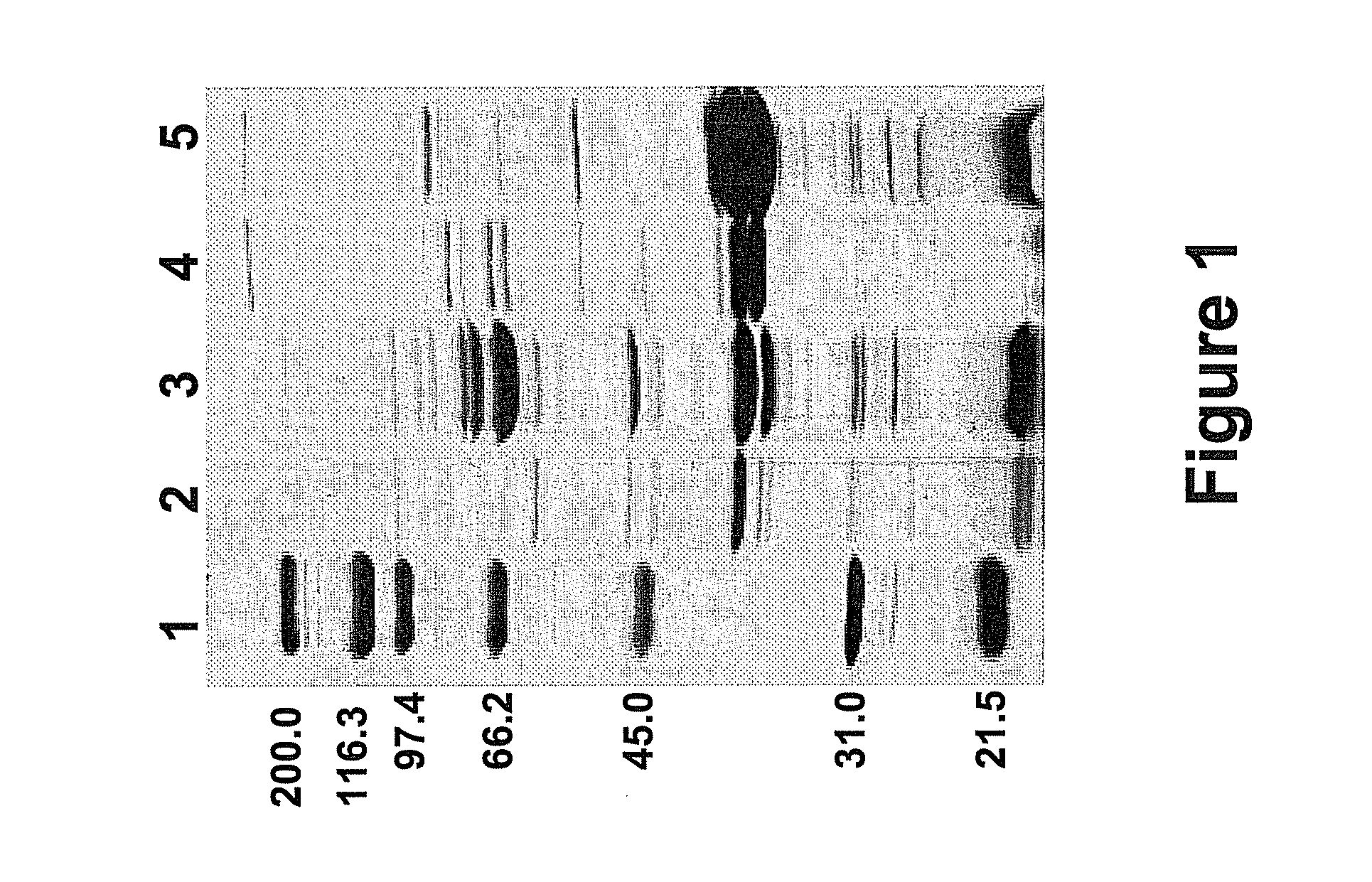
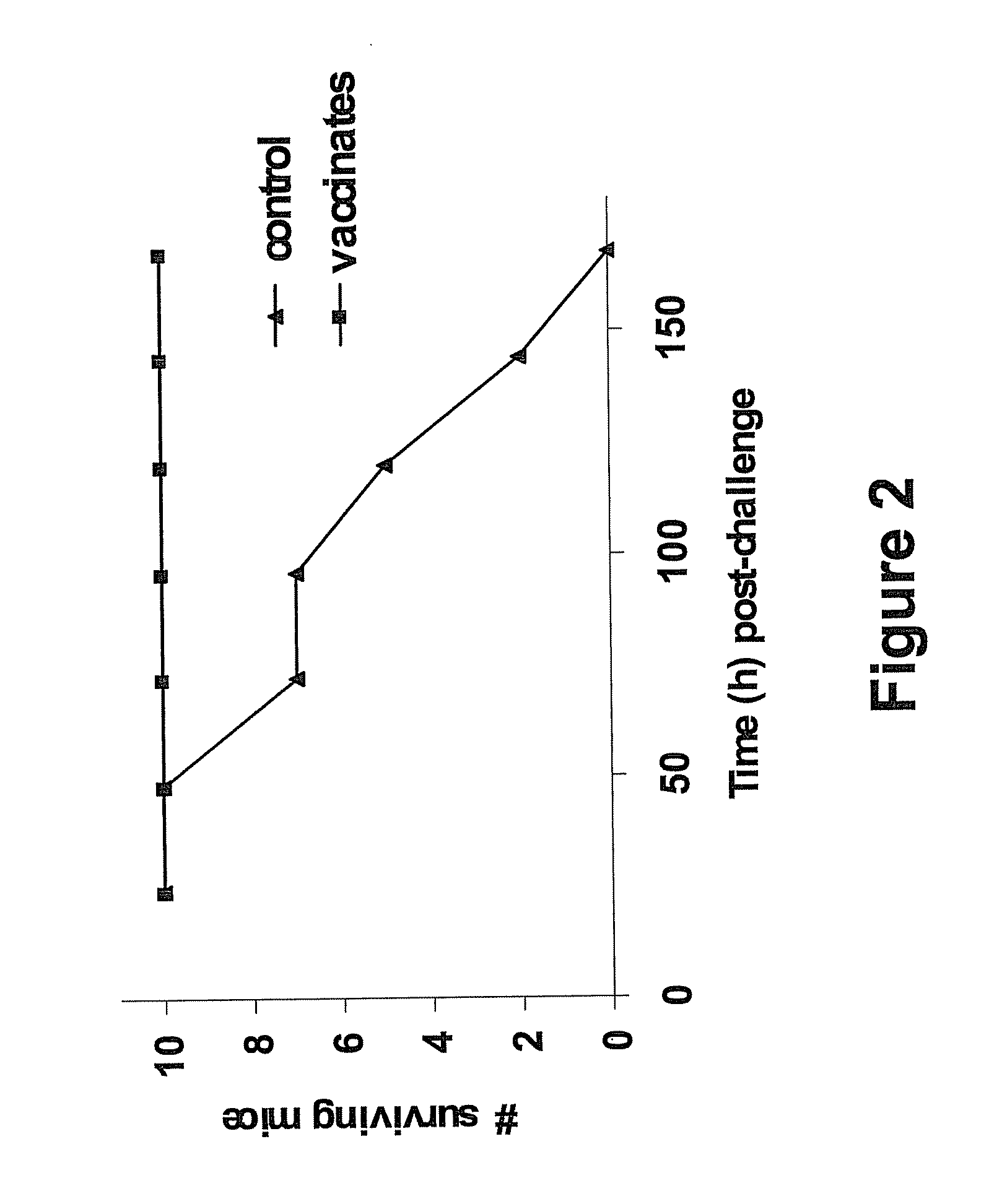
Patents
Literature
106 results about "Yersinia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yersinia is a genus of bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. Yersinia species are Gram-negative, coccobacilli bacteria, a few micrometers long and fractions of a micrometer in diameter, and are facultative anaerobes. Some members of Yersinia are pathogenic in humans; in particular, Y. pestis is the causative agent of the plague. Rodents are the natural reservoirs of Yersinia; less frequently, other mammals serve as the host. Infection may occur either through blood (in the case of Y. pestis) or in an alimentary fashion, occasionally via consumption of food products (especially vegetables, milk-derived products, and meat) contaminated with infected urine or feces.
Yersinia spp. polypeptides and methods of use
The present invention provides isolated polypeptides isolatable from a Yersinia spp. Also provided by the present invention are compositions that include one or more of the polypeptides, and methods for making and methods for using the polypeptides.
Owner:EPITOPIX LLC
Gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof
InactiveCN102534013AStrong specificityDetermine the typeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisBrucella
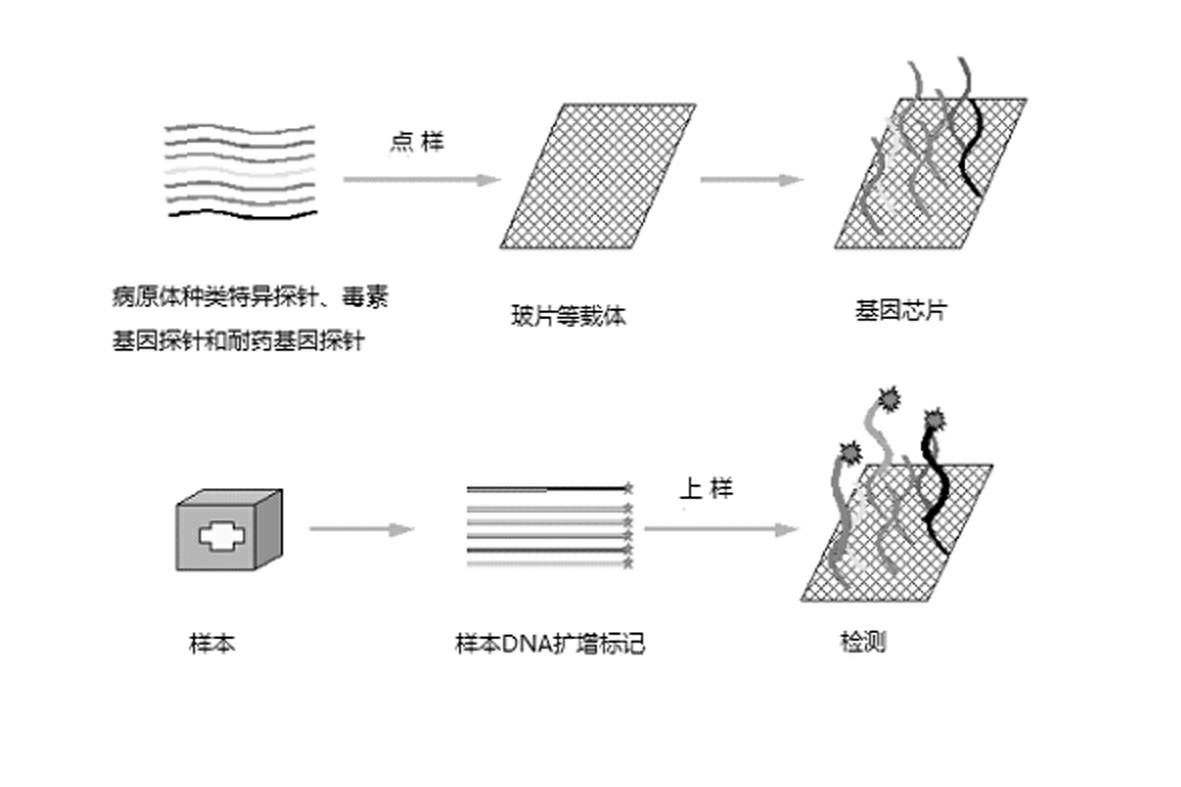
The invention relates to a gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof. The gene comprises (1) a combination of 174 oligonucleotide probes of pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes; and (2) a probe array, which is formed by curing the oligonucleotide probes on a carrier material by arm molecules. The gene chip comprises 174 gene probes, namely 32 pathogen variety specific gene probes of the following 8 pathogens of Burkholderia mallei, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Brucella, salmonella, Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, comma bacillus and the like, 25 toxin gene probe of the following 7 toxins of diphtheria toxin, Shiga toxin, staphylococcus enterotoxin, choleratoxin and the like, and 117 drug-resistant gene probes of 17 drug-resistant genes of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, cephalosporinase, carbapenemase, integrase gene, common gene engineering carrier drug-resistant gene and the like. The gene chip can be used to detect multiple pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes.
Owner:李越希
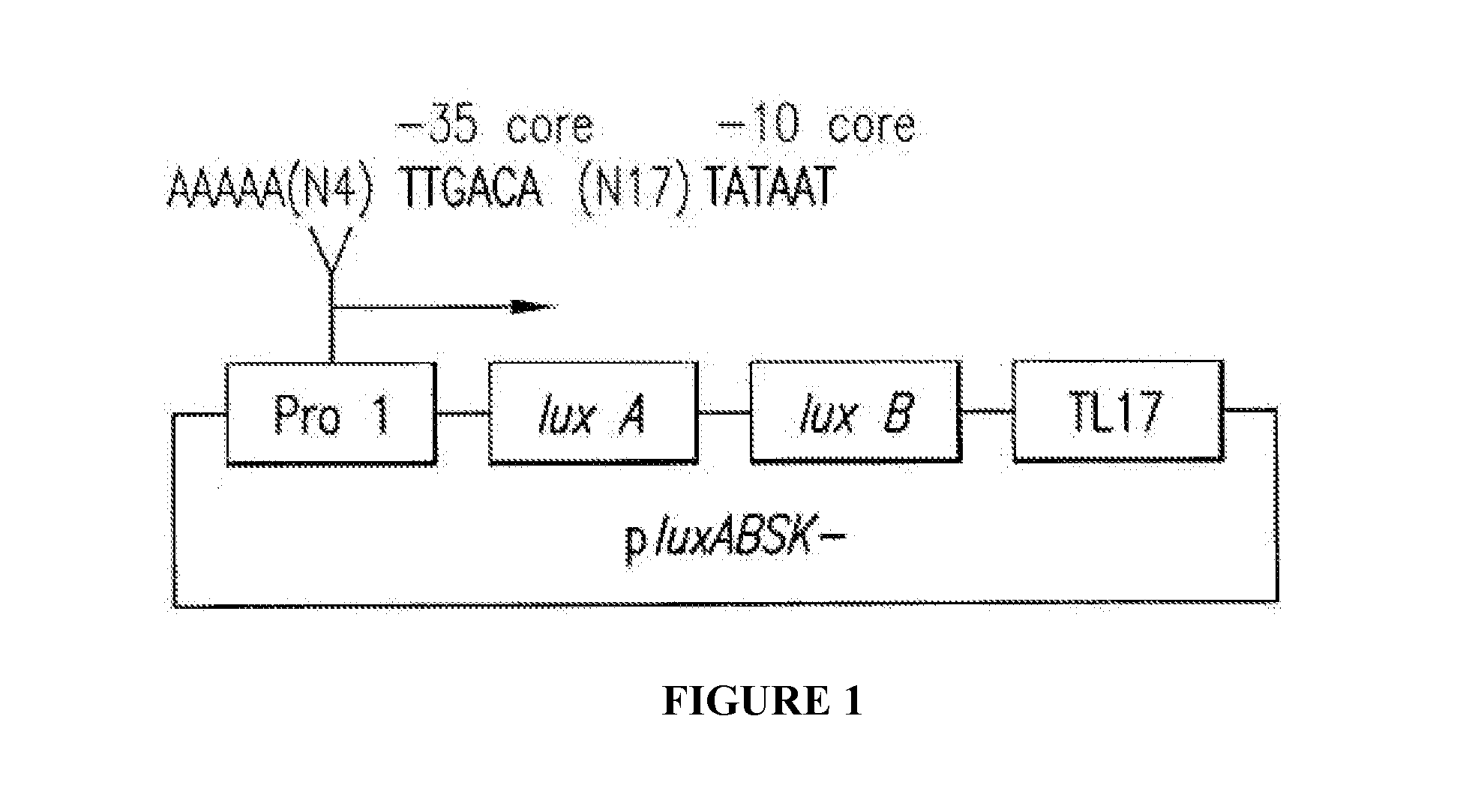
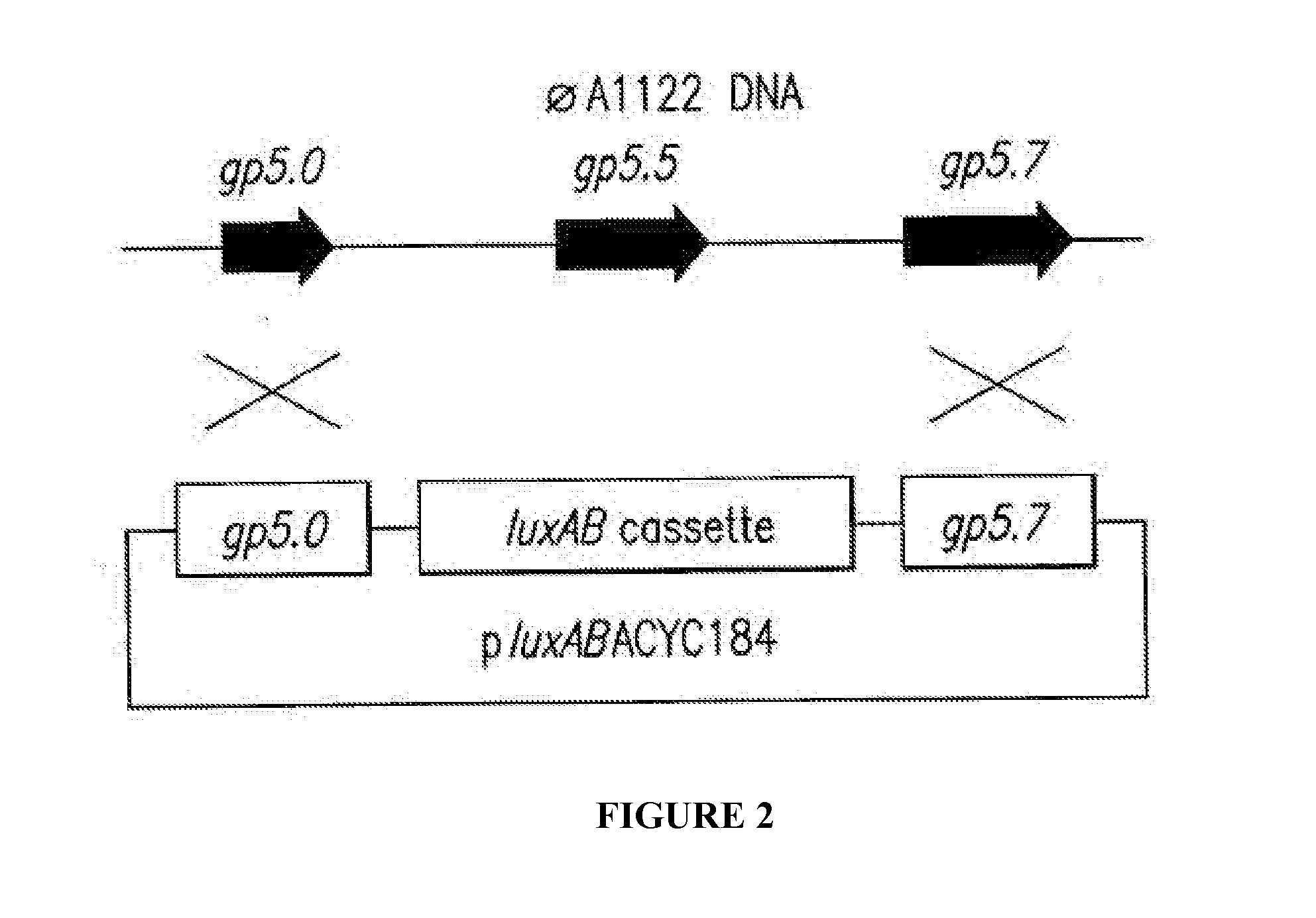
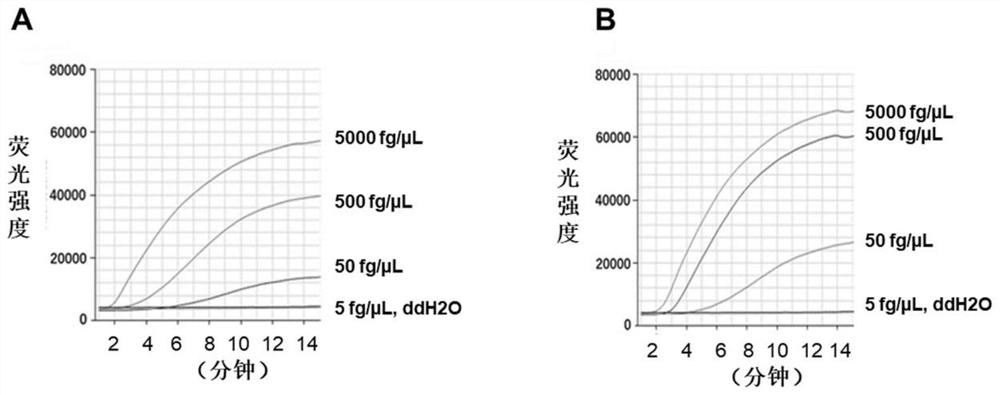
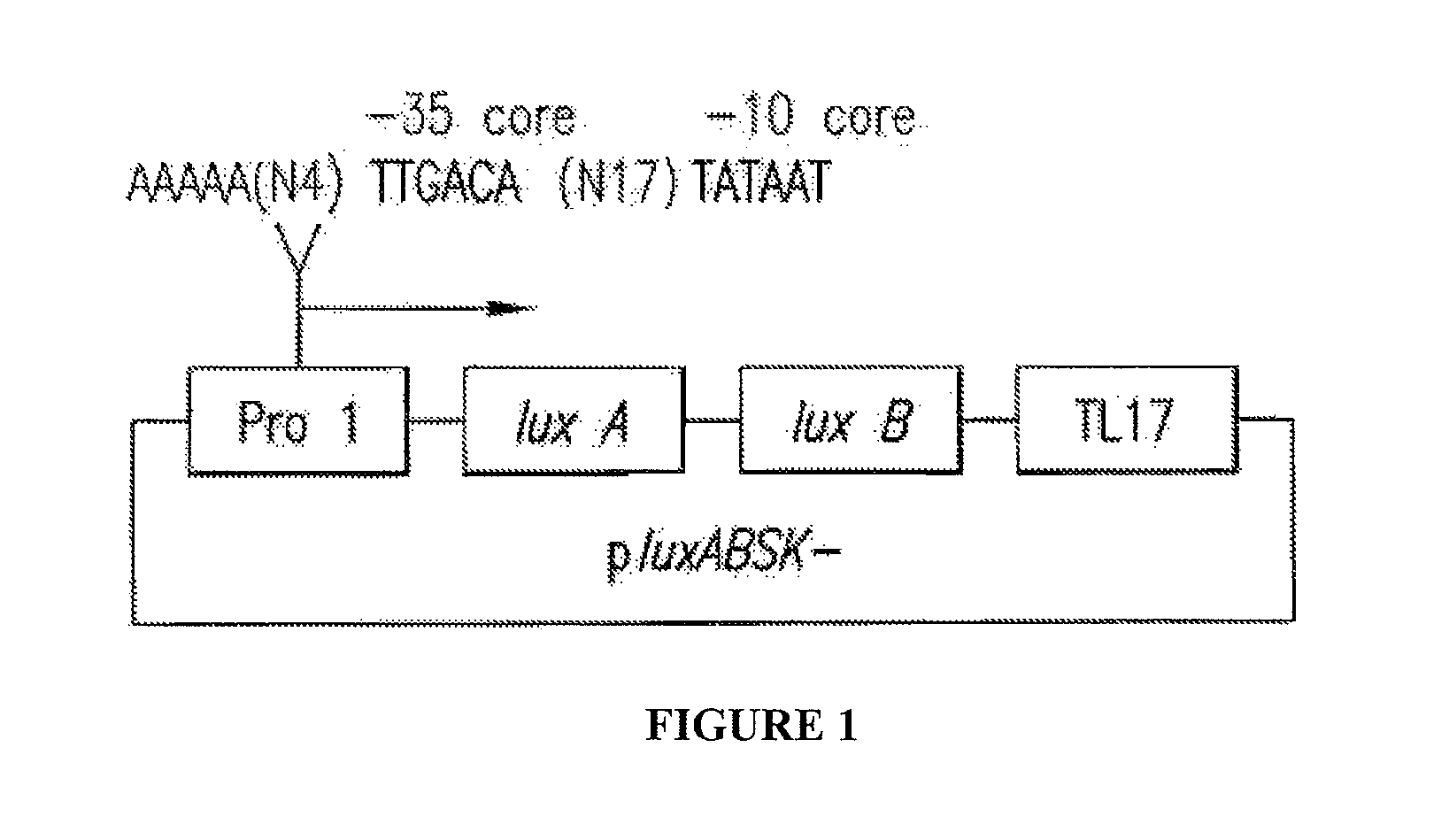
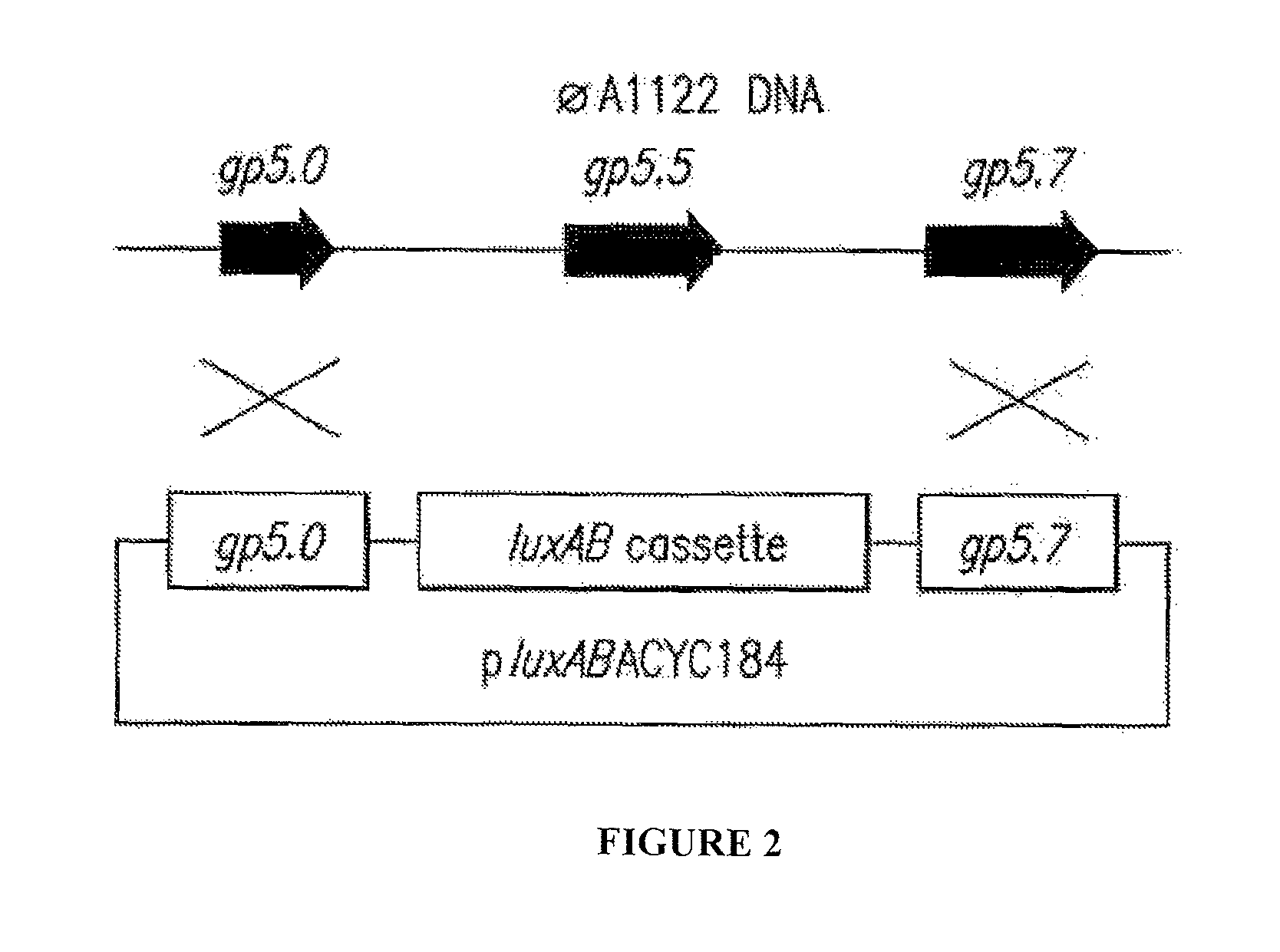
Phage-Mediated Bioluminescent Detection of Yersinia Pestis
InactiveUS20110076672A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismBiotechnology
The present disclosure relates to compositions, methods, systems and kits for the detection of microorganisms of the Yersinia species including Yersinia pestis. The disclosure relates to recombinant phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, the phage comprising a detectable reporter. Detection systems of the disclosure may comprise a phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, and may comprise a reporter nucleic acid expressible upon infection of a Yersinia microorganism by the phage. The system may be operable to detect the expression of the reporter. A detectable reporter may comprise any gene having bioluminescent, colorimetric and / or visual detectability. For example, a detectable reporter may comprise one or more luxAB genes detectable by emission, enhancement and / or change in spectrum of bioluminescent light. Live and infectious Yersinia microbes may be detected by the compositions, methods, systems and kits described herein.
Owner:GUILD ASSOCS
Food-originated pathogenic bactenium quick detection gene chip and its application
InactiveCN1536090AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFood poisoningBeta-hemolytic streptococcus
The present invention provides a gene chip for quickly detecting pathogens from food source, discloses the preparation method of said gene chip and provides 26 oligonucleotide probe sequences for detection. Said gene chip can quickly, accurately and high-effectively detect and identify the class of the pathogens in food, and its detection range includes staphylococcus aureus, Shiga's bacillus, salmonella, colibacillus 0157, bacillus proteus, mononuclear hyperplastic listerella, enterocolitis yersinia, aeruginous pseudomonads, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio cholerae, bacillus cereus, beta hemolytic streptococcus, coconut fermentation pseudomonads, boticin, vibrio jejuni and bacillus perfringens, etc.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Application of Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicine
The invention discloses application of a Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicines. The bacteria is selected from Acinetobacter, Bacillus, Campylobacter, Chlamydia, Chlamydia trachomatis, Clostridium, Citrobacter, Escherichia, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli, enteric bacteria, Enterococcus, Francisella, Haemophilus, helicobacter, Klebsiella Bacillus, Lester monocytogenes, Moraxella, Mycobacterium, Neisseria, proteus, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, shewanella oneidensis, Shigella, Stenotrophomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Yersinia.
Owner:XINJIANG HUASHIDAN PHARMA RES
Preparation and utilization method of yersinia genus rapid detection reagent kit
InactiveCN101200760AGuaranteed reliabilityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBetainePolymerase L
The invention relates to a preparation and using method of a yersinia genus rapid detection kit. The kit includes loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction liquid A, BstDNA polymerase B and chromogenic reagent C. The reaction liquid A contains reaction buffer, dNTP, sulfate magnesium, upstream internal primer 5- CCGGTTTGATCGGTTTCGCCCACTTACAAGATGGGTGTGCC-3, downstream internal primer 5- GTGCGTTTCTGGCCGAGCTTGCAGACGTTTTGCCAGGATT-3, upstream external primer 5- CGCCGTGAAGGTAAAGTTCA-3, downstream external primer 5-CAGAGTTCAGGAACGACAGC-3 and betaine. The method for detecting the yersinia genus includes the DNA extraction of a sample to be detected or bacteria, the loop-mediated isothermal amplification and the chromogenic detection of the yersinia genus. The invention has the advantages of rapid property, strong specificity, high sensitivity and low cost.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Type III bacterial strains for use in medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Bovine brucella indirect ELISA antibody detection kit
InactiveCN105067812AHigh purityIncrease digestionColor/spectral properties measurementsEnterocolitisEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a bovine brucella indirect ELISA antibody detection kit. The kit uses the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of brucella suis S2 acclimated and induced by the application institution in the 1960s as the coating antigen, and improves the sensitivity of detection. The study improves the LPS purification and purity determination method, and endows the developed kit with good specificity. The kit not only can effectively eliminate the interference of conventional Gram negative bacteria to Brucella, but also can get rid of the technical defect that general brucellosis indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) kits cannot distinguish enterocolitis Yersinia O9 and Escherichia coli O157 interference, and improves the specificity of detection. Through improvement and optimization of the main reagent formula, the reaction background of the kit is effectively controlled, and also the time required by detection is shortened.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
Methods and compositions involving LcrV proteins
ActiveUS7875280B2Reduce in quantityReduce riskBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaYersinia pestisYersinia frederiksenii
The present invention concerns methods and compositions involving modified LcrV proteins from Yersinia bacteria. These methods and compositions can be employed to invoke an immune response in a subject against the bacteria, while not suppressing the immune system as much as the native LcrV protein. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to vaccines, as well as methods to protect a subject against Yersinia pestis and plague. Moreover, the present invention concerns methods and compositions for suppressing a subject's immune system using non-native LcrV polypeptides.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
Yersinia spp. polypeptides and methods of use
The present invention provides isolated polypeptides isolatable from a Yersinia spp. Also provided by the present invention are compositions that include one or more of the polypeptides, and methods for making and methods for using the polypeptides.
Owner:VAXXINOVA US INC
Multiplex PCR-based synchronous and rapid method for detecting 13 pathogenic microorganisms in water
InactiveCN102703588AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisEnterobacterales
The invention relates to a multiplex PCR-based synchronous and rapid method for detecting 13 pathogenic microorganisms in water, which comprises the steps of using multiplex PCR to simultaneously amplify gene-specific fragments of the 13 pathogenic microorganisms including escherichia coli, enterohaemorragic escherichia coli o157:h7, legionella pneumophila, salmonella enteritidis, shigella dysenteriae, staphyloccocus aureus, listeria monoeytogenes, helicobacter pylori, mycobacterium tuberculosis, klebsiella pneumonia, vibrio cholera, bacillus anthracis and yersinia pestis, and detecting PCR amplified products through agarose gel electrophoresis, thereby achieving synchronous and rapid detection for the 13 pathogenic microorganisms.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Method and apparatus for growing sprouts
ActiveUS20140237895A1Extended shelf lifeReduce chancePlant phenotype modificationHorticulture methodsPhytochemicalMicrogreen
Provided are methods for growing and shipping sprouts and microgreens in the same container, growing while in shipment using moisture provided in a water-absorbent layer, with optional added beneficials, and including methods for producing sprouts and microgreens for consumption, and for pharmaceutical / nutriceutical use, comprising growth of sprouts in retail-ready containers, the container comprising a moisture-retaining layer of agar media or the like providing water for growth and obviating the need for irrigation during sprout growth. In certain aspects, media is supplemented with beneficial organisms or additives such as probiotic microbes, vitamins (e.g., B12), cofactors, nutrients, and other items (e.g., phytochemicals, natural colors, and antioxidants) which promote the growth of the beneficial microbes on the product, and / or which become incorporated into the product. In certain aspects, added beneficial microorganisms are selected to compete antagonize human pathogens such as Listeria, Salmonella, enterohaemorrhagic E. coli, Yersinia, and / or spoilage organisms (e.g., Erwinia, Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas).
Owner:INST FOR ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
Method for detecting food-borne pseudotuberculosis yersinia genus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification
InactiveCN101182575BAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesBiotechnologyElectrophoresis
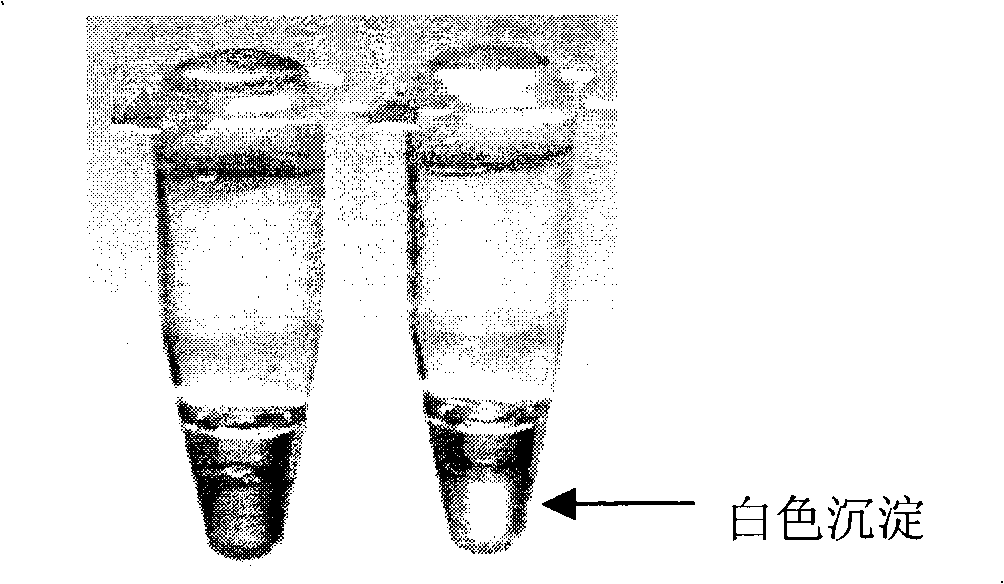
The invention discloses a method for detecting the bacterium Yersini of food-borne pseudonodule with the loop-mediated constant-temperature magnification technology; the method belongs to the bacillus detection technology field and the main technical proposal is that a primer group sequence is designed and the loop-mediated constant-temperature magnification technology is adopted for detection; the loop-mediated constant-temperature magnified product detection methods comprise that 10,000 multiplied g, 5 minutes and room temperature; white sedimentation can be seen at the bottom of the tube in a positive way; visualization reagent is added and the positive result turns green; the process of 1.5 percent agarose gel electrophoresis is implemented and the step-shaped electrophoresis strip is formed; any one of the three loop-mediated constant-temperature magnified product detection methods can be chosen for detection. The method is characterized by accurate detection, strong special andhigh sensibility and with the method, special object bacillus can be identified fast and accurately and the identification efficiency is increased and the time is saved; in this way, the state that the traditional detection system can not meet the requirements of the ever increasing imports and exports.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Reagent kit and method for detection of artificial tuberculosis yersinia genus with ring mediated isothermality amplification method
InactiveCN101492733AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEngineeringYersinia
The invention discloses a method for detecting food origin Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by using loop-mediated constant temperature PCR technology, belonging to the food sanitation field. The technical proposal is as follows: Yersinia pseudotuberculosis 16S-23S regions are used as target detection sequences, and four specific primers containing the whole region sequences are designed. The method comprises extraction of four specific primers of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis 16S-23S regions and food origin Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, detection method for loop-mediated constant temperature PCR amplification. The method fills the gap of a method for detecting food origin Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by using loop-mediated constant temperature PCR amplification technology, and is used for checking Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in import and export foods. The method has the characteristics of low cost, high efficiency, simple operation and convenience.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Microorganisms as carriers of nucleotide sequences coding for antigens and protein toxins, process of manufacturing and uses thereof
ActiveUS8669091B2Efficient tumor therapyEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenTransport system
A Escherichia, Salmonella, Yersinia, Vibrio, Listeria, Shigella, or Pseudomonas bacterium that has the following components: (I) a polynucleotide encoding a heterologous antigenic determinant that induces a CTL response against a tumor cell; (II) a polynucleotide encoding a heterologous protein toxin or toxin subunit; and (III) (a) a polynucleotide encoding a transport system that expresses the products of (I) and (II) on the outer surface of the bacterium or that secretes products of (I) and (II) from the bacterium; and (IV) a polynucleotide that activates the expression of one or more of (I). (II), and / Or (III) in the bacterium wherein polynucleotides (I), (II), (III) and (IV) are different from each other and polynucleotides (I), (II) and (III) encode proteins that are different from each other.
Owner:SOCIUM THERAPEUTICS INC
Inhibition of yersinia pestis
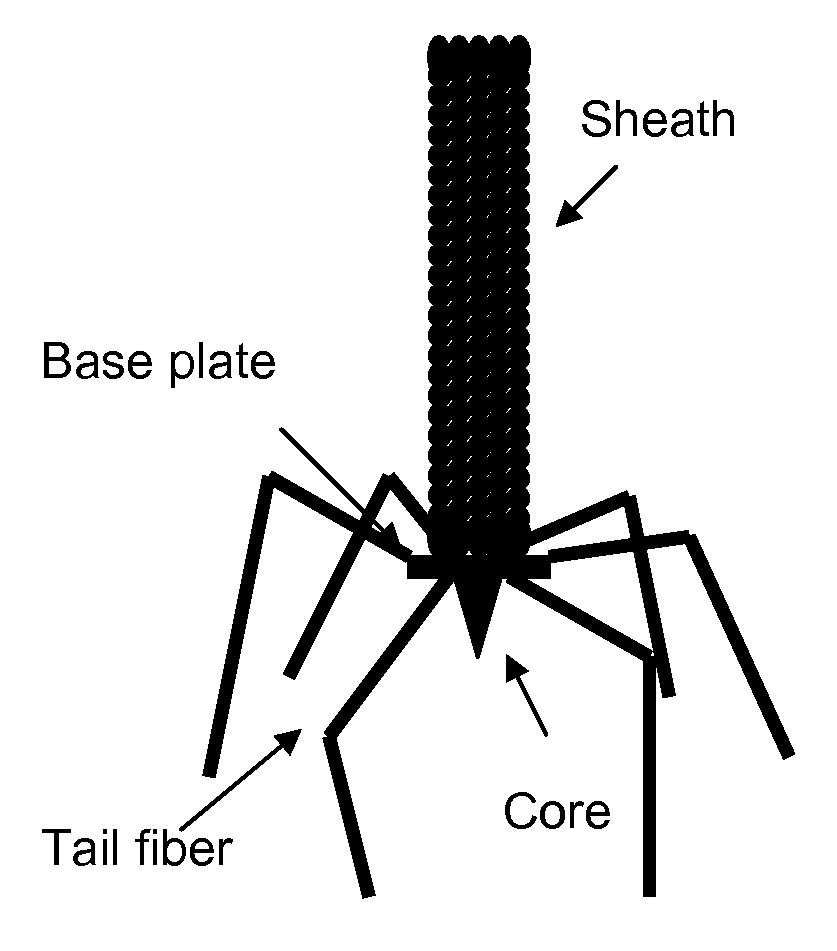
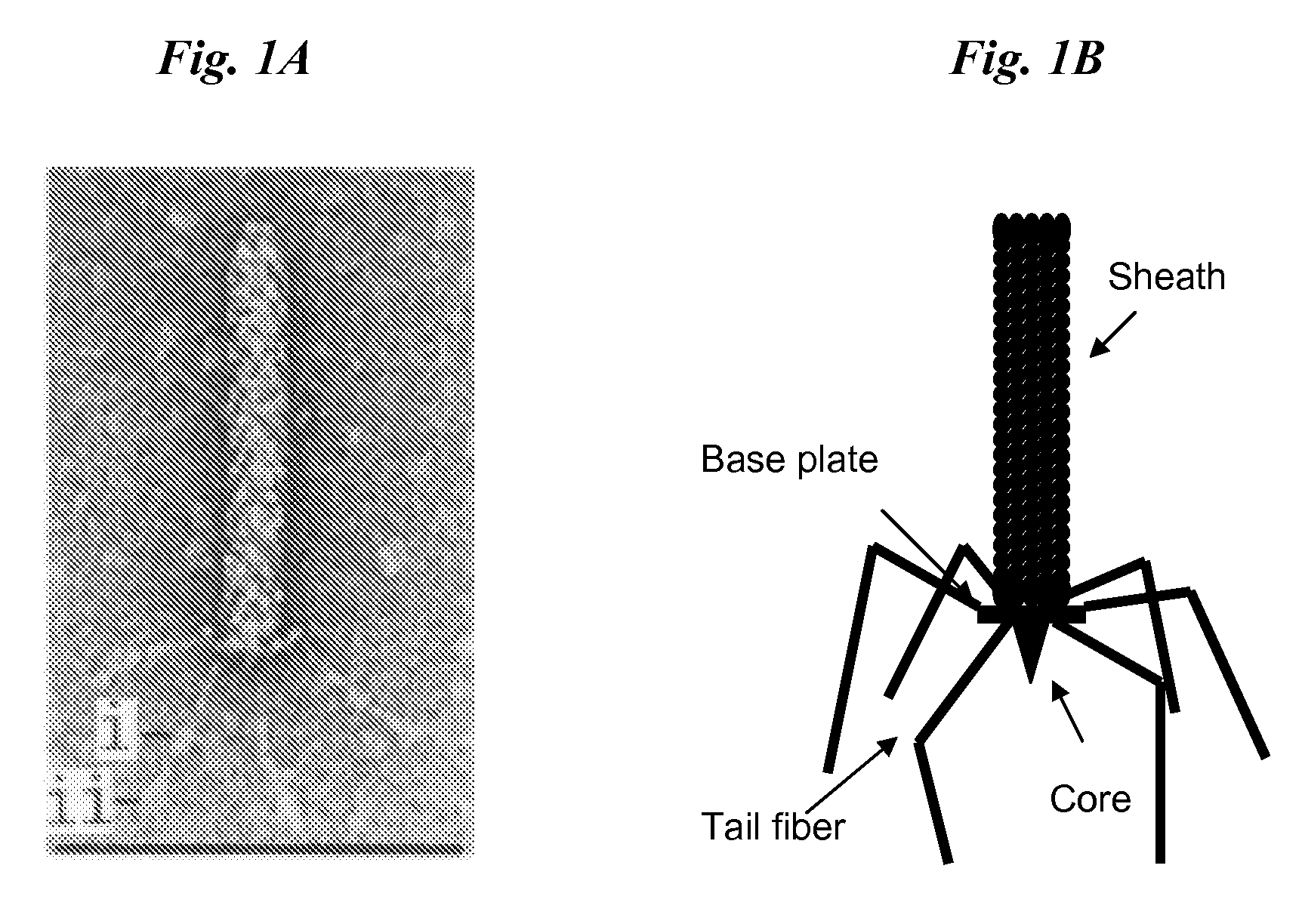
The disclosure relates to the targeting of Y. pestis mediated by the binding activity of tail fibers from naturally occurring R-type pyocins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The targeting may be mediated by a macromolecular complex such as the pyocin itself, a high molecular weight (hmw) bacteriocin modified to have the tail fiber's binding activity, or a bacteriophage modified to have the tail fiber's binding activity. Compositions comprising such complexes are described. Also disclosed are methods for the use of a complex, such as to inhibit the growth of a Yersinia species like Y. pestis, by compromising the integrity of its cytoplasmic membrane are also described. Additional methods include use of the binding activity to identify Y. pestis.
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Degrading bacterium agent for kitchen waste treatment and application thereof
InactiveCN111548963AImprove biological activityImprove degradation rateFungiBio-organic fraction processingCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides a degrading bacterium agent for kitchen waste treatment. The degrading bacterium agent is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20 to 30 parts of bacillus subtilis, 10 to 15 parts of lysine bacillus, 10 to 20 parts of bacillus licheniformis, 15 to 25 parts of trichoderma viride, 5 to 10 parts of candida glabrata, 5 to 10 parts of yersinia lipolytica and1 to 5 parts of a biological surfactant. The invention further provides an application of the degrading bacterium agent in kitchen waste integrated treatment equipment. The degradation microbial inoculum can rapidly decompose proteins, grease, starch polysaccharides, cellulose, hemicellulose and other macromolecular organic matters in the kitchen waste, so that the macromolecular organic matters are rapidly stabilized, the degradation efficiency of the kitchen waste is improved, the space utilization rate of a fermentation bin is further improved, and the quality of the kitchen waste degradation product organic fertilizer is improved.
Owner:中铁环境科技工程有限公司
Compositions and methods for inducing an immune response against yersinia pestis
The invention provides a gene transfer vector for inducing an immune response against Yersinia pestis in a mammal. The gene transfer vector comprises a nucleic acid sequence encoding an immunogenic portion of one or more proteins of Yersinia pestis and / or a nucleic acid sequence encoding a monoclonal antibody directed against Yersinia pestis. The invention further provides a method of producing an immune response against Yersinia pestis in a mammal comprising administration of the gene transfer vector to the mammal. The invention also provides a monoclonal antibody directed against the Virulence (V) antigen of Y. pestis, as well as a hybridoma cell line producing same and a nucleic acid sequence encoding same.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Reagent kit and method for detection of enterocolitis yersinia genus with ring mediated isothermality amplification method
InactiveCN101492732AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnterocolitisYersinia enterocolitica
The invention discloses a method for detecting food origin enterocolitis Yersinia by using loop-mediated constant temperature PCR technology, belonging to the food sanitation field. The technical proposal is as follows: enterocolitis Yersinia 16S-23S regions are used as target detection sequences, and four specific primers containing the whole region sequences are designed. The invention comprises extraction of four specific primers of enterocolitis Yersinia 16S-23S regions and food origin enterocolitis Yersinia, detection method for loop-mediated constant temperature PCR amplification and interpretation of results. The method fills the gap of a method for detecting food origin enterocolitis Yersinia by using loop-mediated constant temperature PCR amplification technology, and is used for checking enterocolitis Yersinia in import and export foods. The method has the characteristics of low cost, high efficiency, simple operation and convenience.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Yersinia SPP. Polypeptides and Methods of Use
The present invention provides isolated polypeptides isolatable from a Yersinia spp. Also provided by the present invention are compositions that include one or more of the polypeptides, and methods for making and methods for using the polypeptides.
Owner:EPITOPIX LLC
Coloring culture medium for detecting food-borne pathogenic Yersinia
ActiveCN106591416AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNovobiocinYeast
The present invention discloses a coloring culture medium for detecting food-borne pathogenic Yersinia, wherein the culture medium contains soybean peptone, yeast powder, sodium chloride, sodium oxalate, agar, a beta-riboside chromogenic substrate, a beta-galactoside chromogenic substrate, esculin, ammonium ferric citrate, bile salt No.3, cephalosporin, novobiocin, and the balance of water. According to the present invention, the coloring culture medium has characteristics of simple formula and convenient preparation operation, can be used for the separation and the detection of food-borne pathogenic Yersinia, and further has advantages of specificity, high efficiency, rapidness, low cost, simple result determination, wide application prospect, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING JUNLIKANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Gene chip-based method for synchronously and rapidly detecting thirteen pathogenic microorganisms in water body
InactiveCN102703589AOptimizing gene chip detection methodStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisListeria monocytogenes
The invention discloses a gene chip-based method for synchronously and rapidly detecting thirteen pathogenic microorganisms in a water body. The method is characterized in that specific gene segments of the pathogenic microorganisms are amplified simultaneously by adopting multiple polymerase chain reactions (PCR), and then, a detection result is obtained through gene chip hybridization and chip scanning image analysis. The detected thirteen pathogenic microorganisms comprise escherichia coli, Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, legionella pneumophila, salmonella enteritidis, Shigella, staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Helicobacter Pylori, mycobacterium tuberculosis, Klebsiella pneumonia, vibrio cholera, Bacillus anthracis and Yersinia pestis.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
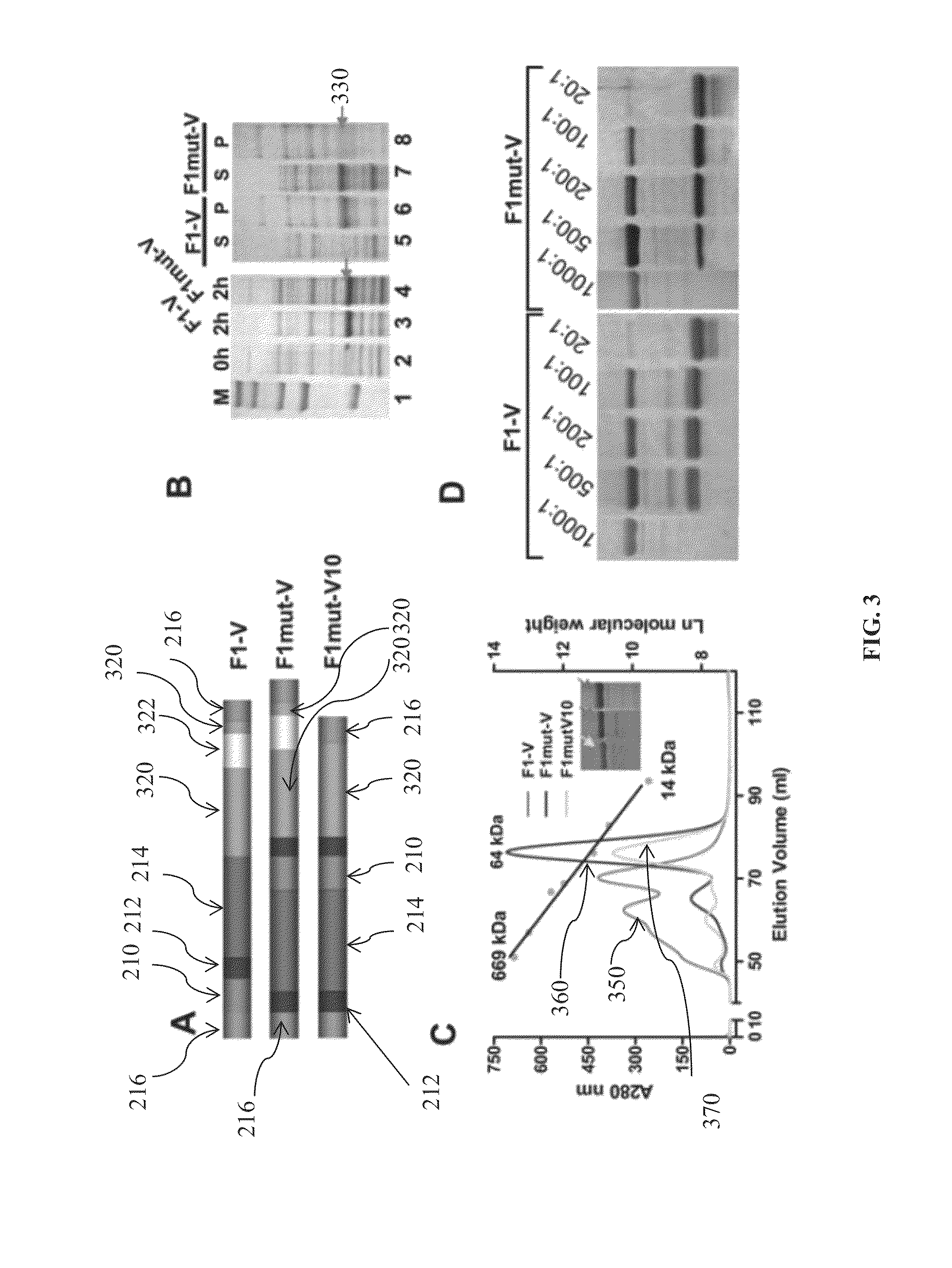
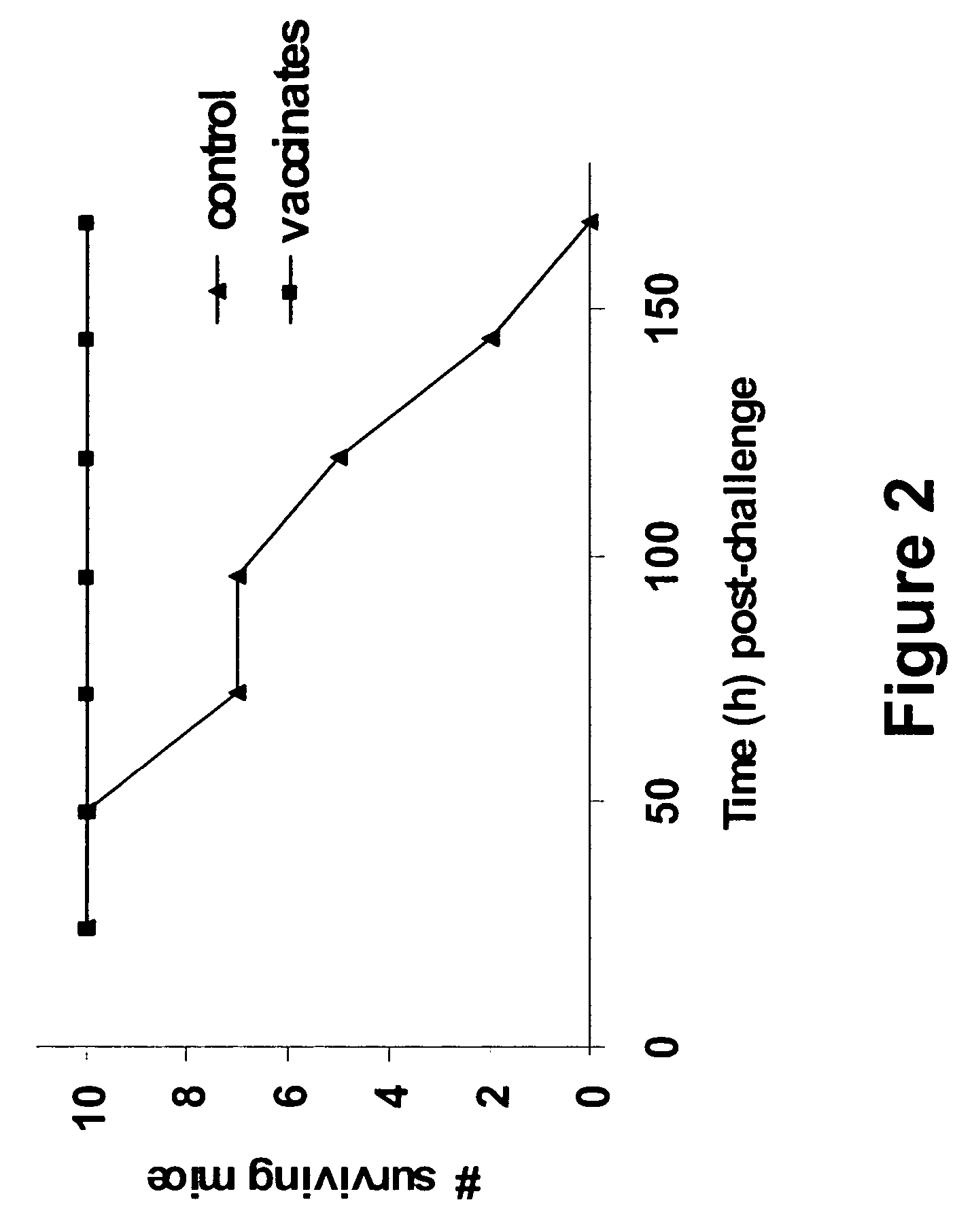
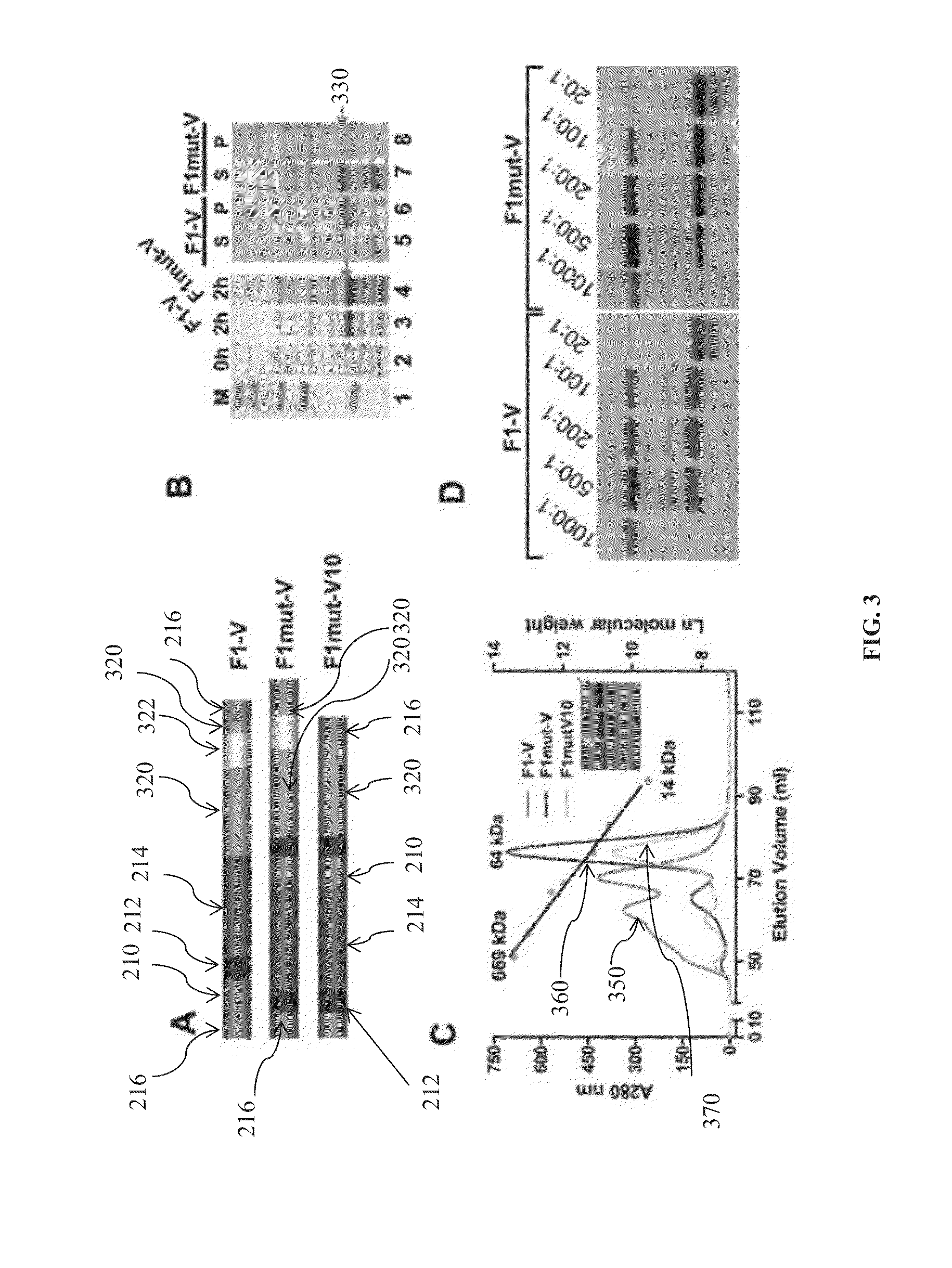
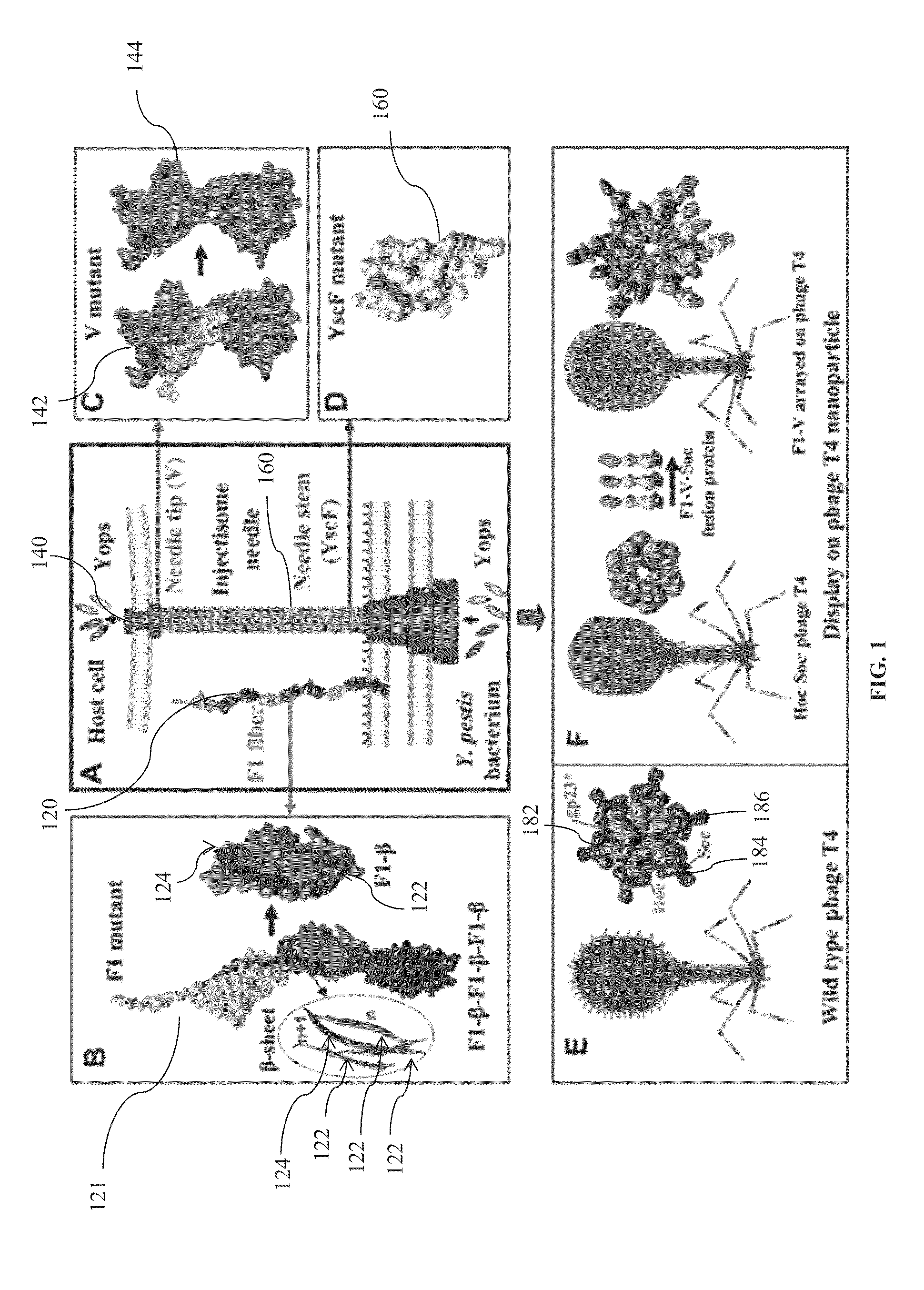
Mutated and bacteriophage t4 nanoparticle arrayed f1-v immunogens from yersinia pestis as next generation plague vaccines
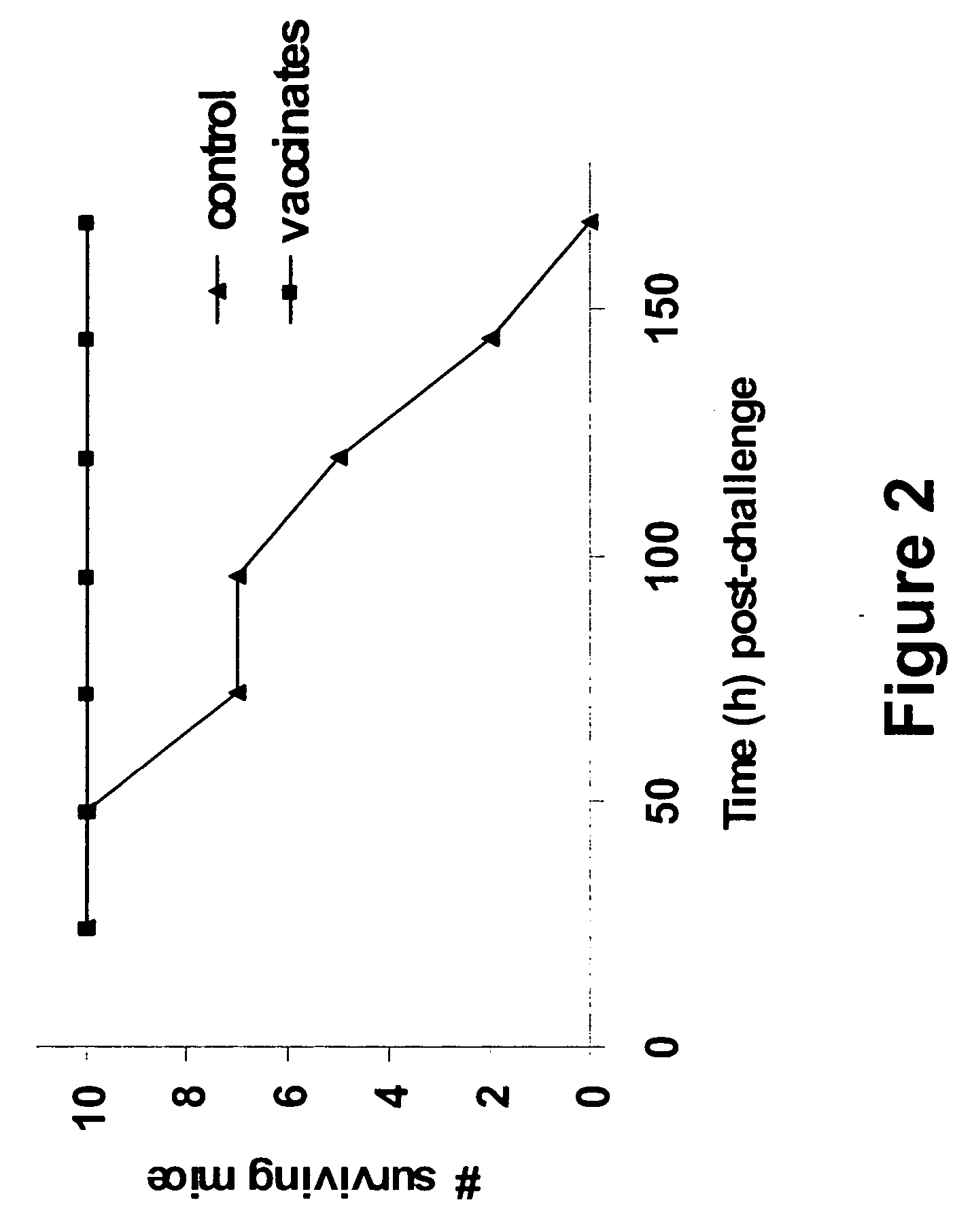
Techniques from two basic approaches, structure-based immunogen design and phage T4 nanoparticle delivery, are developed to construct new plague vaccines. The NH2-terminal β-strand of F1 of Yersinia pestis is transplanted to the COOH-terminus of F1 of Yersinia pestis and the NH2-terminus sequence flanking the β-strand of F1 of Yersinia pestis is duplicated to eliminate polymerization but to retain the T cell epitopes. The mutated F1 is fused to the V antigen of Yersinia pestis to thereby form a fusion protein F1mut-V mutant, which produces a completely soluble monomer. The fusion protein F1mut-V is then arrayed on phage T4 nanoparticles via a small outer capsid protein, Soc, from a T4 phage or a T4-related phage. Both the soluble and T4 decorated F1mut-V provided approximately 100% protection to mice and rats against pneumonic plague evoked by high doses of Yersinia pestis CO92.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Preparation method for pathogenic yersinia enterocolitica test strips
The invention relates to a preparation method for pathogenic yersinia enterocolitica test strips, effectively solving the problems of high time consumption, complexity and poor specificity of existing detection methods. The preparation method includes adding n-caprylic acid to mouse ascites and acetate buffer solution, mixing evenly and centrifuging the mixture, regulating the pH (potential of hydrogen) value of supernatant, adding ammonium sulfate, performing centrifugation, dissolving sediments by PBS solution, and performing dialysis to obtain monoclonal antibodies; activating red, blue and yellow latex particles with carboxyl groups by carbodiimide respectively to obtain suspended activated latex particles; dialyzing to-be-marked antibodies, adding the monoclonal antibodies, dropping the mixture into the activated latex particles, rinsing with NaH2PO4 to enable sediments to be suspended in bovine serum albumin buffer solution, adsorbing markers by glass fibers, drying the markers, and curing anti-mouse IgG (immunoglobulin G) antibodies on fiber films to form quality control areas. The preparation method has the advantages that the advantages of immunoreaction specificity, chromatography rapidity and intuition of the colored latex particles serving as tracers are combined, and accordingly, simplicity, convenience, specificity and sensitiveness are achieved.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Brucella antibody detecting test strip
The invention relates to a Brucella antibody detecting test strip. The Brucella antibody detecting test strip has the following significance: (1) Brucellosis diagnostic methods are enriched; (2) one novel method which is simple and fast and can implement rapid field detection on various animals is provided for Brucellosis diagnosis in China; (3) the test strip overcomes the defect that the conventional Brucellosis diagnostic methods cannot eliminate interference of enterocolitis Yersinia O9 and escherichia coli O157 antiserum in Brucella antibodies, and improves the Brucellosis detecting specificity.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
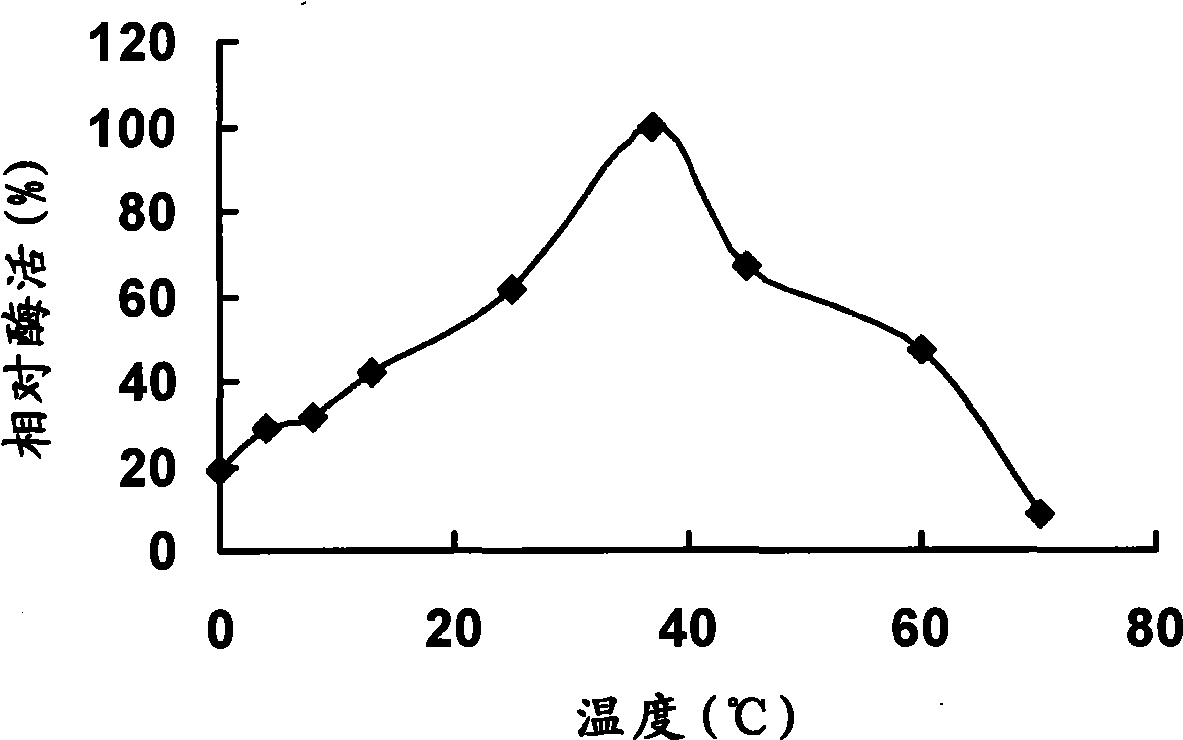
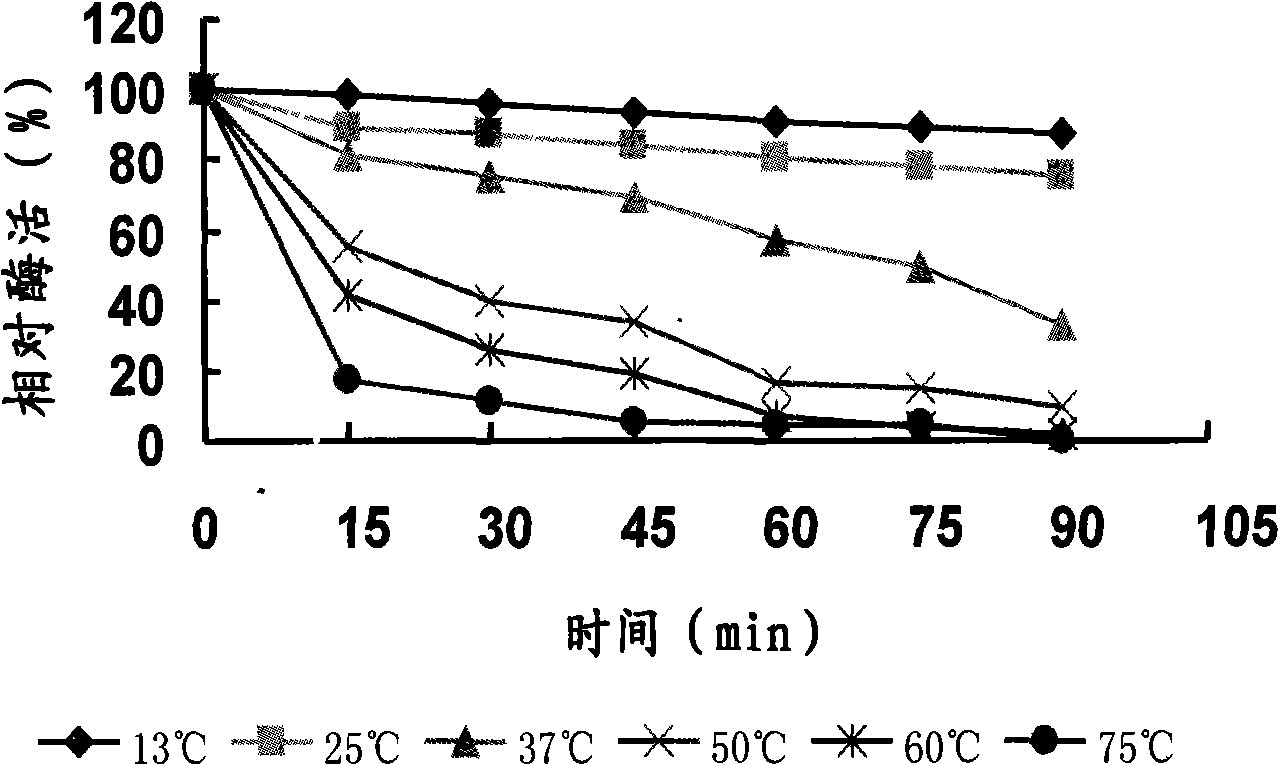
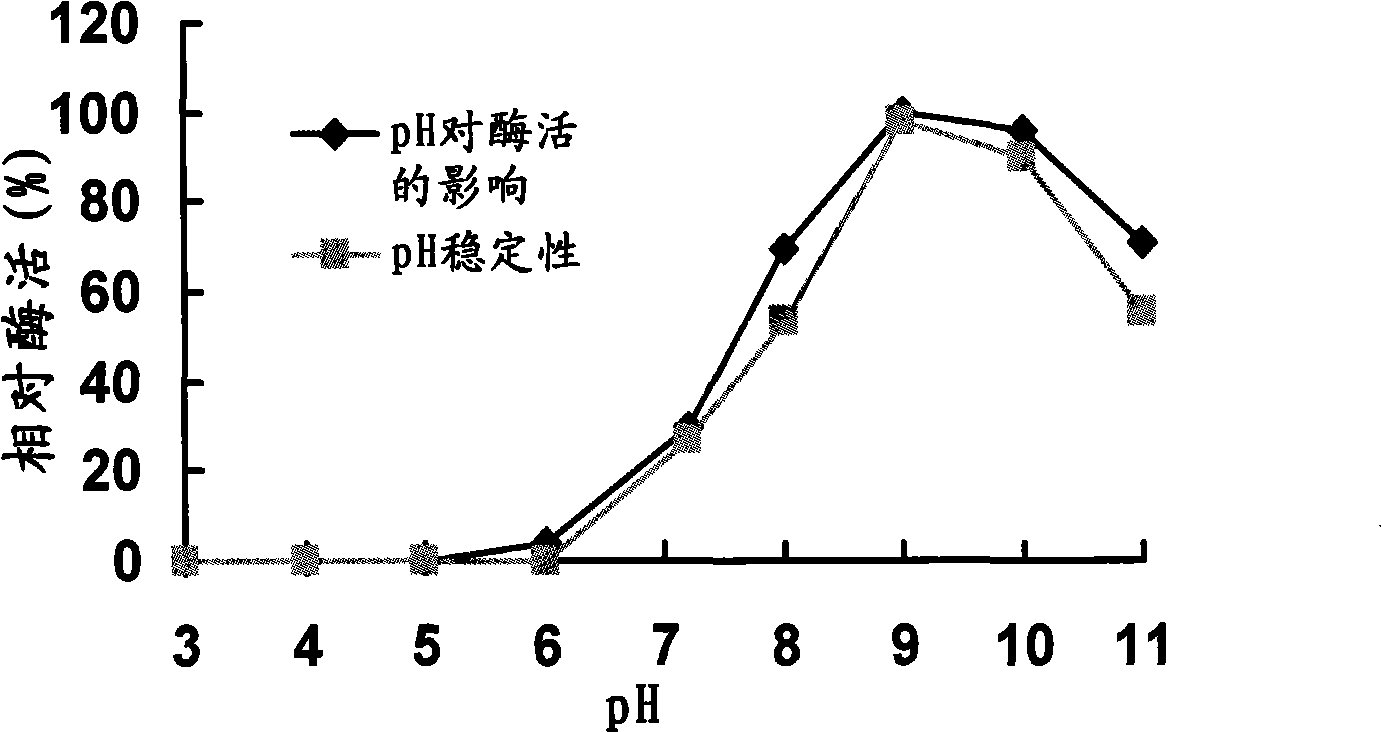
Yersinia strain KM1, low temperature alkaline lipase prepared thereby and purification method thereof
The invention discloses a psychrotrophic bacteria strain Yersinia sp. KM1, a psychrotrophic alkaline lipase that is generated by the strain and resistant to organic solvents, and a separating and purifying method of the psychrotrophic alkaline lipase. The purifying method comprises the steps of ammonium sulfate precipitation of a fermented supernatant, centrifugal concentration with a 10KDa ultrafiltration pipe, Sephacry HRS-100 chromatography and Superdex G-75 chromatography, and finally obtains pure psychrotrophic alkaline lipase under electrophoresis. The purified psychrotrophic alkaline lipase has low reaction temperature, wider pH accommodation range and high resistance to organic solvents, and consequently has huge application potential in the fields of cleaning solvents, food processing, medicine production and biodiesel production, etc.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel isothermal loop-mediated yersinia pestis nucleic acid mark detection reagent
InactiveCN103698516AAvoid pollutionHave immunityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAntigenYersinia pestis
The invention relates to a novel isothermal loop-mediated yersinia pestis nucleic acid mark detection reagent. A front inner primer in a primer group for isothermal loop-mediated amplification is used for marking an antigen, and meanwhile, a rear inner primer in the primer group is used for marking another antigen, so that a yersinia pestis specific target gene can be simultaneously amplified and marked. A matched colloidal gold strip can be used for rapidly detecting an amplification product of the target gene after marking, thereby detecting yersinia pestis. The detection reagent can be simply and rapidly operated, and is high in specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:天津国际旅行卫生保健中心
Yersinia pestis detection kit based on real-time fluorescence RPA technology and application thereof
ActiveCN112899383AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a yersinia pestis detection kit based on a real-time fluorescence RPA technology and application of the yersinia pestis detection kit. The kit package is composed of a primer pair and a probe with the name of YPS723-1-P1, wherein the primer pair is composed of single-stranded DNA with the name of YPS723-F1 and single-stranded DNA with the name of YPS723-R1. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and conveniently detecting yersinia pestis with high sensitivity and good specificity, and is expected to become a rapid diagnosis auxiliary tool for clinical samples.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Phage-mediated bioluminescent detection of Yersinia pestis
The present disclosure relates to compositions, methods, systems and kits for the detection of microorganisms of the Yersinia species including Yersinia pestis. The disclosure relates to recombinant phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, the phage comprising a detectable reporter. Detection systems of the disclosure may comprise a phage operable to infect a Yersinia microorganism, and may comprise a reporter nucleic acid expressible upon infection of a Yersinia microorganism by the phage. The system may be operable to detect the expression of the reporter. A detectable reporter may comprise any gene having bioluminescent, colorimetric and / or visual detectability. For example, a detectable reporter may comprise one or more luxAB genes detectable by emission, enhancement and / or change in spectrum of bioluminescent light. Live and infectious Yersinia microbes may be detected by the compositions, methods, systems and kits described herein.
Owner:GUILD ASSOCS
Mutated and bacteriophage T4 nanoparticle arrayed F1-V immunogens from Yersinia pestis as next generation plague vaccines
Techniques from two basic approaches, structure-based immunogen design and phage T4 nanoparticle delivery, are developed to construct new plague vaccines. The NH2-terminal β-strand of F1 of Yersinia pestis is transplanted to the COOH-terminus of F1 of Yersinia pestis and the NH2-terminus sequence flanking the β-strand of F1 of Yersinia pestis is duplicated to eliminate polymerization but to retain the T cell epitopes. The mutated F1 is fused to the V antigen of Yersinia pestis to thereby form a fusion protein F1mut-V mutant, which produces a completely soluble monomer. The fusion protein F1mut-V is then arrayed on phage T4 nanoparticles via a small outer capsid protein, Soc, from a T4 phage or a T4-related phage. Both the soluble and T4 decorated F1mut-V provided approximately 100% protection to mice and rats against pneumonic plague evoked by high doses of Yersinia pestis CO92.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com