Patents
Literature
106 results about "Cruciate ligament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
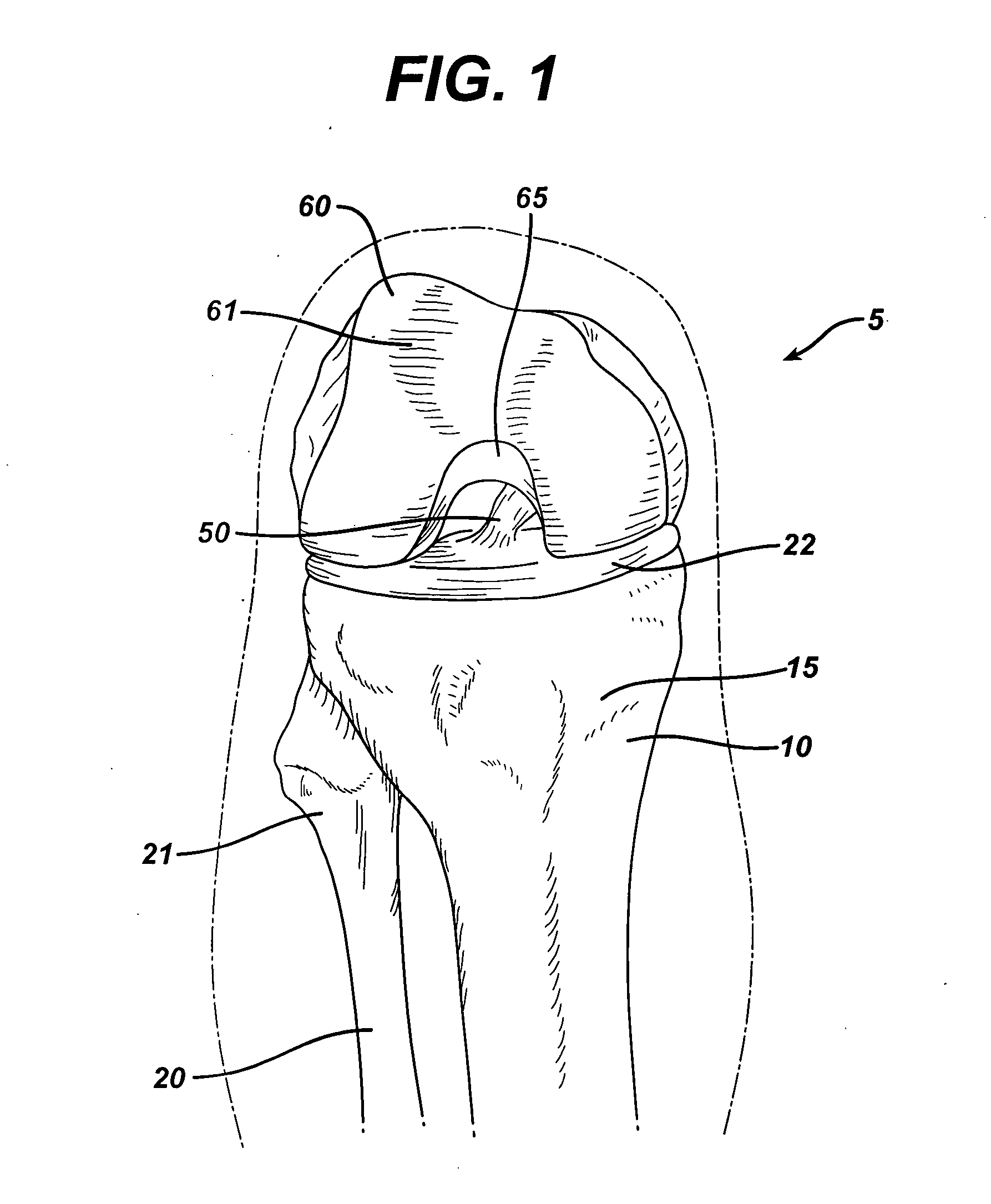
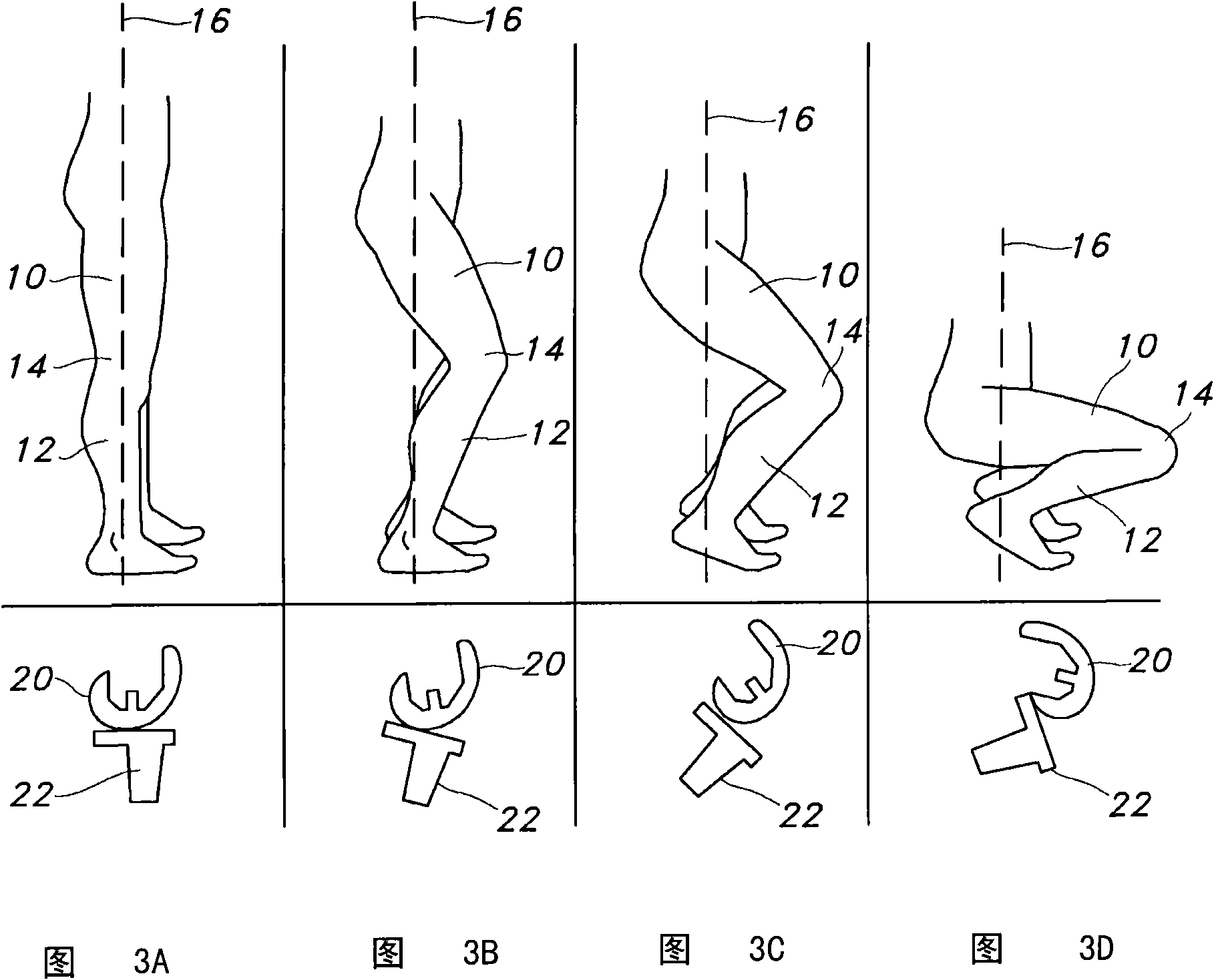
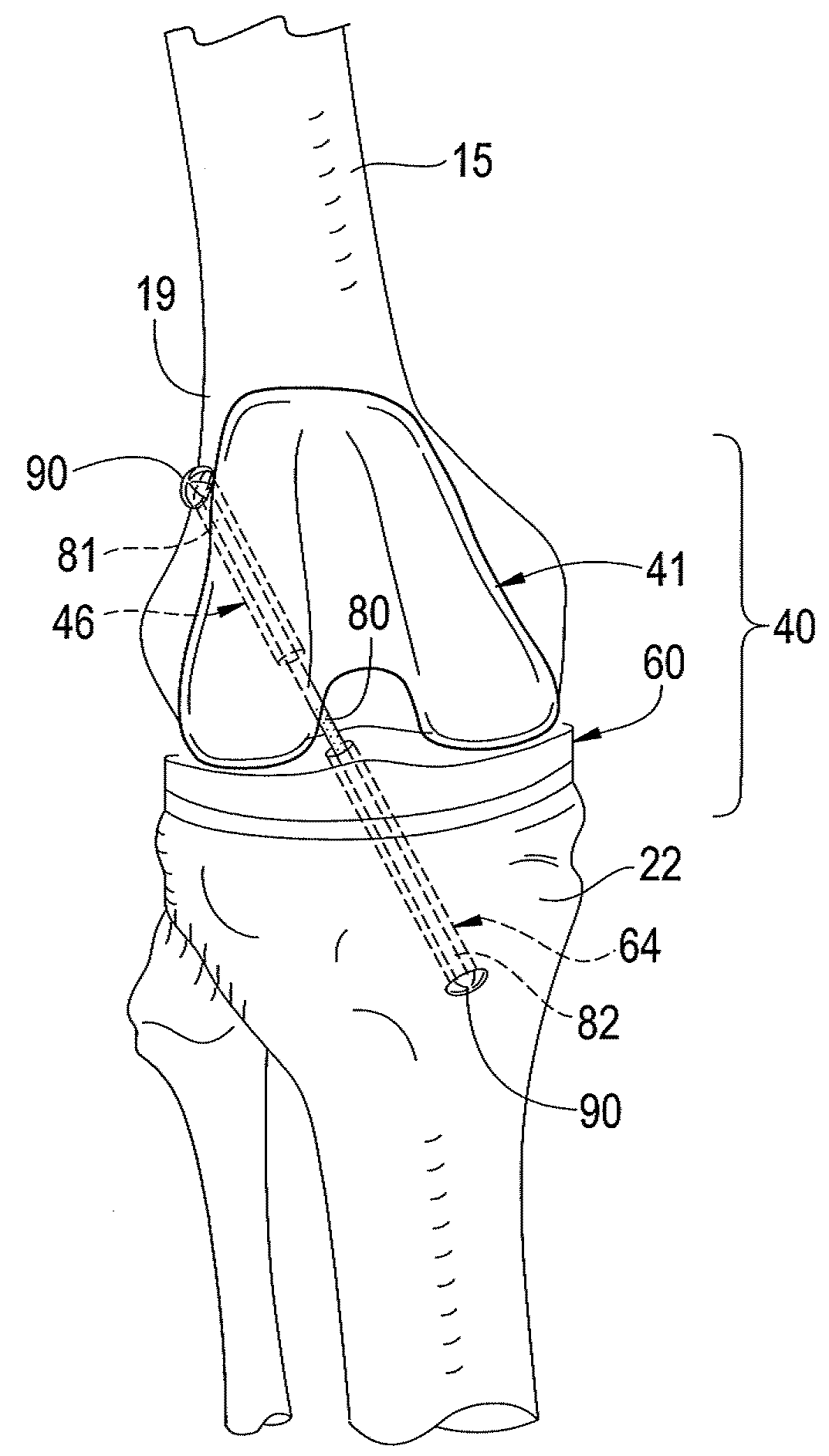
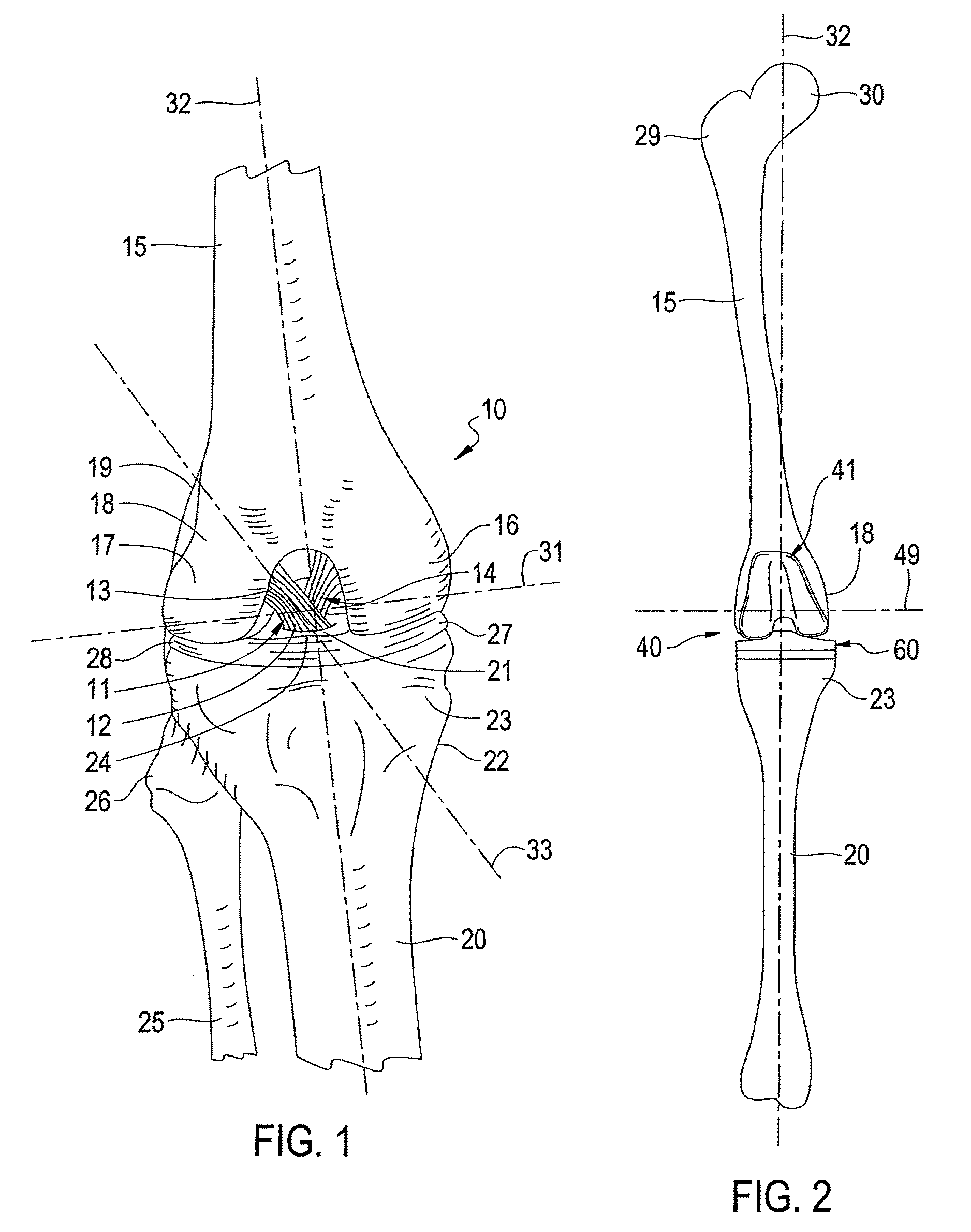
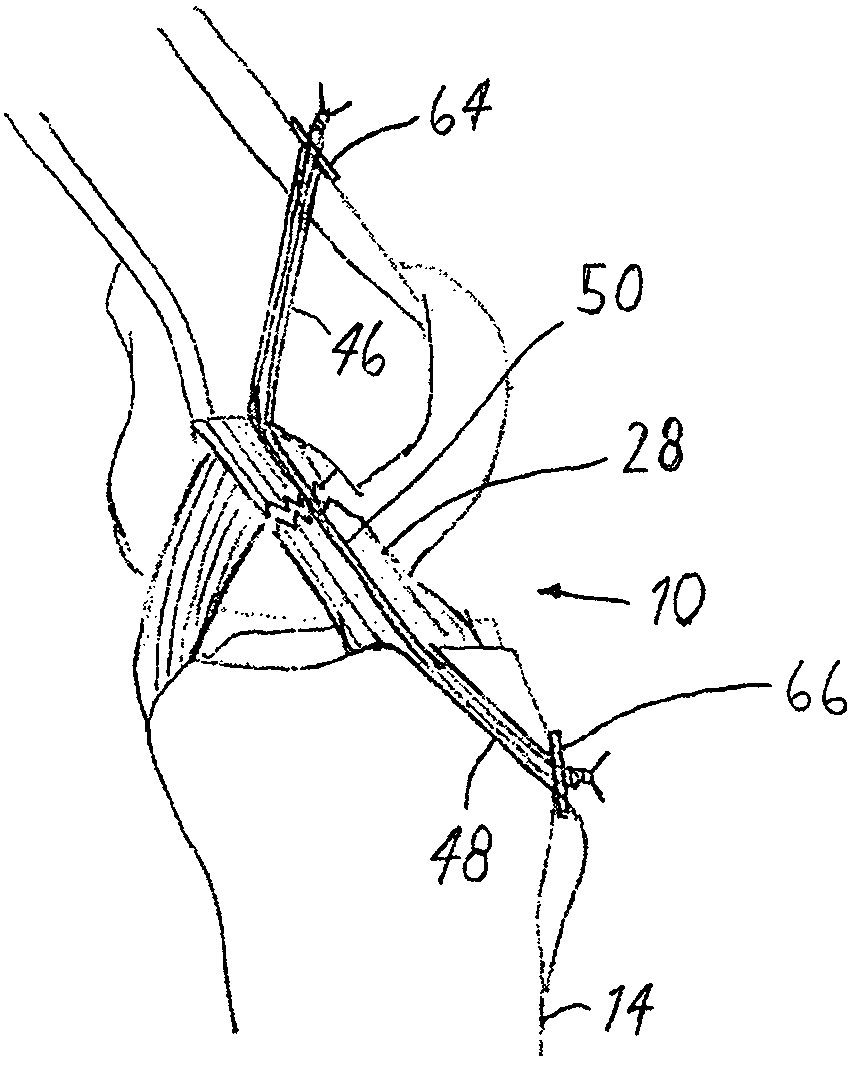
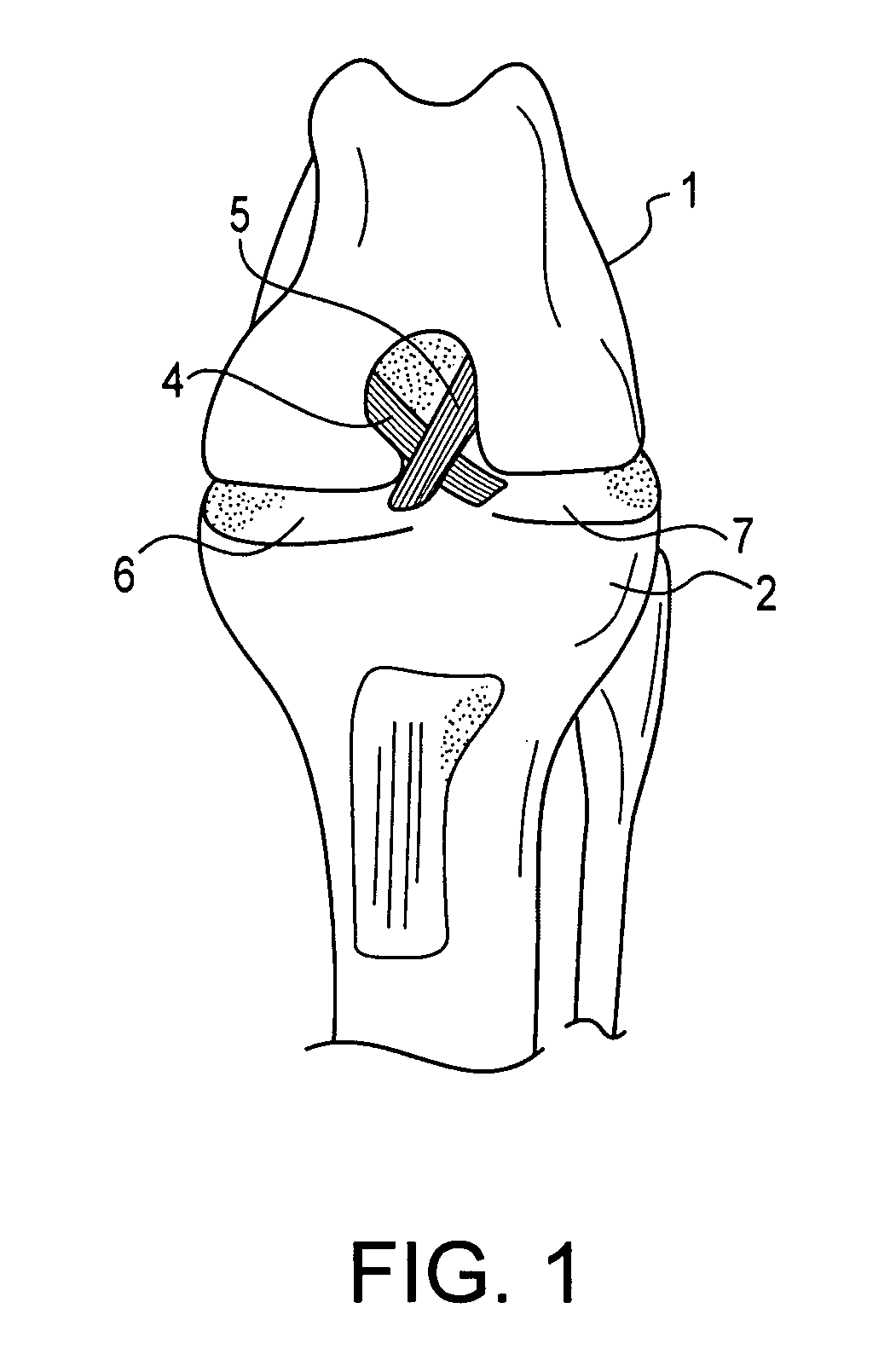
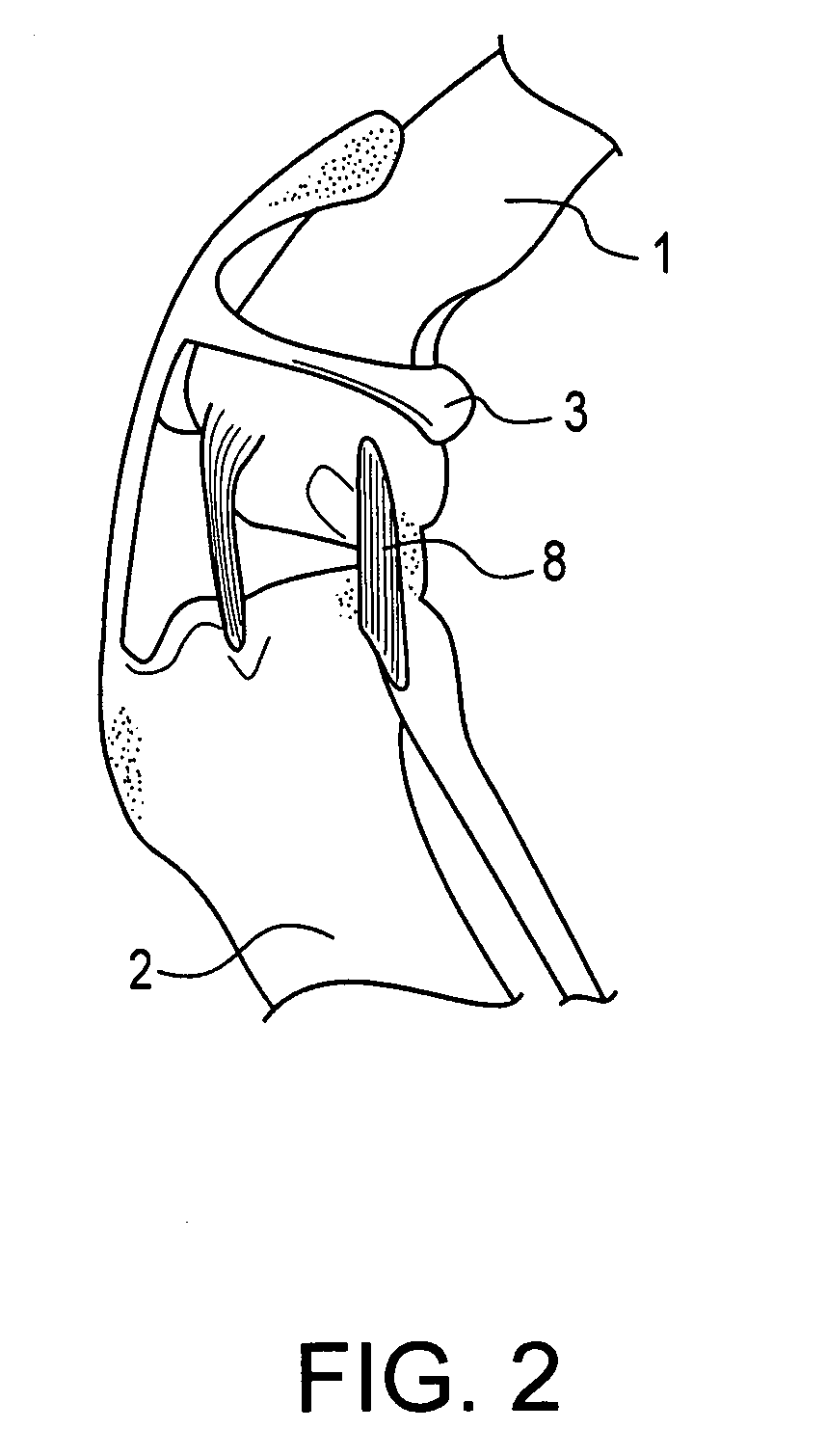
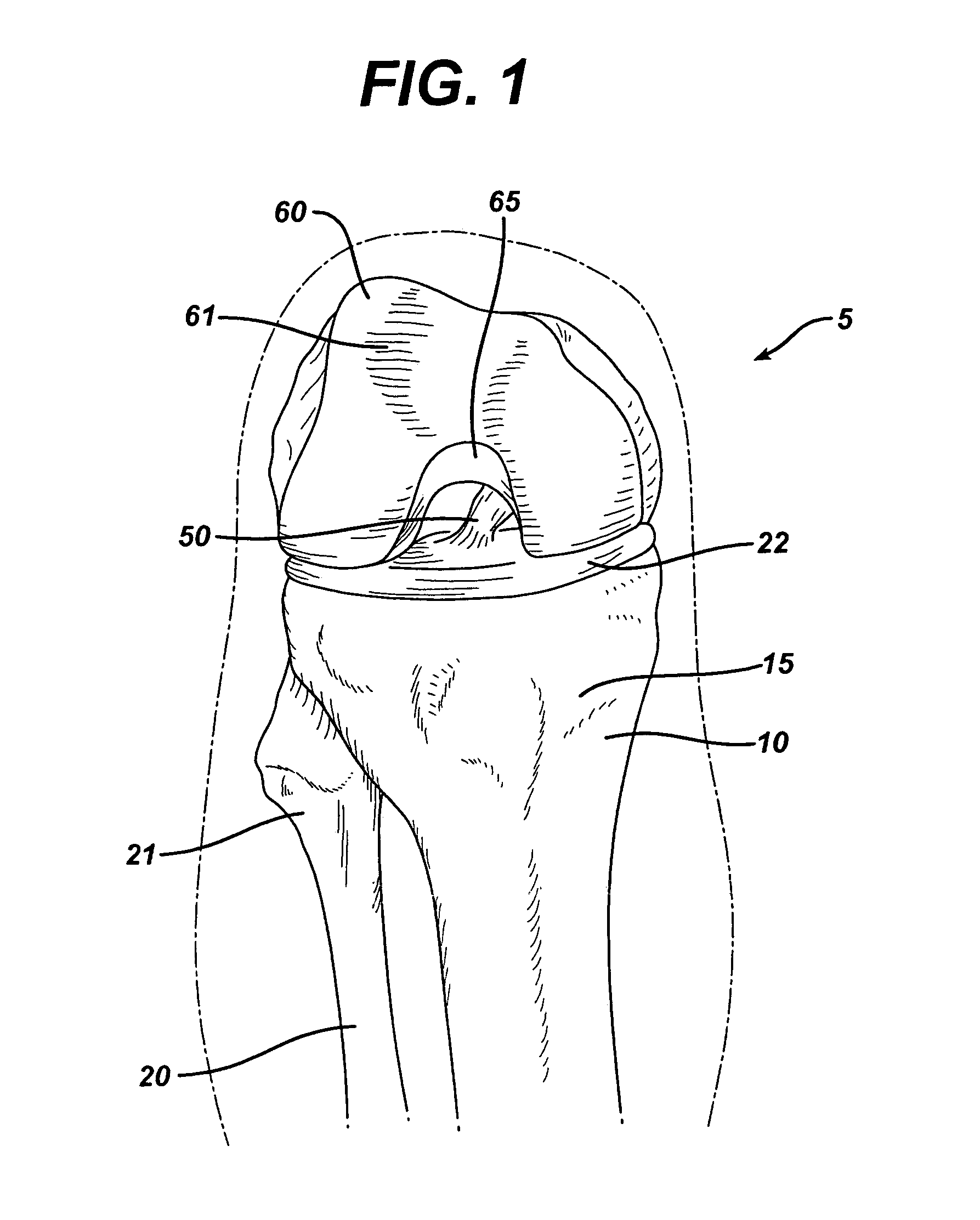
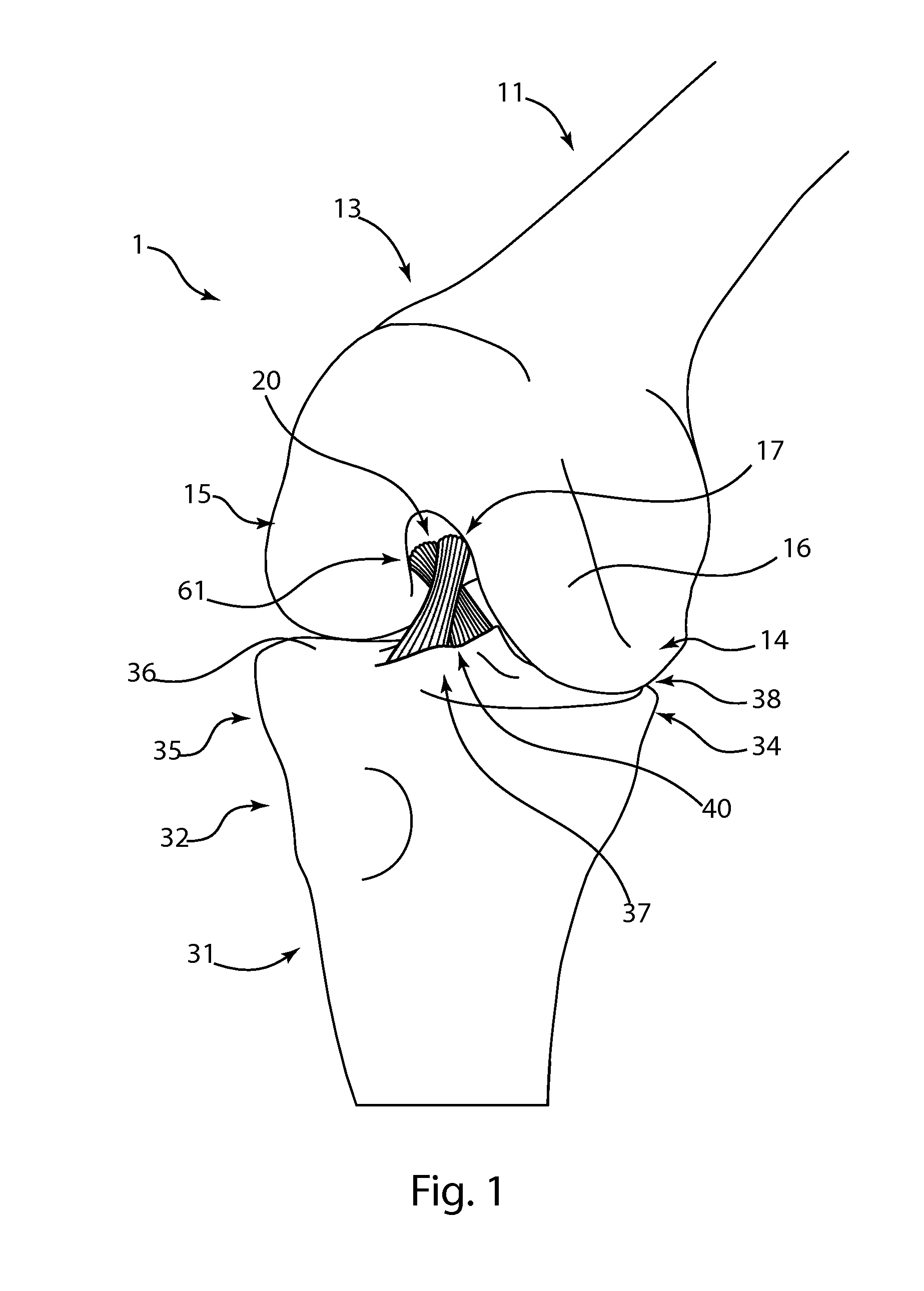
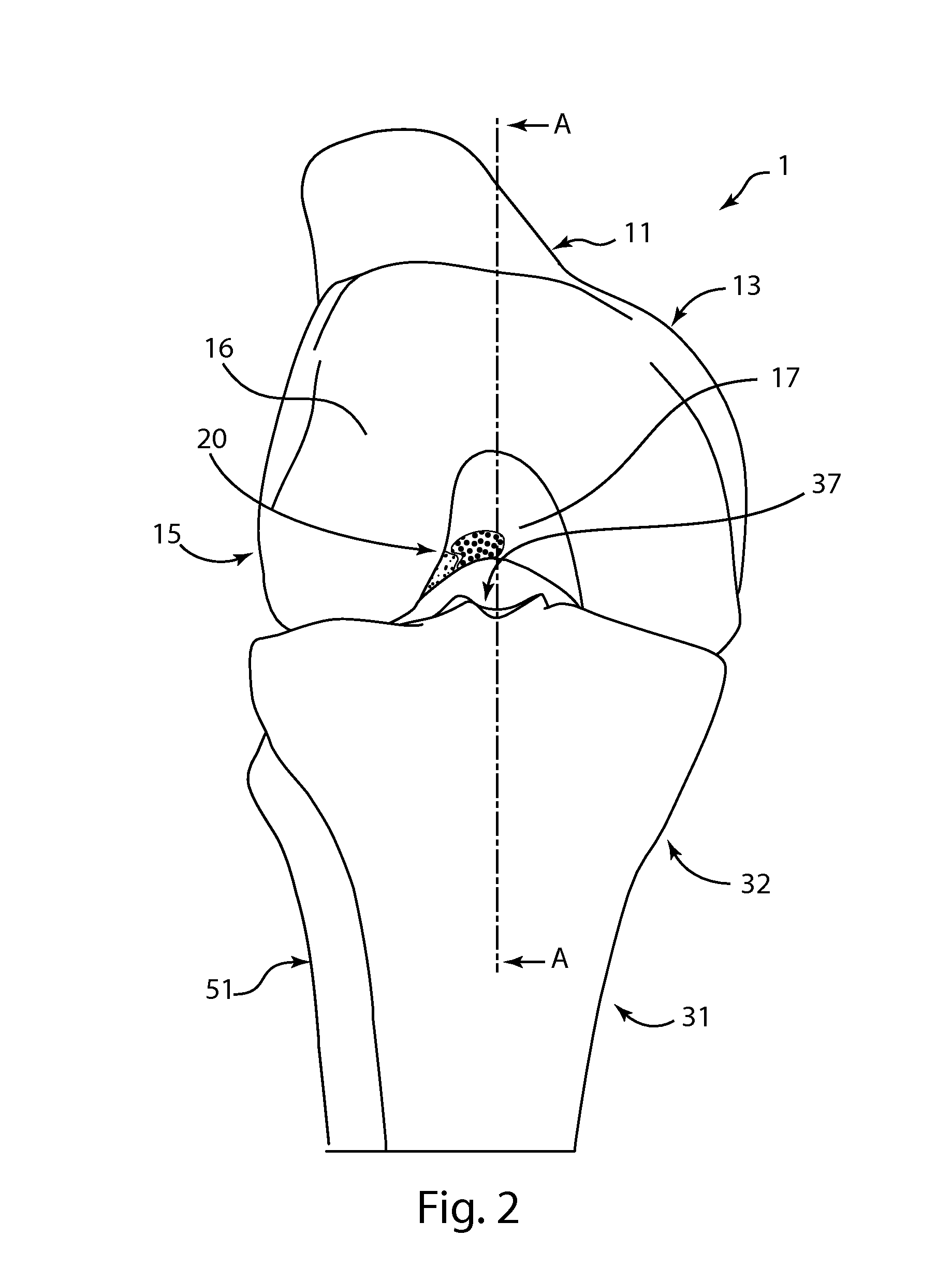
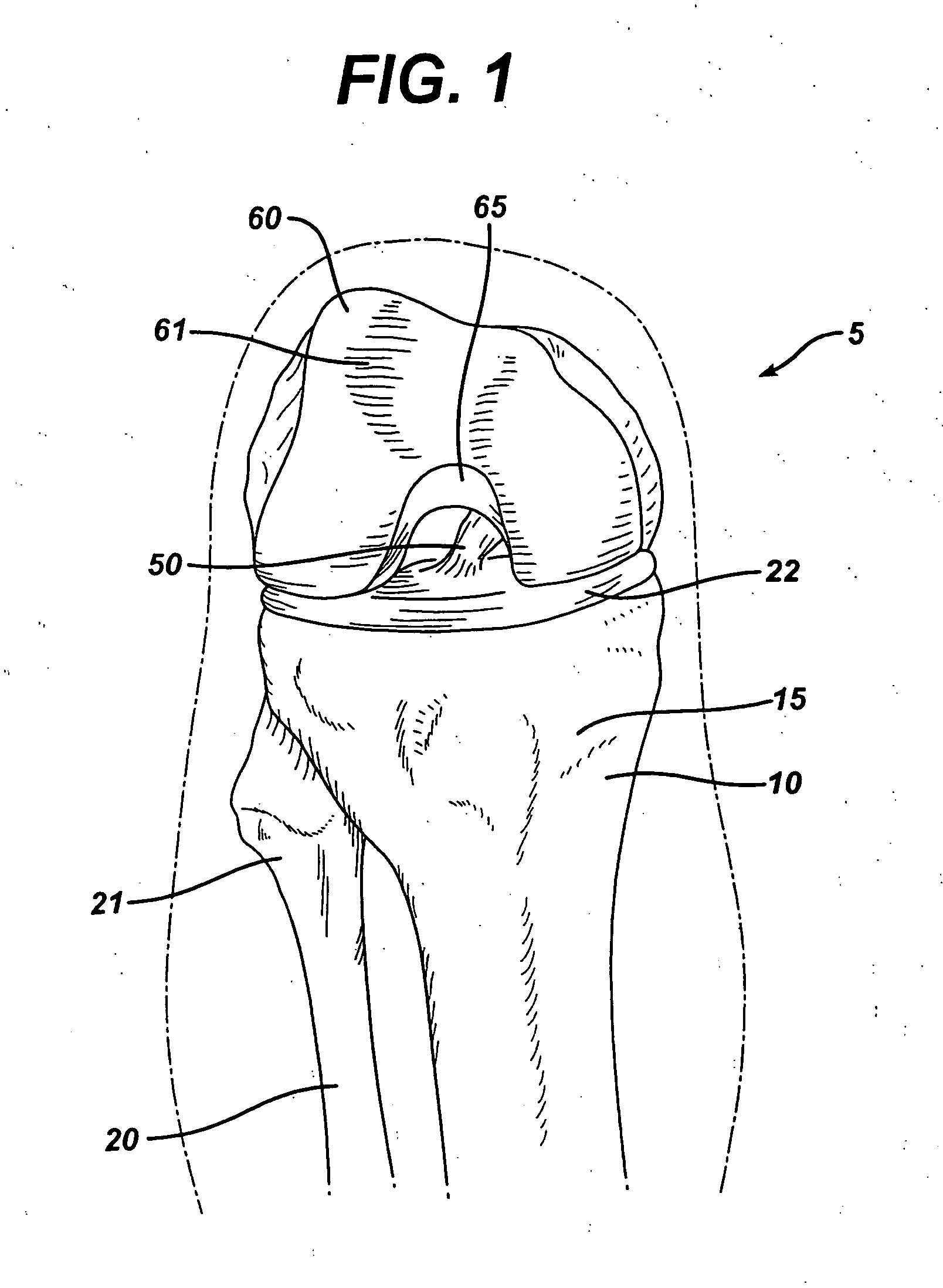
Cruciate ligaments (also cruciform ligaments) are pairs of ligaments arranged like a letter X. They occur in several joints of the body, such as the knee joint and the atlanto-axial joint. In a fashion similar to the cords in a toy Jacob's ladder, the crossed ligaments stabilize the joint while allowing a very large range of motion.
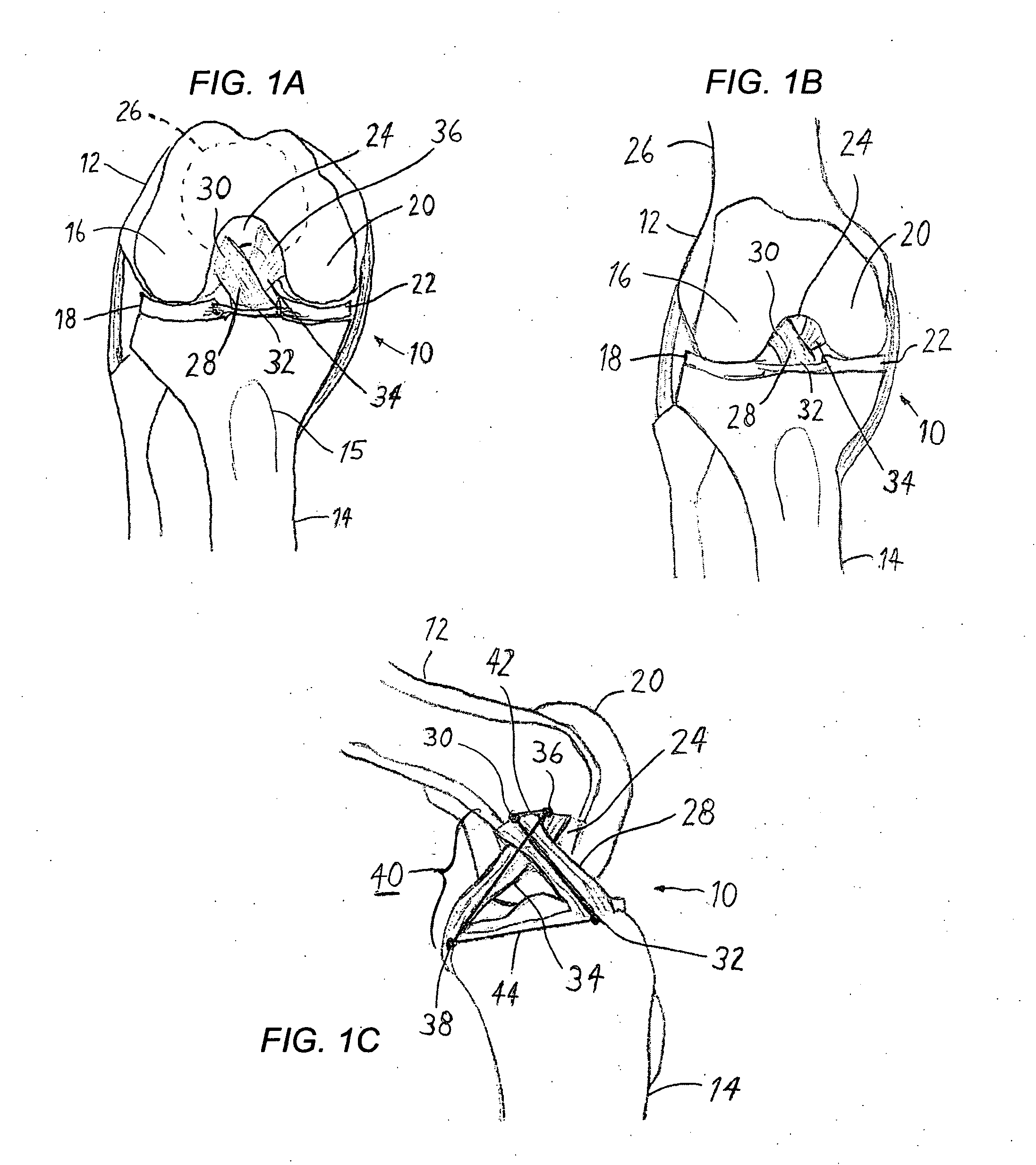
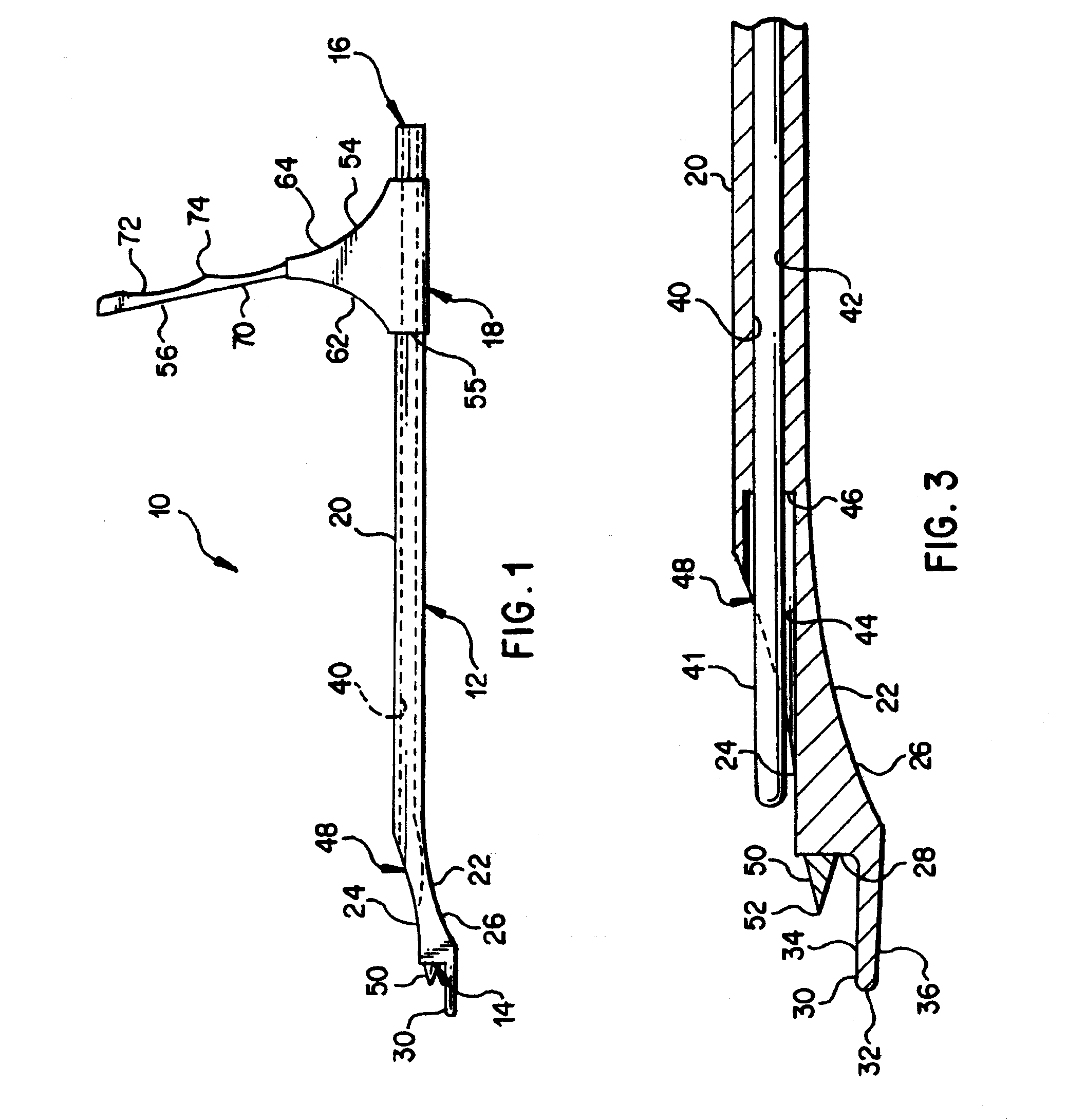
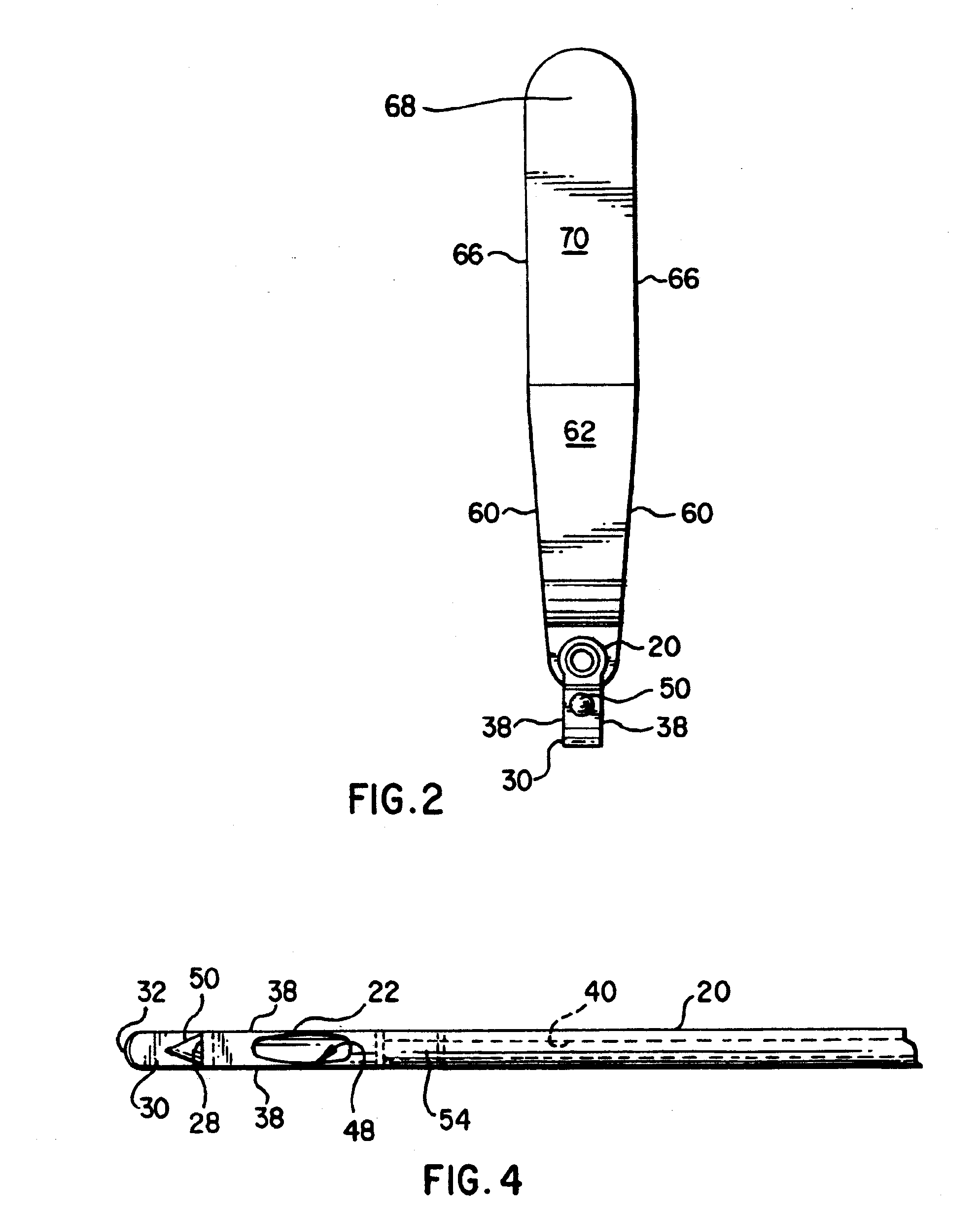
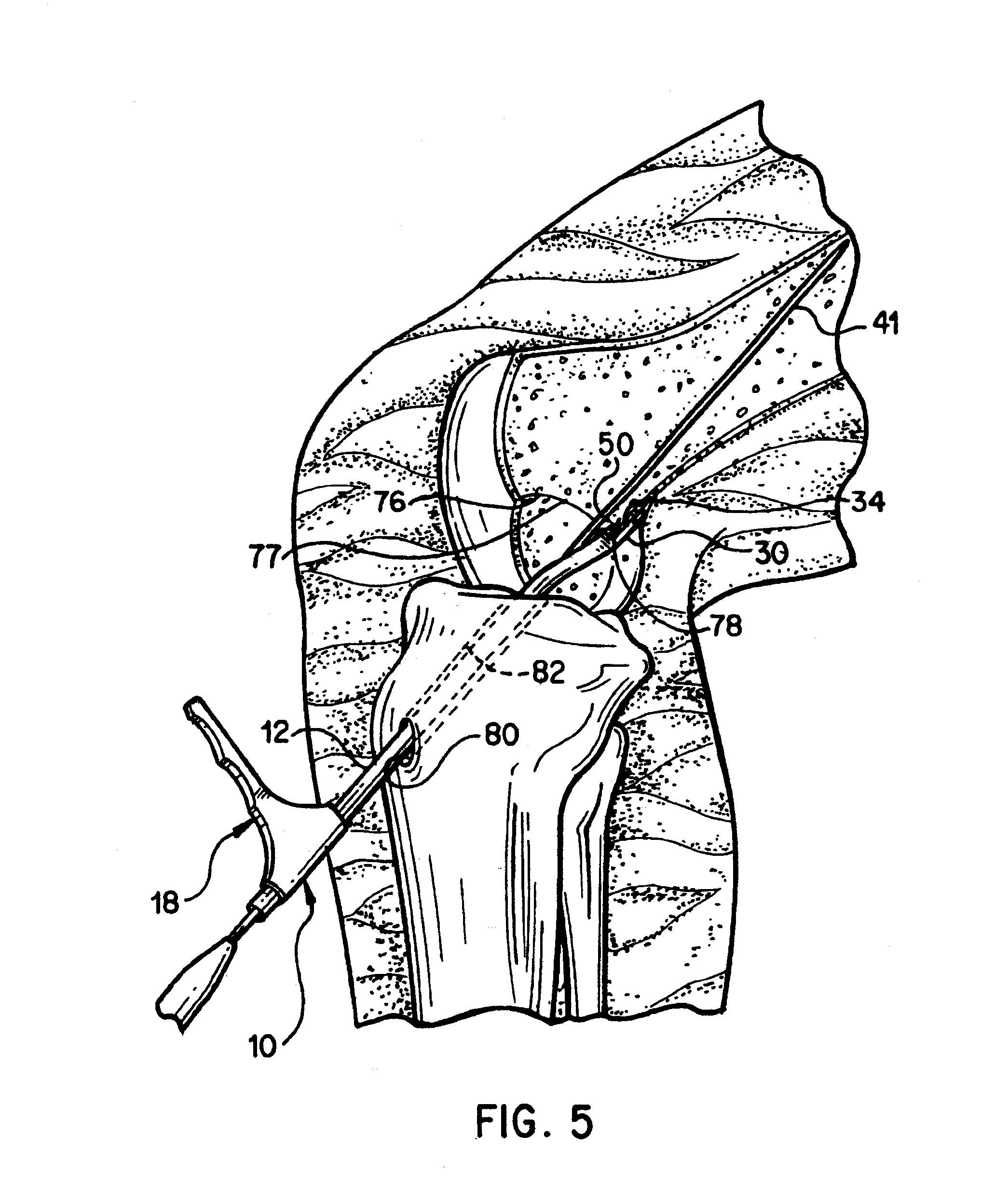
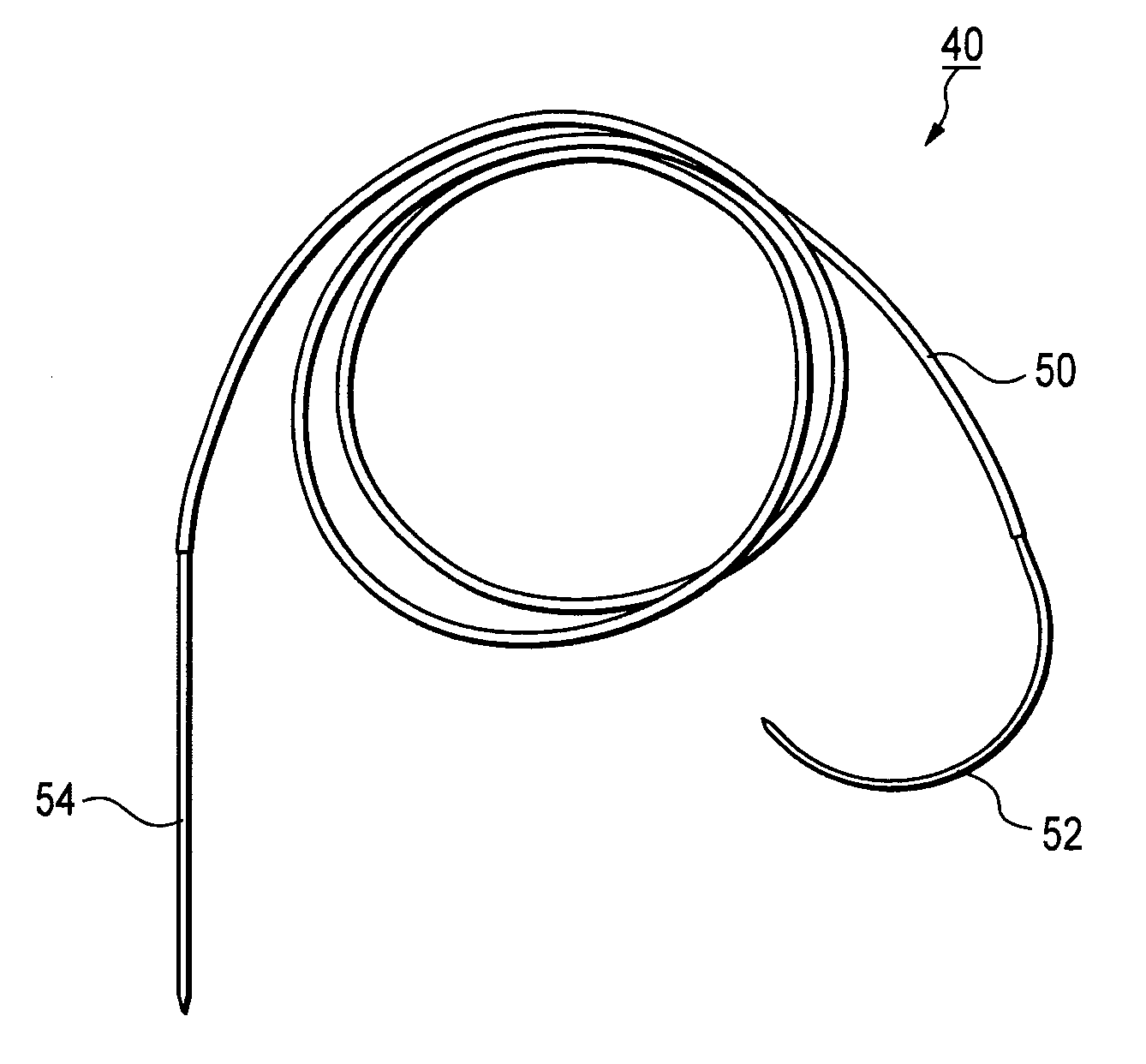
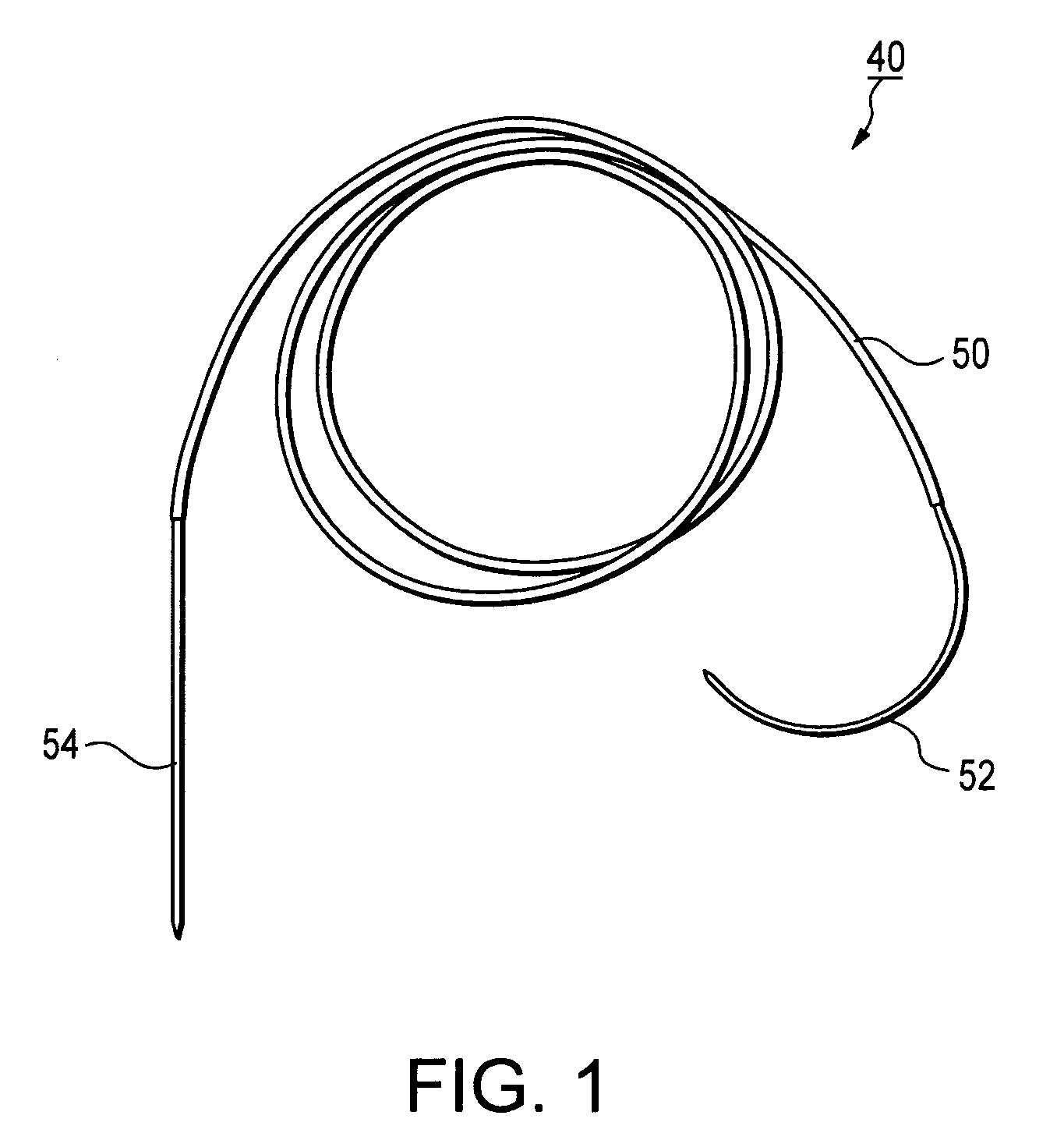
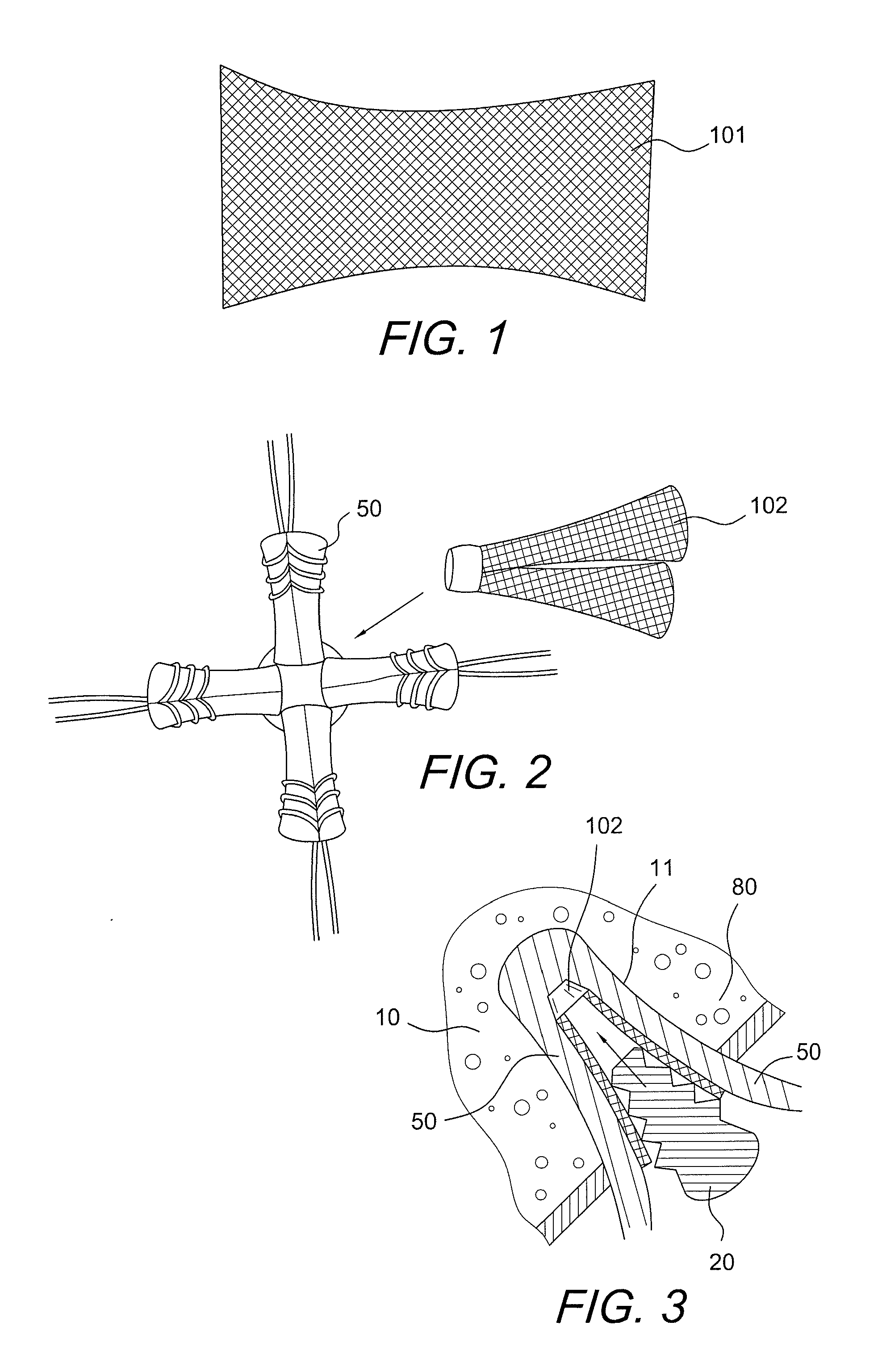
Method of replacing an anterior cruciate ligament in the knee
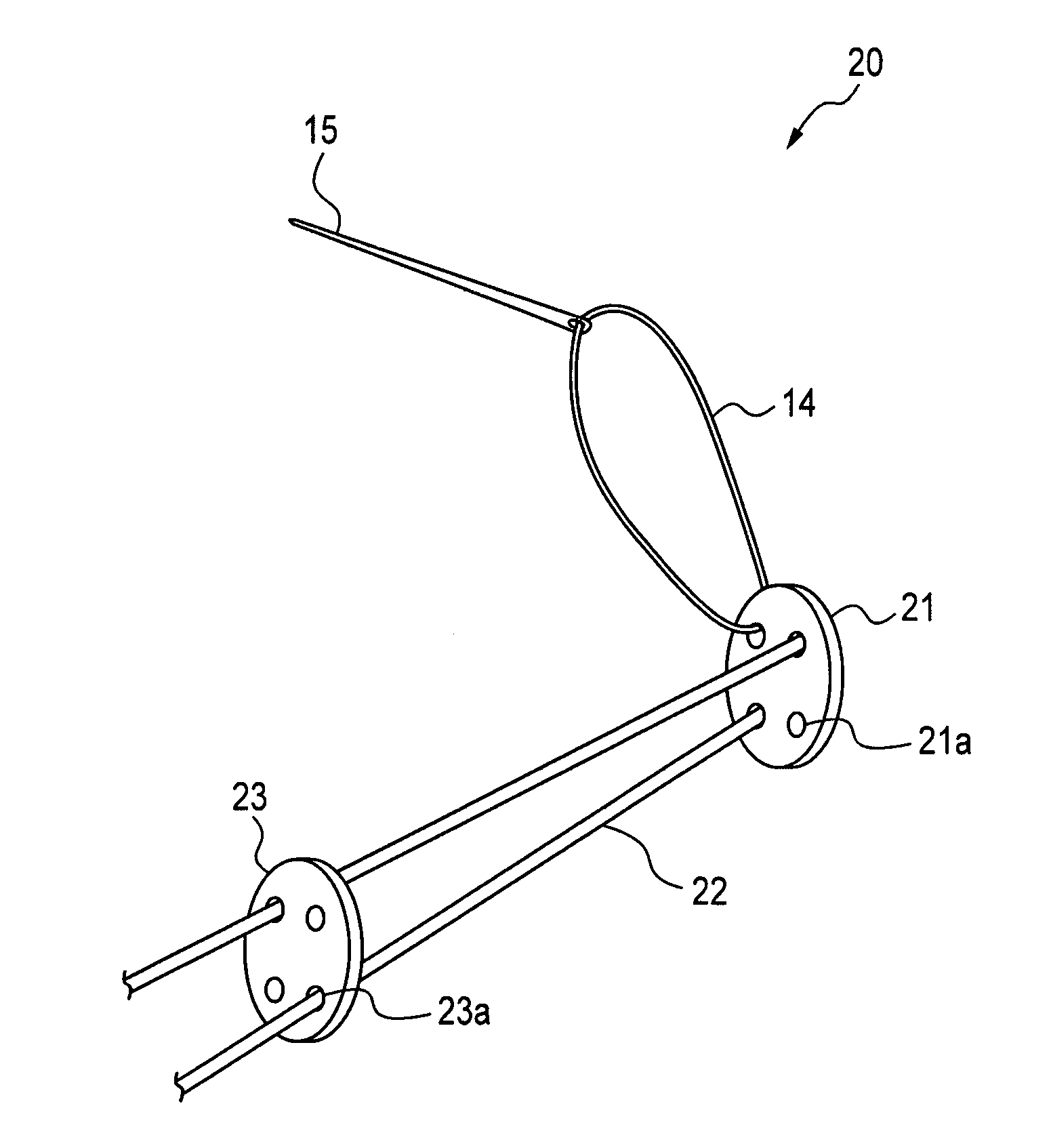
A method of reconstructing a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament in a human knee. Femoral and tibial tunnels are drilled into the femur and tibia. A transverse tunnel is drilled into the femur to intersect the femoral tunnel. A filamentary loop is threaded through the femoral tunnel and tibial tunnel and partially through the transverse tunnel. A replacement graft is formed into a loop and moved into the tibial tunnels using a surgical needle and suture. A flexible filamentary member is simultaneously moved along with the loop into the femoral and transverse tunnels. The filamentary member is used as a guide wire in the transverse tunnel to insert a cannulated cross-pin to secure a top of the looped graft in the femoral tunnel.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US)
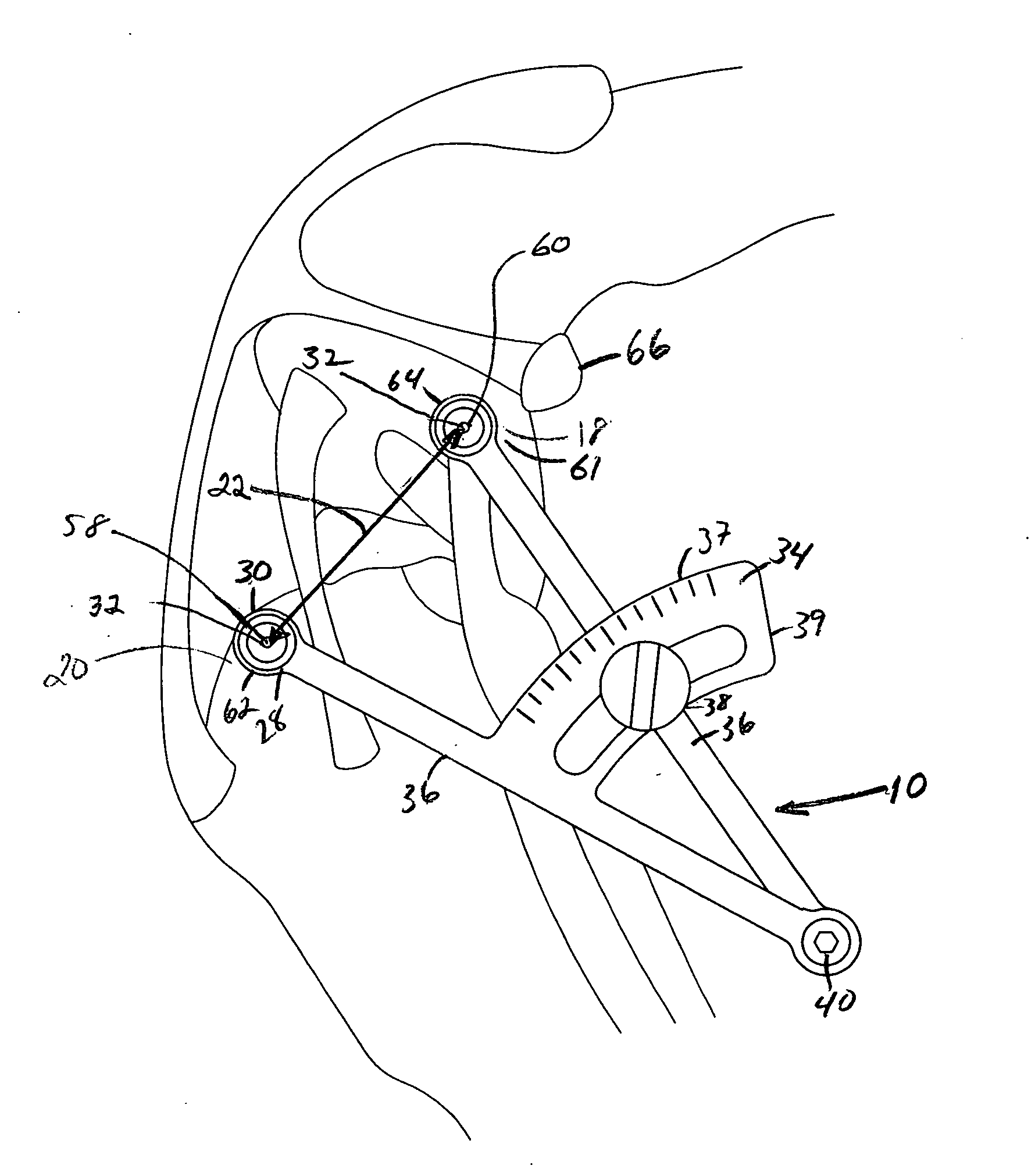
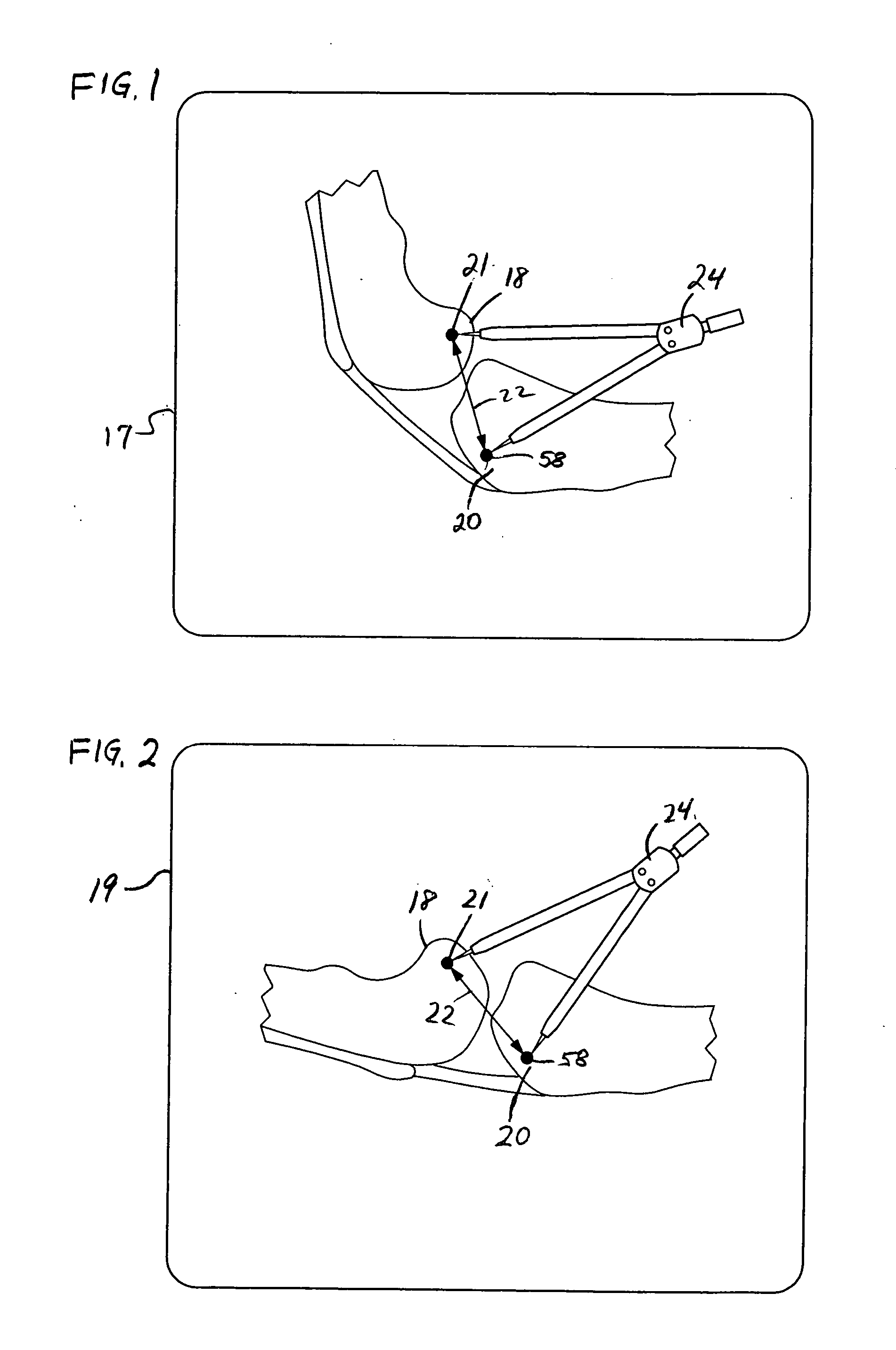
Extracapsular surgical procedure and surgical referencing instrument therefor
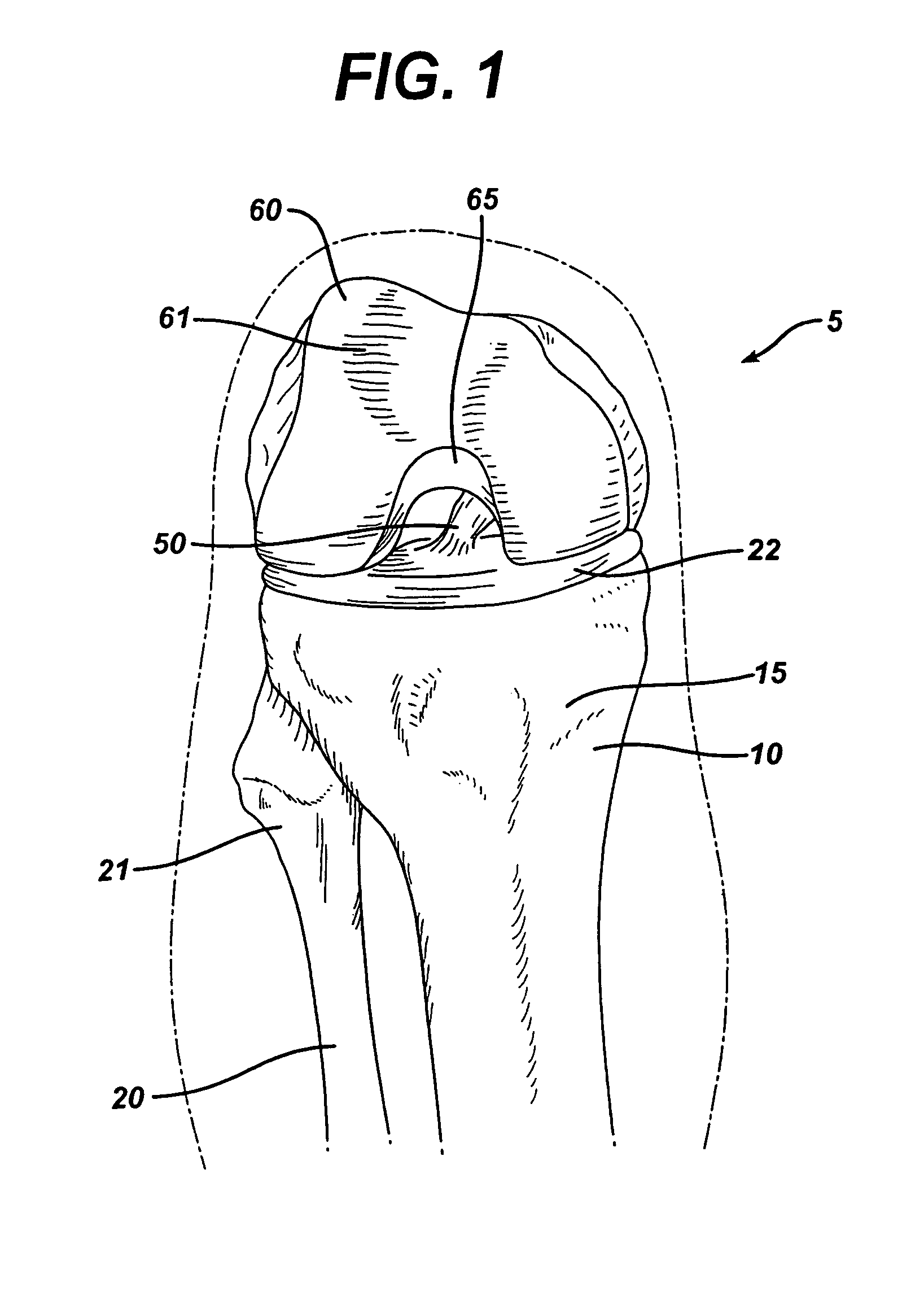
A method and device for finding isometric points in the joints of mammals for use in surgical repair of a joint. Isometric points are first identified in radiographic or other two dimensional images and then located in the actual joint. A method for repairing a cruciate ligament-deficient canine stifle employing the method and device for finding isometric points is described. A method and apparatus for locating the axis of rotation of a joint is also described.
Owner:WHITE RALPH RICHARD
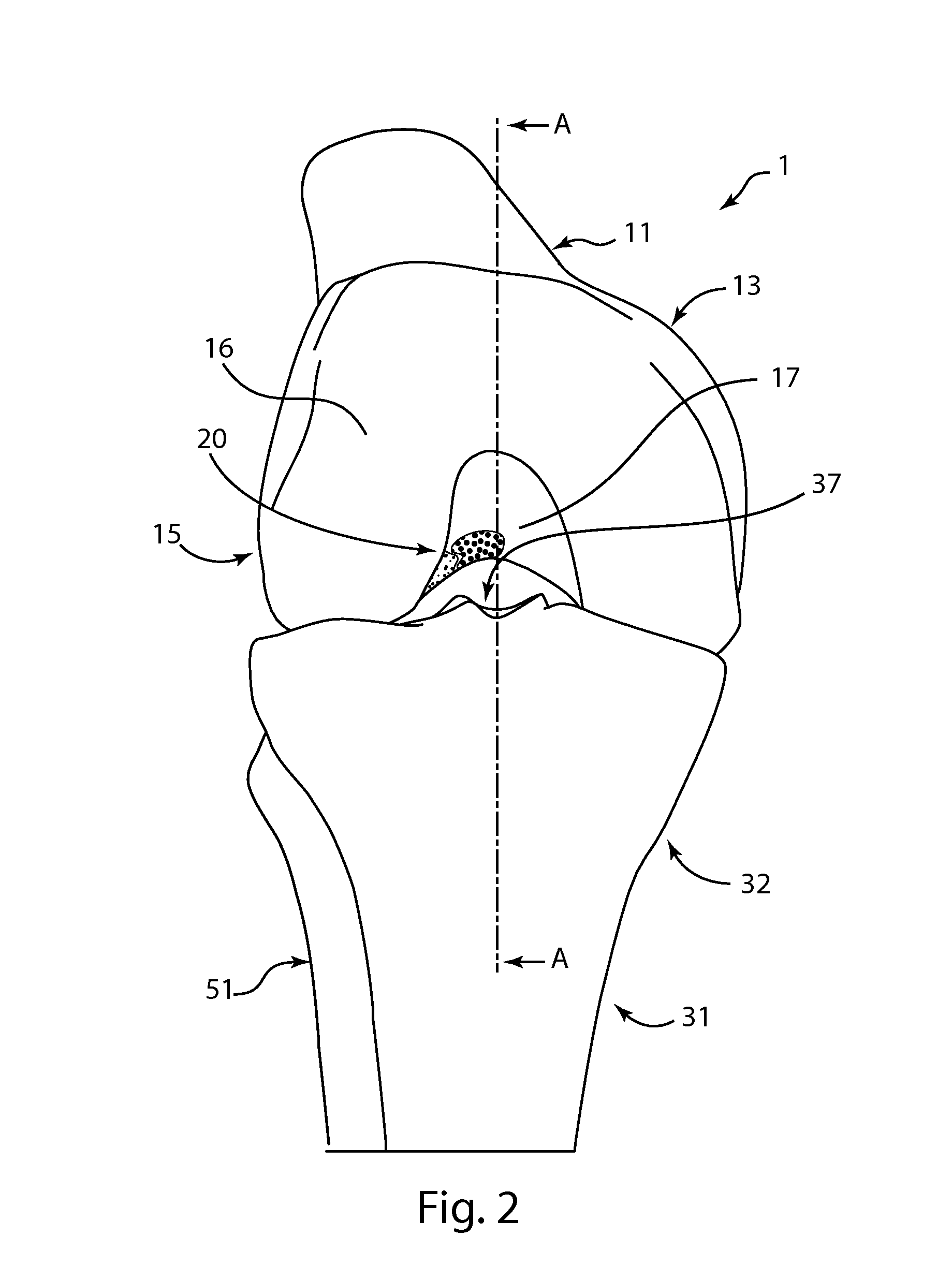
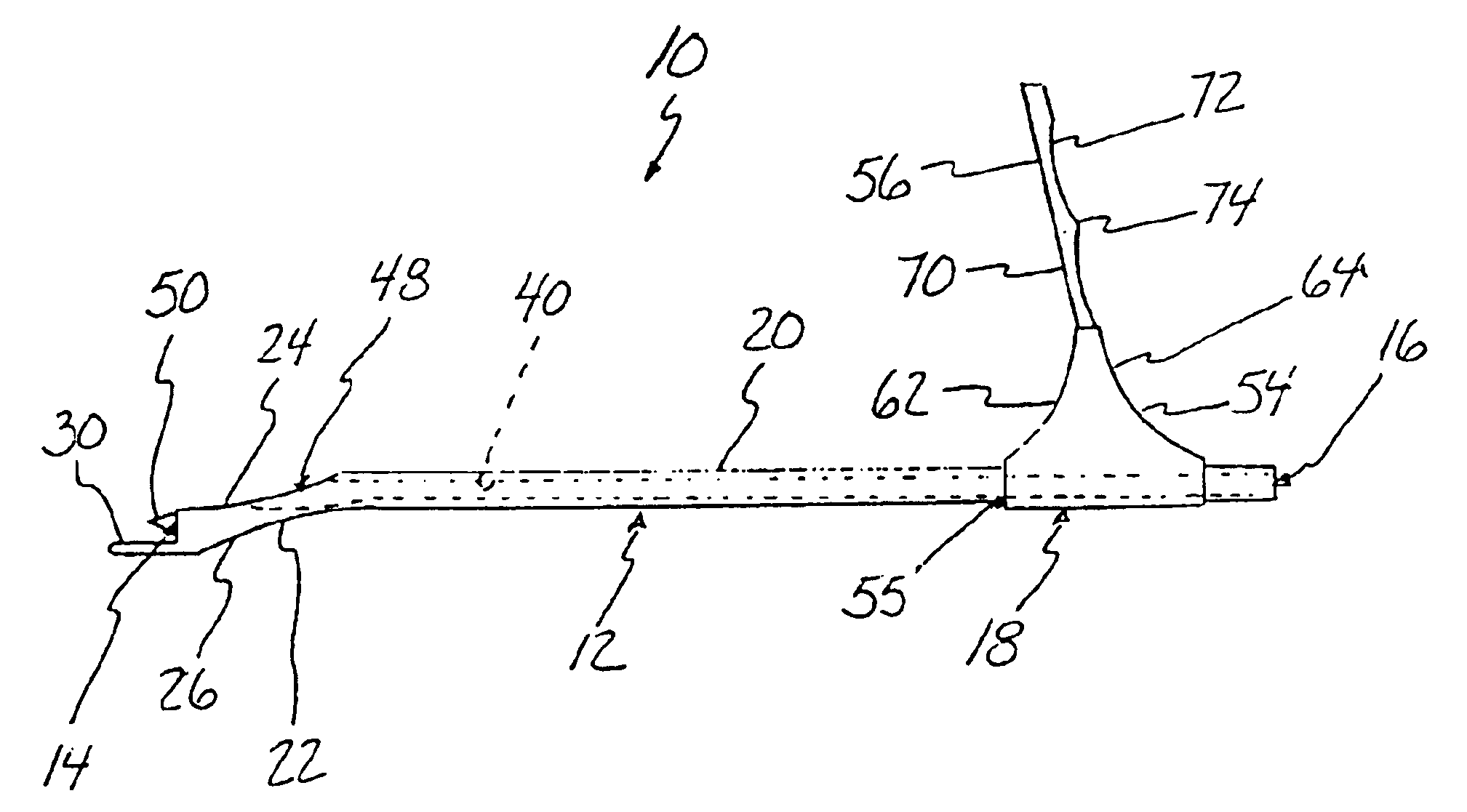
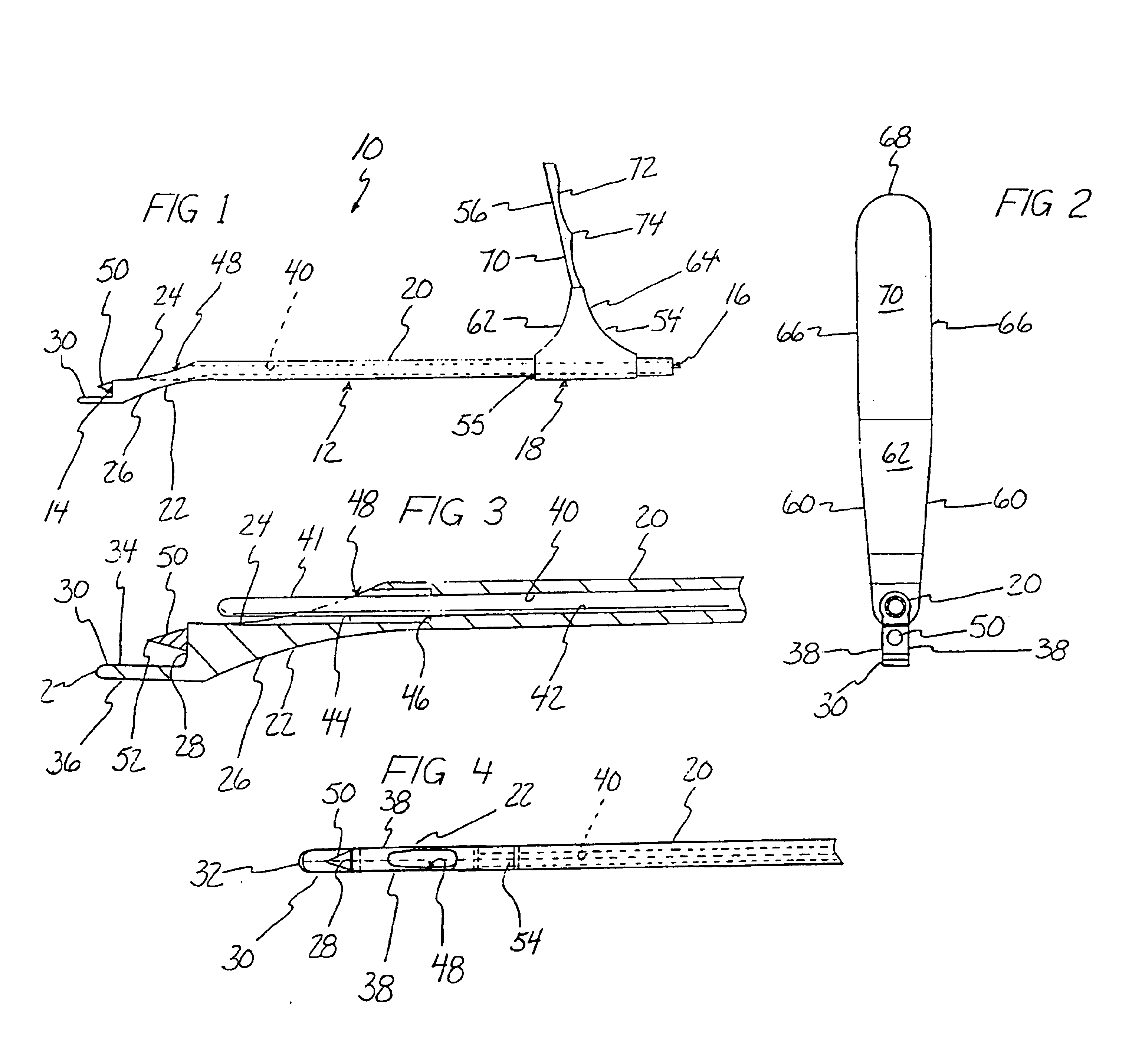
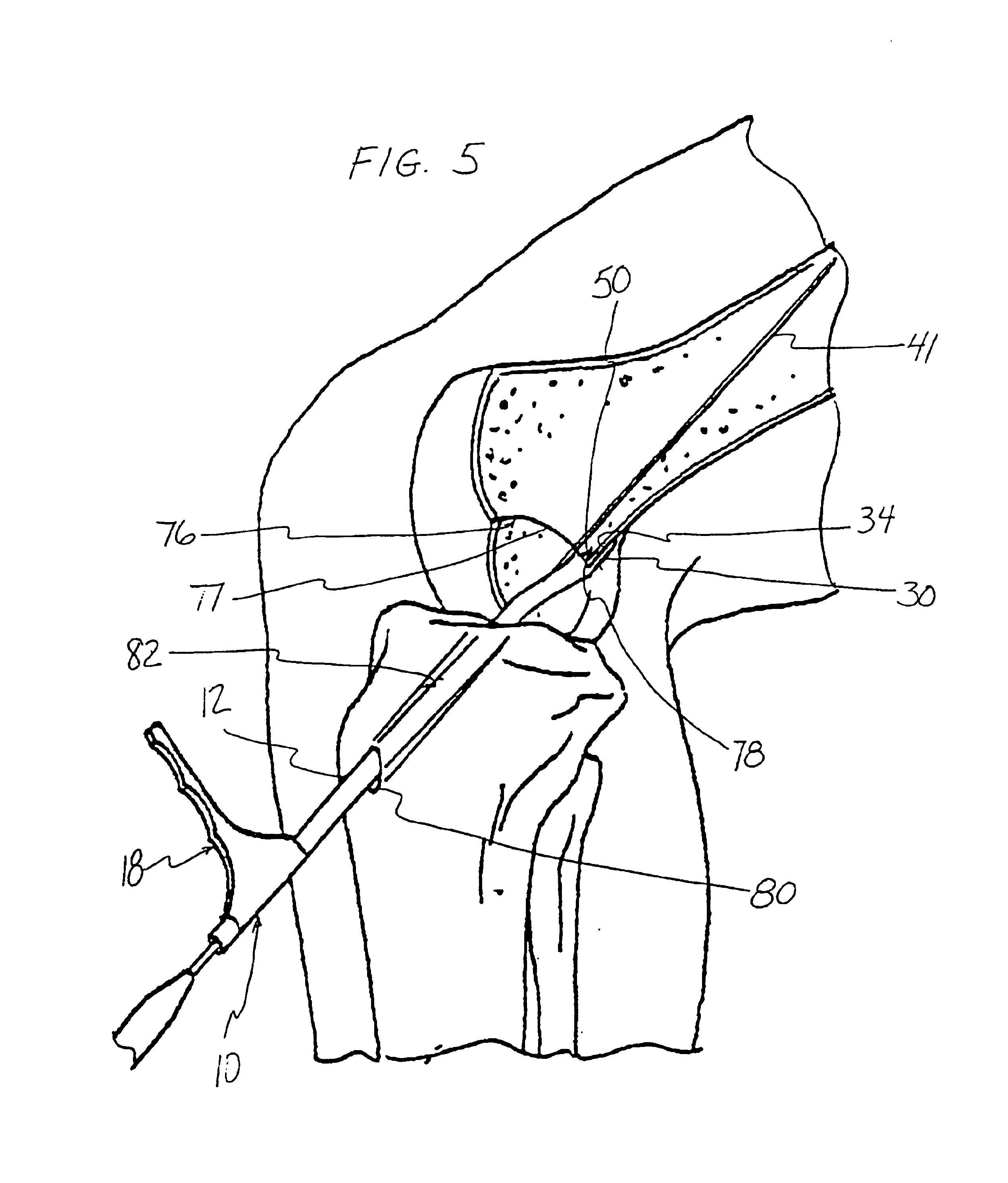
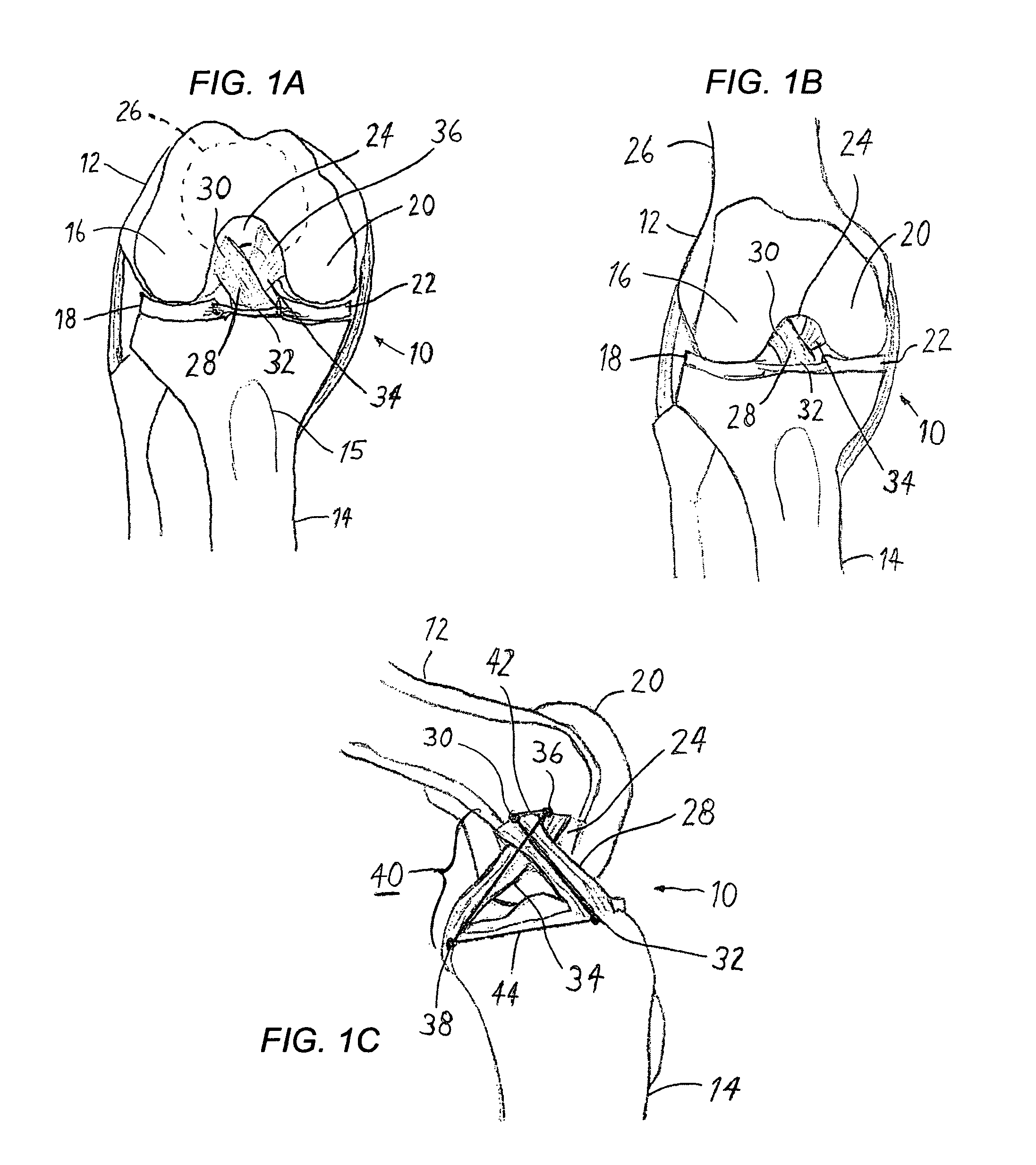
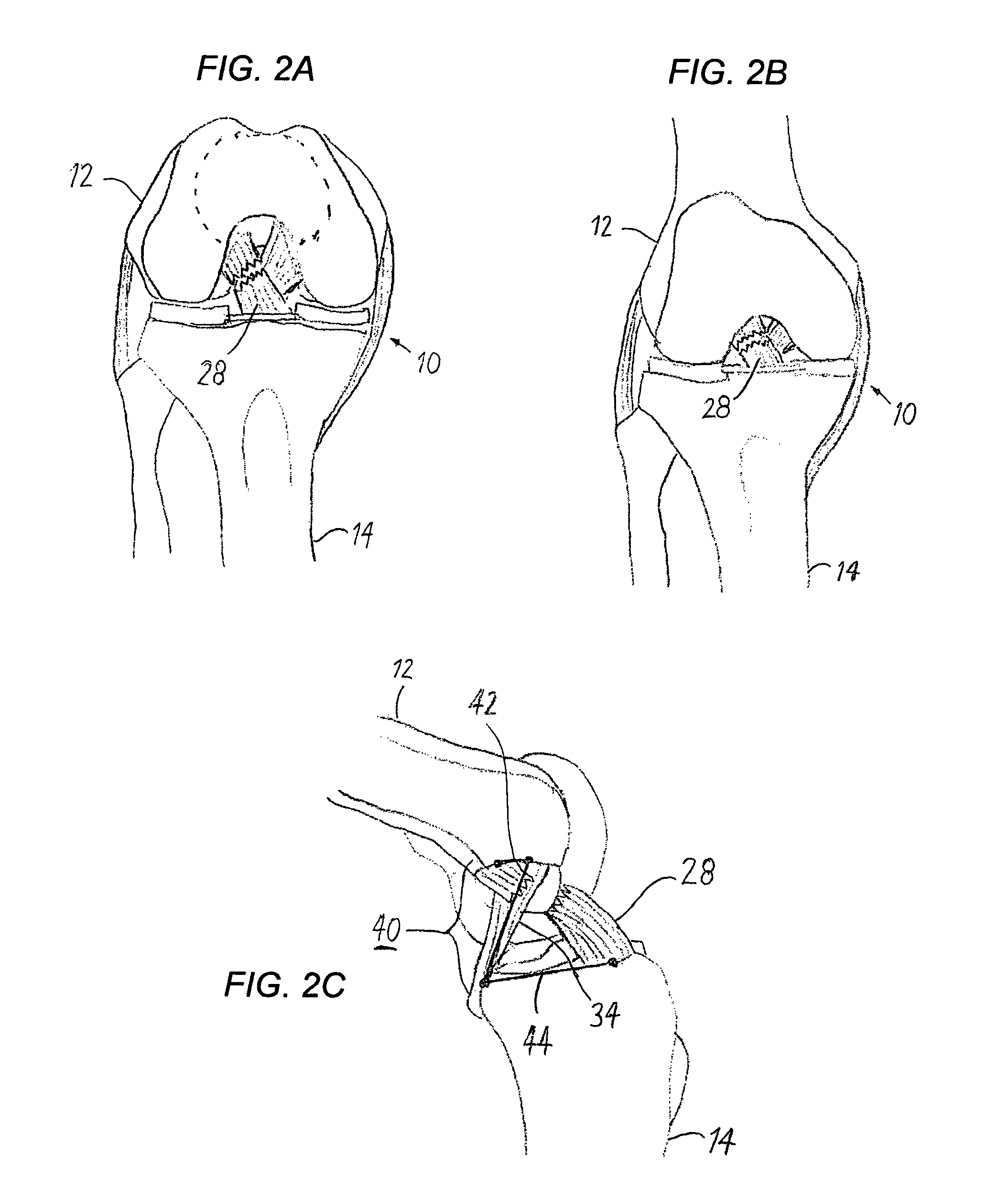
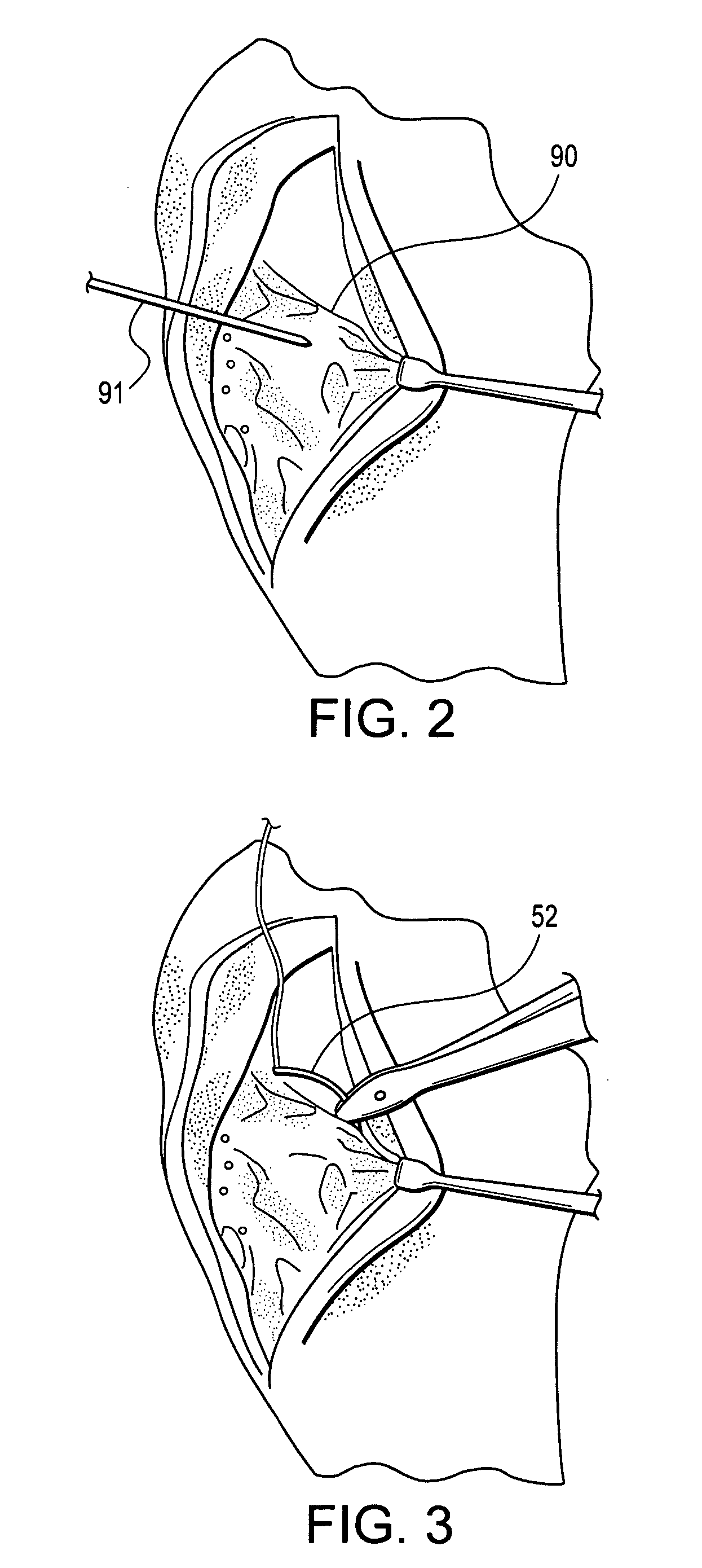
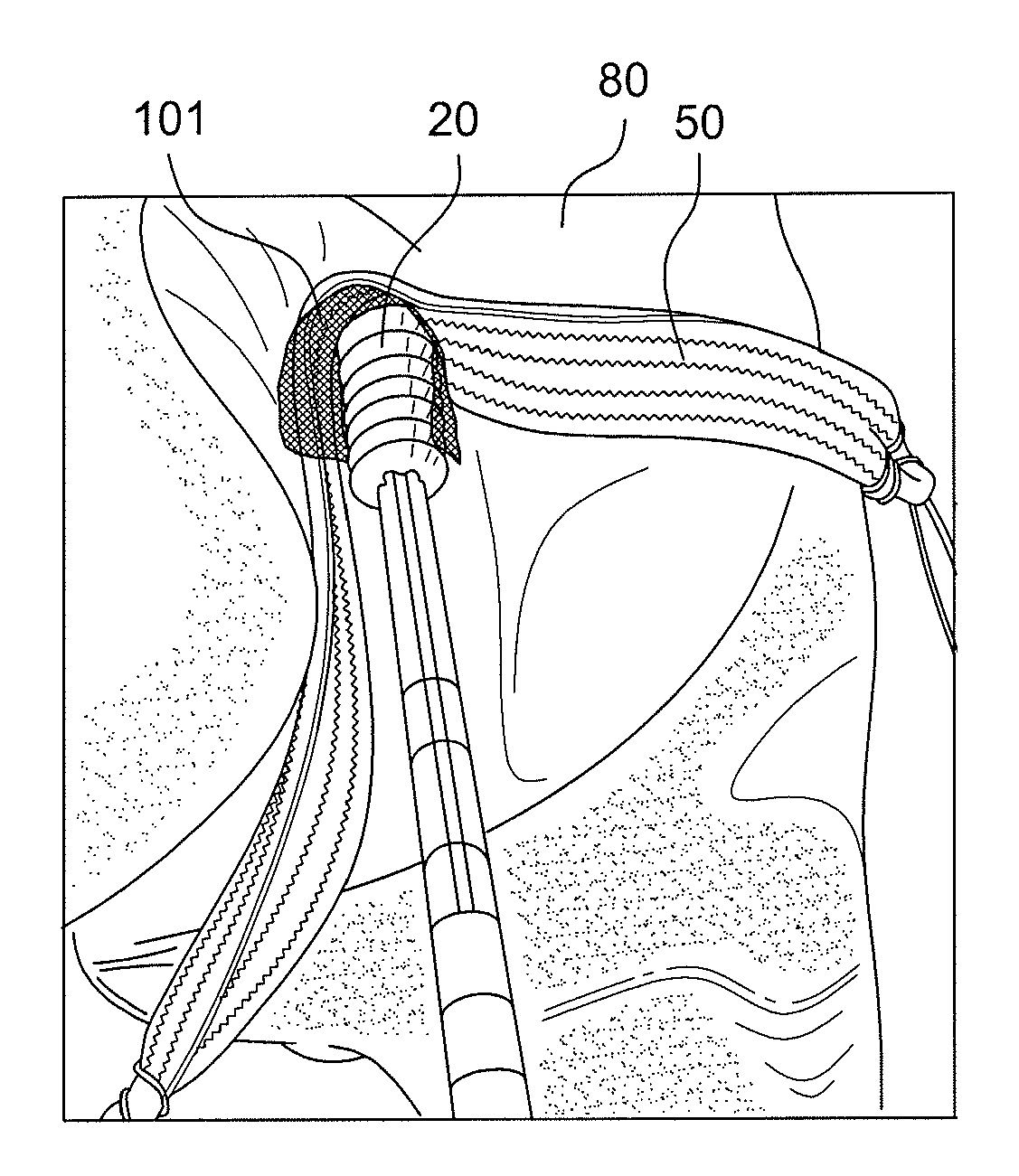
Anterior cruciate ligament tether
A device and method to provide a surgically inserted internal tether between the femur and tibia is provided which will prevent distraction of the healing anterior cruciate ligament in all degrees of flexion and extension, at all times. The anterior cruciate ligament tether preserves the four-bar cruciate linkage, critical for normal knee mechanics. In addition, placement of the tether provides bleeding into the knee in the region of the anterior cruciate ligament attachment sites and the consequent inflow of pluripotential cells and healing mediators.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
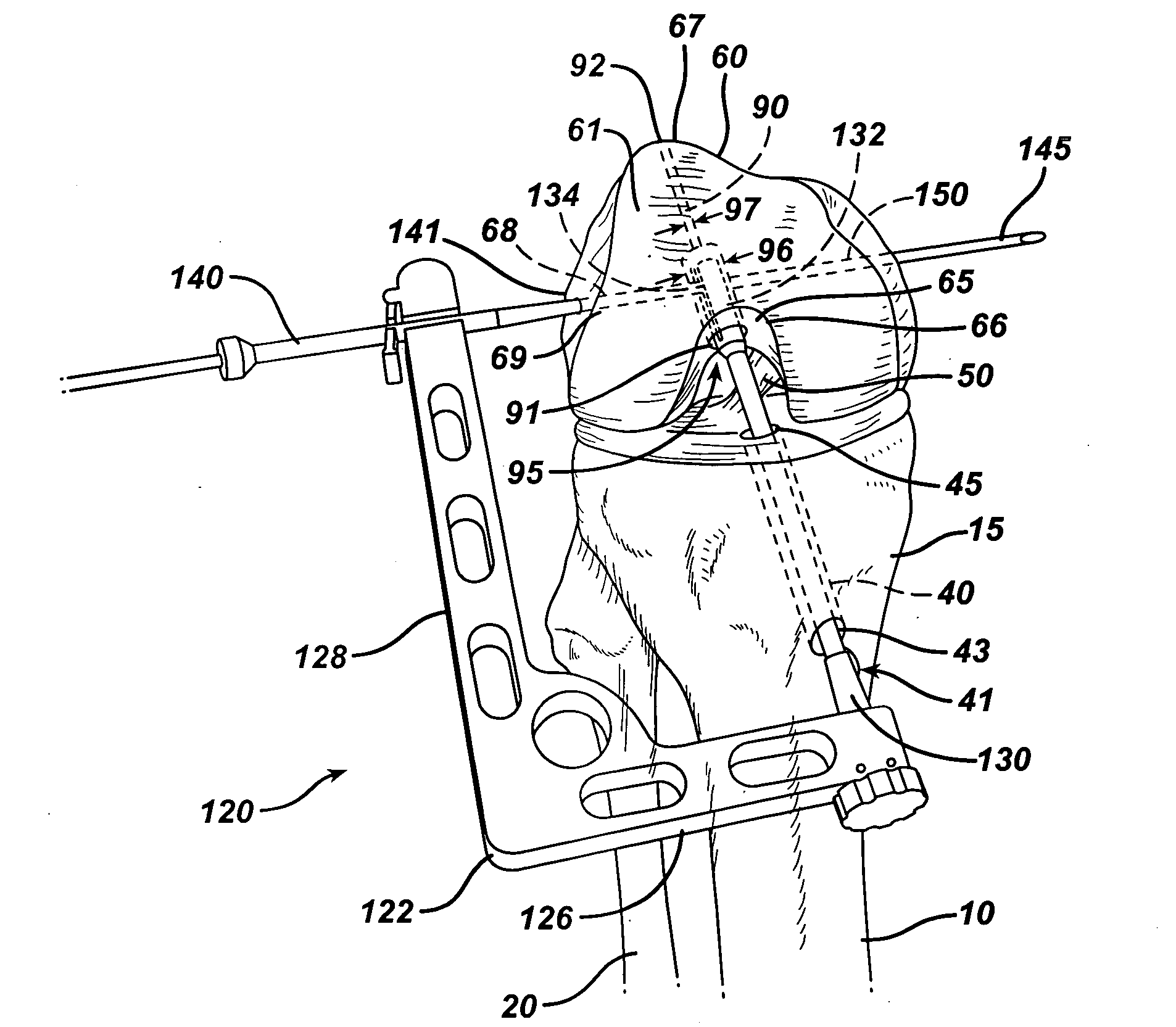
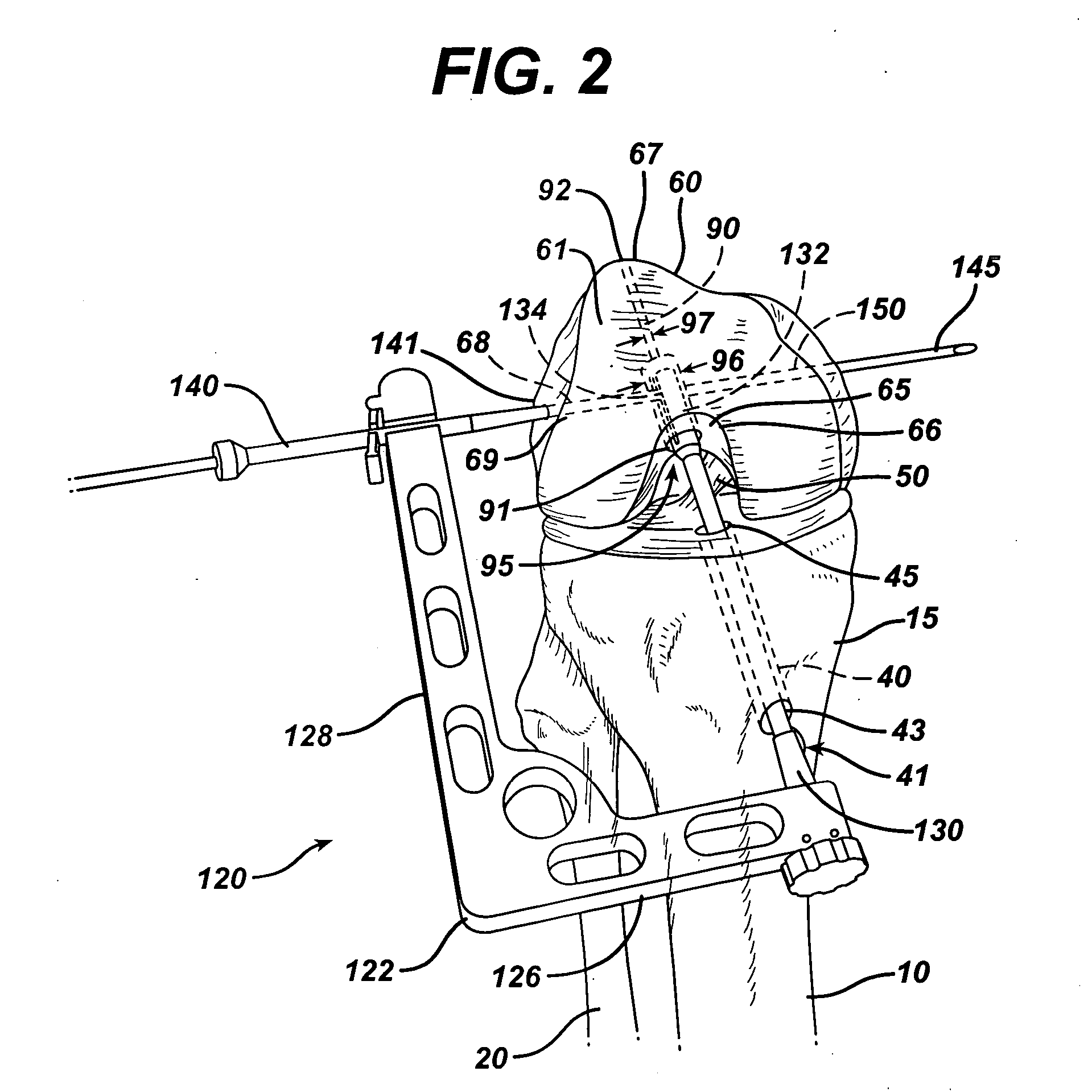
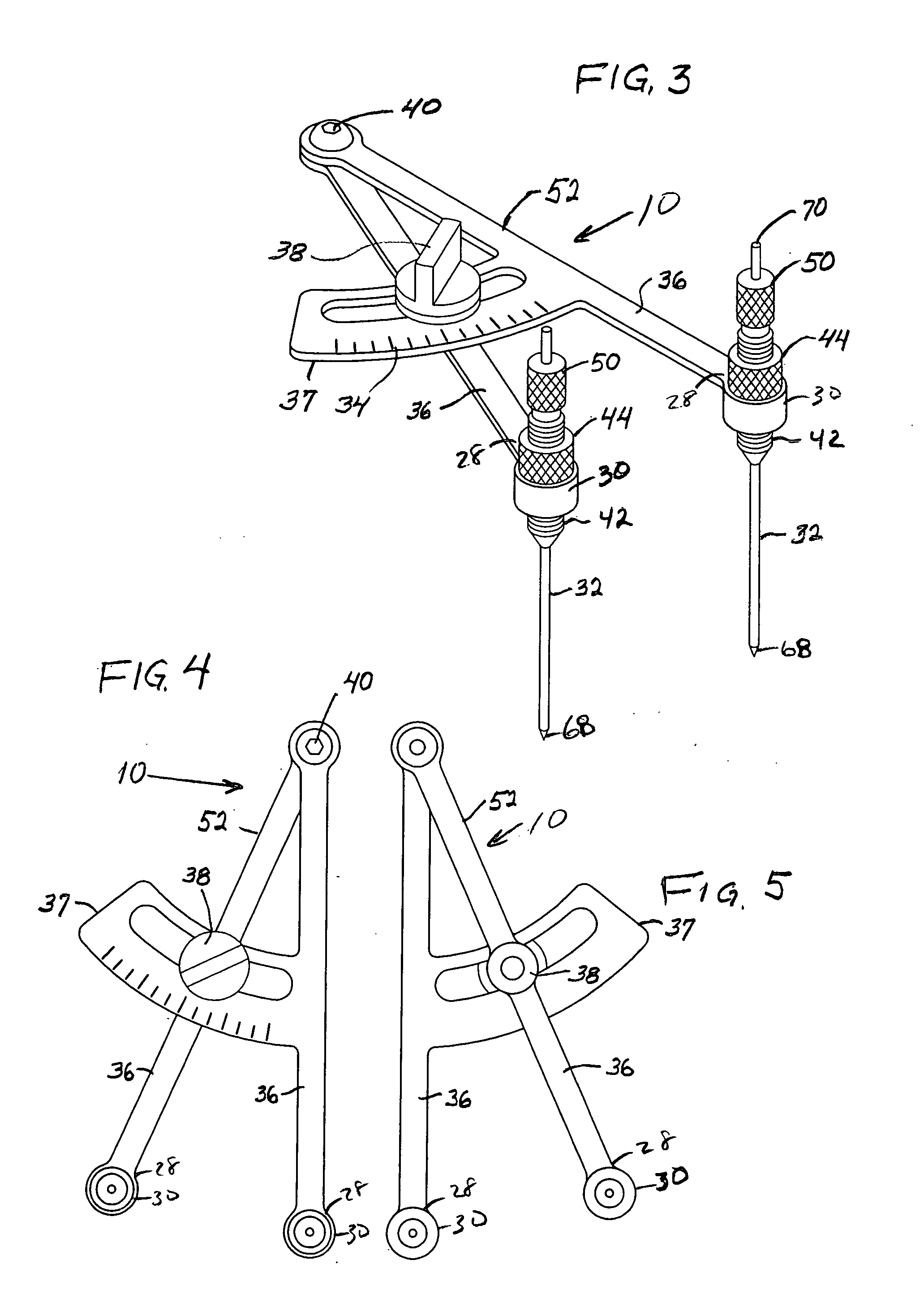
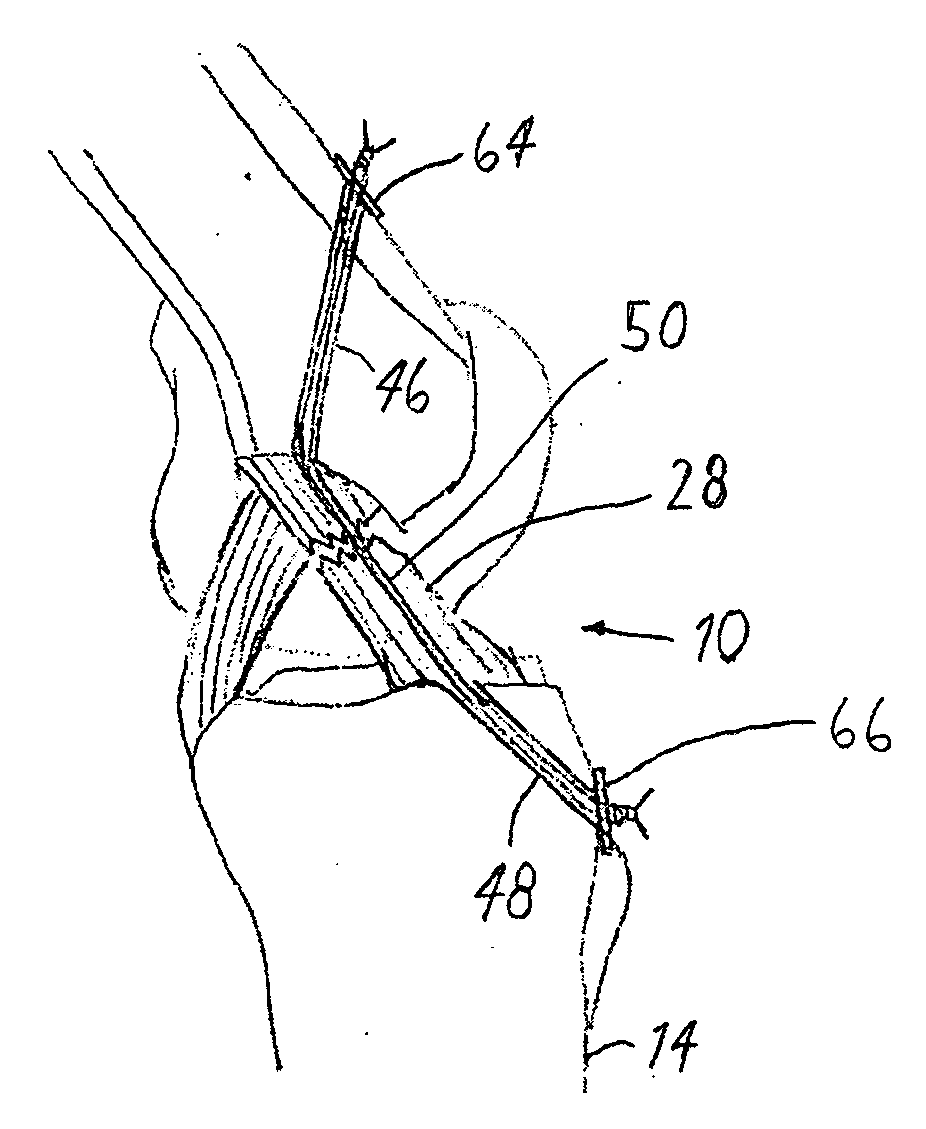
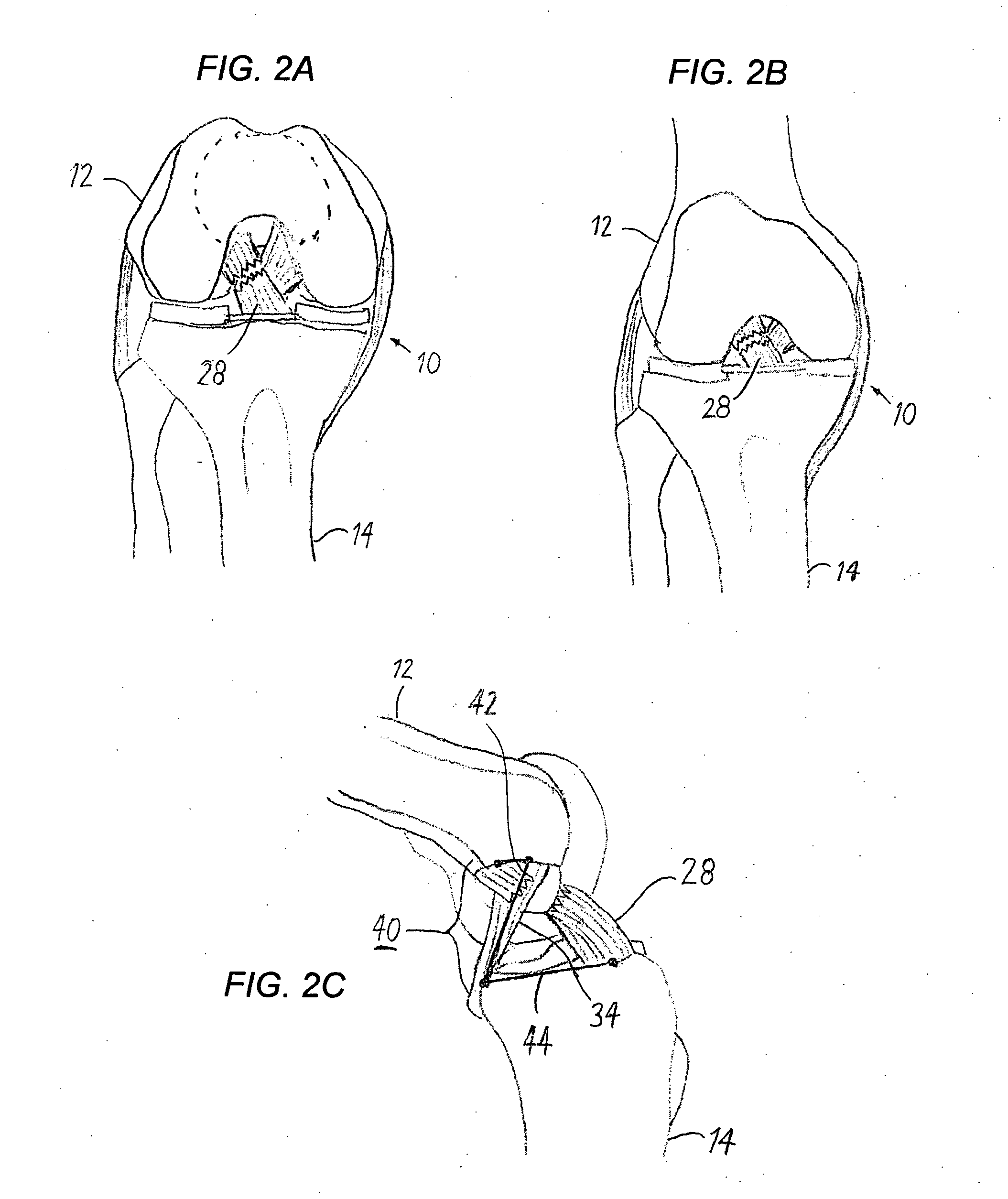
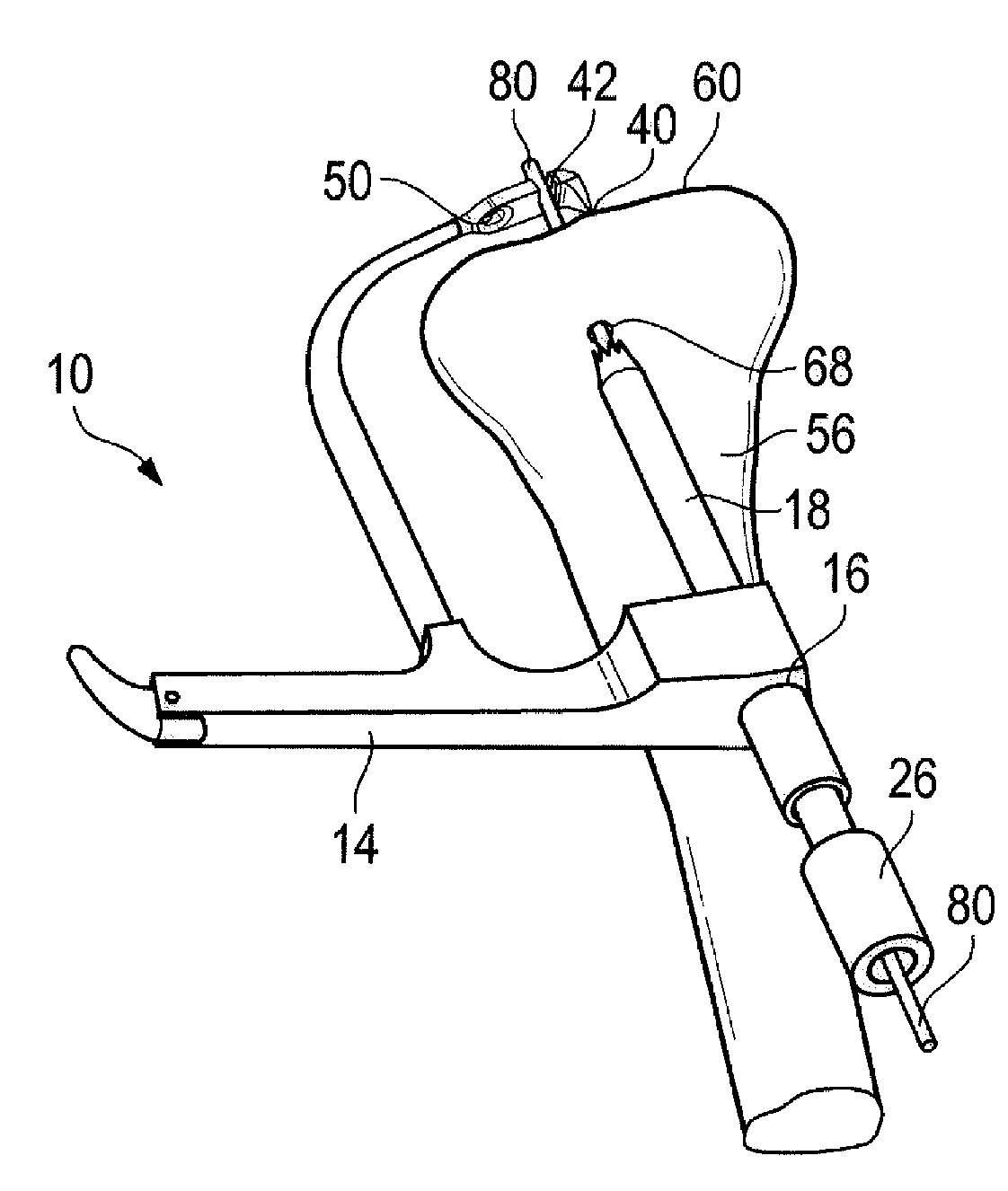
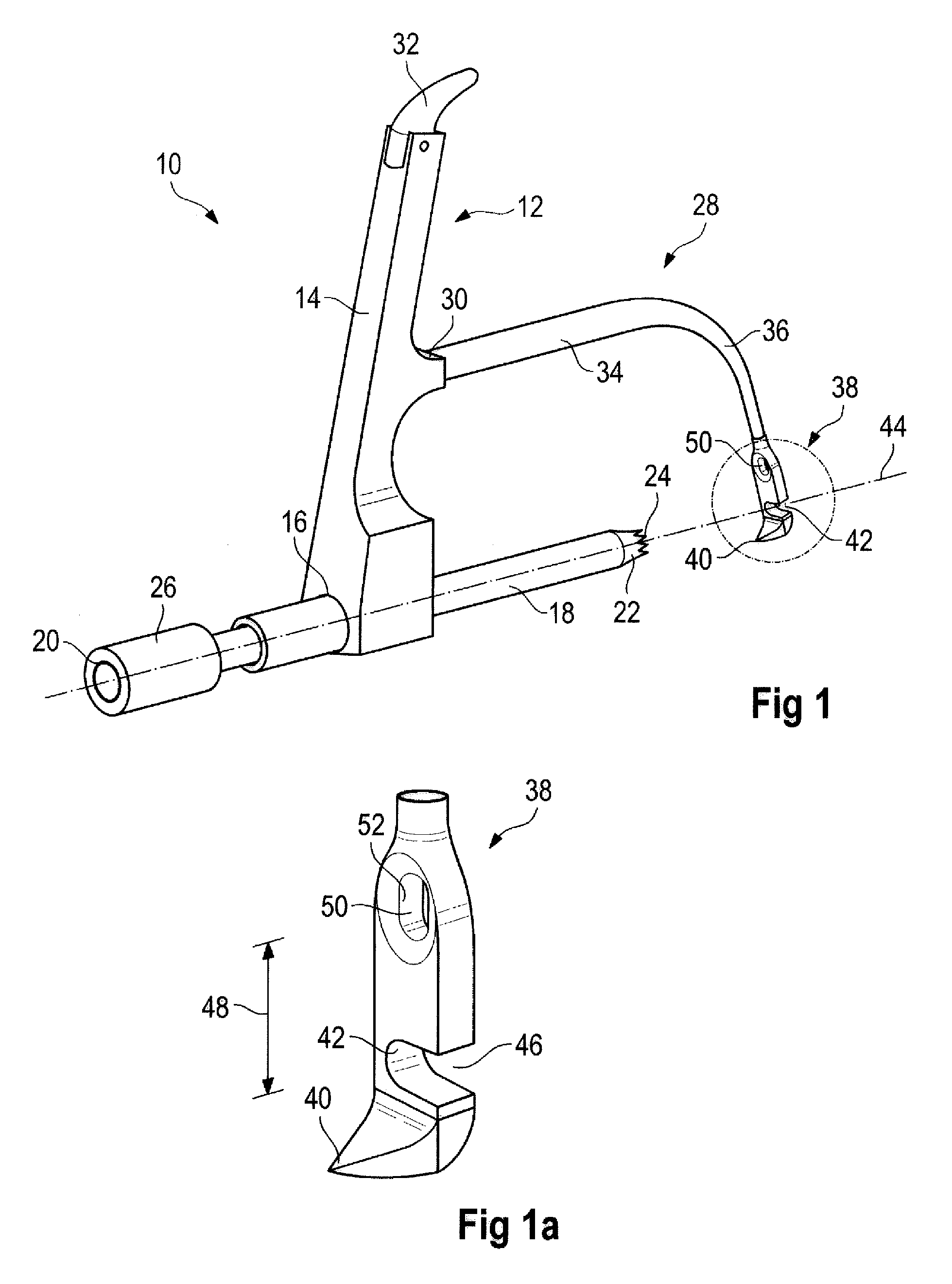
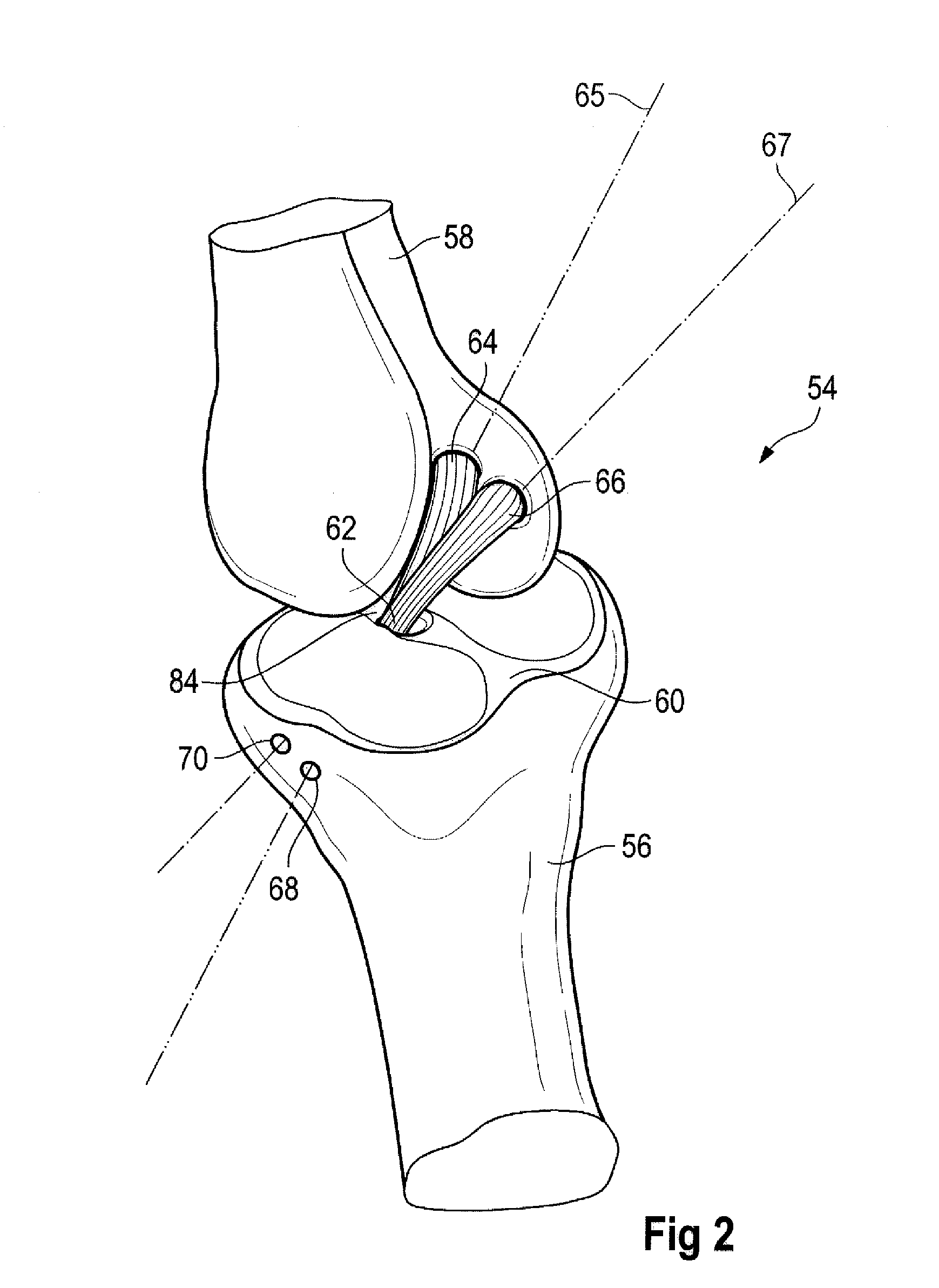
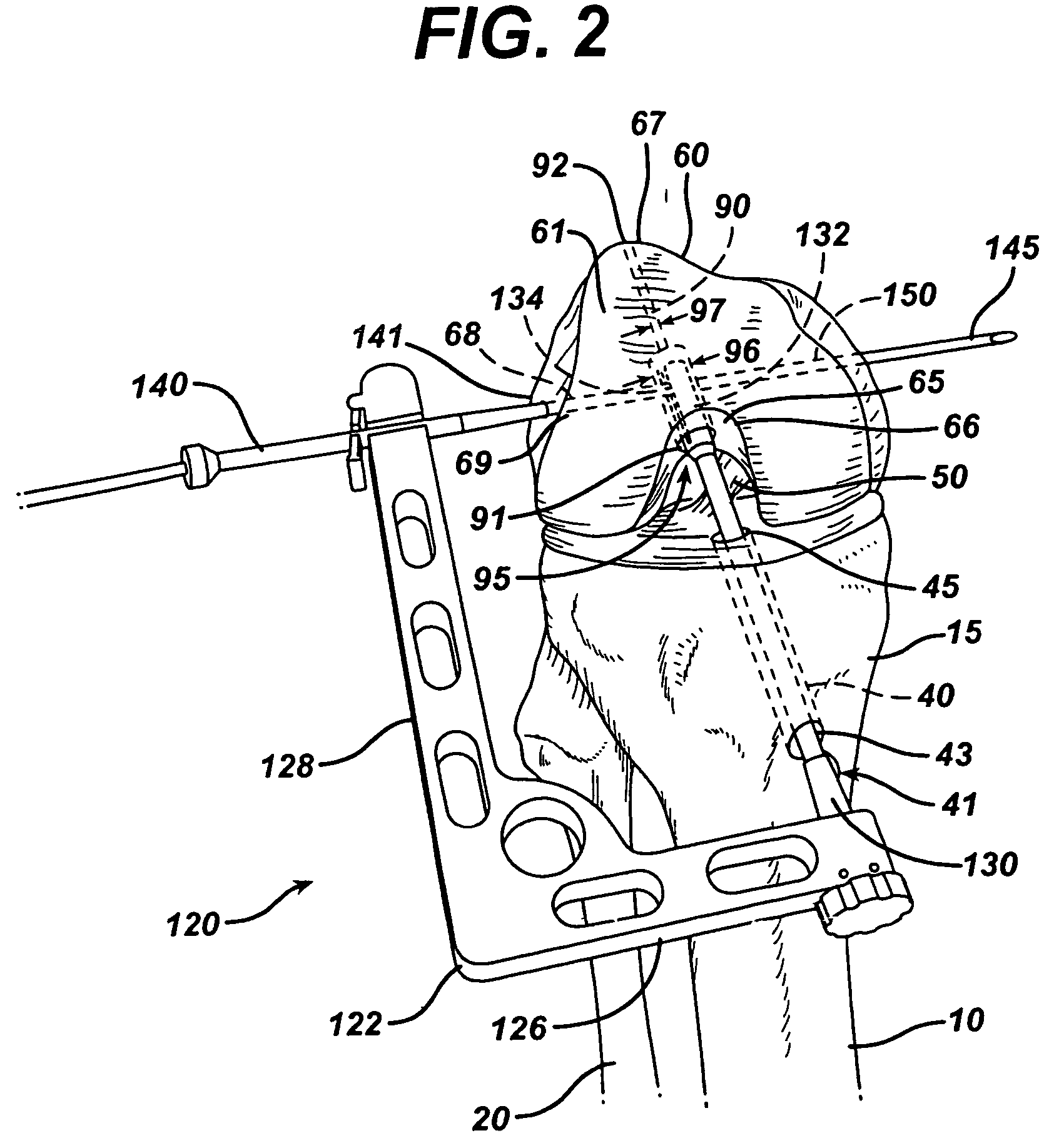
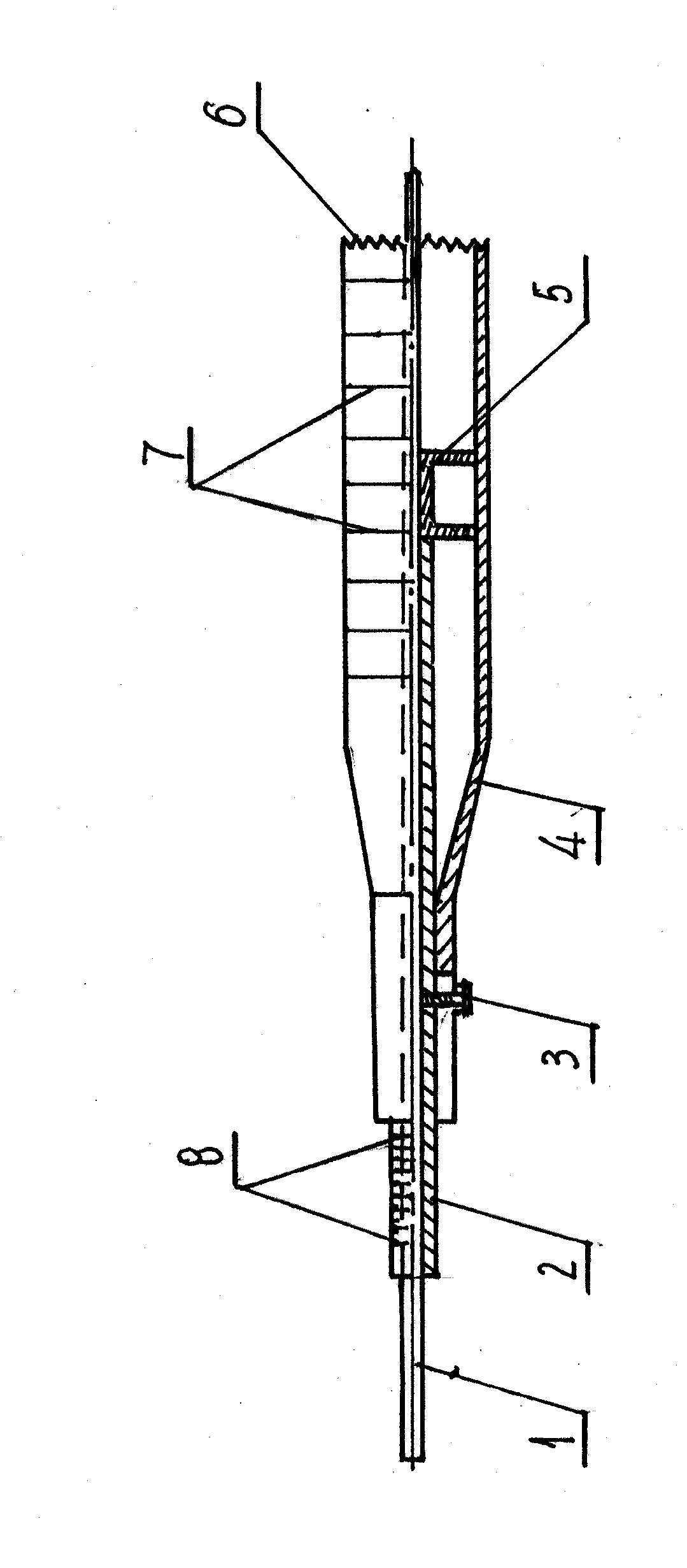
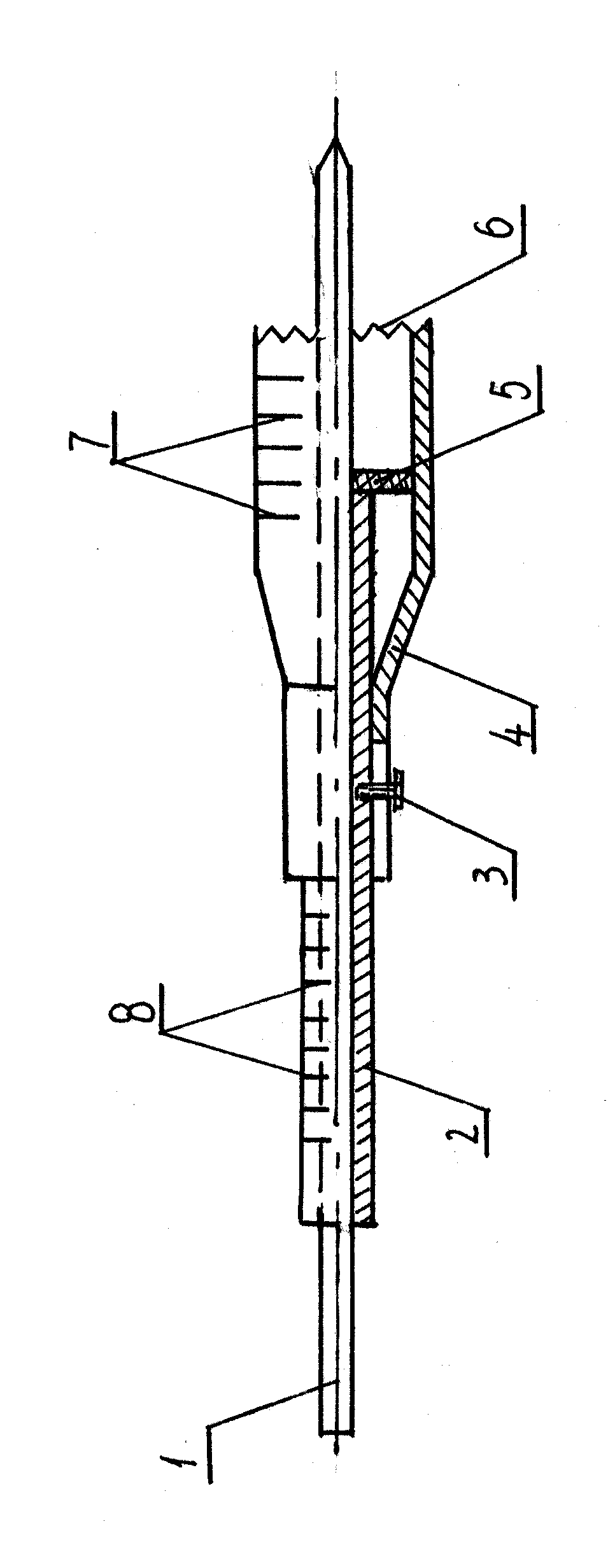
Tibial Aiming Device For The Double Channel Technique
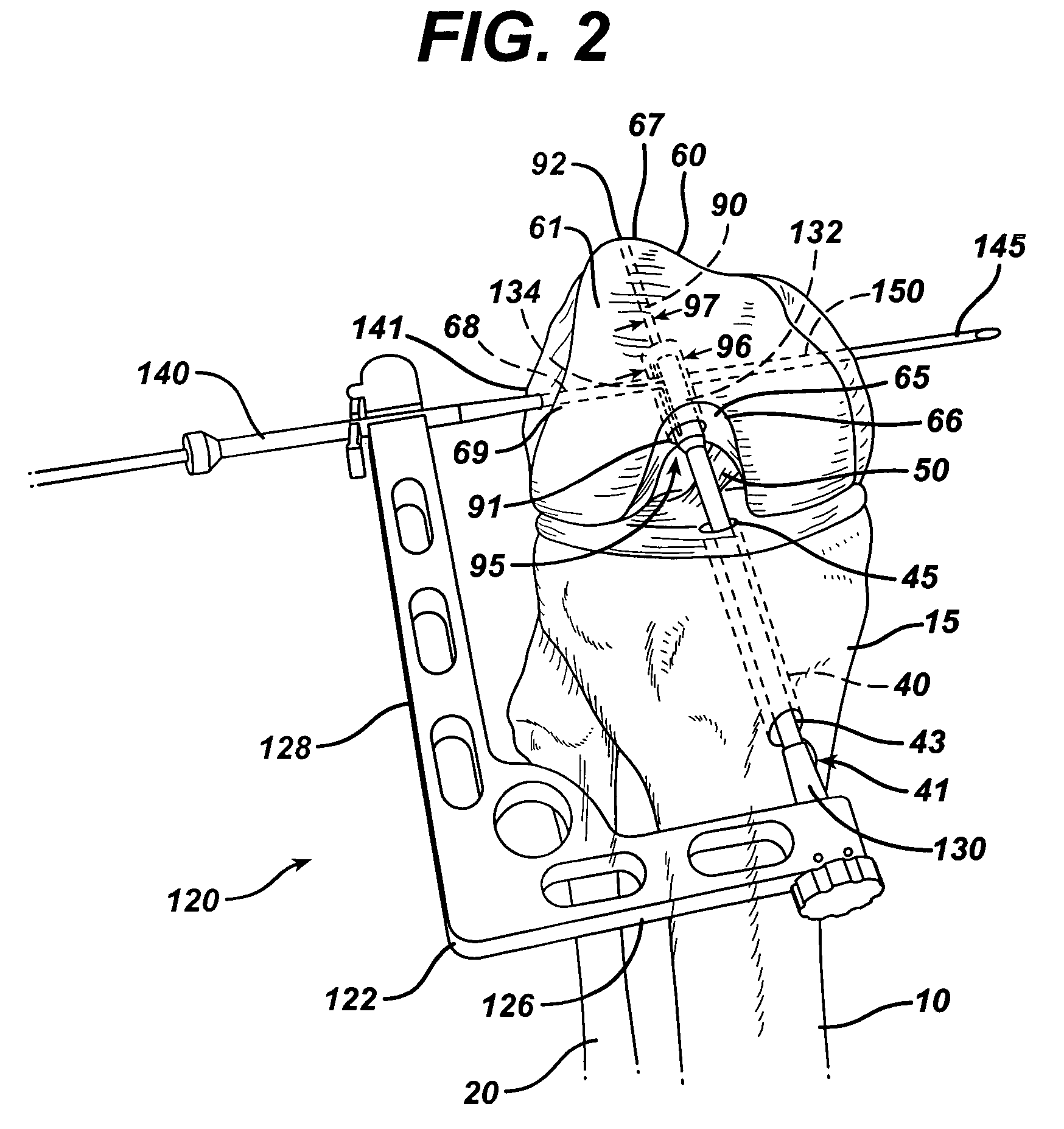
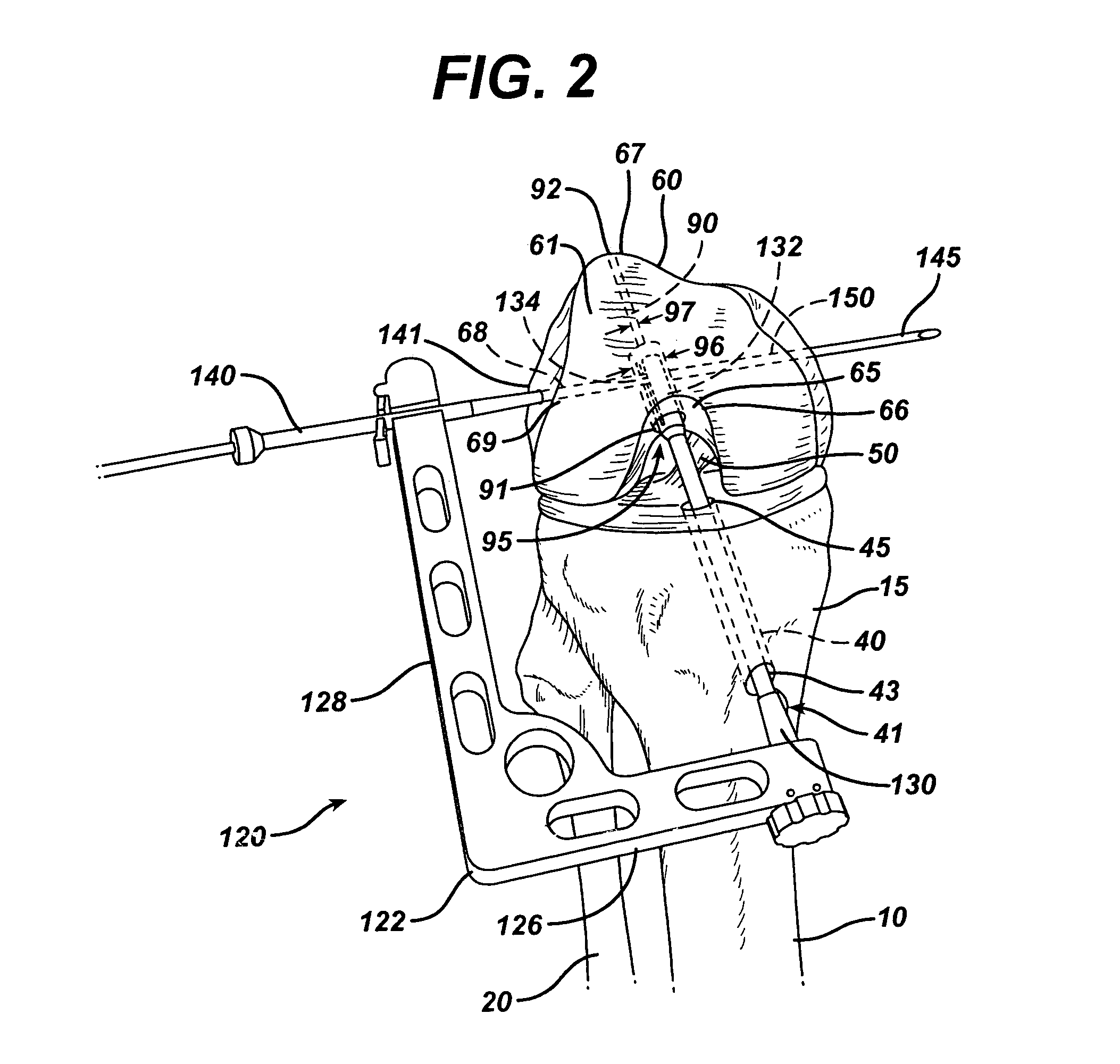
A device (10) serves to target and introduce bore channels into a tibia in the vicinity of a knee joint during reconstruction of the front cruciate ligament. It has a handle (12), a guide sleeve (18) removably attached to said handle, said guide sleeve having a longitudinal axis (44). A distal end of said guide sleeve (18) constitutes a first aiming point. An arm (28) protrudes from said handle (12). A distal end of said arm constitutes a second aiming point. A first opening (42) is provided in a distal end region of said arm, said opening (42) being in alignment with said longitudinal axis (44). A second opening (50) is provided in that distal end region of said arm, said second opening (50) is at a distance from said first opening (42).
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Adjustable suture-button construct for knotless stabilization of cranial cruciate deficient ligament stifle
An adjustable, knotless button / loop / needle construct for fixation of cranial cruciate ligament deficient stifle. The adjustable, knotless construct includes two fixation devices (for example, two buttons), at least one flexible, adjustable loop attached to at least one of the fixation devices (e.g., the buttons), and two needles (each needle being attached to one fixation device, e.g., the buttons). The adjustable, knotless construct has an adjustable loop length and allows adjustment in one direction while preventing or locking the construct from loosening in the opposite direction, due to applied tensile forces. The construct and technique of the present invention provides an improved knotless system for cruciate ligament repair.
Owner:ARTHREX
Double bundle acl repair system
ActiveUS20120059469A1Facilitate circumferential healingIncreased complexitySuture equipmentsLigamentsBone tunnelTibia
A system for single tunnel, double bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction includes implant constructs and instruments. The implant constructs provide a combination of cortical fixation and bone tunnel aperture fixation. The implant constructs separate a graft into distinct bundles. The instruments are used to prepare shaped bone tunnels to receive the implant constructs and graft bundles. Methods for reconstructing the antero-medial and postero-lateral bundles of the anterior cruciate ligament may rely on single femoral and tibial tunnels and a single strand of graft.
Owner:MYERS THOMAS H +1
Methods of precisely forming bone tunnels in cruciate ligament reconstruction of the knee
InactiveUS6878150B1Precise positioningMinimal sizeJoint implantsLigamentsBone tunnelCruciate ligament
A femoral guide for precisely positioning a guide wire on a bone surface of the femur includes a body having a lumen for receiving a guide wire and a tongue protruding from the body for engaging an edge or reference point on the bone surface with the tongue being spaced a predetermined distance from a longitudinal axis of the lumen. The lumen includes an opening allowing a guide wire extending through the lumen to contact the bone surface at a location spaced from the edge substantially the predetermined distance with the tongue engaging the edge. A stylus on the body can be driven into the bone to secure and stabilize the femoral guide prior to driving the guide wire into the bone through the lumen. With the guide wire driven into the bone, a bone tunnel can be formed substantially concentrically or coaxially along the guide wire such that a longitudinal axis of the bone tunnel will be disposed from the edge substantially the predetermined distance. Methods of precisely forming bone tunnels include the steps of engaging an edge of a bone surface with a tongue of the femoral guide, inserting a guide wire through a lumen of the femoral guide, driving the guide wire into the bone through the lumen and forming a bone tunnel in the bone along the guide wire such that a longitudinal axis of the bone tunnel will be disposed from the edge engaged by the tongue a distance substantially equal to the distance that the tongue is disposed from a longitudinal axis of the lumen.
Owner:MCGUIRE DAVID A +1
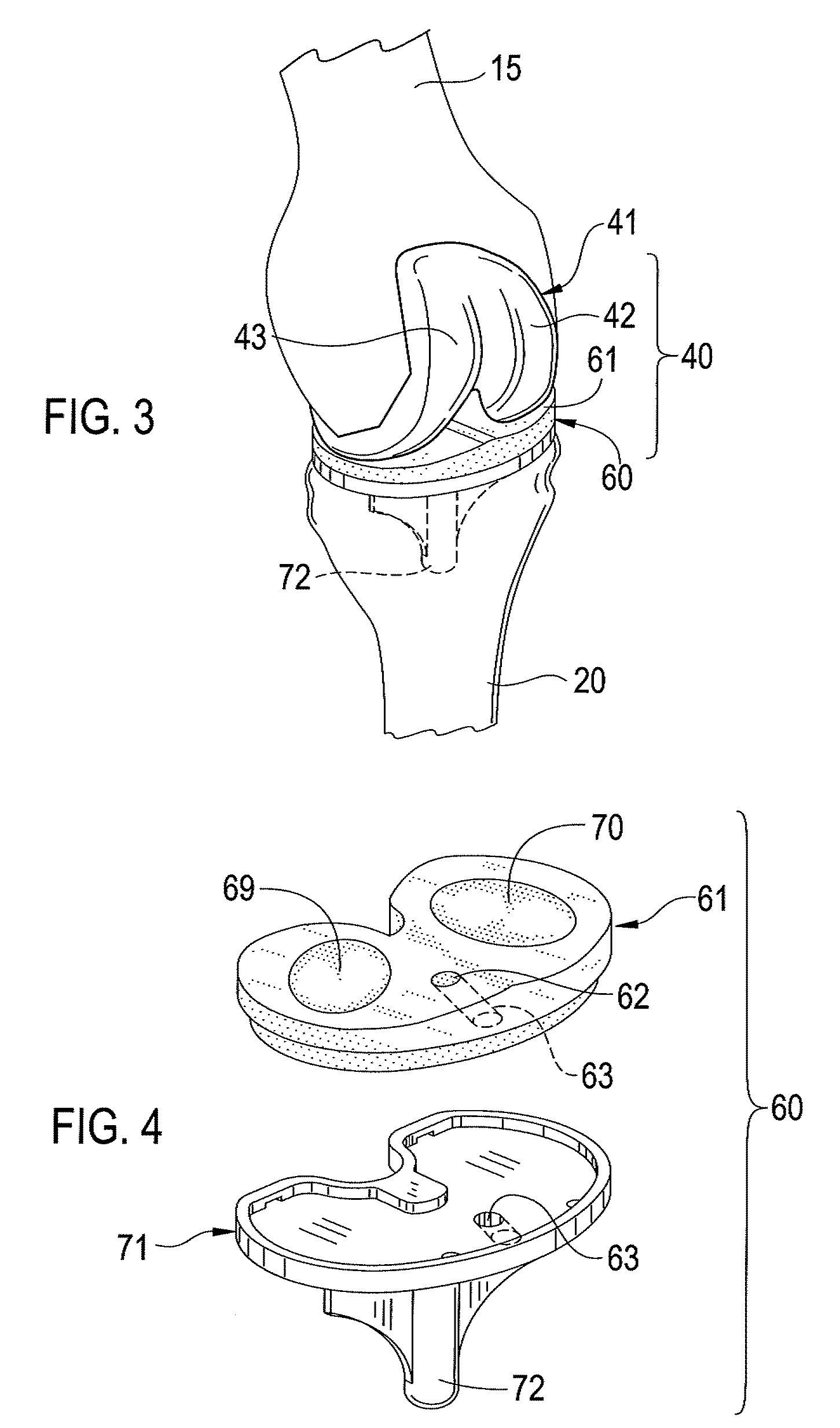
Anterior stabilized knee implant
A posterior cruciate ligament retaining knee implant prosthesis comprising a femoral component including a medial condyle and a lateral condyle separated from one another by an intercondylar channel adapted to accommodate throughput of a native cruciate ligament, both the medial condyle and the lateral condyle posteriorly terminate individually, the medial condyle including a medial condyle bearing surface and the lateral condyle including a lateral condyle bearing surface, the femoral component including an anterior cam, and a tibial component including a medial condyle receiver having a medial condyle receiver bearing surface, the tibial component also including a lateral condyle receiver having a lateral condyle receiver bearing surface, the tibial component also including an anterior post.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
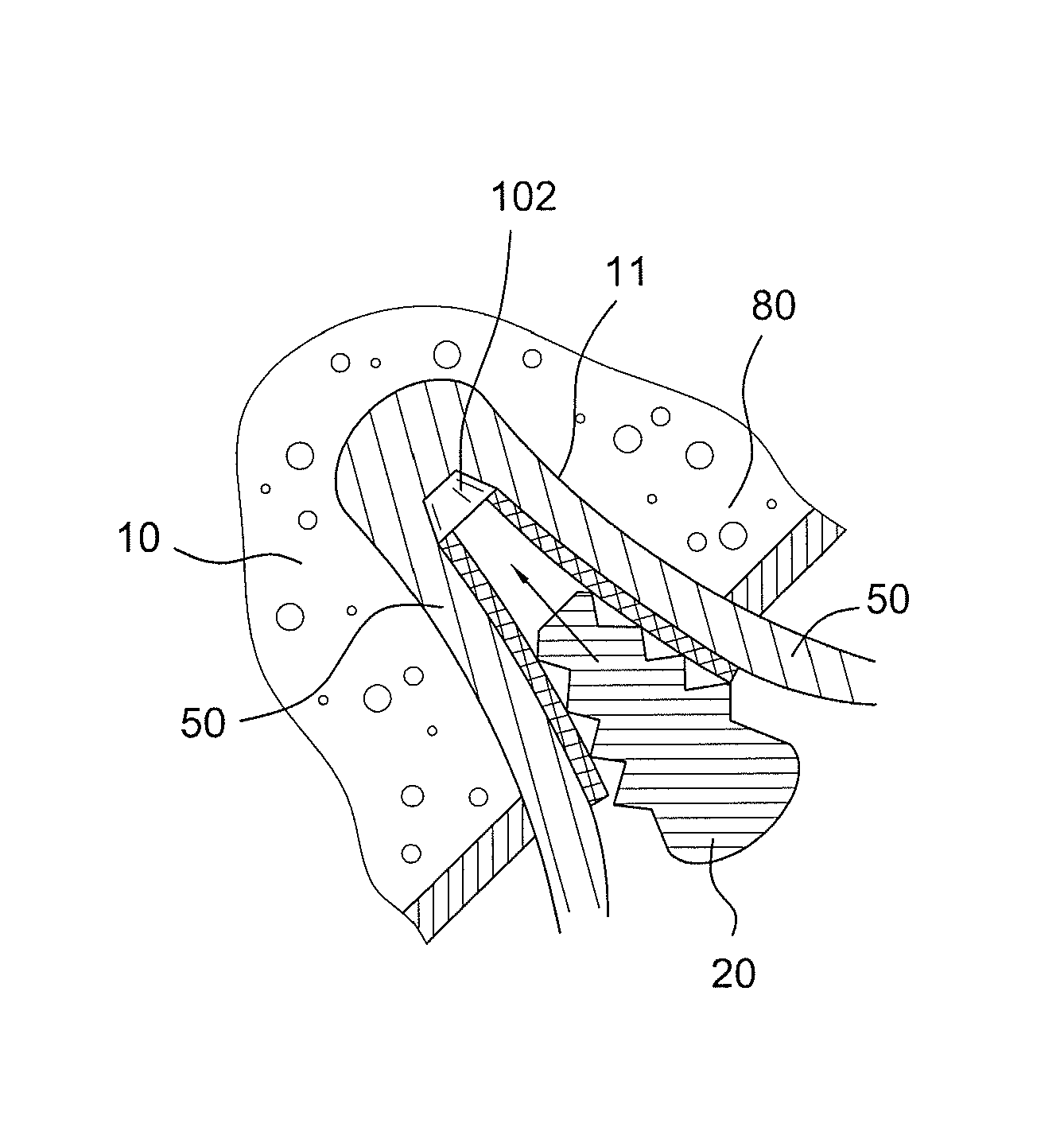
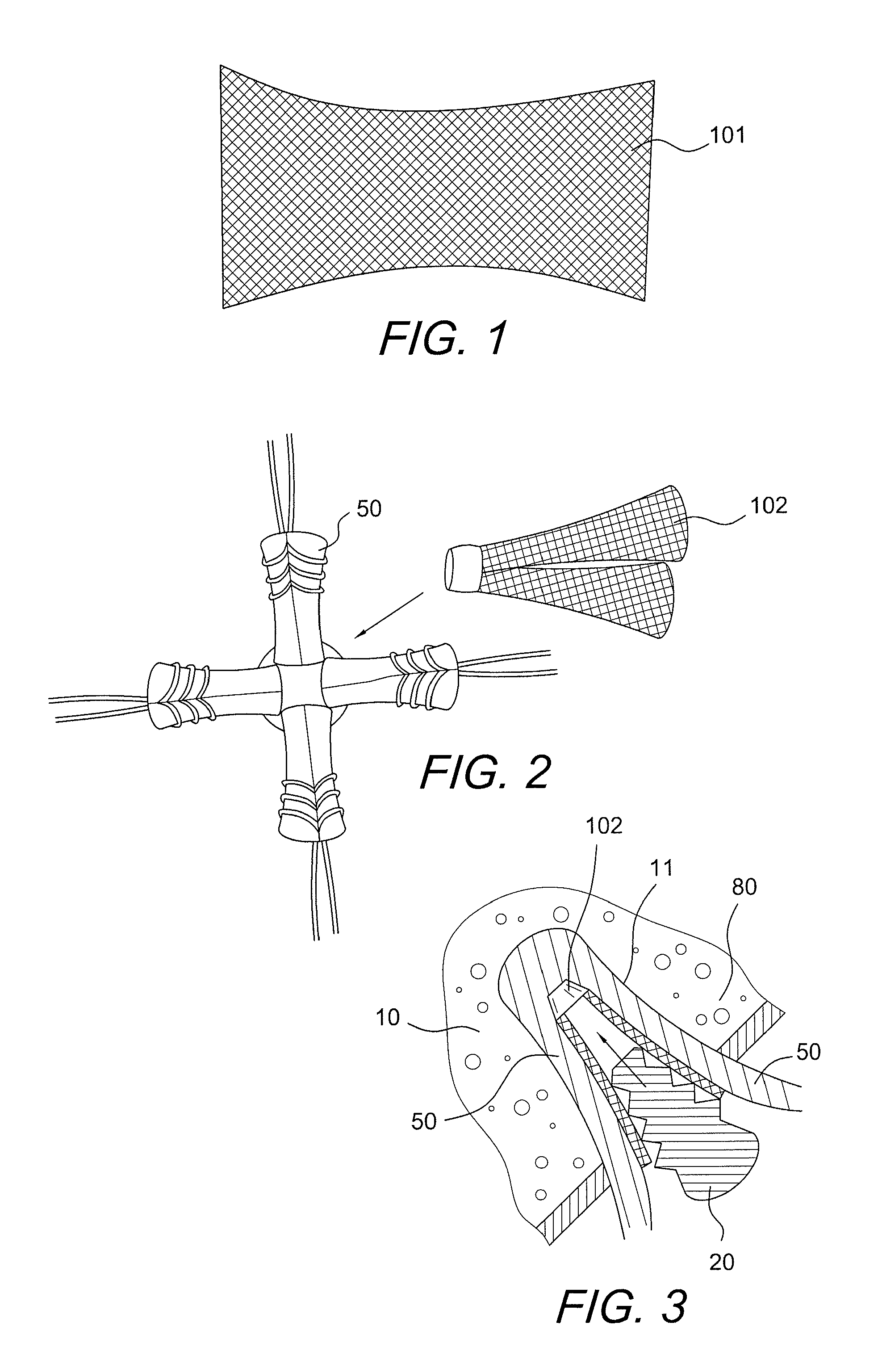
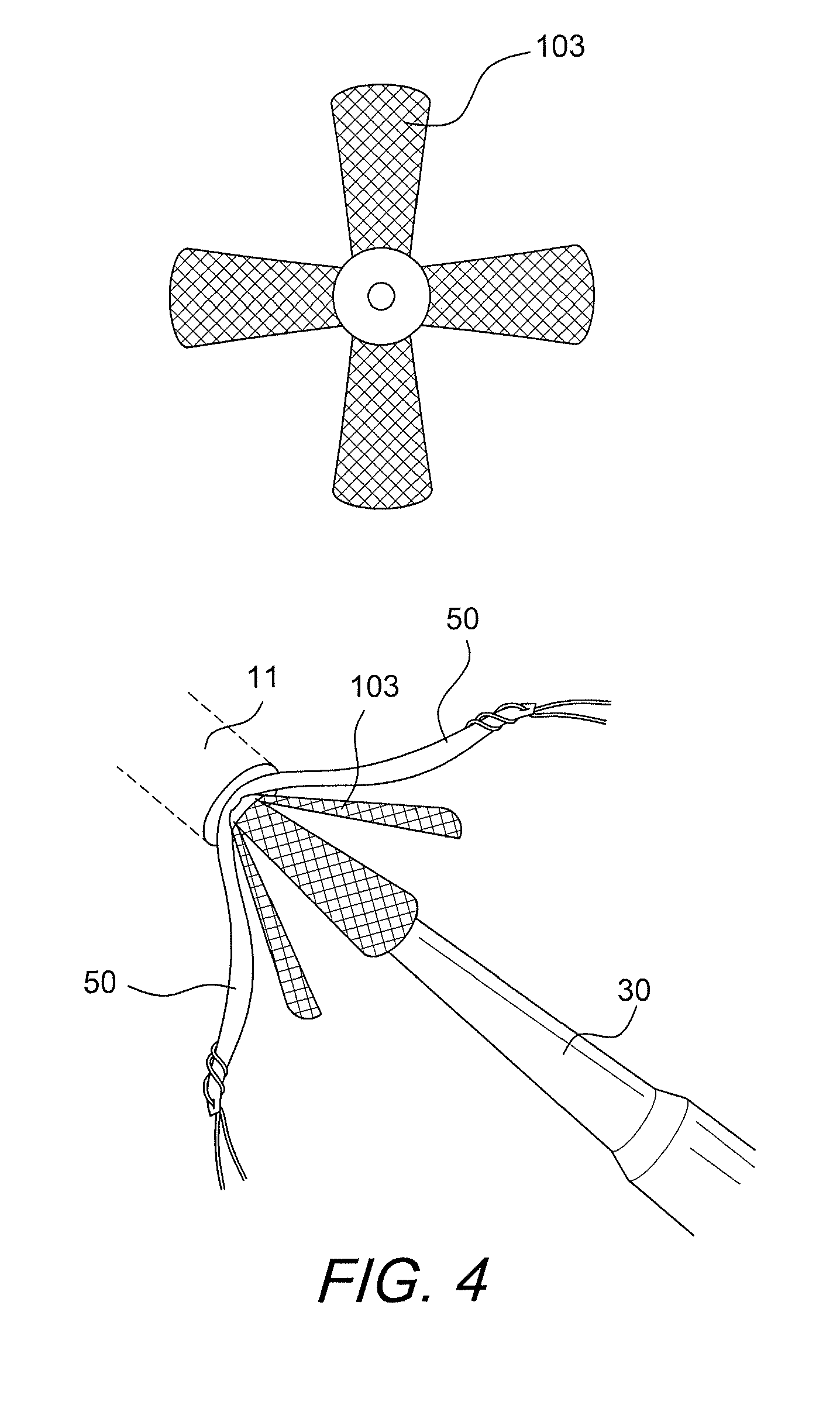
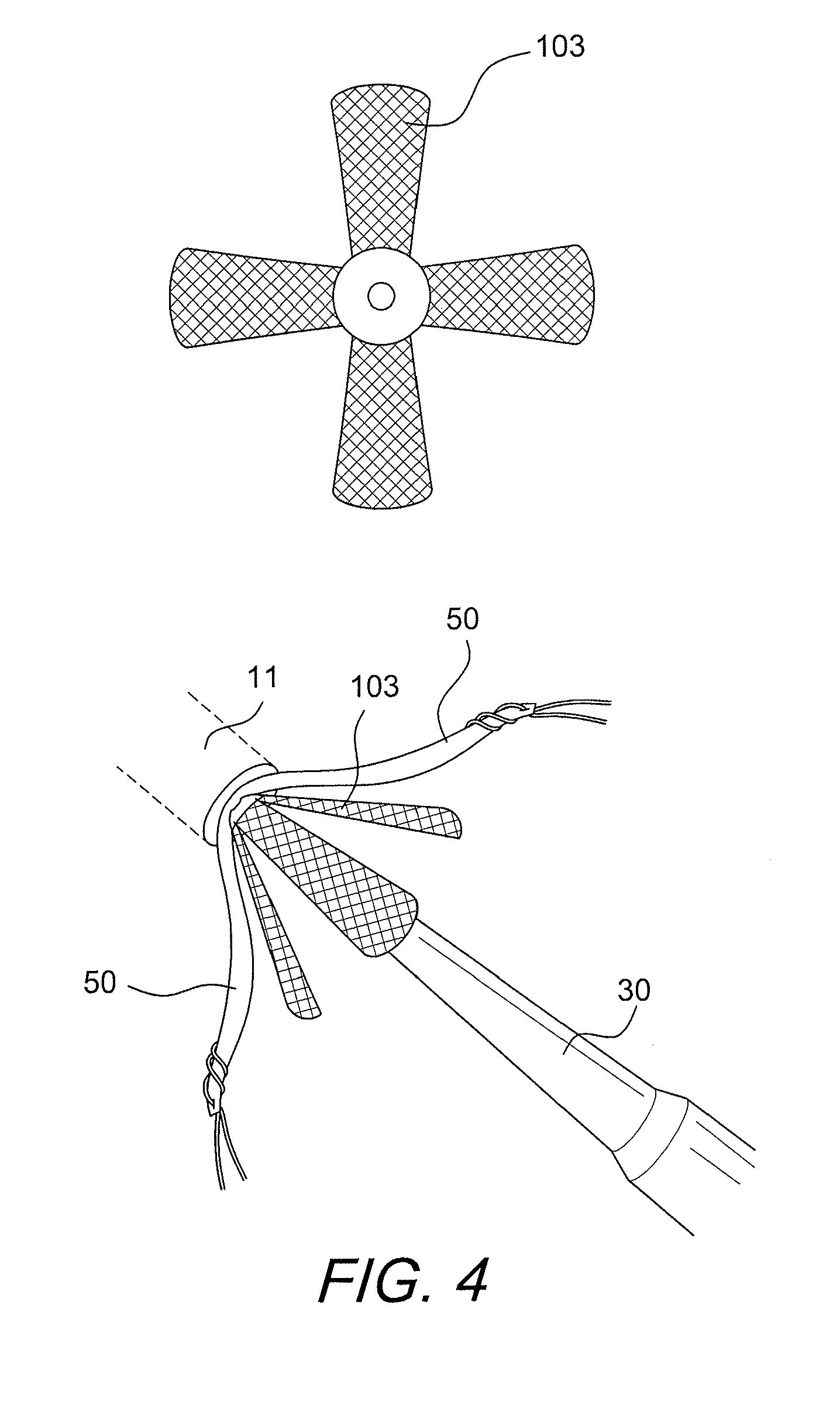
Graft protection mesh and fixation technique
ActiveUS8460350B2Improved strength and structural supportPromote resultsSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCruciate ligamentDouble bundle
A three-dimensional mesh or screen in the shape of a simple flat piece of material that can be provided adjacent the graft (i.e., in between graft bundles, or around the graft, or between the graft and the fixation device) for improved strength and structural support for graft fixation. The mesh provides improved methods for installing and securing ligament grafts (such as double-bundle cruciate ligament grafts) with enhanced reconstruction results.
Owner:ARTHREX
Total Knee Prosthesis and Method for Total Knee Arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a central femoral recess between the condyles providing access to the femur for drilling a channel through which a cruciate ligament substitute may be integrated into the femur. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through which the ligament substitute maybe threaded through the tibia and integrated therein, or anchored upon its surface. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
Anterior cruciate ligament tether
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Method of replacing an anterior cruciate ligament in the knee
A method of reconstructing a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament in a human knee. Femoral and tibial tunnels are drilled into the femur and tibia. A transverse tunnel is drilled into the femur to intersect the femoral tunnel. A filamentary loop is threaded through the femoral tunnel and tibial tunnel and partially through the transverse tunnel. A replacement graft is formed into a loop and moved into the tibial tunnels using a surgical needle and suture. A flexible filamentary member is simultaneously moved along with the loop into the femoral and transverse tunnels. The filamentary member is used as a guide wire in the transverse tunnel to insert a cannulated cross-pin to secure a top of the looped graft in the femoral tunnel.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US)
Single Tunnel, Double Bundle Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Using Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone Grafts
ActiveUS20110196490A1Accurate anatomical reconstructionLess complicatedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTibiaCruciate ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction methods and devices are designed to achieve an anatomically accurate double bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by using a single femoral and tibial tunnel. The method and devices reconstruct the two bundles of the anterior cruciate ligament in a single femoral and tibial tunnel using a bone-patellar tendon-bone graft. The methods and devices enable an accurate anatomical reconstruction of the anteromedial and posterolateral bundles by creating a single femoral and tibial tunnel as opposed to creating two tunnels in the tibia and femur.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and suture-button construct for stabilization of cranial cruciate ligament deficient stifle
An apparatus and method for stabilization of a cranial cruciate ligament deficient stifle in canines using a suture-button construct. The method includes the steps of drilling a femoral hole across a distal femur, passing a needle with a pull-through suture strand of a suture-button construct through the femoral hole, and applying a tensile force to the pull-through suture strand and a suture tape or strand of the construct such that a first button of the suture-button construct lies sideways for passage through the femoral hole, advancing the first button through the femoral hole by pulling the pull-through suture strand until the first button exits the femoral hole, drilling a tibial hole and passing the needle with the pull-through suture strand through the tibial hole, applying a tensile force to the pull-through suture strand and the suture tape or strand of the construct such that the first button lies sideways for passage through the tibial hole, flipping the first button to engage the first button against the medial tibial cortex and subsequently cutting and removing the pull-through suture strand, pulling free ends of the suture tape or strand to advance a second button of the suture-button construct and to seat the second button against the femur, and securing the second button against the femur.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method of replacing an anterior cruciate ligament in the knee
A method of reconstructing a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament in a human knee. Femoral and tibial tunnels are drilled into the femur and tibia. A transverse tunnel is drilled into the femur to intersect the femoral tunnel. A replacement graft is formed into a loop and moved into the femoral and tibial tunnels using a surgical needle and suture. A flexible filamentary member is simultaneously moved along with the loop into the femoral and transverse tunnels. The filamentary member is used as a guide wire in the transverse tunnel to insert a cannulated cross-pin to secure a top of the looped graft in the femoral tunnel.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Double bundle ACL repair system
ActiveUS8535377B2Facilitate circumferential healingIncreased complexitySuture equipmentsLigamentsBone tunnelTibia
A system for single tunnel, double bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction includes implant constructs and instruments. The implant constructs provide a combination of cortical fixation and bone tunnel aperture fixation. The implant constructs separate a graft into distinct bundles. The instruments are used to prepare shaped bone tunnels to receive the implant constructs and graft bundles. Methods for reconstructing the antero-medial and postero-lateral bundles of the anterior cruciate ligament may rely on single femoral and tibial tunnels and a single strand of graft.
Owner:MYERS THOMAS H +1
Femoral Guide and Methods of Precisely Forming Bone Tunnels in Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction of the Knee
InactiveUS20010016746A1Precise positioningShorten the timeJoint implantsLigamentsBone tunnelCruciate ligament
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A femoral guide for precisely positioning a guide wire on a bone surface of the femur includes a body having a lumen for receiving a guide wire and a tongue protruding from the body for engaging an edge or reference point on the bone surface with the tongue being spaced a predetermined distance from a longitudinal axis of the lumen. The lumen includes an opening allowing a guide wire extending through the lumen to contact the bone surface at a location spaced from the edge substantially the predetermined distance with the tongue engaging the edge. A stylus on the body can be driven into the bone to secure and stabilize the femoral guide prior to driving the guide wire into the bone through the lumen. With the guide wire driven into the bone, a bone tunnel can be formed substantially concentrically or coaxially along the guide wire such that a longitudinal axis of the bone tunnel will be disposed from the edge substantially the predetermined distance. Methods of precisely forming bone tunnels include the steps of engaging an edge of a bone surface with a tongue of the femoral guide, inserting a guide wire through a lumen of the femoral guide, driving the guide wire into the bone through the lumen and forming a bone tunnel in the bone along the guide wire such that a longitudinal axis of the bone tunnel will be disposed from the edge engaged by the tongue a distance substantially equal to the distance that the tongue is disposed from a longitudinal axis of the lumen.
Owner:MCGUIRE DAVID A +1
Method of replacing an anterior cruciate ligament in the knee
A method of reconstructing a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament in a human knee. Femoral and tibial tunnels are drilled into the femur and tibia. A transverse tunnel is drilled into the femur to intersect the femoral tunnel. A replacement graft is formed into a loop and moved into the femoral and tibial tunnels using a surgical needle and suture. A flexible filamentary member is simultaneously moved along with the loop into the femoral and transverse tunnels. A pin passing member maintains one end of the filamentary wire in the transverse tunnel as the graft is being moved into place in the femoral and tibial tunnels. The filamentary member is used as a guide wire in the transverse tunnel to insert a cannulated cross-pin to secure a top of the looped graft in the femoral tunnel.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US)
Method of replacing an anterior cruciate ligament in the knee
A method of reconstructing a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament in a human knee. Femoral and tibial tunnels are drilled into the femur and tibia. A transverse tunnel is drilled into the femur to intersect the femoral tunnel. A replacement graft is formed into a loop and moved into the femoral and tibial tunnels using a surgical needle and suture. A flexible filamentary member is simultaneously moved along with the loop into the femoral and transverse tunnels. A pin passing member maintains one end of the filamentary wire in the transverse tunnel as the graft is being moved into place in the femoral and tibial tunnels. The filamentary member is used as a guide wire in the transverse tunnel to insert a cannulated cross-pin to secure a top of the looped graft in the femoral tunnel.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US)
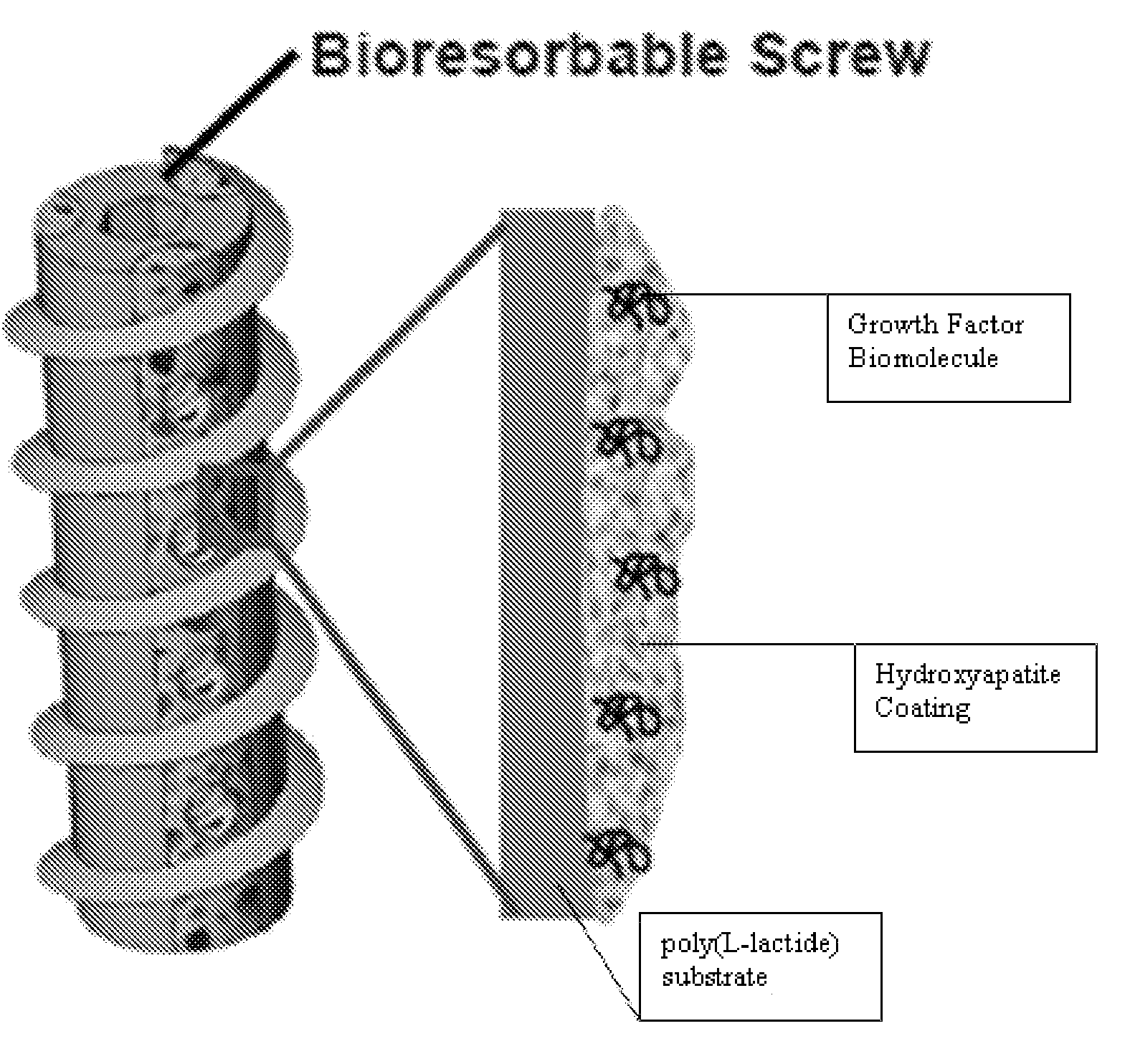
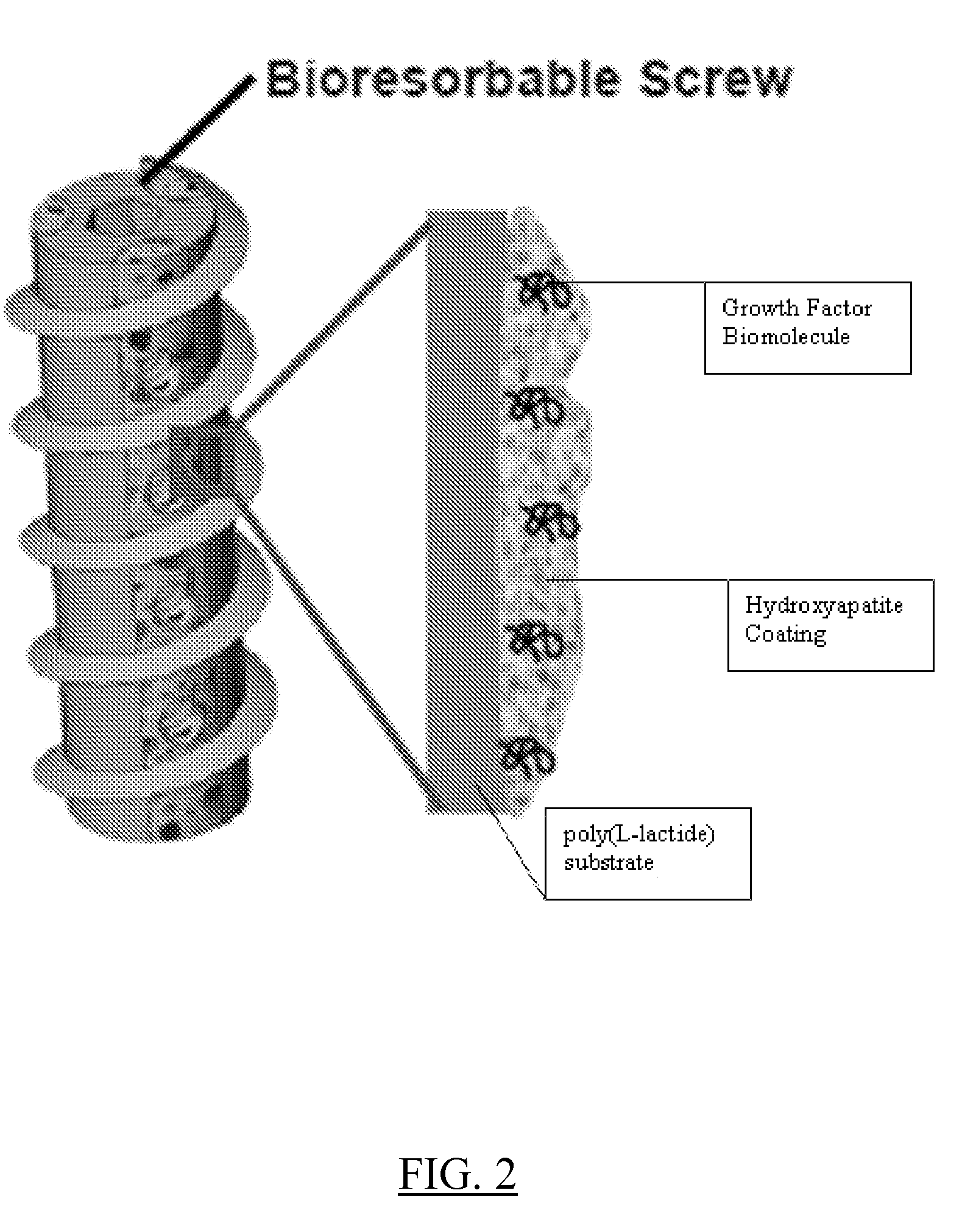
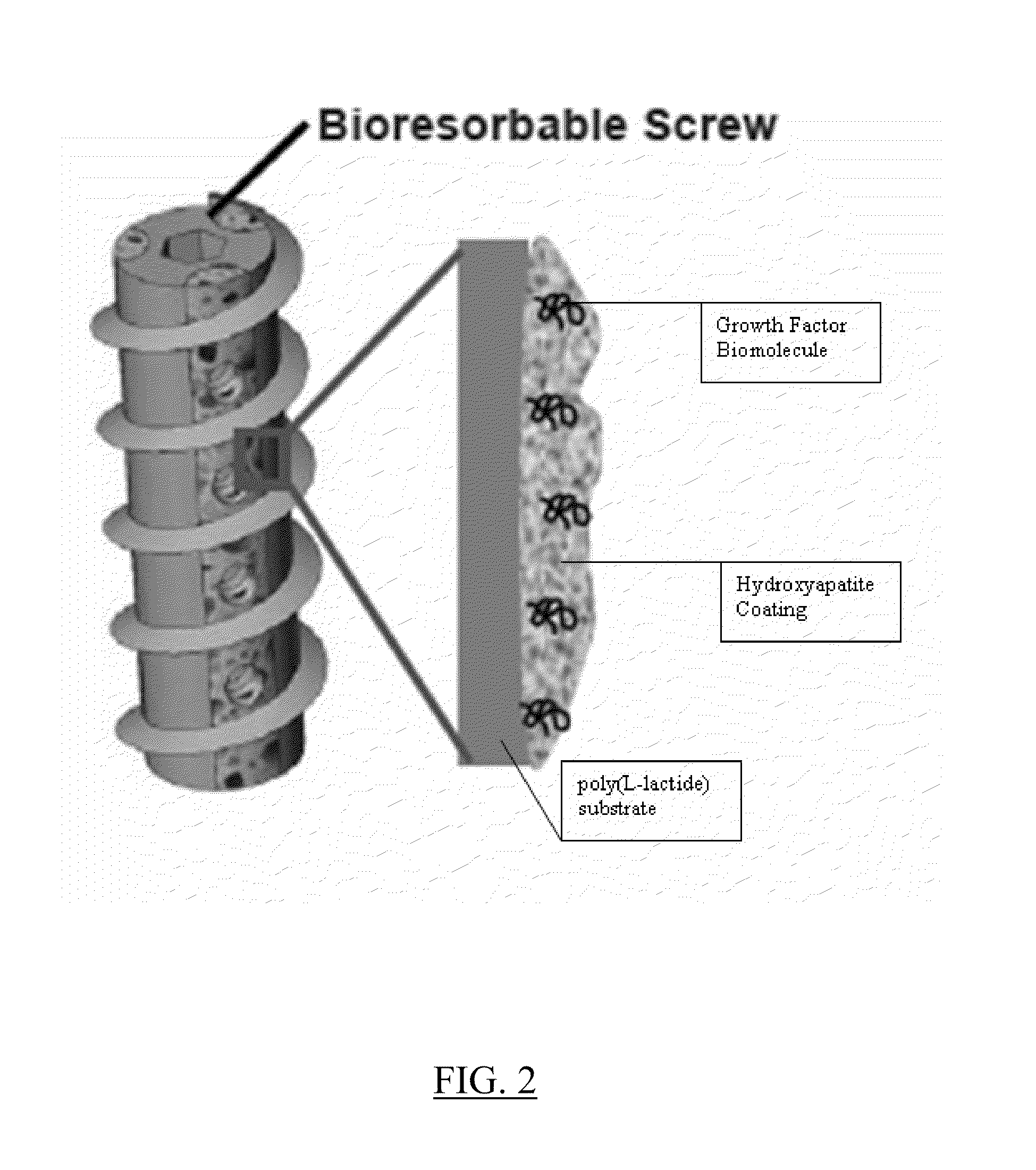
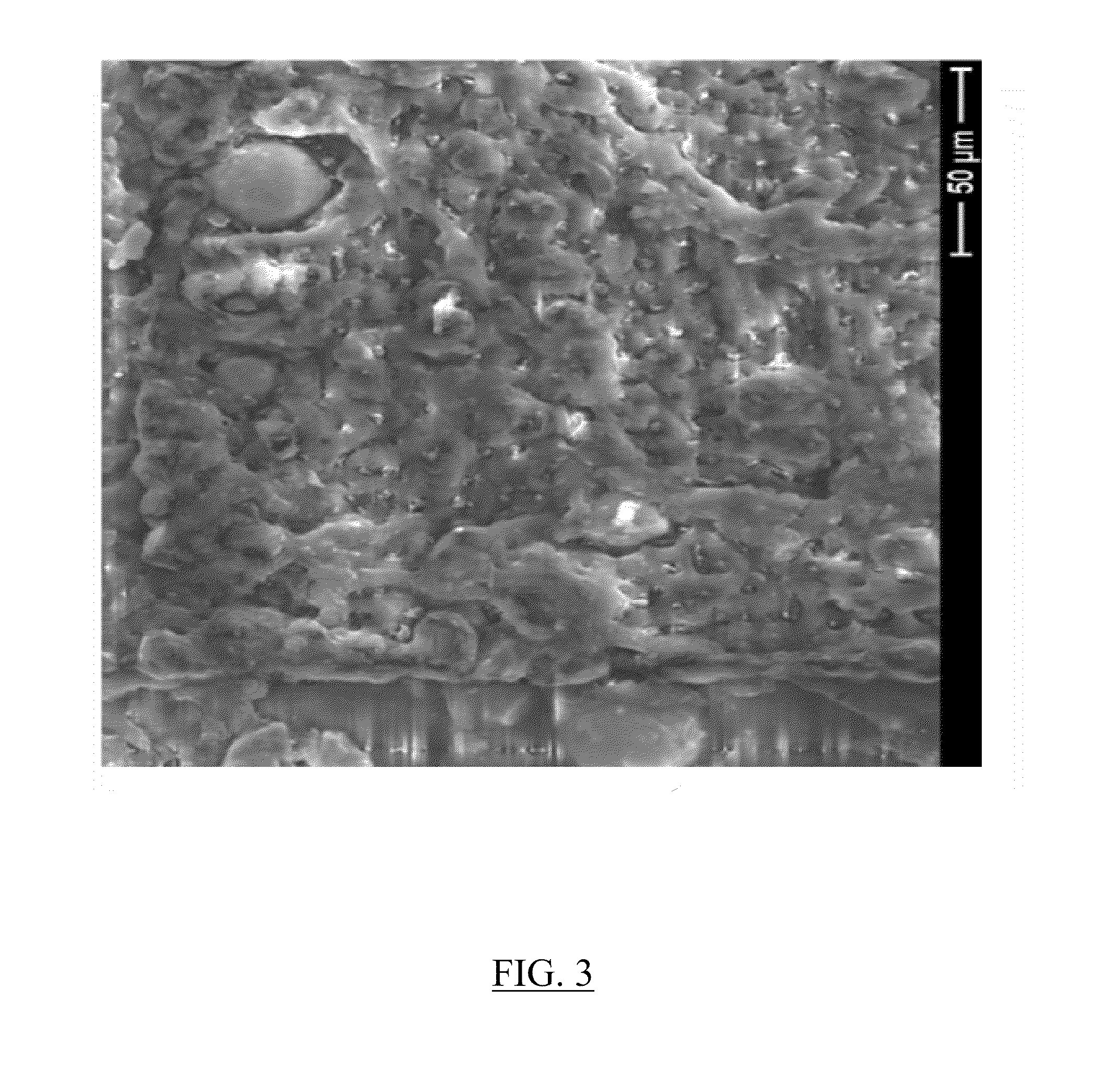
Controlled release of biopharmaceutical growth factors from hydroxyapatite coating on bioresorbable interference screws used in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery
Controlled release of biopharmaceutical growth factors from a hydroxyapatite coating on a bioresorbable interference screw used in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery on a human. Biologically active scaffolds, such as interference bone screws used for ligament fixation, made by growing calcium phosphate-based hydroxyapatite coatings on bioresorbable poly(α-hydroxy ester) scaffolds that provide controlled mineral dissolution and controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2. The biologically active scaffold provides improved bioavailability of BMP-2 growth factor that in turn provides enhanced graft-bone healing in the tibial bone tunnel. The coating method uses surface hydrolysis and modified simulated body fluid incubation which does not require solvent or heat and is conducted at room temperature.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Tibia tunnel locating device and method based on personalized navigation template
ActiveCN104083204AIncrease success ratePrevent the error from being magnified when drilling into the tunnelDiagnosticsOsteosynthesis devicesCruciate ligamentPersonalization
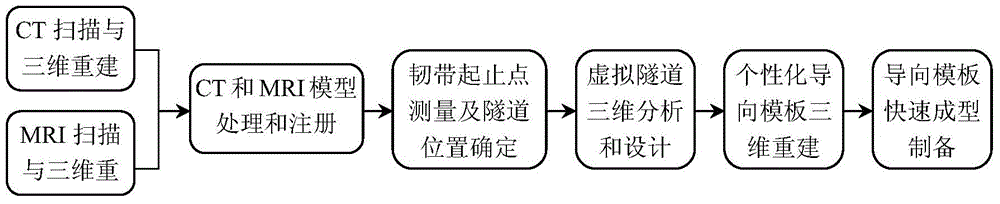
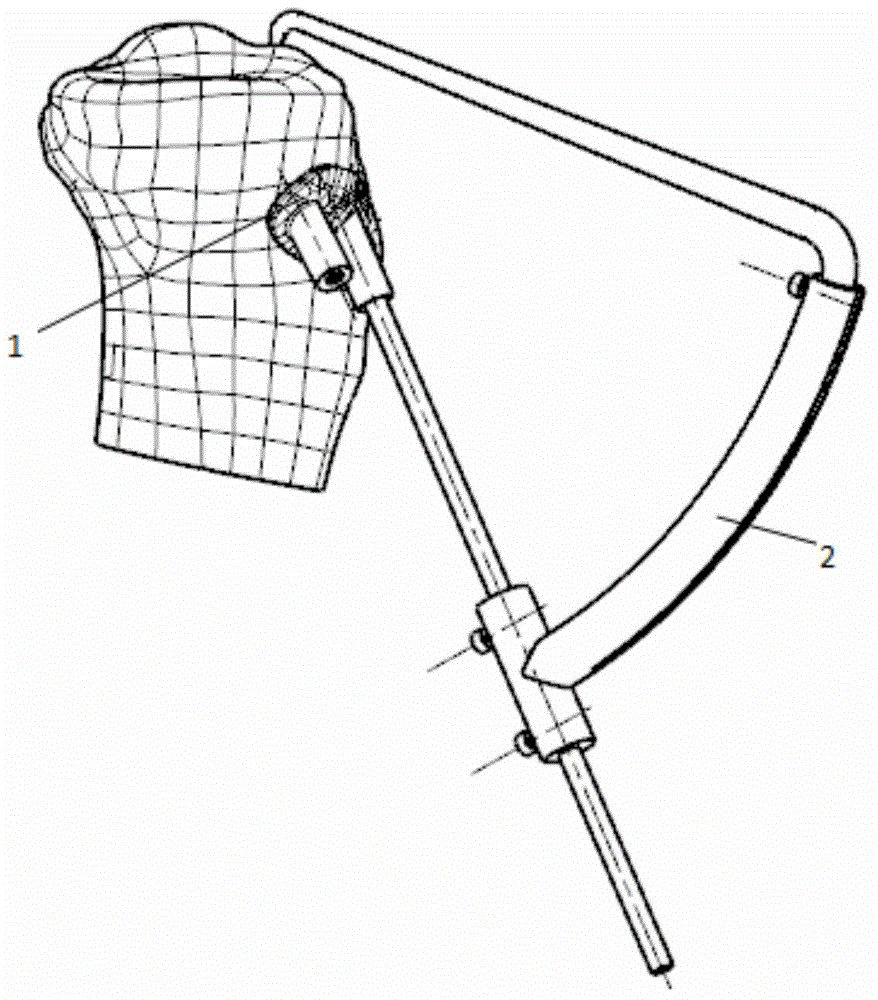
The invention relates to a tibia tunnel locating device and method based on a personalized navigation template and belongs to cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. The method comprises the steps that firstly, CT data and MRI data of a patient are collected, a data model is processed, and three-dimensional reestablishment is conducted on the data model; secondly, according to the three-dimensional model, the position of a tunnel is measured and determined, a bone surface needed by locating is obtained through partition, and a navigation template model is established; thirdly, the navigation template is manufactured through the rapid forming technology; finally, locating and verification are conducted through the navigation template and a locating device of a guider, and then a Kirschner wire is inserted through drilling. According to the tibia tunnel locating device and method based on the personalized navigation template, the navigation template is easy to locate and easy to operate, due to the auxiliary locating calibration of the guider, it is avoided that the error of the Kirschner wire inserted into the inner opening of the tunnel through drilling is amplified due to navigation template catheter small-angle swing deviation caused by soft tissues residues and other factors, the locating precision can be effectively guaranteed, and the surgical effect is more reliable.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Regenerative implant of cruciate ligament and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a regenerative implant of a cruciate ligament and a preparation method and application thereof. A surgical suture-shaped structure made of a degradable high molecule polymerization material is used as an initial mechanical support structure; a membrane-shaped structure made of a composite electrostatic spinning timbering material is used as a core structure for tissue remodeling and regeneration to be tightly wrapped in a winding mode on the initial mechanical support structure so as to form ligament regeneration elements; the multiple ligament regeneration elements form a ligament regeneration element set which is the regenerative implant of the ligament. The results of a goat animal experiment confirms that the implant is completely degraded within 52 weeks after being implanted to an organism, is induced to form an autogenous ligament tissue in the cavity of a knee joint, and induces the bone tunnel interface of a tibia and a femur to form tendon-bone healing; the maximum pulling force of the regenerated ligament is 20-60% that of a normal ligament tissue within 12 months after the implant is implanted to the organism.
Owner:SHANGHAI P & P BIOTECH
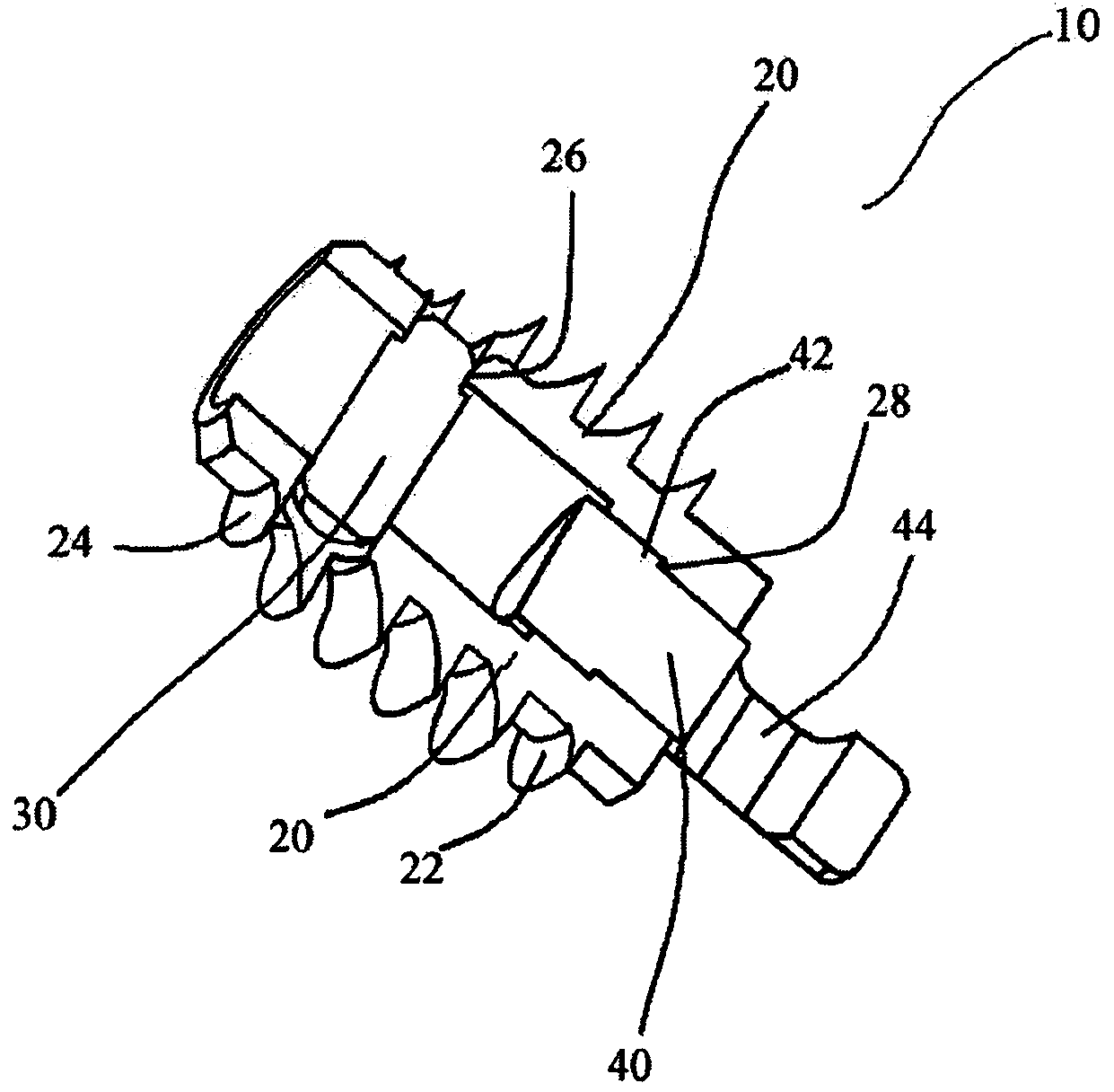
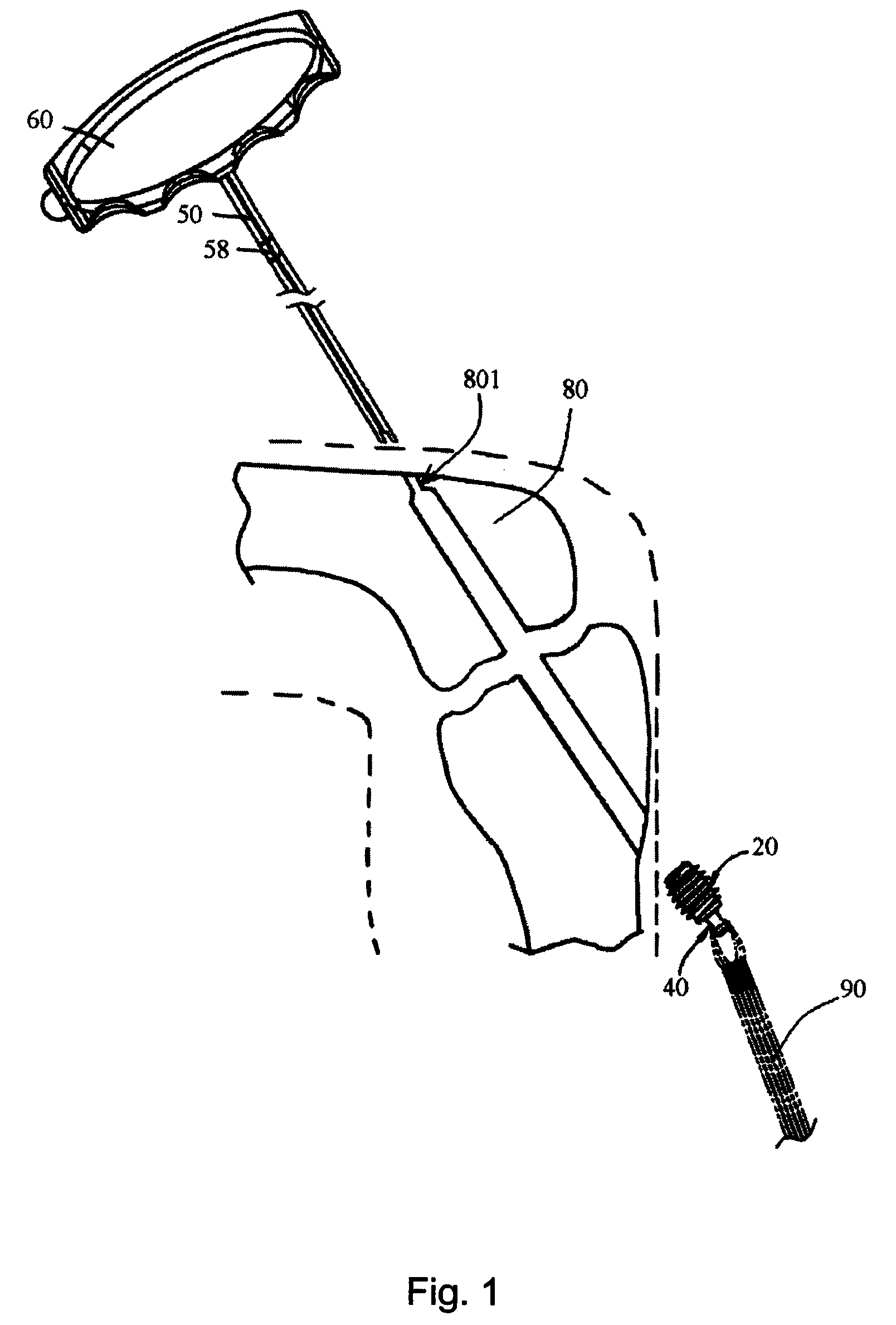
Graft attachment device for ligament reconstruction
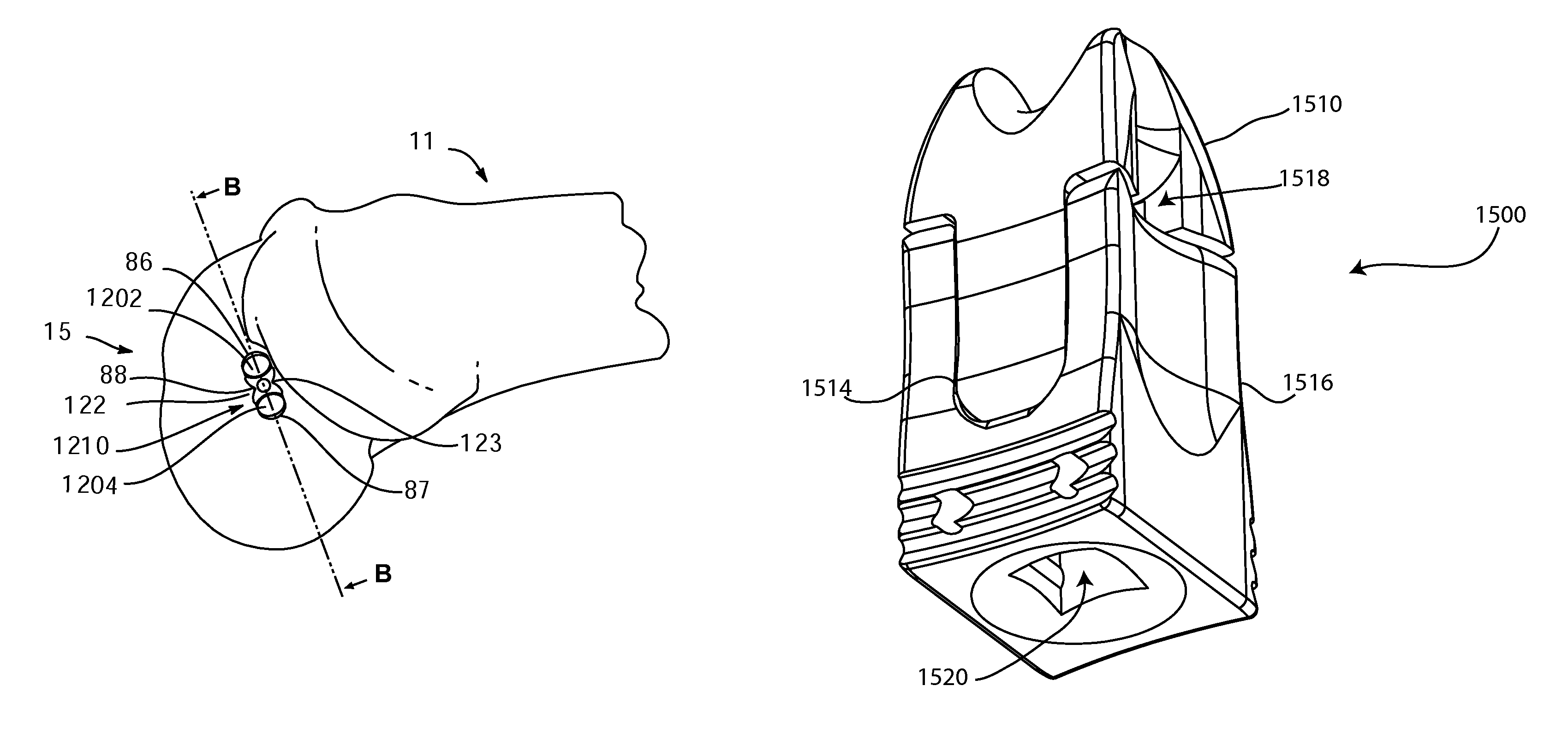
InactiveUS20100217389A1Easy to operateAvoid formingLigamentsMusclesCruciate ligamentSutural ligament
The present invention discloses a graft attachment device for cruciate ligament reconstruction comprises a body having a screw portion with a threading area on the front end of the body, a connection member disposed on the front end, a gap formed between the front end and a predetermined portion of the body adapted for a rope-type member pass through, a pivoting member pivoted on the rear end of the body with its front end, the rear end of the pivoting member having a juncture portion for fixing a ligament, thereby the device could be screwed and fixed on a bone when rotating the device, and seamed a ligament on the rear end of the device.
Owner:NATIONAL YANG MING UNIVERSITY
Tensile integrated bionic knee joint
ActiveCN106361475ALimit the range of motion of bionic jointsAchieve swingProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsRubber materialCruciate ligament
The invention discloses a tensile integrated bionic knee joint which comprises a first rigid compression unit, a stay rope unit and a second rigid compression unit, wherein the first rigid compression unit is composed of a first rigid compression unit main body, a first support rod, a second support rod, a third support rod and a fourth support rod; the stay rope unit is composed of a first bionic cruciate ligament, a second bionic cruciate ligament, a bionic accessory ligament, a first stay rope and a second stay rope. According to the tensile integrated bionic knee joint, through the cooperative use of the bionic ligaments and other stay ropes, a rigid connecting shaft in the middle of the joint is avoided while realizing the movement of the joint on a sagittal plane, so that the friction and wearing between rigid bodies do not exist when the joint moves, and the service life of the joint is prolonged. Meanwhile the stay rope unit is made of rubber materials, has strong elasticity, can absorb a certain impact loads in the working process and improves the stability.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method and suture needle construct for cruciate ligament repair
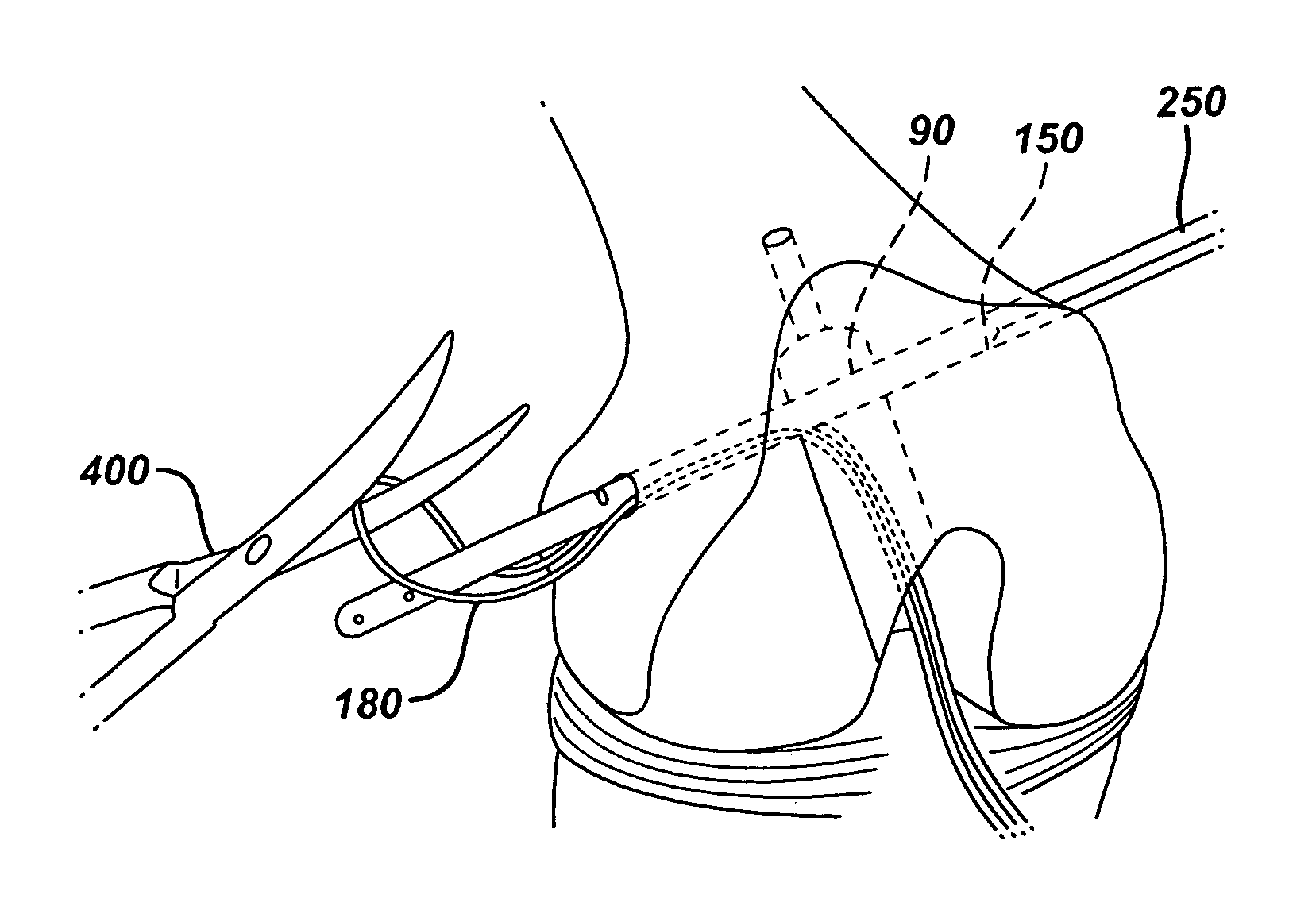
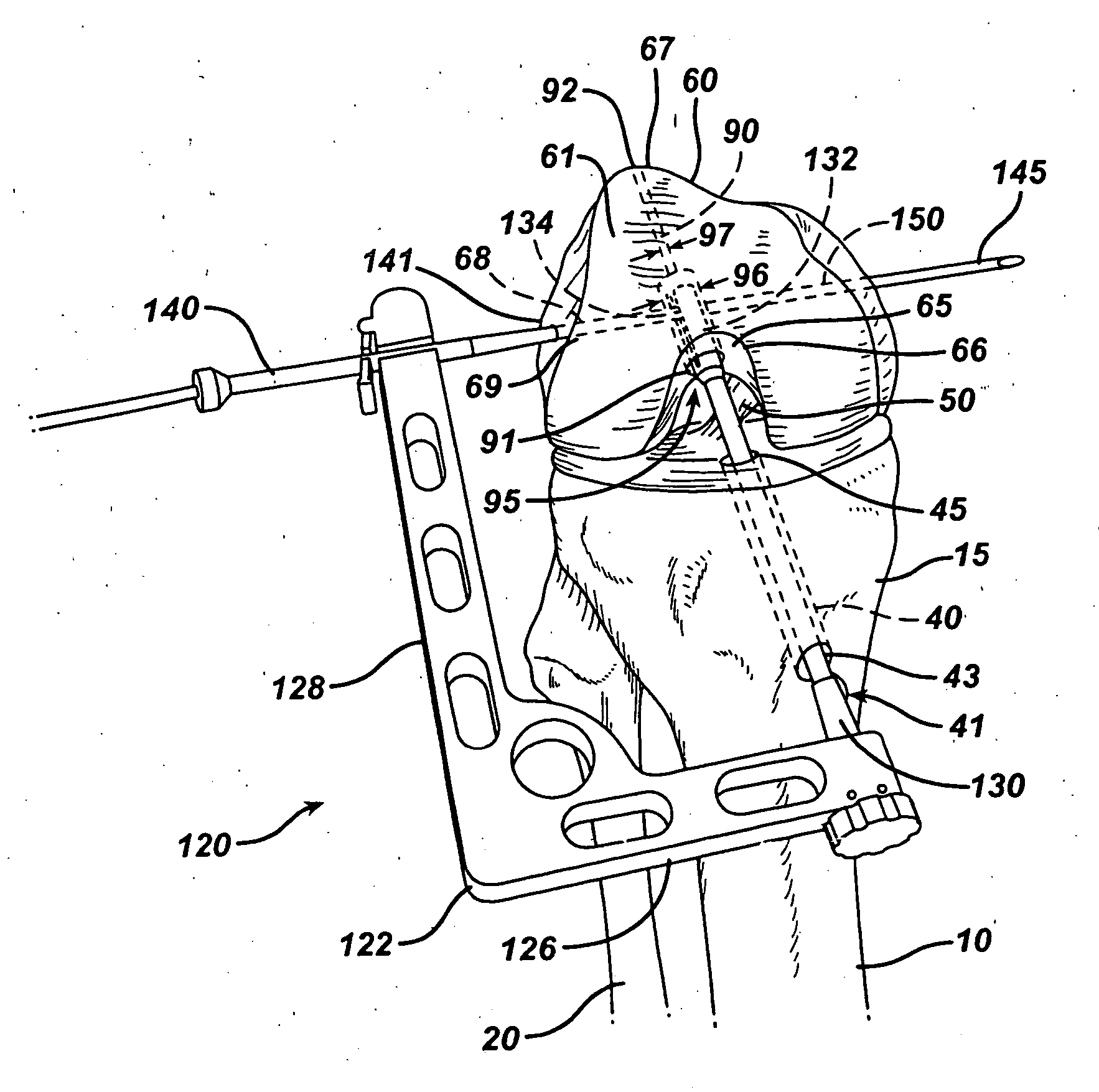
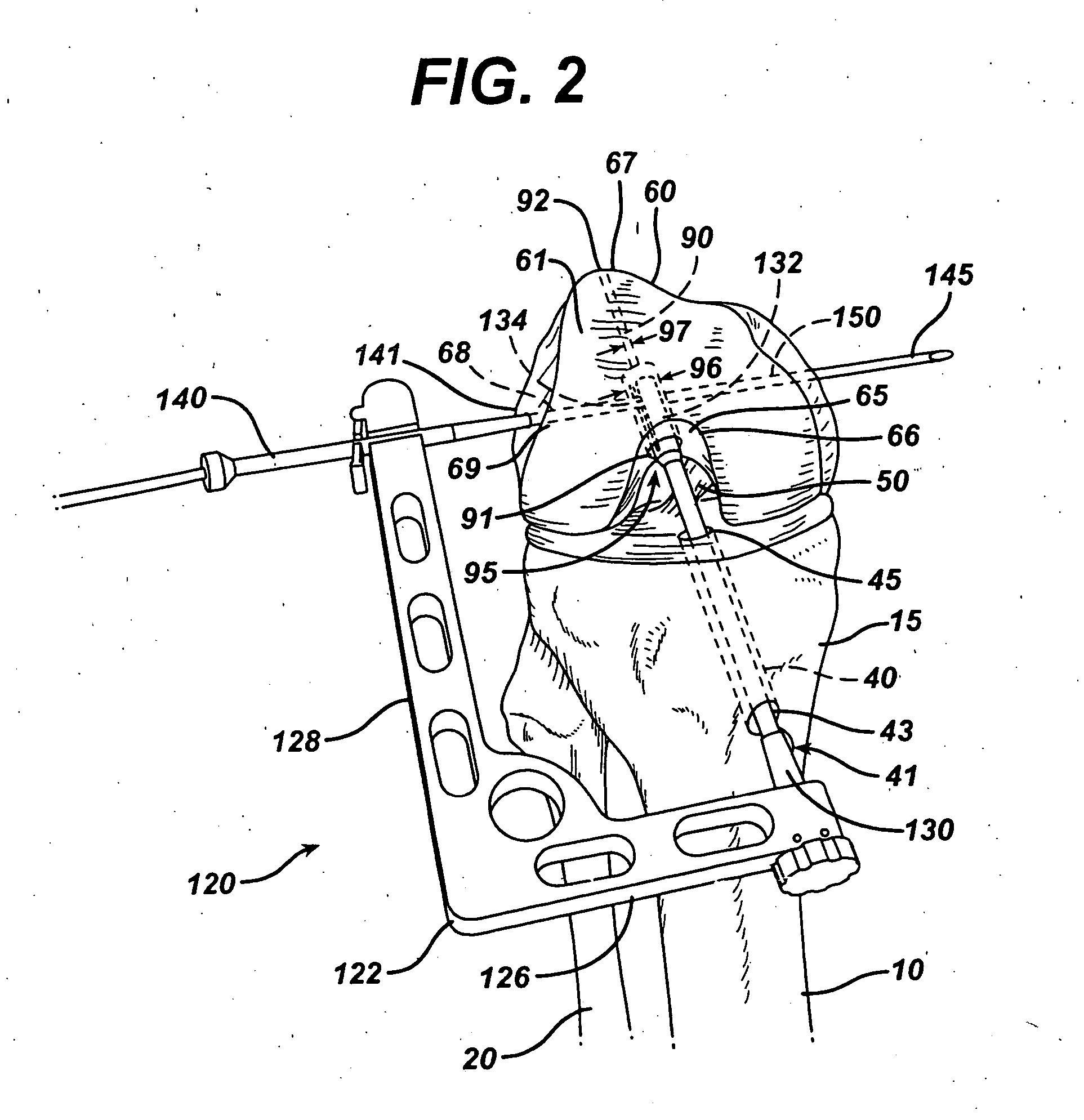
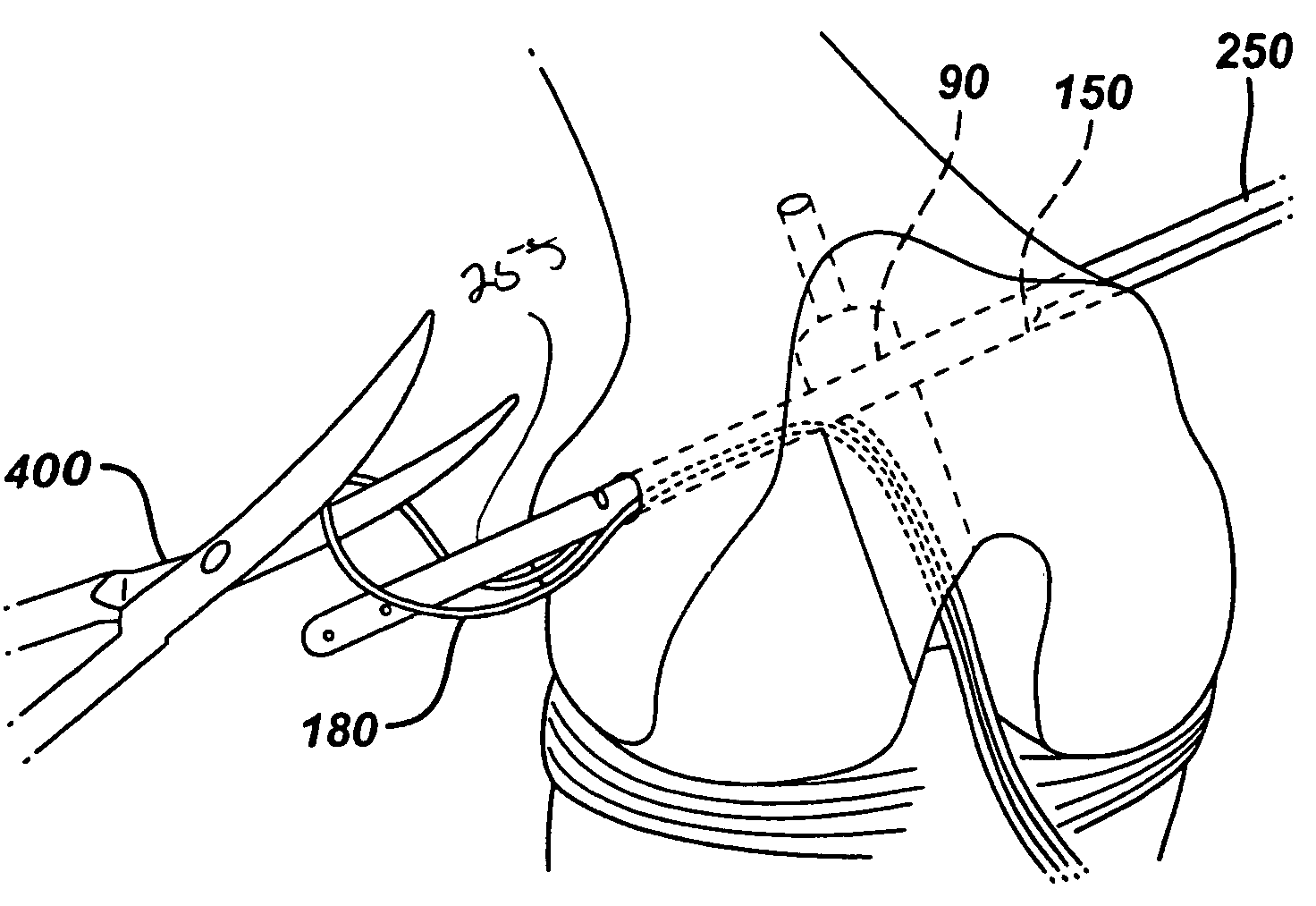
A suture needle construct and method for extracapsular ligament reconstruction in mammals. The joint is first is first explored, and the damaged ligament and meniscus are debrided. The joint capsule is closed and a tunnel is created at the appropriate location in the proximal tibia for tibial fixation. Subsequent to the formation of the tibial tunnel, a suture having a substantially curved needle at one end and a substantially straight needle at the other end is brought in the proximity of the joint. The suture is passed around the lateral fabella using the substantially curved needle, then deep to the patellar ligament using the substantially straight needle, and through the tibial tunnel using the straight needle. The needles are cut off, and the sutures are tensioned over repair site.
Owner:ARTHREX
Graft protection mesh and fixation technique
ActiveUS20100324608A1Easy to fixDecrease insertion torqueSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCruciate ligamentLigament structure
A three-dimensional mesh or screen in the shape of a simple flat piece of material that can be provided adjacent the graft (i.e., in between graft bundles, or around the graft, or between the graft and the fixation device) for improved strength and structural support for graft fixation. The mesh provides improved methods for installing and securing ligament grafts (such as double-bundle cruciate ligament grafts) with enhanced reconstruction results.
Owner:ARTHREX
Endoprosthesis for reestablishment of knee joint cruciate ligaments under full arthroscope
ActiveCN105055049AAvoid the disadvantage of low healing rateGood curative effectLigamentsMusclesCruciate ligamentTibia
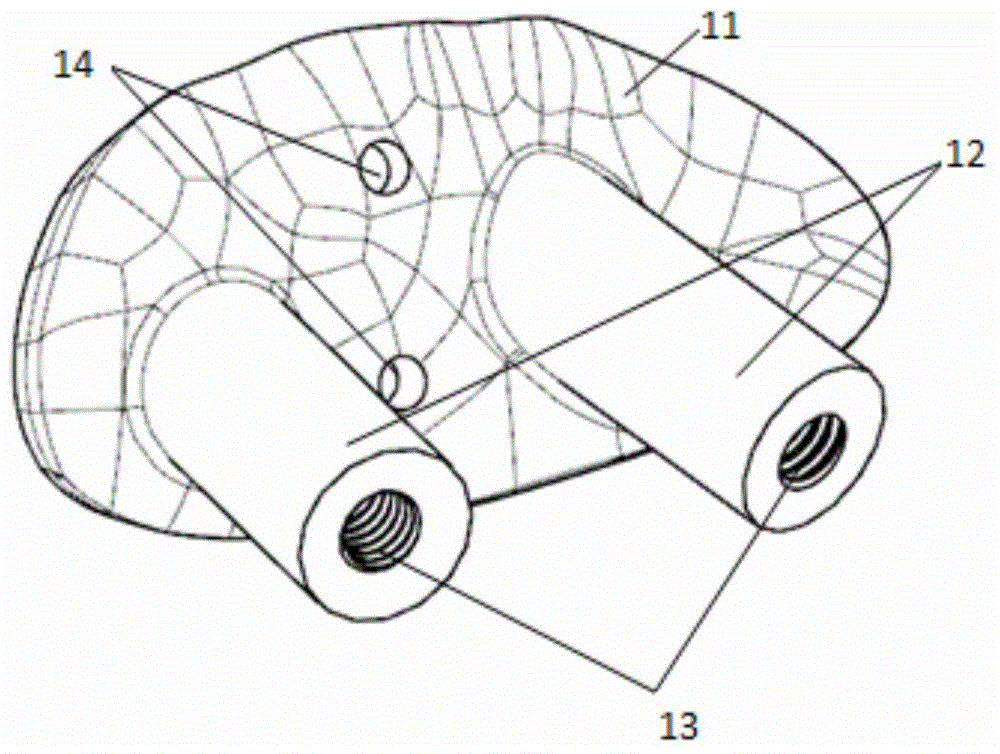
The invention discloses an endoprosthesis for reestablishment of knee joint cruciate ligaments under a full arthroscope. The endoprosthesis comprises a first bolt prosthesis and a second bolt prosthesis which are connected to a thighbone and a shinbone respectively, wherein an artificial tendon prosthesis is connected between the first bolt prosthesis and the second bolt prosthesis; each of the first bolt prosthesis and the second bolt prosthesis comprises a bolt prosthesis front section and a bolt prosthesis back section, and the bolt prosthesis front section and the bolt prosthesis back section are in detachable connection with each other; the bolt prosthesis front section is provided with a self-tapping external thread capable of tapping into the thighbone and the shinbone; the outer surface of the bolt prosthesis back section is provided with an external thread continuously butted with the self-tapping external thread of the bolt prosthesis front section, and adopts a material capable of growing together with bones; and muscle tendon fixation forcing screws are arranged between the first bolt prosthesis and the artificial tendon prosthesis and between the second bolt prosthesis and the artificial tendon prosthesis. Physical fixation and biological fixation are combined to realize the reestablishment of the knee joint cruciate ligaments without establishing a bone channel penetrating through the thighbone, a knee joint cavity and the shinbone, so that operation difficulty is obviously reduced, various complications are avoided, the tensile force of the reestablished artificial ligaments can be adjusted, the operation accuracy is improved and the operation curative effect is promoted.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
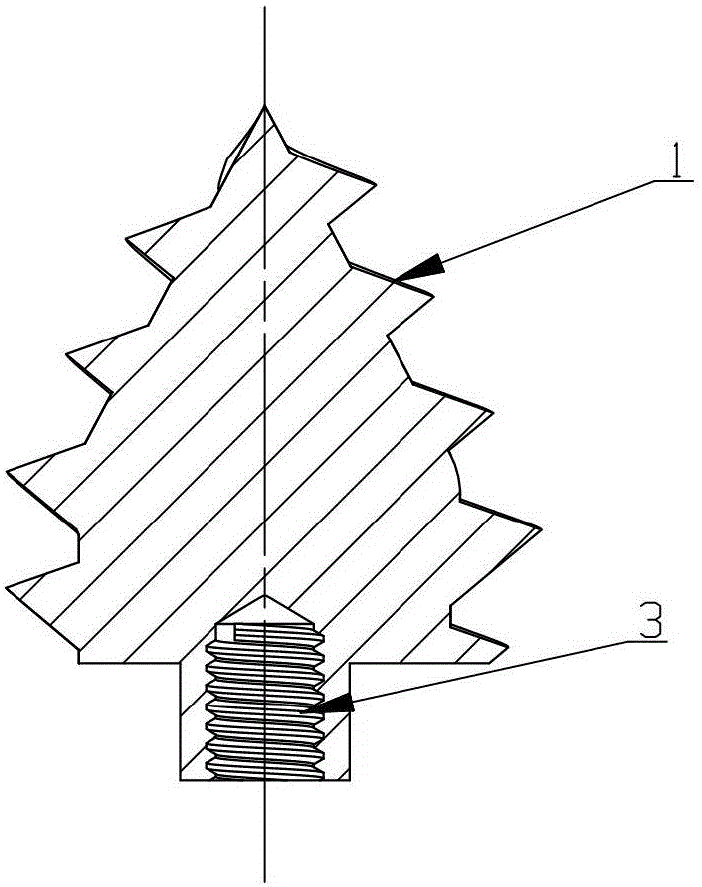
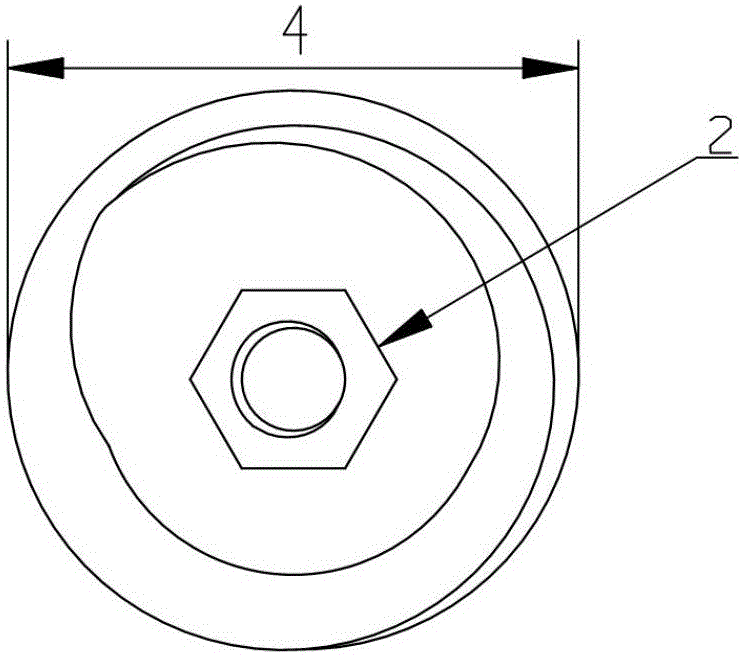
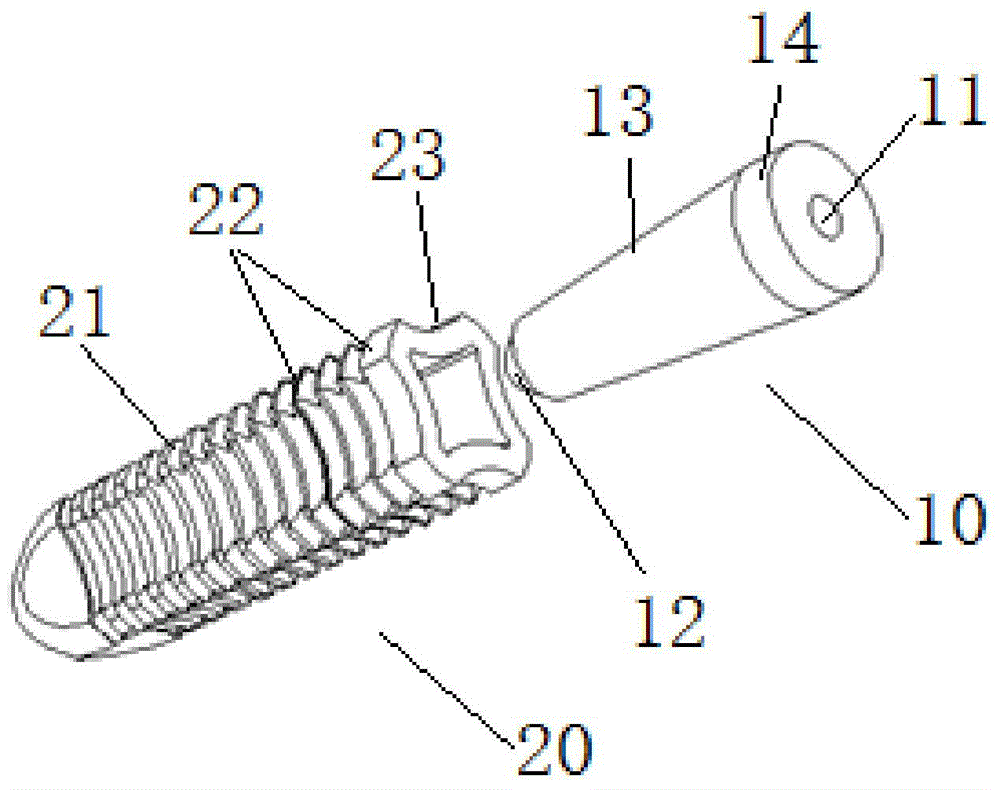
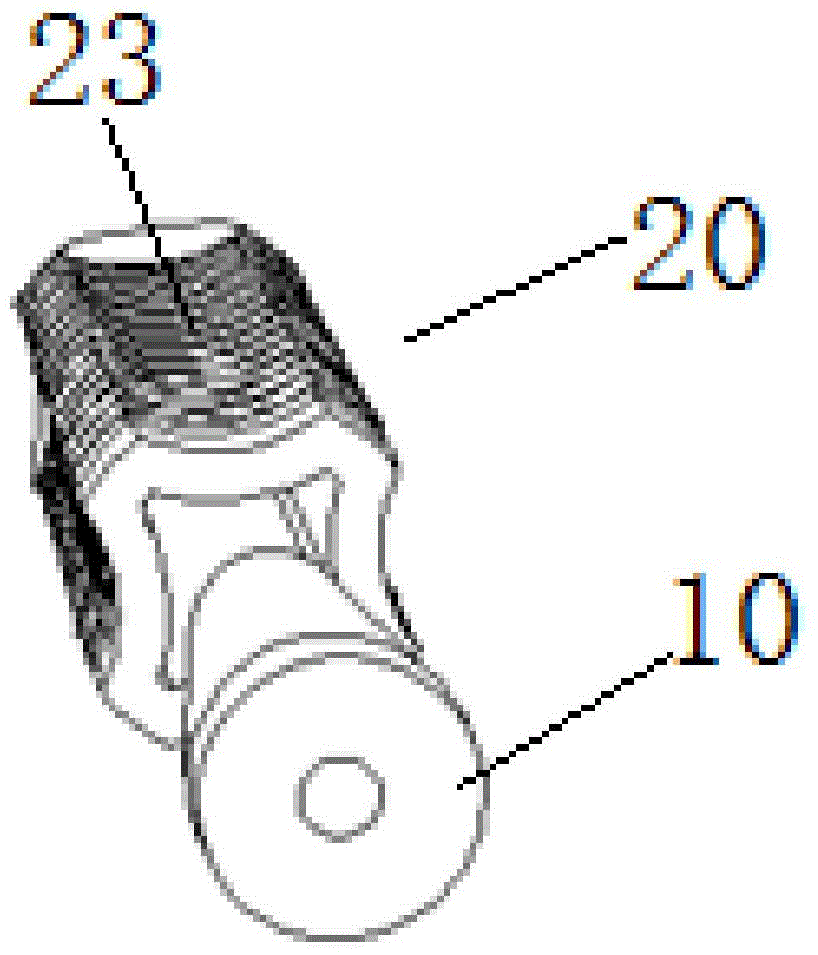
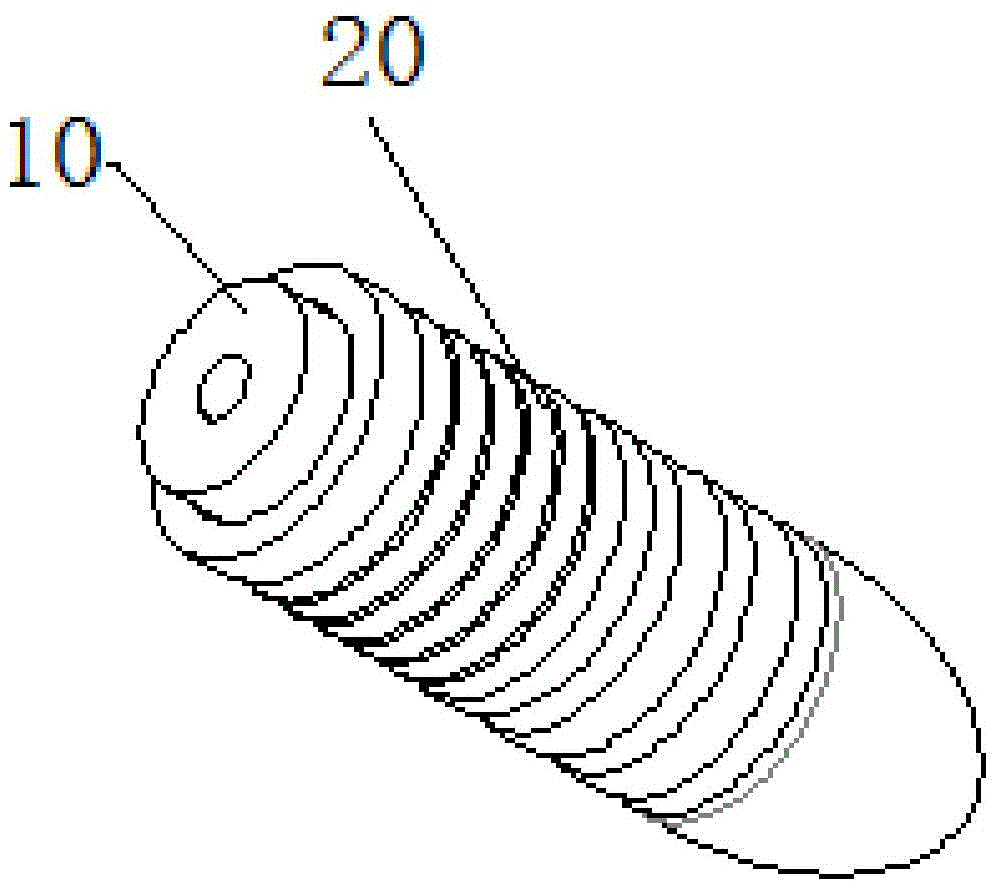
Fixing device, fixing method and application method for reconstruction of cruciate ligaments
The invention discloses a fixing device, a fixing method and an application method for reconstruction of cruciate ligaments. The fixing device comprises a driven nail and an expansion nail sleeve. In an unexpanded state, four axially-extending grooves are formed on the peripheral side surface of a sleeve body in an inwardly and radial sinking mode. By means of the grooves, splitting of ligaments is achieved. In an expansion state, the driven nail is inserted into a sleeve body by means of an opening. Under the effect of the driven nail, the grooves are outwardly extruded so that expansive fixation is achieved. The fixing device, fixing method and application method for reconstruction of cruciate ligaments have following beneficial effects: 360-degree uniform expansion of the expansion nail sleeve is ensured; the expansion nail sleeve is prevented from being broken; transported tendons are not cut by the surgery of reconstruction of ligament; tendons are divided into four bundles by extrusion in a radial direction for effective fixation; fine fixation effect is obtained; full contact among transported tendons and a bone tunnel is achieved; recovery of tendons and bones is further promoted so that the fixing device is suitable for operative habits of a doctor; and the fixing device is easily and conveniently used without additional learning.
Owner:SHANGHAI KINETIC MEDICAL
Cruciate ligament rebuilding hollow trephine
A cruciate ligament rebuilding hollow trephine belongs to medical apparatuses and instruments. A bone residue removing rod is arranged in an axial center hole of the trephine in an insertion mode, and the bone residue removing rod and the trephine are positioned as a whole through the fastening matching of a fastening screw mounted on the bone residue removing rod with an axial sliding hole on the side wall of the trephine. A piston is mounted at the front end of the bone residue removing rod in the axial center hole of the trephine. Sawteeth of the trephine are arranged on the front side end surface of the trephine. Kirschner wires are inserted into the bone residue removing rod, the piston and the axial center hole of the trephine sequentially, and the outer surfaces of the Kirschner wires match with the inner surfaces of the bone residue removing rod, the piston and the axial center hole in a contact mode, so that the Kirschner wires can be positioned radially. The cruciate ligament rebuilding hollow trephine is simple in structure, high-quality and effective in bone-side tunnel establishment and simple in postoperation bone residues removing.
Owner:潘海乐
Controlled release of biopharmaceutical growth factors from hydroxyapatite coating on bioresorbable interference screws used in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery
Controlled release of biopharmaceutical growth factors from a hydroxyapatite coating on a bioresorbable interference screw used in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery on a human. Biologically active scaffolds, such as interference bone screws used for ligament fixation, made by growing calcium phosphate-based hydroxyapatite coatings on bioresorbable poly(α-hydroxy ester) scaffolds that provide controlled mineral dissolution and controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2. The biologically active scaffold provides improved bioavailability of BMP-2 growth factor that in turn provides enhanced graft-bone healing in the tibial bone tunnel. The coating method uses surface hydrolysis and modified simulated body fluid incubation which does not require solvent or heat and is conducted at room temperature.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com