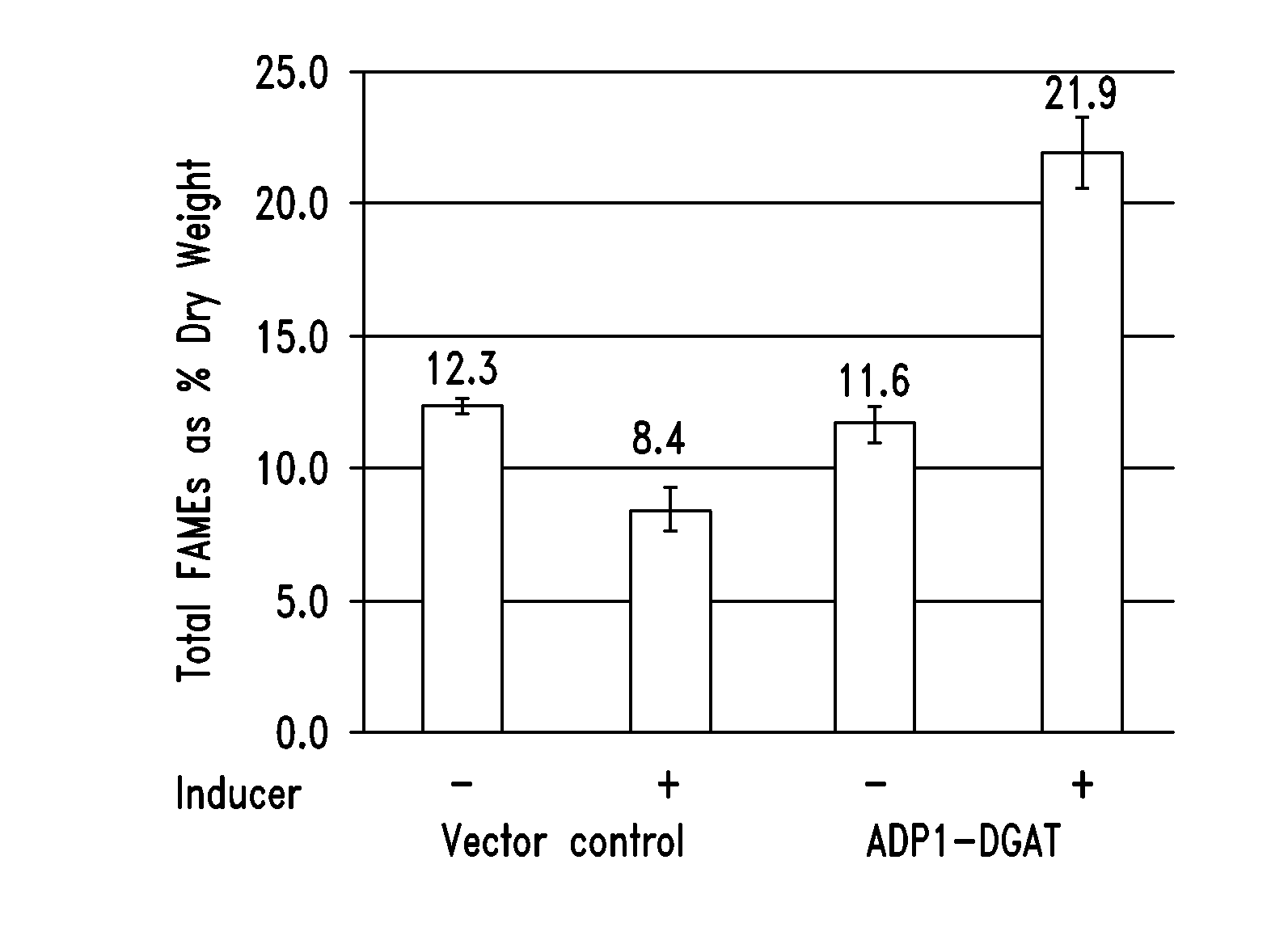
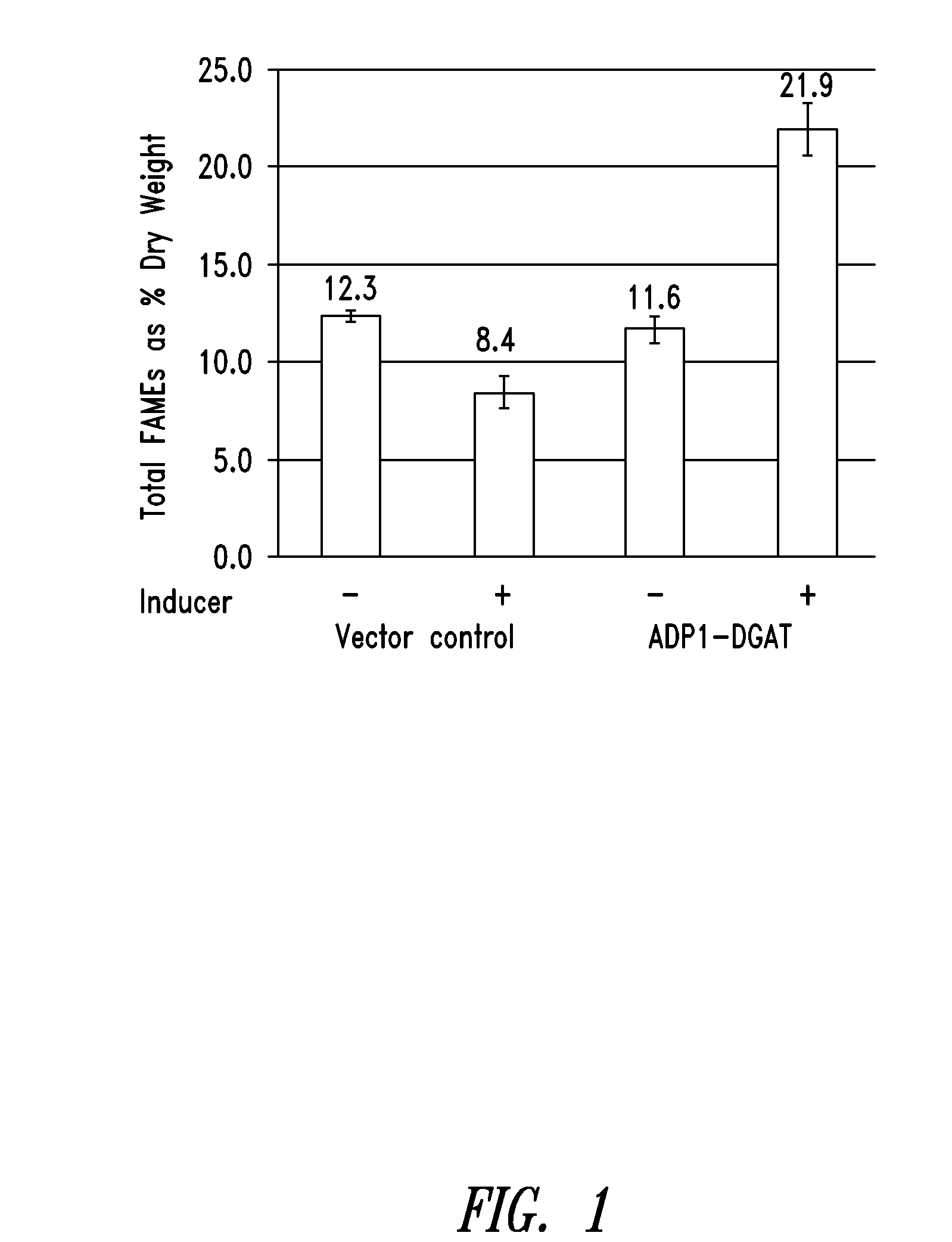
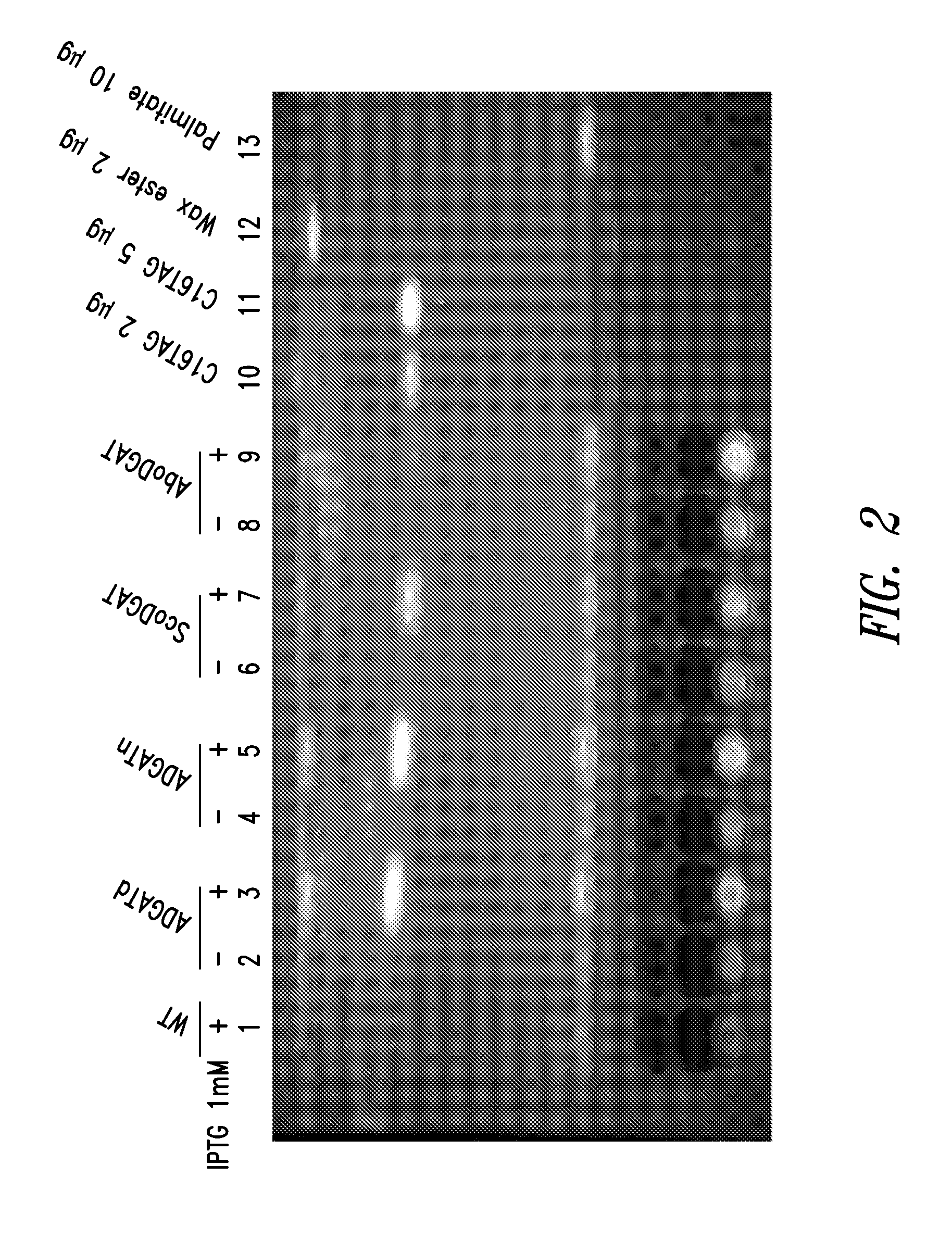
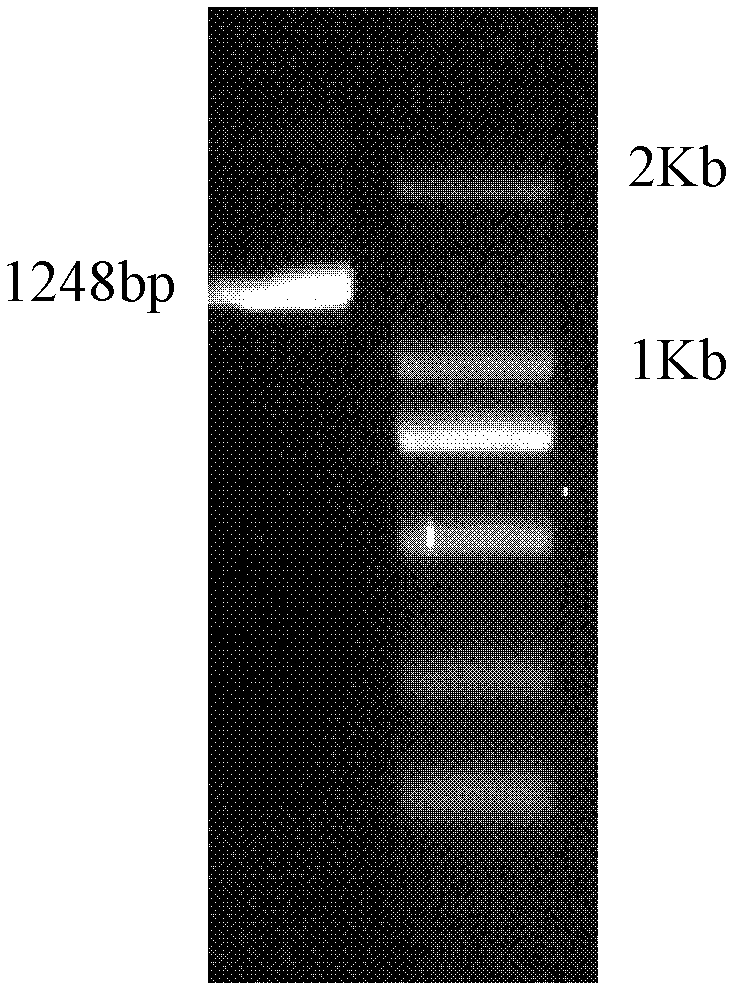
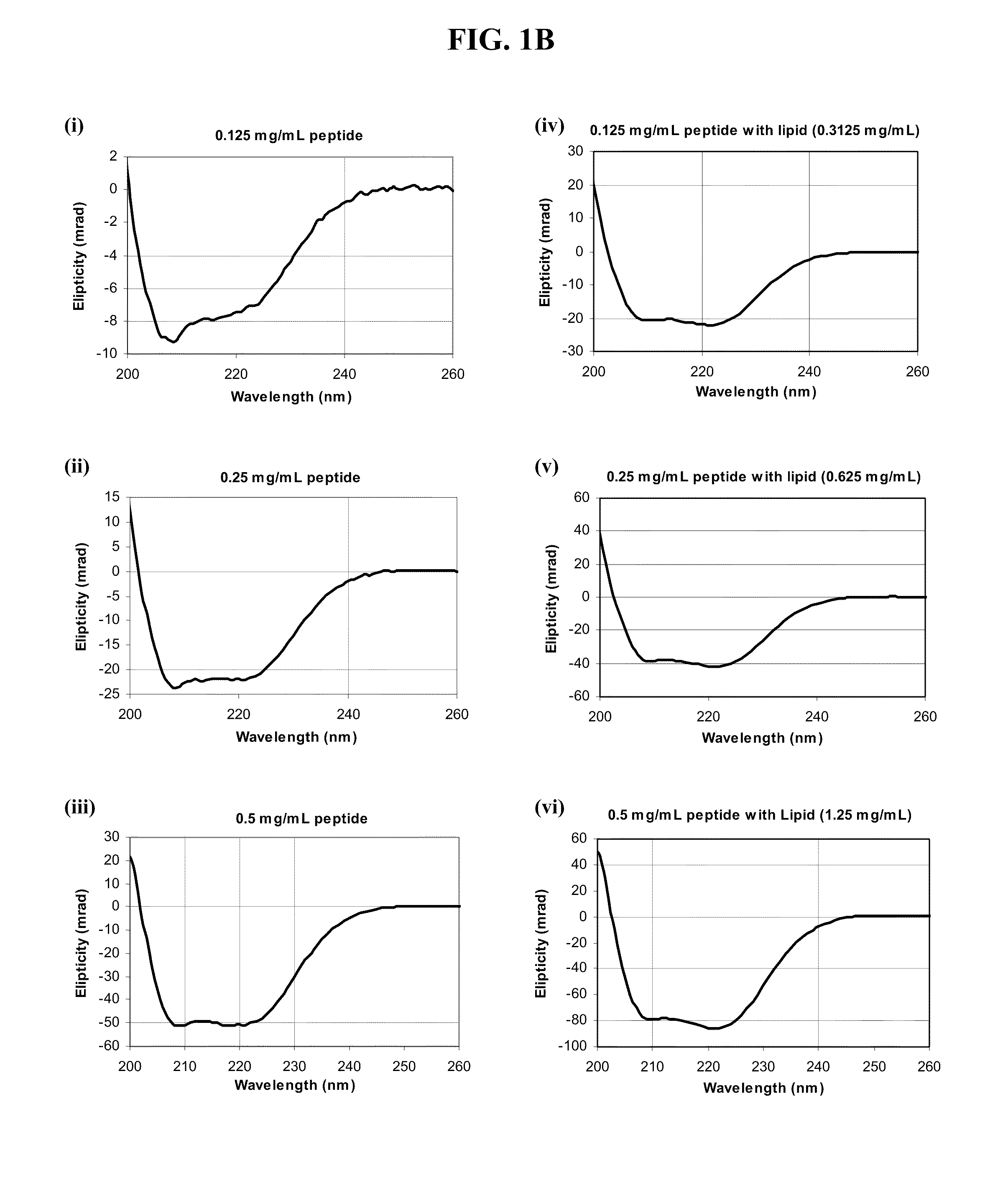
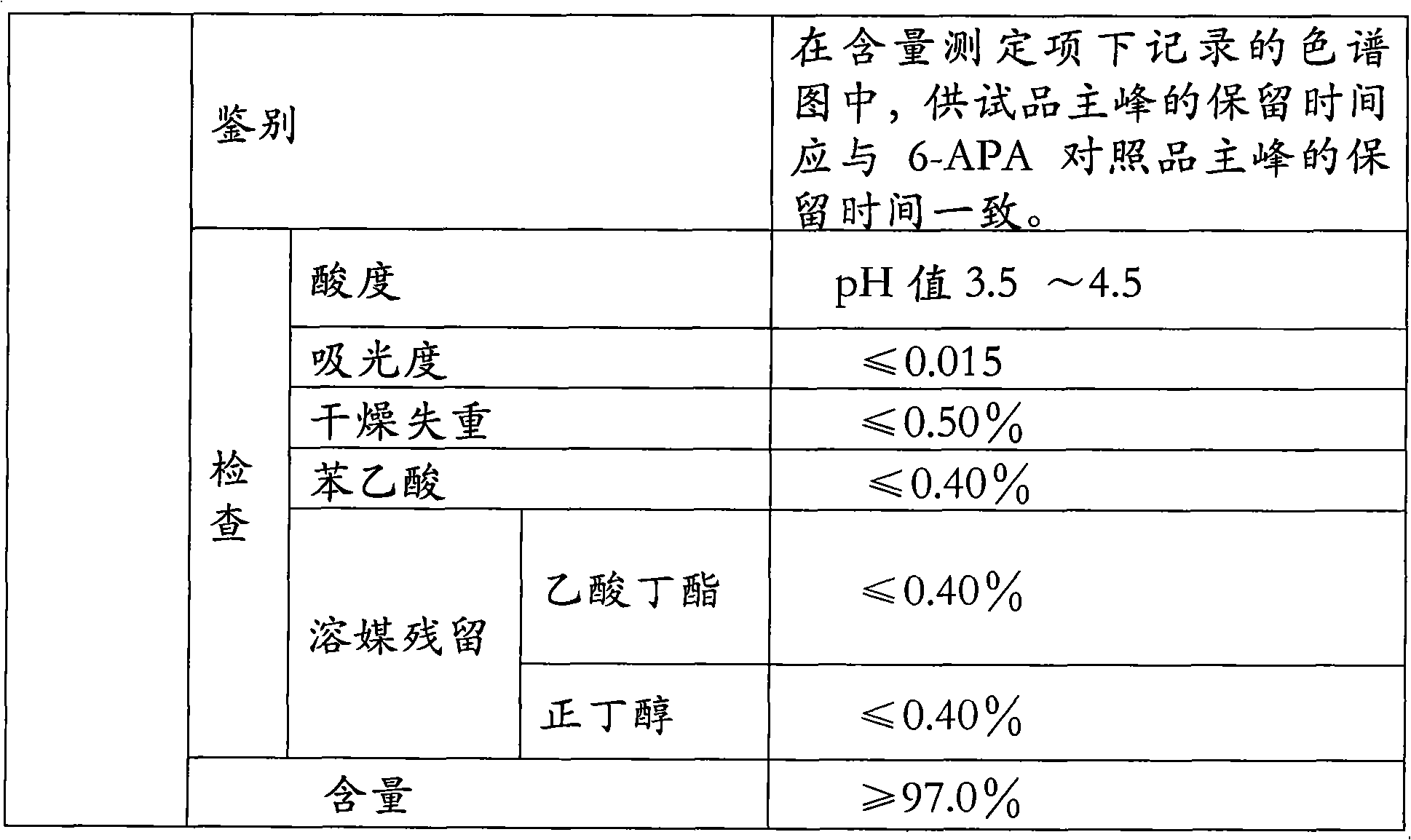
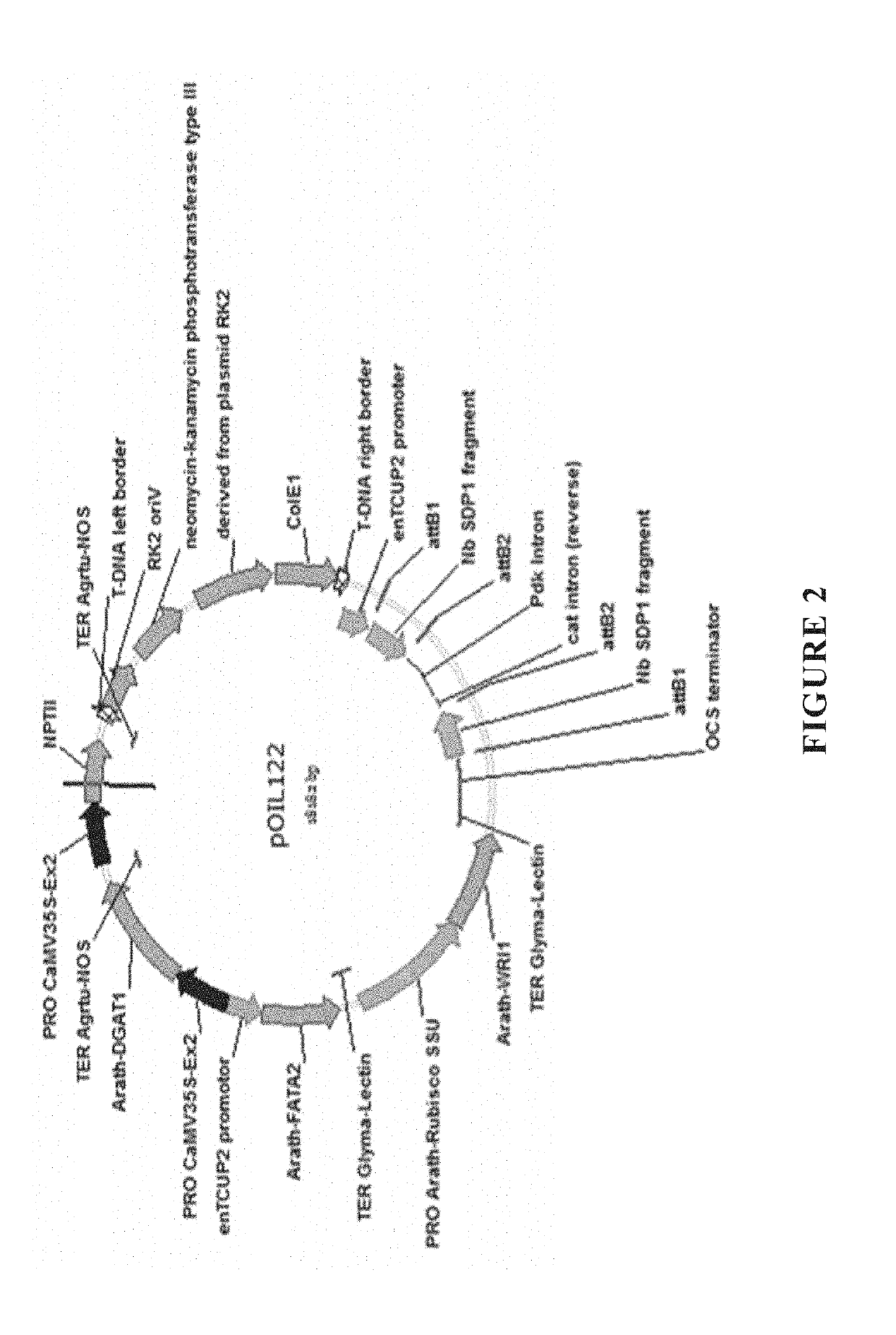
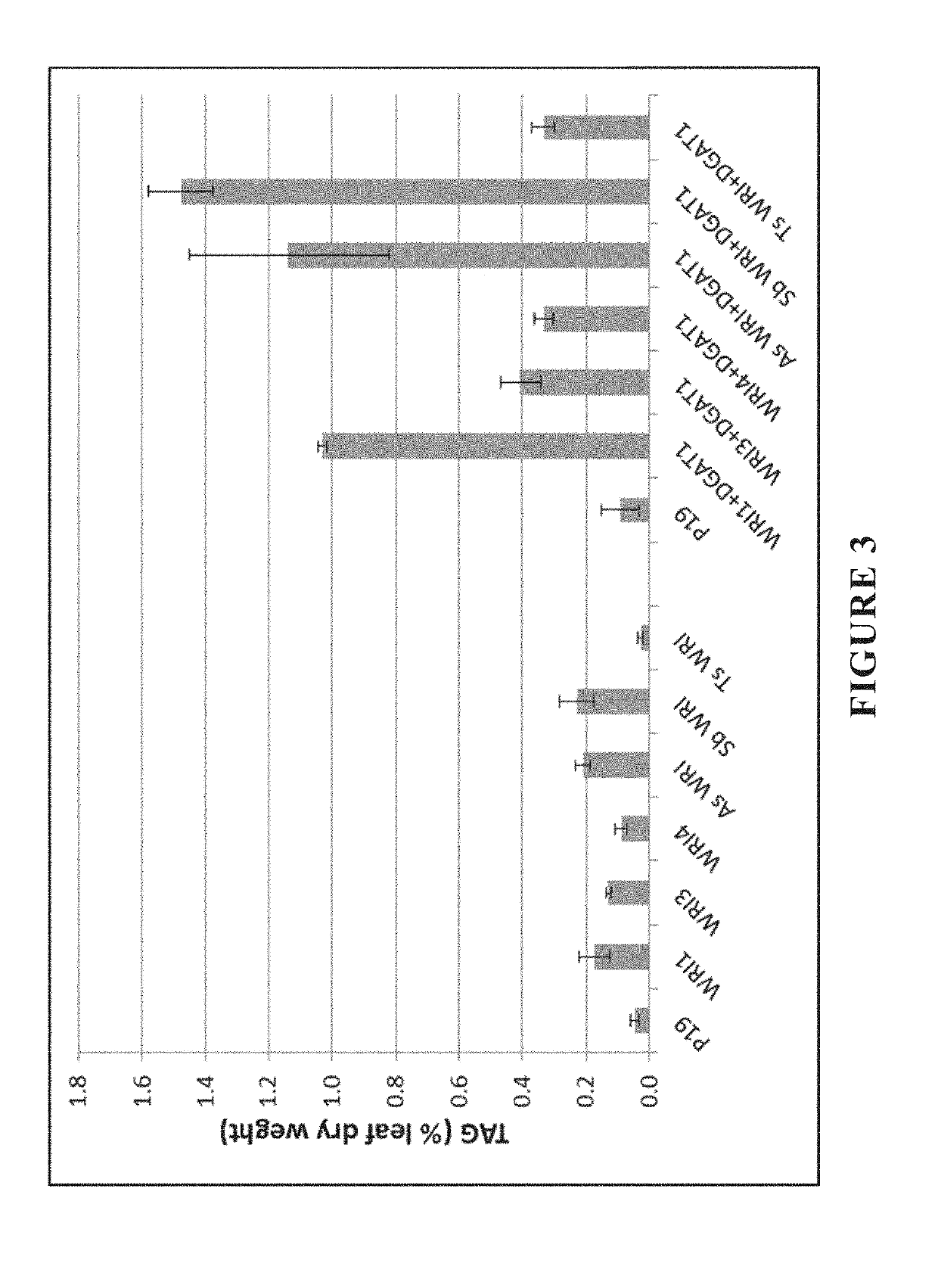
Patents
Literature
167 results about "Acyltransferases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
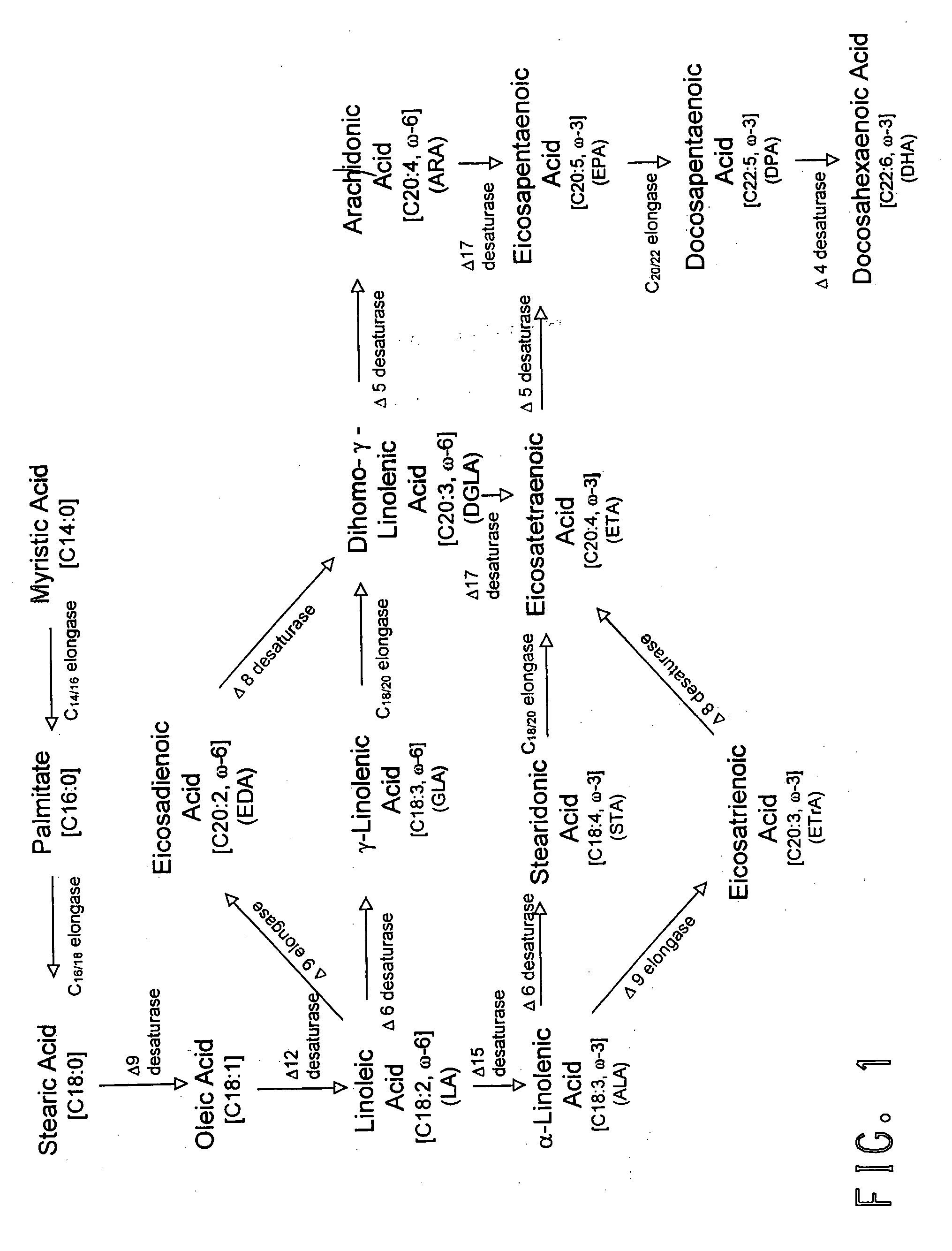
Enzymes from the transferase class that catalyze the transfer of acyl groups from donor to acceptor, forming either esters or amides. (From Enzyme Nomenclature 1992) EC 2.3.
High eicosapentaenoic acid producing strains of Yarrowia lipolytica
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
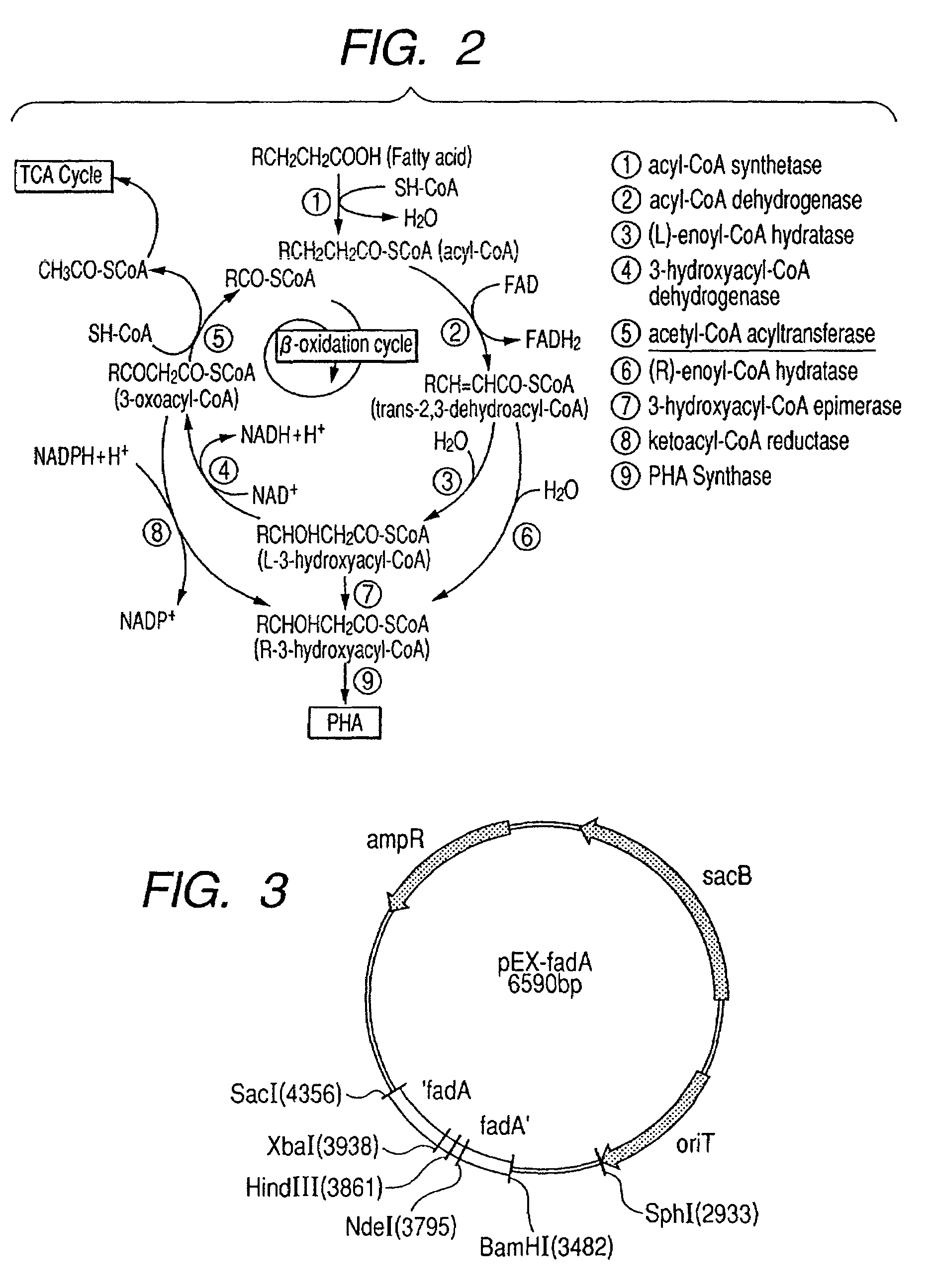
Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene disrupted bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using the same
A method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate with improved productivity and composition is provided. Polyhydroxyalkanoate is produced by a bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate in which a gene encoding acetyl-CoA acyltransferase is disrupted.
Owner:CANON KK
Mortierella alpina glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Process to remove impurities from triacylglycerol oil
ActiveUS20110003370A1Large water/oil interfaceImprove scalabilityFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationCavitationPhospholipase
The present invention is directed to a process to remove impurities from triacylglycerol oil including mixing the oil and a fluidic agent, pumping the mixture through a flow-through hydrodynamic cavitation apparatus at a pre-determined inlet pump pressure, creating hydrodynamic cavitation in the mixture, maintaining the hydrodynamic cavitation for a pre-determined period of time, moving the impurities from the oil to the fluidic agent, and then separating the fluidic agent from the oil. The impurities can include phytosterols, sterol glucosides, acylated sterol glucosides, in which case the fluidic agent is water, an alkali hydroxide, an inorganic base, an organic base, phosphoric acid, citric acid, acetic acid or a mixture thereof. The impurities may also include phosphatides, in which case and the fluidic agent comprises water and an enzyme such as phospholipase, a lipid acyltransferase or a mixture thereof.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
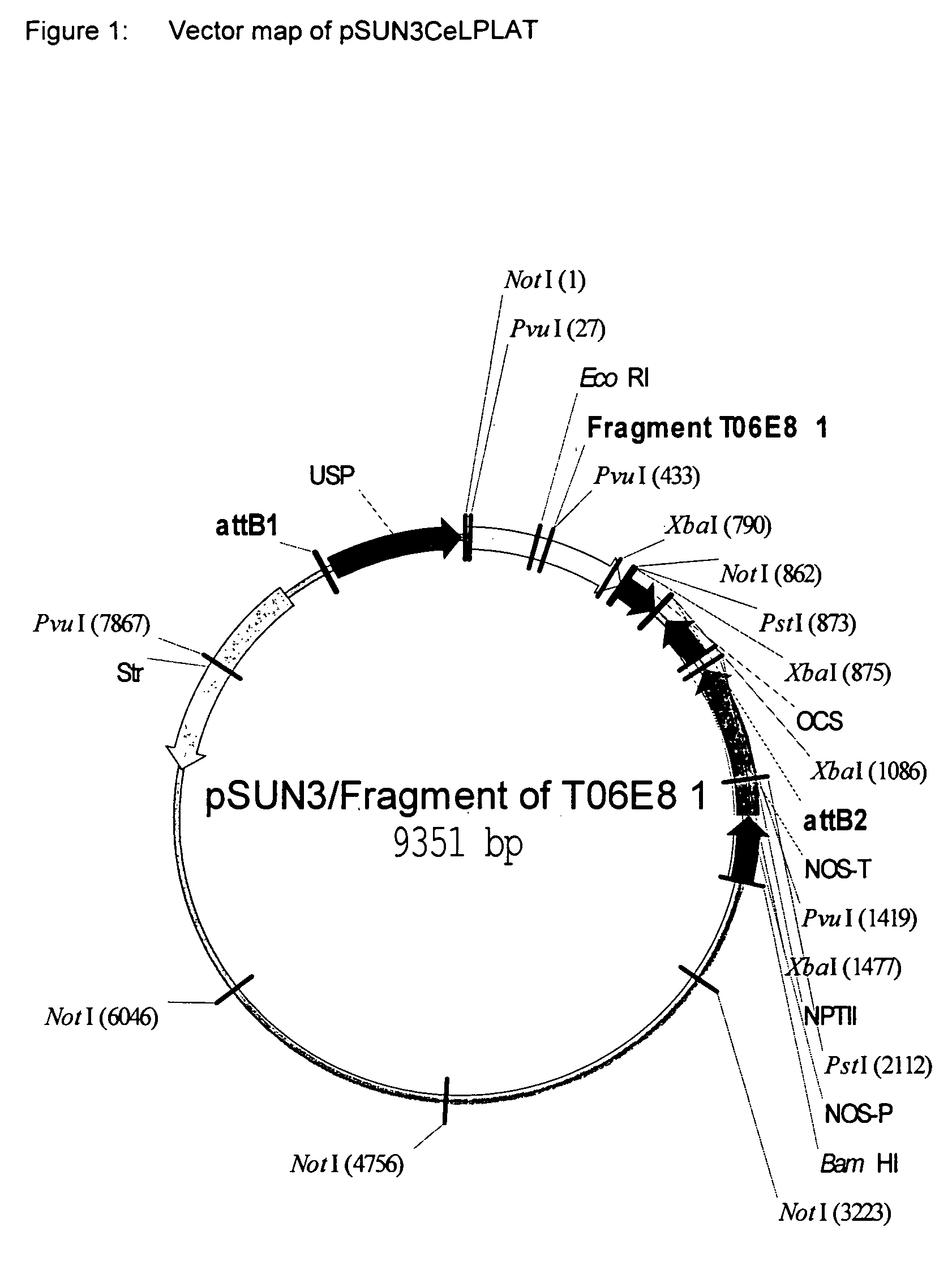
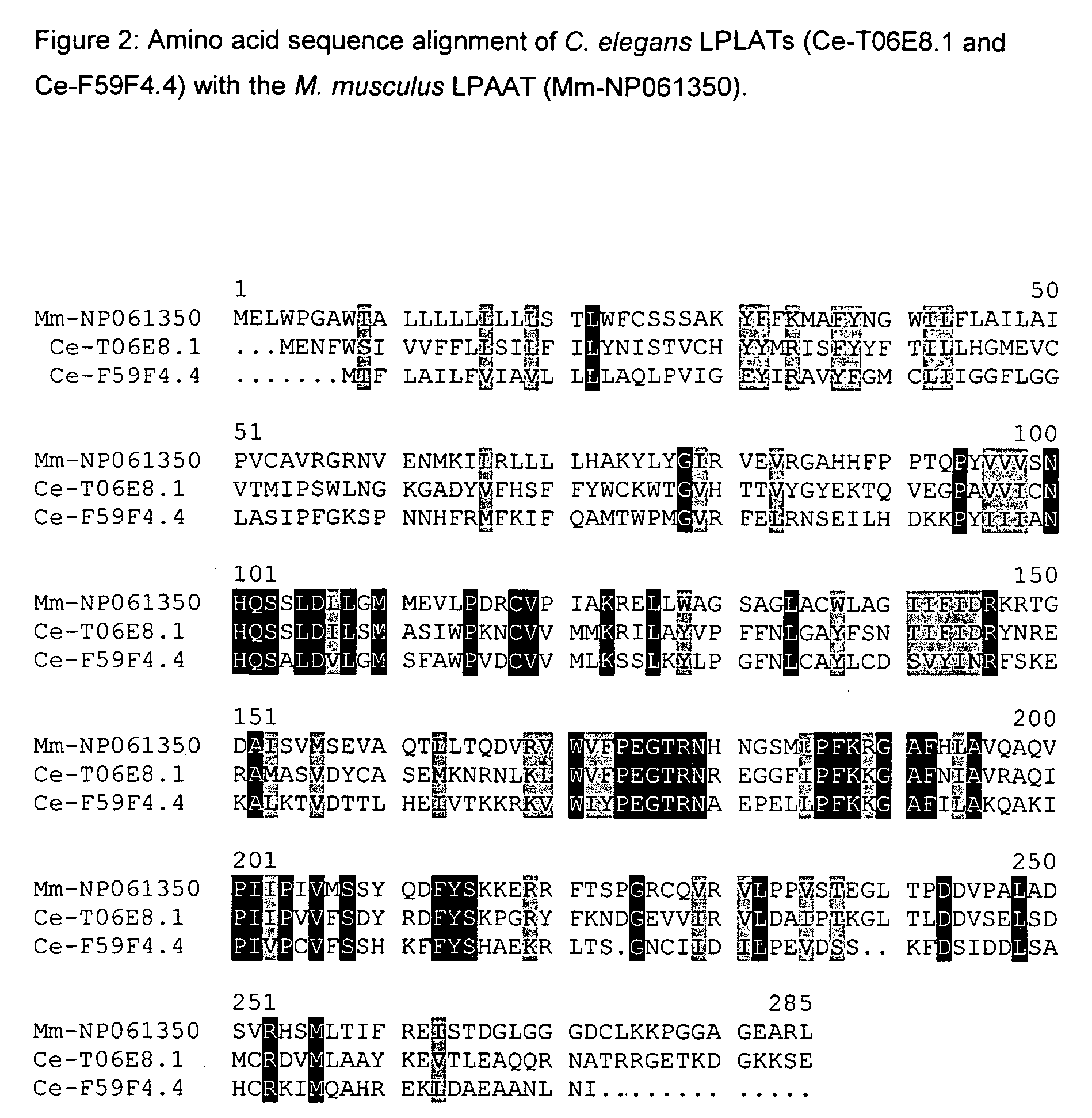
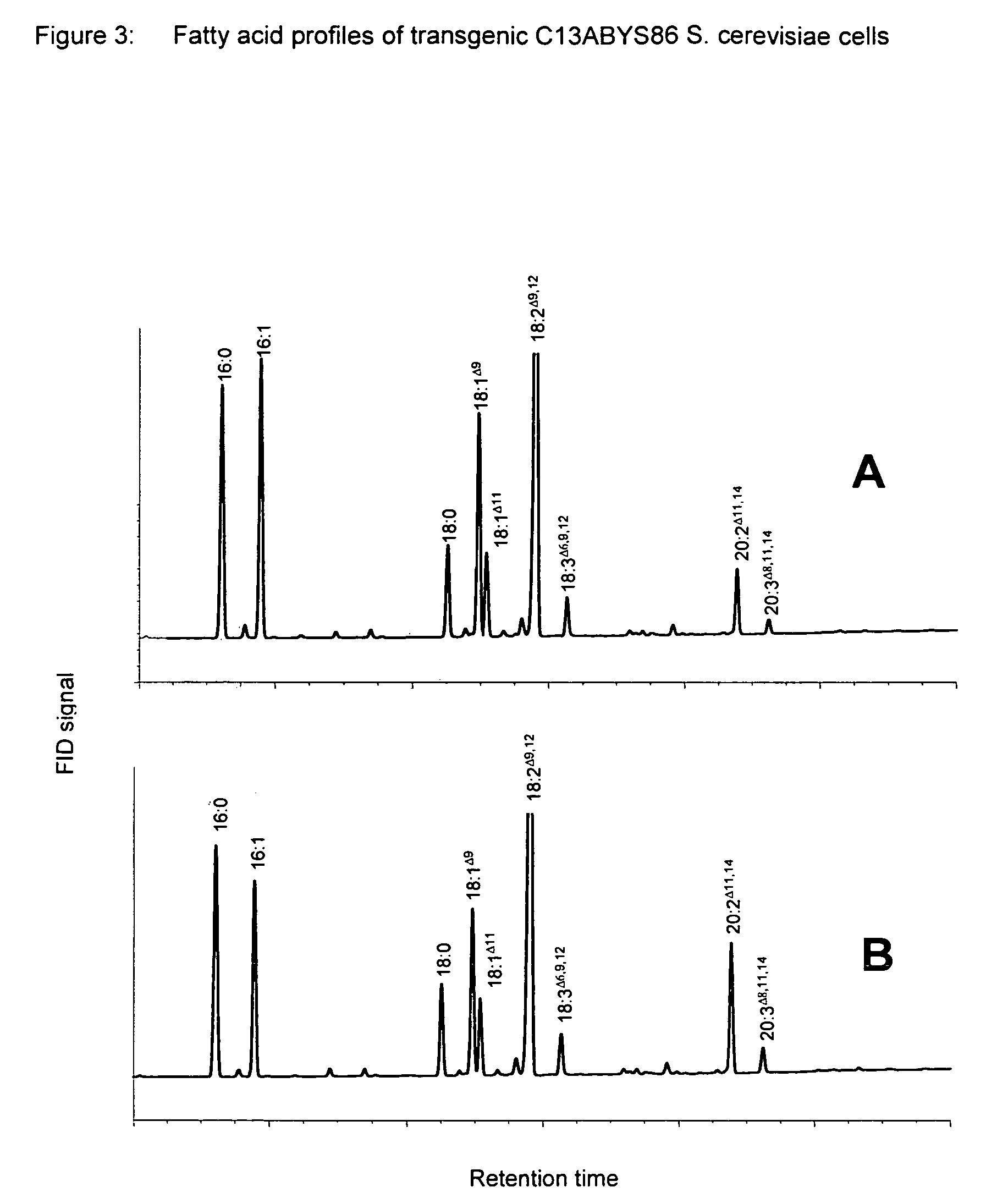
Plant acyltransferases specific for long-chained, multiply unsaturated fatty acids
The present invention relates to a process for the production of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in an organism by introducing, into the organism, nucleic acids which code for polypeptides with acyl transferase activity. These nucleic acid sequences, if appropriate together with further nucleic acid sequences which code for polypeptides of the fatty acid or lipid metabolism biosynthesis, can advantageously be expressed in the organism. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for the production of oils and / or triacylglycerides with an elevated content of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids.The invention furthermore relates to the nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and organisms comprising the nucleic acid sequences according to the invention, vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences and / or the nucleic acid constructs and to transgenic organisms comprising the abovementioned nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs and / or vectors.A further part of the invention relates to oils, lipids and / or fatty acids produced by the process according to the invention and to their use.
Owner:UNIV OF BRISTOL
Variant polypeptides and methods of making
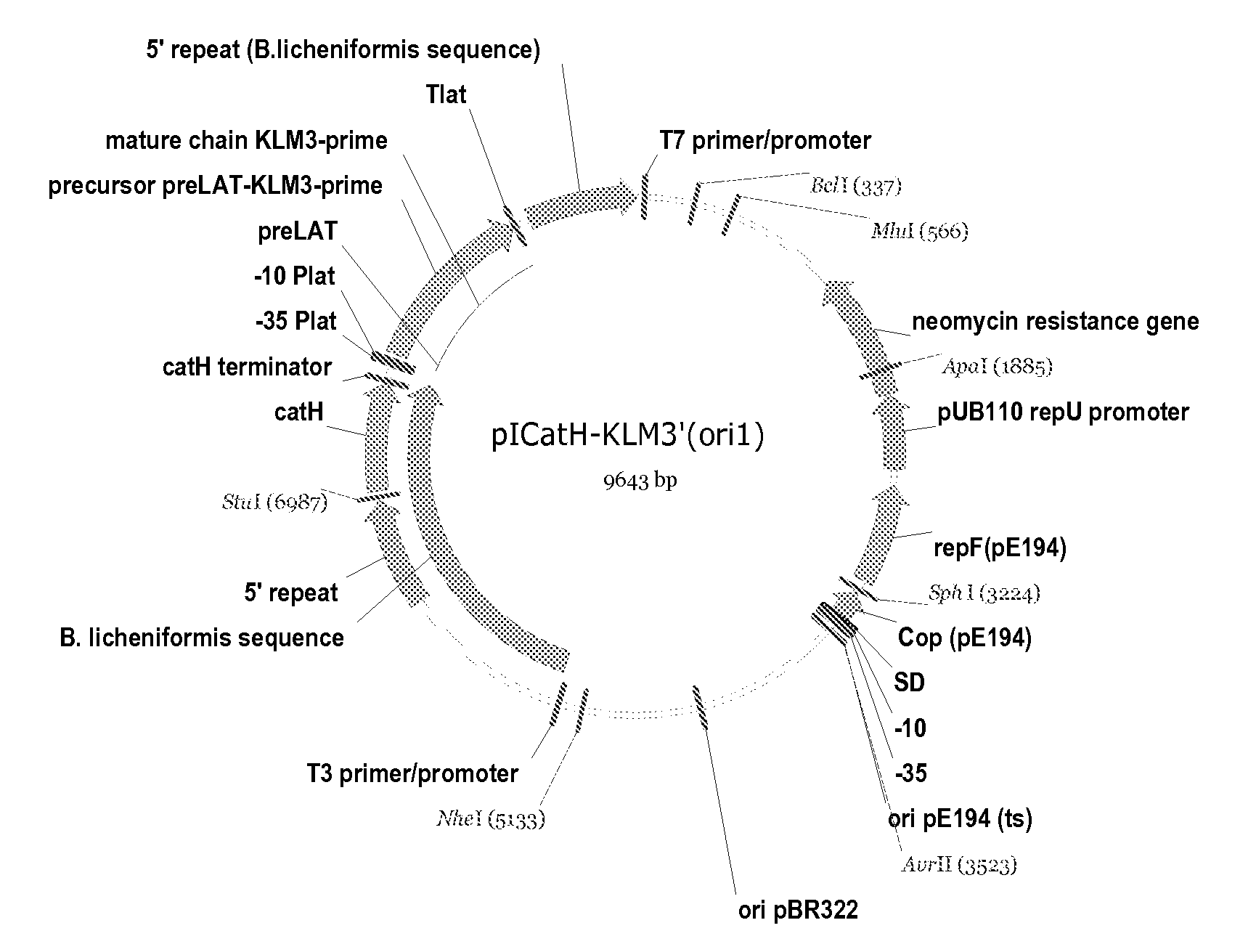
InactiveUS20080070287A1High hydrolytic activityIncreased activity transferase activityBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisLipid formation
The present invention relates to a method for the production of a variant lipid acyltransferase comprising the steps of: (i) selecting a parent enzyme which is a lipid acyltranserase enzyme; (ii) modifying one or more amino acids to produce a variant lipid acyltransferase; (iii) testing the activity of the variant lipid acyltransferase on a galactolipid and / or phospholipid and / or triglyceride substrate; (iv) selecting a variant enzyme with enhanced activity towards galactolipids compared with the parent enzyme; (v) providing a Bacillus licheniformis cell; (vi) transforming the Bacillus licheniformis cell with a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding said variant lipid acyltransferase; and (iii) expressing said variant lipid acyltransferase in the cell under the control of a promoter sequence. The variant lipid acyltransferase can undergo post-translations modification, truncation and / or clipping, i.e., to remove a signal peptide. In addition, the present invention further relates to the use of Bacillus licheniformis to express a lipid acyltransferase, a Bacillus licheniformis host cell comprising a heterologous lipid acyltransferase and a vector comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a lipid acyltransferase operably linked to a promoter sequence homologous to B. licheniformis.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method
The present invention relates to a method of reducing and / or removing diglyceride from an edible oil, comprising a) admixing an edible oil with an acyl acceptor substrate and a diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase, wherein the diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase is characterized as an enzyme which in an edible oil is capable of transferring an acyl group from a diglyceride to glycerol. Preferably, the diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase comprises the amino acid sequence motif GDSX, wherein X is one or more of the following amino acid residues L, A, V, I, F, Y, H, Q, T, N, M or S. Furthermore the present invention relates to the use of a diglyceride:glycerol acyltransferase characterized as an enzyme which in an edible oil is capable of transferring an acyl group from a diglyceride to glycerol, in the manufacture of an edible oil, for reducing and / or removing (preferably selectively reducing and / or removing) diglyceride from said edible oil and to the use of said enzyme in the manufacture of a foodstuff comprising an edible oil for improving the crystallization properties of said foodstuff.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
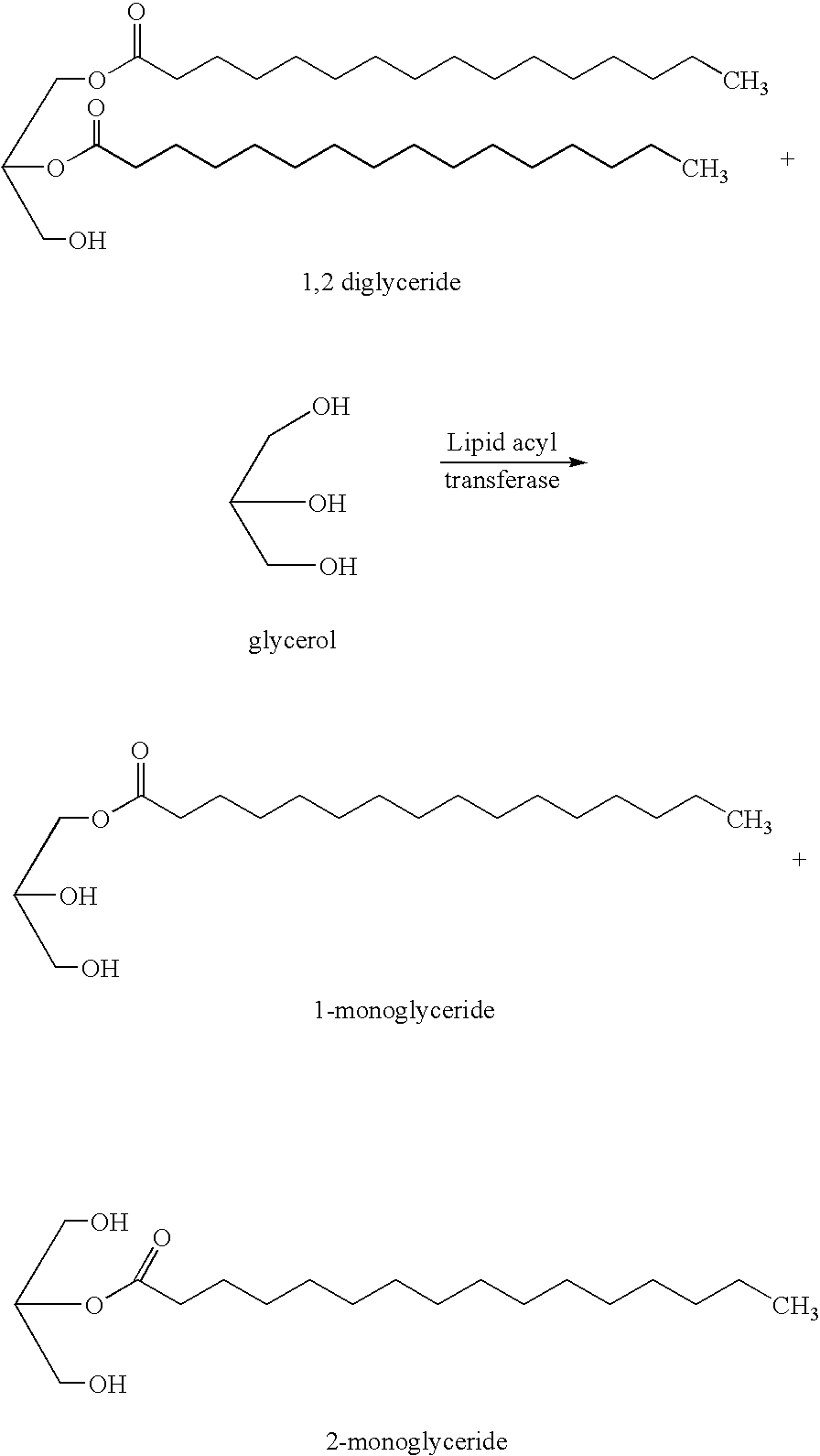
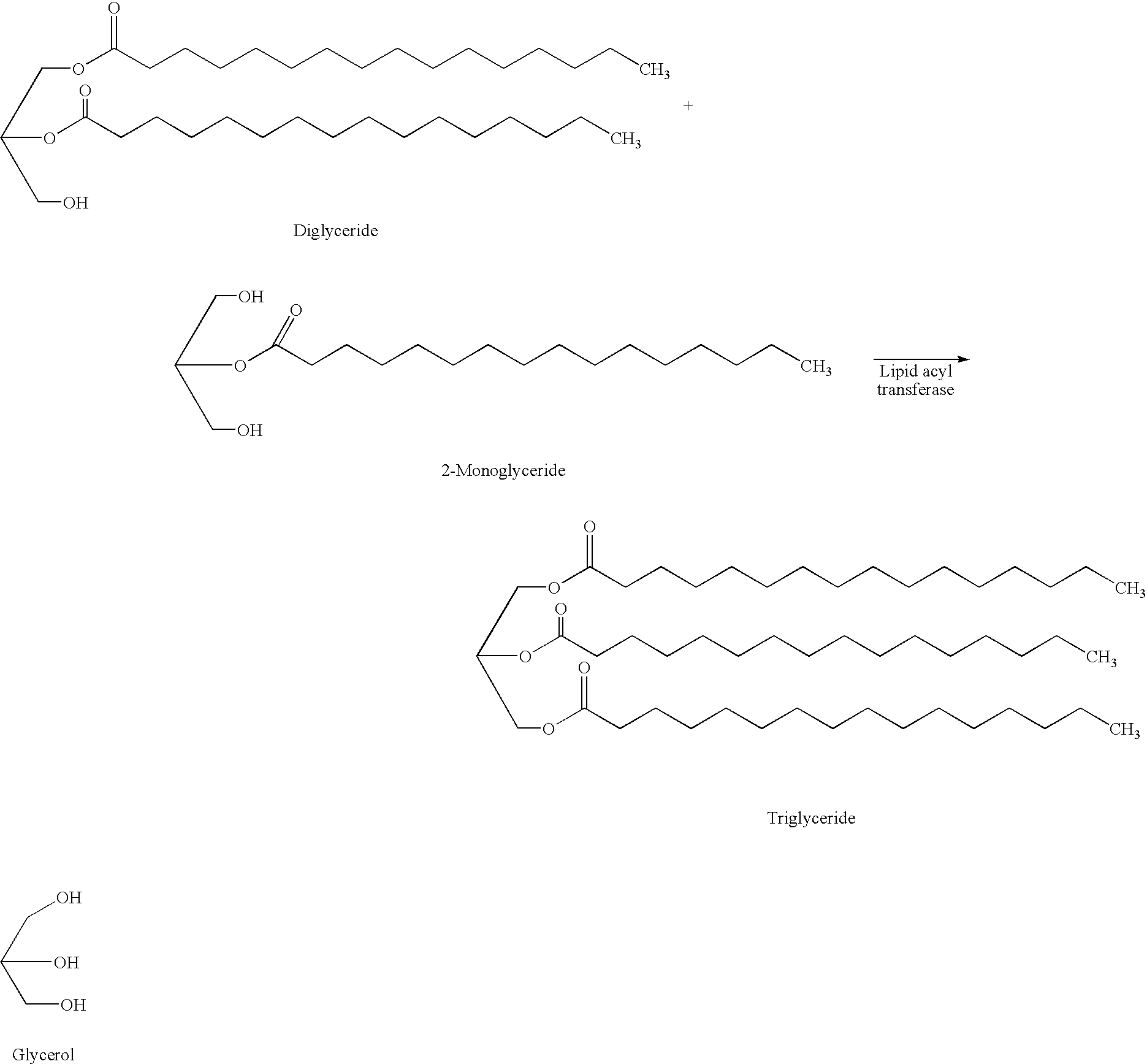
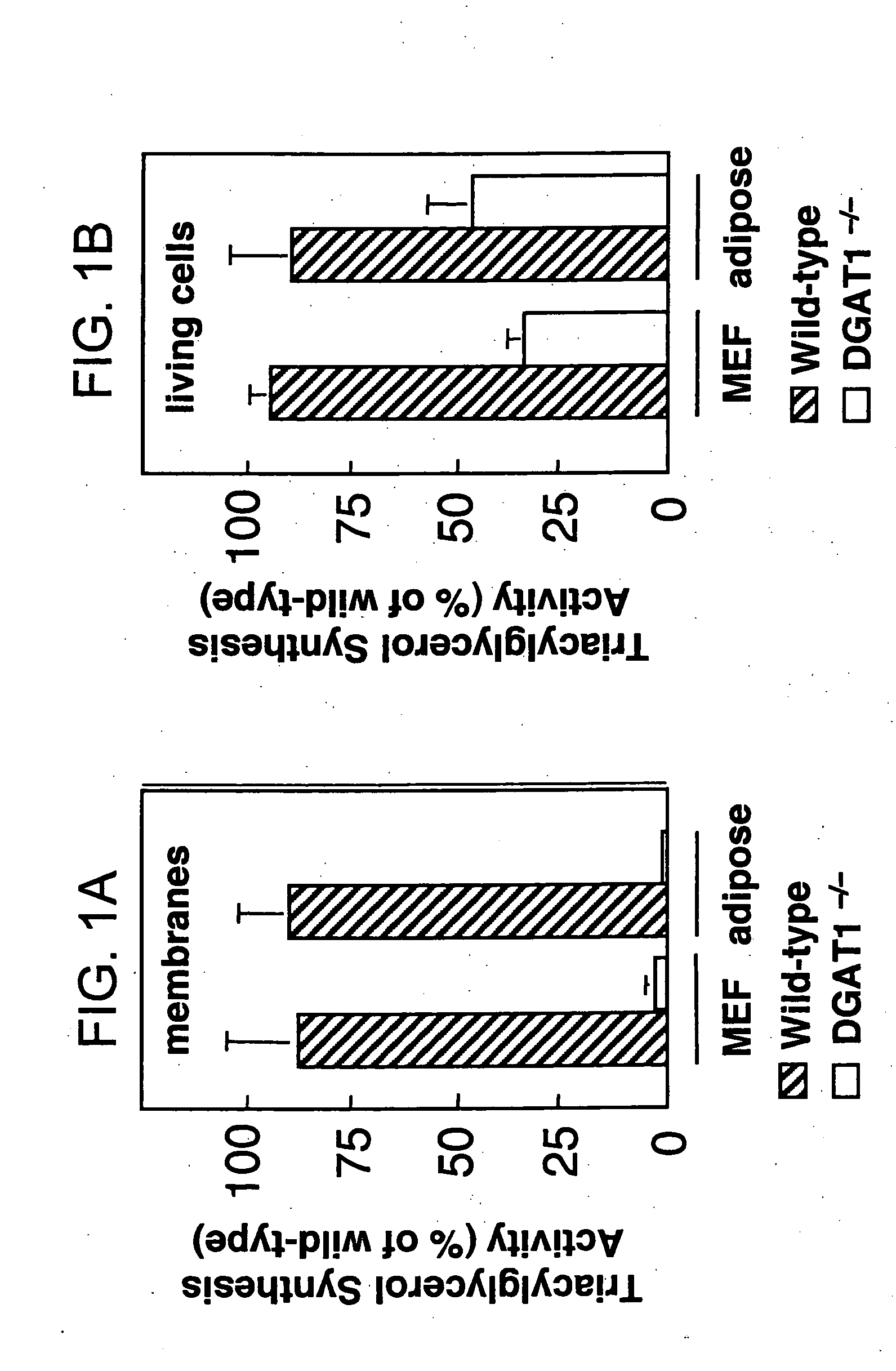
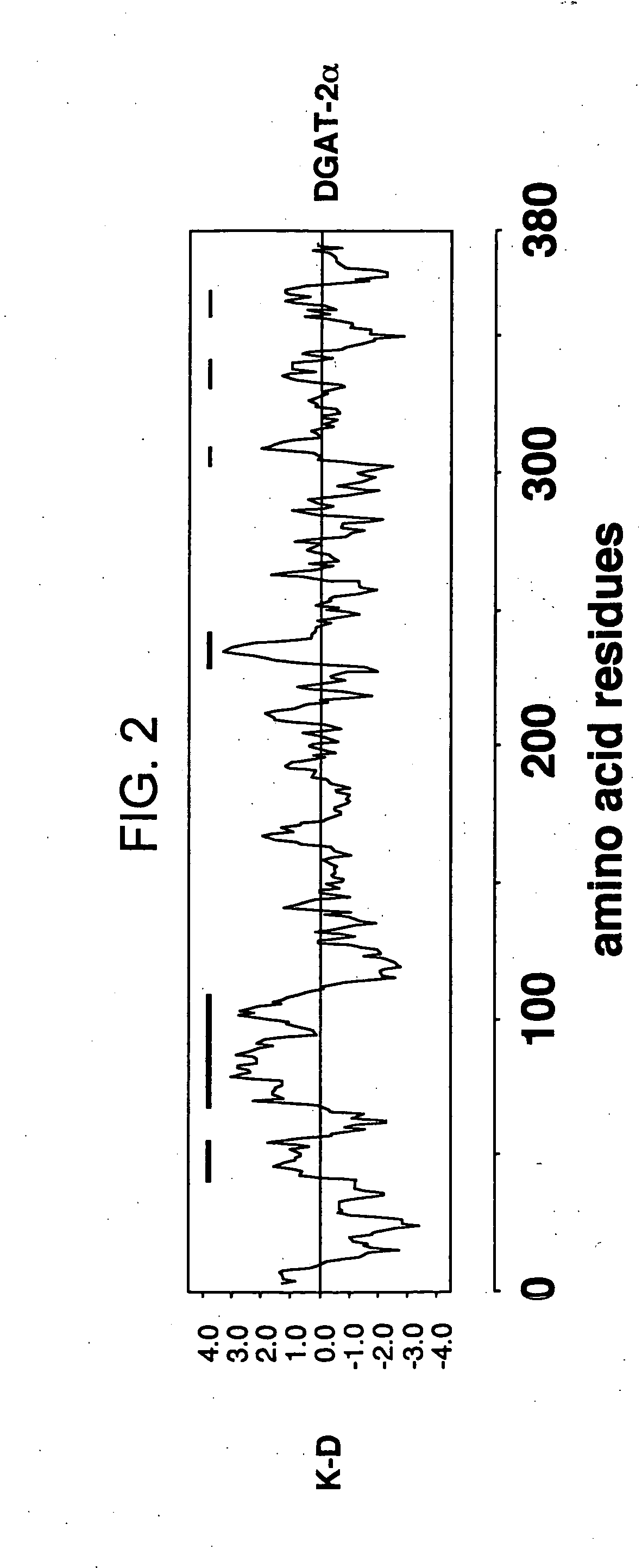
Mono-and diacylglycerol acyltransferases and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050106697A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsMonoacylglycerol acyltransferaseDiglyceride acyltransferase
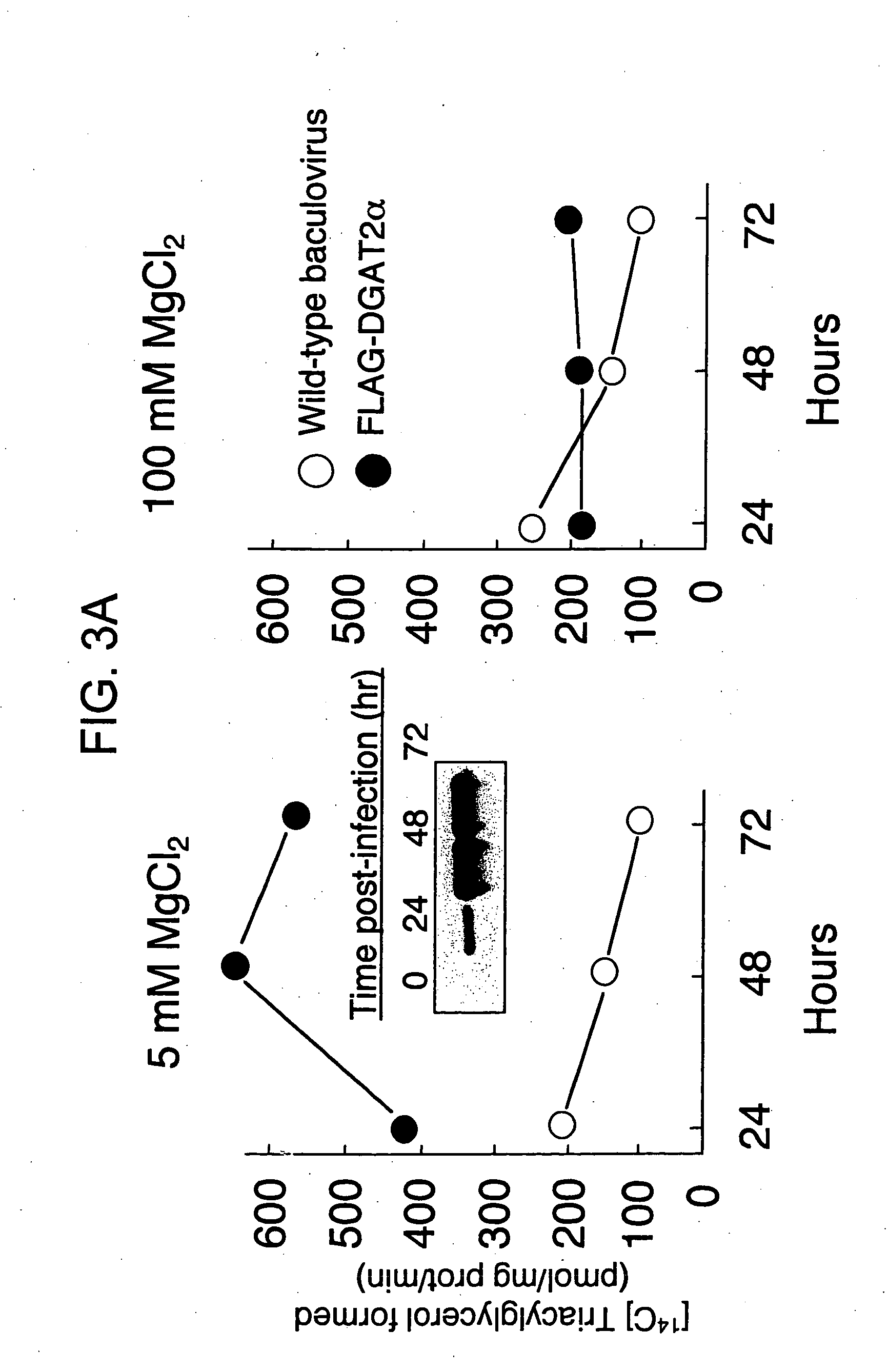
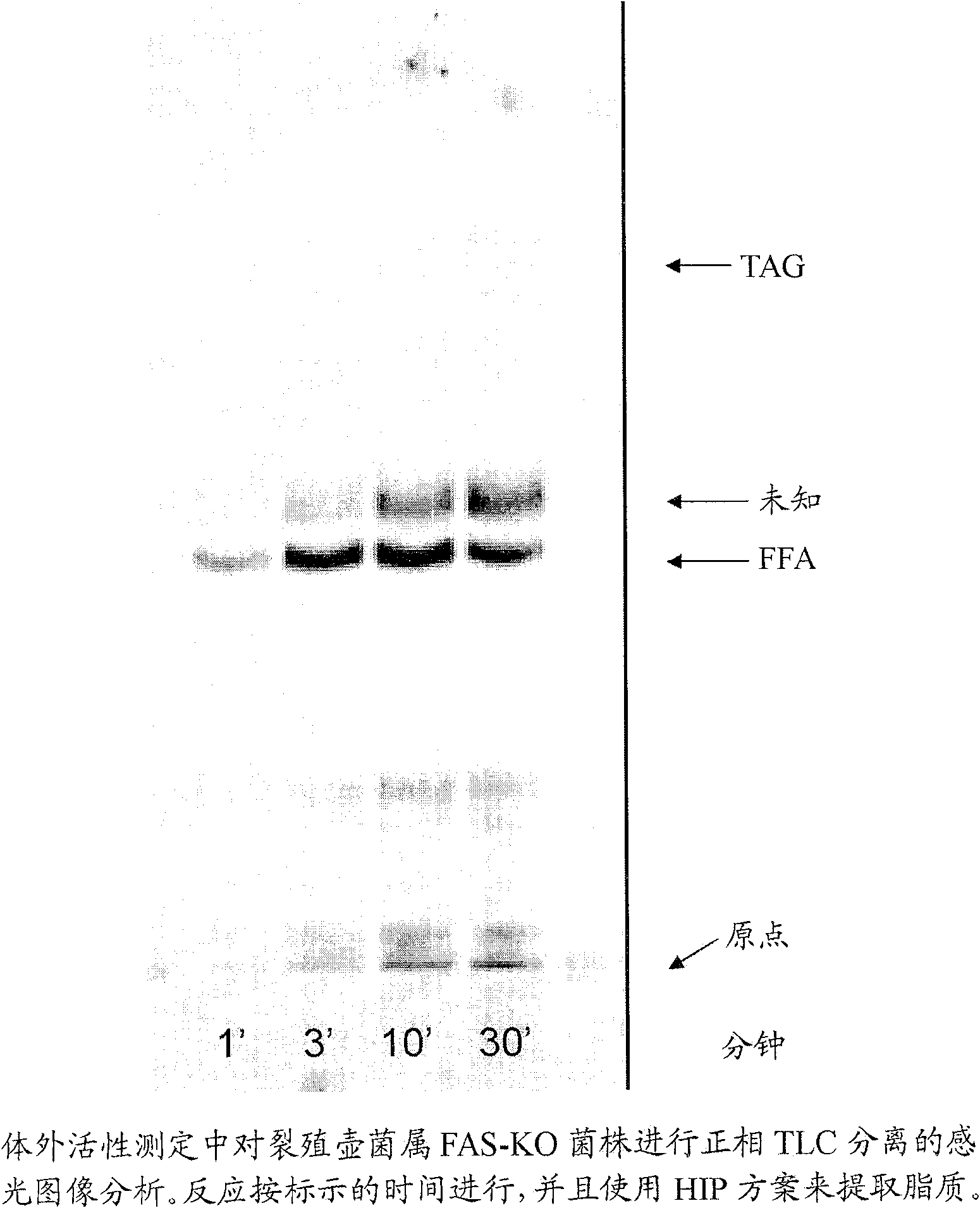
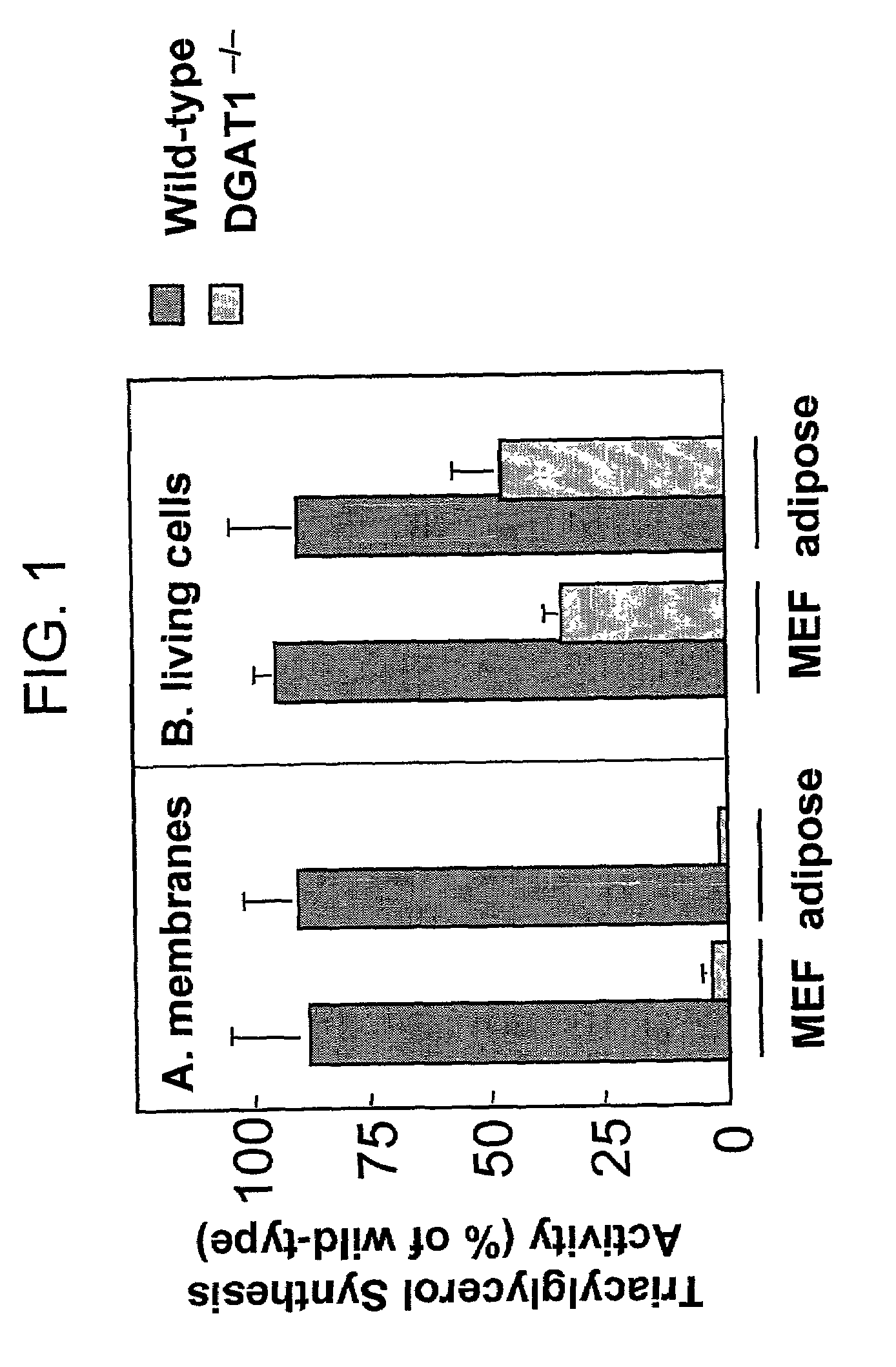
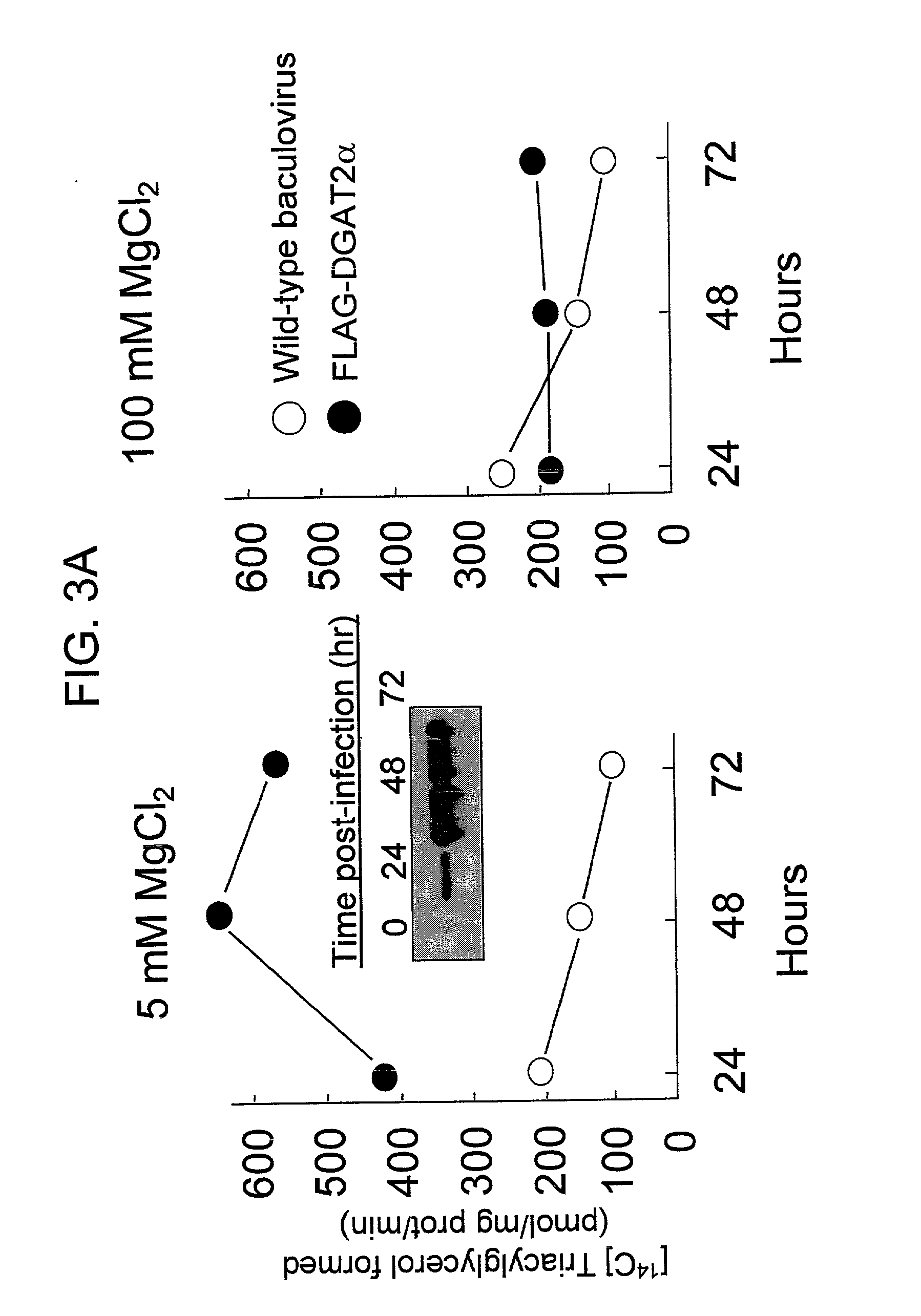
Nucleic acid compositions encoding polypeptide products with diglyceride acyltransferase and / or monoacylglycerol acyltransferase activity, as well as the polypeptide products encoded thereby, i.e., mammalian DGAT2α, MGAT1, or MGAT2 polypeptide products, and methods for producing the same, are provided. Also provided are: methods and compositions for modulating DGAT2α, MGAT1, or MGAT2 activity; DGAT2α, MGAT1, or MGAT2 transgenic cells, animals and plants, as well as methods for their preparation; and methods for making diglyceride, diglyceride compositions, triglycerides and triglyceride compositions, as well as the compositions produced by these methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including research, medicine, agriculture and industry applications.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
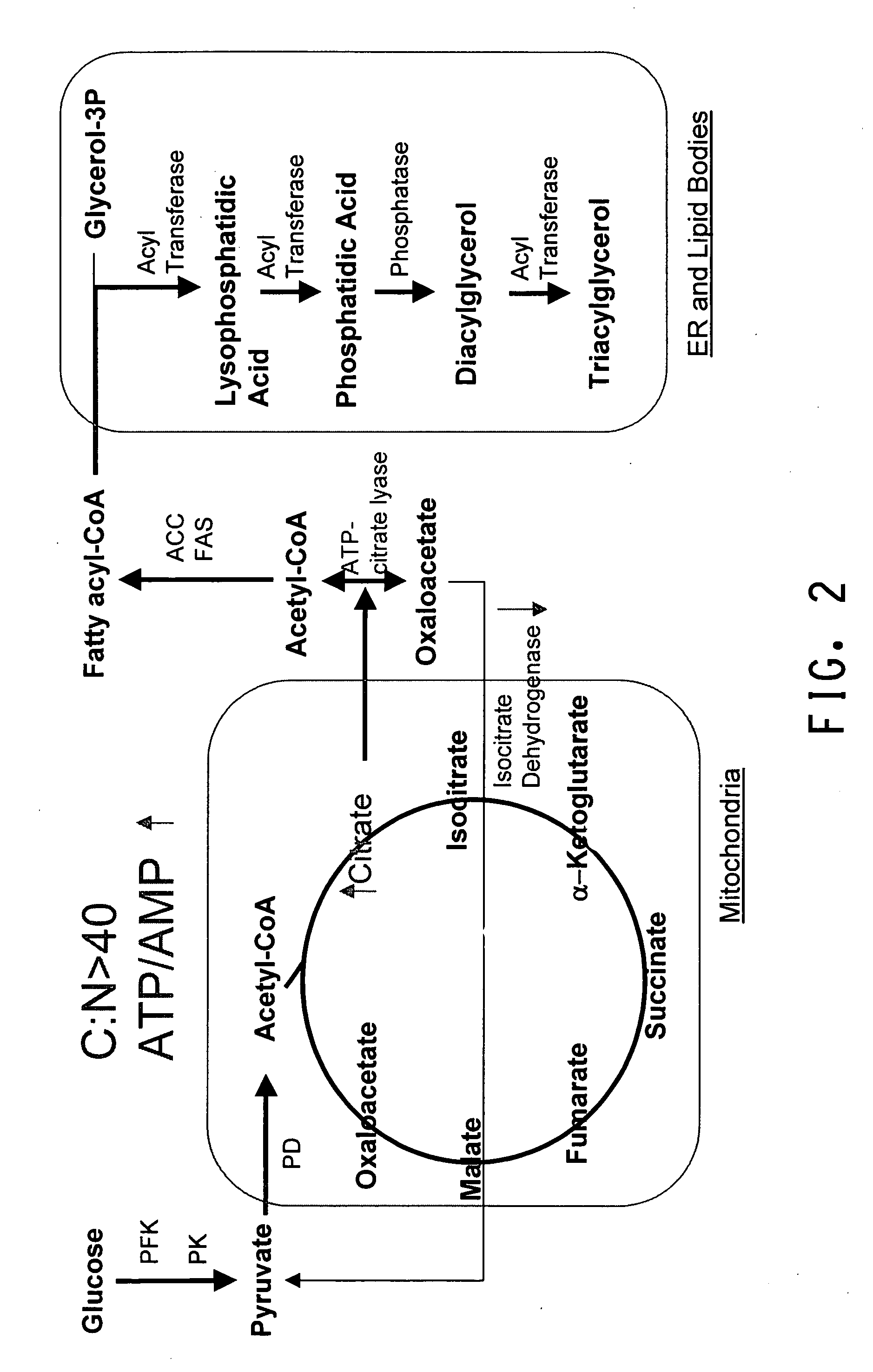
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
ActiveUS20110250659A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeHydrolasesUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaLipid formation
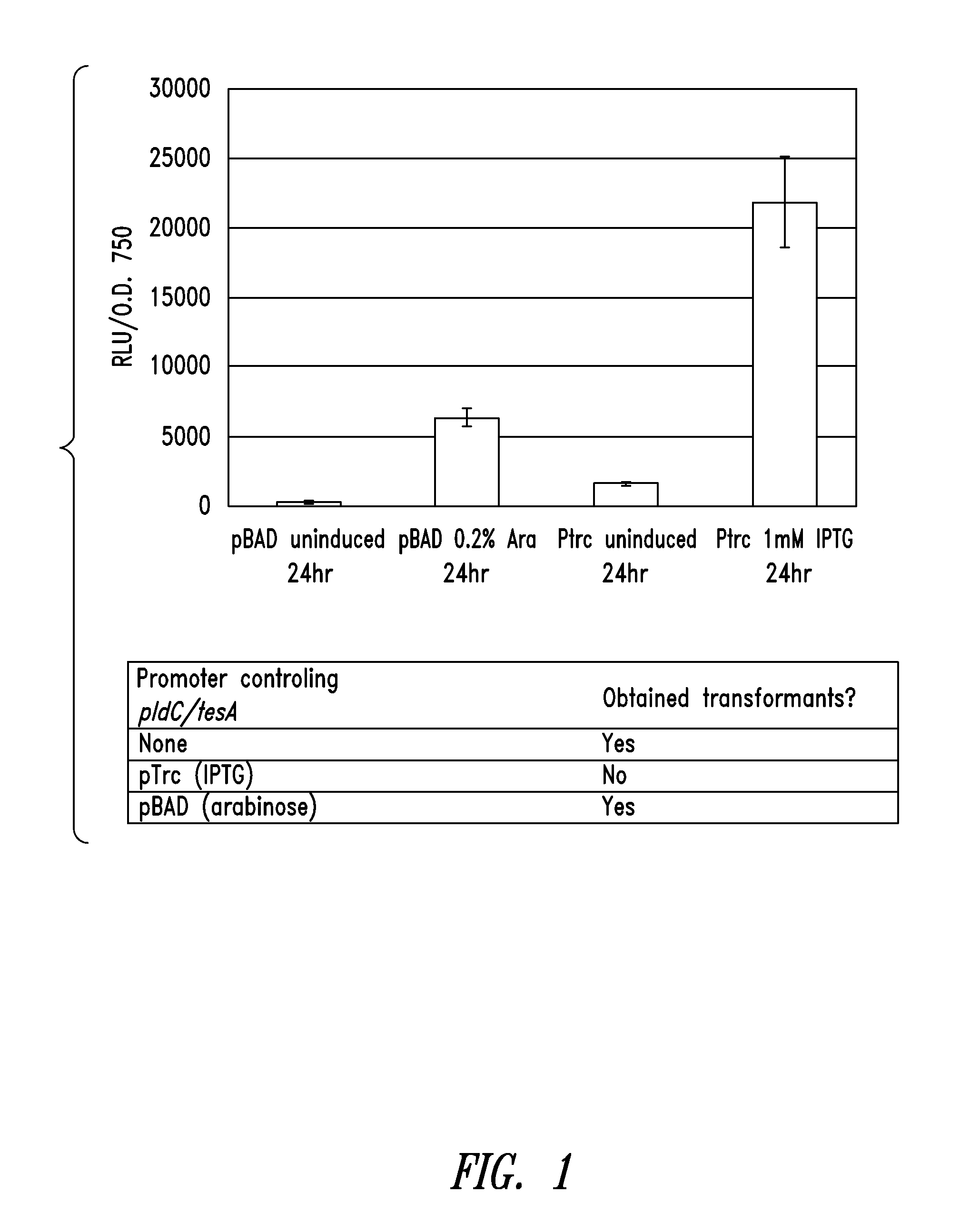
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a phospholipase and / or thioesterase, which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. This disclosure also describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides, as well as photosynthetic microorganism comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene disrupted bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using the same
A method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate with improved productivity and composition is provided. Polyhydroxyalkanoate is produced by a bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate in which a gene encoding acetyl-CoA acyltransferase is disrupted.
Owner:CANON KK
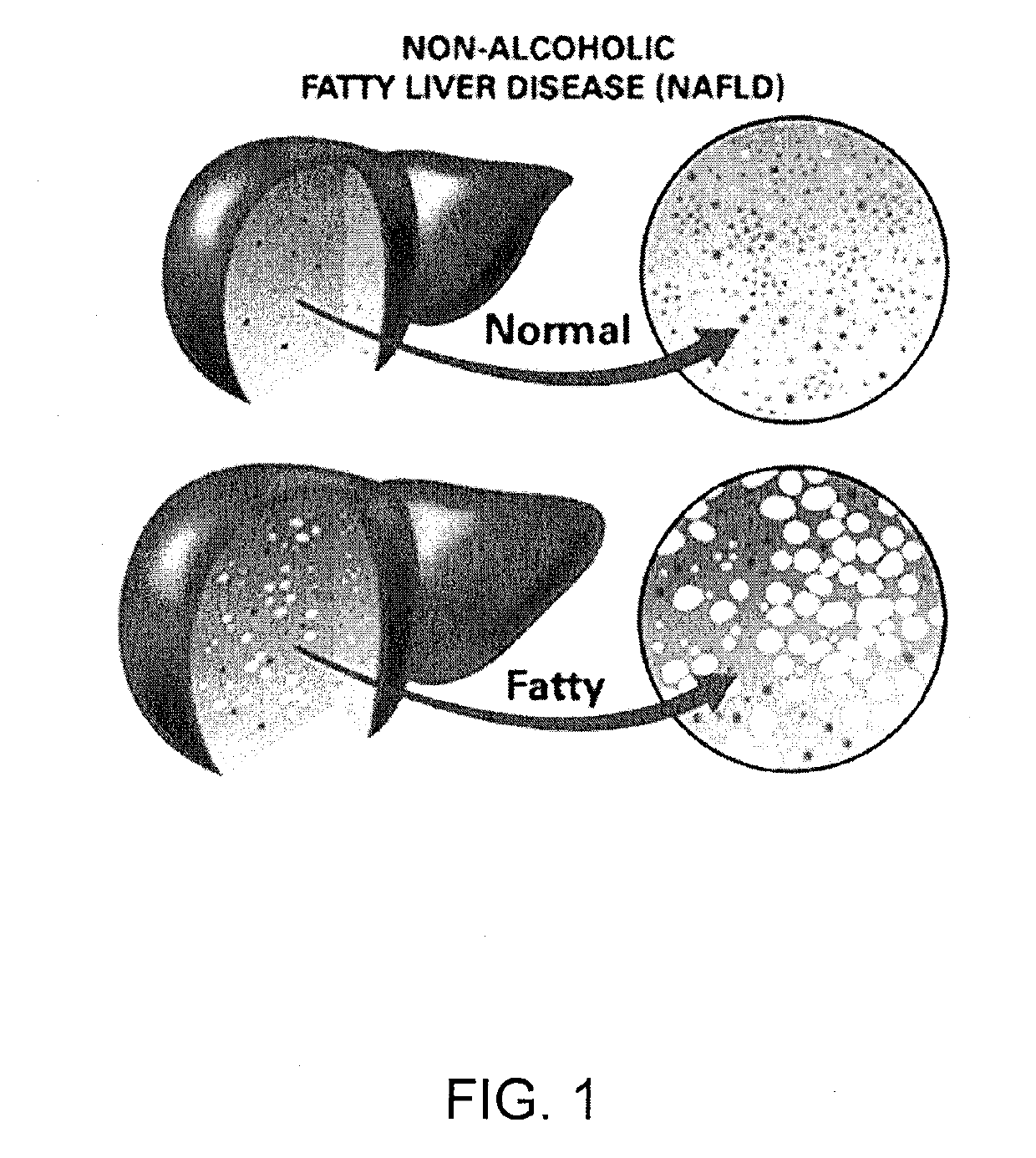
Method and system for reducing the likelihood of developing liver cancer in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ActiveUS20190117709A1Inhibit progressEarly detectionOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemFiberMonoacylglycerol acyltransferase
A method for reducing the likelihood of developing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in an individual diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease involves providing in the gut of an individual a population of beneficial bacteria selected from the group consisting of Lactobacillus species, and at least 6 grams per day of fiber to the individual to maintain a therapeutically effective amount of the beneficial bacteria in the gut of the individual. In certain embodiments, monoacylglycerolacyltransferase-3 (MGAT3) synthesis is inhibited to lower triacylglycerol (TAG) production, while in others, expression of diacylglycerolacyltransferase-2 (DGAT-2) is inhibited. The beneficial bacteria are preferably modified to produce increased amounts of butyrate and are also encapsulated in a frangible enclosure. Levels of Roseburia are preferably increased while the levels of Akkermansia spp. in the individual's gut microbiome are reduced.
Owner:SEED HEALTH INC
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
InactiveCN101573451AImprove the level ofReduce competitionMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or toincrease the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils o btained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Mono- and diacylglycerol acyltransferases and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7045326B2BacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMonoacylglycerol acyltransferaseDiglyceride acyltransferase
Nucleic acid compositions encoding polypeptide products with diglyceride acyltransferase and / or monoacylglycerol acyltransferase activity, as well as the polypeptide products encoded thereby, i.e., mammalian DGAT2α and MGAT1 polypeptide products, and methods for producing the same, are provided. Also provided are: methods and compositions for modulating DGAT2α and MGAT1 activity; DGAT2α and MGAT1 transgenic cells, animals and plants, as well as methods for their preparation; and methods for making diglyceride, diglyceride compositions, triglycerides and triglyceride compositions, as well as the compositions produced by these methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including research, medicine, agriculture and industry applications.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Modified Photosynthetic Microorganisms With Reduced Glycogen and Their Use in Producing Carbon-Based Products
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen as compared to a wild type Cyanobacterium, and which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms also contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids or fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Production method for C8:0/C10:0/C12:0/C14:0 medium-chain fatty acid and ethyl ester thereof
InactiveCN102586350AImprove low temperature performanceSimple extraction processMicroorganism based processesFermentationCupheaThiogalactosides
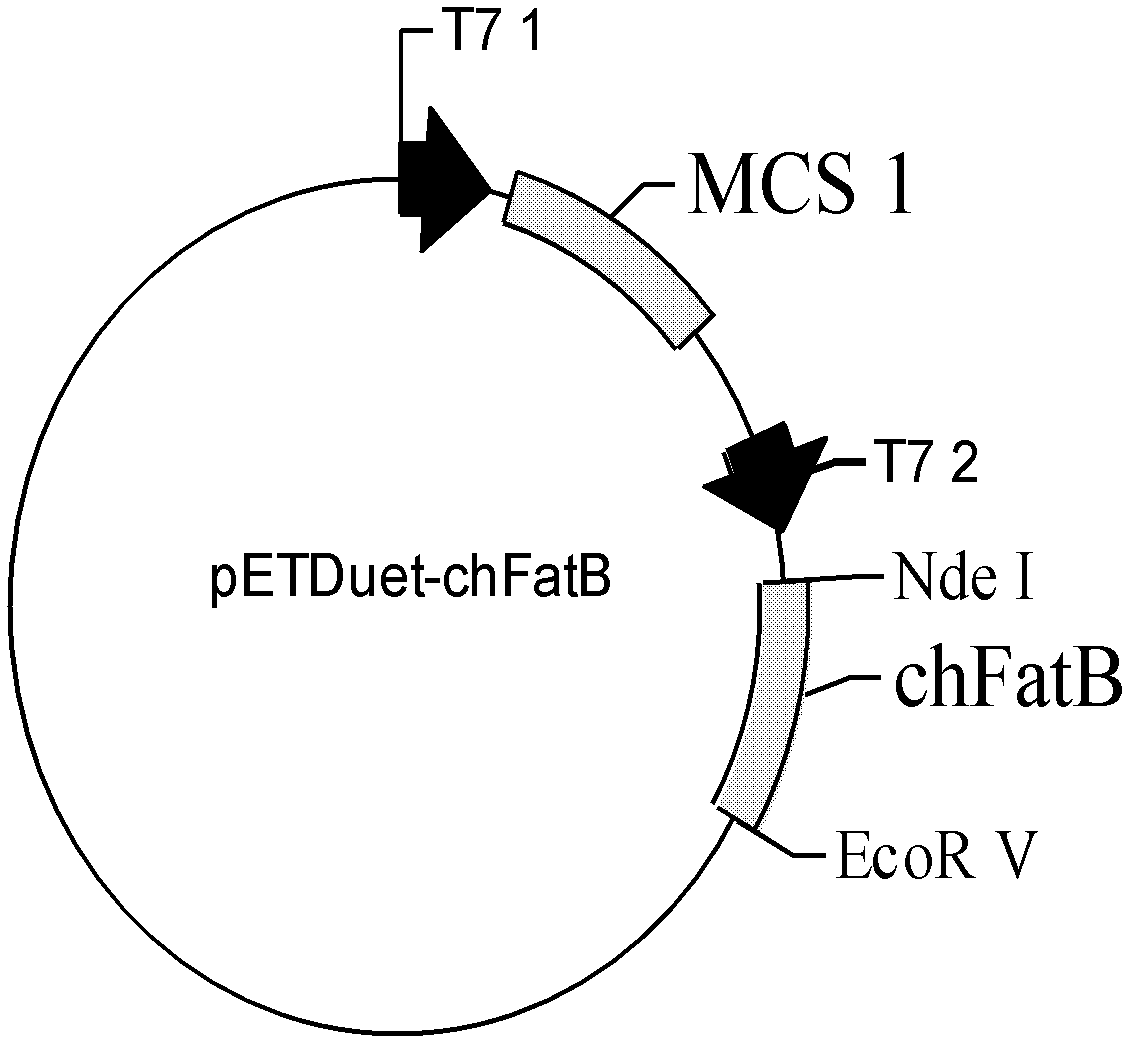
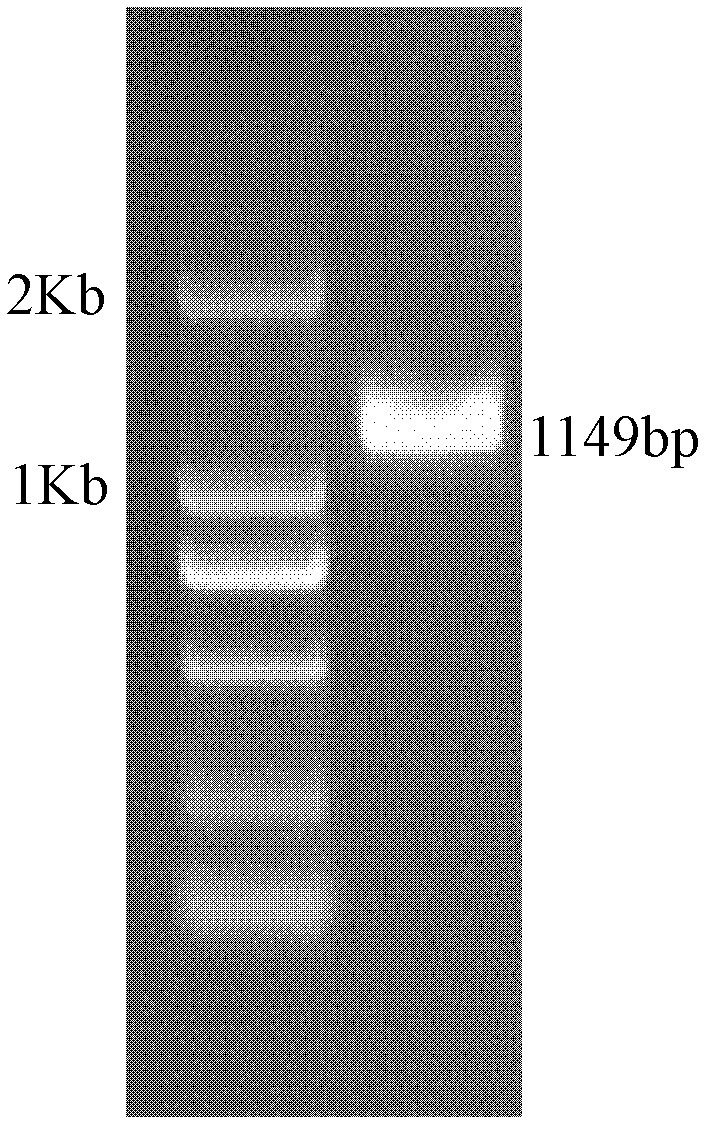
The invention relates to a production method for synthesizing C8:0 / C10:0 / C12:0 / C14:0 medium-chain fatty acid and ethyl ester thereof by using engineering Escherichia coli. The production method comprises the following steps of: cloning thioesterase genes with different specificities chFatB / ucFatB / ccFatB in cuphea / laurel / camphorwood into an expression vector pETDuet-1 to obtain a corresponding recombinant plasmid; transferring the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21, performing isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPDT) induction expression, and specifically hydrolyzing acyl carrier protein (ACP) with specific chain length by using the expressed thioesterase to obtain medium-chain fatty acid; cloning acyltransferase gene (atfA) in acinetobacter into expression vectors pETDuet-chFatB / pETDuet-ucFatB / pETDuet-ccFatB to obtain corresponding recombinant plasmids; and transferring the recombinant plasmids into the Escherichia coli BL21, performing IPTG induction expression, performing acyl transfer reaction on exogenously fed ethanol and acyl-CoA formed by the medium-chain fatty acid intracellularly by using the co-expressed acyltransferase to obtain fatty acid ethyl ester.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Process
A process of water degumming an edible oil (preferably a crude edible oil) comprising the steps of: a) admixing approximately 0.1-5% w / w water with an edible oil (preferably a crude edible oil) and a lipid acyltransferase, b) agitating the admixture for between about 10 minutes and 180 minutes at about 45 to about 900 C, and c) separating the oil phase and the gum phase. Preferably said lipid acyltransferase is a polypeptide having lipid acyltransferase activity which polypeptide is obtained by expression of the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 49 or a nucleotide sequence which as has 70% or more identity therewith; and / or is obtained by expression of a nucleic acid which hybridises under medium stringency conditions to a nucleic probe comprising the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ No. 49; and / or is a polypeptide having lipid acyltransferase activity which polypeptide comprises the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 68 or an amino acid sequence which as has 70% or more identity therewith. In one embodiment the lipid acyltransferase is preferably used in combination with a phospholipase C enzyme. A process for modifying the gum phase of a degummed oil using a lipid acyltransferase is also taught herein.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Process to remove impurities from triacylglycerol oil
ActiveUS8945644B2Improve scalabilityPrevents unsaturated fatty acid from deteriorationFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteDough treatmentPhospholipaseCavitation
The present invention is directed to a process to remove impurities from triacylglycerol oil including mixing the oil and a fluidic agent, pumping the mixture through a flow-through hydrodynamic cavitation apparatus at a pre-determined inlet pump pressure, creating hydrodynamic cavitation in the mixture, maintaining the hydrodynamic cavitation for a pre-determined period of time, moving the impurities from the oil to the fluidic agent, and then separating the fluidic agent from the oil. The impurities can include phytosterols, sterol glucosides, acylated sterol glucosides, in which case the fluidic agent is water, an alkali hydroxide, an inorganic base, an organic base, phosphoric acid, citric acid, acetic acid or a mixture thereof. The impurities may also include phosphatides, in which case and the fluidic agent comprises water and an enzyme such as phospholipase, a lipid acyltransferase or a mixture thereof.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
Plant sterol acyltransferases
InactiveUS7157619B1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant sterol
The present invention is directed to lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase-like polypeptides (LCAT) and acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferases-like polypeptides (ACAT). The invention provides polynucleotides encoding such cholesterol:acyltansferases-like polypeptides, polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides, and the use of such polynucleotides to alter sterol composition and oil production in plants and host cells. Also provided are oils produced by the plants and host cells containing the polynucleotides and food products, nutritional supplements, and pharmaceutical composition containing plants or oils of the present invention. The polynucleotides of the present invention include those derived from plant sources.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
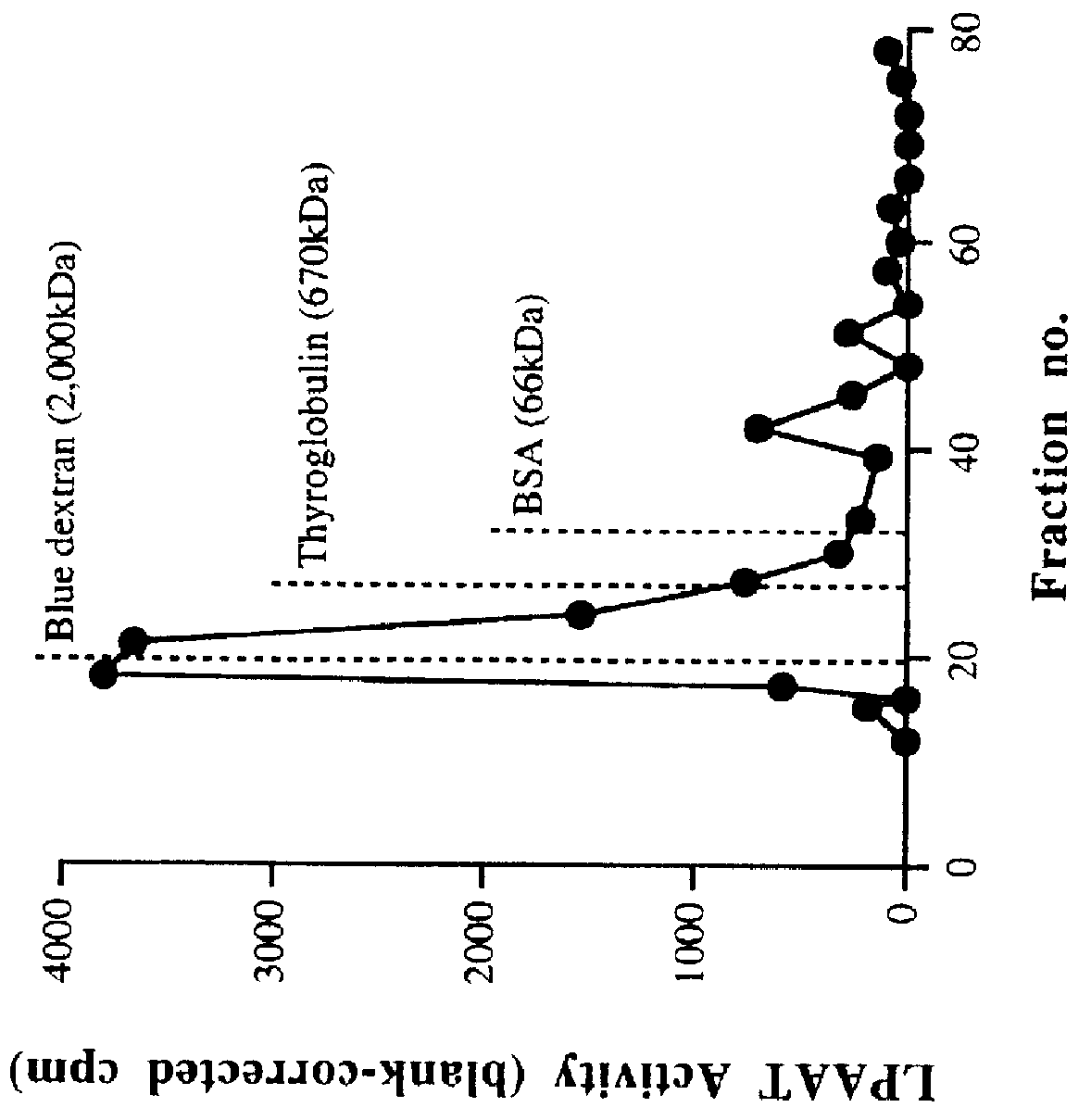
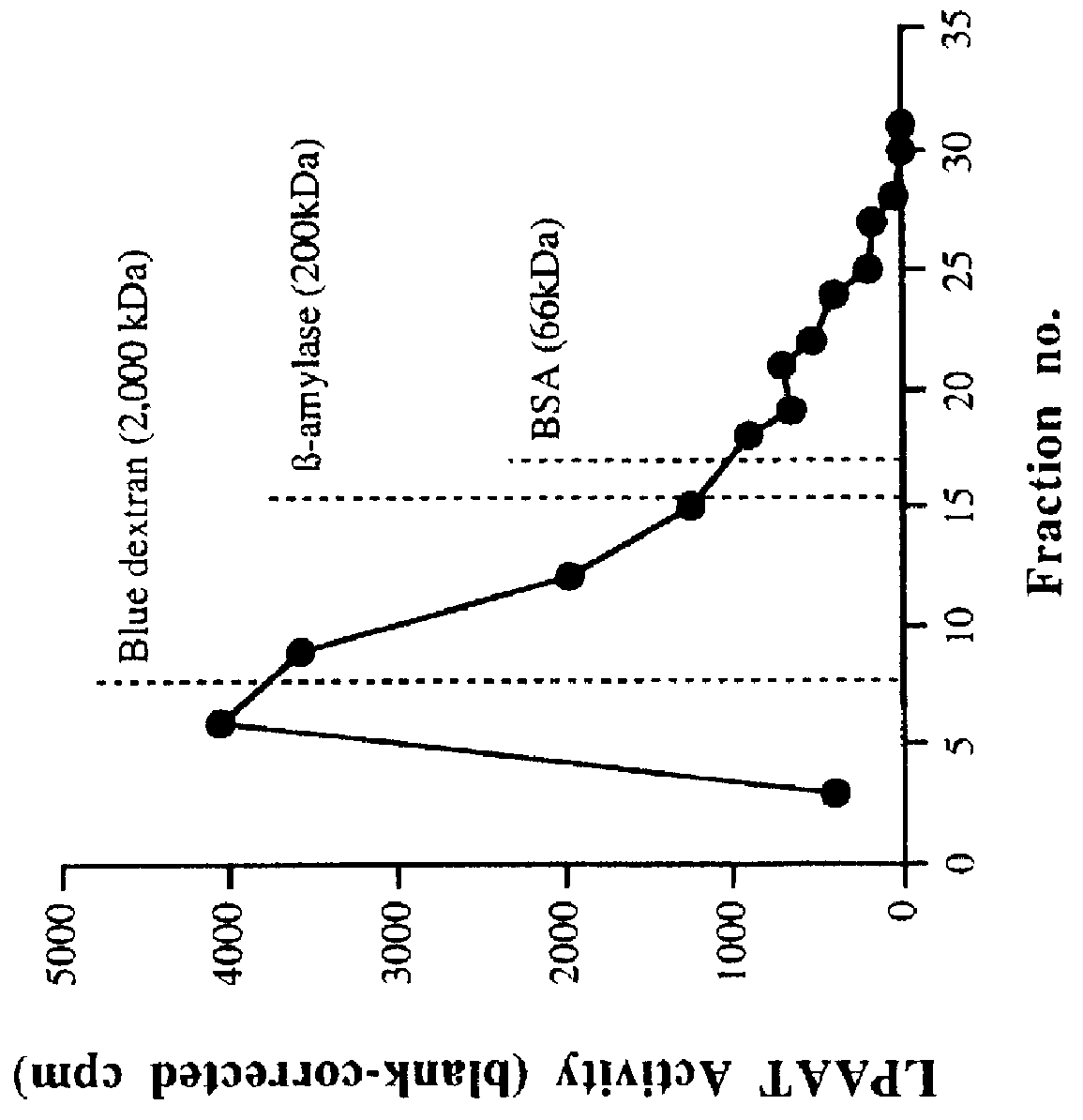
Plant lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferases
This invention relates to plant LPAATs, means to identify such proteins, amino acid and nucleic acid sequences associated with such protein, and methods to obtain, make and / or use such plant LPAATs. Purification, especially the removal of plant membranes and the substantial separation away from other plant proteins, and use of the plant LPAAT is provided, including the use of the protein as a tool in gene isolation for biotechnological applications. In addition, nucleic acid sequences encoding LPAAT protein regions are provided, and uses of such sequences for isolation of LPAAT genes from plants are considered.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
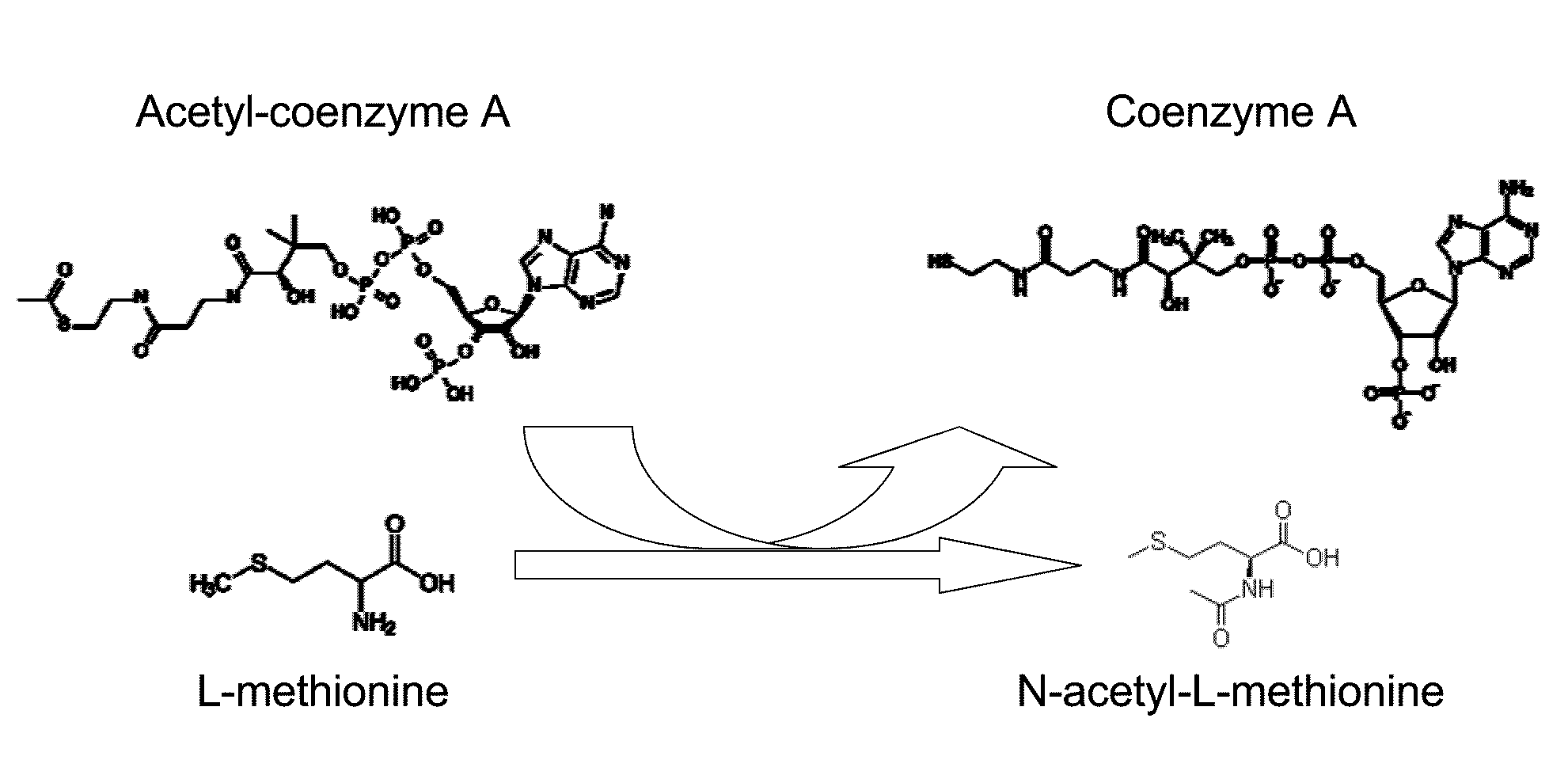
Production of N-acylated sulphur-containing amino acids with microorganisms having enhanced N-acyltransferase enzymatic activity
The present invention claims an isolated polypeptide having L-amino-acid-N-acyl transferase enzymatic activity and a modified microorganism in which this enzyme is overexpressed. Substrates of said enzyme include mainly methionine and their derivatives or analogs. Overexpression in sulphur-containing amino acid producing microorganisms permits the production of large amounts of N-acylated sulphur-containing amino acids. The isolation of the N-acylated sulphur-containing amino acids from the fermentation medium is also claimed.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
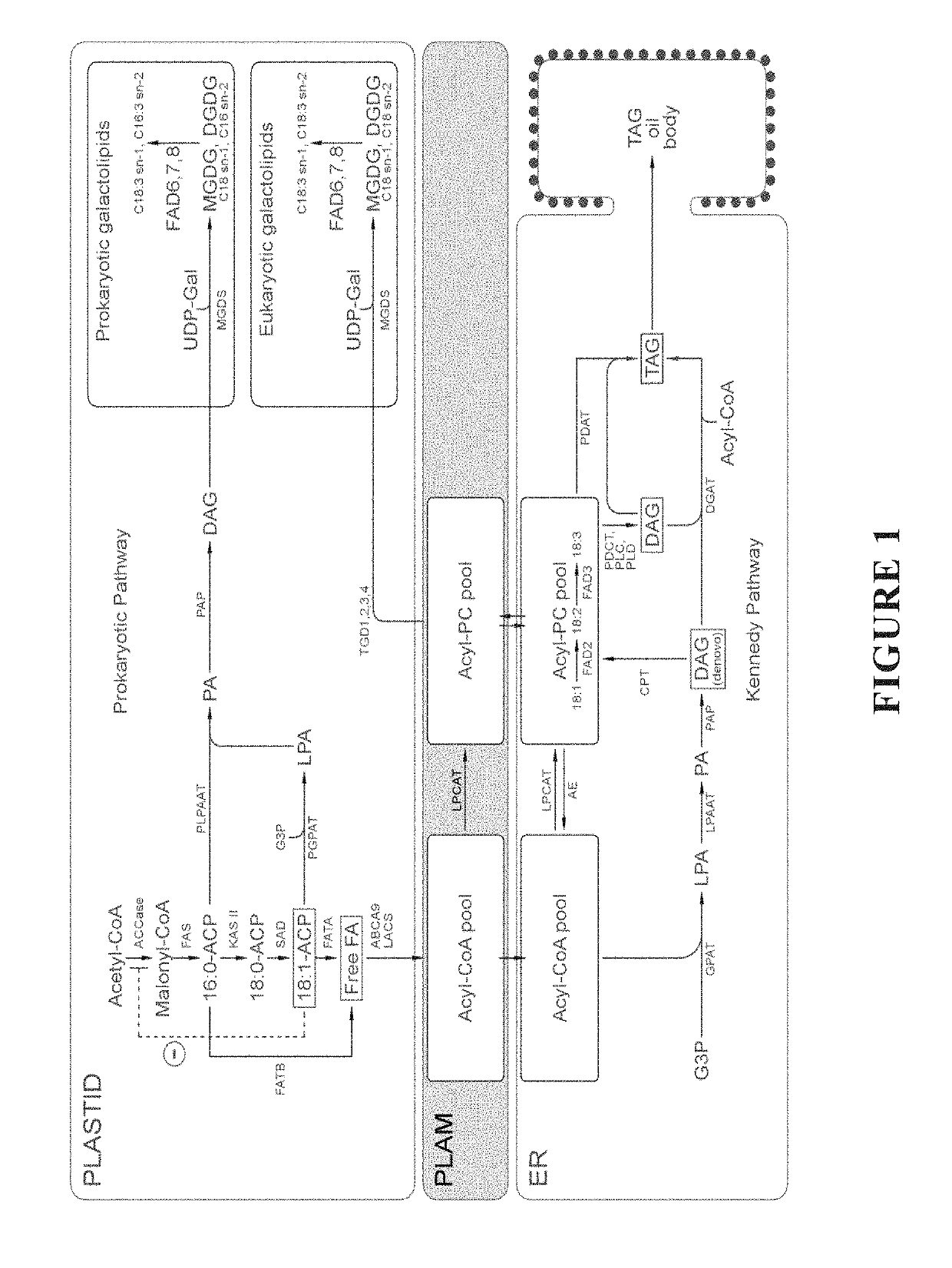
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase genes, proteins, and uses thereof
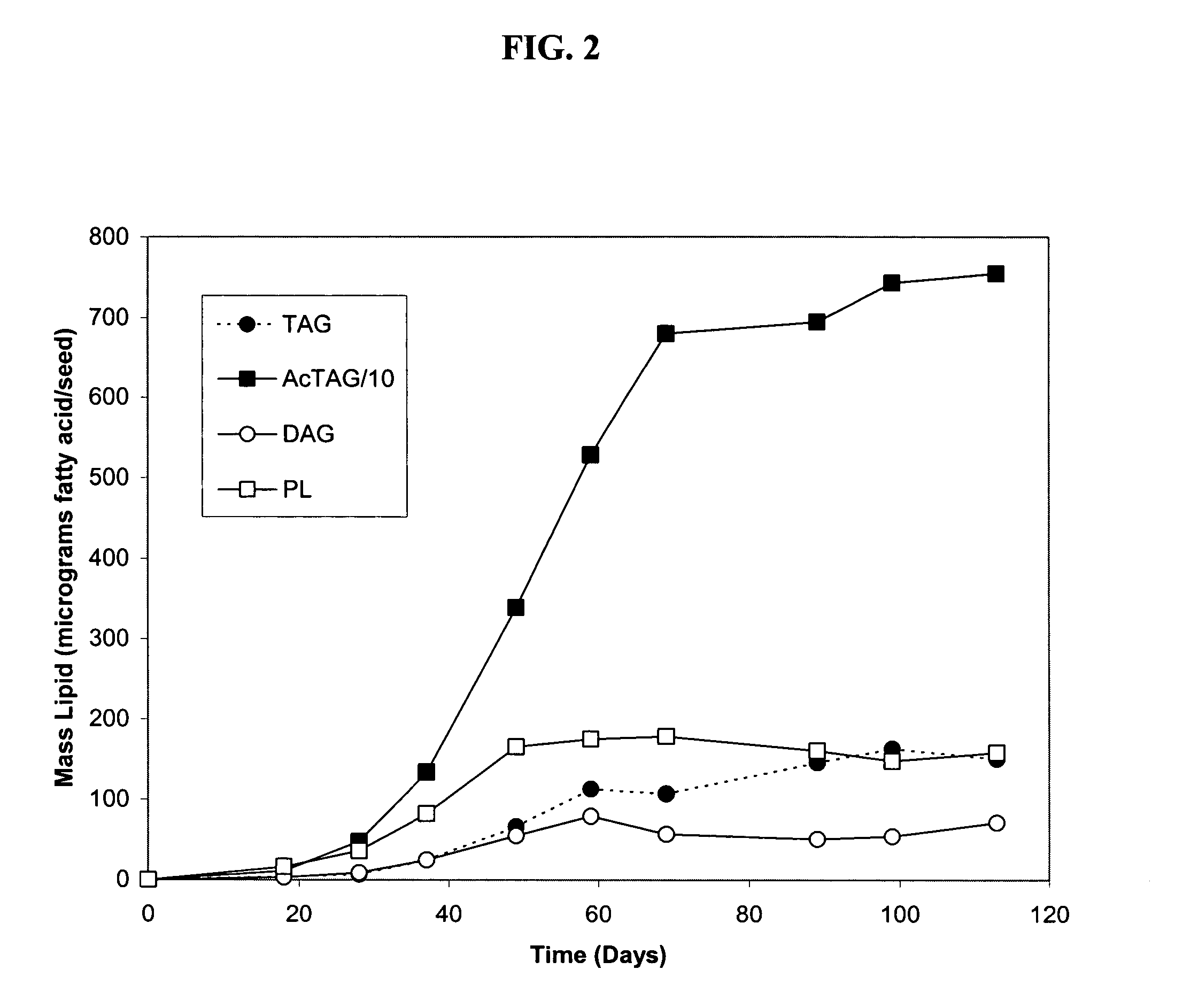
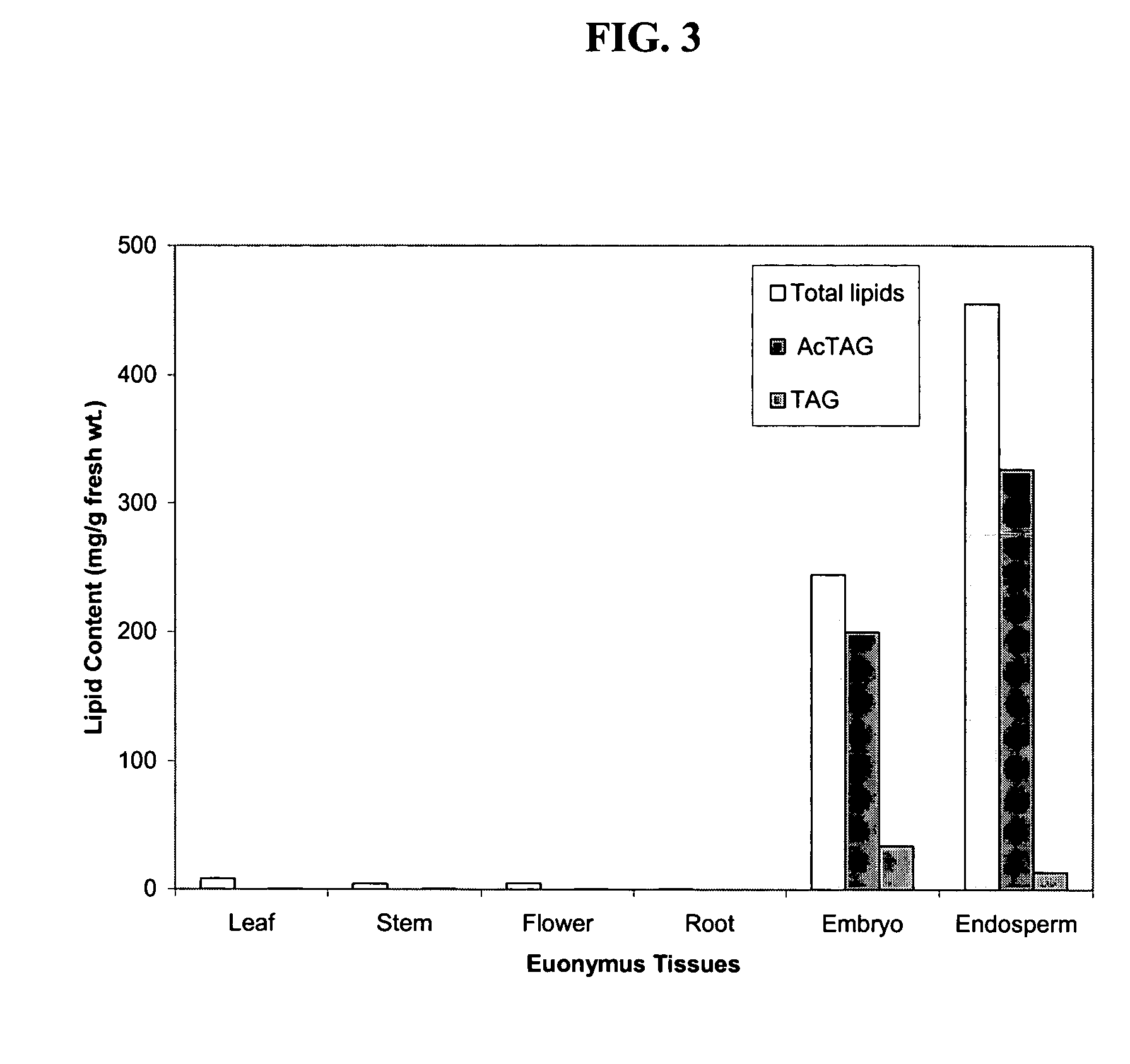
The present invention relates to diacylglycerol acyltransferase genes and proteins, and methods of their use. In particular, the invention describes genes and proteins that exhibit both long-chain acyltransferase and acetyltransferase activity. The present invention encompasses both native and recombinant wild-type forms of the transferase, as well as mutants and variant forms, some of which possess altered characteristics relative to the wild-type transferase. The present invention also relates to methods of using diacylglycerol acyltransferase genes and proteins, including in their expression in transgenic organisms and in the production of acetyl-glycerides in plant oils, and in particular seed oils.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081299A1Improve concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
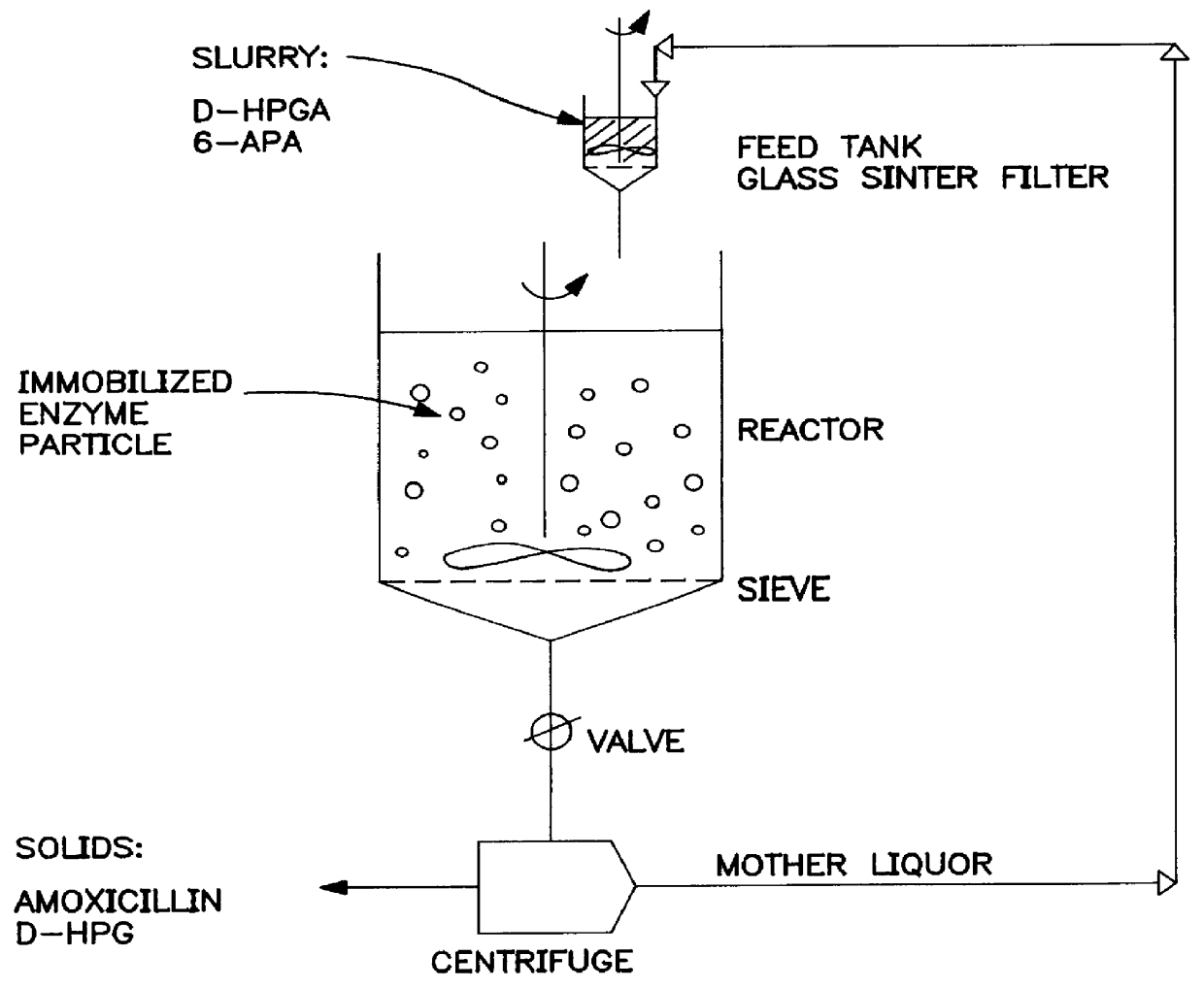
Improved method for preparing amoxicillin by enzymic method
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, and provides an improved method for preparing amoxicillin by an enzymic method, and a product obtained by the improved method for preparing amoxicillin by the enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) dissolving 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) at the temperature of between 10 and 20 DEG C by using water or / and aqueous solution of ammonia which has the pH value of 7.0 to 8.0, and adding D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine methyl ester hydrochlorid and penicillin G acyltransferase; 2) adjusting the pH value of a solution obtained in the step 1) to be 6.0 to 6.5, and reacting at the temperature of between 21 and 30 DEG C until the content of 6-APA is less than 5mg / ml to obtain a solution of an amoxicillin product; and 3) separating the penicillin G acyltransferase from the solution of the amoxicillin product, adjusting by using hydrochloric acid until the solution of the amoxicillin product is clarified, adding the aqueous solution of ammonia, adjusting the pH value to be 5.5 to 6.5, and crystallizing at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C to obtain amoxicillin. By the improved method for preparing amoxicillin by the enzymic method, the quality of the amoxicillin product is greatly improved, and the medication safety of the amoxicillin product is further improved.
Owner:UNITED LAB INNER MONGOLIA CO LTD
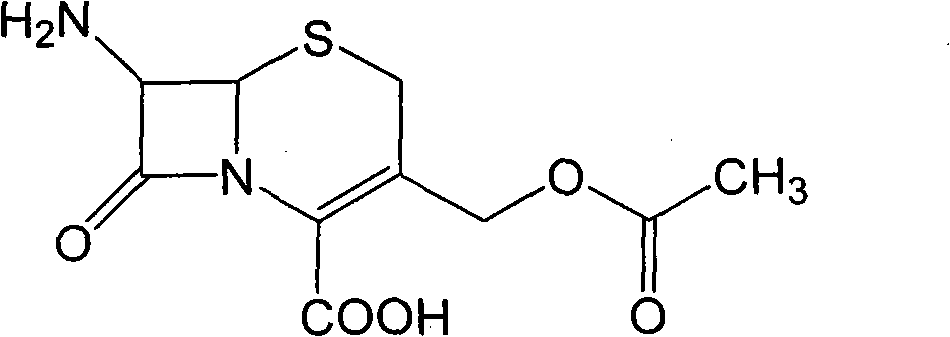
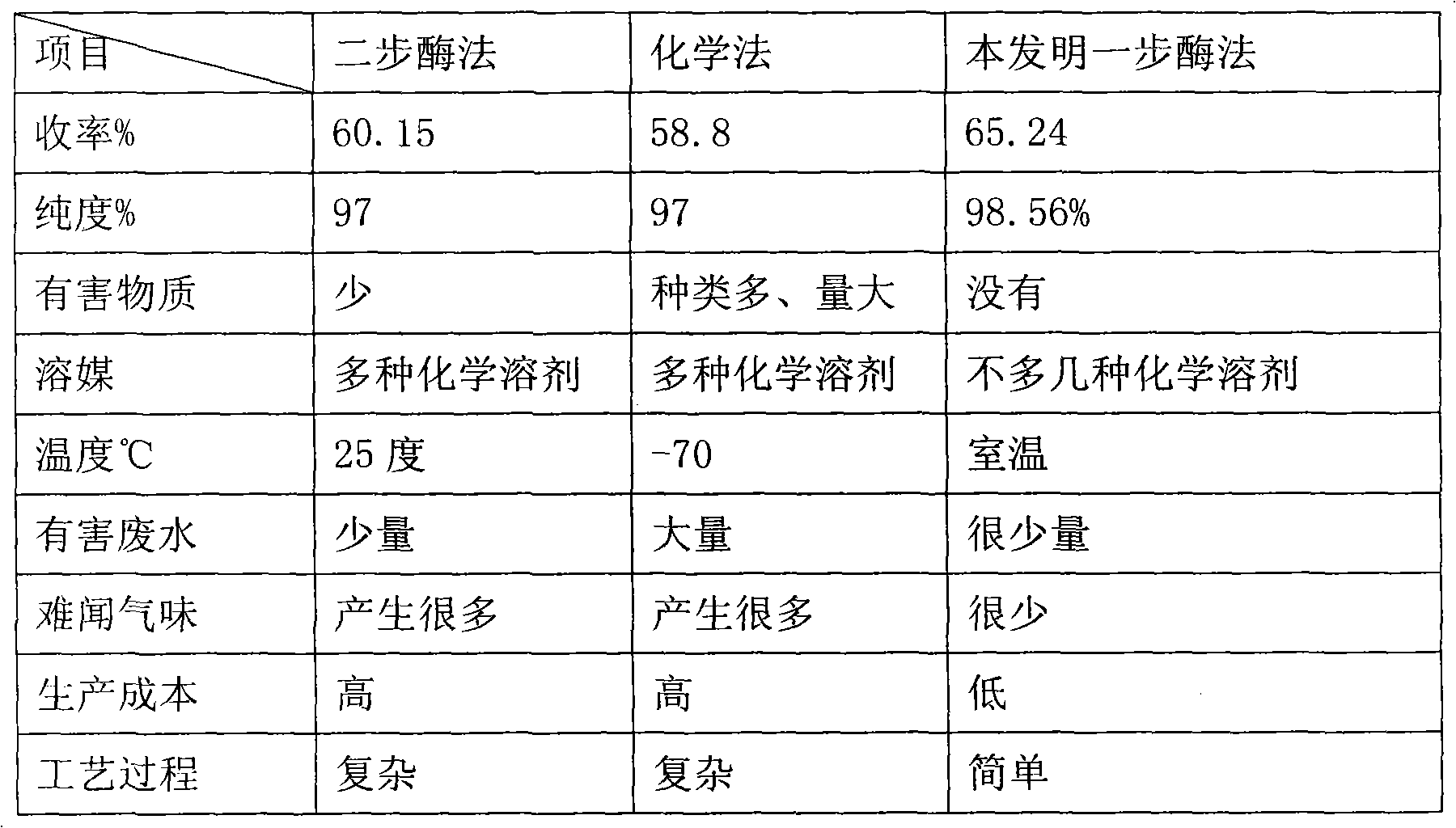
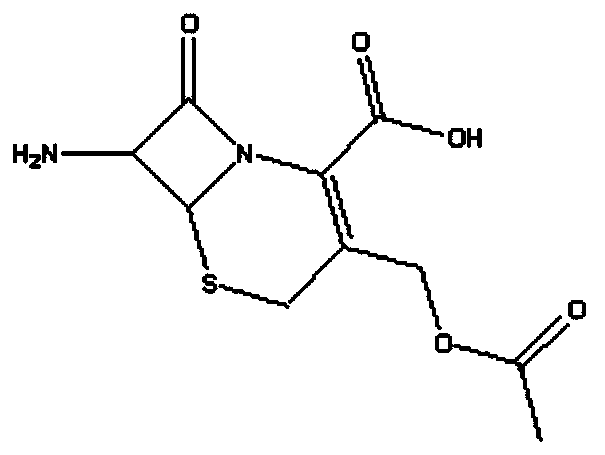
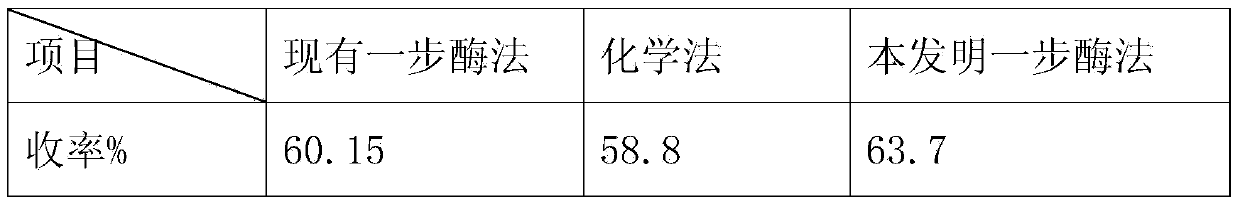
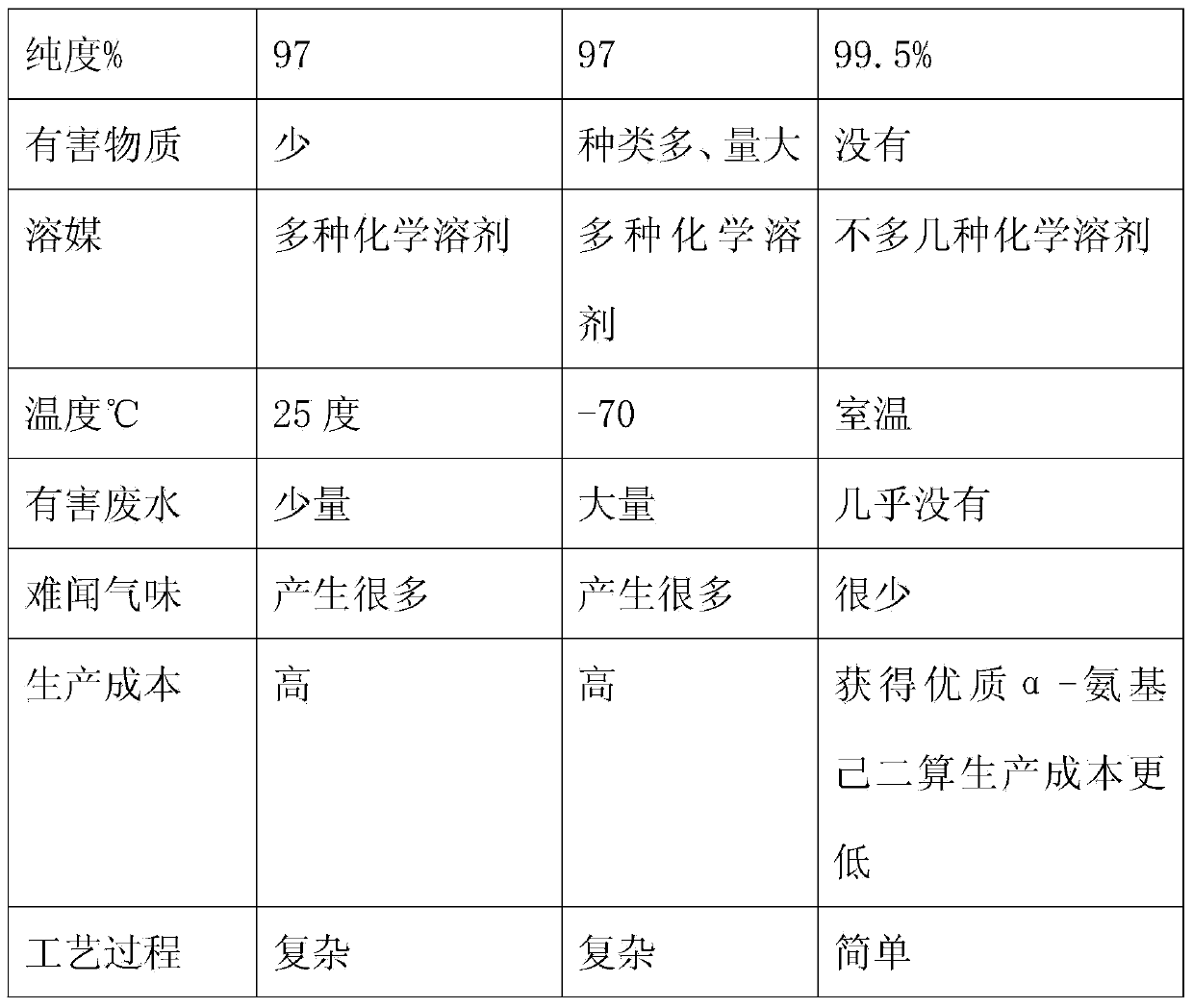
One-step enzymatic method for preparing 7-aminocephalosporanic acid
The invention relates to a one-step enzymatic method for preparing 7-aminocephalosporanic acid. The method for preparing the 7-aminocephalosporanic acid comprises four steps of: 1, treating fermentation liquid of cephalosporin C; 2, performing enzymolysis of the cephalosporin C under the action of acyltransferase of the cephalosporin C to obtain the 7-aminocephalosporanic acid; 3, treating the lysate of 7-aminocephalosporanic acid obtained through the enzymolysis; and 4, crystallizing and drying the 7-aminocephalosporanic acid.
Owner:HARBIN PHARMA GRP CO LTD GENERAL PHARMA FACTORY
Enzyme Directed Oil Biosynthesis In Microalgae
The present invention is related to biosynthetic oil compositions and methods of making thereof. In some embodiments, the invention relates to the use of endogenous enzymes in plants capable of synthesizing oil. In preferred embodiments, said plants are algae. In further embodiments, said algae are from the family Chlamydomonas, Nannochloropsis, Dunaliella, Chlorella and Scenedesmus. In still further embodiments, said endogenous enzymes are diacylglycerol acyltransferases.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for preparing 7-ACA (aminocephalosporanic acid) and obtaining alpha-aminoadipic acid by one-step enzymatic reaction
The invention relates to a method for preparing 7-ACA (aminocephalosporanic acid) and obtaining alpha-aminoadipic acid. The method comprises the following steps of (1) treating cephalosporin C fermentation liquid; (2) performing an enzymolysis reaction of cephalosporin C under the effect of cephalosporin C acyltransferase to obtain 7-ACA; (3) treating the 7-ACA lysate after the enzymolysis; (4) separating out the 7-ACA; (5) separating alpha-aminoadipic acid from the separated 7-ACA lysate.
Owner:HARBIN PHARMA GRP CO LTD GENERAL PHARMA FACTORY
Process for preparation of beta -lactams at constantly high concentration of reactants
InactiveUS6048708AIncrease the molar ratioEconomic impactHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierHigh concentrationAmidase
PCT No. PCT / EP95 / 02876 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 19, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 19, 1997 PCT Filed Jul. 18, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 02663 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 1, 1996An improvement for enzymatically syhnthesizing a beta -lactam compound is presented. The improvement comprises catalyzing the acylation of an amino beta -lactam with an acylating agent for at least 5 hours with an amidase or acylase, wherein the concentration of each reactant is constantly higher than 70% of the lowest value of the saturated concentration of both reactants.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV
Preparation method of glutaryl-7-aminocefaphytanic acid acyltransferase
The method for preparing glutaryl-7-aminocephaphylanic acid acylase is characterized by that it utilizes colibacillus gene engineering bacterium to make shake-flask strain culture in culture medium, fermentation strain culture and fermentation culture, then utilizes centrifuge to collect thallus, soakes to extract enzyme liquor, makes the enzyme liquor undergo the processes of plate-frame filtration, ultrafiltration concentration, purification and fixation so as to obtain the invented product GL-7-ACA ACY.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method of producing L-alanyl-L-glutamine from recombinant escherichia coli
InactiveCN104480172AHigh activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliL-alanyl-l-glutamine
The invention discloses a method of producing L-alanyl-L-glutamine from recombinant escherichia coli, wherein the method of producing L-alanyl-L-glutamine from recombinant escherichia coli is follows: in an aqueous solution with a determined pH value, acting on free L-glutamine and L-alanine methyl ester hydrochloride to generate L-alanyl-L-glutamine, recombining a gene segment of the protein with the amino-acid ester acyltransferase of the L-alanyl-L-glutamine into a carrier and transferring into host bacteria, thereby obtaining the host bacteria with the recombinant DNA and capable of strengthening the activity of an L-alanyl-L-glutamine biological synthesis system. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing a larger number of recombinant escherichia coli cells for expressing the amino-acid ester acyltransferase; (2) excessively expressing the amino-acid ester acyltransferase in the step (1); and (3) taking the amino-acid ester acyltransferase in the step (2) as a crude enzyme source, adding the crude enzyme source into a buffer solution containing L-glutamine and L-alanine methyl ester hydrochloride substrate amino acid to react, thereby realizing efficient production of the L-alanyl-L-glutamine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
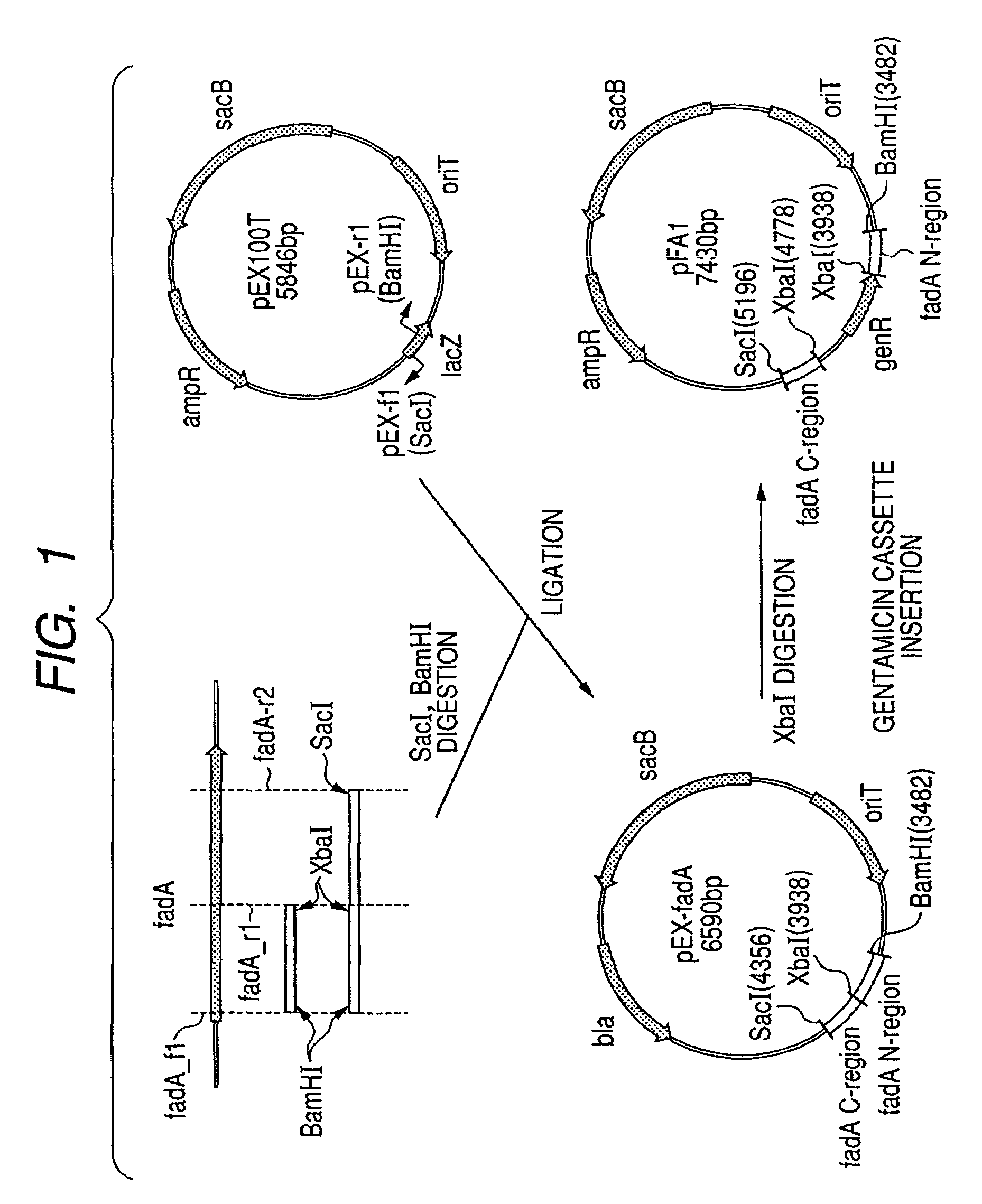
Plants producing modified levels of medium chain fatty acids
The present invention relates to methods of producing industrial products from plant lipids, particularly from vegetative parts of plants. In particular, the present invention provides oil products such as biofuel, and processes for producing these products, as well as plants having an increased level medium chain fatty acids such as lauric acid and myristic acid. In one particular embodiment, the present invention relates to combinations of modifications in a fatty acid thioesterase and one or more acyltransferases. In an embodiment, the present invention relates to a process for extracting lipids. In another embodiment, the lipid is converted to one or more hydrocarbon products in harvested plant vegetative parts to produce alkyl esters of the fatty acids which are suitable for use as a renewable biofuel.
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com