Patents
Literature
87 results about "Shiga toxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
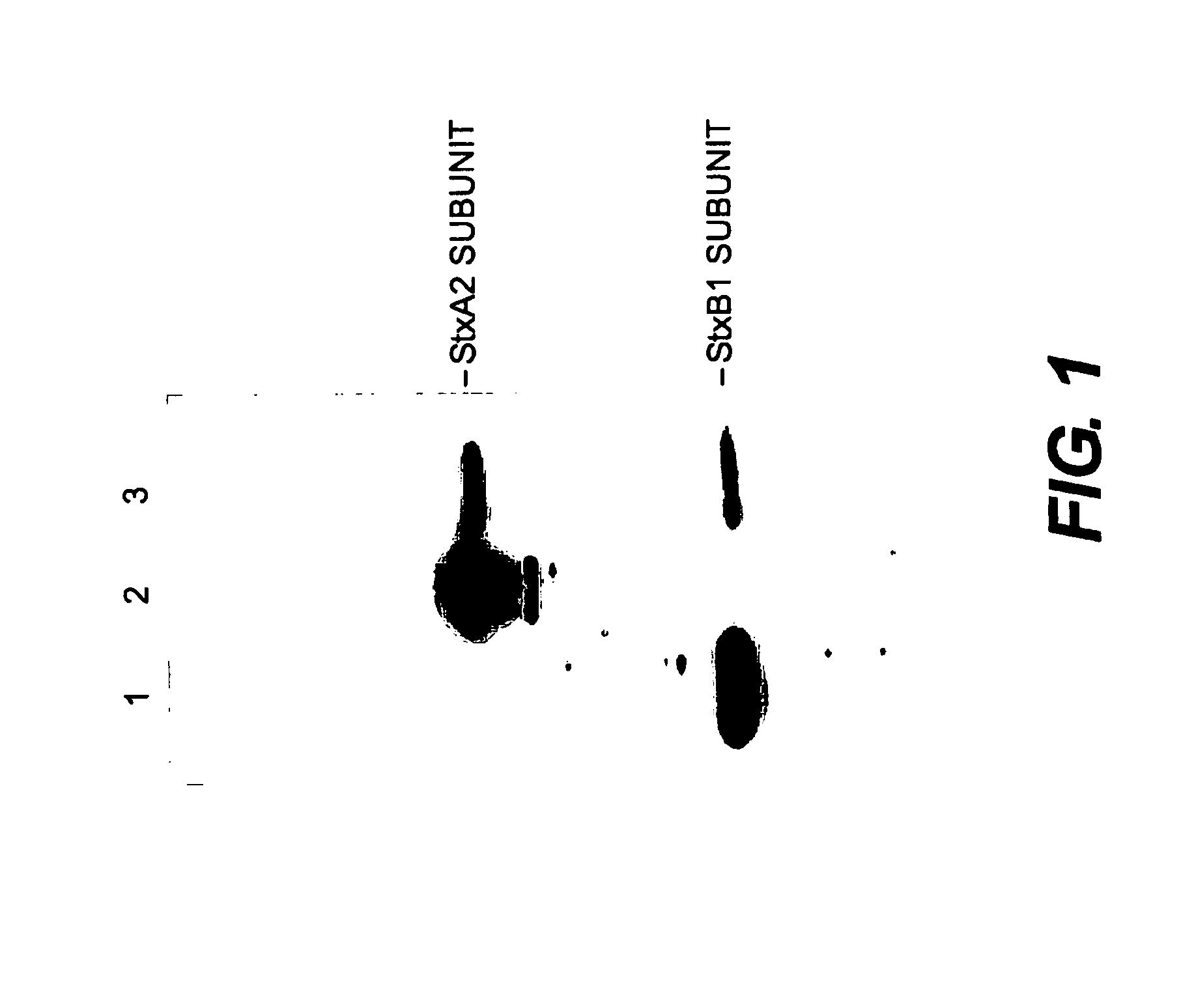
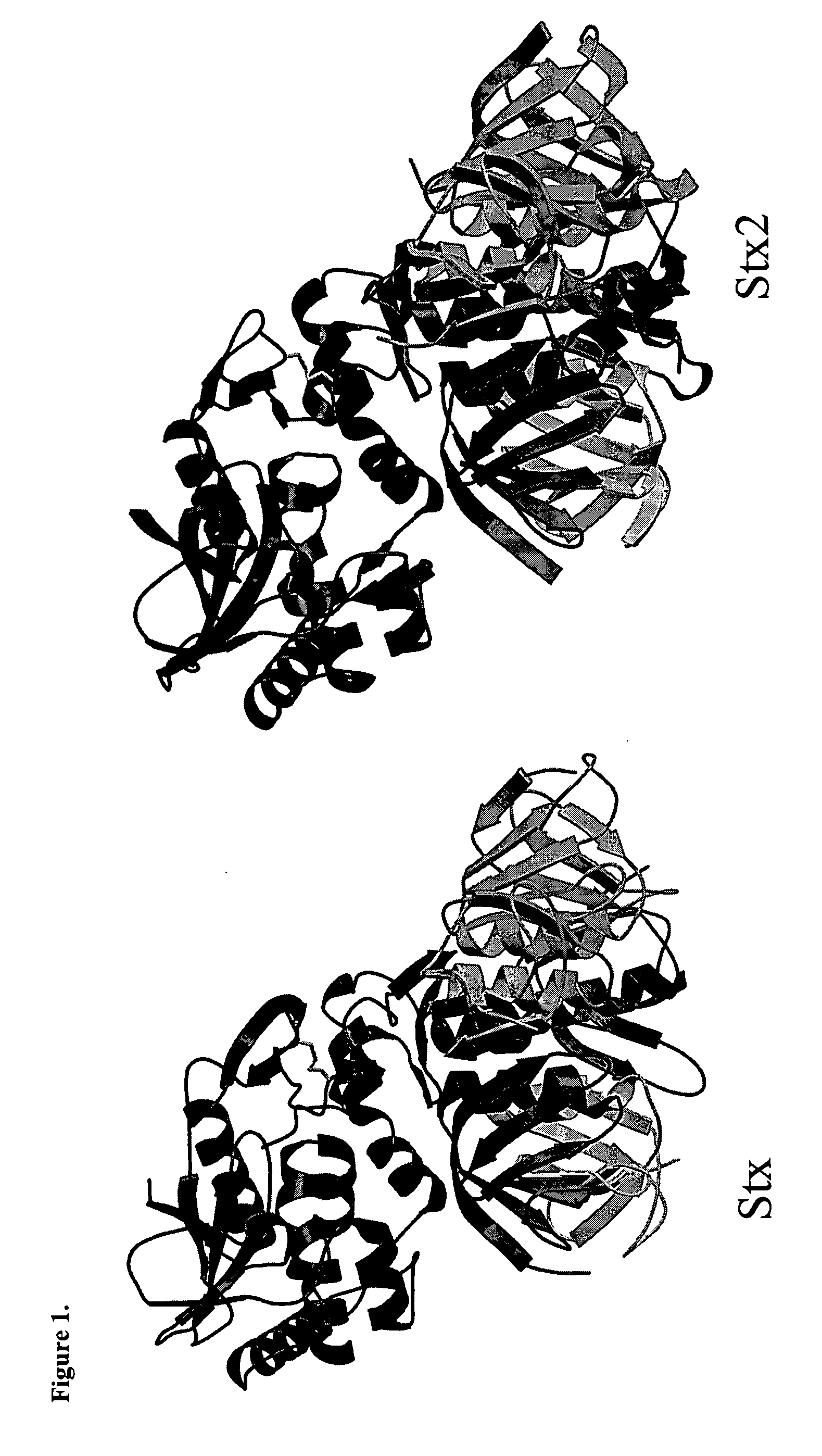
Shiga toxins are a family of related toxins with two major groups, Stx1 and Stx2, expressed by genes considered to be part of the genome of lambdoid prophages. The toxins are named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first described the bacterial origin of dysentery caused by Shigella dysenteriae. Shiga-like toxin (SLT) is a historical term for similar or identical toxins produced by Escherichia coli. The most common sources for Shiga toxin are the bacteria S. dysenteriae and some serotypes of Escherichia coli (STEC), which includes serotypes O157:H7, and O104:H4.
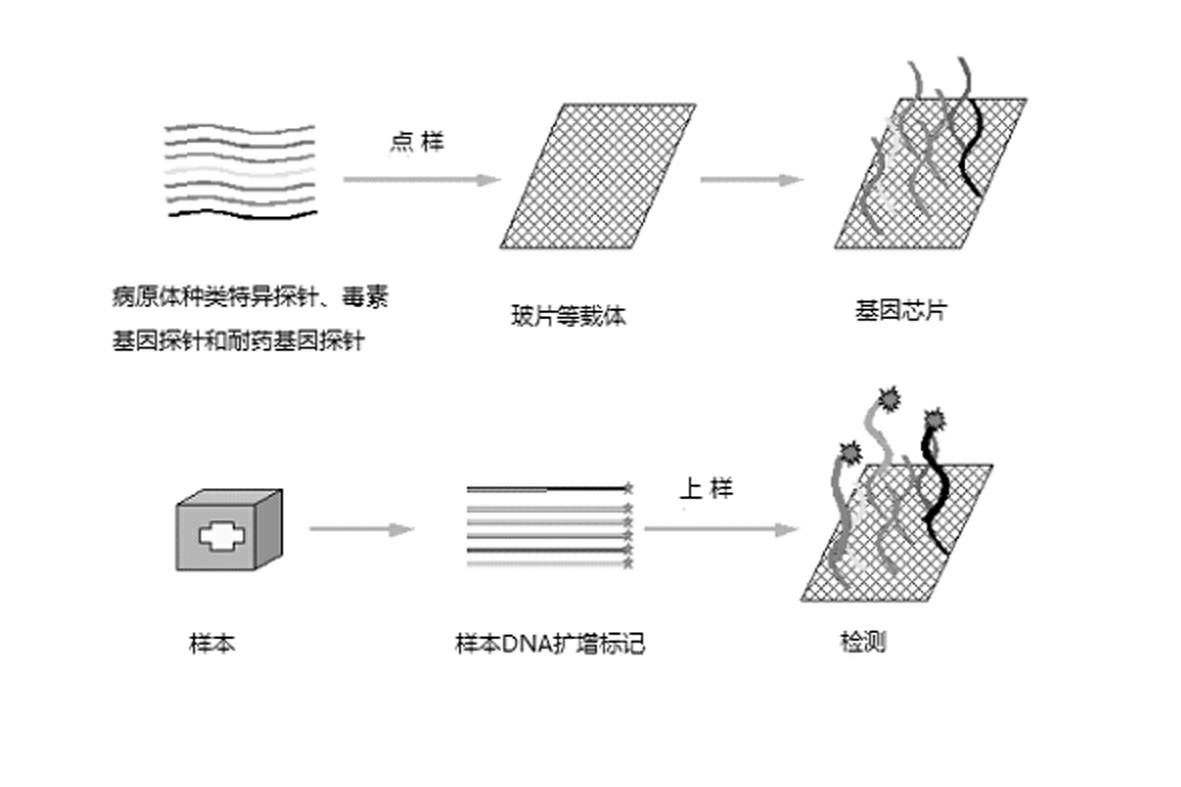
Gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof
InactiveCN102534013AStrong specificityDetermine the typeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisBrucella
The invention relates to a gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof. The gene comprises (1) a combination of 174 oligonucleotide probes of pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes; and (2) a probe array, which is formed by curing the oligonucleotide probes on a carrier material by arm molecules. The gene chip comprises 174 gene probes, namely 32 pathogen variety specific gene probes of the following 8 pathogens of Burkholderia mallei, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Brucella, salmonella, Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, comma bacillus and the like, 25 toxin gene probe of the following 7 toxins of diphtheria toxin, Shiga toxin, staphylococcus enterotoxin, choleratoxin and the like, and 117 drug-resistant gene probes of 17 drug-resistant genes of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, cephalosporinase, carbapenemase, integrase gene, common gene engineering carrier drug-resistant gene and the like. The gene chip can be used to detect multiple pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes.
Owner:李越希
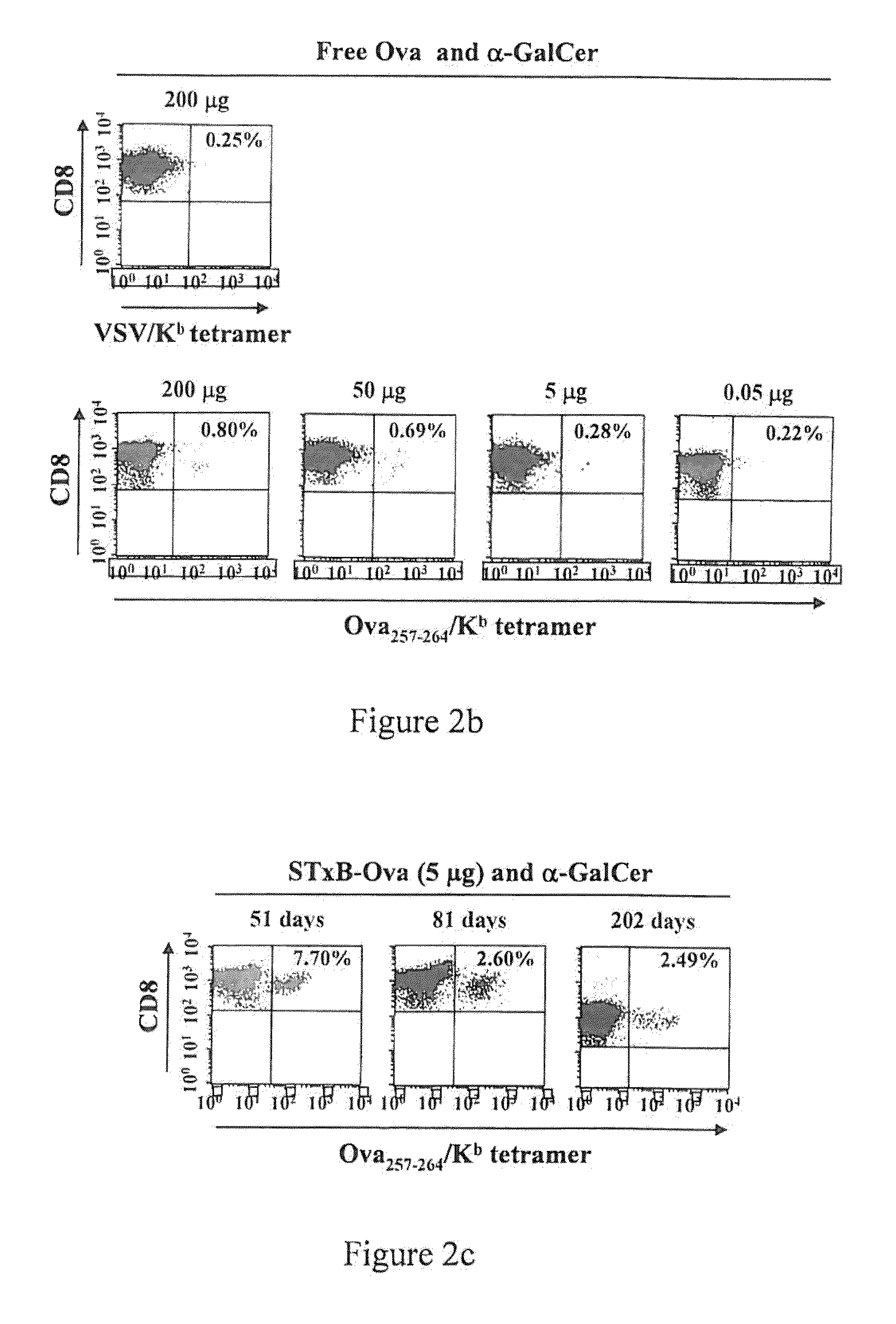
Compositions comprising a B subunit of Shiga toxin and a means stimulating NKT cells
The present invention relates to a composition comprising a) a B subunit of Shiga toxin or a functional equivalent thereof which is able to bind the Gb3 receptor, complexed with an antigen and b) at least one ligand of CDI capable of stimulating NK T cells; and to a pharmaceutical composition and a medicament comprising said composition.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +3
Compositions comprising a b subunit of shiga toxin and a means stimulating nkt cells
Owner:UNIV RENE DESCARTES PARIS V
Ricin inhibitors and methods for use thereof
Ricin A-chain is an N-glycosidase that attacks ribosomal RNA at a highly conserved adenine residue. Crystallographic studies show that not only adenine and formycin, but also pterin-based rings can bind in the ricin active site. For a better understanding of the recognition mode between ricin, and adenine-like rings, the interaction energies and geometries were calculated for a number of complexes. Shiga toxin, a compound essentially identical to the protein originally isolated from Shigella dysenteriae, has an active protein chain that is a homologue of the ricin active chain, and catalyzes the same depurination reaction. The present invention is drawn to identifying inhibitors of ricin and Shiga toxin, using methods molecular mechanics and ab initio methods and using the identified inhibitors as antidotes to ricin or Shiga toxin, or to facilitate immunotoxin treatment by controlling non-specific cytotoxicity.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Methods and compositions based on shiga toxin type 2 protein
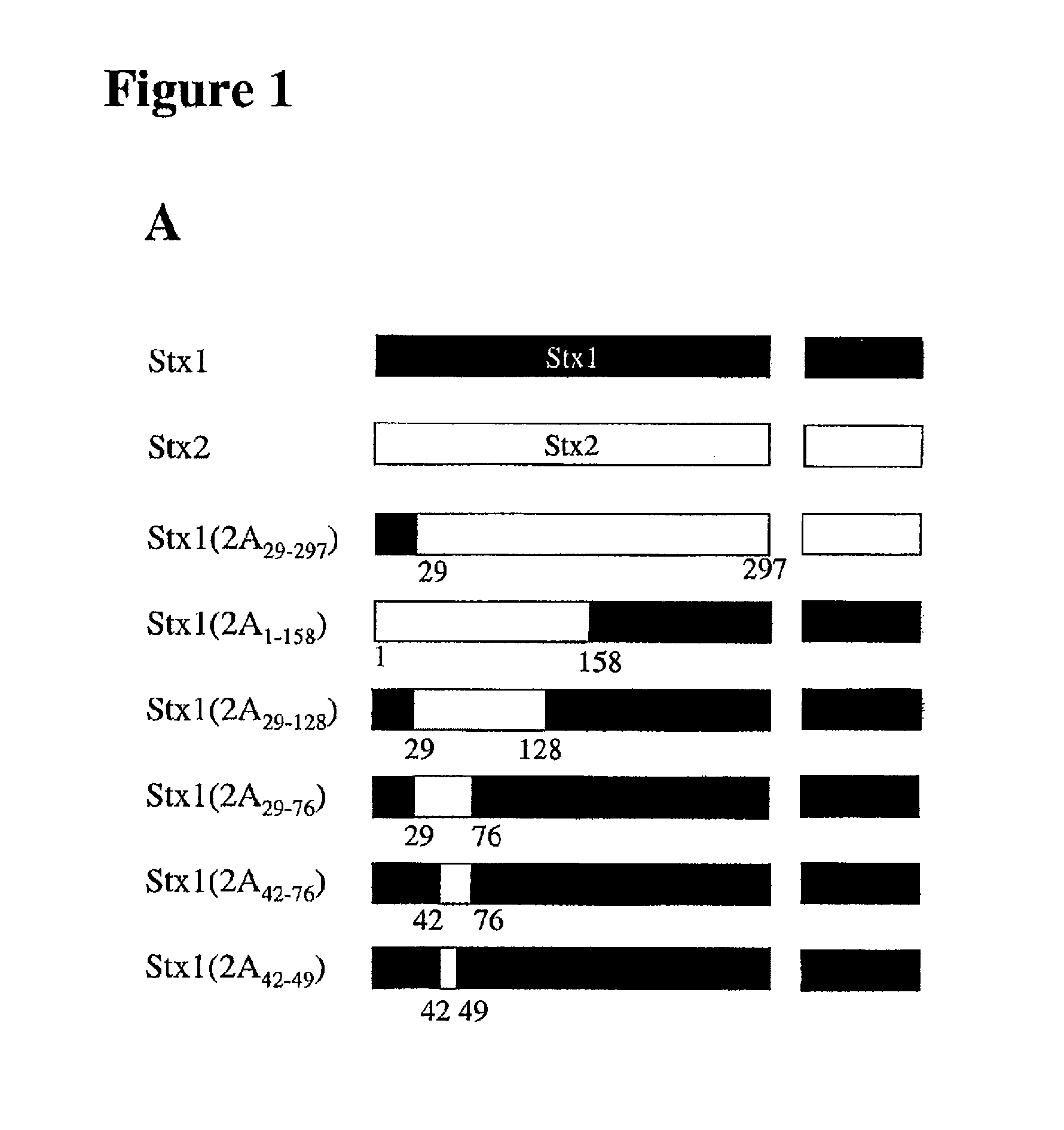
The invention is based on the discovery of the epitope in the Stx2 protein for the 11 E1O antibody. The invention features compositions containing non-full length Stx2 polypeptides that include the 11 E1O monoclonal antibody epitope. The invention also features methods of producing anti-Stx2 antibodies specific for the 11 E1O epitope of the Stx2 protein. Additionally, the invention features methods for treating a subject having, or at risk of developing, a Shiga toxin associated disease (e.g., hemolytic uremia syndrome and diseases associated with E. coli and S. dysenteriae infection) with a polypeptide that includes the 11 E1O epitope or with an anti-Stx2 antibody developed using the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the invention features the detection of Stx2 in a sample using the antibodies developed using the methods of the invention.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
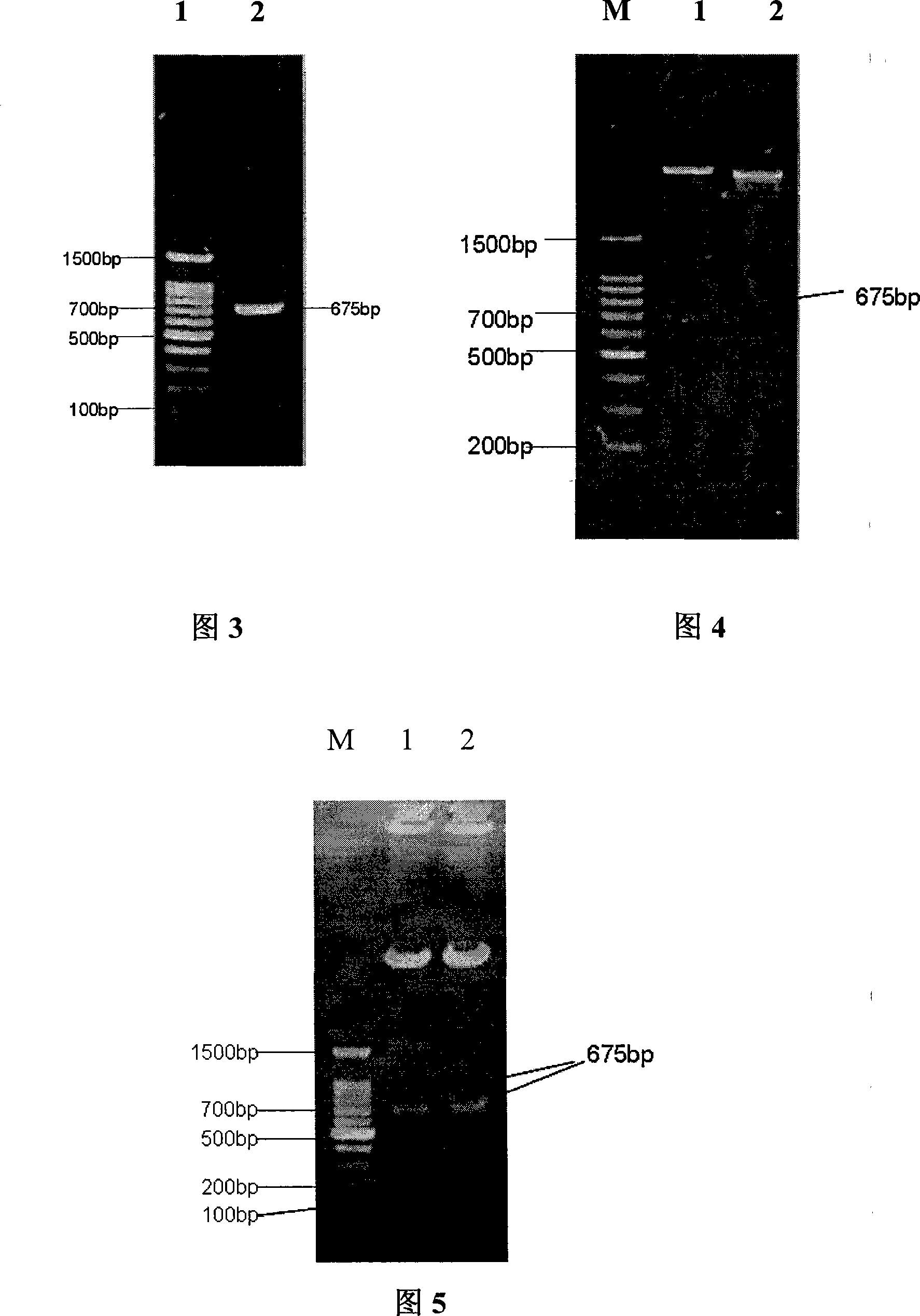
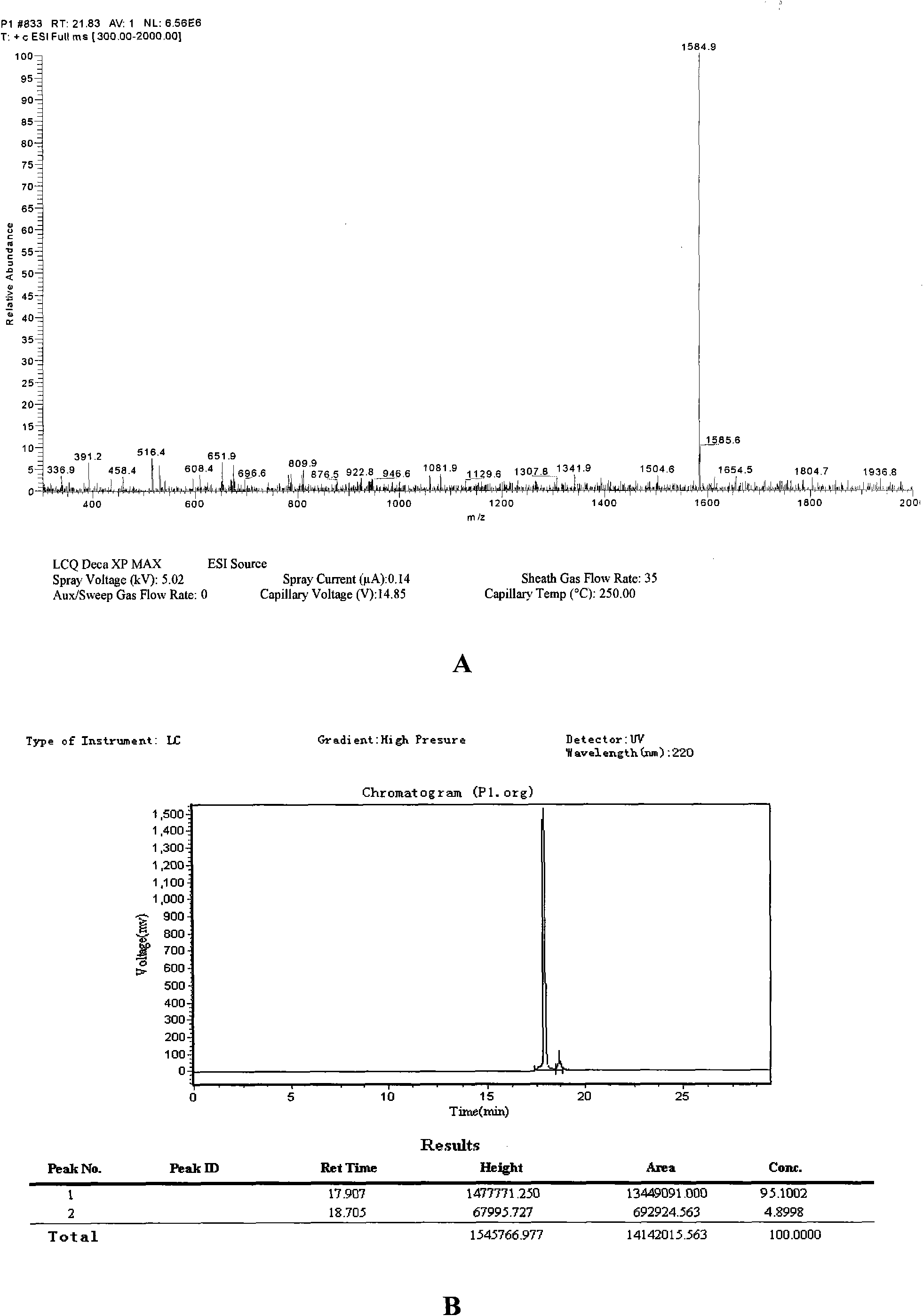
Short peptide for inhibiting Shiga toxin and application thereof
ActiveCN101016332AAvoid toxicityPlay a protective effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a making method of short peptide to inhibit shigellosis with amino acid as list 1, which is characterized by the following: adding chemical group, amino acid, peptide, protein, PEG, marked material to N and C ends to do kinds of chemical or biological decoration; optimizing the stability or other applying property and using scale; fitting for treat shigellosis, enterorrhagia escherichia coli O157 and cholera vibrio.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Proteins comprising amino-terminal proximal shiga toxin a subunit effector regions and cell-targeting immunoglobulin-type binding regions
InactiveUS20160376328A1Reduces and eliminates cytotoxicityFacilitates cellular internalizationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular pathwaysCytotoxicity
The present invention provides proteins comprising immunoglobulin-type binding regions for cell-type specific targeting and Shiga toxin A Subunit effector regions for Shiga toxin effector functions (e.g. cellular internalization, directing subcellular routing, and / or cytotoxicity), wherein the binding regions and Shiga toxin effector regions are combined such that the Shiga toxin effector regions are proximal to the amino-terminals of the proteins. The presently disclosed proteins can comprise additional exogenous materials, such as, e.g., antigens, cytotoxic agents, and detection-promoting agents, and are capable of targeted delivery of these additional exogenous materials into the interiors of target cells. The proteins of the present invention have uses in methods such as, e.g., methods involving targeted killing of target cells, delivering exogenous materials into target cells, labeling subcellular compartments of target cells, and diagnosing and / or treating a variety of conditions including cancers, tumors, other growth abnormalities, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Shiga Toxoid Chimeric Proteins
InactiveUS20090226469A1Reducing and eliminating enzymatic activityReduced enzymatic activityImmunoglobulinsFermentationImmunogenicityShiga bacillus Dysentery
A chimeric Shiga toxoid according to the invention contains an enzymatically-inactivated StxA subunit and a native StxB subunit. This hybrid Shiga toxoid induces the production of broadly cross-reactive species of antibodies against Shiga toxin following immunization. The StxA subunit is modified so that it is enzymatically inactive. The invention thus encompasses the Shiga toxoid or fragments thereof and the nucleic acid sequence of the Shiga toxoid or fragments thereof. The invention further encompasses the production of a Shiga toxoid, the production of antibodies using the Shiga toxoid and methods of productions, and an immunogenic composition containing the Shiga toxoid.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
De-immunized shiga toxin a subunit effector polypeptides for applications in mammals
InactiveUS20160340394A1Reduced antigenicReduced immunogenic potentialAntibacterial agentsHydrolasesCell type specificImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to Shiga toxin effector polypeptides with reduced antigenic and / or immunogenic potential. Immunogenicity can be a limitation for the repeated administration to mammals of proteins and polypeptides derived from Shiga toxins. The Shiga toxin effector polypeptides of the present invention have uses as components of therapeutics, diagnostics, and immunization materials. The cytotoxic proteins of the present invention have uses for selective killing of specific cell types and as therapeutics for the treatment of a variety of diseases, including cancers, immune disorders, and microbial infections. The proteins of the present invention also have uses for detecting specific cell types, collecting diagnostic information, and monitoring the treatment of a variety of diseases, such as, e.g., cancers, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Proteins comprising binding regions, shiga toxin a subunit effector regions, and carboxy-terminal, endoplasmic reticulum localization signal motifs
The present invention provides proteins comprising binding regions for cell-type specific targeting, Shiga toxin effector regions derived from A Subunits of members of the Shiga toxin family for providing Shiga toxin effector functions (e.g. cellular internalization and cytotoxicity), and carboxy-terminal endoplasmic reticulum localization signal motifs. The presently disclosed proteins can comprise additional exogenous materials, such as, e.g., antigens, cytotoxic agents, and detection-promoting agents, and are capable of targeted delivery of these additional exogenous materials into the interiors of target cells. The proteins of the present invention have uses in methods such as, e.g., methods involving targeted killing of target cells, delivering exogenous materials into target cells, labeling subcellular compartments of target cells, and diagnosing and / or treating a variety of conditions including cancers, tumors, other growth abnormalities, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Hemorrhagic bacillus coli of intestine 0157:H7 shiga toxin IIB epitope peptide and uses thereof
InactiveCN101314616AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntestinal structureBacillus coli
The invention belongs to the pharmaceutical biotechnology field, and relates to enterohemorrhagic E.coli O157:H7 Shiga toxin IIB epitope peptide and the application thereof. Four preferred polypeptides are derived from B-cell epitope of the subunit (Stx2A1) of EHEC O157:H7 Shiga toxin IIB epitope peptide. The product can be applied for preparing pharmaceuticals for the diagnosis and treatment of EHEC O157 infection and complications thereof.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Protease-cleavage resistant, shiga toxin a subunit effector polypeptides and cell-targeted molecules comprising the same
ActiveUS20170101636A1Reduces protease-cleavage sensitivityImproved in vivo tolerabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenTolerability
The present invention provides protease-cleavage resistant molecules comprising Shiga toxin effector polypeptides capable of exhibiting potent, Shiga toxin functions (e.g. subcellular routing and cytotoxicity). The present invention also provides protease-cleavage resistant, cell-targeting molecules for targeting specific cell types, e.g., infected or malignant cells. Certain molecules of the present invention are cytotoxic, and certain cell-targeting molecules of the present invention may be used for the targeted killing of specific cell types and the treatment of a variety of diseases, disorders, and conditions, including cancers, tumors, growth abnormalities, immune disorders, and microbial infections. Certain cell-targeting molecules of the invention exhibit improved, in vivo tolerability as compared to related cell-targeted molecules comprising protease-cleavage sensitive, wild-type, Shiga toxin effector polypeptides. The cell-targeting molecules of the invention can deliver additional materials, such as, e.g., antigens, cytotoxic agents, and detection-promoting agents, into the interiors of target cells.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Cholera Toxin Chimera and its Use as a Staph Vaccine
The present invention relates to chimeric protein vaccines and methods of use thereof in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus. One embodiment of the present invention provides a method of generating an immune response in a mammal, that includes administering to the mammal, a composition having a chimeric protein having at least one of: a portion of a cholera toxin, a portion of a heat-labile toxin, and a portion of a shiga toxin; and an antigen having at least one of an antigenic material from S. aureus and an antigenic material from a S. aureus-specific polypeptide.
Owner:BOISE STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions based on Shiga toxin type 1 protein
The invention is based on the discovery of the epitope in the Stx1 protein for the 13C4 antibody. The invention features non-full length Stx1 polypeptides that include the epitope for the 13C4 monoclonal antibody epitope. The invention also features methods of producing anti-Stx1 antibodies specific for the 13C4 epitope of the Stx1 protein. Additionally, the invention features methods for treating a subject having, or at risk of developing, a Shiga toxin associated disease (e.g., hemolytic uremia syndrome and diseases associated with E. coli and S. dysenteriae infection) with a polypeptide that includes the 13C4 epitope or with an anti-Stx1 antibody developed using the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the invention features the detection of Stx1 in a sample using the antibodies developed using the methods of the invention.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Cholera Toxin Chimera and its Use as a Staph Vaccine
ActiveUS20130266607A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention relates to chimeric protein vaccines and methods of use thereof in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus. One embodiment of the present invention provides a method of generating an immune response in a mammal, that includes administering to the mammal, a composition having a chimeric protein having at least one of: a portion of a cholera toxin, a portion of a heat-labile toxin, and a portion of a shiga toxin; and an antigen having at least one of: an antigenic material from S. aureus and an antigenic material from a S. aureus-specific polypeptide.
Owner:BOISE STATE UNIVERSITY
Cell-targeting molecules comprising protease-cleavage resistant, Shiga toxin A subunit effector polypeptides and carboxy-terminal moieties
ActiveUS10815469B2Improve the usefulnessReduced likelihoodAntibacterial agentsHydrolasesAntigenCell type specific
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Fusion protein SAmB as well as coding gene and applications thereof
The invention discloses a fusion protein SAmB as well as a coding gene and applications thereof. The fusion protein provided by the invention is named as SAmB, and comprises an A-subunit mutant protein of N-end II-type shiga toxin and a B-subunit protein of C-end I-type shiga toxin, wherein, the A-subunit mutant protein is a protein which mutates the active site amino acid residue of the A-subunit protein of the N-end II-type shiga toxin. The fusion protein SAmB provided by the invention can be used as a drug used for preventing and / or treating the shiga toxin pathogenic bacterial infection or infection complication.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Methods and compositions based on Shiga toxin type 1 protein
The invention is based on the discovery of the epitope in the Stx1 protein for the 13C4 antibody. The invention features non-full length Stx1 polypeptides that include the epitope for the 13C4 monoclonal antibody epitope. The invention also features methods of producing anti-Stx1 antibodies specific for the 13C4 epitope of the Stx1 protein. Additionally, the invention features methods for treating a subject having, or at risk of developing, a Shiga toxin associated disease (e.g., hemolytic uremia syndrome and diseases associated with E. coli and S. dysenteriae infection) with a polypeptide that includes the 13C4 epitope or with an anti-Stx1 antibody developed using the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the invention features the detection of Stx1 in a sample using the antibodies developed using the methods of the invention.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Shiga toxoid chimeric proteins
InactiveUS8846058B2Reducing and eliminating enzymatic activityBacterial antigen ingredientsDigestive systemAntiendomysial antibodiesImmunogenicity
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Vaccine against colibacillosis
InactiveUS20170028046A1Control performanceImprove performanceAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliToxin
The present invention provides an agent for controlling colibacillosis including a fusion protein comprising a subunit of Shiga toxin and a subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD +1
Primer, kit and method for detecting bacillus coli shiga toxin through PSR (Polymerase Spiral Reaction) isothermal amplification reaction detection
PendingCN108796098AGuaranteed reliabilityNo loss of timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses a primer, a kit and a method for detecting bacillus coli shiga toxin through PSR (Polymerase Spiral Reaction) isothermal amplification reaction detection. The primer comprisesa detection primer Ft and a detection primer Bt, wherein a nucleotide sequence of the detection primer Ft is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; a nucleotide sequence of the detection primer Bt is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a kit for detecting the bacillus coli shiga toxin through the PSR isothermal amplification reaction. The kit comprises the primers, BstDNA polymerase and a mixed solution of calcein and manganese chloride; detection of polymerase spiral reaction on the bacillus coli shiga toxin can be carried out, time loss and short time consumption cannot be caused by the changeof a temperature; a reaction process is simple and convenient, a detection period is short, the specificity is strong, and detection results can be observed by naked eyes. According to the primer, thekit and the method for detecting the bacillus coli shiga toxin through the PSR isothermal amplification reaction detection disclosed by the invention, significance on amplification development of a novel constant-temperature amplification technology and detection on site of microorganism can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods, compositions, and kits for treating shiga toxin associated conditions
The invention features methods, compositions, and kits for treating a subject having a Shiga toxin associated disease with chimeric anti-Shiga Toxin 1 (cαStx1) and anti-Shiga Toxin 2 (cαStx2) antibodies.
Owner:THALLION PHARMA
Anti-I type Shiga toxin IgY antibody as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101570574AInhibition of biological effectsEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliAntigen
The invention discloses an anti-I type Shiga toxin IgY antibody, and the antibody can be prepared by the following method: non-toxic Shiga toxin immune antigen is prepared by the method of chemical synthesis or gene recombinant expression, egg-laying hens are immunized, eggs are collected, and the biological chemical method is applied in extracting and purifying egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY antibody). The antibody has the effects of neutralizing Shiga toxin and effectively inhibiting the toxicity of the Shiga toxin, can be used as an oral antitoxin for preventing and treating complications caused by toxin-producing Shigella, entero-hemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157, vibrio cholerae and the like and can be simultaneously applied in the detection and the infection diagnosis of type I Shiga toxin and pathogen thereof.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Primers, kit and method for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by PSR (polymerase spiral reaction)
ActiveCN109355408AReduce sensitivityGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliFluorescence
The invention discloses primers, kit and method for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by PSR (polymerase spiral reaction). The primers for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I are designedaccording to specific target sequence stx1 of Shiga toxin I and include detection primer Ft and detection primer Bt, as well as acceleration primer IF and acceleration primer IB, and their nucleotidesequences are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 to 4. The invention also provides a kit for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by PSR; the kit includes the above primers, Bst DNA polymerase, and a mixed solution of calcein and manganese chloride, is suitable for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by polymerase spiral reaction; after developing with a fluorescent dye, the results can be judged witheyes. The kit is simple and quick to operate, low in detection cost and suitable for field detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Compositions comprising a b subunit of shiga toxin and a means stimulating nkt cells
InactiveUS20100196417A1Stimulate immune responseAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenToxin
The present invention relates to a composition comprising a) a B subunit of Shiga toxin or a functional equivalent thereof which is able to bind the Gb3 receptor, complexed with an antigen and b) at least one ligand of CDI capable of stimulating NK T cells; and to a pharmaceutical composition and a medicament comprising said composition.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +3
Enterorrhagia colibacillus 0157:H7 Shiga toxin 2A1 subunit active segment Stx2a1 recombination protein, expression method and application
InactiveCN101240019AImproving immunogenicityStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsDepsipeptidesEscherichia coliShiga bacillus Dysentery
The invention discloses a enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 shiga toxin 2A1 subunit active fragment Stx2a1 recombinant protein, including 1) enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 shiga toxin 2A1 subunit active fragment Stx2a1 and expression vector fragment; or 2) enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 shiga toxin 2A1 subunit active fragment Stx2a1 protein carboxyl terminal acquires protein and expression vector fragment with similar function by losing and adding one or more amino terminals. The invention also discloses preparation of aforementioned enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 shiga toxin 2A1 subunit active fragment Stx2a1 recombinant protein, application thereof in preparation of test reagent box and preparation of subunit vaccine for prevention and cure infection of EHEC O157:H7.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
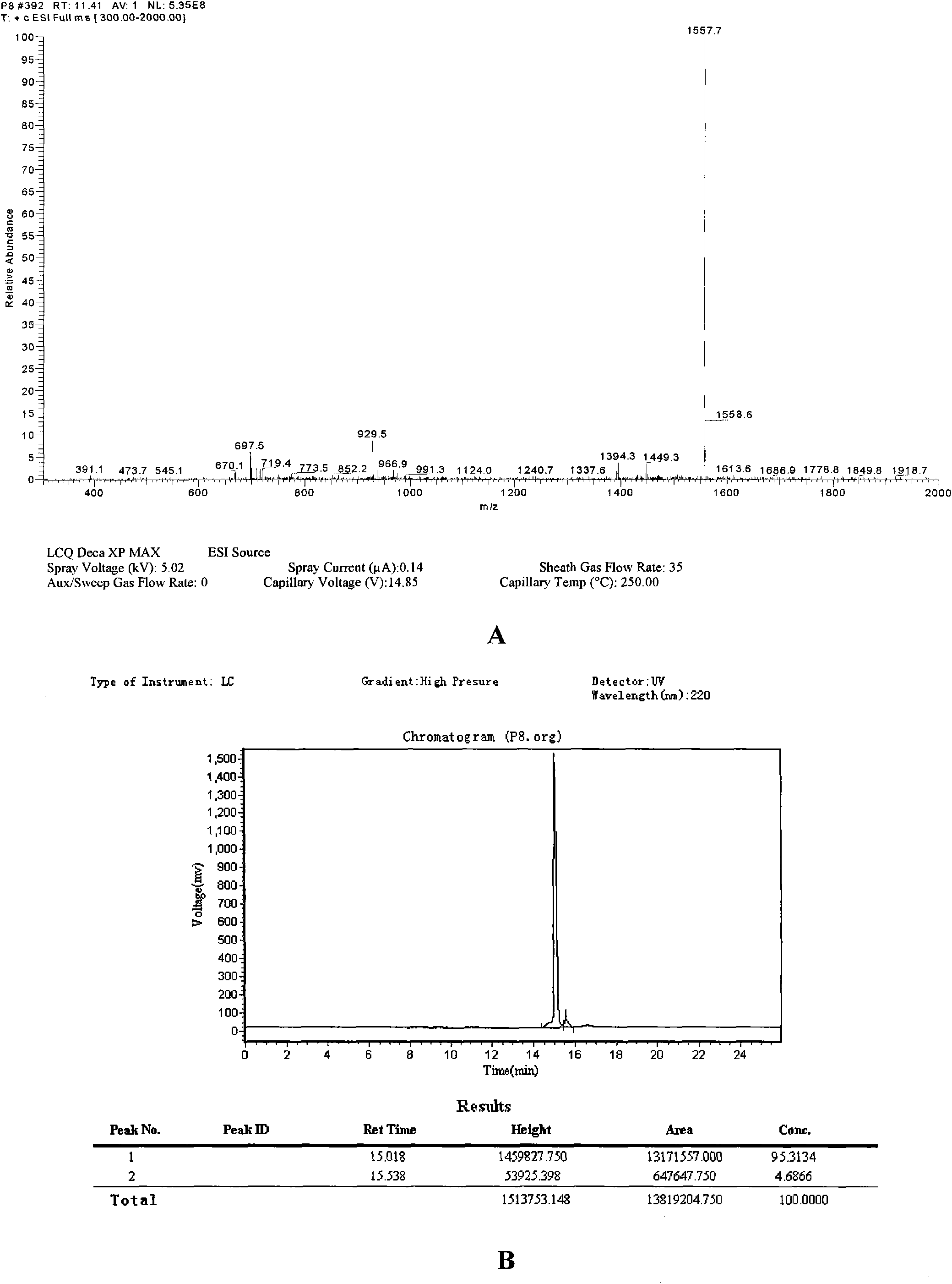
Polypeptide WA8 for inhibiting type-2 shiga toxin activity and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a polypeptide WA8 for inhibiting type-2 shiga toxin activity and a coding gene and application thereof. The polypeptide provided by the invention is named as WA8 (also named P8), and the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is expressed as a sequence 2 in a sequence table. The polypeptide P8 can be prepared into a medicament for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by type-2 shiga toxin or pathogenic bacteria which can generate the type-2 shiga toxin.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Cd20-binding immunotoxins for inducing cellular internalization and methods using same
The present invention provides cytotoxic proteins comprising immunoglobulin-type binding regions for mediating cell-type specific targeting and Shiga toxin effector regions derived from A Subunits of members of the Shiga toxin family for effectuating cytotoxicity. The cytotoxic proteins have uses for selective killing of specific cell types and as therapeutics for the treatment of a variety of diseases, including cancers, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Monoclonal antibody, Fab antibody and application for neutralizing enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli o157:H7 shiga toxin II
The invention belongs to the technological field of medicine bioengineering, which more particularly relates to a monoclonal antibody neutralizing enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 shiga toxin II, Fab antibody sequences and the application. The monoclonal antibody is prepared by hybridoma cell lines with the preservation number of CCTCC: C200822. The antibody of the invention can be used for preparing medicines for diagnosing and treating EHEC O157 infections and the complicating diseases thereof.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Plasmid standard molecules for detecting Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and application thereof
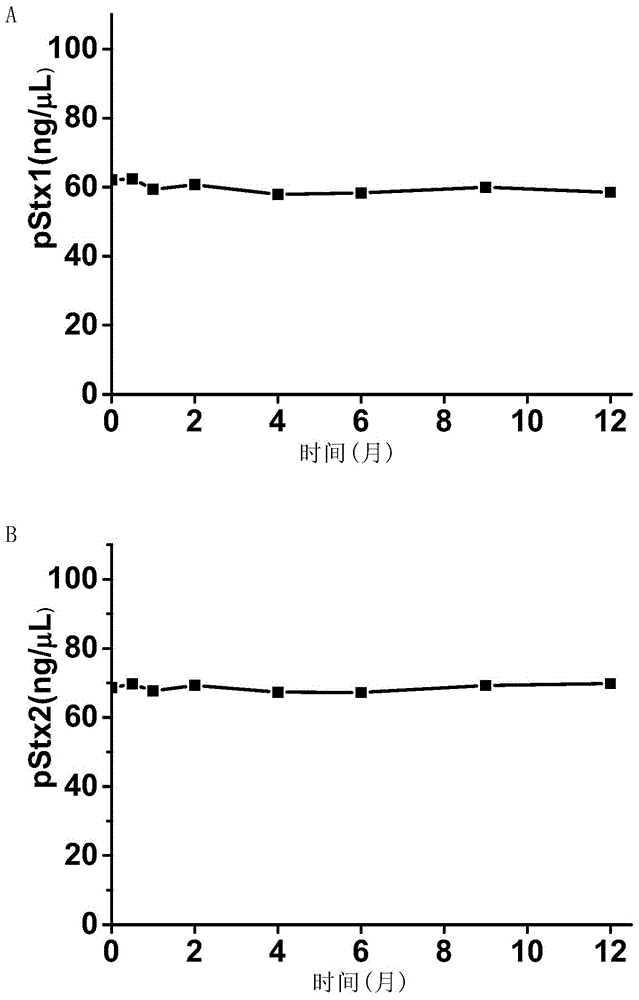
ActiveCN104946736AImprove uniformityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention discloses plasmid standard molecules PLW03 and PLW04 for detecting Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and application thereof. The invention particularly discloses a polynucleotide for Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli PCR detection and a primer pair matched with the polynucleotide. The polynucleotide sequence is prepared into the standard plasmid molecules by using an appropriate framework plasmid. When being matched with the primer pair to perform real-time fluorescent PCR detection, the standard plasmid molecules have the advantages of excellent specificity, excellent sensitivity and favorable stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com