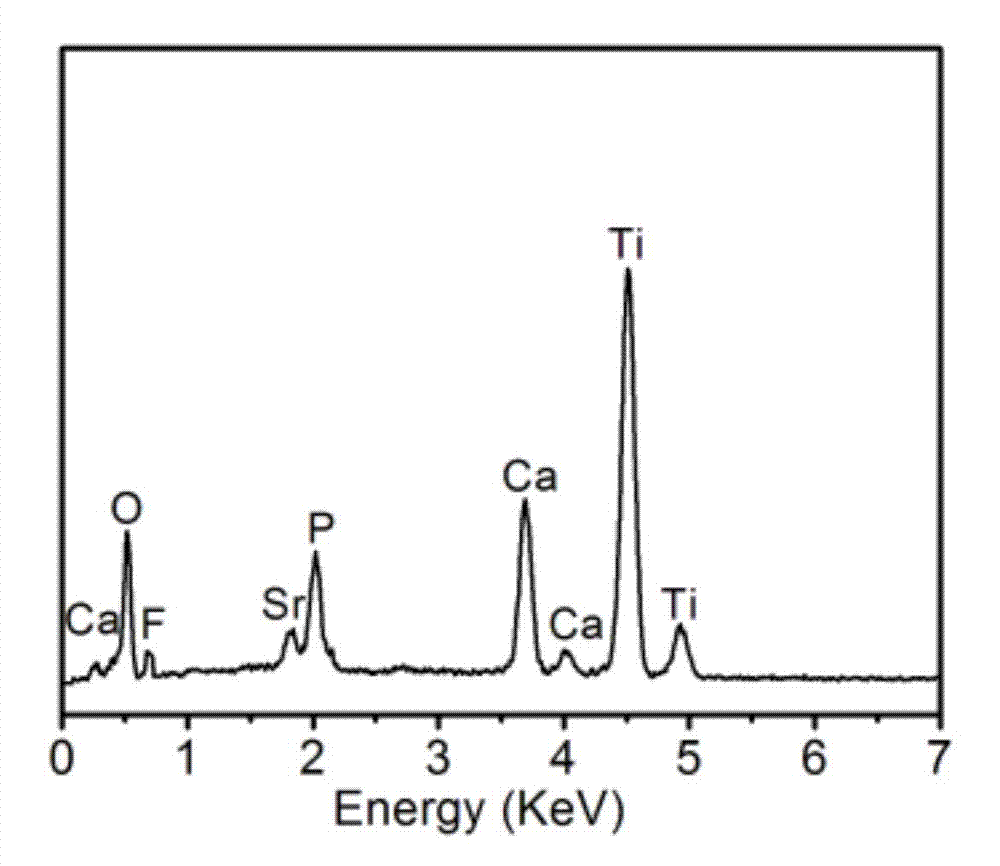
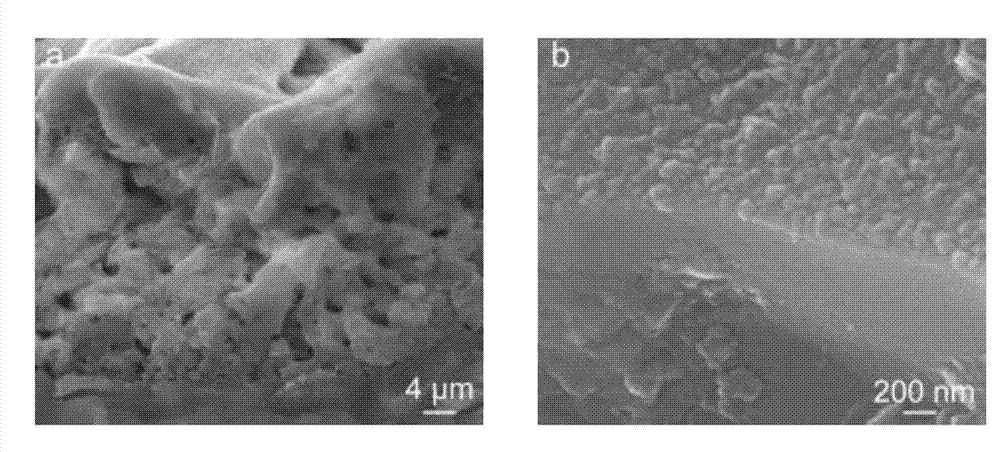
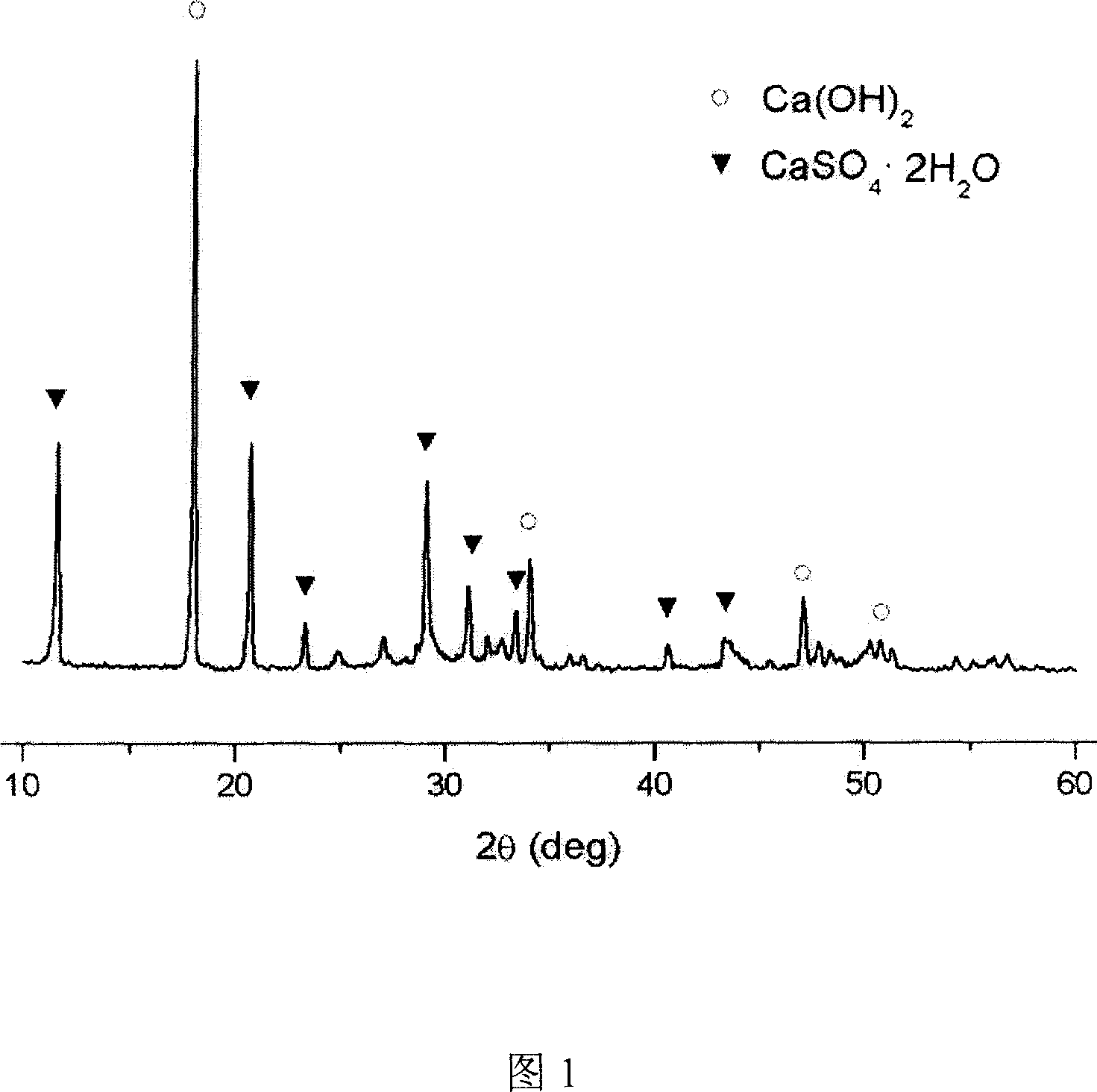
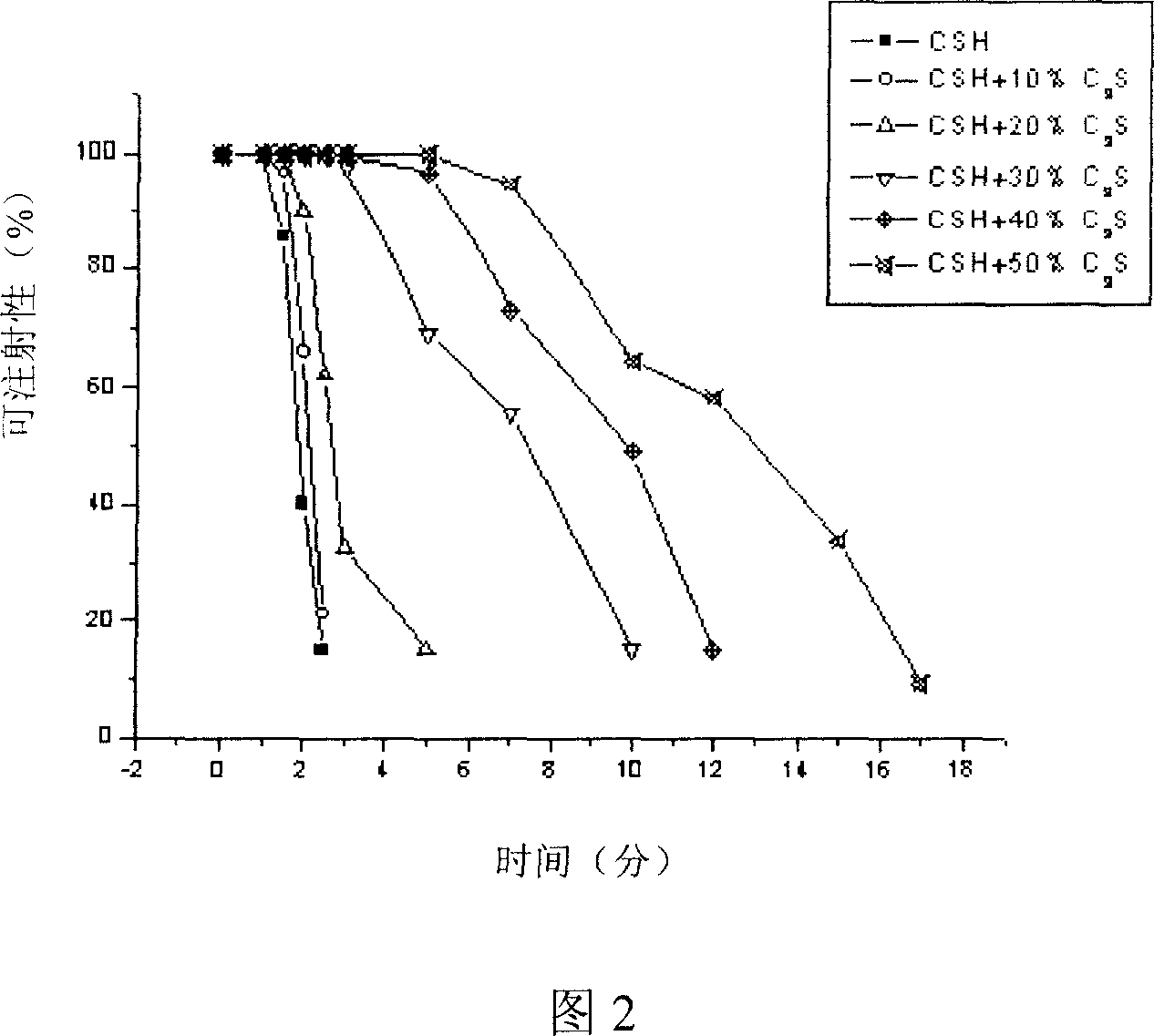
Patents
Literature
241 results about "Simulated body fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
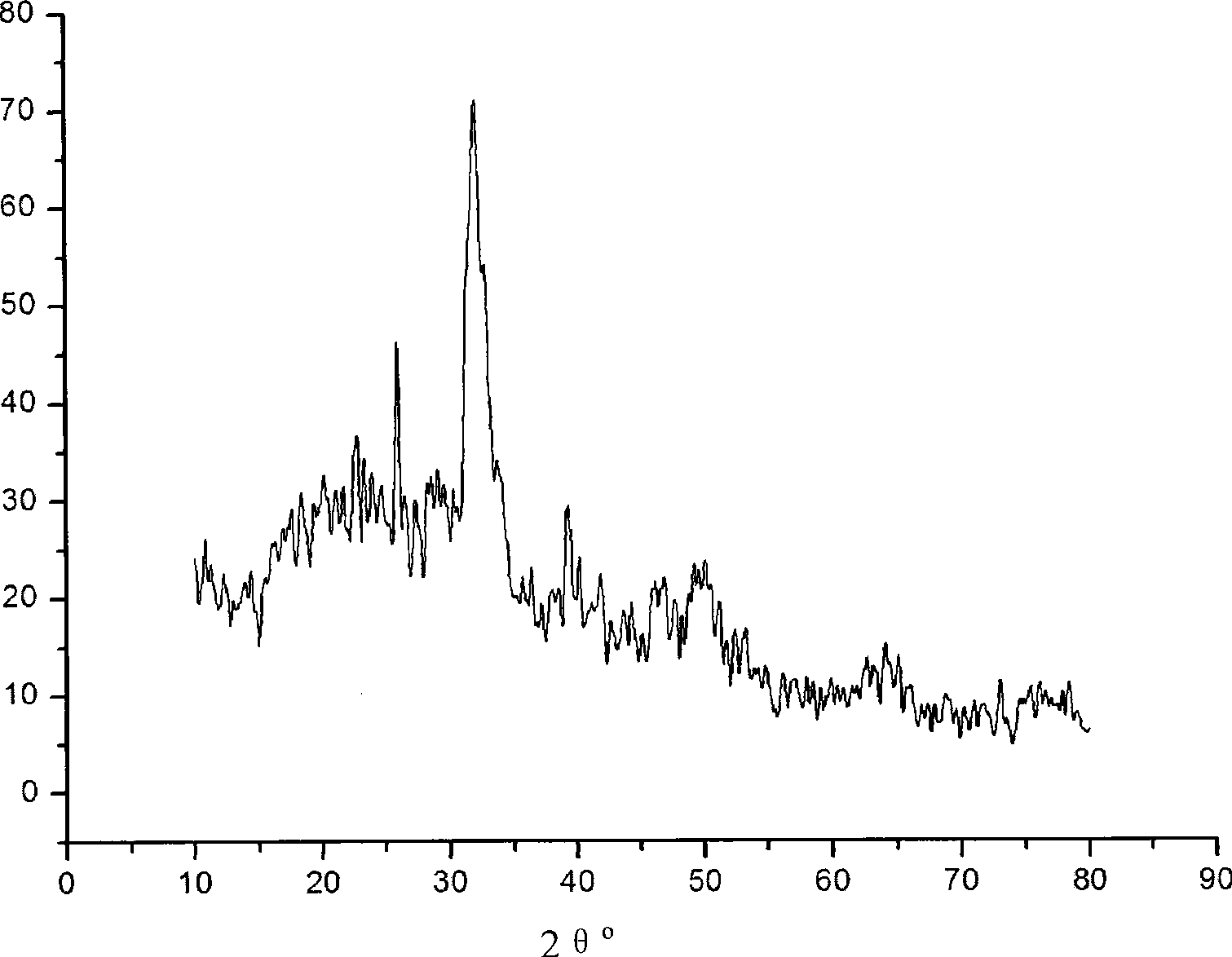
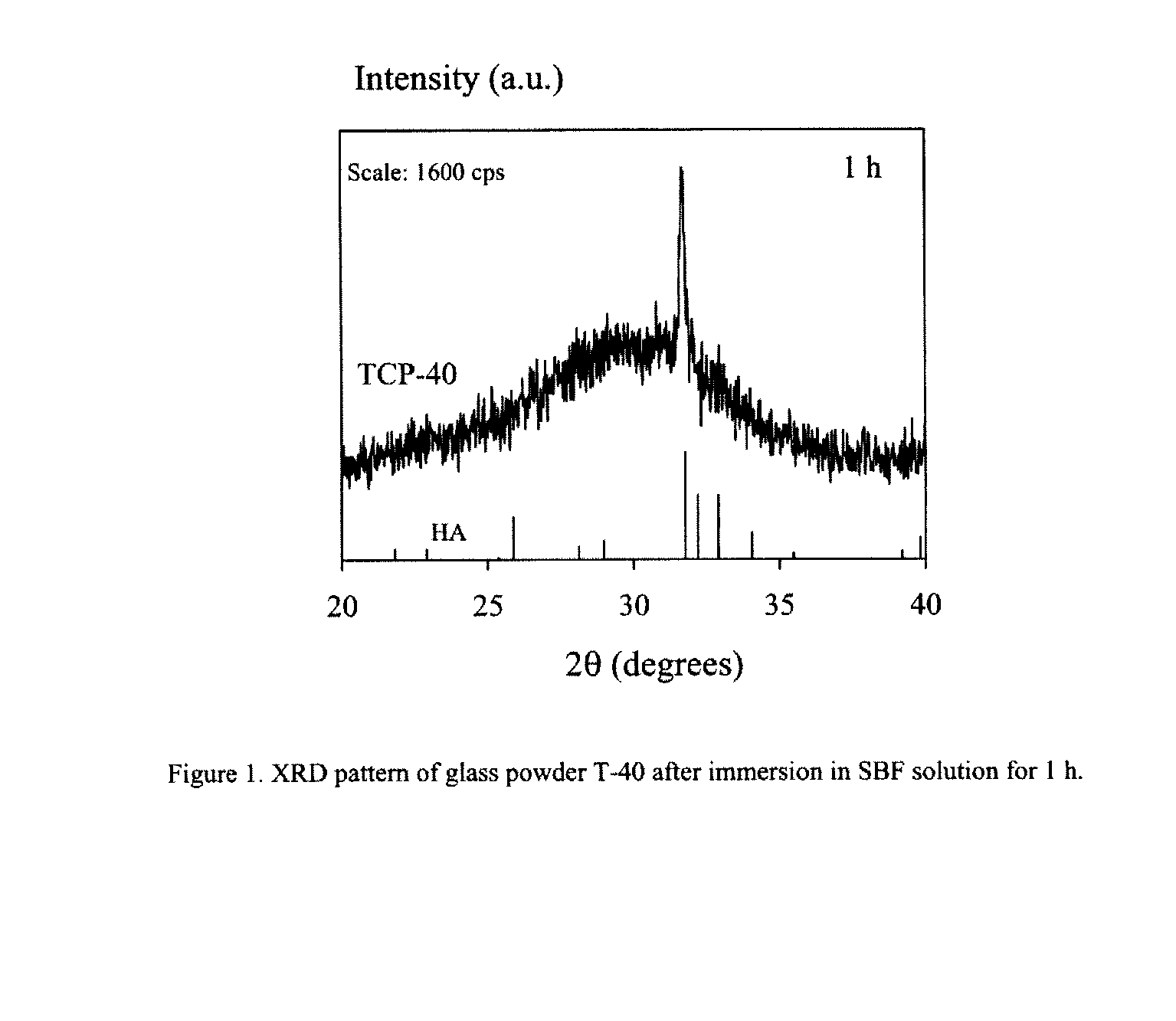
A simulated body fluid (SBF) is a solution with an ion concentration close to that of human blood plasma, kept under mild conditions of pH and identical physiological temperature. SBF was first introduced by Kokubo et al. in order to evaluate the changes on a surface of a bioactive glass ceramic. Later, cell culture media (such as DMEM, MEM, α-MEM, etc.), in combination with some methodologies adopted in cell culture, were proposed as an alternative to conventional SBF in assessing the bioactivity of materials.
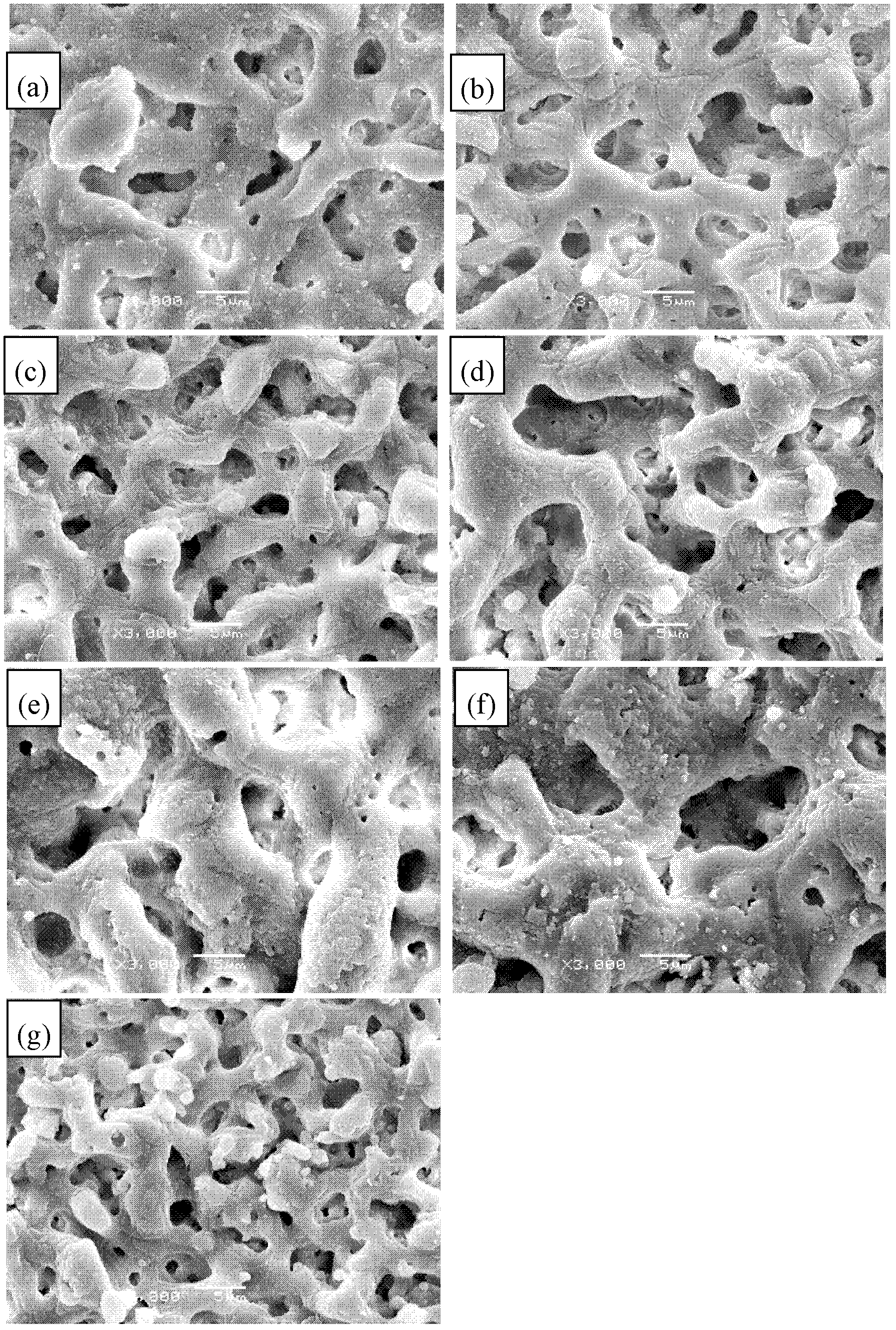
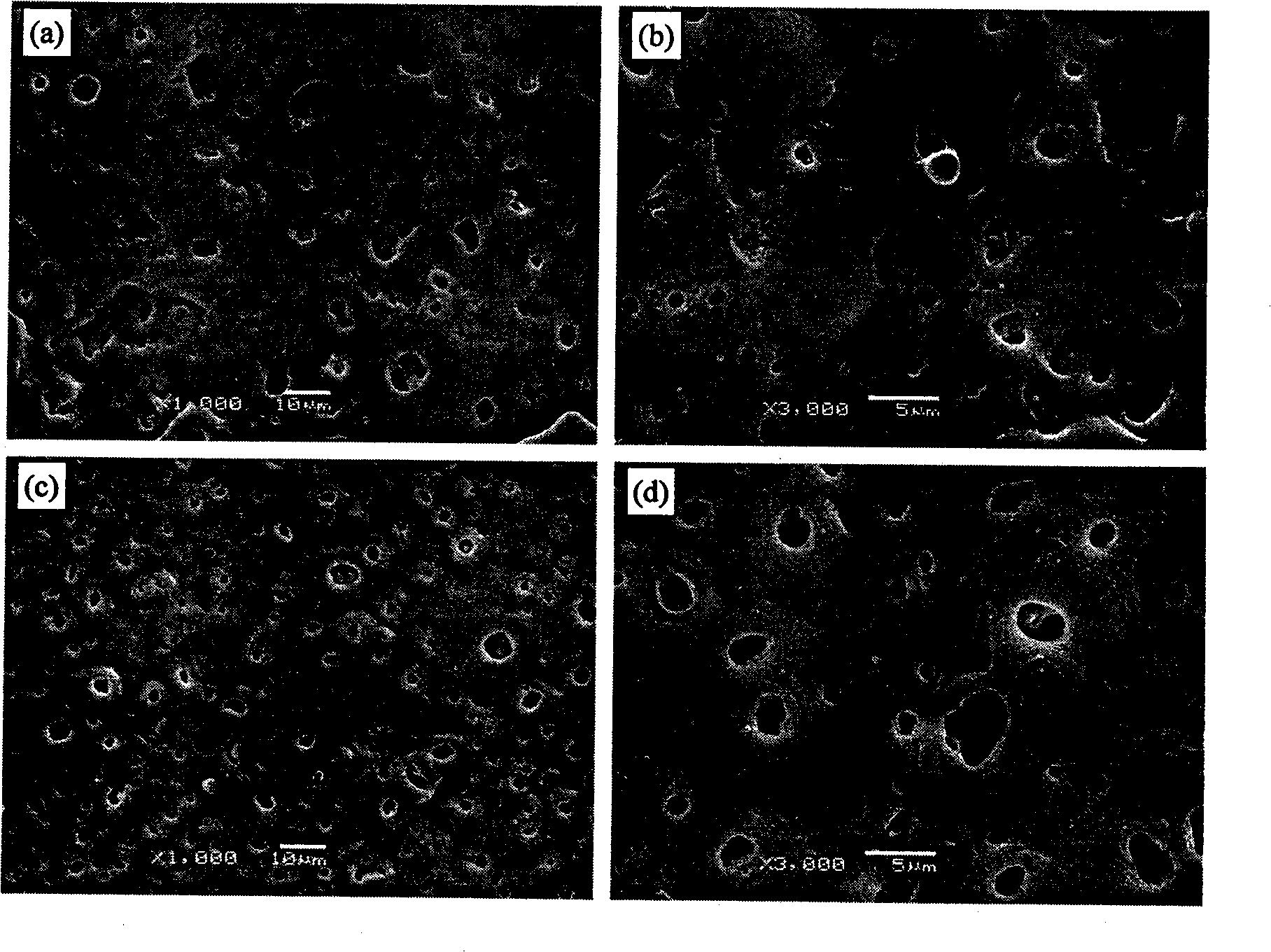
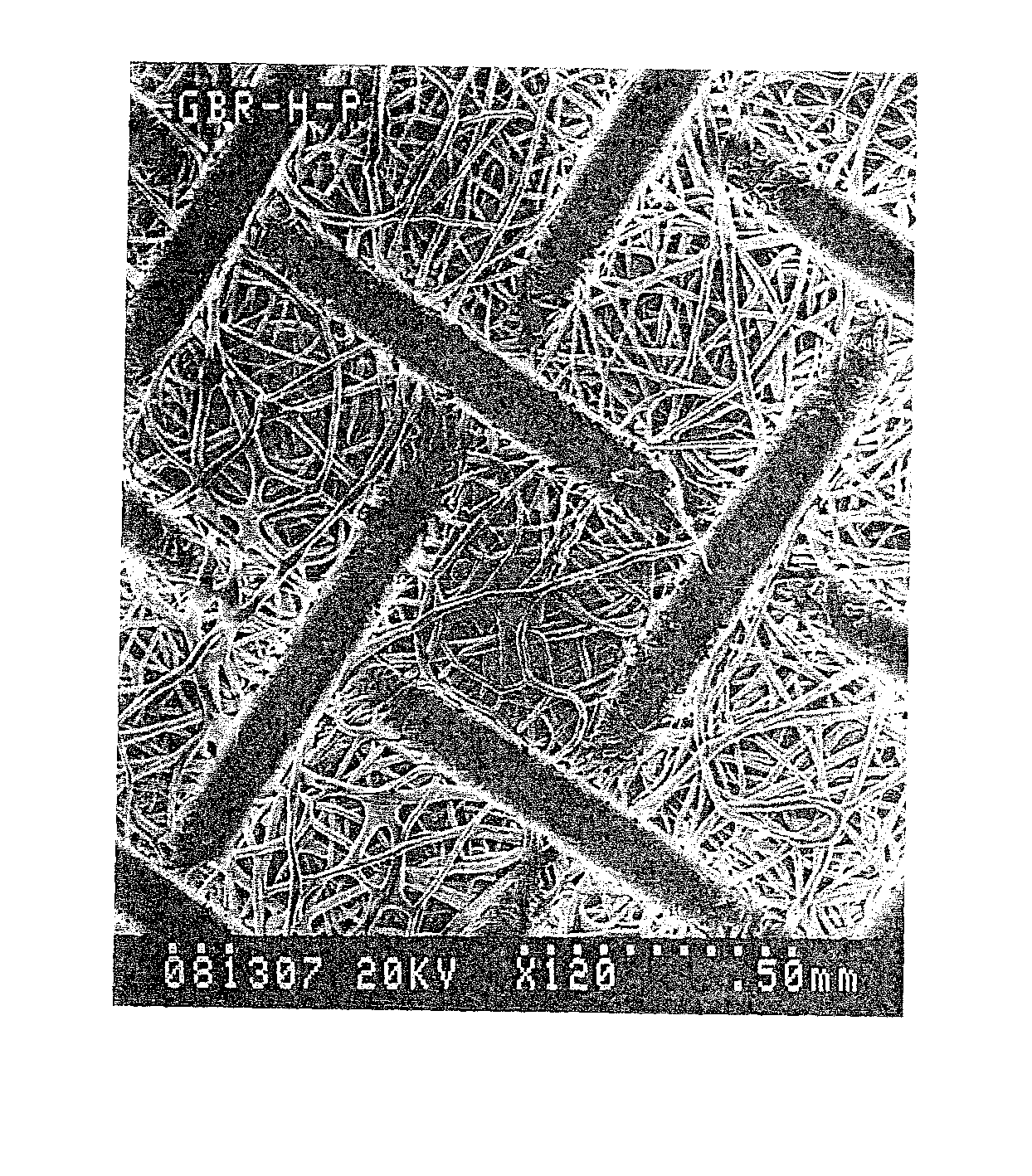
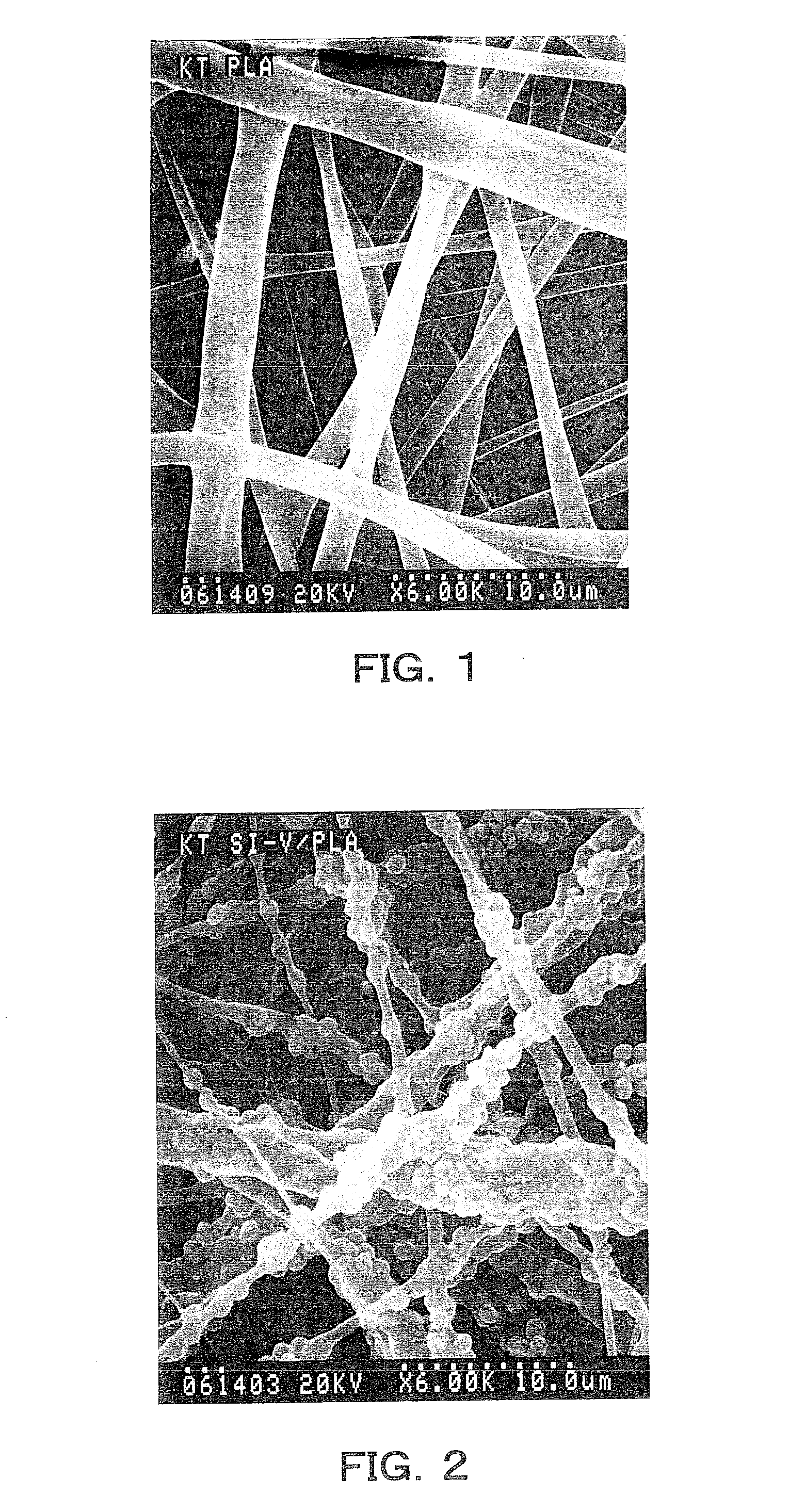
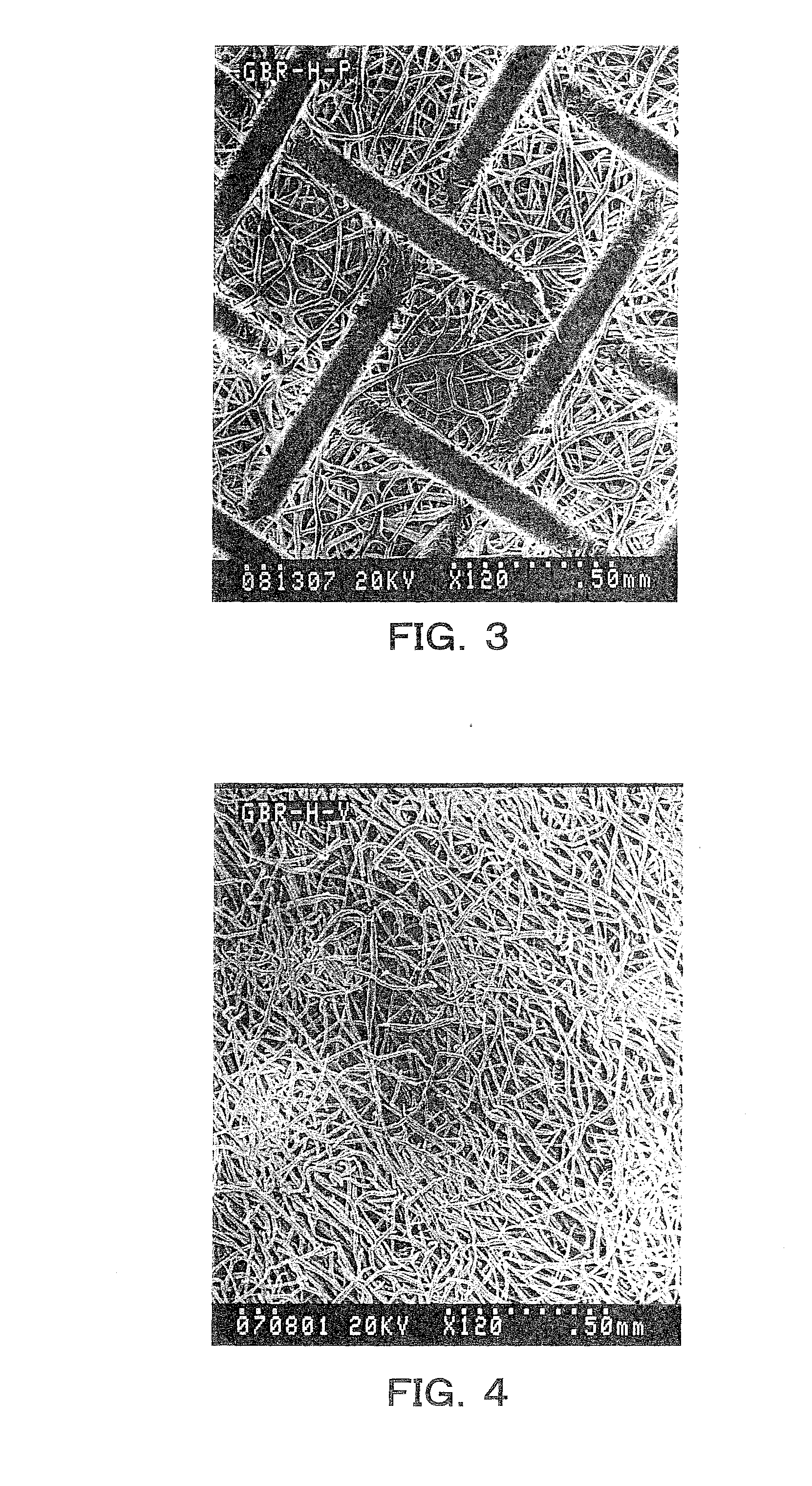
Guided bone regeneration membrane and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100119564A1Improve cell affinityImproving osteogenic abilityBiocideElectric discharge heatingManufacturing technologySimulated body fluid
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +2
Bracket material for bone tissue engineer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101417145AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityProsthesisDrug biological activityProtein C
The invention relates to a bracket material used for an osseous tissue project, and a preparation method thereof. Firstly, the bracket of a type I collagen is extracted from a small fresh pigskin by a mature extracting technique. Then, the bracket is further expanded in a Tris cushion liquid, the pH of which is equal to 8.8 to obtain a natural porous collagen bracket by the treatments of freezing and drying. The bracket is respectively and repeatedly mineralized in a CaCl2 liquid and in (NH4)2HPO4 liquid or mineralized in simulated body fluid for a long period to lead the weakly crystallized HA to be uniformly settled into the collagen bracket; and then a pigskin collagen-hydroxyapatite ossein is obtained by the treatments of freezing and drying to replace the natural bracket material. The invention not only maintains the natural bracket structure of the collagen in an organism, but also has the advantages of low material cost, simple devices, short period and easy operation. The obtained compound bracket material used for the pigskin collagen-hydroxyapatite osseous tissue project has the characteristics of high intensity, large toughness, non-antigenicity, higher biological activity as well as degradation and releasing control.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing biodegradable magnesium alloy intravascular stent
The invention discloses a method for preparing a biodegradable magnesium alloy intravascular stent in the technical field of biological materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing stress relief annealing treatment on a magnesium alloy extrusion bar of phi20mm; processing the annealed bar into a tube blank, and extruding the tube blank; performing stress relief annealing treatment on the extruded capillary tube; cutting the annealed capillary tube to form a stent blank by laser; acid-washing and ultrasonically cleaning the cut stent in an ultrasonic cleaner to remove thecut residues; and performing electrochemical polish, ultrasonic cleaning and passivation on the stent. The extruded magnesium alloy capillary tube has uniform tube wall thickness and smooth surface, the tensile strength of the capillary tube can reach 320 to 370MPa, the yield strength can reach 260 to 300MPa, the elongation can reach 24 to 30 percent, and the corrosion rate of the capillary tube in simulated body fluid is 0.14 to 0.24mm / year. The polished intravascular stent has flat, smooth and bright internal and external surfaces. The preparation method provided by the invention can prepare the biodegradable intravascular stent meeting the clinical requirement.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOVATON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Bioactive glass composition, its applications and respective preparation methods
ActiveUS20140193499A1Easy to sinterHigh in vitro biomineralization rateBiocideCosmetic preparationsFlexural strengthChemistry
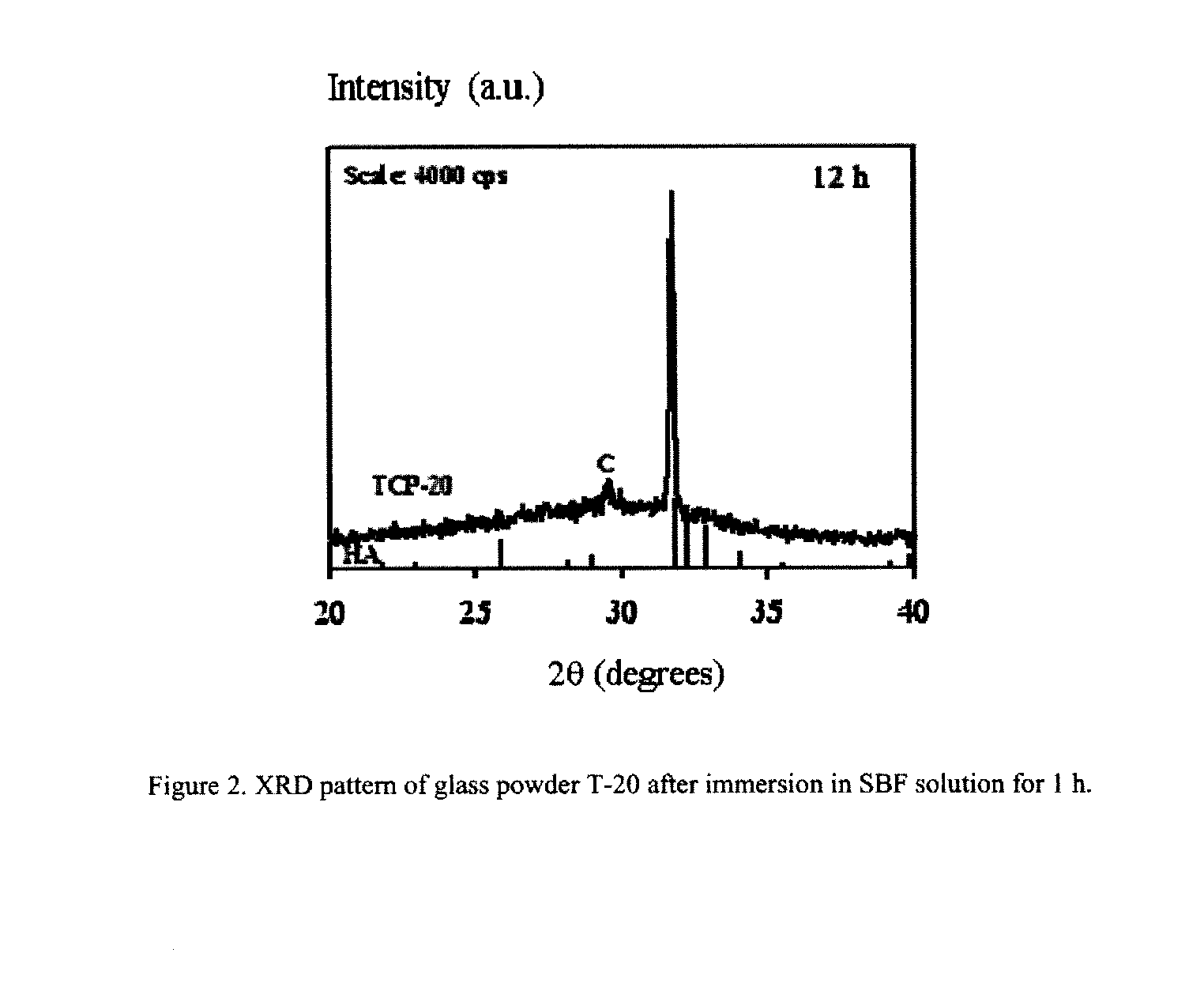
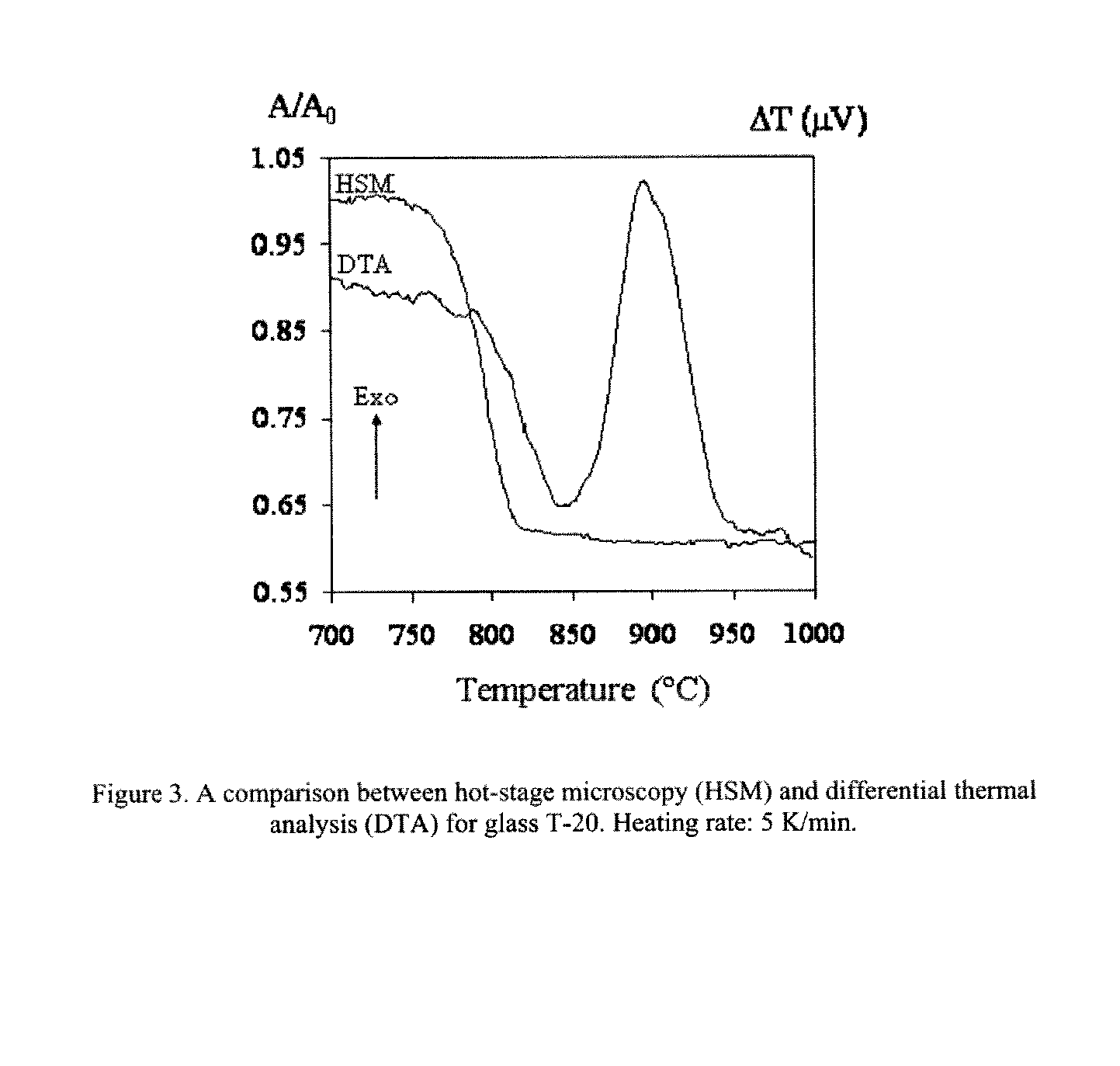
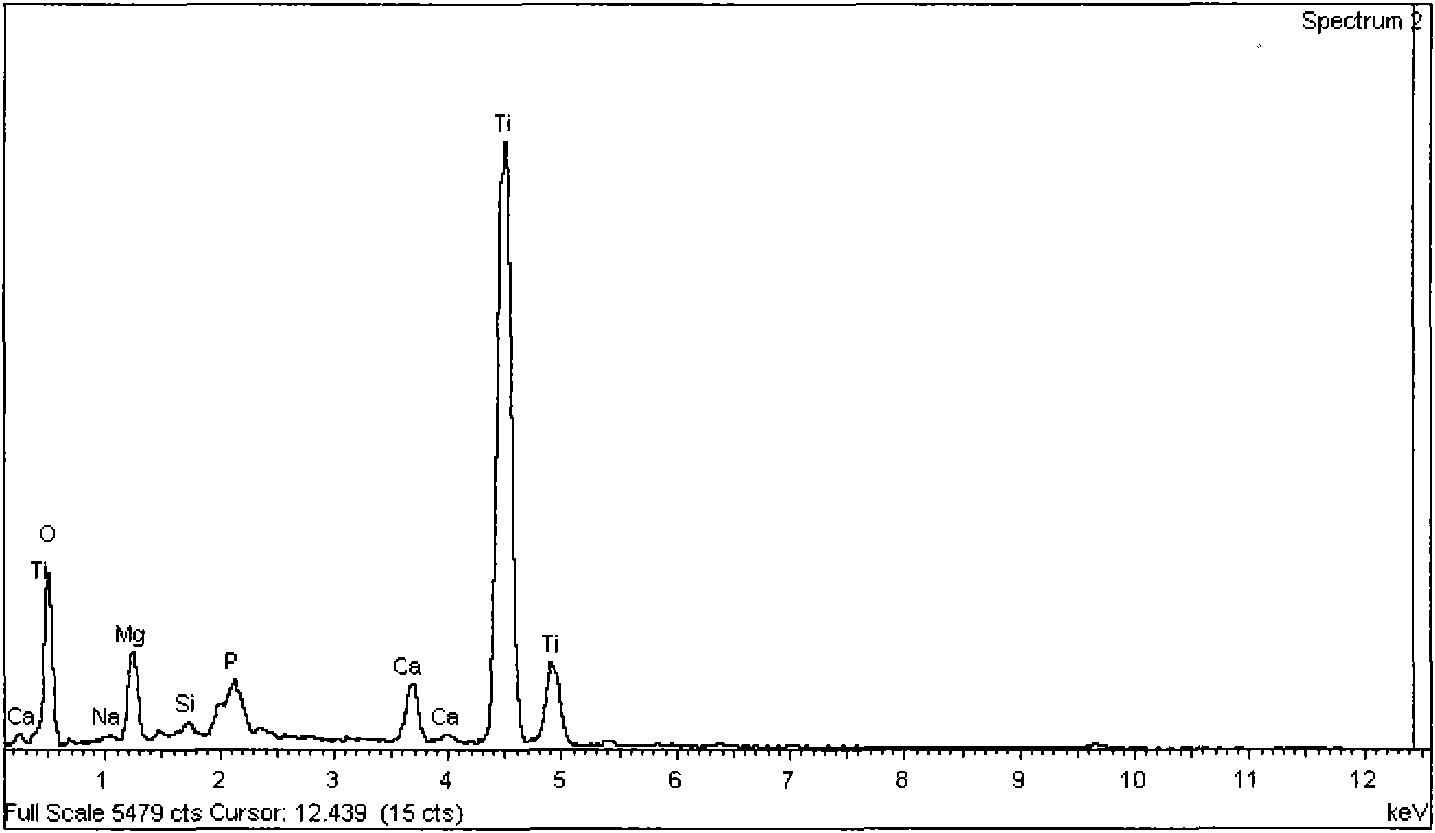
The present invention relates to development of bioactive glass / glass-ceramic composition that are able to promote a fast deposition layer of carbonated hydroxyapatite upon immersion in simulated body fluid (SBF) for time periods as short as one hour. Such composition might include fluorides, and a variety of oxides (or their precursor compounds), such as Na2O—Ag2O—SrO—CaO—MgO—ZnO—P2O5—SiO2—Bi2O3—B2O3—CaF2, be prepared by the melt route or by the sol-gel process, with the specific composition and the preparation route selected according to the intended functionalities, which can present controlled biodegradation rate and bactericidal activity. The powders derived from glass melts purred in cold water (frits) may completely densify by sintering at temperatures up to 800° C. without devitrification, resulting in bioglass compacts with high flexural strength (˜85 MPa). The bioactive glass powders prepared by sol-gel densify at lower temperatures due to their higher specific surface area and reactivity.
Owner:REG4LIFE REGENERATION TECH
Biodegradable Mg-Gd-Zn-Ag-Zr series magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103184379AAccelerated corrosionUniform corrosion morphologySurgerySimulated body fluidIntravascular stent
The invention relates to biodegradable Mg-Gd-Zn-Ag-Zr series magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of medical alloy. The alloy consists of Gd, Zn, Ag, Zr and Mg in percentage by weight: 5-10 percent of Gd, 0.5-3 percent of Zn, 0.1-1 percent of Ag, 0.1-1 percent of Zr and the balance of Mg. Through reasonably designing the alloy elements, a long-period stacking order structure (LPSO structure) is formed in an alloy structure; and with the adoption of the structure, the alloy can be strengthened and toughened, and the corrosion resistance and the local corrosion resistance of the alloy can be improved. Through deformation processing and heat treatment, the strong toughness and the corrosion resistance of the magnesium alloy can be further improved. The magnesium alloy provided by the invention is uniformly corroded in simulated body fluid, so that the overall failure of an implant material due to local corrosion is avoided, and no remarkable cytotoxicity exists; and the magnesium alloy can be used as a fixed implant material in the department of orthopedics. After solid solution treatment, the biodegradable Mg-Gd-Zn-Ag-Zr series magnesium alloy has good secondary shaping capability and can be used as an implant material in a blood vessel.
Owner:JIANGSU KONSUNG MEDICAL EQUIPMENT CO LTD +1
Preparation method of calcium orthophosphate bone cement degradable to pore in human body
The invention relates to a preparation method for calcium phosphate aggregate cement that can degradate in human body, which comprises: preparing said cement powder by alpha-type tricalcium phosphate, calcium biphosphate and calcium carbonate powder; adding chitose microsphere in prepared analog body fluid, clearing and drying to mix with said solid powder to prepare composite powder; using buffle solution to add baking soda and sodium alginate to prepare solidification liquid; finally, mixing the powder and liquid to prepare composite slurry.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Biological active coating on surface of titanium or titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101537208AImprove surface bioactivityImprove bindingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisHydroxylapatiteSodium titanate
The invention relates to the field of surface modification of biomedical materials, in particular to a biological active coating on the surface of titanium or a titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The coating is a composite gradient coating; the inner layer is a titanium oxide film layer with the thickness between 0.5 and 10 mu m; the intermediate layer is a sodium titanate gel film layer with the thickness between 0.1 and 10 mu m; and the outer layer is a hydroxylapatite layer with the thickness between 1 and 15 mu m. A method combining anodization and alkali treatment is adopted to prepare the biological active coating on the surface of the titanium or the titanium alloy, which comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing an oxide film with certain thickness on the surface of the titanium or the titanium alloy by an anodization method; secondly, forming a layer of porous netty sodium titanate gel film layer on the surface of the oxide film by an alkali treatment method; and finally, depositing the bone-like hydroxylapatite layer on the surface of a sample after the treatments in a simulated body fluid. The method can effectively improve the biological activity on the surface of the titanium or the titanium alloy; and the surface has a coarse porous structure, so the bonding force of the hydroxylapatite layer and the adhesive ability of cells are improved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-toughness corrosion-resistant magnesium alloy implanted material capable of being degraded in organism
The invention relates to a high-toughness corrosion-resistant magnesium alloy implanted material capable of being degraded in an organism, belonging to the technical field of biological materials. The material of the invention comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 1-4% of Nd, 0.1-1.0% of Zn, 0.1-1.0% of Ag, 0.3-0.8% of Zr and balance of Mg. The invention strengthens magnesium alloy through alloy elements, refines grains, improves plasticity, and further strengthens the magnesium alloy through extrusion deformation and heat treatment processes. The corrosion rate of the magnesium alloy provided by the invention in the simulated body fluid is 0.22-0.28mm / year, meeting the requirement of the implanted material for the corrosion rate; and the material of the invention does not have obvious cytotoxicity and has good blood compatibility, thereby meeting the requirements of the implanted material for biological compatibility. The high-plasticity medium-strength magnesium alloy provided by the invention can be used for support intravascular stent materials, and the high-strength medium-plasticity magnesium alloy provided by the invention can be used for implanted materials in orthopaedics.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOVATON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of biologically active nanometer composite layer on medical-use metal surface
InactiveCN1769527AGood combinationImprove biological activitySuperimposed coating processApatiteBiological activation
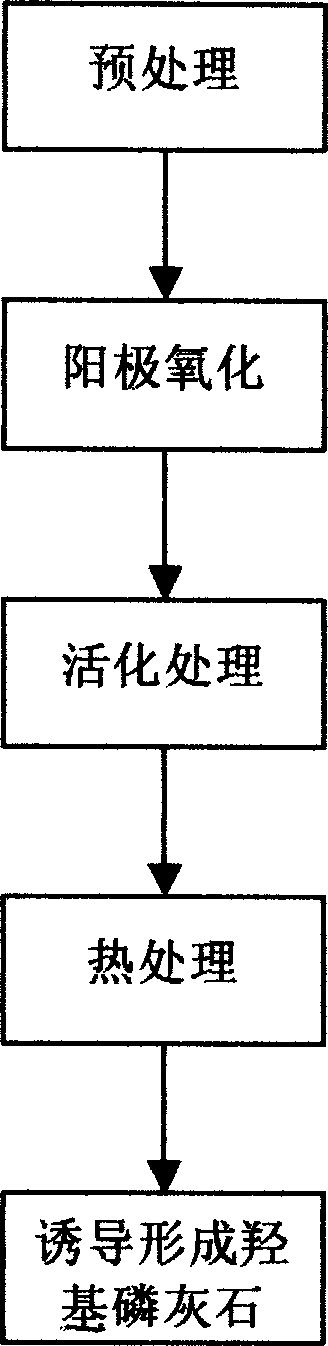
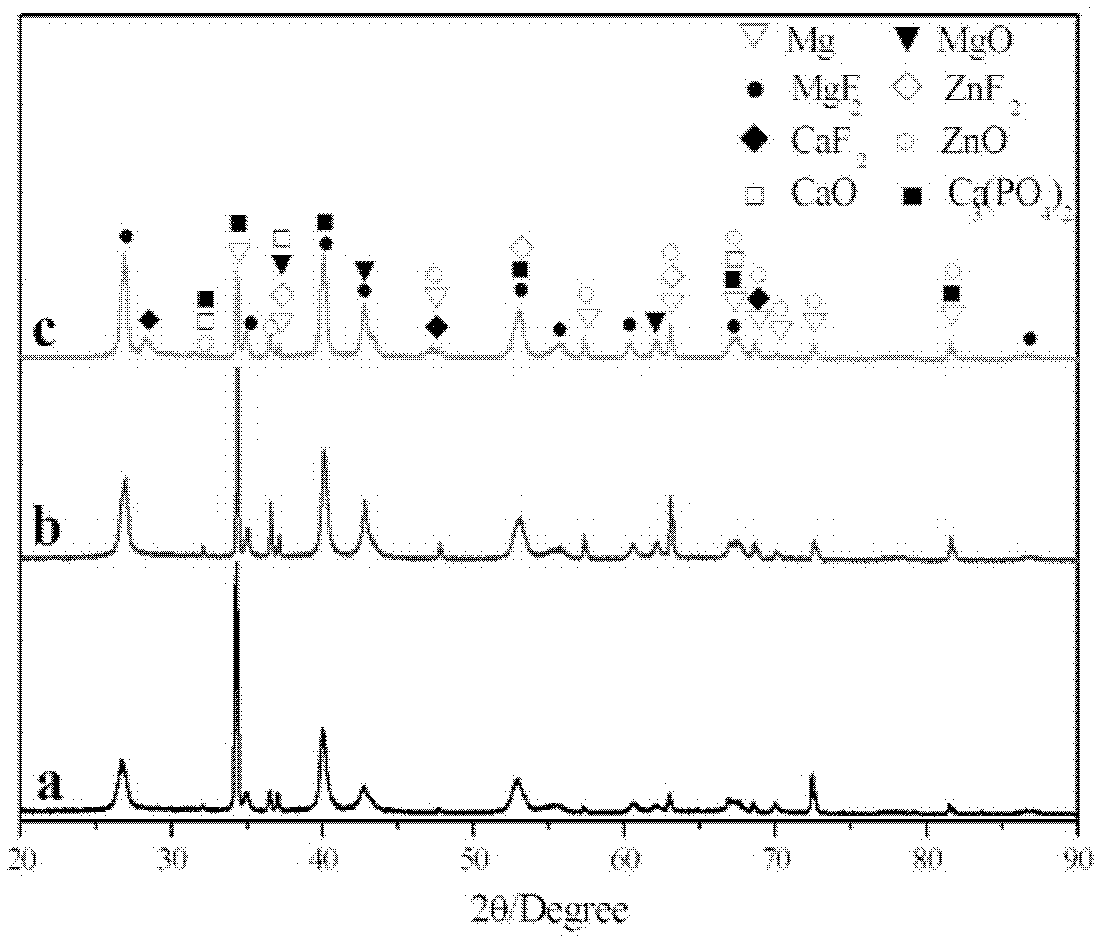
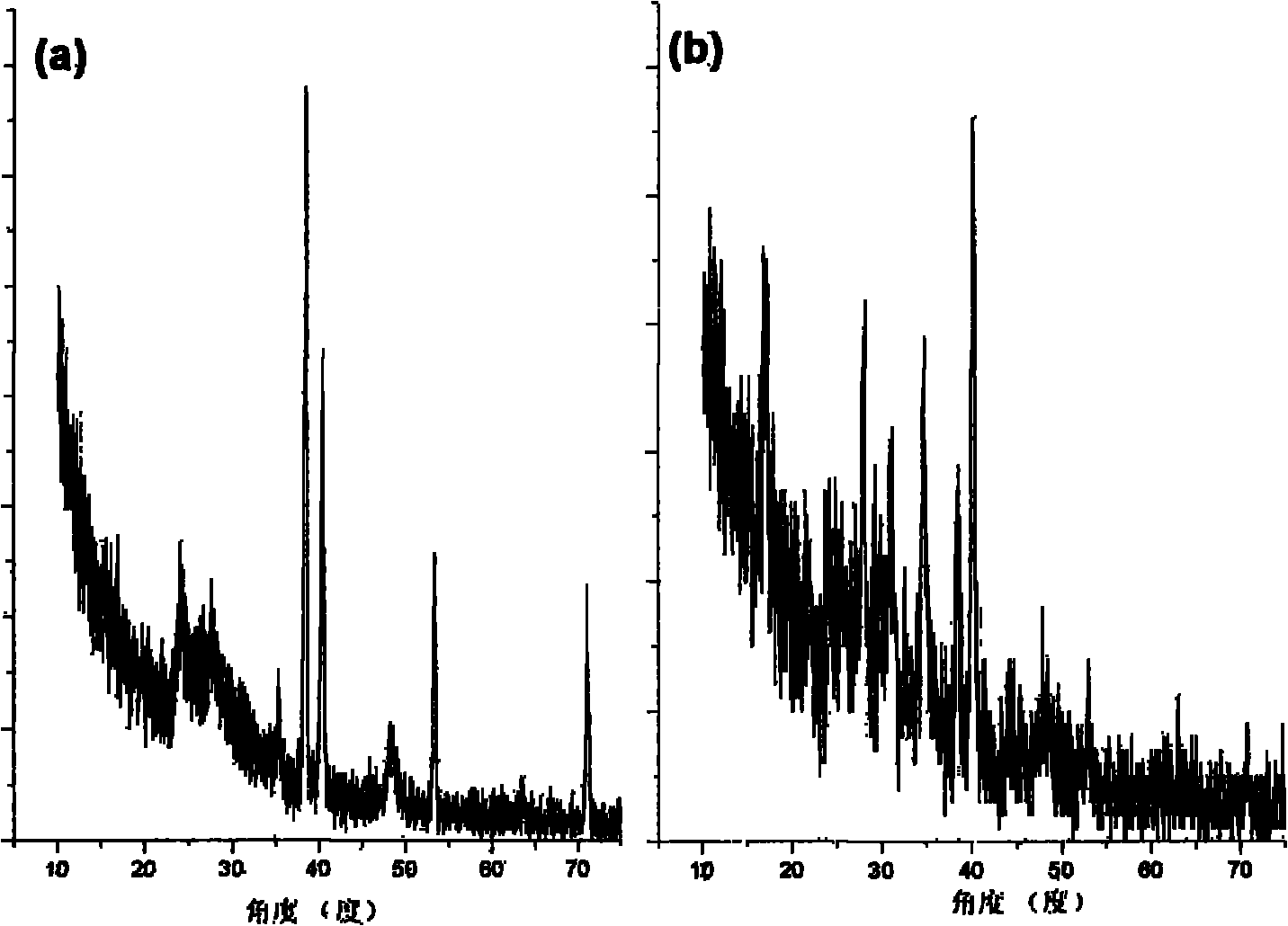
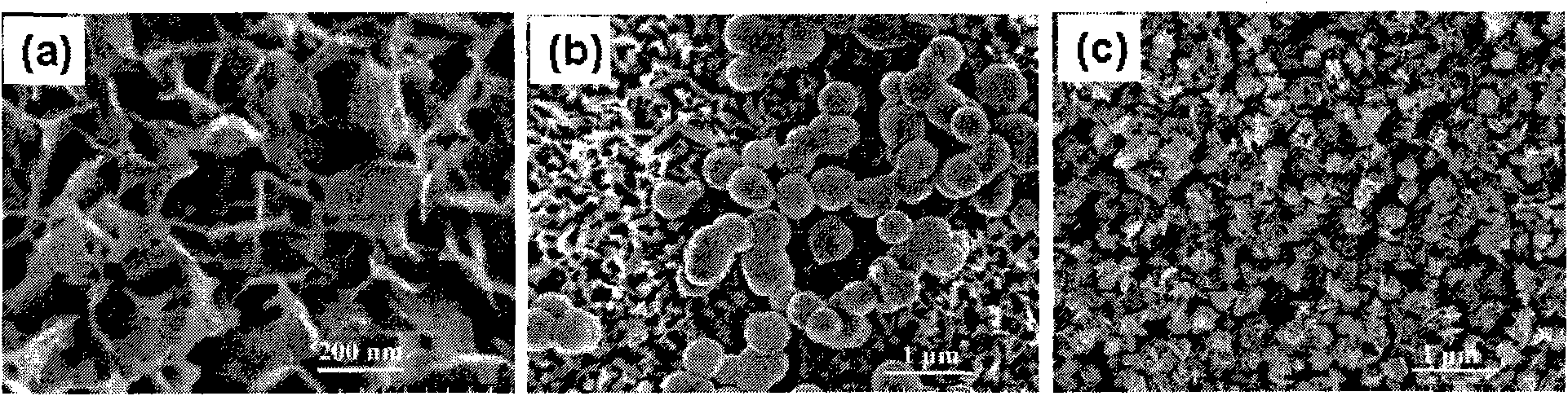
This invention relates to a biological active nanometer compound layer making method for the medical metal surface, which includes the following steps: putting the medical metal titanium and its alloy radix into the diluent acid liquid to do corrad pretreatment; using the pretreated titanium and its alloy radix as the anode to do anode oxidation to create the compact titanium dioxide nanometer tube film on the surface of the metal; putting them into the alkali lye to do activation treatment, then doing heat treatment with them under 450íµí½650íµ for 0.5í½3 hours; Then putting them into the simulate liquid to produce hydroxyl apatite. The charater of this invention is that it provides a method that combines the anode oxidation and alkali heat treatment, and this invention impoves the biological compatibility of the medical metal greatly.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Preparation method of biological ceramic coating rich in calcium and phosphate phases on surface of magnesium alloy
ActiveCN102220620AHigh hardnessHigh densityAnodisationPhosphatisationPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biological ceramic coating rich in calcium and phosphate phases on the surface of magnesium alloy, comprising the following steps of: adding (C6H5O7)2Ca3.4H2O and Na3PO4 to deionized water, and simultaneously adding KOH, NH4HF2, N(CH2CH2OH)3, C3H8O3 and H2O2 to prepare an electrolyte with a certain concentration ratio of calcium and phosphate; disposing the magnesium alloy in the electrolyte as an anode which is prepared through micro arc oxidation energization reaction. The calcium-phosphate ceramic coating obtained by the preparation methodconsists of three layers of a loose layer, a transition layer and a compact layer, wherein the surface of the loose layer consists of a plurality of uniformly distributed micropores, the transition layer is between the loose layer and the compact layer, and the compact layer and a substrate body form good metallurgical bonding; therefore, the coating has high rigidity, high density, high bonding force and good corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance; simultaneously, the mouse acute systemic toxicity test indicates that the coating has good biocompatibility, and the simulated body fluid soaking test indicates that the coating has good biological activity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Implant surface biomimetic coating material for promoting sacralization and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an implant surface biomimetic coating material for promoting the sacralization and a preparation method thereof. The coating material is a compound of calcium phosphate cooperatively doped with various trace elements and organic macromolecules. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: immersing an artificial implant pretreated by acid or alkali in simulated body fluid containing various trace element ions and organic macromolecules; carrying out chemical precipitation treatment between 35 DEG C and 150 DEG C to ensure that the surface of the implant is subjected to calcium phosphate salt core forming and growth; and forming a continuous coating of calcium phosphate salt cooperatively doped with various trace elements and the organic macromolecules. The surface of the coating has a nanoscale fine structure, and the effects of slowly degrading and releasing active ions of calcium, phosphorus and various trace elements and promoting the sacralization of implants for diseased intraosseous injuries, bone fracture internal fixation and tooth root internal fixation in the oral cavity. The coating material has the characteristics of simple preparation process, controllable coating thickness, trace element content, crystallinity and degradation rate, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnesium base degradable implant material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101559239AImprove biological activityIncreased microhardnessAnodisationProsthesisMicro arc oxidationPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention discloses a magnesium base degradable implant material, belonging to the technical field of biological materials. The implant material is composed of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy matrix and micro-arc oxidation coating; the micro-arc oxidation coating is formed by micro-arc oxidation treatment by electrolyte formed by solving the sodium silicate, potassium hydroxide, potassium fluoride, soluble phosphate and trolamine in pure water; each liter of electrolyte contains 12-18g of sodium silicate, 3-8g of potassium hydroxide, 2-7g of potassium fluoride, 5-20g of soluble phosphate and 5-10ml of trolamine. The implant material has not only high micro hardness but also excellent decay resistance; and after dipping in simulated body fluid, the surface has phosphorite deposition, which shows that the material has certain biological activity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Titanium dioxide/strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104726921AEase of mass productionSimple and fast operationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisSolubilityPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention provides a titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an electrolyte containing calcium ions, strontium ions, fluorine ions and phosphate anions; and then by taking titanium or a titanium alloy as an anode and stainless steel as a cathode, directly preparing the titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating on the surface of a titanium or titanium alloy substrate by virtue of a micro-arc oxidation technology. The coating consists of an inner layer combined on the surface of the substrate and a surface layer combined on the surface of the inner layer, wherein the inner layer is a titanium dioxide layer in a form of a nano crystal and the surface layer is a nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer. No non-continuous interfaces are available between the coating and the substrate and the coating has high combining strength and structural stable performance; the coating is relatively small in solubility in a simulated body fluid, so that the coating is effectively implanted and used; and the nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer in the surface layer can remarkably promote the osteogenic function of the cells to form new bones and inhibit bacterial adhesion and growth.
Owner:宝鸡卡斯特医疗科技有限公司
Calcium sulfate semihydrate group combined self-curing bio-active material, preparation and application thereof
The invention relates to a self-solidification biological active material of hemigydrate calcium sulfate base, relative production and application. Wherein, the invention is characterized in that: said material is paste formed by harmony liquid, hemigydrate calcium sulfate / tricalcium silicate composite powder, while their mass ratio is 0.8-1.2:1; said harmony liquid is one of deionized water, analogue humor, inorganic salt solution or inorganic solution; the content of tricalcium silicate in the hemigydrate calcium sulfate / tricalcium silicate composite is 1-50%. The invention can be shaped freely, without cell toxicity, while it can be degraded stepped with adjustable speed, and it can induce the generation of skeleton agustite, with higher activity then calcium sulfate material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
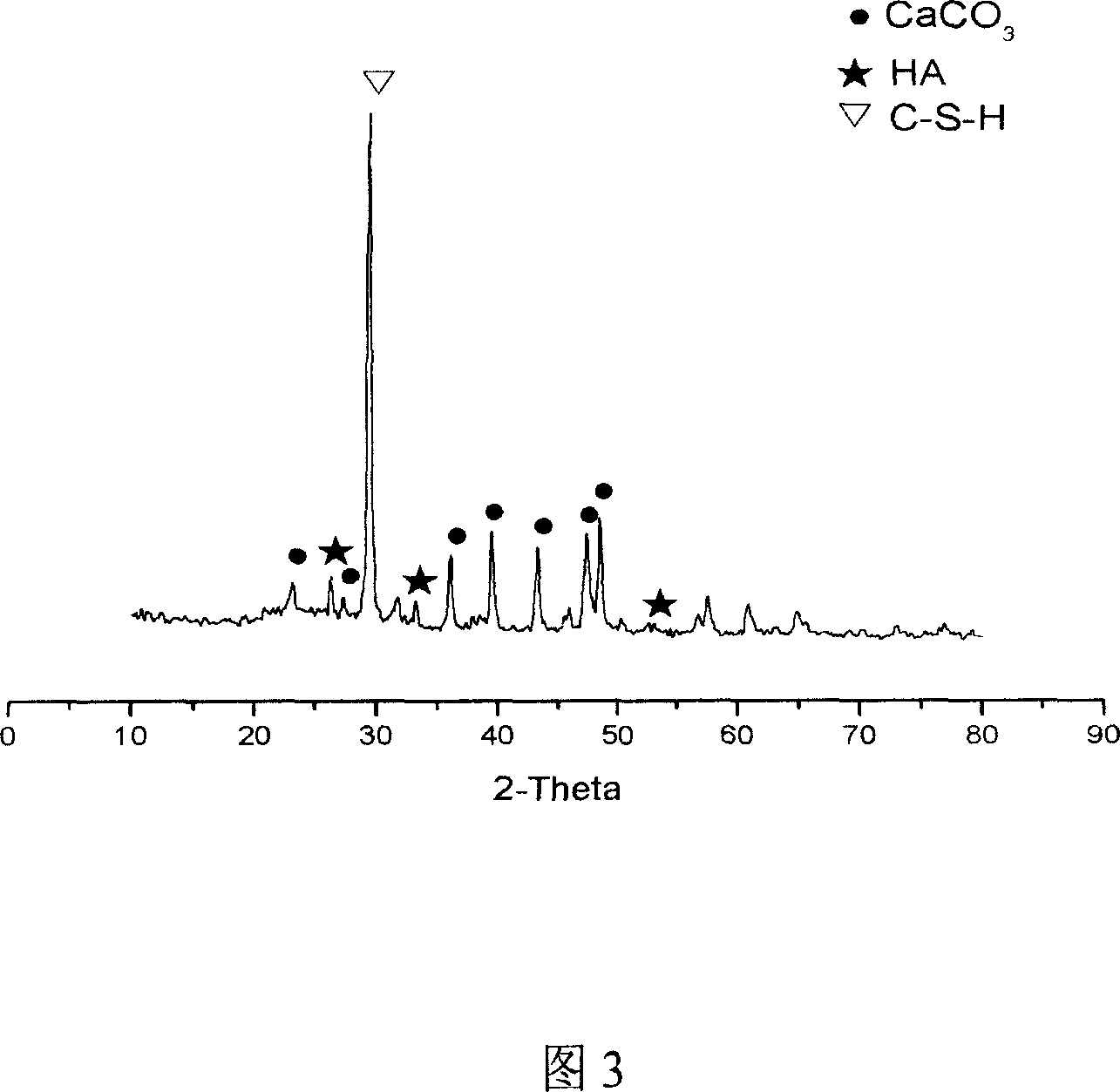
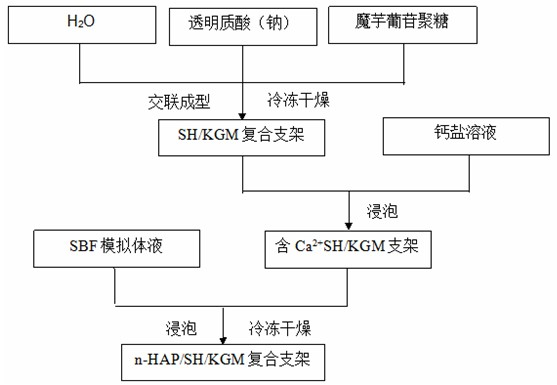
Hydroxyapatite, sodium hyaluronate and konjac glucomannan composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102380128APromote growthImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisCalcificationMechanical property
The invention relates to a hydroxyapatite, sodium hyaluronate and konjac glucomannan porous scaffold composite material for bone defect restoration and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedical materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: cross-linking sodium hyaluronate and konjac glucomannan serving as raw materials to obtain a sodium hyaluronate and konjac glucomannan porous scaffold material, and preparing a hydroxyapatite, sodium hyaluronate and konjac glucomannan porous scaffold material by a pre-calcification and simulated body fluid (SBF) solution soaking bionic mineralization method. Reaction conditions are mild, the used materials are safe, non-toxic and low in cost, and the preparation process is simple; meanwhile, the scaffold material has high mechanical properties and a unique three-dimensional structure and meets the requirement of bone tissue engineering.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
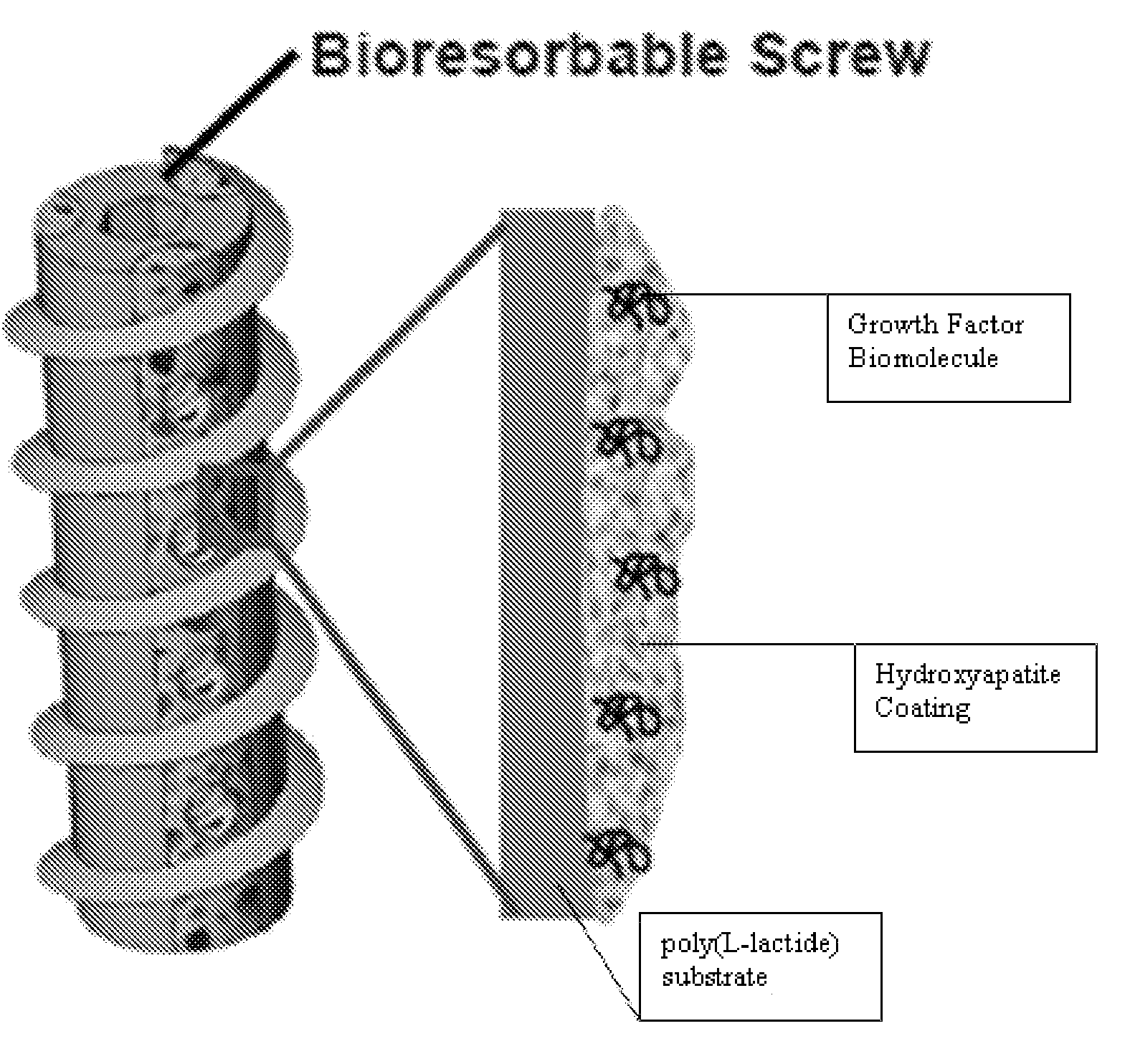
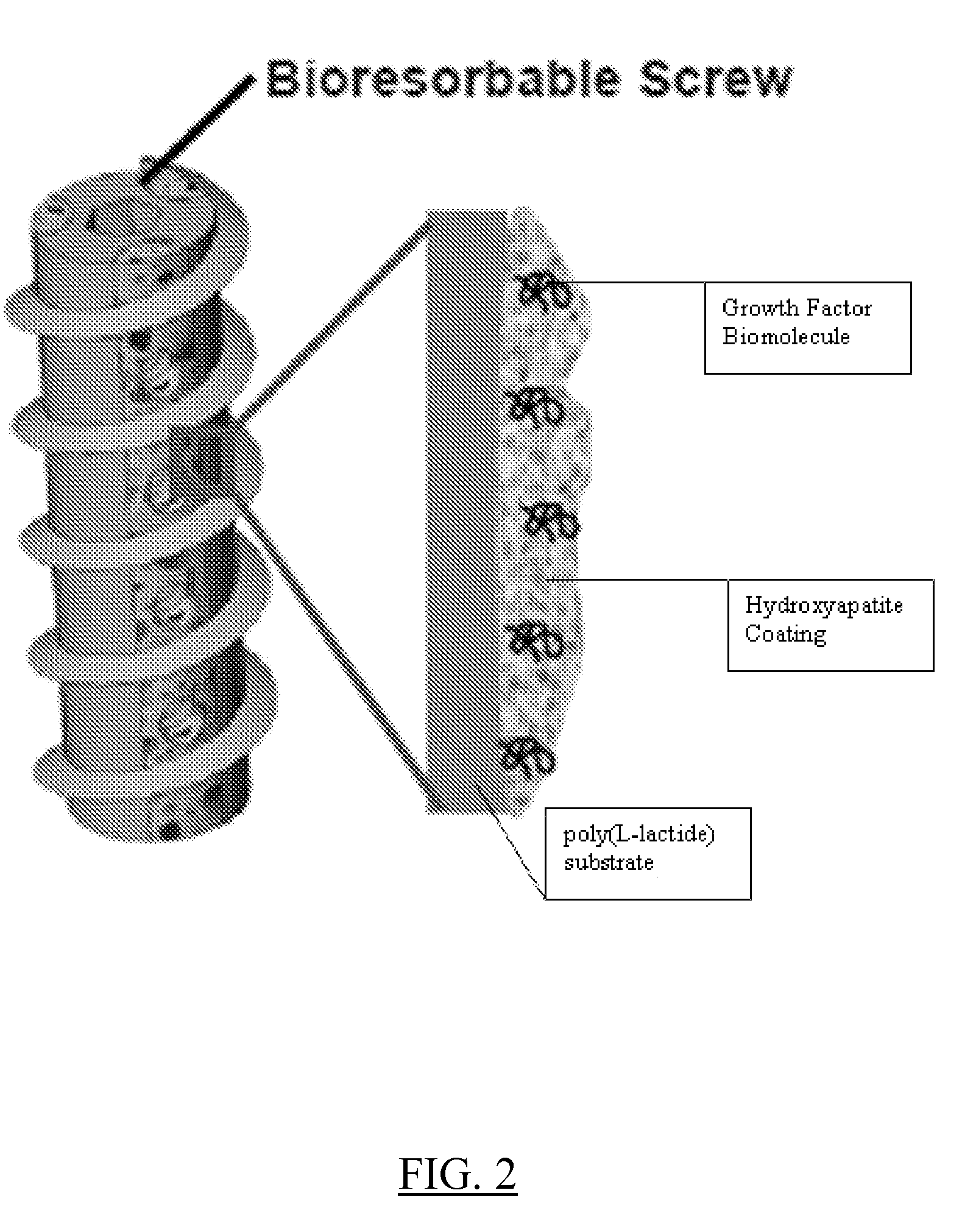
Controlled release of biopharmaceutical growth factors from hydroxyapatite coating on bioresorbable interference screws used in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery
Controlled release of biopharmaceutical growth factors from a hydroxyapatite coating on a bioresorbable interference screw used in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery on a human. Biologically active scaffolds, such as interference bone screws used for ligament fixation, made by growing calcium phosphate-based hydroxyapatite coatings on bioresorbable poly(α-hydroxy ester) scaffolds that provide controlled mineral dissolution and controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2. The biologically active scaffold provides improved bioavailability of BMP-2 growth factor that in turn provides enhanced graft-bone healing in the tibial bone tunnel. The coating method uses surface hydrolysis and modified simulated body fluid incubation which does not require solvent or heat and is conducted at room temperature.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
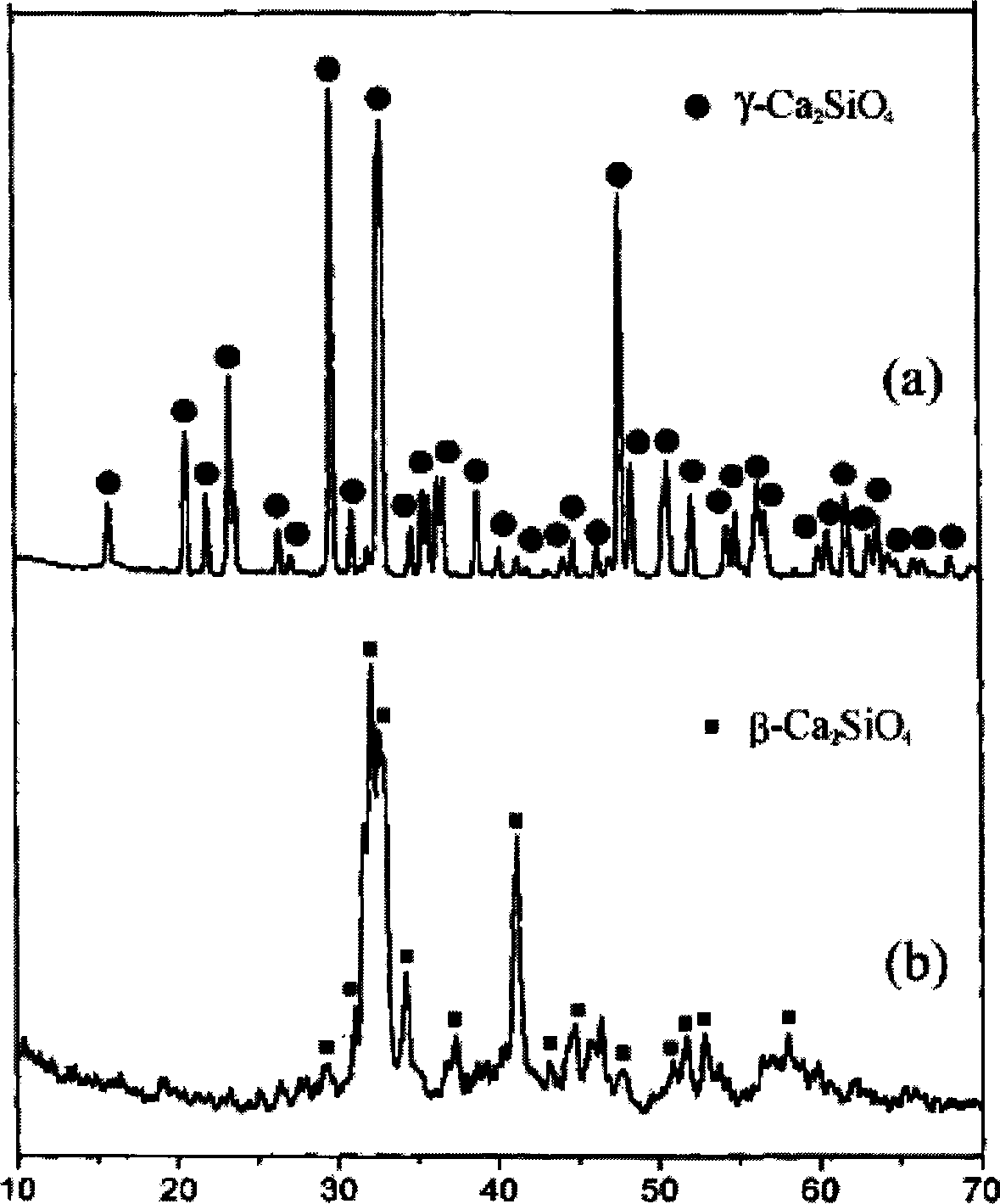
Dicalcium silicate coating layer-titanium alloy loading bone replacement material and its preparation method
The present invention relates to a bone substituted material. Said bone substitute material is dicalcium silicate coating layer deposited on the surface of titanium alloy of Ti-6Al-4V, said coating layer is formed from beta-Ca2SiO4 and glass phase, and its thickness if 50-400 micrometers. Its preparation method incldues the following steps: firstly, synthesizing gamma-Ca2SiO4, then using atmospheric plasma spraying process to deposit the dicalcium silicate coating layer on the titanium alloy base body, and the combination strength of said coating layer and base body is greater than 34-40 MPa.The tests show that the bone apatite can be formed on the surface of dicalcium silicate, and cell can quickly grow and proliferate on the beta-Ca2SiO4 coating layer surface, so that said substitute material possesses good biological activity and compatibility.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing intravascular stent upon 3D (three-dimensional) printing technology
The invention discloses a method for preparing an intravascular stent upon the 3D (three-dimensional) printing technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly establishing a 3D model of the intravascular stent in a computer; inputting data of the established model into corollary equipment of a 3D printer and setting a printing program; bonding a mixed powder material, consisting of stainless steel powder or nickel-titanium powder and stearic acid powder, with a bonder through 3D printing program control to form an intravascular stent blank; performing degreasing, vacuum sintering and cooling treatment on the blank in sequence to obtain the intravascular stent. According to the preparation method, the personalized model can be designed according to the actual requirement of a patient, and the required intravascular stent blank can be rapidly and accurately prepared; the further prepared intravascular stent has a complete surface and has no defects of deformation or cracking and the like; especially, the prepared intravascular stent has no rejection reaction in 24 days in simulated body fluid, is good in biocompatibility and completely meets the medical requirement; the cost for preparing the intravascular stent by a traditional laser cutting method is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUNAN HANDLIKE MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY CO LTD
Ti-TiN-CNx gradient multilayer film and preparation method thereof
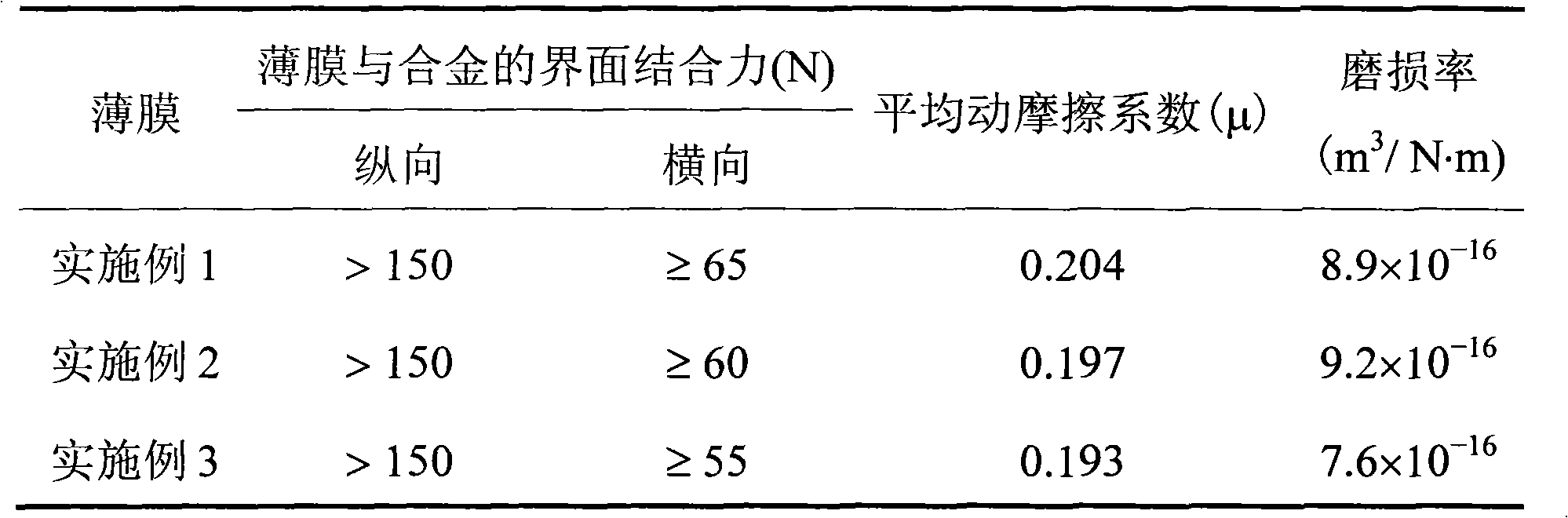
ActiveCN101804708AImprove bindingReduce coefficient of frictionLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingBiocompatibility TestingAlloy substrate
The invention discloses a Ti-TiN-CNx gradient multilayer film. A pure Ti combining layer, a TiN / CNx gradient multilayer transition layer formed by alternating TiN and amorphous CNx and an amorphous CNx film layer with a graphite similar structure are sequentially arranged on a Ti alloy substrate from top to bottom. The Ti-TiN-CNx gradient multilayer film is prepared by adopting an unbalance magnetic sputtering method. The pure Ti combining layer and the TiN / CNx gradient multilayer transition layer improve the bonding force of the film and the substrate, the amorphous CNx film with a graphite similar structure has the hardness of reaching 25-35 GPa and contains lower internal stress, and the gradient multilayer film has controllable thickness. A biological friction property test is carried out in Tyrode's simulated body fluid, and the gradient multilayer film has lower friction coefficient and abrasion rate, shows excellent friction-reducing and wear-resisting property and biocompatibility, can be used for surface protection and modification of a biological material for replacing heart valve prosthesis and joint prosthesis, and greatly prolongs the service life of the material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Composite porous calcium phosphate bone cement and method for making same
InactiveCN1927416APromote degradationPromote growthProsthesisCalcium biphosphateSimulated body fluid
The invention relates to compound porous calcium orthophosphate skeleton cement. Wherein, said cement is formed by calcium orthophosphate skeleton cement powder, 3-hydroxy butanoic acid-CO-3-hydroxy pentanoic acid polymer microball, and solidify liquid. And the production comprises: preparing orthophosphate skeleton cement solid powder; preparing analogue humor; mixing the PHVV microball radiated by Co60 gama-ray; washing, drying and emerging it in the analogue humor, to be washed and dried; then mixing the PHBV microball and solid powder, to be added with solidify liquid to obtain the product. The invention has high strength, quick degradation and controllable degradation speed. And it can be used to repair skeleton hurt and used as skeleton support.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Biodegradable Mg-Gd-Zn-Ag-Zr series magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103184380AAccelerated corrosionUniform corrosion morphologySimulated body fluidOrder structure
The invention relates to biodegradable Mg-Gd-Zn-Ag-Zr series magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of medical alloy. The alloy consists of Gd, Zn, Ag, Zr and Mg in percentage by weight: 5-10 percent of Gd, 0.5-3 percent of Zn, 0.1-1 percent of Ag, 0.1-1 percent of Zr and the balance of Mg. Through reasonably designing the alloy elements, a long-period stacking order structure (LPSO structure) is formed in an alloy structure; and with the adoption of the structure, the alloy can be strengthened and toughened, and the corrosion resistance and the local corrosion resistance of the alloy can be improved. Through deformation processing and heat treatment, the strong toughness and the corrosion resistance of the magnesium alloy can be further improved. The magnesium alloy provided by the invention is uniformly corroded in simulated body fluid, so that the overall failure of an implant material due to local corrosion is avoided, and no obvious cytotoxicity exists. The biodegradable Mg-Gd-Zn-Ag-Zr series magnesium alloy can be used as a bone plate, a bone nail and other fixing and implant materials in the orthopeadic surgery.
Owner:JIANGSU KONSUNG MEDICAL EQUIPMENT CO LTD +1
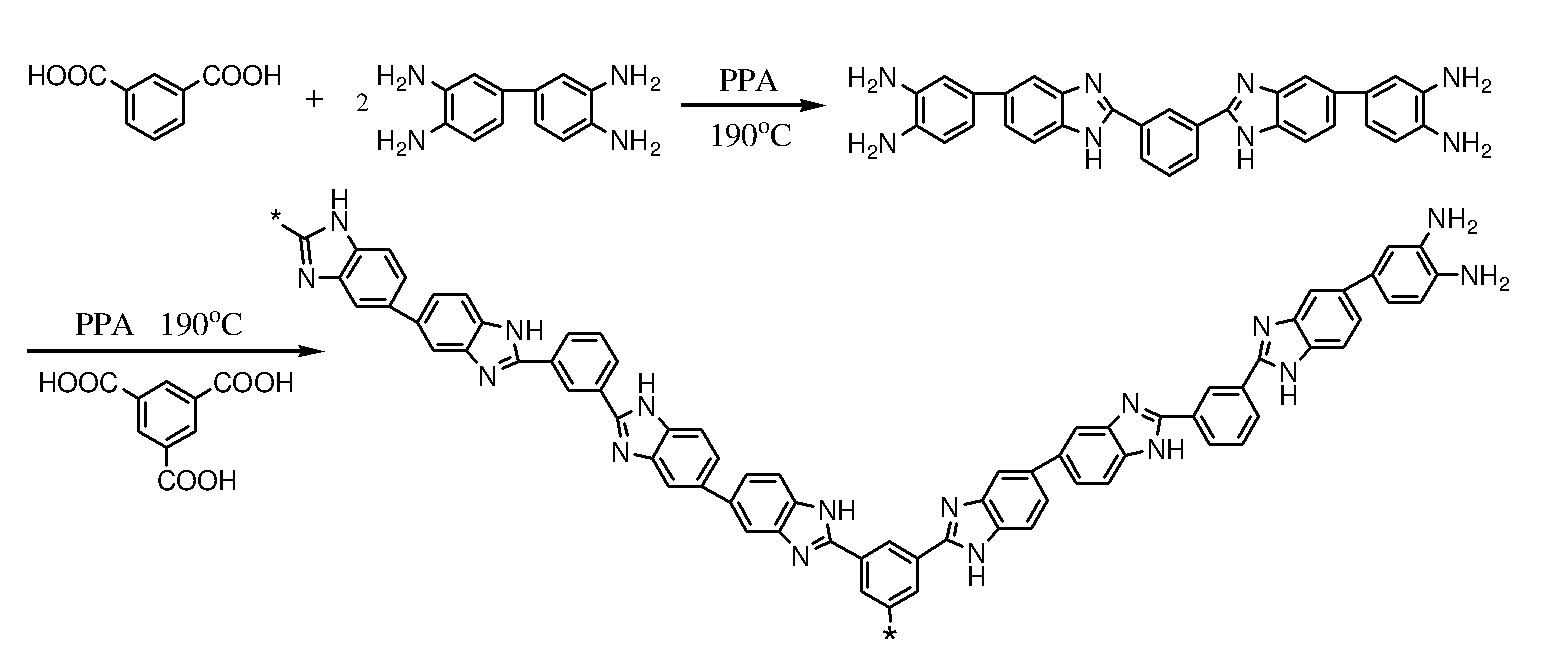
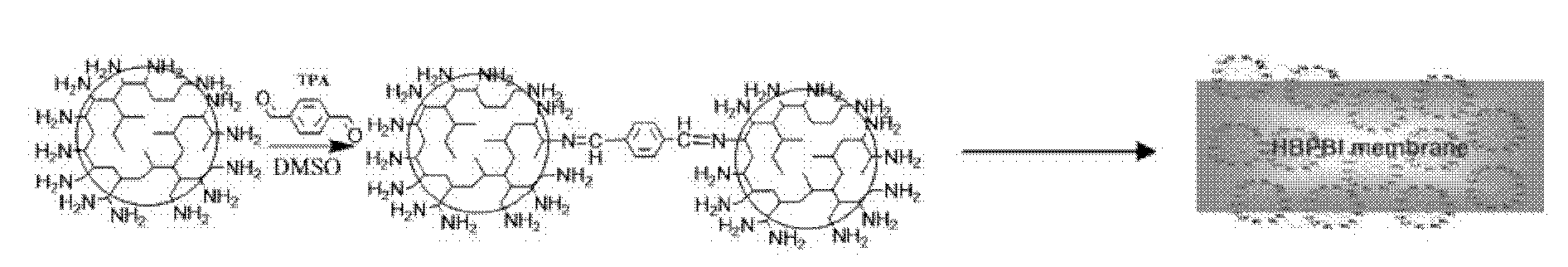
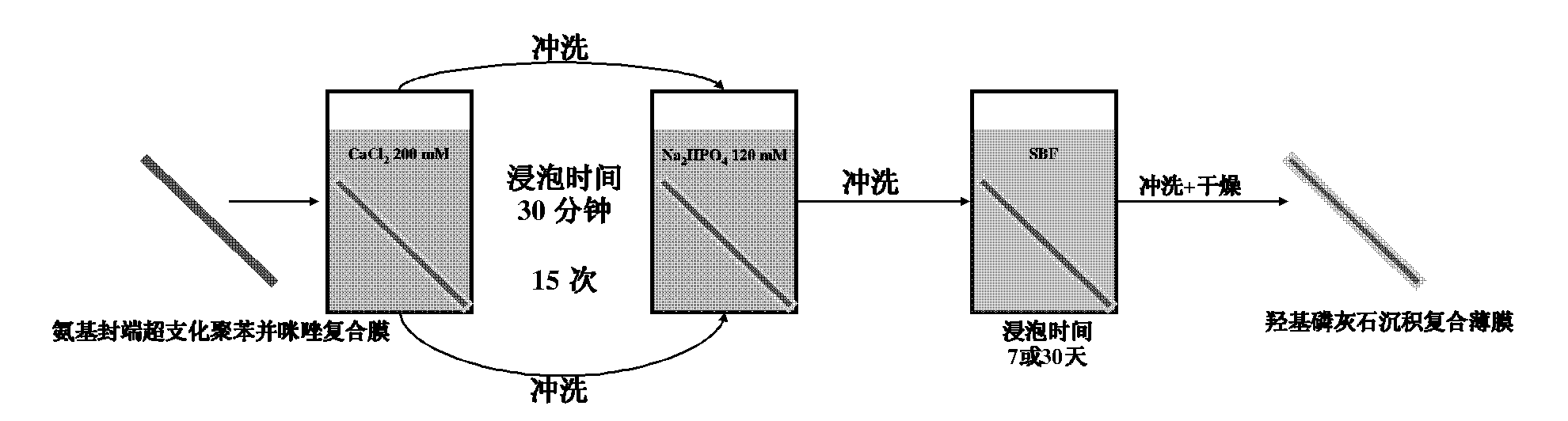
Preparation method of amino-terminated hyperbranched polybenzimidazole composite film
ActiveCN101879331AGood compatibilityGood bone conductionSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsComposite filmApatite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an amino-terminated hyperbranched poly benzimidazole composite film, belonging to the technical field of composite thin films. The preparation method comprises the following two steps of compositing an amino-terminated hyperbranched poly benzimidazole thin film matrix, and precipitating hydroxyapatite, wherein the matrix is composited with a methodusing tetramine as an A2 monomer and benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid as a B3 monomer; and the hydroxyapatite is precipitated by combining alternative immersing and simulated body fluid immersing. The invention provides a method for preparing the composite thin film using an alkaline group as a matrix at normal temperature and pressure. The formed hydroxyapatite and polymeric matrix are in a sandwich structure. The hydroxyapatite can be properly fixed on the surface of the composite thin film so that not only the biocompatibility and the bone conductivity of the thin film can be improved but also the hydrophilicity of the thin film can be increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN DALTON ELECTRONICS MATERIAL CO LTD
Bioactive graded zirconia-based structures
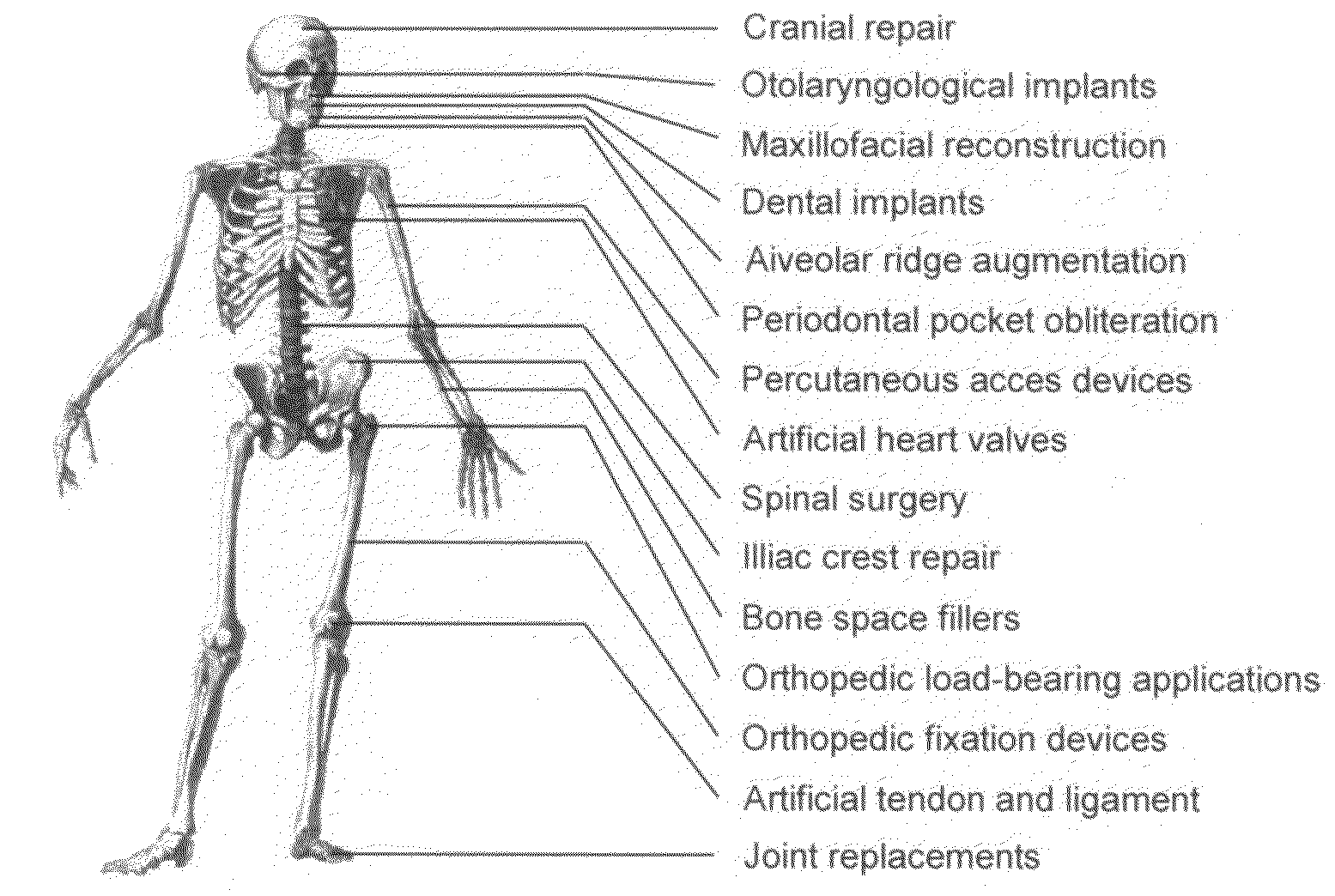
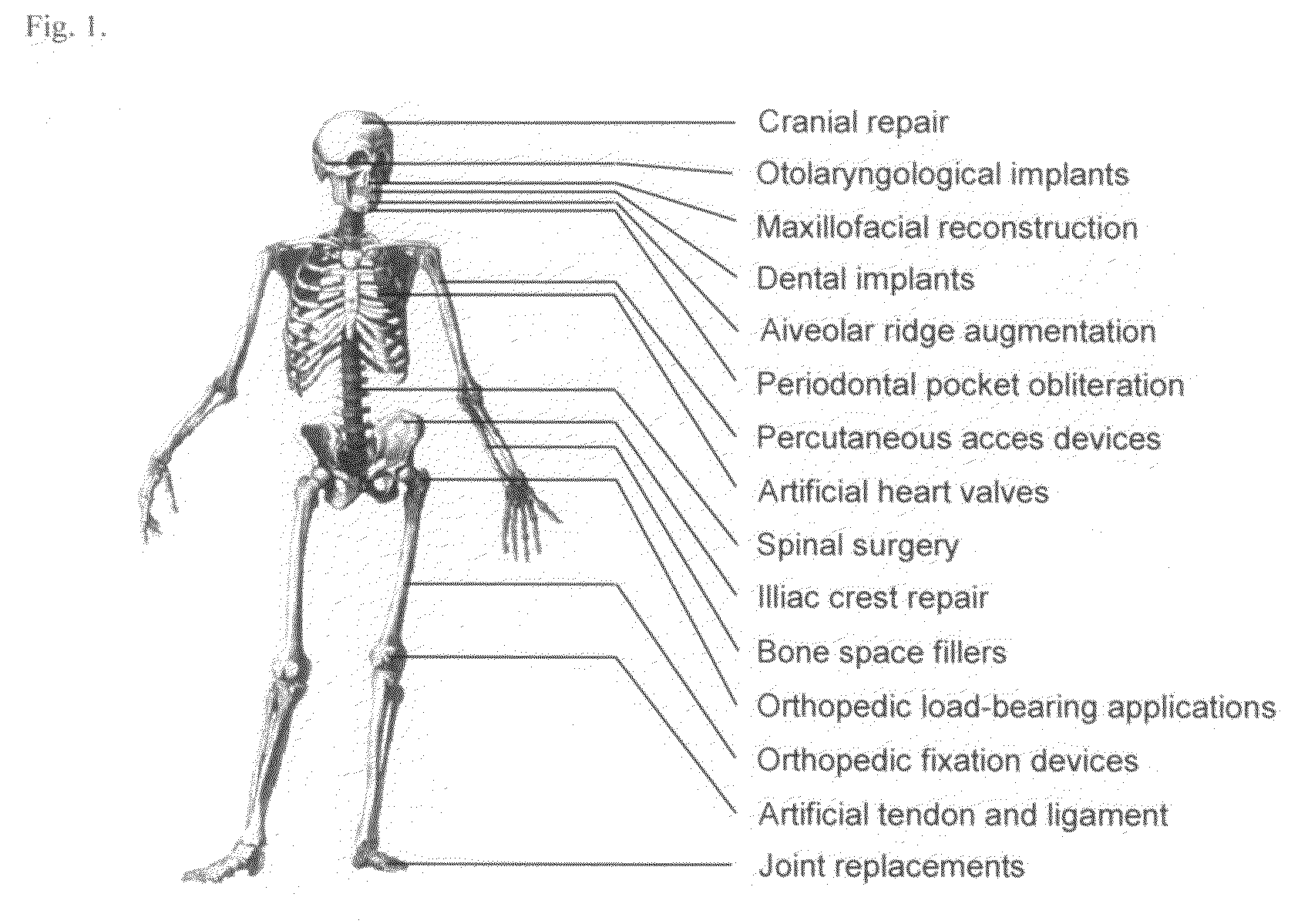
The present invention provides a functionally graded bioactive glass / ceramic composite structure or bioactive glass / ceramic / bioactive glass sandwich structure for use in such applications as damage resistant, ceramic dental implants, immediate tooth replacement, endodontic posts, orthopedic prostheses, orthopedic stems, bone substitutes, bone screws, plates, and anchors, nonunion fractures repair, alveolar ridge augmentation, missing small bone parts (e.g. fingers, toes, etc), maxilla facial reconstruction, spinal fusion, and scaffolds for bone regeneration, comprising a residual bioactive glass or glass-ceramic layer at all accessible surfaces, followed by an underlying graded glass-ceramic layer, and then an dense interior ceramic. The residual bioactive glass or glass-ceramic layer can be further transformed to a carbonate apatite (CHA) layer by immersing in calcifying solution or simulated body fluid (SBF) with electrolyte composition similar to that of serum. The interior ceramic preferably contains yttria-tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP) or ceria stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Ce-TZP) or magnesia stabilized zirconia (Mg-PSZ) or calcia stabilized zirconia (Ca-PSZ) or alumina or zirconia-alumina composites. Further, the invention provides methods for making the same functionally graded bioactive glass / ceramic composite structure or graded bioactive glass / ceramic / bioactive glass sandwich structure.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for forming osteolith class layer on surface of calcium phosphate ceramics
InactiveCN1562894AImprove surface activityFast depositionBone implantCalcium biphosphateSimulated body fluid
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Alumina-based biologic active ceramic composite material
InactiveCN101250058AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove biological activityCeramic compositeNitrogen gas
The invention relates to an aluminum dioxide substrate biological active ceramic composite material with better mechanical properties and biological activity, belonging to the technical field of bioceramic material, which contains 80-99% of aluminum dioxide and 1-20% of diopside, referring to mass percentage. The preparation method comprises using aluminum dioxide balls to ball grind mixed raw materials, screening the powder material via a screen of 100 meshes to prepare mixed powder, arranging the mixed powder into a graphite mould to be died and shaped, thermally pressing and sintering in nitrogen gas or argon gas, while the sintering temperature is 1400-1500DEG C, sintering pressure is 25-30MPa, keeping the temperature and pressure for 30-40min. Tests prove that the sample immersed in simulated body fluid has much carbonate hydroxyapatite sediment generated at surface and the composite material has better biological activity. The composite material has simple preparation, low material cost, low production investment and wide application for the preparation of artificial bone.
Owner:张木蕃
Bacteria cellulose/gelatin/hydroxyapatite composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101947335ASolve the problem of low mechanical propertiesPromote growthProsthesisFiberSimulated body fluid
The invention relates to a bacteria cellulose / gelatin / hydroxyapatite composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material contains the raw materials of bacteria cellulose gel sheeting, gelatin, procyanidin, CaCl2 and simulated body fluid, and the mass ratio of the bacteria cellulose gel sheeting, the gelatin, the procyanidin and the CaCl2 is 100-200:1-5:4-6:6-10. The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly crosslinking the gelatin by using the procyanidin as crosslinking agent so that the gelatin is coated on the fiber surface of the bacteria cellulose to prepare a bacteria cellulose / gelatin composite material, and the bacteria cellulose / gelatin / hydroxyapatite composite material is further prepared by adopting biomimetic mineralization method. The composite material according to the invention has excellent mechanical properties, unique three-dimensional nano-network structure and more structural and componential similarity to bionics, and meets the demand of the engineering material for cartilage tissues of human body. The composite material according to the invention has the advantages of safe and nontoxic reagents adopted, low cost and simple preparation technology.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
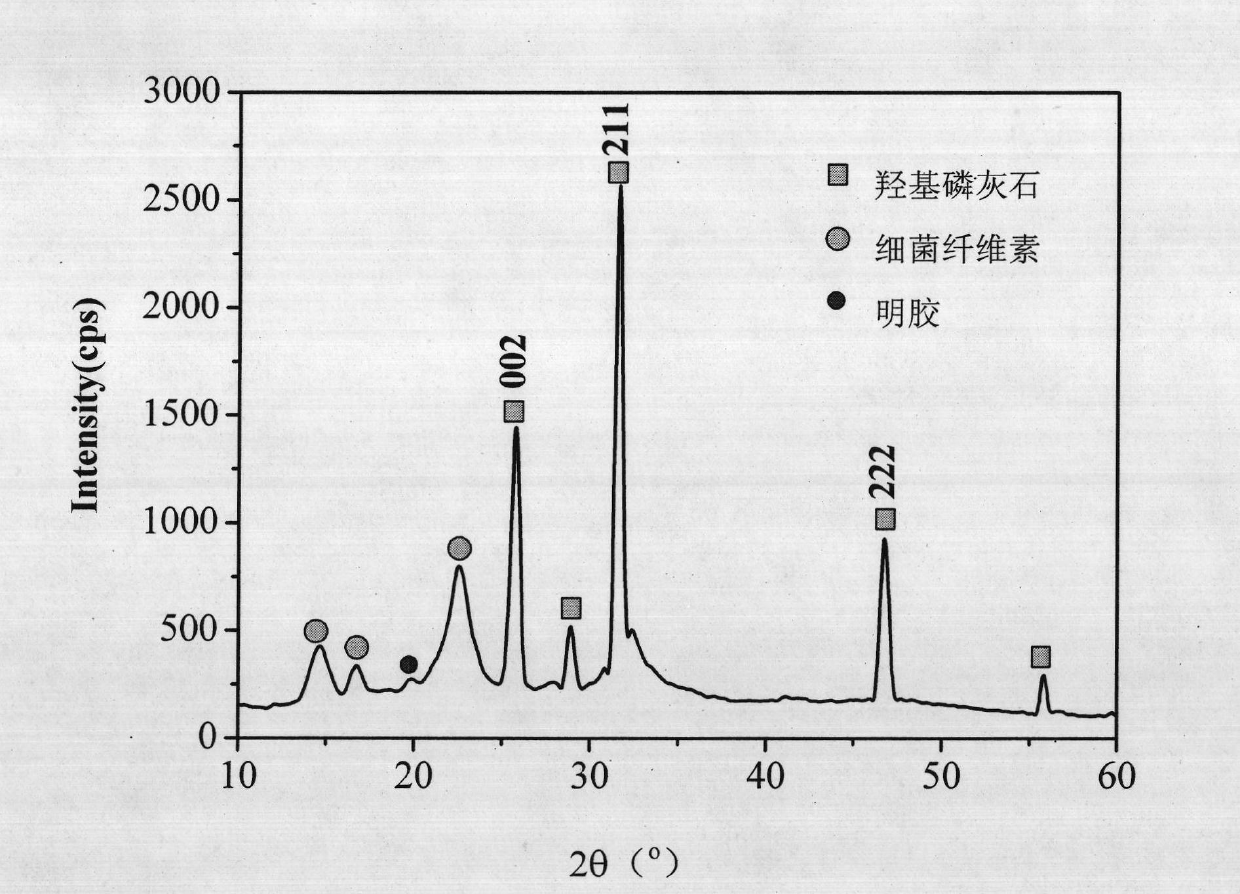
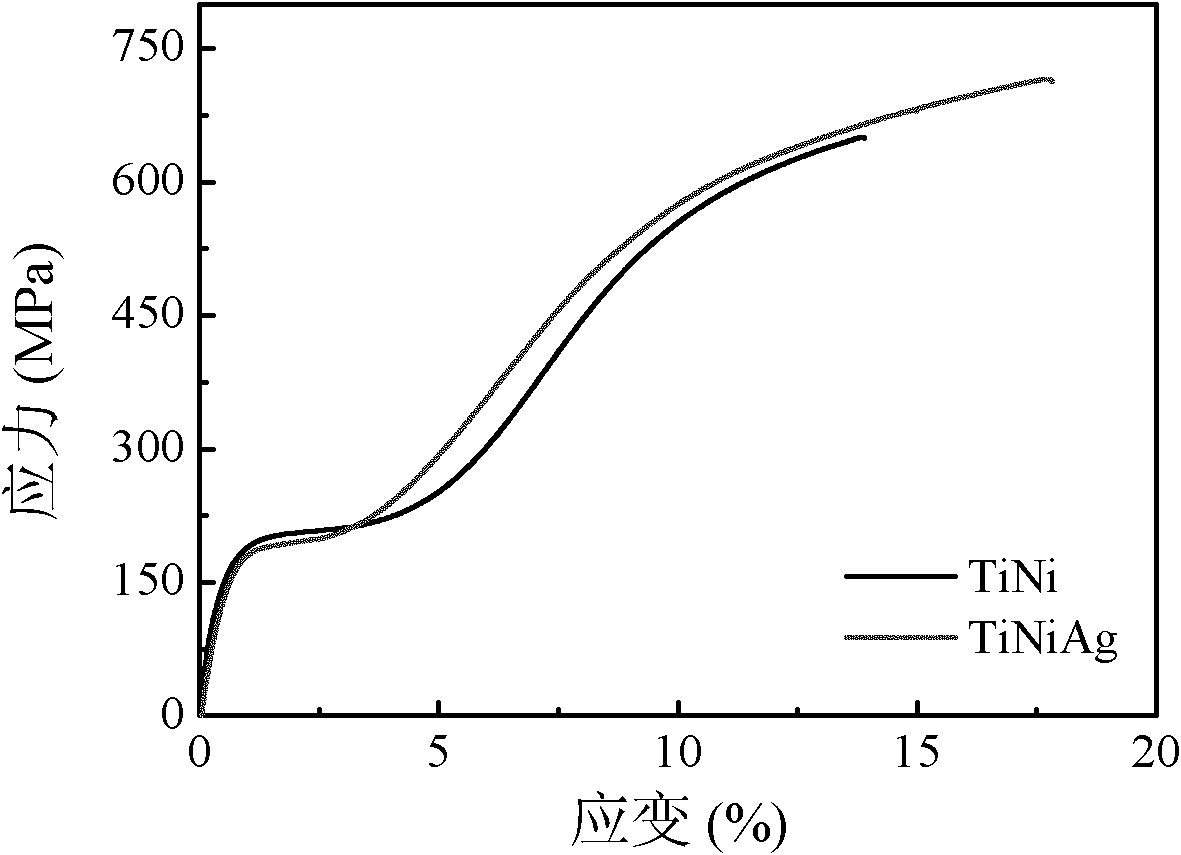
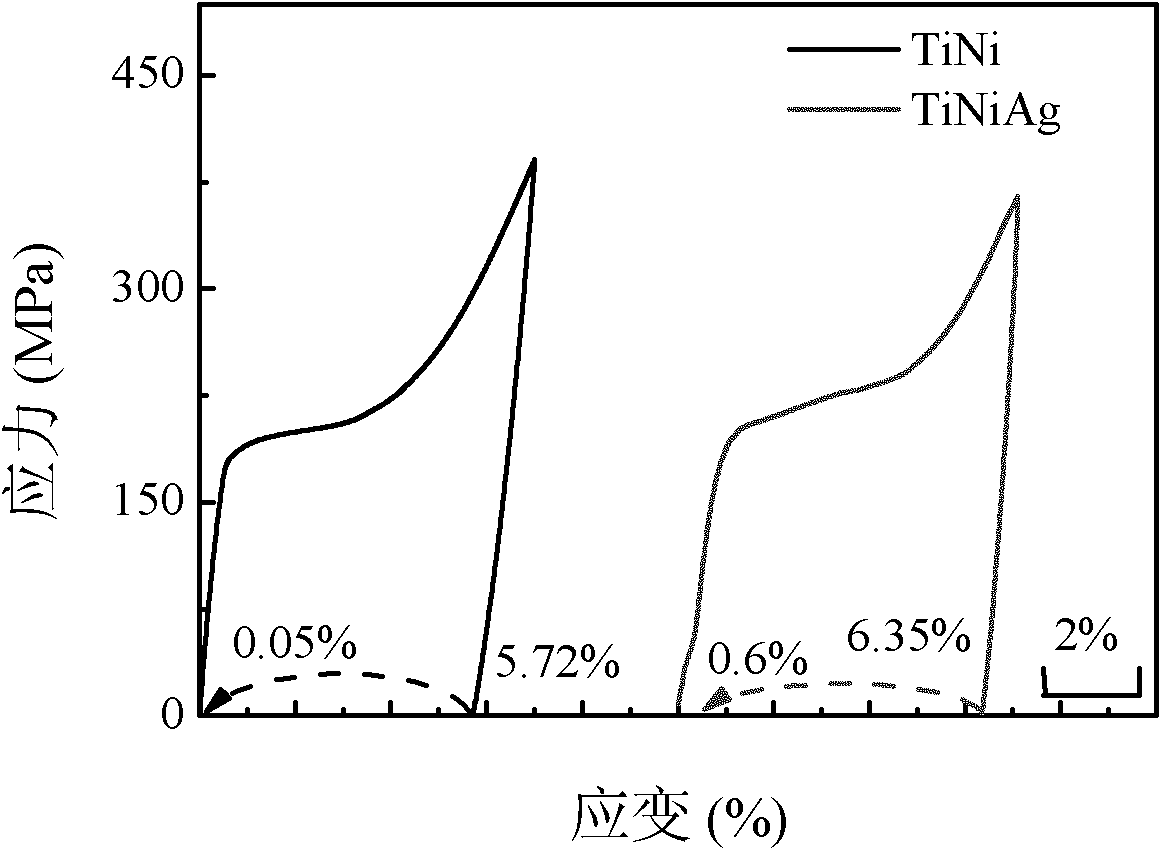
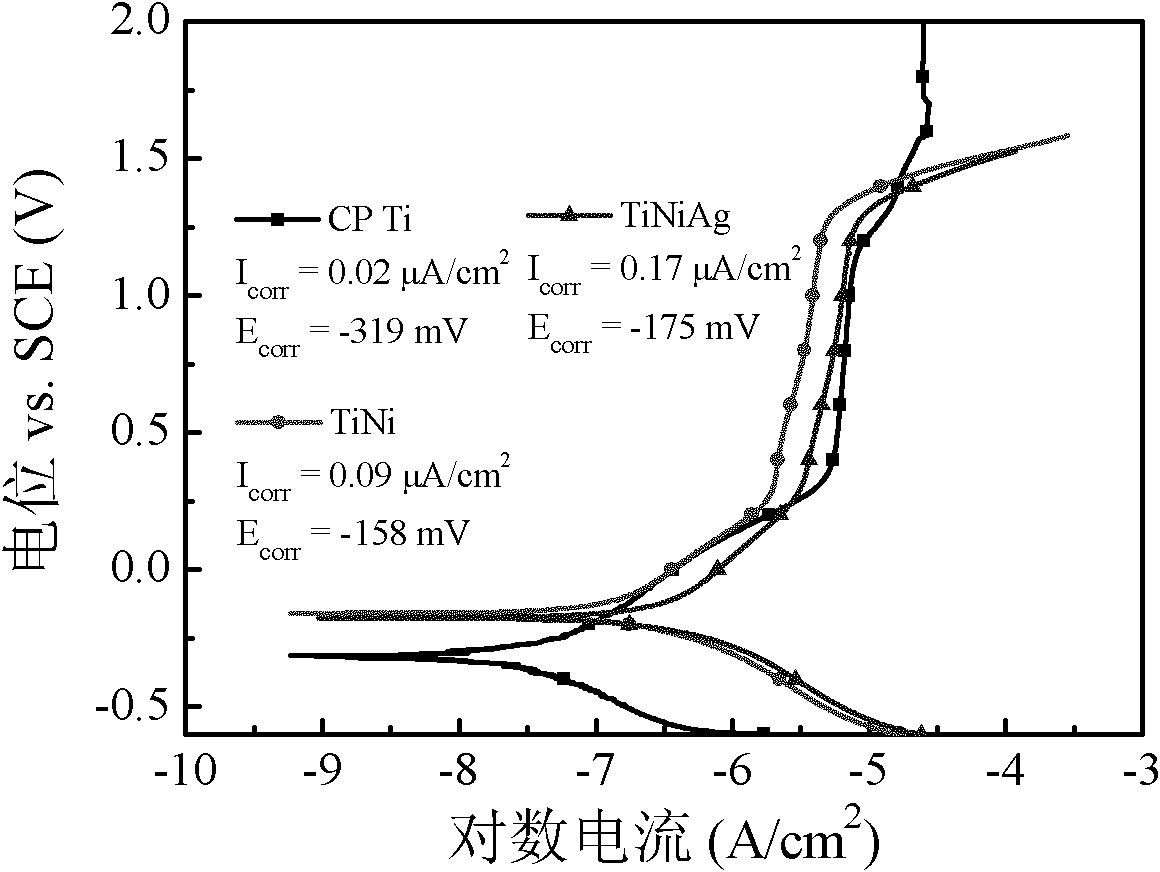
TiNiAg memory alloy with antibacterial function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101988166AGood shape memory effectIncrease elasticityEscherichia coliBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a TiNiAg memory alloy with the antibacterial function and a preparation method thereof. The TiNiAg memory alloy contains 20%-80% of nickel, 0.1%-10% of silver and the balance of titanium by atomic percent. The alloy not only has good shape memory effect and superelasticity, but also has good matching of mechanical properties. Simultaneously, the alloy material has good corrosion resistance and biocompatibility in simulated body fluid, and cytotoxicity is in the same level of a TiNi alloy. In addition, the alloy material has a broad antimicrobial spectrum and can well inhibit Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus epidermidis and other gram-negative and positive bacteria.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
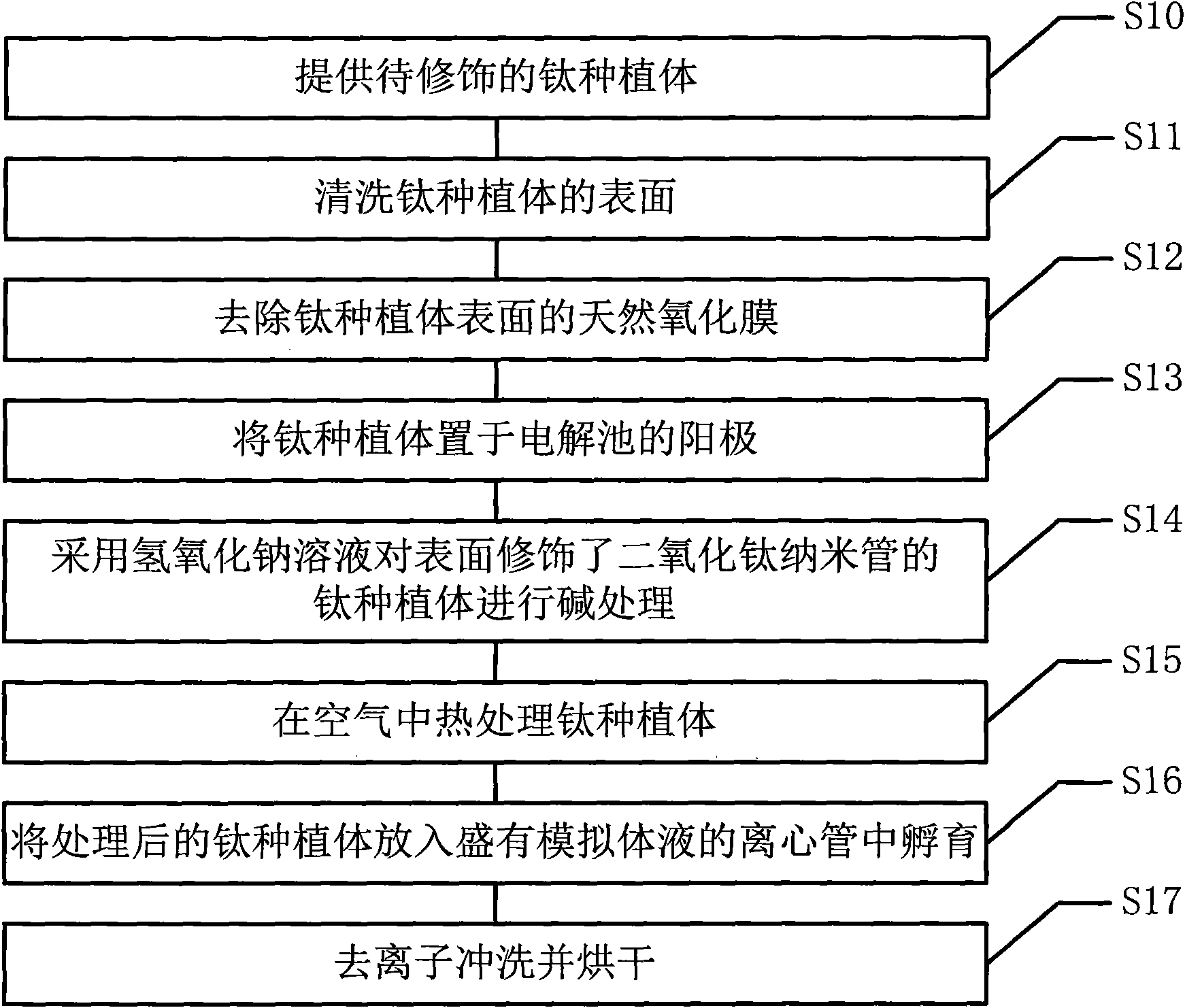
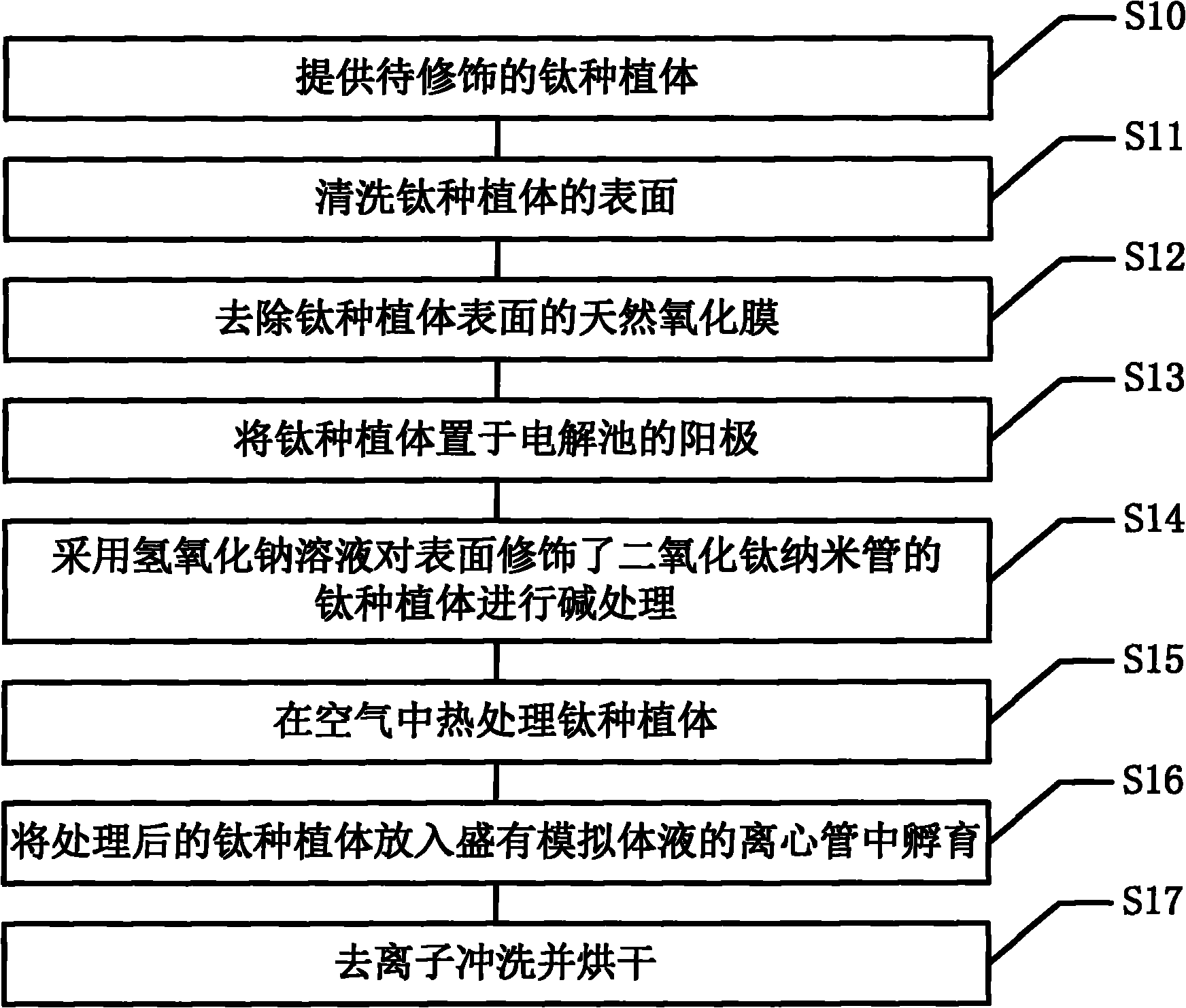
Biomimetic modification method of controllable titanium dioxide nano-tube on surface of titanium planting body and planting body
InactiveCN102383163APromotes Adhesive GrowthHas bone conduction propertiesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingNanotubeSurface modification
The invention relates to a biomimetic modification method of a controllable titanium dioxide nano-tube on a surface of a planting body, which comprises the following steps that: a titanium planting body to be modified is provided; the surface of the titanium planting body is washed; a natural oxidized film on the surface of the titanium planting body is removed; the titanium planting body is arranged on anode of an electrolytic cell to be oxidized to obtain a titanium dioxide nano-tube structure; sodium hydroxide solution is adopted for the alkaline treatment of the titanium planting body with the surface being modified by the titanium dioxide nano-tube; heat treatment on the titanium planting body is undertaken in the air; the titanium planting body after being treated is placed into a centrifugal pipe with simulation body liquid to incubate; and the titanium planting body is de-ionized, washed and dried. The biomimetic modification method has the advantages that: a unique structure of the titanium dioxide (TiO2) nano-tube is used for building a biomimetic nano calcium-phosphous coating on the surface of the planting body, after the planting body is planted into a human body, on the one hand, the planting body is in a nano-grade structure and can provide contact for osteoplast byssus to promote the adhesion growth of cells, and on the other hand, the calcium-phosphous coating is consistent with inorganic composition of natural bone, so an osteoacusis characteristic can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for preparing composite ceramic membrane on surface of magnesium alloy intravascular stent by micro-arc oxidation
InactiveCN103882497AFast growthImprove fracture toughnessAnodisationStentsElectrolytic agentMicro arc oxidation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a composite ceramic membrane on the surface of a magnesium alloy intravascular stent by micro-arc oxidation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing an electrolyte; 2) performing micro-arc oxidation treatment by taking the magnesium alloy intravascular stent as an anode, taking a stainless steel plate as a cathode and taking a stainless steel wire with the surface coated with an insulating plastic membrane as an auxiliary cathode so as to in-situ grow a layer of uniform composite ceramic membrane on the surface of the magnesium alloy intravascular stent. Micron-grade holes which are uniformly distributed in the prepared composite ceramic membrane can be used as carriers for directly transporting a medicament to a lesion part in a tubular cavity. When the composite ceramic membrane is not subjected to hole sealing post-treatment, the resistance to corrosion of neutral NaCl salt mist can be up to 500h, the resistance to corrosion of a simulated body fluid environment can be up to 2400h, and the fracture toughness is obviously improved. The preparation process disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency and energy conservation.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for preparing artificial head bones made from composite material and for modifying surface
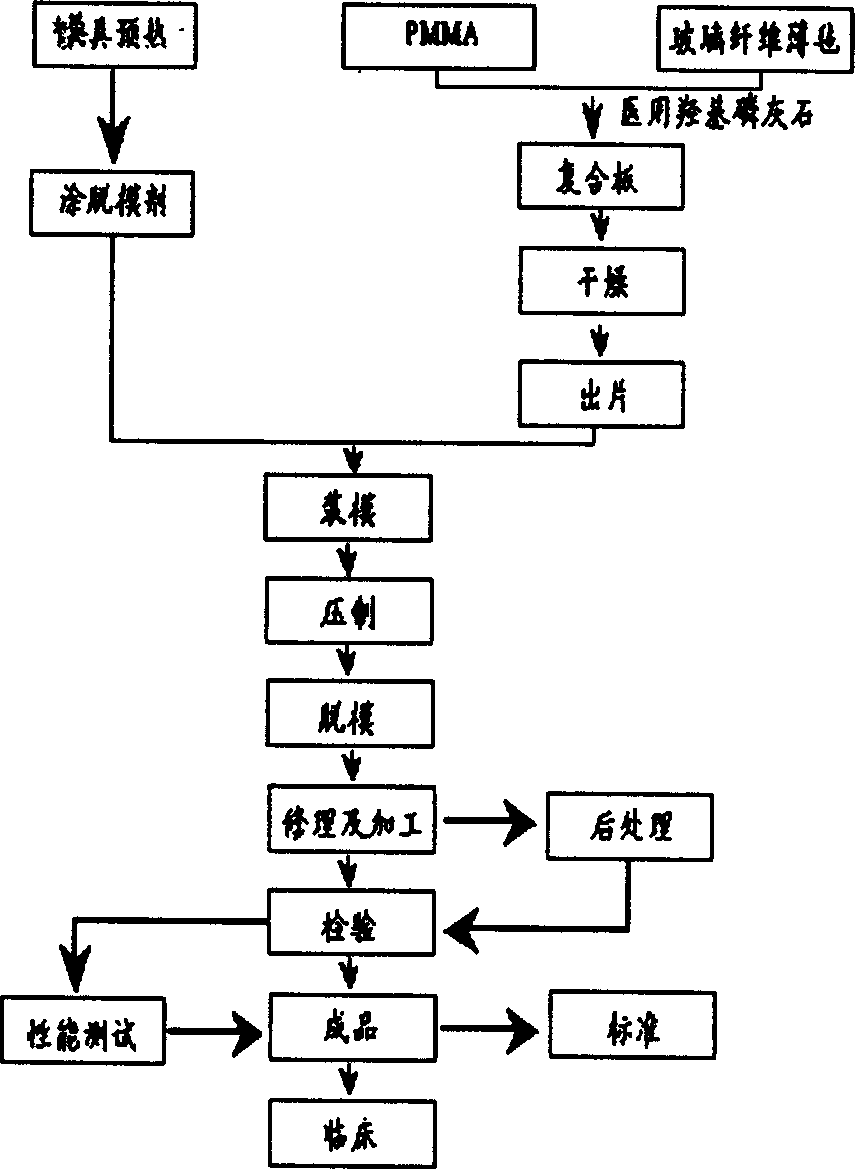
An artificial skull with high surficial bioactivity is prepared from methyl polymethacrylate, biological carbon (or glass) fibres and hydroxy apatite (or beta-tricalcium phosphate) micropowder through laminating or hot pressing, and immersing in simulative body fluid.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com