Patents
Literature
73 results about "Yersinia pestis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yersinia pestis (formerly Pasteurella pestis) is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, rod-shaped, coccobacillus bacterium, with no spores. It is a facultative anaerobic organism that can infect humans via the Oriental rat flea. It causes the disease plague, which takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic plagues. All three forms were responsible for a number of high-mortality epidemics throughout human history, including the sixth century's Plague of Justinian; the Black Death, which accounted for the death of at least one-third of the European population between 1347 and 1353; the Great Plague of London of 1665, which was ended in 1666 by the Great Fire of London; and the Third Pandemic, sometimes referred to as the Modern Plague, which began in the late 19th century in China and spread by rats on steamboats, claiming close to 10,000,000 lives. These plagues likely originated in China and were transmitted west via trade routes. Recent research in 2018 indicated that the pathogen may have been the cause of what was described as the Neolithic Decline, in which European populations declined significantly. This would push the date to much earlier and might be indicative of an origin in Europe rather than Eurasia.
Transformed Saccharomyces cerevisiae Engineered for Xylose Utilization
InactiveUS20100112658A1High ethanol productionEfficient growth processFungiBacteriaHeterologousNucleotide
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae produced by transformation with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding for xylulokinase (XKS) from Yersinia pestis and xylose isomerase (XI) are capable of xylose utilization. The transformants express these heterologous polynucleotides at a sufficient functional level to grow aerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. Further transformation of the recombinant yeasts to overexpress one or more of the S cerevisiae genes PIP2, IMG2, MAK5, VPS9, COX10, ALE1, CDC7, and MMS4, permits the yeast to grow anaerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. When grown under anaerobic conditions on a culture medium comprising both glucose and xylose, the transformed yeast exhibit increased ethanol productivity, with the yeast growing on the xylose to increase their biomass and fermenting the glucose to ethanol.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
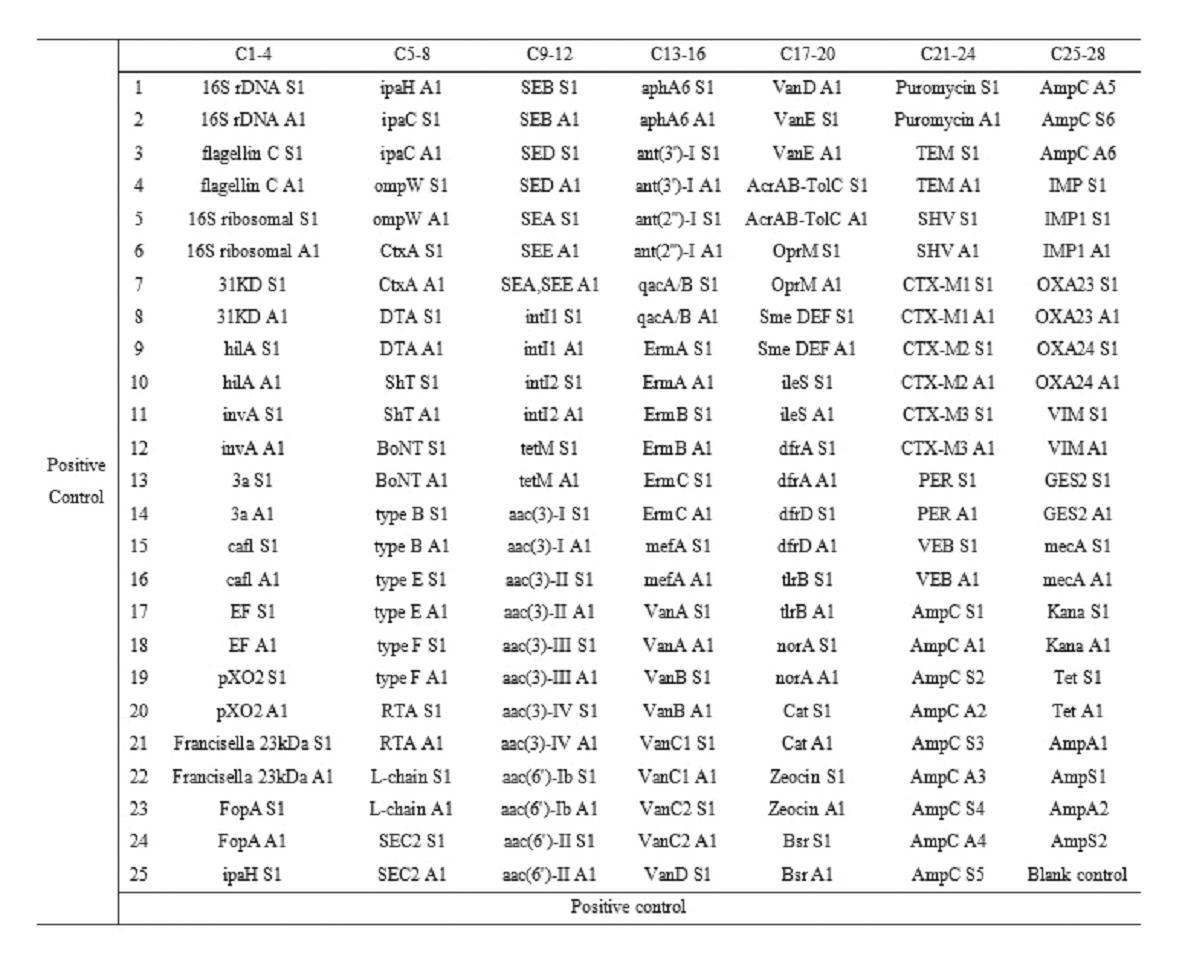
Gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof
InactiveCN102534013AStrong specificityDetermine the typeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisBrucella
The invention relates to a gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof. The gene comprises (1) a combination of 174 oligonucleotide probes of pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes; and (2) a probe array, which is formed by curing the oligonucleotide probes on a carrier material by arm molecules. The gene chip comprises 174 gene probes, namely 32 pathogen variety specific gene probes of the following 8 pathogens of Burkholderia mallei, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Brucella, salmonella, Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, comma bacillus and the like, 25 toxin gene probe of the following 7 toxins of diphtheria toxin, Shiga toxin, staphylococcus enterotoxin, choleratoxin and the like, and 117 drug-resistant gene probes of 17 drug-resistant genes of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, cephalosporinase, carbapenemase, integrase gene, common gene engineering carrier drug-resistant gene and the like. The gene chip can be used to detect multiple pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes.
Owner:李越希
Phage-Mediated Bioluminescent Detection of Yersinia Pestis
InactiveUS20110076672A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismBiotechnology
The present disclosure relates to compositions, methods, systems and kits for the detection of microorganisms of the Yersinia species including Yersinia pestis. The disclosure relates to recombinant phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, the phage comprising a detectable reporter. Detection systems of the disclosure may comprise a phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, and may comprise a reporter nucleic acid expressible upon infection of a Yersinia microorganism by the phage. The system may be operable to detect the expression of the reporter. A detectable reporter may comprise any gene having bioluminescent, colorimetric and / or visual detectability. For example, a detectable reporter may comprise one or more luxAB genes detectable by emission, enhancement and / or change in spectrum of bioluminescent light. Live and infectious Yersinia microbes may be detected by the compositions, methods, systems and kits described herein.
Owner:GUILD ASSOCS
Method for detecting Yersinia pestis by utilizing a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)
InactiveCN101665832AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a novel method for detecting Yersinia pestis, the loop-mediated isothermal amplification LAMP is adopted. The invention substantially improves a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method to enhance the detecting specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Plating media for the identification of Yersinia pestis
Owner:R&F PROD
Substrate peptide sequences for plague plasminogen activator and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090069248A1Antibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementEgg proteinProteinase activity
The present invention is directed to peptide sequences that were identified from combinatorial libraries and could serve as substrates of plague plasminogen activator (Pla). Another aspect of the present invention is drawn to peptides derived from the substrates for Pla as a result of chemical modifications leading to specific inactivation of the proteolytic activity of Pla. Additionally, the present invention is directed to the use of the substrates identified herein in the detection of bacteria expressing omptin family of proteases which includes Y. pestis. Furthermore, the present invention is also directed to the use of the inhibitors identified herein in the prevention and treatment of infection caused by these bacteria.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Live bacterial vaccine
The present invention relates, e.g., to a Lactobacillus bacterium, which (1) expresses a recombinant polypeptide containing a lipoprotein signal sequence from the OspA protein of Borrelia burgdorferi, or an active variant of the leader sequence, operably linked to one or more heterologous polypeptide(s) of interest and / or (2) which comprises an expressible polynucleotide encoding a recombinant polypeptide, wherein the polynucleotide encodes a lipoprotein signal from the OspA protein of Borrelia burgdorferi, or an active variant thereof, which is operably linked to one or more heterologous polypeptide(s) of interest. In one embodiment, the heterologous polypeptide is from Yersinia pestis, the etiologic agent of plague. In another embodiment, the heterologous polypeptide is from Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiologic agent of Lyme disease. Also described are immunogenic compositions, such as live bacterial vaccines, comprising the bacterium; methods for eliciting an immune response against the polypeptide using the bacterium; and kits comprising the bacterium.
Owner:LACTRYS OCTROOI +1
Multivalent nanoemulsion vaccines
ActiveUS20120107349A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVaccinationPaenibacillus lactis
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the stimulation of immune responses. Specifically, the present invention provides methods of inducing an immune response against one or a plurality of pathogens (e.g., vaccinia virus, H5N1 influenza virus, Bacillus anthracis, C. botulinum, Y. pestis, Hepatits B, and / or HIV, etc.) in a subject (e.g., a human subject) and compositions useful in such methods (e.g., immunogenic composition comprising nanoemulsion and one or a plurality of pathogens (e.g., inactivated by the nanoemulsion) and / or pathogen products and / or pathogen components). Compositions and methods of the present invention find use in, among other things, clinical (e.g. therapeutic and preventative medicine (e.g., vaccination)) and research applications
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method and kit for detecting pathogens of infectious diseases
InactiveCN101603096AThe detection process is fastImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSARS coronavirusAvian influenza virus
The invention discloses a method for detecting pathogens of infectious diseases, which possibly exist in a biological sample. The pathogens of the infectious diseases comprise avian influenza virus H5 subtype, avian influenza virus H7 subtype, SARS coronavirus, hanta virus, plague yersinia pestis and bacillus anthracis. The method comprises amplifying a nucleic acid fragment of a biological sample and detection by a probe. The invention also provides a primer for amplification and a probe for detection. The invention also provides a kit including the primer. The method has the advantages of high flexibility, strong specificity, easy operation, wide sample range, the detection for the pathogens of various infectious diseases at the same time and the suitability for early diagnosis of respiratory infectious diseases.
Owner:HAI KANG LIFE
Methods and compositions involving LcrV proteins
ActiveUS7875280B2Reduce in quantityReduce riskBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaYersinia pestisYersinia frederiksenii
The present invention concerns methods and compositions involving modified LcrV proteins from Yersinia bacteria. These methods and compositions can be employed to invoke an immune response in a subject against the bacteria, while not suppressing the immune system as much as the native LcrV protein. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to vaccines, as well as methods to protect a subject against Yersinia pestis and plague. Moreover, the present invention concerns methods and compositions for suppressing a subject's immune system using non-native LcrV polypeptides.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
Multiplex PCR-based synchronous and rapid method for detecting 13 pathogenic microorganisms in water
InactiveCN102703588AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisEnterobacterales
The invention relates to a multiplex PCR-based synchronous and rapid method for detecting 13 pathogenic microorganisms in water, which comprises the steps of using multiplex PCR to simultaneously amplify gene-specific fragments of the 13 pathogenic microorganisms including escherichia coli, enterohaemorragic escherichia coli o157:h7, legionella pneumophila, salmonella enteritidis, shigella dysenteriae, staphyloccocus aureus, listeria monoeytogenes, helicobacter pylori, mycobacterium tuberculosis, klebsiella pneumonia, vibrio cholera, bacillus anthracis and yersinia pestis, and detecting PCR amplified products through agarose gel electrophoresis, thereby achieving synchronous and rapid detection for the 13 pathogenic microorganisms.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Genetic liquid phase chip for joint detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101560557AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisPathogenic bacteria
The invention discloses a genetic liquid phase chip for rapid detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria of bacillus anthracis, yersinia pestis, brucella bacteria, francisella tularensis and burkholderia pseudomallei. The liquid phase chip for detecting the five drastic pathogenic bacteria has the advantages of large flux, less required sample capacity, strong specificity, high sensitivity, accuracy, high efficiency, and the like.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Kit for simultaneously detecting four pathogenic bacteria and non-diagnostic detection method thereof
ActiveCN105950759AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTime efficientYersinia pestis
The invention discloses a kit for simultaneously detecting four pathogenic bacteria Yersinia pestis, Frencisella tularensis, Burkholderia pseudomallei and Brucella by using fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and a non-diagnostic detection method. The kit comprises specific primers and probes corresponding to the four pathogenic bacteria. The kit disclosed by the invention is convenient to use, and has the advantages of low reagent consumption, low cost, high detection specificity and high sensitivity. The detection method can detect four pathogenic bacteria for one sample, thereby greatly simplifying the operational process, reducing the repetitive operation steps, saving the time, reducing the labor consumed by repetitive operation, effectively saving the cost and implementing quick screening.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Inhibition of yersinia pestis
The disclosure relates to the targeting of Y. pestis mediated by the binding activity of tail fibers from naturally occurring R-type pyocins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The targeting may be mediated by a macromolecular complex such as the pyocin itself, a high molecular weight (hmw) bacteriocin modified to have the tail fiber's binding activity, or a bacteriophage modified to have the tail fiber's binding activity. Compositions comprising such complexes are described. Also disclosed are methods for the use of a complex, such as to inhibit the growth of a Yersinia species like Y. pestis, by compromising the integrity of its cytoplasmic membrane are also described. Additional methods include use of the binding activity to identify Y. pestis.
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Compositions and methods for inducing an immune response against yersinia pestis
The invention provides a gene transfer vector for inducing an immune response against Yersinia pestis in a mammal. The gene transfer vector comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding an immunogenic portion of one or more proteins of Yersinia pestis and / or a nucleic acid sequence encoding a monoclonal antibody directed against Yersinia pestis. The invention further provides a method of producing an immune response against Yersinia pestis in a mammal comprising administration of the gene transfer vector to the mammal. The invention also provides a monoclonal antibody directed against the Virulence (V) antigen of Y. pestis, as well as a hybridoma cell line producing same and a nucleic acid sequence encoding same.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Primer group for detecting Yersinia pestis, rapid diagnosis kit and detection method
ActiveCN101824468AStrong specificityReduce background effects in amplification reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlYersinia pestis
The invention discloses a primer group for detecting Yersinia pestis, a rapid diagnosis kit and a detection method, wherein the primer group consists of the following four primers: an external primer F3, an external primer B3, an inner primer FIP and an inner primer BIP. The kit consists of the primer group, Bst DNA polymerase, sample pretreatment solution, stabilizing solution, reaction solution, colored solution and positive control solution, and the seven kinds of solutions are placed in a vessel. Both the primer group and the kit can detect the Yersinia pestis with high efficiency and high specificity, as well as are based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology, apply six segments, four primers and one constant temperature, complete an amplification reaction within 1 hour, and are low in detection cost, short in detection time, high in yield and specificity, obvious in negative and positive result color developing difference, high in verification rate, obvious and reliable in verification.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAFENG BIOTECH
Pesticin and phage lysozyme fusion protein and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a pesticin and phage lysozyme fusion protein and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The fusion protein sequentially contains a pesticin protein Pst of yersinia pestis and a lysozyme e of a phage Bp7 from an amino terminal to a carboxyl terminal; the fusion protein gene is composed of 990 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence of the fusion protein is encoded, so that the obtained fusion protein has a relatively good effect in preventing or / and treating staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method and kit for detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN102796810AImprove throughputAddresses issues with reduced sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesHighly pathogenic
The invention provides a method and kit for detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria, particularly a method for simultaneously detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria, which comprises the following steps: in a polymerase reaction system, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) on high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria by using a specific primer set, thereby obtaining an amplification product; and detecting with a specific probe or probe microsphere. The invention also provides a corresponding kit. The invention can sensitively and conveniently detect and identify multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria, including Bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis, Clostridium botulinum, Brucella, Streptococcus suis, Vibrio cholerae, Francisella tularensis, Pseudomonas mallei (or Pseudomonas pseudomallei), Coxiella burnetii and Legionella pneumophila.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELLGEN LIFE SCI CO LTD
Immunity-chropadography test paper for detecting Yersinia pestis infection and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an immunity-chropadography test paper for detecting Yersinia pestis infection, comprising a layer of cellulose nitrate film, wherein a detection line and a quality control lineare arranged on the cellulose nitrate film, and the detection is Yersinia pestis polysaccharide antigen and the quality control line is antibody capable of being combined with staphylococcus aureus protein A and the cellulose nitrate film is arranged on a water absorption pad and a gold-label pad is arranged on the cellulose nitrate film and and a sample pad is arranged on the gold-label pad The invention also provides a preparation method of the immunity-chropadography test paper for detecting Yersinia pestis infection. Compared with the prior method, the immunity-chropadography test paper for detecting Yersinia pestis infection and preparation method thereof are simpler, more quick and more suitable for clinical and special condition with strong specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAITAI JINXIN BIOMOLECULAR DETECTION TECH
Gene chip-based method for synchronously and rapidly detecting thirteen pathogenic microorganisms in water body
InactiveCN102703589AOptimizing gene chip detection methodStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisListeria monocytogenes
The invention discloses a gene chip-based method for synchronously and rapidly detecting thirteen pathogenic microorganisms in a water body. The method is characterized in that specific gene segments of the pathogenic microorganisms are amplified simultaneously by adopting multiple polymerase chain reactions (PCR), and then, a detection result is obtained through gene chip hybridization and chip scanning image analysis. The detected thirteen pathogenic microorganisms comprise escherichia coli, Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, legionella pneumophila, salmonella enteritidis, Shigella, staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Helicobacter Pylori, mycobacterium tuberculosis, Klebsiella pneumonia, vibrio cholera, Bacillus anthracis and Yersinia pestis.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Human monoclonal antibodies protective against bubonic plague
In this application are described fully human monoclonal antibodies which specifically recognize F1 or V antigen of Y. pestis and epitopes recognized by these monoclonal antibodies. Also provided are mixtures of antibodies of the present invention, as well as methods of using individual antibodies or mixtures thereof for the detection, prevention, and / or therapeutical treatment of plague infections in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Extraction, purification process for yersinia pestis natural F1 antigen
InactiveCN101220086AHigh purityImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenMolecular sieve
The invention discloses an extraction and purification method for the natural F1 antigen of the Yersinia pestis, which adopts a proposal combining glass bead treatment, ammonium sulfate precipitation and molecular sieve filtration to successfully extract and purify natural F1 antigen with high purity from the Yersinia pestis cultures. The immunological detection and the animal protection experiment prove that the natural F1 antigen obtained by the method has higher protective immune function and detection sensitivity. If detecting the F1 monoclonal antibody of the same mouse ascites sample with the natural F1 antigen in the invention and the reformed F1 antigen (rF1) obtained from expression having the same concentration, the result indicates that the antibody titer detected by the natural F1 antigen is obviously higher than the detection result by the rF1. The extraction and purification method for the natural F1 antigen of the Yersinia pestis can play an important role in the development of Sub-unit Vaccine of plague and the detection and diagnosis of plague (e.g. immunological detection, etc.), which has a broad application prospect.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid sequence, kit and method used for isothermal amplification detection of yersinia pestis and application
PendingCN112391483AStrong specificityGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismYersinia pestis
The invention relates to the field of pathogen microorganism detection, in particular to a nucleic acid sequence, kit and method used for isothermal amplification detection of yersinia pestis and application. The nucleic acid sequence of the invention includes strand displacement primer sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, probes as shown in SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No.4, and a cross amplification primer sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.5. The kit and the detection method of the invention have the technical advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, simple steps and high repeatability.
Owner:内蒙古自治区综合疾病预防控制中心 +1
Protein suspension chip method capable of quantitatively determining yersinia pestis
InactiveCN101493468ACoating volume improvementReduce the amount of coatingBiological testingYersinia pestisBiology
The invention aims at providing a protein suspension chip which can quantitatively detect the bacteria and a detection method thereof, particulary relates to a method for detecting the protein suspension chip which is suitable for quantitative detection and analysis of Yersinia pestis (Y.pestis). The method has high sensitivity, strong specificity, good detection capacity and wide dynamic range, and establishes a new detection mode platform.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Novel isothermal loop-mediated yersinia pestis nucleic acid mark detection reagent
InactiveCN103698516AAvoid pollutionHave immunityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAntigenYersinia pestis
The invention relates to a novel isothermal loop-mediated yersinia pestis nucleic acid mark detection reagent. A front inner primer in a primer group for isothermal loop-mediated amplification is used for marking an antigen, and meanwhile, a rear inner primer in the primer group is used for marking another antigen, so that a yersinia pestis specific target gene can be simultaneously amplified and marked. A matched colloidal gold strip can be used for rapidly detecting an amplification product of the target gene after marking, thereby detecting yersinia pestis. The detection reagent can be simply and rapidly operated, and is high in specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:天津国际旅行卫生保健中心
Yersinia pestis detection kit based on real-time fluorescence RPA technology and application thereof
ActiveCN112899383AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a yersinia pestis detection kit based on a real-time fluorescence RPA technology and application of the yersinia pestis detection kit. The kit package is composed of a primer pair and a probe with the name of YPS723-1-P1, wherein the primer pair is composed of single-stranded DNA with the name of YPS723-F1 and single-stranded DNA with the name of YPS723-R1. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and conveniently detecting yersinia pestis with high sensitivity and good specificity, and is expected to become a rapid diagnosis auxiliary tool for clinical samples.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Orally-administered live bacterial vaccines for plague
The invention provides live, attenuated Salmonella bacterial strains that express one or more plague antigens of Yersinia pestis for use in live vaccine compositions that can be orally administered to an individual to protect against plague.
Owner:AVANT IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS
Phage-mediated bioluminescent detection of Yersinia pestis
The present disclosure relates to compositions, methods, systems and kits for the detection of microorganisms of the Yersinia species including Yersinia pestis. The disclosure relates to recombinant phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, the phage comprising a detectable reporter. Detection systems of the disclosure may comprise a phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, and may comprise a reporter nucleic acid expressible upon infection of a Yersinia microorganism by the phage. The system may be operable to detect the expression of the reporter. A detectable reporter may comprise any gene having bioluminescent, colorimetric and / or visual detectability. For example, a detectable reporter may comprise one or more luxAB genes detectable by emission, enhancement and / or change in spectrum of bioluminescent light. Live and infectious Yersinia microbes may be detected by the compositions, methods, systems and kits described herein.
Owner:GUILD ASSOCS
Transformed Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose utilization
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae produced by transformation with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding for xylulokinase (XKS) from Yersinia pestis and xylose isomerase (XI) are capable of xylose utilization. The transformants express these heterologous polynucleotides at a sufficient functional level to grow aerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. Further transformation of the recombinant yeasts to overexpress one or more of the S cerevisiae genes PIP2, IMG2, MAK5, VPS9, COX10, ALE1, CDC7, and MMS4, permits the yeast to grow anaerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. When grown under anaerobic conditions on a culture medium comprising both glucose and xylose, the transformed yeast exhibit increased ethanol productivity, with the yeast growing on the xylose to increase their biomass and fermenting the glucose to ethanol.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com