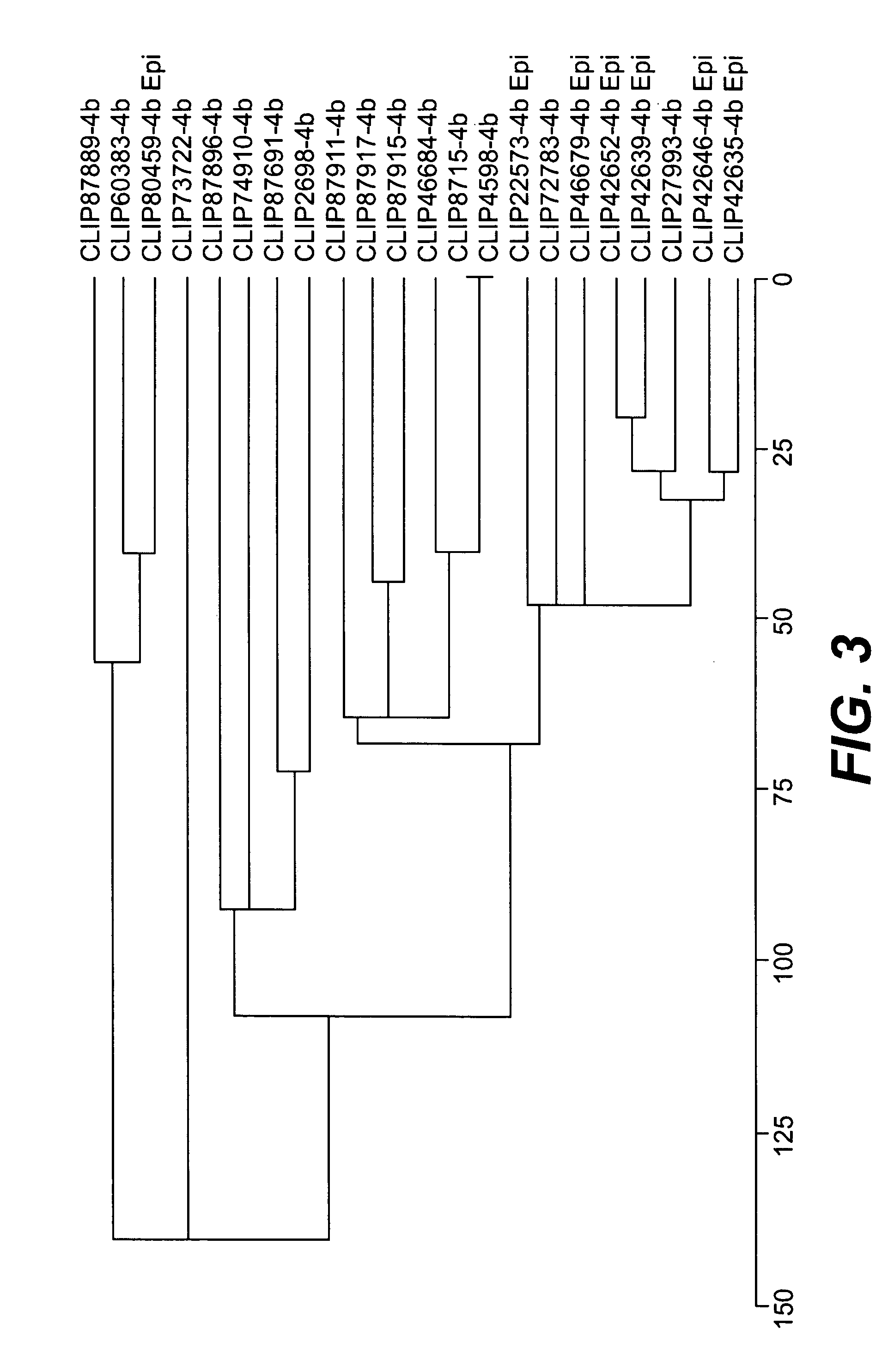
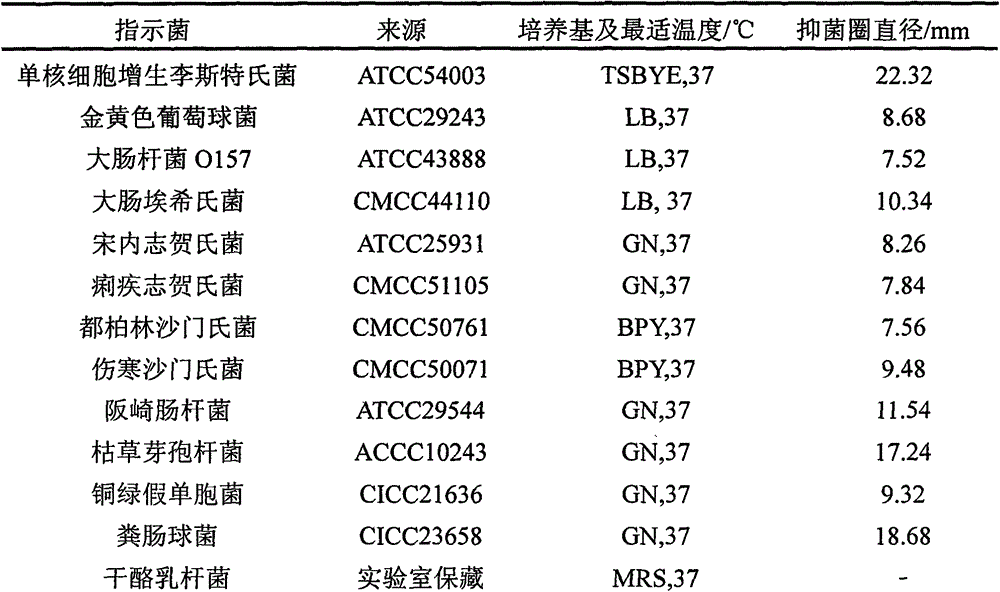
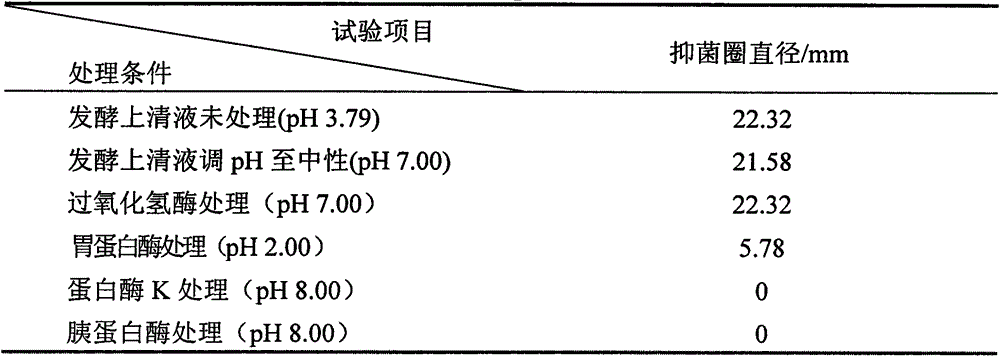
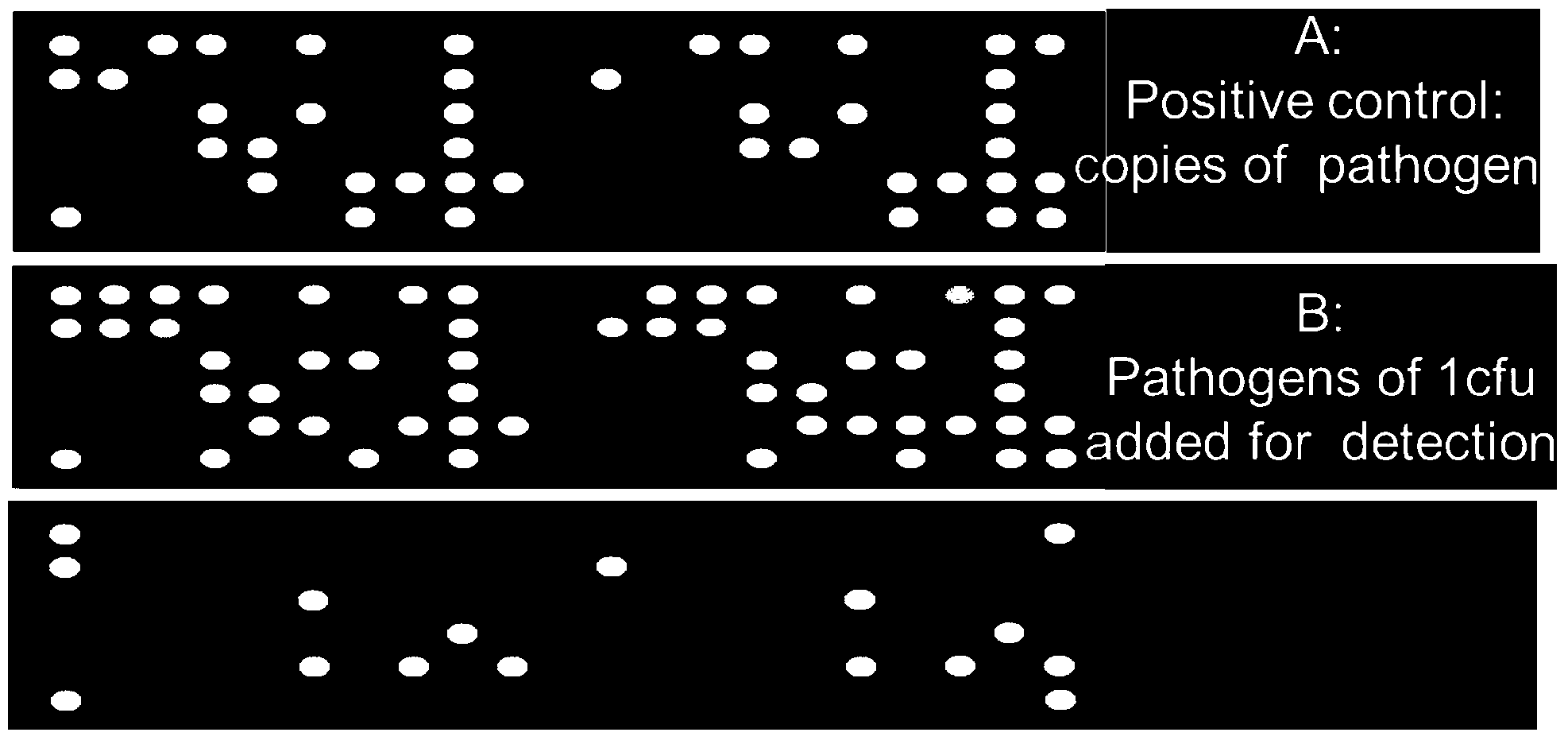
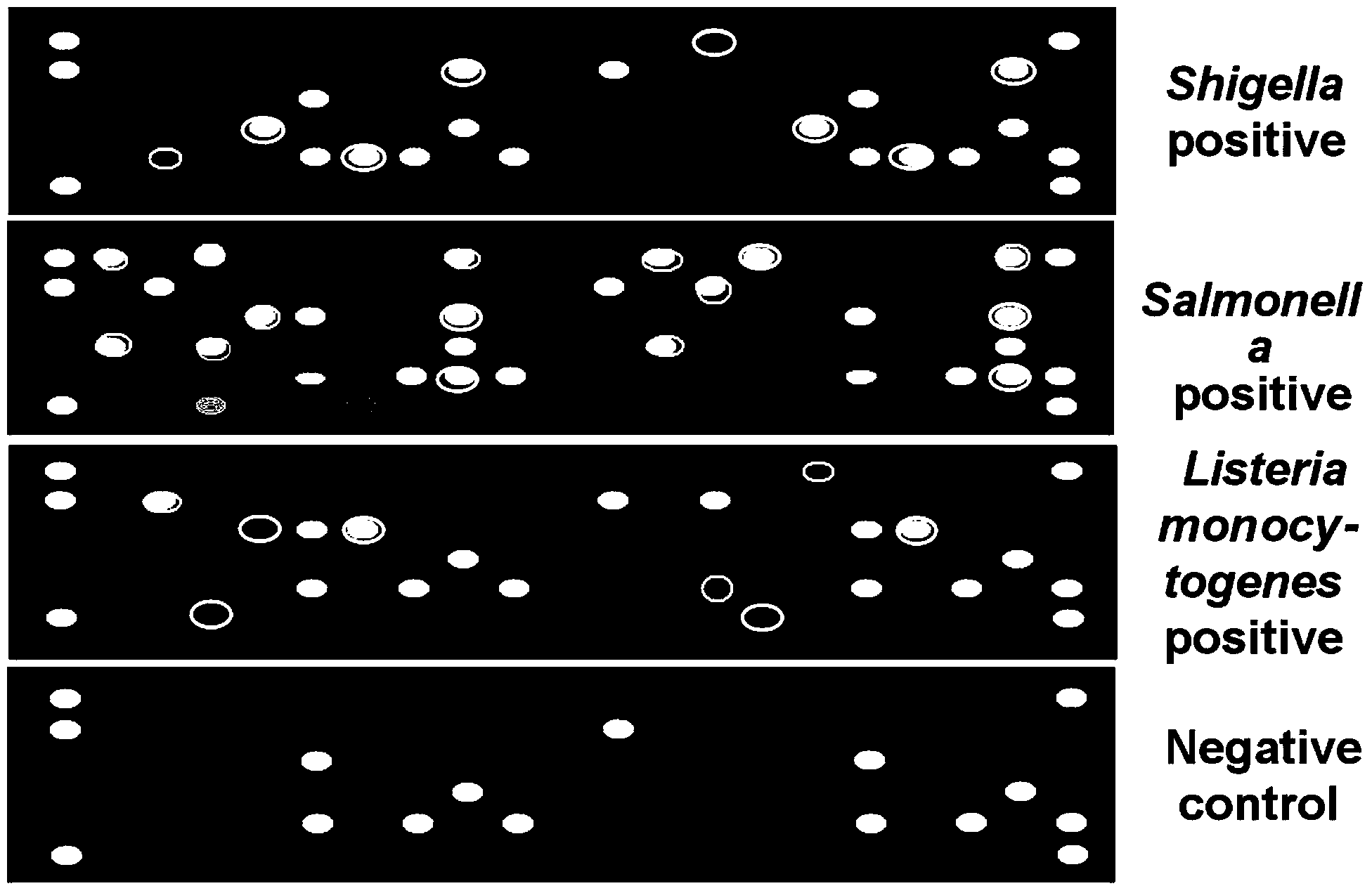
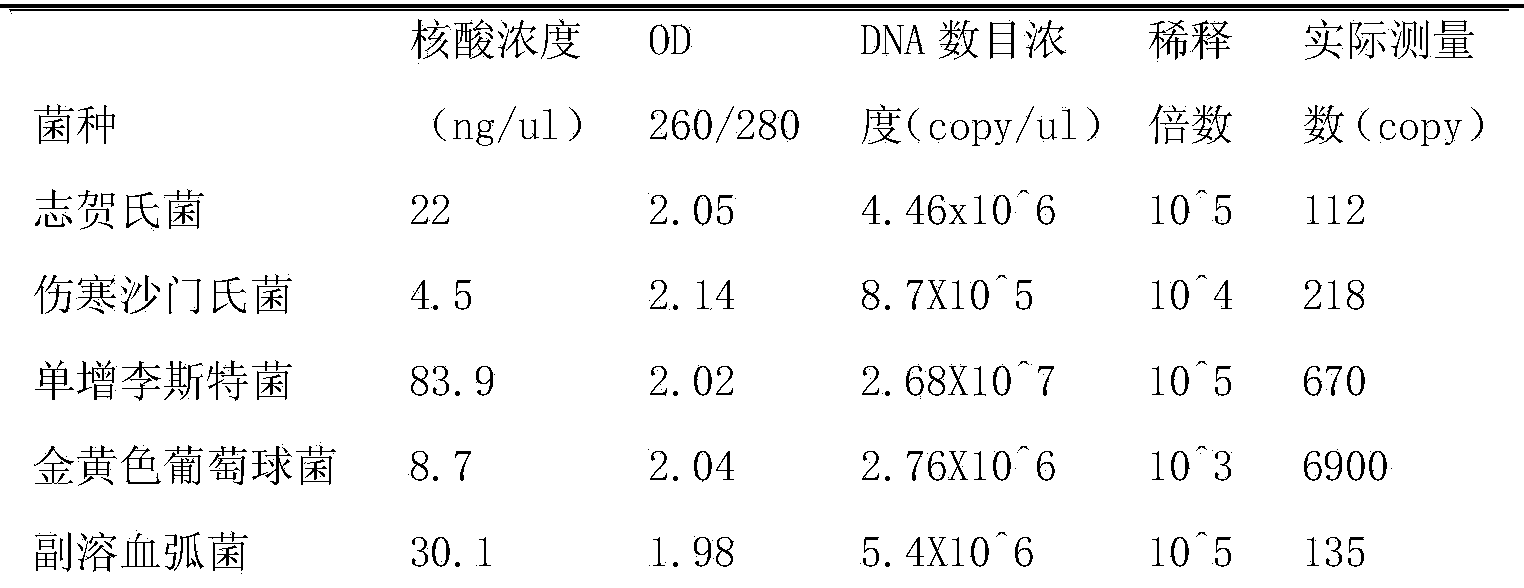
Patents
Literature
592 results about "Listeria monocytogenes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Listeria monocytogenes is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host's cells and is one of the most virulent foodborne pathogens, with 20 to 30% of foodborne listeriosis infections in high-risk individuals may be fatal. Responsible for an estimated 1,600 illnesses and 260 deaths in the United States annually, listeriosis ranks third in total number of deaths among foodborne bacterial pathogens, with fatality rates exceeding even Salmonella spp. and Clostridium botulinum. In the European Union, listeriosis follows an upward trend that began in 2008, causing 2,161 confirmed cases and 210 reported deaths in 2014, 16% more than in 2013. Listeriosis mortality rates are also higher in the EU than for other foodborne pathogens.
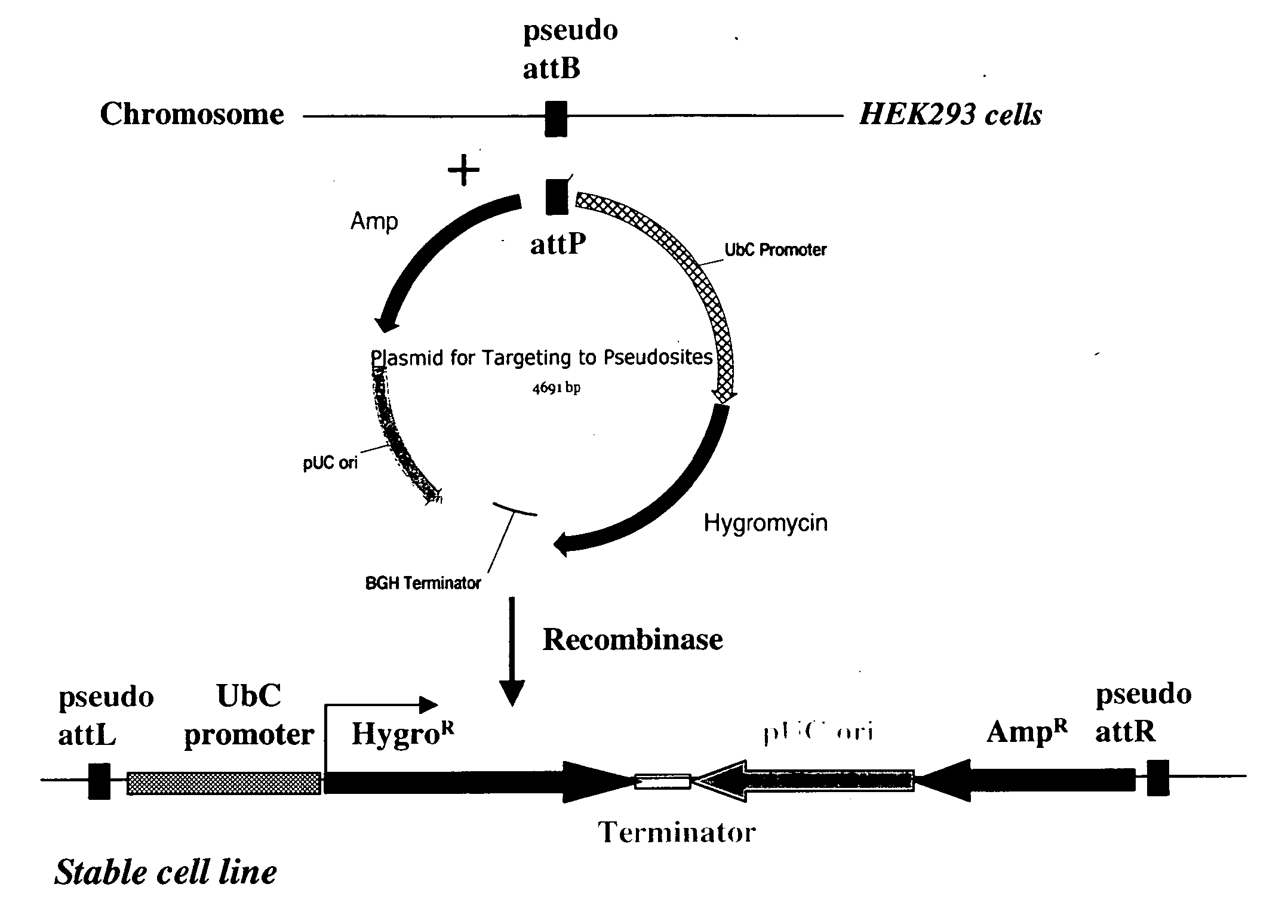
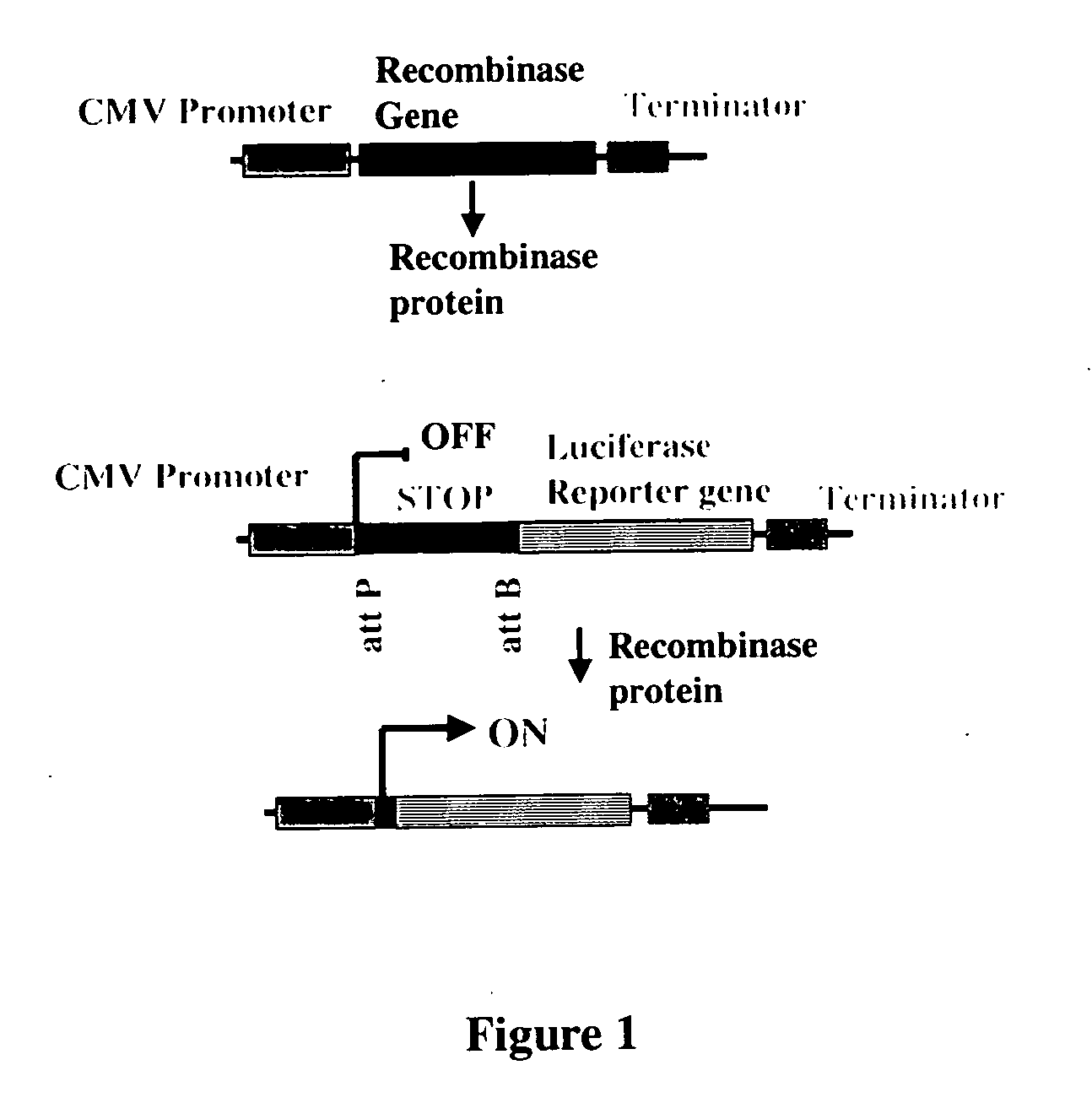
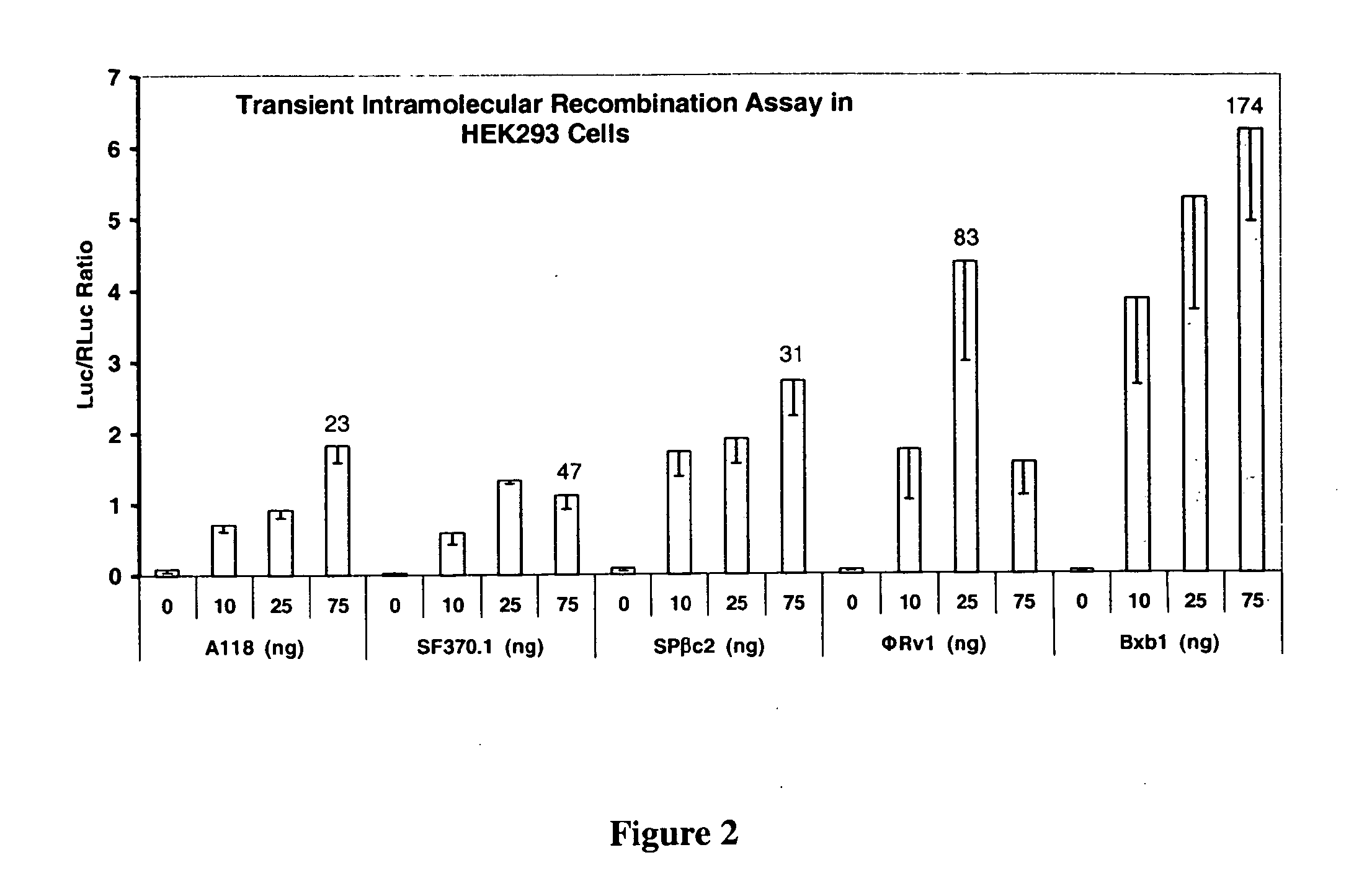
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
InactiveUS20080020465A1Antibacterial agentsHydrolasesStreptococcus pyogenesSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PADIDAM MALLA
MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry)-assisted identification method for listeria monocytogenes
InactiveCN102253111AAccurate identificationSimple sample preparation in operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTime-of-flight mass spectrometryMicroorganism
This invention relates to an MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption / Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry)-assisted identification method for listeria monocytogenes, comprising the following steps of: (1) selecting 35 to 40 strains of fresh cultures of listeria monocytogenes, pre-treating the samples; (2) collecting maps of all bacterial strain samples; (3) analyzing and unifying the obtained maps by using BioTyper software to obtain a standard map of listeria monocytogenes; (4) preparing a sample of a microorganism to be detected by adopting the method in the step (1); (5) collecting the MALDI-TOF-MS map of the sample to be detected according to the method in the step (2); comparing the obtained MALDI-TOF-MS map of the sample to be detected in step (5) with the obtained standard map of listeria monocytogenes in the step (3), judging the detection results according to matching fractions. According to the invention, a mass spectrogram database and the standard map in listeria monocytogenes identification are created successfully, and the accurate identification with convenience, microscale and high automation for listeria monocytogenes can be realized.
Owner:曹际娟 +1
Methods and compositions for the targeting of a systemic immune response to specific organs or tissues
The invention provides methods and compositions for targeting a separately generated immune response to a specific organ or tissue, e.g. one affected by cancer, using one or more agents with a tropism for the organ or tissue or that can be specifically localized to the desired organ or tissue. For example, the invention provides methods ands compositions for treating liver metastases from colorectal cancer using a combination of a granulocyte / macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) augmented tumor cell vaccination and Listeria monocytogenes (LM) infection.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
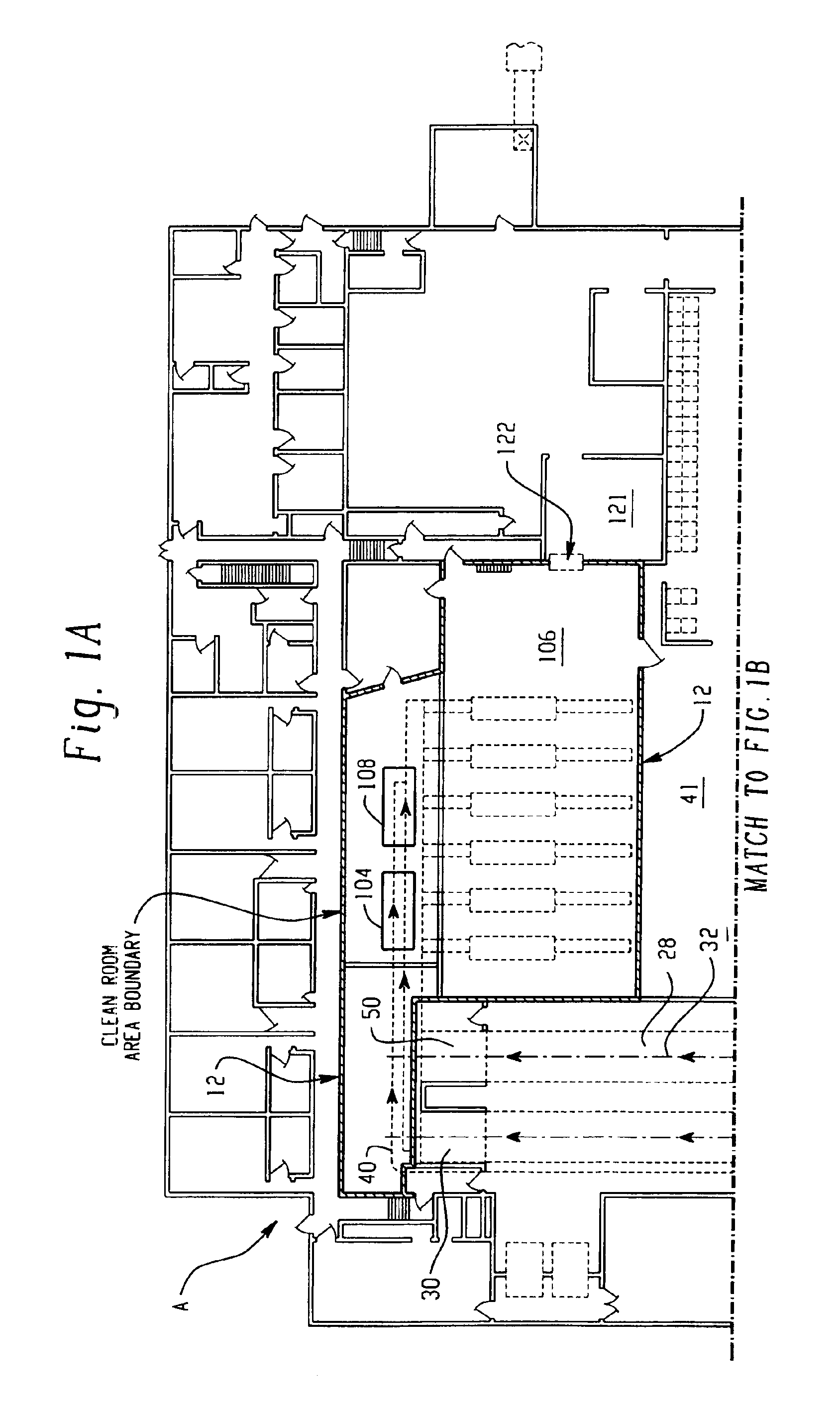
System for handling processed meat and poultry products
InactiveUS6964788B2Apparent advantageObvious advantagesMeat/fish preservation using liquidsSausage casingsPathogenic microorganismPoultry product
Food products, such as precooked meats, sausages, and the like are microbially decontaminated in their cooking packages to remove surface microorganism contamination from the packages. The cooking packages are removed and the food products optionally subjected to further processing, such as slicing, and then packaged in aseptic packaging. The microbial decontamination step, further processing and packaging are carried out in a clean room which is maintained to a high level of sterilization or disinfection to minimize or eliminate contamination of the food products with pathogenic microorganisms such as Listeria Monocytogenes. The food products thus leave the packaging plant with a much higher assurance of food safety than is found in a conventional packaging plant.
Owner:STERIS CORP
Antibacterial composition and method of production
An electrolysis method is described for generating an aqueous solution of copper citrate that has bacteriocidal activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. Gram positive bacteria are known to be relatively more sensitive to the bacteriocidal activities of copper ions than are Gram negative bacteria. Situations exist in which a disinfectant that is relatively more toxic for Gram positive bacteria will be advantageous over a more broadly active disinfectant, such as that provided by most other disinfectants. In particular, a disinfectant that is relatively selective for Gram positive bacteria could help preserve various non-pathogenic Gram negative microbial populations. The residual Gram negative bacteria can potentially compete with, and thereby lessen the chances of the reintroduction of pathogenic Gram positive bacteria, such as MRSA, Streptococcus, Clostridium difficile and Listeria monocytogenes.
Owner:MI HOPE
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20040185478A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Listeria monocytogenes nucleic acid chromatography detection kit, its detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN102520172AGuaranteed SensitivityGuaranteed FeaturesMaterial analysisDNA extractionMicrobiology
The invention discloses a listeria monocytogenes nucleic acid chromatography detection kit, its detection method and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and immunology. According to the invention, with the combination of a polymerase chain reaction technology in molecular biology and an immunochromatography technology, rapid detection of listeria monocytogenes in food is accomplished. The kit provided by the invention includes three parts of DNA extraction, PCR amplification and strip detection. The combination of the molecular biology technology and the immunochromatography technology is accomplished by modification of primers and selection of corresponding coatings and markers in strip preparation so as to achieve specific amplification product detection of listeria monocytogenes in food. Compared with a traditional biochemistry method, the method provided by the invention is used to greatly save detection time and simplify operation steps, has characteristics of accuracy, rapidity, convenience and safety, and is suitable for detection of a large number of samples.
Owner:北京陆桥技术股份有限公司
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20060263810A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNeisseria meningitidisListeria monocytogenes
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6′-IIa, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6′)-aph(2″), aad(6), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Pathogenic microorganism DNA detecting chip and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101113476ASensitive hybridization detectionAccurate readingMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to a pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip and the chip comprises a carrier and a nucleic acid probe on the carrier. The nucleic acid probe is provided with a target detection probe used for detecting target gene of pathogenic microorganism. The pathogenic microorganism comprises but not limits to vibrio cholerae, pathogenic escherichia coli, campylobacter jejuni, Yersinia enterocolitica, parahemolytic vibrio, salmonella, and shigella and Listeria monocytogenes. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip and provides applications of the pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip in detection of pathogenic microorganism. Also a pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip kit is provided.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Annular mediated isothermal amplification-nano cadmium sulphide mark electrochemistry checking method for Listeria monocytogenes
InactiveCN101260424AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater bathsLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a method for detection Listeria monocytogenes with loop-mediated isothermal amplification-CdS nanoparticles labeling electrochemistry. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of: obtaining double-stranded target sequence of amplification reagent-Listeria monocytogenes to be detected by means of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction; pyrolyzing a double-stranded target sequence in water bath into a single-stranded target sequence, then self assembling and fixing at the surface of gold electrode, so that the target sequence modified electrode of the Listeria monocytogenes to be detected is obtained; afterwards, labeling the probe sequence coming from the Listeria monocytogenes by CdS nanoparticles to obtain a labeled probe sequence; carrying out molecular hybridization on the labeled probe sequence and the target sequence of the target sequence modified electrode, and carrying out electrochemical detection by simultaneity plating Hg anodic stripping method; detecting out cadmium ions corresponding to the species-specific genes (actA) of the detected Listeria monocytogenes. The method has the advantages of speediness, strong specificity, high sensitivity and convenient use.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20030049636A1Low costRapid positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:BERGERON MICHEL G +3
Fourteen-food-borne pathogenic bacterium multiplex PCR detection primer set and kit
ActiveCN103484546ATo achieve the detection effectMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a fourteen-food-borne pathogenic bacterium multiplex PCR detection primer set and a kit. The detection primer set is composed of primer pairs for detecting salmonella, Shigella, Vibrio parahemolyticus, campylobacter jejuni, campylobacter coli, staphylococcus aureus, bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, yersinia enterocolitica, enterobacter sakazakii, Escherichia coli, vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli O157, aeromonas hydrophila and internal positive control. A multiplex PCR detection method based on an ordinary PCR platform is built, multiplex PCR reactions are carried out on genomic DNA, extracted from a sample to be tested, of bacteria in the same reaction system through the primer pairs acquired through analysis and design, and whether the food-borne pathogenic bacteria are contained in the sample or not is judged through the electrophoretic analysis of reaction products.
Owner:北京卓诚惠生生物科技股份有限公司
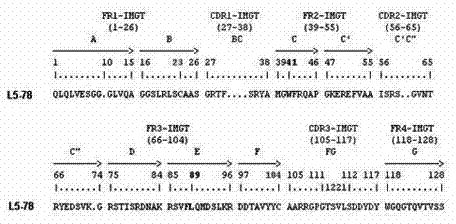
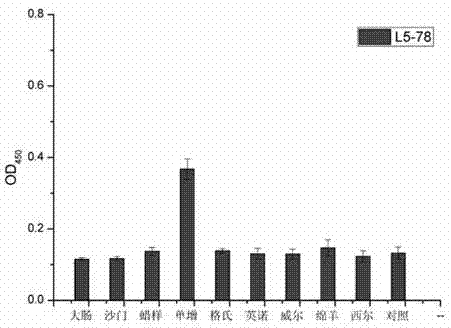
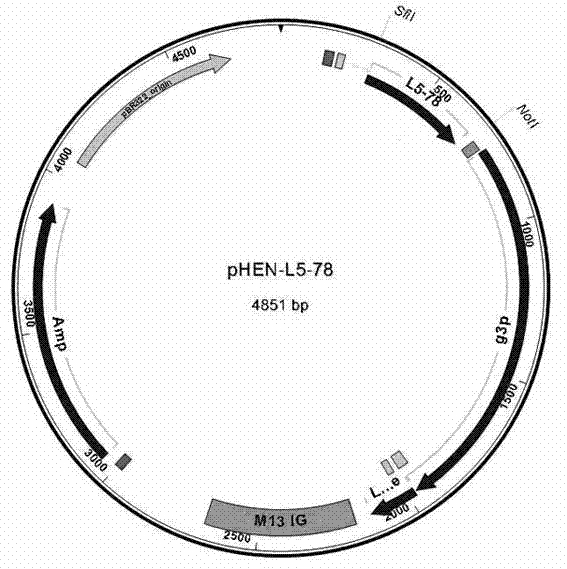
Single-domain heavy chain antibody L5-78 for Listeria monocytogenes
InactiveCN103497252AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAntigenADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to a single-domain heavy chain antibody and polypeptide for Listeria monocytogenes. The antibody has the protein or polypeptide with the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:1, and can be used in the fields of immune detection, antigen enrichment purification and the like. The amino acid sequence provided by the invention can be used as a precursor, can be modified by using a random or site-directed mutagenesis technique to obtain a mutant with better properties (affinity, specificity, stability and the like), and is used for developing proteins or polypeptides which are further used in medicine, industry and agriculture.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
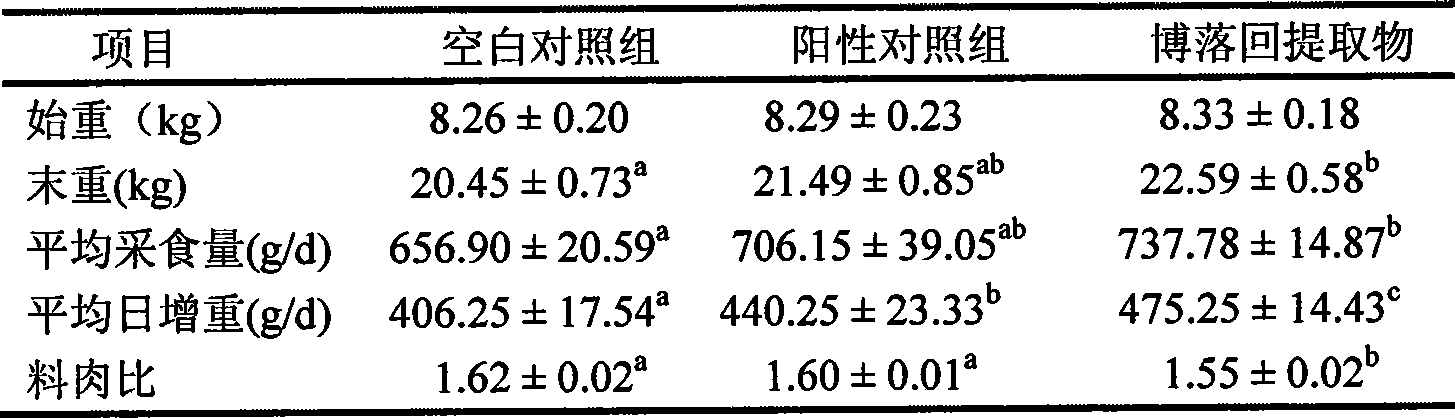
Application of pink plumepoppy herb extract in veterinary drugs of economic animals
ActiveCN101530475APromote growthImprove conversion rateAntibacterial agentsAnimal feeding stuffFeed conversion ratioFeed additive
The invention relates to an application of pink plumepoppy herb extract in veterinary drugs of economic animals; the pink plumepoppy herb extract is used for preparing medical feed additives of the veterinary drugs which are used for enhancing the growth of the economic animals and increasing conversion rate of the feed or veterinary drugs which has better inhibiting action and disinfecting action to common pathogenic bacteria in livestock and poultry, such as listeria monocytogenes, haemophilus and pasteurella.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria by using nucleic acid test strip based on hyper-branched rolling cycle amplification and kit
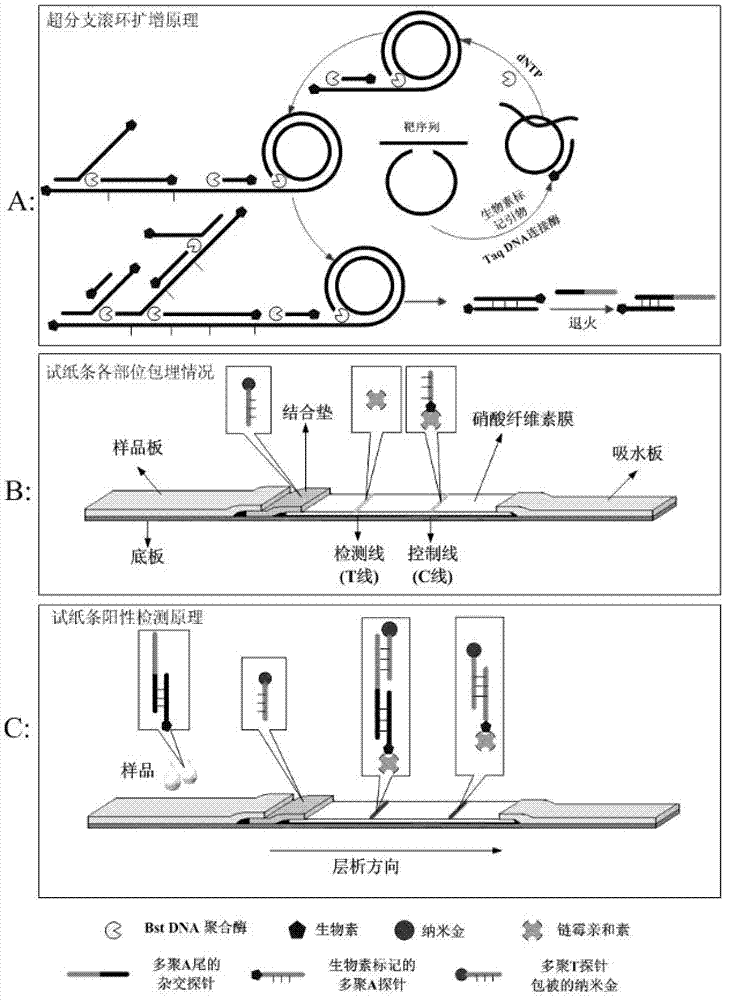
InactiveCN102816855AReduce the chance of non-specific amplificationLess prone to false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesListeria monocytogenesNucleic acid test
The invention discloses a method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria by using a colloidal gold nucleic acid test strip based on hyper-branched rolling cycle amplification and a kit for detecting Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella, belonging to the technical field of biological detect. The method comprises the following main steps: (1) performing extraction and enzyme digestion on the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of food-borne pathogenic bacteria; (2) designing an amplification primer and a nucleic acid probe sequence; (3) performing hyper-branched rolling cycle amplification reaction; (4) annealing and hybridizing; (5) preparing a nano gold probe; (6) preparing a colloidal gold nucleic acid test strip; and (7) detecting a sample. When the sample contains a target gene segment, both a T line and a C line of the colloidal gold nucleic acid test strip are formed into red lines; and if the sample does not contain the target gene segment, only the C line of the colloidal gold nucleic acid test strip is formed into a red line. According to the invention, food-borne pathogenic bacteria in the food sample can be detected quickly, specifically, sensitively, qualitatively and quantitatively; and the invention is simple in probe design, short in operation steps and favorable for popularization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Stabilization of fresh mozzarella cheese using fermented whey
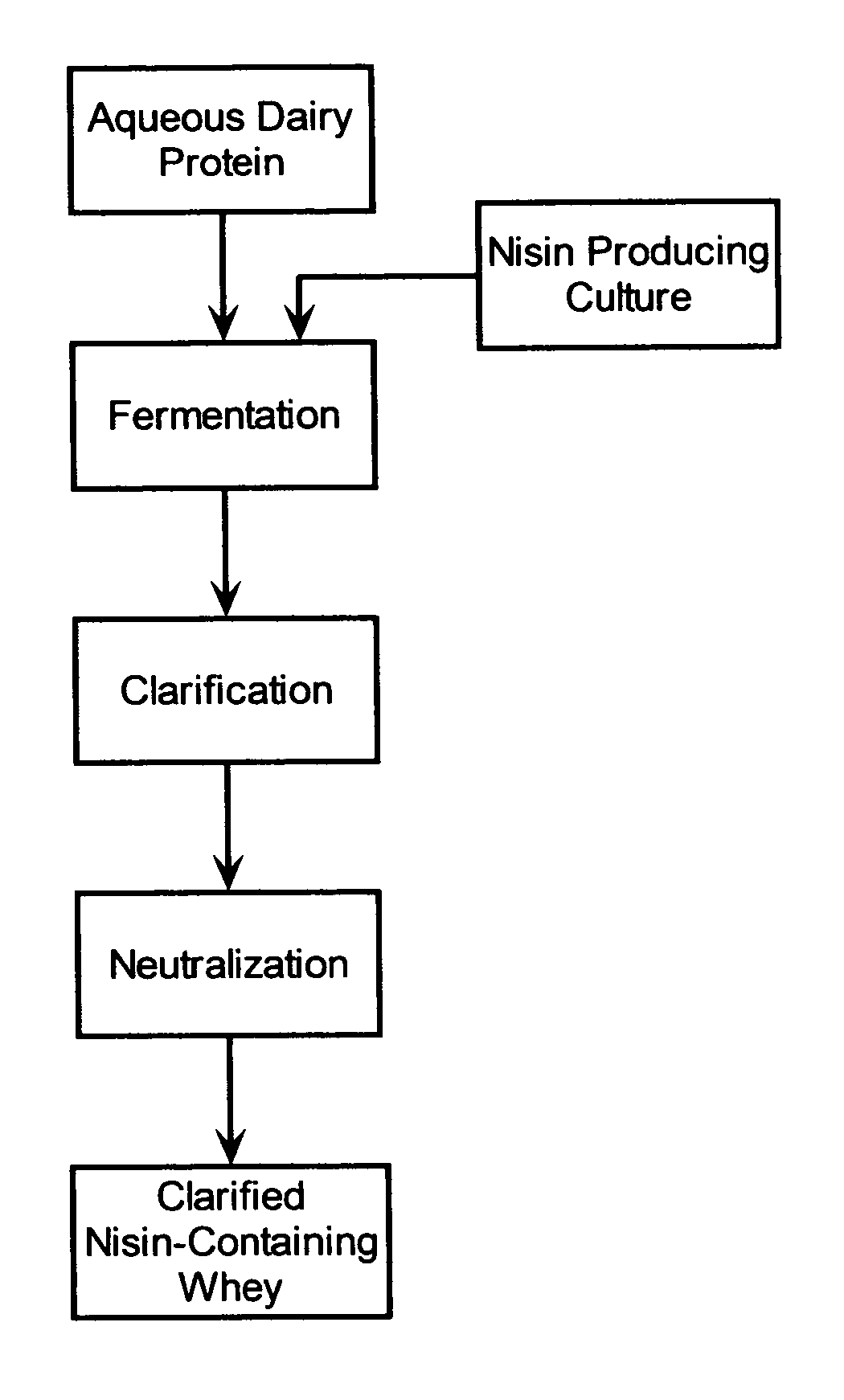
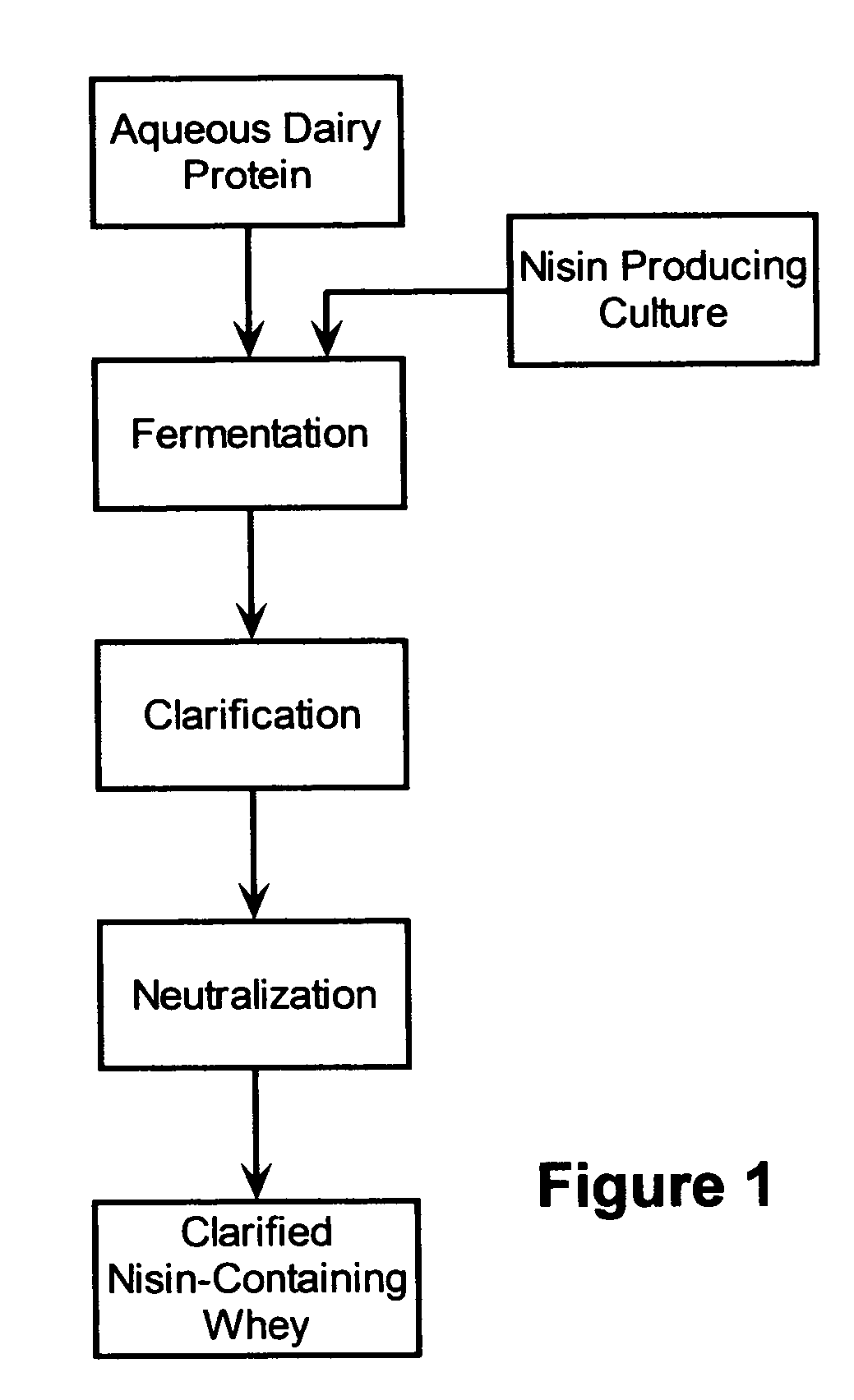
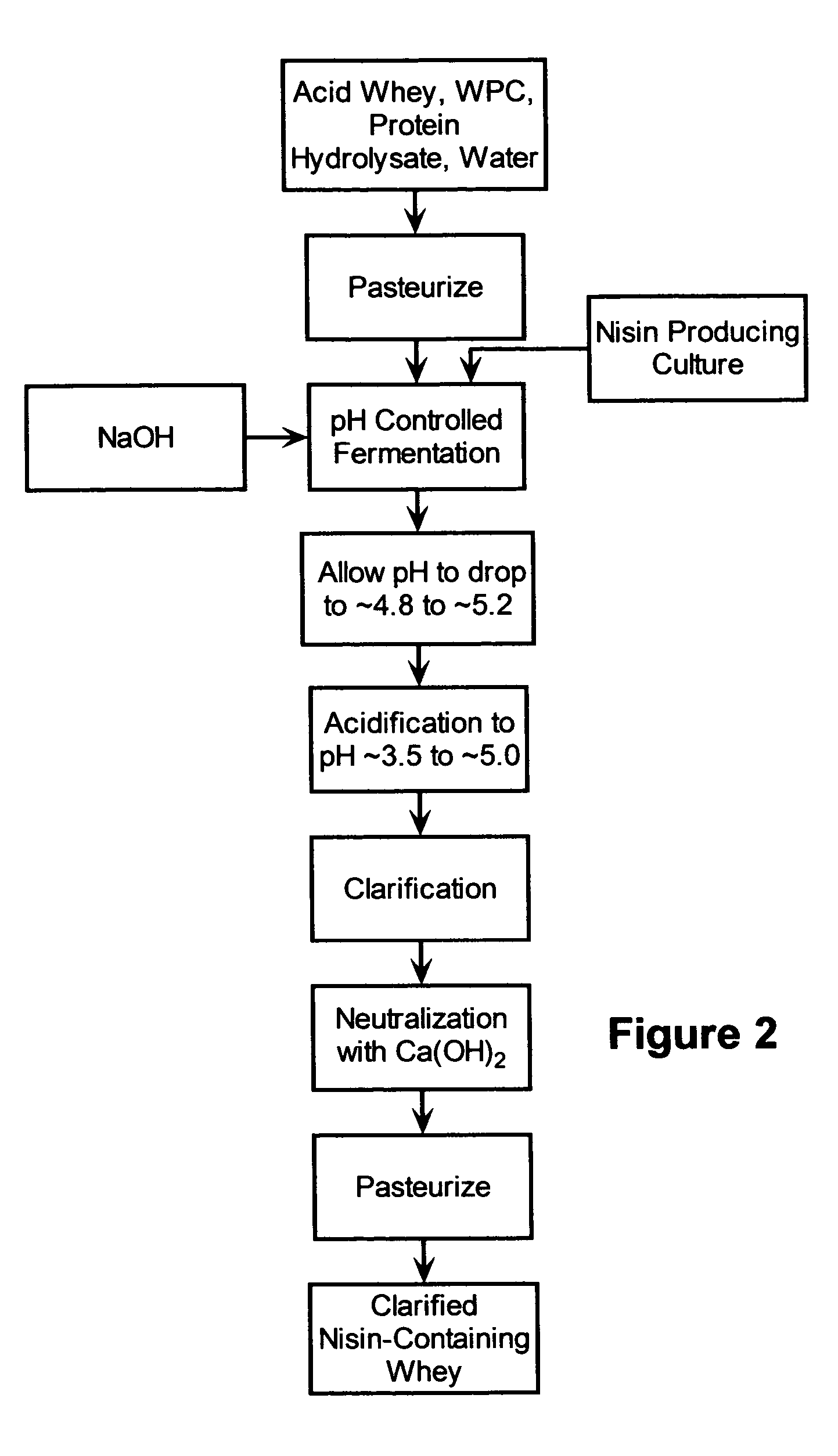
InactiveUS20050287272A1Reduce riskReduce detection limitMilk preparationDough treatmentMozzarella cheeseNisin
The invention is directed to a fermented and clarified nisin-containing whey and a method of making that can be used to produce a stabilized food product by adding, for example, to the pack water of fresh mozzarella cheese. The resulting stabilized food product retards or limits below detection levels the growth of toxins from pathogenic bacterial contaminants when the nisin-containing whey is added in amounts between about 10 to about 30% to the food product. The stabilized food product improves the safety of the food by retarding the growth of Listeria monocytogenes and improves the shelf life of the product by retarding the growth of gas forming bacteria such as bacteria from the Leuconostoc species.
Owner:KRAFT FOODS GRP BRANDS LLC
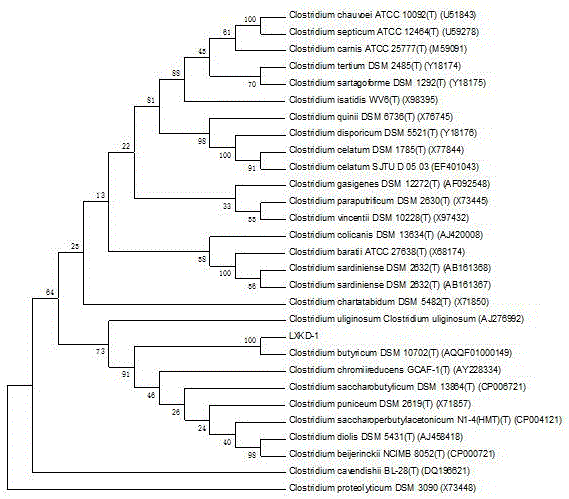
Preparation and application of Clostridium butyricum and live Clostridium butyricum preparation
ActiveCN106479924APromote growthPrevent diarrheaBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEggshell
The invention discloses preparation and application of Clostridium butyricum and a live Clostridium butyricum preparation; Clostridium butyricum LXKJ-1 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on 24 March, 2016 under CCTCC NO: M201613. A seed medium, fermentation medium formulation, culture conditions for Clostridium butyricum and a production of a preparation of live Clostridium butyricum are also disclosed. The Clostridium butyricum provided herein is tolerant to acids, bases and high temperature, is highly capable of producing butyric acid, can inhibit animal pathogens, such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Clostridium perfringens, and can prevent diarrhea in livestock and poultry due to Escherichia coli, Salmonella and Clostridium perfringens, improving intestinal flora balance, promoting the growth of livestock and poultry, relieving constipation in sows, improving egg weight for layers, improving eggshell quality for layers, and decreasing egg-feed ratio.
Owner:湖北绿雪生物科技有限公司
Culture medium for composite enrichment of salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101412978AShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLithium chlorideStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses a complex enrichment medium used for salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and staphylococcus aureus and a method for preparing the same. The complex enrichment medium comprises the following components in weight portion: 15 to 19 portions of tryptone, 2 to 4 portions of peptone, 2 to 3 portions of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 to 3 portions of glucose, 0.5 to 1.5 portions of aesculin, 1, 000 portions of distilled water, 1 to 2.5 portions of sodium pyruvate, 3 to 10.0 portions of mannitol, 1.0 to 25.0 portions of sodium chloride, 1 to 2.5 portions of lithium chloride, 0.0001 to 0.0002 portion of potassium tellurite, and 0.005-0.015 portion of nalidixic acid, wherein the pH value is between 7.1 and 7.5. The complex enrichment medium can inhibit the growth of other pathogenic microorganisms while performing enrichment on three target pathogens, thus the complex enrichment medium can be directly applied to the isolation culture and the biological assay test of target bacteria, and can also be directly applied to a detection technology of a plurality of pathogens based on one detection platform for multiple PCR and the like to make a diagnostic report.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
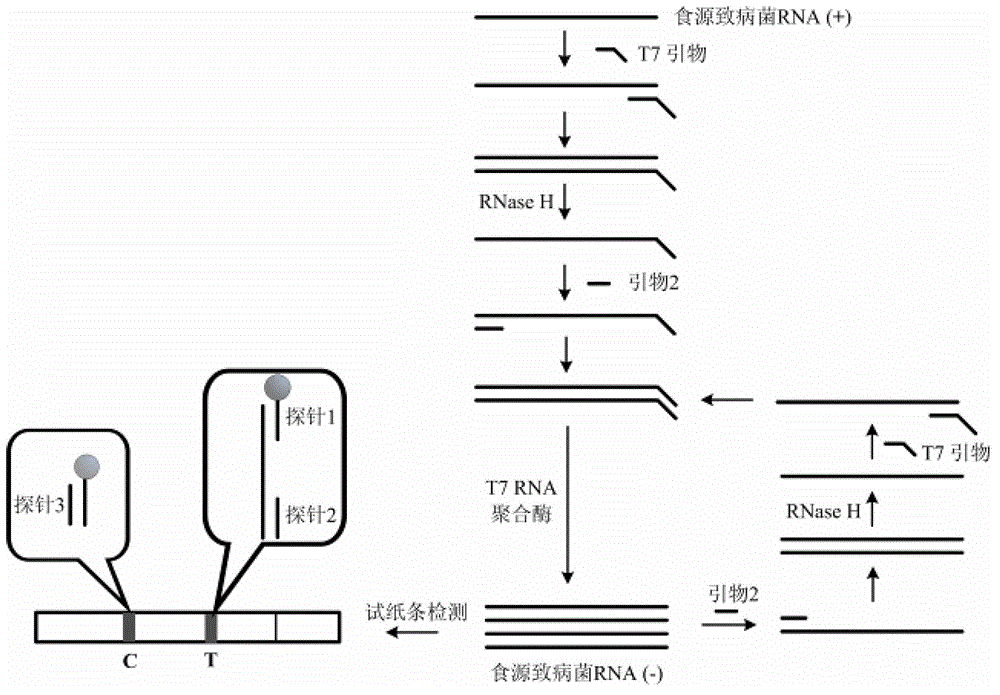
Method and kit for detecting pathogenic bacterium of food source by test strip based on NASBA (Nucleic Acid Sequence Based Amplification)
ActiveCN103146835AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid sequence based amplificationMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting pathogenic bacterium of a food source by a test strip based on NASBA (Nucleic Acid Sequence Based Amplification) and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting RNA of pathogenic bacterium of the food source; (2) designing an amplification primer; (3) performing NASBA reaction; (4) designing a catching probe; (5) preparing a nano-gold probe; (6) preparing a collaurum nucleic acid strip; and (7) detecting the samples. The kit using the method to detect Listeria monocytogenes comprises primers (as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and 2), enzyme, buffer solution, RNaseH, RNA enzyme inhibitor, dNTPs, NTPs, probes (as shown in SEQ ID NO. 4, 5 and 6) and collaurum nucleic acid strip, etc. By combining NASBA with detection of the test strip, the method disclosed by the invention can realize qualitative or quantitative detection, and has low cost, high detection speed, good specificity, high sensitivity and safety in use.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
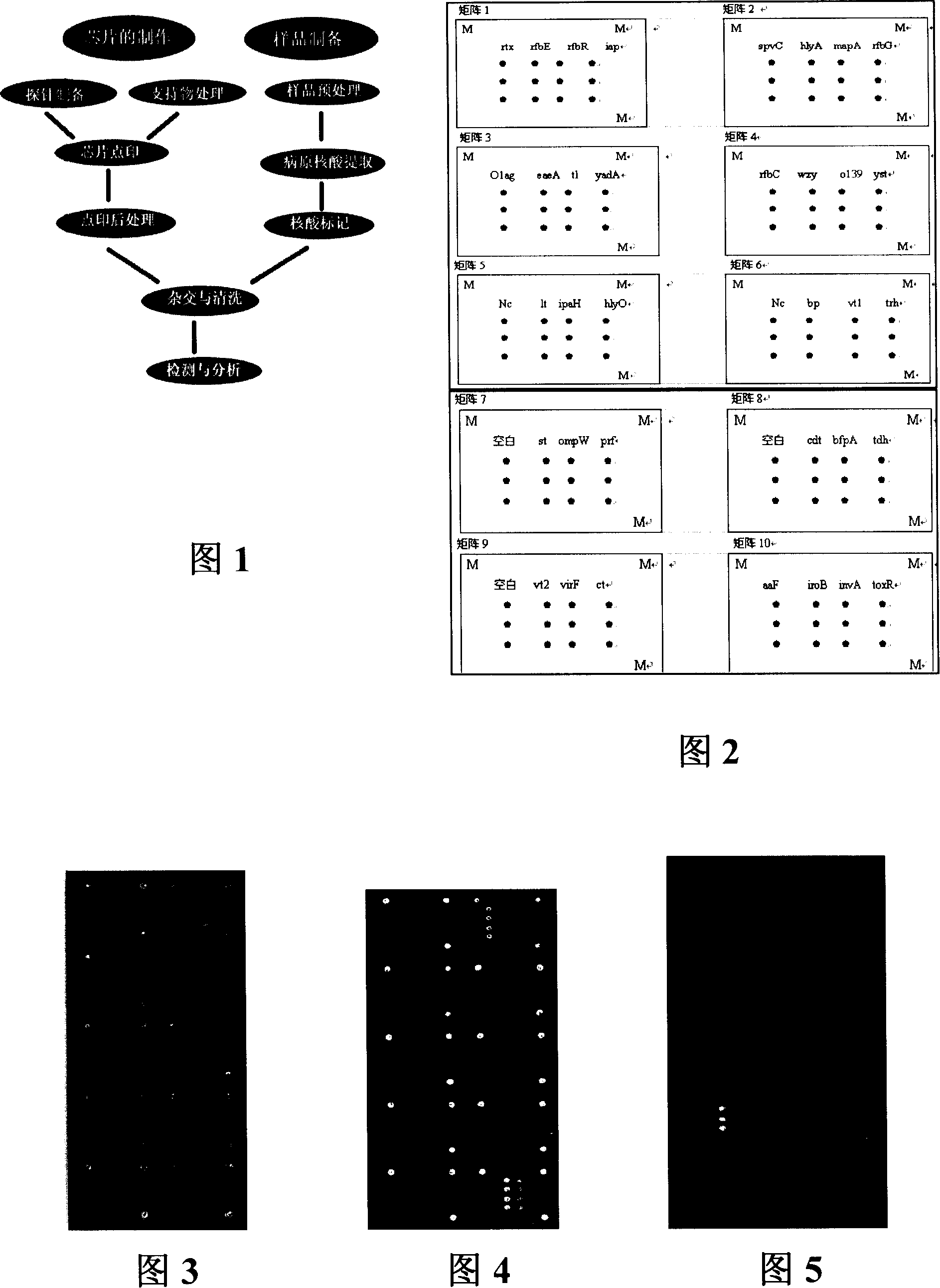
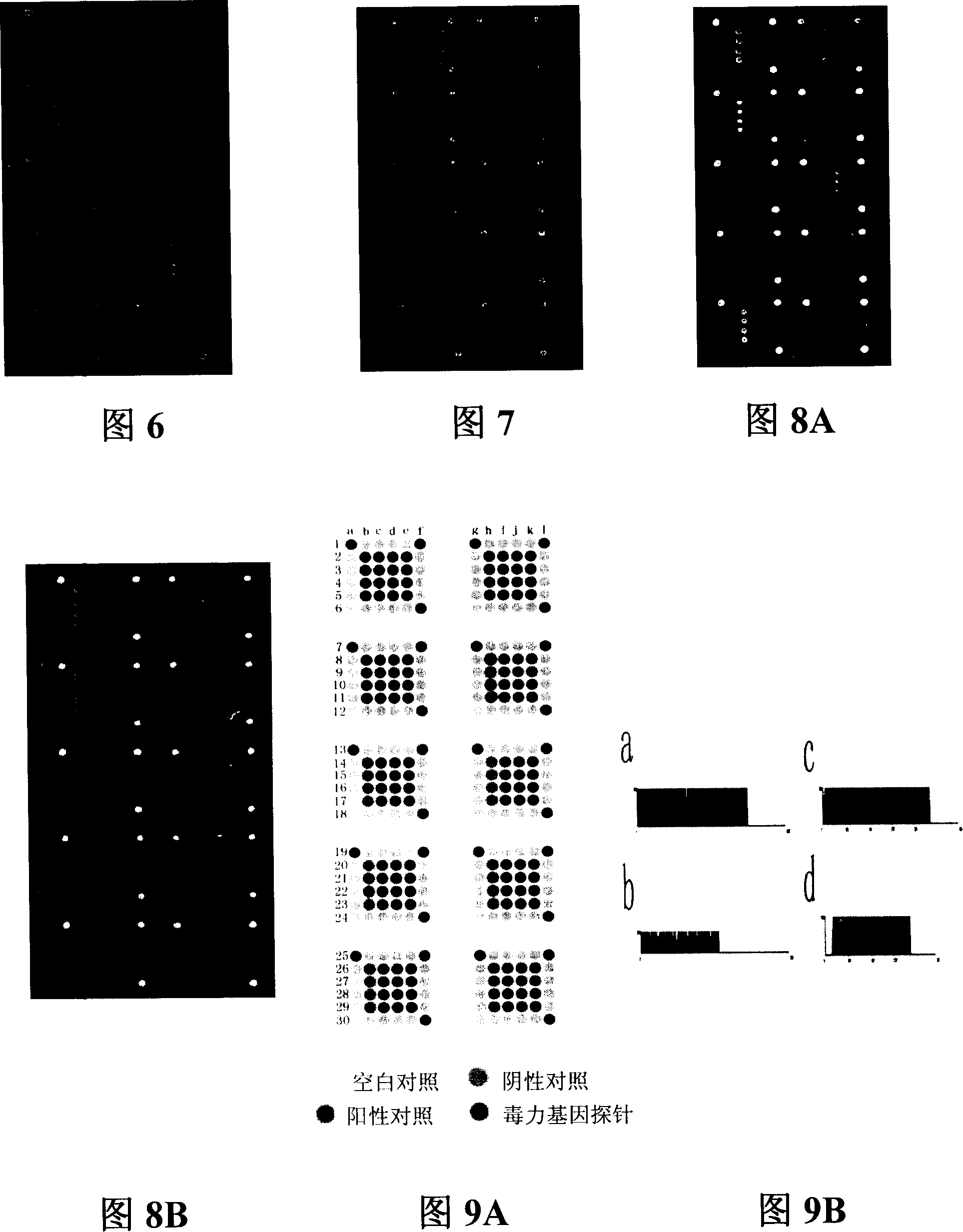
Molecular typing of listeria monocytogenes, hybridization supports and kits for said molecular typing
InactiveUS20060257894A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular typingHybridization probe
Owner:DOUMITH MICHEL +7
Preparation method of (Lactobacillus planetarium subsp. plantarum)Zhang-LL and its listeria monocytogene-resistant bacteriocin
ActiveCN104531562ASource securityStable sourceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood borneListeria murrayi
The invention relates to a preparation method of (Lactobacillus planetarium subsp.plantarum)Zhang-LL and its listeria monocytogene-resistant bacteriocin. The preparation method is suitable for preservation and fresh-keeping of meat and meat products, milk and milk products, fruits and vegetable, and instant foods. The (Lactobacillus planetarium subsp.plantarum)Zhang-LL (CGMCC No.6936) is selected from bacon on the Fujian farmer's market. A bacteriocin production broth is obtained by fermentation of a Zhang-LL strain, and the Zhang-LL strain bacteriocin is extracted and purified by a pH-dependent adsorption-desorption method, a cation exchange chromatography and a reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography so that titer is improved by 32 times and purity is improved by 36.65 times. The bacteriocin can inhibit a plurality of food-borne pathogenic bacteria such as listeria monocytogenes, has high bacteriostatic activity, good heat, acid and base stability, can be degraded by human protease and is a natural and safe biological preservative. The preparation method has the advantages of simple processes, stability, high efficiency, source convenience, low cost and industrial production feasibility.
Owner:BEIJING BEINONG HONGZE BIOTECH CO LTD
Modified coconut oils with broad antimicrobial spectrum
InactiveUS20100016430A1Improve antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliCandida famata
Owner:MALAYSIAN AGRI RES & DEV INST MARDI
Quick high-throughput intestines source pathogenic bacterium detection method
InactiveCN103898208AMeet the requirements of safety testingMeet the testing requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesStaphylococcus aureusA-DNA
The invention relates to a quick, sensitive and high-throughput intestines source pathogenic bacterium detection method. The detection method provided by the invention integrates two powerful molecular biological techniques: polymerase chain reaction PCR and a micro-array, and directly fixes a probe of PCR hybridization in a hybridization cabin of the micro-array on a same chip with a PCR reaction chamber. The detection method comprises the following steps of enriching bacteria; extracting a DNA solution; carrying out PCR amplification; hybridizing; cleaning; and judging the result. The method provided by the invention can quickly detect genes of vibrio parahaemolyticus, Shigella, staphylococcus aureus, listeria monocytogenes and salmonella in high throughput, and the detection efficiency of front-line inspection and quarantine personnel of import and export ports can be greatly improved, thereby not only reducing the workload, but also solving the undetected positive result problem probably caused by conventional detection method to the maximum extent. Therefore, food safety incidents are prevented to the maximum extent.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF P R C
Oligonucleotide primer for detecting common pathogenic bacteria by adopting fluorescent quantitation PCR (Rich Client Platform) technology, method thereof for detecting common pathogenic bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN101928773AEfficient and wideWide range of applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyFood poisoning
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide primer for detecting common pathogenic bacteria by adopting a fluorescent quantitation PCR (Rich Client Platform) technology, a method thereof for detecting common pathogenic bacteria and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: providing 10 pairs of specific oligonucleotide primer sequences at annealing temperature of 50-60 DEG C without differing 5 DEG C; and simultaneously, quickly, accurately and effectively identifying and quantificationally detecting various pathogenic bacteria at the same time. A detection range comprises bacillus cereus, enterobacter sakazakii, vibrio parahaemolyticus, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157, salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, Shigella, campylobacter jejuni, pseudomonas aeruginosa, klebsiella pneumoniae, and the like. The invention also can be used for the fields of disease diagnosis, environmental monitoring, water-quality and food supervision and detection, food poisoning pathogenicbacteria detection, bacteriological classification, epidemiological investigation, biological agent detection, and the like, is convenient, quick, accurate and effective and has wide application range.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogen in dairy products
ActiveCN101240335AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsKlebsiella oxytocaStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention provides a gene chip for detecting common pathogen in dairy, which comprises a solid-phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase vector, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes DNA fragment or its complementary DNA or RNA sequence selected from E. sakazakii, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Listeria monocytogenes, salmonella and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region of Bacillus cereus, as well as ipaH gene of Shigella or gyrB gene of citrobacter freundii. The invention further provides a reagent box which uses the gene chip to detect pathogen in dairy. The gene chip and the reagent box of the invention for detecting pathogen in dairy are easy to operate, highly precise and greatly repeatable.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD +1
Multiplex PCR based primer pair and kit for detecting multiple intestinal pathogens
ActiveCN104531898AQuick checkMultiple testing sites at one timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnteroinvasive E. coliEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a multiplex PCR based primer pair and kit for detecting intestinal pathogens, particularly relates to a multiplex PCR based primer pair and kit for detecting 14 intestinal pathogens, and belongs to the technical field of PCR application. The 14 intestinal pathogens comprise vibrio cholerae (group O1 phage, group O139 phage and group non-O1 / O139 phage), listeria monocytogenes, enteropathogenic escherichia coli (EPEC), enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli (EHEC), enterotoxigenic escherichia coli (ETEC), enteroinvasive escherichia coli (EIEC), enteroaggregative escherichia coli (EAEC), shigella, intestinal virus EV71, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7, clostridium difficile, vibrio parahaemolyticus, salmonella enteritidis and salmonella typhimurium. The multiplex PCR based primer pair and kit can change the situation that only a few intestinal pathogens can be detected in one time and can be used for detecting 14 intestinal pathogens and 26 genes simultaneously.
Owner:AGCU SCIENTECH
Multiplex LAMP detection primer, kit and method for six food-borne pathogenic bacteria in fruits and vegetables
InactiveCN107022644AStrong specificityHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses a multiplex LAMP detection primer, kit and method for six food-borne pathogenic bacteria in fruits and vegetables and belongs to the technical field of bacterial gene detection. A rapid detection primer set for the six pathogenic bacteria including listeria monocytogenes, enterobacter sakazakii, shigella spp, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella spp and escherichia coli O157:H7 is designed, and multiplex LAMP reaction is performed on the genome DNA of the bacteria extracted from a sample to be detected in the same reaction system by use of the detection kit including the primer set to determine whether the sample contains the six food-borne pathogenic bacteria or not. The multiplex LAMP detection primer is high in specificity and sensitivity and can accurately detect the genome DNA of the six food-borne pathogenic bacteria in the same reaction system, can realize simple and convenient, quick and accurate detection, is suitable for on-site rapid detection and has significance on improving the pathogenic bacterium analysis and detection technology and the fruit and vegetable edible quality security.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARDS & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Culture medium capable of simultaneously enriching five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria and preparation method for culture medium
ActiveCN102660474AImprove detection efficiencyLow costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention relates to a culture medium for simultaneous composite enrichment of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria, namely Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and Shigella, and a preparation method for the culture medium. Food-borne pathogenic bacteria are a significant reason to cause food positioning, so the rapid and accurate detection of the food-borne pathogenic bacteria has an important practical significance for preventing and controlling food safety incidents. The culture medium is characterized by comprising the following components: 10.0 g of peptone, 10.0 g of sodium chloride, 9.0 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.5 g of monopotassium phosphate, 0.1 g of cholate, 0.1 mg of potassium tellurite, 1.0 g of lithium chloride, 3.0 g of glucose, 2.0 g of mannitol, 2.5 g of sodium pyruvate, 1.0 g of aesculin and 1,000 mL of distilled water, wherein the pH value is 7.1 to 7.5. The culture medium can simultaneously enrich five kinds of target pathogenic bacteria, can be used for separation and identification of target bacteria, can also be used for the molecular detection of multiple pathogenic bacteria on the same detection platform, provides technical support for a method for rapidly detecting five kinds of pathogenic bacteria in food, and meets the requirement of simultaneous detection of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES +1
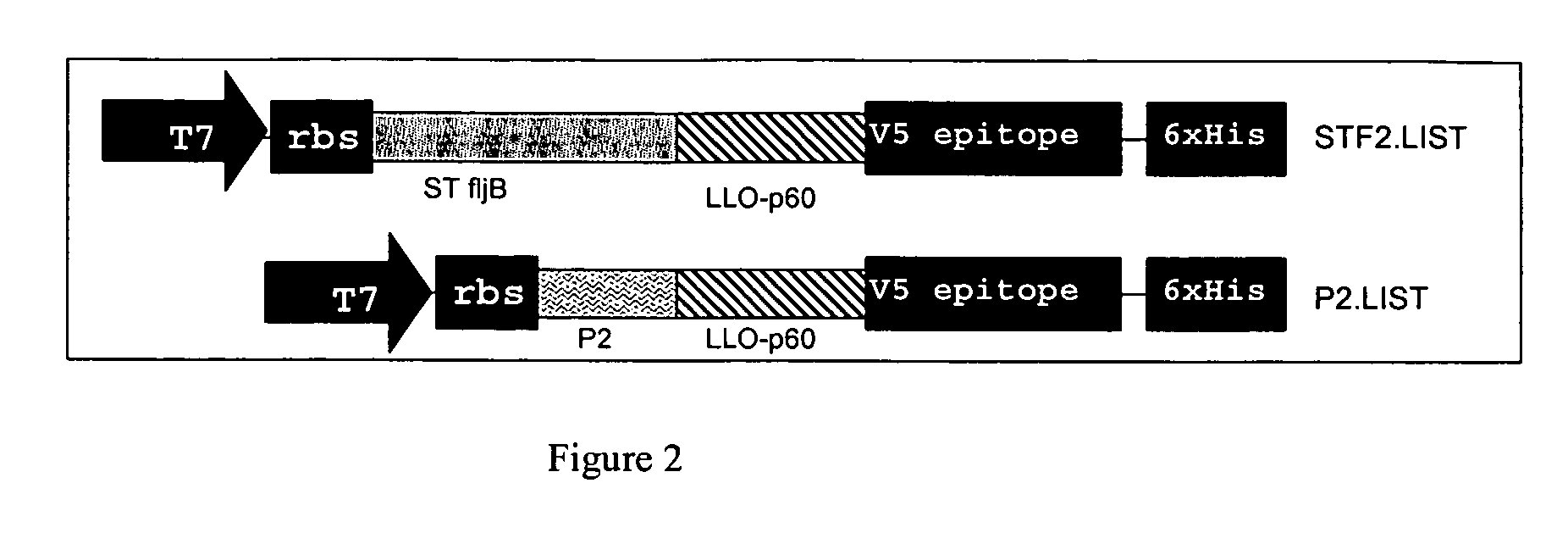
Compositions of pamps and Listeria monocytogenes and methods of use
InactiveUS20090081725A1Antibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenPathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules
A composition comprising a pathogen associated molecular pattern (PAMP) protein that activates toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) or toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) signaling and at least two distinct antigens of Listeria monocytogenes. Amino acids, nucleotides, vectors, cell lines, and the methods for production and use of the compositions are provided.
Owner:VAXINNATE +1
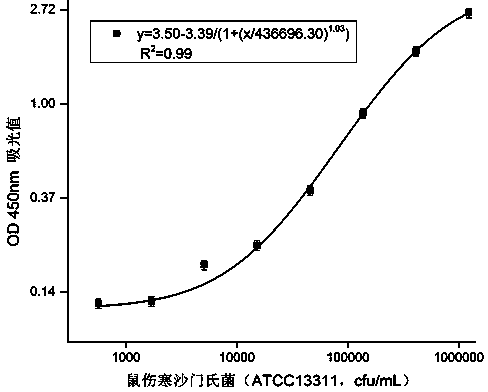
Double-antibody sandwich method for detecting salmonella typhimurium in food based on monoclonal antibodies
The invention discloses a double-antibody sandwich method for detecting salmonella typhimurium in food based on monoclonal antibodies, belonging to the technical field of immunoassay. Salmonella typhimurium ATCC13311 and smooth salmonella typhimurium LPS are adopted for mixed immunity of a 7-week BALB / c mouse, 10 LPS monoclonal antibodies are obtained by immunity, fusion and screening, horse radish peroxidases (HRP) are labeled respectively, and the salmonella typhimurium is paired two by two. A sandwich enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) method is established by taking 6E2 CGMCC No.7206 monoclonal antibodies as coated antibodies and enzyme-labeled antibodies and by taking the salmonella typhimurium as standards, and the LOD is 500cfu / mL. The sandwich method, established by using the monoclonal antibodies which are highly uniform in physicochemical property and high in specificity and can be prepared on a large scale, is high in sensitivity and low in cost; the salmonella typhimurium is not in cross reaction with salmonella enteritidis, salmonella arizonae, E.coli, E.coliO157:H7, enterobacter sakazakii, staphylococcus aureus and listeria monocytogenes; a quick and efficient analysis way is provided for detection of the salmonella typhimurium in the food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com