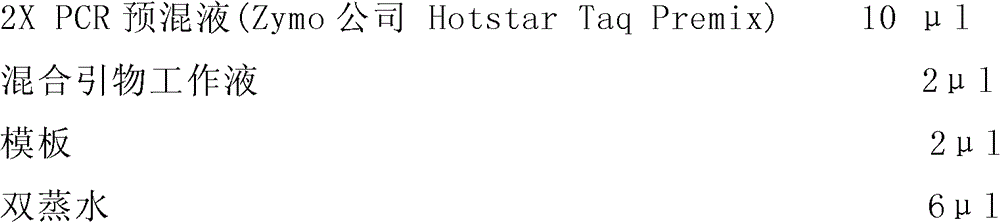Method and kit for detecting multiple high-pathogenicity pathogenic bacteria
A highly pathogenic and pathogenic bacteria technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and nucleic acid detection, can solve the problems of lack of highly pathogenic pathogens, low sensitivity, cumbersome process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] Example 1 Detection of highly pathogenic pathogens
[0121] 1. Probe microsphere coating:
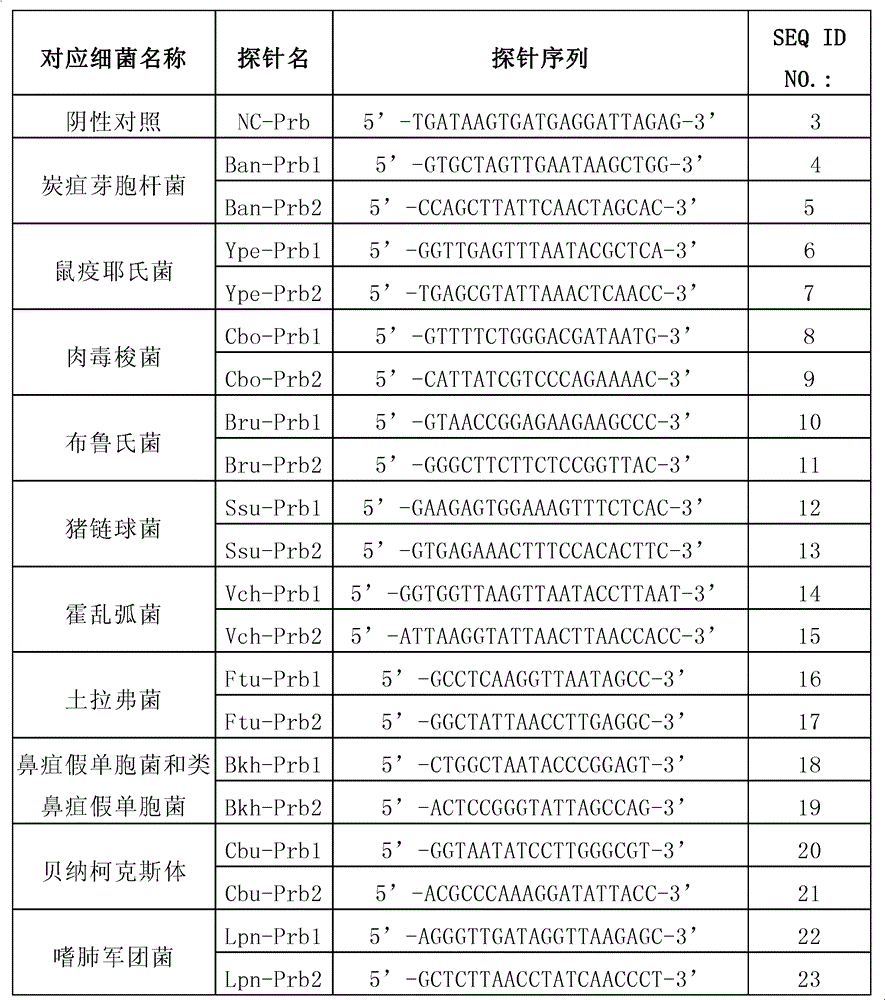
[0122] 1. Follow the list below to synthesize the probe
[0123]
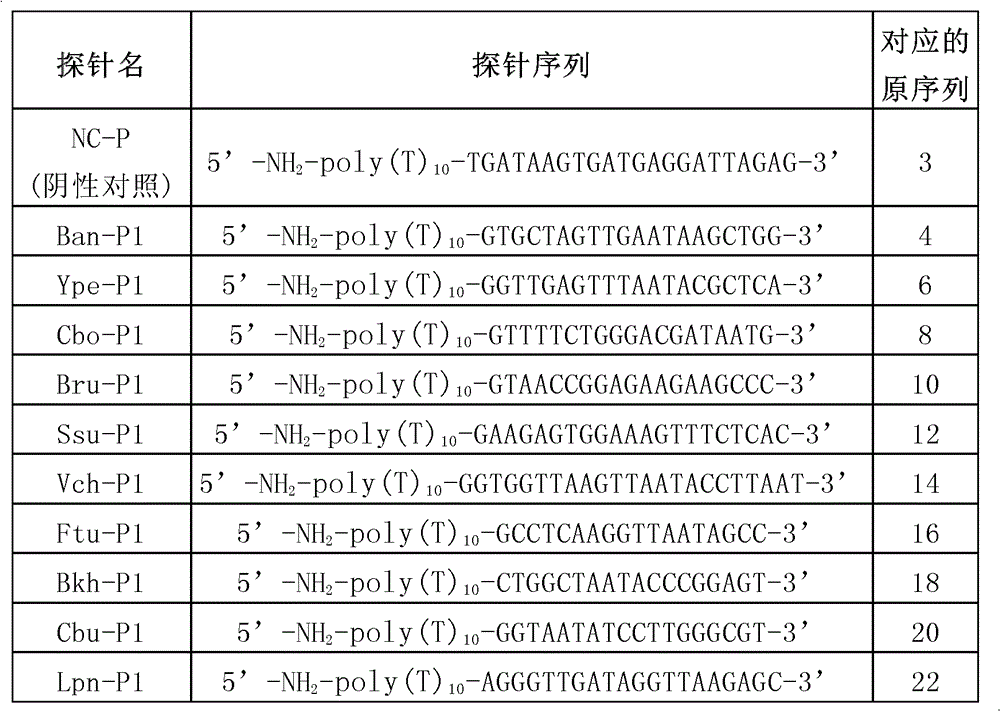
[0124] Note: The spacer arm is a poly(T) composed of 10 Ts 10 -, so the probe Ban-P1 is equal to poly(T) 10 +SEQ ID NO.: 3, probe Ype-P1 is equal to poly(T) 10 +SEQ ID NO.: 4, and so on.
[0125] 2. Select 11 kinds of fluorescent coded microspheres No. 22, 24, 26, 28, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, and 42 [Luminex Company], and perform probe analysis corresponding to each probe in the table above. Coating, the method is as follows:
[0126] (1) Put all kinds of microspheres and a portion of EDC powder stored at -20°C to equilibrate at room temperature for 30 minutes;
[0127] (2) Take each corresponding probe and dissolve it with double distilled water, the concentration is 0.01mM (10pmol / μL);
[0128] (3) Mix the microspheres uniformly with an oscillator;
[0129] (4) Take 50ul each (6.0×10 5 ) The microspheres are placed in a clea...
Embodiment 2
[0195] 1. Probe microsphere coating:
[0196] 1. Follow the list below to synthesize the probe
[0197]
[0198] Note: The spacer arm is -HEG-.
[0199] 2. Select 11 kinds of fluorescent coded microspheres No. 22, 24, 26, 28, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, and 42 [Luminex Company], and perform probe analysis corresponding to each probe in the table above. Coating, the method is as follows:
[0200] (1) Put all kinds of microspheres and a portion of EDC powder stored at -20°C to equilibrate at room temperature for 30 minutes;
[0201] (2) Take each corresponding probe and dissolve it with double distilled water, the concentration is 0.01mM (10pmol / μL);
[0202] (3) Mix the microspheres uniformly with an oscillator;
[0203] (4) Take 50μl each (6.0×10 5 ) The microspheres are placed in a clean 1.5ml centrifuge tube with a pre-marked number;
[0204] (5) Centrifuge at 8000g centrifugal force for 5 minutes to precipitate the microspheres, carefully discard the supernatant;
[0205] (6) Add 100μl of d...
Embodiment 3
[0265] Example 3 Detection of highly pathogenic pathogens
[0266] Repeat Example 2 with the difference that samples 16-27 are replaced with samples Nos. 28 and 29. Among them, the No. 1 and No. 16 samples were combined to form the No. 28 sample. Combine No. 3 and No. 25 samples as No. 29 sample.
[0267] The test results showed that sample No. 28 contained Clostridium botulinum and Streptococcus suis; sample No. 29 contained Tulaversa and Legionella pneumophila. The test result is consistent with the actual situation of the sample.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com