Patents
Literature
1381 results about "Alloy substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
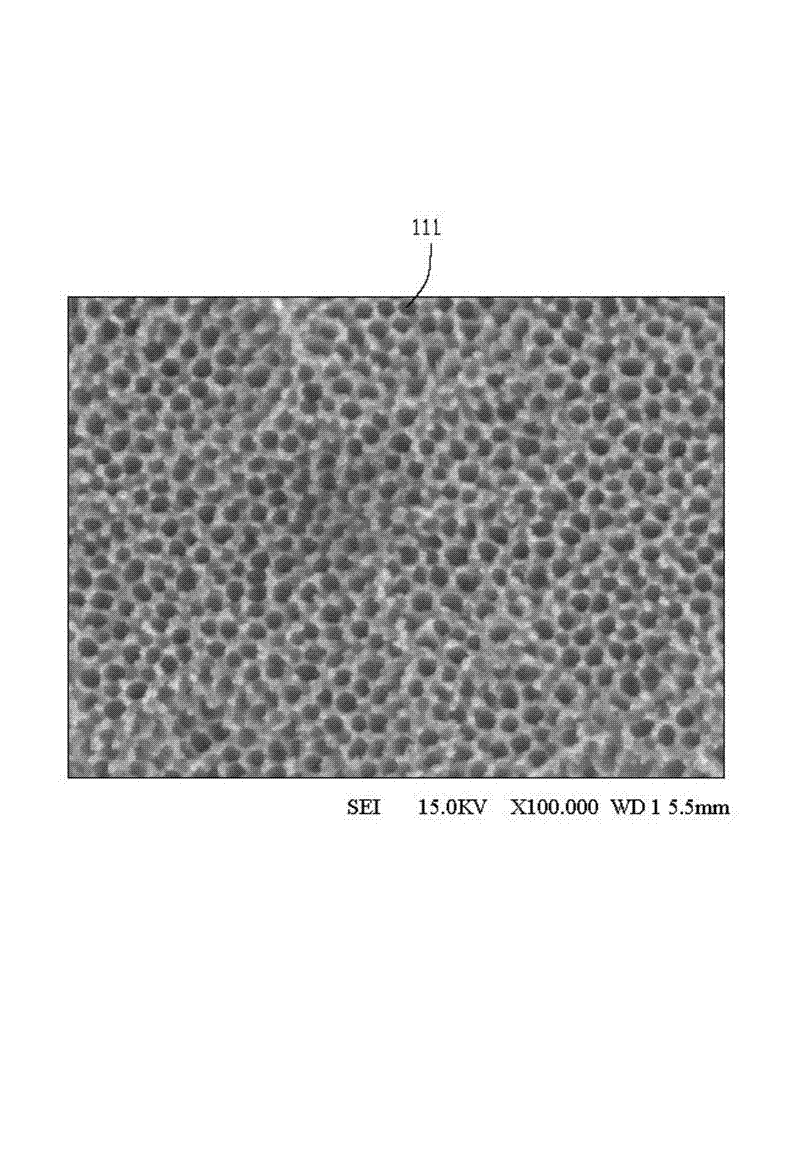
Clean, dense yttrium oxide coating protecting semiconductor processing apparatus
ActiveUS20050037193A1Extended service lifeExcellent plasma corrosion-resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPlasma coatingChemical vapor deposition
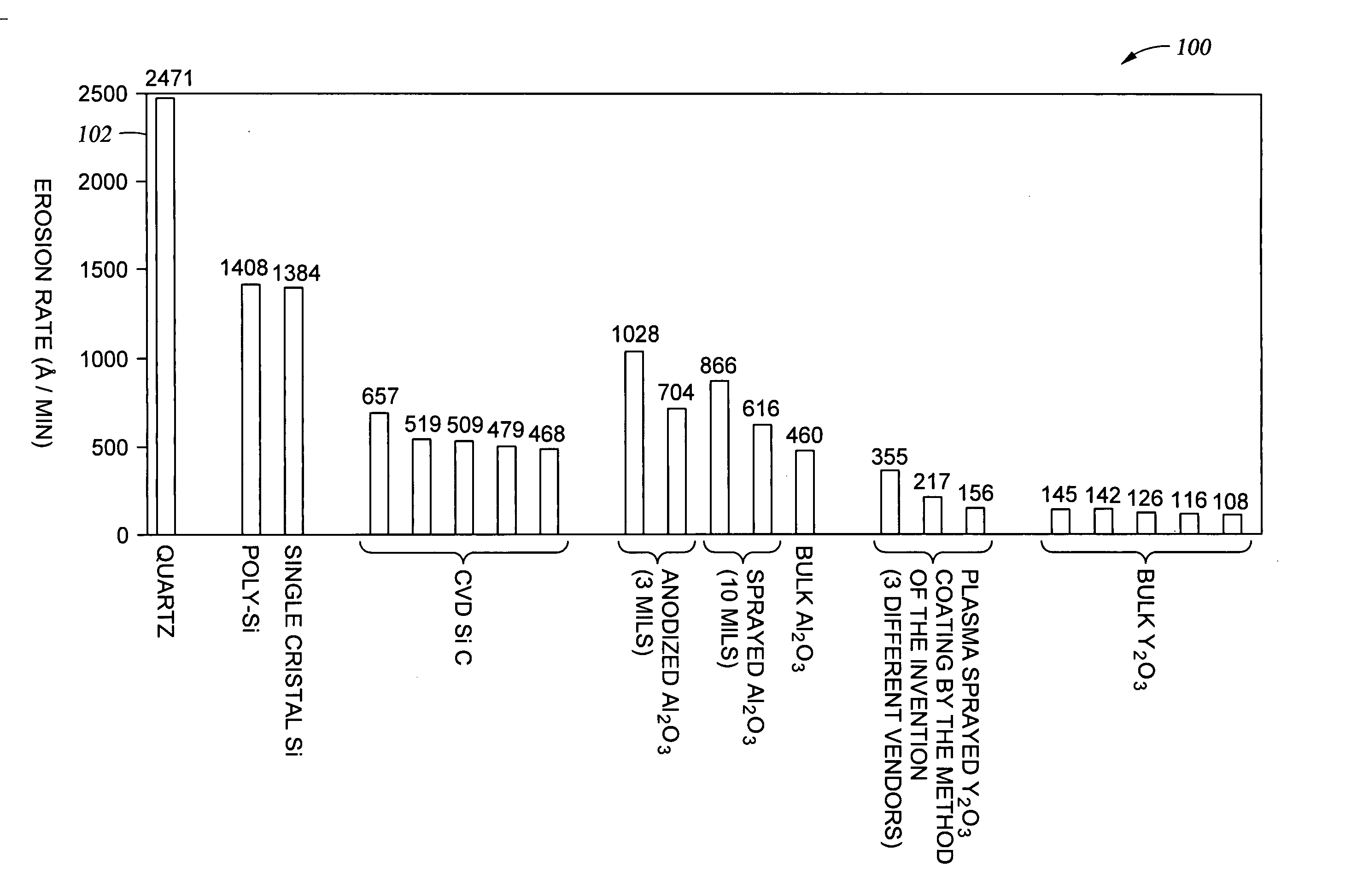
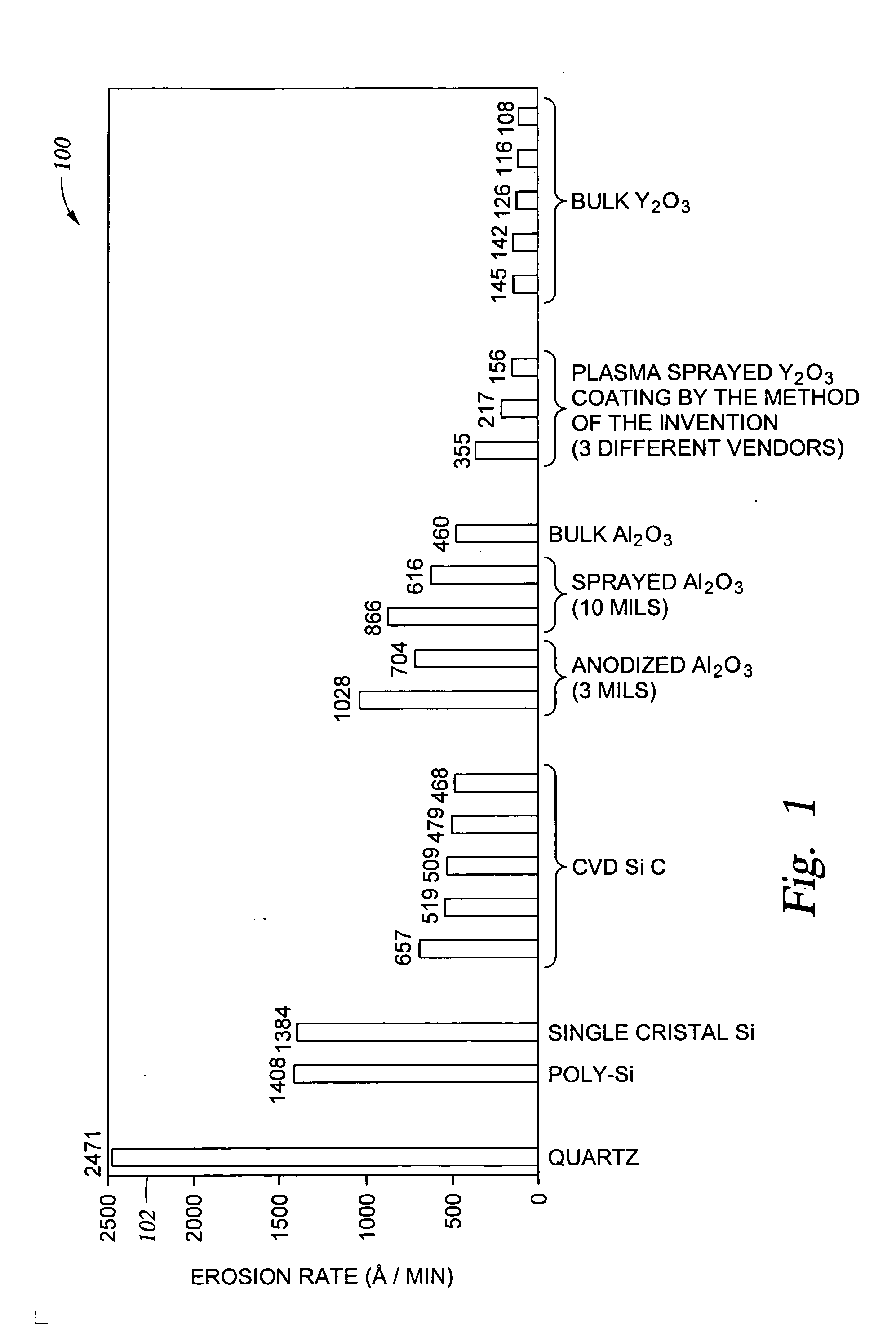
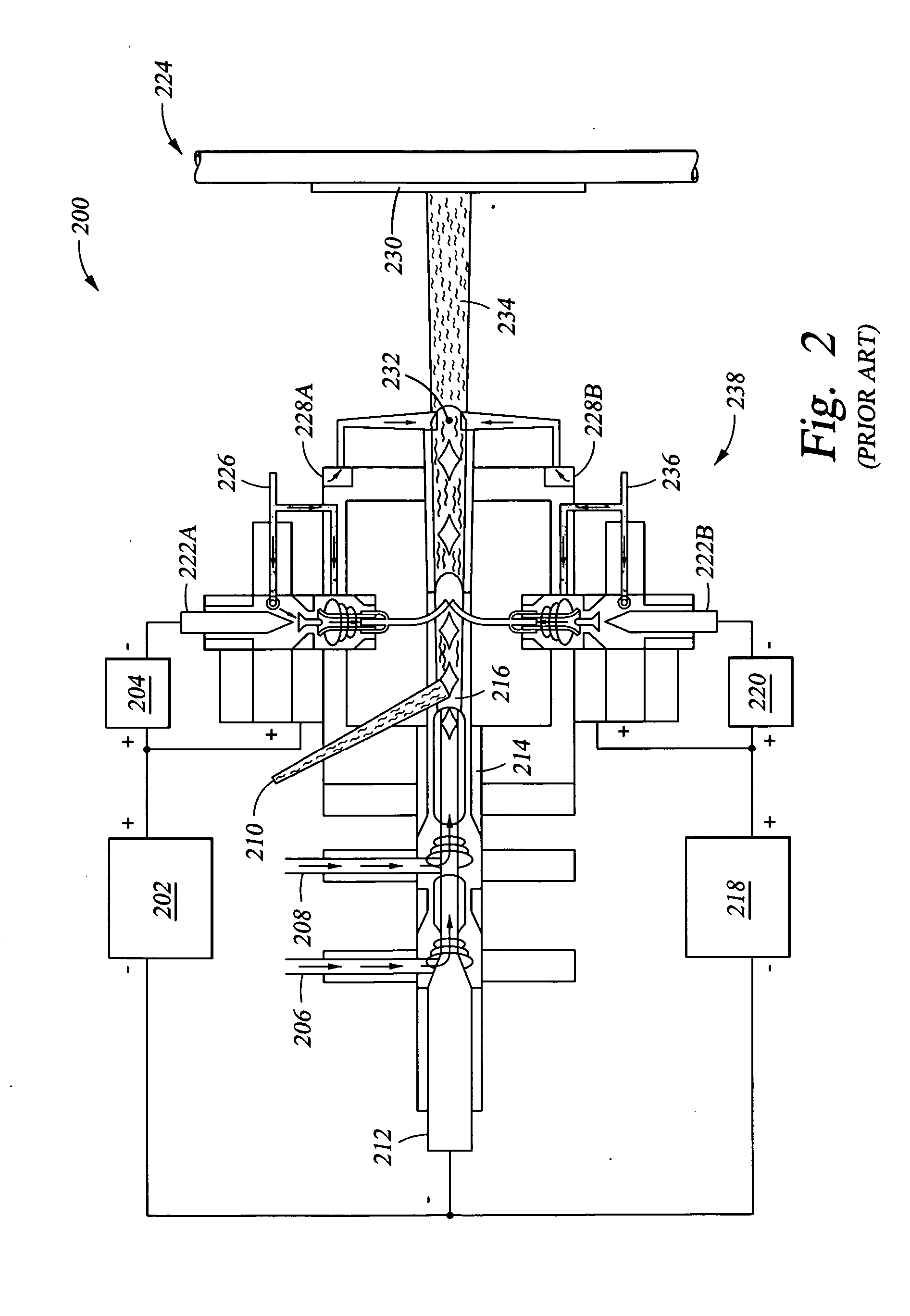
Disclosed herein is a method for applying plasma-resistant coatings for use in semiconductor processing apparatus. The coatings are applied over a substrate which typically comprises an aluminum alloy of the 2000 series or the 5000 through 7000 series. The coating typically comprises an oxide or a fluoride of Y, Sc, La, Ce, Eu, Dy, or the like, or yttrium-aluminum-garnet (YAG). The coating may further comprise about 20 volume % or less of Al2O3. The coatings are typically applied to a surface of an aluminum alloy substrate or an anodized aluminum alloy substrate using a technique selected from the group consisting of thermal / flame spraying, plasma spraying, sputtering, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). To provide the desired corrosion resistance, it is necessary to place the coating in compression. This is accomplished by controlling deposition conditions during application of the coating.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for preparing single-layer graphene
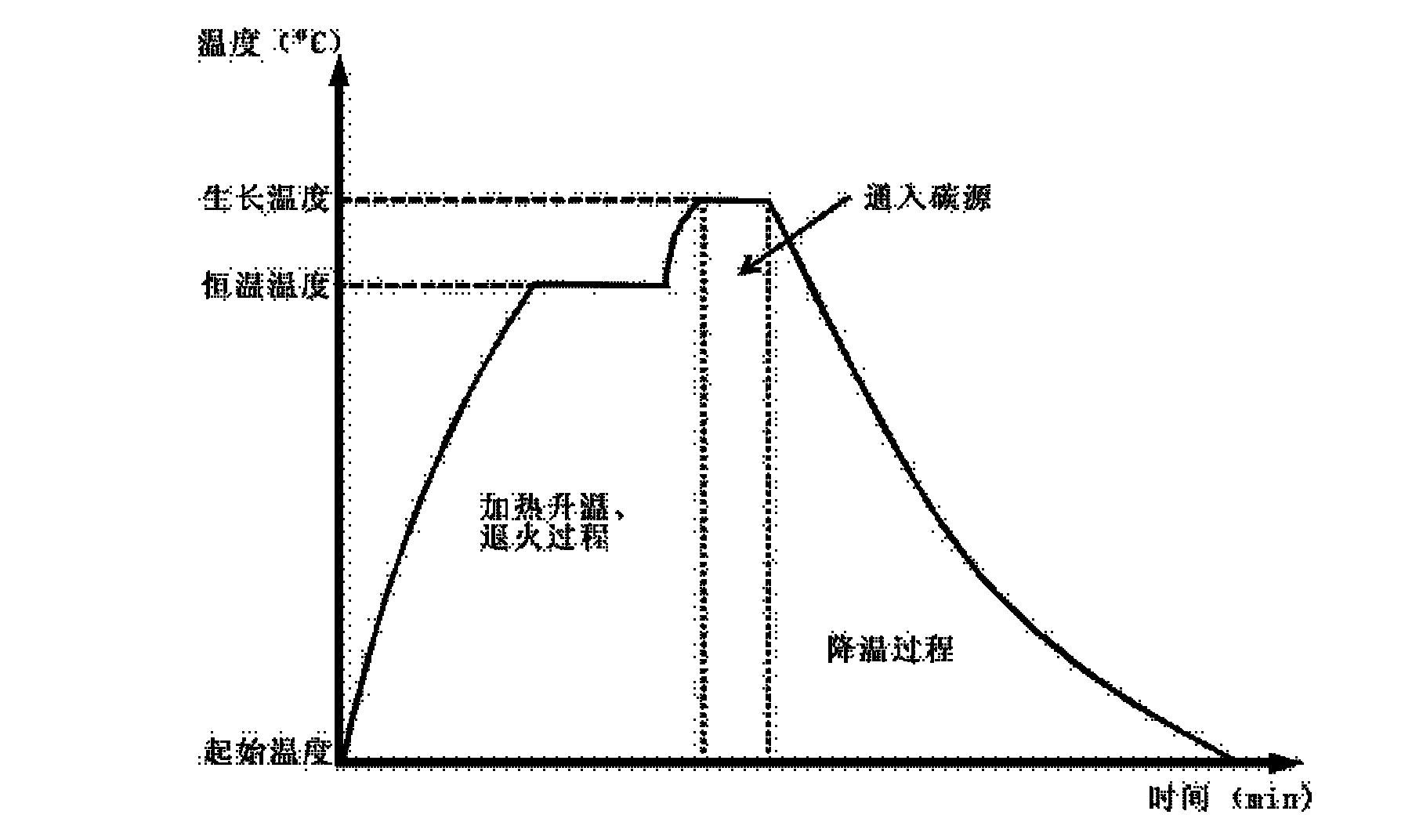
The invention discloses a method for preparing single-layer graphene. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing an alloy substrate; and 2) in the hydrogen and inert atmosphere, catalyzing to grow graphene on the surface of the alloy substrate obtained in the step 1) by a chemical vapor deposition method, thereby finishing the preparation of the single-layer graphene. The method makes use of the characteristics of two or more alloy metals in the alloy substrate, realizes control on the decomposition, diffusion and precipitation processes of a carbon source, simply and efficiently restrains the precipitation process of carbon dissolved in the metal substrate to enable the graphene to be capable of growing in a surface catalytic manner to obtain the single-layer graphene withuniform layer distribution, and is suitable for industrial production and particularly for the controllable preparation of single-layer or few-layer graphene.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Members with multi-layer coatings
InactiveUS6254984B1Improve adhesionGuaranteed uptimeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCarbideCrystal orientation
In the multi-layer-coated member composed of an ultra-hard alloy substrate and a multi-layer coating formed thereon, the multi-layer coating comprises two or more first layers each composed of at least one of carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides of elements of Groups 4a, 5a and 6a of the Periodic Table and Al, and two or more second layers each composed of at least one of oxides, carboxides, oxinitrides and carboxinitrides of elements of Groups 4a, 5a and 6a of the Periodic Table and Al laminated alternately. The first layers adjacent via the second layer are continuous in crystal orientation.
Owner:HITACHI TOOL ENG LTD
Composite body of aluminum or aluminum alloy and plastic and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102268183AImprove bindingAnodisationMetallic material coating processesThermoplasticMetallurgy
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Method of making diamond nanopillars
ActiveUS20090233445A1High application potentialMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanopillarAlloy substrate
A method for fabricating diamond nanopillars includes forming a diamond film on a substrate, depositing a metal mask layer on the diamond film, and etching the diamond film coated with the metal mask layer to form diamond nanopillars below the mask layer. The method may also comprise forming diamond nuclei on the substrate prior to forming the diamond film. Typically, a semiconductor substrate, an insulating substrate, a metal substrate, or an alloy substrate is used.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
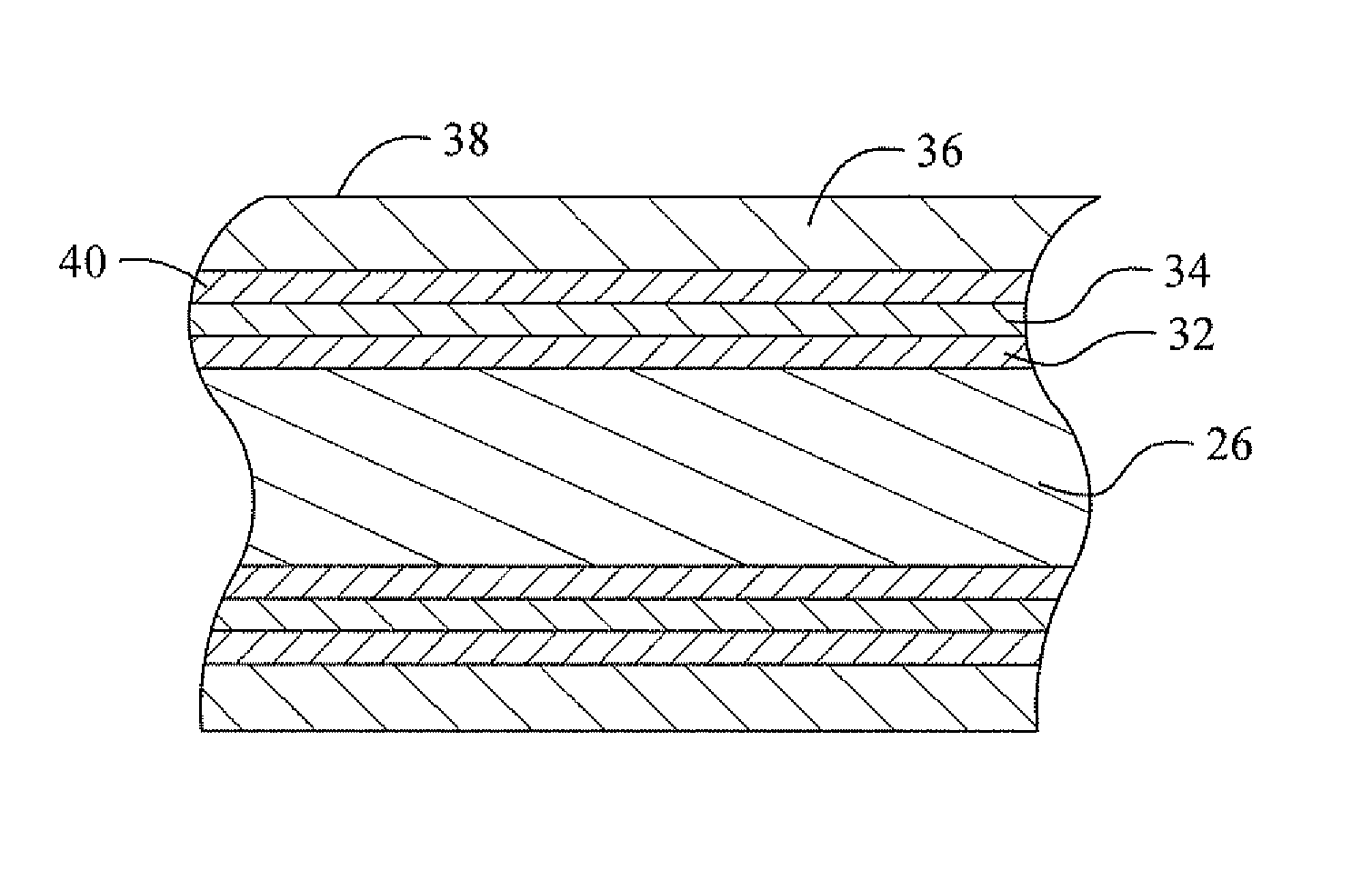
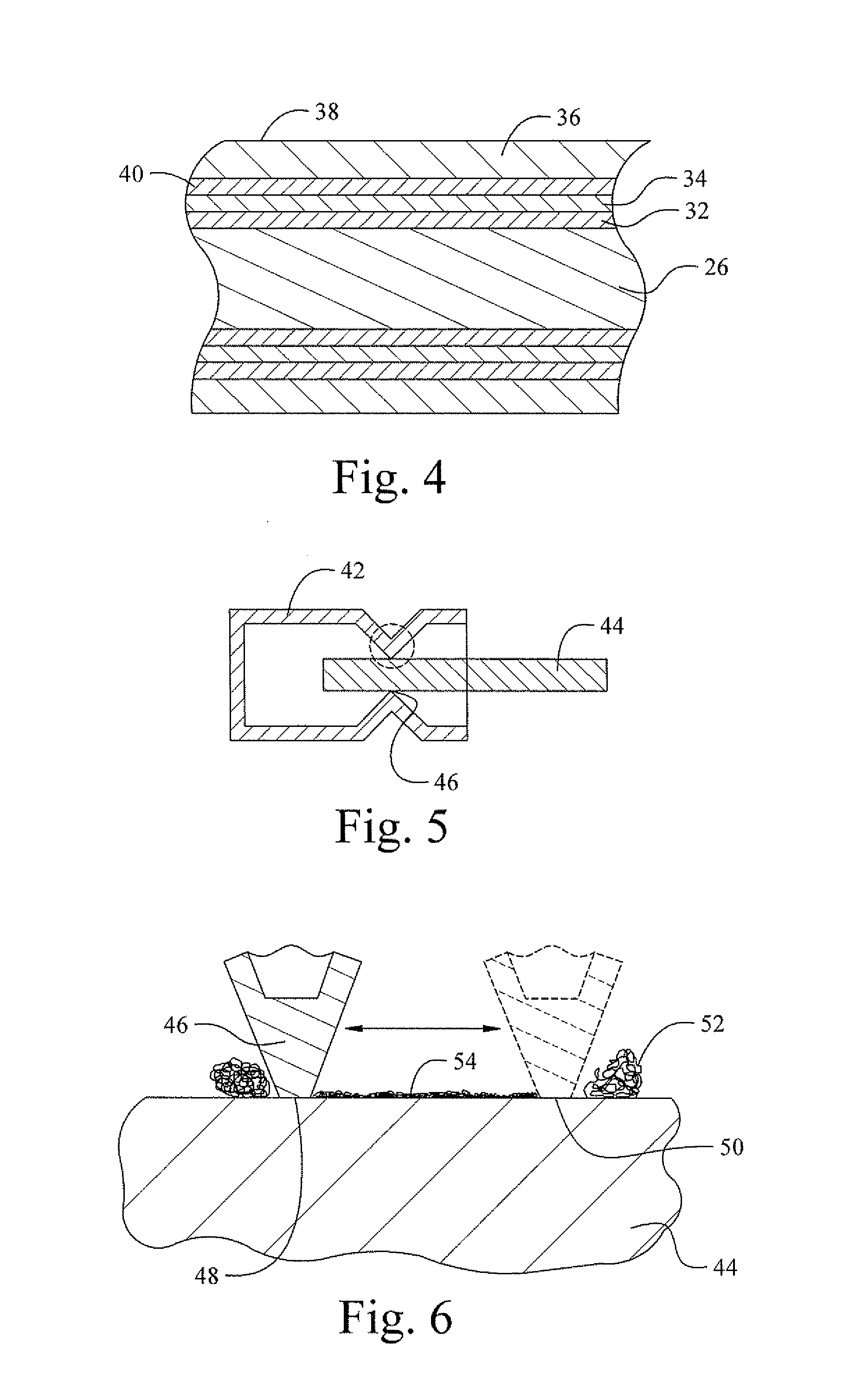
Fretting and whisker resistant coating system and method
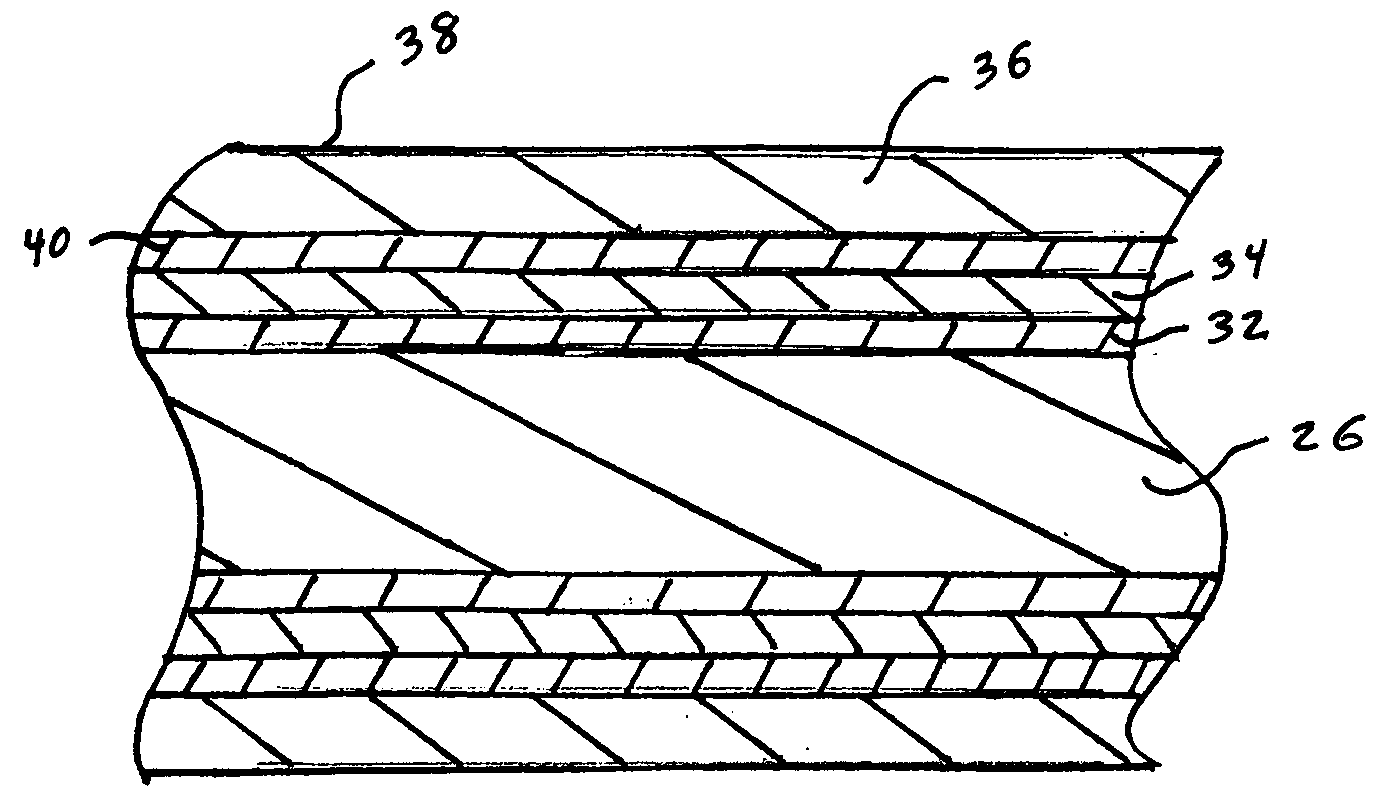
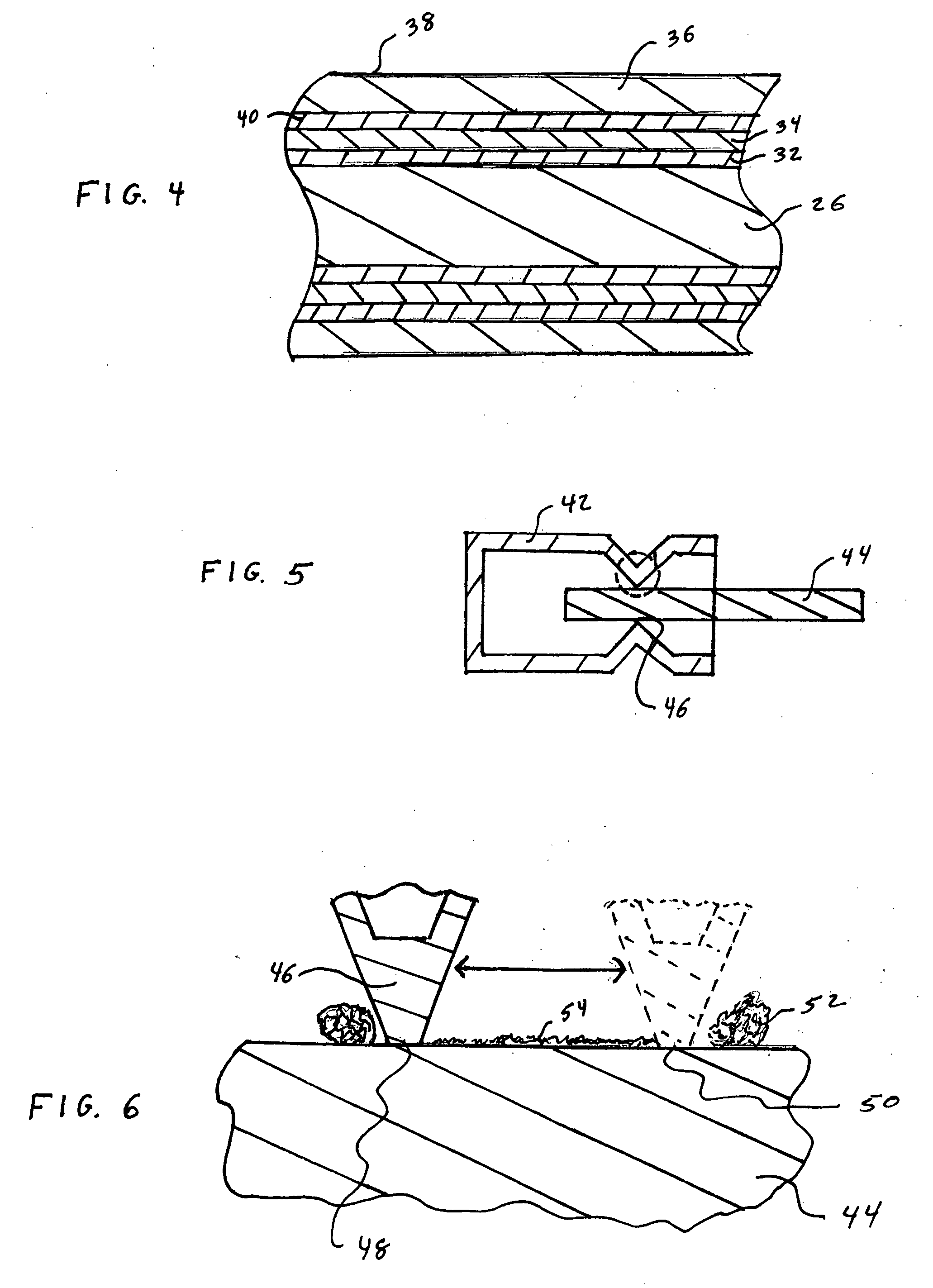
ActiveUS20050106408A1Minimized increaseHigh resistivityAnodisationHot-dipping/immersion processesCoating systemFlexible circuits
A coated electrically conductive substrate has particular utility where there are multiple closely spaced leads and tin whiskers constitute a potential short circuit. Such substrates include leadframes, terminal pins and circuit traces such as on printed circuit boards and flexible circuits. This electrically conductive substrate has a plurality of leads separated by a distance capable of bridging by a tin whisker, a silver or silver-base alloy layer coating at least one surface of at least one of the plurality of leads, and a fine grain tin or tin-base alloy layer directly coating said silver layer. An alternative coated electrically conductive substrate has particular utility where debris from fretting wear may oxidize and increase electrical resistivity, such an in a connector assembly. This electrically conductive substrate has a barrier layer deposited on the substrate that is effective to inhibit diffusion of constituents the substrate into a plurality of subsequently deposited layers. The subsequently deposited layers include a sacrificial layer deposited on the barrier layer that is effective to form intermetallic compounds with tin, a low resistivity oxide metal layer deposited on said sacrificial layer, and an outermost layer of tin or a tin-base alloy directly deposited on the low resistivity oxide metal layer. In this alternative embodiment, the barrier layer is preferably nickel or a nickel-base alloy and the low resisitivity oxide metal layer is preferably silver or a silver-base alloy. When heated, the coated substrate of this second embodiment forms a unique structure having a copper or copper-base alloy substrate, an intervening layer formed from a mixture or metals including copper and tin, and an outermost layer which is a mixture of a copper-tin intermetallic containing phase and a silver-rich phase. It is believed that this silver-rich phase is particularly beneficial to reduce an increase in resistivity due to oxidation of fretting wear debris.
Owner:WIELAND ROLLED PROD NORTH AMERICA LLC
Aluminum laminate
InactiveUS6235409B1Light weightHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesAdhesive processesAlloy substrateAlclad
A bright finish aluminum alloy on high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy lamination is disclosed including a bright finish top sheet, a high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate, and an adhesive bonding the bright finish metal top sheet to the high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate to provide a bright finish aluminum on high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy lamination product having brighter finish than a sheet product of said high strength aluminum or aluminum alloy and higher strength than a sheet product of said bright finish aluminum of the same thickness as said lamination product, wherein said lamination product withstands galvanic corrosion. In one aspect, the bright finish metal top sheet is 5657 aluminum foil. In one aspect, the high strength aluminum alloy is 5182 alloy sheet.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
High temperature component with thermal barrier coating and gas turbine using the same
There is provided a high temperature component with a thermal barrier coating, which can be used as a high temperature component for a gas turbine, an aircraft gas turbine engine, or the like. A top coat is formed of a ceramic on a bond coat, the bond coat being formed on a heat resistant alloy substrate composed mainly of at least one element of nickel and cobalt, wherein the bond coat contains at least one of nickel and cobalt, chromium and aluminum, and further contains at least one selected from a group consisting of tantalum, cesium, tungsten, silicon, platinum, manganese and boron in a range of 0 to 20 wt %. The high temperature component according to the present invention has very high durability of a thermal-insulating ceramic layer, and is less susceptible to spalling damage.
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY +1
Methods for treating superalloy articles, and related repair processes
A method is described, for treating a superalloy substrate which includes at least one cavity containing adherent metal oxide material on its surface. A short-pulsed, high repetition rate laser beam is directed against the cavity surface for a period of time sufficient to remove substantially all of the adherent metal oxide material. The laser beam is characterized by a peak power density in the range of about 10 megawatts / cm2 to about 10 gigawatts / cm2. In another embodiment, a high-power, short-pulsed, high repetition rate laser beam is directed to a region on the substrate which includes the cavity, under laser operational conditions which are capable of cutting into the superalloy material; so that a boundary region is formed within the substrate, which encloses the cavity. The cavity can be a crack in a turbine blade, and the crack can be repaired after treatment, by welding, or by another suitable technique.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
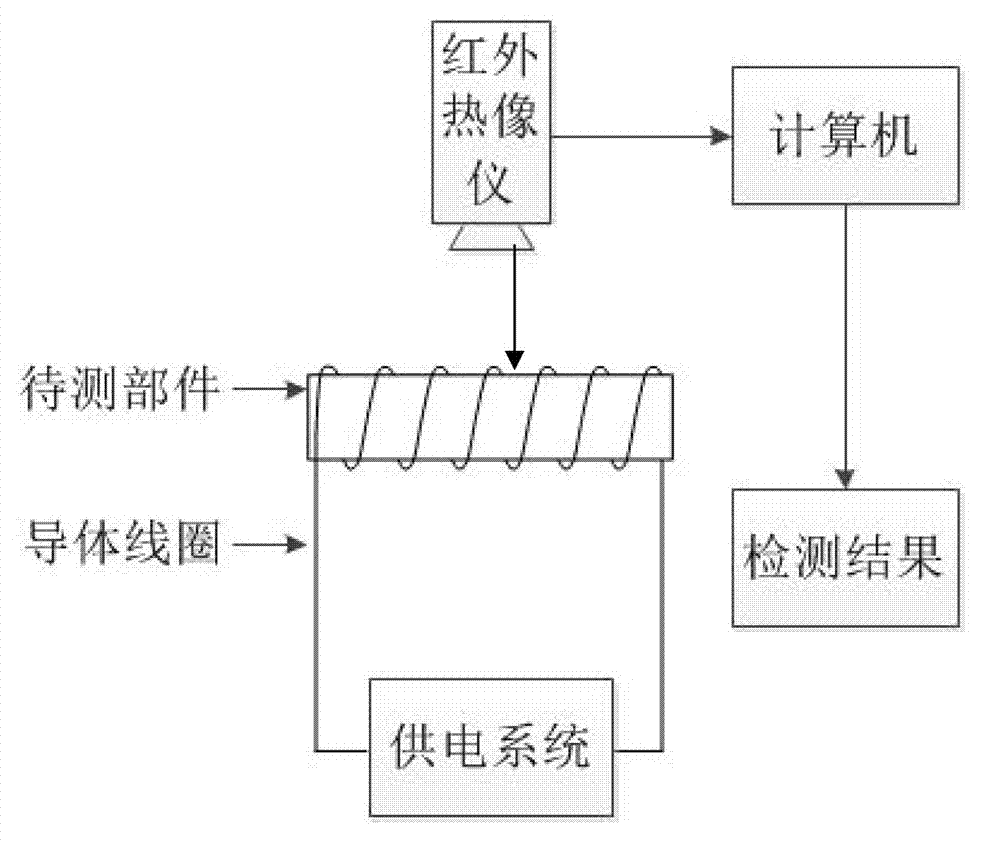
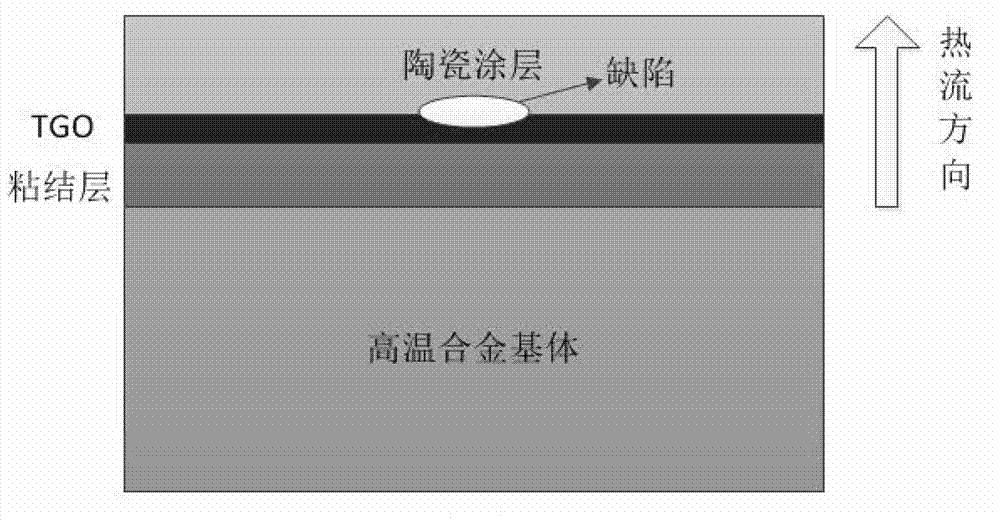
Thermal barrier coating part electromagnetic eddy current thermal imaging non-destructive detection system and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102954968AHigh precisionEvenly distributedOptically investigating flaws/contaminationElectrical conductorCeramic coating
The invention relates to a thermal barrier coating part electromagnetic eddy current thermal imaging non-destructive detection system and a detection method thereof. The detection system comprises an electromagnetic heating device connected with a thermal barrier coating part requiring detection, an infrared thermal imager, and a computer connected with the infrared thermal imager. The detection method comprises that: a conductor coil of the electromagnetic heating device is wound on a thermal barrier coating part requiring detection, the conductor coil is connected with a power supply system, the infrared thermal imager is adopted to carry out infrared image acquisition on a coating surface temperature field of the thermal barrier coating part requiring detection, the acquired image is input into the computer, and computer processing is performed to finally obtain the detection result. According to the present invention, electromagnetic induction is adopted to heat a high temperature alloy substrate, and the ceramic coating surface temperature field is monitored to obtain defect distribution; heat generated by eddy current is uniformly distributed, the detection result has high accuracy, and errors due to different heat flow injection directions are avoided; the detection process does not cause damage on the thermal barrier coating part requiring detection; and detection speed is rapid, efficiency is high, operation is convenient, and cost is low.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Laser cladding Co-based alloy powder for conductor roll
InactiveCN101187022ASolve repair problemsImprove performanceMetallic material coating processesChemical compositionAlloy substrate
Provided is cobalt-based alloy powder for laser cladding electricity conducting roller, the weight percentages of the chemical components of the material are that Cr is 24-30%, W is 6-10%, Mo is 3-6%, Ni takes 6-12%, Fe holds 2-10%, Mn is 0.5-2%, Si holds 0.2-2%, V is 0.1-0.6%, B takes 0.3-1.5%, C holds 0.5-2.5%, Y2O3 is 0-0.5%, Hf takes 0-0.5%, La2O3 holds 0-0.5%, Ce is 0-0.5%, and the rest is Co. The invention has the advantages that with multiple strengthened methods, the alloy substrate is strengthened and the crystal boundary quality is improved, which enables the alloy to achieve perfect combination property, thereby achieving medium rigidity and relatively high intensity of the alloy, simultaneously forming self-fluxing alloy and reducing alloy melting point, and increasing properties of oxidation resistance, abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, and certain electricity conduction.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER TECH
Compound of aluminum or aluminum alloy and plastics and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102229266AImprove bindingReduce usageAnodisationSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticAlloy substrate
The invention provides a compound of aluminum or an aluminum alloy and plastics and a manufacturing method thereof. The compound comprises an aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate and a plastic piece which is combined with the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate through injection molding, wherein the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is subjected to electrochemical etching, thus the surface of the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is etched from the surface to the inside to form a plurality of nano holes; and the plastic piece is made of crystalline thermoplastic plastics. The manufacturing method of the compound comprises the following steps: providing the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate; carrying out electrochemical etching treatment on the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate, thus the surface of the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is etched from the surface to the inside to form the plurality of nano holes; and placing the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate subjected to electrochemical etching into an injection molding mould, and combining the injection molding piece on the surface of the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate, thus the compound is obtained, wherein the molding piece is made of crystalline thermoplastic plastics.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Preparation of super-hydrophobic surface for metal anti-corrosive and self-cleaning effects
InactiveCN101440510AGood environmental stabilityEasy to operateElectrolytic organic material coatingElectrochemical responseAlloy substrate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a super-hydrophobic surface with metal corrosion protection and self-cleaning functions, which comprises the following steps: 1) washing a metal or an alloy substrate clean by using acetone, deionized water and ethanol sequentially; 2) using the cleaned metal or the alloy substrate as an anode and a cathode respectively and putting the anode and the cathode into a fatty acid CH3(CH2)n-2COOH electrolyte solution with the concentration of between 0.001 and 0.5 mol per liter, wherein n is equal to between 10 and 14; and applying voltage of between 0.5 and 25 volts between the cathode and anode to perform an electrochemical reaction for 0.5 to 6 hours so as to deposit a layer of a fatty acid salt super-hydrophobic surface with the metal corrosion protection and self-cleaning functions on the surface of the metal or the alloy substrate serving as the cathode. The method has simple operation and low equipment requirement, is not limited by the shape of a substrate, is easy to achieve industrialization, and has comparatively wide practical value.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Composite reinforcing and treating method for alumium or alumium alloy substrate surface through ion implantation and deposition
InactiveCN1858296AImprove carrying capacityImprove wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDiamond-like carbonMetallic materials
The present invention provides composite reinforcing treatment process for aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate surface through both ion implantation and deposition. The present invention solves the problems of great residual stress, lower binding force and poor bearing capacity of diamond-like carbon film on aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate, and the low wear resistance of DLC film under high speed and heavy load condition. The composite reinforcing treatment process includes the following steps: ultrasonic cleaning of aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate; Ar ion sputtering cleaning; Ti ion implantation; PIIID deposition of Ti film; PIIID deposition of TiN film; PIIID deposition of Ti(CN) film; PIIID deposition of TiC film and synthesis of diamond-like carbon film. All the steps but the first mentioned one are completed in vacuum chamber. The DLC film of the present invention has 10 times over raised wear life compared with single DLC film in the same thickness and friction coefficient lower than 0.1.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Chromium(VI)-free, aqueous acidic chromium(III) conversion solutions
InactiveUS20070243397A1Improve protectionSolid state diffusion coatingMetal layered productsAlloy substrateZinc alloys
An essentially chromium(VI)-free, chromium(III)-containing corrosion resistant conversion solution, or layer thereof for treating metals such as zinc, zinc alloy, aluminum, or aluminum alloy substrates. The conversion solution, is substantially free of chromium(III)-chelates, is capable of producing thick conversion films even at low temperatures, has good corrosion resistance, and is self healing with regard to scratches and the like.
Owner:COLUMBIA CHEM , A CORP OF OH
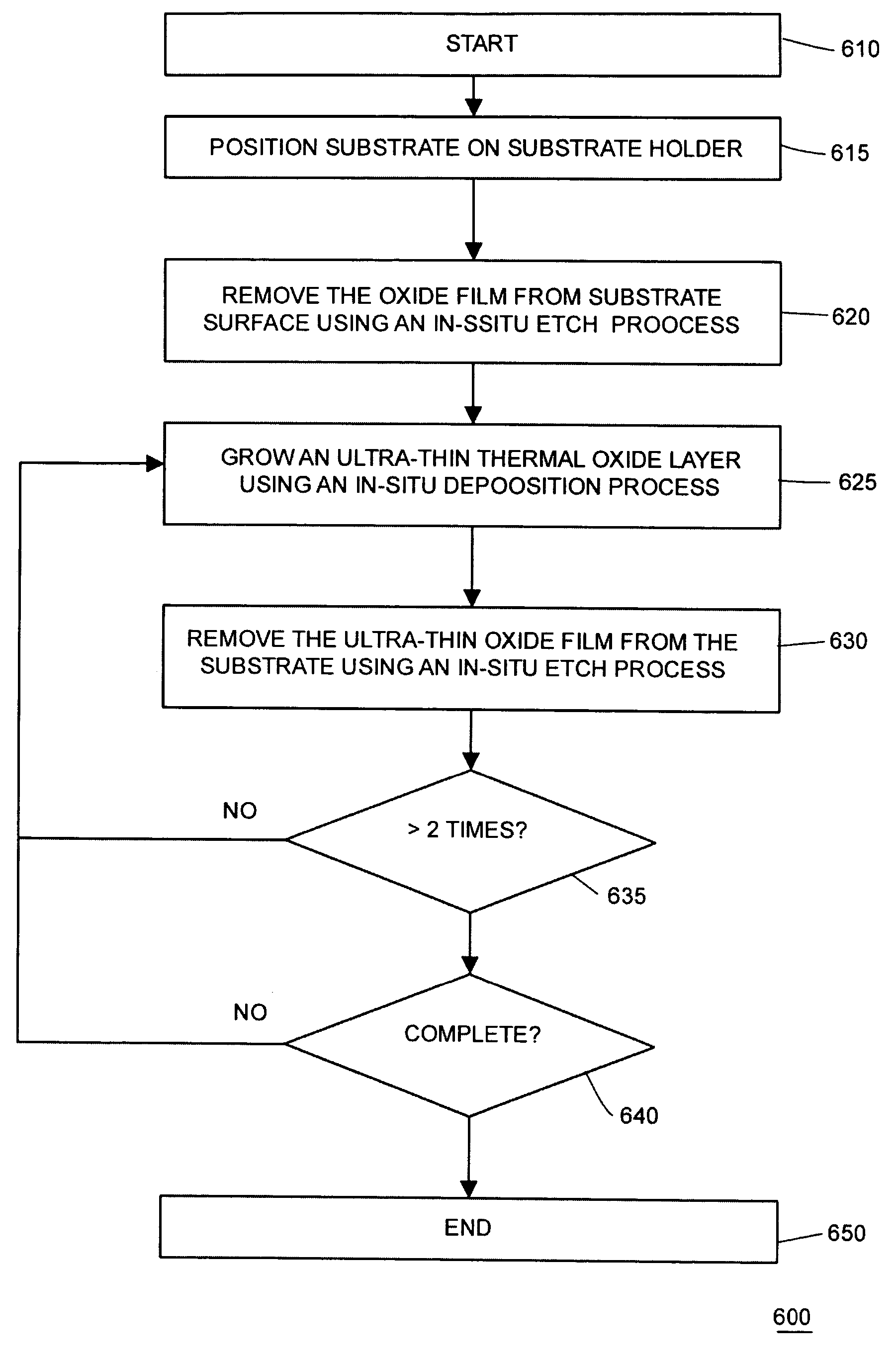
Multiple grow-etch cyclic surface treatment for substrate preparation
InactiveUS20050048742A1Simple interfaceFree from defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAlloy substrateThermal oxide
This invention provides a method for modifying the surface properties of a Si or Si alloy substrate by performing repeated etch-grow cycles of thermal oxide to yield a more defect free substrate with a more uniform nucleating surface which provides an improved interface for dielectric formation. Additionally, this method of processing does not expose the substrate to ambient atmosphere and preserves the improved surface until subsequent processing steps are performed.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Fretting and whisker resistant coating system and method
ActiveUS7391116B2High resistivityInhibited DiffusionHot-dipping/immersion processesAnodisationCoating systemAlloy substrate
Owner:WIELAND ROLLED PROD NORTH AMERICA LLC
Material and method for preparing aluminum alloy structural member by using laser 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing technology
InactiveCN104759625AImprove performanceIncrease profitAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer Aided DesignMaterial synthesis
The invention discloses a material and method for preparing an aluminum alloy structural member by using a laser 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing technology. Technologies such as a CAD (Computer Aided Design) three-dimensional entity model slicing technology, a digital programming technology and a laser quick forming technology and a material synthesis technology are combined integrally; under the condition that no any special mold or tool is used, multi-layer cladding accumulation is performed through quick melting and solidification of a laser beam on an aluminum alloy substrate by taking the powder of Al, Fe, Cu, Si, Ti, B, Mn, C and Ce according to the mass percentage of 80.0, 3.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 3.0, 1.5, 2.0 and 1.5 as a raw material; an aluminum alloy structural member with good comprehensive performance such as high performance, full compactness and high fatigue life is directly finished from a part digital model in one step. The method has the characteristics of low cost, short period and high material utilization rate, and is suitable for integrated quick forming manufacturing of large-sized and complex aluminum alloy structural members; the shapes and the sizes of the prepared parts are not limited, and the requirement on structural integration can be met.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
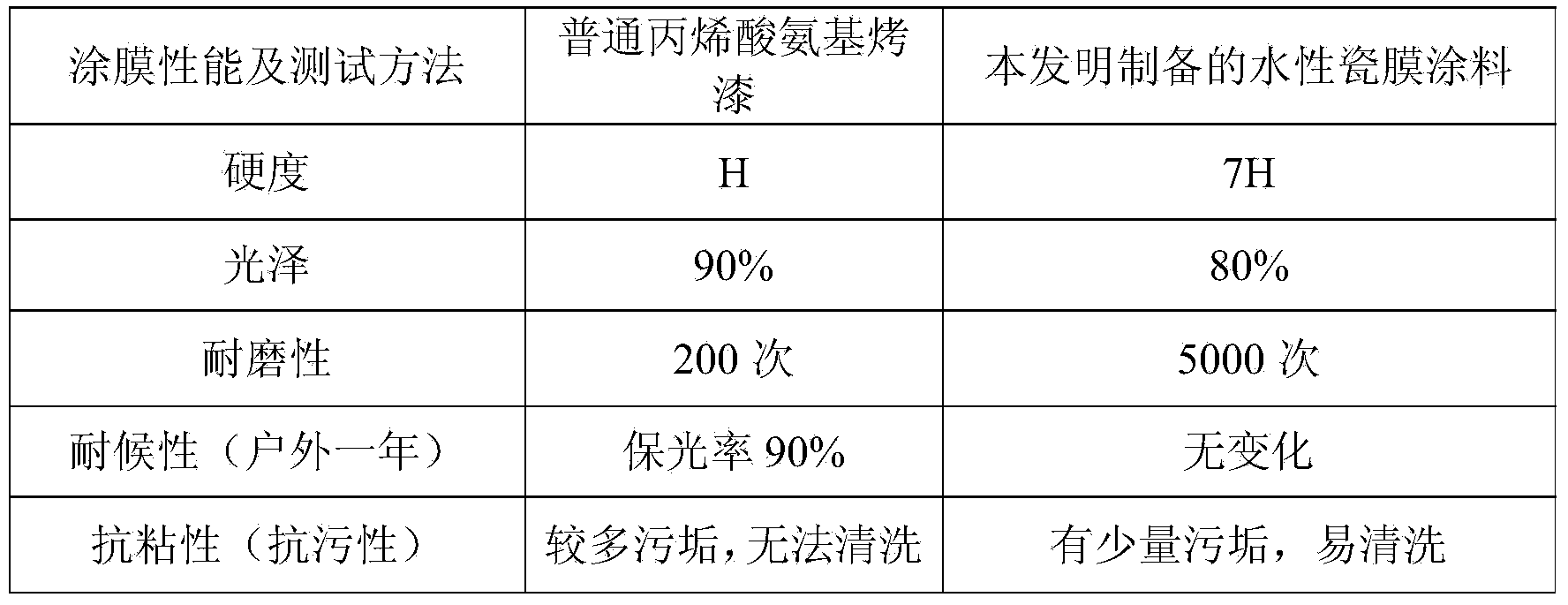
Water-based porcelain film coating and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a water-based porcelain film coating. The formula of the water-based porcelain film coating comprises the following components in parts by weight: 45% to 55% of colloidal silica dispersion liquid, 30% to 45% of a silane coupling agent, 5% to 15% of an inorganic pigment, 2% to 5% of alumina packing, 0.5% to 1% of a flatting agent, 1% to 2% of hydroxy silicone oil with low molecular weight and 1% to 1.5% of an organic acid catalyst, wherein the colloidal silica dispersion liquid is prepared by mixing colloidal silica with big and small particle diameters according to the mass ratio of (1-3):1, wherein the particle diameters of the colloidal silica with the small particle diameters are distributed within 10nm to 15nm while the particle diameters of the colloidal silica with the big particle diameters are distributed within 40nm to 50nm; the silane coupling agent is prepared by mixing methyl trimethoxysilane and methyl triethoxysilane according to the mass ratio of (1-2):1; the organic acid catalyst can be a formic acid or an acetic acid or can be a mixture of the formic acid and the acetic acid. The water-based porcelain film coating has the good adhesive force and the good waterproof and cohesive-proof on an aluminum alloy substrate.
Owner:广东四方威凯新材料有限公司
Laminar titanium aluminum composite plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101450542ALow densityImprove mechanical propertiesRoll mill control devicesExplosivesAlloy substrateVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a laminated titanium aluminum clad plate and a preparation method thereof. The laminated titanium aluminum clad plate is characterized in that the titanium aluminum clad plate consists of an aluminum alloy substrate layer and a titanium-coated layer; and the total thickness is 1.5 mm. Compared with a TAI plate material with thickness of 1.5 mm, the laminated titanium aluminum clad plate can save a titanium material by 80 percent around so as to reduce the material cost and also reduce the whole density of the plate material by about 35 percent; and compared with a 2024 plate material with the thickness of 1.5 mm, the laminated titanium aluminum clad plate not only improves anticorrosive performance and thermal shock resistance of the material but also improves the whole mechanical performance of the plate material.
Owner:有研金属复材技术有限公司
Method for producing white anodized aluminum oxide
A method for forming substantially white anodized aluminum oxide on an aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is provided. A porous aluminum oxide layer is formed on the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate by anodization in an acid electrolyte. Following formation of the anodized porous layer of aluminum oxide, the aluminum / aluminum alloy substrate is sequentially immersed in at least two reaction material solutions. The two or more reaction materials react to deposit a substantially white pigment material in the pores of the anodized aluminum oxide.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Three-dimensional orthotropic carbon fiber reinforced aluminum-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a three-dimensional orthotropic carbon fiber reinforced aluminum-based composite material and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of carbon fibers. The material consists of the following components in percentage by volume: 30 to 60 percent of carbon fiber reinforcement and 40 to 70 percent of aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate, wherein the aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0 to 13 percent of Si, 0 to 11 percent of Mg, 0 to 10 percent of Zn, 0 to 8 percent of Cu, 0 to 2 percent of Mn, 0 to 1 percent of Ti and the balance of Al. The defect when a three-dimensional orthotropic carbon fiber structure is compounded with metal in the prior art is effectively overcome, three-dimensional orthotropic carbon fibers are taken as the reinforcement in the metal-based composite material, and the compounding of the three-dimensional orthotropic carbon fibers and aluminum or an aluminum alloy is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Iron-based alloy and nitridation treatment for PEM fuel cell bipolar plates
A corrosion resistant electrically conductive component that can be used as a bipolar plate in a PEM fuel cell application is composed of an alloy substrate which has 10-30 wt. % Cr, 0.5 to 7 wt. % V, and base metal being Fe, and a continuous surface layer of chromium nitride and vanadium nitride essentially free of base metal. A oxide layer of chromium vanadium oxide can be disposed between the alloy substrate and the continuous surface nitride layer. A method to prepare the corrosion resistant electrically conductive component involves a two-step nitridization sequence by exposing the alloy to a oxygen containing gas at an elevated temperature, and subsequently exposing the alloy to an oxygen free nitrogen containing gas at an elevated temperature to yield a component where a continuous chromium nitride layer free of iron has formed at the surface.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
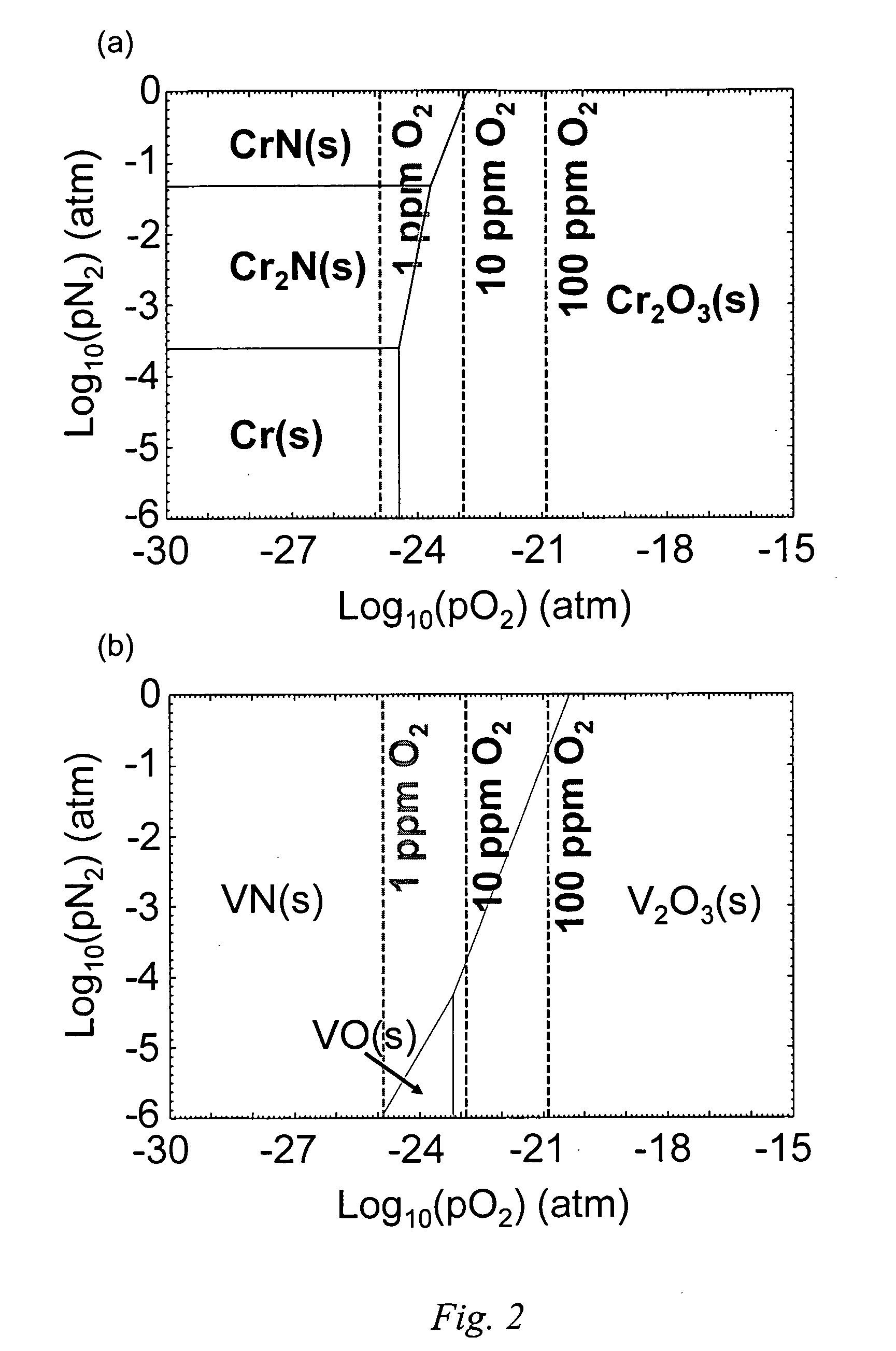
Aluminum alloy substrate for magnetic disk
InactiveUS20170327930A1Improve rigidityFlat surfaceBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMetallurgyAlloy substrate
An aluminum alloy substrate for a magnetic disk includes 0.5 mass % or more and 24.0 mass % or less of Si, 0.01 mass % or more and 3.00 mass % or less of Fe, and the balance of Al and unavoidable impurities. The aluminum alloy substrate for a magnetic disk includes a smooth plated surface and has high rigidity.
Owner:FURUKAWA SKY ALUMINUM CORP +1
Multifunctional alumina/metal micro-laminated coating
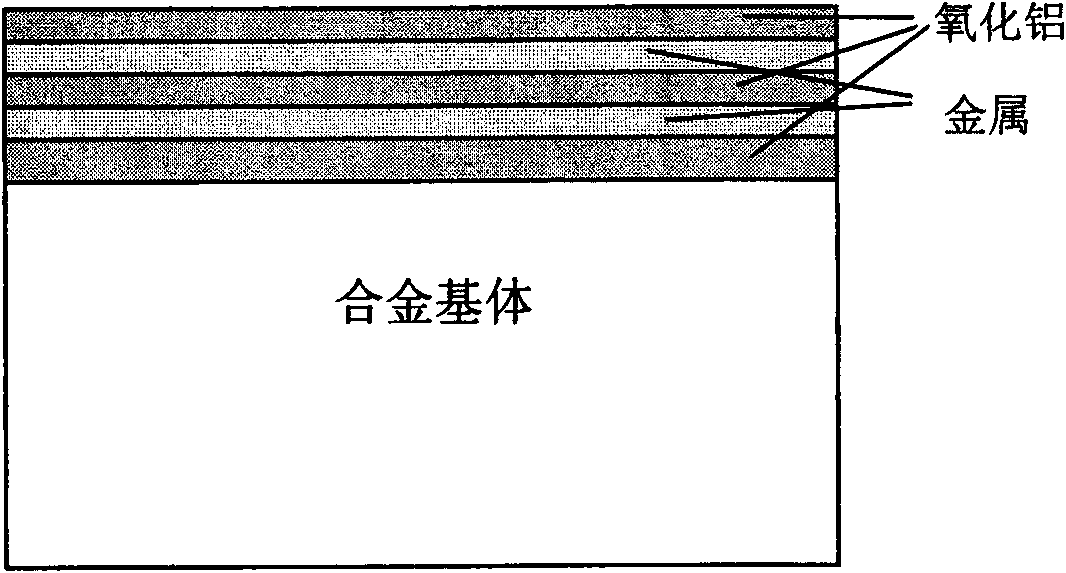
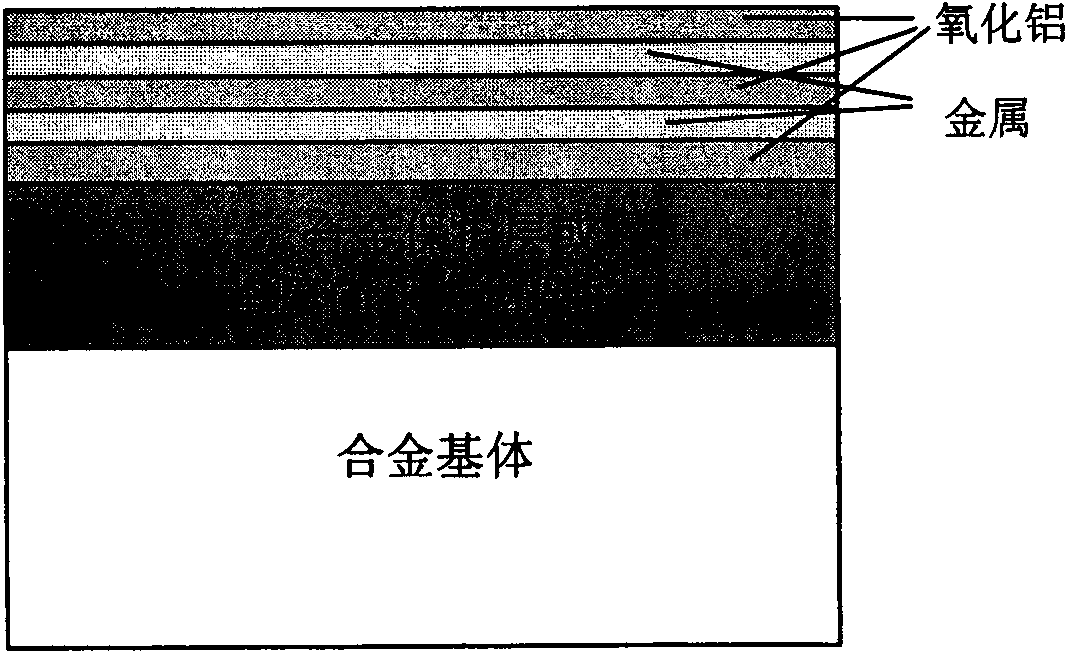
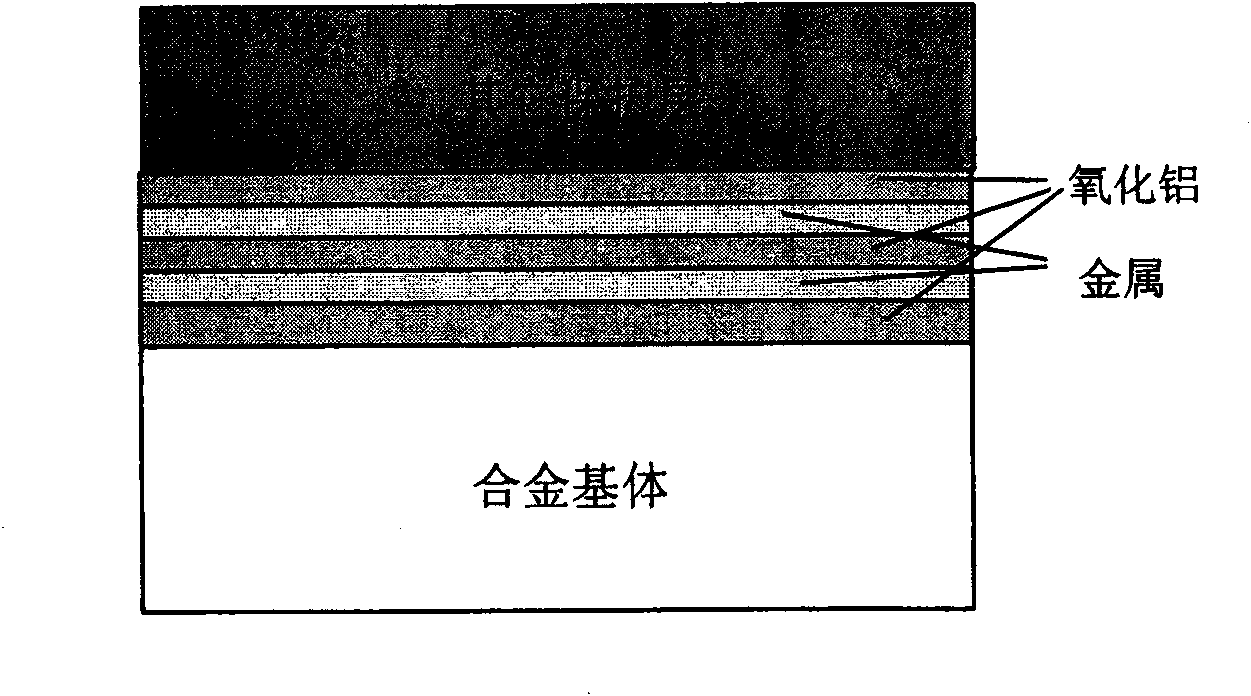
The invention provides a multifunctional alumina / metal micro-laminated coating, which belongs to composite material made from metals and ceramic and coating technology thereof and is used for high-temperature protection, anti-tritium permeation, and anti-hydrogen damage of alloys with wide temperature scope. The micro-laminated coating adopts a high-pure alumina or alumina doped with a small amount of rear earth oxide, or alumina doped with a small amount of zirconia as an alumina coating, wherein the metals can be Pt, or Rh, or Ir, or Au, or alloys of all, or M-Cr-Al-rare earth alloy, or Fe, Co, Ni-based aluminum-containing alloy. The thickness of each laminated coating is 20-1000nm. The micro-laminated coating can be obtained by adopting a plurality of methods through the alternative sedimentation of the alumina coating and a metal coating. The micro-laminated coating has the following characteristics: (1) excellent binding force with the alloy substrate; (2) excellent high-temperature protection performance and anti-tritium penetration performance, and anti-hydrogen damage performance; (3) wide operating temperature range from room temperature to 2000 DEG C; (4) the evaporation inhibition of precious metal coatings at high temperature; and (5) and synergistic protective effect with other coatings.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing nano-structured nitrogen silicon zirconium coating on surface of hard alloy substrate
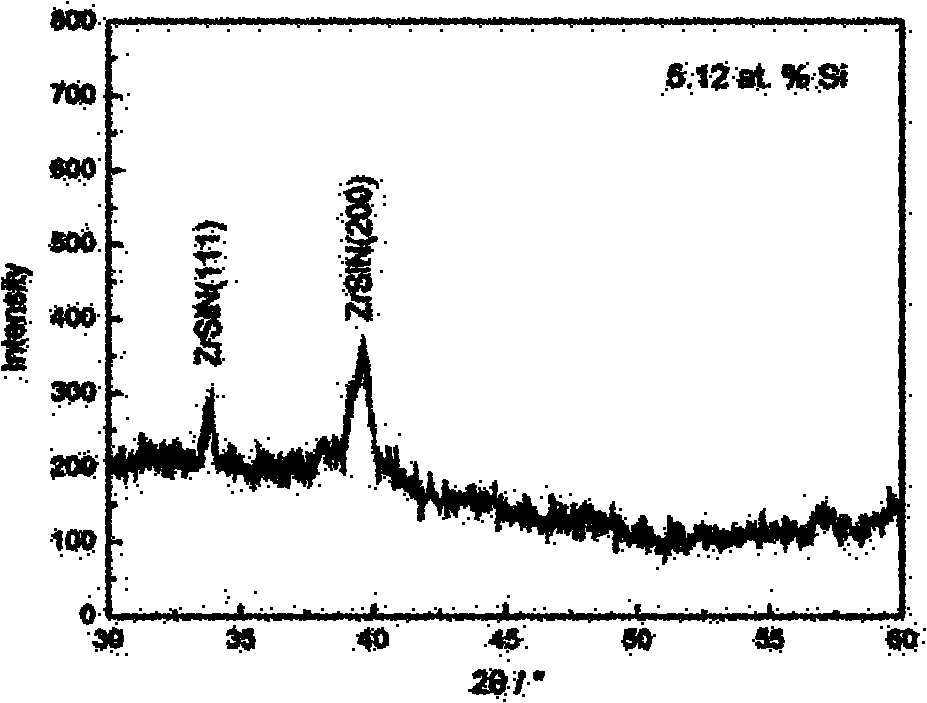
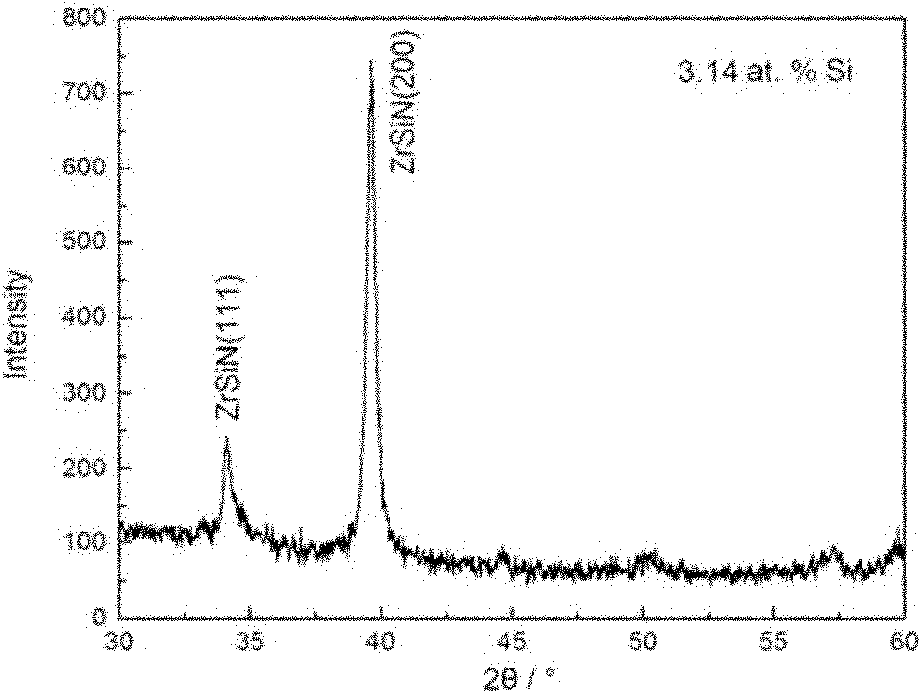
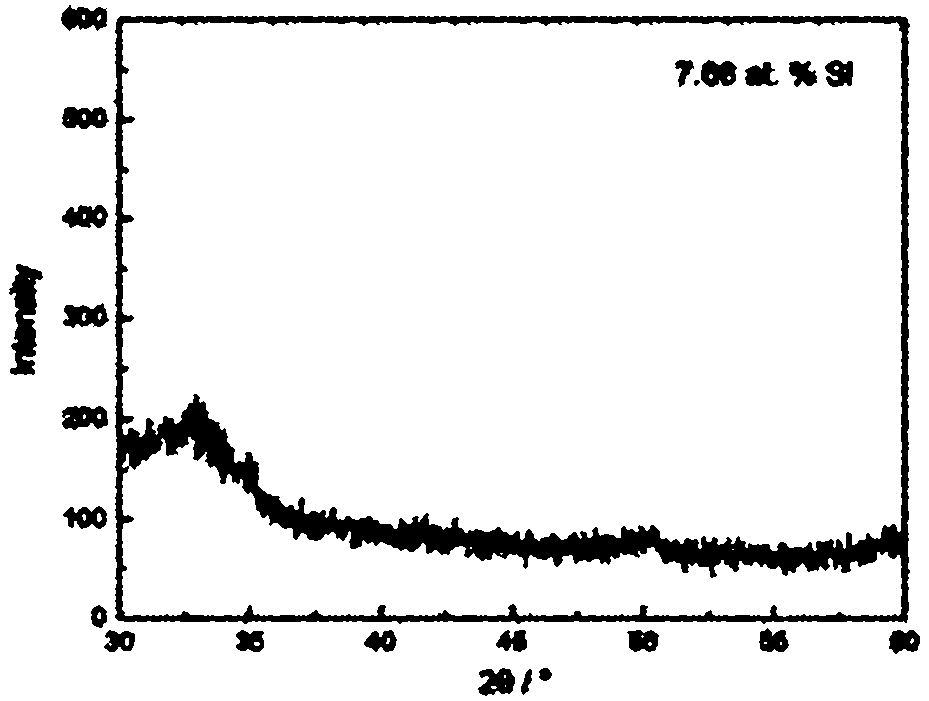
InactiveCN101921982AHigh hardnessGrowth inhibitionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNano structuringAlloy substrate
The invention provides a method for preparing a nano-structured nitrogen silicon zirconium coating on the surface of a hard alloy substrate, relating to a hard alloy. A direct-current and radio frequency reaction co-sputtering method is used to prepare the nano-structured nitrogen silicon zirconium coating through controlling the power of a Si target. When the content of Si in a ZrSiN coating is reduced, the Si atoms in the coating exist in the mode of replacing Zr atoms, the ZrSiN coating with low content of Si is solid solution, and the cross section of the ZrSiN coating is in a column structure. The solid solubility and the hardness of the ZrSiN coating are increased with the increment of the content of Si. When the content of Si in the coating reaches a definite amount, excessive element of Si can form amorphous Si3N4 at crystal boundary with element of N. When the content of Si in the coating is further increased, a great amount of amorphous Si3N4 is generated, thus seriously inhabiting the growth of ZrN crystal particles and influencing the degree of crystallization of the coating, in addition, the coating is changed to be in an amorphous state and is in a non-column equiaxial structure.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
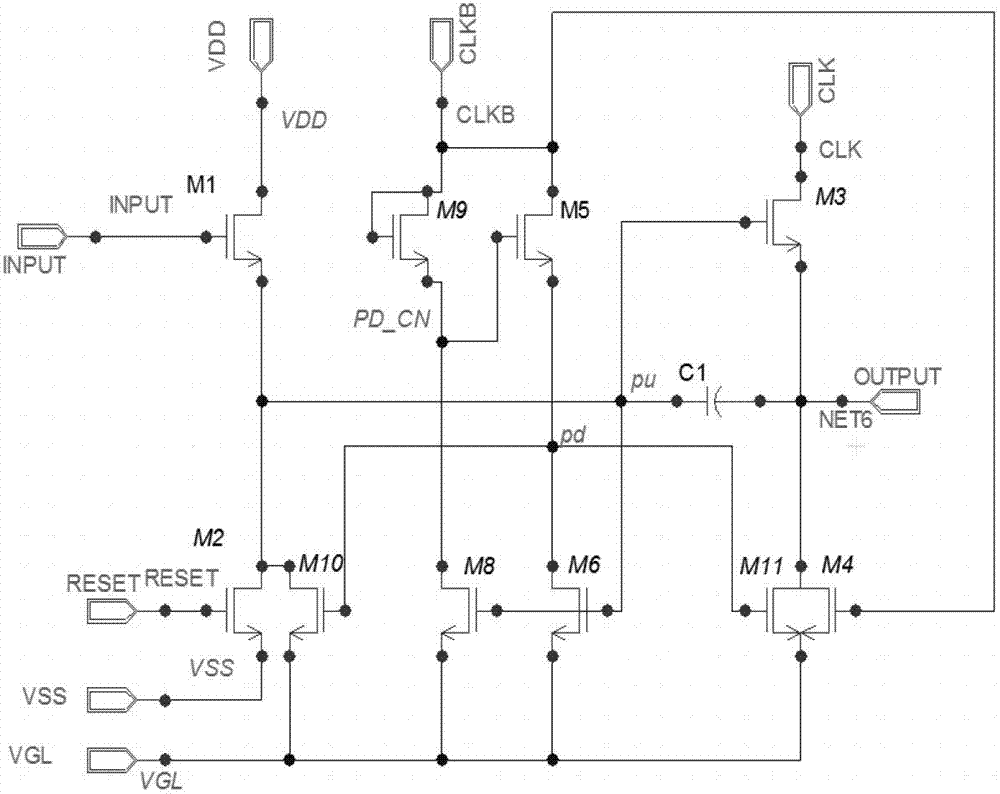
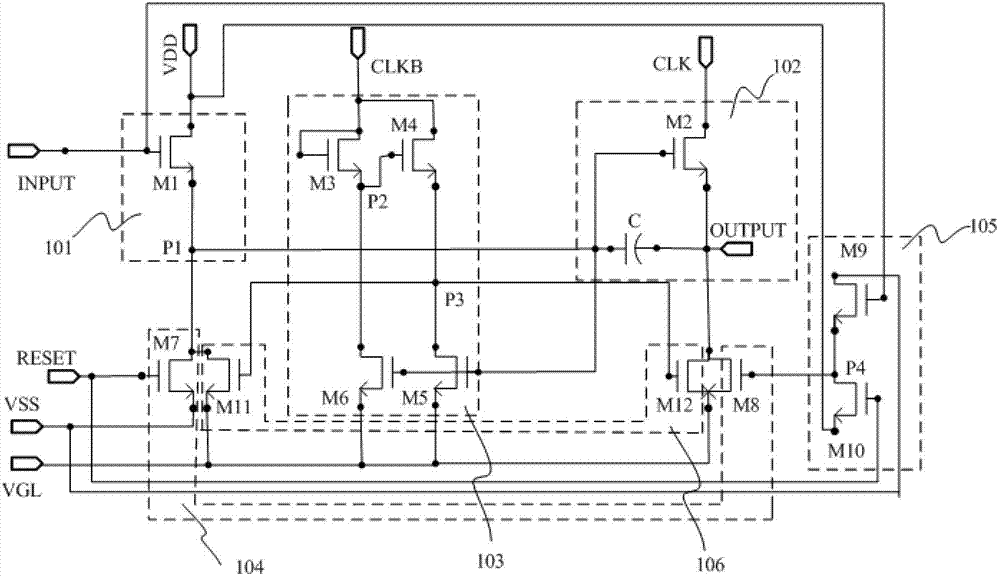
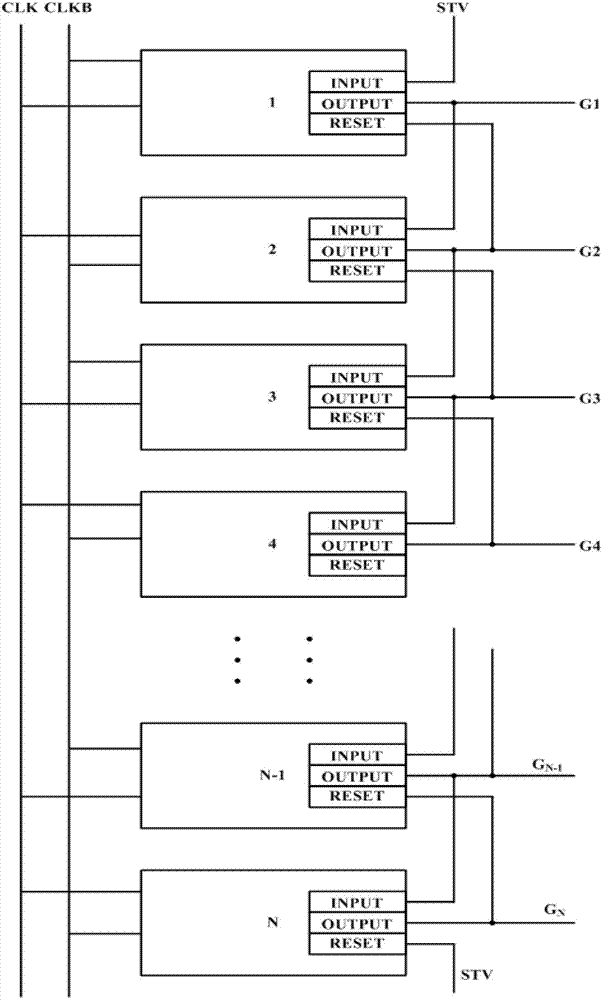
Shifting register and alloy substrate electrode driving device
ActiveCN103093825AImprove stabilityReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerAlloy substrate
The embodiment of the invention provides a shifting register and an alloy substrate electrode driving device, and aims at shortening the operation time of a part of thin film transistors, improving the stability of the shifting register and also reducing the energy consumption of the shifting register. The shifting register comprises a pull-up node charging unit, an output unit, a pull-down control unit, a pull-up node discharging unit and an output discharging unit, wherein the output discharging control unit is used for responding to an input signal, used for providing a second voltage signal to the pull-up node discharging unit through a fourth node of the output discharging control unit, and used for responding to a reset signal to provide a first voltage signal to the pull-up node discharging unit through the fourth node of the output discharging control unit.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
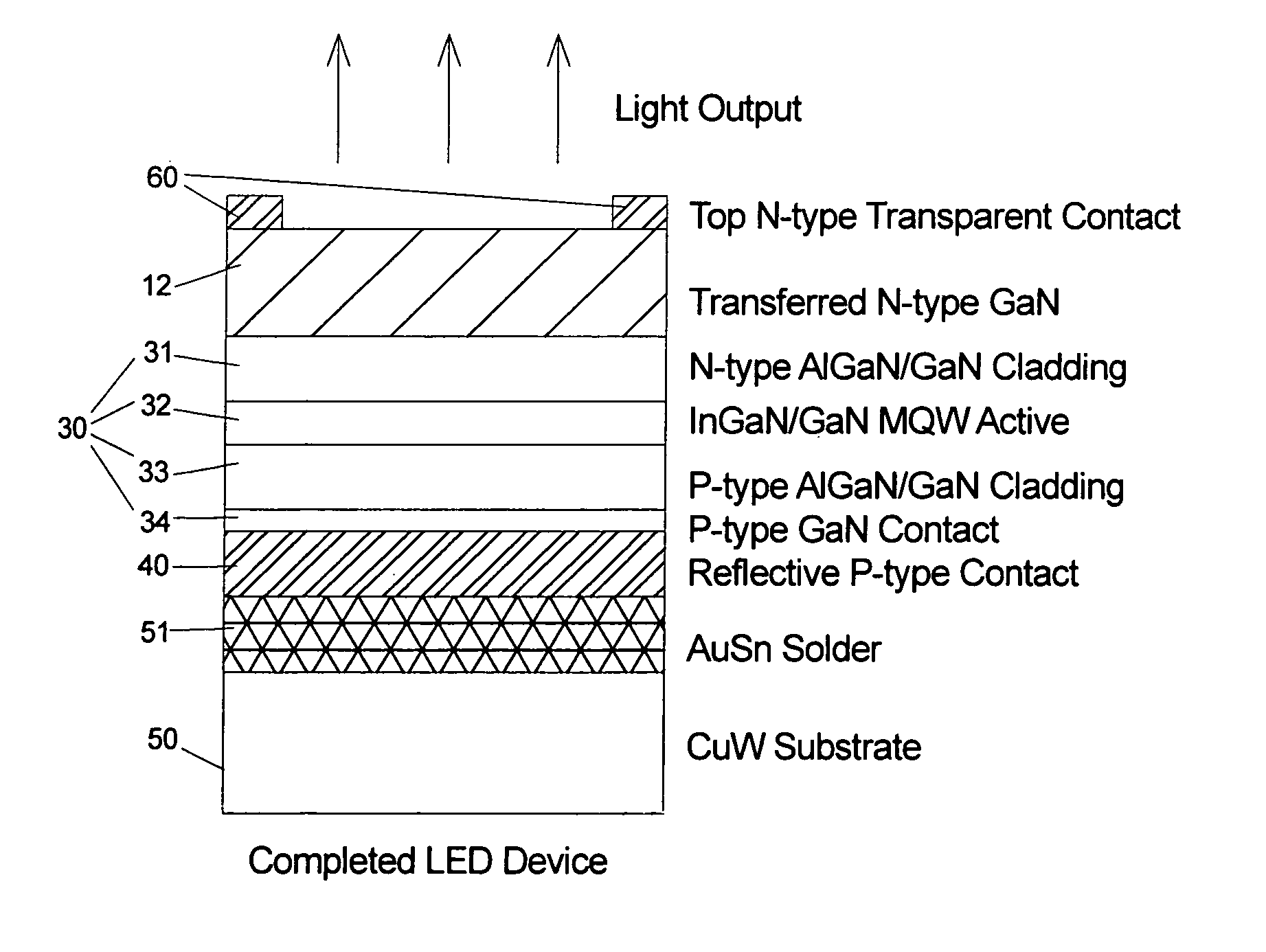
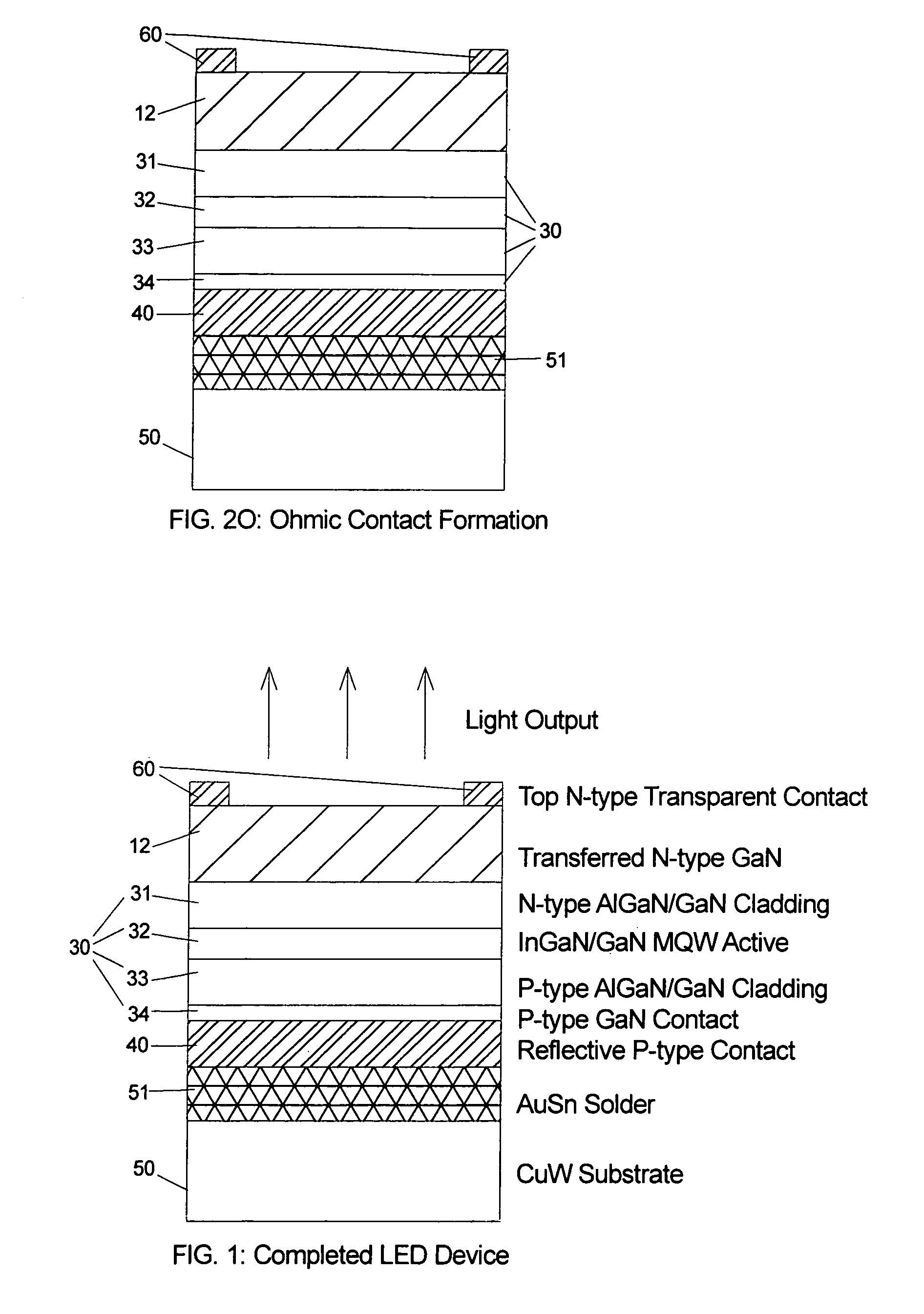
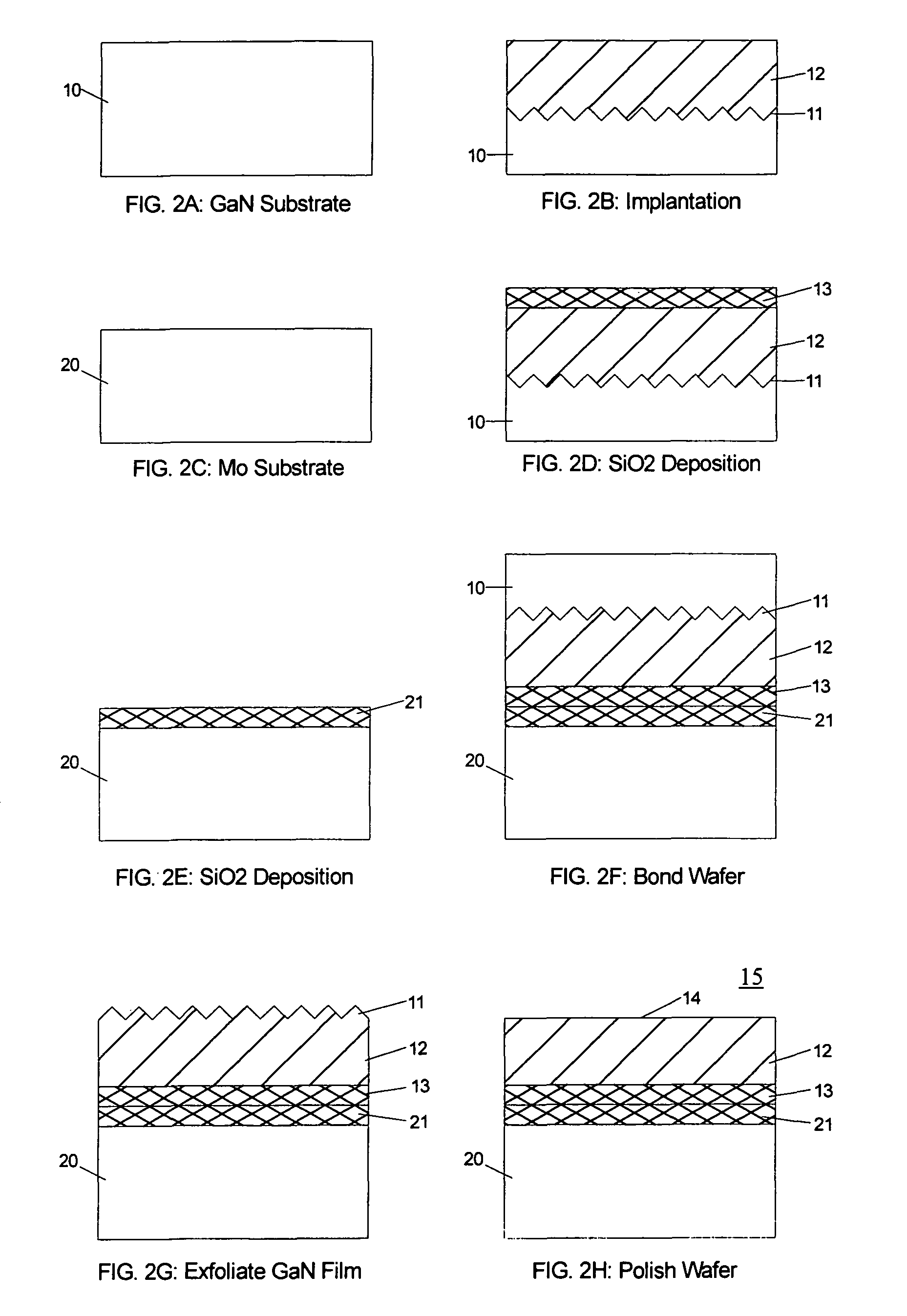
Bonded intermediate substrate and method of making same
ActiveUS8101498B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal alloyThin layer
An intermediate substrate includes a handle substrate bonded to a thin layer suitable for epitaxial growth of a compound semiconductor layer, such as a III-nitride semiconductor layer. The handle substrate may be a metal or metal alloy substrate, such as a molybdenum or molybdenum alloy substrate, while the thin layer may be a sapphire layer. A method of making the intermediate substrate includes forming a weak interface in the source substrate, bonding the source substrate to the handle substrate, and exfoliating the thin layer from the source substrate such that the thin layer remains bonded to the handle substrate.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Process for anodizing aluminum-alloy substrate
The invention relates to a process for anodizing an aluminum-alloy substrate. The process comprises the following steps of: (S1) degreasing; (S2) washing for the first time; (S3) washing by an alkali; (S4) washing for the second time; (S5) polishing; (S6) washing for the third time; (S7) anodizing; (S8) washing for the fourth time; (S9) carrying out electrolytic coloring; (S10) washing for the fifth time; (S11) sealing holes; (S12) washing for the sixth time to finally obtain a dense anodic oxide film. The whole anodizing process is carried out in the environment of normal temperature, less energy is consumed, the sulfuric acid used for anodizing can be reused for degreasing, the utilization rate of raw materials is high, the production cost is low, the holes are sealed after carrying out the anodizing reaction, the anodizing film can effectively protect the aluminum and the aluminum-alloy, the surface of the anodizing film has no honeycomb-like porous structure, is highly smooth and can be kept to be smooth for a long time.
Owner:CHENGDU SUNSHINE ALUMINUM
Preparation method of titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure
The invention provides a preparation method of a titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure. The preparation method comprises the steps that (a) a titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure model is sliced and layered according to 20-30 mu m layer thickness; (2) titanium alloy powder is uniformly paved on a titanium alloy substrate, a laser beam which is emitted by a laser is used for selectively melting a titanium alloy powder layer according to the determined scan locus of the laser beam to complete the processing of one layer of titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure; (c) the titanium alloy powder is paved on the layer of formed titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure again, the laser beam which is emitted by the laser is used for selectively melting the titanium alloy powder layer according to the determined scan locus of the laser beam; (d) the titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure is processed layer by layer, and the titanium alloy thin-wall honeycomb structure is finally formed. According to the method, the stress accumulation and the deformation of a forming piece in the forming process are reduced, the flexibility degree is high, and a thin-wall honeycomb component with variable honeycomb distance and a three-dimensional dot matrix structure can be prepared.
Owner:CAPITAL AEROSPACE MACHINERY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com