Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
a serine recombinase and site-specific technology, applied in the field of site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use, can solve the problems of high integration frequency, unidirectional integration, unsatisfactory chromosomal rearrangement, etc., and achieve site-specific recombination stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design, Synthesis, and Cloning of Recombinase Genes and Intramolecular Recombination Assay Plasmids
[0195] After analyzing the published literature and sequences available in Genbank, numerous site-specific recombinases were selected and assayed for DNA integration, excision, inversion, and replacement in mammalian and plant cells. The amino acid sequences for large site-specific recombinases of serine family (Smith, M. C. and H. M. Thorpe 2000 Diversity in the serine recombinases. Mol. Microbiol., 44:299-307) were obtained from GenBank and reverse translated to DNA. Since the sources of recombinases were from bacteria or bacterial viruses, we optimized the DNA sequence for recombinase expression in mammalian cells without changing the encoded amino acid sequence. The genes were totally synthesized using the codons for high-level human and mouse expression and with convenient restriction enzyme sites for cloning. In addition, regions of very high (>80%) or very low (<30%) GC content...
example 2
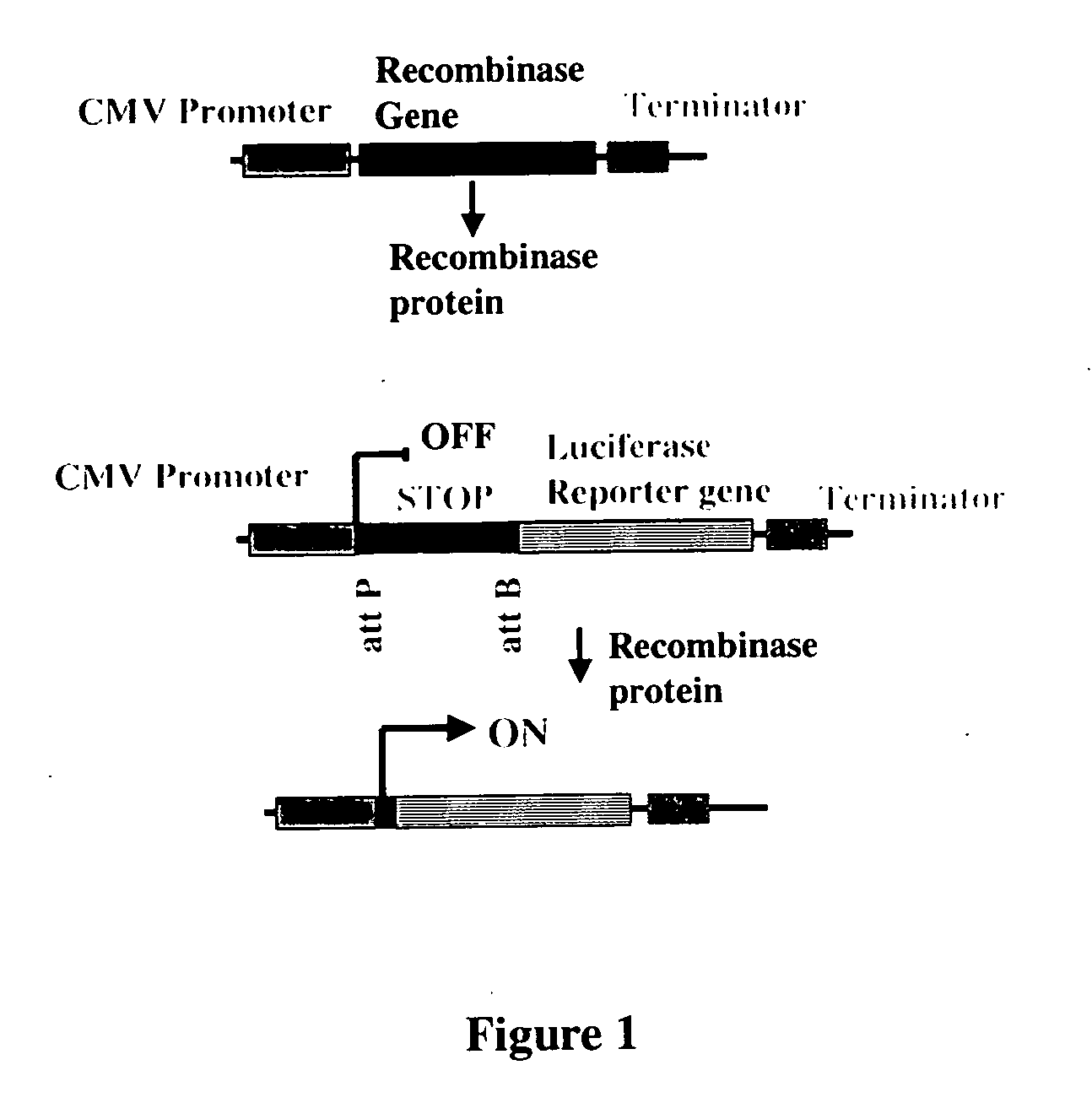
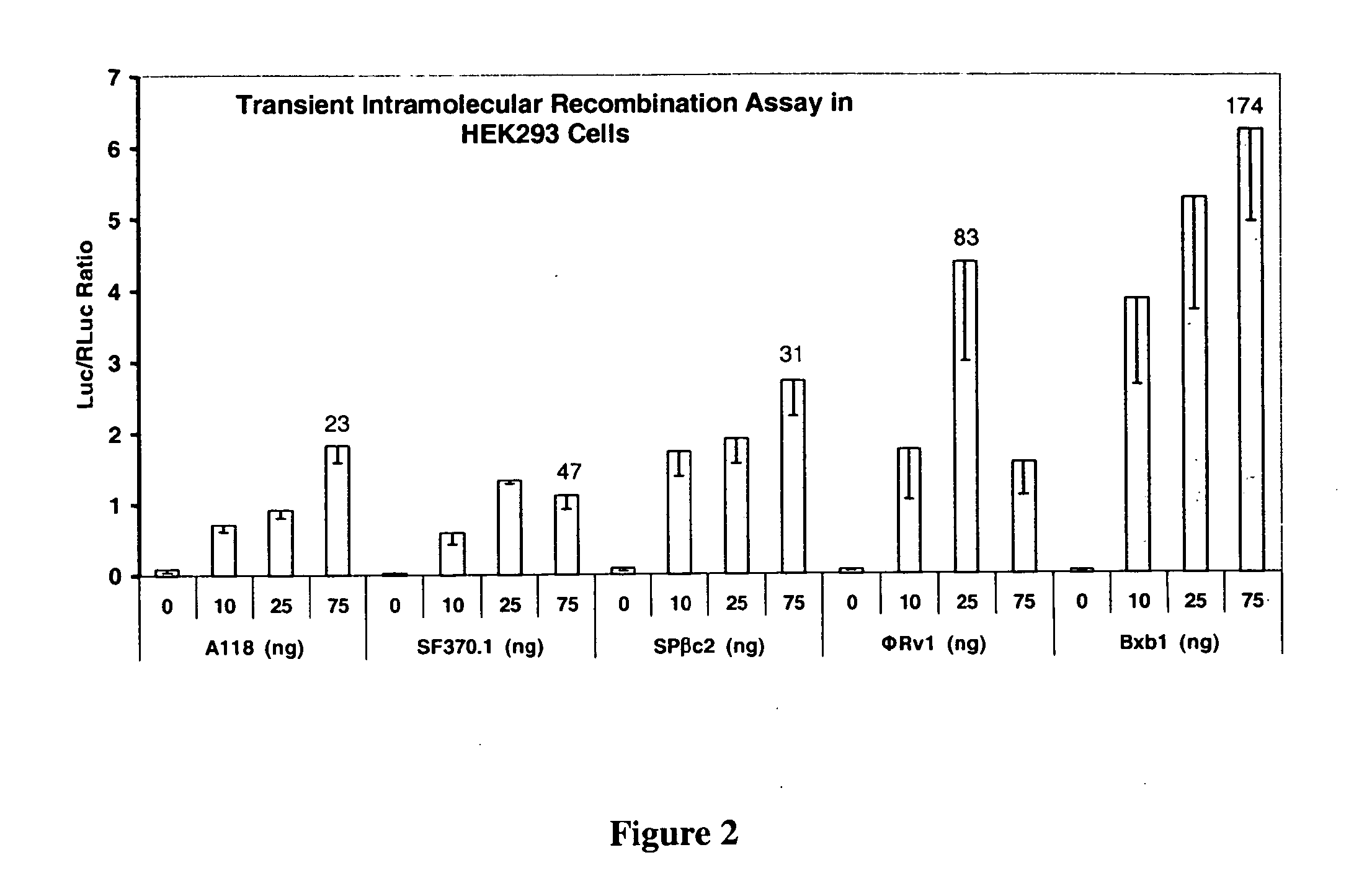
Transient Intramolecular Recombination Assays
[0215] In order to determine the activity of the recombinases in mammalian and plant cells, a transient assay was developed. Briefly, the assay consisted of cloning the recombinase gene into an expression plasmid, making the corresponding intramolecular recombination assay plasmid, introducing both plasmid DNAs into cells by transfection, and assaying for luciferase enzyme activity. The recombinase assay plasmids contained CMV Promoter-attP:STOP:attB-Luciferase Reporter gene-Terminator sequences. The STOP sequence is a transcription termination signal sequence. In the absence of recombination, expression of the luciferase reporter gene is prevented by the STOP sequence present between the promoter and reporter gene. Recombination between the attP and attB sites due to the introduced recombinase results in deletion of the STOP sequence and activation of reporter gene. This assay is sensitive and robust because it is an OFF to ON format an...
example 3
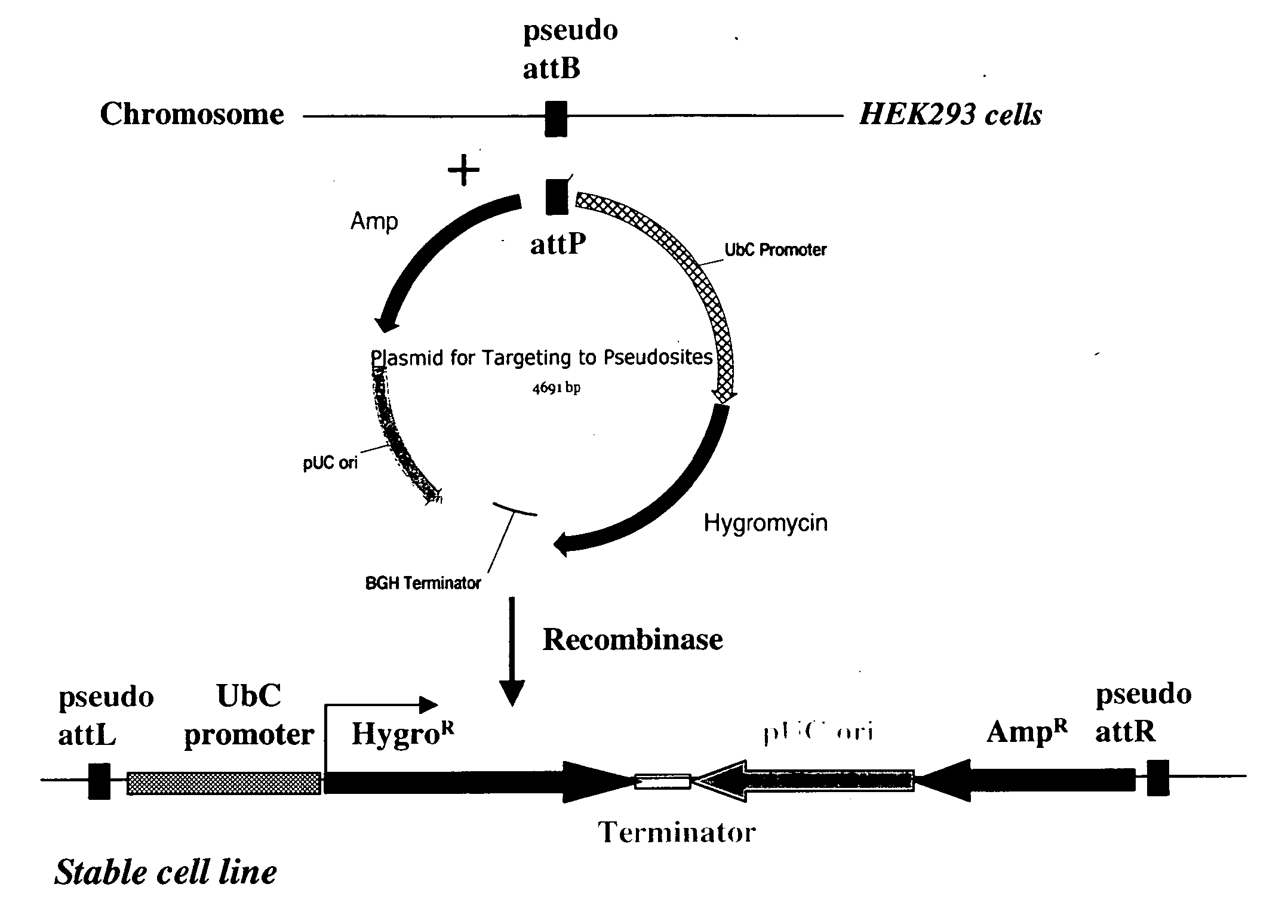
Stable Integration of Plasmid DNA Containing attP or attB Sequence into HEK293 Chromosome Containing the attB or attP Site
[0231] Assay for the integration of plasmid DNA at attP or attB site on the chromosome was done in a two-step process. In the first step, a stable cell line containing a single copy of attP or attB site of each enzyme was generated and characterized. In the second step, a plasmid containing the attP or attB site was integrated at the chromosomal attB or attP, respectively, in the presence of the recombinase expression plasmid.
Generation of Stable HEK293 Clones with attP or attB Sequence in the Chromosome
[0232] A single copy of attP or attB sequence of each recombinase (SEQ ID Numbers 11, 13-21) was introduced at the FRT locus in Flp-In™-293 cells obtained from Invitrogen [Carlsbad, Calif. (catalog #R750-07)] following the procedure recommended by the manufacturer. The FRT locus in Flp-In™-293 cells has a CMV promoter, FRT integration site for Flp recombinase,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com