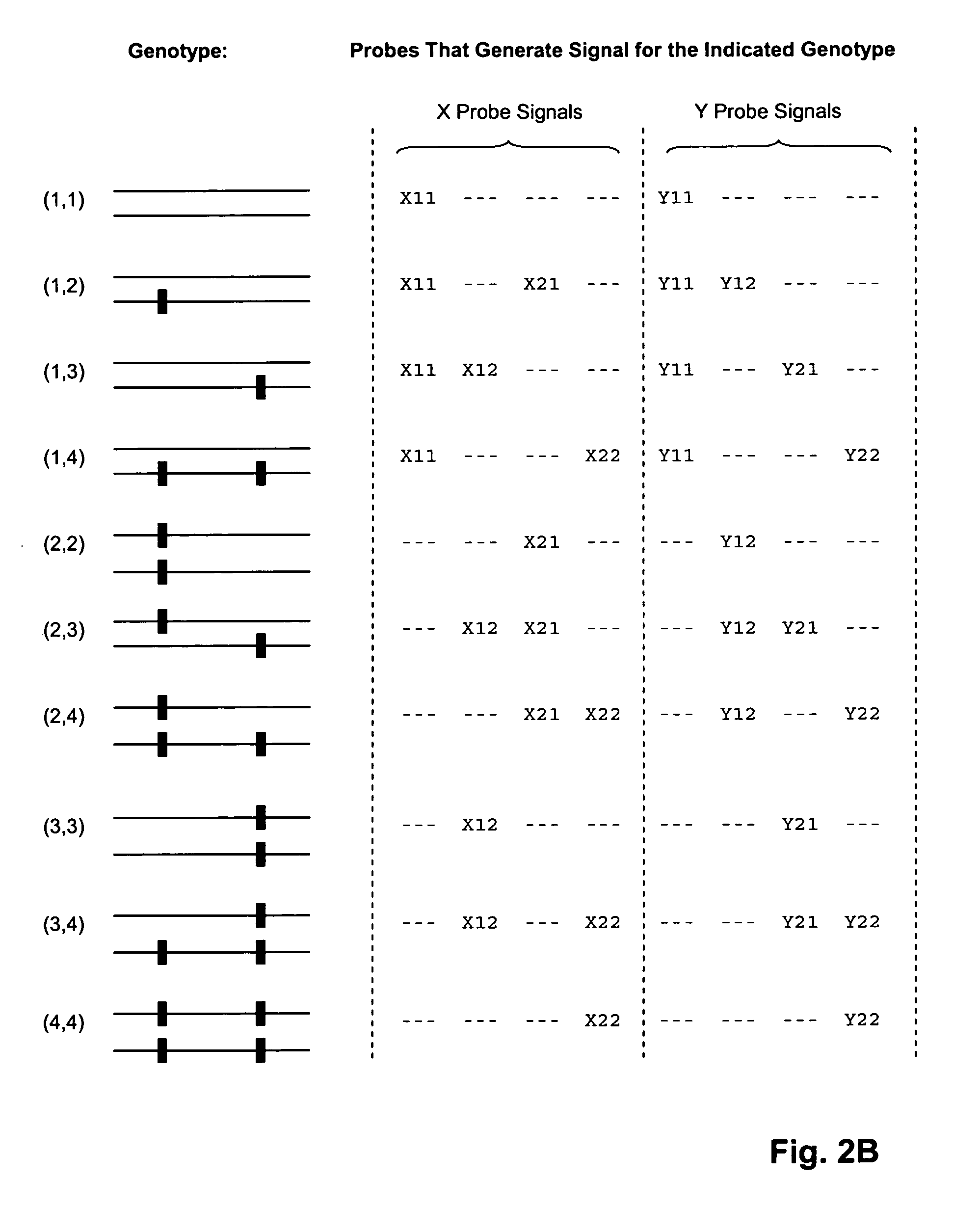
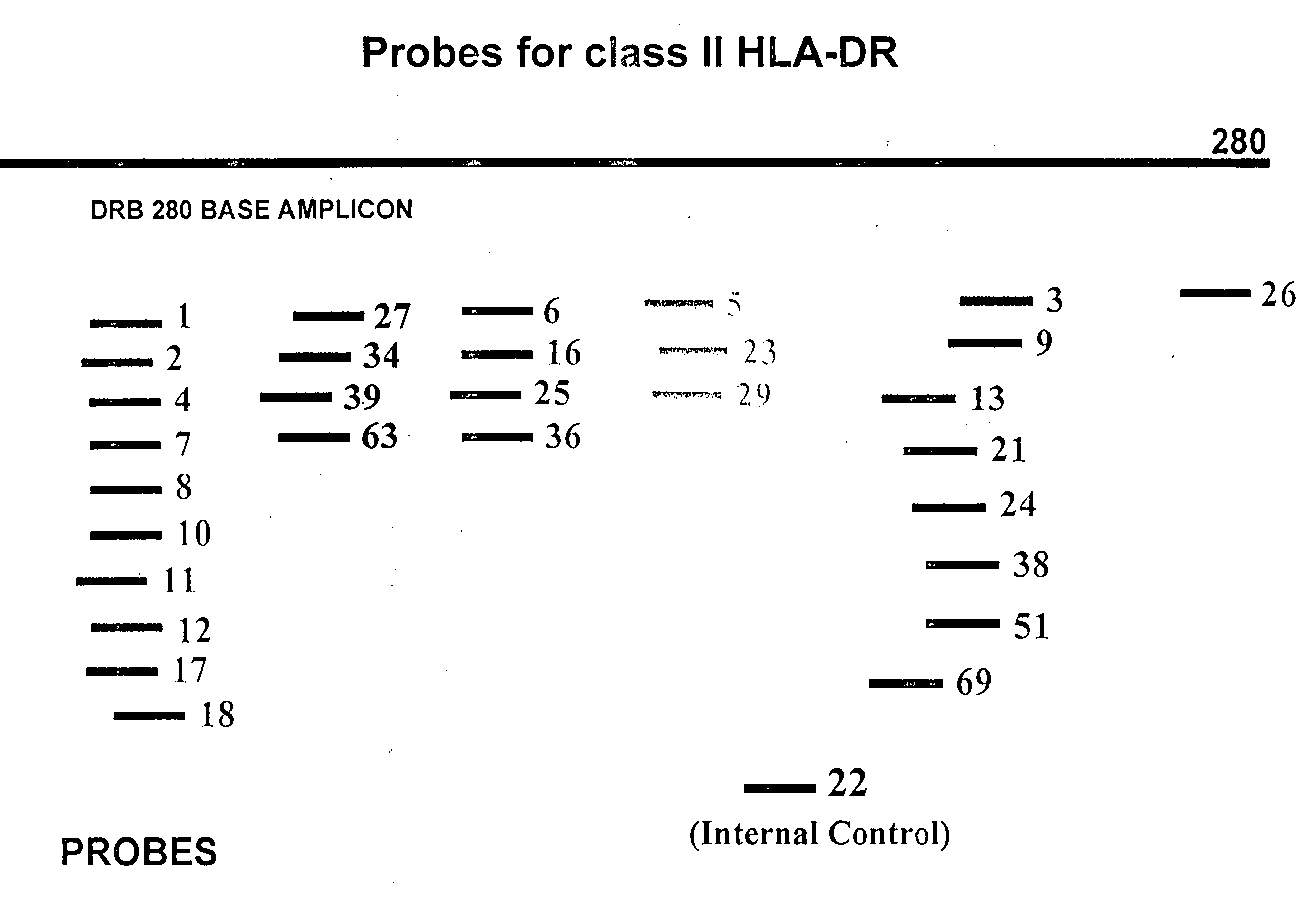
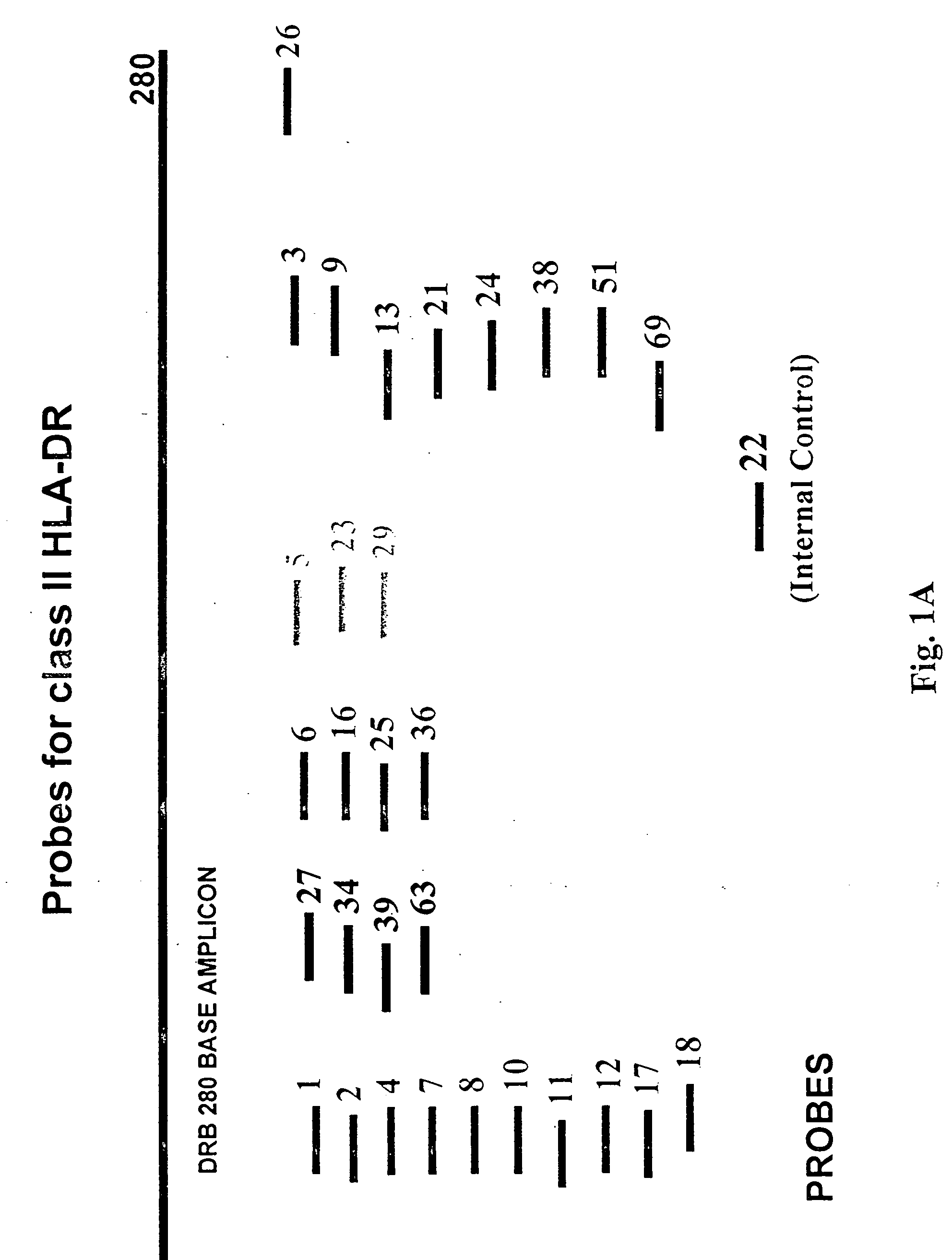
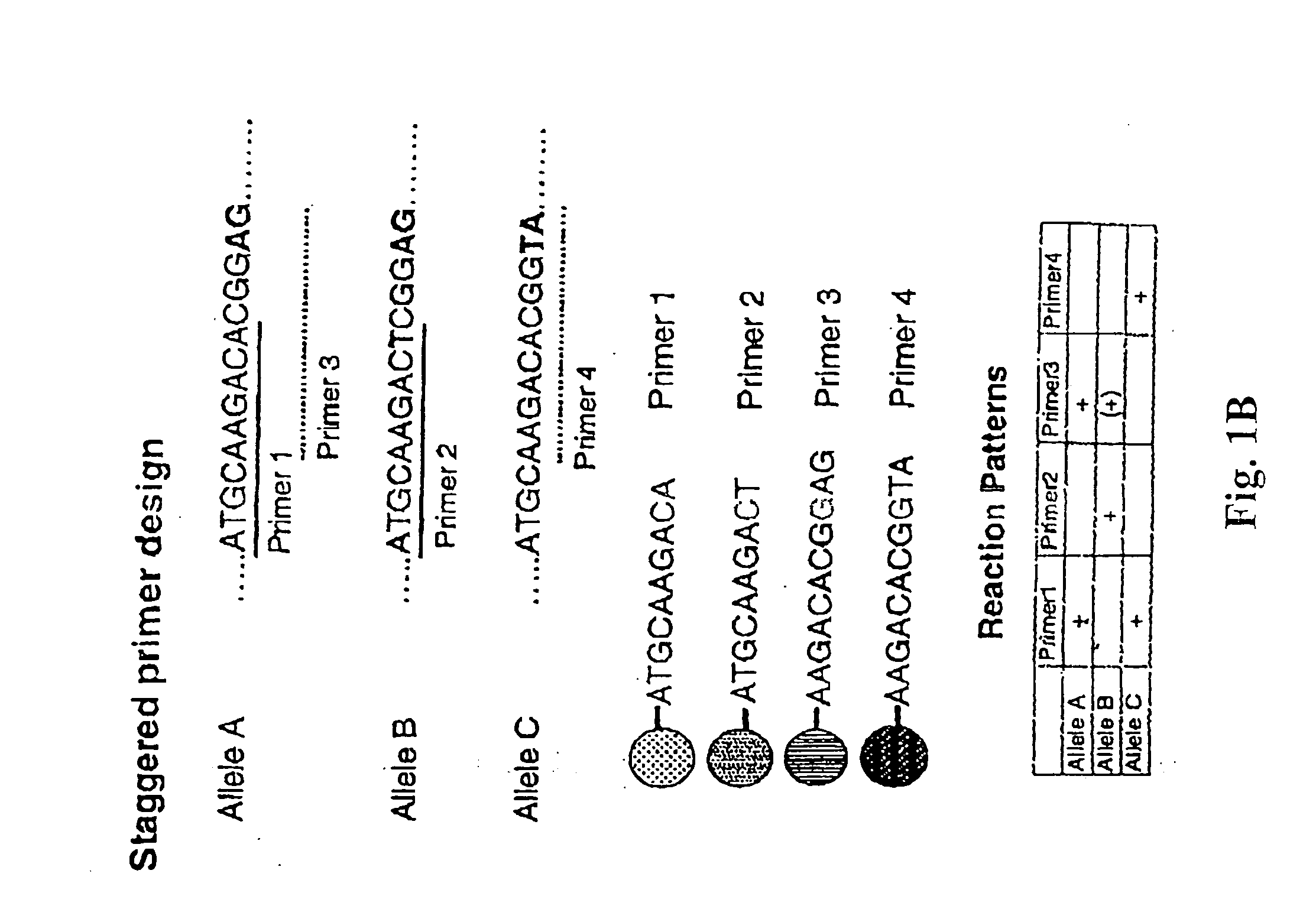
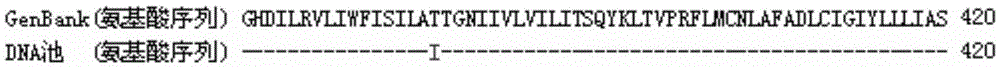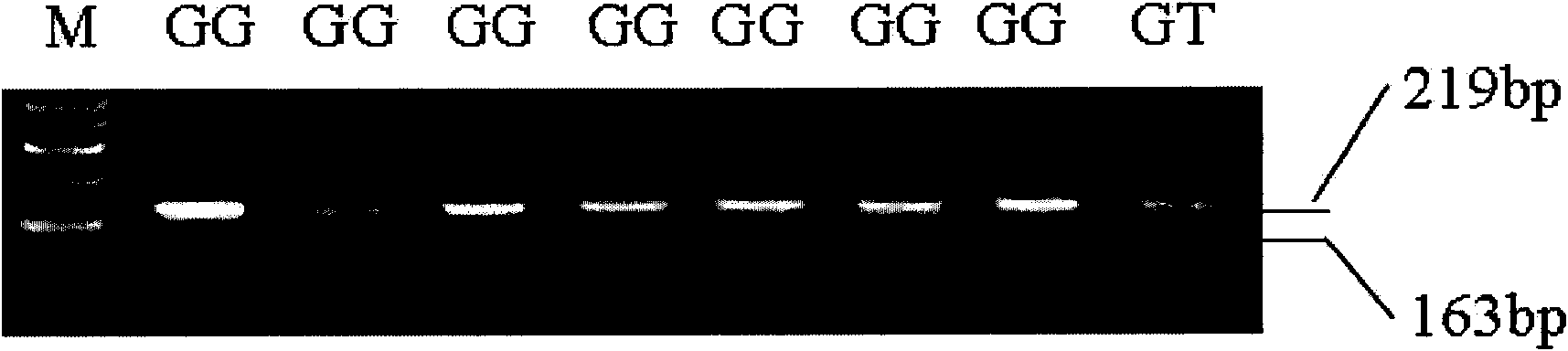Patents
Literature
166 results about "Polymorphic locus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
, B.S in Zoology with Entomology Minor. A polymorphic loci has 2 or more alleles. This allows for multiple possible genotypes and phenotypes depending on whether one of the alleles are dominant, how complete the dominance is, etc.
Analysis of genetic polymorphisms and gene copy number
InactiveUS6468744B1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsCytochrome P450Drug biotransformation
The invention provides methods for detecting variations in polymorphic sites and / or variations in gene copy number. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of biotransformation genes, such as cytochromes P450.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
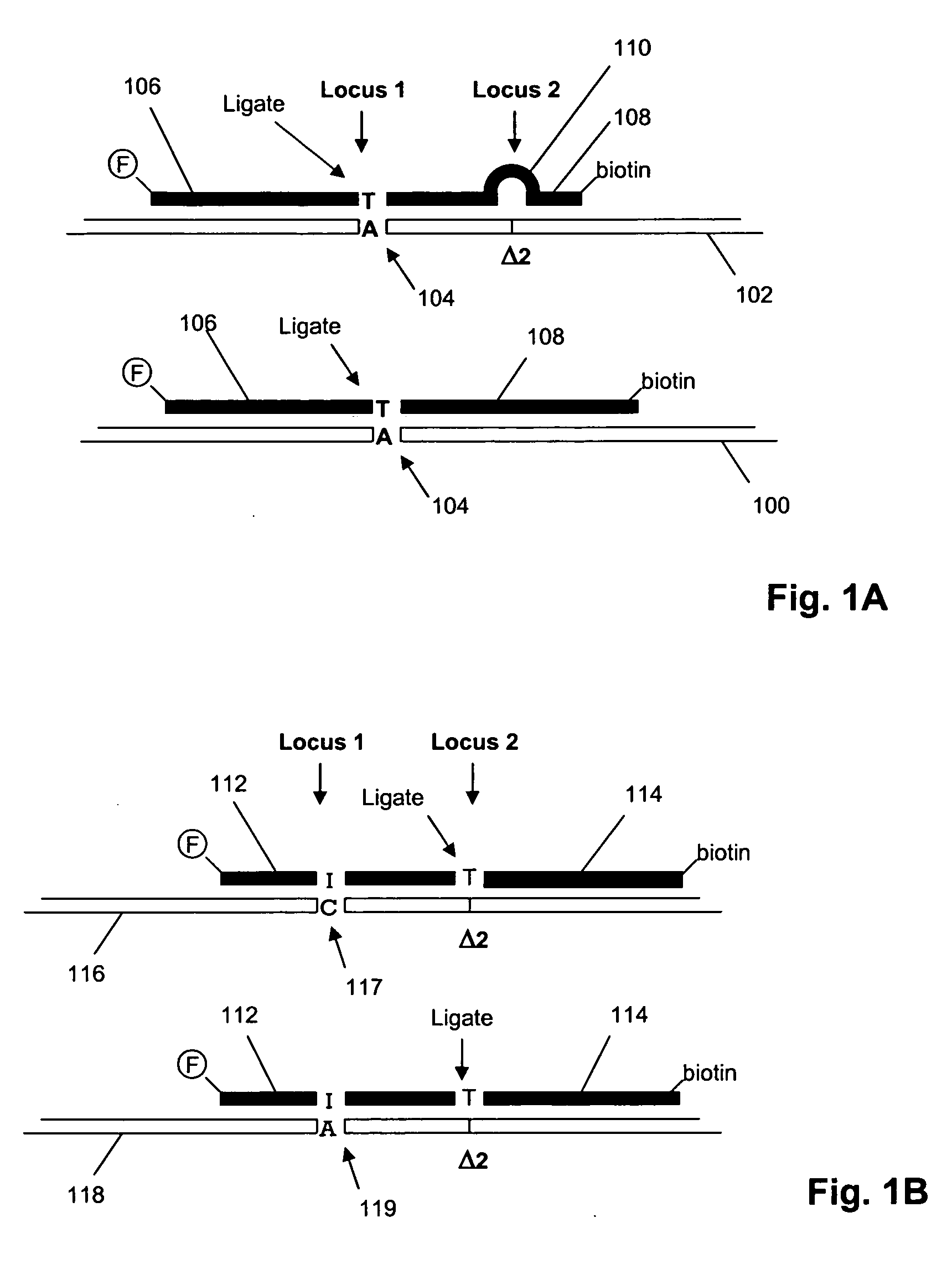
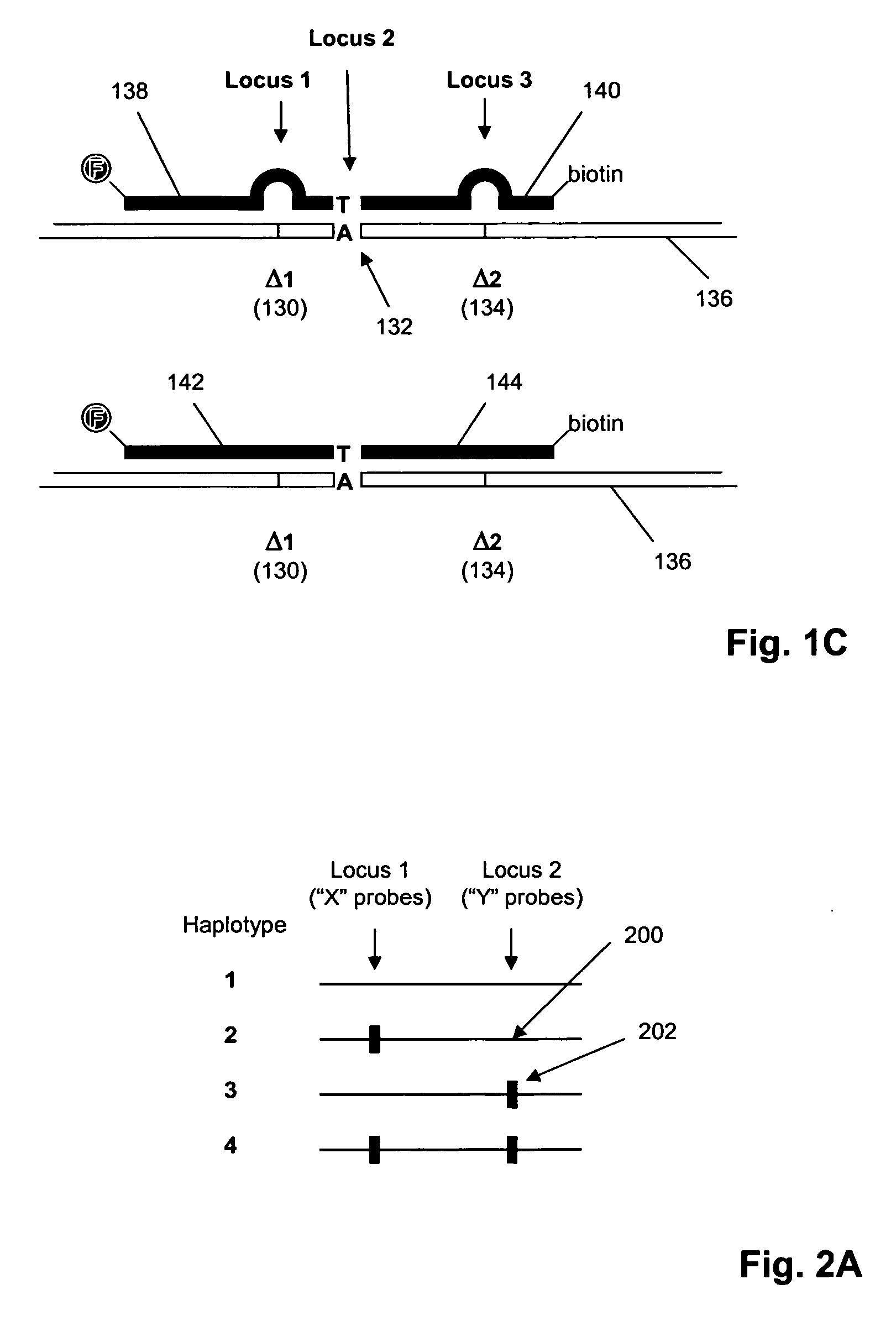
Methods for determining genetic haplotypes and DNA mapping
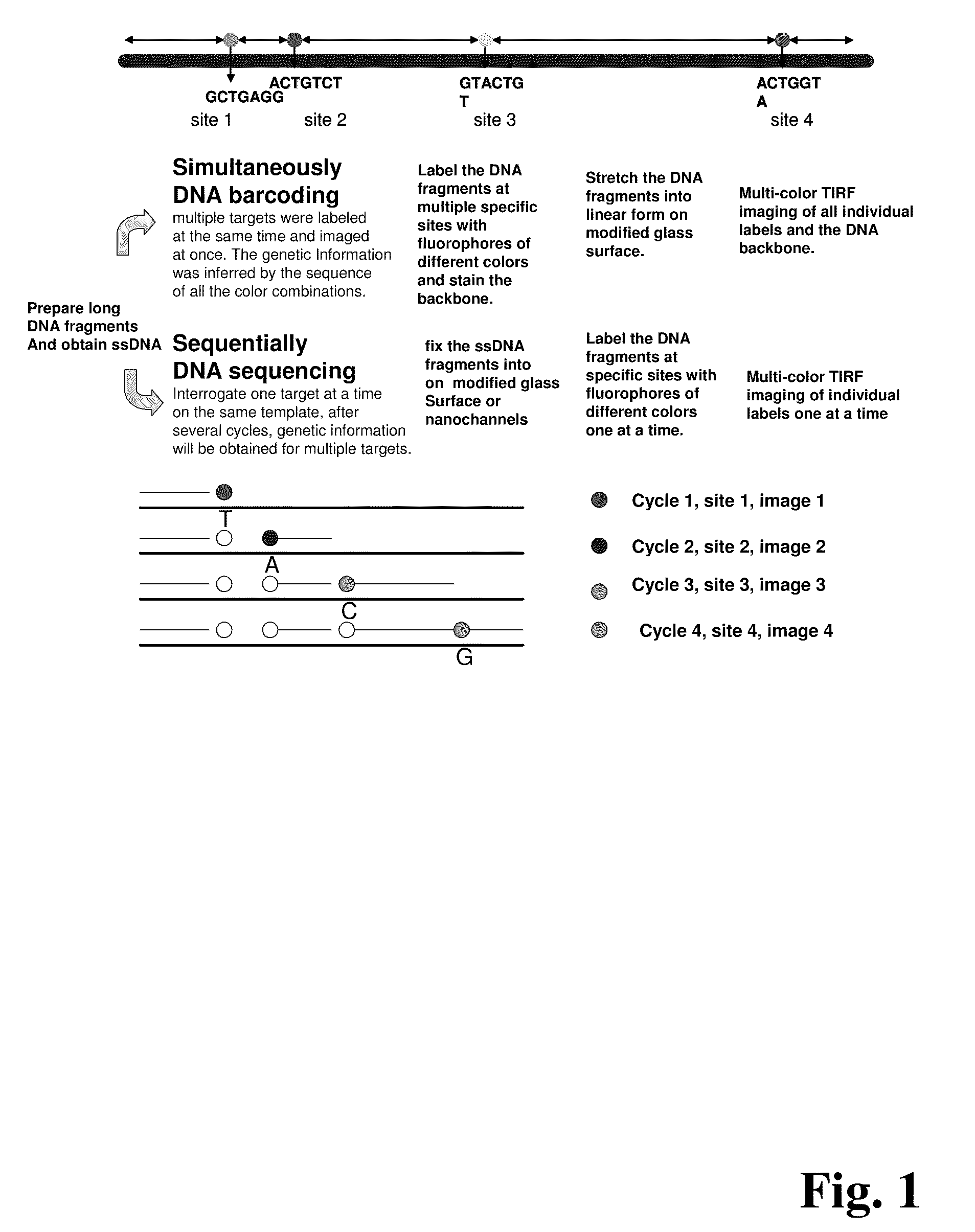
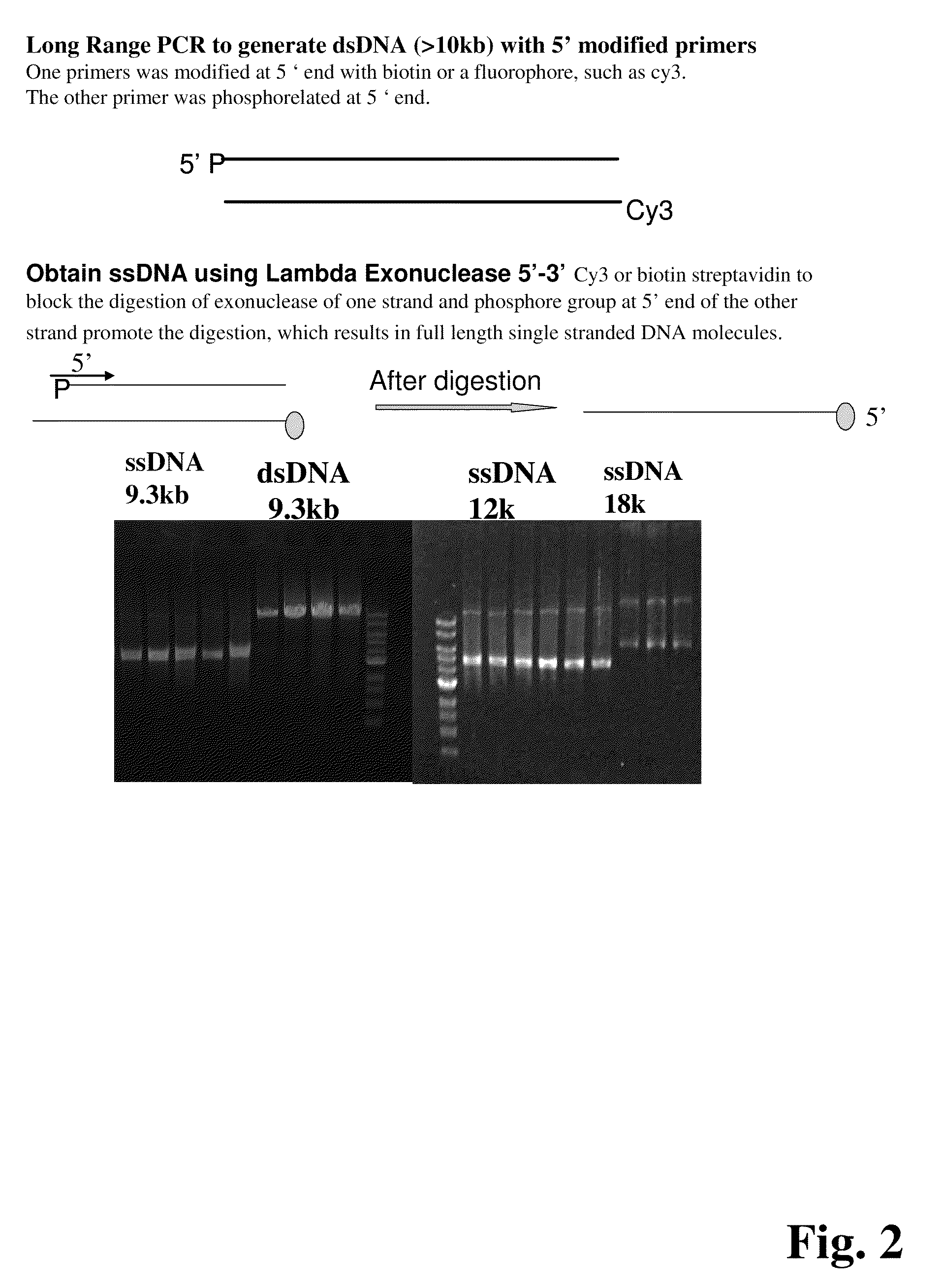
ActiveUS20090155780A1Improve labeling efficiencyStable labelingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDirect imagingDNA barcoding
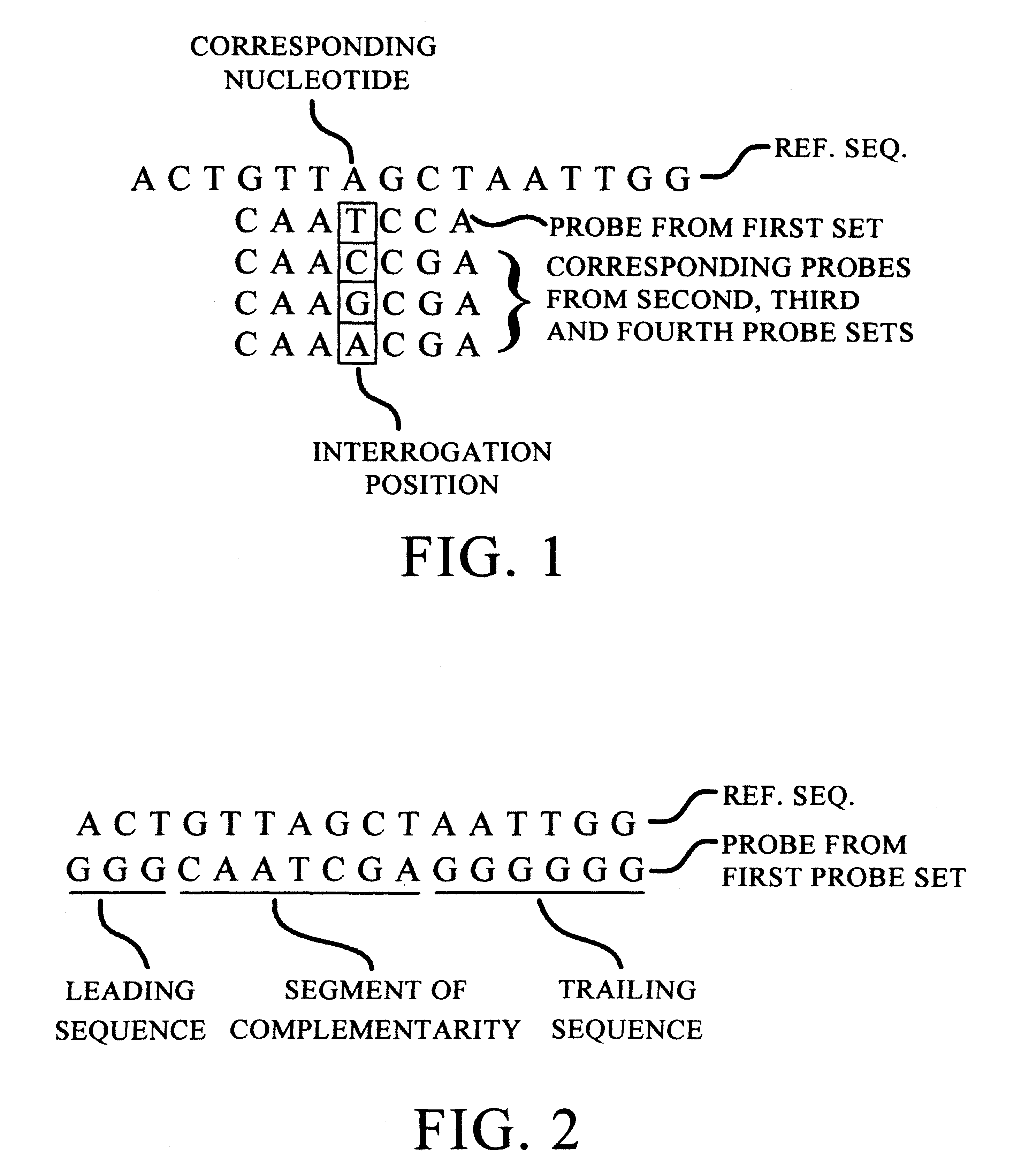
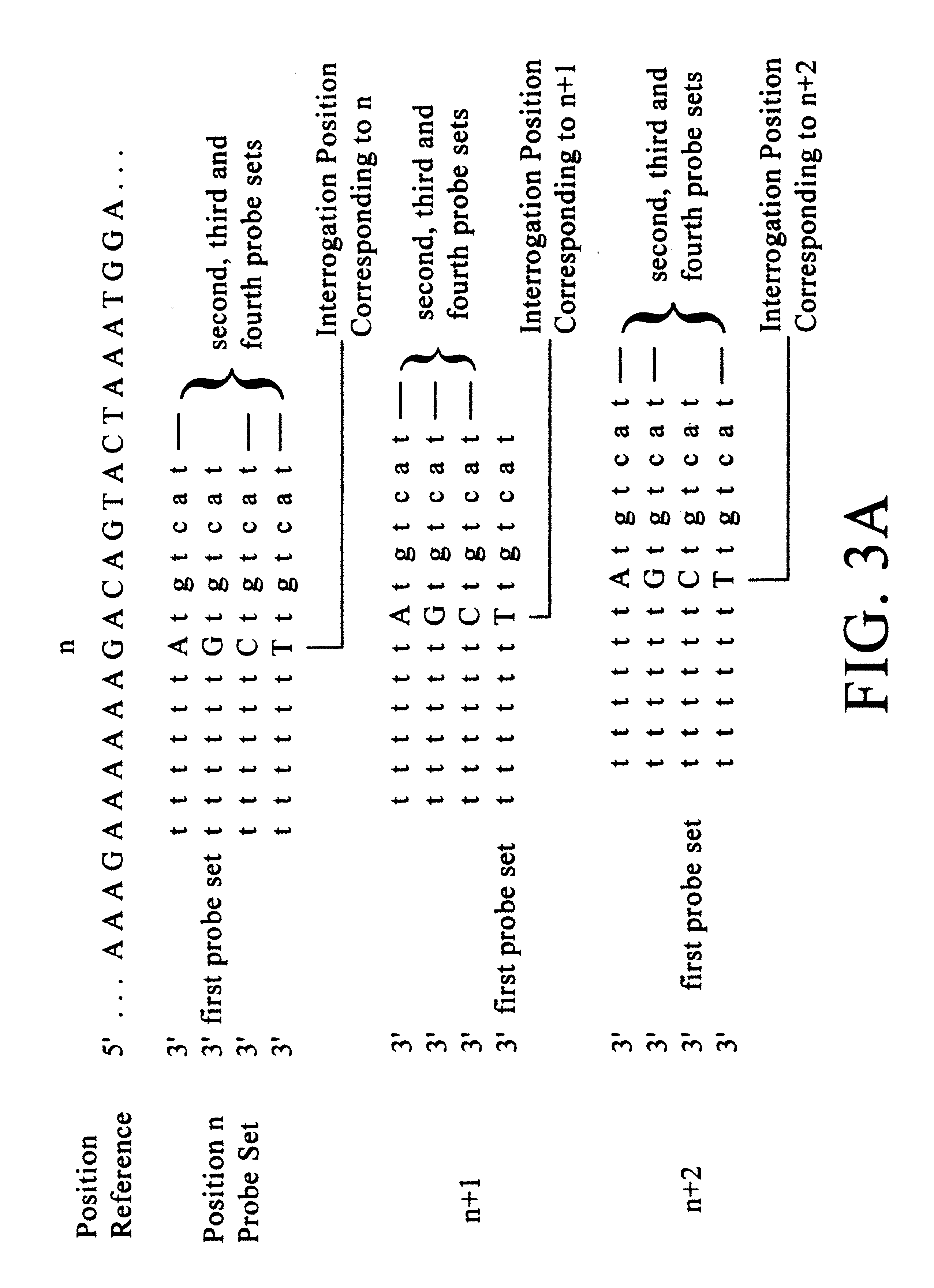
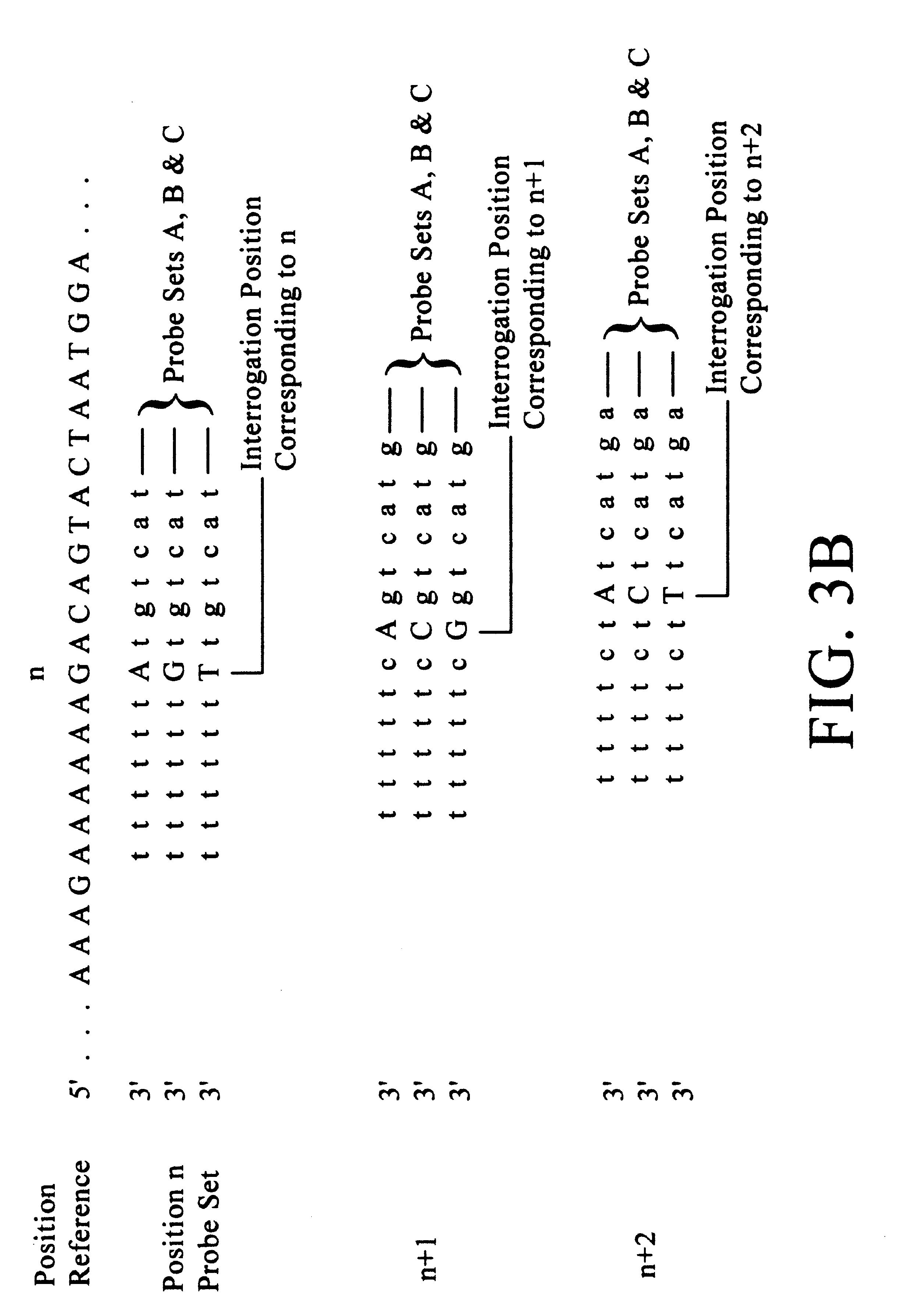
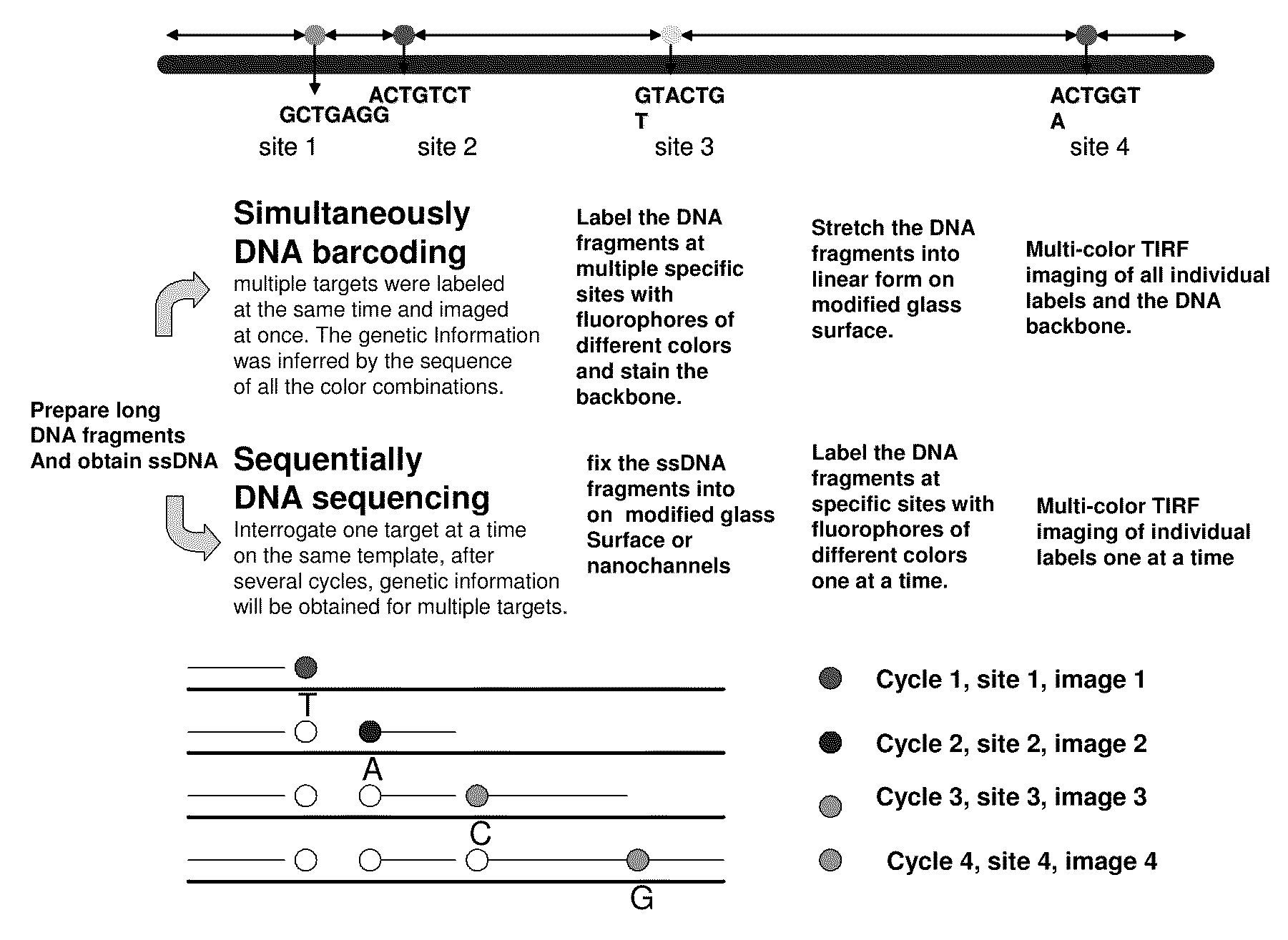
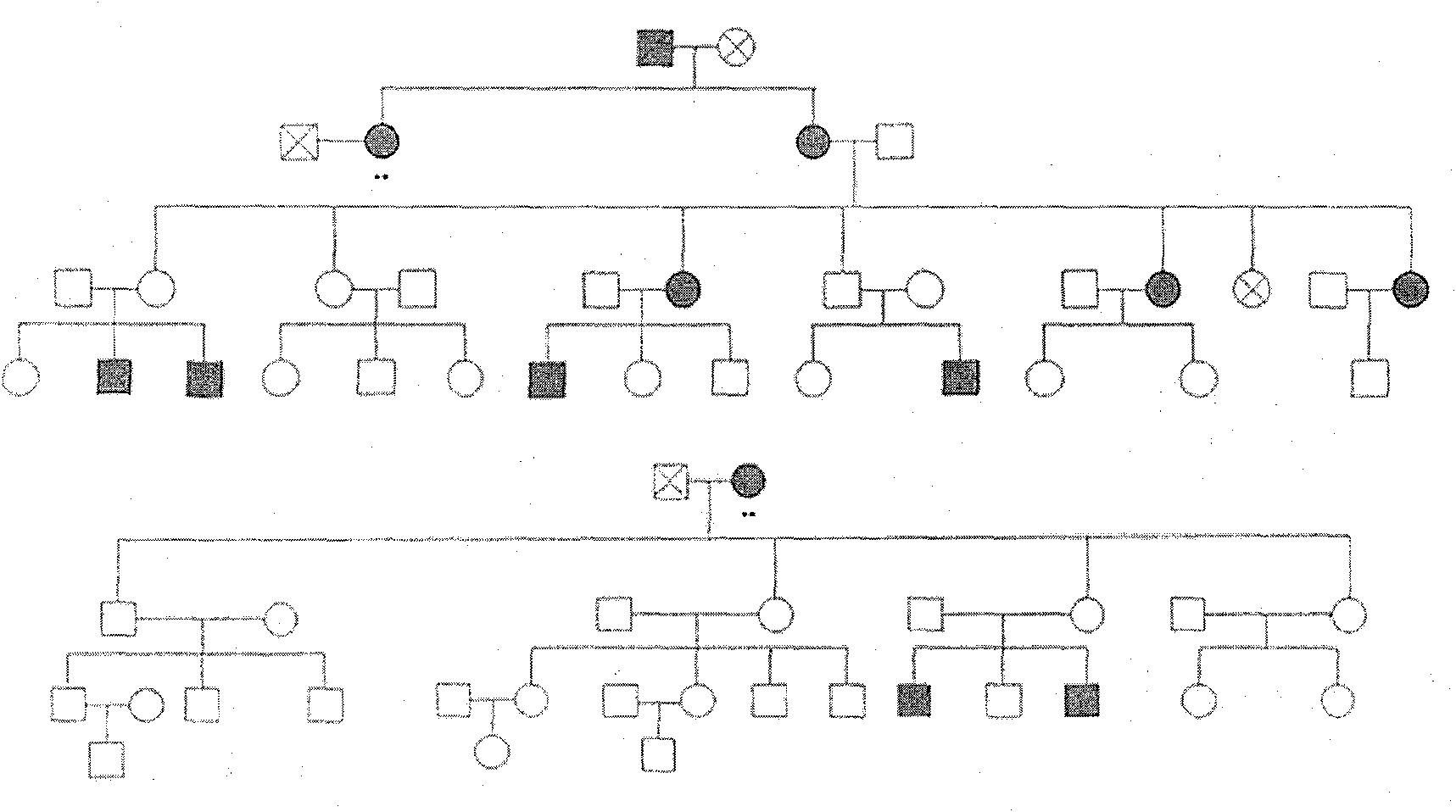
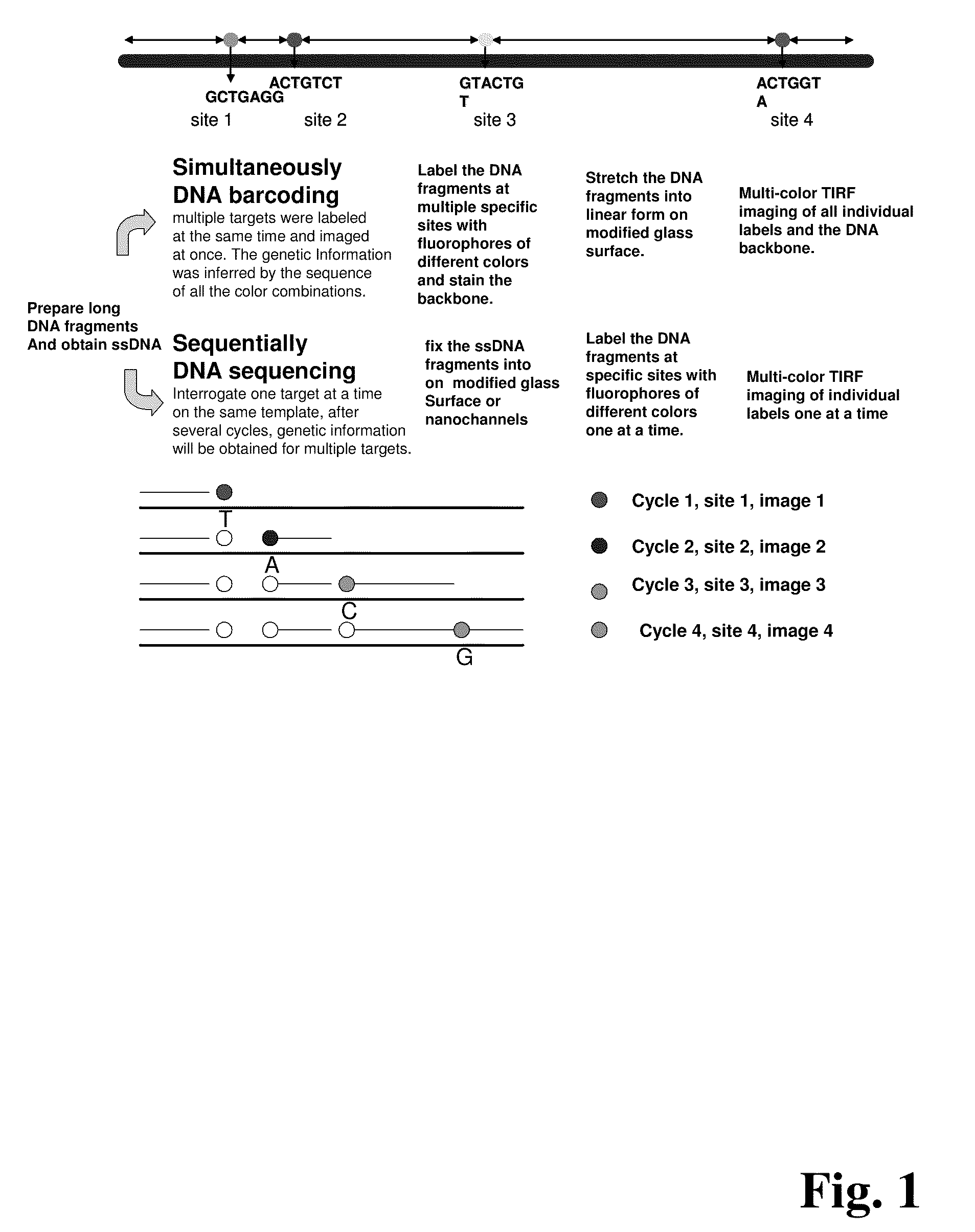
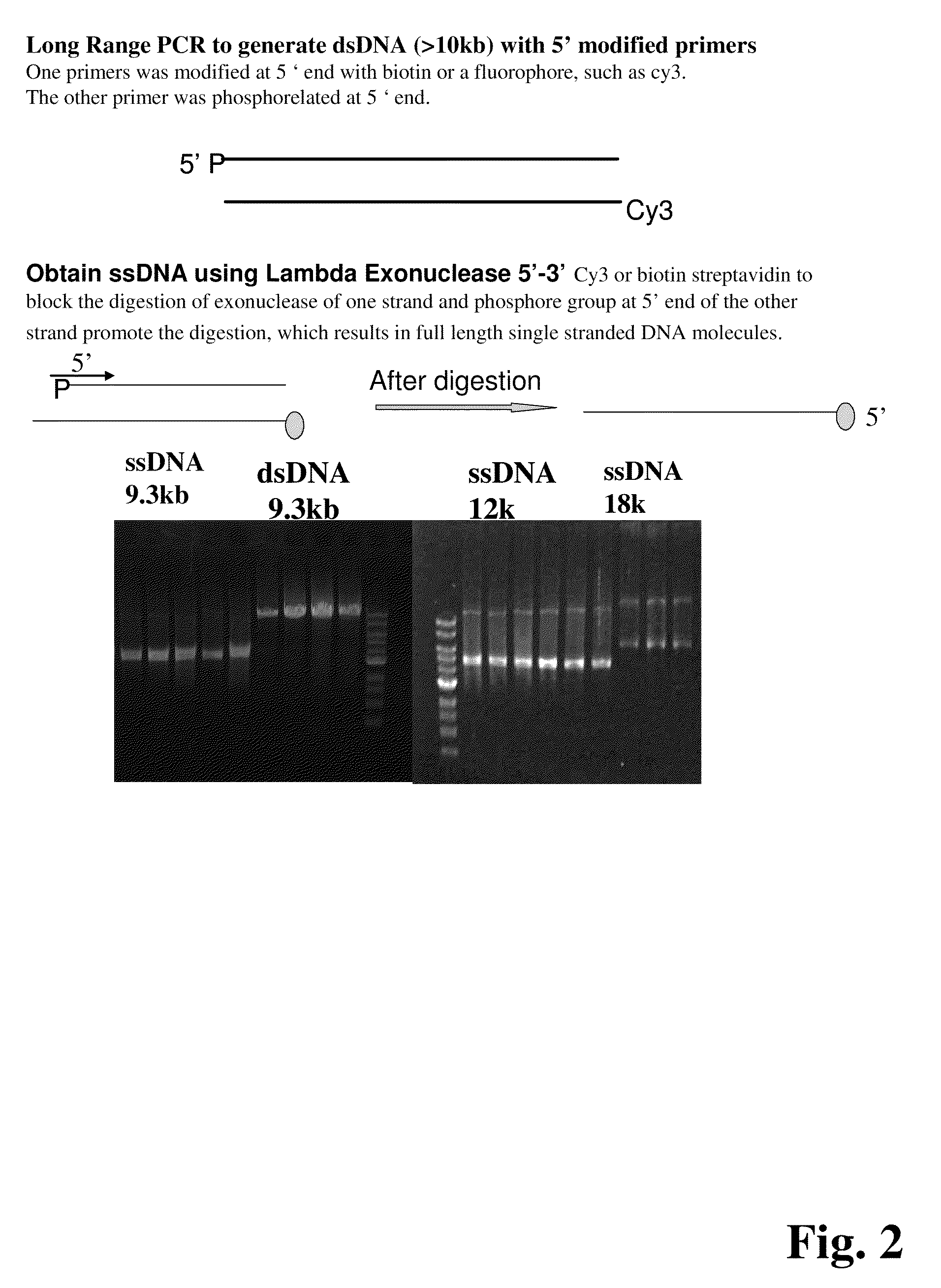
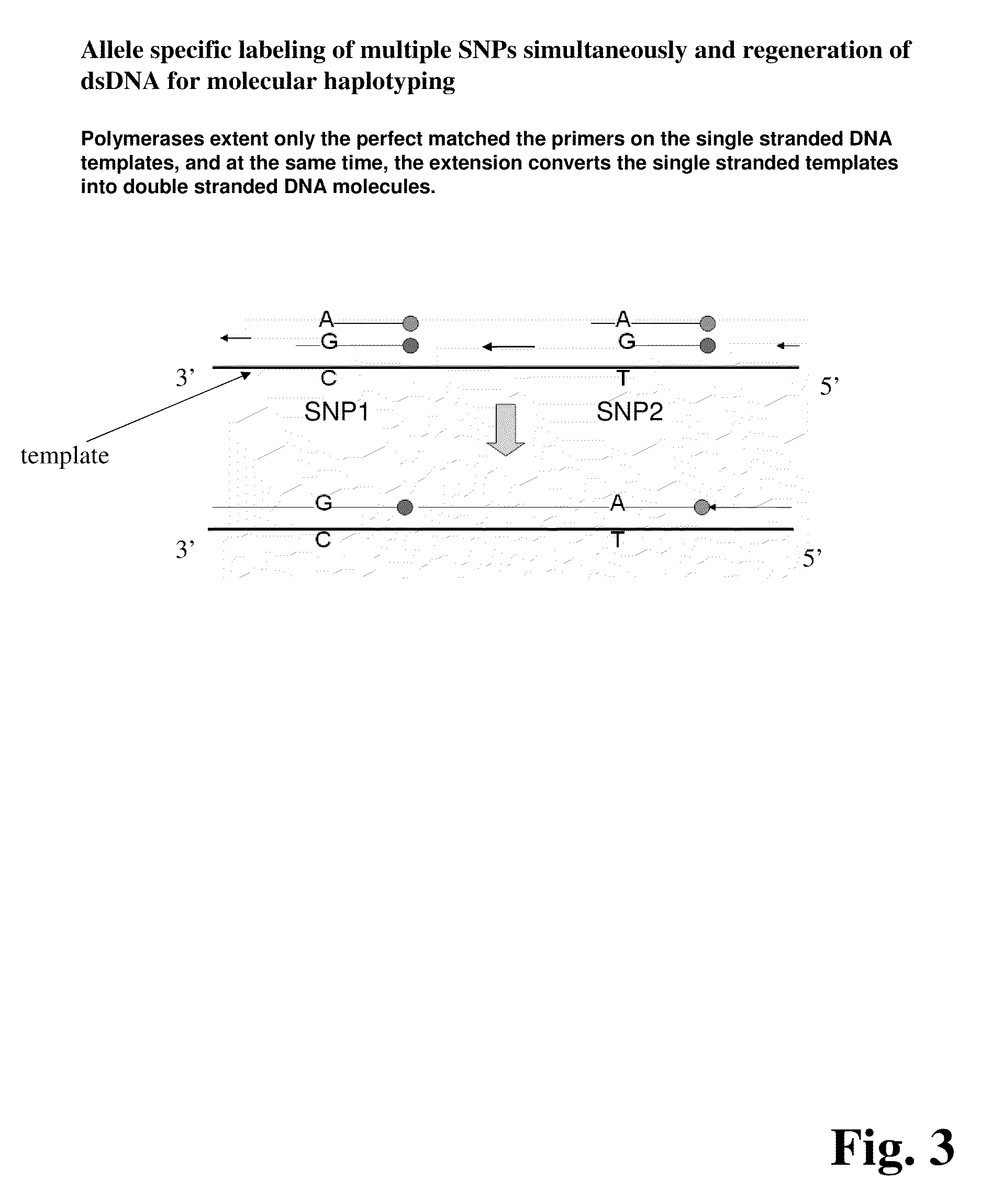
Improved methods of genetic haplotyping and DNA sequencing and mapping, including methods for making amplified ssDNA, methods for allele determination, and a DNA barcoding strategy based on direct imaging of individual DNA molecules and localization of multiple sequence motifs or polymorphic sites on a single DNA molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Method and kits for multiplex hybridization assays
ActiveUS20060281098A1Improve matchSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAPolynucleotide
The invention provides a method for genotyping interfering polymorphic loci in a target polynucleotide, such as a strand of genomic DNA, in a multiplex hybridization-based assay. The invention also provides nucleic acid standards for validating the performance of such hybridization-based assays. In one aspect, the method of the invention is carried out by providing for each interfering polymorphic locus one or more probes so that at least one probe is capable of forming a perfectly match duplex at the locus regardless of the characteristic sequence of an adjacent polymorphism.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Multiplexed analysis of polymorphic loci by concurrent interrogation and enzyme-mediated detection
InactiveUS20080167195A1Strong specificityDegree of reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHla genesEnzyme
The invention provides methods and processes for the identification of polymorphisms at one or more designated sites, without interference from non-designated sites located within proximity of such designated sites. Probes are provided capable of interrogation of such designated sites in order to determine the composition of each such designated site. By the methods of this invention, one or more mutations within the CFTR gene and the HLA gene complex can be can be identified.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Set of chloroplast SNP and INDEL molecular marker combination for maternal traceability of maize
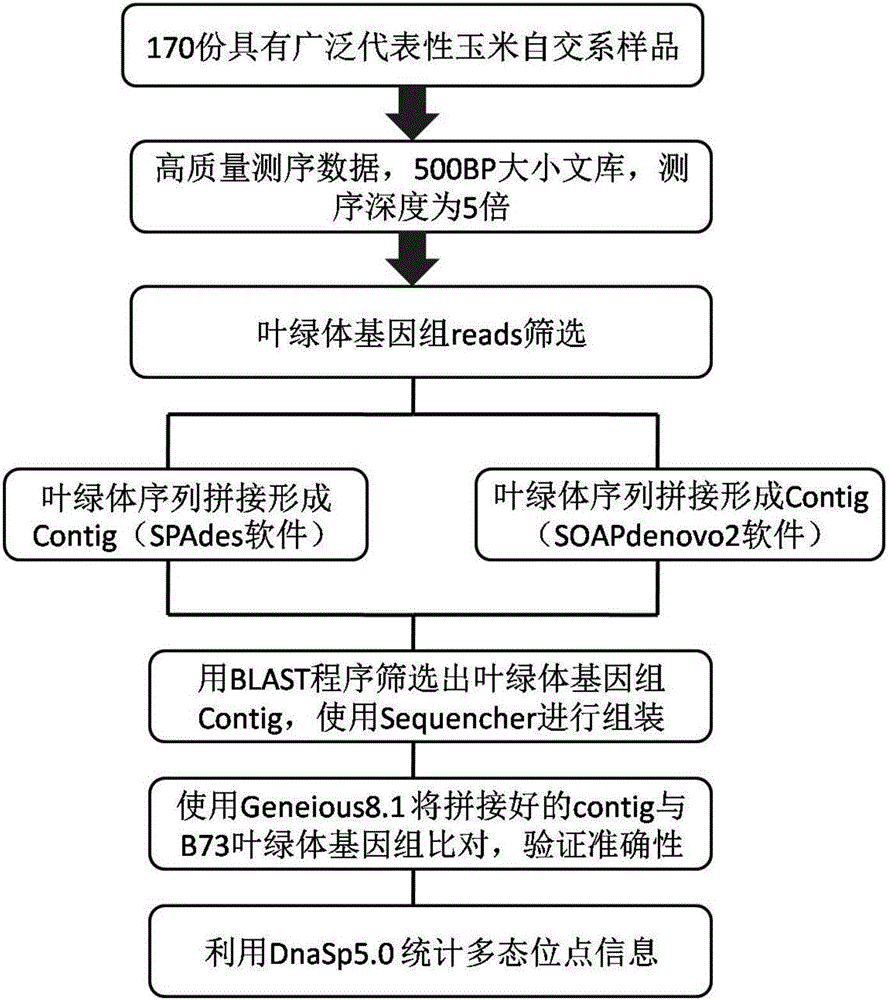
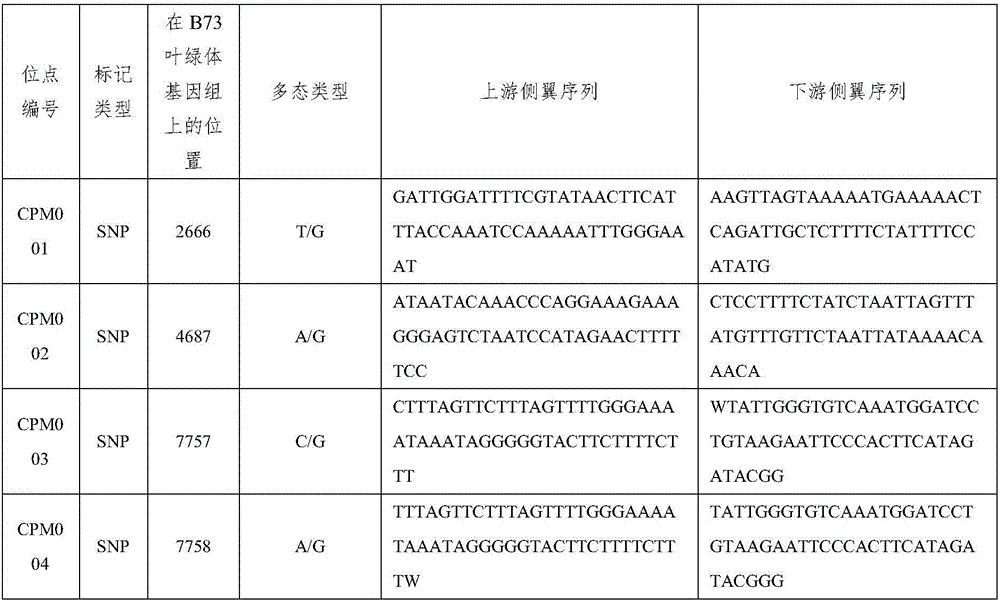
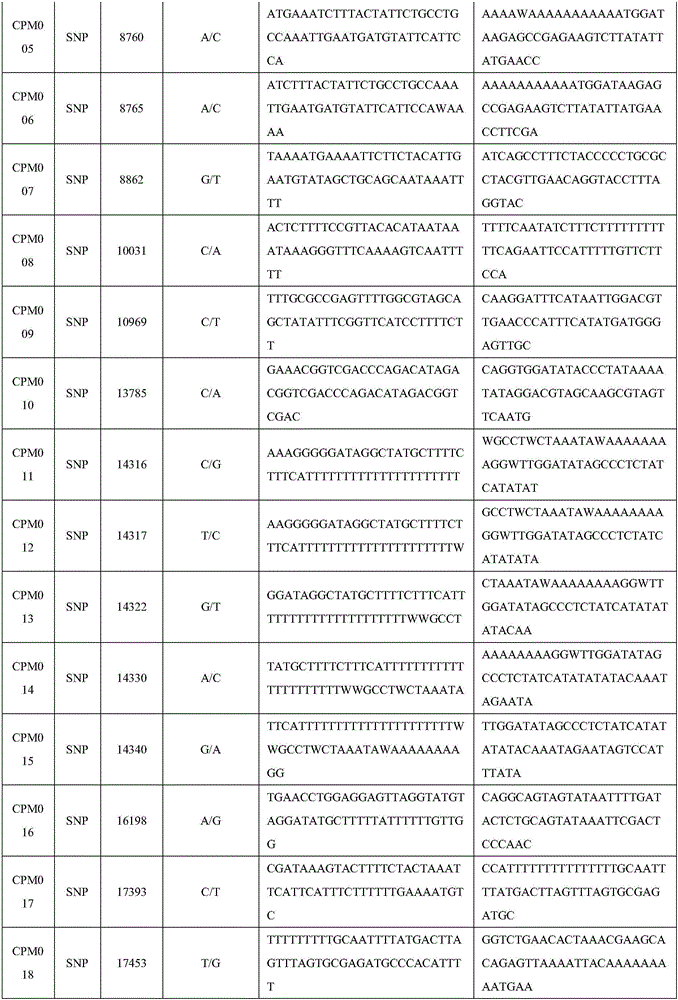
The invention relates to a set of chloroplast SNP and INDEL molecular marker combination for maternal traceability of maize. On the basis of high quality resequencing data, the invention develops a set of maize chloroplast genome polymorphic locus combination, the polymorphic loci are CPM001-CPM100, which include 96 SNP loci and 4 IDNEL loci. The 100 chloroplast loci can be applied to construction of a maize chloroplast DNA fingerprint database, parental traceability, and reciprocal cross identification. Through application of the chloroplast polymorphic loci, the range of available marker loci for maize on the genomic level is expanded; and a new idea and method are provided for maize varieties, germplasm resource identification, genetic relationship evaluation, cytoplasmic genetic characteristics and other studies.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Methods and kits comprising AFLP primers, and ramp primers with a part complementary to a compound microsatellite repeat and an anchor part complementary to nucleotides adjacent to the repeat
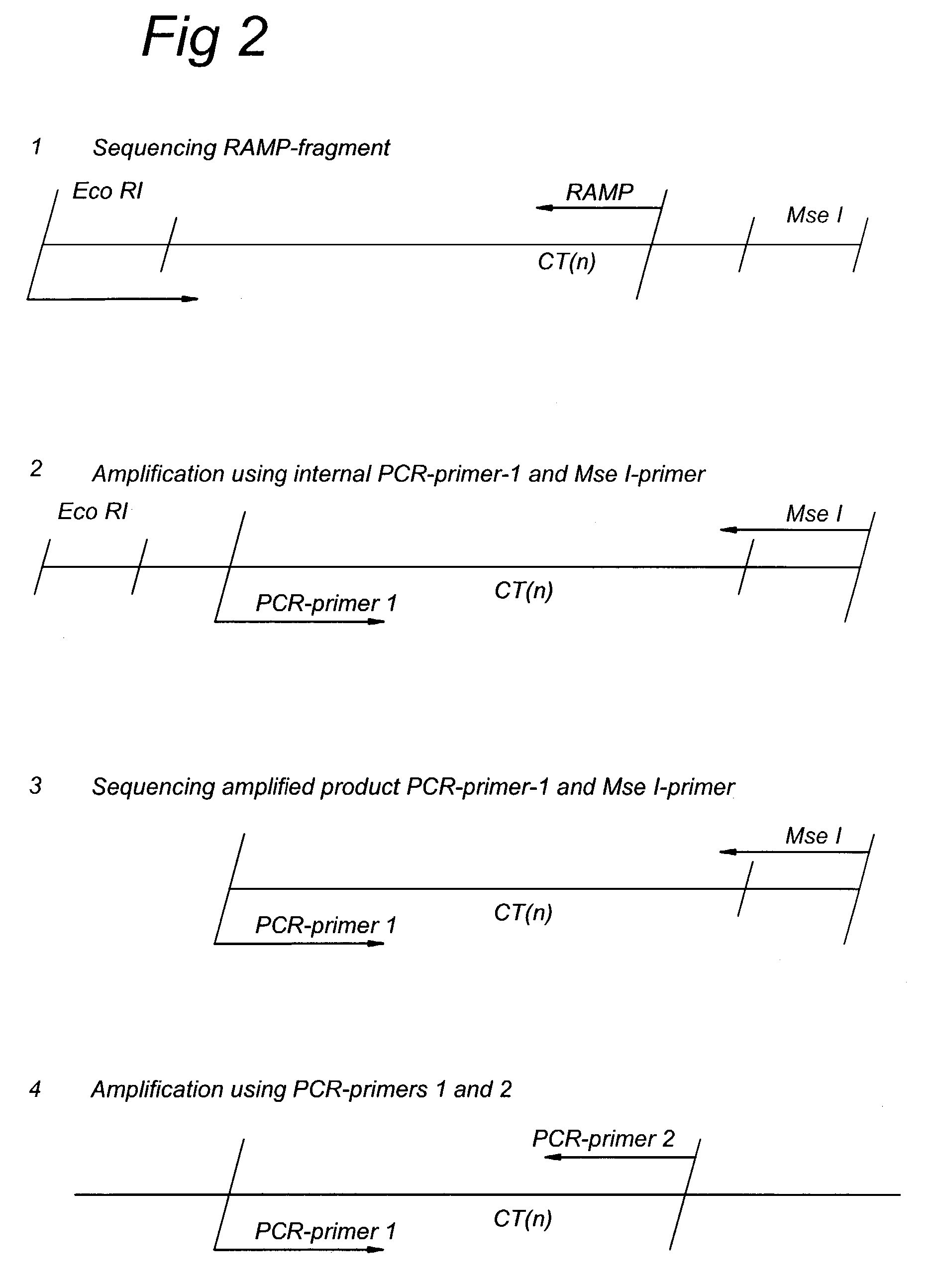
InactiveUS7217516B2Quick identificationReliable and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleotide
The present invention discloses methods for identifying and analysing microsatellite-associated polymorphisms between different DNA samples. Different DNA samples, e.g. from different individuals, are analysed using a PCR based on the combination of a RAMP-primer and an AFLP-primer and polymorphisms between the different DNA samples are identified. The polymorphisms thus identified may be isolated and further analysed by e.g. DNA sequence analysis both upstream and downstream from the microsatellite-associated polymorphism. These sequences may subsequently be used to devise and synthesise new means for analysis of the polymorphic locus, such as e.g. PCR-primer pairs or oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Chinese population linkage analysis single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker sets and use method and application thereof
InactiveCN102121046AEnsure reliabilityEnsure comprehensivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic linkage disequilibriumInternational HapMap Project
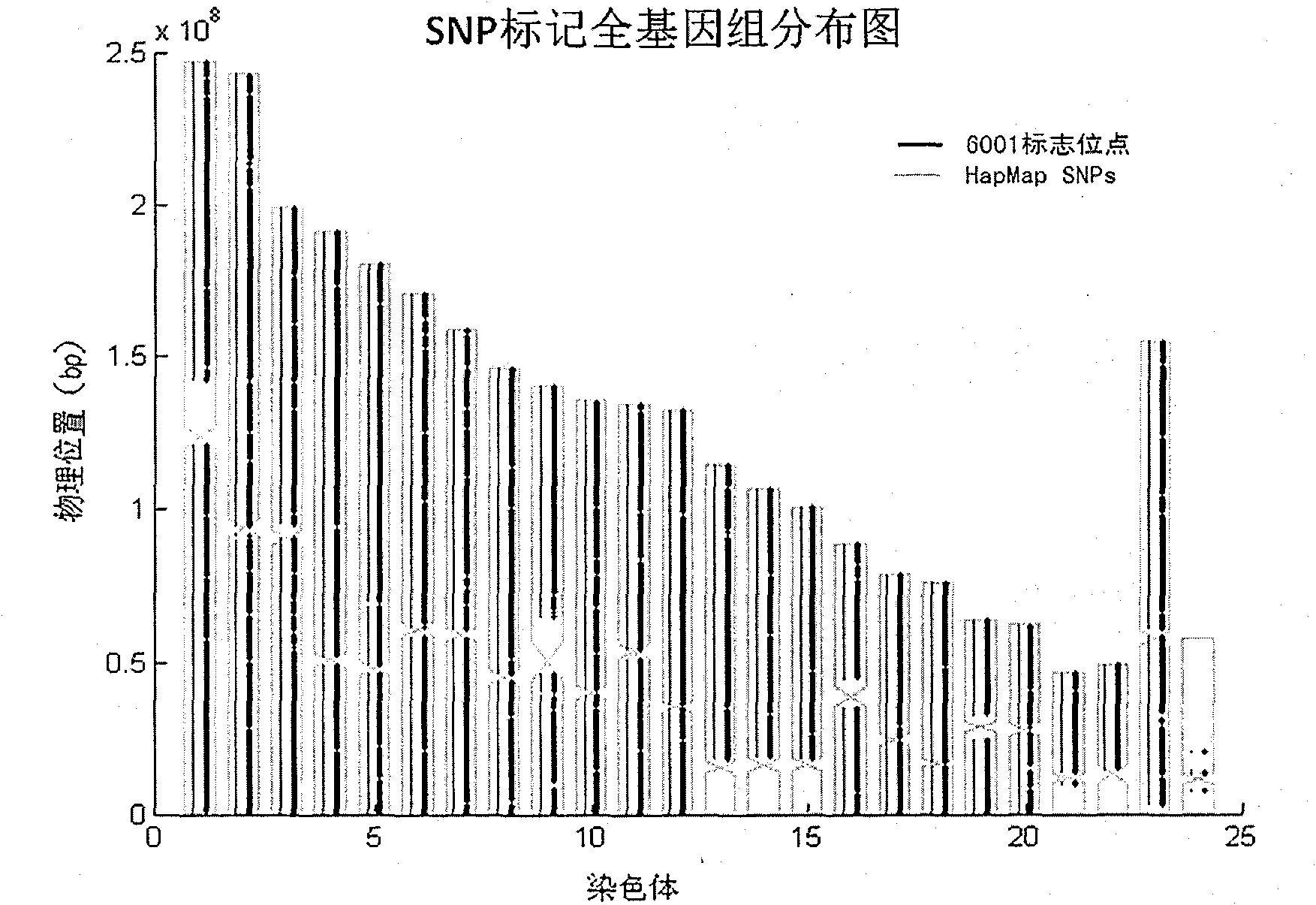
The invention relates to Chinese population linkage analysis single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker sets and a use method and application thereof. On the basis of hundreds of millions of Chinese Han population data results in the mass data of the International HapMap Project, medium-density and high-density SNP marker sets for linkage analysis are constructed and optimized, according to the statistical comparisons of multiple parameters such as the linkage disequilibrium, the polymorphism level, the typing success rate, the distribution position and density of genomes and the functional characteristic, and the multi-level selections and experimental verifications. The two marker sets separately contain 3000 and 6001 loci, wherein the 6001 loci contain the 3000 loci. The SNP sets aim at the Han genetic background in design, have high polymorphism in Chinese and can realize the aim of efficiently marking the Chinese family sample genomes. The selection of polymorphic loci is based on the neutral evolution principle, and all the loci are in a non-gene function region, thus the influence of evolution on the gene function can be avoided. Meanwhile, the characteristics that the marking loci have high typing detectability and can uniformly cover the whole genomes can ensure that the whole genomes can be screened completely and new pathogenic genes can be located and found. The two sets of SNP markers are used to customize probes or chips and perform whole-genome genotyping to family samples; and the typing data are used for linkage analysis, and the haplotyping and fine locating of the linkage candidate region are also adopted, thus the use method has more accurate locating result than the traditional method while the cost is lower and the speed is higher. The distribution and coverage of the 6001 SNP marker set in human chromosomes are shown in the appended drawings.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Methods for determining genetic haplotypes and DNA mapping
ActiveUS7771944B2Improve labeling efficiencyStable labelingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDirect imagingHaplotype
Improved methods of genetic haplotyping and DNA sequencing and mapping, including methods for making amplified ssDNA, methods for allele determination, and a DNA barcoding strategy based on direct imaging of individual DNA molecules and localization of multiple sequence motifs or polymorphic sites on a single DNA molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Methods and compositions for genetically detecting improved milk production traits in cattle
InactiveUS20050123929A1Convenient lifeHigh pregnancy rateAnimal reproductionSugar derivativesHeifer calfHaplotype
An isolated nucleic acid molecule comprising a polymorphic site selected from the group consisting of positions 164, 269, 284, 407 and 989 of SEQ ID NO: 1, an array or a kit comprising the same. Also provided are a method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in bovine proteinase inhibitor (PI) gene, a method for haplotyping a bovine cell, a method for progeny testing of cattle based on said haplotyping, a method for selectively breeding of cattle based on haplotyping a parent animal. The present invention further provides a method for testing a dairy cattle for its milk production trait, comprising haplotyping its cells, wherein a cattle having haplotypes 1, 3, 4 or 5 indicates that the cattle has desirable milk production trait. Haplotype 1 indicates that the cattle has the most desirable milk production trait.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
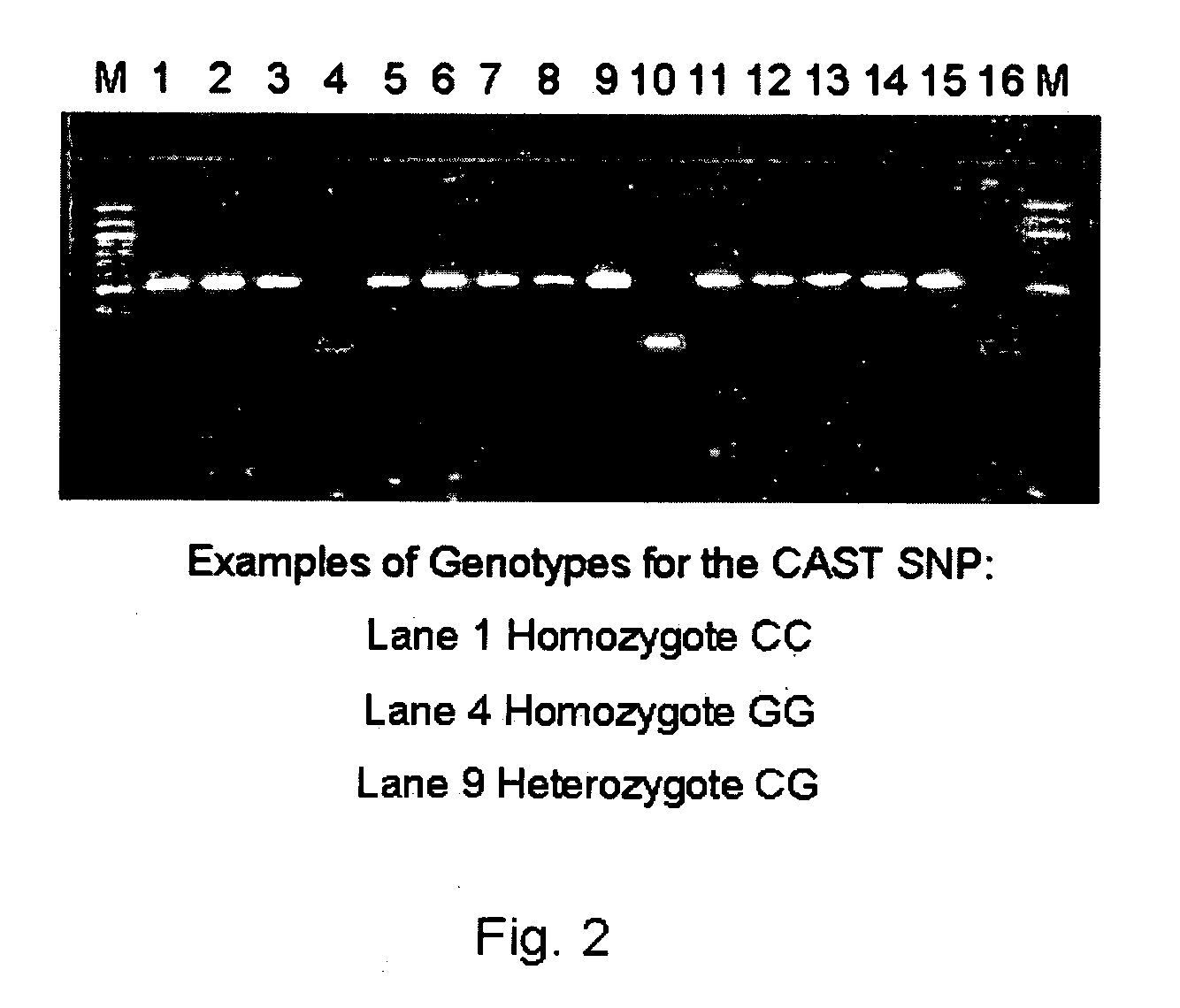
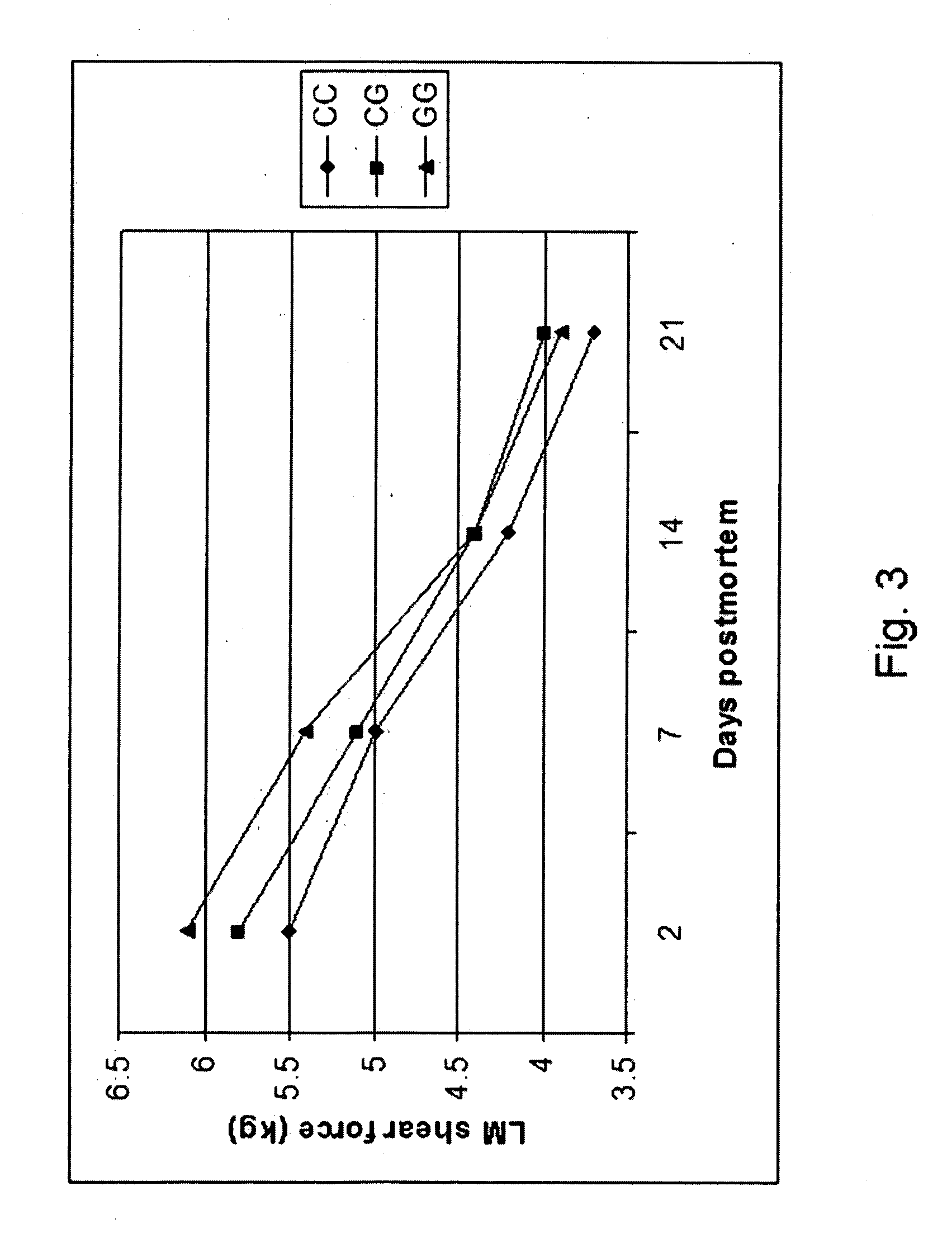
Bovine CASTgene SNP and meat tenderness
ActiveUS20060211006A1Increase productivityHigh frequencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideComputer-aided
The present invention relates to the identification of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) within the bovine CAST locus encoding the calpastatin protein, wherein the allelic variation of the SNP is a G / C transversion associated with post-mortem muscle tenderness. The invention further relates to oligonucleotides useful in identifying the genotype of bovines as it relates to the CAST locus polymorphic site. The invention also encompasses computer-assisted methods and systems for improving the production efficiency for livestock having marketably tender meat using multiple data, and in particular the genotype of the animals as it relates to the CAST SNP. These methods of the invention encompass obtaining a genetic sample from each animal in a herd of livestock, determining the genotype of each animal with respect to specific quality traits as defined by a panel of at least two single polynucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), one SNP corresponding to a site between exons 5 and 6 of the bovine CAST locus, grouping animals with like genotypes, and optionally, further sub-grouping animals based on like phenotypes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Method and kits for multiplex hybridization assays
The invention provides a method for genotyping interfering polymorphic loci in a target polynucleotide, such as a strand of genomic DNA, in a multiplex hybridization-based assay. The invention also provides nucleic acid standards for validating the performance of such hybridization-based assays. In one aspect, the method of the invention is carried out by providing for each interfering polymorphic locus one or more probes so that at least one probe is capable of forming a perfectly match duplex at the locus regardless of the characteristic sequence of an adjacent polymorphism.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for testing DNA mononucleotide pleomorphism
InactiveCN101220395AEasy to handleEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePolymer
The invention discloses a detection method of DNA single nucleotide polymorphism. The method which is provided by the invention uses a fluorescent substance for marking the DNA of a sample to be detected, and the nucleotide of the polymorphism site of the target single nucleotide of the DNA to be detected is determined by the fluorescence resonance energy transfer situation of the fluorescent substance and a water-soluble conjugated polymer. The invention has simple and convenient processing, which omits various separation and purification steps; the nucleotide of the polymorphism site of the single nucleotide can be detected by a small amount of DNA, thus the invention has great significance for the development of drugs and the clinical diagnosis of hereditary diseases.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of detecting sequence differences
InactiveUS20110300537A1Reduce the impactRequires setSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleotideGenomic DNA
The invention relates to methods of genotyping single nucleotide differences in a nucleic acid sample. More particularly, the invention provides methods of identifying the nucleotide at a polymorphic site or a group of polymorphic sites in a sample of genomic DNA. The method uses tagged primer extension in which a set of tag sequences correspond to the identity of the nucleotides at the polymorphic sites. Primer extension products are PCR amplified using a common set of tag-specific primers, the downstream primers bearing distinguishable labels. Following separation by size and / or charge, the detection of distinguishable label in a product of the anticipated size determines the identity of the nucleotide at the polymorphic site. The method is well-suited for the genotyping of multiple single-nucleotide differences in one series of reactions.
Owner:PRIMERADX
Methods for polymorphism identifcation and profiling
InactiveUS20020048749A1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsEpidemiologyProbe array
The invention provides methods of using probe arrays for polymorphism identification and profiling. Such methods entail constructing a first array of probes that span and are complementary to one or more known DNA sequences. This array is hybridized with nucleic acid samples from different individuals to identify a collection of polymorphisms. A second array is then constructed to determine a polymorphic profile of an individual at the collection of polymorphic sites. The polymorphic profile is useful for, e.g., genetic mapping, epidemiology, diagnosis and forensics.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Hypertension genetic test kit
InactiveCN101608219AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNucleotideFluorescence
The invention discloses a kit for testing the genetic risk of hypertension. The kit comprises specific primer pairs for testing the single nucleotide polymorphic locus genotypes of an angiotensin converting enzyme gene (ACE), an angiotensin II receptor type1 gene (AGTR1) and an endothelial type nitric oxide synthase gene (NOS3) as well as specific fluorescent probe pairs, fluorescent quantitative PCR regular components, PCR reaction components and the like. The kit estimates the individual genetic risk of hypertension by synchronously testing the polymorphic locus genotypes of the genes closely related to the genetic risk of hypertension.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal trisomy by allelic ratio analysis using targeted massively parallel sequencing
InactiveUS20130267425A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationMassive parallel sequencingTrisomy 22
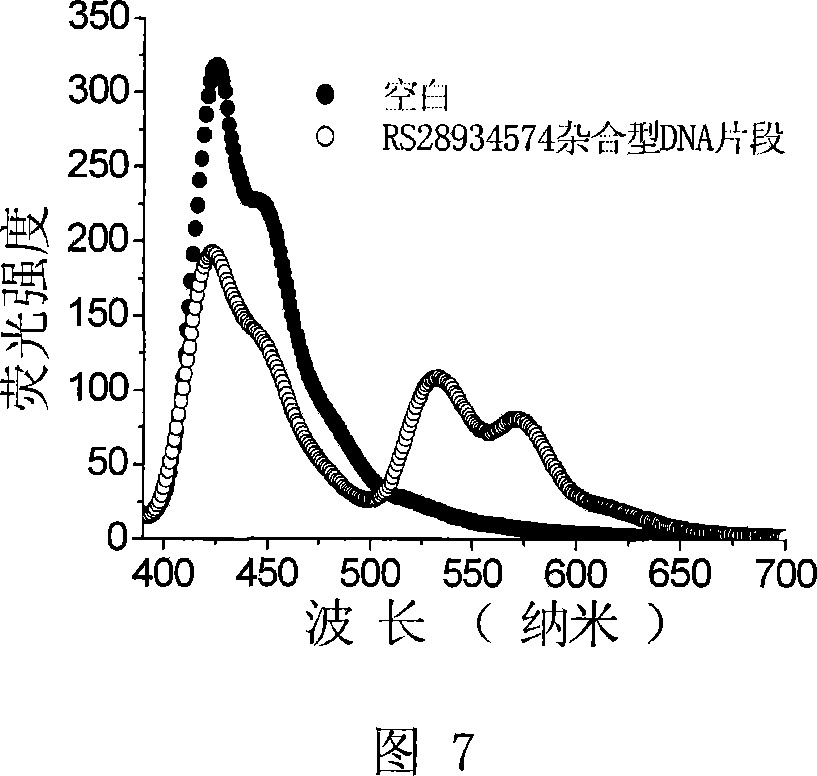
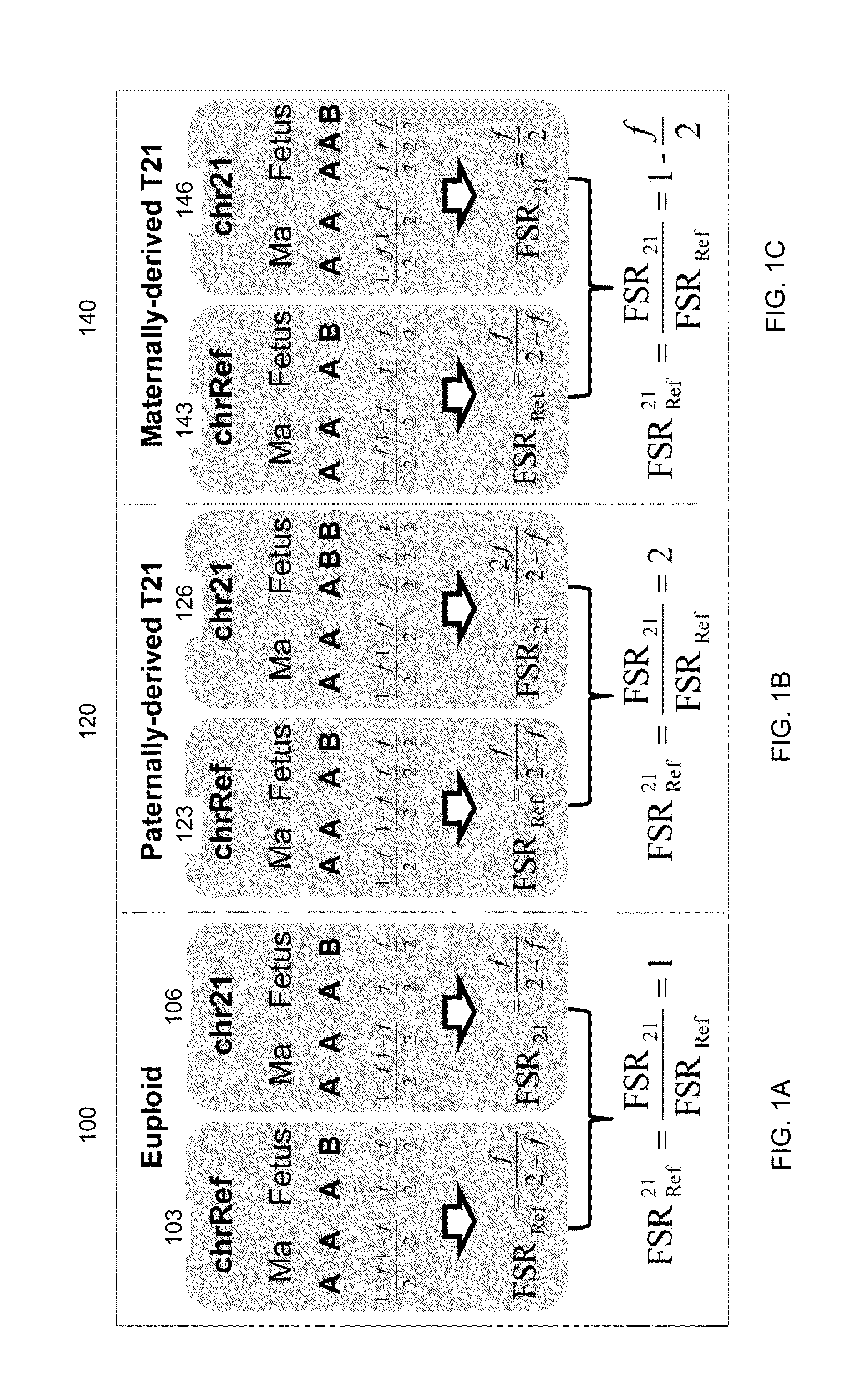
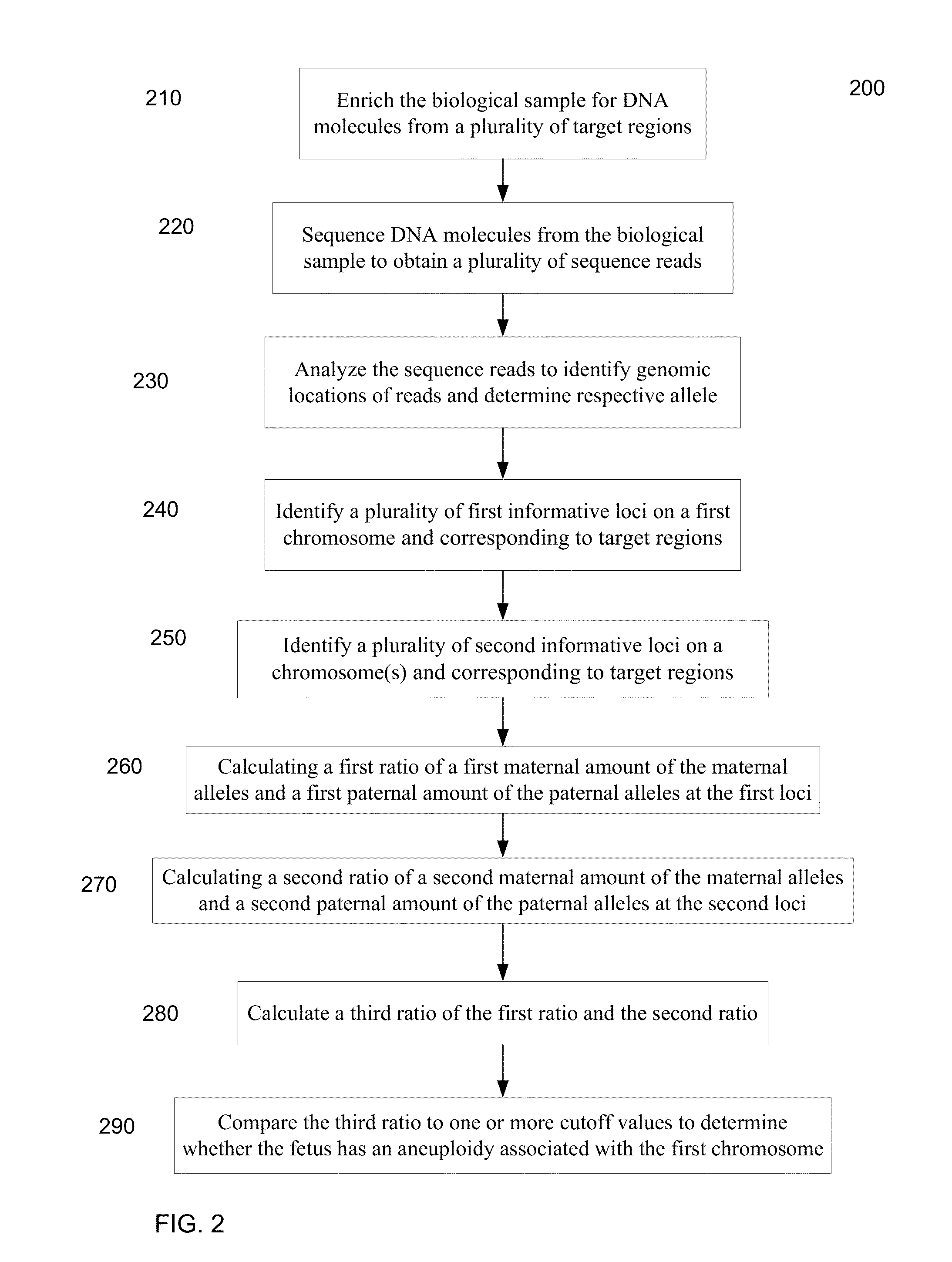
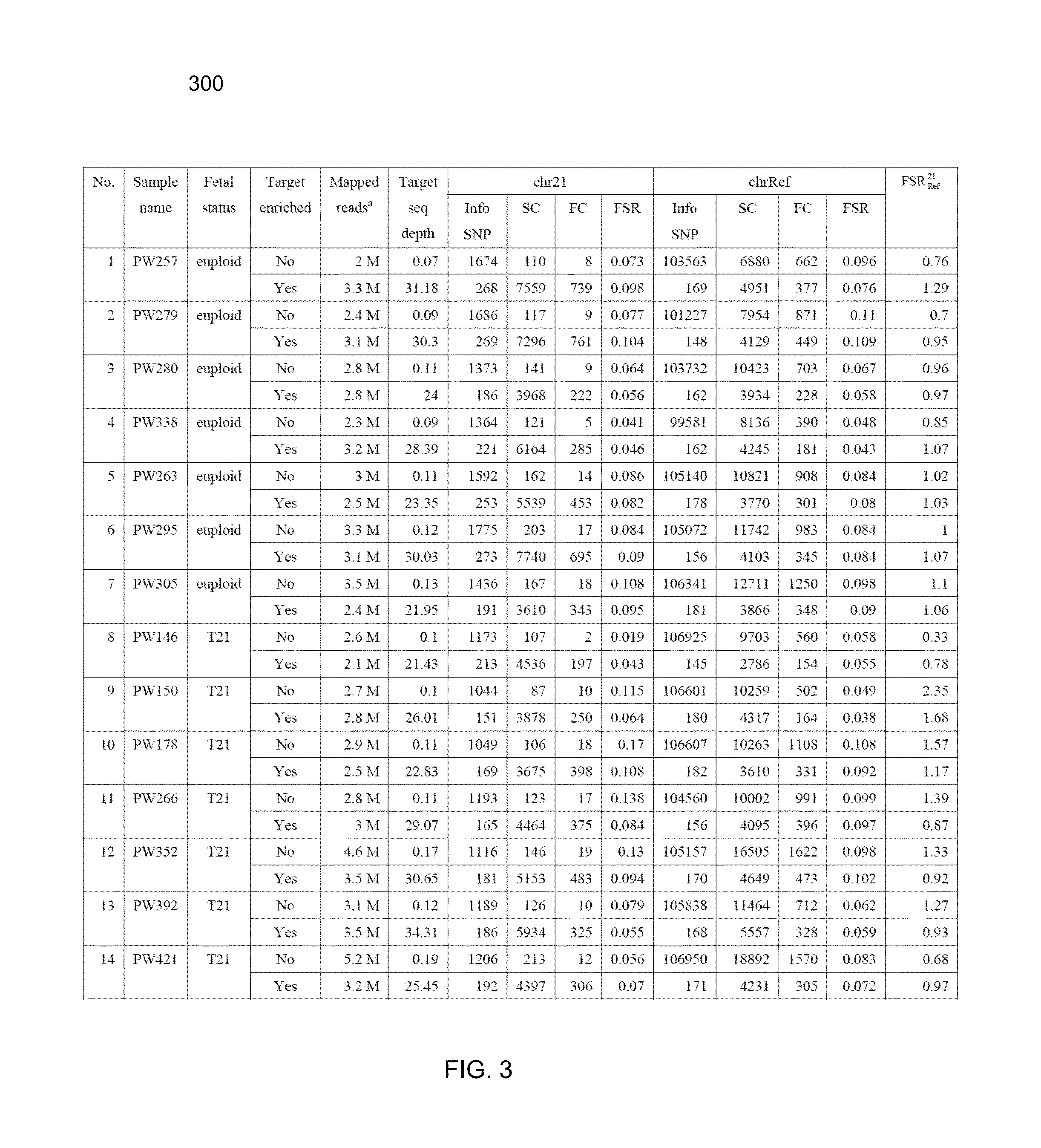
Whether a fetus has an aneuploidy associated with a first chromosome is detected using ratios of alleles detected in a maternal sample having a mixture of maternal and fetal DNA. DNA from the sample is enriched for target regions associated with polymorphic loci and then sequenced. Polymorphic loci (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms) in the target regions with fetal-specific alleles are identified on a first chromosome and on one or more reference chromosomes. A first ratio of the fetal-specific alleles and shared alleles is determined for the loci on the first chromosome. A second ratio of the fetal-specific alleles and shared alleles is determined for the loci on the reference chromosome(s). A third ratio of the first and second ratio can be compared to a cutoff to determine whether an aneuploidy is present, and whether the aneuploidy is maternally-derived or paternally-derived.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Molecular marker of loin-eye area character-related gene SVEP1 and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN105969845AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotide sequencingBiology
The invention relates to the field of preparation of a swine molecular marker, in particular to a molecular marker of a loin-eye area character-related gene SVEP1 and an application of the molecular marker. According to the molecular marker, the sequence of the SVEP1 gene comprises an SNP site which is located on the 44660bpth part of a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the site is an A / G base mutation which causes SfanI-RFLP polymorphism. The base mutation, which is located within the 3rd intron of the SVEP1 gene, cannot change an amino acid sequence which is translated by the base mutation. Therefore, a sequence, which is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, of the molecular marker can be obtained by designing a primer nearby the SNP site of the SVEP1 gene sequence, and subsequently, loin-eye area characters can be identified. According to the patent, on the basis of an existing PCR-RFLP technology, the A / G mutation is discovered on the 44660bpth part of the SVEP1 gene, and it discovers that the polymorphic site is significantly related to the loin-eye area characters; therefore, the patent is helpful for swine growth character researches to a certain degree.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
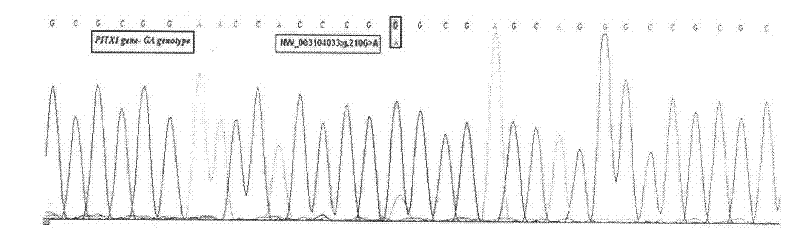
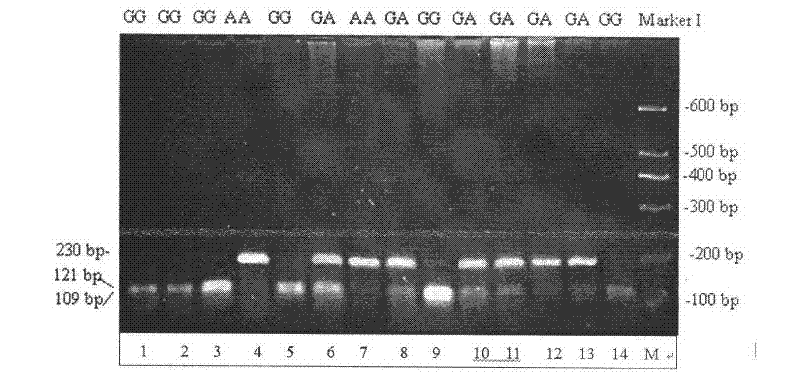
Single nucleotide polymorphic locus of milk goat PITX1 gene, and detection method and application of single nucleotide polymorphic locus
InactiveCN102649956AAccurate detectionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionMarker-assisted selection
The invention relates to a single nucleotide polymorphic locus of a milk goat PITX1 gene, and a detection method and application of the single nucleotide polymorphic locus, and belongs to the technical field of animal molecular genetic breeding. The gene single nucleotide polymorphic locus comprises the single nucleotide polymorphic locus of the milk goat PITX1 gene with the 201st position is G or A, wherein the genotype is GG, GA and AA. The detection method comprises the following steps: performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on the milk PITX1 gene by using the DNA sequence of the PITX1 gene as a template and a primer pair P as a primer; performing enzyme digestion on the PCR product by using restriction endonuclease MspI; and detecting the enzyme-digested product through agarose gel electrophoresis to identify the single nucleotide polymorphic locus of the milk goat PITX1 gene. Through the adoption of the method, the milk goat species with excellent genetic resources can be established quickly in marker assisted selection (MAS) breeding of the milk goat. The method has the advantages of simplicity and quickness in operation, low cost and high detection precision.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Susceptible/resistant MUC13 molecular marker capable of identifying F4 weaning brash of piglets and application
InactiveCN101532052AReduce mortalityImprove resistance to diarrheal diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a susceptible / resistant MUC 13 molecular marker capable of identifying F4 weaning brash of piglets of western pig breeds and application thereof to genetic improvement of pig breeds. The molecular marker firstly identifies single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) A157G, and then adopts a SNaPshot method to perform genotype judgment on the SNPA157G. The invention detects a polymorphic site through modern molecular biology technology, utilizes the marker assisted selection (MAS) to select advantageous allelotype reserved individual breed, can obviously improve weaning brash resistance of species groups, and greatly reduces the death rate of the piglets.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
FSHR (follicle stimulating hormone receptor) gene based molecular marker related to porcine reproduction traits as well as detection method and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN105087820AEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideFshr gene
The invention discloses an FSHR (follicle stimulating hormone receptor) gene based molecular marker related to porcine reproduction traits as well as a detection method and an application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is a porcine FSHR gene segment which contains a polymorphic locus, and the polymorphic locus is at the 1,166th site in a sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 and has C / T base variation. The detection method comprises the following steps: a primer is designed according to the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker; PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed with genomic DNA of a to-be-detected pig as a template; the type of a polymorphic locus in a PCR amplification product is judged. The invention further discloses the application of the molecular marker in selection of the porcine reproduction traits. According to an FSHR gene mutation site, the FSHR gene based molecular marker related to the porcine reproduction traits as well as the detection method and the application of the molecular marker are provided, and foundation is provided for porcine molecular breeding and development of a physiological mechanism for porcine reproduction.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Esophageal cancer genetic test kit
InactiveCN101608218AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceNucleotide
The invention discloses a kit for testing the genetic risk of esophageal cancer, which comprises specific premier pairs for testing the single nucleotide polymorphic locus genotypes of a cytochrome P450 1A1 gene (CYP1A1), a cytochrome P450 2E1 gene (CYP2E1), a glutathione-S-transferase M1 gene (GSTM1), a 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofo late reductase gene (MTHFR), a reduction type coenzyme I quinone oxido-reductase gene (NQ01), an oncoprotein 53 gene (P53), an X-ray repair cross-complementing gene 1 (XRCC1) and a xeroderma pigmentosum complementary set A gene (XPA) as well as specific fluorescent probe pairs, fluorescent quantitative PCR regular components, PCR reaction components and the like. The kit of the invention estimates the individual genetic risk of esophageal cancer by synchronously testing the polymorphic locus genotypes of the genes closely related to the genetic risk of esophageal cancer.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
Application of insertion/deletion polymorphic locus in sudden unexplained death detecting kit
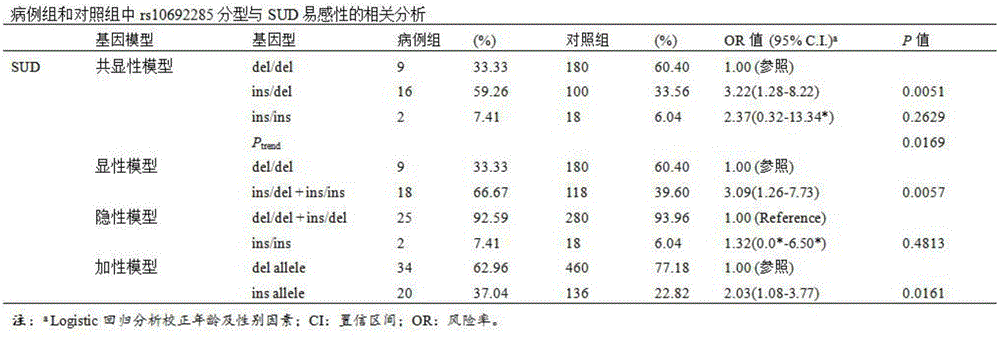
ActiveCN106367482AIncreased risk of SUDPredict susceptibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSudden unexplained deathRyanodine receptor
The invention relates to an application of a No.rs10692285 insertion / deletion polymorphic locus on the gene of a Ryanodine receptor type 2 in detecting sudden unexplained death, and the invention also discloses a kit for detecting the sudden unexplained death. The kit comprises a specific primer pair for detecting the No.rs10692285 insertion / deletion polymorphic locus on the gene of the Ryanodine receptor type 2, wherein the specific primer pair is as follows: a sense primer: 5'GCATGTTTATTATGCAAGTT3', and an antisense primer: 5'ATACAATTAAGCCCACGA3'; or the sequence of a sense primer: 5'CATTCATTGCATGTTTATTATG3', and the sequence of an antisense primer: 5'CATTATTTCACAGCACCCG3'; or the sequence of a sense primer: 5'TAAATGAACAAAGAAAACCTTC\3', and the sequence of an antisense primer: 5'CTCGGTCACAGTAGGTGG3'. The kit provided by the invention, by detecting and analyzing the gene carrying type of the rs10692285 locus on the gene of the Ryanodine receptor type 2 of an individual, can predict the susceptibility of the individual to the sudden unexplained death.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
bPrimer batch PCR primer design method based on Primer 3
ActiveCN105718759AReduce amplification failureHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsFailure causes
The invention provides a bPrimer batch PCR primer design method based on a Primer 3.The method includes the steps that an original sequence of a target DNA sequence is obtained; a high-frequency polymorphic locus in DNA polymorphic data is extracted; the high-frequency polymorphic locus is labeled; an annotated sequence of the labeled high-frequency polymorphic locus is output, and the annotated sequence and the original sequence are identical in basic group length; the annotated sequence is read to generate candidate primers; the candidate primers are screened.The bPrimer batch PCR primer design method based on the Primer 3 can avoid the high-frequency polymorphic locus, reduces amplification failure caused by genetic diversity of target population, can detect specificity of primers in batches, reduces amplification failure caused by nonspecific amplification, primer dimer and other reasons, can be used for evaluating specificity of existing primers, and can automatic segment long target segments.
Owner:HUNAN SHENGWEI GENE TECH
Kit for detecting bladder cancer-related risk genes
The invention discloses a kit for detecting bladder cancer-related risk genes. The kit includes a specific primer pair and a specific fluorescent probe pair for simultaneously detecting a No. rs9642880 SNP locus on an MYC gene and a No. rs2294008 SNP locus on a PSCA gene, a conventional component for fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection and the like. The kit can assess risk that an individual suffers from bladder cancer through simultaneously detecting MYC and PSCA single nucleotide polymorphic locus genotypes which are closely related to psoriasis.
Owner:浙江爱易生物医学科技有限公司
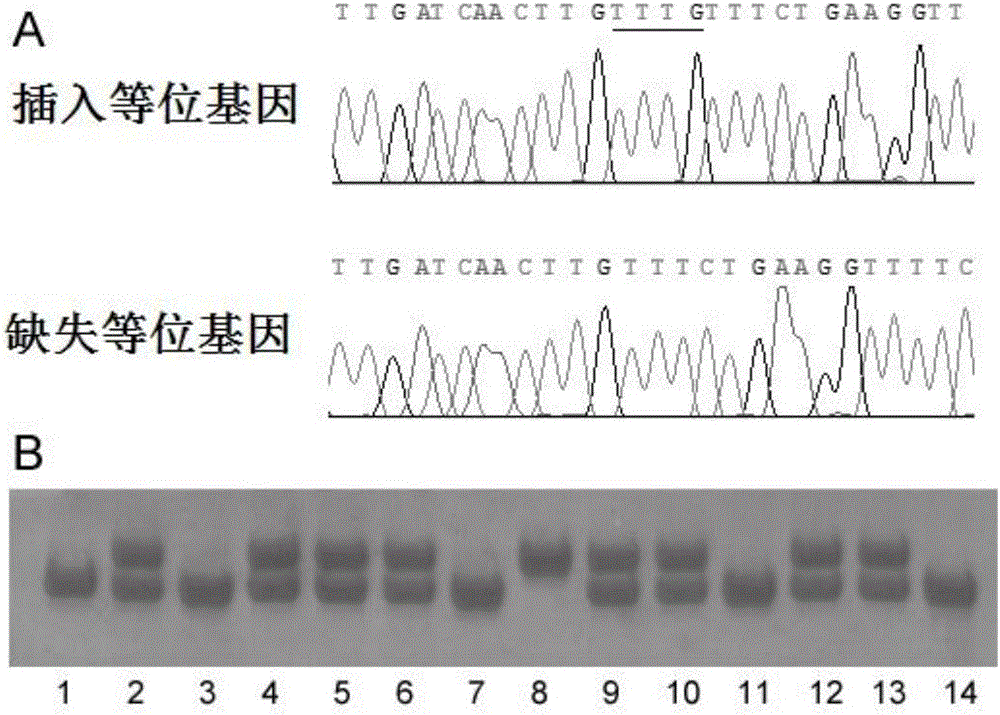
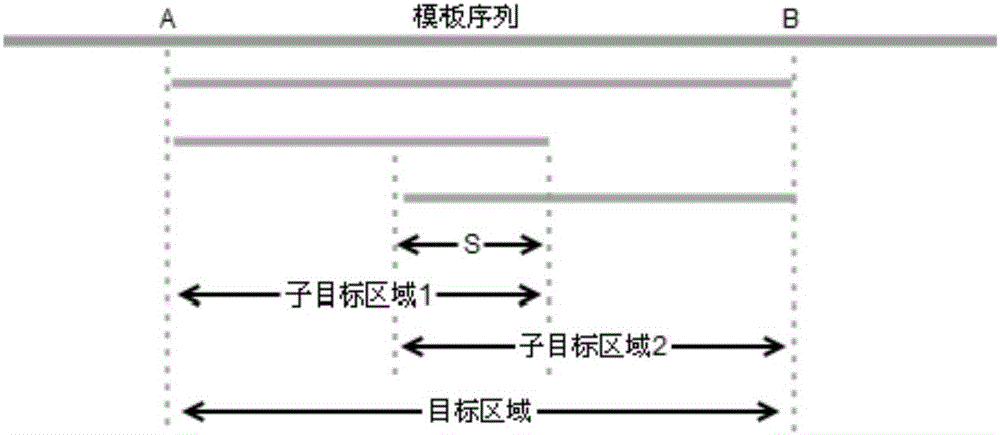
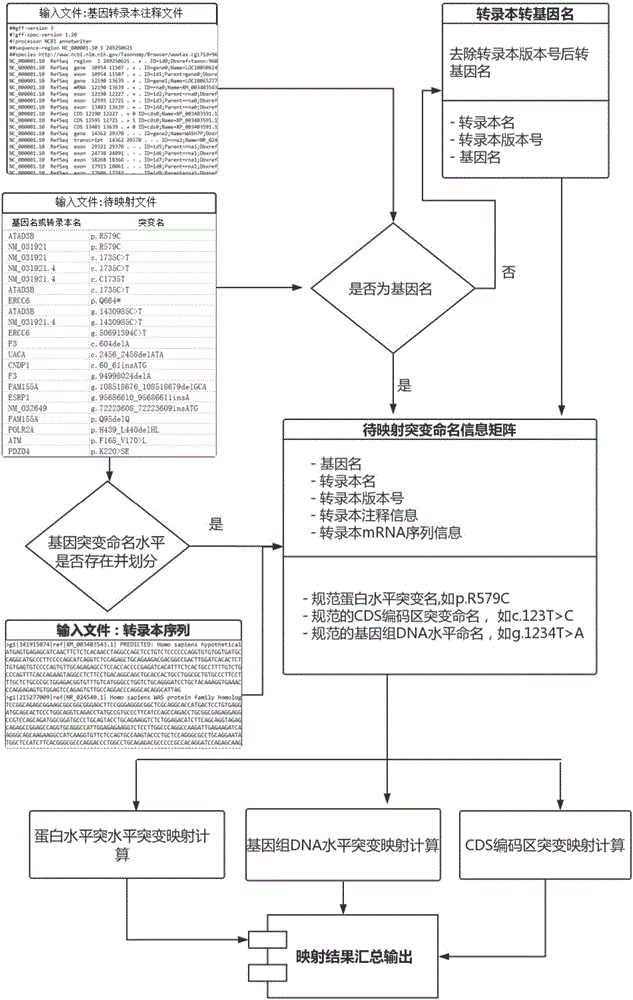
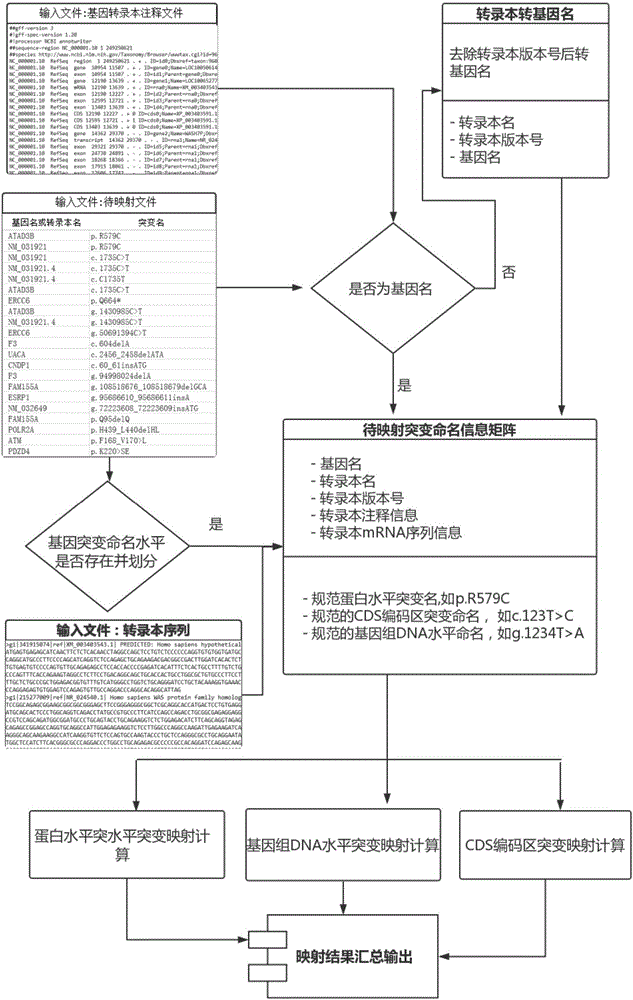
DNA and protein level mutation analysis method
The invention discloses a DNA and protein level mutation analysis method. The method comprises the steps of 1, reading a gene mutation file, and formatting the file into a standard name; 2, indexing a transcript sequence, gene information and gene transcript annotation information, thereby forming an amino acid codon corresponding relationship table; judging a mutation level and a mutation mode, and judging whether a mutation name is protein level mutation, genome DNA level mutation or CDS code area mutation; and 4, entering different level mutation mapping processes according to a judging result of the step 3, thereby obtaining mapping relationships of three mutation names. According to the method, the mapping relationships of various mutation names are output by carrying on phenotypic correlation gene mutation and polymorphic sites mined from literatures, thereby finishing annotating correspondence between pathogenic variation mined from the literatures, and gene mutation and polymorphic sites identified by sequencing.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Method for predicting susceptibility of coronary heart disease and kit thereof
InactiveCN102154445ASimple and fast operationThe result is stableMicrobiological testing/measurementCoronary artery diseaseWhite blood cell
The invention provides a method for predicting the susceptibility of coronary heart disease and a kit thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, picking up the genome DNA of human peripheral blood leukocytes; 2, for the polymorphic locus, namely 396D / I of the DDAH1 gene in a tested individual, which is shown as SEQ ID 1 in a sequence table, specifically amplifying the polymorphic locus from the DNA by F and R oligonucleotide primer sequences shown as the SEQ ID 2 and 3 in the sequence table, and detecting different genotypes of the DDAH1 gene, namely 396 focus by using the Taqman probe base sequence shown as SEQ ID 4 and 5 in the sequence table; and 3, introducing the I / I, D / I and D / D genotypes of the DDAH1 gene, namely 396 focus of the tested individual into a non-conditional Logistic regression analysis model to predict the susceptibility of coronary heart disease. By the method, through the specific combination of the probe and different genotypes of the polymorphic locus, the different genotypes are detected.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
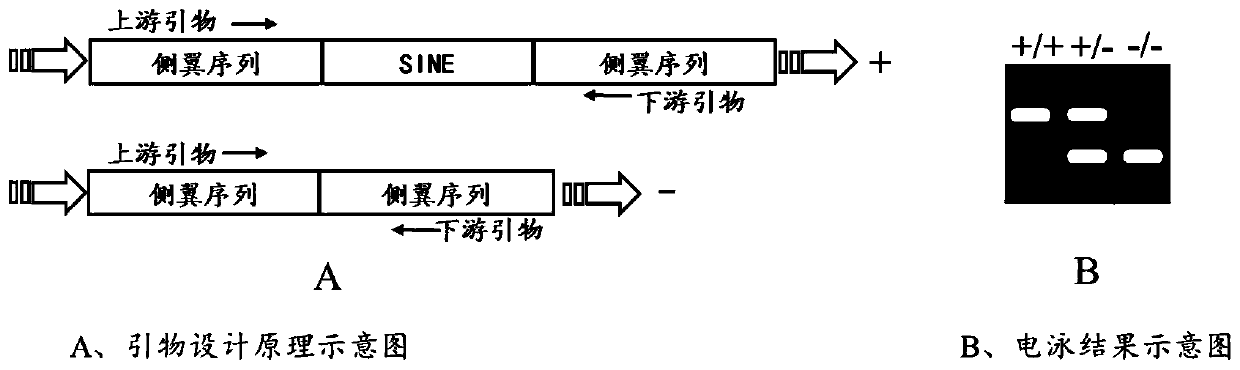
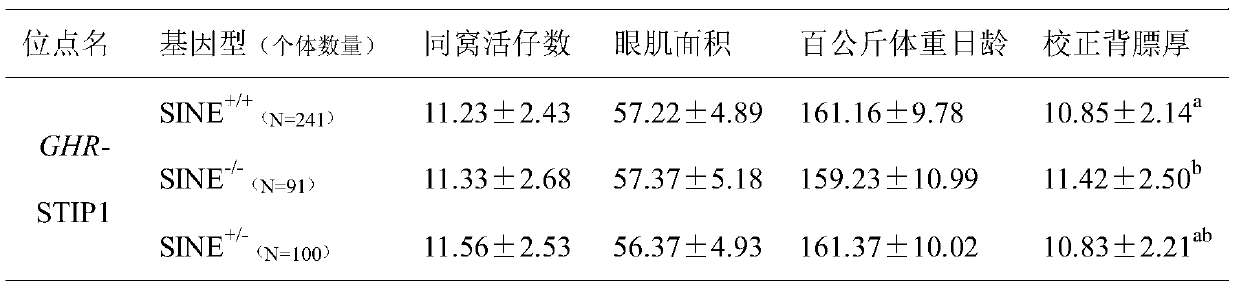
Polymorphic molecular marker for SINE transposon inside GHR gene related to pig back fat thickness, detection method and application
ActiveCN110157811AEasy to insertLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a polymorphic molecular marker for a SINE transposon inside a GHR gene related to pig back fat thickness, a detection method and application. The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the molecular marker comes from a GHR gene, an insertion polymorphic locus of a reverse SINE transposon exists on each of 200-493 loci of the sequence, the lociare shown as three gene types of SINE+ / +, SINE+ / - or SINE- / -, the body back fat thickness of the homozygous insertion gene type (SINE+ / +) is remarkably smaller than that of the body of the homozygousnon-insertion gene type (SINE- / -). The polymorphic molecular marker for the SINE transposon inside the GHR gene can be used for early selection of family breeding, and the molecular basis can be supplied in apolegamy. The powerful auxiliary effect is supplied to breeding of the back fat character, the breeding process is accelerated, and the breeding cost is lowered. The polymorphic molecular marker for a SINE transposon inside the GHR gene supplies a novel method for screening the pig back fat thickness.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Identification and application of pig MHC II TA gene as immunity related molecular labels
InactiveCN101570789AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionTemplate design
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular label preparation, in particular relates to molecular label preparation and application as auxiliary selection and related to pig immunity property. The molecular label takes mRNA sequence of a pig MHCIITA gene as a template design primer to carry out PCR amplification, PCR product purification and sequencing so as to acquire a nucleic acid shown as a sequence table SEQ ID NO:2; 9 single-chain nucleic acid polymorphic sites (SNP) are found in the nucleic acid sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO:2, and a PCR-PvuII-RFLP method is developed to detect the molecular label on the 188th bp of the nucleic acid sequence, namely base mutation C188-T188. The invention discloses the sequence amplifying a partial code region and a non-translational region of the pig MHCIITA gene, the primer used in PCR amplification and a detection method for the molecular label.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) and protein level mutation analysis system
The invention provides a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) and protein level mutation analysis system, which comprises a reading and indexing judgment module and a mapping module, wherein the reading and indexing judgment module is used for readubg a gene mutation file, carrying out formatting processing on the gene mutation file to obtain a standard name, indexing a transcript sequence, gene information and gene transcript annotation information, constructing an amino acid codon corresponding correlation chart, and judging a mutation generation level and mutation mode, and judging whether mutation naming is protein level mutation or genome DNA level mutation or CDS (Coding Sequence) coding region mutation; and the mapping module is used for independently entering different level mutation mapping flows according to the judgment result of the reading and indexing judgment module to obtain the mapping relationship of three types of mutation naming. The system undertakes the phenotype relevant gene mutation and the polymorphic site of literature mining, and outputs the mapping relationship of various types of mutation naming so as to achieve a purpose of finishing the correspondence and the like of the gene mutation and the polymorphic sites of the pathopoiesia variation and the sequencing identification of the literature mining.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Sheep back fat trait-related SNP and application thereof
InactiveCN101942438AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionGene type
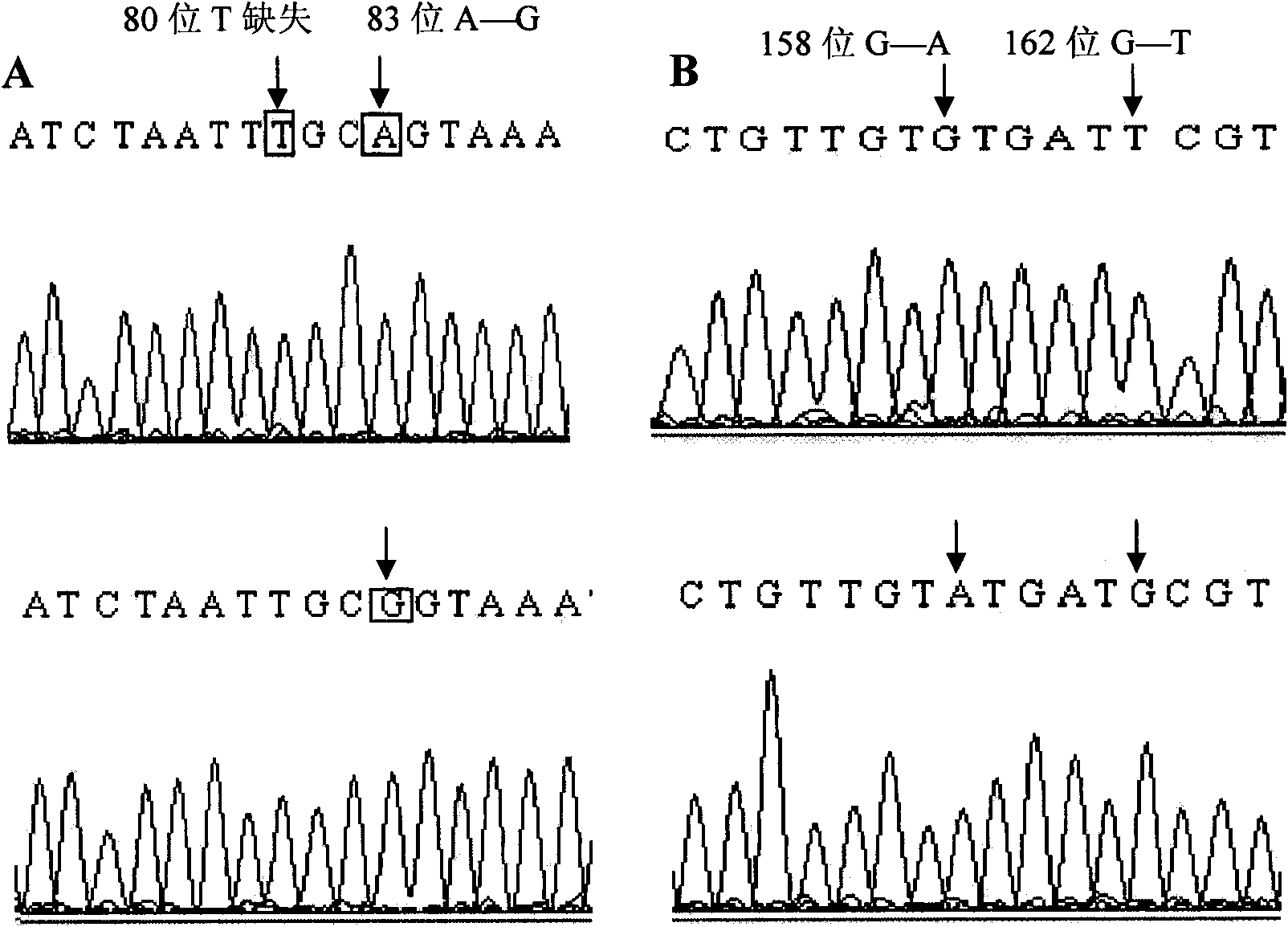
The invention relates to the field of biological engineering, in particular to a method for predicating sheep back fat trait by using single nucleotide polymorphism. The method comprises the following steps of: performing PCR amplification on total DNA of the sheep by using primers in SEQ ID No: 2 and SEQ ID No: 3; and detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism by using PCR amplified products, and determining whether the 162nd position basic group at the 5' end of SEQ ID No: 1 in a sequence list is G or T, wherein the back fat thickness of the GT gene type is obviously thicker than that of the GG gene type. The detected polymorphic loci provide new materials for molecular breeding and provide scientific evidence for marker-assisted selection of the sheep back fat thickness.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com