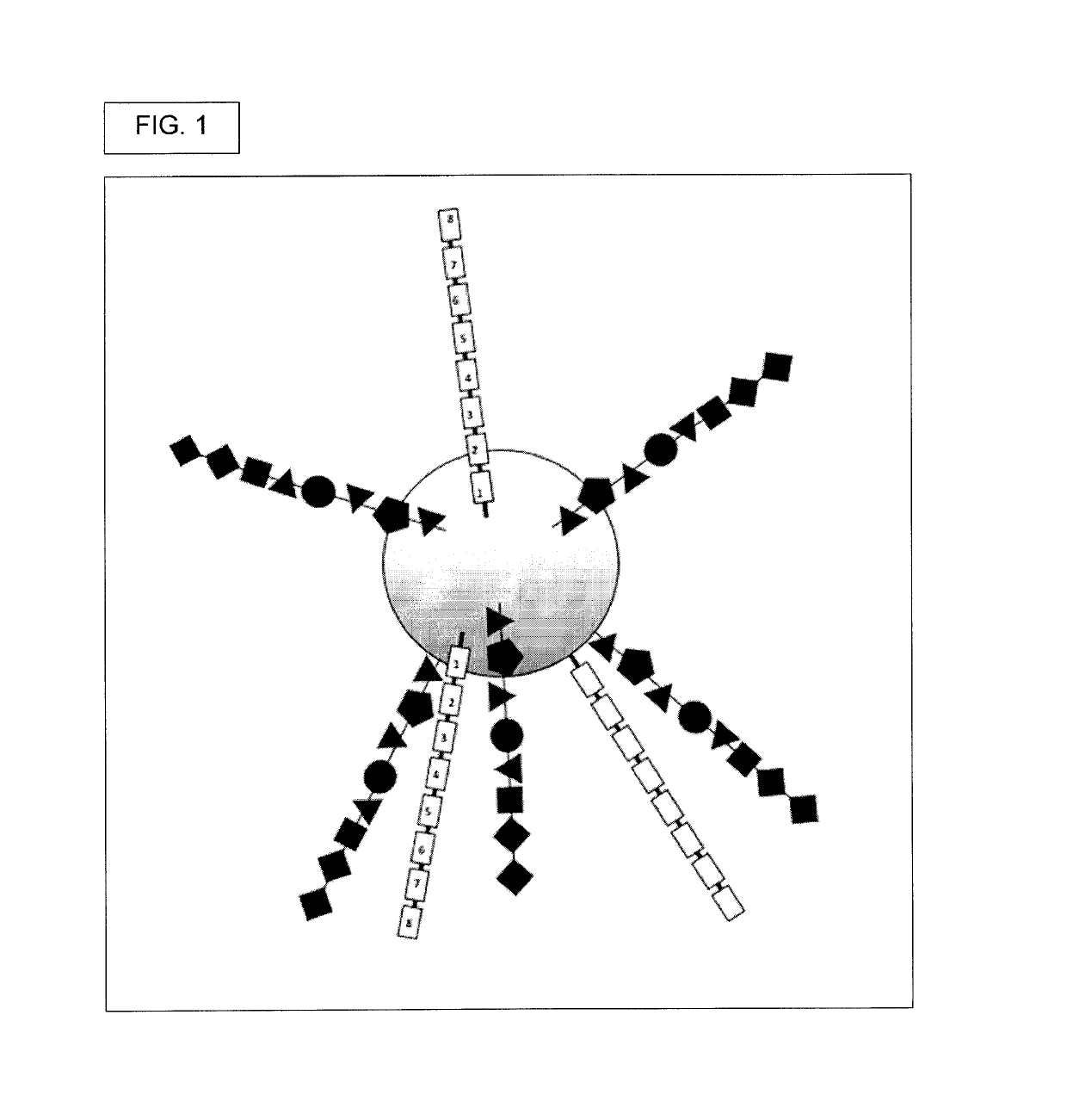
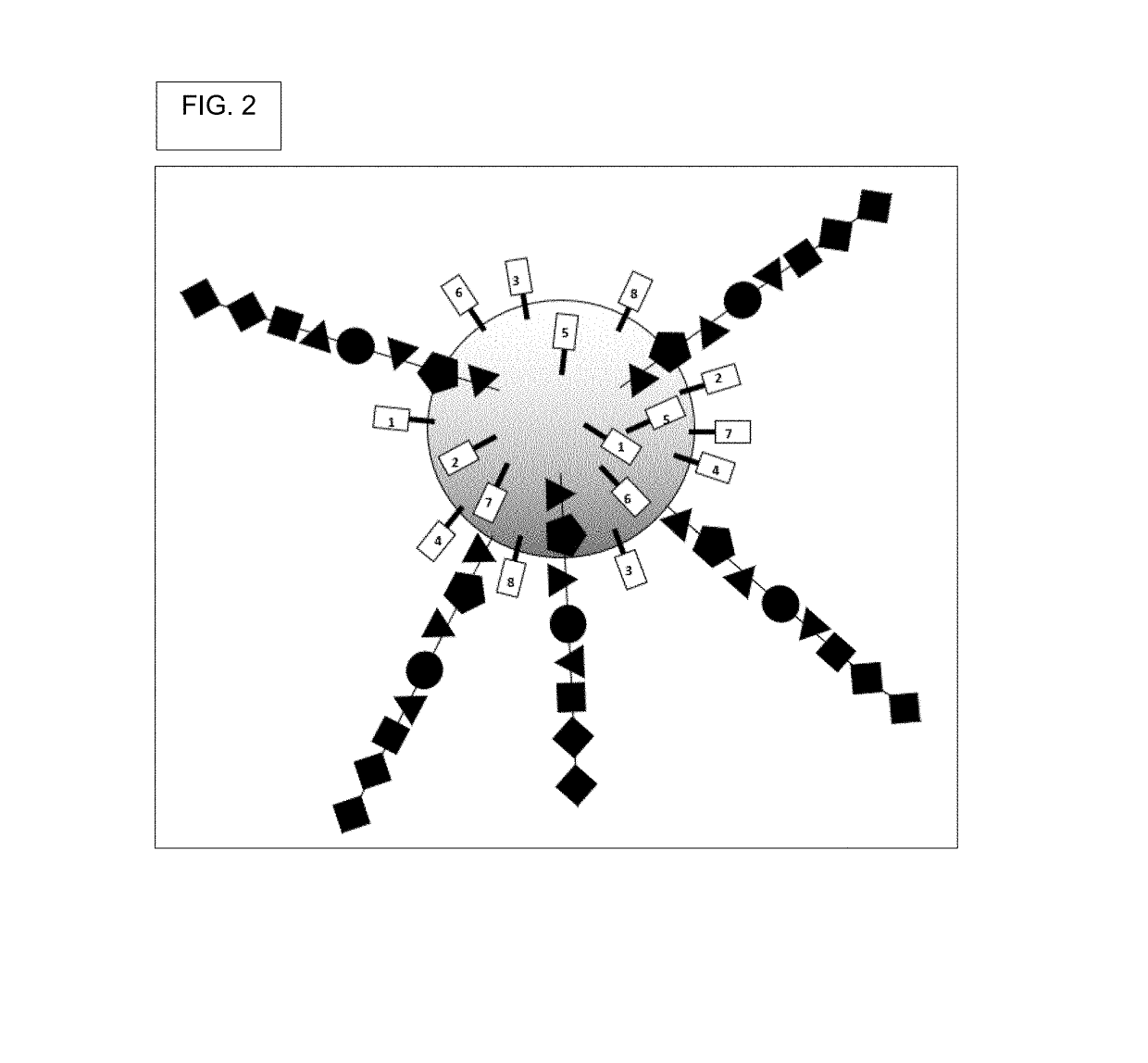
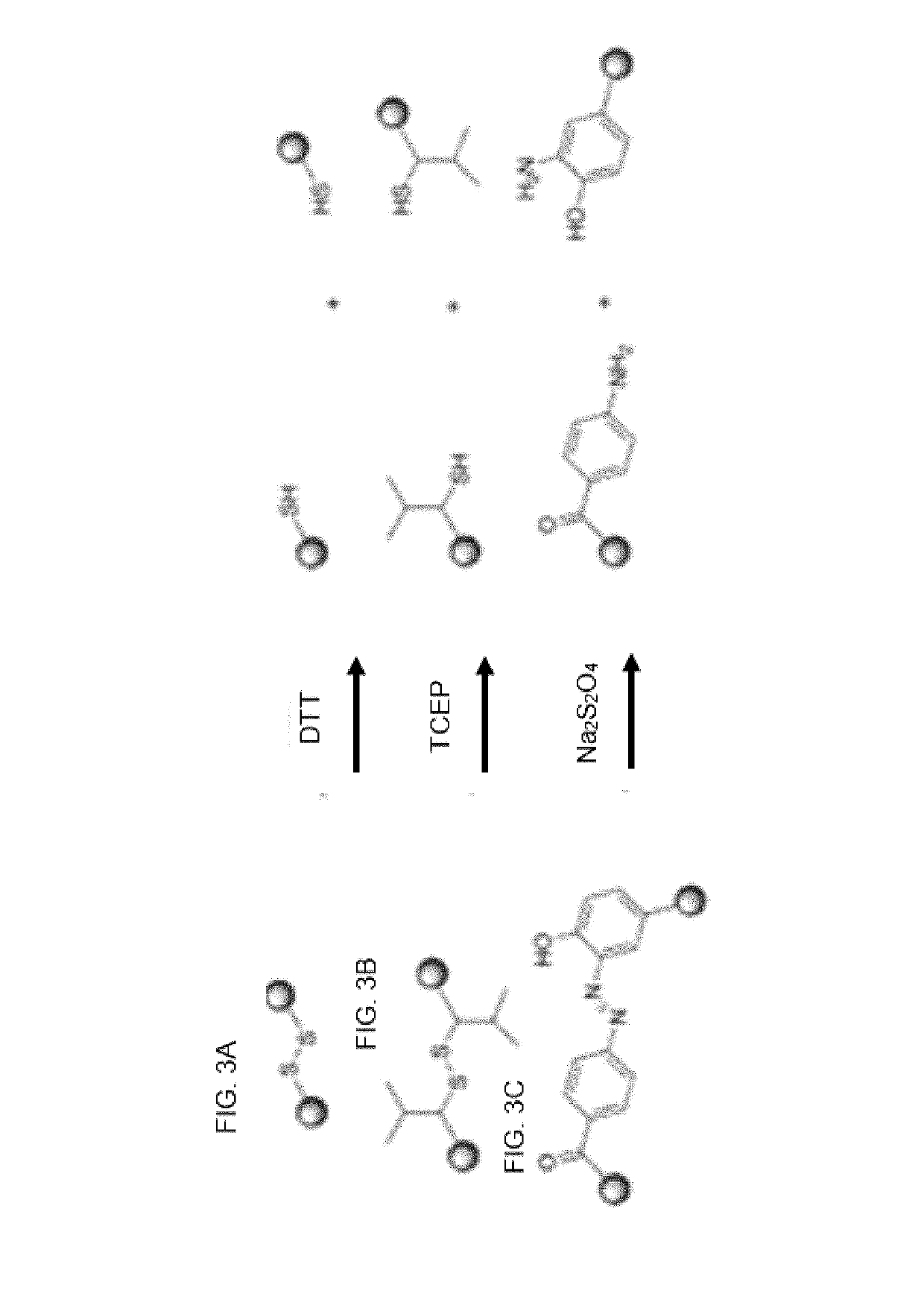
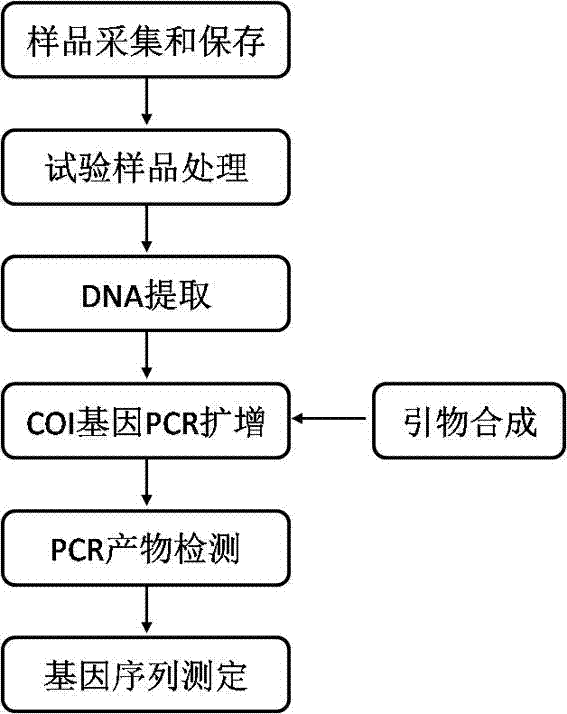
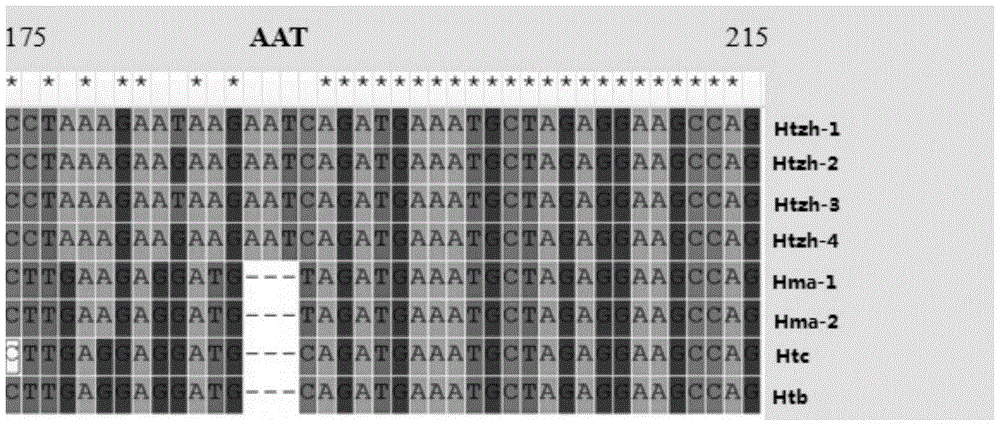
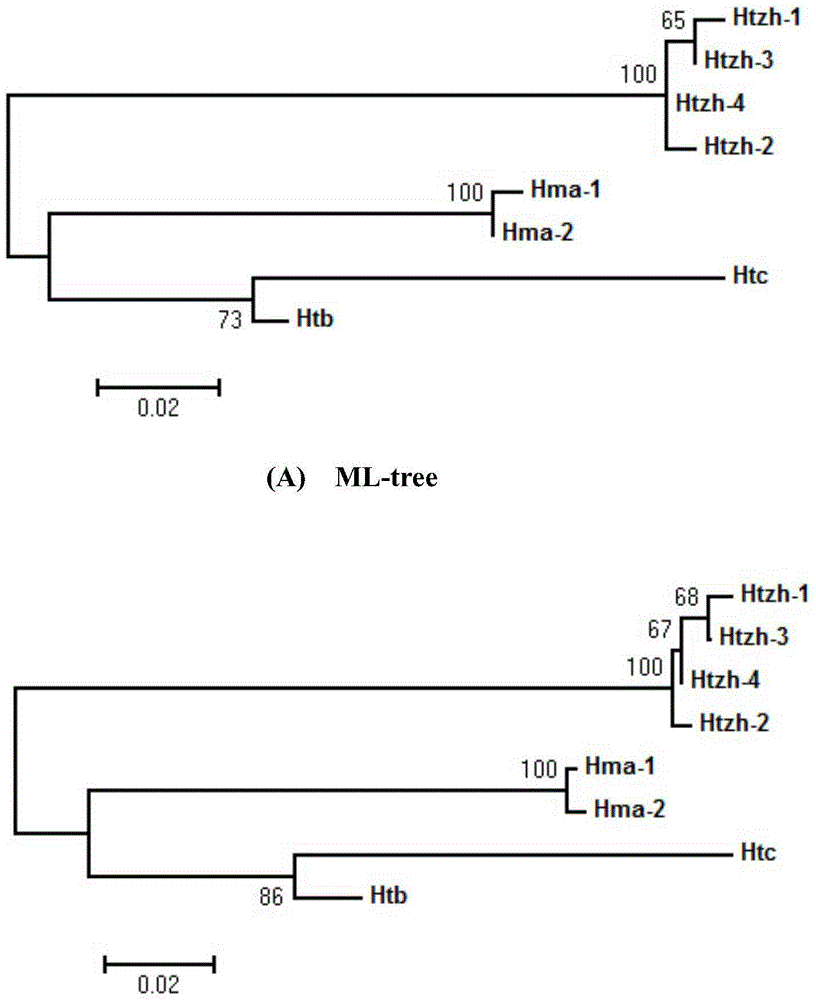
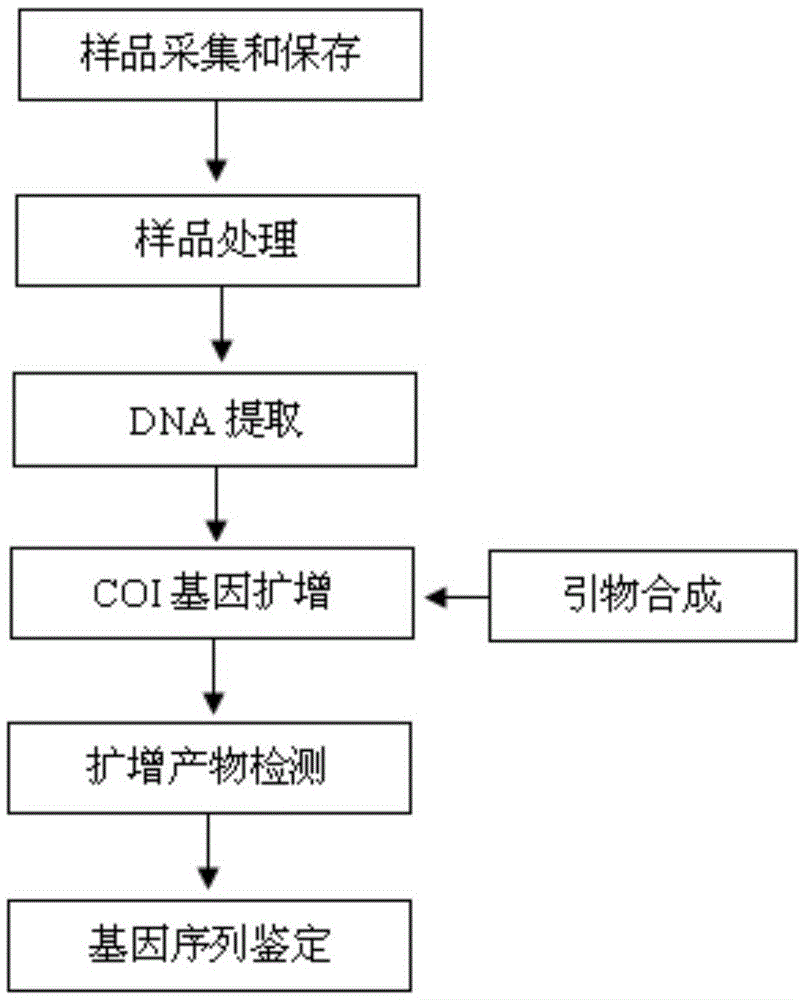
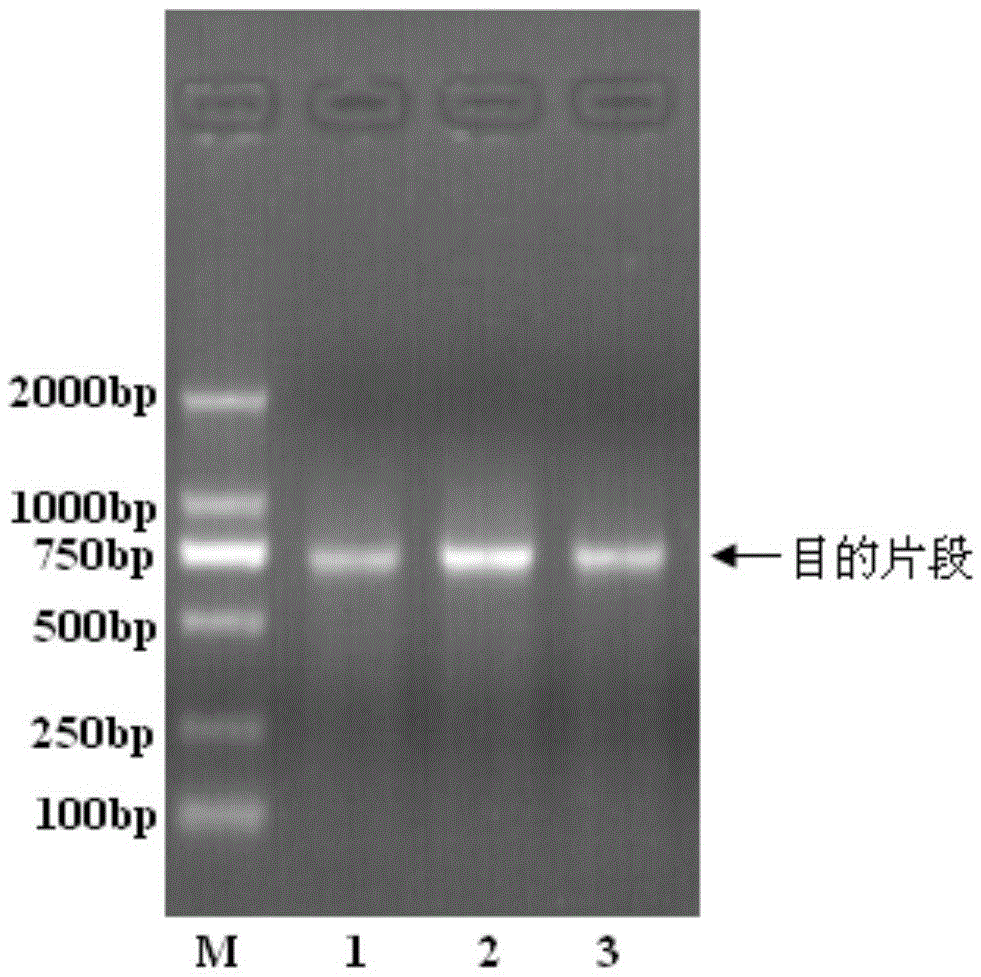
Patents
Literature
196 results about "DNA barcoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that, by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called "sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, in the same way that a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species, parts of an organism, or simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries.
Methods for determining genetic haplotypes and DNA mapping
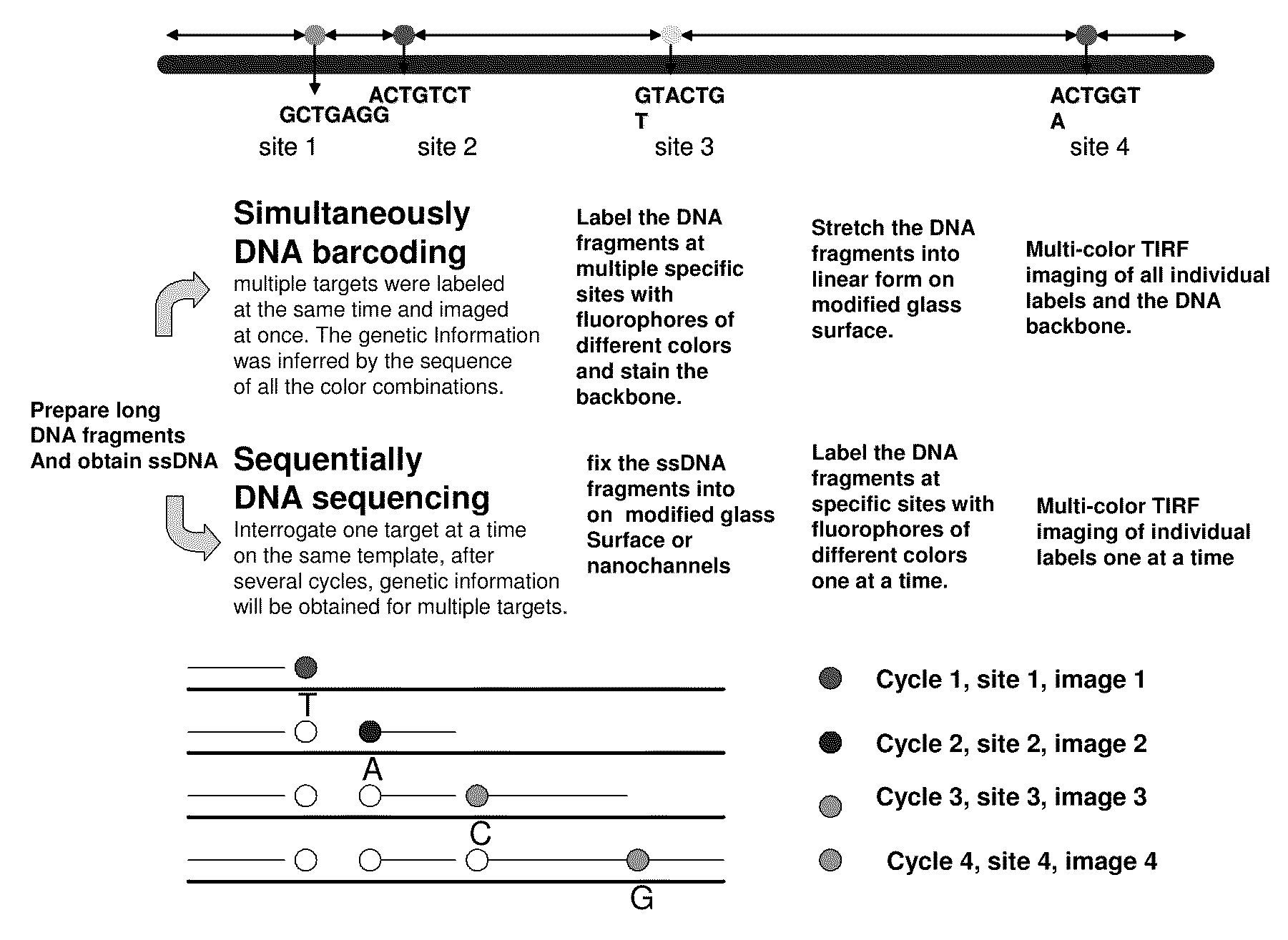
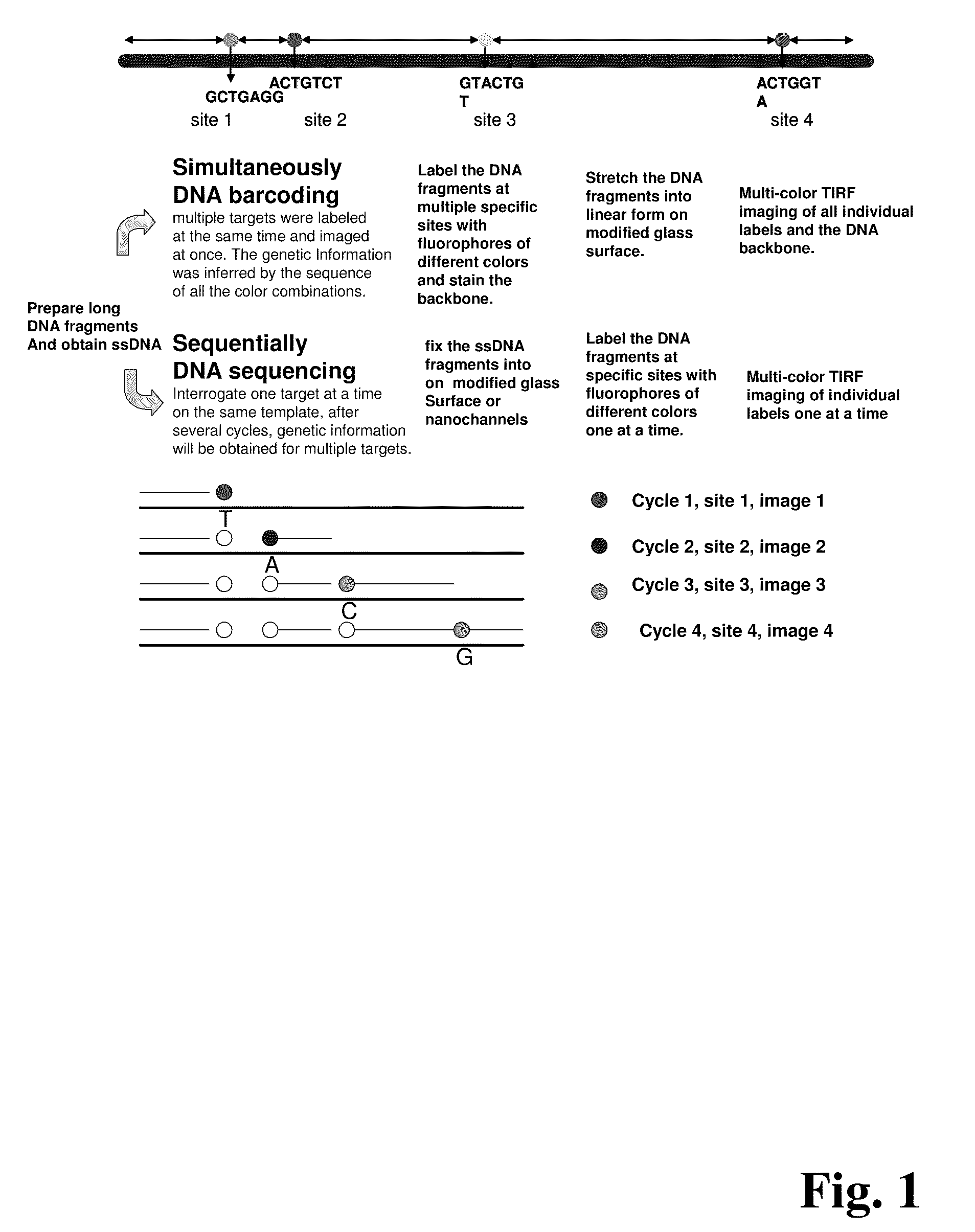
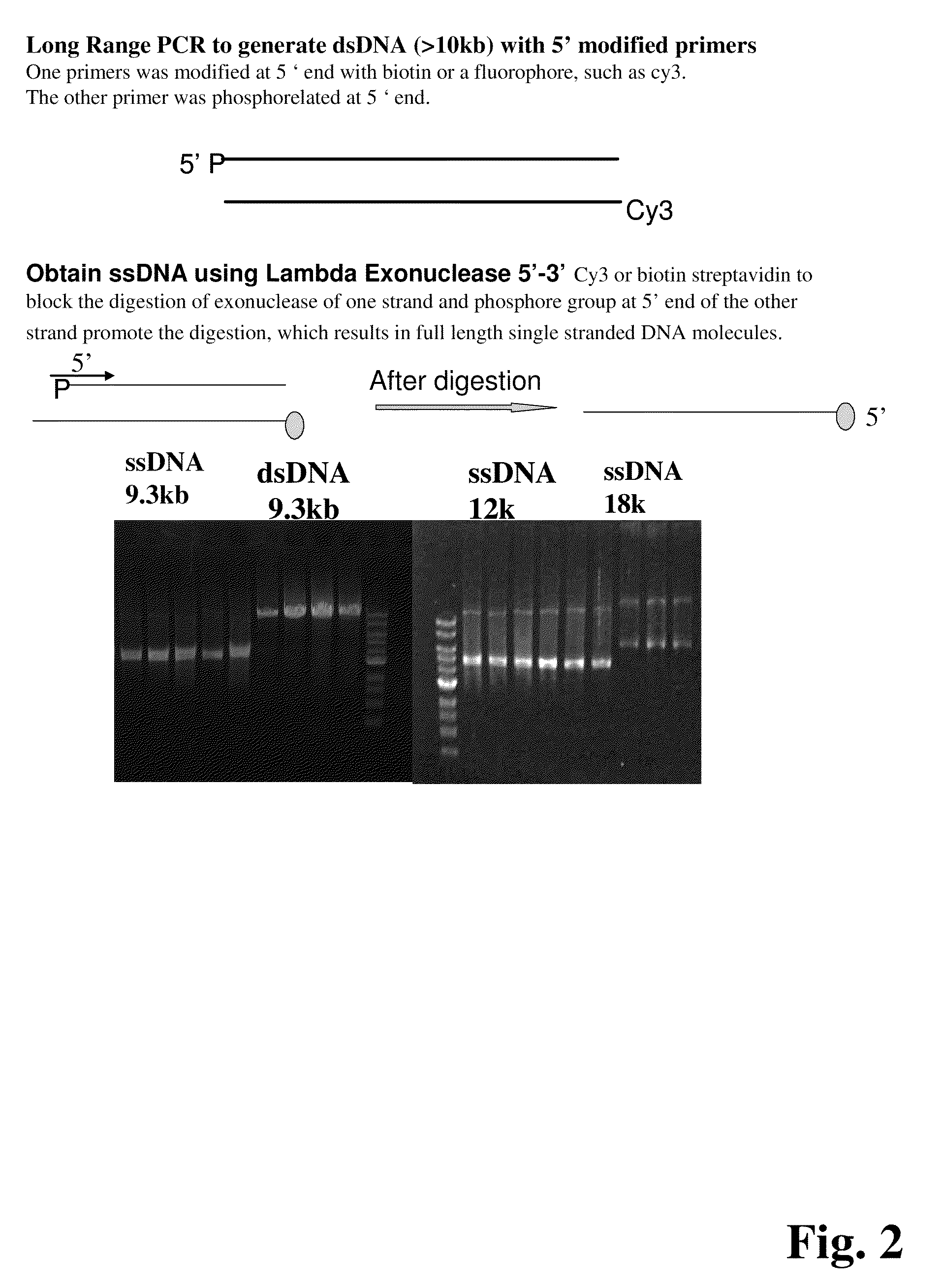
ActiveUS20090155780A1Improve labeling efficiencyStable labelingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDirect imagingDNA barcoding
Improved methods of genetic haplotyping and DNA sequencing and mapping, including methods for making amplified ssDNA, methods for allele determination, and a DNA barcoding strategy based on direct imaging of individual DNA molecules and localization of multiple sequence motifs or polymorphic sites on a single DNA molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
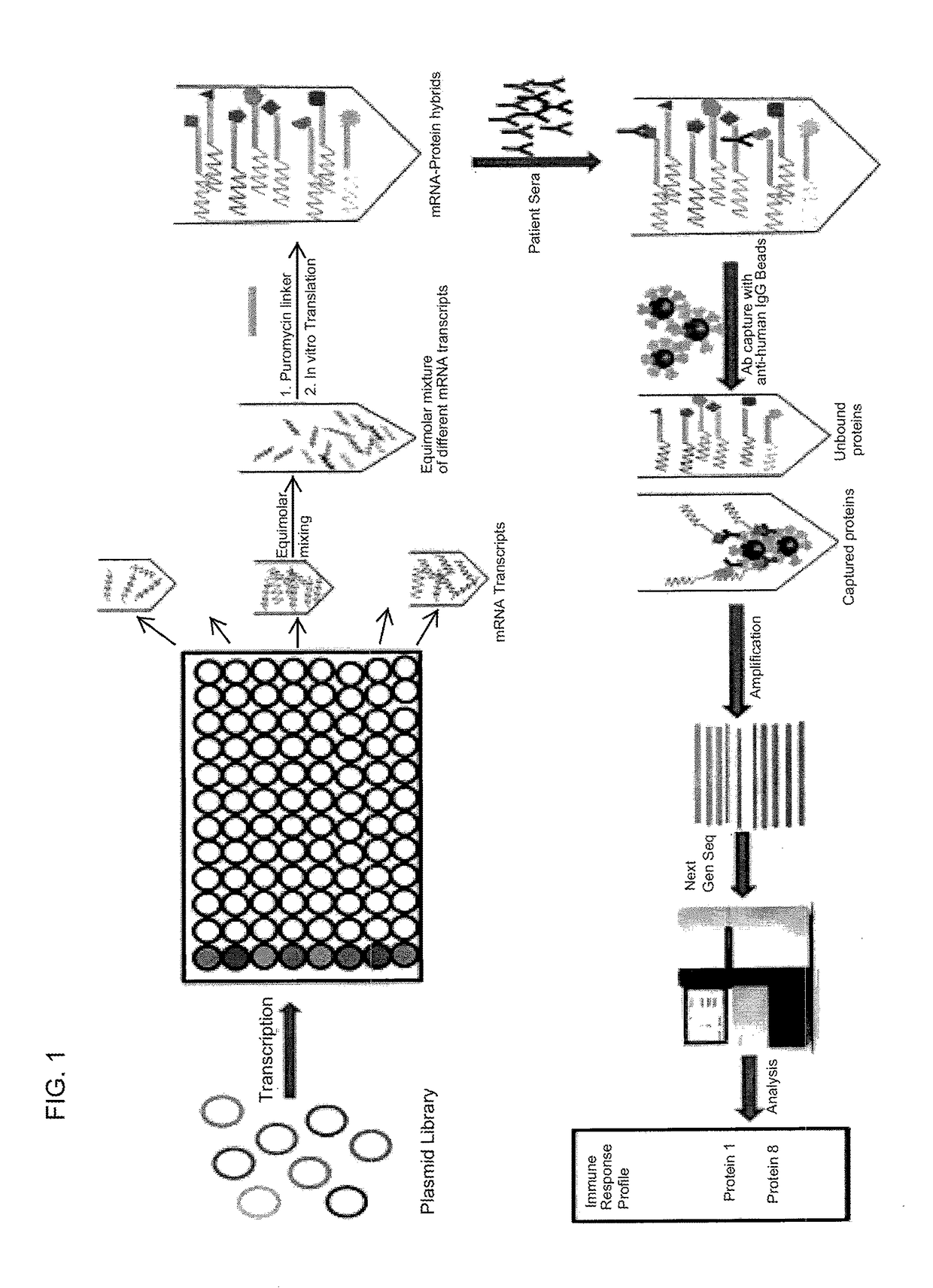
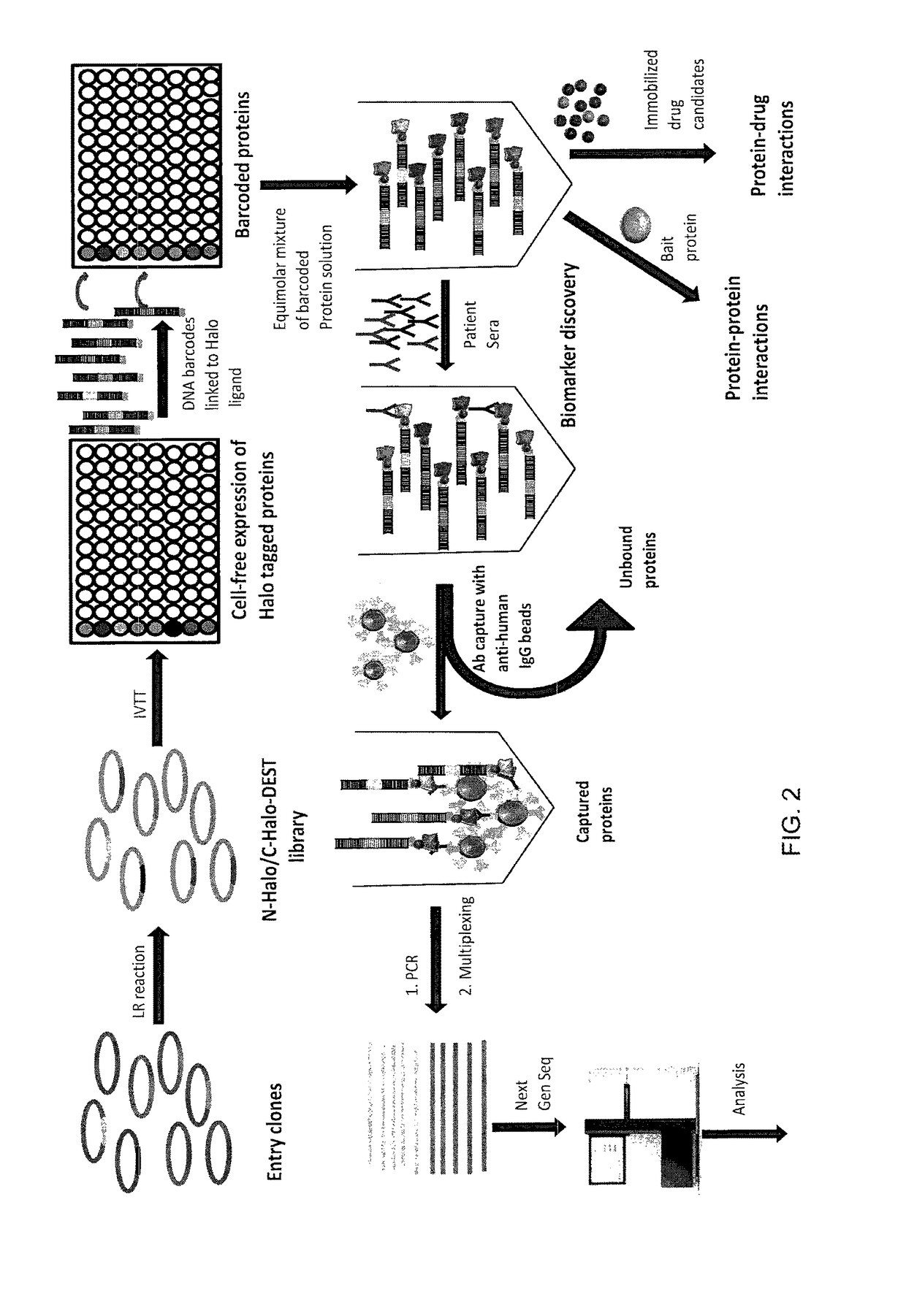
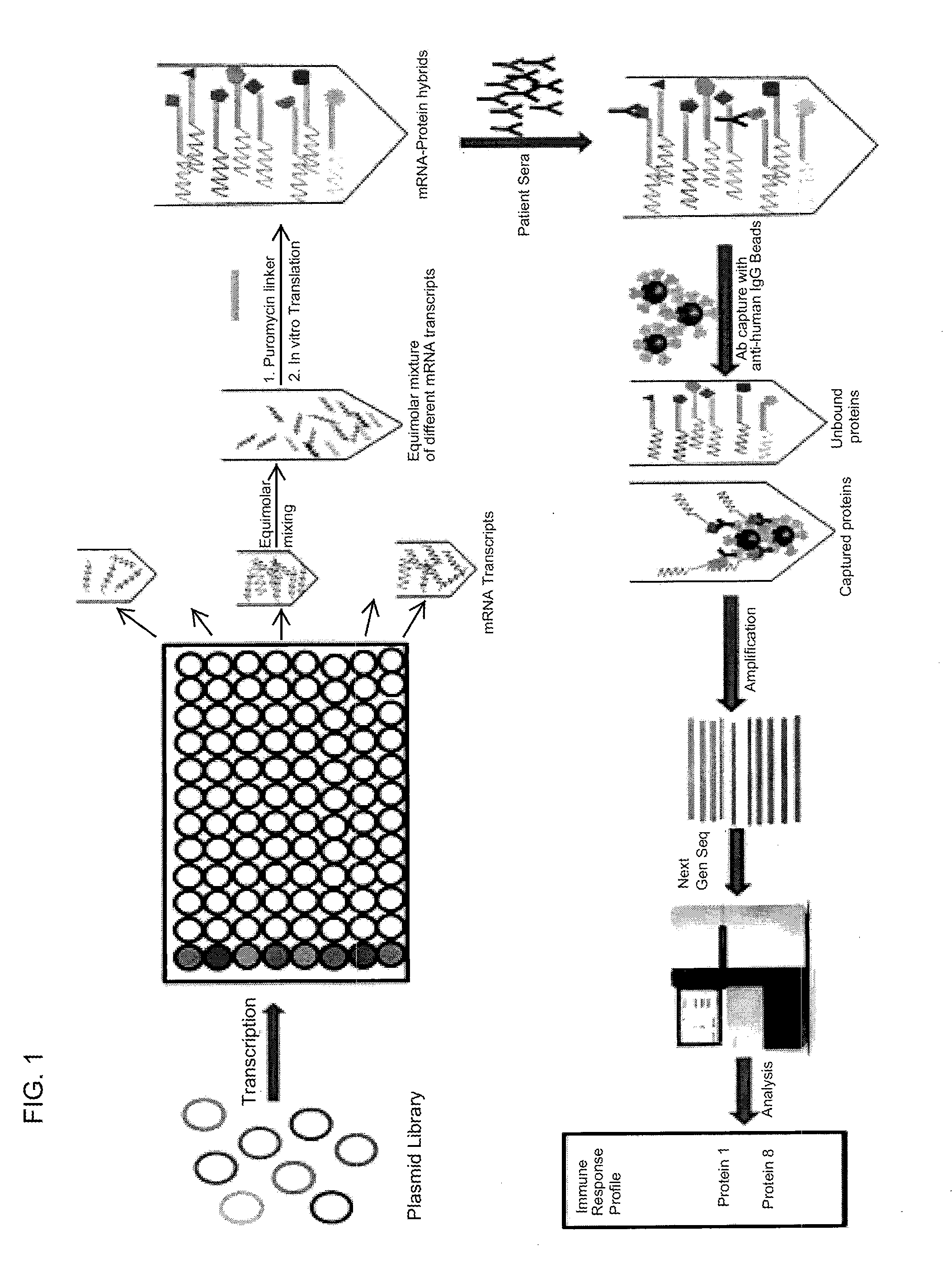
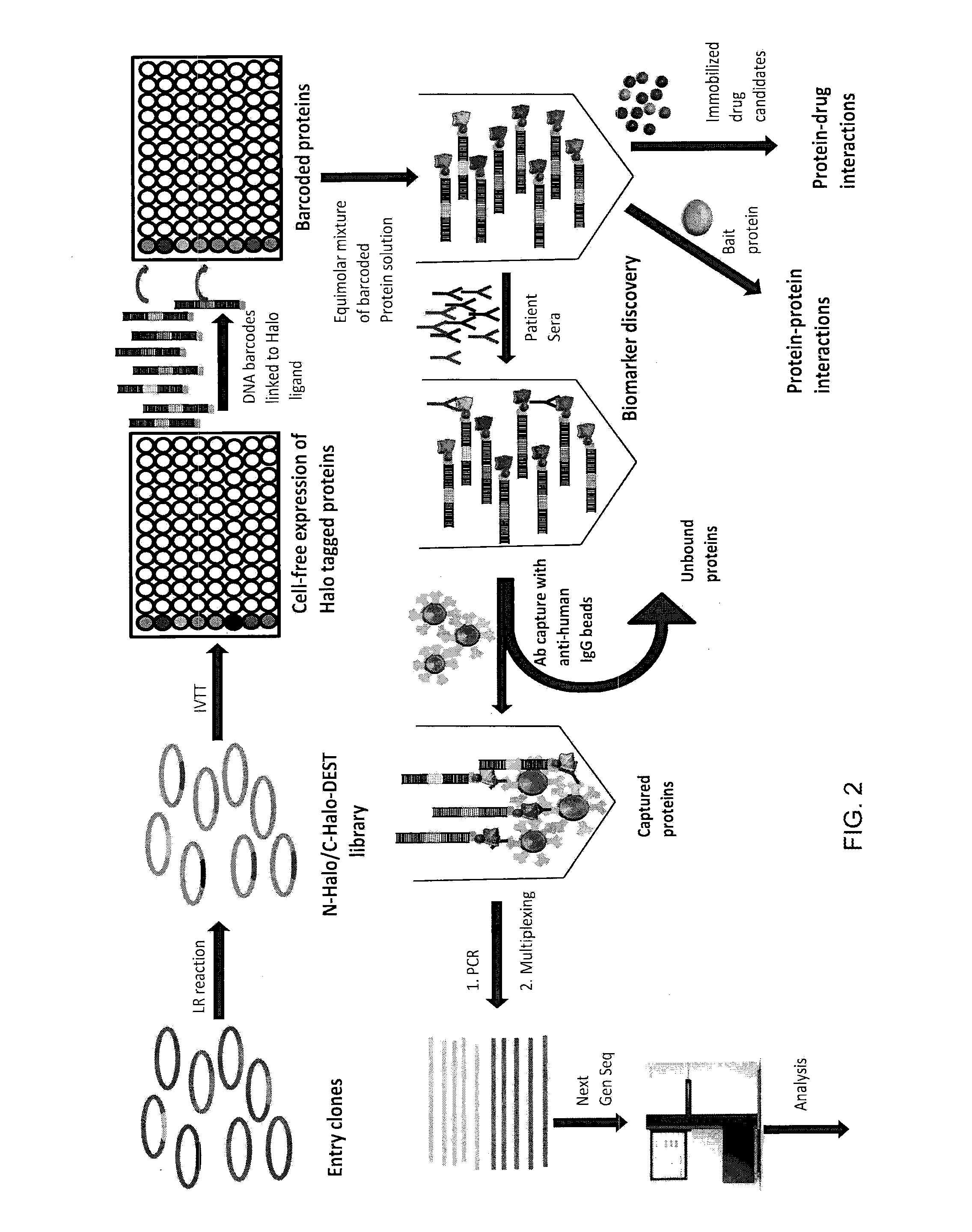
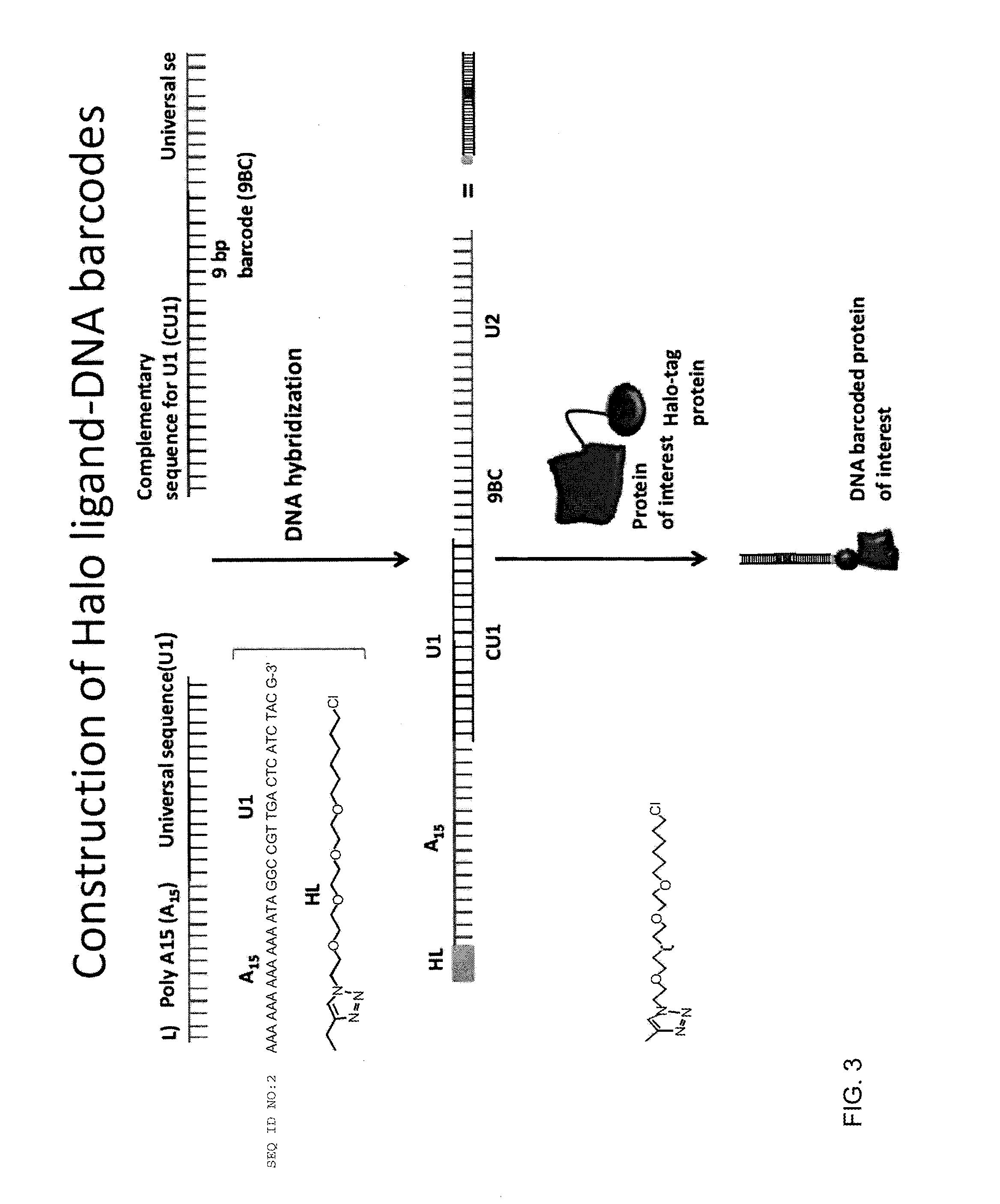
Nucleic acid-tagged compositions and methods for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling
Methods and compositions for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling (e.g., immunoprofiling), based on nucleic acid tagging of polypeptides (e.g., by RNA display) are described. In some embodiments the described compositions and methods utilize a library of prey polypeptide targets linked to prey RNAs encoding them, and a population of bait polypeptides, e.g., a mixture of antibodies, that bind to one or more of the prey polypeptide targets and are used to isolate and identify the bound prey polypeptide targets by amplification of their associated prey RNAs and sequencing of the corresponding cDNAs. In other embodiments the prey polypeptide targets are linked to DNA Bar Codes, which serve as unique identifiers of the tagged polypeptide.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid-tagged compositions and methods for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling
ActiveUS20160122751A1Nucleotide librariesLibrary member identificationDNA barcodingUnique identifier
Methods and compositions for multiplexed protein-protein interaction profiling (e.g., immunoprofiling), based on nucleic acid tagging of polypeptides (e.g., by RNA display) are described. In some embodiments the described compositions and methods utilize a library of prey polypeptide targets linked to prey RNAs encoding them, and a population of bait polypeptides, e.g., a mixture of antibodies, that bind to one or more of the prey polypeptide targets and are used to isolate and identify the bound prey polypeptide targets by amplification of their associated prey RNAs and sequencing of the corresponding cDNAs. In other embodiments the prey polypeptide targets are linked to DNA Bar Codes, which serve as unique identifiers of the tagged polypeptide.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Application of nucleotide sequence of rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) ITS (internal transcribed spacer)-D3 region in establishment of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code identification system for medicinal plants
InactiveCN102191318AImprove versatilitySequence alignment is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideDNA barcoding
The invention relates to a method for identifying medicinal plants by utilizing nucleotide sequences, in particular to an application of a nucleotide sequence of an rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) ITS (internal transcribed spacer)-D3 region in establishment of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code identification system for medicinal plants. The application comprises the following steps of: firstly, detecting the nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions of medicinal plants, and establishing a DNA bar code database; then, detecting the nucleotide sequence of the ITS-D3 region of a sample to be identified; constructing a clustering tree by the detected nucleotide sequence and the nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions in the DNA bar code database; determining the medicinal plant having the closest genetic relationship with the sample to be identified in the DNA bar code database according to the clustering tree, and comparing the difference between the nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions of the medicinal plant and the sample to be identified; and then, by taking the name of the species of the medicinal plant having the closest genetic relationship with the sample to be identified in the database as a reference and combining information such as morphological characteristics and the like, determining the name of the species of the sample to be identified. In the invention, the DNA bar codes have the characteristics of good primer universality, accurate sequence comparison and strong species distinguishing capability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE +1
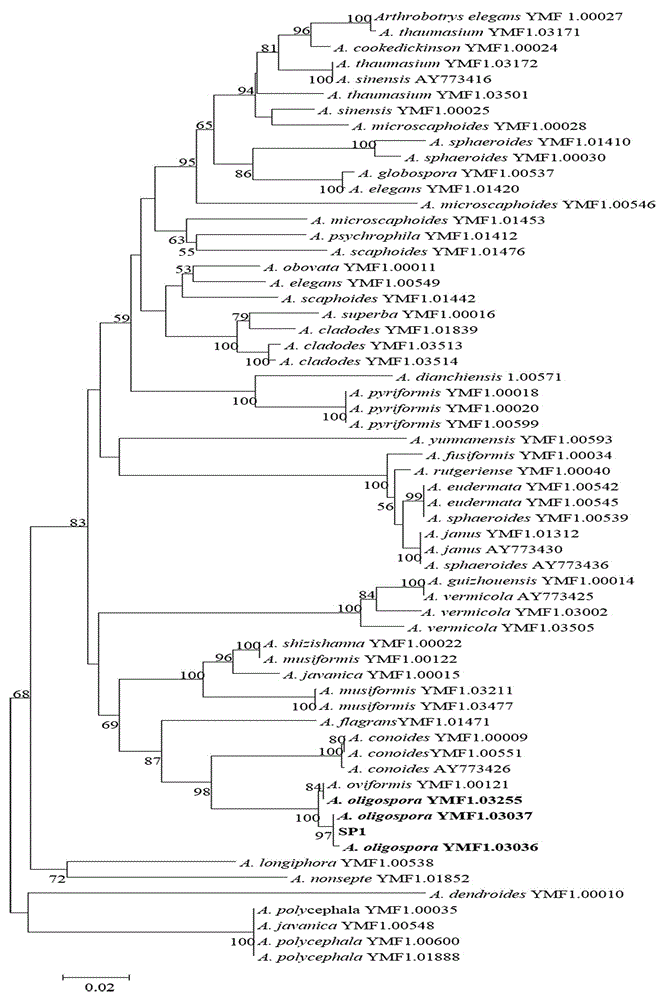
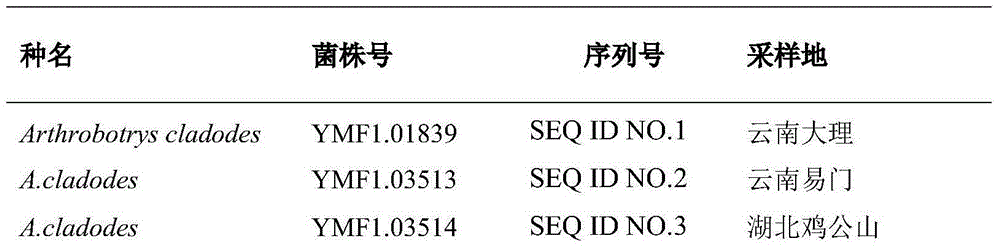
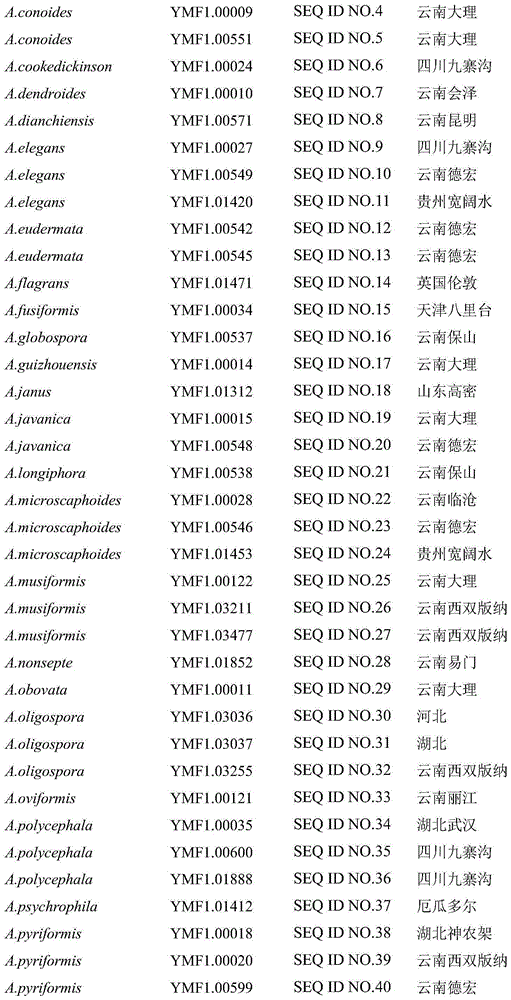
Method for identifying predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys through DNA bar codes
InactiveCN105063761AEasy to expandEasy to compareLibrary creationSpecial data processing applicationsDNA barcodingGermplasm
The invention provides a method for identifying predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys through DNA bar codes and belongs to the field of fungus species identification. According to the method, RPB2 genes serve as target DNA bar code genes for identifying the predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys, combined arthrobotrys sample experiment data and target fungus data merged strategy is adopted to establish a high-cavity database, meanwhile, RPB2 genes to be identified are compared with a gene library, an identifying rule is established based on a system generation tree method of genetic distance method and clustering analysis of the Kimura-2-parameter probability to identify species. The method has the advantages that the RPB2 genes serve as the DNA bar codes most suitable for identifying the nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys, and the method is universal and easy to amplify and compare. The identifying efficiency and the reliability and accuracy of the identifying method are greatly superior to those of a conventional DNA bar code method, and the method makes up for the blank of the nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys DNA bar code molecular markers and the method provides a useful research tool for researches on germplasm resource excavation, biocontrol application and genetic diversity of nematophagous hyphomycete.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method based on DNA bar code
InactiveCN106701914AClear scopeClear lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method based on a DNA bar code. Common bacterial contaminants in a medicine production environment can be effectively and accurately identified. The bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method comprises the steps that 1, a monoclonal bacterial strain is obtained through culture; 2, a genome DNA of the monoclonal bacterial strain obtained in the step 1 is extracted; 3, PCR is performed by using a general nucleic acid sequencing primer to amplify a specific sequence of nucleic acids; 4, a PCR product is extracted and purified; 5, a nucleic acid sequence of the PCR product obtained in the step 4 is determined; 6, a sequence analysis software is applied to perform sequence splicing, positioning is performed by using a general nucleic acid sequencing primer pair, a primer region is removed, and a DNA sequence of a corresponding fragment is obtained; 7, the DNA sequence of the corresponding fragment in the step is imported into a DNA bar code standard sequence core database or a GenBank database for sequence comparison, and bacteria are identified.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Specific primer pair for identification of spermatophyte species and applications of specific primer pair
InactiveCN102978208AEfficient identificationImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentation3-deoxyriboseDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a specific primer pair for identification of spermatophyte species and applications of the specific primer pair. The invention provides a pair of specific primers consisting of a single stranded DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) A and a single stranded DNA B. The single stranded DNA A is 15-40bp and has a DNA fragment same as the DNA fragment shown as a sequence I in a sequence table. The single stranded DNA B is 15-40bp and has a DNA fragment same as the DNA fragment shown as a sequence II of the sequence table. In the invention, with the ycflb gene of a plant to be tested as a template, the DNA fragment obtained by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification with the specific primer pair is also protected. The DNA fragment can be used for assisting identification of the spermatophyte species. The specific primer pair can be used for developing general kits, effectively identifying land plant species, and promoting the development of plant DNA bar codes, contributing to social progress.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DNA barcode compositions and methods of in situ identification in a microfluidic device
PendingUS20190345488A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCell specificSequence analysis
Apparatuses, compositions and processes for DNA barcode deconvolution are described herein. A DNA barcode may be used to provide a bead specific identifier, which may be detected in situ using hybridization strategies. The DNA barcode provides identification by sequencing analysis. The dual mode of detection may be used in a wide variety of applications to link positional information with assay information including but not limited to genetic analysis. Methods are described for generation of barcoded single cell sequencing libraries. Isolation of nucleic acids from a single cell within a microfluidic environment can provide the foundation for cell specific sequencing library preparation.
Owner:BERKELEY LIGHTS
Method for identifying DNA bar code molecule of earthworm
InactiveCN103898234AIdentification is conducive to the realizationIdentification achievedMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a method for identifying a DNA bar code molecule of an earthworm and a COI sequence of the DNA bar code molecule of the earthworm. The method comprises the steps of amplifying the gene of a sample COI through polymerase chain reaction (PCR), verifying the PCR product by agarose gel, then sending to a biological sequencing company for sequencing, according to the sequencing result, sequence splicing through manual correcting, comparing with a public sequence, then confirming the tissue to be tested as the source of pheretima aspergillum or pheretima vulgaris if the homology of the spliced sequence and the gene sequence SEQ ID NO.1-NO.4 is over 99%. By adopting the reliable DNA molecular identification technology, the method can rapidly and accurately identify the earthworm varieties specified by the 'pharmacopoeia of China' and non-medicinal material earthworm varieties without conducting morphological identification on the earthworm varieties, can further distinguish the pheretima aspergillum varieties from pheretima vulgaris varieties, improves the accuracy and reliability, and guarantees the safety of the earthworm as the medicinal material.
Owner:MUDANJIANG YOUBO PHARMA CO LTD
Molecular identification method for DNA bar code of lumbricus
InactiveCN106834467AIdentification is conducive to the realizationIdentification achievedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a molecular identification method for a DNA bar code of lumbricus and a CO I sequence thereof. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying a sample CO I gene through polymerase chain reaction (PCR); verifying the PCR product through agarose gel and then sending to a biological sequencing company for sequencing; manually correcting and splicing sequence for the sequencing result; comparing with a public sequence; and if the homology of the gene sequence SEQ ID NO.1-NO.4 is above 99%, confirming a to-be-detected tissue as a source of pheretima aspergillum or Shanghai lumbricus. According to the invention, a reliable DNA molecular identification technique is adopted; the morphological identification for lumbricus varieties is not required; the lumbricus varieties and non-drug lumbricus varieties specified in Chinese Pharmacopoeia can be quickly and accurately identified; besides, the pheretima aspergillum and the Shanghai lumbricus can be further distinguished; the accuracy and the reliability can be enhanced; the safety of the lumbricus used as a medicinal material can be guaranteed.
Owner:MUDANJIANG YOUBO PHARMA CO LTD
Method for discriminating two closely-related species of shellfish or identifying their hybrid generation
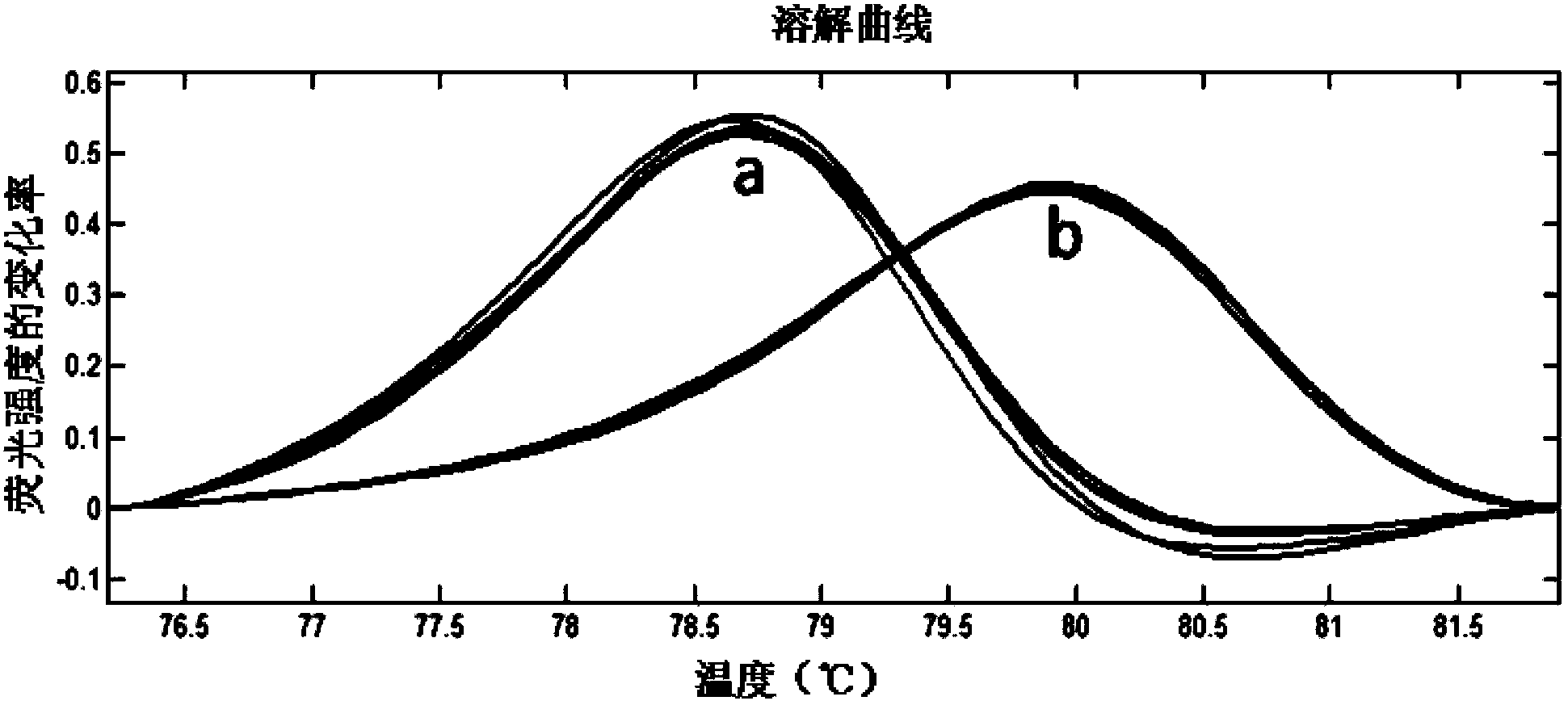
ActiveCN104046683BSimple methodNo cumbersome experimental operations are requiredMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsDNA barcoding
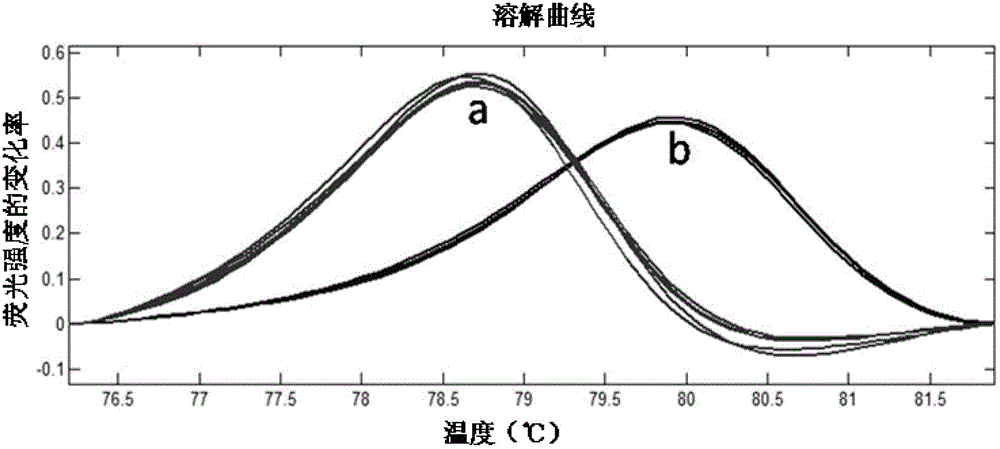
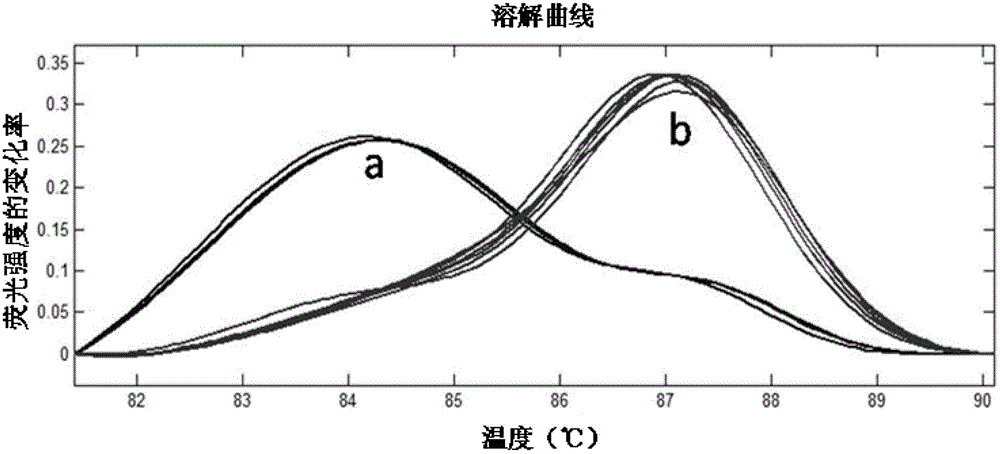
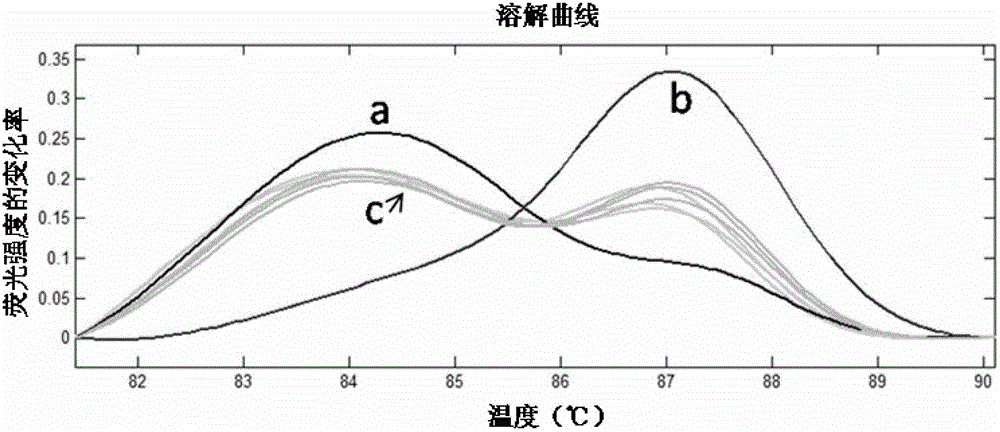
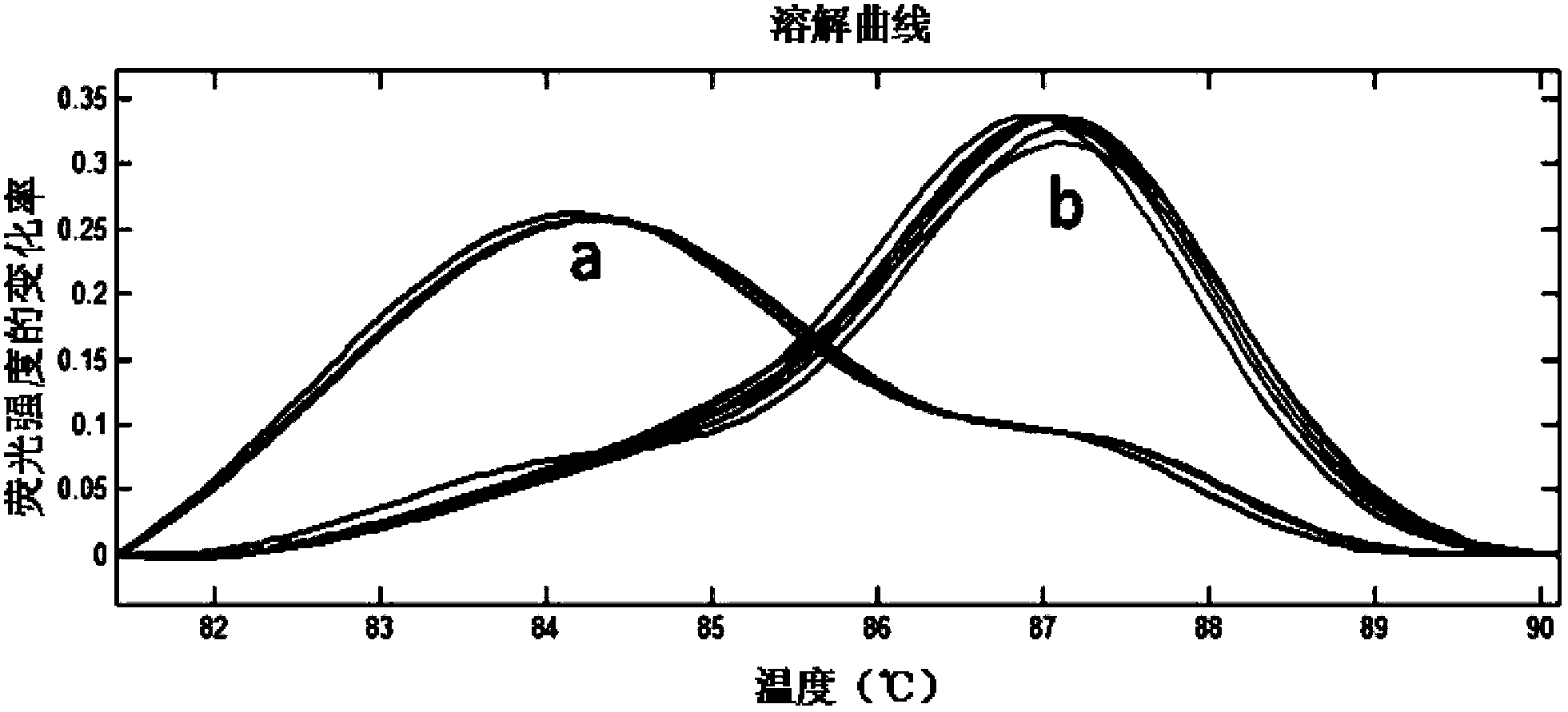
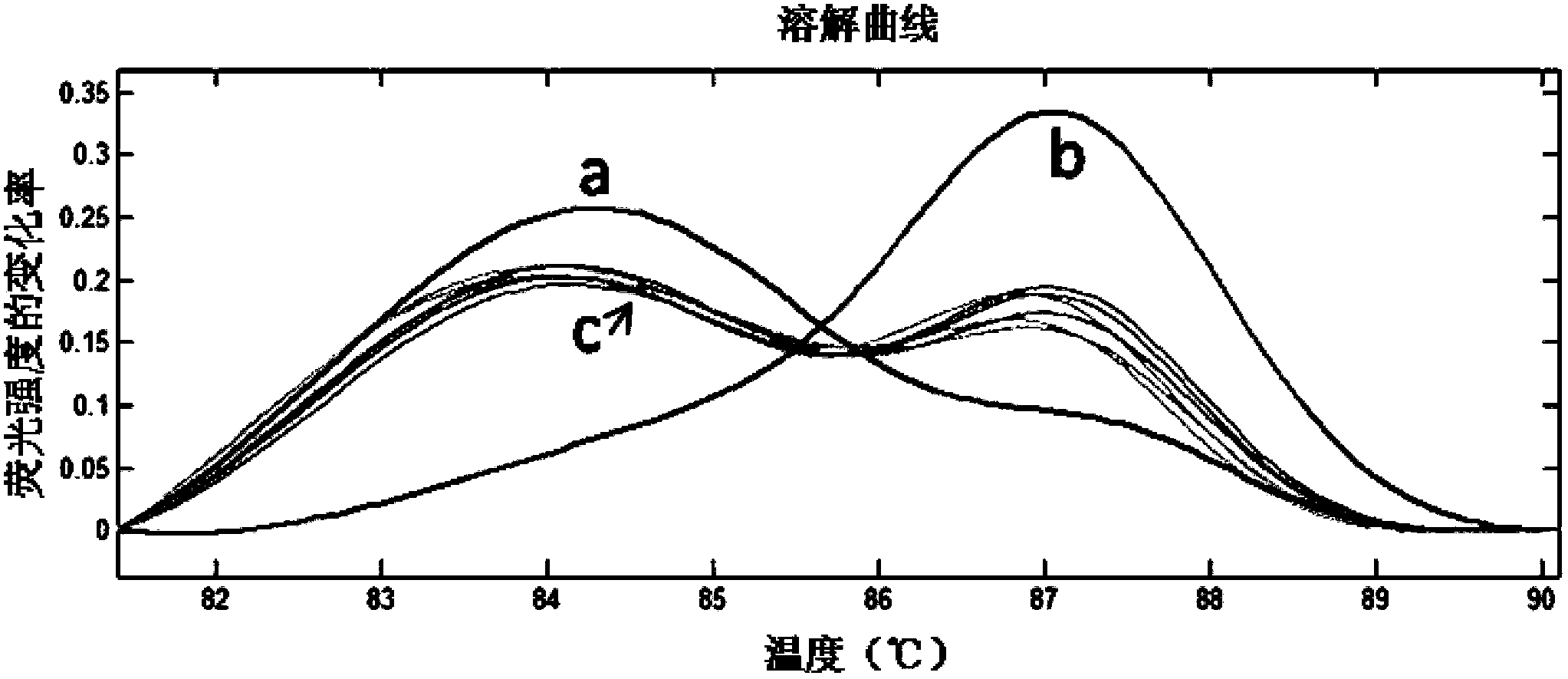
The invention relates to specie discriminating and identification technology and especially relates to a method for discriminating two closely-related species of shellfish or identifying their hybrid generation. Through combination of endonuclear DNA bar code gene PCR amplification technology and high resolution melting (HRM), the method realizes discriminating of closely-related species or identification of their hybrid generation. Through the method, time from sample preparation to result acquisition is a half day and most processes are carried out in a machine without complex experiment operation. Through a dissolving curve showing method, different peak shapes represent different sequence characteristics and thus a visual determination result is obtained. The result obtained by the method is acquired by a genetic material DNA and can be accepted by domestic and international persons in the same industry or experts. A common phenotype identification method for determining specie names and determining if the specie is hybrid generation is accepted by experts difficultly.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Target bar code gene of bar codes of plants in18 species in melilotus miller and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105603095AImprove accuracyAccurate classification and storageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingGermplasm
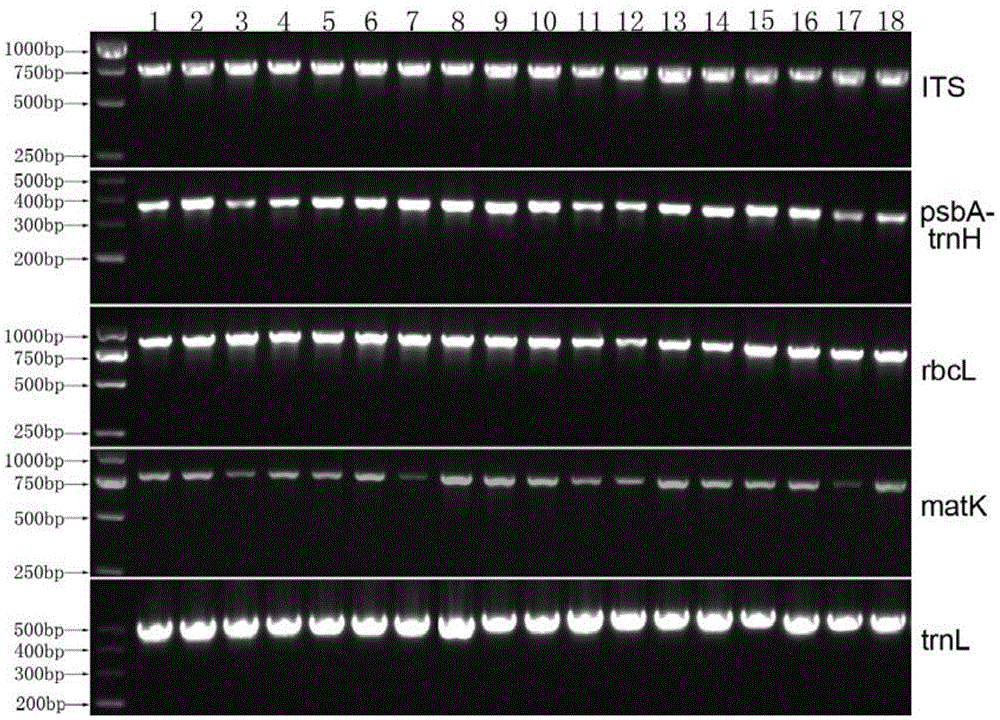
The invention relates to a technology for identifying DNA bar codes of plants in 18 species in melilotus miller and an application method thereof. Five genes of ITS, psbA-trnH, rbcL, matK and trnL are selected and integrated to serve as a target DNA bar code gene for identifying 18 species in melilotus miller. Based on data organization, data editing and analysis methods of ContigExpress, a multi-sequence alignment method of ClustalW, a Neighbor-Joining algorithm based on a minimum evolution principle and a no of difference method, a clustering chart is built, and a basic using method of the technology for identifying the DNA bar codes of plants in 18 species in melilotus miller is formed, and a standard classification bar code gene and a corresponding sequence are determined. By means of the technology, the fast, efficient and high-accuracy method for identifying the DNA bar codes of different species in melilotus miller is built, and the method has great significance in differentiation of various species in melilotus miller and utilization of germplasm resources.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Specific primer pair based on rbcL gene and used for identifying land plant species and application thereof
InactiveCN103305620AGood amplification effectEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a specific primer pair based on a rbcL gene and used for identifying land plant species and an application thereof. The specific primer pair provided by the invention is composed of a single stranded DNA A and a single stranded DNA B, wherein the single stranded DNA A is 15-40bp and comprises a DNA fragment of the DNA fragments as shown by a sequence 1 of a sequence table; and the single stranded DNA B is 15-40bp and comprises a DNA fragment of the DNA fragments as shown by a sequence 2 of the sequence table. The single stranded DNA A can be the DNA fragment as shown by the sequence 1 of the sequence table; and the single stranded DNA B can the DNA fragment as shown by the sequence 2 of the sequence table. The specific primer pair provided by the invention can be used for developing a universal kit, effectively identifying the land plant species and prompting the development and social service of plant DNA bar code.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Oligonucleotide encoded chemical libraries
InactiveUS20190210018A1Preventing and minimizingMinimizing and preventing leakage of fluidMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA barcodingChemical compound
This application provides a bead with a covalently attached chemical compound and a covalently attached DNA barcode and methods for using such beads. The bead has many substantially identical copies of the chemical compound and many substantially identical copies of the DNA barcode. The compound consists of one or more chemical monomers, where the DNA barcode takes the form of barcode modules, where each module corresponds to and allows identification of a corresponding chemical monomer. The nucleic acid barcode can have a concatenated structure or an orthogonal structure. Provided are method for sequencing the bead-bound nucleic acid barcode, for cleaving the compound from the bead, and for assessing biological activity of the released compound.
Owner:PLEXIUM INC
DNA barcoding standard gene sequence of Rizhao Blepharipoda liberata and species identification method based thereon
InactiveCN103937802AFacilitate the realization of molecular identificationAchieve molecular identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMolecular identificationForward primer
Relating to the technical field of species identification, the invention specifically relates to a DNA barcoding standard gene sequence of Rizhao Blepharipoda liberata and species identification method based on the gene sequence. The DNA barcoding standard gene is COI gene, which has a gene sequence shown as SEQIDNO.1. The identification method includes: conducting extraction separation of DNA on a to-be-tested tissue, and amplifying a target gene by polymerase chain reaction. A pair of primers used in the amplification reaction are shown as the following: a forward primer 5'-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG-3', and a reverse primer 5'-TAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAAAAATCA-3'. The gene sequence obtained in the invention is in favor of realizing molecular identification of the Rizhao Blepharipoda liberata, and can effectively shorten the identification time of the Rizhao Blepharipoda liberata.
Owner:刘丰铭
DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood product, and application method thereof
InactiveCN104404131ALarge capacityReduce dependenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA barcodingPhylogenetic tree
The invention discloses a DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and an application method thereof. The technology is as below: constructing a high capacity database through a strategy by merging database of rosewood samples experiment data and a target plant; sequencing a DNA bar code sequence of the rosewood samples; merging the sequencing sequences with homologous sequences published in the Genbank database to construct a rosewood DNA bar code gene database with wide range of data sources; and establishing an algorithm and decision rules for the identification database by using matK+rbcL genes as the target DNA bar code gene for rosewood identification, and using a search tool method of a local alignment algorithm based on frequency, a genetic distance method based on Kimura-2-parameter probability and a phylogenetic tree method based on clustering analysis. The DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and the application method thereof establish an accurate and quick rosewood DNA bar code identification technology.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
Chinese patent medicine biological species constituent component monitoring method based on SMRT (single molecule real-time) sequencing technique
InactiveCN106498050ARealize monitoringMaintain securityMicrobiological testing/measurementOriginal dataDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a Chinese patent medicine biological species constituent component monitoring method based on an SMRT (single molecule real-time) sequencing technique. The Chinese patent medicine biological species constituent component monitoring method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting genome DNA of a sample to be detected; 2) by taking the DNA as a template, amplifying an ITS2 sequence and a psbA-trnH sequence of the DNA; 3) based on a Pacbio RSII sequencing platform, performing library construction on a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) product according to standard operation procedures of the platform, and performing SMRT sequencing; 4) filtering original data by using SMRT Analysis Server 2.3.0 software, obtaining circular-consensus sequencing (CCS) on the basis of the RS_ReadsOfInsert.1 operation procedures, and clustering by using the CCS sequence by using CD-HIT (cluster database at high identity with tolerance) software, so as to obtain an ITS2 sequence and a psbA-trnH sequence for later analysis finally; 5) putting the sequences into a traditional Chinese medicinal material DNA bar code identification system (http: / / www.tcmbarcode.cn / china / ), performing BLAST(basic linear algebra subprograms) comparison, thereby obtaining species identification results. By adopting the method, monitoring on Chinese patent medicine biological species constituent components can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for discriminating two closely-related species of shellfish or identifying their hybrid generation
ActiveCN104046683ASimple methodNo cumbersome experimental operations are requiredMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsDNA barcoding
The invention relates to specie discriminating and identification technology and especially relates to a method for discriminating two closely-related species of shellfish or identifying their hybrid generation. Through combination of endonuclear DNA bar code gene PCR amplification technology and high resolution melting (HRM), the method realizes discriminating of closely-related species or identification of their hybrid generation. Through the method, time from sample preparation to result acquisition is a half day and most processes are carried out in a machine without complex experiment operation. Through a dissolving curve showing method, different peak shapes represent different sequence characteristics and thus a visual determination result is obtained. The result obtained by the method is acquired by a genetic material DNA and can be accepted by domestic and international persons in the same industry or experts. A common phenotype identification method for determining specie names and determining if the specie is hybrid generation is accepted by experts difficultly.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for rapidly discriminating species of cotton
InactiveCN103468672AEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingBarcode
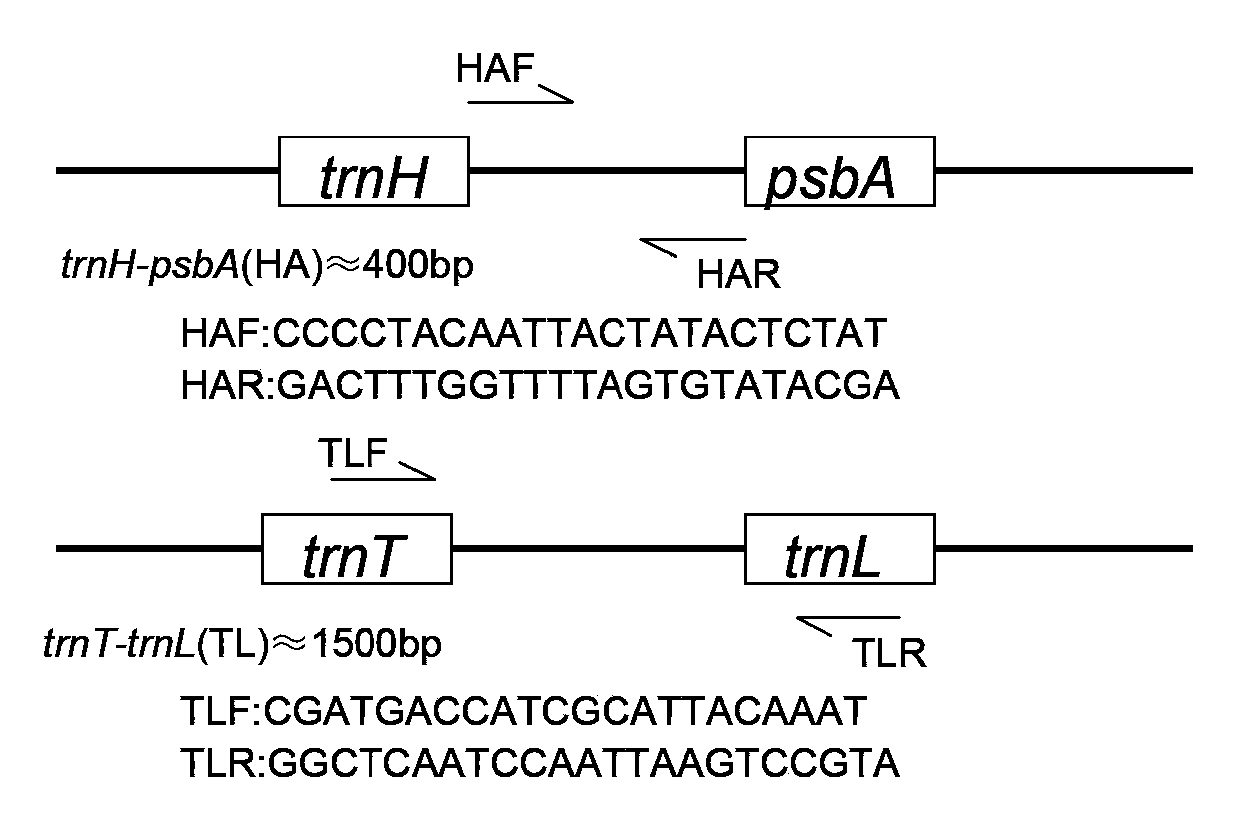
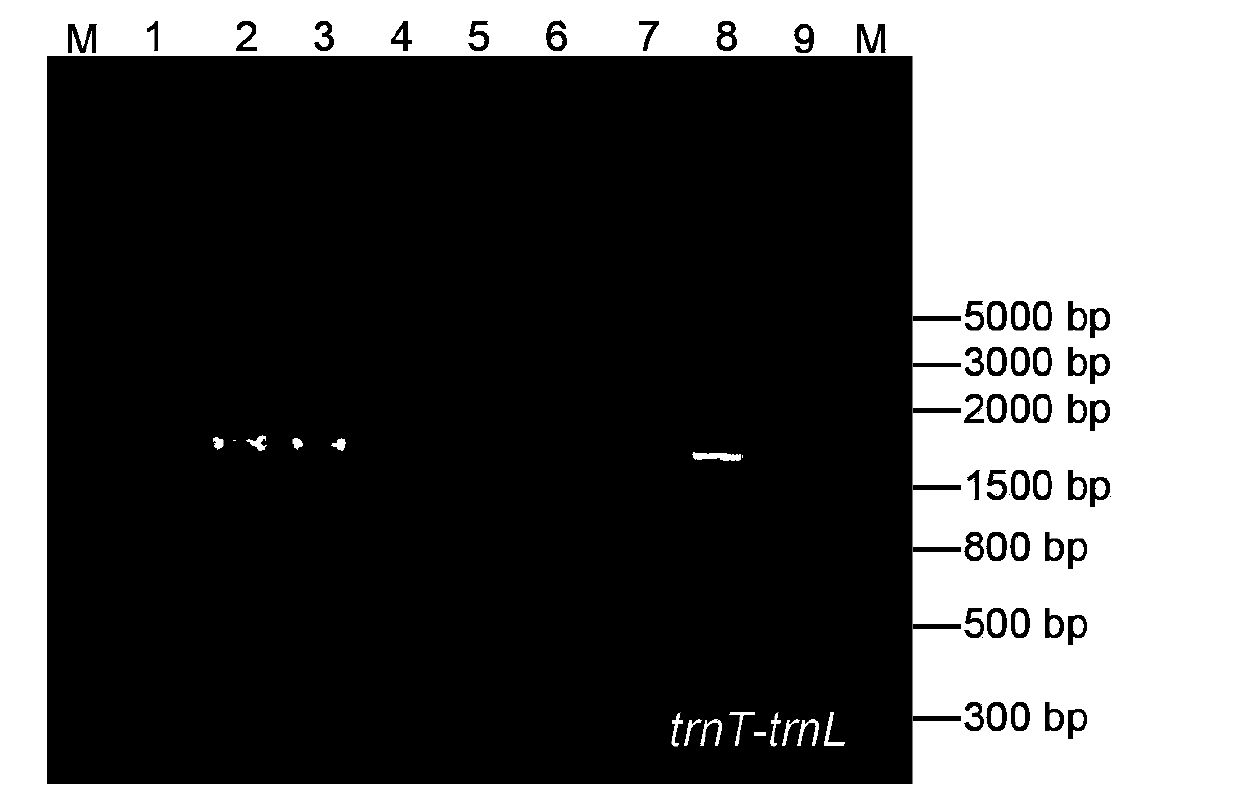
The invention relates to the molecular biology field, and concretely relates to a cotton species DNA barcode and a method for rapidly and accurately identifying the species of cotton. The method comprises the following steps: sampling, carrying out total DNA extraction, carrying out PCR amplification, cloning, sequencing, and carrying out sequence alignment. In the invention, cotton chloroplast genome specific primer pair total DNA is adopted to carry out specific amplification of trnT-trnL and trnH-psbA sequences, so convenience, fastness, no individual extraction of chloroplast DNA are realized; a combination of the trnT-trnL and trnH-psbA sequences adopted as the cotton species DNA barcode has a moderate length, has a high cotton species identification capacity, and can rapidly identifies the cotton species. The method does not rely on traditional identification classification experiences, and has the advantages of simple operation and high accuracy.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
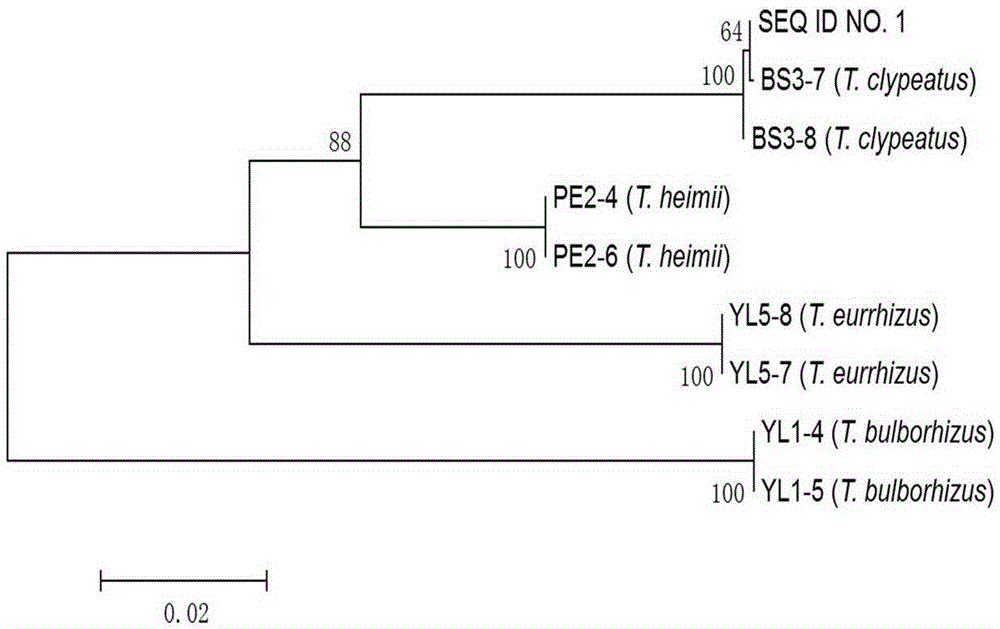
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcode reference gene of termitomyces clypeatus and application of DNA barcode reference gene of termitomyces clypeatus
InactiveCN105238794AEasy to expandEasy to compareMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMolecular identificationReference genes
The invention belongs to the field of fungus species identification and relates to a reference gene for molecular identification of Termitomyces clypeatus and a molecular identification method. Sequences of adopted primers are RPB2B-f: 5'-CCGCAAAGGCTGGTGTATC-3' and RPB2B-r: 5'-TTCGAATGAGTTCAAGTGT-3', and the primers can be used for amplification of large-subunit gene (RPB2) of RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymerase II of the termitomyces clypeatus to obtain a reference detection gene. The termitomyces clypeatus can be quickly and accurately identified according to RPB2 gene DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence differences. The RPB2 gene overcomes the defect of difficulty in identification of traditional termitomyces clypeatus forms and has the advantages of universality and easiness in amplification and comparison, reliability and accuracy in identification are greatly improved, and a powerful research implement is provided for excavation, protection and utilization of genetic resources of the termitomyces clypeatus.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method for identifying composition species of mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder by utilizing denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE)
InactiveCN106191294AMake up for the defect that the mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder cannot be identifiedResolving constituent species identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA barcodingGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to identification of composition species of mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder. A technology comprises the steps of extracting genome DNAs of the mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder, and using a specific primer modified by a specific GC clamp structure to perform polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; causing PCR amplification products to undergo electrophoretic separation and dyeing in denaturant gel, performing denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis to obtain DGGE denaturing gel electrophoresis bands; cutting a single DNA band, recycling DNAs, and performing second round PCR amplification; causing an obtained DNA sequence to undergo sequence splicing and cutting, and submitting the DNA sequence to a public database to perform sequence alignment, and taking highest sequence similarity species as identification results, so as to distinguish species composition of the mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder. According to the method, DNA bar codes and a DGGE technology are combined, the shortcoming that the DNA bar codes cannot be used for identifying the mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder is overcome, and identification of composition species of the mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder or a compound preparation and traditional Chinese medicine adulteration identification are performed effectively. The method has the advantages of being quick, accurate, high in repeatability and low in cost and the like.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN ZHONGZHI PHARMA GRP
Cultivation method of genuine salvia
ActiveCN103828705AIncrease productionHigh content of active ingredientsPlant genotype modificationSalvia miltiorrhizaDNA barcoding
The invention relates to a cultivation method of genuine salvia, which comprises the following steps of: establishment of a salvia germplasm resource garden, selection of representative genuine salvia germplasm resources, identification of genuine salvia genome karyotype structure, determination of genuine salvia DNA bar codes, artificial mutation to obtain autotetraploid, sexual hybridization to obtain triploid salvia permanent hybrids, detoxification treatment, tissue culture seedling cloning and proliferation, bottle seedling transplanting, transplanted seedling management, new species comparison and testing, determination of the medicinal material yield and the main drug effective components, and genuine salvia new species determination and species identification. The genuine salvia obtained in the invention is, so far, the only population that has two great natural advantages: the polyploid advantage and the heterosis, and the advantages are giant and irreplaceable. Therefore, the method of the invention is an effective method for cultivating genuine traditional Chinese medicine with strong biotic stress and abiotic stress capability by using traditional Chinese medicine genuine functional genomes and feature genes and based on inherent genes of genuine traditional Chinese medicine.
Owner:陈瑞阳
Sequence of standard gene of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcode of aedes and application thereof
InactiveCN105039364ARapid identificationShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMolecular identificationDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a sequence of a standard gene of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcode of aedes. The sequence is characterized in that the gene is a CO I (cytochrome oxidase subunit) gene of aedes (verrallina) iriomotensis; the sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table. The invention also discloses an application of the sequence of the standard gene of the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcode of aedes to detection and identification of aedes (verrallina) iriomotensis. The sequence provided by the invention is beneficial to achieving fast identification of aedes (verrallina) iriomotensis and shortening the identification time. An identification method fills in gaps in the field of molecular identification of aedes (verrallina) iriomotensis, is more efficient and convenient than traditional morphological identification methods and has the effects of reducing errors and ensuring that the results have reliability.
Owner:珠海国际旅行卫生保健中心
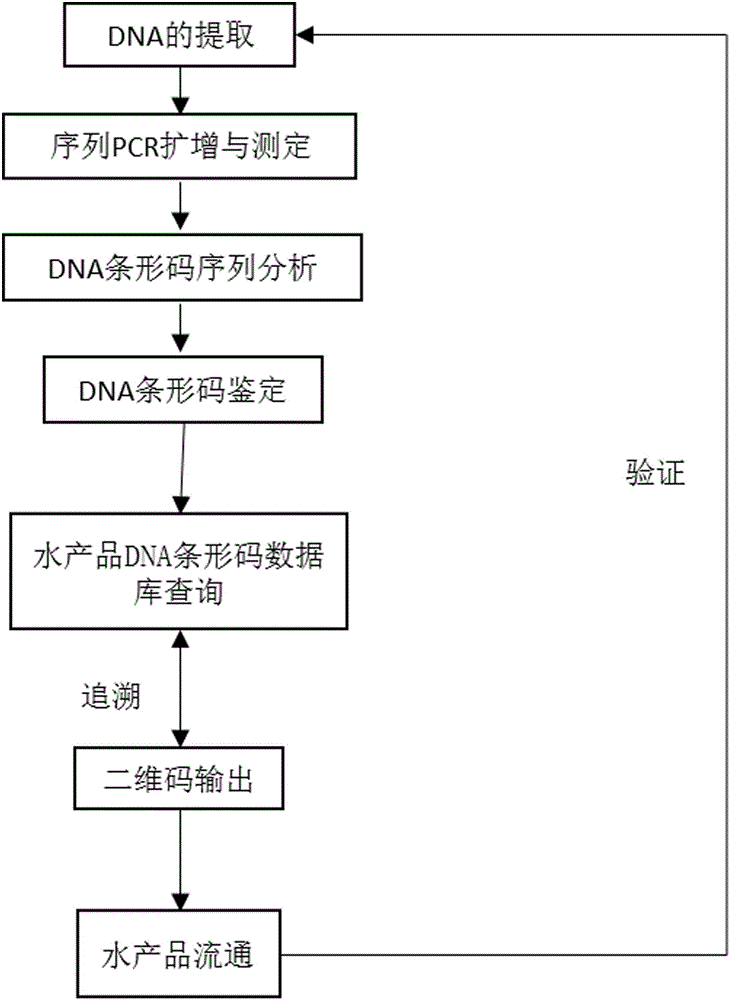
Method and system for supervising fish and quality of raw meat product of fish based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code technique
InactiveCN106282380AAccurate identificationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationDNA barcoding
The invention relates to a method and a system for supervising fish and quality of a raw meat product of the fish based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code technique and a system. The method includes the steps: (1) extracting DNA of the fish and raw meat product of the fish, and acquiring molecular bar code sequences, namely, mitochondrion COI homologous sequences; (2) performing species identification by a DNA bar code database, converting molecular identification results and product information into a two-dimensional code image, and pasting the two-dimensional code image on the surface of a package; (3) acquiring information such as production places, kinds, processing records and product detection by a consumer by scanning a single two-dimensional code of a commodity through intelligent devices in the circulation process of the fish and raw meat product of the fish. According to the method, automatically supervising of fish products in commercial circulation is achieved by the aid of molecular biology bar code and two-dimensional bar code technology.
Owner:CHINESE STURGEON RES INST CHINA THREE GOR
Method for identifying tea tree variety by using DNA bar code
InactiveCN104946745AAccurate identificationSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementStainingDNA barcoding
The present invention relates to a tea tree variety identifying method, specifically to a method for identifying the tea tree variety by using DNA bar code. The method comprises: respectively extracting DNA from a plurality of tea tree varieties; screening SSR primers; respectively preparing PCR reagents from the plurality of the extracted NDA, and carrying out reaction amplification; carrying out gel electrophoresis on each PCR reaction product, staining, and shooting and recording by using a gel imager; and combining the letters corresponding to the variety conversion on the SSR primers to form the DNA bar code. According to the present invention, the molecular marker technology is utilized, the method for identifying the tea tree variety by using the DNA bar code is established through the technical combination of genome DNA extraction, labeling screening, PCR amplification, product analysis, stripe data reading, letter bar code establishing and the like, and compared with the traditional morphology identifying method, the method of the present invention has the following characteristics that: the method is not affected by the environmental conditions, the method is simple, rapid and accurate, and the accurate identifying can be performed on the tea variety authenticity.
Owner:湖南省茶叶研究所
DNA barcoding standard detection sequence for acrossocheilus beijiangensis and applications of DNA barcoding standard detection sequence
InactiveCN105986021AAccurate identificationShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMolecular identificationDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a DNA barcoding standard detection sequence for acrossocheilus beijiangensis, which is shown as SEQ ID NO;1, and a molecular identification method based on the standard detection sequence. Due to the application of the DNA barcoding standard detection sequence for acrossocheilus beijiangensis provided by the invention, the reliable DNA molecular identification technology for the incomplete individuals which can not be accurately identified and for the complete individuals in samples is realized, therefore, the technical defect that in the prior art, the incomplete individuals basically can not be identified, and the complete individuals need to be identified by the professionals who are very familiar to the morphological traits of acrossocheilus beijiangensis is overcome, and compared with the traditional morphological identification method, the DNA barcoding standard detection sequence provided by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately identifying acrossocheilus beijiangensis.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
DNA bar code primer pair, kit and method for identifying Taxus chinensis species
InactiveCN105177151AEfficient identificationRich genetic variationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA bar code primer pair, kit and method for identifying Taxus chinensis species. The kit comprises the following DNA bar code primer pair including an upstream primer Taxus Indel-F(SEQ ID NO.1) and a downstream primer Taxus Indel-R(SEQ ID NO.2). DNA bar codes include the Taxus chinensis DNA bar code, the Taxus chinensis var.mairei DNA bar code, the Taxus cuspidata DNA bar code, and the Taxus baccata DNA bar code, wherein the sequence of the Taxus chinensis DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.3 to SEQ ID NO.6, the sequence of the Taxus chinensis var.mairei DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.7 to SEQ ID NO.8, the sequence of the Taxus cuspidata DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.9, and the sequence of the Taxus baccata DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.10. The kit and the identifying method are simple, easy to implement and capable of being effectively used for Taxus species identification, protection and related research, and results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
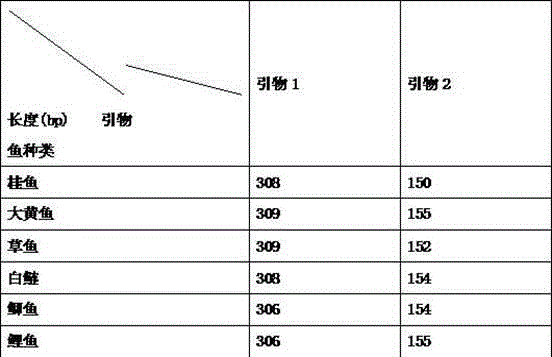
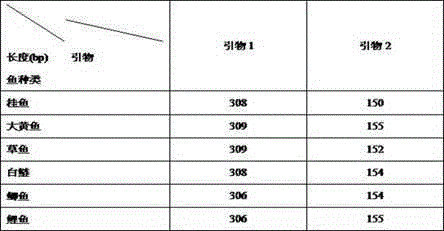
Six common fish identification kits based on DNA Barcoding
The invention discloses an identification method of six common fishes (mandarin fish, large yellow croaker, grass carp, silver carp, crucian and carp). The six common fishes and raw fish products thereof are identified by comparing the lengths of base sequences compiled. The method is established based on DNA Barcoding and is not limited by shape of the identified material. Even if the individual is a tissue fragment, an accurate result can be obtained. Therefore, the kit can be widely applied to accurately identifying fishes and raw fish products thereof.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Sinilabeo rendahli DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code standard detection gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105483227AAccurate identificationIdentification is conducive to the realizationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMolecular identificationNucleotide
The invention discloses a sinilabeo rendahli DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code standard detection gene and application thereof. The DNA bar code standard detection gene is of a COI gene of which a nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.1. A sinilabeo rendahli DNA bar code species identification method disclosed by the invention adopts a reliable DNA molecular identification technology, and the sinilabeo rendahli is rapidly and accurately indentified. Compared with a traditional morphological identification method, the standard detection gene sequence obtained by the method is conducive to realizing the molecular identification of the sinilabeo rendahli, and can effectively shorten the identification time.
Owner:深圳华大海洋科技有限公司
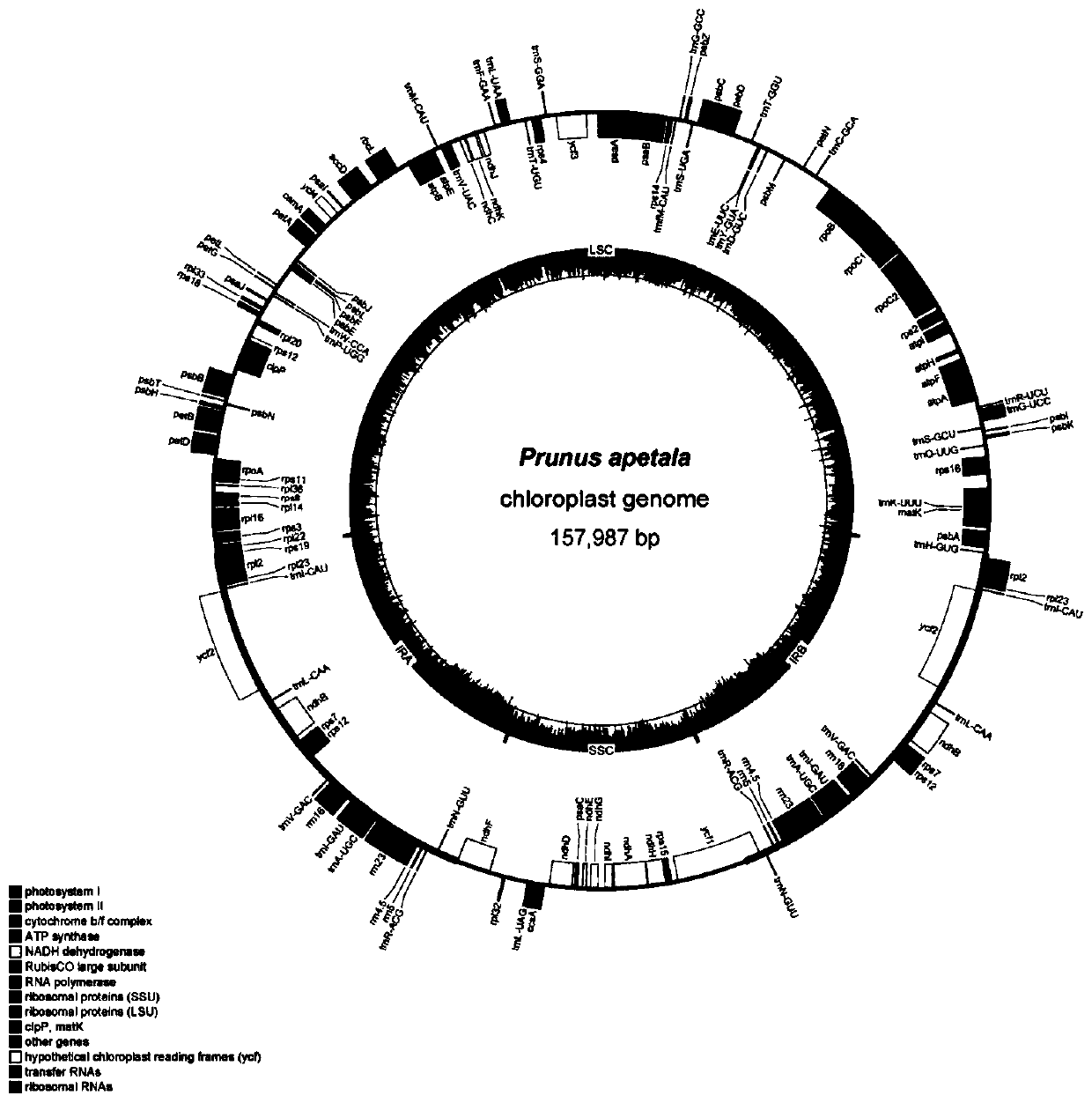
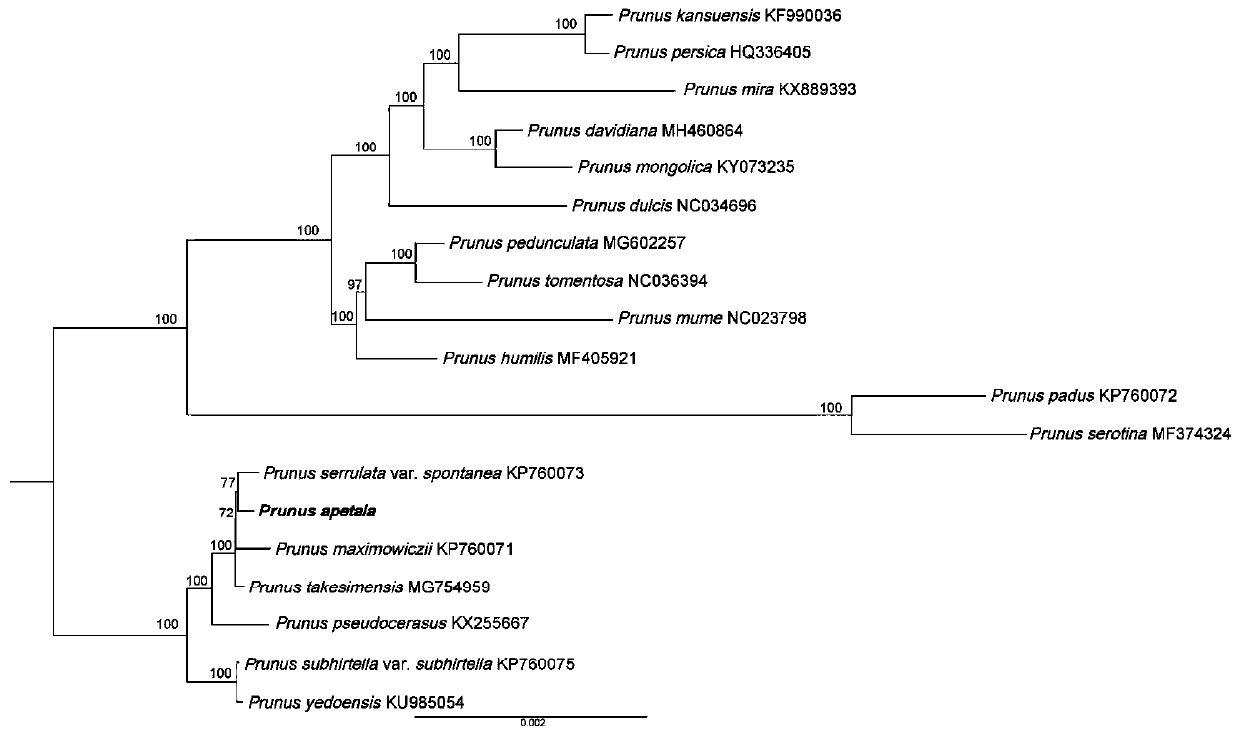
Prunus apetala chloroplast genome and application thereof
The invention discloses a prunus apetala chloroplast genome for the first time. The prunus apetala chloroplast genome is applied to a phylogenetic study of prunus apetala, and a phylogenetic status of the prunus apetala in prunus is analyzed. A phylogenetic relationship of a prunus subgenus species is established through the prunus apetala chloroplast genome by methods of molecular systematics and phylogenetic genomics; on the basis, the whole chloroplast genome is used as a super DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code of a prunus subgenus for identifying an oriental cherry variety; a technical support is provided for protection of an oriental cherry germplasm resource and species identification; and the chloroplast genome has an important significance for evaluation, protection and utilization of seed breeding and genetic diversity of a typical prunus subgenus plant.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com