Patents
Literature
246 results about "Attachment site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
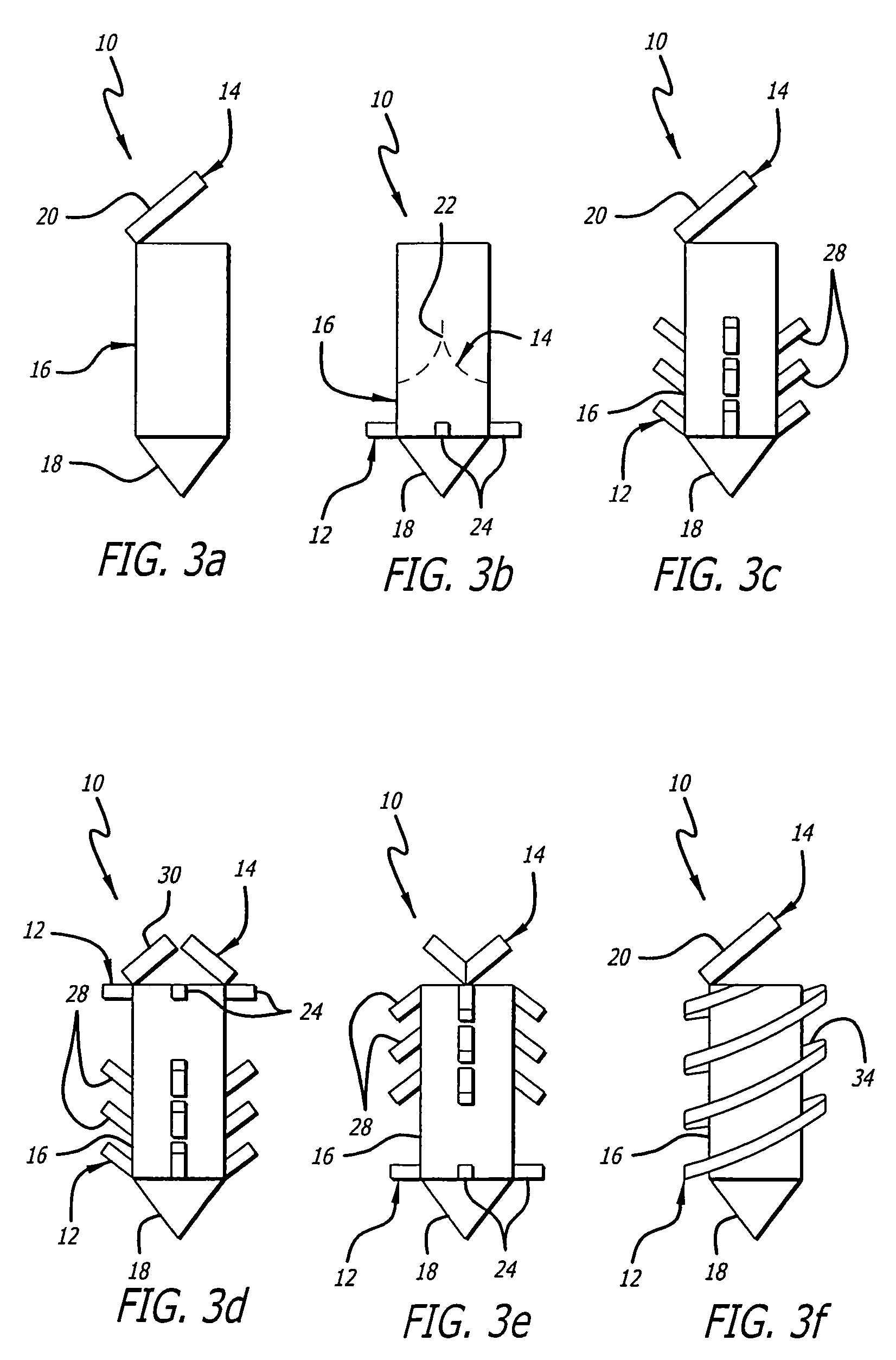
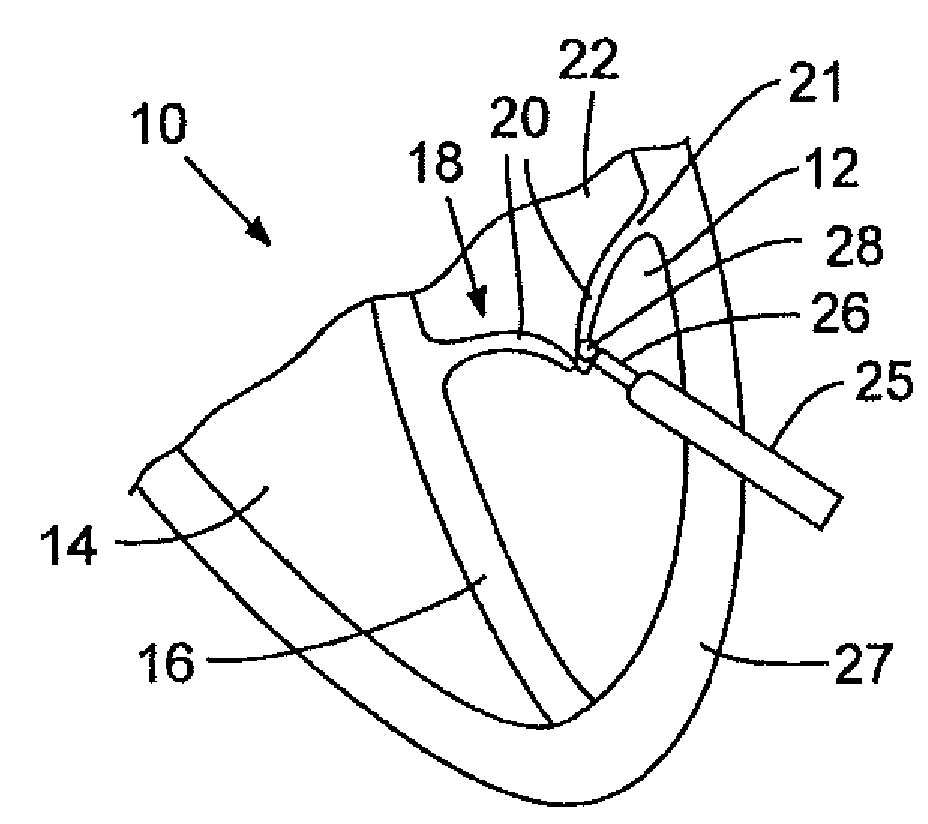
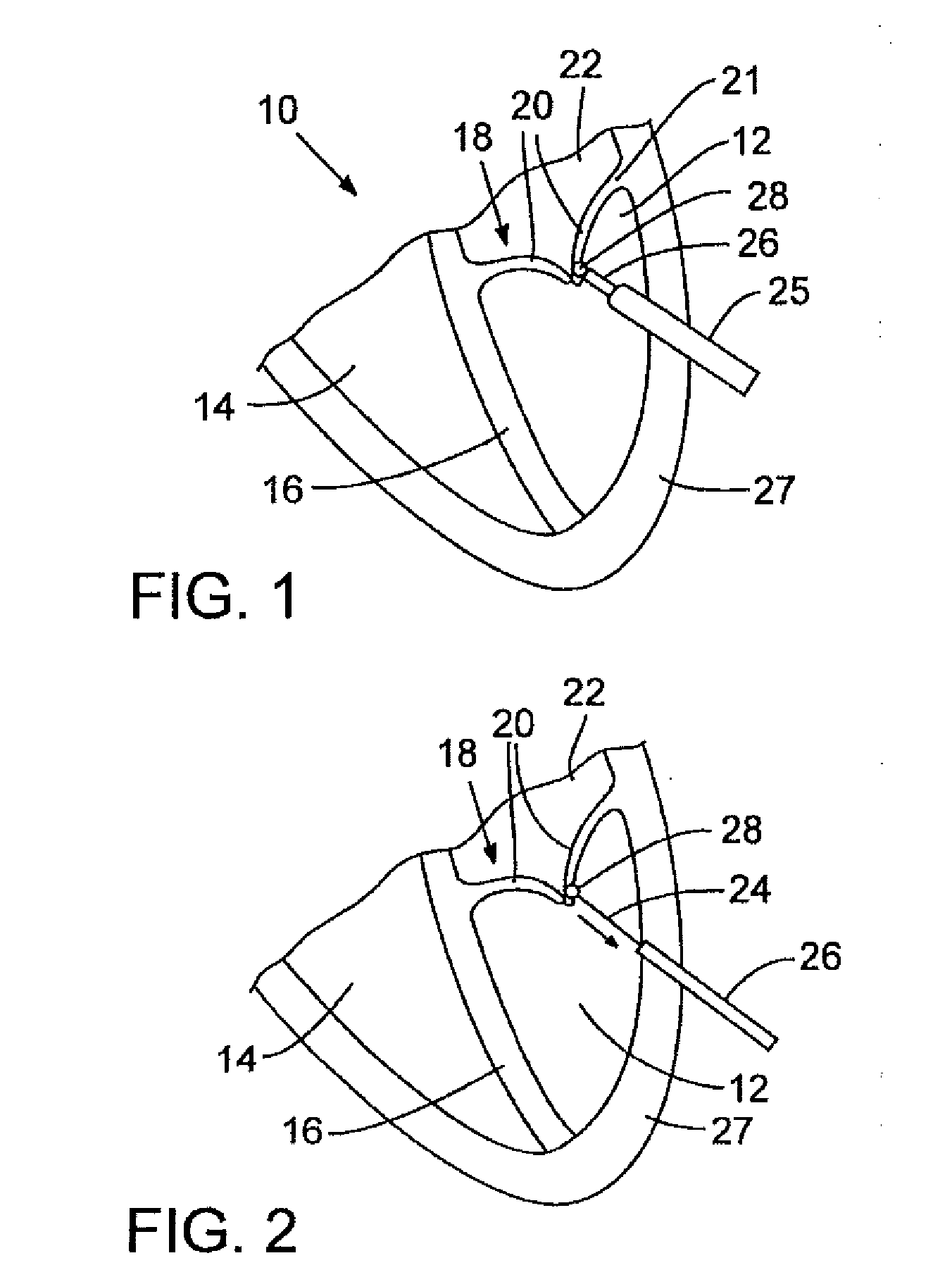
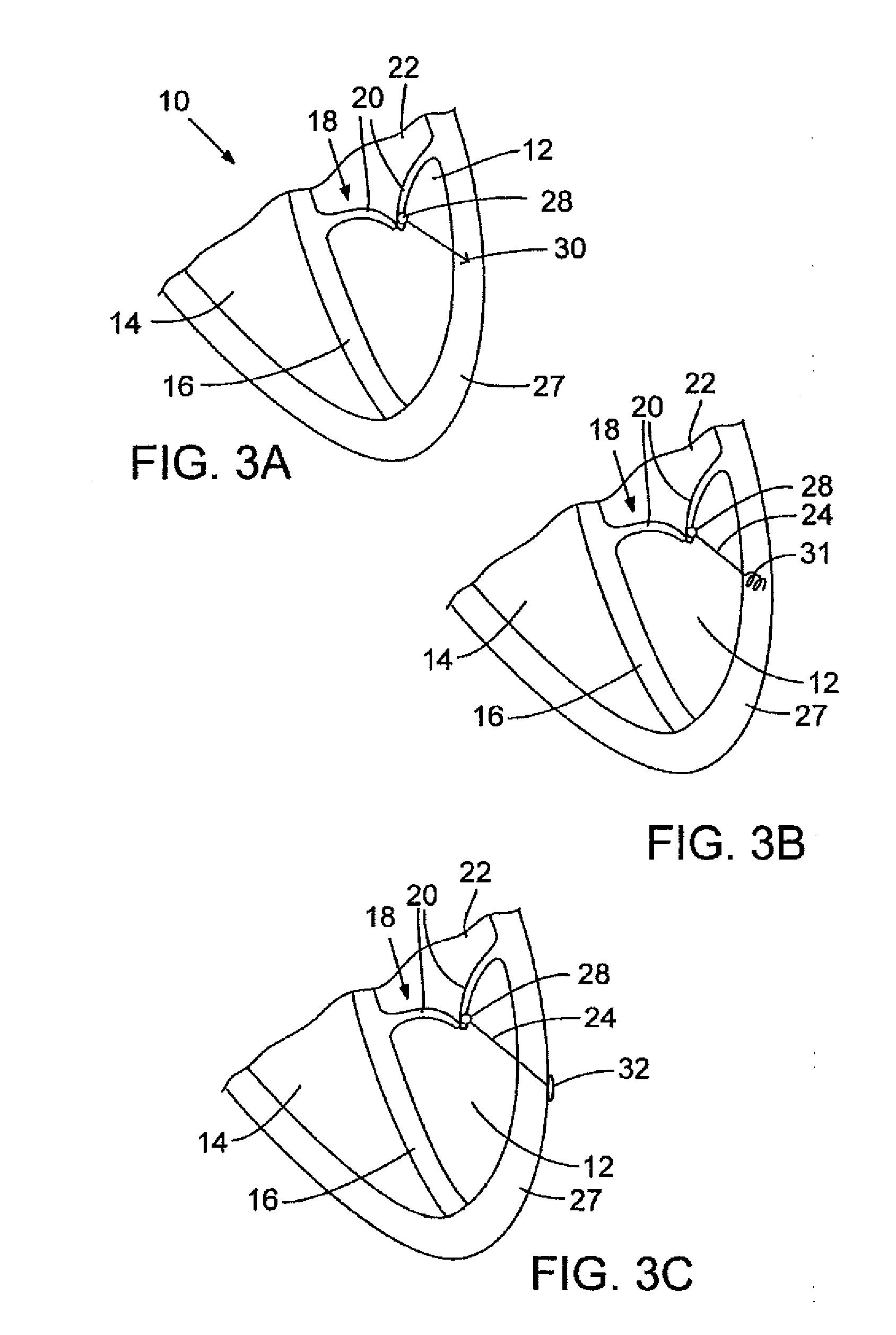
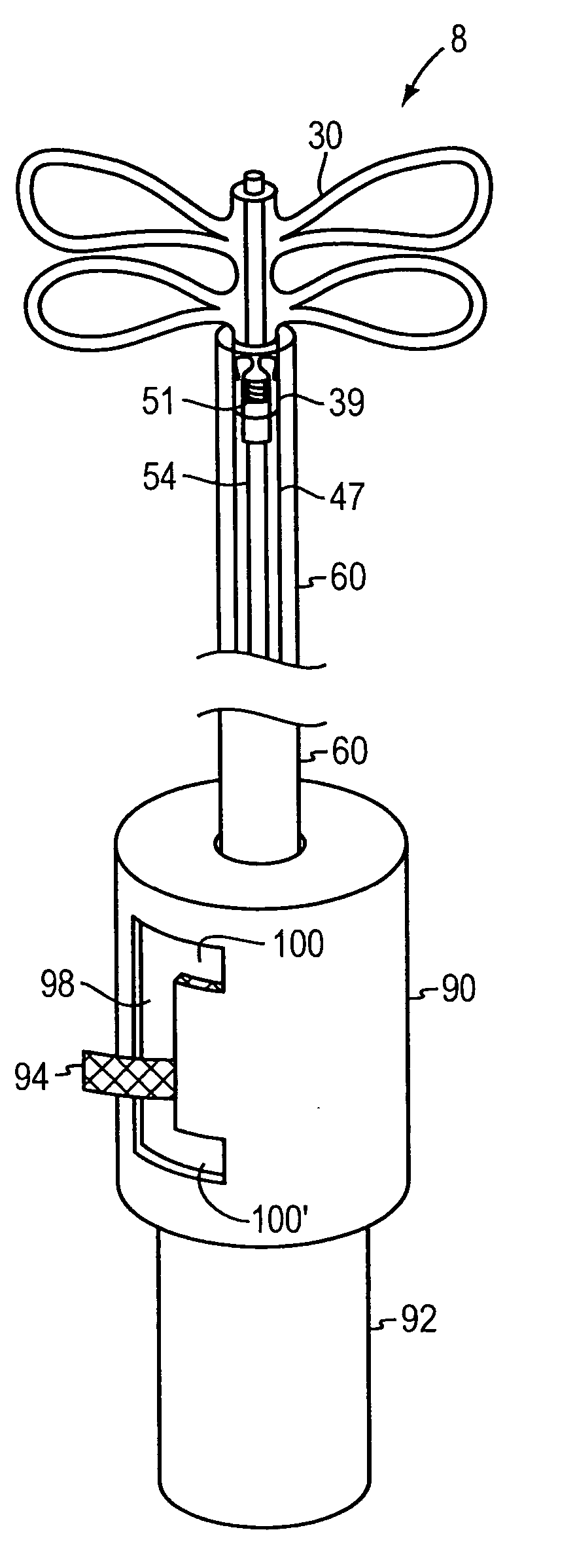
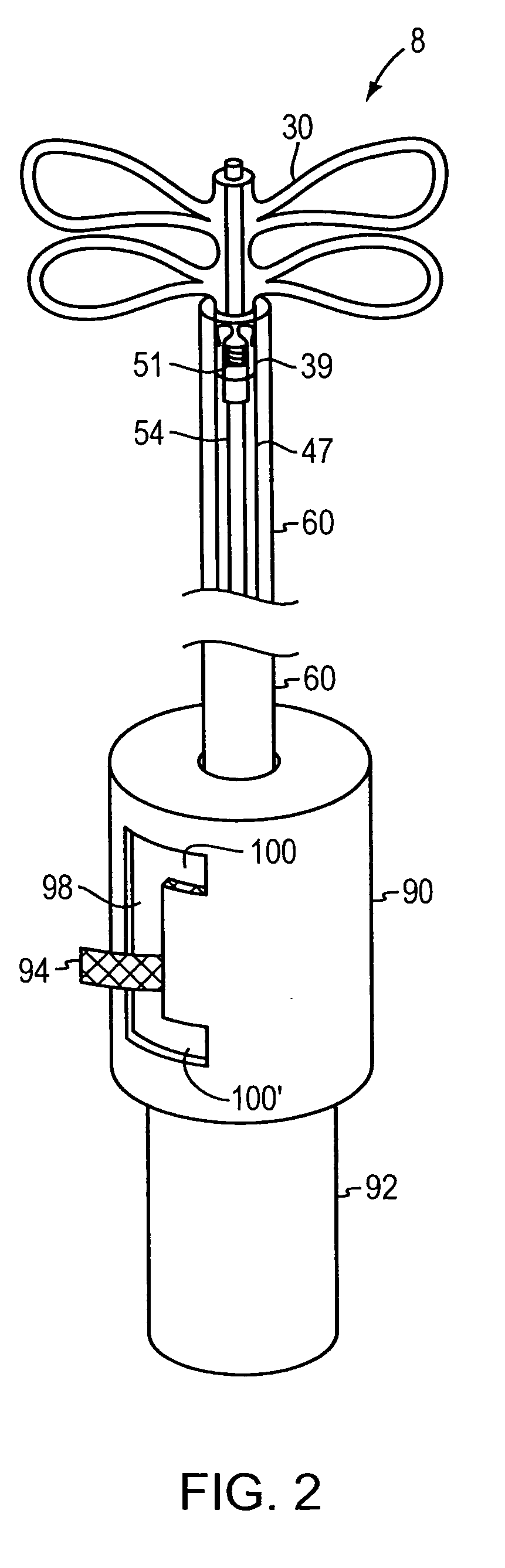
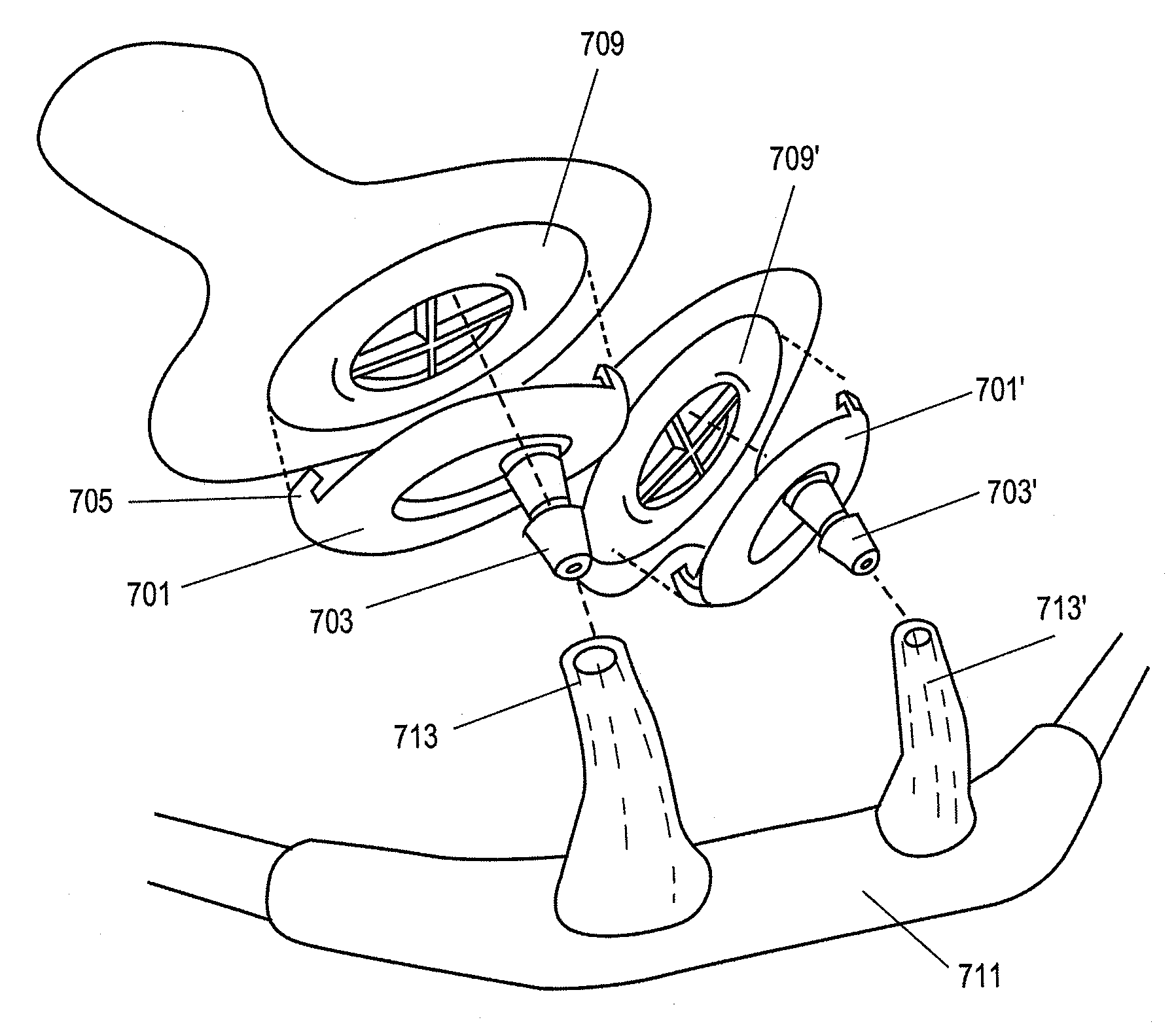
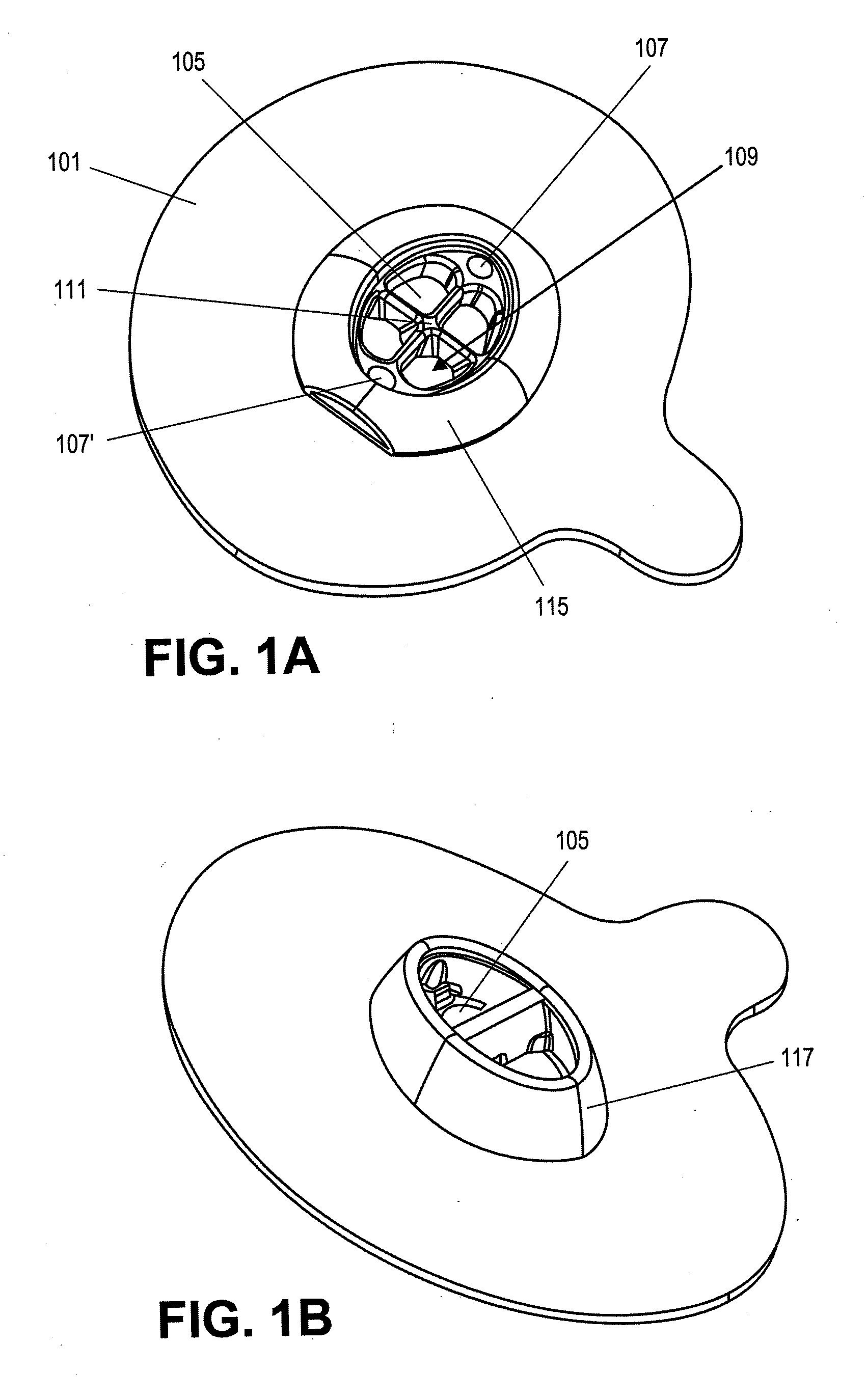
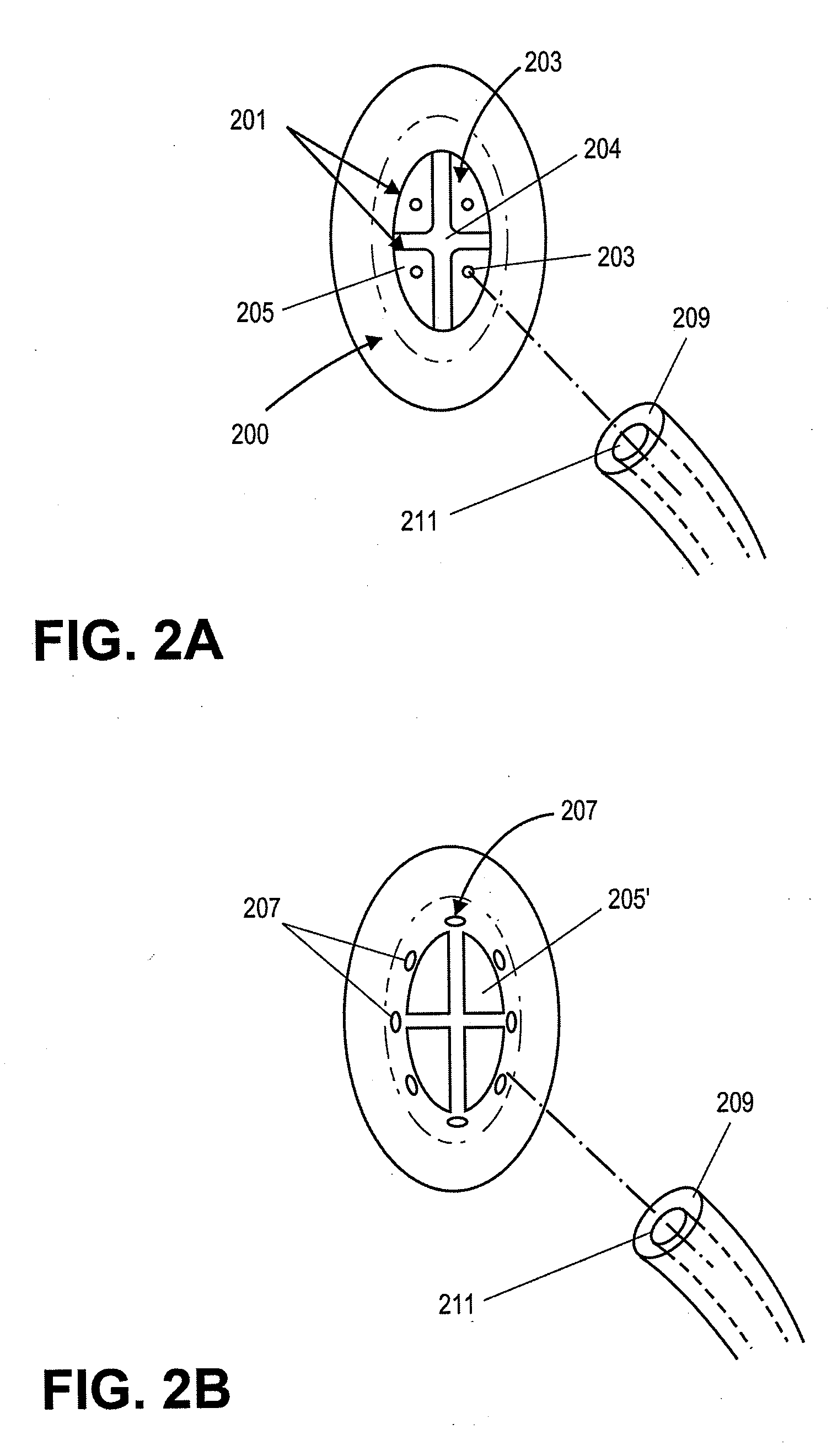
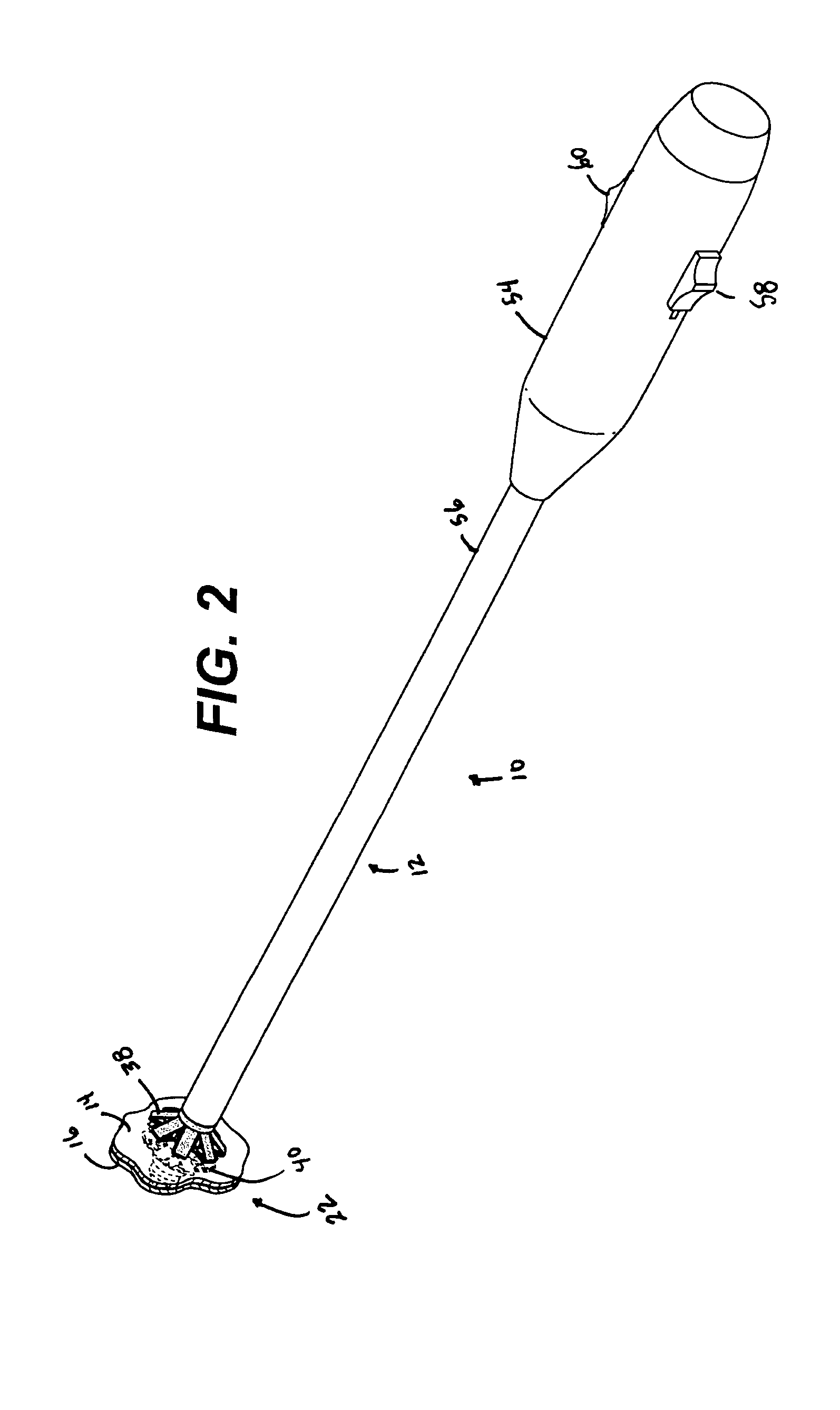
Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker with Secondary Fixation Capability
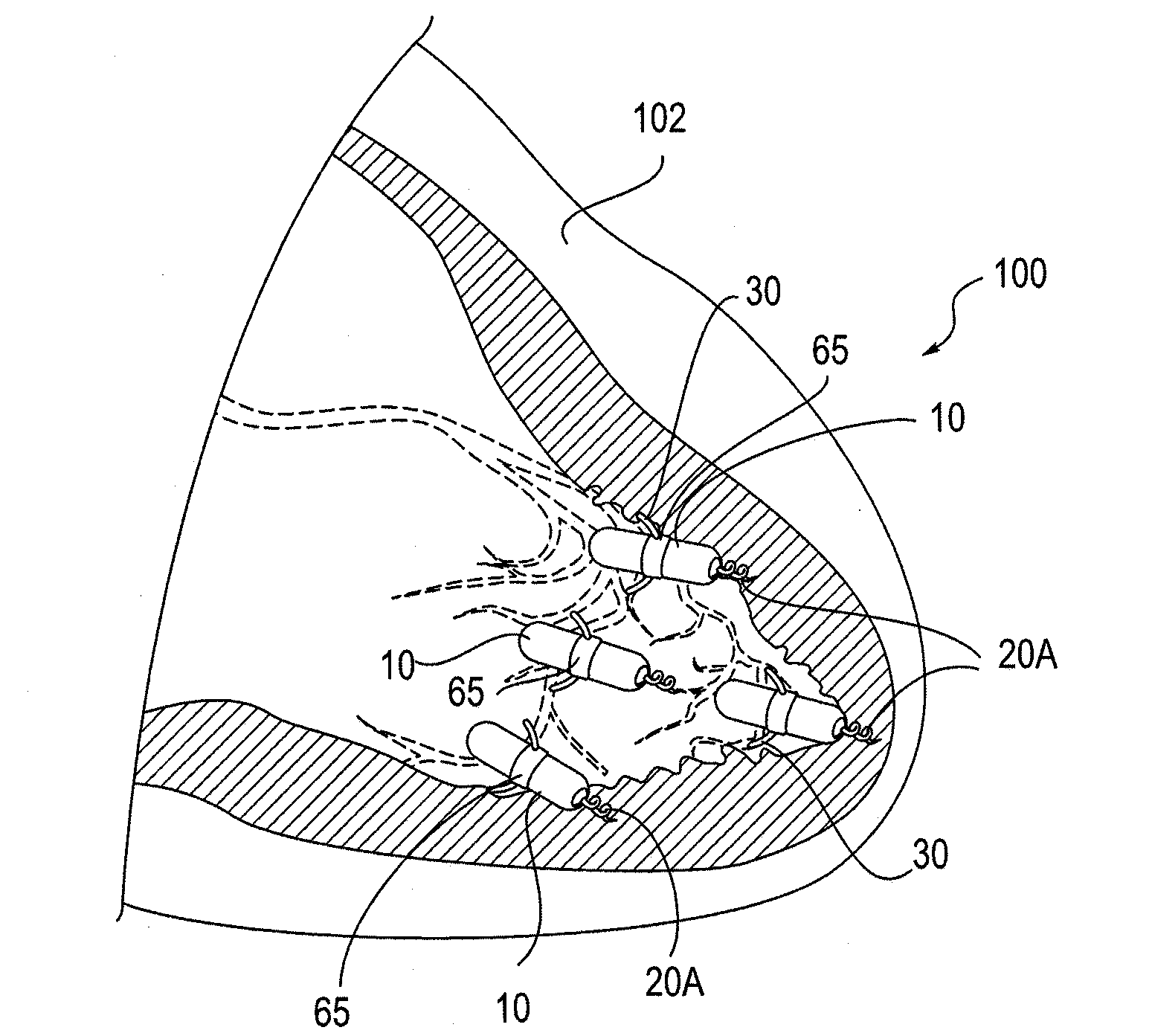
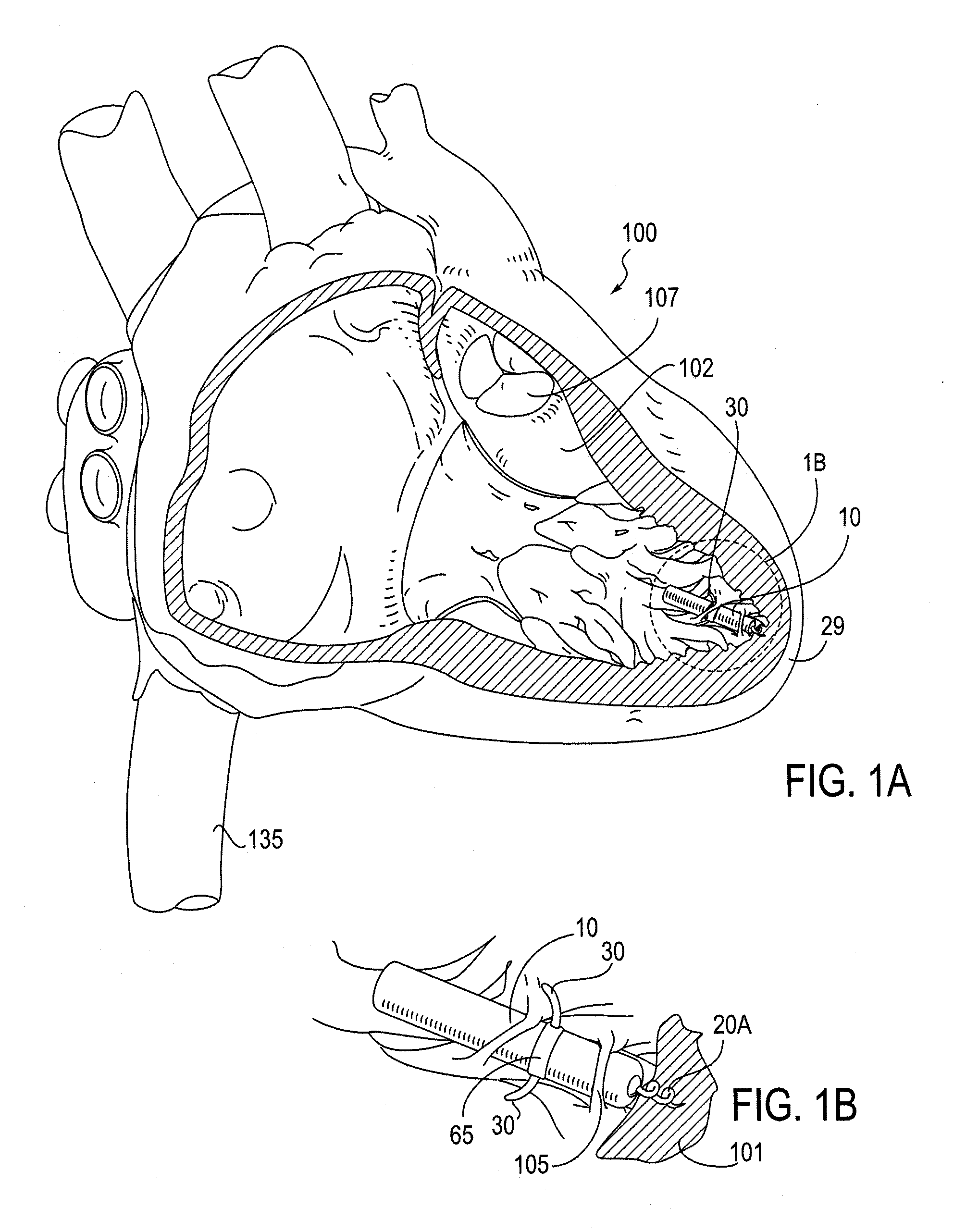
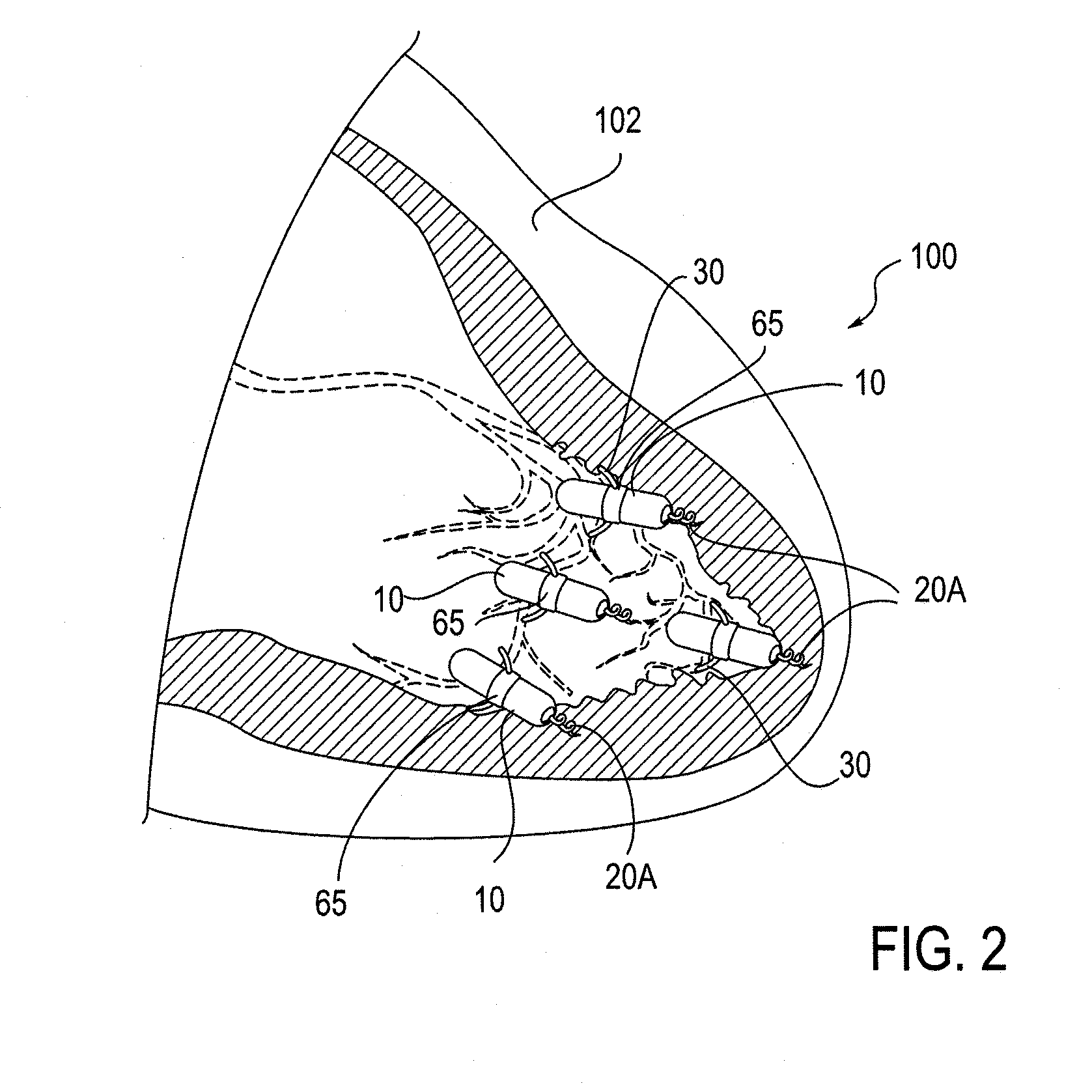
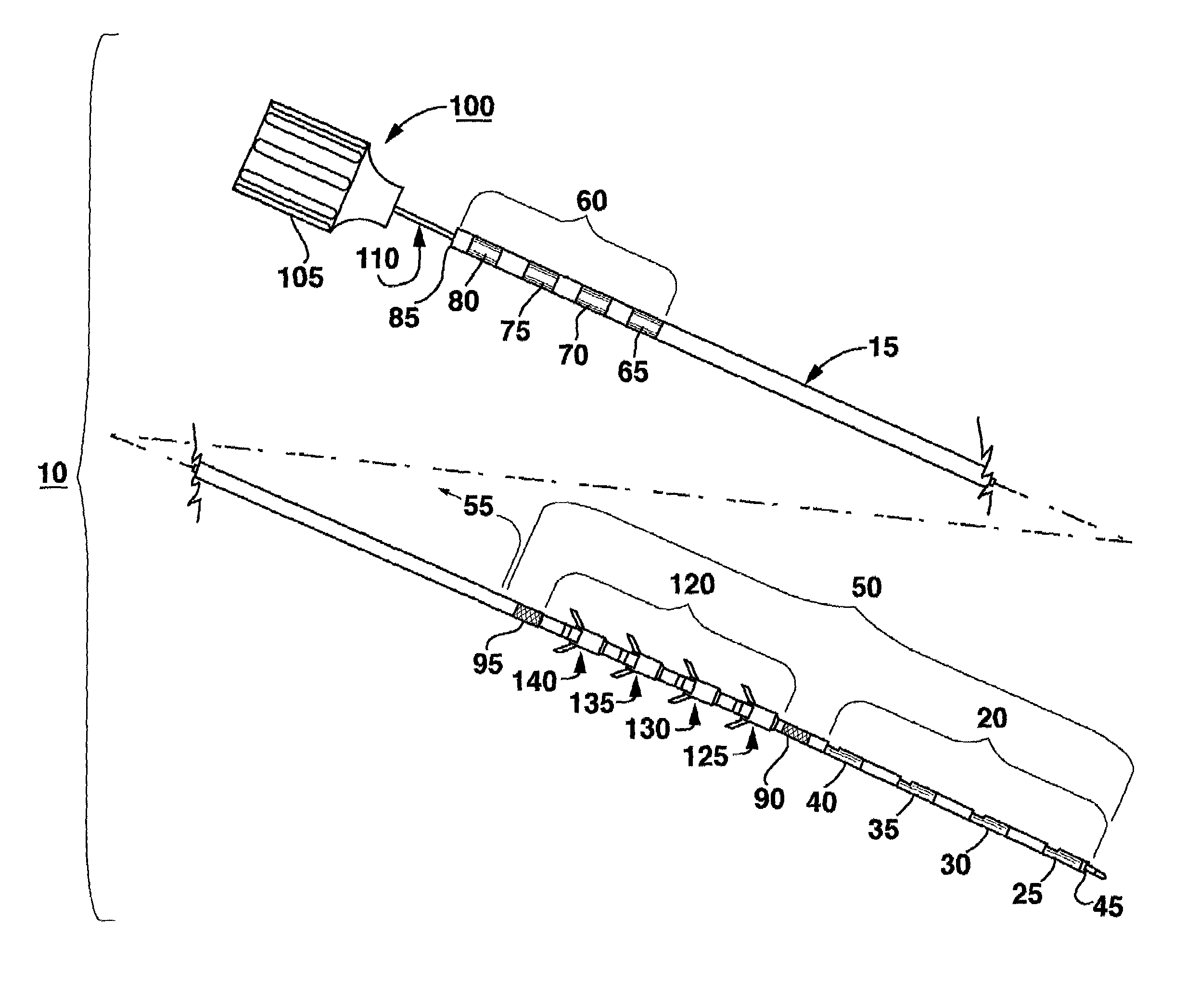
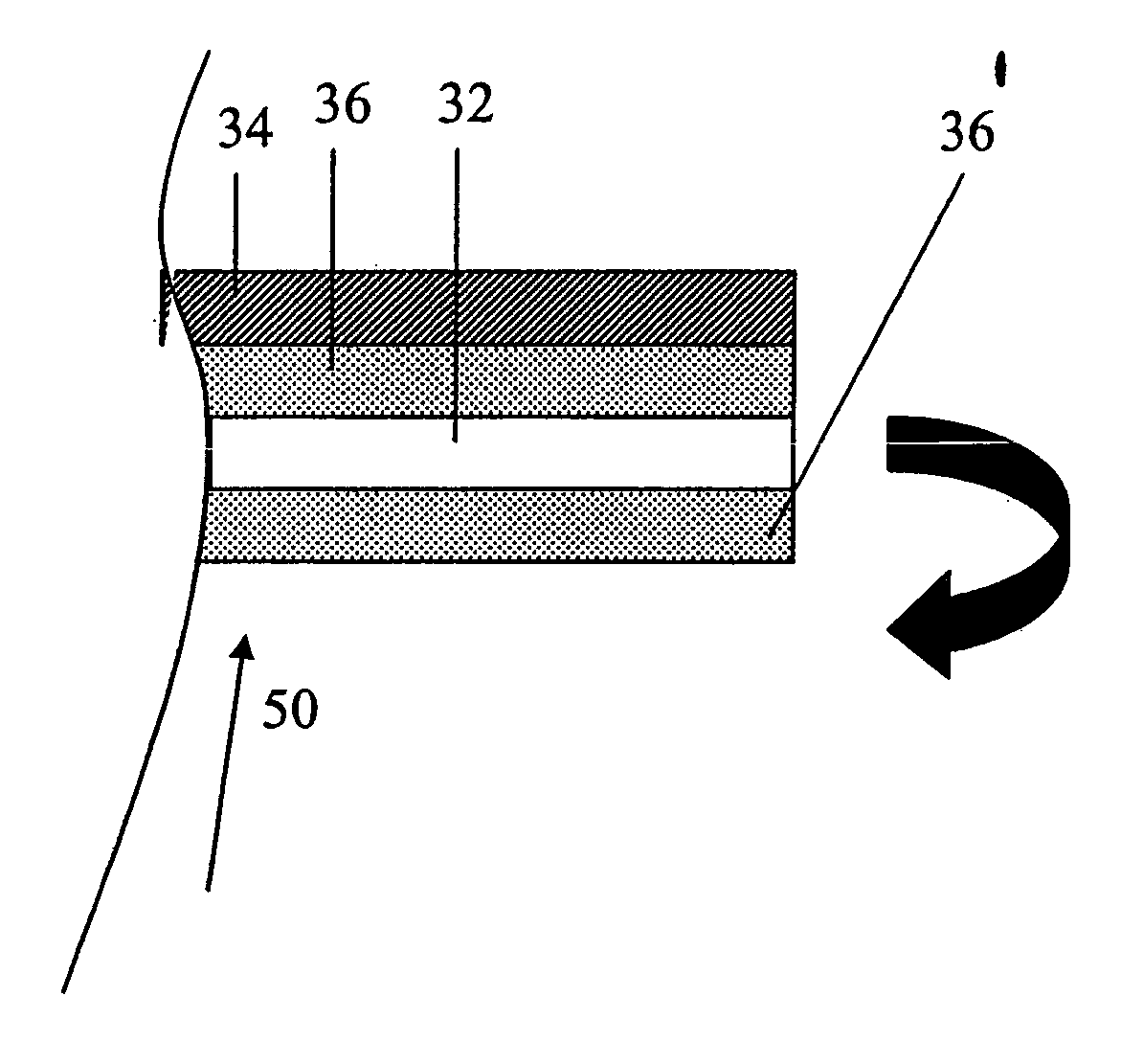
The invention relates to leadless cardiac pacemakers (LBS), and elements and methods by which they affix to the heart. The invention relates particularly to a secondary fixation of leadless pacemakers which also include a primary fixation. Secondary fixation elements for LBS's may either actively engage an attachment site, or more passively engage structures within a heart chamber. Active secondary fixation elements include a tether extending from the LBS to an anchor at another site. Such sites may be either intracardial or extracardial, as on a vein through which the LBS was conveyed to the heart, the internal or external surface thereof. Passive secondary fixation elements entangle within intraventricular structure such as trabeculae carneae, thereby contributing to fixation of the LBS at the implant site.
Owner:NANOSTIM
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6999819B2Optimize locationQuick placementSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMuscle tissueMedicine
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Delivery device for leaflet valve
InactiveUS7335218B2Reduce riskHeart valvesSurgical needlesAttachment siteAortocoronary bypass surgery
Owner:HLT INC
Method and apparatus for repairing or replacing chordae tendinae
ActiveUS20100042147A1Adjustable lengthFunction increaseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
A method and apparatus for performing mitral valve chordal repair on a patient include attaching at least one filament to a mitral valve leaflet and to a papillary muscle. A first end of a filament can be attached to the mitral valve leaflet and the length of the filament can be adjusted by adjusting the tension of the filament in a catheter. The second end of the filament can be attached to an attachment site.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
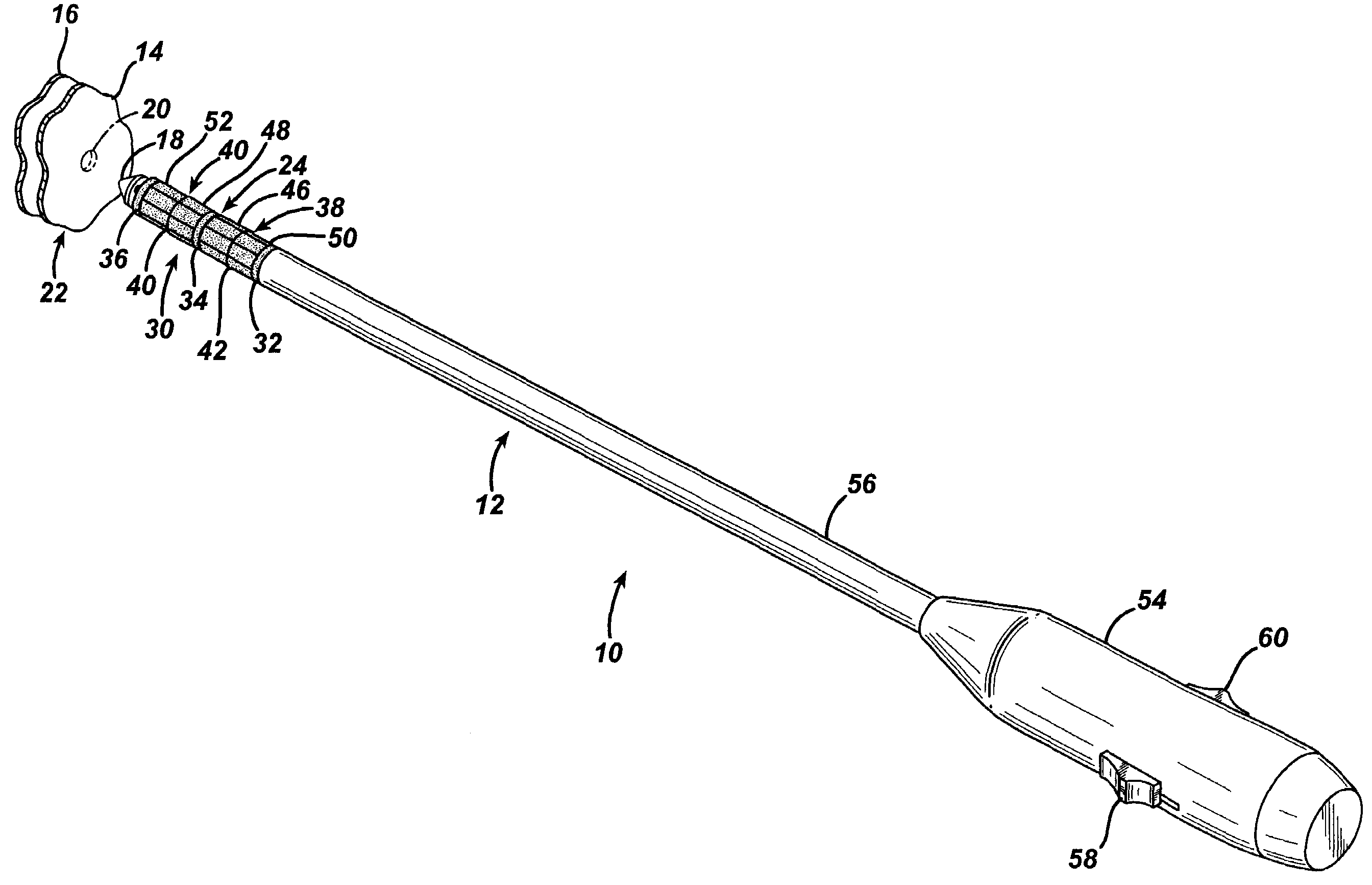
Slip-fit handle for hand-held instruments that access interior body regions
A first surgical instrument has a bore extending therethrough and includes a handle attachment site. A second surgical instrument is sized and configured for passage through the bore of the first instrument. The handle is adapted for manipulating the first instrument when in use and includes a component configured to removably engage the handle attachment site. The handle includes a passageway accommodating passage of the second instrument through the bore of the first instrument while the first instrument is removably engaged by the handle.
Owner:KYPHON
Bone milling instrument
InactiveUS7255702B2Complex and anatomically correct implant shapeAccurate shapeProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAttachment siteBiomedical engineering
A bone milling instrument is disclosed for creating a shaped cavity from an initial cavity in a bone, the bone milling instrument comprising a reference frame, a centering member at the distal end of the reference frame, a registration surface for engaging a portion of the initial cavity, and an attachment site provided proximally of the registration surface, a guidance support member, an attachment mechanism at the first end of the guidance support member, and a constrained pathway extending between the ends of the guidance support member; a shuttle having a first connection element configured for positionably attaching the shuttle to the guidance support member, and a second connection element configured to provide a rotational coupler; and a cutting device having a cutting portion configured at a distal end thereof, and an attachment portion provided at a proximal end.
Owner:SHALBY ADVANCED TECH INC
Single lumen access deployable ring for intralumenal anastomosis
Creating an anastomosis, or the surgical formation of a passage between two normally distinct vessels or lumens, is enhanced by an applier that introduces a ring device without the need for a separate anvil to form a hollow rivet shaped attachment. Moreover, the ring device may be advantageously formed in a cylindrical shape from molded polymer material or stamped from sheet metal with proximal and distal rings connected by proximal and distal arms that respectively form hinged, ring shaped so appose tissue walls. A center ring or portion sits in the attachment site. The applier causes actuating by moving the rings relative to one another. A latching mechanism locks the rings in the actuating state.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
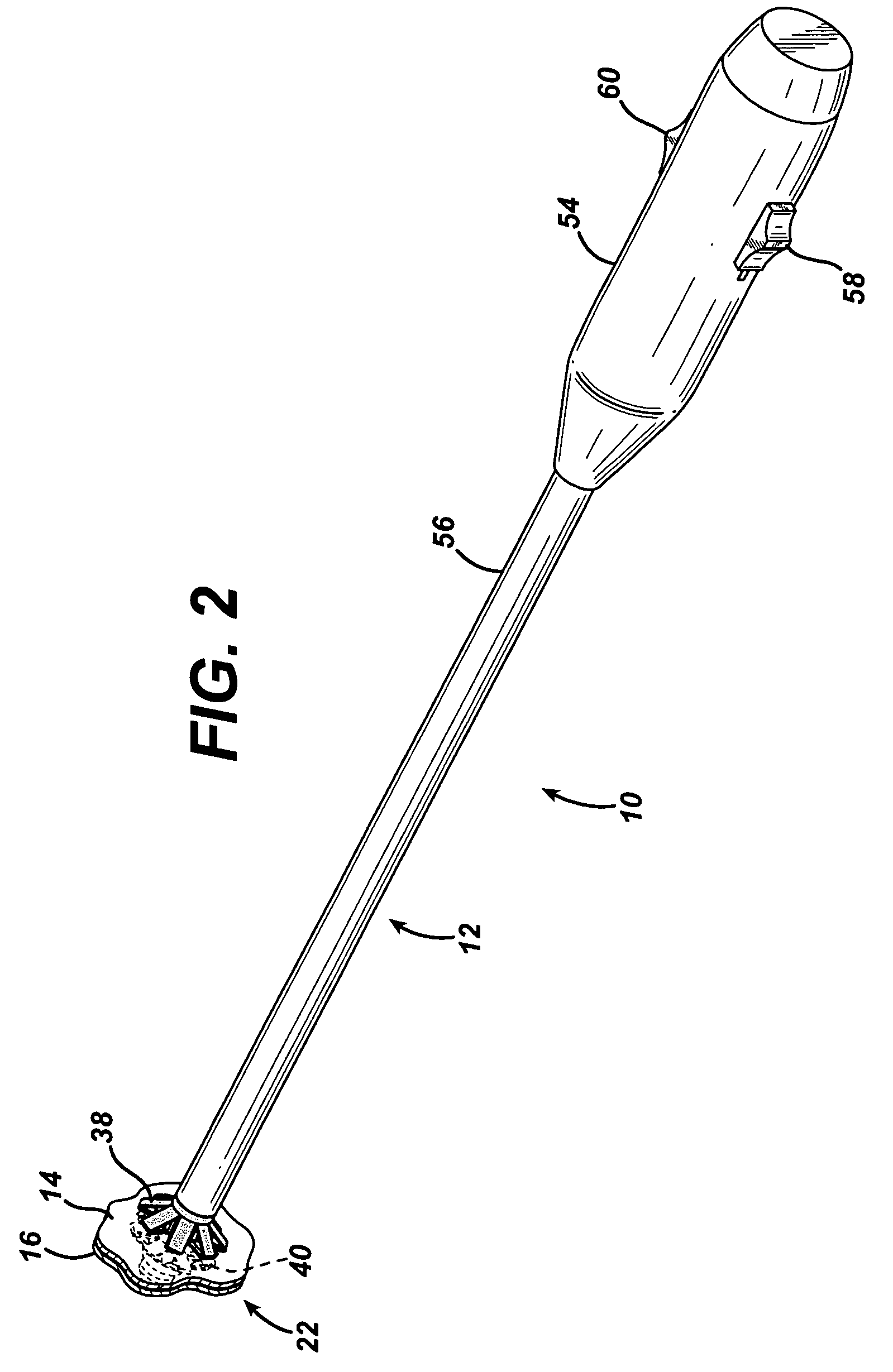
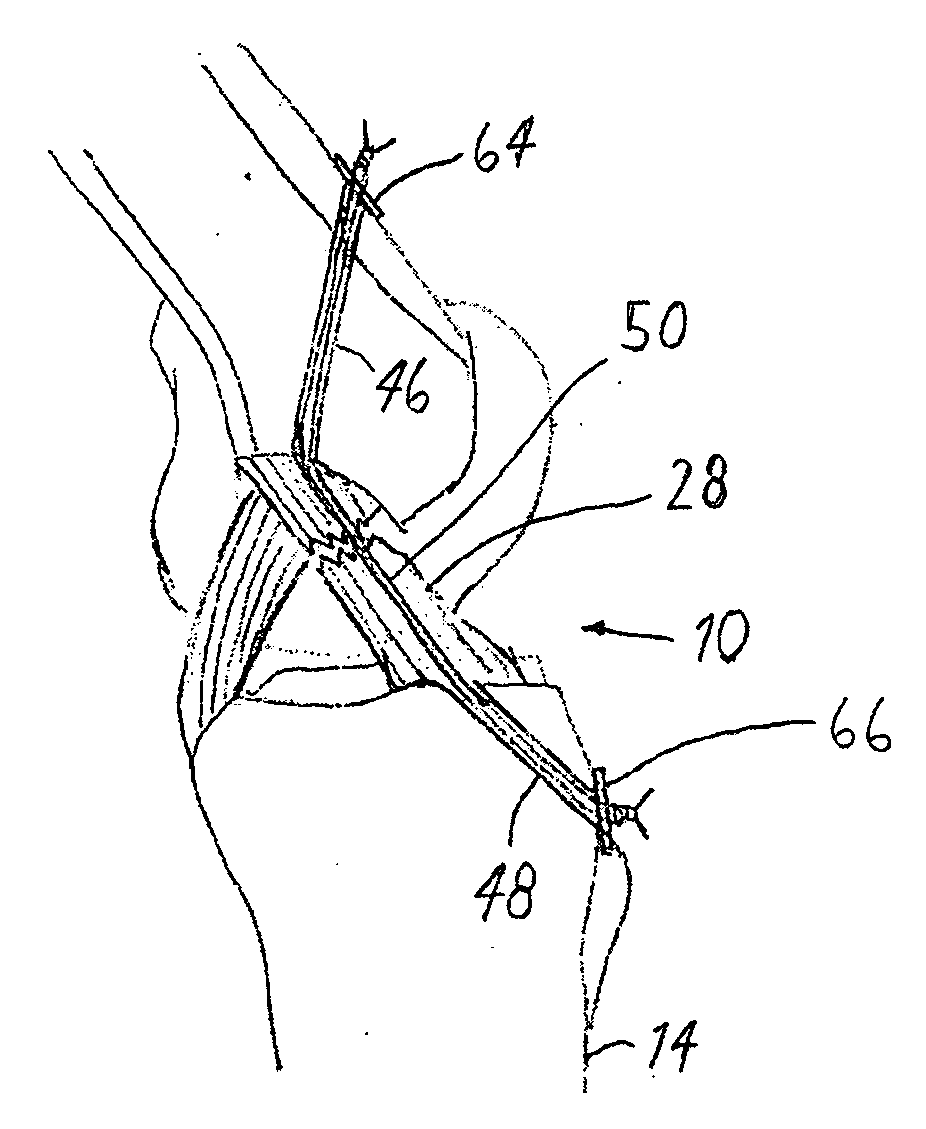
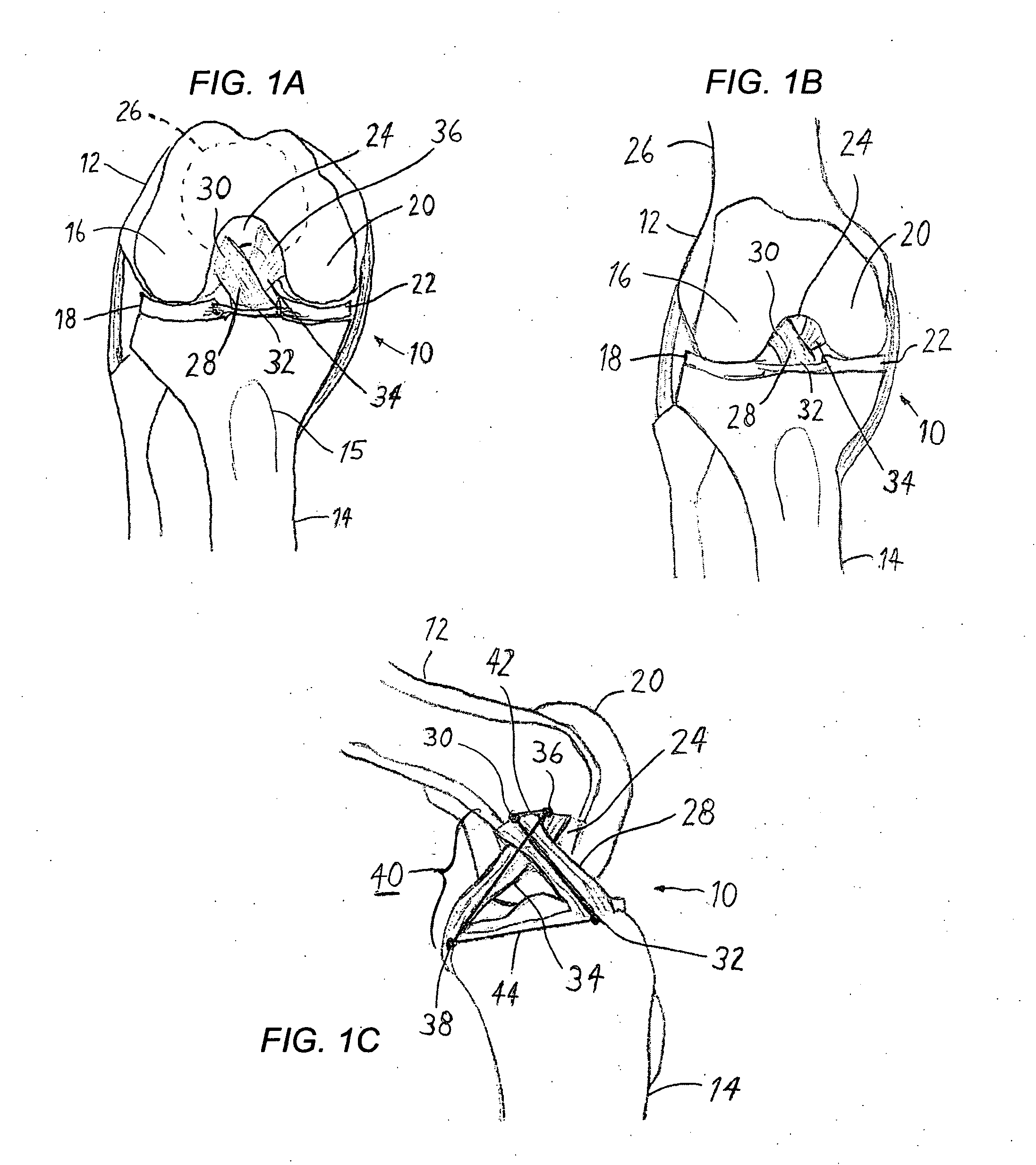
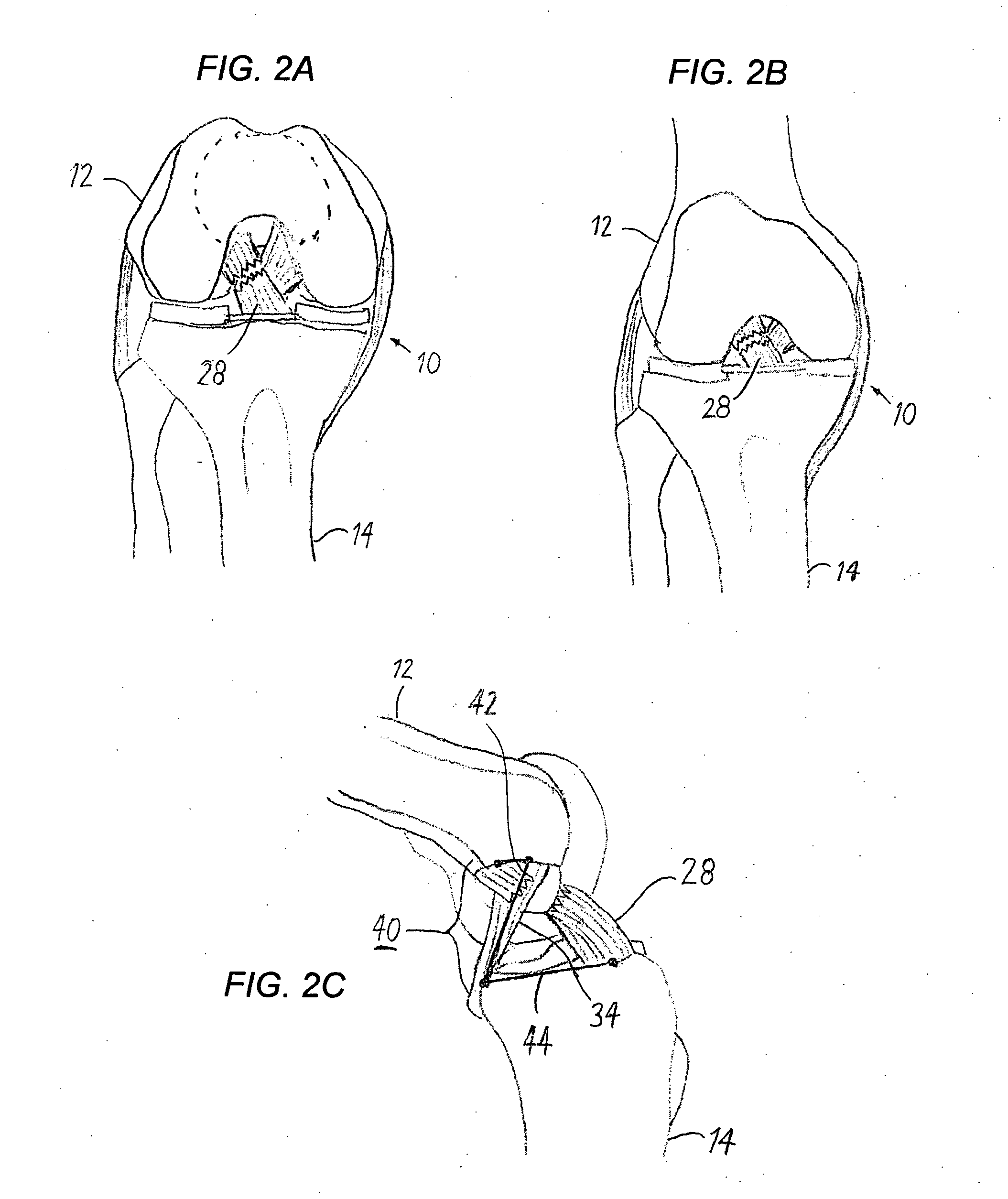
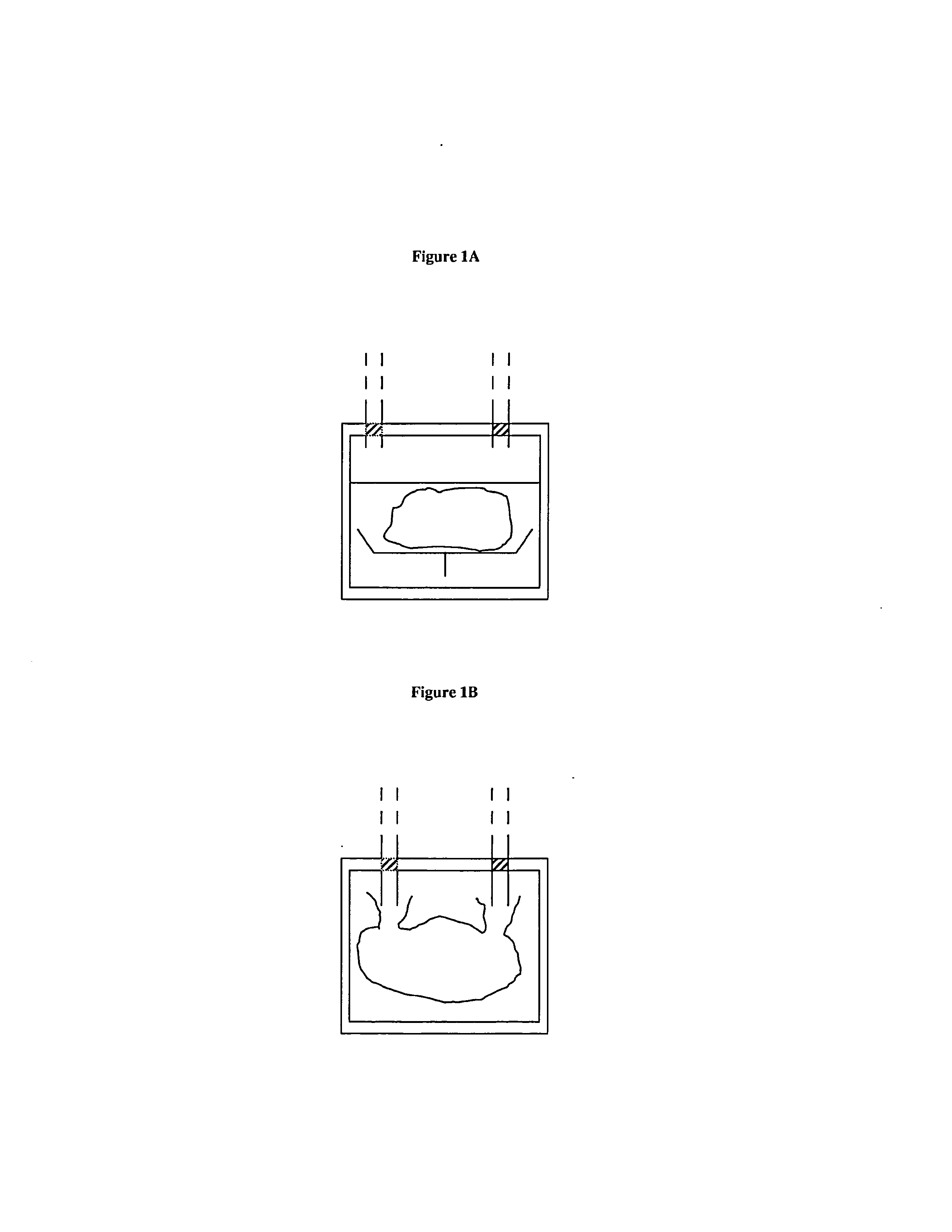
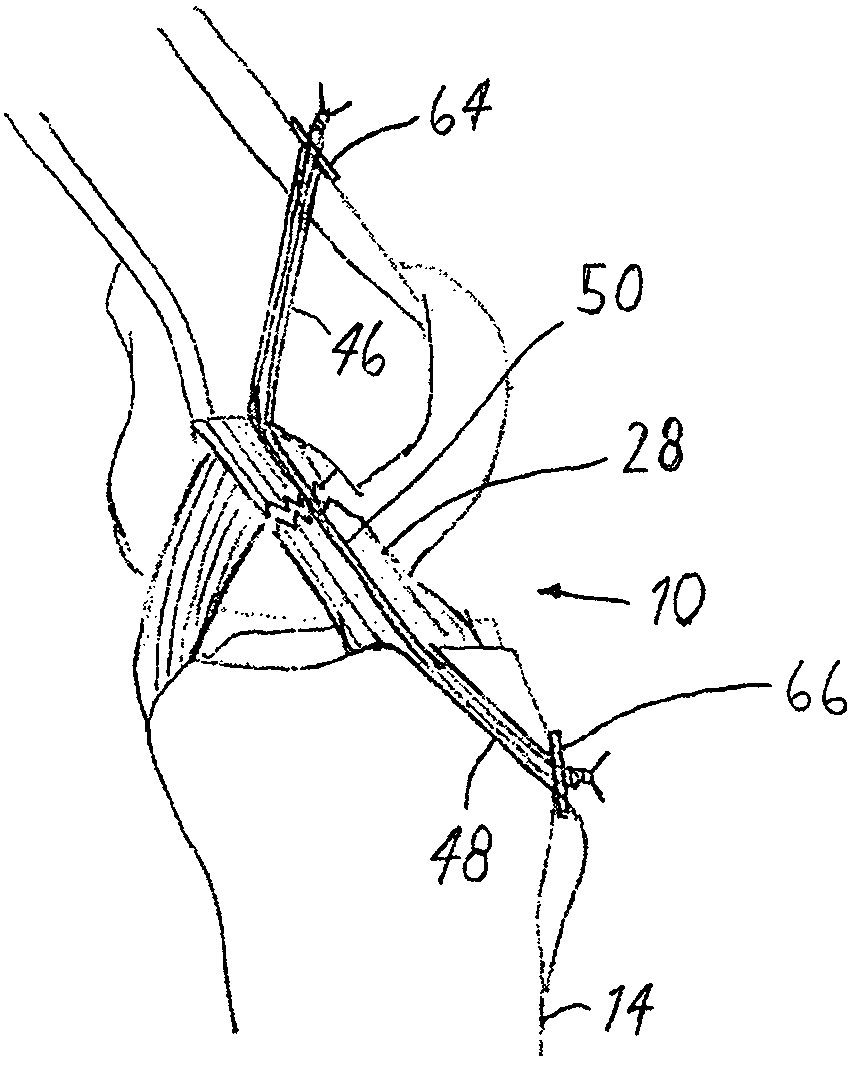
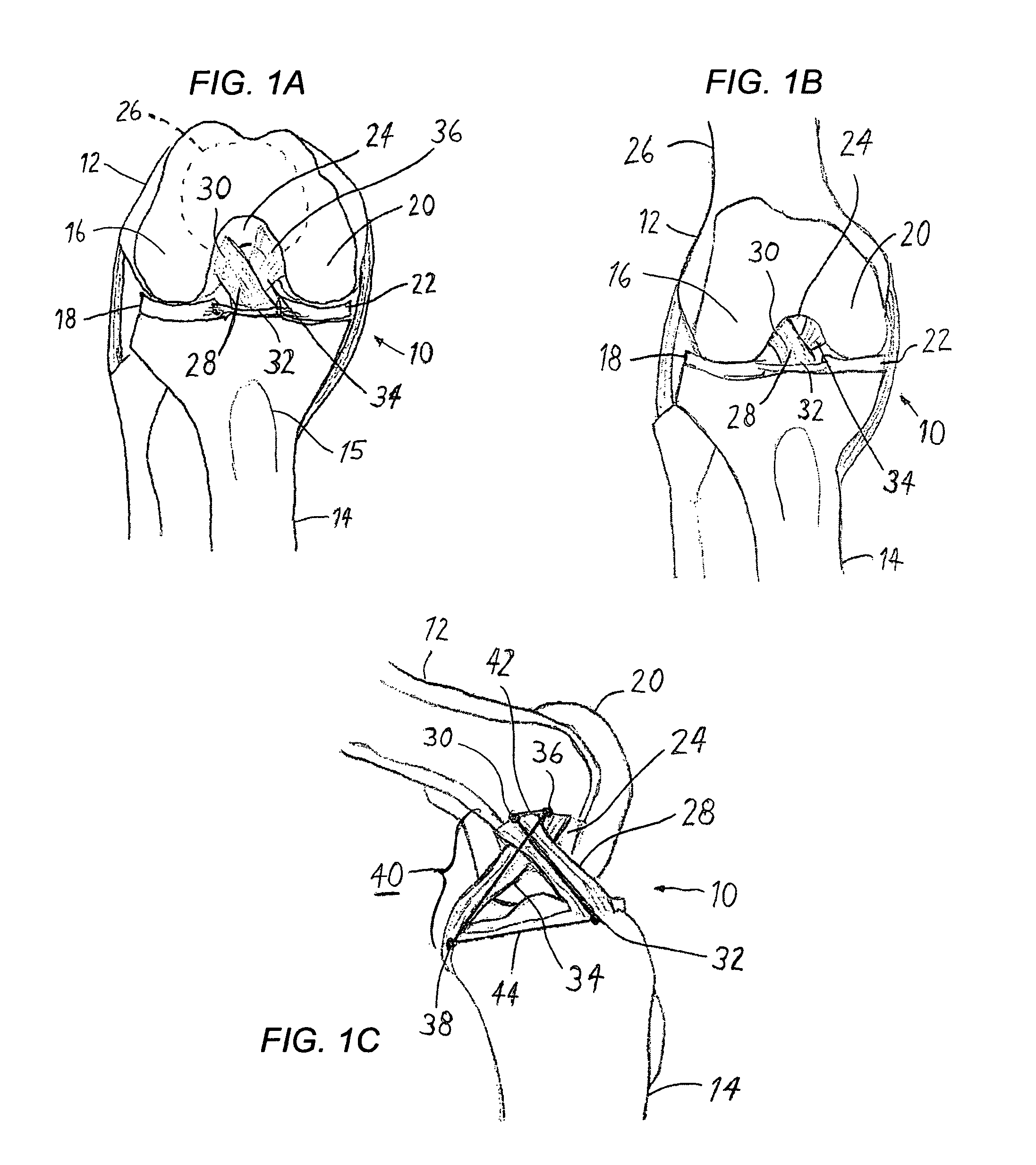
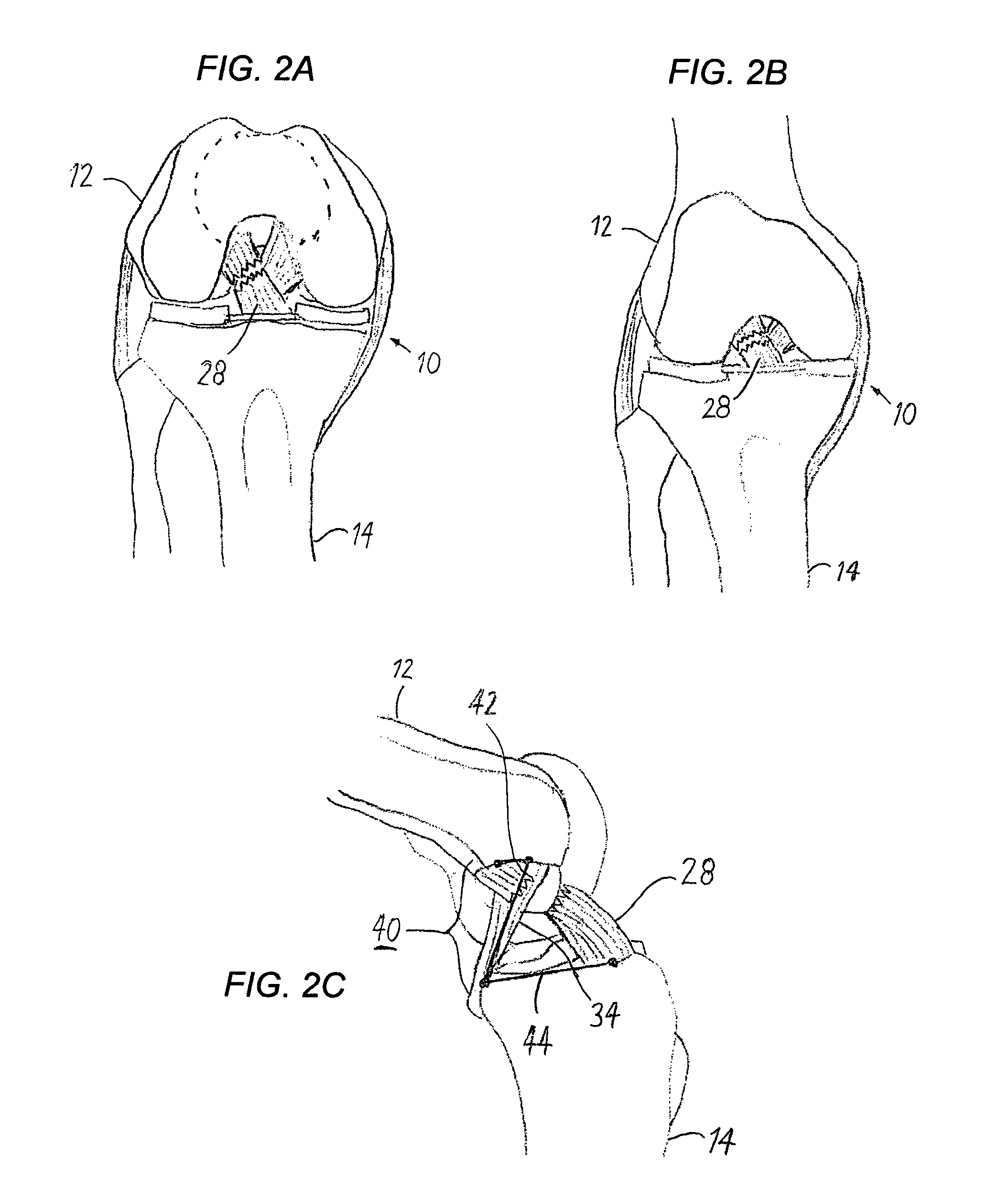
Anterior cruciate ligament tether
A device and method to provide a surgically inserted internal tether between the femur and tibia is provided which will prevent distraction of the healing anterior cruciate ligament in all degrees of flexion and extension, at all times. The anterior cruciate ligament tether preserves the four-bar cruciate linkage, critical for normal knee mechanics. In addition, placement of the tether provides bleeding into the knee in the region of the anterior cruciate ligament attachment sites and the consequent inflow of pluripotential cells and healing mediators.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Delivery device for implant with dual attachment sites
InactiveUS20070088388A1Improve accuracyEasy to controlSurgical veterinaryWound clampsSurgeryAttachment site
The invention generally relates to systems and methods for percutaneous closure of intra-cardiac openings, such as a patent foramen ovale (PFO). In one embodiment, a delivery system includes a first attachment mechanism and a second attachment mechanism attached to a closure device for implantation in an intra-cardiac opening. The delivery system can be used to deliver a closure device to the intra-cardiac opening, or to retrieve or re-position a closure device within the intra-cardiac opening.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
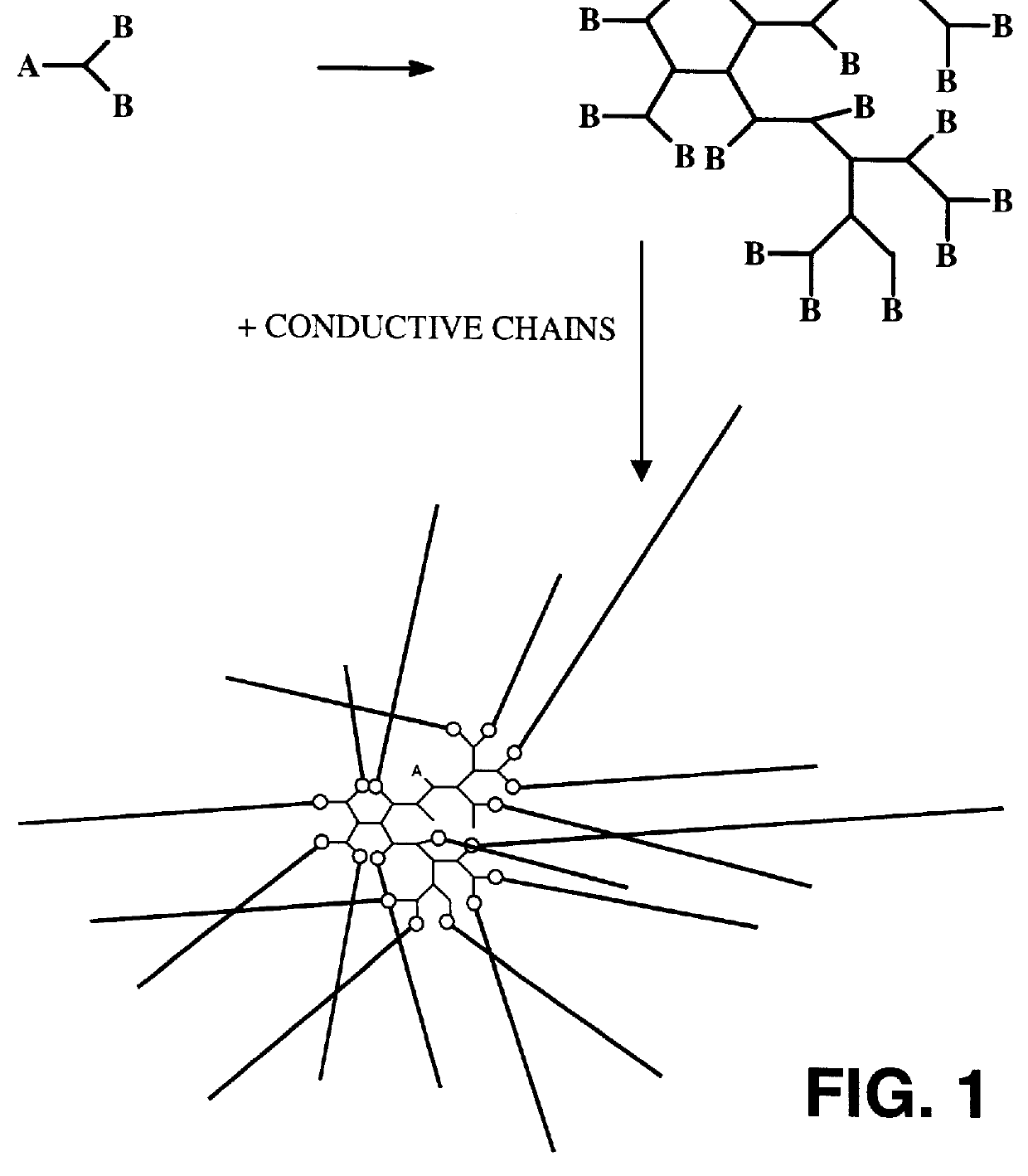
Reflective and conductive star polymers
Conductive polymers having a star structure comprising a central core with multiple attachment sites and conjugated charge transporting arms radiating therefrom. The cores are derived from hyperbranched polymers, dendrimers, or other molecules with a multiplicity of attachment sites. The arms are derived from conjugated oligomers and polymers such as polythiophene, polyaniline or polyphenylene. The subject polymers allow assembly of the macromolecules in all three dimensions in the solid state. A ramification of the compact assembly is the realization of highly reflective, smooth coatings simply applied from solution. A preferred embodiment having a 1,3,5 hyperbranched polyphenylene core and poly (3-hexylthiophene) arms provides lustrous reflective gold coatings.
Owner:EIC LAB
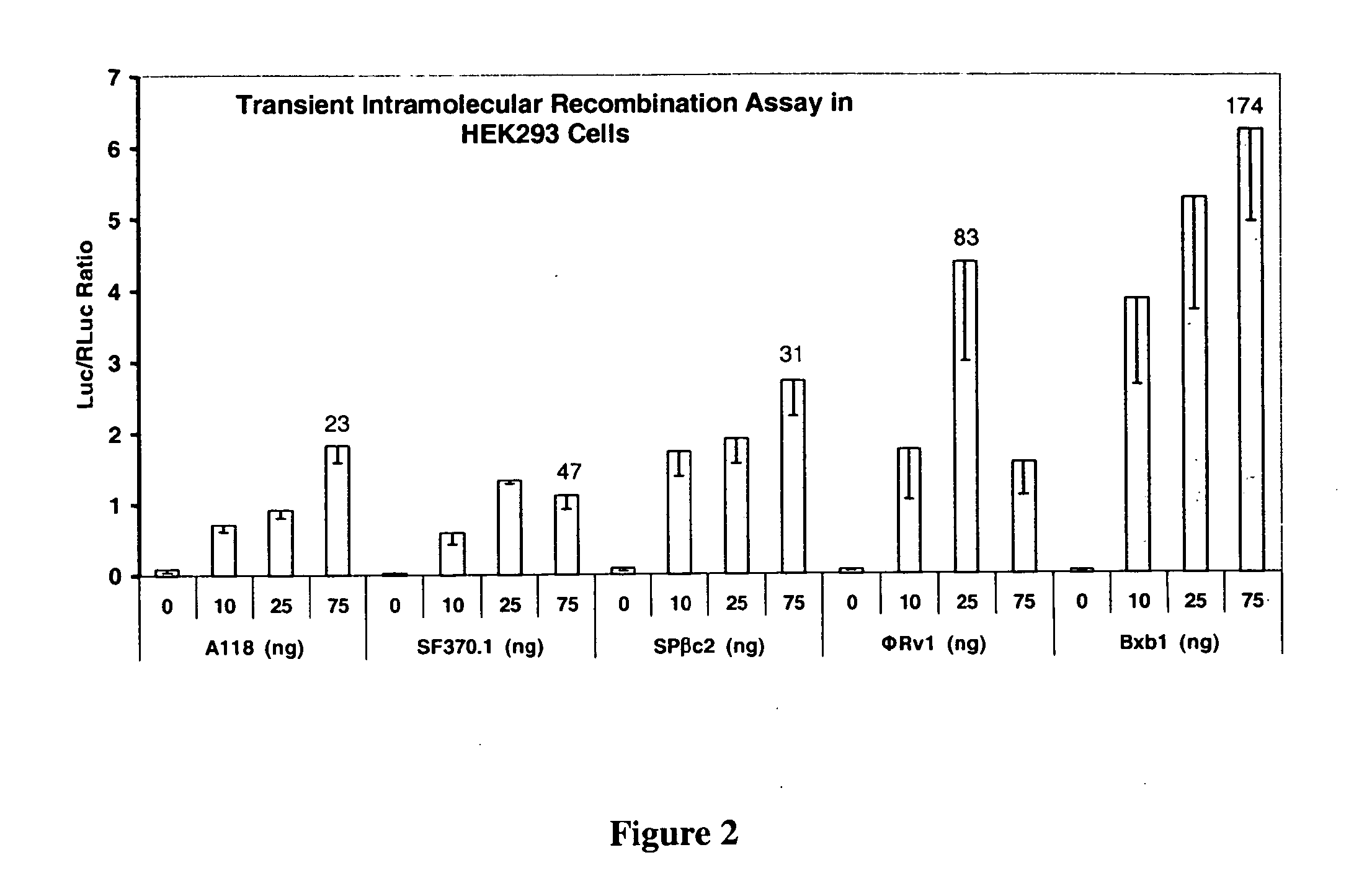
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
InactiveUS20080020465A1Antibacterial agentsHydrolasesStreptococcus pyogenesSite-specific recombination
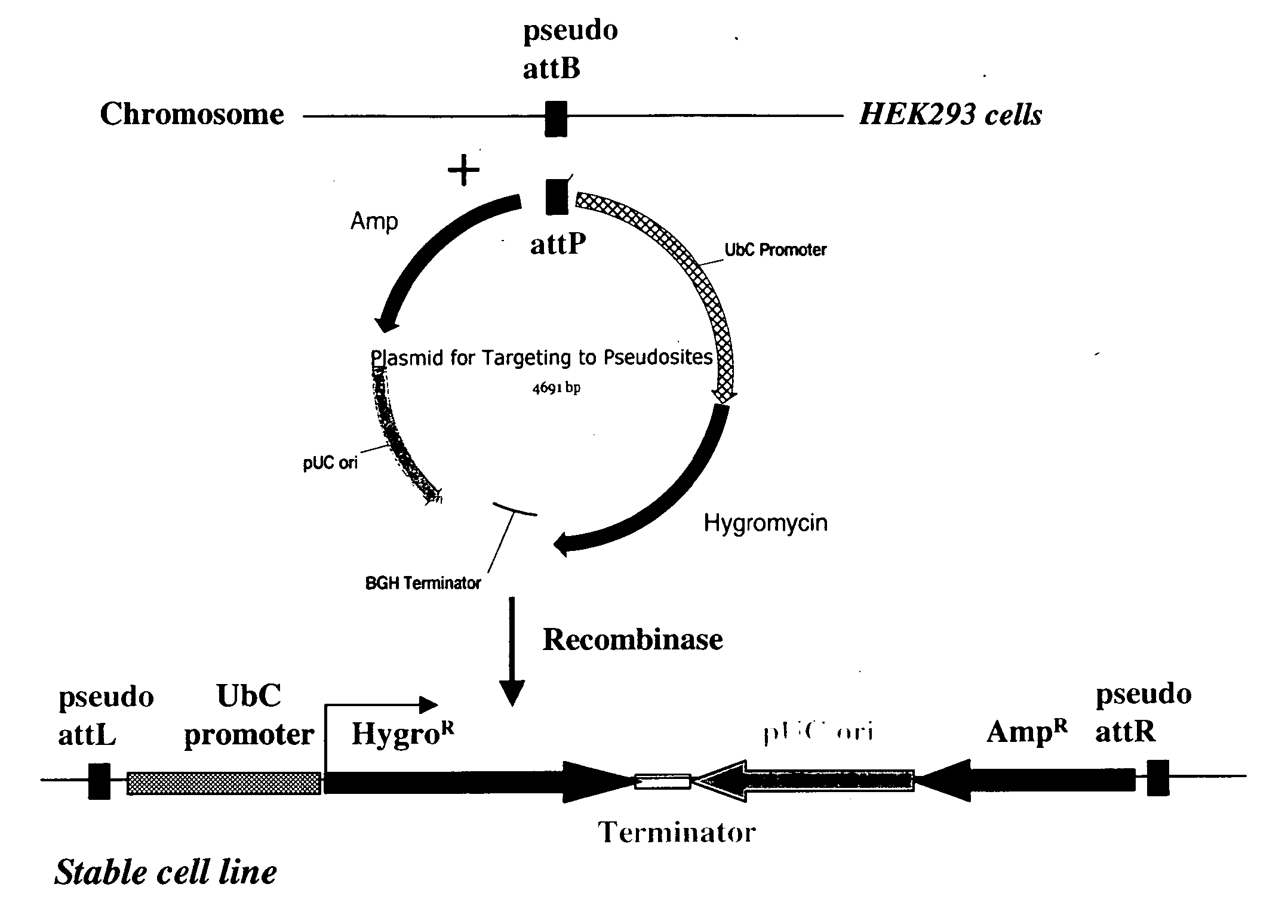
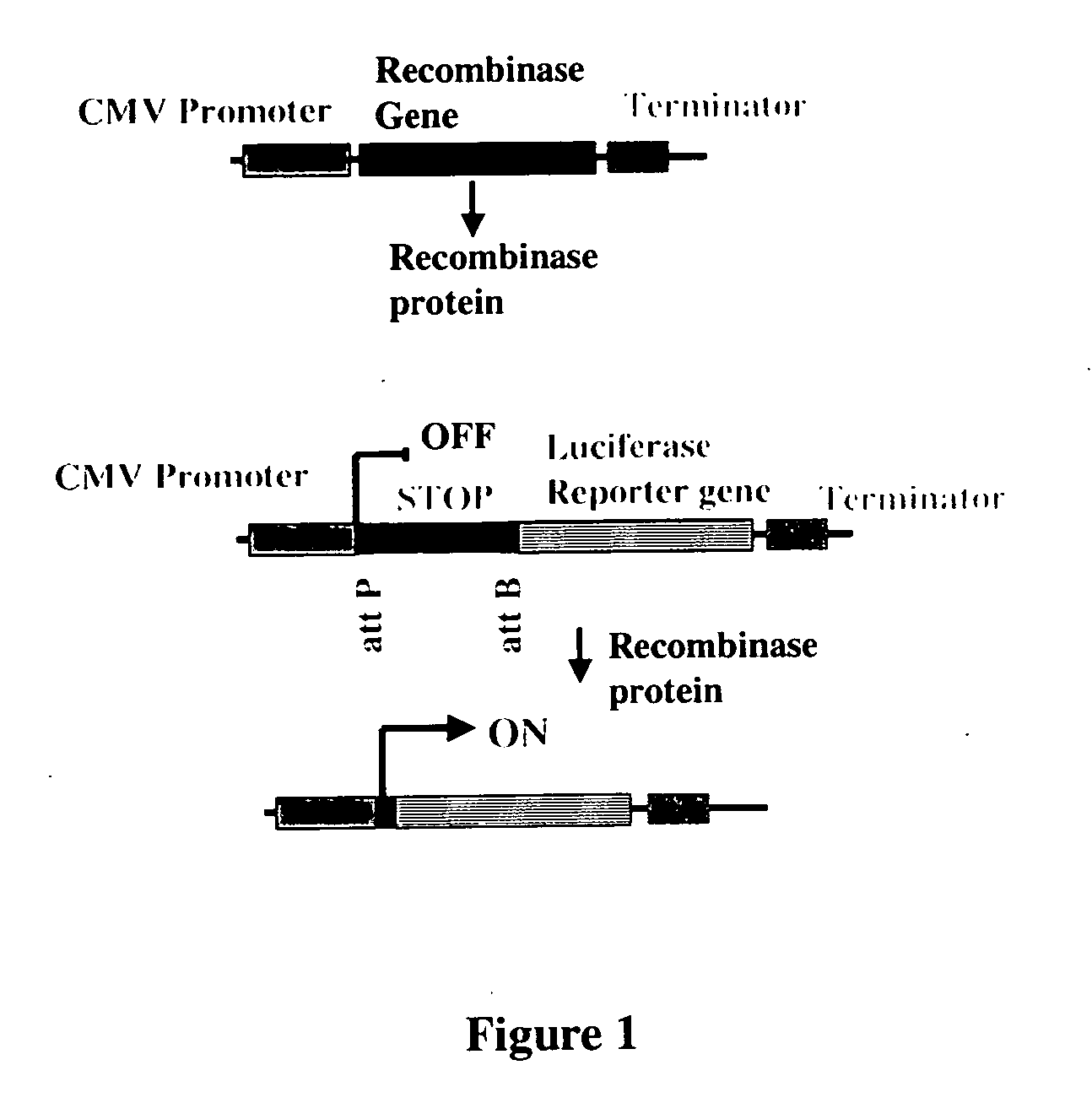
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PADIDAM MALLA
Method of treating diseased valve
A device and method for improving flow through a native blood vessel valve, such as the aortic valve, are provided. The present invention allows a miniature valve to be implanted into affected leaflets percutaneously, obviating the need for coronary bypass surgery. The method includes the cutting of small holes, on the order of 4 mm, in the leaflets of a targeted valve, thereby allowing blood to flow through the newly formed holes. The holes are used as attachment sites for the miniature valves of the present invention.
Owner:HLT INC
System for delivery of magnetic stimulation
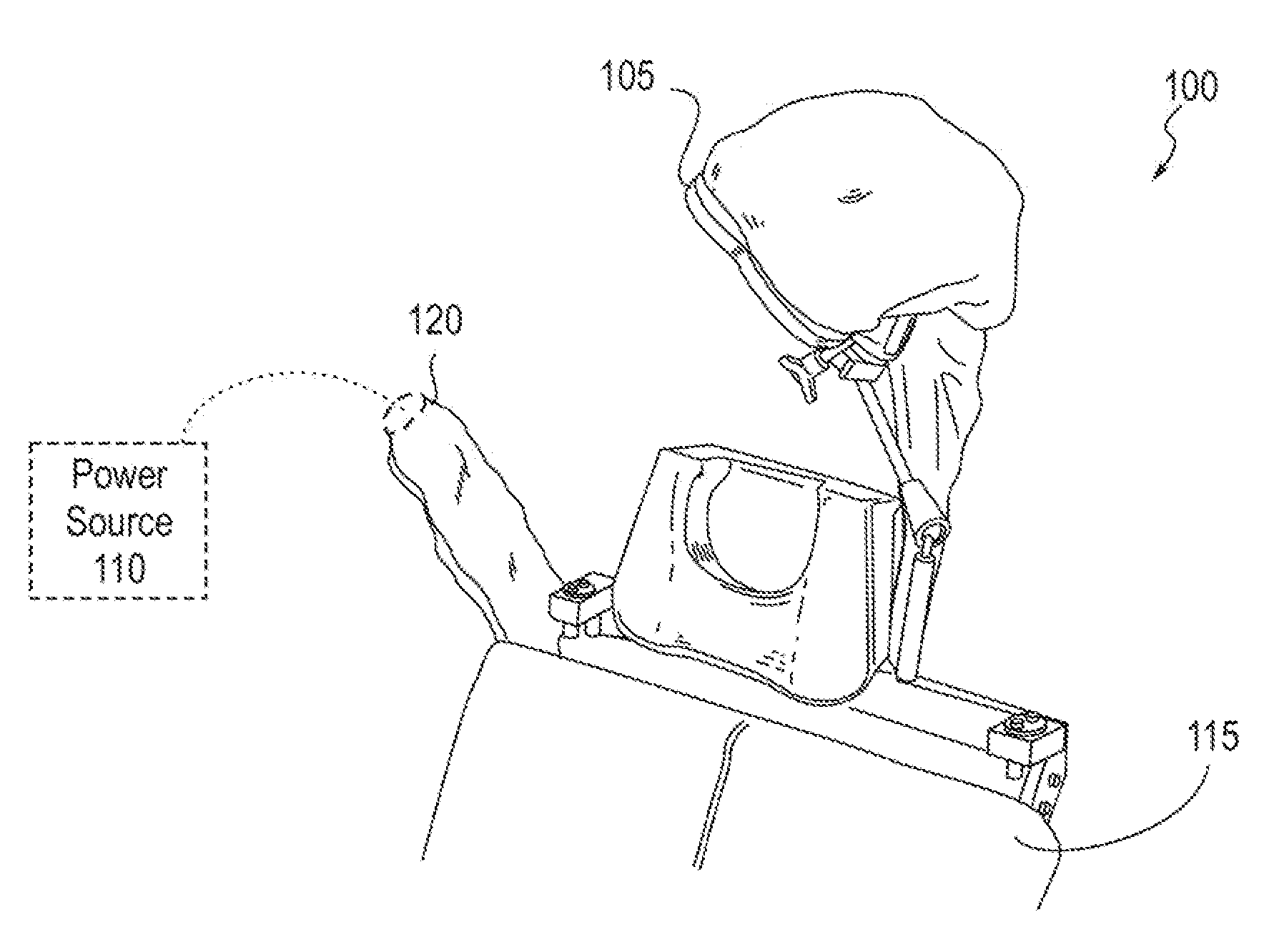
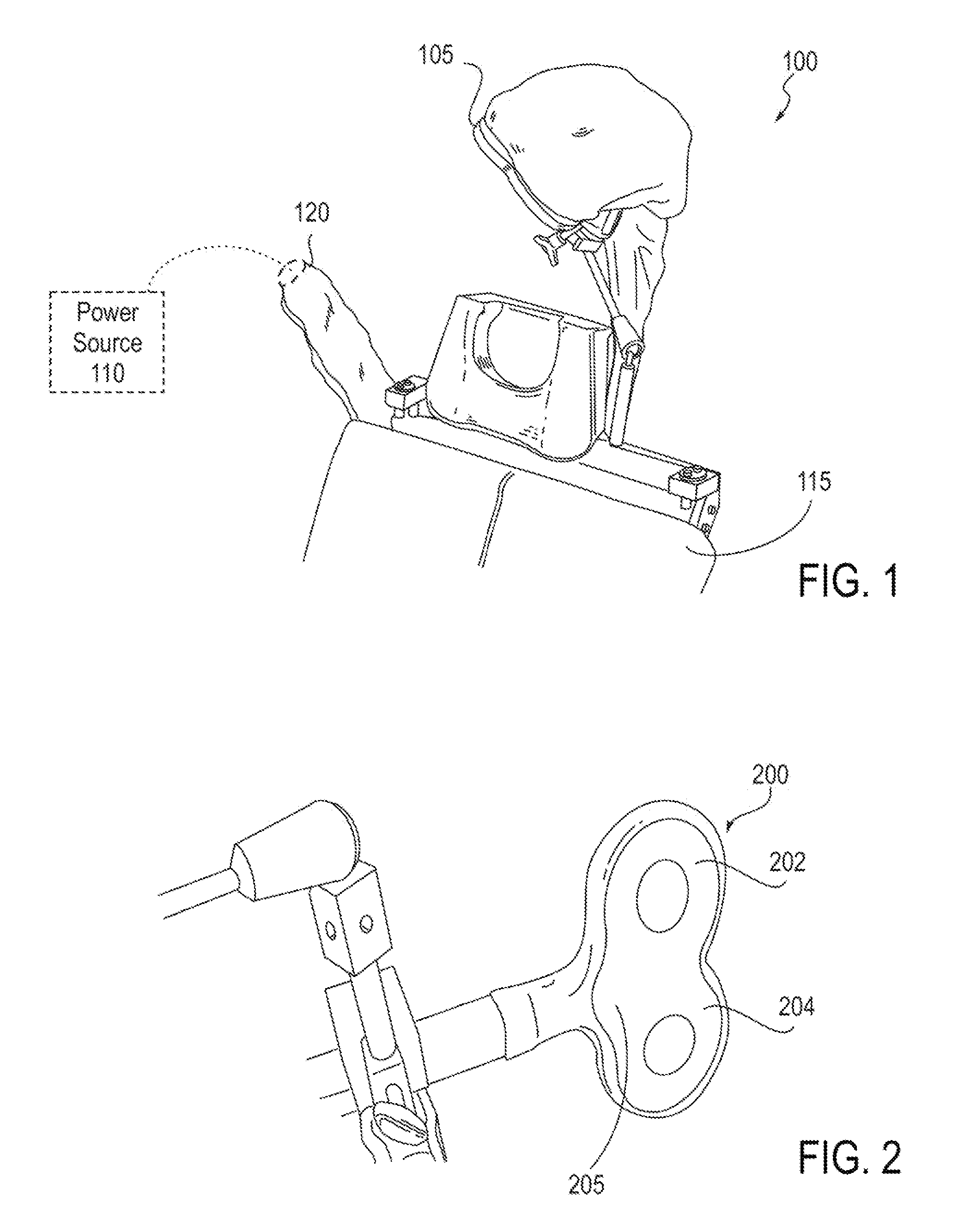
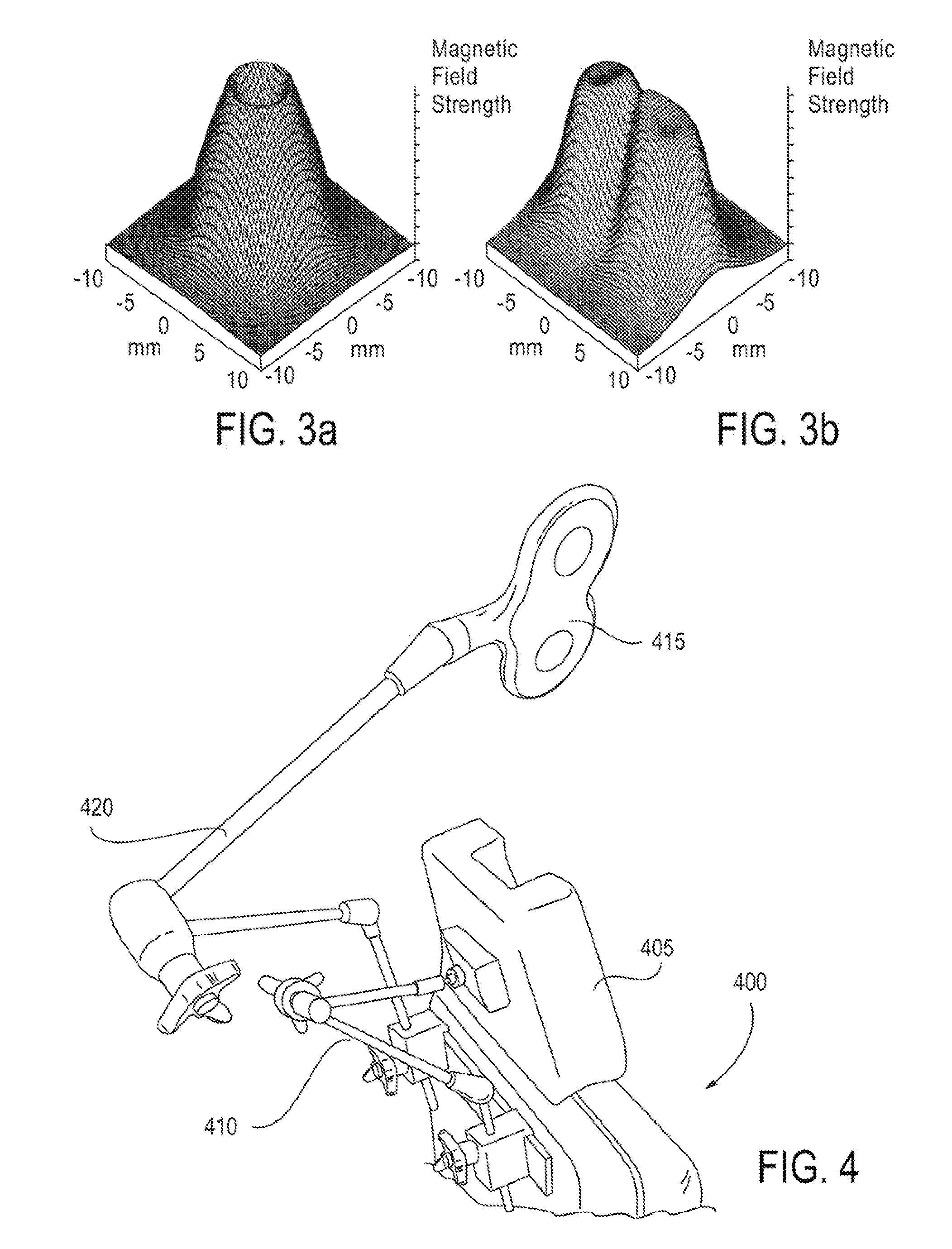
A system for delivering magnetic stimulation to a subject that has a magnetic stimulation coil, a power source, and a patient-positioning device is provided. The magnetic stimulation coil is movably connected to patient-positioning device for fixably positioning the magnetic stimulation coil to stimulate a region of a subject and electrically connected to the power source. A cooling system maintains the magnetic stimulation coil between a temperature of about 5° C. and about 40° C. during operation of the coil for a period of at least 90 minutes. An attachment site for a second magnetic stimulation coil is provided, and the second magnetic stimulation coil is optionally movably connected to the patient-positioning device for positioning the second magnetic stimulation coil independently of the first magnetic stimulation coil to provide a combination delivery of magnetic stimulation to a second region of the subject.
Owner:ETIS INVESTMENTS
Methods and devices for placing a conduit in fluid communication with a target vessel and a source of blood
InactiveUS20050192604A1Shorten the lengthReduce morbiditySuture equipmentsStentsSynthetic materialsEngineering
Devices and methods for placing a conduit in fluid communication with a target vessel to communicate the target vessel with a source of blood. A conduit is coupled to the target vessel by first and second securing components that compress or sandwich the vessel wall. The conduit may be preshaped to assume a desired orientation when in an unbiased state, for example, to allow the conduit to be deformed during delivery and then regain its desired orientation once which is regained when deployed. The first and second securing components may be any shape but are preferably elongated in the direction of the vessel axis, e.g., elliptical or rectangular, such that a minimum amount of material is present at the outlet to closely approximate the cross-sectional area of the native target vessel. The securing components do not significantly occlude the target vessel lumen, may be secured to the vessel wall in non-penetrating fashion, and provides a fluid-tight seal around the attachment site. The conduit may comprise tissue, synthetic material, etc., and one or both securing components may be constructed or provided with means for attaching an autologous vessel.
Owner:CARSON DEAN F +8
Water-stable photoluminescent semiconductor nanocrystal complexes and method of making same
InactiveUS6872450B2Reduces and prevents quantum yield reductionReduces ability of oxygenMixing methodsGlass/slag layered productsPhotoluminescenceSemiconductor nanocrystals
Owner:EVIDENT TECH
Method and apparatus for repairing or replacing chordae tendinae
ActiveUS8778016B2Adjustable lengthFunction increaseSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsPapillary muscleMitral valve leaflet
A method and apparatus for performing mitral valve chordal repair on a patient include attaching at least one filament to a mitral valve leaflet and to a papillary muscle. A first end of a filament can be attached to the mitral valve leaflet and the length of the filament can be adjusted by adjusting the tension of the filament in a catheter. The second end of the filament can be attached to an attachment site.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Respiratory sensor adapters for nasal devices
Described herein are nasal respiratory devices including an attachment site for a sensors and sensor adapters for securing at least a portion of a sensor to a nasal respiratory device. Sensor adapters typically have a body frame having at least two regions: an attachment region for securing the sensor adapter to the nasal respiratory device; and a sensor connector region for securing a sensor across from an outlet of the nasal respiratory device.
Owner:VENTUS MEDICAL INC
Applier for fastener for single lumen access anastomosis
ActiveUS7452363B2Easy to controlPrecise positioningSuture equipmentsDiagnostic markersRing deviceMedicine
Creating an anastomosis, or the surgical formation of a passage between two normally distinct vessels or lumens, is enhanced by an applier that introduces a ring device without the need for a separate anvil to form a hollow rivet shaped attachment. Moreover, the ring device may be advantageously formed in a cylindrical shape from molded polymer material or stamped from sheet metal with proximal and distal rings connected by proximal and distal arms that respectively form hinged, ring shaped so appose tissue walls. A center ring or portion sits in the attachment site. The applier causes actuating by moving the rings relative to one another. A latching mechanism locks the rings in the actuating state.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Controlled detachment of intra-luminal medical device
InactiveUS20050222537A1Easy to controlEliminate the problemElectrotherapySurgerySurgical departmentMedical device
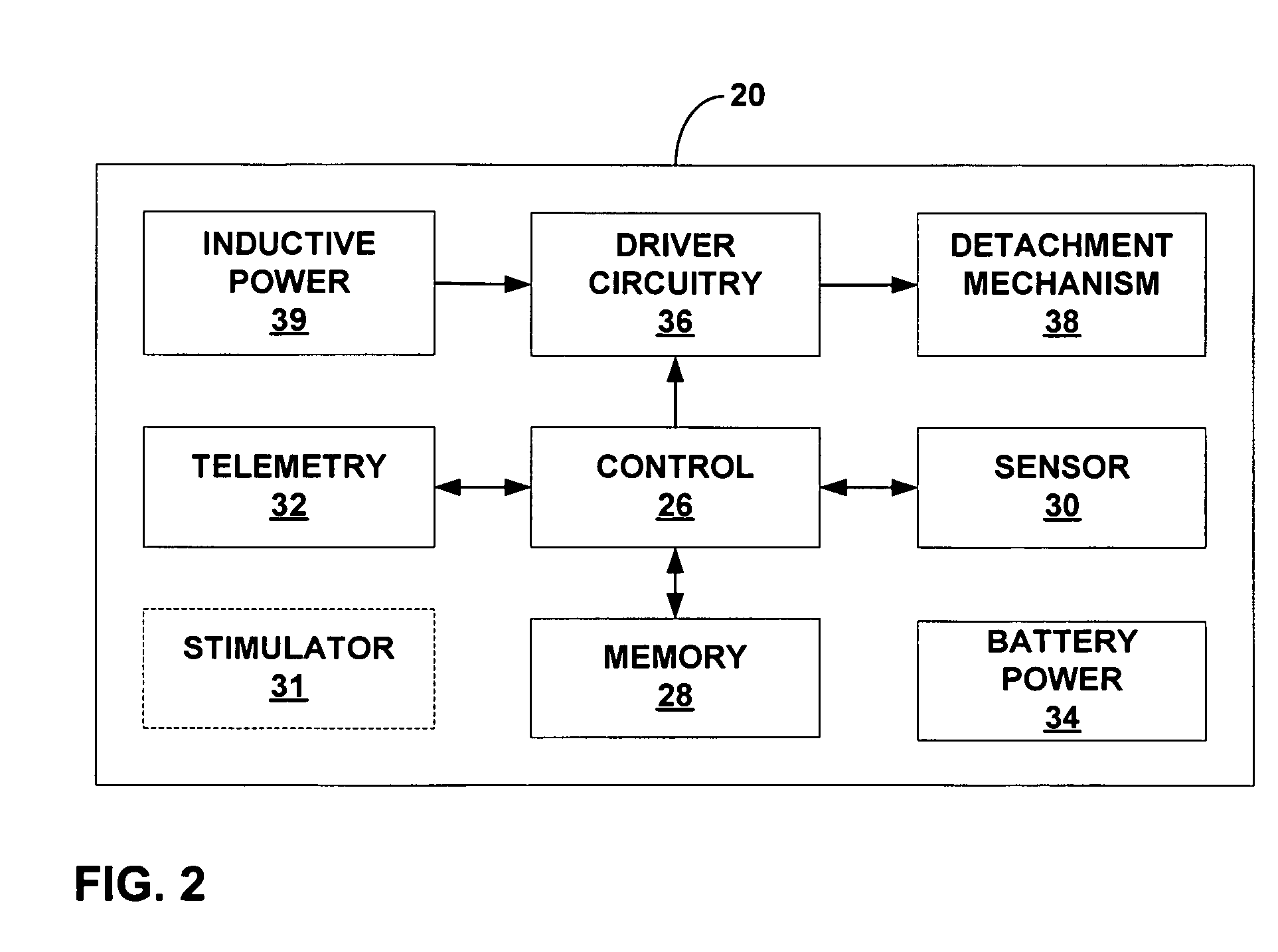
An intra-luminal medical device includes a fixation mechanism to attach the medical device to tissue within a body lumen, and a detachment mechanism to permit selective detachment of the medical device from the tissue attachment site without the need for endoscopic or surgical intervention. An electromagnetic device may be provided to mechanically actuate the detachment mechanism. Alternatively, a fuse link may be electrically blown to detach the medical device. As a further alternative, a rapidly degradable bonding agent may be exposed to a degradation agent to detach the medical device from a bonding surface within the body lumen. The medical device may eliminate problems associated with uncertain and inconsistent detachment of intra-luminal medical devices.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Methods and systems for intraoperative measurement of soft tissue constraints in computer aided total joint replacement surgery
InactiveUS20050119661A1Maintaining soft tissue balance of the replacement kneeDraw tensionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaMathematical model
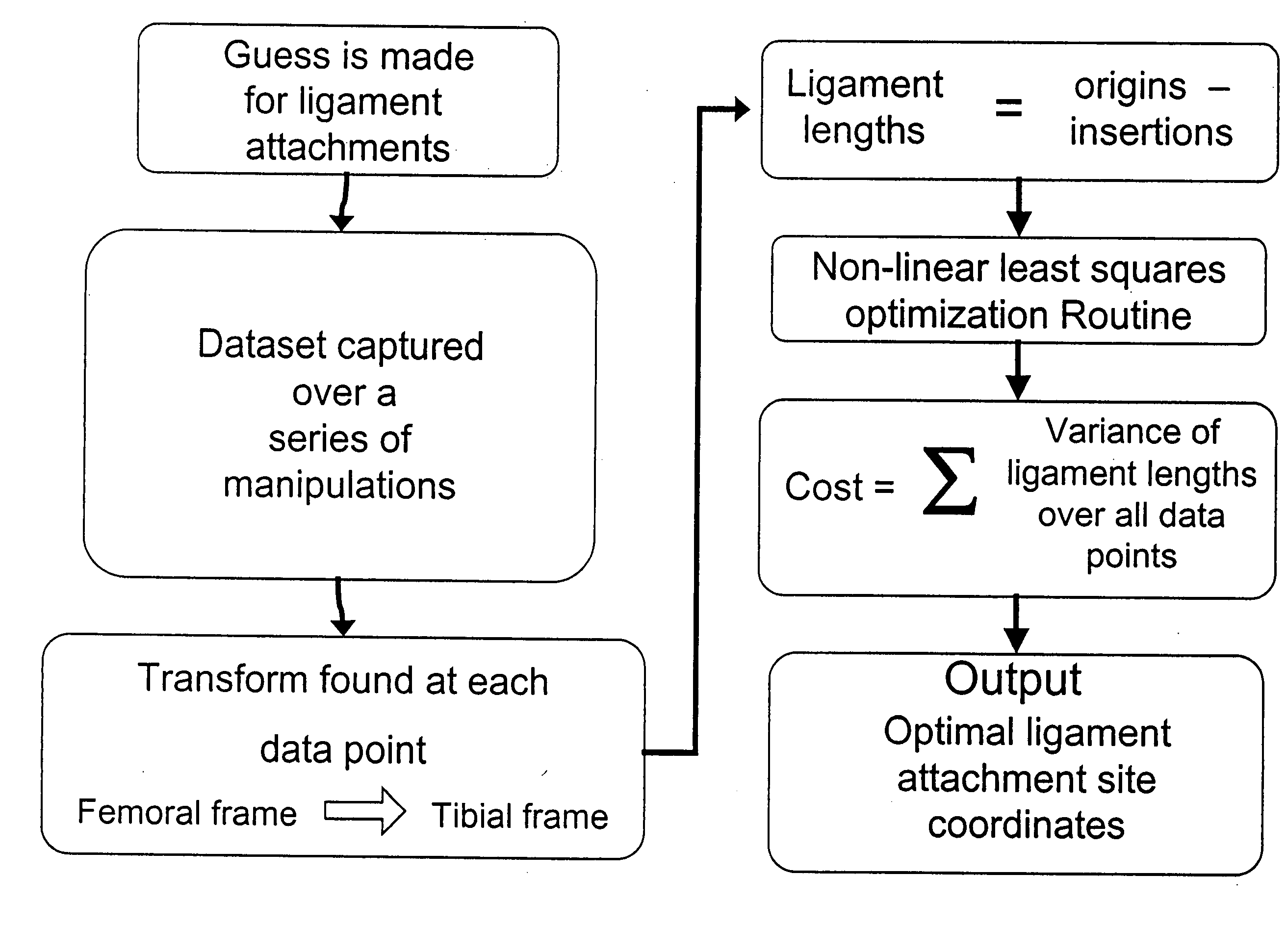
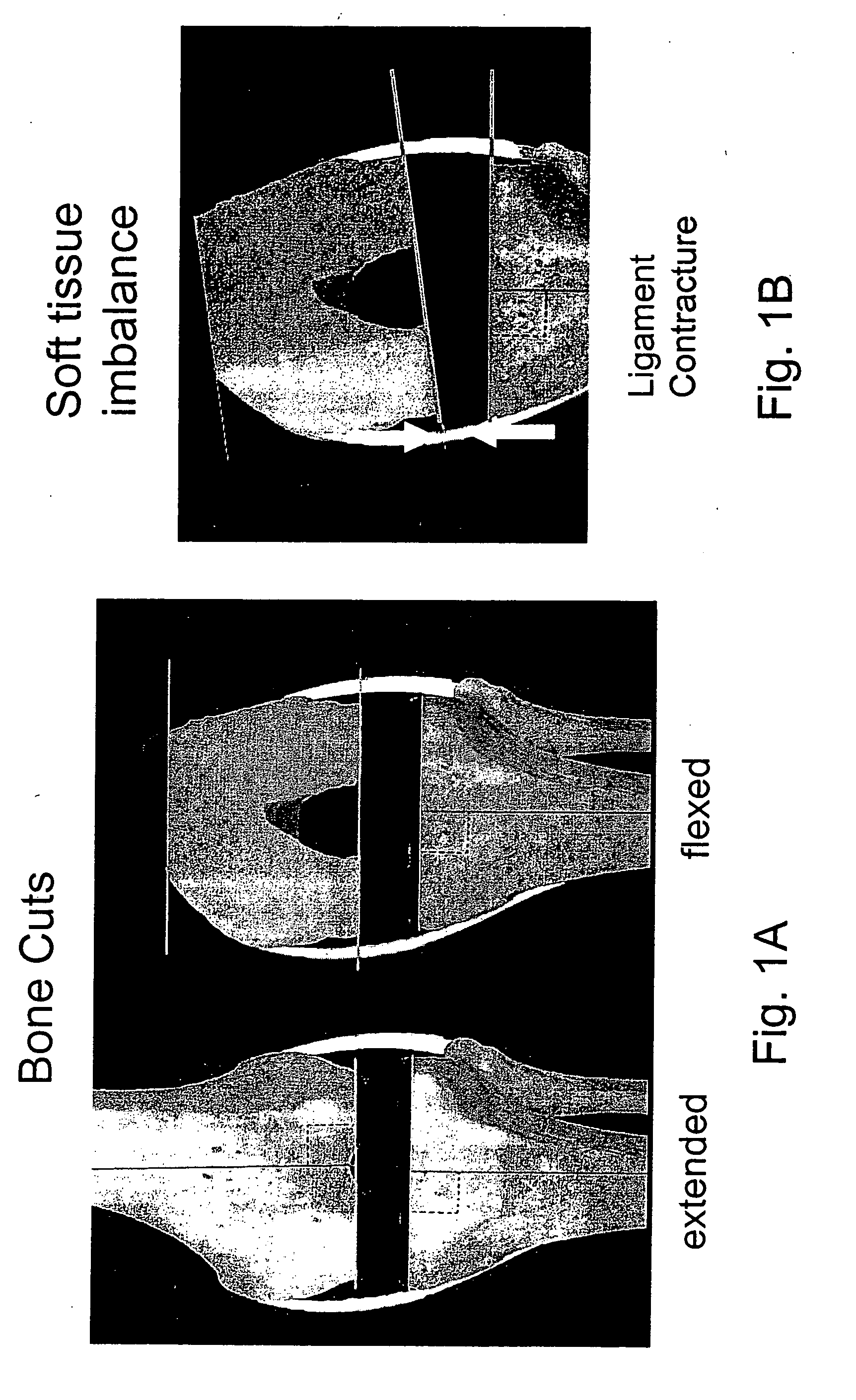
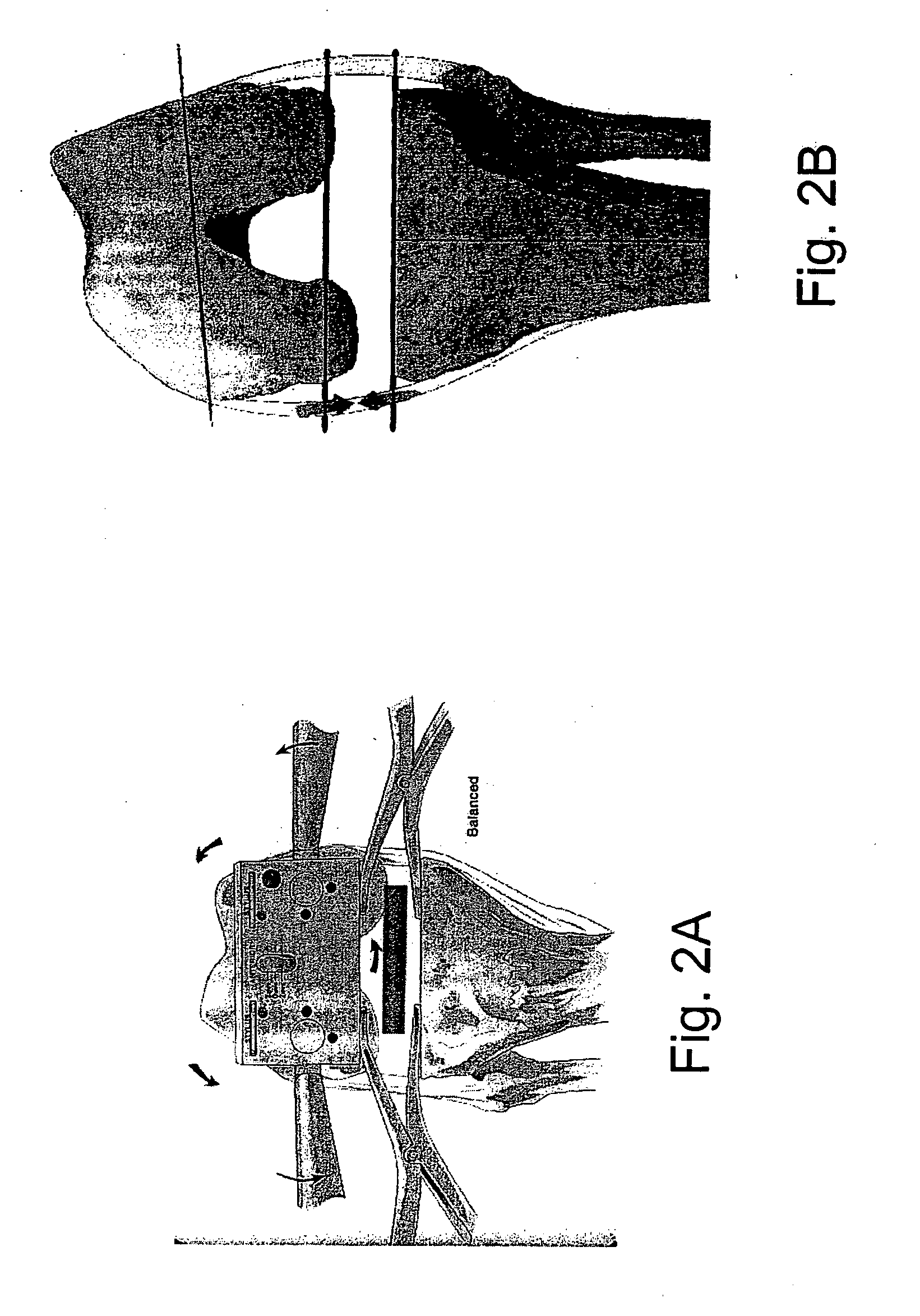
Methods and systems are described to quantitatively determine the degree of soft tissue constraints on knee ligaments and for properly determining placement parameters for prosthetic components in knee replacement surgery that will minimize strain on the ligaments. In one aspect, a passive kinetic manipulation technique is used in conjunction with a computer aided surgery (CAS) system to accurately and precisely determine the length and attachment sites of ligaments. These manipulations are performed after an initial tibial cut and prior to any other cuts or to placement of any prosthetic component. In a second aspect, a mathematical model of knee kinematics is used with the CAS system to determine optimal placement parameters for the femoral and tibial components of the prosthetic device that minimizes strain on the ligaments.
Owner:HODGSON ANTONY J +1
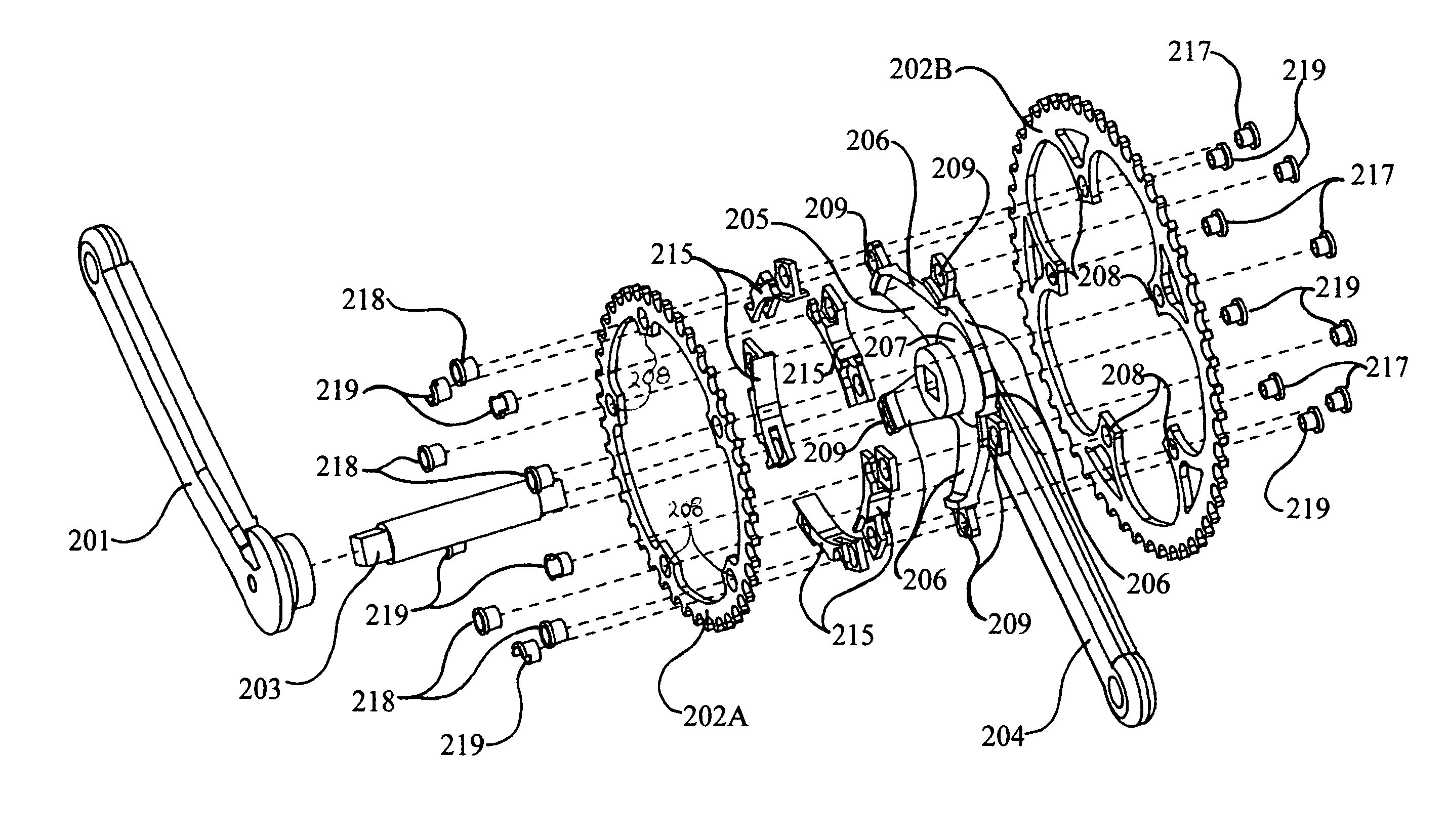
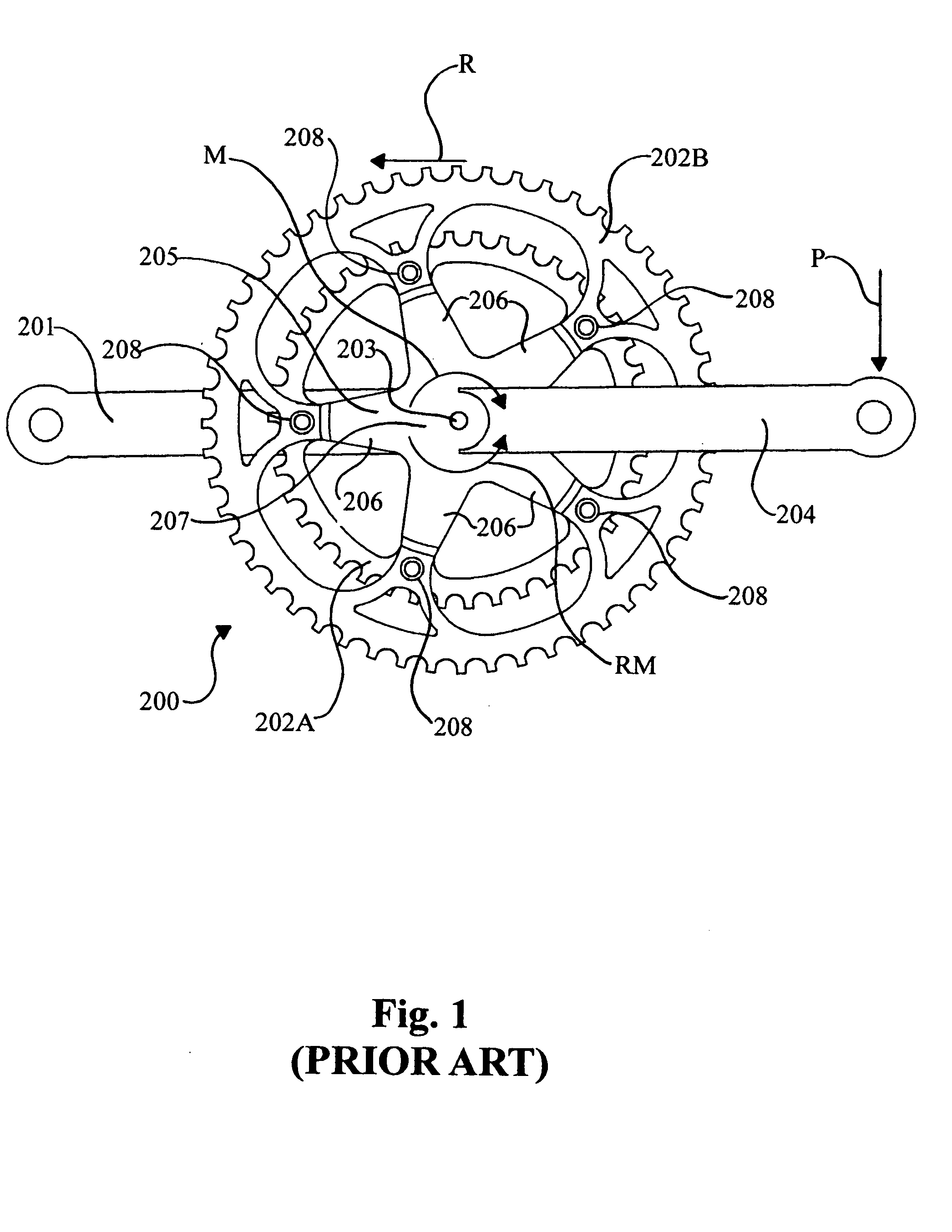
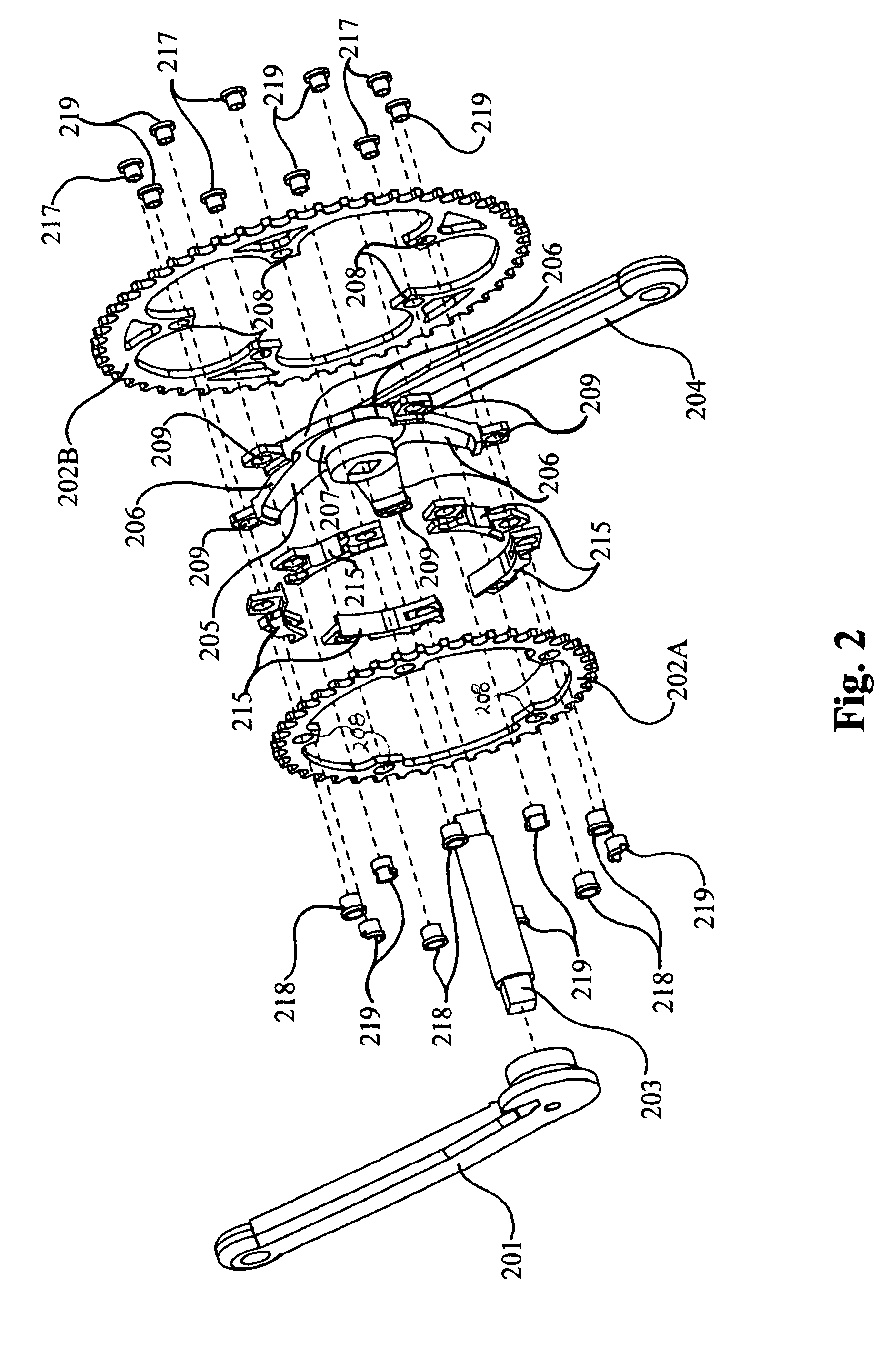
Load measurement apparatus and methods utilizing torque sensitive link for pedal powered devices
InactiveUS20050178210A1Easy to installEasy maintenanceChain/belt transmissionForce measurementEngineeringSprocket
Apparatus and methods for use in measurement of applied load at a chainring assemblage of a pedal powered device are provided. The apparatus includes a link adapted for interposition between a chainring attachment site located on a conventional chainring mount, or spider, and a corresponding chainring attachment locale at a conventional chainring. The link has a geometry and / or material composition selected to accommodate measurement of load exhibited between the attachment site and the corresponding chainring attachment locale. Means for measuring the load exhibited thereby is associated with the link.
Owner:FORZA
Follicle stimulating hormones
Heterodimeric polypeptide conjugates exhibiting FSH activity, comprising a dimeric polypeptide comprising an FSH-.alpha. subunit and an FSH-.beta. subunit, wherein at least one of the FSH-.alpha. and FSH-.beta. subunits differs from the corresponding wildtype subunit in that at least one amino acid residue acid residue comprising an attachment group for a non-polypeptide moiety has been introduced or removed, and having at least one non-polypeptide moiety bound to an attachment group of at least one of said subunits are provided. Preferably, at least one attachment group, e.g., an N- or O-glycosylation site or an attachment site for a polymer molecule such as polyethylene glycol, has been introduced, e.g., at an N-terminal. The polypeptide conjugates exhibit improved properties, in particular an increased half-life, compared to human FSH.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Implantable valves and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20060064174A1Enhance and strengthen bondingMore efficientVenous valvesBlood vesselsSand blastingBiocompatible coating
An implantable valve composed of a frame structure monolithically formed and covered with a biocompatible coating or soft structure. The implantable valve can have various shapes, openings, anchoring sites, attachment sites and is flexible, expendable, and easy to attach to body tissue. In some embodiments, the implantable valve is made by first determining a two or three dimensional configuration of the frame structure, which has an open end and a tapered end. The configuration may be scaled to obtain a desired size, e.g., length and diameter. One or more frame structure may be cut, stamped, etched, or machined from a single material, which could be metal or plastic with various thickness profiles and may have superelasticity and / or shape memory. The biocompatible coating selectively seals the valve to control / prevent fluid passage. To enhance bonding, the frame structure surface is treated with etching, polishing, sand blasting, plating, nanotechnology surface modification, etc.
Owner:ZADNO REZA
Applier for fastener for single lumen access anastomosis
ActiveUS20050070926A1Easy to controlPrecise positioningSuture equipmentsDiagnostic markersRing deviceAttachment site
Creating an anastomosis, or the surgical formation of a passage between two normally distinct vessels or lumens, is enhanced by an applier that introduces a ring device without the need for a separate anvil to form a hollow rivet shaped attachment. Moreover, the ring device may be advantageously formed in a cylindrical shape from molded polymer material or stamped from sheet metal with proximal and distal rings connected by proximal and distal arms that respectively form hinged, ring shaped so appose tissue walls. A center ring or portion sits in the attachment site. The applier causes actuating by moving the rings relative to one another. A latching mechanism locks the rings in the actuating state.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
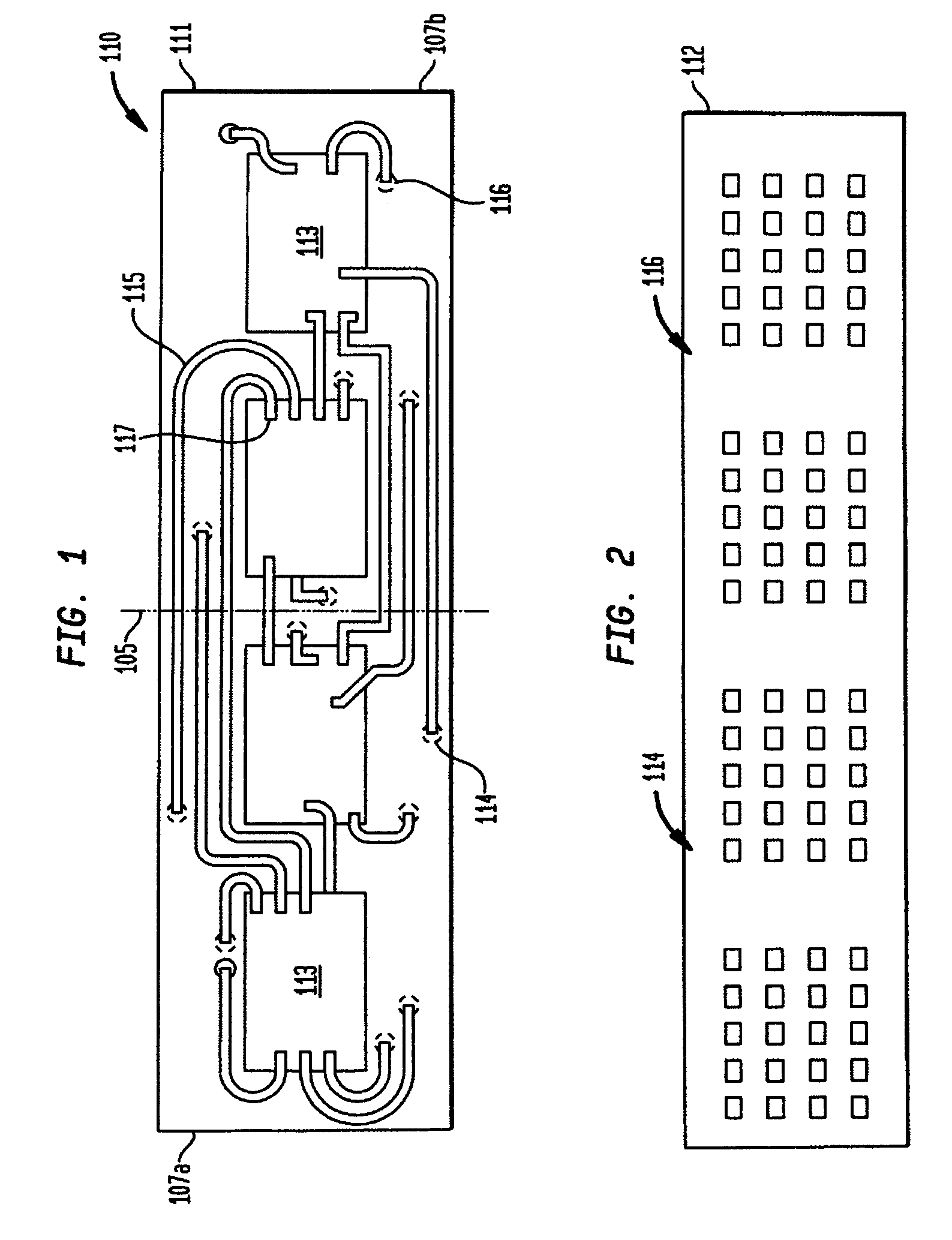
Stacked microelectronic assemblies
InactiveUS7149095B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted electric component incorporationEngineeringAttachment site
A stacked microelectronic assembly includes a plurality of microelectronic subassemblies. Each subassembly includes a substrate having at least one site, a plurality of first contacts and a plurality of second contacts. Each subassembly also has at least one microelectronic element assembled to the at least one attachment site and electrically connected to at least some of the first and second contacts. The substrate is folded so that the first contacts are accessible at a bottom of a subassembly and the second contacts are accessible at a top of a subassembly. The plurality of subassemblies are stacked one on top of another in a generally vertical configuration. The substrate of at least one of the subassemblies has a plurality of attachment sites and a plurality of microelectronic elements assembled to the attachment sites. The substrate is folded so that at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements are disposed alongside one another.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Polymer conjugates of GLP-1
ActiveUS8293869B2Rapid clearanceGood release effectMetabolism disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsWater solubleMethyl group
Conjugates of a GLP-I moiety may be covalently attached to one or more water-soluble polymers. For instance, a GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety releasably attached at its N-terminus to a water-soluble polymer. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety possesses an N-methyl substituent. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached at a polymer attachment site to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety is glycosylated at a site separate from the polymer attachment site.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
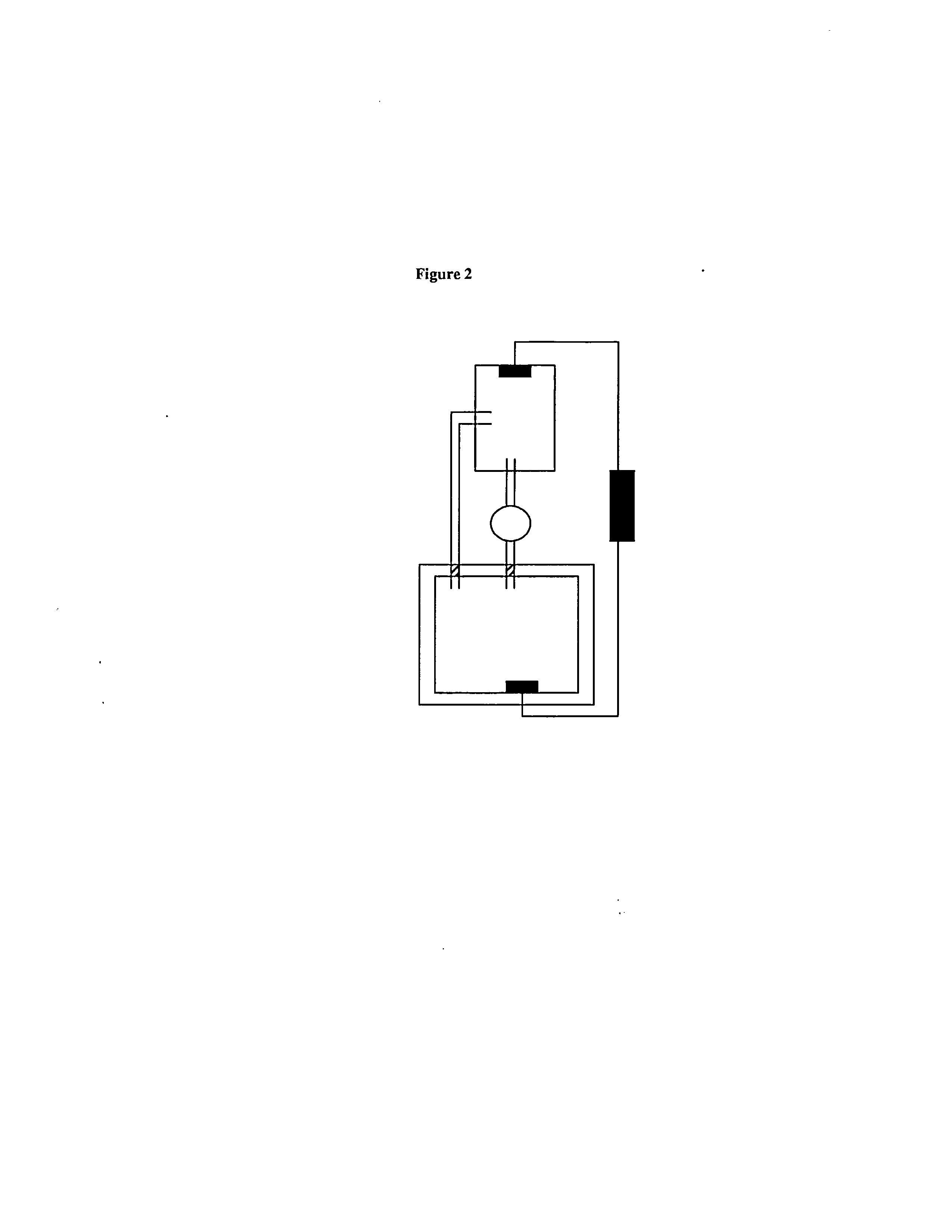
Bioreactors, systems, and methods for producing and/or analyzing organs
InactiveUS20130177972A1Speed up the processImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyAttachment site
Articles and methods for growing or analyzing tissues and organs using bioreactors or other devices and components are provided. In some embodiments, a bioreactor is configured to provide a growth chamber having one or more inlets, outlets, sensors, organ attachment sites, and / or organ identifiers.
Owner:BIOSTAGE INC
Anterior cruciate ligament tether
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Mesoporous permeation layers for use on active electronic matrix devices
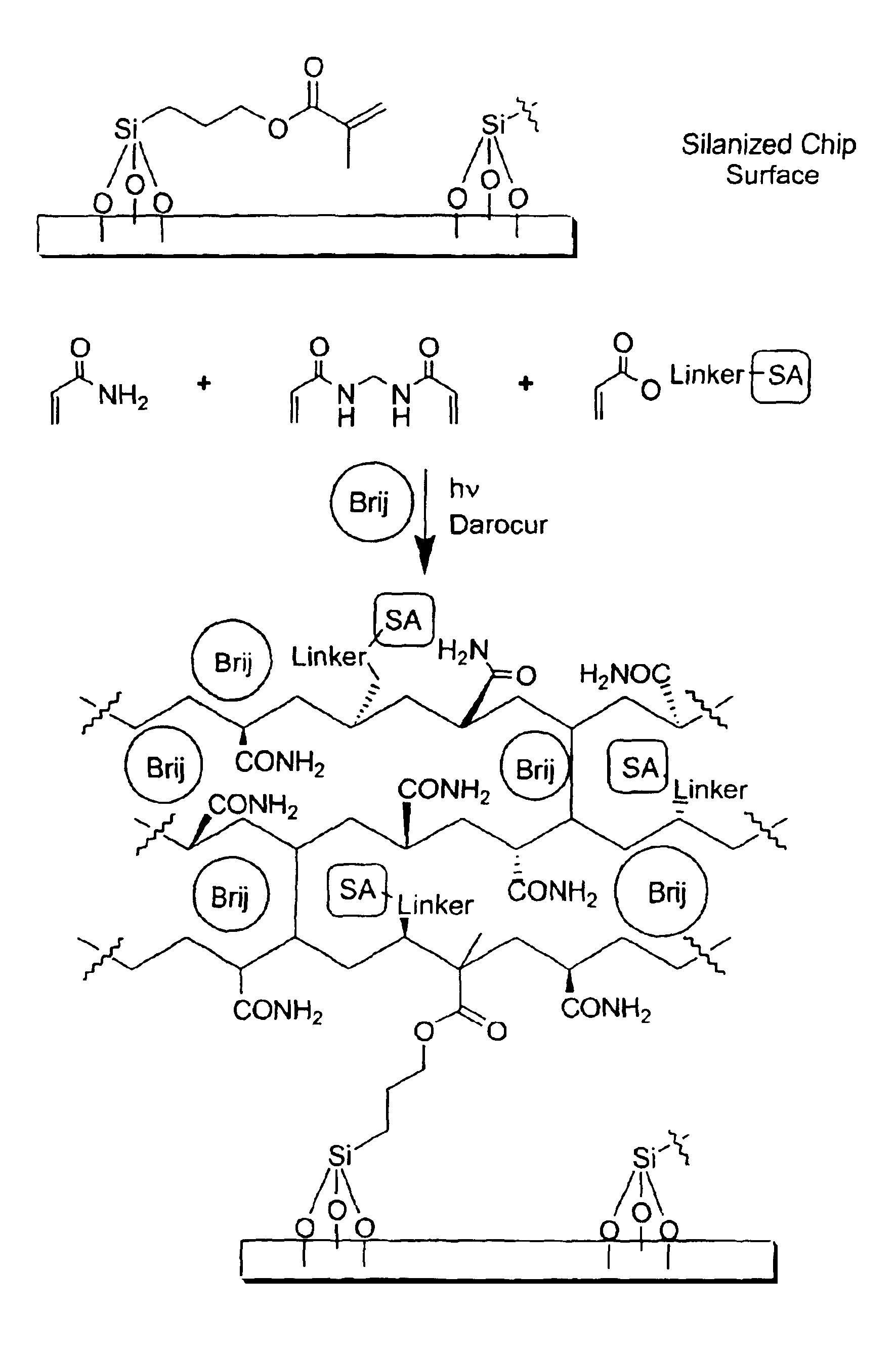
The present invention provides improved synthetic polymer hydrogel permeation layers for use on active electronic matrix devices for biological assays. The permeation layers have a defined porous character, with mesopores in a size range between about 100 nanometers and about 1000 nanometers, and may also have micropores in the micrometer size range. The mesoporous synthetic hydrogel permeation layers demonstrate improved signal intensity and linearity characteristics as compared to nanoporous synthetic hydrogel permeation layers on active electronic matrix devices. In addition, the present invention also provides synthetic polymer hydrogel permeation layers which contain copolymerized attachment sites for nucleic acid probes or other biomolecules.
Owner:NANOGEN INC +1
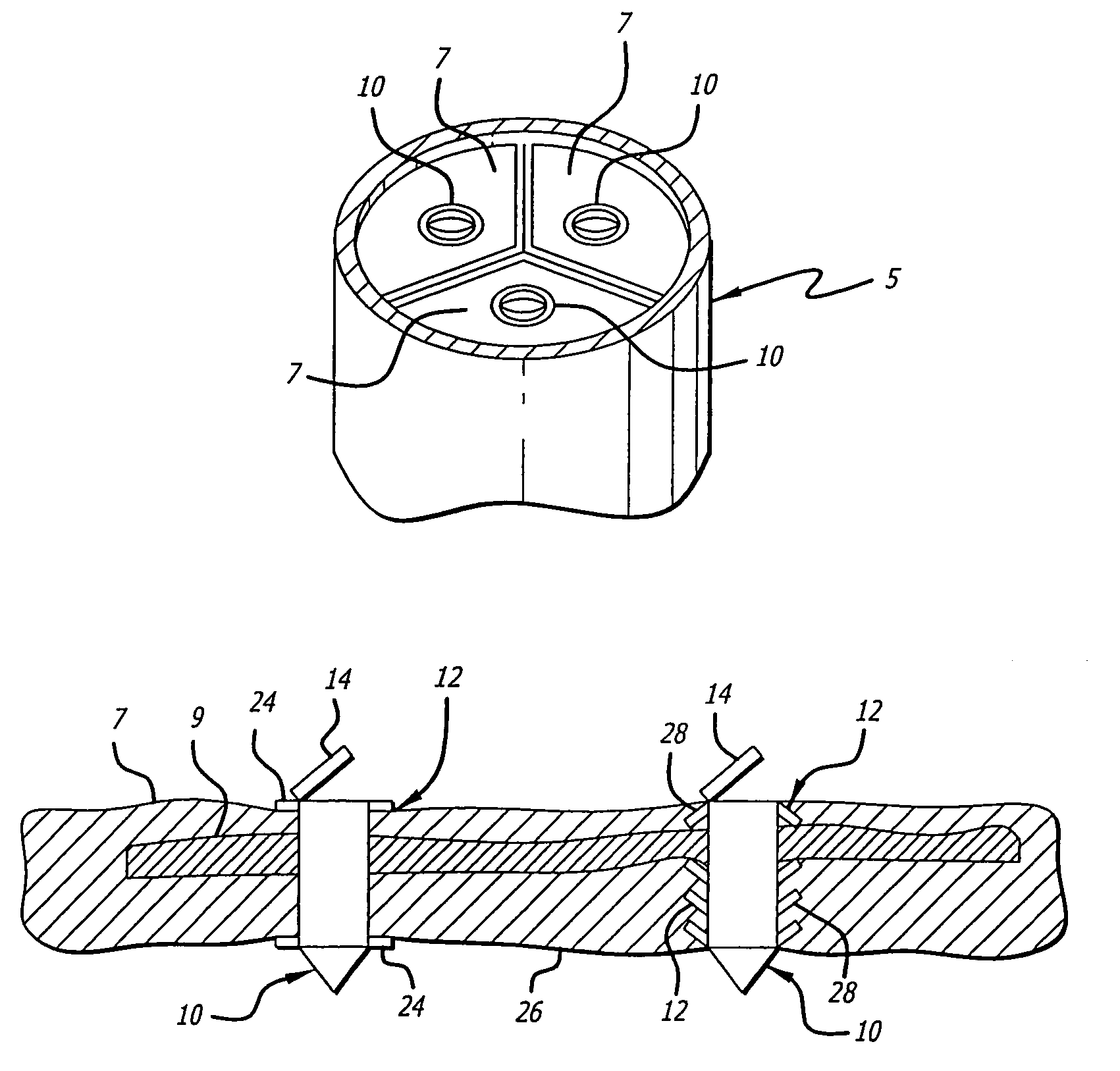
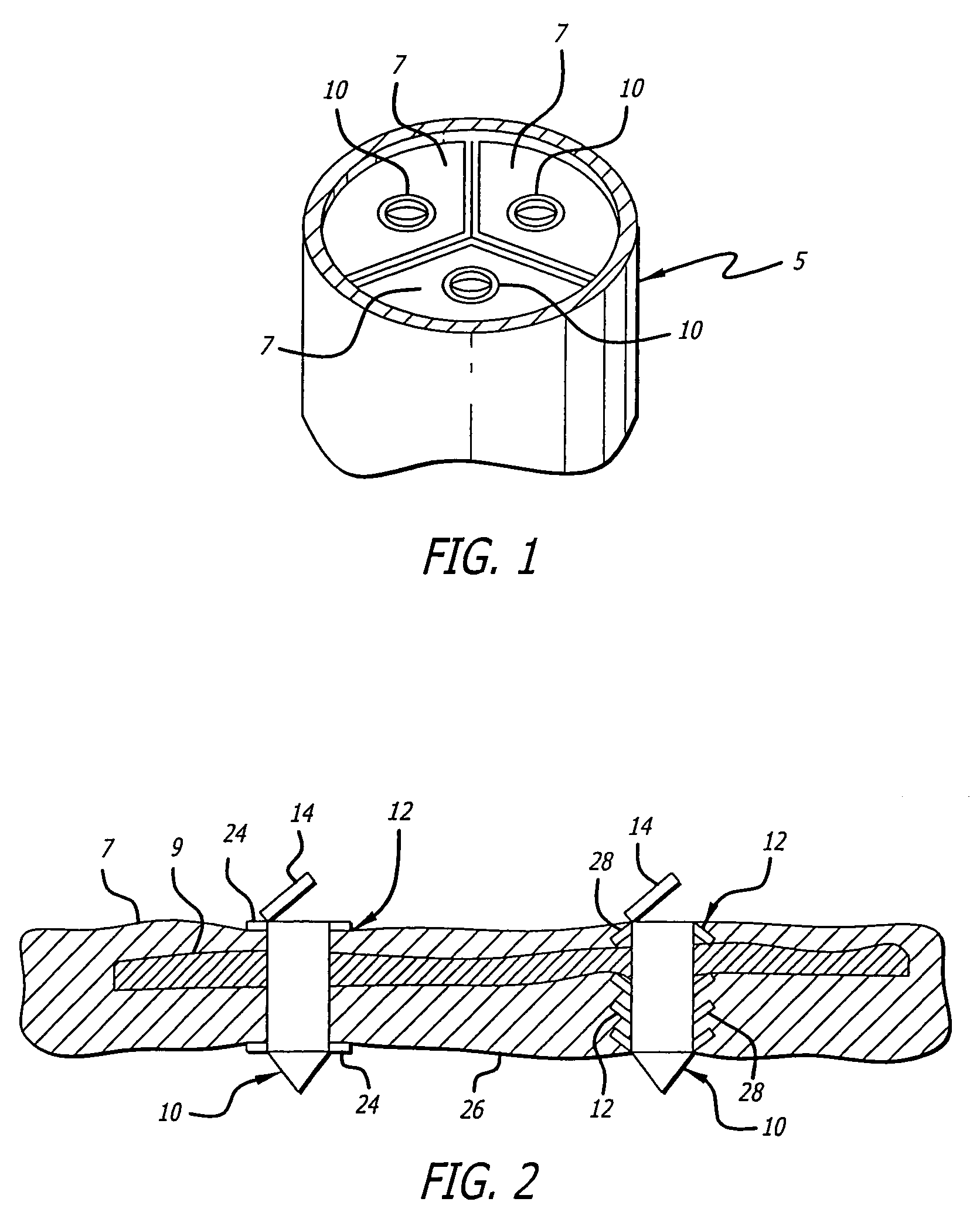
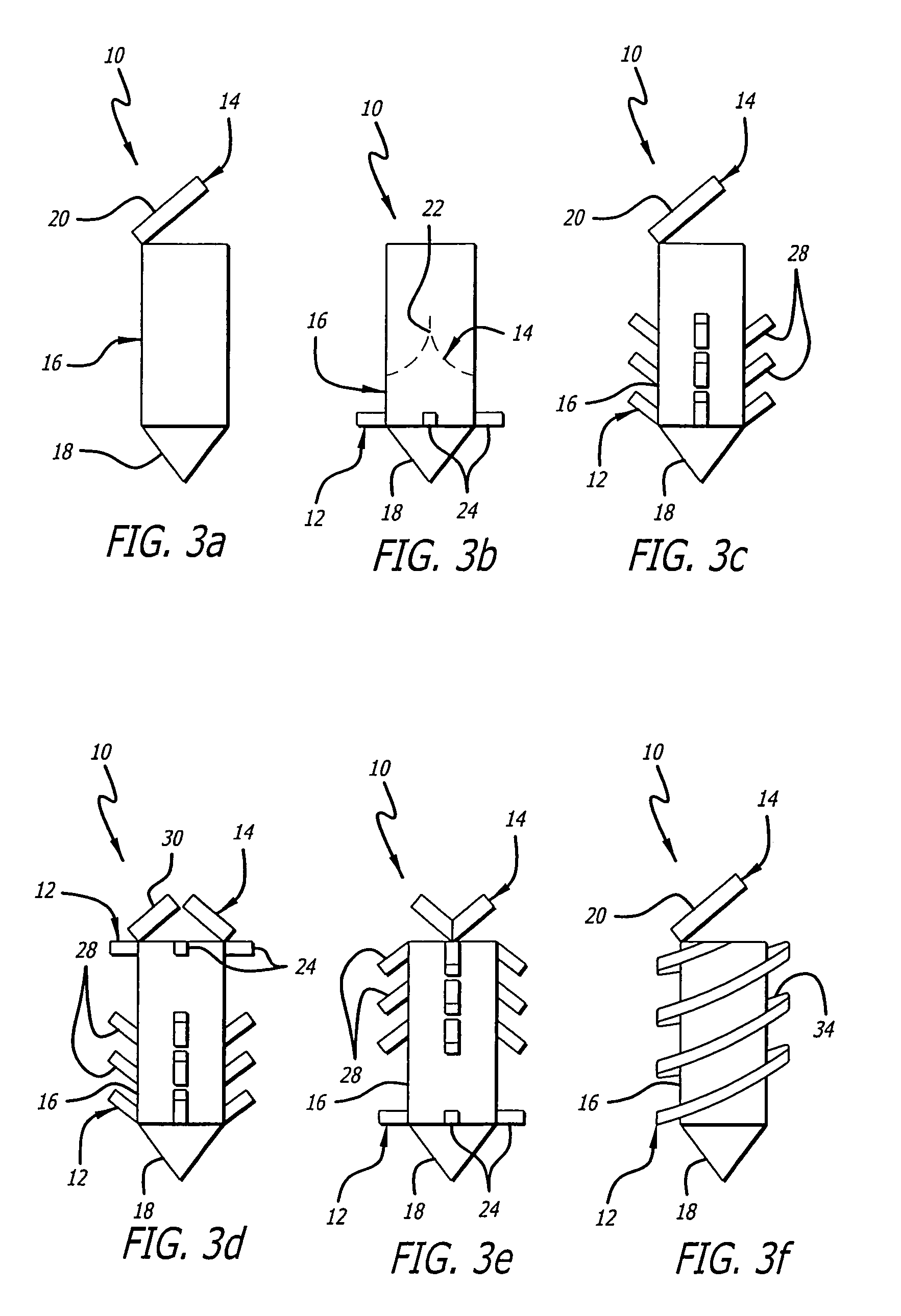
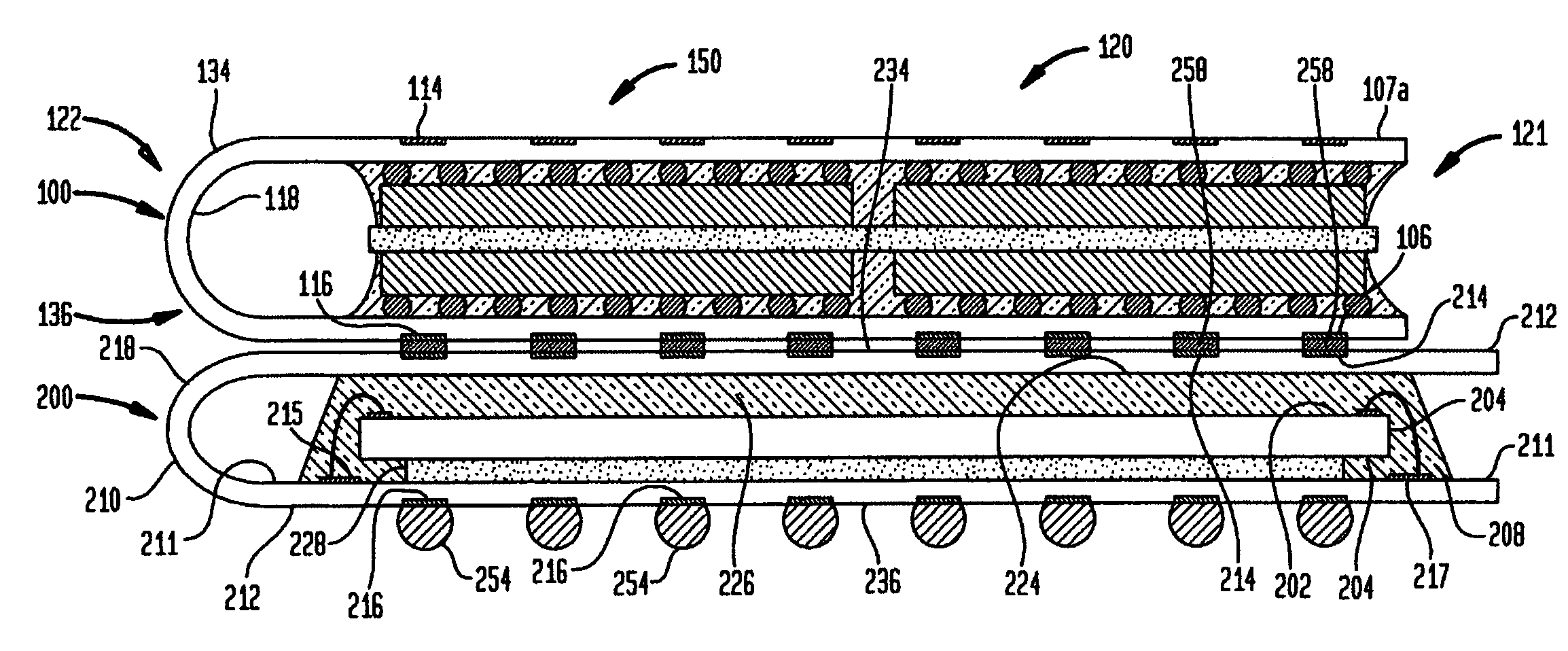
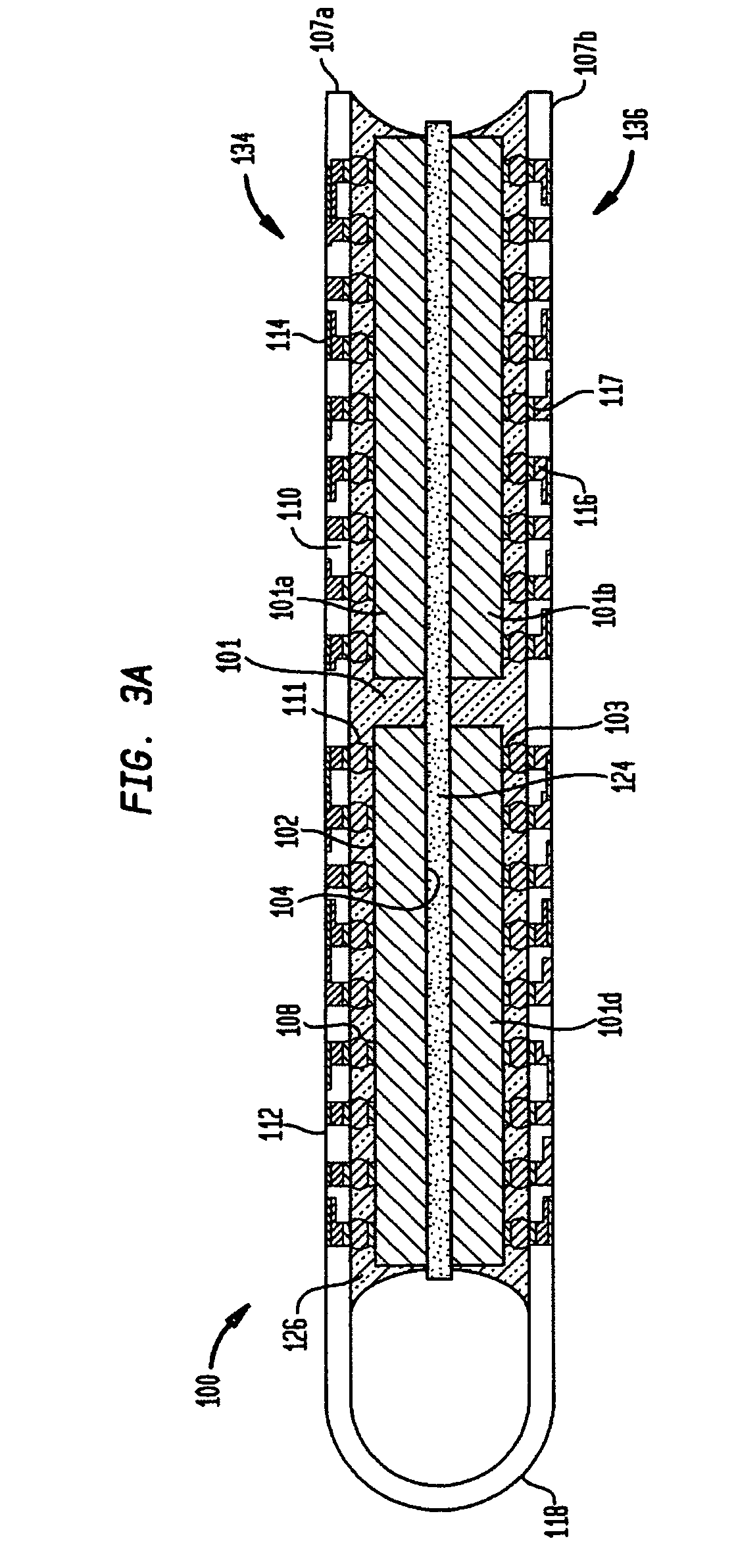
Implantable prosthesis having reinforced attachment sites
The present invention provides an implantable graft that includes an elongate graft tube having opposing ends defining an attachment site for attaching the graft to a stent. The graft further includes a reinforcement member attached adjacent to at least one of the ends of the graft for establishing a reinforced attachment site for the graft, thereby preventing elongation of a suture hole in the material. Furthermore, the present invention provides a graft wherein at least one end of the graft is folded over itself and glued or sutured to itself and / or the stent, thereby forming a reinforcement thereto.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com