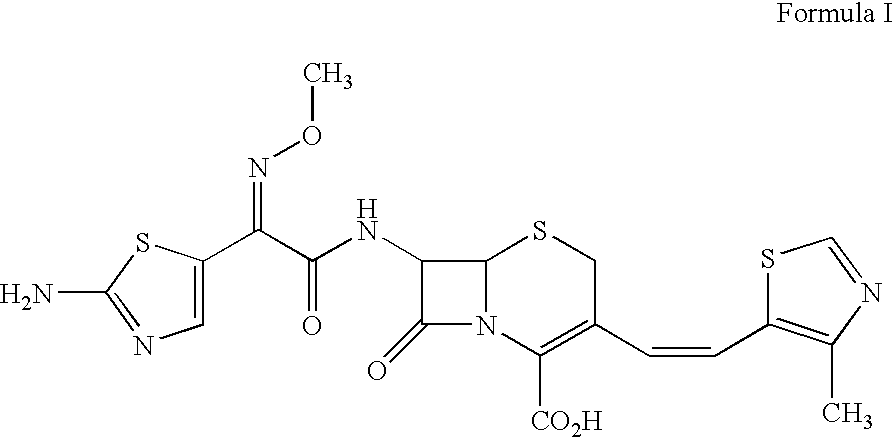
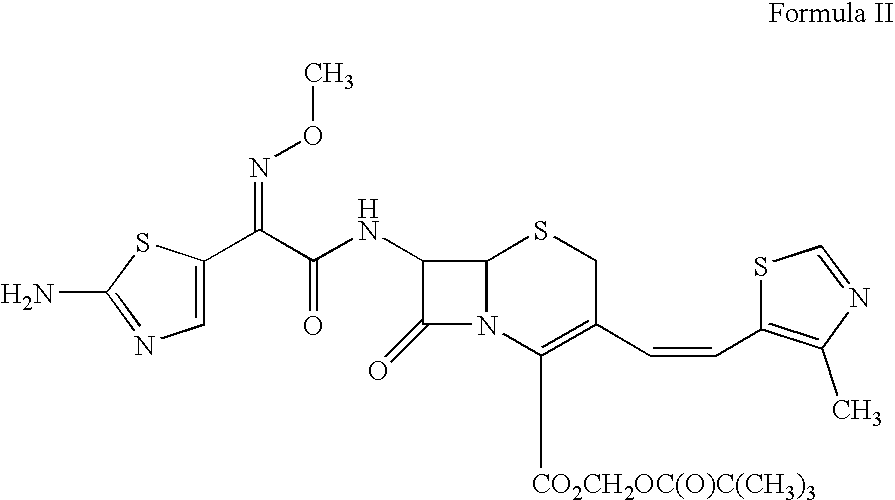
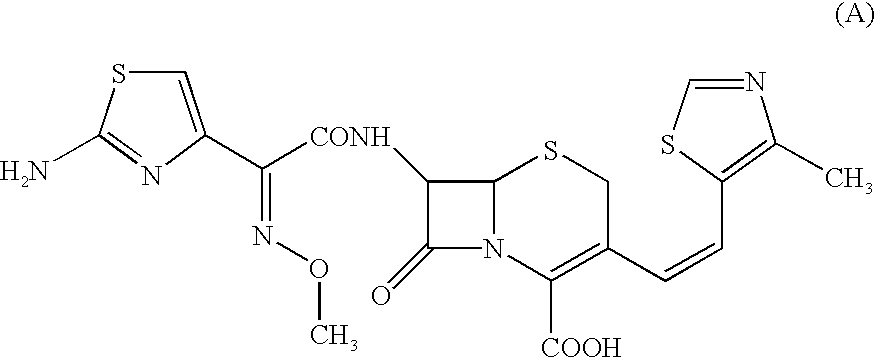
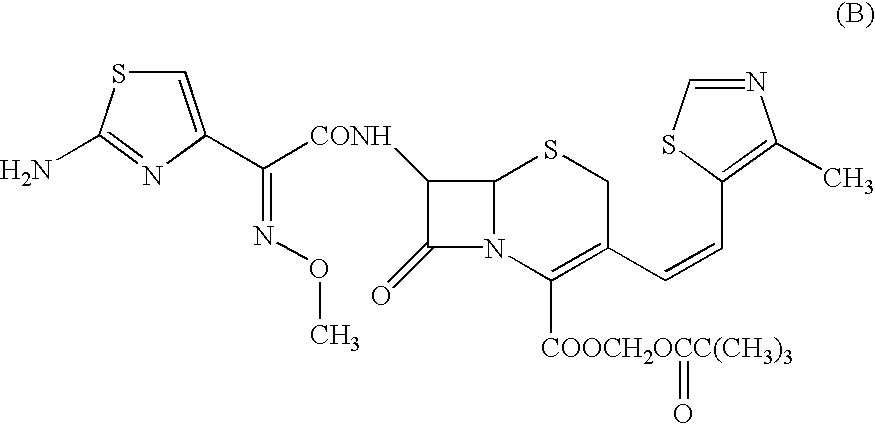
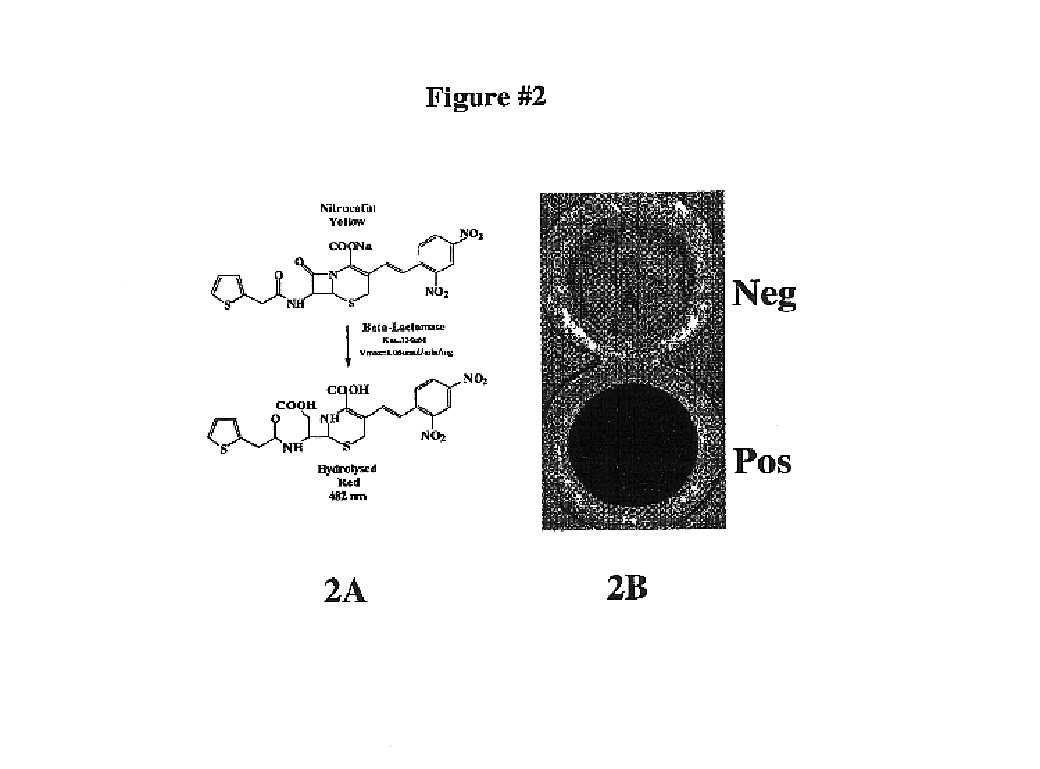
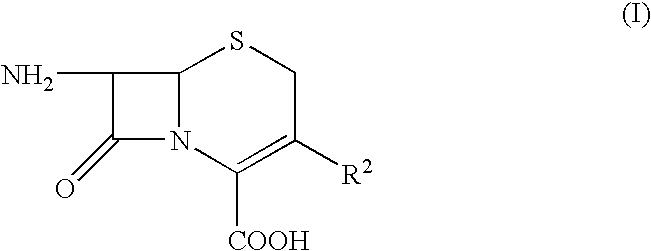
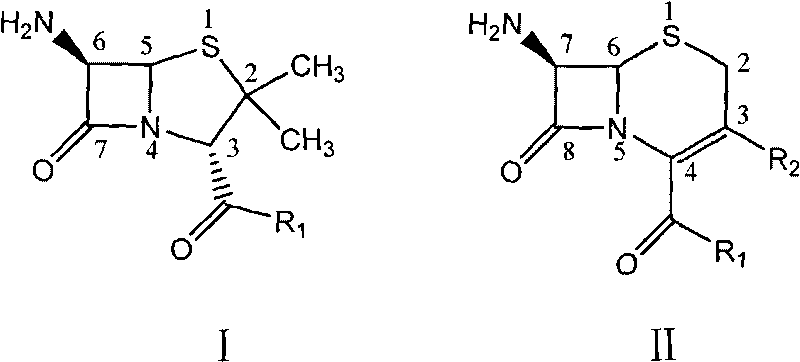
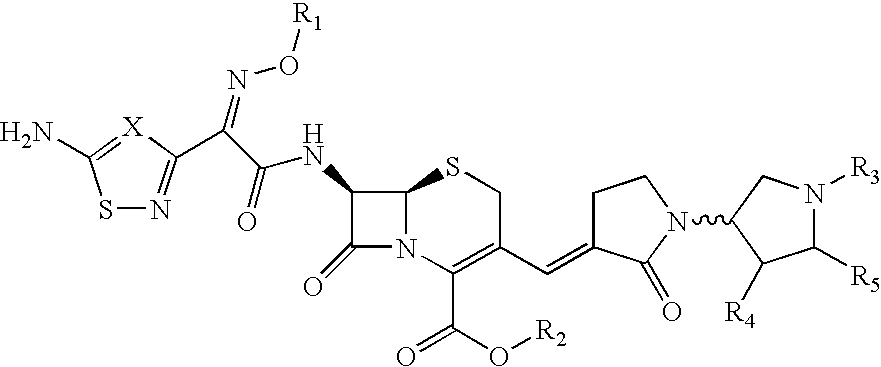
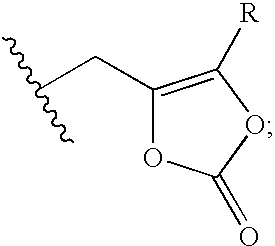
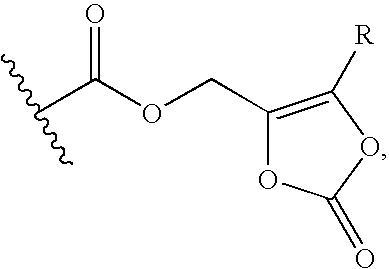
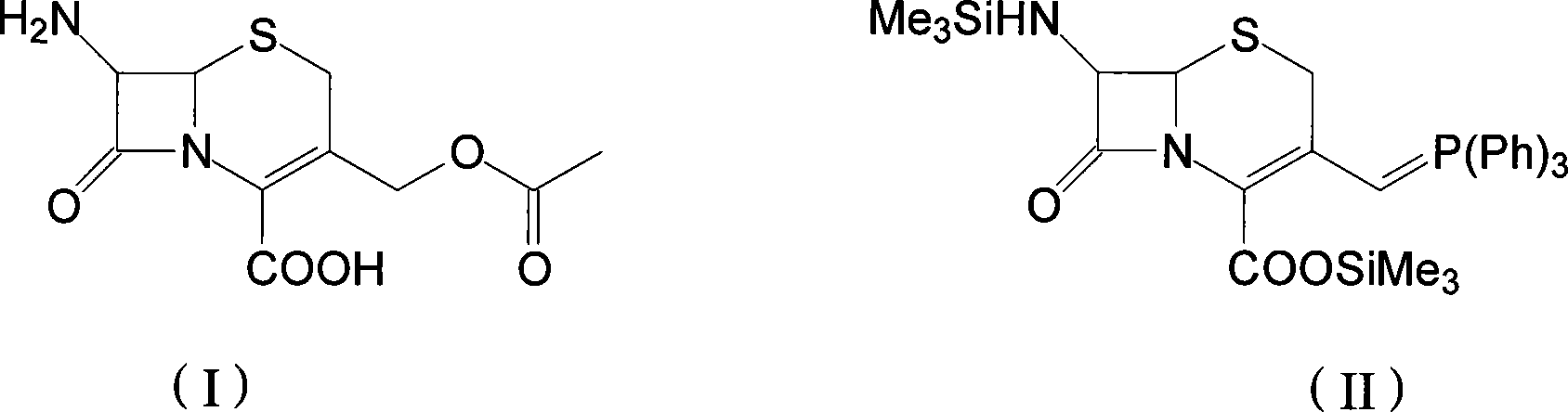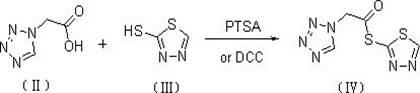Patents
Literature
531 results about "Cephalosporin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cephalosporins (sg. /ˌsɛfələˈspɔːrɪn, ˌkɛ-, -loʊ-/) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as "Cephalosporium". Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964.
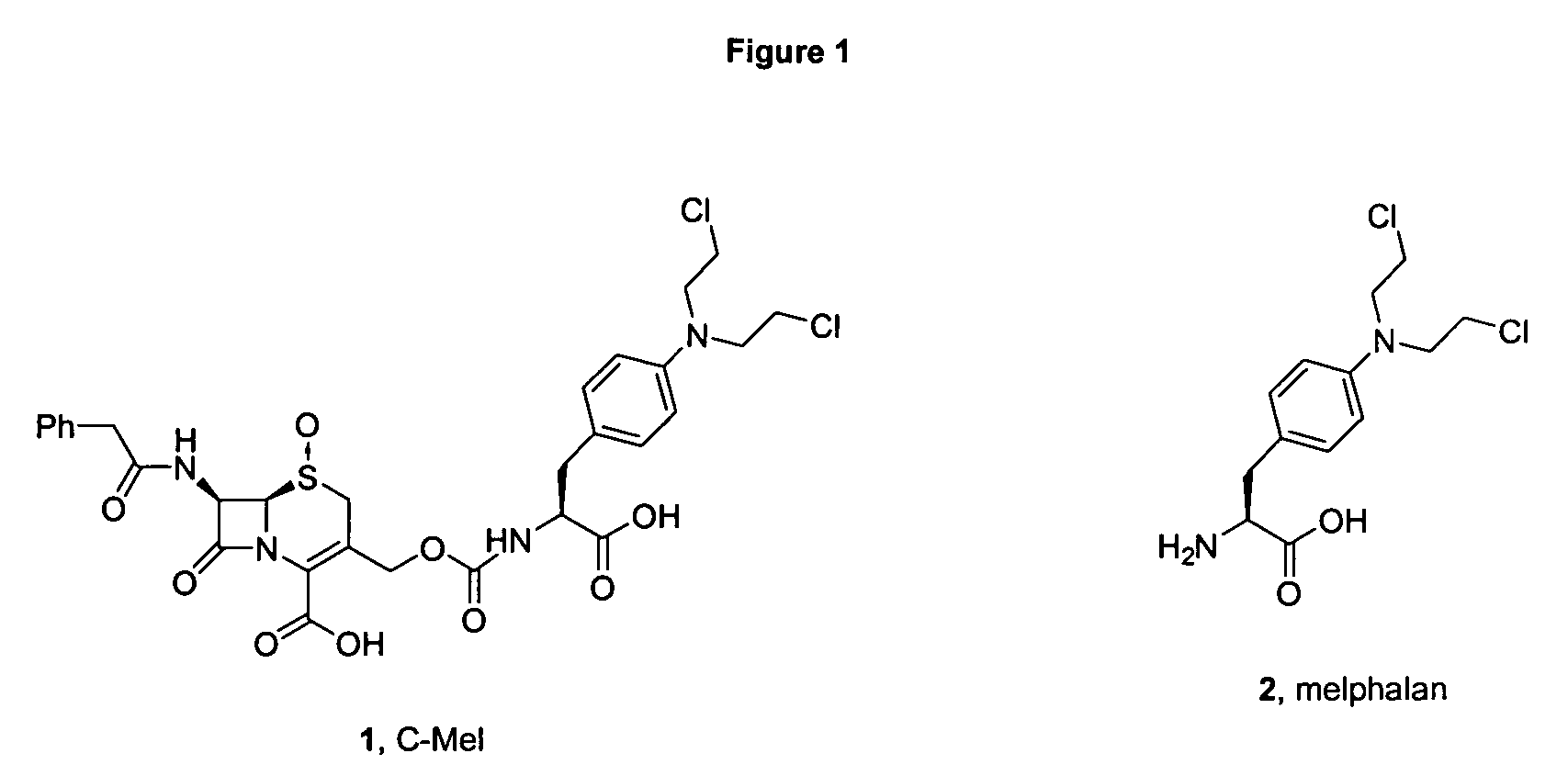
Melphalan prodrugs
InactiveUS20050214310A1High specificity of actionImprove stabilityNanomedicineAntibody ingredientsSolubilityTherapeutic window
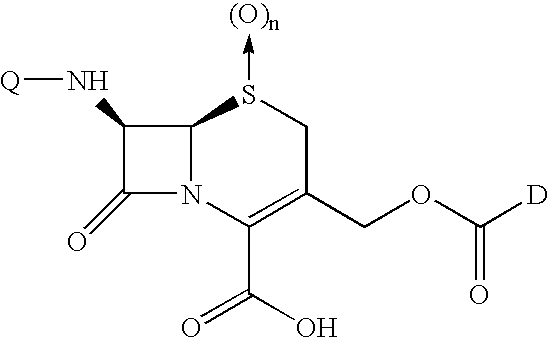
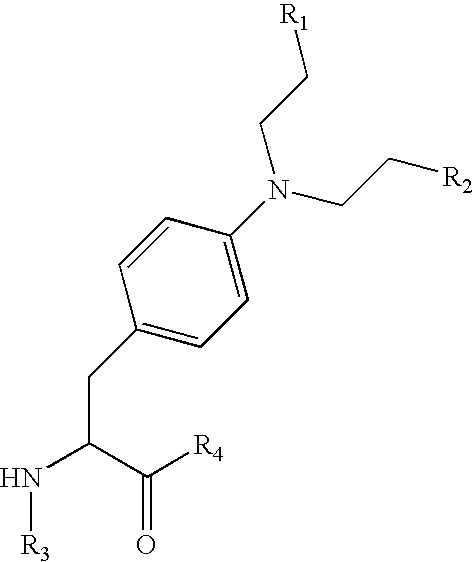
Shown and described are the synthesis of more potent forms of C-Mel, a prodrug used in Antibody-Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy, that releases the clinically used anticancer alkylating agent melphalan extracellularly. Shown and described are the synthesis of a variety of melphalan analogues with the intention to promote facile intracellular drug access. Esters, amides, and peptides of melphalan are shown. Cephalosporin prodrugs of the most interesting melphalan derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for potency, toxicity, therapeutic window, plasma stability, and solubility.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
Nanoparticulate and controlled release compositions comprising a cephalosporin
InactiveUS20070160675A1Minimize changesMinimizes and eliminates variationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseNanoparticle
The present invention provides a composition comprising cephalosporin useful in the treatment and prevention of a bacterial infection. In one embodiment, the composition comprises nanoparticulate particles comprising cephalosporin and at least one surface stabilizer. The nanoparticulate particles have an effective average particle size of less than about 2000 nm. In another embodiment, the composition comprises a modified release composition that, upon administration to a patient, delivers cephalosporin in a bimodal, multimodal or continuous manner. The invention also relates to dosage forms containing such compositions, and to methods for the treatment and prevention of a bacterial infection.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
Enhancement of oral bioavailability of non-emulsified formulations of prodrug esters with lecithin
InactiveUS20050113337A1Prevent degradationImprove efficiencyBiocideDispersion deliveryAntibiotic YLiposome
A method for enhancing the oral bioavailability of a prodrug ester by formulating the ester as a non-emulsified formulation with lecithin; as well as a pharmaceutical composition of at least one antibiotic and lecithin in a non-emulsified formulation; a method of treating infections with the non-emulsified formulation, and a method for preparing tablets by direct compression of blends of drugs with lecithin are disclosed. Non-emulsified formulations include solids, tablets, capsules, lozenges, suspensions, elixirs and solutions, and exclude emulsions, liposomes, lipid matrix systems and micro-emulsions. A suitable prodrug ester is a cephalosporin β-lactam antibiotic such as cefditoren pivoxil, and a suitable non-emulsified formulation is a solid formulation.
Owner:TAP PHARM PROD INC
Composition comprising a crystallographically stable, amorphous cephalosporin and processes for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS6486149B2Good water solubilityImprove solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsWater solubleAqueous solution
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Method for preparing cephalosporin propylene
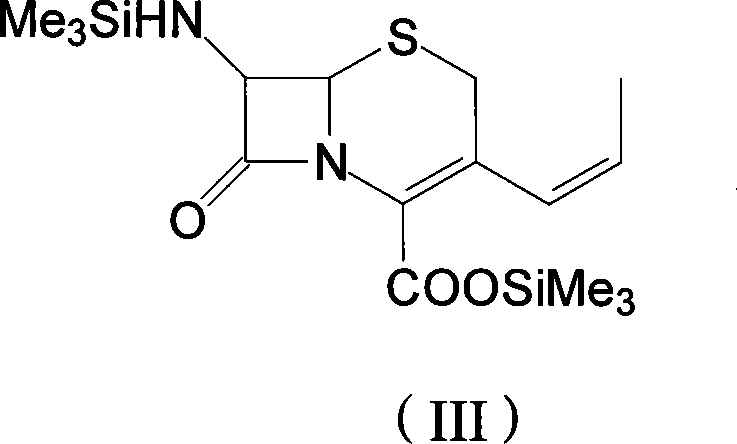
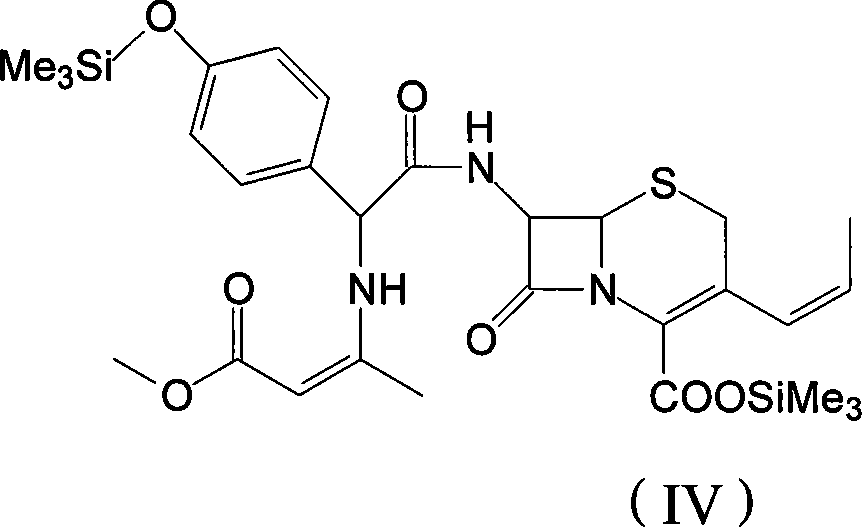
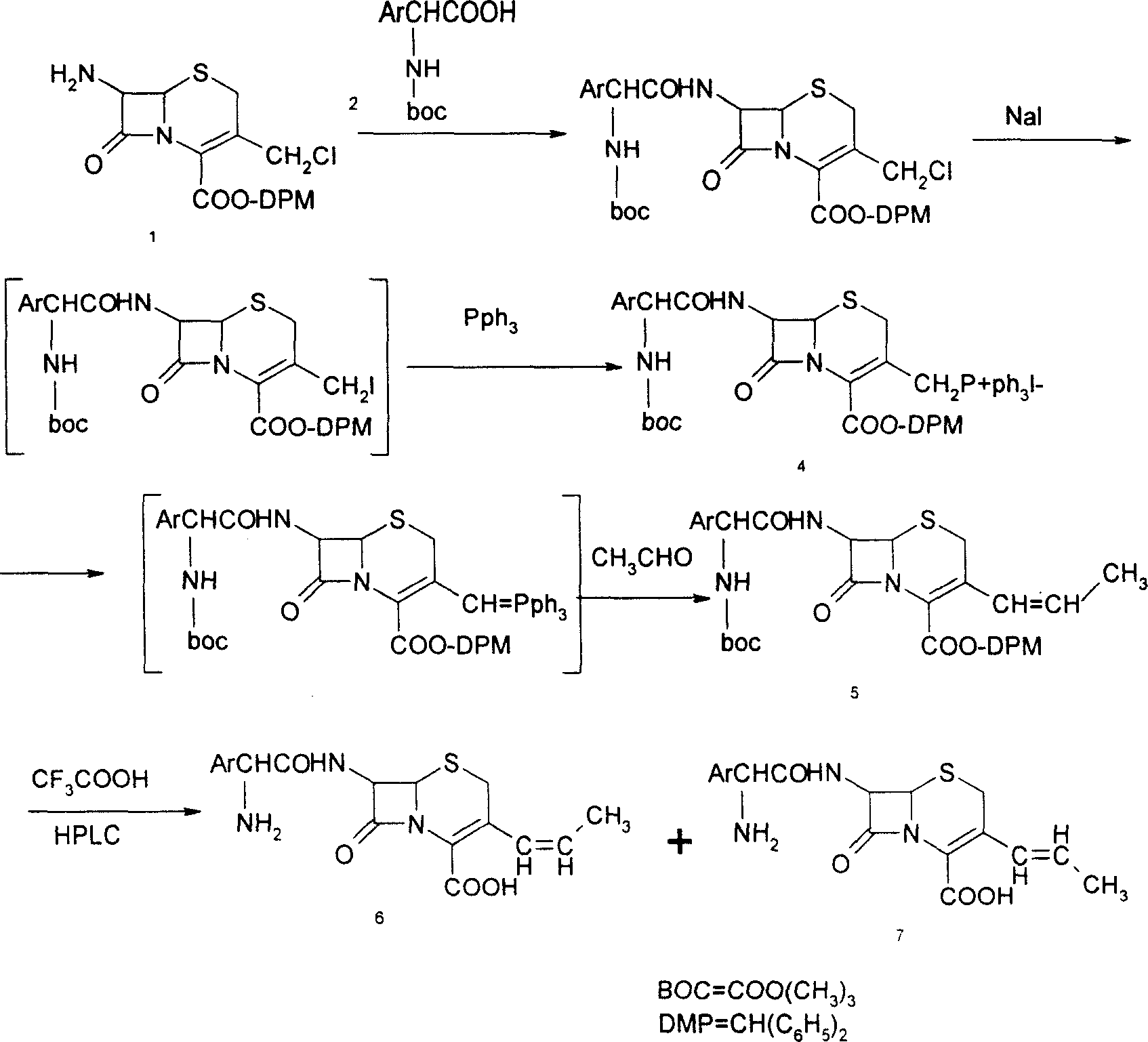
The invention discloses a preparation method of cefprozil, which comprises: 7-amin cethalosporanic acid (7-ACA) reacts with triphenyl phosphine to get 7- trimethylsilyl amino-3-triphenyl phosphate methylene-4-cethalosporanic acid trimethylsilyl ester through silanization protection and iodination reagent replacing under the condition of catalyst existing; WITTIG reaction is made for the product and acetaldehyde to get 7-trimethylsilyl amino -3-(propenyl-1-alkenyl)-4-cethalosporanic acidtrimethylsilyl ester; then the compound reacts with D-para hydroxybenzene glycine dane potassium salt to geta compound (6R, 7R)-7-[(2R)-2- ethoxycarbonyl-1-methyl - ethylene amino (4-trimethylsilyl oxyphenyl) acetamido group(amide)]-8-oxo-3- (1- propenyl)-5-thio-1- heterobicycle [4.2.0] octylene-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid trimethylsilyl ester; hydrolytic treatment is then used to get the cefprozil. The invent adopts the method of one pot and can participate in next reaction without separating intermediateproducts. The preparation method of cefprozil has the advantages of low cost, convenient operation and high overall yield, adapting to demands of industrial production.
Owner:南通康鑫药业有限公司
Chphalosporin-derived mercaptans as inhibitors of serine and metallo-beta-lactamases
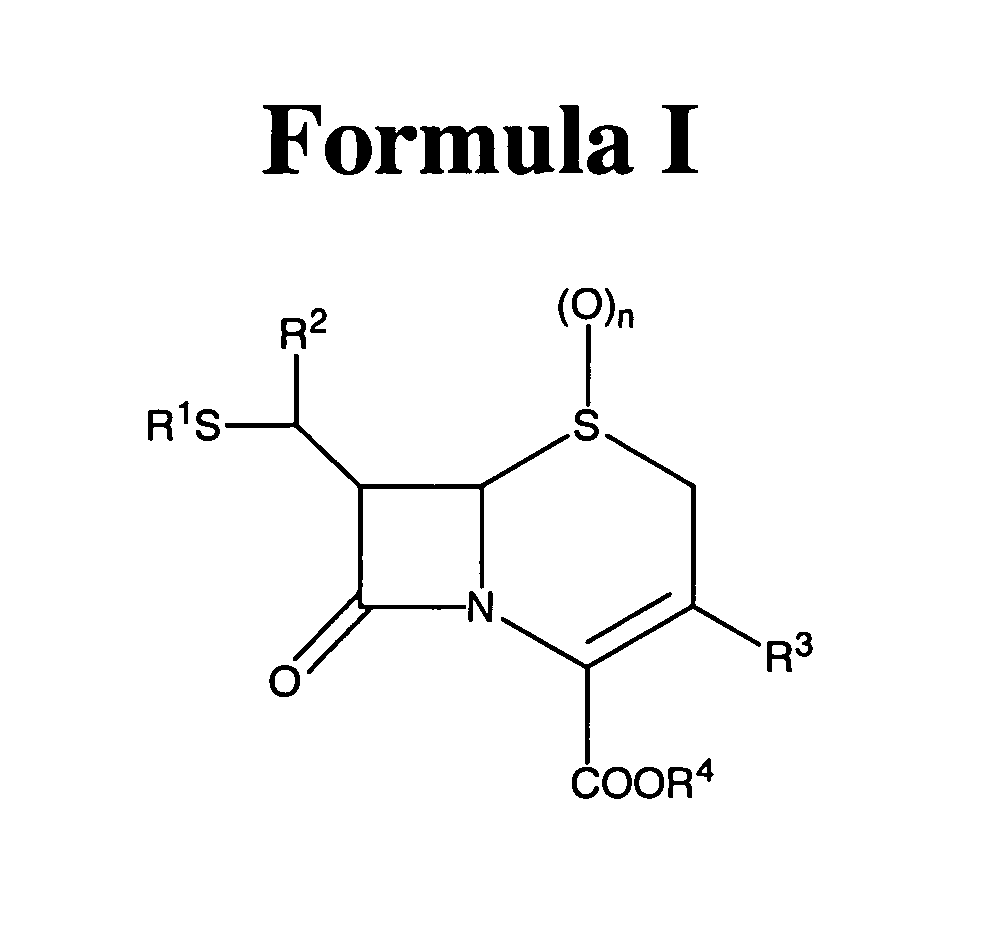
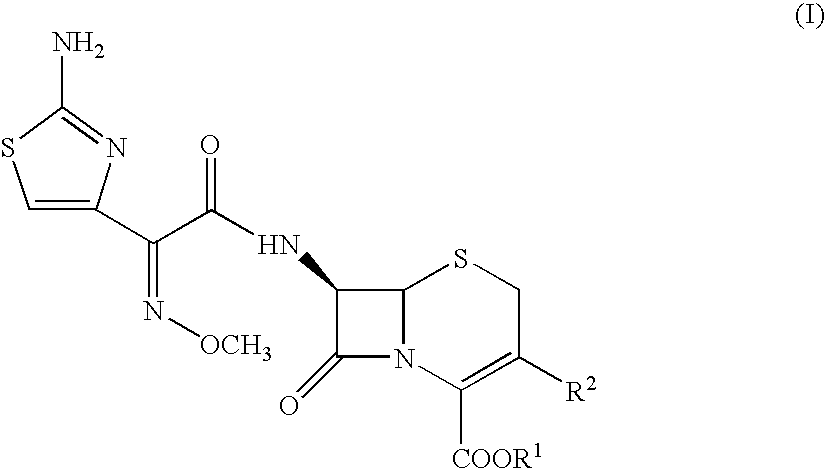
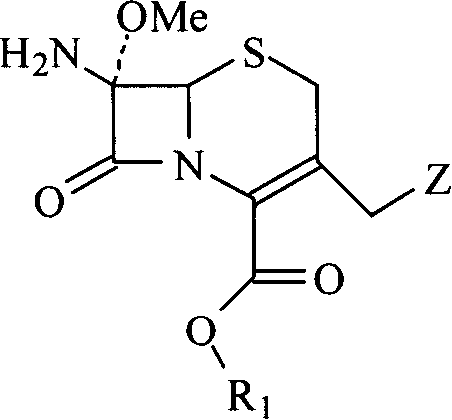
Compounds of formula I: See Formula I in Figures Section wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 and n have any of the values defined in the specification, and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, are useful for inhibiting simultaneously serine and metallo-β-lactamase enzymes, for enhancing the activity of β-lactam antibiotics, and for treating β-lactam resistant bacterial infections in a mammal. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions, processes for preparing compounds of formula I, and novel intermediates useful for the synthesis of compounds of formula I.
Owner:BUYNAK JOHN D +1
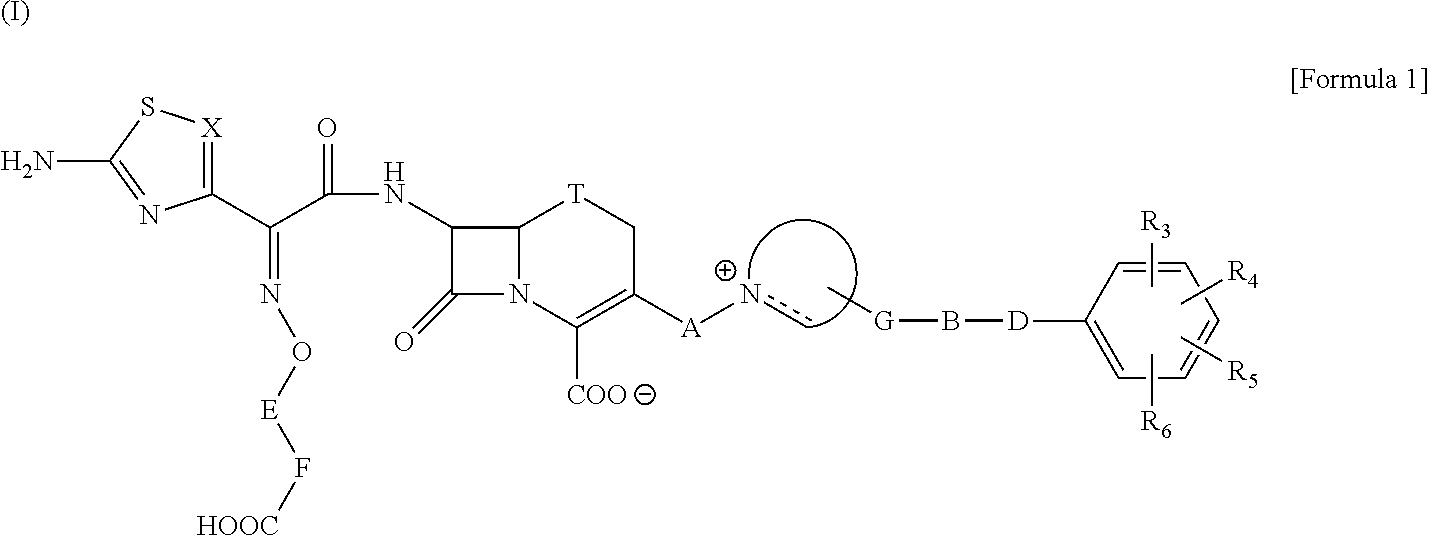
Cephalosporin having catechol group
ActiveUS20110190254A1Potent antimicrobial spectrumHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainPharmaceutical medicine
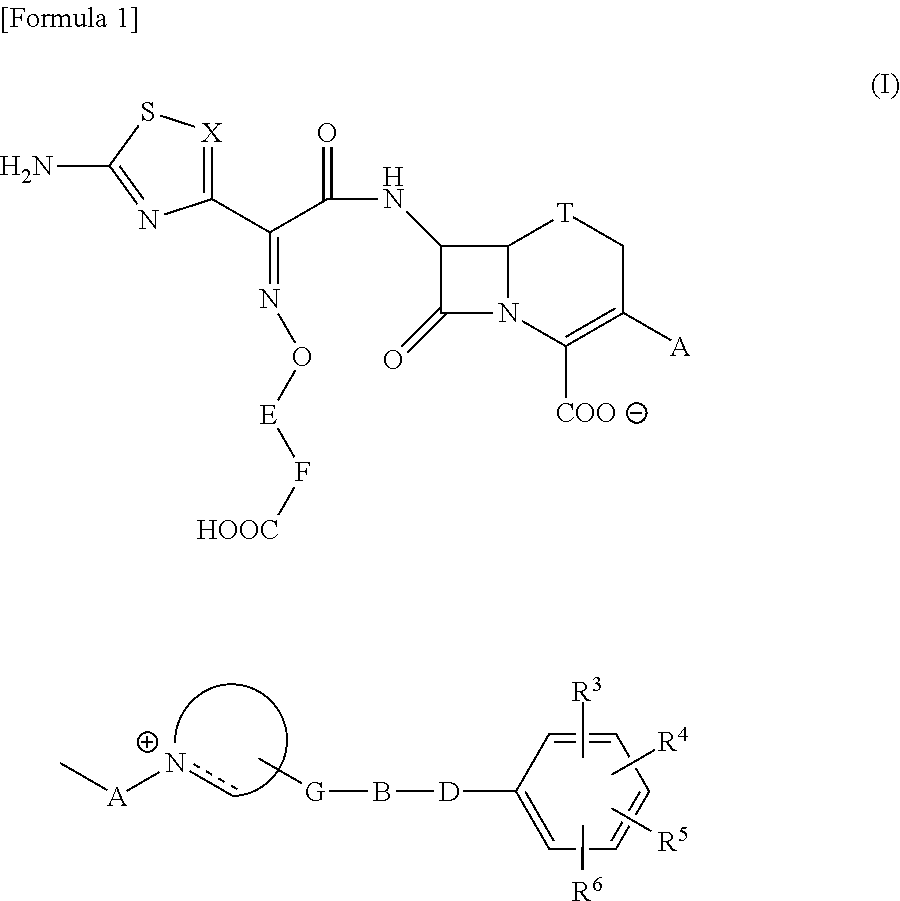
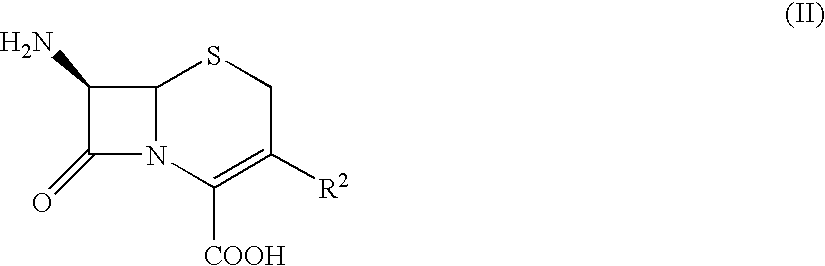
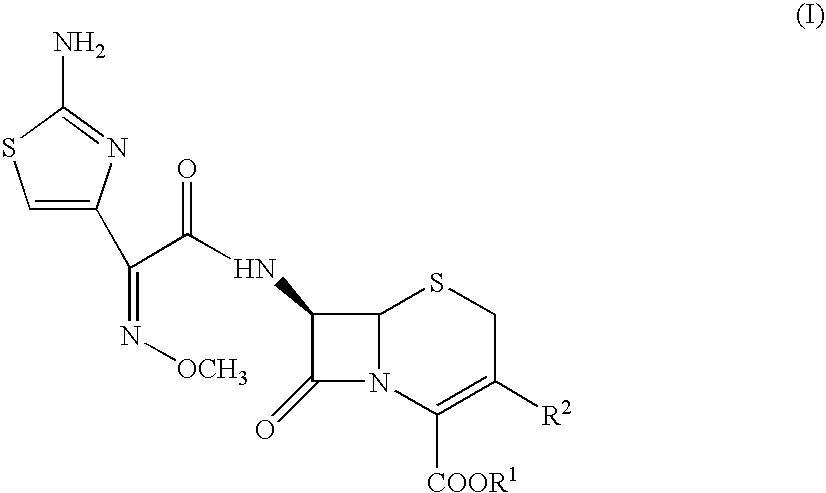
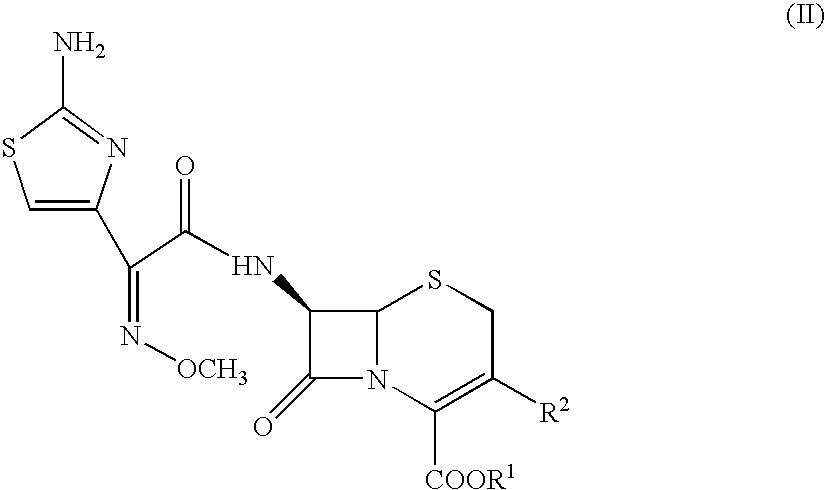
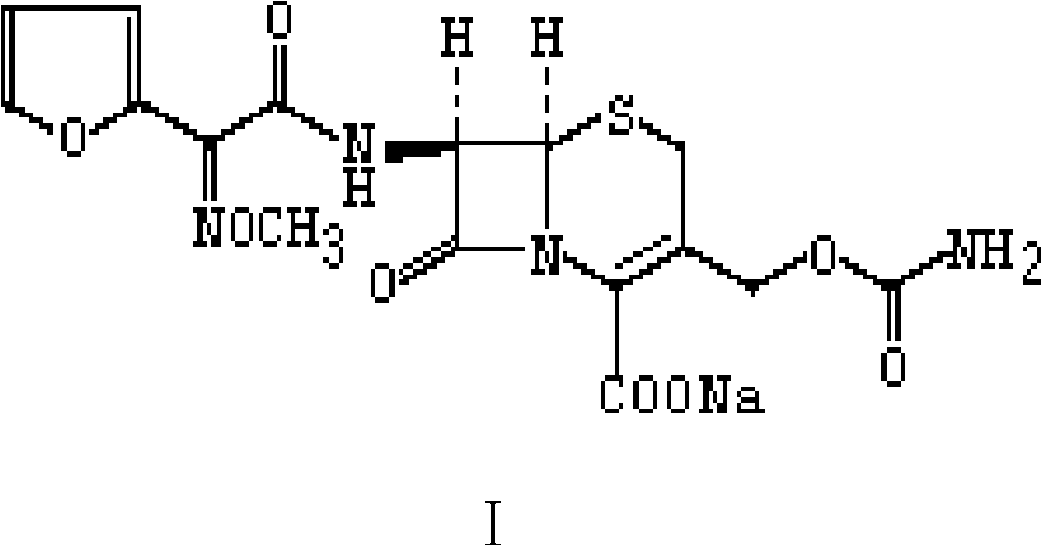
The present invention provides Cephem compounds which have a wide antimicrobial spectrum and have potent antimicrobial activity against beta-lactamase producing Gram negative bacteria as follows:A compound of the formula:wherein,X is N, CH or C—Cl;T is S or the like;A and G are lower alkylene or the like;B is a single bond or the like;D is a single bond, —NR7—, —CO—, —CO—NR7—, —NR7—CO—, —NR7—CO—NR7—, or the like;E is optionally substituted lower alkylene;F is a single bond or optionally substituted phenylene;R3, R4, R5 and R6 each is independently hydrogen, halogene, nitrile, or the like;or an ester, a compound protected at the amino on the ring in the 7-side chain, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, or a solvate thereof.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Method for preparing oral non-ester-type autibiotic cetprozil
The invention supplies a manufacture method for oral taken inester antibiotic cephalosporin propylene. It has the advantages of short reacting method, mild reacting condition, easy to operate, etc.
Owner:上海医药科技发展有限公司
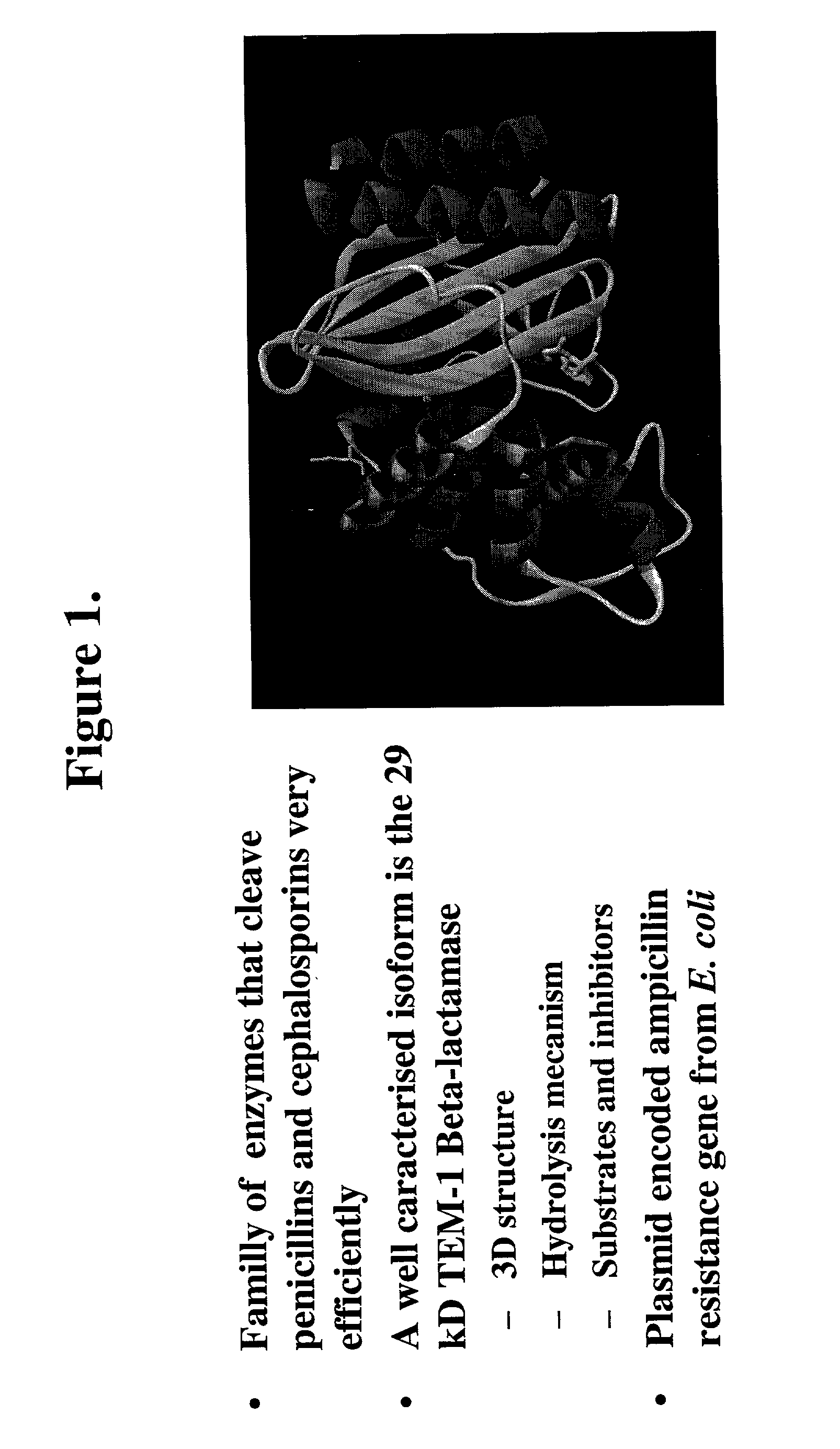
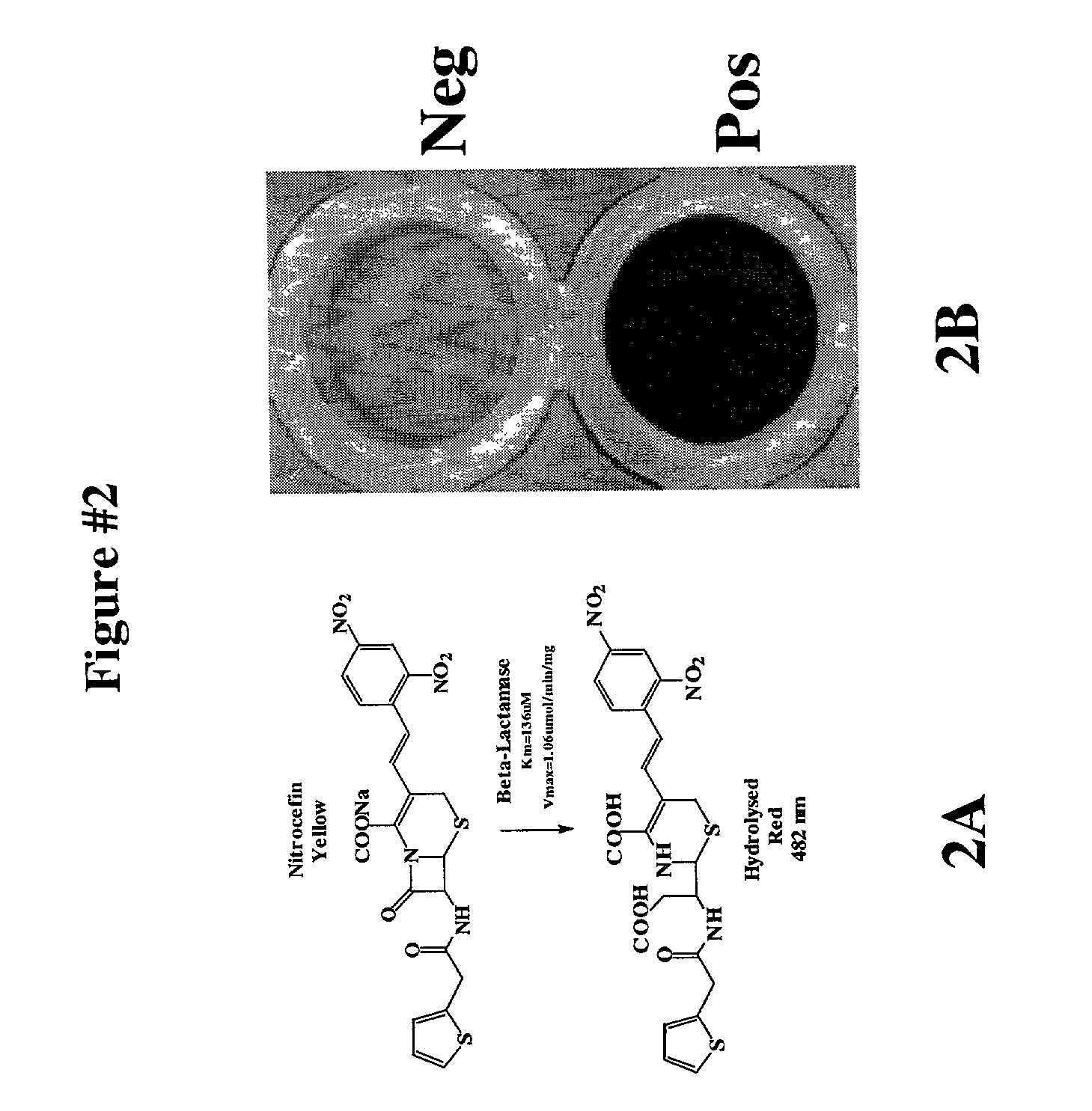
Protein fragment complementation assay (PCA) for the detection of protein-protein, protein-small molecule and protein nucleic acid interactions based on the E. coli TEM-1 beta-Lactamase
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
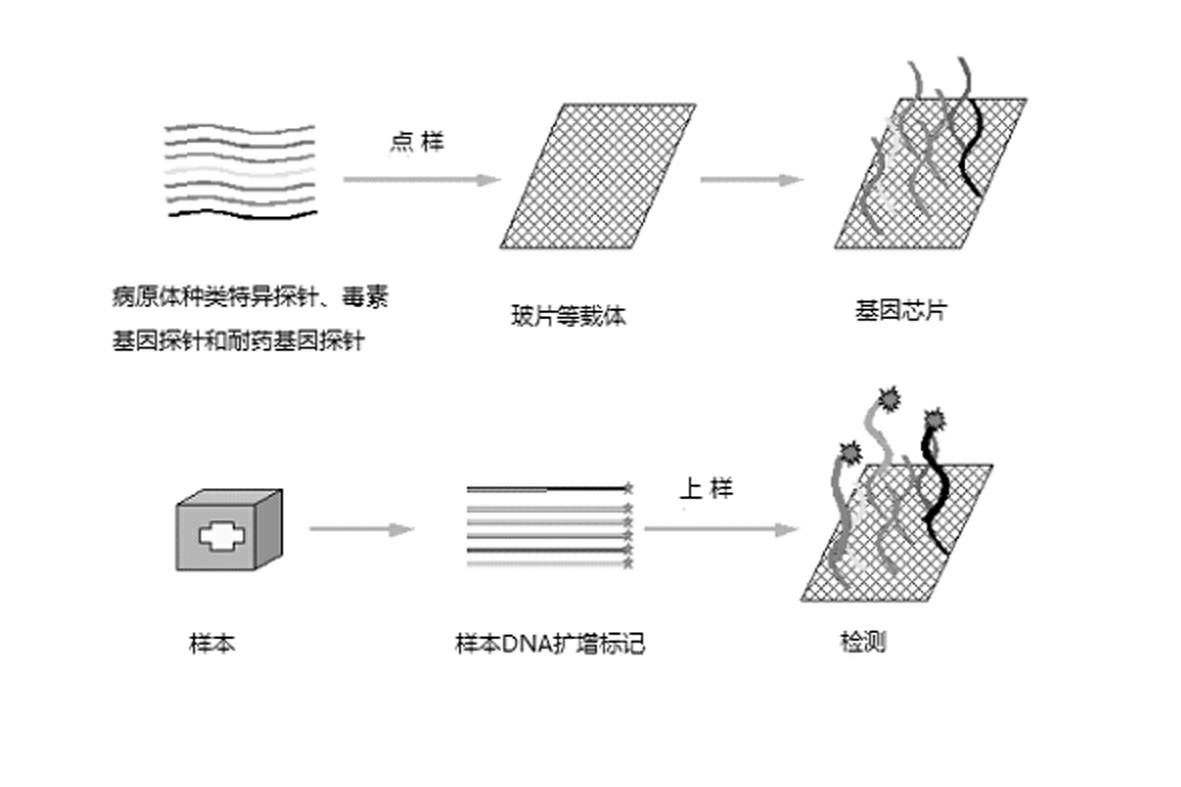
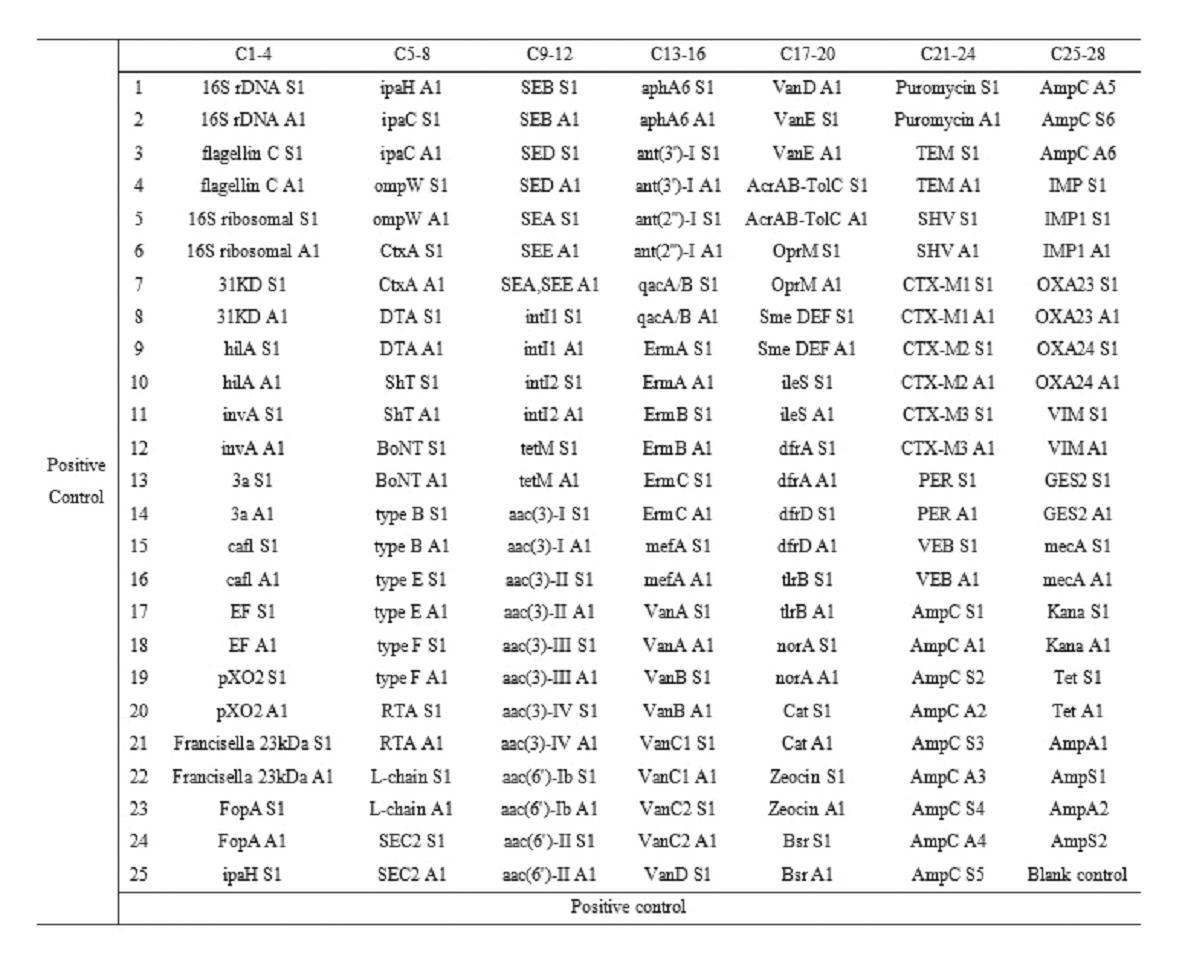
Gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof
InactiveCN102534013AStrong specificityDetermine the typeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisBrucella
The invention relates to a gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof. The gene comprises (1) a combination of 174 oligonucleotide probes of pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes; and (2) a probe array, which is formed by curing the oligonucleotide probes on a carrier material by arm molecules. The gene chip comprises 174 gene probes, namely 32 pathogen variety specific gene probes of the following 8 pathogens of Burkholderia mallei, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Brucella, salmonella, Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, comma bacillus and the like, 25 toxin gene probe of the following 7 toxins of diphtheria toxin, Shiga toxin, staphylococcus enterotoxin, choleratoxin and the like, and 117 drug-resistant gene probes of 17 drug-resistant genes of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, cephalosporinase, carbapenemase, integrase gene, common gene engineering carrier drug-resistant gene and the like. The gene chip can be used to detect multiple pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes.
Owner:李越希
Process for preparing cephalosporins with salified intermediate
InactiveUS20050119244A1Promote crystallizationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry7-ACASilanes
Cephalosporins may be conveniently prepared by a process in which 7-ACA is silylated, acylated, desilylated and then salified to give an intermediate which is eventually cyclized with thiourea.
Owner:ACS DOBFAR SPA
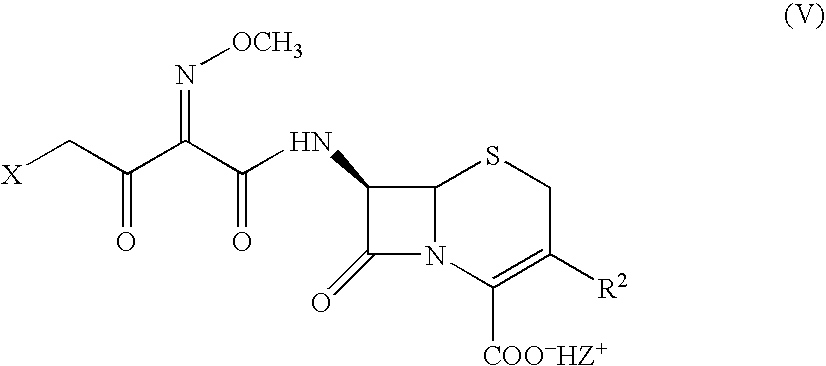
Process for preparing cephalosporins with salified intermediate
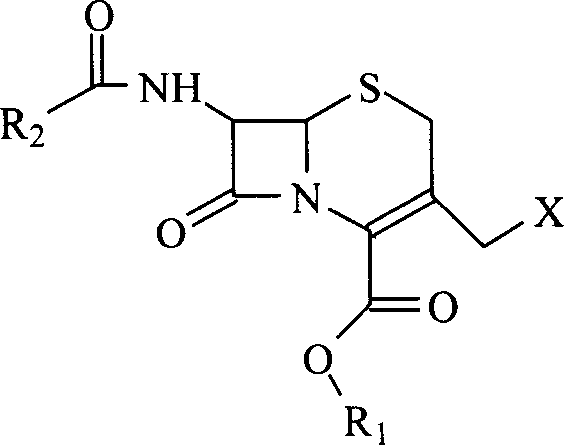
Cephalosporins may be conveniently prepared by a process in which a benzathinium salt of formula (V) wherein: Z is benzathine; and X and R2 are as defined in the specification, is reacted with thiourea. The resulting product may be crystallized as a sodium salt, as an internal salt, or as a pharmaceutically acceptable salt.
Owner:ACS DOBFAR SPA
Processing method for cephalosporin dreg
ActiveCN103146761AEasy to handleDeal with economical and thoroughWaste based fuelSludge processingActivated sludgeResource utilization
The invention discloses a processing method for cephalosporin dreg. The processing method comprises the following process steps of: (A) thermal alkaline hydrolysis and separation treatment: uniformly mixing cephalosporin dreg, water and alkali, carrying out constant-temperature alkaline hydrolysis reaction, and carrying out solid-liquid separation at a certain temperature after the constant-temperature alkaline hydrolysis reaction, so as to obtain sediments to be standby; and (B) anaerobic digestion treatment: inoculating anaerobic activated sludge into an anaerobic fermentation tank, mixing the sediments obtained in the step (A) with excess sludge produced by utilizing wastewater biological treatment, injecting the mixture into the fermentation tank, carrying out constant-temperature stirring, and carrying out biogas residue discharging and feeding during fermentation. According to the processing method for the cephalosporin dreg, drug residues in the cephalosporin dreg can be completely removed, the problem that the anaerobic fermentation of single cephalosporin dreg cannot be effectively sustained is solved, and the reduction and innocent treatment to the cephalosporin dreg are realized; and biogas residues produced during the processing process can be used for preparing raw materials of organic fertilizers, the produced sewage gas can be used as clean fuels, and safe and effective disposition and resource utilization to the cephalosporin dreg are realized.
Owner:河北华药环境保护研究所有限公司
The preparation method of ceftezole sodium
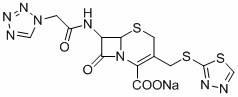
InactiveCN102286001AReduce generationReduce pollutionOrganic chemistryCeftezole SodiumP-Toluenesulfonic acid
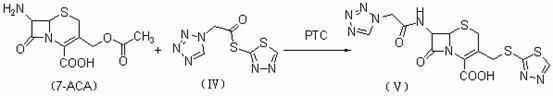
The invention discloses a preparation method of ceftizole sodium, which belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry. The method uses 1H-tetrazolium acetic acid and 2-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole as raw materials, and generates 1H-tetrazolium acetic acid-1 under the catalysis of p-toluenesulfonic acid or dicyclohexylcarbodiimide ,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thioester (active ester), and then the active ester and 7-aminocephalosporanic acid are "one-pot" synthesis of ceftizole acid under the action of quaternary ammonium salt phase transfer catalyst, and then Sodium salt is generated, and further recrystallization and purification can obtain high-purity ceftiazole sodium. The preparation process is simple and feasible, the atom utilization rate is high, the product quality is good, and the industrial production requirements are met.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Novel arabinose-fermenting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20100304454A1Improve stabilityAvoid recombinationFungiHydrolasesPropanoic acidGlucose repression
The present invention relates to eukaryotic cells which have the ability to convert L-arabinose into D-xylulose 5-phosphate. The cells have acquired this ability by transformation with nucleotide sequences coding for an arabinose isomerase, a ribulokinase, and a ribulose-5-P-4-epimerase from a bacterium that belongs to a Clavibacter, Arthrobacter or Gramella genus. The cell preferably is a yeast or a filamentous fungus, more preferably a yeast is capable of anaerobic alcoholic fermentation. The may further comprise one or more genetic modifications that increase the flux of the pentose phosphate pathway, reduce unspecific aldose reductase activity, confer to the cell the ability to directly isomerise xylose into xylulose, increase the specific xylulose kinase activity, increase transport of at least one of xylose and arabinose into the host cell, decrease sensitivity to catabolite repression, increase tolerance to ethanol, osmolarity or organic acids; and / or reduce production of by-products. The cell preferably is a cell that has the ability to produce a fermentation product such as ethanol, lactic acid, 3-hydroxy-propionic acid, acrylic acid, acetic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, amino acids, 1,3-propane-diol, ethylene, glycerol, -lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins. The invention further relates to processes for producing these fermentation products wherein a cell of the invention is used to ferment arabinose into the fermentation products.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
Slow-release preparation containing beta-lactamase inhibitor and cephalosporin and its use
The present invention relates to a slow-released preparation containing beta-lactamase inhibitor and cephalosporin. Said slow-released preparation can be made into antibiotic slow-released injection or slow-released implant preparation. Said injection is formed from slow-released microsphere and solvent, the slow-released microsphere contains slow-released auxiliary material and beta-lactamase inhibitor with antibacterial effective dose and cephalosporin, the solvent is special one containing suspension adjuvant of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium, etc. and its viscosity is 100 cp-3000 cp (20 deg.C-30 deg.C). The slow-released auxiliary material is selected from EVAc, polylactic acid copolymer, sebacic acid copolymer, albumin glue and gelatin, etc. The slow-released implant preparation is prepared by using slow-released microsphere or adopting melting process. Said invention also provides its application method. and can obtain obvious therapeutic effect for curing various infective diseases.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
Protein fragment complementation assay (PCA) for the detection of protein-protein, protein-small molecule and protein nucleic acid interactions based on the E. coli TEM-1 beta-lactamase
The present invention describes an assay method comprising: (A) generating (1) at least a first fragment of a reporter molecule linked to a first interacting domain and at least a second fragment of a reporter molecule linked to a second interacting domain, or (2) nucleic acid molecules that code for (A)(1) and subsequently allowing said nucleic acid molecules to produce their coded products; then, (B) allowing interaction of said domains; and (C) detecting reconstituted reporter molecule activity, where said reporter molecule can react with a penicillin- or a cephalosporin-class substrate.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Preparation of cefixime cephalosporin and fine purification method
InactiveCN101220040AImprove product qualityEasy to operateOrganic chemistryIce waterPurification methods
The invention relates to a preparation and refining method for cefixime, which is conducted as in the following technical steps: the first step, cefixime methyl triethyl amine salt is dissolved in an organic solvent, filtered and washed after reaction with formic acid anhydrous and 98 percent of concentrated sulfuric acid below 0 DEG C, and dried in vacuum at 50 DEG C to obtain cefixime monohydrate monosulphate; the second step, the cefixime monohydrate monosulphate is dissolved in deionized water below 0 DEG C, the pH value is adjusted by ammonia, after being discolored and filtrated by activated carbon, the filtrate is added with ethanol and then 4mol / L of hydrochloride is used for adjusting the pH value, and after filtering, washing by icing water and drying at 30 DEG C in vacuum, cefixime trihydrate acid products are obtained. The method has the advantages of simple operation, little pollution, low manufacturing cost, good quality of prepared cefixime, great convenience for industrialization manufacturing and substantial economic benefits. Simultaneously, as the product of cefixime is presented as white powder with content over 98 percent, guarantees are provided for safe medication in the quality of medicines.
Owner:四川方向海瑞实业有限责任公司
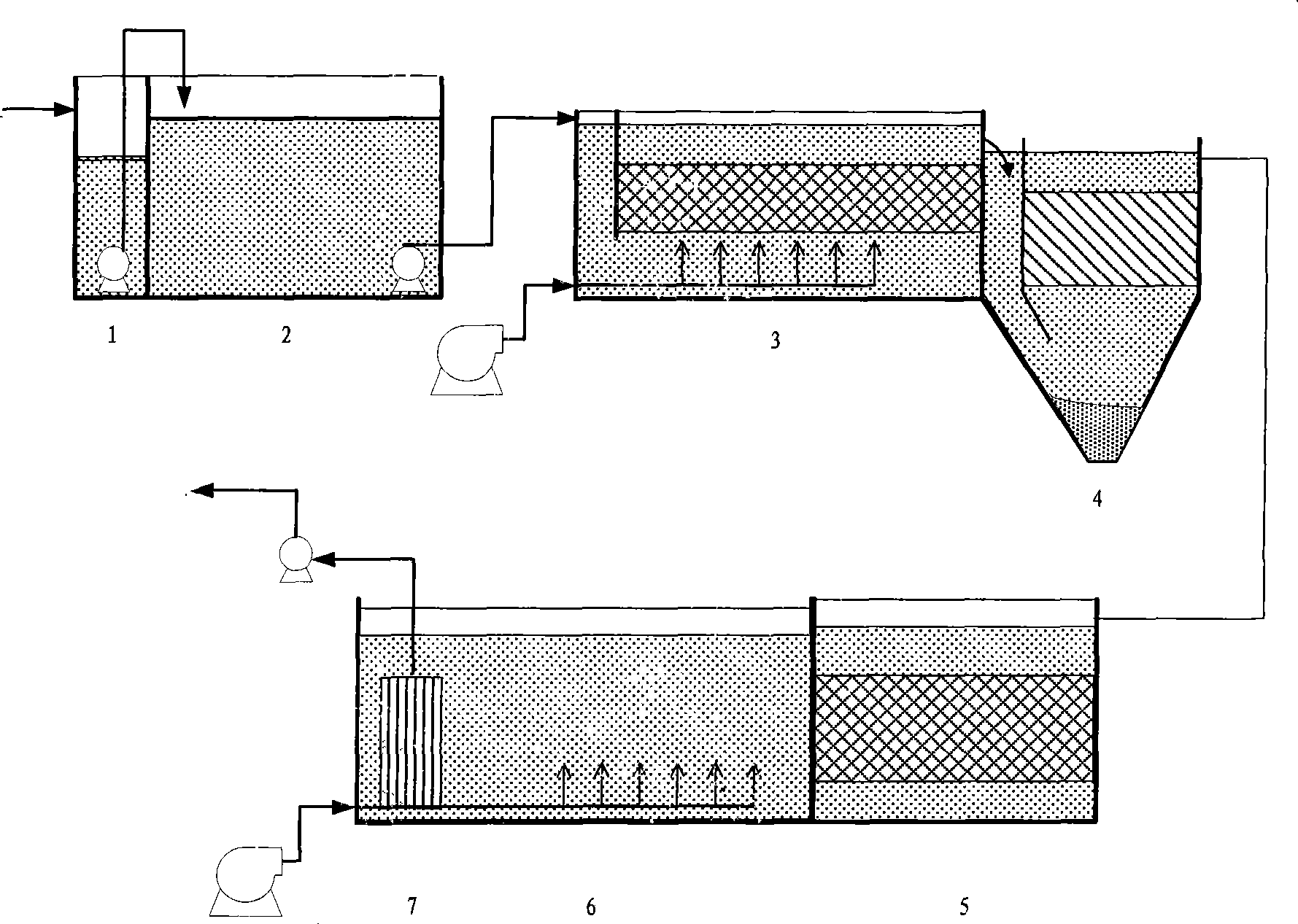
Processing method for wastewater from cephalosporin synthesis pharmaceutical production
InactiveCN101434437AIncrease concentrationWon't be lostTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesUltrafiltrationCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to a treatment method of wastewater produced by cephalo synthetic drug manufacturing, which mainly comprises three parts, namely, aerobe catalytic oxidation, anoxia hydrolytic acidification and a membrane biological reactor; firstly, organic matters having better biodegradability in the wastewater are removed in a biological contact oxidation pond, then biological hydrolytic acidification is carried out in an anoxic pond, and then the wastewater flows into the membrane biological reactor to carry out final aerobic Bioremediation; the wastewater after the treatment passes through an ultrafiltration membrane in the membrane biological reactor and is pumped out by a pump and then discharged to an effluent pipe after reaching standards or recycled to the production technology; the membrane biological reactor consists of an aeration zone and a membrane filtering zone, wherein, the aeration zone carries out aeration by adopting a disc-shaped millipore aeration head, the ultrafiltration membrane is positioned in the membrane filtering zone, the organic matters in the wastewater after being treated with aerobe contact oxidation and anoxia hydrolytic acidification are basically biodegraded, the wastewater is pumped out through the ultrafiltration membrane, and microbes in the reactor are blocked in the reactor. The method has the advantages of simple technique, good effect of treating wastewater, small occupation area, and low treatment cost, and is especially suitable for the wastewater produced by the cephalo synthetic drug manufacturing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUANGYI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH DEV
Production method for biological bacteria ecological fertilizer
InactiveCN102898253AImprove fertilityImprove qualityBio-organic fraction processingProductsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a production method for biological bacteria ecological fertilizer, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing main straw material; (2) preparing humic scorched earth; (3) preparing enhanced adhesive; (4) preparing a complex nutrient; (5) preparing fermentation decomposing agent; (6) preparing complex cephalosporin bacteria cultivated species; (7) preparing straw complex bacteria strain material; and (8) preparing biological bacteria fertilizer. According to the method disclosed by the invention, wastes in industrial and agricultural production and people lives are fully utilized and are prepared into the bacteria fertilizer by the action of the microorganism; the biotechnology is used for accelerating the agricultural productivity; and the production method has the advantages that waste materials are changed into things of value, comprehensive utilization is realized, the nature is greened, the environment is purified, and the virtuous circle of the ecological organic agriculture can be favorably carried out. The prepared biological bacteria ecological fertilizer has all advantages of the organic fertilizer and has a better fertilizer efficiency and a better effect, the soil regeneration capability can be restored, the ecological environment is protected, the stress resistance capability of crops is improved, diseases and pests can be reduced, the soil can be favorably improved, the soil fertility is increased, the production and income of the crops as well as fruits and vegetables can be increased, the quality is improved, and the biological bacteria ecological fertilizer is suitable to use as base fertilizer for the crops.
Owner:刘仕海
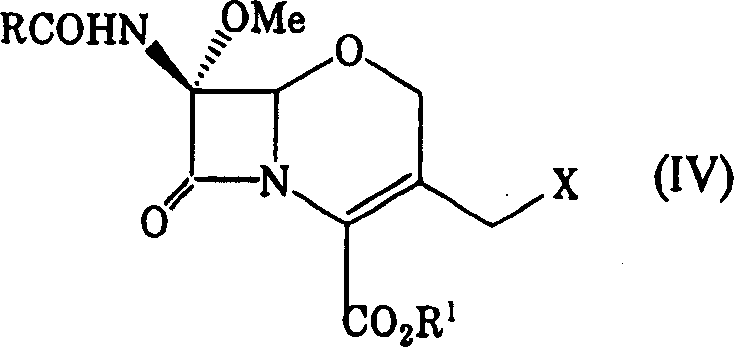
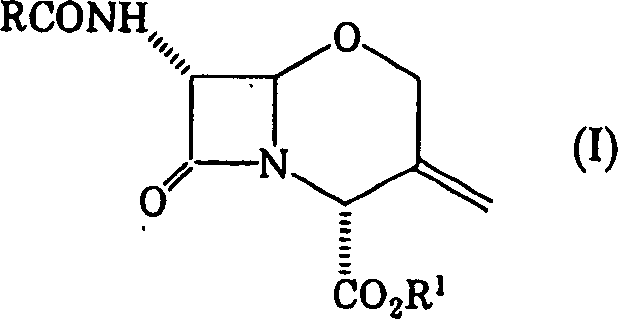
Process for producing 1-oxacephalosporin-7alpha-methoxy-3-chloromethyl derivative
To provide a novel production method of oxacephem compound. [Solution] A method of producing Compound (IV) shown by the formula: (wherein R represents an acyl residue; R 1 represents carboxy protecting group; Me represents methyl and X represents halogen), the method comprising the steps of: (First step) letting Compound (I) shown by Formula: (wherein, R represents an acyl residue; R 1 represents carboxy protecting group) react with a halogenating agent in the presence of a base; (Second step) adding MOMe (M represents alkaline metal; Me represents methyl) in the presence of a halogenating agent after completion of the first step; and (Third step) adding a reducing agent after completion of the second step.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Process for producing Cefepime and cephalosporin analogues
Process for producing Cefepime, Cefpirome and Cefquinome, whereby a cephalosporin containing a quaternary ammonium group is reacted with thiourea to provide the aforesaid cephalosporins.
Owner:ACS DOBFAR SPA
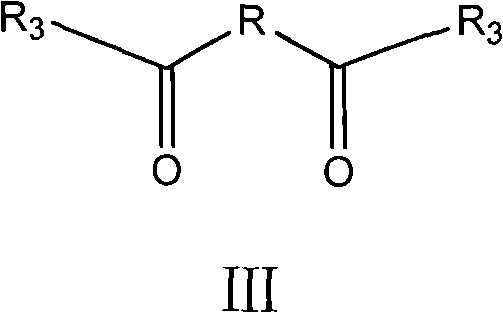
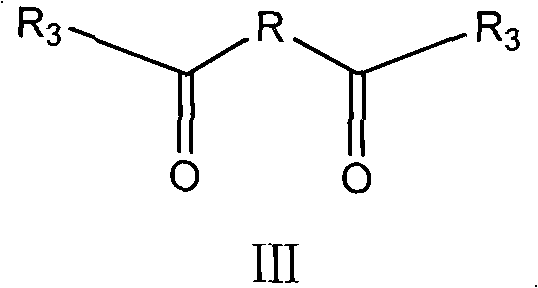
Beta-lactam twin antibiotic compound, preparation method thereof and use thereof
InactiveCN101723961AStrong antibacterial activityAvoid drug resistanceAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryChemical structureAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, in particular to a twin antibiotic compound formed by bonding each two parent nucleuses with the same structure of a beta-lactam antibiotic compound or of a derivative of the beta-lactam antibiotic compound with a dicarboxylic acid by two amido bonds, preparation method thereof and use thereof. The chemical structural general formula of the twin antibiotic compound is represented by a formula III. In the formula, R3 is a parent nucleus structure of a molecule of a penicillin compound or a derivative of the penicillin compound or a molecule of a cephalosporin compound or a derivative of the cephalosporin compound; and R may be alkyl and aryl or heteroaryl or substituted alkyl and substituted aryl or heteroaryl. In-vitro antibacterial experiments show that the beta-lactam twin antibiotic compound of the invention has remarkable antibacterial activity and is a novel antibacterial compound. The beta-lactam twin antibiotic compound of the invention can be used in the preparation of bacteriostats or bacteriacides as well as anti-infection medicaments. According to the general knowledge of pharmacy, the compound of the invention can be made into pharmaceutically acceptable salts or hydrates.
Owner:刘超美
Cephalosporin derivative formulation
InactiveUS20080103121A1Improve stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFreeze-dryingCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to a freeze-dried formulation for cephalosporin derivatives having increased stability and a method for preparing such a formulation using certain excipients for stabilizing the formulation.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
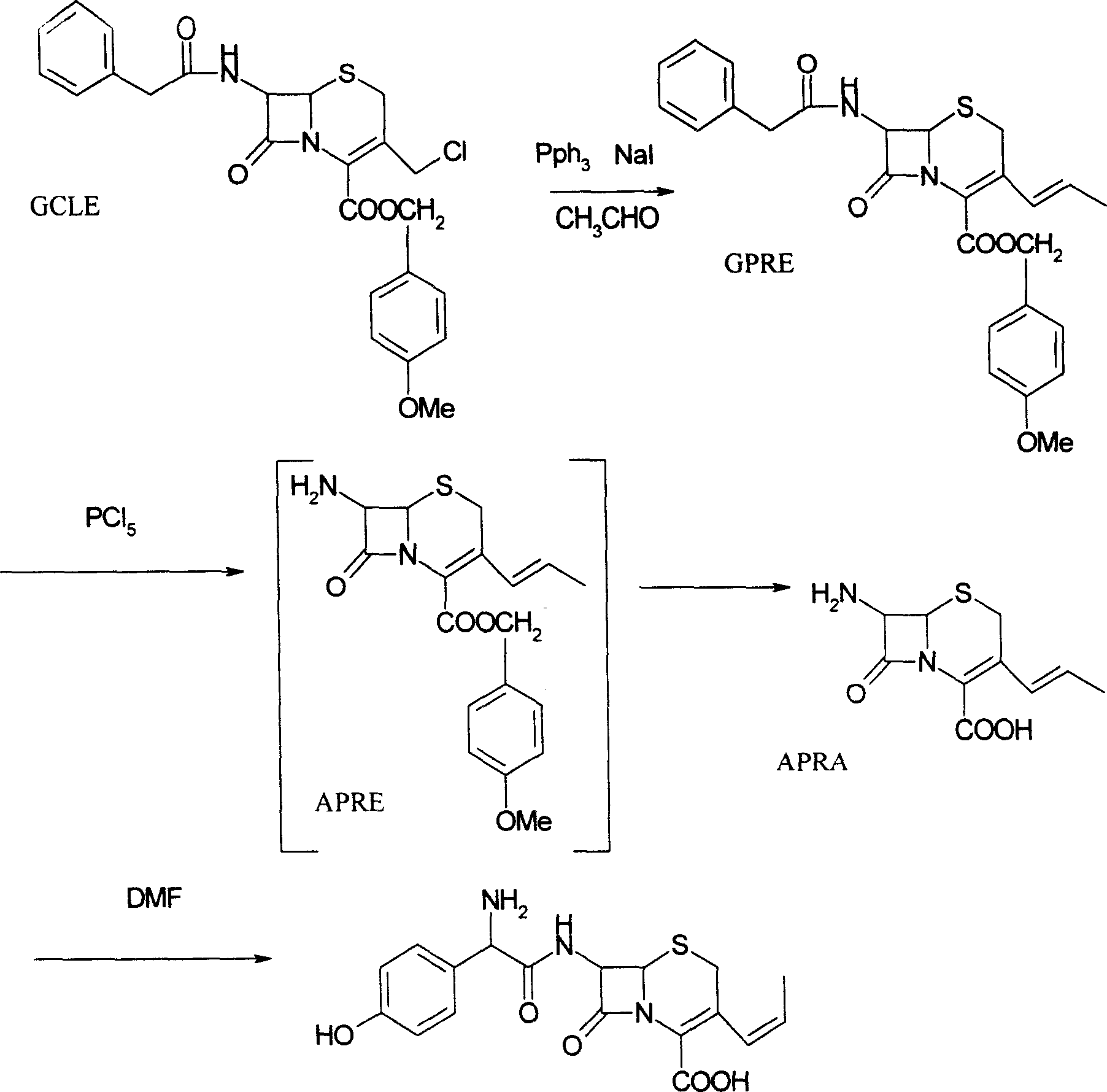
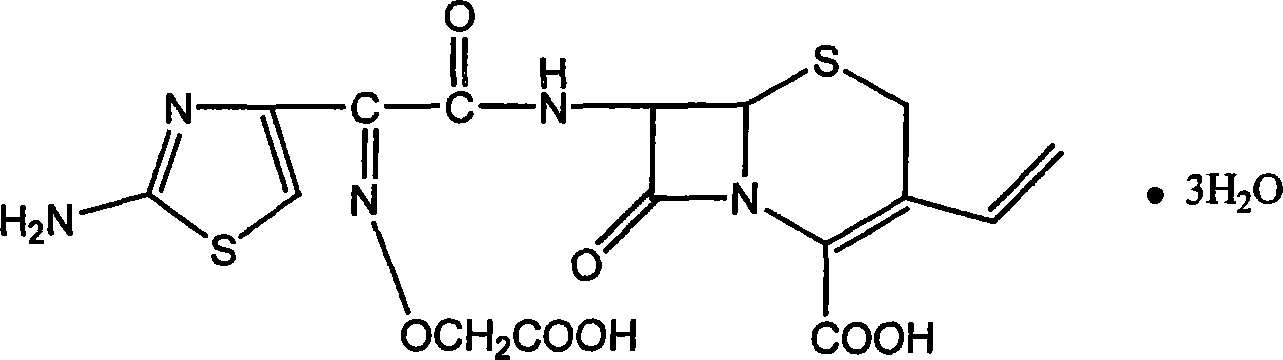
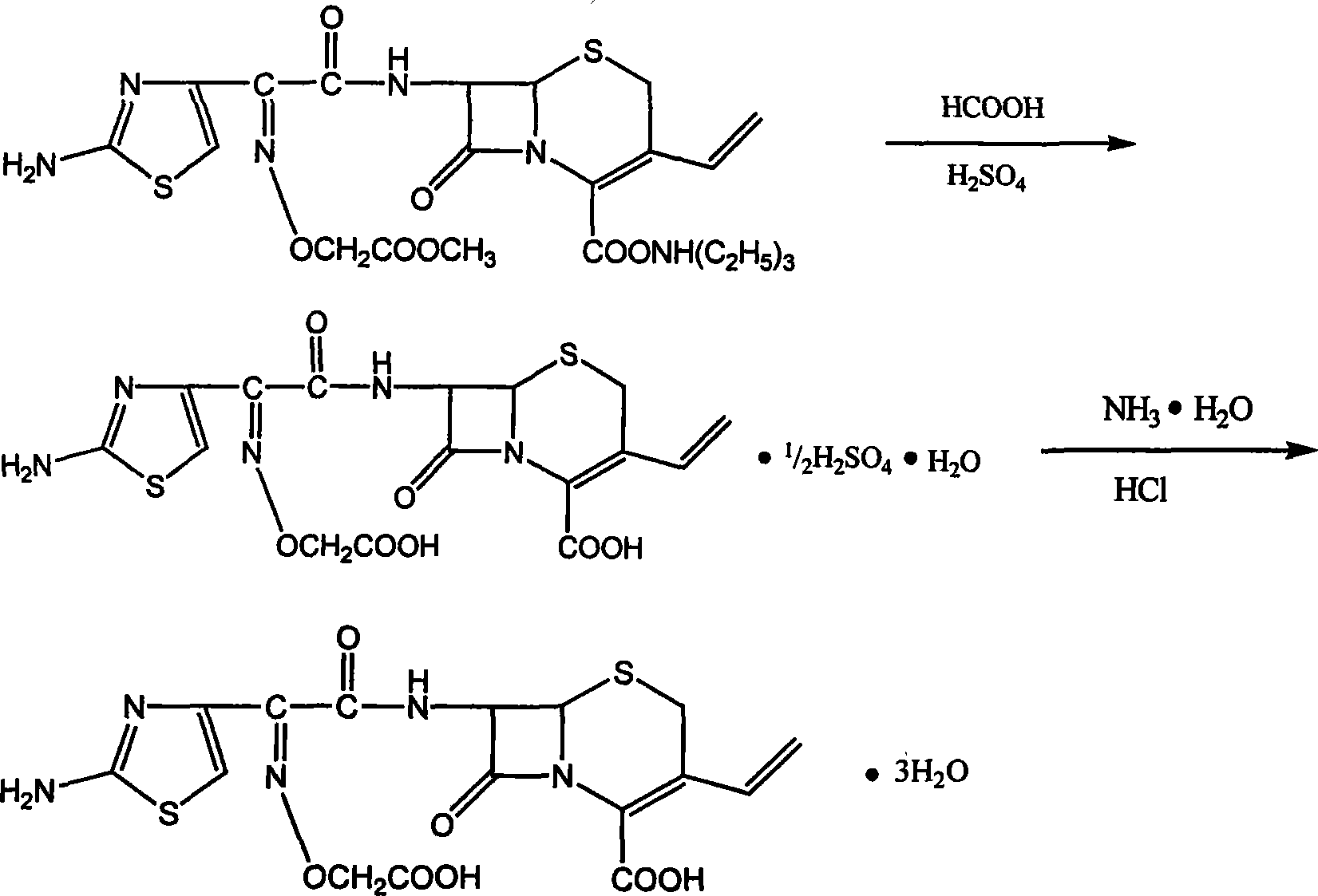
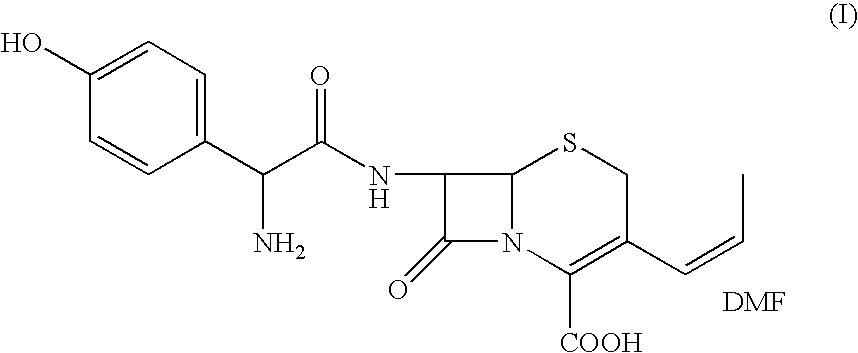
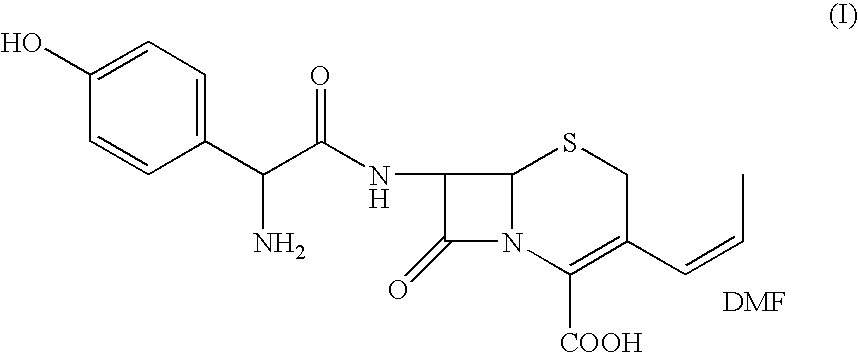
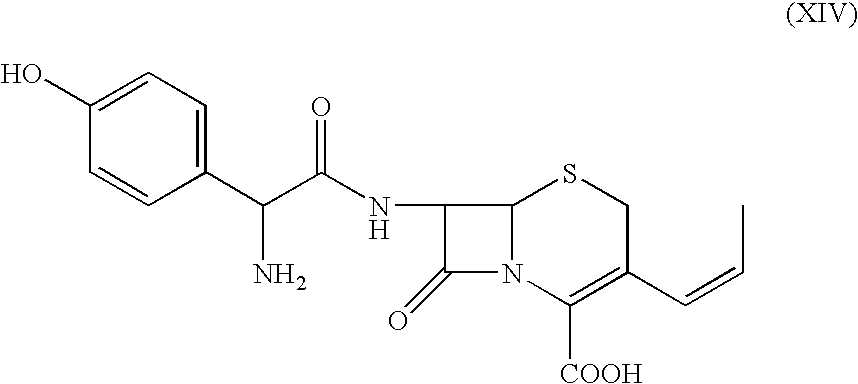
Process for the preparation of 3-propenyl cephalosporin DMF solvate
InactiveUS6903211B2High purityHigh yieldAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryEnzymatic hydrolysisBis(trimethylsilyl)amine
The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of cefprozil DMF solvate of formula (I), which is useful for the preparation of cefprozil, comprising:i) reacting a compound of formula (VIII) with acetaldehyde to produce a compound of formula (IX),ii) deesterifying the carboxy protecting group of the compound of formula (IX) using an acid to yield a compound of formula (X),iii) converting the compound of formula (X) to a compound of formula (XI),iv) neutralizing the compound of formula (XI) followed by enzymatic hydrolysis to produce an APCA of formula (V),v) silylating the APCA using a mixture of trimethylsilylchloride and hexamethyldisilazane to produce silylated APCA of formula (XII), andvi) condensing the silylated APCA with a mixed anhydride to produce the DMF solvate compound of formula (I).
Owner:ORCHID CHEM & PHARM LTD
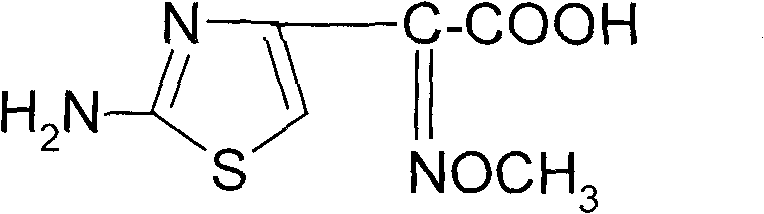
Synthetic method of 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid
ActiveCN101805311AIncrease reaction rateShorten the production cycleOrganic chemistryEthyl acetateHydrolysis
The invention relates to a synthetic method of 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid, which belongs to the synthetic methods of heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole ring. The synthetic method is characterized by comprising the following operation steps: 1) homogeneous oximation reaction: preparing 2-hydroxamic ethyl acetoacetate; 2) methylation reaction: preparing 2-methoxyimino ethyl acetoacetate; 3) triphosgene chlorination reaction: preparing 4-chloro-2-methoxyimino ethyl acetoacetate; 4) cyclization reaction: preparing 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid ethyl ester; 5) hydrolysis: preparing a crude product of the 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid; and 6) refining: preparing a product of the 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid. The invention provides an oximating agent system which is applicable to homogeneous nitrosification reaction. The invention provides a triphosgene chlorinating agent which has the advantages of small toxicity, safe and convenient storage, transportation and use, easy control of process operation and high yield. The yield of the 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid ethyl ester is not less than 95.4%; the yield of the crude product of the 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid is not less than 94.4%; and the yield of the finished product of the 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid is not less than 90.5%. The purity of the finished product of the 2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-(Z)-methoxyimino acetic acid is not less than 99.06%, and the melting point is 182.1 DEG C-183.9 DEG C. The synthetic method is used for synthesizing raw materials of the third generation of cephalosporins.
Owner:YIYUAN XINQUAN CHEM
Resourceful treatment method for antibiotics mushroom dregs
InactiveCN105642652AAdapt to resource processingReasonable process combinationSolid waste disposalBiotechnologyPenicillin
The invention provides a resourceful treatment method for antibiotics mushroom dregs, wherein mushroom dregs produced during production of antibiotics such as penicillin, erythrocin and cephalosporin are treated by the steps of intensified hydrolysis, mushroom dregs blending, two-phase anaerobic digestion, deep dehydration, resource utilization and the like. Aiming at the practical problems of a large quantity of antibiotics mushroom dregs and great treatment difficulty, the antibiotics mushroom dregs are subjected to harmless and resourceful treatment, thus providing basis for difficulties urgent to be solved of pharmaceutical enterprises.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Methoxy cephalosporin intermediate
The invention relates to a synthesis method of an intermediate of methoxyl cephalosporin. C3 site methyl halide of a cephems compound with C4,7 site being protected, instead of the ordinary 7-ACA, is used as a material, functionalized at C3 site, and then methoxylated at C7 site, finally de-protected, and the intermediate of methoxyl cephalosporin is prepared. The compound can be conveniently used in the synthesis of various methoxyl cephalosporin medicines. The invention has apparent advantages of clear synthesis route, less steps, less and inexpensive reagents, comparatively single solvent, convenience for recovery and recycling, low material cost and operation expenses.
Owner:北京金源化学集团有限公司
Preparation method of stable cefuroxime sodium
InactiveCN102838622ALess impuritiesImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryCefuroxime SodiumCrystallization
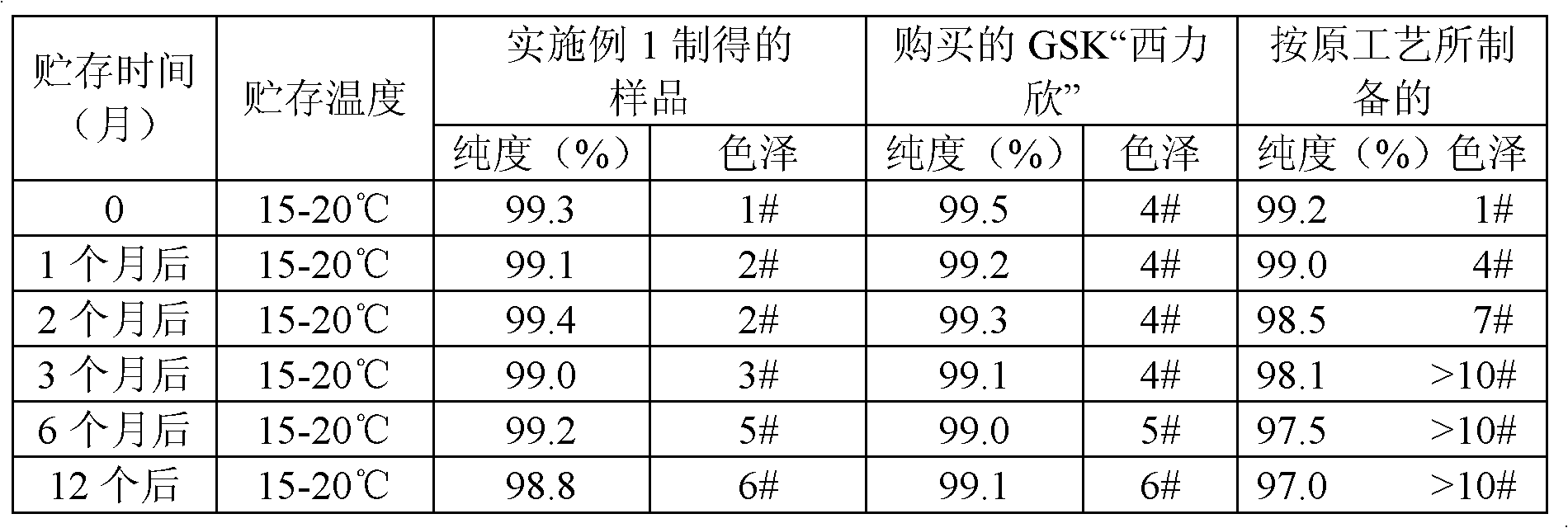
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, relates to a preparation method of cephalosporin, and more specifically relates to a preparation method of a stable cefuroxime sodium. According to the invention, a process control technique and a multiscale simulation technology are utilized to conduct on-line crystallization control of cefuroxime sodium, so as to obtain a cefuroxime sodium product with stable quality and crystal form, and moderate particles. The quality and especially the stability of the product are improved greatly, and product quality achieves a same level as that of ''Xilixin'' from an original researching factory.
Owner:SHANXI WEIQIDA PHARMA IND
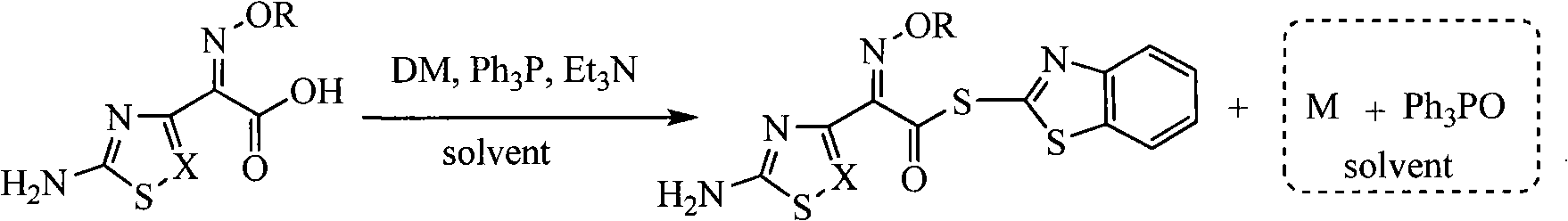
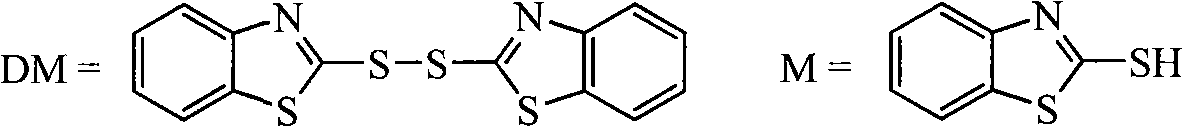
Process for recovering triphenyl phosphine oxide and 2-mercaptobenzothiazole from production waste liquid of cephalothin active ester
The invention discloses a method for recycling triphenyl phosphine oxide and 2-mercaptobenzothiazole from the production waste liquid of cephalosporin active ester, which includes the following steps: 1 to 10 percent sodium hydroxide solution is added drop by drop into the production waste liquid of the cephalosporin active ester under 0 to 80 DEG C; the pH value of the system is adjusted to be 10 to 12, and then the waste liquid is mixed fully for 0.5 to 6 hours, standing still and layering; an organic layer is decompressed to recycle an organic solvent; the solid waste slag is recrystallized directly to obtain the triphenyl phosphine oxide; the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole is extracted and obtained from water layer by a using acid neutralization method. The recycling method of the invention has the advantages of the simple operation, the high recycling rate, the good product purity, the good atom economy, etc., which effectively solves the problems existing in the prior art, such as the complicated operation, the high energy consumption, the low yield rate, the serious environment pollution, etc., thus having a wide implementary value and potential social economic benefits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com