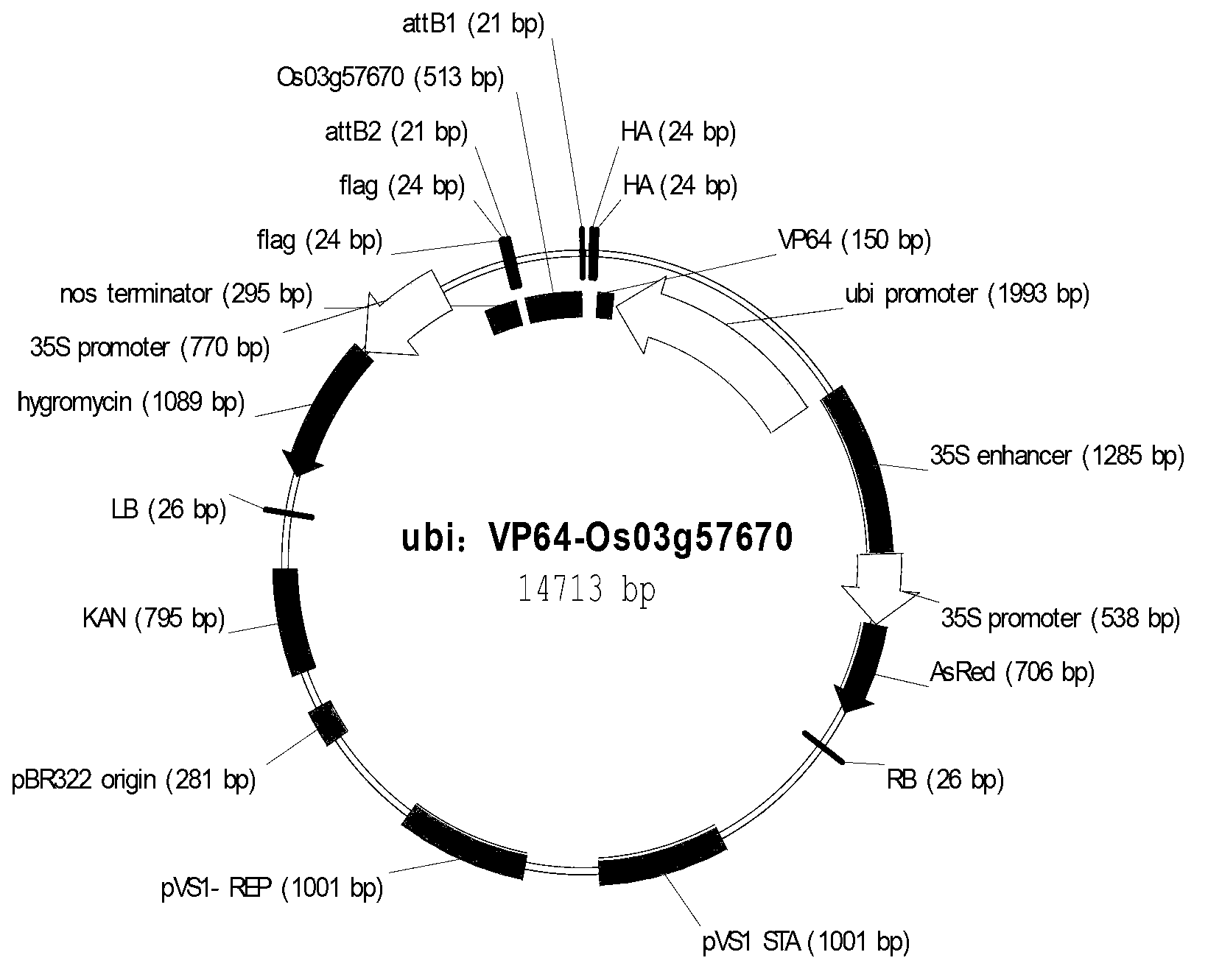
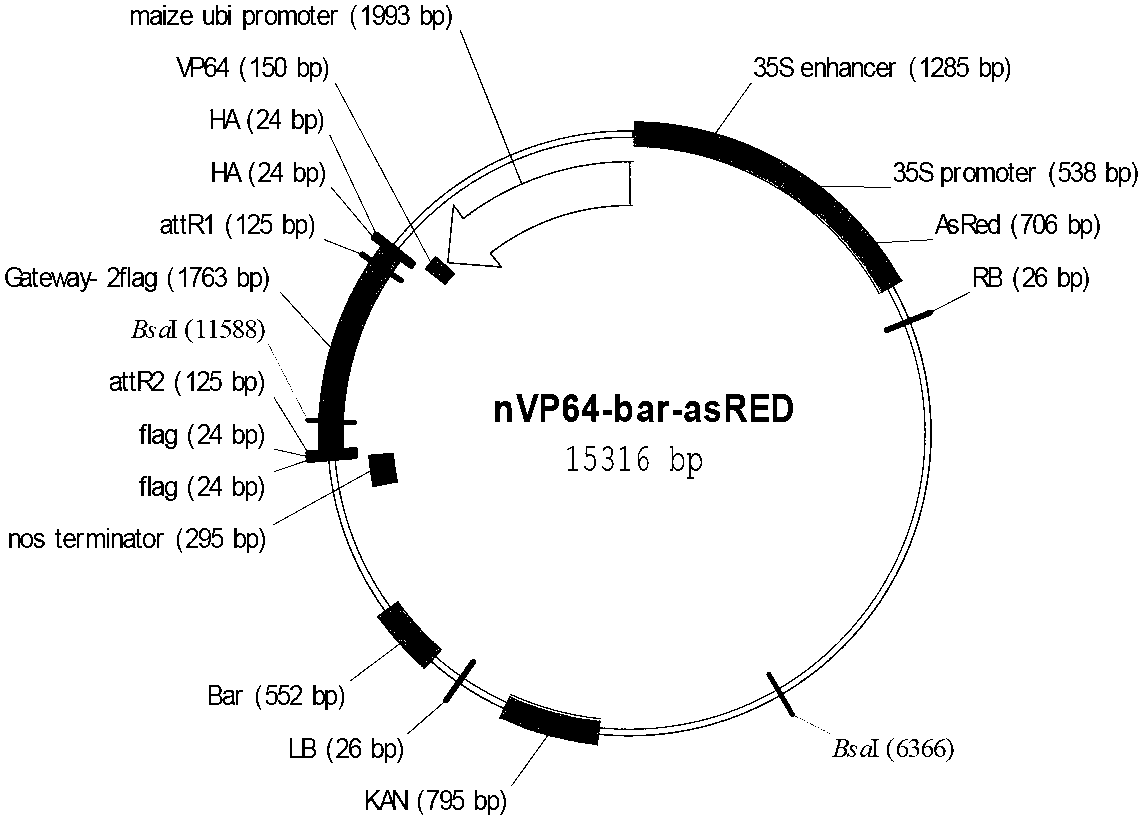
Application of synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os03g57670
ActiveCN103214581AChange traitsEnhanced coercion capabilitiesBacteriaHybrid peptidesGenetically modified riceSequence motif
The invention provides an application of a synthetic transcription factor VP64-Os03g57670. The synthetic transcription factor is constructed by fusing a transcription factor activated sequence motif VP64 (namely four transcription factor activated sequence motifs VP16) and paddy transcription factor Os03g57670 gene, and is converted to the paddy, so as to change the grain characteristic of paddy, so that the transgenic paddy seed is remarkably shorter, wider, and lighter in thousand seed weight, and paddy blade is crimped, therefore, the paddy has a better market application prospect.
Owner:CROPEDIT BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
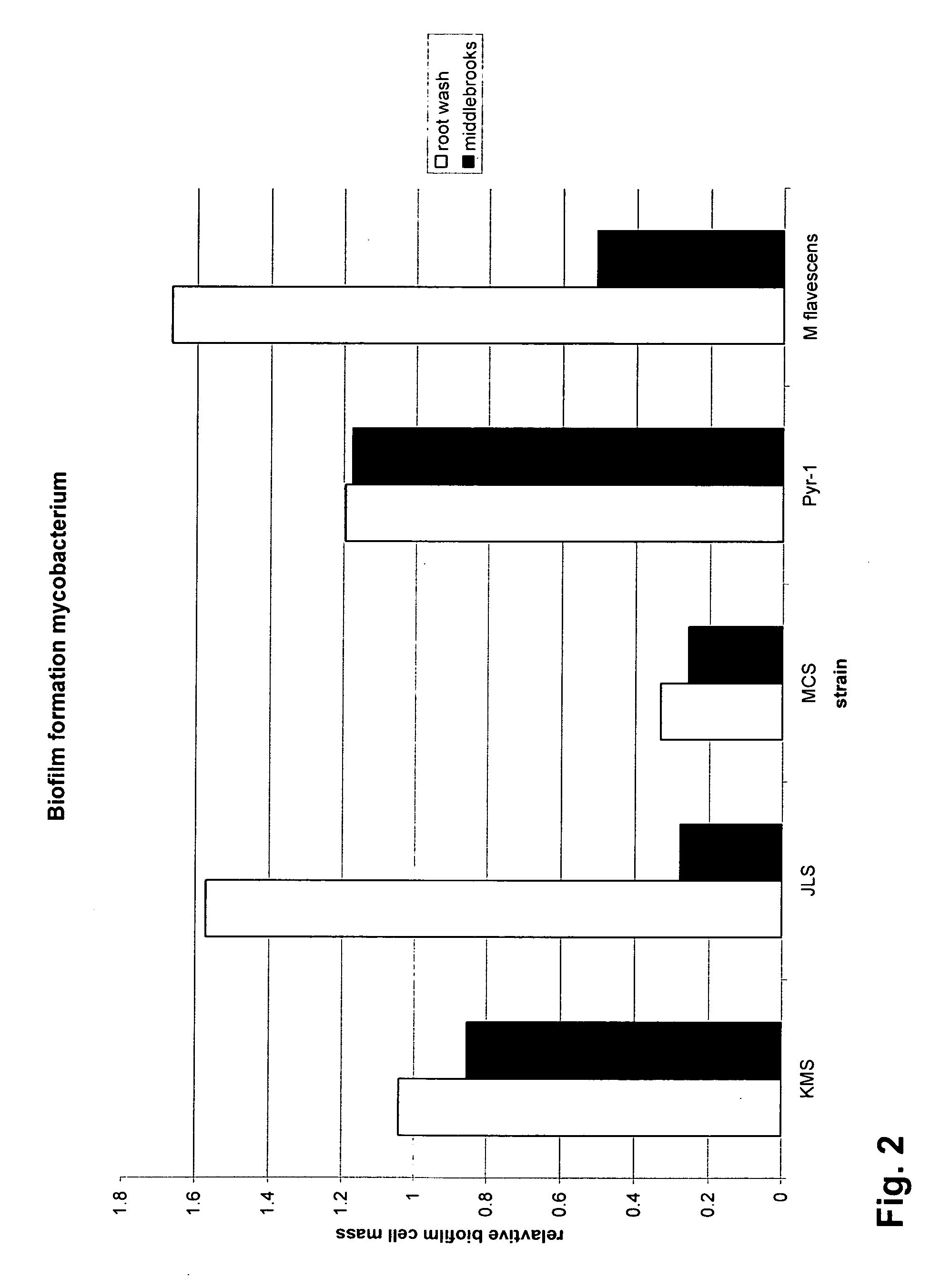
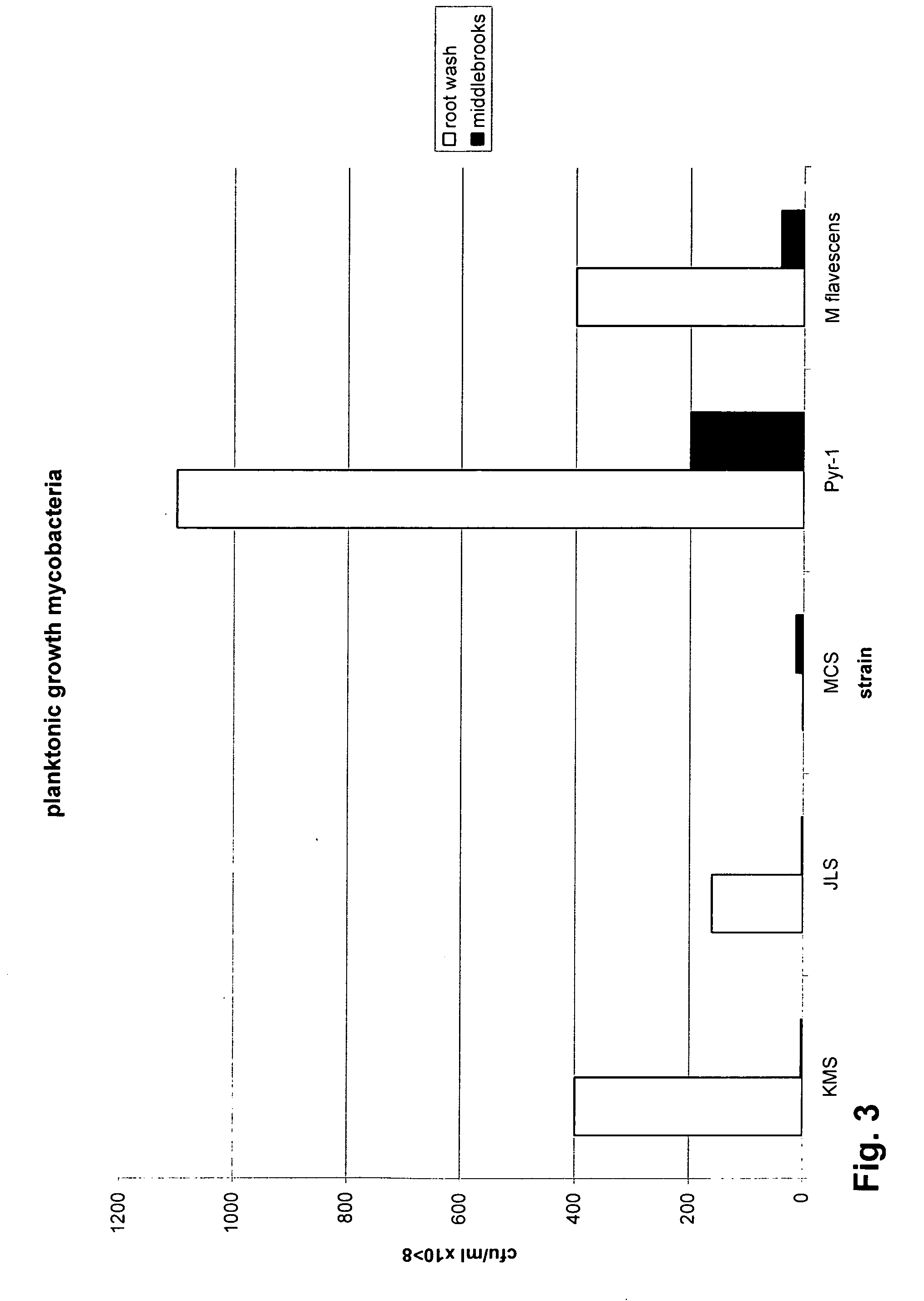
Mycobacteria compositions and methods of use in bioremediation
The present invention includes a contaminant-degrading composition for use in remediation of contaminated soil having a selected contaminant. Such a composition can include a seed for a plant capable of growing in the presence of the selected contaminant, and a contaminant-degrading mycobacteria on the seed. Additionally, the present invention includes a contaminant-degrading system for use in remediation of contaminated soil having a selected contaminant. Such a system can include a plant growing in the contaminated soil, and contaminant-degrading mycobacteria colonized on a root of the plant, wherein the mycobacteria is capable of degrading the selected contaminant. The mycobacteria can be capable of degrading the selected contaminant, such as PAHs, PCPs, MTBEs, and the like. Additionally, the contaminant-degrading mycobacteria can be at least one of M. KMS, M. JLS, or M MCS. Also, the contaminant-degrading mycobacteria can have nid dioxygenase genes, which can further include a nidB-nidA sequence motif.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
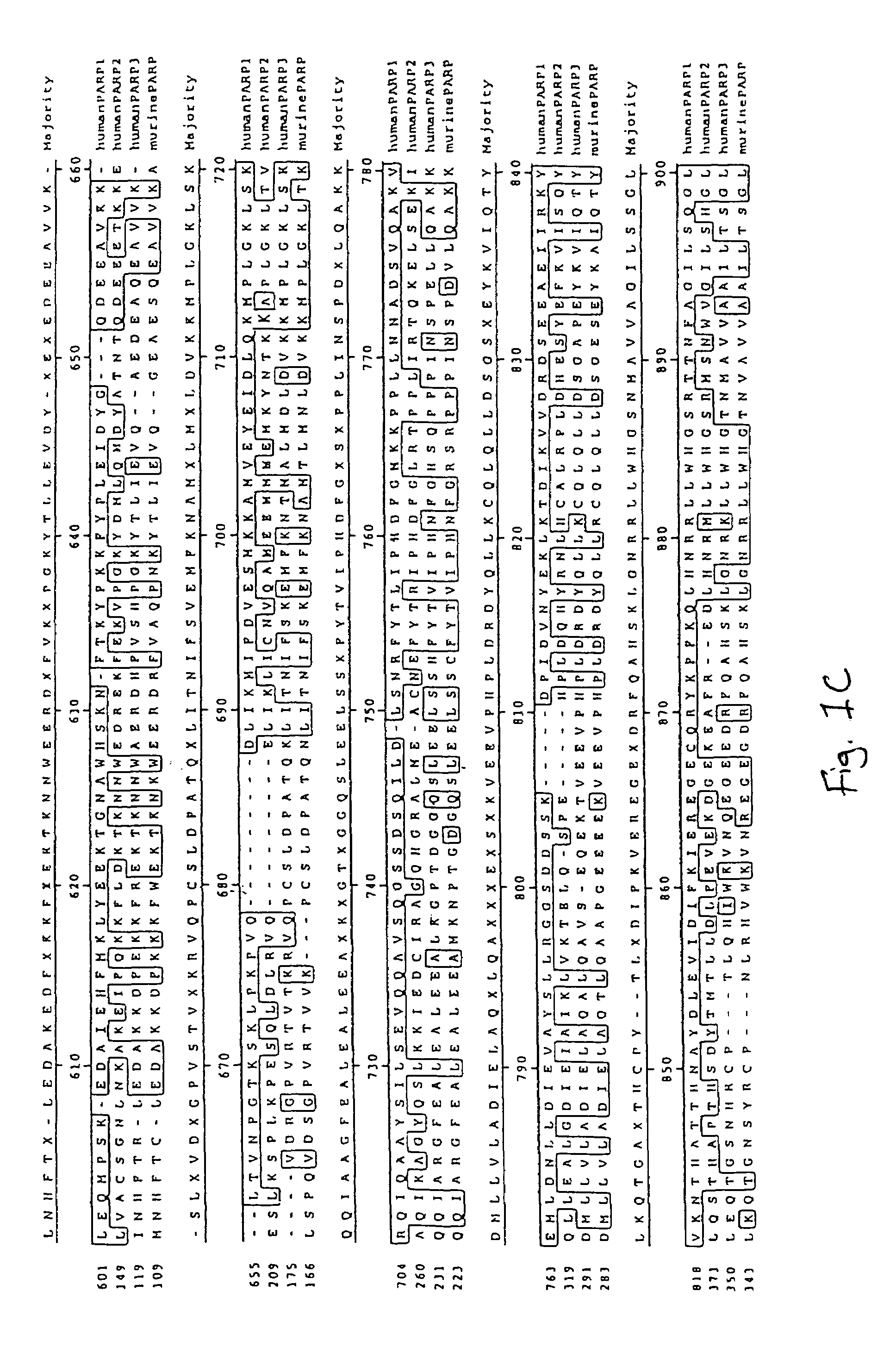
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-gene
The invention relates to poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) homologs which have an amino acid sequence which hasa) a functional NAD+ binding domain andb) no zinc finger sequence motif of the general formulaCX2CXmHX2C in which m is an integral value from 28 or 30, and the X radicals are, independently of one another, any amino acid;and the functional equivalents thereof; nucleic acids coding therefor; antibodies with specificity for the novel protein; pharmaceutical and gene therapy compositions which comprise products according to the invention; methods for the analytical determination of the proteins and nucleic acids according to the invention; methods for identifying effectors or binding partners of the proteins according to the invention; novel PARP effectors; and methods for determining the activity of such effectors.
Owner:BASF AG +1
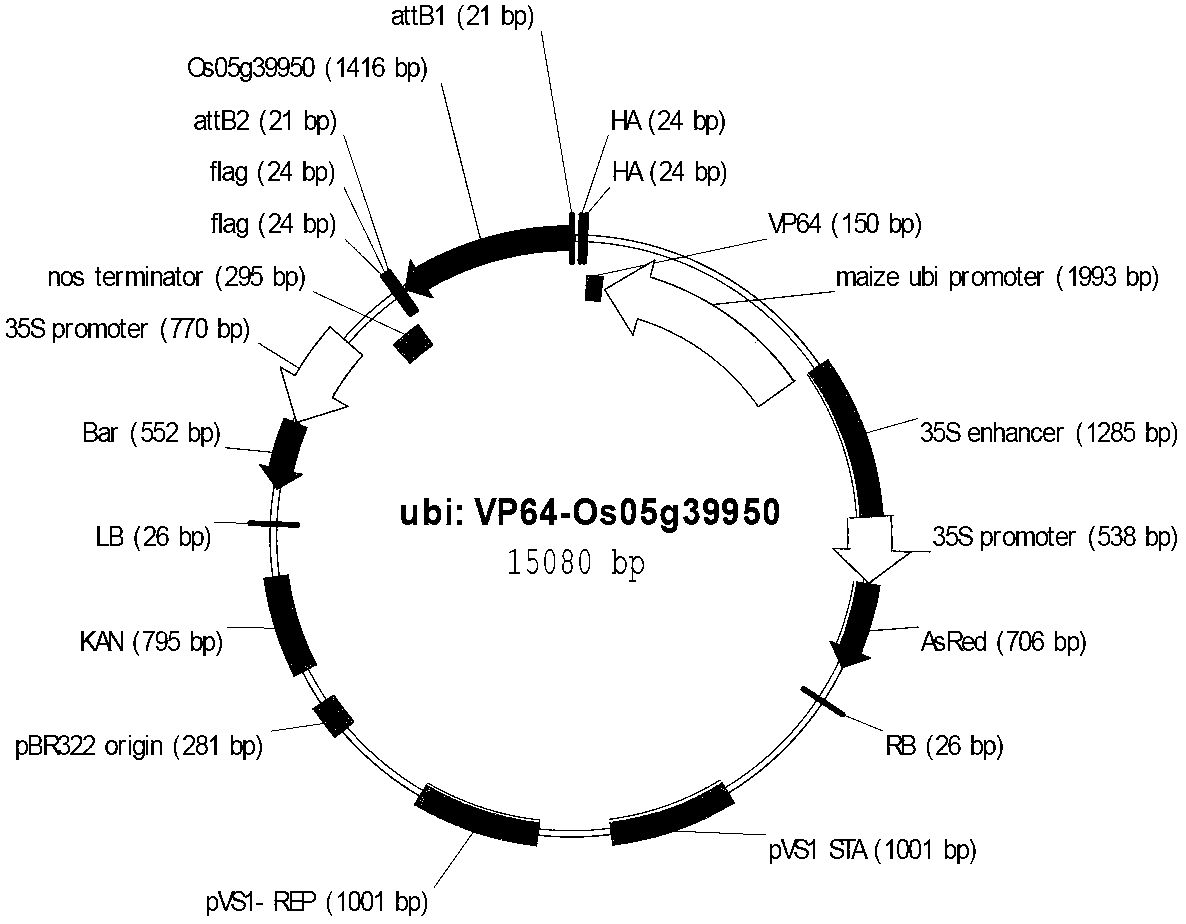
Application of rice transcription factor Os05g39950 gene
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Peptides for use as translocation factors
InactiveUS20040234527A1Ameliorate any conditionGood effectCosmetic preparationsNervous disorderADAMTS ProteinsProtein translocation
Proteins that contain the amino acid sequence motif X<1>X<1>X<2>X<3>X<1>, where X<1>=R or K and X<2 >and X<3>=any amino acid have been found to translocate and can therefore be used in the manufacture of compositions for therapeutic applications. The proteins may also be used as translocation factors to deliver proteins or nucleic acids into a cell.
Owner:IMPLYX
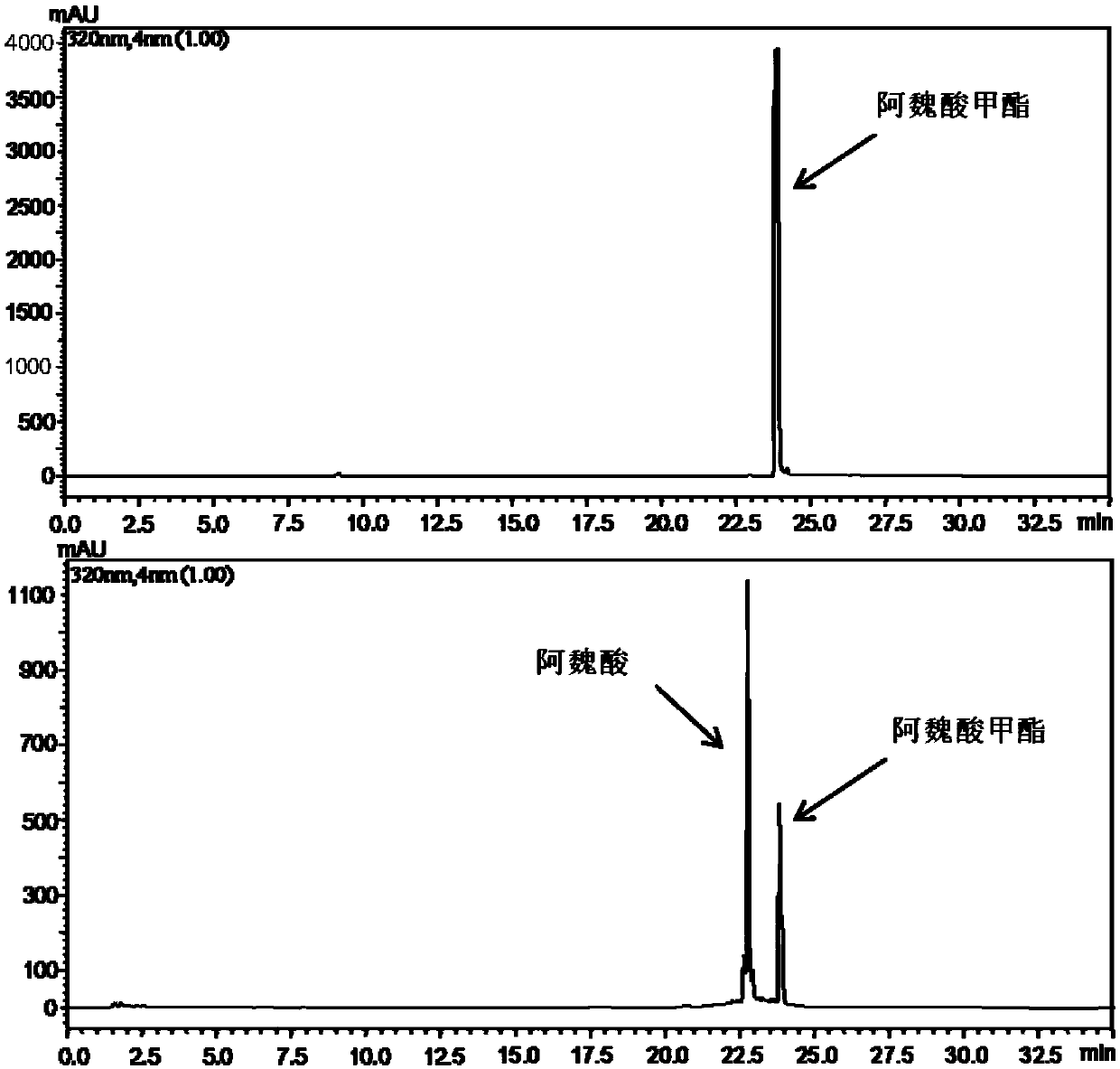
Feruloyl esterase and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109652392AIncrease enzyme activityHigh hydrolytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCefazolin
The invention provides feruloyl esterase and a preparing method and application thereof. A feruloyl esterase gene coming from a soil macro gene library have the nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The gene contains a tetrapeptide SXXK sequence motif which is rarely seen, and after the esterase gene is inserted into plasmid pET28a(+), the gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to achieve heterogeneous expression. The molecular weight of purified recombinase (DLFae4) is 38.3 kDa. Besides, it is put forward for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze penbritin, penicillin, cefazolin and other lactam antibiotics. As is shown by site-directed mutagenesis experiments, a catalysis triplet of DLFae4 is composed of serine(S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302), and the mutation of any of serine (S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302) can cause loss of the catalysis capability of DLFae4. DLFae4 has a high hydrolytic activity on methyl ferulate and has good heat stability. In the presence of cellulase, DLFae4 can obviously increase the amount of ferulic acid released from destarched wheat bran. Due to peculiar activities and enzymatic characteristics of novel feruloyl esterase, novel feruloyl esterase can be applied to feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and other fields.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for analysis of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7270958B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleic acid cloning
Disclosed are a number of methods that can be used in a variety of embodiments, including, creation of a nucleic acid terminated at one or more selected bases, sequence analysis of nucleic acids, mapping of sequence motifs within a nucleic acid, positional mapping of nucleic acid clones, and analysis of telomeric regions. The methods utilize double-stranded templates, and in most aspects involve a strand replacement reaction initiated at one or more random or specific locations created in a nucleic acid molecule, and in certain aspects utilizing an oligonucleotide primer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Immunogenic compositions and methods of use
InactiveCN101365724AReliable controlImprove utilizationAntibacterial agentsMaterial nanotechnologyPolyelectrolyteSequence motif
Disclosed herein is a multilayer film comprising two or more layers of polyelectrolytes, wherein adjacent layers comprise oppositely charged polyelectrolytes. A first layer polyelectrolyte comprises a composite polypeptide comprising one or more surface adsorption regions covalently linked to one or more functional regions, wherein the functional regions generate a single polypeptide chain, and the one or more surface adsorption regions have amino acid sequence motifs composed of 5 to 15 amino acid residues. The one or more functional regions comprise 3 to 250 amino acid residues.
Owner:路易斯安那科技大学研究基金会
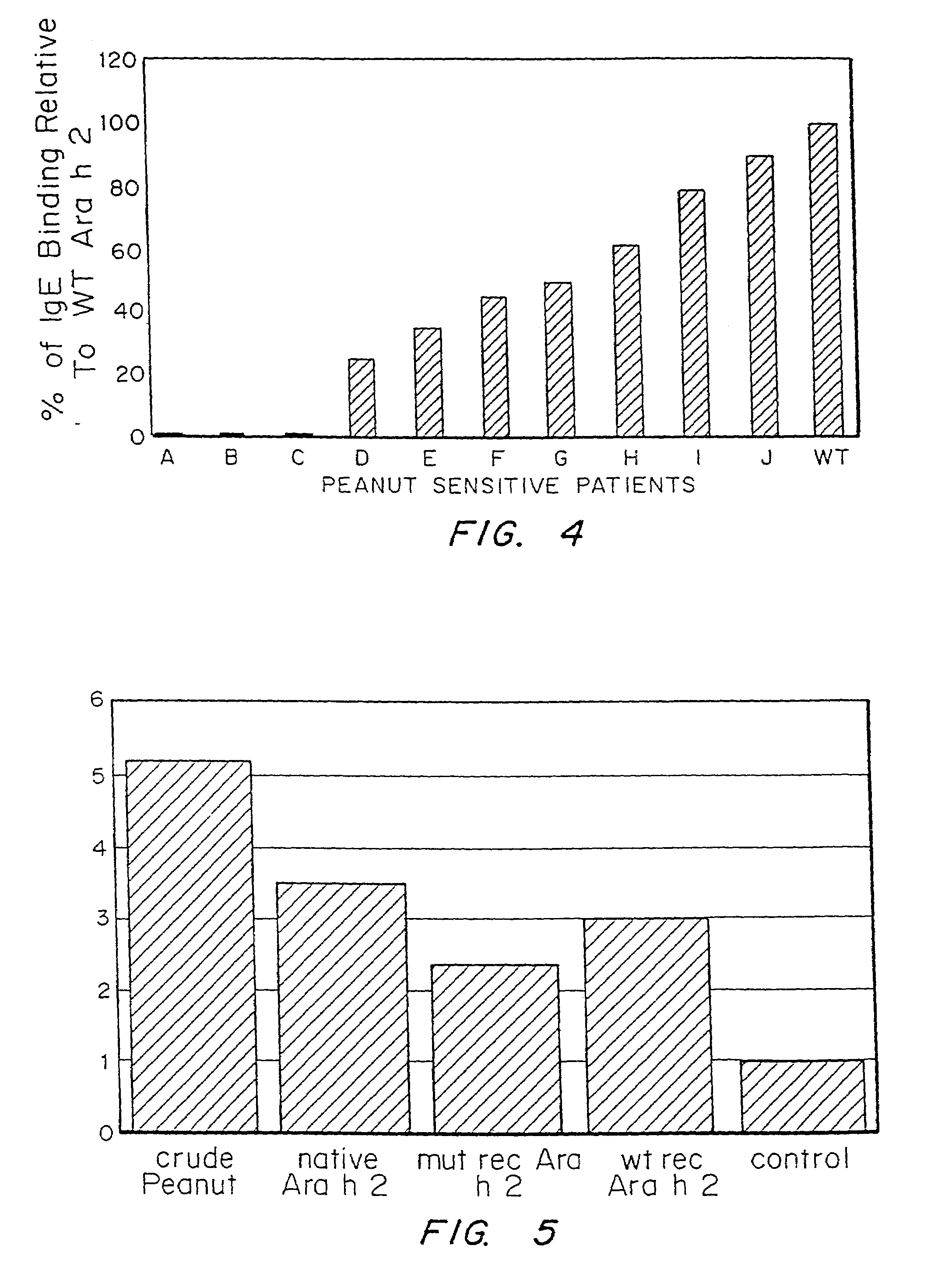
Nucleic acids encoding ara h 3 polypeptides
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity. The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Pharmaceutical Compositions Containing Antifungal Peptides
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing, in a pharmaceutical carrier, a peptide comprising at least one sequence motif of the following general formula (I) Hel1-HB-Hel2. The invention also relates to the use and production of said pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for screening restriction endonucleases
InactiveUS6905837B2Facilitate characterizationPromote productionSugar derivativesHydrolasesOpen reading frameCytotoxicity
A method is provided for identifying a restriction endonuclease, which includes the steps of (a) screening a target DNA sequence for the presence of known methylase sequence motifs, (b) identifying any open reading frames which lie close to the methylase sequence motifs screened in step (a), and (c) assaying the protein products of these open reading frames for restriction endonuclease activity.Methods for identifying isoschizomers of known restriction endonucleases, which isoschizomers possess a desired physical property, such as thermostability, are also provided by the present invention, as are several novel restriction endonucleases isolated from M. jannaschii, MjaIII and MjaIV. Additionally, a gene was identified that encoded a previously observed endonuclease activity, designated MjaII.Also provided by the present invention are vectors suitable for cloning a DNA sequence encoding a cytotoxic protein, via independent transcription promotors which may be selectively controlled by several conditions. A method for producing these cytotoxic proteins using such vectors is also provided, as are stable clones of PacI and NlaIII.
Owner:GOSS INT AMERICAS
Methods and reagents for decreasing clinical reaction to allergy
InactiveUS20070213507A1Less allergicEliminate IgE bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsFungi peptidesBinding siteT cell
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE-binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than-within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
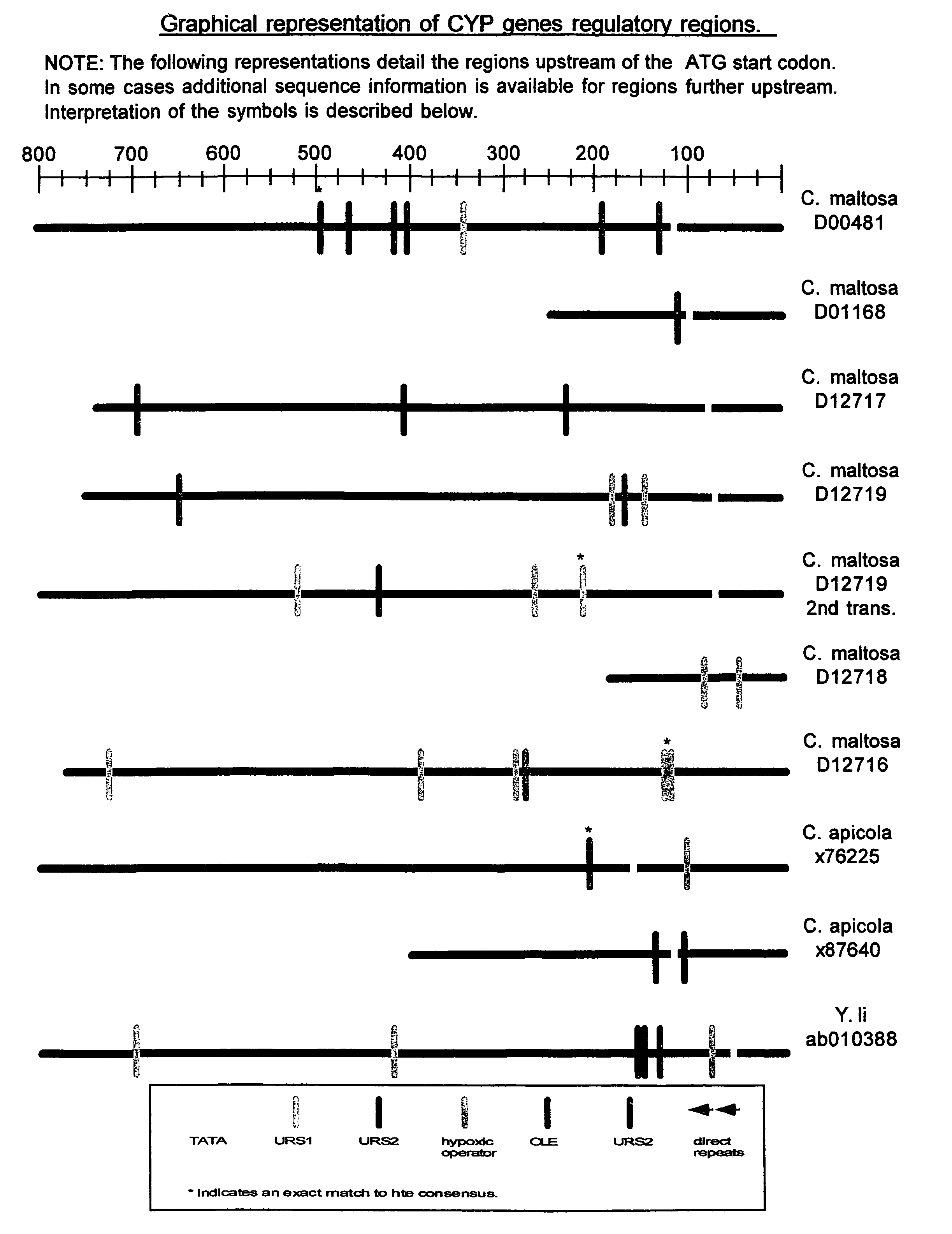
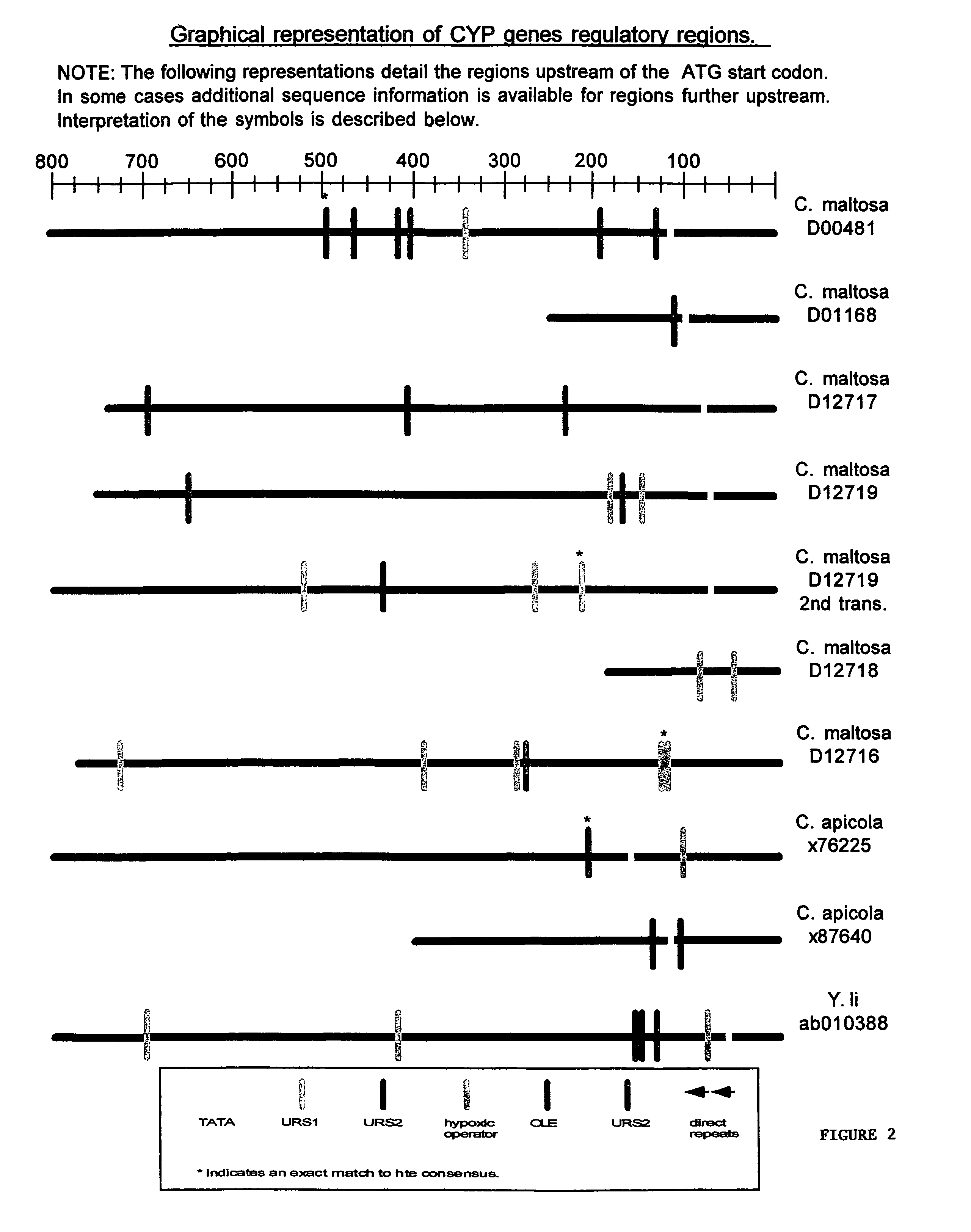
Promoter motifs in Candida tropicalis
The present invention provides modified promoters from Candida troplicalis CYP and POX4 genes. The modified promoters have various sequence motifs added, deleted, or altered in order to modulate expression of a coding sequence operably linked thereto. The sequence motifs comprise repressors of gene induction (URS sequences) and activators of gene induction (UAS sequences) as well as oleic acid response elements (ORE sequences). Yeast host cells comprising such modified promoters are also provided. Methods of altering expression of a protein of the beta or omega oxidation pathways using a subject modified promoter are also provided.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Multilayer films, coatings, and microcapsules comprising polypeptides
ActiveUS7550557B2Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsPolyelectrolyteEthylene Homopolymers
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
Multilayer films, coatings, and microcapsules comprising polypeptides
ActiveUS20070077275A1Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsPolyelectrolyteEthylene Homopolymers
Disclosed herein are multilayer films comprising two or more layers of polyelectrolytes, wherein adjacent layers comprise oppositely charged polyelectrolytes. A first layer polypeptide comprising one or more first amino acid sequence motifs, wherein the one or more first amino acid sequence motifs has a length of 5 to 15 amino acids residues, and wherein the balance of charge in the first amino acid sequence motif at pH 7 is greater than or equal to approximately one-half of the length of the first amino acid sequence motif, wherein the first layer polypeptide is not a homopolymer. Further, a second layer comprises second layer polyelectrolyte comprising a nonprotein polyelectrolyte having a charge opposite that of the first layer polypeptide.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors
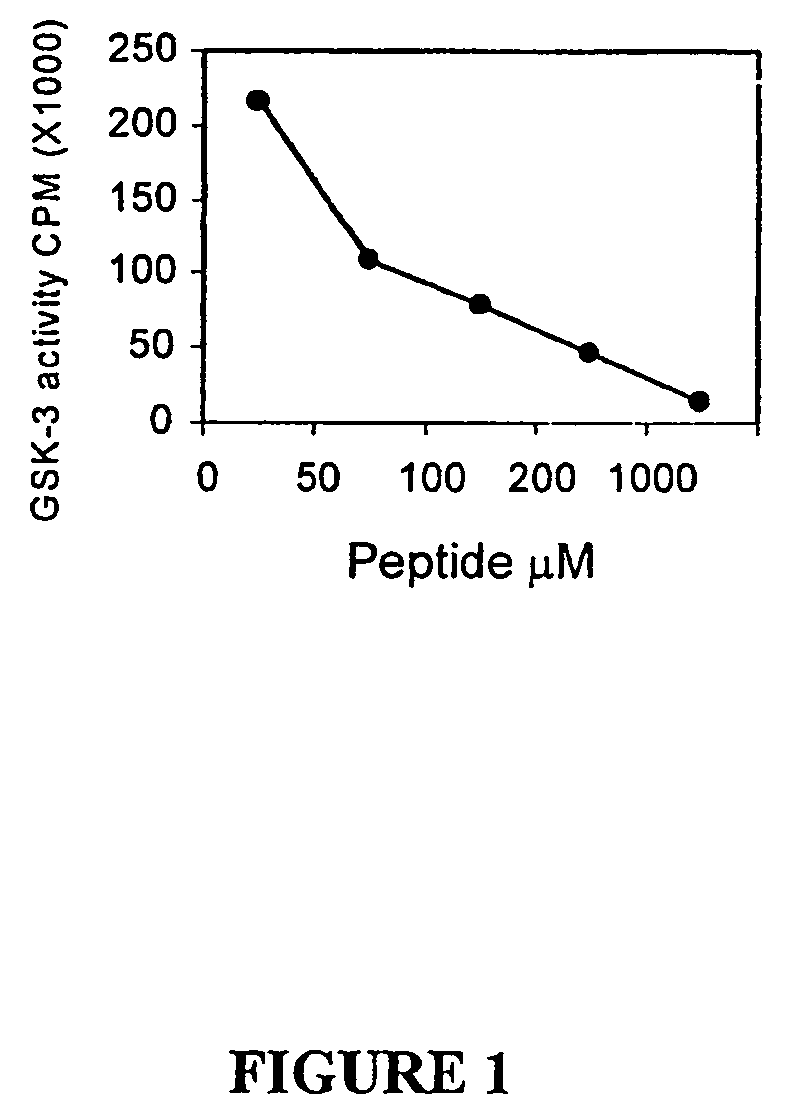
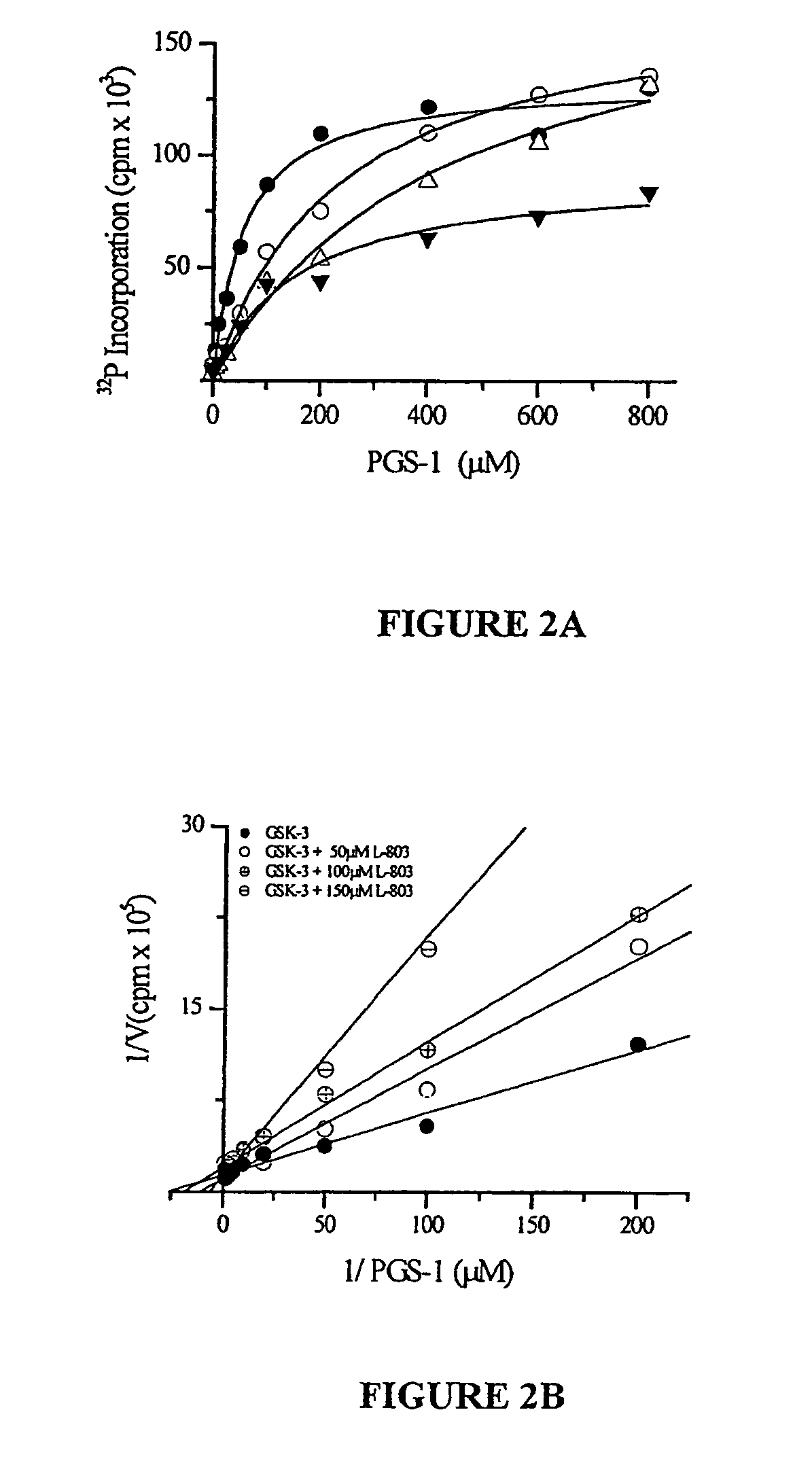
Peptide inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) having an amino acid sequence motif of XZXXXS(p)X, wherein S(p)=phosphorylated serine or phosphorylated threonine, X=any amino acid, and Z=any amino acid except serine or threonine. These inhibitors, which are about 7 to 20 amino acids long, are specific for GSK-3 and strongly inhibit the enzyme with an IC50 of about 150 μM. Also provided are methods of treating biological conditions mediated by GSK-3 activity, such as potentiating insulin signaling in a subject, treating or preventing type 2 diabetes in a patient, and treating Alzheimer's Disease by administering peptide inhibitors. Compositions of these peptide inhibitors and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers are also provided, as is a method for identifying inhibitors of GSK-3. The invention further relates to a computer-assisted method of structure based drug design of GSK-3 inhibitors using a three-dimensional structure of a peptide substrate of GSK-3.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
Method for developing SSR molecular markers on large scale
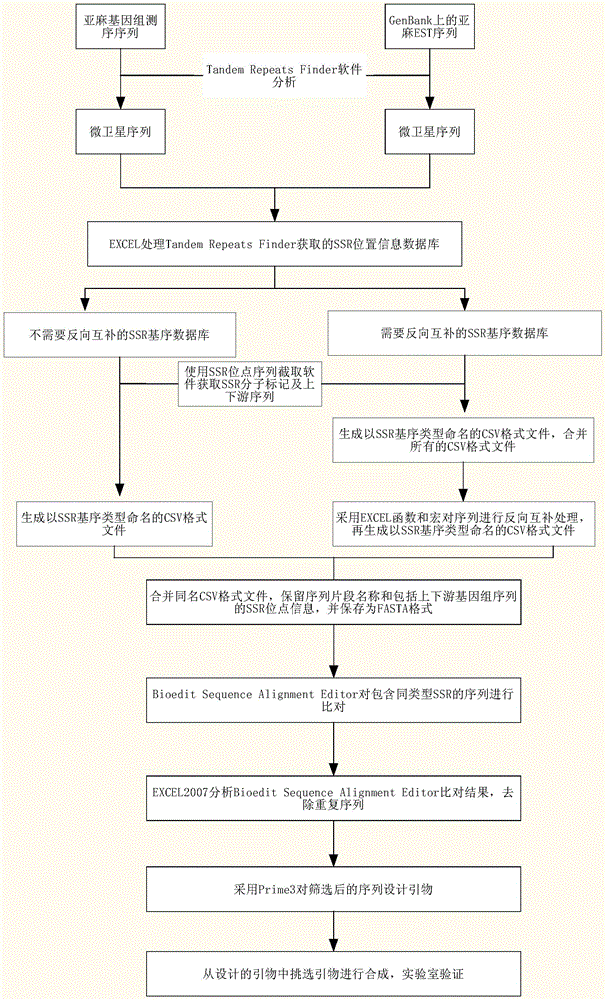
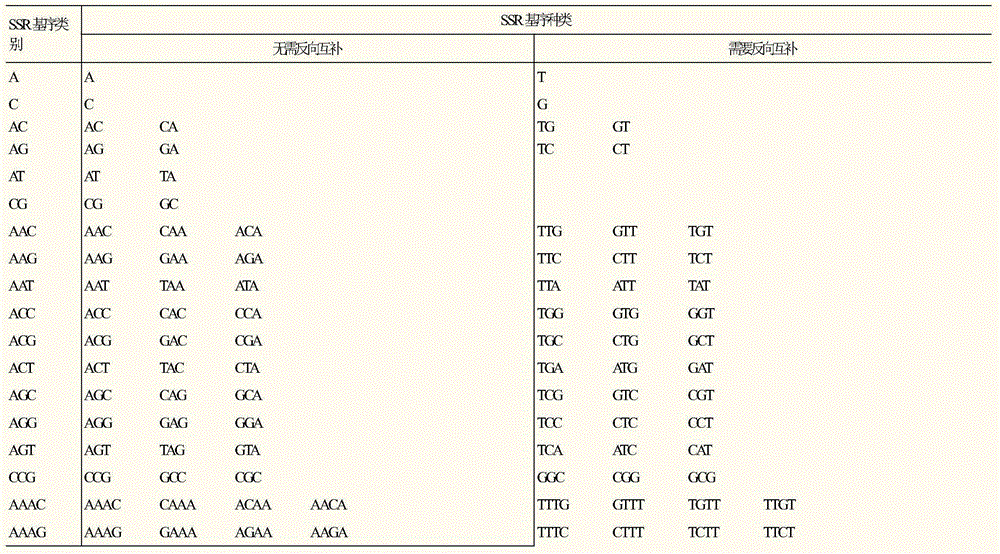
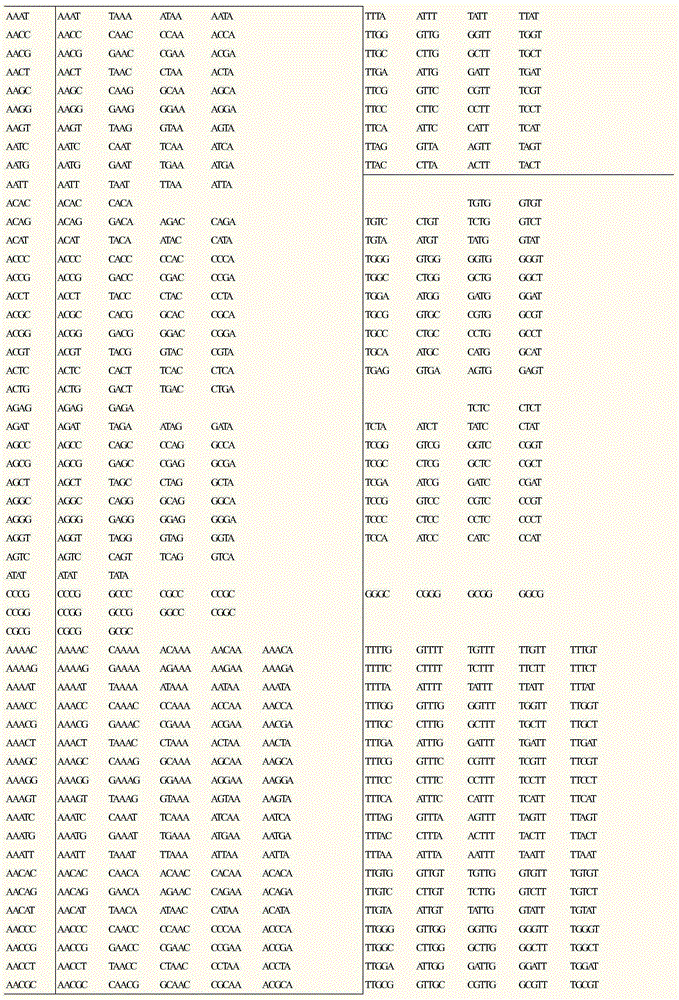
InactiveCN104830832ASolve the problem of high design repetition rate and low effectivenessImprove development efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenomic sequencingSequence database
The invention relates to a method for developing SSR molecular markers on a large scale. The method for developing the SSR molecular markers on the large scale comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a genomic sequencing sequence or an EST sequence on GenBank; secondly, acquiring SSR locus information of the genomic sequencing sequence or the EST sequence on the GenBank; thirdly, classifying SSR locus according to SSR sequence motif types; fourthly, carrying out reverse complementary treatment on SSR locus information of a database 3.CSV; fifthly, acquiring SSR molecular markers and upstream and downstream sequences in a database 4.CSV and a database 5.CSV by adopting SSR locus sequence interception software, and creating a sequence database according to the sequence motif types; and sixthly, screening repeated or similar SSR locus in CSV files of SSRs of the same type. The method for developing the SSR molecular markers on the large scale has the advantages that SSR marker locus in a genome can be located, SSR sequence fragments can be intercepted on the large scale, repeatability analysis can be carried out on different SSR sequences, and SSR molecular marker development efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chimeric Compositions and Methods for Regulating Plant Gene Expresssion
InactiveUS20110271396A1High expressionHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotidePlant cell
The invention provides a method for producing a chimeric promoter polynucleotide capable of controlling transcription of an operably linked polynucleotide in a plant cell or plant, wherein the method comprises combining: a) at least one sequence motif comprising a sequence with at least 70% identity to SEQ ID NO:1, 11 or 12, and b) another polynucleotide sequence. The invention also provides chimeric promoters polynucleotides comprising the sequences defined in a) and b). The invention also provides constructs, vectors, host cells, plant cells and plants comprising the chimeric promoter polynucleotides of the invention. The invention also provided methods for modifying gene expression and phenotype of plant cells and plants by transforming the plant cells and plants with the chimeric promoter polynucleotides of the invention.
Owner:THE NEW ZEALAND INST FOR PLANT & FOOD RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com