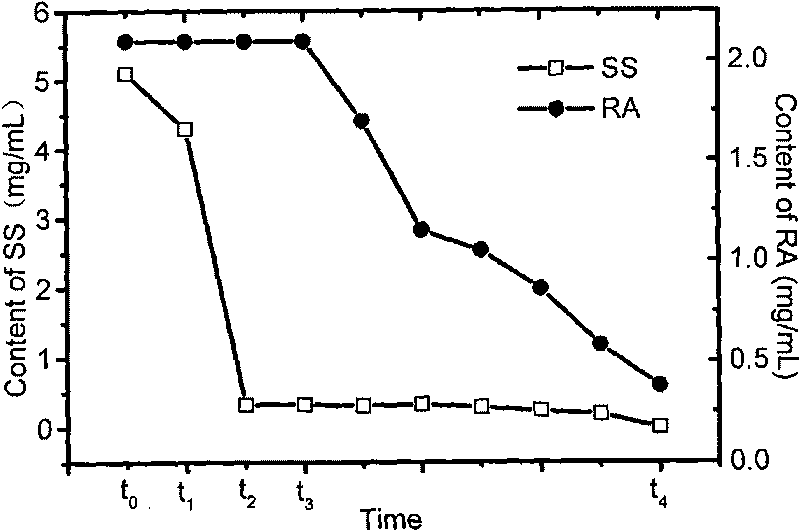
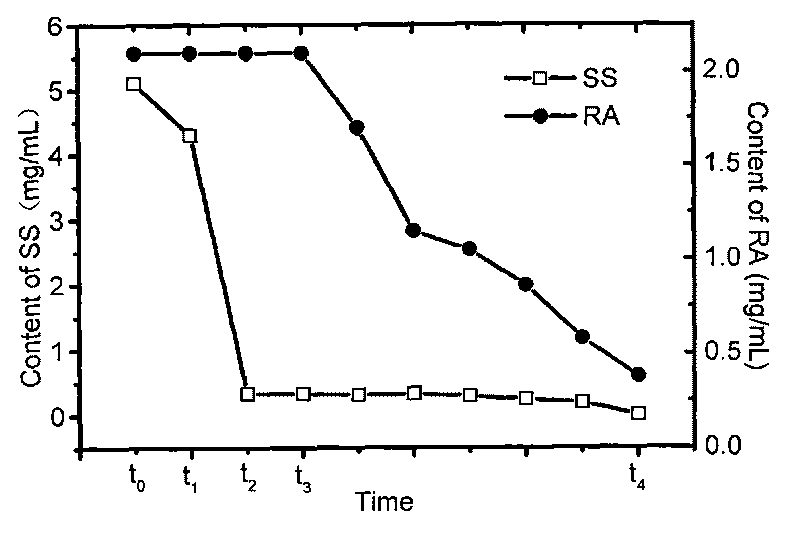
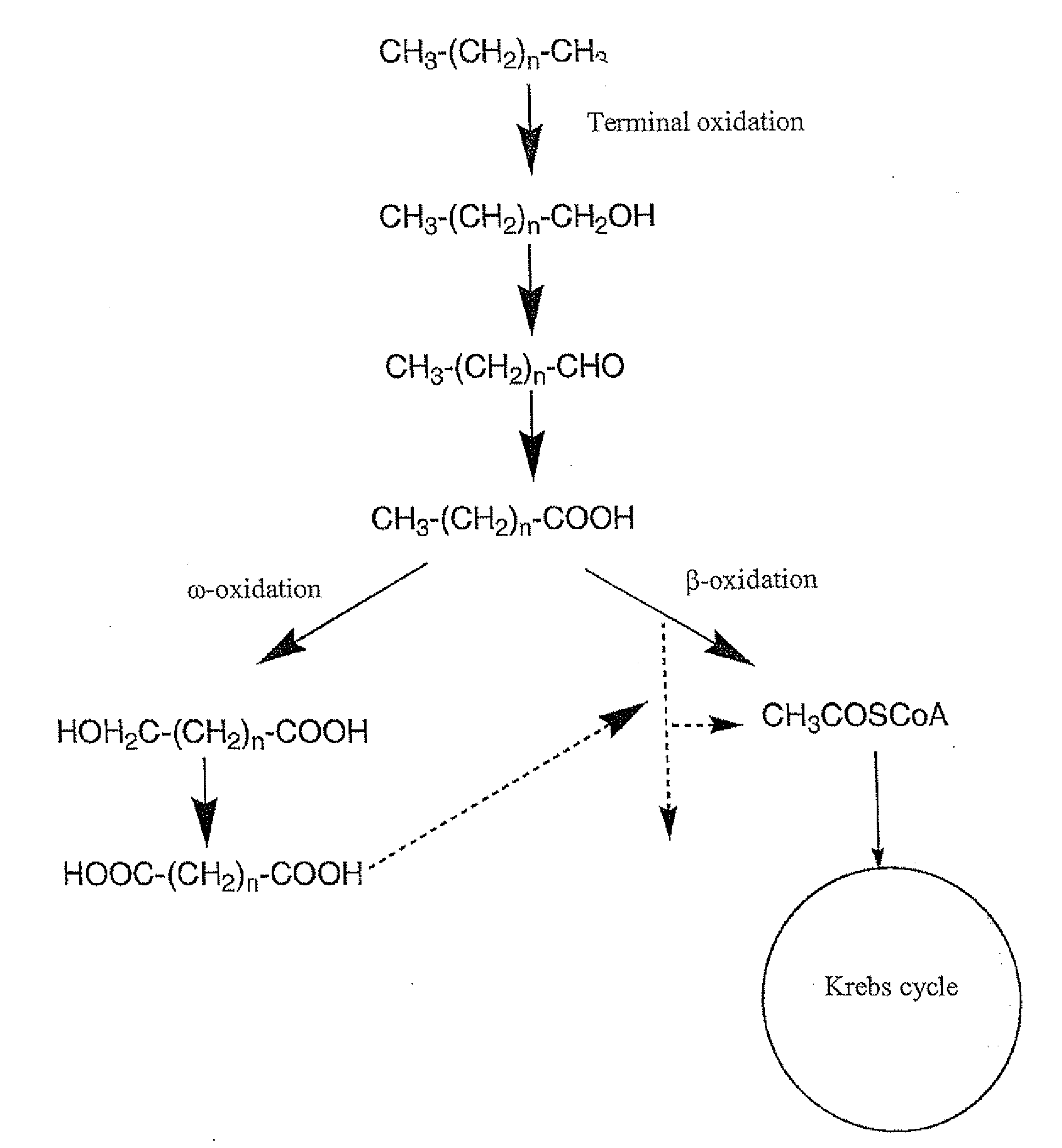
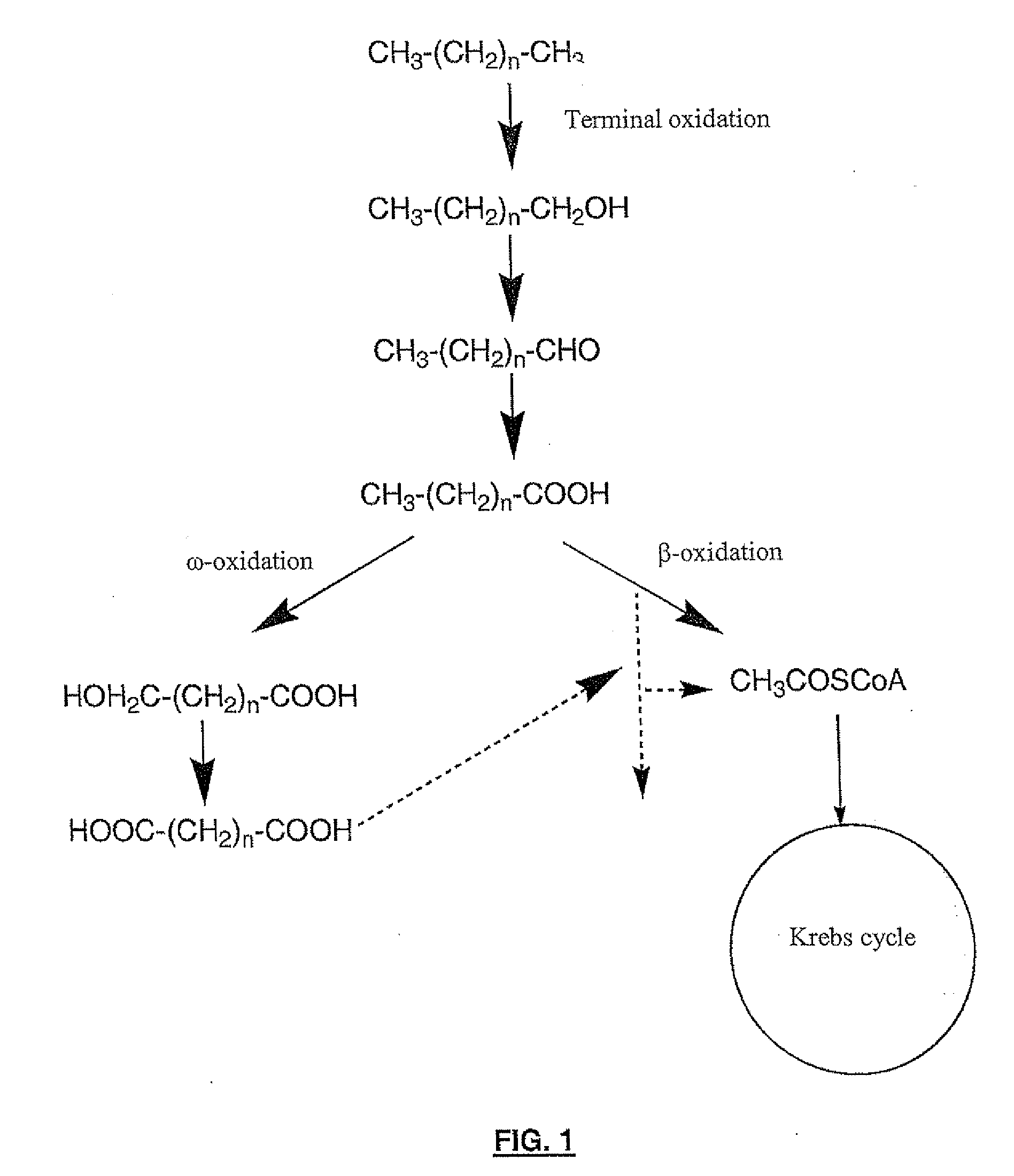
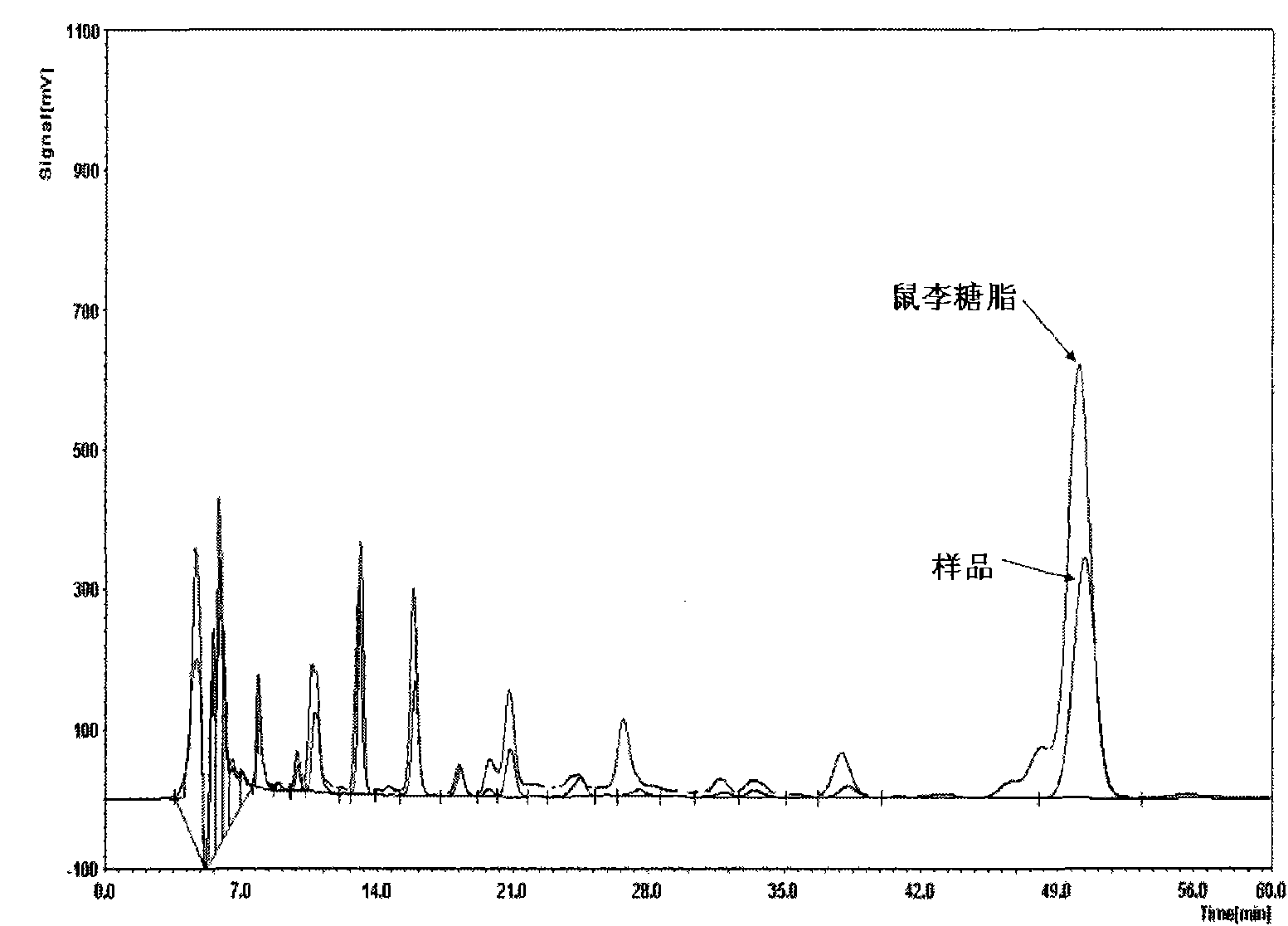
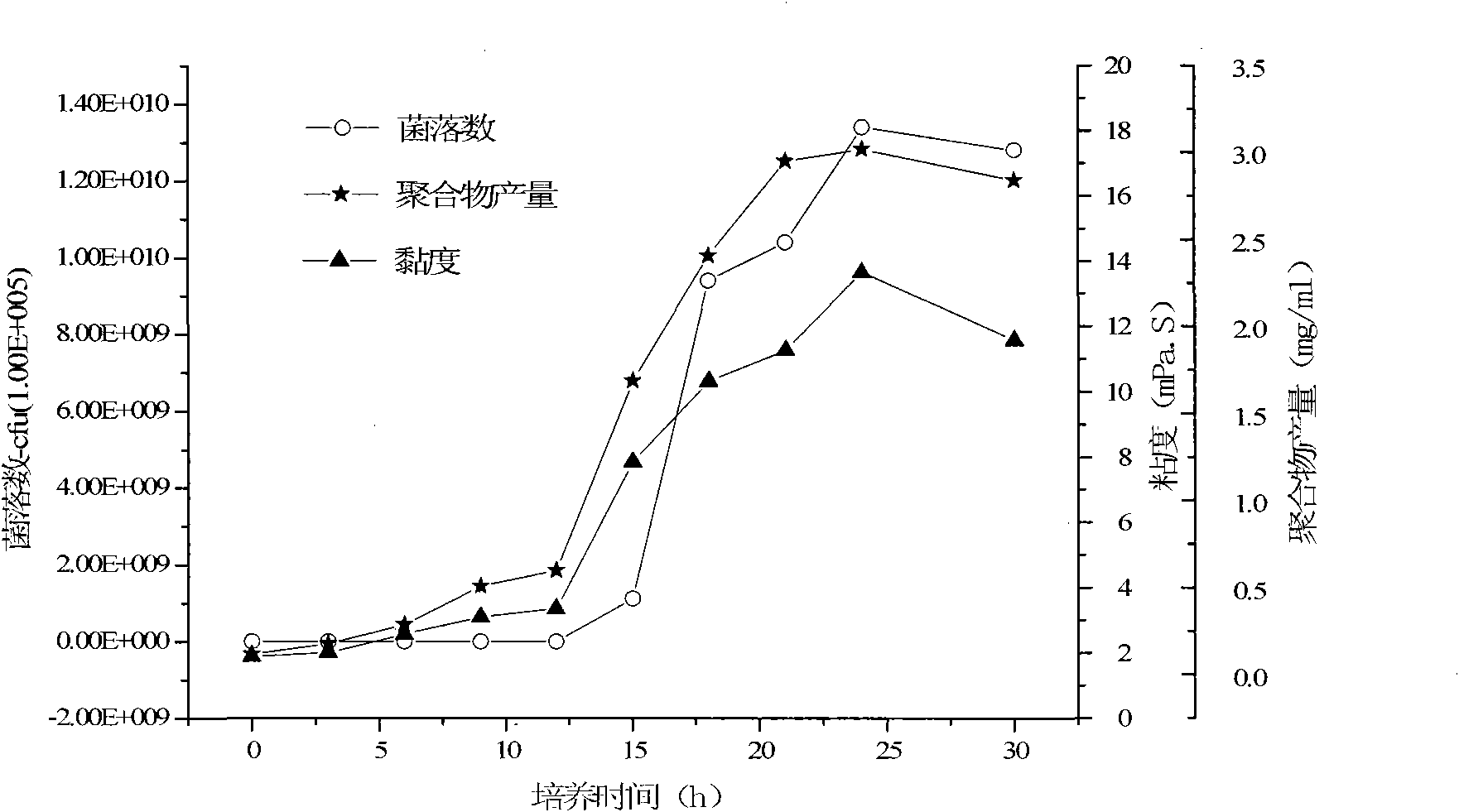
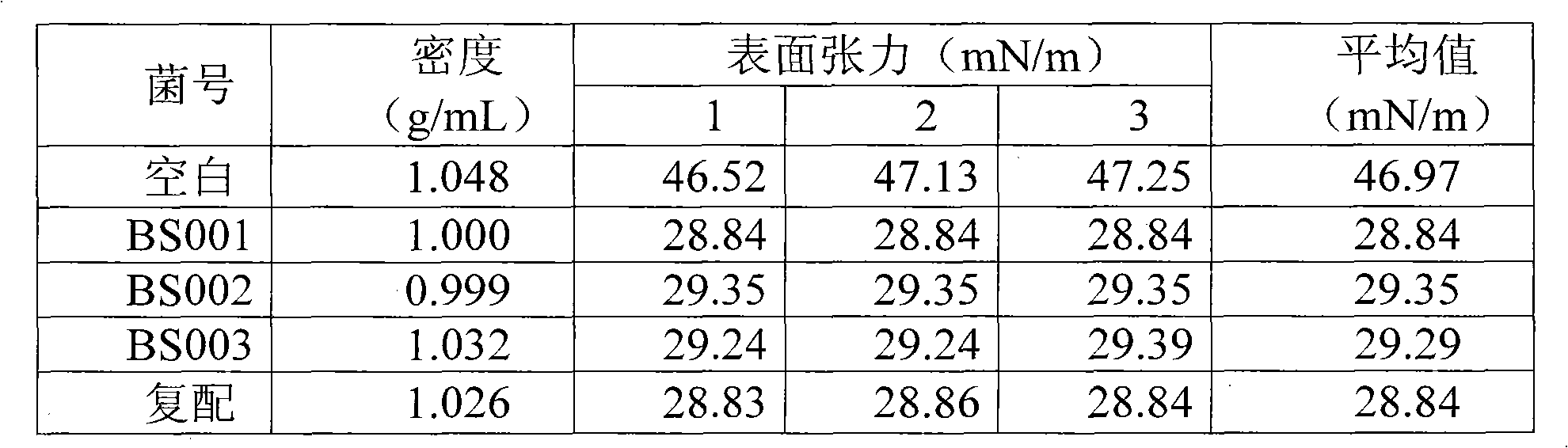
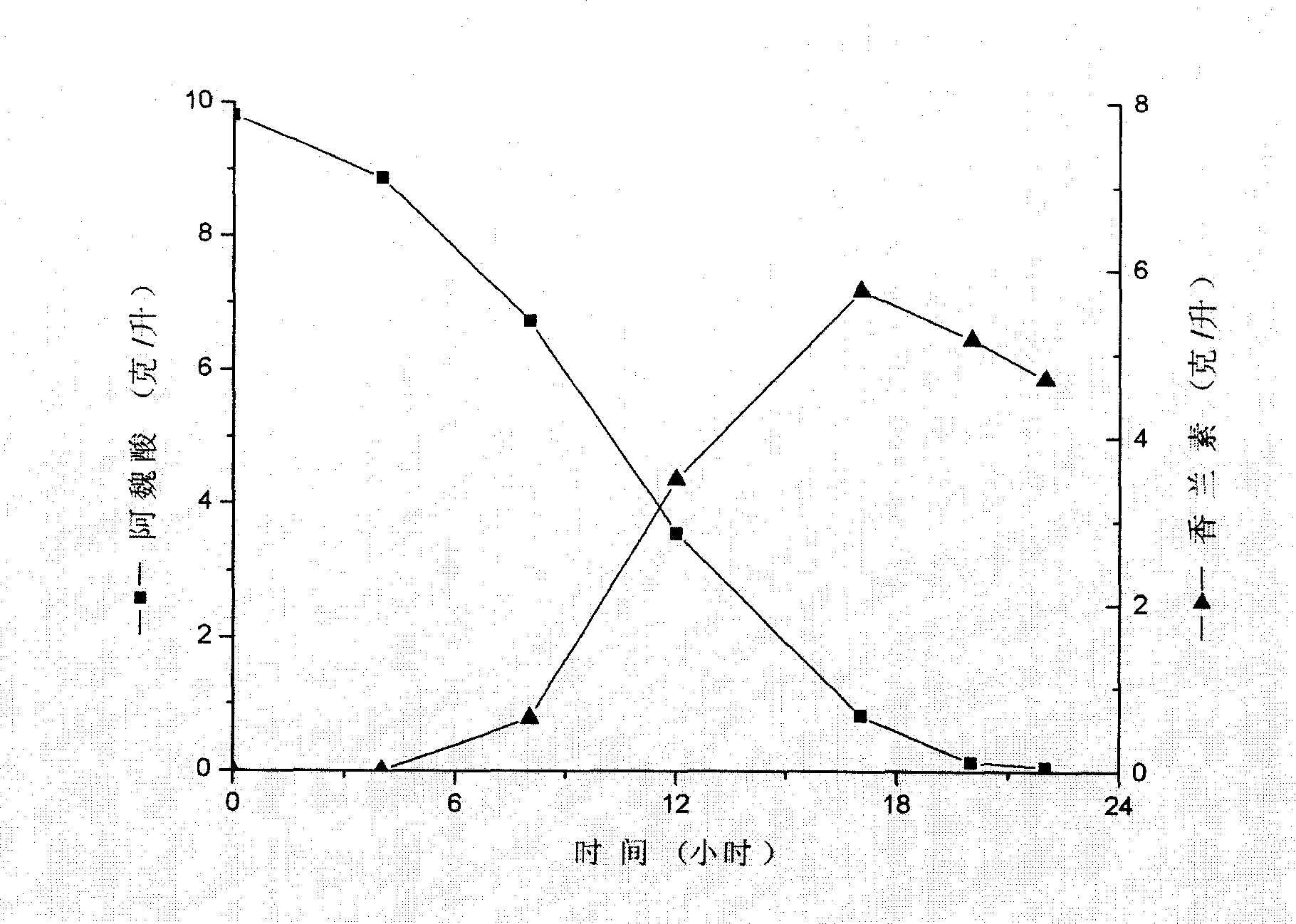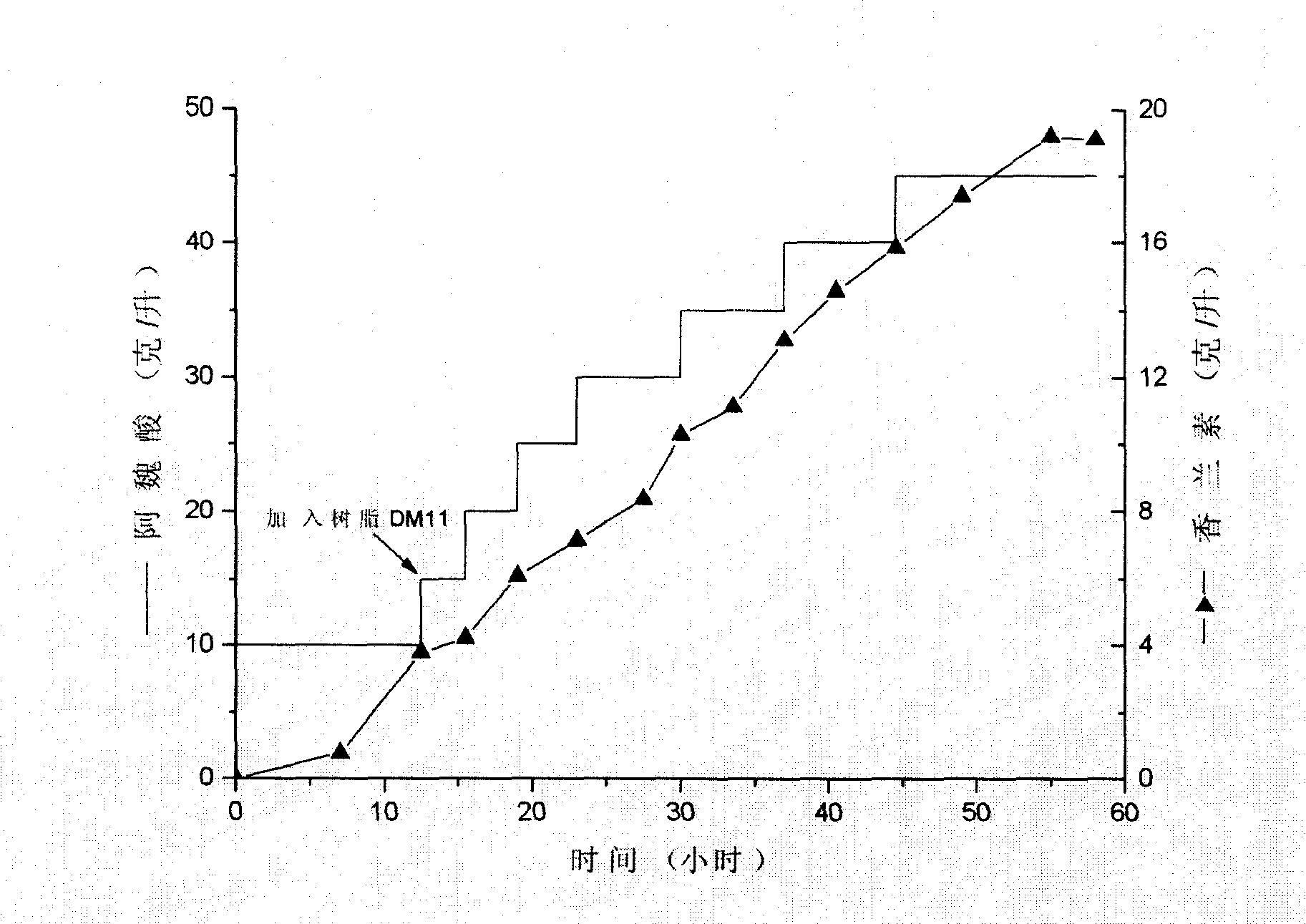Patents
Literature
1037 results about "Drug biotransformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
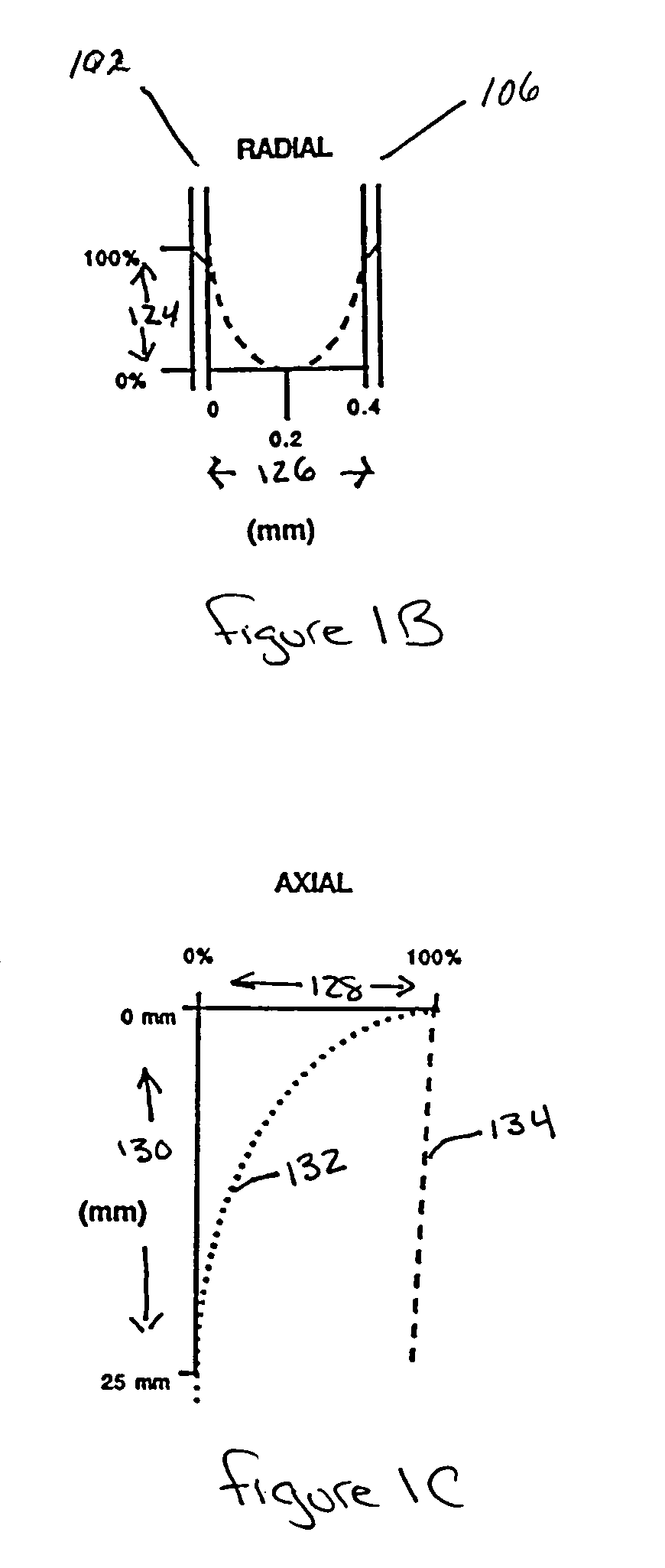
Biotransformation means chemical alteration of chemicals such as nutrients, amino acids, toxins, and drugs in the body. It is also needed to render non-polar compounds polar so that they are not reabsorbed in renal tubules and are excreted.
Analysis of genetic polymorphisms and gene copy number
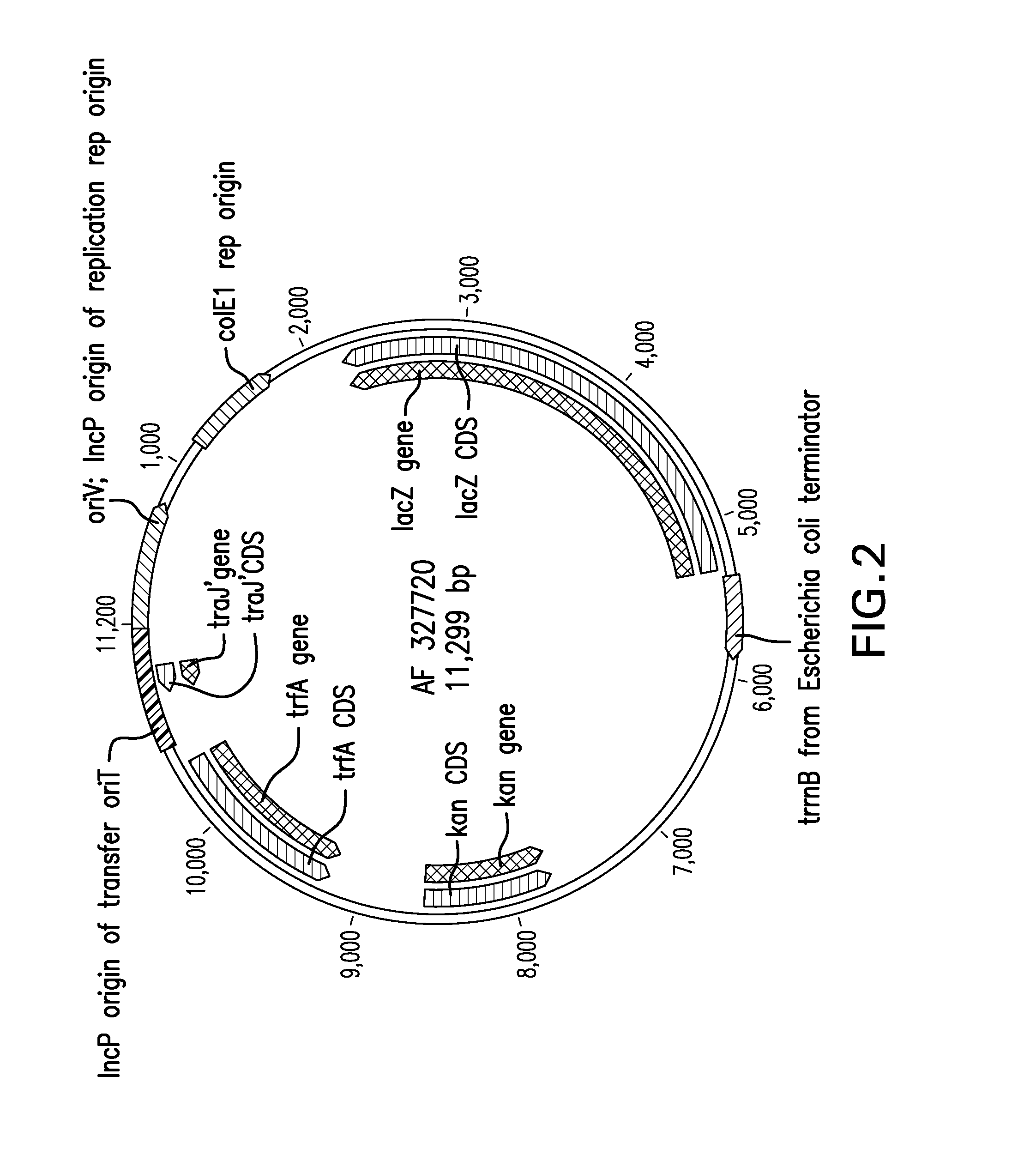
InactiveUS6468744B1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsCytochrome P450Drug biotransformation
The invention provides methods for detecting variations in polymorphic sites and / or variations in gene copy number. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of biotransformation genes, such as cytochromes P450.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Solubilization of algae and algal materials
InactiveUS20100068772A1Speed up the processIncrease ratingsMicroorganism lysisWaste based fuelLipid formationAlcohol
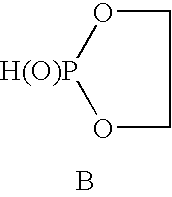
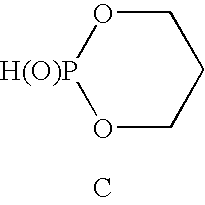
Methods for solubilizing algae or algal material are provided to facilitate the recovery of oil or lipids, as well as hydrocarbons and carbohydrates, from algae or algal material. The methods involve contacting algae or algal material with an oxoacid ester or thioacid ester of phosphorus or a mixture of an oxoacid of phosphorus and / or an alcohol to form a mixture thereof under conditions effective to solubilize the algae or algal material. These methods optionally further comprise bioconversion of the solubilized algae or algal material to form a composition suitable for recovery of oils and non-oil chemicals.
Owner:CIRIS ENERGY INC
Bioreactor design and process for engineering tissue from cells
InactiveUS6979308B1Easy to adjustEnhance effective transferBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationFiber
A scaled-up multi-coaxial fiber bioreactor, and variations of this bioreactor. The device is characterized by a hollow housing and an array of from about 20 to about 400 modules of hollow fibers, where each module includes at least three coaxial semipermeable hollow fibers. The innermost fiber provides a boundary for an innermost compartment which is connected to inlet and outlet ports. Arranged coaxially around the central hollow fiber are several other hollow fibers with their respective compartments, each compartment defined by a respective annular space between adjacent fibers and each including inlet and outlet ports. An outermost compartment for permitting integral aeration is the space between the outer side of the outermost fibers and the inner side of the housing, and has inlet and outlet ports. The hollow housing has inlet and outlet manifolds and flow distributors for each of the compartments. In a preferred embodiment the bioreactor is used as an extracorporeal liver. Liver cells, are introduced into one or more annular compartments and media and aeration are provided in others. Plasma from an ailing patient is introduced into another compartment for biotransformation of blood-borne toxins and biosynthesis of proteins, lipids, and other metabolic products.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
In-situ biological repairing method for biomass intensified petroleum contaminative soil
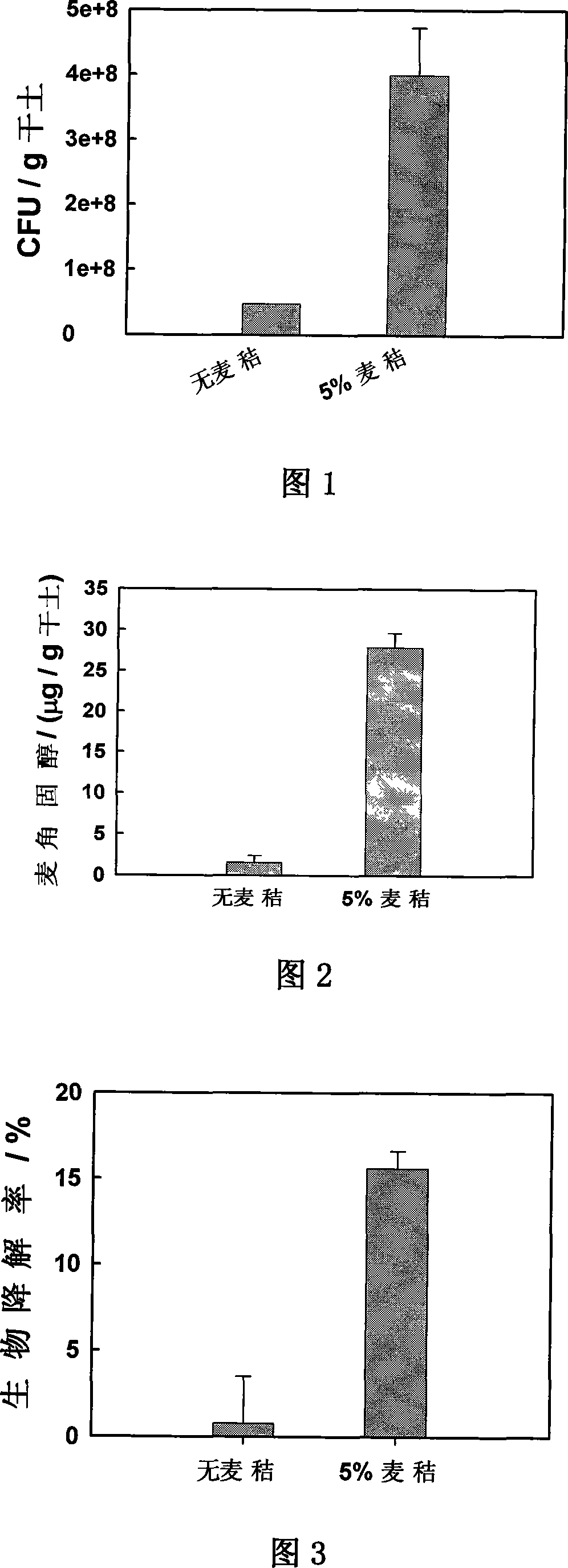
ActiveCN101104177APromote accumulationIncrease intakeFungiBacteriaBiomass degradationIn situ bioremediation
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for preparing food function factor gamma-amino-butyric acid
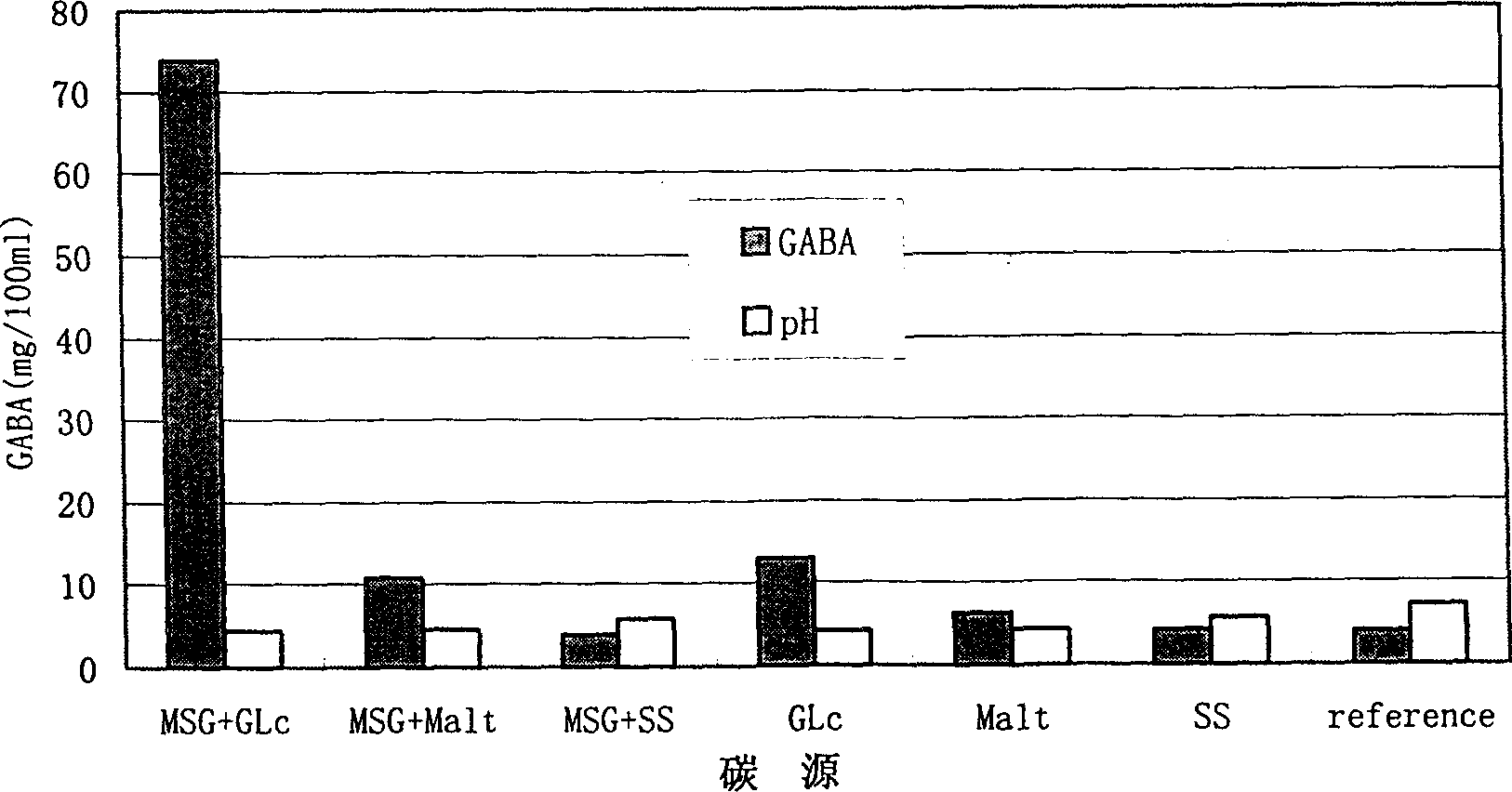
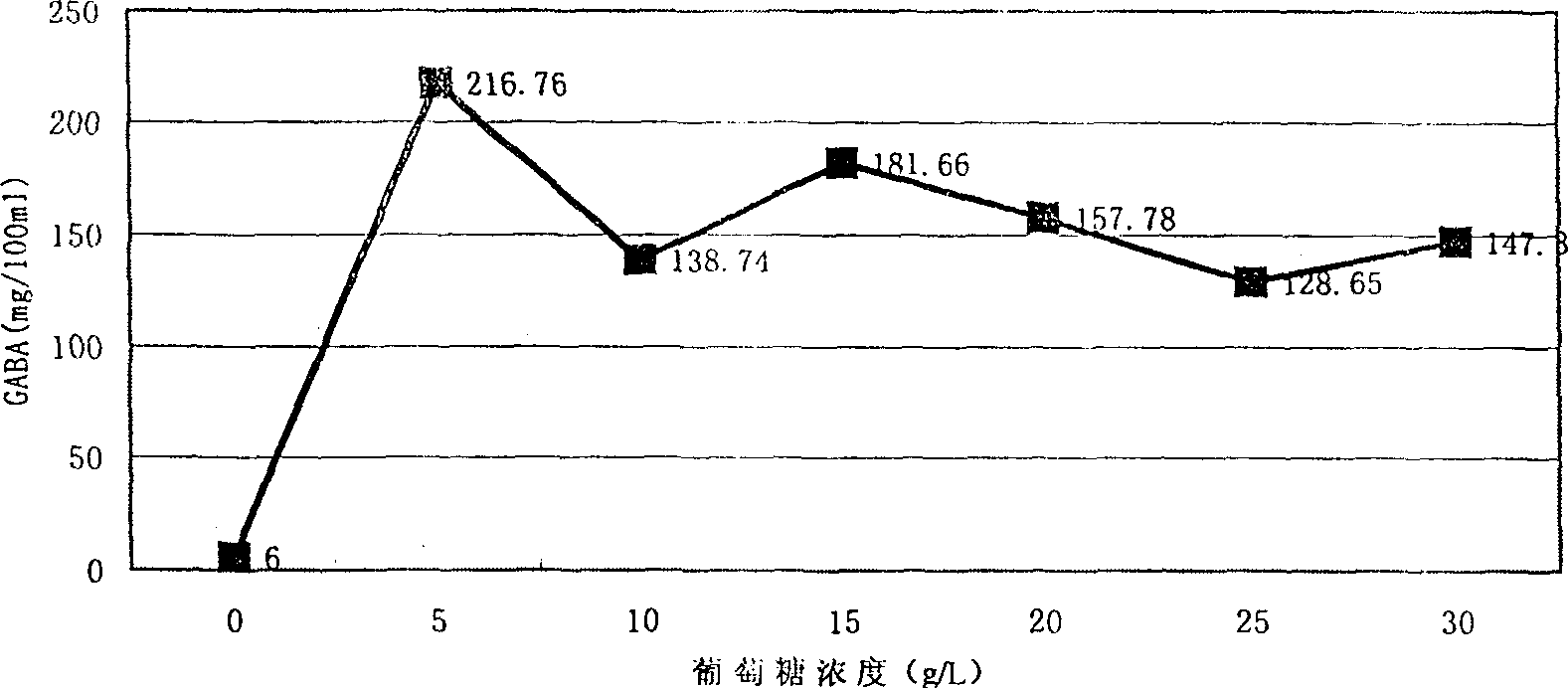
The present invention belongs to the field of food biotechnology and is especioally microbial conversion process of preparing gamma-amino butyric acid. Gamma-amino butyric acid is prepared with lactic acid bacteria or lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycete mixture as bacteria strain, sodium L-glutamate as converting substrate and through fermentating process with fermenting medium with carbon source, nitrogen source and inorganic salt. The selected lactic acid bacteria can growth well in MRS or PYG culture medium at 25-40 deg.c and may be used as culture seed liquid. Of the culture medium, the carbon source is glucose, and the nitrogen source may be one or several selected from corn paste, yeast paste, defatted peanut cake powder, etc. After fermentation, the concentration of gamma-aminoacid may reach as high as 300-500 ml / 100 ml.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
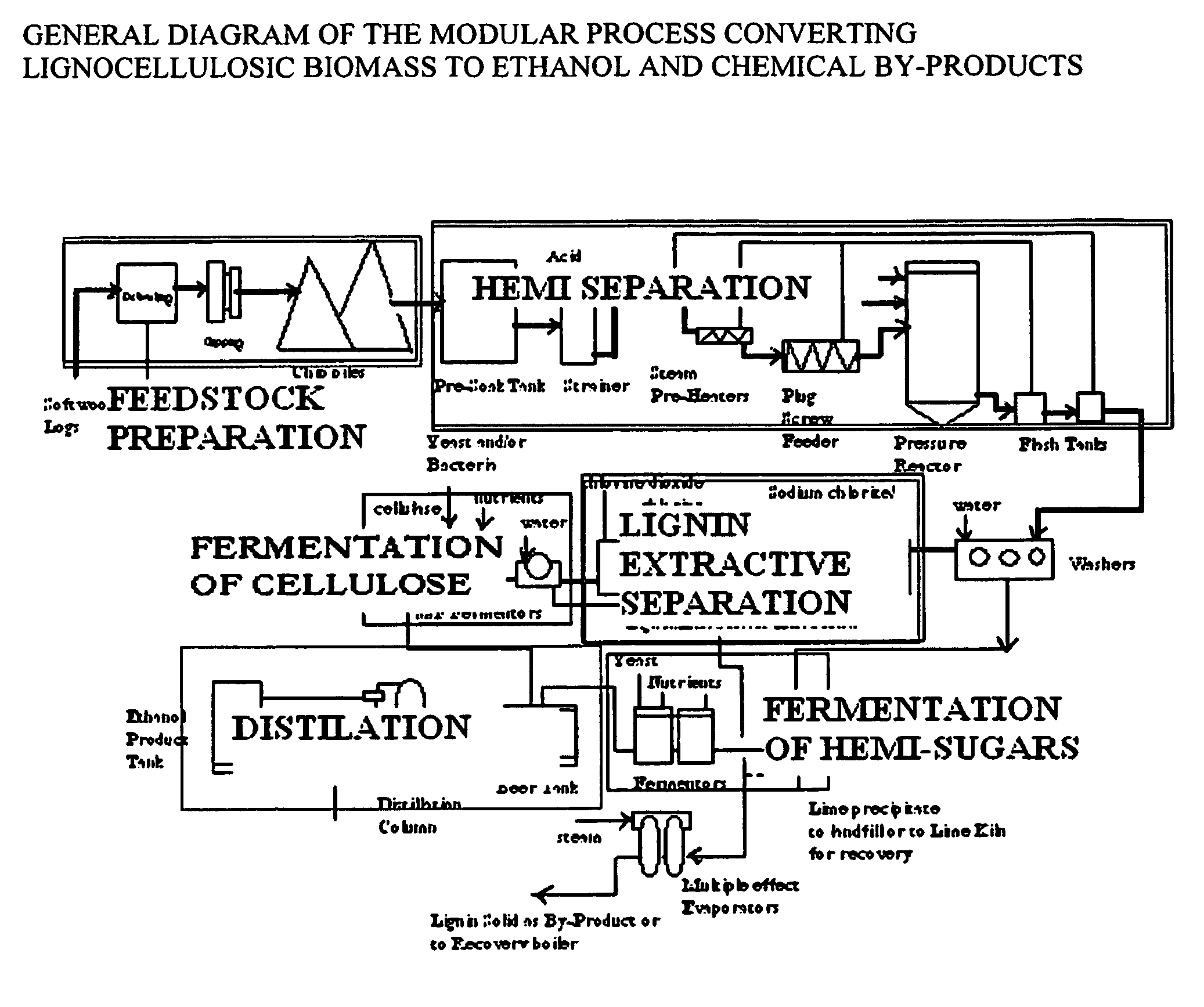
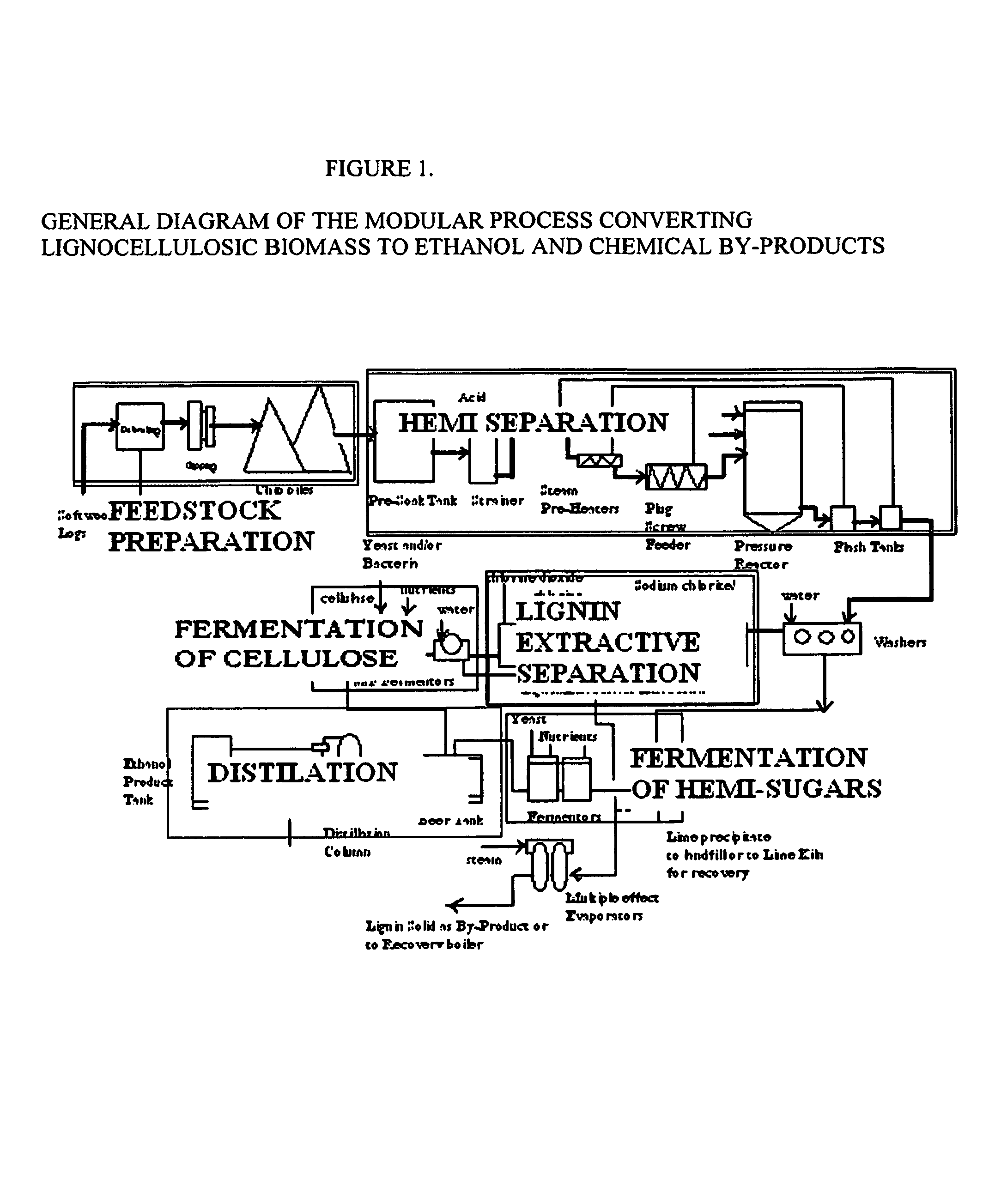
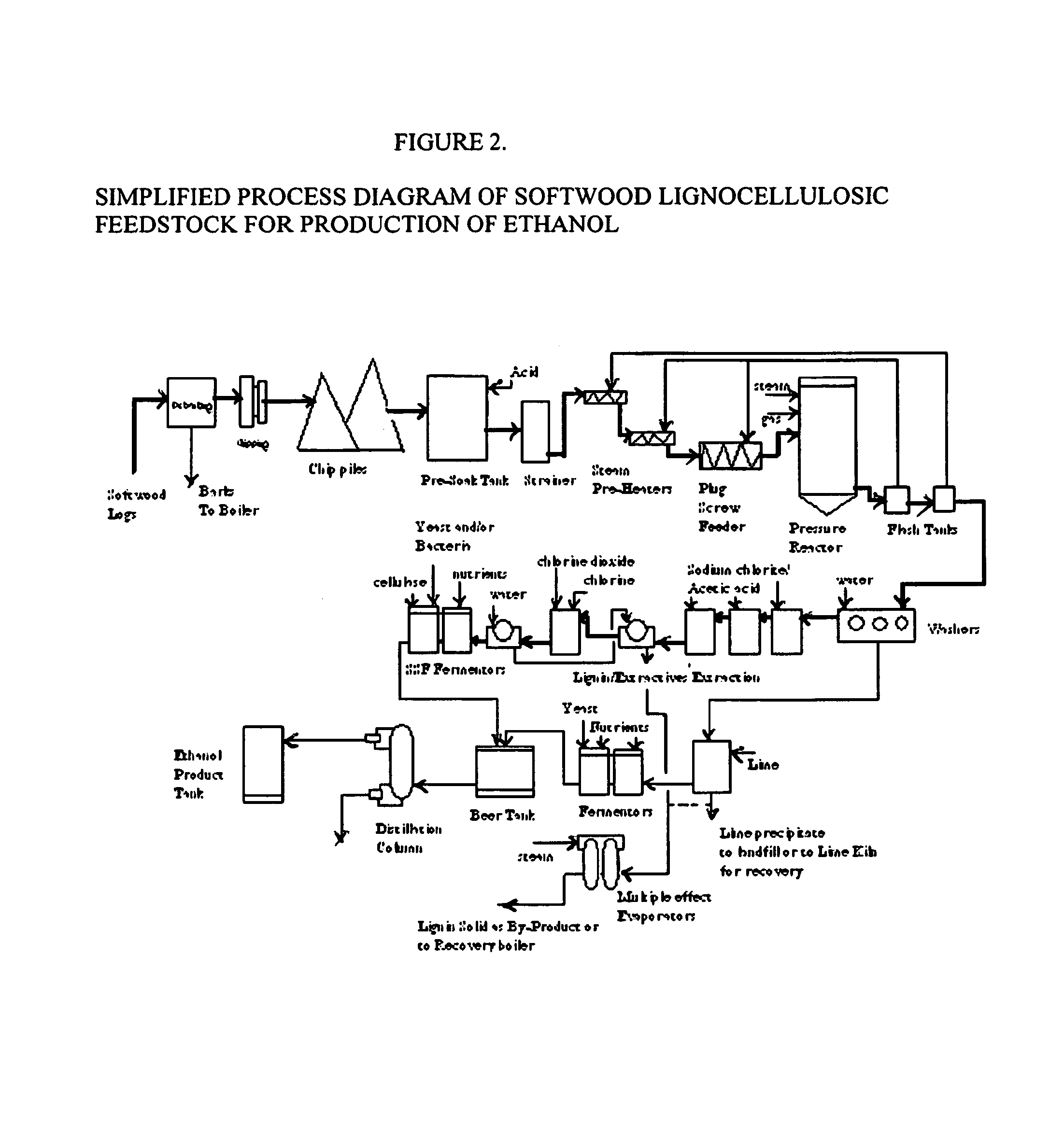
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS7666637B2Robust and cost-effectiveImproving biological reactivity of celluloseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentHydrolysate
The invented process separates main components in lignocellulosic biomass, specifically hardwoods, softwoods into lignin and fractions of high purity sugars which are used for ethanol production. The invented process comprises of treatment stages at high temperature and high pressure with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Residual lignin and extractives in the cellulosic solid fraction are selectively removed by chemical treatments of sodium chlorite, anhydrous acetic acid, chlorine and chlorine dioxide to enhance the purity and biological conversion of cellulose to ethanol. The pre-hydrolysate generated from the acid treatment stage, containing xylose, arabinose, galactose, glucose and the purified cellulosic fraction are enzymatically hydrolyzed and fermented to produce ethanol. Significant amount of lignin from the process is recovered as a by-product.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Nanoemulsions for delivering lipophilic substances into cells
InactiveUS6265180B1Low toxicityDecreased cell growthMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processTriglycerideLinoleic acid
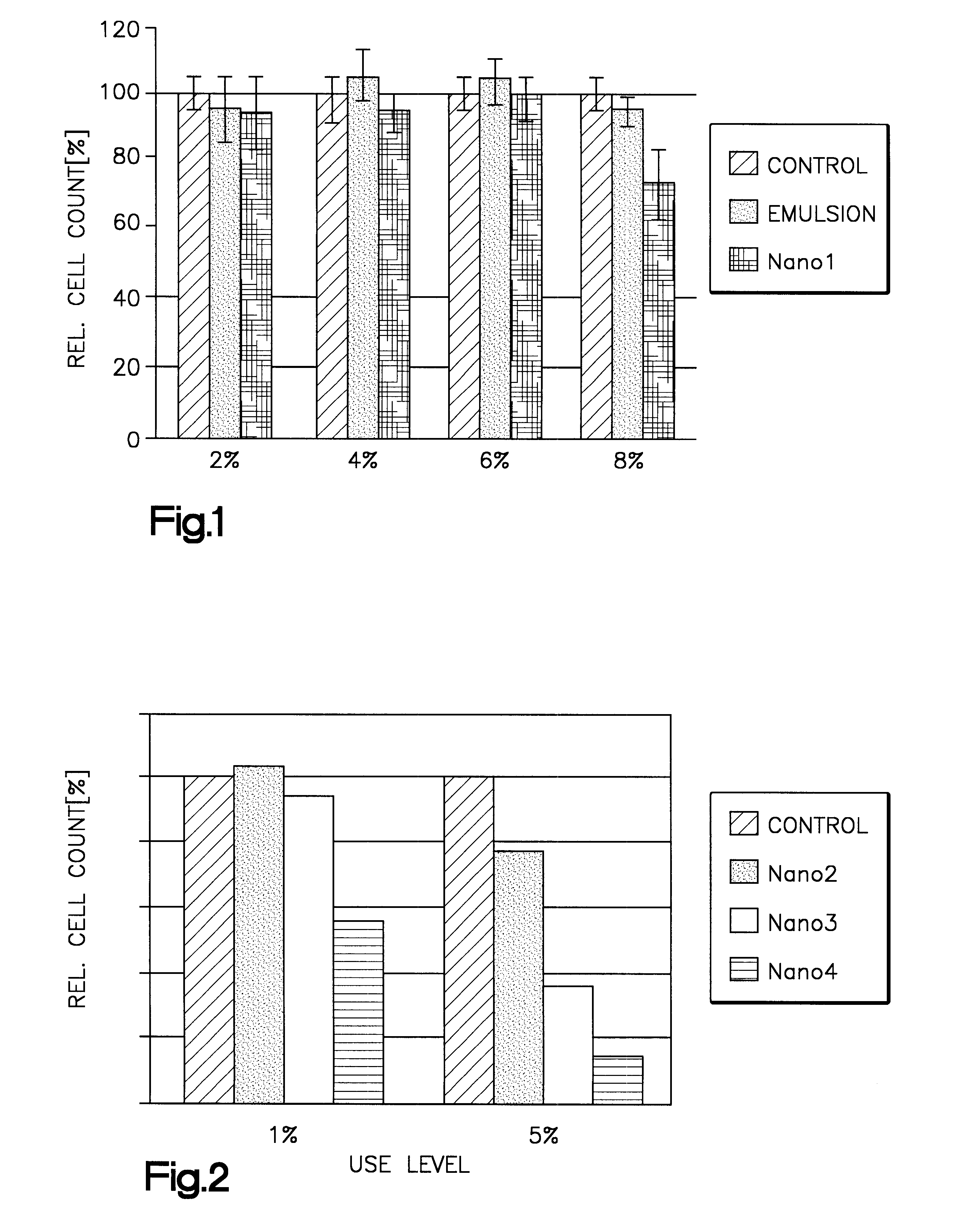
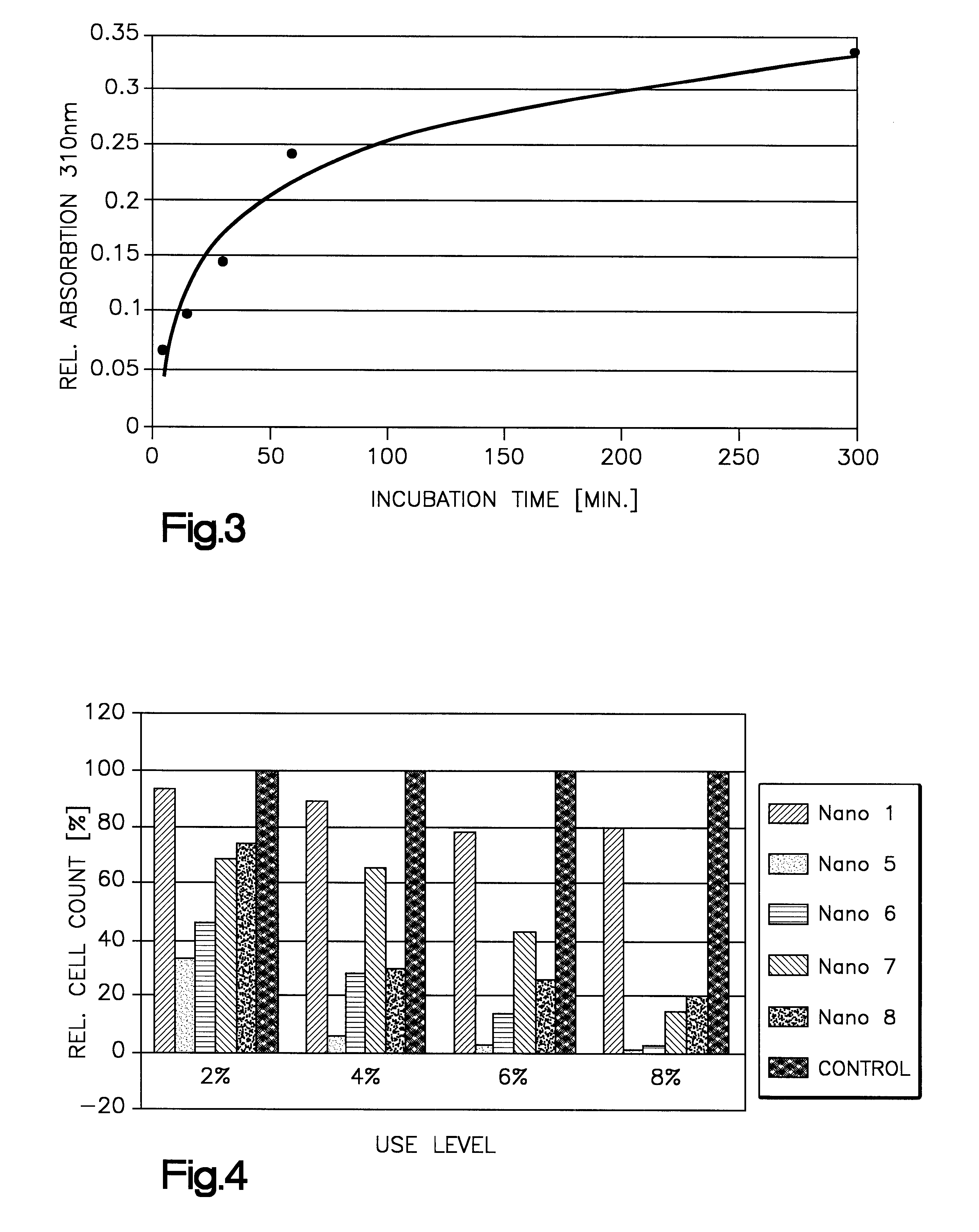
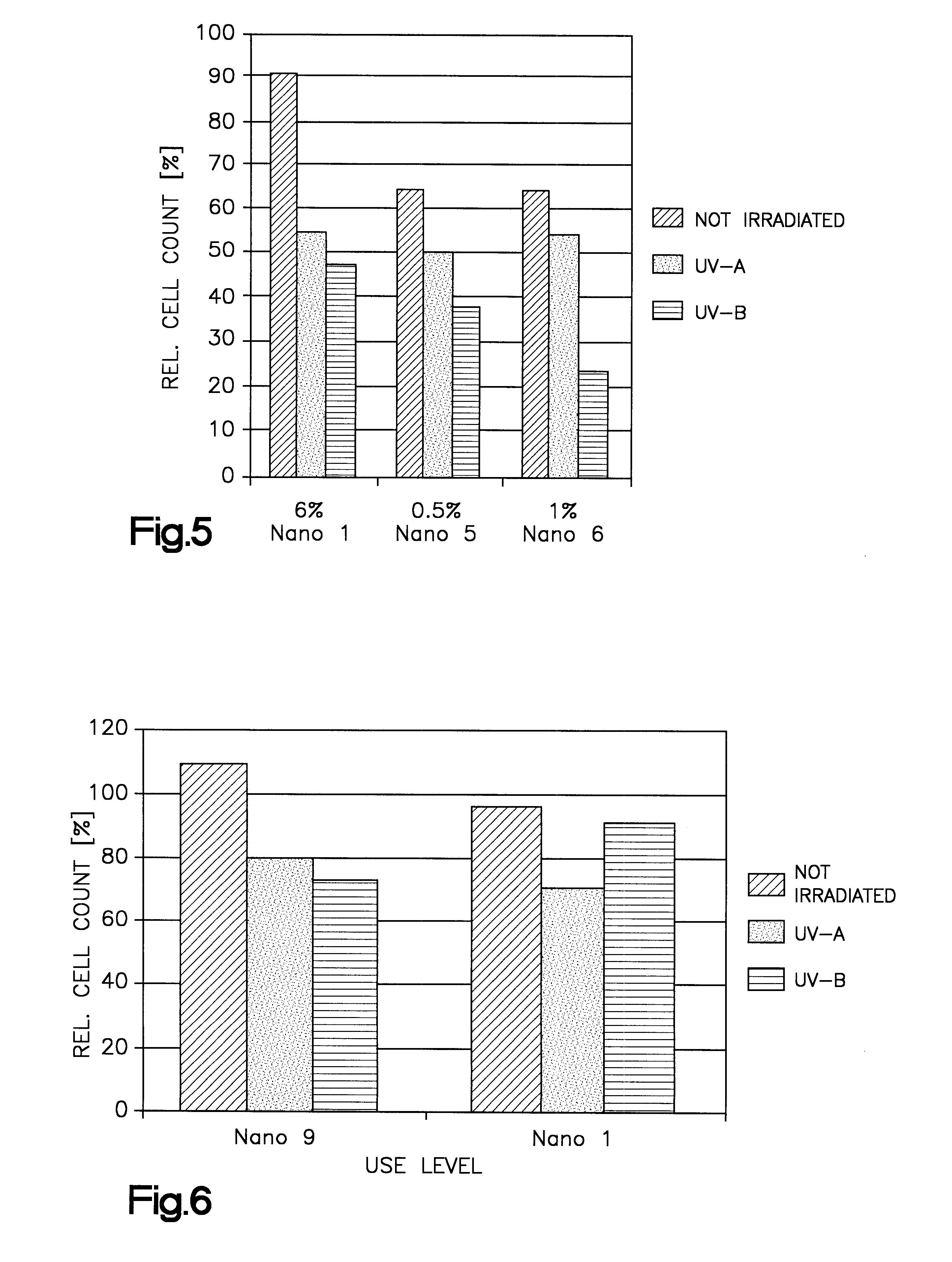
Sterile nanoemulsions are prepared containing oily droplets of a diameter of less than 100 nm in an aqueous phase. The oily droplets contain a lipophilic substance, and have on their surface an amphoteric emulsifier in an amount of preferably 0.65 to 0.75 parts by weight amphoteric emulsifier for one part by weight of oily component forming the droplets. The oily component of the droplets is preferably a triglyceride containing oleic acid and / or linoleic acid. The nanoemulsions are used for delivering into cells the lipophilic substance contained by the oily droplets. This delivery can be used to biotransform the lipophilic substance, promote cell differentiation, growth or biosynthesis of a desired substance, or to test for toxicity of the lipophilic substance.
Owner:MIBELLE COSMETICS
Method for planting lentinus edodes by using mulberry branch wood chips as planting material
InactiveCN101627697AShorten the growth cycleHigh biotransformation rateHorticultureFertilizer mixturesDrug biotransformationFunctional food
The invention discloses a method for planting lentinus edodes by using mulberry branch wood chips as a planting material, mainly comprising the following steps: preparing the planting material; sterilizing the planting material at high temperature; inoculating and managing the output of the lentinus edodes; the method reasonably controls the material mixture ratio of the planting material through science and strictly controls technological conditions, such as temperature, humidity and the like in the planting process, therefore, the planted lentinus edodes has short growth period, high biotransformation rate, high yield, uniform individuals and abundant nutrition and belongs to a functional food of a novel generation.
Owner:巫溪县万统野生资源开发有限责任公司
Method for culturing rare edible fungi including tricholoma lobayense heim and clitocybe maxima by using vine shoot dust
InactiveCN102187787AAchieve biotransformationMaterials are readily availableHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologySucrose
The invention discloses a method for culturing rare edible fungi including tricholoma lobayense heim and clitocybe maxima by using vine shoot dust. The method comprises the following steps of: A, preparation of a fermentation culture solution; B, preparation of liquid spawn; C, preparation of granular spawn; D, preparation of a culture medium: selecting 68-72 percent of vine shoot dust, 8-12 percent of cotton seed hull, 8-12 percent of broken dry broad-leaved tree fallen leaves, 8 percent of bran, 1 percent of sucrose and 1 percent of calcined lime in a weight ratio, stirring in a material-water ratio of 1:1.4, bagging, performing conventional sealing, and sterilizing for later use; E, inoculating culture; and F, harvesting. The vine shoot is treated and developed into a raw material for culturing the rare edible fungi including the tricholoma lobayense heim and the clitocybe maxima, a natural culture medium is provided for the fungi culture industry, the biotransformation utilization of the vine shoot is realized, and the culture costs of the tricholoma lobayense heim and the clitocybe maxima are reduced.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
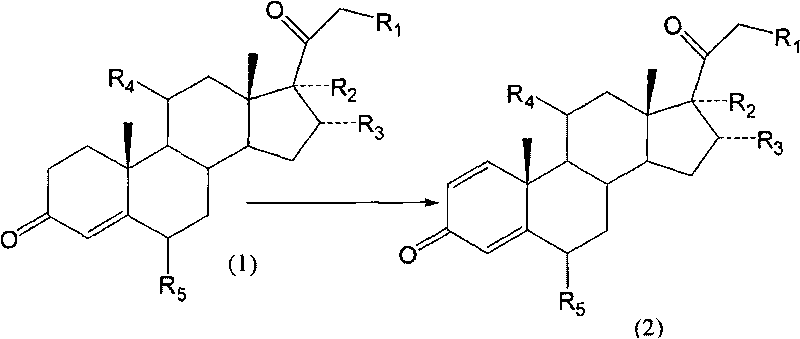
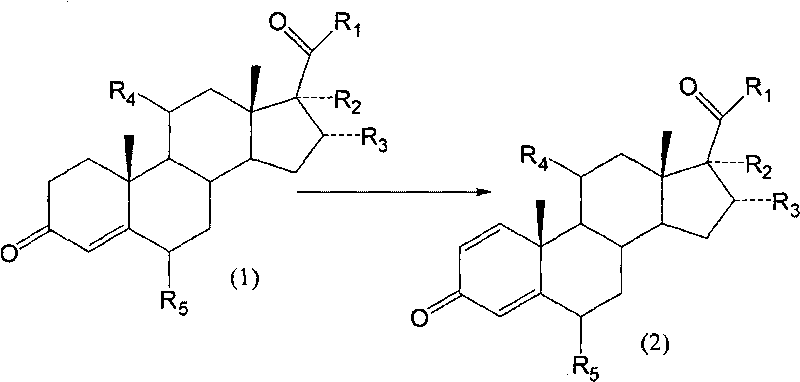
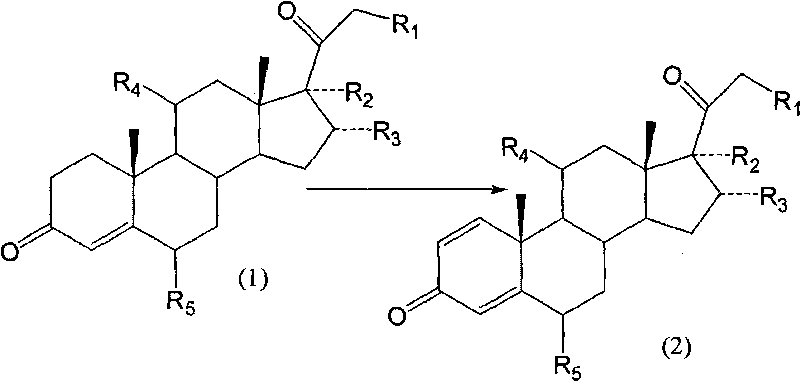
Biological dehydrogenation preparation method of steroid drug intermediate
InactiveCN101760496AAvoid residueAvoid toxicityMicroorganism based processesFermentationArthrobacter simplexSolvent
A biological dehydrogenation preparation method of steroid drug intermediate takes the formula (1) compound as a substrate, and adopts an arthrobacter simplex biological dehydrogenation method to obtain formula (2) compound; the special process comprises the following steps: smashing or dissolving the formula (1) compound with solvent, putting into a fermentation tank in which arthrobacter is cultivated for biotransformation, extracting, separating and refining, and drying to obtain dehydrogenated polymer, i.e. compound (2); and the dehydrogenation transformation rate can reach 70 to 90 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN JINYAO GRP
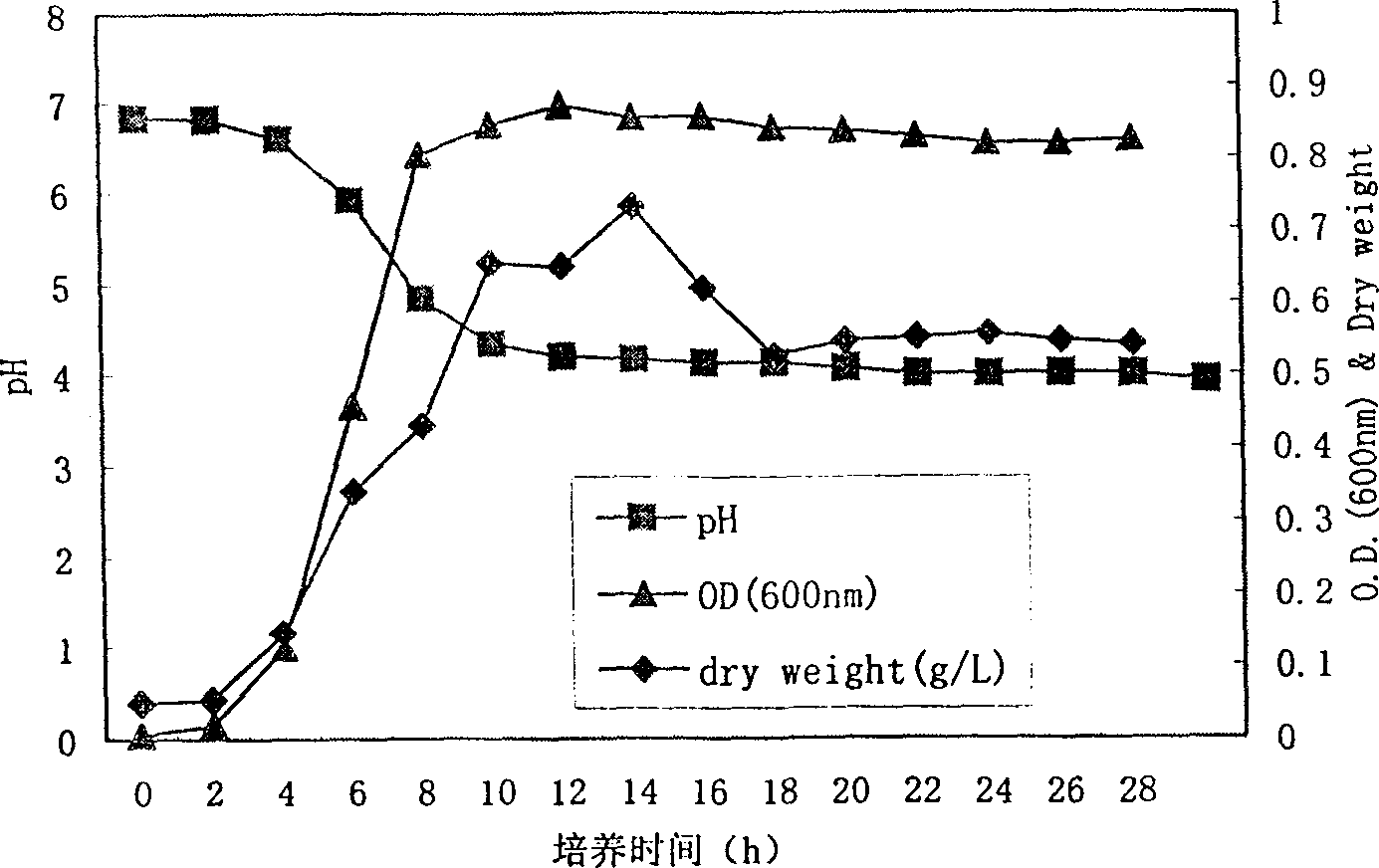
Microbe fermenting process of producing perfume phenylethanol
The present invention is the microbe fermenting process of producing perfume phenylethanol with tobacco material. The technological process includes using tobacco as precursor for biological conversion, adding proper culture medium, selecting proper bacteria strain, fermentation culture in certain technological conditions., degrading the lignin, pectin and polyphenol compounds to convert into phenylethanol and final purifying via extraction or ion exchange resin adsorption. The obtained phenylethanol product has pure fragrance and may be used for food product. The production process is simple and has wide application foreground.
Owner:华宝香化科技发展(上海)有限公司
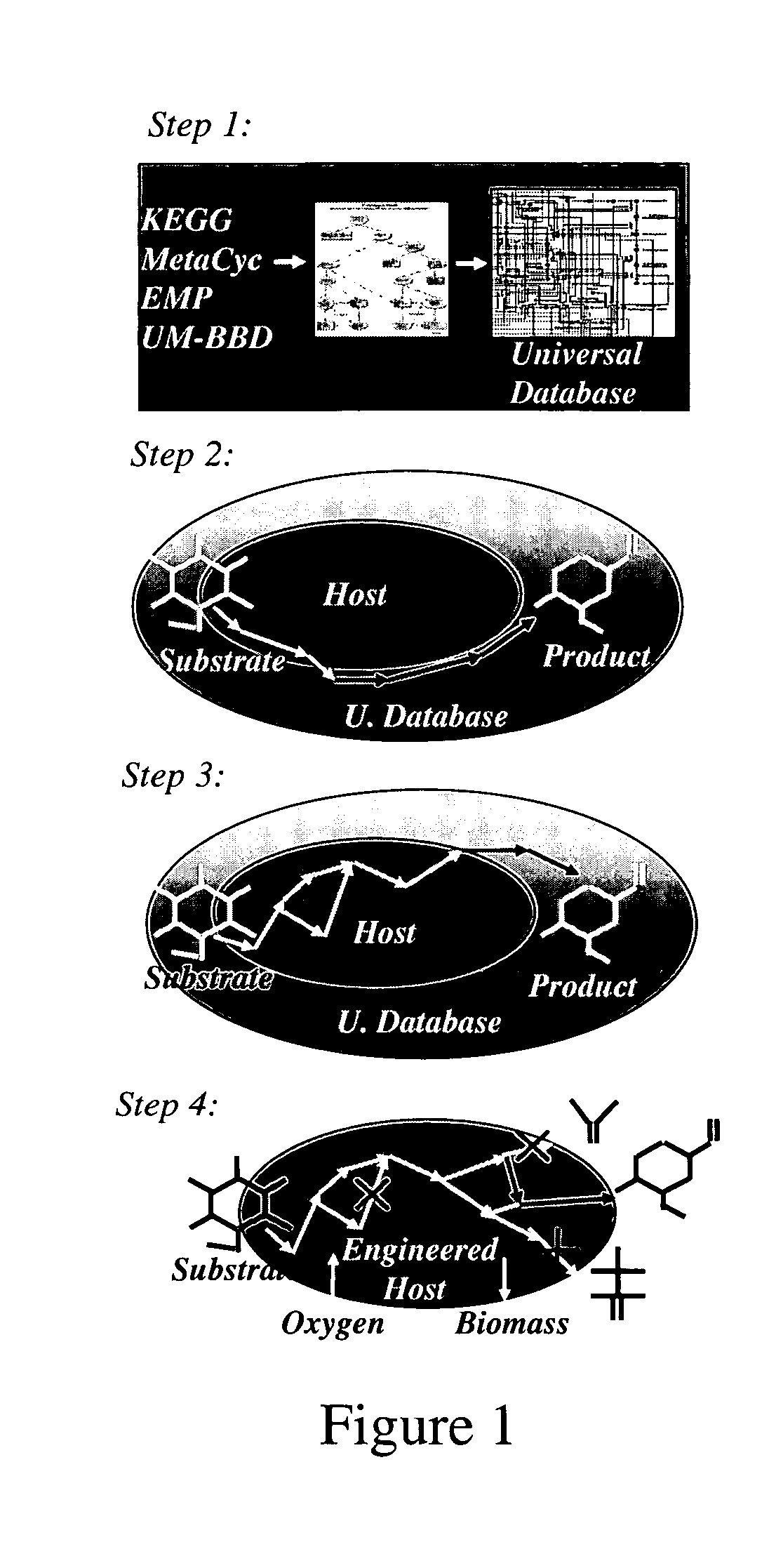
Method for redesign of microbial production systems
A computer-assisted method for identifying functionalities to add to an organism-specific metabolic network to enable a desired biotransformation in a host includes accessing reactions from a universal database to provide stoichiometric balance, identifying at least one stoichiometrically balanced pathway at least partially based on the reactions and a substrate to minimize a number of non-native functionalities in the production host, and incorporating the at least one stoichiometrically balanced pathway into the host to provide the desired biotransformation. A representation of the metabolic network as modified can be stored.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
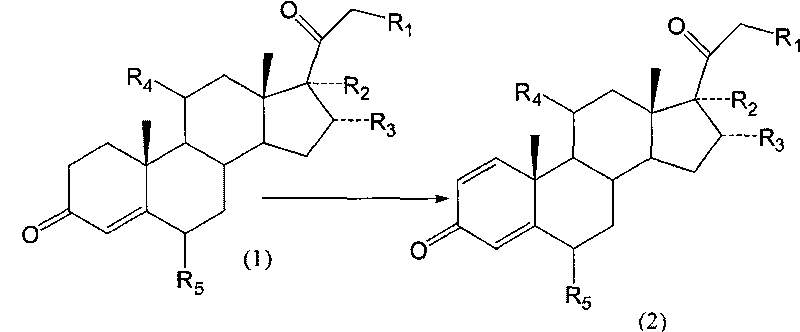
Biological dehydrogenation preparation method of 6 alpha-methylprednisolone intermediate
ActiveCN101760495AAvoid residueFlexible choiceMicroorganism based processesFermentationDehydrogenationMethylprednisolone
The invention relates to a biological dehydrogenation preparation method of a 6 alpha-methylprednisolone intermediate, which uses a compound of formula (1) as a substrate and obtains a compound of formula (2) by adopting a simple arthrobacterium biological dehydrogenation method. The process comprises the following steps of: crushing the formula (1) compound or dissolving the formula (1) compoundby using a solvent; adding to a fermentation tank with cultivated arthrobacterium to perform biotransformation; extracting, separating, and refining; drying, and then obtaining a dehydrogenation matter, i.e. the formula (2) compound. The invention can achieve the biotransformation rate of 70-90 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN JINYAO GRP
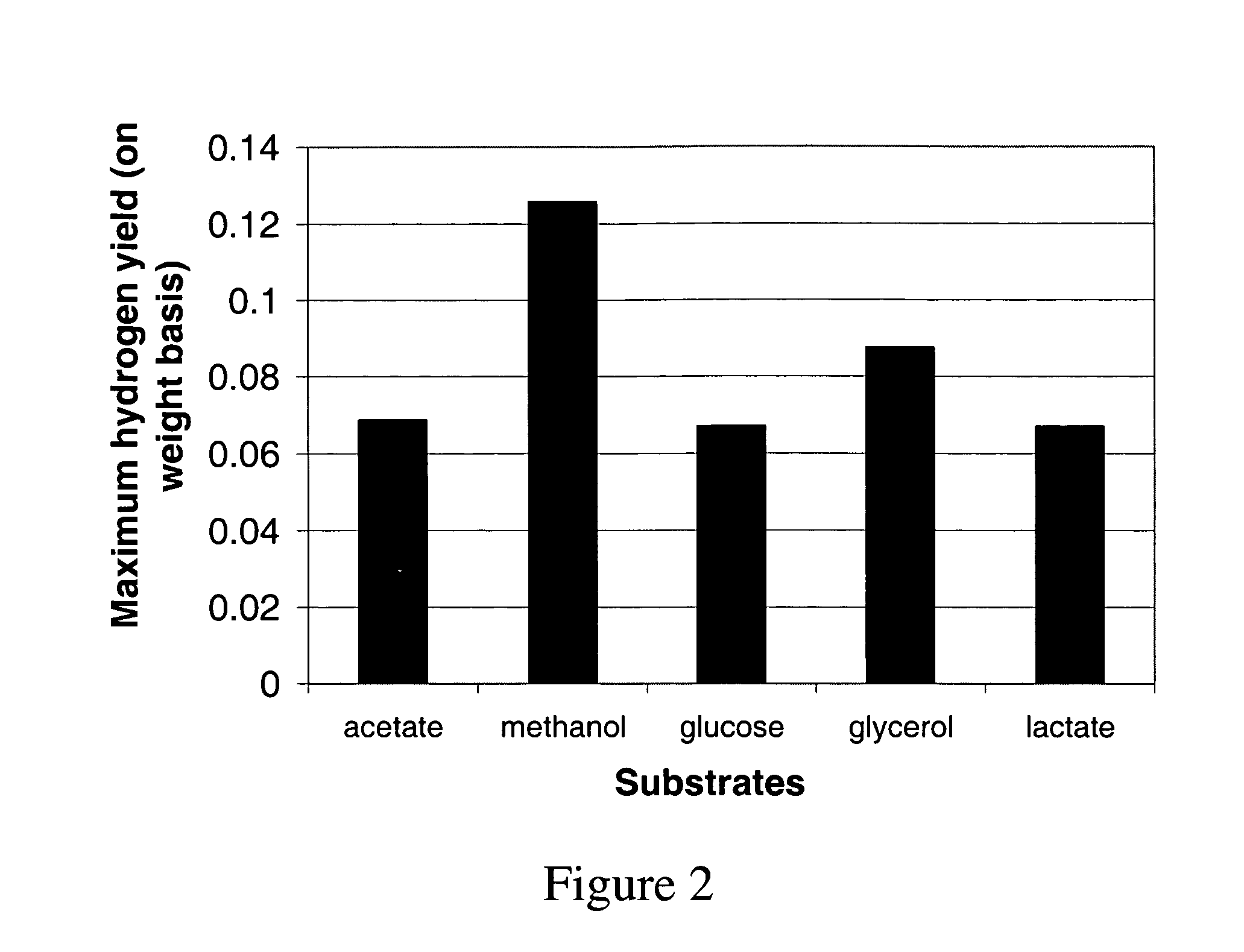
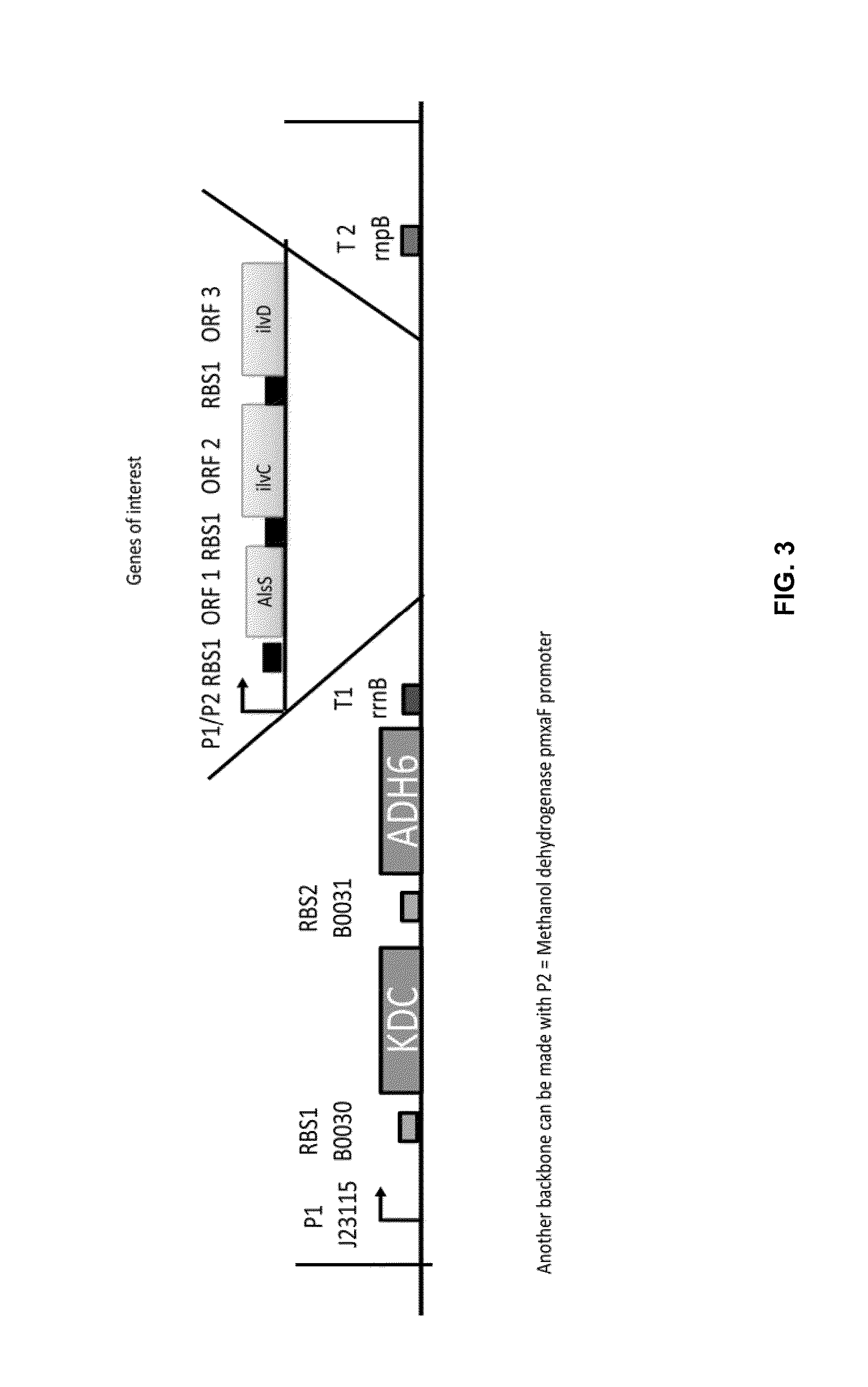
Biological Conversion of Multi-Carbon Compounds from Methane
Multi-carbon compounds such as ethanol, n-butanol, sec-butanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, fatty (or aliphatic long chain) alcohols, fatty acid methyl esters, 2,3-butanediol and the like, are important industrial commodity chemicals with a variety of applications. The present invention provides metabolically engineered host microorganisms which metabolize methane (CH4) as their sole carbon source to produce multi-carbon compounds for use in fuels (e.g., bio-fuel, bio-diesel) and bio-based chemicals. Furthermore, use of the metabolically engineered host microorganisms of the invention (which utilize methane as the sole carbon source) mitigate current industry practices and methods of producing multi-carbon compounds from petroleum or petroleum-derived feedstocks, and ameliorate much of the ongoing depletion of arable food source “farmland” currently being diverted to grow bio-fuel feedstocks, and as such, improve the environmental footprint of future bio-fuel, bio-diesel and bio-based chemical compositions.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Streptomycete and method for producing vanillin by using the same to biologically transform ferulic acid
ActiveCN101165168AReduce pollutionMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationChemical synthesis
The present invention is one Streptomyces strain and the process of utilizing the Streptomyces strain in converting ferulic acid to produce high concentration vanillin. The Streptomyces strain is Streptomyces sp.V-1 in the preservation number of CCTCC M 206065. In the GY converting culture medium with the Streptomyces strain, ferulic acid may be converted to produce high concentration vanillin fermenting liquid. Adding macroporous adsorption resin DM11 into the converting culture medium can increase the concentration of vanillin fermenting liquid greatly. The present invention has the advantages of less environmental pollution, high product concentration, less side products, short production period, low cost, etc.
Owner:APPLE FLAVOR & FRAGRANCE GRP +2
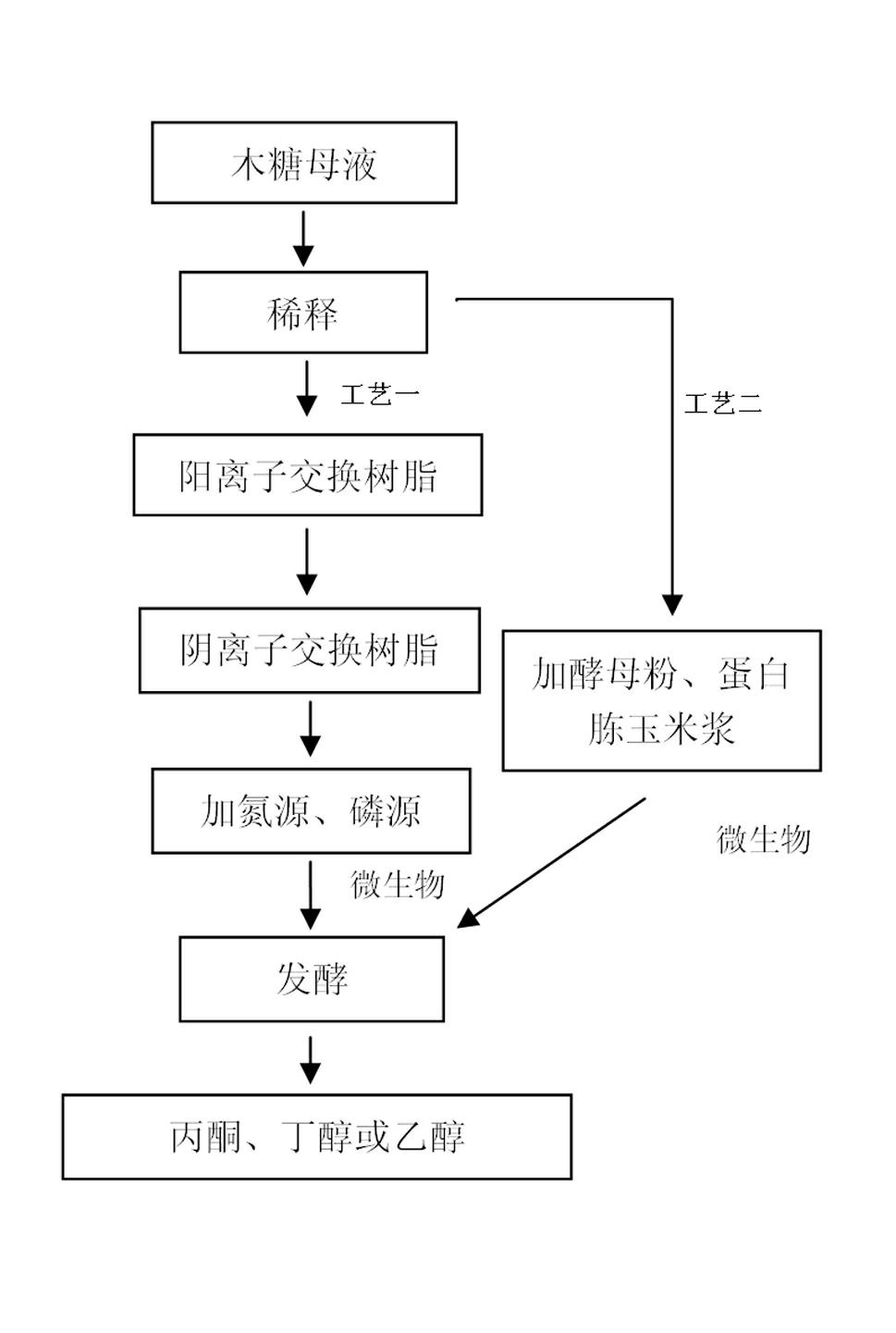
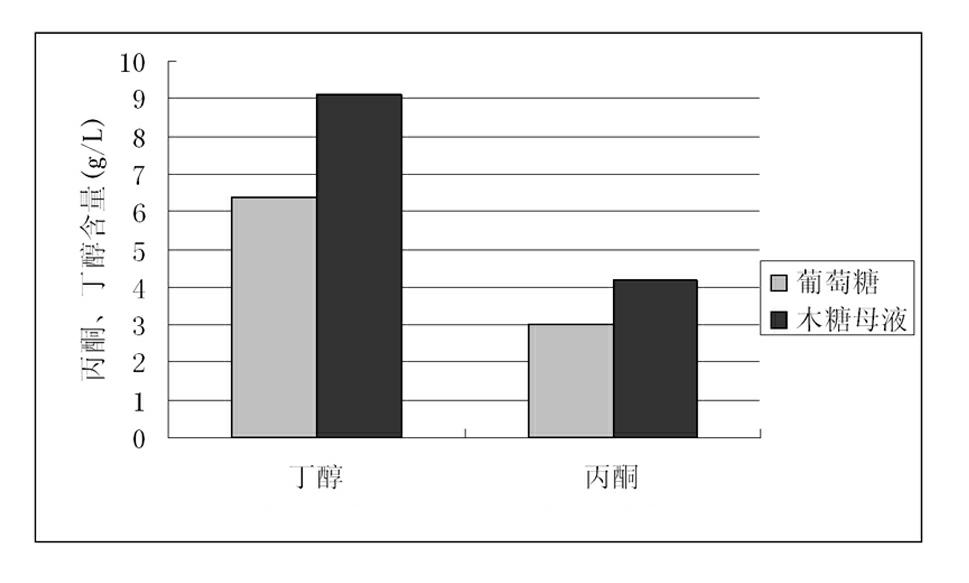
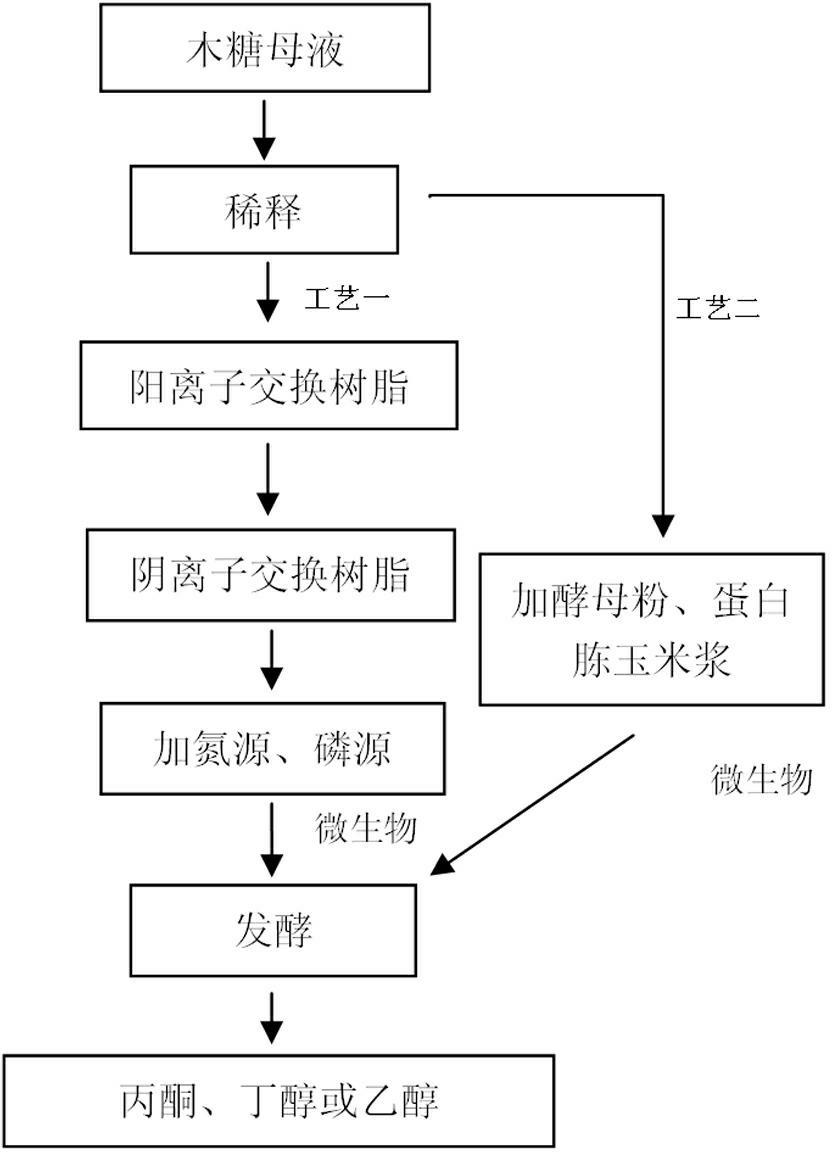
Method using xylose production waste liquid to produce acetone and butanol
A method using the xylose production waste liquid to produce acetone and butanol belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering, utilizes the xylose production waste liquid as the raw material, utilizes the microbial fermentation technology and the biotransformation sugar source to produce chemical products of acetone and butanol, and has the specific technological steps of culture medium preparation, bacterial strain activation, inoculation and fermentation, so the products of ethanol, acetone and butanol are obtained. The invention has advanced technology and a low equipment input cost; the utilization problem of the xylose production waste liquid is solved, and the additional value is high; compared with chemical synthesis, fossil resources are also saved; meanwhile, compared with the production method which takes the grain crop as the fermentation raw material, the price of the raw material is low, the method does not compete with the human being for food, and does not compete with the grain forest for land; and the comprehensive utilization of the xylose production waste liquid is realized, the comprehensive cost of the xylose production is reduced, the utilization efficiency of the biomass resource is improved, the industrial by-products are reused, the environment pollution is less, the energy consumption is low, and the social benefit is obvious.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGLIVE BIO TECH CO LTD
Production method of selenium-enriched pork
The invention relates to a production method of selenium-enriched pork. A feed fed when live pigs are bred is a selenium-enriched nutritional feed processed by corn, wheat bran, soybean meal, fish meal, feed grade calcium hydrophosphate, mountain flour, trace elements and selenium-enriched ryegrass hay, wherein the content of the hay in the feed is not lower than 15wt%, and the selenium content in the hay is not less than 1,000mug / kg. The selenium-enriched ryegrass hay is obtained by drying ryegrass the reaped or harvested leaf surfaces of which are sprayed and applied with a sodium selenite nutrient solution the concentration of which is not lower than 200ppm. In the invention, the selenium-enriched pork is obtained by the two-time biotransformation of inorganic selenium and has ruddy meat color, tender quality, fragrant taste and no any fishy smell of a pigpen, the selenium content in each kilogram of pork is not less than 80mug, and the lowest selenium demand of a human body can bemet as long as an adult eats more than 100g of selenium-enriched pork every day.
Owner:CHAOHU WANDA FARMING
Culture medium and cultural method for cultivating coprinus comatus
InactiveCN102924156AHigh biotransformation rateGrowth inhibitionBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationFecesLivestock manure
The invention provides a culture medium for cultivating coprinus comatus, which is composed of chestnut shells, crop straws or corncobs, dry livestock manure, calcium superphosphate, quick lime, enzyme bacterium and water. The method utilizing the culture medium to cultivate the coprinus comatus comprises the following steps: first, uniformly stirring all raw materials to produce a base material; second, stacking the base material for fermentation; third, bagging the fermented base material for inoculation so as to produce bacteria sticks; fourth, placing the bacteria sticks in a bacteria cultivating room; fifth, debagging the bacteria sticks so as to allow the bacteria sticks to be stood in a bed and is covered with soil; sixth, carrying out water spray management; and seventh, picking the coprinus comatus. According to the invention, the chestnut shells are basic material of the culture medium which is green and pollution-free, the cultivating process is simple, and the production cost is low; and the coprinus comatus is high in yield, good in quality, and high in biotransformation efficiency.
Owner:柞水县海林菌业有限责任公司 +1
Preparation method of porous inorganic filling materials-fixed quinone compound
InactiveCN101862680AImprove catalytic performanceSolve the technical bottleneck of secondary pollutionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWater contaminantsSulfonyl chlorideAnaerobic reactor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous inorganic filling materials-fixed quinone compound, belonging to the technical field of water treatment in environmental engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting porous inorganic filling materials such as ceramsites, volcanics and the like; plating gamma-aluminum oxide on the surface of the materials; aminating, so that the surfaces of the porous inorganic filling materials contain a certain quantity of primary amidogen; putting the aminated materials into hydrochloric solution to have reaction for protecting the primary amidogen; and putting the reacted porous inorganic filling materials into sodium hydroxide solution, adding sulfonyl chloride group-containing anthraquinone compound which is dissolved in dichloromethane, and reacting for 6-10h under the room temperature to fix the water-soluble quinone compound. The quinone compound-containing macroporous polymer is applied to an anaerobic reactor to be capable of improving the biotransformation speed of an organic matter which is hardly degraded. The method covalently fixes the quinone compound on the macroporous polymer of a biologic carrier, so that the redox medium is easily contacted with the microbe, thereby overcoming the problem of the secondary pollution since the water-soluble quinone compound flows out with the water.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing macroporous polymer fixed quinonoid compound
InactiveCN101698699AImprove catalytic performanceIncrease contactTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesDrug biotransformationDichloromethane
The invention discloses a method for preparing a macroporous polymer fixed quinonoid compound and belongs to the technical field of water treatment in environment engineering. The method is characterized by selecting hydroxyl group containing macroporous polymers for aminating treatment so as to make the macroporous polymers contain primary amino groups in certain quantity. At the room temperature, the macroporous polymers are added in solution of sodium hydroxide, then anthraquinone compounds, which are dissolved in methylene chloride and contain sulfonic acid chloride groups, are added, andthe mixed solution stirred for reaction for 0.5 to 2 hours, so that the fixture of the quinonoid compounds are realized. The macroporous polymers containing quinonoid compounds can be applied to an anaerobic reactor to improve the biological conversion rate of hardly degradable organic matters. The method has the advantages that: the quinonoid compounds are covalently fixed on a biological carrier which is macroporous polymers, so that a redox mediator is more easily contacted with microorganisms; and the problem of secondary pollution caused by emission of water soluble quinonoid compounds along with discharge water is solved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving sweetness of stevia sugar
InactiveCN101691389AIncrease sweetnessSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationMicroorganismAdditive ingredient
Stevioside is a novel sweeter which is extracted from stevia leaves, and the stevioside in the stevia leaves mainly comprises two components of stevioside and rebaudioside A. The sweetness and mouthfeel of the rebaudioside A are both excellent, while the stevioside has certain lingering bitterness; and as the structure and nature of the rebaudioside A are approximate to the structure and nature of the stevioside, the separation of rebaudioside A and stevioside features high cost and great technical difficulty. In the invention, microorganisms are transformed for 20h-150h under the conditions that the concentration of the stevioside is 0.01%-5% (W / W), the temperature is 25-80 DEG C, the quantity of inverting enzyme or bacterial solution is 0.1%-10% (W / W), and the pH value is 2.0-7.0, and the stevioside contained in the rebaudioside A solution can be selectively degraded, thus obtaining high purity rebaudioside A containing no stevioside. The biotransformation method used in the invention has temperate conditions, does not use toxic methanol and other chemicals or macroporous resin with high cost, thus being a novel technology with safety, greenness and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Production of dicarboxylic acids by improved mutant strains of yarrowia lipolytica
The invention concerns a method for producing dicarboxylic acids (DCA) with long hydrocarbon chains, also called diacids, which consists in culturing a mutant strain of Yarrowia lipolytica obtained by mutagenesis directed and more particularly disrupted at least for the POX2, POX3, POX4 and POX5 genes encoding acyl-CoA oxydase, in a medium consisting essentially of an energetic substrate including at least one carbon source and one nitrogen source and in subjecting said strain to a bioconversion substrate selected among n-alkanes of at least 10 carbon atoms, fatty acids of at least 10 carbon atoms, their alkyl esters and natural oils.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +2
Method for cultivating selenium-rich bean sprouts
InactiveCN102090313AAdvantages of production processNo pollution in the processCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationSoybean sproutDrug biotransformation
The invention relates to selenium-rich bean sprouts and a production process thereof. The production process is to use sprouting of soybeans to perform the biotransformation of selenium to obtain a bean sprout product rich in organic selenium. The invention belongs to the field of deep processing of farm products, and also belongs to the field of the production of functional food. The production process comprises the following steps of: performing selection and impurity removal on the soybeans, then soaking in solution of sodium selenite, draining water, and then ensuring that the soybeans sprout in a mode of water spraying cultivation to obtain the selenium-rich bean sprouts.
Owner:常州五星禾绿蔬菜食品有限公司
Biomass Pyrolysis Refining-Method of Hierarchical Directional Conversion
InactiveCN102266864ADifferent pyrolysis propertiesBiological substance pretreatmentsSilicaSlagDrug biotransformation
The invention relates to a biomass pyrolysis refining-grading directional conversion process. Based on the fact that the main chemical components (cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, etc.) of biomass raw materials have different thermal decomposition characteristics, the present invention uses pyrolysis refining as the technical platform to propose a technology of gradient heating and step-by-step collection scheme, the pyrolysis products are graded and directed transformations as platform compounds. Among them, the water-soluble pyrolysis oil fraction has fermentation properties and can undergo selective biotransformation; the fat-soluble pyrolysis oil fraction is used to refine high-quality bio-oil, and the pyrolysis residue is used to prepare high-quality activated carbon or nano-silica. Biomass pyrolysis refining-graded directional conversion solves the problems of the use of a large number of enzyme catalysts and the difficulty of collecting, transporting and storing raw materials in the process of using biomass raw materials as energy. It is a high-efficiency and high-value utilization process of biomass.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Artificial cultivation method capable of realizing highland cultivation of wild ganoderma tsugae murr
InactiveCN102870595AAvoid temperature dropLight intensityHorticultureAnimal scienceGanoderma pseudoferreum
The invention relates to an artificial cultivation method of lucid ganoderma, in particular to an artificial cultivation method capable of realizing highland cultivation of wild ganoderma tsugae murr. The artificial cultivation method comprises the following steps: (1), a stock culture is prepared; (2), a pre-culture spawn is prepared; (3), a production spawn is prepared; (4), inoculating and cultivation are conducted; and (5), ganoderma tsugae murr growing management is conducted till a white edge of a fungi pileus is turned to yellow completely, and then the ganoderma tsugae murr is picked. According to the artificial cultivation method, the total biotransformation rate can reach 55-85%; the taste of the obtained ganoderma tsugae murr is relatively bitter; the ganoderma tsugae murr has the taste of ganoderma lucidum, and has effects of improving the immunity, preventing a cancer and the like; and requirements of the ganoderma tsugae murr in a wide range can be met through the artificial cultivation.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM +1
Production method and strain of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
InactiveCN102154393ASimplify production stepsReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate decarboxylaseDrug biotransformation
The invention discloses a production method and strain of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a glutamate decarboxylase gene into a glutamic acid production bacterium to construct a gene engineering bacterium; and removing a carboxyl from a self-accumulated glutamic acid by using glutamate decarboxylase secreted by the gene engineering bacterium to synthesize the GABA. In the invention, fermentation of glutamic acid is combined with transformation of the GABA, so that the production steps of the GABA are simplified; moreover, glucose, urea and the like are taken as culturing raw materials, so that the production cost of the method disclosed by the invention is remarkably lowered compared with a biological transformation method in which L-glutamic acid or L-sodium glutamate serving as a precursor needs to be exogenously added.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for biotransformation of kitchen waste through hermetia illucens
InactiveCN107716508ARealize one-time feedingMeet growth needsSolid waste disposalHermetia illucensDrug biotransformation
The invention provides a process for biotransformation of kitchen waste through hermetia illucens. The process includes the following steps that ingredients are added into the sorted and smashed kitchen waste, the relative humidity is adjusted, processing materials are obtained, EM bacteria are added, and a mixture is obtained after even mixing is carried out; and the mixture is paved on a cultivation disc, five-day-age larva of the hermetia illucens is added, feeding is carried out at the temperature ranging from 28 DEG C to 32 DEG C and the relative humidity ranging from 70% to 90%, and after feeding is completed, hermetia illucens mature larva and remnant materials are separated. According to the process, one-time putting of the kitchen waste can be achieved, the growth requirement of the hermetia illucens larva can be met, the processing process can be greatly simplified, and efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF APPLIED BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Method for producing mannitol by taking jerusalem artichoke as raw materials through biotransformation
InactiveCN101736058AGreat tasteAvoid raising blood sugar levelsMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh concentrationLactarius
The invention relates to saccharification processing technology of jerusalem artichoke by utilizing high-quality fructose biomass as a raw material and strain selection and technology optimization for producing mannitol by taking jerusalem artichoke as carbon source through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) crushing jerusalem artichoke tuber into coarse particles, filtering after water leaching and enzymolysis for 6 hours, supernating at 42 DEG C, rotating, evaporating and concentrating to obtain saccharification jerusalem artichoke juice with high concentration of fructose; 2) establishing high performance liquid chromatography analysis and detection conditions which can synchronously analyze the content of fermentation liquor substrate (glucose and fructose) and products (mannitol); and 3) inspecting the capacity for producing lactic acid and mannitol through fermentation by seven lactic acid bacteria by utilizing saccharification jerusalem artichoke juice with different concentration of total sugar, thus determining lactic acid bacteria with high transformation rate and production intensity of fructose, and optimizing production fermentation conditions and the highest concentration of tolerant substrate. Through feed-batch fermentation, production efficiency can be improved and mannitol can be continuously produced in large scale. The method not only generates no byproduct of sorbitol, but also has low production cost, wide raw material sources, simple technology, and mature technical route and can be implemented in industrialization.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite bacterial agent and biological method for treating flow-back fracturing fluid to obtain oil displacement active water
InactiveCN101935615ACapable of recyclabilityWith oil displacement abilityFungiBacteriaMetaboliteFracturing fluid
The invention discloses a composite bacterial agent and a biological method for treating flow-back fracturing fluid to obtain oil displacement active water, which relate to biotransformation and reutilization technology of fracturing flow-back fluid. In the method, the fracturing flow-back fluid is treated by a microbial fermentation method, and a residual organic substance harmful to environment in the flow-back fluid is transformed into biological active water with certain function. The composite bacterial agent and the method are applied to reinjection water of water injection wells, reinjection water for single-well soaking, reinjection water for oil field blockage removal, reinjection water for other purposes, water for medicament preparation in a technical process and the like. The composite bacterial agent comprises biosurfactant, organic acid, organic ester, organic ketone, biogas and other metabolites produced by microbial metabolism of the fracturing flow-back fluid.
Owner:DALIAN BITEOMICS INC
Fibrized cellulomonas cartae, hydrolase and application thereof in taxane conversion aspect
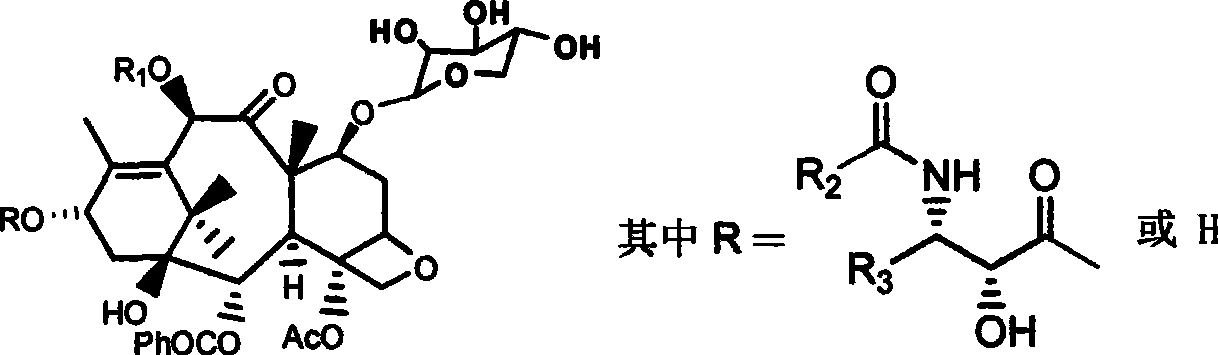
The invention provides a fibration Cellulomonas spp and a hydrolytic enzyme thereof for effectively transforming taxane xyloside into taxol or the analogues thereof, and an effective new method for preparing the taxol or the analogues thereof through biotransformation reaction. The method can prepare the taxol or the analogues thereof with high efficiency, low cost and environmental protection, which provides an effective approach adapting to industrial production for making full use of taxane resources.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com