Patents
Literature
191 results about "Yarrowia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
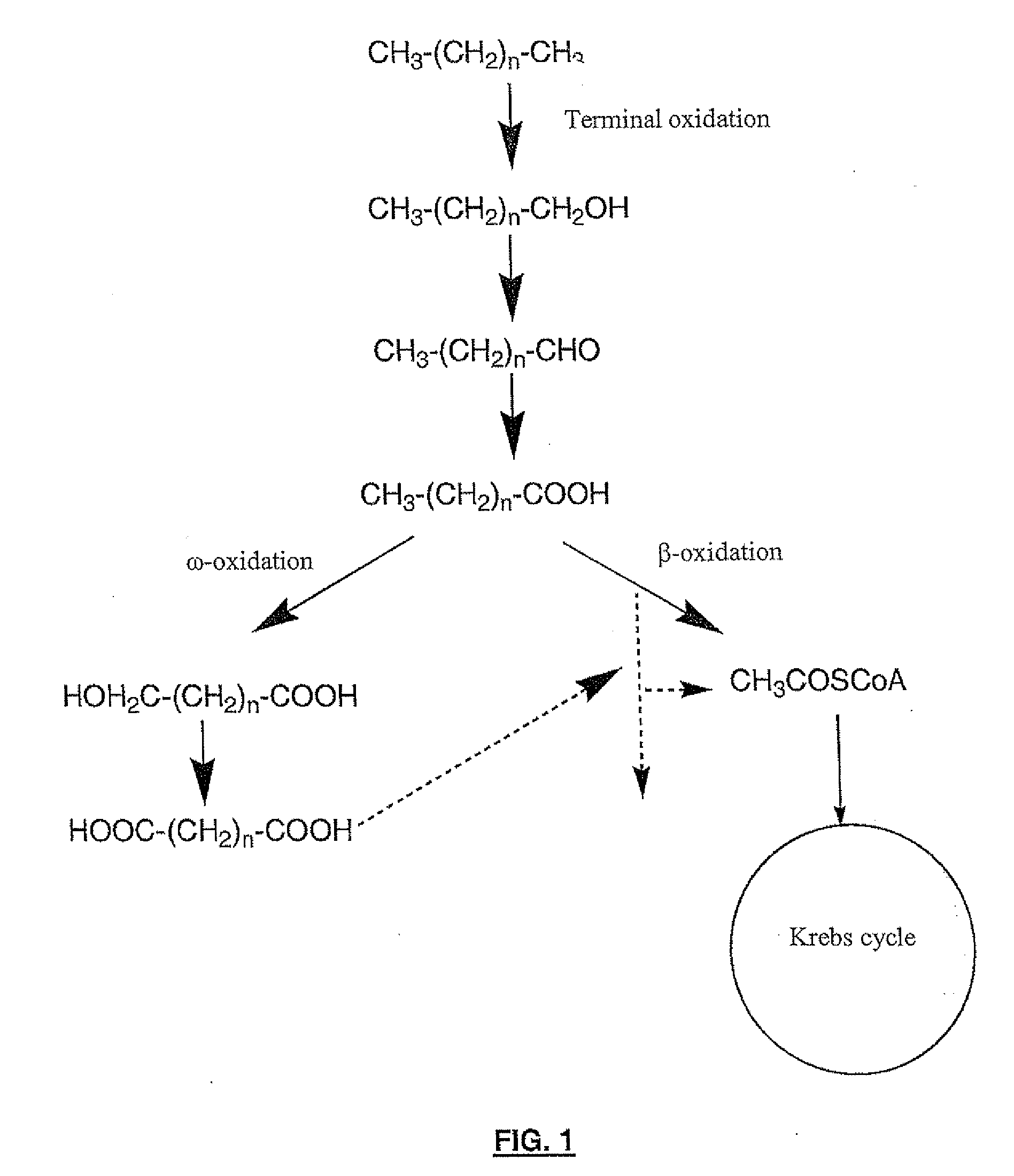
Yarrowia is a fungal genus in the family Dipodascaceae. For a while the genus was monotypic, containing the single species Yarrowia lipolytica, a yeast that can use unusual carbon sources, such as hydrocarbons. This has made it of interest for use in industrial microbiology, especially for the production of specialty lipids. Molecular phylogenetics analysis has revealed several other species that have since been added to the genus.
High eicosapentaenoic acid producing strains of Yarrowia lipolytica
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Docosahexaenoic acid producing strains of Yarrowia lipolytica
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
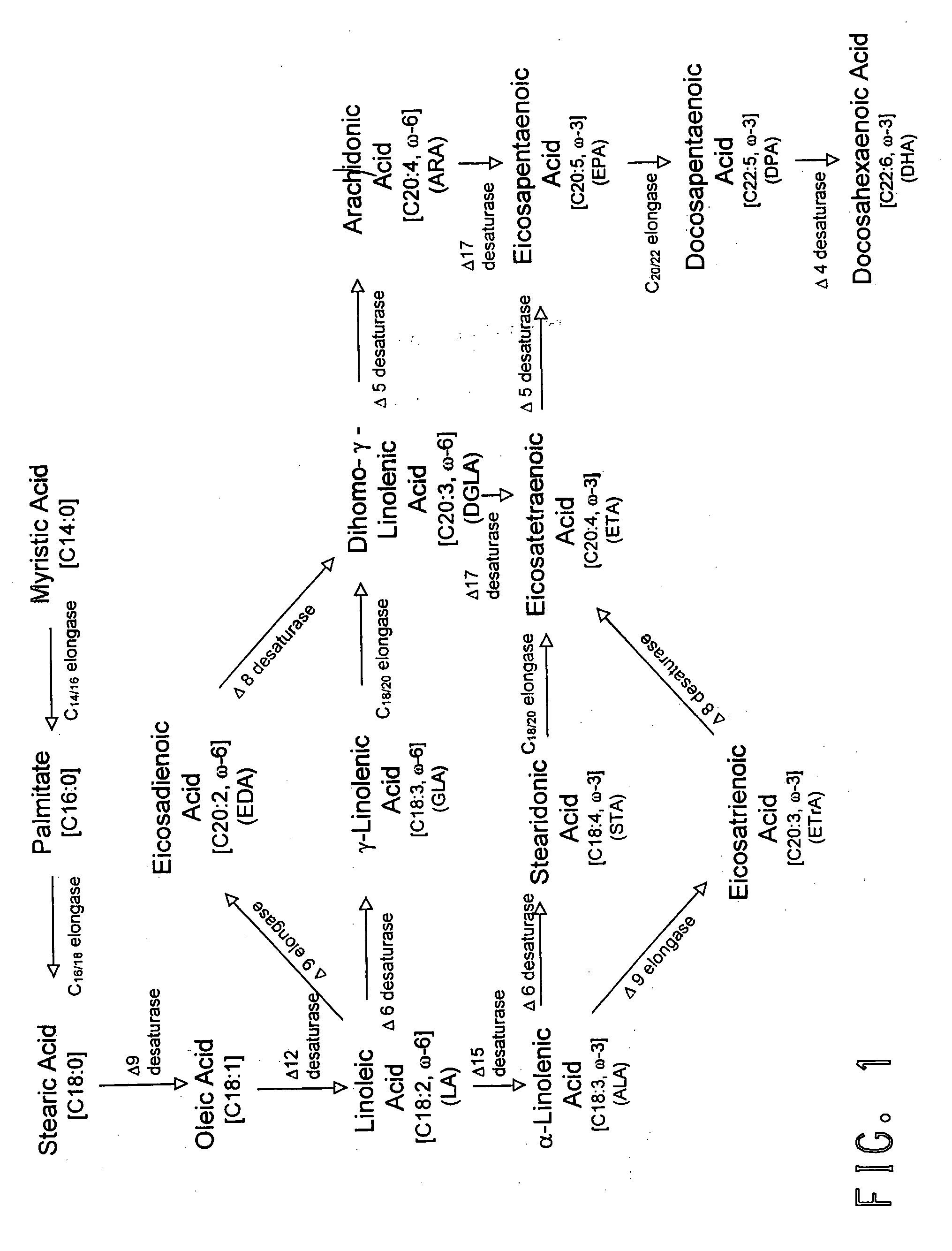
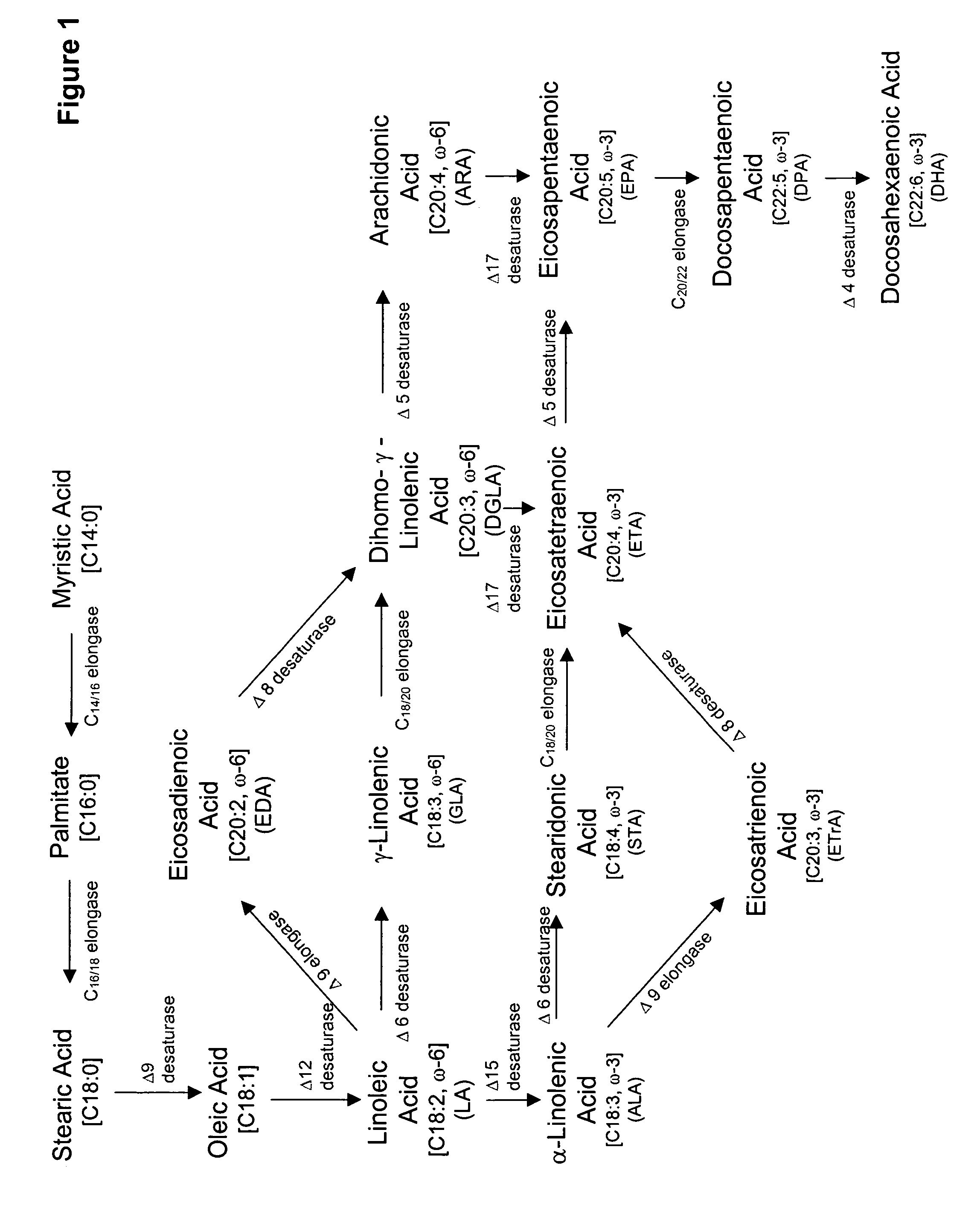
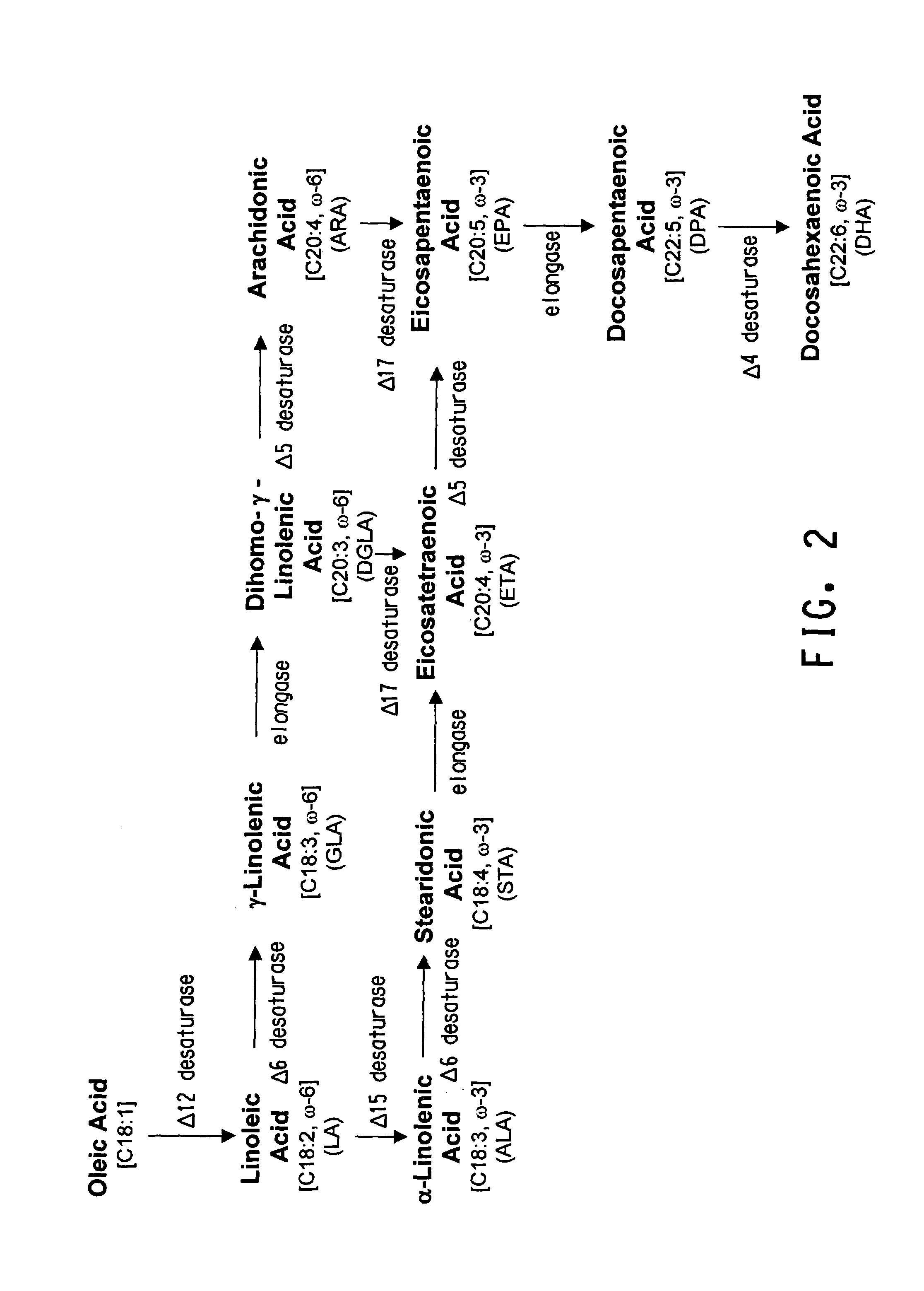
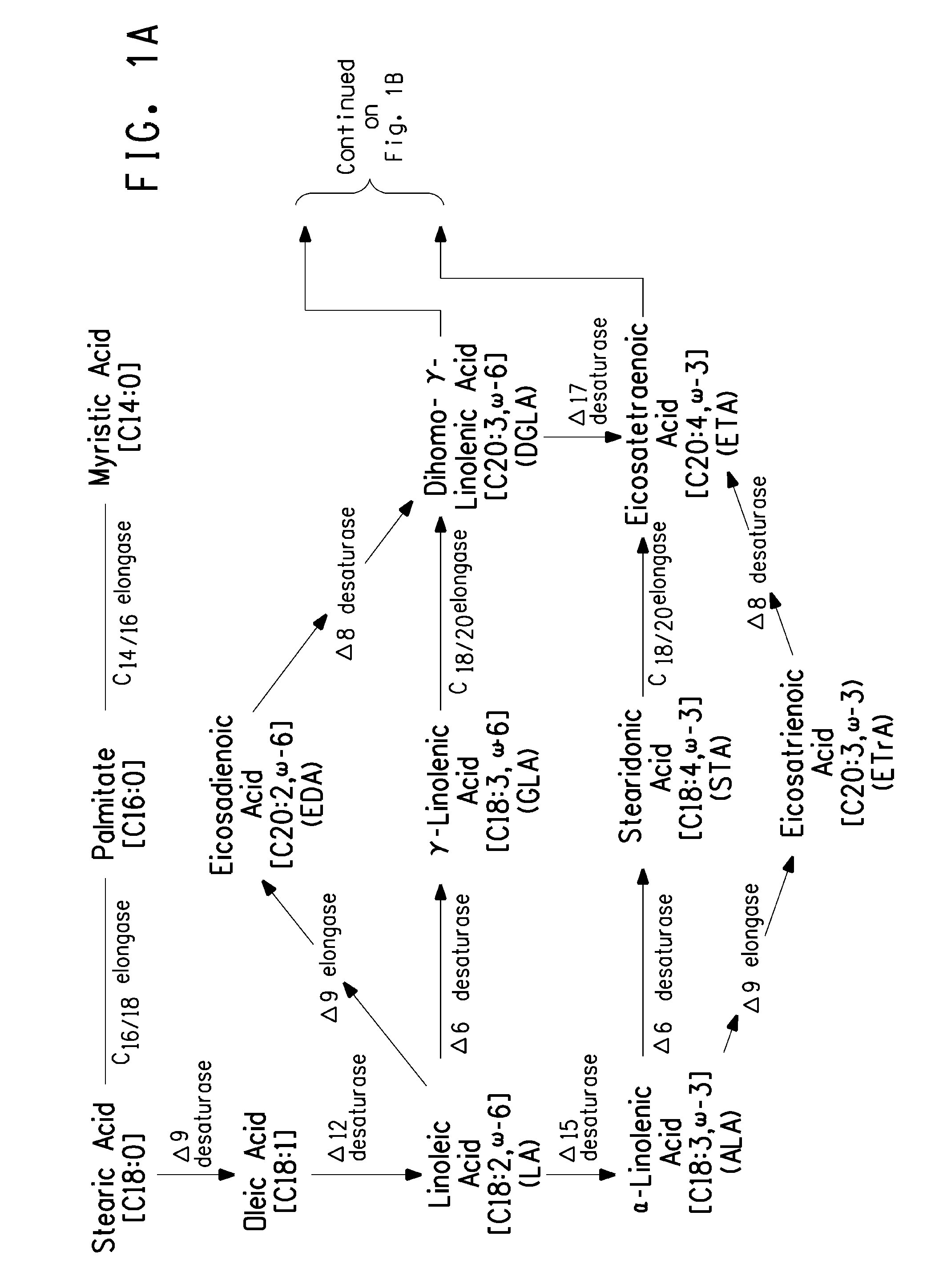
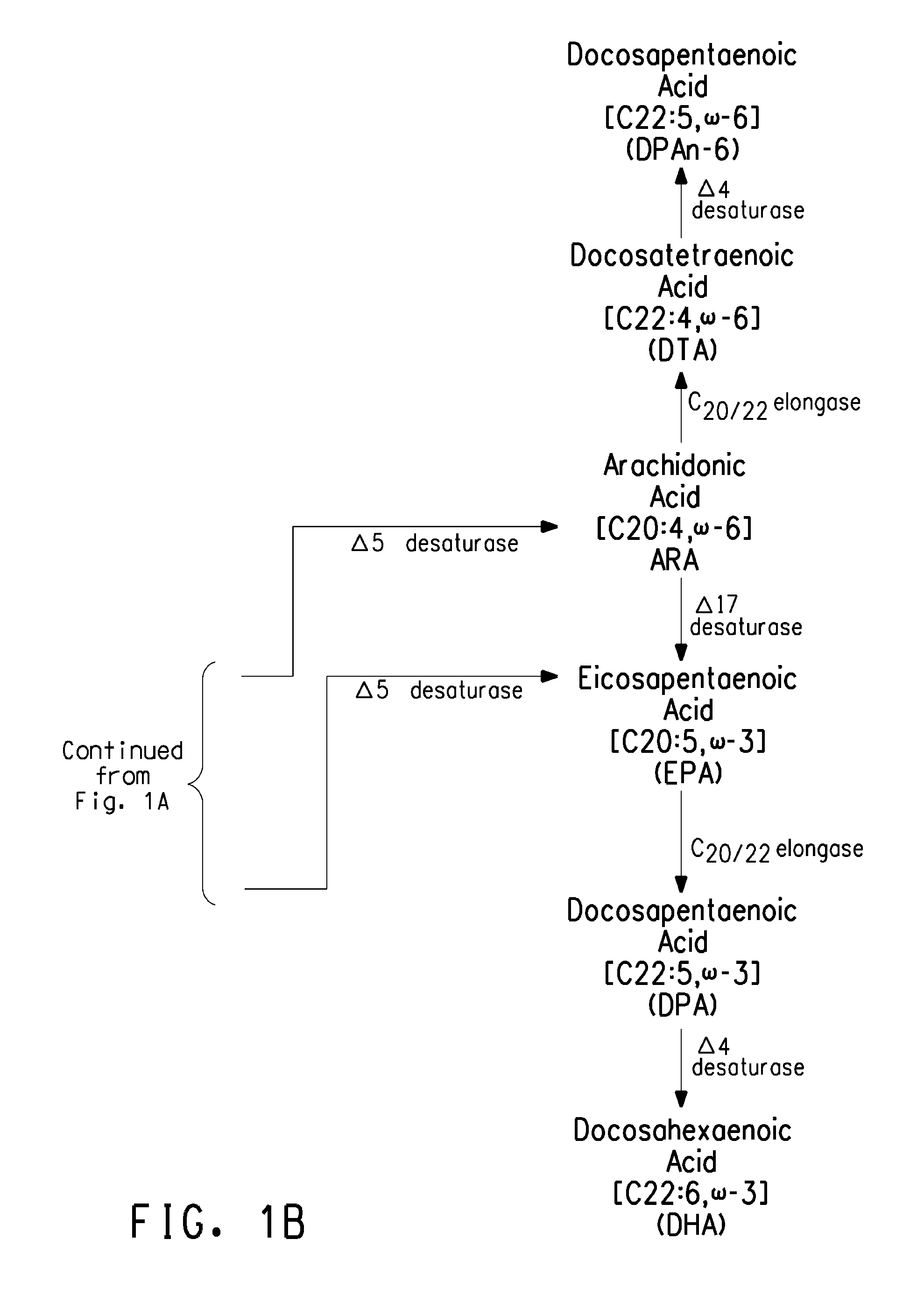
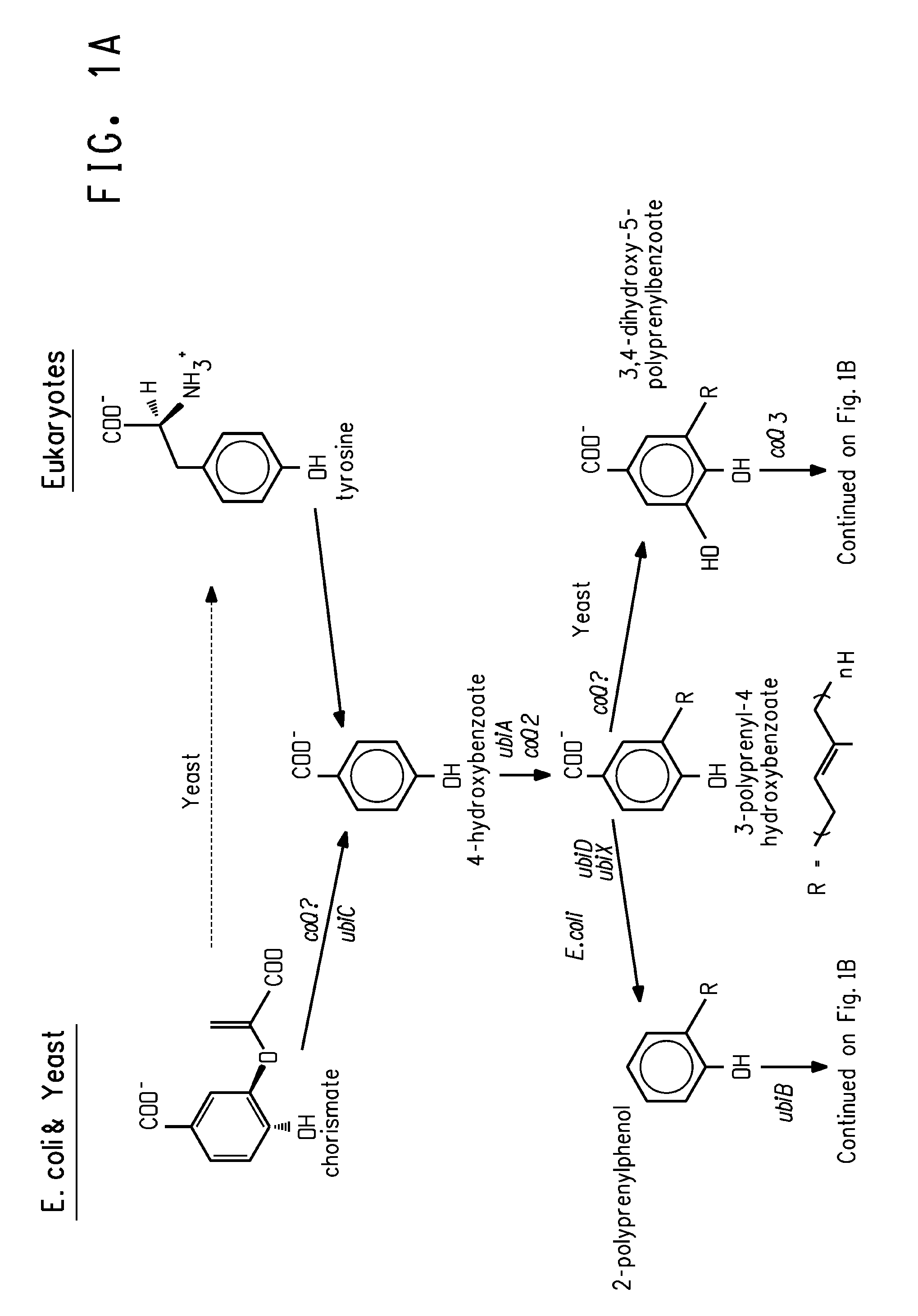
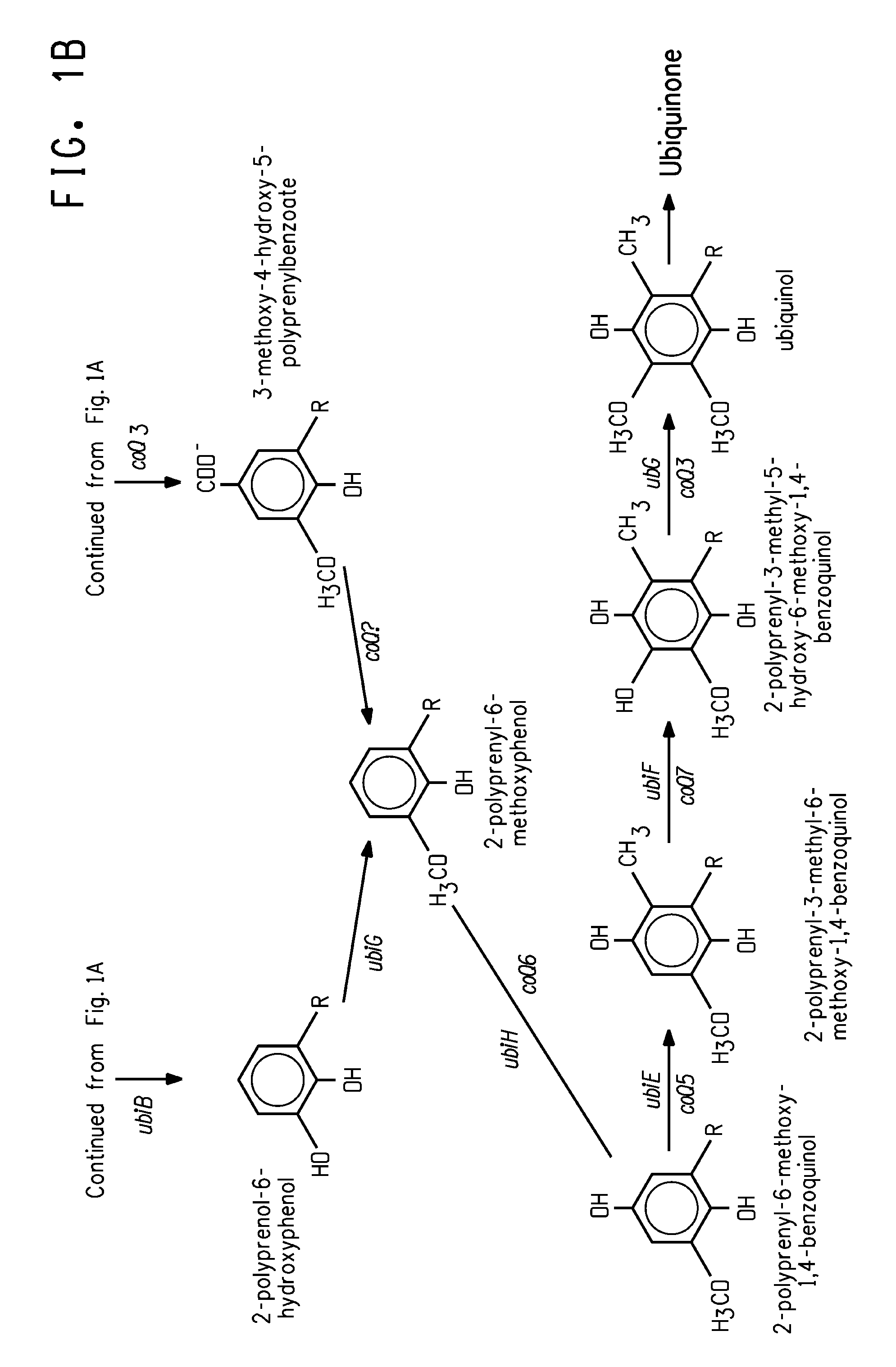
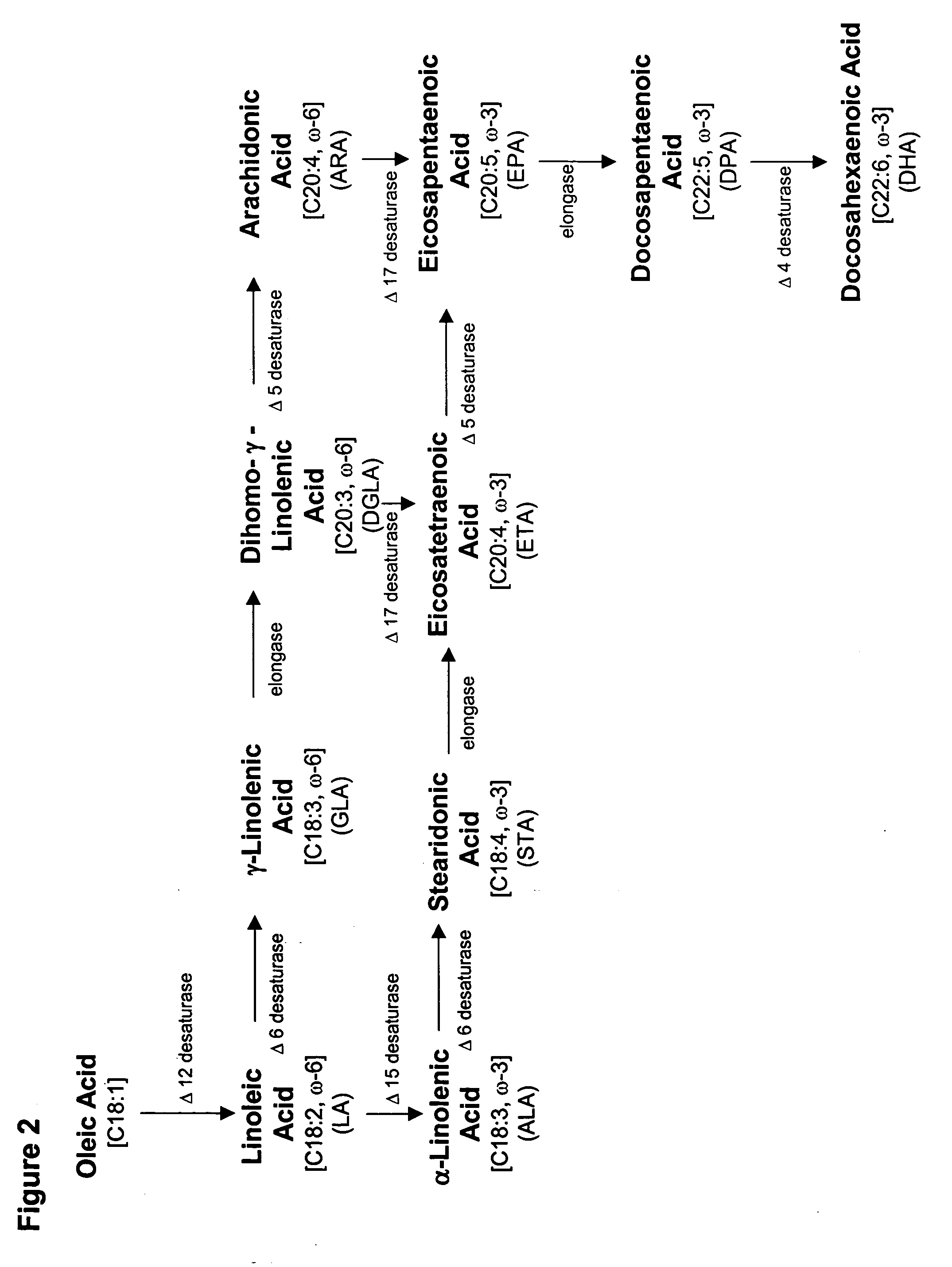
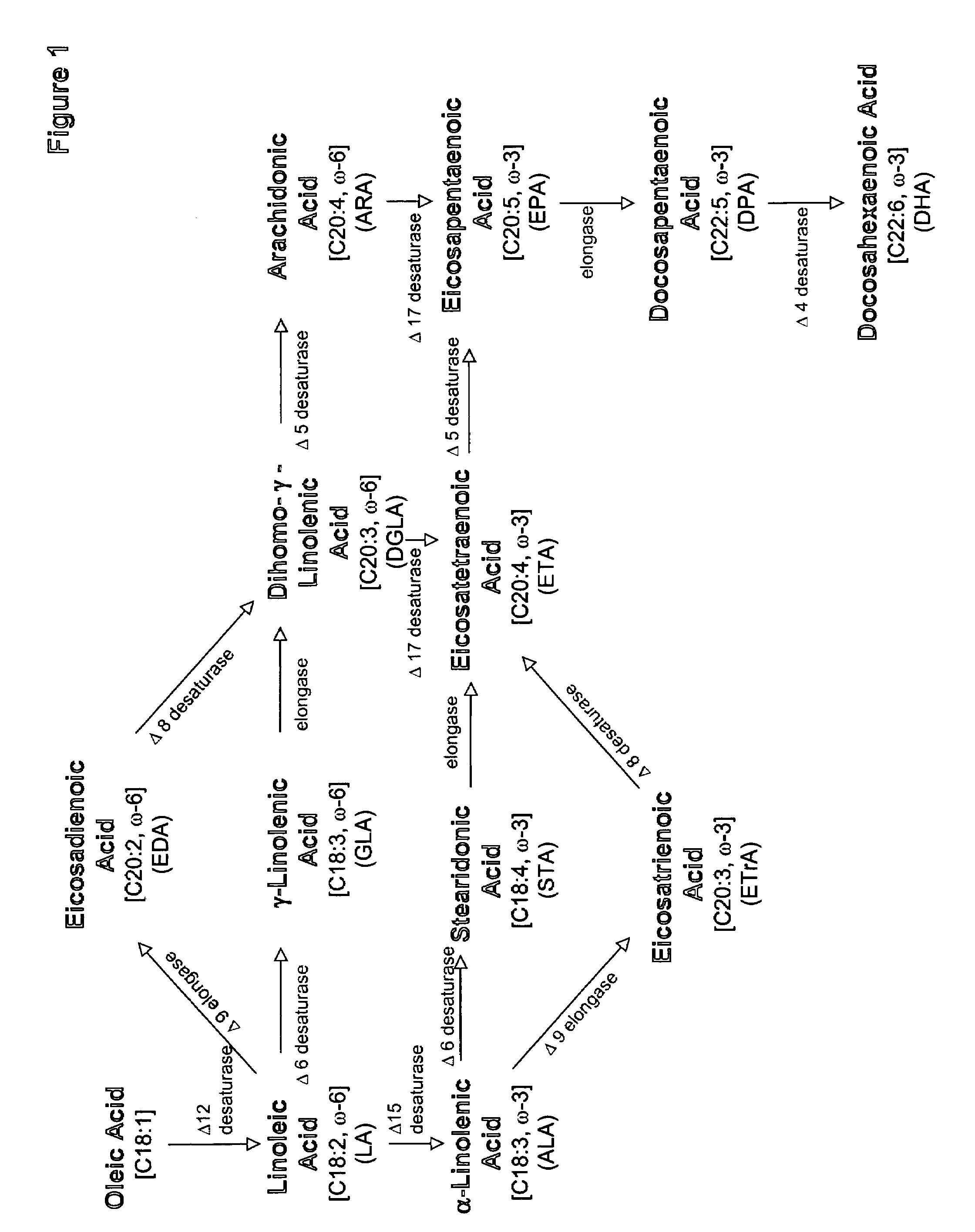
The present invention relates to methods for the production of ω-3 and / or ω-6 fatty acids in oleaginous yeast. Thus, desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to arachidonic acid (ARA); ETA to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); DGLA to ETA; EPA to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and ARA to EPA have been introduced into the genome of Yarrowia for synthesis of ARA and EPA.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Optimized strains of yarrowia lipolytica for high eicosapentaenoic acid production
Engineered strains of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica capable of producing greater than 50 weight percent of eicosapentaenoic acid [“EPA”], an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, in the total oil fraction are described. These strains over-express heterologous Δ9 elongases, Δ8 desaturases, Δ5 desaturases, Δ17 desaturases, Δ12 desaturases and C16 / 18 elongases, and optionally over-express diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferases. Preferred gene knockouts are also described. Production host cells, methods for producing EPA within said host cells, and products comprising EPA from the optimized Yarrowia lipolytica strains are claimed.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
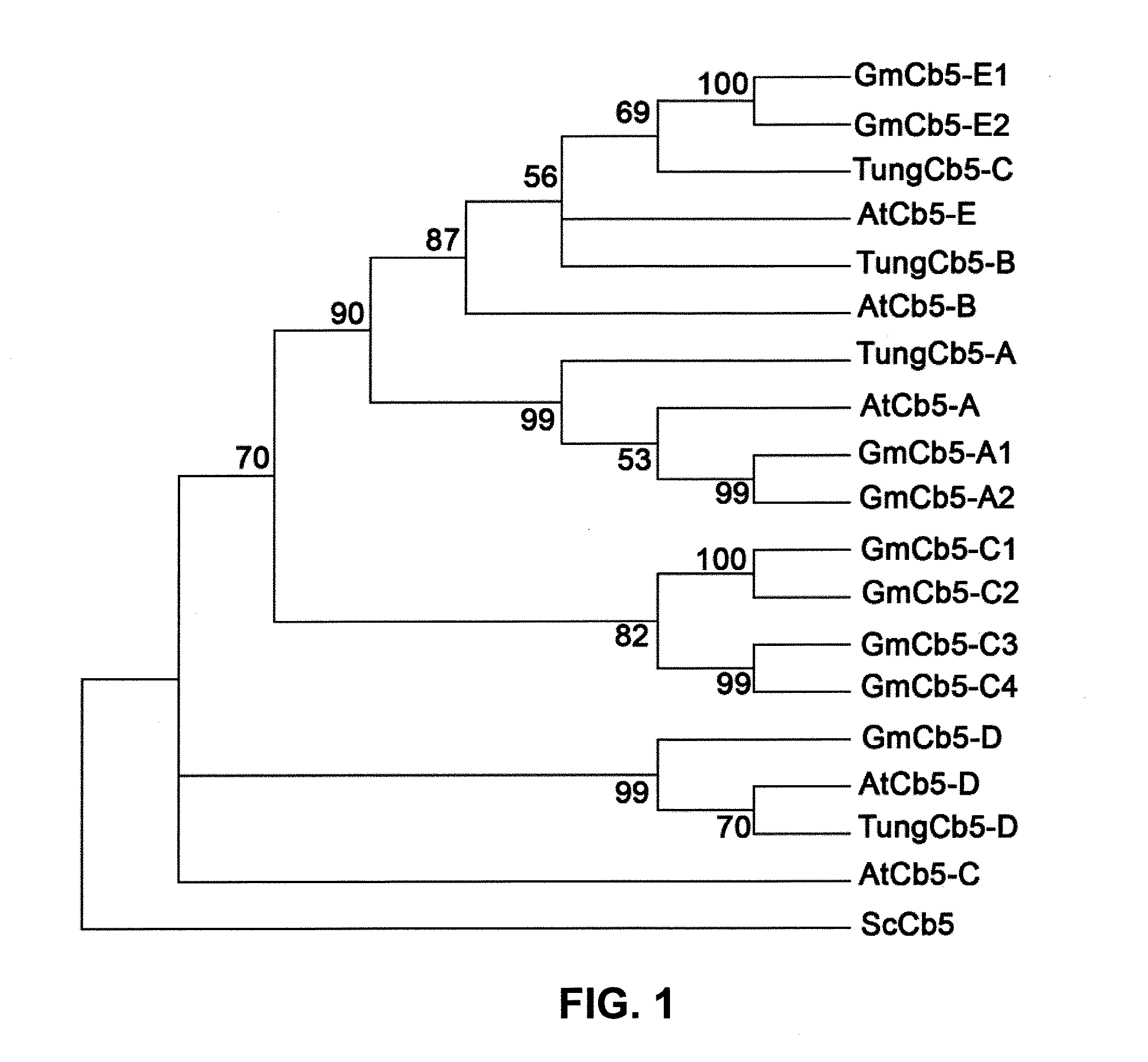
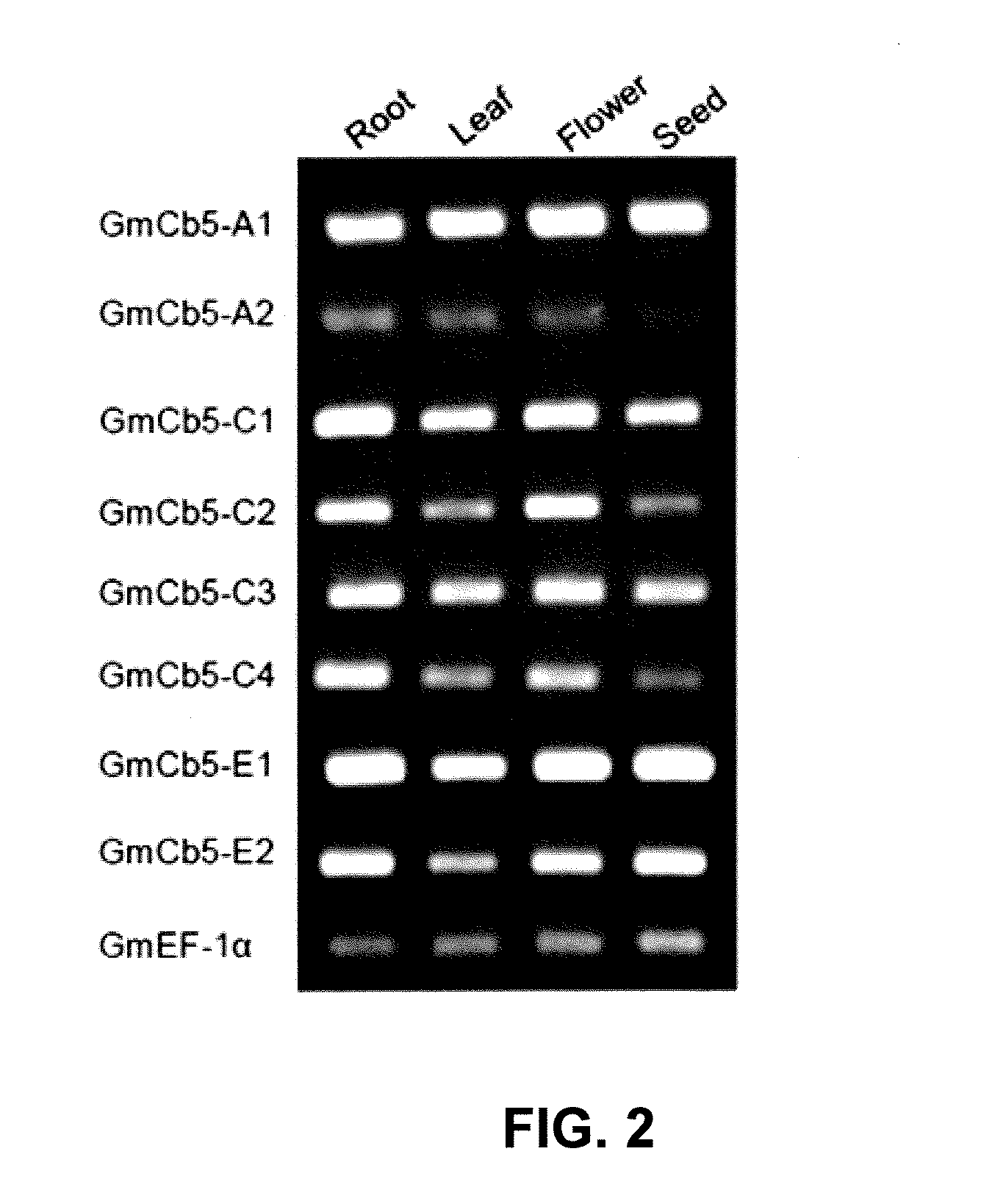
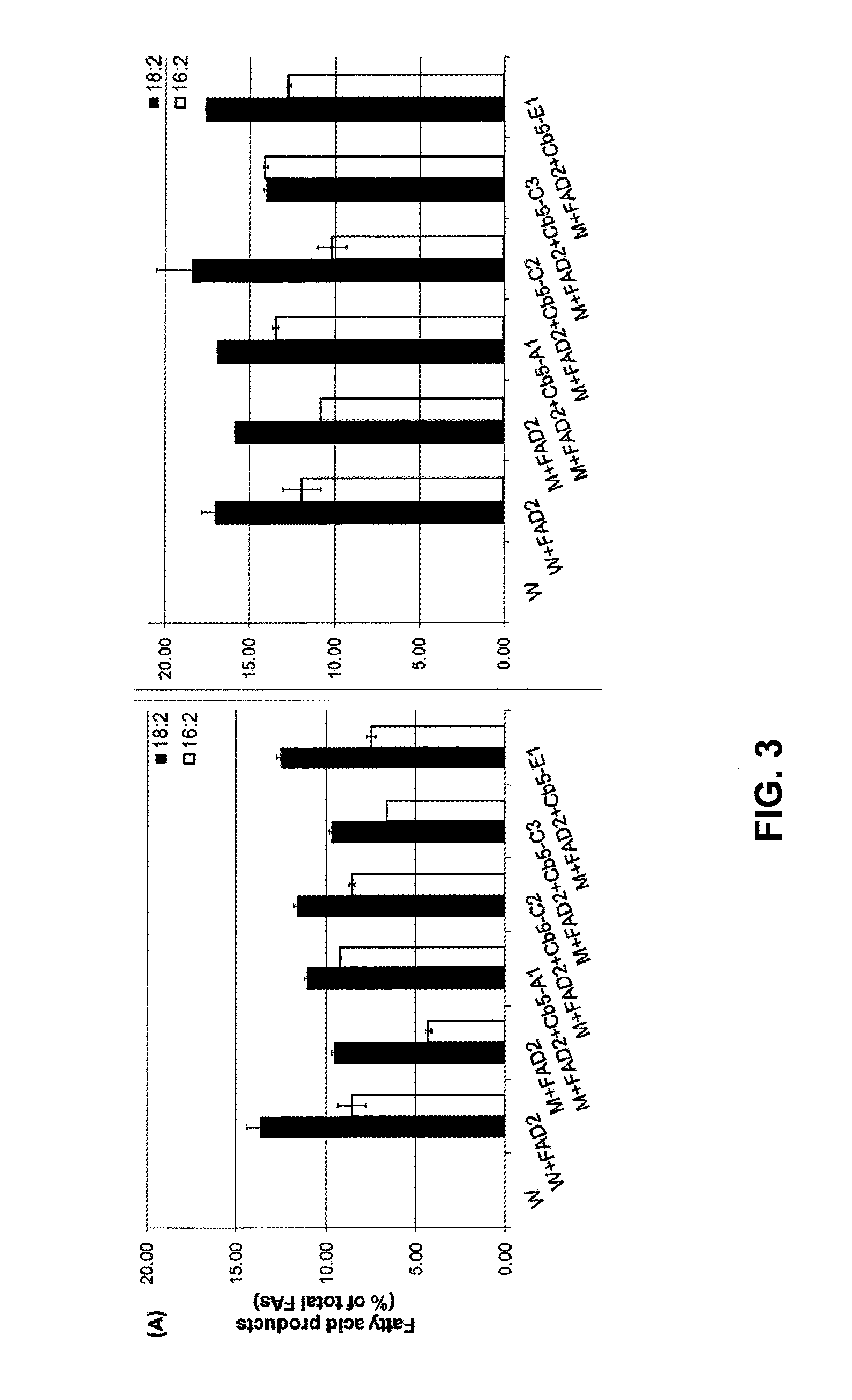
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
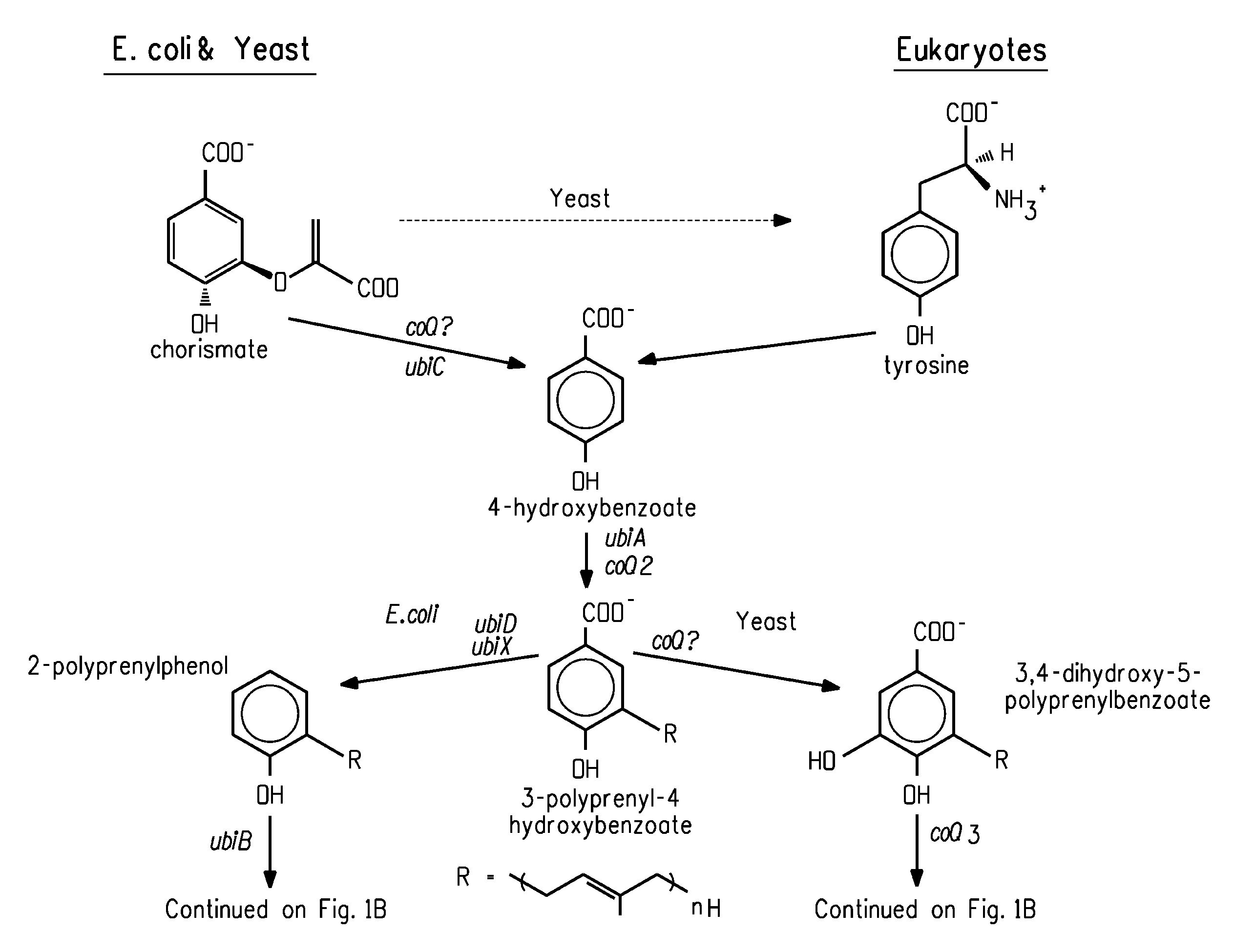
Coenzyme Q10 Production in a Recombinant Oleaginous Yeast
Engineered strains of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica capable of co-producing coenzyme Q10 and at least one ω-3 / ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid are provided. The strains may also be engineered to co-produce at least one C40 carotenoid. Methods of using the antioxidant products obtained (e.g., biomass and / or pigmented oils) in food and feed applications are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
The present invention relates to methods for the production of ω-3 and / or ω-6 fatty acids in oleaginous yeast. Thus, desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to arachidonic acid (ARA); ETA to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); DGLA to ETA; EPA to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and ARA to EPA have been introduced into the genome of Yarrowia for synthesis of ARA and EPA.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
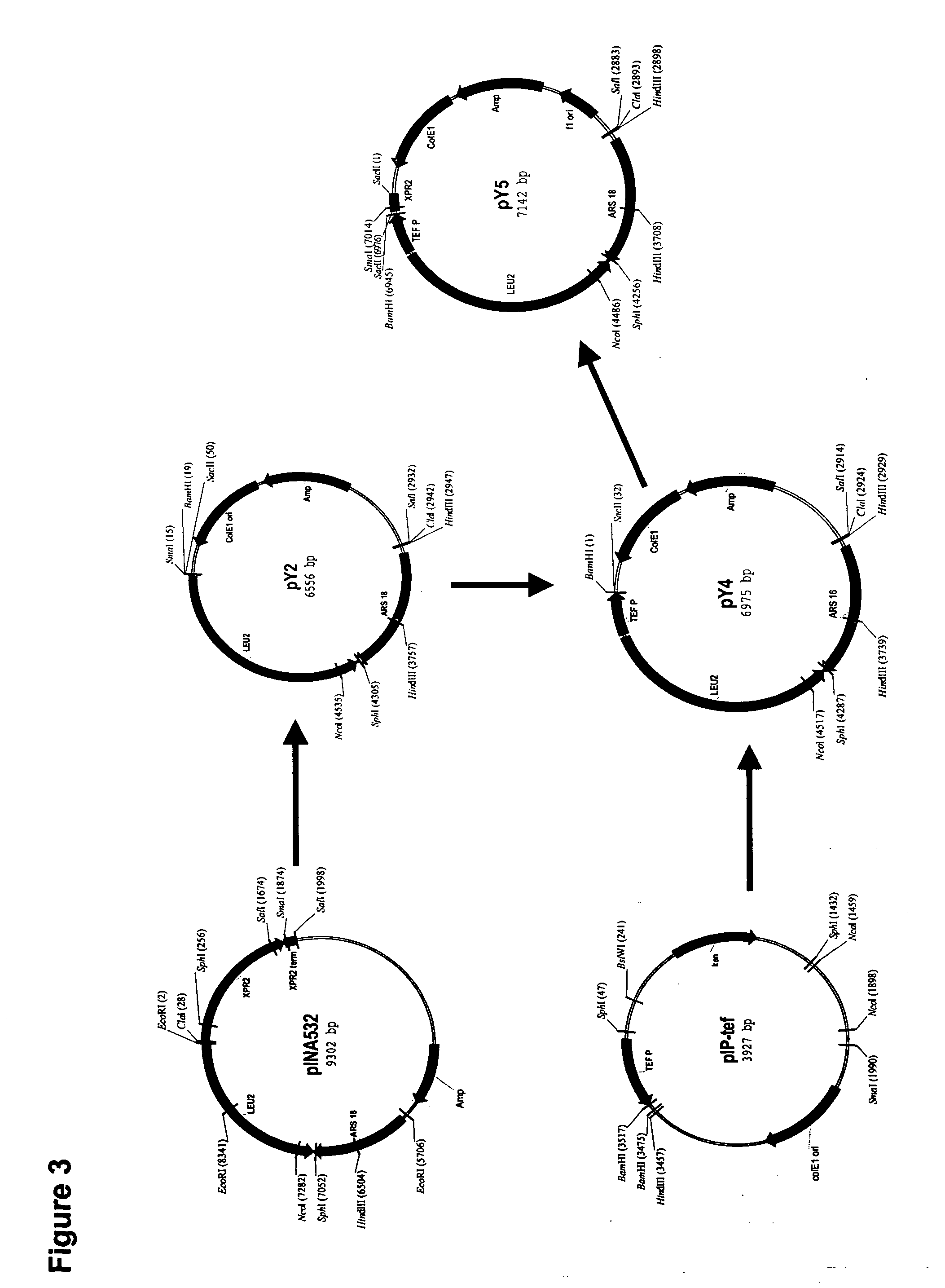
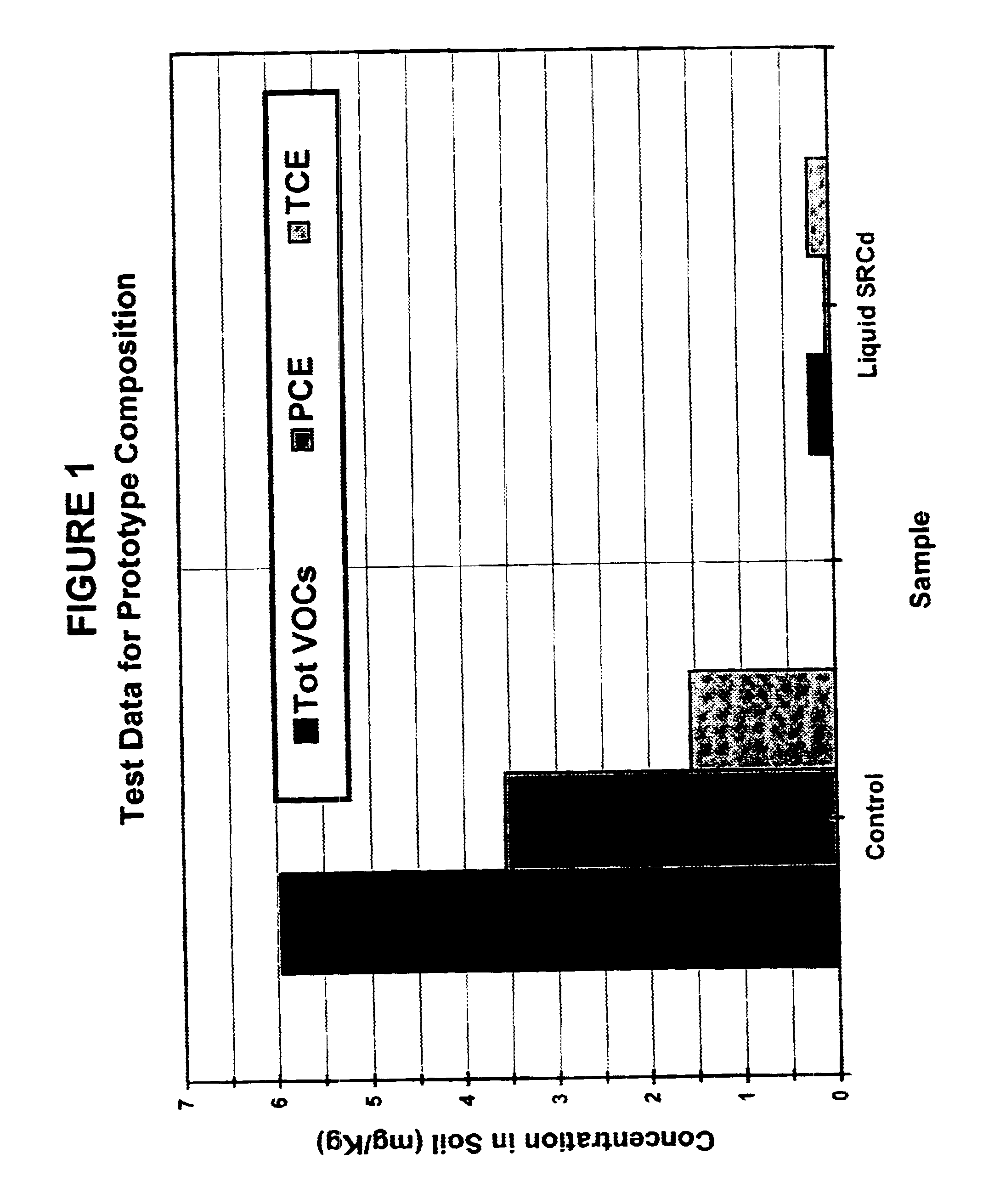
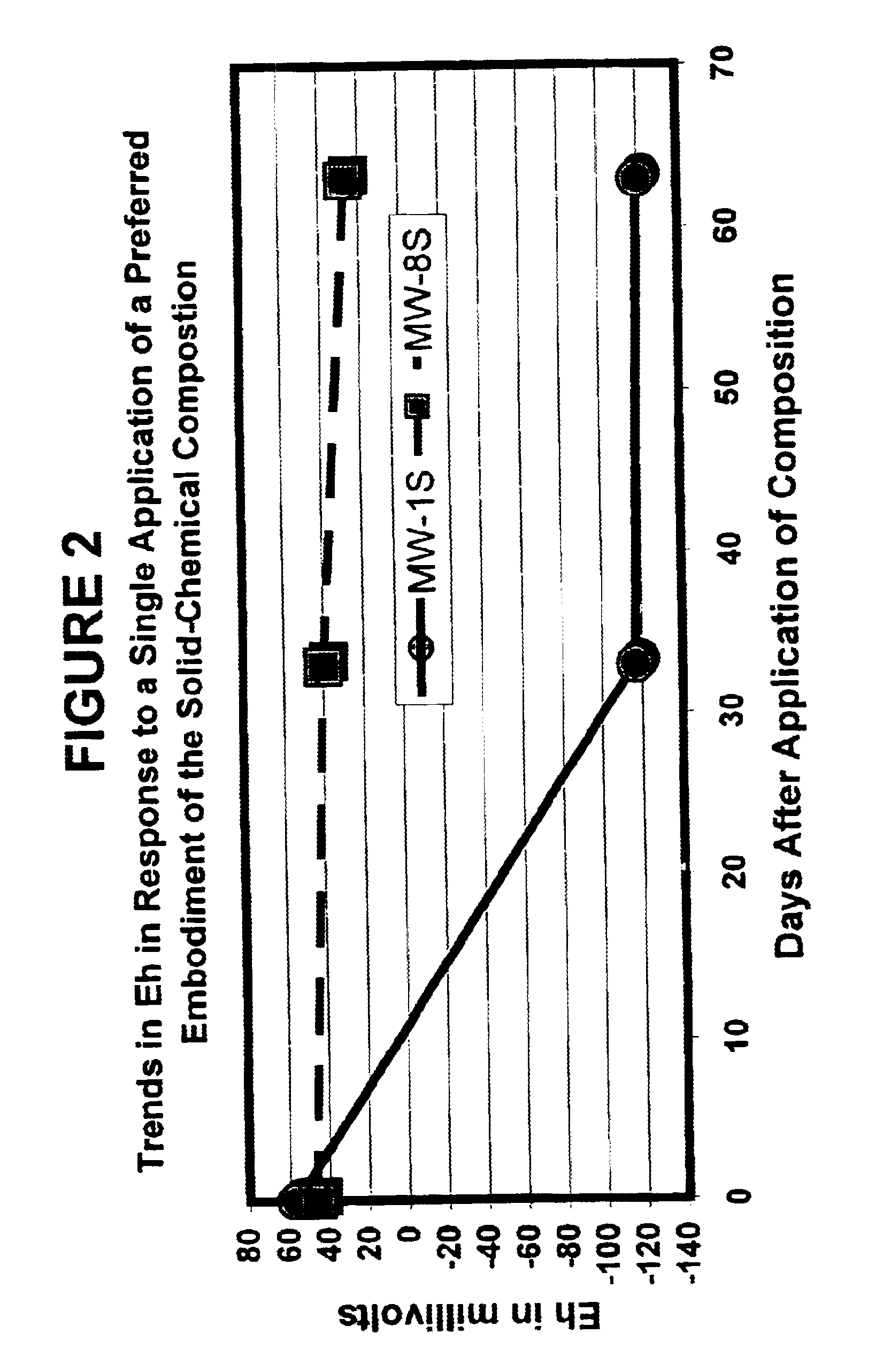
Solid-chemical composition for sustained release of organic substrates and complex inorganic phosphates for bioremediation
InactiveUS6620611B2Improve solubilityIncreasing speed and effectivenessBacteriaWater treatment compoundsPseudomonasTrichoderma spp
A slow-release solid chemical composition for environmental bioremediation is provided. The composition comprises a source of soluble organic substrates which include sugars, soluble organic polymers and mixtures of them in an amount of 7% to 90%, insoluble organic substrates an amount of 10% to 70%, complex inorganic phosphates in an amount of 0.5% to 7% and soluble organic salts in an amount of 2% to 70%. The insoluble organic substrates include fibrous plant materials, starches, cellulosic materials and mixtures of these substrates. The complex inorganic phosphates include ringed metaphosphates, linear polyphosphates and mixtures. The organic salts include lactates, formates, acetates, citrates, etc. Also the composition further comprises microorganisms which include Bacillus spp., Rhizobium spp., Bradyrhibzobium spp., Fibrobacter spp., Clostridium spp., Pseudomonas. spp., Geobacter spp., Arthrobacter spp., Nocardia, spp., aspergillus spp., Trichoderma spp., Candida spp., Yarrowia spp. and combinations of these microorganisms. The composition can be prepared in various forms, including granules, briquettes, pellets, tablets or capsules.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Yarrowia lipolytica strain and method thereof for synthesizing erythritol
ActiveCN103374534AHigh ability to synthesize erythritolImprove conversion rateFungiMicroorganism based processesContinuous fermentationInorganic salts
The invention discloses a yarrowia lipolytica strain and a method thereof for synthesizing erythritol. The yarrowia lipolytica strain is yarrowia lipolytica BLC13 CGMCC NO. 7326. The method for synthesizing the erythritol by the yarrowia lipolytica strain comprises the following steps of: taking a carbon source with an initial fermentation concentration of 100-400g / L, a nitrogen source with an initial fermentation concentration of 2-35g / L and inorganic salt as raw materials, treating for 30 minutes at 80-90 DEG C, cooling down and subsequently inoculating the yarrowia lipolytica strain, carrying out continuous fermentation or in-batch fed-batch fermentation under an aerobic condition, and after the fermentation is accomplished, purifying the erythritol from a fermentation liquid. The yarrowia lipolytica strain disclosed by the invention is used for synthesizing the erythritol from glucose, the conversion rate is high, and the Chinese erythritol standard is met.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Production of gamma-linolenic acid in oleaginous yeast
The present invention relates to methods for the production of γ-linolenic acid (GLA) in oleaginous yeast. Thus, Δ12 and Δ6 desaturases able to catalyze the conversion of oleic acid to GLA have been introduced into the genome of Yarrowia, using zeta-directed integration. Transformed strains produced over 25% GLA in the total lipids, as opposed to wildtype Yarrowia that is unable to synthesize any GLA. Metabolic engineering and fermentation methods are provided to further enhance GLA productivity in oleaginous yeast.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Lipase, its gene, yalulipolytic geast for producing said enzyme and its application
ActiveCN1948470AWide substrate adaptabilityImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesFungiConservative mutationAmino acid
This invention relates to a preparation of a kind of lipase and the method of using the lipase to compound ester. Exactly is that amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO:1 or its lipase of conservative mutation sequence, it also relates to the gene coding this lipase, Yarrowia lipolytica generating this lipase.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing biodegradable oil residue fertilizer
InactiveCN101863686AChange physical statePromote growthFertiliser formsOrganic fertilisersField experimentINCREASED EFFECT
The invention relates to a method for preparing a biodegradable oil residue fertilizer, which comprises the following steps of: degrading grease in oil residue by using microbial fermentation liquor of bacillus subtilis and microbial fermentation liquor of Yarrowia lipolytica; performing high-temperature treatment at normal pressure on the oil residue of which the grease is degraded; and decomposing proteins in the oil residue by using protease generated by microbial fermentation liquor of geotrichum candidum and microbial fermentation liquor of lactobacillus plantarum so as to generate various amino acids and bioactive substances favorable for crop growth. The method has the advantages of short time for treating the oil residue, reducing environmental pollution, and fully utilizing specific nitrogen nutrition of the oil residue; and the prepared fertilizer has obvious yield increasing effect through field experiments.
Owner:SHANDONG GUANGDA FERTILIZER INDAL TECHCO
Production of dicarboxylic acids by improved mutant strains of yarrowia lipolytica
The invention concerns a method for producing dicarboxylic acids (DCA) with long hydrocarbon chains, also called diacids, which consists in culturing a mutant strain of Yarrowia lipolytica obtained by mutagenesis directed and more particularly disrupted at least for the POX2, POX3, POX4 and POX5 genes encoding acyl-CoA oxydase, in a medium consisting essentially of an energetic substrate including at least one carbon source and one nitrogen source and in subjecting said strain to a bioconversion substrate selected among n-alkanes of at least 10 carbon atoms, fatty acids of at least 10 carbon atoms, their alkyl esters and natural oils.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +2
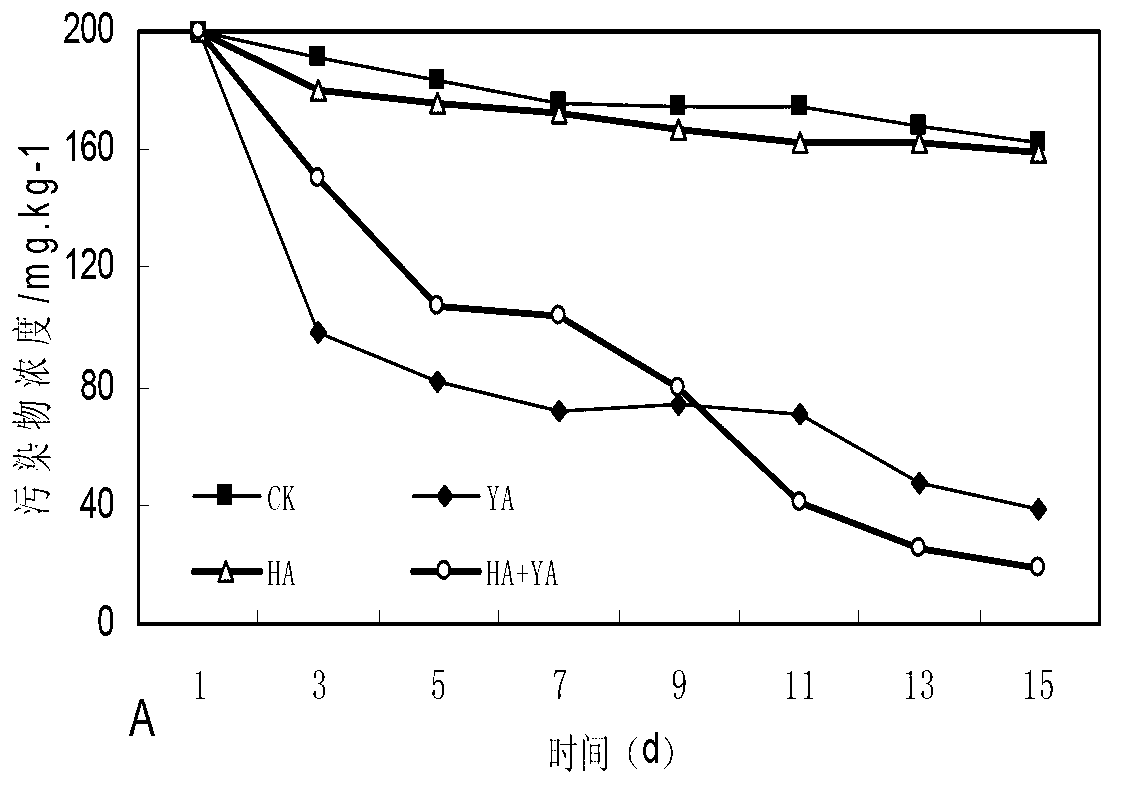
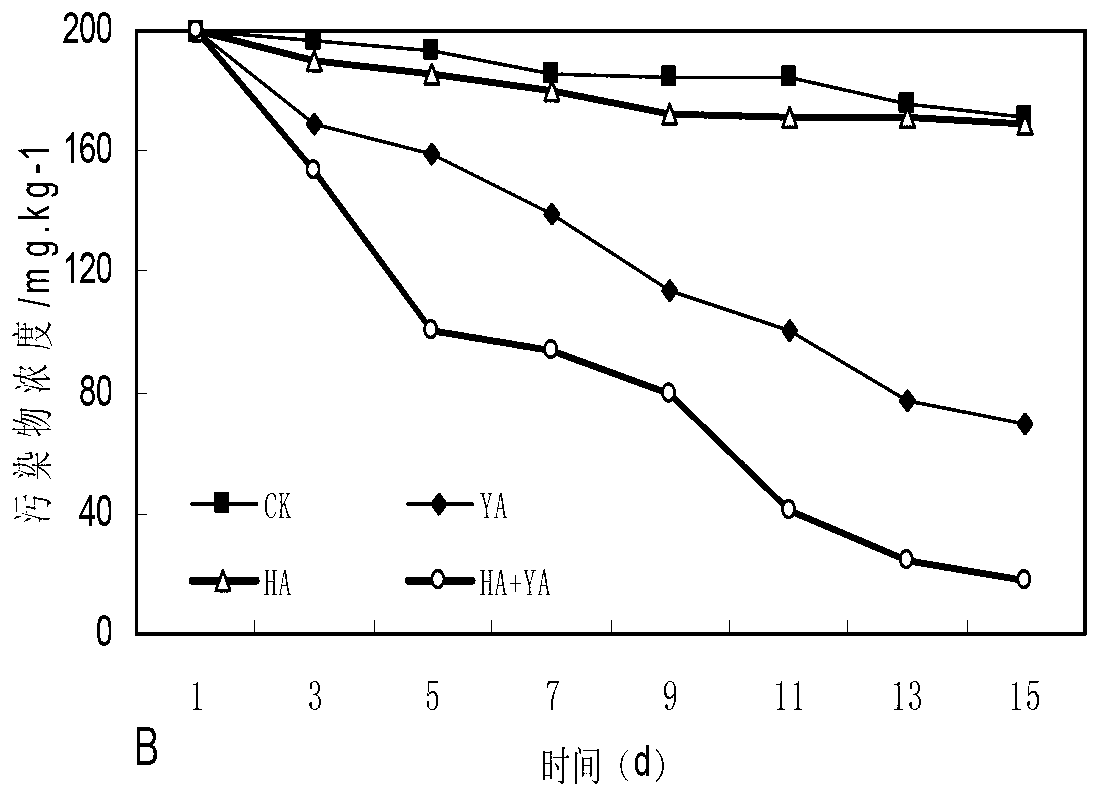
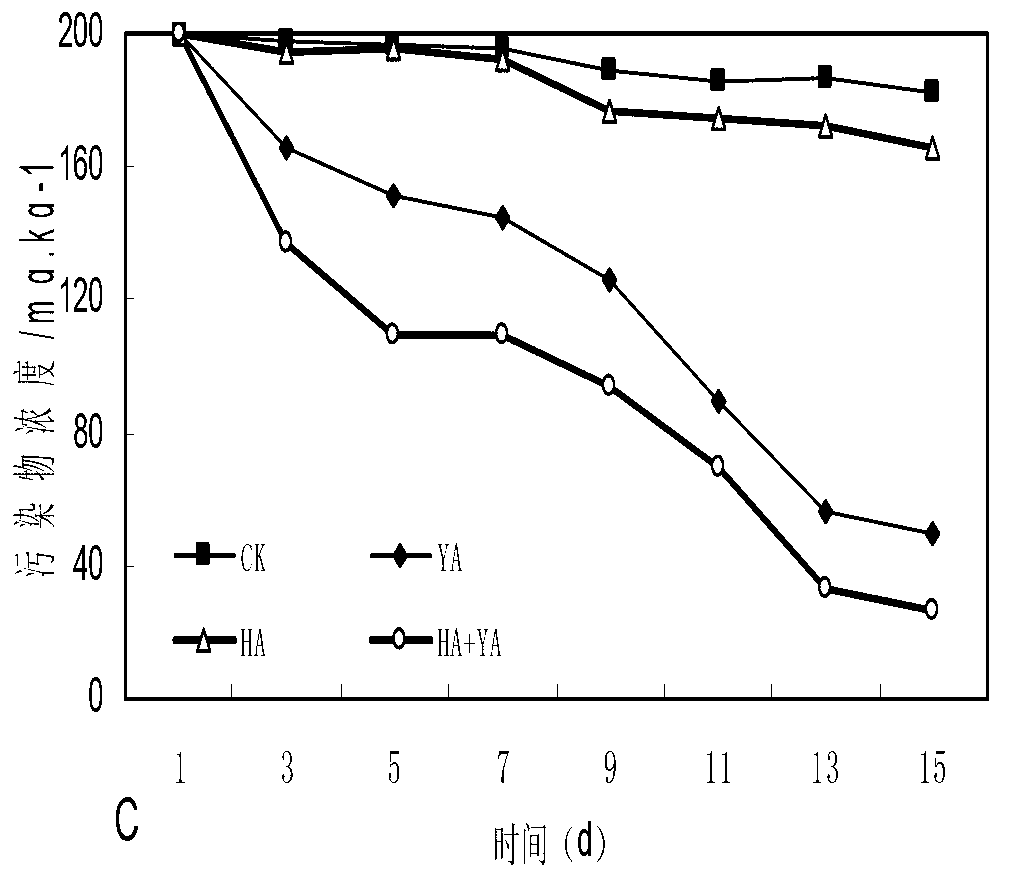
Bacterial strain for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application of bacterial strain cooperated with surface active agent in soil remediation
InactiveCN102994404APromote degradationImprove degradation rateFungiContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical fields of environmental engineering and microbial engineering, and in particular relates to Yarrowia lipolytica tzyx3 for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application of the Yarrowia lipolytica tzyx3 cooperated with a surface active agent in soil remediation. The preservation number of the Yarrowia lipolytica tzyx3 in China center for type culture collection is CCTCC NO: M 2012241, and the Yarrowia lipolytica tzyx3 is capable of degrading the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The Yarrowia lipolytica tzyx3 has synergistic effect with the surface active agent and can be used for remediation of soil polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:杭州韦尔茂通环境技术有限公司
Alpha-ketoglutarate producing yeast engineering strain and construction method thereof
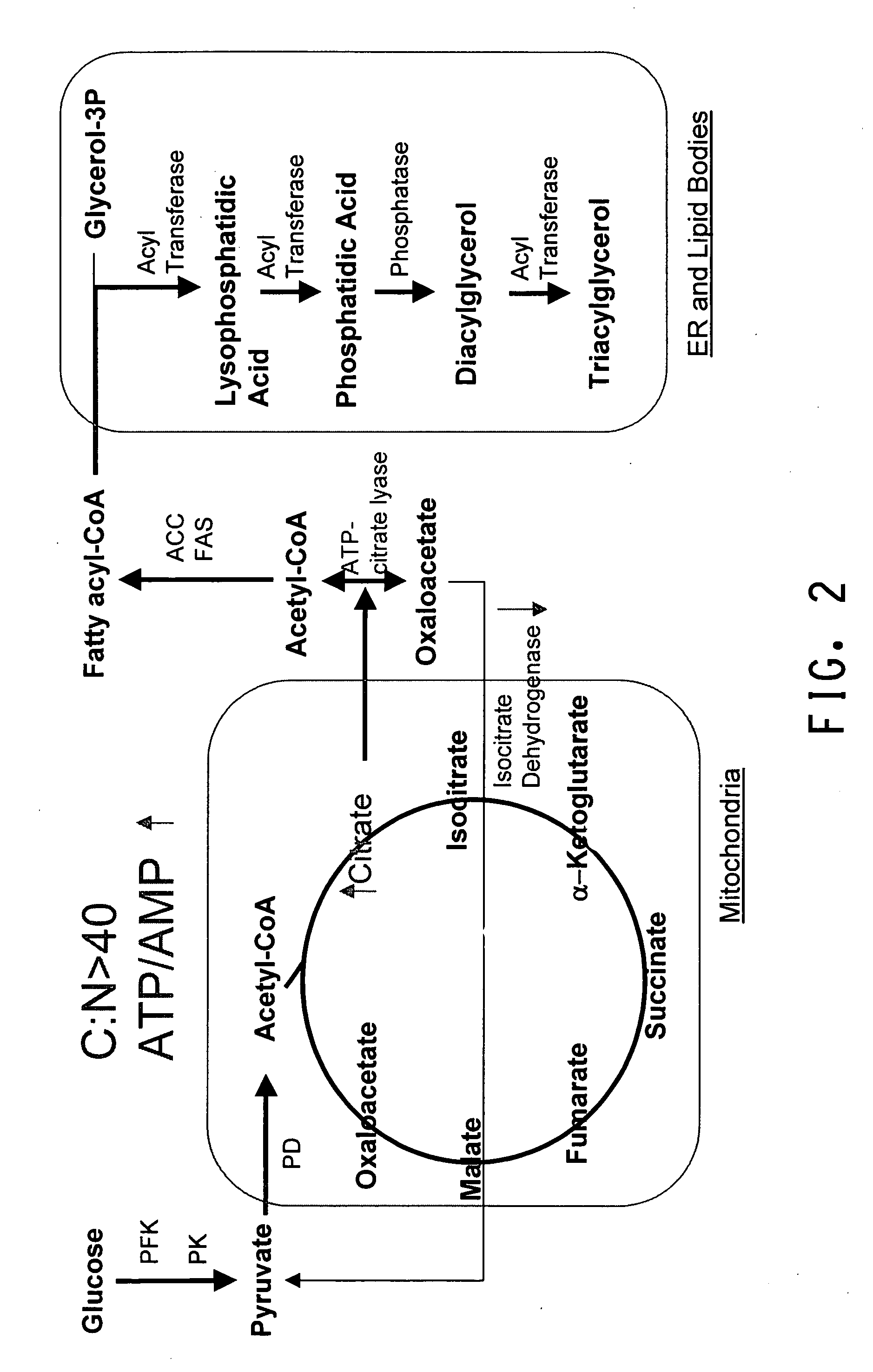
The invention discloses an alpha-ketoglutarate producing yeast engineering strain and a construction method thereof, which belong to the field of genetic engineering. In the method, a molecular approach is adopted, and the yeast engineering strain Y.lipolytica ACL with improved ATP-citrate lyase activity is obtained by over-expressing an ATP-ATP-citrate lyase ACL coding gene from a mouse into a strain Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06 for producing alpha-ketoglutarate by a fermentation method. Compared with a parent strain, the genetic engineering strain provided by the invention can intracellularly accumulate acetyl coenzyme A with the dry cell weight (DCW) of 0.89 mM / g by adopting glycerol as the unique carbon source so as to achieve the ACL activity of 3.56 U / mg protein improved by 7.5 times, achieve the alpha-ketoglutarat yield of 45.3 g / L which is 1.29 times that of parent protein and reduce the pyruvic acid yield to 17.2 g / L which is 68.8 percent of that of the parent strain, and has vast application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Thermally stable lipase as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN105950585ASave manpower and material resourcesImprove accuracyHydrolasesFermentationHalf-lifeAmino acid
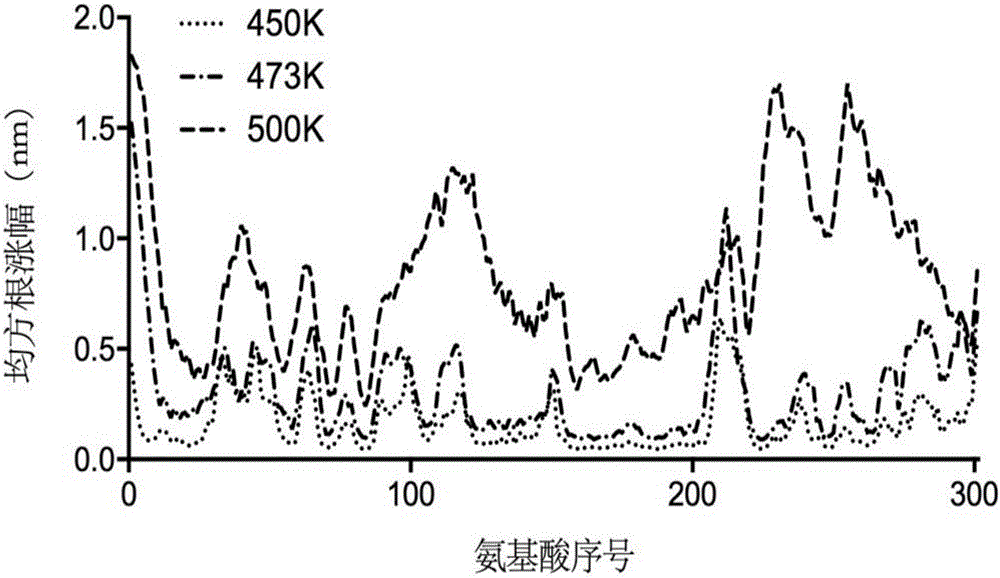
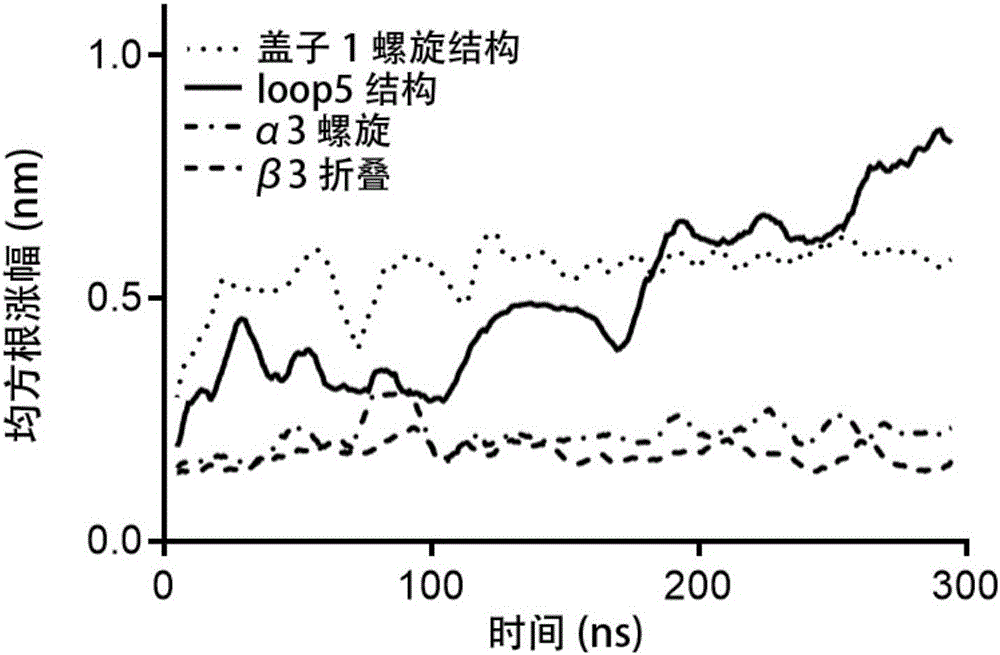
The invention discloses a thermally stable lipase as well as a preparation method and applications of the thermally stable lipase. The lipase is S2-210 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, S8-214 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2, S14-216 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.3, or S191-241 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.4. According to the thermally stable lipase and the preparation method thereof, the unfolding process of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase 2 is stimulated through the long-time high-temperature molecular dynamics simulation, and the main area of protein unfolding and the critical steps for forming the wet molten-globule state are analyzed, so that the key site for transforming the kinetic stability are effectively screened. The thermally stable lipase is heat-resisting, is long in half-life period, and is particularly suitable for being applied in the industry.
Owner:GUANGDONG RUISHENG TECH GRP CO LTD
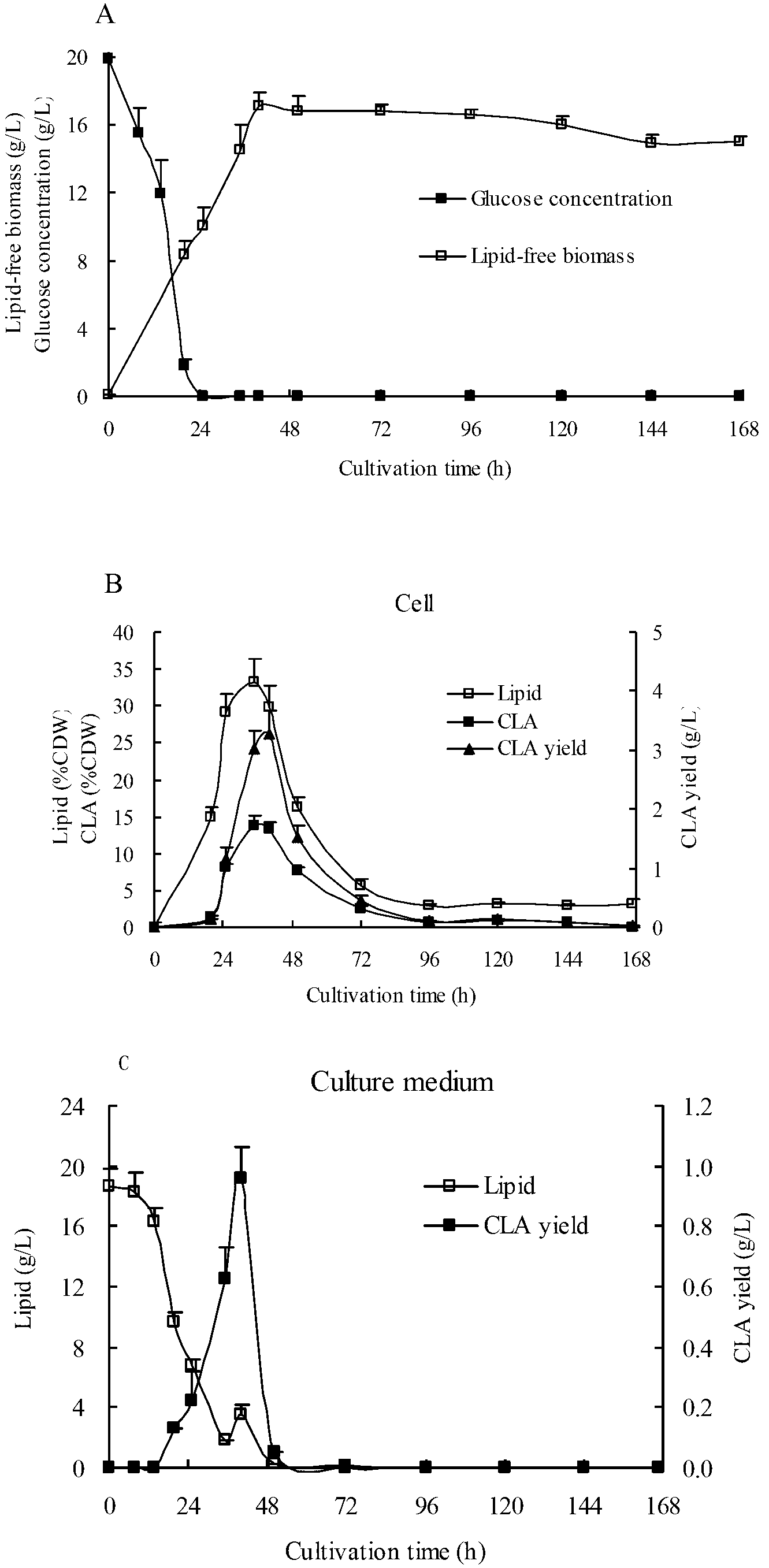
Method for optimizing conjugated linoleic acid synthesis by using Yarrowia lipolytica yeast recombinant strain based on genetic engineering strategy
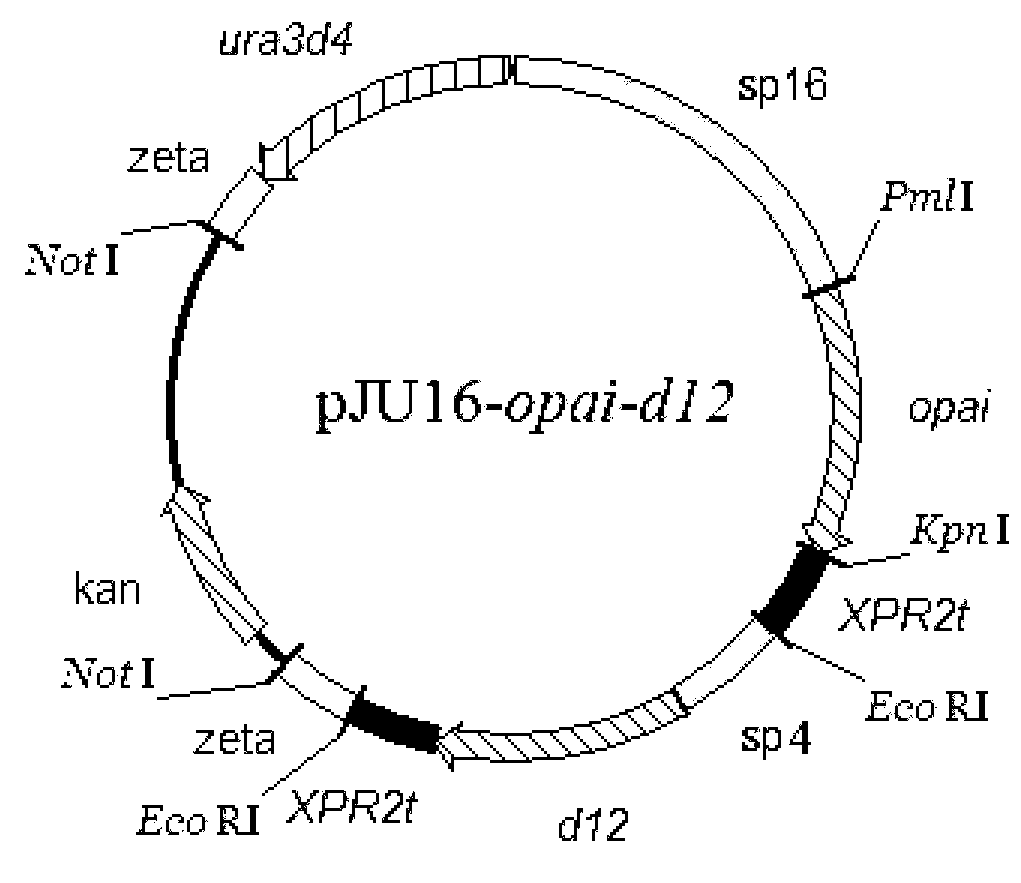
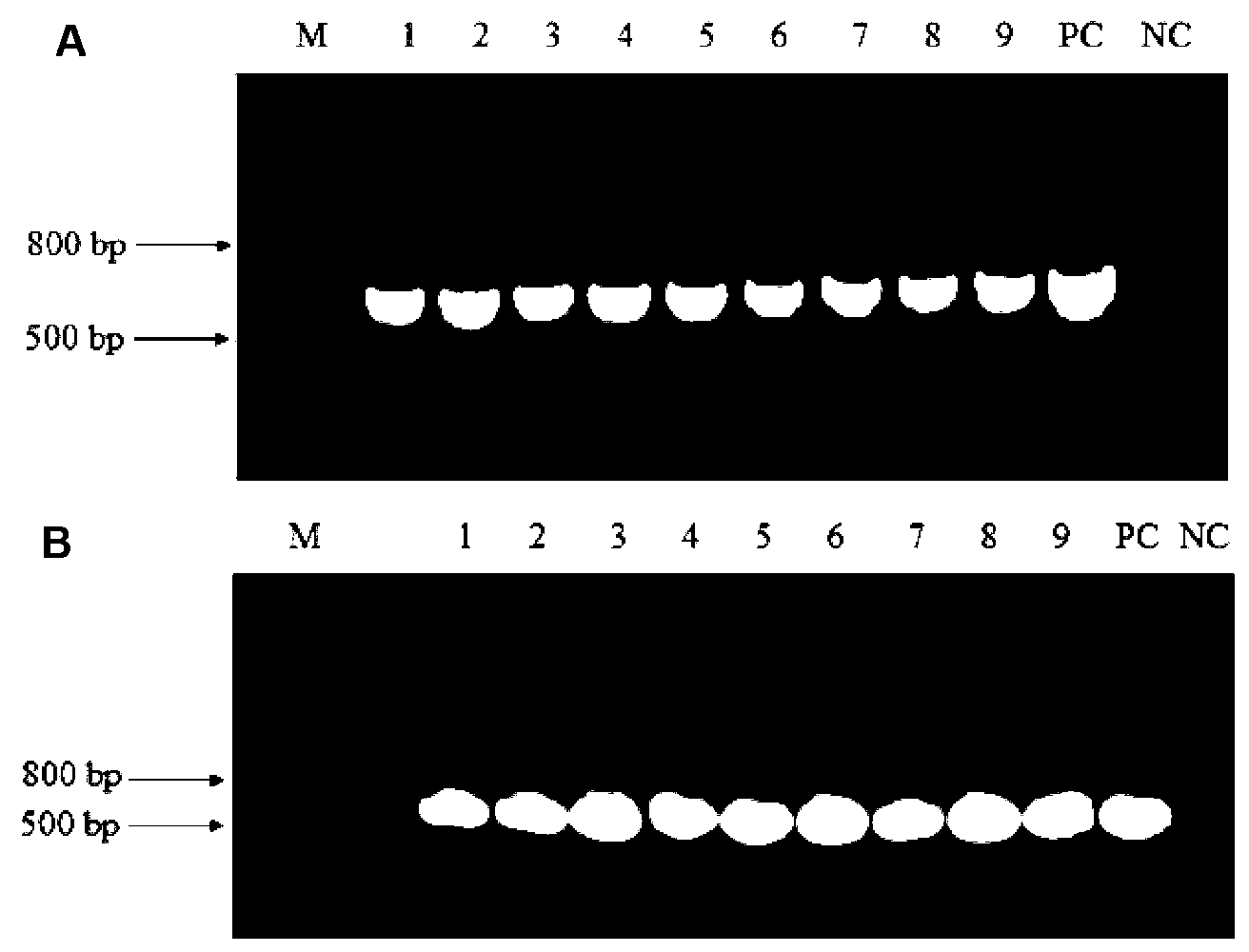
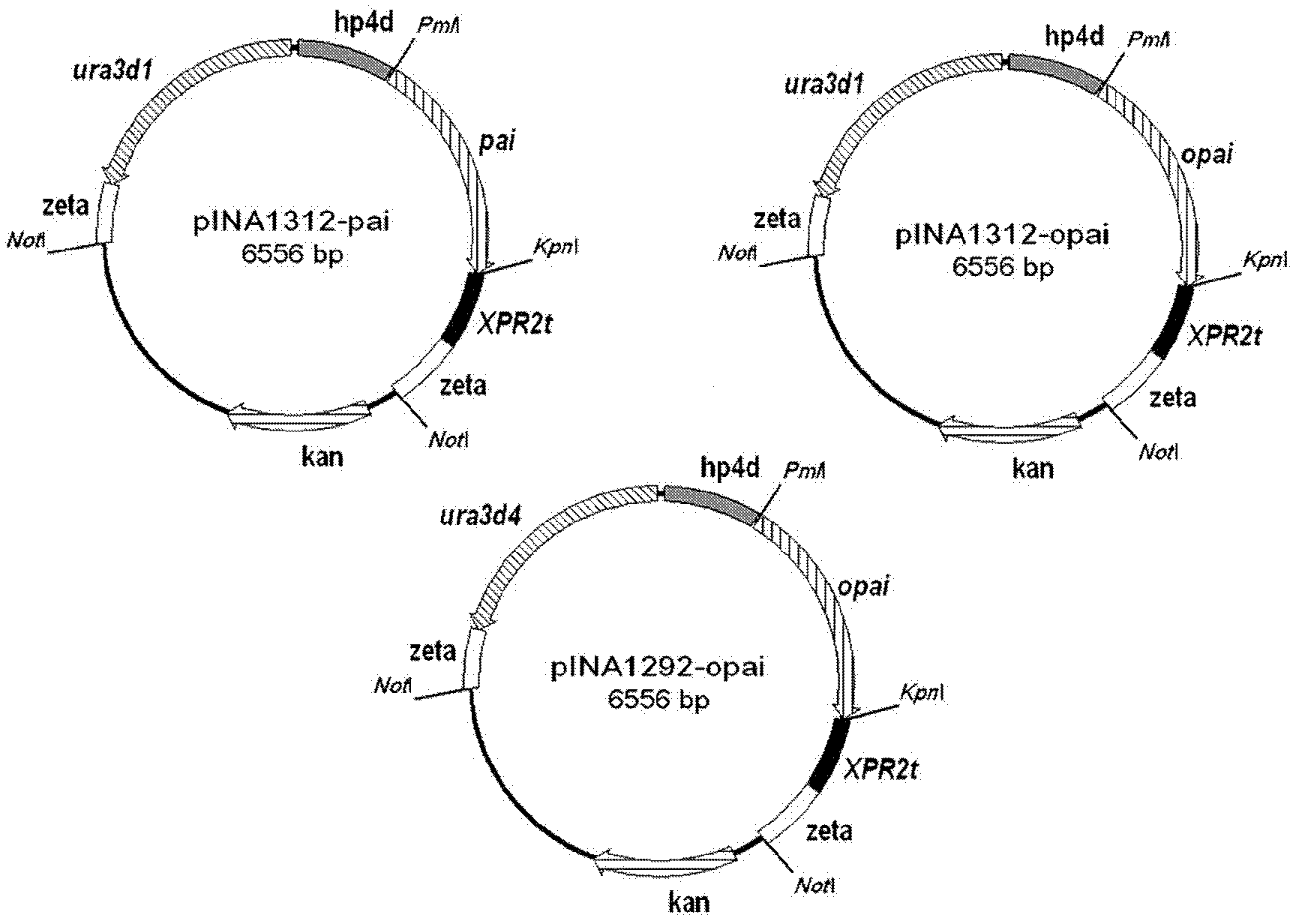
According to the invention, delta-12 desaturase gene (FADS12, d12) from mortierella alpine ATCC32222 (M. alpina ATCC32222) is amplified, such that multi-copy expression plasmid with inserted opai / d12 co-expression gene and recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast strain are prepared. According to the invention, the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast strain assists in increasing endogenous substrate linoleic acid (LA) amount and outer soybean oil increased substrate LA amount in fermentation medium, through expressing d12. In the strain, opai gene and d12 gene expression and transcript levels are increased with a multi-copy integration manner, such that conjugated linoleic acid t10 and c12-CLA specific isomer synthesis amount in recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast strain can be further improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Yarrowia lipolytica and applications thereof
ActiveCN107164249AImprove conversion rateEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIndustrial biotechnology
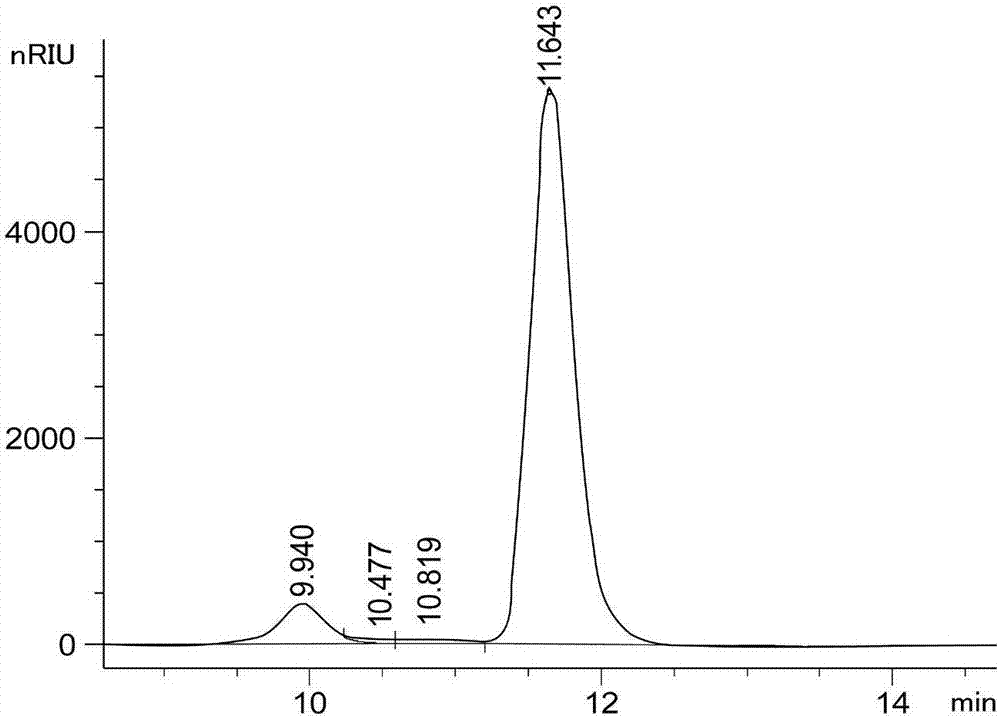
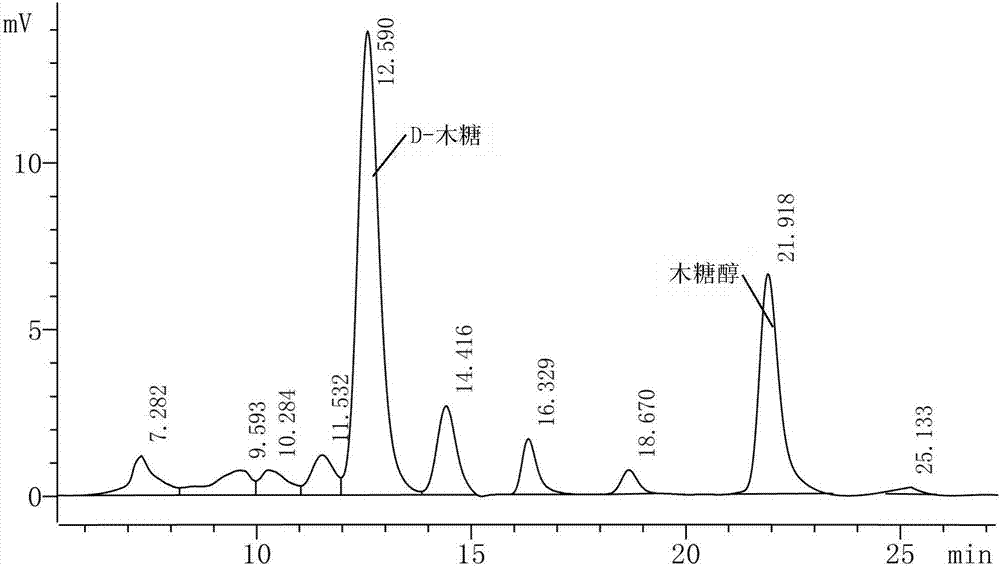
The invention discloses a Yarrowia lipolytica and applications thereof, and belongs to the field of industrial biotechnology. A strain obtained after separation is named as Yarrowia lipolytica BBE-17. The strain can produce erythritol through fermentation using glucose as a carbon source, a high conversion rate can be realized without fed batch or continuous fermentation, and the adjustment of the pH value is not needed in the whole fermentation process, so the technologic operation is simplified, and the strain has certain industrial application potential. The strain also can produce xylitol through fermentation using a D-xylose mother liquor as a carbon source, so the strain a new potential way for the preparation of polyol products from non-food raw materials through a biological technology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Special fertilizer for Xinjiang Hami melon
InactiveCN101891551AReasonable ratio of nutrientsIncrease productionFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesGeotrichumAmmonium sulfate
The invention relates to a special fertilizer for Hami melon, which is an organic-inorganic compound fertilizer consisting of enzymolysis oil residue, ammonium sulfate, diammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, zinc sulfate and boric acid, wherein the enzymolysis oil residue is a product produced by utilizing lipase in bacillus subtilis zymotic fluid and yarrowia lipolytica zymotic fluid and protease in geotrichum candidum zymotic fluid and lactobacillus plantarum zymotic fluid to carry out biodegradation on oil residue. The special fertilizer is specially configured against the absorption rules of nutrients of Xinjiang Hami melon and the nutrient status of the soil of a main producing region of the Hami melon, and can fully utilize the special nitrogen nutrient of the oil residue, increase the output and improve the quality.
Owner:SHANDONG GUANGDA FERTILIZER INDAL TECHCO
Heatproof mutation lipase with high catalytic activity as well as preparation method and application of heatproof mutation lipase
ActiveCN106047838ASave manpower and material resourcesQuick filterHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesThermal stabilityMolecular dynamics
The invention discloses heatproof mutation lipase with high catalytic activity as well as a preparation method and an application of the heatproof mutation lipase. The lipase is S118-177 mutation lipase with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and S122-196 mutation lipase with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The key unfolding subregion of a lipase lid 1 region is analyzed through long-time high-temperature molecular dynamic simulation of the unfolding process of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase 2, and key mutation sites are effectively screened. The mutation lipase obtained through actual measurement and screening has high heat stability and catalytic activity and is particularly suitable for being applied industrially.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Special fertilizer for Zhanhua winter jujubes, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101955390AReasonable ratio of nutrientsHigh yieldFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesGeotrichumNutrient absorption
The invention relates to a special fertilizer for Zhanhua winter jujubes, a preparation method and the application thereof. The special fertilizer for Zhanhua winter jujubes comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 50 to 70 parts of zymolysing oil residues, 10 to 20 parts of urea, 5 to 15 parts of DAP (diammonium phosphate), 10 to 18 parts of potassium sulfate, 0.5 to 1 part of ferrous sulphate, 0.3 to 0.7 part of zinc sulfate and 0.2 to 0.4 part of boric acid, wherein the zymolysing oil residue is a product produced by carrying out biodegradation on the oil residues by using lipases in bacillus subtilis fermentation broth and yarrowia lipolytica fermentation broth and proteases in geotrichum candidum fermentation broth and lactobacillus plantarum fermentation broth. The special fertilizer of the invention is prepared especially according to the nutrient status of soils in the main producing areas of Zhanhua winter jujubes and the regulation of nutrient absorption of the jujubes, and has the advantages of reasonable nutrient ratio and strong pertinence. The special fertilizer can reduce the salt damages caused by fertilizing and the organic and inorganic combination can improve the soil fertility.
Owner:SHANDONG GUANGDA FERTILIZER INDAL TECHCO
Mutant of glutamine transaminase expressed by active form
ActiveCN107574159AAchieve active expressionSimplify production stepsFungiTransferasesBacterial strainMutant
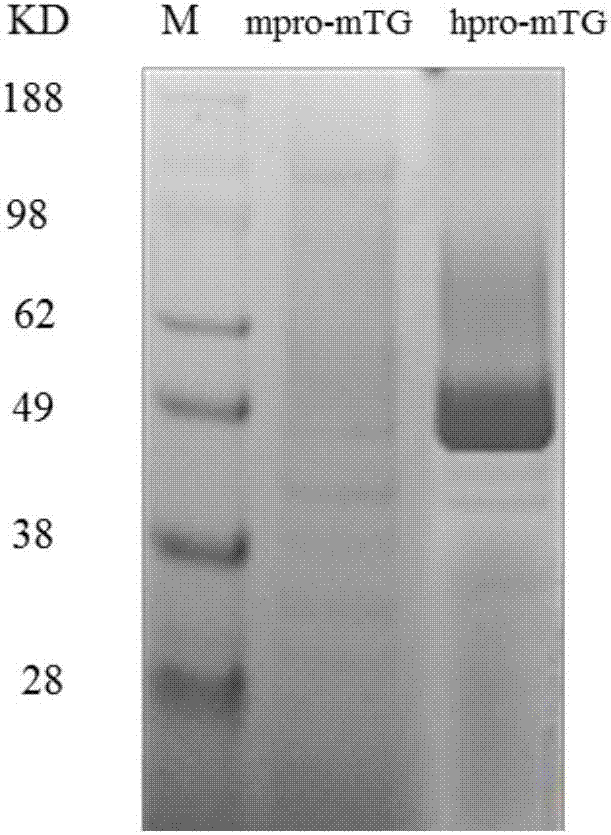
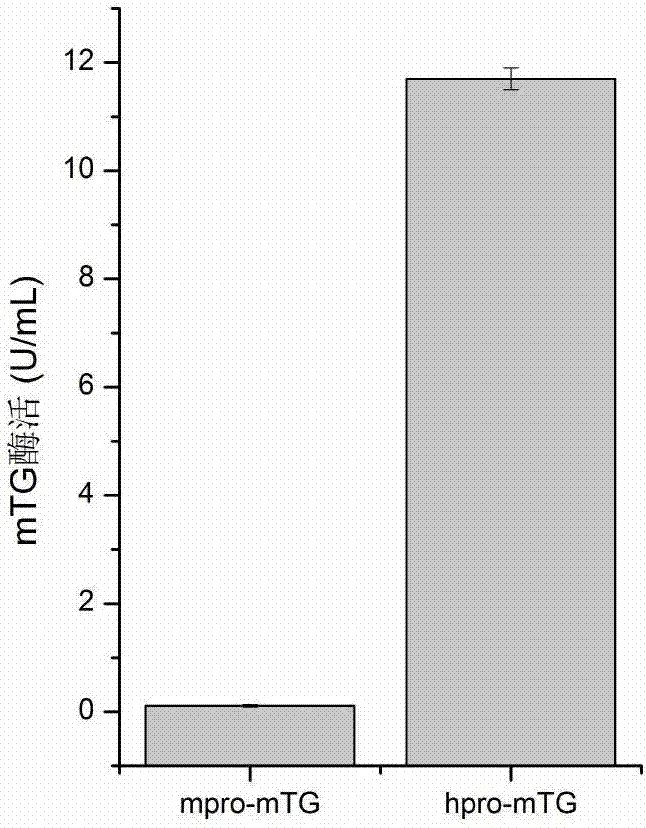
The invention discloses a mutant of glutamine transaminase expressed by an active form, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A genetically engineered bacterium po1h / hpro-mTG of high-output glutamine transaminase is structured by using yarrowia lipolytica as a host. The bacterial strain is high in enzyme production level; the fermenting enzyme activity of a shake flask is up to 11.7 U / mL, and improved by 106 times in comparison to that before transformation; the fermenting enzyme activity of a fermenting tank is up to 43.7 U / mL. Through co-expressing proteases TAMEP and hpro-mTG, the activity expression of glutamine transaminase is realized; the fermenting enzyme activity of the shake flask can reach 6.7U / mL, and the fermenting enzyme activity of the fermenting tank can reach 21.4U / mL. The fermenting enzyme production level of the recombinant bacteria is high, the production cost of the glutamine transaminase is reduced; the mutant is good for the industrial production of the glutamine transaminase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glutamine transaminase mutant with improved enzymatic activity
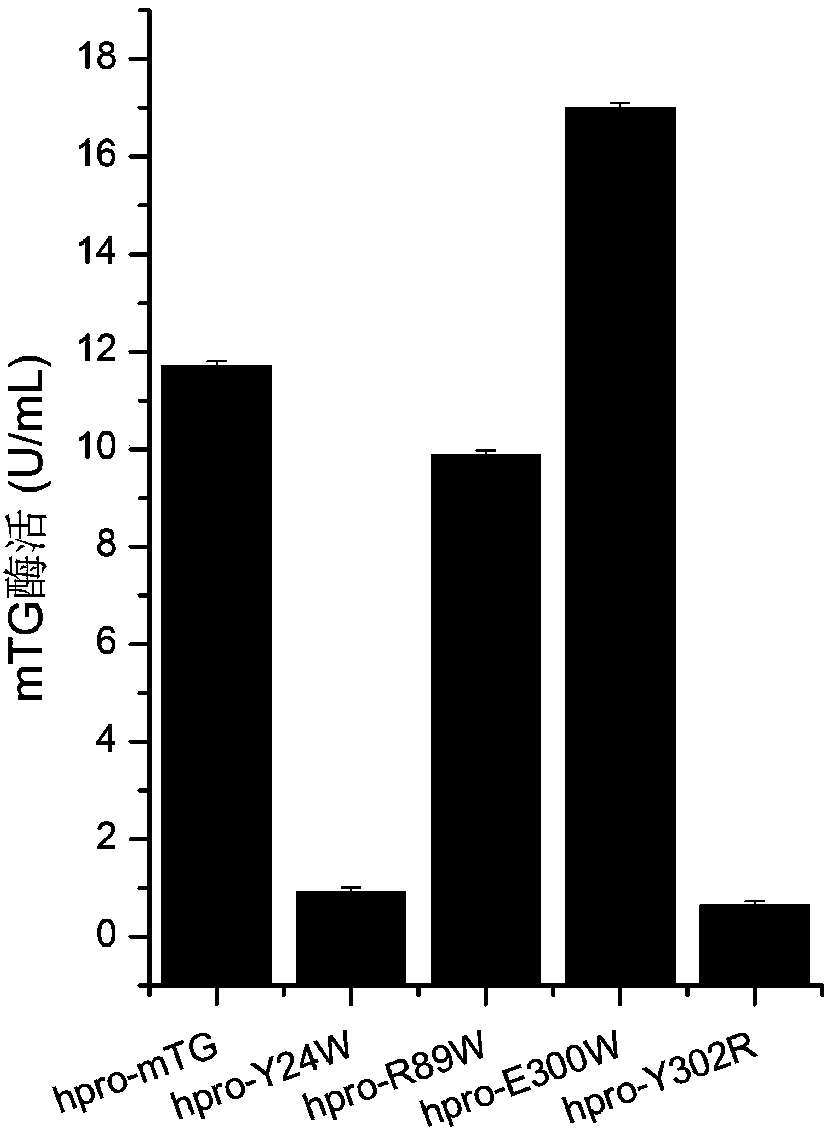
ActiveCN107739734AEasy to separate and purifyEasy to trainFungiAcyltransferasesAmine transaminase activityReactive site
The invention discloses a glutamine transaminase mutant with improved enzymatic activity, which belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The site-specific mutagenesis is performed on glutamine transaminase, an amino acid residue close to an active site of the glutamine transaminase is changed, so that the catalytic efficiency of the glutamine transaminase is improved, and the enzymatic activityof the glutamine transaminase is further improved. Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica with improved enzymatic activity is established by the glutamine transaminase mutant, the enzymatic activity of theglutamine transaminase is improved by 1.45 times compared with an original strain, the enzymatic activity of the shake flask fermentation can reach 16.995U / mL, and the enzymatic activity of the fermenting tank fermentation can reach 59.85U / mL which is the highest fermentation value reported at present.
Owner:TAIXING DONGSHENG FOOD TECH
Pentose phosphate pathway upregulation to increase production of non-native products of interest in transgenic microorganisms
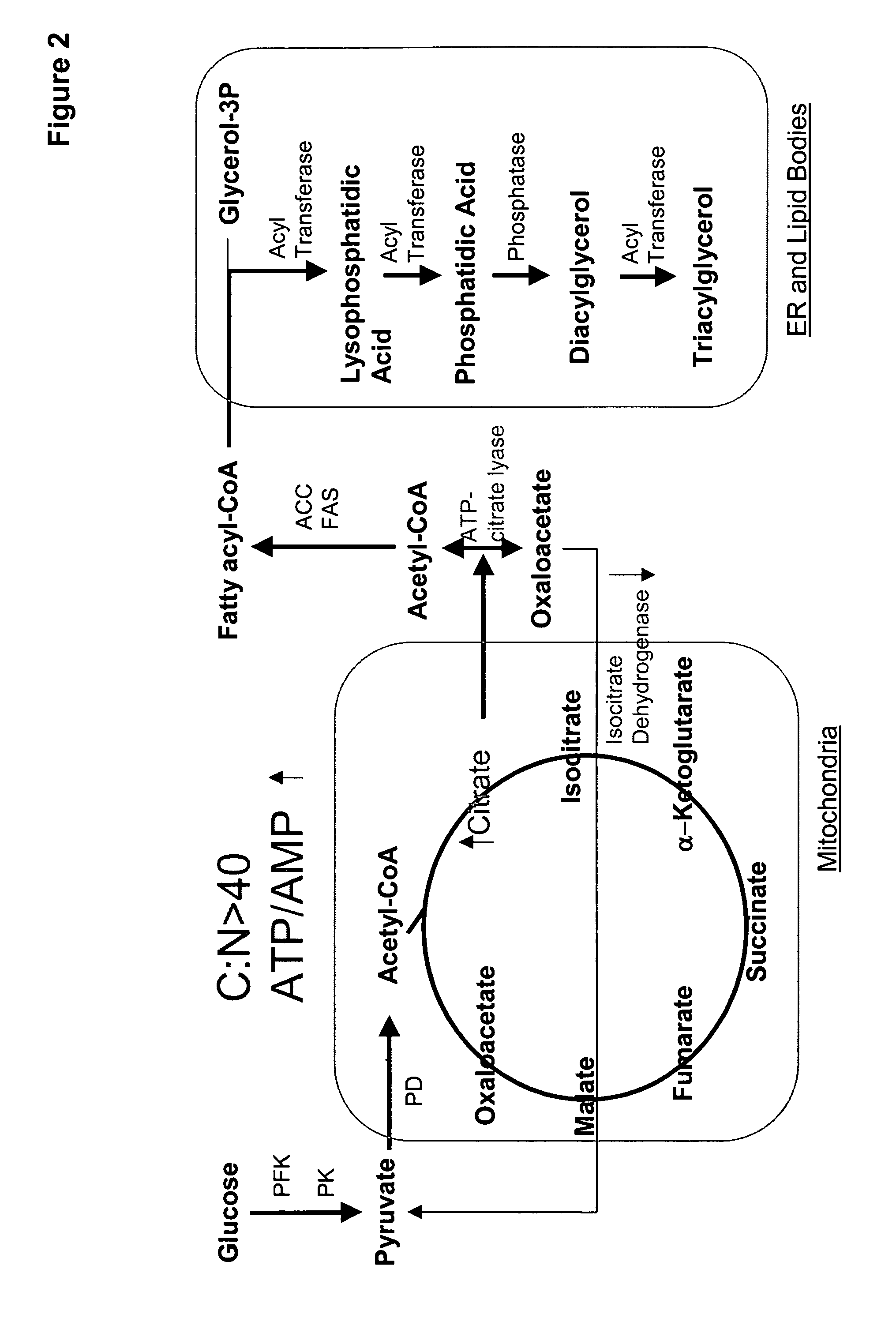
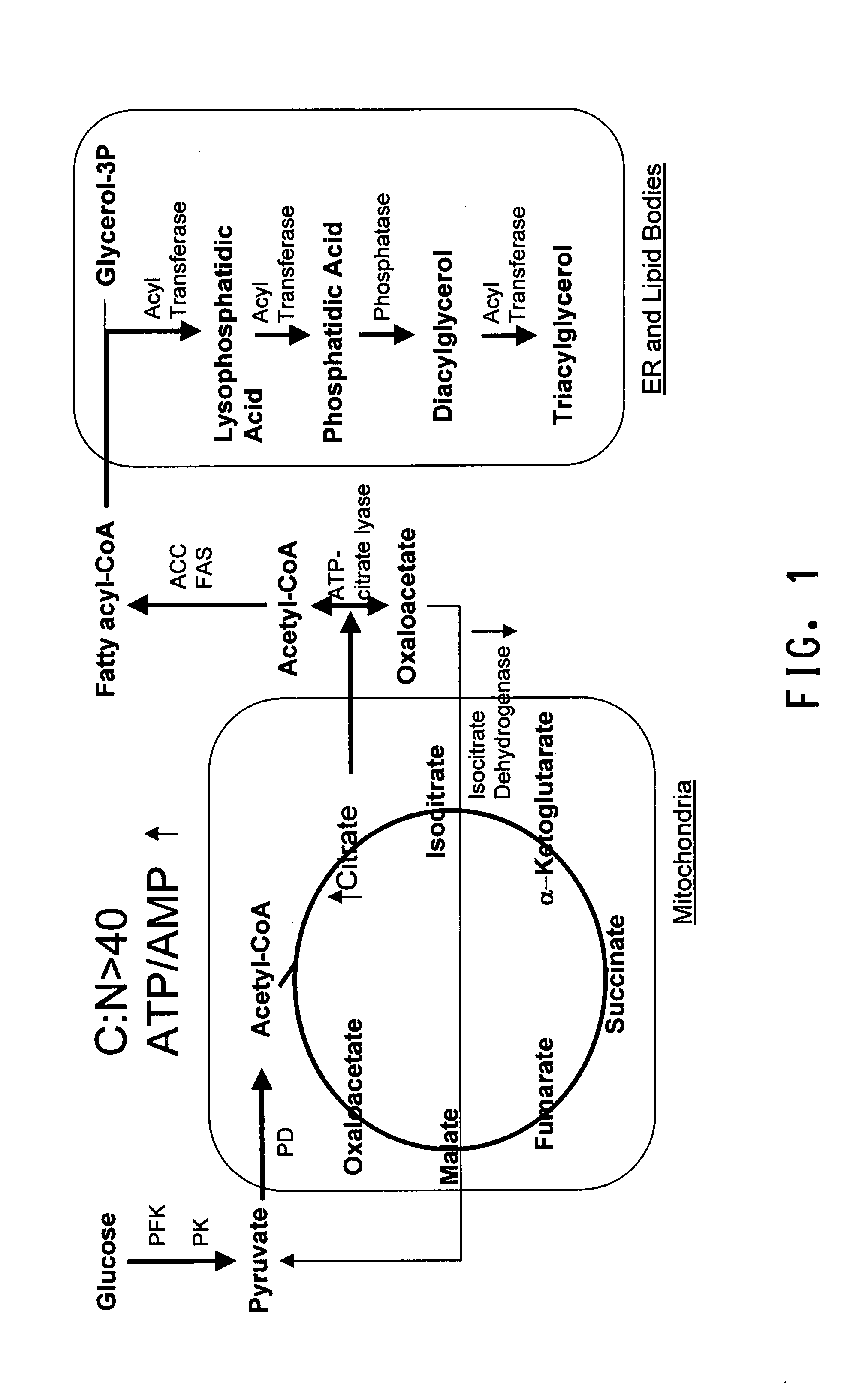
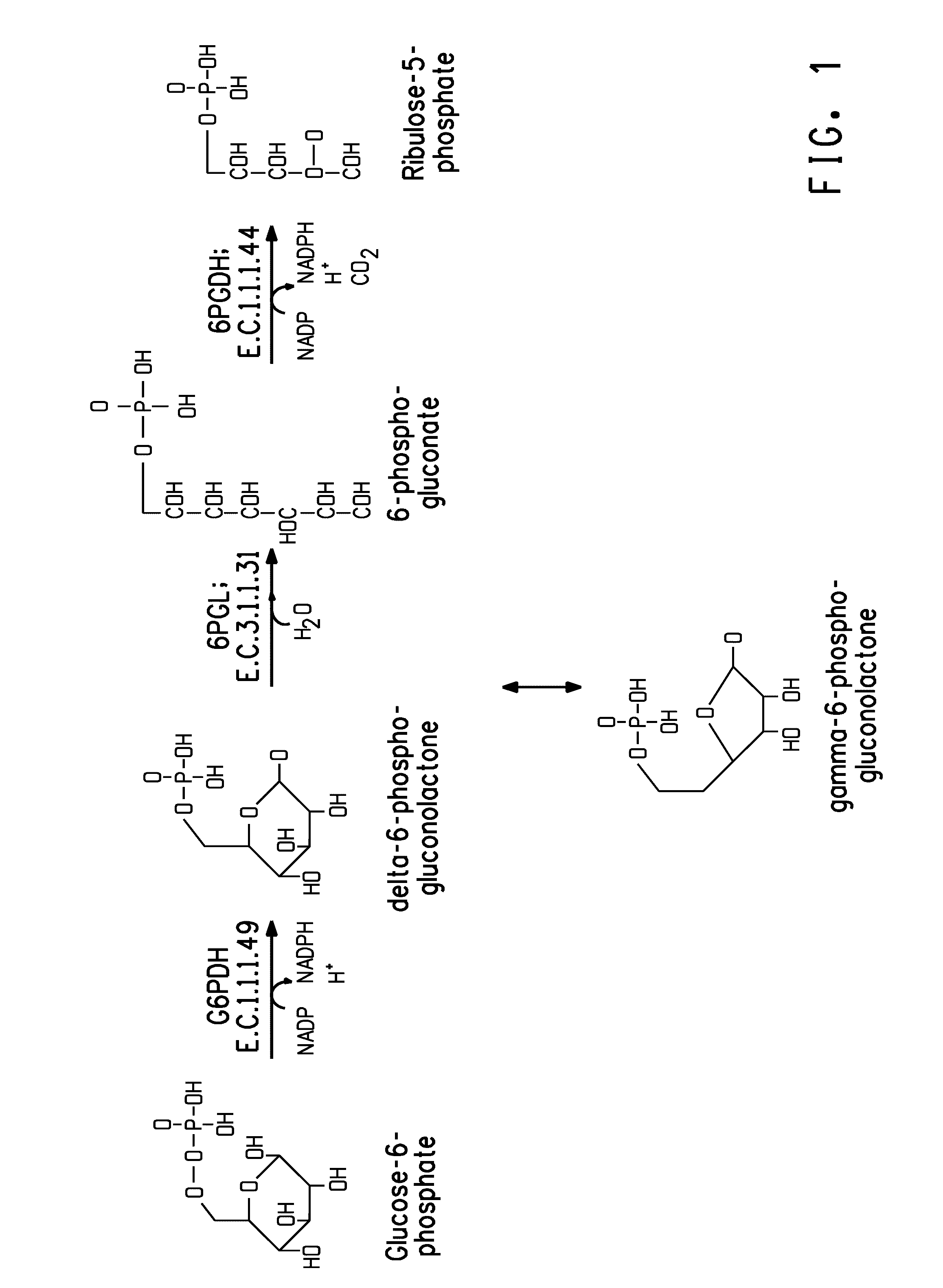
Coordinately regulated over-expression of the genes encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase [“G6PDH”] and 6-phospho-gluconolactonase [“6PGL”] in transgenic strains of the oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica, comprising a functional polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”] biosynthetic pathway, resulted in increased production of PUFAs and increased total lipid content in the Yarrowia cells. This is achieved by increased cellular availability of the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate [“NADPH”], an important reducing equivalent for reductive biosynthetic reactions, within the transgenic microorganism.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
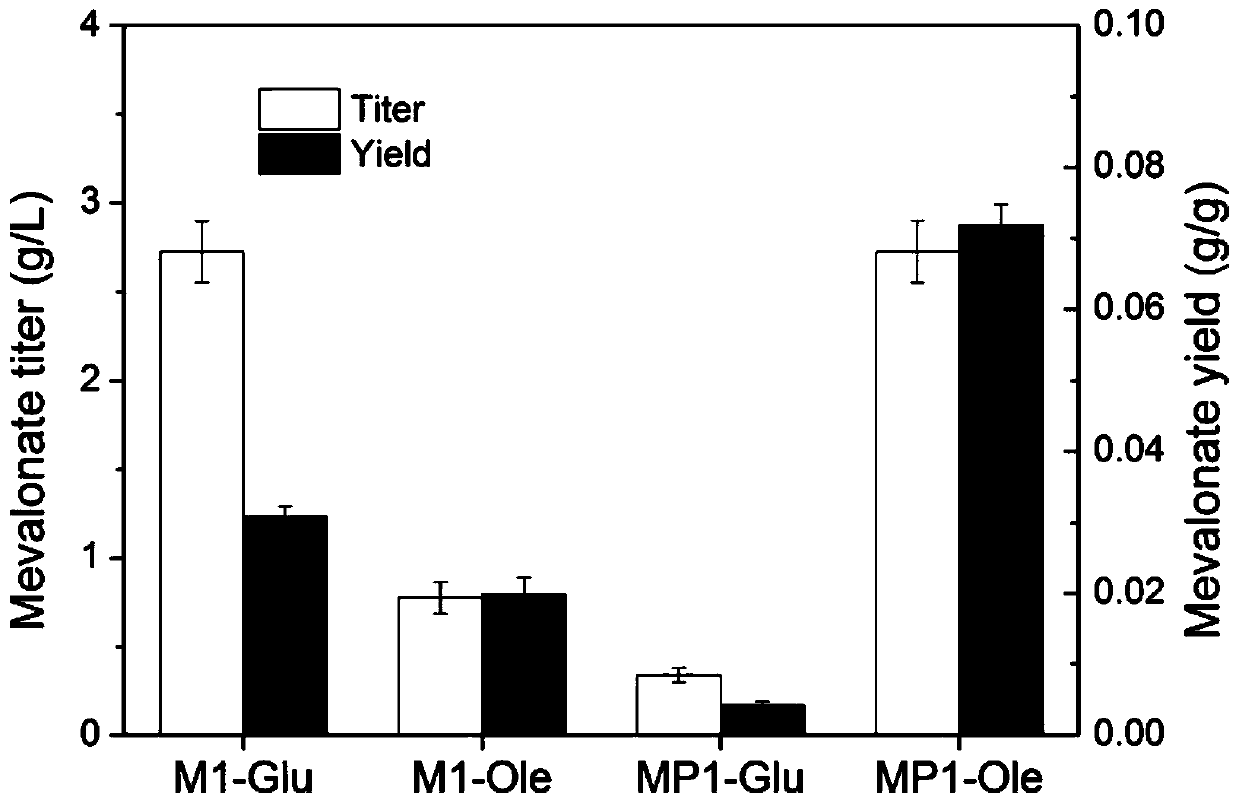
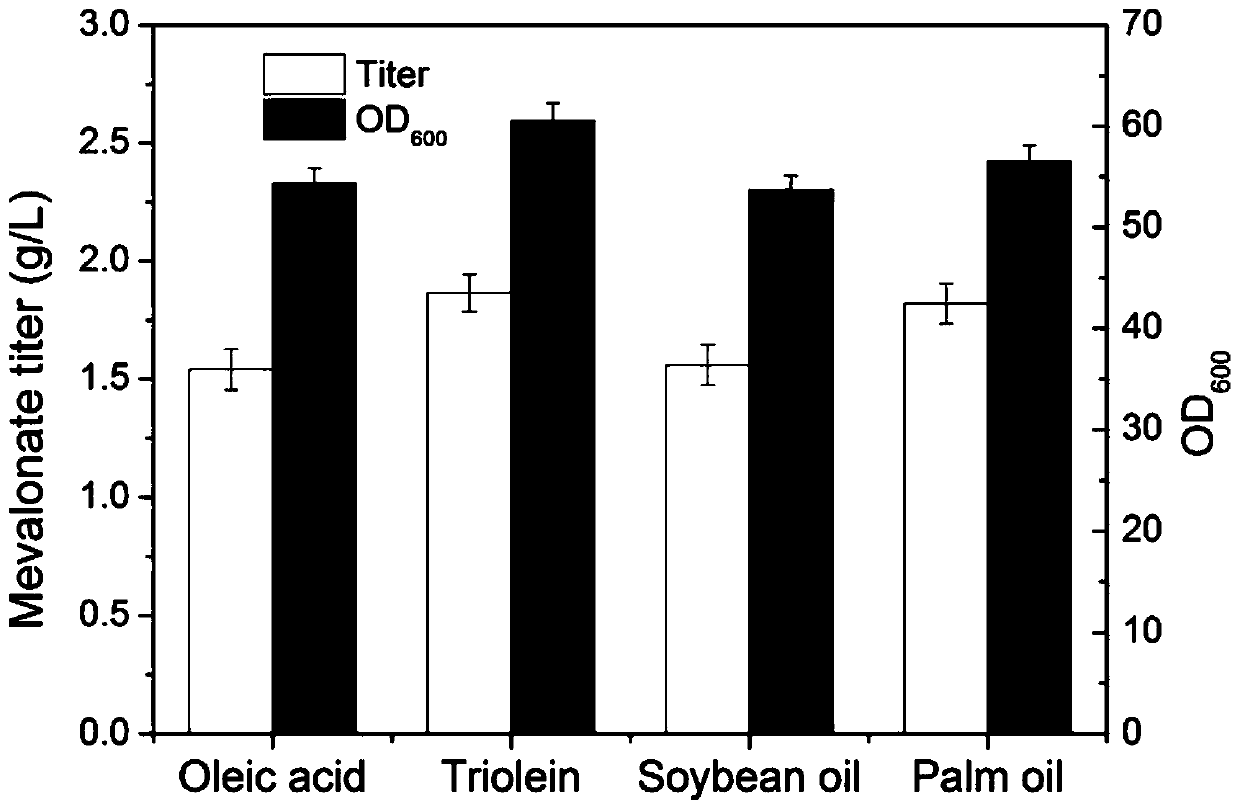
Method for positioning and synthesizing terpenoids by means of Yarrowia lipolytica way
ActiveCN110106209AHigh synthetic yieldImprove the added value of the applicationMicroorganism based processesFermentationHMG-CoA reductaseAlpha-farnesene
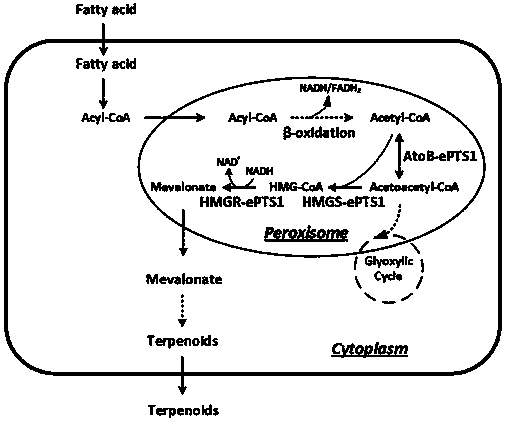
The invention discloses a method for positioning and synthesizing terpenoids by means of the Yarrowia lipolytica way. The method comprises the steps that an acetoacetyl coenzyme A thiolase, HMG-CoA synthetase and HMG-CoA reductase in the synthetic route of mevalonic acid in Yarrowia lipolytica are over-expressed and positioned to the peroxisome, and engineering bacteria MP1 are obtained; on the basis of the engineering bacteria MP1, the alpha-farnesene synthesis way is expressed, and engineering bacteria FP1 are obtained; or, the beta-carotene synthesis way is expressed, and engineering bacteria CP1 are obtained; or, the linalool synthesis way is expressed, engineering bacteria LP1 are obtained; the bacteria FP1 or CP1 or LP1 can synthesize the terpenoids under the aerobatic condition by means of a culture medium containing fatty acid or grease, and the yield of the synthesized terpenoids is higher compared with a traditional method. According to the method, fatty acid, grease and cheap food waste oil can be used for generating mevalonic acid downstream terpenoids, and the considerable application prospect and the economic value are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
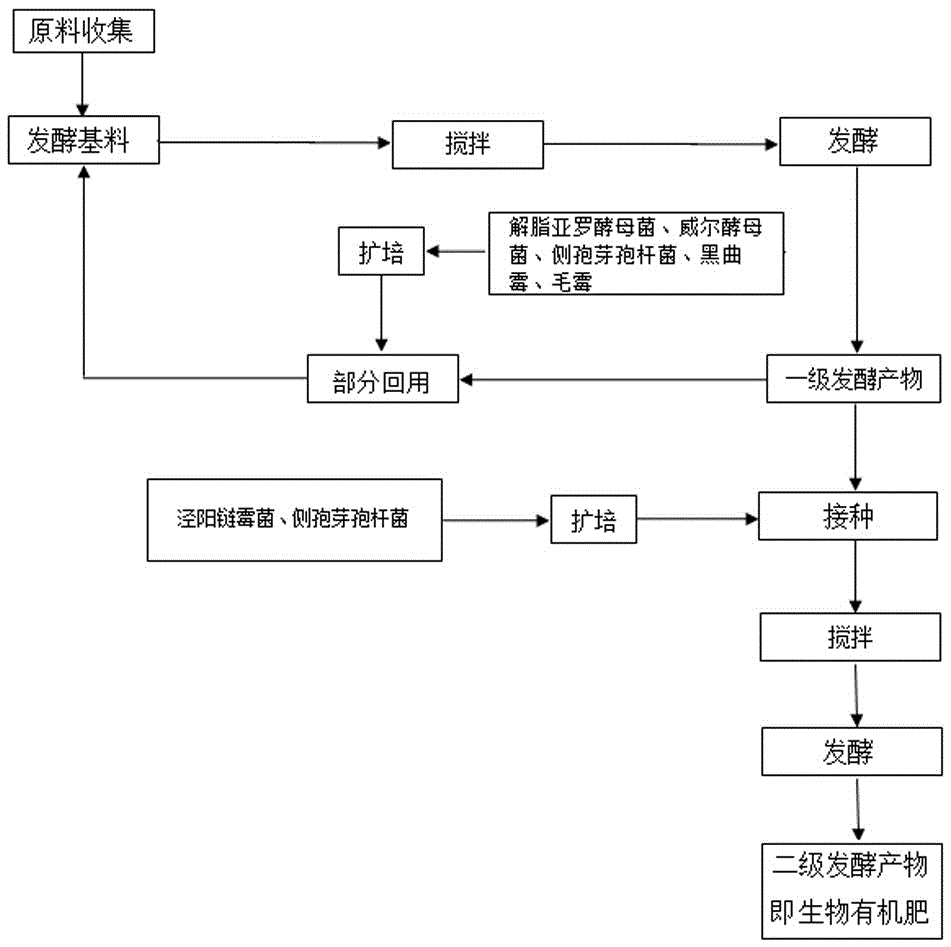
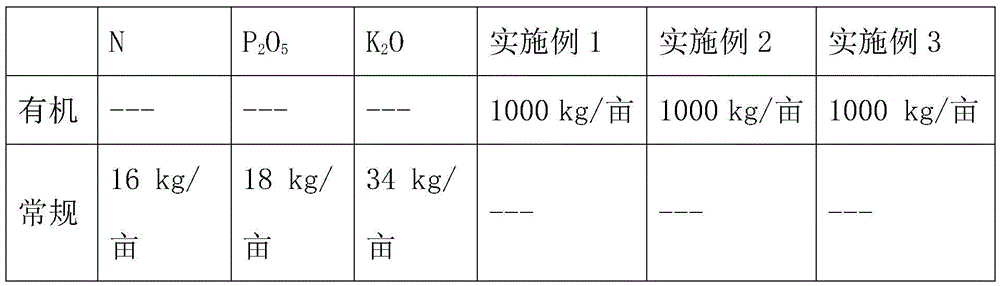
Method for producing bio-organic fertilizers by quick fermentation of kitchen wastes
InactiveCN105565917AHigh salinityEasy to solveBio-organic fraction processingBioloigcal waste fertilisersBiotechnologyDisease damage
The invention discloses a method for producing bio-organic fertilizers by quick fermentation of kitchen wastes. The bio-organic fertilizers are obtained by primary fermentation and secondary fermentation. Since primary fermentation products are partially returned to a fermentation matrix, fermentation rate is increased. According to characteristics of the kitchen wastes, yarrowia lipolytica, Saccharomyces willianus and bacillus laterosporus are selected for zymolysis of the kitchen wastes. Functional bacteria including streptomyces jingyangensis and the bacillus laterosporus are added, the streptomyces jingyangensis is capable of generating antibiotics to protect crops from pest and disease damages, and the bacillus laterosporus is resistant to high temperature, high salinity, dryness and high permeability and capable of improving soil salinity and alkalinity after being applied to soil and continuing decomposing macromolecular substances in the soil to provide nutrition for the crops, so that efficacies of the bio-organic fertilizers are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN CHAOYI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
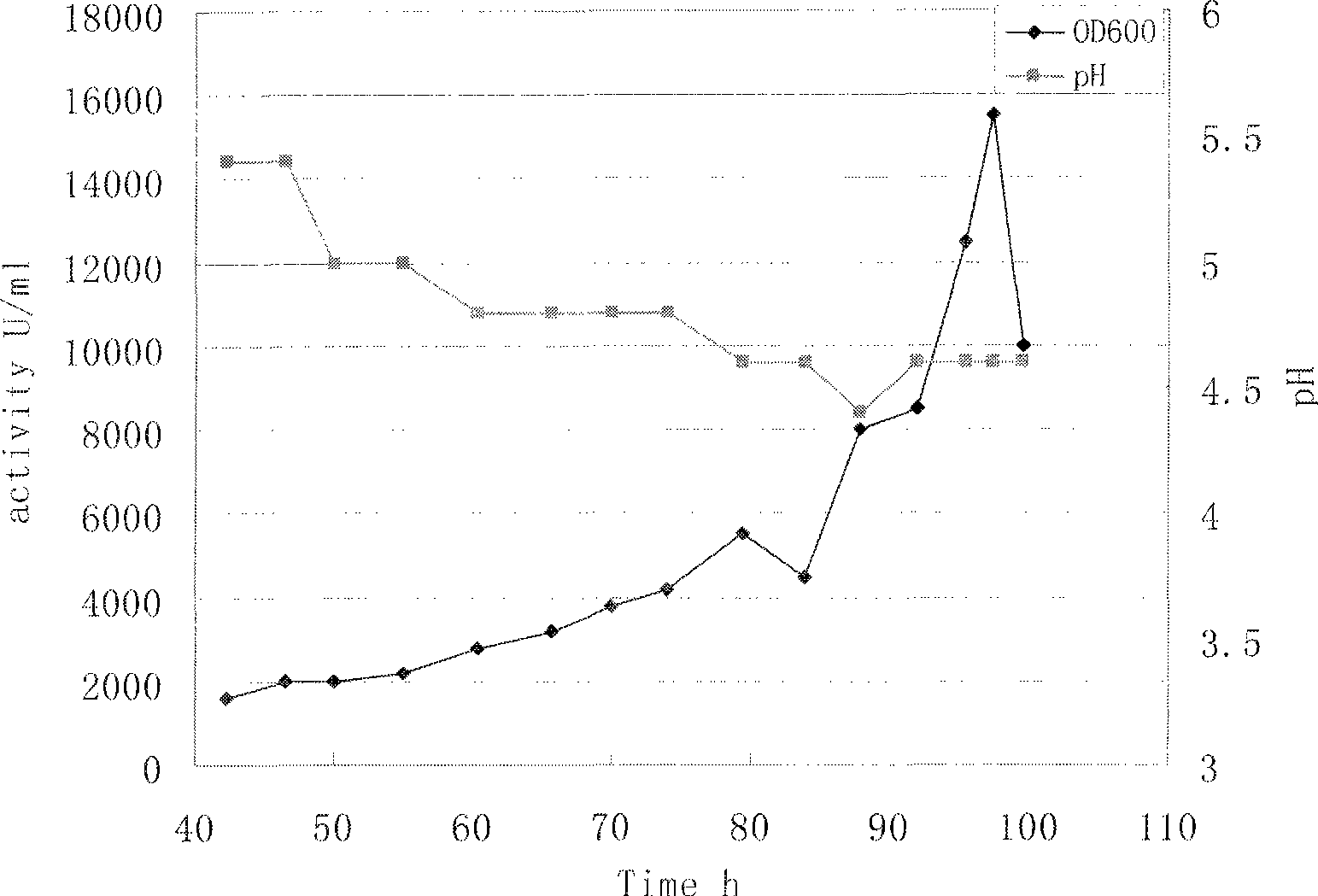
A strain of Yarrowia lipolytica mutant strain capable of highly yielding lipase, cultivation method and use of enzyme thereof
The invention provides a Yarrowia lipolytica lipase high-yield strain LW1 (CGMCC No.2707) obtained through an ultraviolet mutagenesis method, a fermentation culture method, a lipase purification method, and a method for catalyzing the methyl esterification of fatty acid thereof. Yarrowia lipolytica CGMCC No.2707 is cultured for 97.5 h through fed-batch fermentation on a fermentation tank with the capacity of 100L, the lipase production level is 15,500U / ml, and the activity of produced lipase powder is 30,000U / g. The obtained lipase powder or a zymotic fluid can be directly applied to a reaction of catalyzing the methyl esterification of the fatty acid. The conversion rate for 30h is more than 90 percent when the fatty acid and methanol are added according to the equal mol ratio and the using amount of the lipase in a system is 1,000-3,000U per gram of fatty acid.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Recombinant yeast strain capable of producing conjugated linoleic acid and application thereof
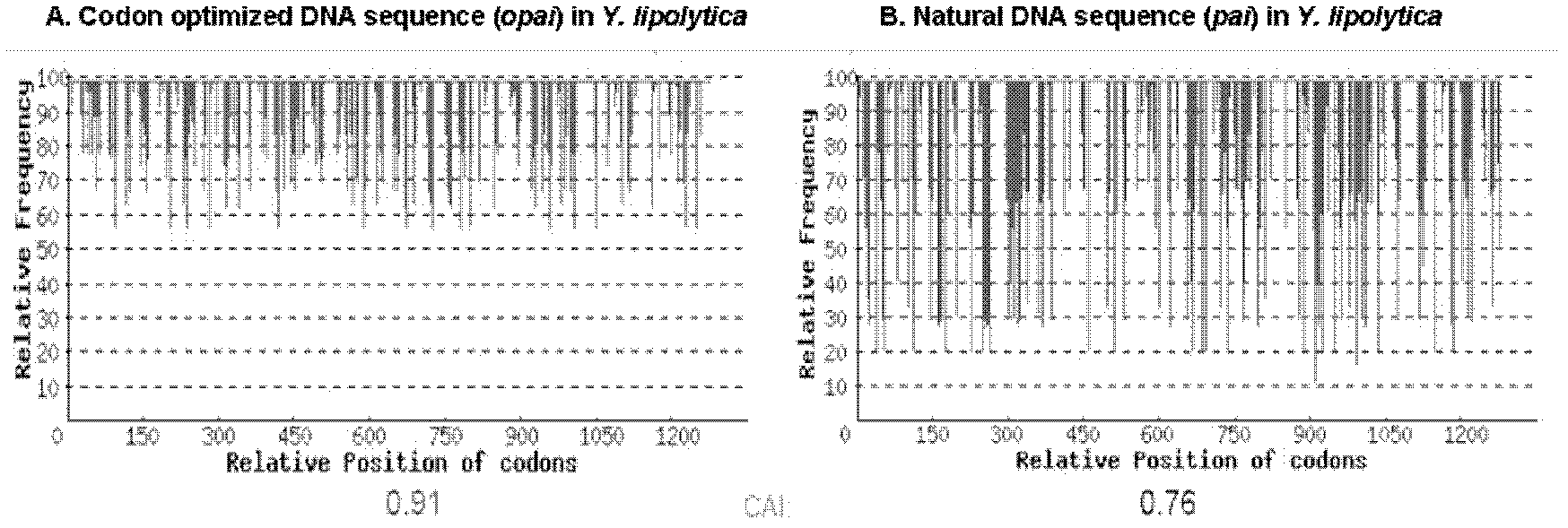
The invention relates to a recombinant yeast strain capable of producing conjugated linoleic acid and an application thereof. In the invention, codon optimization is carried out on linoleate isomerase in propionibacterium acnes (PAI) gene to obtain an optimized gene opai, recombinant expression plasmid and recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica bacterium which contain the opai gene are prepared, and therecombinant Yarrowia lipolytica bacterium which expresses the opai gene is utilized to produce conjugated linoleic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for producing erythritol by utilizing Yarrowia lipolytica strains
InactiveCN102352393AFulfil requirementsHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEvaporation
The invention relates to a process for producing erythritol by utilizing Yarrowia lipolytica strains, belonging to the technical field of fermentation engineering. In the process, artificial breeding and reproduction is carried out on Yarrowia lipolytica screed in nature so as to produce erythritol, wherein the steps of strain culture of Yarrowia lipolytica and production of erythritol with the strains comprise: strain preparation, primary and secondary seed culture, fermentation to obtain fermentation broth, ceramic membrane filtration, nanofiltration, evaporation and concentration, activated carbon decolorization, ion exchange, vacuum crystallization, auxiliary crystallization, centrifugation, drying, screening and package. In the invention, a mother liquid obtained by centrifugation reaches the standard of ceramic membrane filtrate after being subjected to nano filtration and purification, thus the ceramic membrane filtrate can be mixed and enters into the next process, thereby greatly improving the yield of the product; and the purity of the finished product is more than 99.5%, and the moisture of the finished product is about 0.16%. The process has the advantages of low production cost, short fermentation period, high production efficiency and the like.
Owner:FUTASTE PHARM CO LTD
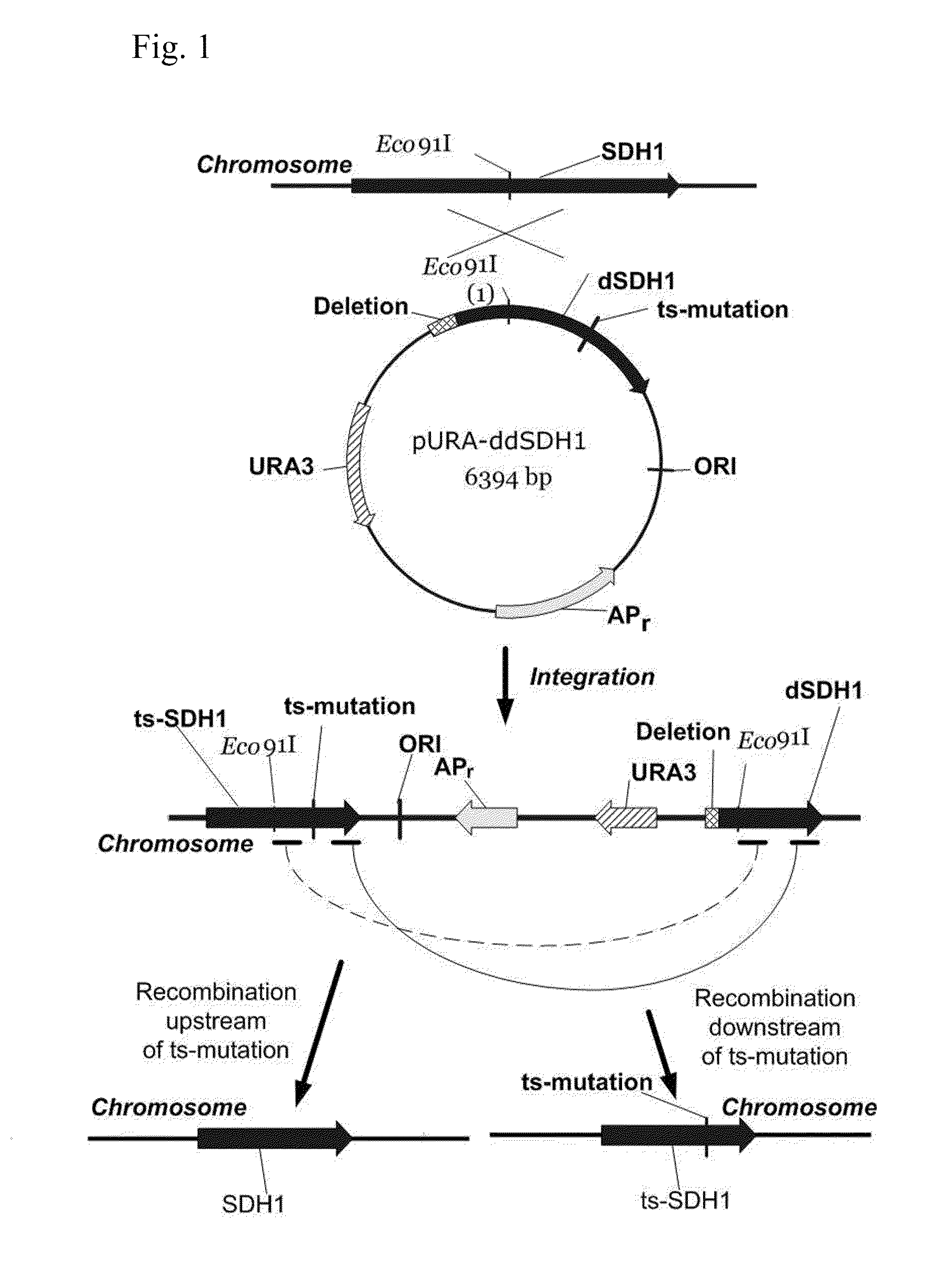
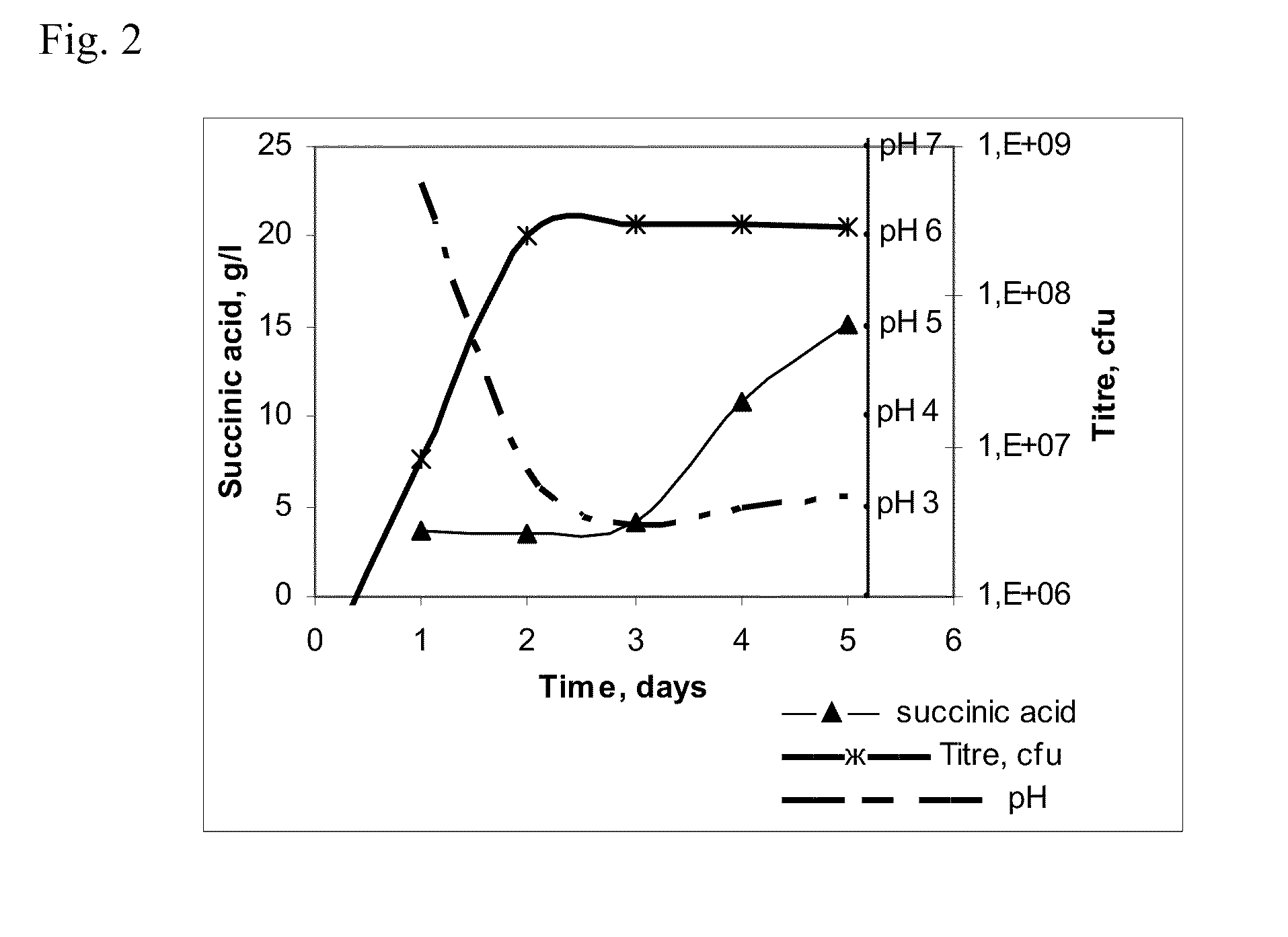
METHOD FOR PRODUCING SUCCINIC ACID USING A YEAST BELONGING TO THE GENUS Yarrowia
ActiveUS20120015415A1Improve productivityProducing succinic acidFungiOxidoreductasesSuccinic acidSuccinate dehydrogenase
The present invention provides a method for producing succinic acid using a yeast belonging to the genus Yarrowia, which has been modified to reduce activity of succinate dehydrogenase in said yeast.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com